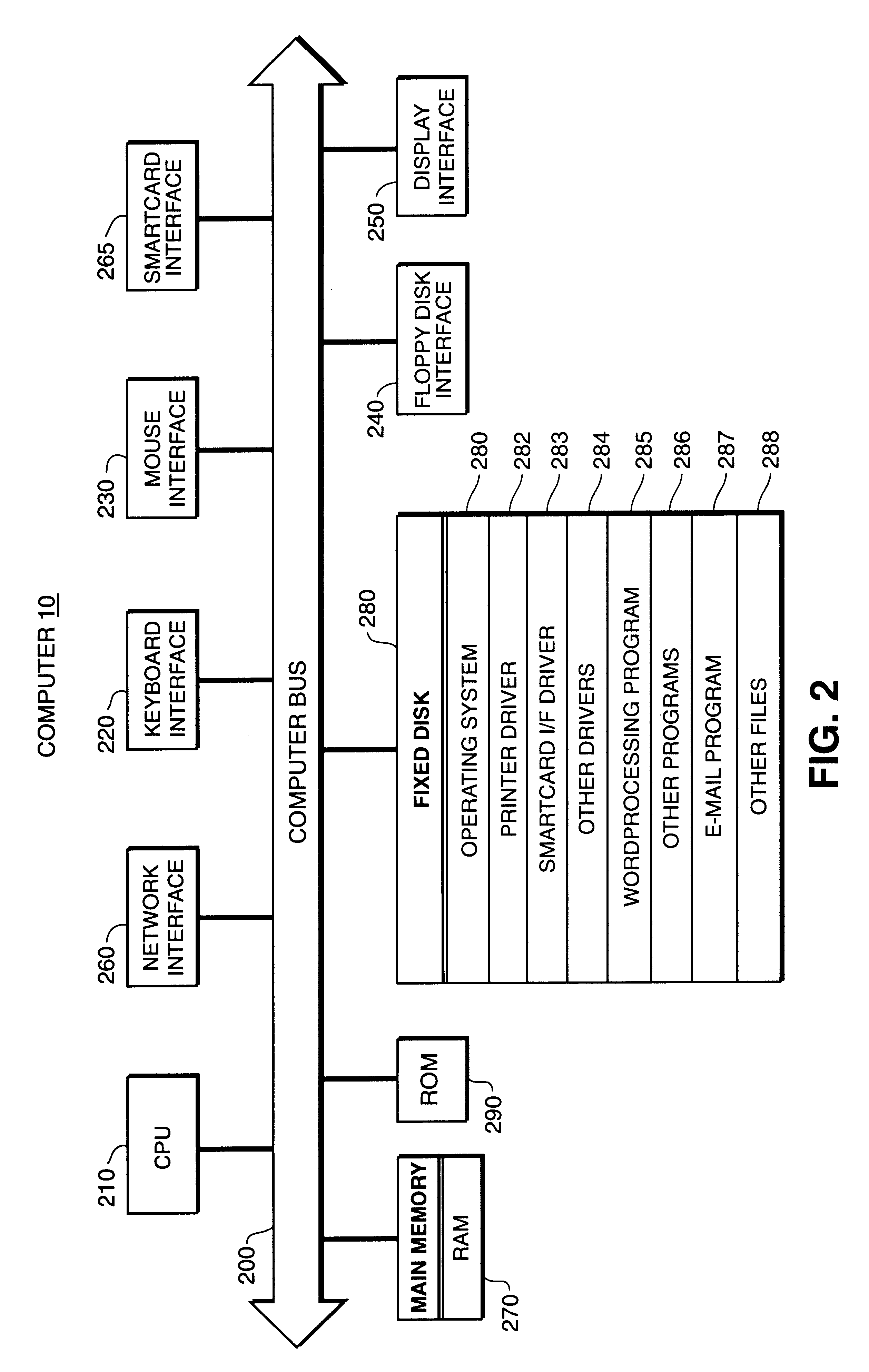
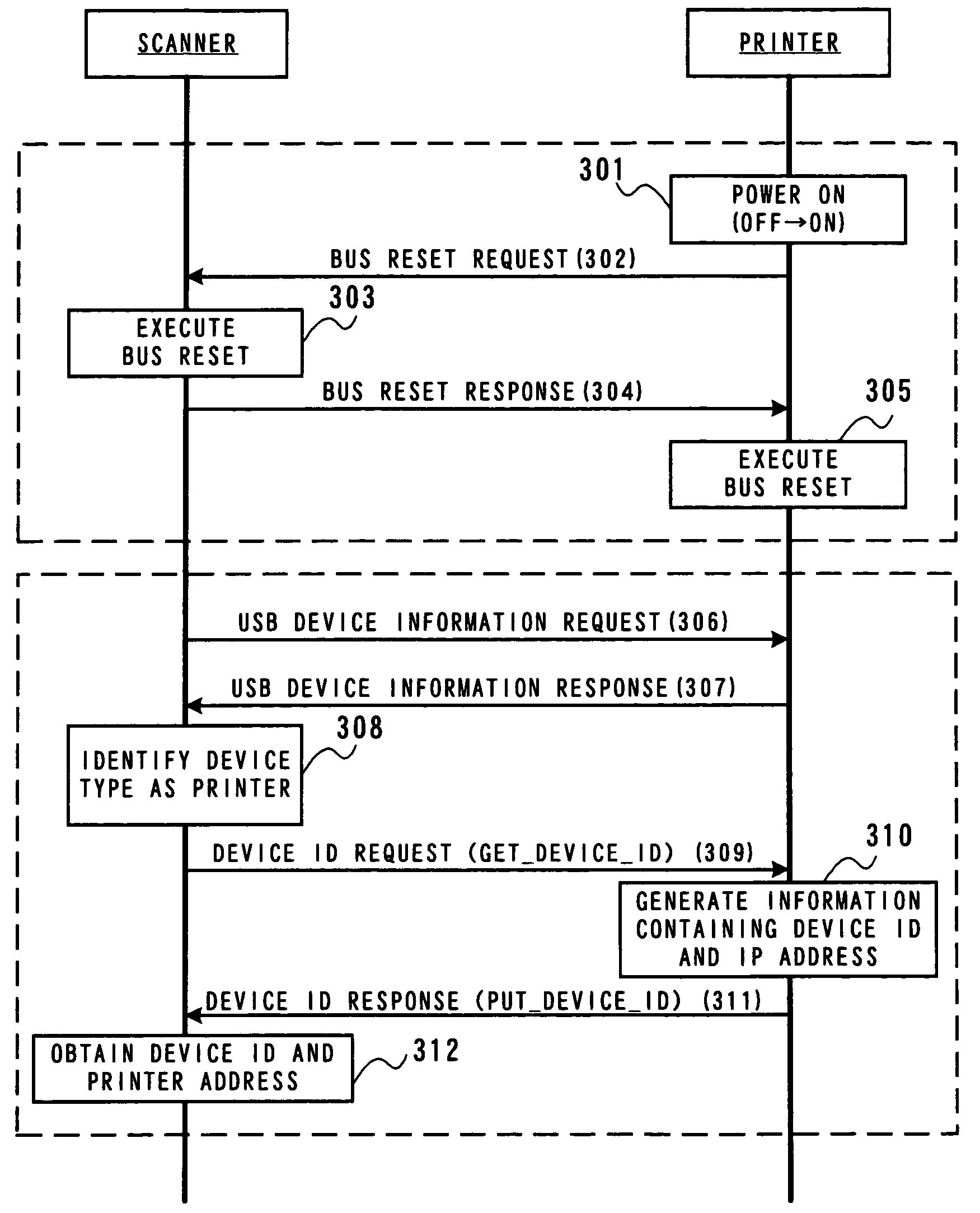
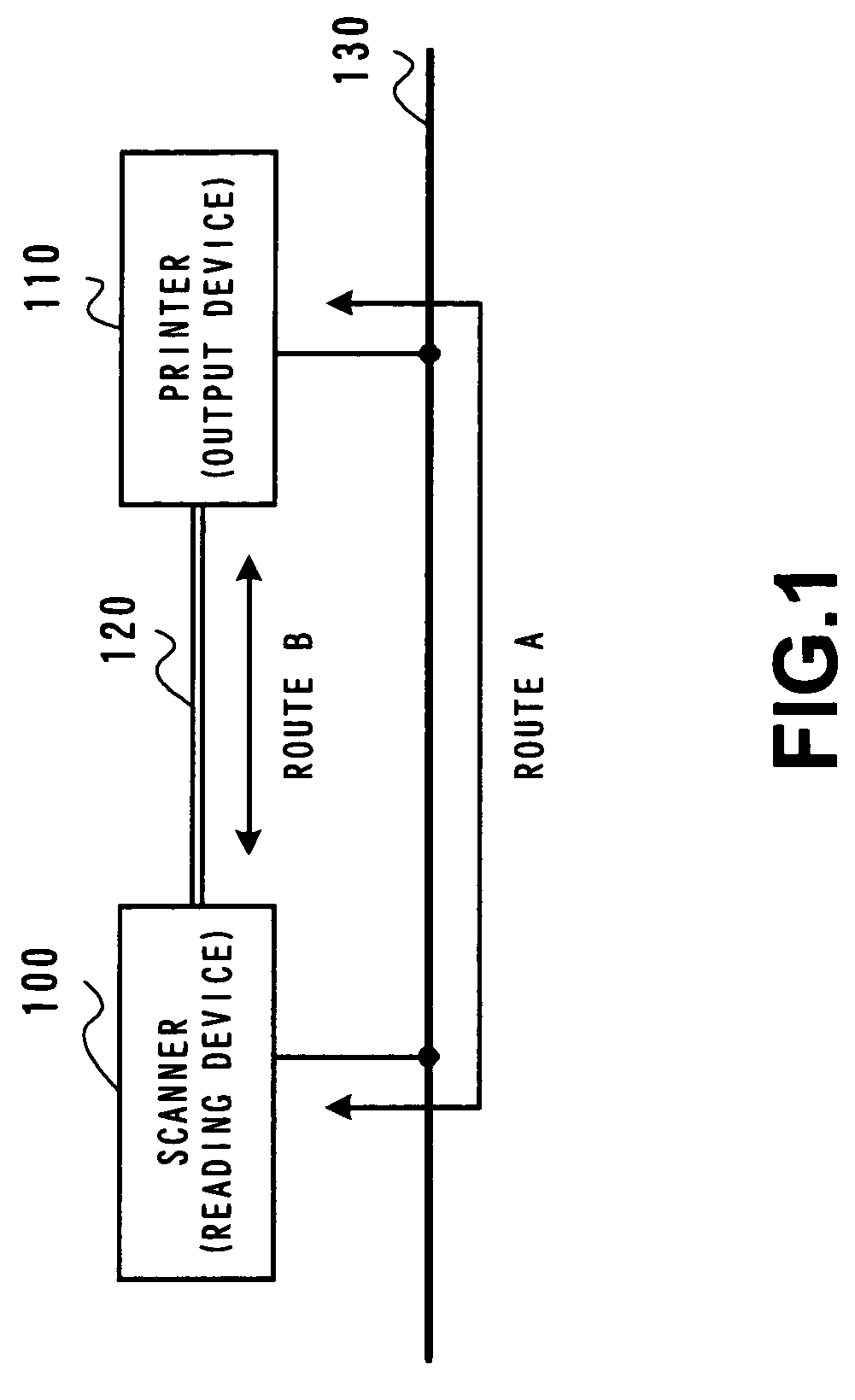
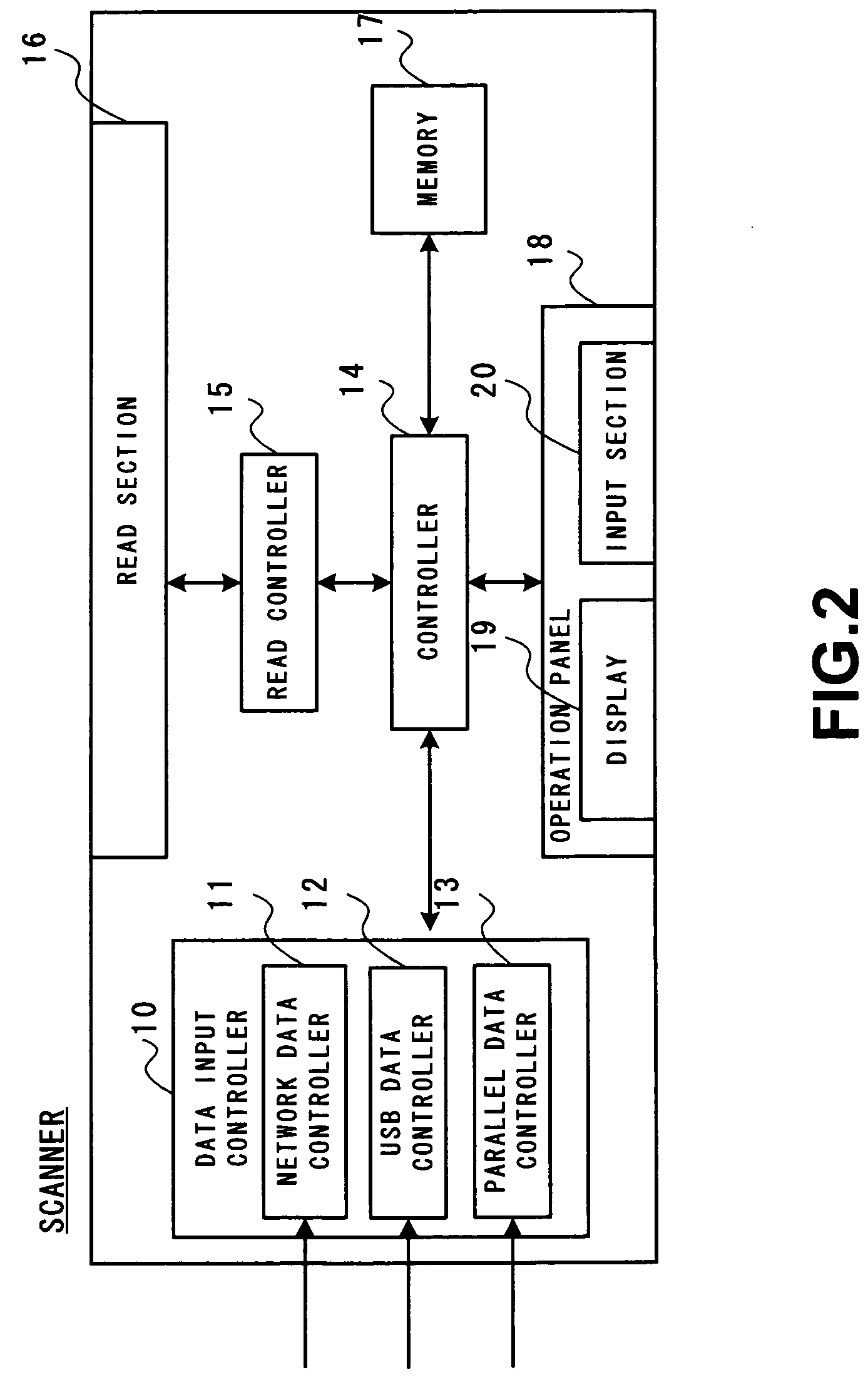
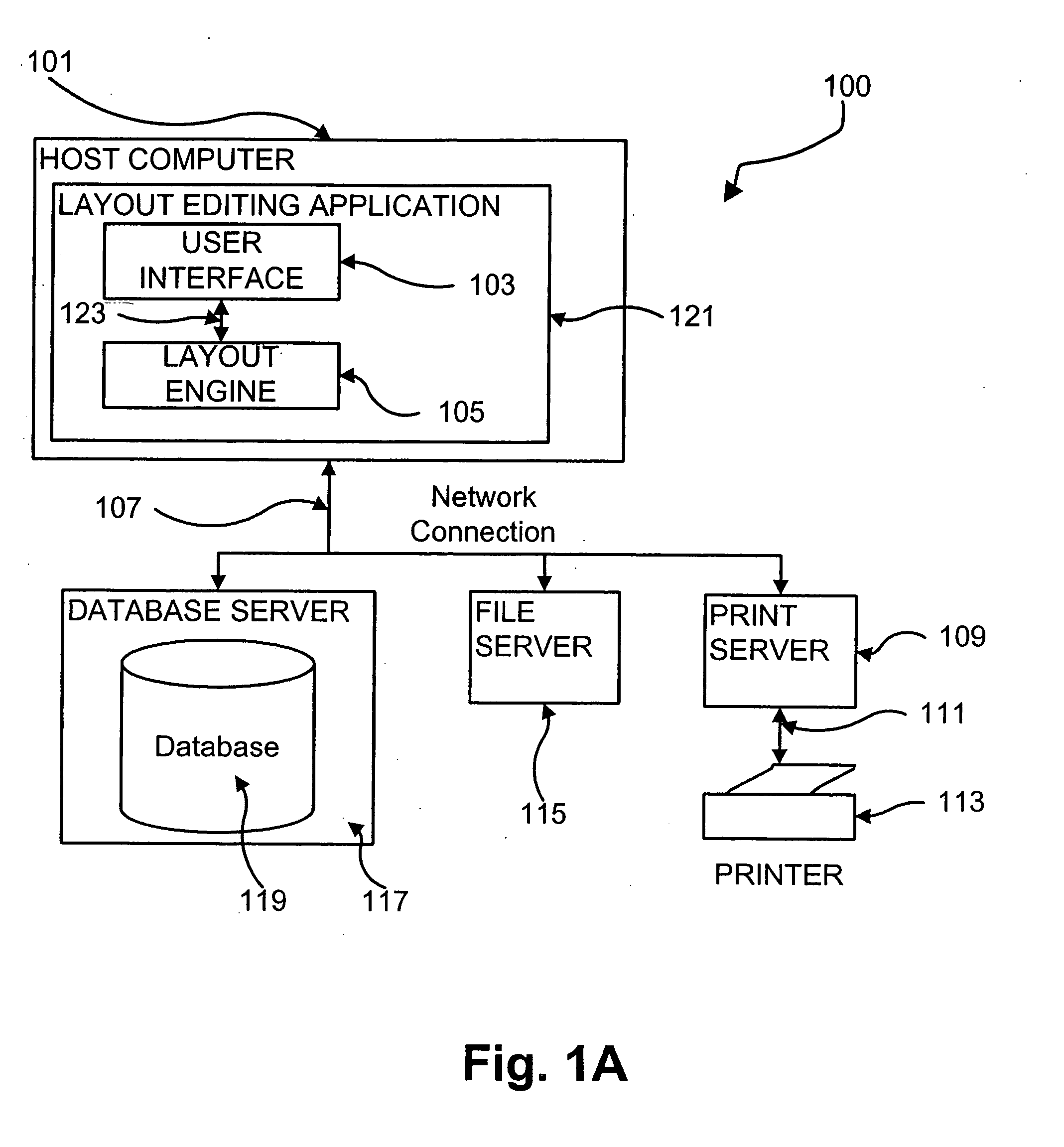
Patents
Literature
7557results about "Visual presentation using printers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
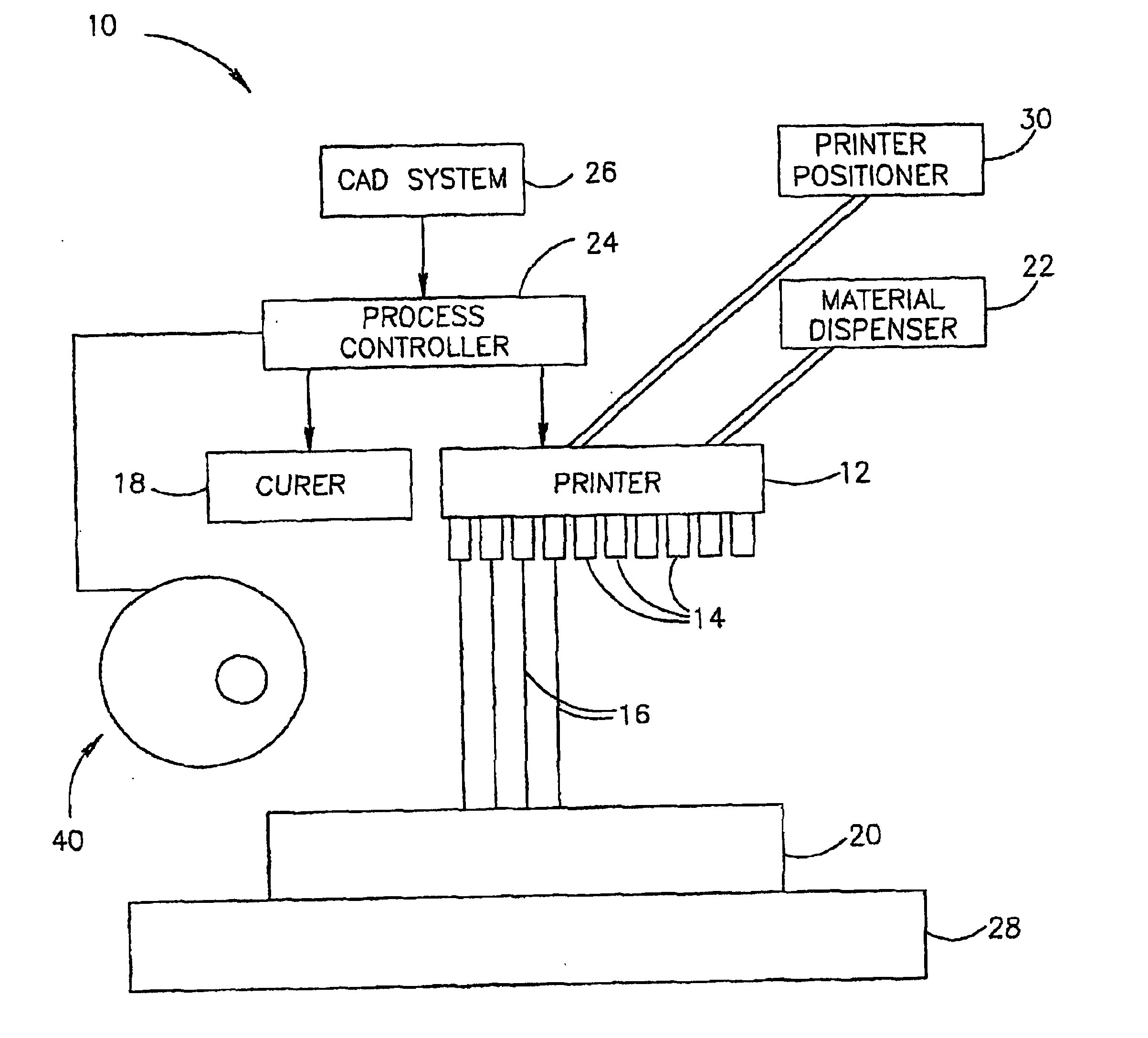
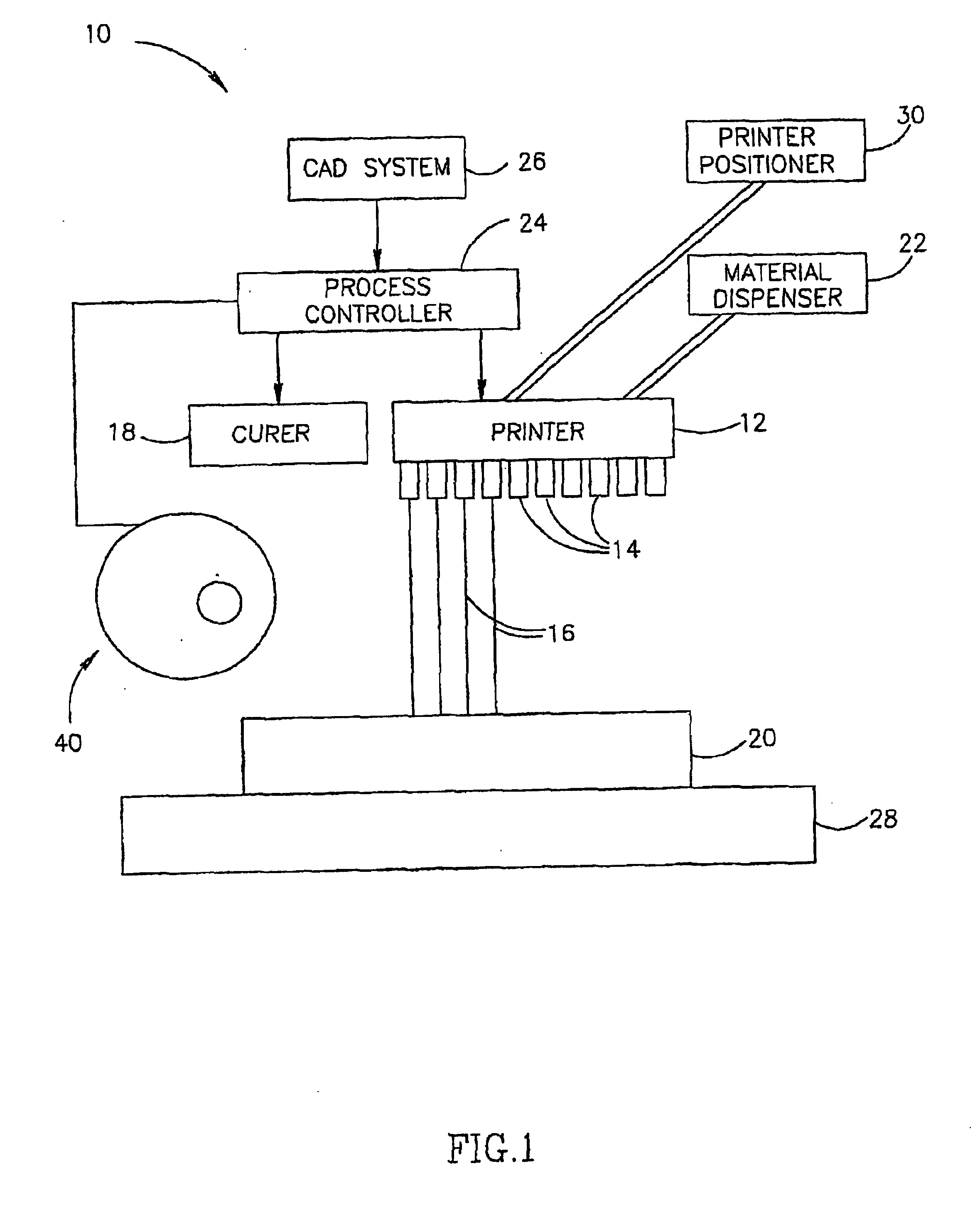
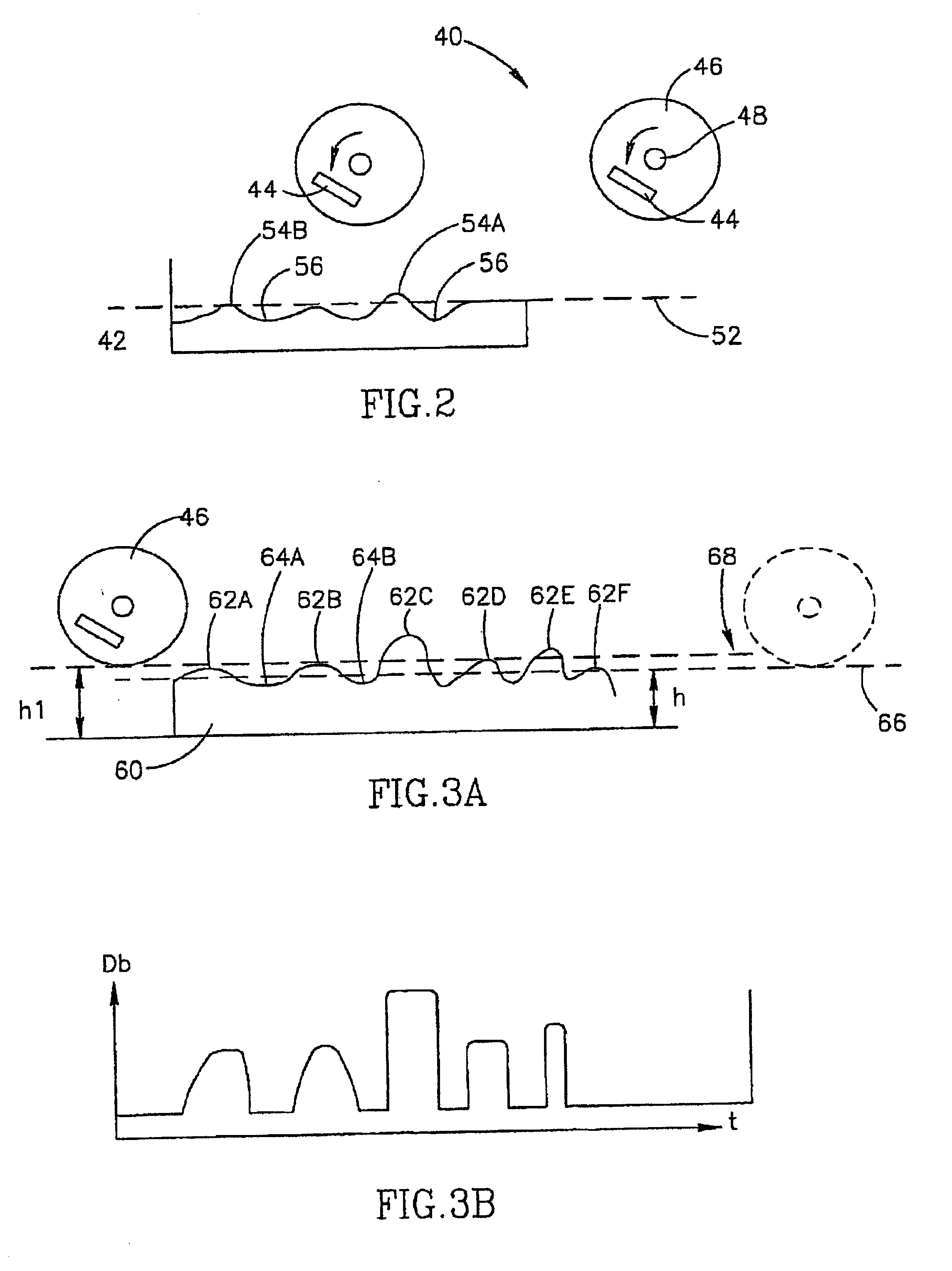
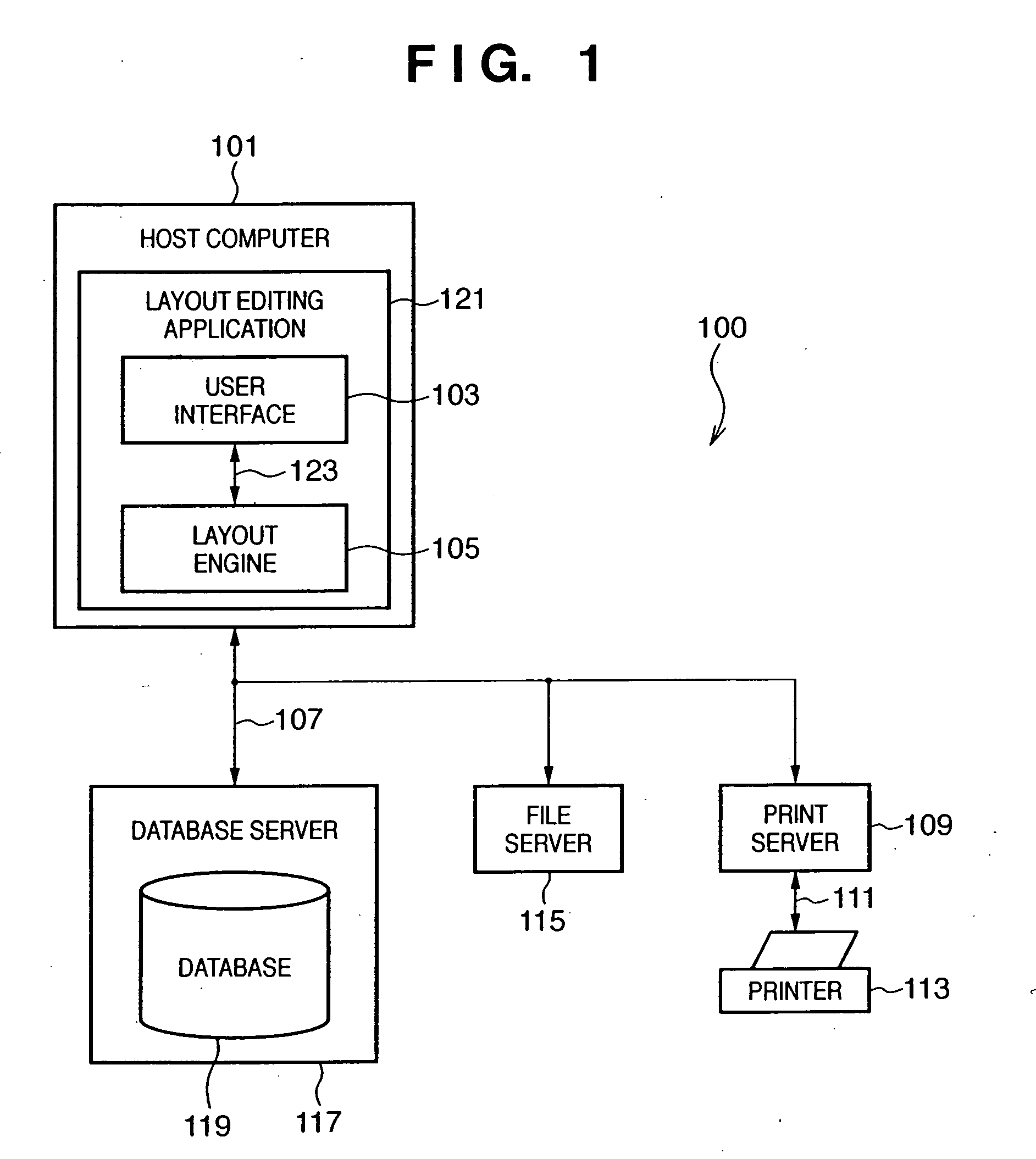
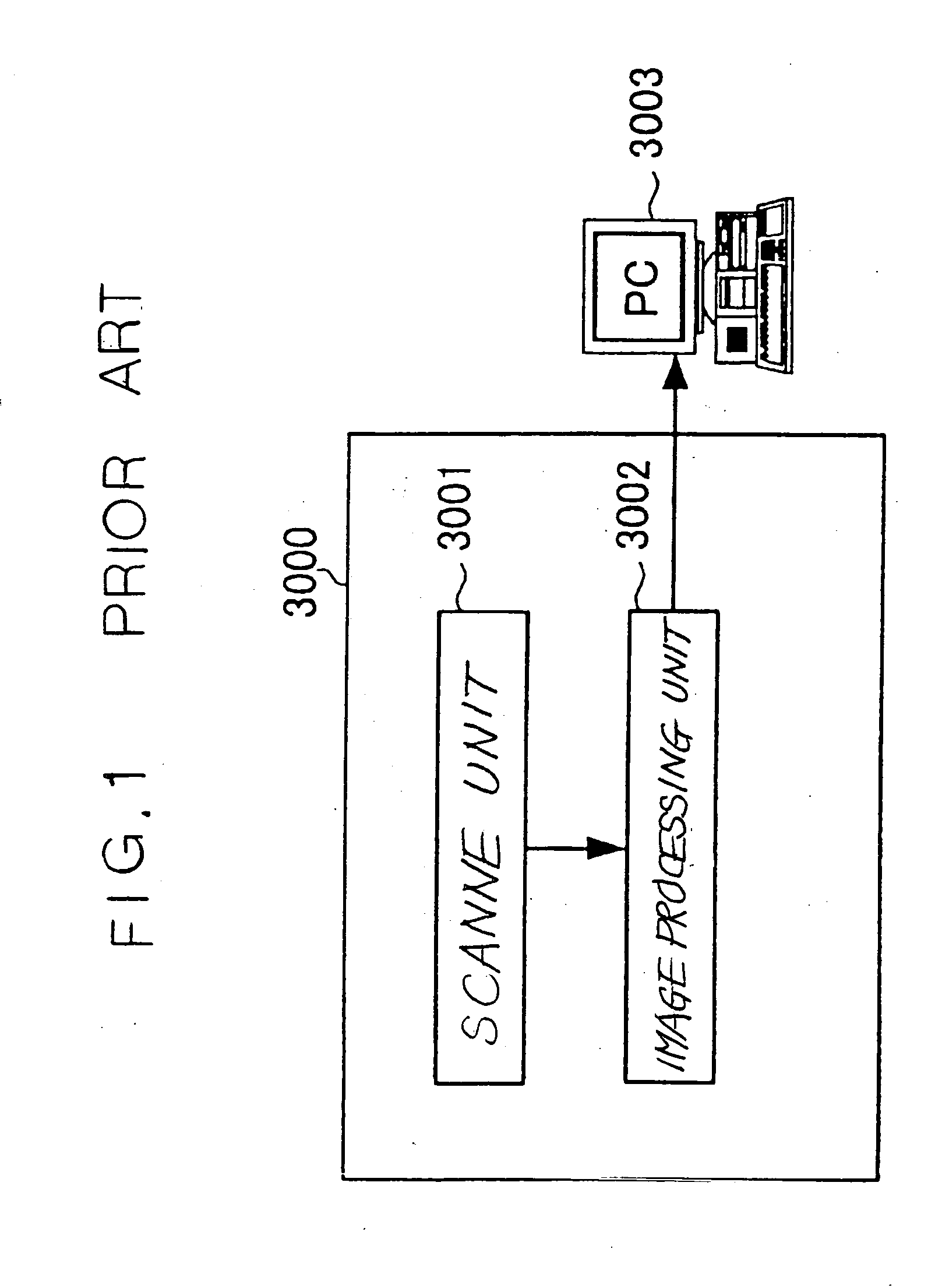
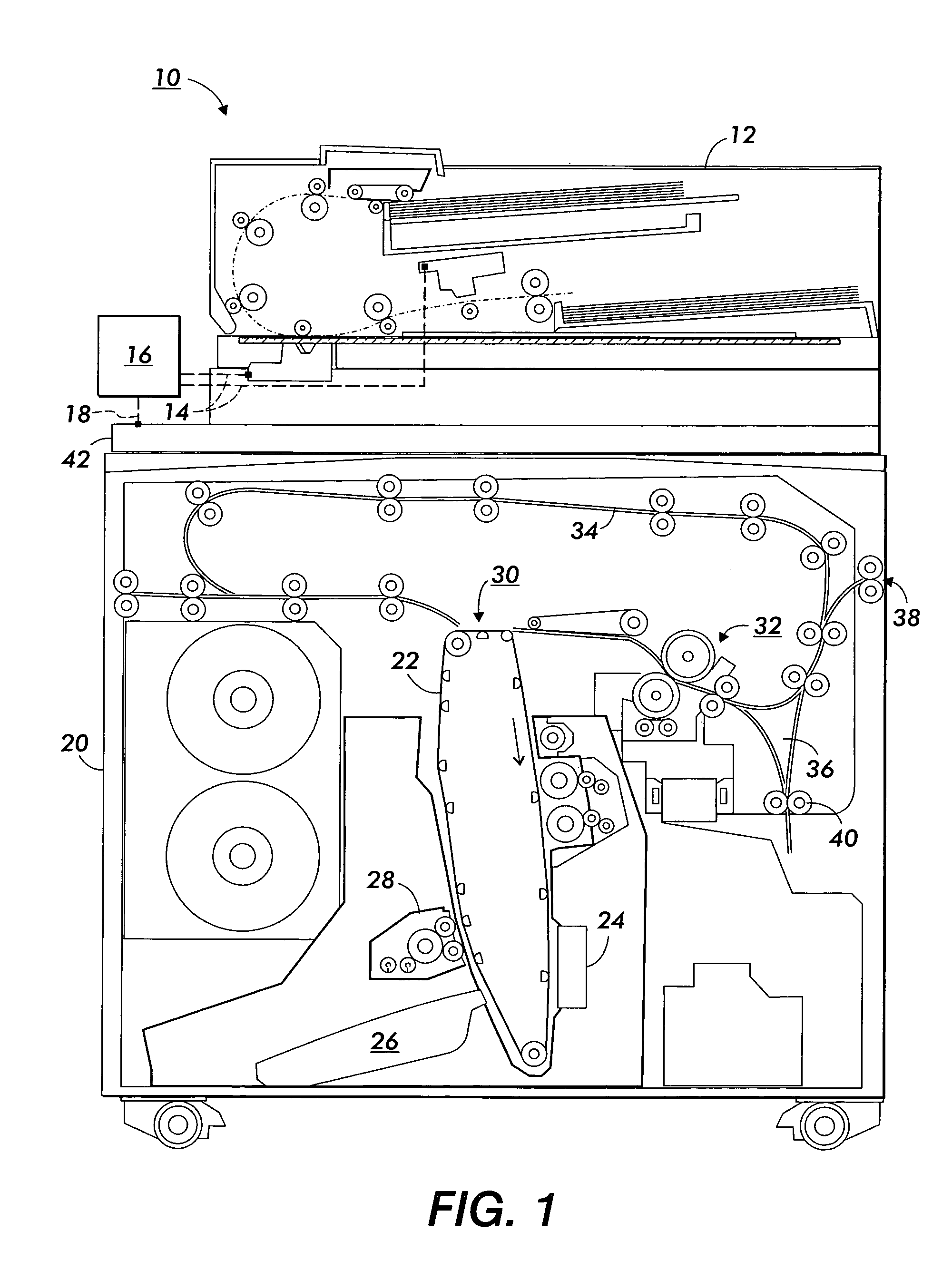
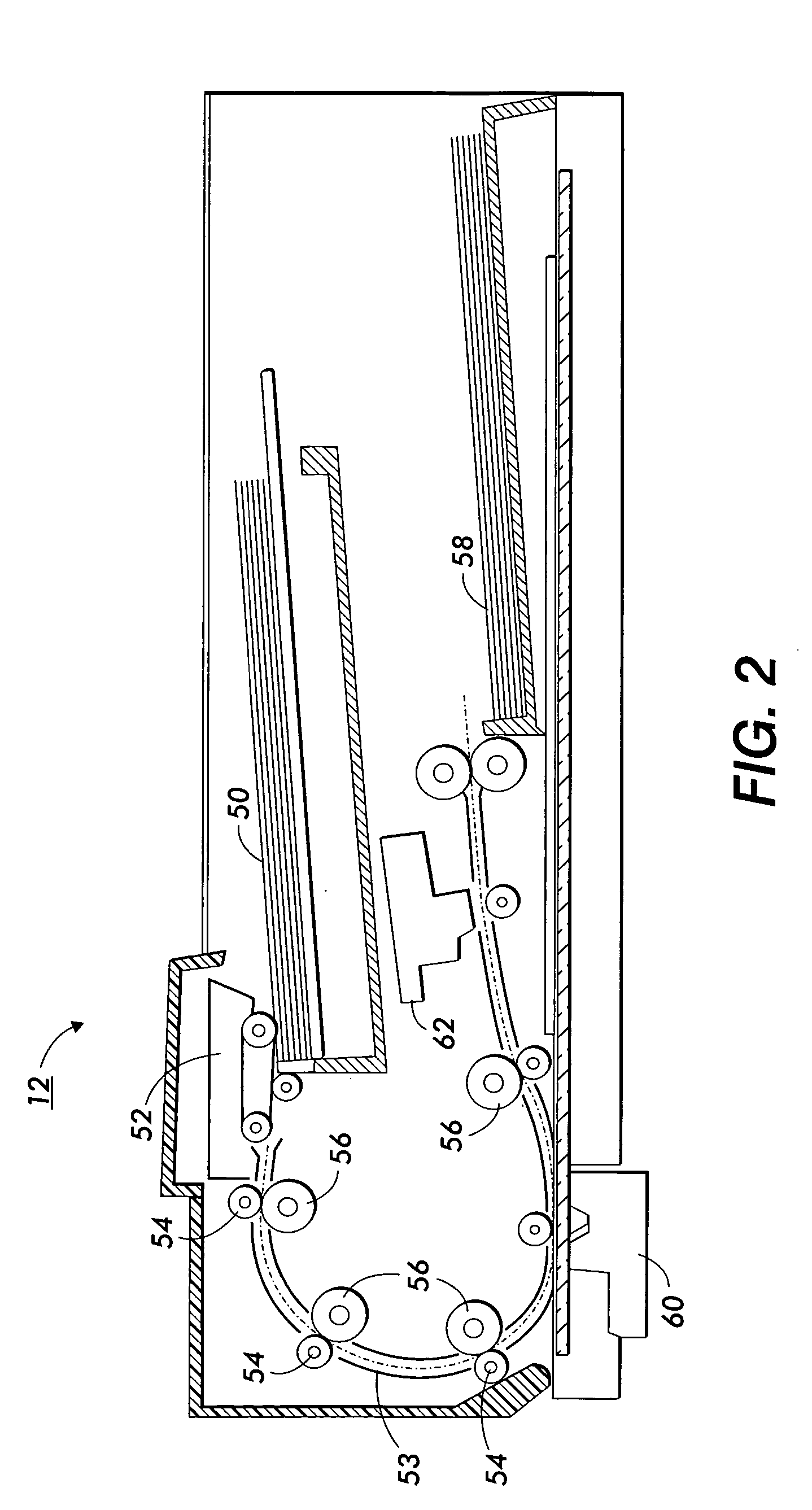
System and method for three dimensional model printing
InactiveUS6850334B1Digitally marking record carriersAdditive manufacturing apparatusInterface layer3 dimensional printing
A system and a method for printing of three-dimensional models and apparatus for controlling the height and thickness of the layers of interface material forming the 3-D models being printed, is provided. The method includes the steps of dispensing a pre-determined quantity of interface material from at least one printing head to form at least one interface layer; leveling the dispensed interface material to a pre-determined height; curing the leveled interface material; and repeating the steps of dispensing, leveling and curing thereby producing a plurality of interface layers to a configured pattern layer for forming the three-dimensional model.
Owner:STRATASYS LTD
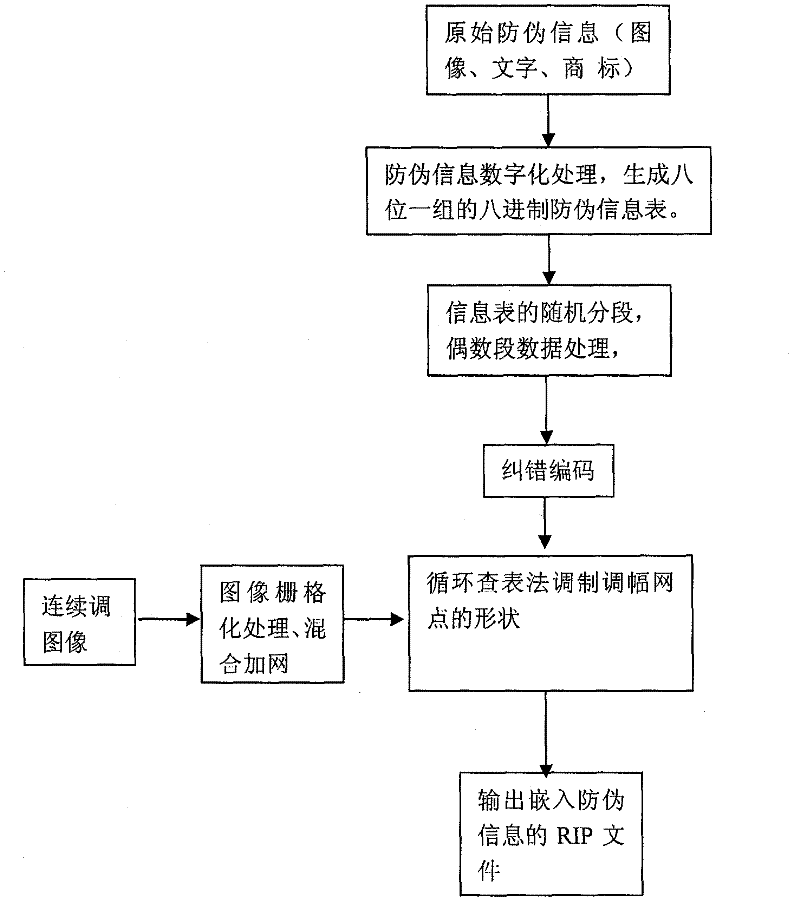
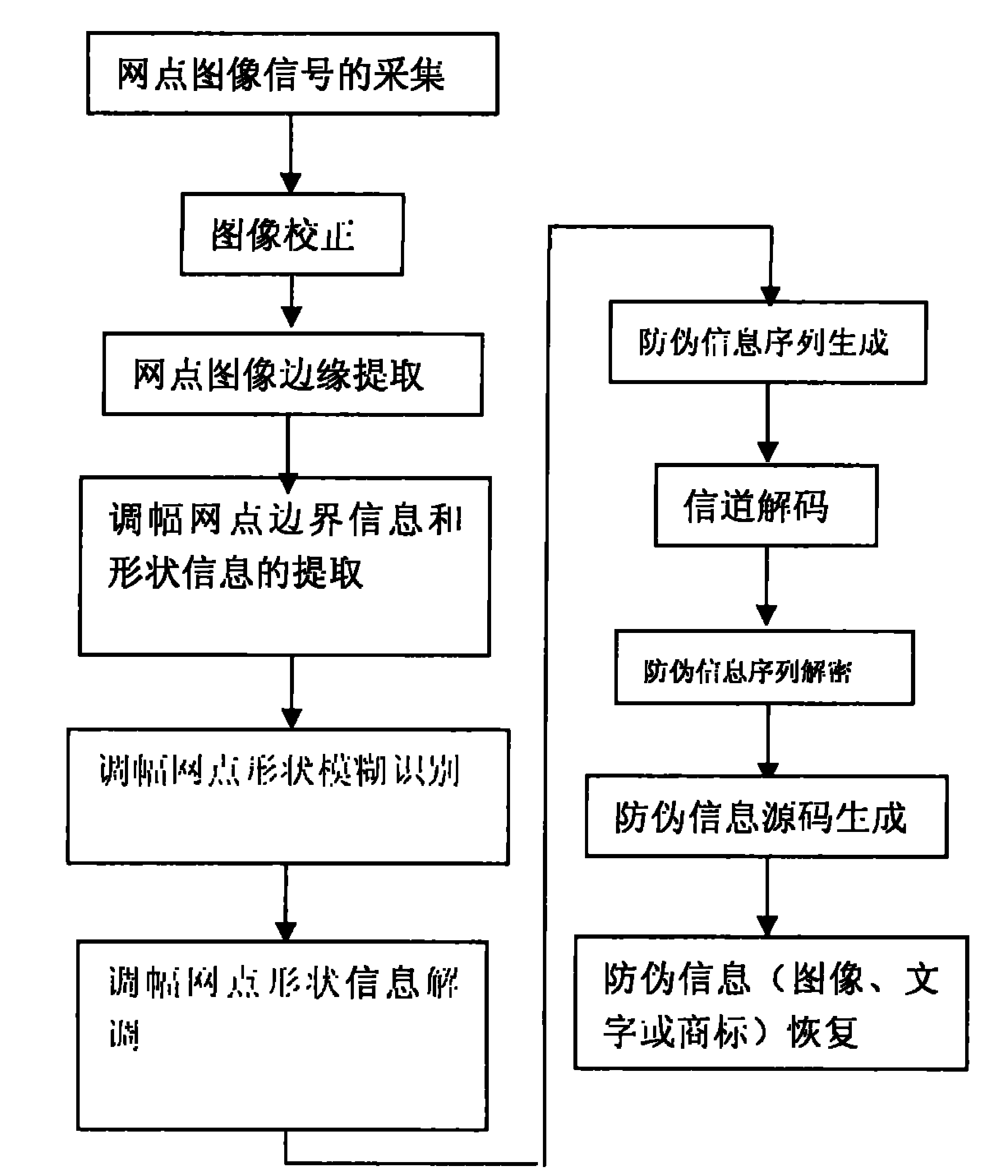
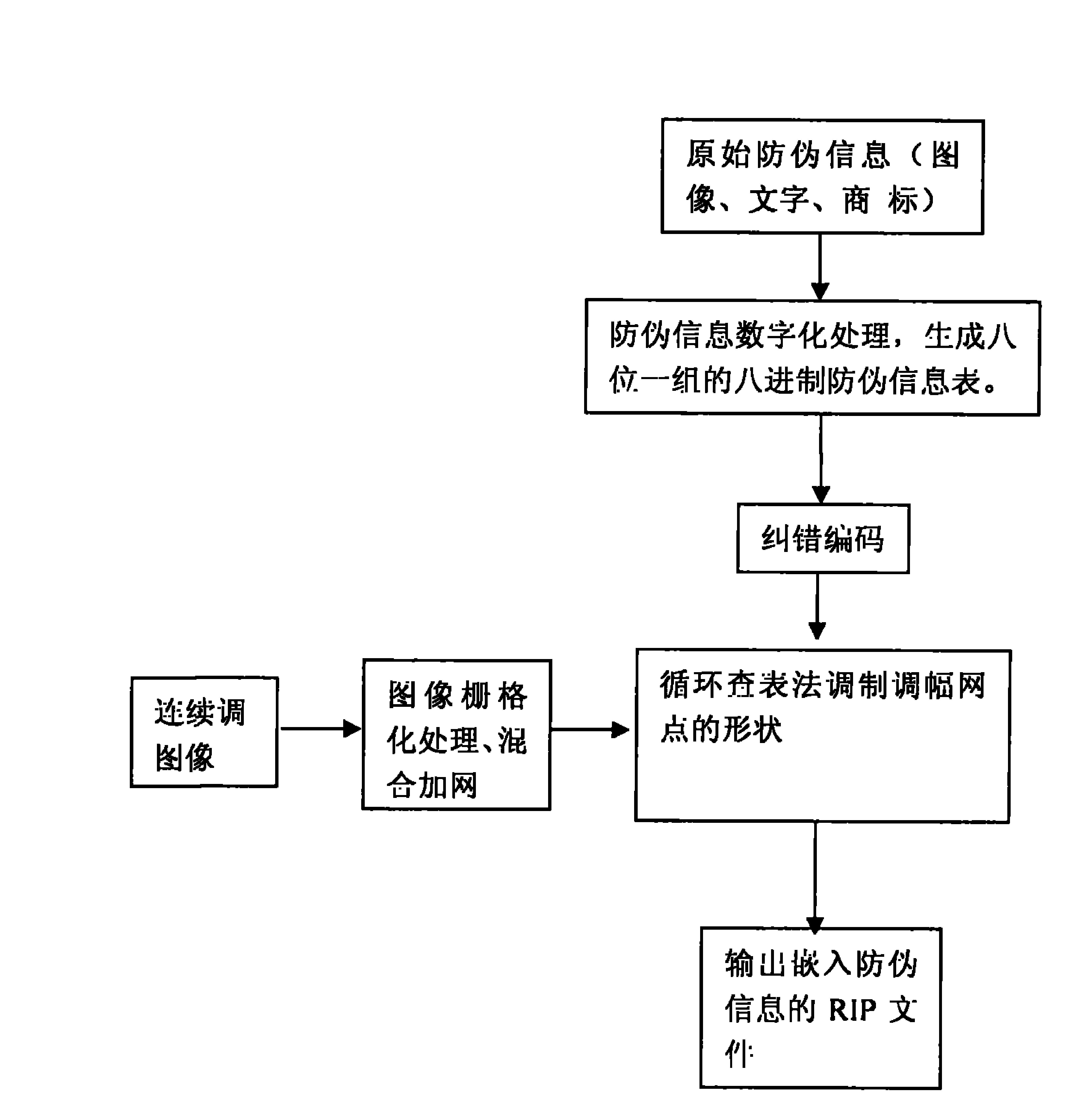
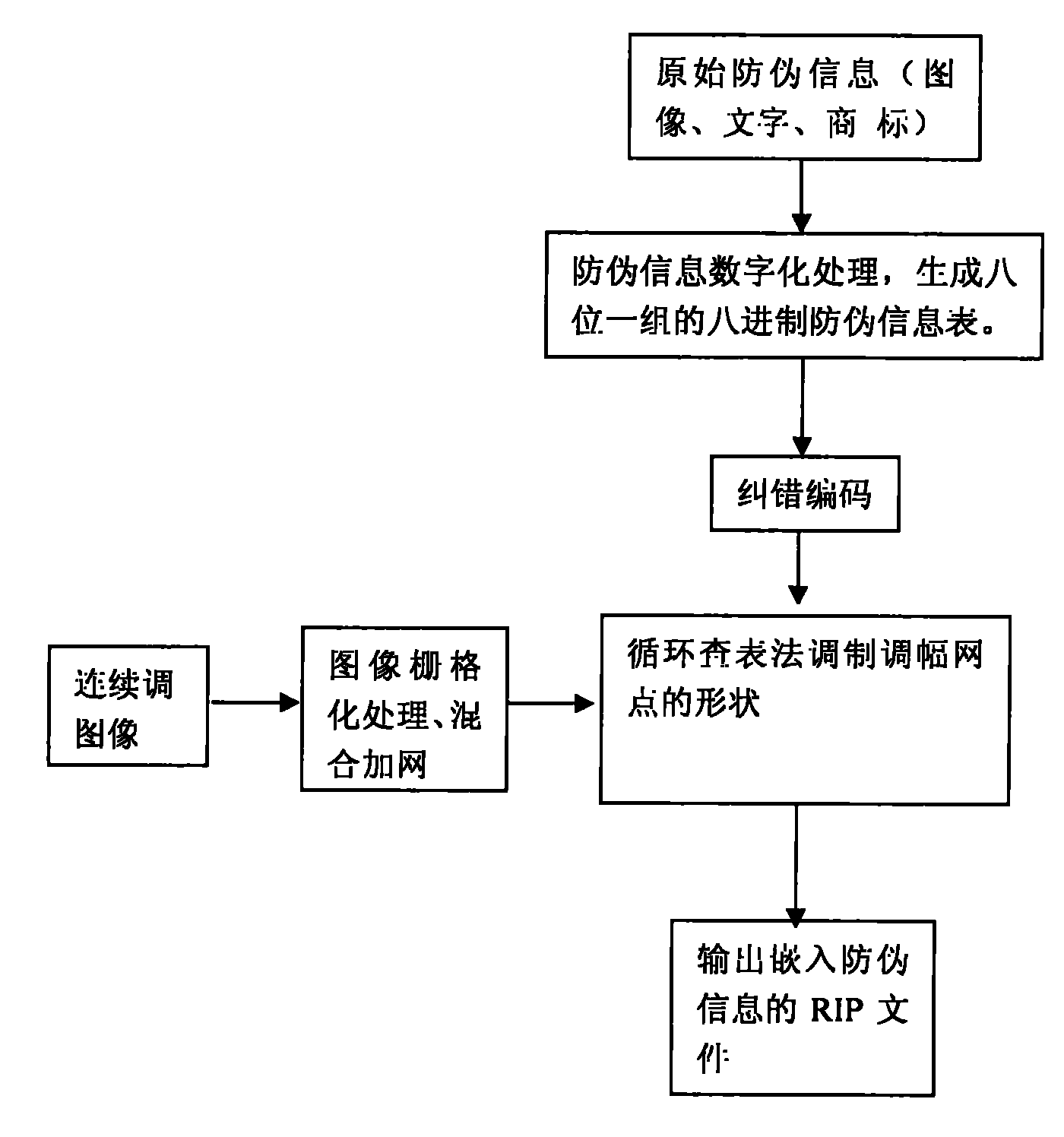
Multi-dimensional encryption anti-counterfeiting printing technology based on binary signals
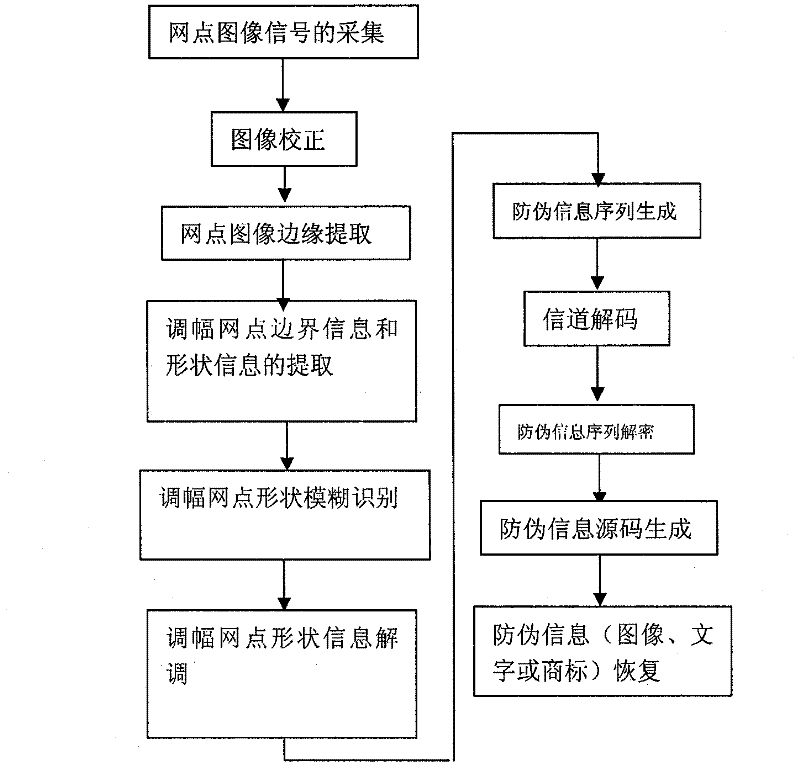
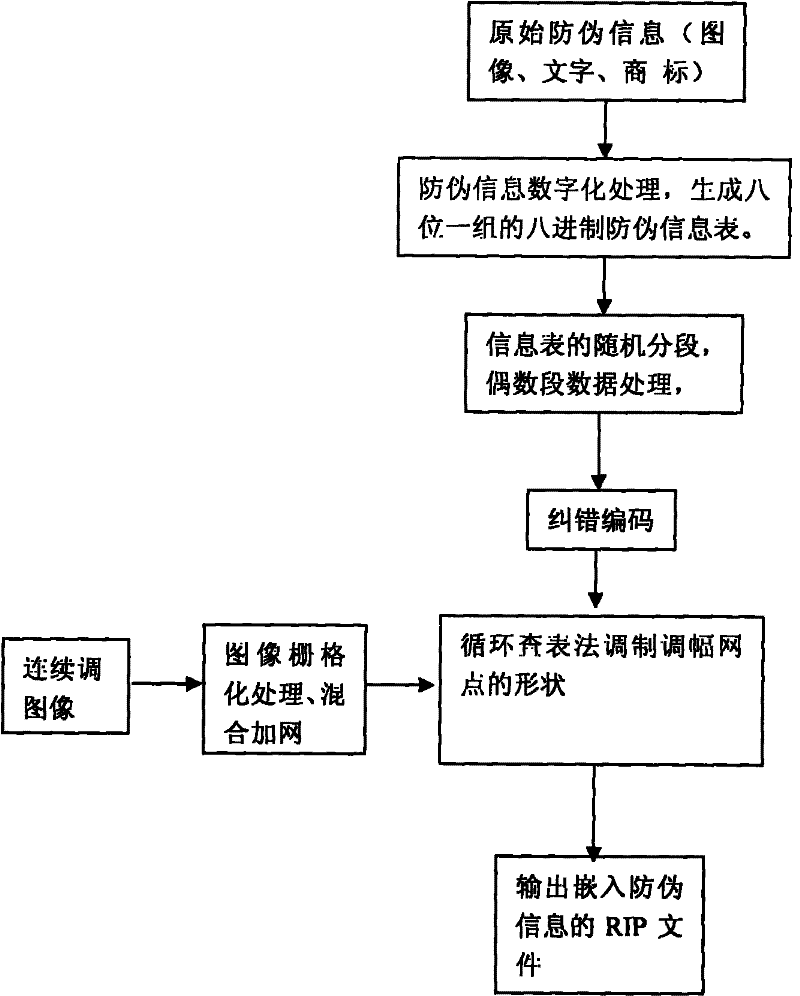
InactiveCN102402696ACombating Illegal CopyingStrong anti-counterfeiting abilityVisual presentation using printersRecord carriers used with machinesElectronic documentMulti dimensional
The invention discloses a multi-dimensional encryption anti-counterfeiting printing technology based on binary signals. According to the anti-counterfeiting printing technology, two-dimensional encryption anti-counterfeiting information can be generated into binary modulation signals by encryption and channel coding, and the anti-counterfeiting information is orderly changed in an amplitude modulation screening form and embedded into a whole page in a modulation mode of a circulating table look-up method, so that the anti-counterfeiting information can be identified from a random fragment during presswork identification. The technology has strong fragment resistance, can resist illegal copying behaviors based on a camera, a scanner, an electronic document and the like more effectively, and can be widely applied in the anti-counterfeiting field of presswork.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
Authenticated secure printing
InactiveUS6862583B1Guaranteed normal transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareMultiple image
Authorized printout of an image corresponding to print data received at a print node from a network. The authorized printout comprises encrypting print data by a print node and storing the encrypted print data without printout, receiving authentication of an intended recipient to print the print data, and decrypting the encrypted print data by the print node and printing the decrypted print data by an image forming device, responsive to receipt of authentication in the receiving step. The print node may be the image forming device itself or a gateway to multiple image forming devices. The print node encrypts the print data with either a symmetric key or an asymmetric key.
Owner:CANON KK
Image forming system, image forming method and information terminal device
InactiveUS7869073B2Visual presentation using printersMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunication unitTerminal equipment
An image forming system comprising an information terminal device and a printing device that is connected to the information terminal device through a network and a local connection and performs a printing process of image data sent from the information terminal device, in which the information terminal device includes a network identifier acquisition unit that obtains through the local connection a network identifier of the printing device on the network at the time of the local connection between the information terminal device and the printing device, and a data communication unit that performs data communications with the printing device through the network according to the network identifier obtained by the network identifier acquisition unit.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Encrypting anti-counterfeiting printing technology for modulating shapes of amplitude modulation dots of printed work through binary-system encrypting signal
InactiveCN102184428ACombating Illegal CopyingStrong anti-counterfeiting abilityVisual presentation using printersRecord carriers used with machinesElectronic documentDocumentation
The invention discloses an encrypting anti-counterfeiting printing technology for modulating the shapes of amplitude modulation dots of a printed work through a binary-system encrypting signal. In the anti-counterfeiting printing technology, anti-counterfeiting information is subjected to encryption and channel coding to form a binary-system modulating signal and the anti-counterfeiting information is embedded into a whole page by sequentially changing the shapes of the amplitude modulation dots in a circulating table lookup modulation way. During recognition of the printed work, the anti-counterfeiting information can be recognized from any fragment, so the anti-breakage performance is high, the illegal replication based on a camera, a scanner, an electronic document and the like can be more effectively prevented and the technology can be extensively applied to the field of printed work anti-counterfeiting.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
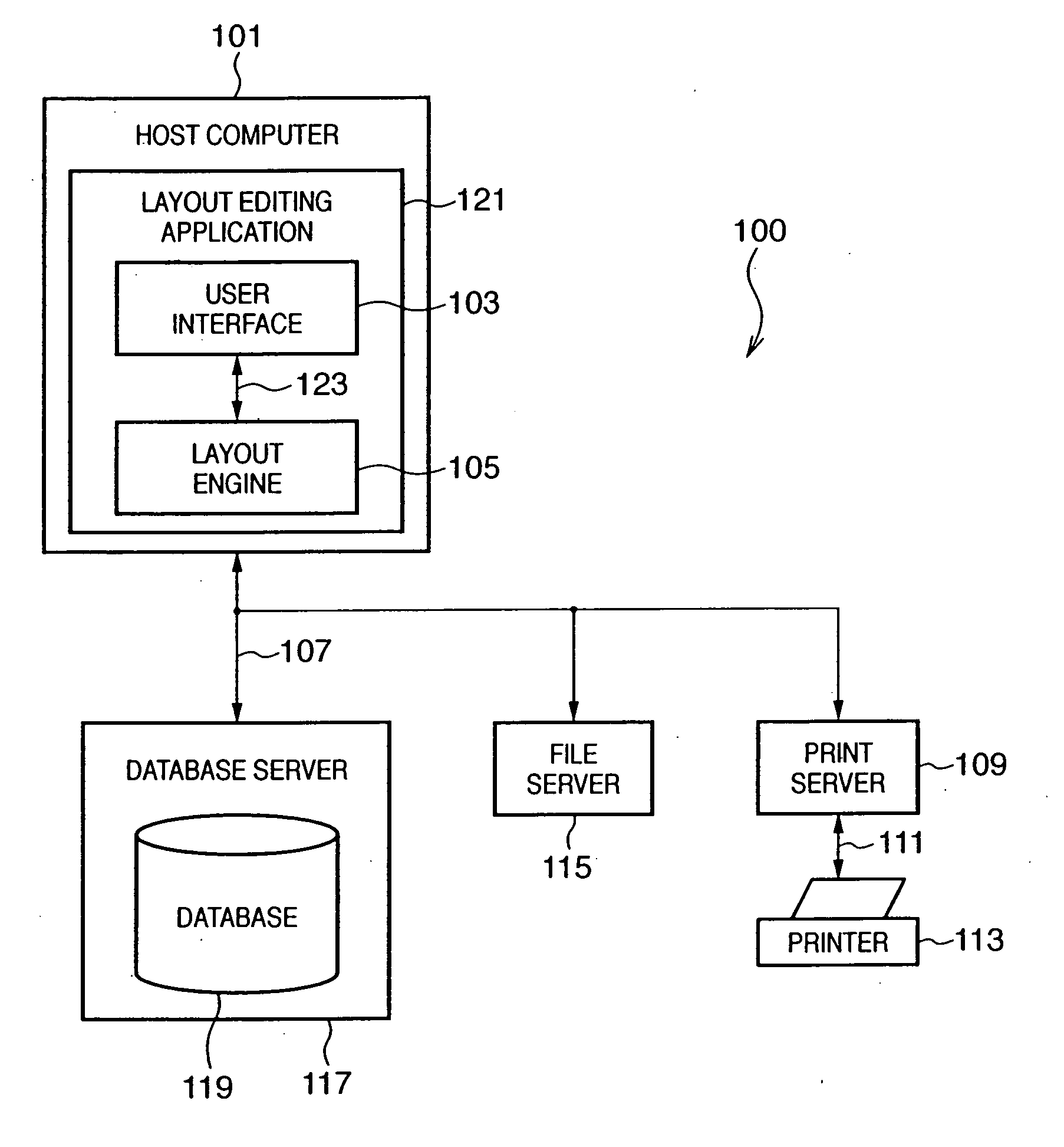
Layout adjustment method and apparatus and layout adjustment program
InactiveUS20050168782A1Increase the use of spaceVisual presentation using printersNatural language data processingImage basedZeroisation
In determining the layout of a page on the basis of layout information representing the intra-page layout of a plurality of containers in which images based on assigned data are visually drawn, the layout information has designation information to designate whether to zeroise the container size when data assigned to the container is empty. In adjusting the layout, a container to which empty data is assigned is detected from the plurality of partial regions. It is determined whether designation information corresponding to the detected container is designation to zeroise the size. If zeroisation is designated, the layout of the page is adjusted while regarding the size of the detected container as zero.
Owner:CANON KK
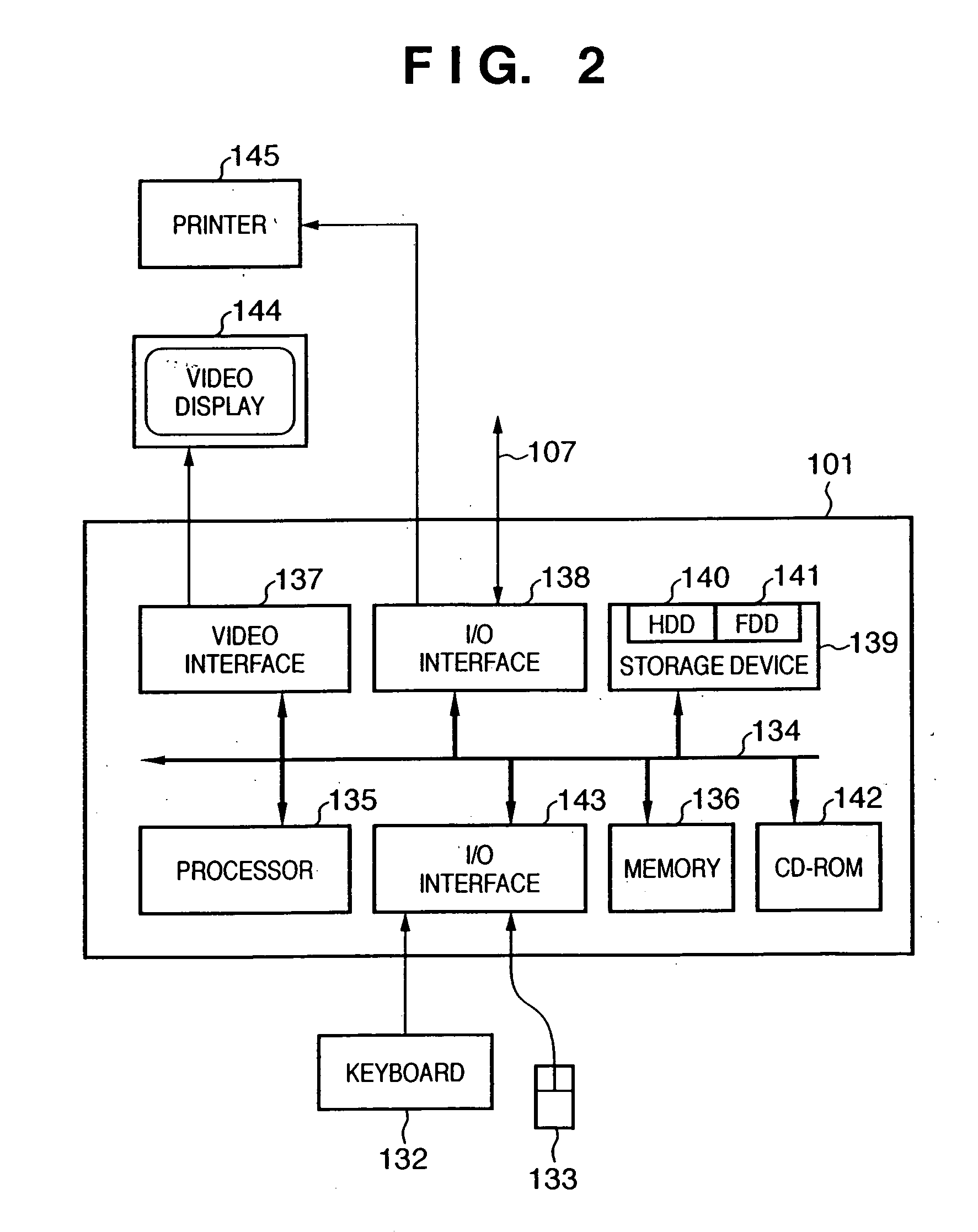
Automated wysiwyg previewing of font, kerning and size options for user-selected text
InactiveUS20060132812A1Visual presentation using printersNatural language data processingComputer graphics (images)Text editing
A font control application detects a user selection of text being edited in a text-editing application. In response to a single user command, the font control application presents a font preview menu including the selected text automatically rendered multiple times in different fonts. In response to receiving a user selection of one rendition of the selected text from the font preview menu, the font control application instructs the text-editing application to change a font of the selected text to the font of the selected rendition.
Owner:YOU SOFTWARE
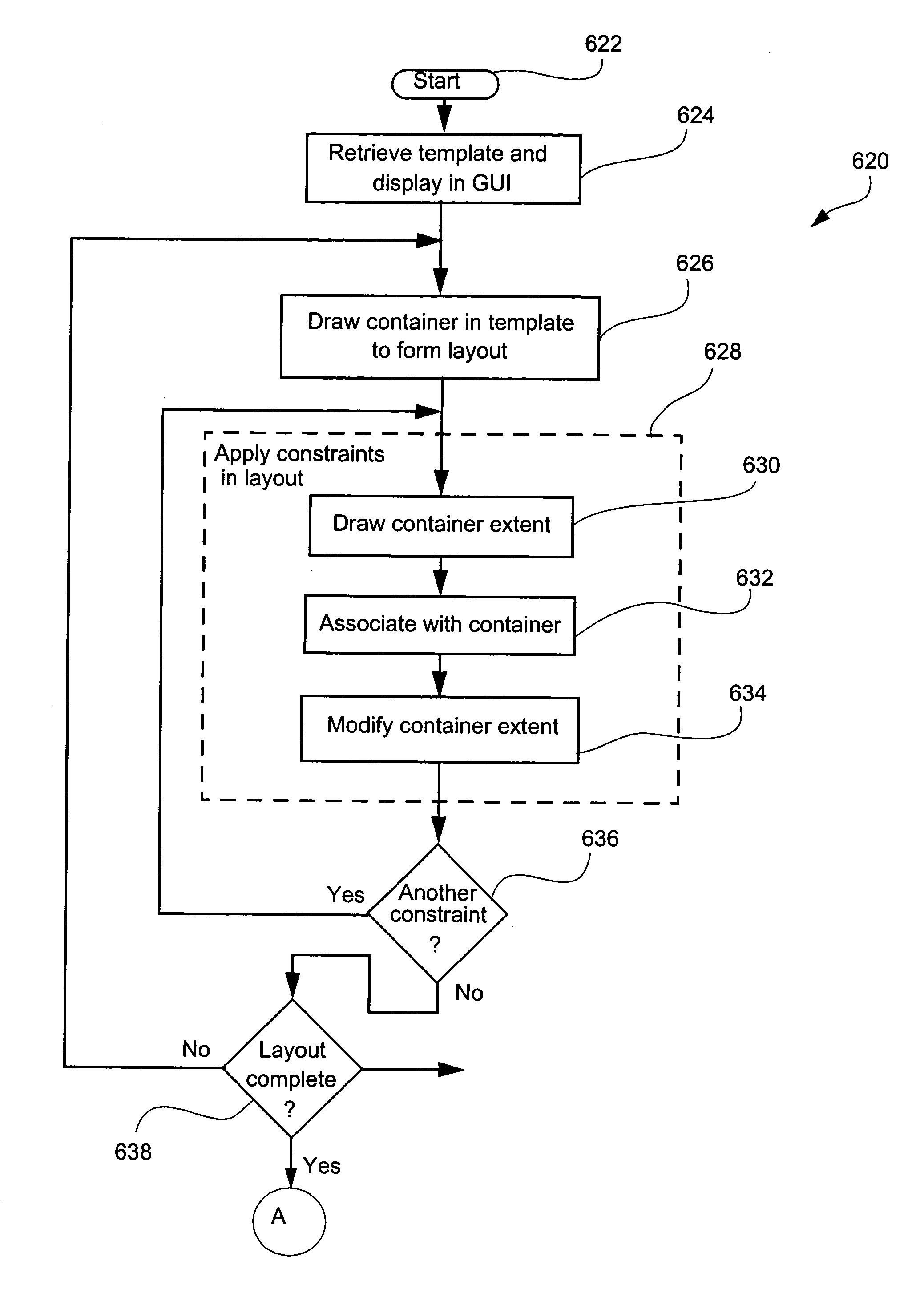
Selective preview and proofing of documents or layouts containing variable data
InactiveUS20050094205A1Visual presentation using printersNatural language data processingPaper documentData content
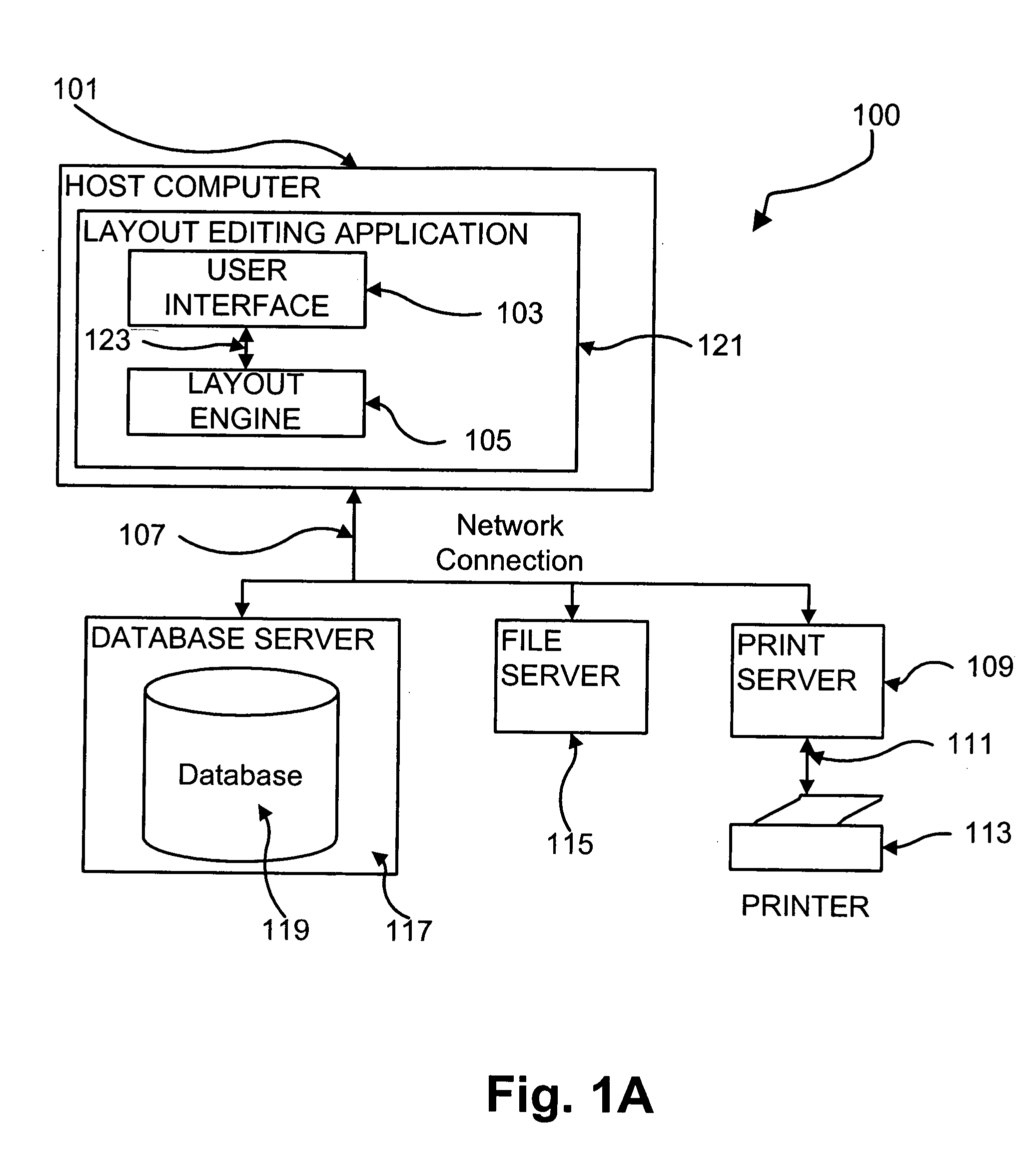
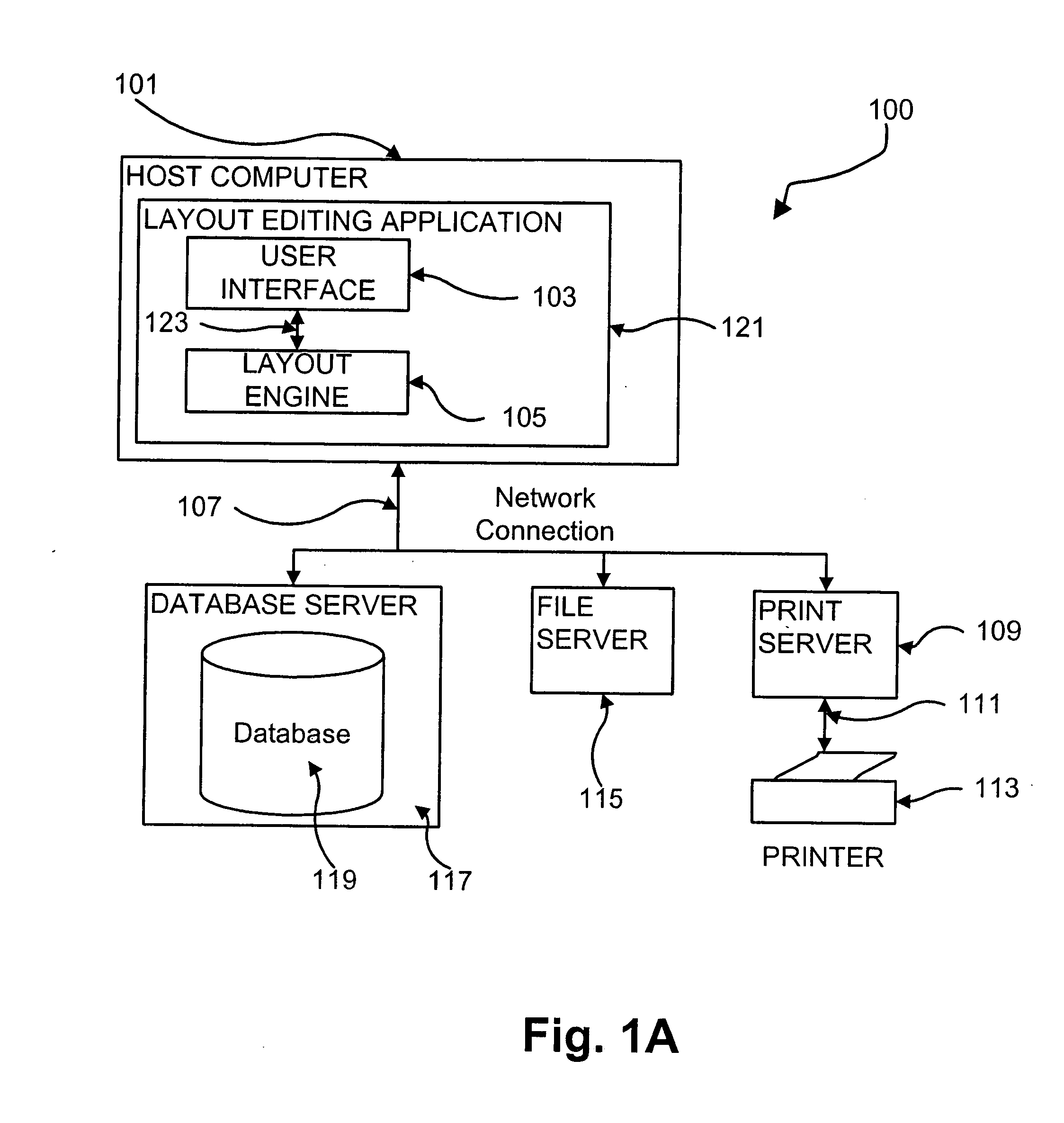
Methods and apparatus for proofing (644) a variable document intended for printing are disclosed in which a GUI (2000) is configured to allow user manipulation of layout rules associated with content containers within a template for variable document generation. Selective proofing (2100) involves proofing a plurality of variable data documents each formed from a common layout in which variable data content is placed into containers having locations and sizes within the layout and defined by layout rules. Measures of variation (2103, 2106) and measures of deviation (2109, 2110) are calculated. The measures of deviation are processed (2112) to give a deviation value. Once completed for each document, the deviation values of the documents are compared (2114) to identify at least one group of the documents for presentation for further assessment. Live proofing includes creating a layout (2002) for a variable data document based upon a template established in the GUI. A container (2010) is set in the template to form the layout, which is then modified to thereby generate an exemplary document by placing exemplary content into the container, wherein a dimension of the container and / or a position of the container are varied based upon a property of the placed content. The exemplary document is displayed in the layout via the GUI to enable visual proofing by the user.
Owner:CANON KK
User interface for creation and editing of variable data documents
InactiveUS20050094207A1Visual presentation using printersNatural language data processingGraphical user interfaceLayout
Methods and apparatus for variable document printing are disclosed in which a graphical user interface is configured to allow user manipulation of layout rules associated with content containers within a template for variable document generation. One method involves creating a layout for a variable data document based upon a template. The method firstly sets at least one container in the template to form the layout, and then establishes at least one constraint associated with each selected one of at least one feature of the container, the establishing including, for each feature, detecting a user instigated selection of the corresponding feature. The layout is then modified to thereby generate the document by placing content into the containers, wherein at least one dimension of the least one container and / or a position of the at least one container in the layout are varied based on a property of the placed content on a condition that each constraint in the layout is satisfied.
Owner:CANON KK
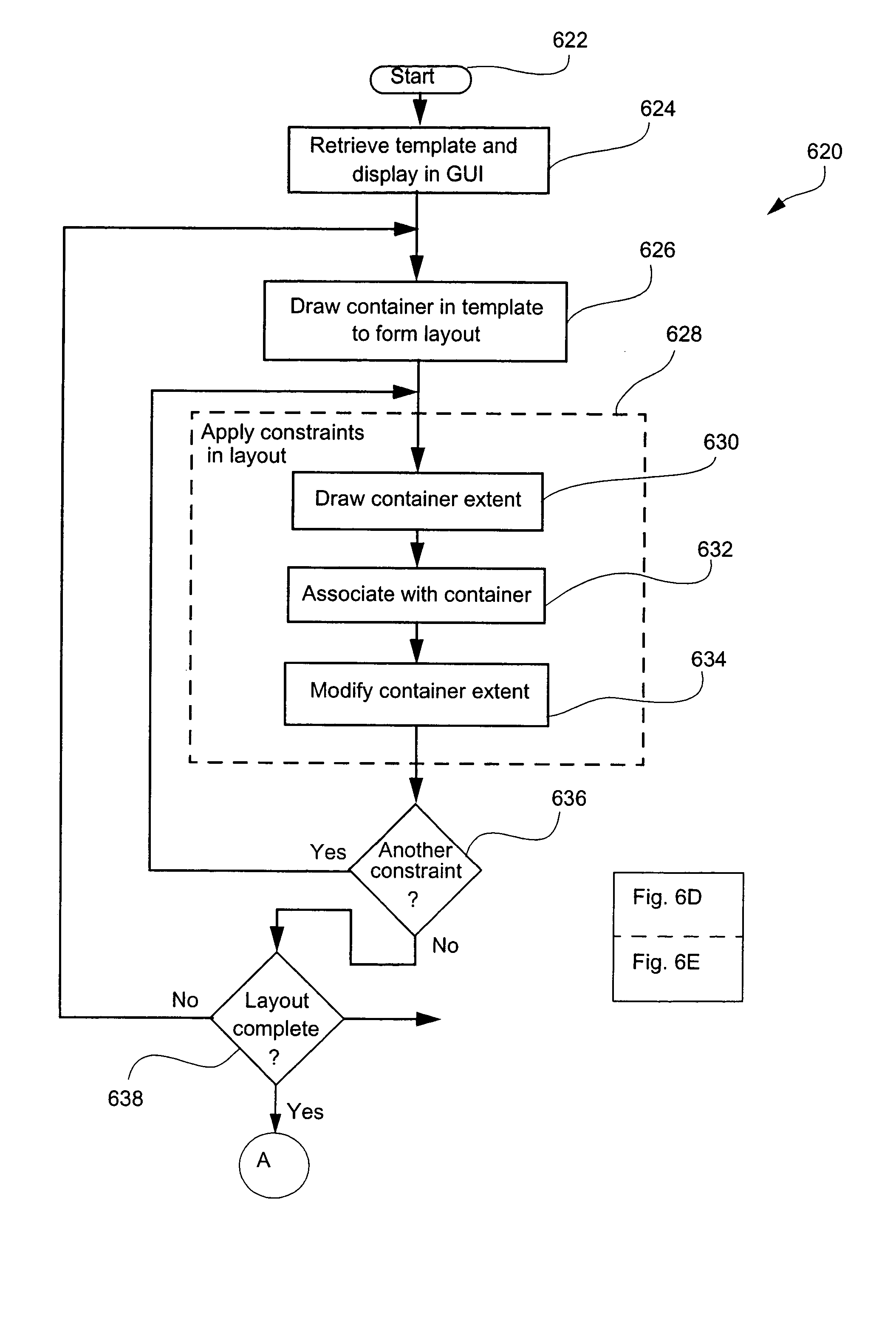
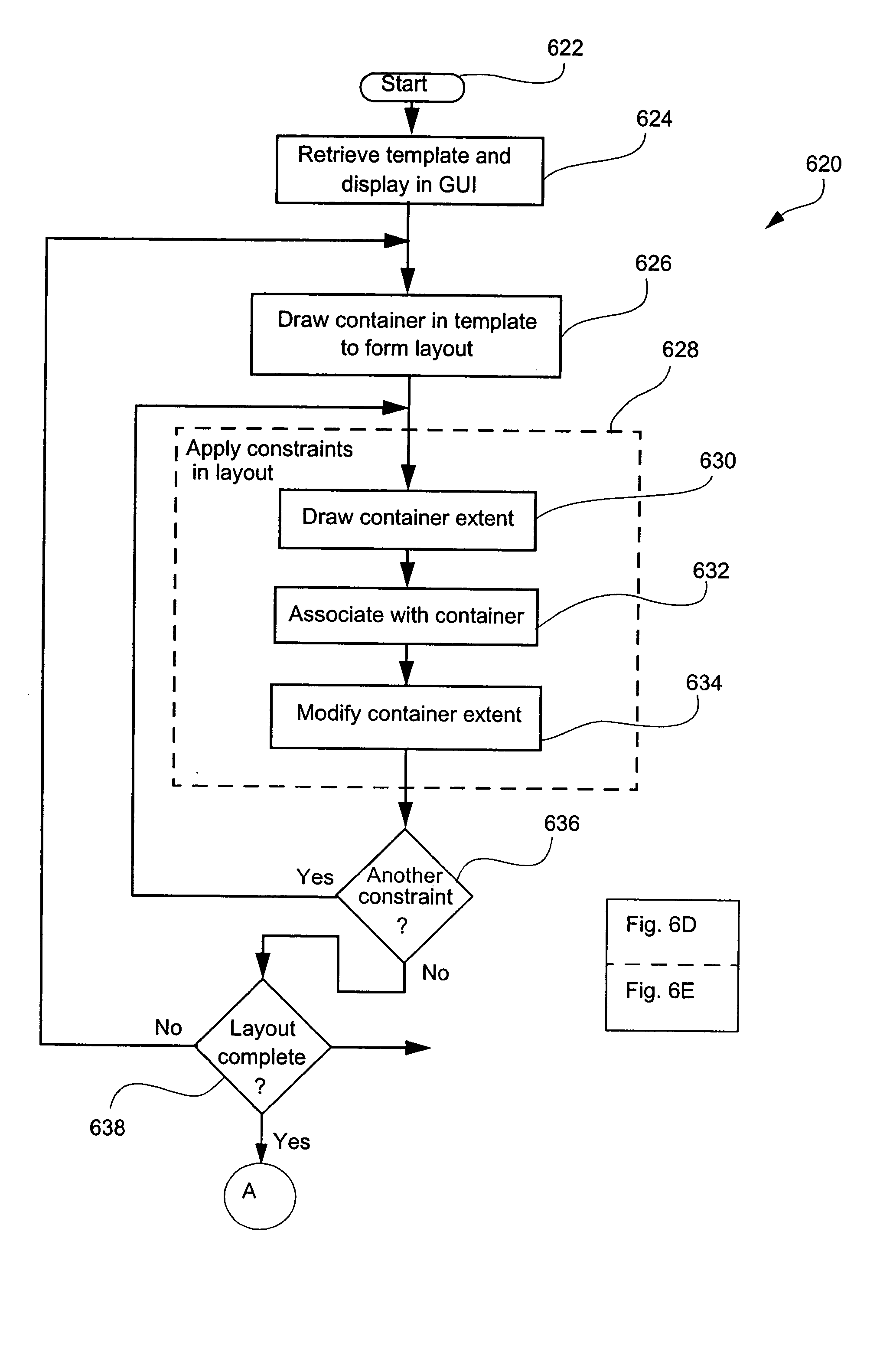
Document layout method
InactiveUS20050094206A1Visual presentation using printersNatural language data processingGraphical user interfaceAlgorithm
Methods and apparatus for variable document printing are disclosed in which a graphical user interface is configured to allow user manipulation of layout rules associated with content containers within a template for variable document generation. One method involves laying out (626) container objects (407, 408) forming part of a template (624) intended for a variable data document. The objects each have a rectangular boundary in two-dimensional space, and the method comprises detecting an operation (628, 2800) to modify a position of at least one edge of at least one of the objects. Then, rules of association between edges of the objects having a corresponding orientation to the one edge are identified. A position of at least the one edge is then modified whilst observing the rules of association between all the correspondingly oriented edges. Finally an objective function derived from the rules of association between the correspondingly oriented edges is minimized (3009) to thereby balance a layout of the objects in at least the dimension of modification. Other methods involve maintaining the objective function for a group of edges, the addition and removal of constraints in respect of correspondingly oriented edges, the removal, addition and then removal of constraints in modifying the width of a container, the calculation of text container sizes, and the creation of tables, particularly for text containers.
Owner:CANON KK
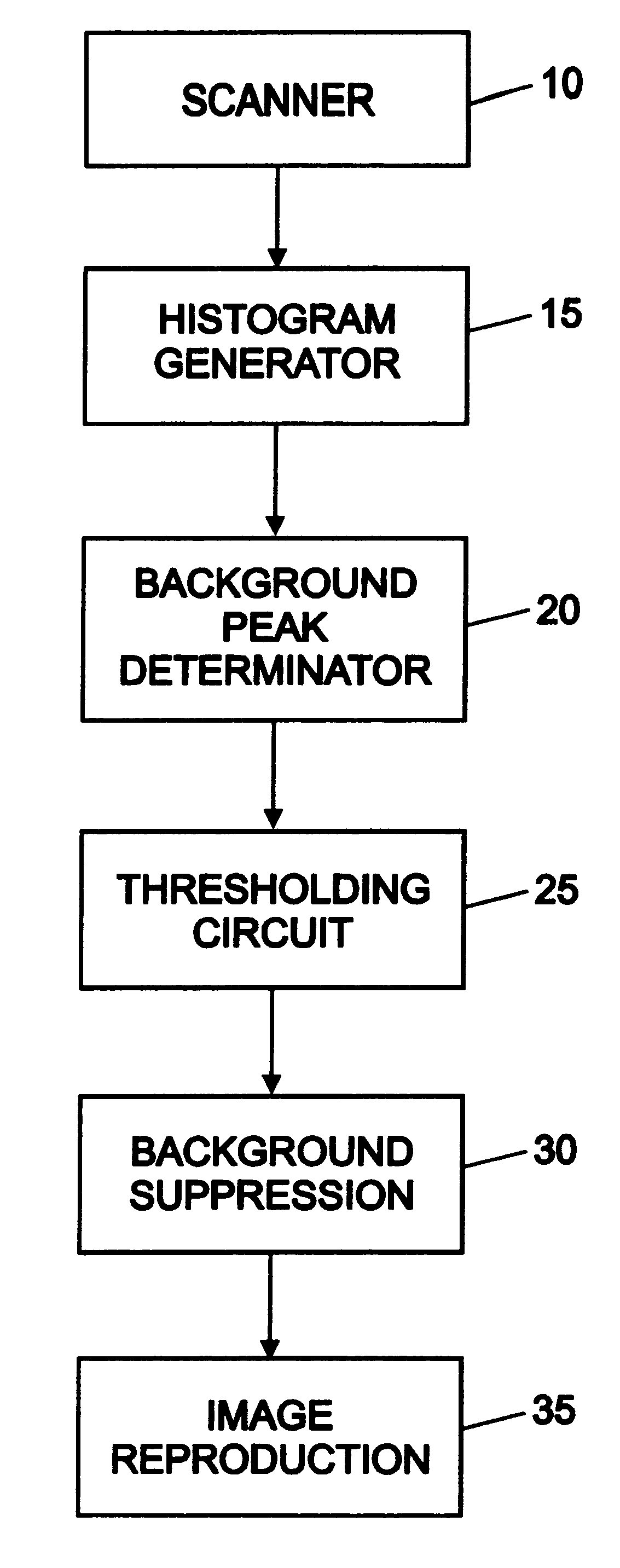
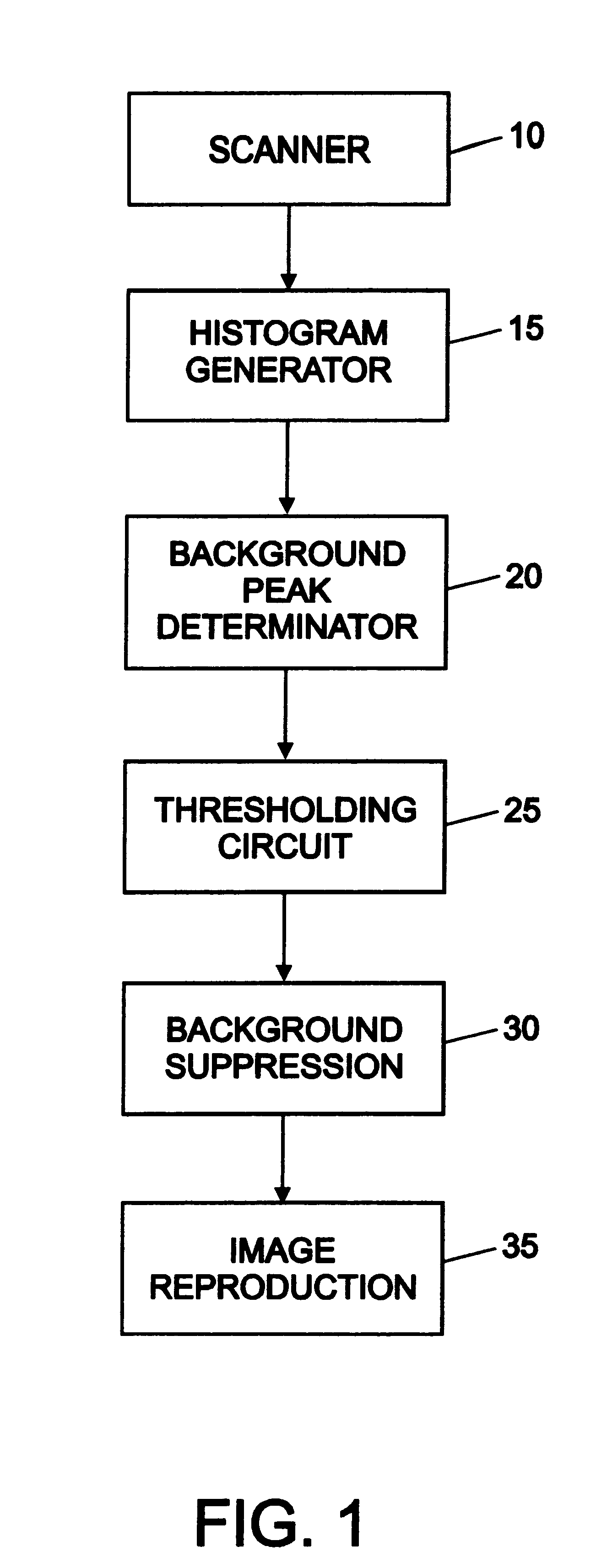
System and method for eliminating background pixels from a scanned image
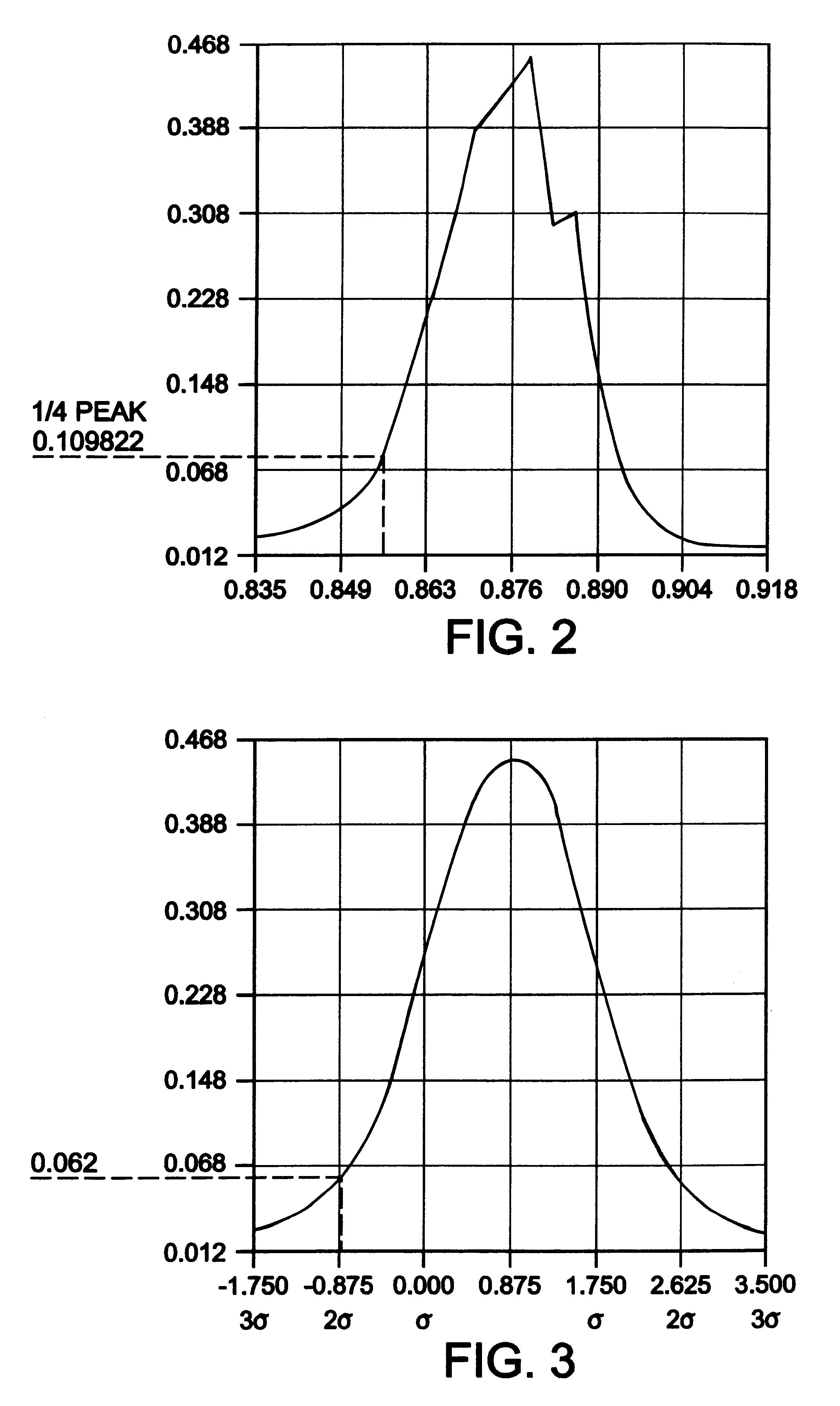
InactiveUS6222642B1Promote reproductionMore valueImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersPeak valueHistogram
An image desired to be reproduced is scanned to determine its video pixel gray values. A histogram generator generates a histogram distribution representing a frequency of the gray values. The histogram distribution is analyzed to determine a background peak gray value of the image and a standard deviation of the histogram distribution based on a Gaussian approximation. A thresholding circuit dynamically adjusts the background peak value based on the standard deviation and a selected scaling factor to generate a background threshold value. The background threshold value expands a range of background gray values in the image which are eliminated during image reproduction. Eliminating substantially all background gray values improves the quality of the reproduced image.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Thermal response correction system
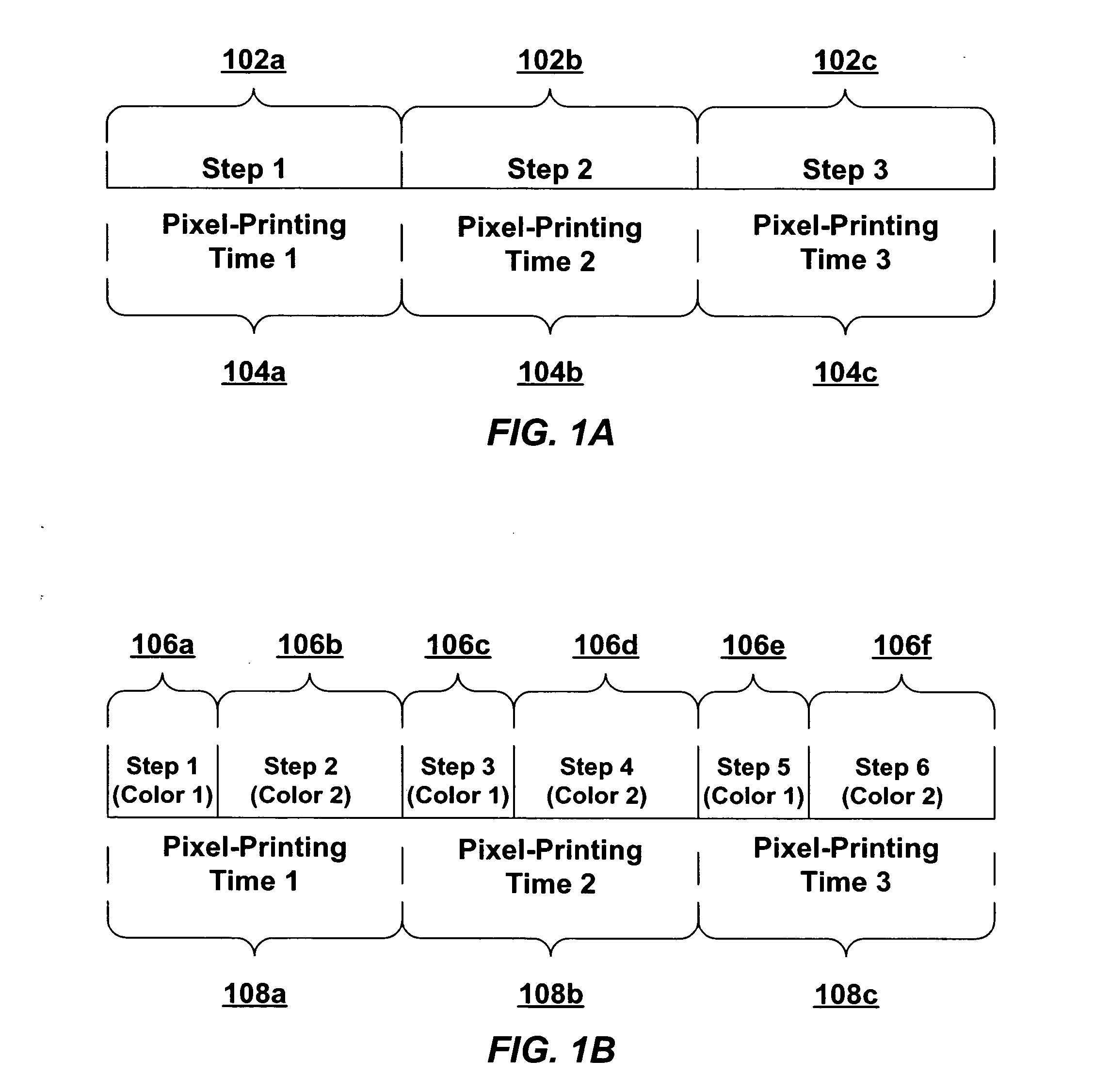
Techniques are disclosed for performing thermal history control in a thermal printer in which a single thermal print head prints sequentially on multiple color-forming layers in a single pass. Each pixel-printing interval may be divided into subintervals, which may be of unequal duration. Each sub-interval may be used to print a different color. The manner in which the input energy to be provided to each print head element is selected may be varied for each of the subintervals. For example, although a single thermal model may be used to predict the temperature of the print head elements in each of the subintervals, different parameters may be used in the different subintervals. Similarly, different energy computation functions may be used to compute the energy to be provided to the print head in each of the subintervals based on the predicted print head temperature.
Owner:TPP TECH LLC
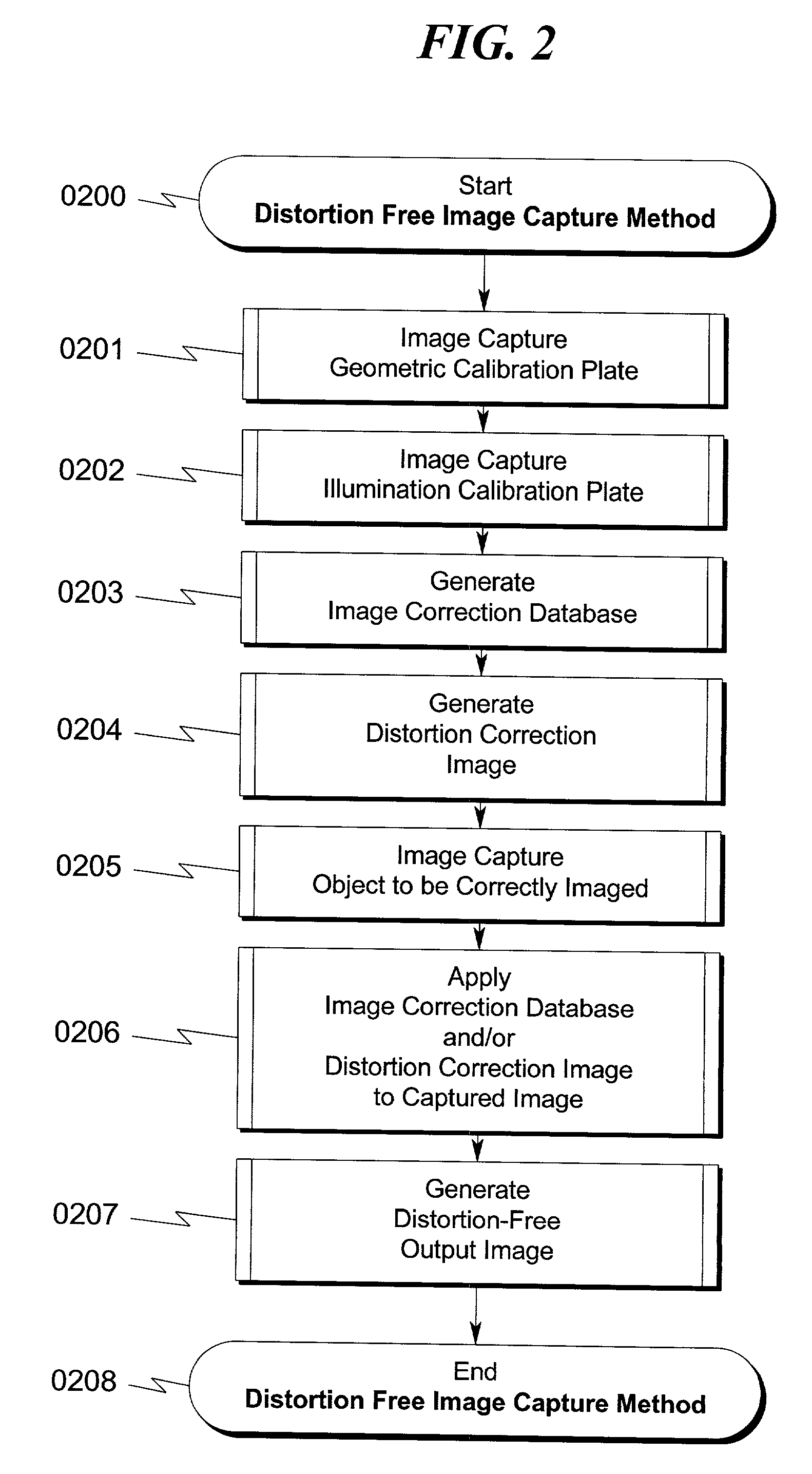
Distortion free image capture system and method
InactiveUS20020041383A1Low costImprove distortionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementOphthalmologyDistortion free
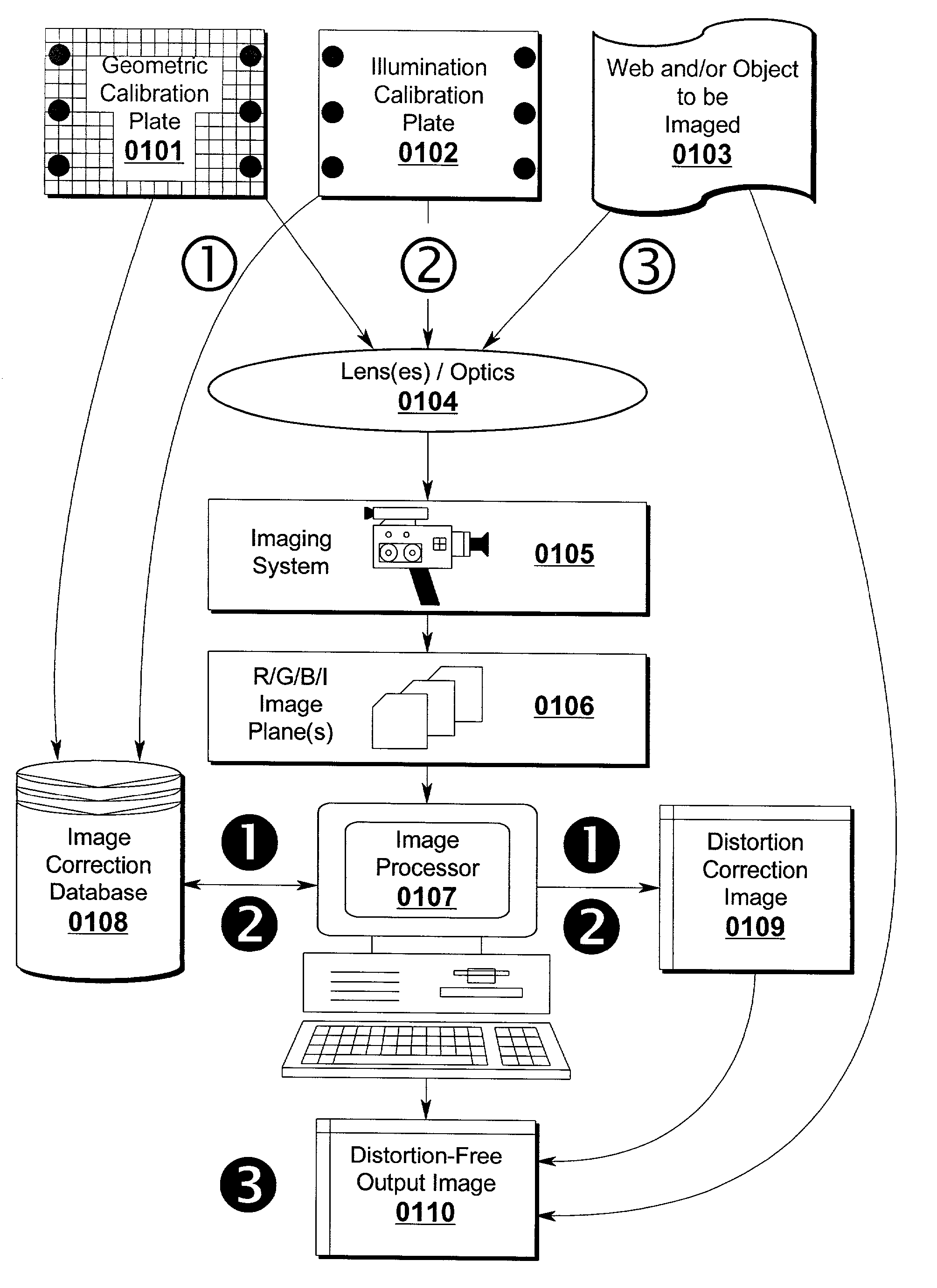
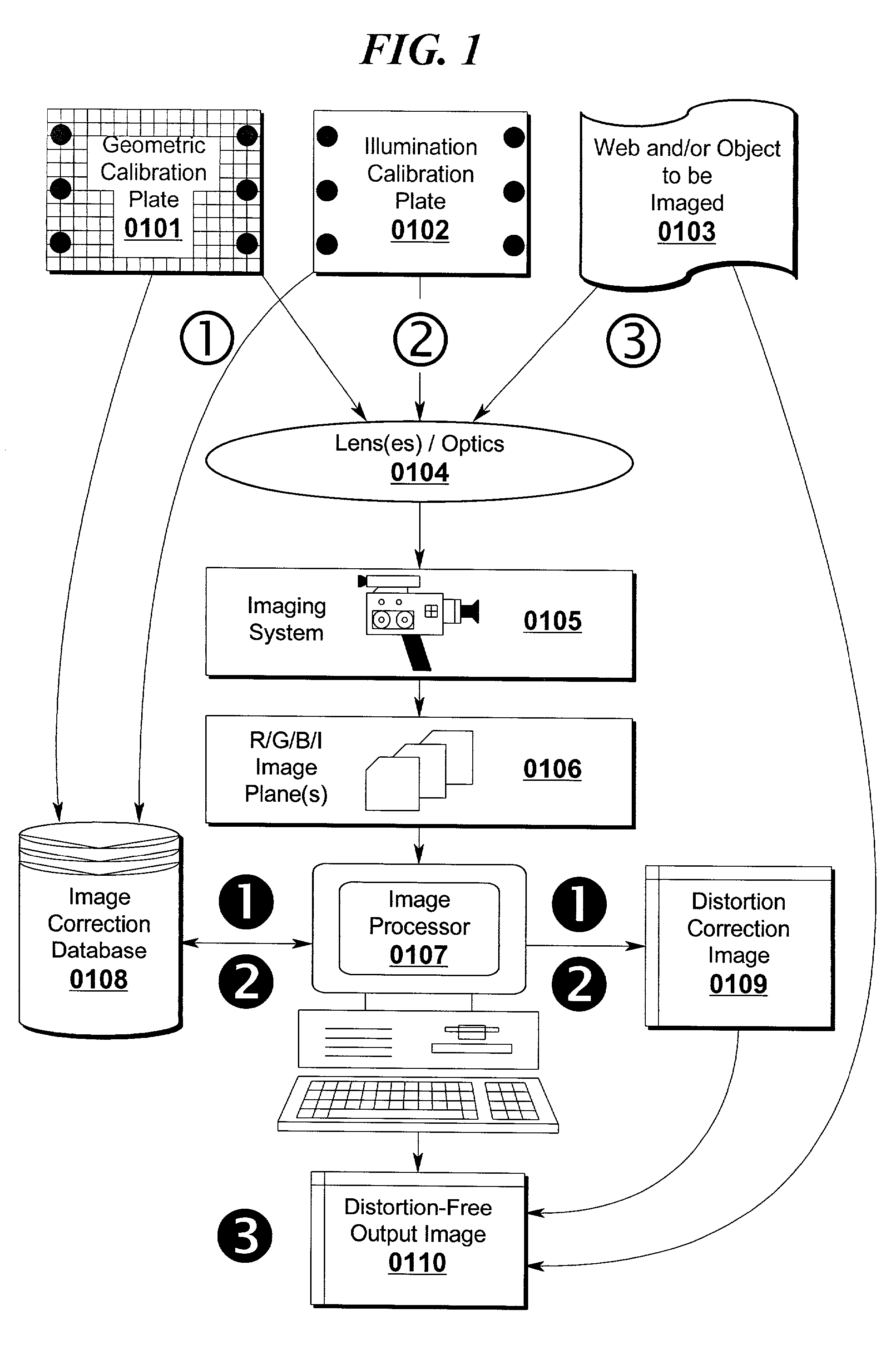
A system and method for correcting distortions that occur in image capture systems is disclosed. The present invention in some preferred embodiments includes provisions to correct or change magnification differences for all causes including position errors in zoom lens positioning mechanisms as well as those caused by chromatic aberration, CCD alignment errors, lens distortion off center variations, pincushion / barrel lens distortion, magnification distortions, camera and lens misalignment errors, and lighting variations (including flash-to-flash illumination variations). A significant feature of the present invention in contrast with the prior art is that with the use of a movable calibration plate in the present invention it is possible to image capture both the calibration plate and the input object image in a single image capture, thus permitting simultaneous compensation for a variety of lighting and illumination variations not possible with the prior art.
Owner:LEWIS JR CLARENCE A +1
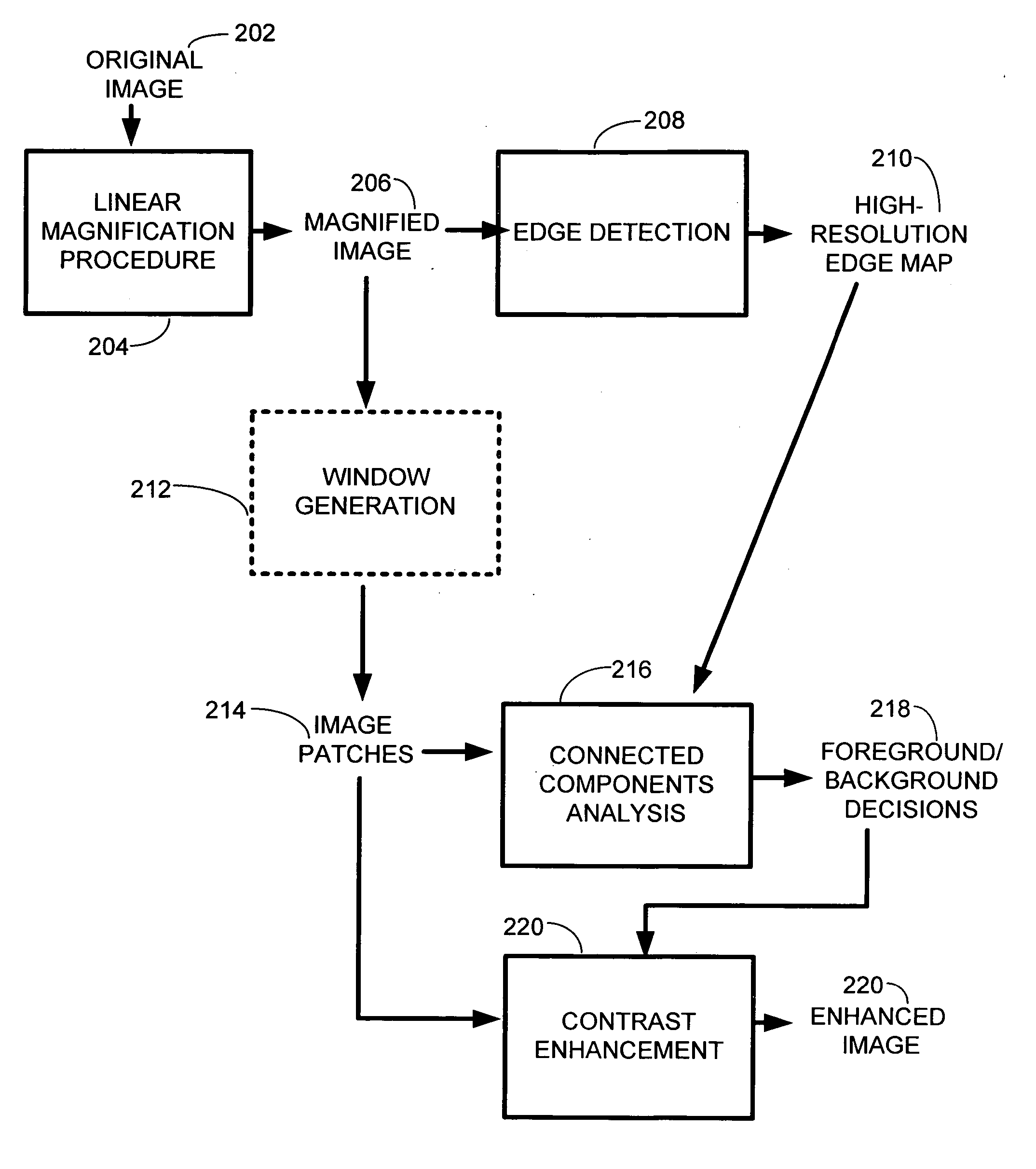
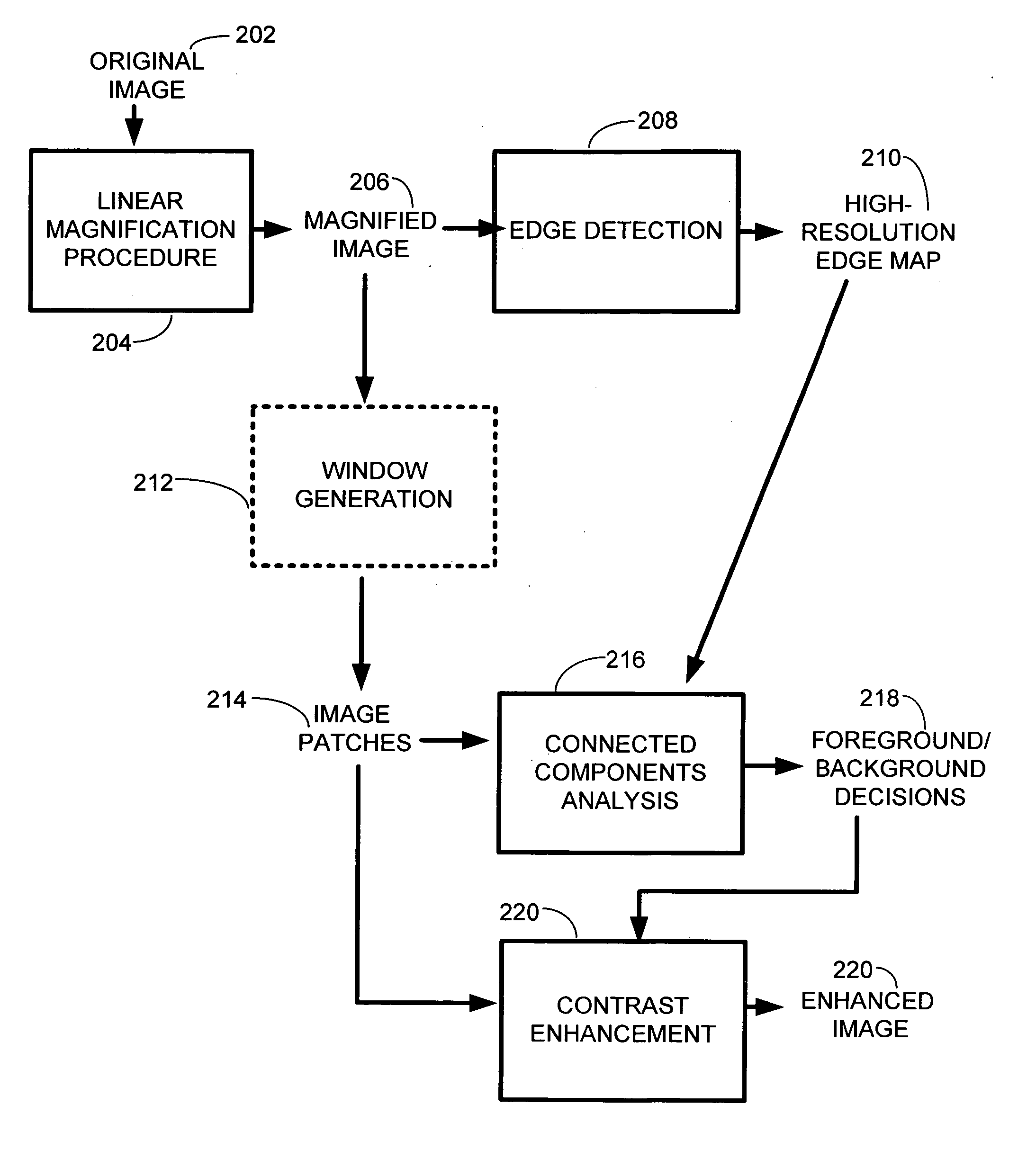
Image superresolution through edge extraction and contrast enhancement
InactiveUS20060290950A1Remove jaggednessAccurate descriptionImage enhancementDigitally marking record carriersImage resolutionEdge extraction
A technique for generating high-resolution bitmaps from low-resolution bitmaps. A low-resolution bitmap is magnified to form a magnified image. Edge detection is performed on the magnified image to find high contrast edges. A plurality of image patches of the magnified image are generated. These images patches are analyzed by performing connected components analysis on each of them using the high contrast edges to produce a plurality of foreground and background decisions determining whether a portion of an image patch is a background or a foreground region. Then the contrast of one or more pixels in each of the plurality of image patches is enhanced based on the foreground and background decisions. Finally, the system and method of the invention combines the luminance of the enhanced output pixels with the color values generated by the magnification algorithm. This produces a high-resolution bitmap from the contrast-enhanced pixels.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
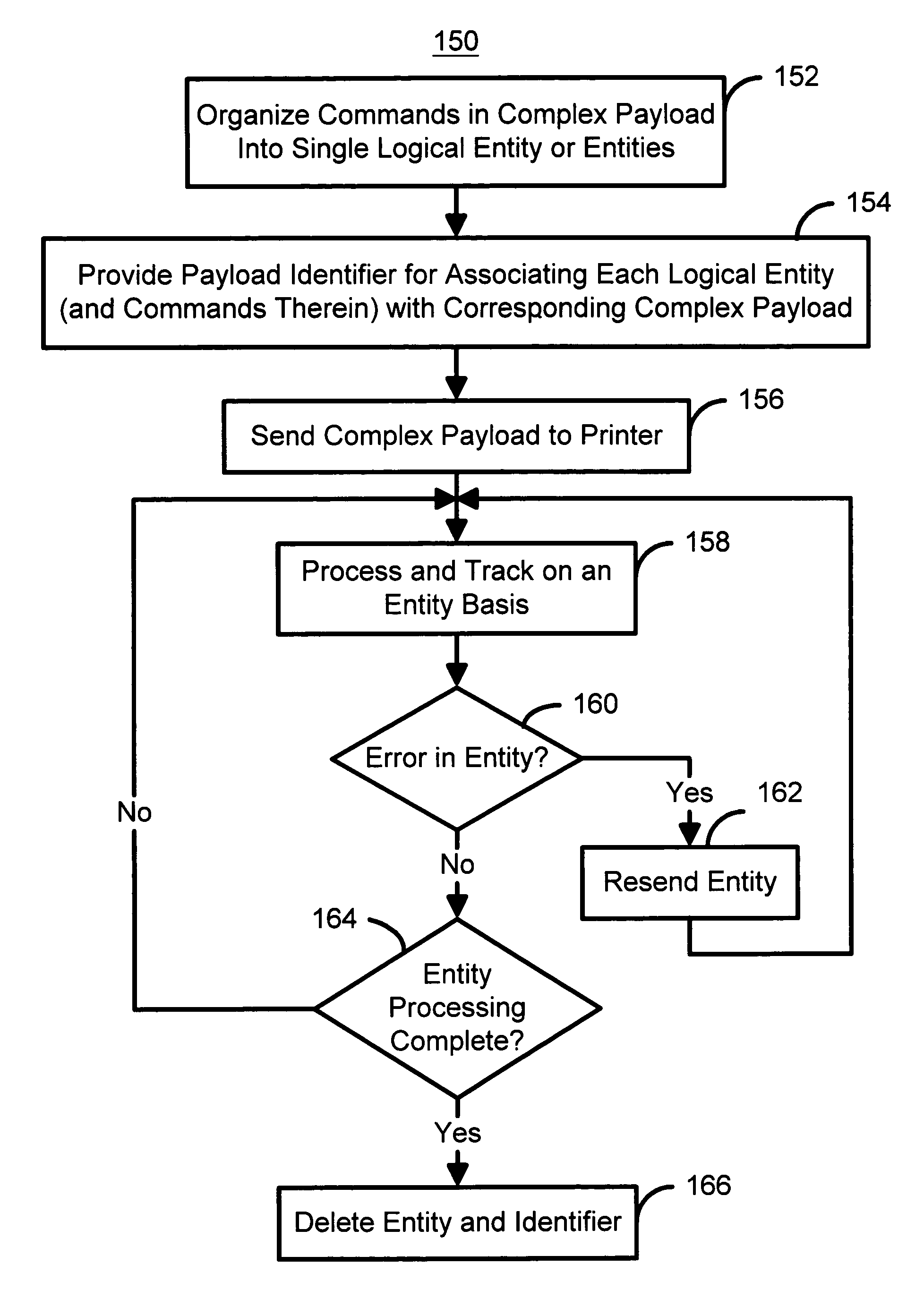
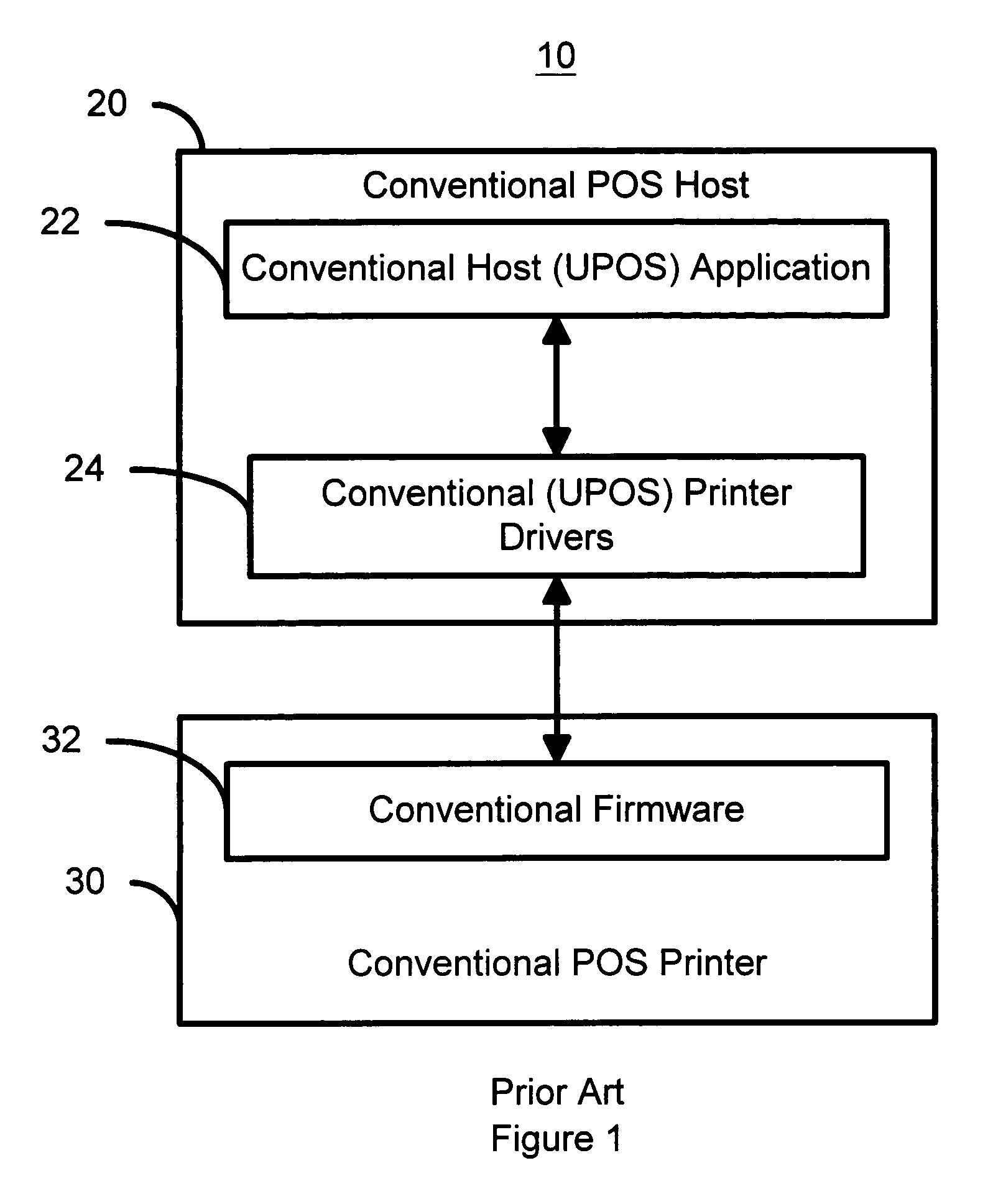
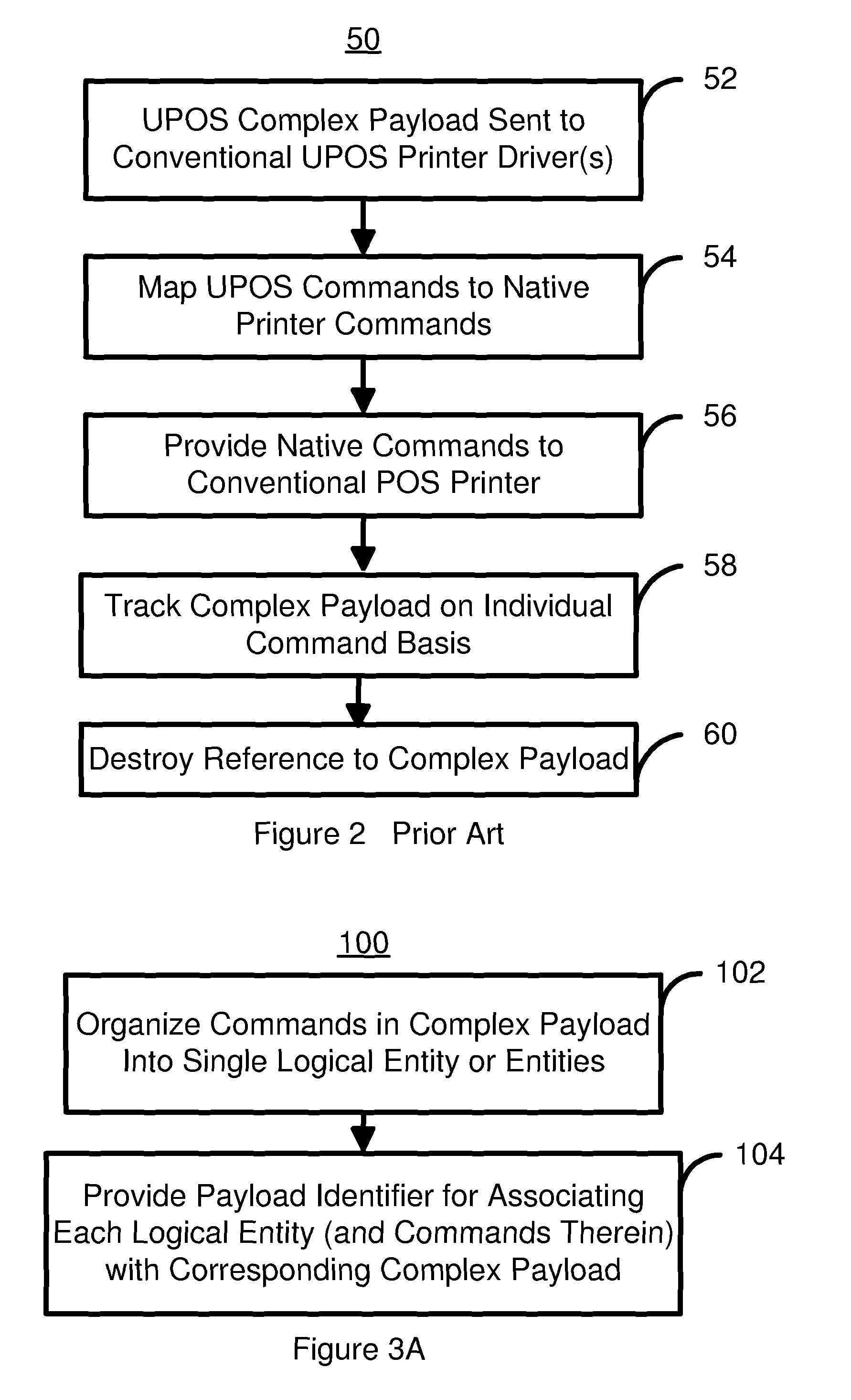
Method for more efficiently managing complex payloads in a point of sale system
ActiveUS7889384B2Easy to operateEfficient managementDigitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersSingle entityPoint of sale
Owner:TOSHIBA GLOBAL COMMERCE SOLUTIONS HLDG
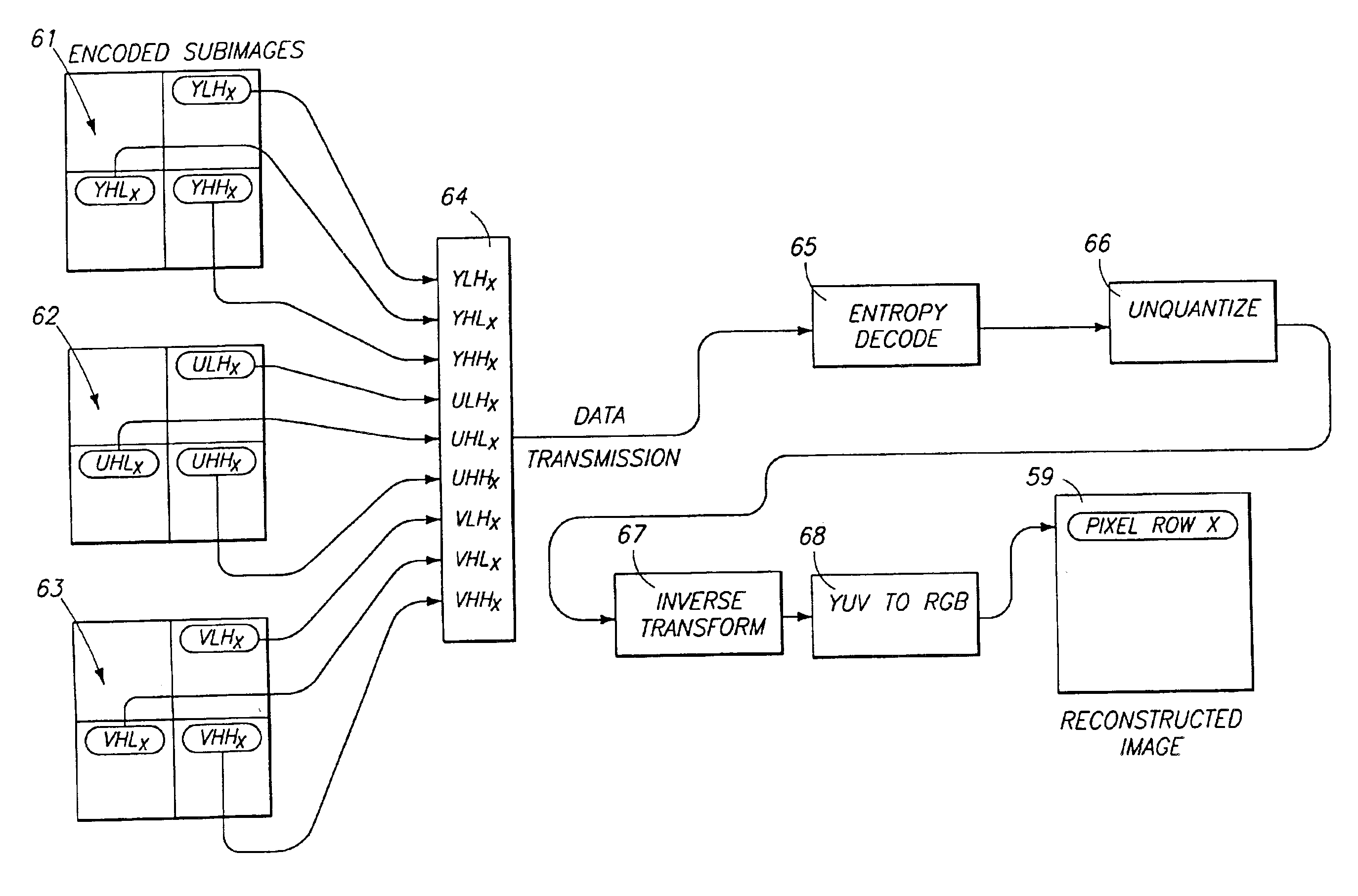
Progressive image transmission using discrete wavelet transforms
InactiveUS6847468B2Convenient previewImprove the level ofDigitally marking record carriersGeometric image transformationDecompositionImage transfer
Disclosed herein is a method of storing and of progressively transferring a still image so that it can be conveniently previewed during the transfer and so that a user can terminate the transfer at an early stage if the image turns out to be undesirable. The methods of the invention include transforming the image into a plurality of decomposition levels using a discrete wavelet transform. Each decomposition level comprises a plurality of subimages which allow reconstruction of an image representation of the still image. The decomposition levels are transmitted beginning with a base decomposition level providing a low level of image resolution and then proceeding with decomposition levels providing increasingly higher levels of image resolution. Within each decomposition level, rows of the various subimages are arranged or interlaced together in contiguous blocks, so that all data for a single row, at a single decomposition level, is transmitted together. At the receiving end of the transfer, the row blocks are reconstructed and displayed as they are received. The invention enables the initial display of a low resolution image which is gradually updated and sharpened, on a row-by-row basis, until a desired high resolution is achieved. The user may terminate the transfer at any point.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
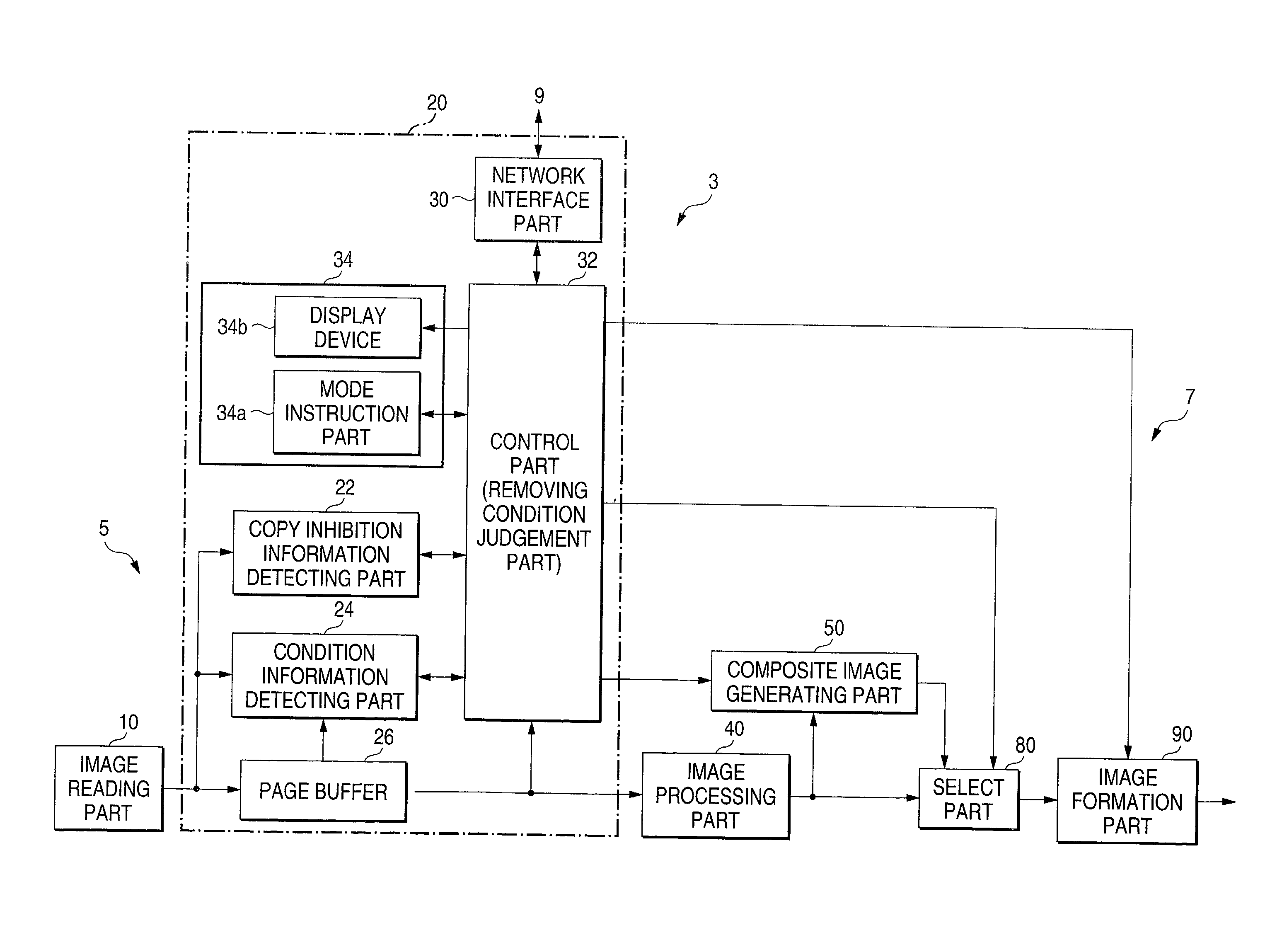
Image generating method, device and program, and illicit copying prevention system
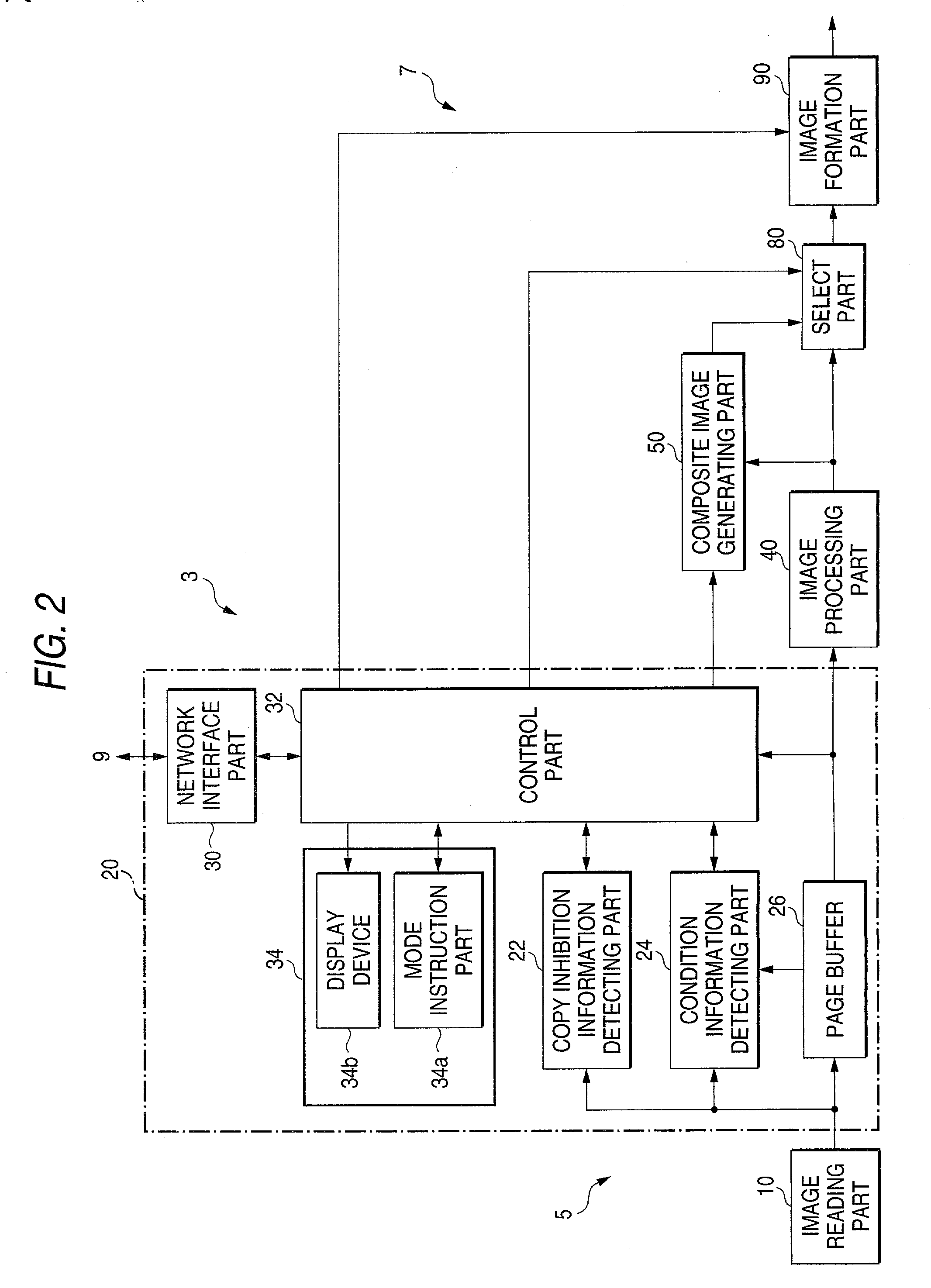
InactiveUS20030179412A1User identity/authority verificationVisual presentation using printersComputer graphics (images)Paper document
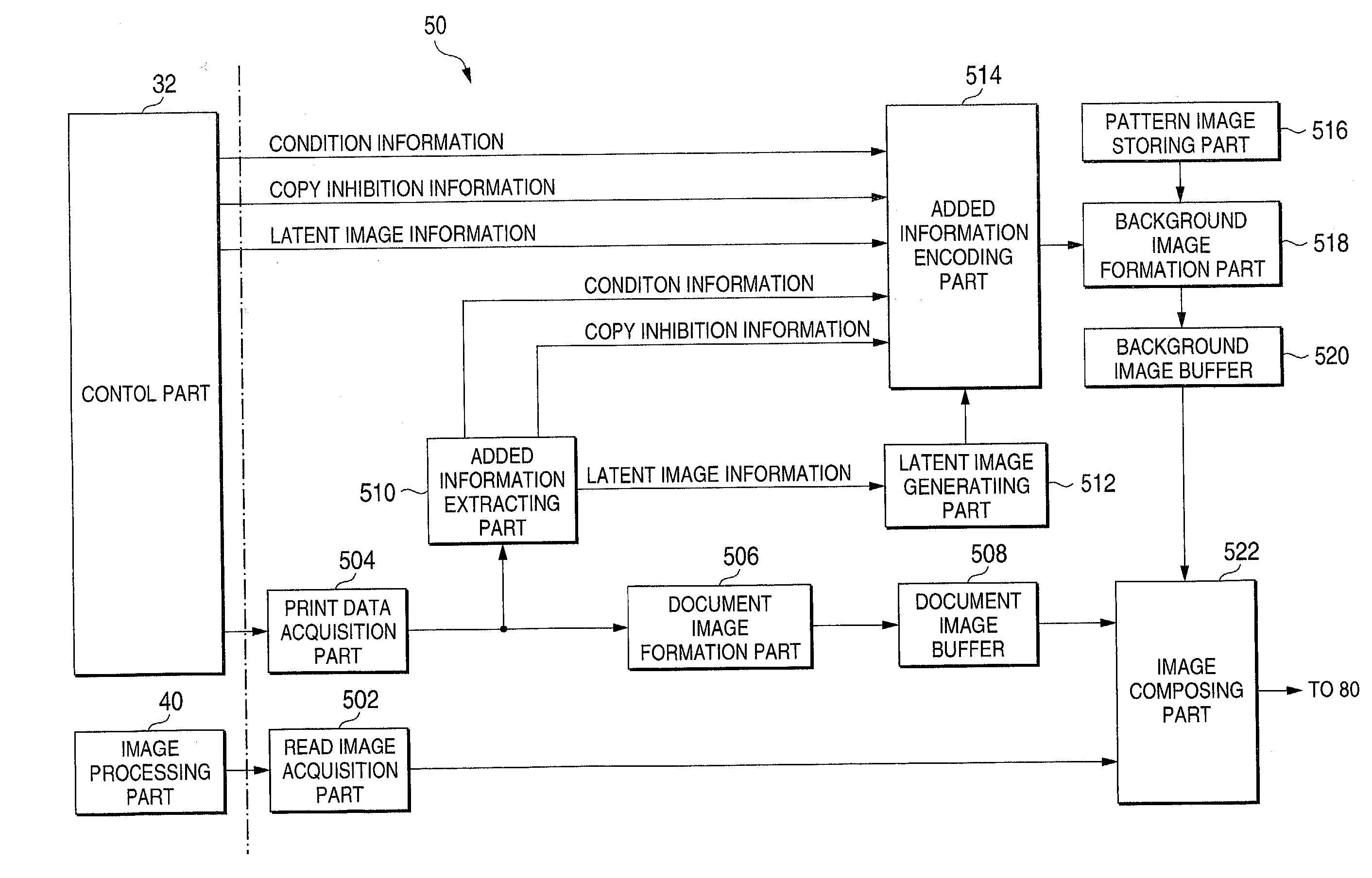
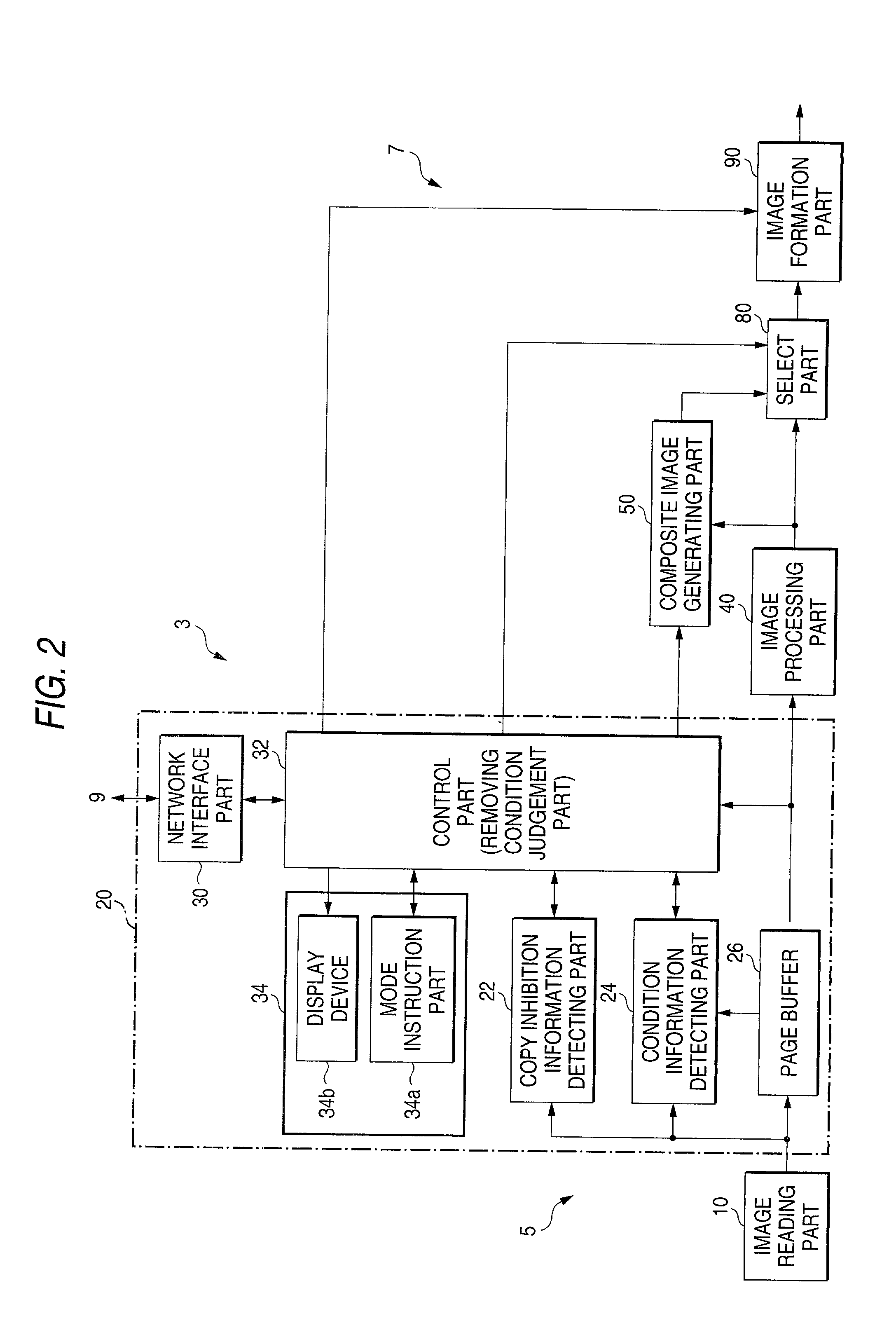
An added information encoding part repeatedly arranges two kinds of copy inhibition code arrays of the unit two-dimensional arrays to which copy inhibition codes are assigned, and condition code arrays of the unit two-dimensional arrays to which codes for removing the copy inhibition are assigned, into a two-dimensional array according to given rules. A background image formation part generates a background image in which copy inhibition pattern image areas and condition pattern image areas are repeatedly and two-dimensionally arranged according to given rules, while referring to this array, and the pattern images corresponding to respective codes stored in the background image formation part, and stores the generated background image into a background image buffer. An image composing part reads out document images from a document image buffer, and the background image from the background image buffer, and superimposes them into a composite image.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Authoring tools using a mixed media environment
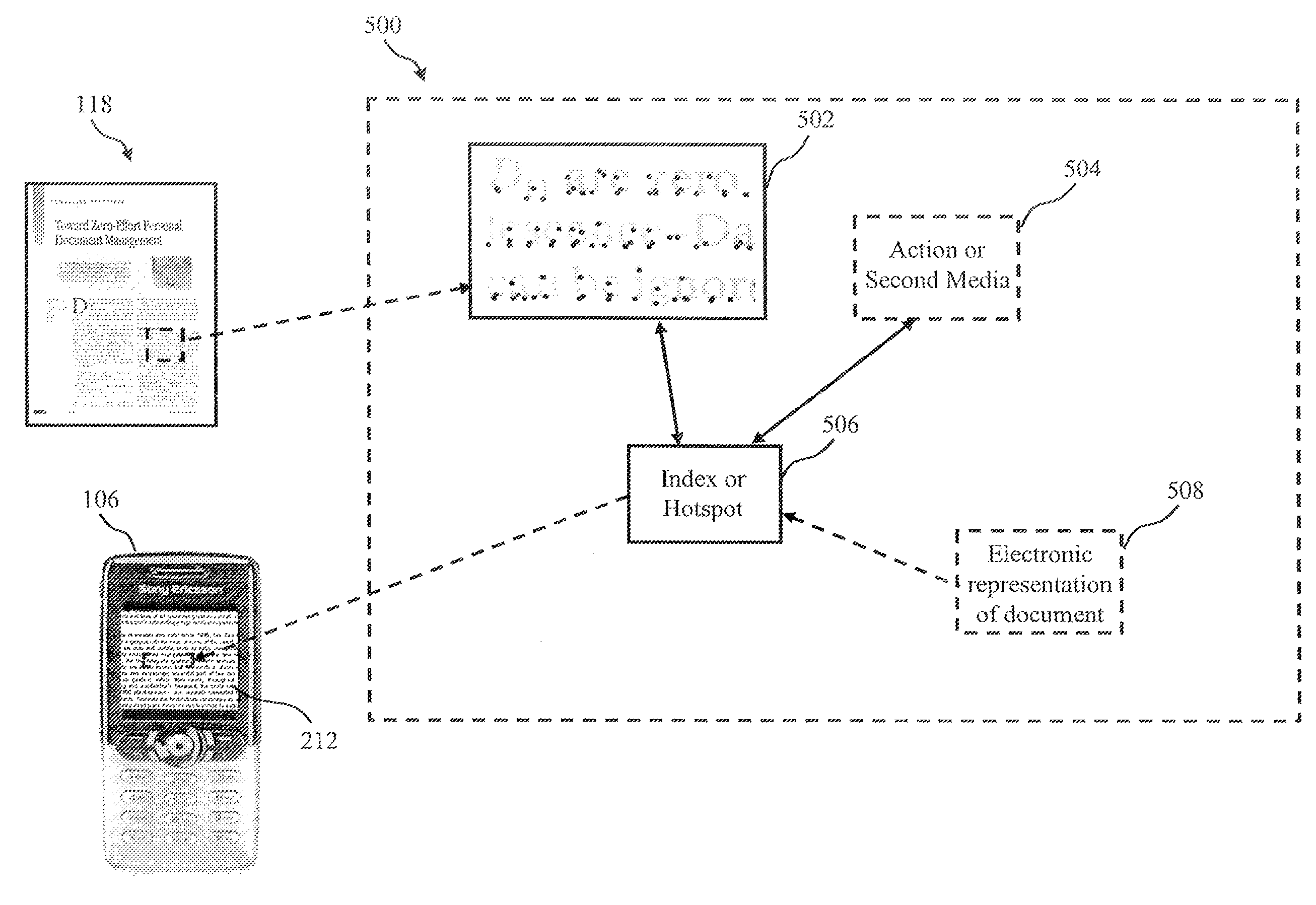
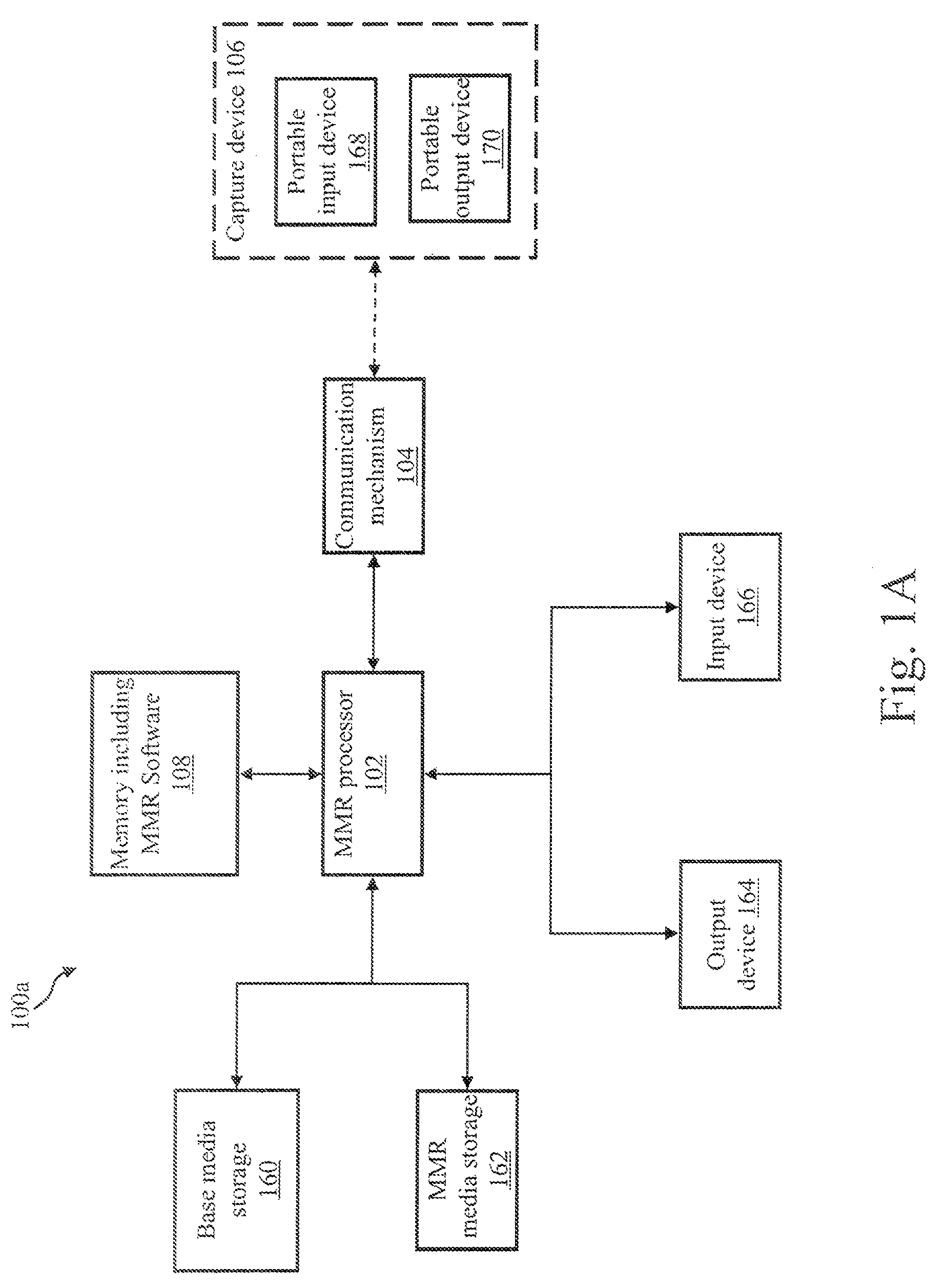
ActiveUS7639387B2Visual presentation using printersCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital contentNumber content
A Mixed Media Reality (MMR) system and associated techniques are disclosed. The MMR system provides mechanisms for forming a mixed media document that includes media of at least two types (e.g., printed paper as a first medium and digital content and / or web link as a second medium). In one particular embodiment, the MMR system provides a method to associate related documents. The method acquires two associated documents and associates the related portions together. When the method acquires a portion of one of the document, it identifies the portion acquired, and provides the related portion of the other document.
Owner:RICOH KK
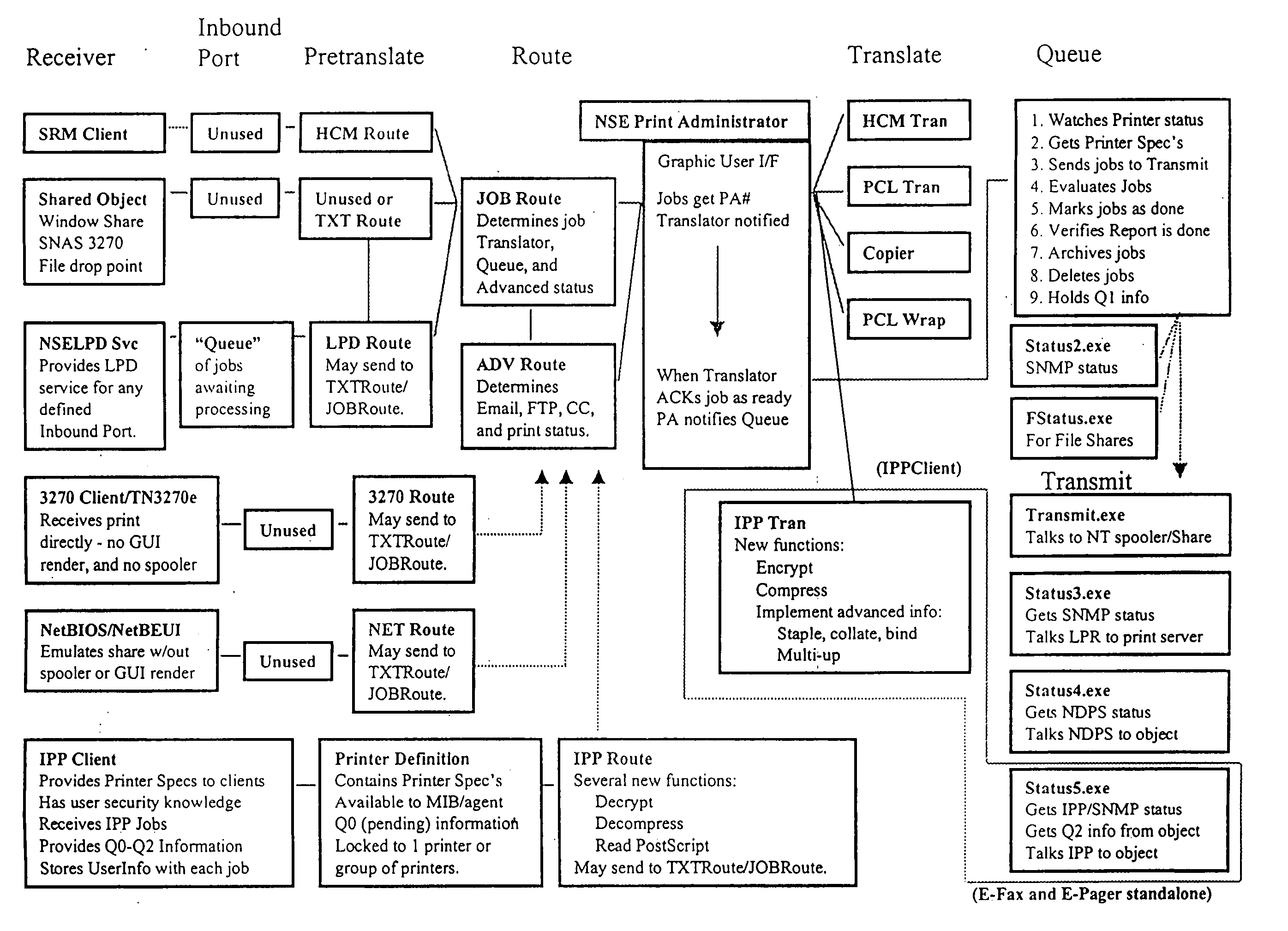
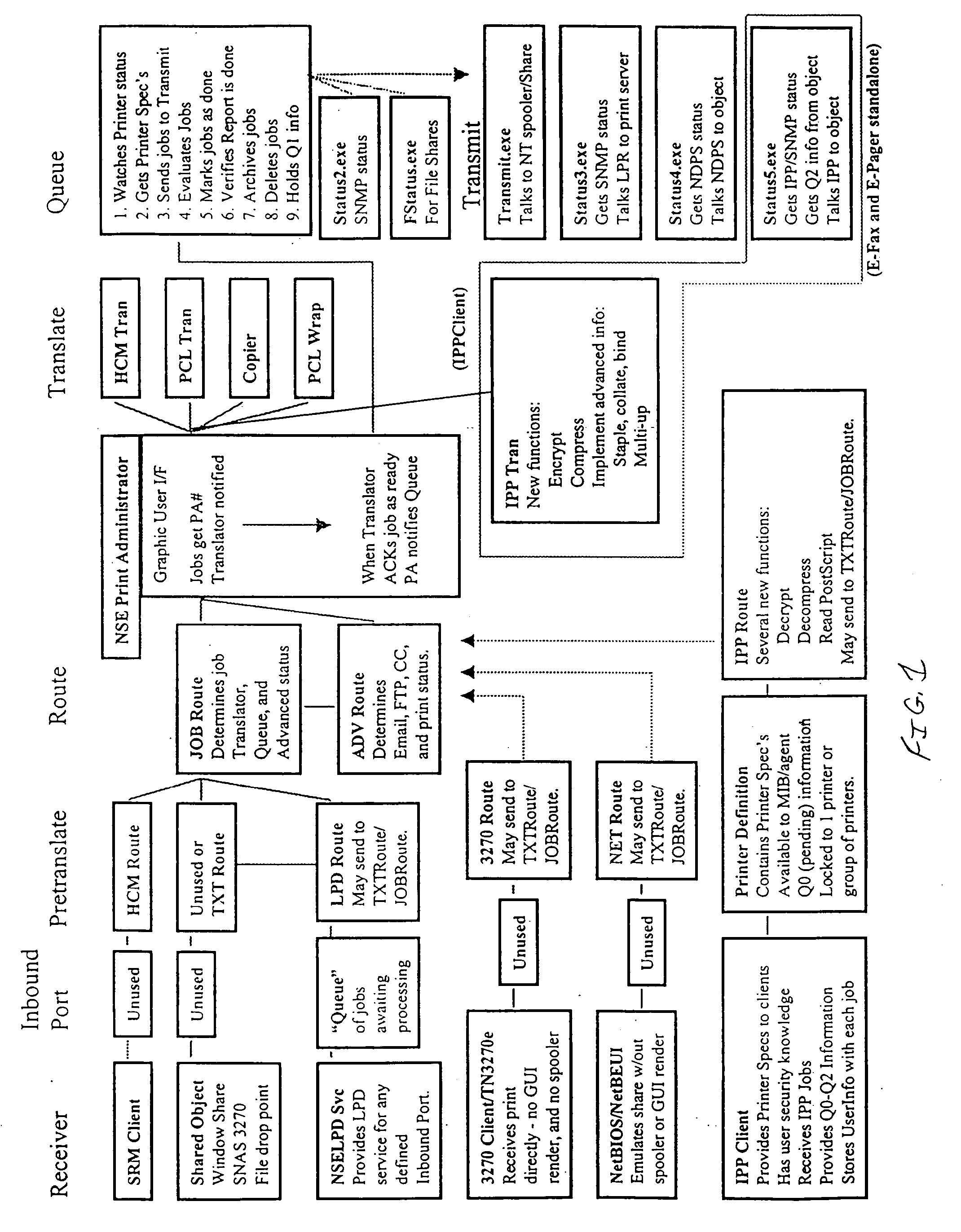
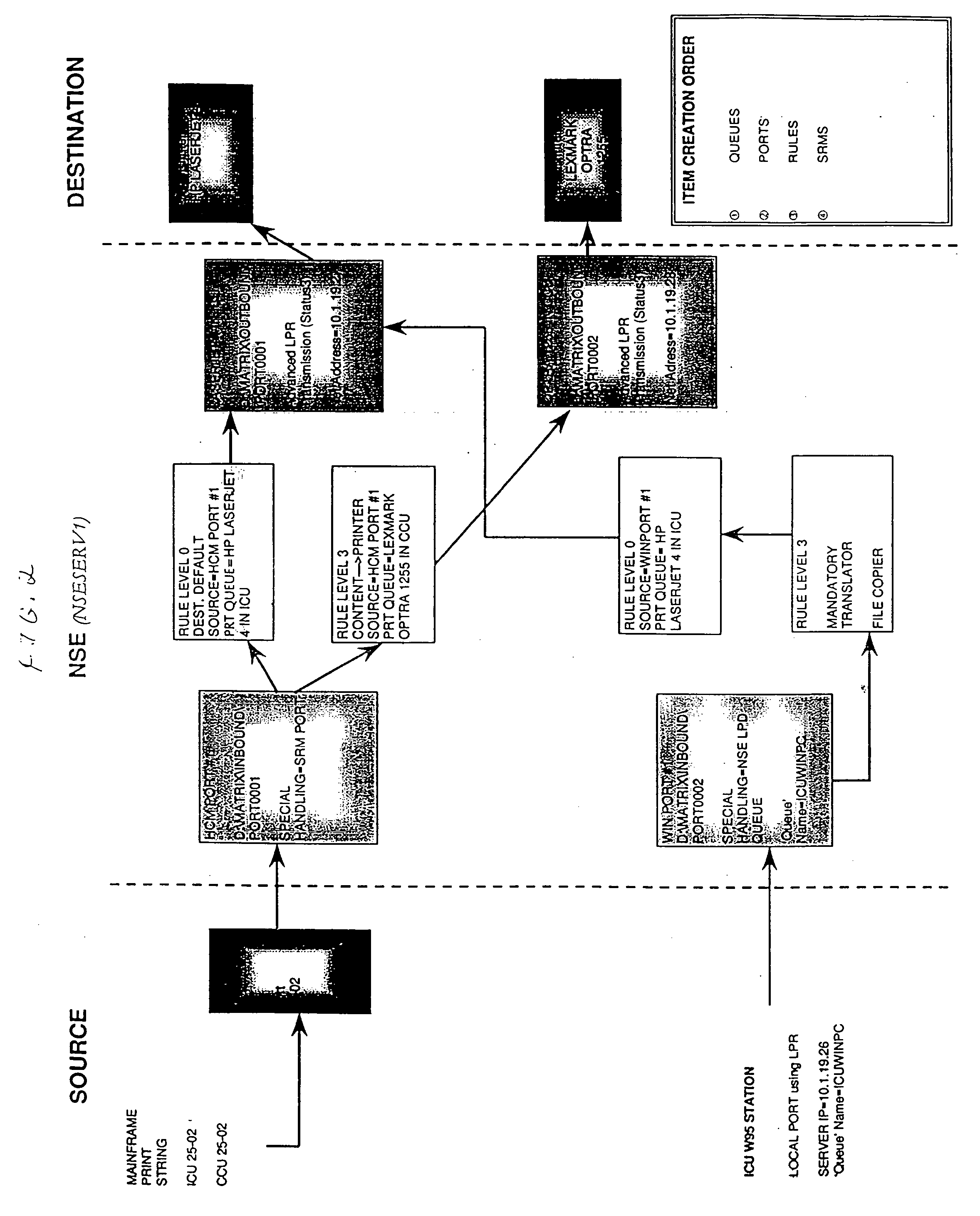
Printer control and document management system
InactiveUS20040105122A1Digital data processing detailsVisual presentation using printersComputer printingElectronic form
A printer control and information management system is provided employing numerous individual satellite modules, and providing an enterprise-wide output system capable of receiving all types of input and redirecting of all types of output. Data can be inputted from any location in an enterprise system and coordinated into a coherent format for reporting and forms processing. Forms can be automatically generated based on the data inputted, which forms can be directed to the appropriate personnel. The system provides for notifications to the appropriate personnel in order to resolve problems which may arise from the operation of the various equipment utilized in the enterprise network system. Information can be redirected to anyone within the system, the user identifying the manner and format of the information to be presented. Thus, inbound reports can be received from different systems and outputs delivered in the format that is preferred by the user. Report recognition is provided for any application, with the ability to merge textual information with electronic forms. Additionally, the forms can be completed with bar code information to prevent inadvertent disclosure of sensitive information. Large and contiguous host generated reports can be electronically distributed to users, as well as the ability to automatically fax any type of report directly to any recipient. The system can be accessed via the Internet for ease of inputting and reviewing information at any location.
Owner:ST CLAIR MANAGEMENT RESOURCES
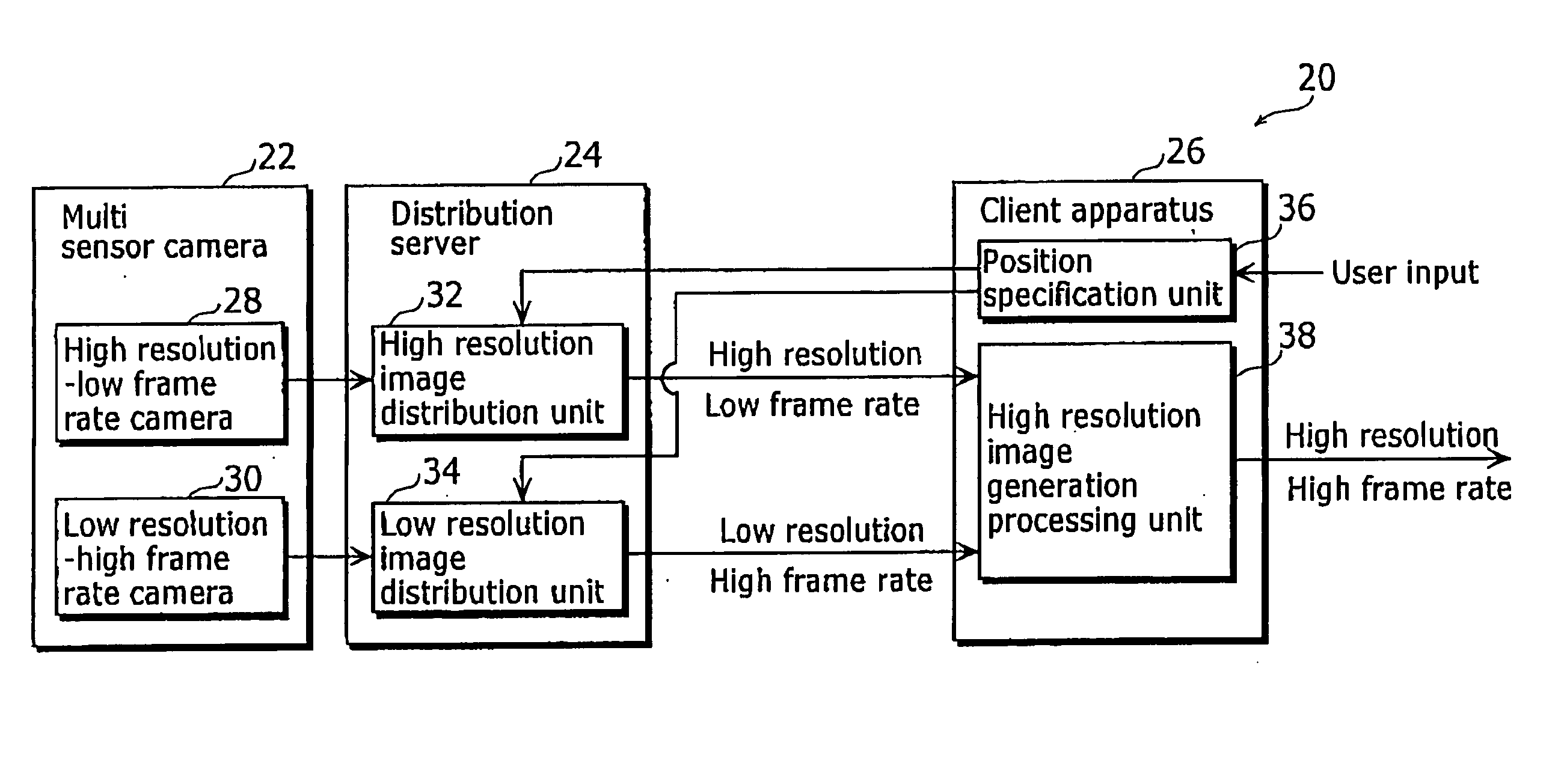
Imaging system, image data stream creation apparatus, image generation apparatus, image data stream generation apparatus, and image data stream generation system
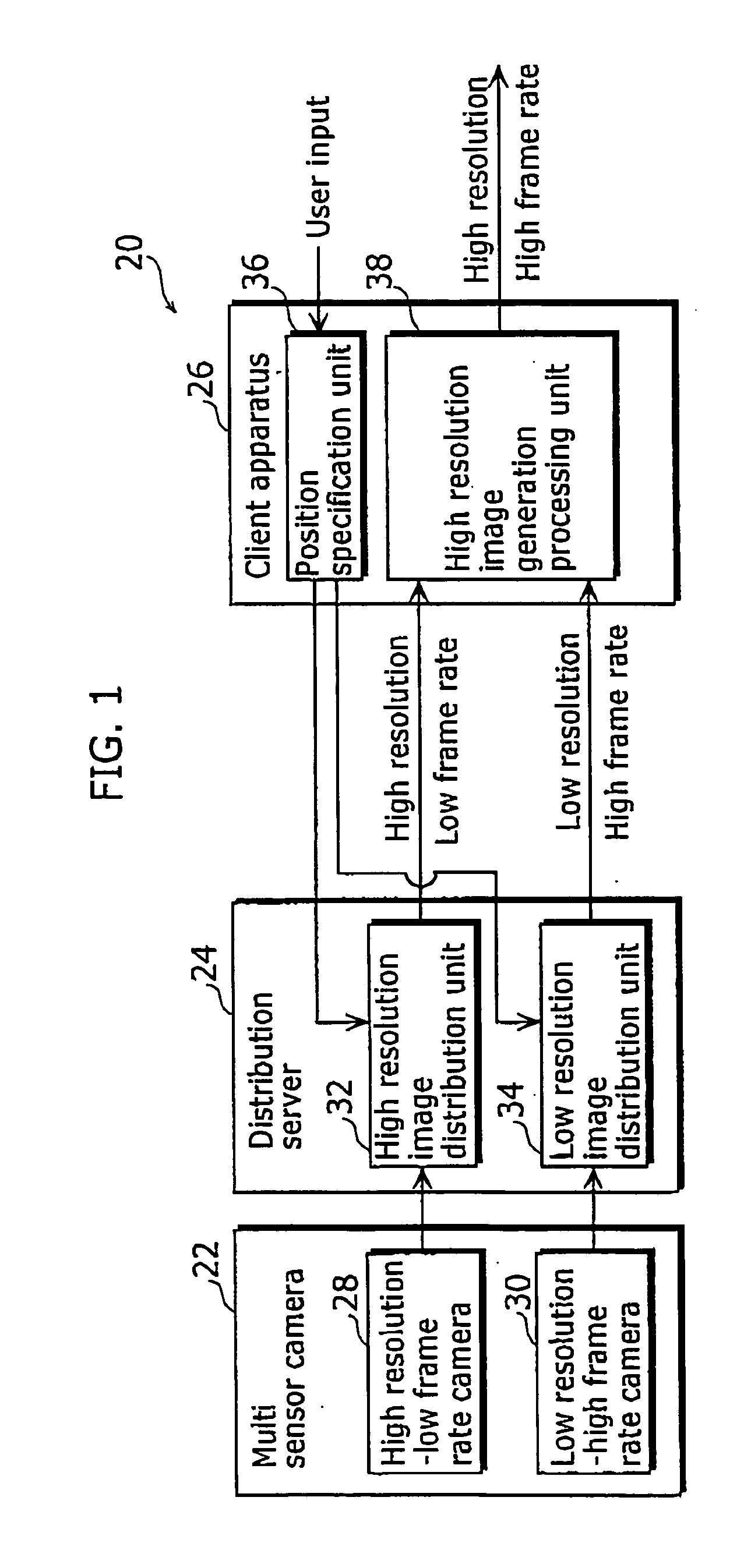
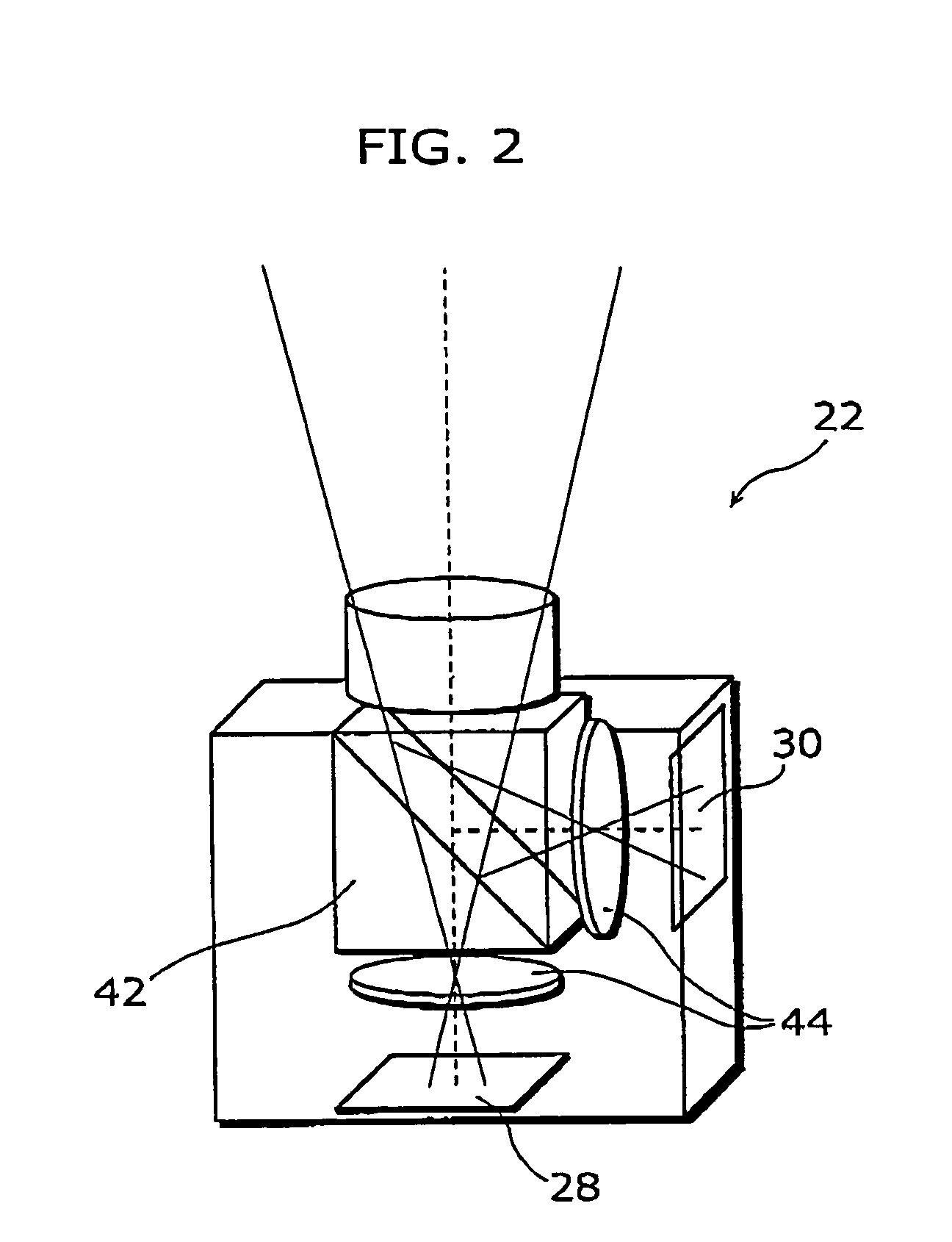
InactiveUS20050219642A1Low costHigh frame rateTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersData streamBeam splitter
An imaging system that is capable of generating high resolution and high frame rate video includes of a beam splitter, two lenses, a high resolution-low frame rate camera, and a low resolution-high frame rate camera. The beam splitter reflects a part of an incident ray. The two lenses gather the ray reflected from the beam splitter and the ray penetrating the beam splitter, respectively. The low resolution-high frame rate camera is a sensor that takes an image of the ray gathered by one of the lenses at a low resolution and a high frame rate. The high resolution-low frame rate camera is a sensor that takes an image of the ray gathered by the other of the lenses at a high resolution and a low frame rate.
Owner:YACHIDA MASAHIKO +1
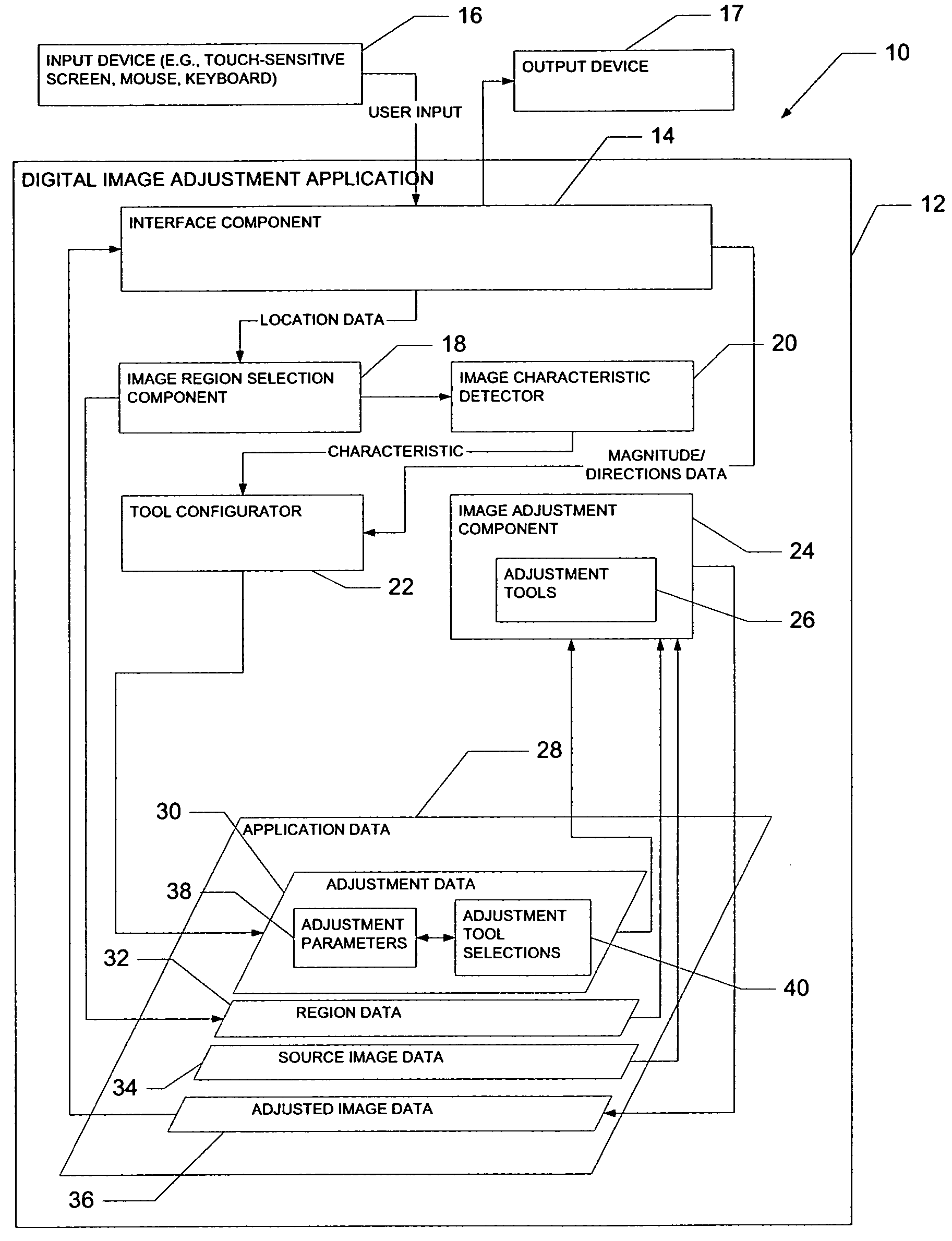
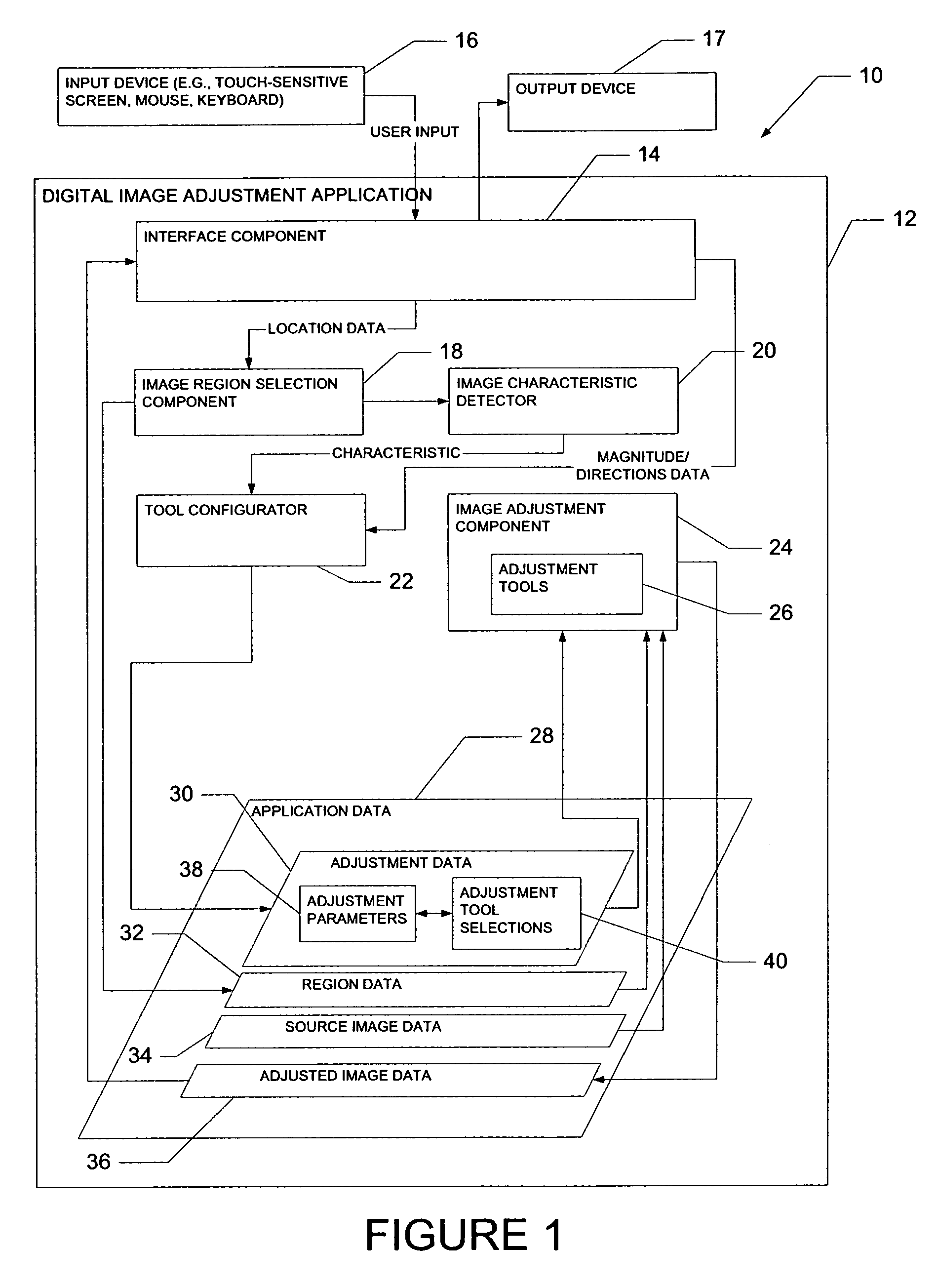
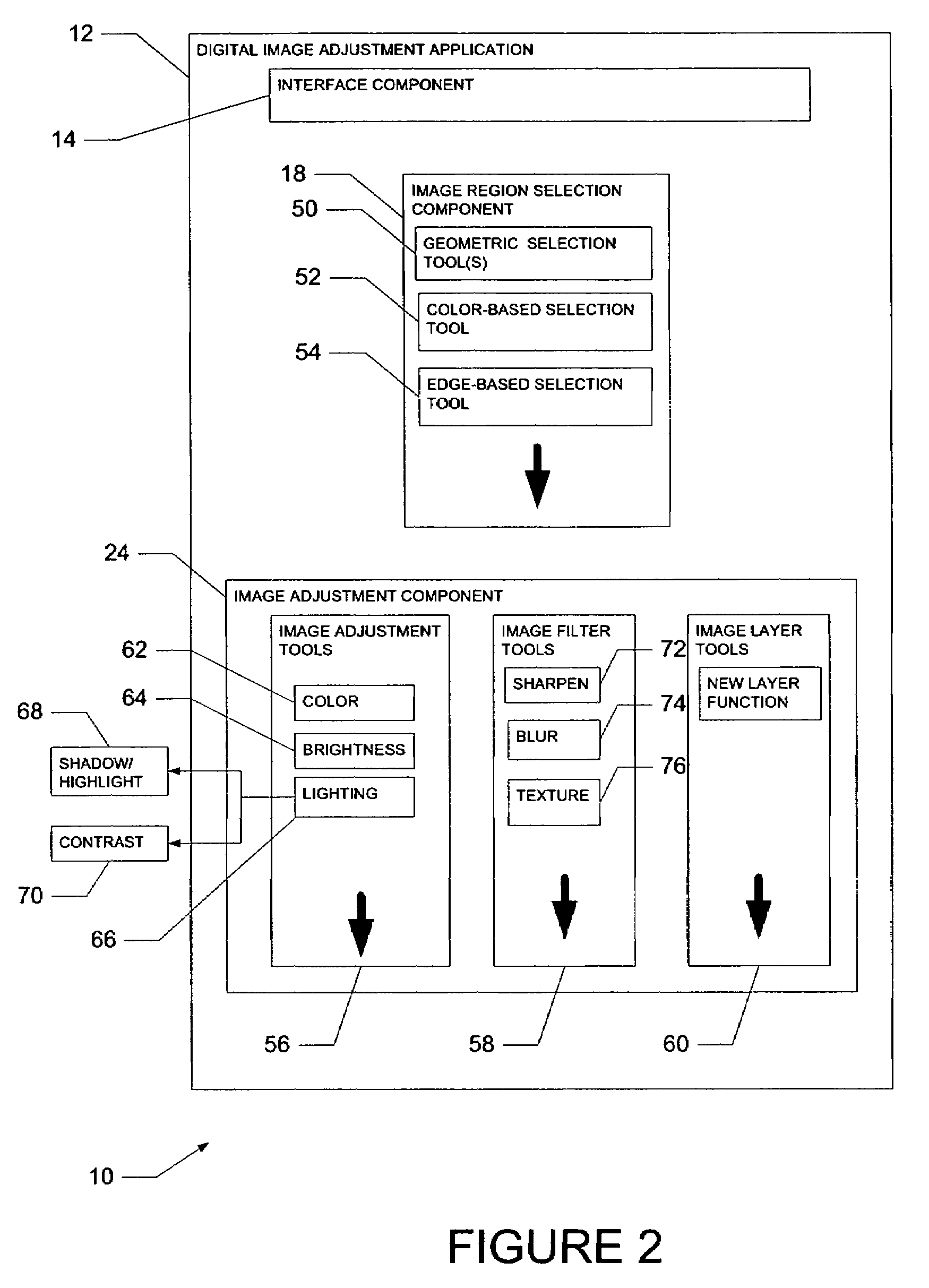
Multi-behavior image correction tool
A system to perform modifications, or adjustments, to a digital image includes an interface component to receive selection input to enable selection of the digital data to be modified. A detector then detects a characteristic of the digital data. A configurator automatically configures a function, supported by a data modification component, to modify the digital data. The automatic configuration of the function is performed using the detected characteristic of the digital data to be modified.
Owner:ADOBE INC
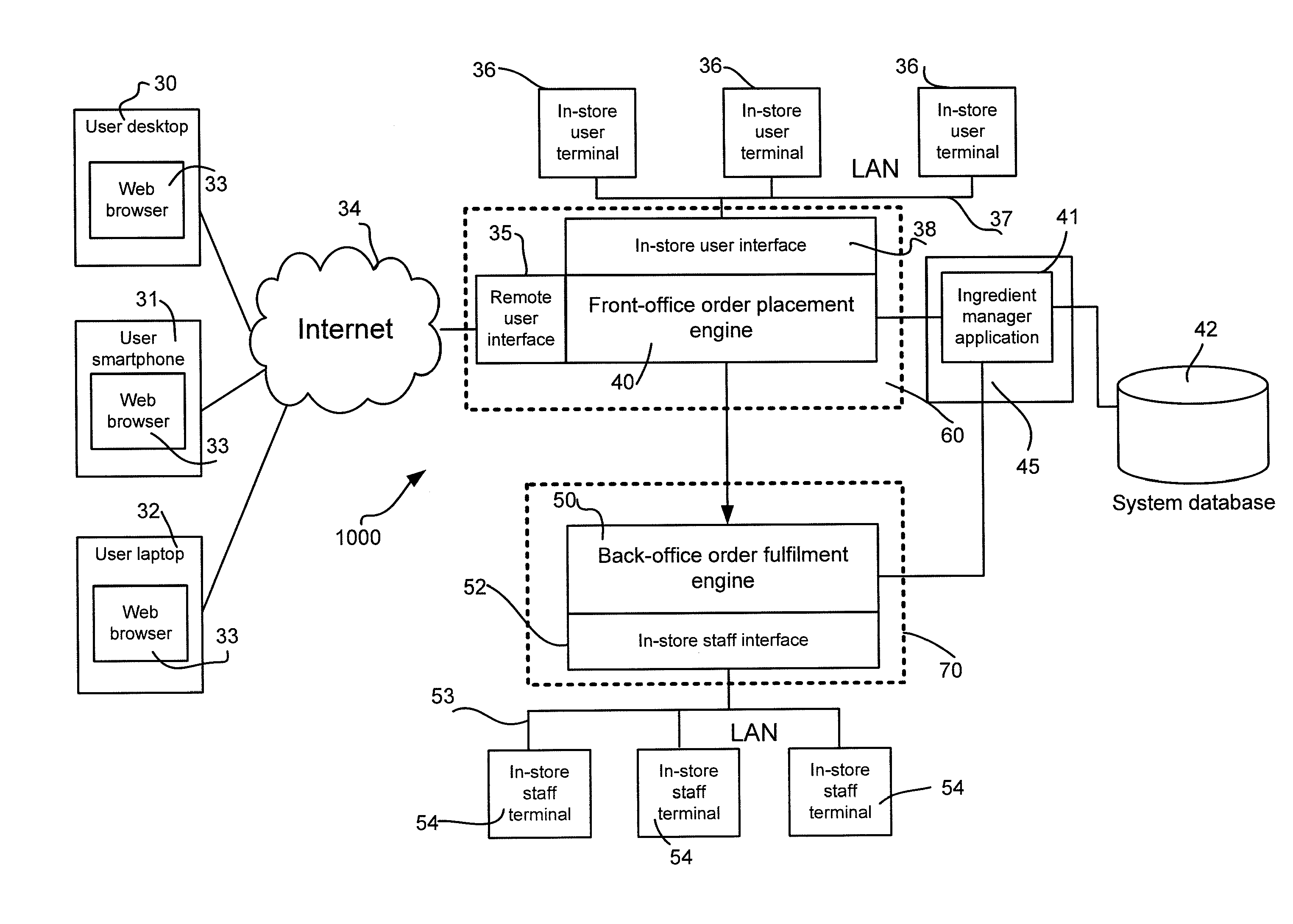
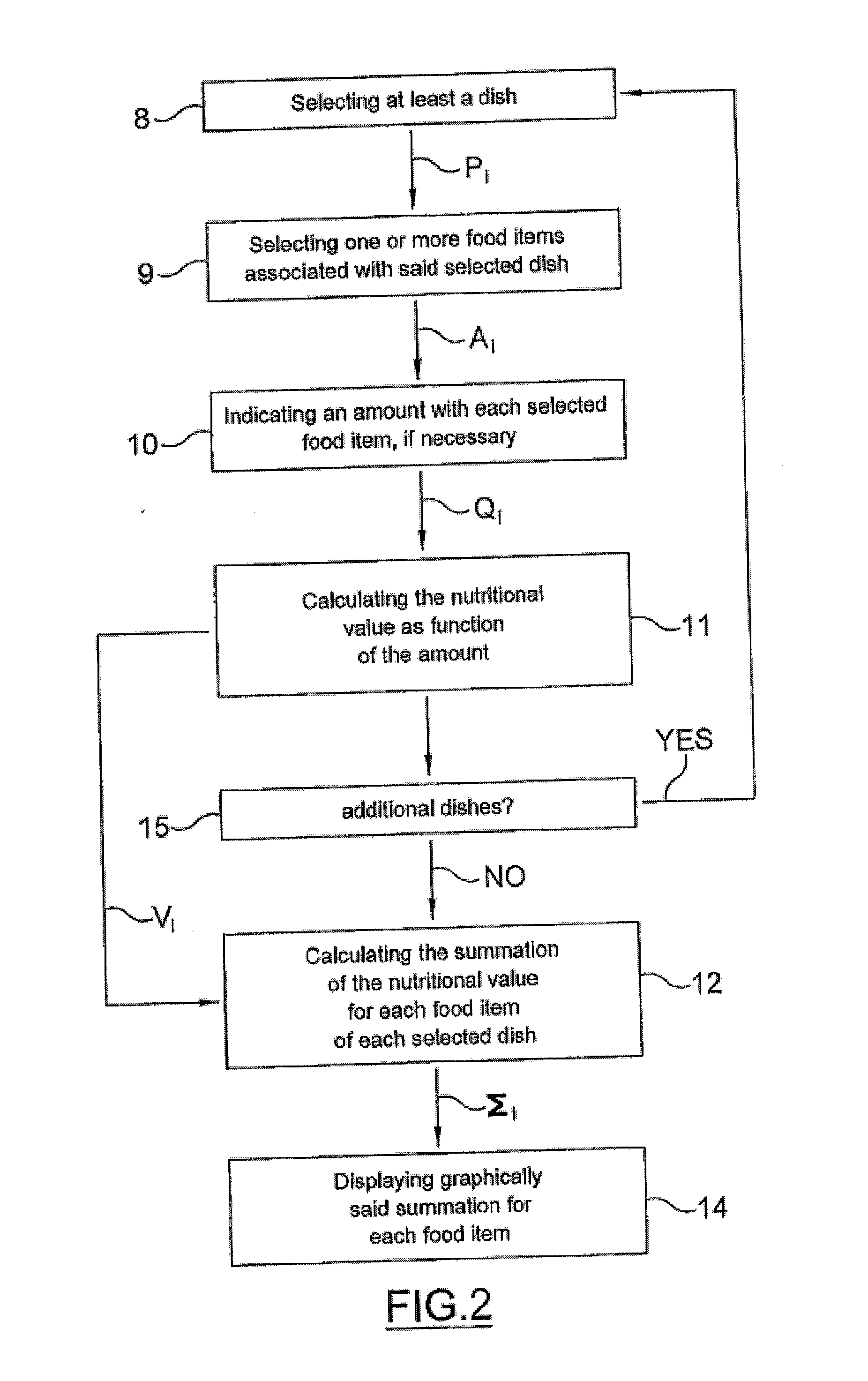
Food and beverages ordering, preparation, management and pricing system and method
InactiveUS20100280895A1Discounts/incentivesDigital data processing detailsAdditive ingredientOrder form
A computerized food and beverages ordering apparatus implements an ordering service for meeting requirements of purchasers. A database comprises records representative of a plurality of ingredients, and at least two attributes are associated with each ingredient. One of the attributes associated to each ingredient is a nutritional parameter for a specific amount of the ingredient, and another attribute is a personal parameter. The personal parameter can be a parameter capable of describing the suitability of the associated ingredient in respect of a medical condition of a purchaser, or it can be a parameter capable of describing the suitability of the associated ingredient in respect of a taste requirement of a purchaser. A user interface is operated by, or under the instruction of, a purchaser to input an order for a meal. The meal comprises one or more of said plurality of ingredients, and each ingredient has an associated quantity. An order placement processor is connected to the user interface and to the database, and it is configured to output to the user interface at least two output parameters. One of the output parameters is a total nutritional parameter computed from the total quantities of ingredients comprised in the meal. Another output parameter is a personal parameter.
Owner:IDEANDO LTD
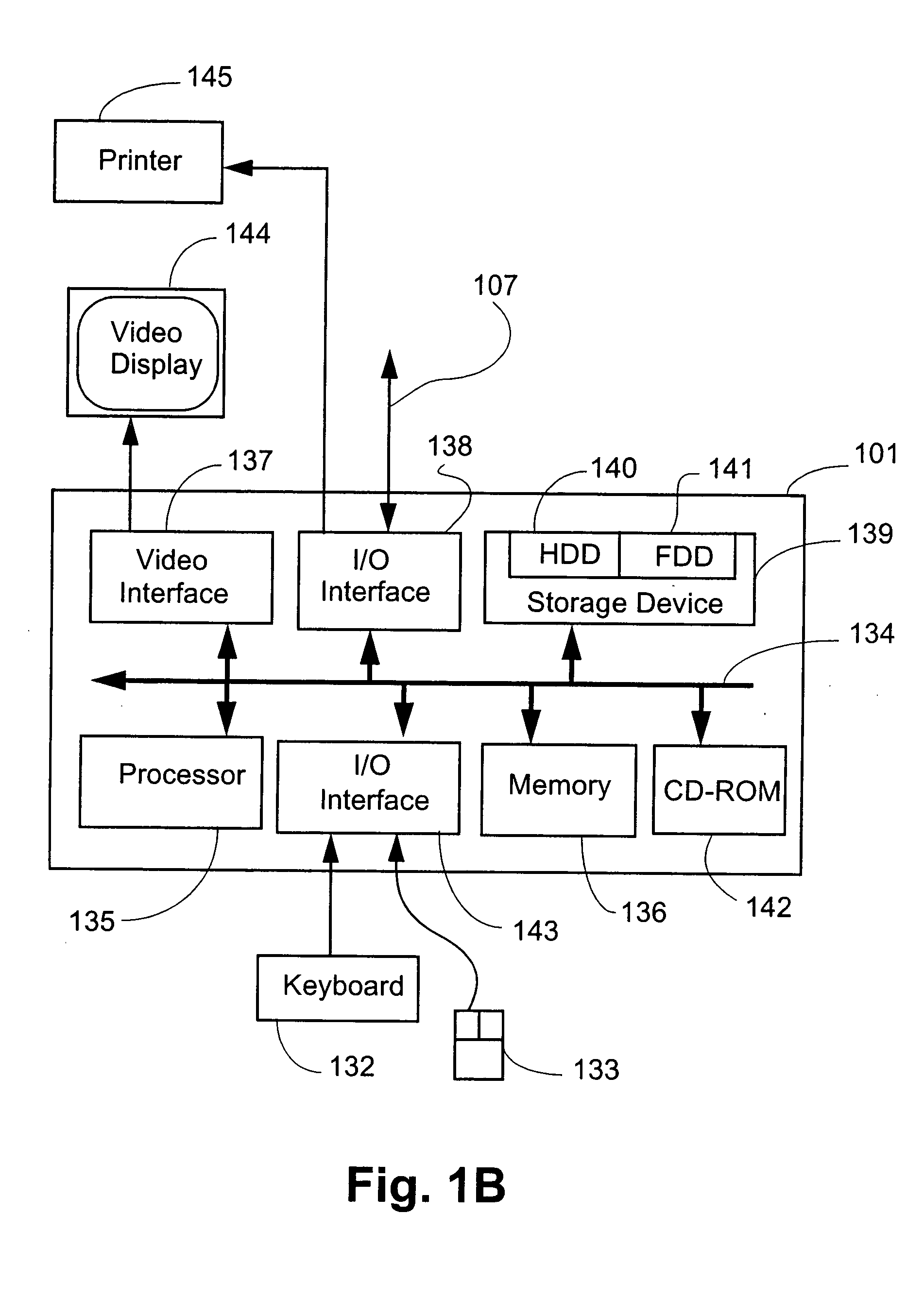
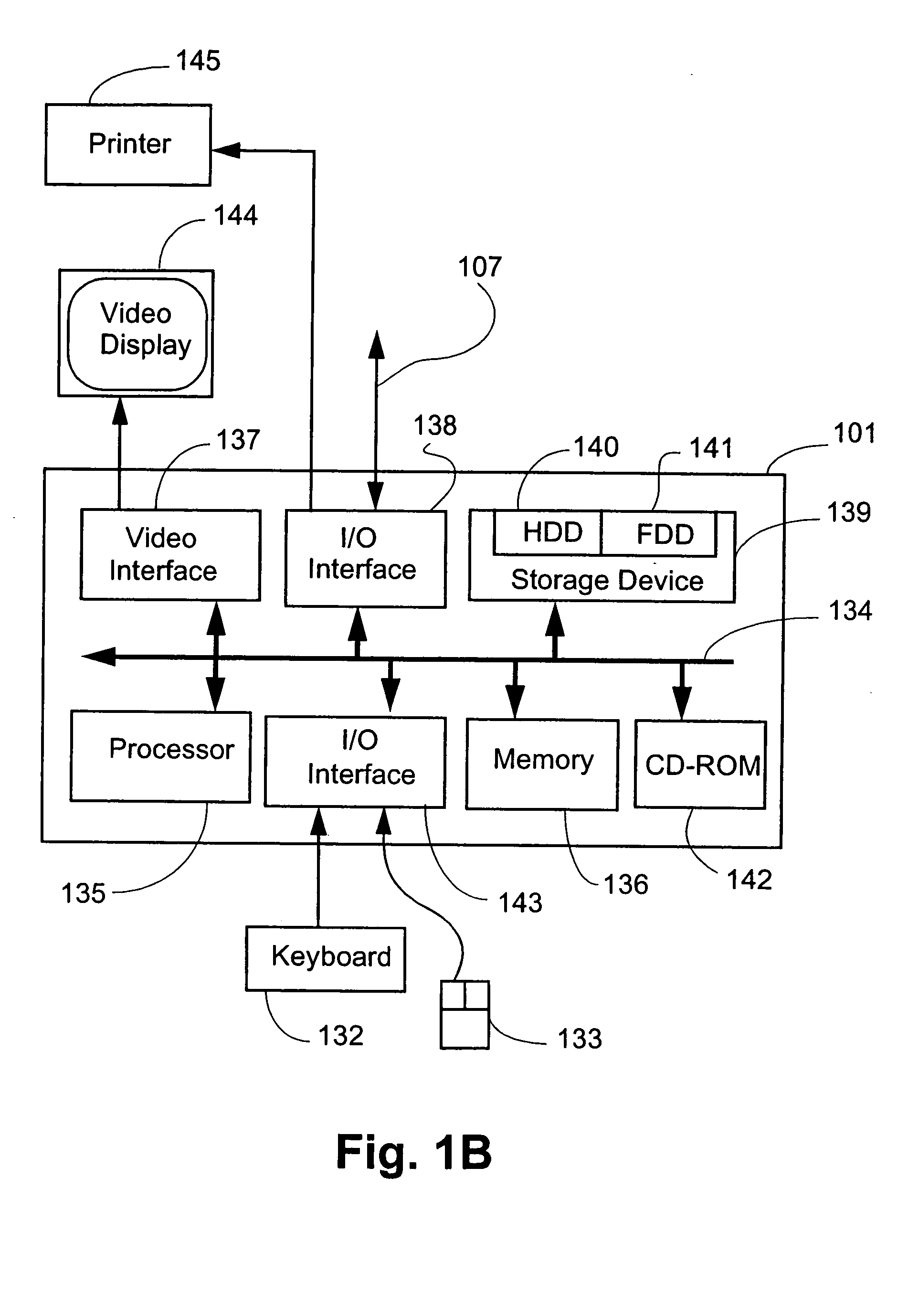
Image recording device and computer accessible storage storing program therefor
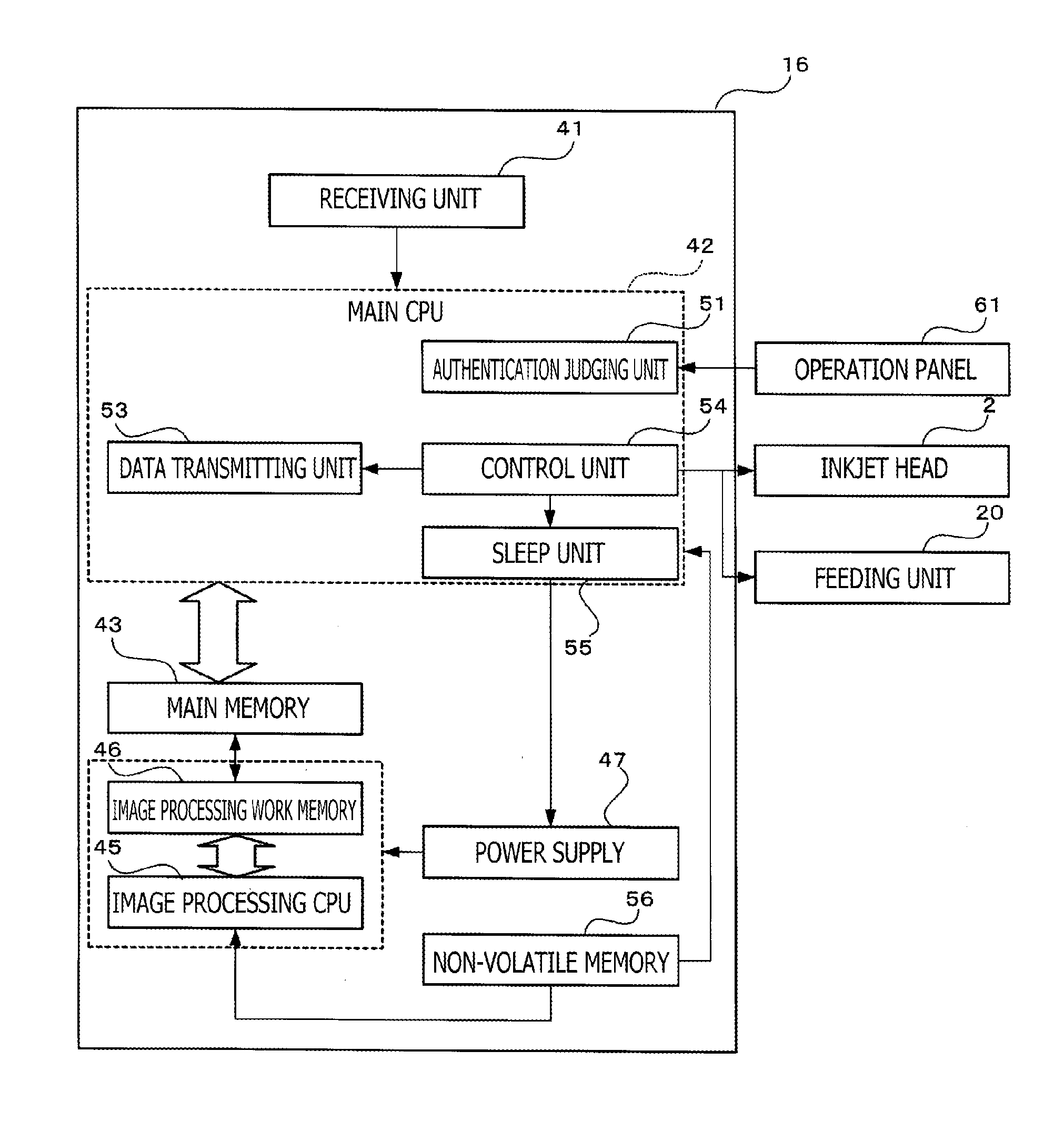
ActiveUS20120162693A1Save powerImprove performanceVisual presentation using printersComputer hardwareImage recording
An image recording device is provided with a first memory which is a volatile memory, a second memory, an input unit through which authentication information is input, an authentication judging unit. The recording unit is controlled to print an image on the printing sheet based on the drive data, which is converted from the image data stored in the first memory or the second memory and is stored in the first memory or the second memory. The drive data or the image data is stored in each of the first memory and the second memory is transmitted therebetween. The image recording device further includes a restricting unit capable of restricting power supply to the converting unit and the first memory in a sleep mode.
Owner:BROTHER KOGYO KK
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, and image processing program
ActiveUS20060215204A1Digitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printersImaging processingComputer graphics (images)
An image processing apparatus implements appropriate image processing on image data stored in a storage unit of the image processing apparatus easily and efficiently, and distributes the image data to an external apparatus. An image format conversion-unit implements image processing such as resolution conversion processing, filter processing, γ correction processing, and halftone processing on image data stored in an HDD serving as an image data storage unit so that the image data conform to conditions, such as image quality and format, specified by an external client apparatus. The image-processed image data are then distributed to the external client apparatus.
Owner:RICOH KK
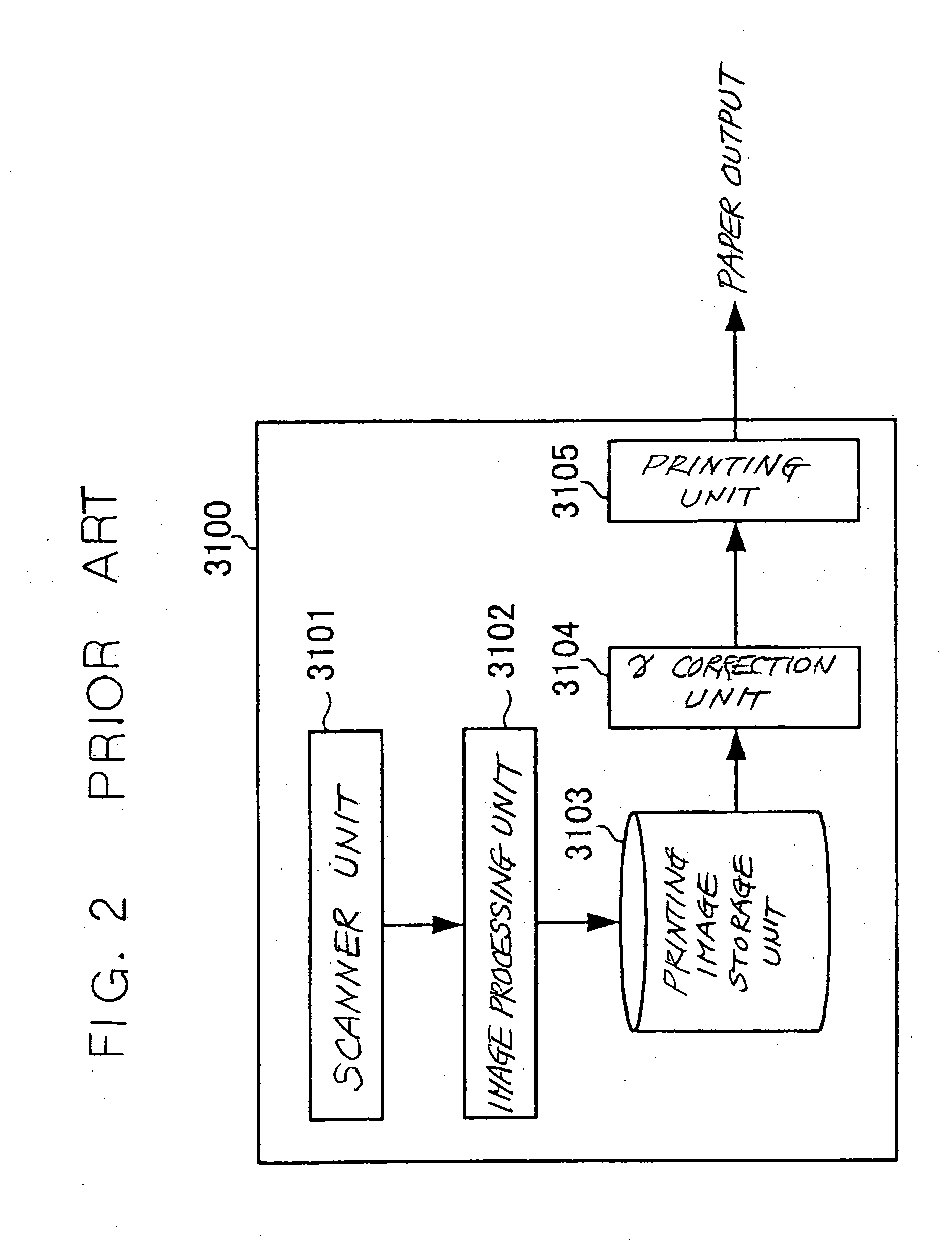
Image reader and copier
InactiveUS20030179399A1Reliable preventionImprove processingImage enhancementImage analysisProgramming languageCondition Code
An image, in which a pattern image is arranged so as to express a control information for inhibiting copying or for removing the inhibition, is defined as an image to be read. A copy inhibition code or a condition code for removing the inhibition is assigned for the pattern image. In a "normal copy mode" of a copier, a copy inhibition information detecting part detects the copy inhibition code in an obtained image, and a controller halts the copying when the copy inhibition code is detected. A condition information detecting part detects the condition code in the obtained image. A copy mode is provided in which the copying operation is permitted when the condition matches. The controller permits copying when a condition, such as permitting a specific user to perform copying or the elapse of a predetermined day and time delimited period, is established.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Apparatus and method for converting image display mode
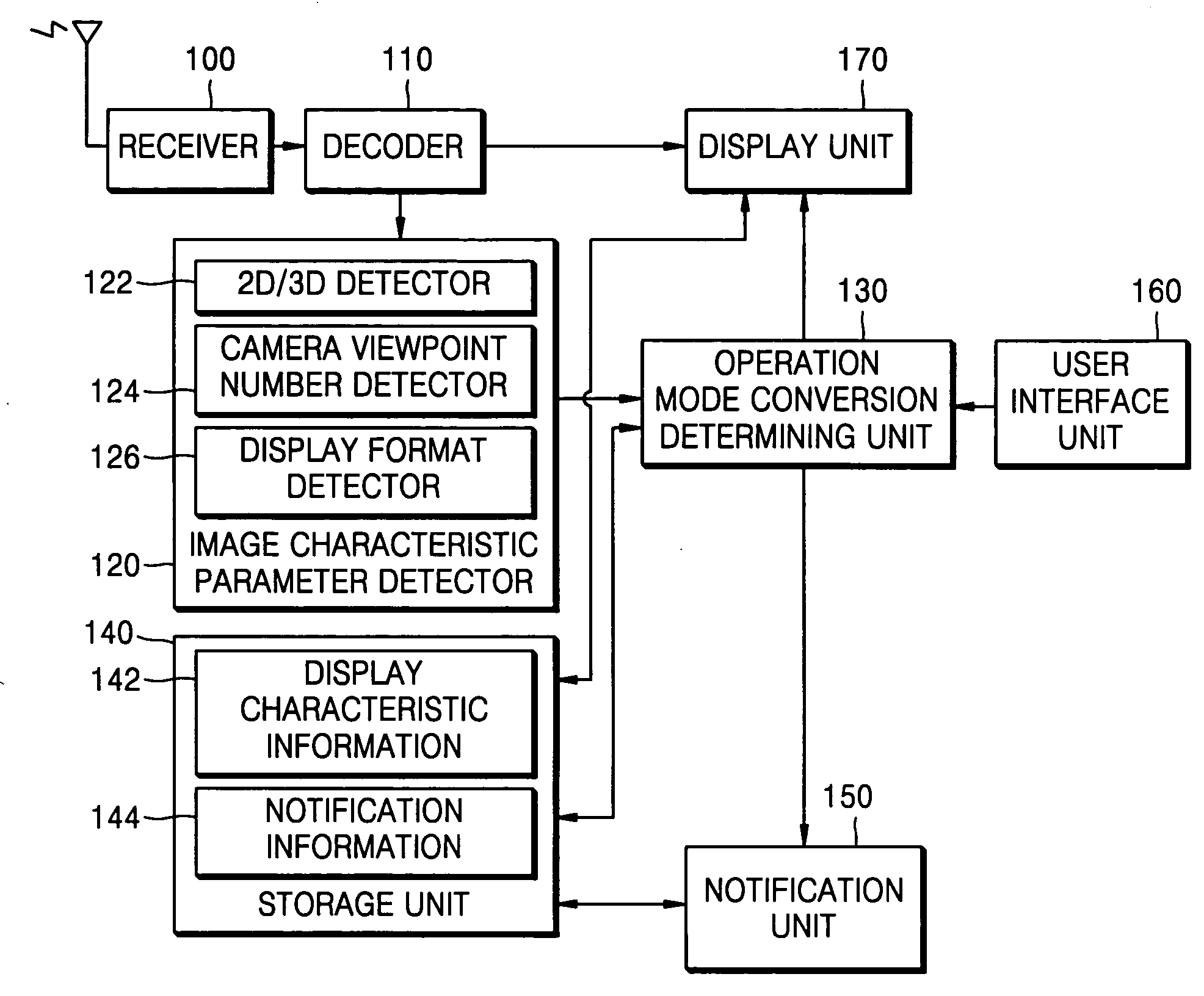
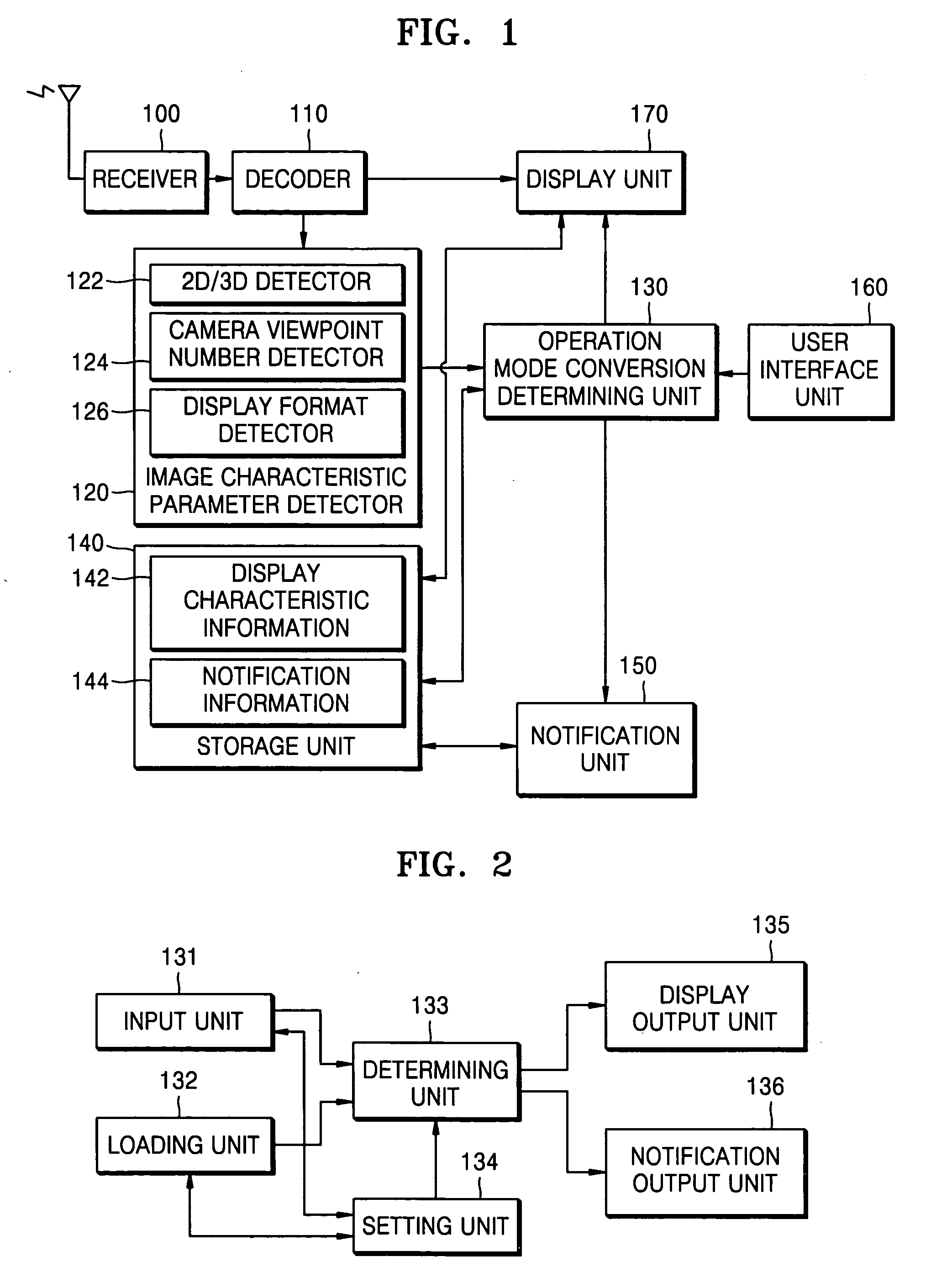
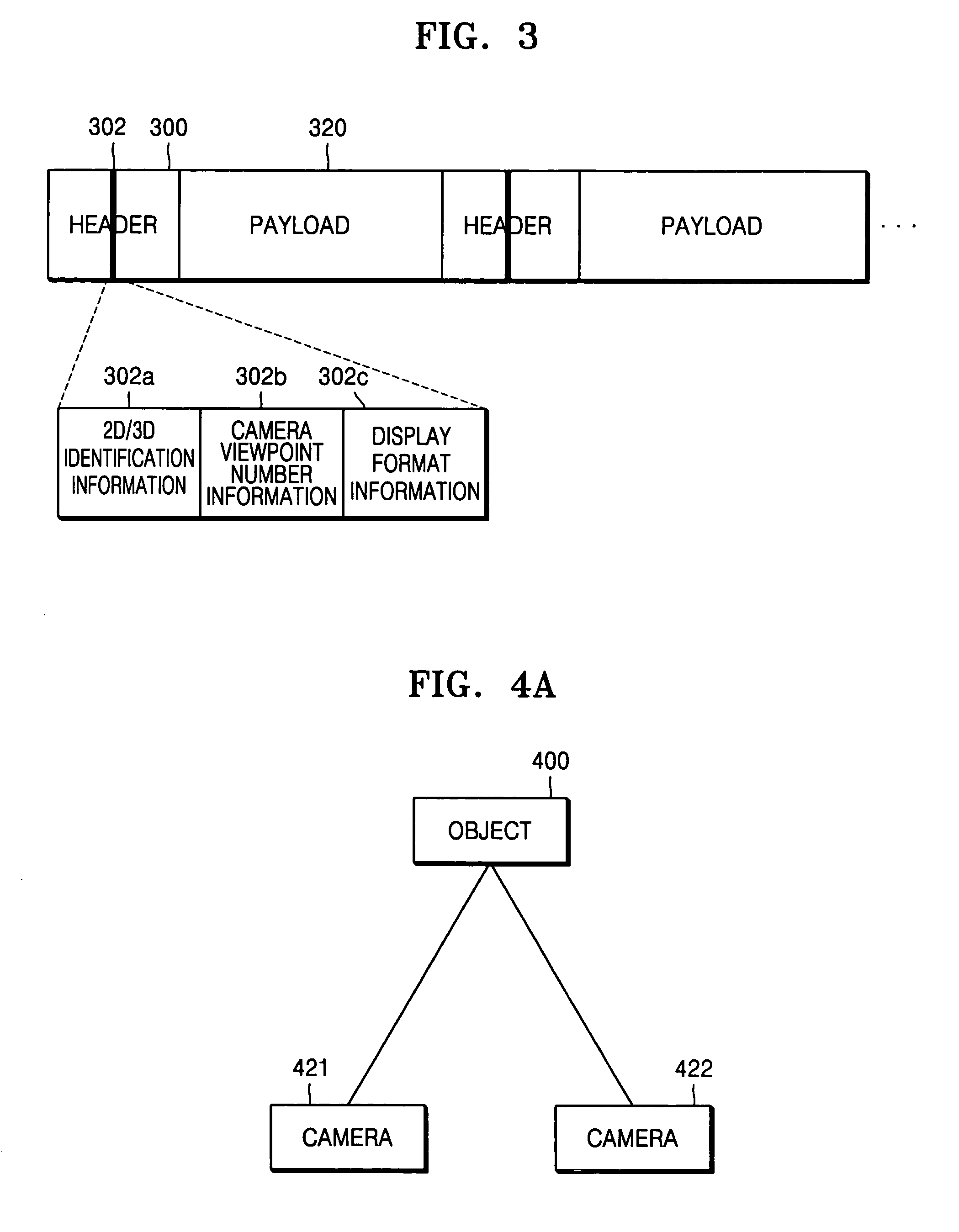
InactiveUS20060279750A1Digitally marking record carriersVisual presentation using printers3d imageImage signal
An image display mode conversion apparatus and method, the apparatus having a display unit displaying image data included in an image signal, an image characteristic parameter detector detecting an image characteristic parameter which is information regarding whether the image data included in the image signal represents a two-dimensional (2D) image or a three-dimensional (3D) image, and an operation mode conversion determining unit receiving the detected image characteristic parameter, determining whether or not an operation mode of the display unit should be converted, and outputting an operation mode conversion signal to the display unit according to the determination result. Therefore, it is possible to provide more convenience to users in various fields, such as a 3D image broadcasting and so on, by implementing the image display mode conversion apparatus in a digital broadcast standard system.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
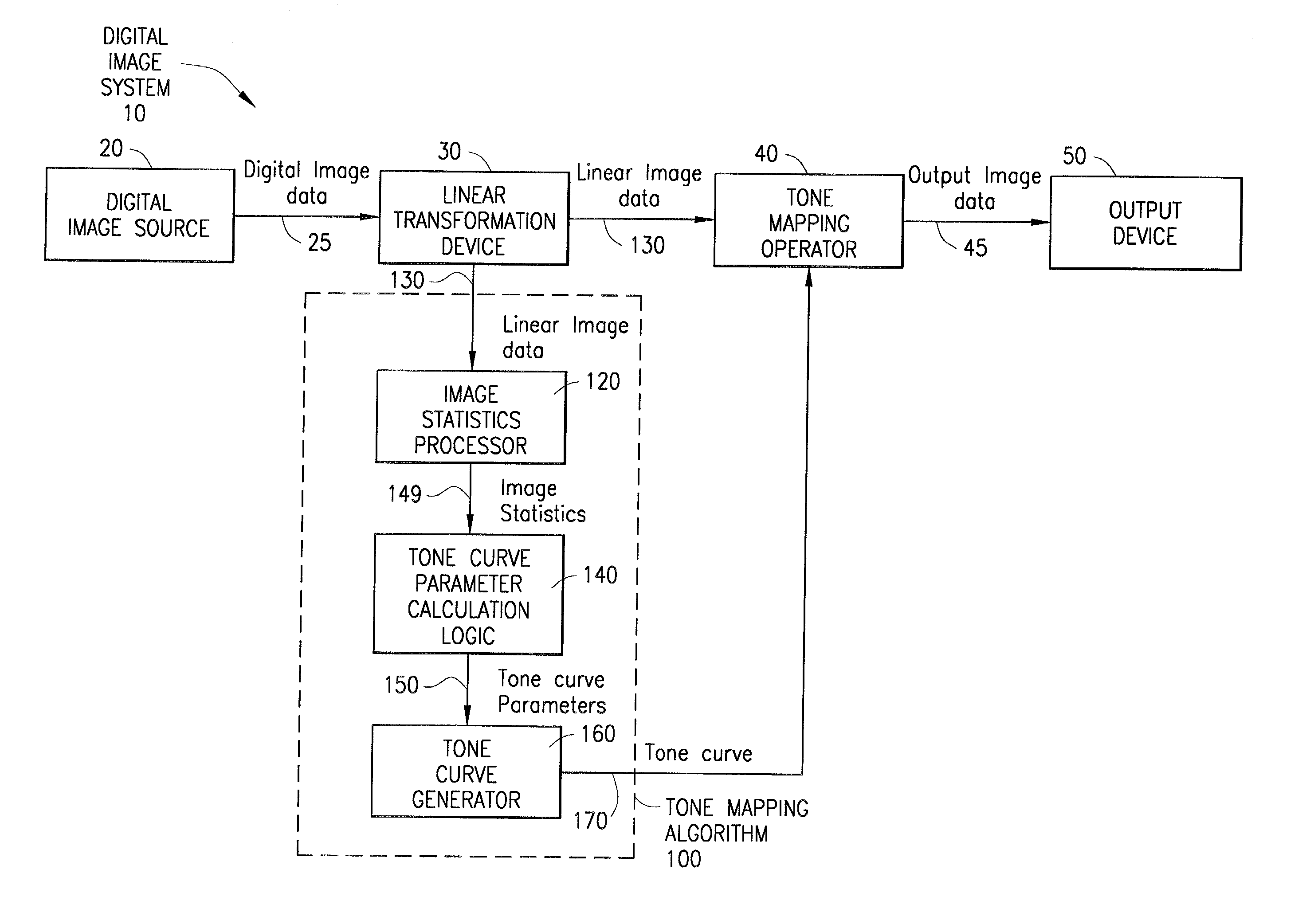
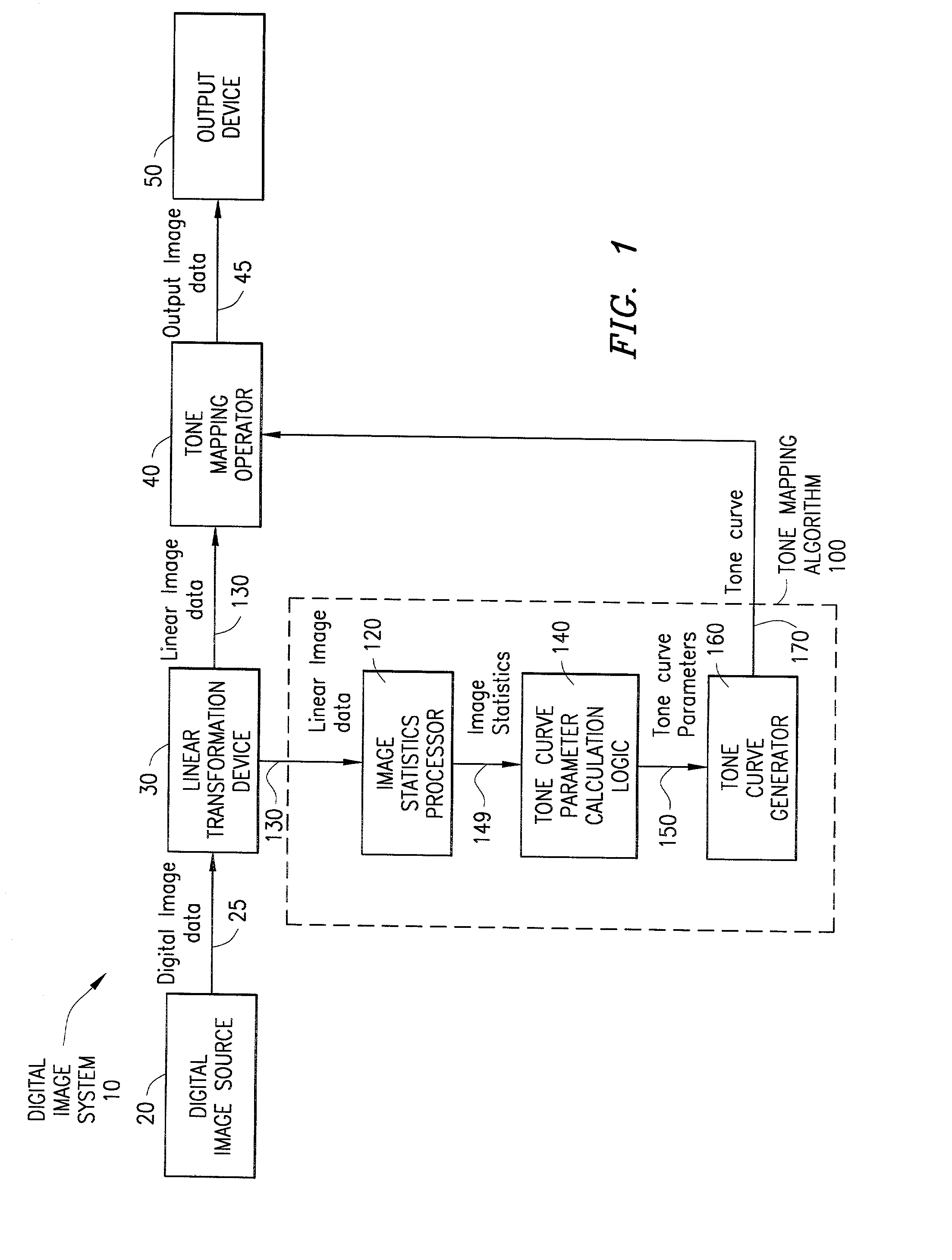
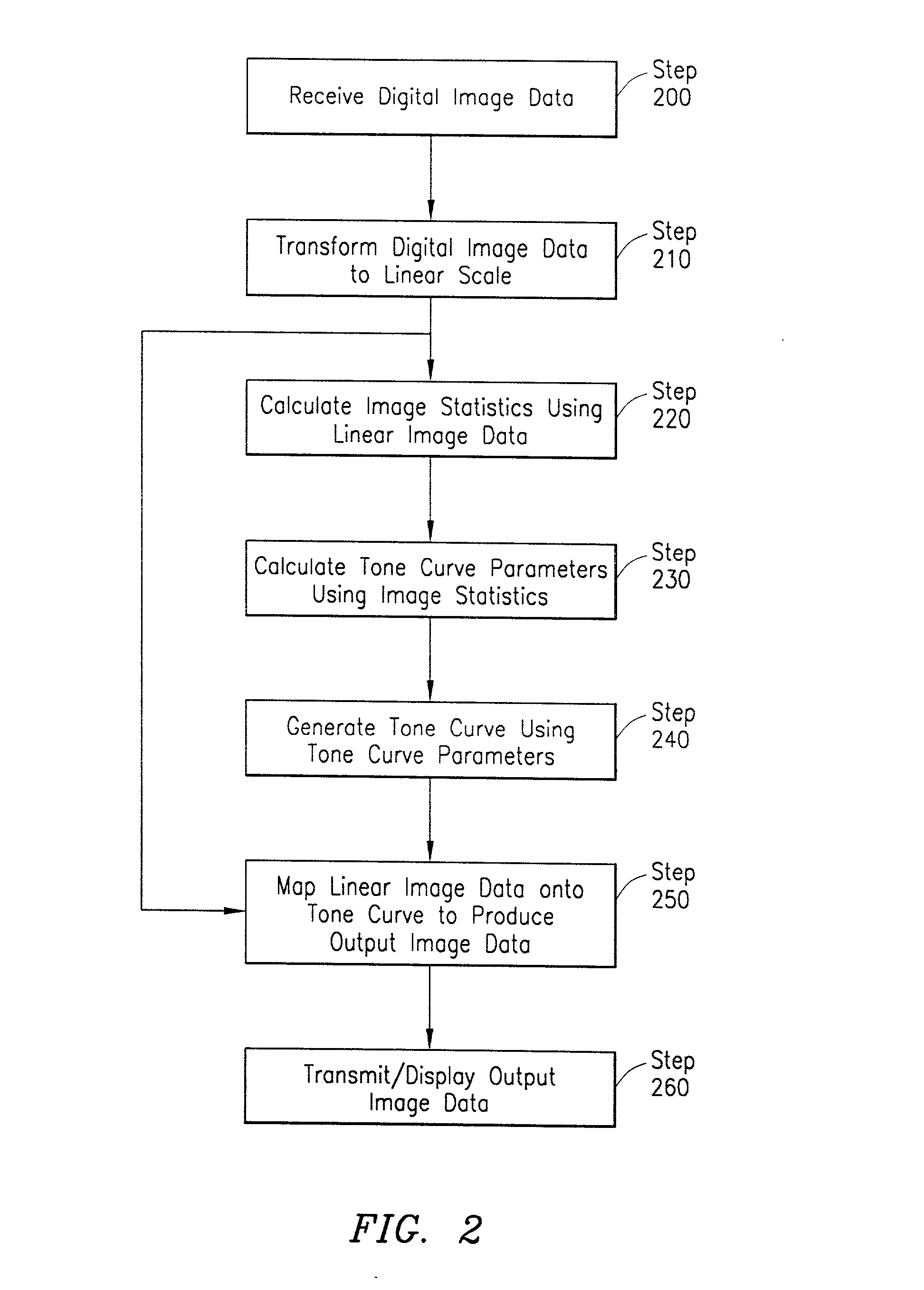
System and method for digital image tone mapping using an adaptive sigmoidal function based on perceptual preference guidelines
InactiveUS20020171852A1Image enhancementDigitally marking record carriersTone mappingTagged Image File Format
An adaptive image tone mapping curve based on perceptual preference guidelines is generated as a sigmoidal function, in which the sigmoidal function parameters (slope and shift) are determined by original image statistics. Tone curves generated for different images each have a smooth sigmoidal shape, so that the tone mapping process does not change the image histogram shape drastically. The sigmoidal function has the form: <math-cwu id="MATH-US-00001"> <number>1< / number> t it ( x ) = 100 1 + exp it ( - alpha it ( x / 100 - beta ) ) , <mathematica-file id="MATHEMATICA-00001" file="US20020171852A1-20021121-M00001.NB" / > <image id="EMI-M00001" wi="216.027" he="18.96615" file="US20020171852A1-20021121-M00001.TIF" imf="TIFF" ti="MF" / > < / math-cwu> where alpha is the slope parameter and beta is the shift parameter. The input value x in the sigmoidal function varies in the range [0, 100], because the tone curve is generated on an L* scale, which has values from 0 to 100. The sigmoidal tone curve calculation can be implemented efficiently using simple arithmetic operations by pre-calculating and storing various factors used in the calculation of alpha and beta and by pre-generating a pair of fixed tone curves with two extreme slopes and interpolating between the curves.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
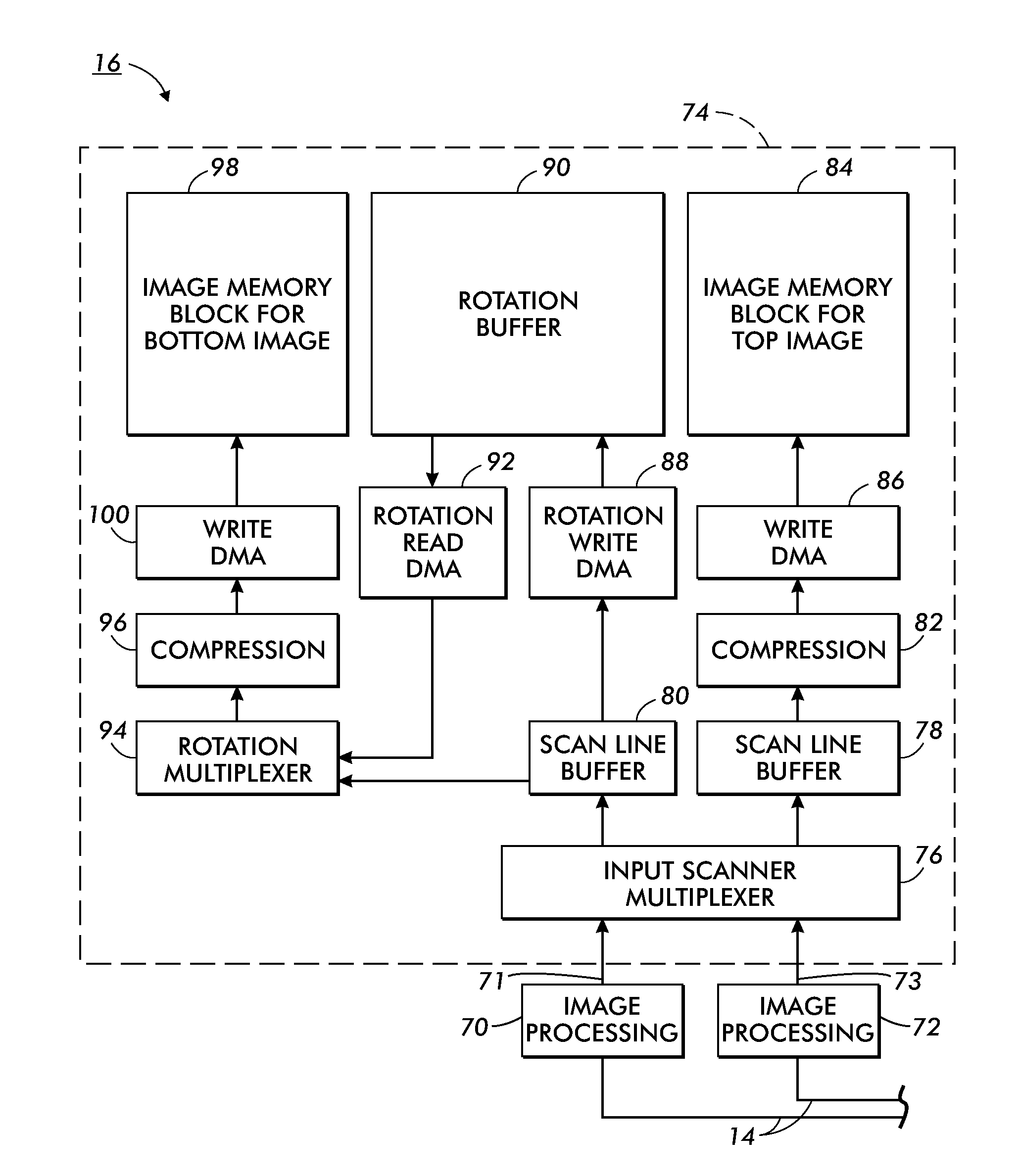
System and method for image rotation
InactiveUS7894094B2Digitally marking record carriersGeometric image transformationReverse orderComputer graphics (images)
A system and method to provide 180-degree rotation of image data at full throughput. The system includes a memory access controller that writes bursts of image data into a rotation buffer. The image data is then read out of the rotation buffer in the reverse order from which it was written to thereby accomplish rotation. By alternating the position in the rotation buffer in which the image data is written such that an image is either written into the buffer from top and read from the bottom or written into the buffer from the bottom and read out from the top, a one page rotation buffer of can be used to concurrently process two pages.
Owner:XEROX CORP
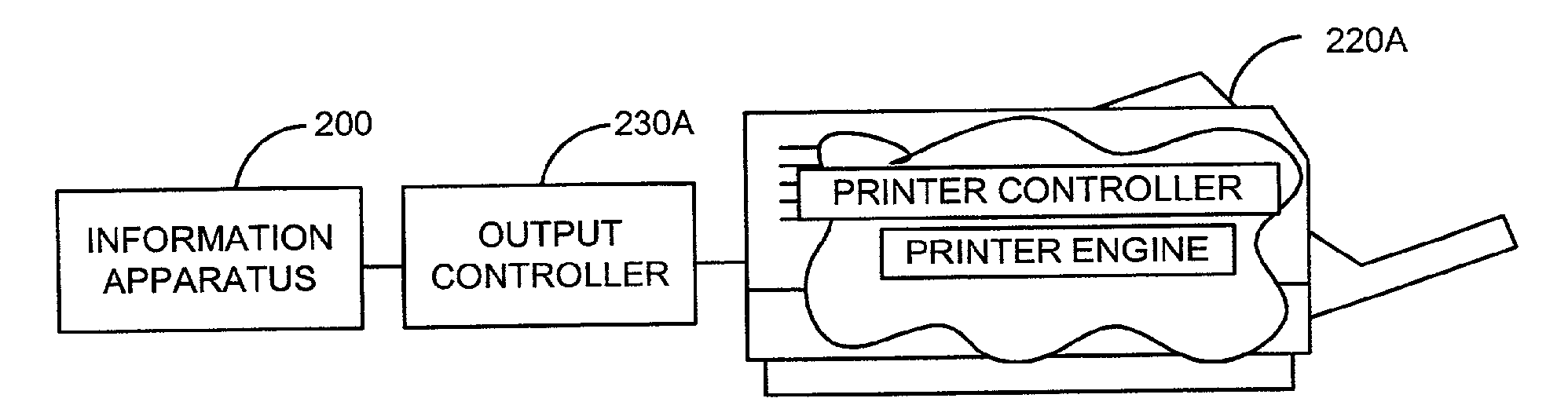
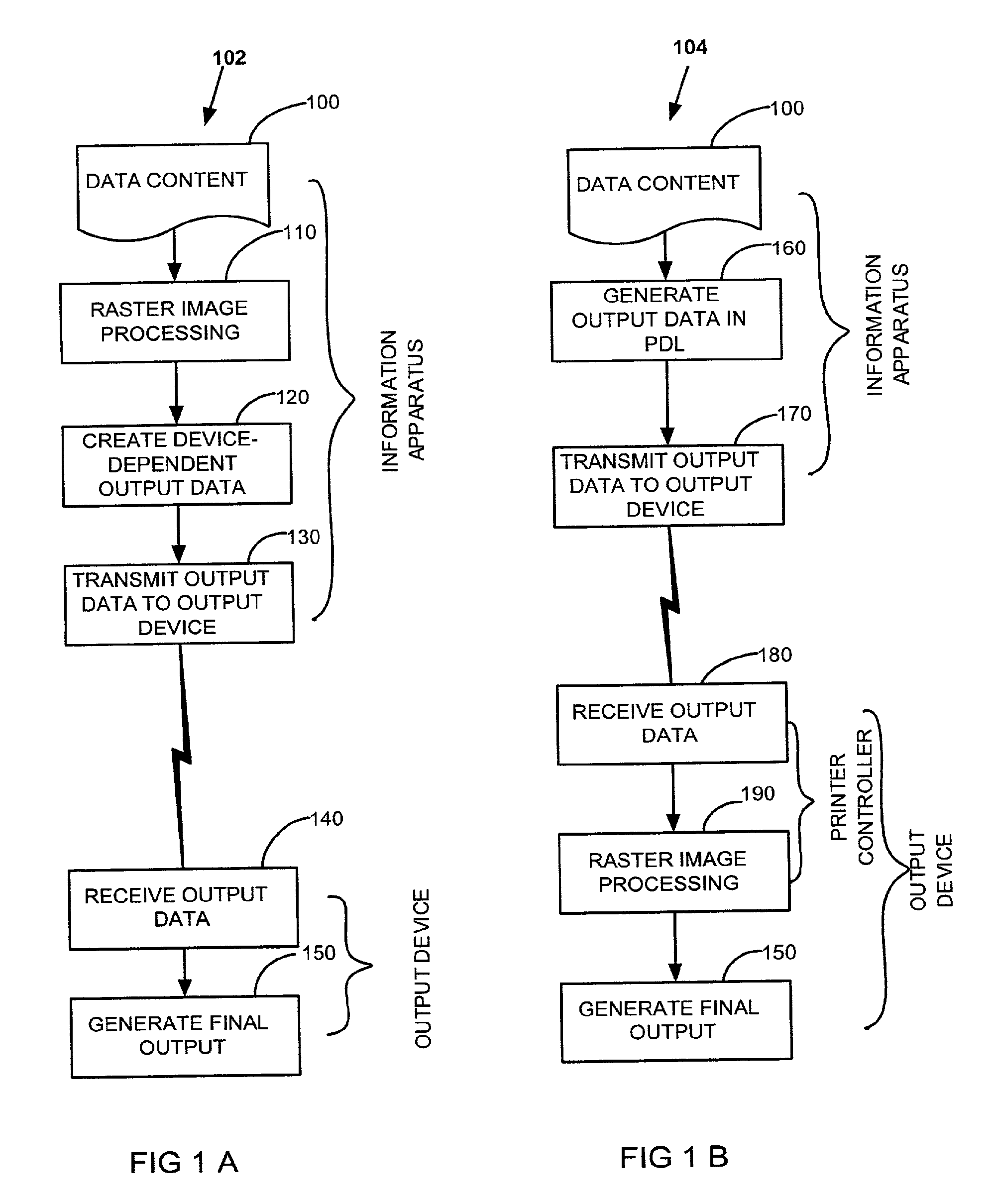
Wireless information apparatus for universal data output
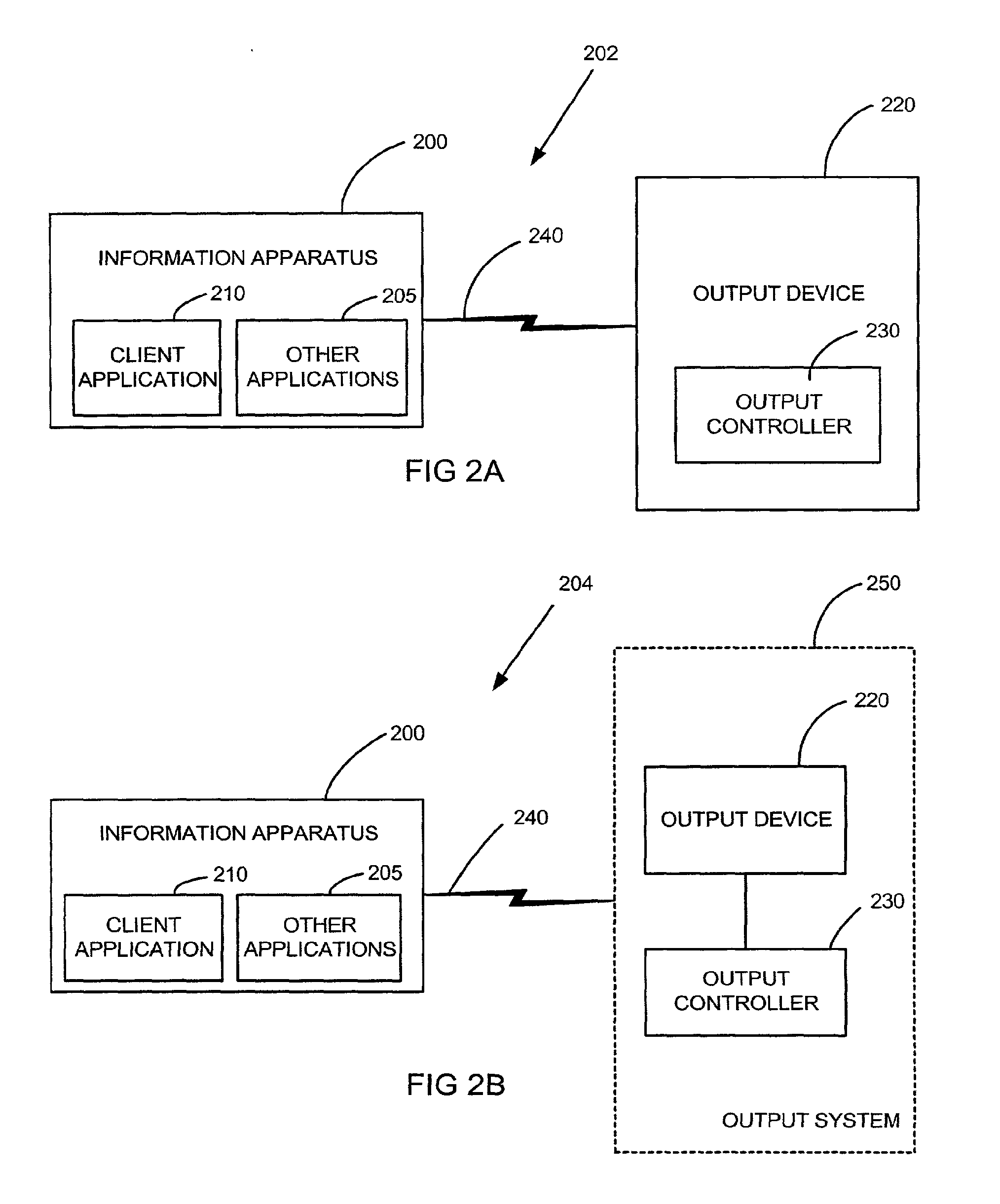
InactiveUS20100039669A1Eliminate needHigh outputEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsOutput deviceData content
A data output method for rendering at an output device content accessible with an information apparatus, includes obtaining at the information apparatus one or more rasterization parameters corresponding to the output device and conforming at the information apparatus at least part of the data content into one or more output images with said one or more rasterization parameters. An intermediate output data is transmitted from the information apparatus to an output controller that is distinct from the information apparatus and associated with the selected output device, the intermediate output data including said one or more output image. The intermediate output data is converted at the output controller into an output data acceptable for rendering at the output device.
Owner:FLEXIWORLD TECH
Printing medium certificate documents and false proof handling method of copy thereof
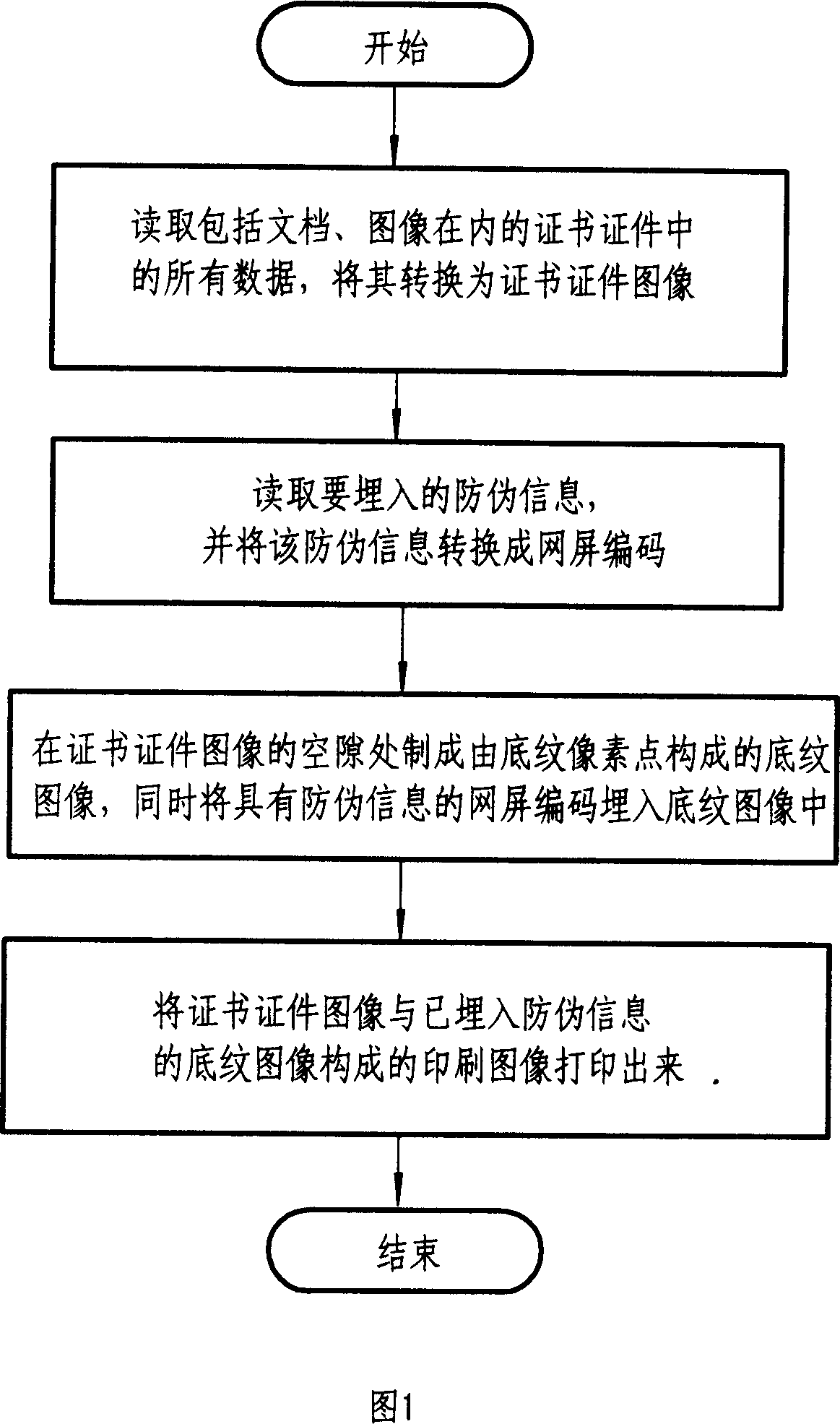
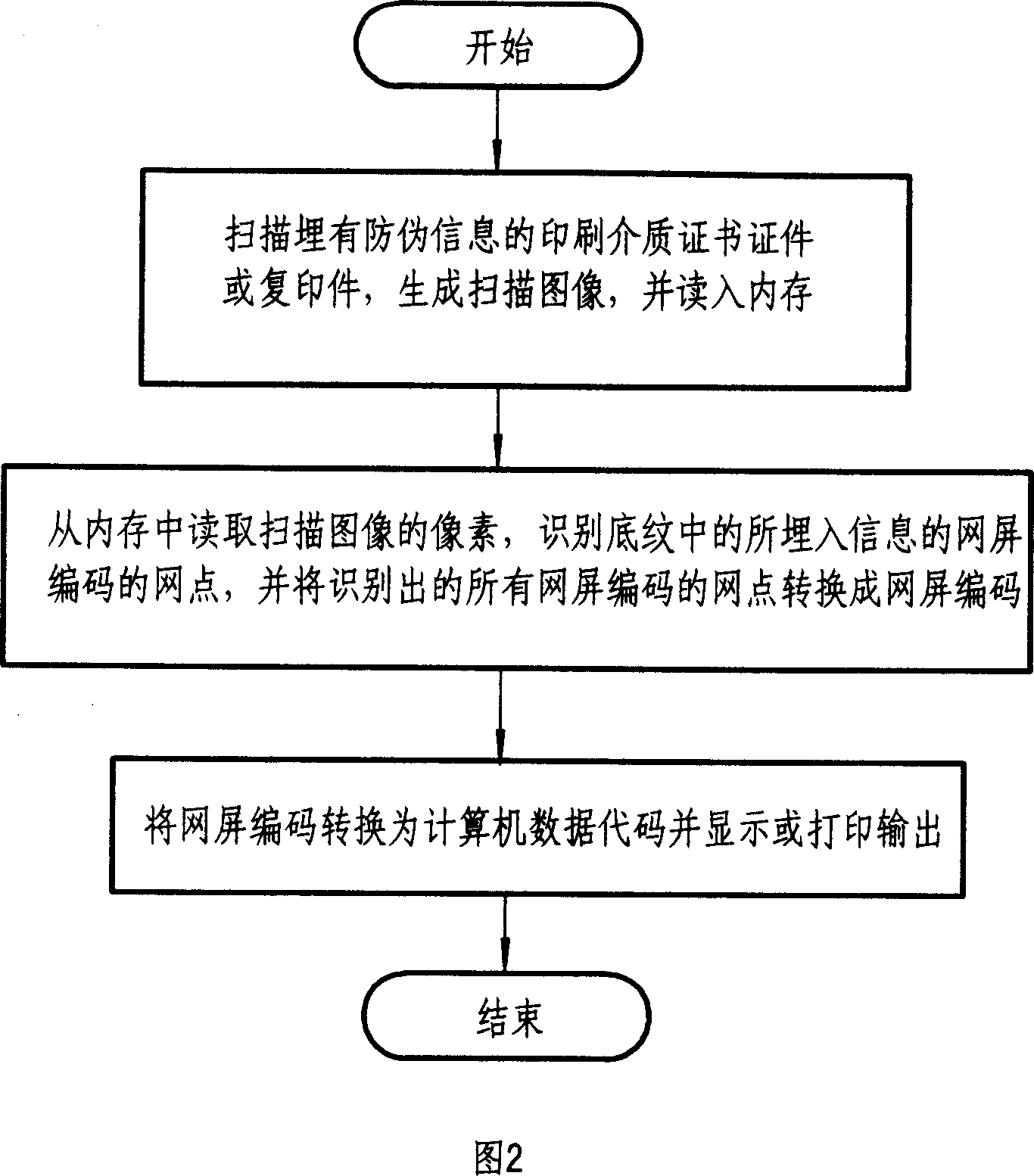
ActiveCN1928916ARealize anti-counterfeiting and anti-tampering processing methodVisual presentation using printersImage data processing detailsPrint mediaInformation embedding
The related false proof information embedding method for print-media certificate comprises: printing the false proof shading image in certificate content gap, and embedding the false proof information of screen code on the shading without changing shading pixel feature. The corresponding recognition method comprises: scanning the print media to recognize the false proof information, and comparing both the false proof information and certificate or copy together. This invention can also recognize the copy, needs low cost, and benefit to spread.
Owner:顾泽苍
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com