Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Decrease shift" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
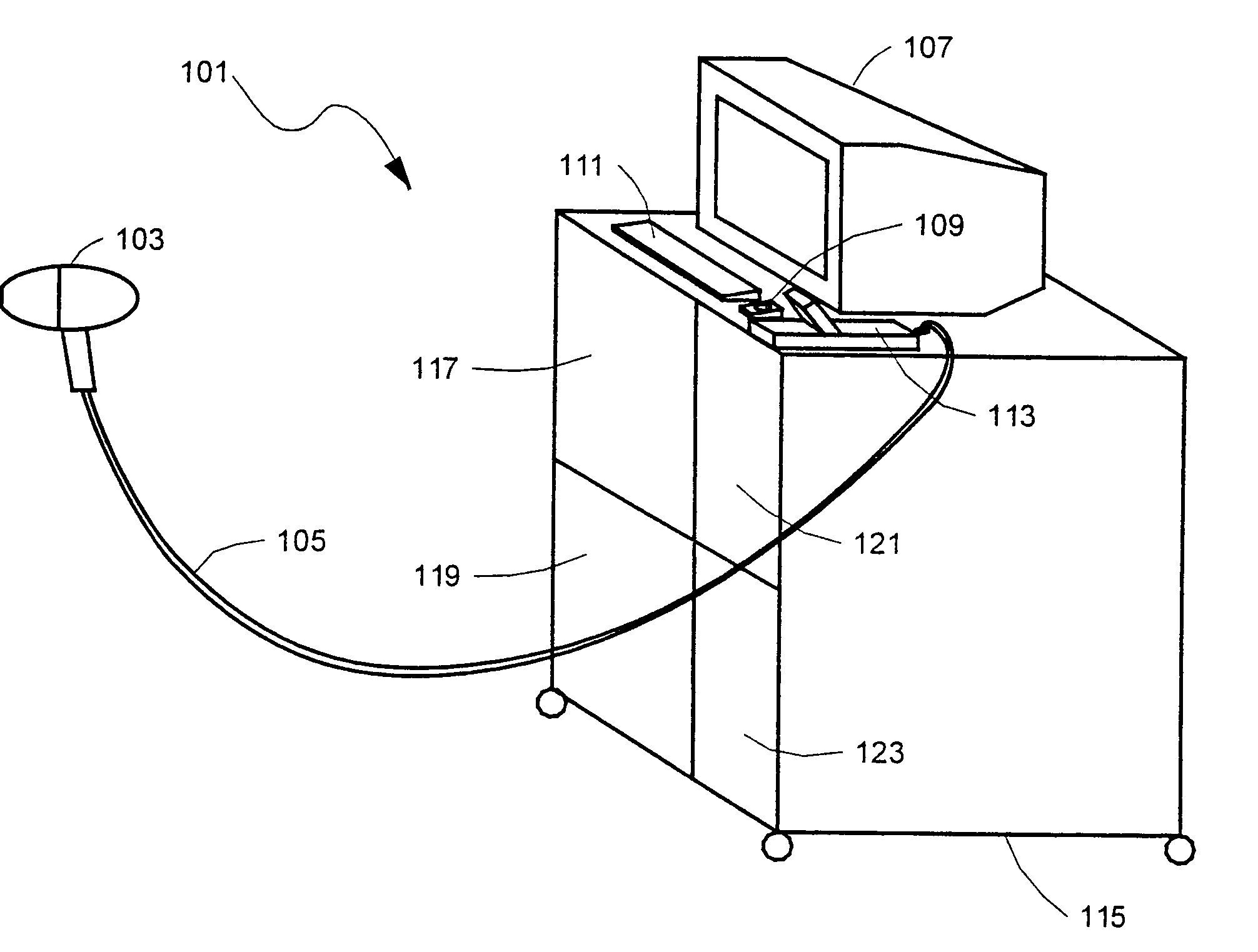
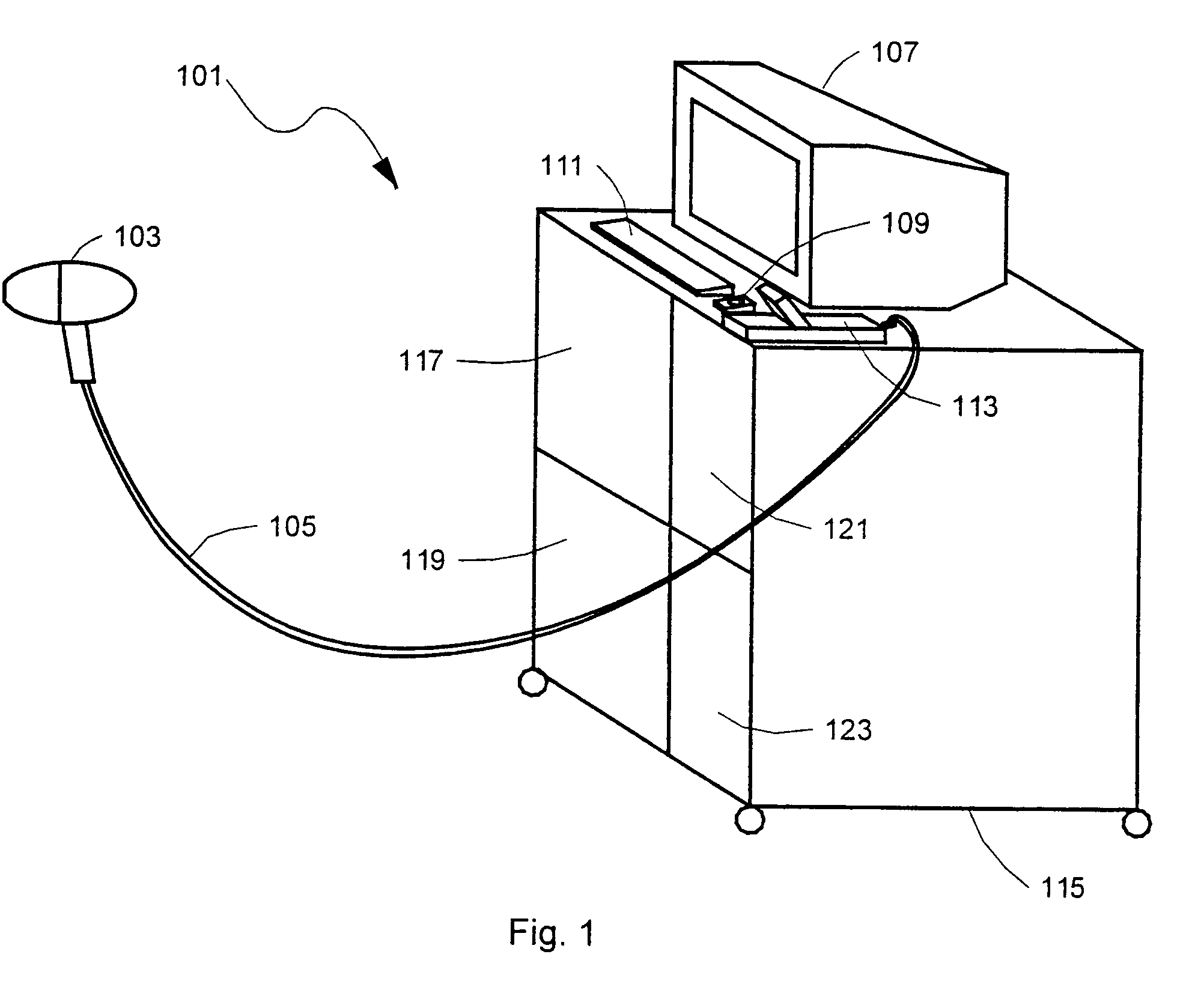
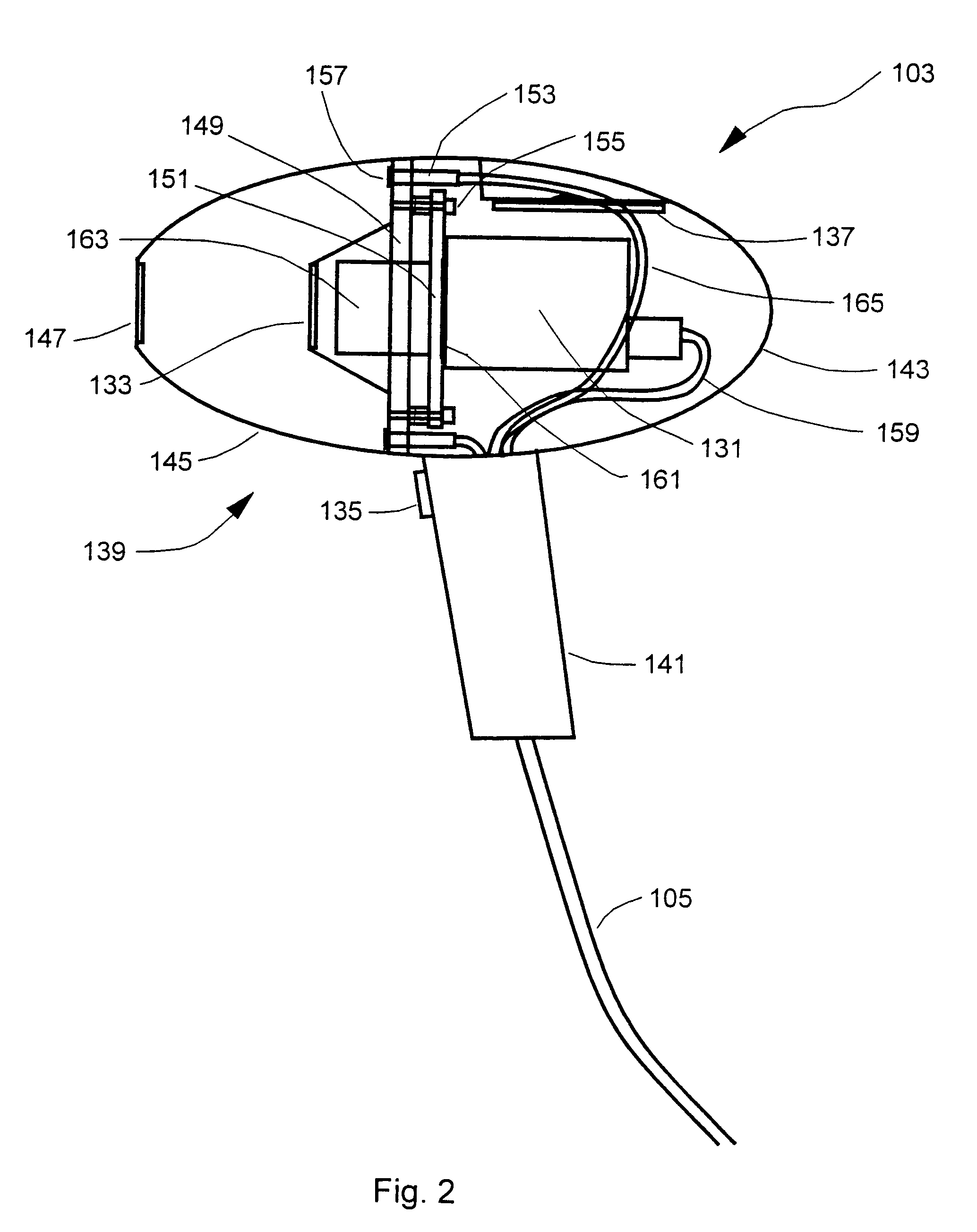
System and method for examining, recording and analyzing dermatological conditions
InactiveUS6993167B1Minimise edge contributionDecrease shiftDiagnostics using lightSurgeryMelanomaHand held
A system for collecting, storing and displaying dermatological images for the purpose of monitoring and diagnosis of skin conditions and skin cancers, including melanoma. A hand-held unit illuminates a section of the patient's skin, and an imaging device generates imaging signals from light derived from a skin section. Pairs of light output ports in the hand-held unit are arranged such that their intensity distributions overlap at their half-intensity levels so that the resulting summation of their intensities has a flat central region. Three image stores are maintained, one for lesion images, one for “nearby skin” images, and one for reference-white images. The “nearby skin” images are used by the system software to automatically determine the skin / lesion border. The reference white images are used to set the dynamic range of the instrument and to compensate for lighting irregularities. Two images of the same lesion taken at different times may be displayed simultaneously so that changes in the lesion may be determined. The calibration system is designed so that image data taken on any of multiple machines built to the same specification will be corrected back to a common reference standard to ensure absolute accuracy in colour rendition.
Owner:POLARTECHNICS
Method of manufacturing wiring board and method of manufacturing semiconductor package
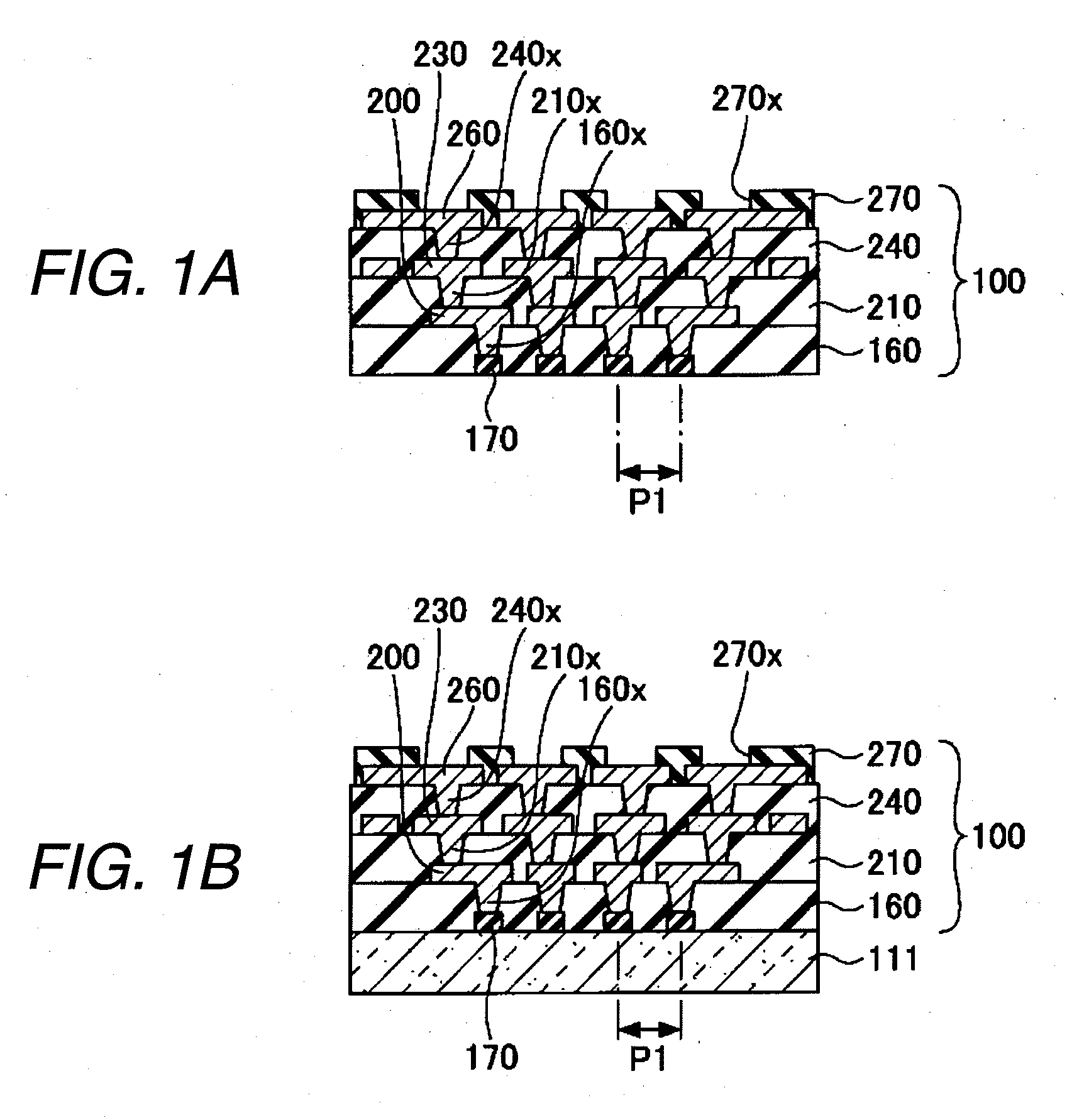
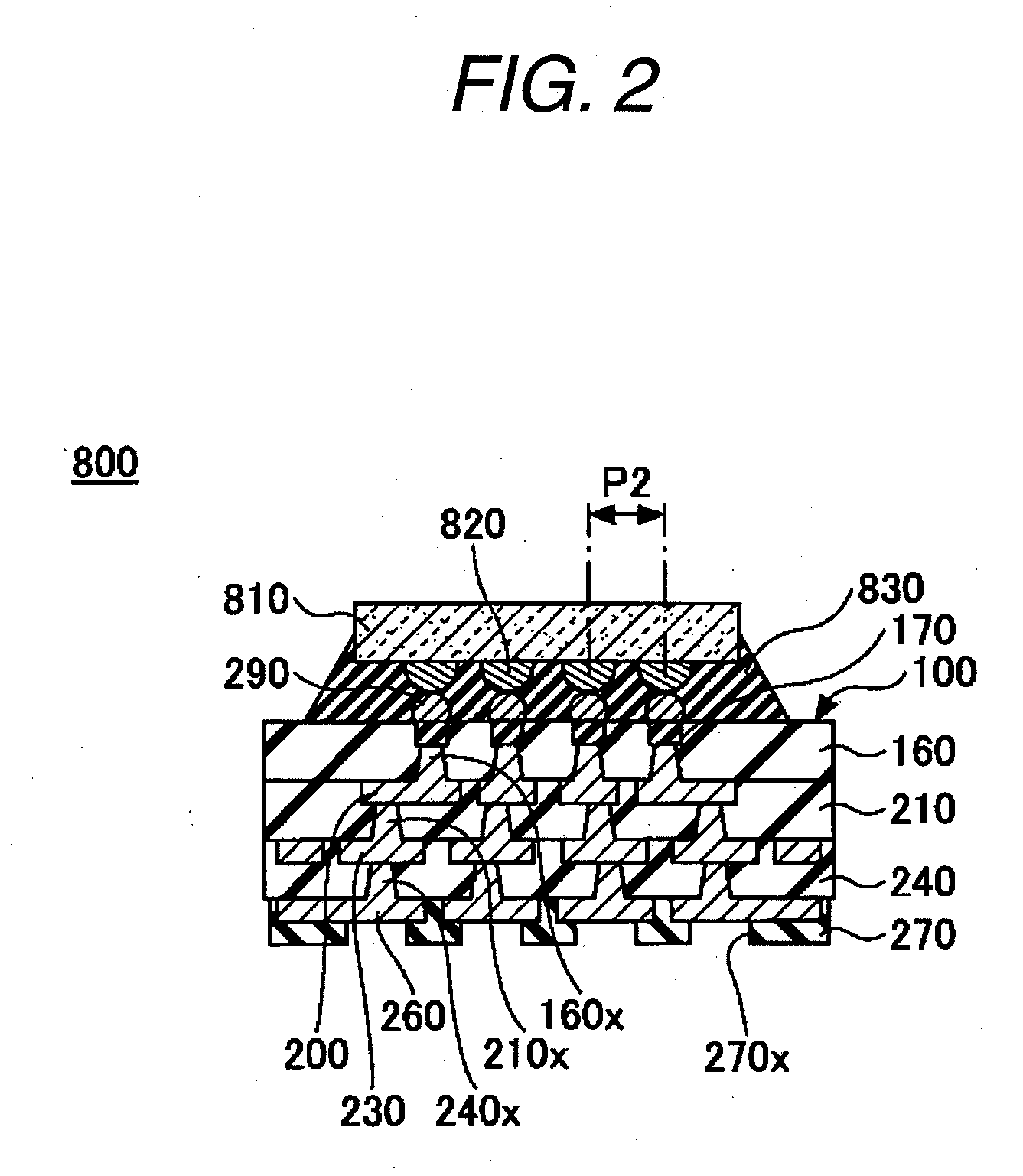
ActiveUS20090223046A1Decrease shiftReduce a shift of the pitchPrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringSemiconductor chip
A method of manufacturing a wiring board having a semiconductor chip mounting surface for mounting a semiconductor chip thereon which is manufactured by a process including a step of forming a wiring layer and an insulating layer on a support board and a step of removing the support board, including a peeling layer forming step of forming a peeling layer on the support board formed by a material having a coefficient of thermal expansion which is equal to that of a semiconductor substrate constituting the semiconductor chip, and a support board removing step of removing the support board by carrying out a predetermined treatment over the peeling layer.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
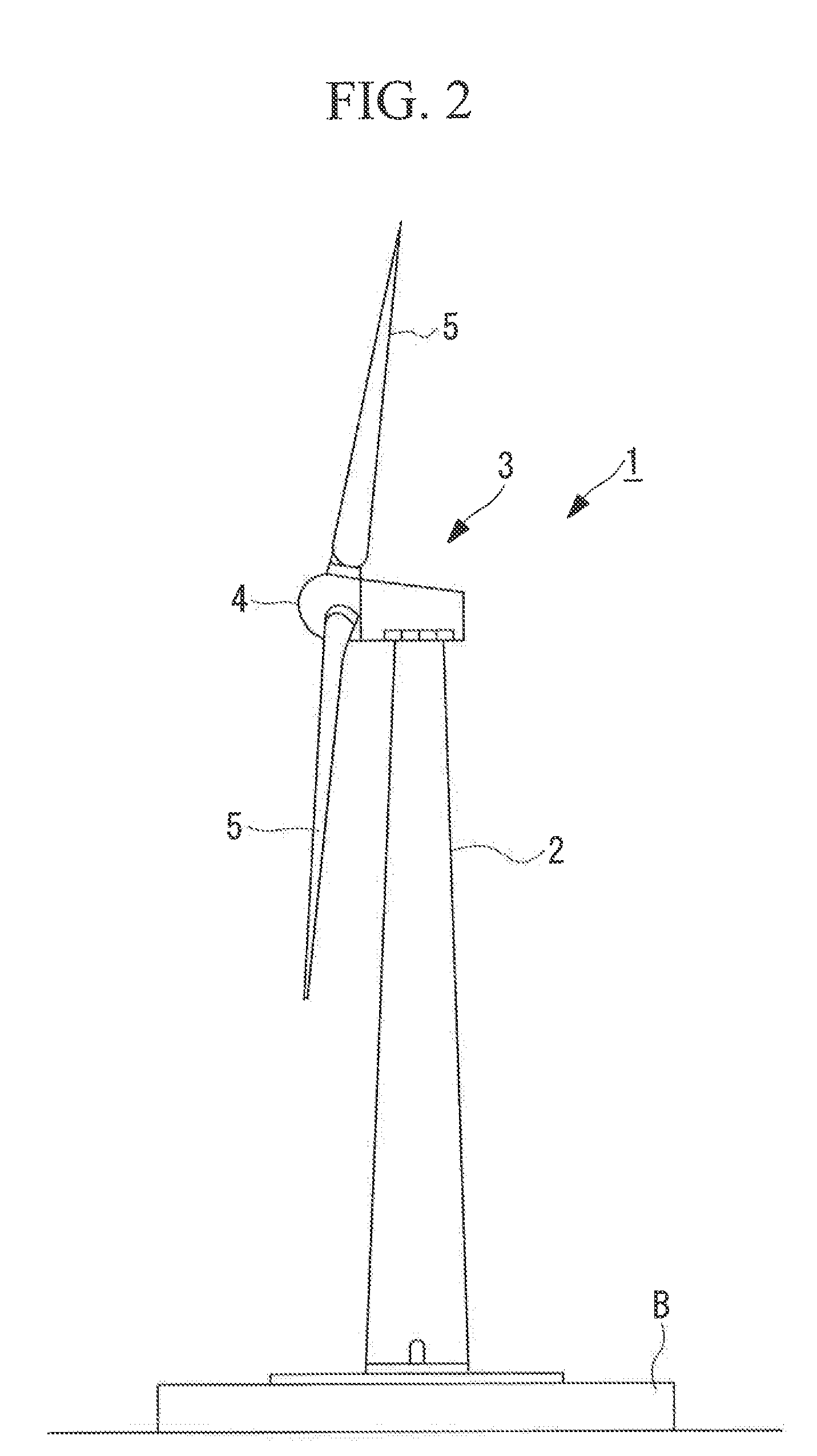
Wind turbine generator
InactiveUS20110233939A1Easily adjust clearanceGuaranteed uptimeRotary combination bearingsRoller bearingsNacelleHearing perception
A wind turbine generator provided with a sliding bearing as a yawing ring bearing that can reduce shifting of an axial center by making radial-direction clearances small. In a wind turbine generator in which a nacelle installed at the top of a tower is turnably supported via a yawing sliding bearing, the yawing sliding bearing is provided with a sliding member 33 disposed between top and bottom support surfaces of a flange formed mainly at a stationary portion and a turning portion; and a rolling element disposed between the stationary portion of the yawing sliding hearing and the turning portion.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
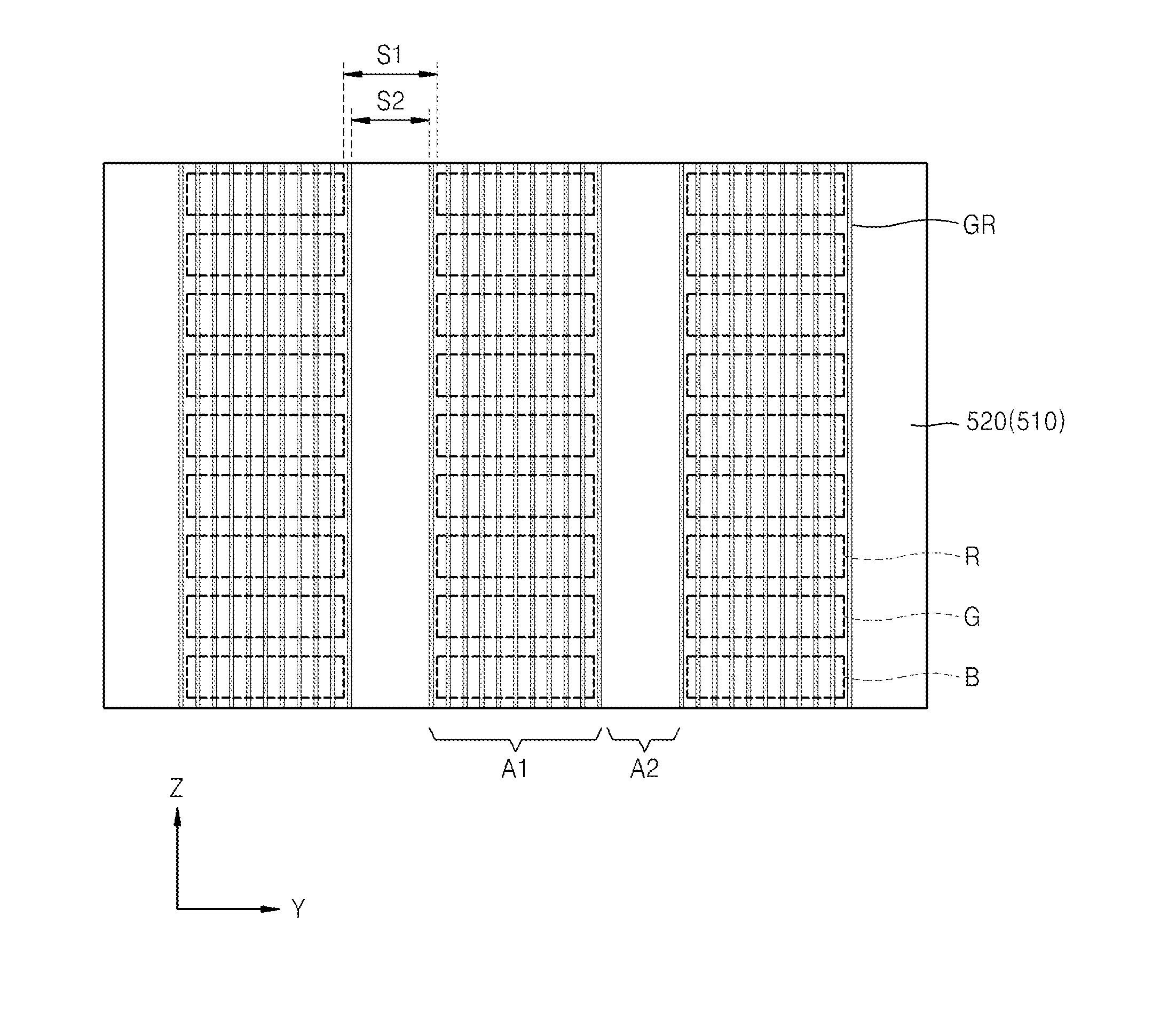
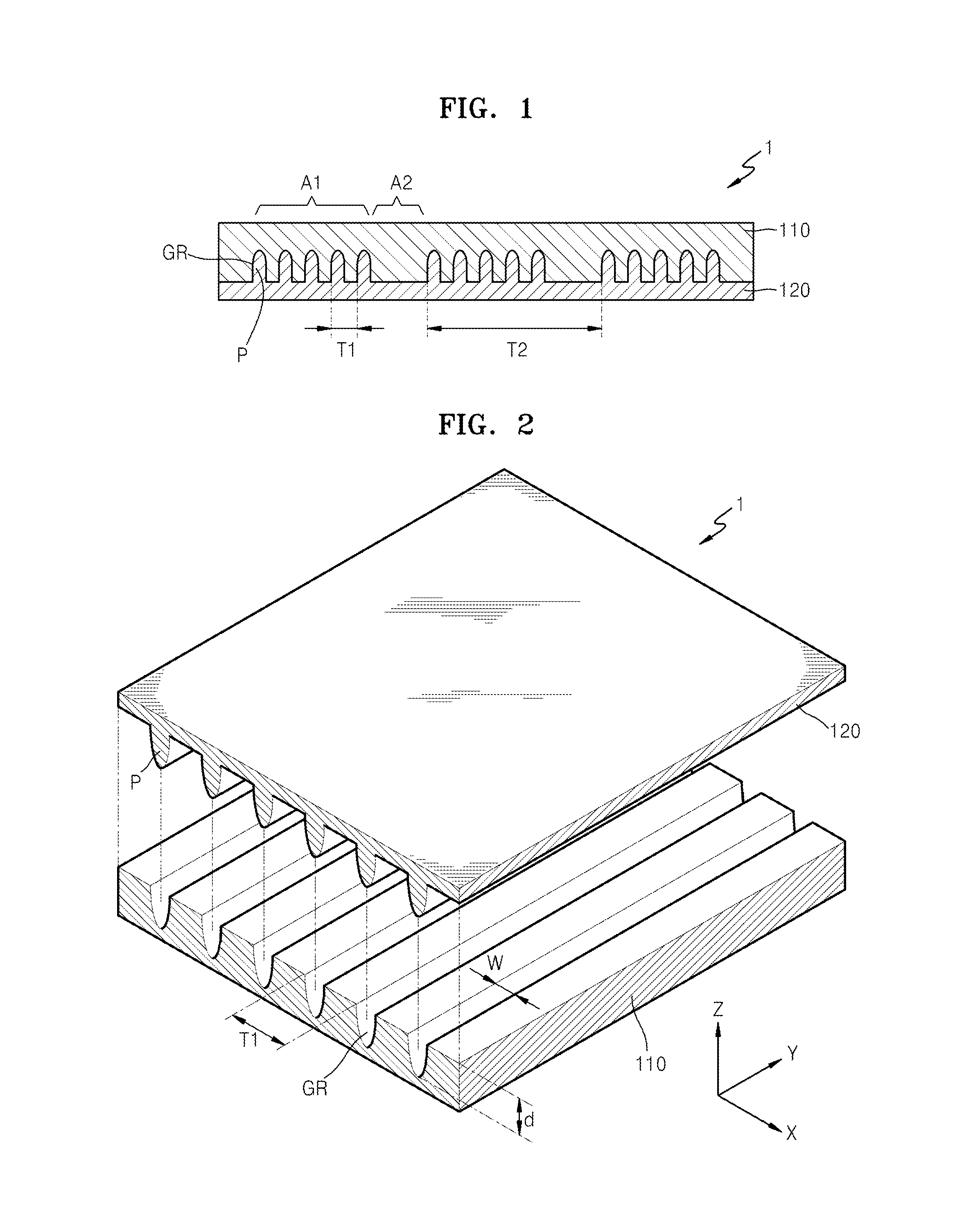
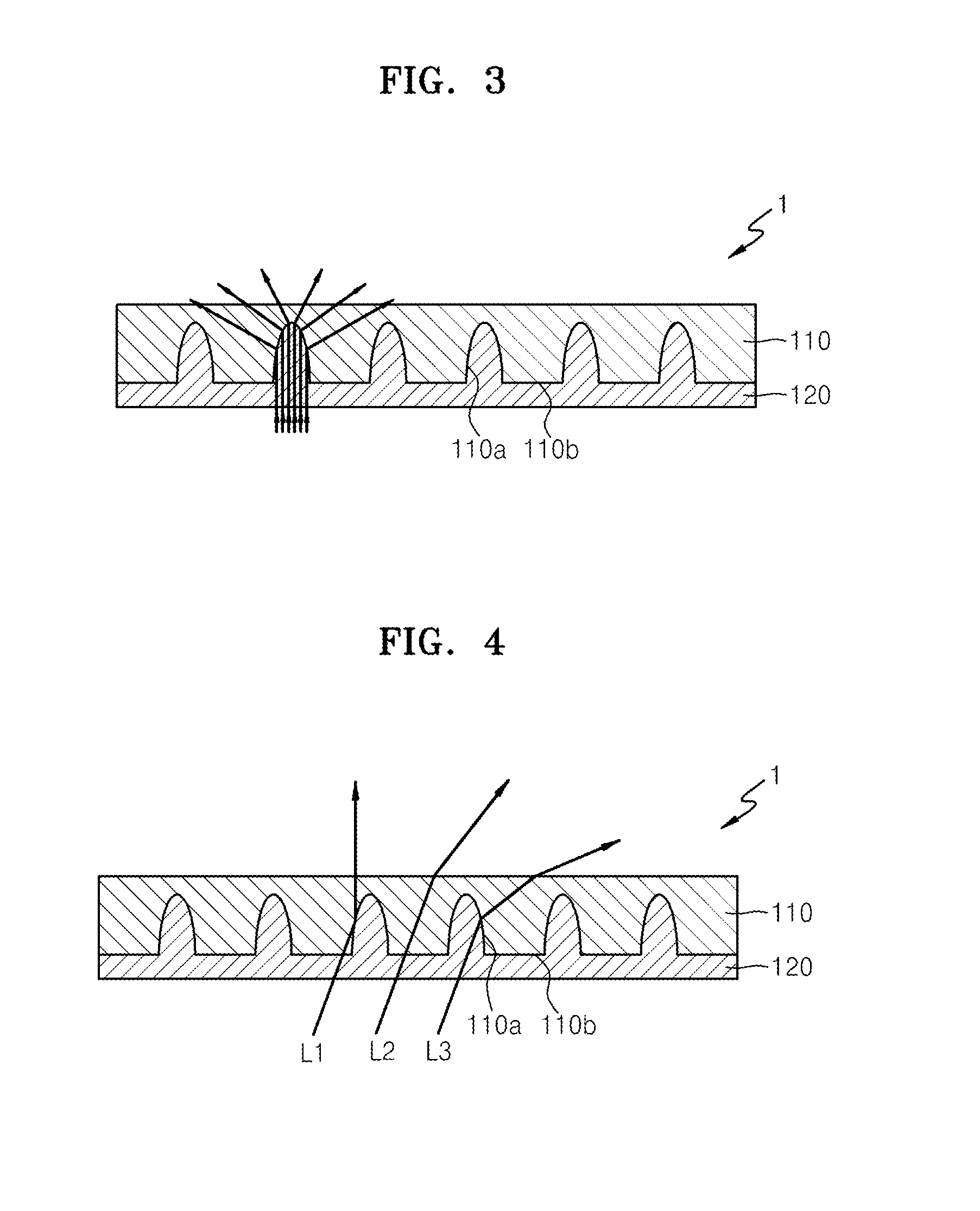
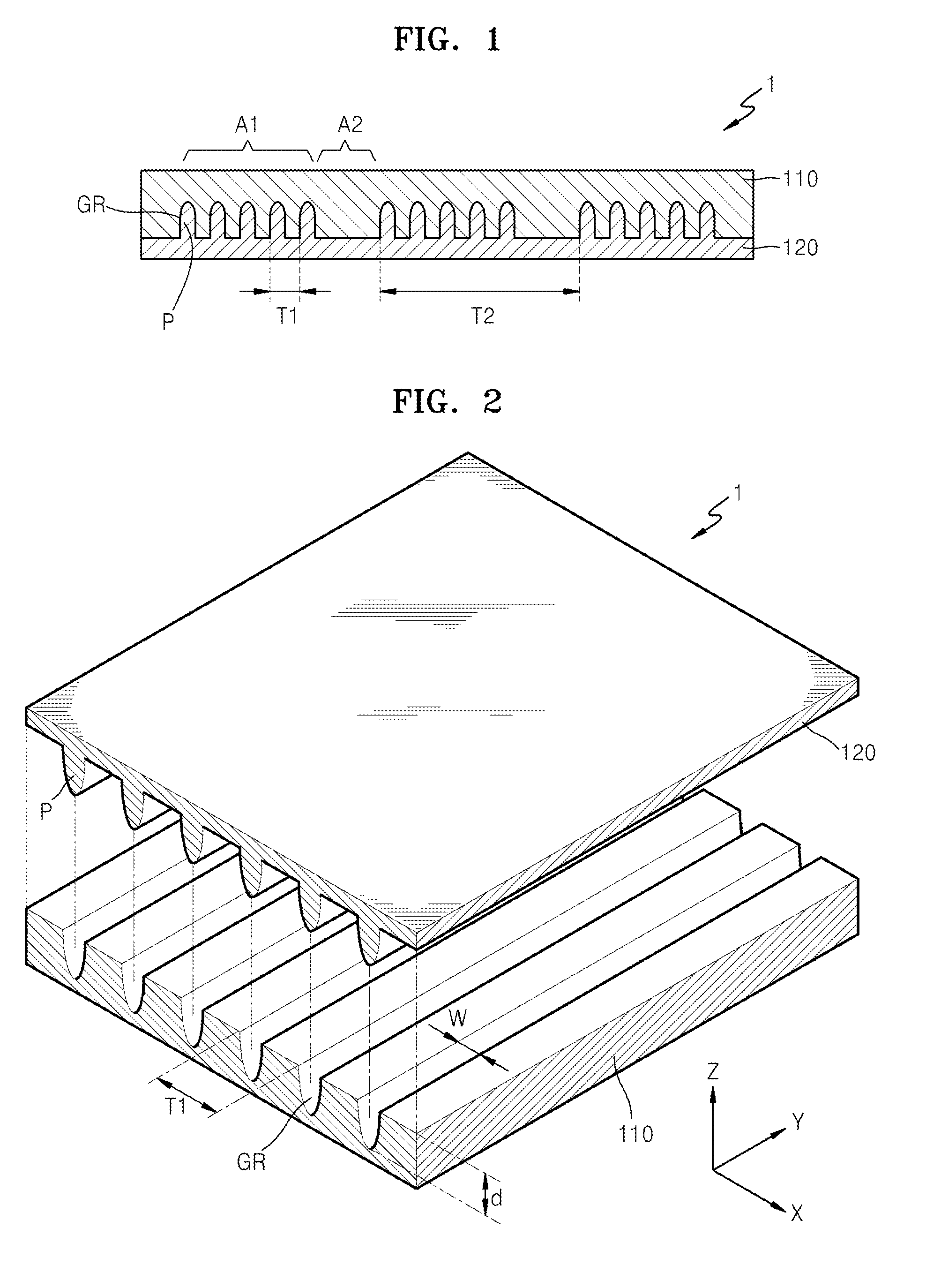
Optical films for reducing color shift and organic light-emitting display devices employing the same
ActiveUS20140353626A1Reduce color castDecrease shiftStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesColor shiftRefractive index
Optical films, and organic light-emitting display devices employing the same, include a high refractive index pattern layer including a lens pattern region and a non-pattern region alternately formed, wherein the lens pattern region includes a plurality of grooves each having a depth larger than a width thereof, and the non-pattern region has no pattern; and a low refractive index pattern layer formed of a material having a refractive index smaller than a refractive index of the high refractive index pattern layer, wherein the low refractive index pattern includes a plurality of filling portions filling the plurality of grooves.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC +1
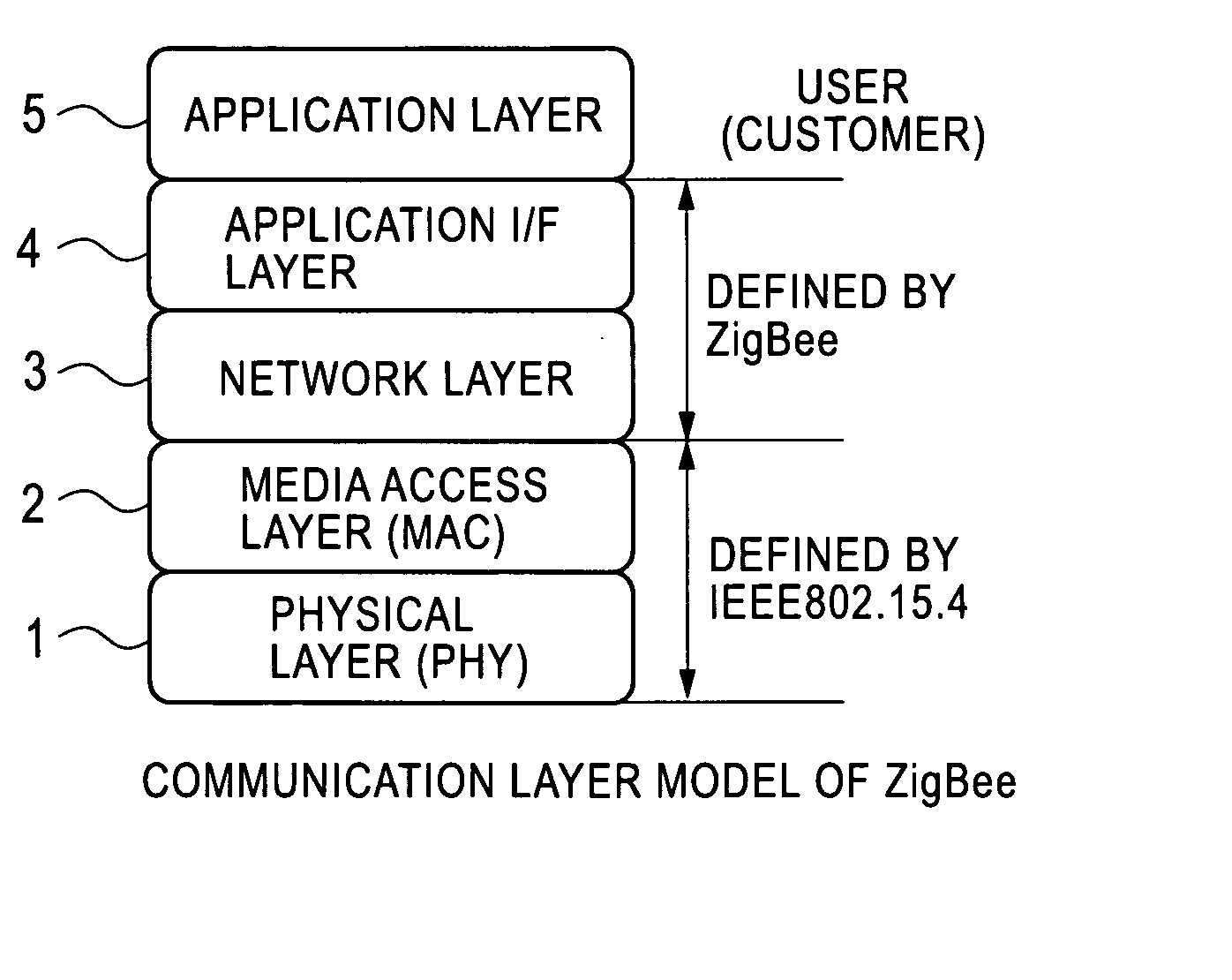
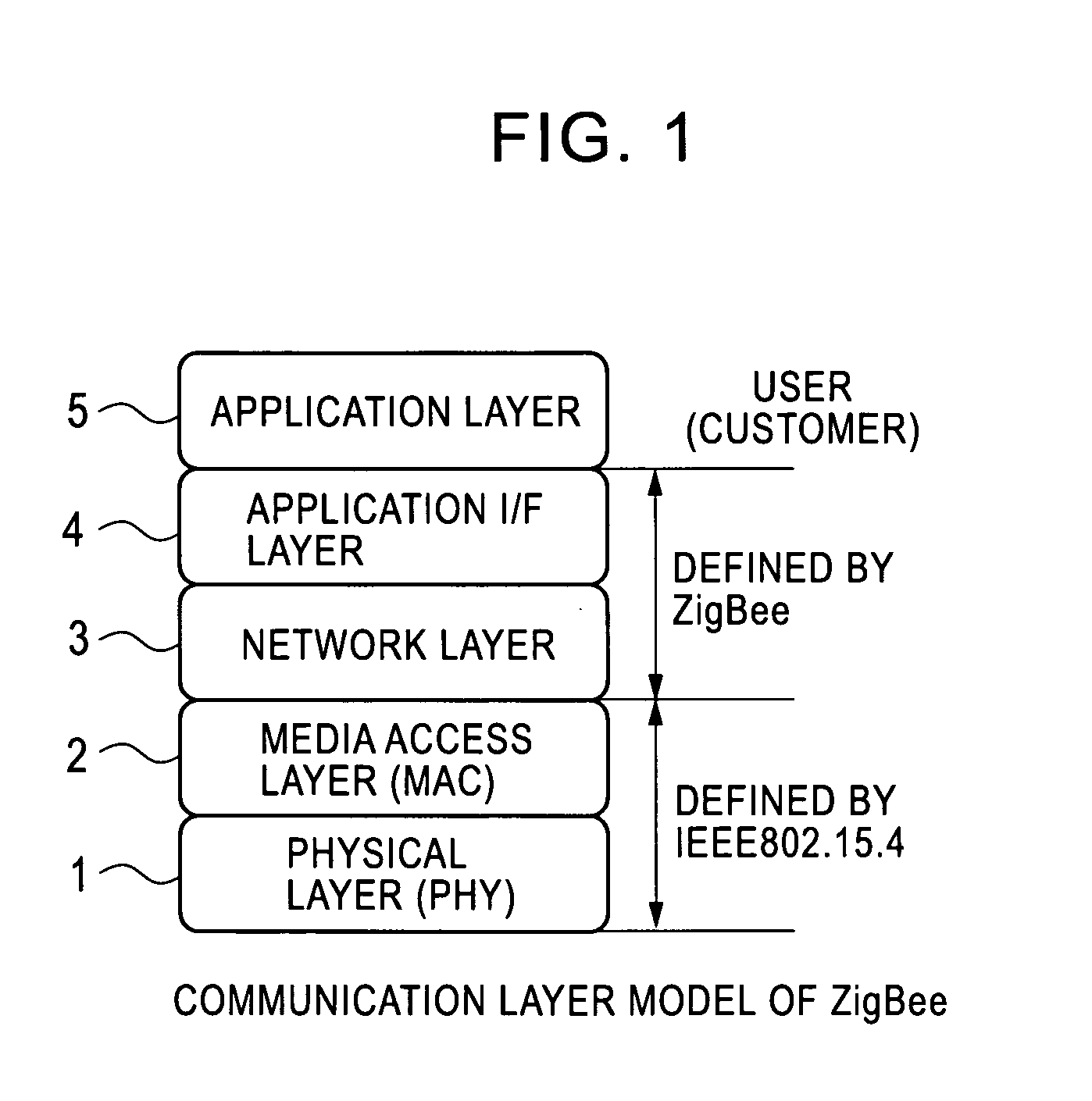
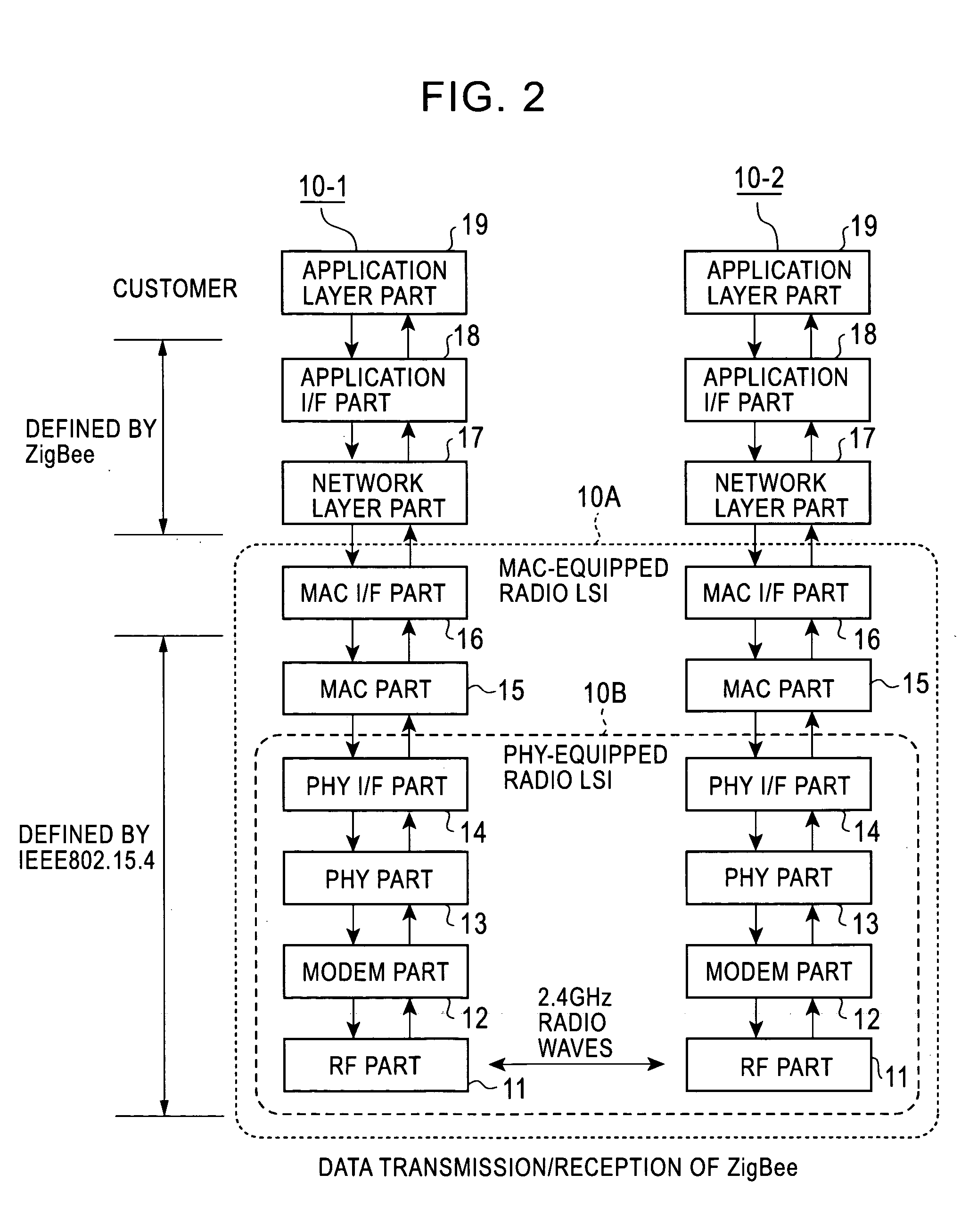
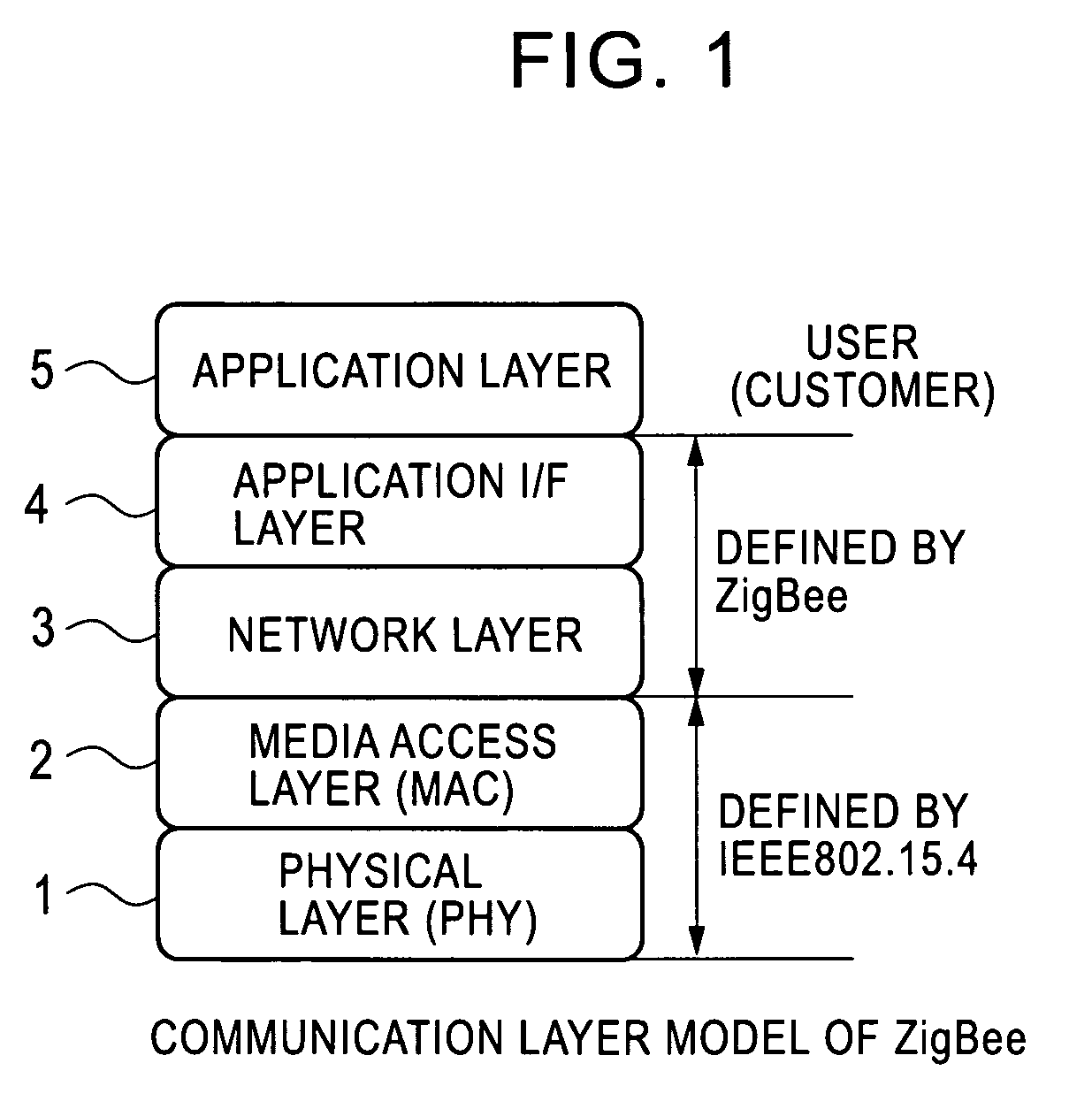
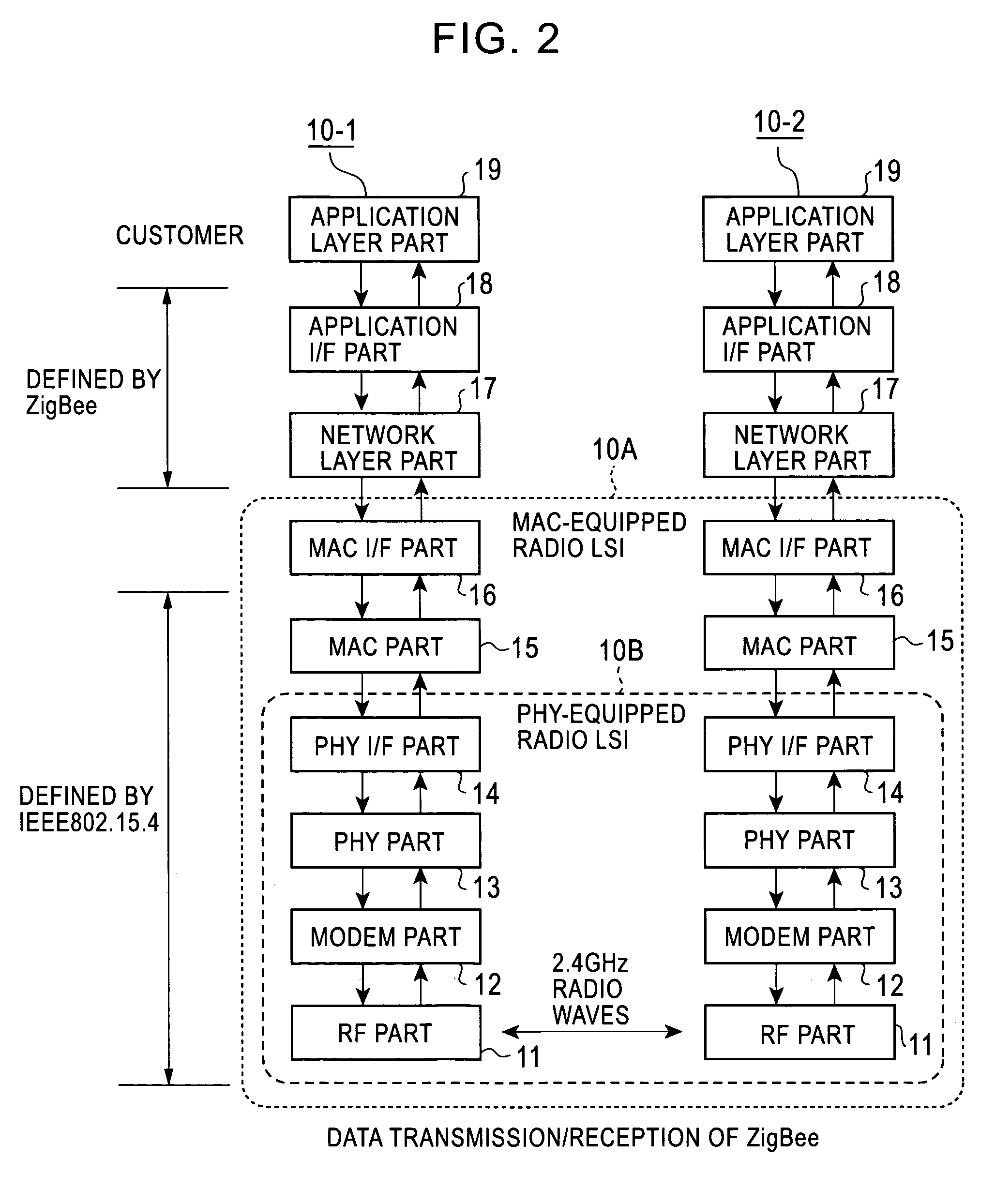
Radio integrated circuit and radio communication method
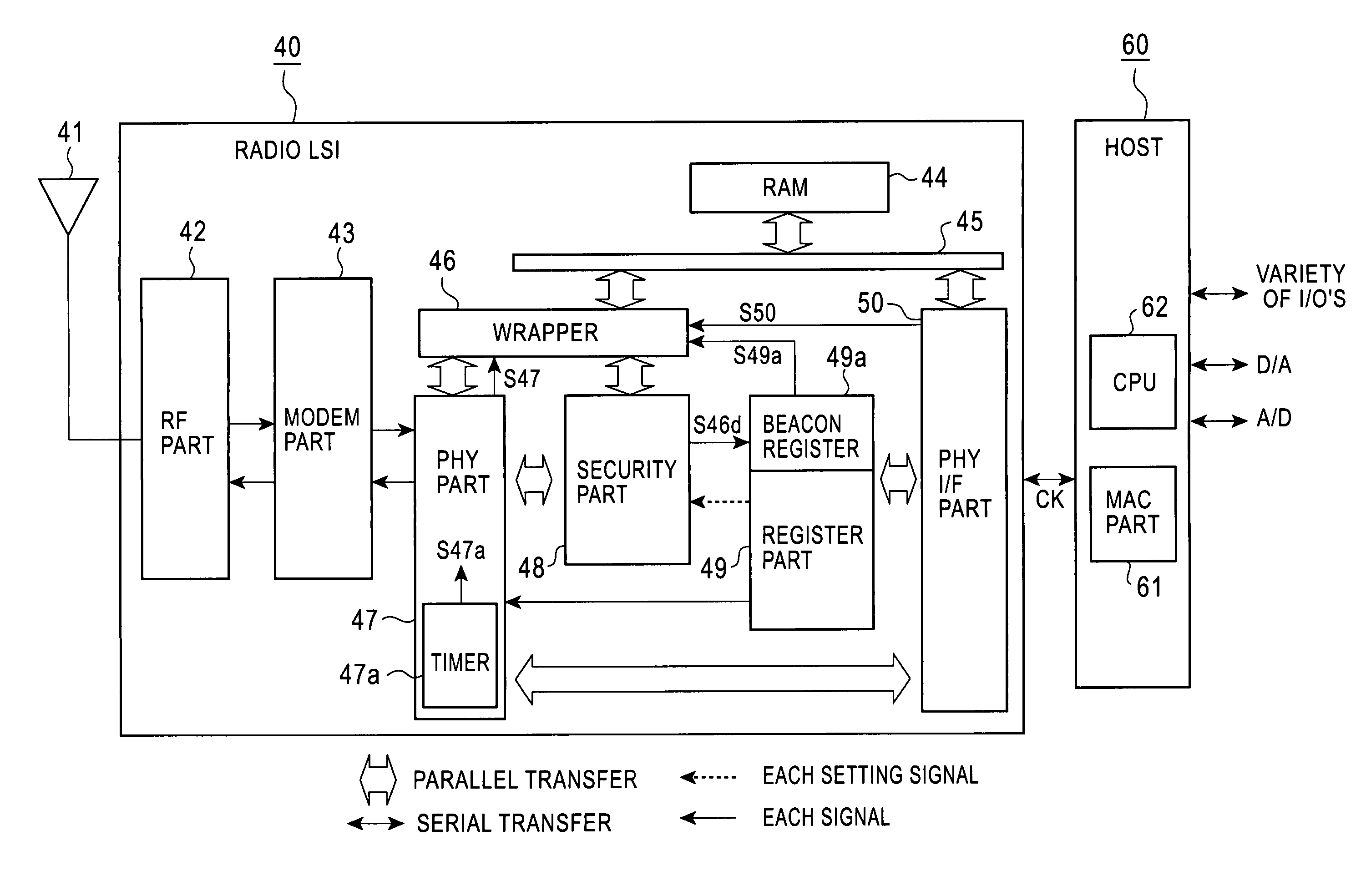
InactiveUS20060187961A1Reduce relative shiftDecrease shiftTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData transmissionIntegrated circuit
A PHY-equipped radio LSI and a radio communication method capable of transmitting data without fail while maintaining a beacon interval. Using a selector which is switched by a beacon transmission signal output from a beacon register, a data transmission request signal is switched for transmitting data from a RAM to a PHY part, and a transfer is started when this signal goes to “1. ” In this way, for transmitting beacon data, the beacon data has been previously transferred to the RAM, and the beacon data is transmitted at the time of beacon transmission interval with the PHY part remaining in a transmission state, so that the beacon interval can be maintained. In addition, it is possible to prevent a failure in the transmission of transfer data due to the state of the PHY part.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
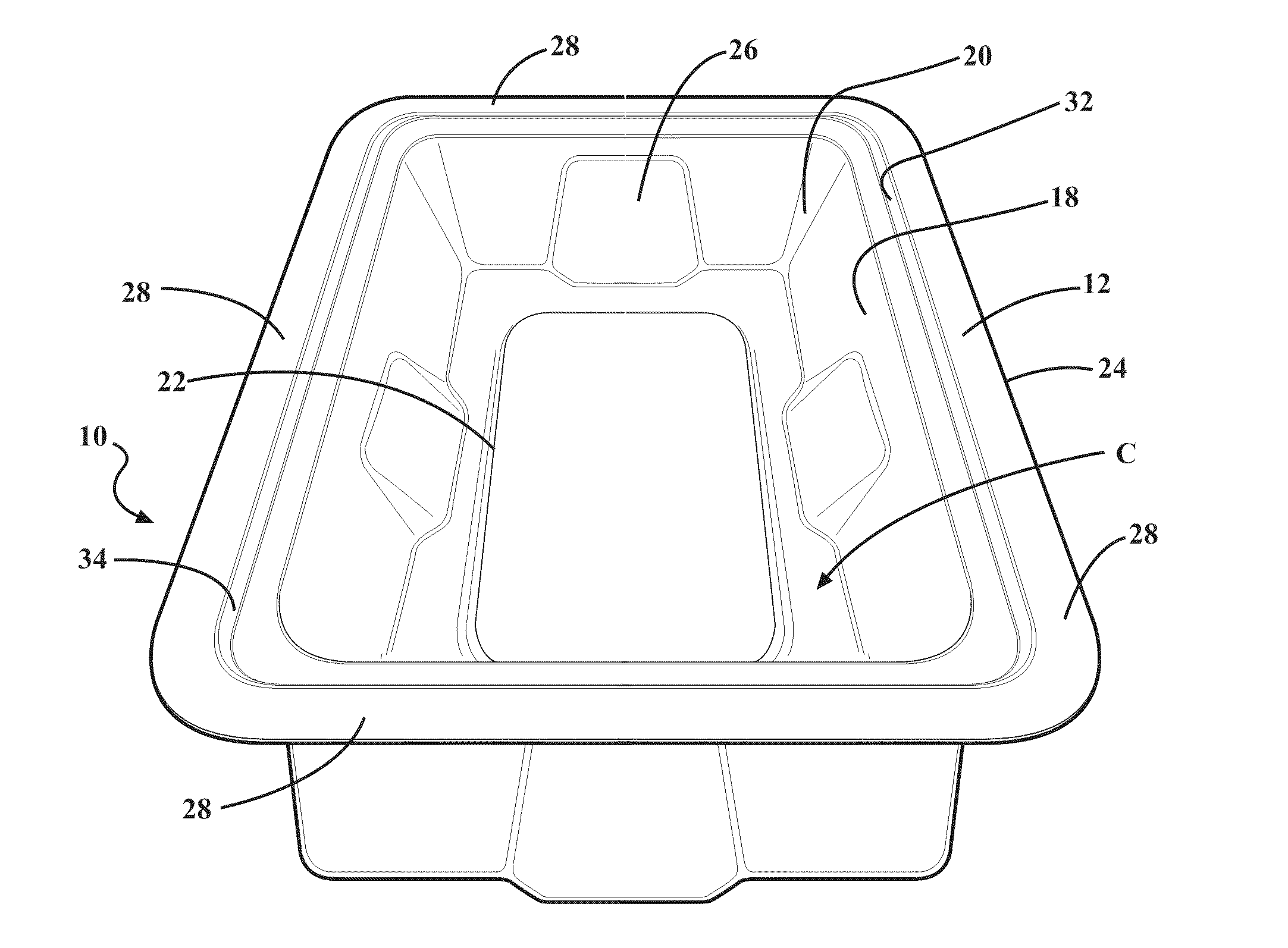
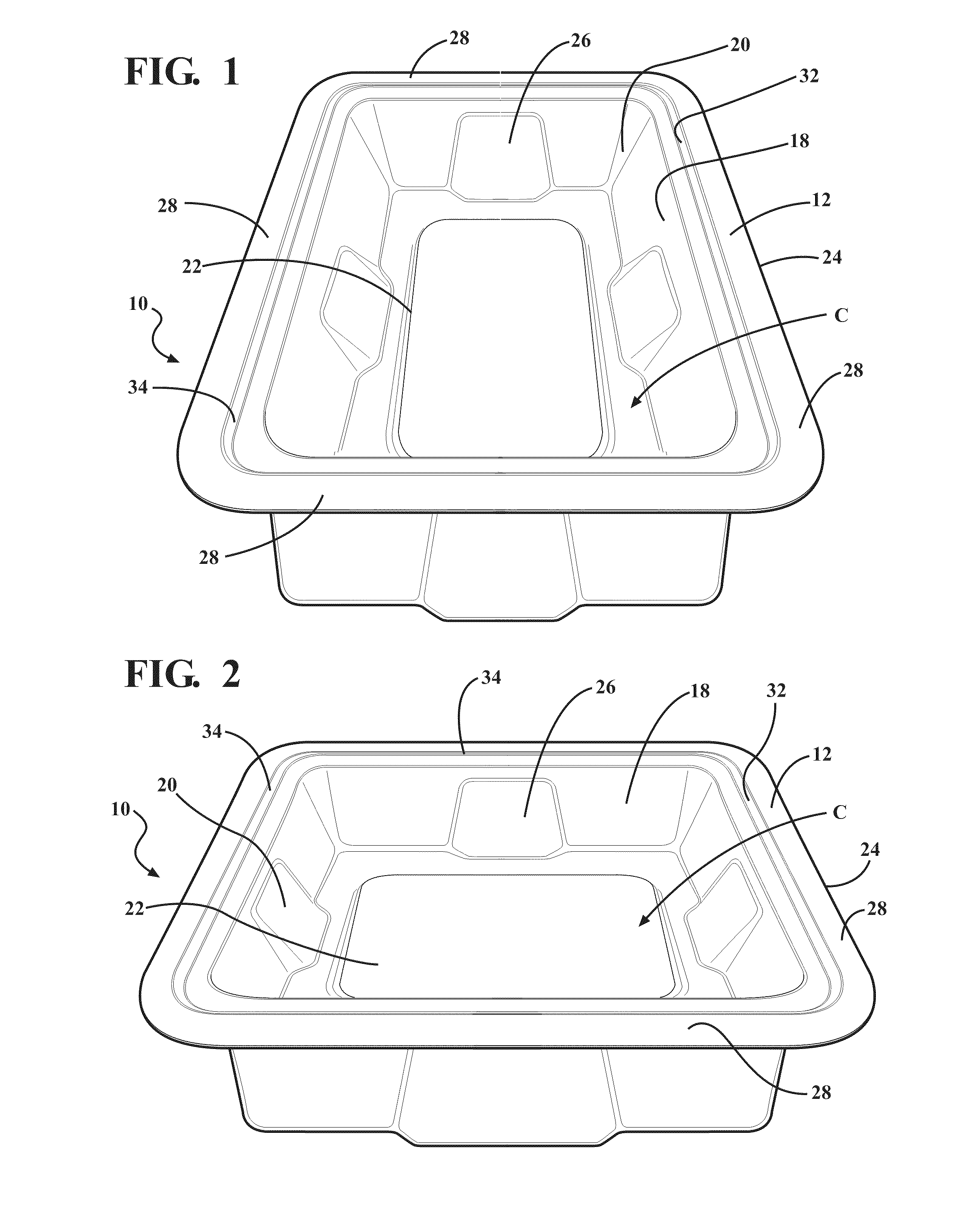
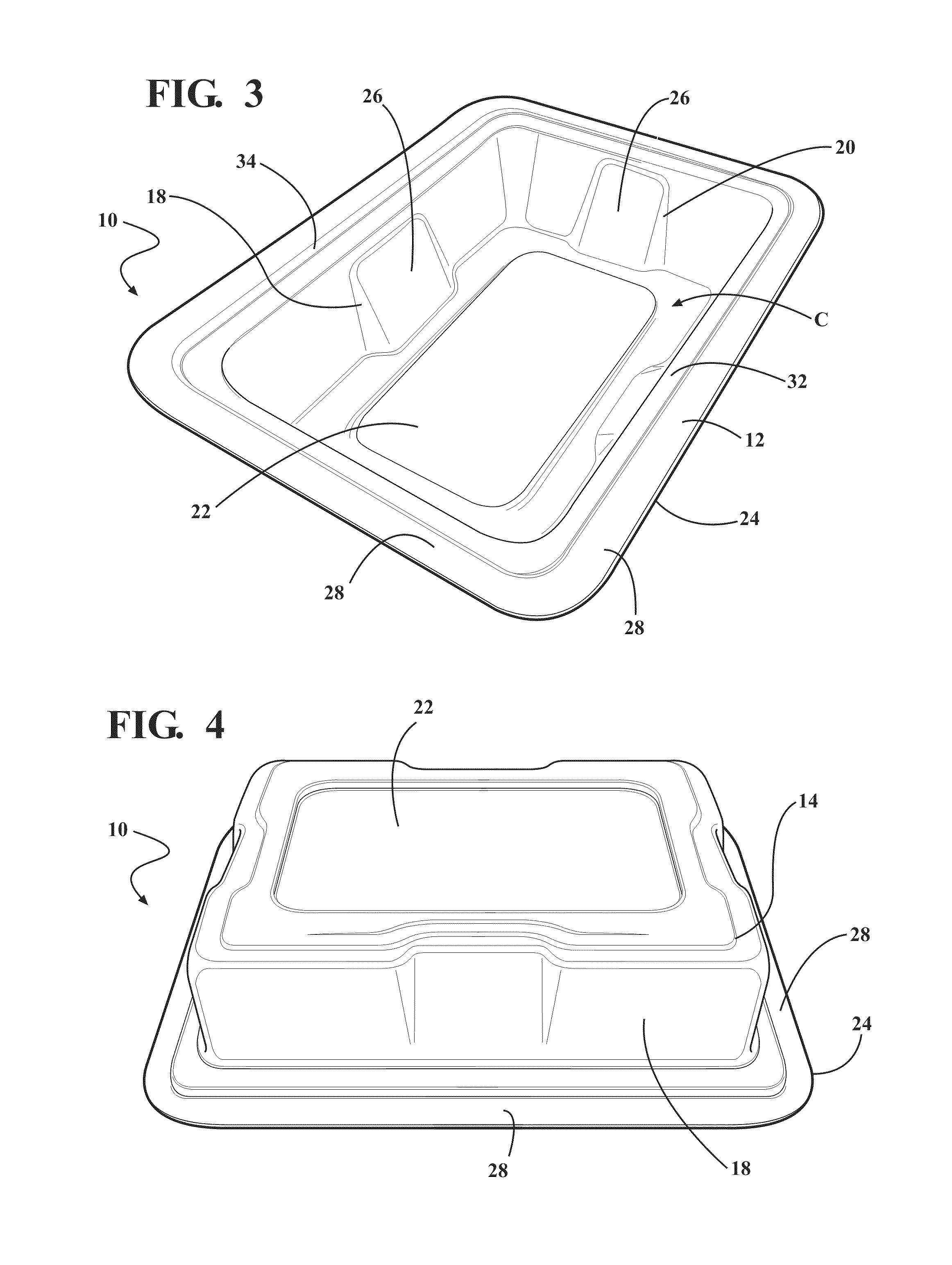
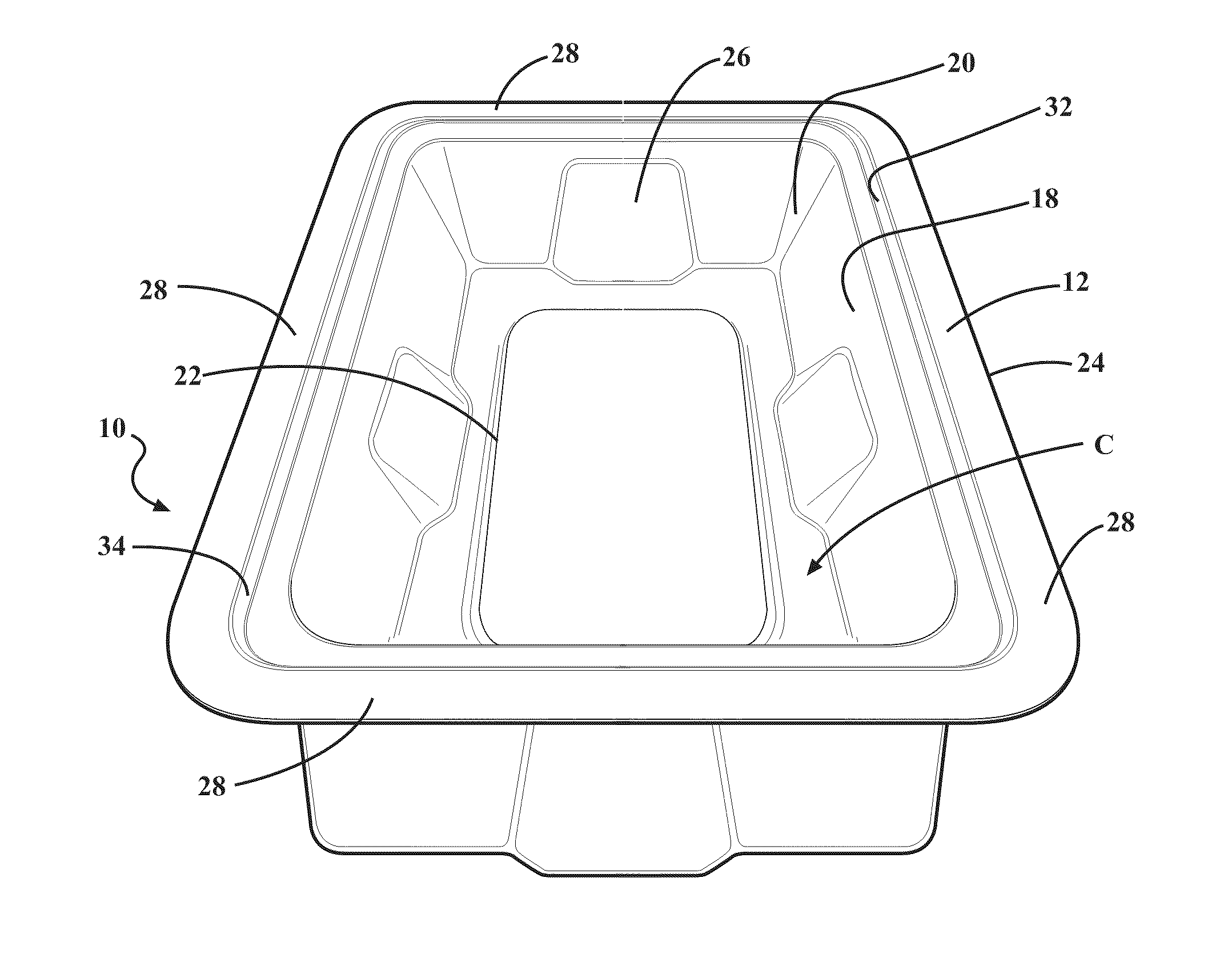
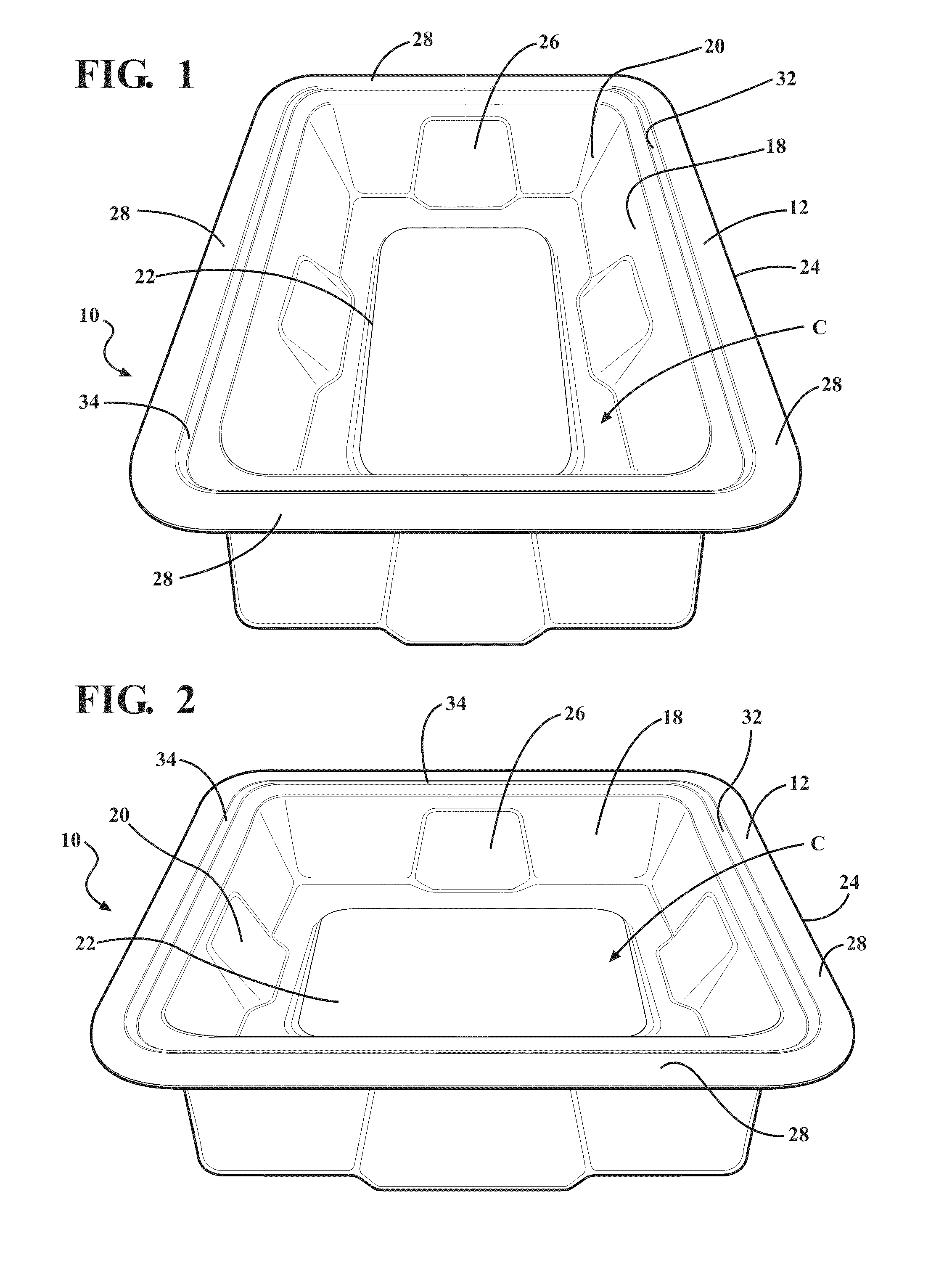
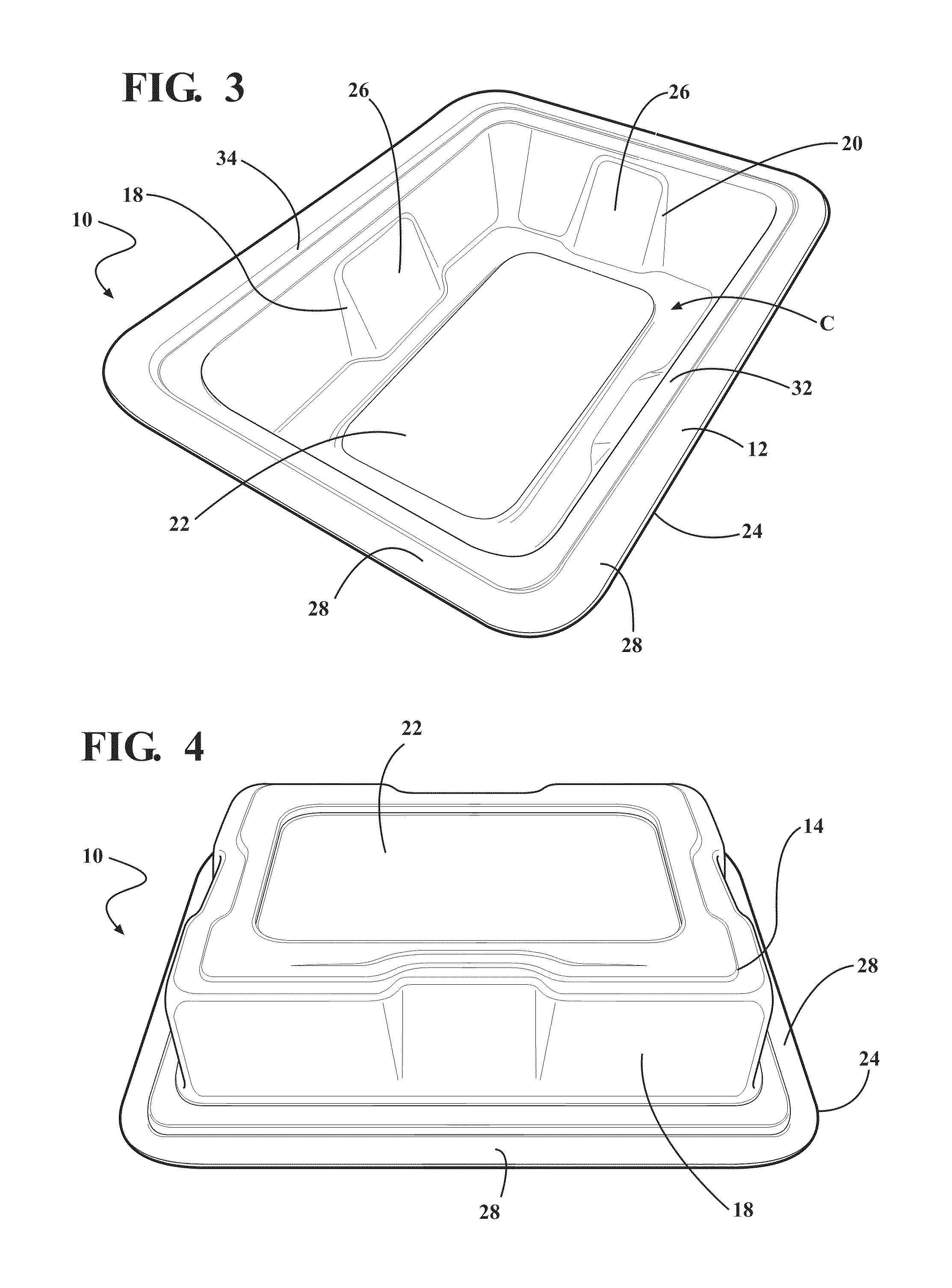
Composite for packaging a medical device and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20110036736A1Reduce abrasion and generationReduces shiftFlexible coversWrappersBiomedical engineeringMedical treatment
A composite for packaging a medical device has a first layer including an aromatic polyether polyurethane and a second layer. The first layer forms a base that has a plurality of walls extending therefrom to define a cavity for receiving the medical device. The second layer is disposed on the first layer opposite the cavity. The composite is formed from a method that includes the step of disposing the first layer on the second layer. The composite may also be included with a container to form a packaging system.
Owner:UFP TECHNOLOGIES
Composite for packaging a medical device and method of forming the same
ActiveUS9144464B2Increase resistanceReduce abrasion and generationFlexible coversWrappersPolyether polyurethaneEngineering
A composite for packaging a medical device has a first layer including an aromatic polyether polyurethane and a second layer. The first layer forms a base that has a plurality of walls extending therefrom to define a cavity for receiving the medical device. The second layer is disposed on the first layer opposite the cavity. The composite is formed from a method that includes the step of disposing the first layer on the second layer. The composite may also be included with a container to form a packaging system.
Owner:UFP TECHNOLOGIES
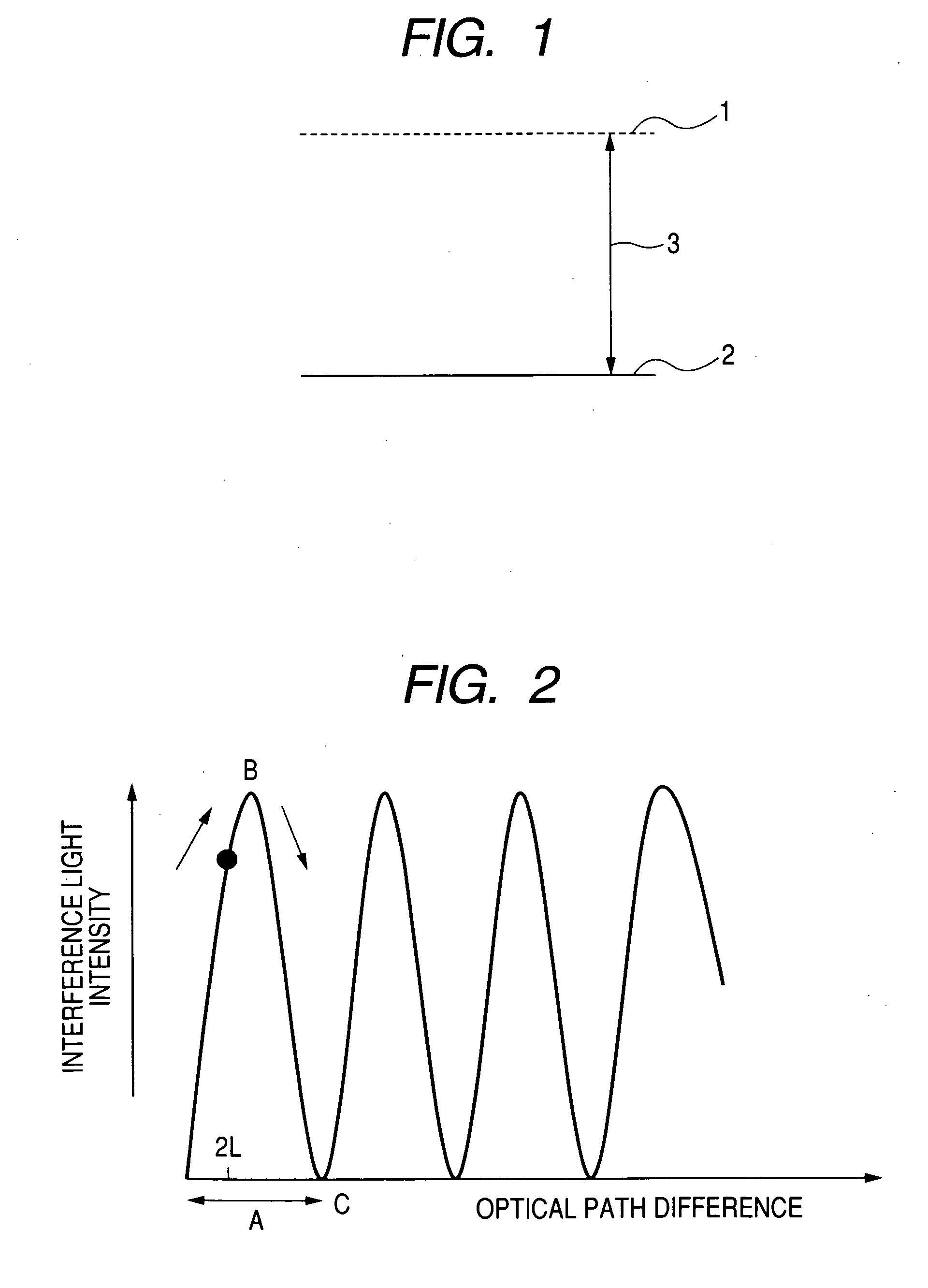
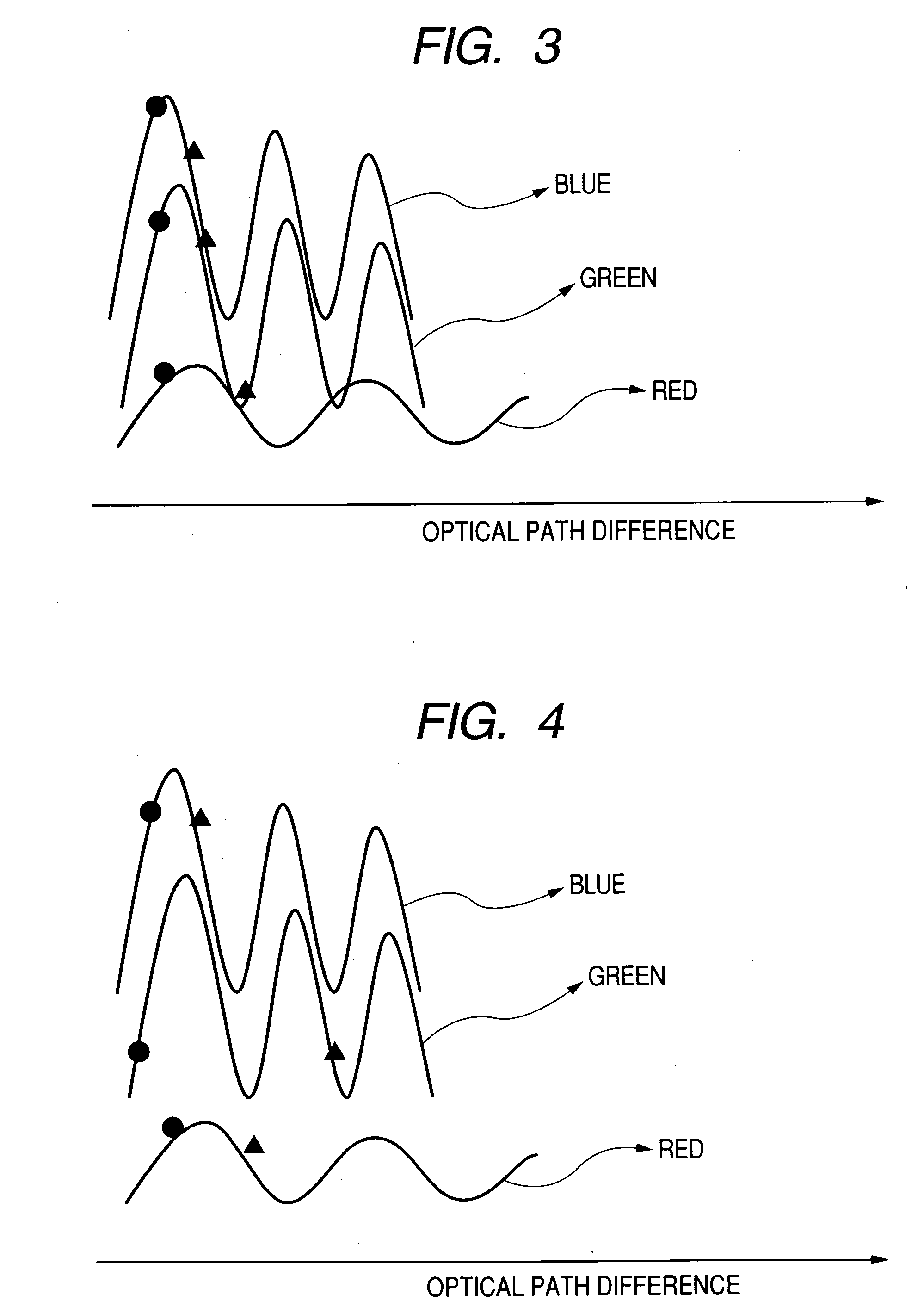
Organic light-emitting device array and display
ActiveUS20060091380A1Reduce relative shiftReduce colorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical pathOptical pathlength
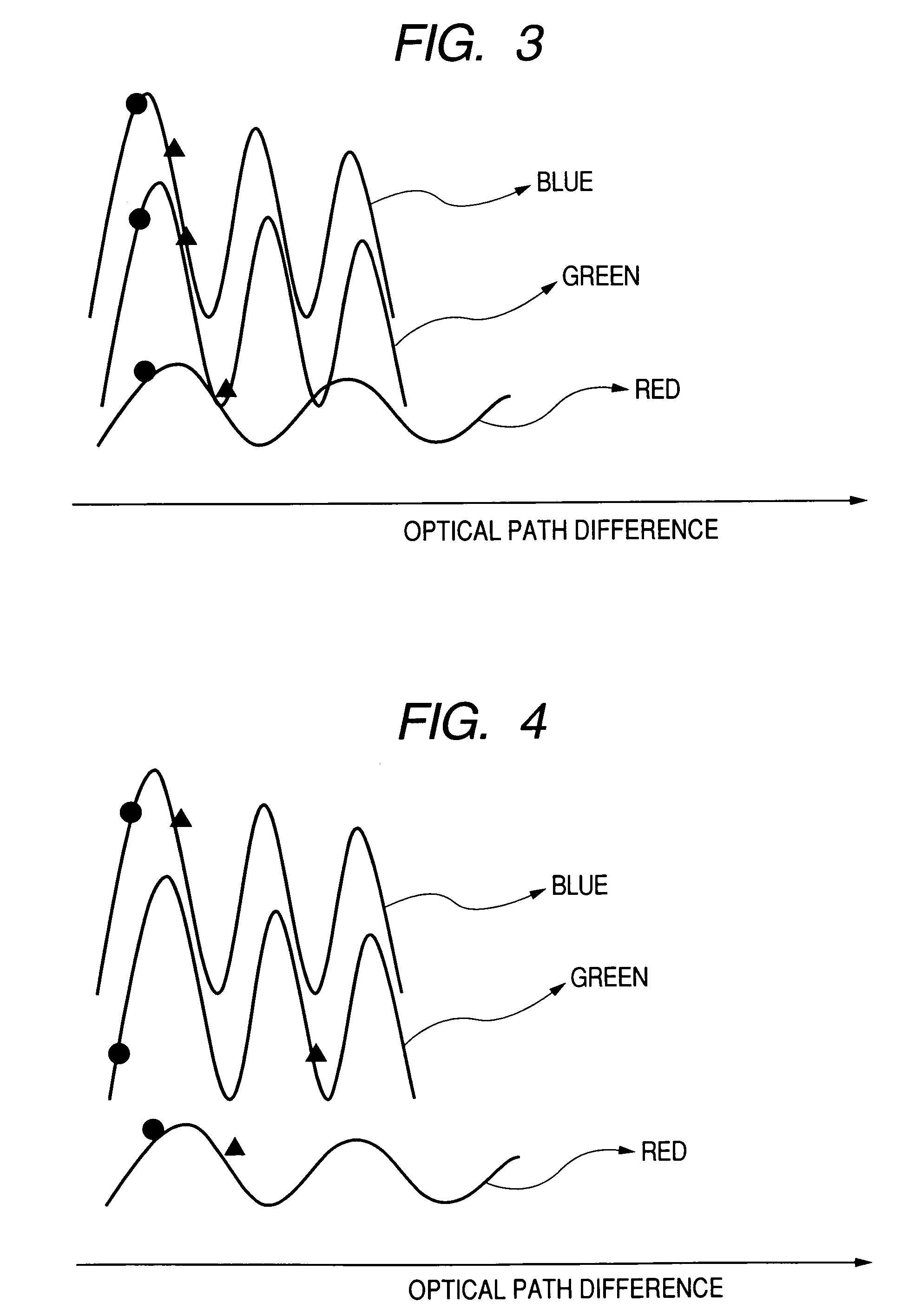
The present invention provides an organic light emitting device array which reduces the change of white balance even if an observation angle is changed. In an organic light emitting device array comprising a plurality of organic light emitting devices which emit lights of different colors, an optical path difference is set such that signs of gradients at an optical path difference of 2L of interferograms for all the plurality of organic light emitting devices are identical to each other.
Owner:CANON KK
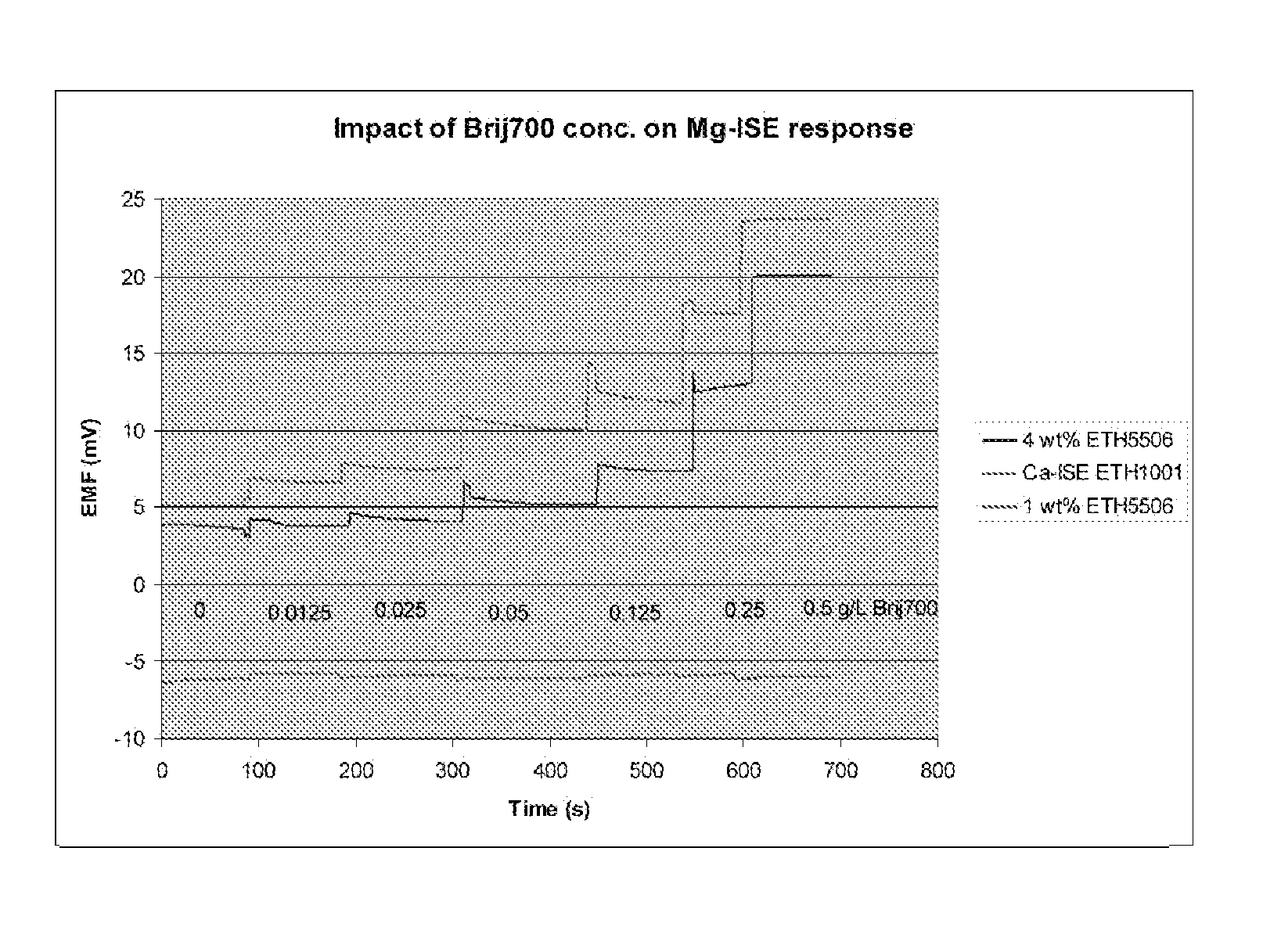
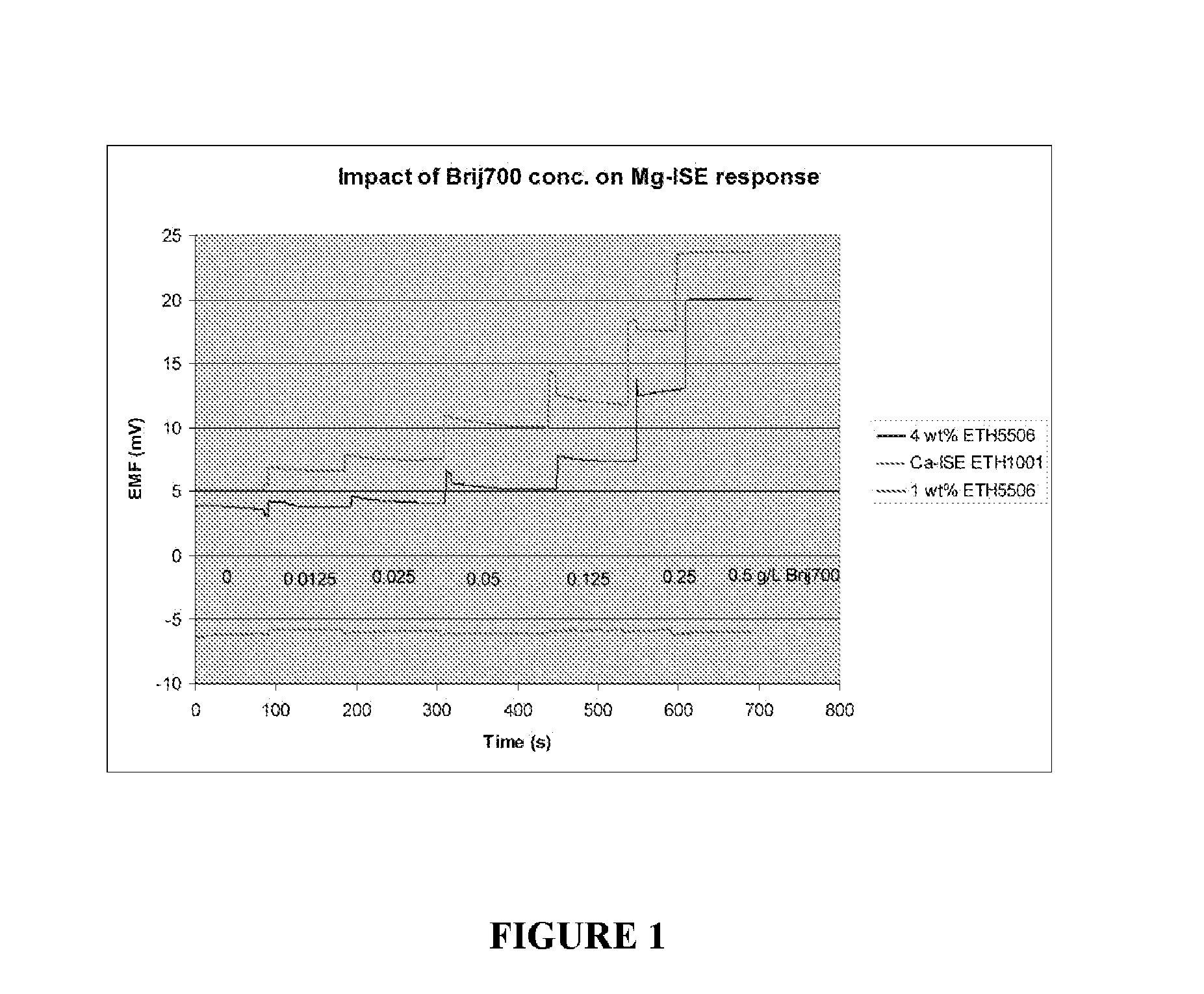
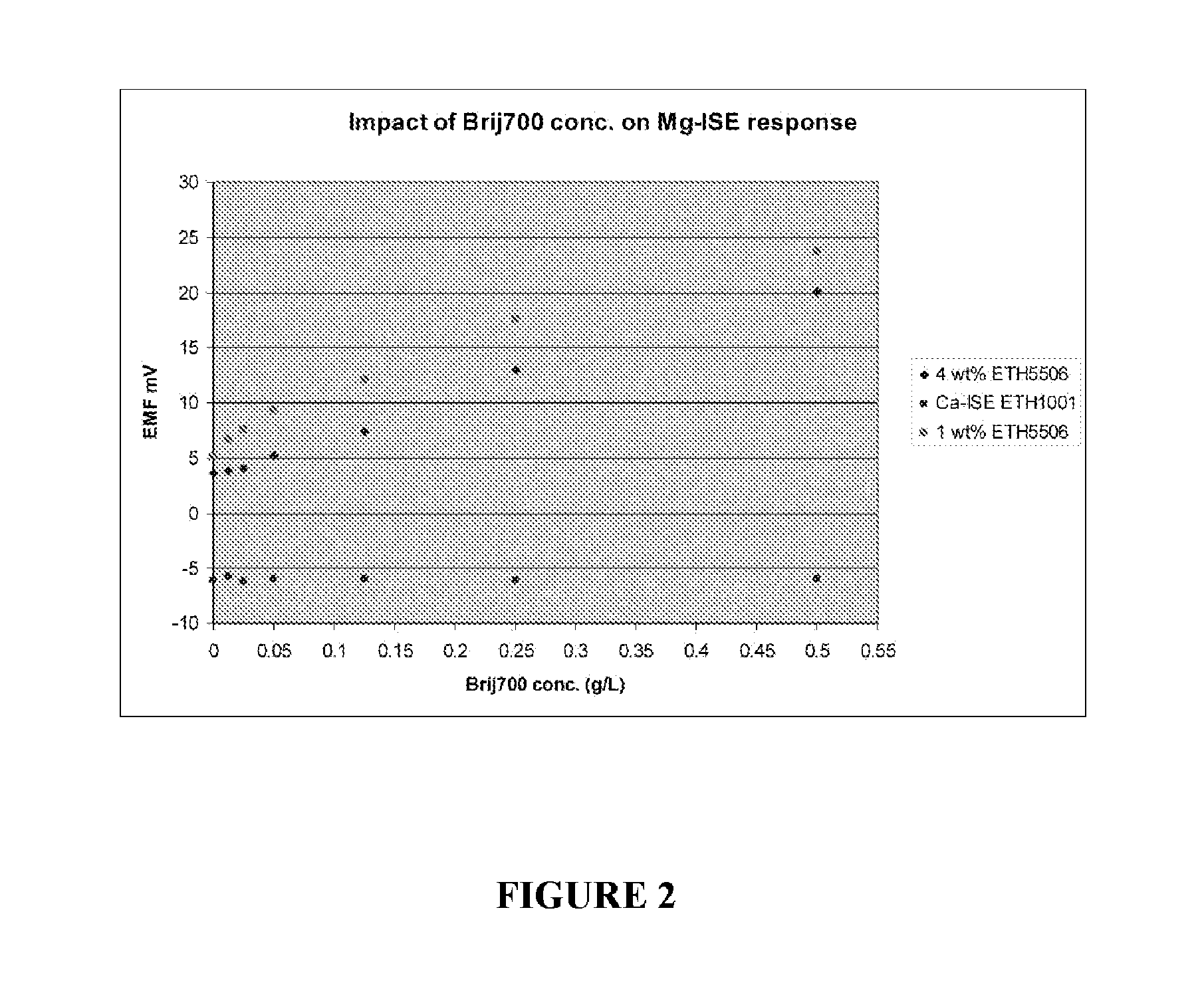
Use of Polyoxyalkylene Nonionic Surfactants with Magnesium Ion Selective Electrodes
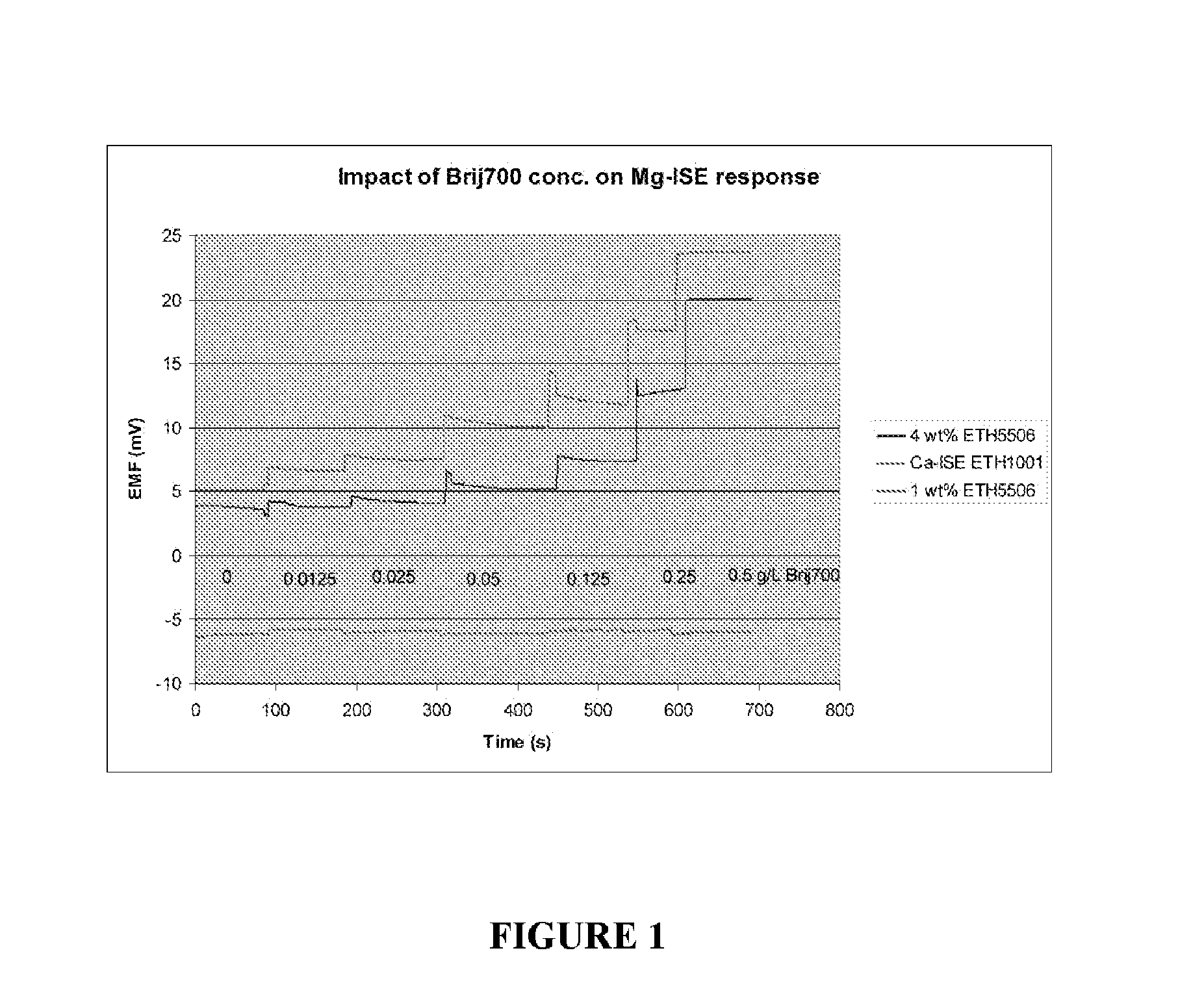
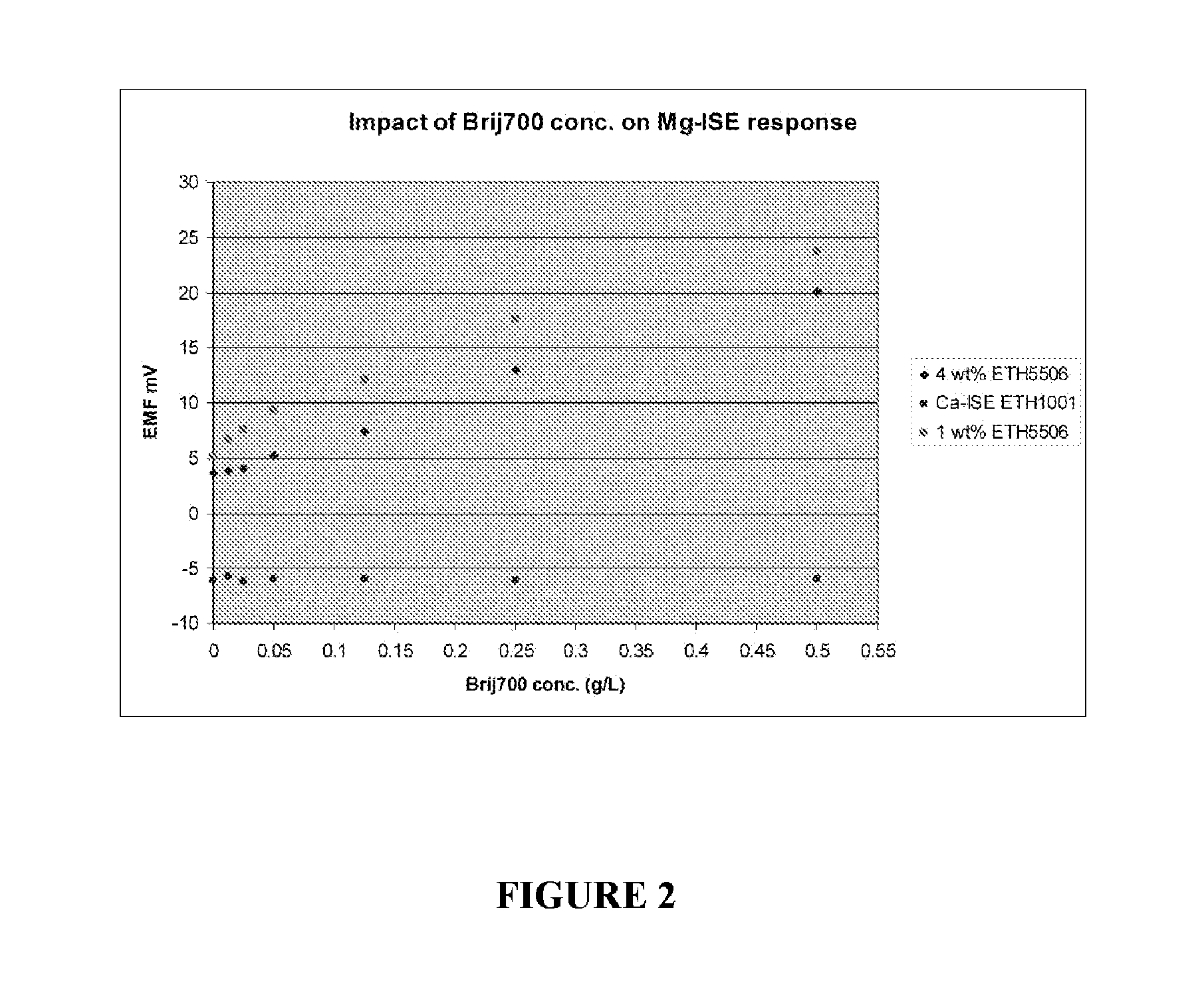
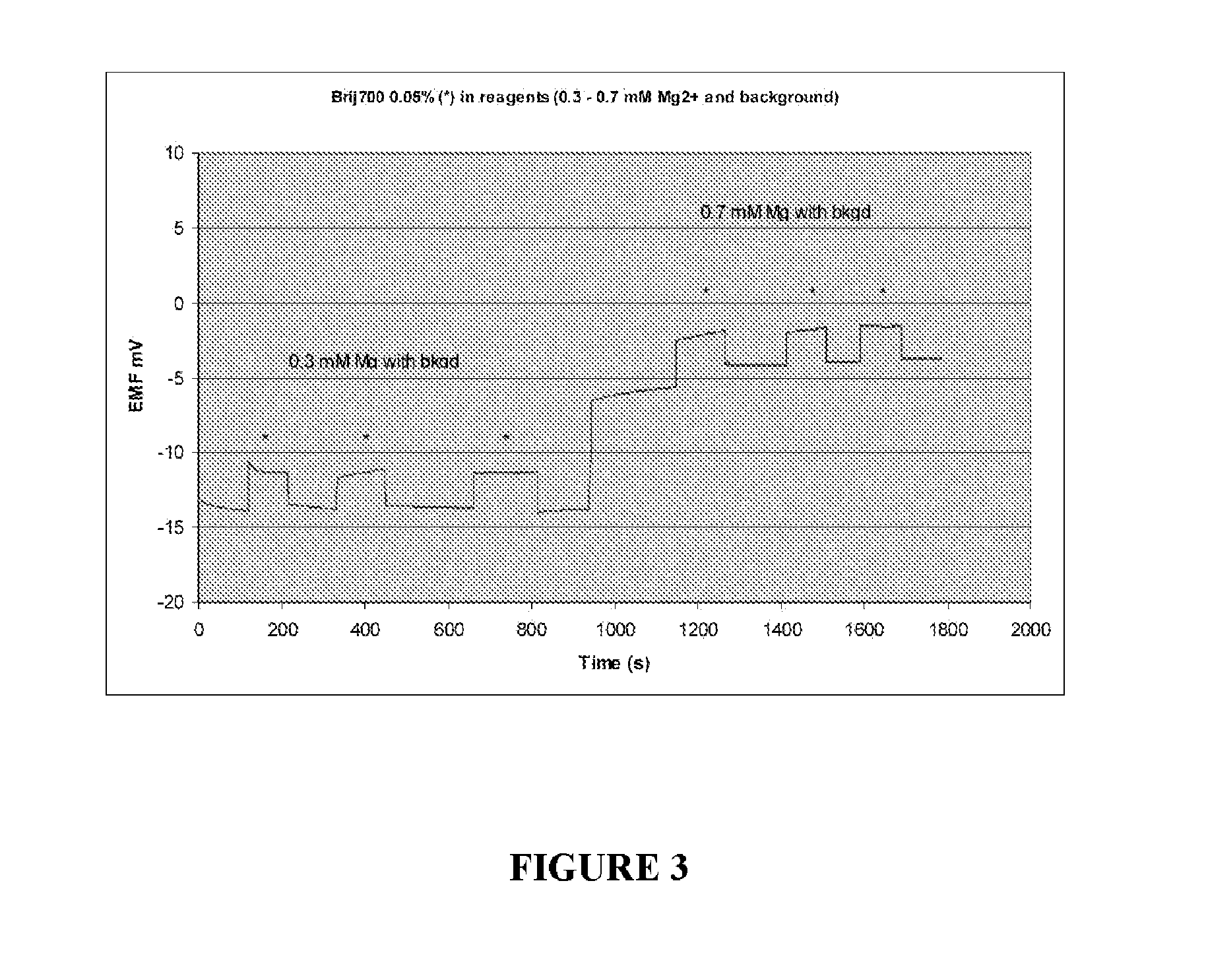
ActiveUS20110139638A1Reduce relative shiftDecrease shiftOrganic chemistryWeather/light/corrosion resistanceEtherBlood electrolytes
Methods are disclosed for reducing the shift in EMF bias in a magnesium ion selective electrode, comprising the step of: contacting the electrode with a composition comprising a polyoxyalkylene nonionic surfactant; wherein the polyoxyalkylene nonionic surfactant has an HLB greater than about 18. Additional aspects of the present invention are directed to methods, comprising the steps of: contacting a magnesium ion selective electrode with a composition comprising a polyoxyalkylene nonionic surfactant, wherein the polyoxyalkylene nonionic surfactant has an HLB greater than about 18; and measuring a biologically relevant level of a blood electrolyte in a blood composition with the electrode. In certain embodiments, the polyoxyalkylene nonionic surfactant is polyoxy ethylene (100) stearyl ether and the blood electrolyte is magnesium ion.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
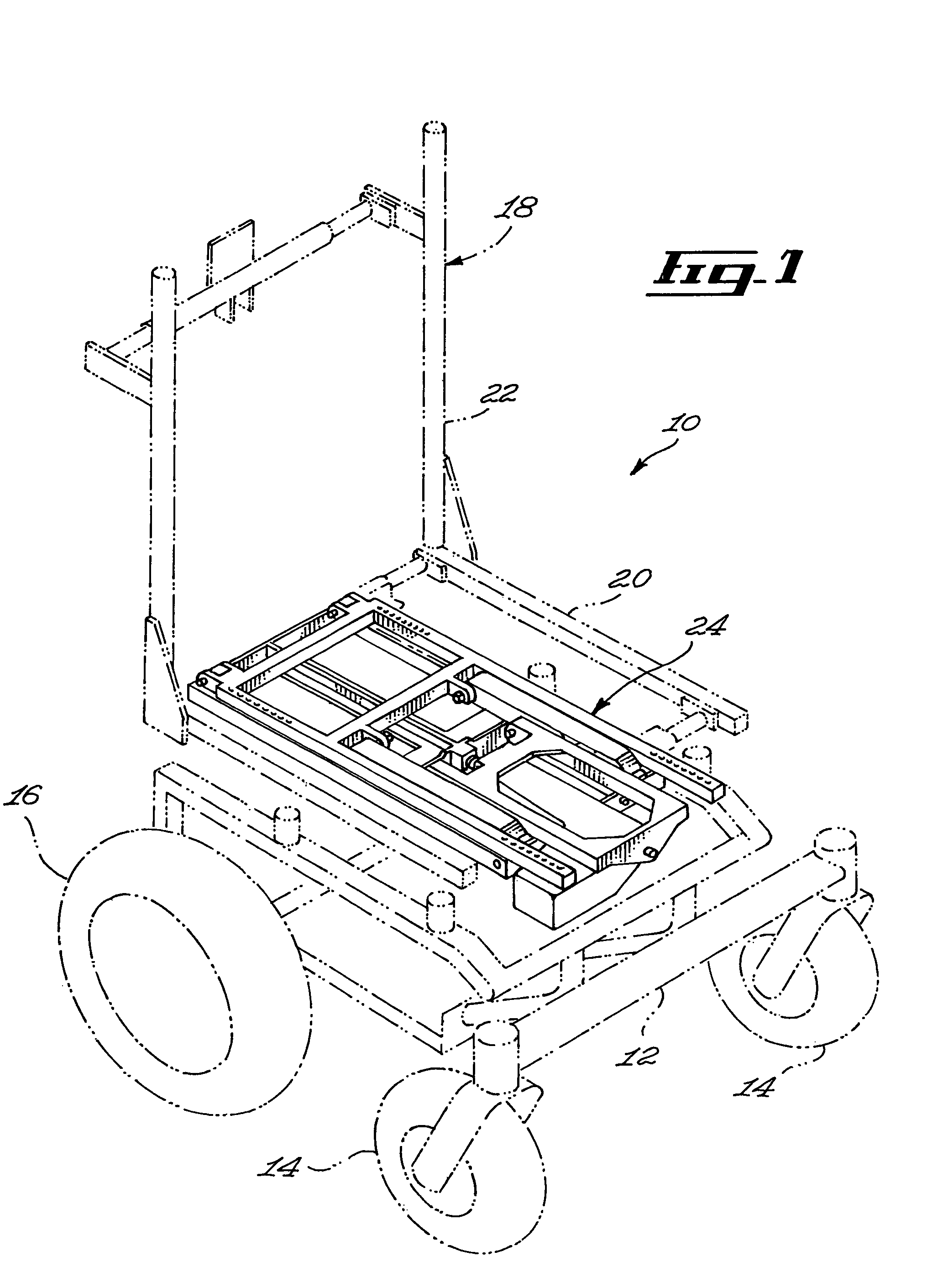
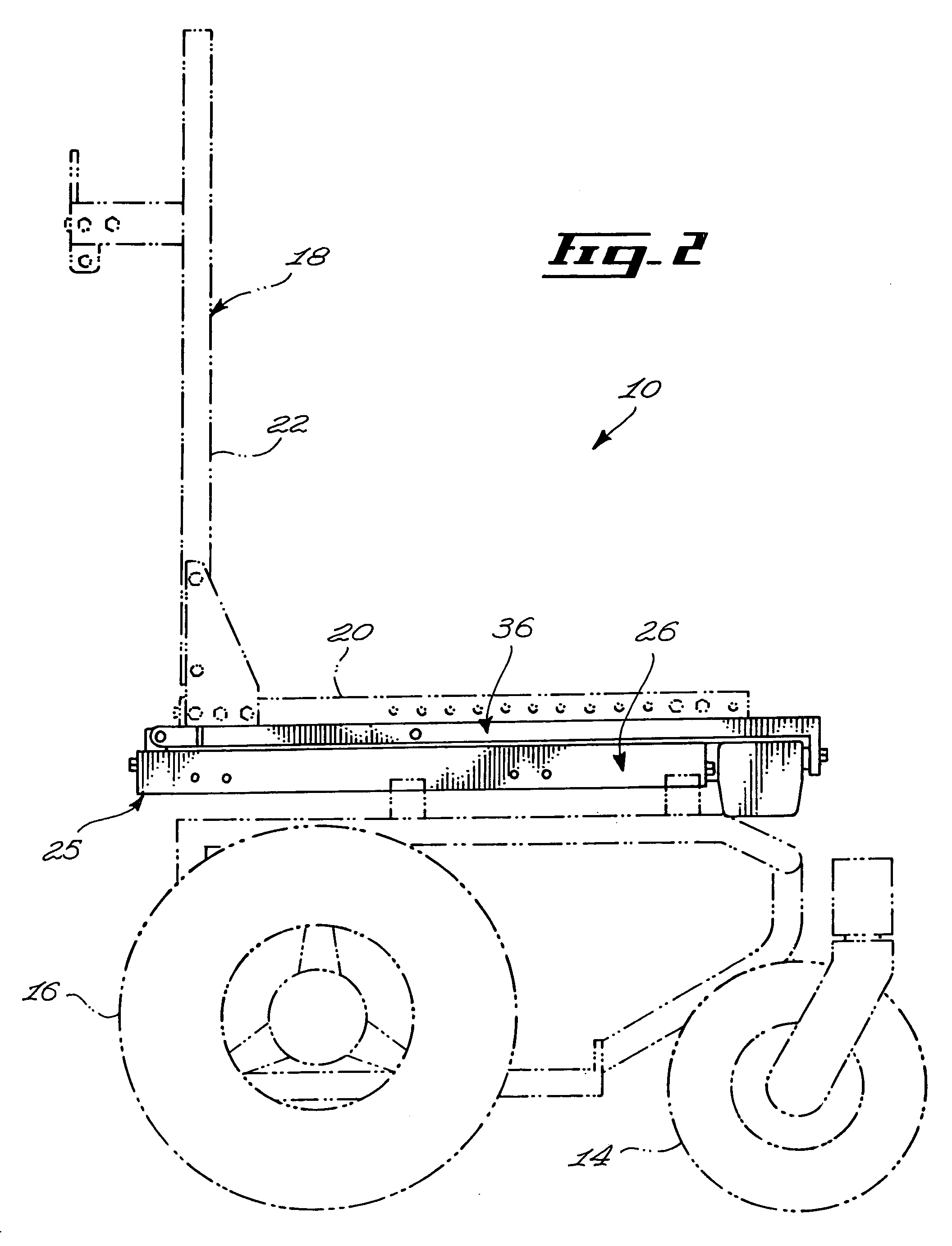
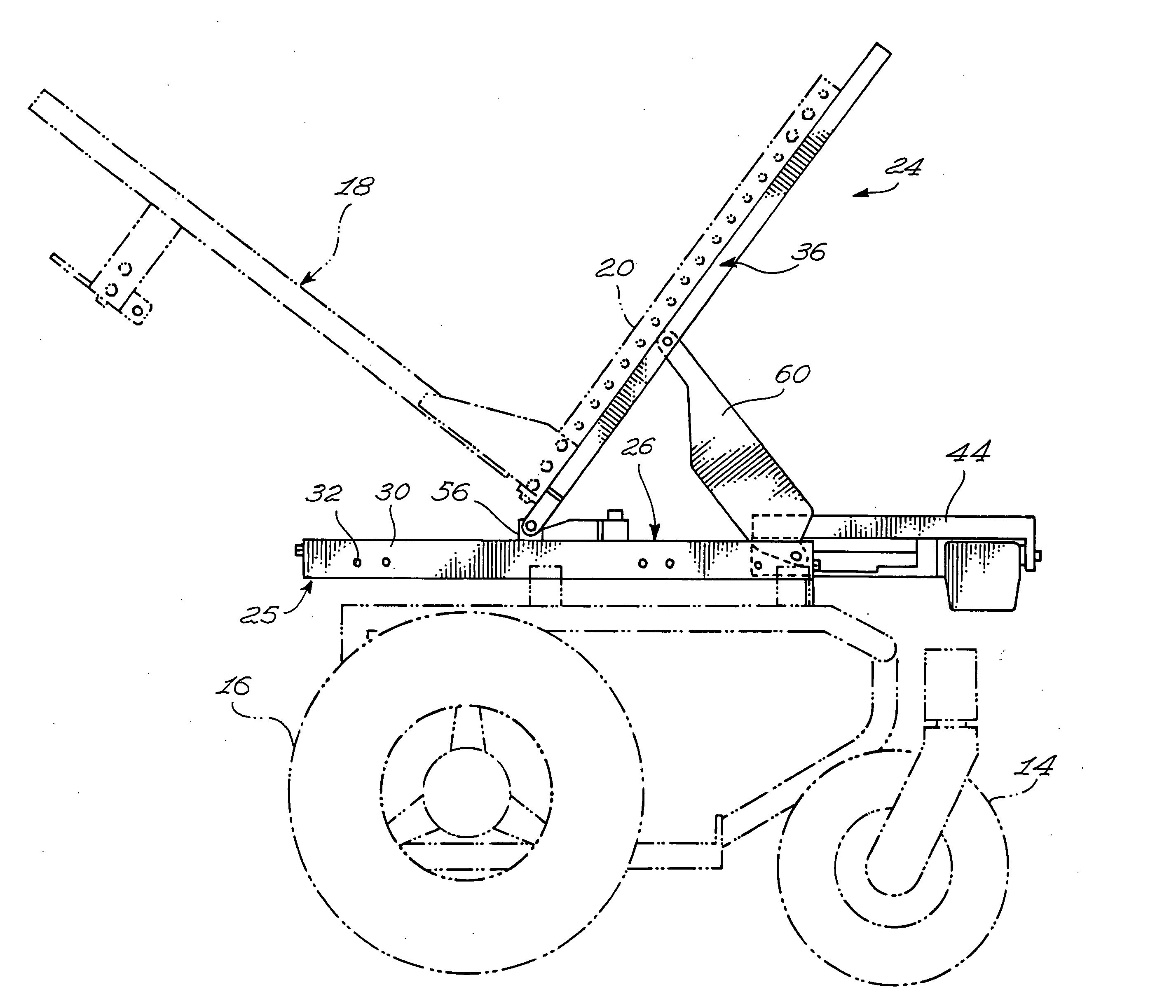
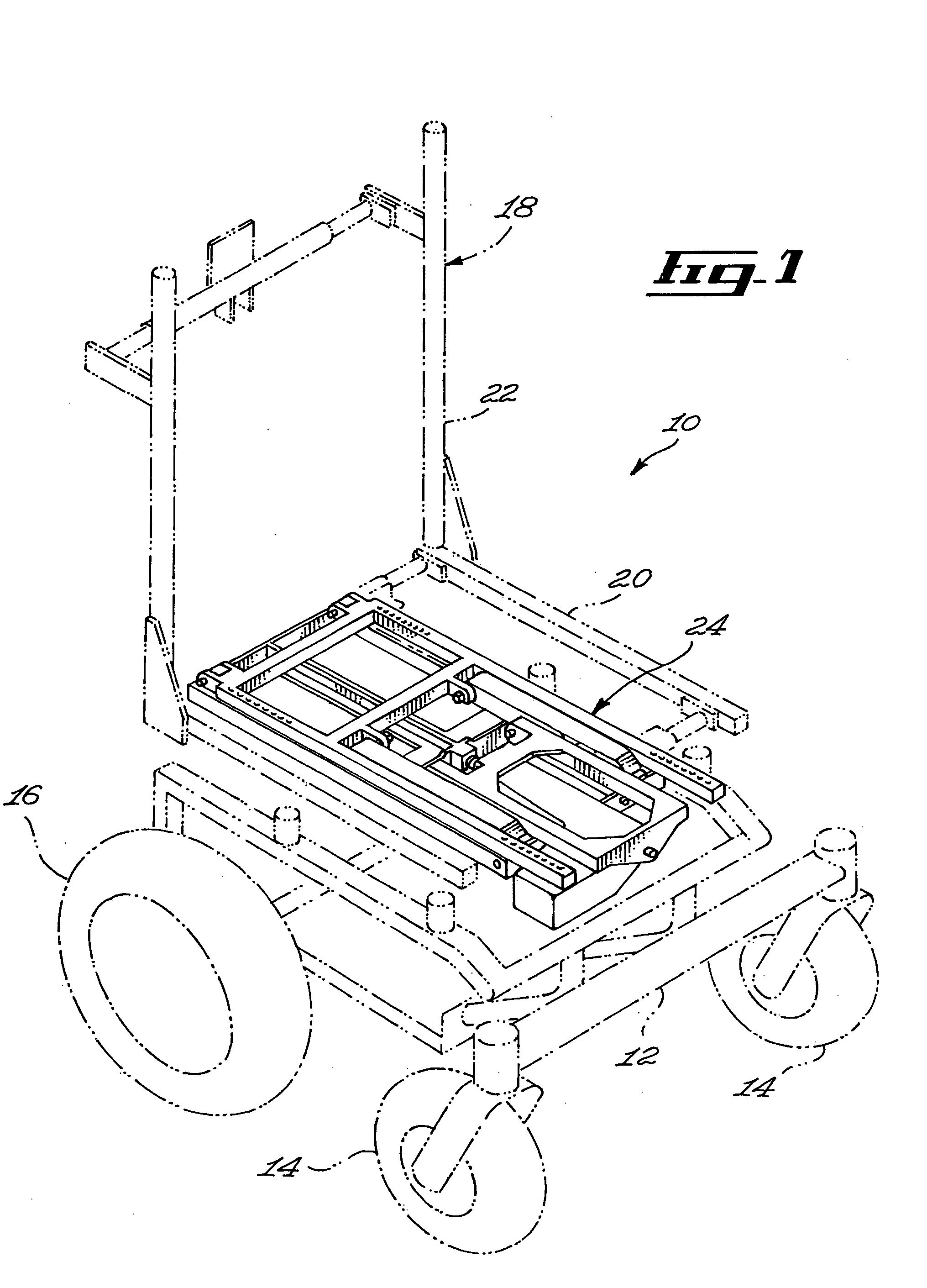
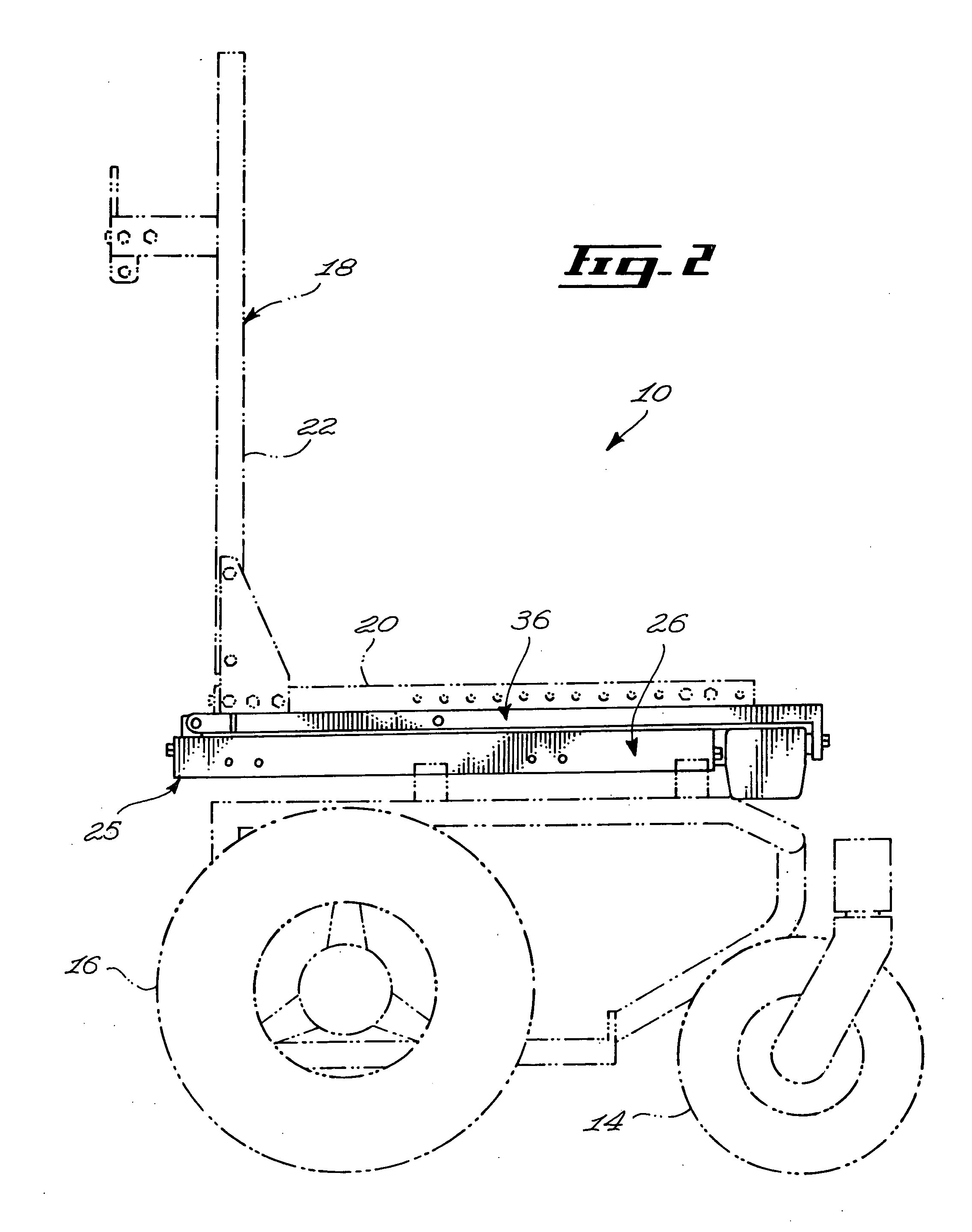
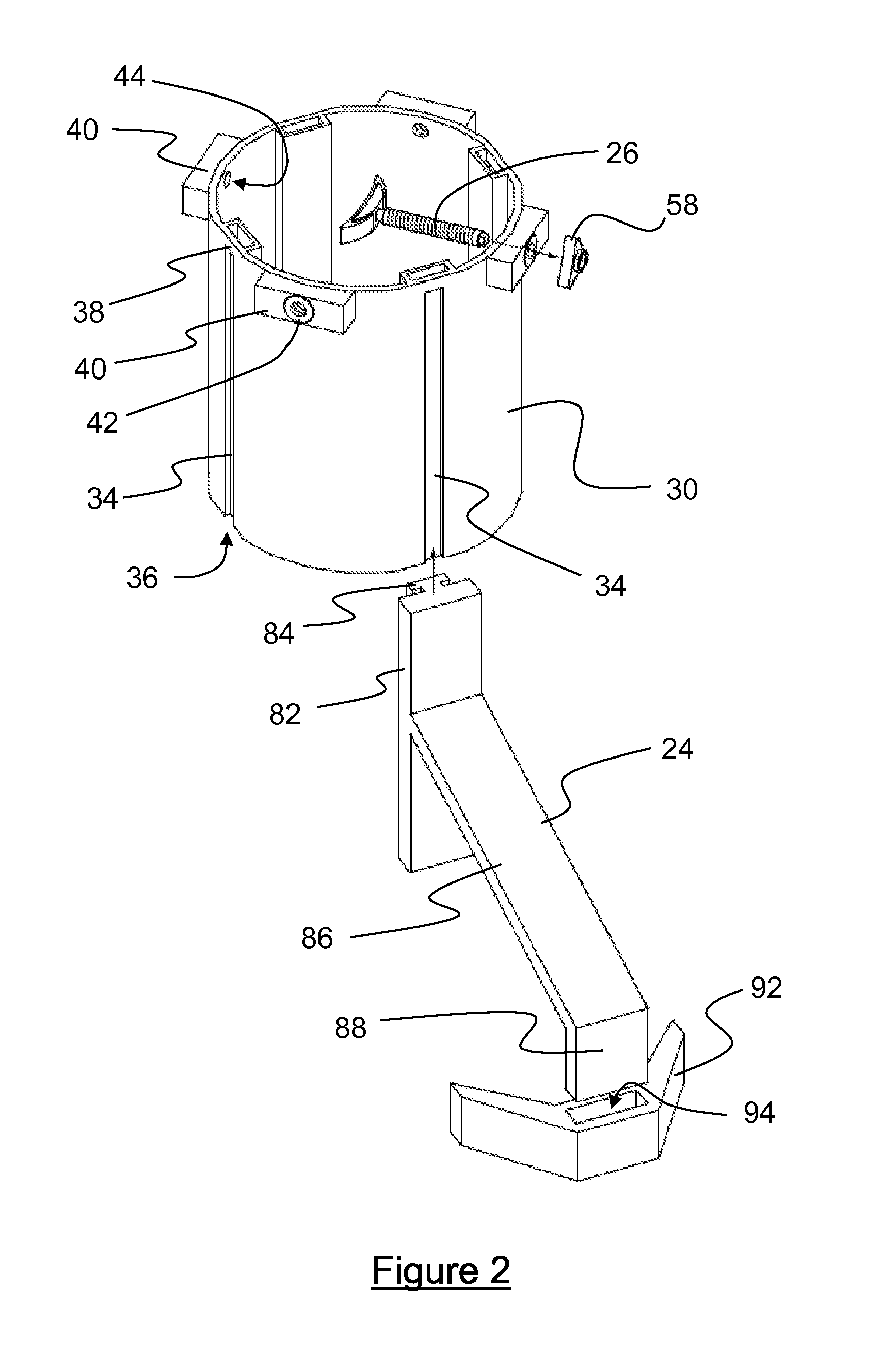
Seat supporting assembly and wheelchair including same
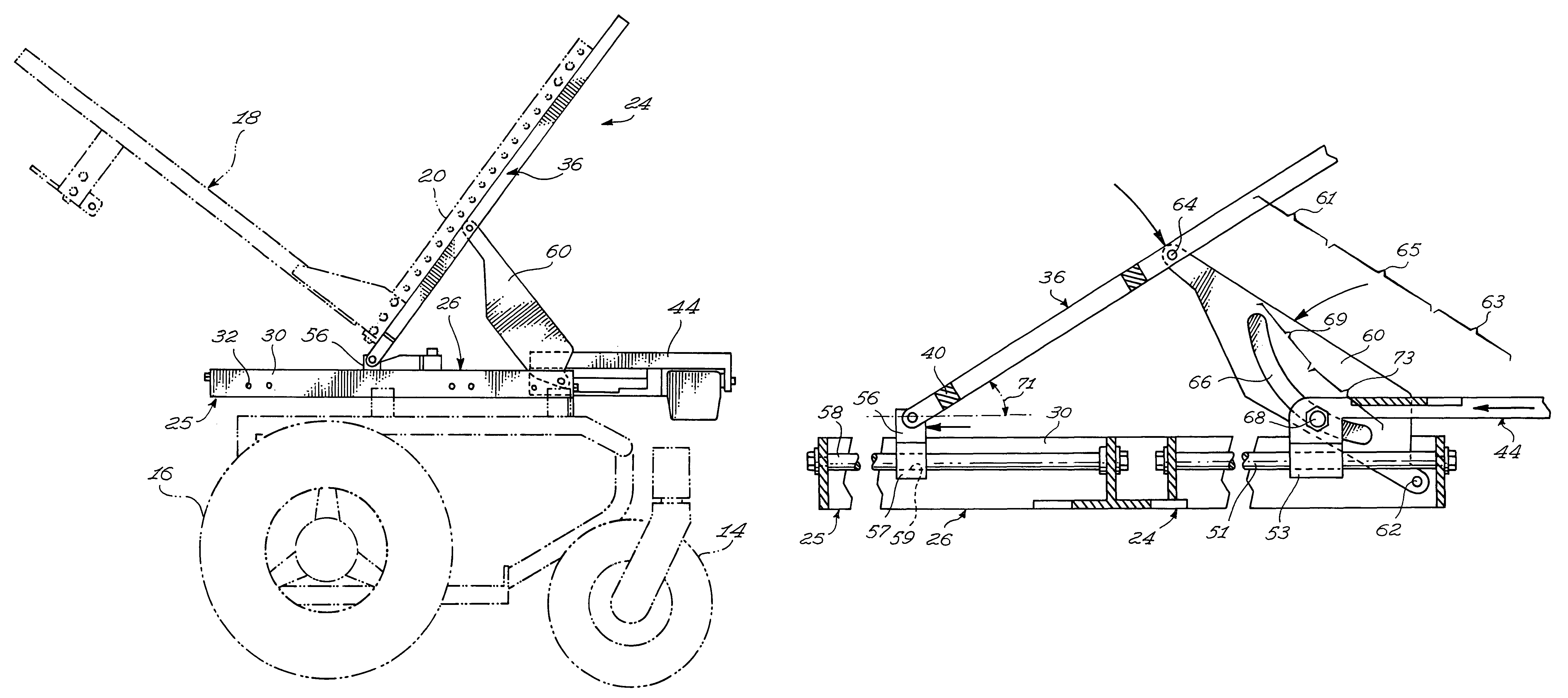
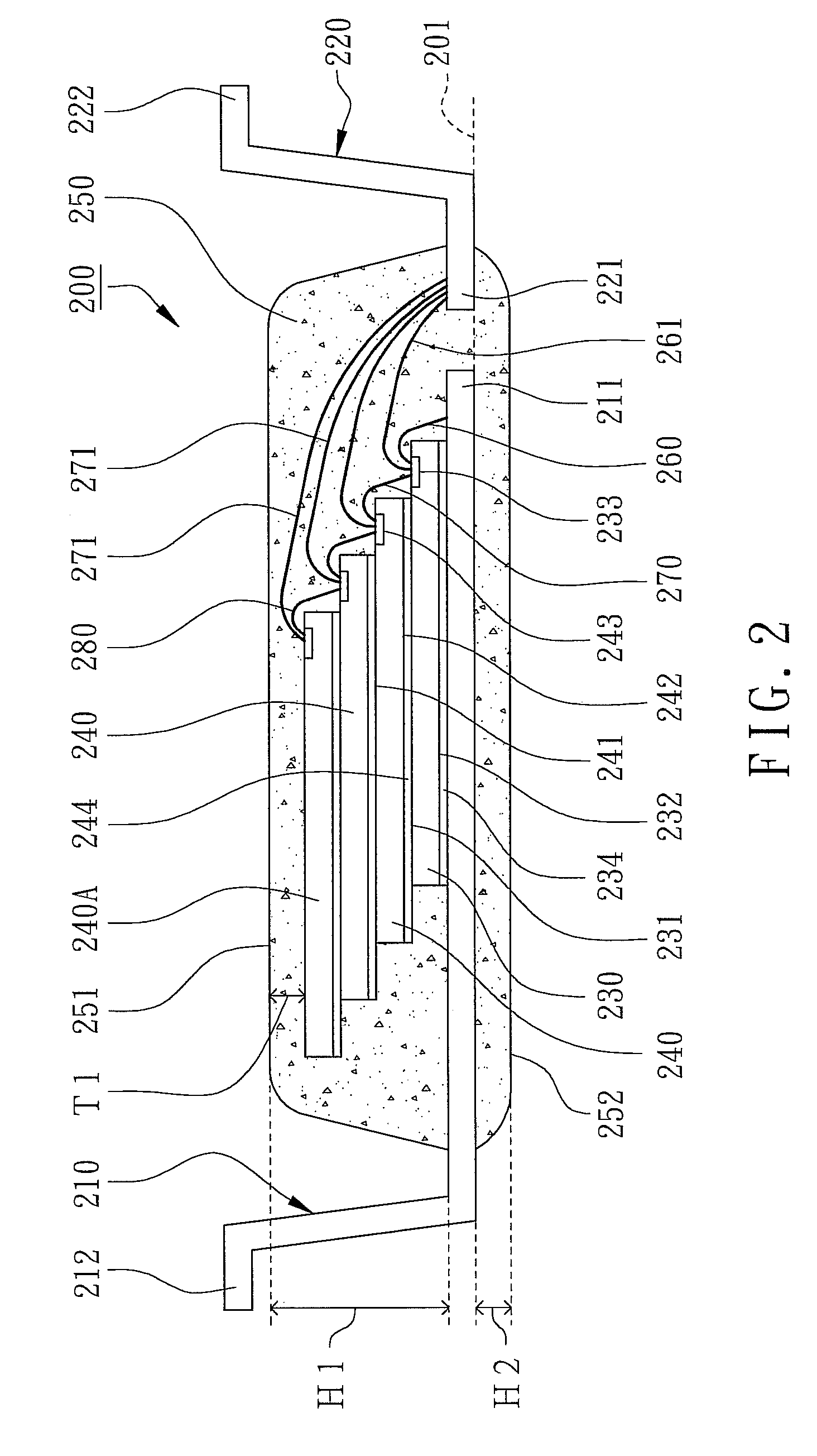
ActiveUS8297641B2Reduce needDecrease shiftCarriage/perambulator accessoriesOperating chairsWheelchairEngineering
A seat supporting assembly (24) for supporting a seat (18), the assembly comprising a base (25) including a substantially elongated guiding rod (58), a seat support (36), a seat support-to-base linking member (56) pivotally coupled to the seat support (36) and sliding on the base guiding rod (58), a substantially elongated tilting member (60) having a guiding groove (66) and being pivotally attached to the seat support (36) and to the base (25). An actuating assembly (44) is coupled to the base (25) and includes a motion transmitting member (68) mounted within the guiding groove (60). The force from the actuating assembly moves the tilting member (60) according to the geometry of the guiding groove (66), which causes the seat supporting assembly (24) to move between tilted and upright configurations by pivoting the tilting member (60) relative to the seat support (36) and the base (25) and substantially simultaneously moving the seat support-to-base linking member (56) longitudinally relative to the guiding rod (58). The assembly is designed to maintain the location of the center of gravity of a user as the seat tilts rearwardly by automatically moving the seat forwardly during tilting. The guiding groove (66) in the tilting member (60) may be curved such that the tilting motion occurs with a constant angular velocity The seat assembly is particularly useful for wheelchairs.
Owner:AMYLIOR
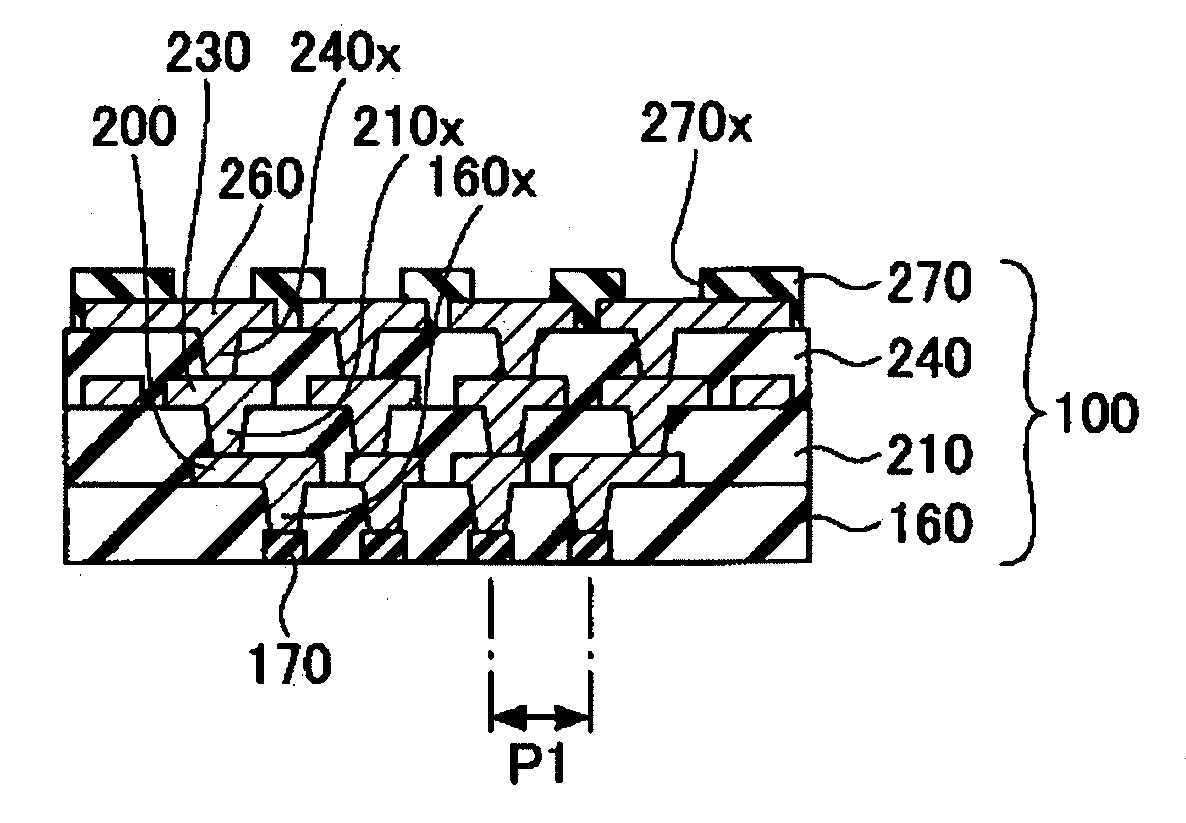
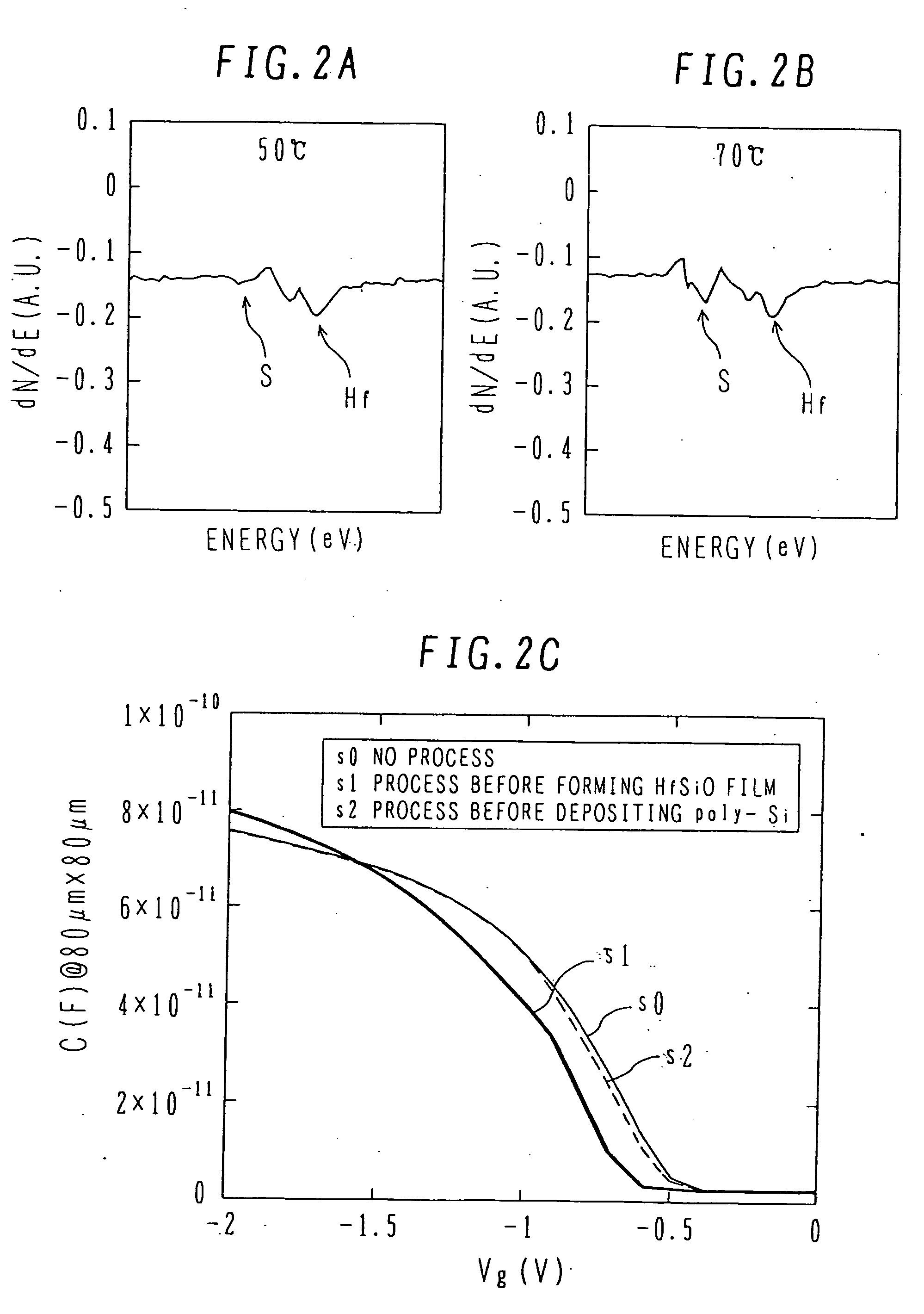
Semiconductor device having high dielectric constant gate insulating layer and its manufacture method
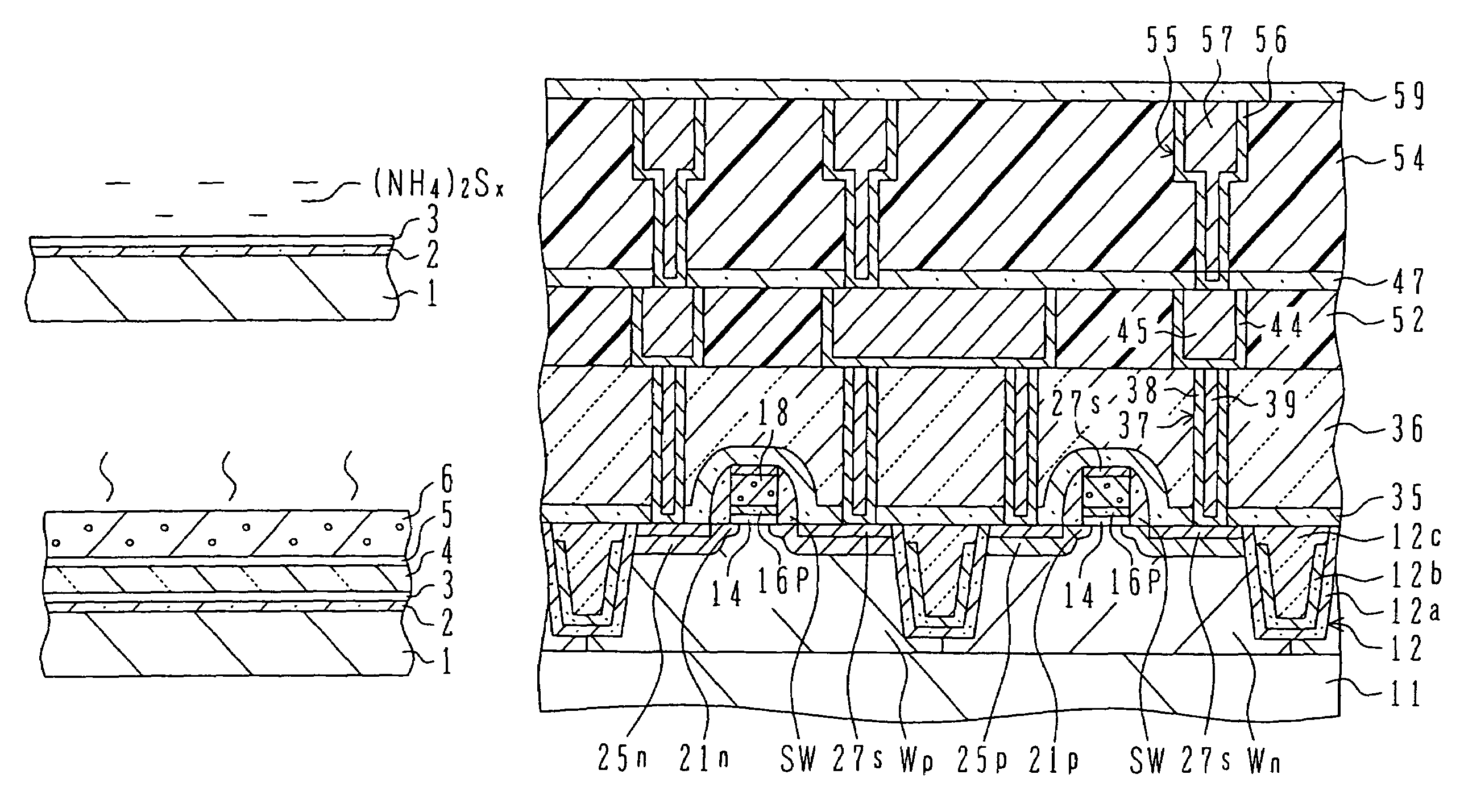
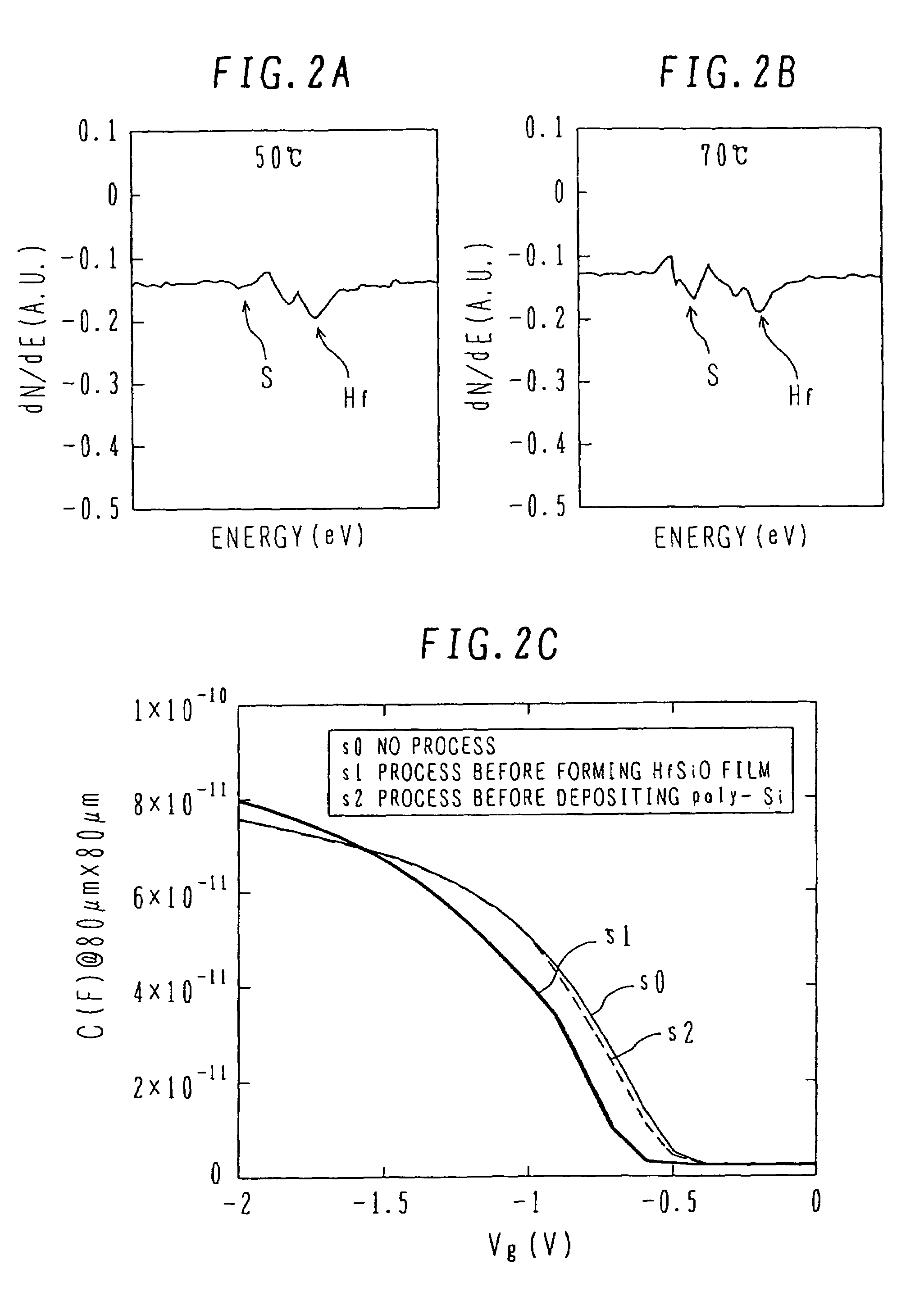
InactiveUS20060172498A1High dielectric constantDecrease shiftSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialInterface layer
A semiconductor device manufacture method has the steps of: (a) forming an interface layer of SiO or SiON on the surface of an active region of a silicon substrate; (b) forming a high dielectric constant gate insulating film such as HfSiON having a dielectric constant higher than that of silicon oxide, above the interface layer; (c) forming a gate electrode of polysilicon above the high dielectric constant gate insulating film; (d) passivating the substrate surface at least before or after the high dielectric constant gate insulating film is formed; (e) forming an insulated gate electrode structure by patterning at least the gate electrode and the high dielectric constant gate insulating film; and (f) forming source / drain regions in the active region on both sides of the insulated gate electrode structure. The semiconductor device has the high dielectric constant insulating film having a dielectric constant higher than that of silicon oxide.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Seat Supporting Assembly and Wheelchair Including Same
ActiveUS20090230652A1Reduce needReduce relative shiftCarriage/perambulator accessoriesOperating chairsWheelchairEngineering
A seat supporting assembly (24) for supporting a seat (18), the assembly comprising a base (25) including a substantially elongated guiding rod (58), a seat support (36), a seat support-to-base linking member (56) pivotally coupled to the seat support (36) and sliding on the base guiding rod (58), a substantially elongated tilting member (60) having a guiding groove (66) and being pivotally attached to the seat support (36) and to the base (25). An actuating assembly (44) is coupled to the base (25) and includes a motion transmitting member (68) mounted within the guiding groove (60). The force from the actuating assembly moves the tilting member (60) according to the geometry of the guiding groove (66), which causes the seat supporting assembly (24) to move between tilted and upright configurations by pivoting the tilting member (60) relative to the seat support (36) and the base (25) and substantially simultaneously moving the seat support-to-base linking member (56) longitudinally relative to the guiding rod (58). The assembly is designed to maintain the location of the center of gravity of a user as the seat tilts rearwardly by automatically moving the seat forwardly during tilting. The guiding groove (66) in the tilting member (60) may be curved such that the tilting motion occurs with a constant angular velocity The seat assembly is particularly useful for wheelchairs.
Owner:AMYLIOR
Use of polyoxyalkylene nonionic surfactants with magnesium ion selective electrodes
ActiveUS8496800B2Decrease shiftOrganic chemistryWeather/light/corrosion resistanceEtherBlood electrolytes
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC
COL (Chip-On-Lead) multi-chip package
InactiveUS7622794B1Reduce relative shiftDecrease shiftSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSealant
A Chip-On-Lead (COL) multi-chip package is revealed, primarily comprising a plurality of leads, a first chip disposed on the first leads, one or more second chips stacked on the first chip, and an encapsulant. The leads have a plurality of internal leads encapsulated inside the encapsulant where the internal leads are fully formed on a downset plane toward and parallel to a bottom surface of the encapsulant. The height between the internal leads to a top surface of the encapsulant is three times or more greater than the height between the internal leads and the bottom surface. Since the number and the thickness of the second chips is under controlled, the thickness between the top surface of the encapsulant and the most adjacent one of the second chips is about the same as the one between the internal leads and the bottom surface of the encapsulant. Therefore, the internal leads of the leads without downset bends in the encapsulant can balance the upper and lower mold flows and carry more chips without shifting nor tilting.
Owner:POWERTECH TECHNOLOGY
Col (chip-on-lead) multi-chip package
InactiveUS20090302441A1Decrease shiftSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSealant
A Chip-On-Lead (COL) multi-chip package is revealed, primarily comprising a plurality of leads, a first chip disposed on the first leads, one or more second chips stacked on the first chip, and an encapsulant. The leads have a plurality of internal leads encapsulated inside the encapsulant where the internal leads are fully formed on a downset plane toward and parallel to a bottom surface of the encapsulant. The height between the internal leads to a top surface of the encapsulant is three times or more greater than the height between the internal leads and the bottom surface. Since the number and the thickness of the second chips is under controlled, tile thickness between the top surface of the encapsulant and the most adjacent one of the second chips is about the same as the one between the internal leads and the bottom surface of the encapsulant. Therefore, the internal leads of the leads without downset bends in the encapsulant can balance the upper and lower mold flows and carry more chips without shifting nor tilting.
Owner:POWERTECH TECHNOLOGY INC
Telescoping Leg Lock and Portable Elevated Platform with Same
InactiveUS20090250571A1Decrease shiftReduce noiseMachine framesRod connectionsBearing surfaceMechanical engineering
A telescoping leg for supporting an elevated platform includes an outer leg. An inner leg is slidably disposed within the outer leg. An off-axis slot is disposed through a sidewall of one of either the inner leg or the outer leg and an aperture is disposed in the other. The inner leg is slidably positionable within the outer leg to align the off-axis slot with the aperture. A pin is disposable through the aperture and the slot when the aperture and the slot are aligned such that a bearing surface of the pin contacts a bearing surface of the slot to laterally push the inner leg against the outer leg.
Owner:MITY-LITE
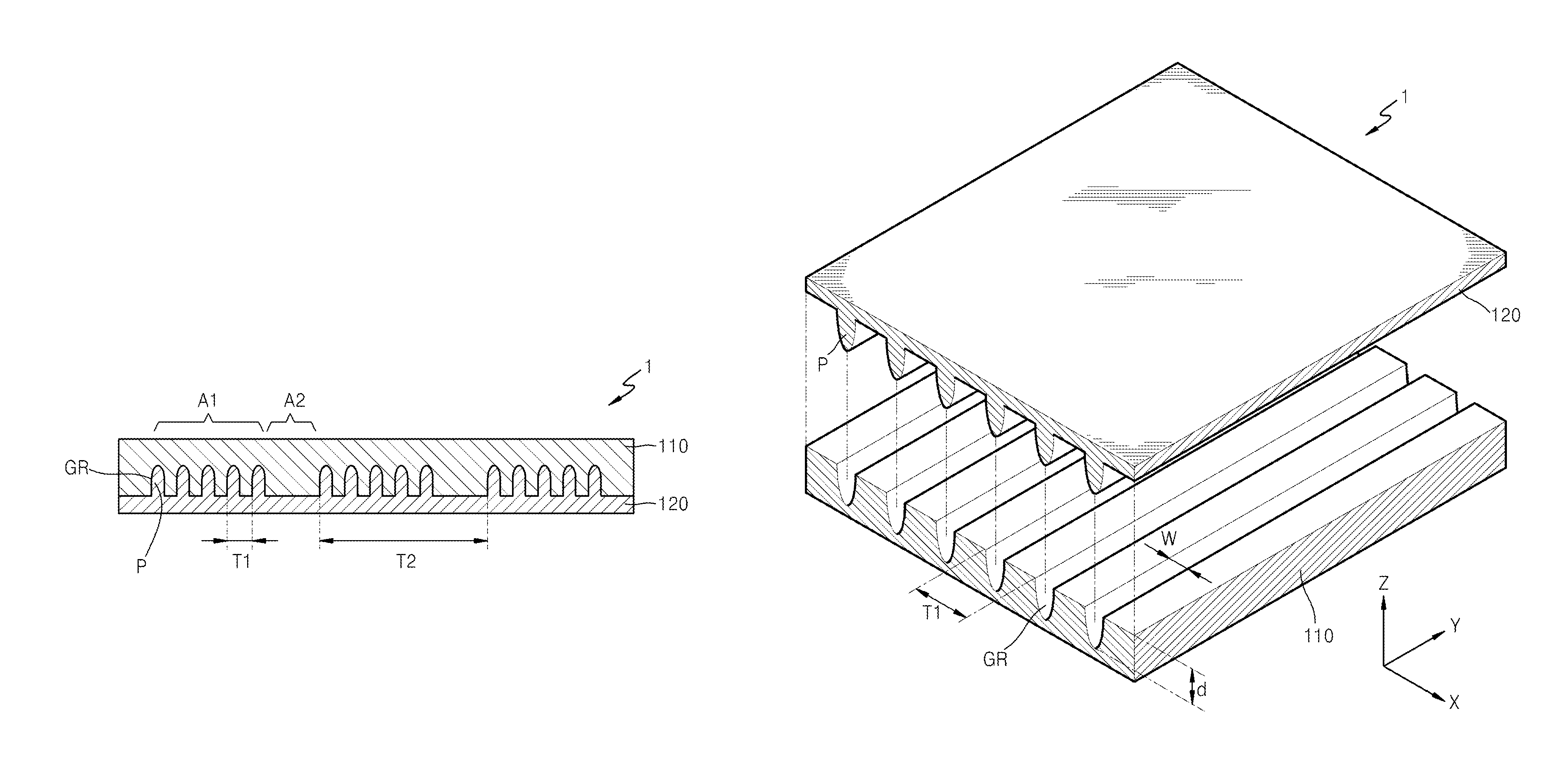
Optical film for reducing color shift and organic light-emitting display device employing the same
ActiveUS20150323707A1Decrease shiftStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesColor shiftRefractive index
Optical films, and organic light-emitting display devices employing the same, include a high refractive index pattern layer including a lens pattern region and a non-pattern region alternately formed, wherein the lens pattern region includes a plurality of grooves each having a depth larger than a width thereof, and the non-pattern region has no pattern; and a low refractive index pattern layer formed of a material having a refractive index smaller than a refractive index of the high refractive index pattern layer, wherein the low refractive index pattern includes a plurality of filling portions filling the plurality of grooves.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
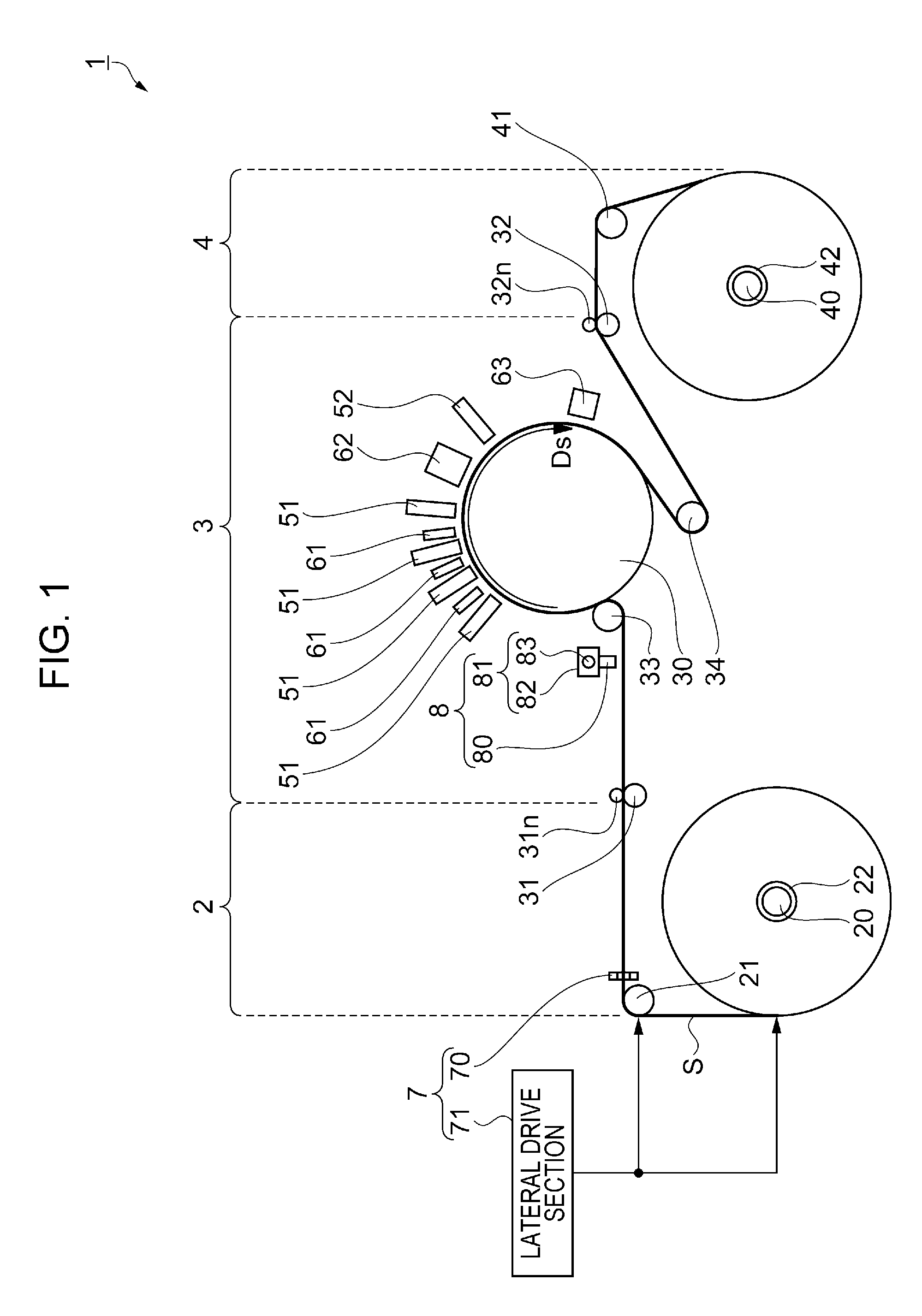
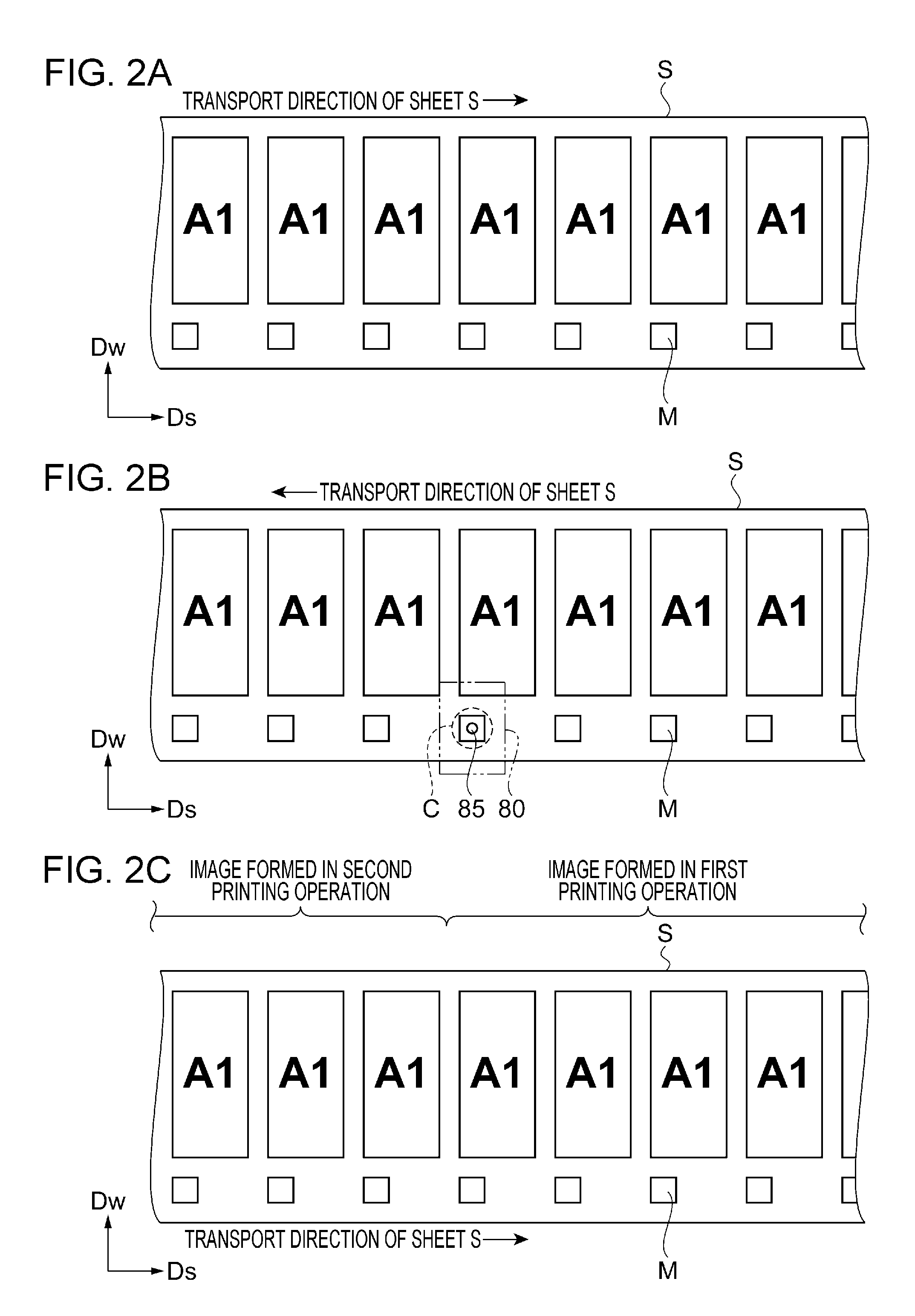
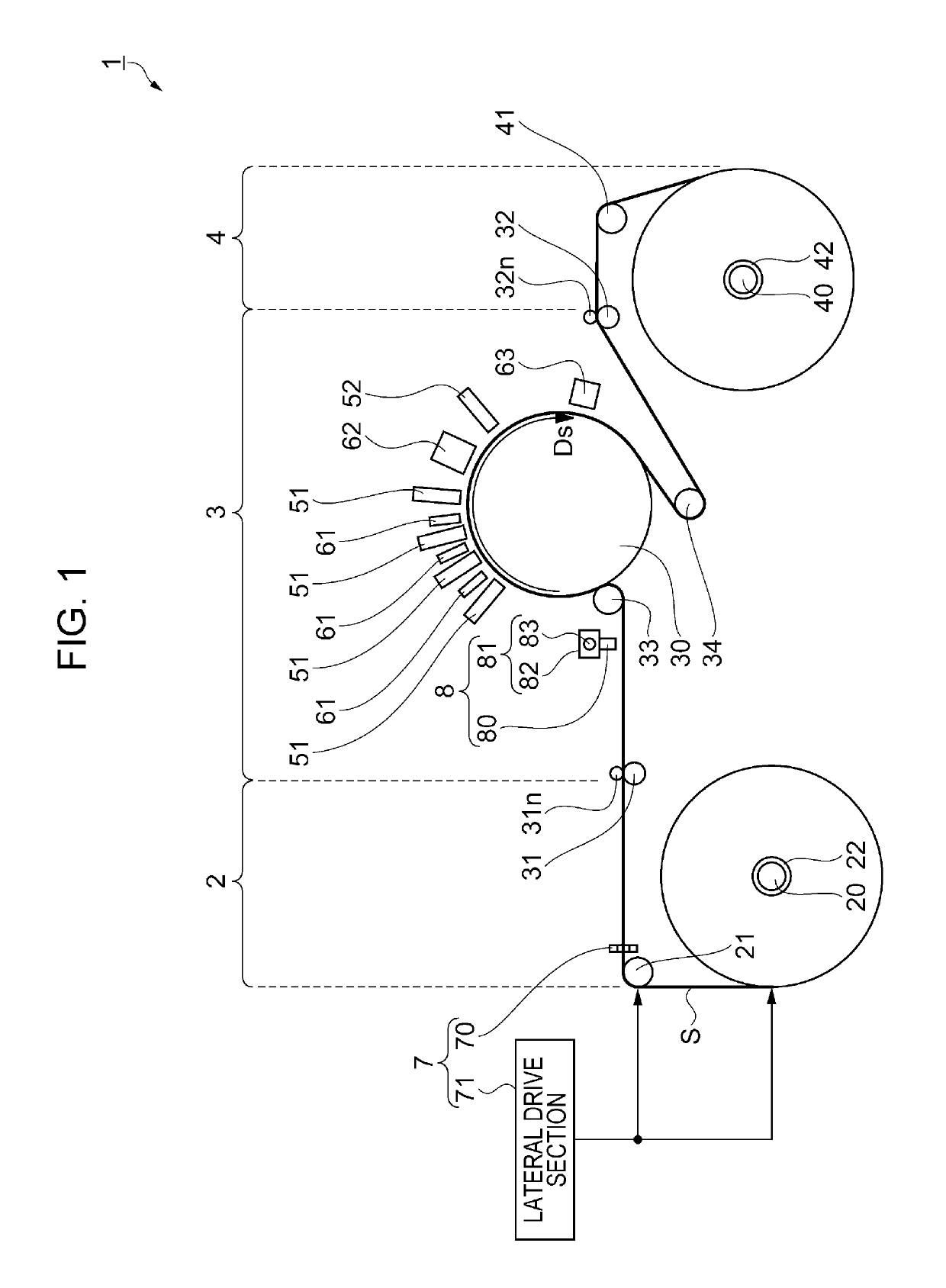
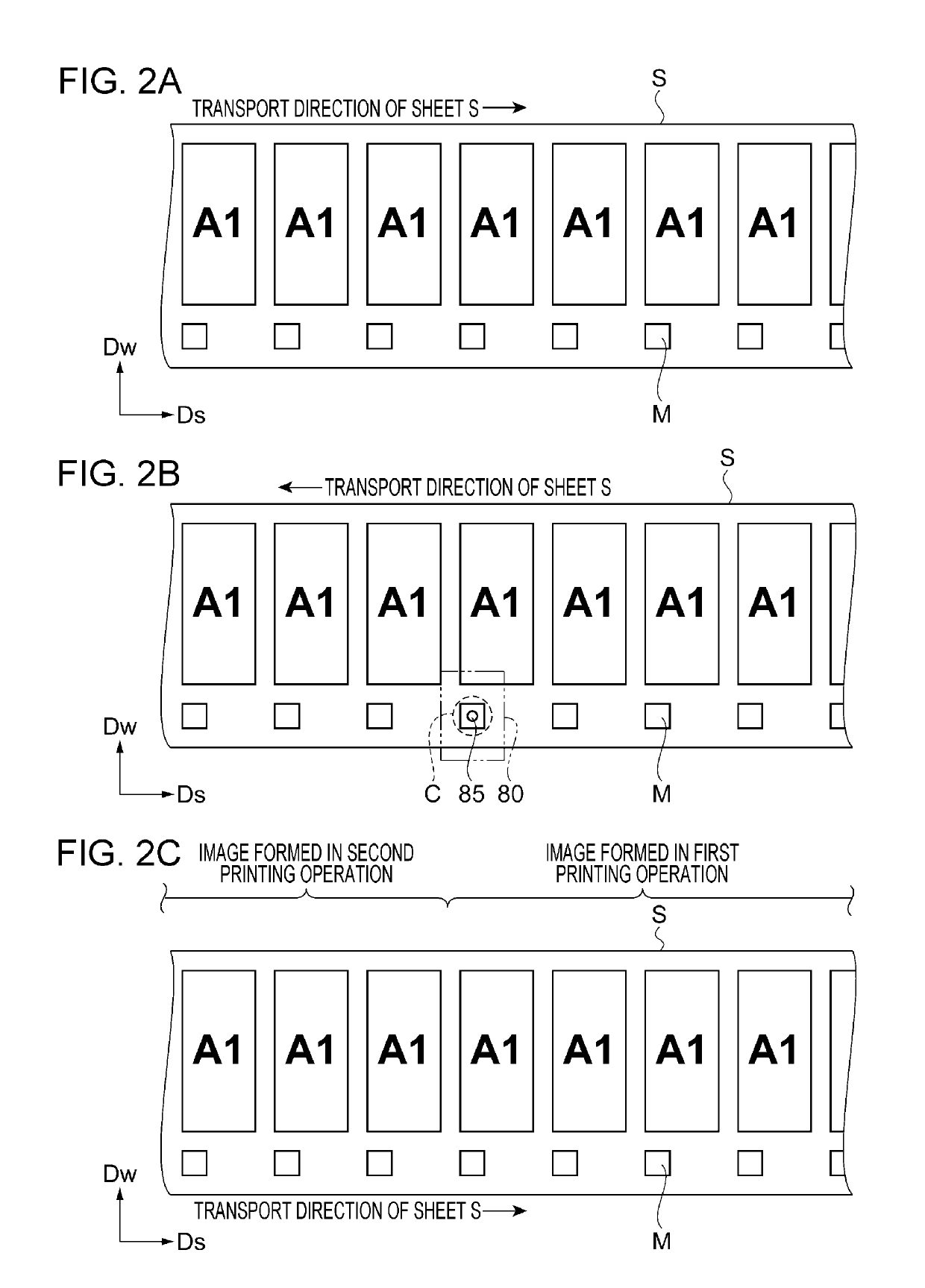
Mark detection method using printing apparatus and printing apparatus
InactiveUS20160272451A1Stable detectionDecrease shiftFunction indicatorsVisual presentation using printersMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical films for reducing color shift and organic light-emitting display devices employing the same
Optical films, and organic light-emitting display devices employing the same, include a high refractive index pattern layer including a lens pattern region and a non-pattern region alternately formed, wherein the lens pattern region includes a plurality of grooves each having a depth larger than a width thereof, and the non-pattern region has no pattern; and a low refractive index pattern layer formed of a material having a refractive index smaller than a refractive index of the high refractive index pattern layer, wherein the low refractive index pattern includes a plurality of filling portions filling the plurality of grooves.
Owner:CHEIL IND INC +1
Method of manufacturing a FeRAM with annealing process
InactiveUS6908867B2Decrease shiftPrevent degradationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitorMaterials science
There are contained the steps of forming sequentially a first conductive film, a dielectric film, and a second conductive film on a first insulating film, forming an upper electrode of a capacitor by patterning the second conductive film, patterning the dielectric film to leave under the upper electrode, forming a lower electrode of the capacitor by patterning the first conductive film, covering the capacitor and the first insulating film with a second insulating film, and annealing at least one of the first insulating film and the second insulating film in an inert-gas atmosphere and then exposing the film to an N2O plasma.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
Semiconductor device having high dielectric constant gate insulating layer and its manufacture method
InactiveUS7265401B2High dielectric constantDecrease shiftSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesInterface layerSilicon oxide
A semiconductor device manufacture method has the steps of: (a) forming an interface layer of SiO or SiON on the surface of an active region of a silicon substrate; (b) forming a high dielectric constant gate insulating film such as HfSiON having a dielectric constant higher than that of silicon oxide, above the interface layer; (c) forming a gate electrode of polysilicon above the high dielectric constant gate insulating film; (d) passivating the substrate surface at least before or after the high dielectric constant gate insulating film is formed; (e) forming an insulated gate electrode structure by patterning at least the gate electrode and the high dielectric constant gate insulating film; and (f) forming source / drain regions in the active region on both sides of the insulated gate electrode structure. The semiconductor device has the high dielectric constant insulating film having a dielectric constant higher than that of silicon oxide.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Radio integrated circuit and radio communication method
InactiveUS7756158B2Decrease shiftTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData transmissionComputer science
A PHY-equipped radio LSI and a radio communication method capable of transmitting data without fail while maintaining a beacon interval. Using a selector which is switched by a beacon transmission signal output from a beacon register, a data transmission request signal is switched for transmitting data from a RAM to a PHY part, and a transfer is started when this signal goes to “1.” In this way, for transmitting beacon data, the beacon data has been previously transferred to the RAM, and the beacon data is transmitted at the time of beacon transmission interval with the PHY part remaining in a transmission state, so that the beacon interval can be maintained. In addition, it is possible to prevent a failure in the transmission of transfer data due to the state of the PHY part.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Christmas tree stand and kit therefor
A Christmas tree stand comprises a container having a base and a sidewall extending therefrom, the sidewall having a plurality of outer longitudinal slots; a plurality of removable legs, each removable leg configured to be accommodated within a respective longitudinal slot; and a plurality of grippers threadably connected to the sidewall. Each gripper has a flexible padding layer disposed thereon for securely gripping a trunk of a Christmas tree
Owner:DUNCAN GALYNA
Lens System
A lens system includes a first lens. The first lens is an IR absorptive lens. The first lens includes a first surface facing the object side, and a second surface facing the image side.
Owner:SINTAI OPTICAL SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
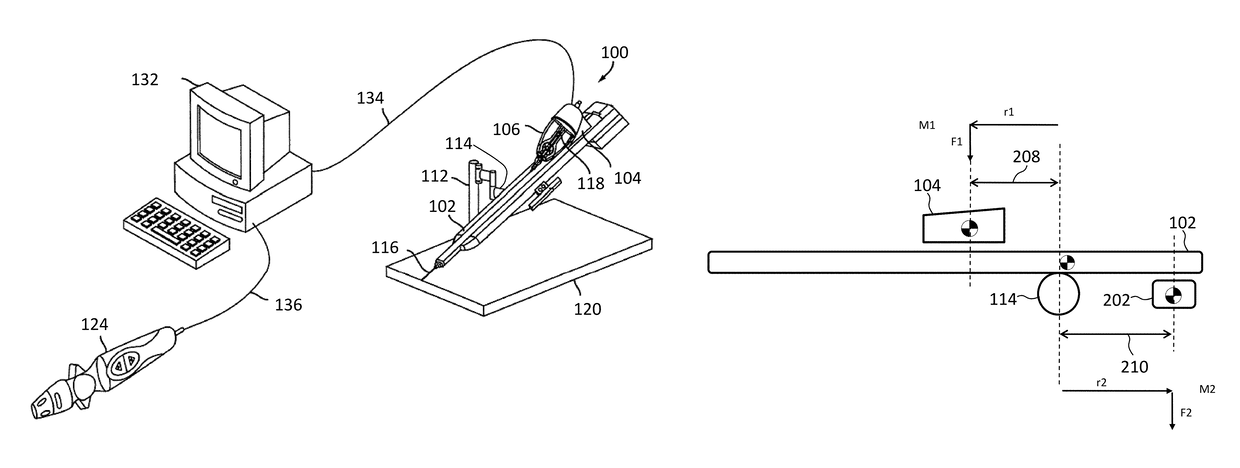
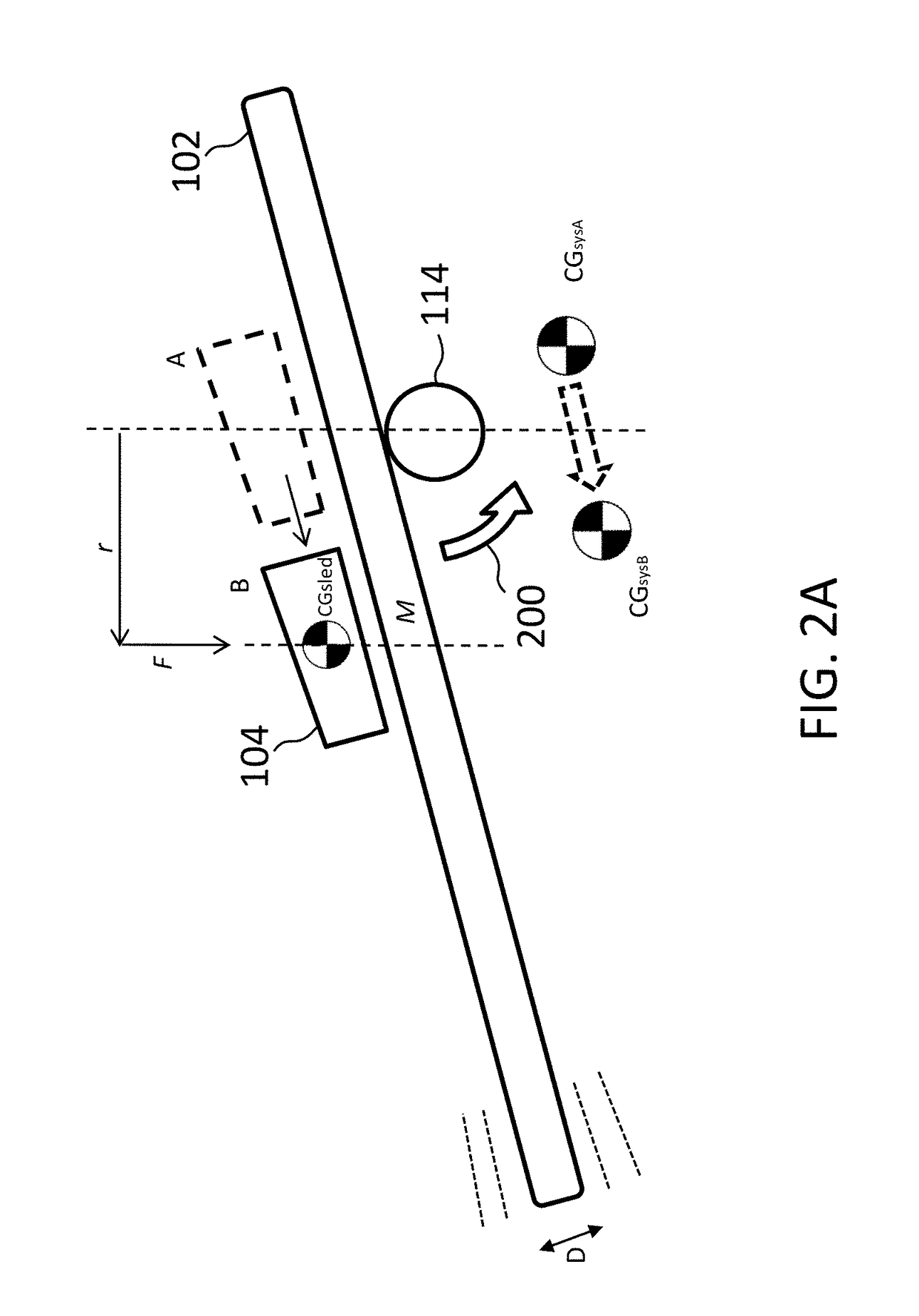
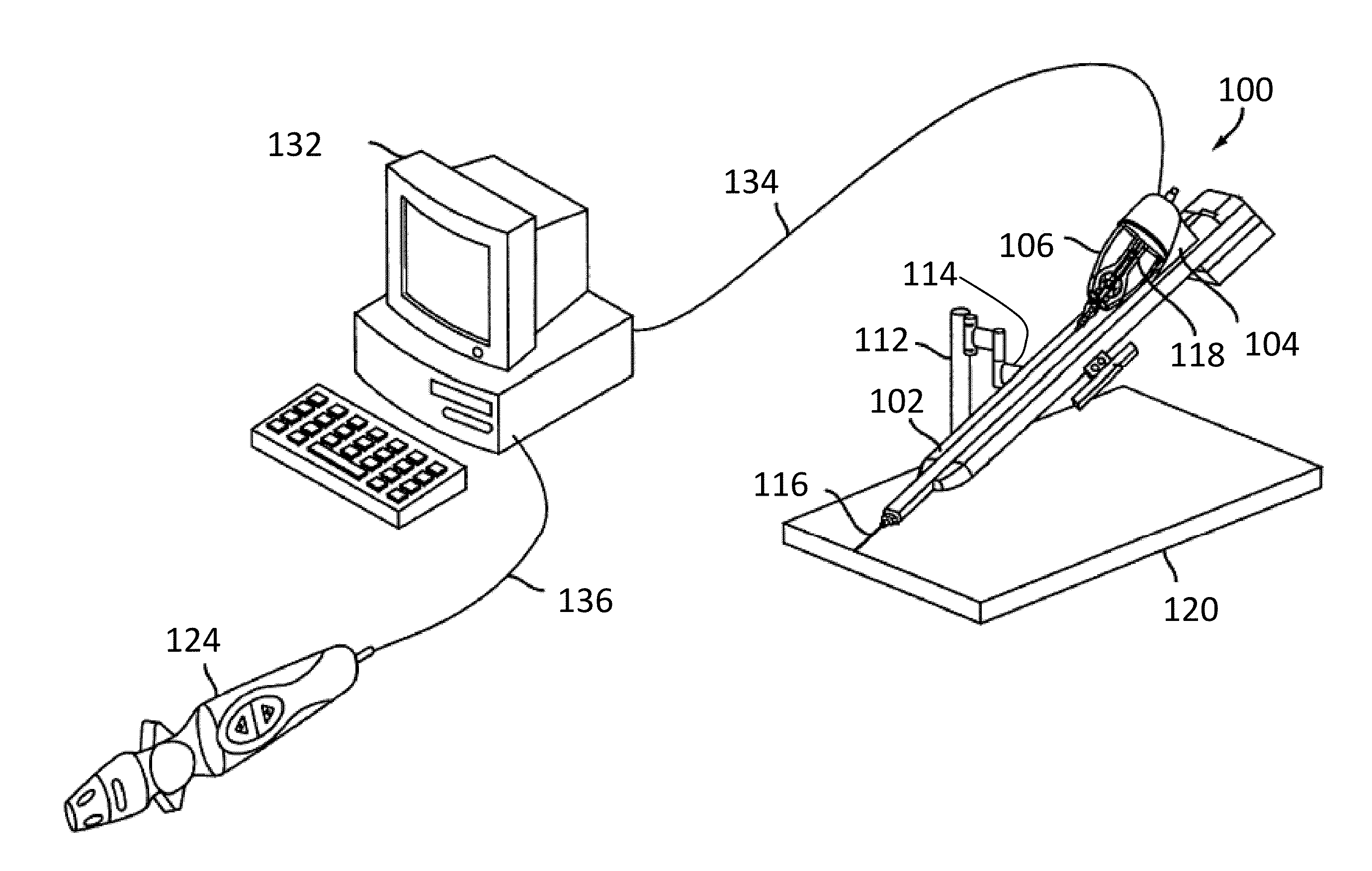
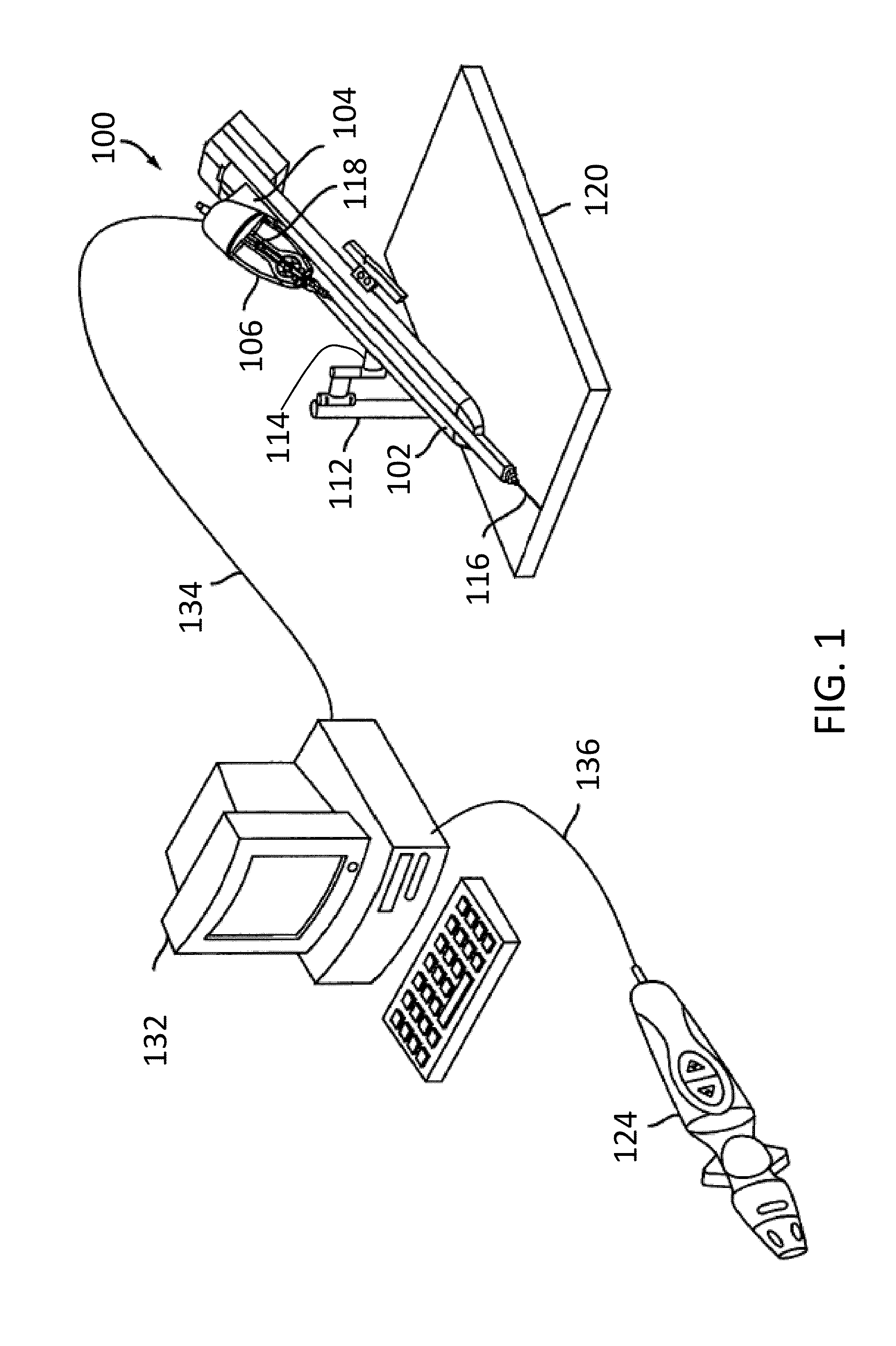
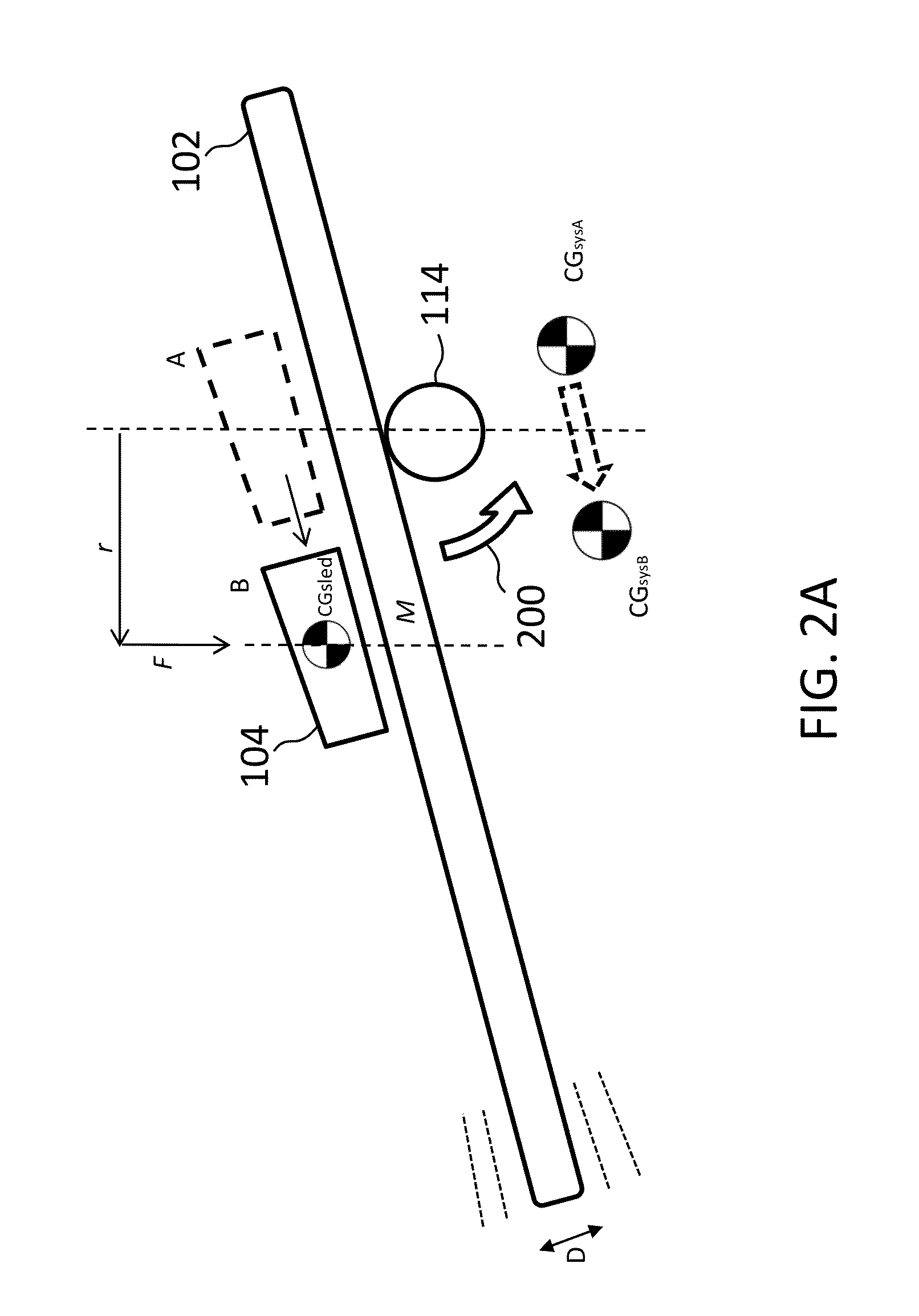
Components and methods for balancing a catheter controller system with a counterweight
Various embodiments provide systems and methods for controlling a catheter with a catheter positioning device by using a remote controller. As the catheter is advanced by the catheter positioning device, a counterweight may be adjusted to balance the catheter positioning system. In further embodiments, the counterweight may be configured to move to balance a sled member such that any total moment exerted on a sled base remains constant. In further embodiments, the counterweight may be controlled by a control system based on one or more sensors coupled with the catheter positioning system.
Owner:CATHETER PRECISION INC
Components and methods for balancing a catheter controller system with a counterweight
ActiveUS20150066052A1Reduce relative shiftDecrease shiftDiagnosticsMedical devicesControl systemPositioning system
Various embodiments provide systems and methods for controlling a catheter with a catheter positioning device by using a remote controller. As the catheter is advanced by the catheter positioning device, a counterweight may be adjusted to balance the catheter positioning system. In further embodiments, the counterweight may be configured to move to balance a sled member such that any total moment exerted on a sled base remains constant. In further embodiments, the counterweight may be controlled by a control system based on one or more sensors coupled with the catheter positioning system.
Owner:CATHETER PRECISION INC
Mark detection method using printing apparatus and printing apparatus
InactiveUS10273105B2Stable detectionDecrease shiftFunction indicatorsWebs handlingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Anti-skid material for ears or fastening tabs of absorbent article
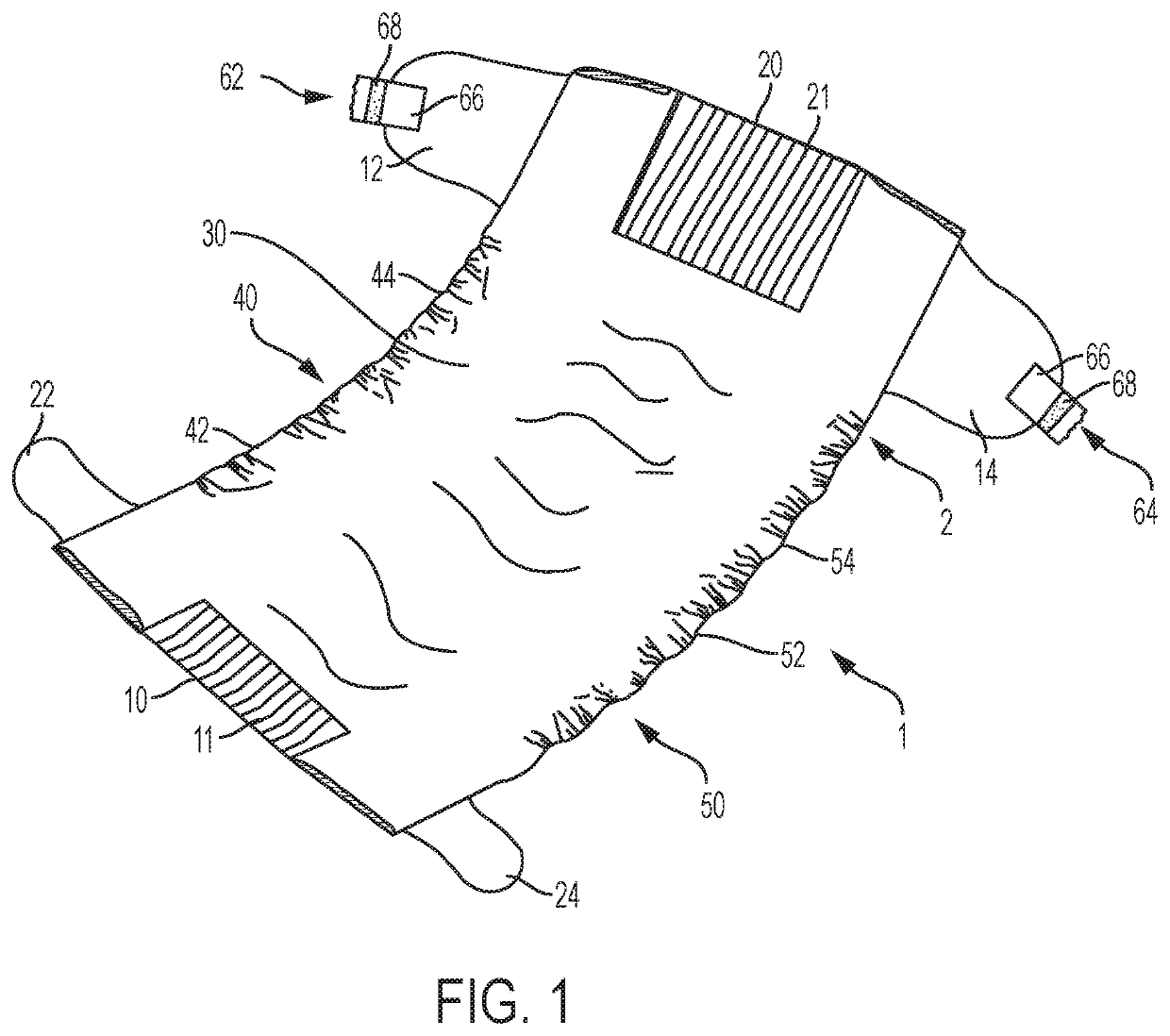
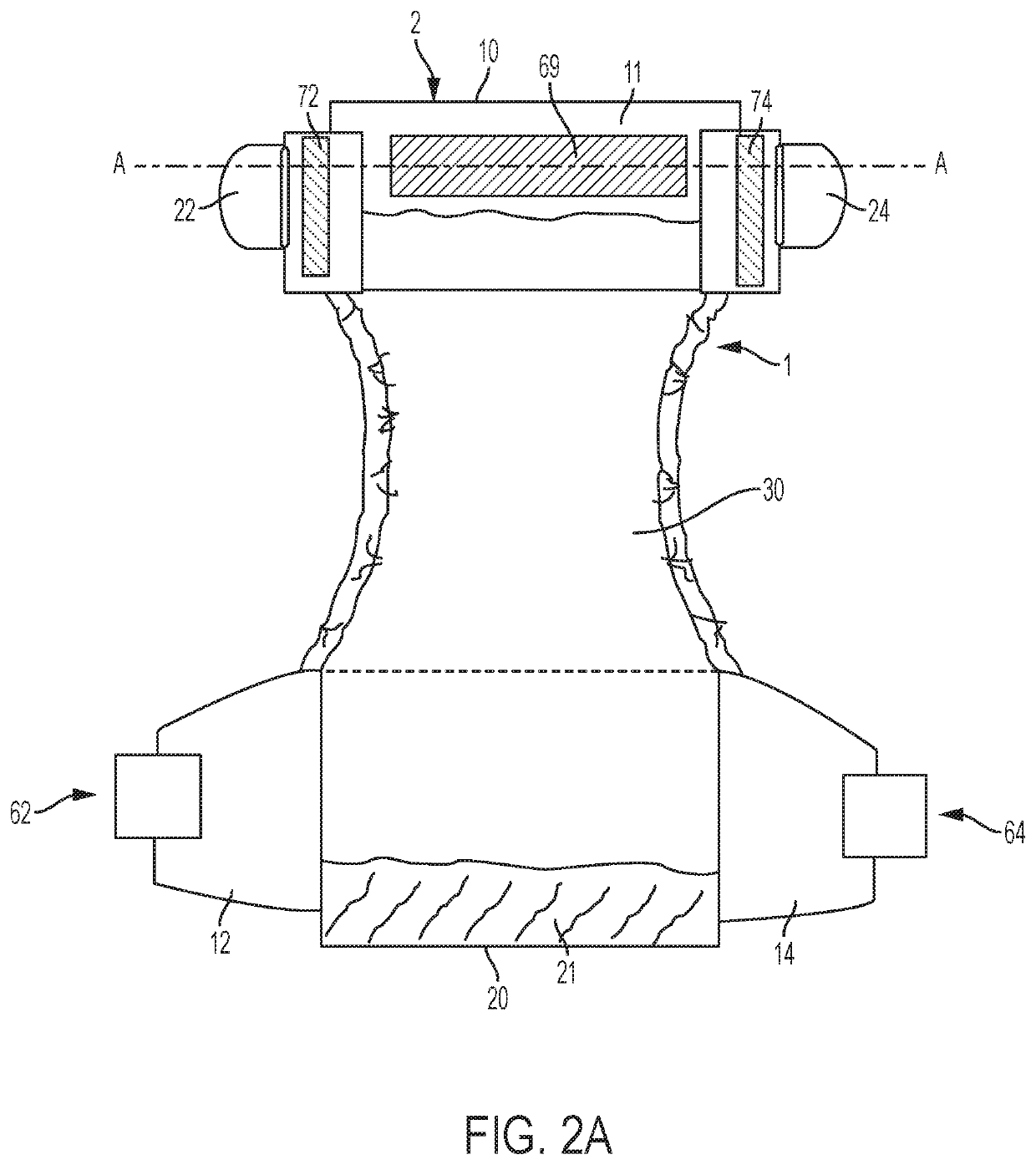
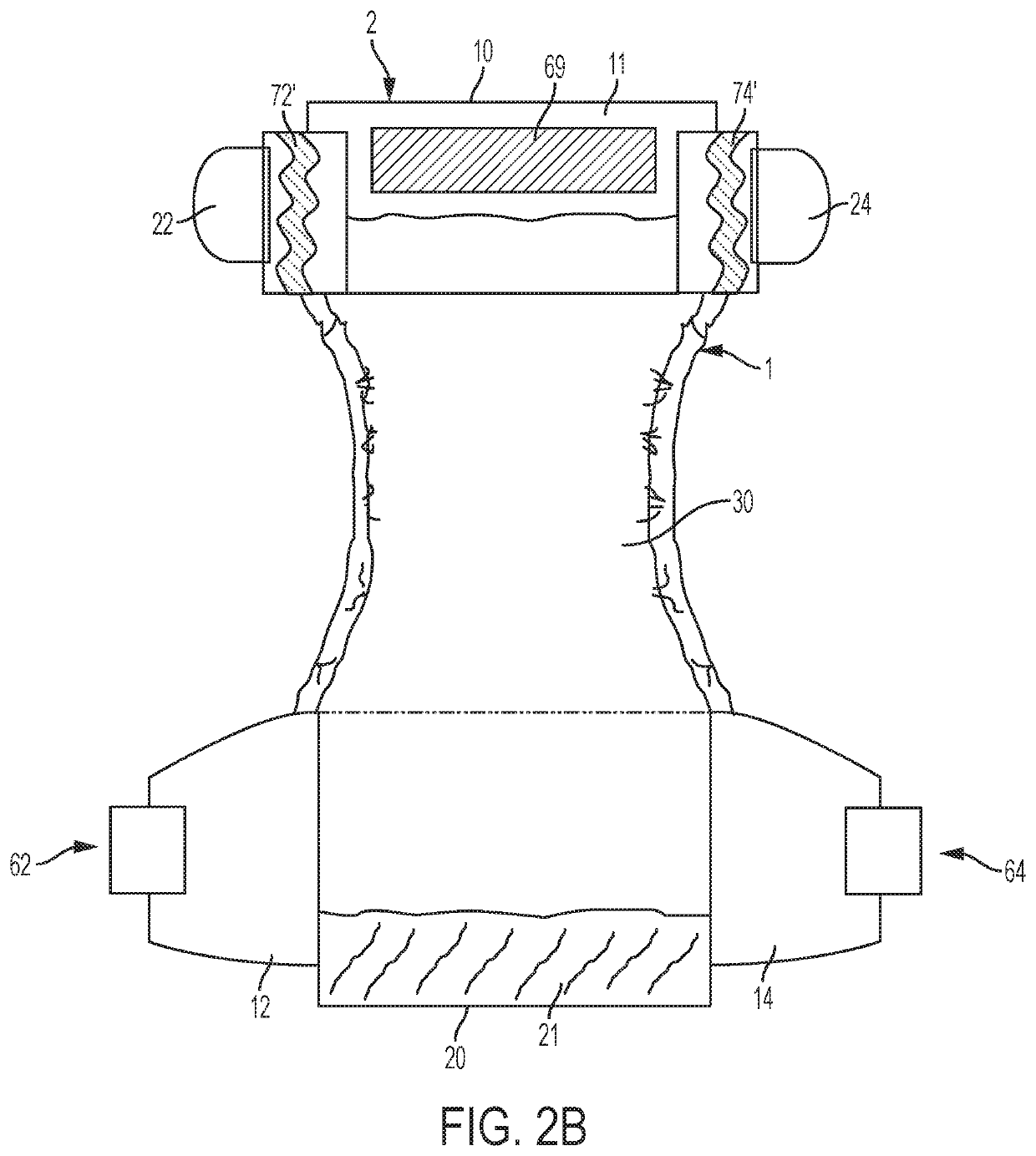
ActiveUS10716718B2Decrease shiftPrevent shifting and saggingAbsorbent padsBandagesElastomerEngineering
An absorbent article that has a reduced tendency to shift when worn. The absorbent article includes a chassis with a front waist portion, a crotch portion, and a back waist portion. Side panels or ears are attached to the front and back waist portions of the chassis, and fastening components are attached to the back ears. Anti-skid elements are added to the outside surface and / or inside surface of the front side panels or ears and / or to the inside surface of the fastening tabs, such as by applying an elastomeric strip in a substantially vertical direction. When the absorbent article is fastened to the wearer attaching the fastening components on the back ears to the front waist portion of the absorbent article, the anti-skid elements interface with the front waist portion, the front ears, and / or the wearer to exert friction and thereby reduce shifting of the fastened absorbent article.
Owner:FIRST QUALITY BABY PROD
Multi-fluid jetting device
An improved multi-fluid jetting device. The jetting device includes a nozzle plate having a substantially planar surface for ejecting a fluid therefrom. The nozzle plate has at least 10 or more nozzles wherein groups of three adjacent nozzles are arranged in a triad orientation and wherein at least two adjacent nozzles in said triad orientation are coupled to two different fluid sources for fluid ejection from said adjacent nozzles substantially perpendicular to said nozzle plate surface.
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com