Patents
Literature
6507results about "Coding details" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
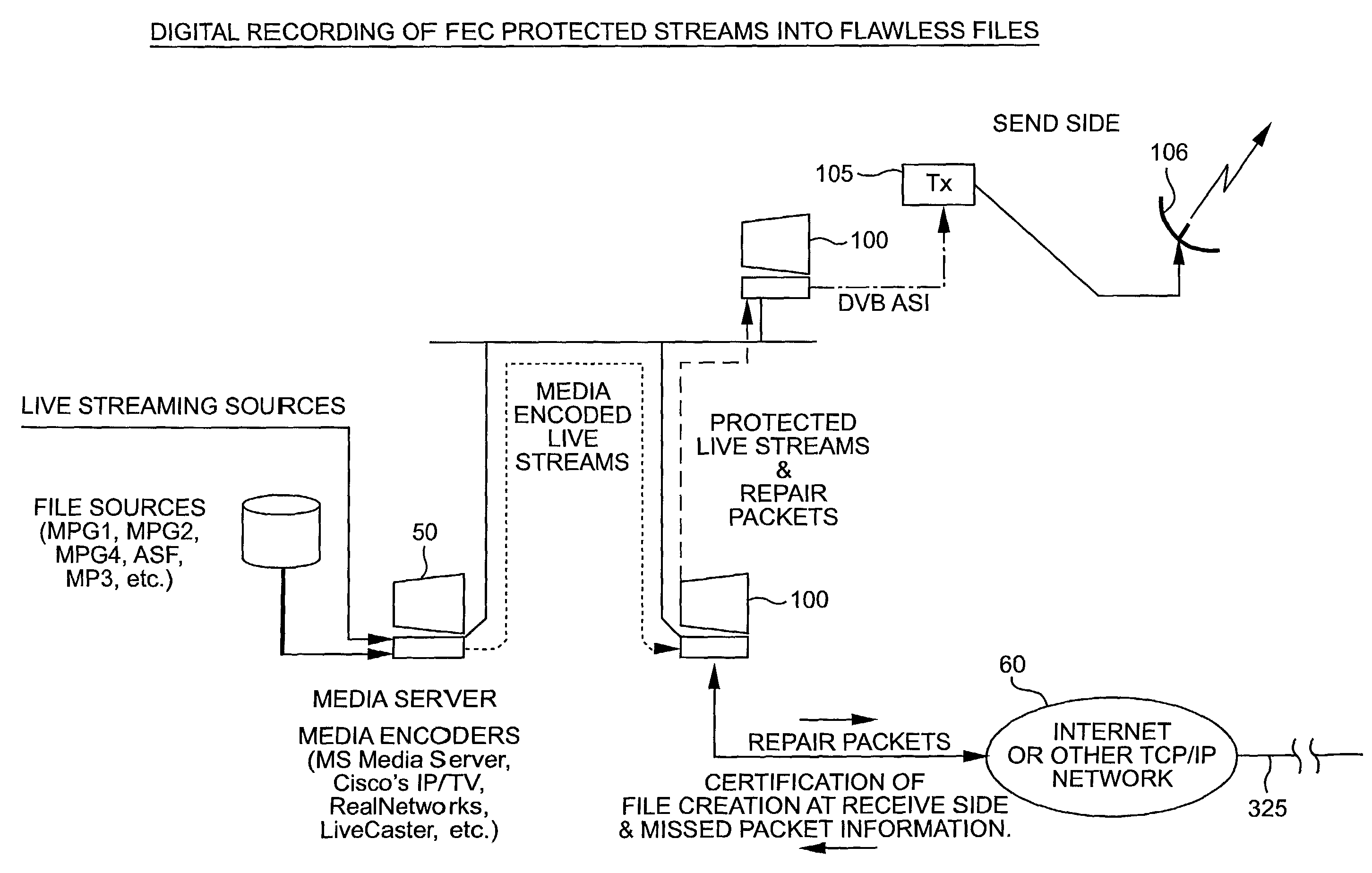
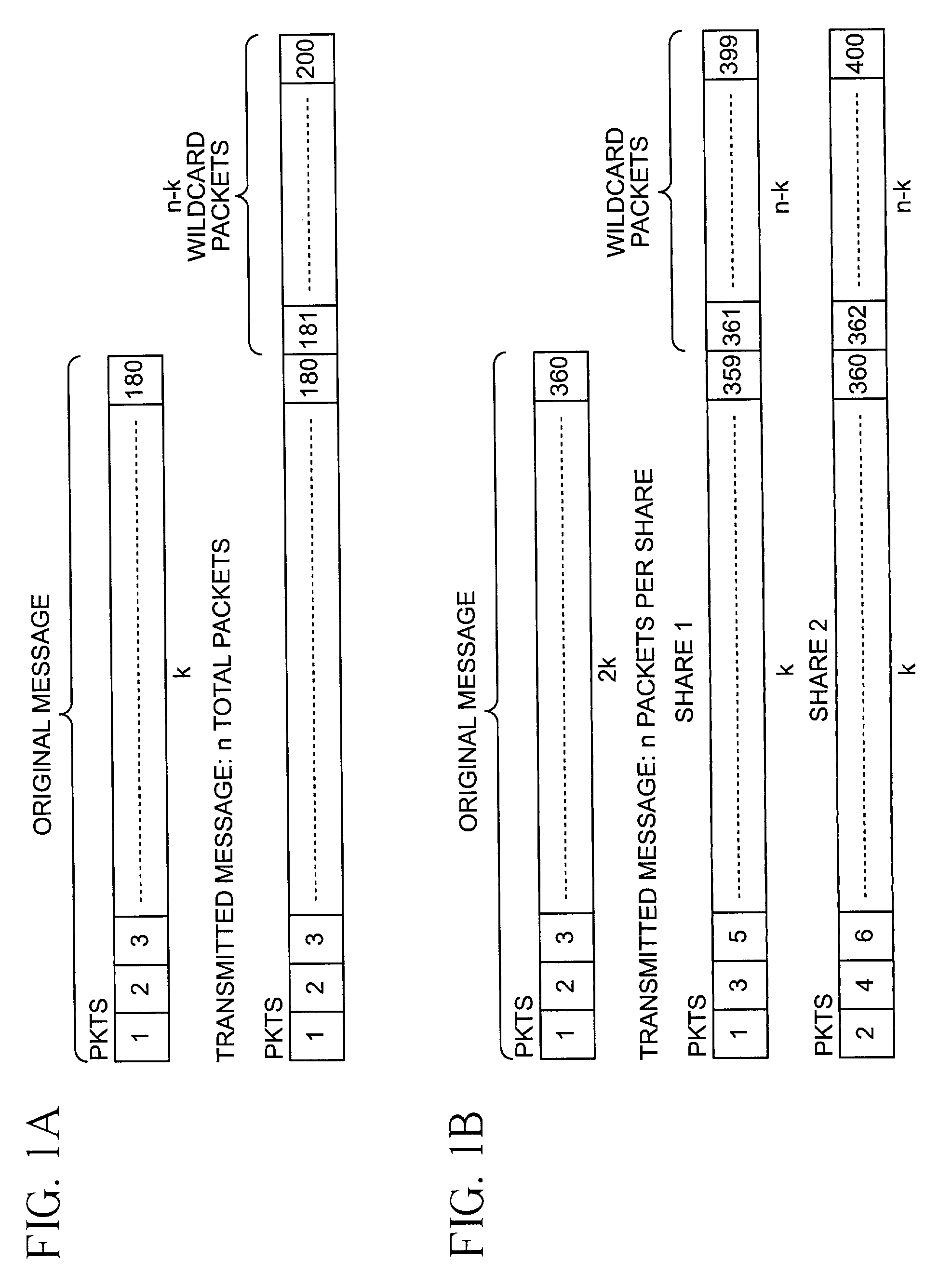
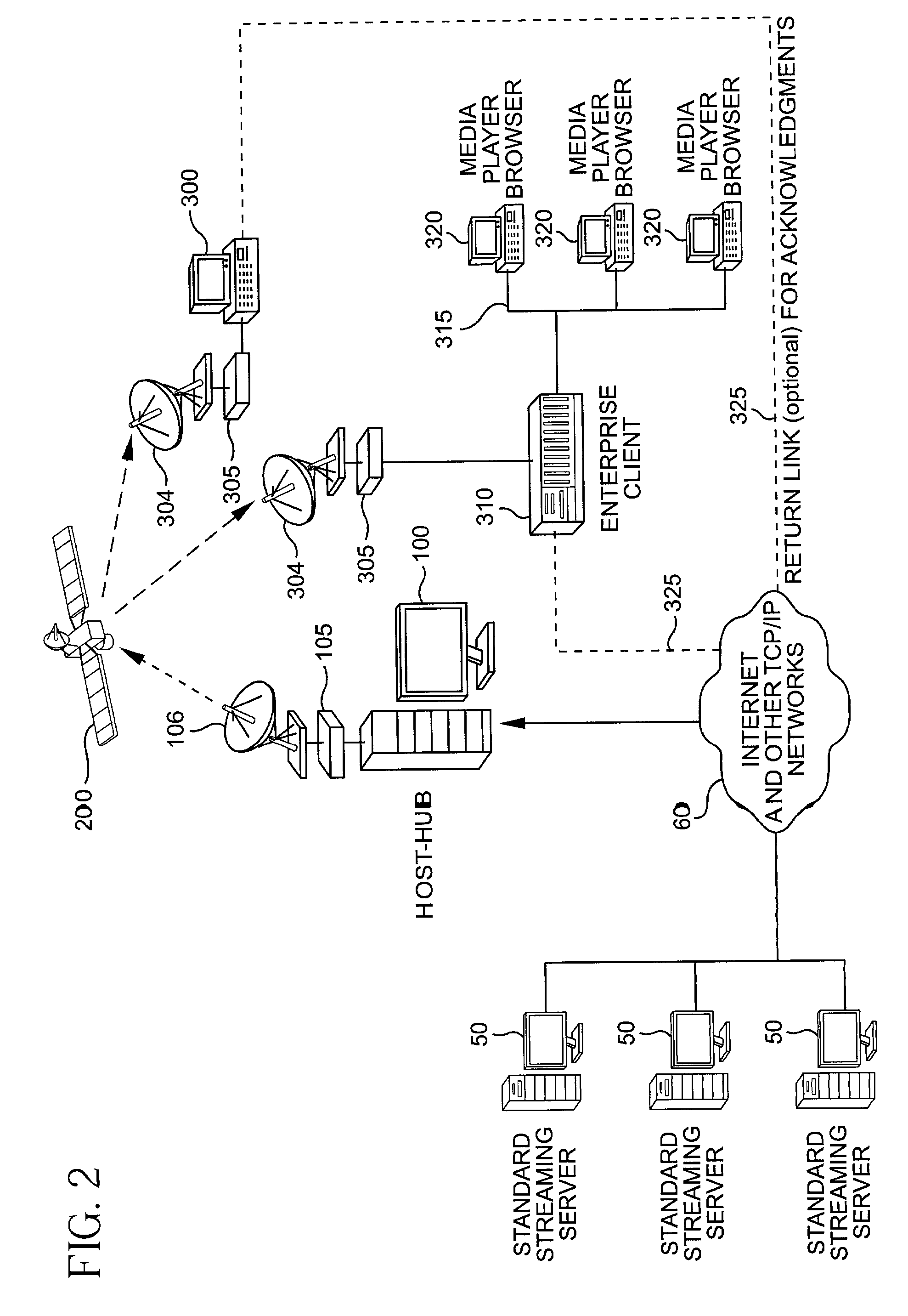
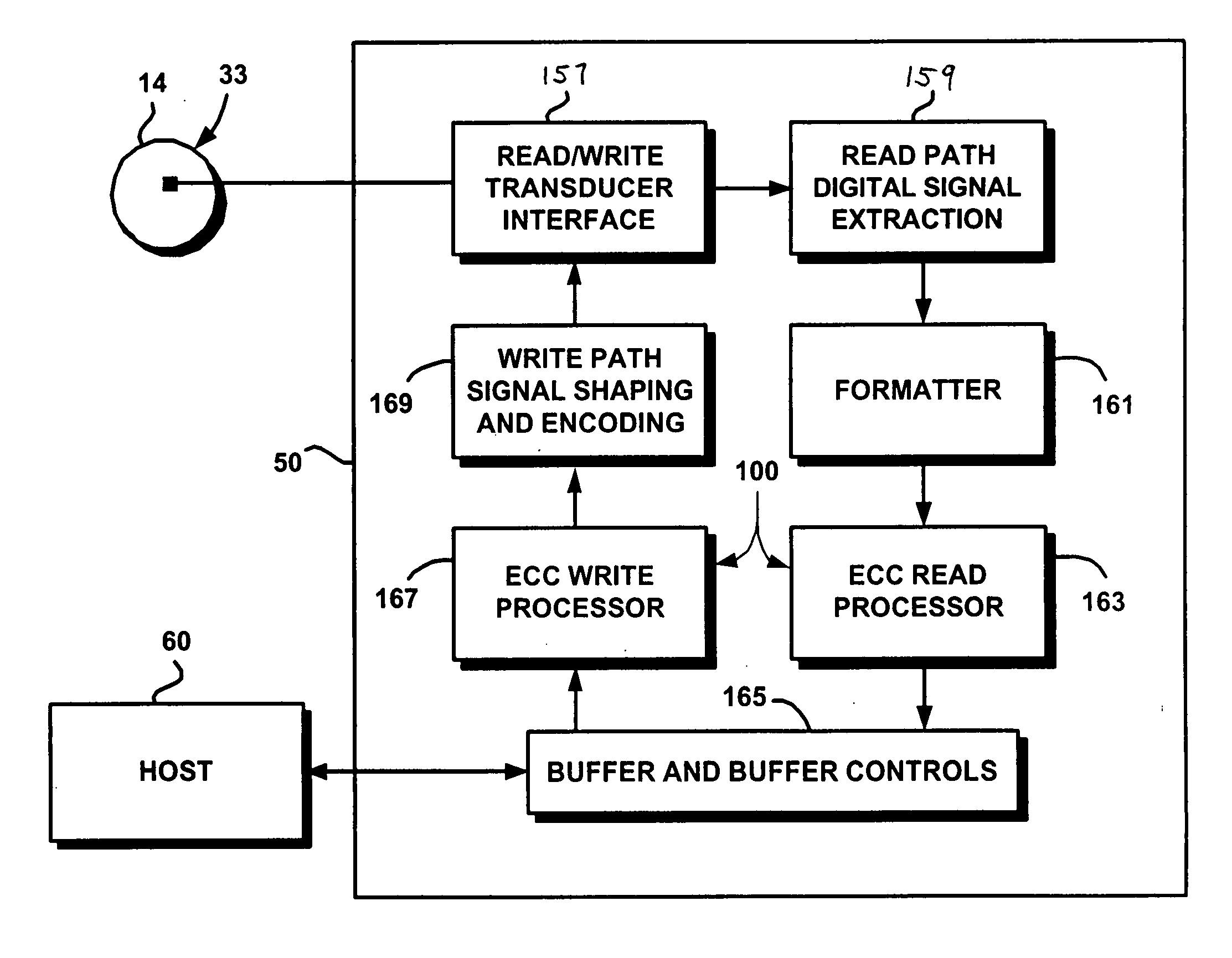
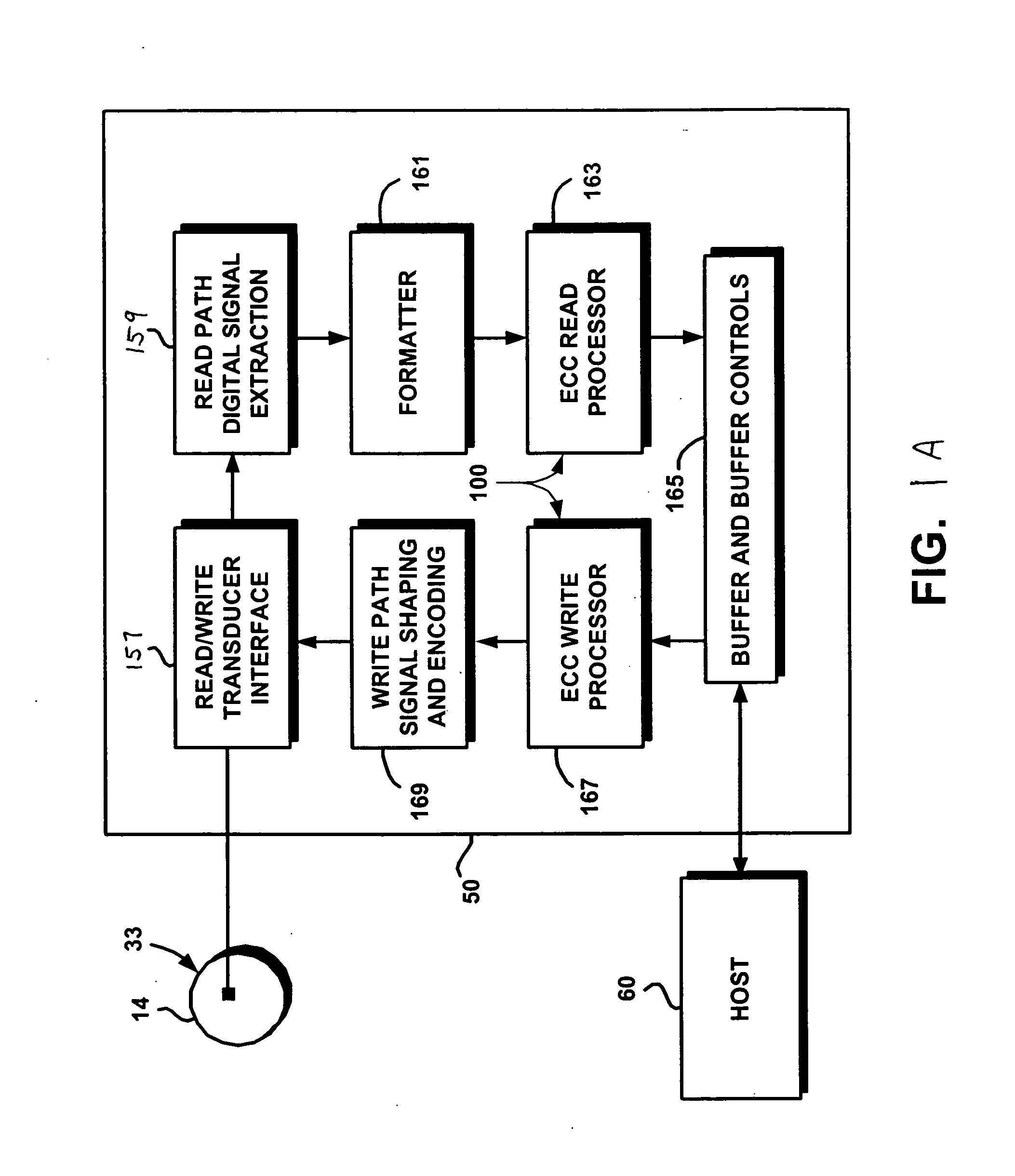
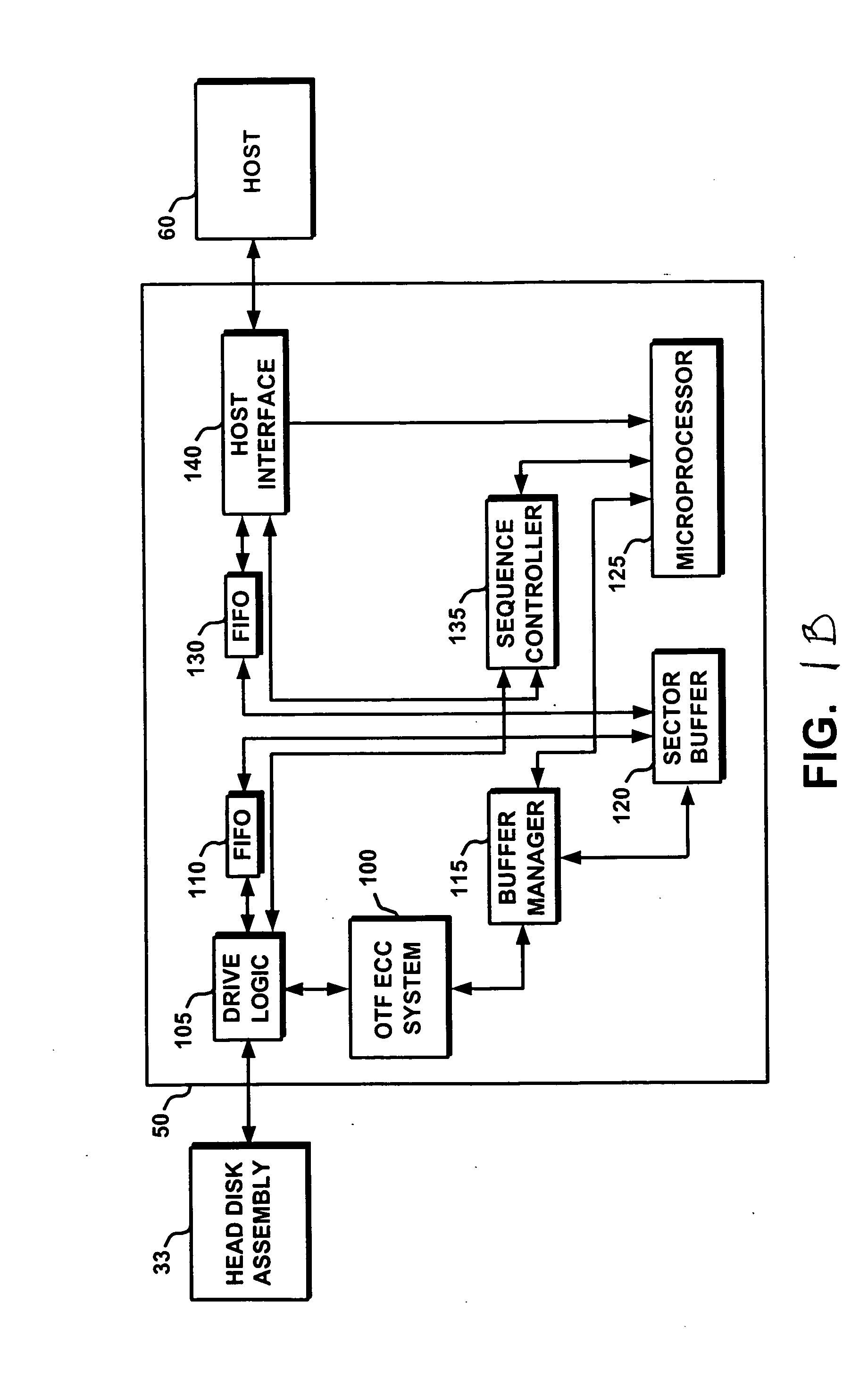
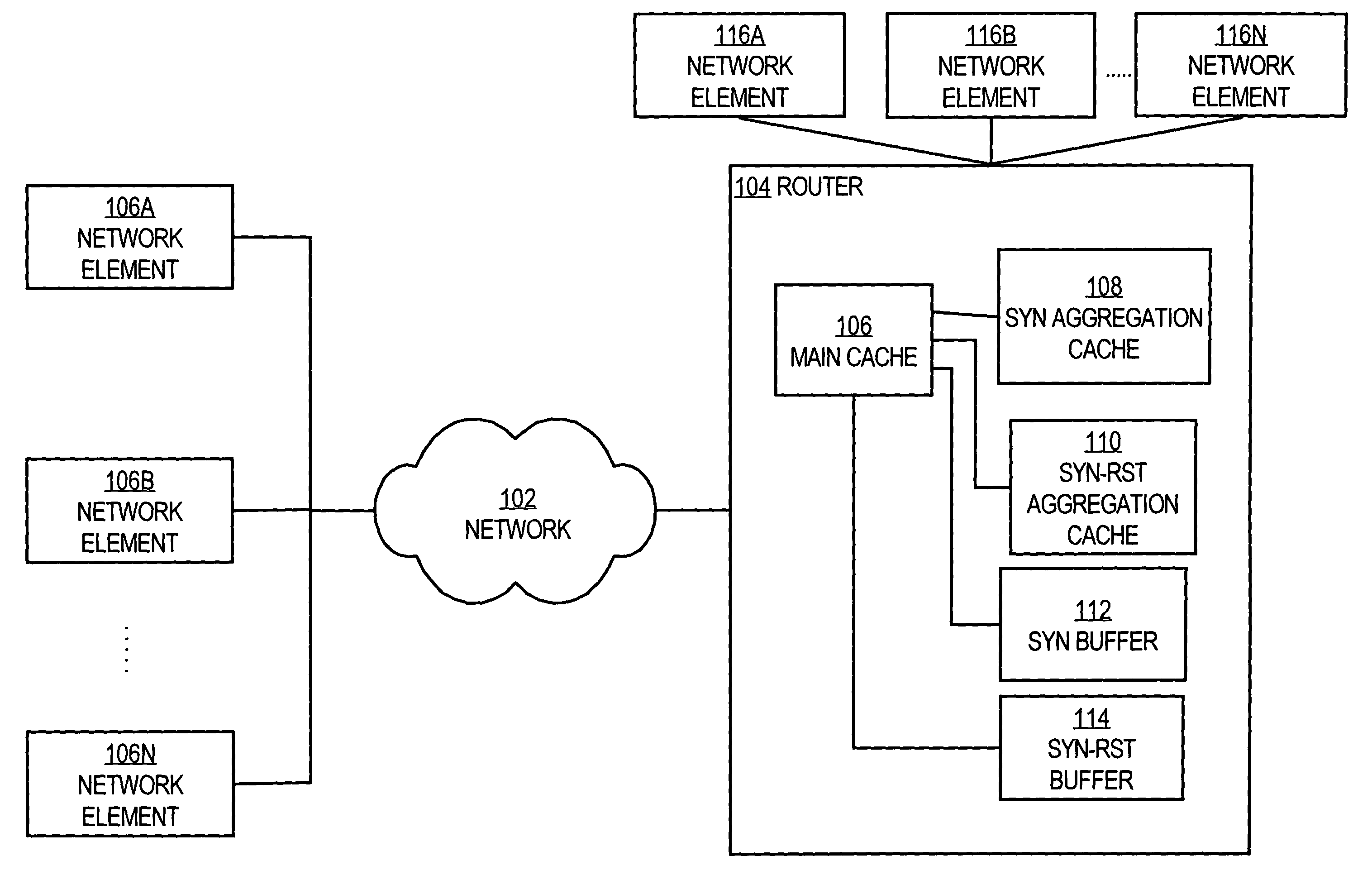
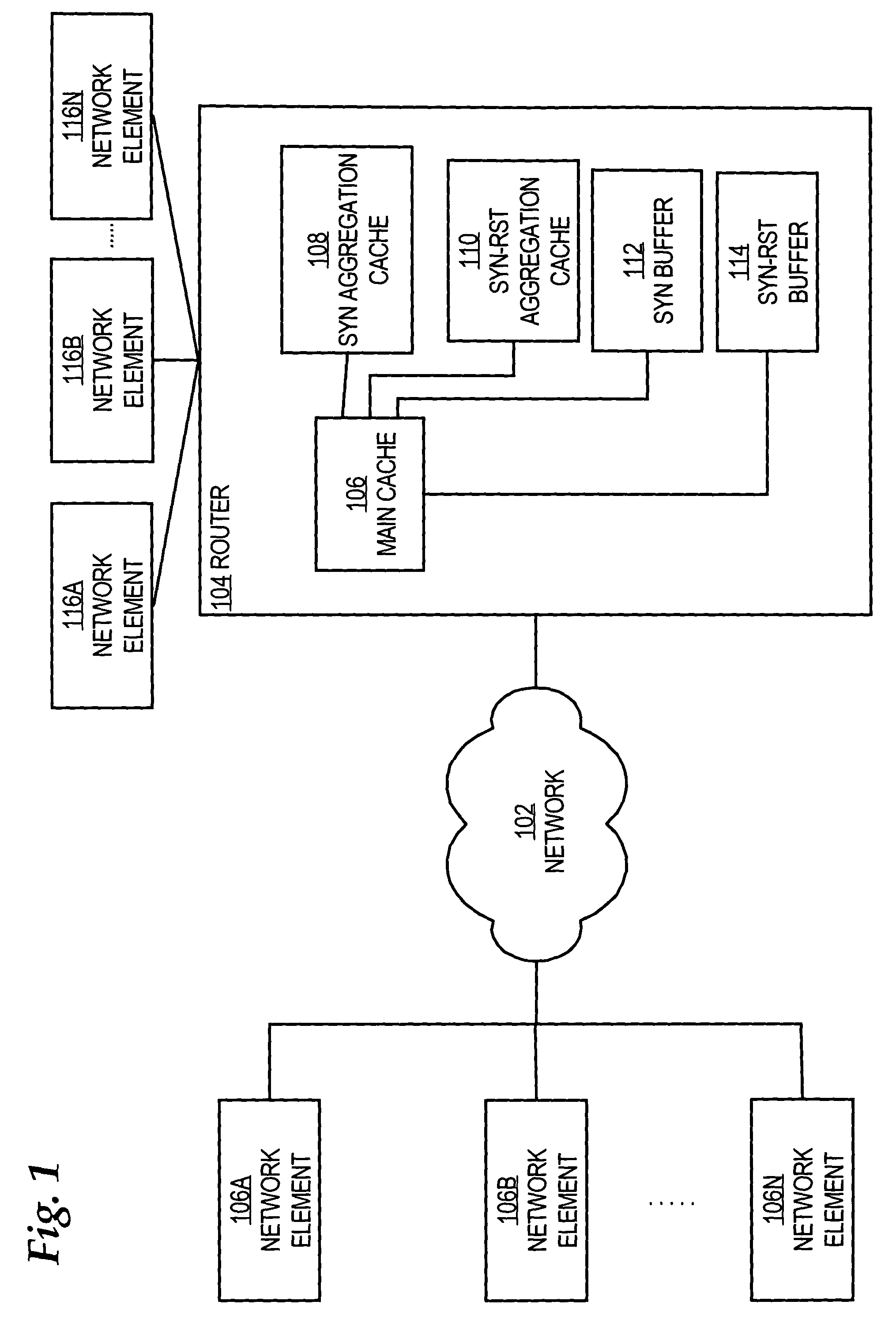
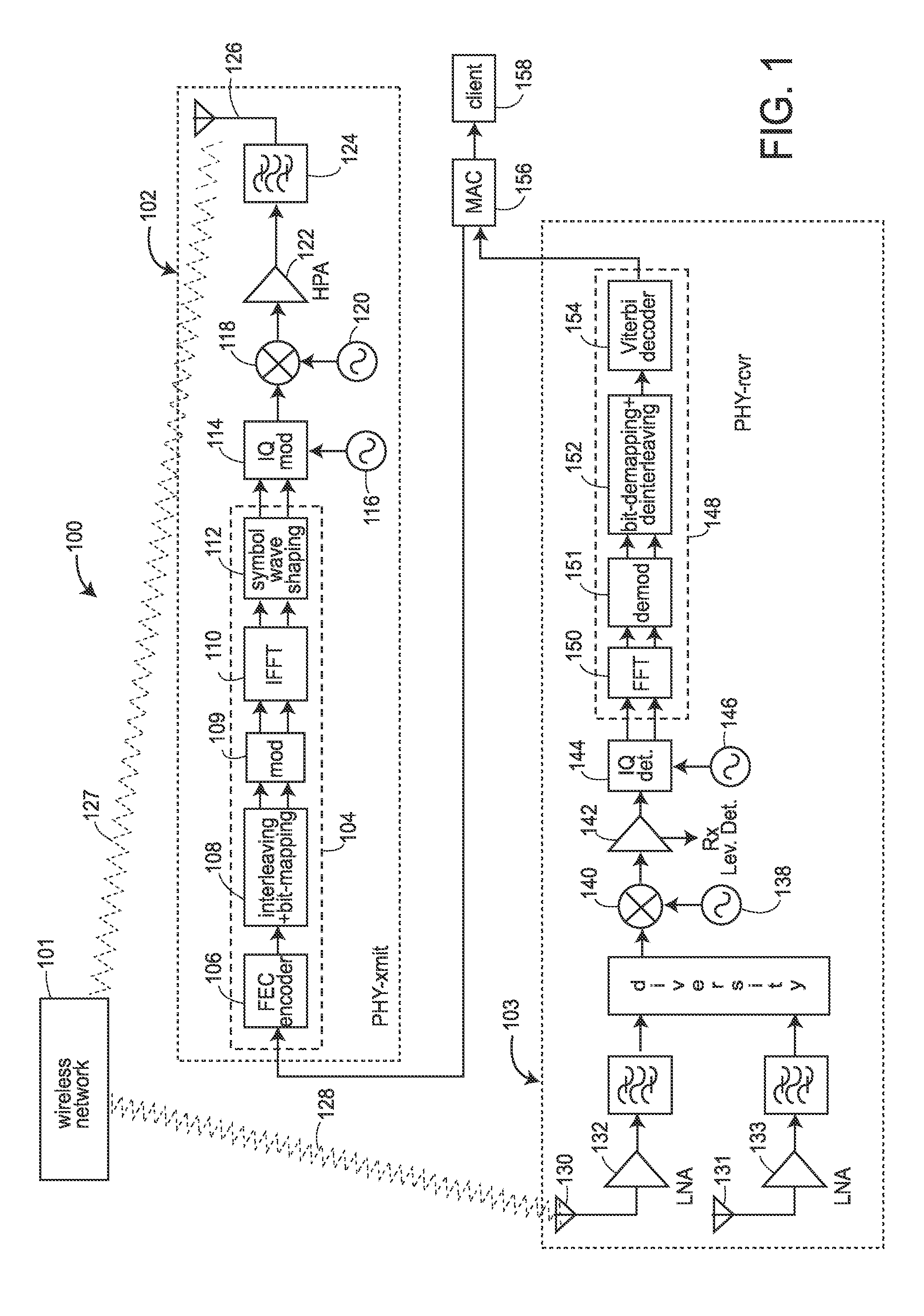
System for protecting the transmission of live data streams, and upon reception, for reconstructing the live data streams and recording them into files
ActiveUS7024609B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsData streamReal-time data
The present invention relates to a system for (1) protecting the transmission of packet streams between a host computer and one or more client computers, and (2) upon reception, (a) reconstructing any outage damage caused during the transmission to the packet streams, and (b) digitally recording the reconstructed packet streams to a file. The present invention also relates to a method for dynamically generating a file index table as the packet stream is being digitally recorded.
Owner:KENCAST
Techniques for detecting and correcting errors using multiple interleave erasure pointers
InactiveUS20050229069A1Correction capabilityTransmission systemsCode conversionBlock codeError location
Techniques for detecting and correcting burst errors in data bytes formed in a two-level block code structure. A second level decoder uses block level check bytes to detect columns in a two-level block code structure that contain error bytes. The second level decoder generates erasure pointers that identify columns in the two-level block structure effected by burst errors. A first level decoder then uses codeword check bytes to correct all of the bytes in the columns identified by the erasure pointers. The first level decoder is freed to use all of the codeword check bytes only for error byte value calculations. The first level decoder does not need to use any of the codeword check bytes for error location calculations, because the erasure pointers generated by the second level decoder provide all of the necessary error locations. This techniques doubles the error correction capability of the first level decoder.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV +1
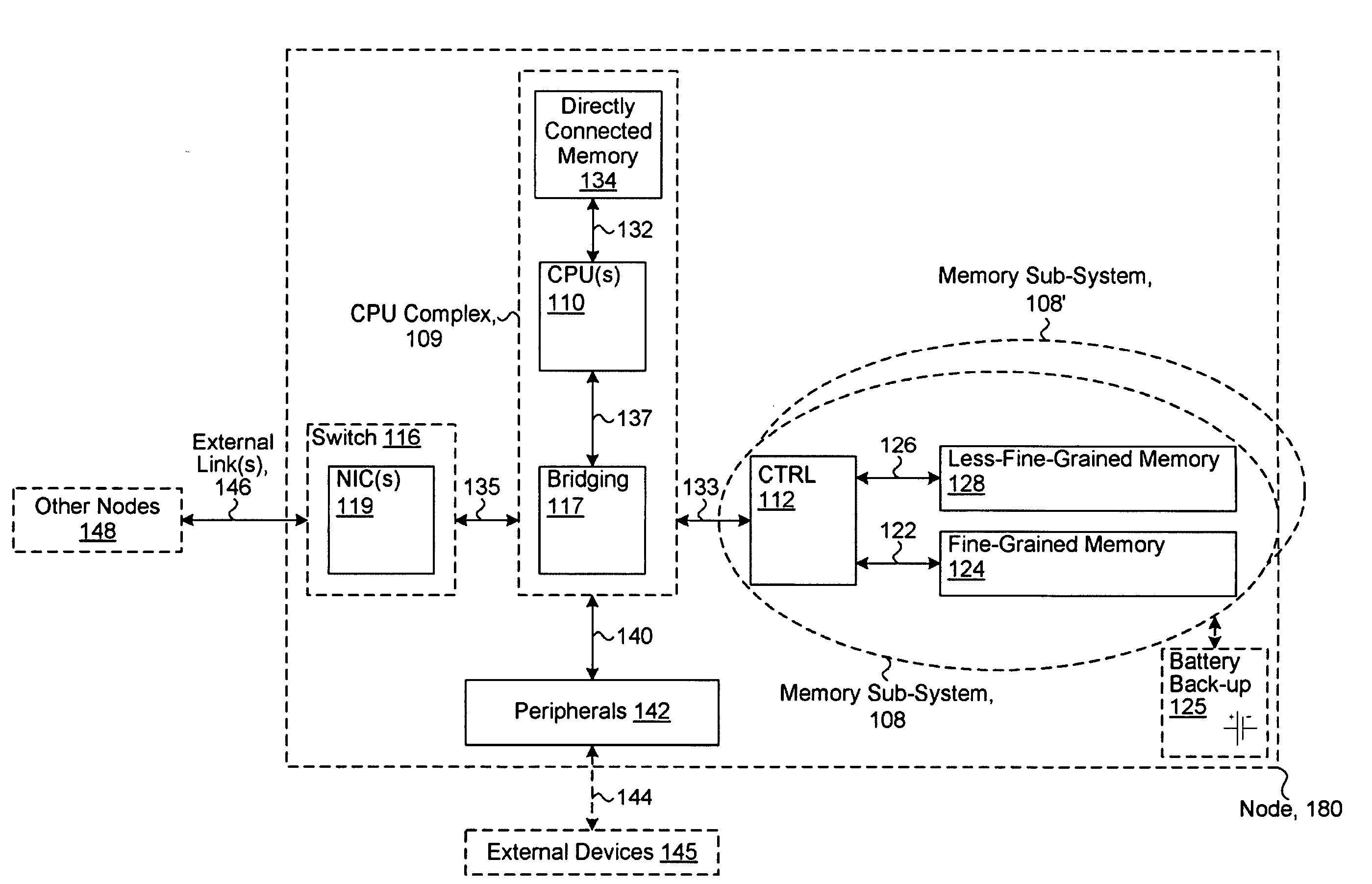
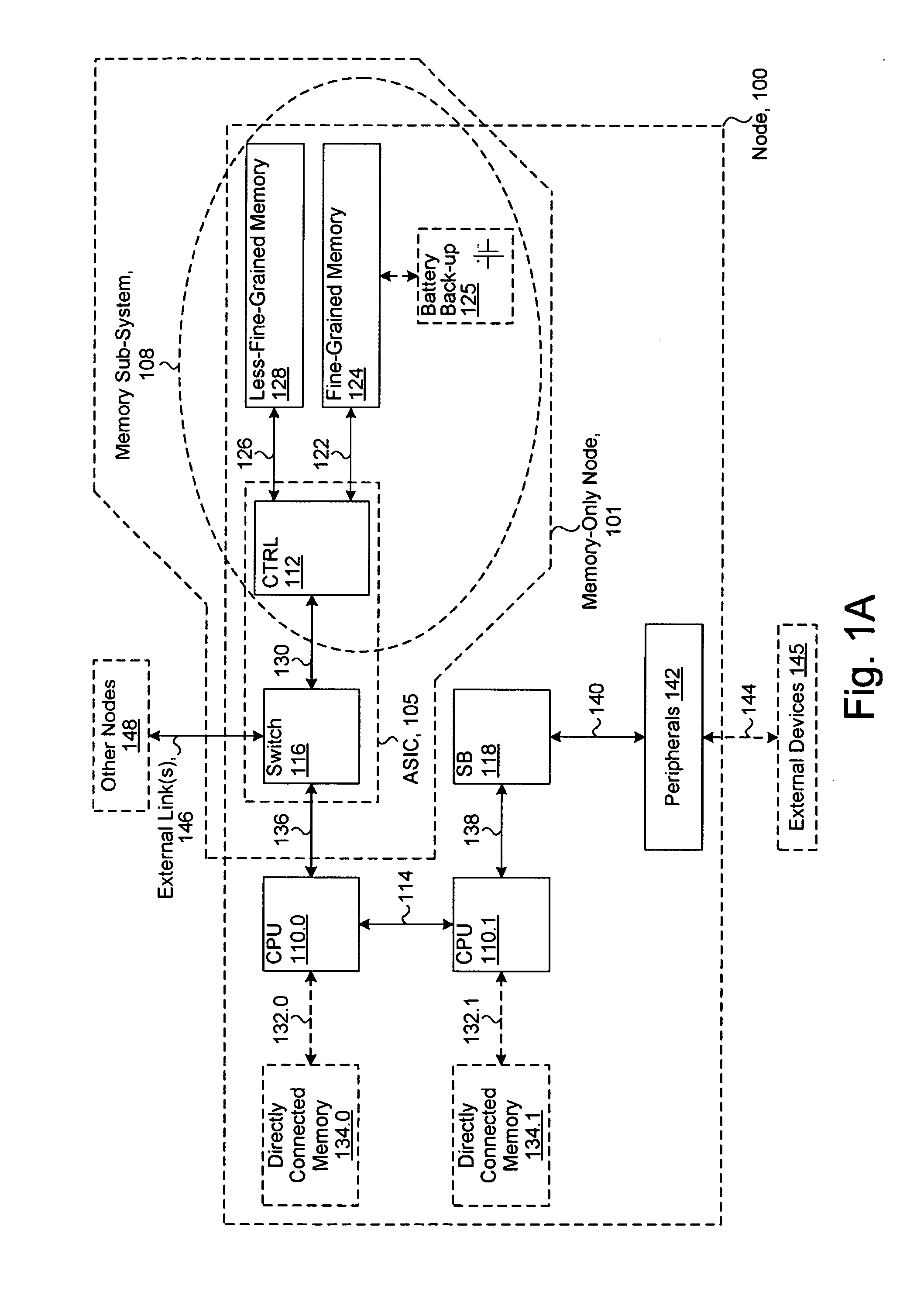
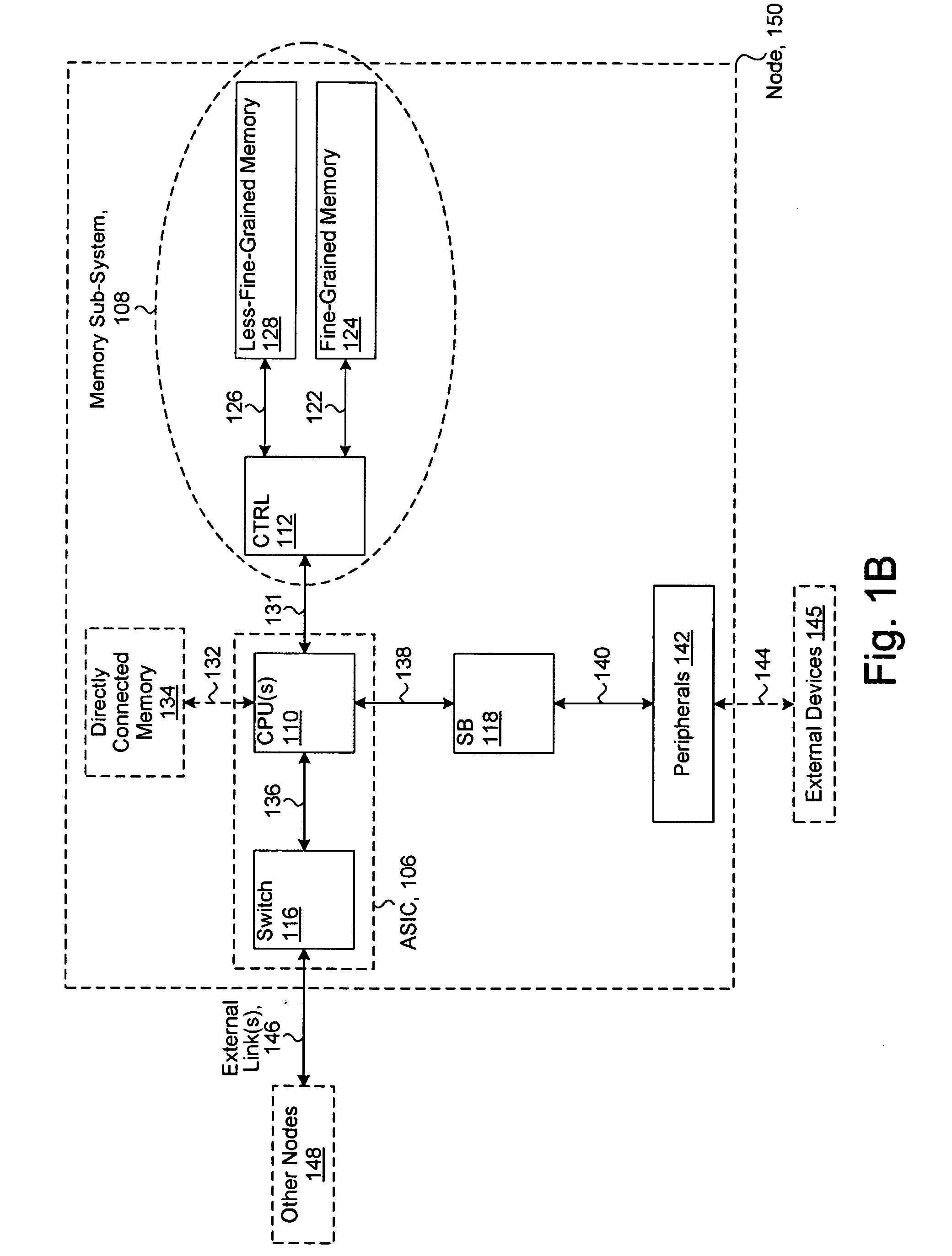
System including a fine-grained memory and a less-fine-grained memory
ActiveUS20080301256A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTData processing systemWrite buffer
A data processing system includes one or more nodes, each node including a memory sub-system. The sub-system includes a fine-grained, memory, and a less-fine-grained (e.g., page-based) memory. The fine-grained memory optionally serves as a cache and / or as a write buffer for the page-based memory. Software executing on the system uses n node address space which enables access to the page-based memories of all nodes. Each node optionally provides ACID memory properties for at least a portion of the space. In at least a portion of the space, memory elements are mapped to locations in the page-based memory. In various embodiments, some of the elements are compressed, the compressed elements are packed into pages, the pages are written into available locations in the page-based memory, and a map maintains an association between the some of the elements and the locations.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
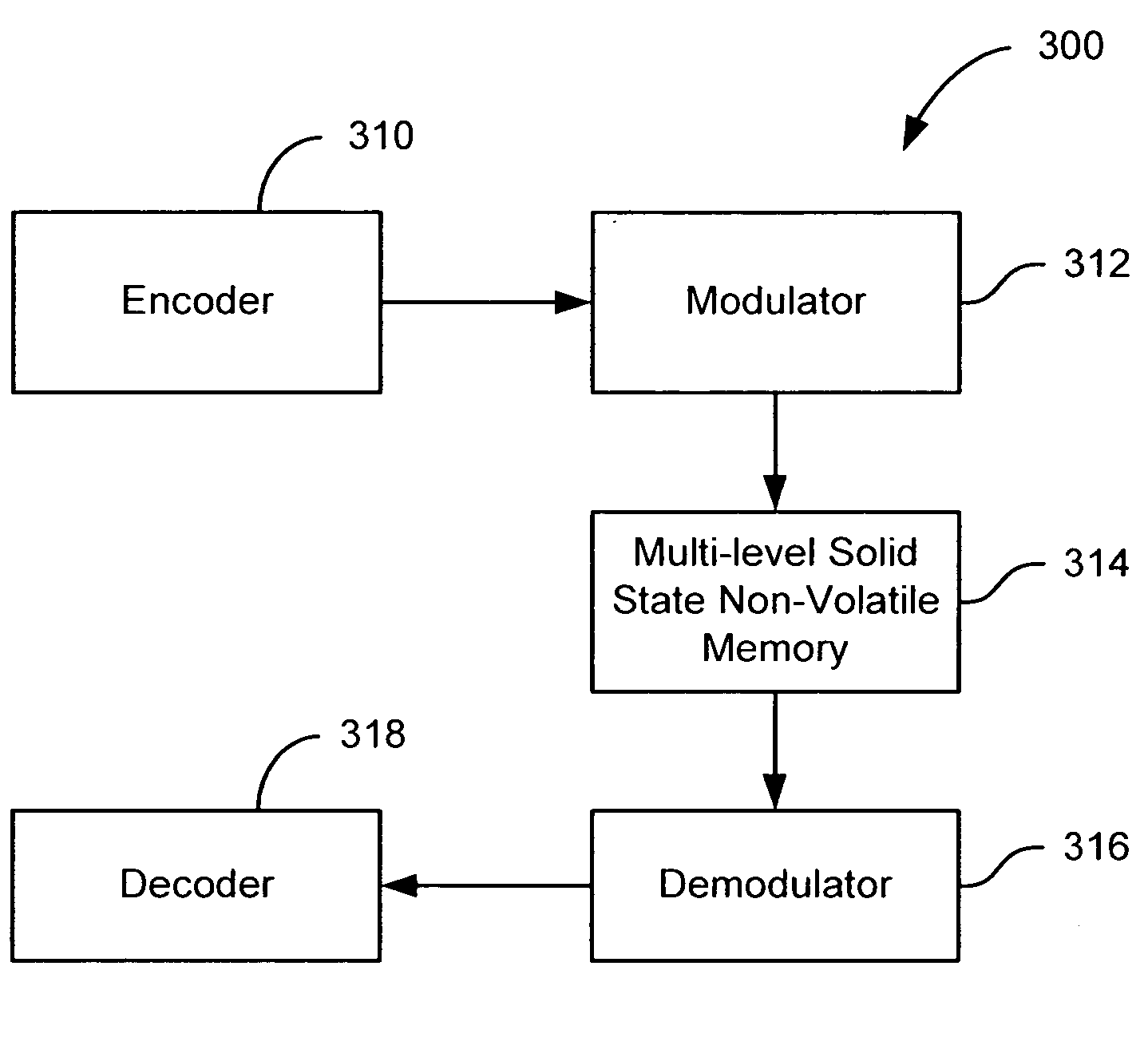
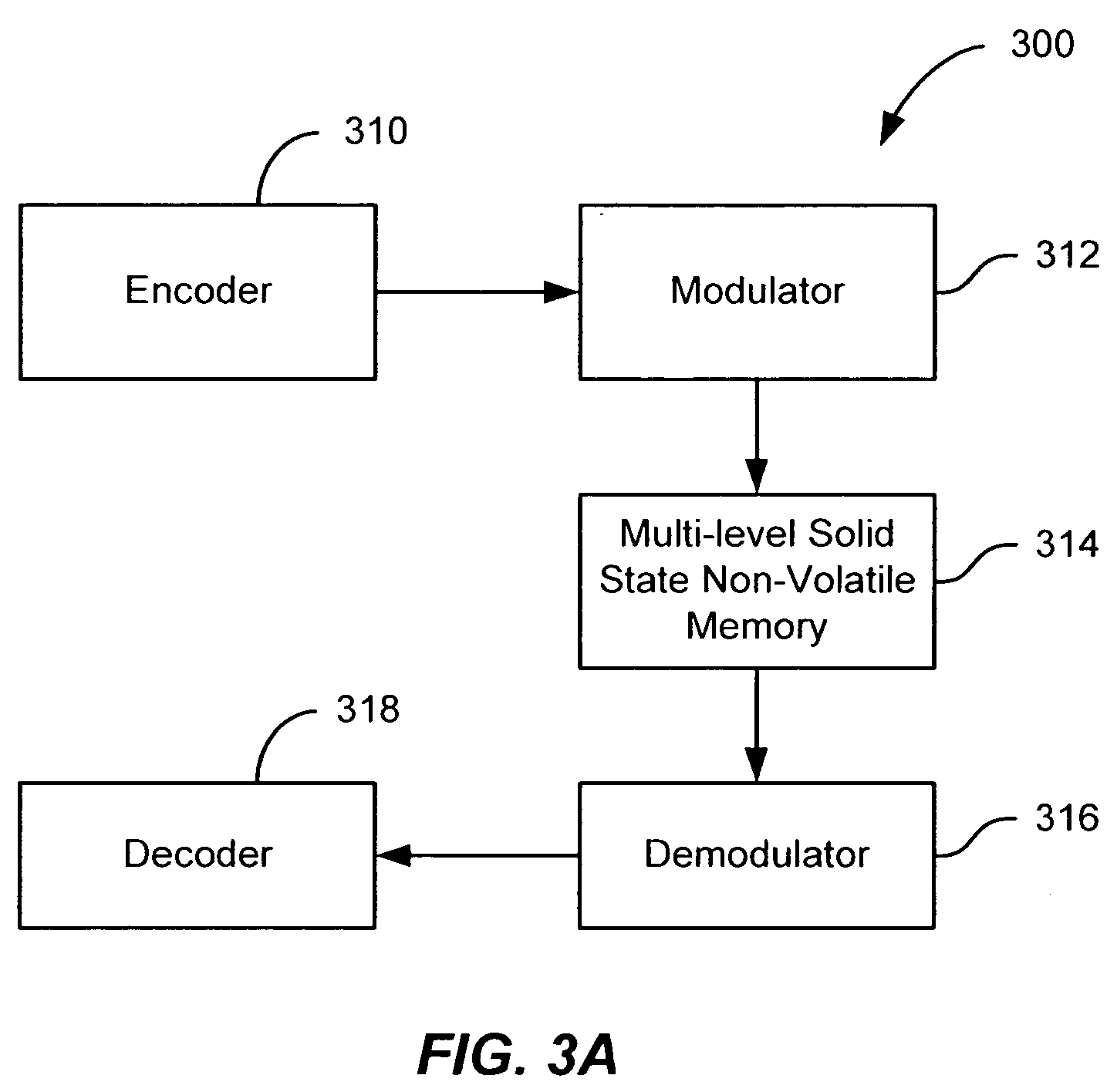
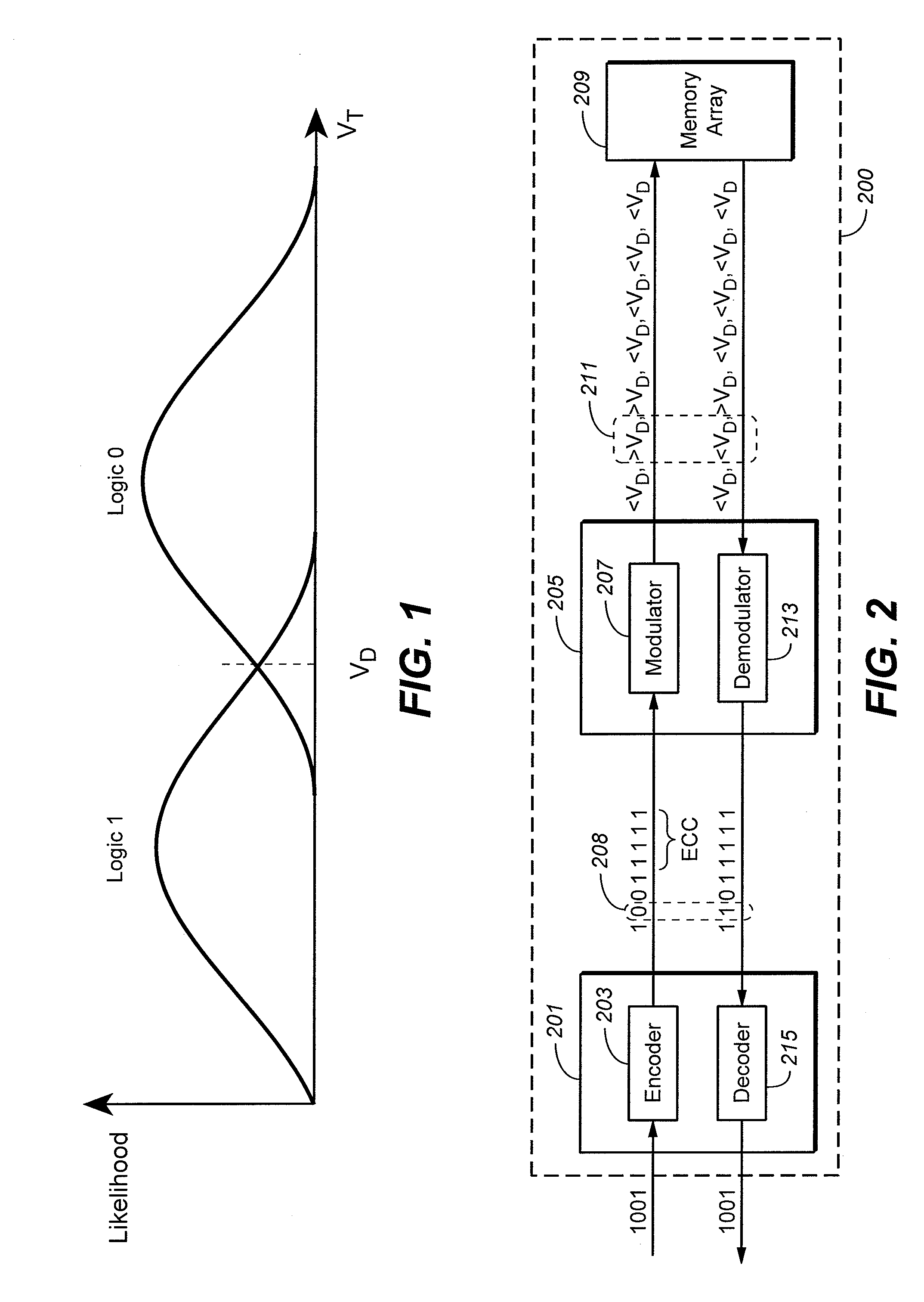
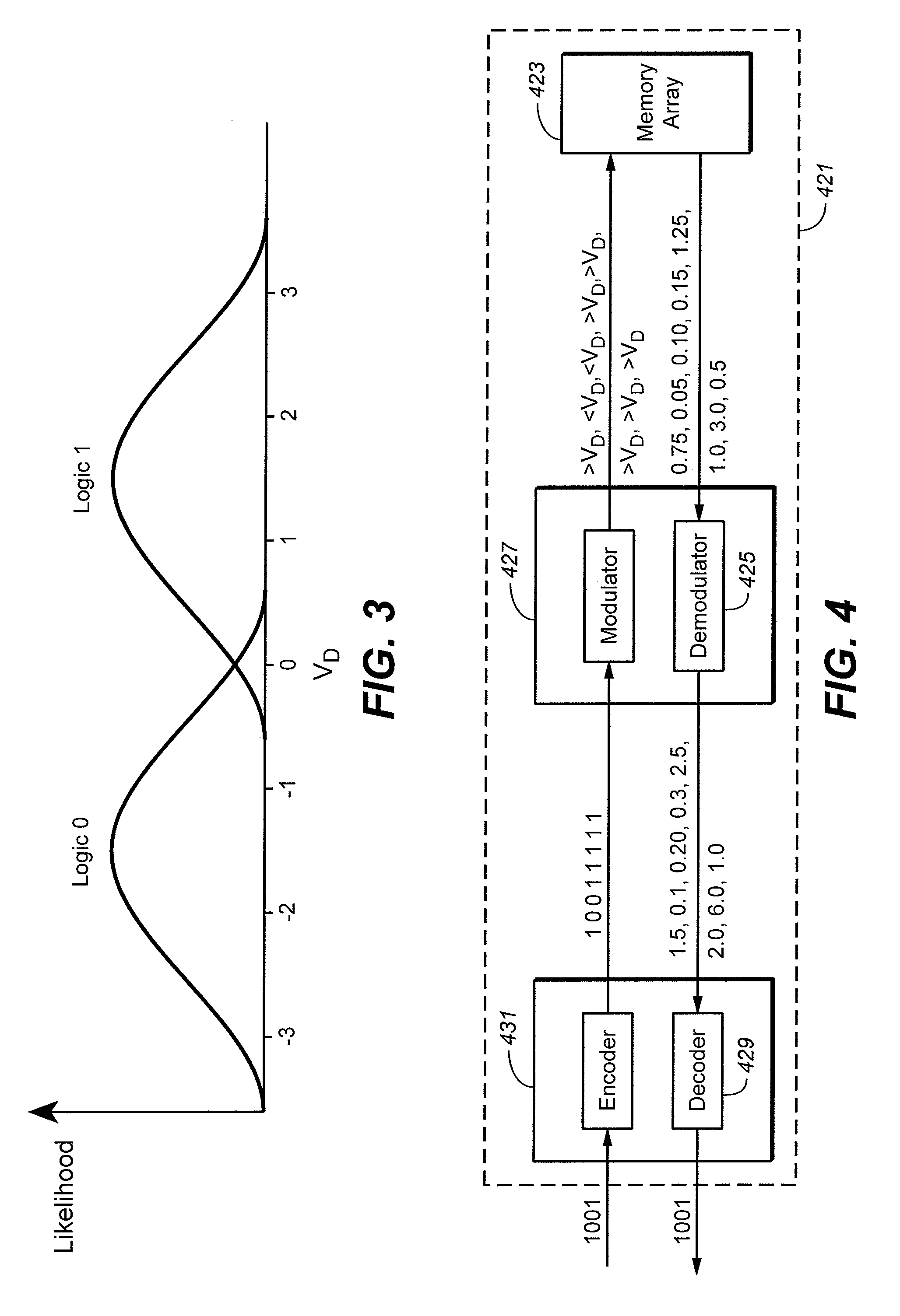
Flash memory with coding and signal processing
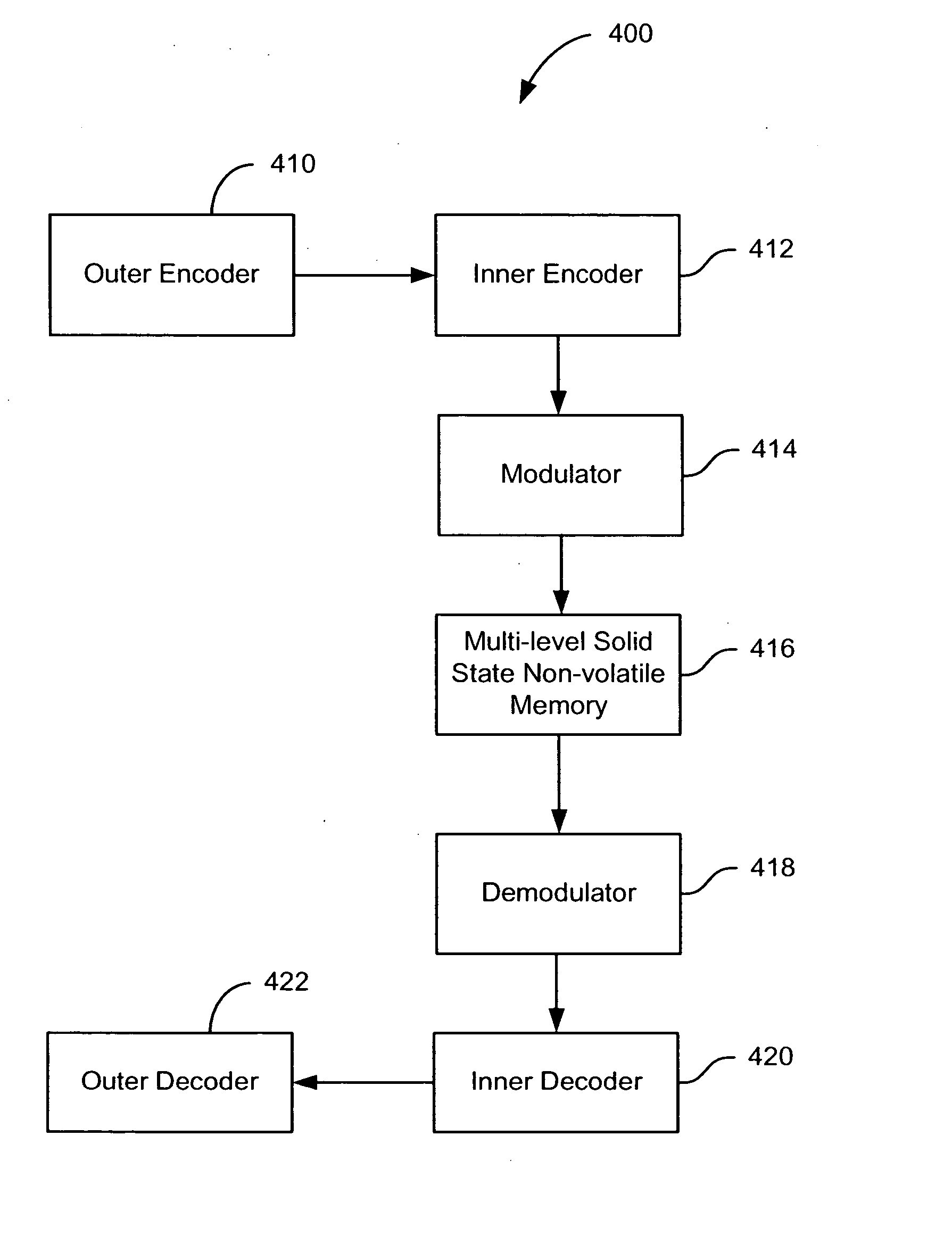
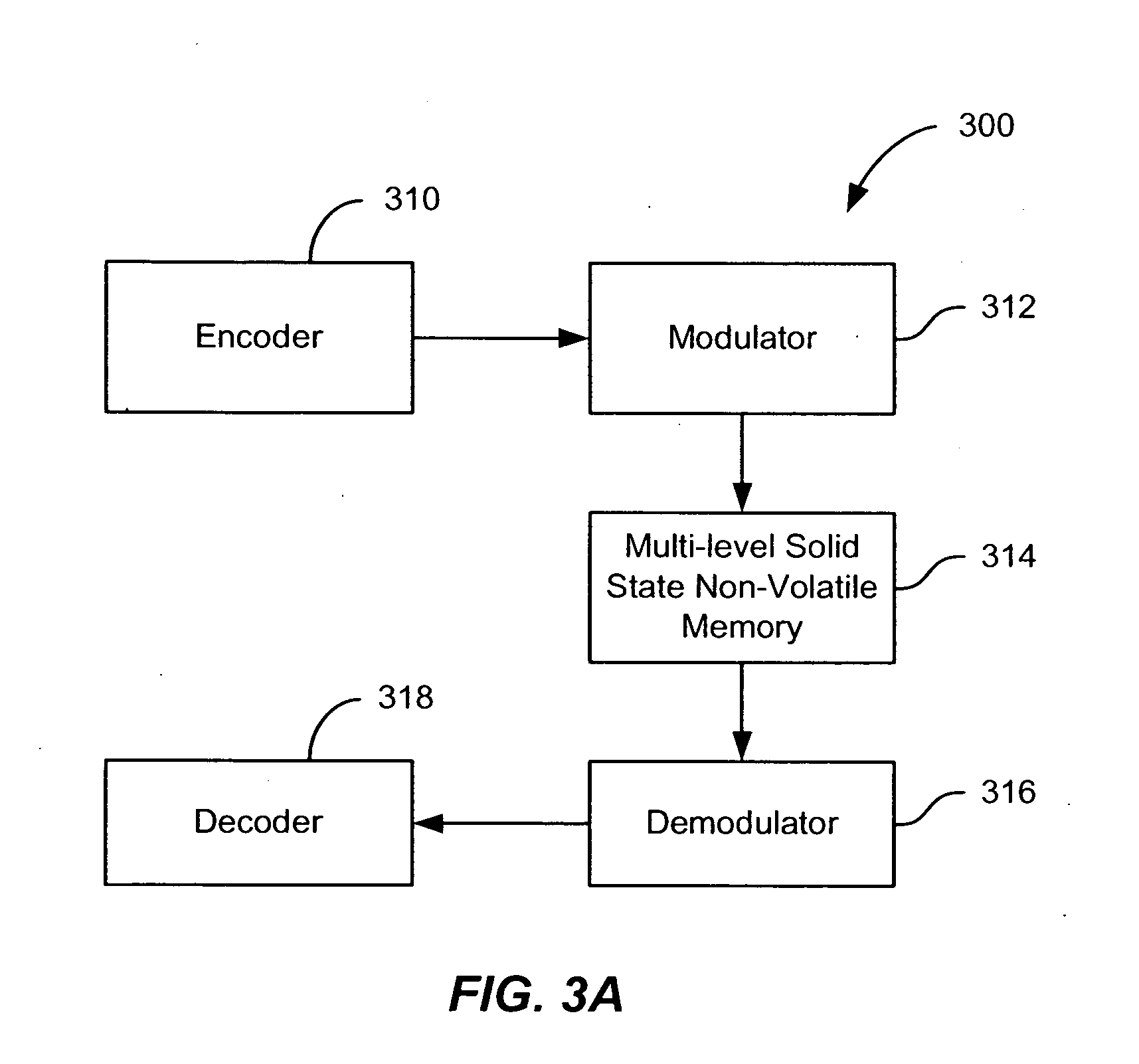
A solid state non-volatile memory unit includes, in part, an encoder, a multi-level solid state non-volatile memory array adapted to store data encoded by the encoder, and a decoder adapted to decode the data retrieved from the memory array. The memory array may be a flash EEPROM array. The memory unit optionally includes a modulator and a demodulator. The data modulated by the modulator is stored in the memory array. The demodulator demodulates the modulated data retrieved from the memory array.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Multi-Level Striping and Truncation Channel-Equalization for Flash-Memory System
InactiveUS20090240873A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError preventionLogical block addressingData access
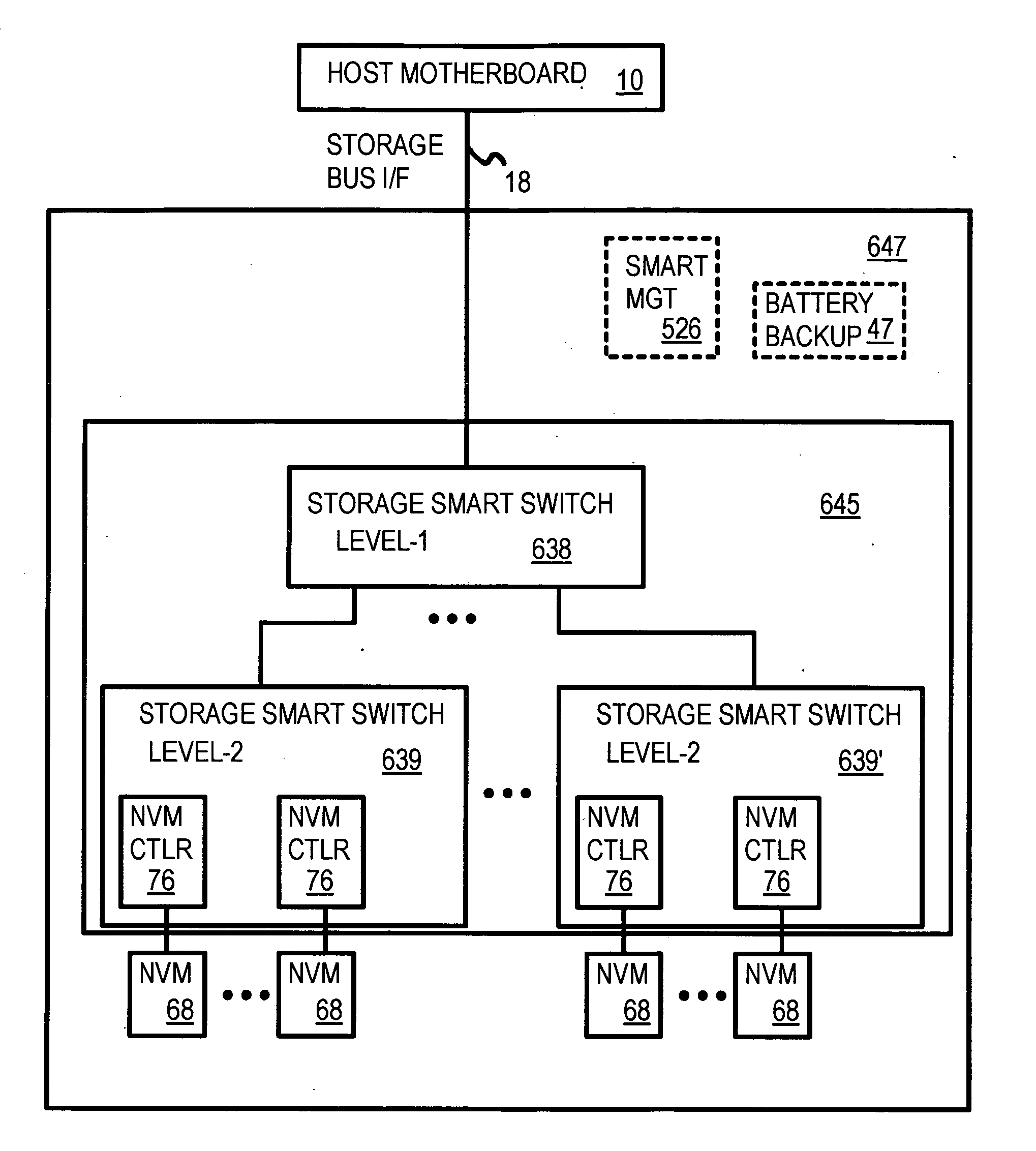
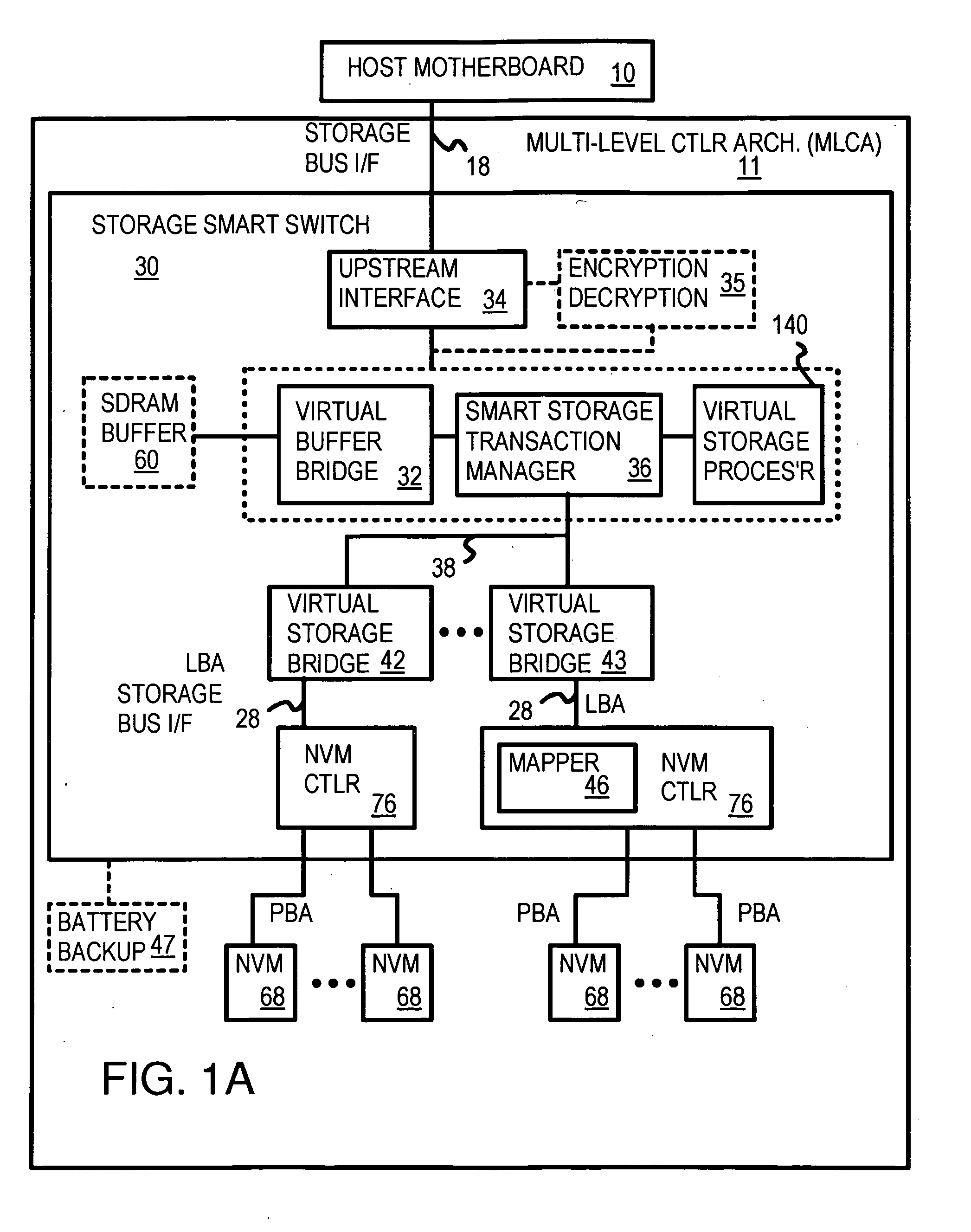
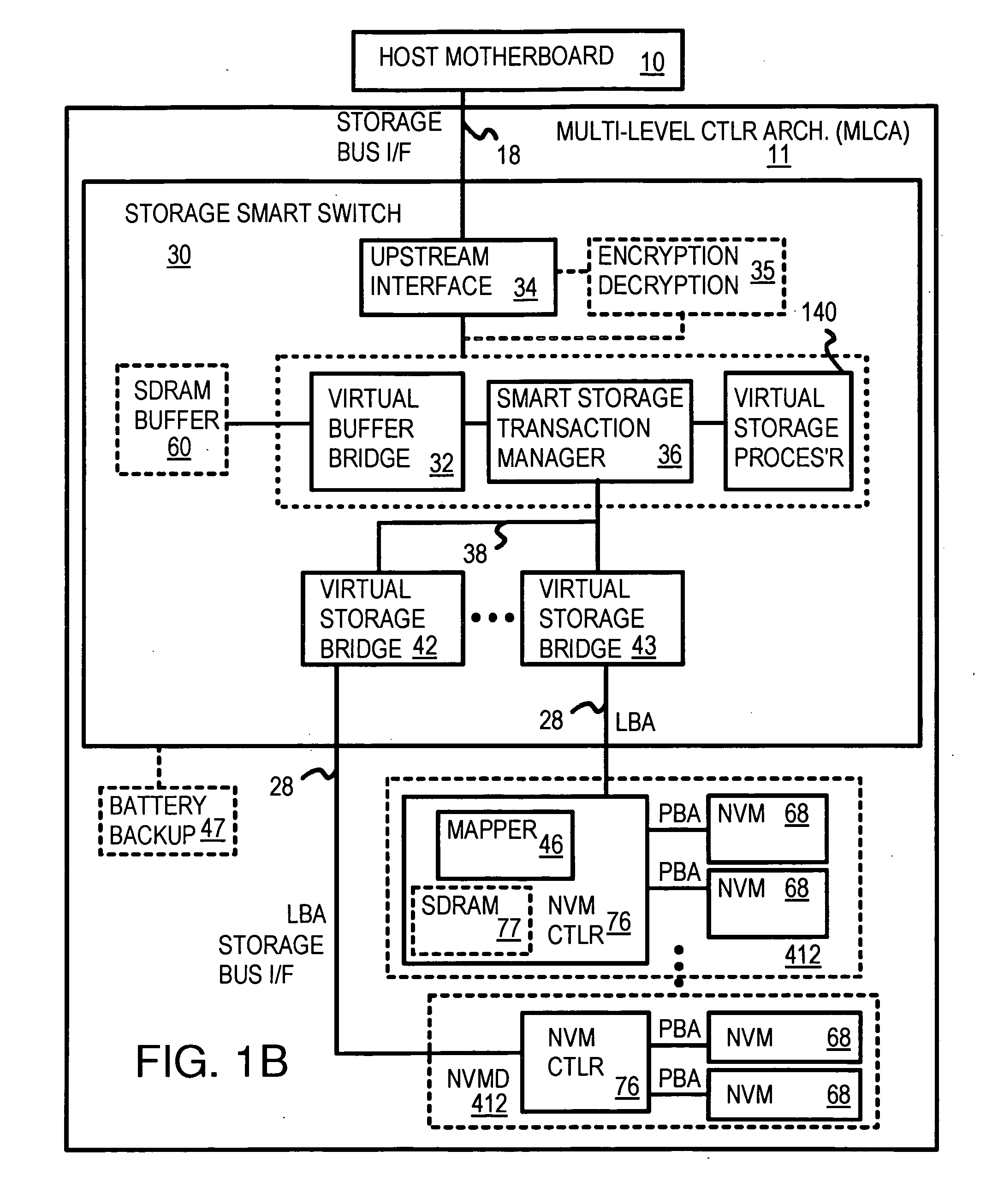
Truncation reduces the available striped data capacity of all flash channels to the capacity of the smallest flash channel. A solid-state disk (SSD) has a smart storage switch salvages flash storage removed from the striped data capacity by truncation. Extra storage beyond the striped data capacity is accessed as scattered data that is not striped. The size of the striped data capacity is reduced over time as more bad blocks appear. A first-level striping map stores striped and scattered capacities of all flash channels and maps scattered and striped data. Each flash channel has a Non-Volatile Memory Device (NVMD) with a lower-level controller that converts logical block addresses (LBA) to physical block addresses (PBA) that access flash memory in the NVMD. Wear-leveling and bad block remapping are preformed by each NVMD. Source and shadow flash blocks are recycled by the NVMD. Two levels of smart storage switches enable three-level controllers.
Owner:SUPER TALENT TECH CORP
Generating and matching hashes of multimedia content
ActiveUS20020178410A1RobustRobust hashingElectrophonic musical instrumentsCode conversionFrequency spectrumAlgorithm
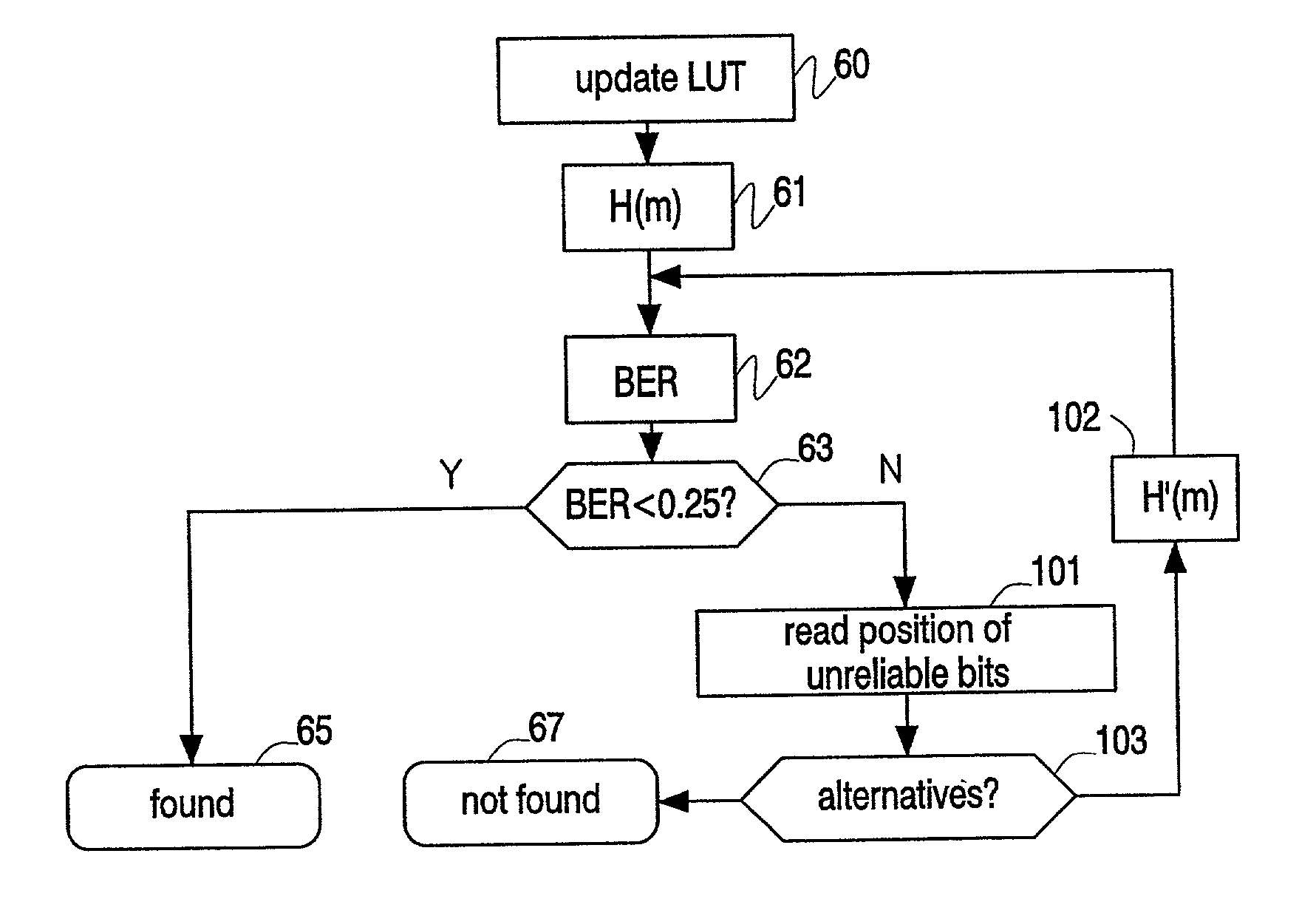
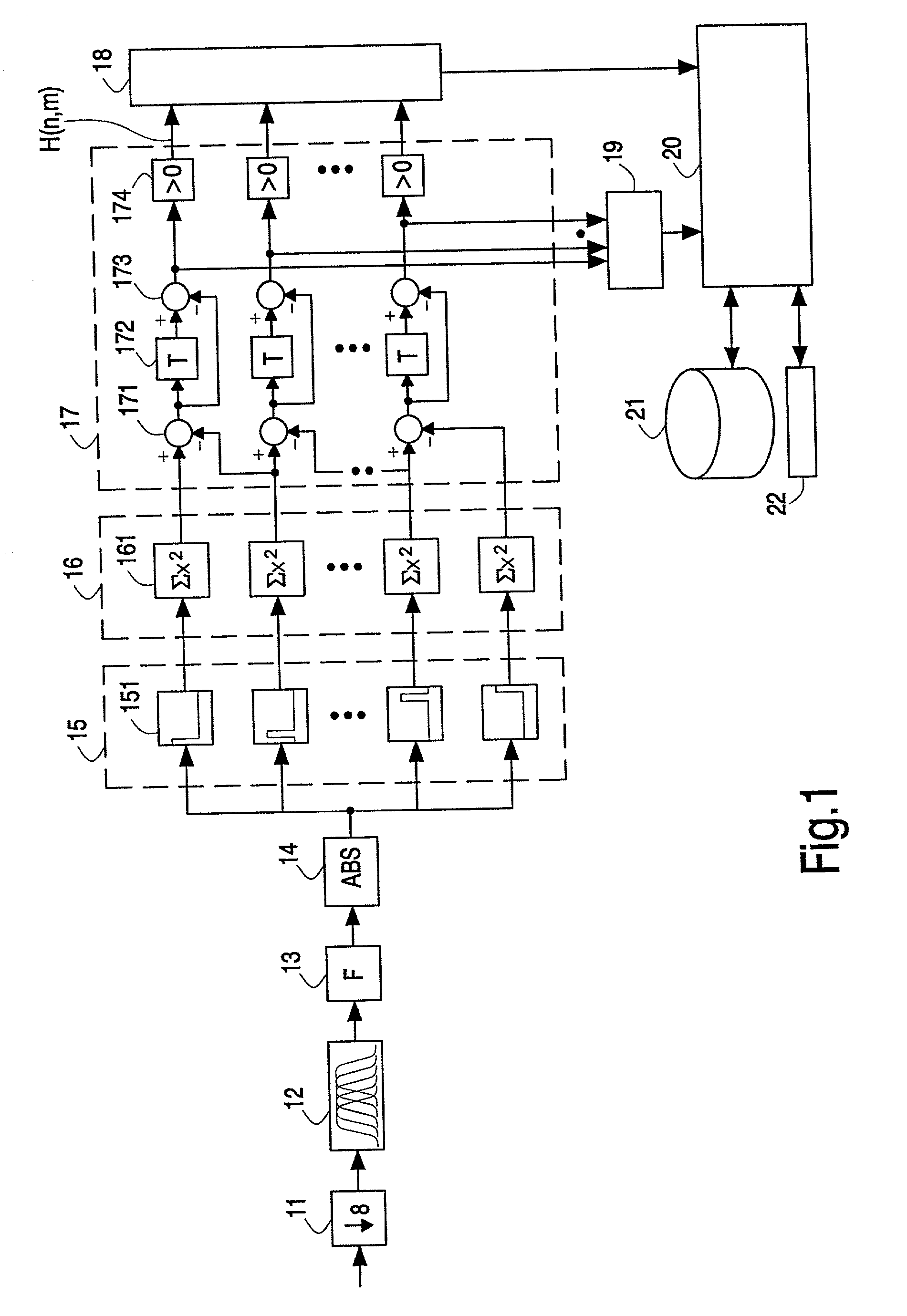
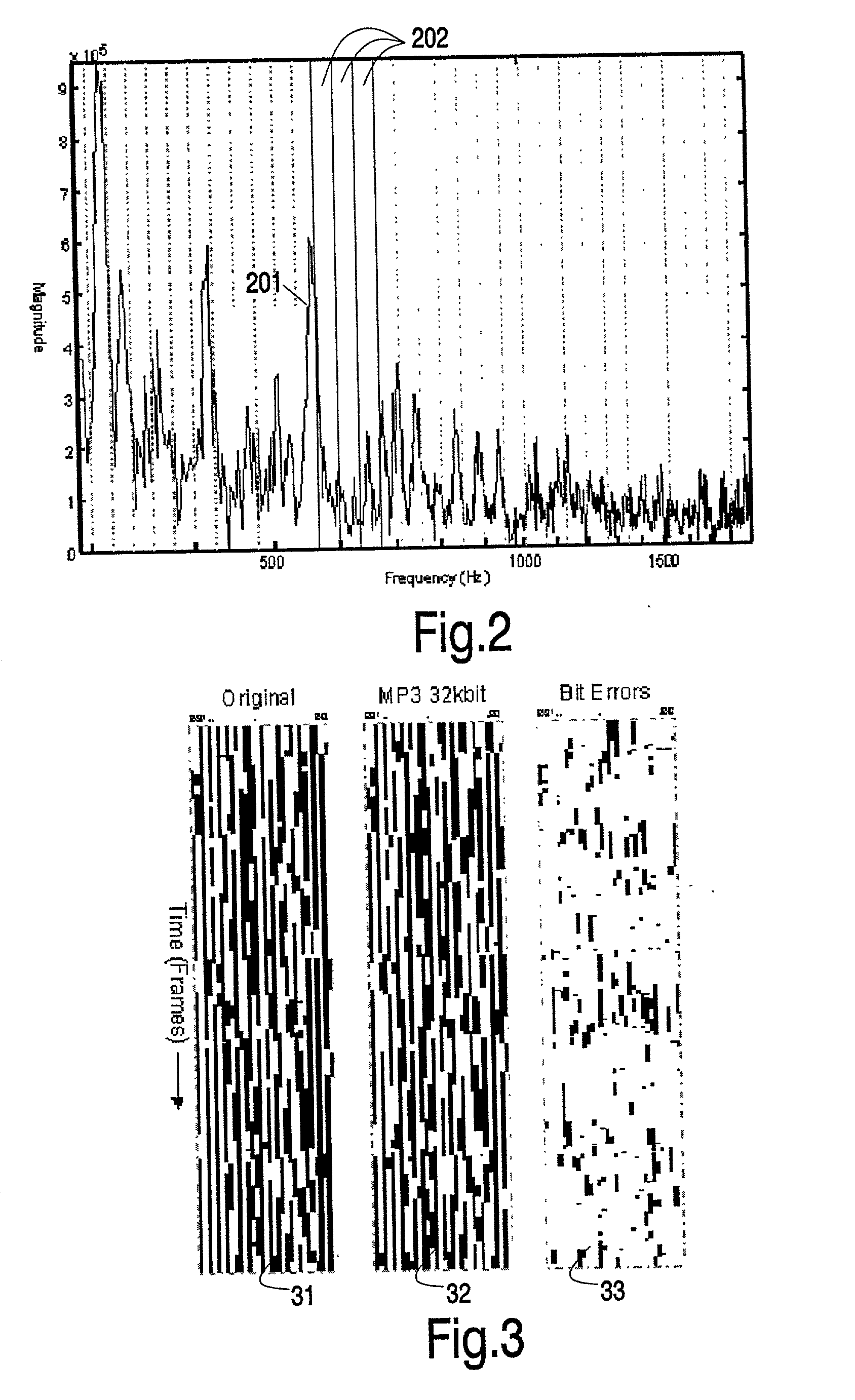
Hashes are short summaries or signatures of data files which can be used to identify the file. Hashing multimedia content (audio, video, images) is difficult because the hash of original content and processed (e.g. compressed) content may differ significantly. The disclosed method generates robust hashes for multimedia content, for example, audio clips. The audio clip is divided (12) into successive (preferably overlapping) frames. For each frame, the frequency spectrum is divided (15) into bands. A robust property of each band (e.g. energy) is computed (16) and represented (17) by a respective hash bit. An audio clip is thus represented by a concatenation of binary hash words, one for each frame. To identify a possibly compressed audio signal, a block of hash words derived therefrom is matched by a computer (20) with a large database (21). Such matching strategies are also disclosed. In an advantageous embodiment, the extraction process also provides information (19) as to which of the hash bits are the least reliable. Flipping these bits considerably improves the speed and performance of the matching process.
Owner:GRACENOTE
Robust visual passwords
InactiveUS7219368B2Easy to rememberKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationGraphicsUser input
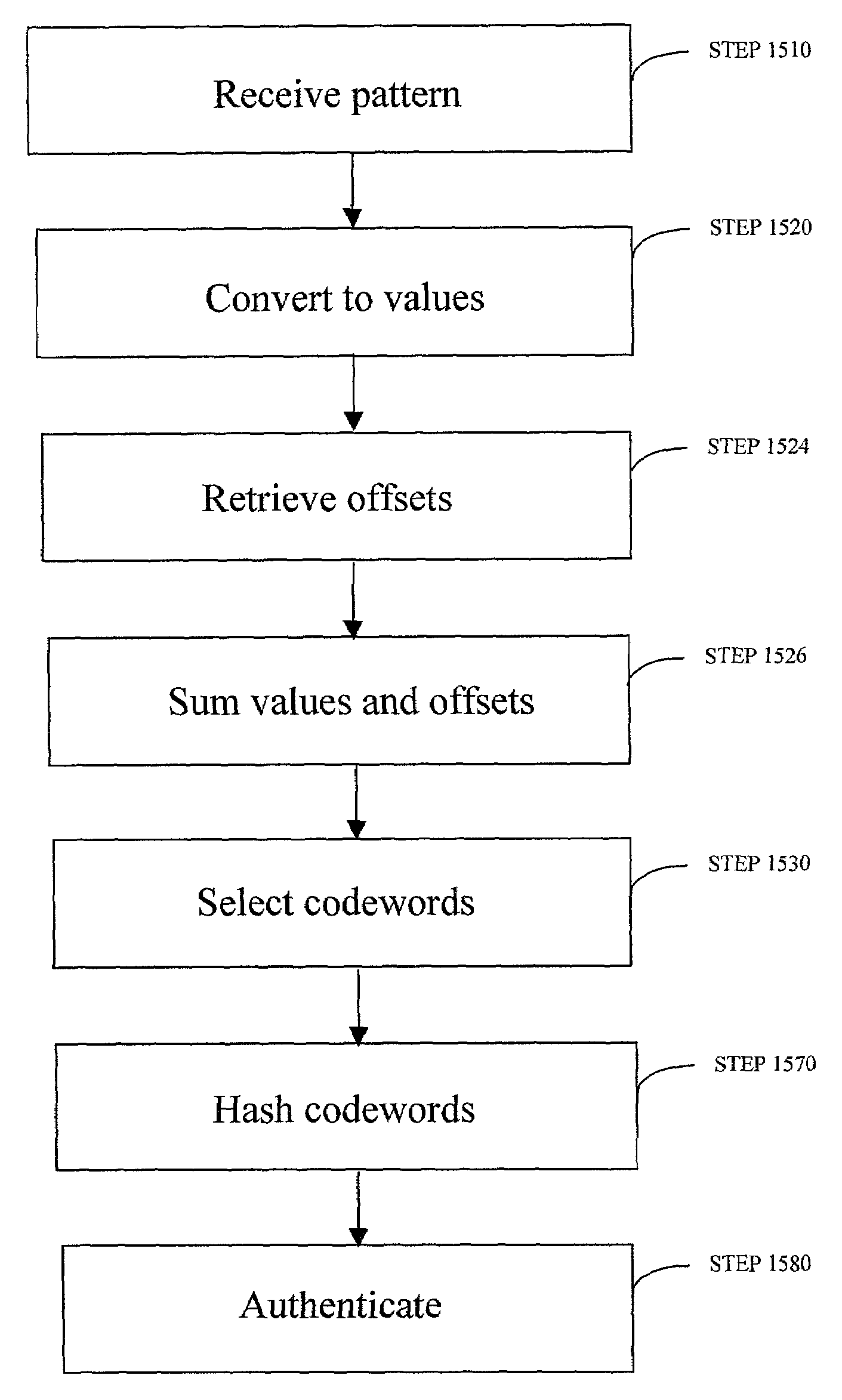
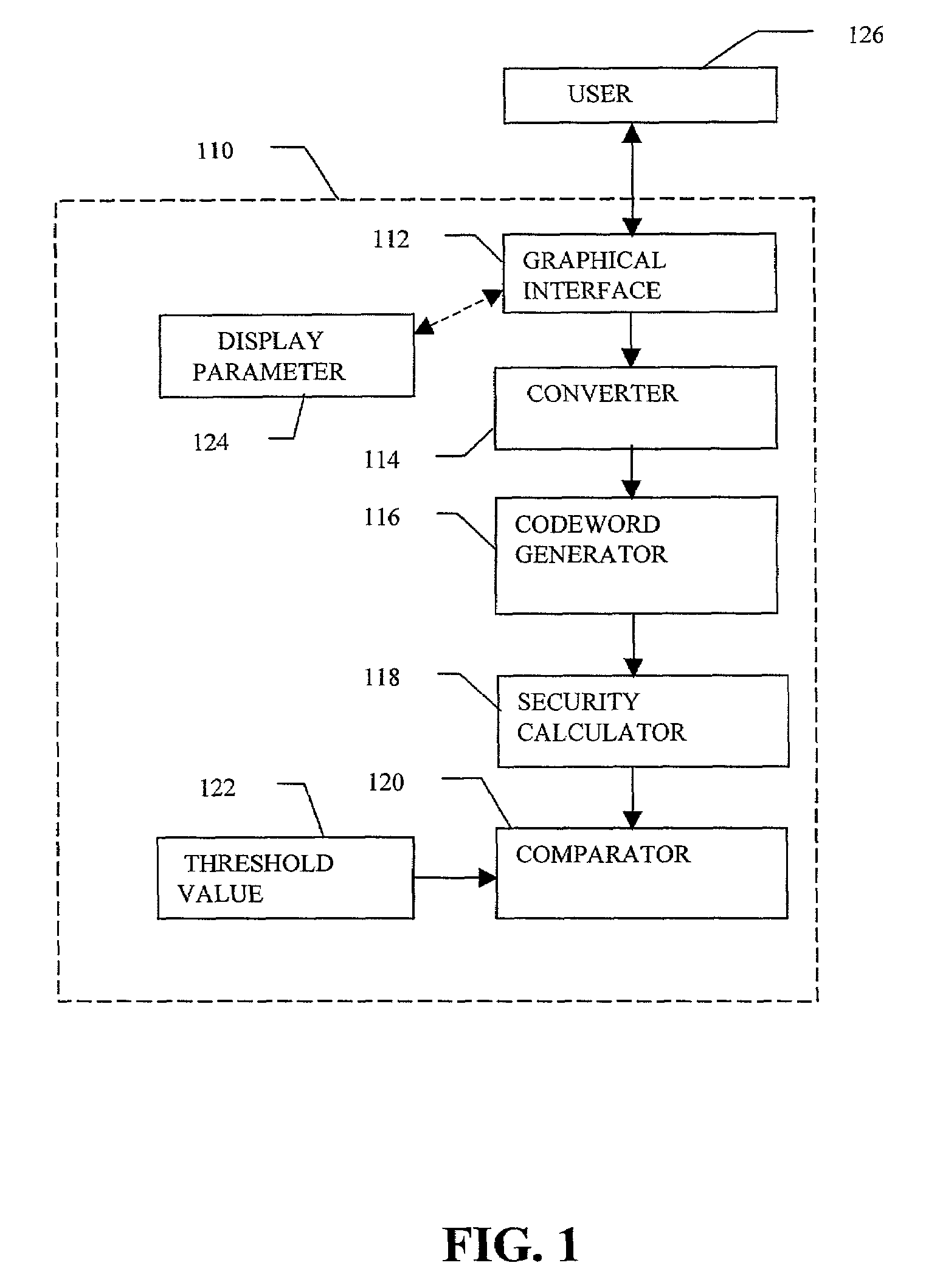
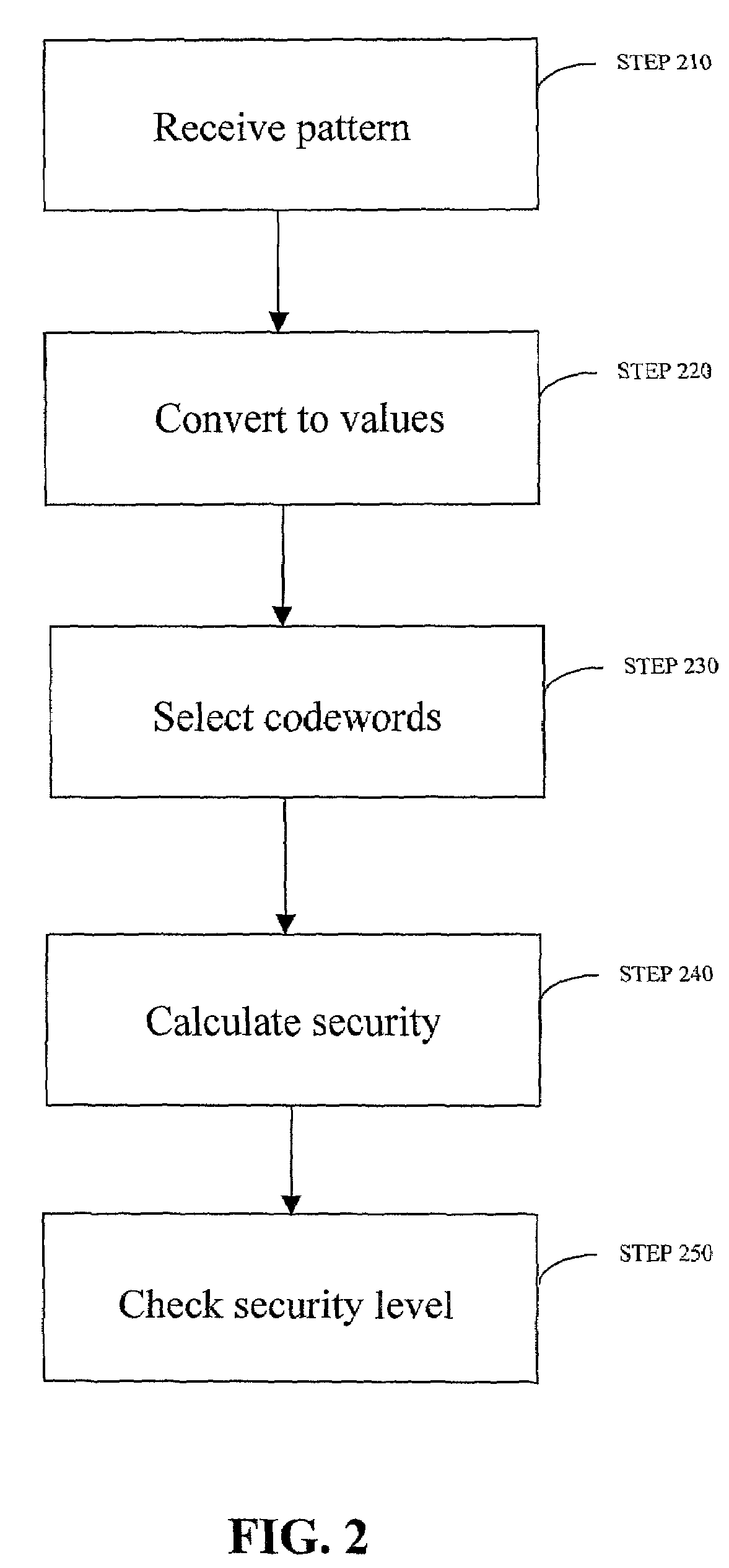
Enrollment and authentication of a user based on a sequence of discrete graphical choices is described. A graphical interface presents various images and memory cues that a user may associate with their original graphical choices. Enrollment may require the input to have a security parameter value that meets or exceeds a threshold. An acceptable sequence of graphical choices is converted to a sequence of values and mapped to a sequence of codewords. Both a hash of the sequence of codewords and a sequence of offsets are stored for use in authenticating the user. An offset is the difference between a value and its corresponding codeword. Authentication requires the user to enter another sequence of discrete graphical choices that is approximately the same as original. The offsets are summed with the corresponding values before mapping to codewords. Authentication requires the sequence of codewords, or a hash thereof, to match.
Owner:RSA
Method and system for error correction in flash memory
ActiveUS20070171730A1Improve storage densityImprove reliabilityMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionA d converterData memory
A solid state non-volatile memory unit. The memory unit includes a multi-level solid state non-volatile memory array adapted to store data characterized by a first number of digital levels. The memory unit also includes an analog-to-digital converter having an input and an output. The input of the analog-to-digital converter is adapted to receive data from the multi-level solid state non-volatile memory array. The output of the analog-to-digital converter is adapted to output a digital signal characterized by a second number of digital levels greater than the first number of digital levels.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method and device for efficient frame erasure concealment in linear predictive based speech codecs
ActiveUS20050154584A1Improve concealmentPromote recoveryError preventionTransmission systemsStability parameterFrequency spectrum
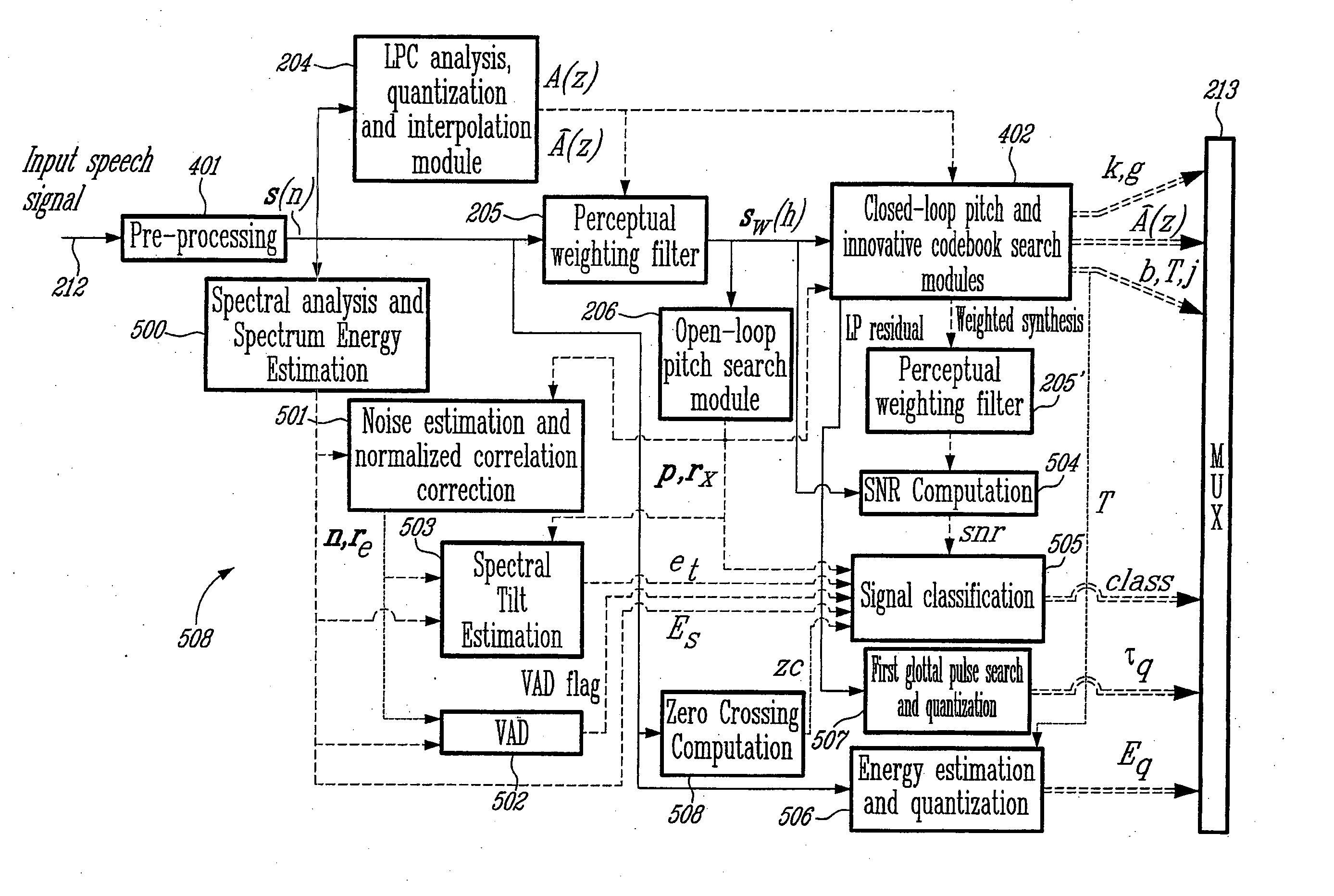
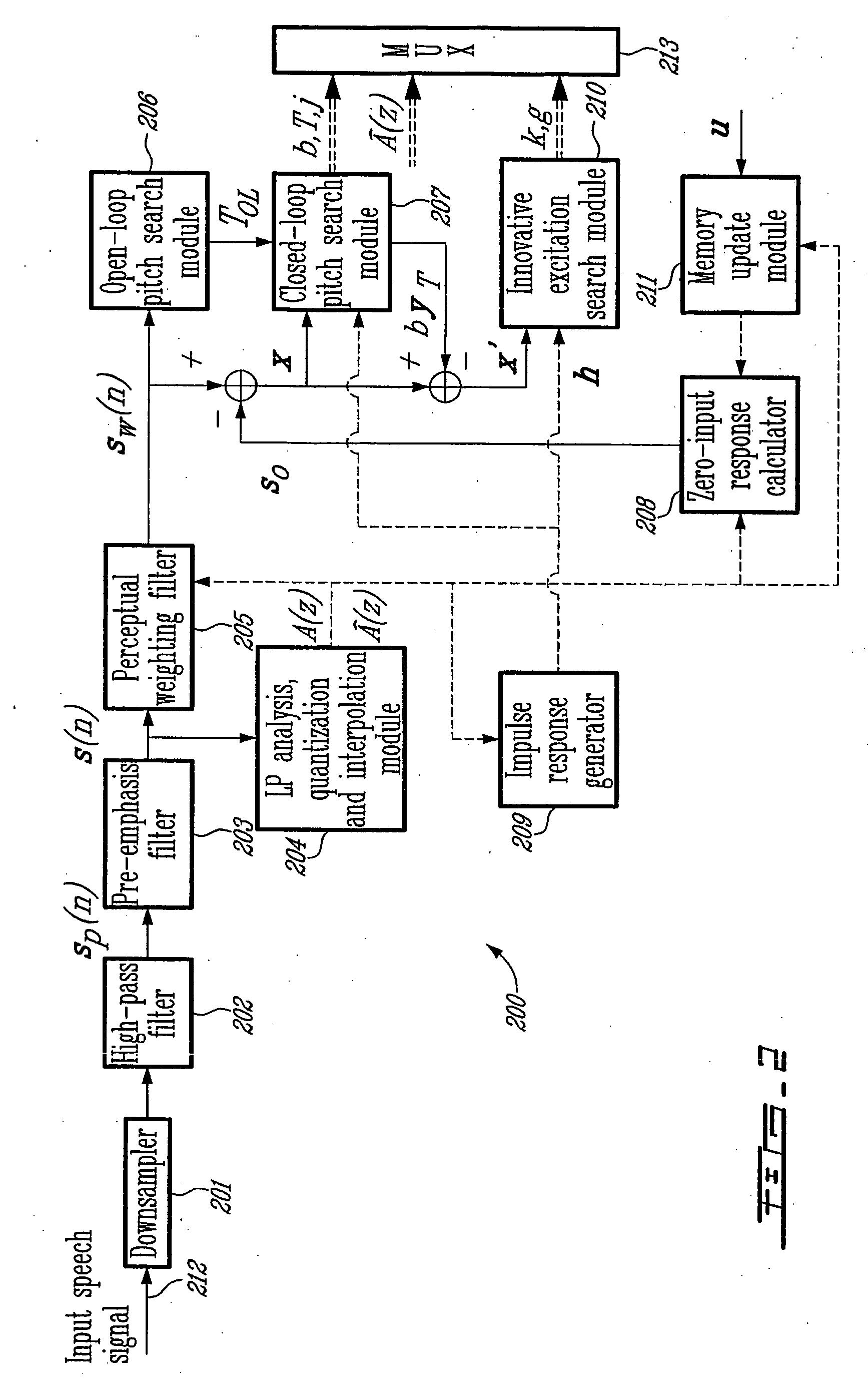
The present invention relates to a method and device for improving concealment of frame erasure caused by frames of an encoded sound signal erased during transmission from an encoder (106) to a decoder (110), and for accelerating recovery of the decoder after non erased frames of the encoded sound signal have been received. For that purpose, concealment / recovery parameters are determined in the encoder or decoder. When determined in the encoder (106), the concealment / recovery parameters are transmitted to the decoder (110). In the decoder, erasure frame concealment and decoder recovery is conducted in response to the concealment / recovery parameters. The concealment / recovery parameters may be selected from the group consisting of: a signal classification parameter, an energy information parameter and a phase information parameter. The determination of the concealment / recovery parameters comprises classifying the successive frames of the encoded sound signal as unvoiced, unvoiced transition, voiced transition, voiced, or onset, and this classification is determined on the basis of at least a part of the following parameters: a normalized correlation parameter, a spectral tilt parameter, a signal-to-noise ratio parameter, a pitch stability parameter, a relative frame energy parameter, and a zero crossing parameter.
Owner:VOICEAGE EVS LLC
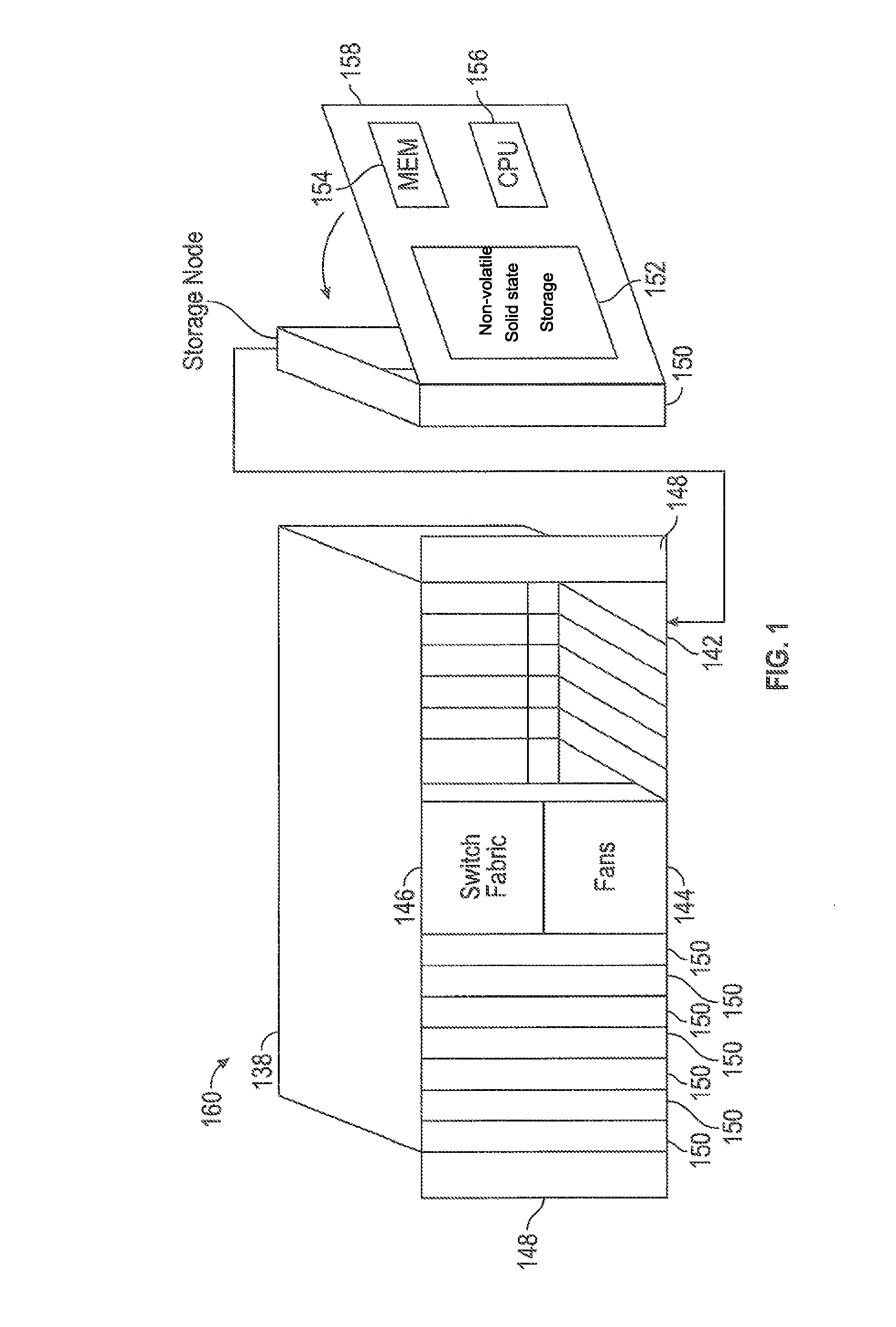
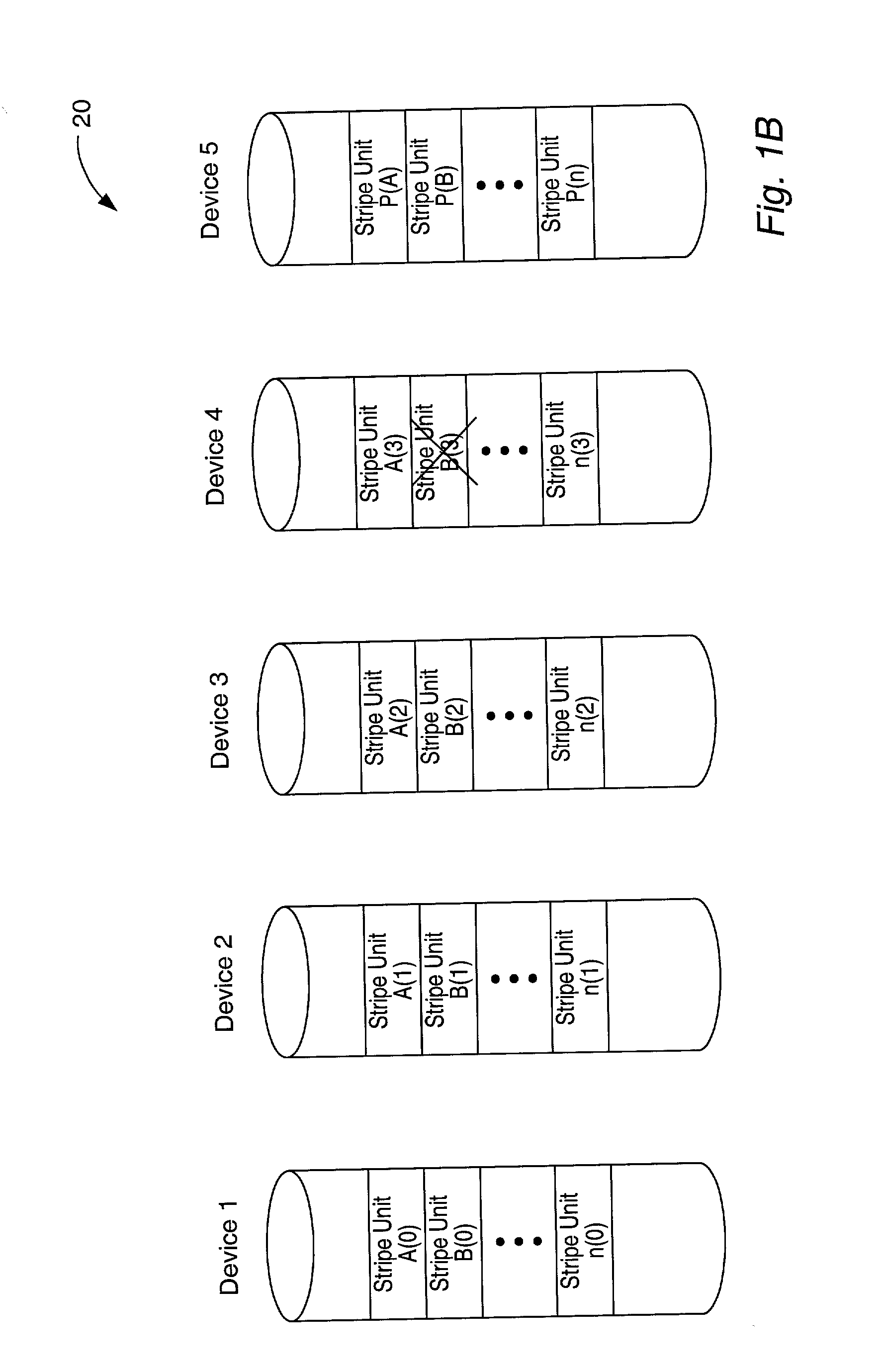
Storage cluster
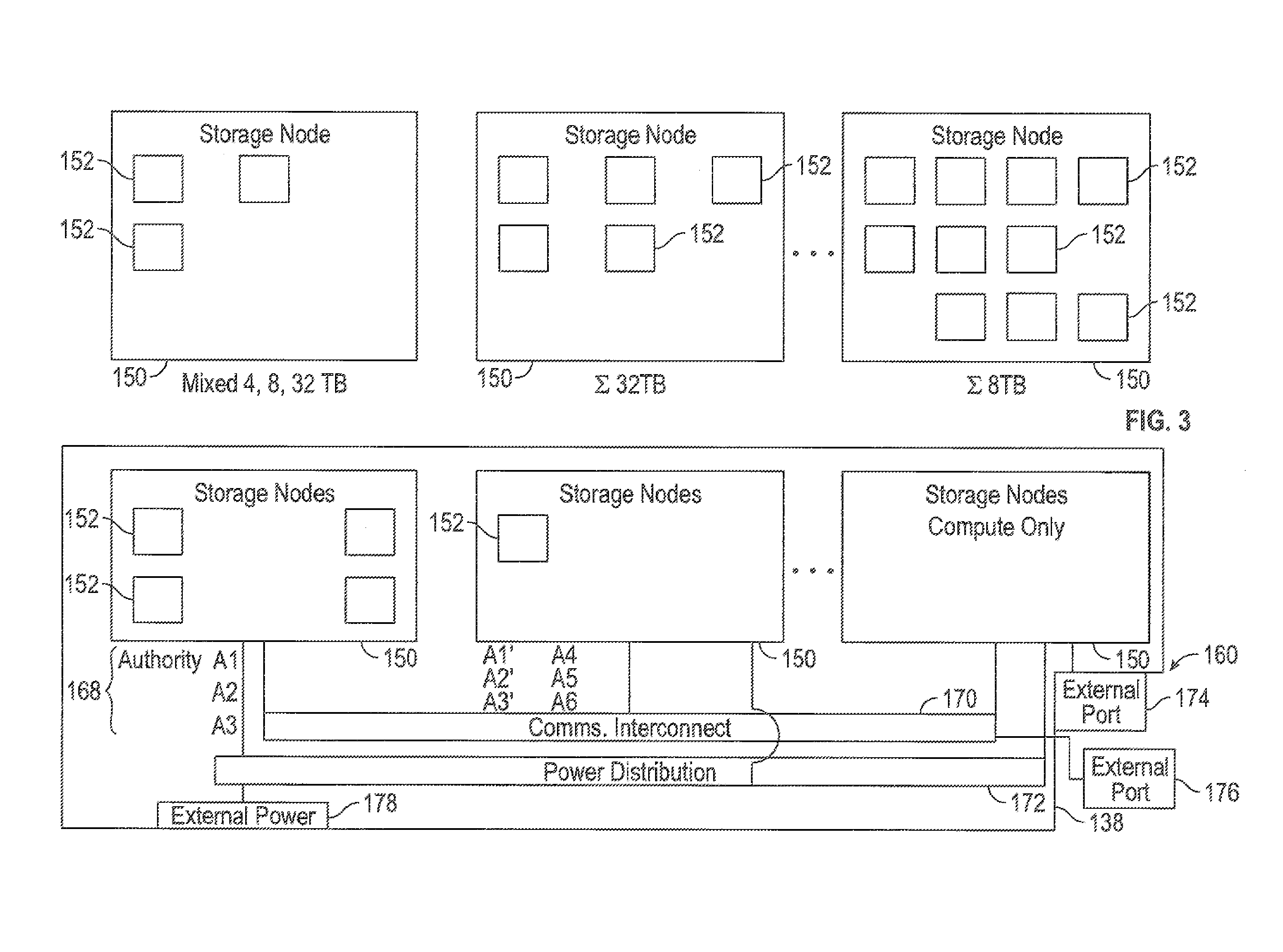
ActiveUS8850108B1Maintain abilityMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersData storeSolid state memory
A plurality of storage nodes in a single chassis is provided. The plurality of storage nodes in the single chassis is configured to communicate together as a storage cluster. Each of the plurality of storage nodes includes nonvolatile solid-state memory for user data storage. The plurality of storage nodes is configured to distribute the user data and metadata associated with the user data throughout the plurality of storage nodes such that the plurality of storage nodes maintain the ability to read the user data, using erasure coding, despite a loss of two of the plurality of storage nodes. The chassis includes power distribution, a high speed communication bus and the ability to install one or more storage nodes which may use the power distribution and communication bus. A method for accessing user data in a plurality of storage nodes having nonvolatile solid-state memory is also provided.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
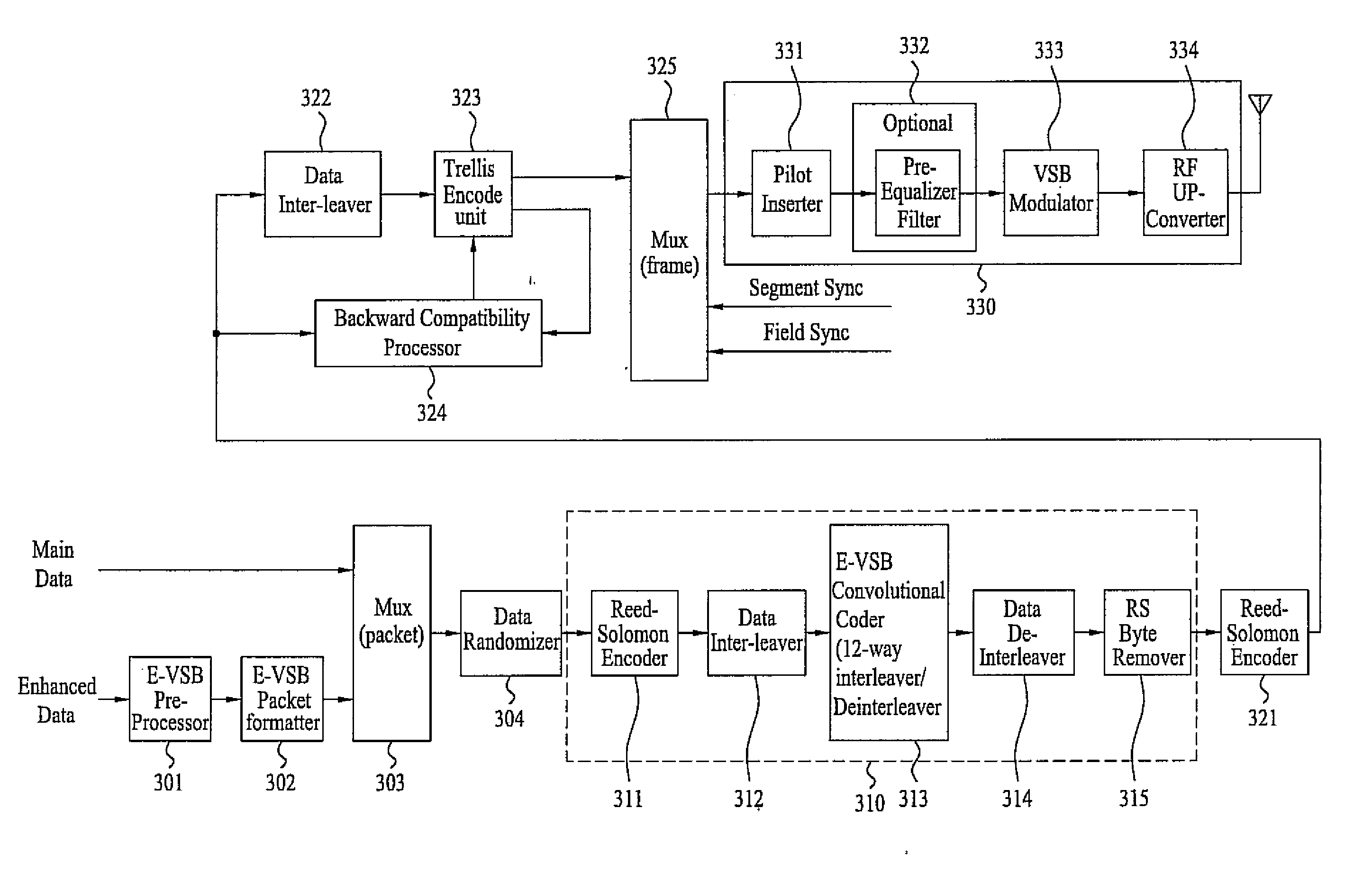
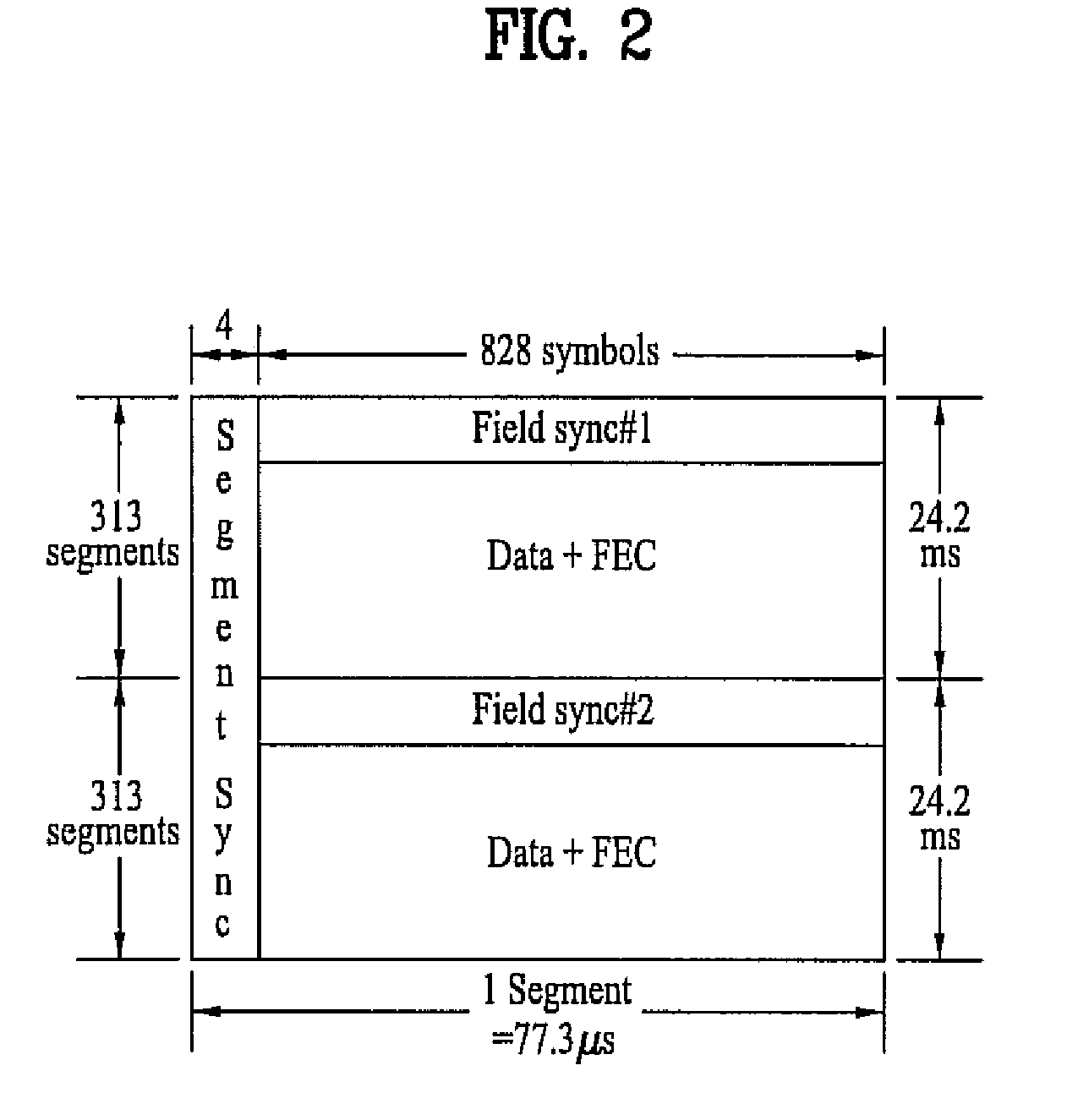
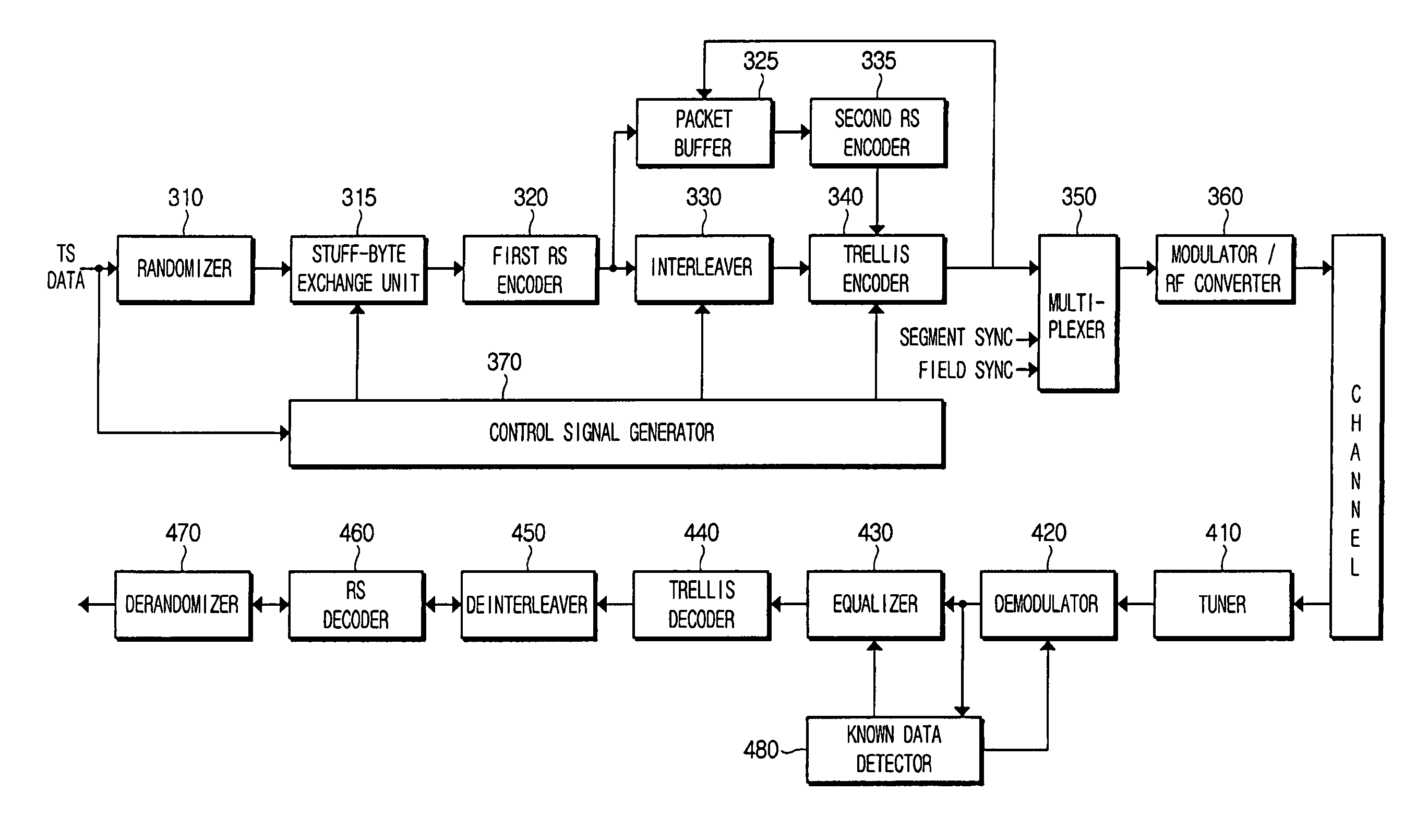
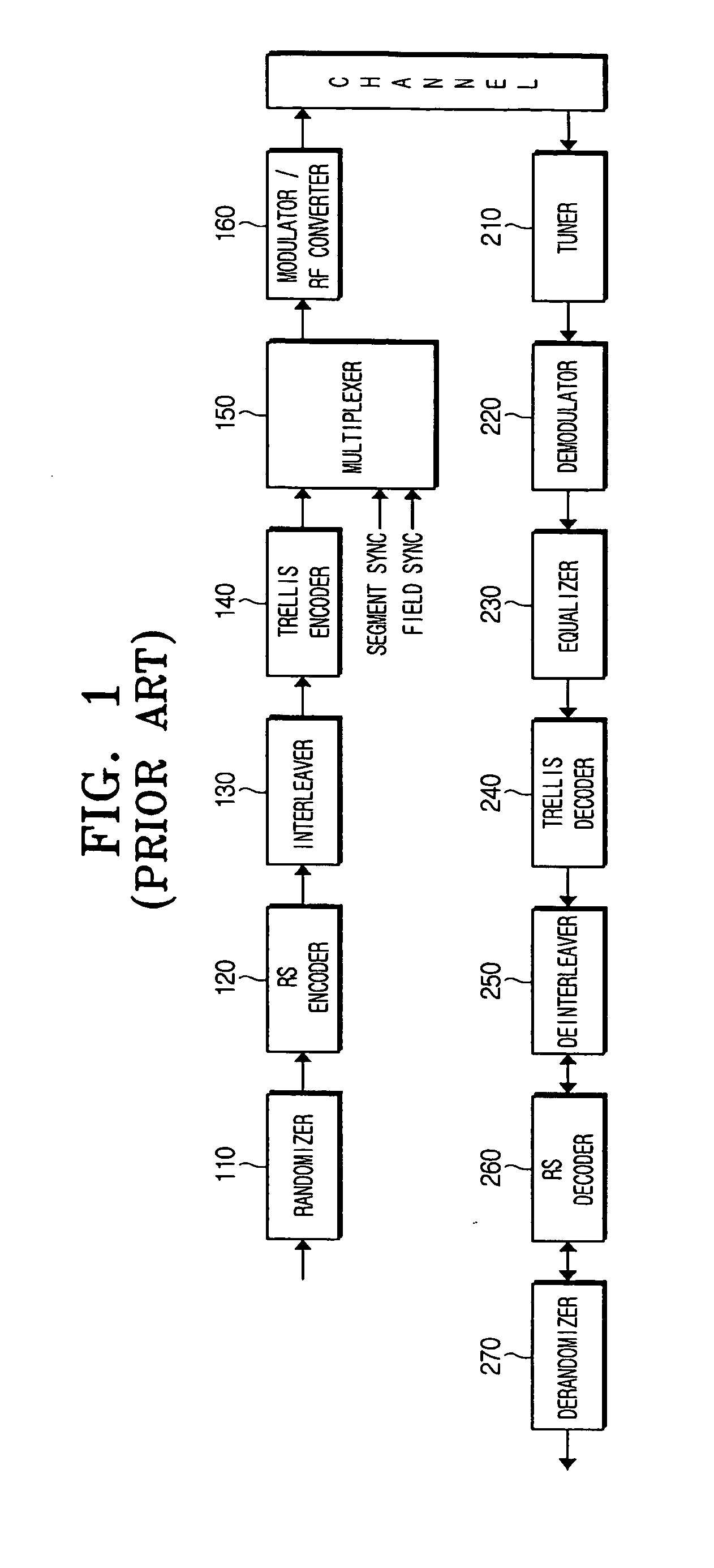
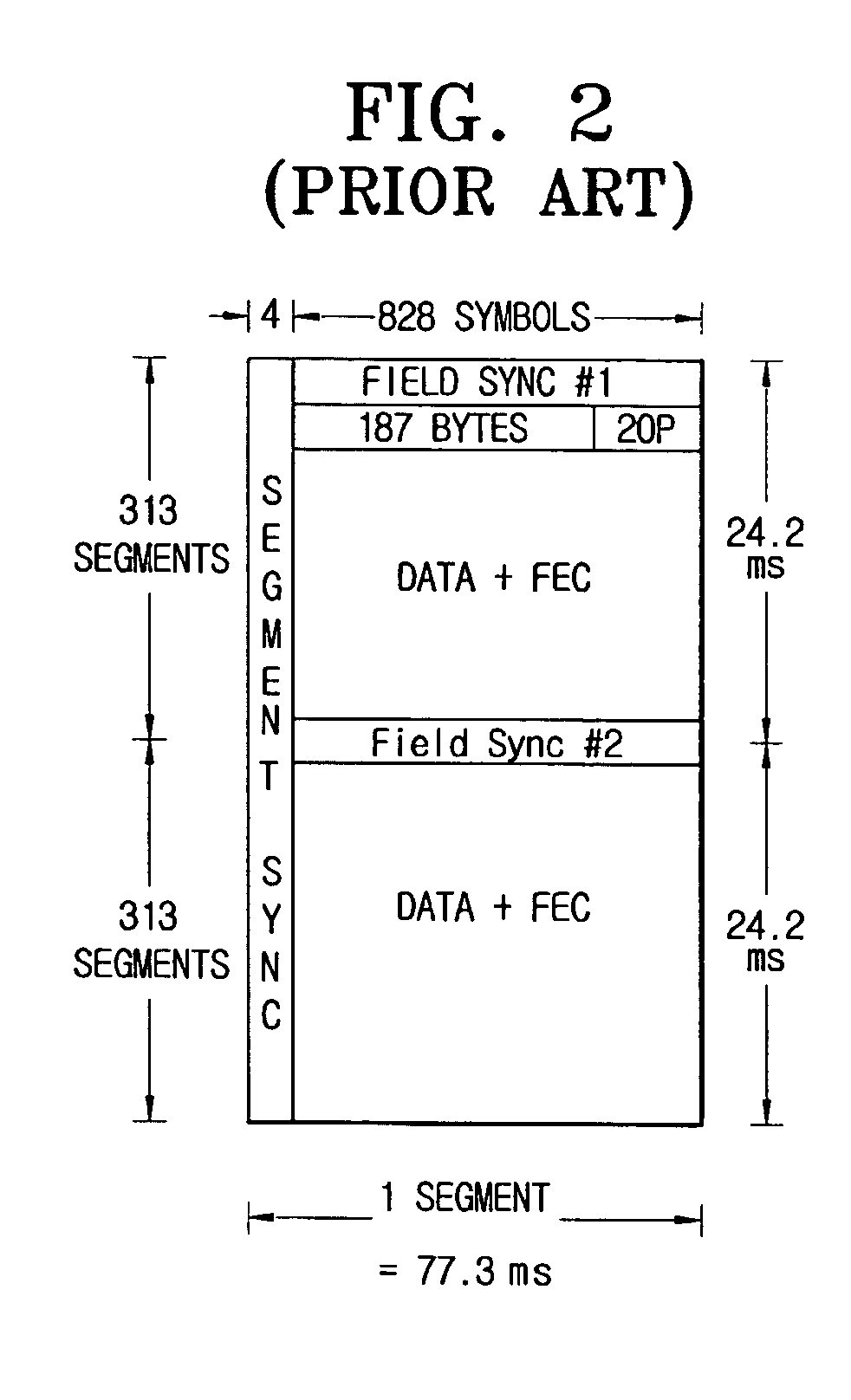
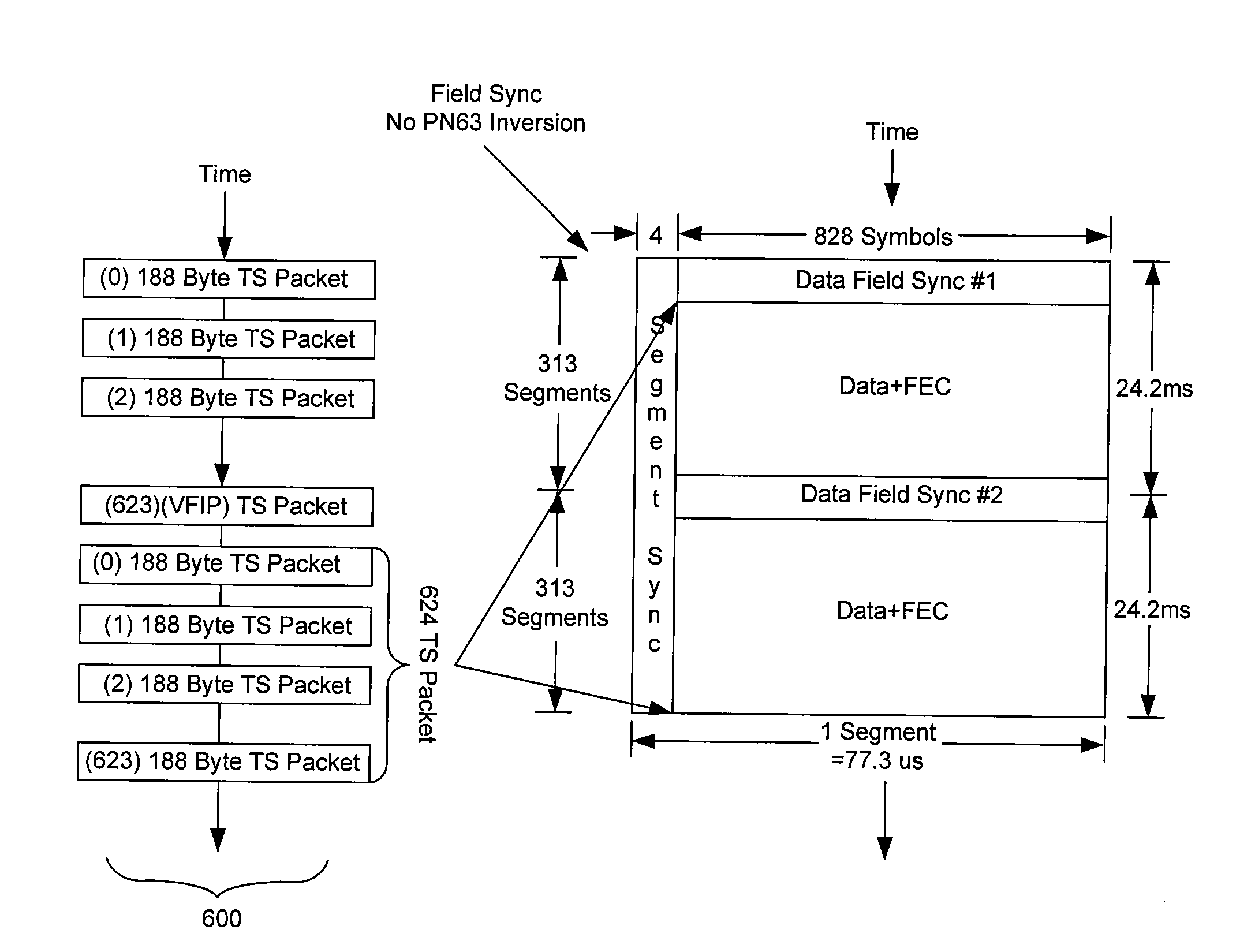
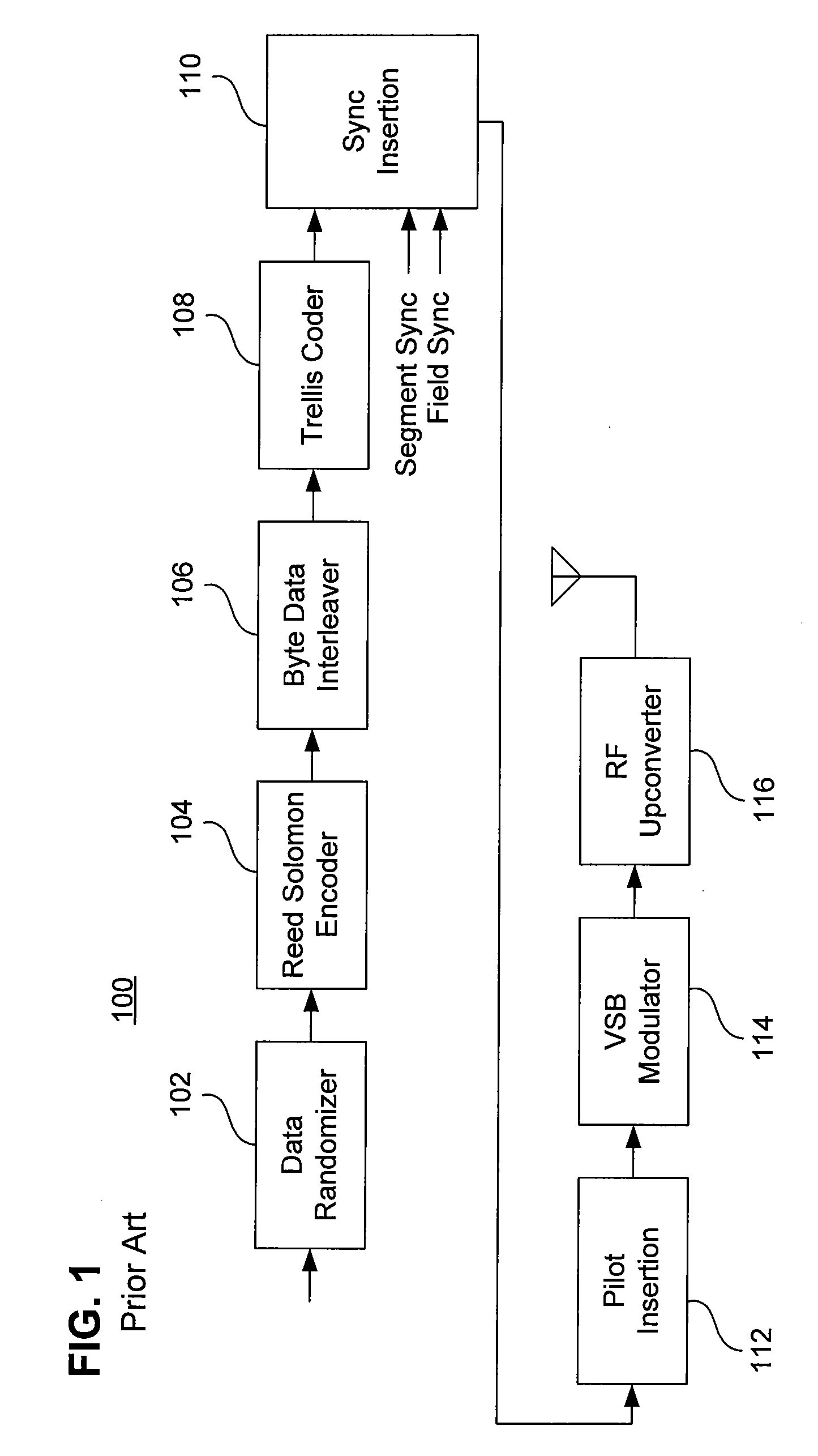
Digital television transmitter and method of coding data in digital television transmitter
InactiveUS20070071110A1Enhance decoding functionImprove reception qualityPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionMultiplexingMultiplexer
A digital television (DTV) transmitter and a method of coding data in the DTV transmitter method are disclosed. A pre-processes enhanced data by coding the enhanced data for forward error correction (FEC) and expanding the FEC-coded enhanced data. A data formatter generates enhanced data packets including the pre-processed enhanced data and inserting known data to at least one of the enhanced data packets. A first multiplexer multiplexes main data packets with the enhanced data packets, and a data randomizer randomizes the multiplexed data packets. A Reed-Solomon (RS) encoder RS-codes the randomized data packets by adding first parity data, and a data interleaver interleaves the RS-coded data packets. A trellis encoder trellis-encodes the interleaved data packets, wherein the trellis encoder may be initialized when a known data sequence is inputted thereto.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
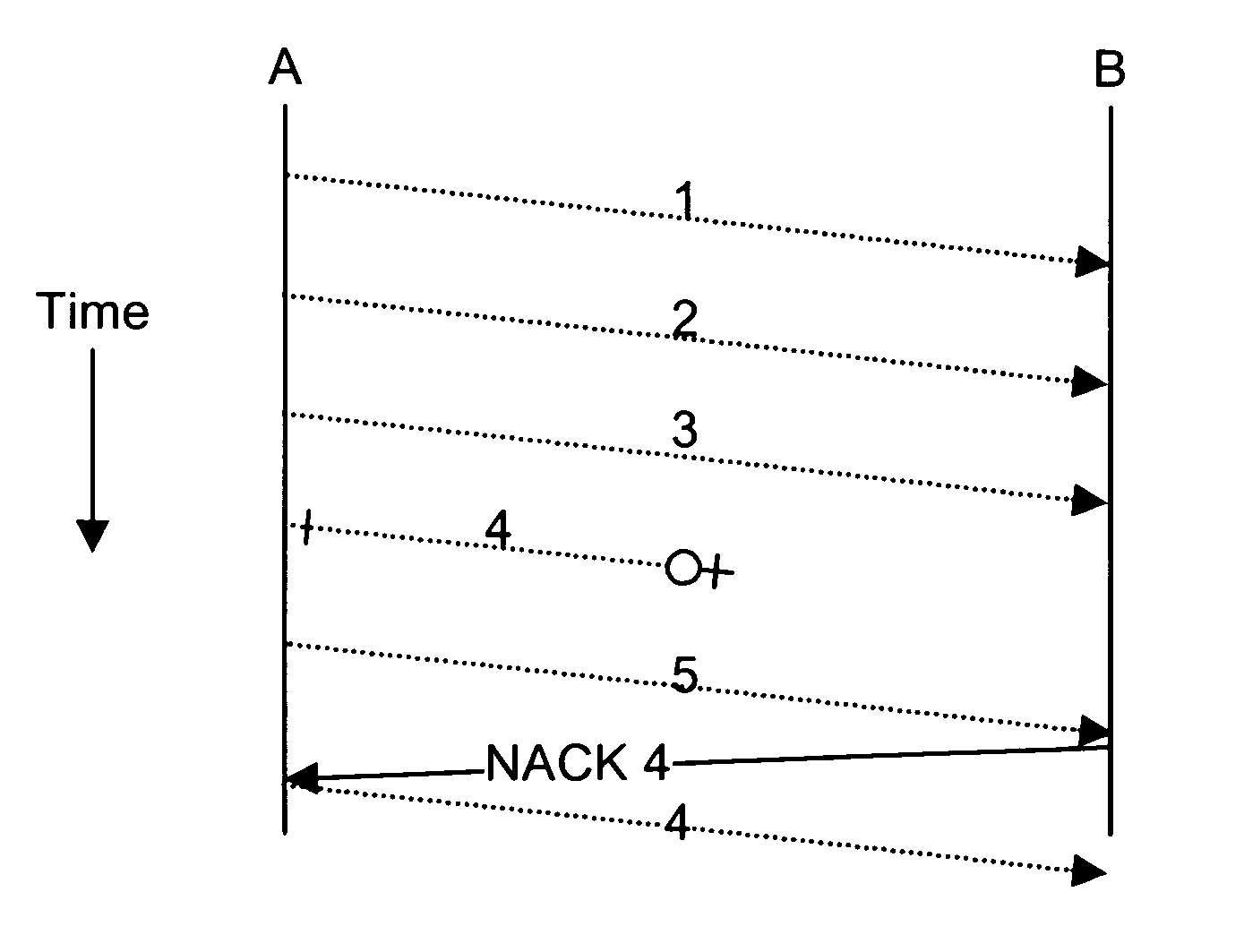
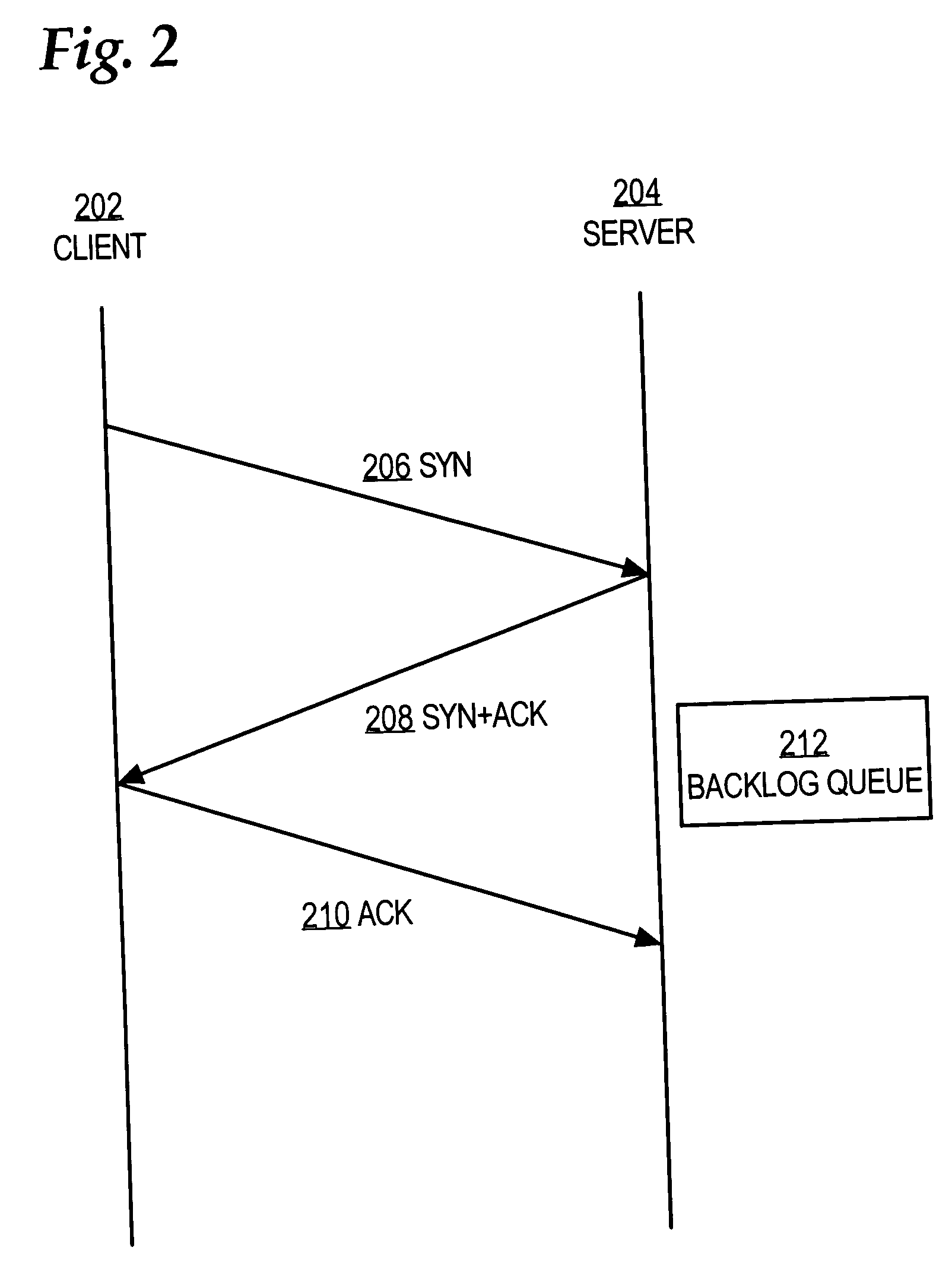
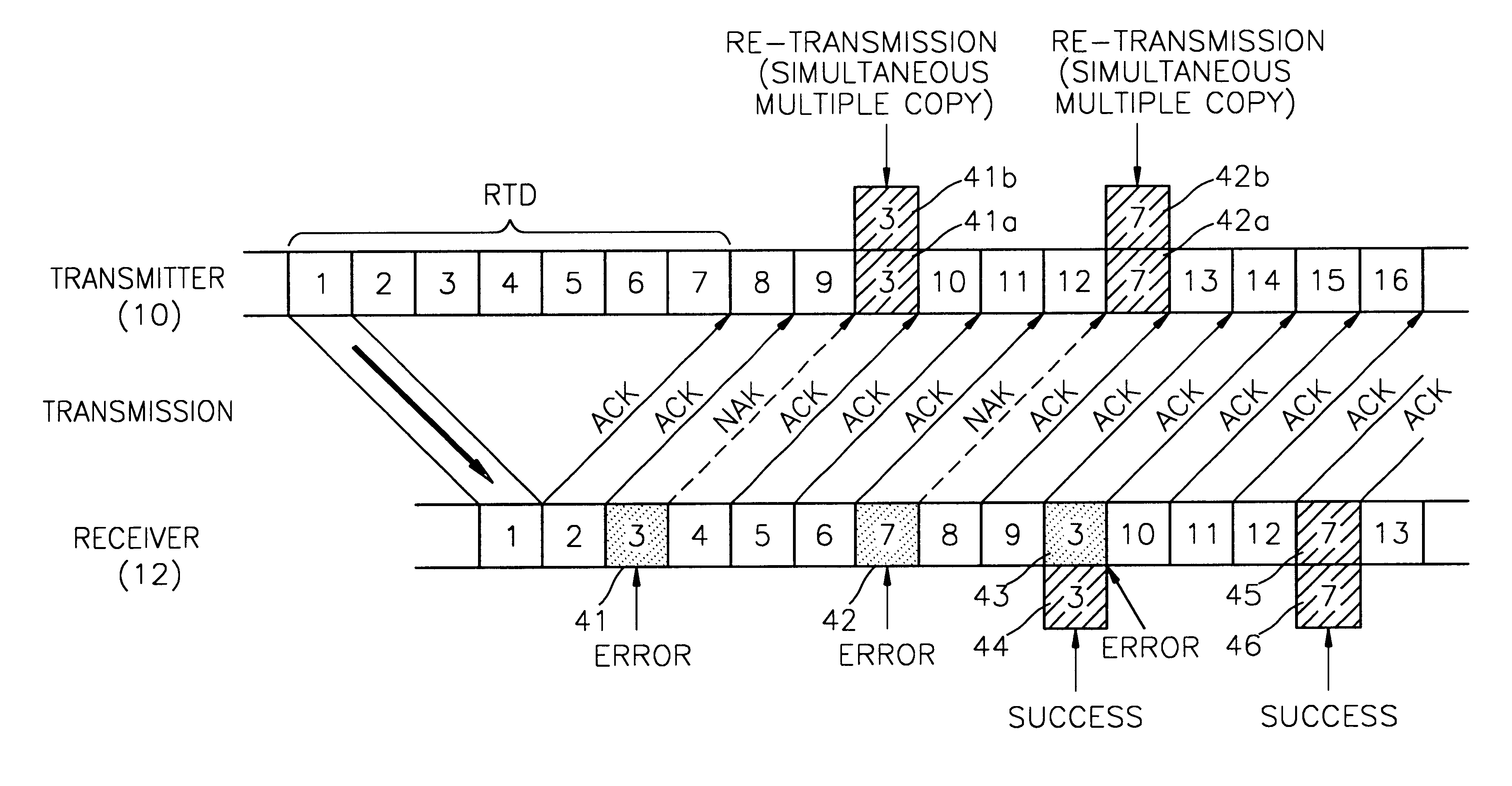
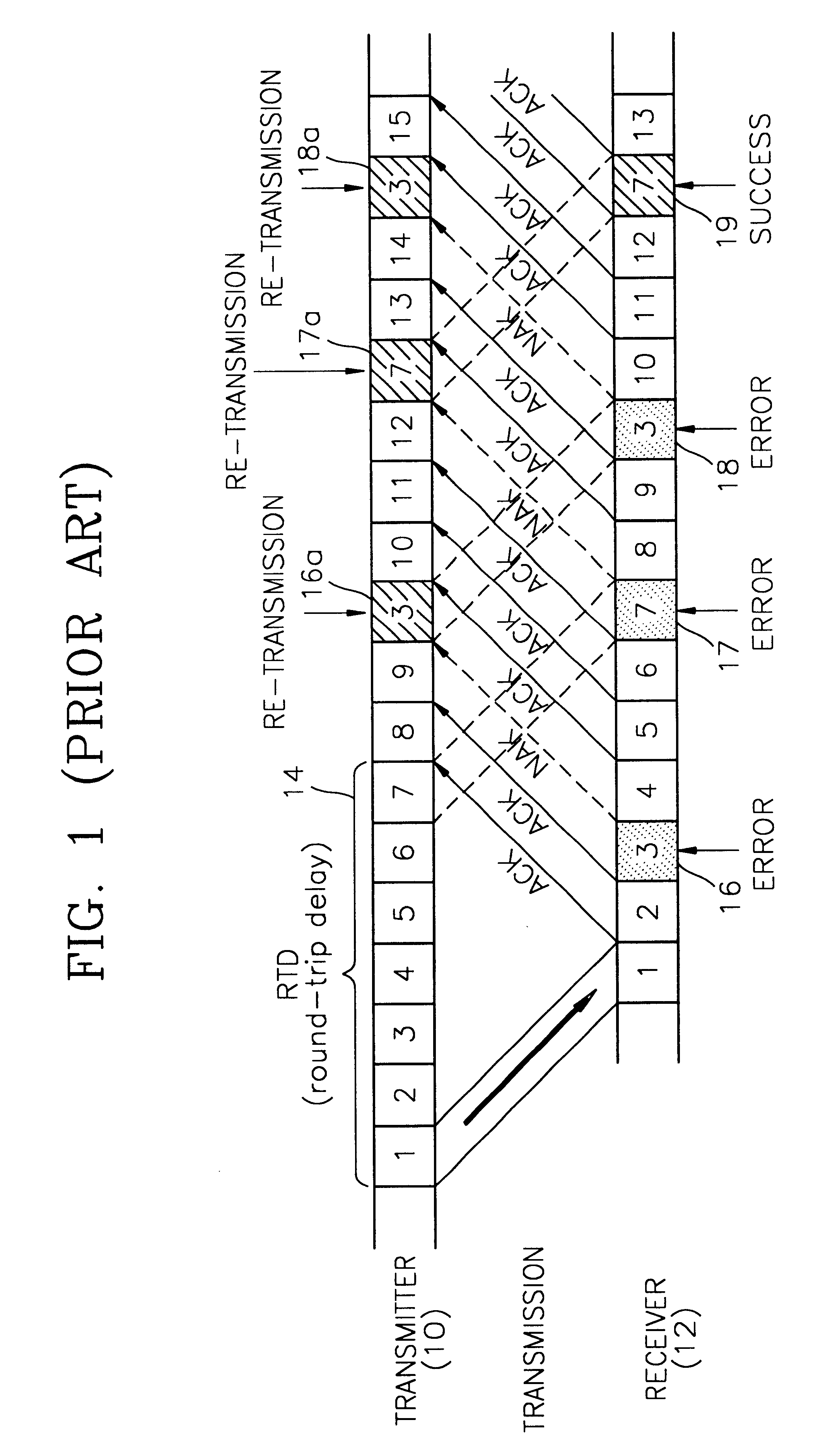
System and method for a negative acknowledgement-based transmission control protocol
InactiveUS7035214B1Shorten the lengthError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsCongestion windowTraffic capacity
A system and method for transmitting data in a data communications network, using a transmission control protocol, to provide reduced acknowledgment control traffic, error recovery and congestion control. A communications link is established between a transmitter and a receiver. Setting the communications link includes setting a network congestion window to an initial length. A sequence, or stream, of data packets is sent from the transmitter to the receiver. The receiver detects any missing packets, by examining the sequence numbers of the incoming packets, and sends negative acknowledgments, generally no more than four, to the transmitter identifying the missing data packet. When the transmitter receives a negative acknowledgment, it decreases the length of the congestion window, and re-transmits the missing packet. Detection and use of round-trip time, re-transmission time-out are provided.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Method and device for multi phase error-correction
InactiveUS20070124652A1Error detection/correctionCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceMulti phase
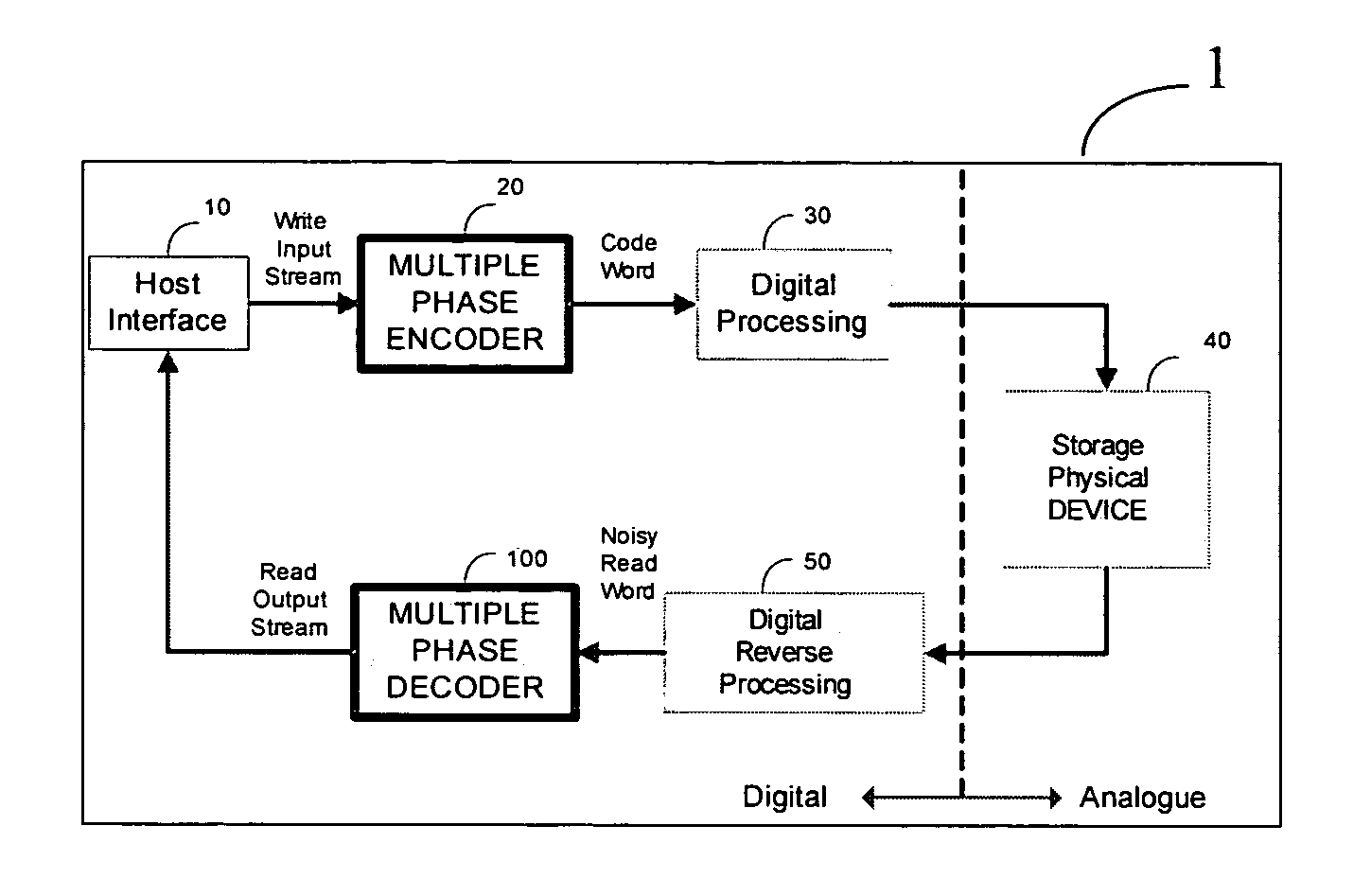
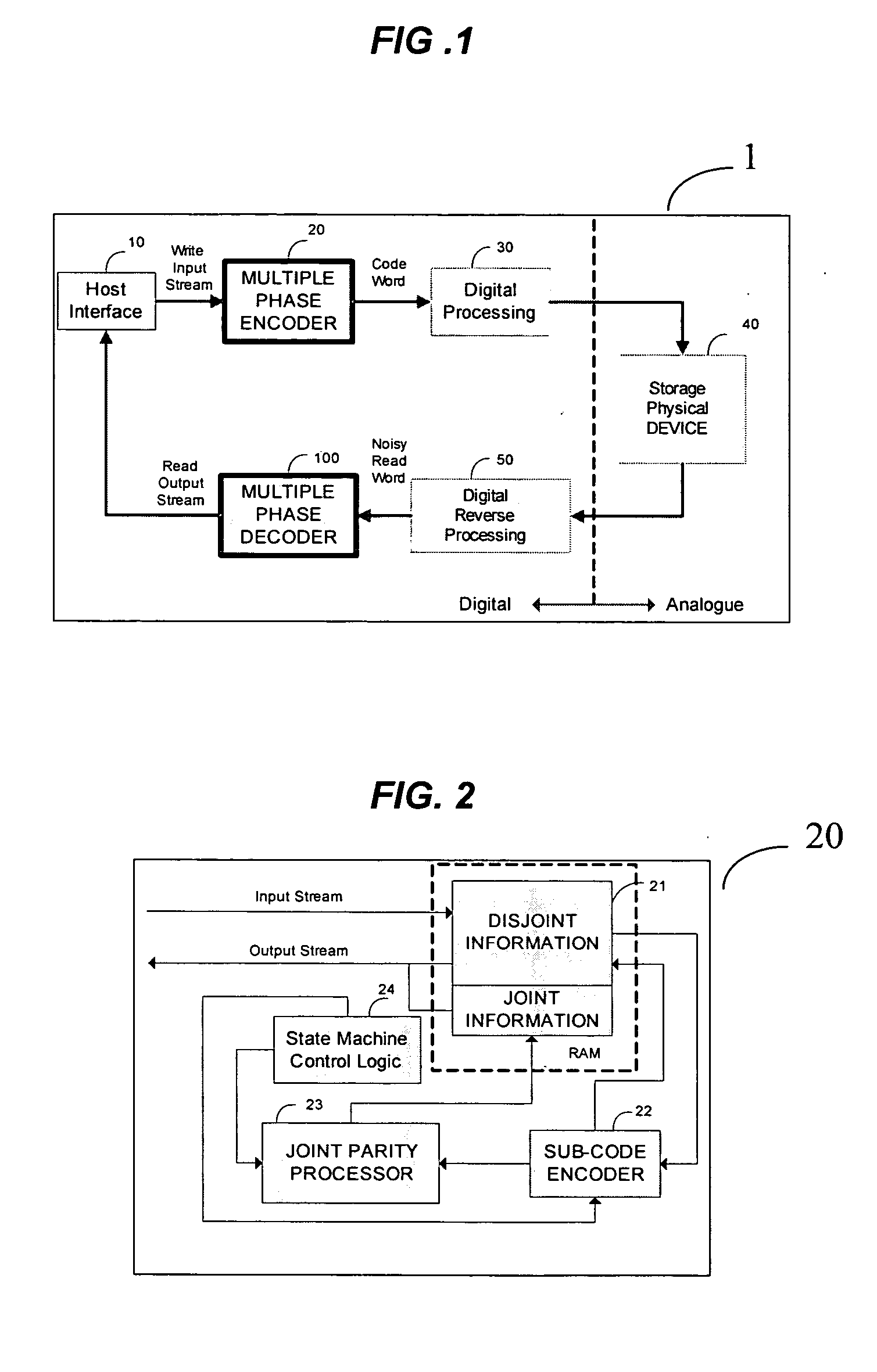
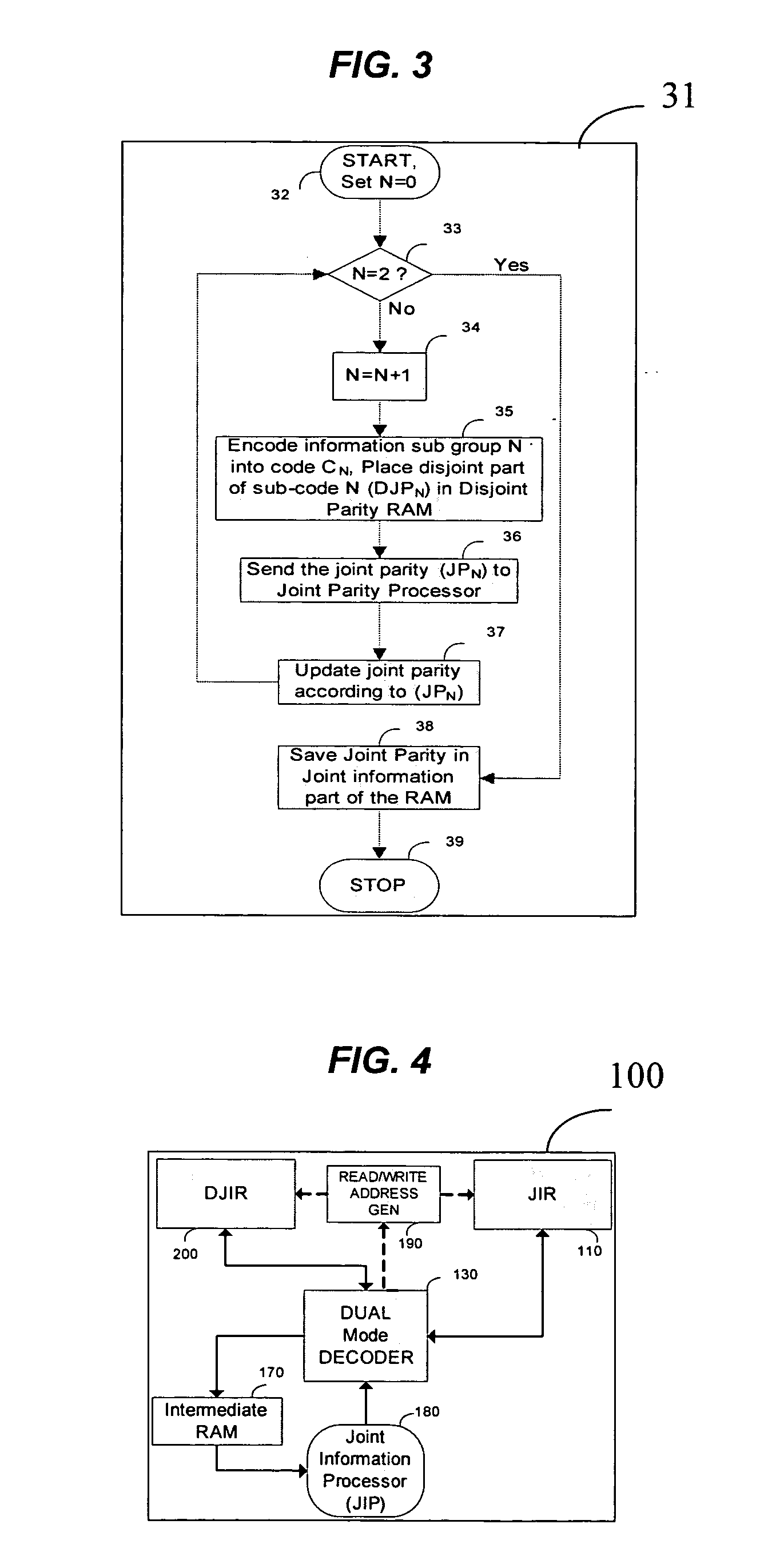
Data bits to be encoded are split into a plurality of subgroups. Each subgroup is encoded separately to generate a corresponding codeword. Selected subsets are removed from the corresponding codewords, leaving behind shortened codewords, and are many-to-one transformed to condensed bits. The final codeword is a combination of the shortened codewords and the condensed bits. A representation of the final codeword is decoded by being partitioned to a selected subset and a plurality of remaining subsets. Each remaining subset is decoded separately. If one of the decodings fails, the remaining subset whose decoding failed is decoded at least in part according to the selected subset. If the encoding and decoding are systematic then the selected subsets are of parity bits.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Electronic device having a plurality of modes of operation
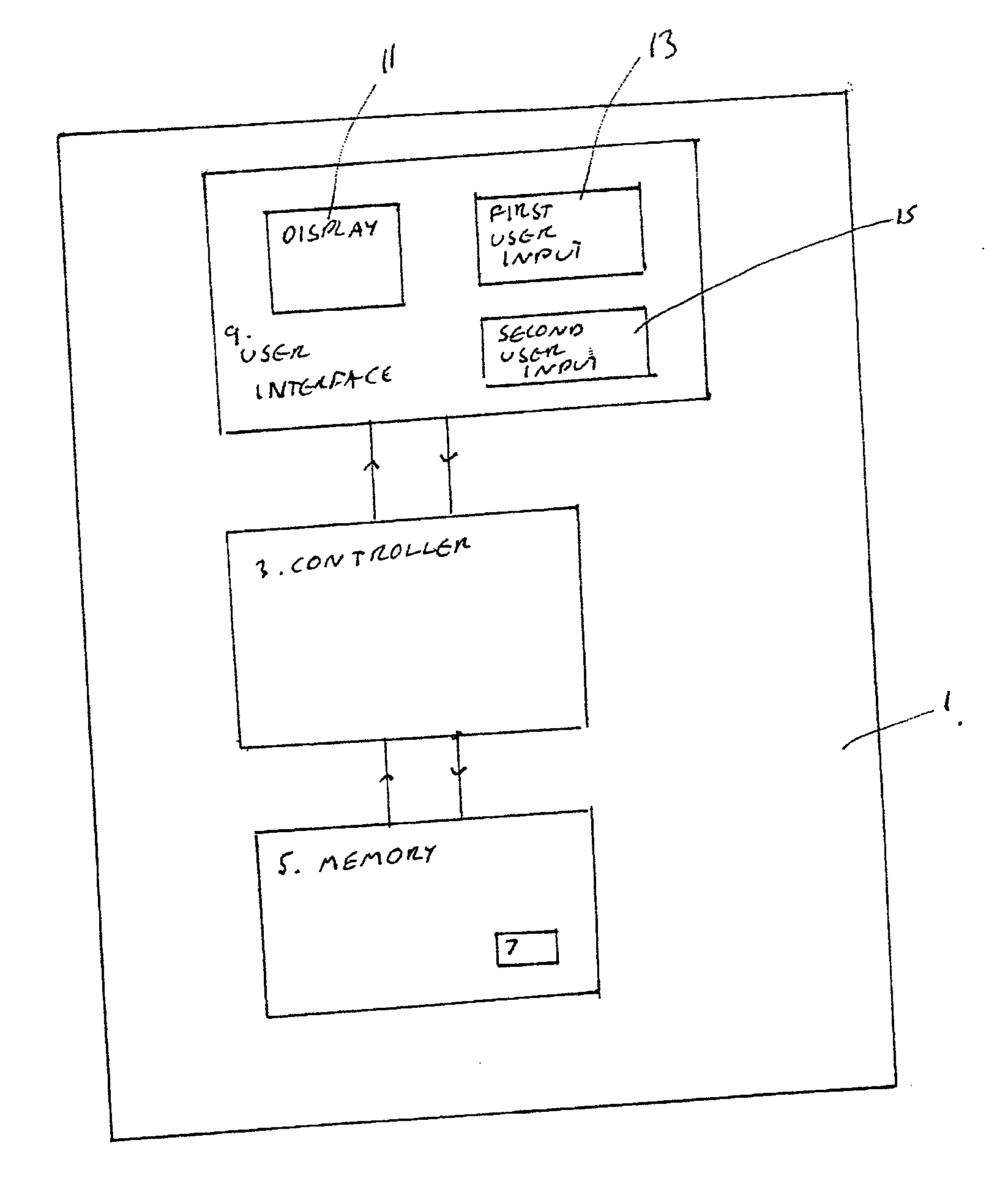
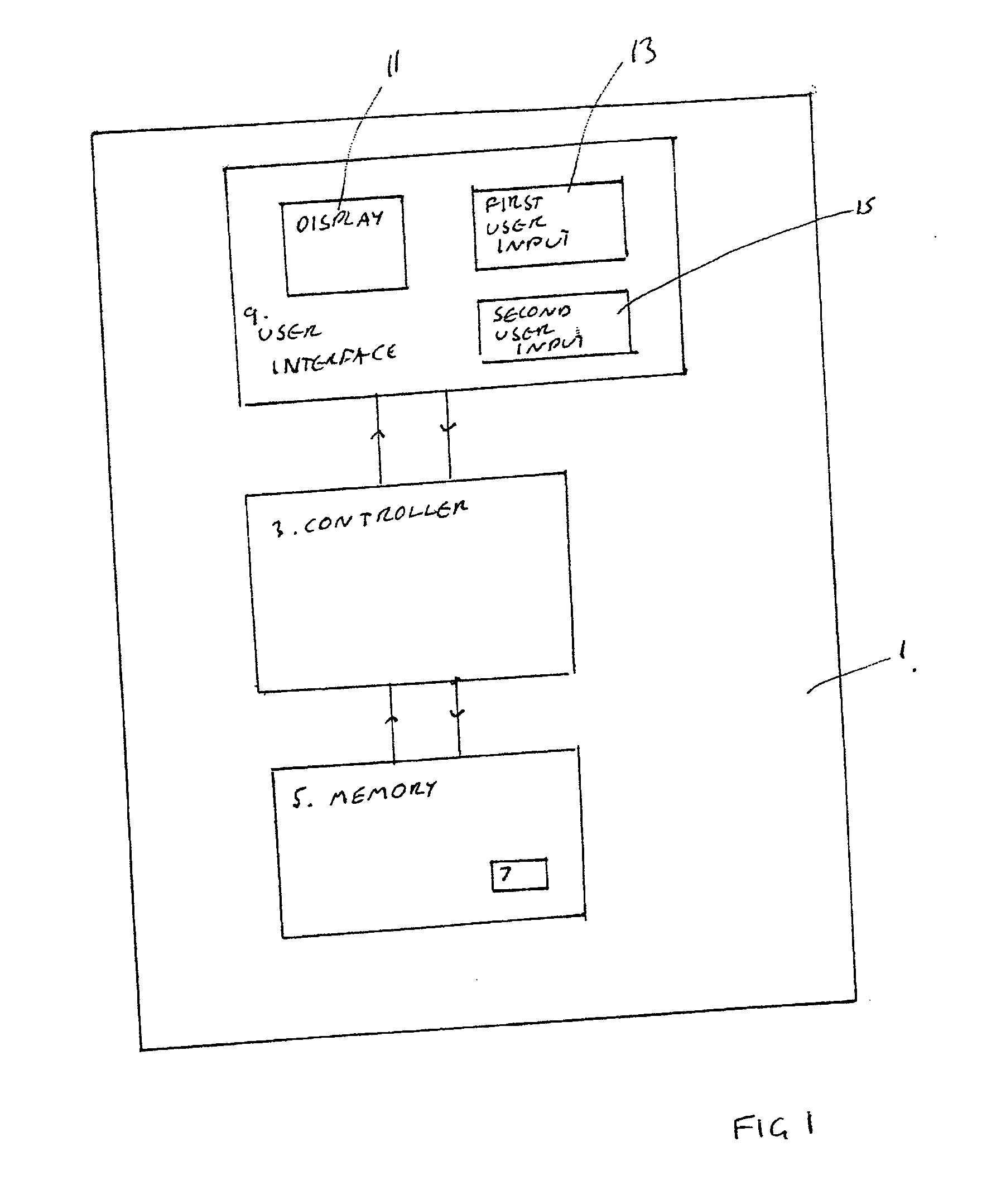
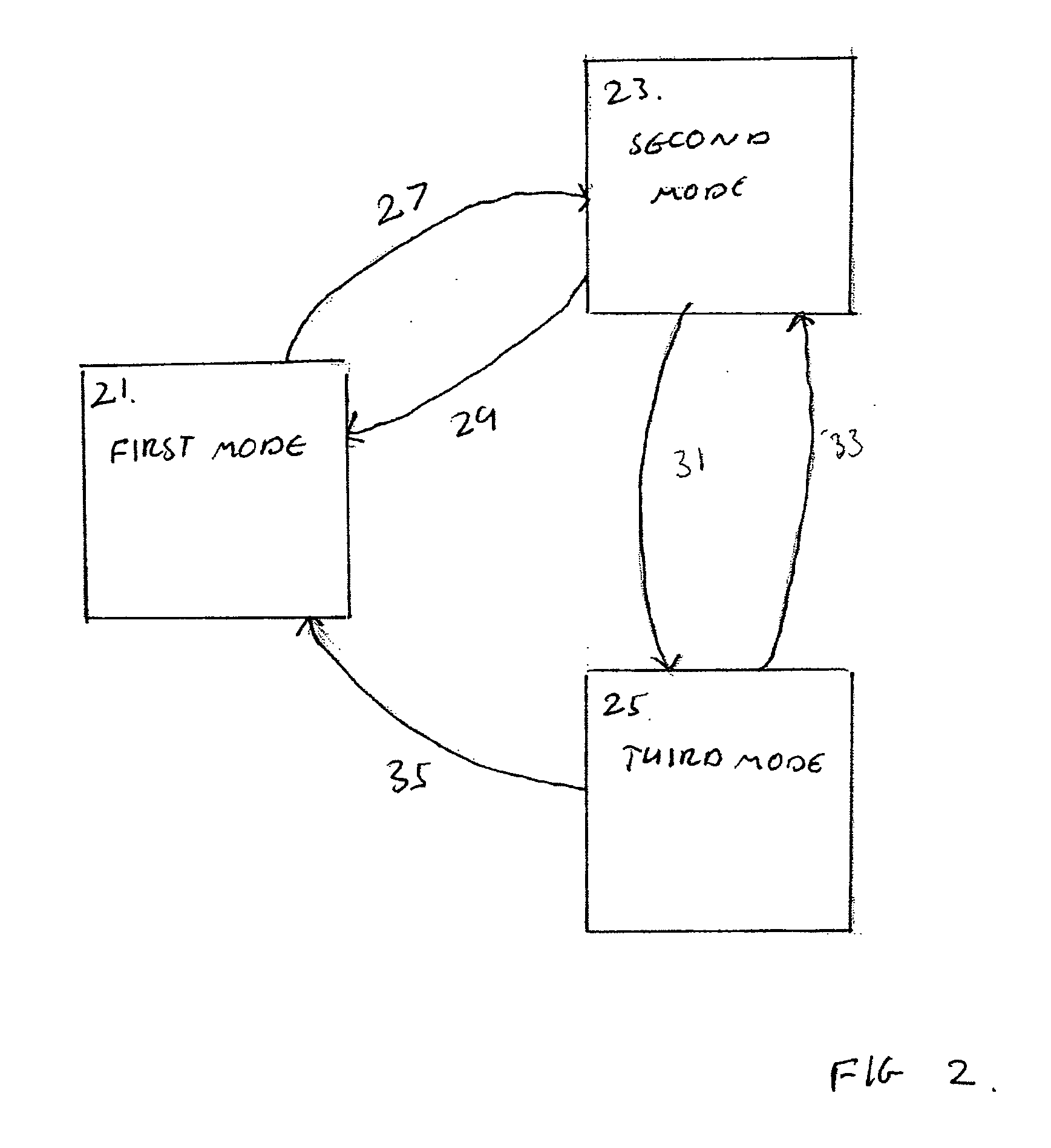
InactiveUS20070300140A1Easy accessAvoid performanceError preventionTransmission systemsUser inputDisplay device
An electronic device including a display, a first user input, for enabling access to a plurality of functions, a second user input, and a controller, operable, in response to an input, to change the mode of operation of the device from a first, active mode of operation, in which the controller is operable to enable a user access to a plurality of functions, to a second, restricted mode of operation in which the controller is operable to disable user access to the plurality of functions, and operable, in response to an input via the second user input, to change the mode of operation of the device from the second, restricted mode of operation to a third, restricted mode of operation in which the controller is operable to disable user access to the plurality of functions and is operable to present information not presentable in the second restricted mode of operation.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
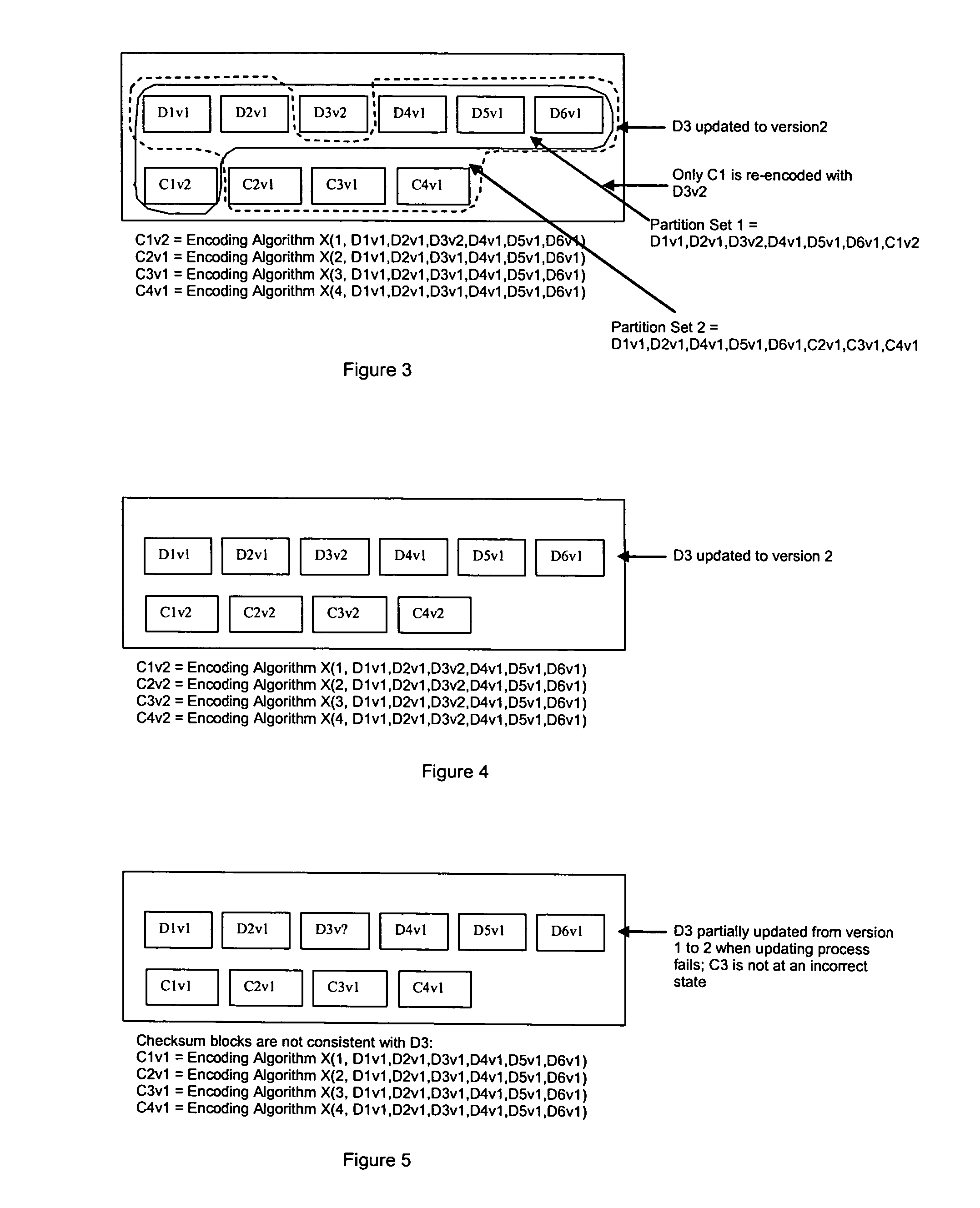
Method for erasure coding data across a plurality of data stores in a network
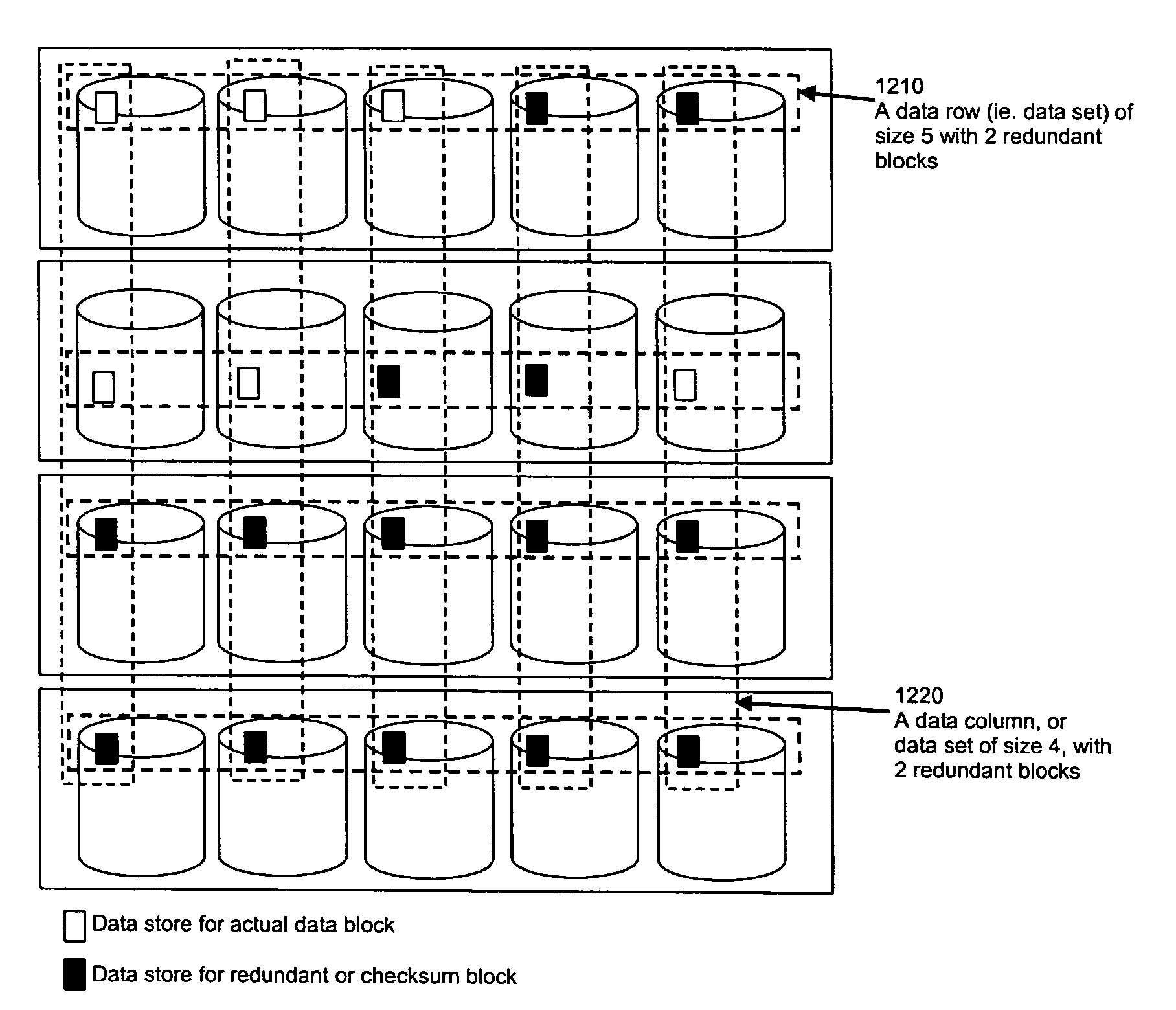
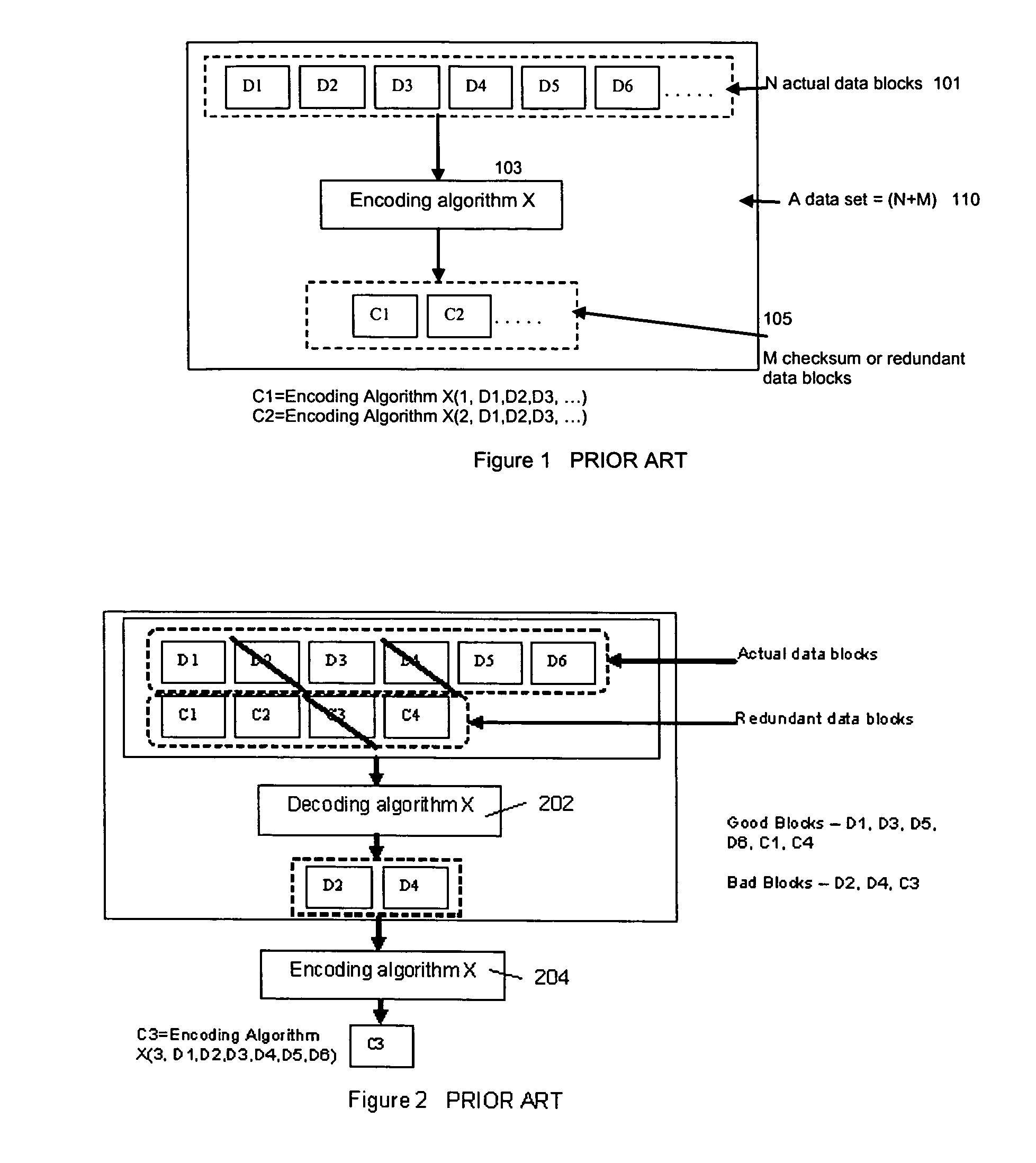
ActiveUS7681104B1Maintain data consistencyEffective applicationError preventionCode conversionData setTheoretical computer science
An efficient method to apply an erasure encoding and decoding scheme across dispersed data stores that receive constant updates. A data store is a persistent memory for storing a data block. Such data stores include, without limitation, a group of disks, a group of disk arrays, or the like. An encoding process applies a sequencing method to assign a sequence number to each data and checksum block as they are modified and updated onto their data stores. The method preferably uses the sequence number to identify data set consistency. The sequencing method allows for self-healing of each individual data store, and it maintains data consistency and correctness within a data block and among a group of data blocks. The inventive technique can be applied on many forms of distributed persistent data stores to provide failure resiliency and to maintain data consistency and correctness.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC
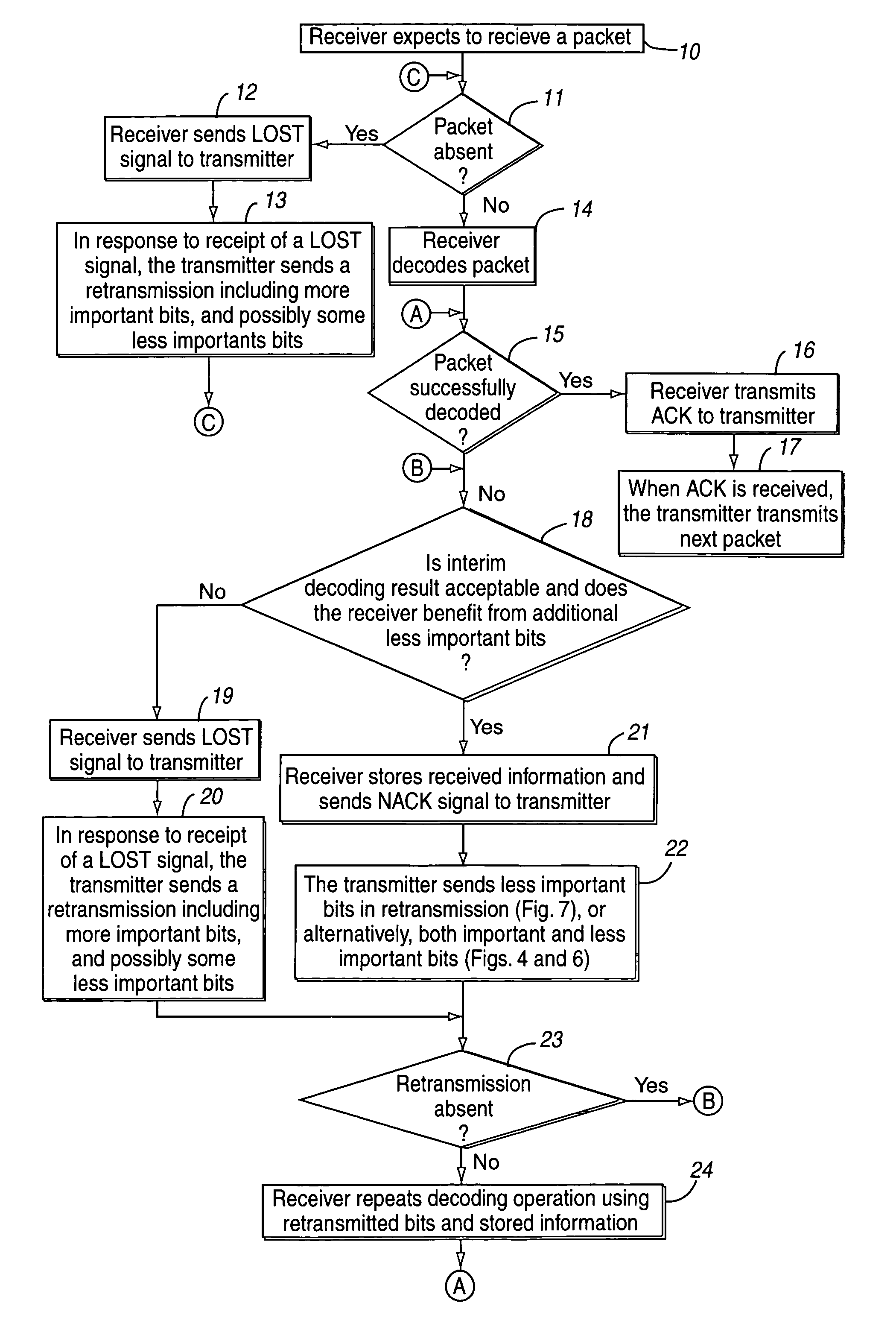
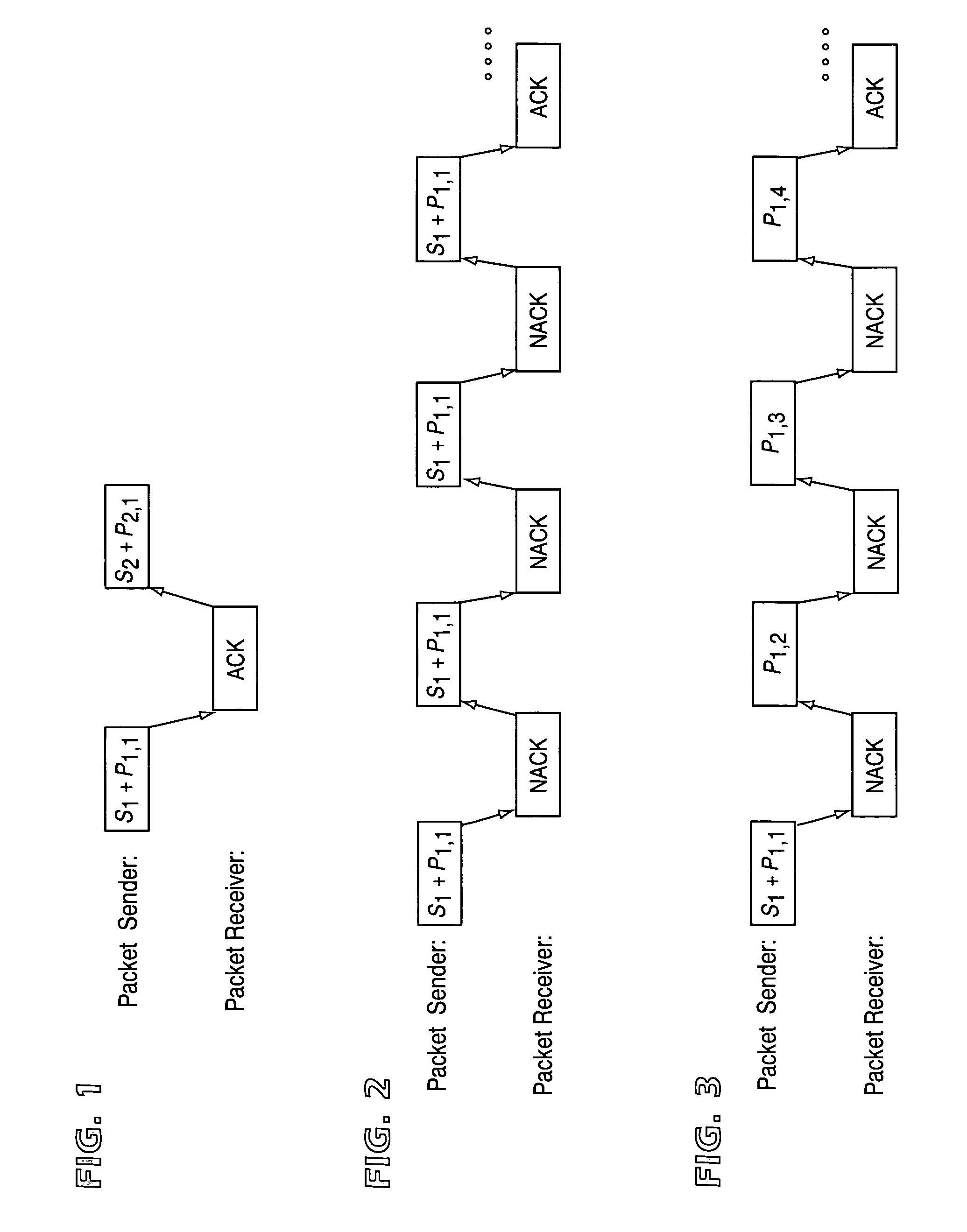
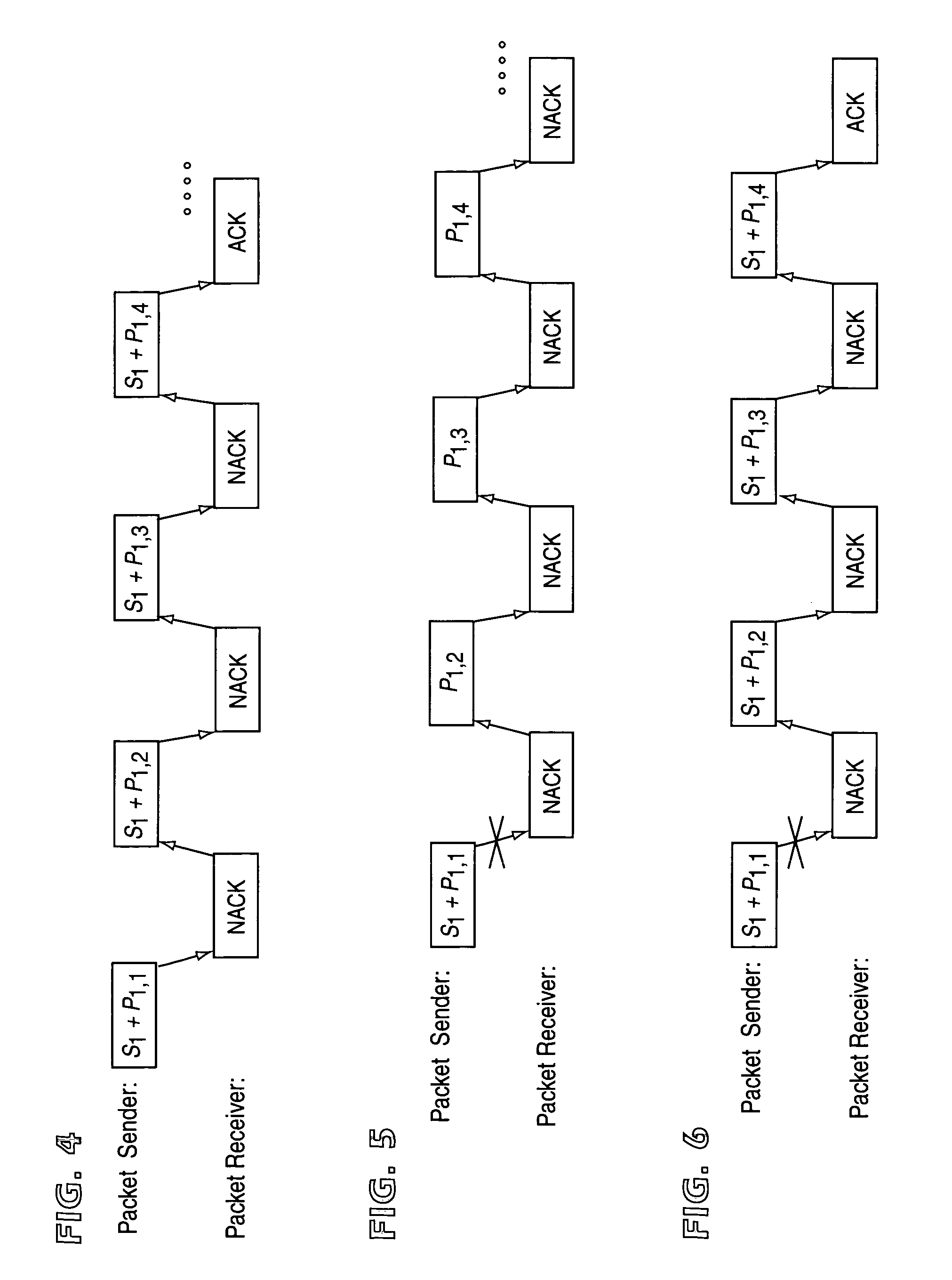
Hybrid ARQ for packet data transmission
InactiveUS6977888B1Improve throughputReduce delaysError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCommunications systemForward error correction
A hybrid ARQ scheme is used incremental data packet combining. In an example embodiment, the hybrid ARQ scheme with incremental data packet combining employs three feedback signaling commands: ACK, NACK, and LOST. Using these three feedback commands, the hybrid ARQ scheme with incremental data packet combining provides both robustness and good performance. This scheme is particularly advantageous in communication systems with unreliable communication channels, e.g., a fading radio channel, where forward error correction (FEC) codes are used and some of the code symbols are more important than other code symbols. Benefits include increased throughput and decreased delay of the packet data communication.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
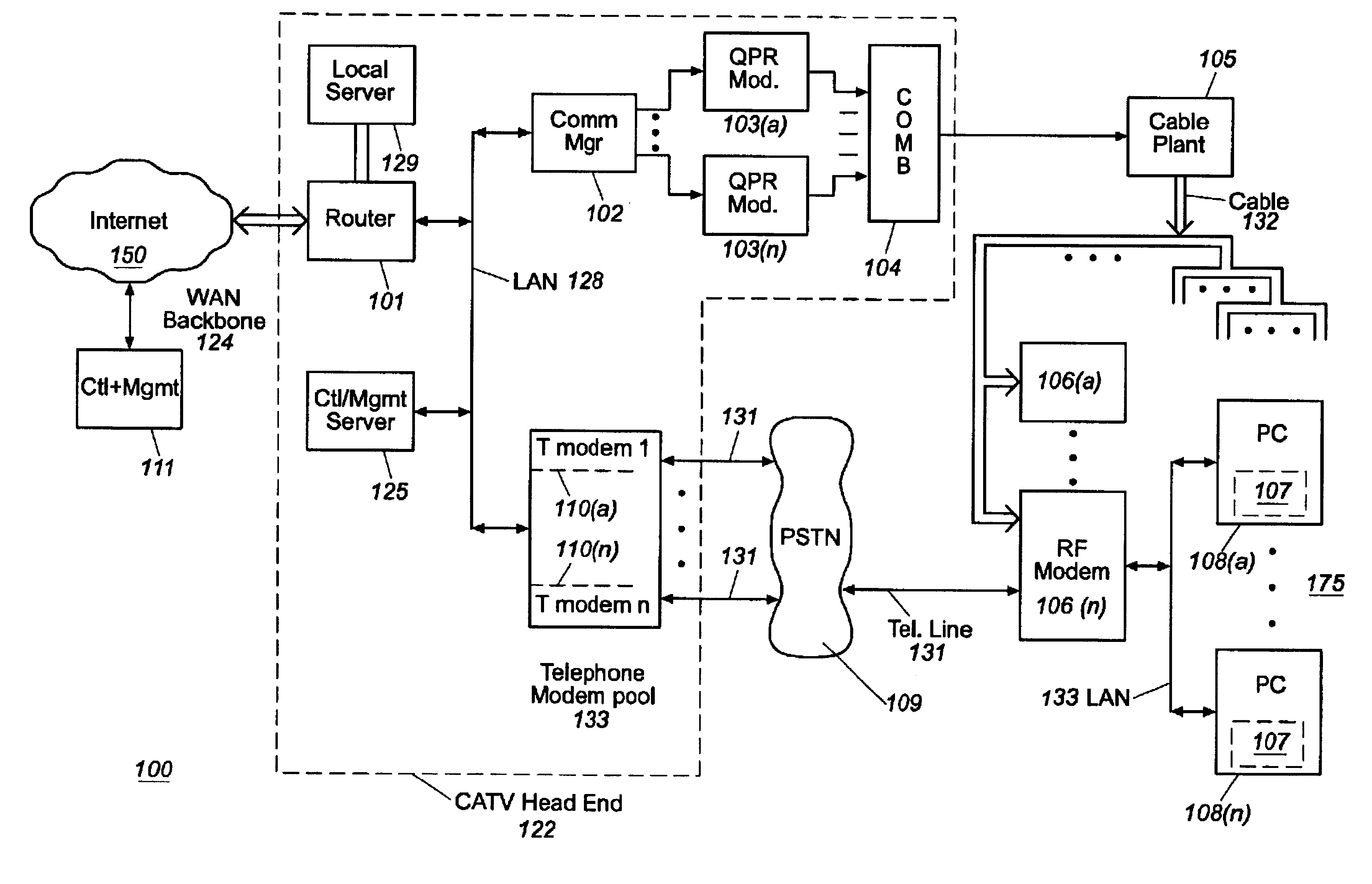
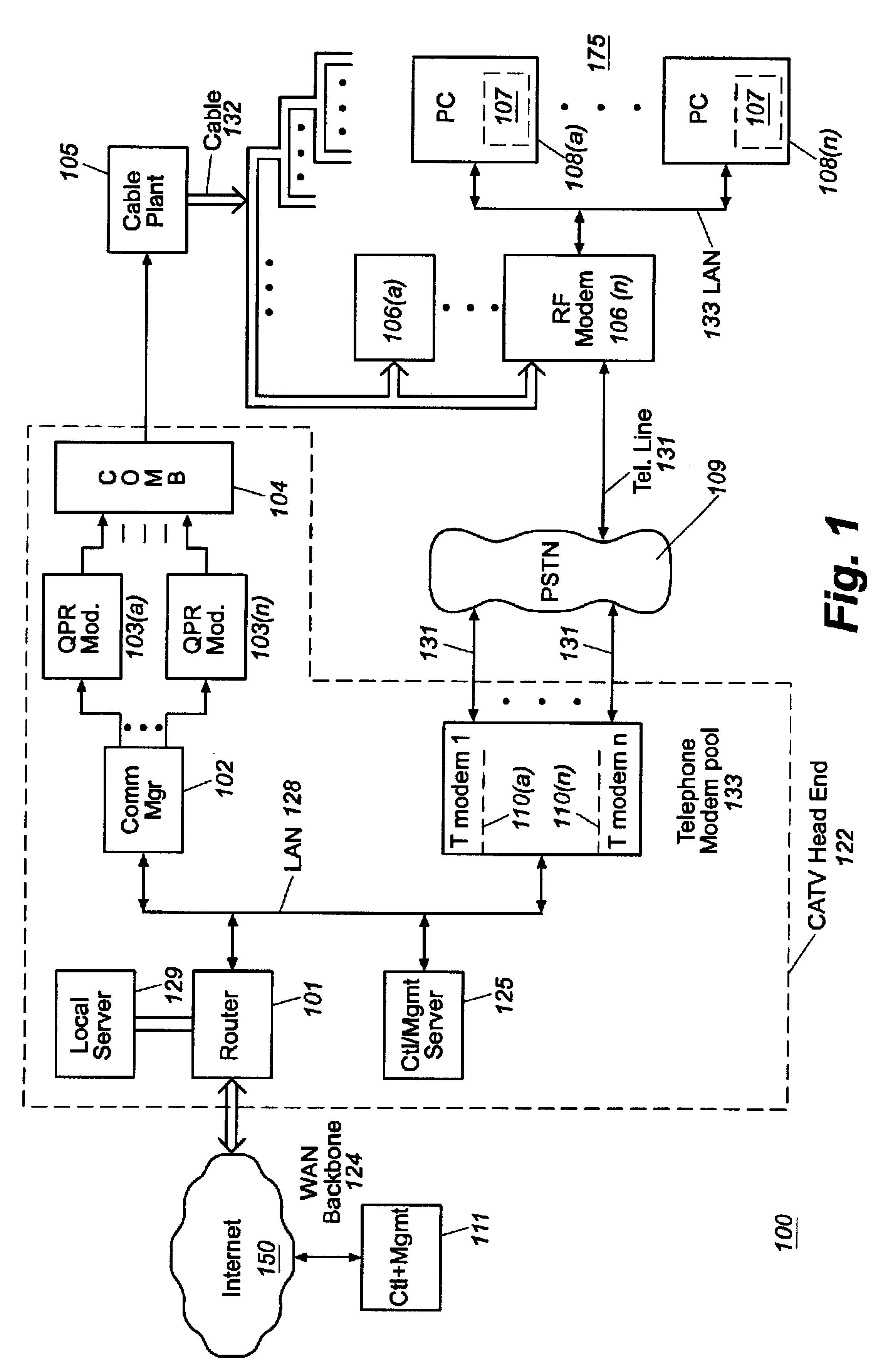
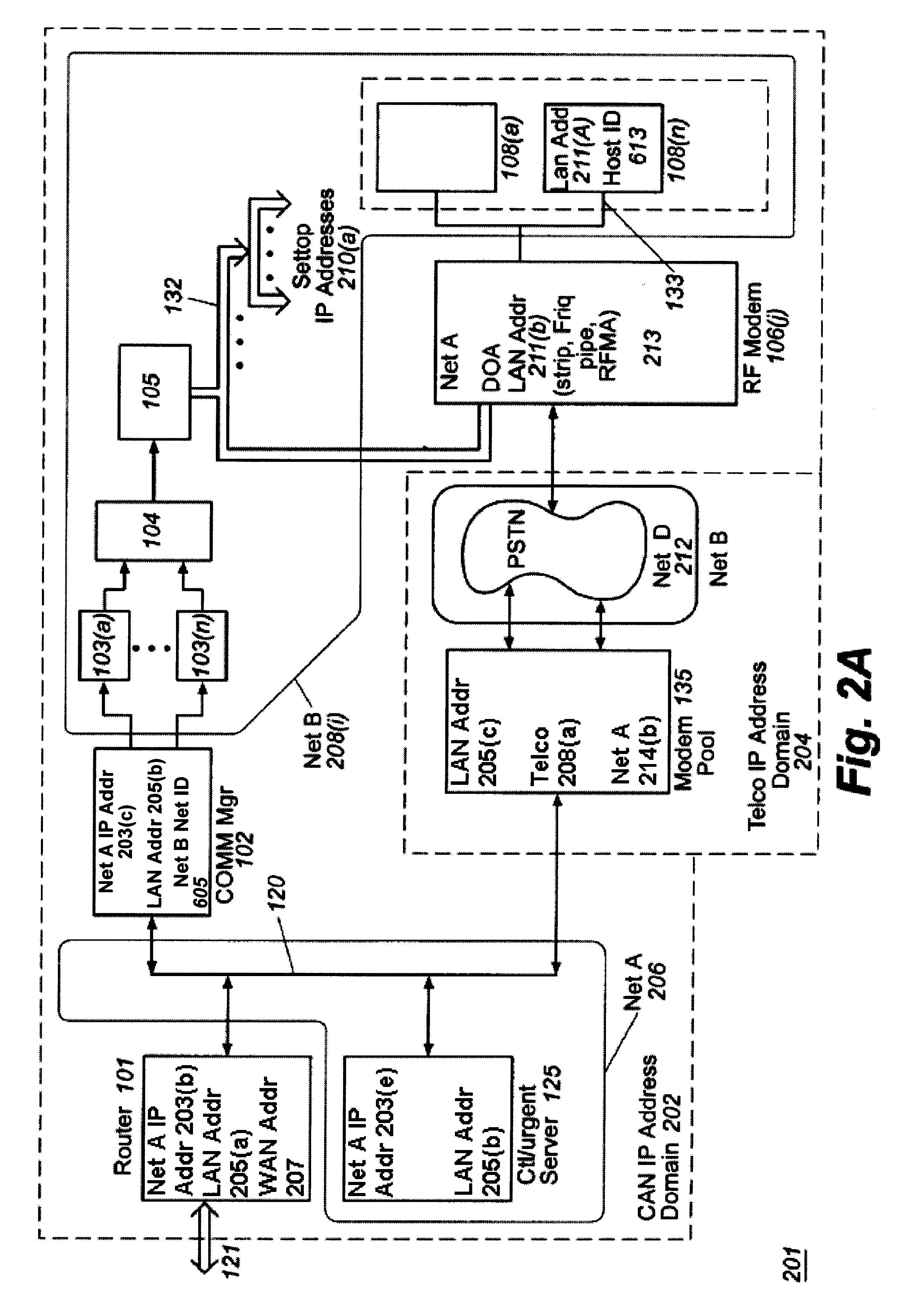
Usage statistics collection for a cable data delivery system
InactiveUS6308328B1Broadband local area networksBroadcast transmission systemsData connectionNetwork management
Apparatus for recording and collecting usage and other statistical data from components of a cable data network comprises a network manager for maintaining and collecting the statistics. Internet protocol addresses are associated with components of the network. The component maintains a software agent that manages a statistics database. Responsive to a manager request generated at a service provider defined time interval, the component software agent provides the usage statistics to the network manager in real-time during an Internet session with a host. When the host to Internet or other data connection is torn down due to failure, disconnect or inactivity time-out, remaining usage statistics data is collected and the session duration updated with the time of tear down. Usage statistics collected include the amount of data transferred to / from a host, the amount of data that is discarded due to insufficient resource capacity and amount of data that cannot be corrected despite forward error correction used in a downstream high capacity channel to the host. Data traps may be defined and downloaded to components of the network for implementation. As a result, billing of users of the cable data network can be usage sensitive and determined based on actual data transferred (including credit given for errored data) and / or time sensitive based on session duration.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Digital broadcast transmitting and receiving system having an improved receiving performance and signal processing method thereof
ActiveUS20050249301A1Improve reception performanceModulation with suppressed carrierCode conversionData streamEqualization
A digital broadcast transmitting and receiving system and a signal processing method thereof that improves the receiving performance of the system. A digital broadcast transmitter can include a randomizer to receive and randomize a data stream into a specified position of which stuff bytes are inserted, a stuff-byte exchange unit to generate known data having a predefined pattern and insert the known data into the specified position of the data stream into which the stuff bytes are inserted, an encoder to encode the data stream output from the stuff-byte exchange unit for an error correction, and a modulator and RF converter to modulate the encoded data stream, RF-convert the modulated data stream and transmit the RF-converted data. The digital broadcast receiving performance can be improved even in an inferior multi-path channel by detecting the known data from the received transmission and using the known data for synchronization and equalization in a digital broadcast receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
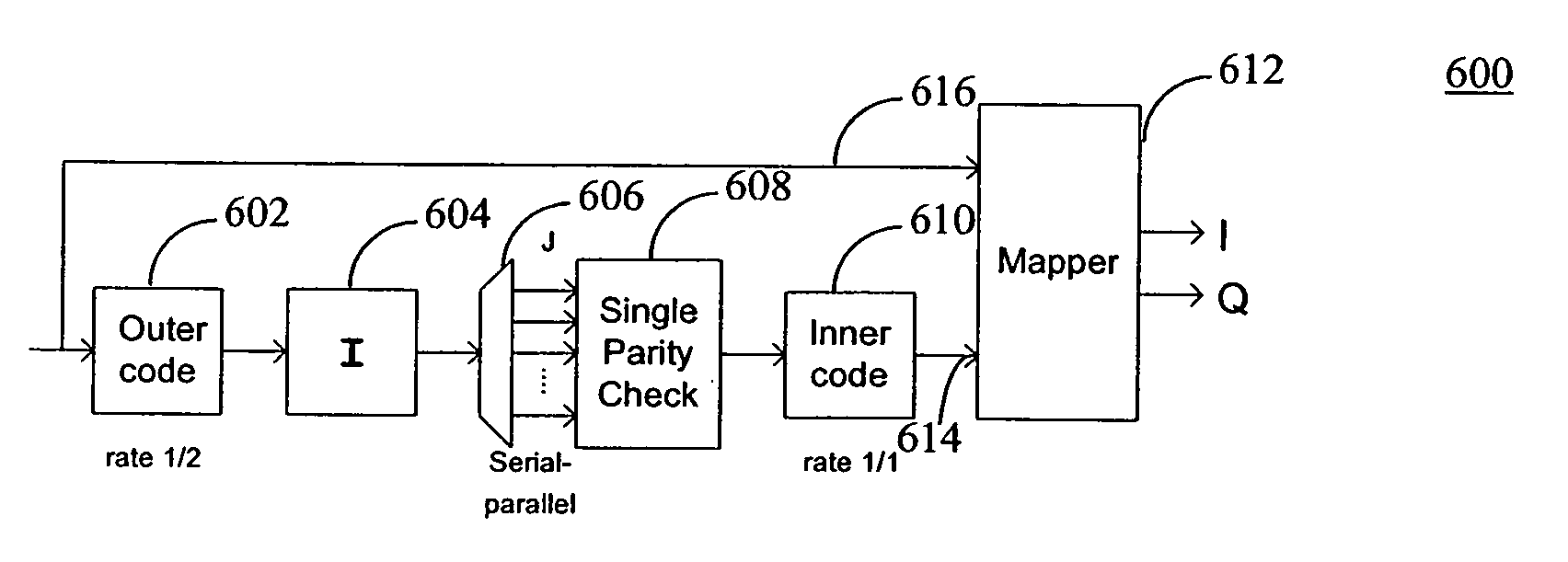
Method and apparatus for communications using improved turbo like codes
ActiveUS20060031737A1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionSingle parity checkConvolutional code
Methods, apparatuses, and systems are presented for performing data encoding involving encoding data bits according to an outer convolutional code to produce outer encoded bits, processing the outer encoded bits using an interleaver and a single parity check (SPC) module to produce intermediate bits, encoding the intermediate bits according to an inner convolutional code to produce inner encoded bits, processing the inner encoded bits using a puncture module to produce punctured bits, and combining the data bits and the punctured bits to produce encoded outputs. Methods, apparatuses, and systems are also presented for performing data decoding based on soft channel metrics derived from a channel using various iterative techniques.
Owner:TRELLIS WARE TECH
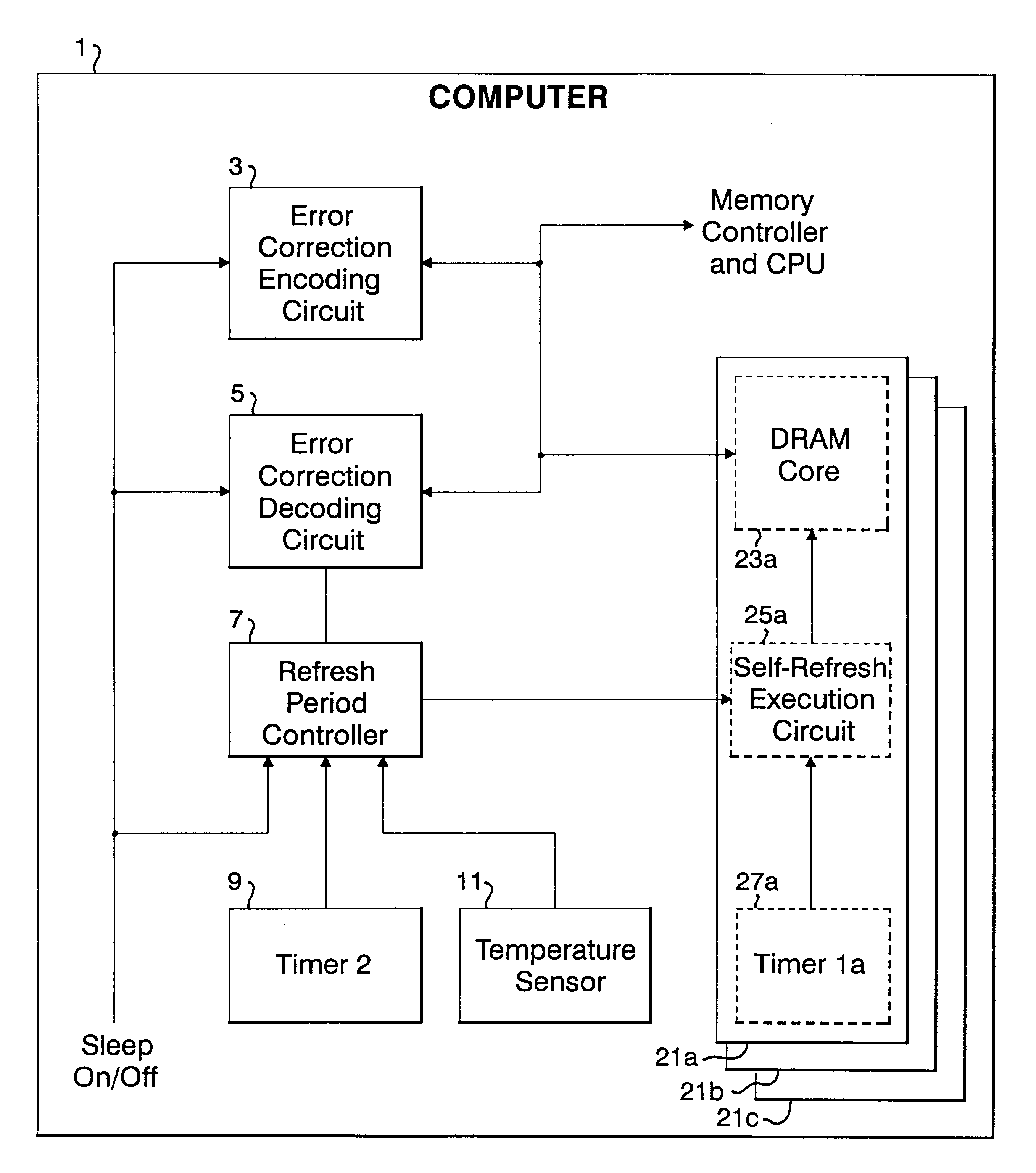
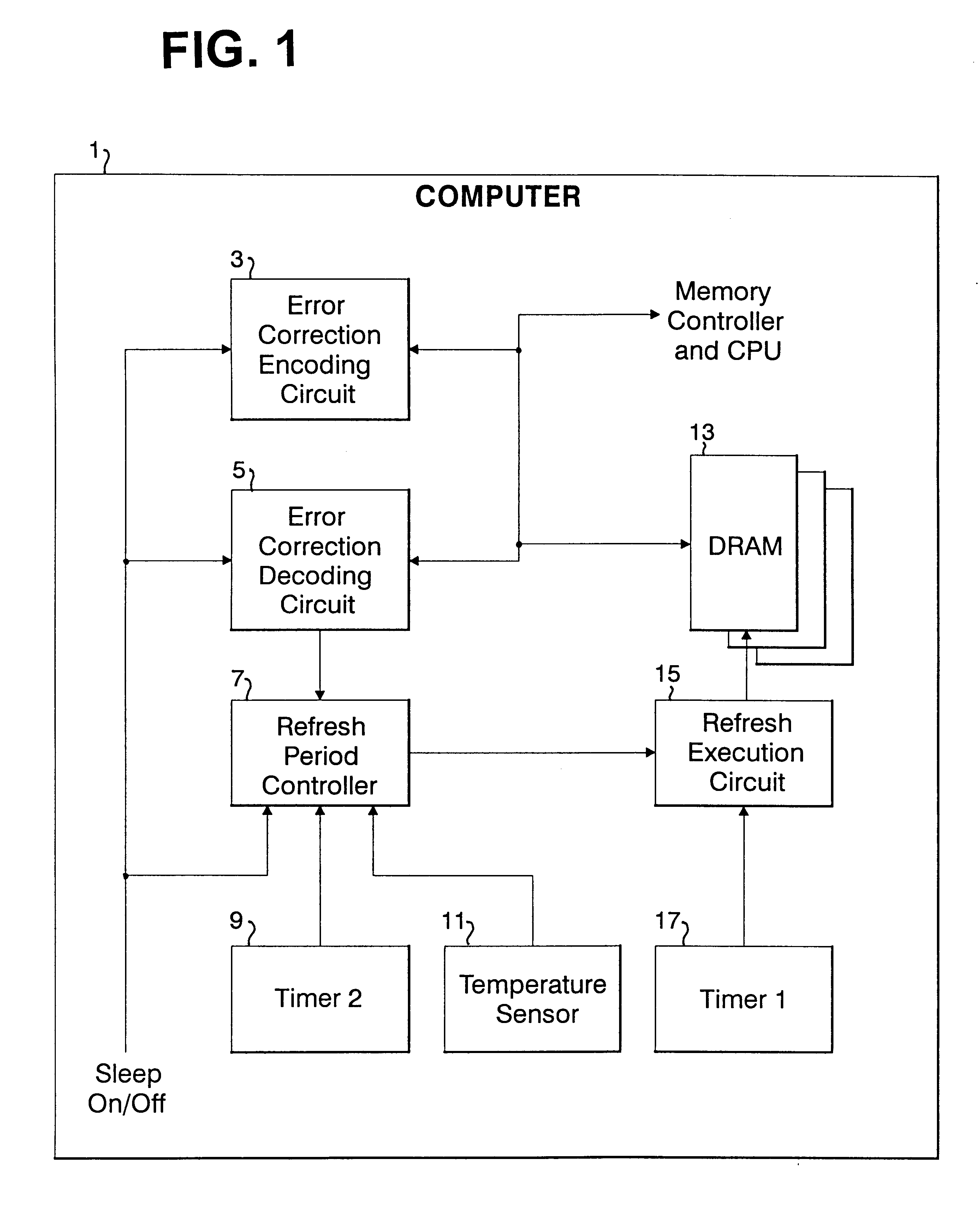
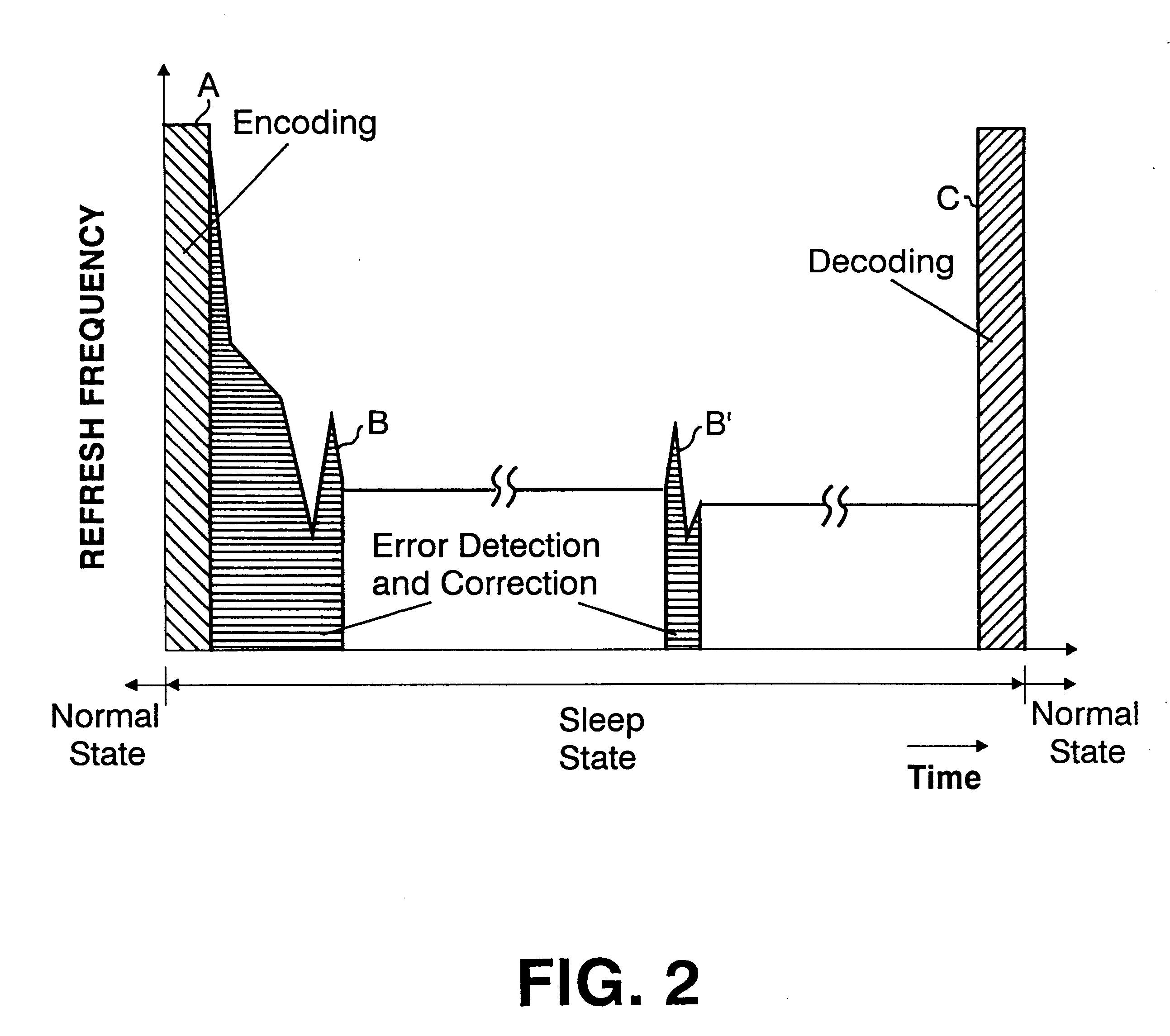
Refresh period control apparatus and method, and computer
InactiveUS6199139B1Highly effective error correction functionLow costEnergy efficient ICTCode conversionComputer hardwareRefresh cycle
The present invention provides a memory system that optimizes, during a sleep mode, a refresh period for a memory device, such as DRAM, which stores meaningful data and for which a refresh operation is required to prevent the loss of data. More particularly, the present invention is directed to an apparatus for controlling, in a sleep mode, a refresh period for a memory device 13 that requires a refresh operation, comprises: an encoding circuit 3 for encoding data to obtain code that can be used to correct errors equal to or more than dual errors; a decoding circuit 5 for correcting errors and for decoding the corrected code; and a refresh period controller 7 for, following a transition to the sleep mode, changing a refresh period by using data, which is stored in the memory device 13 and encoded by the encoding circuit 3, until the refresh period becomes longest in a condition where there is no error that can not be corrected by the decoding circuit 5 and the number of correctable errors does not exceed a predetermined count, and where a refresh execution circuit 15 for performing the refresh operation for the memory device can deal with the changed refresh period, and for, following the first end of the change of the refresh period, setting the refresh execution circuit 15 so that the refresh of the memory device 13 is performed at the refresh period at the first end of the change of the refresh period.
Owner:IBM CORP
Detecting network denial of service attacks
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
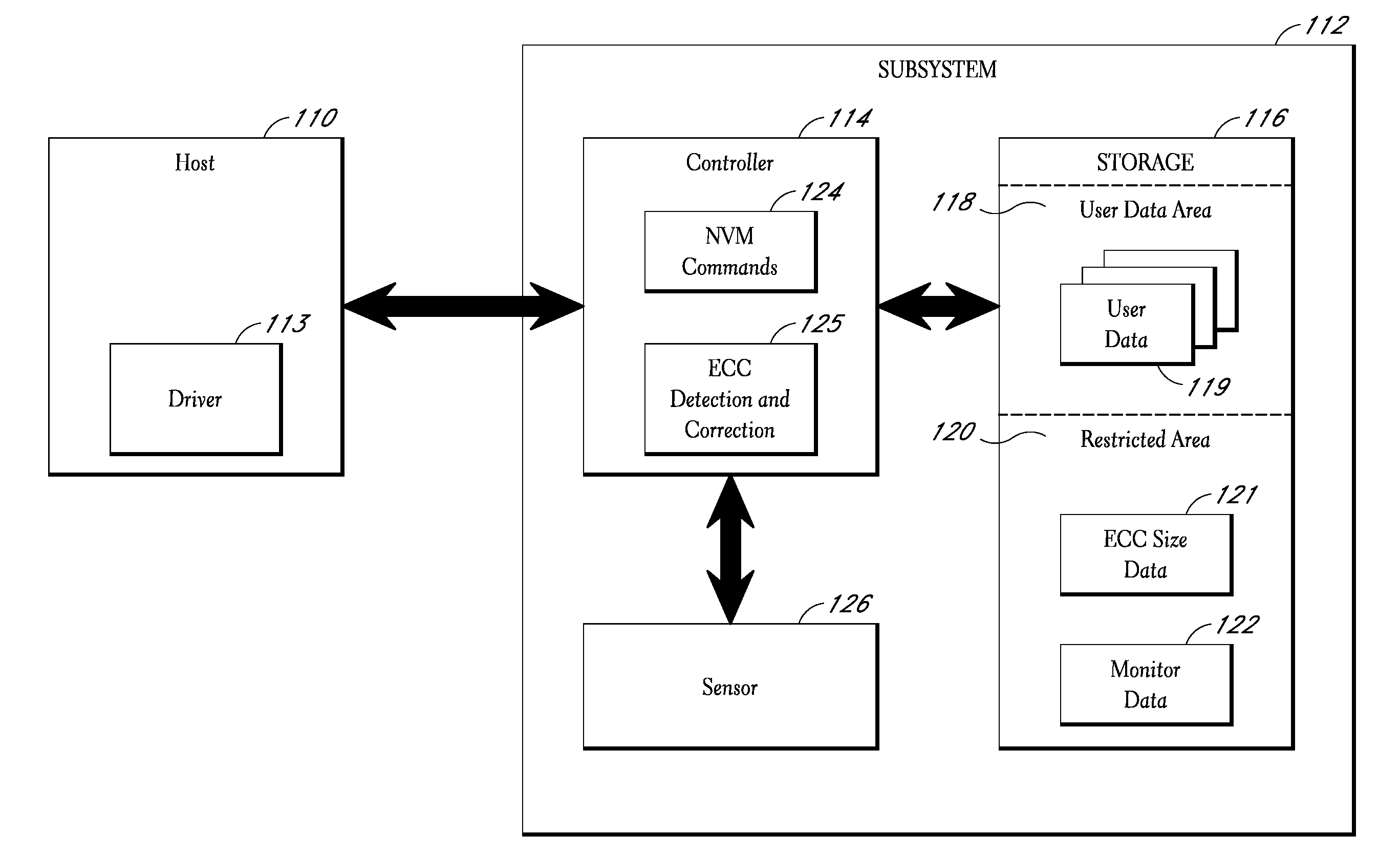
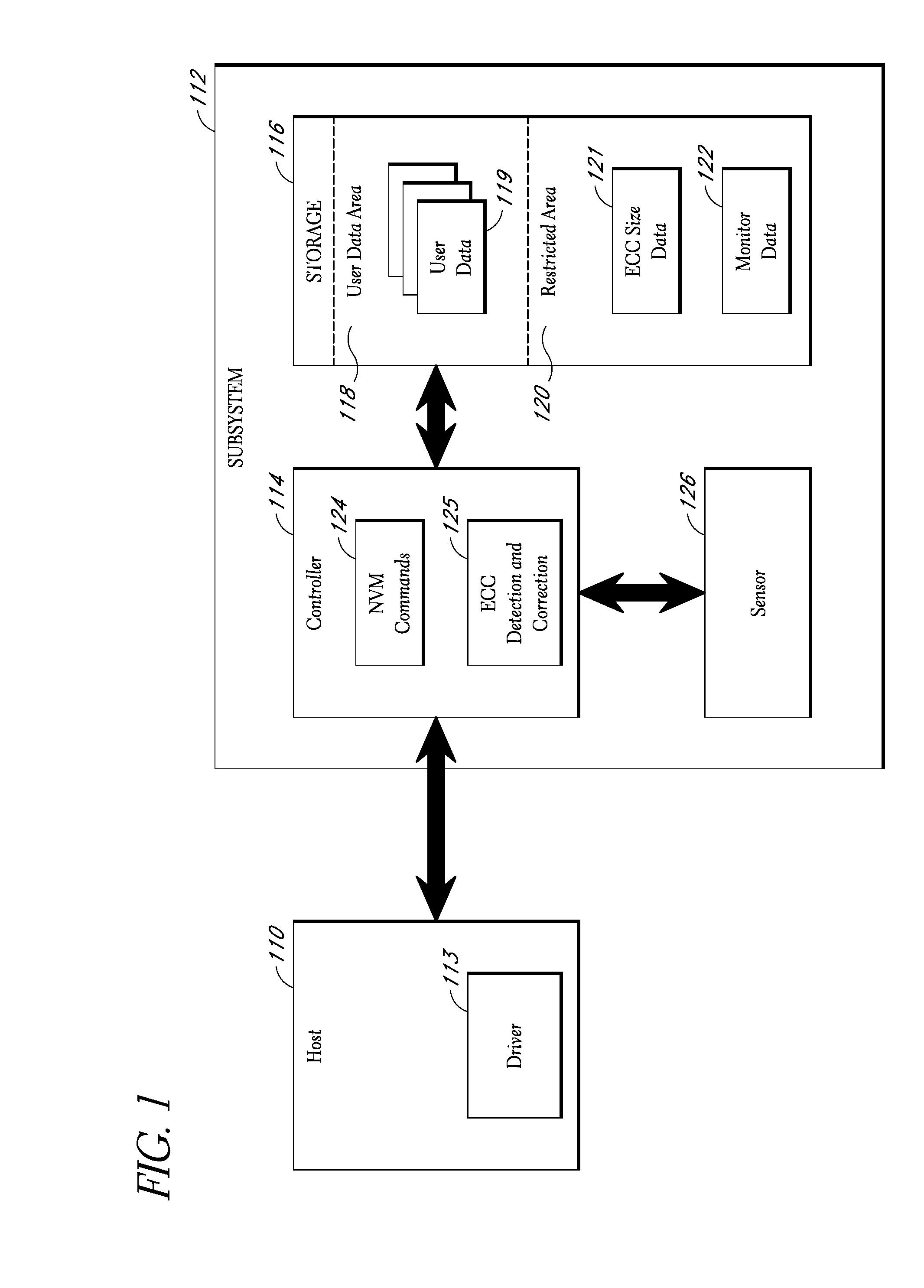
Storage subsystem capable of adjusting ECC settings based on monitored conditions
ActiveUS8095851B2Effective balanceImprove the level ofError detection/correctionCode conversionMultiple criteriaData error
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
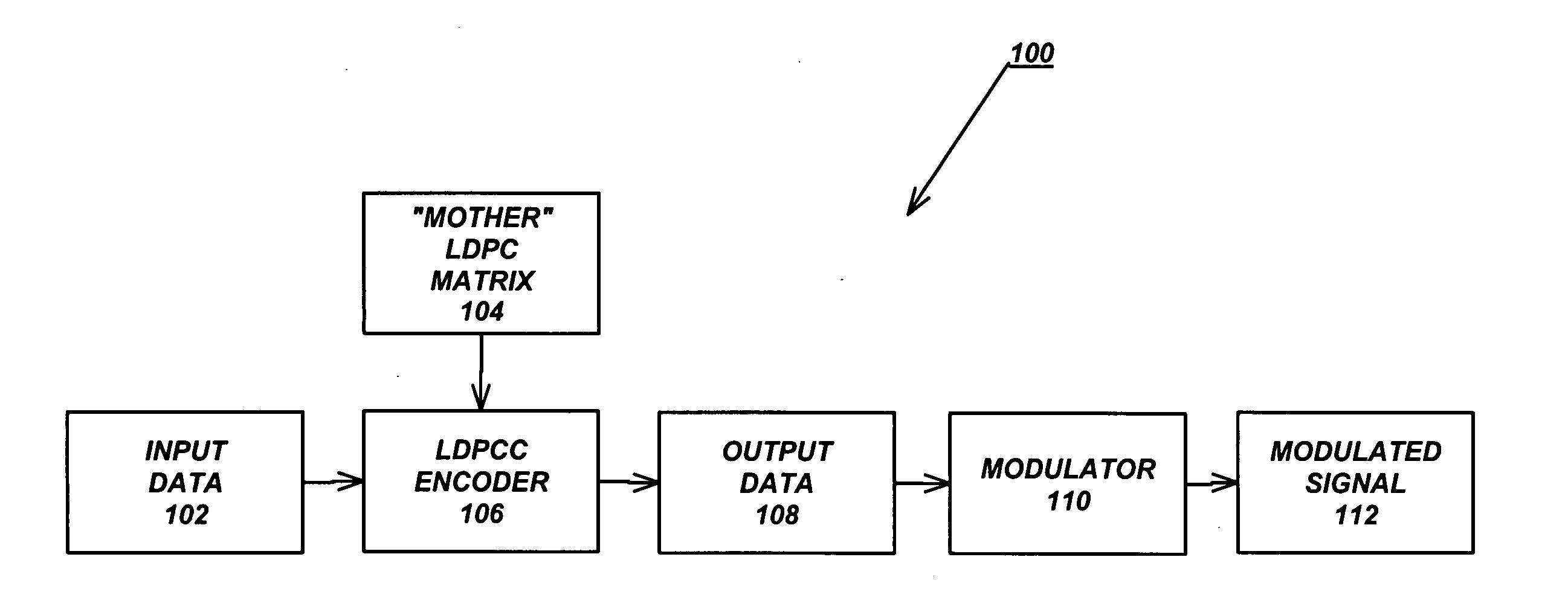
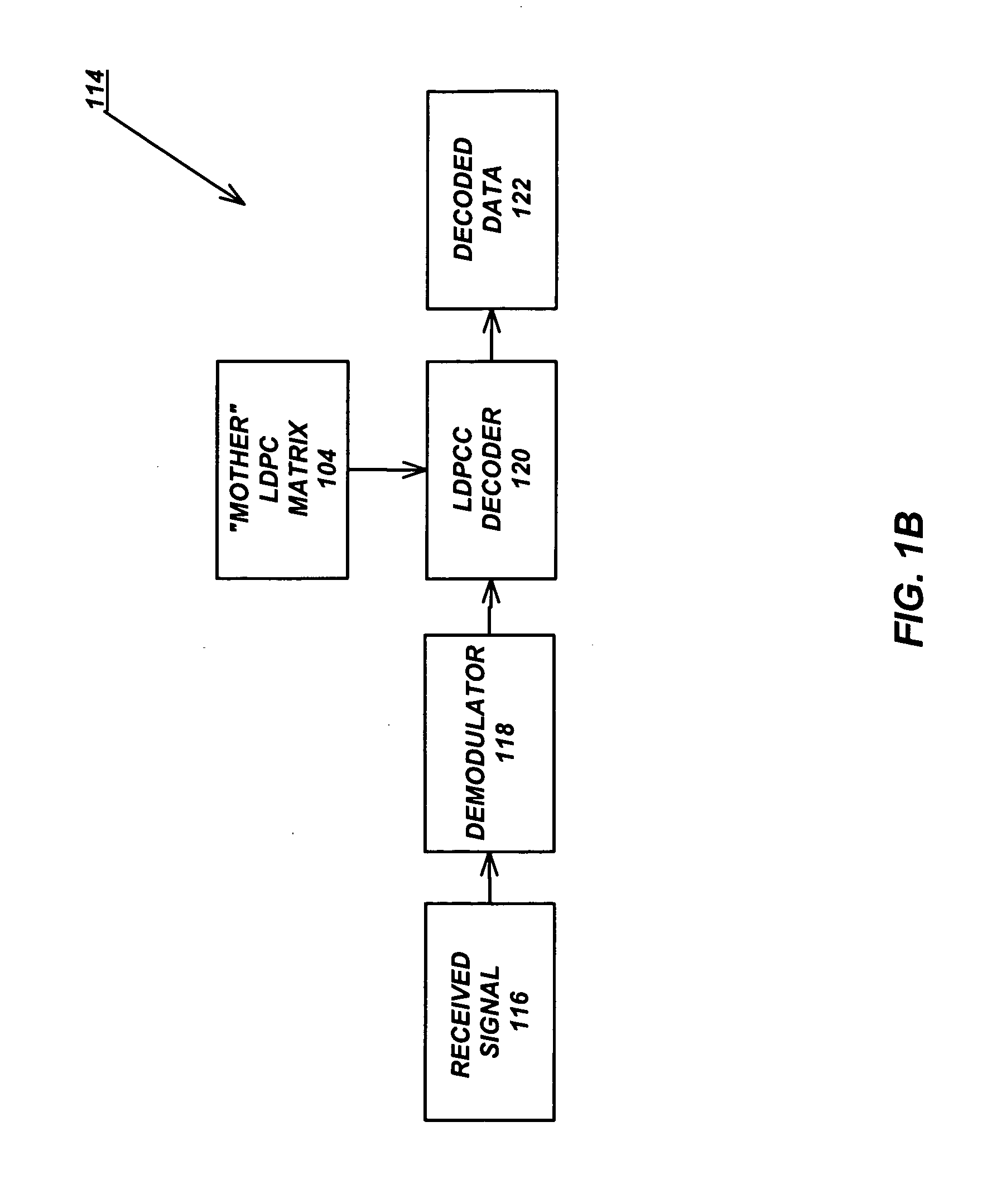
Variable-rate low-density parity check codes with constant blocklength
Low density parity check (LDPC) codes (LDPCCs) have an identical code blocklength and different code rates. At least one of the rows of a higher-rate LDPC matrix is obtained by combining a plurality of rows of a lower-rate LDPC matrix with the identical code blocklength as the higher-rate LDPC matrix.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
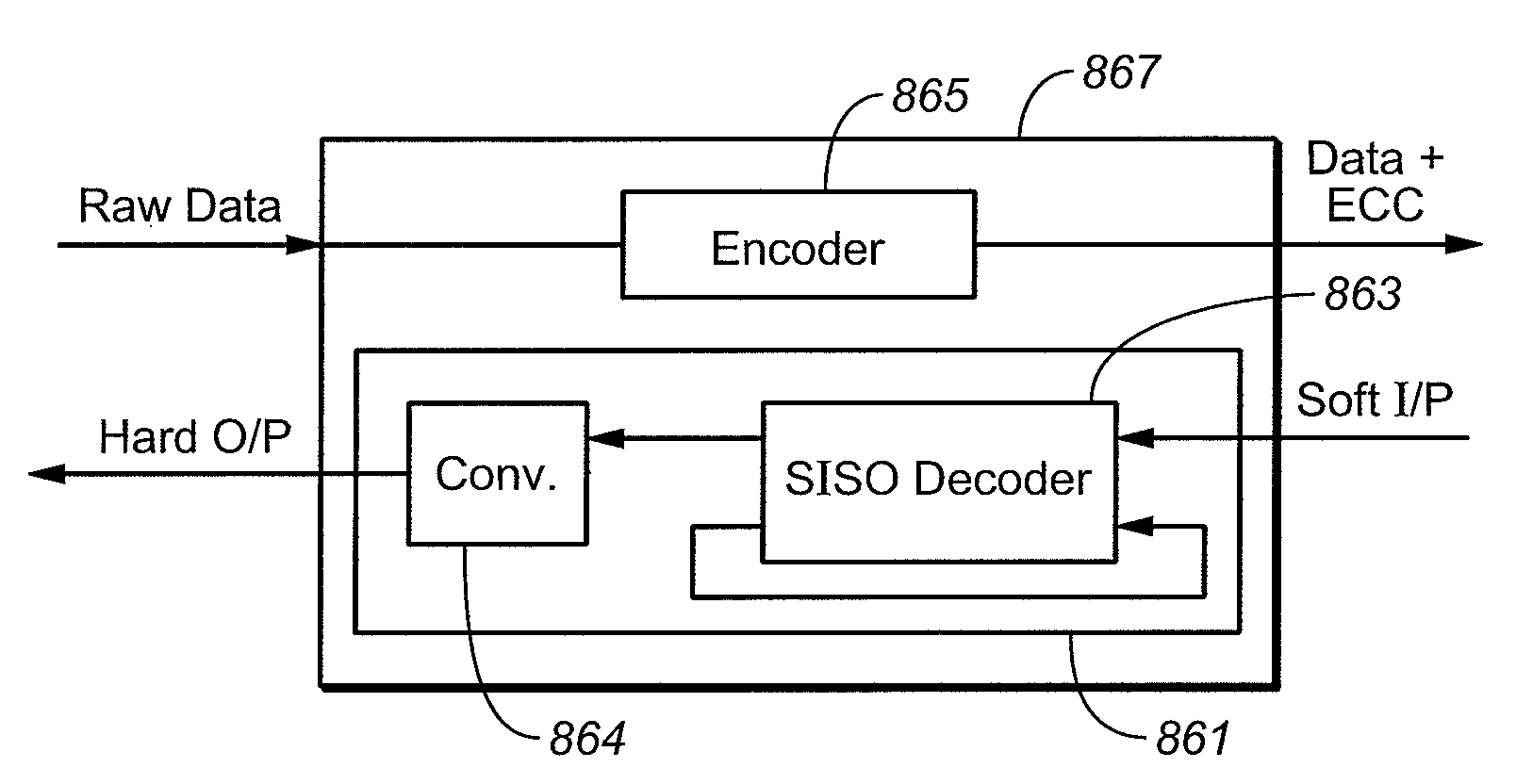
Soft-Input Soft-Output Decoder for Nonvolatile Memory
ActiveUS20080082897A1Error detection/correctionRead-only memoriesOperating systemNon-volatile memory
In a nonvolatile memory system, data is read from a memory array and used to obtain likelihood values, which are then provided to a soft-input soft-output decoder. The soft-input soft-output decoder calculates output likelihood values from input likelihood values and from parity data that was previously added according to an encoding scheme.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Apparatus, systems, methods and computer products for providing a virtual enhanced training sequence
InactiveUS20060244865A1Variable lengthTelevision system detailsCode conversionSystems approachesComputer science
A system, method, apparatus and computer code for communicating a training sequence for initializing an equalizer in a digital receiver are provided including receiving a digital signal containing data to be broadcast from a digital RF transmitter and inserting the training sequence into the digital signal deterministically such that a predetermined sequence of symbols are communicated to the receiver.
Owner:ROHDE & SCHWARZ GMBH & CO KG
Method for controlling errors in link layer in wideband wireless communication and computer readable media therefor
InactiveUS6615382B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsDelayed timeData link layer
A method for controlling errors in a wireless link layer using a simultaneous multiple copy scheme and an adaptive forward error correction (FEC) scheme in a wideband wireless communication is provided. The method for controlling errors in a link layer in wideband wireless communication using an automatic repeat request (ARQ) scheme, in which a wideband wireless channel is used for communication between a first node and a second node, includes the steps of (a) estimating the error ratio of a forward (a direction in which a cell is transmitted from the first node to the second node) channel using the state of a backward (a direction in which a cell is transmitted from the second node to the first node) channel, and transmitting a cell, in which a forward error correction (FEC) code having an encoding ratio that varies depending on the estimated error ratio is included in a protocol data unit (PDU) of a wireless link layer, through the forward channel and (b) re-transmitting the copy of a cell transmitted in the step (a), when feedback information that indicates that an error exists in the cell transmitted in the step (a) is received through the backward channel. It is possible to reduce the number of times of re-transmission by improving the probability of correcting forward errors using more error controlling bits as the state of the channel is worse and to minimize the waste of resources using less error controlling bits as the state of the channel is better, to thus obtain the optimal performance and guarantee the minimum delay time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
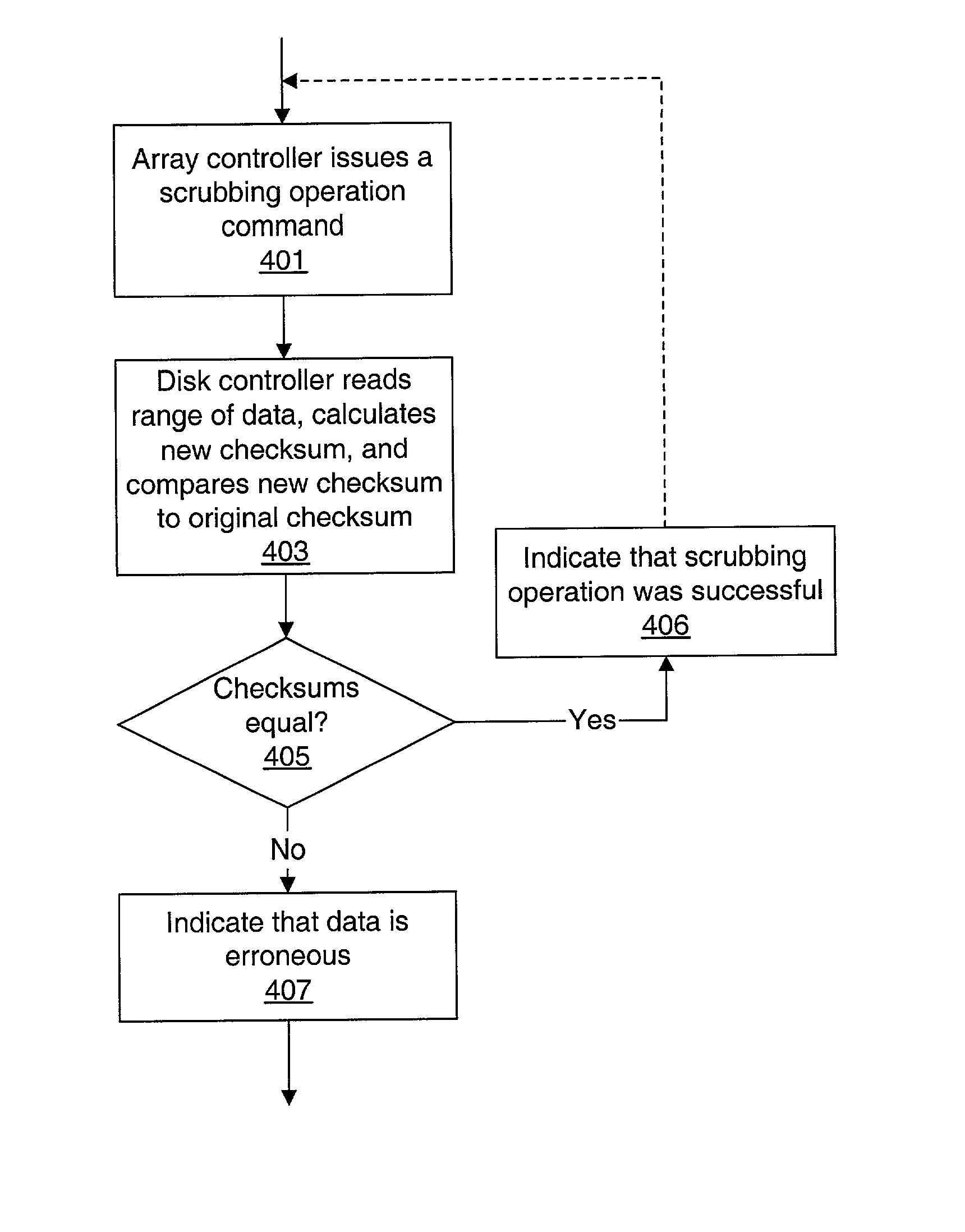
Storage array employing scrubbing operations at the disk-controller level
A storage system comprises a storage array controller and a storage array, which includes multiple disk drives and disk drive controllers. The storage array controller issues scrubbing operation commands to one or more of the disk drive controllers. In response, each disk drive controller that receives a scrubbing operation command reads data from within a data range from at least one of the disk drives, calculates a new checksum for the data, and compares the new checksum to a preexisting checksum for the data. If the new checksum doesn't equal the preexisting checksum, the data within the data range is determined to be erroneous.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
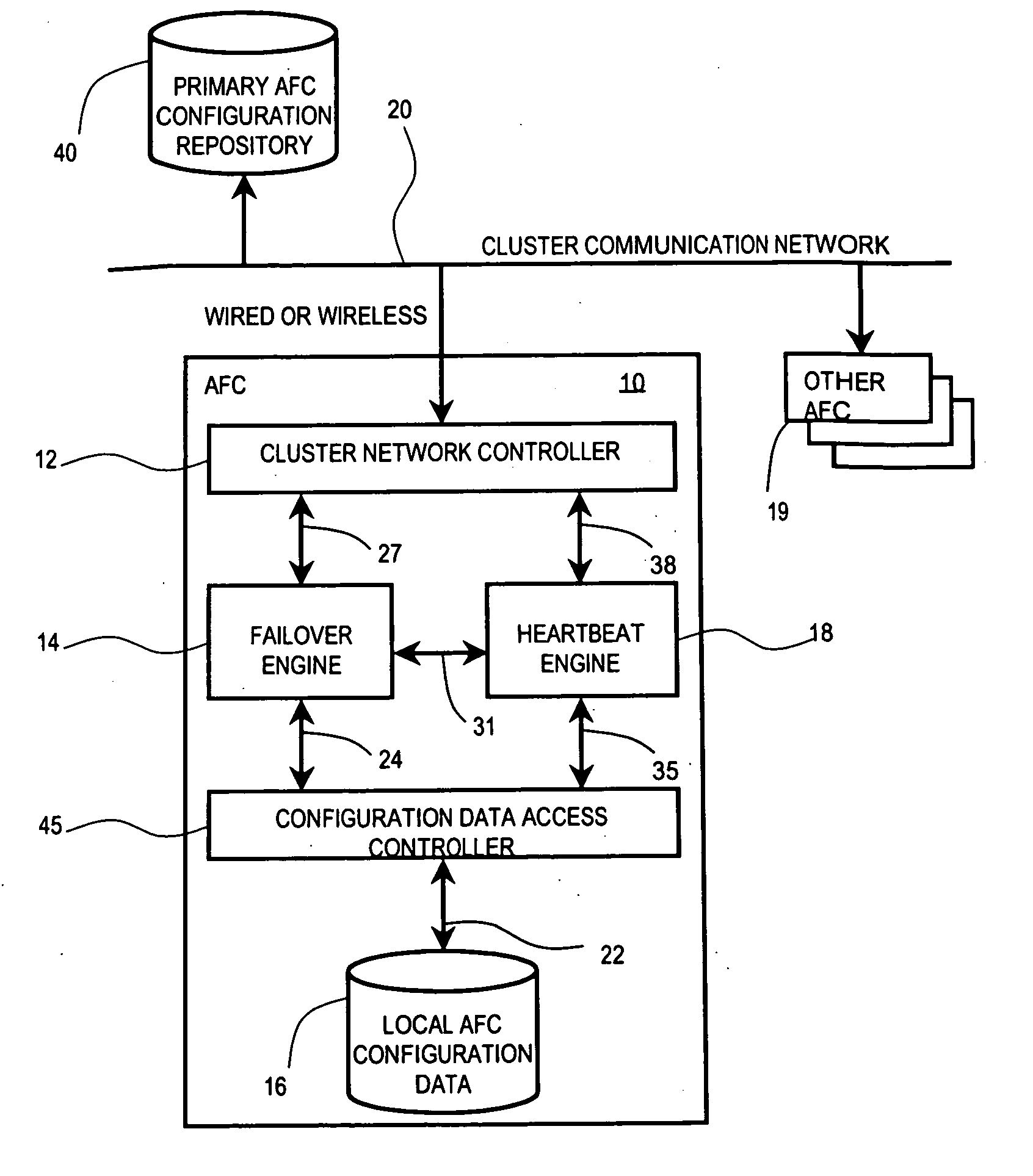
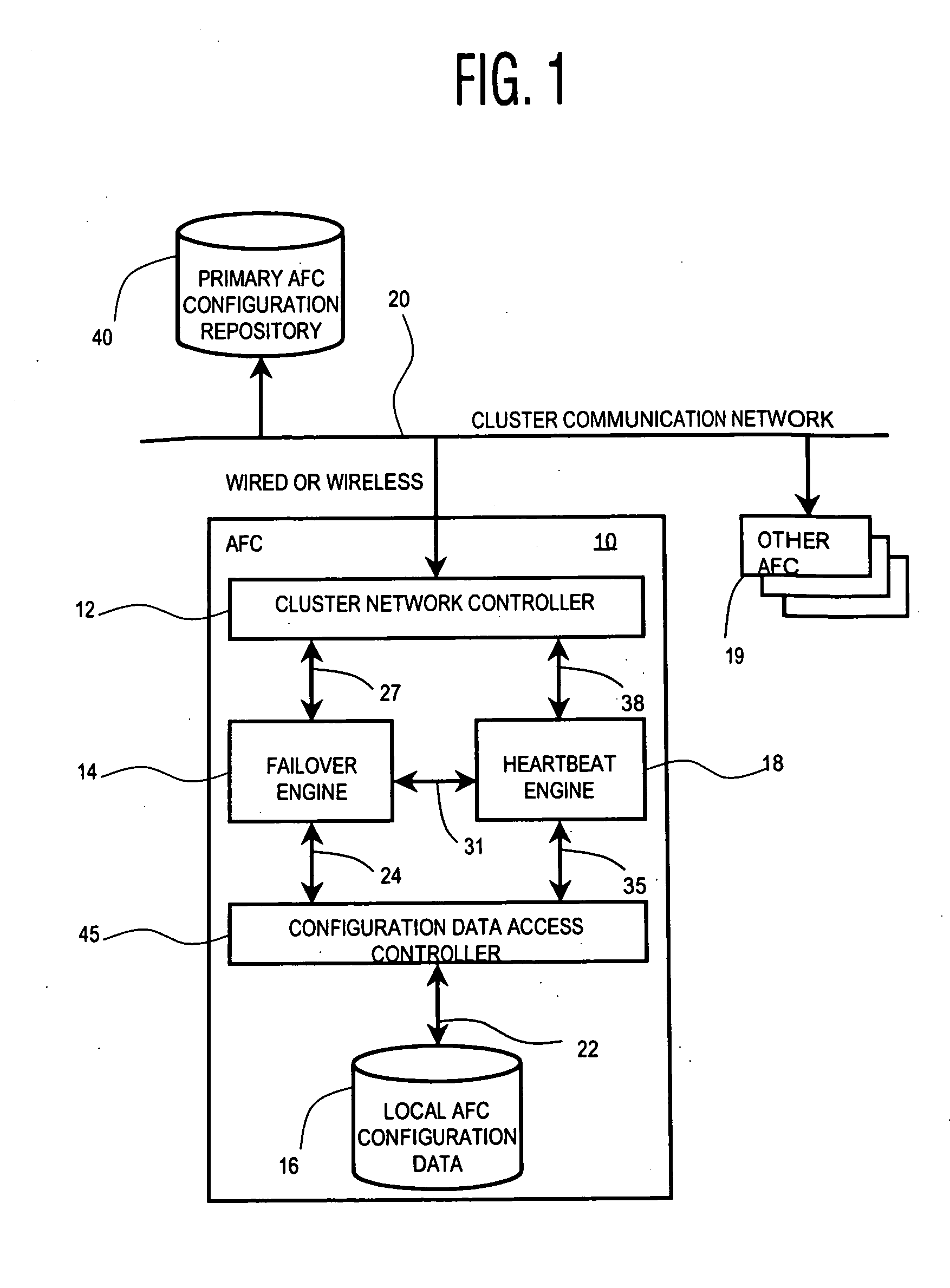
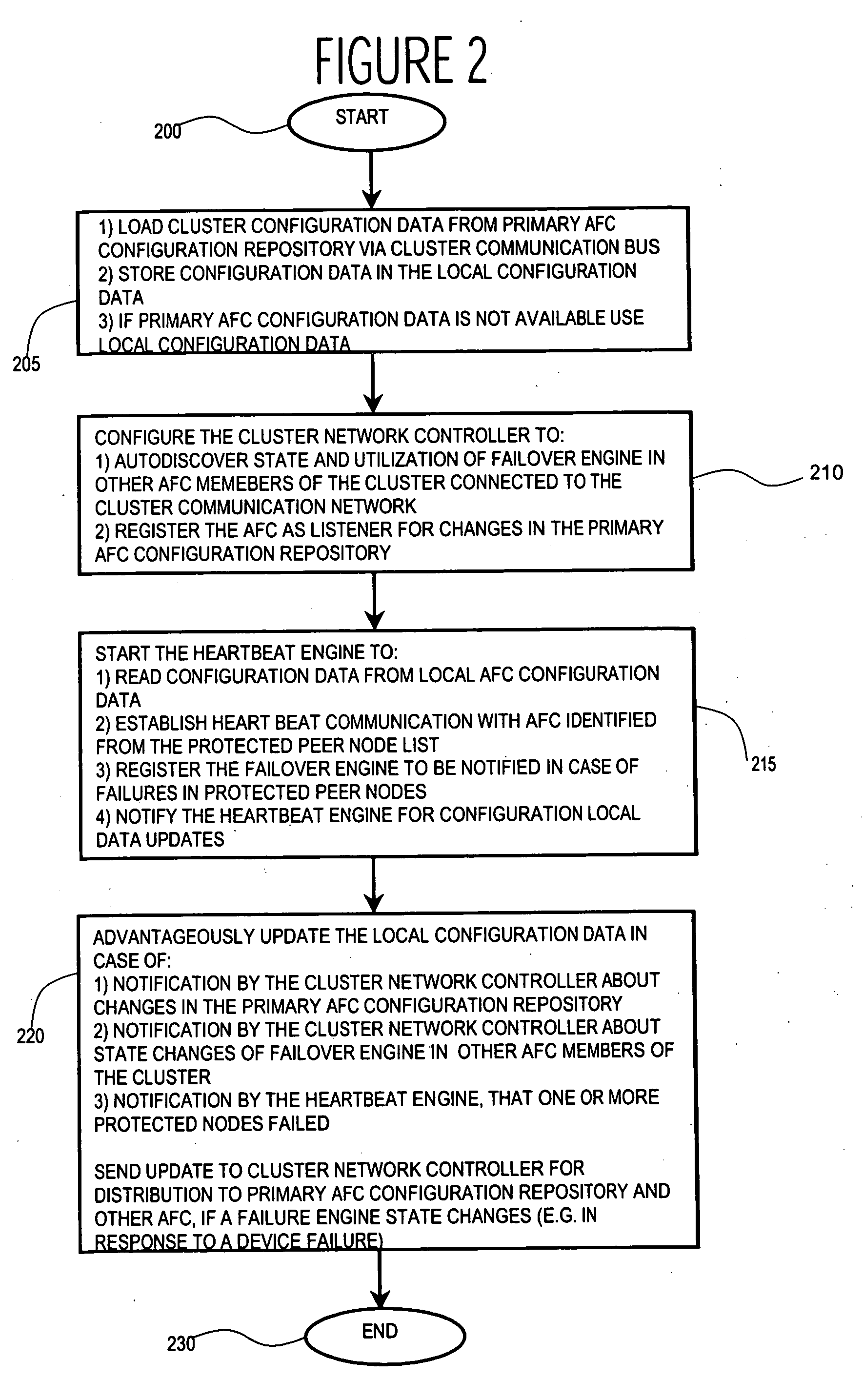
Processing device management system
ActiveUS20050138517A1Improve usabilityLow costError preventionTransmission systemsFailoverHigh availability
A system automatically adaptively modifies a fail-over configuration priority list of back-up devices of a group (cluster) of processing devices to improve availability and reduce risks and costs associated with manual configuration. A system is used by individual processing devices of a group of networked processing devices, for managing operational failure occurrences in devices of the group. The system includes an interface processor for maintaining transition information identifying a second processing device for taking over execution of tasks of a first processing device in response to an operational failure of the first processing device and for updating the transition information in response to a change in transition information occurring in another processing device of the group. An operation detector detects an operational failure of the first processing device. Also, a failure controller initiates execution, by the second processing device, of tasks designated to be performed by the first processing device in response to detection of an operational failure of the first processing device.
Owner:III HLDG 3
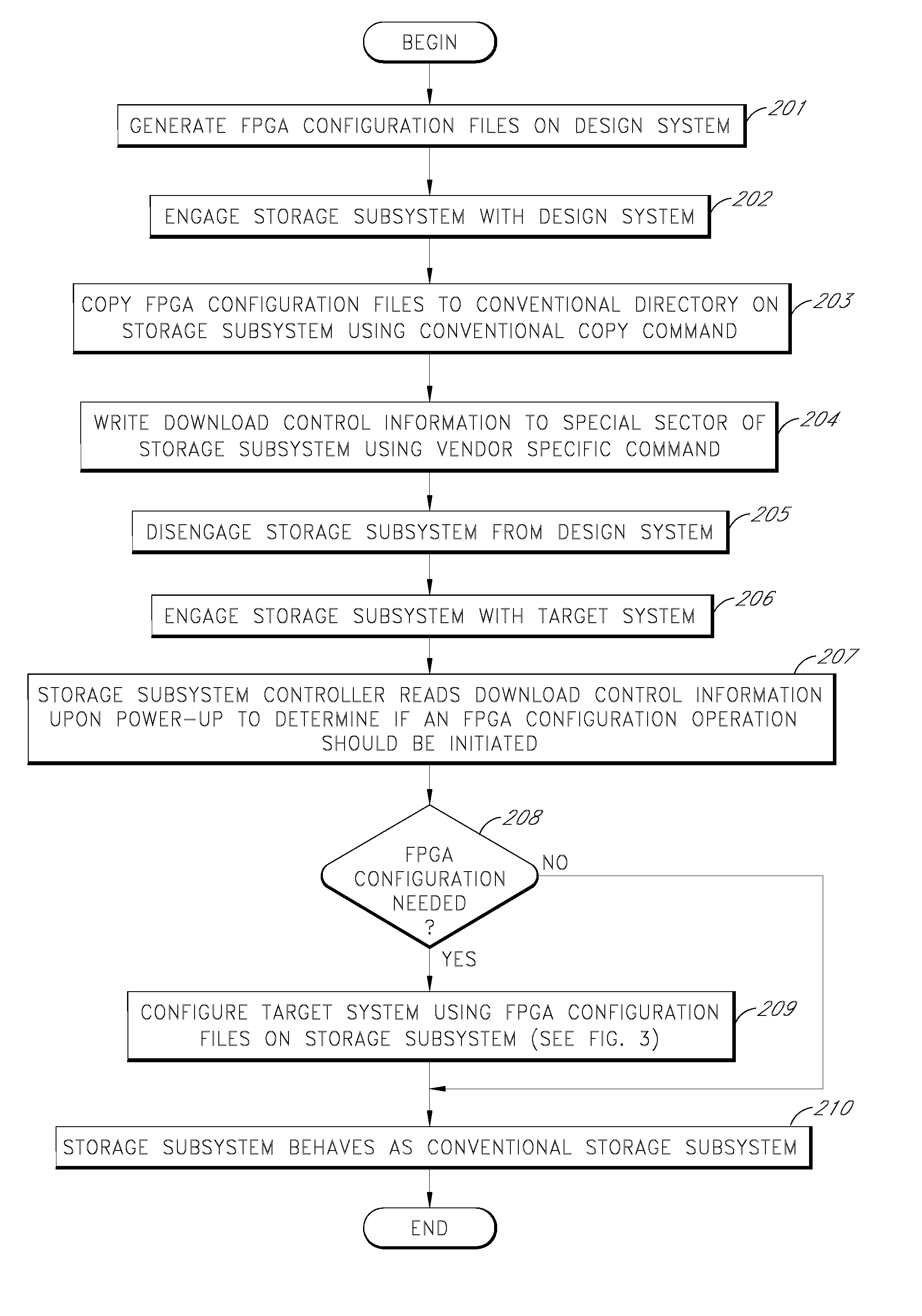
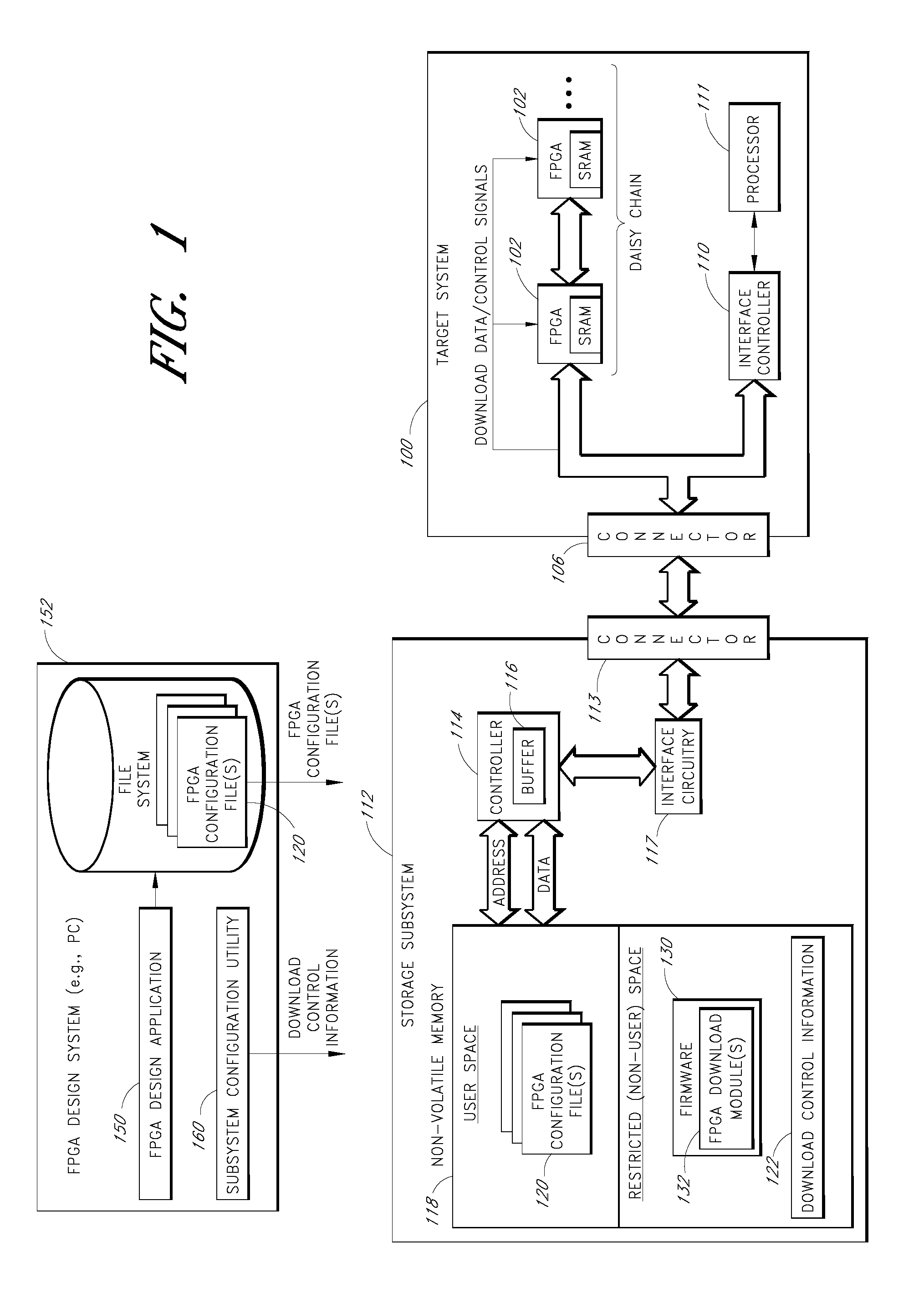
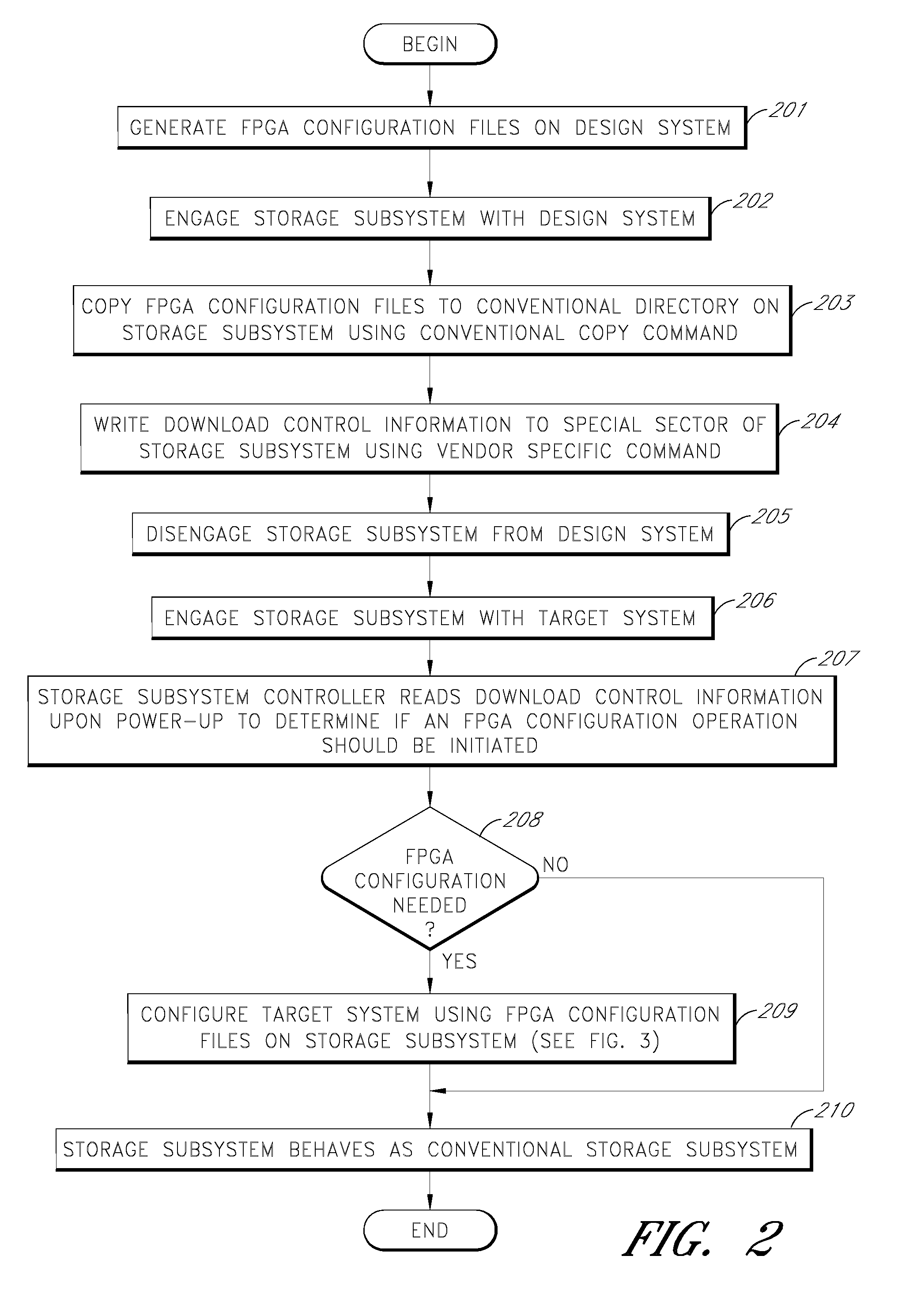
Storage subsystem capable of programming field-programmable devices of a target computer system
InactiveUS8161227B1Avoid the needInput/output to record carriersError preventionProgrammable logic deviceGoal system
A non-volatile storage subsystem is capable of serving as a configuration controller for configuring / programming one or more field-programmable devices, such as FPGAs, of a target computer system. The storage subsystem may be in the form of a memory card or drive that plugs into a standard slot or external port of the target system. When connected to the target system, the storage subsystem uses the appropriate download interface / protocol to stream or otherwise send configuration data stored in its non-volatile storage to the target system's field-programmable device(s). Thus, the need for a configuration controller in the target system is avoided. Once the configuration process is complete, the storage subsystem preferably acts as a standard storage subsystem, such as an ATA storage drive, that may be used by the target system to store data.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
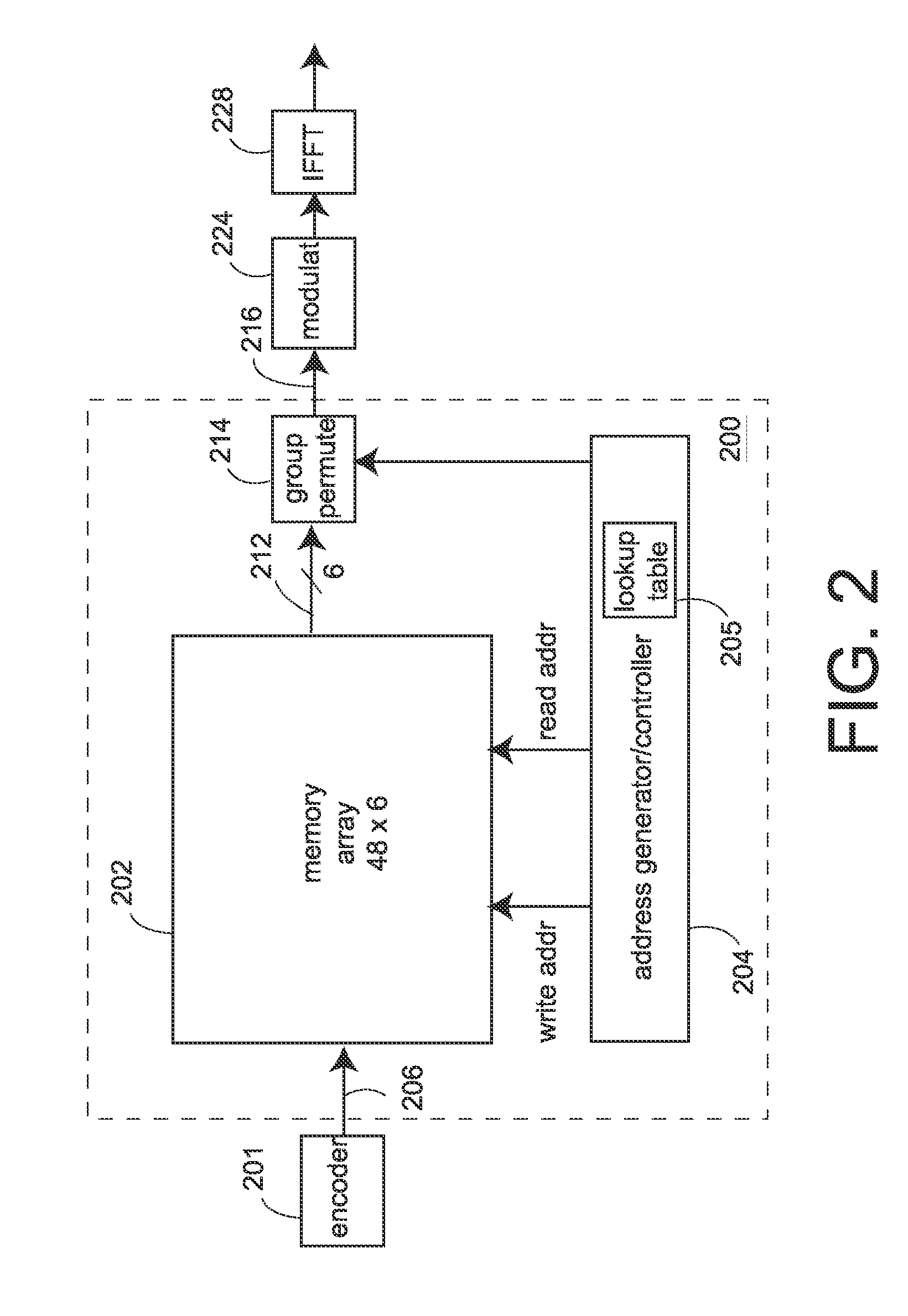
Interleaver, deinterleaver, interleaving method, and deinterleaving method for OFDM data
ActiveUS7170849B1Saving in latencySave powerCode conversionCoding detailsParallel computingMemory block
An interleaver and interleaving method each includes two stages, and is useful in coded orthogonal frequency division multiplexed (COFDM) wireless local area networks. A first stage performs a first block permutation and a second stage performs bit order permutation to effectuate a second group permutation. A corresponding de-interleaver does just the opposite at the receiver. A double-buffer version includes writing data into one memory block in a first order while reading data from the second block in a second order, with the first and second orders selected to effectuate the first block permutation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Popular searches
Multiple digital computer combinations Digital signal error detection/correction Transmission link error control system Electric digital data processing Record information storage Hardware monitoring Forward error control use Digital computer details Redundant data error correction Energy efficient computing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com