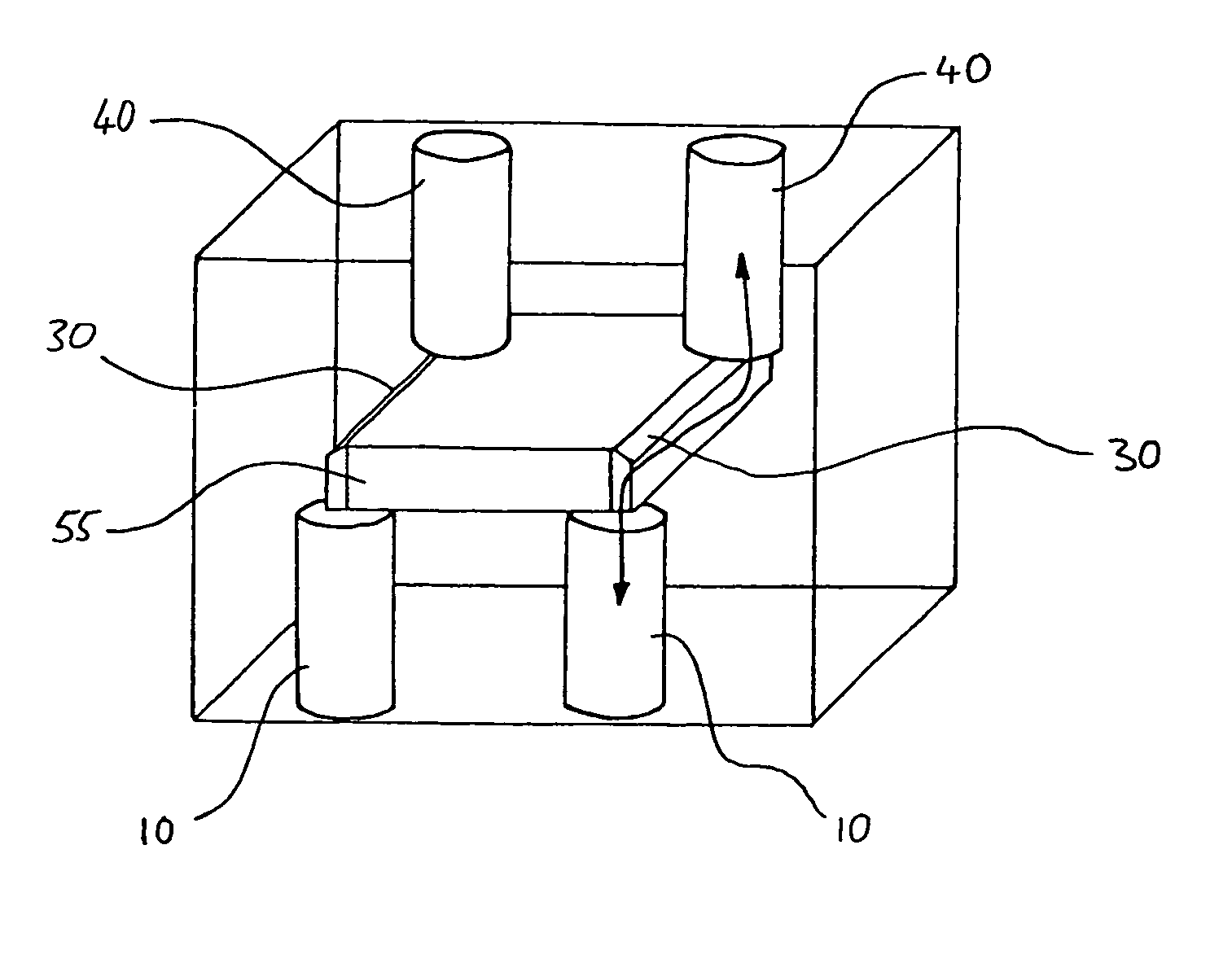
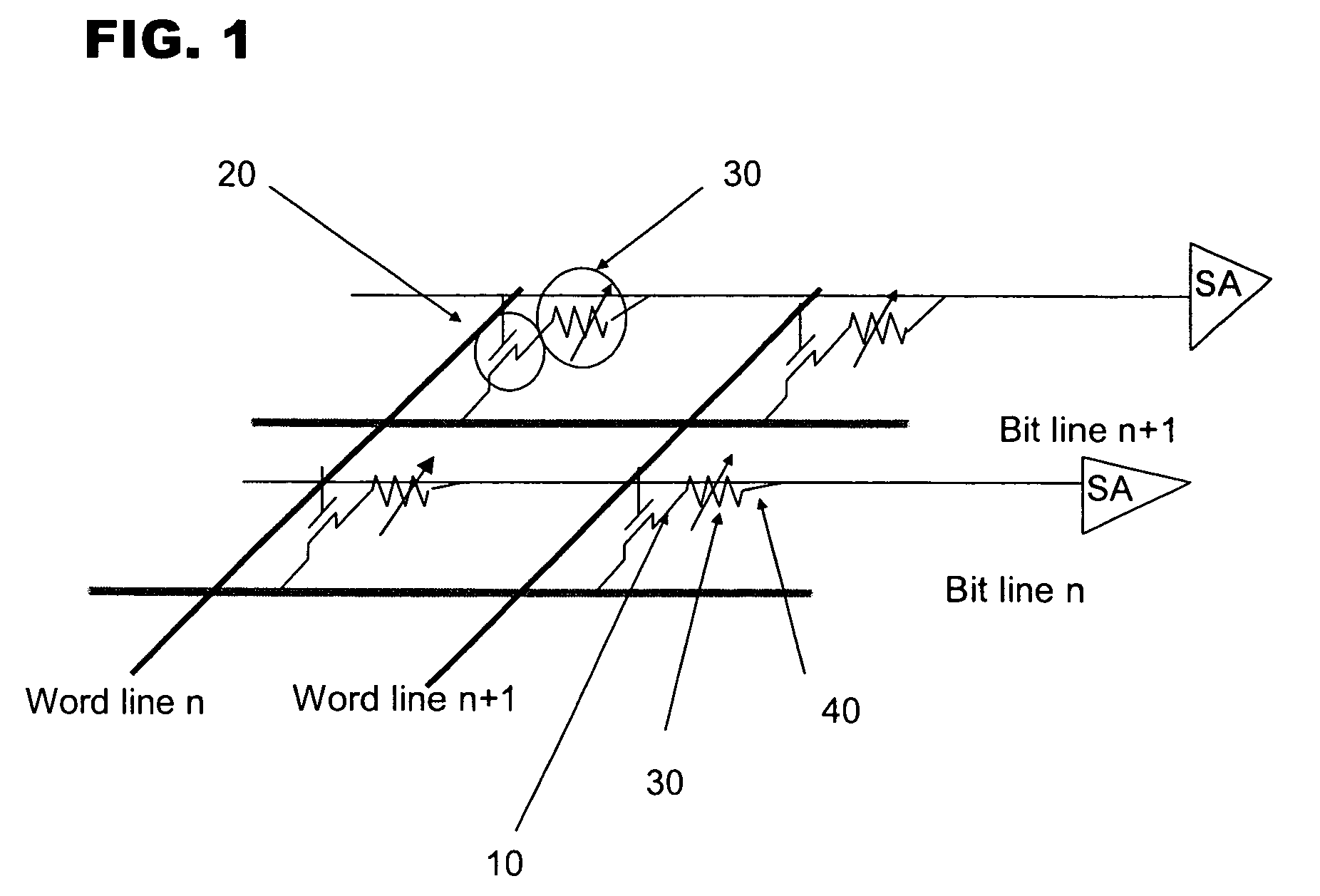
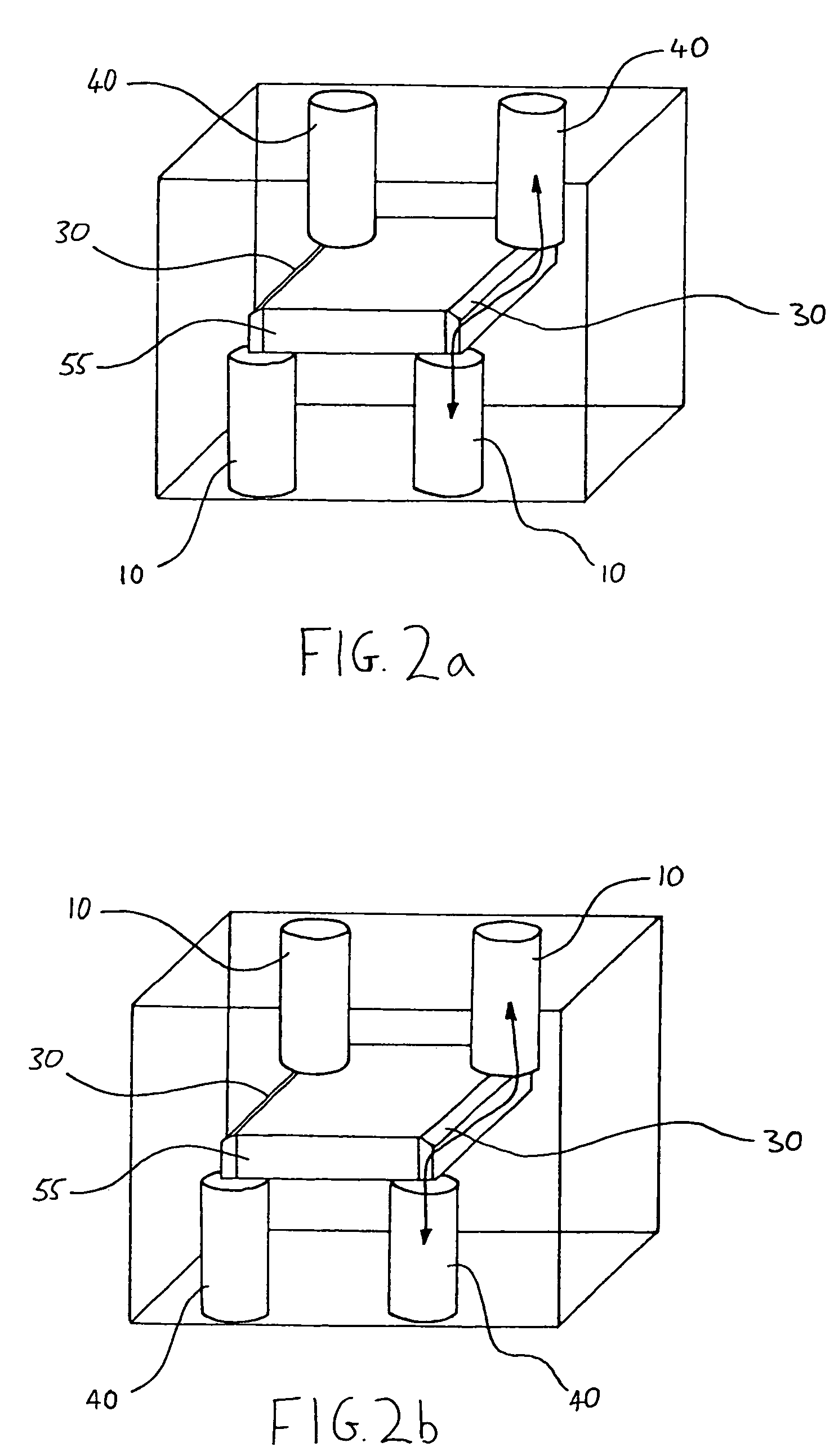
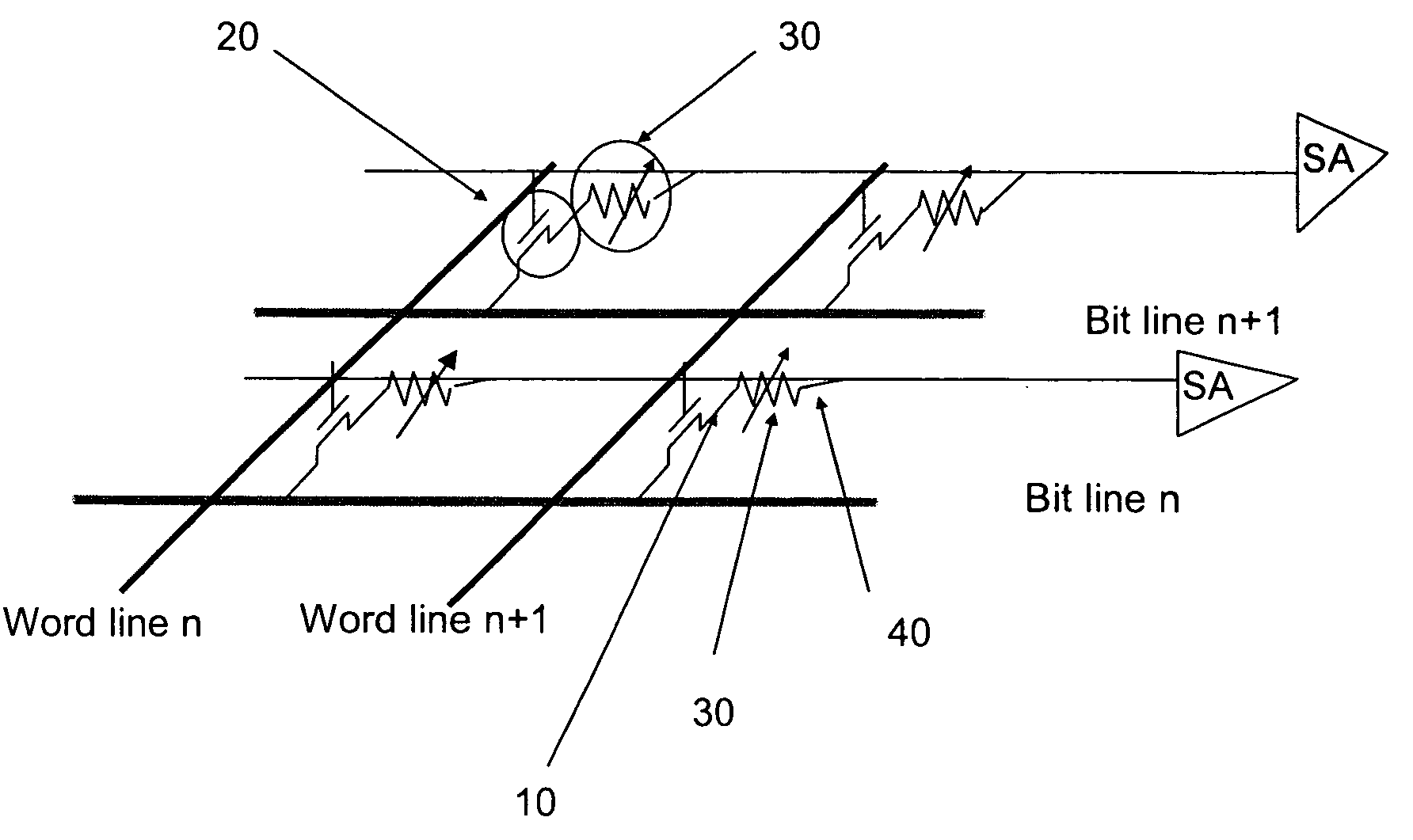
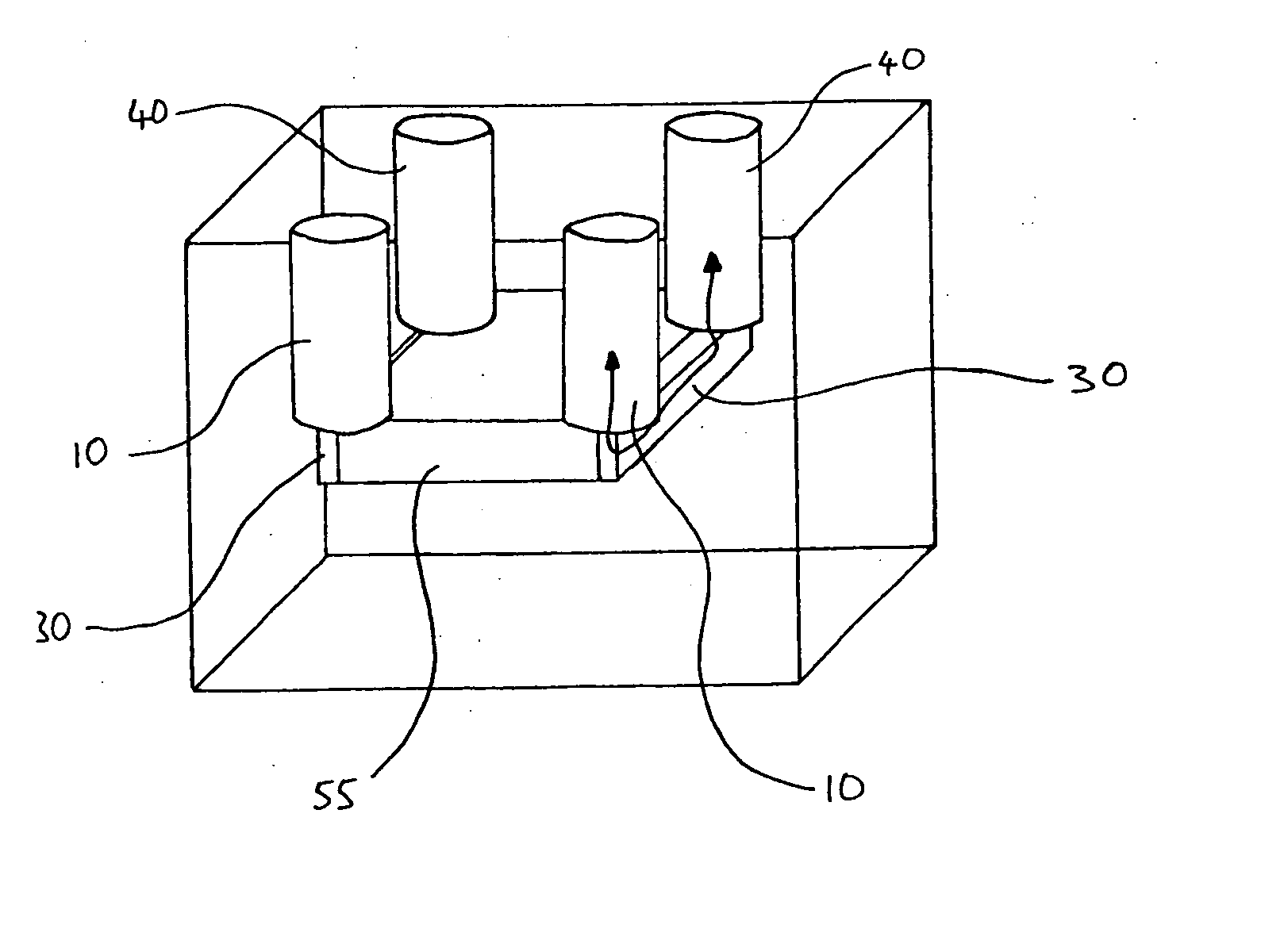
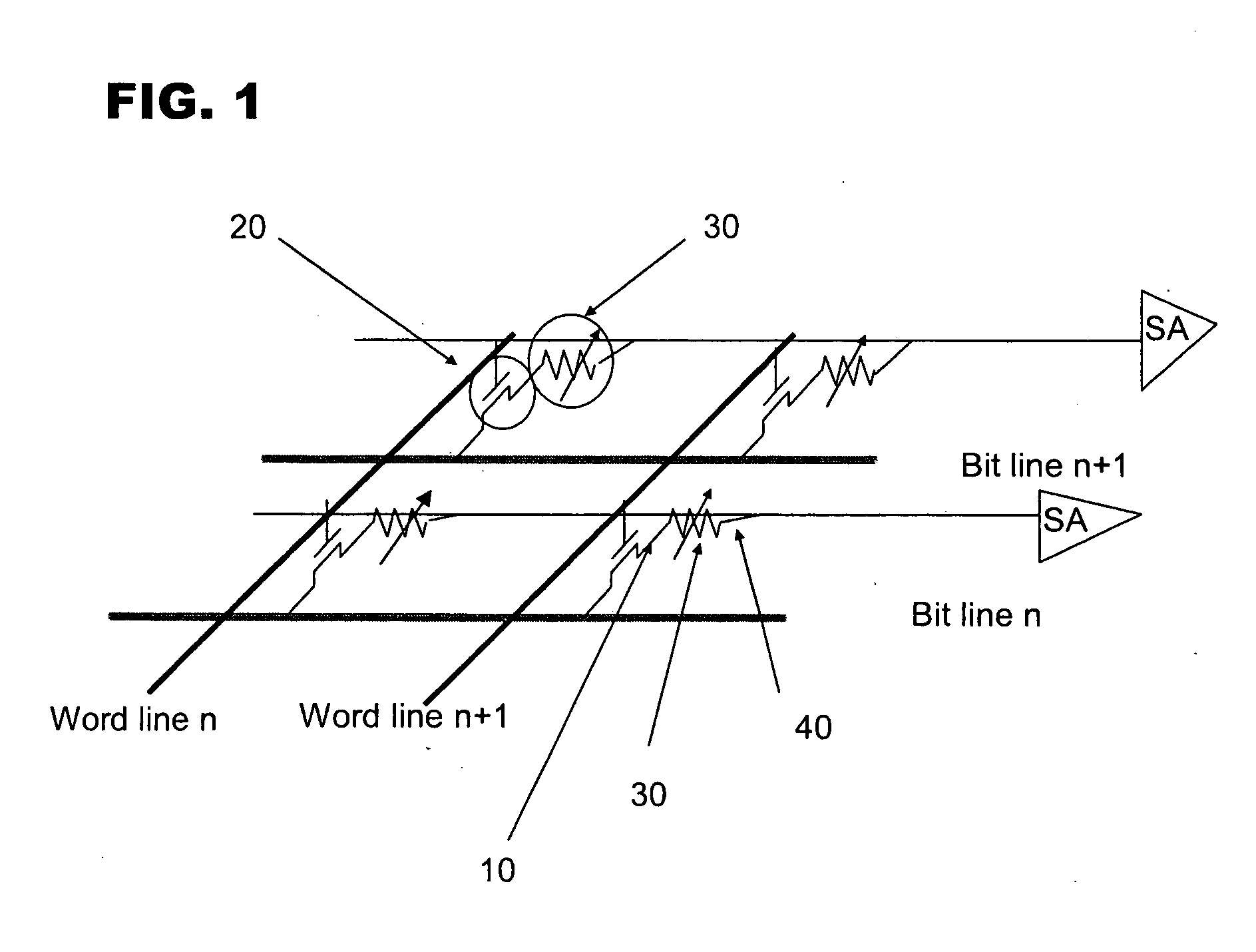
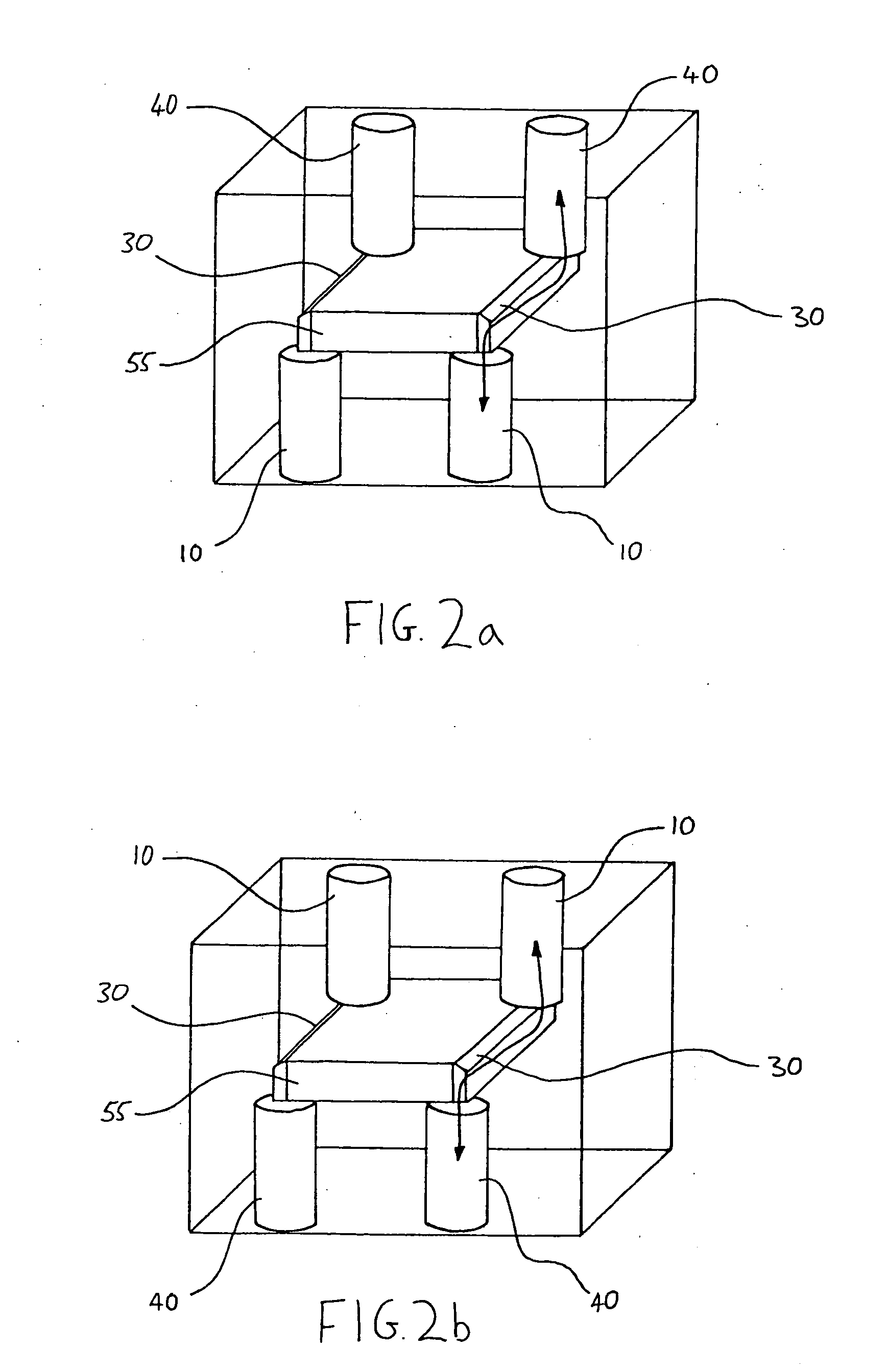
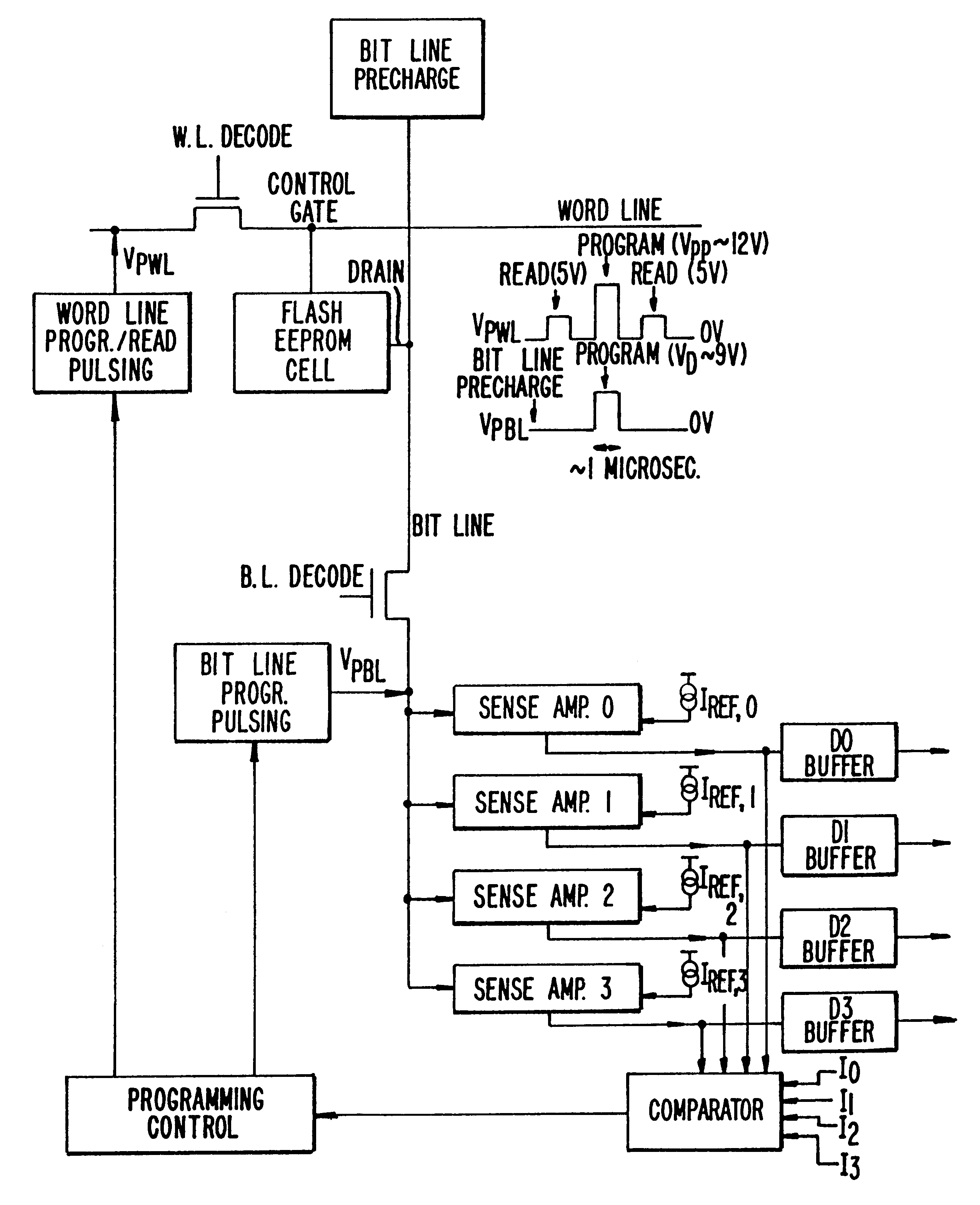
Patents
Literature
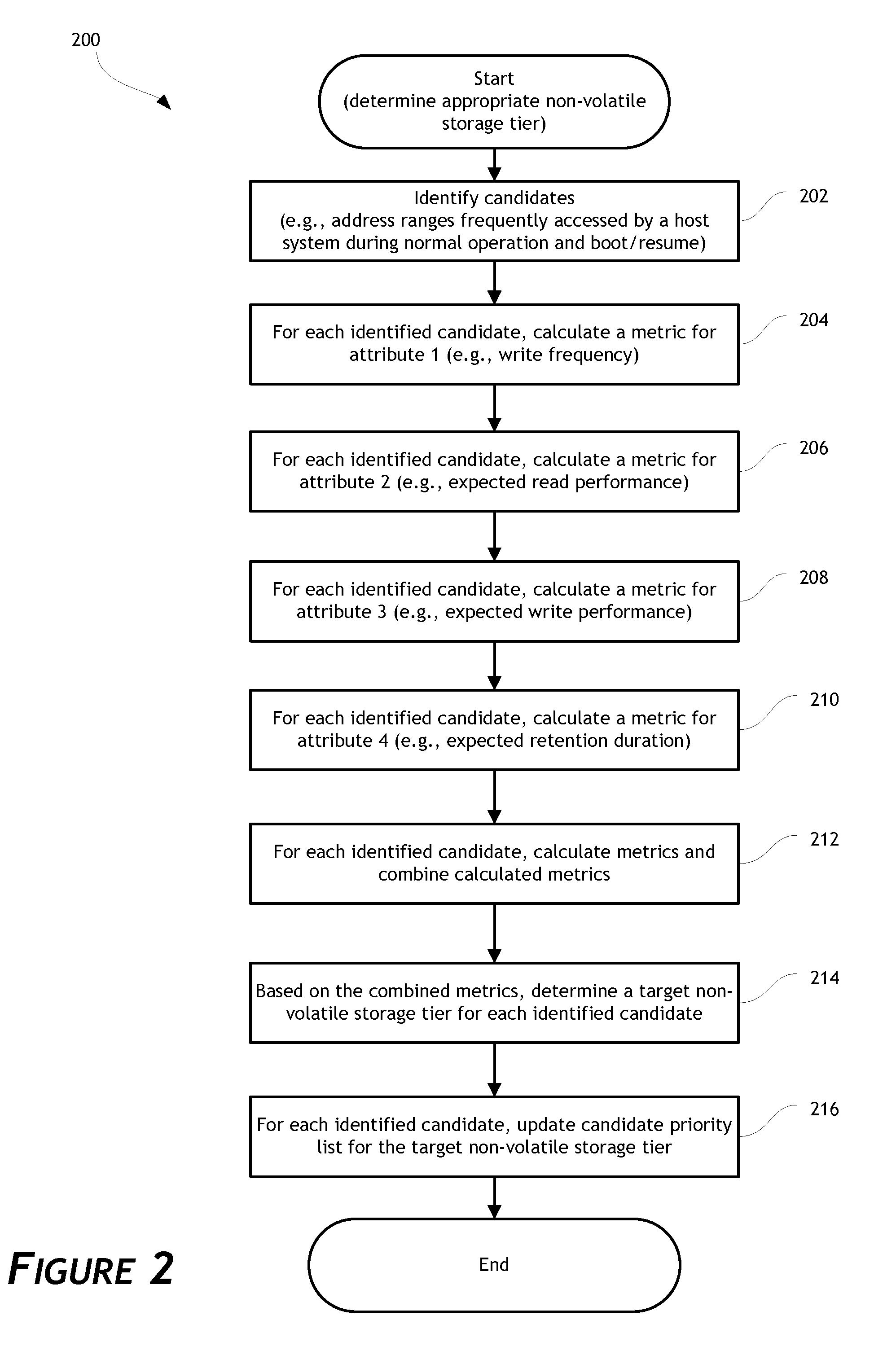
611 results about "Solid state memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
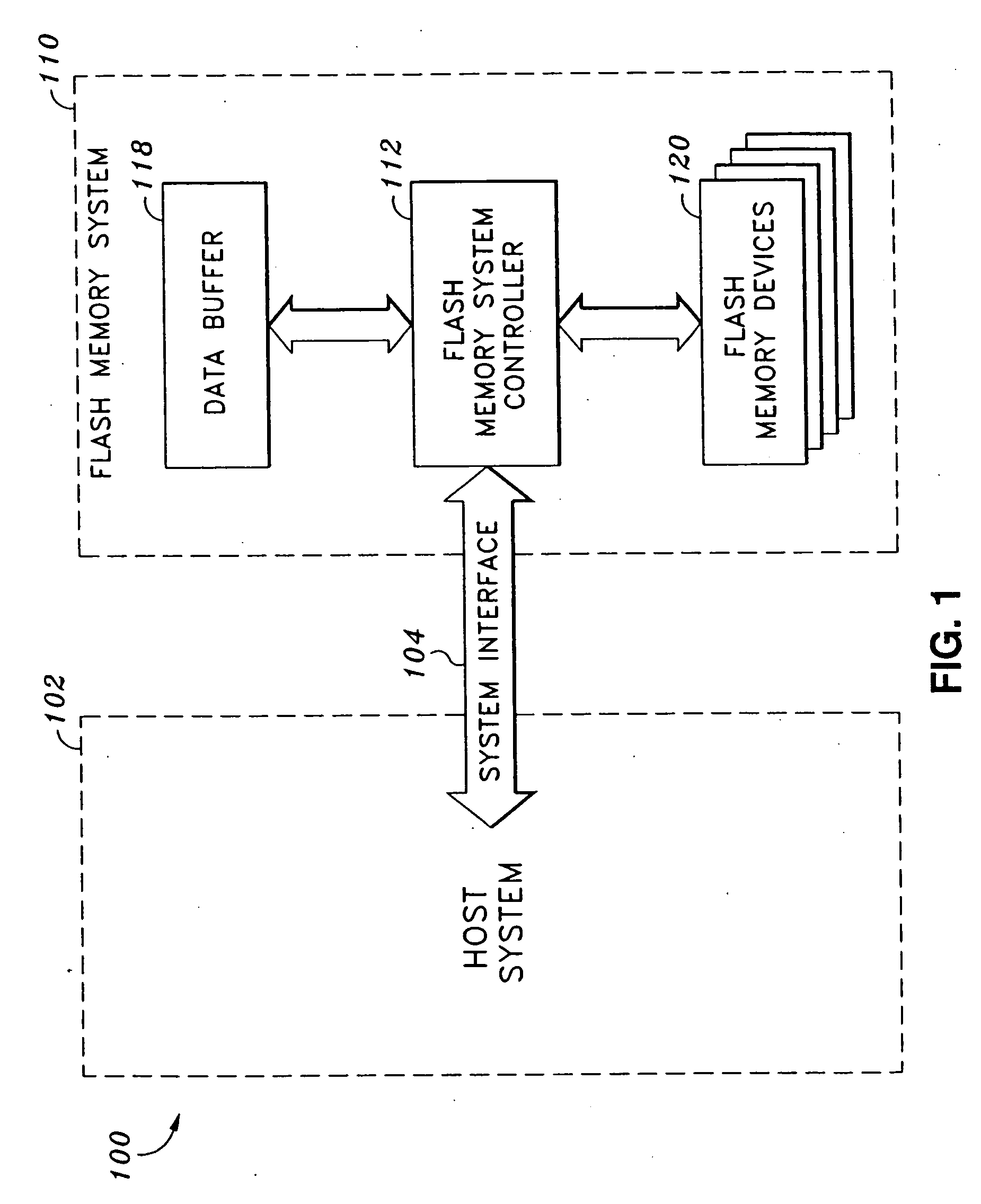
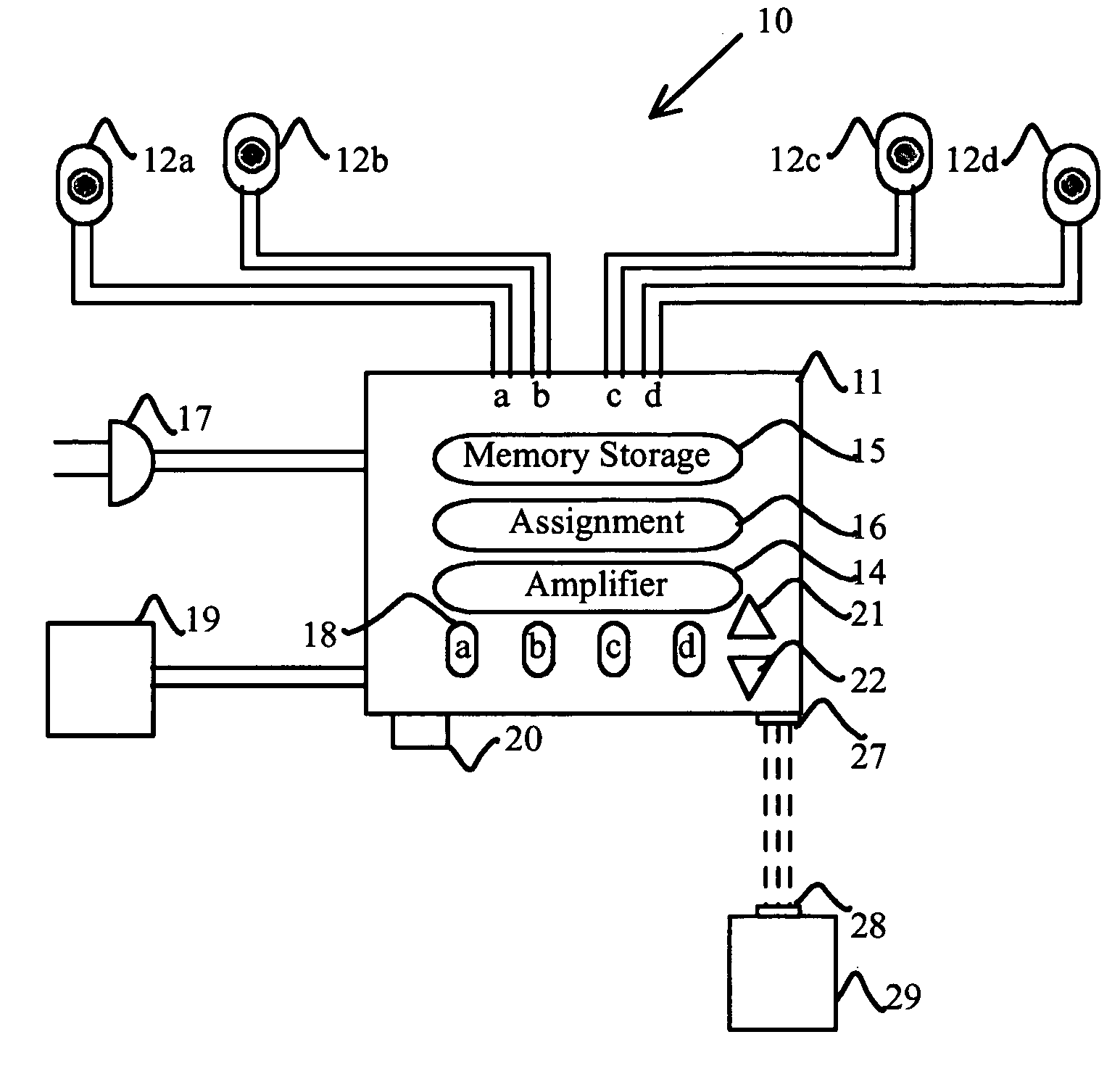
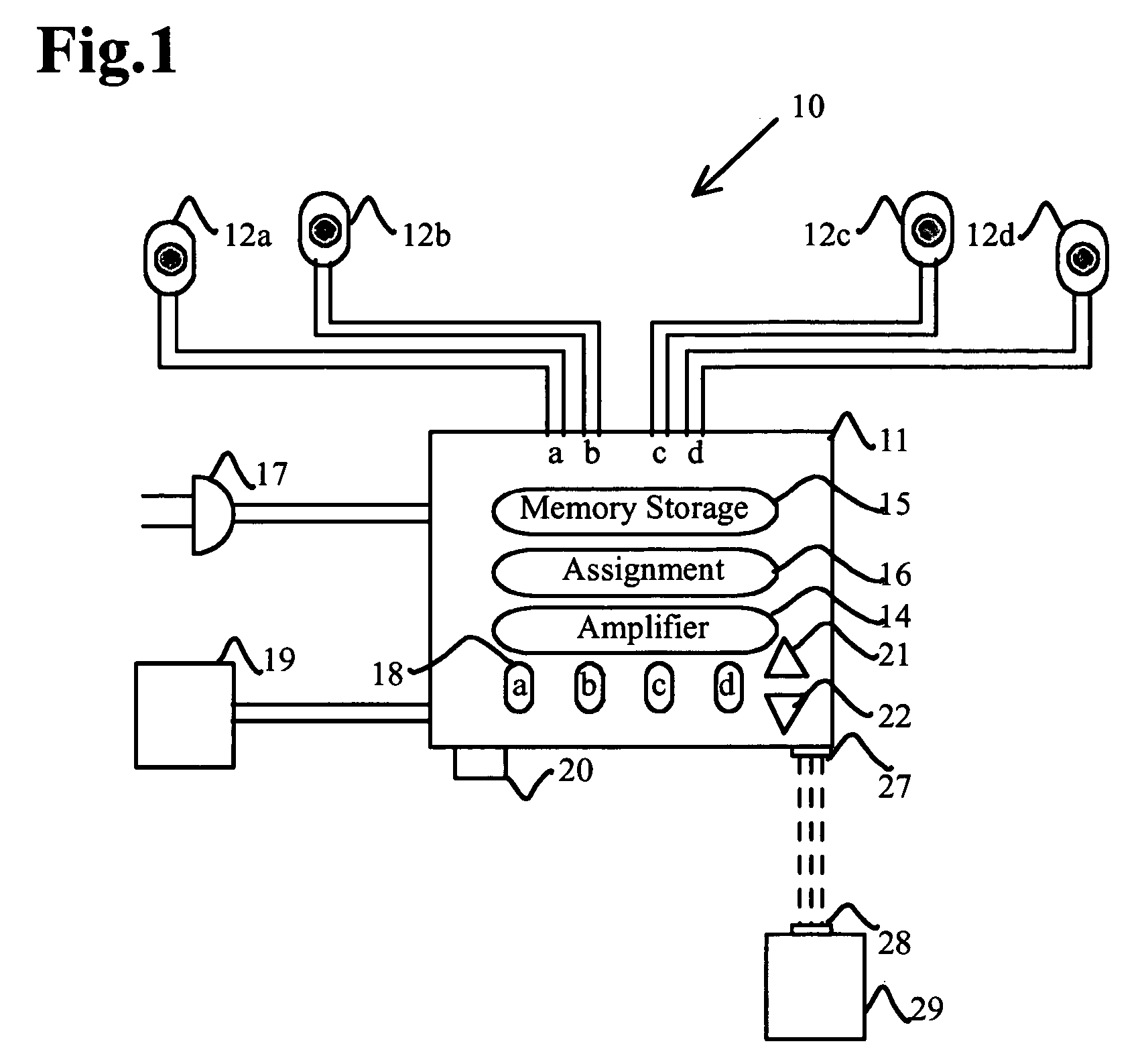
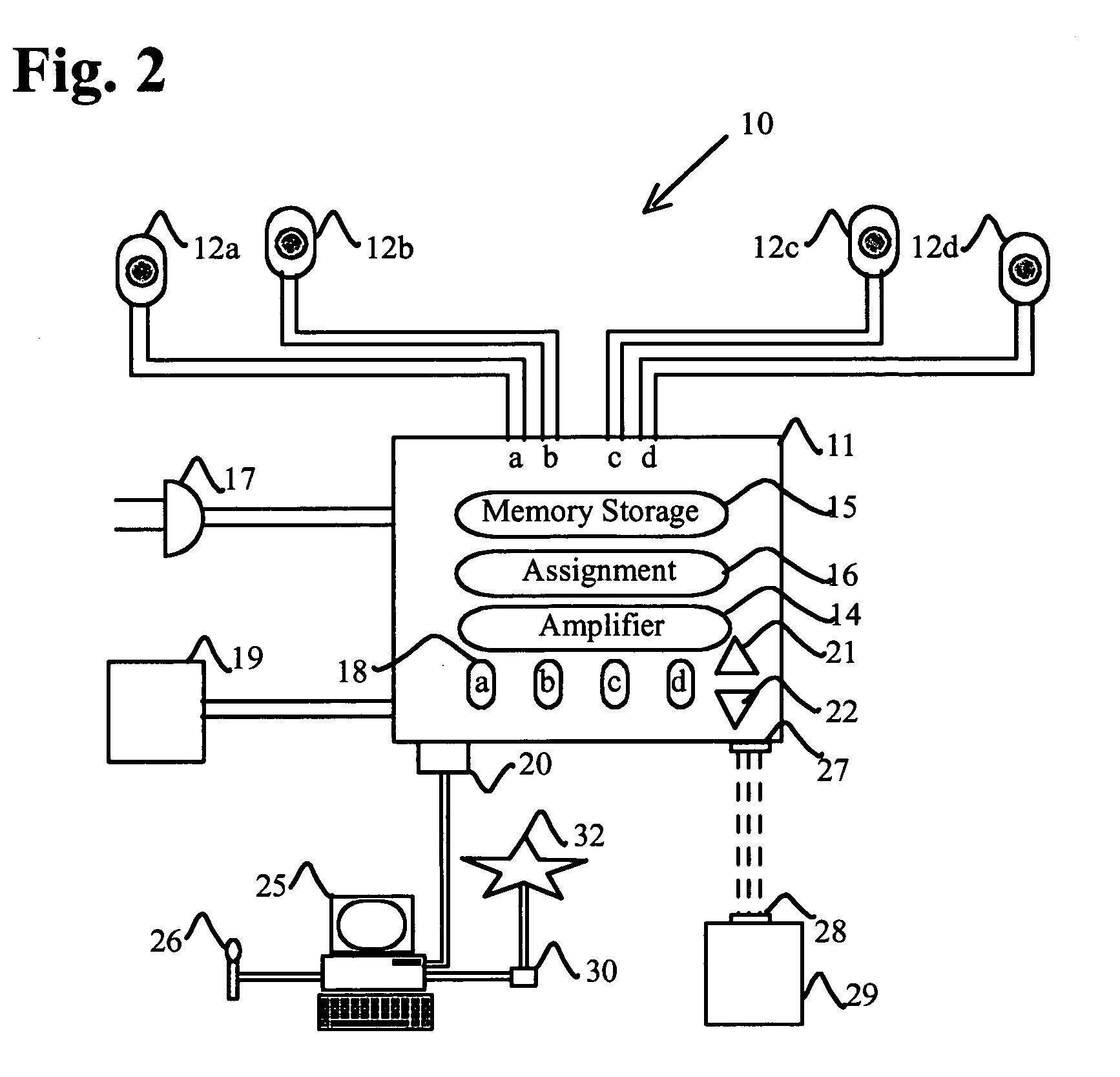
Solid-state memory. Updated: 04/26/2017 by. Solid-state memory is a computer memory that is stored within a hardware device that contains no moving parts. For example, CompactFlash memory is commonly a solid-state non-volatile memory.
Solid state memory (SSM), computer system including an ssm, and method of operating an ssm
InactiveUS20090049234A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingData storing
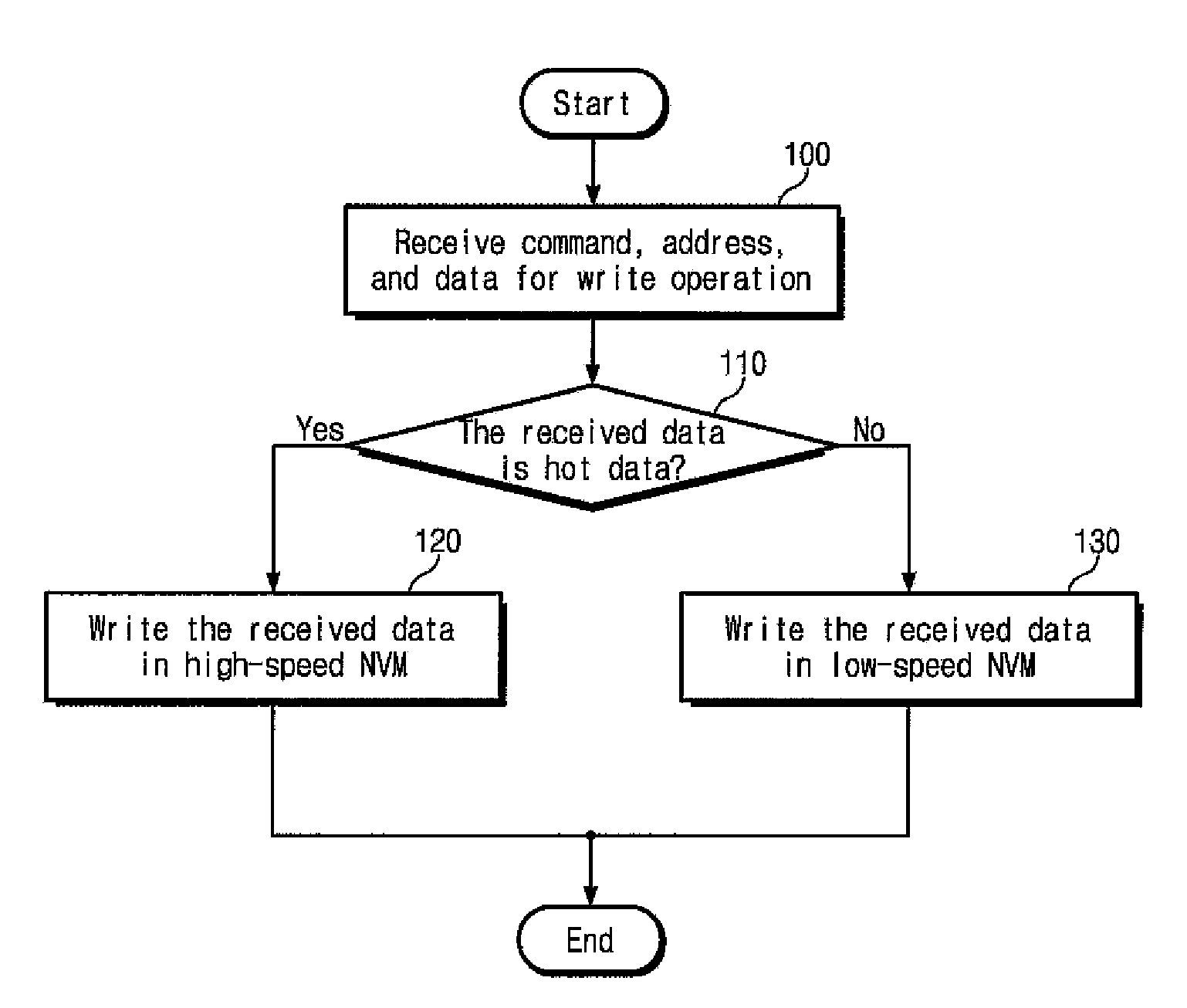
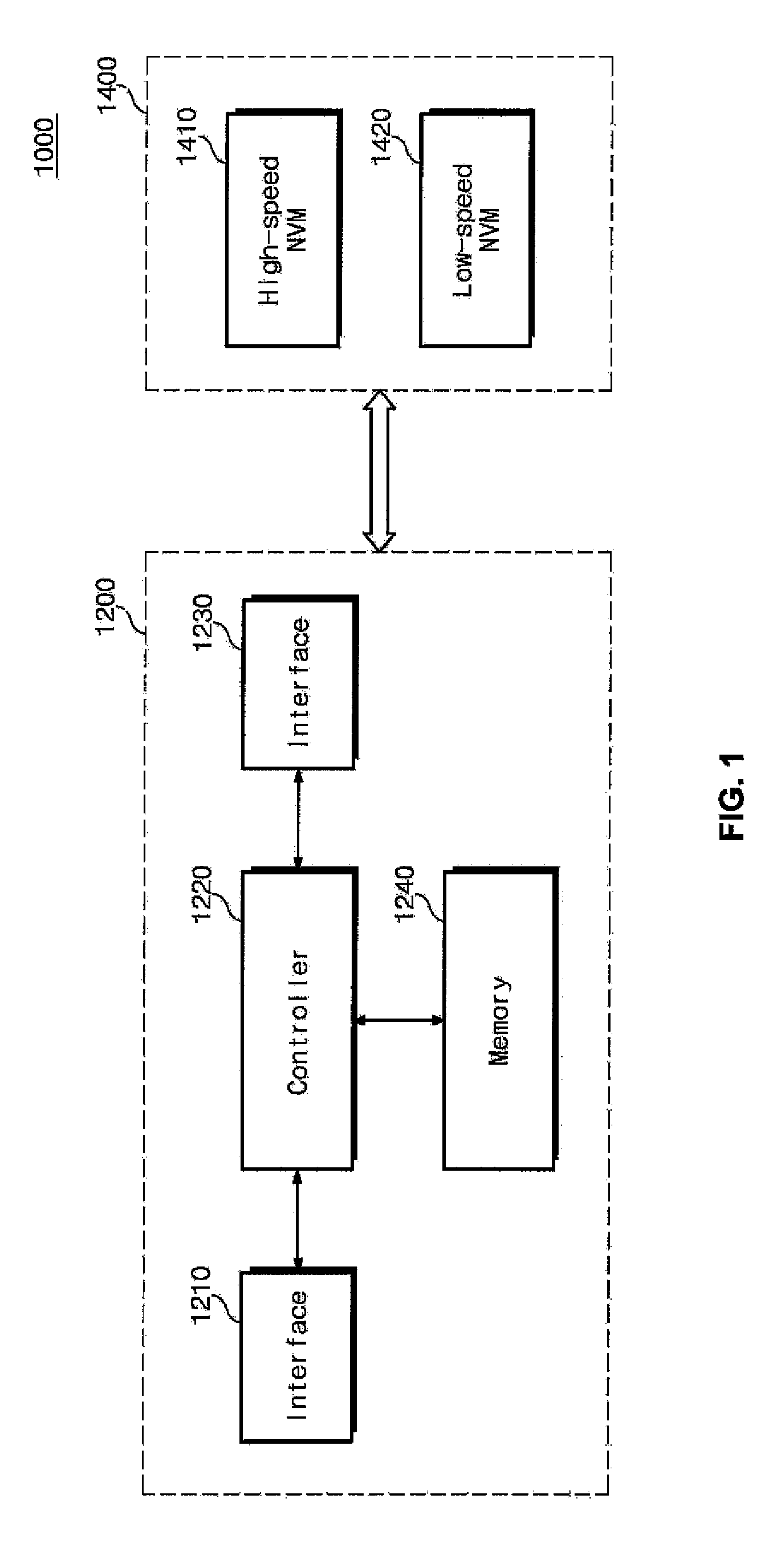
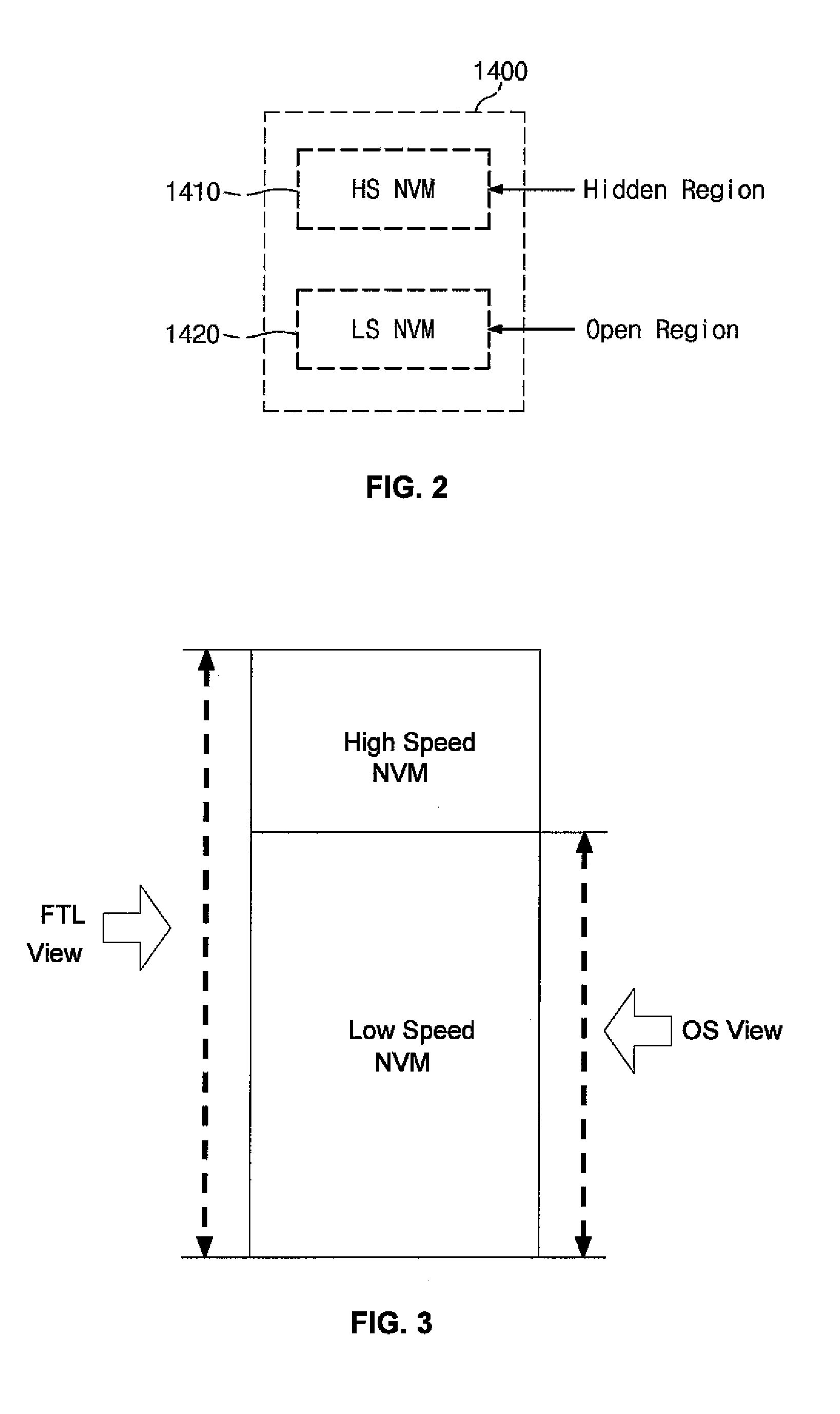
In one aspect, data is stored in a solid state memory which includes first and second memory layers. A first assessment is executed to determine whether received data is hot data or cold data. Received data which is assessed as hot data during the first assessment is stored in the first memory layer, and received data which is first assessed as cold data during the first assessment is stored in the second memory layer. Further, a second assessment is executed to determine whether the data stored in the first memory layer is hot data or cold data. Data which is then assessed as cold data during the second assessment is migrated from the first memory layer to the second memory layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
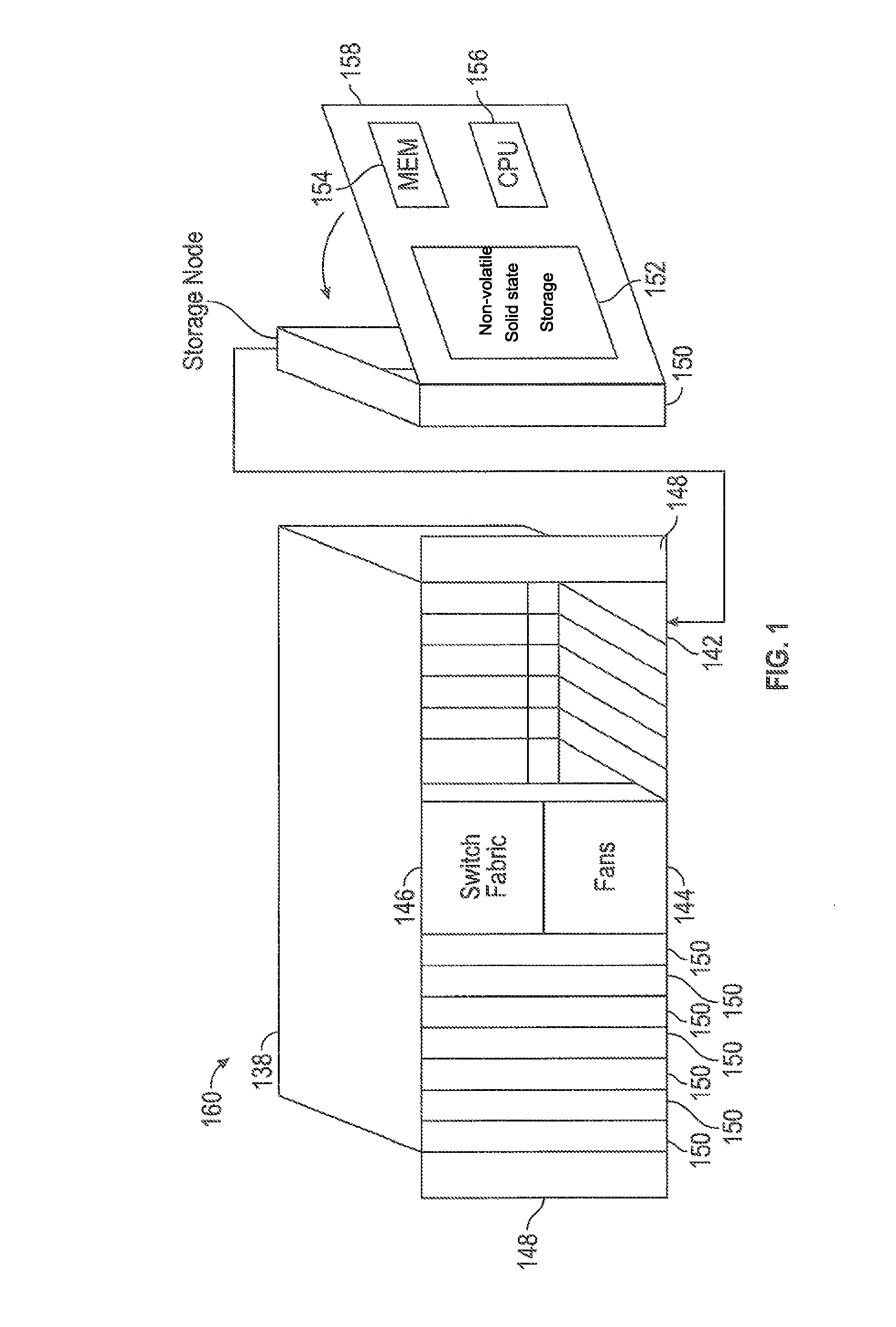
Storage cluster
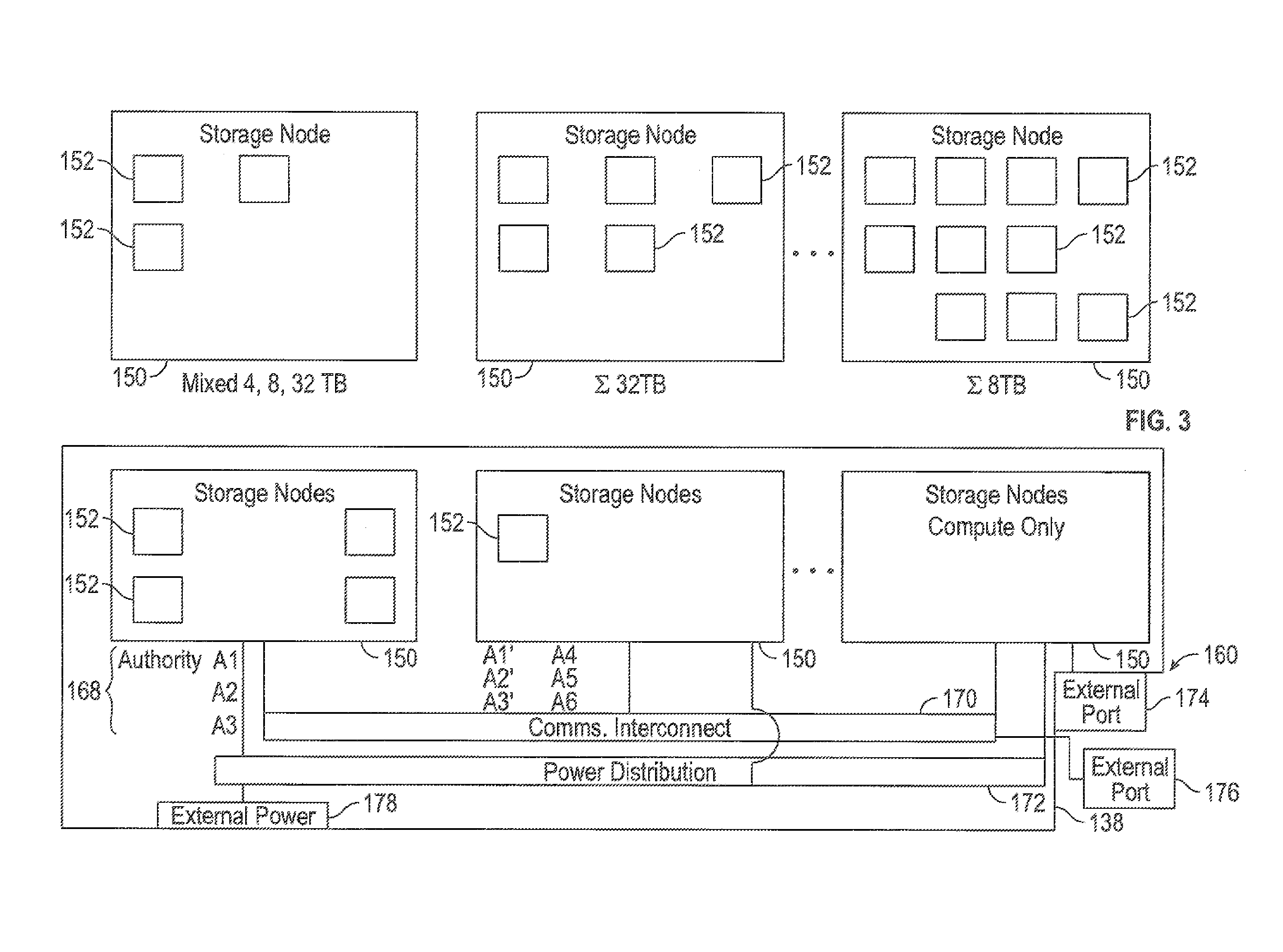
ActiveUS8850108B1Maintain abilityMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersData storeSolid state memory
A plurality of storage nodes in a single chassis is provided. The plurality of storage nodes in the single chassis is configured to communicate together as a storage cluster. Each of the plurality of storage nodes includes nonvolatile solid-state memory for user data storage. The plurality of storage nodes is configured to distribute the user data and metadata associated with the user data throughout the plurality of storage nodes such that the plurality of storage nodes maintain the ability to read the user data, using erasure coding, despite a loss of two of the plurality of storage nodes. The chassis includes power distribution, a high speed communication bus and the ability to install one or more storage nodes which may use the power distribution and communication bus. A method for accessing user data in a plurality of storage nodes having nonvolatile solid-state memory is also provided.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
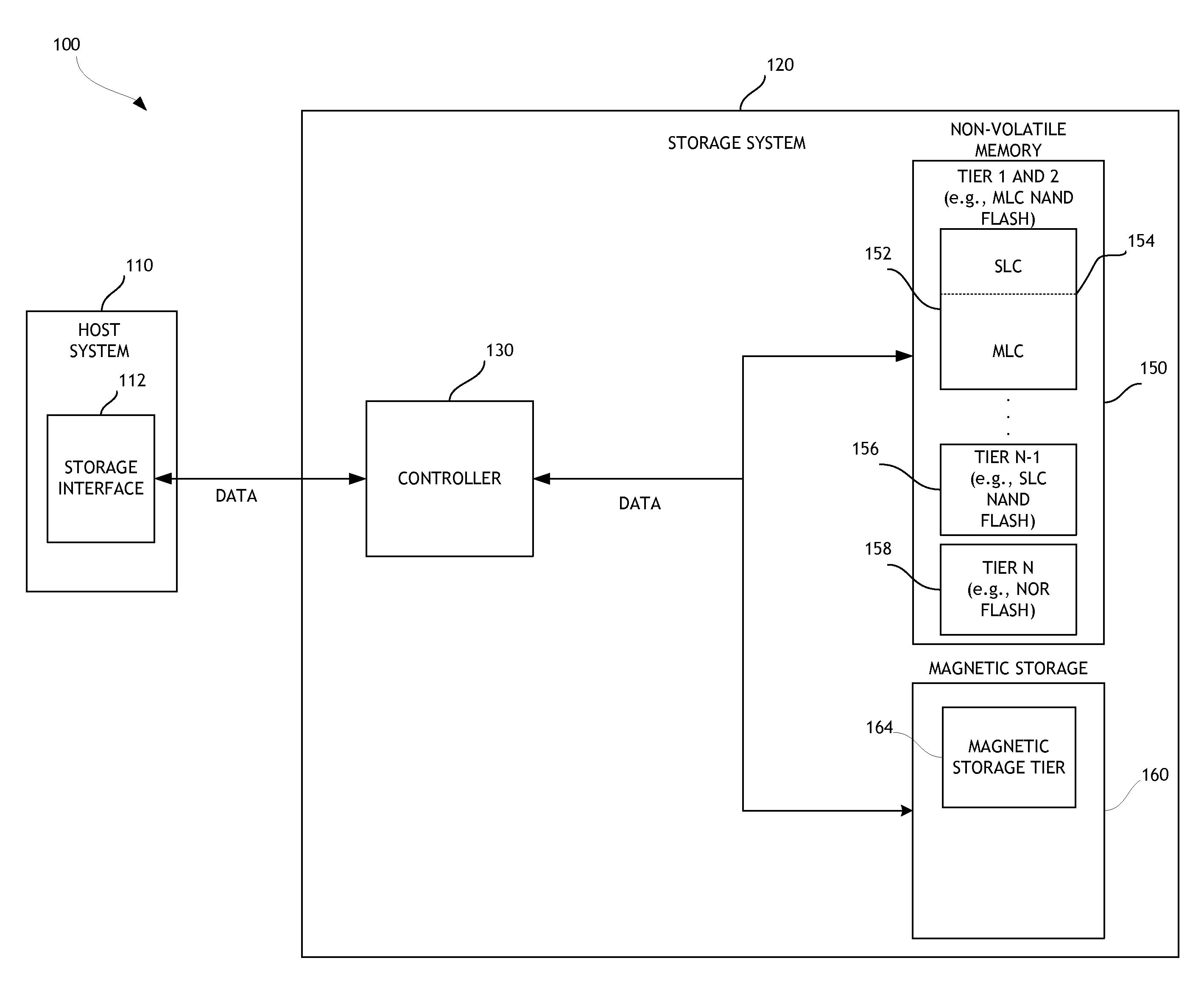
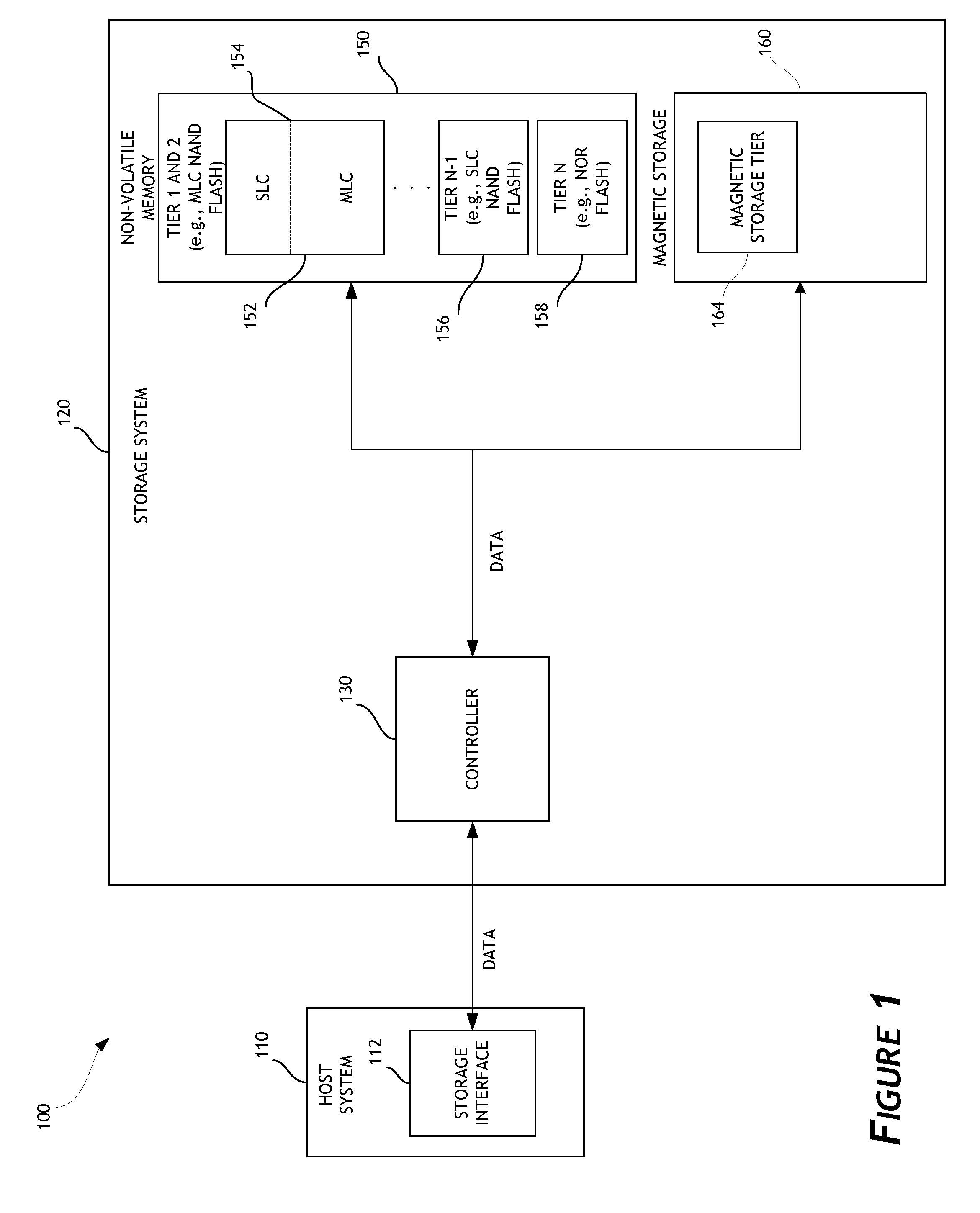
Disk drive data caching using a multi-tiered memory
ActiveUS20130132638A1Limit usable lifeReduce dataMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTSingle levelComputer science
A disk drive is disclosed that utilizes multi-tiered solid state memory for caching data received from a host. Data can be stored in a memory tier that can provide the required performance at a low cost. For example, multi-level cell (MLC) memory can be used to store data that is frequently read but infrequently written. As another example, single-level cell (SLC) memory can be used to store data that is frequently written. Improved performance, reduced costs, and improved power consumption can thereby be attained.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
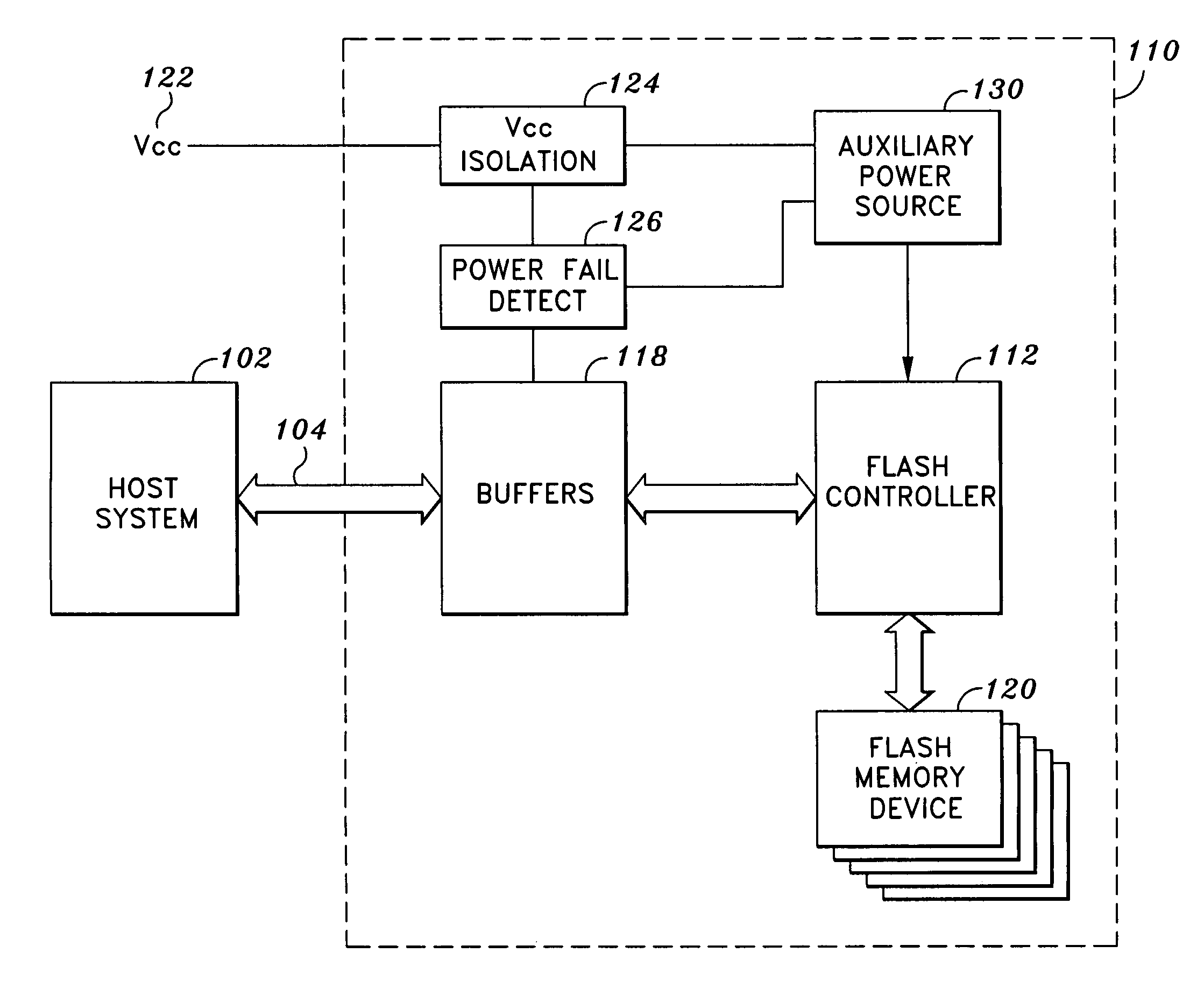
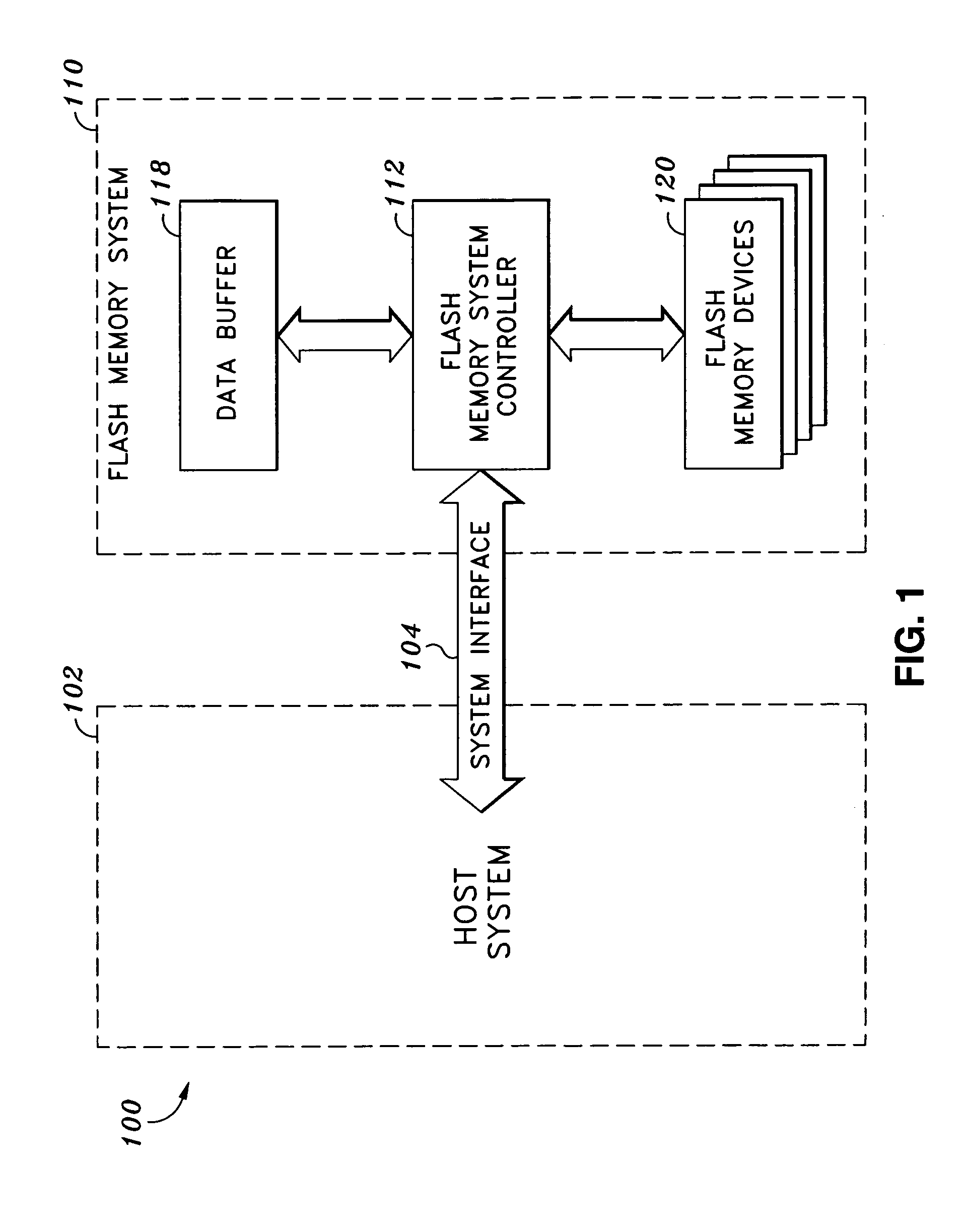
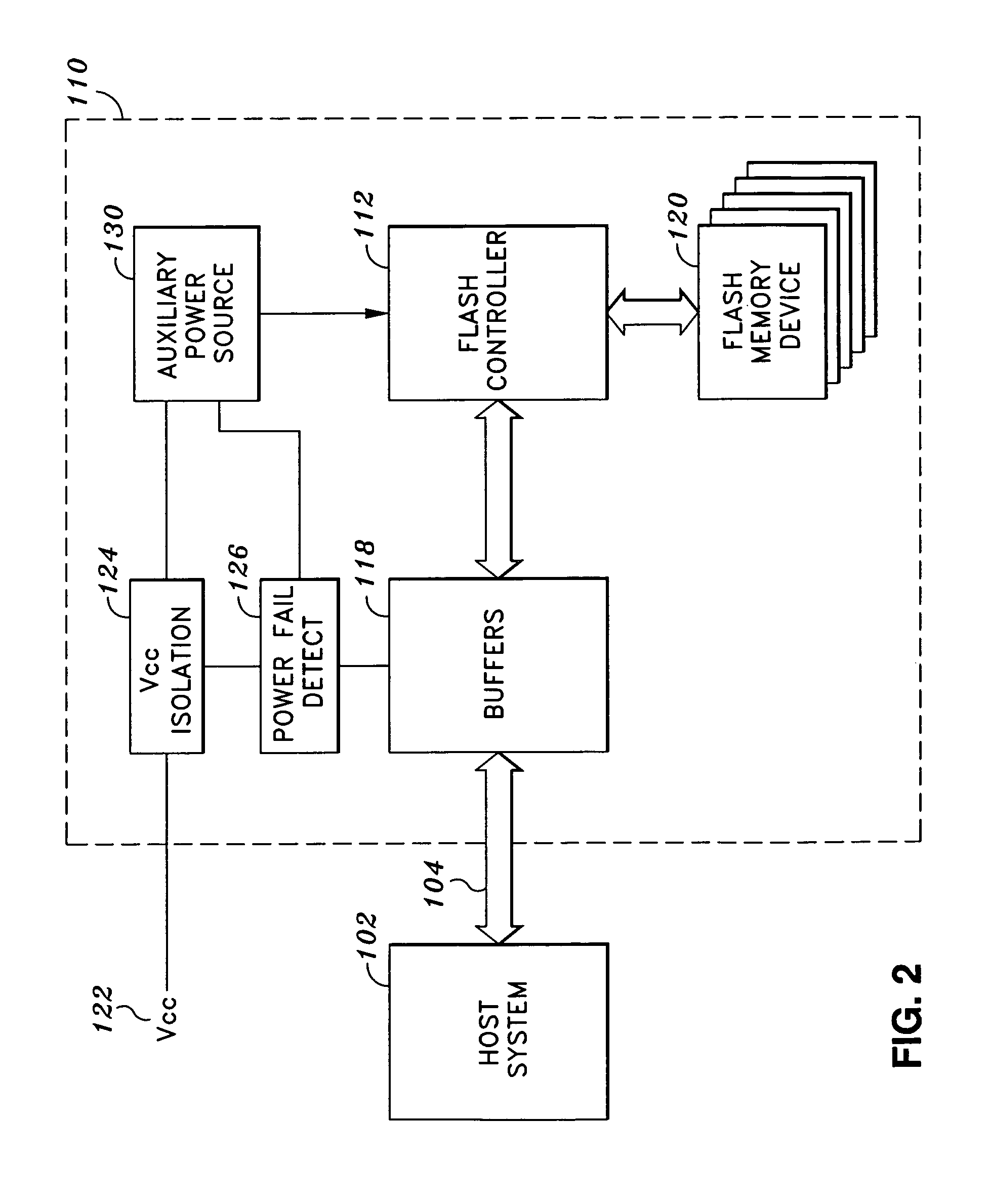
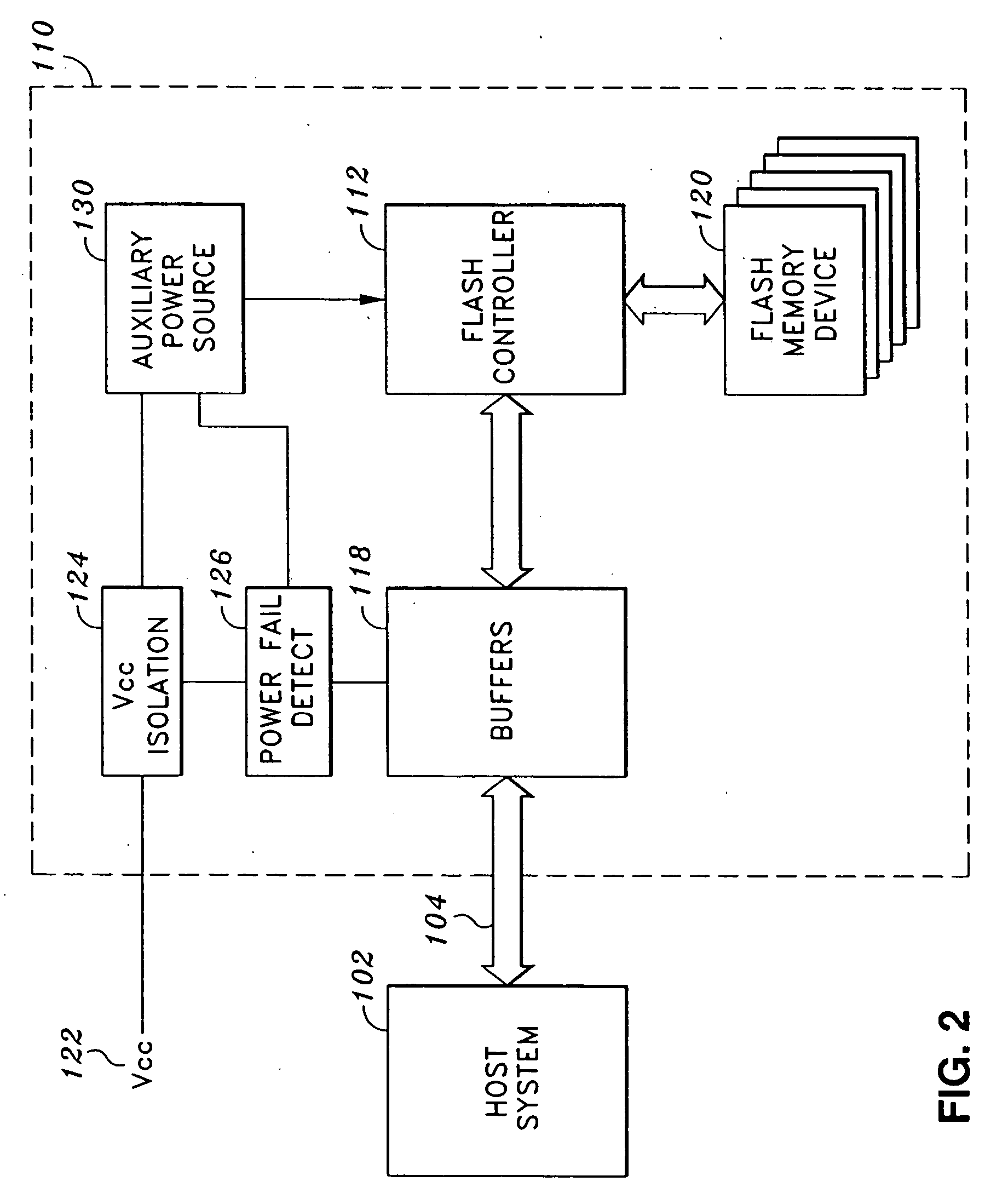
System and method for preventing data corruption in solid-state memory devices after a power failure
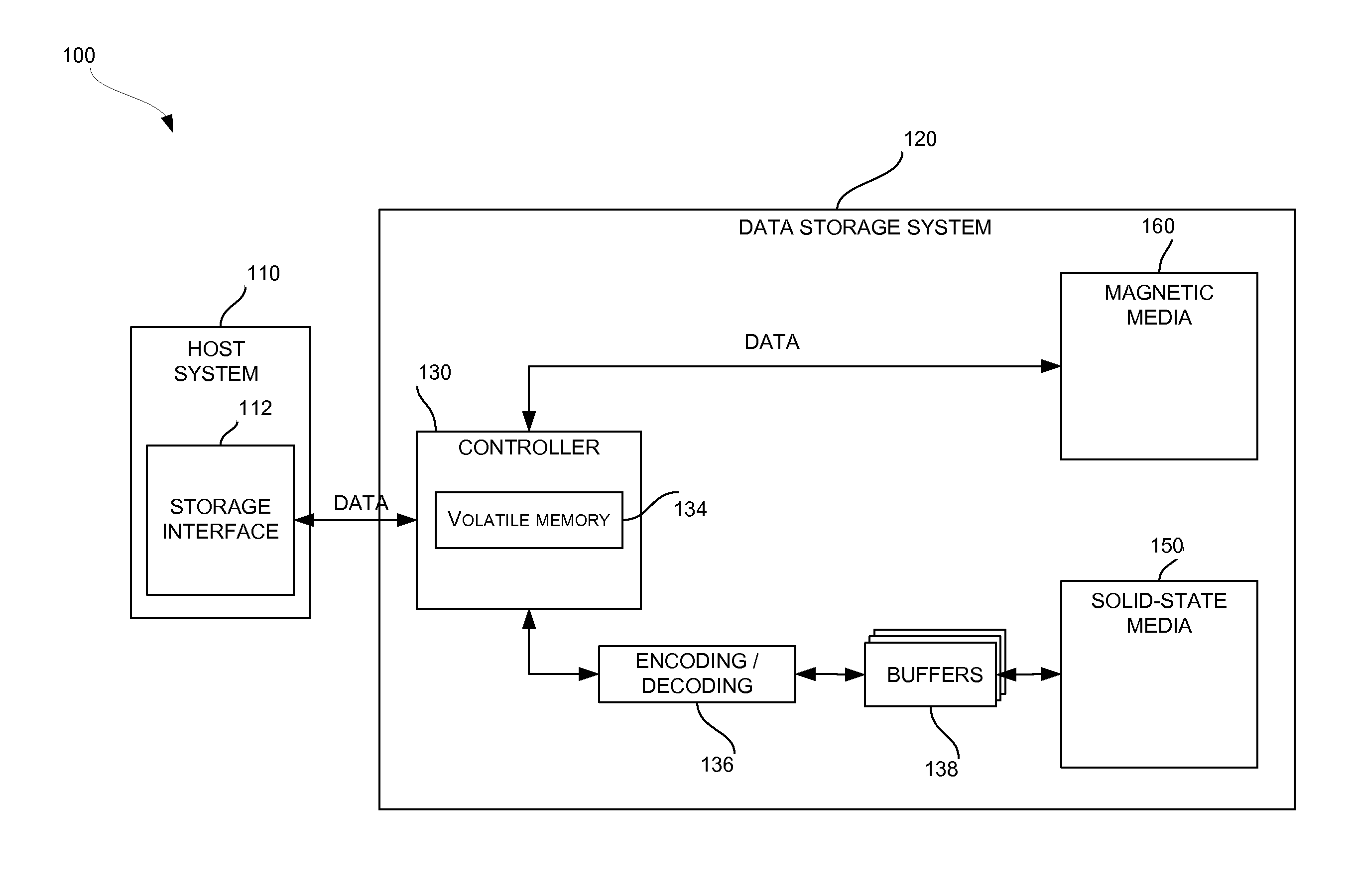
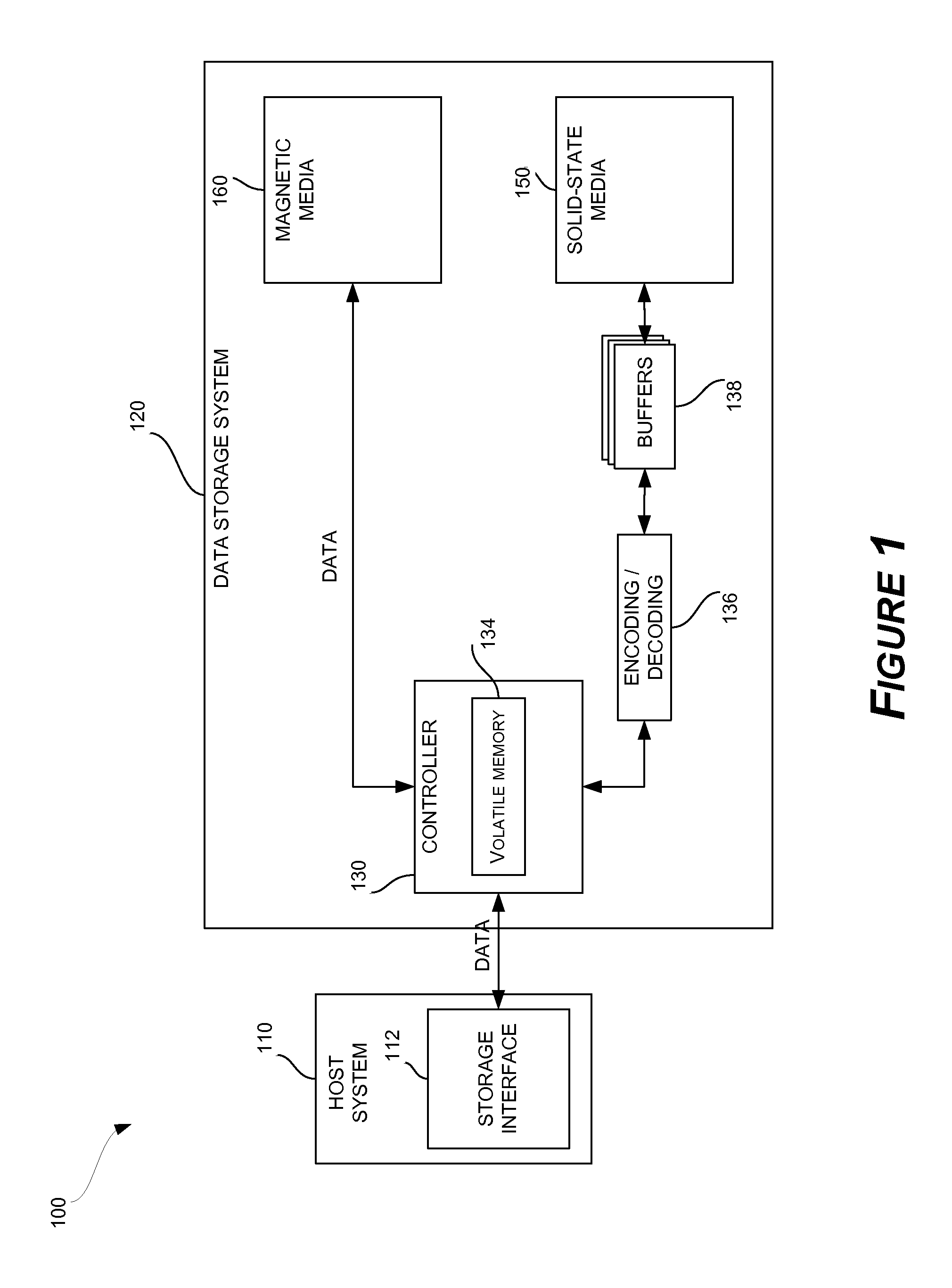
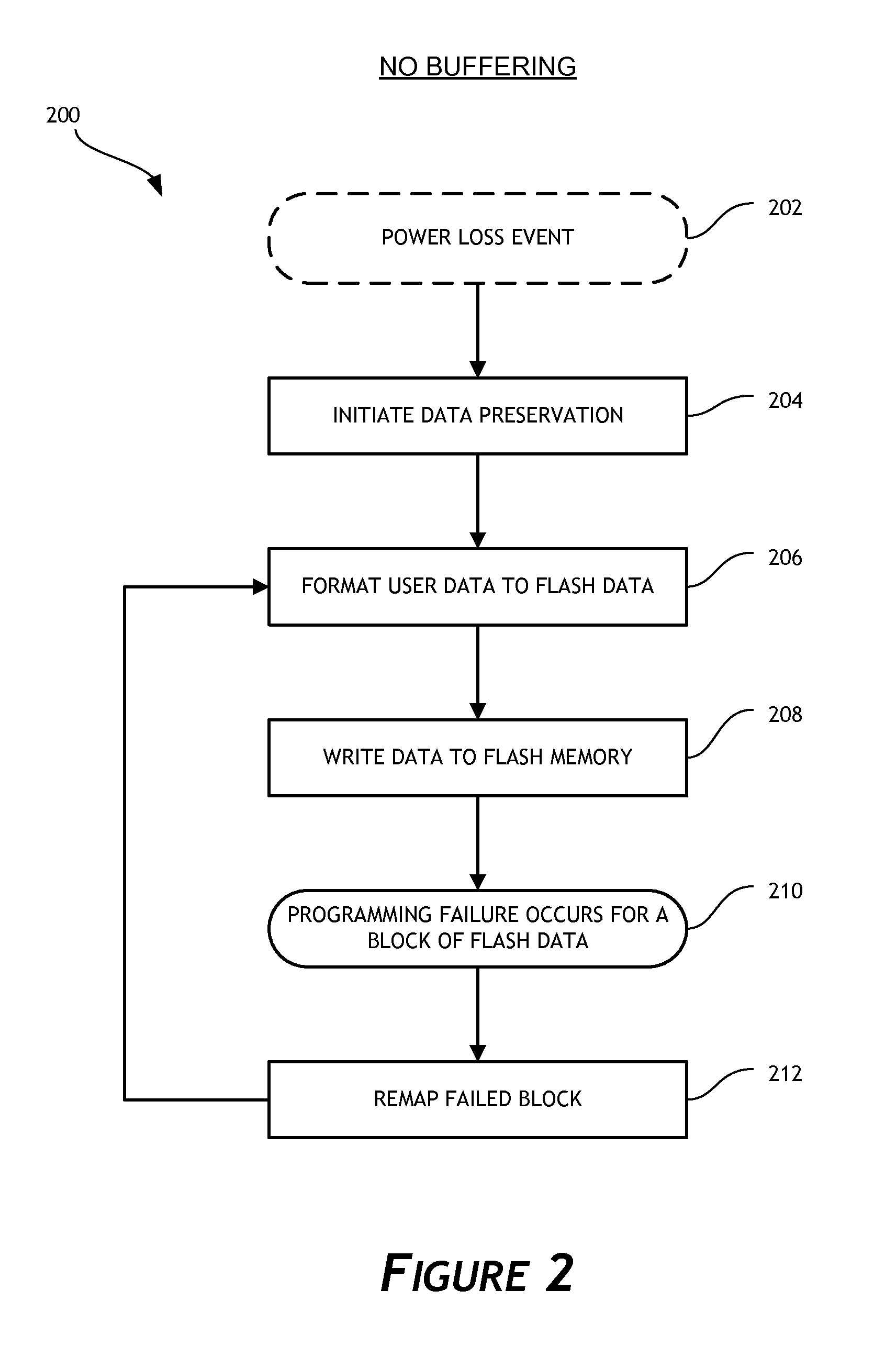
A data preservation system for flash memory systems with a host system, the flash memory system receiving a host system power supply and energizing an auxiliary energy store therewith and communicating with the host system via an interface bus, wherein, upon loss of the host system power supply, the flash memory system actively isolates the connection to the host system power supply and isolates the interface bus and employs the supplemental energy store to continue write operations to flash memory.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
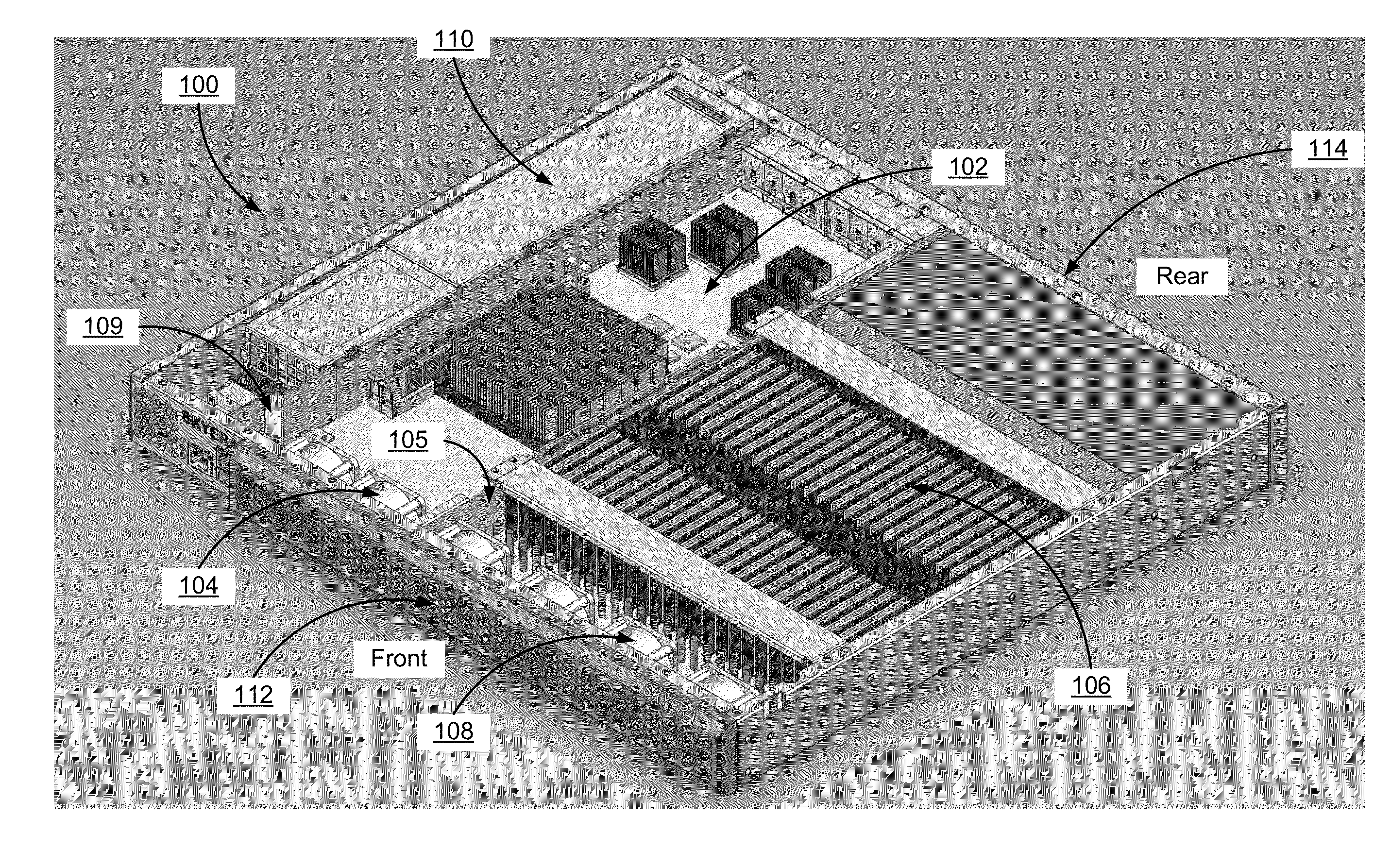
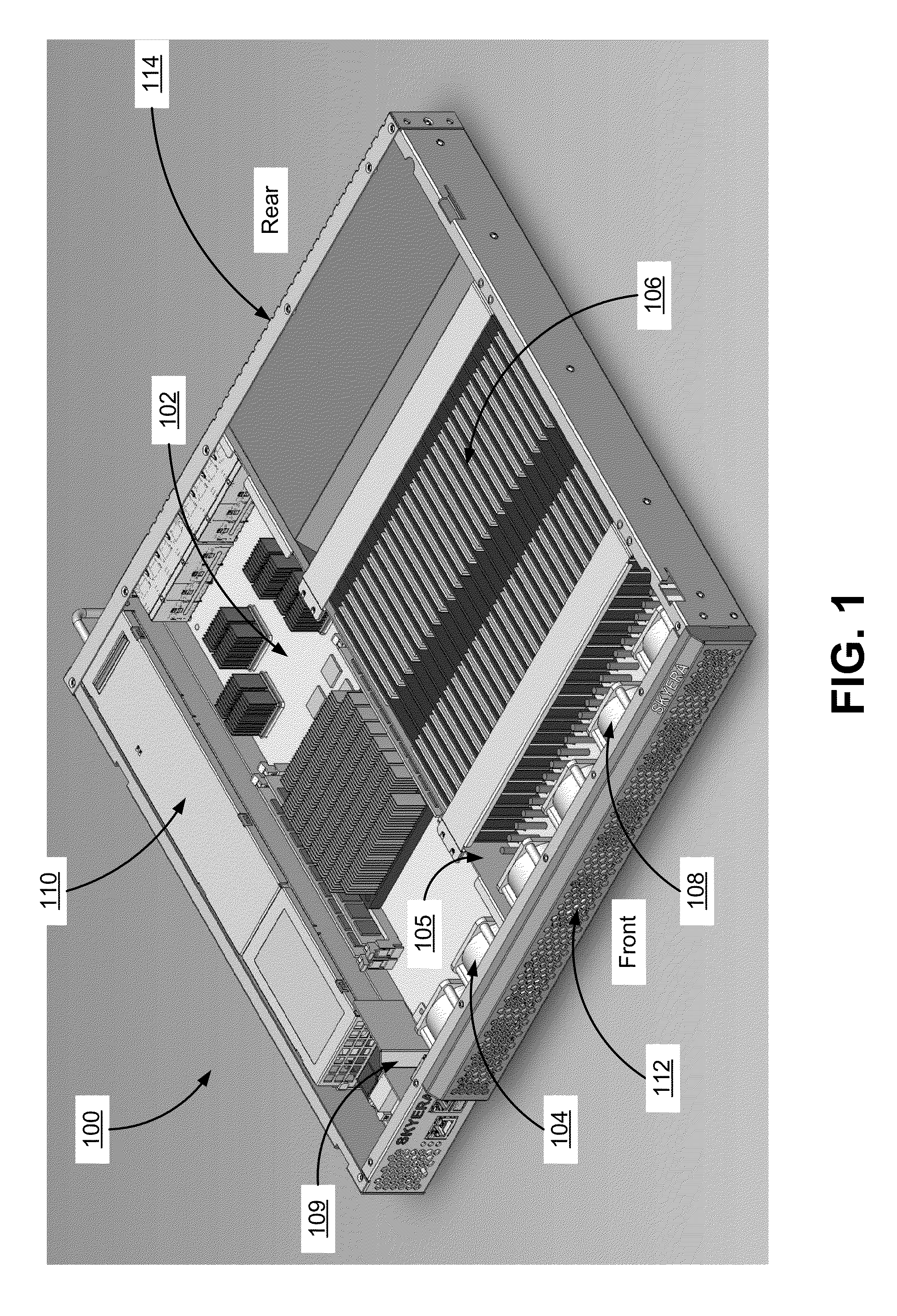
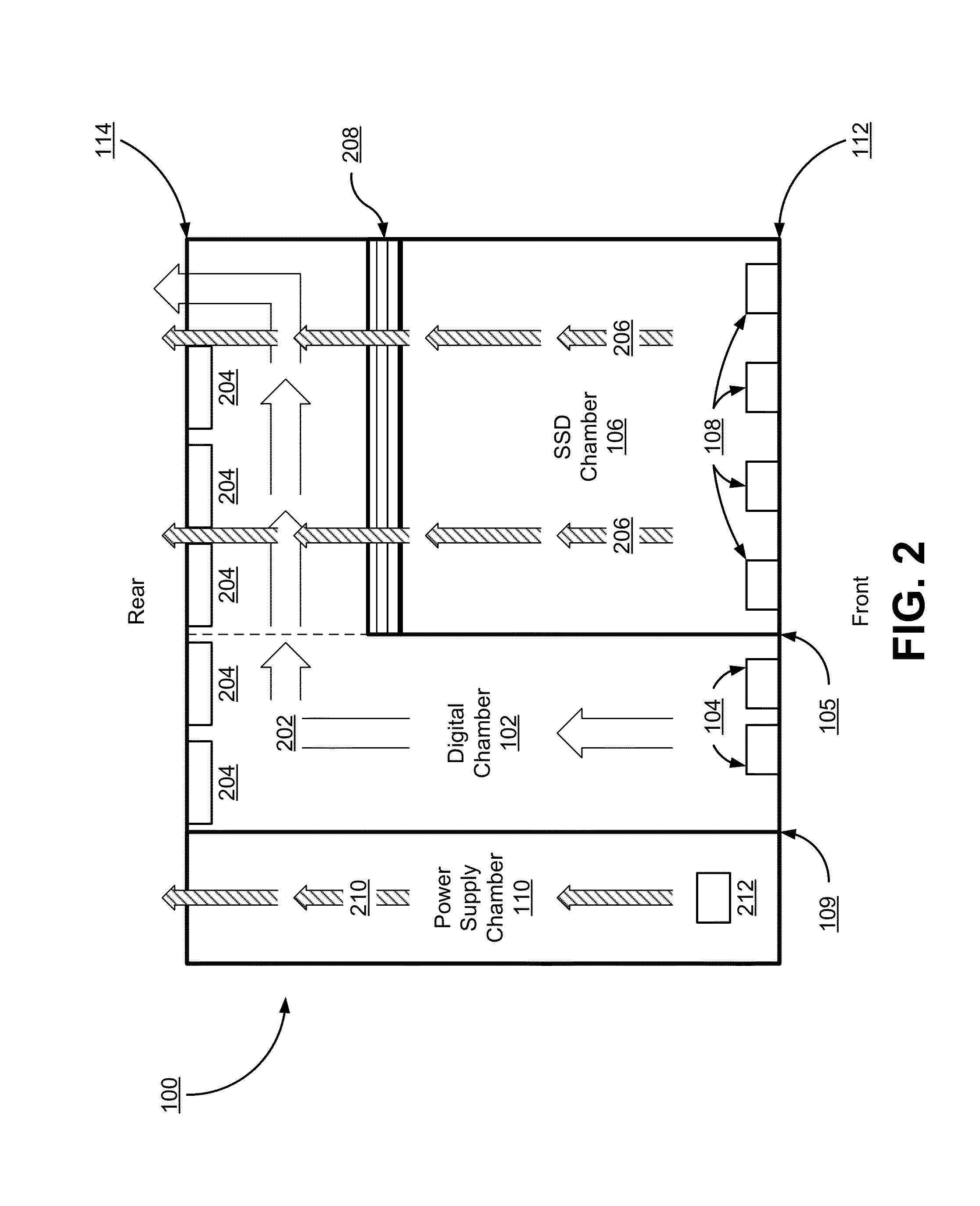
Chassis with separate thermal chamber for solid state memory
ActiveUS20140063721A1Extended service lifeServersTemperatue controlTemperature controlJunction temperature
A chassis for a network storage system contains a first thermal chamber that houses conventional electronic components and a second thermal chamber that houses non-volatile solid state memory such as flash memory. A cooling system keeps the electronics in first thermal chamber below their maximum junction temperature. Meanwhile, a temperature regulating system maintains the solid state memory in the second thermal chamber within a range of a preferred operating temperature selected to extend the lifetime and / or improve the reliability of the solid state memory. Thus, the chassis provides dual zone temperature control to improve performance of the network storage system.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
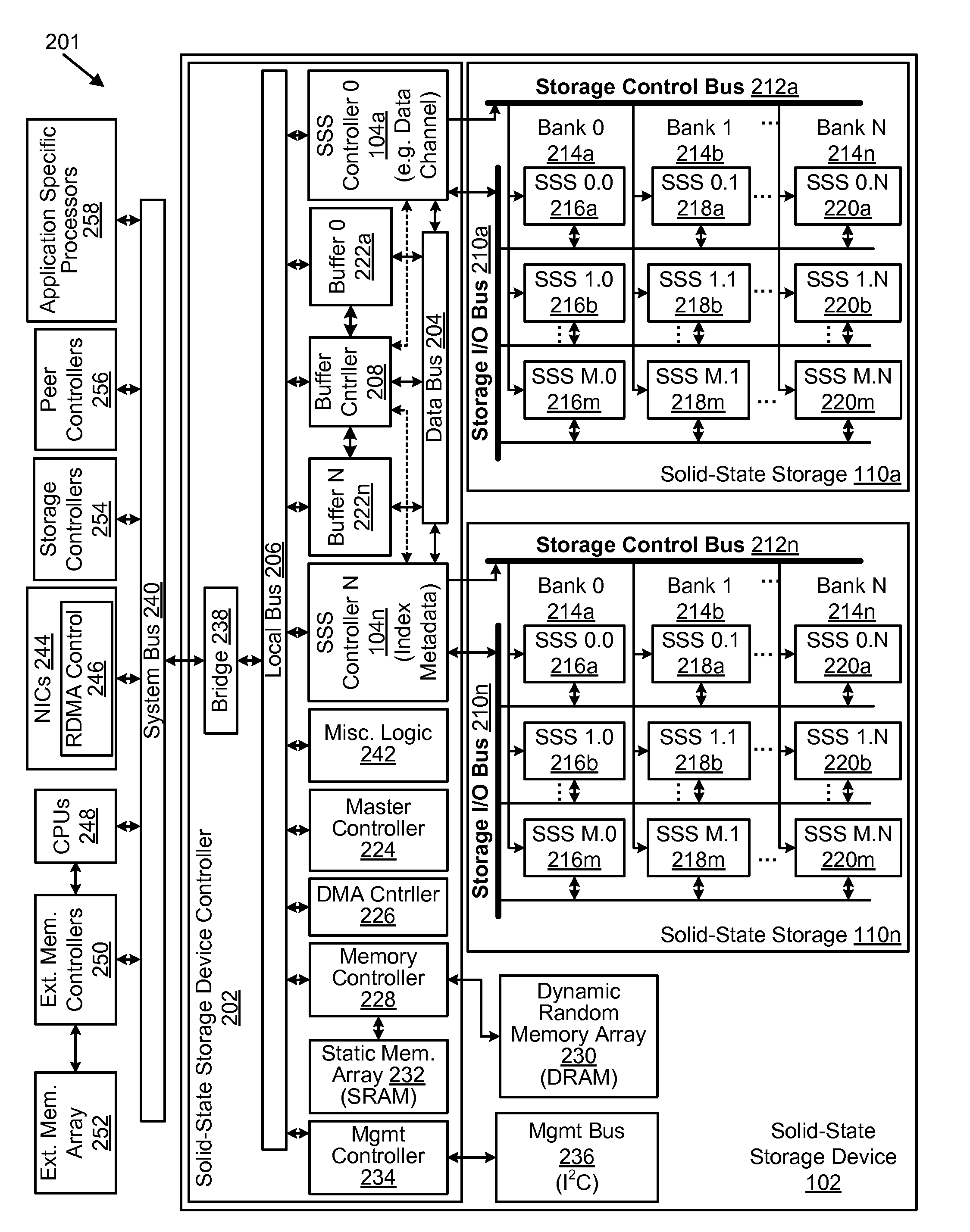
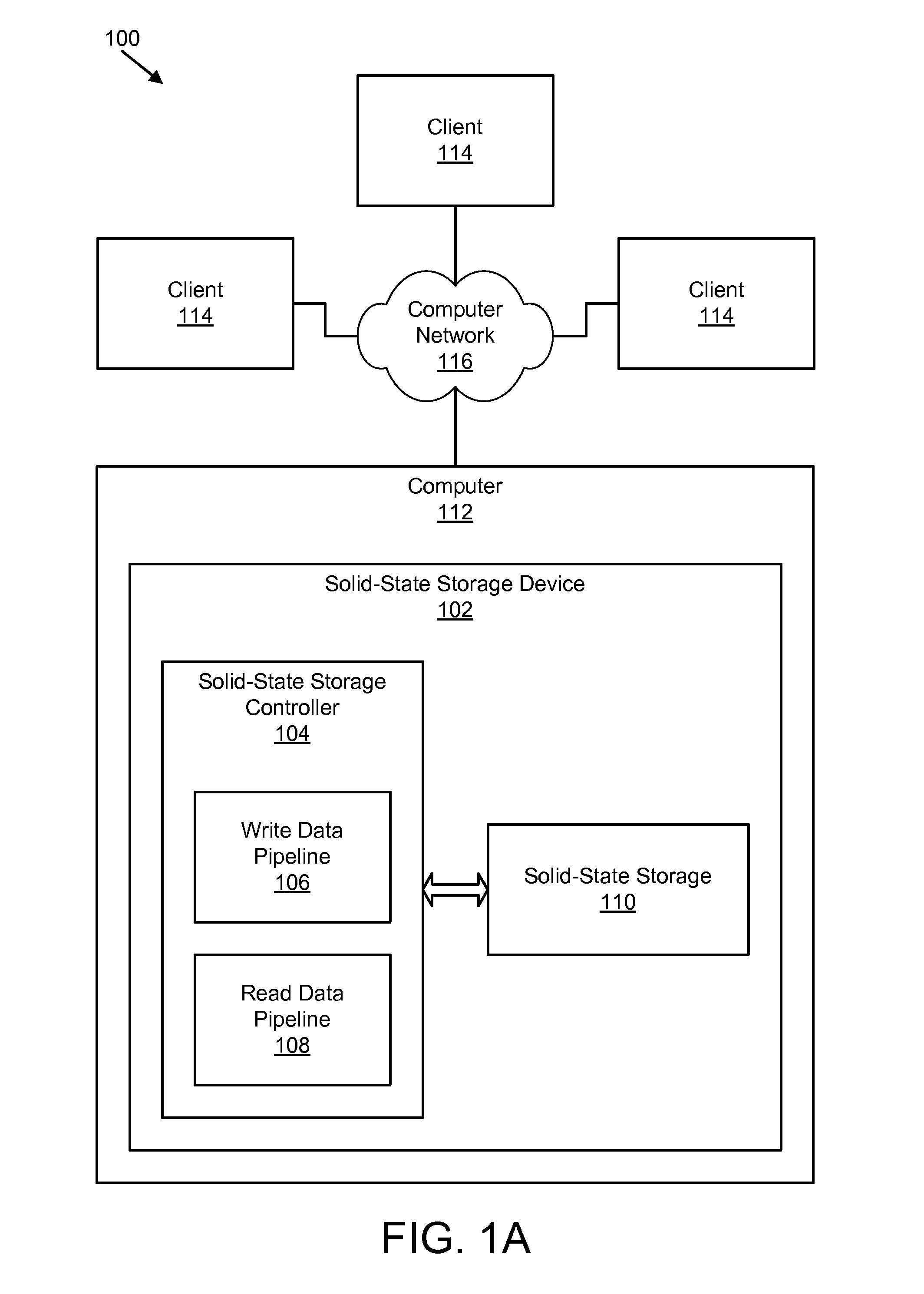
Apparatus, system, and method for managing data using a data pipeline
ActiveUS20080141043A1Energy efficient ICTInput/output to record carriersSolid-state storageData segment
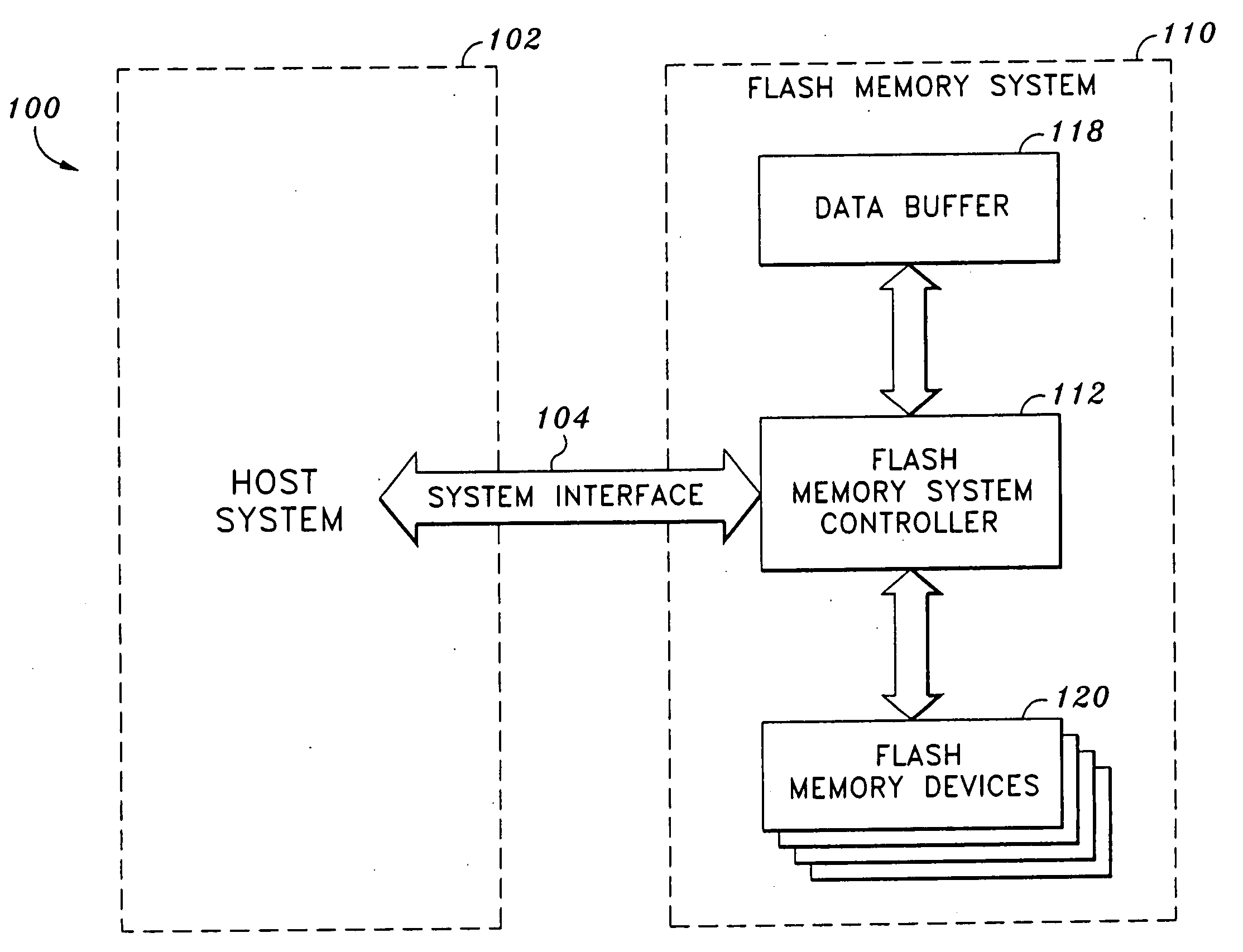
An apparatus, system, and method are disclosed for managing data in a solid-state storage device. A solid-state storage and solid-state controller are included. The solid-state storage controller includes a write data pipeline and a read data pipeline The write data pipeline includes a packetizer and an ECC generator. The packetizer receives a data segment and creates one or more data packets sized for the solid-state storage. The ECC generator generates one or more error-correcting codes (“ECC”) for the data packets received from the packetizer. The read data pipeline includes an ECC correction module, a depacketizer, and an alignment module. The ECC correction module reads a data packet from solid-state storage, determines if a data error exists using corresponding ECC and corrects errors. The depacketizer checks and removes one or more packet headers. The alignment module removes unwanted data, and re-formats the data as data segments of an object.
Owner:UNIFICATION TECH LLC
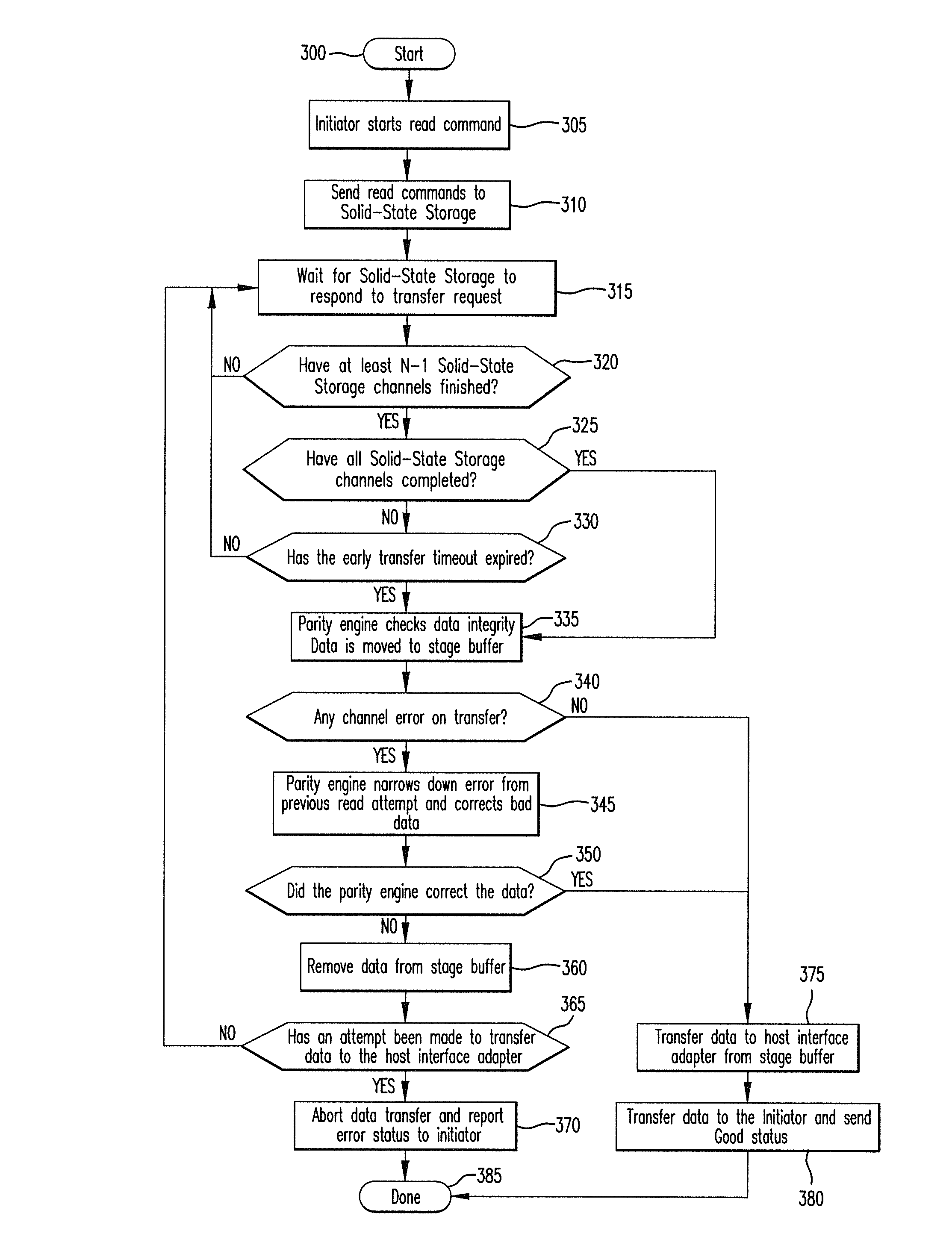
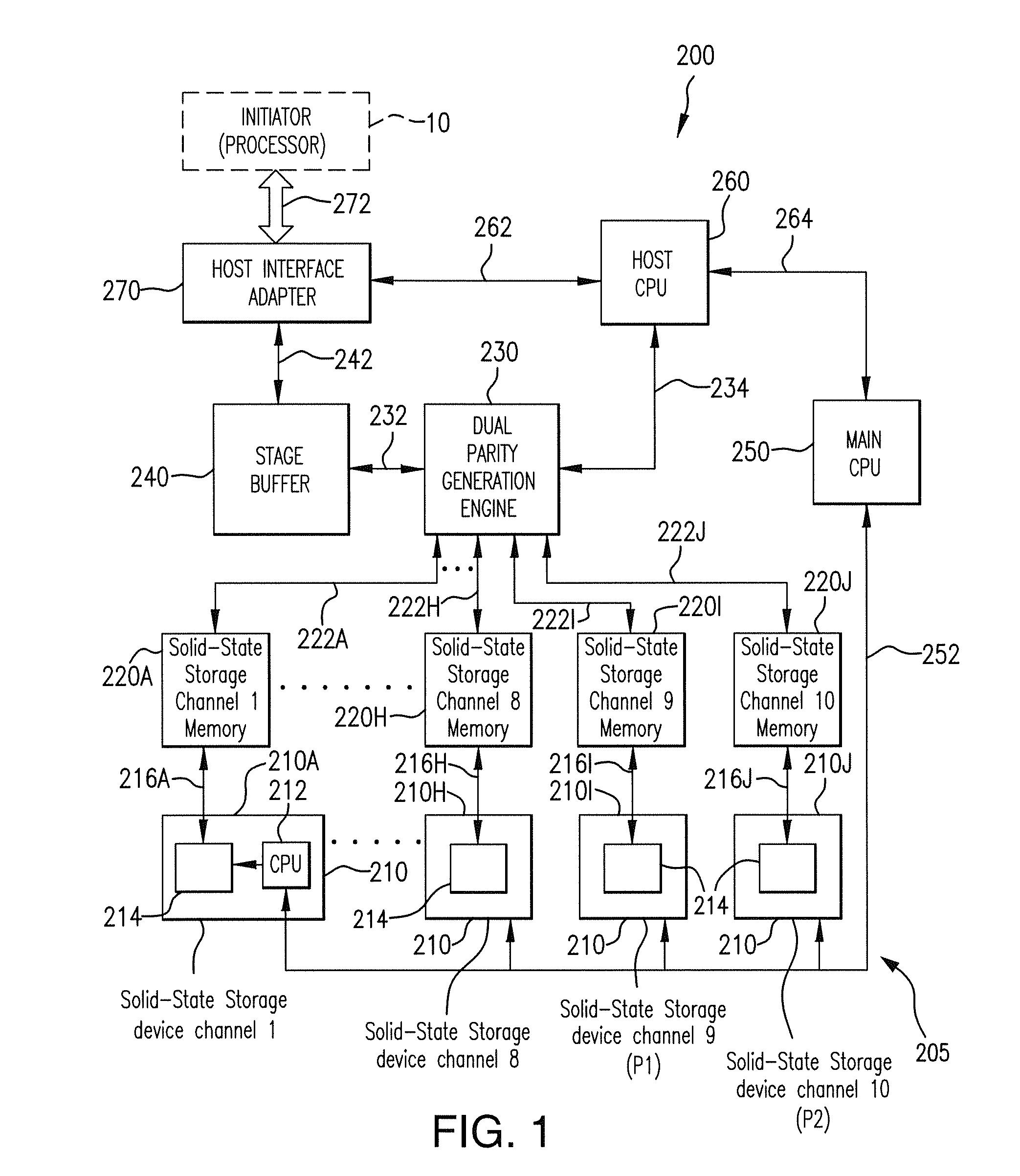
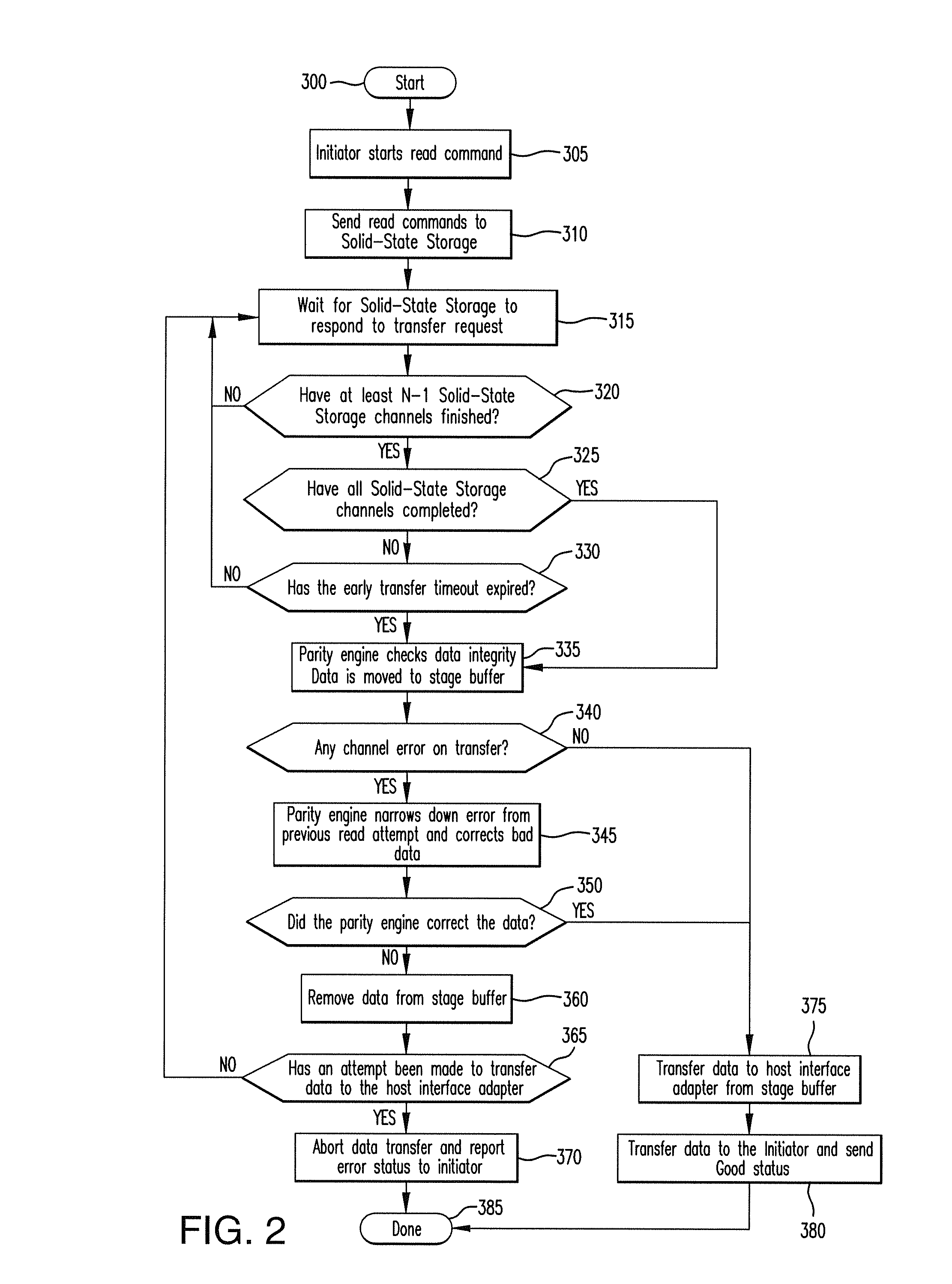
Method for reducing latency in a solid-state memory system while maintaining data integrity
ActiveUS8661218B1Easy accessReduce energy consumptionError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsSolid-state storageFault tolerance
A latency reduction method for read operations of an array of N solid-state storage devices having n solid-state storage devices for data storage and p solid-state storage devices for storing parity data is provided. Utilizing the parity generation engine fault tolerance for a loss of valid data from at least two of the N solid-state storage devices, the integrity of the data is determined when N−1 of the solid-state storage devices have completed executing a read command. If the data is determined to be valid, the missing data of the Nth solid-state storage device is reconstructed and the data transmitted to the requesting processor. By that arrangement the time necessary for the Nth solid-state storage device to complete execution of the read command is saved, thereby improving the performance of the solid-state memory system.
Owner:DATADIRECT NETWORKS
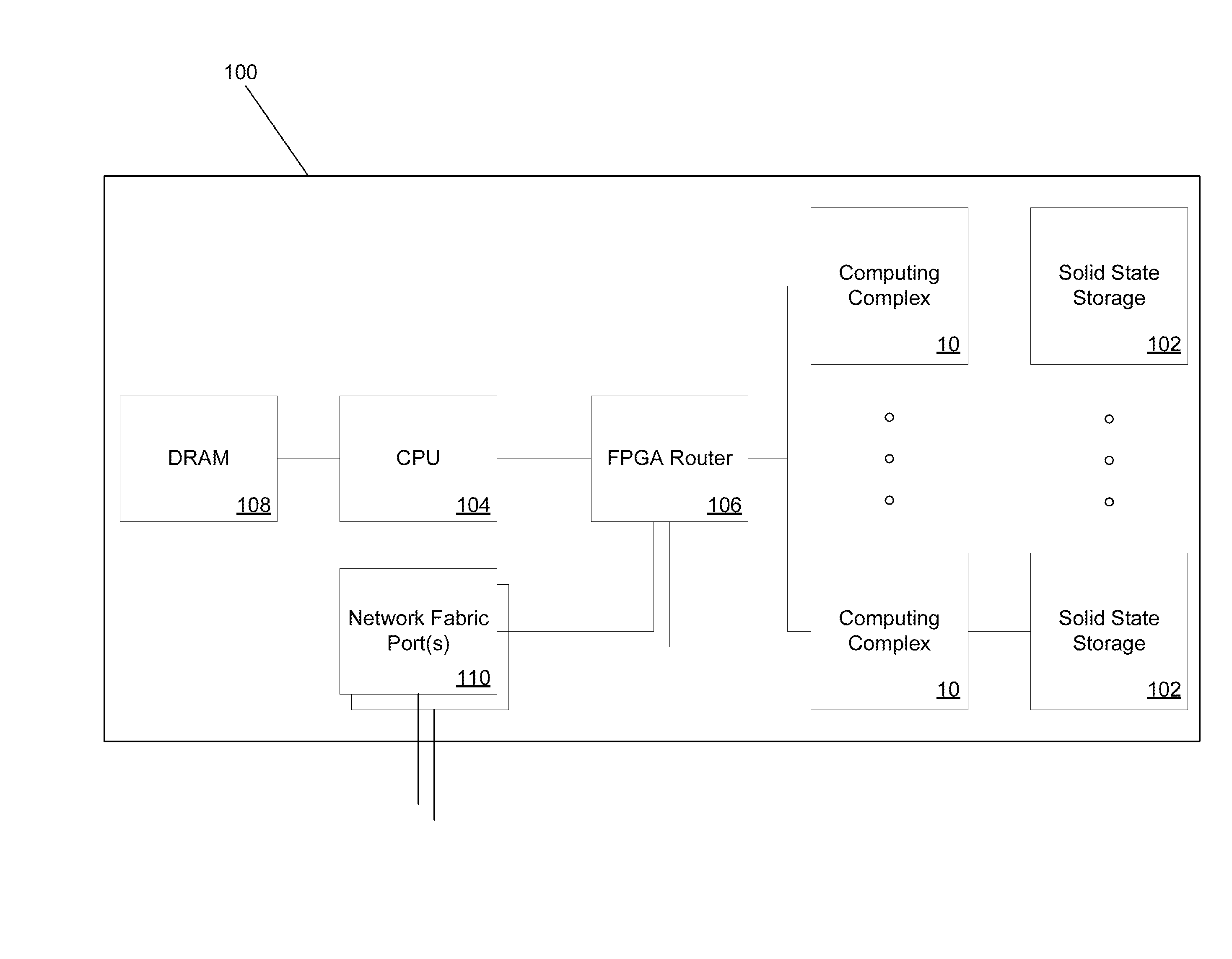
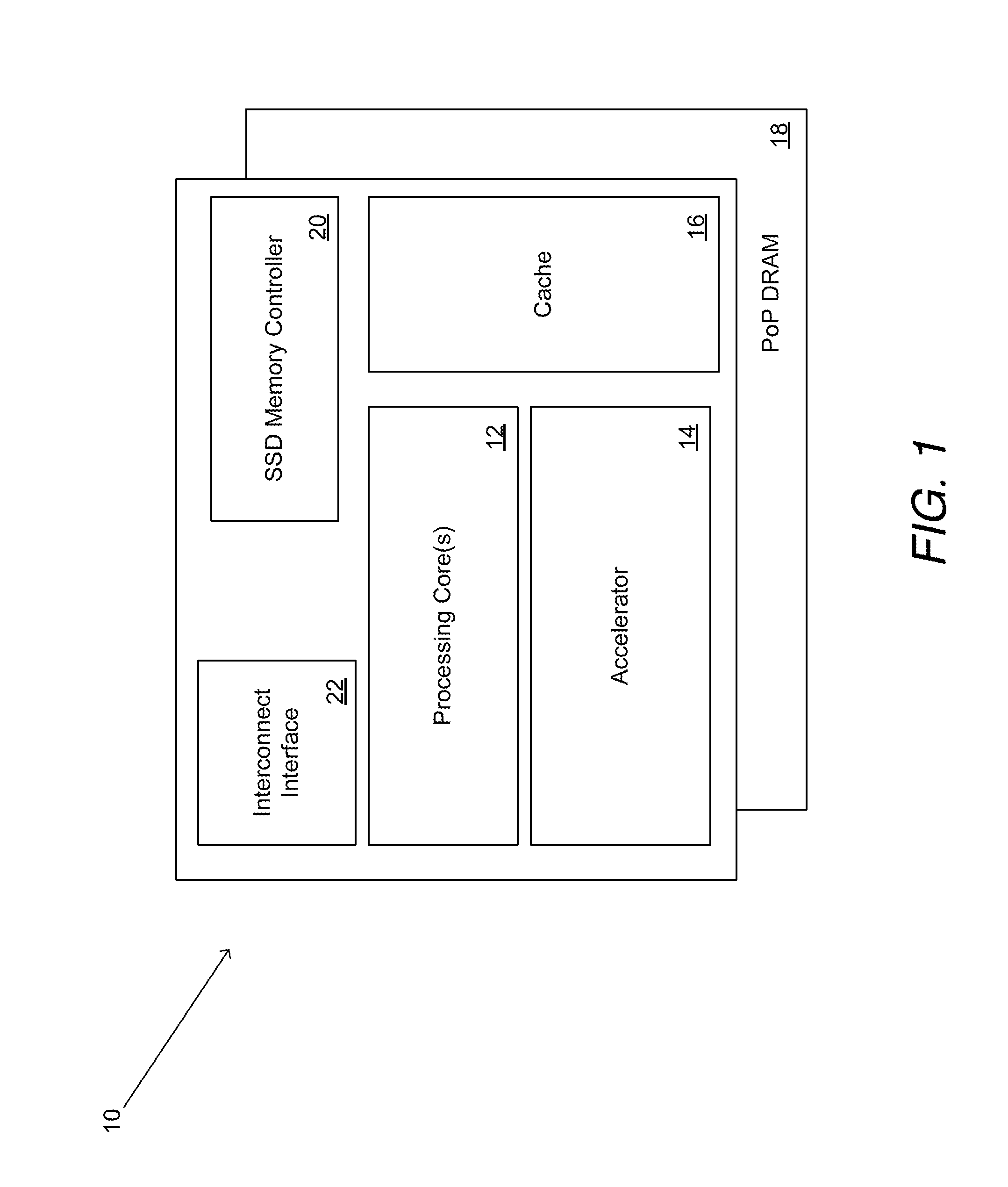
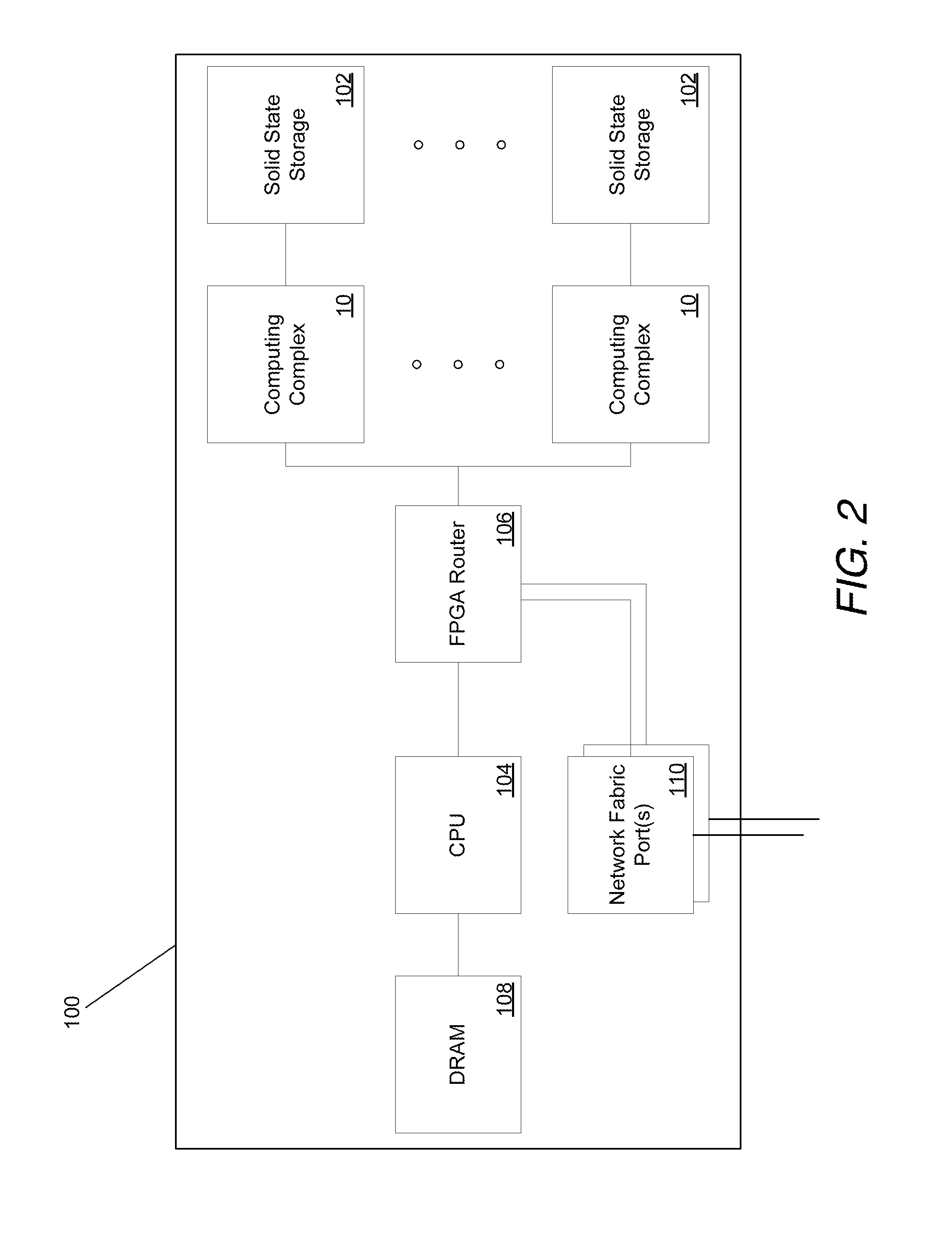
Systems and methods for rapid processing and storage of data
ActiveUS9552299B2Faster bandwidthImprove latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMassively parallelProcessing core
Systems and methods of building massively parallel computing systems using low power computing complexes in accordance with embodiments of the invention are disclosed. A massively parallel computing system in accordance with one embodiment of the invention includes at least one Solid State Blade configured to communicate via a high performance network fabric. In addition, each Solid State Blade includes a processor configured to communicate with a plurality of low power computing complexes interconnected by a router, and each low power computing complex includes at least one general processing core, an accelerator, an I / O interface, and cache memory and is configured to communicate with non-volatile solid state memory.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
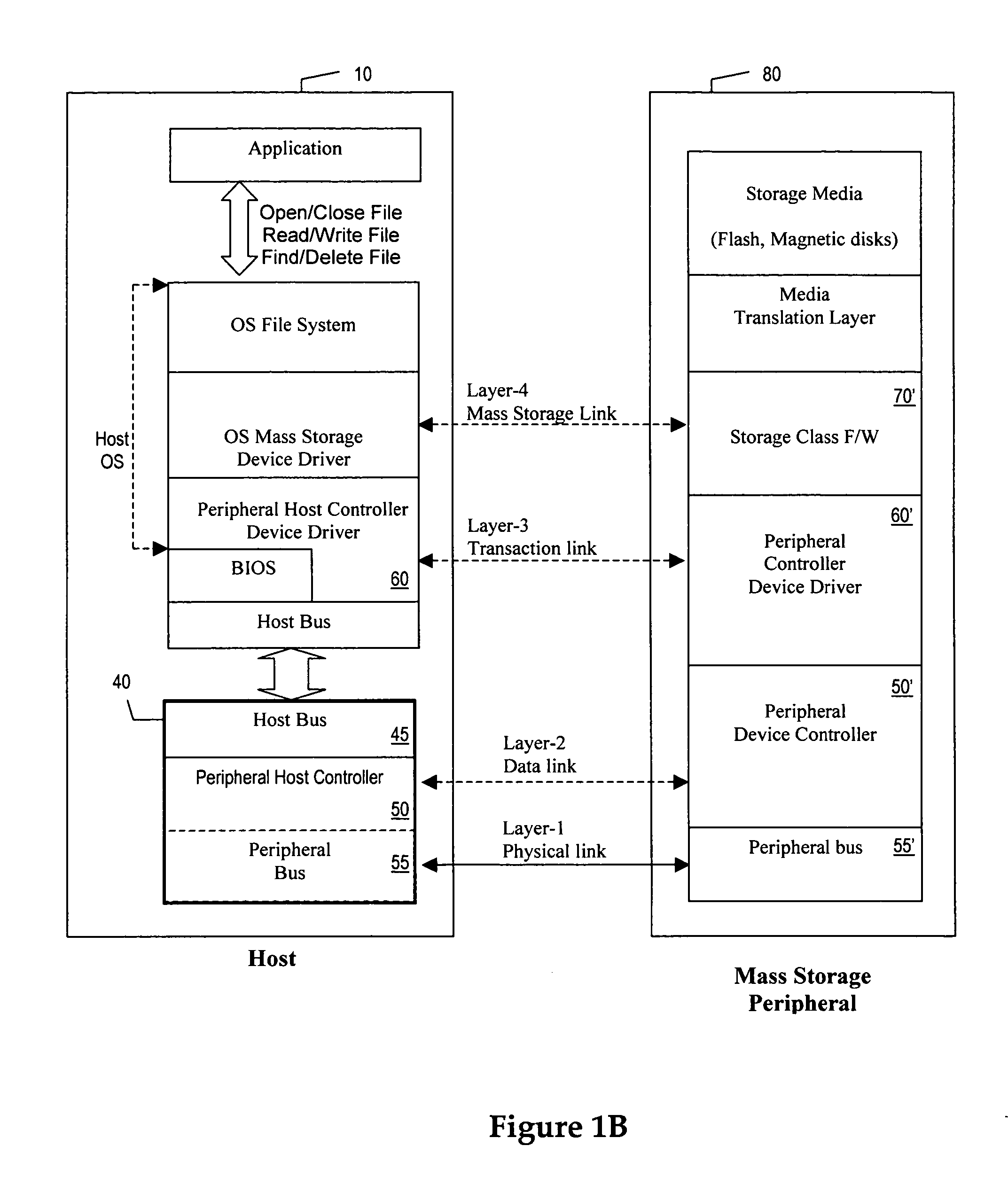
Mass storage system and method using hard disk and solid-state media
ActiveUS20110320690A1Minimal degradationReduce access latencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionPrinted circuit boardSolid state memory
Methods and systems for mass storage of data over two or more tiers of mass storage media that include nonvolatile solid-state memory devices, hard disk devices, and optionally volatile memory devices or nonvolatile MRAM in an SDRAM configuration. The mass storage media interface with a host through one or more PCIe lanes on a single printed circuit board.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Flash memory device with ATA/ATAPI/SCSI or proprietary programming interface on PCI express
InactiveUS20050240713A1Easy to useOvercome difficultiesInput/output to record carriersSCSIComputer compatibility
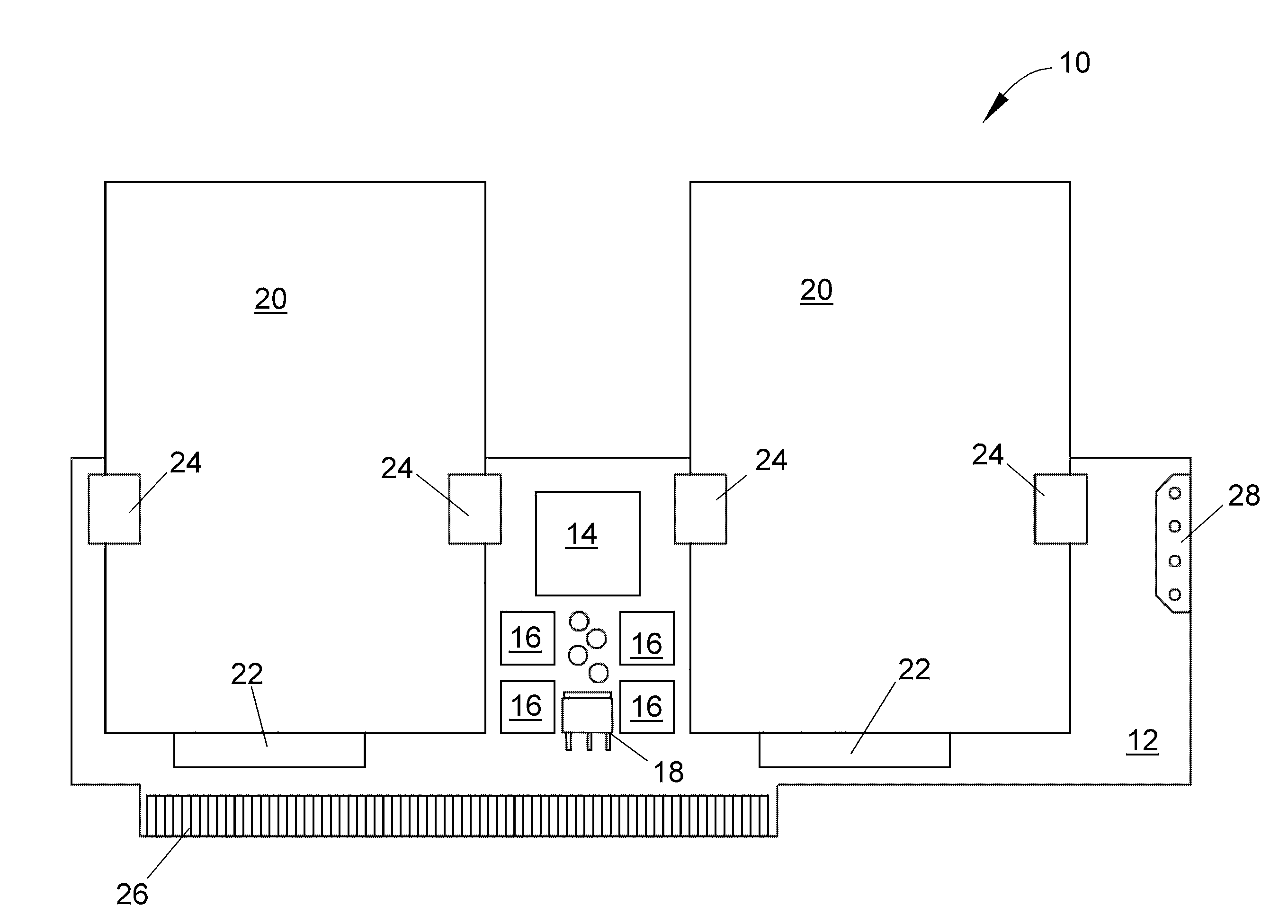
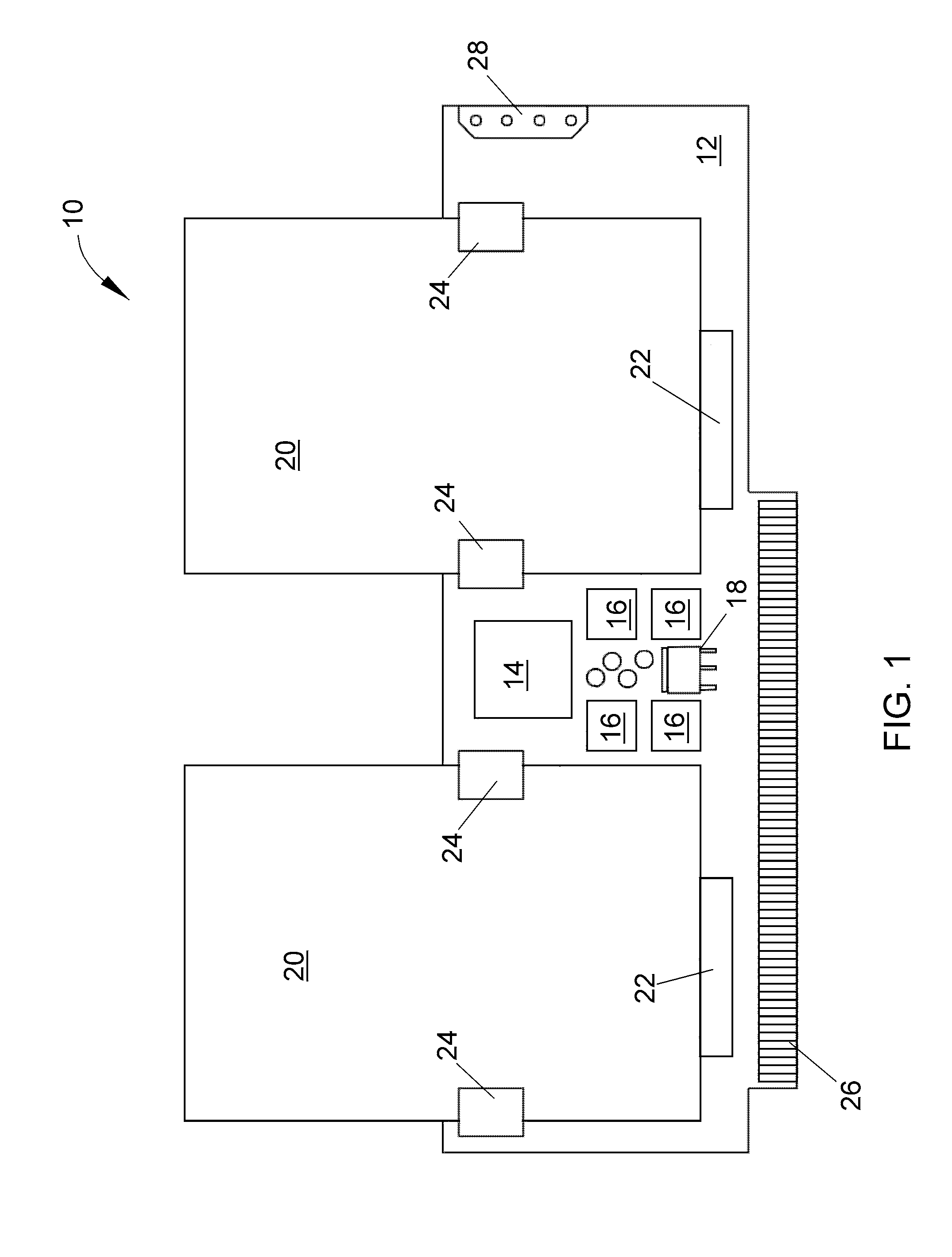
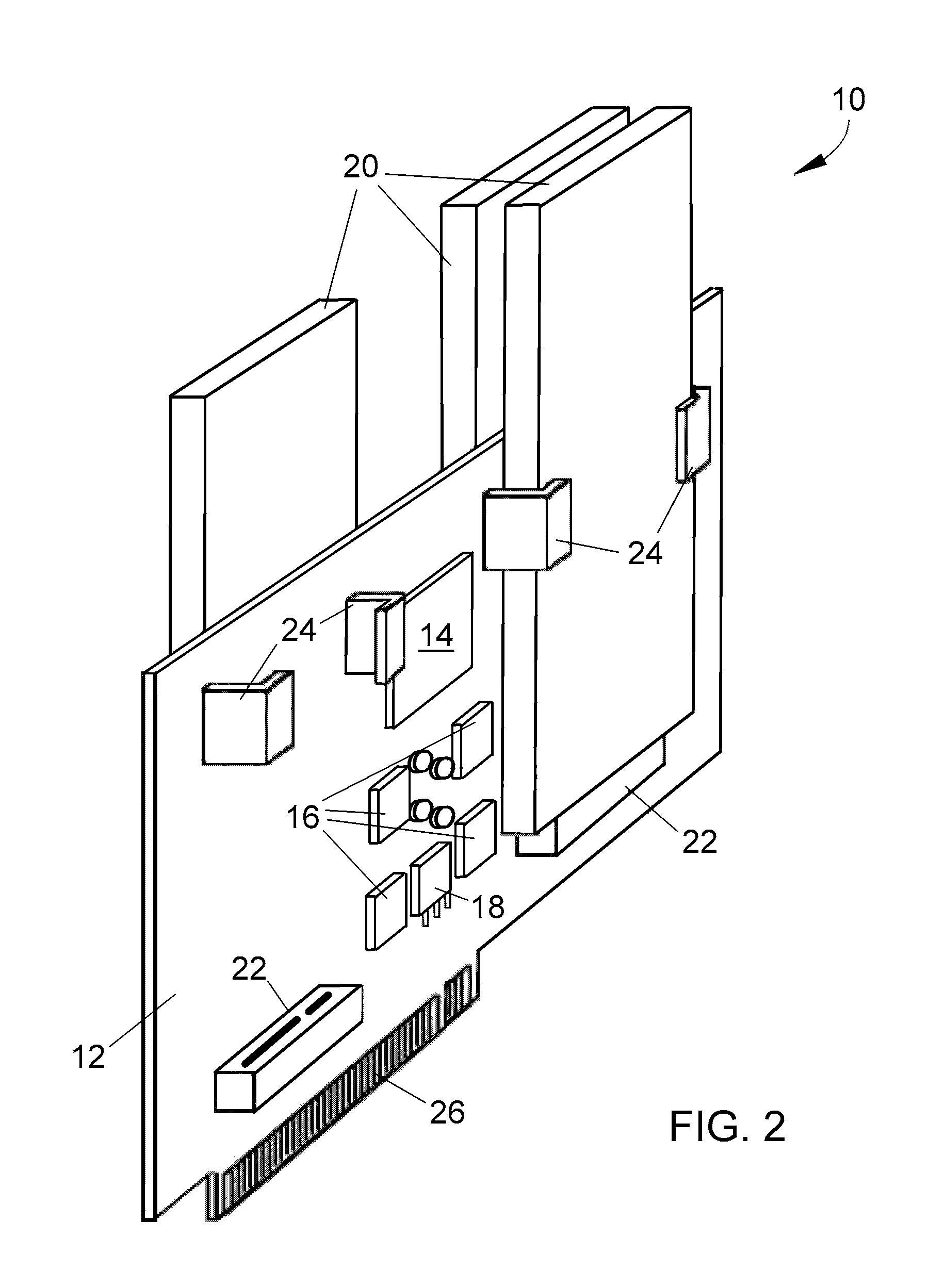
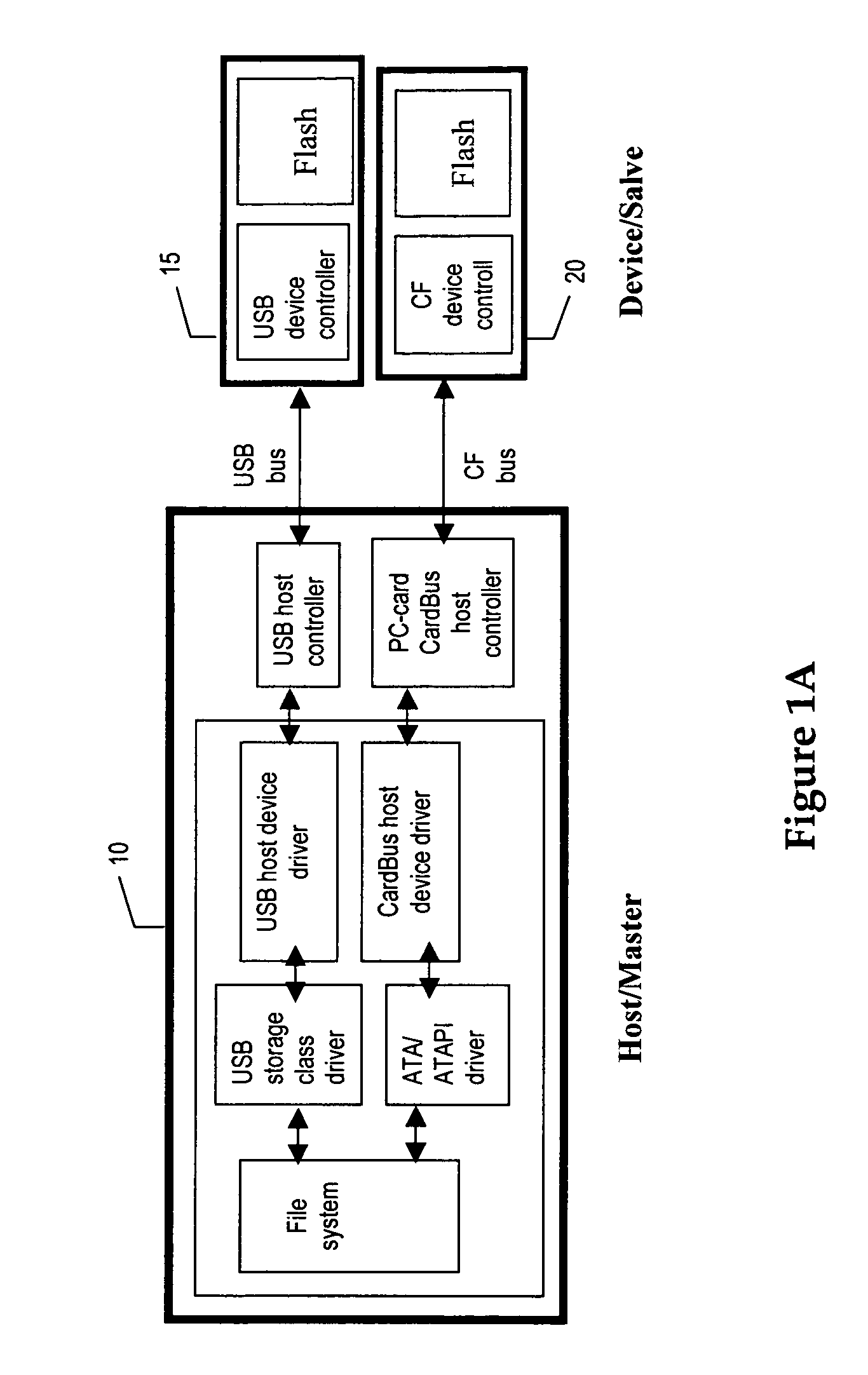
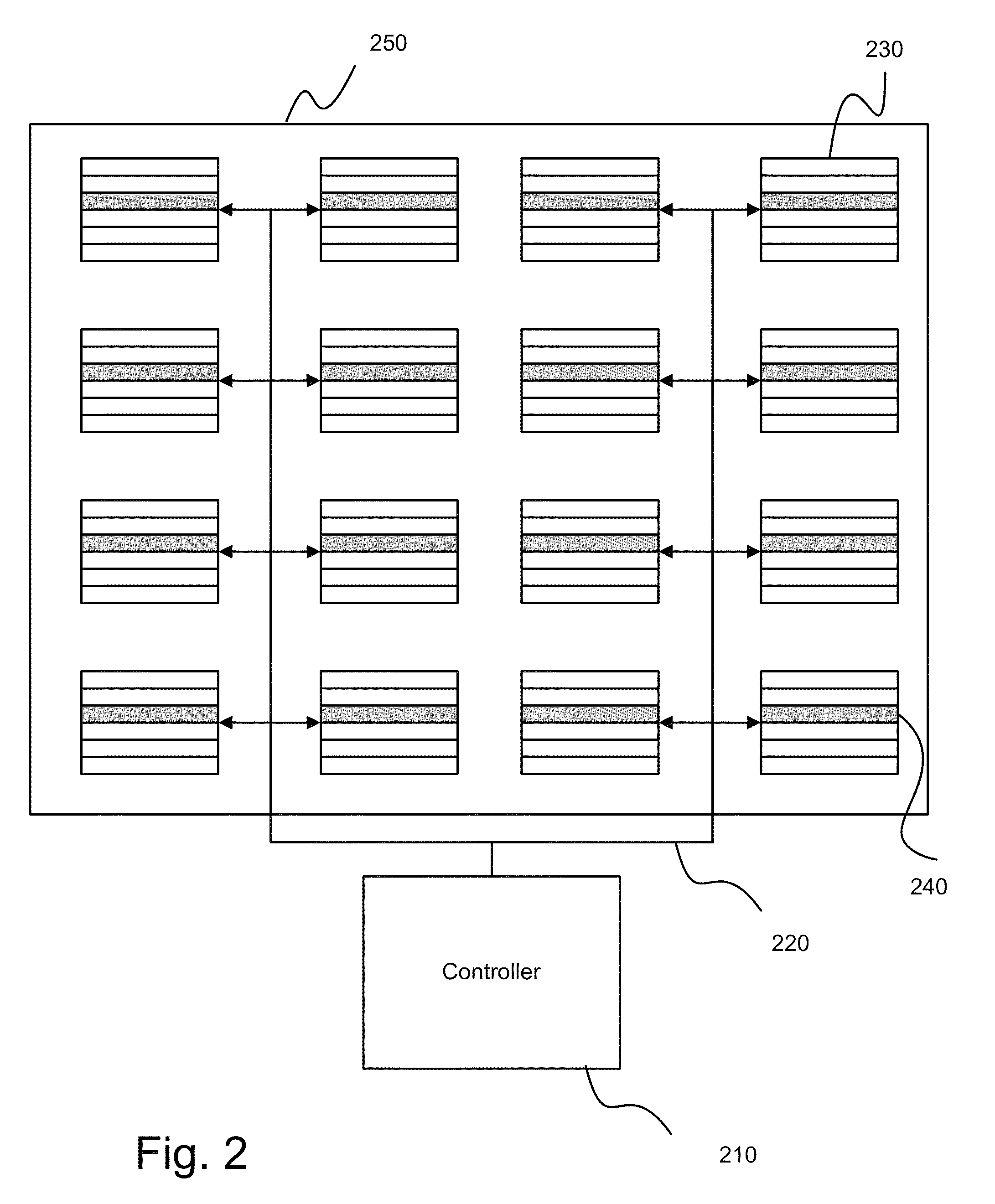
A storage device made of flash memory module(s) and a storage device controller and a PCI Express interface unit, is implemented to be compatible with (1) either ATA, ATAPI, SCSI or proprietary specification, and (2) PCI Express platform such as, with then, ExpressCard Standard or PCI Express Card Specification or PCI Express Mini Card Specification. The device includes memory module(s), which can accept data transfer and configuration and status report to / from non-volatile solid-state memory herein referred to as flash memory module(s). The storage device controller and the PCI Express interface unit work together to provide (A) PCI Express interface functionality and compatibility, and (B) ATA, ATAPI or SCSI or proprietary programming interface functionality and compatibility, alone with common flash memory operations such as programming reading, writing, erasing, and data transferring from / to PCI Express host platform.
Owner:V TECH CO LTD
System and method for reducing contentions in solid-state memory access
ActiveUS8769190B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsInternal memorySolid-state storage
Embodiments of the invention are directed to enabling concurrent commands from command requesters in a non-volatile solid-state storage subsystem in a manner that reduces contentions among the commands. Embodiments group blocks of memory into multiple sets of superblocks and associate a command requester to each superblock set. In one embodiment, the superblock sets are dynamically associated with a requester. In one embodiment, the superblock sets are dynamically associated with requesters based in part on at least one of internal memory management needs and host command throughput. In one embodiment, an erase command is executed on a superblock within a set and a simultaneous write command is executed on a superblock within another set.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Solid state memory device with PCI controller
ActiveUS8086791B2Memory systemsInput/output processes for data processingSolid-state storageProcessor register
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Efficient retry mechanism for solid-state memory failures
ActiveUS8788880B1Improve performanceReduce allocationError detection/correctionRead-only memoriesSolid-state storageTheoretical computer science
A data storage subsystem is disclosed that implements a solid-state data buffering scheme. Prior to completion of programming in solid-state storage media, data that is formatted for storage in solid-state media is maintained in one or more buffers. The system is able to retry failed programming operations directly from the buffers, rather than reprocessing the data. The relevant programming pipeline may therefore be preserved by skipping over a failed write operation and reprocessing the data at the end of the current pipeline processing cycle.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Solid-state memory device with protection against power failure
A data preservation system for flash memory systems with a host system, the flash memory system receiving a host system power supply and energizing an auxiliary energy store therewith and communicating with the host system via an interface bus, wherein, upon loss of the host system power supply, the flash memory system actively isolates the connection to the host system power supply and isolates the interface bus and employs the supplemental energy store to continue write operations to flash memory.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEMORY SYST INC
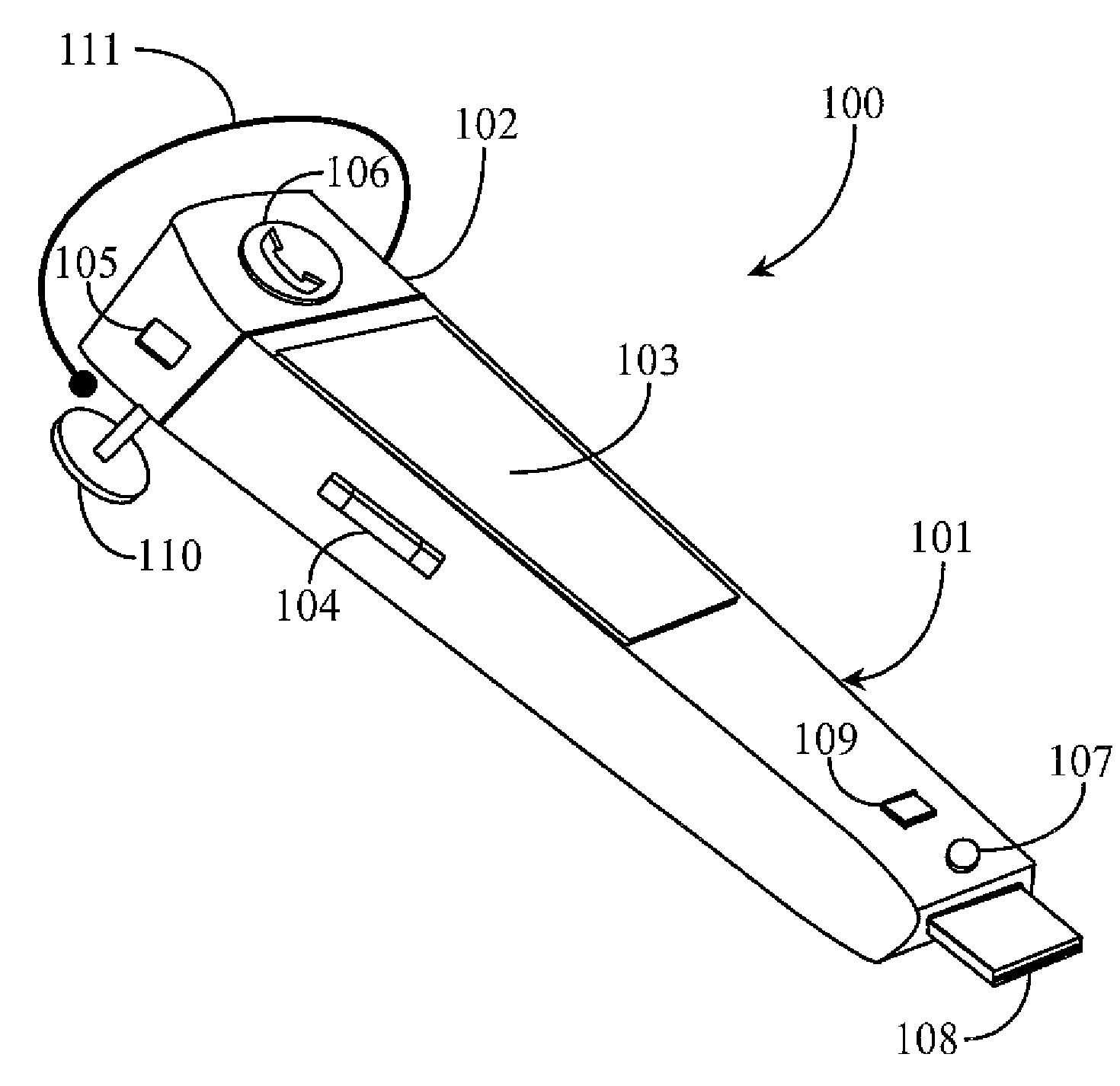
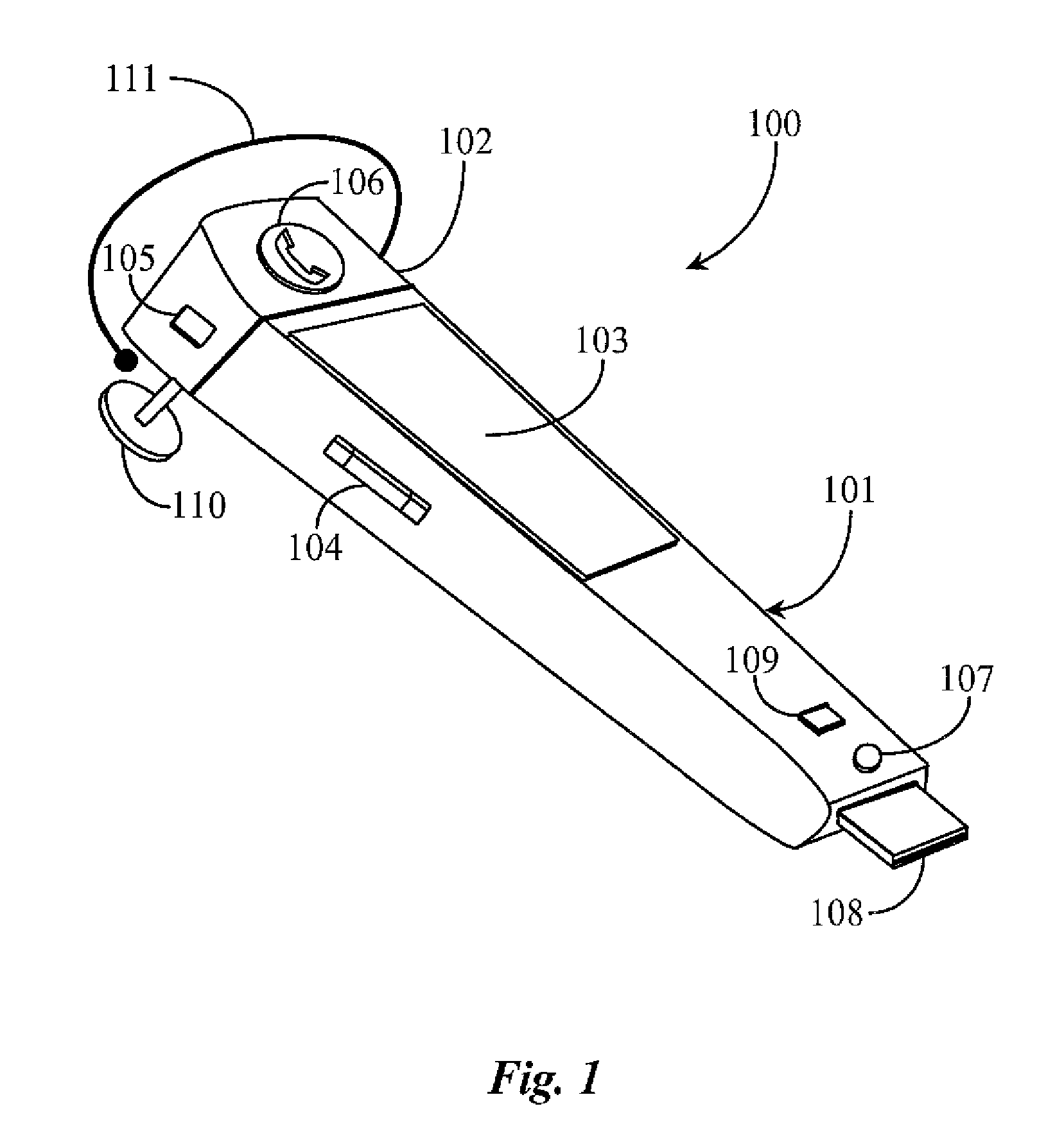
Multi-Function Electronic Ear Piece
InactiveUS20090191920A1Increase resourcesImprove task performanceTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsTransceiverMusic player
An electronic device includes a transceiver, a solid state memory, a charge port, at least one speaker, and a software music player. The device is adapted by toggle interface to function as a telephone hands free earpiece, a wireless flash drive, or a wireless music player.
Owner:OI HLDG 1 LLC
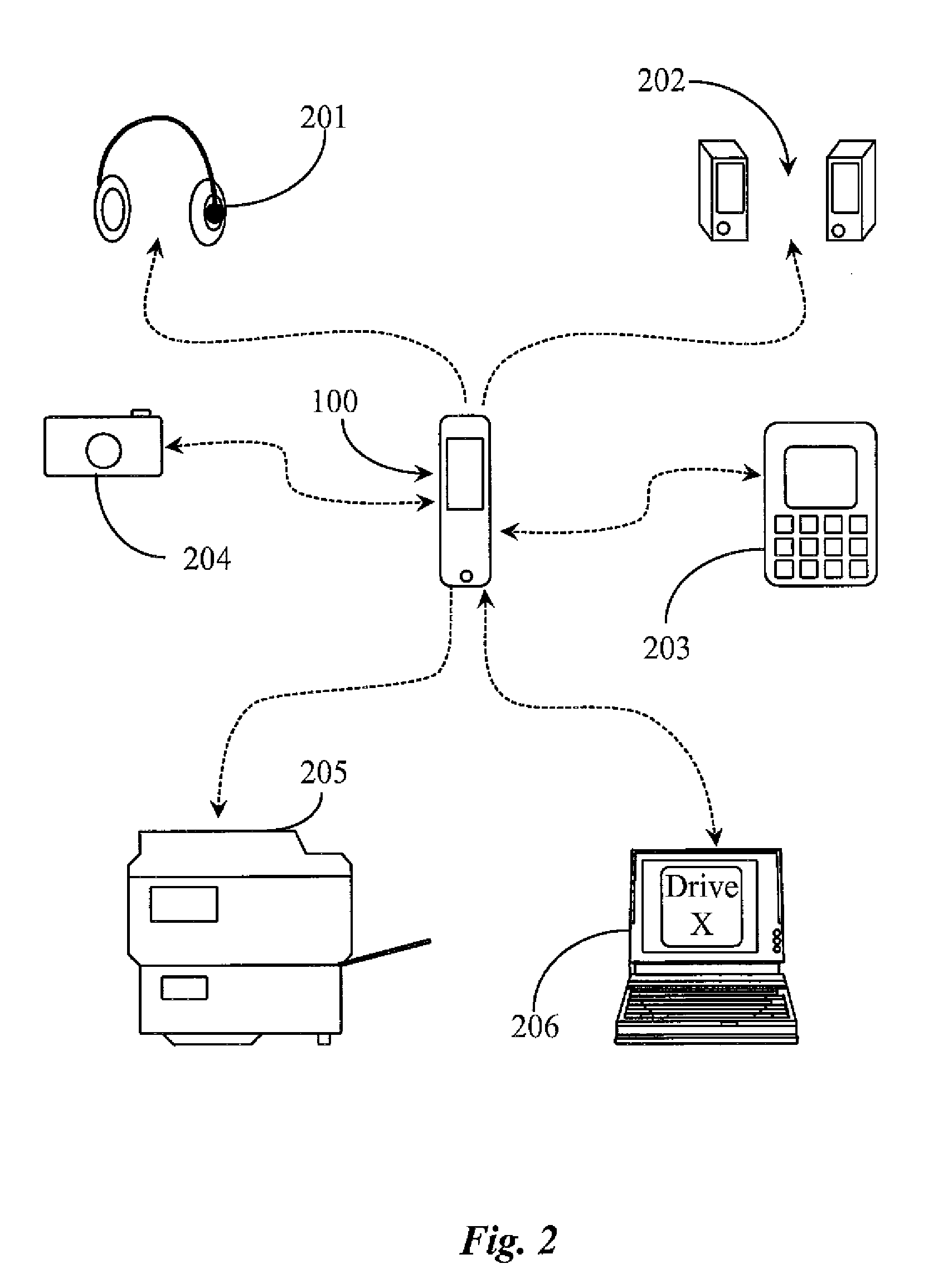
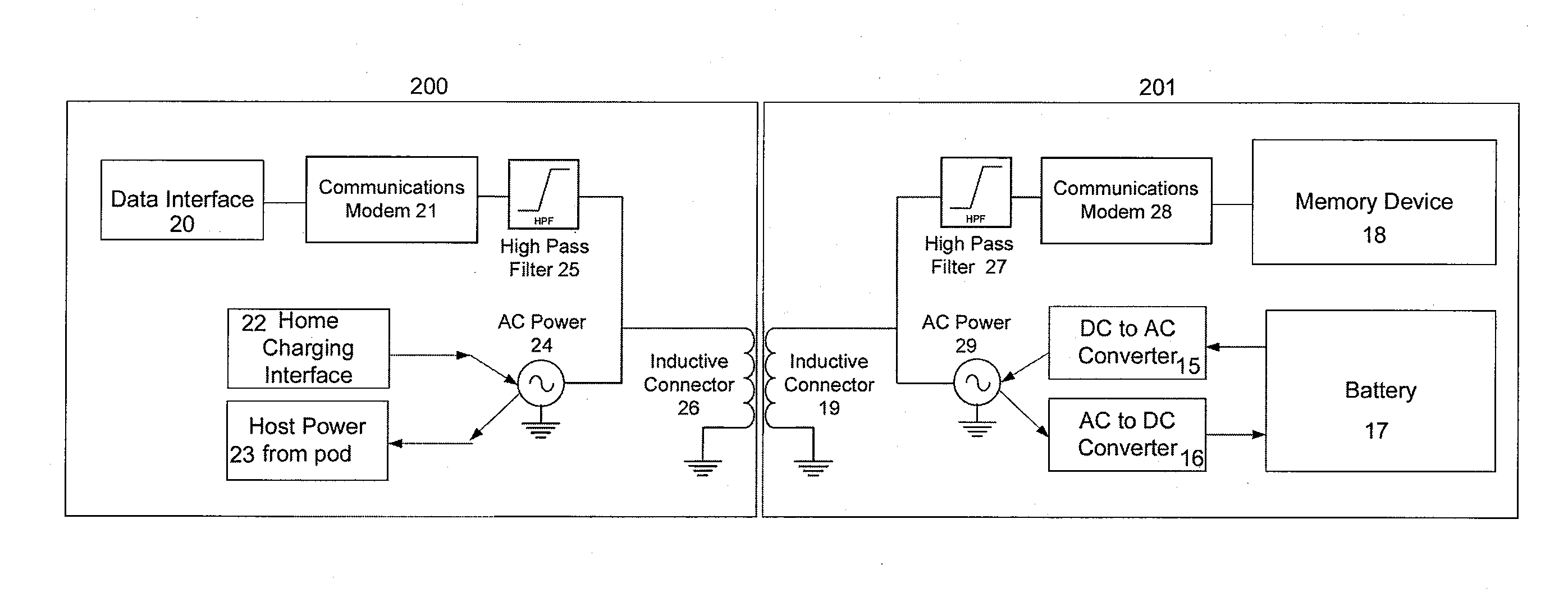
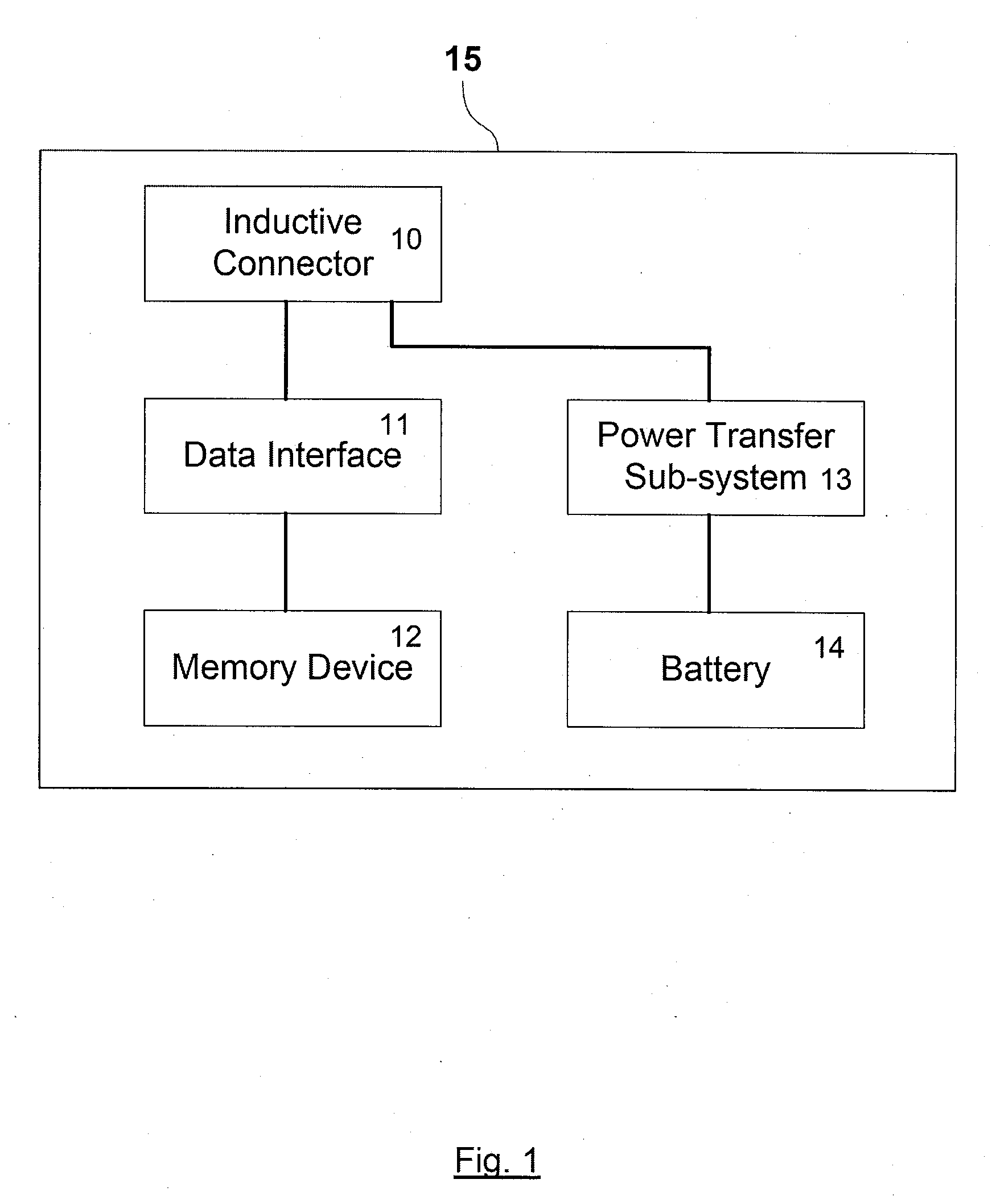
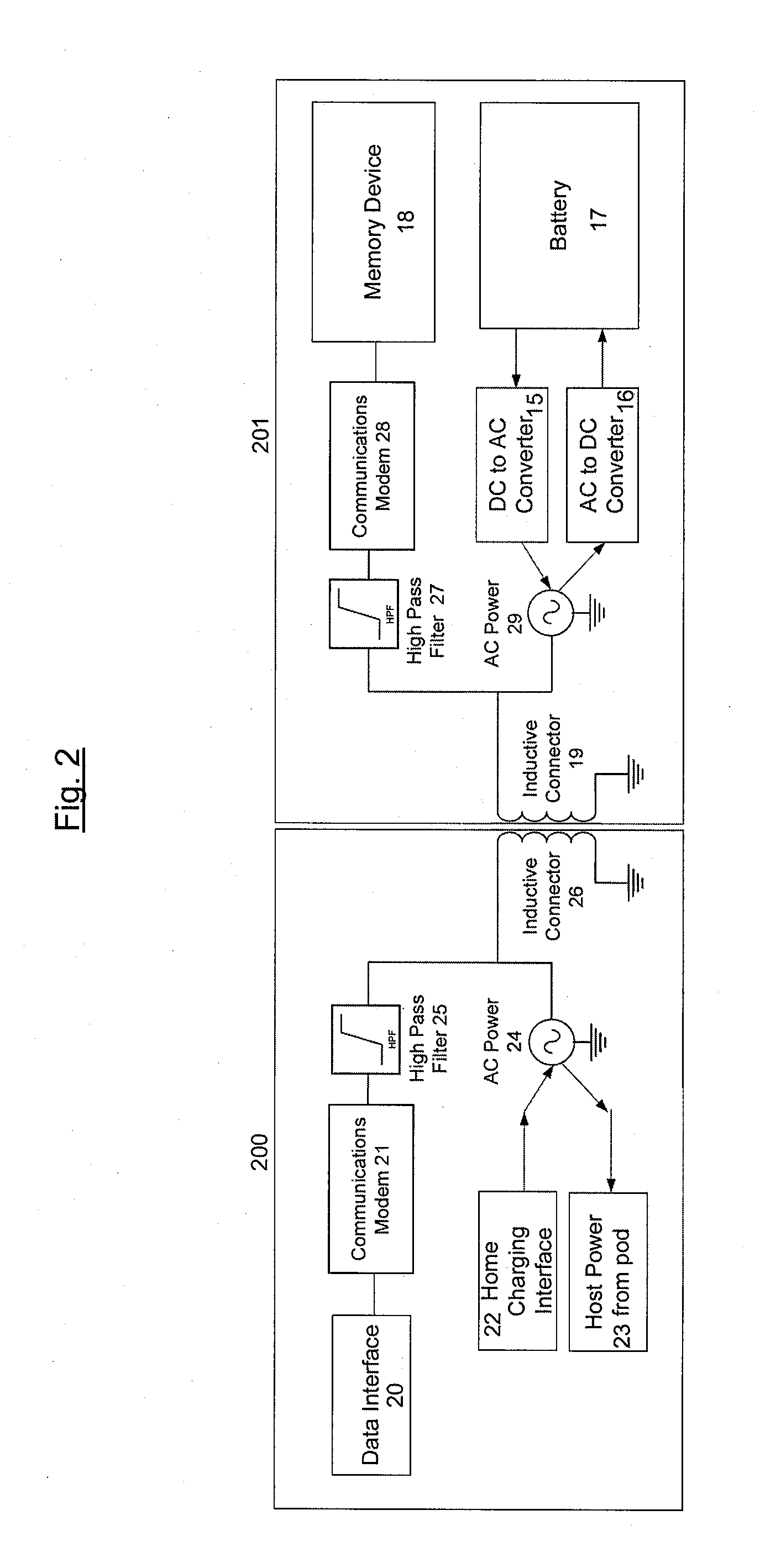
Inductively coupled data and power transfer system and apparatus
The present invention provides a system and apparatus for transferring electronic data and / or power from one station to another by means of a transportable pod comprising a solid state memory device and further provided with an inductively linked, electrically insulated connector. The transportable pod comprises a battery which is used to power a remote host docking station, which may be used in an underwater environment for the collection of subsea data. The transportable pod can be transferred alternately from a home docking station, where it is charged up, and where it's stored data is uploaded and to a remote host docking station where is provides power, and where it collects and stores data collected by the remote host docking station.
Owner:WFS TECH
Horizontal chalcogenide element defined by a pad for use in solid-state memories
ActiveUS7038230B2Decreased current/power requirementRemove restrictionsSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPhase-change memorySemiconductor
A process for fabricating phase-change elements having ultra small cross-sectional areas for use in phase change memory cells specifically and in semiconductor devices generally in which pads are implemented to create horizontally aligned phase change elements is disclosed. The elements thus defined may be used within chalcogenide memory cells or other semiconductor devices.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Horizontal chalcogenide element defined by a pad for use in solid-state memories
ActiveUS20050145984A1Decreased current/power requirementRemove restrictionsSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPhase-change memoryDevice material
A process for fabricating phase-change elements having ultra small cross-sectional areas for use in phase change memory cells specifically and in semiconductor devices generally in which pads are implemented to create horizontally aligned phase change elements is disclosed. The elements thus defined may be used within chalcogenide memory cells or other semiconductor devices.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
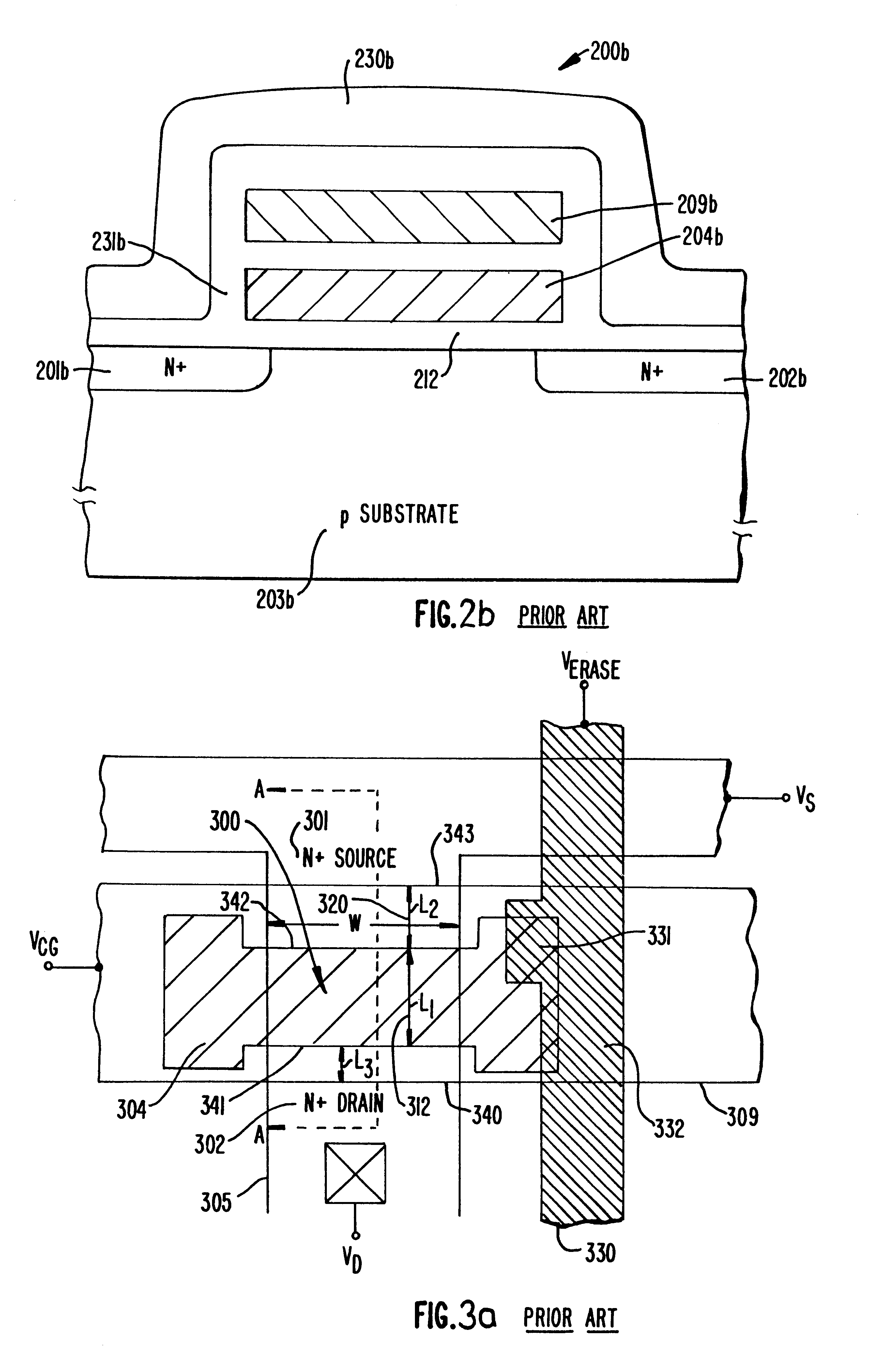
Highly compact EPROM and flash EEPROM devices
Structures, methods of manufacturing and methods of use of electrically programmable read only memories (EPROM) and flash electrically erasable and programmable read only memories (EEPROM) include split channel and other cell configurations. An arrangement of elements and cooperative processes of manufacture provide self-alignment of the elements. An intelligent programming technique allows each memory cell to store more than the usual one bit of information. An intelligent erase algorithm prolongs the useful life of the memory cells. Use of these various features provides a memory having a very high storage density and a long life, making it particularly useful as a solid state memory in place of magnetic disk storage devices in computer systems.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Improved Hybrid Drive
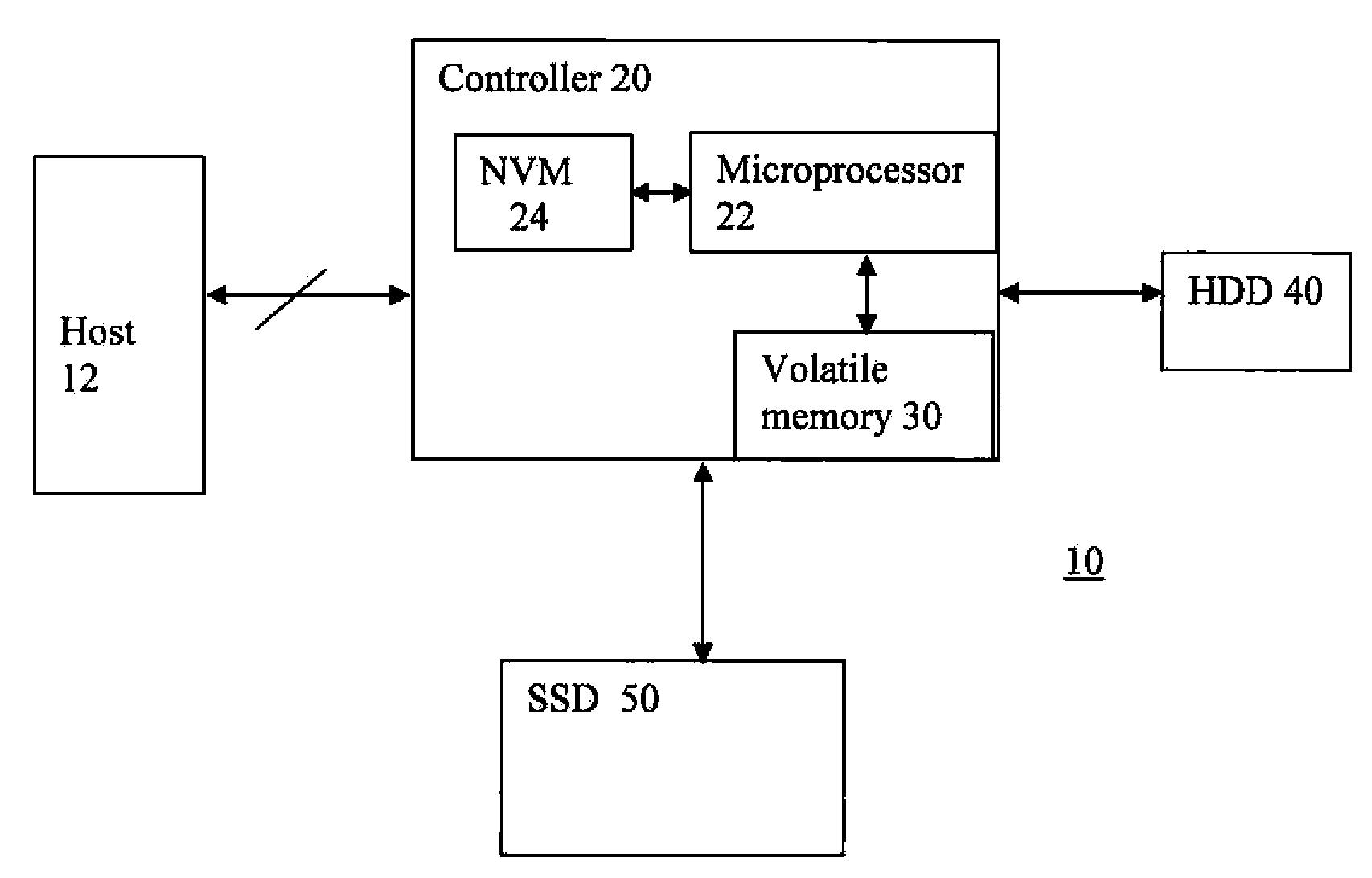
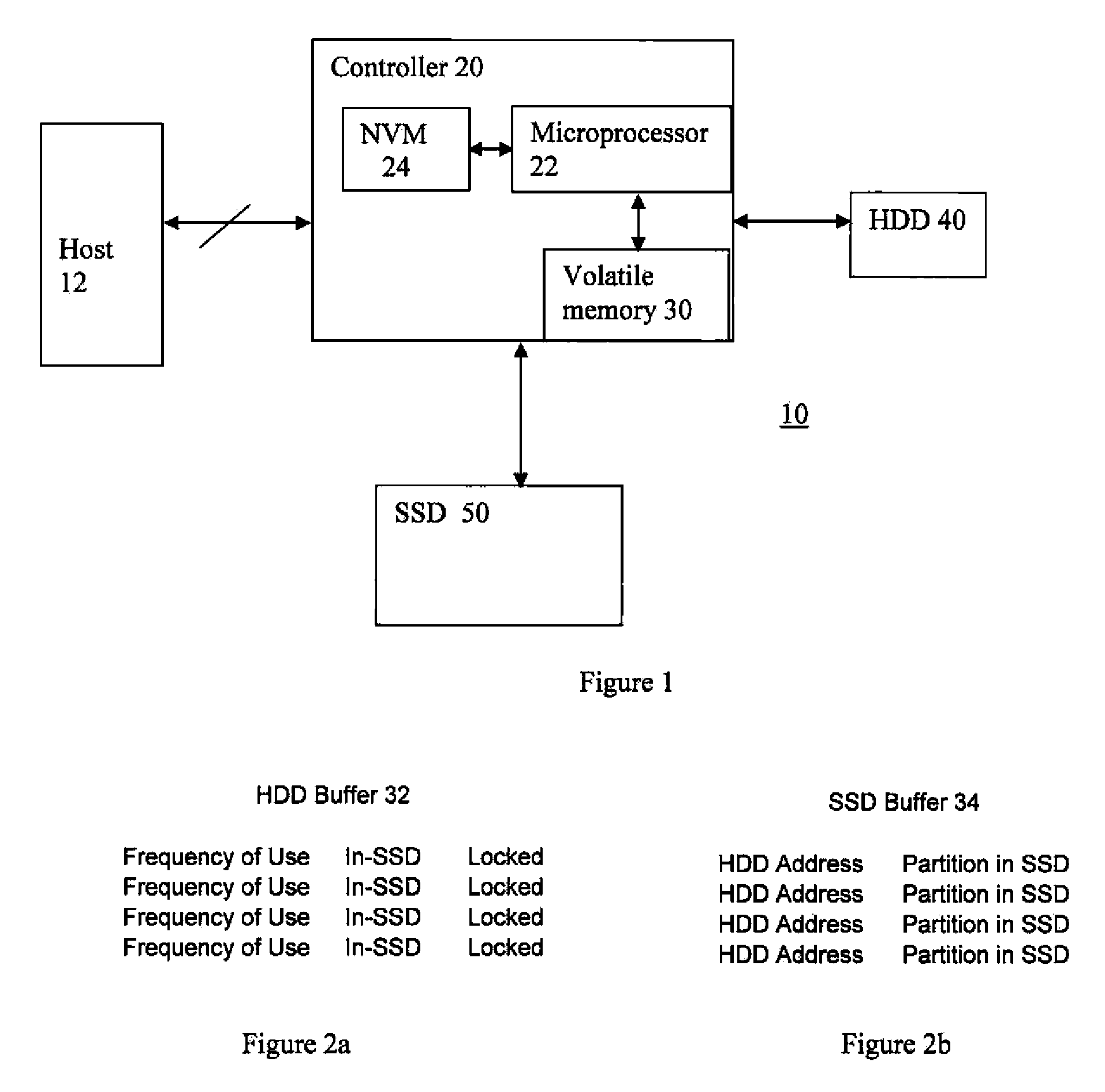
InactiveUS20100088459A1Efficient readingMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTHard disc driveSolid state memory
A non-volatile storage system comprises a hard disk drive (HDD) having a first capacity for storing information therein in a plurality of blocks. The storage system also comprises a non-volatile solid state memory (SSD) having a second capacity, less than the first capacity, for storing information therein. Finally, the storage system comprises a controller having a volatile memory and for controlling the read operation of the HDD and the read / write operation of the SSD. The controller stores in the volatile memory the address of read blocks from the HDD in a first period of time and determines a plurality of the most frequently read blocks in the first period of time, The controller then causes the SSD to store information from the most frequently read blocks from the HDD, and thereafter causes information to be read from the SSD when the storage system is requested to access information from the most frequently read blocks. The controller resets the identity of the most frequently read blocks in the volatile memory after a second period of time, where the second period of time is longer than said first period of time.
Owner:GREENLIANT
Non-volatile memory-based mass storage devices and methods for writing data thereto
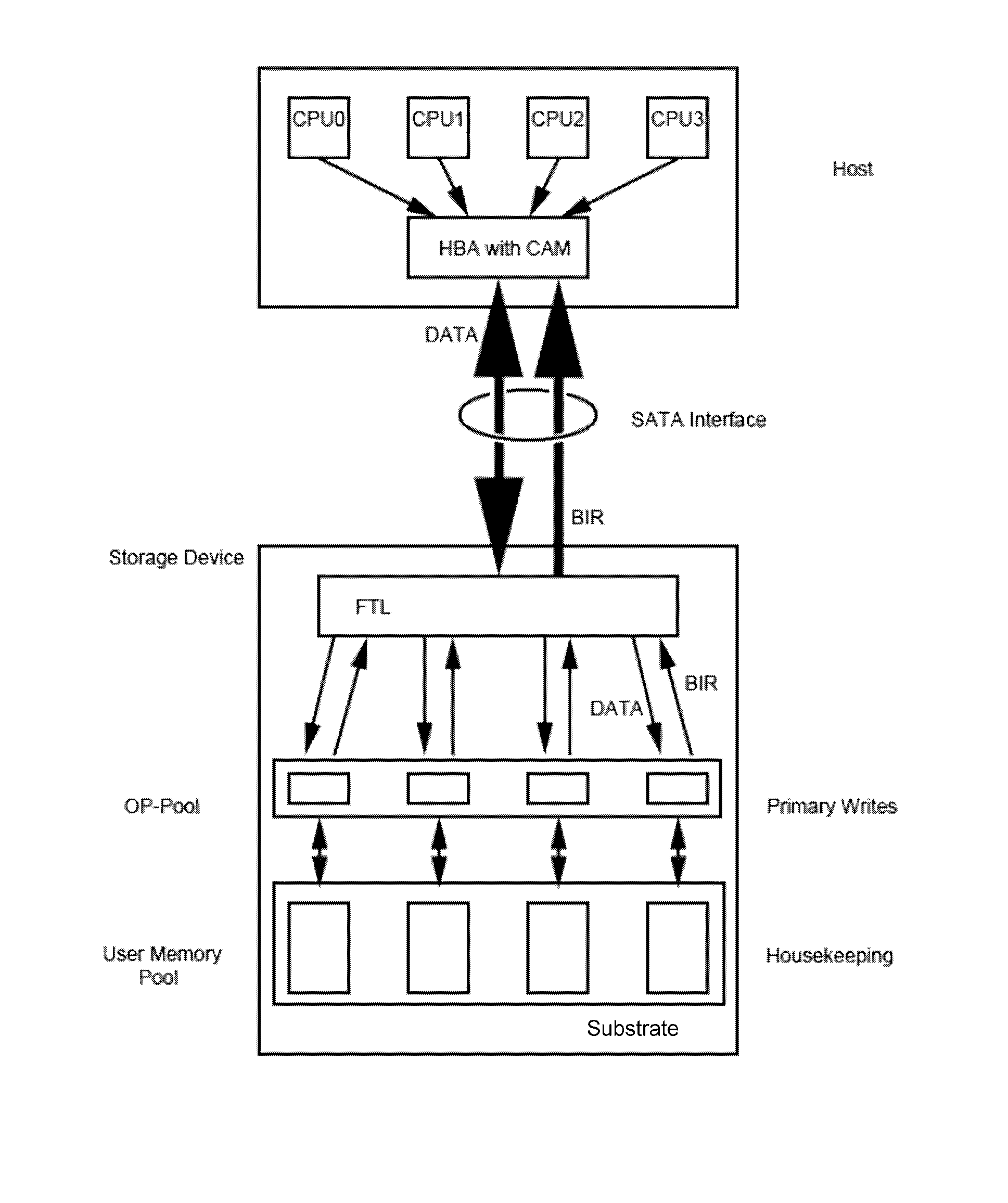
ActiveUS20130067138A1Need for goodMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesMass storageComputer science
A non-volatile solid state memory-based mass storage device having at least one non-volatile memory component and methods of operating the storage device. In one aspect of the invention, the one or more memory components define a memory space partitioned into user memory and over-provisioning pools based on a P / E cycle count stored in a block information record. The storage device transfers the P / E cycle count of erased blocks to a host and the host stores the P / E cycle count in a content addressable memory. During a host write to the storage device, the host issues a low P / E cycle count number as a primary address to the content addressable memory, which returns available block addresses of blocks within the over-provisioning pool as a first dimension in a multidimensional address space. Changed files are preferably updated in append mode and the previous version can be maintained for version control.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Data encoding in solid-state storage devices
ActiveUS8578246B2Improve efficiencyError detection/correctionCode conversionSolid-state storageTheoretical computer science
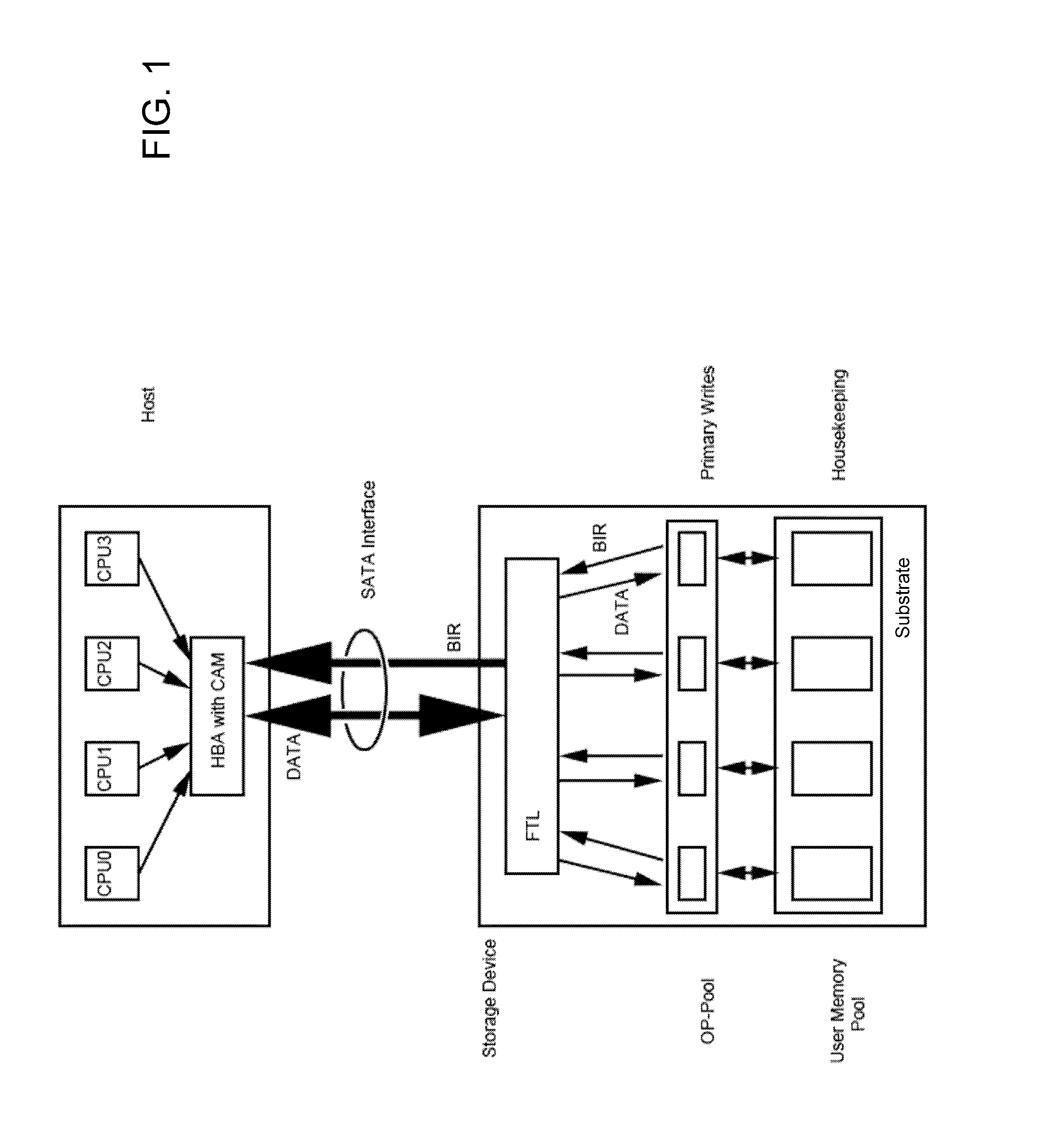
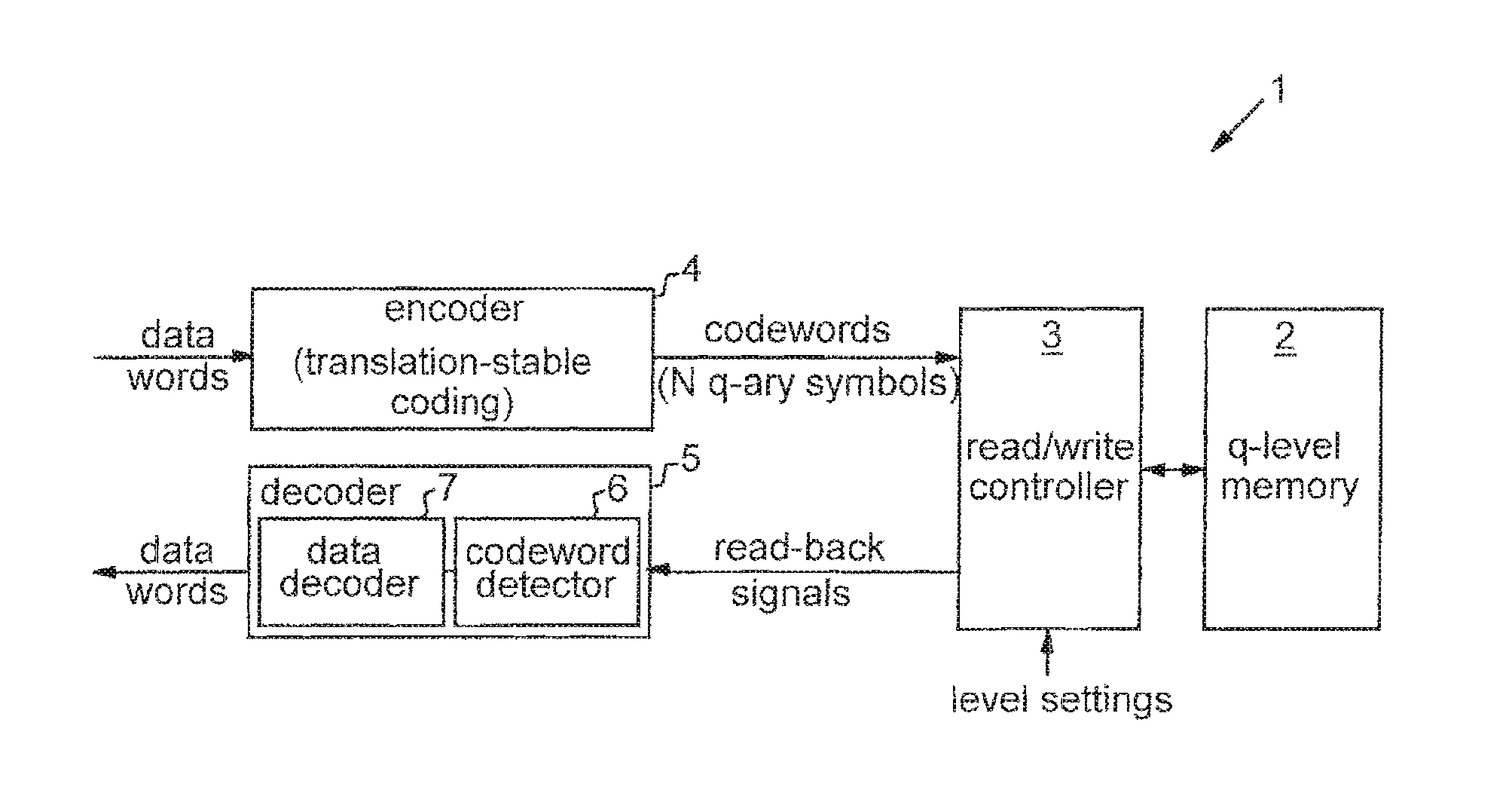
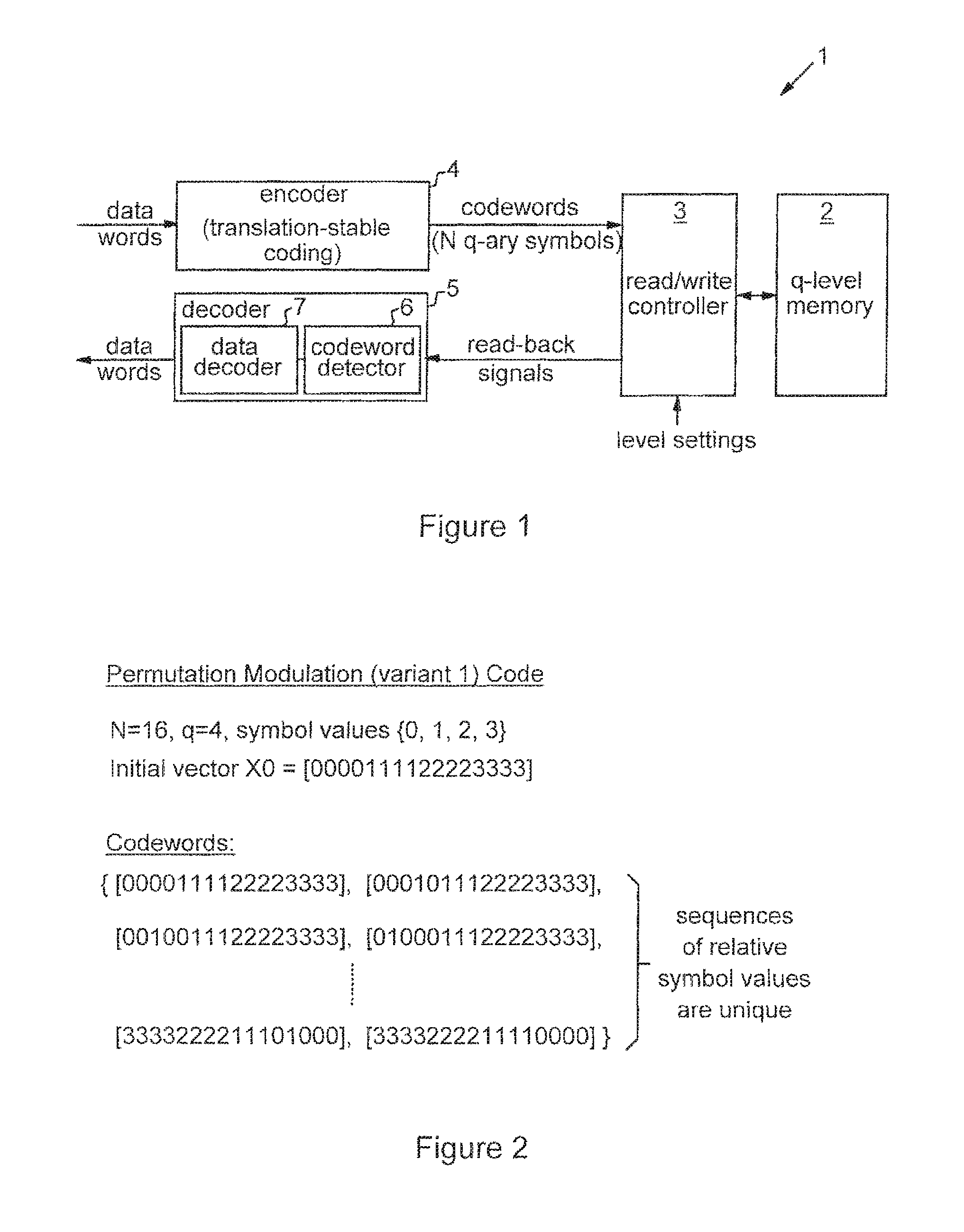
Methods and apparatus are provided for recording input data in q-level cells of solid-state memory (2), where q>2. Input data words are encoded as respective codewords, each having a plurality of symbols. The coding scheme is such that each symbol can take one of q values corresponding to respective predetermined levels of the q-level cells, and each of the possible input data words is encoded as a codeword with a unique sequence of relative symbol values. The symbols of each codeword are then recorded in respective cells of the solid-state memory by setting each cell to the level corresponding to the recorded symbol value. Input data is thus effectively encoded in the relative positions of cell levels, providing resistance to certain effects of drift noise.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
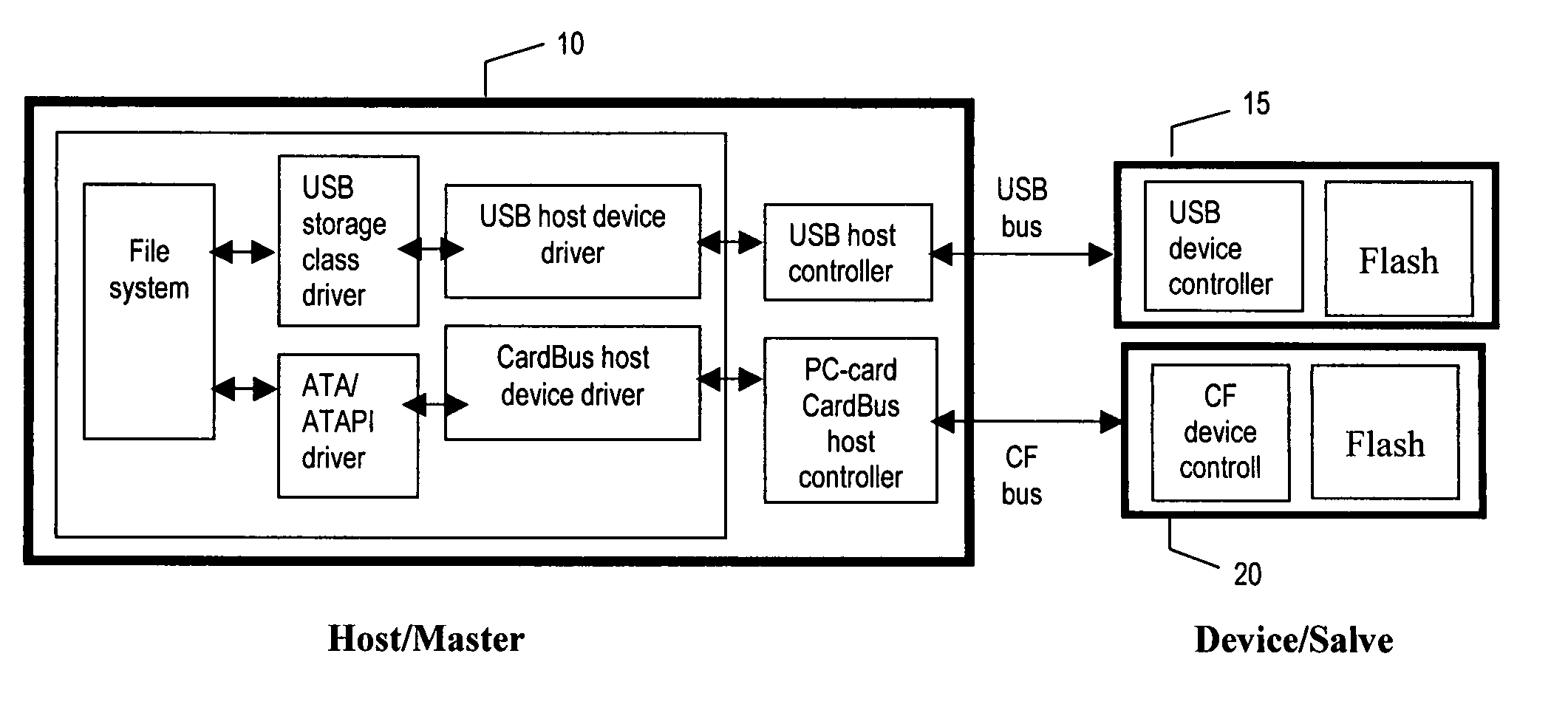
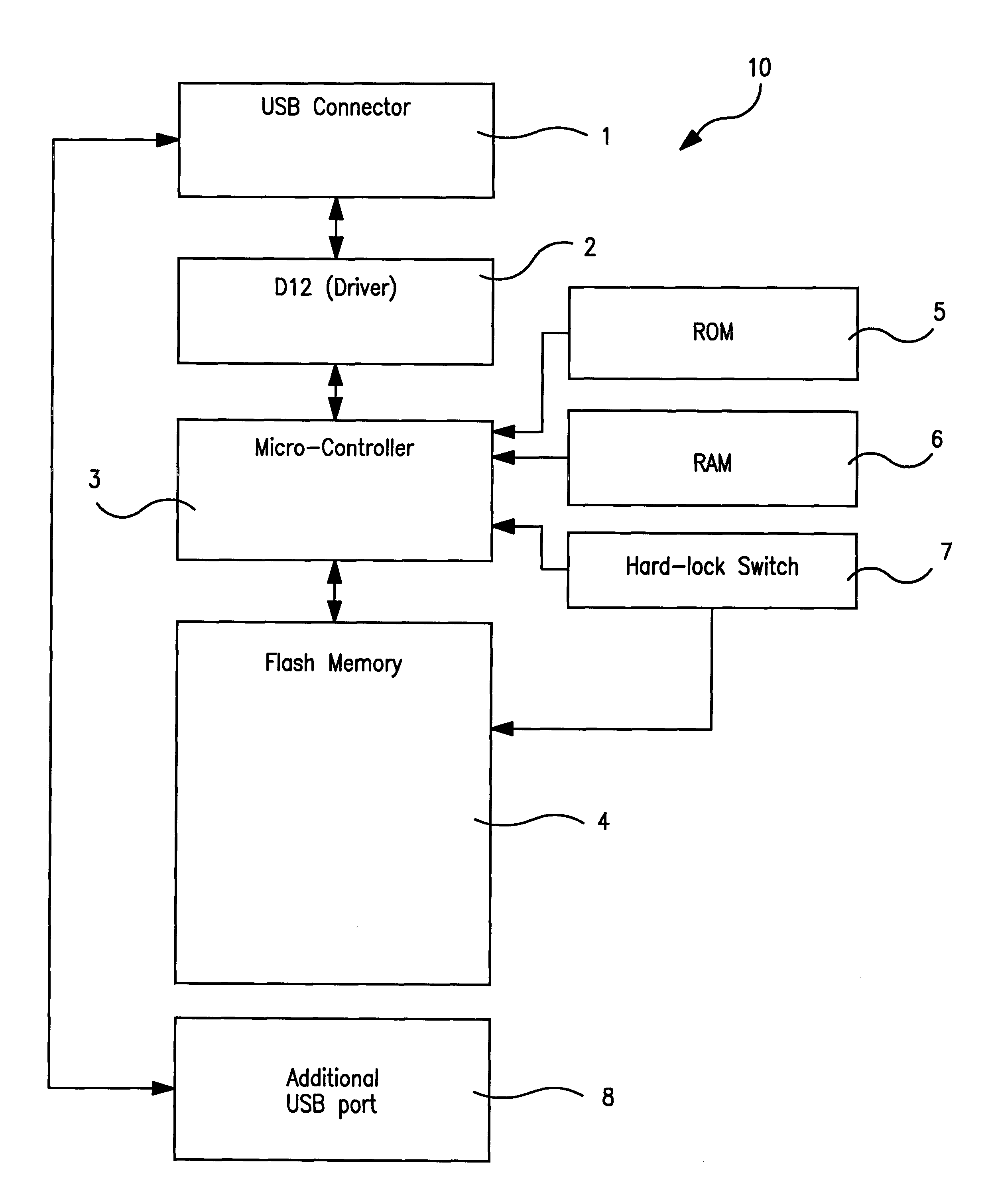
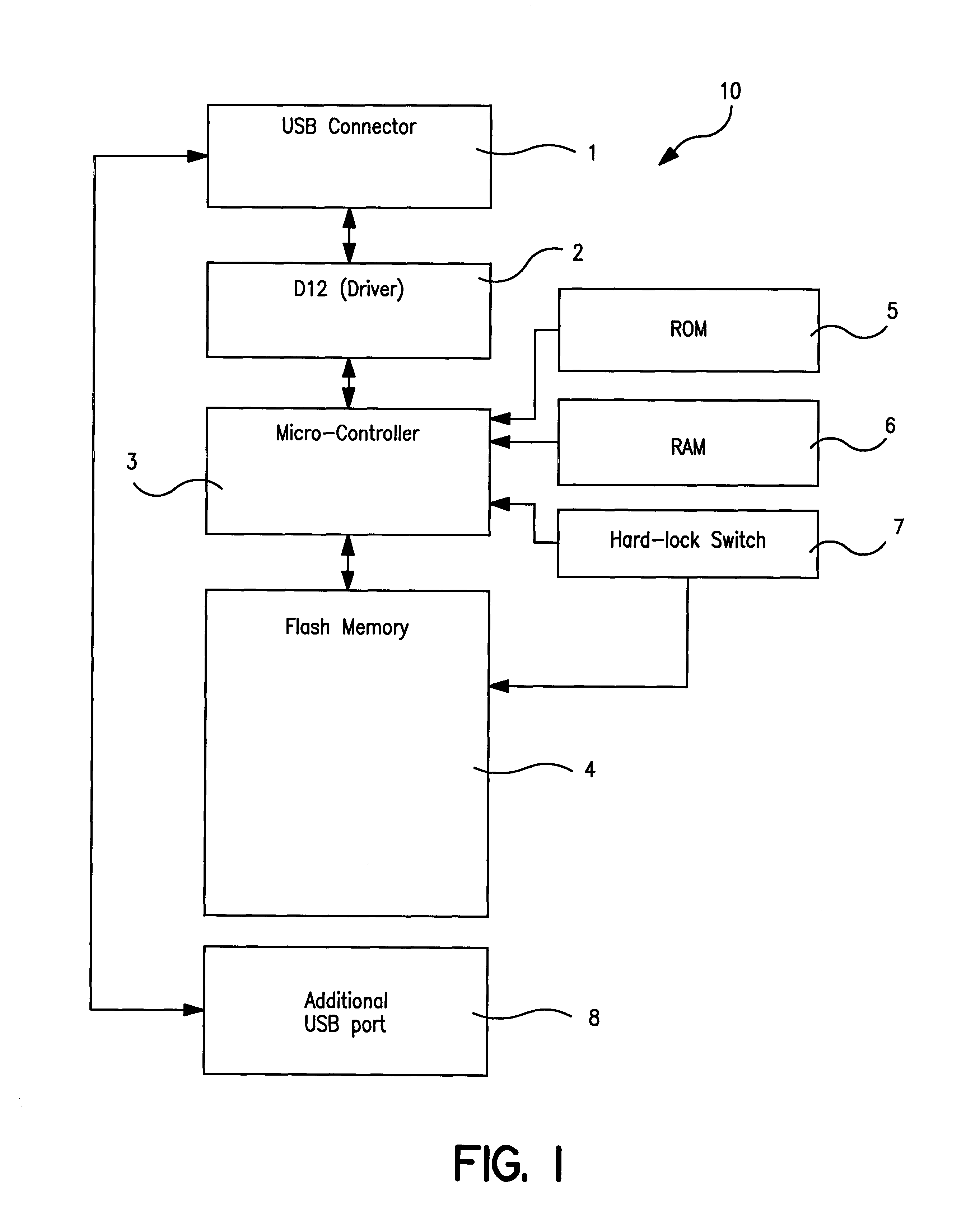
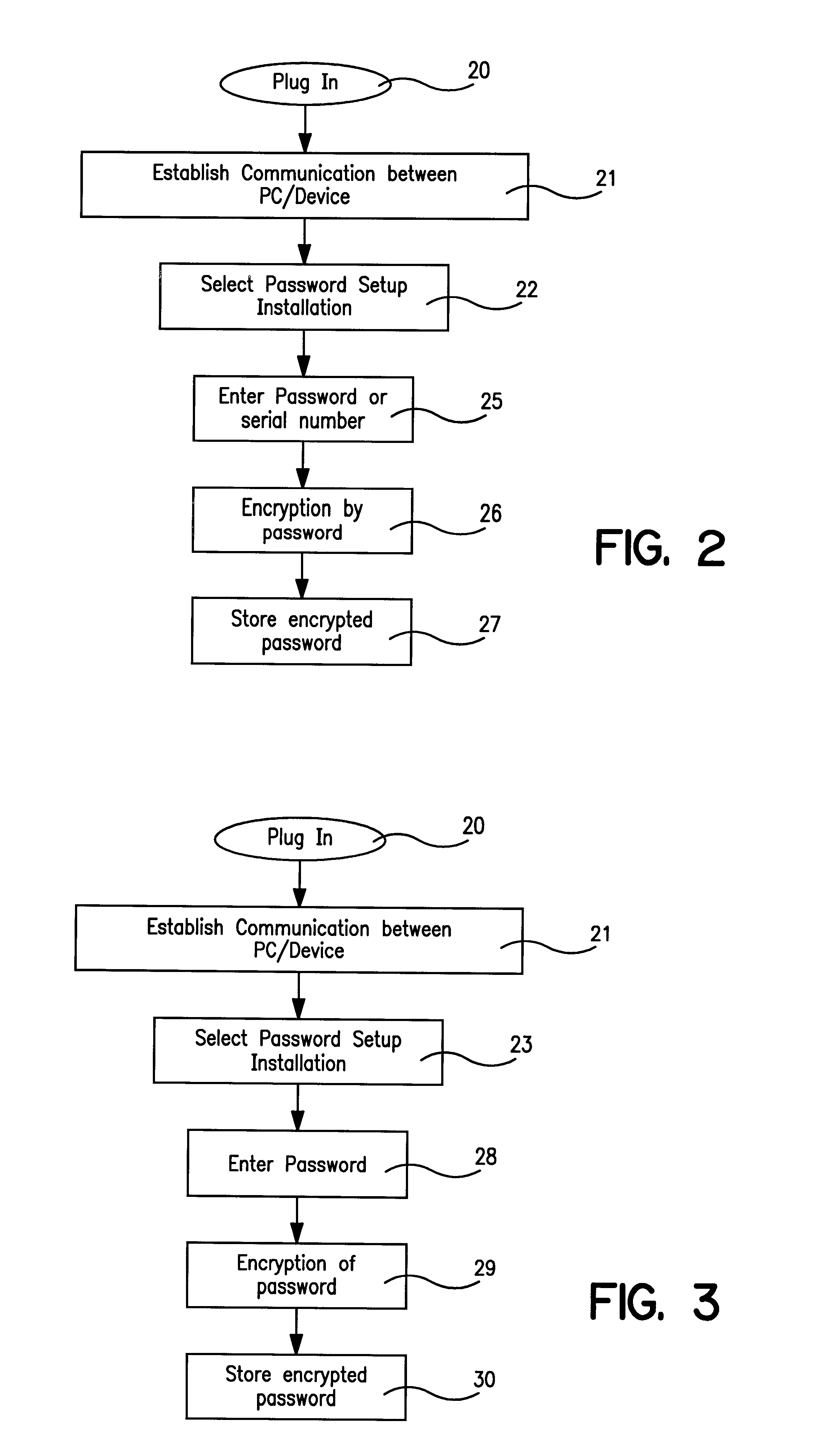
Portable data storage device having a secure mode of operation
A portable data storage device (10) includes a universal serial bus (USB) coupling device (1) and an interface device (2) is coupled to the USB coupling device (1). The portable data storage device (10) also includes a memory control device (3) and a non-volatile solid-state memory device (4). The memory control device (3) is coupled between the interface device (2) and the memory device (4) to control the flow of data from the memory device (4) to the USB coupling device (1).
Owner:TREK TECH SINGAPORE PTE
Horizontal chalcogenide element defined by a pad for use in solid-state memories
InactiveUS20060157681A1Decreased current/power requirementRemove restrictionsSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesPhase-change memoryDevice material
A process for fabricating phase-change elements having ultra small cross-sectional areas for use in phase change memory cells specifically and in semiconductor devices generally in which pads are implemented to create horizontally aligned phase change elements is disclosed. The elements thus defined may be used within chalcogenide memory cells or other semiconductor devices.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Highly compact EPROM and flash EEPROM devices
Structures, methods of manufacturing and methods of use of electrically programmable read only memories (EPROM) and flash electrically erasable and programmable read only memories (EEPROM) include split channel and other cell configurations. An arrangement of elements and cooperative processes of manufacture provide self-alignment of the elements. An intelligent programming technique allows each memory cell to store more than the usual one bit of information. An intelligent erase algorithm prolongs the useful life of the memory cells. Use of these various features provides a memory having a very high storage density and a long life, making it particularly useful as a solid state memory in place of magnetic disk storage devices in computer systems.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
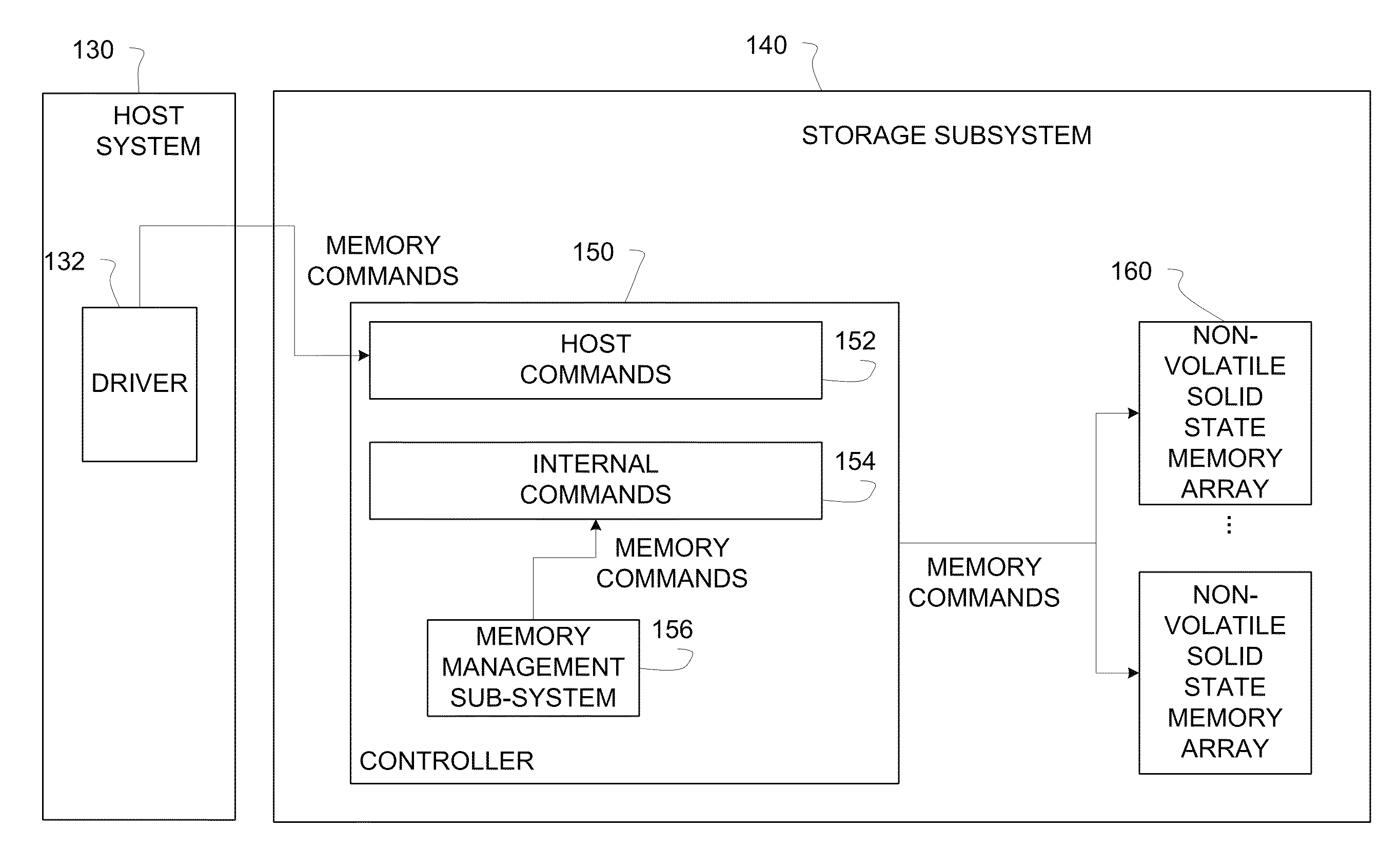
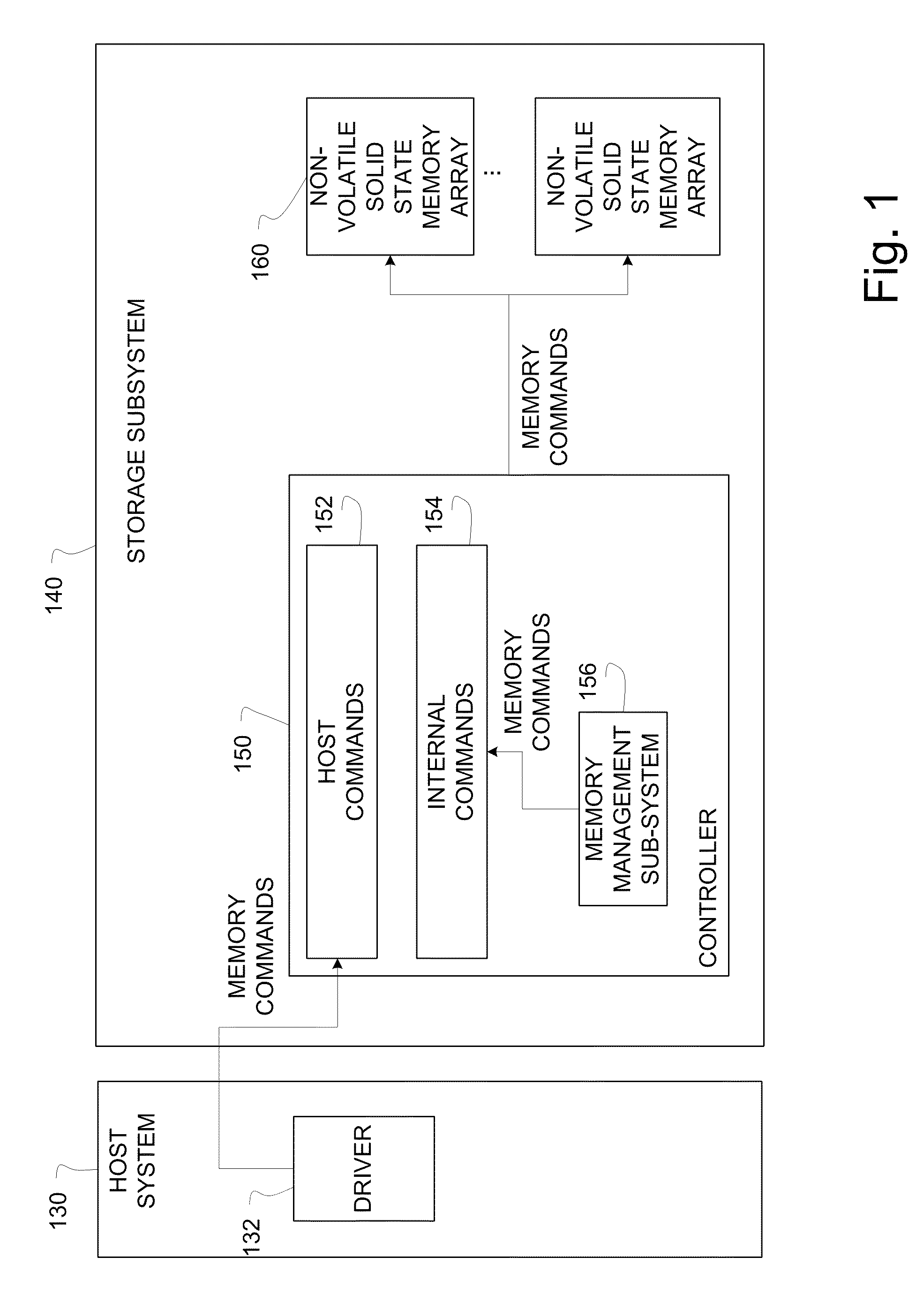
Logical to physical address mapping in storage systems comprising solid state memory devices
ActiveUS20130124794A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPhysical addressHybrid storage system
The present idea provides a high read and write performance from / to a solid state memory device. The main memory of the controller is not blocked by a complete address mapping table covering the entire memory device. Instead such table is stored in the memory device itself, and only selected portions of address mapping information are buffered in the main memory in a read cache and a write cache. A separation of the read cache from the write cache enables an address mapping entry being evictable from the read cache without the need to update the related flash memory page storing such entry in the flash memory device. By this design, the read cache may advantageously be stored on a DRAM even without power down protection, while the write cache may preferably be implemented in nonvolatile or other fail-safe memory. This leads to a reduction of the overall provisioning of nonvolatile or fail-safe memory and to an improved scalability and performance.
Owner:IBM CORP
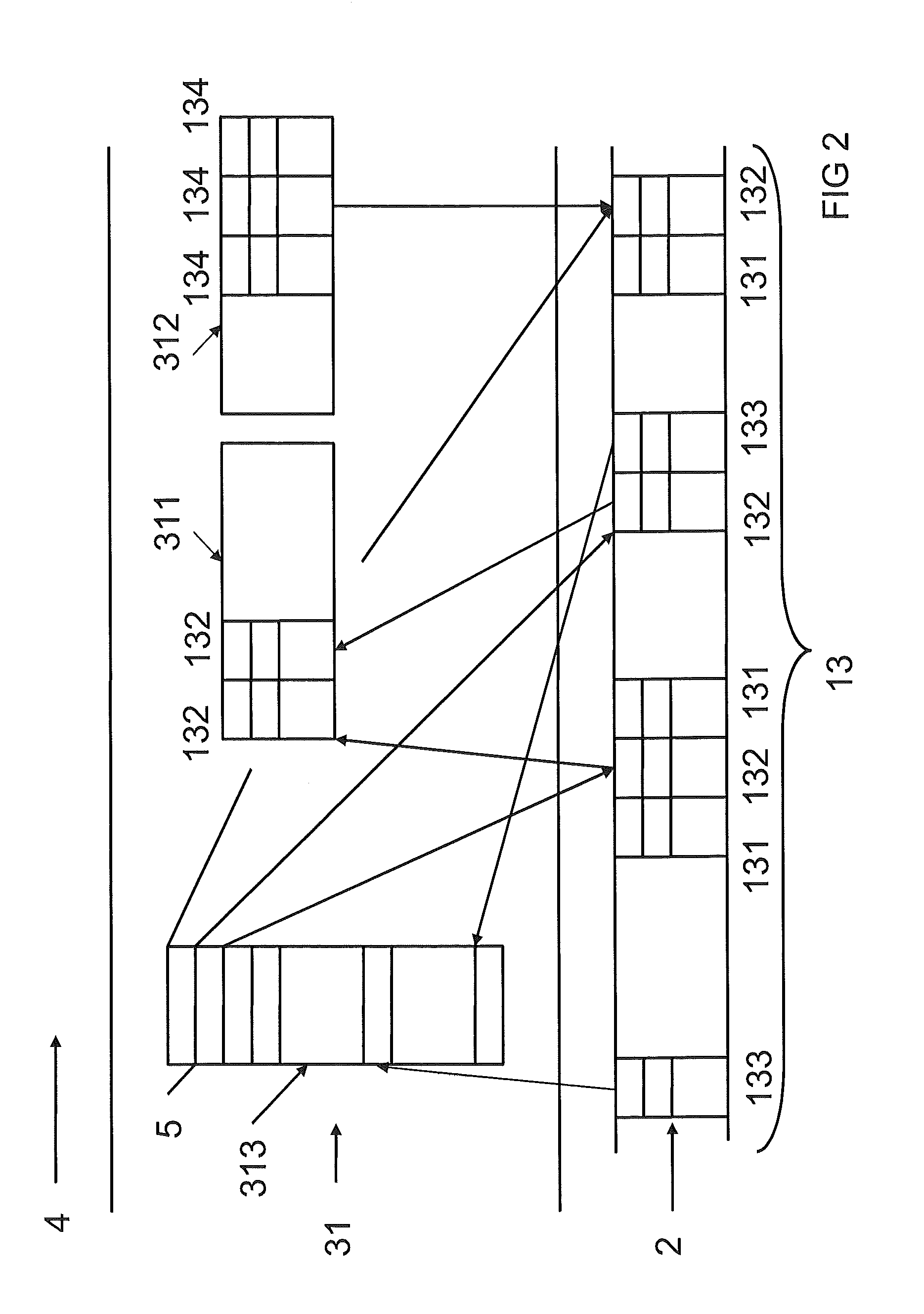
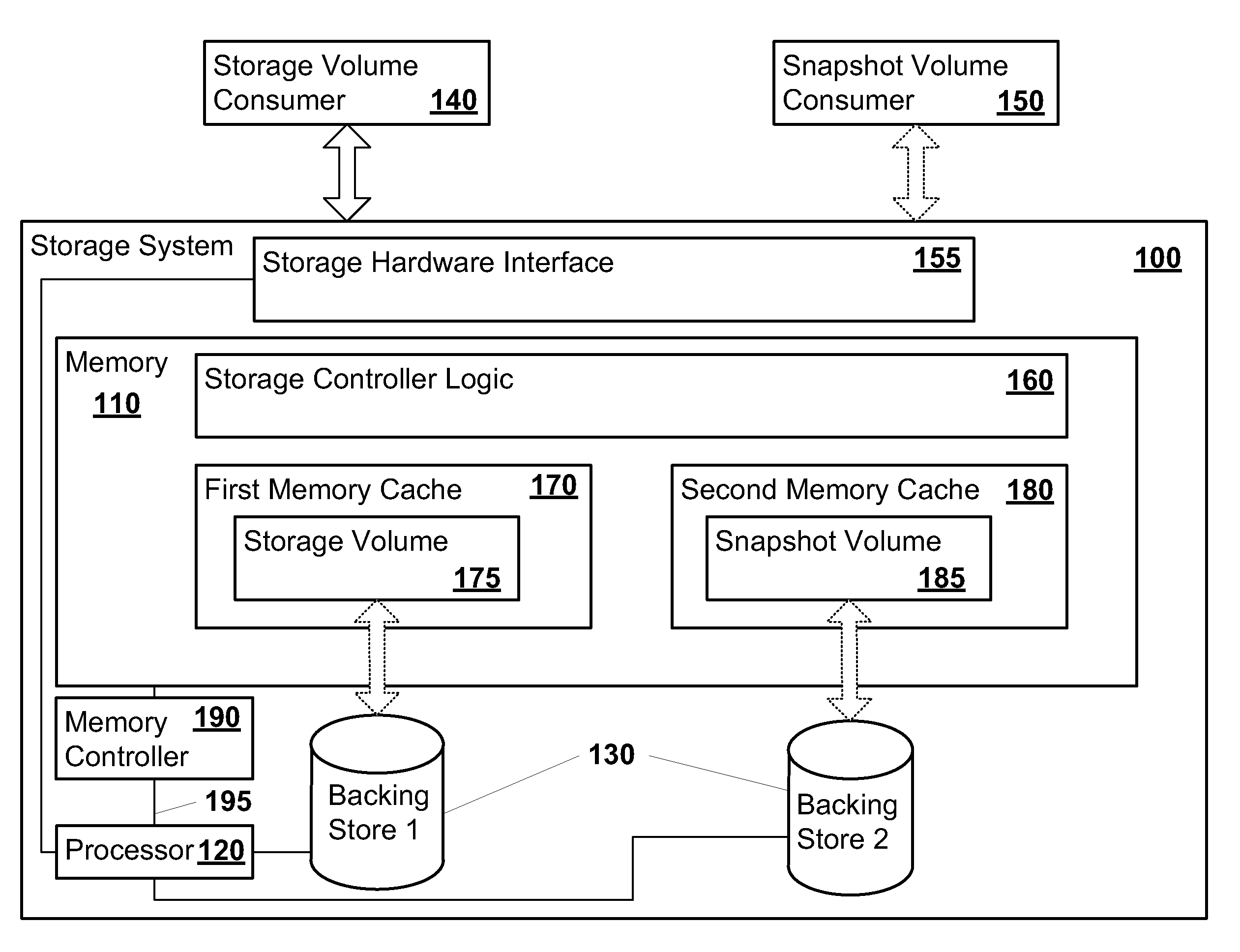
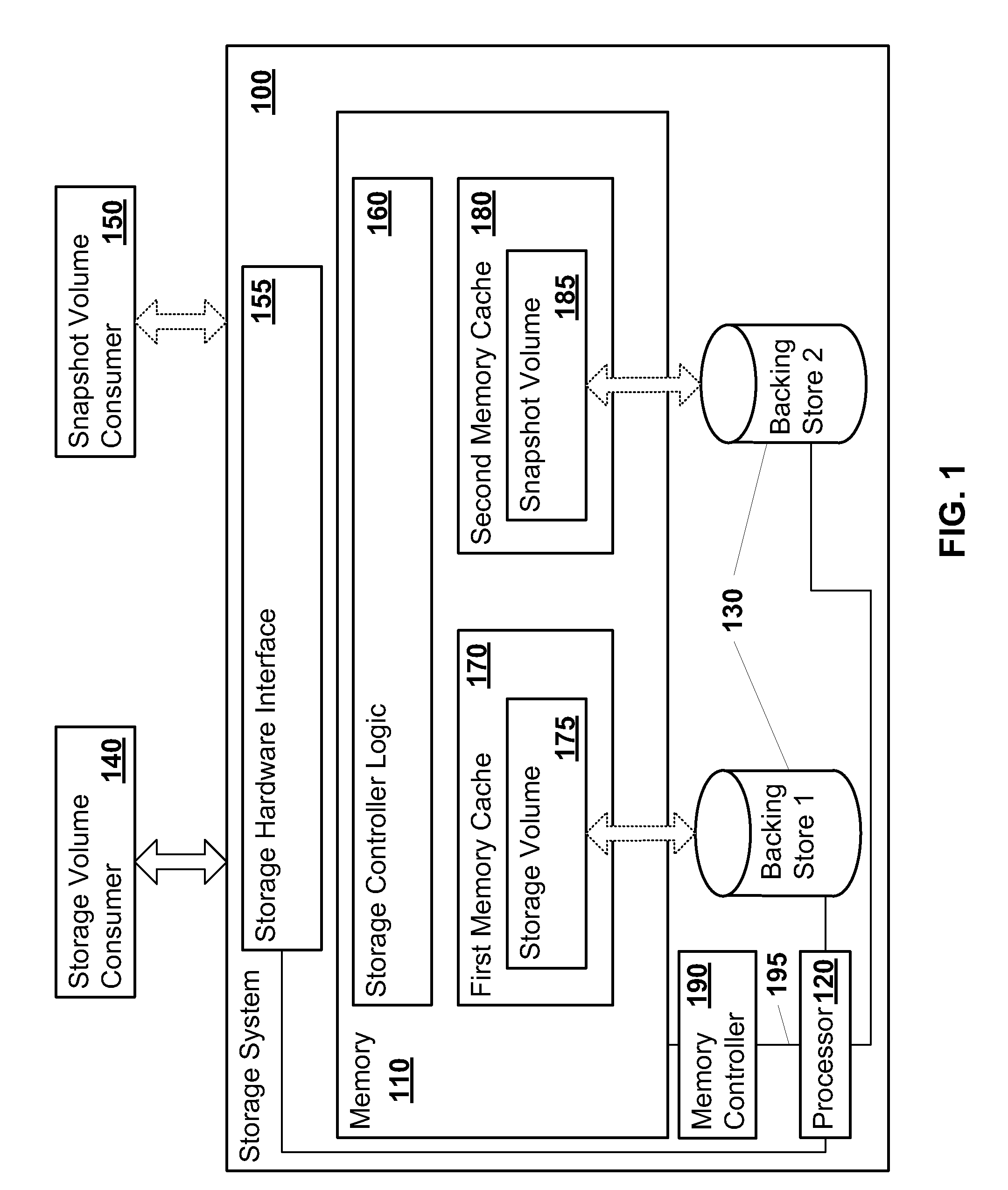
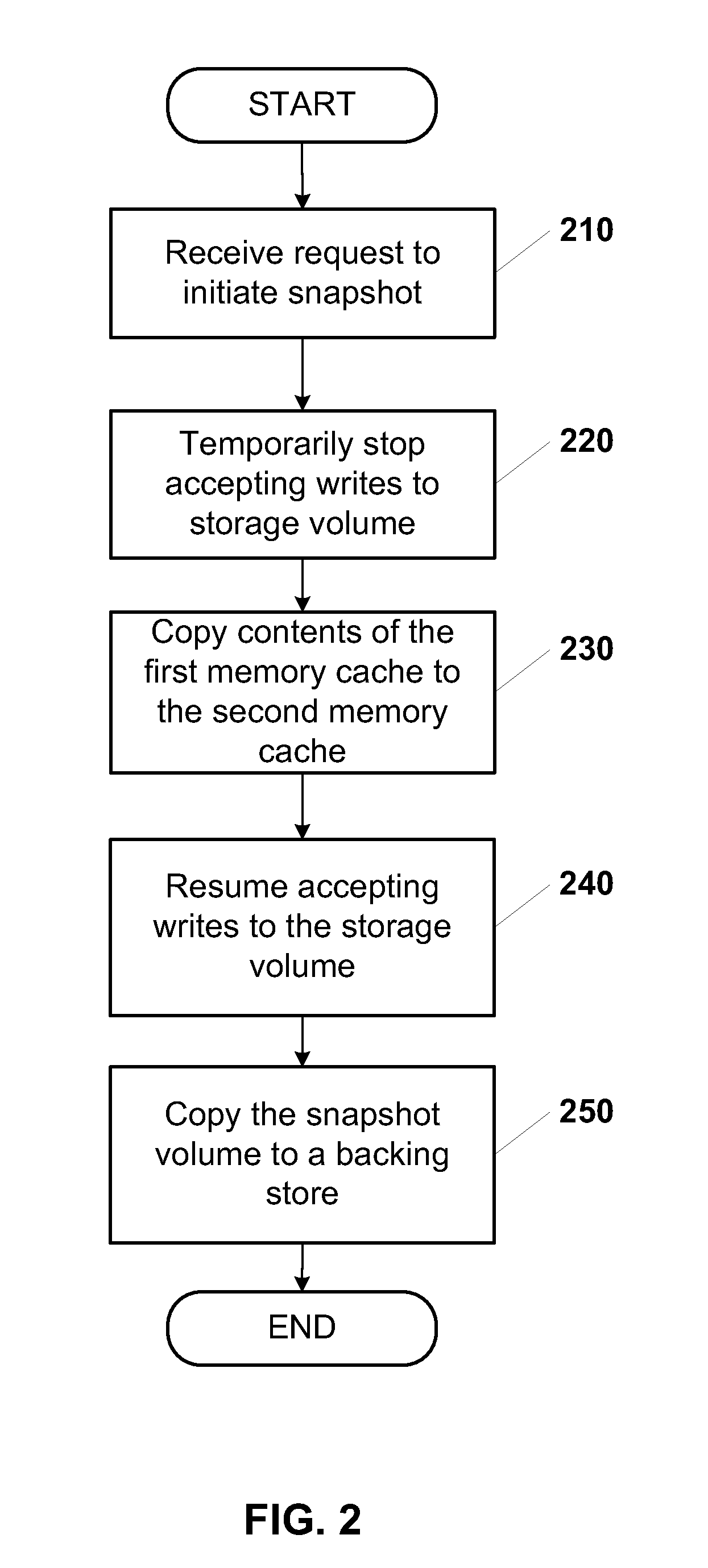
System and method for performing rapid data snapshots
A storage system is provided that includes storage controller logic that performs rapid data snapshots. The storage controller logic may provide block-level access to a storage volume. The storage controller logic may store all data blocks of the storage volume in a first solid state memory cache. The storage controller logic may form a snapshot of the storage volume in a second solid state memory cache. The first and second solid state memory caches are addressable with a processor. The storage system may complete the snapshot extremely quickly because the processor may copy from one memory location to another between the first and second solid state memory caches.
Owner:KOVE IP
Sampling playback doorbell system
InactiveUS20060038663A1Quality improvementEasy constructionSound producing devicesElectric/electromagnetic audible signallingDocking stationDoorbell
A digital sampling playback doorbell system has two or more doorbell buttons and a central unit with solid state memory storage for multiple digitally sampled sound files. User assignment means are provided for assigning a particular sound file to a particular doorbell button. The digital sampling playback doorbell has computer interface of RS-232, or USB, or infrared wireless connection type and relies on computer installed software to download digitally sampled sound files stored in the computer hard drive to the memory of the digital sampling playback doorbell system central unit. The digitally sampled sound files stored in the computer hard drive are obtained by accessing a web site through the Internet or capturing sound through an audio computer connection to a microphone, CD player, radio broadcast or mass music storage device using software resident in the computer. Alternatively, an IPOD can be used as a source for sounds that can be transferred or sent to play on the doorbell. Such sound transfer can take place via a blue tooth communication link, or by a docking station that resides on the doorbell. Taking advantage of the intelligence contained within the IPOD, one can then select sounds or files that have been previously converted by either the IPOD or the computer that the IPOD was previously attached to, and send them to the doorbell.
Owner:PREDOMINANCE
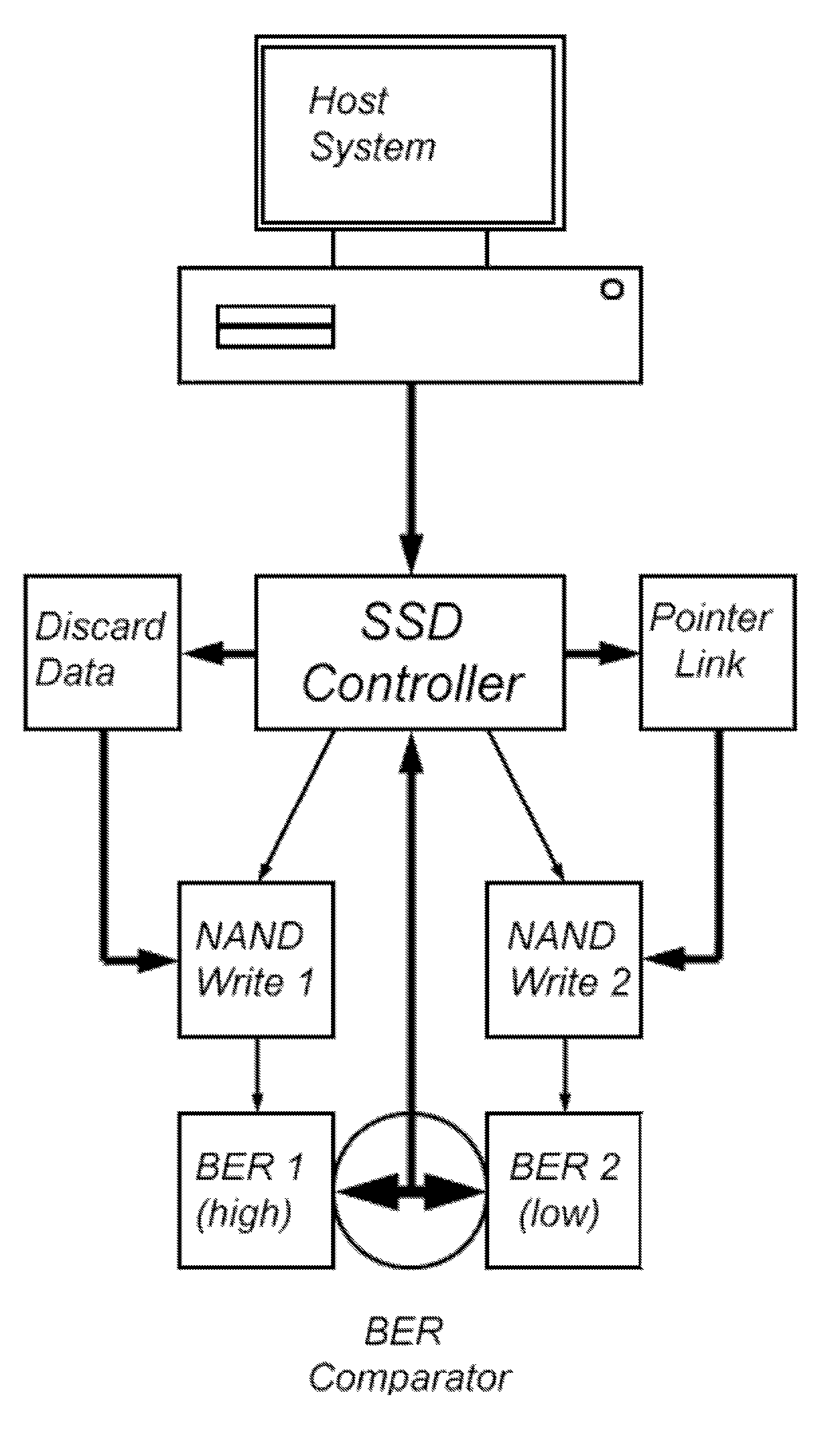
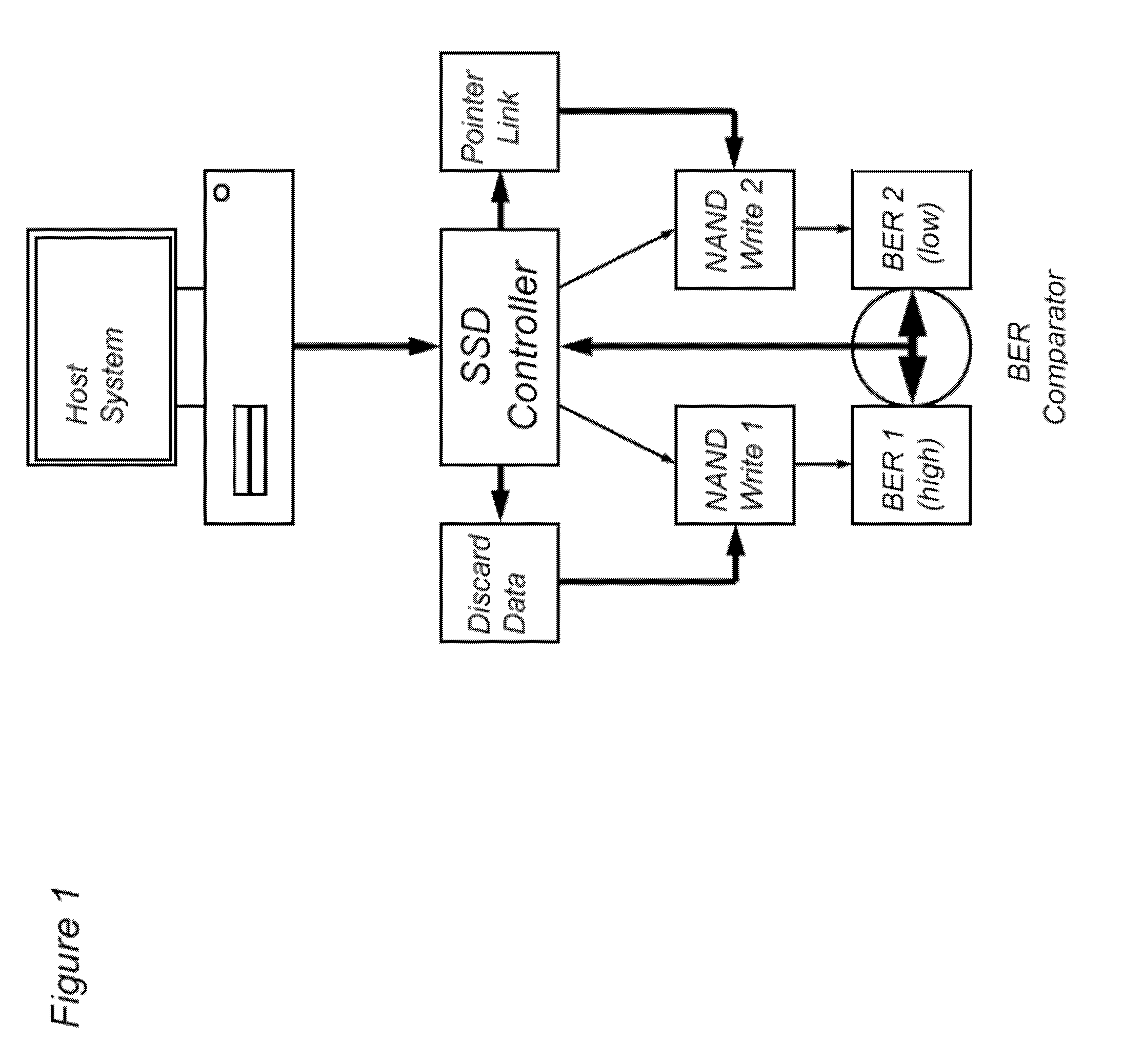
Solid-state memory-based storage method and device with low error rate
InactiveUS20130024735A1Low initial error rateReduce error rateError correction/detection using block codesRedundant data error correctionData setNon-volatile memory
Non-volatile solid-state memory-based storage devices and methods of operating the storage devices to have low initial error rates. The storage devices and methods use bit error rate comparison of duplicate writes to one or more non-volatile memory devices. The data set with a lower bit error rate as determined during verification is maintained, whereas data sets with higher bit error rates are discarded. A threshold of bit error rates can be used to trigger the duplication of data for bit error comparison.
Owner:OCZ STORAGE SOLUTIONS
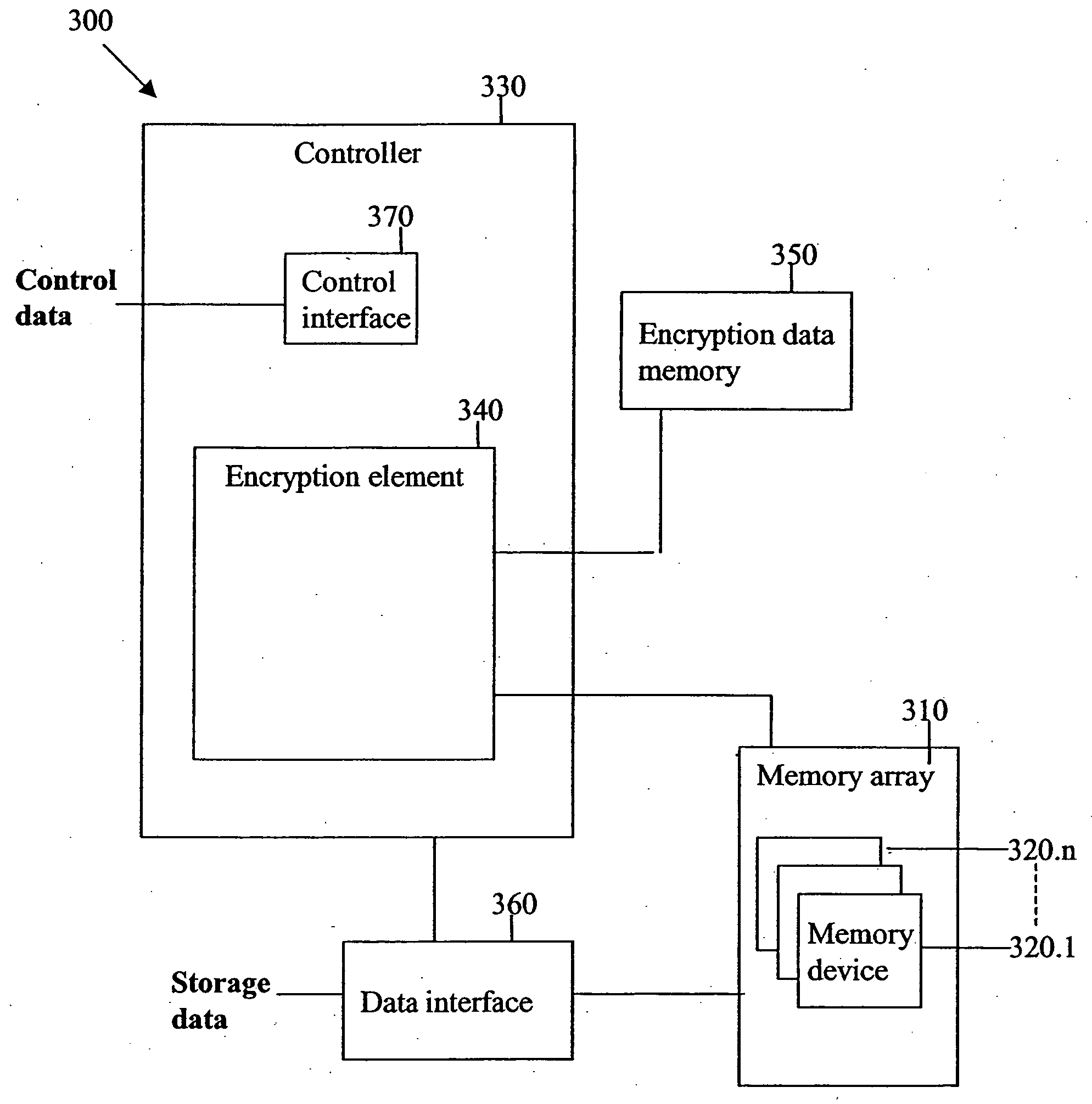
Secured redundant memory subsystem
InactiveUS20060053308A1Easy accessData stream serial/continuous modificationUser identity/authority verificationSolid-state storageRAID
A storage device consists of multiple solid state memory devices and a memory controller. The memory devices are configured as a redundant array, such as a RAID memory array. The memory controller performs data encryption to provide secured access to the array. The encryption may be performed with an encryption data sequence which is stored on a separate memory element.
Owner:RAIDY 2 GO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com