Patents
Literature
318 results about "Write amplification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
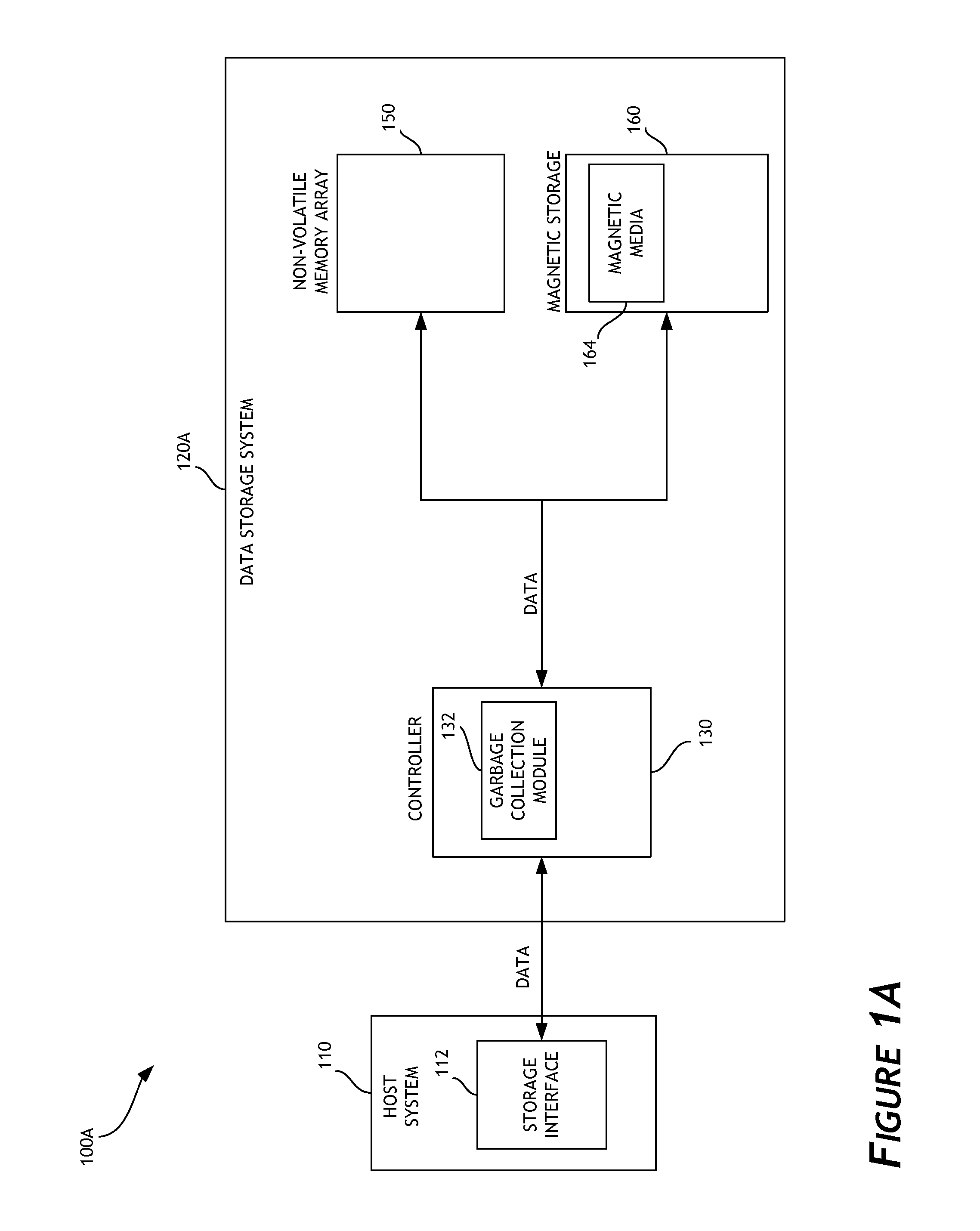
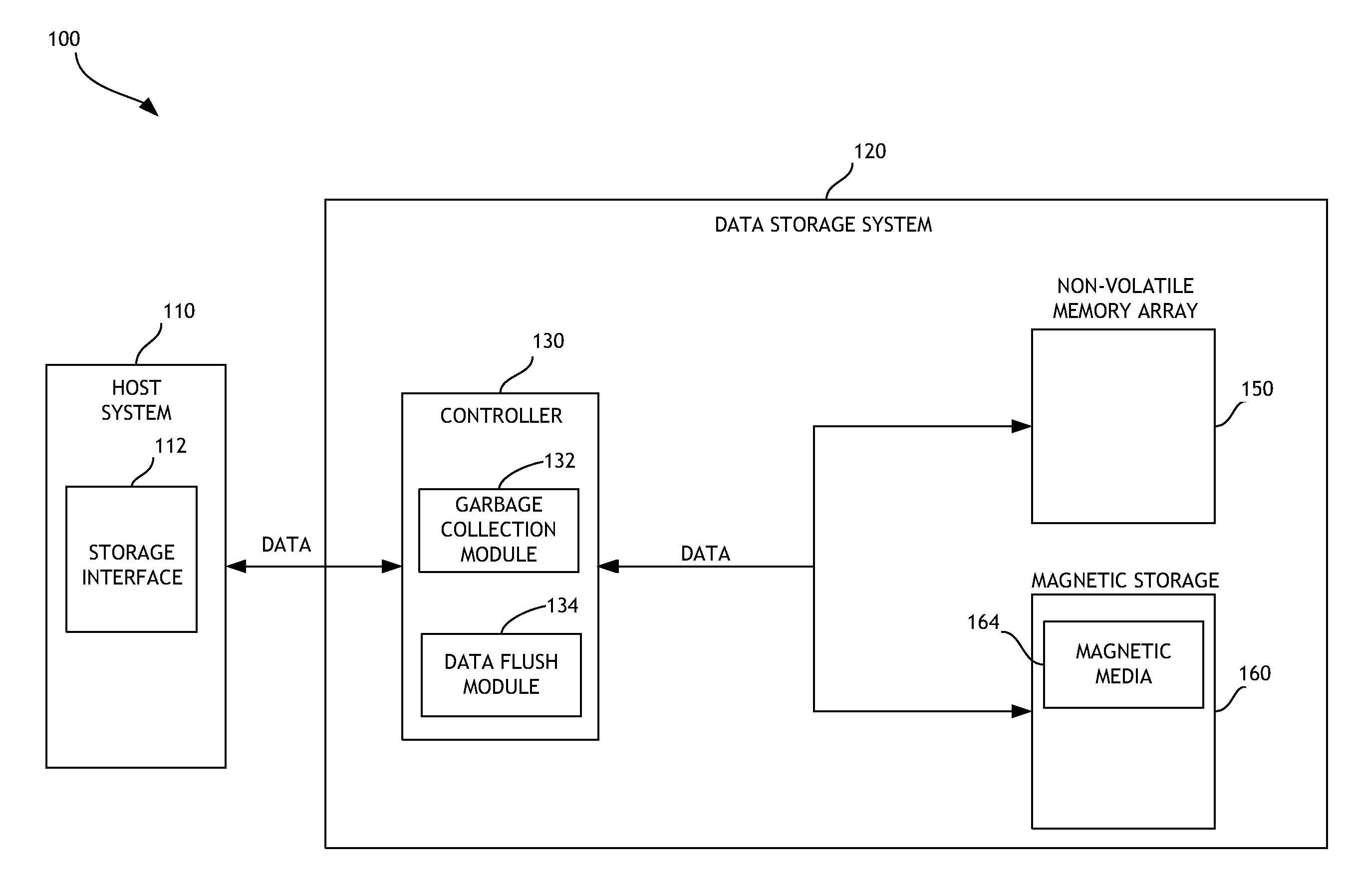
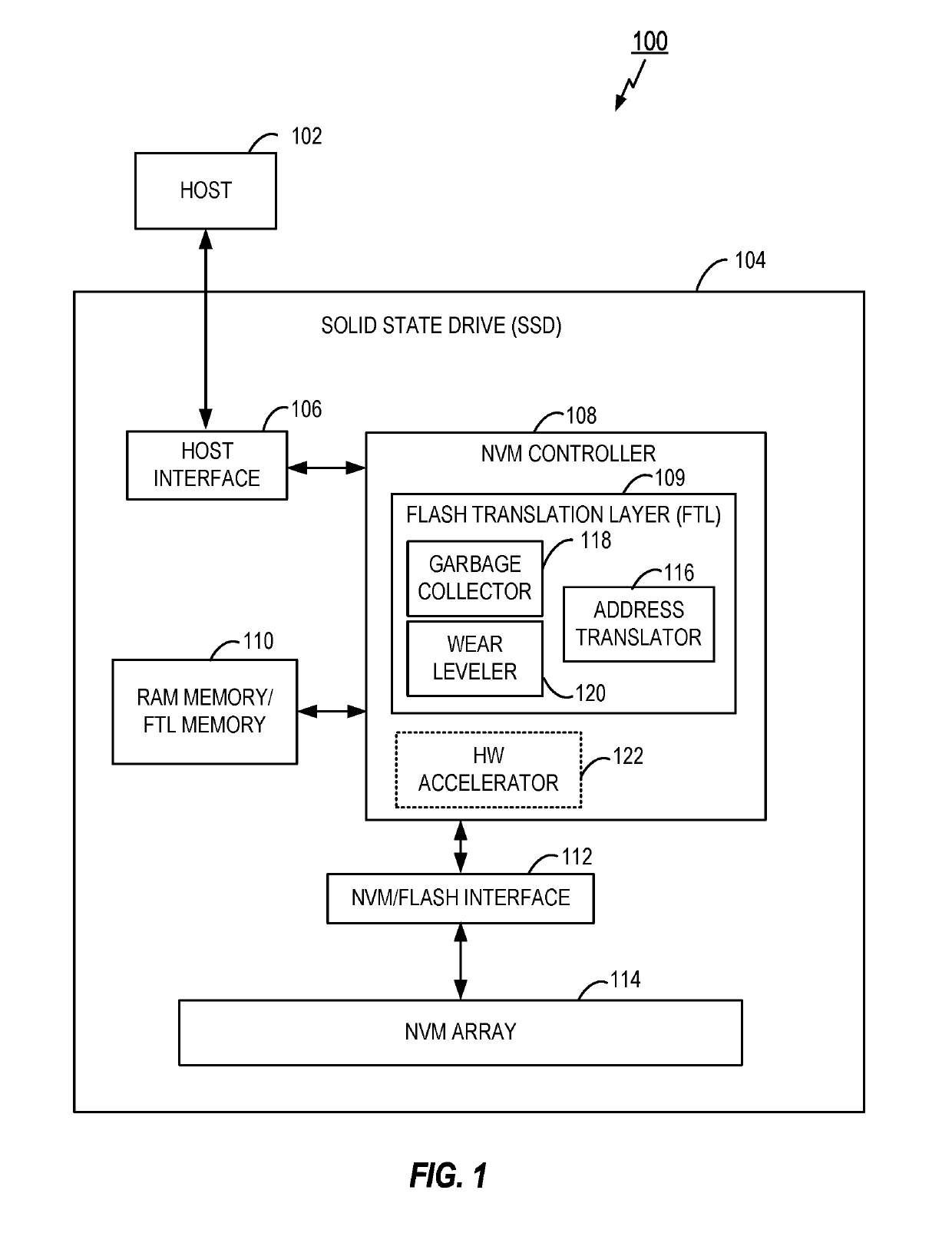
Write amplification (WA) is an undesirable phenomenon associated with flash memory and solid-state drives (SSDs), where the actual amount of information physically-written to the storage media is a multiple of the logical amount intended to be written.
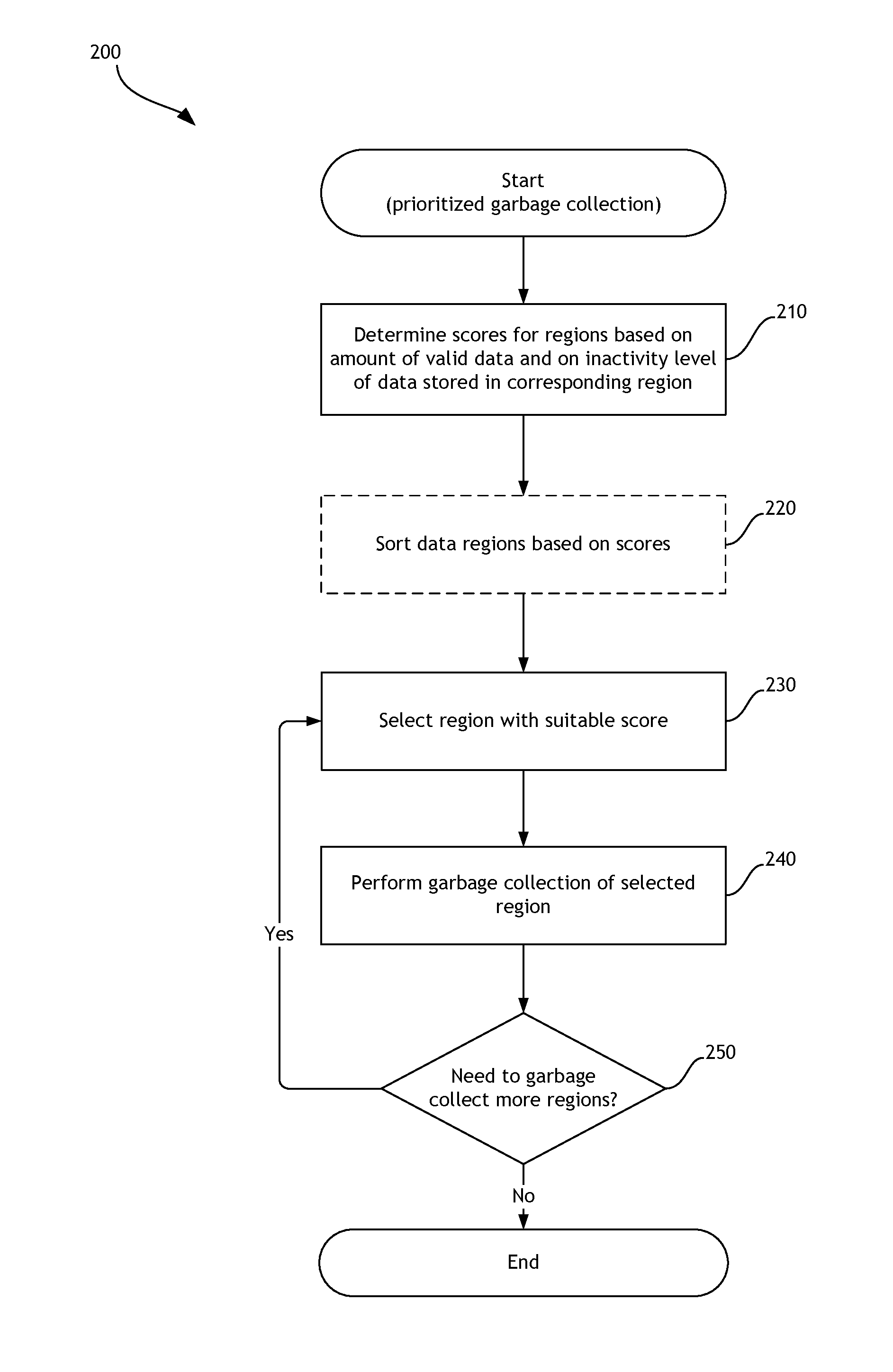
Garbage collection based on the inactivity level of stored data
ActiveUS8788778B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersWrite amplificationWaste collection
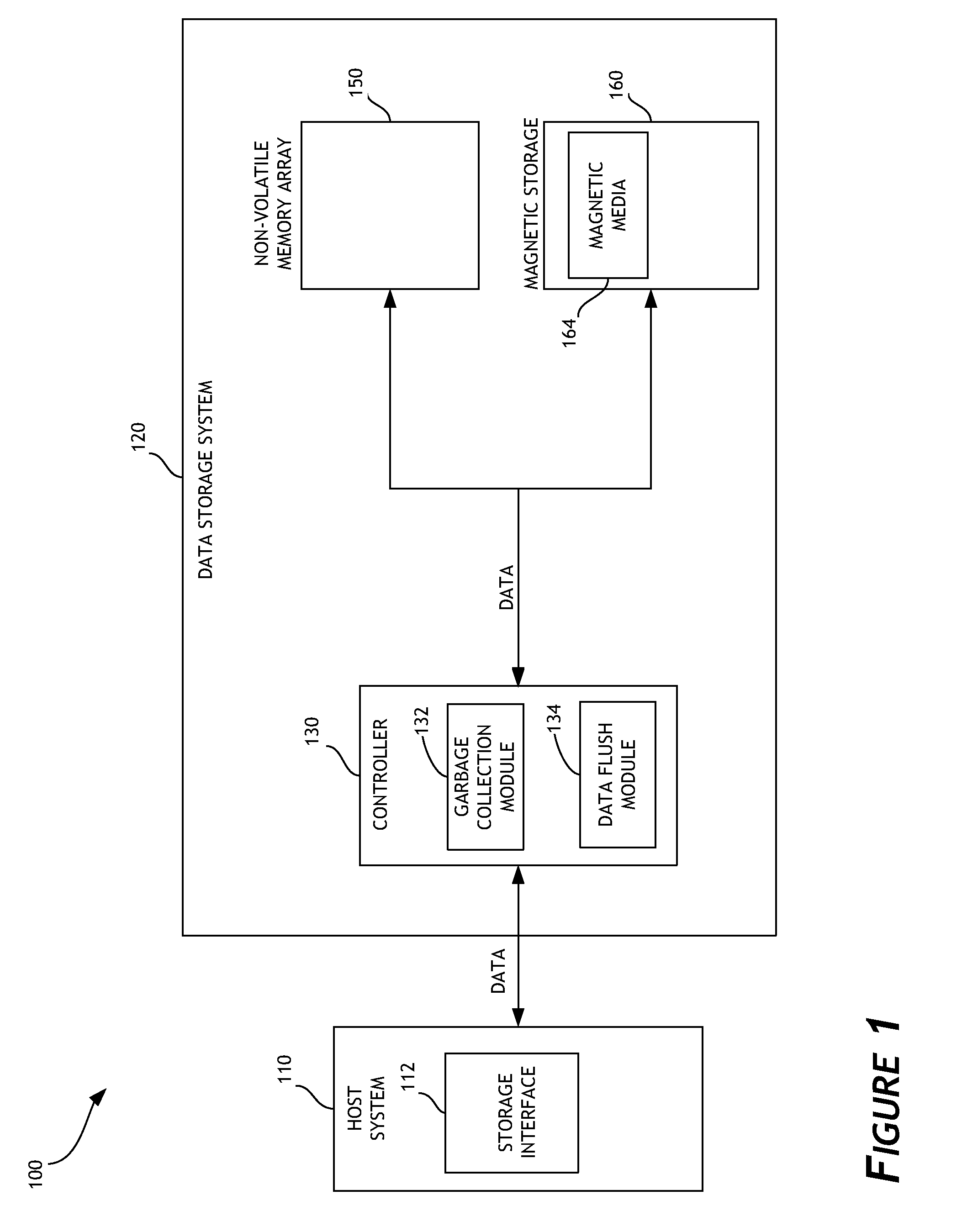
A data storage system implements garbage collection based on the inactivity level of stored data. In one embodiment, the inactivity level of data stored in regions of a data storage system is taken into account when prioritizing regions for garbage collection. Inactivity level of memory regions can be compared to an inactivity threshold. The threshold can be adjusted during operation of the data storage system. Garbage collection can be delayed until data stored in a particular region is unlikely to be updated. Write amplification associated with garbage collection is reduced, and improved performance is attained.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Priority-based garbage collection for data storage systems
ActiveUS20140181432A1Increased longevityImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWrite amplificationWaste collection
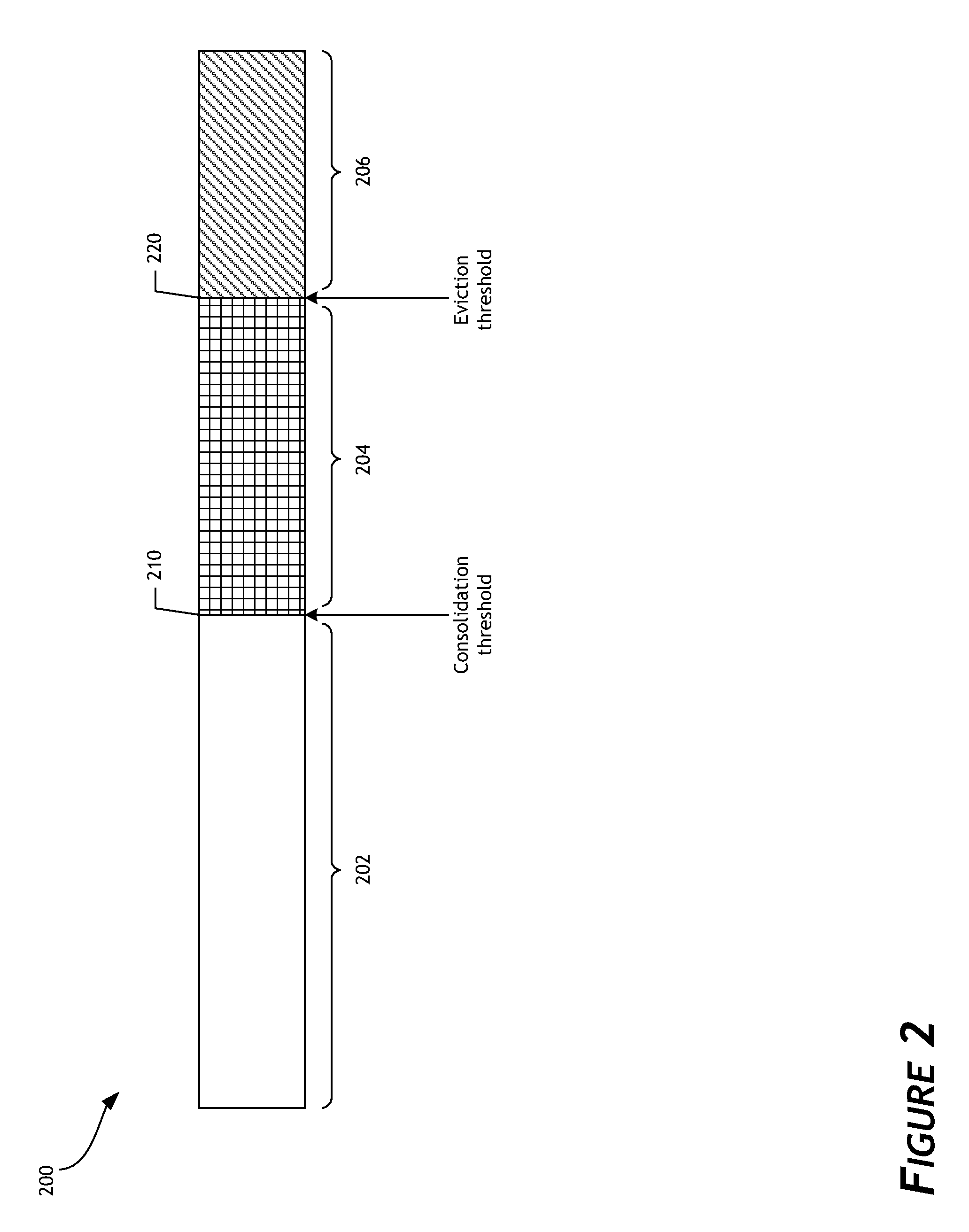
Priority-based garbage collection utilizes attributes of data stored in the non-volatile memory array in order to improve efficiency of garbage collection and of the overall data storage system. A set of low priority data can be selectively evicted from a non-volatile memory array. This can, for example, reduce write amplification associated with garbage collection. Another set of low priority data can be regrouped or consolidated in a different region of the non-volatile memory array. In addition, flushing of data can be performed in order to enhance or optimize garbage collection. Performance and endurance can thereby be improved.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Storage control system with write amplification control mechanism and method of operation thereof
InactiveUS20130061019A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionWrite amplificationControl system
A method of operation of a storage control system includes: partitioning logical addresses into a number of subdrives, the logical addresses associated with a memory device; and monitoring a data write measure of one of the subdrives.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
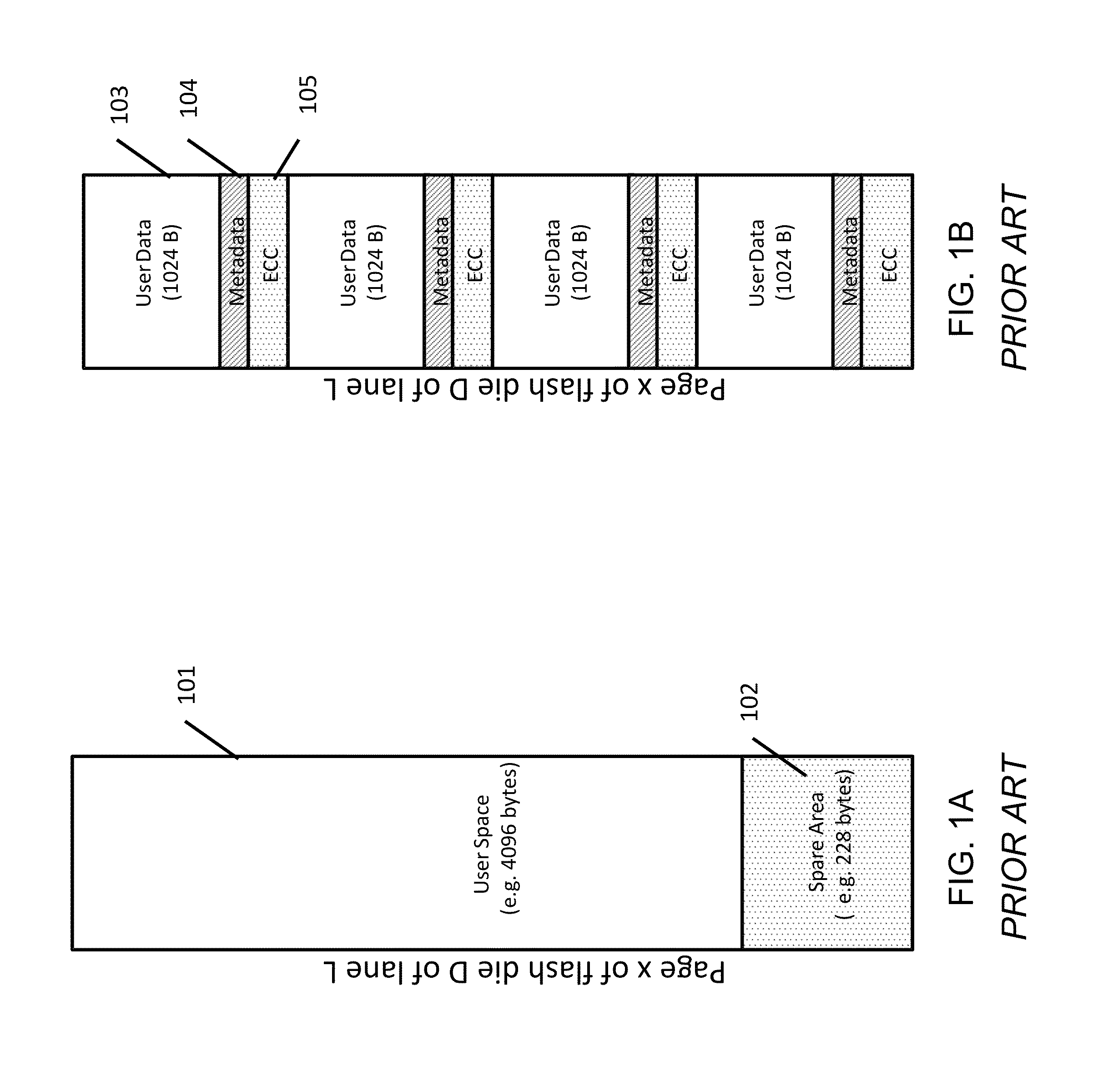
System and method for tolerating a failed page in a flash device
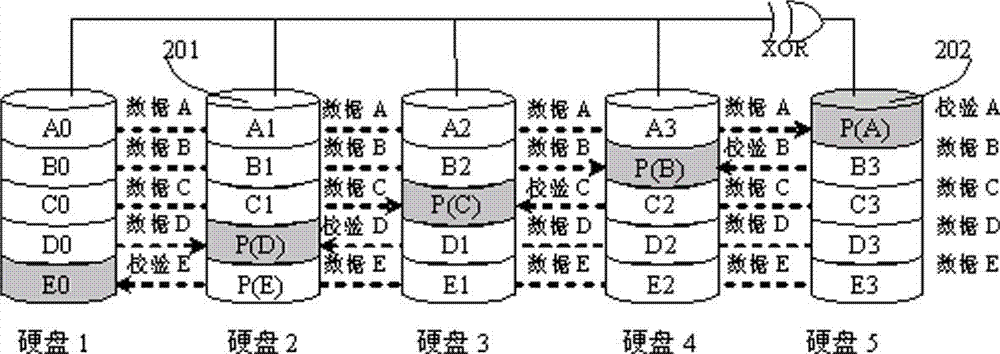
ActiveUS9047214B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeMemory architecture accessing/allocationStatic storageWrite amplificationSolid-state drive
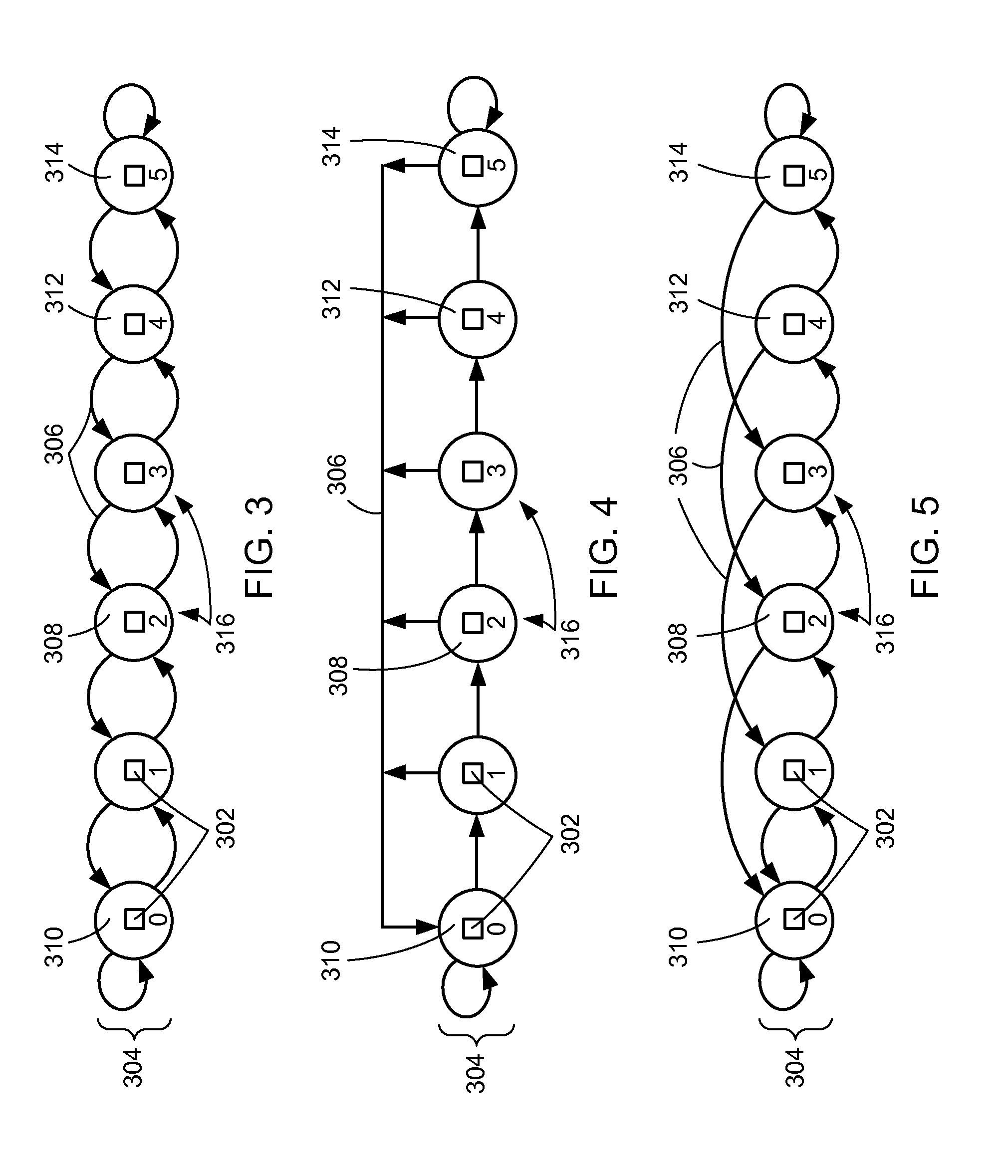
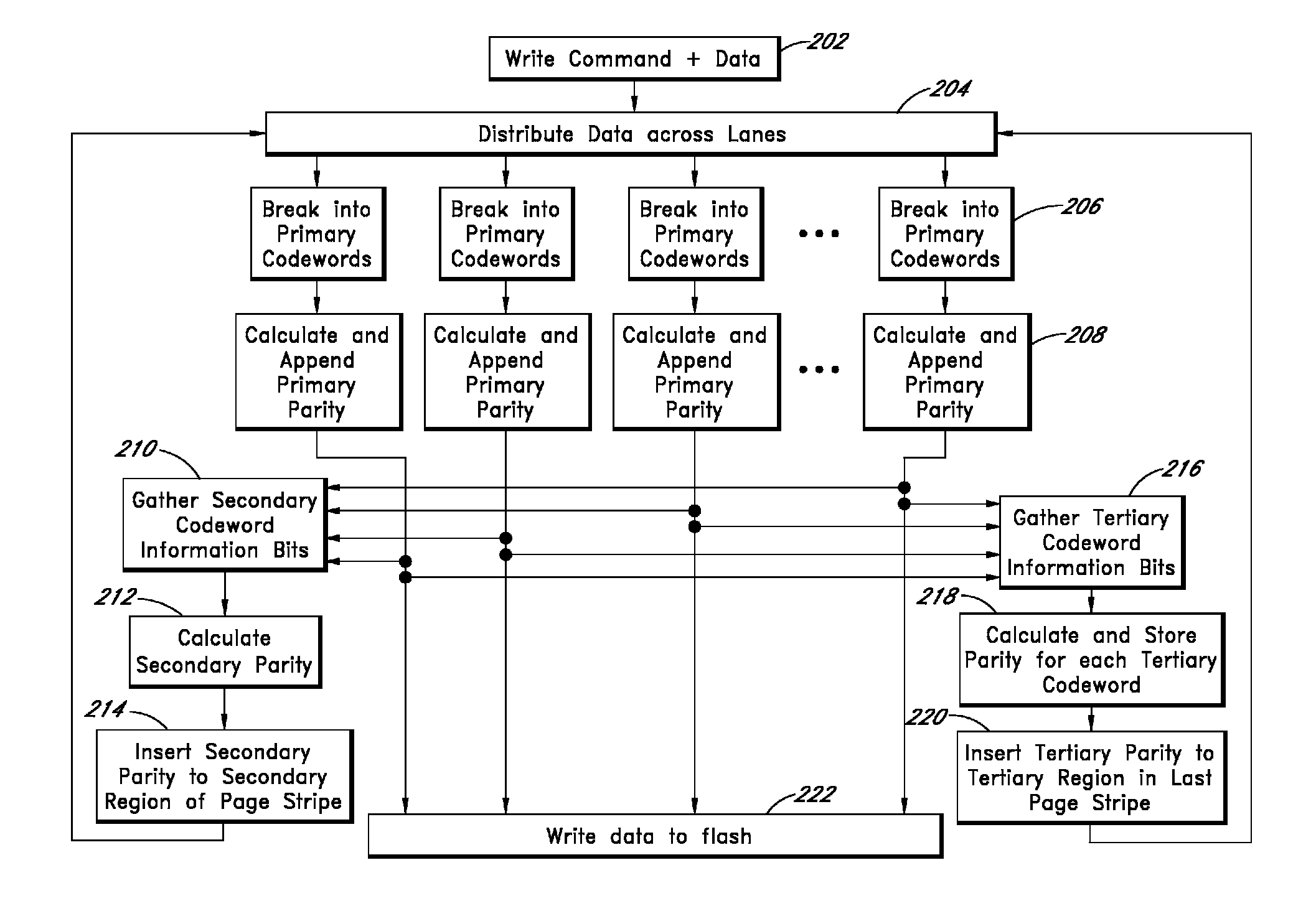
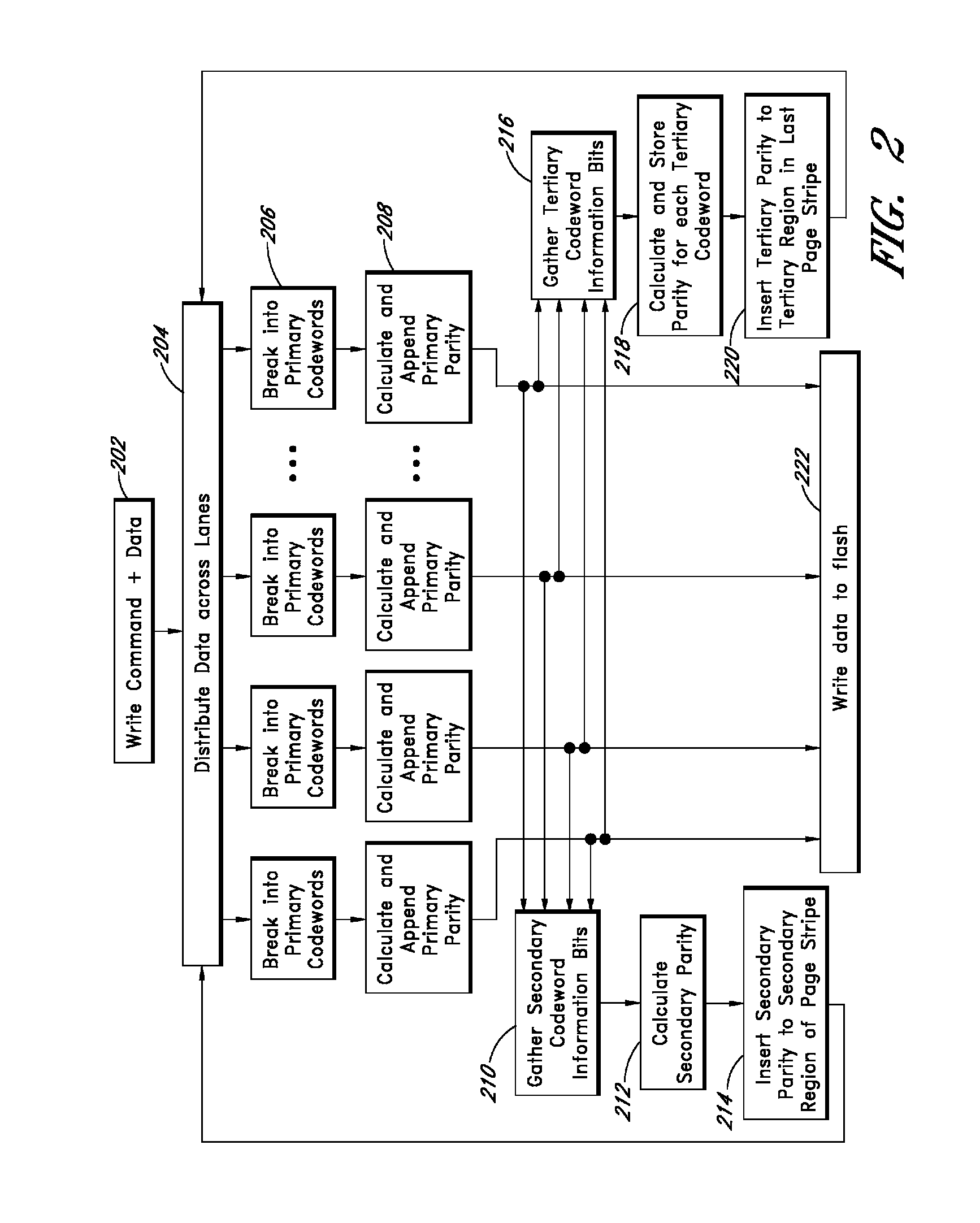
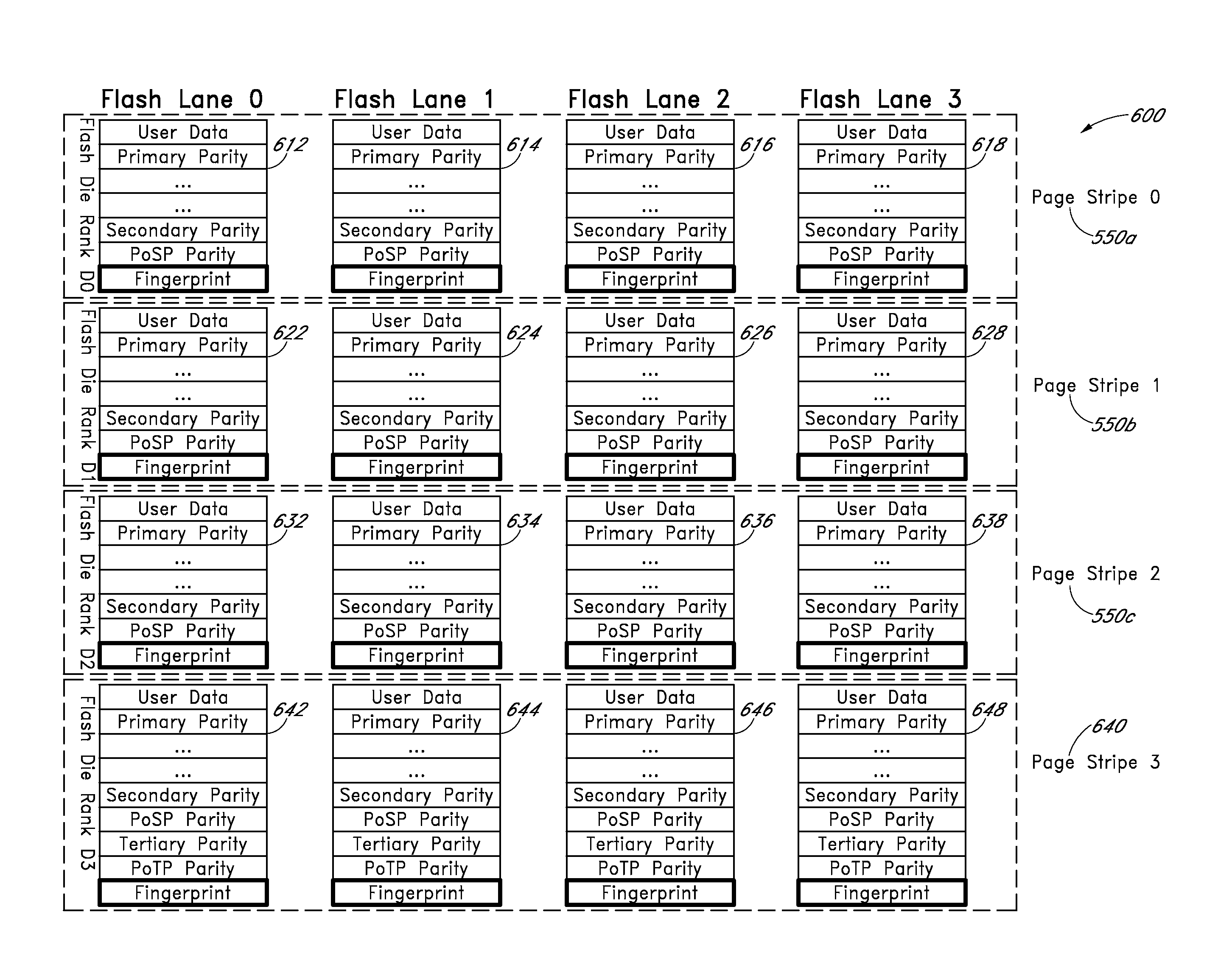
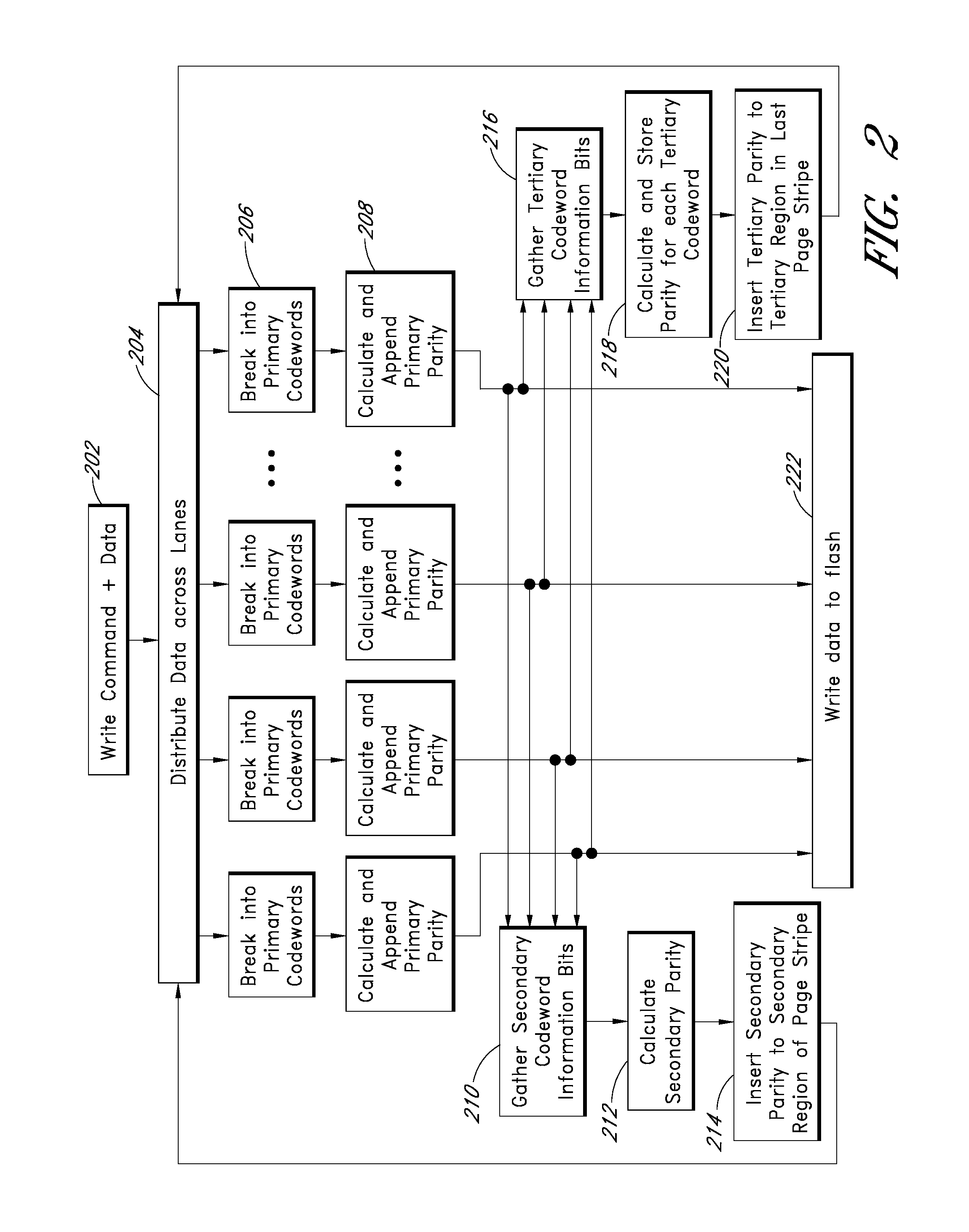
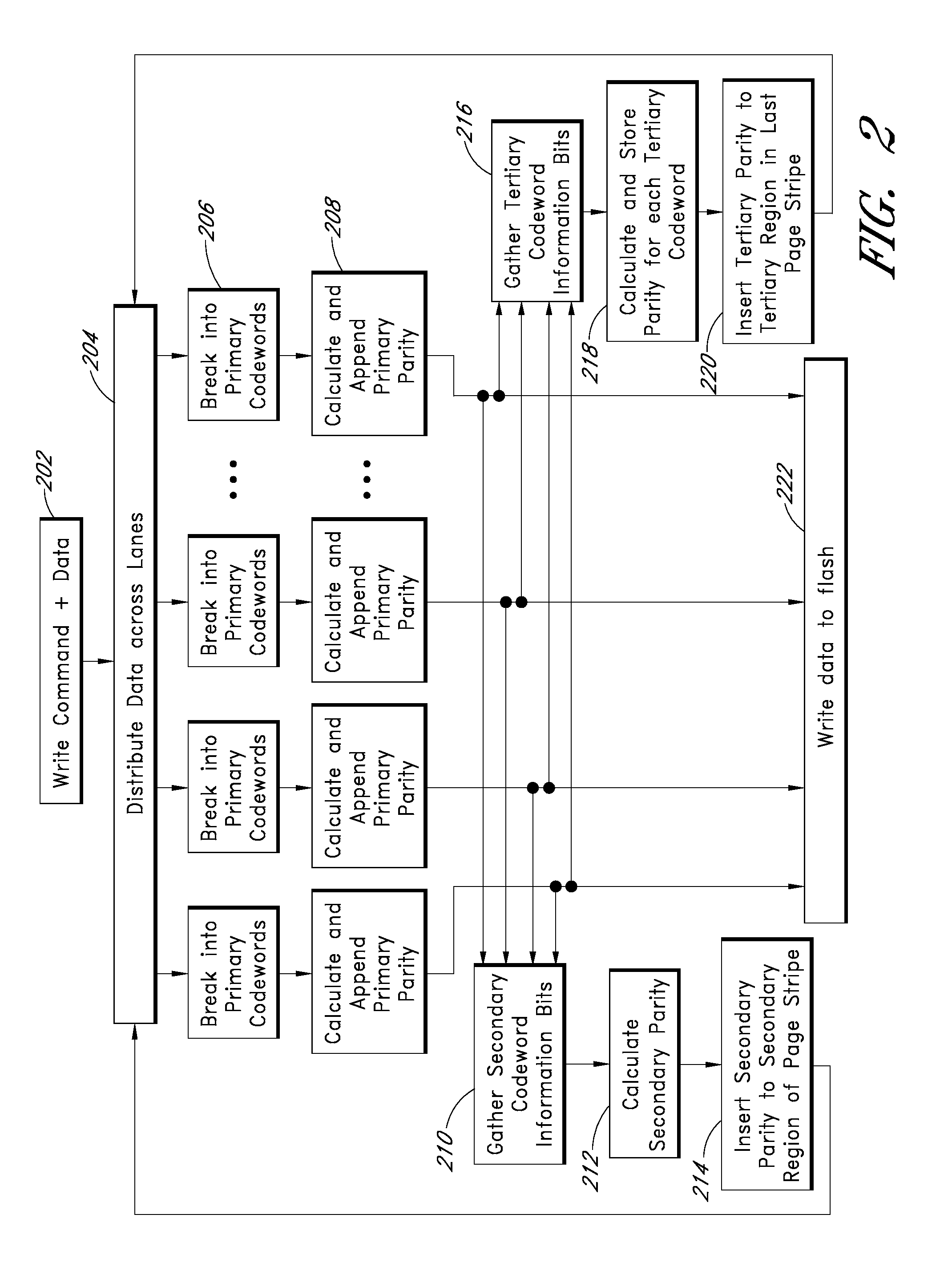
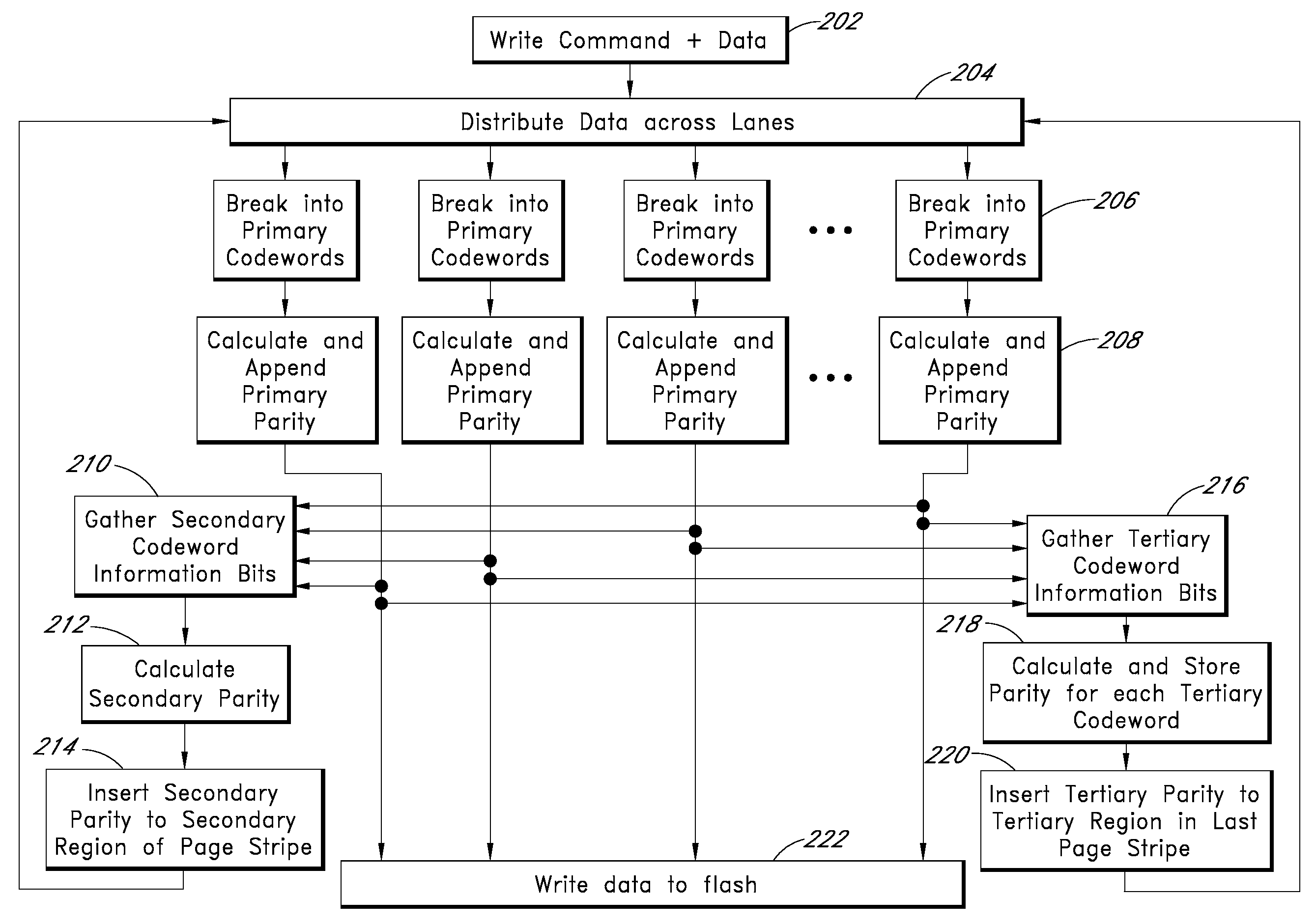
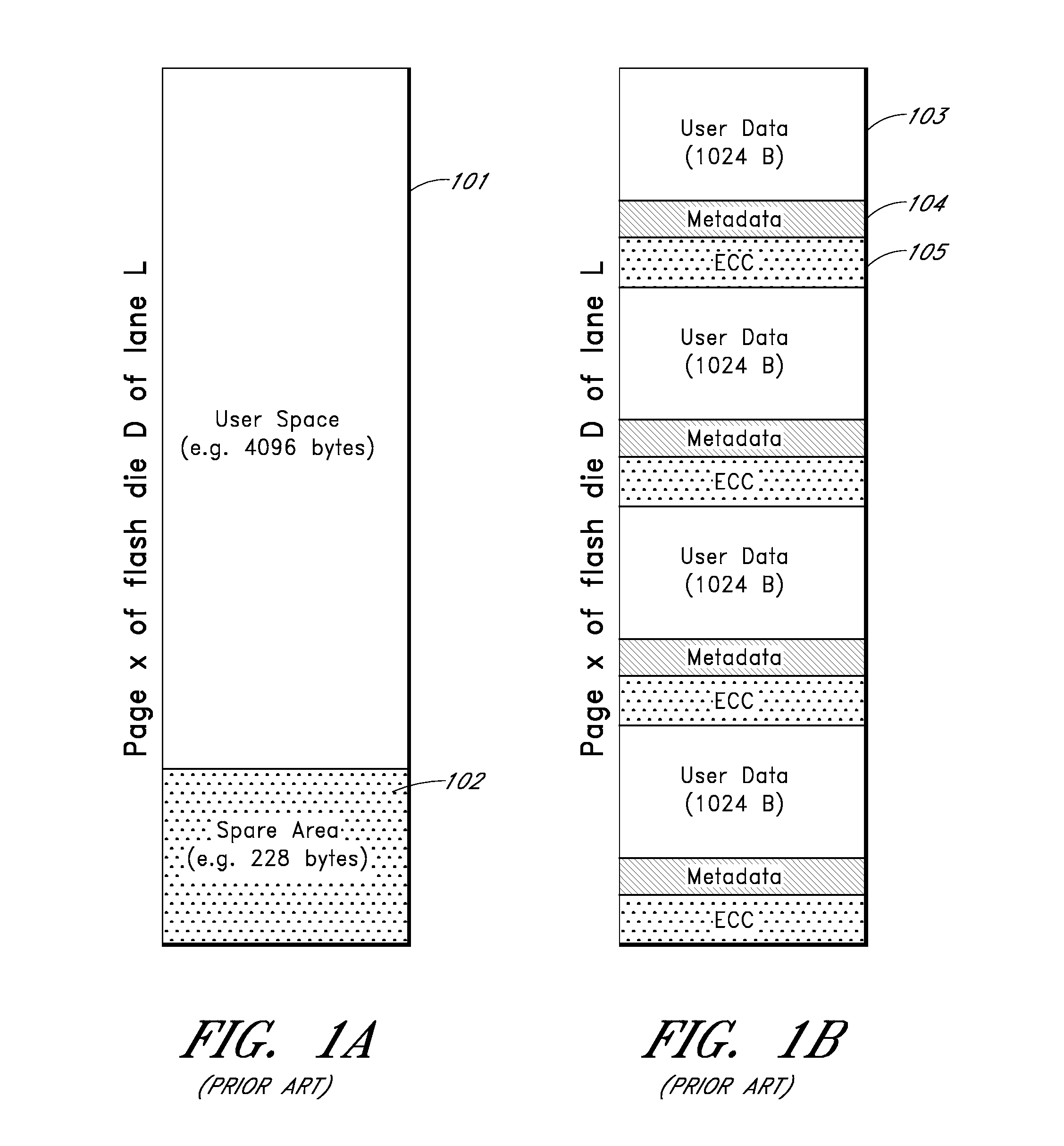
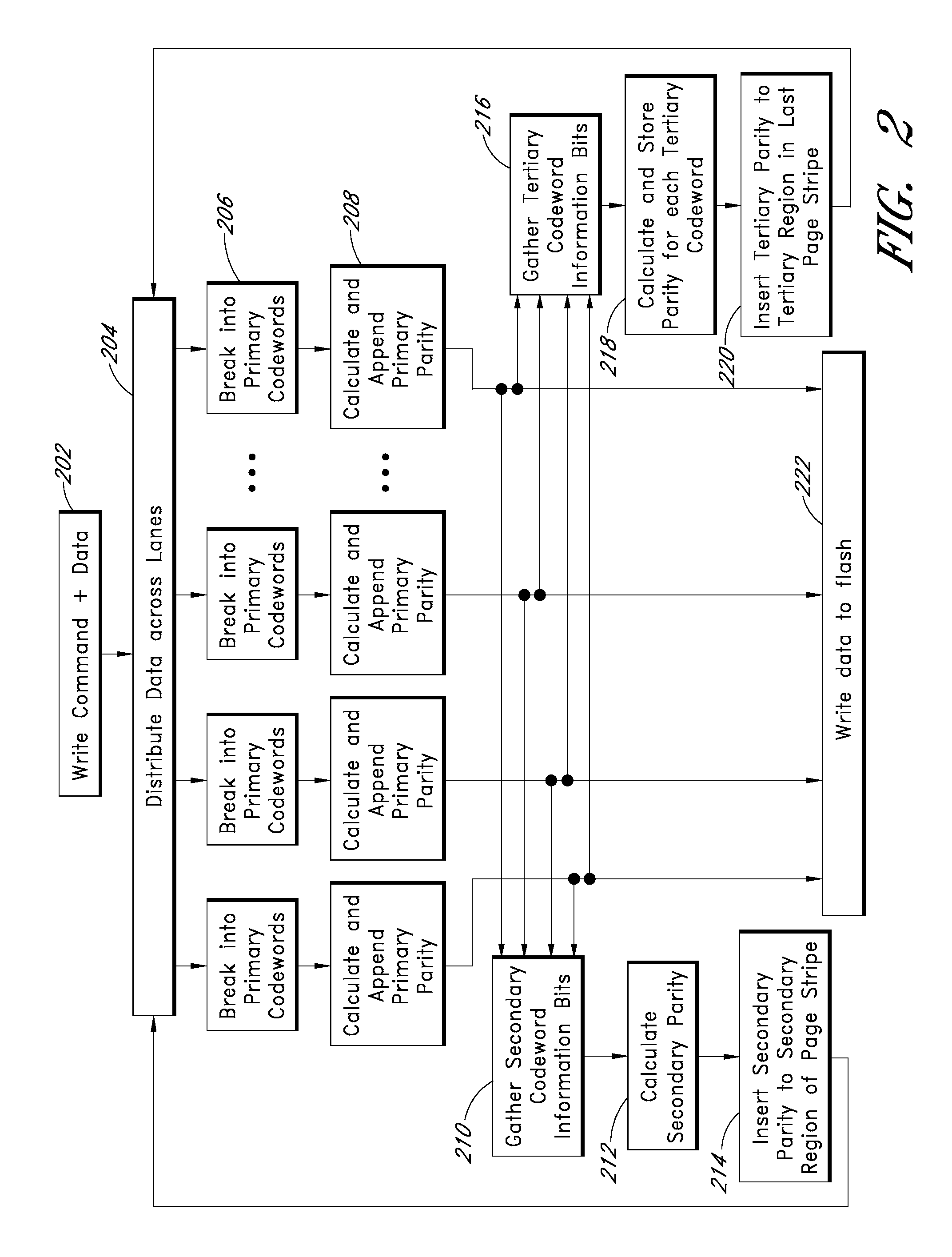
Apparatus and methods provide relatively low uncorrectable bit error rates, low write amplification, long life, fast and efficient retrieval, and efficient storage density such that a solid-state drive (SSD) can be implemented using relatively inexpensive MLC Flash for an enterprise storage application. A page is associated with a set of primary ECC codewords, and a page stripe is associated with a set of secondary codewords and primary over secondary parity (PoSP) ECC codewords. Two or more page stripes can form a page grid, wherein the page grid is associated with a group of tertiary ECC codewords, wherein the last page stripe of the page grid has a reduced payload capacity.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
Systems and methods for adaptively selecting from among a plurality of error correction coding schemes in a flash drive for robustness and low latency
ActiveUS9183085B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeRedundant data error correctionWrite amplificationLatency (engineering)
Owner:POLARIS POWERLED TECH LLC
Low write amplification in solid state drive
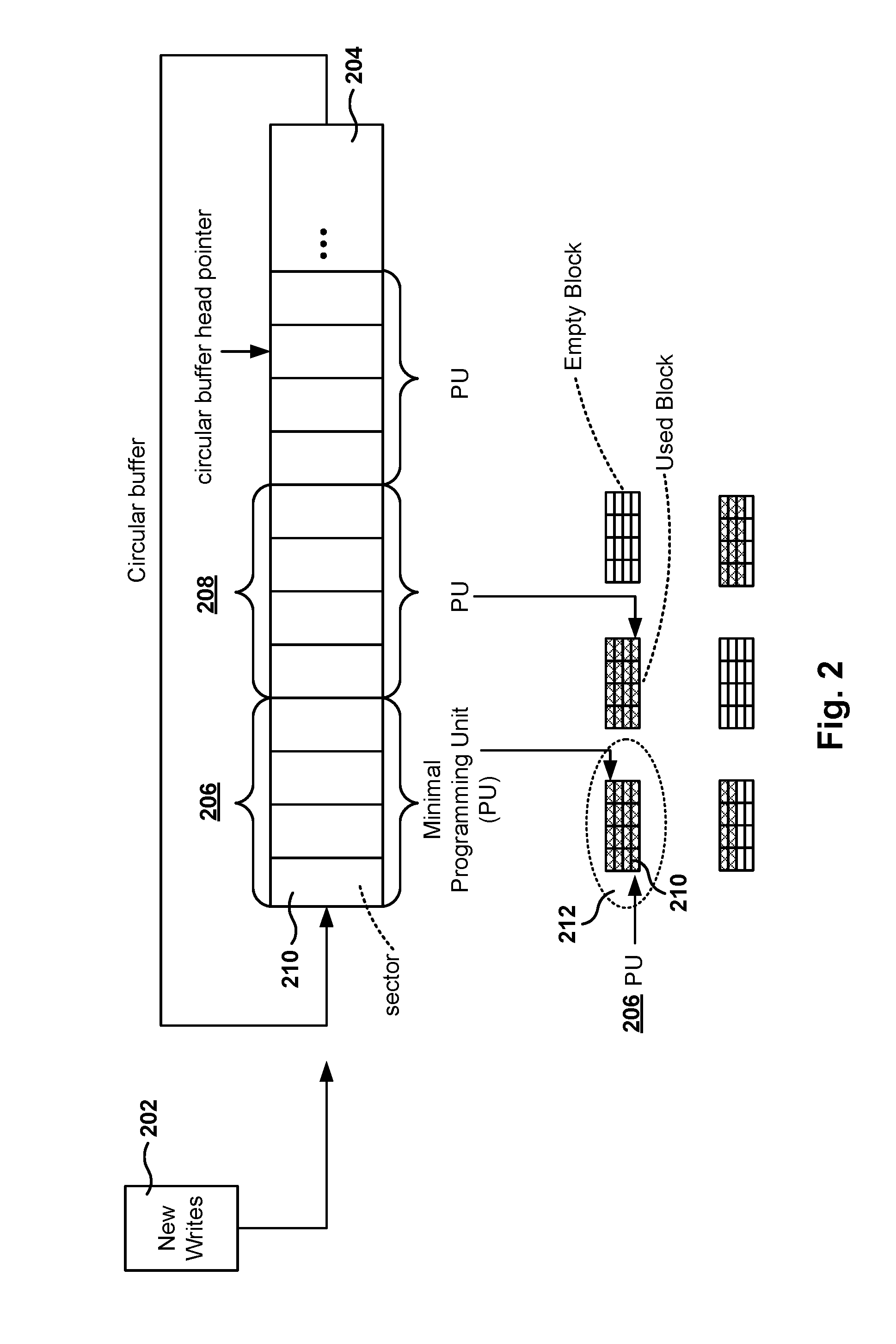
Methods, systems, and computer programs are presented for storing data in a solid state drive (SSD). One method includes an operation for detecting a plurality of streams writing to the SSD, each stream writing in sectors, a page including a plurality of sectors and a block including a plurality of pages. A write operation includes writing at least one complete page, and an erase operation includes erasing at least one complete block. The method further includes operations for allocating a write buffer for each stream in RAM memory, and for storing each received sector of a stream in the corresponding write buffer. When a write buffer stores enough sectors to fill a page, content of the write buffer is written to a page in flash memory such that the page is filled. Further, the write buffer is freed after writing the content of the write buffer to the flash memory.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Systems and methods for reclaiming memory for solid-state memory
ActiveUS9208018B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeStatic storageRedundant data error correctionWrite amplificationSolid-state drive
Apparatus and methods provide relatively low uncorrectable bit error rates, low write amplification, long life, fast and efficient retrieval, and efficient storage density such that a solid-state drive (SSD) can be reliably implemented using various types of memory cells, including relatively inexpensive multi-level cell flash. One embodiment intelligently coordinates remapping of bad blocks with error correction code control, which eliminates the tables used to avoid bad blocks.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
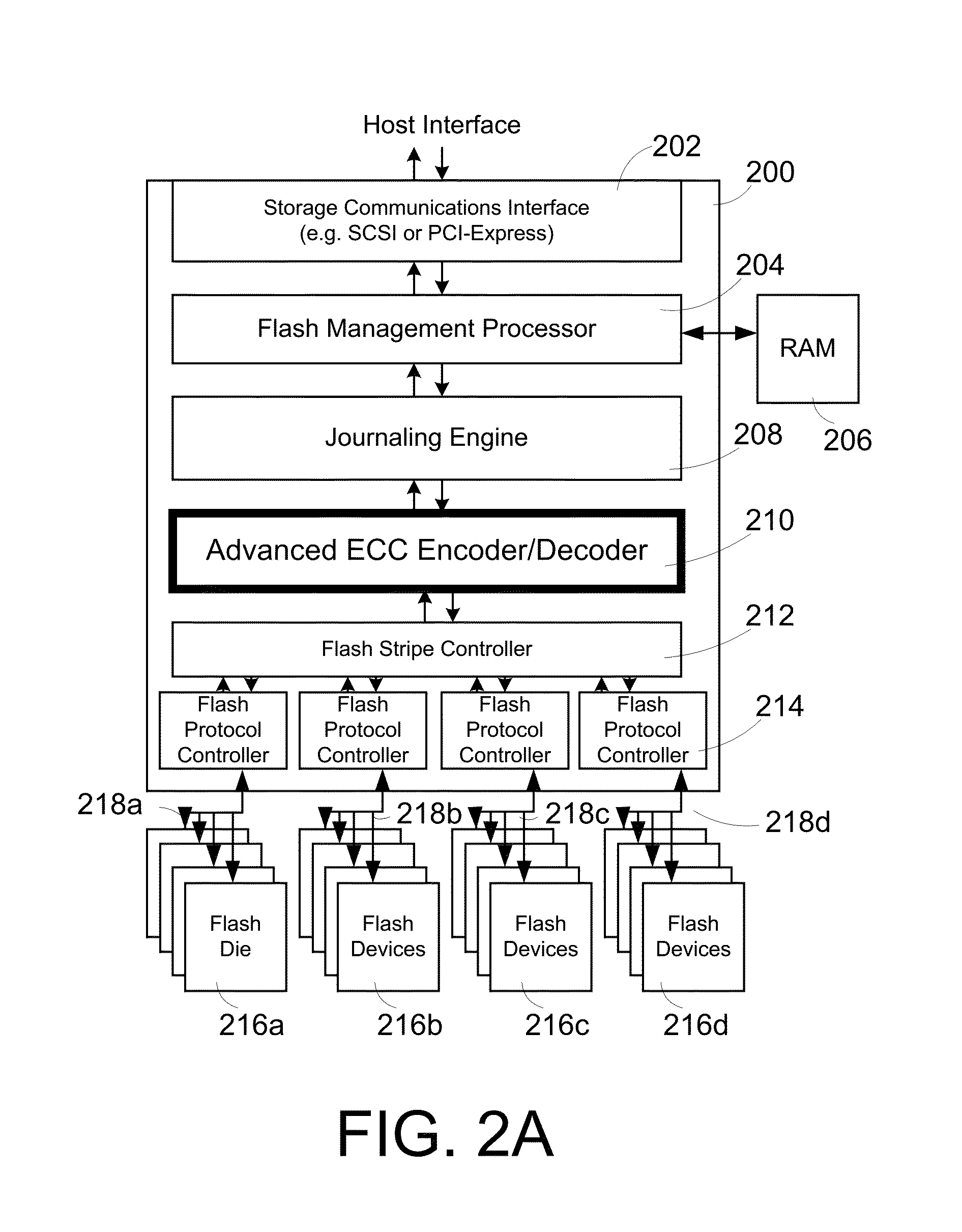
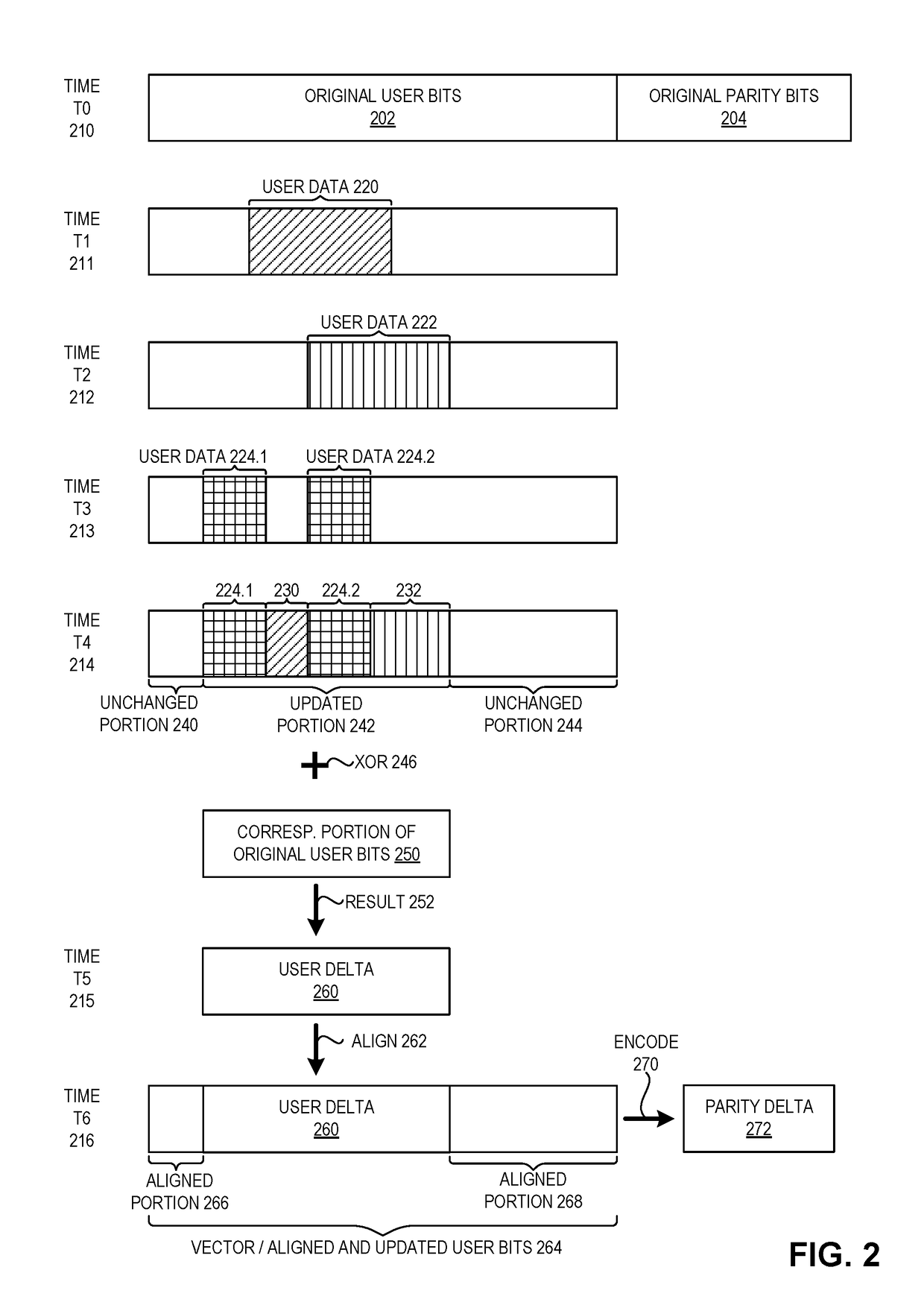
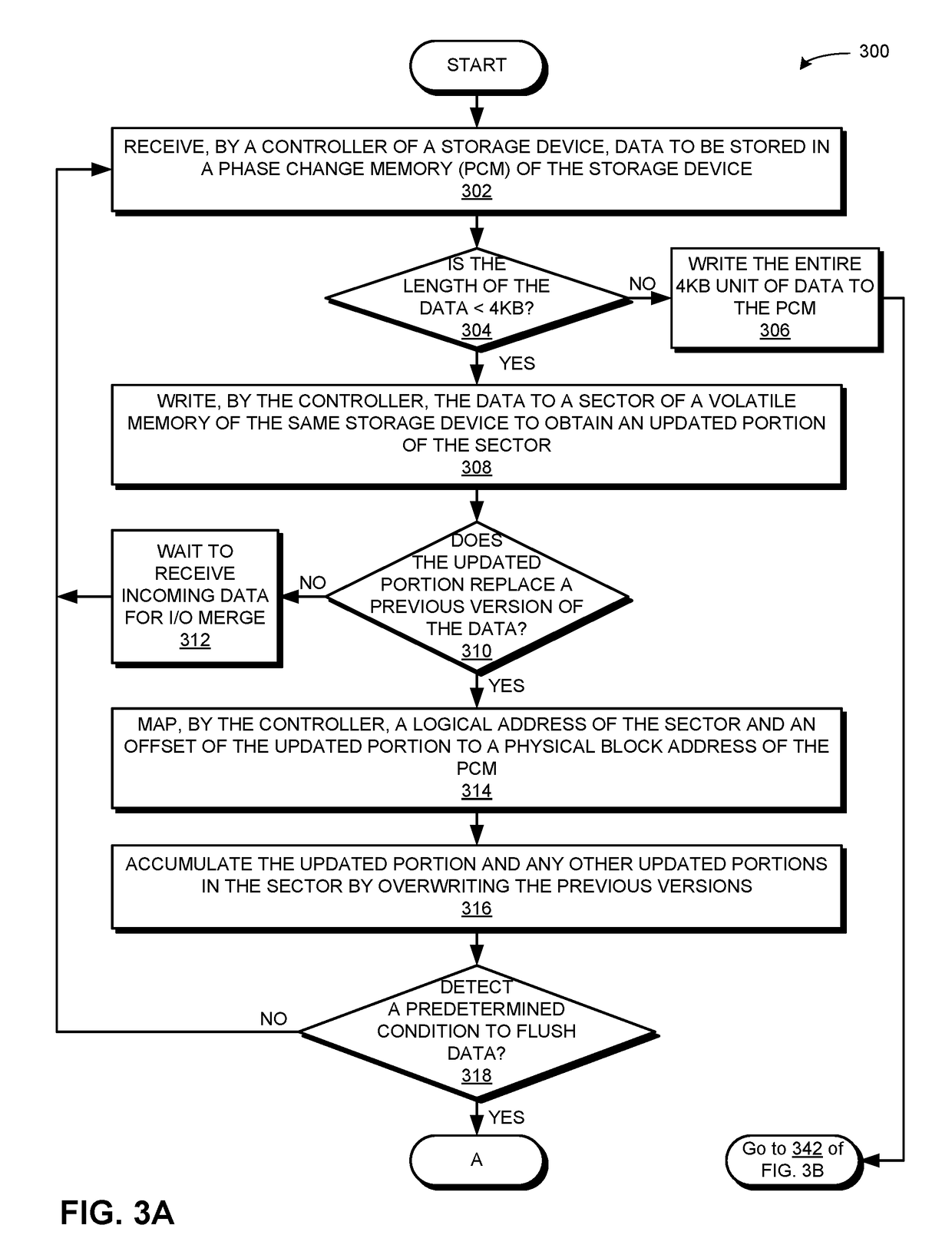
Method and system for mitigating write amplification in a phase change memory-based storage device
ActiveUS20190012111A1Input/output to record carriersMemory systemsComputer hardwareWrite amplification
One embodiment facilitates mitigating write amplification in a phase change memory-based storage device. During operation, the system receives, by a controller of the storage device, data to be stored in a phase change memory (PCM) of the storage device. The system writes, by the controller, the data to a sector of a volatile memory of the same storage device to obtain an updated portion of the sector. In response to detecting a predetermined condition, the system writes the updated portion to the PCM.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Flash management optimization for data update with small block sizes for write amplification mitigation and fault tolerance enhancement
InactiveUS20180321874A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersFault toleranceWrite amplification
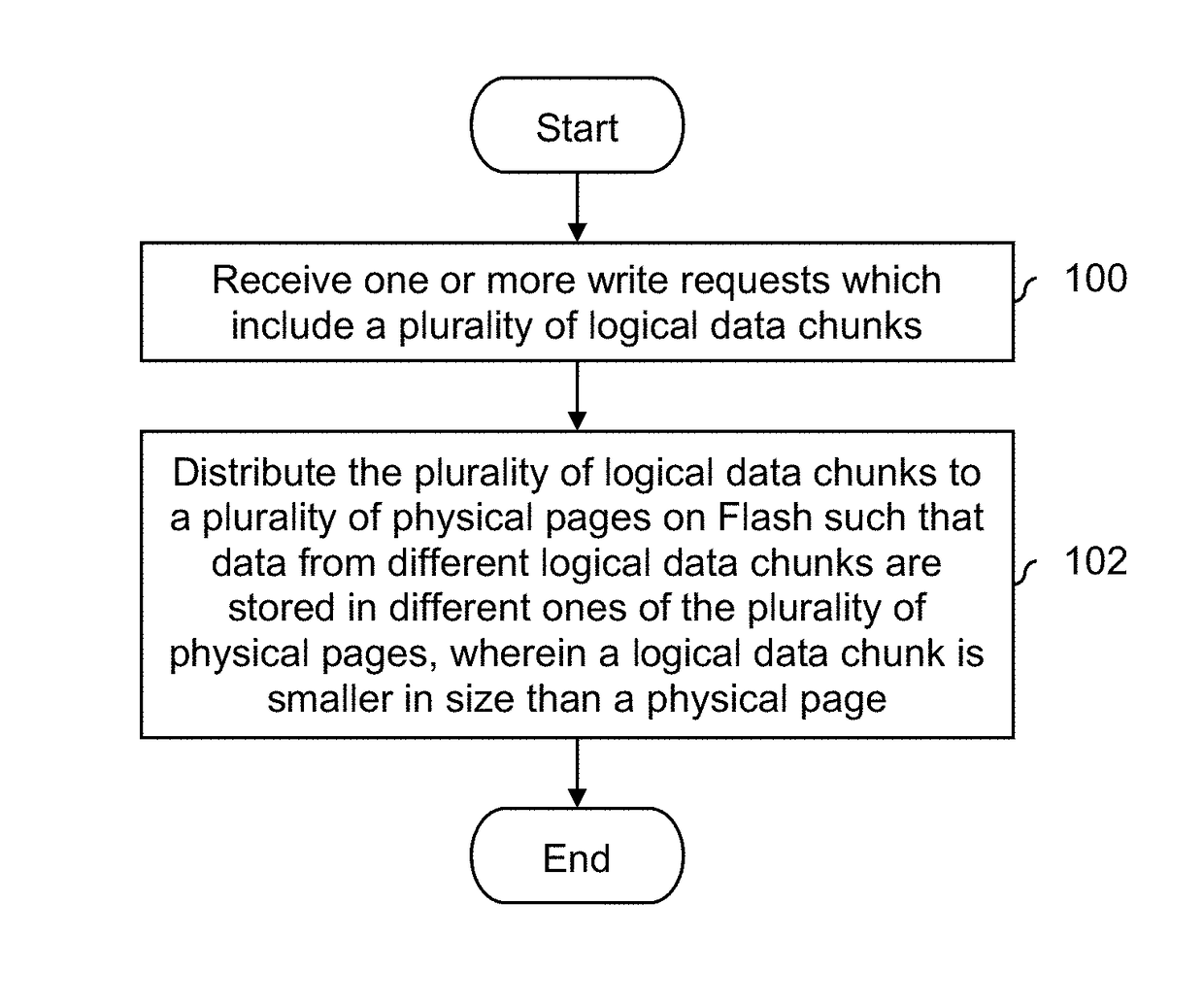
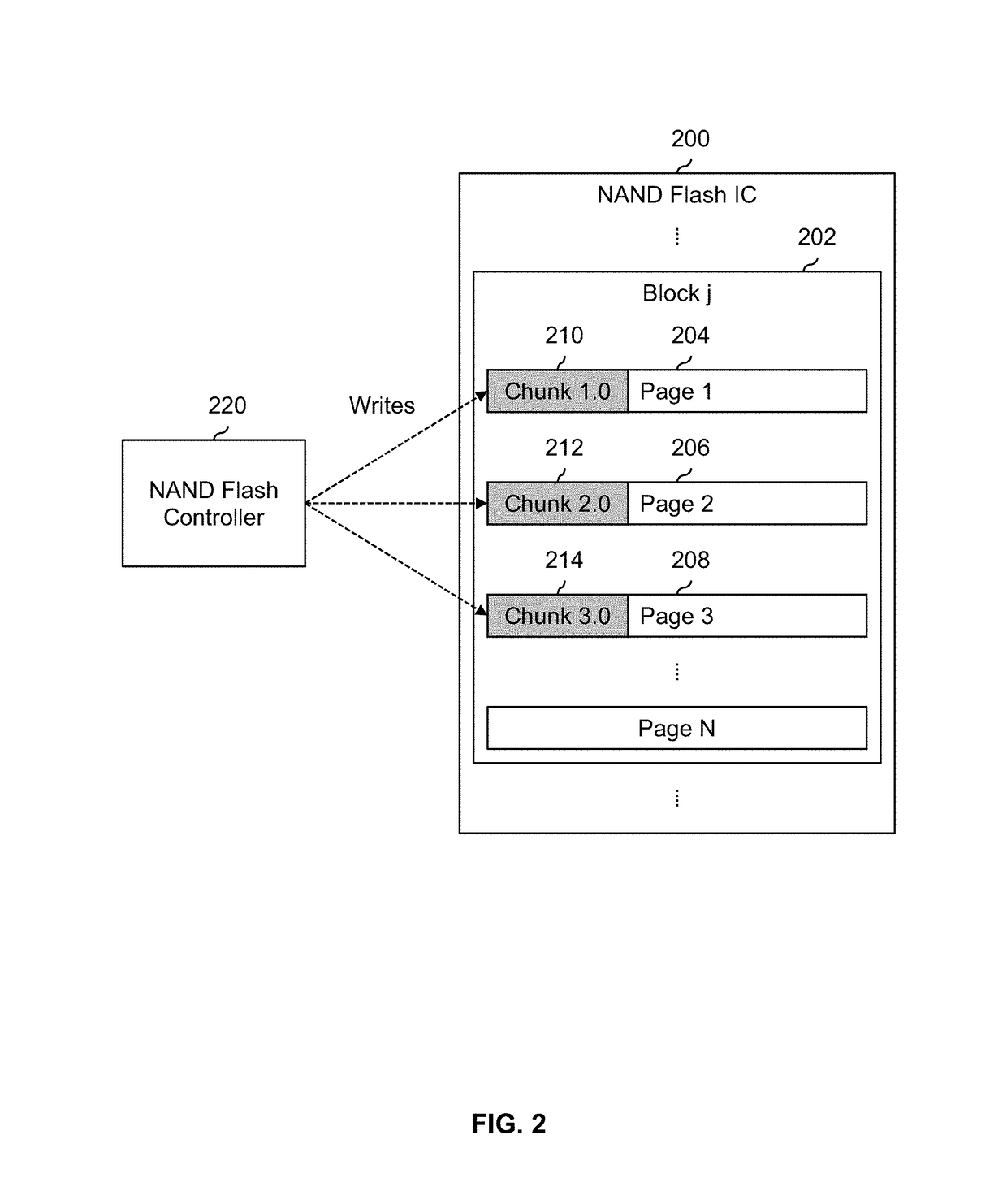
One or more write requests which include a plurality of logical data chunks are received. The plurality of logical data chunks are distributed to a plurality of physical pages on Flash such that data from different logical data chunks are stored in different ones of the plurality of physical pages, wherein a logical data chunk is smaller in size than a physical page.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Reducing write amplification in a flash memory
ActiveUS20130232290A1Reducing write amplificationMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsMemory addressWrite amplification
An apparatus having a memory circuit and a manager is disclosed. The memory circuit generally has (i) one or more Flash memories and (ii) a memory space that spans a plurality of memory addresses. The manager may be configured to (i) receive data items in a random order from one or more applications, (ii) write the data items in an active one of a plurality of regions in a memory circuit and (iii) mark the memory addresses in the active region that store the data items as used. Each data item generally has a respective host address. The applications may be executed in one or more computers. The memory addresses in the active region may be accessed in a sequential order while writing the data items to minimize a write amplification. The random order is generally preserved between the data items while writing in the active region.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Low write amplification in solid state drive
Methods, systems, and computer programs are presented for storing data in a solid state drive (SSD). One method includes an operation for detecting a plurality of streams writing to the SSD, each stream writing in sectors, a page including a plurality of sectors and a block including a plurality of pages. A write operation includes writing at least one complete page, and an erase operation includes erasing at least one complete block. The method further includes operations for allocating a write buffer for each stream in RAM memory, and for storing each received sector of a stream in the corresponding write buffer. When a write buffer stores enough sectors to fill a page, content of the write buffer is written to a page in flash memory such that the page is filled. Further, the write buffer is freed after writing the content of the write buffer to the flash memory.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Systems and methods for reclaiming flash blocks of a flash drive
ActiveUS8793556B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWrite amplificationSolid-state drive
Apparatus and methods provide relatively low uncorrectable bit error rates, low write amplification, long life, fast and efficient retrieval, and efficient storage density such that a solid-state drive (SSD) can be implemented using relatively inexpensive MLC Flash for an enterprise storage application.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
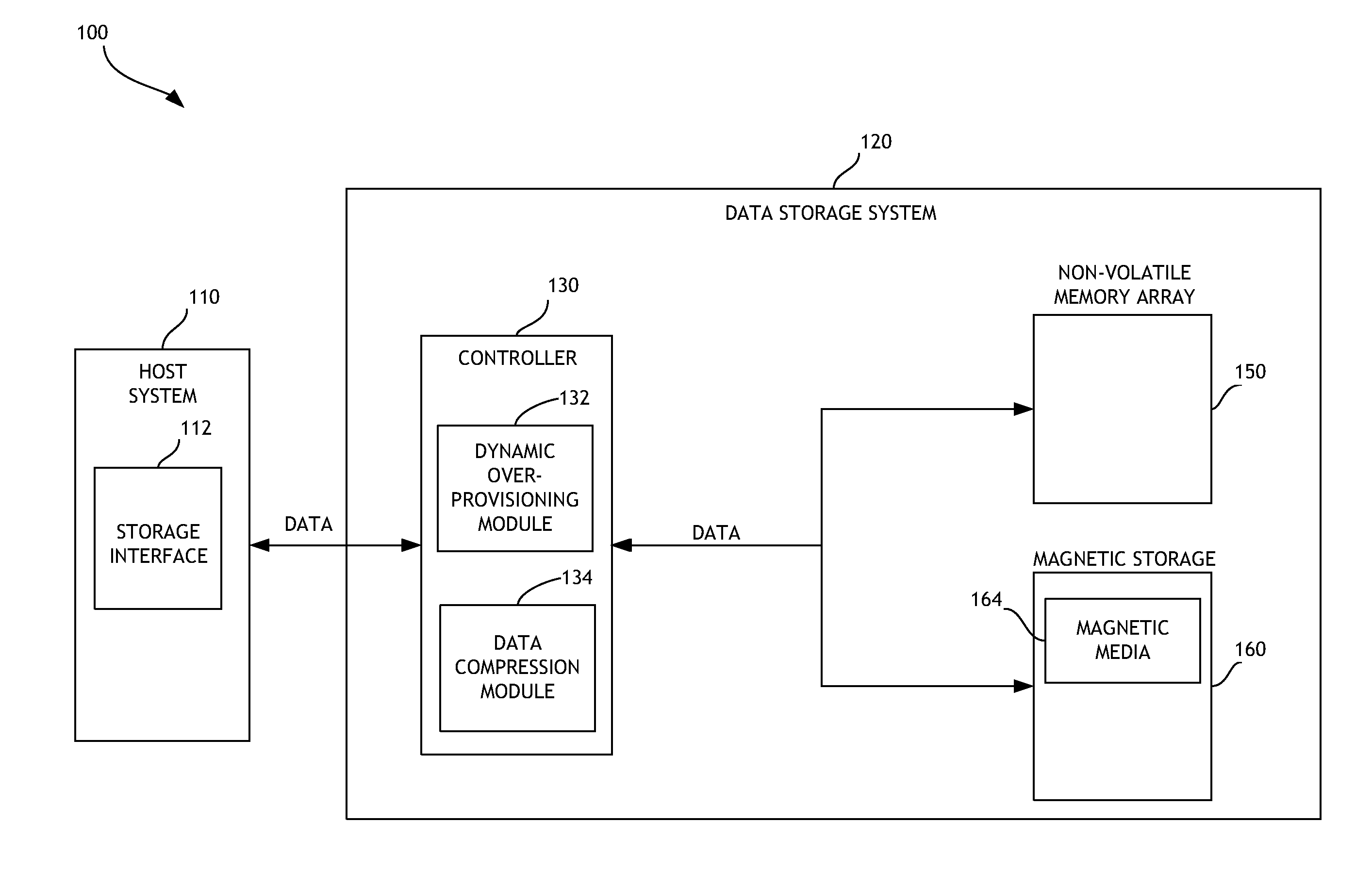
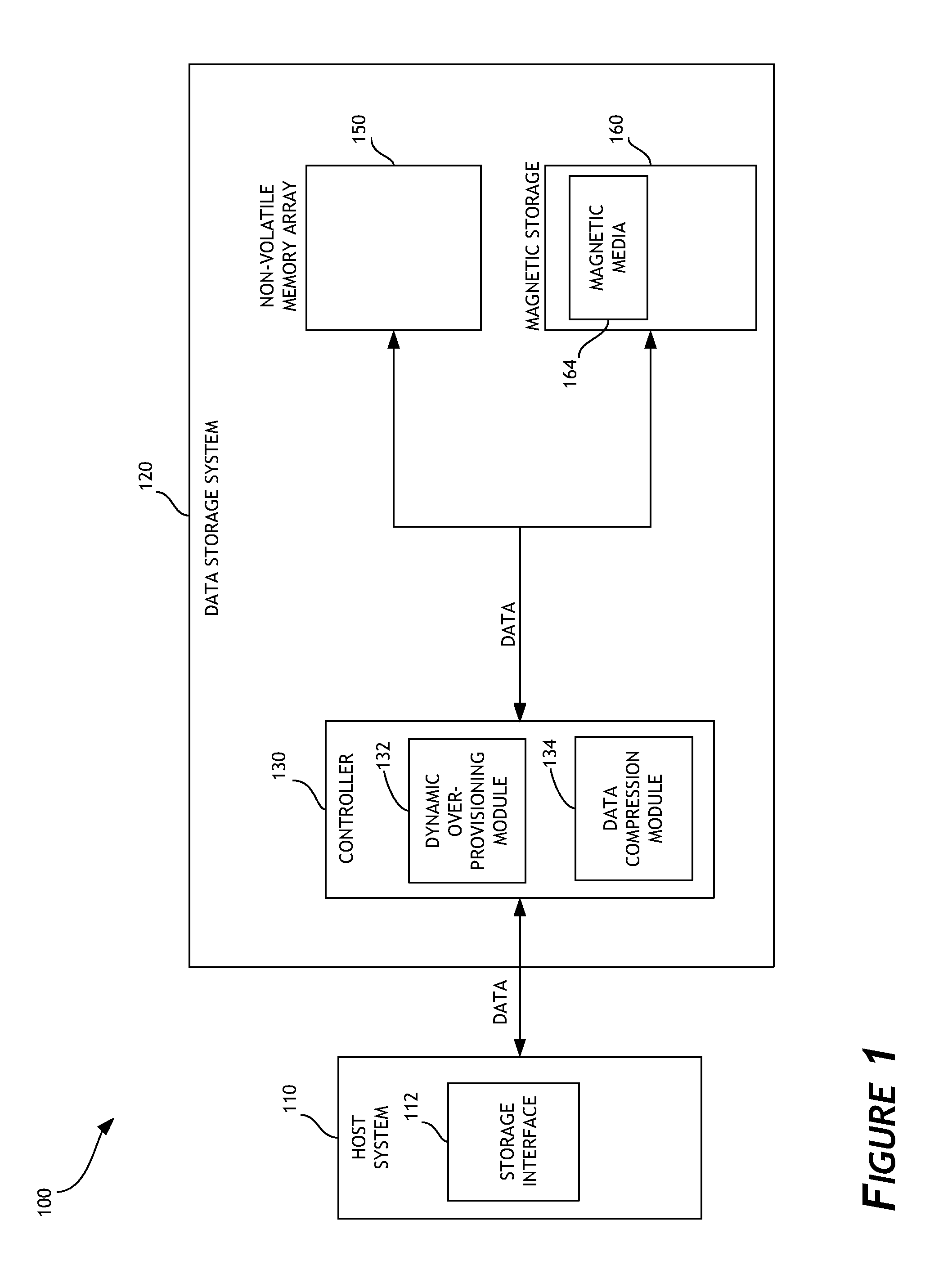
Dynamic overprovisioning for data storage systems
ActiveUS20140181369A1Improve efficiencyIncreased longevityMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWrite amplificationCache hit rate
Disclosed embodiments are directed to systems and methods for dynamic overprovisioning for data storage systems. In one embodiment, a data storage system can reserve a portion of memory, such as non-volatile solid-state memory, for overprovisioning. Depending on various overprovisioning factors, recovered storage space due to compressing user data can be allocated for storing user data and / or overprovisioning. Utilizing the disclosed dynamic overprovisioning systems and methods can result is more efficient utilization of cache memory, reduction of write amplification, increase in a cache hit rate, and the like. Improved data storage system performance and increased endurance and longevity can thereby be attained.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Systems and methods for mapping for solid-state memory
ActiveUS9009565B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesWrite amplificationSolid-state drive
Apparatus and methods provide relatively low uncorrectable bit error rates, low write amplification, long life, fast and efficient retrieval, and efficient storage density such that a solid-state drive (SSD) can be reliably implemented using various types of memory cells, including relatively inexpensive multi-level cell flash. One embodiment intelligently coordinates remapping of bad blocks with error correction code control, which eliminates the tables used to avoid bad blocks.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
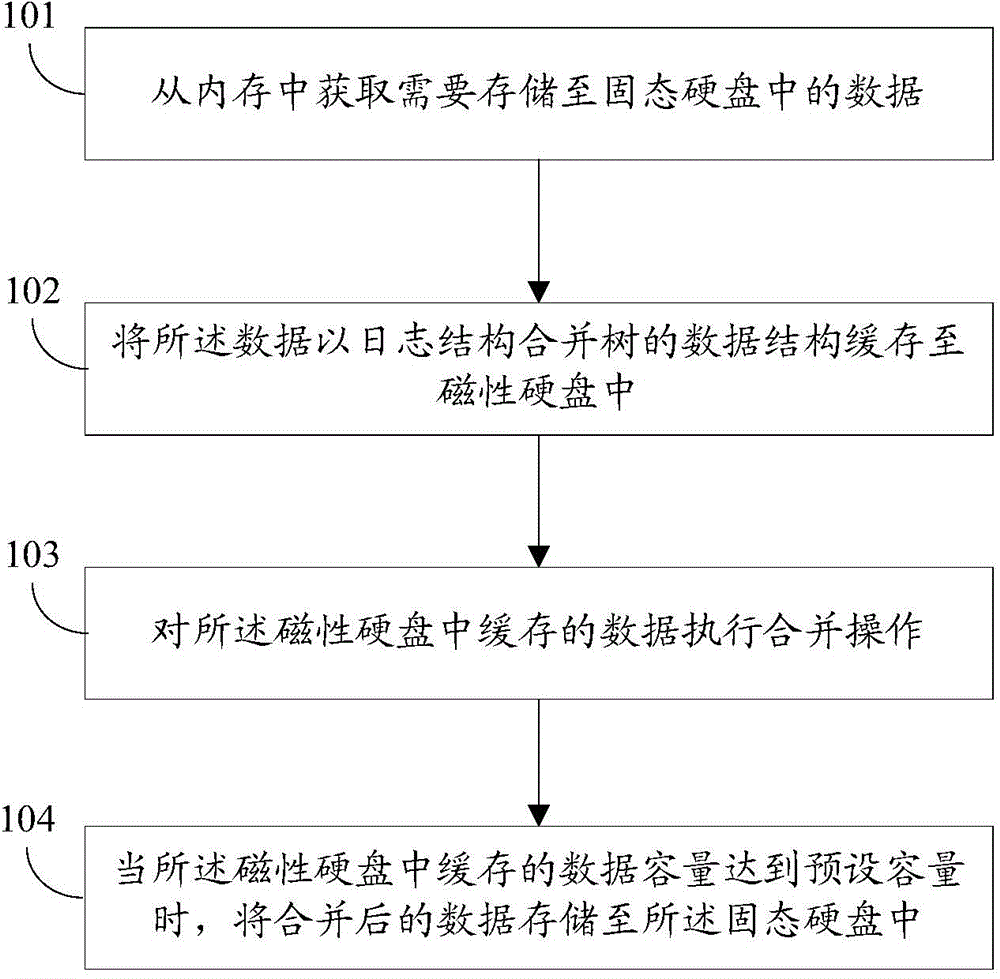
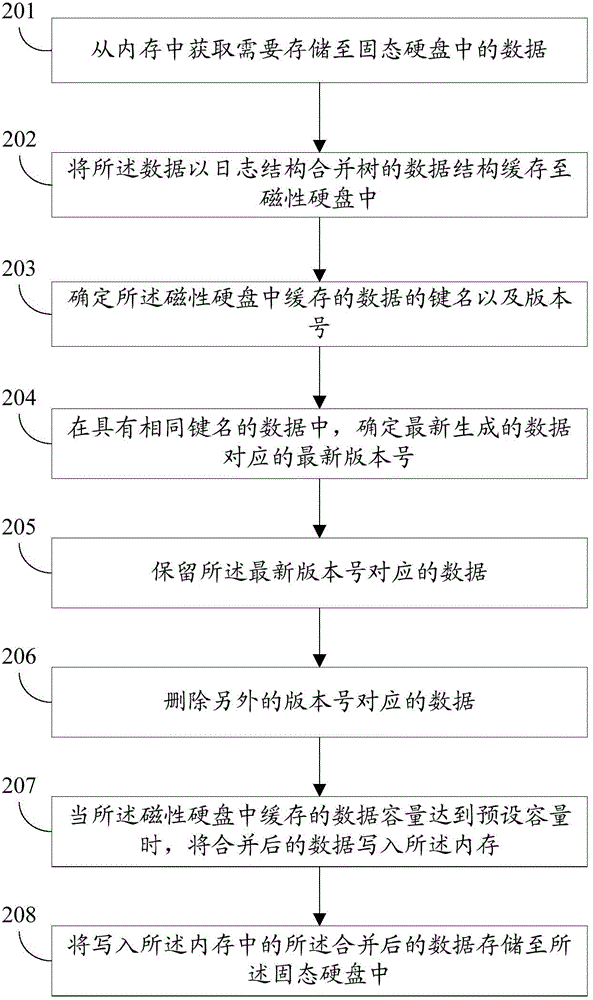
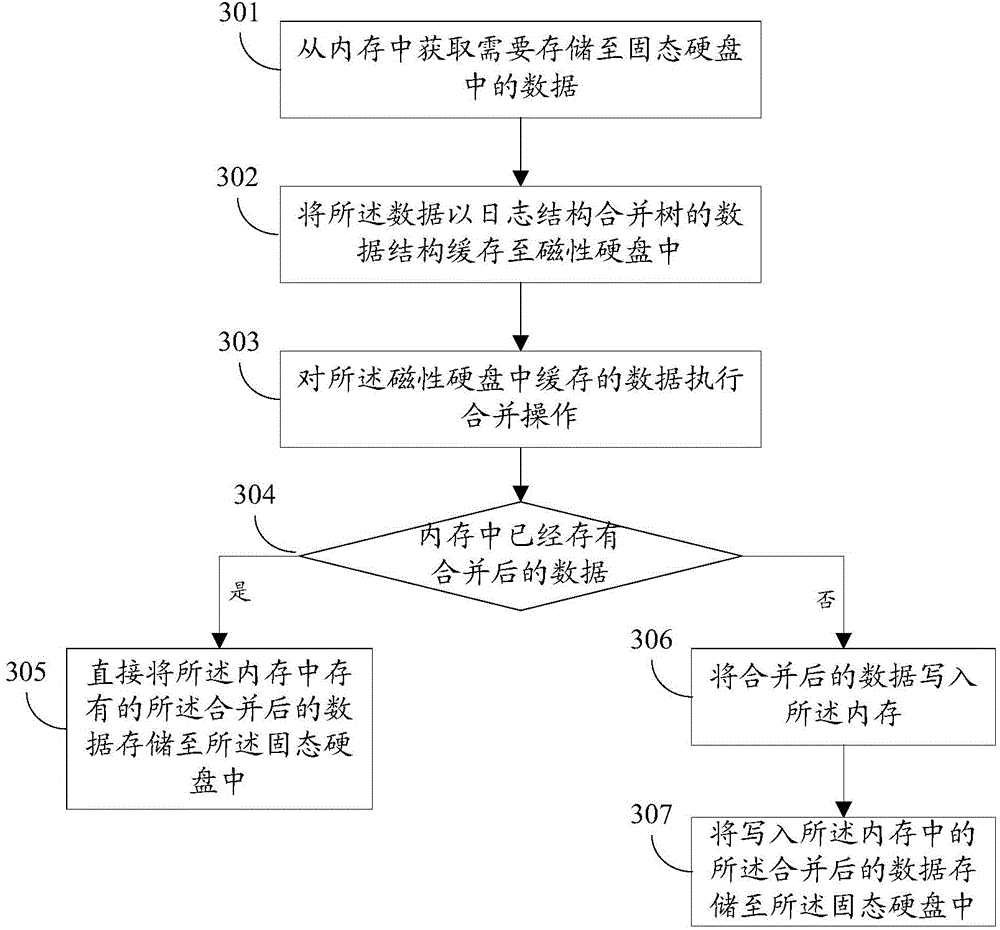
Data storage method and data storage device
ActiveCN105224237ASolve the write amplification problemExtended service lifeInput/output to record carriersData capacityWrite amplification
The invention provides a data storage method and a data storage device. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining data to be stored into a solid-state hard disk from a memory; caching the data into a magnetic hard disk in a data structure being a log structure merging tree; executing a merging operation on the data cached in the magnetic hard disk; and when the volume of the data cached in the magnetic hard disk reaches the preset volume, storing the merged data into the solid-state hard disk. By using the method or the device provided by the invention, the write amplification problem generated during the updating of small-particle-size data can be solved; and the service life of the solid-state hard disk is prolonged.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
System data management using garbage collection and hybrid self mapping
ActiveUS8966205B1Generate and update system data quickly and efficientlyReducing write amplificationMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsWrite amplificationWaste collection
A data storage system is disclosed that utilizes garbage collection and hybrid self-mapping for managing system data. In one embodiment, a system data region having an amount of valid system data that is below a threshold is freed. Write amplification associated with managing and storing system data can be reduced at least in part because only valid system data can be copied during garbage collection of the selected region. Mapping information associating system data with physical locations in non-volatile storage where system data is stored can be generated, which can reduce system data reconstruction time during start-up of the data storage system. Increase in efficiency and reduction in startup and initialization time can be attained.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
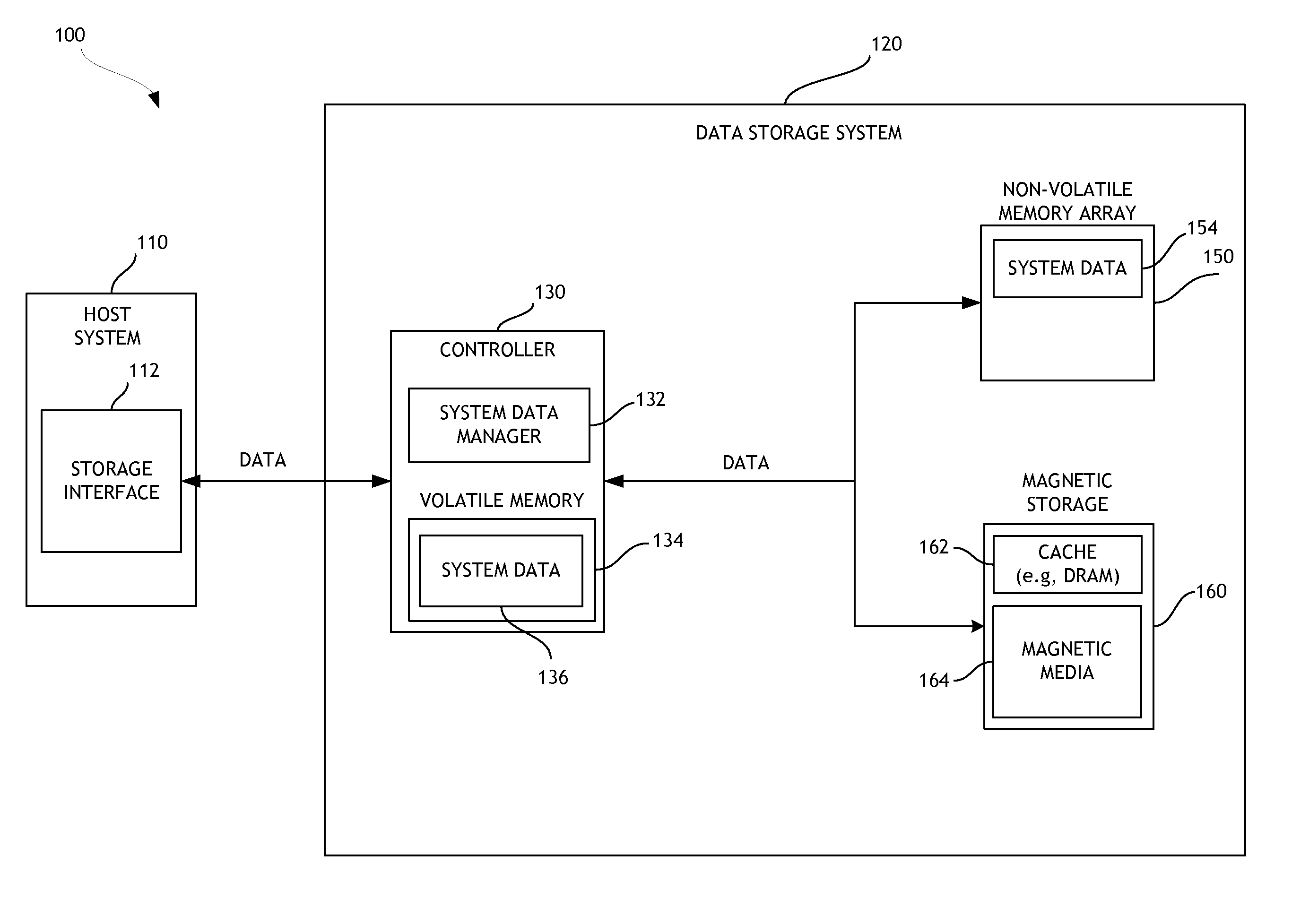
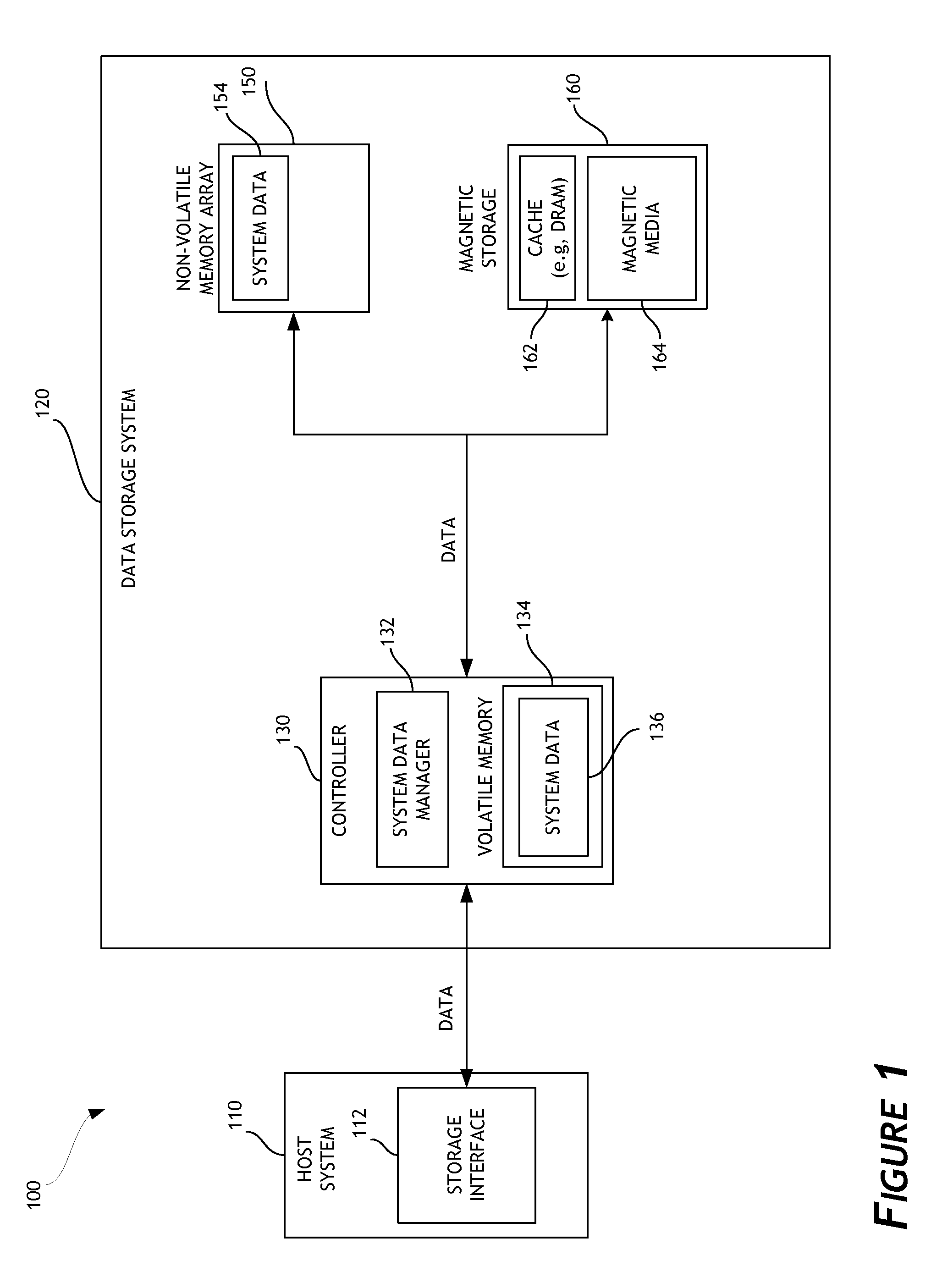
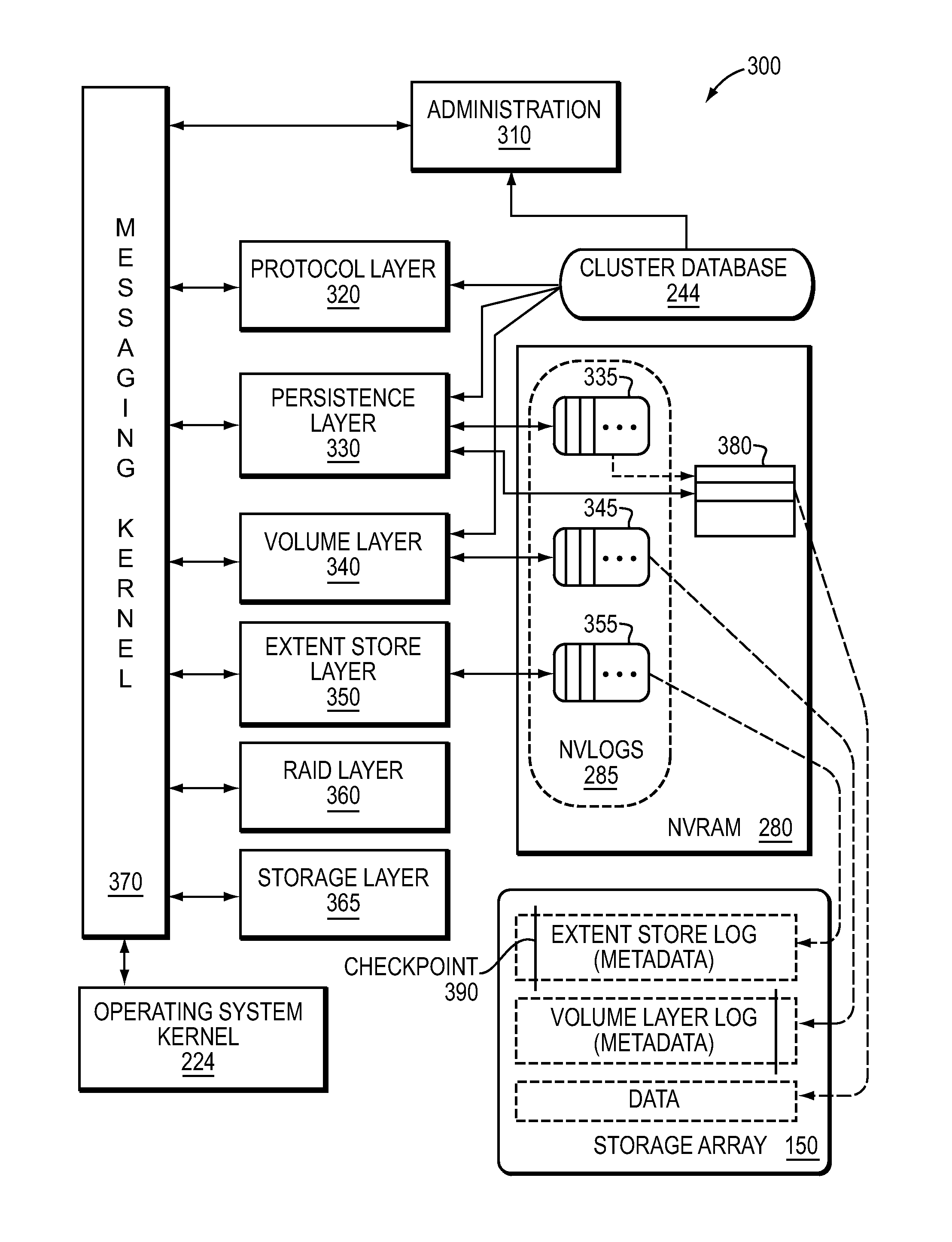
Flash optimized, log-structured layer of a file system
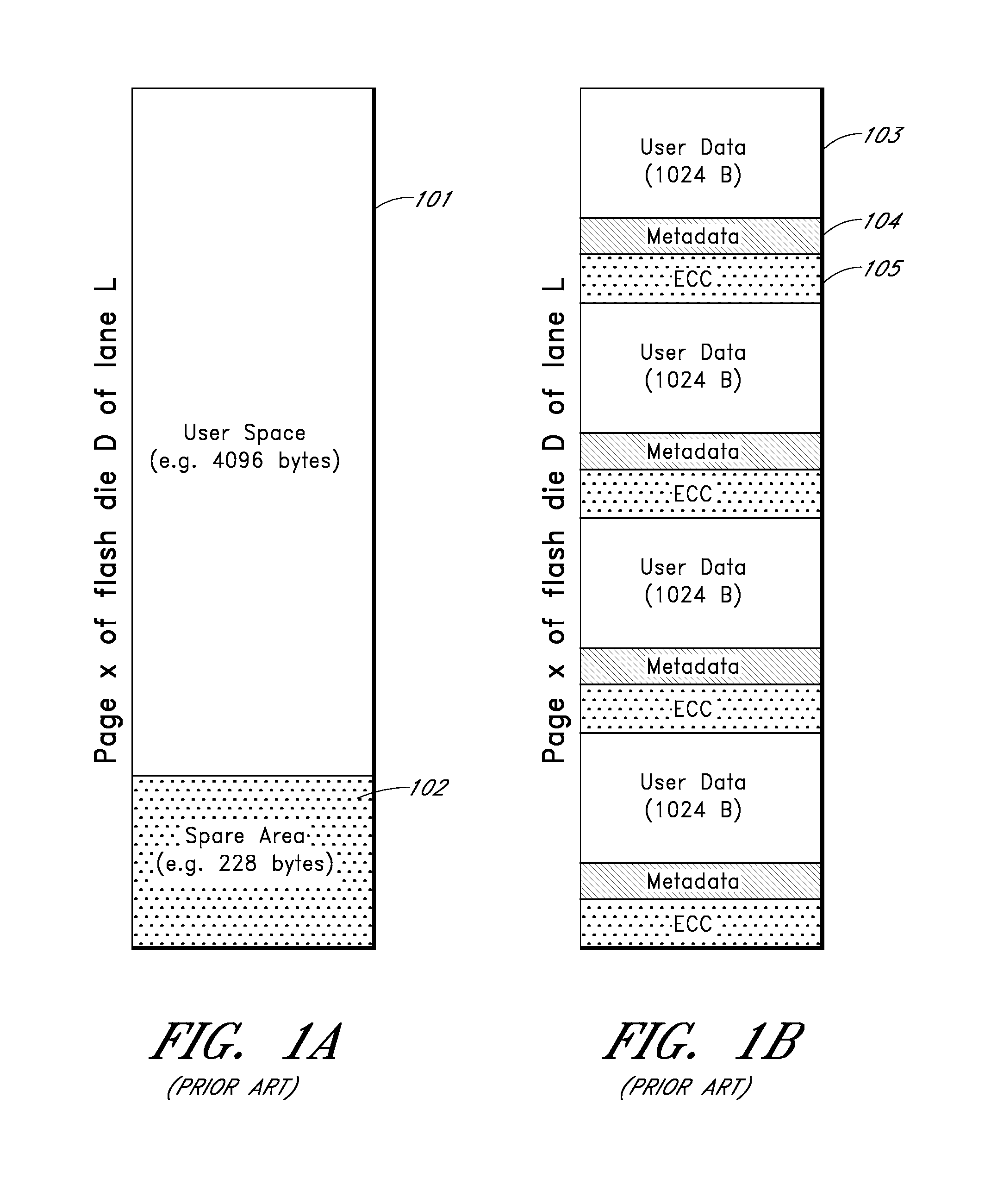
ActiveUS8880788B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersVariable lengthMetadata
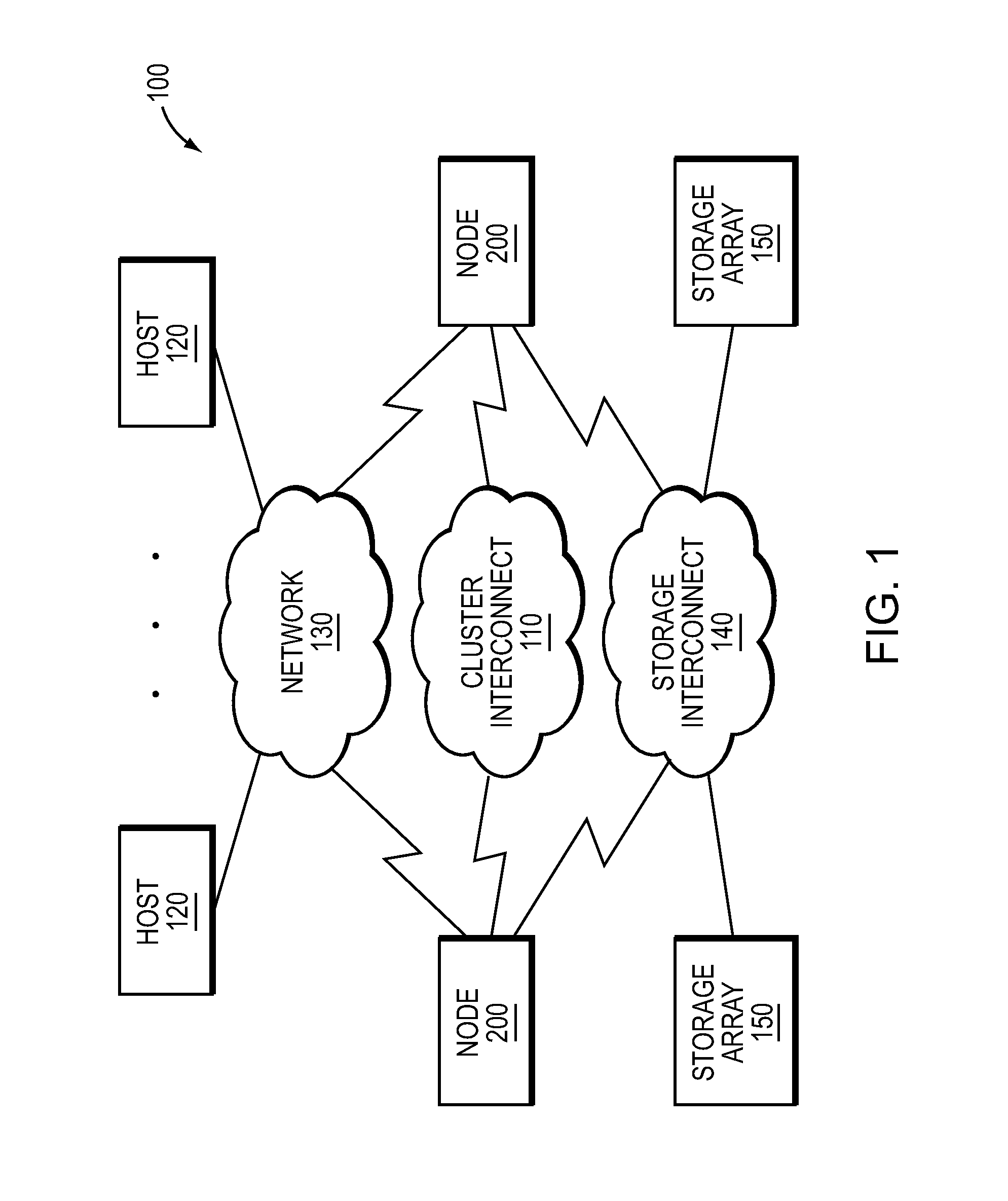
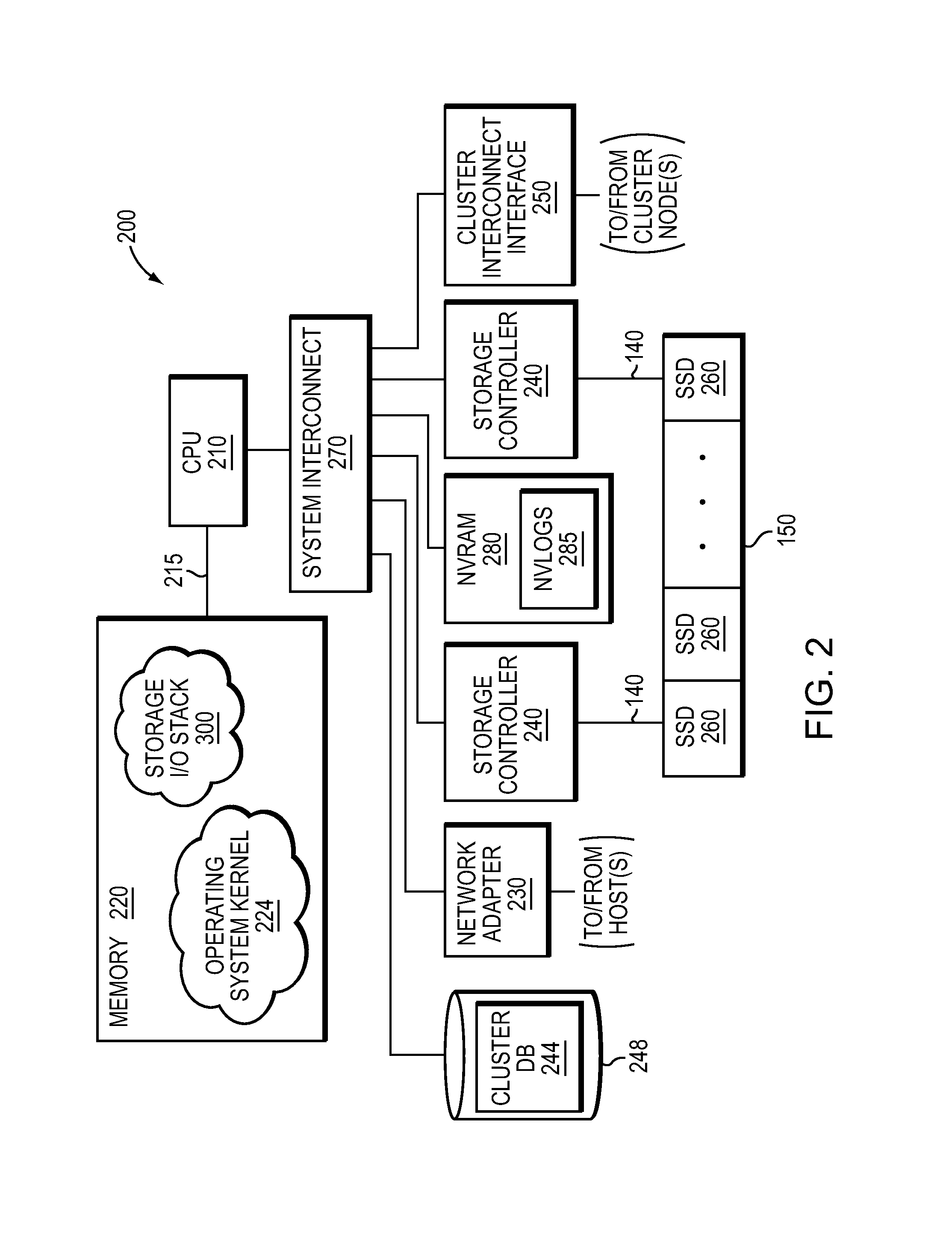
In one embodiment, a flash-optimized, log-structured layer of a file system of a storage input / output (I / O) stack executes on one or more nodes of a cluster. The log-structured layer of the file system provides sequential storage of data and metadata on solid state drives (SSDs) to reduce write amplification, while leveraging variable compression and variable length data features of the storage I / O stack. The data may be organized as an arbitrary number of variable-length extents of one or more host-visible logical units (LUNs). The metadata may include mappings from host-visible logical block address ranges of a LUN to extent keys, as well as mappings of the extent keys to SSD storage locations of the extents. The storage location of an extent on SSD is effectively “virtualized” by its mapped extent key such that relocation of the extent on SSD does not require update to volume layer metadata.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Systems and methods for low latency, high reliability error correction in a flash drive
ActiveUS8788910B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeError detection/correctionStatic storageWrite amplificationLatency (engineering)
Apparatus and methods provide relatively low uncorrectable bit error rates, low write amplification, long life, fast and efficient retrieval, and efficient storage density such that a solid-state drive (SSD) can be implemented using relatively inexpensive MLC Flash for an enterprise storage application.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
RAID5 (redundant array of independent disk 5) write IO optimization processing method
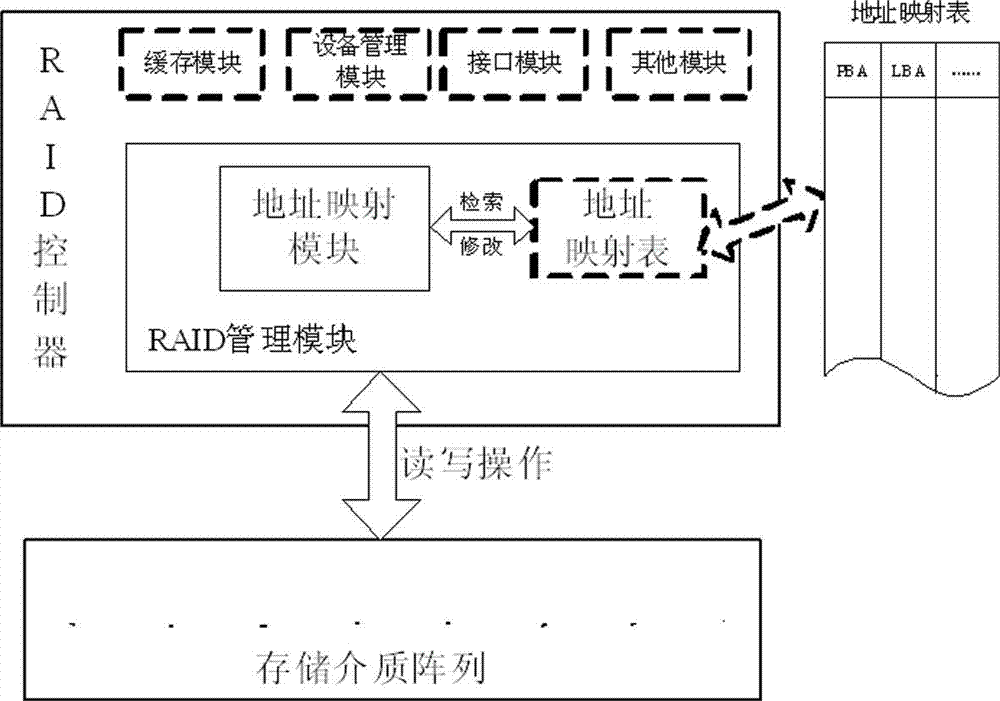
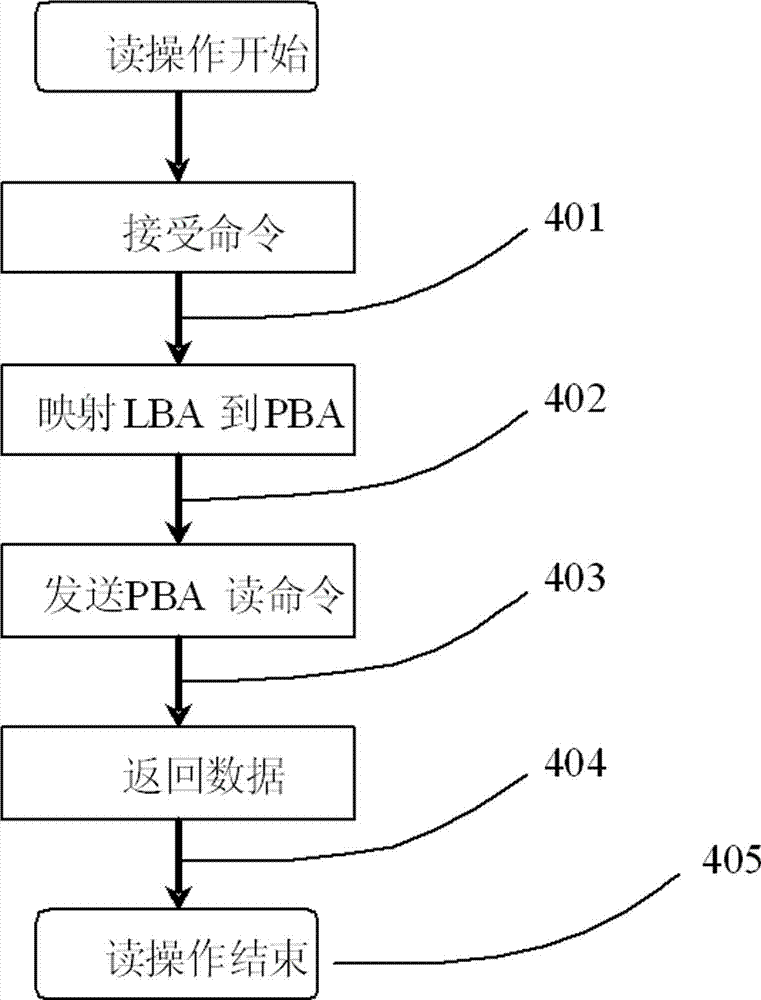
ActiveCN103049222AReduce write amplification effectOperate effectivelyInput/output to record carriersRAIDWrite amplification
Disclosed is an RAID5 (redundant array of independent disk 5) write IO optimization processing method. The method includes following steps: 1), storage system creation; 2), data reading and writing operation; and 3), failure data block recovery and has the advantage of capability of effectively lowering write amplification effect of RAID level disk arrays. For conventional magnetic disks, sequential write performance is much higher than random write performance. The address mapping method enables random write operation to be converted into sequential write operation, write performance of the magnetic disk is effectively brought into play, IO operation needed for computation checking is lowered, and response capability of an RAID system is evidently improved, and power consumption of the system is lowered. In addition, an address mapping module can flexibly choose arrangement positions and the number of checking blocks, so that the RAID5 write IO optimization processing method is not limited to be applicable to disk arrays of RAID5 level and can be popularized for realization of RAID4 and RAID6 levels.
Owner:NO 709 RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
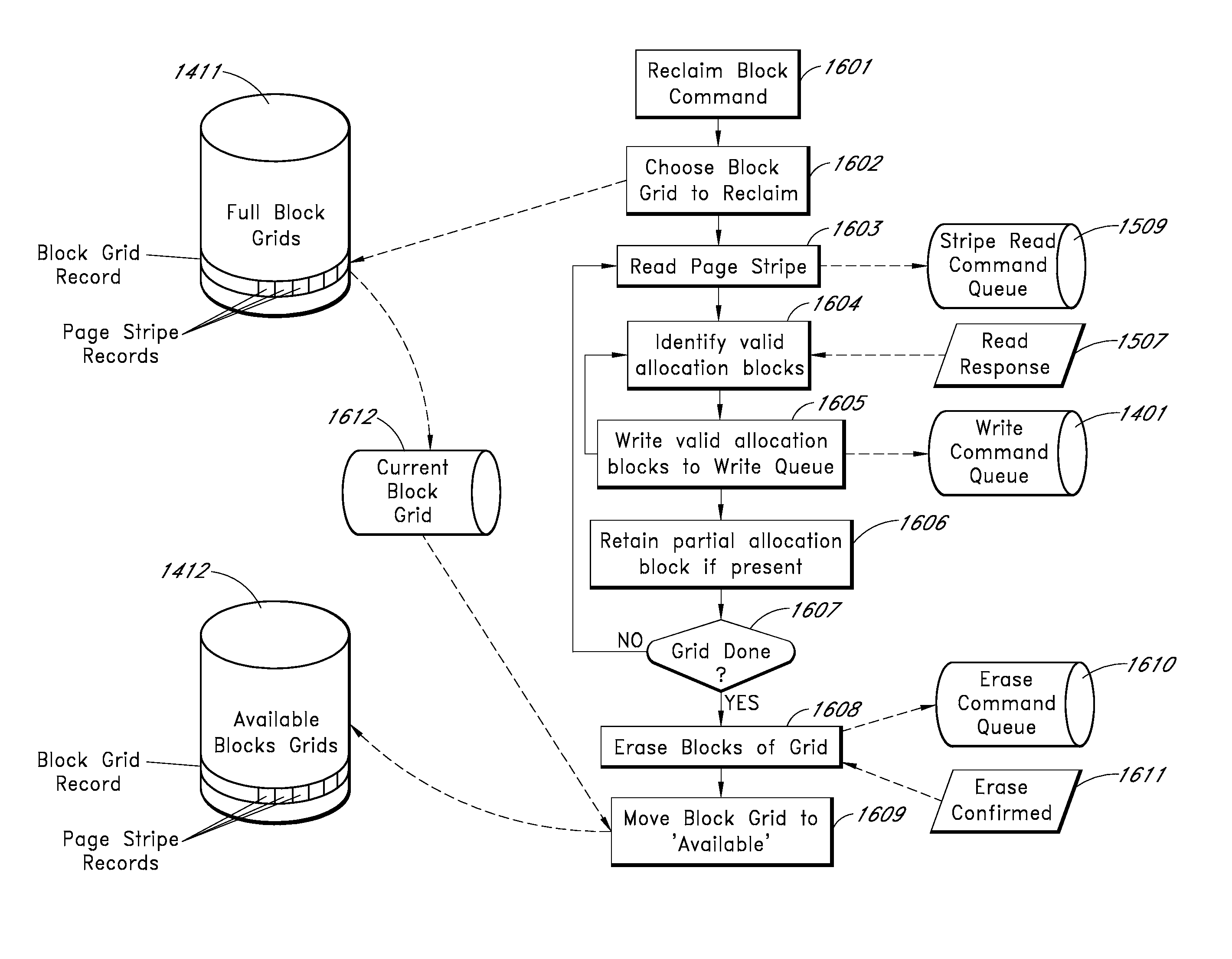
Regrouping data during relocation to facilitate write amplification reduction
ActiveUS20170242788A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionWrite amplificationMetadata
A technique for garbage collection in a storage system includes generating regrouping metadata for one or more pages of at least two logical erase blocks (LEB). The regrouping metadata indicates an associated stream for each of the pages. Multiple of the LEBs that include valid pages associated with a first stream are selected, based on the regrouping metadata, for regrouping. The valid pages associated with the first stream from the selected LEBs are regrouped into a new LEB.
Owner:IBM CORP
Systems and methods for transparently varying error correction code strength in a flash drive
ActiveUS8972824B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeError detection/correctionRead-only memoriesWrite amplificationSolid-state drive
Apparatus and methods provide relatively low uncorrectable bit error rates, low write amplification, long life, fast and efficient retrieval, and efficient storage density such that a solid-state drive (SSD) can be implemented using relatively inexpensive MLC Flash for an enterprise storage application.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
Mapping table management method for solid state disk and solid state disk
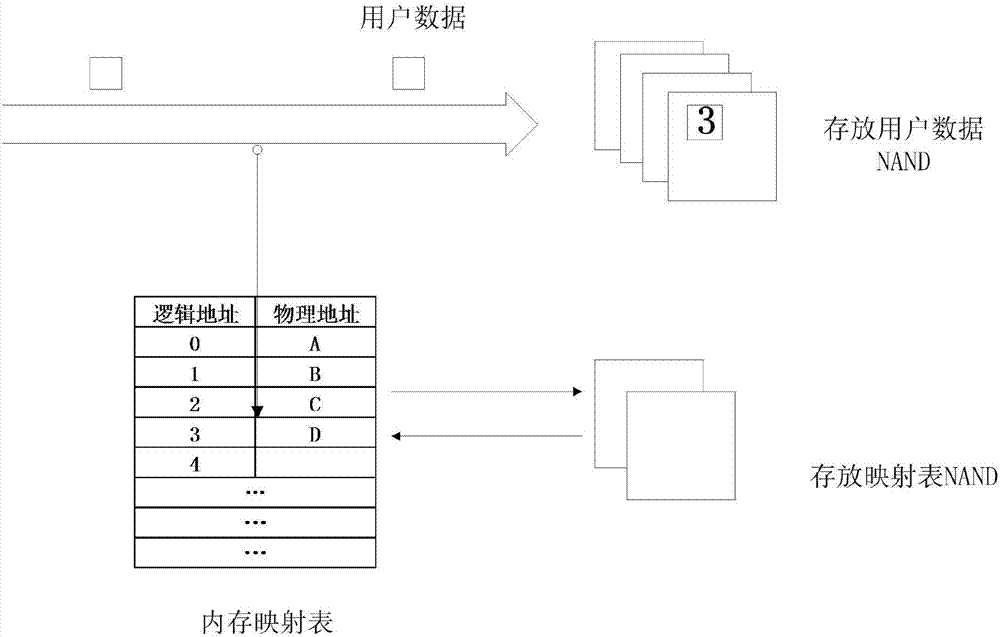
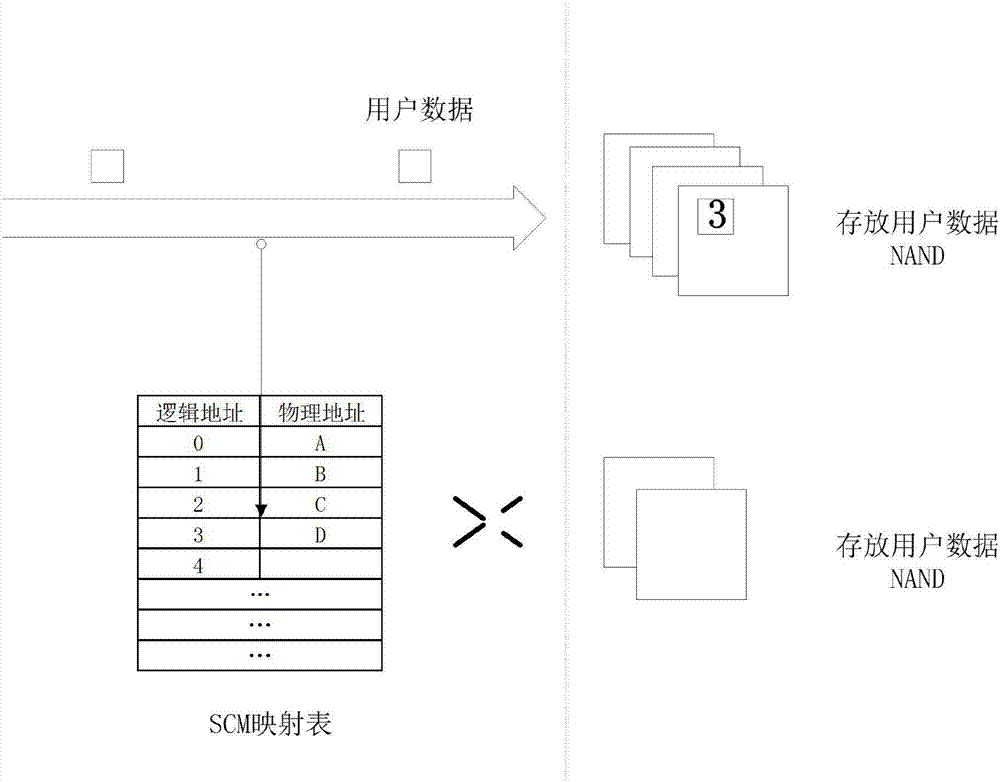
InactiveCN107193758AAvoid occupyingReduce stepsMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWrite amplificationDisk controller
The invention discloses a mapping table management method for a solid state disk and the solid state disk. The method is characterized in that an SCM is added into the solid state disk, a hard disk controller regards the SCM as a solid state disk data cache, and a mapping table used for recording a mapping relation between a specific physical address of an NAND and a logic address accessed by a host is created and stored in the SCM; and when the host writes host data into the solid state disk, the data is written into the SCM first to be cached, and the mapping table is updated synchronously after the data cached in the SCM is actually updated to the NAND or the mapping table is updated synchronously when the data is written into the SCM to be cached. By storing the mapping table in the SCM, the mapping table no longer needs to be stored in the NAND, occupation of space of the NAND is avoided, and therefore the problem of writing amplification caused by frequent updating of the mapping table is avoided. Meanwhile, the operation of loading an initial mapping table from the NAND after startup is omitted, and startup response delay is greatly shortened.
Owner:RAMAXEL TECH SHENZHEN
Systems and methods for adapting to changing characteristics of multi-level cells in solid-state memory
ActiveUS9026867B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeRead-only memoriesDigital storageWrite amplificationSolid-state drive
Apparatus and methods provide relatively low uncorrectable bit error rates, low write amplification, long life, fast and efficient retrieval, and efficient storage density such that a solid-state drive (SSD) can be reliably implemented using various types of memory cells, including relatively inexpensive multi-level cell flash. One embodiment intelligently coordinates remapping of bad blocks with error correction code control, which eliminates the tables used to avoid bad blocks.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
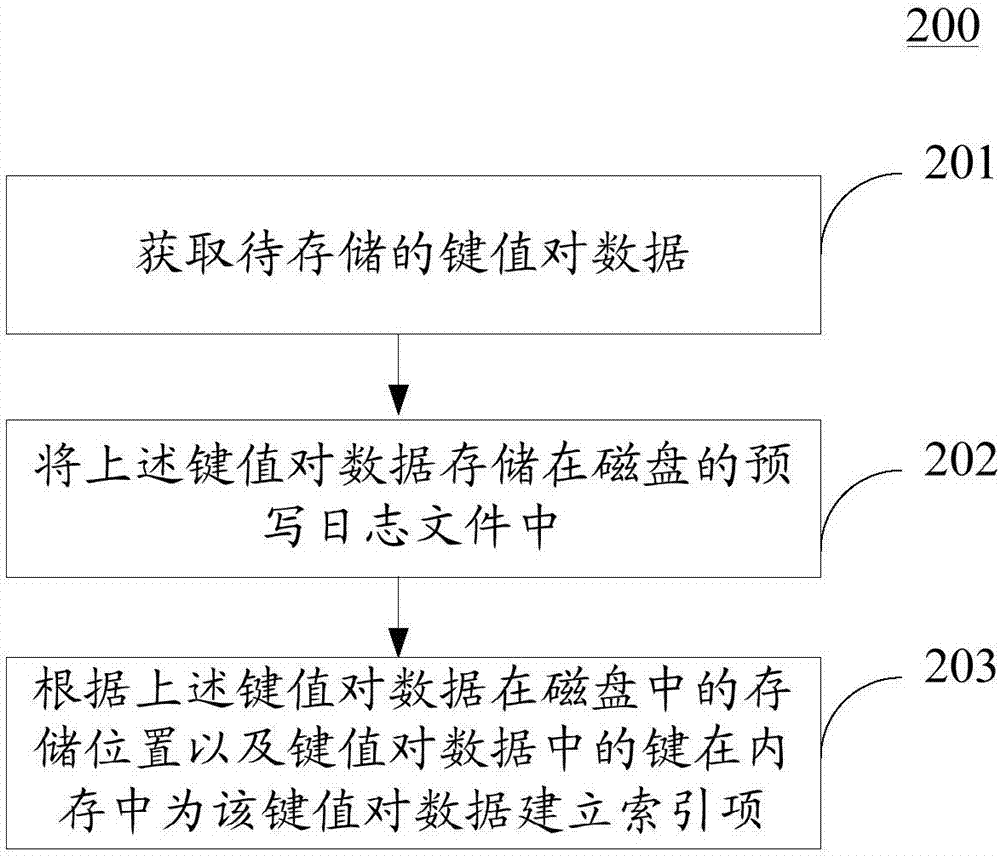
Method and device for storing data
ActiveCN106886375AImprove effectivenessReduce write amplification problemsInput/output to record carriersWrite amplificationPaired Data
The invention discloses a method and device for storing data. The method specifically comprises the steps of obtaining key value pair data to be stored; storing the key value pair data in pre-write log files of a disk; generating an index entry for the key value pair data in a memorizer according to the storing position of the key value data in the disk and keys in the key value pair data so as to execute preset operation on the key value pair data through the index entry, and writing the key value pair data reserved in a pre-write log file which satisfies a preset condition into the disk when the pre-write log file which satisfies a merging settling condition is detected, wherein the storing position comprises at least the file name of the pre-write log file and offset of the key value pair data in the pre-write log file and the initial position of the file. According to the method and device for storing the data, the problem of write amplification can be avoided, and the effectiveness of stored data is improved.
Owner:BAIDU ONLINE NETWORK TECH (BEIJIBG) CO LTD
Reducing write amplification in solid-state drives by separating allocation of relocate writes from user writes
InactiveUS20160092352A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWrite amplificationData stream
In one embodiment, a method includes maintaining a first open logical erase block for user writes, maintaining a second open logical erase block for relocate writes, wherein the first and second open logical erase blocks are different logical erase blocks, receiving a first data stream having the user writes, transferring the first data stream to the first open logical erase block, receiving a second data stream having the relocate writes, and transferring the second data stream to the second open logical erase block. Other systems, methods, and computer program products are described in additional embodiments.
Owner:IBM CORP
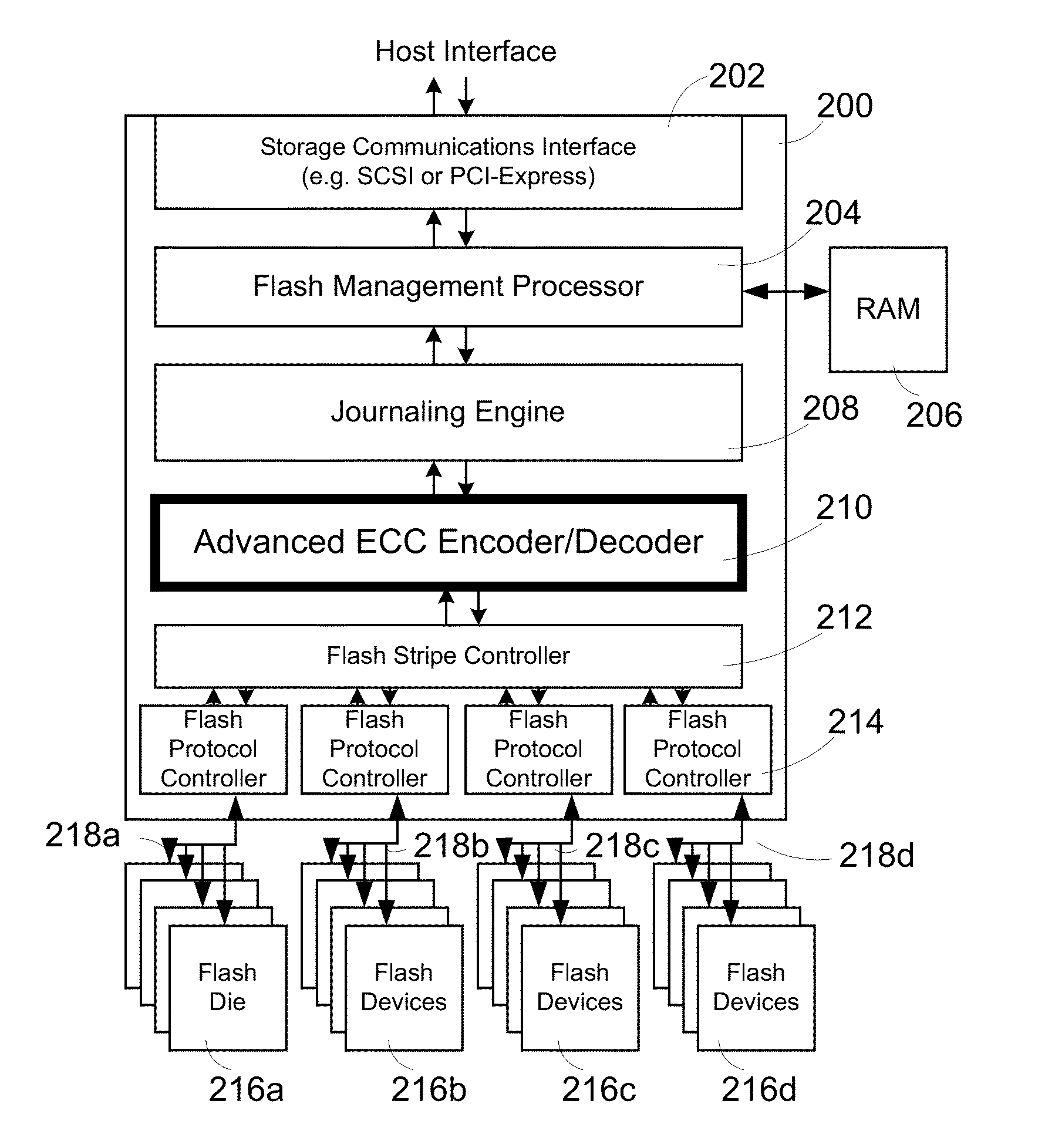
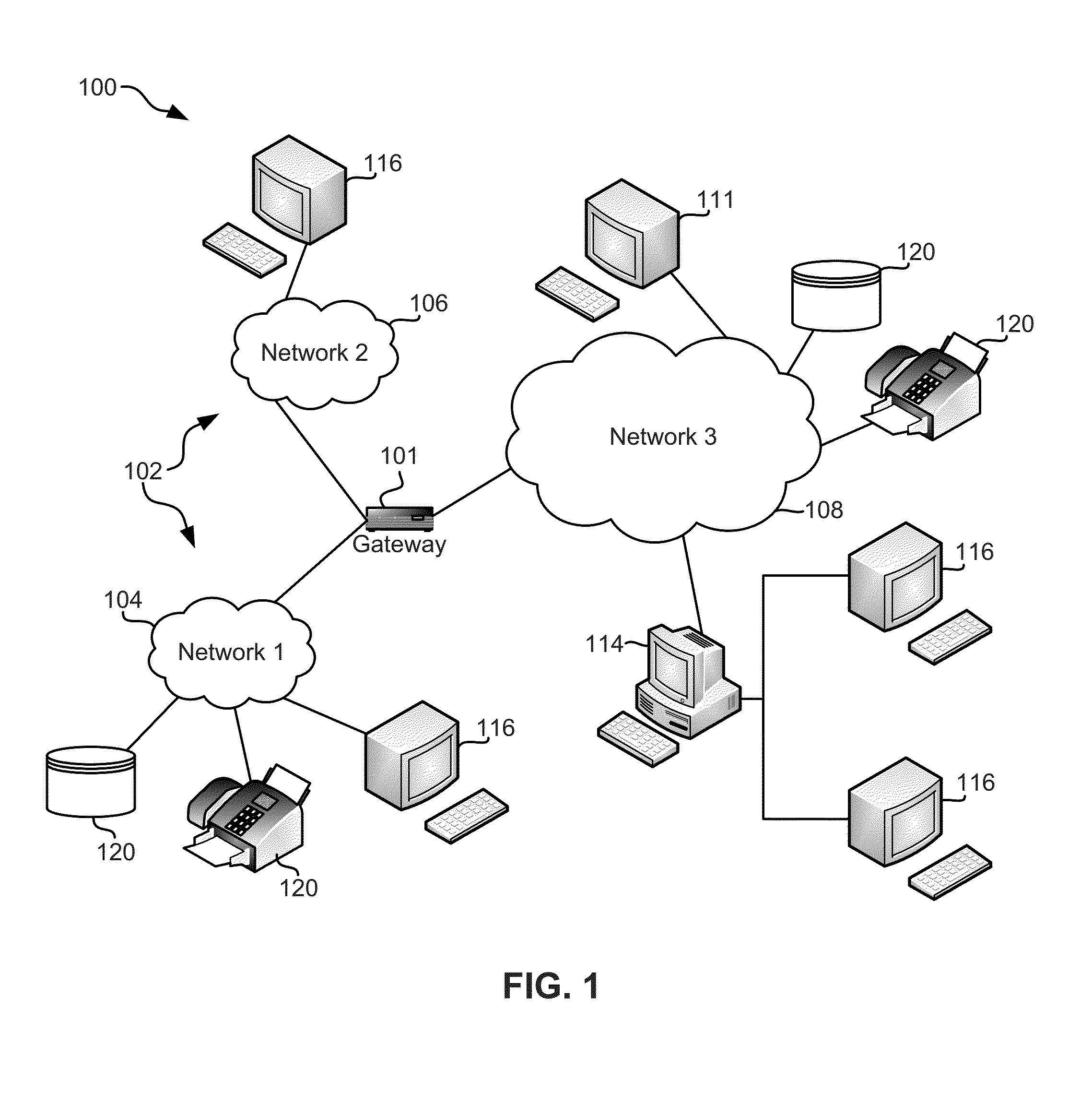
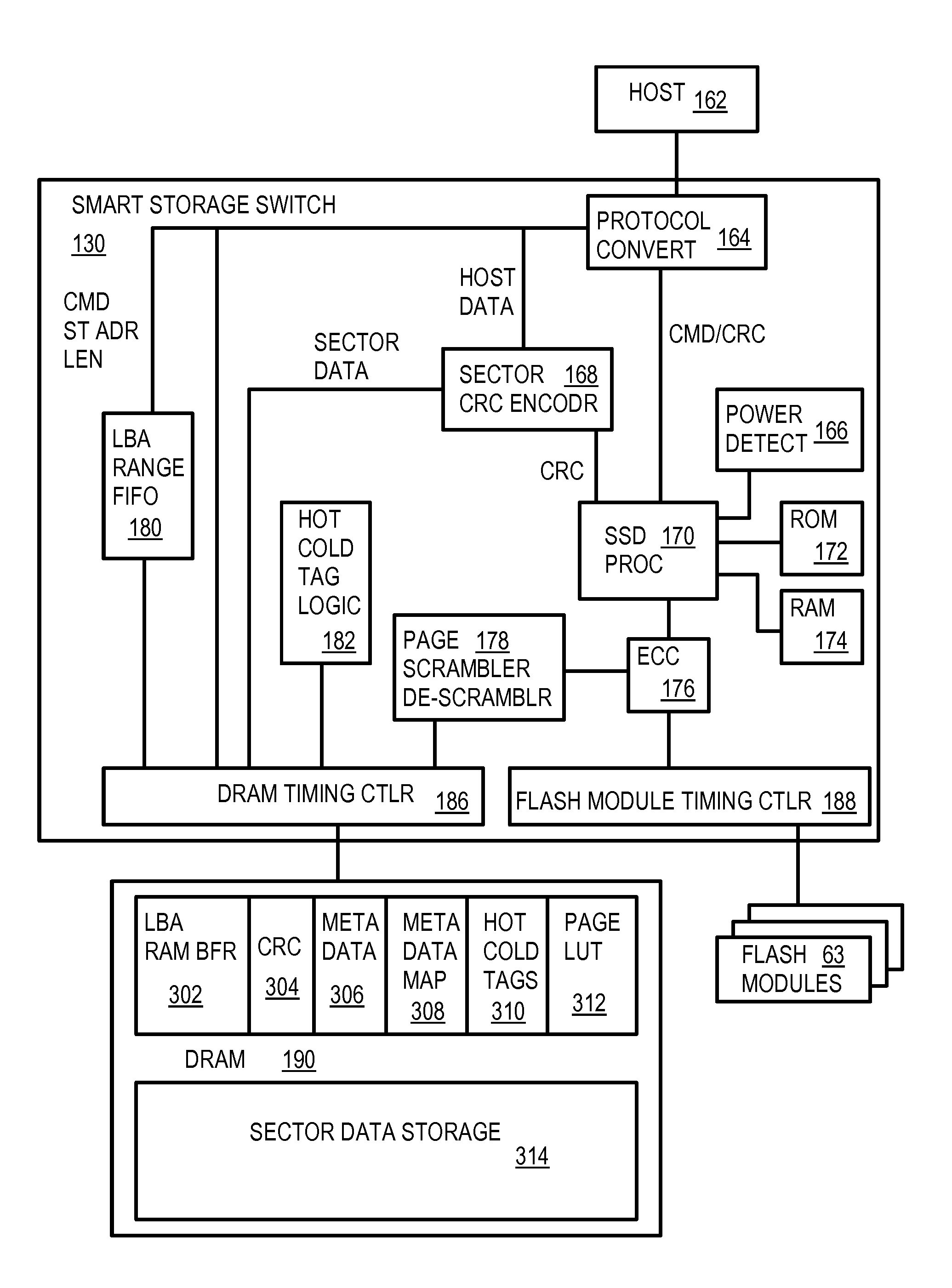
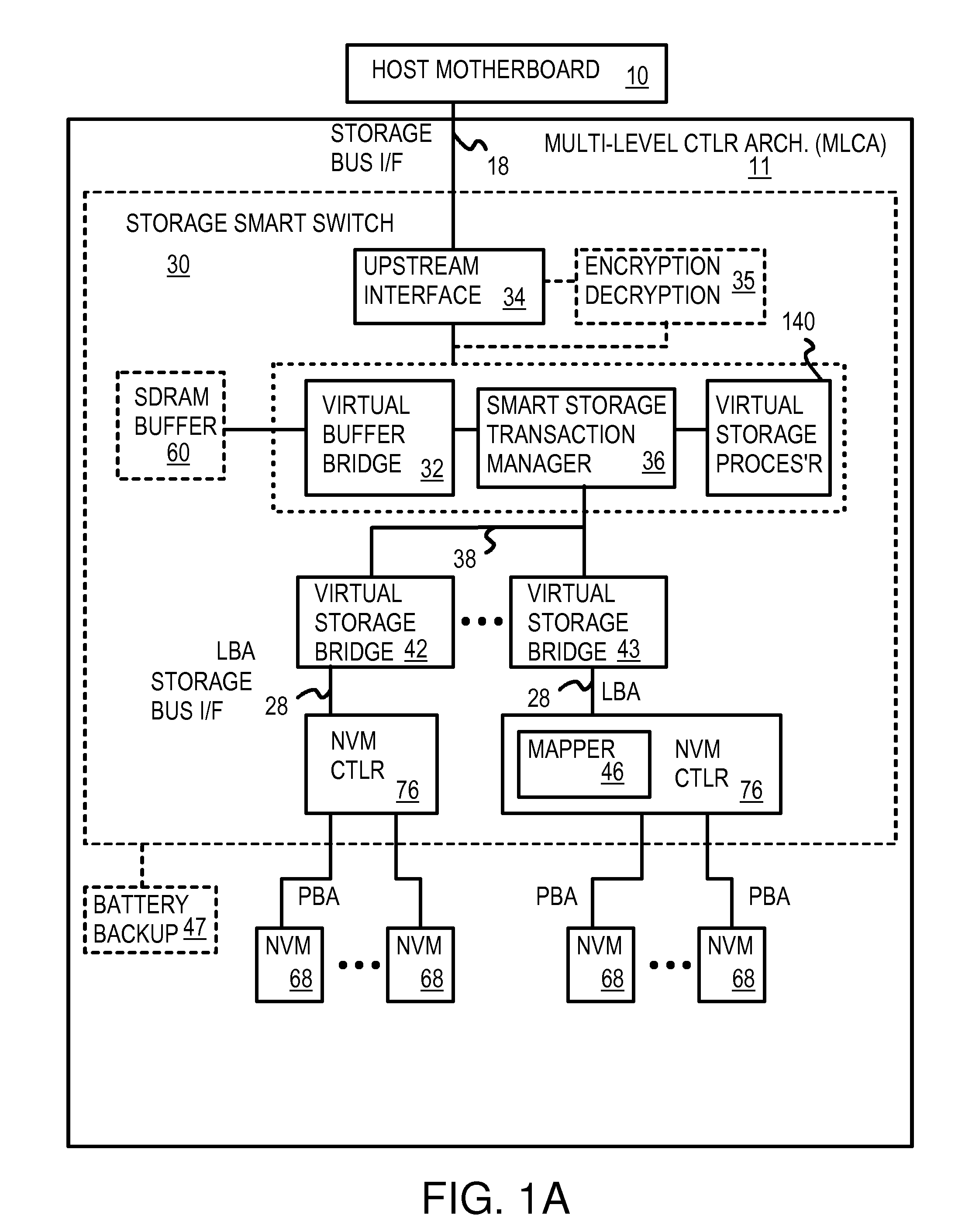
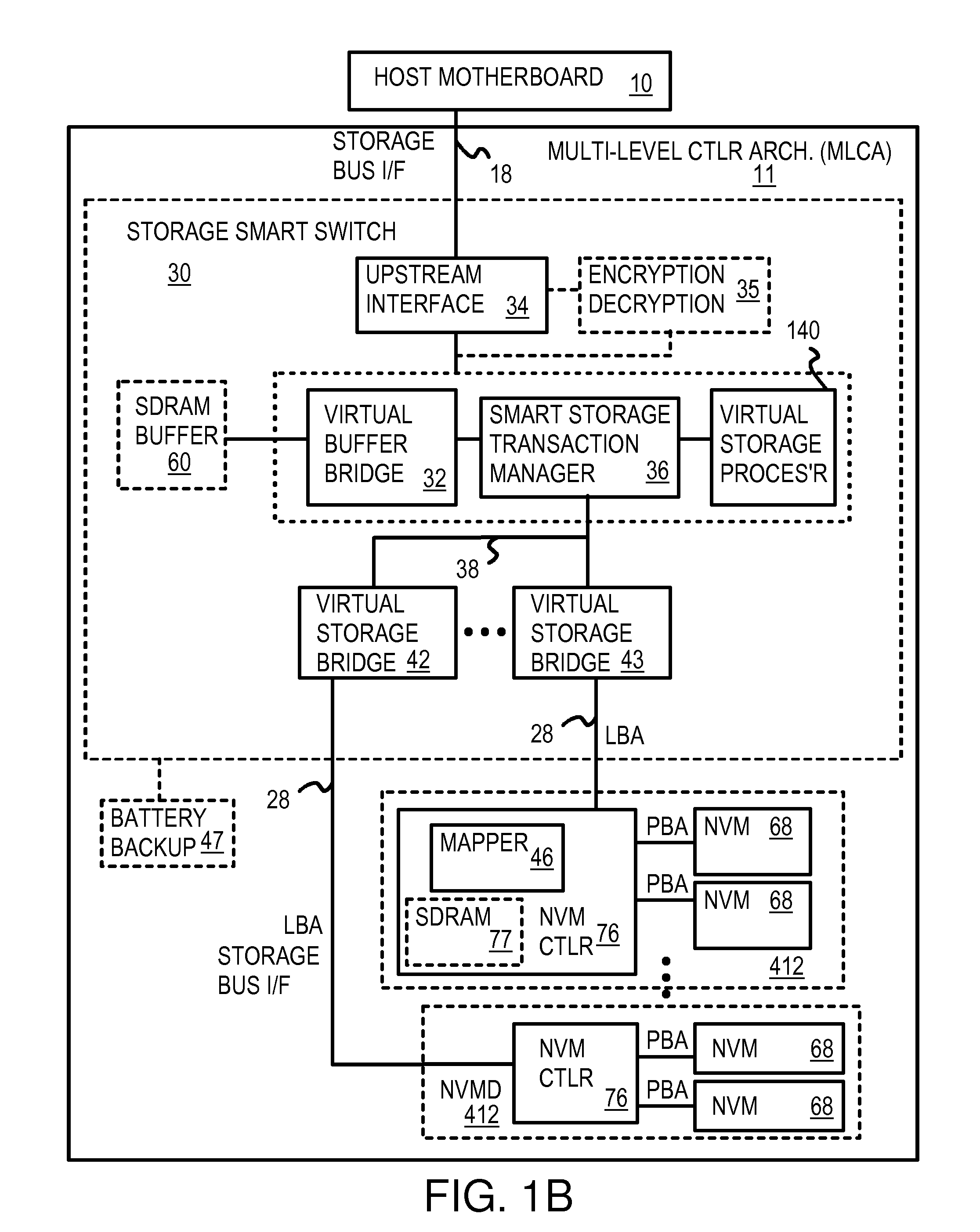
Flash-memory system with enhanced smart-storage switch and packed meta-data cache for mitigating write amplification by delaying and merging writes until a host read
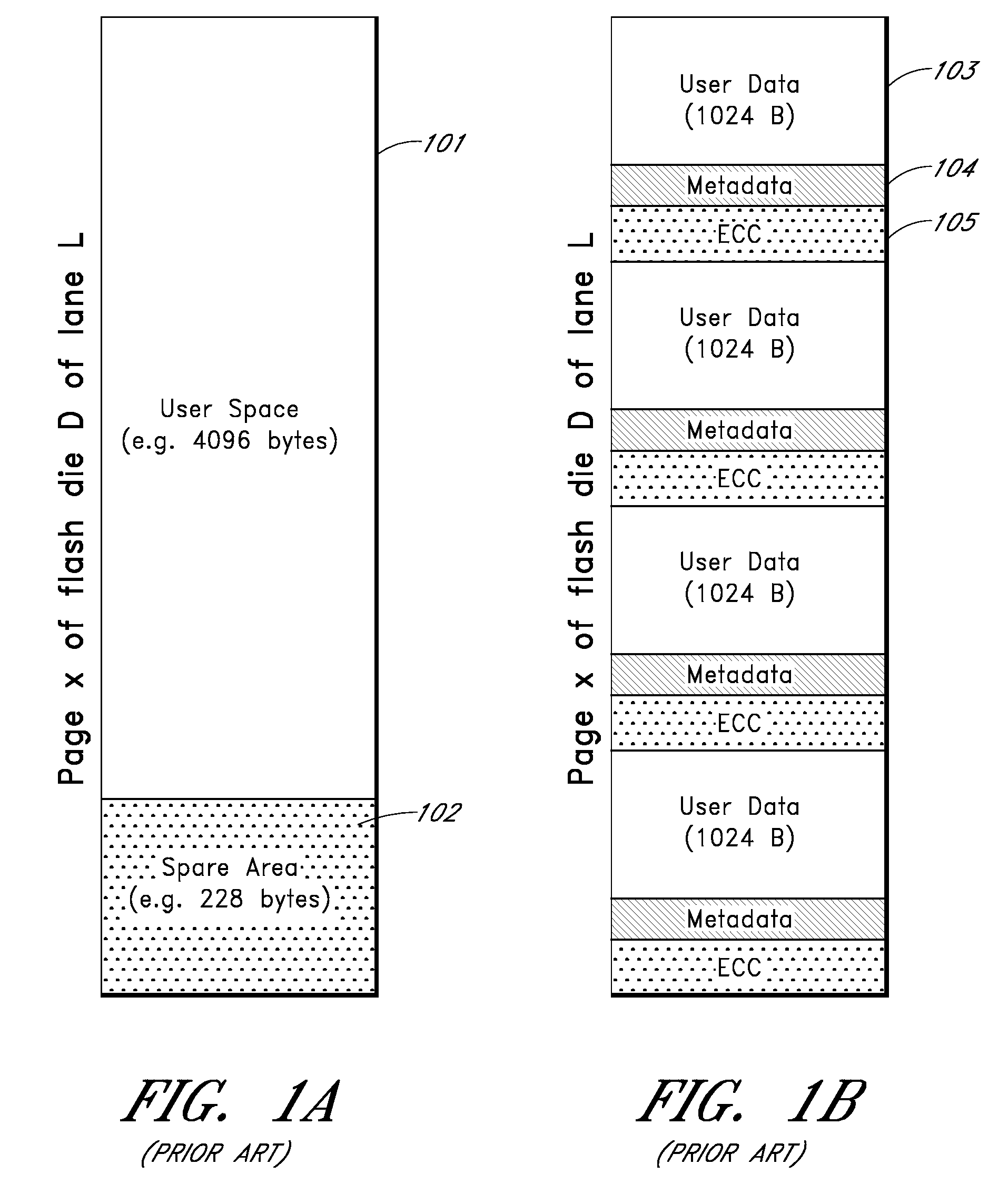
InactiveUS8452912B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesWrite amplificationLogical block addressing
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
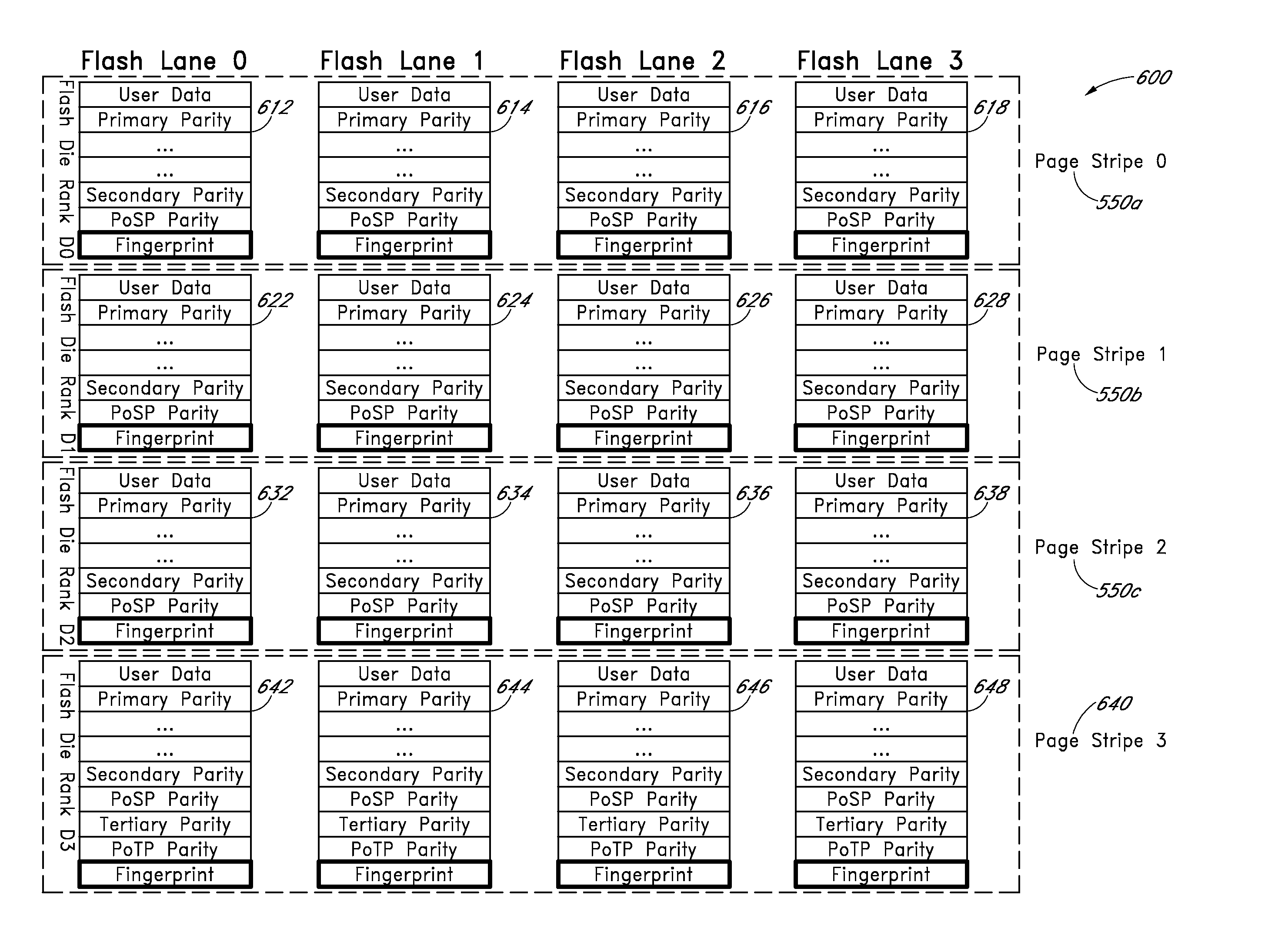
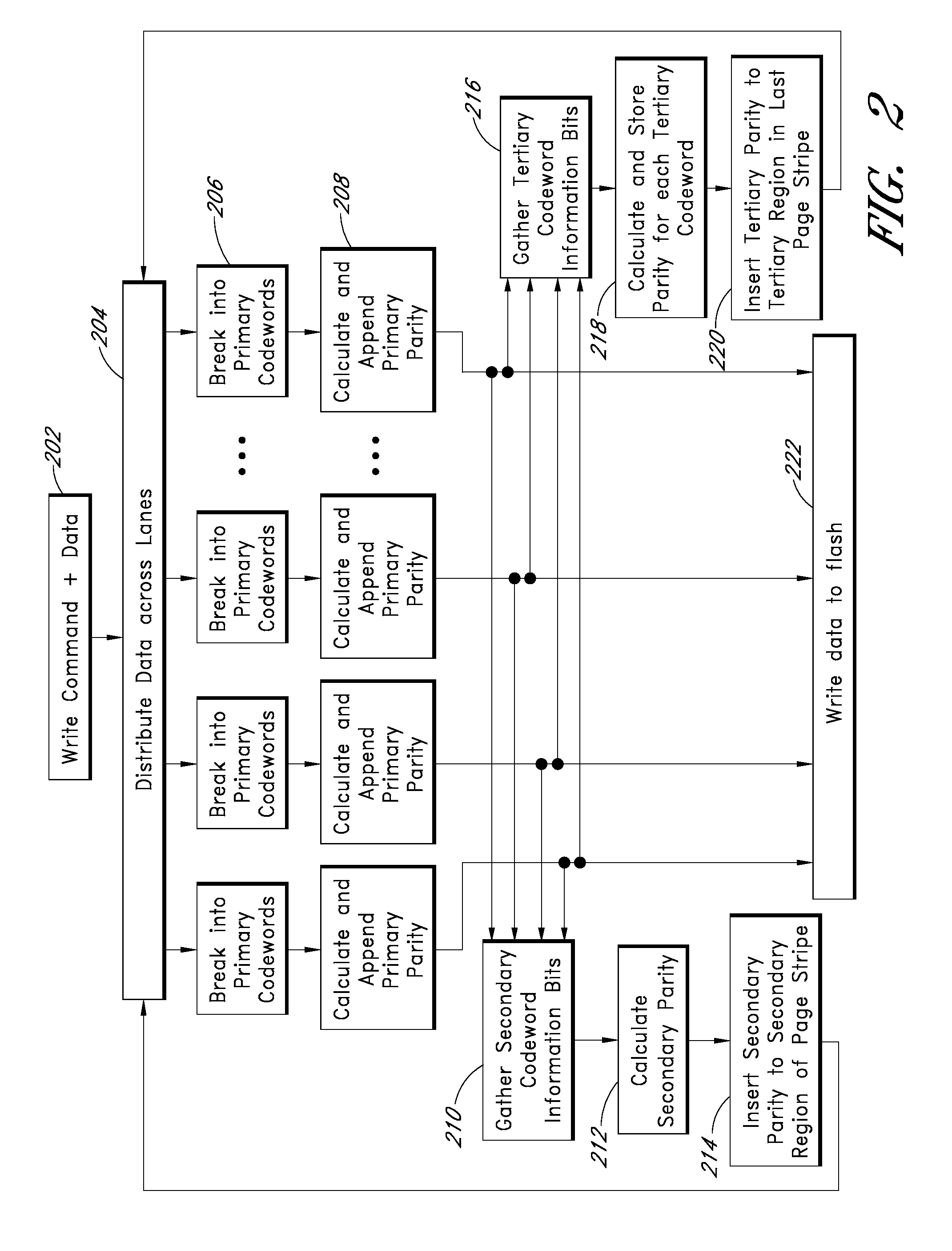
Systems and methods for redundantly storing error correction codes in a flash drive with secondary parity information spread out across each page of a group of pages
ActiveUS9021336B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeCode conversionCoding detailsWrite amplificationSolid-state drive
Apparatus and methods provide relatively low uncorrectable bit error rates, low write amplification, long life, fast and efficient retrieval, and efficient storage density such that a solid-state drive (SSD) can be implemented using relatively inexpensive MLC Flash for an enterprise storage application. Both primary parity symbols for primary codewords and secondary parity symbols for secondary codewords are generated. The secondary parity symbols are spread out across each page of a group of pages.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
Systems and methods for storing data for solid-state memory
ActiveUS9053012B1Low uncorrectable bit error rateSolution to short lifeError detection/correctionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWrite amplificationSolid-state drive
Apparatus and methods provide relatively low uncorrectable bit error rates, low write amplification, long life, fast and efficient retrieval, and efficient storage density such that a solid-state drive (SSD) can be reliably implemented using various types of memory cells, including relatively inexpensive multi-level cell flash. One embodiment intelligently coordinates remapping of bad blocks with error correction code control, which eliminates the tables used to avoid bad blocks.
Owner:IP GEM GRP LLC
Method for selecting garbage collection target block, and solid state disk
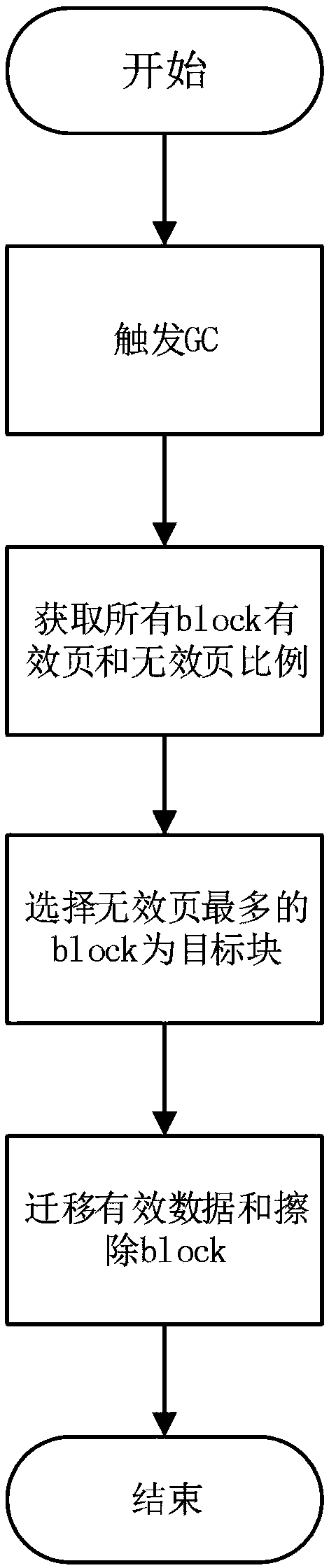
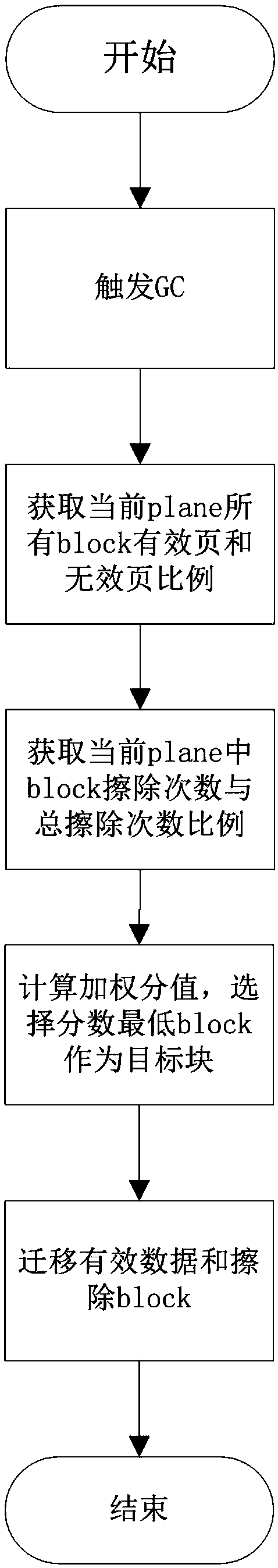
InactiveCN108628758AExtended service lifeReduce the number of migrationsMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwareWrite amplification
The invention discloses a method for selecting a garbage collection target block, and a solid state disk. The method is characterized in that the recovery factor score of each block is calculated according to the proportion and the erasing frequencies of effective pages in each block, and the block with a lowest score is selected as a recovery target block. The effective page ratio and the erasingfrequency weighting score value of each block on the SSD (Solid State Disk) are calculated to comprehensively consider an influence on the read-write performance and the service life of the SSD as far as possible, and the block with a low effective page proportion and few erasing frequencies is selected as the target recovery block of a GC. A wear-leveling thought is used for selecting an optimalblock as a recovery block, block erasing frequencies in the SSD are reduced, data migration frequencies are lowered, write amplification is reduced, and the service life of the SSD is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN YILIAN INFORMATION SYST CO LTD
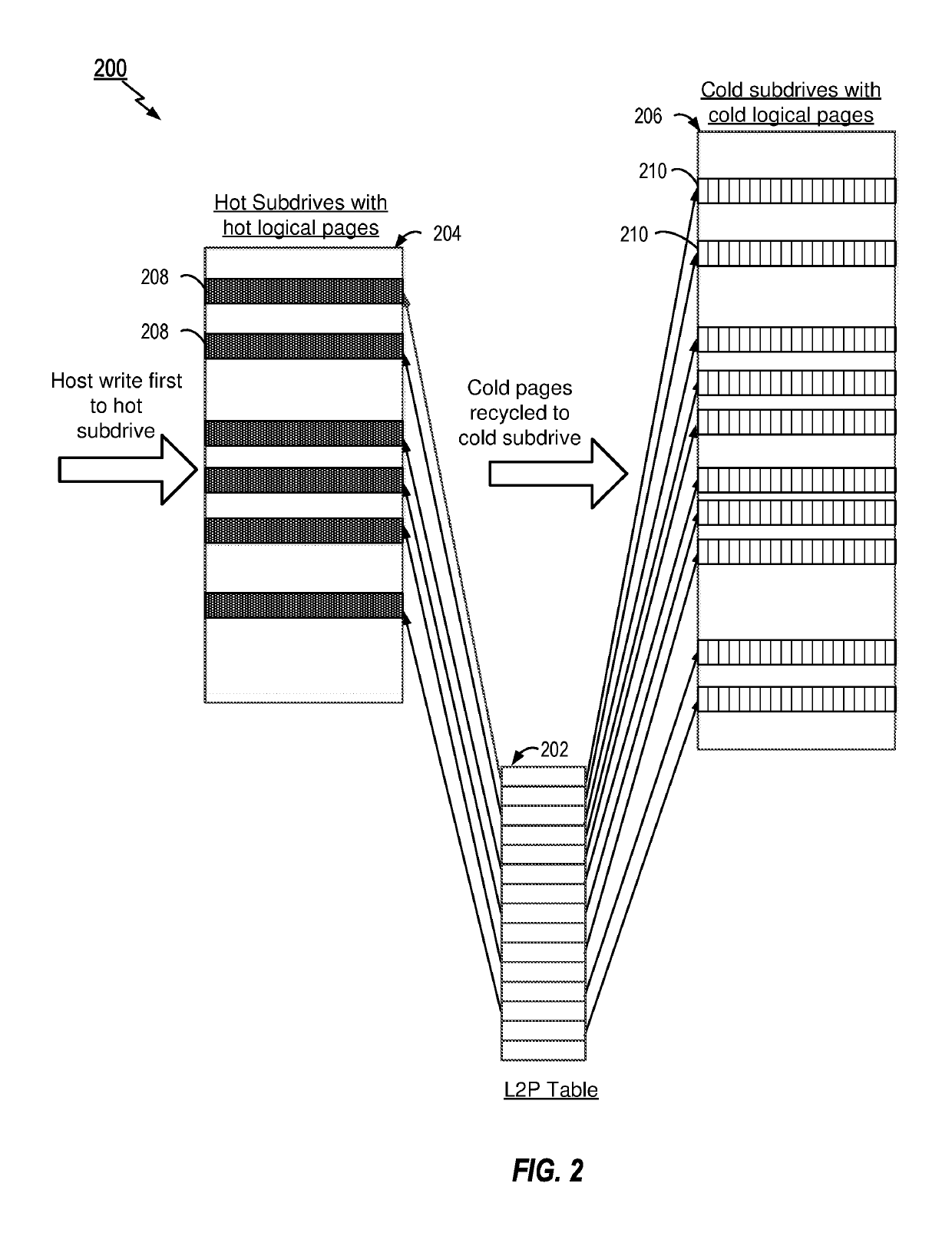
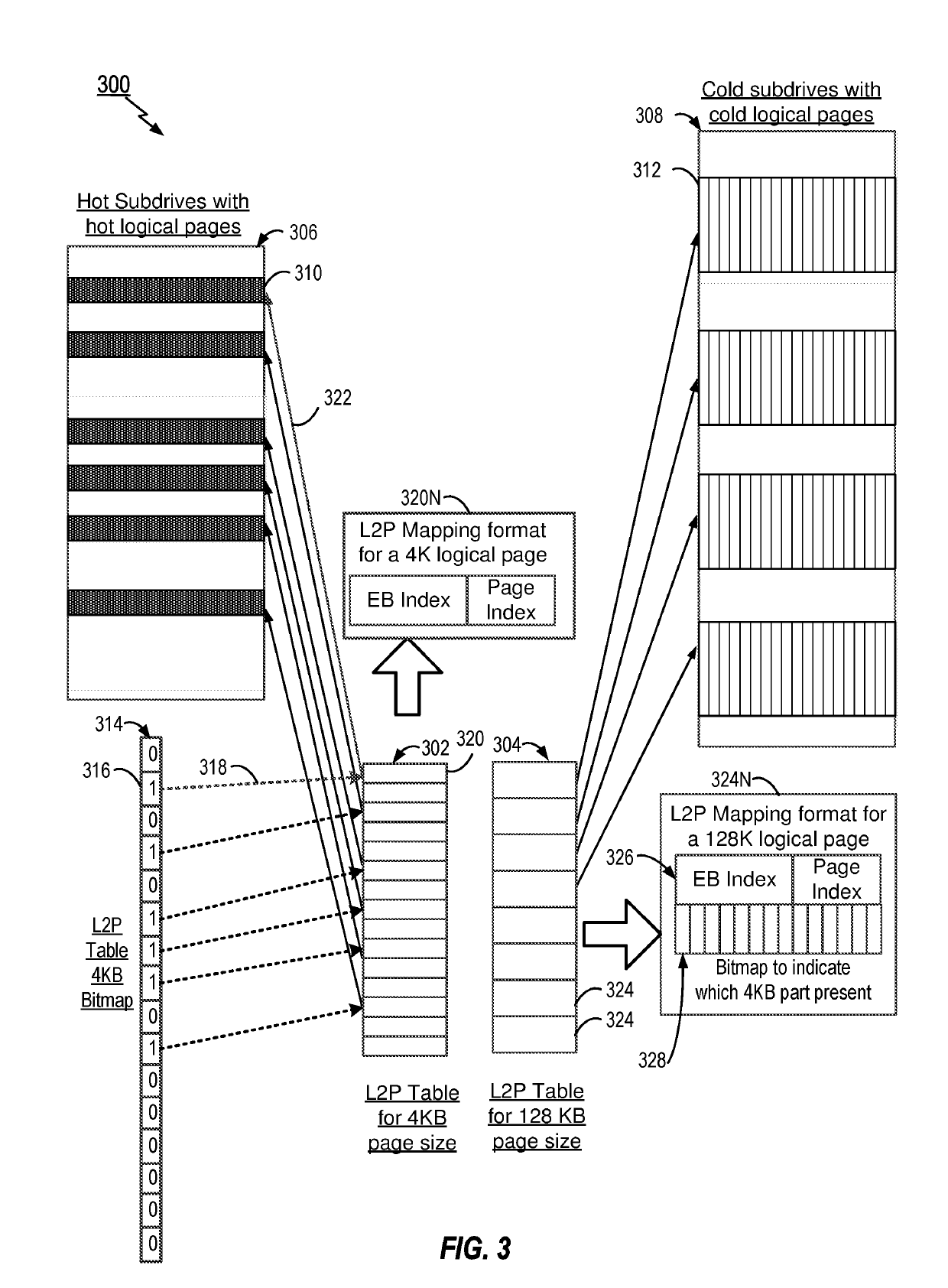
Methods and apparatus for variable size logical page management based on hot and cold data
ActiveUS20190114272A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWrite amplificationSolid-state drive
Aspects of the disclosure provide for management of a flash translation layer (FTL) for a non-volatile memory (NVM) in a Solid State Drive (SSD). The methods and apparatus provide a logical to physical (L2P) table where a first portion of the table is used for mapping frequently accessed hot data to a first subdrive in the NVM. Additionally, a second portion of the L2P table is provided for mapping cold data less frequently accessed than the hot data to a second subdrive, where logical blocks for storing the cold data in the second subdrive are larger than logical blocks storing the hot data in the first subdrive. Separation of the L2P table into hot and cold subdrives reduces the L2P table size that is needed in RAM for logical to physical memory mapping, while at the same time provides lower write amplification and latencies, especially for large capacity SSDs.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com