Solid-state imaging device, driving method of solid-state imaging device, and electronic device
A camera device, solid-state technology, applied in TV, circuit, color TV, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to read the global shutter, and achieve the effects of large dynamic range, expanded effective pixel area, and high frame rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
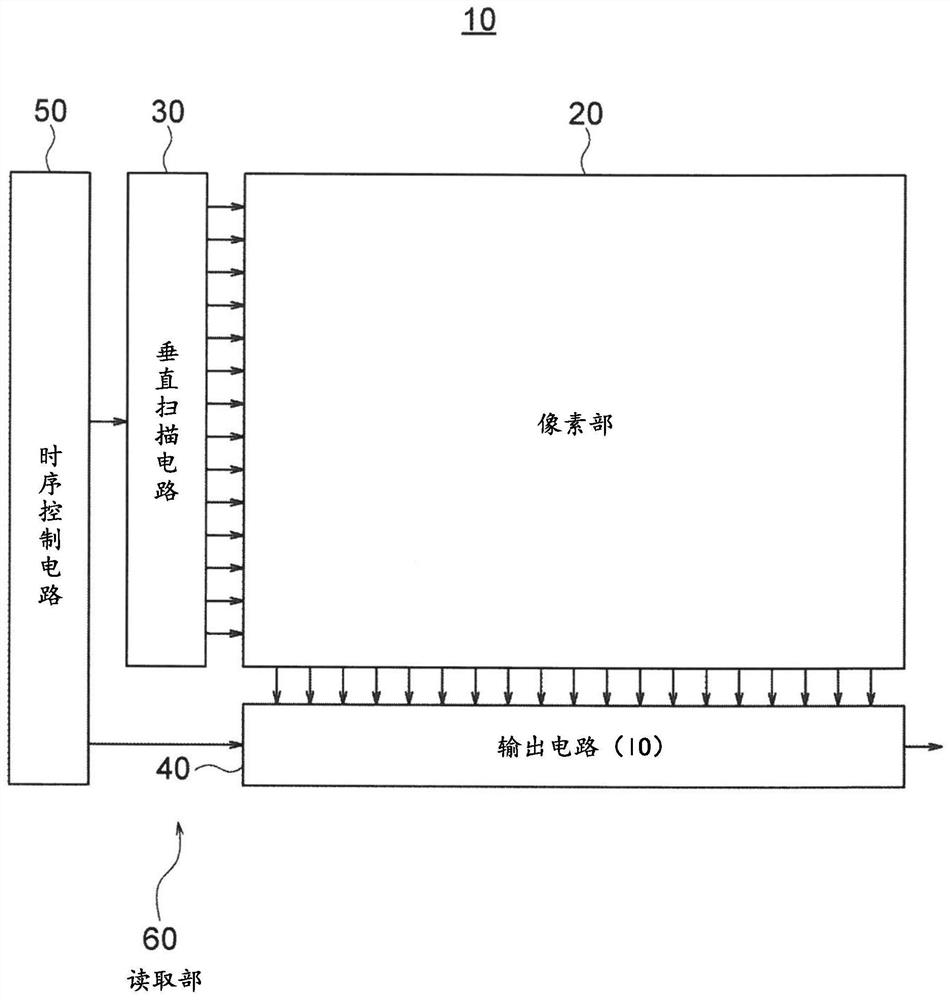
[0073] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing a configuration example of the solid-state imaging device according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0074] In the present embodiment, the solid-state imaging device 10 is constituted by, for example, a CMOS image sensor including digital pixels (Digital Pixels) as pixels.
[0075] like figure 1 As shown, this solid-state imaging device 10 includes a pixel unit 20 as an imaging unit, a vertical scanning circuit (row scanning circuit) 30 , an output circuit 40 , and a timing control circuit 50 as main constituent elements.
[0076] Among these components, for example, the vertical scanning circuit 30 , the output circuit 40 , and the timing control circuit 50 constitute a pixel signal reading unit 60 .
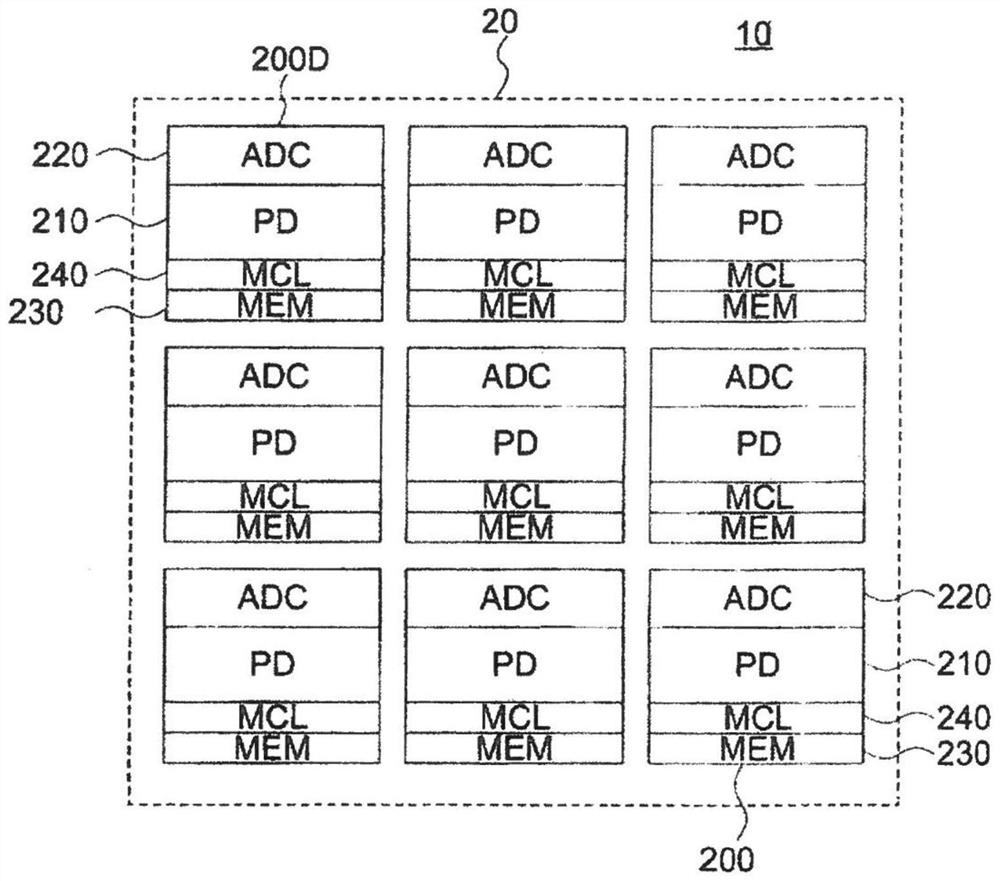
[0077] In the first embodiment, the solid-state imaging device 10 includes, as digital pixels, a photoelectric conversion reading unit, an AD (analog-to-digital) conversion unit, and a memory unit in the pixel u...
no. 2 approach
[0388] Figure 30 It is a diagram for explaining the solid-state imaging device according to the second embodiment of the present invention, and is a diagram showing an example of selection processing between the time stamp ADC mode operation and the linear ADC mode operation.
[0389] The difference between the solid-state imaging device 10A of the second embodiment and the solid-state imaging device 10 of the first embodiment is as follows.
[0390] In the solid-state imaging device 10 according to the first embodiment, the time stamp (TS) ADC mode operation and the linear (Lin) ADC mode operation are continuously performed.
[0391] In contrast, in the solid-state imaging device 10A according to the second embodiment, it is possible to selectively perform a time stamp (TS) ADC mode operation and a linear (Lin) ADC mode operation according to illuminance.
[0392] exist Figure 21 In the example of , in the case of normal illuminance (ST51), the time stamp ADC mode operati...
no. 3 approach
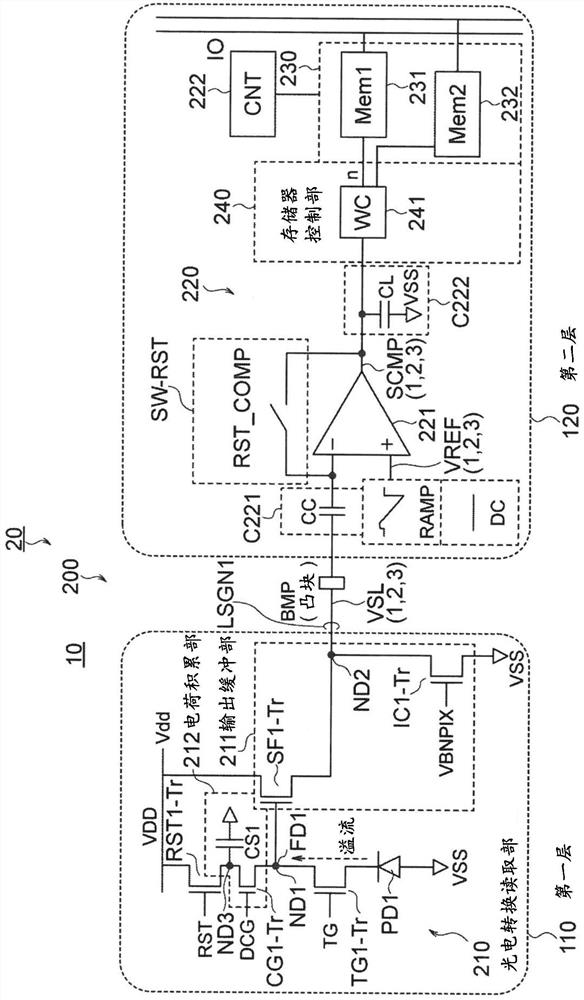
[0397] Figure 31 It is a diagram showing a configuration example of a pixel of a solid-state imaging device according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0398] The difference between the solid-state imaging device 10B of the third embodiment and the solid-state imaging device 10 of the first embodiment is as follows.
[0399] In the solid-state imaging device 10B according to the third embodiment, the current transistor IC1-Tr as a current source is arranged not on the first substrate 110 side, but on the input of the AD converter 220 on the second substrate 120 side, for example. side.
[0400] According to the third embodiment, the same effects as those of the first embodiment can be obtained.
[0401] The solid-state imaging devices 10 , 10A, and 10B described above can be applied as imaging devices to digital cameras or video cameras, portable terminals, or electronic equipment such as monitoring cameras and medical endoscope cameras.
[0402] Figure 3...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com