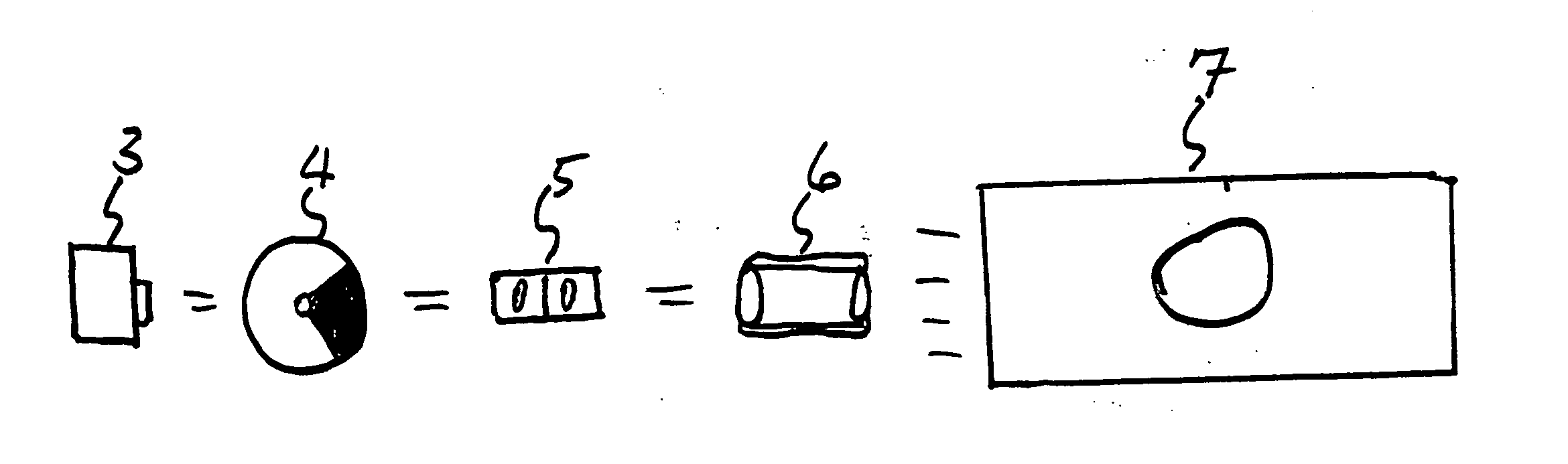Patents
Literature
33results about How to "High frame rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
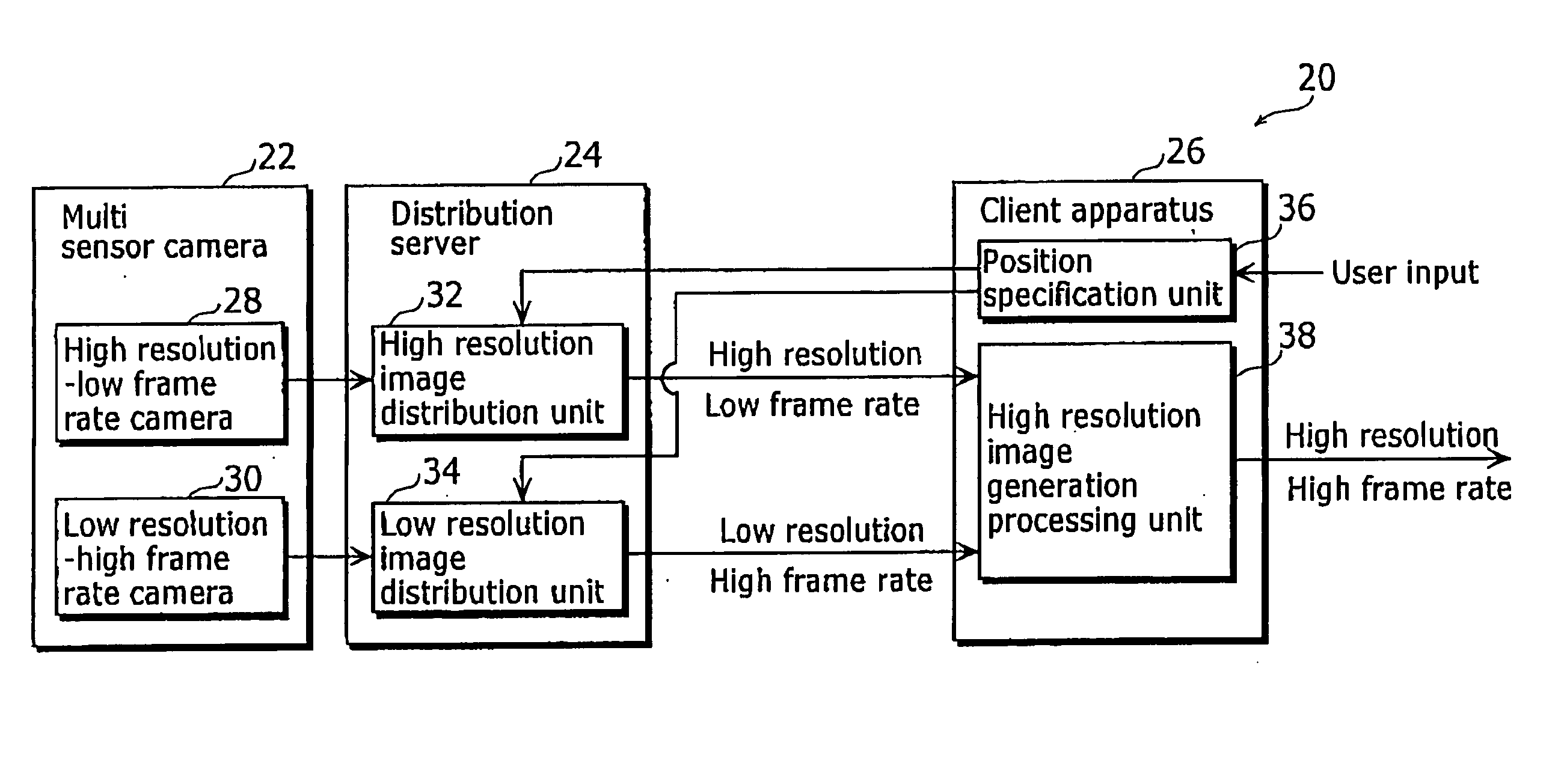
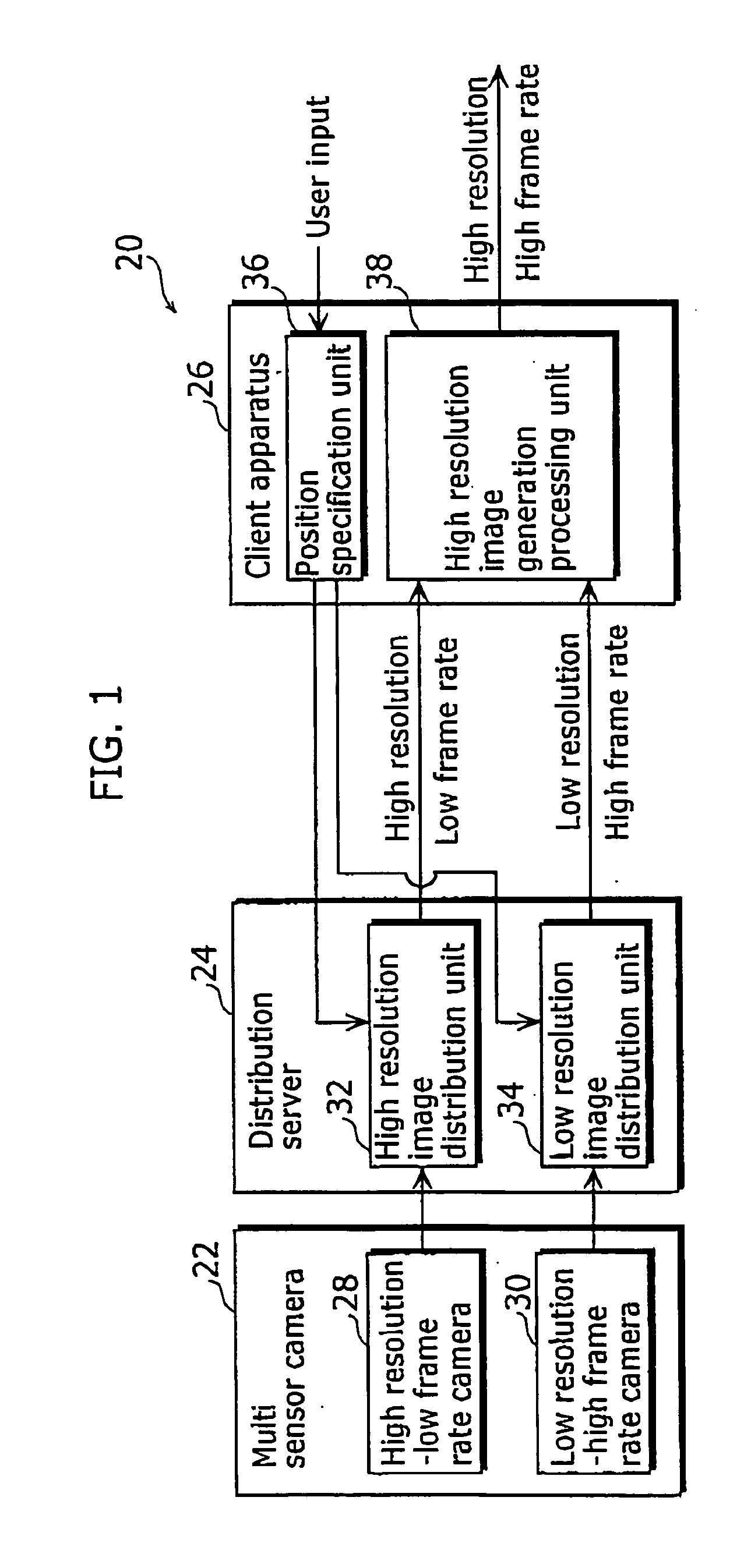
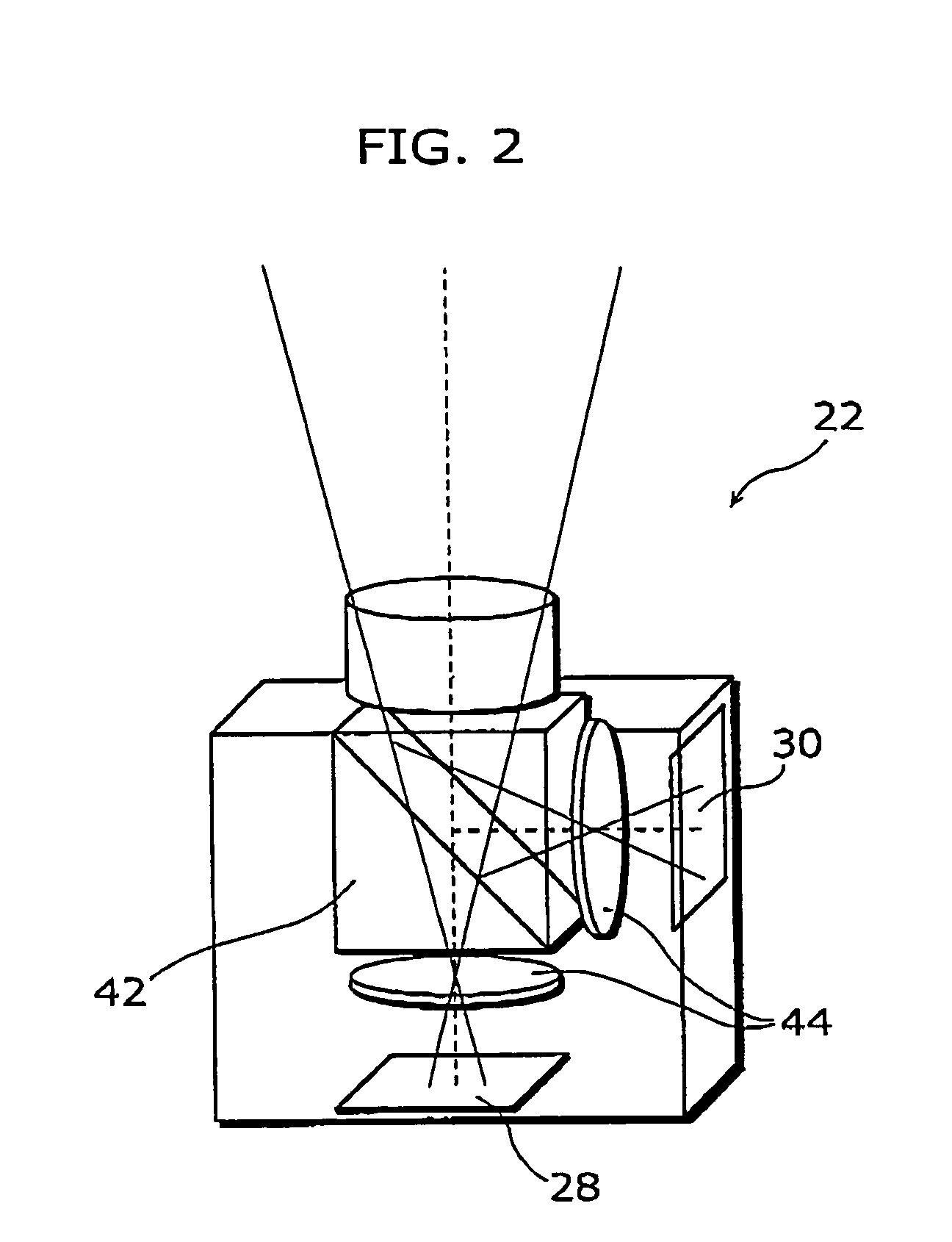
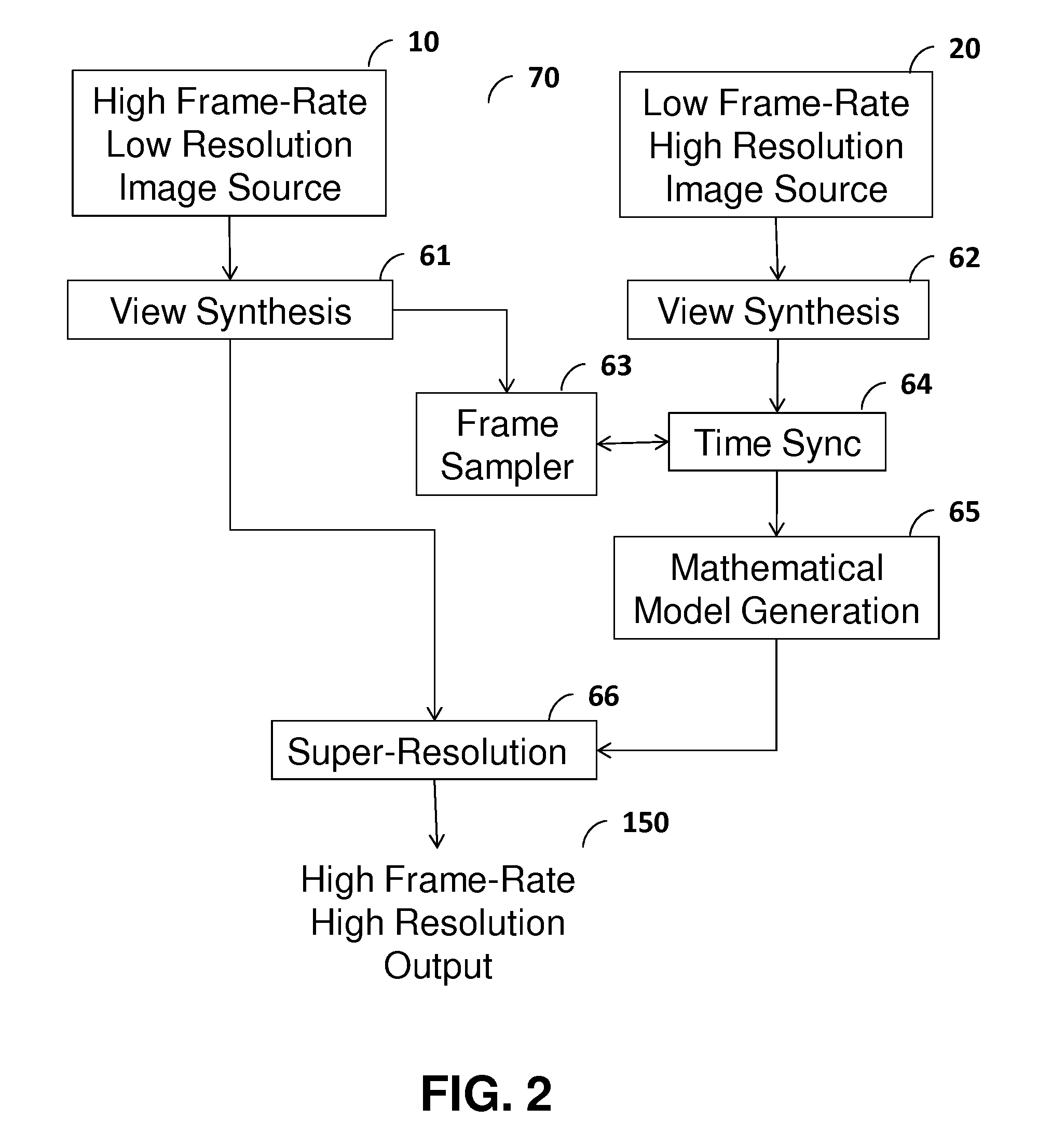
Imaging system, image data stream creation apparatus, image generation apparatus, image data stream generation apparatus, and image data stream generation system
InactiveUS20050219642A1Low costHigh frame rateTelevision system detailsDigitally marking record carriersData streamBeam splitter
An imaging system that is capable of generating high resolution and high frame rate video includes of a beam splitter, two lenses, a high resolution-low frame rate camera, and a low resolution-high frame rate camera. The beam splitter reflects a part of an incident ray. The two lenses gather the ray reflected from the beam splitter and the ray penetrating the beam splitter, respectively. The low resolution-high frame rate camera is a sensor that takes an image of the ray gathered by one of the lenses at a low resolution and a high frame rate. The high resolution-low frame rate camera is a sensor that takes an image of the ray gathered by the other of the lenses at a high resolution and a low frame rate.
Owner:YACHIDA MASAHIKO +1
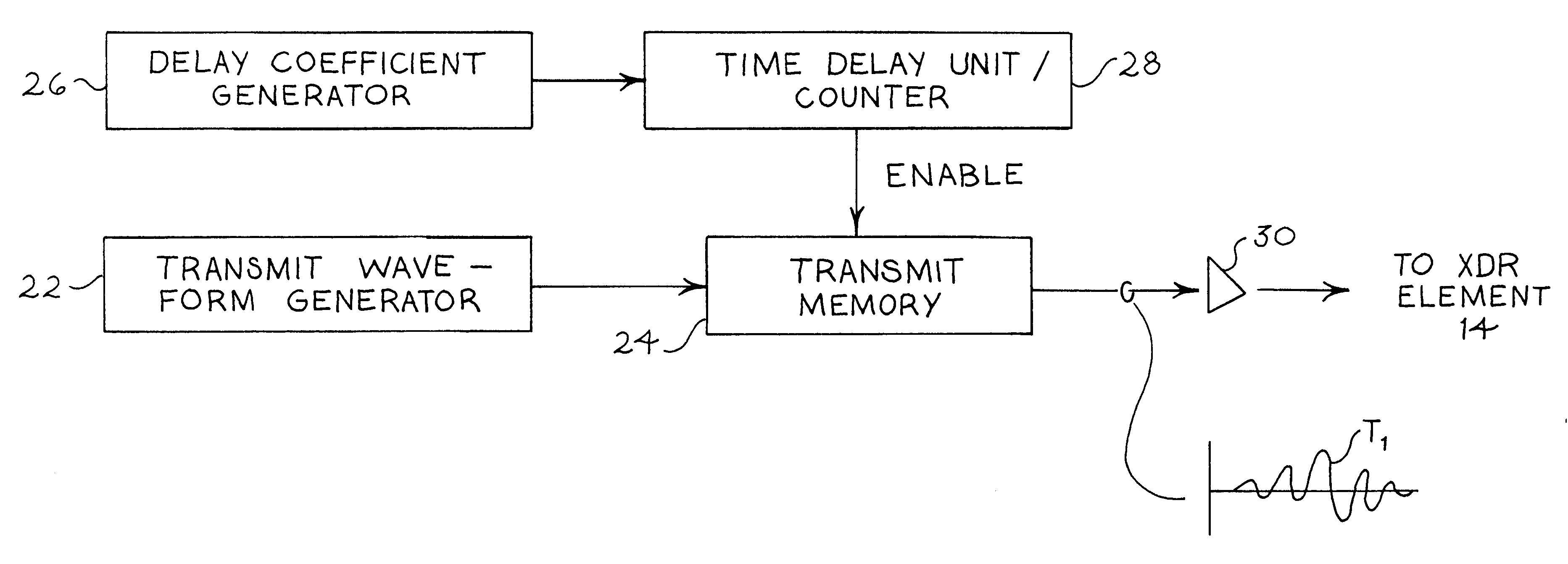
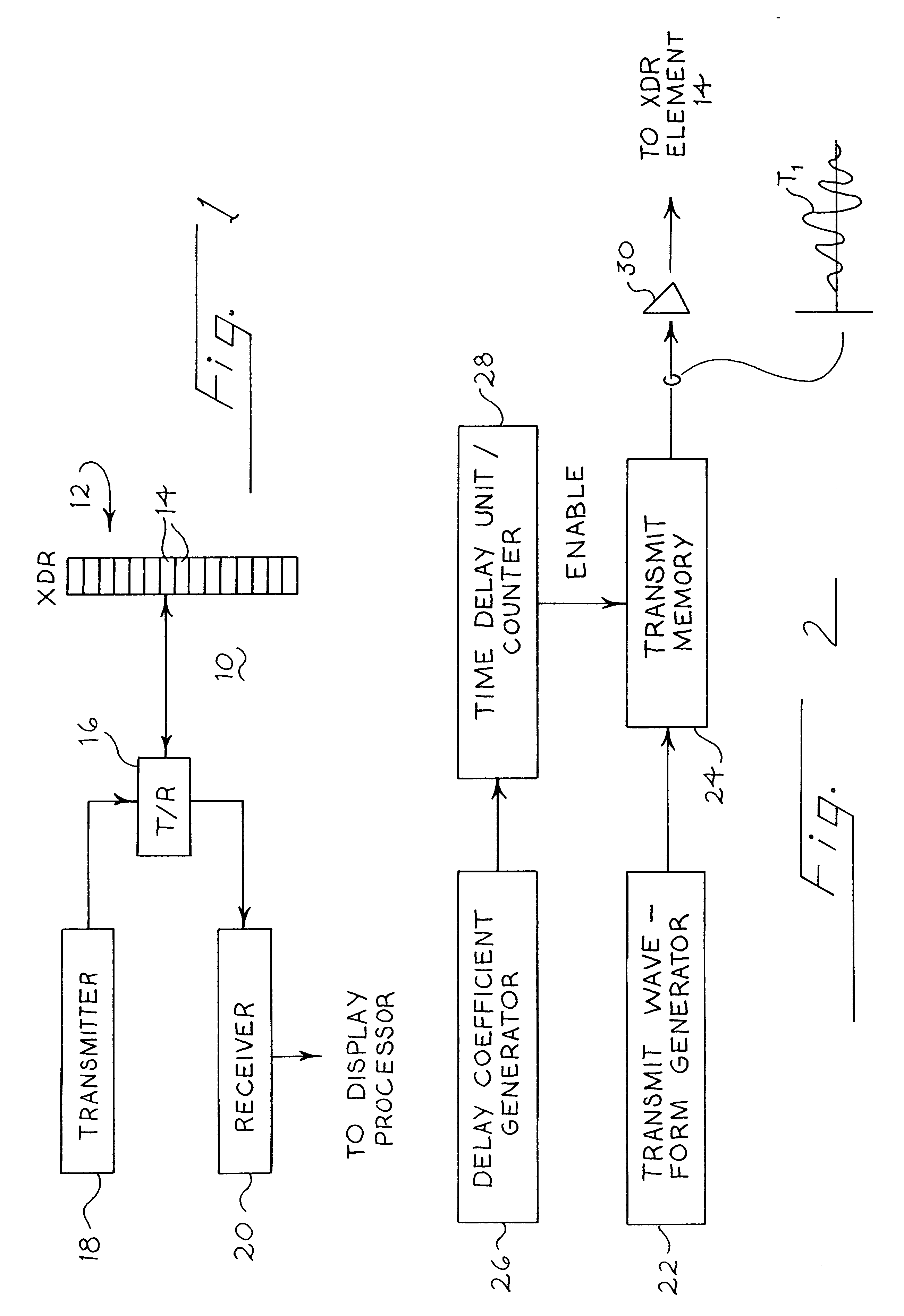
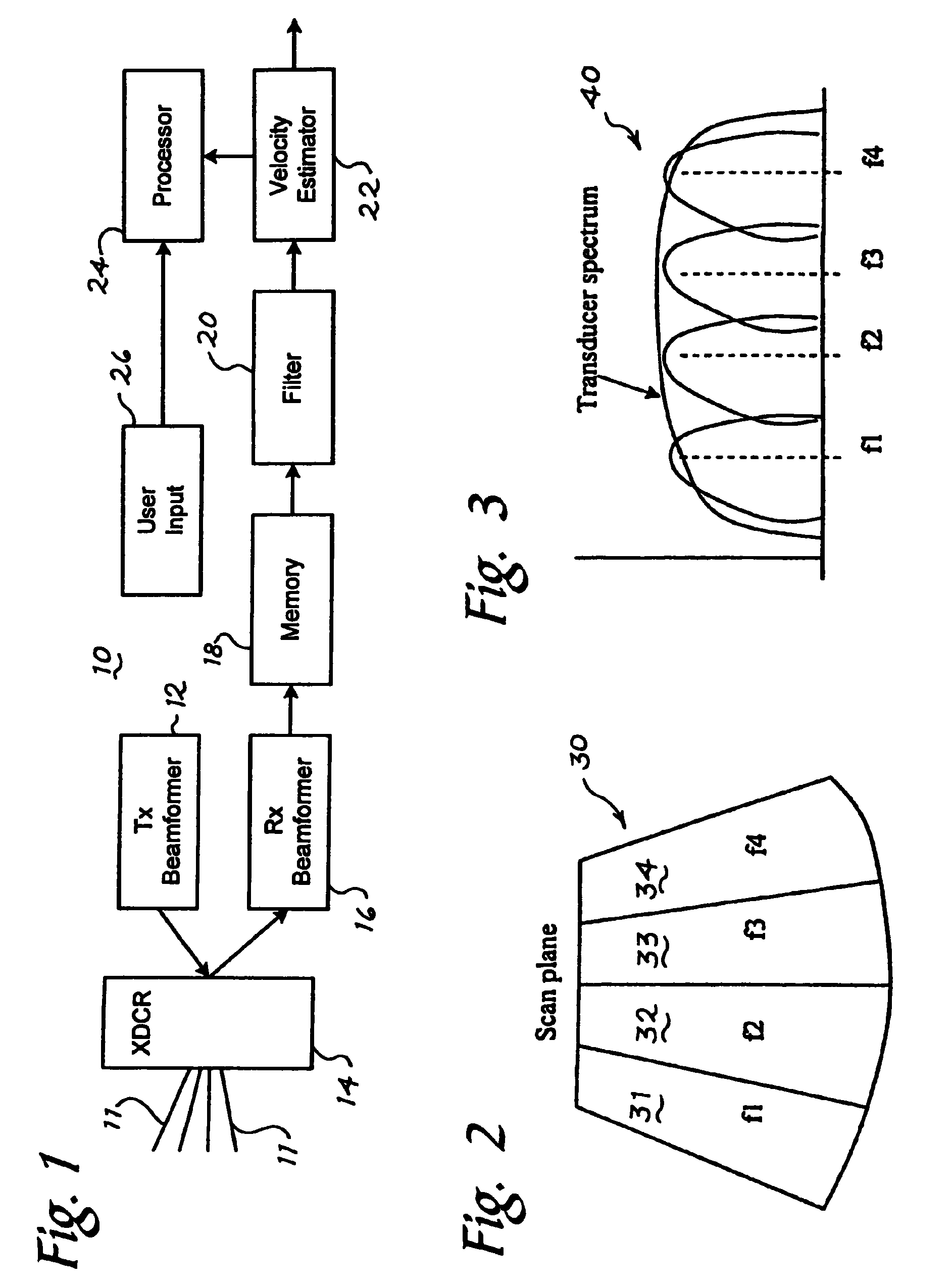
Medical ultrasound imaging system with composite delay profile
InactiveUS6312386B1High frame rateExtend depthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsEngineeringImage system
A medical ultrasound diagnostic imaging system includes a delay system that applies a composite delay profile to signals to or from respective transducer elements. One composite delay profile includes a first, substantially point-focus delay profile for a first set of the transducer elements and a second, substantially point-focus delay profile for a second set of the transducer elements. The first and second delay profiles cause ultrasonic energy from the respective first and second sets of the transducer elements to constructively add at first and second respective spaced focal zones in either transmit or receive. Another composite delay profile includes first and second portions that substantially correspond to respective parts of a point-focus delay profile, and third and fourth portions that are intermediate the point-focus delay profile and respective tangents.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
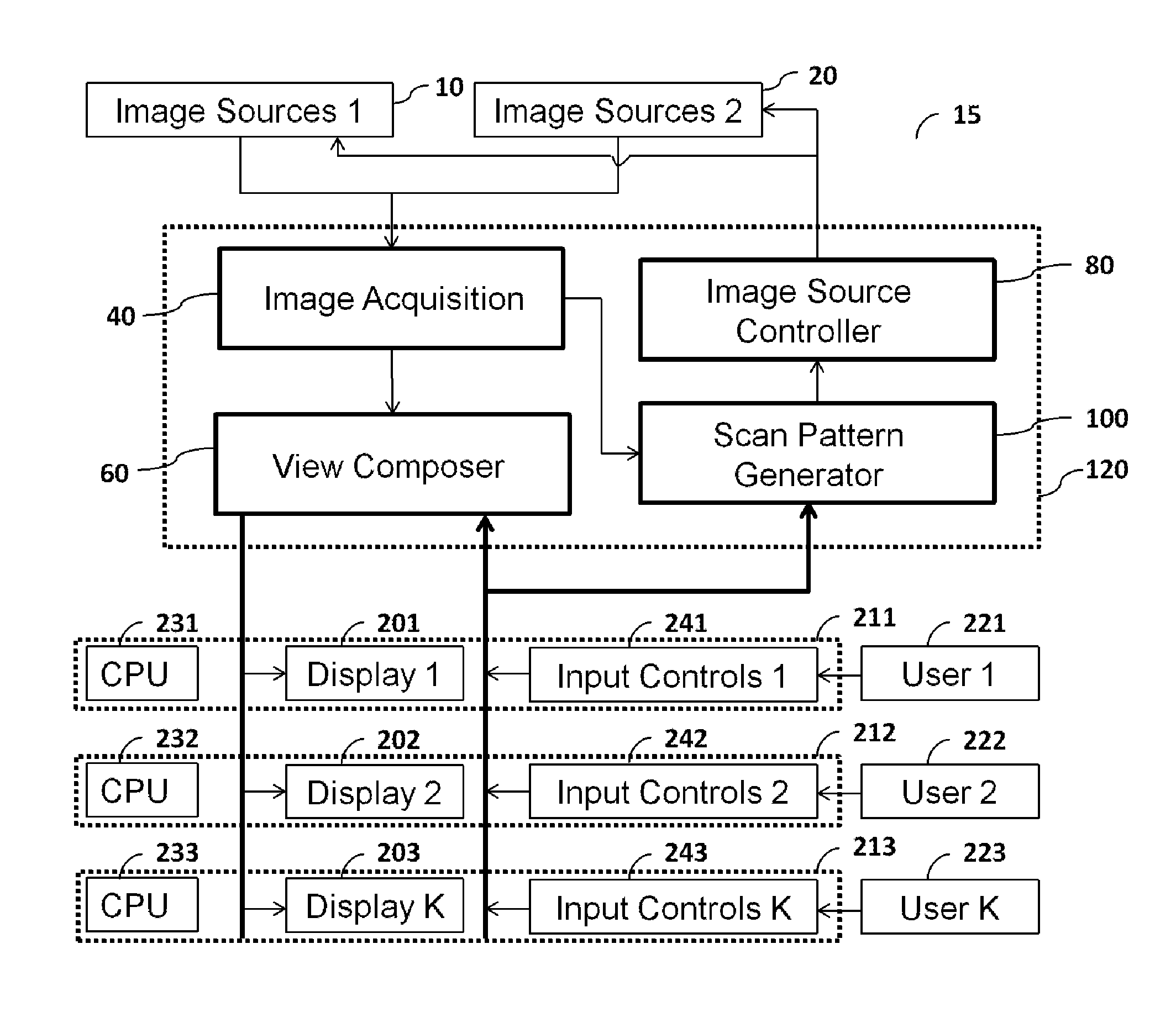
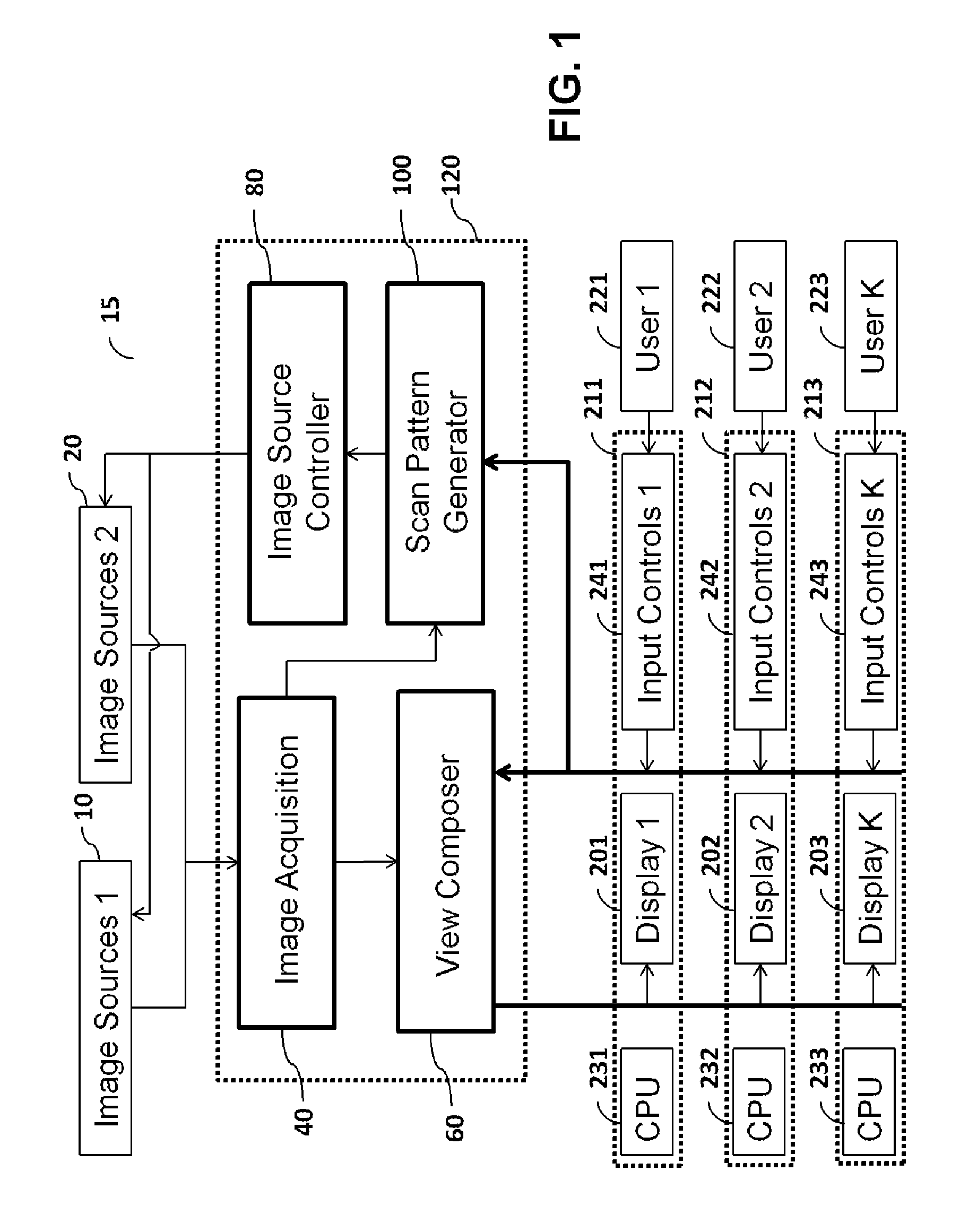
Method and apparatus for multi-user user-specific scene visualization
InactiveUS20100149338A1High magnificationHigh frame rateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsConcurrent userImage resolution
A method and apparatus is described for providing a personalized interactive experience to view a scene to a plurality of concurrent users. A plurality of image sources with different attributes such as frame-rate and resolution, are digitally processed to provide controllable enhanced user-specific visualization. An image source control method is also described to adjust the image sources based on collective requirement of a plurality of users.
Owner:MAMIGO
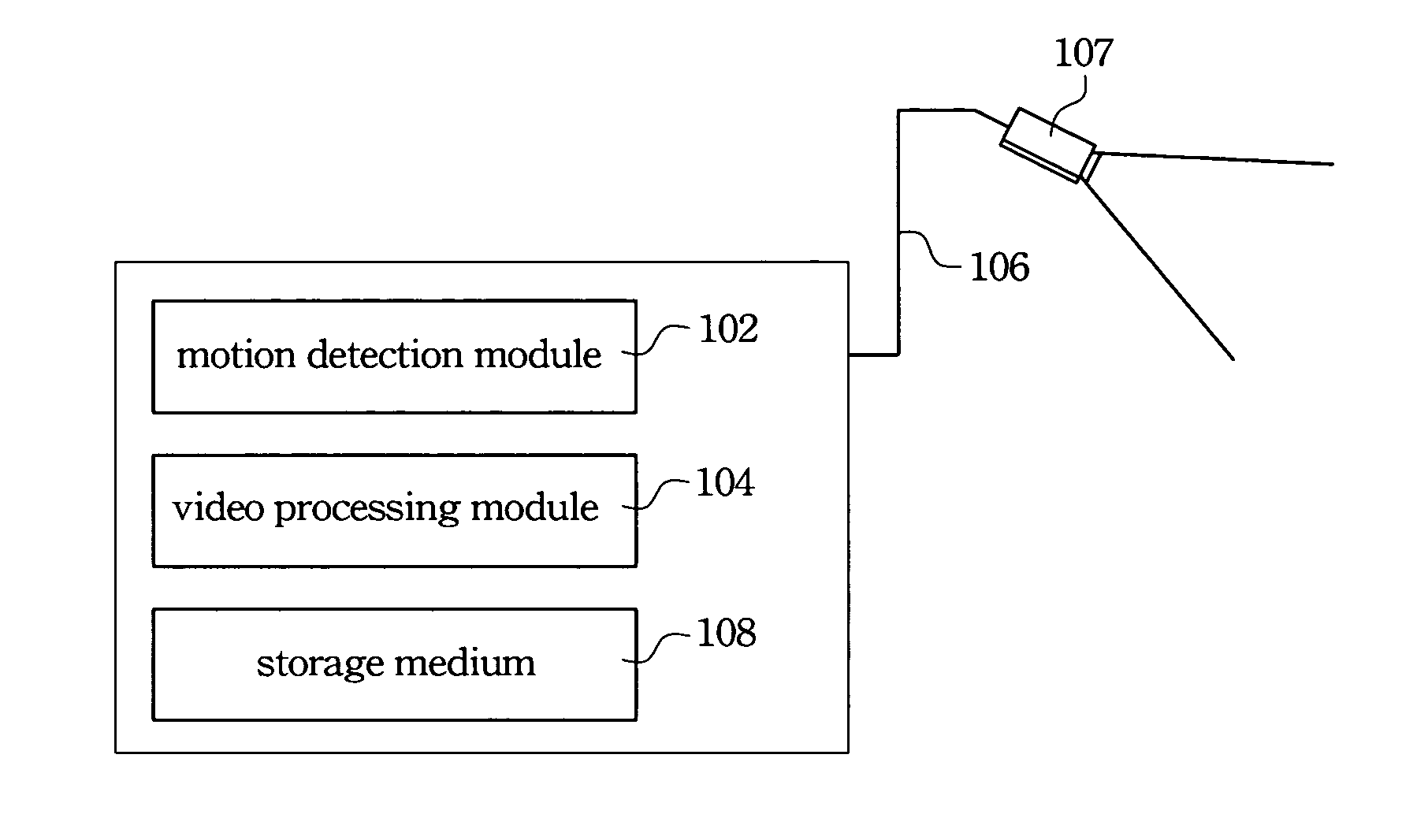
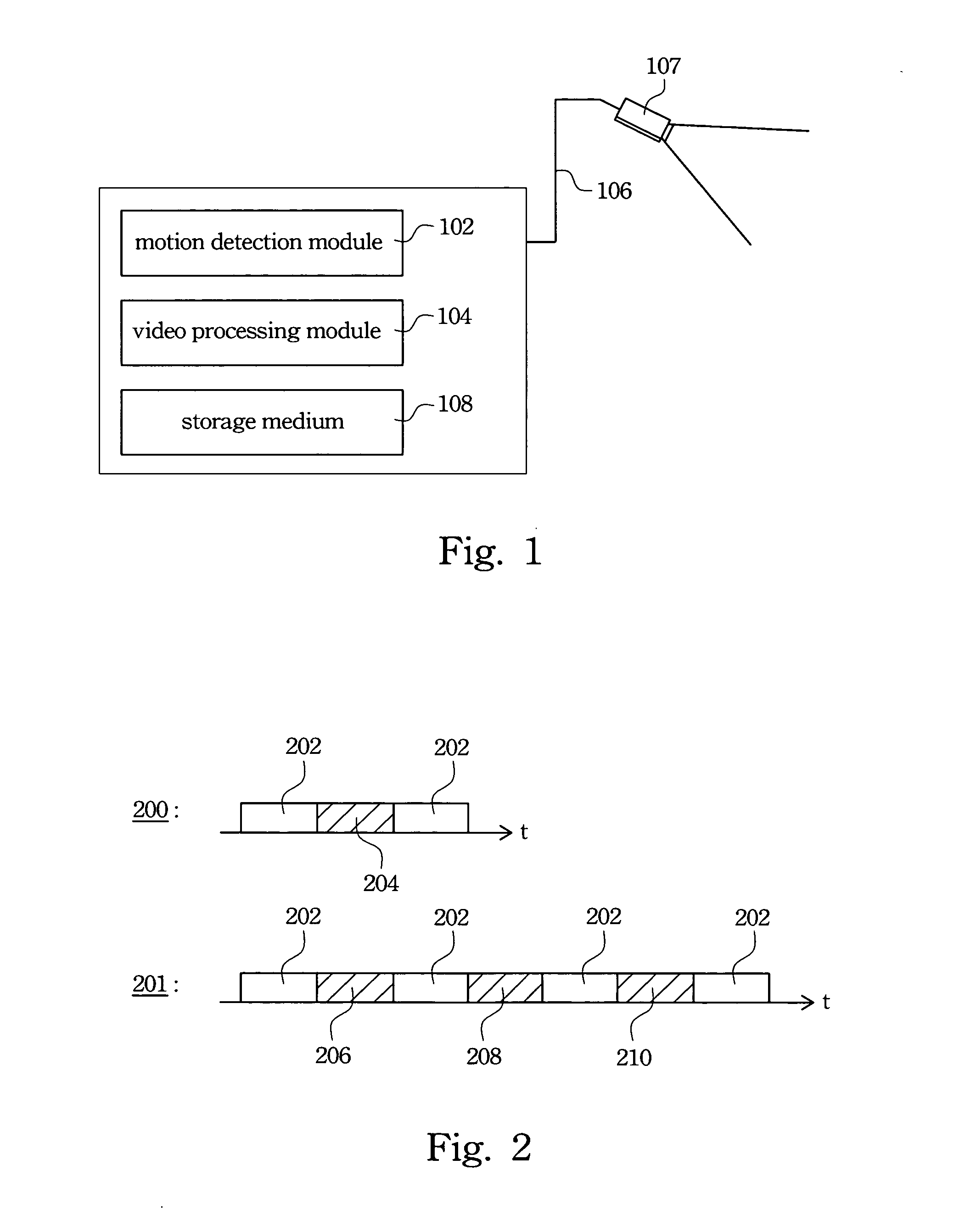
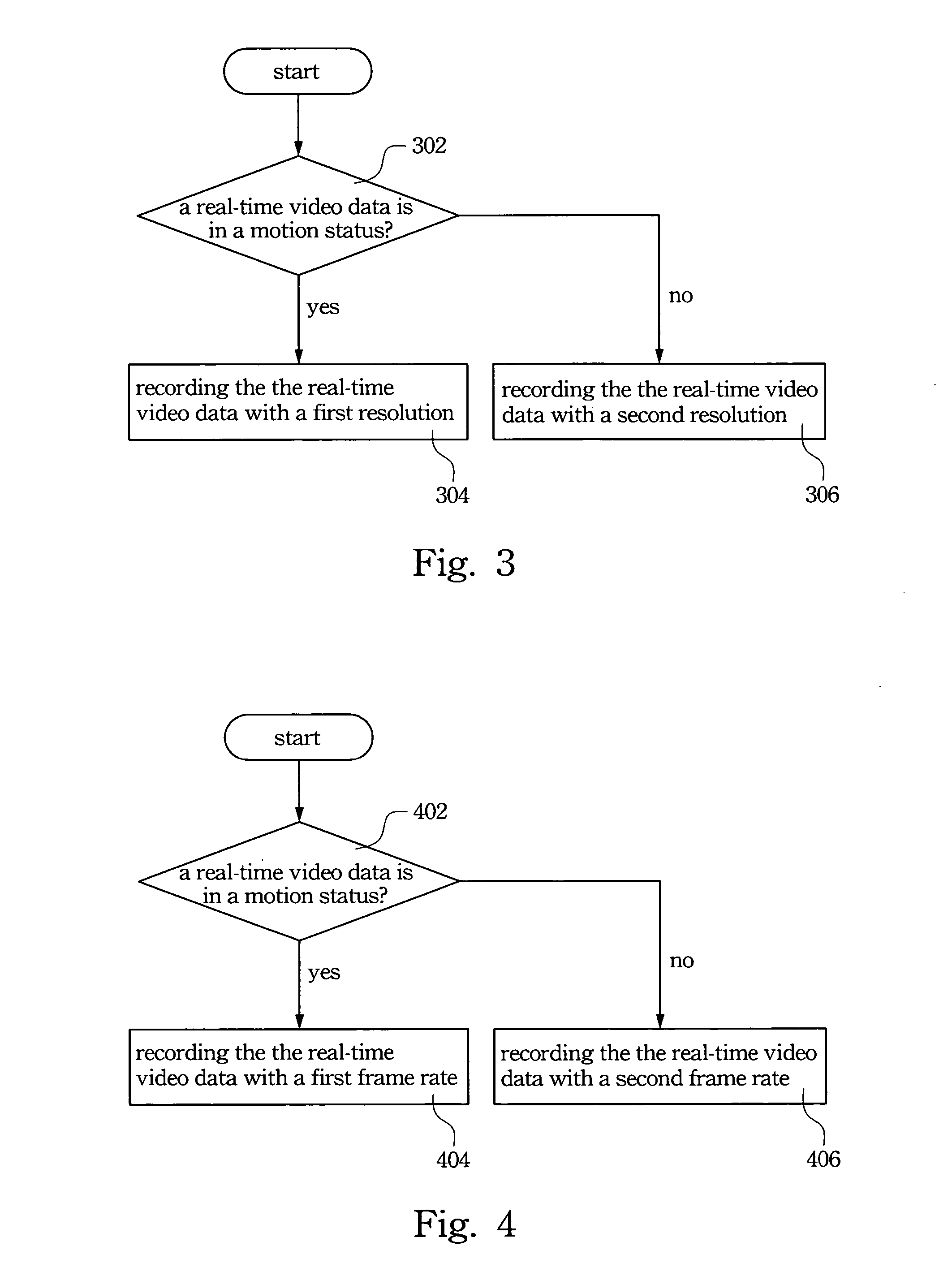
Surveillance system having auto-adjustment functionality
InactiveUS20060203903A1Reduce resolutionHigh frame rateTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesImage resolutionVideo processing
A surveillance system having auto-adjustment functionality is described. The surveillance system includes a motion detection module and a video processing module. The motion detection module detects real-time video data and determines whether the video data is in a motion status. When the real-time video data is in the motion status, the video processing module records the real-time video data into a storage medium with a first resolution. When the real-time video data is not in the motion status, the video processing module records the real-time video data into the storage medium with a second resolution.
Owner:AVER INFORMATION INC
Motion blur compensation
ActiveUS20140022352A1High resolutionHigh frame rateImage enhancementImage analysis3d surfacesRelative motion
Disclosed is a method for compensating for motion blur when performing a 3D scanning of at least a part of an object by means of a 3D scanner, where the motion blur occurs because the scanner and the object are moved relative to each other while the scanning is performed, and where the motion blur compensation comprises:—determining whether there is a relative motion between the scanner and the object during the acquisition of the sequence of focus plane images;—if a relative motion is determined, performing a motion compensation based on the determined motion; and—generating a 3D surface from the sequence of focus plane images.
Owner:3SHAPE AS
Display device and display method
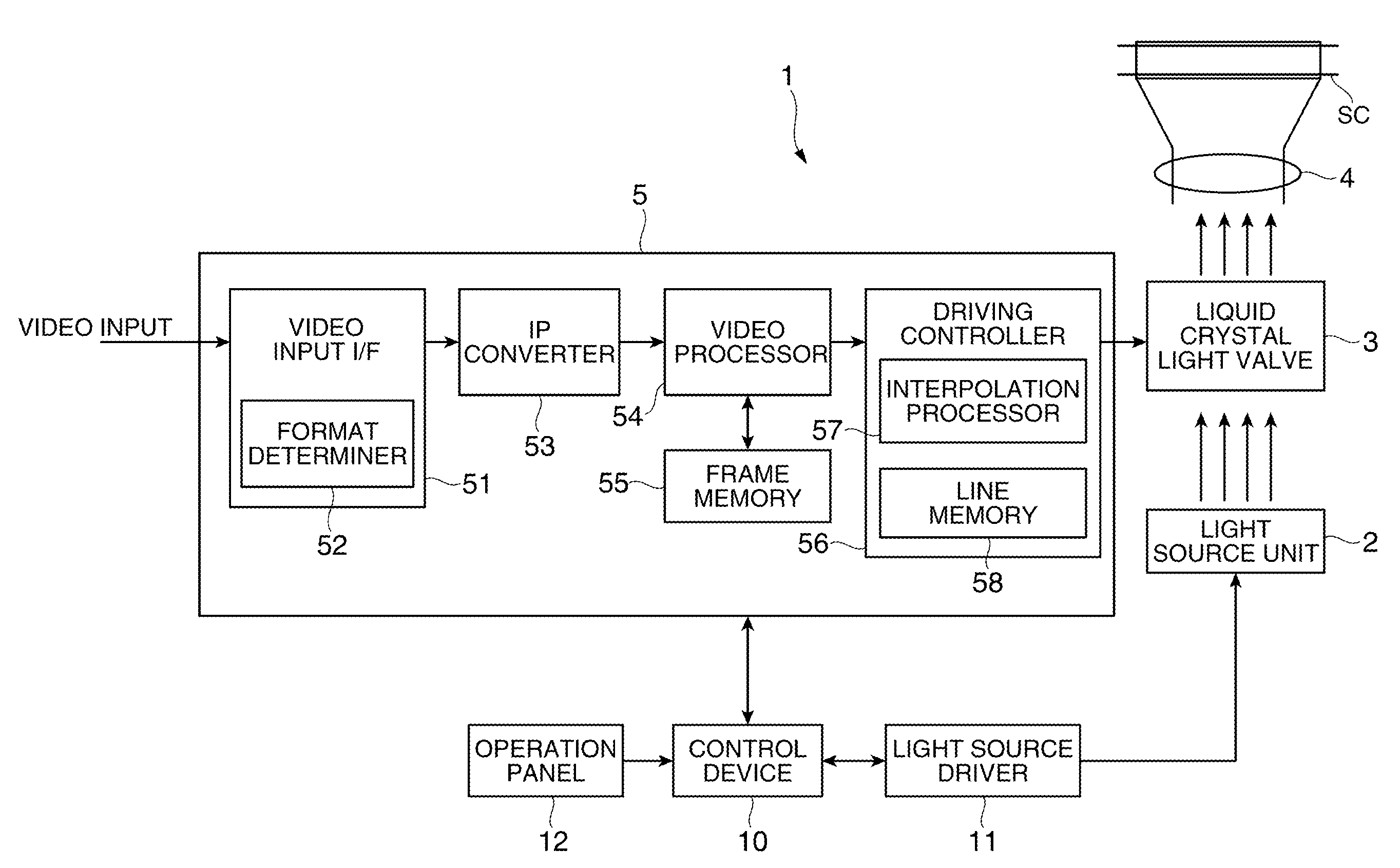
InactiveUS20120069147A1Decrease process loadHigh frame rateSteroscopic systemsImage resolutionDisplay resolution
A display device includes: a determiner that determines a video format of a stereoscopic video picture which is input as an input video picture and includes a right-eye image and a left-eye image; a video processor that generates a right-eye frame and a left-eye frame from the input video picture based on the video format determined by the determiner and outputs a stereoscopic video picture including the right-eye frame and the left-eye frame; a display unit that displays images with a predetermined display resolution; and a display controller that converts the resolution of the respective frames included in the stereoscopic video picture output by the video processor into the display resolution and causes the display unit to display the images.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
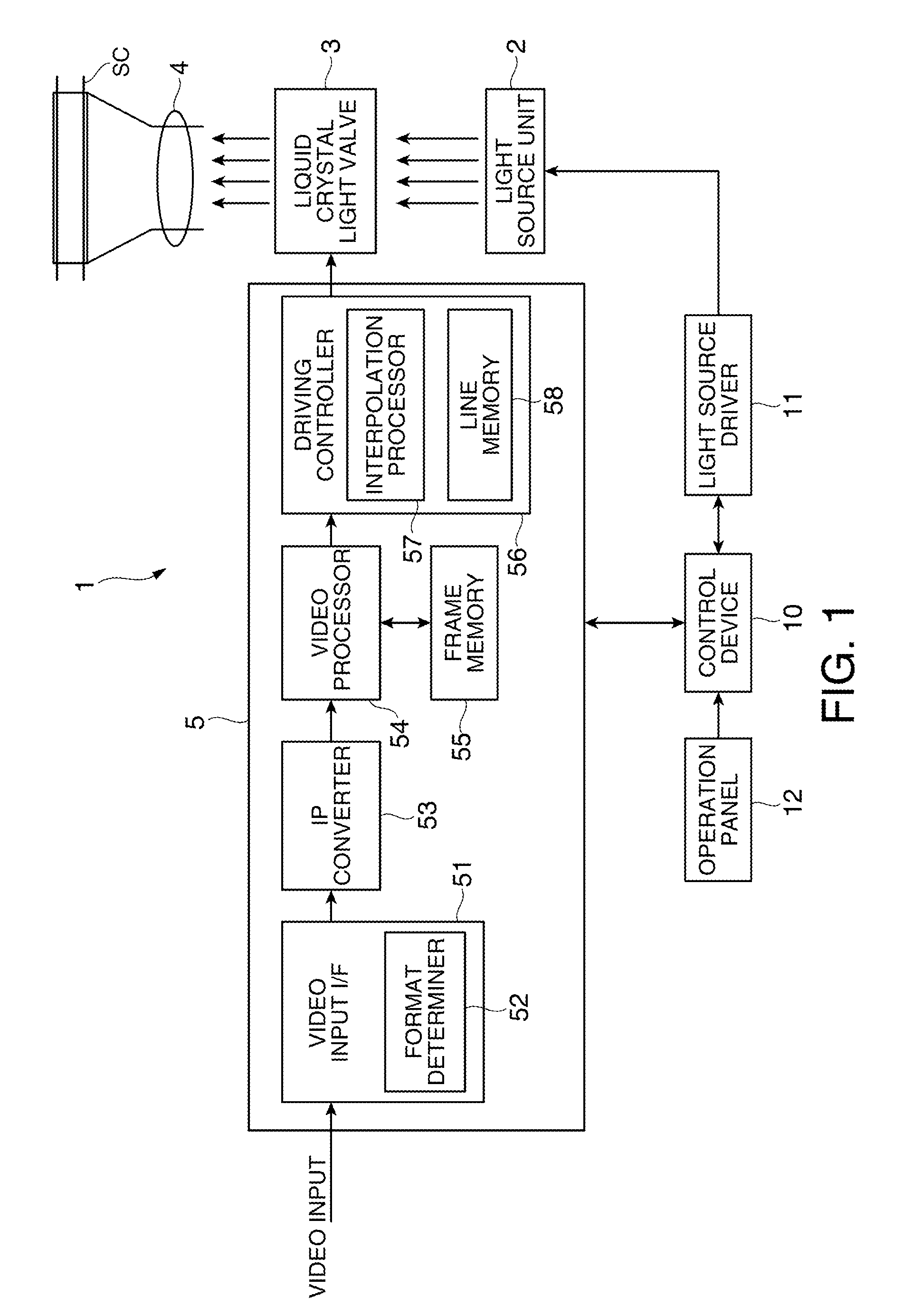
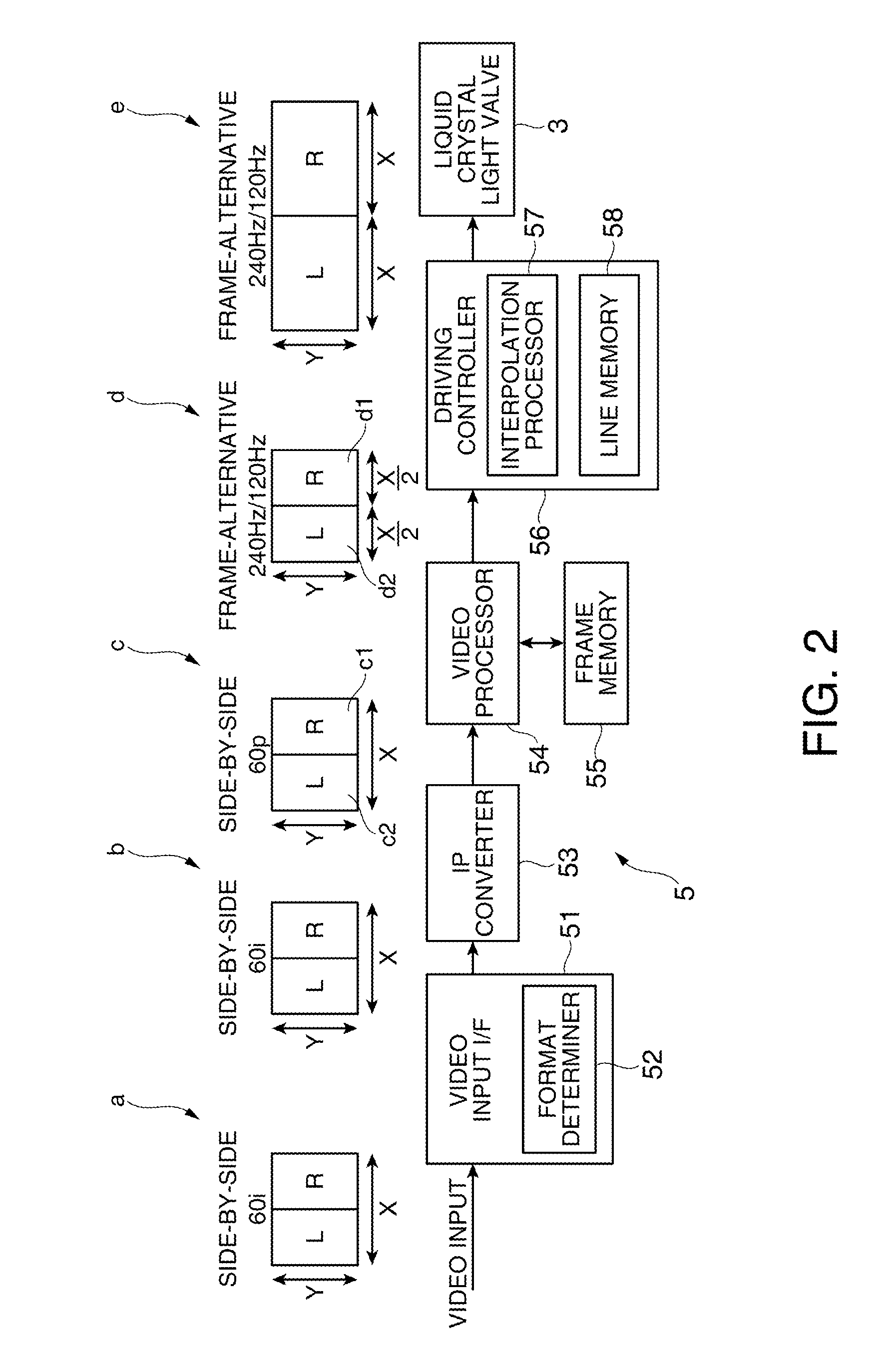
Liquid crystal display device and image display method of the same
ActiveUS20090128478A1High frame rateEnsures brightness of screenCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputer visionLiquid-crystal display
To provide a liquid crystal display device which performs pseudo impulsive driving, ensures brightness of a screen, and can improve the contrast of the screen. An arithmetic device for generating insertion images is provided in a liquid crystal display device for realizing pseudo impulsive driving. A moving object region and a background region are extracted from first image data which is input to the arithmetic device; second image data where the moving object region is displayed as a black image or a white image is generated; and a display panel performs display where the second image data of nth frame is displayed as an insertion image in a period between the first image data of nth frame and the first image data of (n+1)th frame.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Object positioning for an x-y projected capacitive touch panel
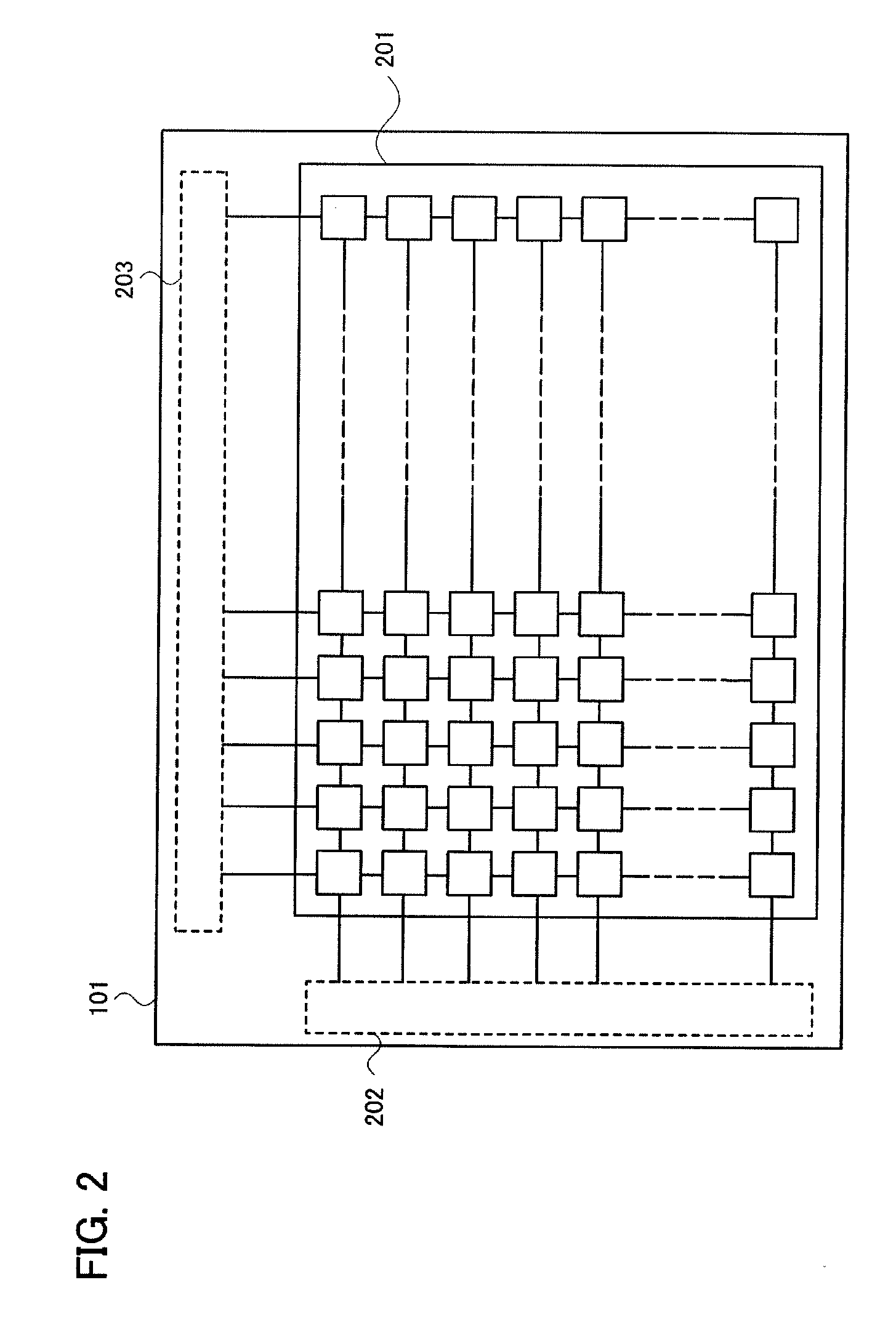
InactiveUS20110050614A1High frame rateLower power consumptionInput/output processes for data processingTouch panelCapacitance
Methods are proposed for object positioning for an X-Y projected capacitive touch panel. In an embodiment, capacitance sensing under inphase excitation of traces is applied to set a base value when the capacitive touch panel is not touched and to obtain capacitances at intersections when the capacitive touch panel is touched, and the base value is compared with the measured capacitances to identify touch points. In other embodiments, X-Y projected sensing and all-point sensing are combined to reduce the amount of calculation and achieve the same positioning effect as an all-point capacitive touch panel.
Owner:ELAN MICROELECTRONICS CORPORATION
Method for producing and exhibiting three-dimensional motion pictures from a single strip of motion picture film
InactiveUS20060072073A1High frame rateProjectorsStereoscopic photographyThree dimensional motionFilm (photographic)
A method is disclosed for producing and exhibiting high-quality three-dimensional (3-D) motion pictures. Stereoscopic images are placed side by side on a strip of motion picture film, such images having been anamorphically compressed to fit into the 70 mm or other film format used for presentation. These images are then reciprocally expanded to produce the aspect ratio of the original images as photographed. A single strip of motion picture film is used and images intended to be seen through the left or right eye of the viewer of such films are slightly different, to create the 3-D effect. To minimize the amount of light projected onto the screen, projection is accomplished by use of a projector capable of accomplishing pulldown between frames in five milliseconds of less and equipped with a single 0-bladed shutter at high frame rates, specifically 48 frames per second or higher. The method described here allows for screen sizes considerably larger than those currently in use for theatrical 3-D presentation. Viewers of films produced by this method can observe the images projected through polarized glasses or by other means known in the art. The 3-D effect can be withdrawn as desired by presenting identical images for the right and left eyes, thus delivering two-dimensional (2-D) presentation. Existing 3-D movies can be converted for exhibition according to the method described, with significant improvement in picture quality and smoother appearance of motion. In addition, films can be made to deliver 3-D effect for certain scenes or sequences within a motion picture presentation, with 2-D presentation for other scenes or sequences within the same motion picture.
Owner:WEISGERBER ROBERT C
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, recording medium, and program
ActiveUS7411617B2High frame rateDeteriorate quality of displayed imageTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData conversionVideo output
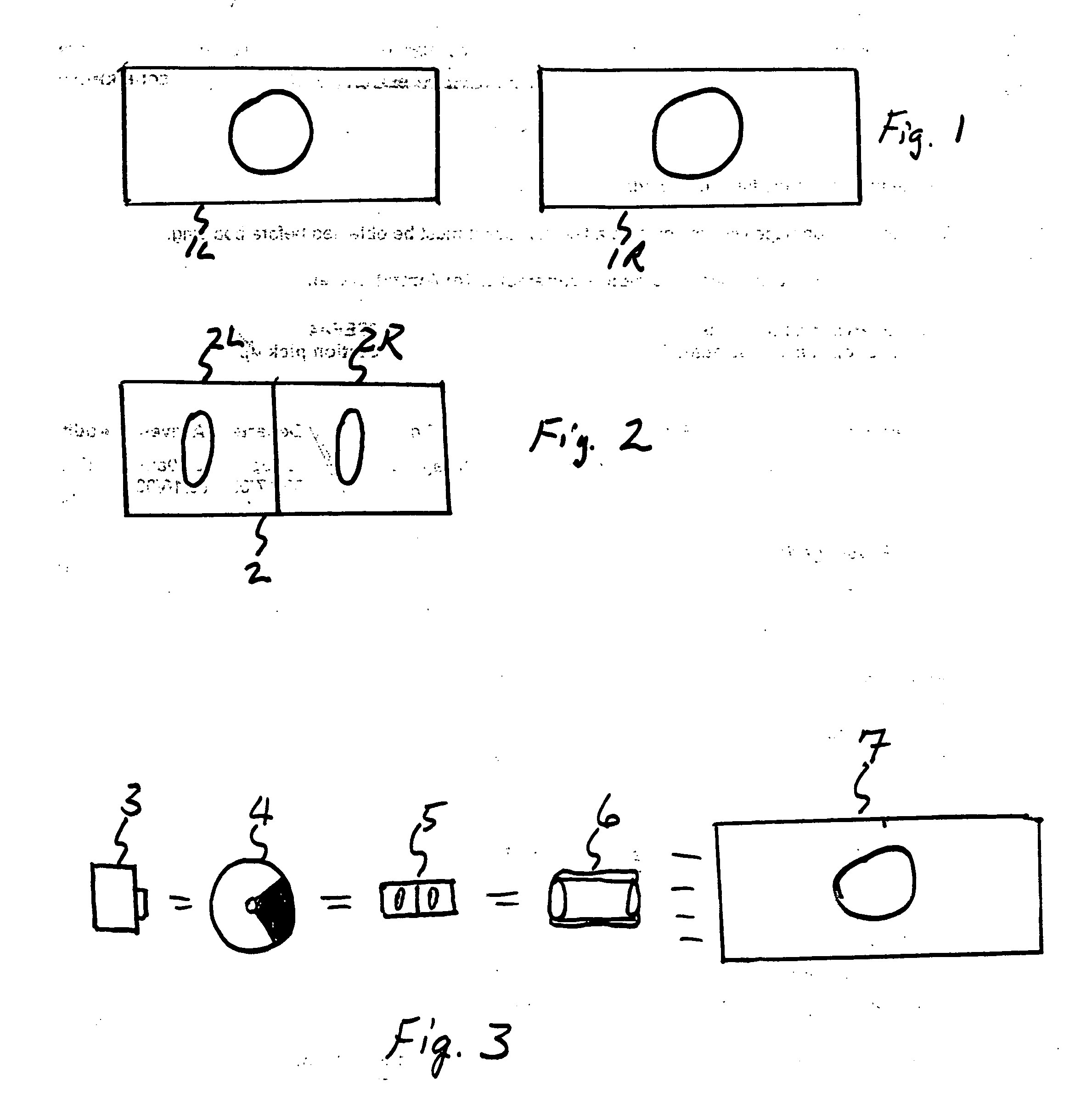
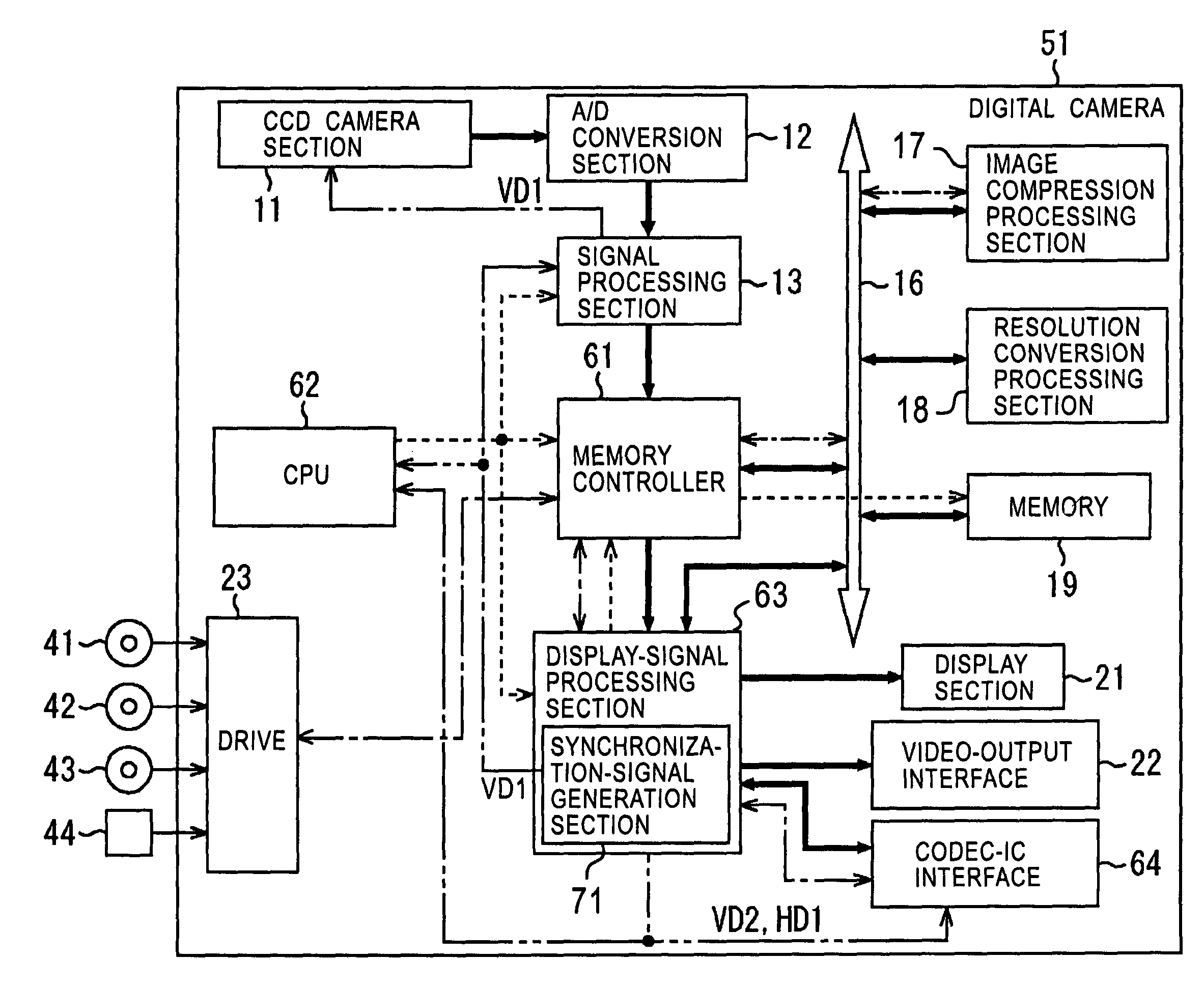
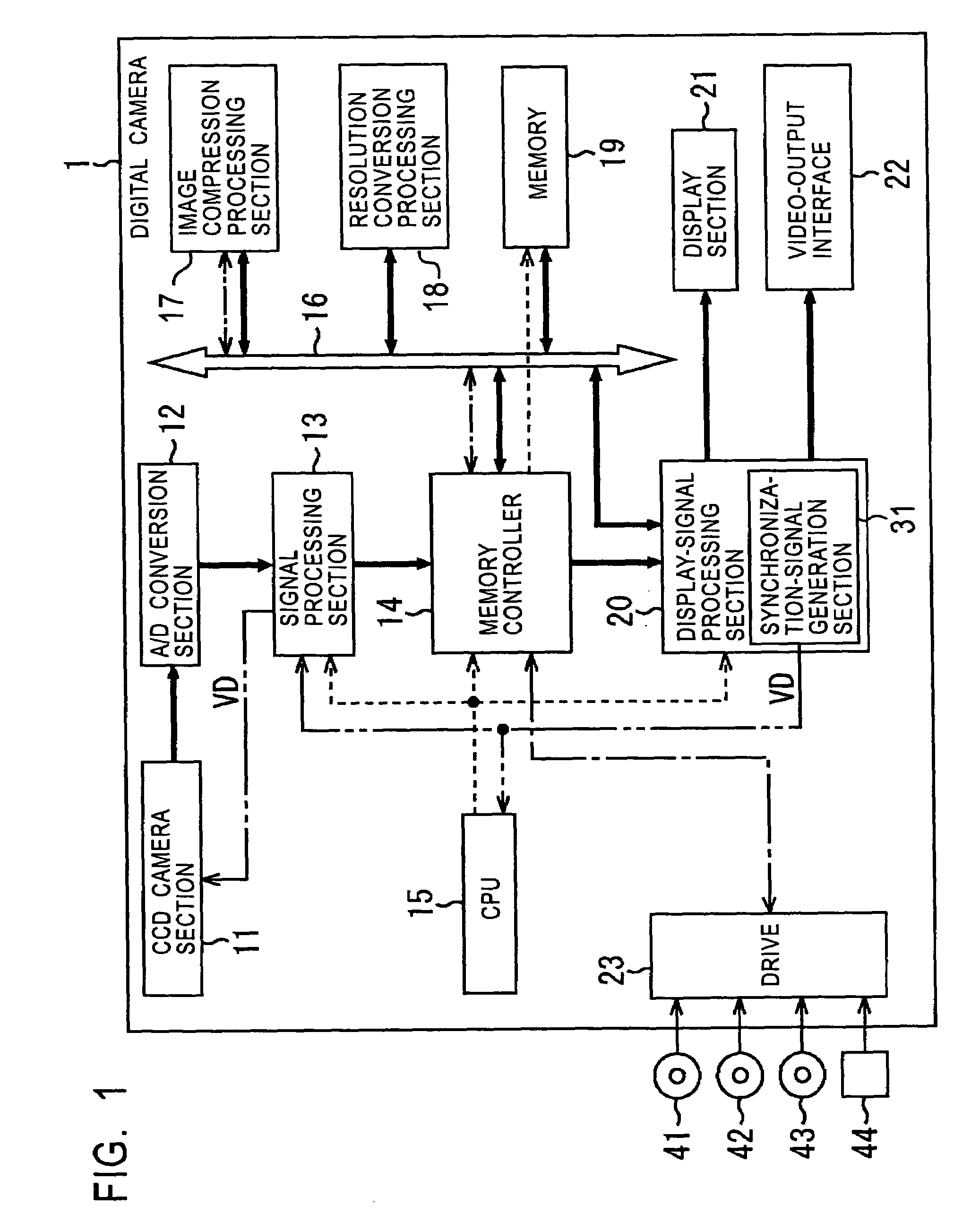
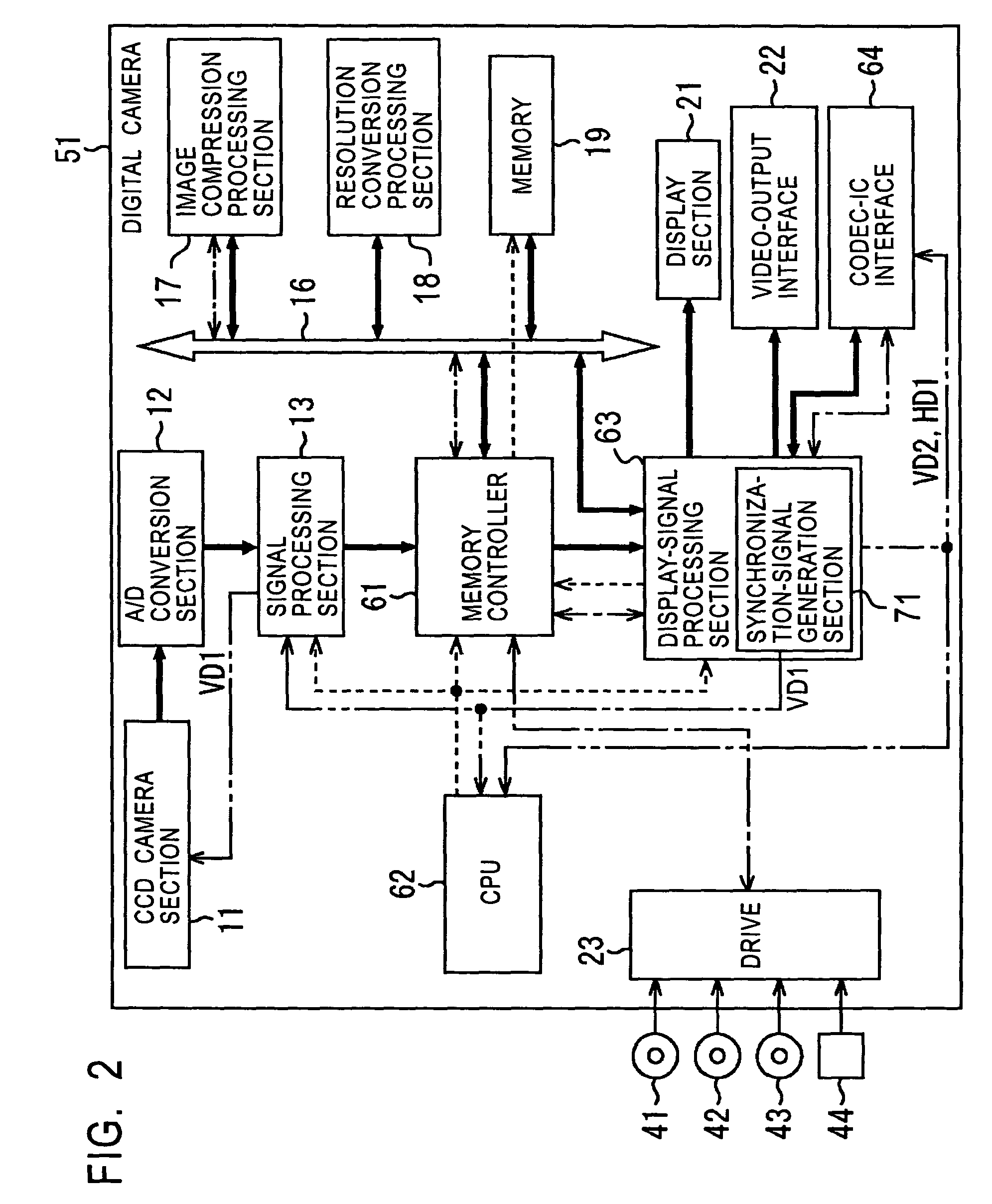
In image-data recording processing performed when a video output conforms to the PAL system, a display-signal processing section receives image data having a frame rate of 30 Hz recorded in a memory, through a bus, converts the image data to image data having an NTSC frame rate of 29.97 Hz by a frame-rate conversion method in which thinning out is performed according to the ratio of frame rates, and outputs it to a display section and a codec-IC interface. The display-signal processing section also converts to image data having a PAL frame rate of 25 Hz, and outputs it to a video-output interface. In other words, image data is processed at a frame rate not related to the output, and then converted to image data having a frame rate suited for the output, and output. This invention can be used in digital cameras.
Owner:SONY CORP
Image sensing apparatus
ActiveUS20140055642A1High continuous shoot speedHigh frame rateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPixel arrayImage sensing
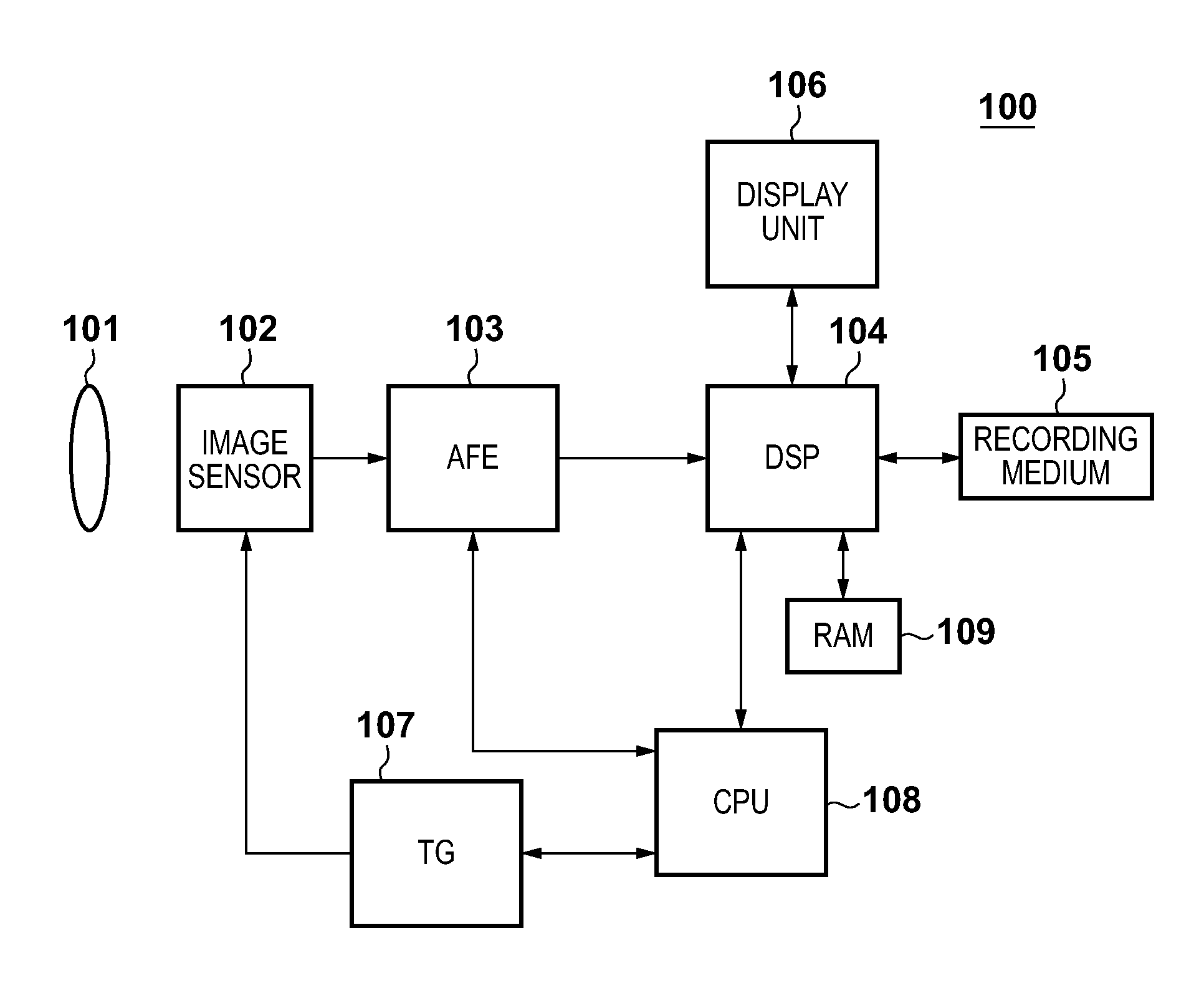
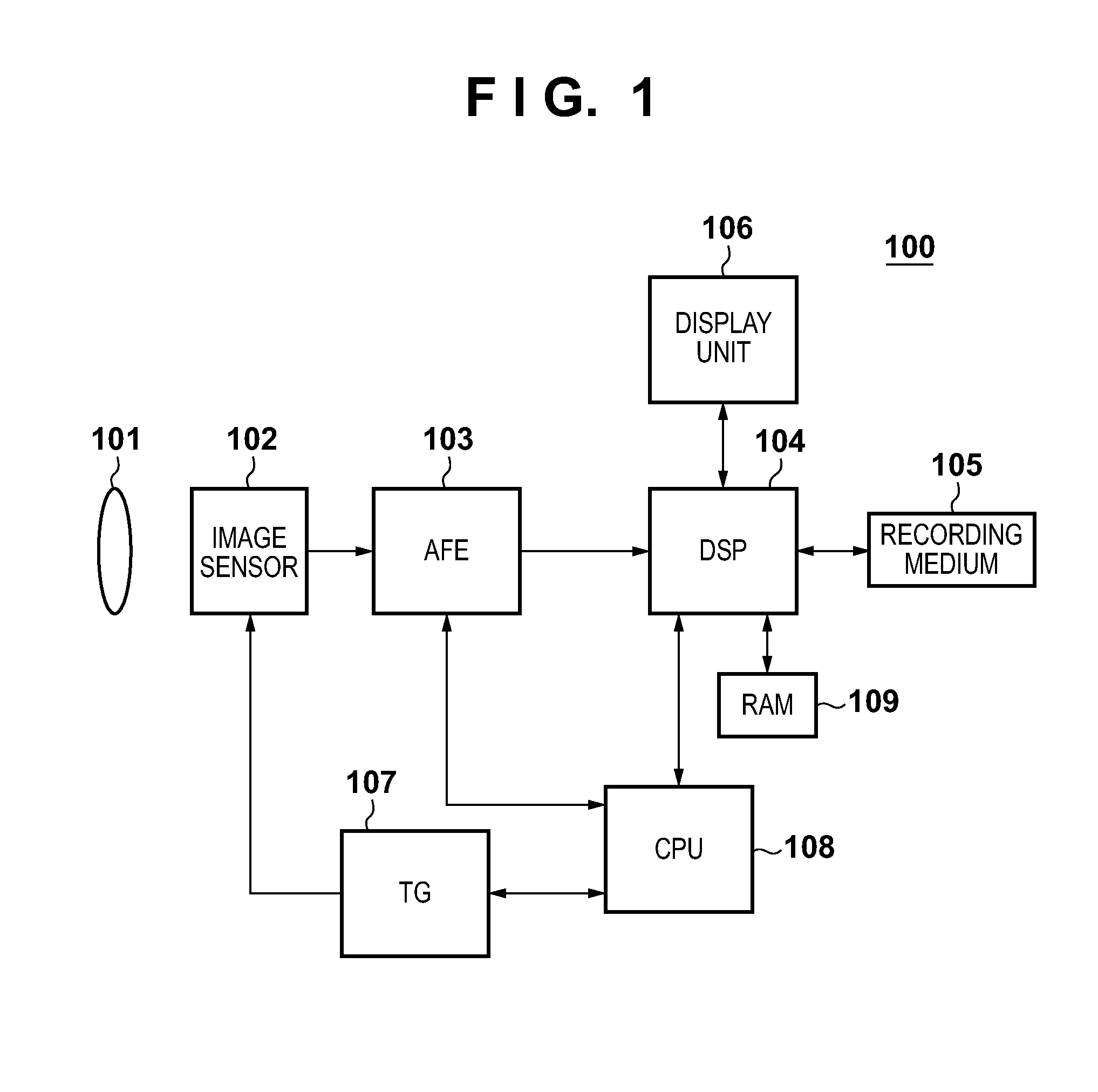
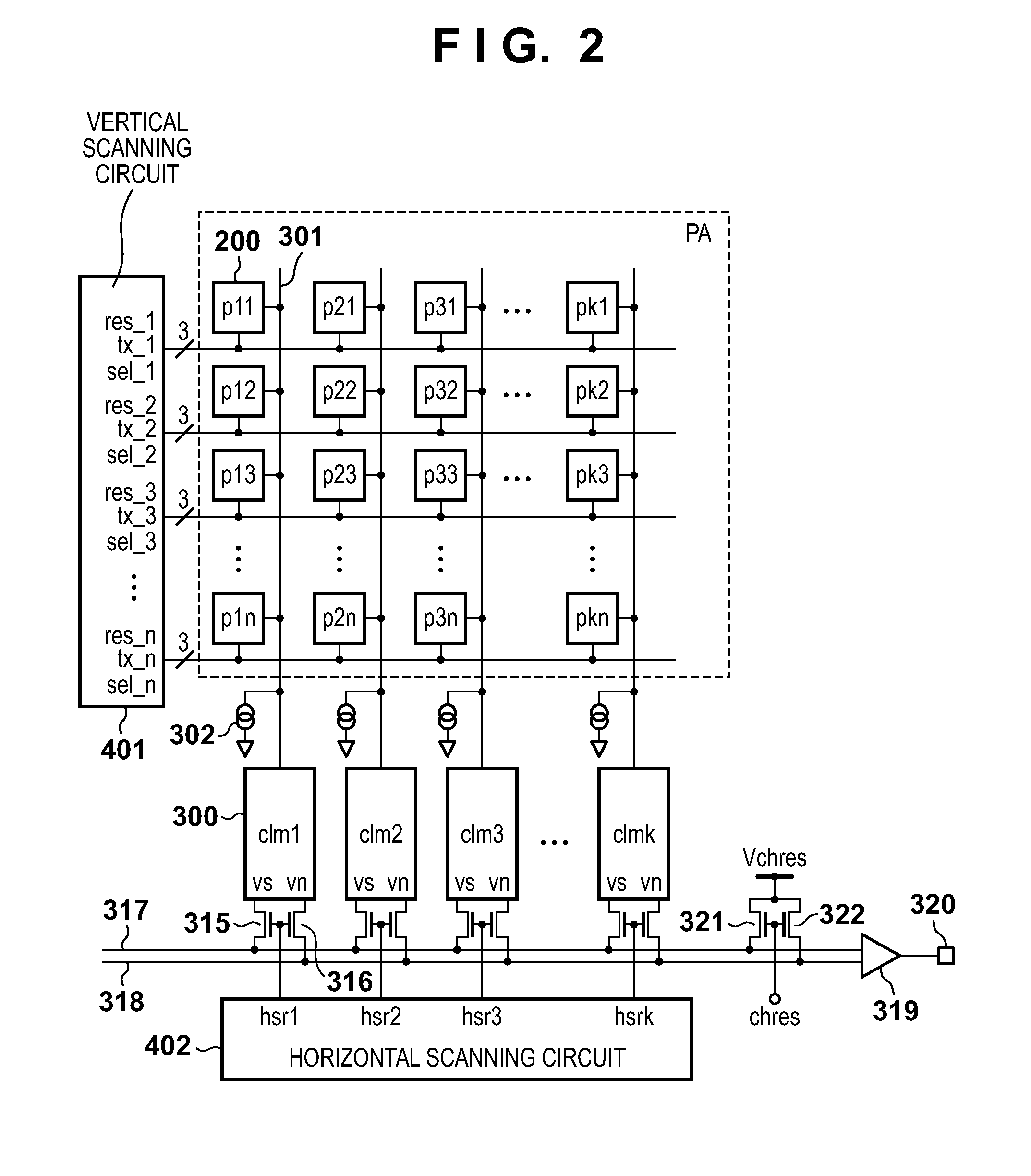
An image sensing apparatus comprises an image sensor including a pixel array in which a plurality of pixels are arrayed in matrix, a first storage unit configured to hold an output signal from the pixel, and a second storage unit configured to hold a signal transferred from the first storage unit, wherein signal transfer from the first storage unit to the second storage unit is started during a signal write operation in the first storage unit.
Owner:CANON KK
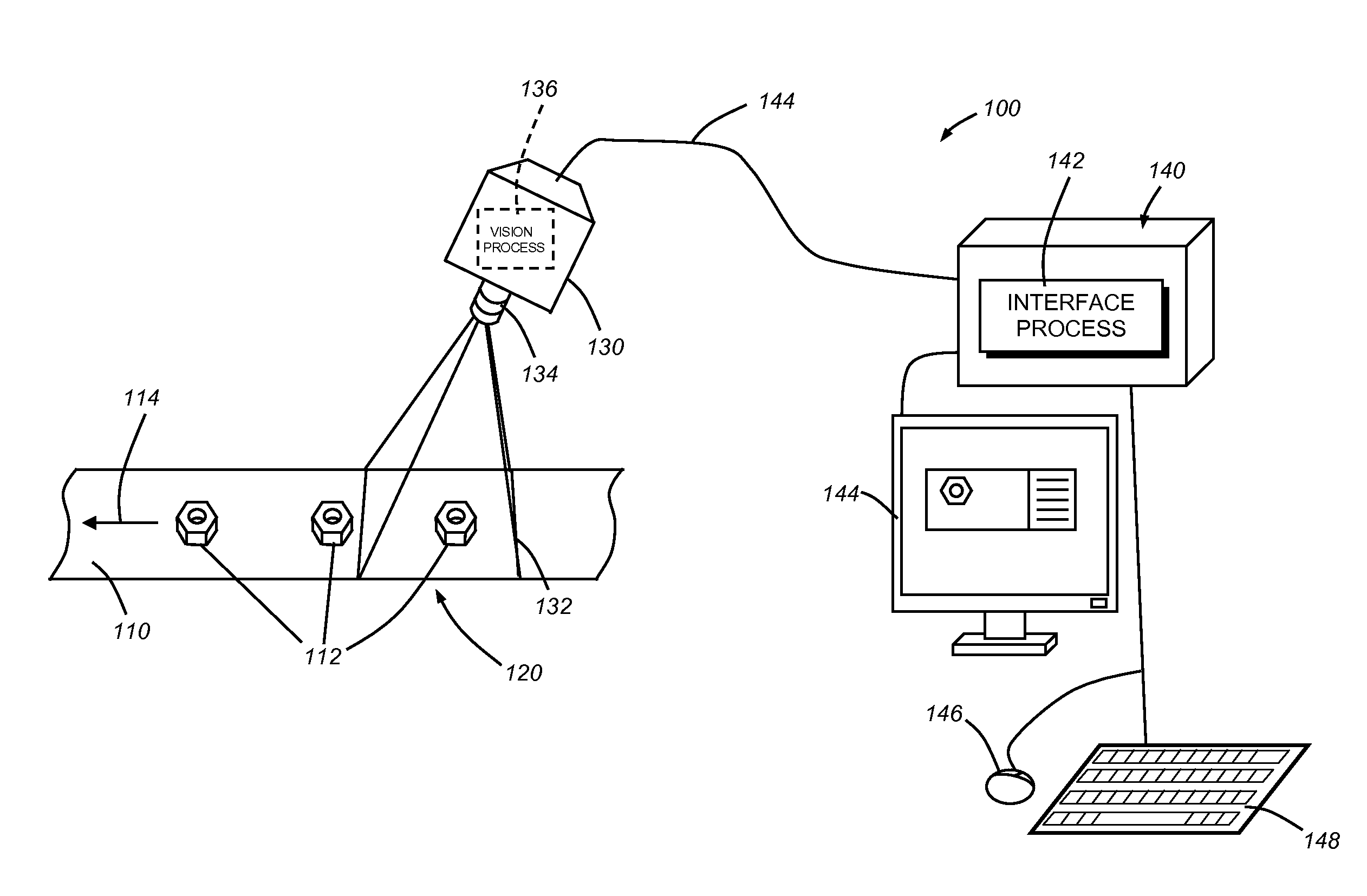
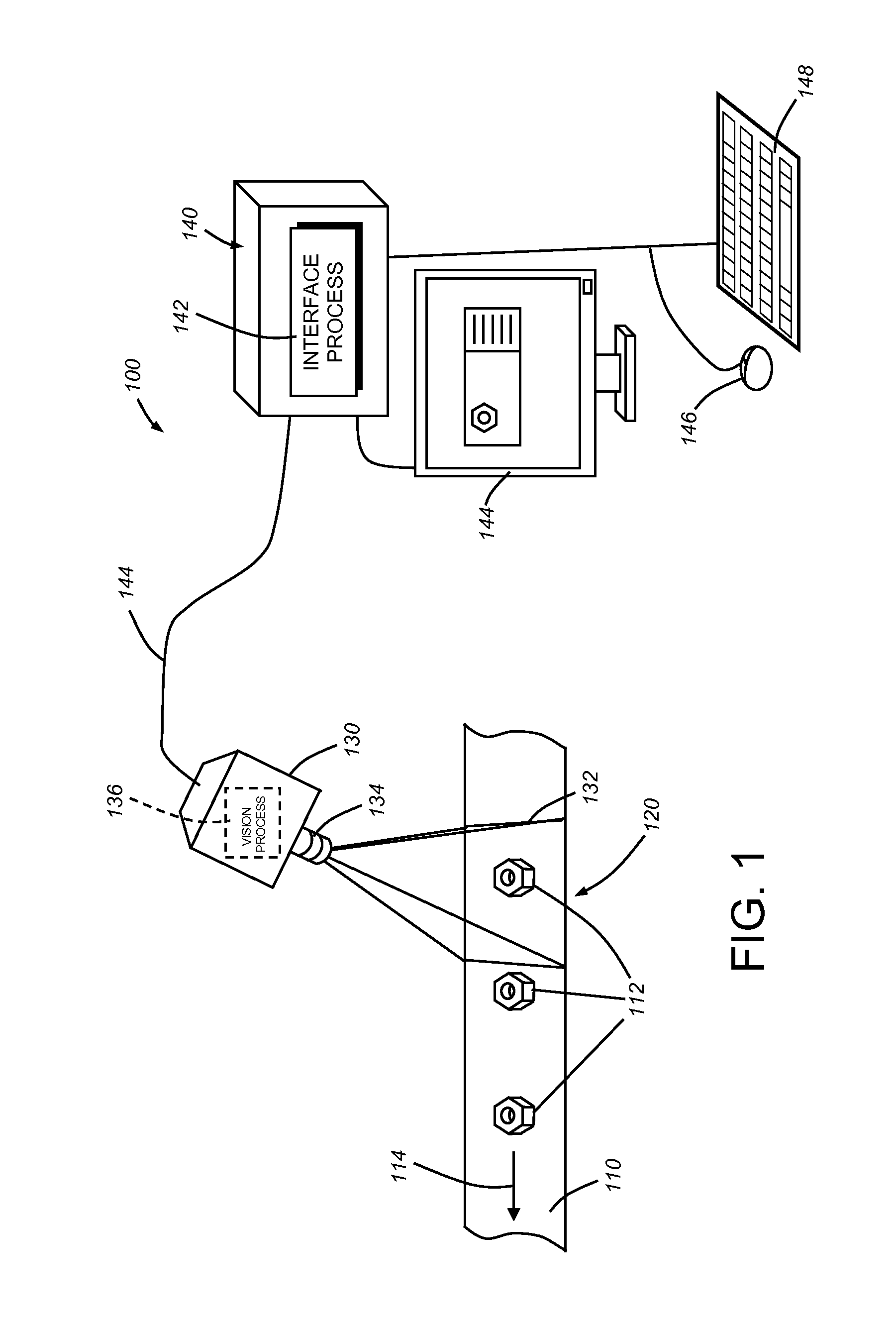
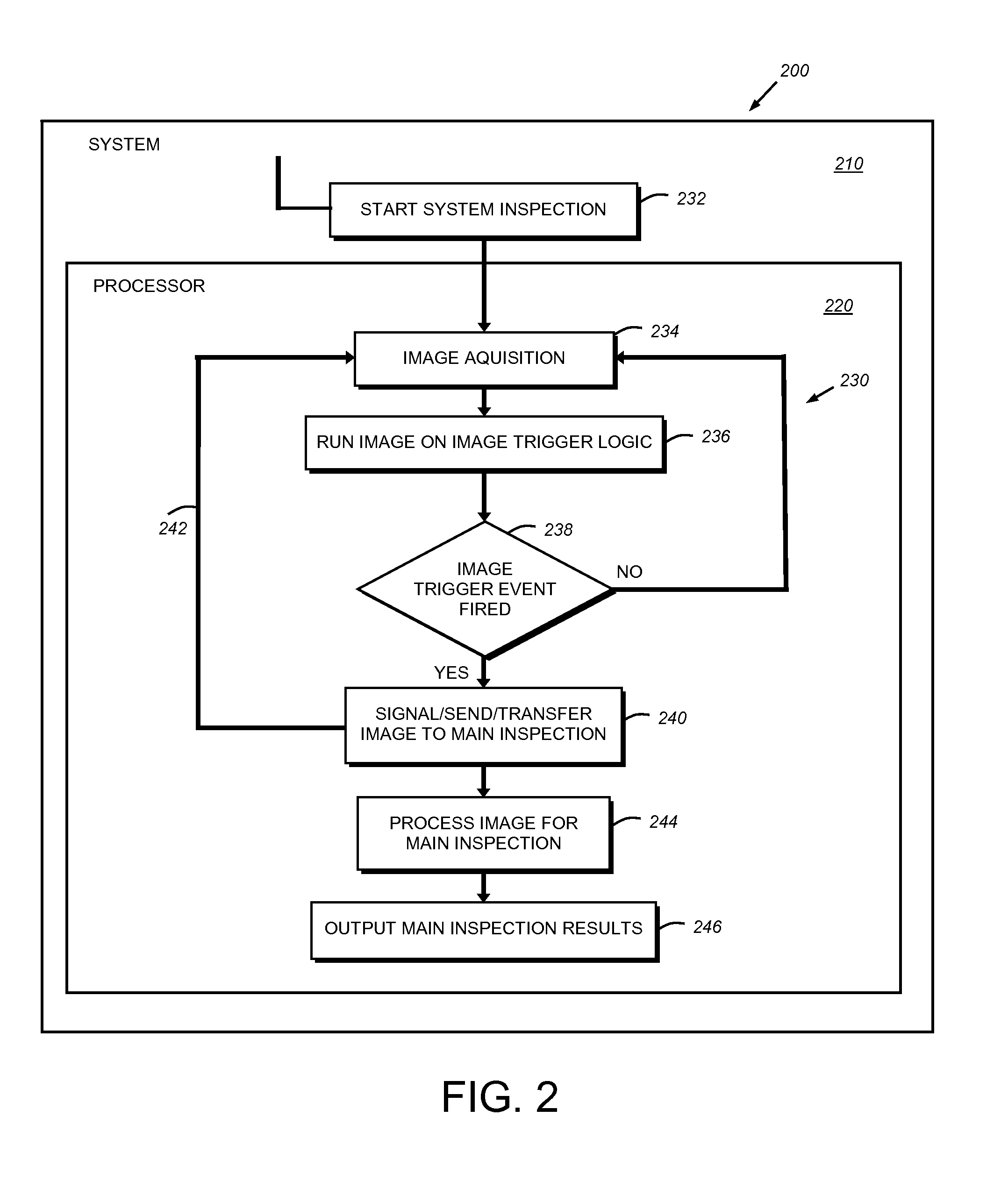
Configurable image trigger for a vision system and method for using the same
ActiveUS20130155220A1Readily configureHigh frame rateMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsBarcodeVisual system
This invention provides a trigger for a vision system that can be set using a user interface that allows the straightforward variation of a plurality of exposed trigger parameters. Illustratively, the vision system includes a triggering mode in which the system keeps acquiring an image of a field of view with respect to objects in relative motion. The system runs user-configurable “trigger logic”. When the trigger logic succeeds / passes, the current image or a newly acquired image is then transmitted to the main inspection logic for processing. The trigger logic can be readily configured by a user operating an interface, which can also be used to configure the main inspection process, to trigger the vision system by tools such as presence-absence, edge finding, barcode finding, pattern matching, image thresholding, or any arbitrary combination of tools exposed by the vision system in the interface.
Owner:COGNEX CORPORATION
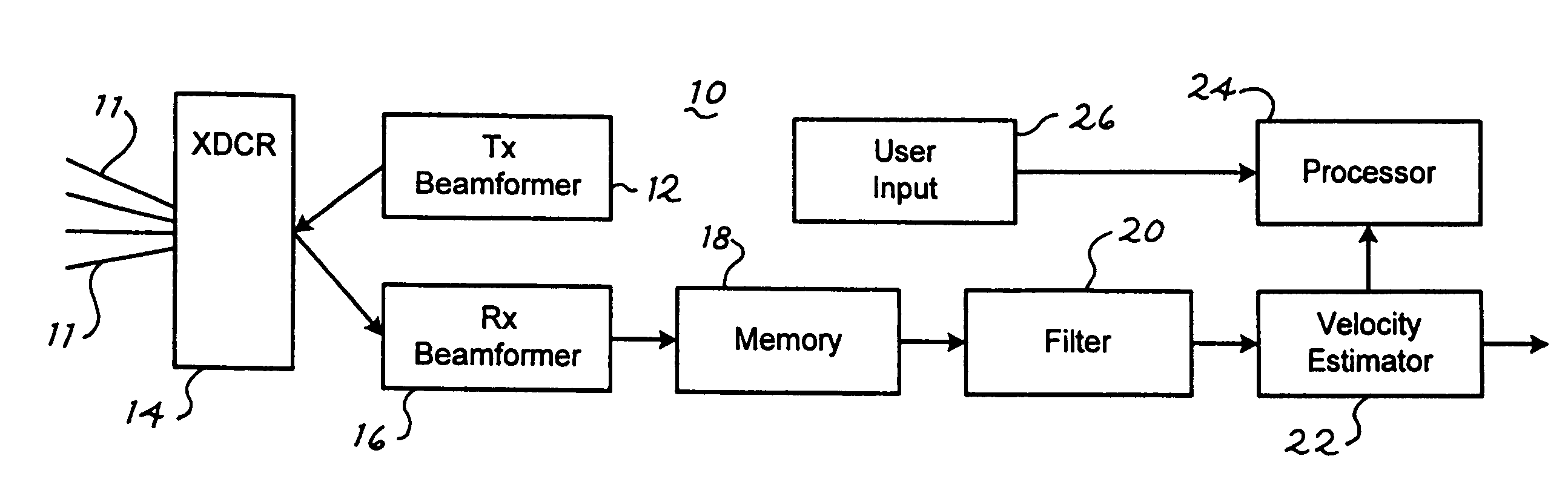
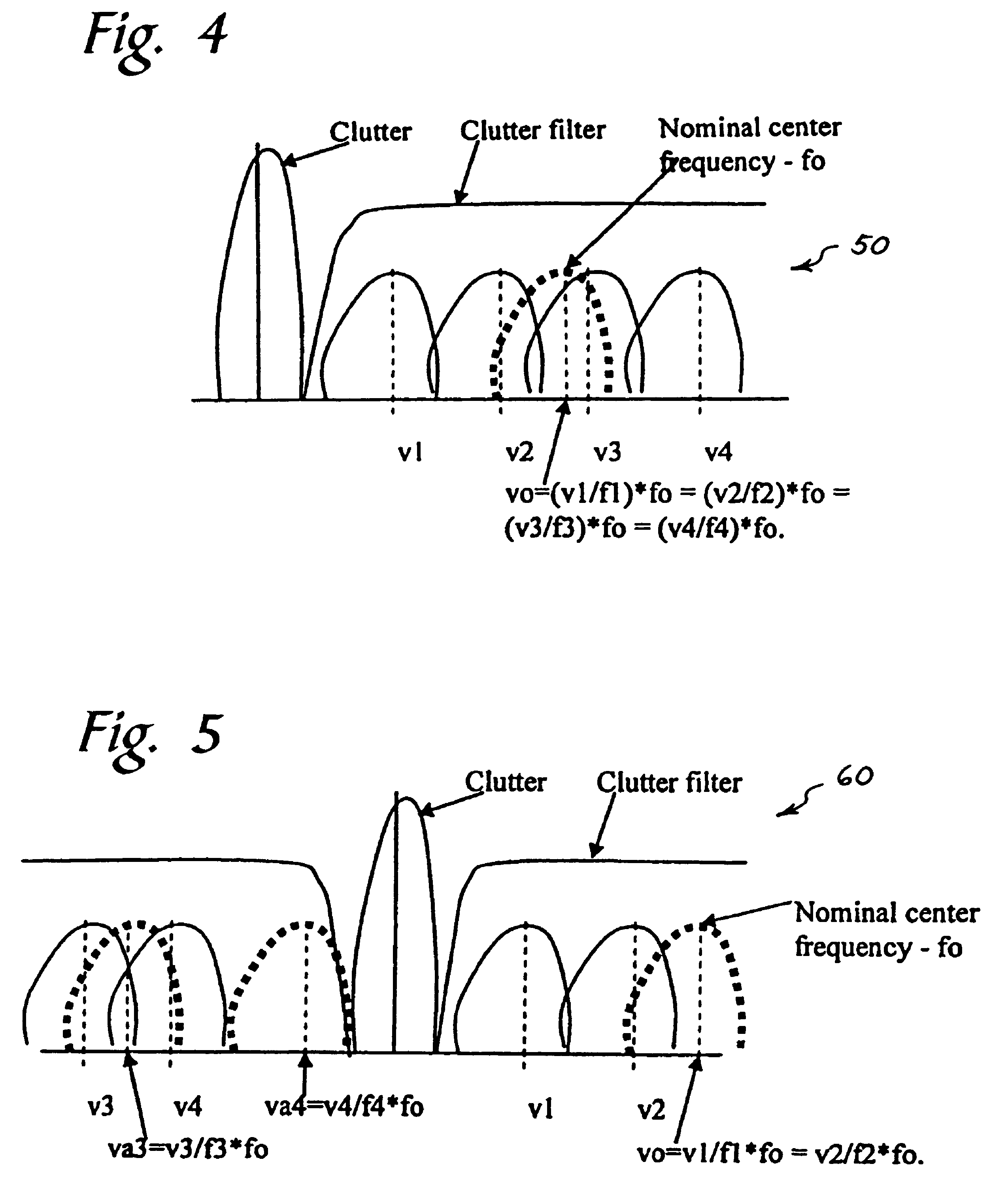
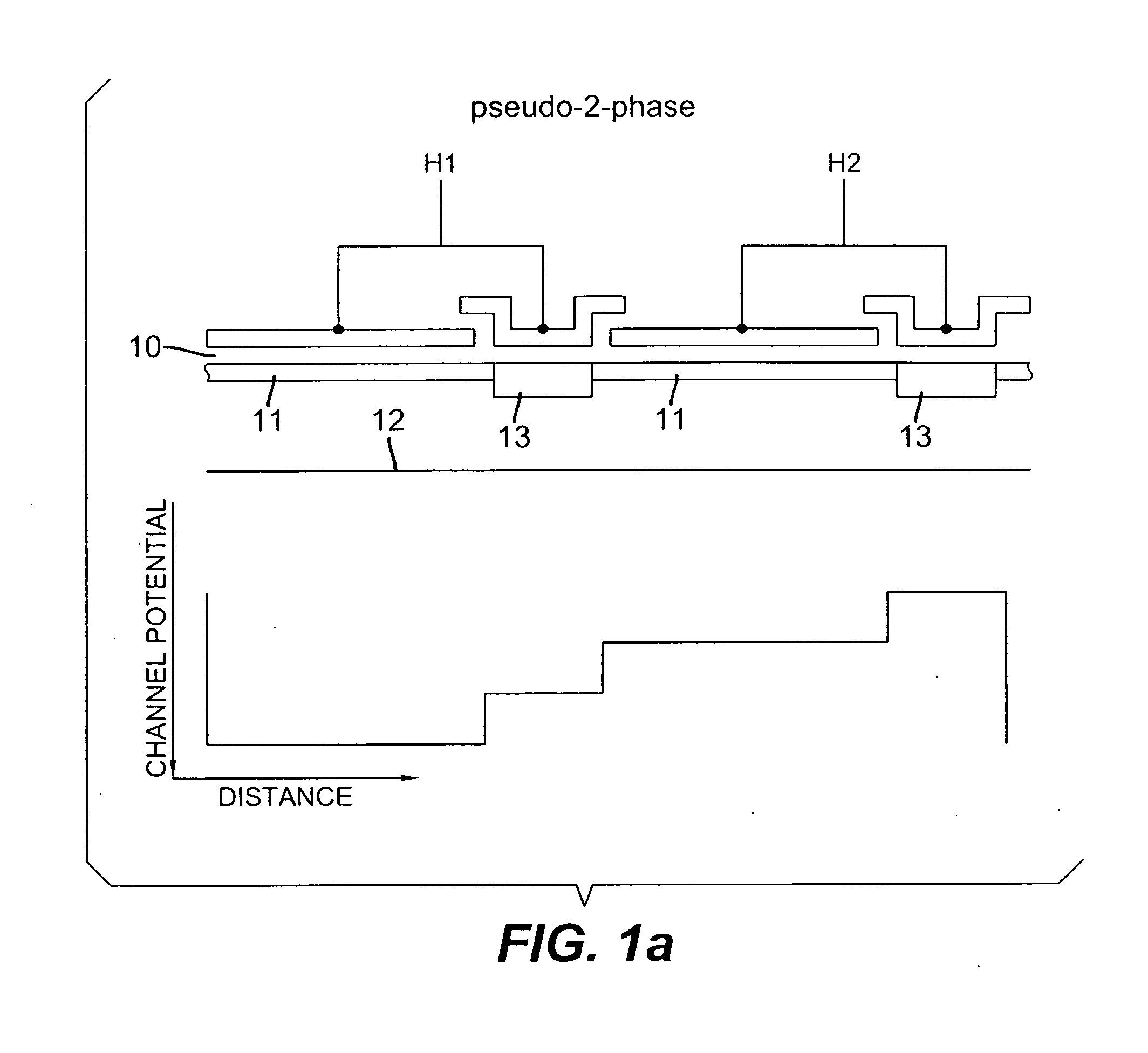
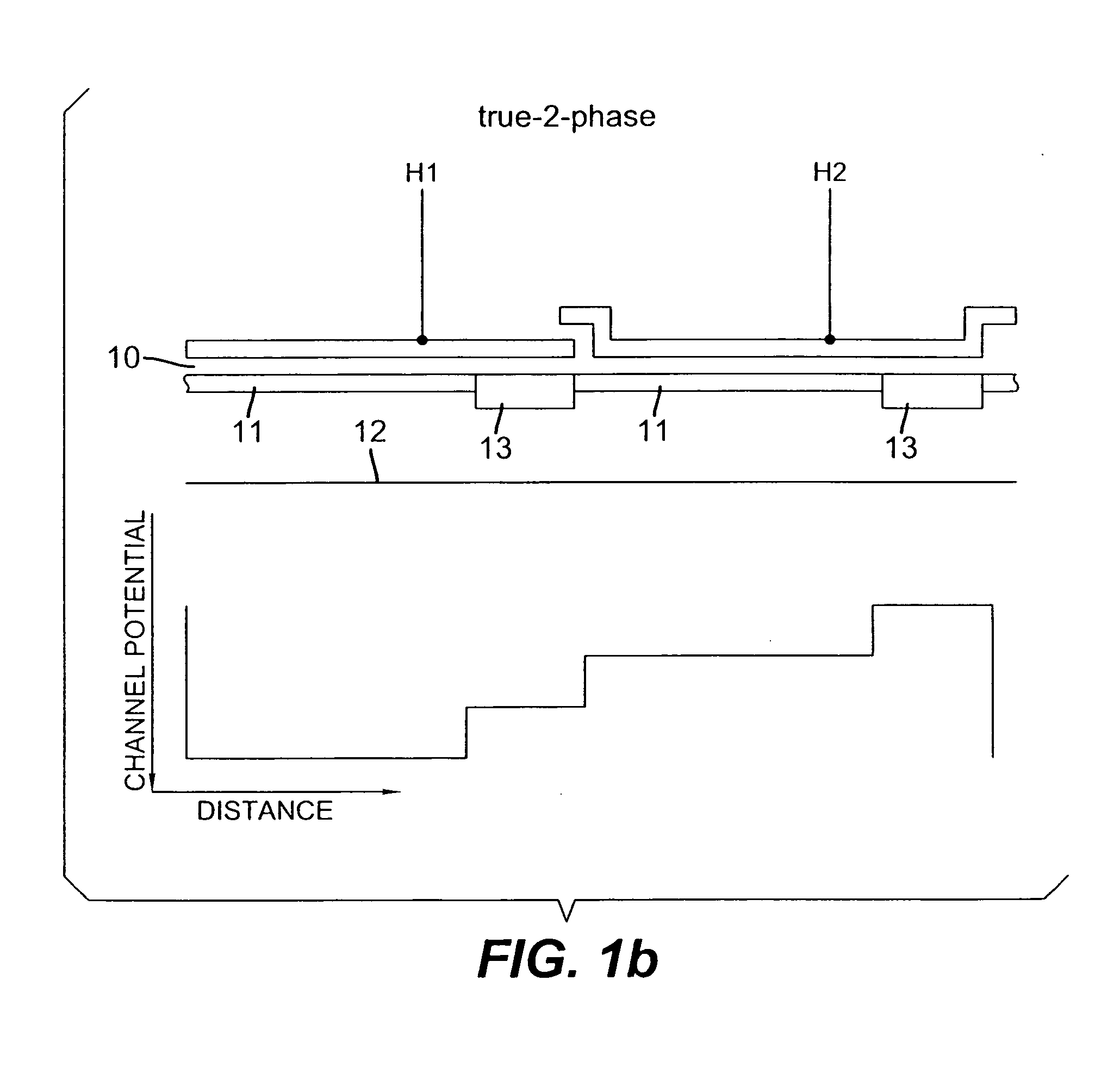
Ultrasound color flow imaging at high frame rates
ActiveUS7946990B2High frame rateBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsFrequency bandBlood stream
A method is provided to improve the frame-rate in color-flow ultrasound imaging using simultaneous spatially-distinct transmit beams with one or more frequency bands per transmit beam. Pulses of different center frequencies are used simultaneously in different (lateral and / or elevational) directions, thereby reducing the scanning time and improving the frame-rates. Optionally, a multi-modal pulse is used, and flow is estimated separately for the different frequencies. The flow estimates for these pulses are appropriately combined to improve low-velocity sensitivity and to reduce aliasing. A flow sample count with two or more different pulse repetition intervals can be used to further improve low-flow sensitivity and minimize aliasing.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
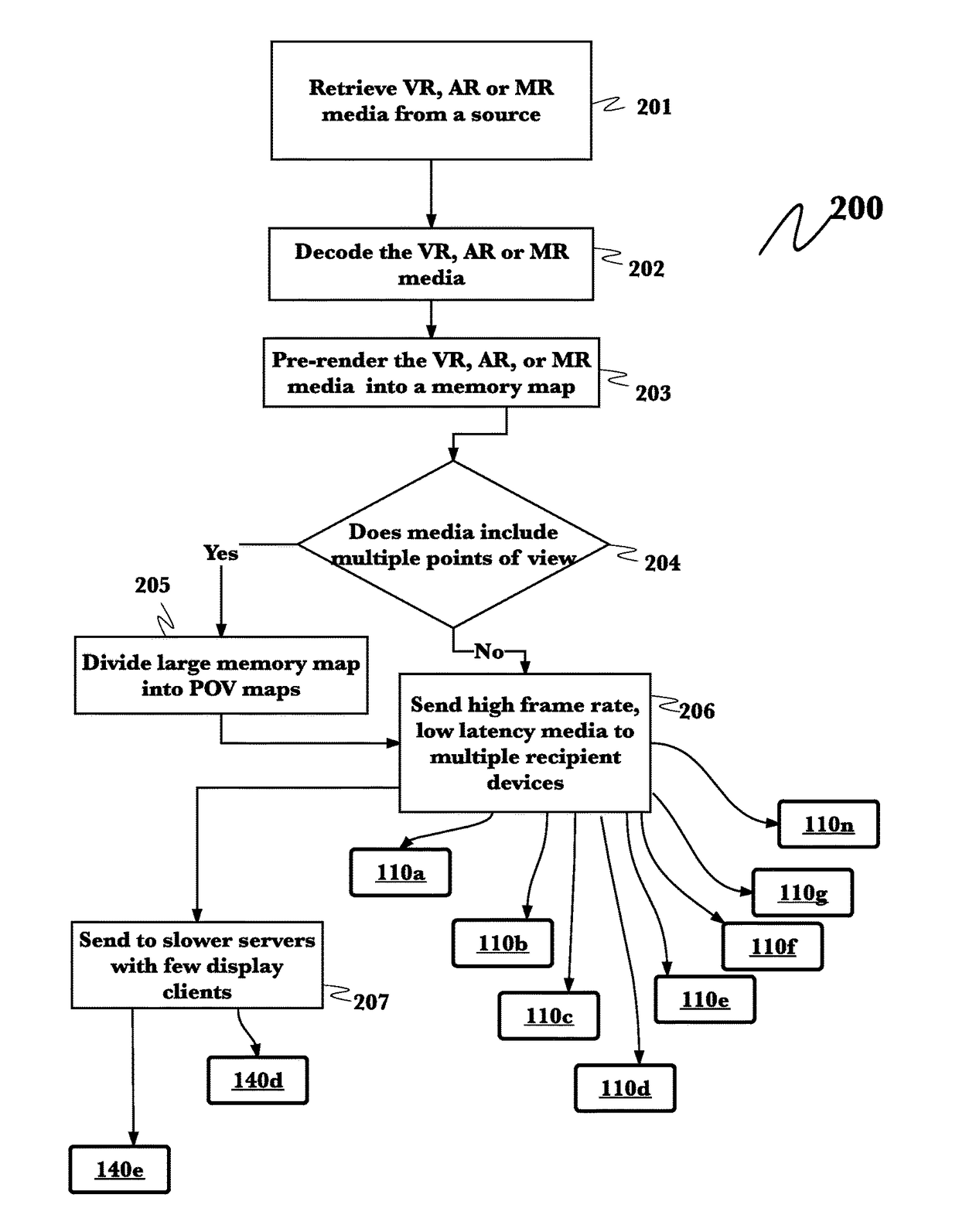
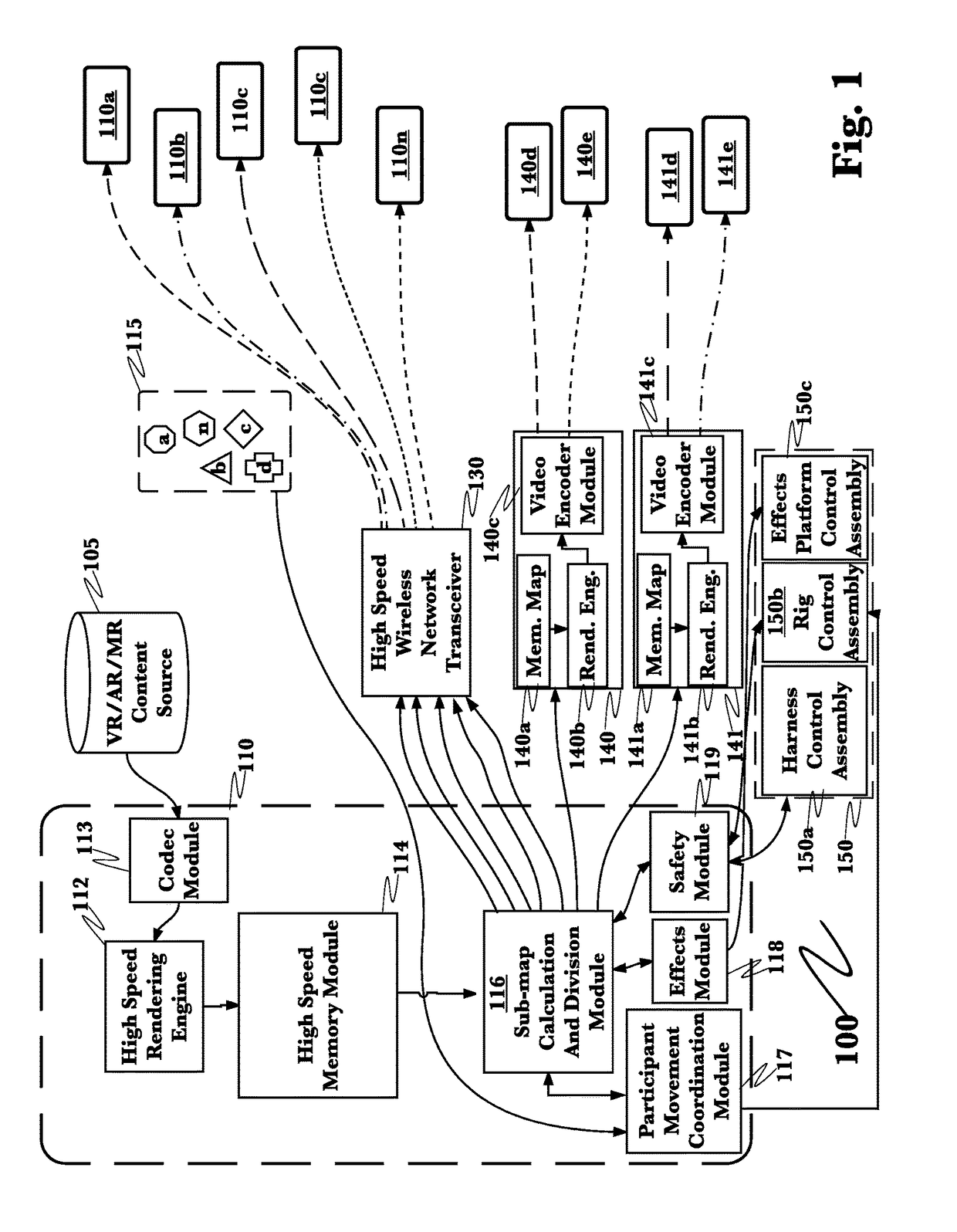
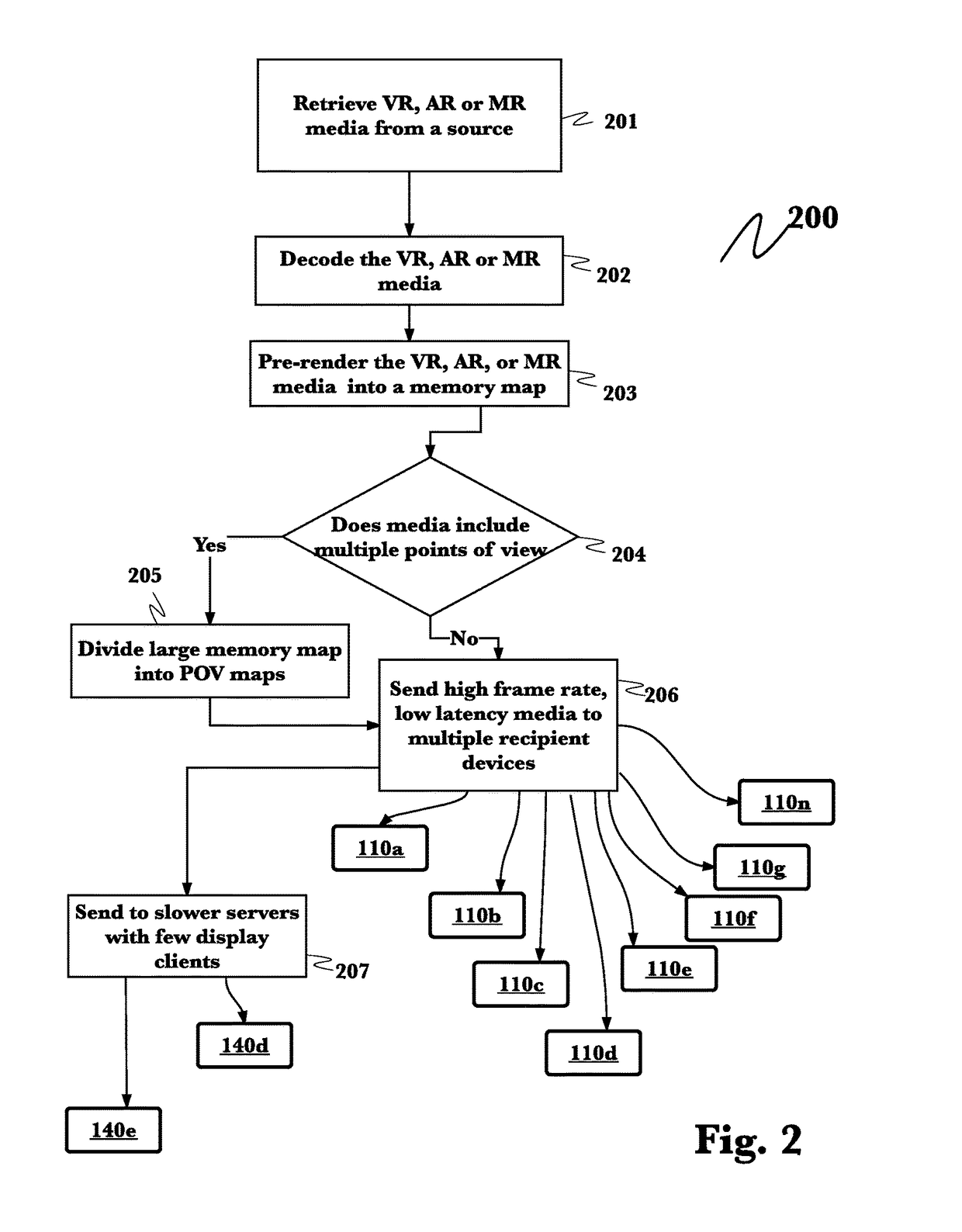
System and method for an enhanced, multiplayer mixed reality experience
InactiveUS20170228916A1High frame rateMinimal latencyInput/output processes for data processing3D-image renderingHigh speed videoMemory map
A system for enhanced, multiplayer mixed reality experience has been developed. A high-speed video content rendering engine retrieves mixed reality content data from a plurality of sources. A high-speed, low latency memory map is then rendered. All or point of view specific sub-portions of this main memory map are then transmitted either to secondary servers of lesser capability, which drive one to three mixed reality goggles or up to ten or more of virtual reality goggles directly. User experience may be enhanced the system providing physical props, sounds or actions based upon clues contained in the mixed reality content data.
Owner:PAPERCLIP PRODN INC
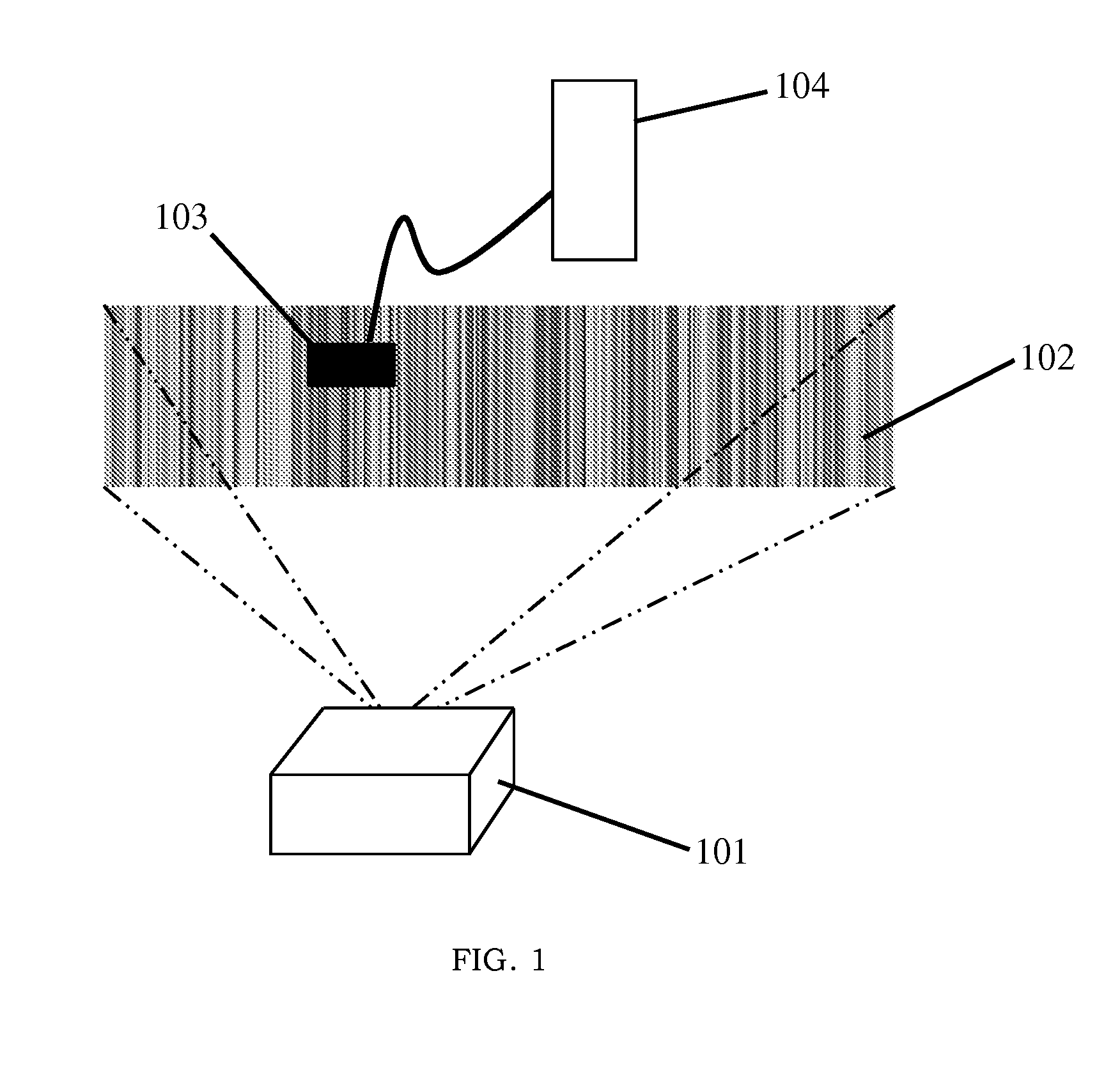
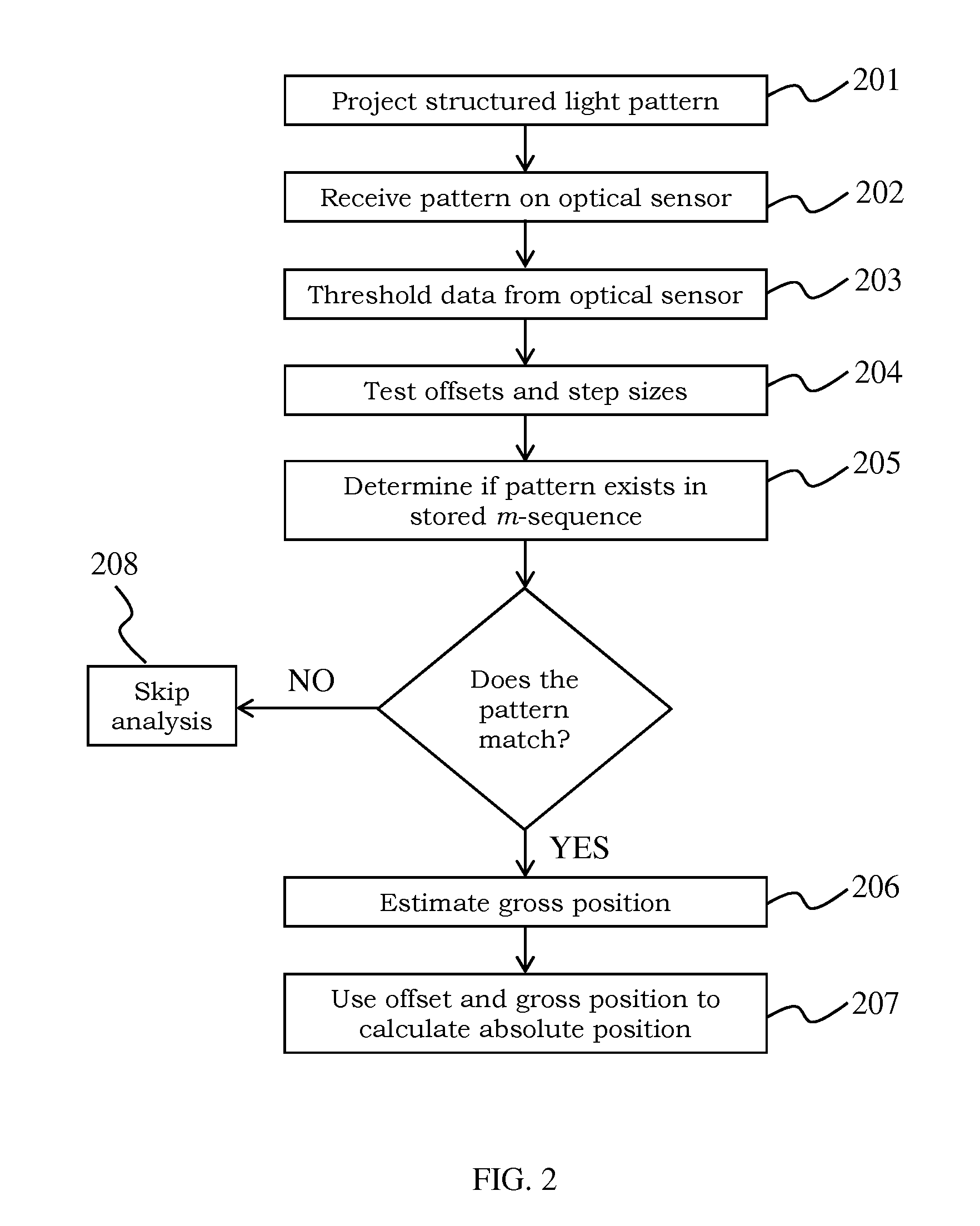
System and Method for Tracking Objects with Projected m-Sequences
ActiveUS20160084960A1High frame rateLow latencyOptical rangefindersPosition fixationComputer visionSix degrees of freedom
According to embodiments of the present invention are a system and method that use projected structured patterns of light and linear optical sensors for motion tracking. Sensors are capable of recovering two-dimensional location within the projection area, while several sensors can be combined for up to six degrees of freedom tracking. The structure patterns are based on m-sequences, in which any consecutive subsequence of m bits is unique. Both digital and static light sources can be used. The system and method of the present invention enables high-speed, high precision, and low-cost motion tracking for a wide range of applications.
Owner:DISNEY ENTERPRISES INC +1
Multiple output charge-coupled devices
ActiveUS20080018767A1High frame rateTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSense amplifierCharge detection
An image sensor includes a plurality of pixels overlaid with a color filter pattern of at least two colors having the same color on every other pixel in one direction; three or more charge-coupled devices oriented parallel to the every other pixel color filter repeat pattern; a charge sensing amplifier at the output of at least two of the charge couple devices; each charge-coupled device having a first and a second gate; a CCD-to-CCD transfer gate connecting adjacent charge-coupled devices with the first gate being on one side of the CCD-to-CCD transfer gate and the second gate being on the opposite side of the CCD-to-CCD transfer gate; all CCD-to-CCD transfer gates are electrically connected together; all first gates are electrically connected; and all second gates are electrically connected.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
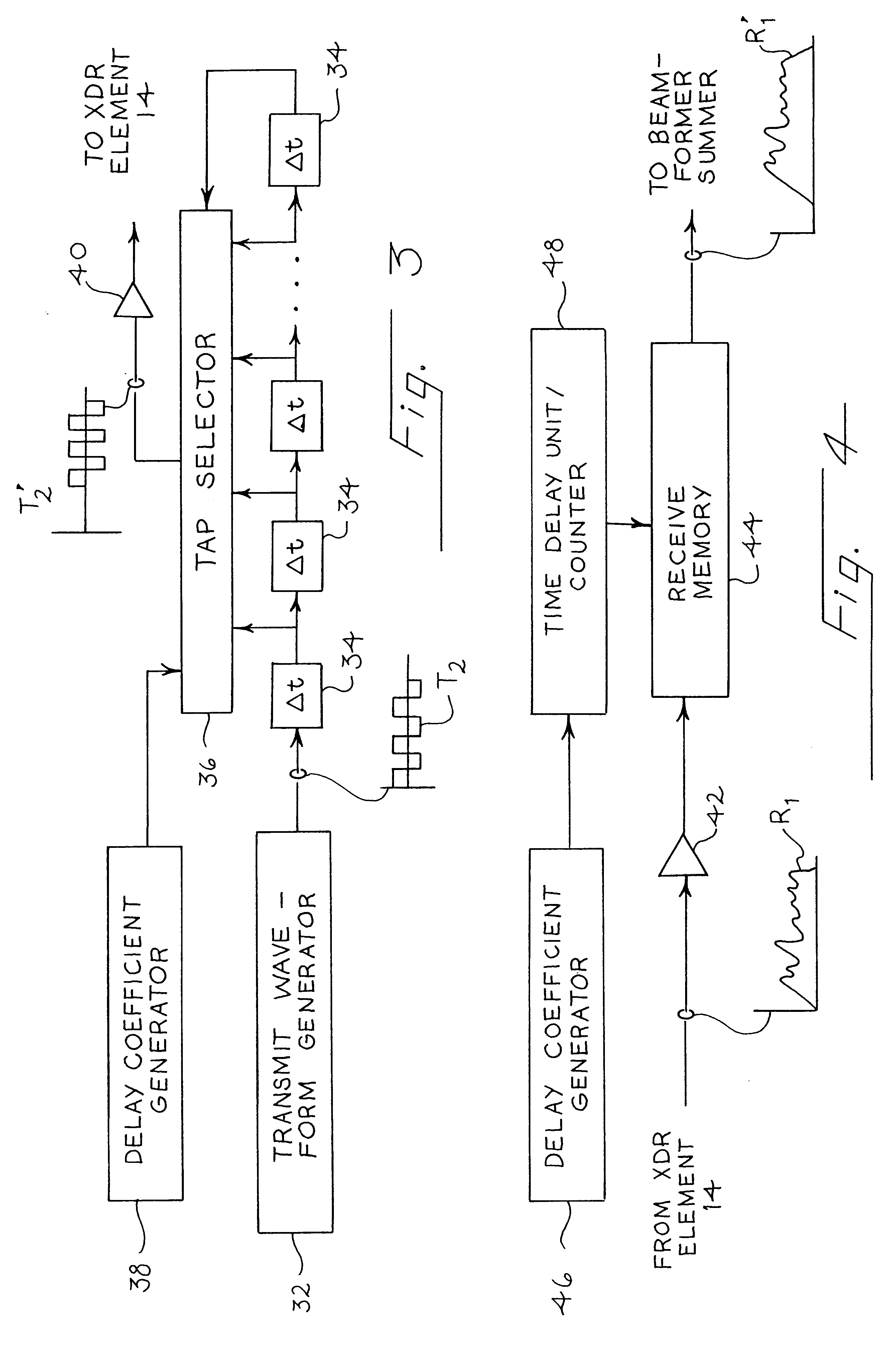
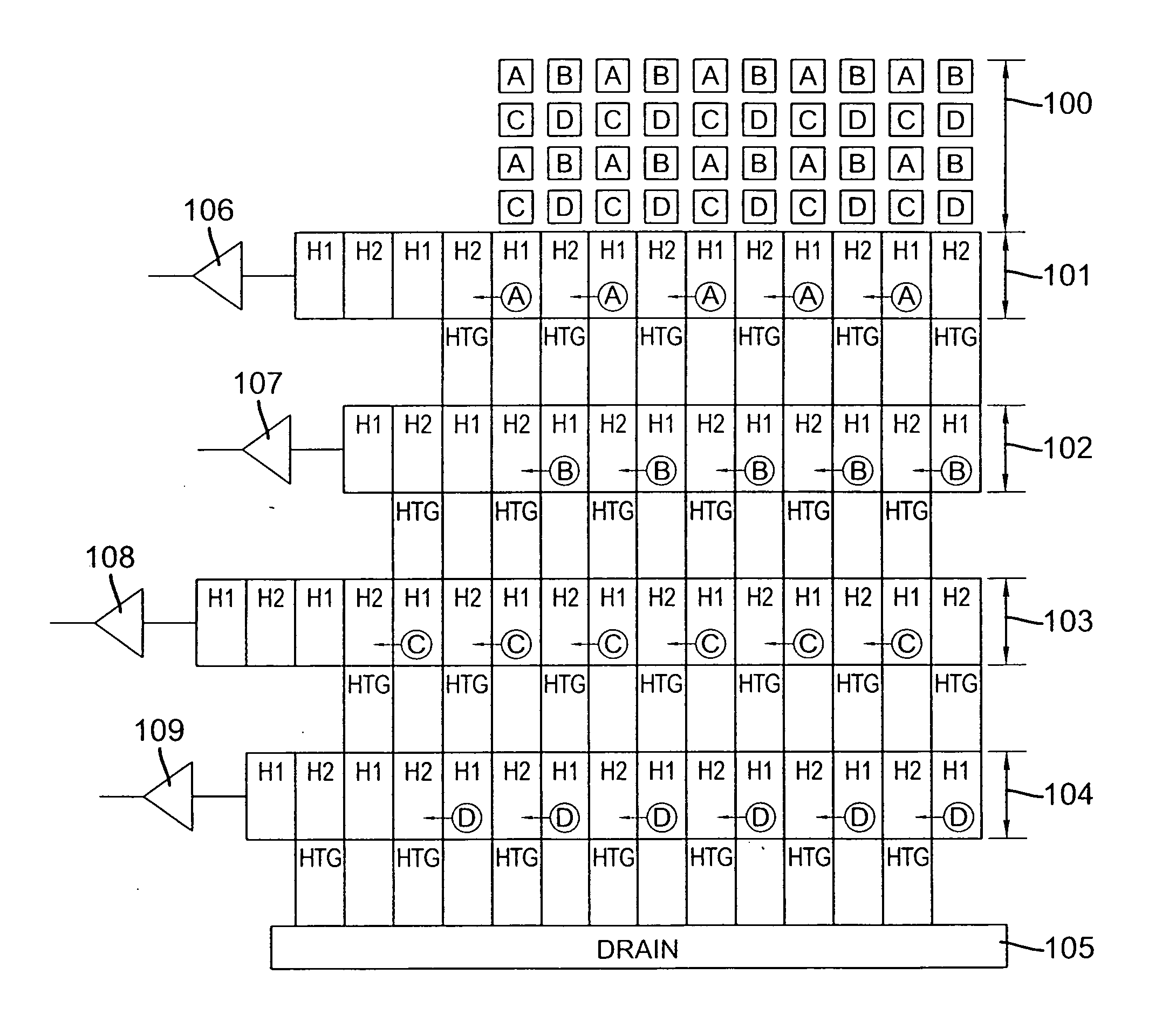
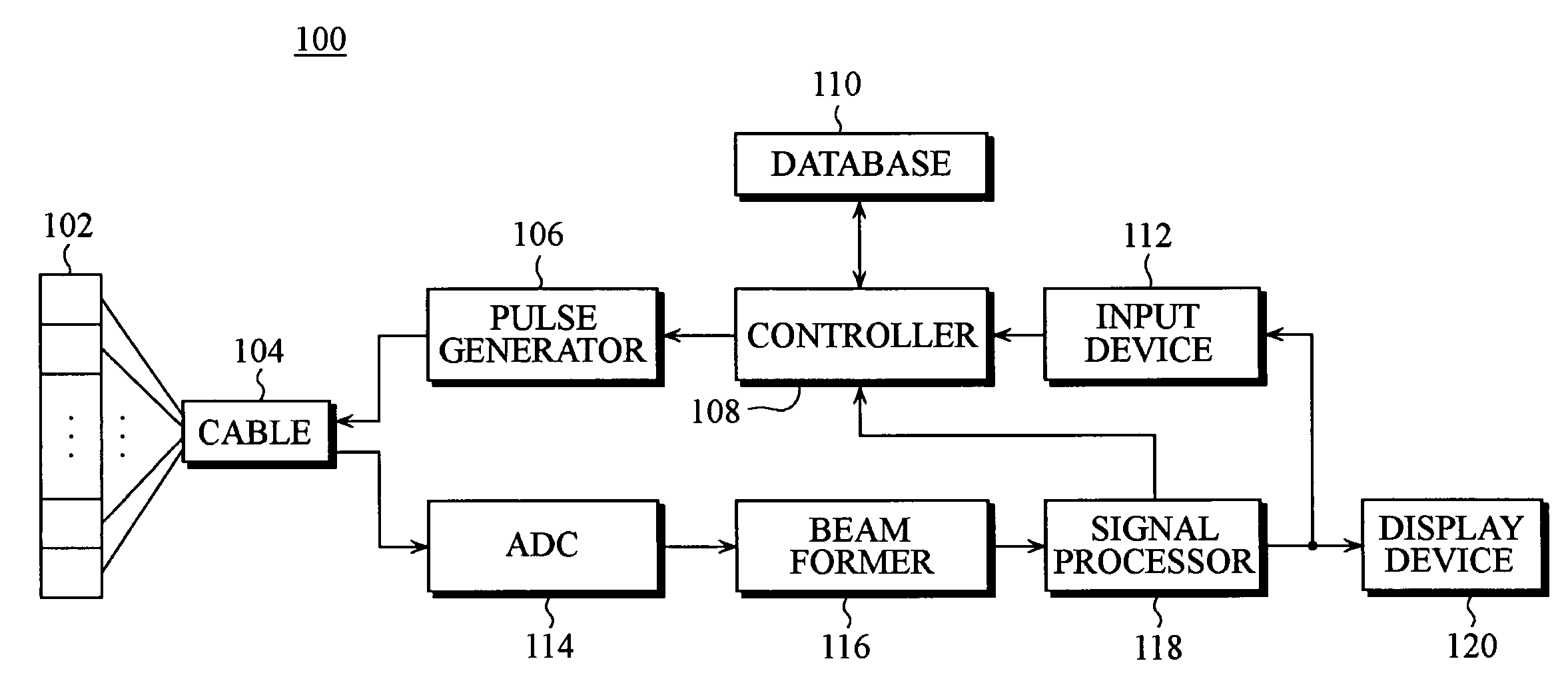
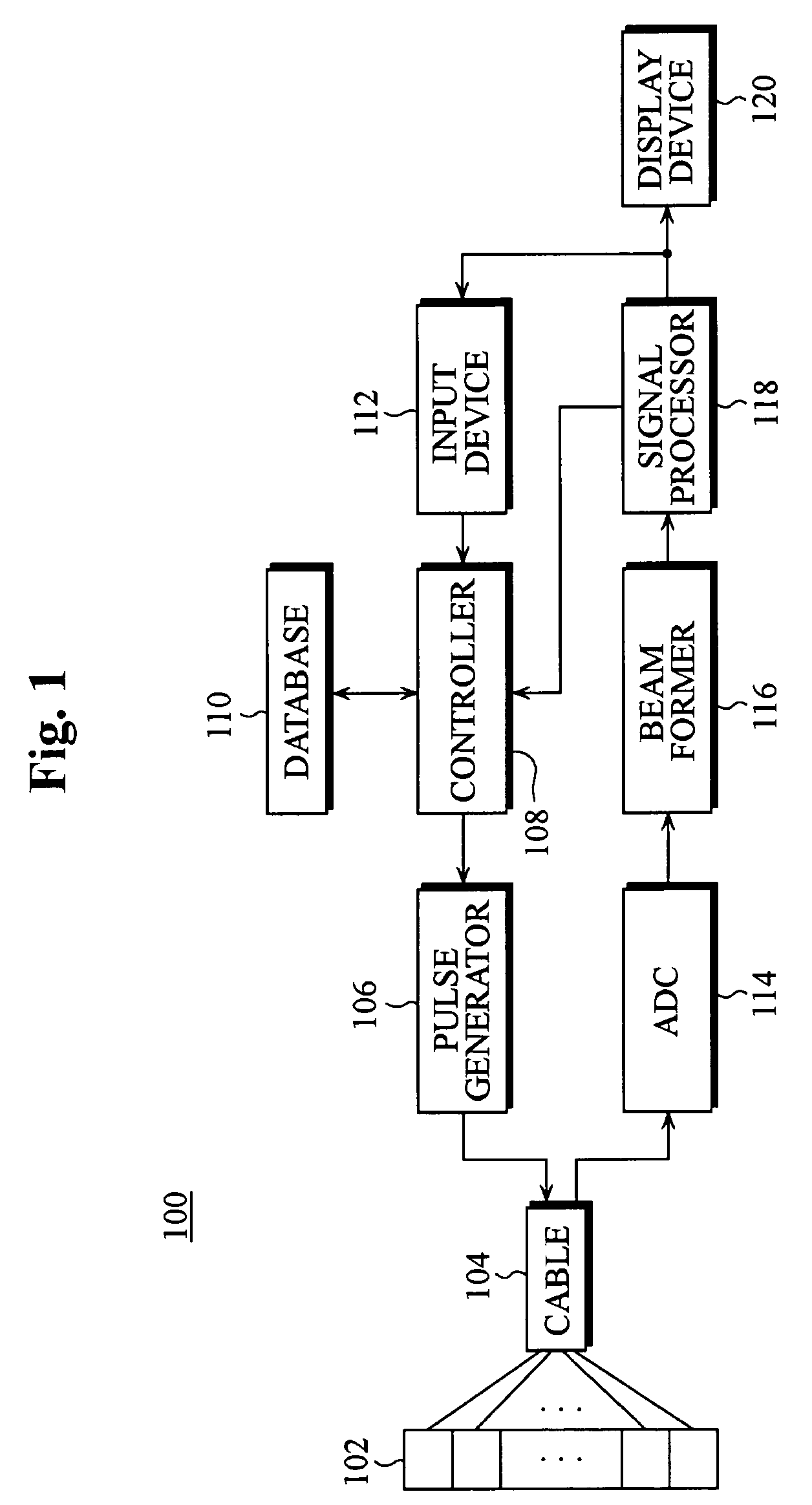
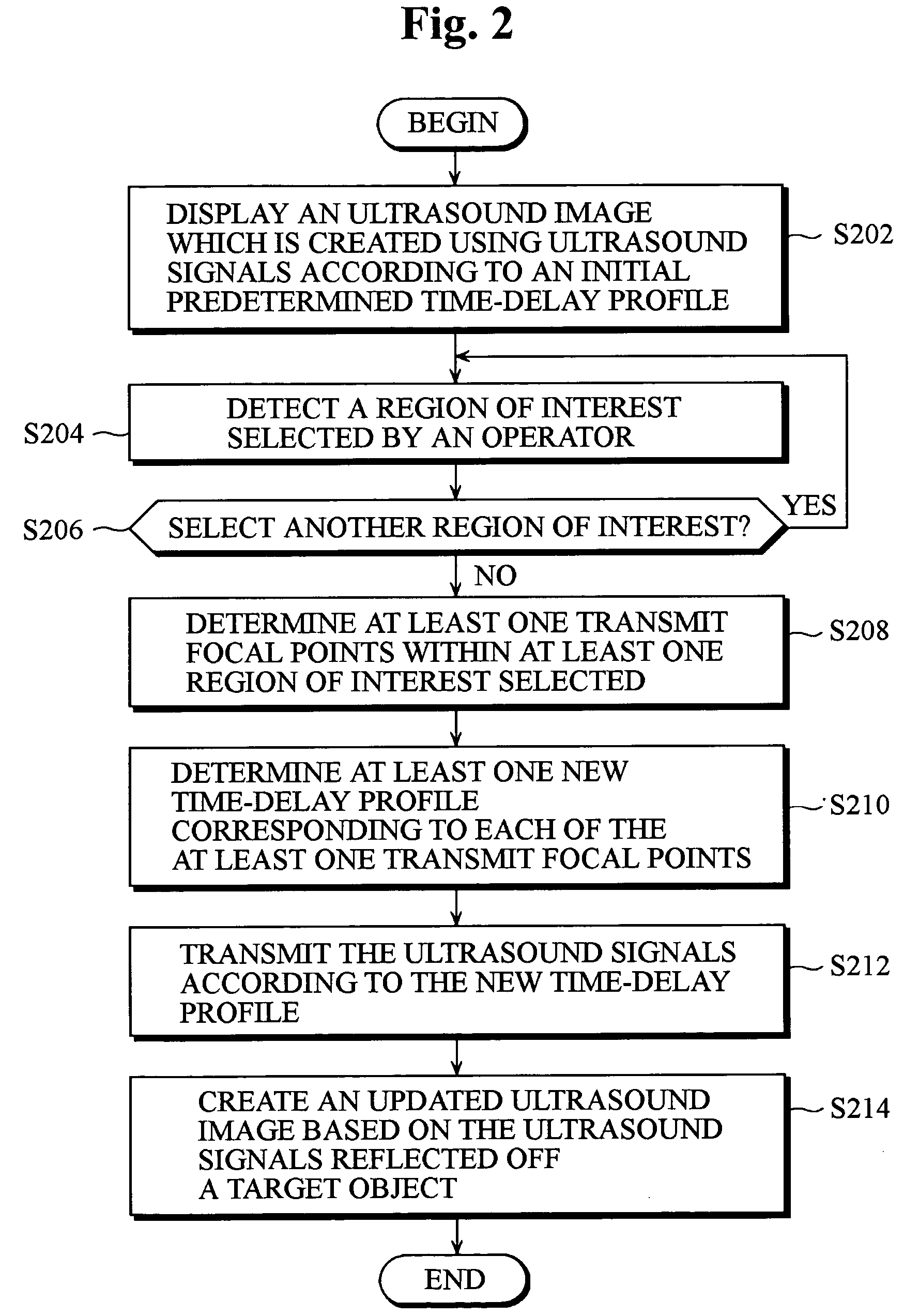
Ultrasound imaging apparatus having a function of selecting transmit focal points and method thereof
InactiveUS20060025687A1High frame rateIncrease frame rateWave based measurement systemsBlood flow measurement devicesUltrasound imageRegion of interest
The present invention relates to an ultrasound imaging apparatus having a function of selecting transmit focal points and method thereof, in which an operator may select at least one transmit focal point, allowing for transmit-focusing ultrasound signals upon the selected focal point to create an ultrasound image of a target object. The ultrasound imaging apparatus includes an ultrasound transducer array, a pulse generator, a controller, a database, an input device, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), a beam former, a signal processor, and a display device. The method for ultrasound imaging comprises the steps of: a) transmitting to a target object ultrasound signals in accordance with a predetermined initial time-delay profile; b) receiving and processing the reflected ultrasound signals from the target object to create an ultrasound image of the target object; c) displaying the created ultrasound image to allow an operator to select at least one region of interest within the displayed ultrasound image; d) in response to the operator's selection, detecting coordinates of the selected region of interest; e) determining at least one transmit focal point corresponding to the detected coordinates of the selected region of interest; f) determining at least one new time-delay profile based on each of the transmit focal points; and g) transmitting the ultrasound signals in accordance with the new time-delay profile to the target object; h) receiving and processing the reflected ultrasound signals off the target object to create an updated ultrasound image of the target object.
Owner:MEDINCELL
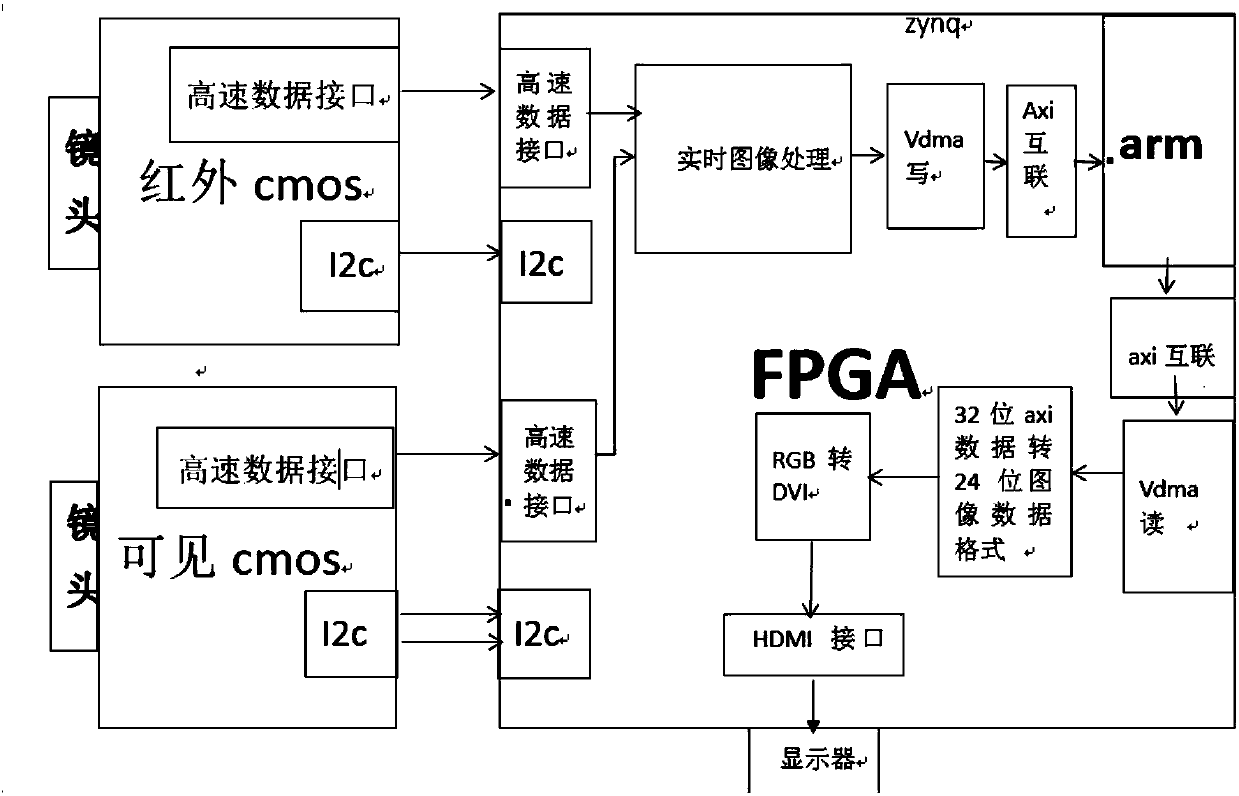
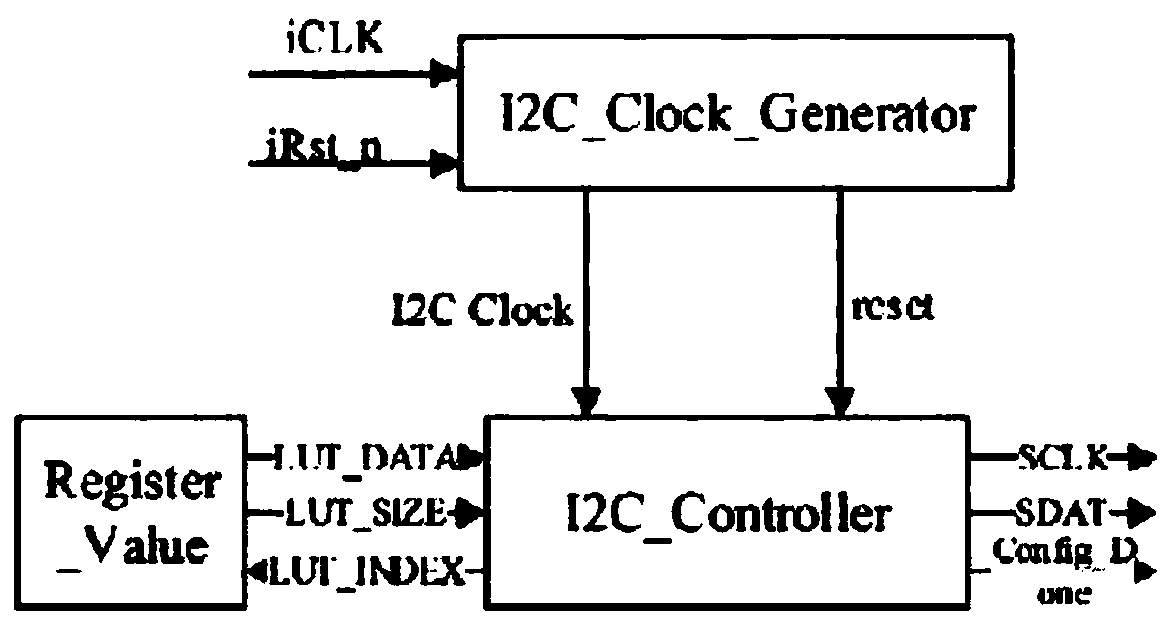
Bispectral high-speed camera based on fpga
InactiveCN109951617ARealize simultaneous acquisitionReal-time image fusionTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsCMOS sensorStereo camera
The invention relates to a dual-spectrum high-speed camera based on fpga. The dual-spectrum high-speed camera comprises an infrared sensor, a visible light sensor, a serial communication master-slaveinterface realized by an I2C interface, an image processing device and an image real-time display device. A register in the cmos sensor is written by using an I2C interface working time sequence, exposure of the cmos sensor is controlled, and automatic white balance opening and closing, frame rate and / or resolution are / is controlled. The infrared-based high-sensitivity cmos sensor improves the imaging speed to realize high frame rate and high speed; and a global exposure mode is adopted by using the cmos sensor, so that the moving shooting of the high-speed object is not distorted.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
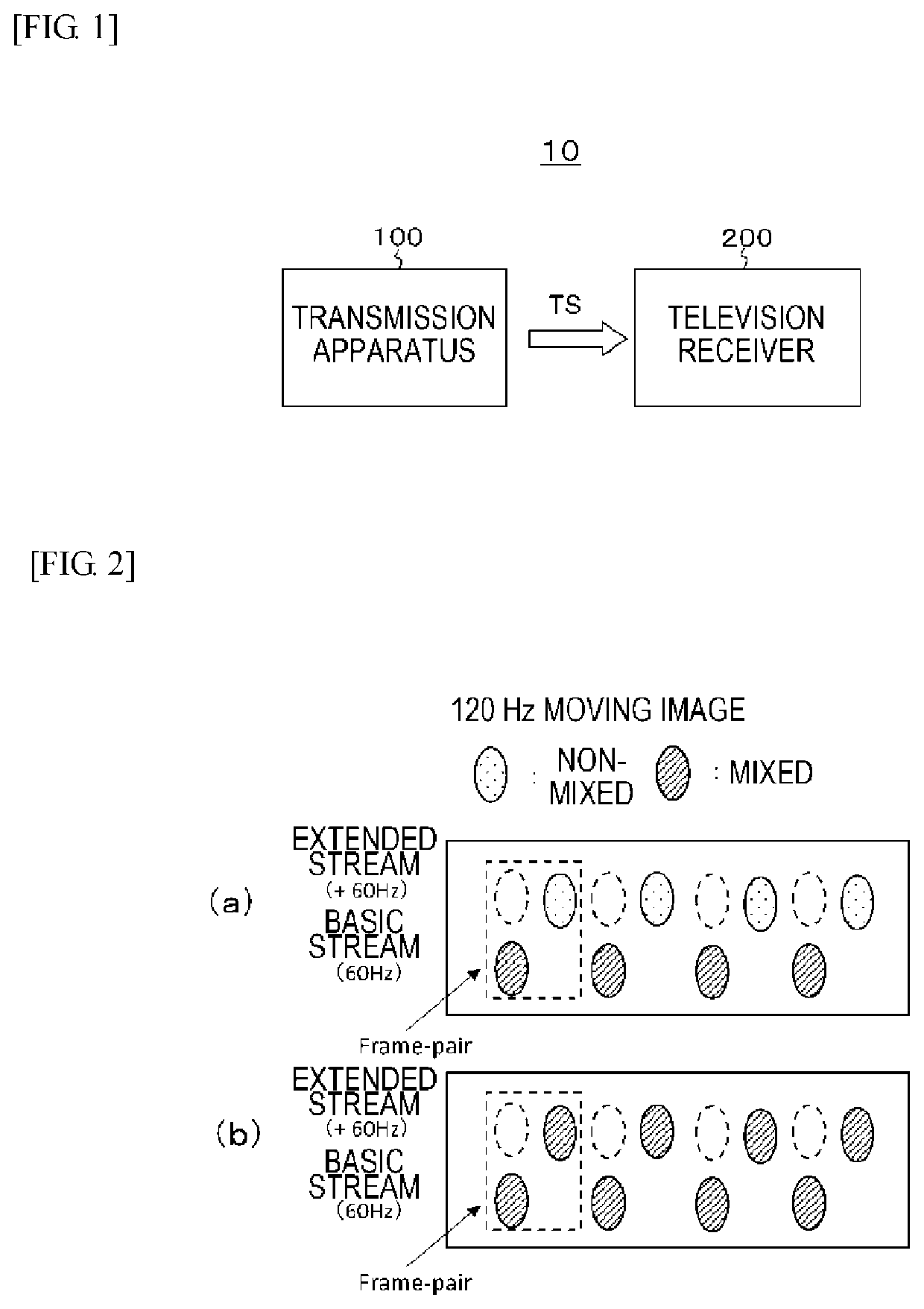
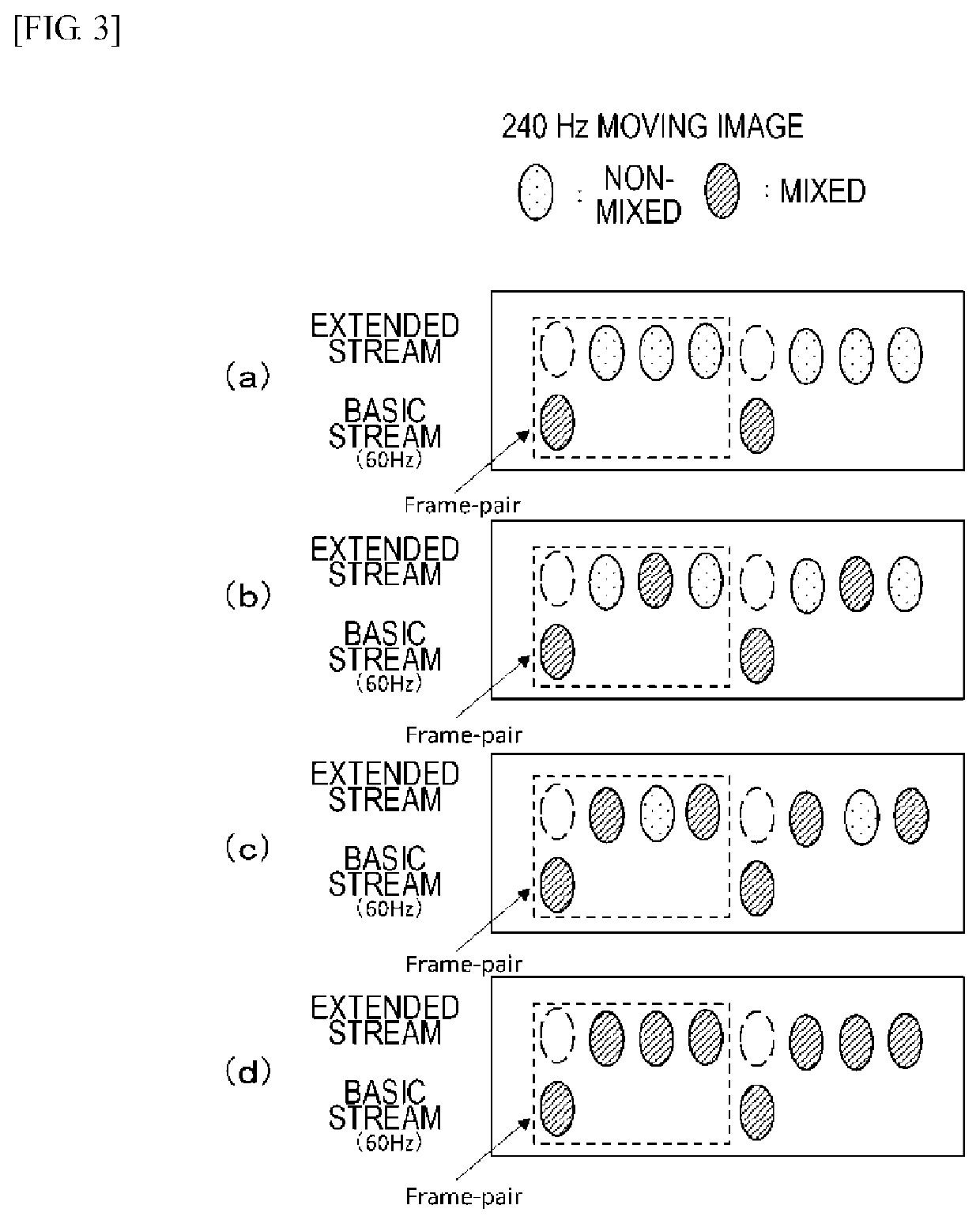
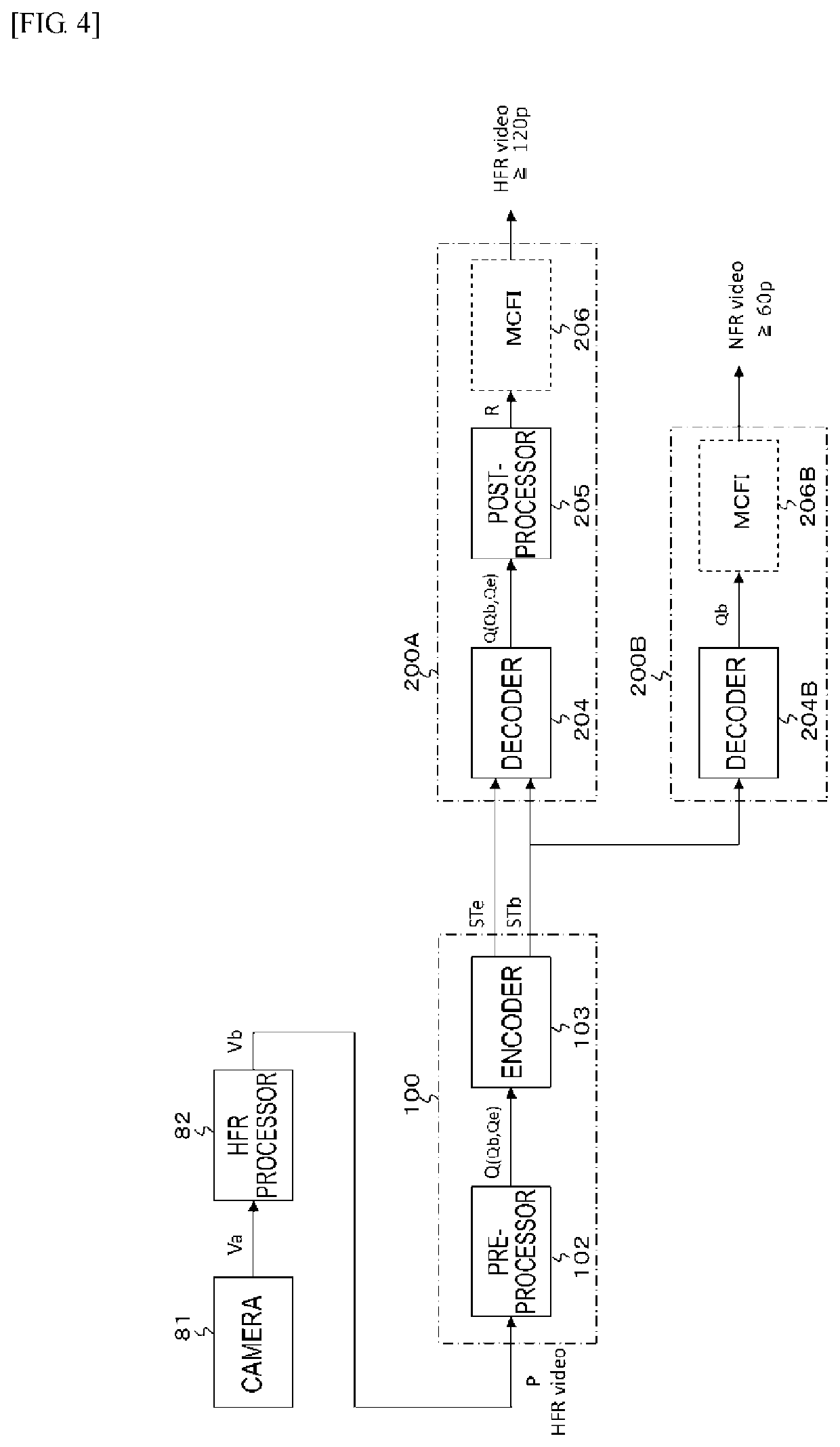
Transmission apparatus, transmission method, reception apparatus, and reception method
ActiveUS20200021869A1High frame rateTransfer satisfactorilyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFrame rateComputer graphics (images)
There is provided a transmission apparatus including: a processing unit that performs processing of mixing, at a mixing rate independent for each frame, image data in peripheral frames with image data in each frame of first moving image data at a first frame rate and obtains second moving image data at the first frame rate. At least image data in a frame corresponding to a second frame rate that is lower than the first frame rate in the image data in each frame that forms the second moving image data is brought into a state in which the image data is mixed with the image data in the peripheral frames.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and method for ultrasonic diagnostic imaging
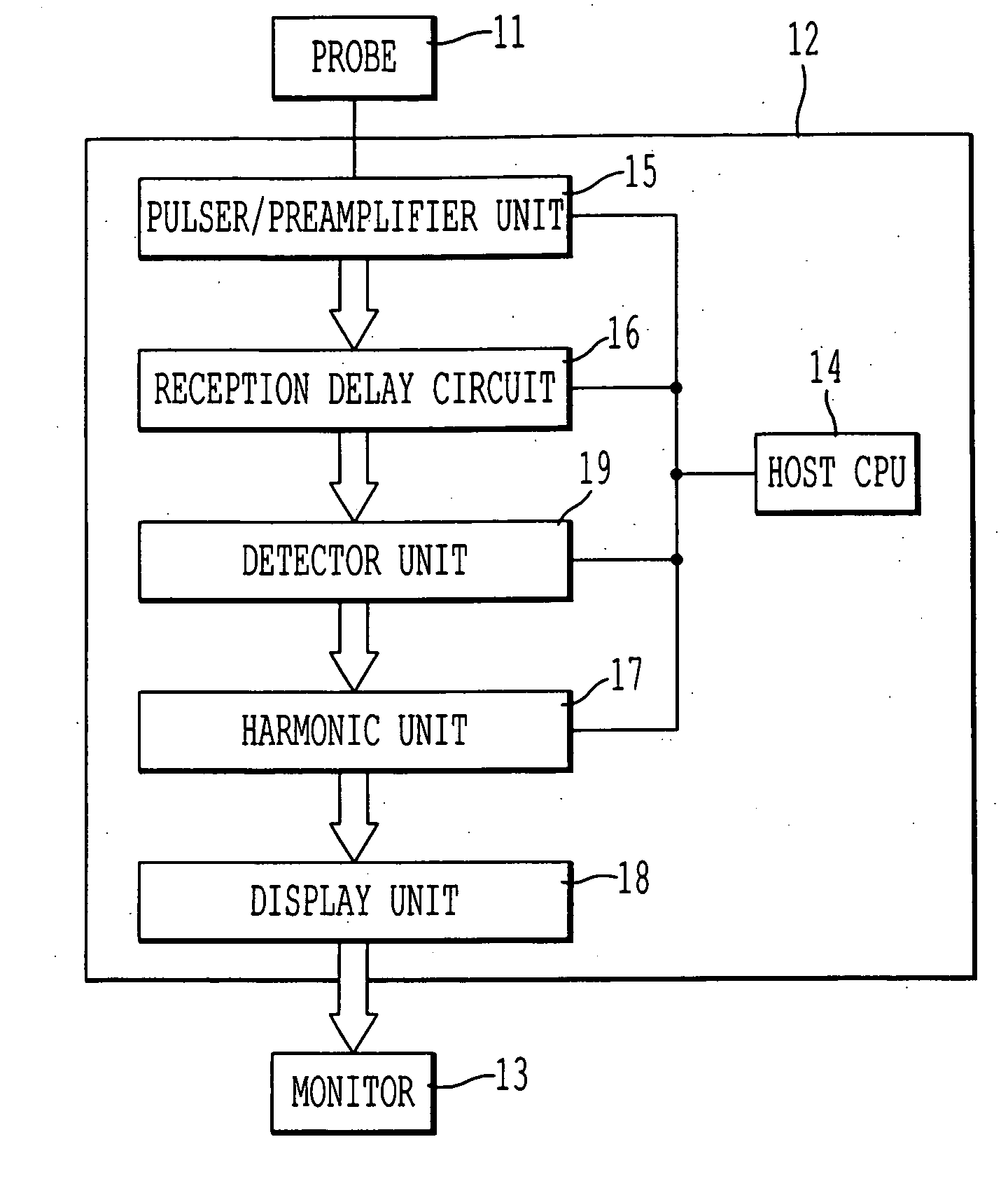
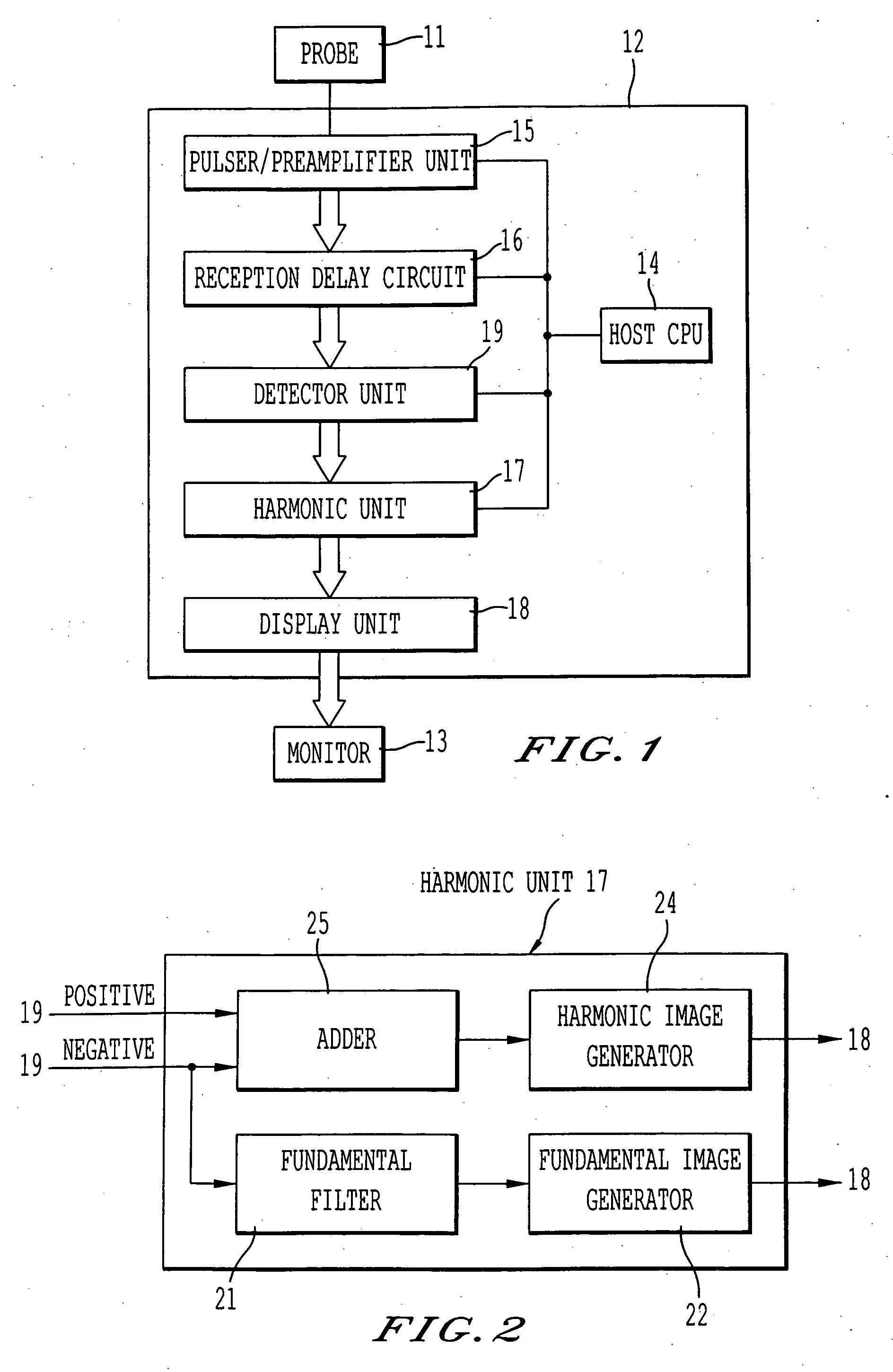
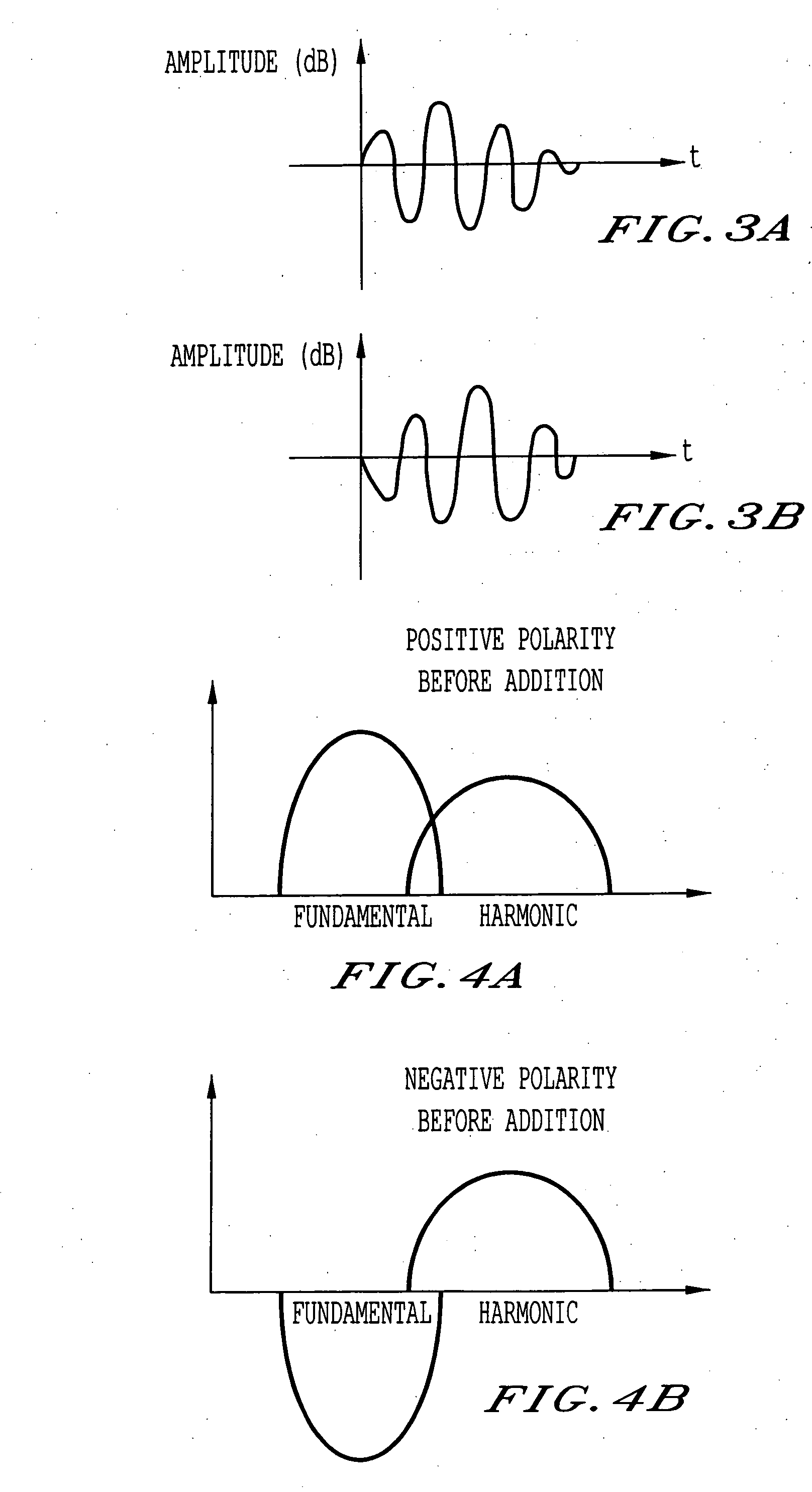
InactiveUS20060086187A1High frame rateVibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSubject specificFrequency band
An ultrasonic diagnosis apparatus and method wherein both imaging of a contrast effect and imaging of a tissue appearance before and after inflow of a contrast medium can be realized on condition that low-power transmission and a high frame rate are maintained. The ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus includes a transmission / reception unit for transmitting subject ultrasonic waves with a band substantially centered at a fundamental frequency and generating a received signal based on an ultrasonic echo from the subject, a harmonic unit for extracting a signal of a harmonic component of the fundamental frequency included in the received signal and extracting a signal of the fundamental component with the band substantially centered the fundamental frequency included in the received signal, and a display unit for generating a display image based on the extracted harmonic and fundamental components.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
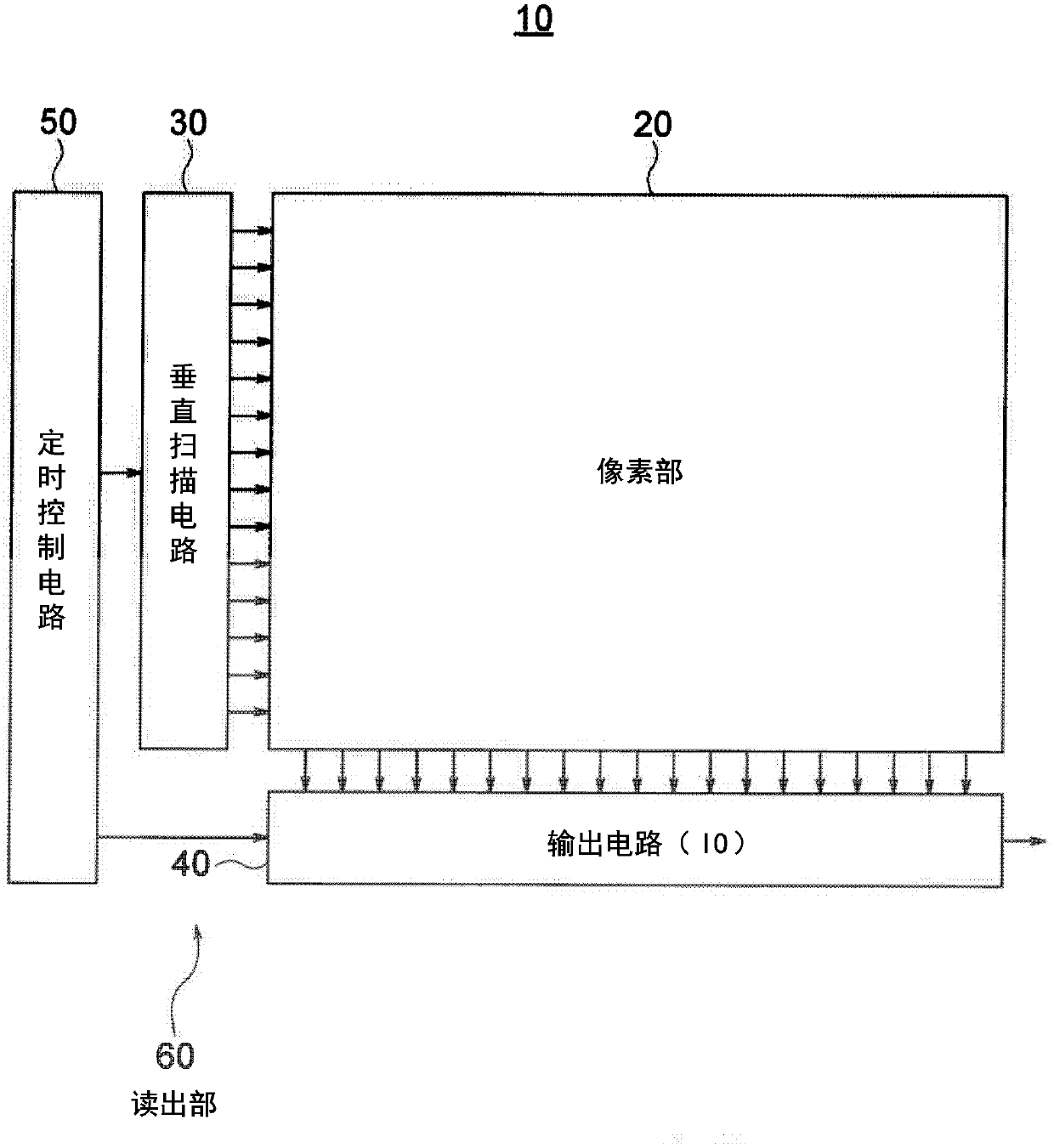
Solid-state imaging device, method for driving solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
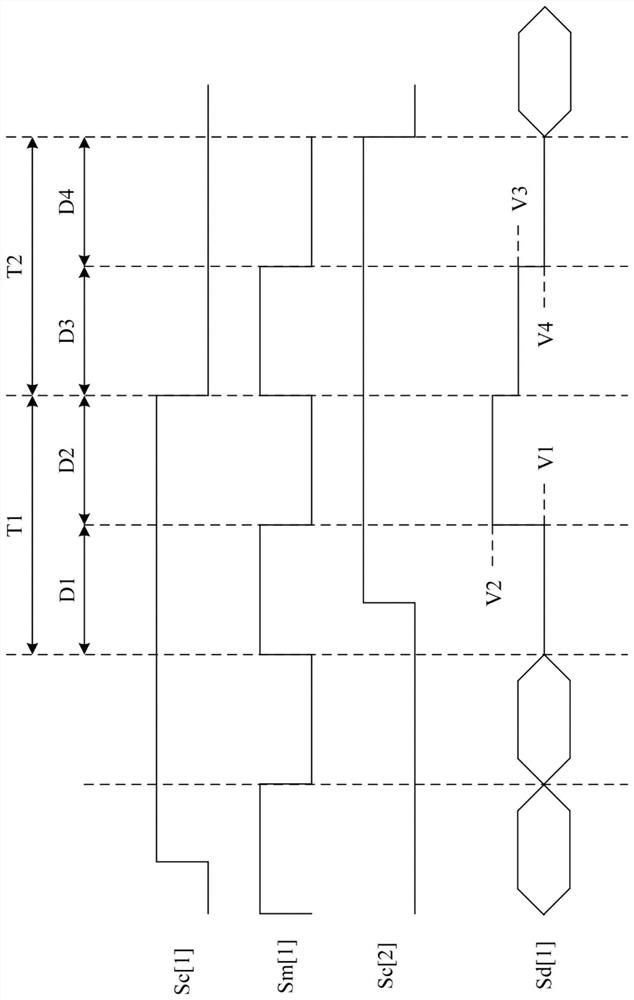
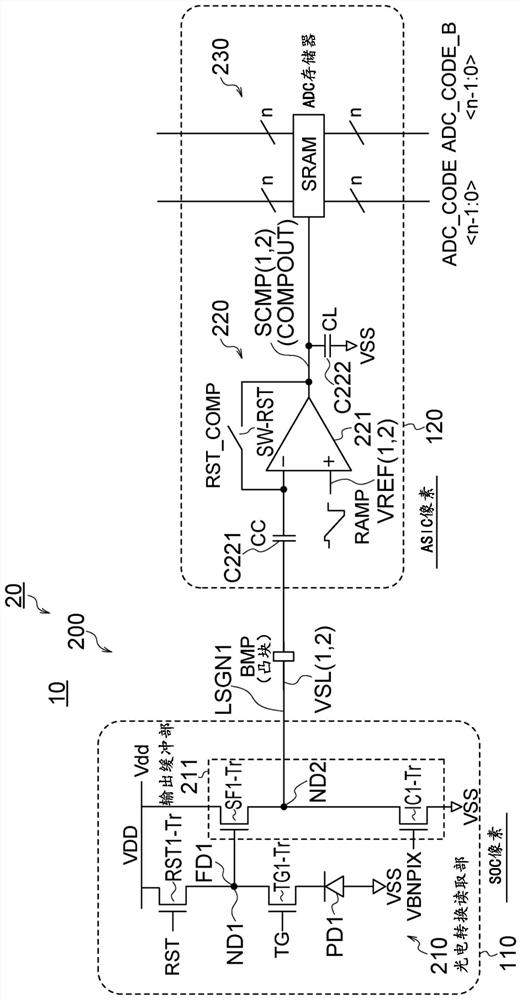
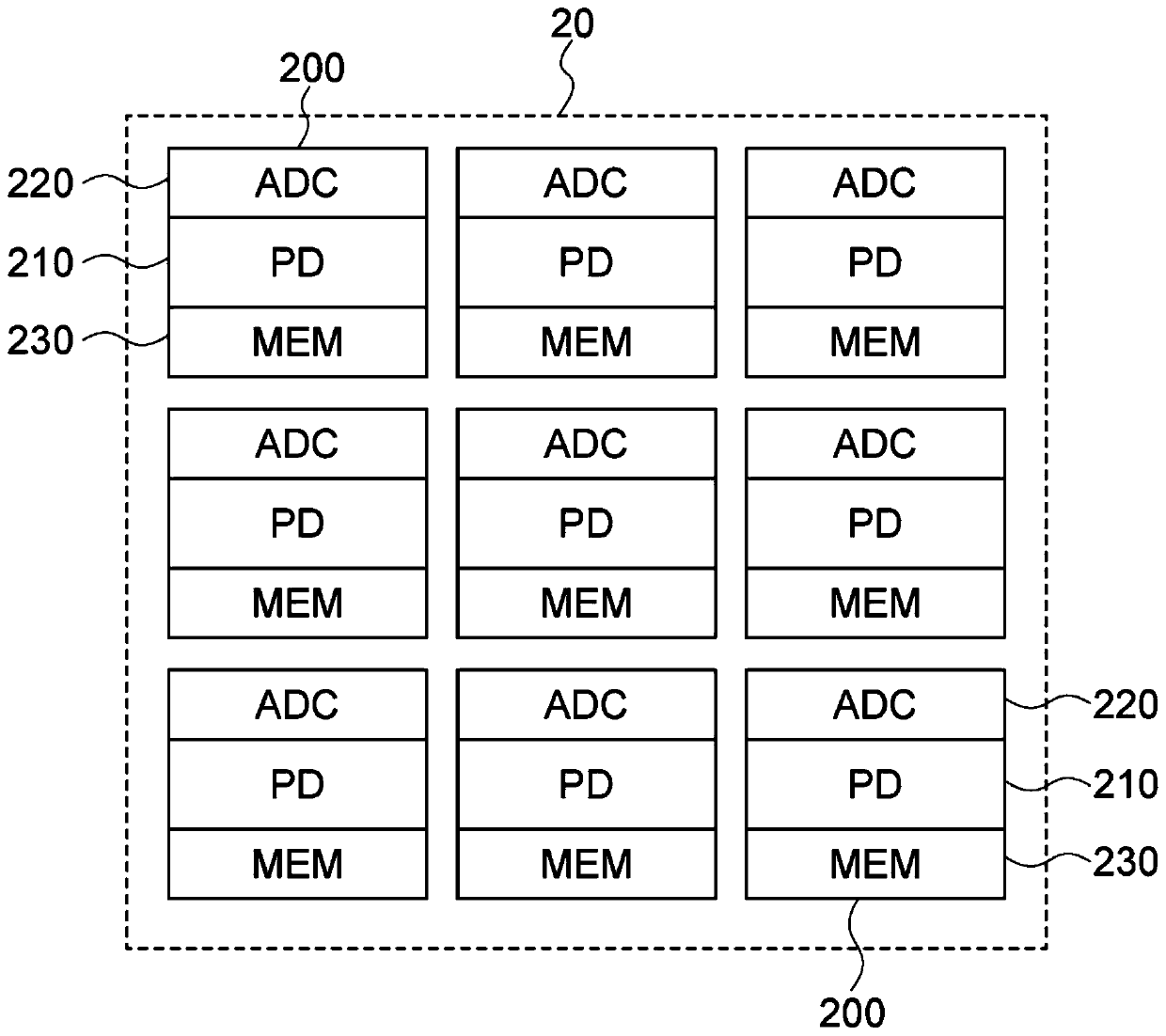
ActiveCN109561264AWide dynamic rangeHigh frame rateAnalogue/digital conversionTelevision system detailsHigh frame rateFloating diffusion
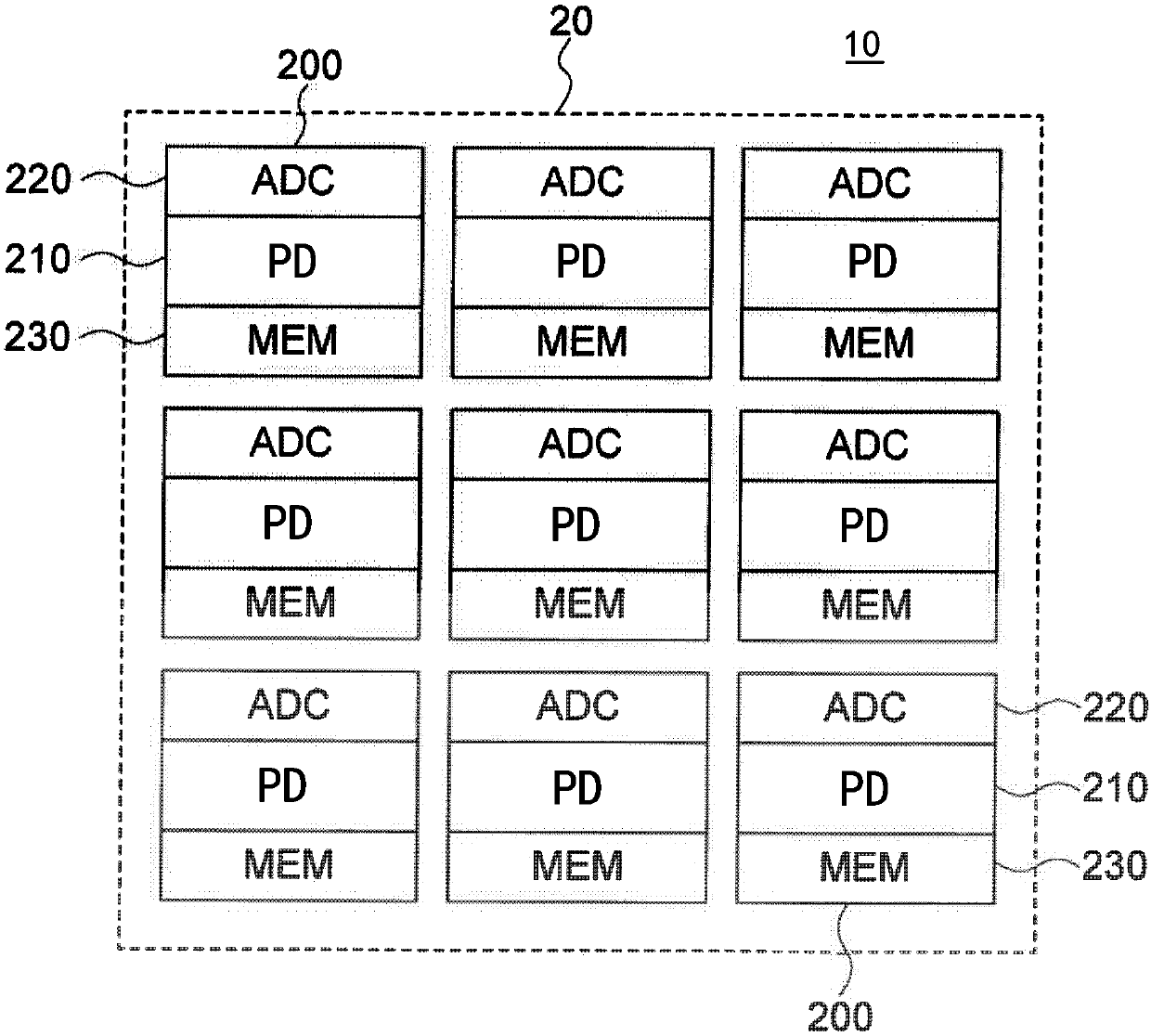
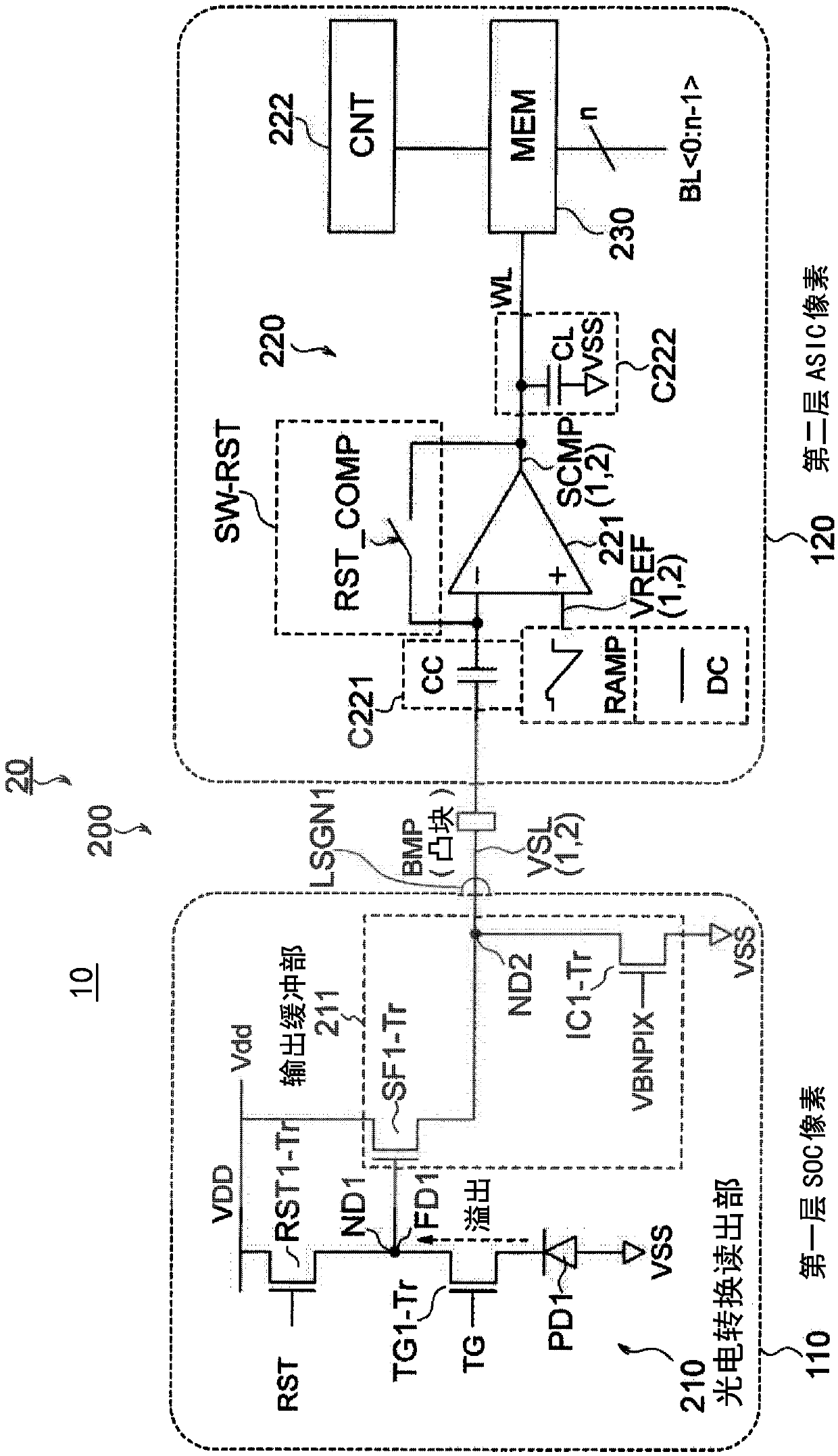
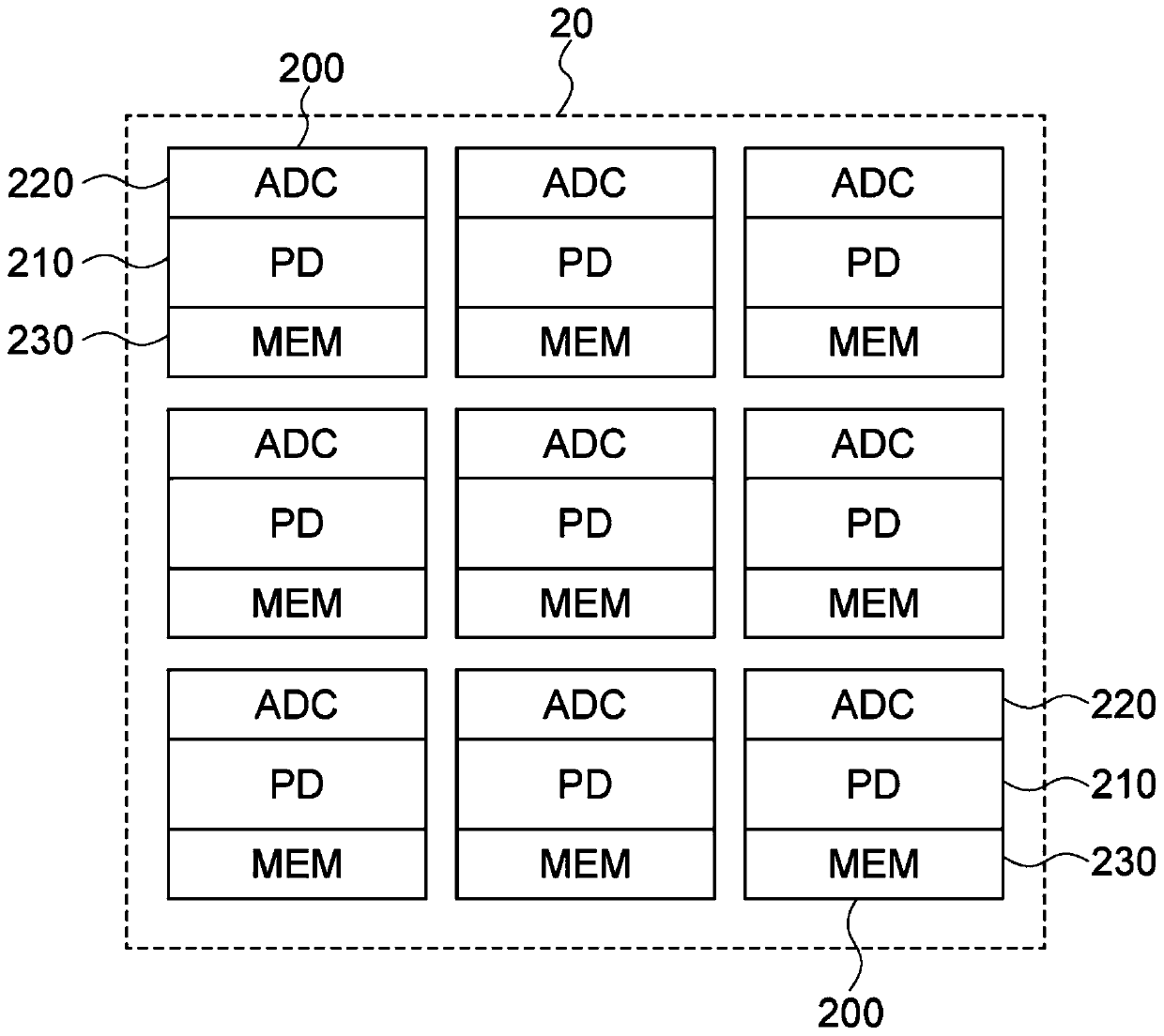
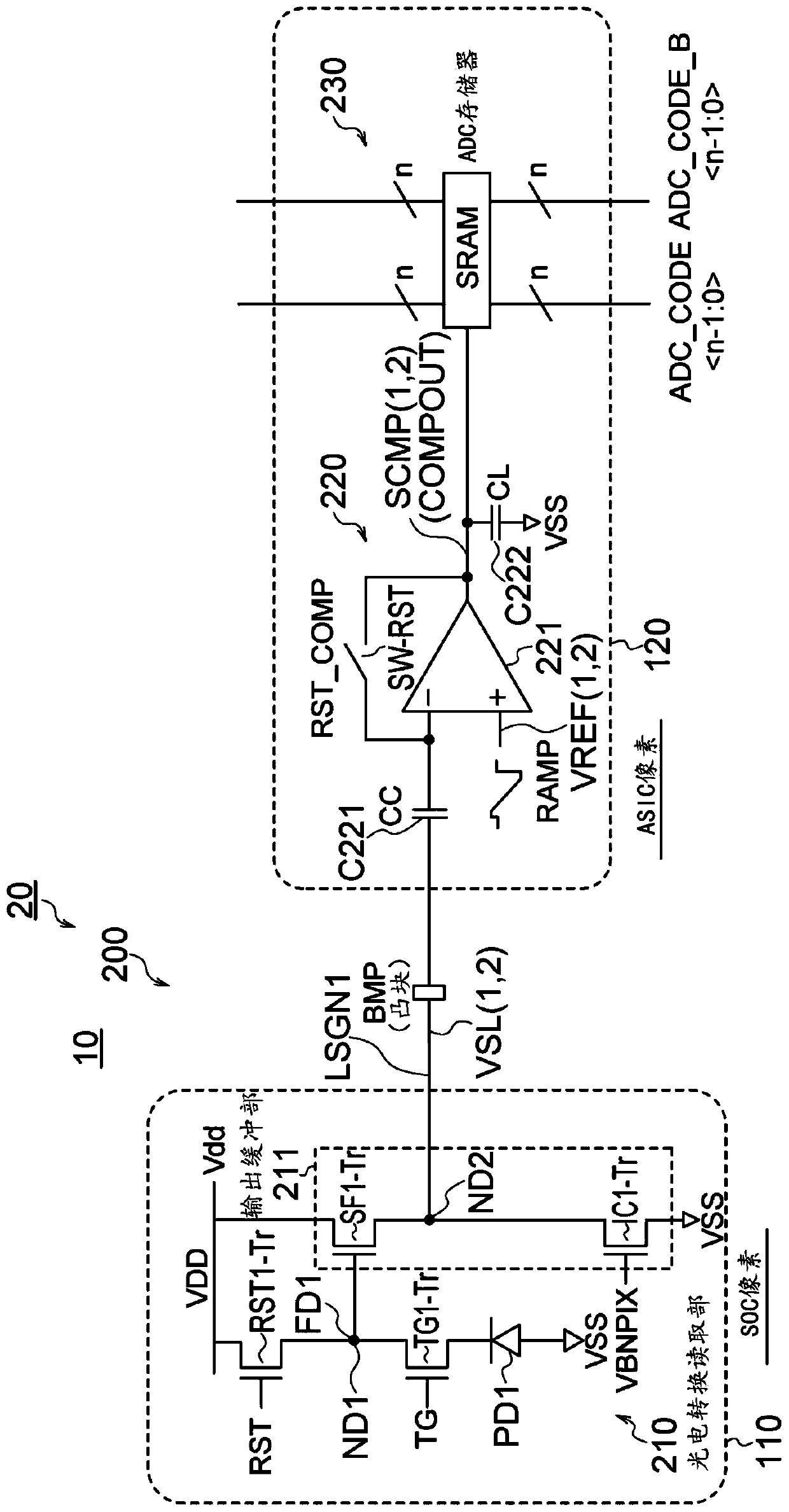
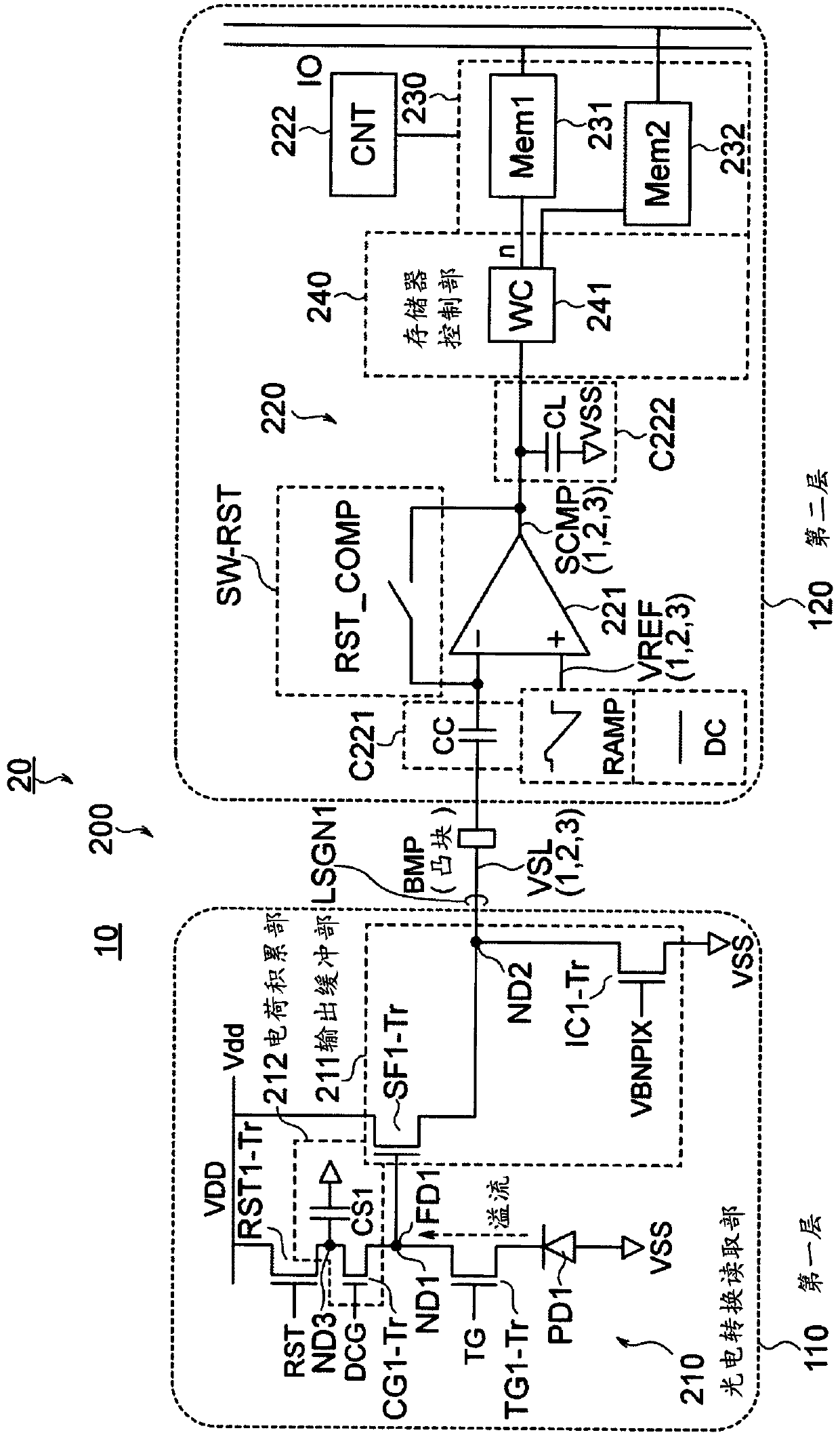
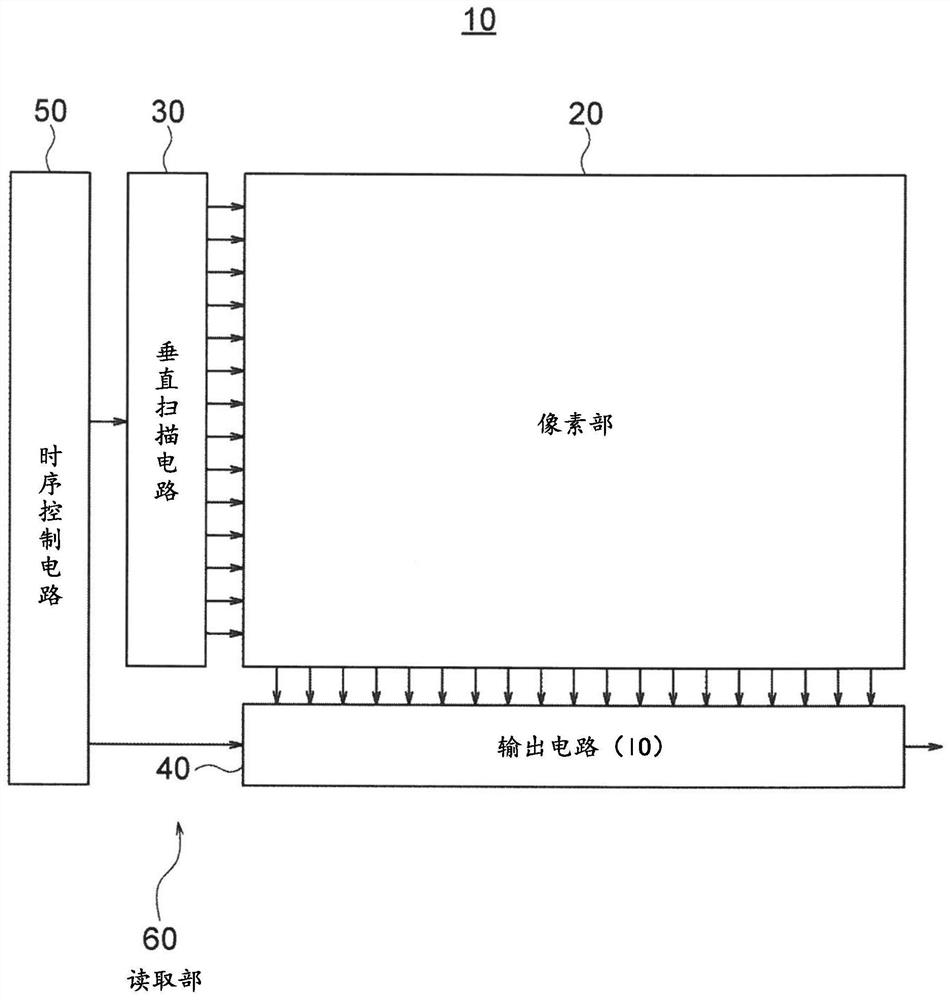
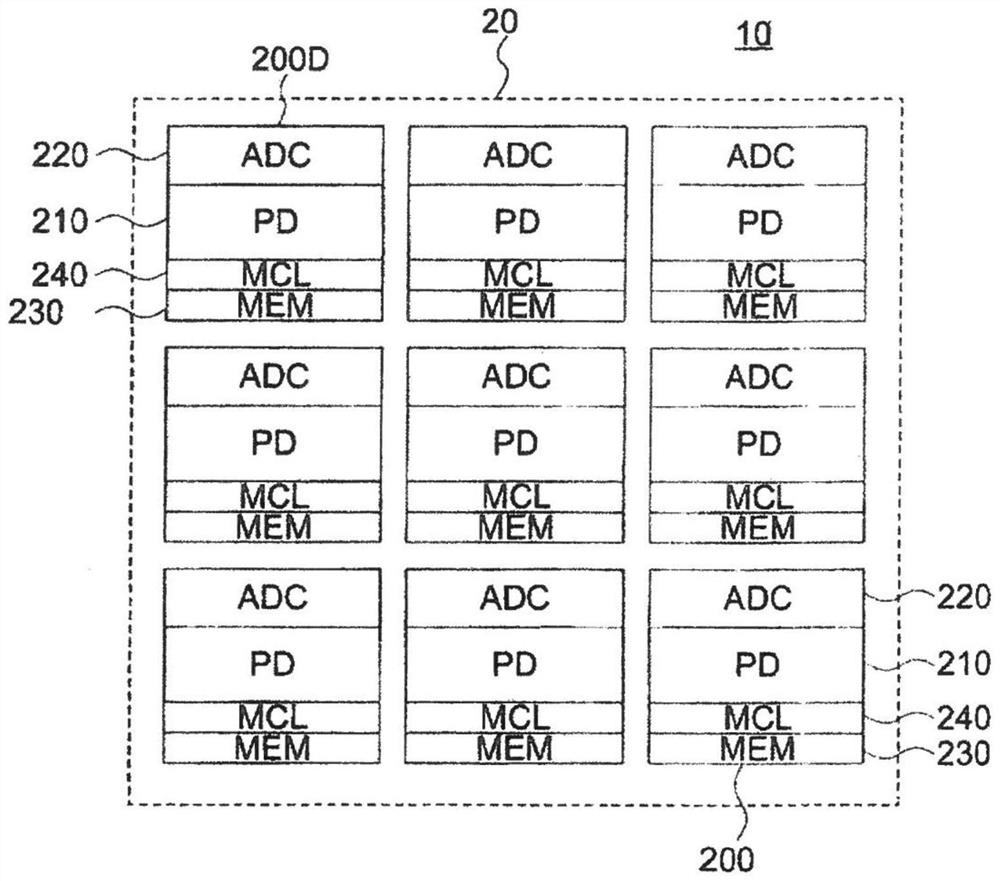
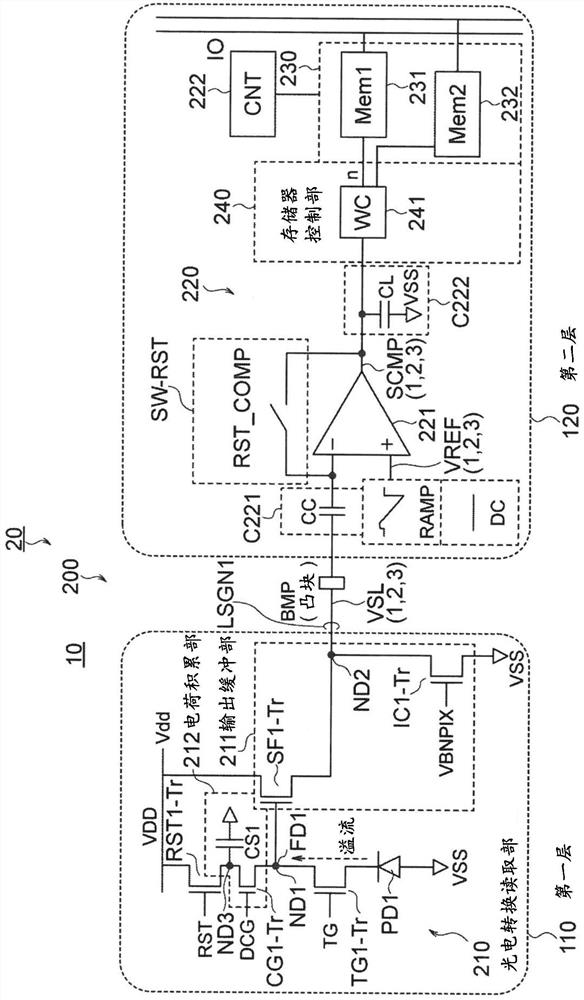
A Solid-state imaging device, A method for driving THE solid-state imaging device, and an electronic apparatus are provided. An AD conversion part (220) has a comparator (221) for performing comparison processing comparing a voltage signal read out by a photoelectric converting and reading part (210) and a reference voltage and outputting a digitalized comparison result signal, the comparator (221), under the control by a reading part (60), performs first comparison processing for outputting a digitalized first comparison result signal with respect to a voltage signal corresponding to an overflow charge overflowing from a photodiode (PD1) to a floating diffusion (FD1) in an integration period and second comparison processing for outputting a digitalized second comparison result signal withrespect to a voltage signal corresponding to an accumulated charge of the photodiode (PD1) transferred to the floating diffusion (FD1) in a transfer period after the integration period. Due to this,it becomes possible to substantially realize a broader dynamic range and a higher frame rate.
Owner:PRILUNICUS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Solid-state imaging device, method for driving solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveCN111435976AAchieve high linearityAchieve scopeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsConvertersLow voltage
Provided are a solid-state imaging device, a method for driving the same and an electronic apparatus where a comparator in an AD converter in a digital pixel is characterized by low power consumptionand low peak current and that are capable of operating at low voltage and achieving high linearity across the entire input range. A comparator 700 is constituted by two stages of preamplifiers 710 and720 with a clamp diode and two serial current-controlling inverters 730 and 740, and every branch is current-controlled. The two stages of the preamplifiers 710 and 720 and the following two consecutive inverters 730 and 740 are all current-controlled such that low power consumption and low peak current are realized. A trade-off can be made between the noise and the comparator speed by controlling the bandwidth of the comparator using the bias current. This is beneficial to more than one comparator operation mode.
Owner:普里露尼库斯新加坡私人有限公司
Solid-state imaging device, method for driving solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
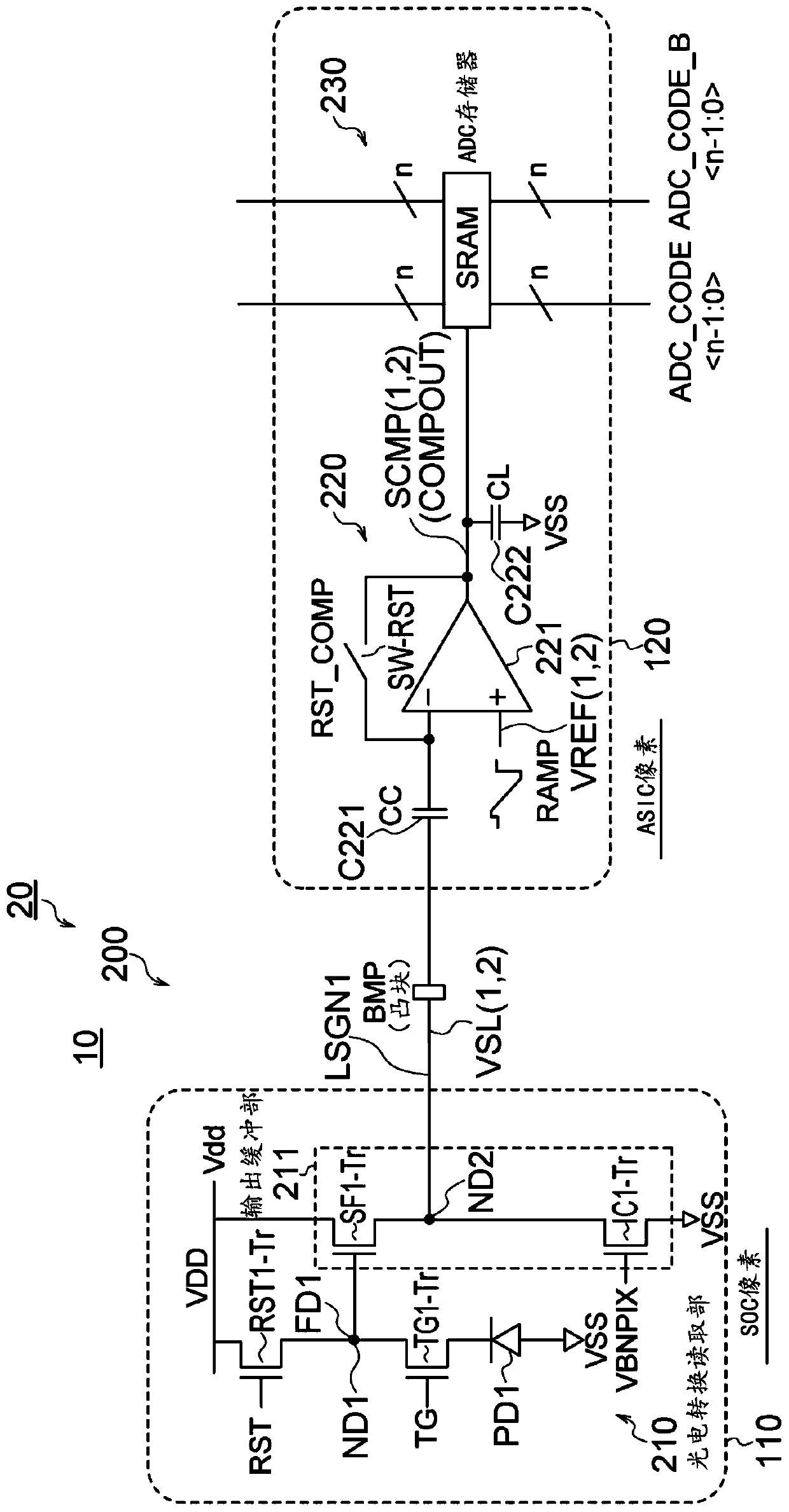
ActiveCN111385501AEfficient accessAchieve large dynamic rangeTransistorTelevision system detailsHigh frame rateSoftware engineering
Provided is a solid-state imaging device, a method for driving solid-state imaging device, and an electronic apparatus, by which large dynamic range, high frame rate, and high effective access of a memory can be essentically achieved. A comparator (221) is configured to perform a first comparing operation of outputting a digital first comparison result signal obtained by processing the overflow charges overflowing from PD1 to FD1 in the storing period, a second comparing operation of outputting a digital second comparison result signal obtained by processing the charges stored in PD1 that aretransferred to FD1 in the transfer period, and a third comparing operation of outputting a digital third comparison result signal obtained by processing the charges stored in PD1 that are transferredto FD1 in the transfer period and the charges stored in the charge storing part, and a memory control part (240) controls whether or not to allow writing of the data corresponding to the third comparison result signal into a memory part (230), depending on the states of the first and second comparison result signals.
Owner:普里露尼库斯新加坡私人有限公司
Solid-state imaging device, driving method of solid-state imaging device, and electronic device
ActiveCN111385501BEfficient accessAchieve large dynamic rangeTransistorTelevision system detailsHigh frame rateEngineering
The present invention provides a solid-state imaging device, a driving method of the solid-state imaging device, and an electronic device capable of substantially realizing a large dynamic range and a high frame rate and efficiently accessing a memory. The comparator 221 may perform a first comparison process of outputting a digitized first comparison result signal corresponding to the overflow charge overflowed from PD1 to FD1 during the accumulation period, compared with the accumulated charge of PD1 transferred to FD1 during the transfer period. In the second comparison process corresponding to the output of the digitized second comparison result signal, the digitized third comparison result signal output corresponding to the accumulated charge of PD1 and the accumulated charge of the charge accumulation part transferred to FD1 during the transfer period is the second comparison process. Three comparison processes, and the memory control unit 240 controls whether to write data corresponding to the third comparison result signal into the memory unit 230 according to the states of the first and second comparison result signals.
Owner:普里露尼库斯新加坡私人有限公司
Laminated image pickup device, image pickup apparatus, image pickup method, and recording medium recorded with image pickup program
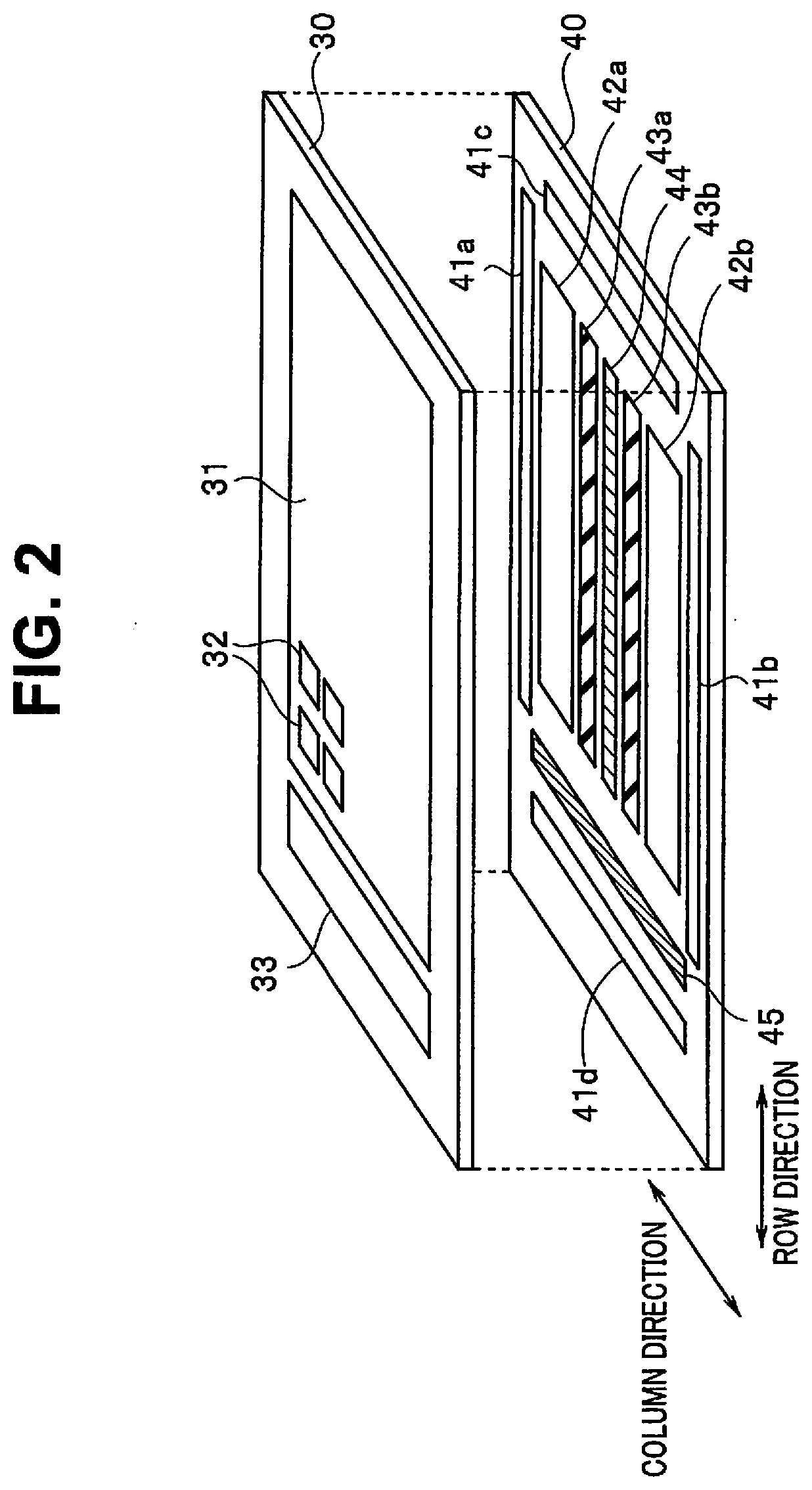
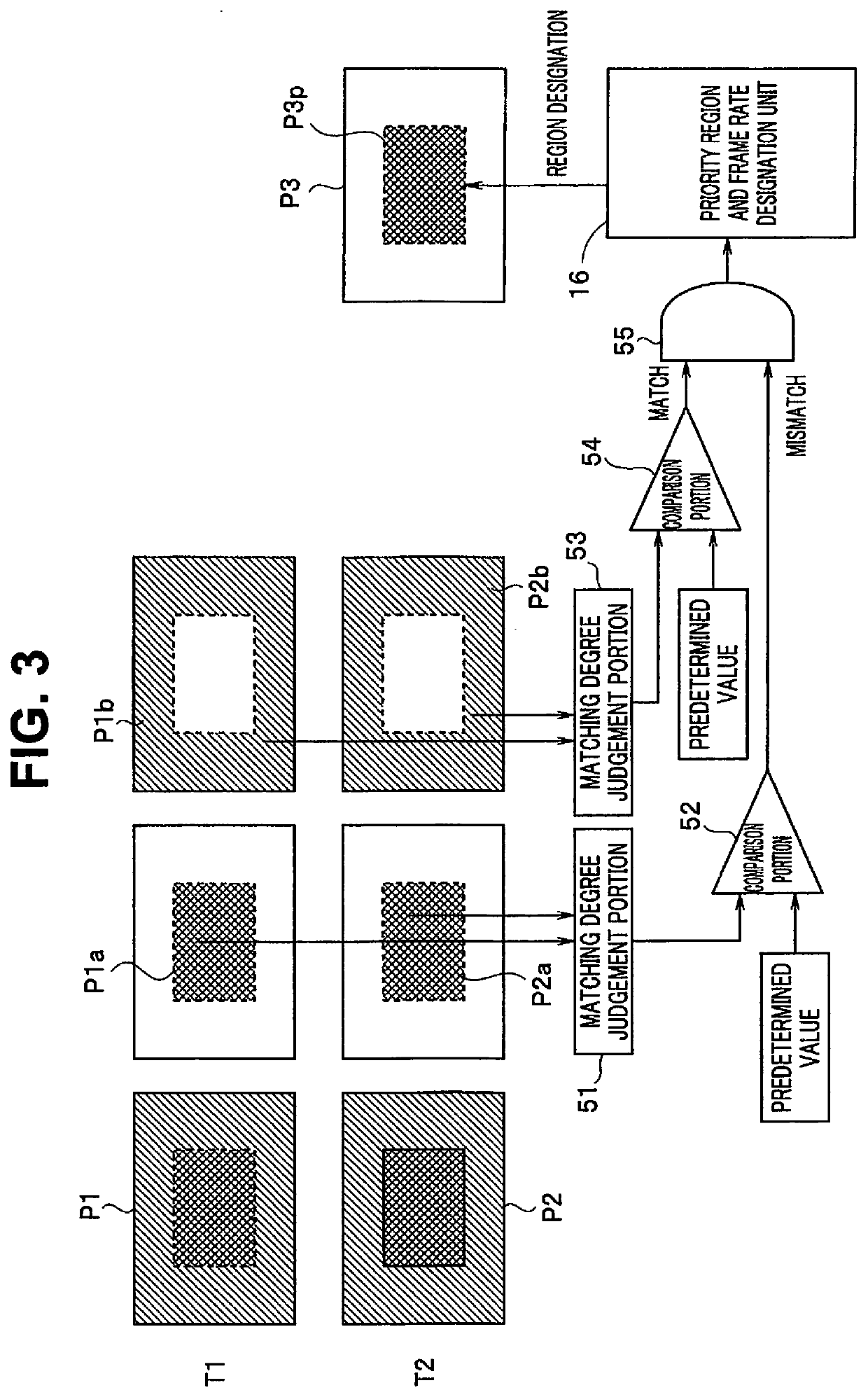
InactiveUS20200412982A1High frame rateTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesNuclear medicineImage based
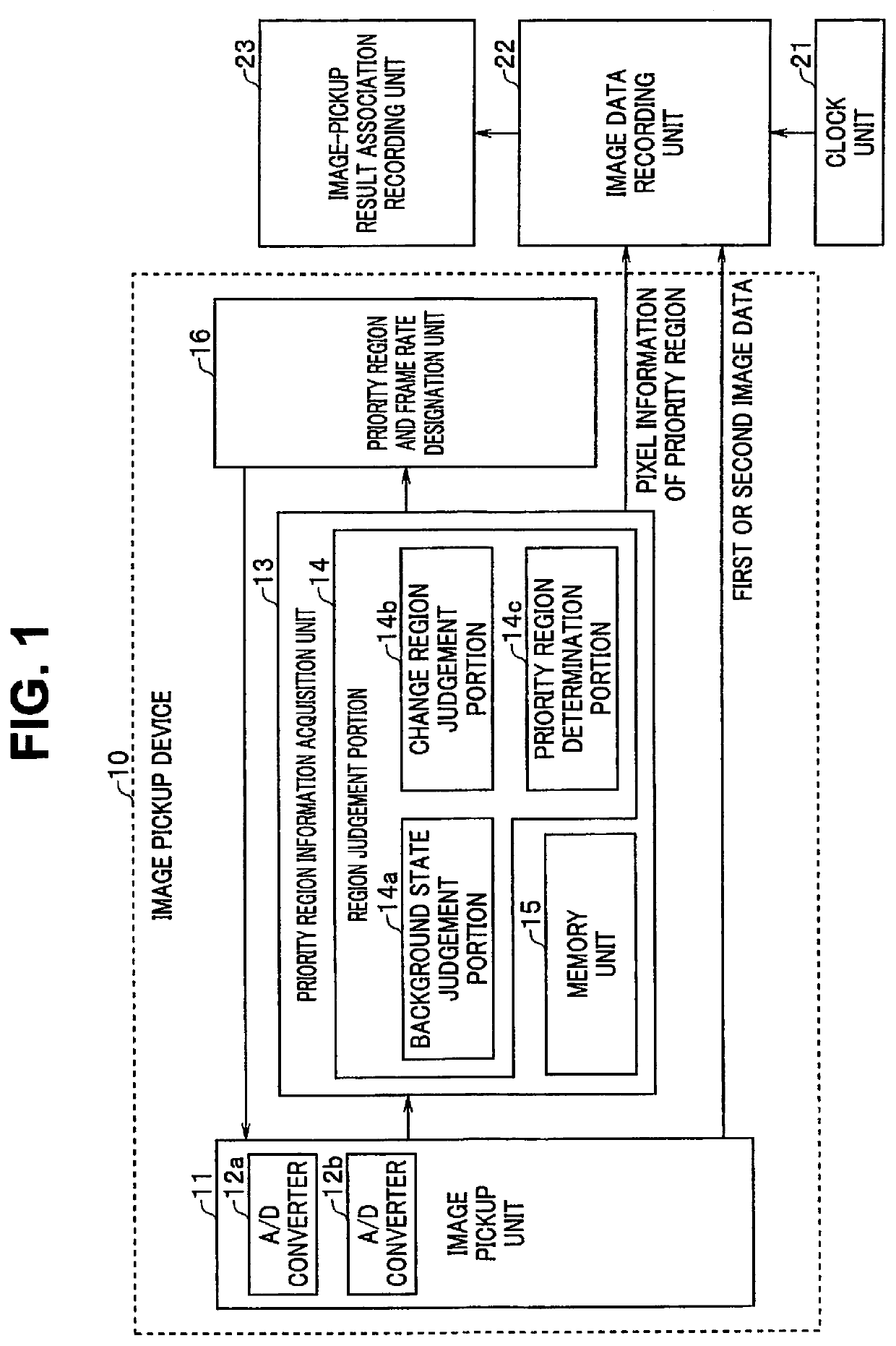
A laminated image pickup device includes: a sensor including a plurality of pixels configured on a sensor substrate and configured to continuously acquire image data at a predetermined frame rate; and a processor. The processor is provided on a substrate other than the sensor substrate, and is configured to perform, based on the image data, region judgement processing of obtaining a priority region including some pixels of the plurality of pixels and to obtain outputs of the some pixels included in the priority region at a higher frame rate than the predetermined frame rate.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
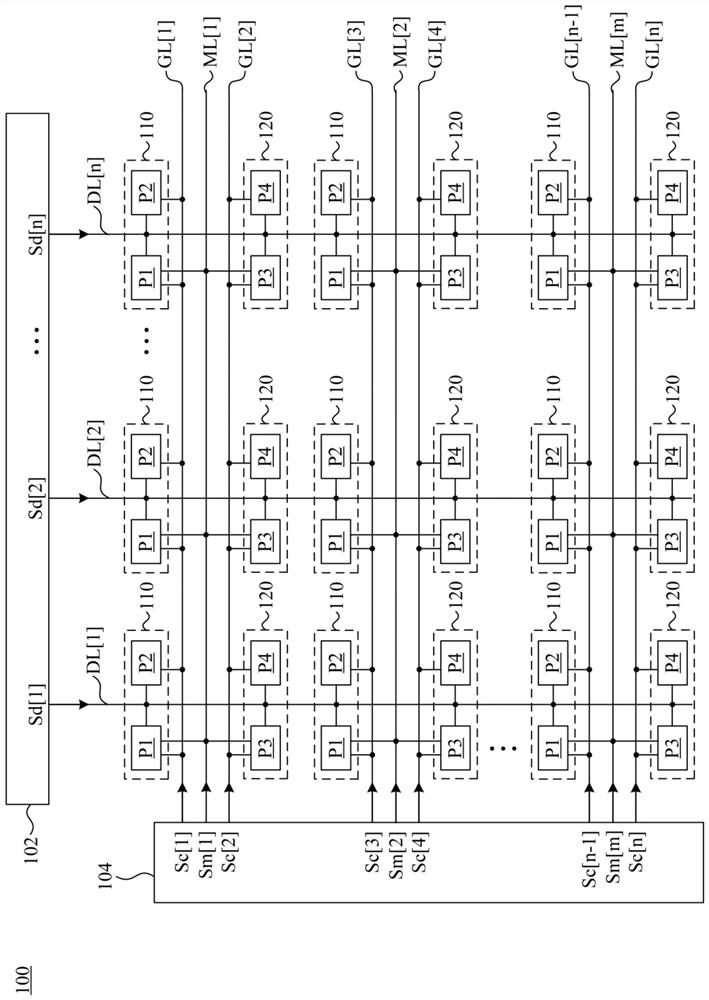
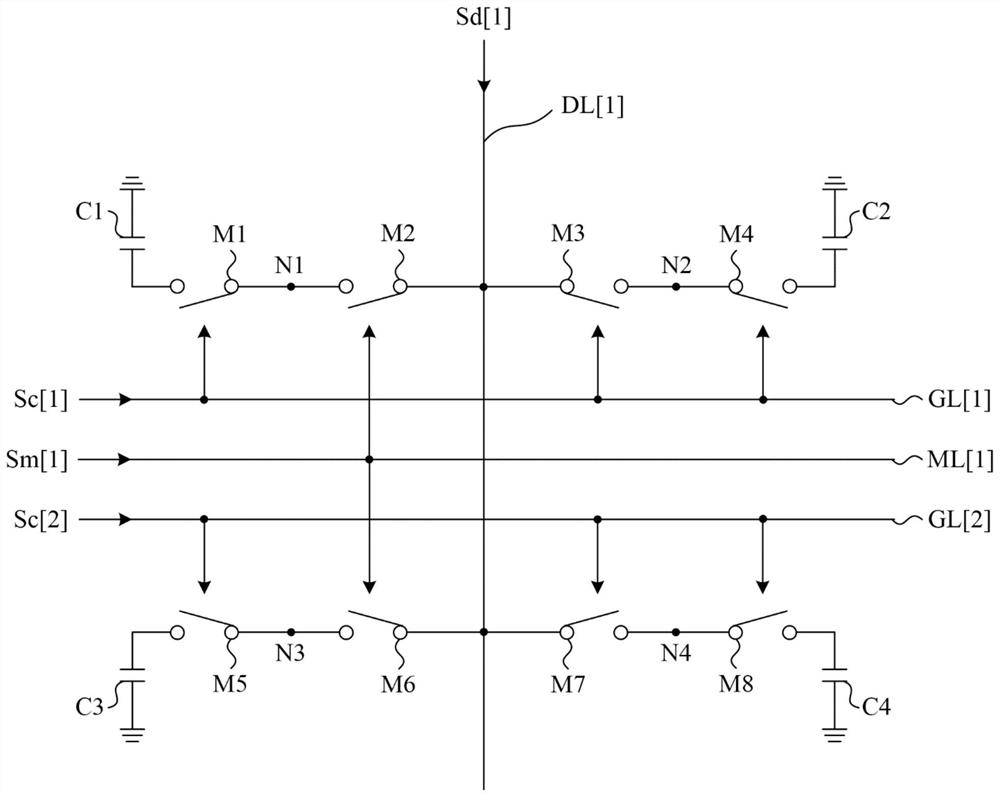
low impedance display
A low impedance display includes a first pixel group, a second pixel group and a first multiplexing driving line. The first pixel group includes first pixels and second pixels. The second pixel group includes third pixels and fourth pixels, wherein the first pixel group and the second pixel group receive data signals from the data lines. The first multiplexing driving line is coupled to the first pixel and the third pixel for receiving the first multiplexing signal. The first multiplexing driving line is also used to control the first pixel and the second pixel to receive the data signal sequentially, and control the third pixel and the fourth pixel to receive the data signal sequentially.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP +1
Solid-state imaging device, driving method of solid-state imaging device, and electronic device
ActiveCN111435975BBlock through currentWrite operation is goodAnalogue/digital conversionTelevision system detailsComputer hardwareEngineering
The present disclosure provides a solid-state imaging device, a driving method of the solid-state imaging device, and an electronic device that can effectively block the through current from the bit cell during the writing operation of the SRAM bit cell and realize a good writing operation. The memory unit 230 is formed of an SRAM 231 as an ADC memory, and performs writing and reading of ADC codes under the control of the reading unit 60 . The SRAM 231 is configured in such a way that power gate transistors are added to both the power supply node (between the power supply and the virtual power supply node) and the ground node (between the virtual reference potential node and the reference potential), and during the write operation Blocks shoot-through current from the bit cell. Furthermore, the power gate transistor is controlled by the reading unit 60 so as to operate as either a weak current source or a switch.
Owner:普里露尼库斯新加坡私人有限公司
Video encoder/decoder (codec) for real-time applications and size/b and width reduction
ActiveUS11245911B1Improved video transmission bandwidthNegligible latencyInput/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsData streamReal time analysis
The present invention has utility of providing systems and methods for video processing for use in real-time interactive display systems which produce improved video transmission bandwidth with negligible latency thus providing a seamless video feed to enhance real-time interactive displays. The present invention solves the unmet need to optimize video image transmission in real time and after the video source image processing stage, allowing for increased bandwidth for video image processing without losing perceptible image quality or adding perceptible latency. Aspects of the present invention provide systems and methods which analyze pixels of video in real-time and encodes an alternate, reduced bandwidth, data stream for immediate transmission to a receiver where another instance of the codec decodes the received data stream and restores the video's images without introducing perceptible latency.
Owner:WHIRLWIND 3D LLC
Solid-state imaging device, method for driving solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveCN111435975AHelp miniaturizationSmall pixelsAnalogue/digital conversionTelevision system detailsComputer hardwareWeak current
Provided are a solid-state imaging device capable of effectively blocking a direct current from a bit cell in an SRAM bit cell write operation and capable of achieving a good write operation, a methodfor driving a solid-state imaging device and an electronic apparatus. A memory part 230 is formed using an SRAM 231 serving as an ADC memory, and an ADC code is written into and read from the memorypart 230 under control of a reading part 60. In the SRAM 231, a power gating transistor is additionally provided to both of a power supply node (between a power supply and a virtual power supply node)and a ground node (between a virtual reference potential node and a reference potential) for the purposes of blocking the shoot-through currents from the bit cells during the writing operation. The power gating transistors are controlled by the reading part 60 so as to operate as either a weak current source or switch.
Owner:普里露尼库斯新加坡私人有限公司
Optical navigation system and optical navigation apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20140218296A1High frame rateHigh precisionInput/output for user-computer interactionDigital data processing detailsOperating systemImaging data
An optical navigation system and an optical navigation apparatus thereof are provided. The optical navigation system comprises a host and the optical navigation apparatus. The host detects a running program to generate a control signal. The optical navigation apparatus, which is connected to the host in a wireless way, receives the control signal and performs a performance configuration according to the control signal to adjust an image data amount that is required for processing.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com