Patents
Literature
269 results about "Cycle count" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A cycle count is an inventory auditing procedure, which falls under inventory management, where a small subset of inventory, in a specific location, is counted on a specified day. Cycle counts contrast with traditional physical inventory in that a full physical inventory may stop operation at a facility while all items are counted at one time. Cycle counts are less disruptive to daily operations, provide an ongoing measure of inventory accuracy and procedure execution, and can be tailored to focus on items with higher value, higher movement volume, or that are critical to business processes. Although some say that cycle counting should only be performed in facilities with a high degree of inventory accuracy (greater than 95%), cycle counting is one means of achieving and sustaining high degrees of accuracy. There are specific procedures to use cycle counting to quickly identify root causes of problems in the processes that control inventories and then monitor the effectiveness of the actions to eliminate the root causes. In fact, doing conventional inventory audits without having previously made the control processes reliable is like trying to weigh dry ice - soon after balances are corrected, the bad processes wrong the balances again. The ideal procedure is to bring the control processes to reliability through root cause elimination with cycle counting, then perform a full physical audit to correct all balances, and then continue to use cycle counting to monitor and sustain. The specific procedures to this approach include the use of control groups, frequent repetition of counts of inaccurate items (e.g., weekly or twice a month), and prioritization based on control process vulnerability rather than item values. This approach faces difficulty with the mindset of making inventory data periodically accurate for accounting books' purposes but it is essential with the mindset of perfecting control processes so inventory data are continuously accurate for minute-to-minute support to operations. The purpose of cycle counting is to verify the inventory accuracy and even though it is not an adequate procedure to be used to correct inventory errors, it is an adequate way to identify the root causes of inventory errors. In contrast, identifying root causes, agreeing on actions to eliminate them and implementing them to the point of perfecting control processes is virtually impossible with traditional inventory audit approaches.
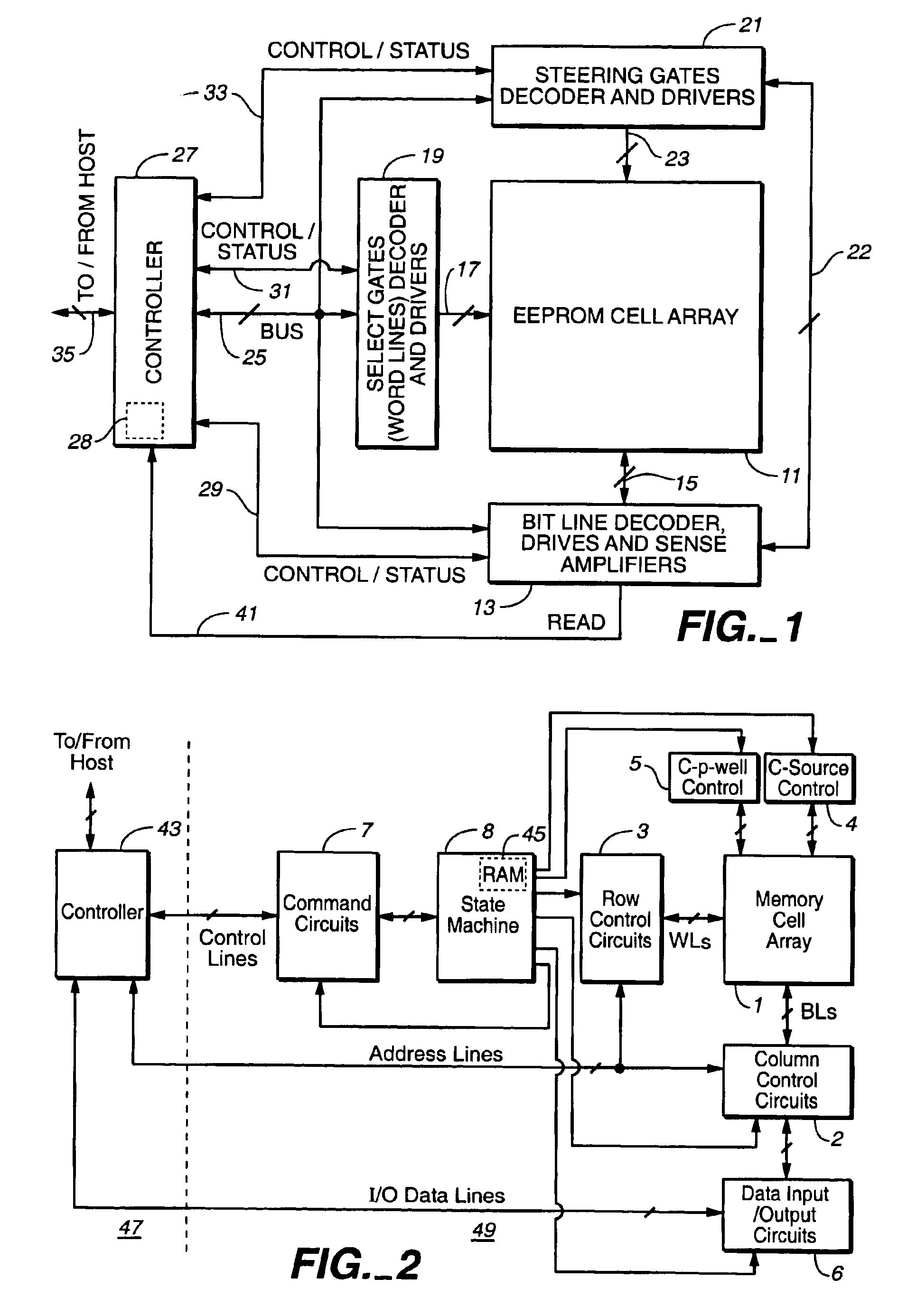
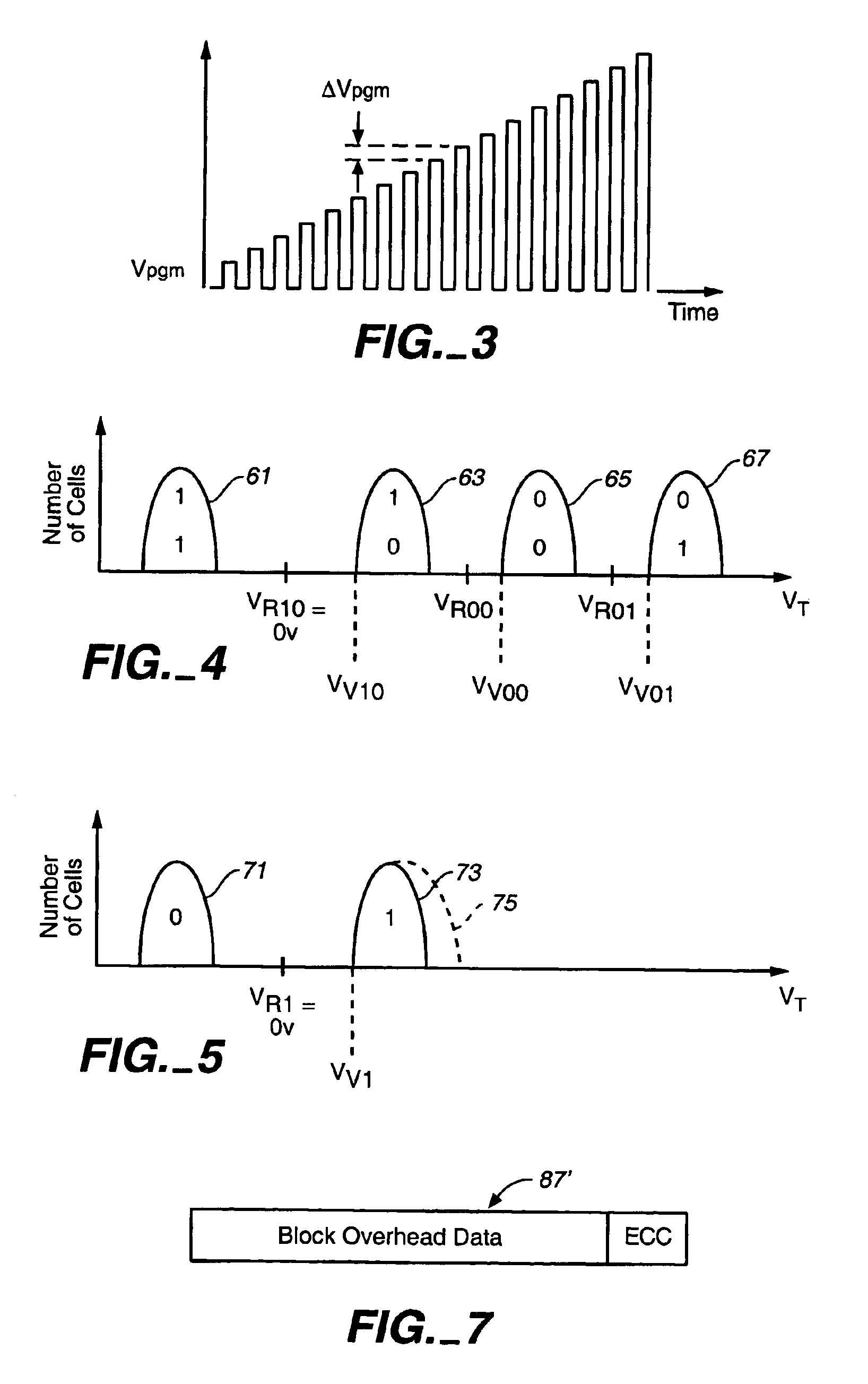
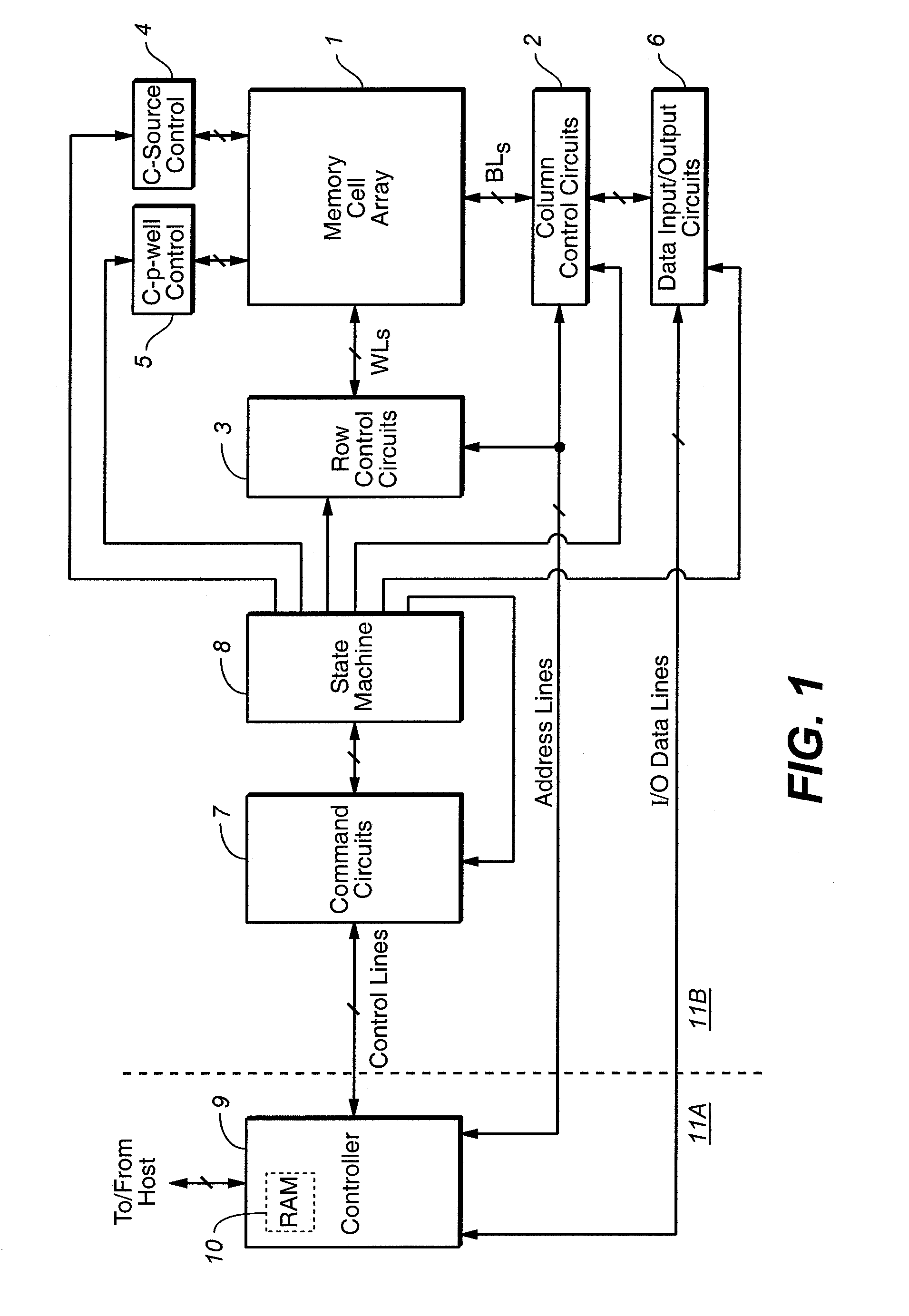
Drift compensation in a flash memory
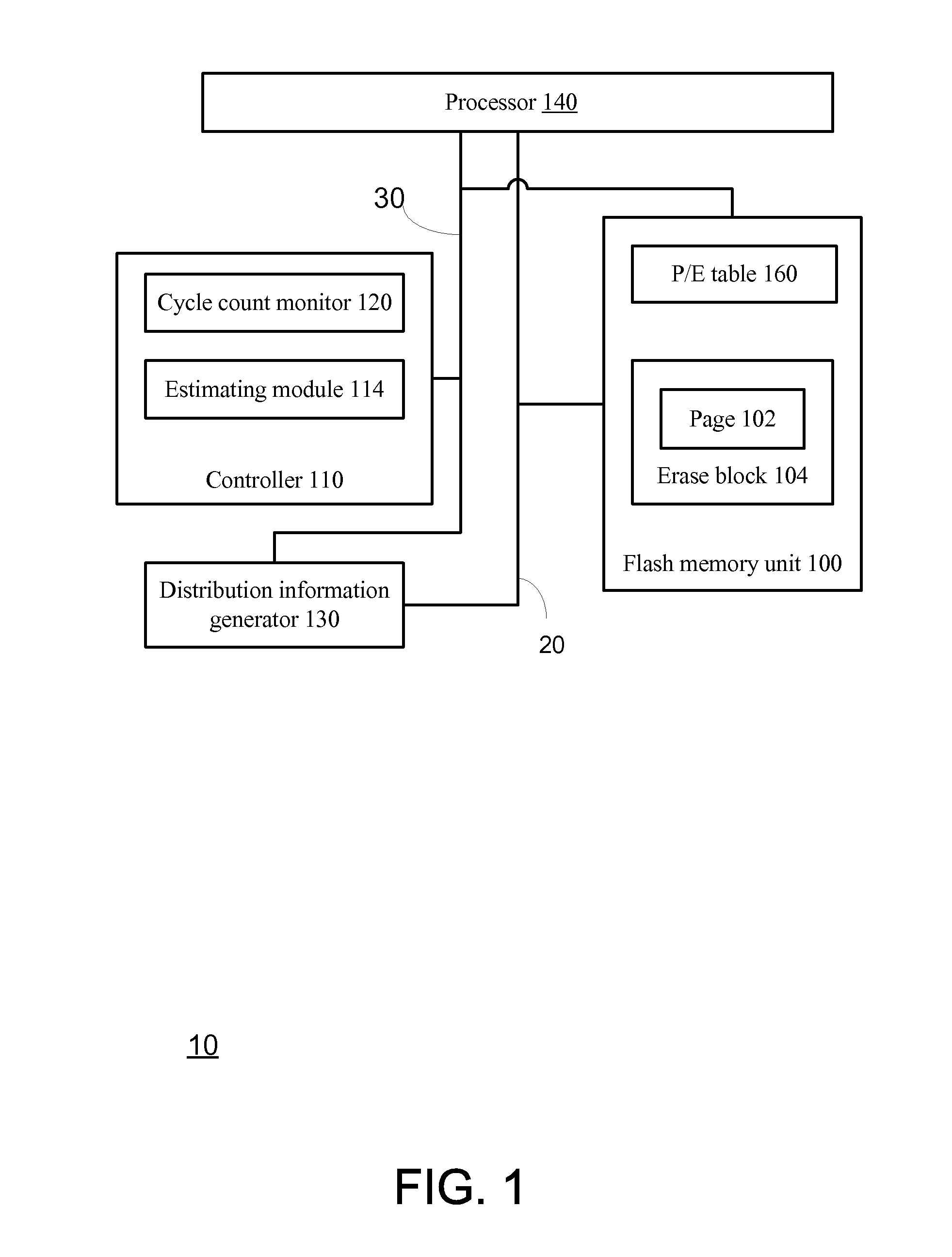
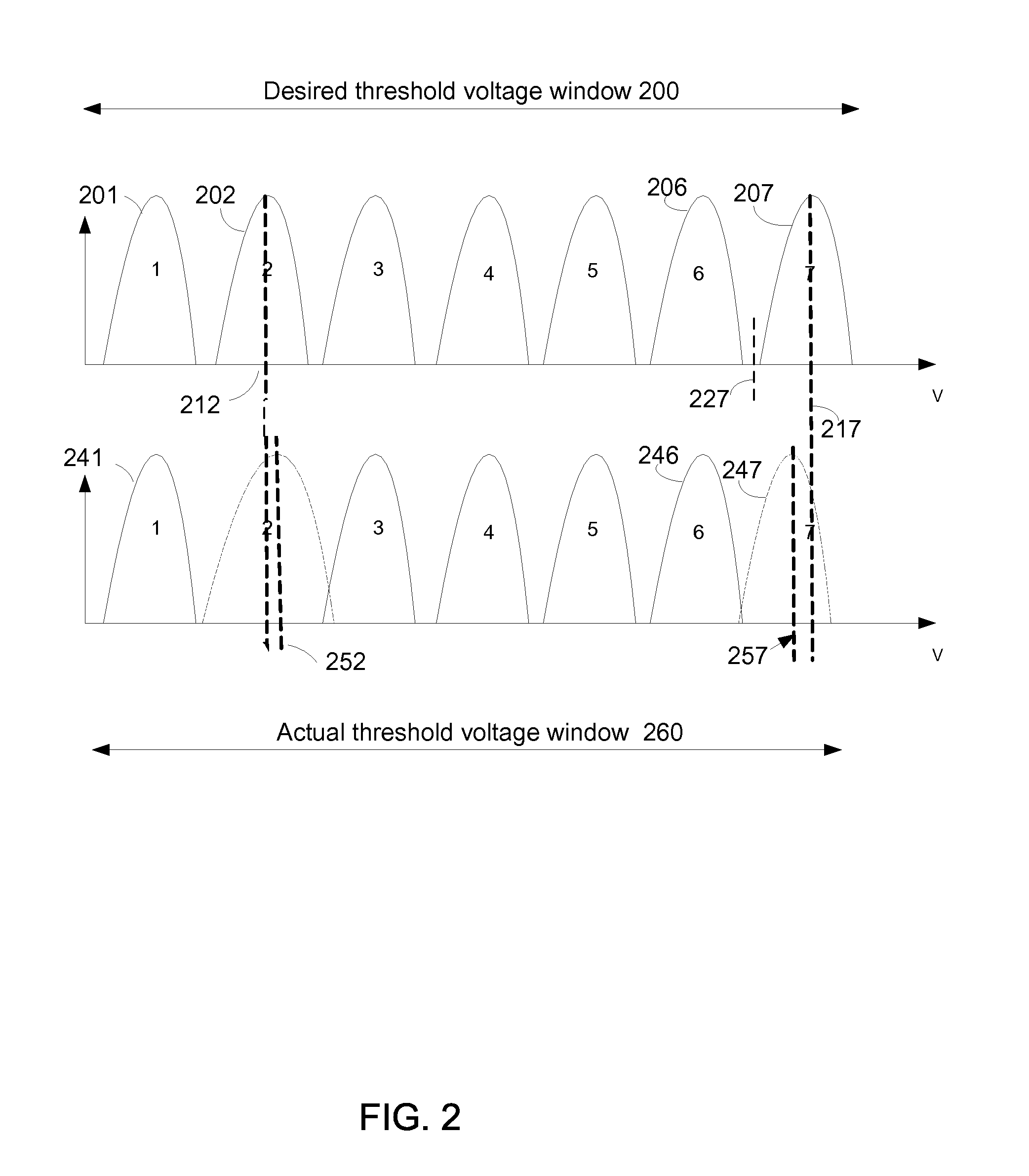
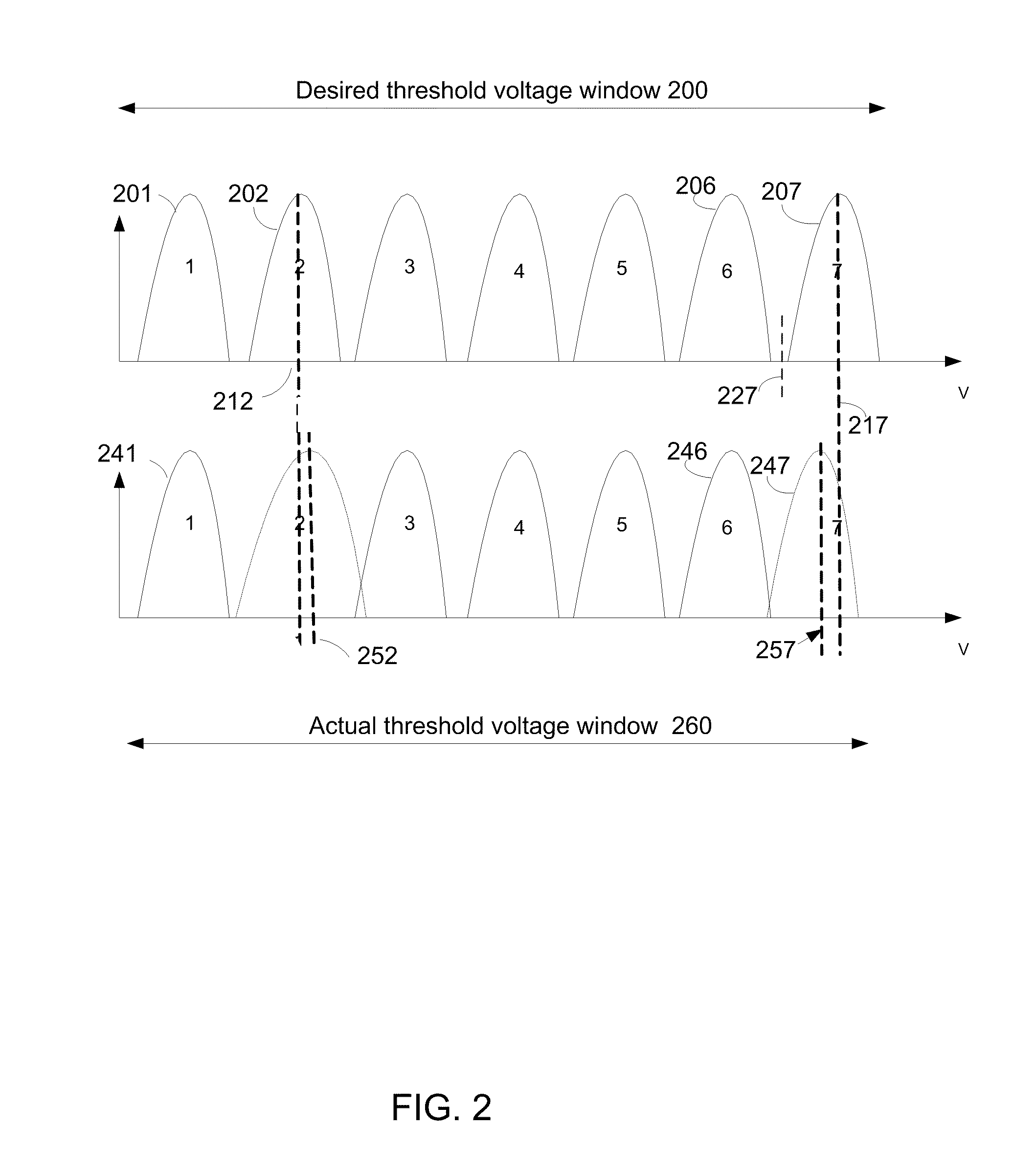
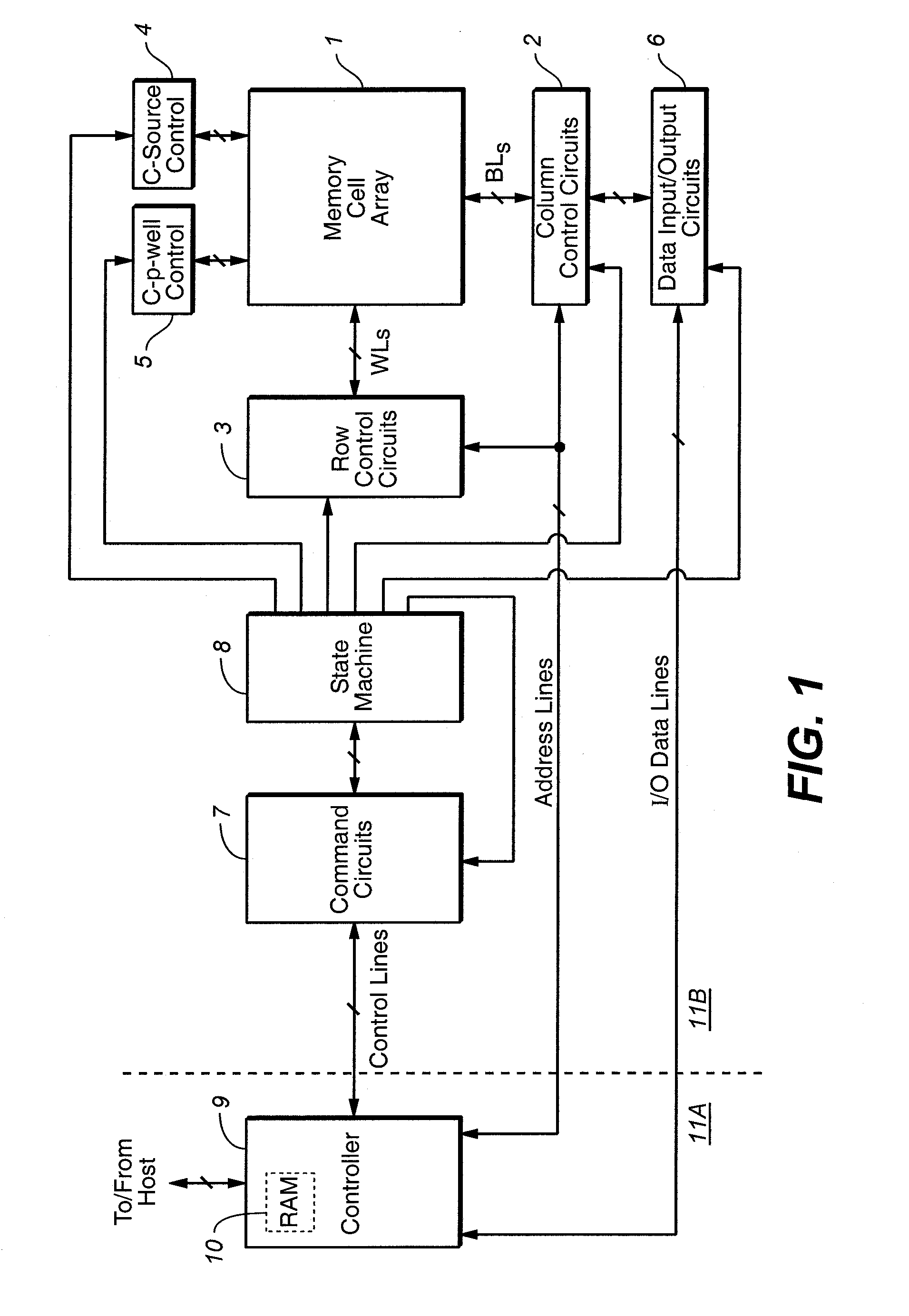
A plurality of memory cells are managed by obtaining values of one or more environmental parameters of the cells and adjusting values of one or more reference voltages of the cells accordingly. Alternatively, a statistic of at least some of the cells, relative to a single reference parameter that corresponds to a control parameter of the cells, is measured, and the value of the reference voltage is adjusted accordingly. Examples of environmental parameters include program-erase cycle count, data retention time and temperature. Examples of reference voltages include read reference voltages and program verify reference voltages. Examples of statistics include the fraction of cells whose threshold voltages exceed initial lower bounds or initial medians.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL ISRAEL LTD
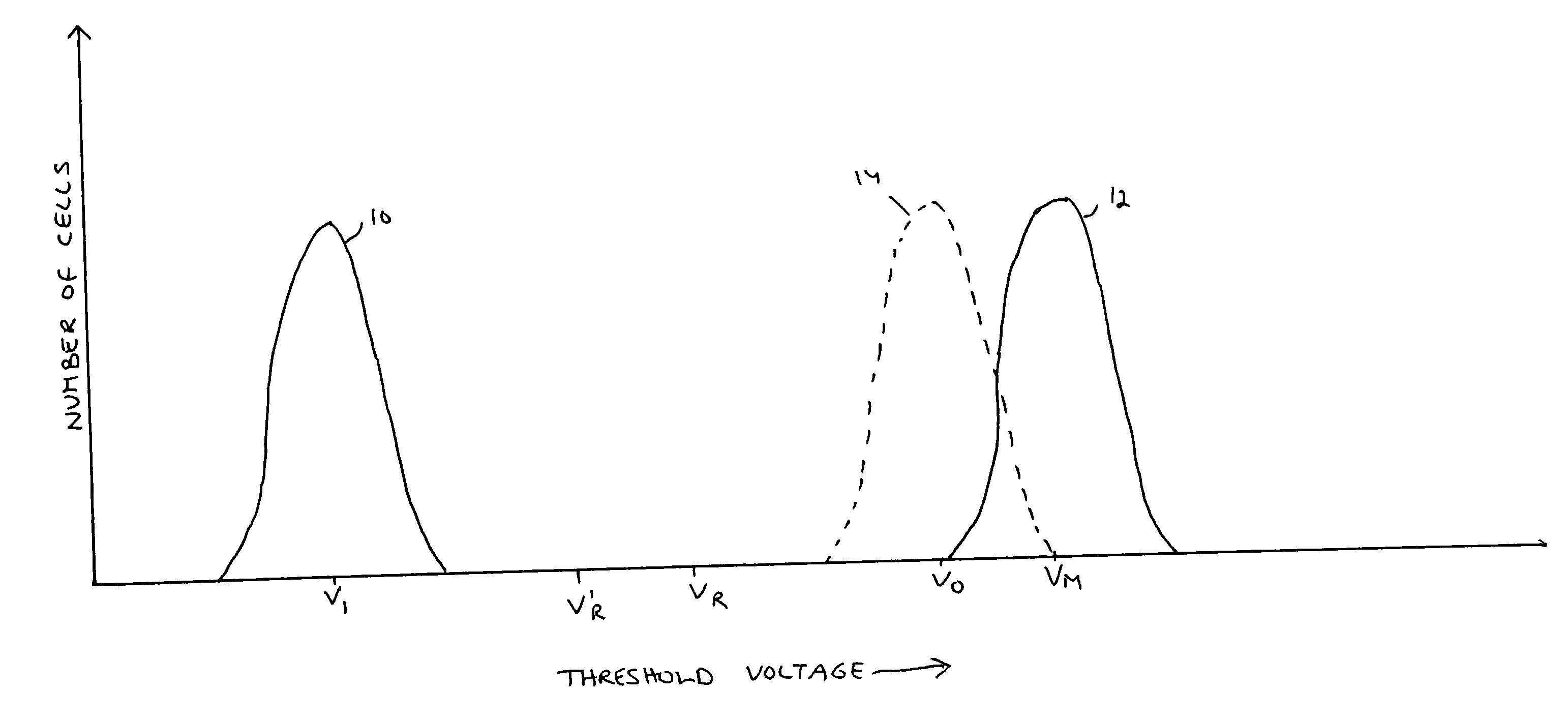
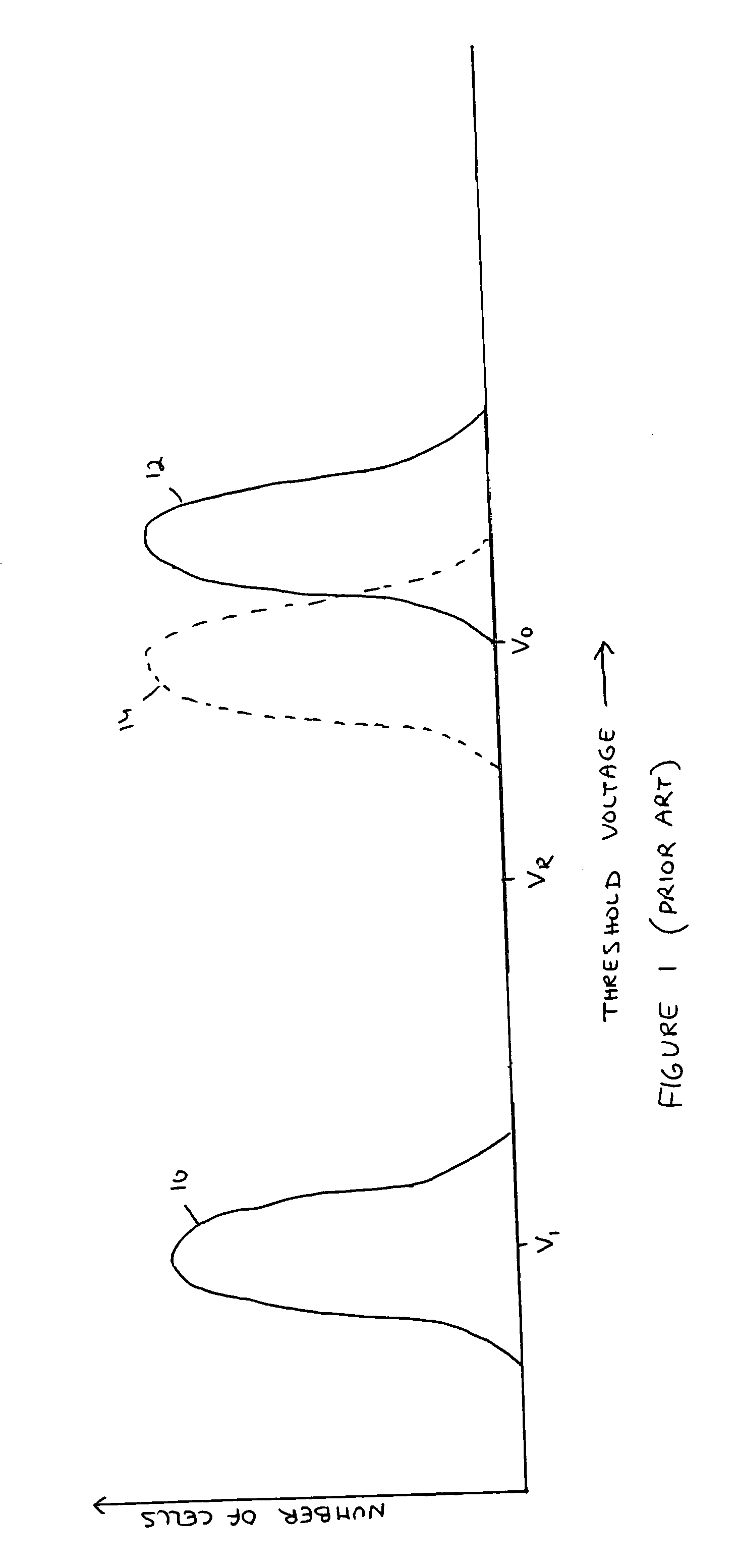
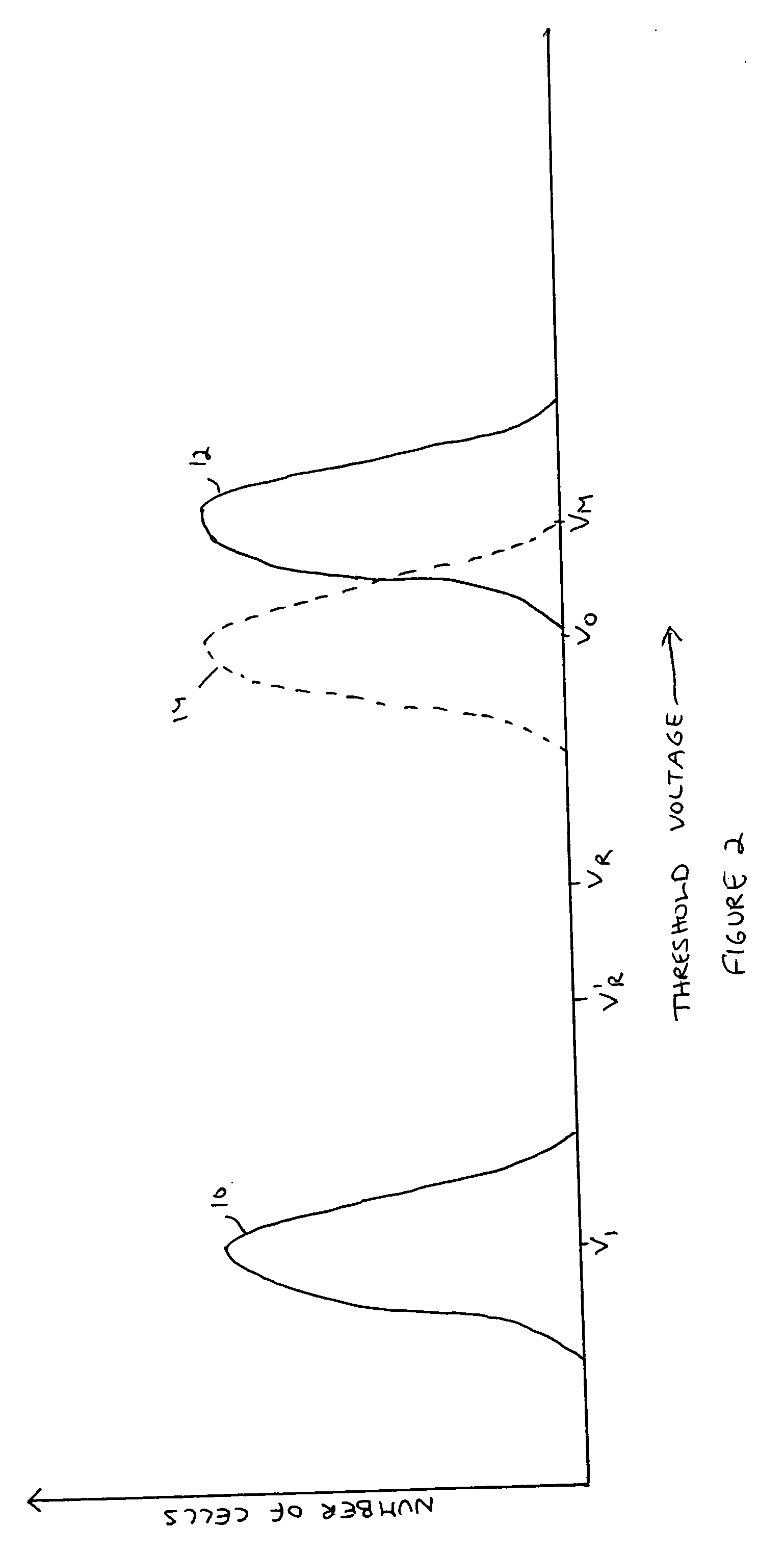
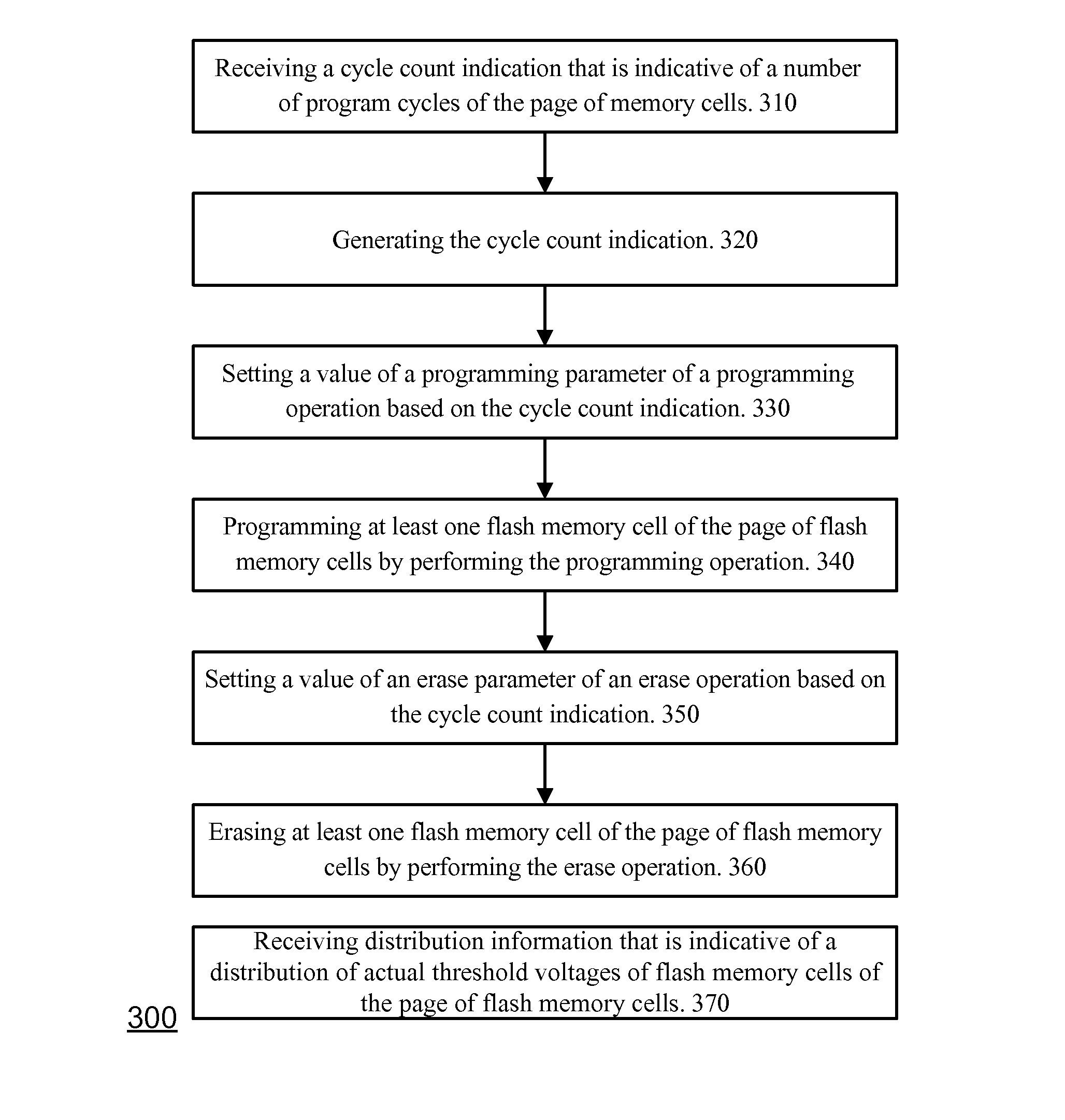
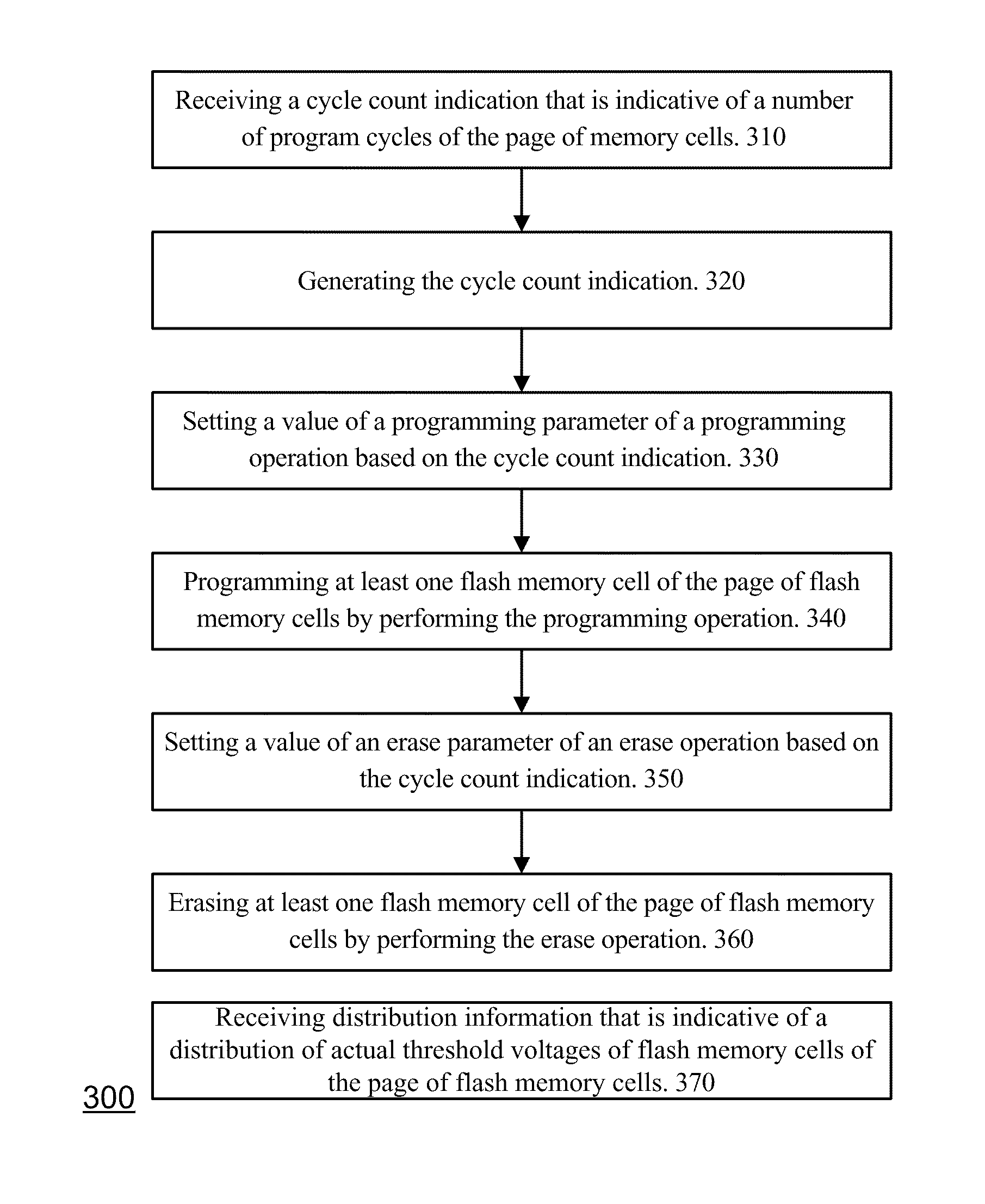
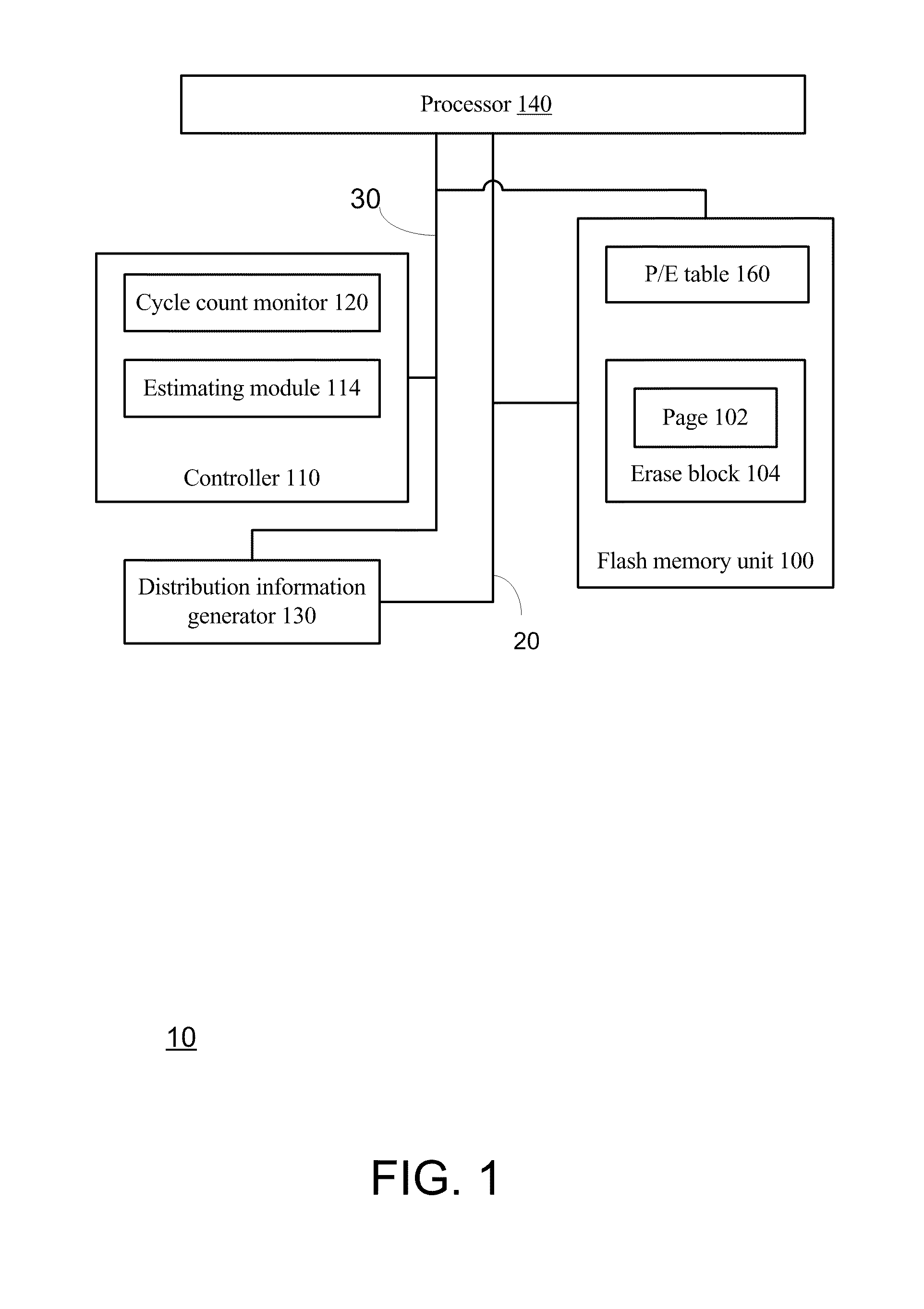
Flash memory module and method for programming a page of flash memory cells
A flash memory module and a method for programming a page of flash memory cells, the method includes: receiving a cycle count indication indicative of a number of program cycles of the page of memory cells; setting a value of a programming parameter of a programming operation based on the cycle count indication; and programming at least one flash memory cell of the page of flash memory cells by performing the programming operation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
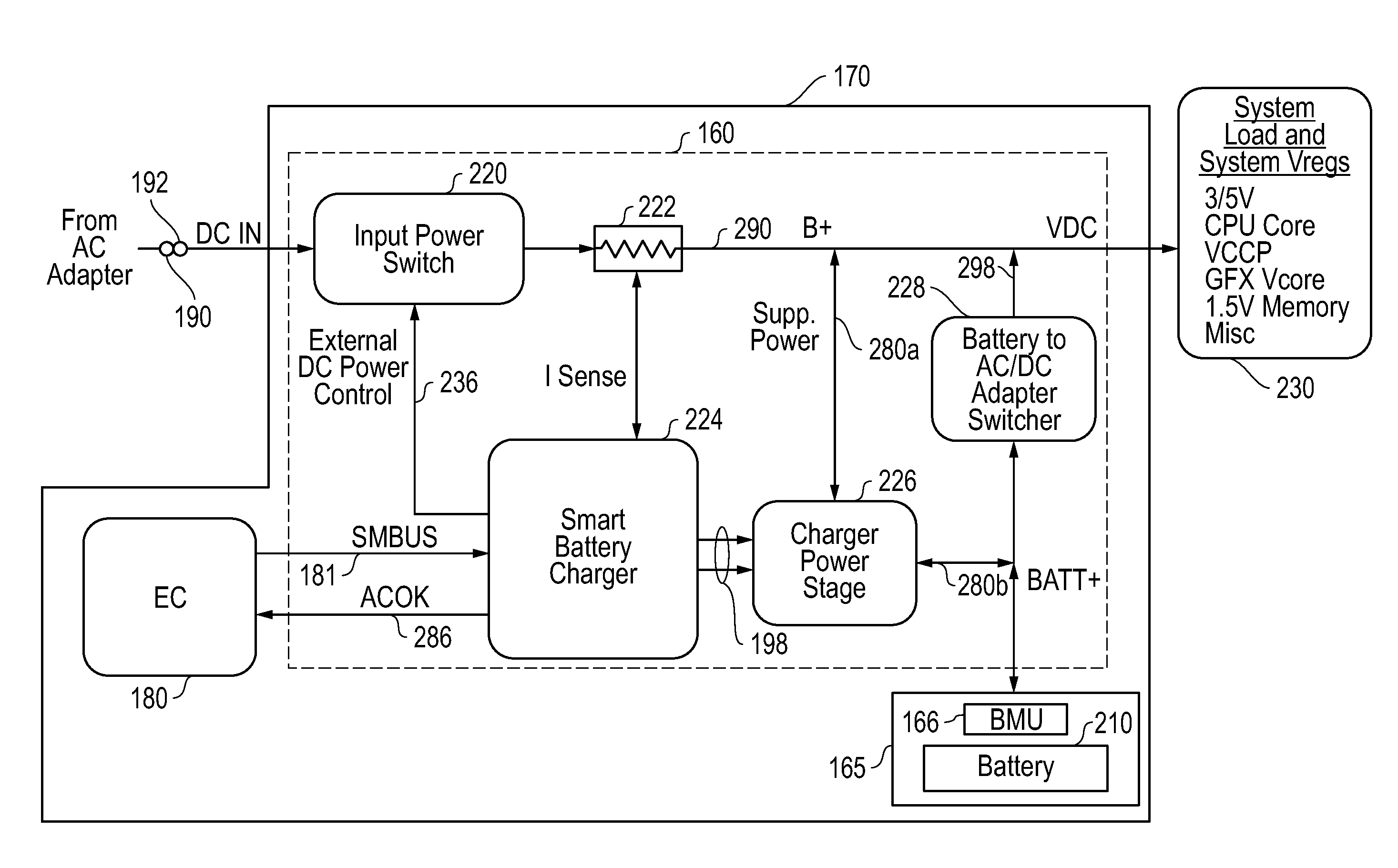
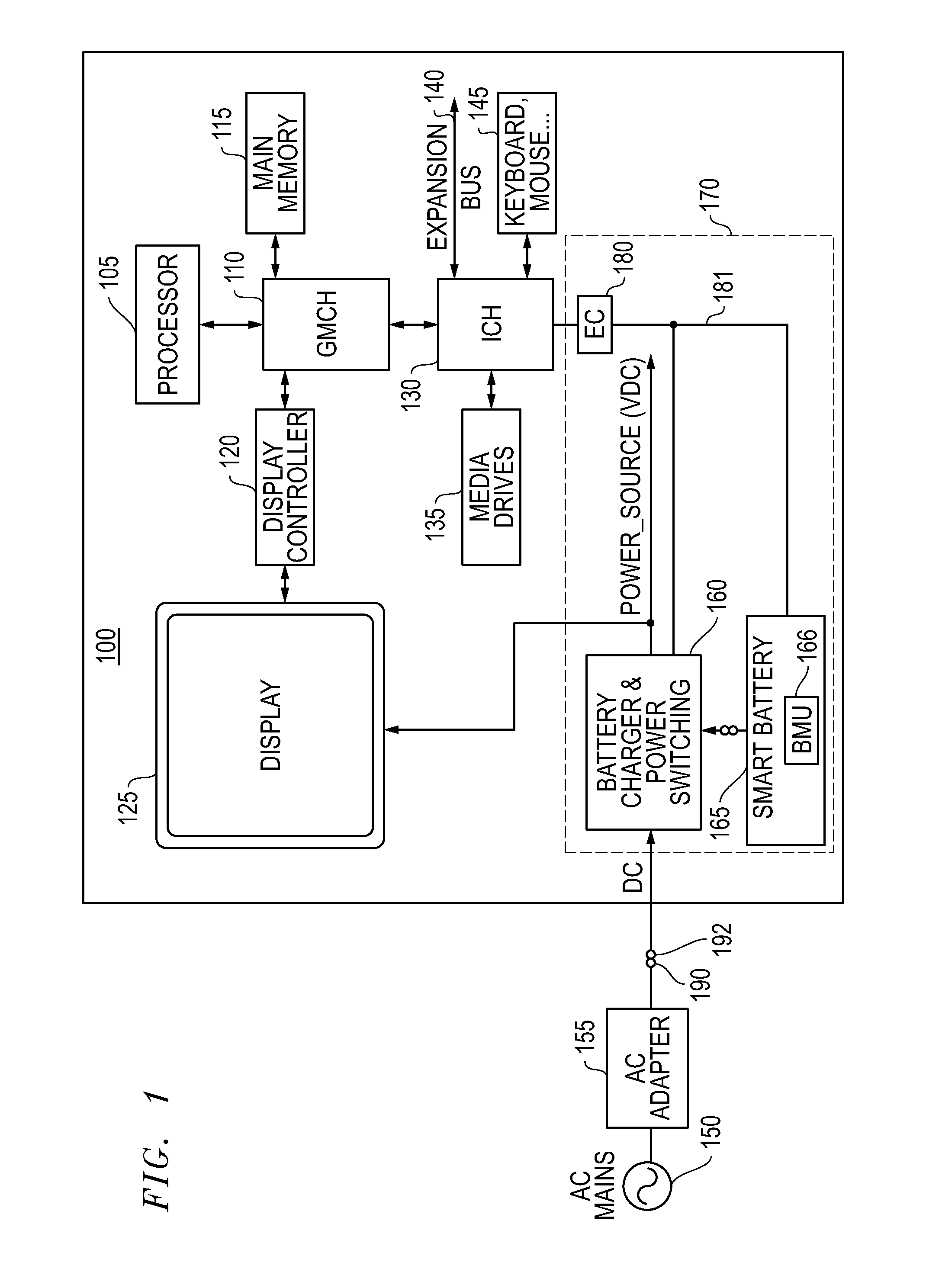
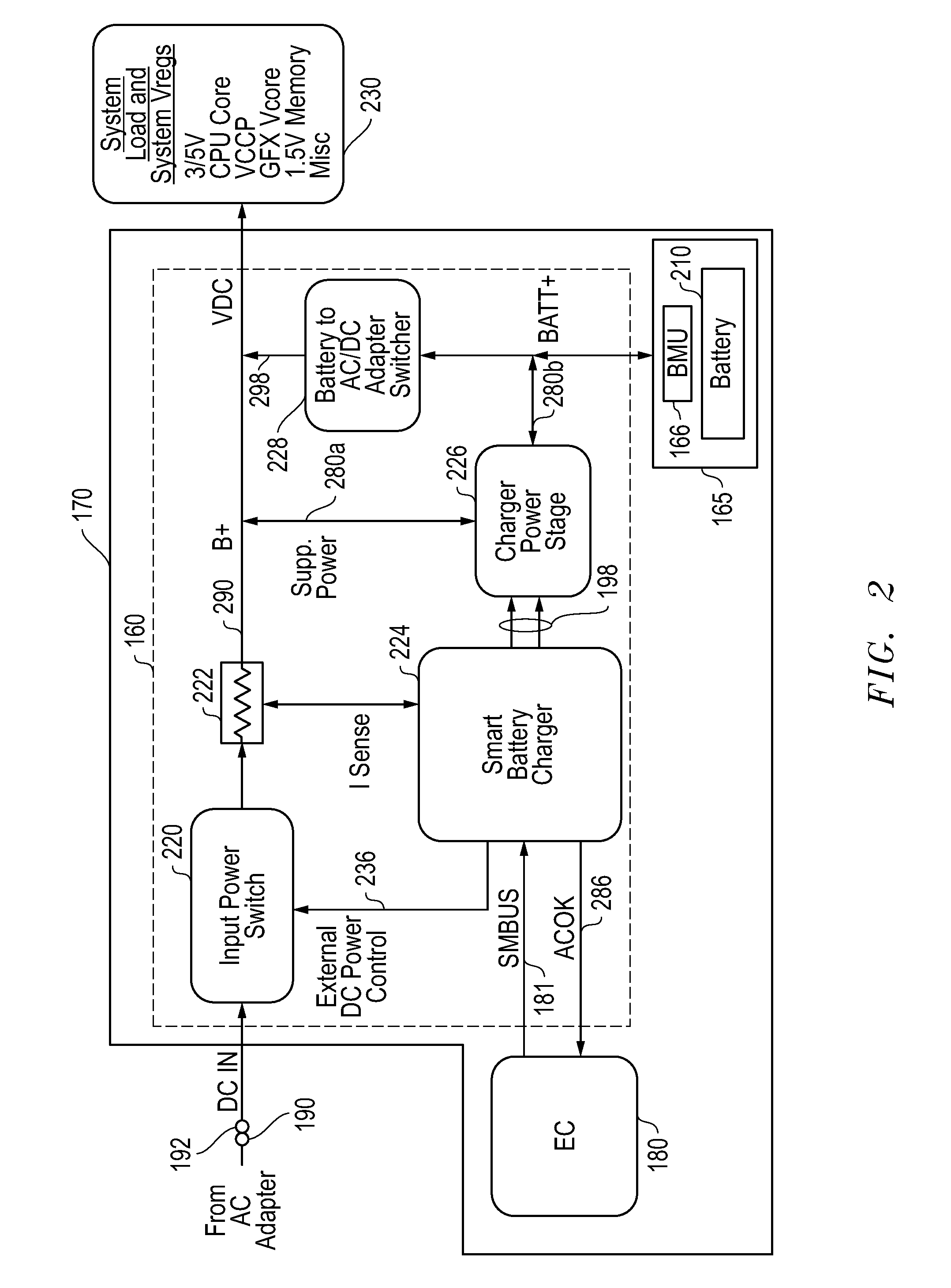
Systems and methods for providing supplemental power to battery powered information handling systems
ActiveUS20130339757A1Raise countMinimize impactVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingBattery chargeElectrical battery
Systems and methods are disclosed for providing supplemental power to a battery powered information handling systems. The disclosed systems and methods may be implemented to intelligently control the selected use of supplemental power so as to reduce or substantially prevent an increase in battery usage cycle count by only allowing use of supplemental power above a given minimum supplemental battery charge level threshold. Battery cycle count may be further enhanced by only again allowing recharging of the system battery pack when its charge level drops below the minimum supplemental battery charge level threshold, and then recharging to a maximum recharge battery charge level threshold which also may be selectable by a user and / or provider of the information handling system.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
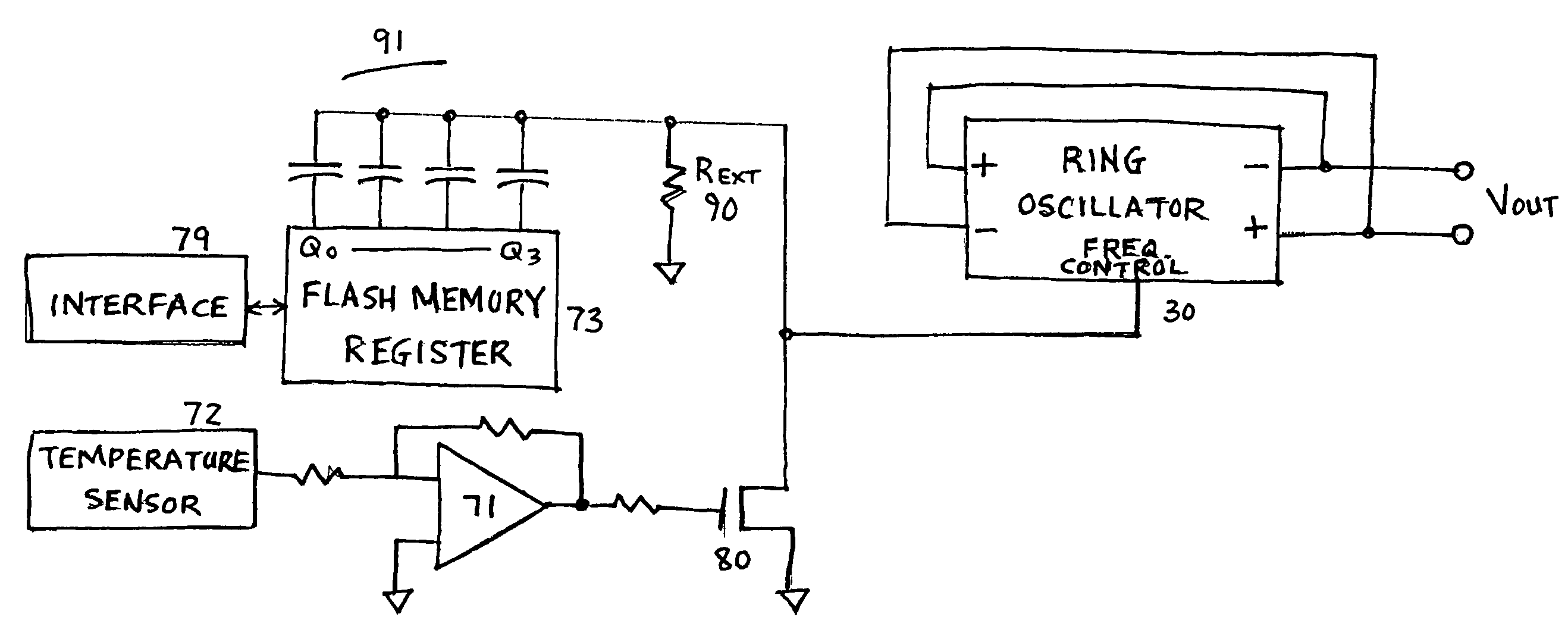
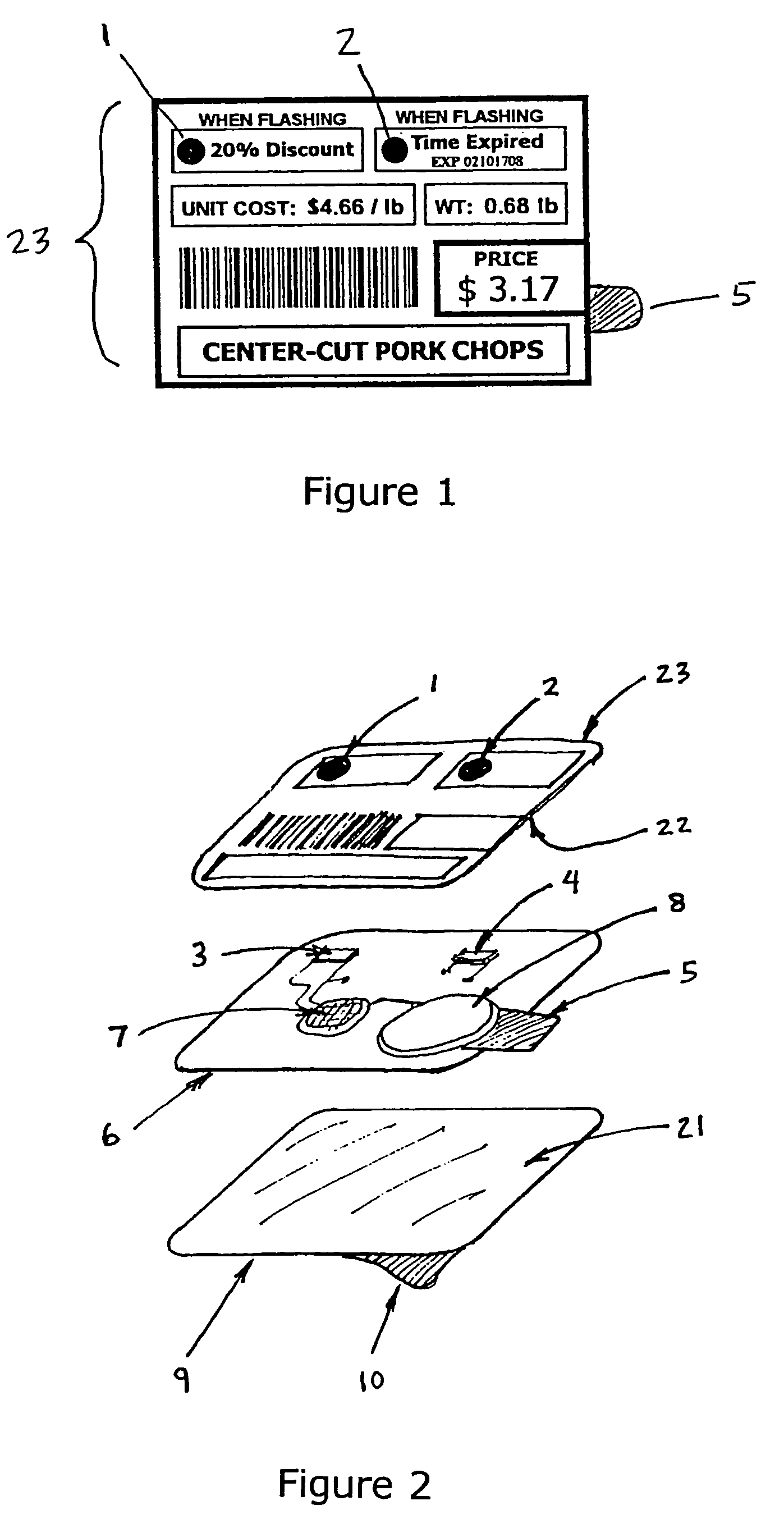
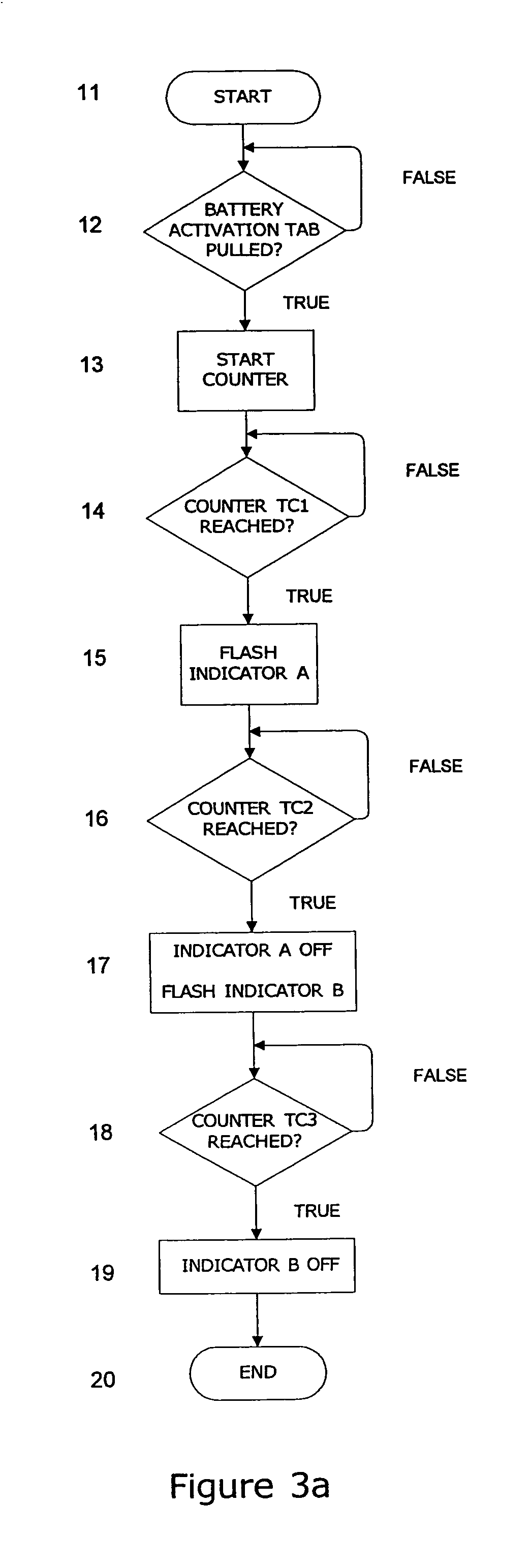
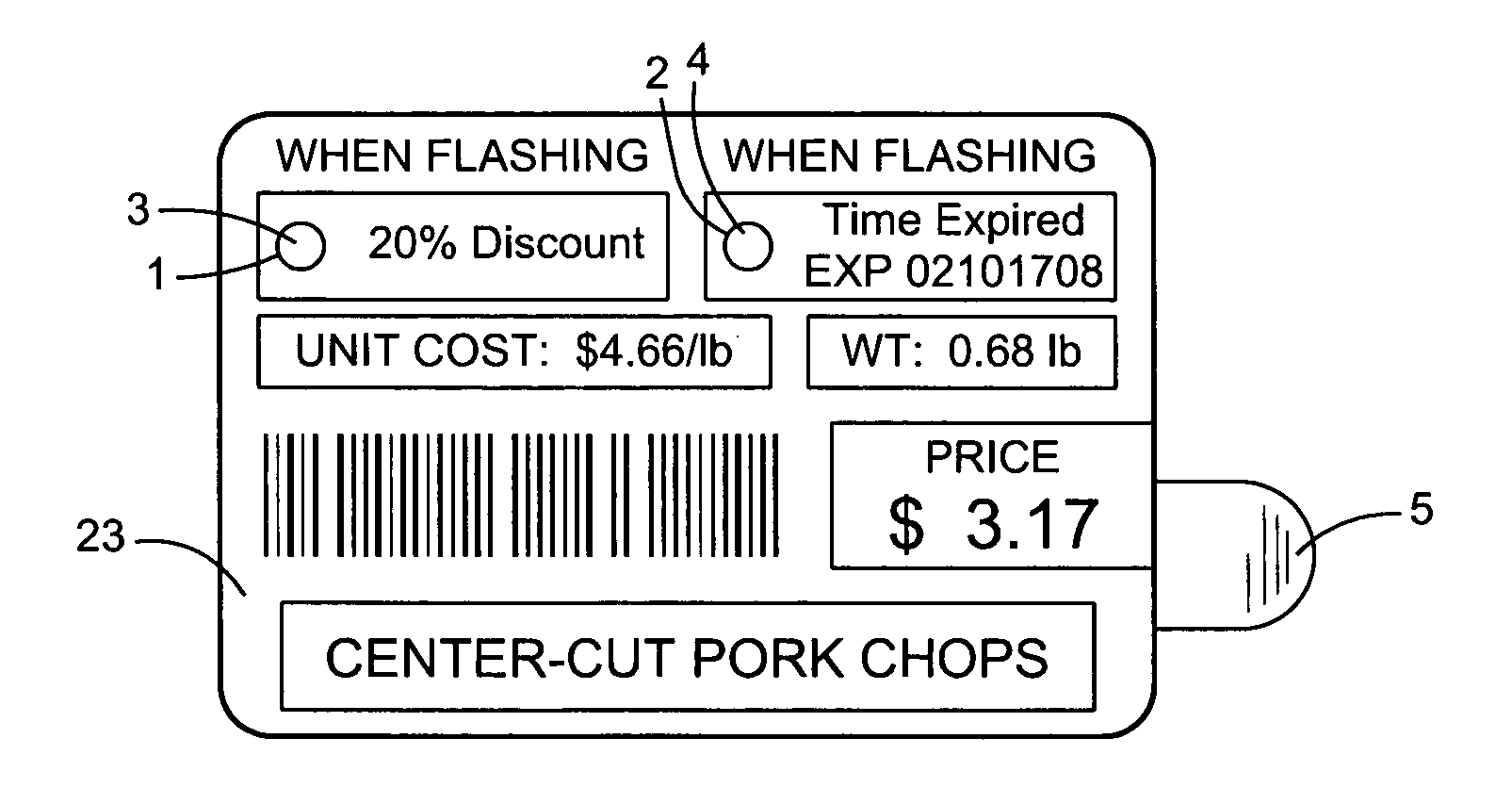
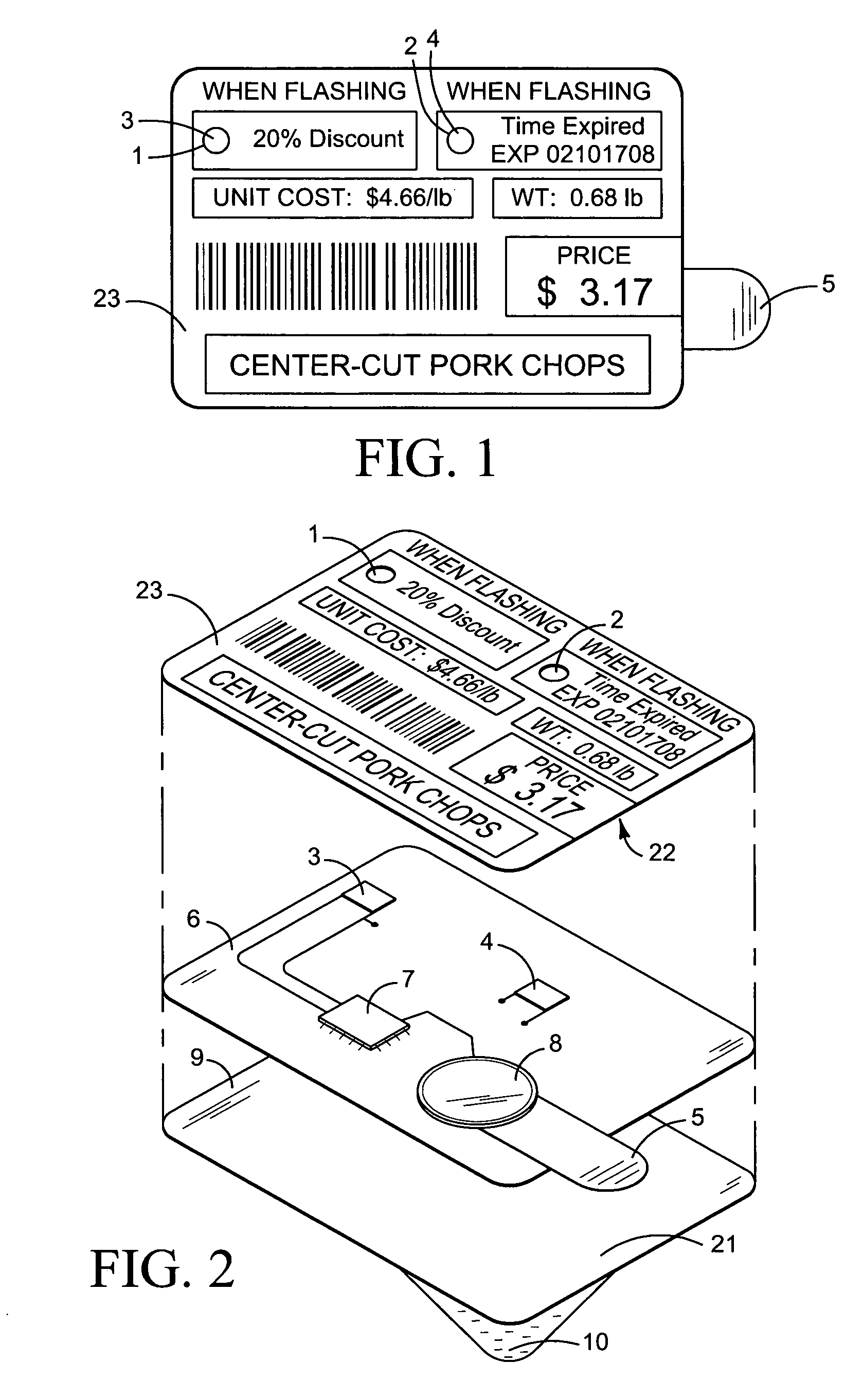
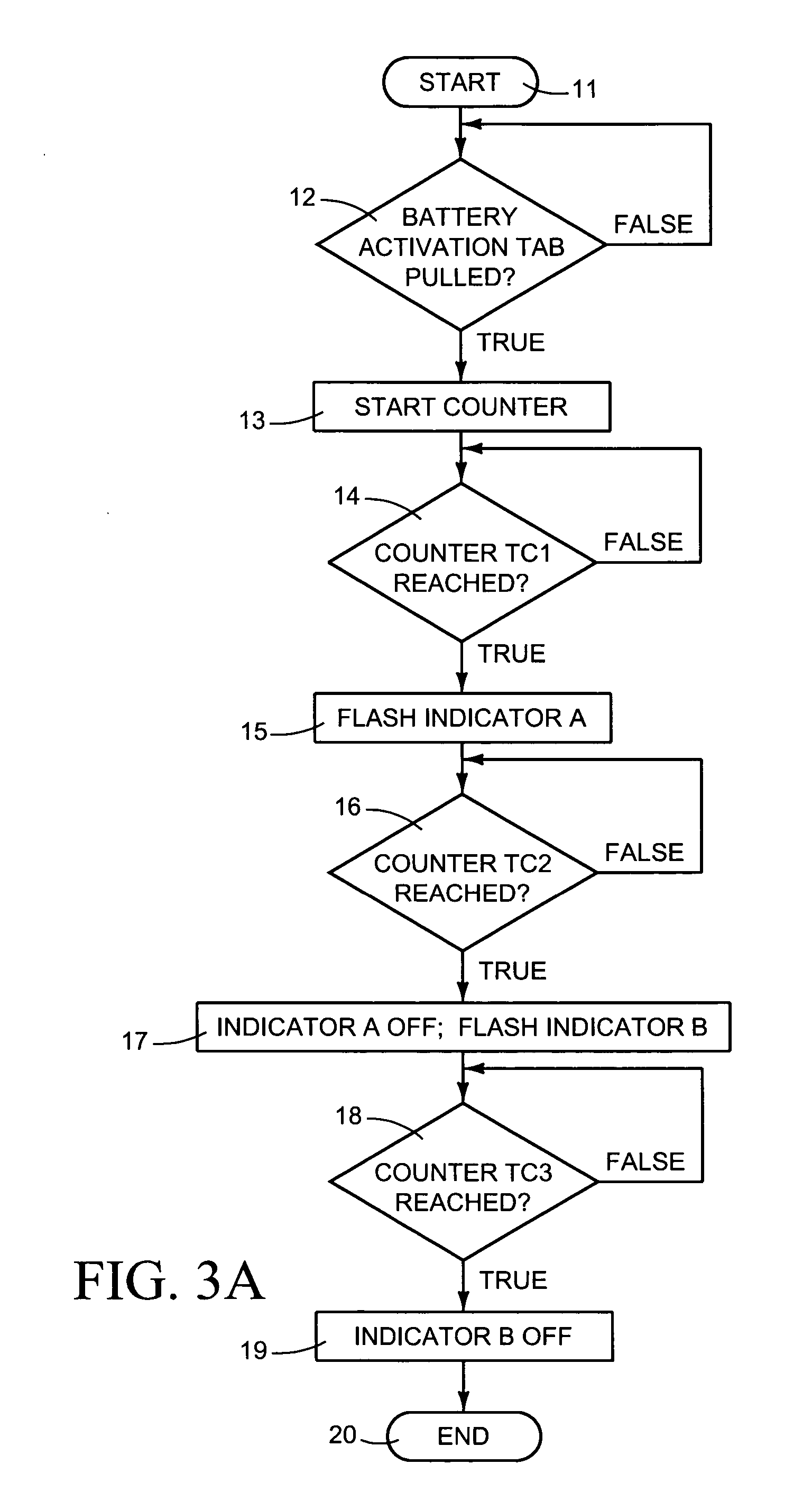
Perishable product electronic label including time and temperature measurement
ActiveUS7057495B2Informed decisionSimpler and more complex calculationStampsElectric signal transmission systemsEngineeringElectronic assemblies
An electronic assembly may be contained in a label that performs time-temperature integration (TTI) and indicates that time and / or temperature levels have been reached that may compromise the quality, shelf life, or safety of the item to which the label is affixed. The label may be used on a wide variety of objects that require careful handling in terms of temperature and / or time elapsed before use. The labeling system includes circuitry that measures and calculates, and indictor(s) that signal that the time has come for discounted sale, and, later, that the time has come for disposal rather than sale. Optionally, the circuitry may act as an “over-temperature alarm” system, to measure, calculate, and indicate when a one-time temperature violation has occurred that is of such a magnitude that the item is immediately considered compromised or spoiled. The label may take the form of a flexible, disposable label that is typically powered by a small battery. Methods may include providing a temperature-variable oscillator or time-base, counting cycles of said oscillator within a logic circuit to determine when one or more preset total cycle counts is / are reached, and signaling when said total cycle count(s) is / are reached.
Owner:COPELAND COLD CHAIN LP
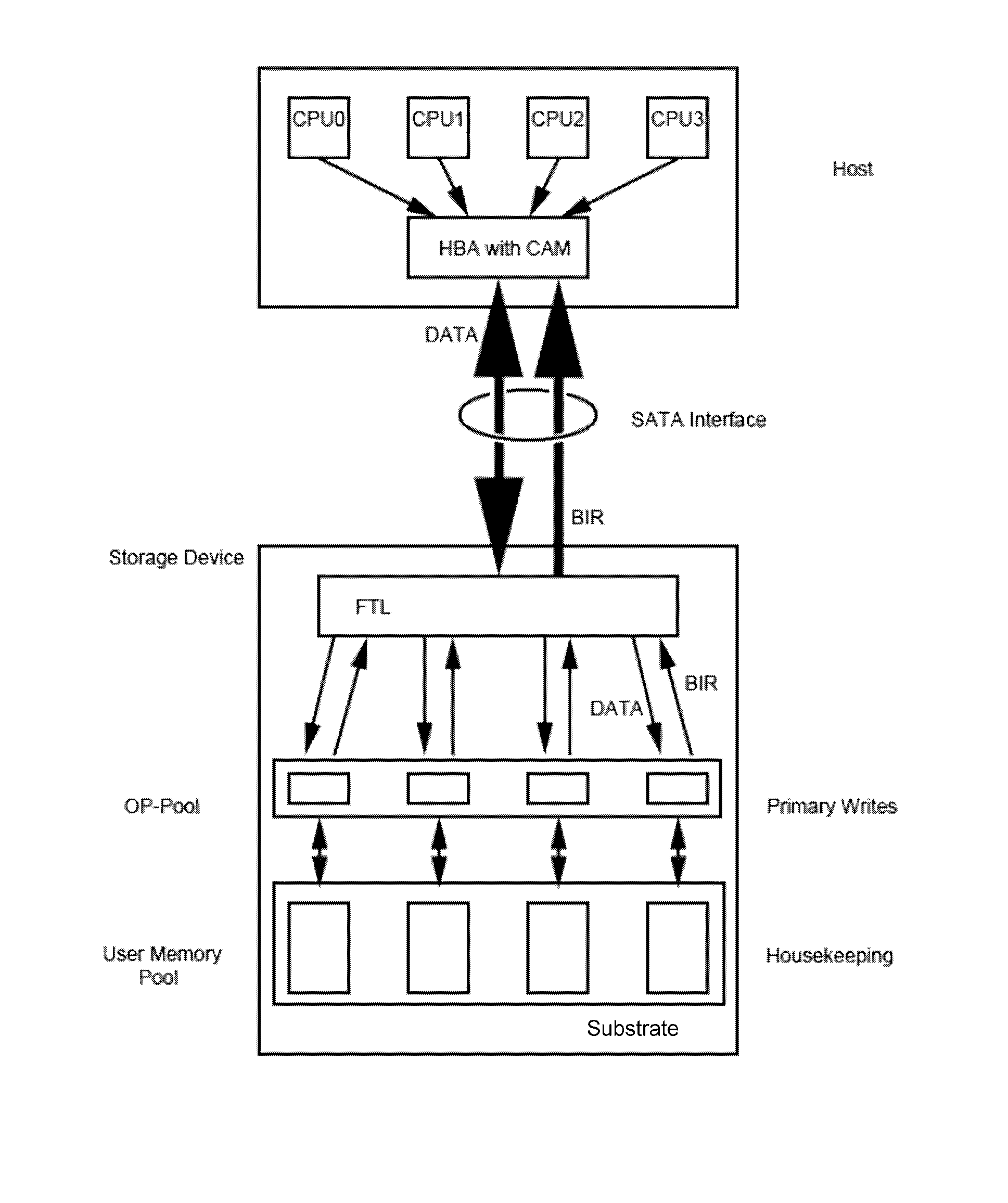
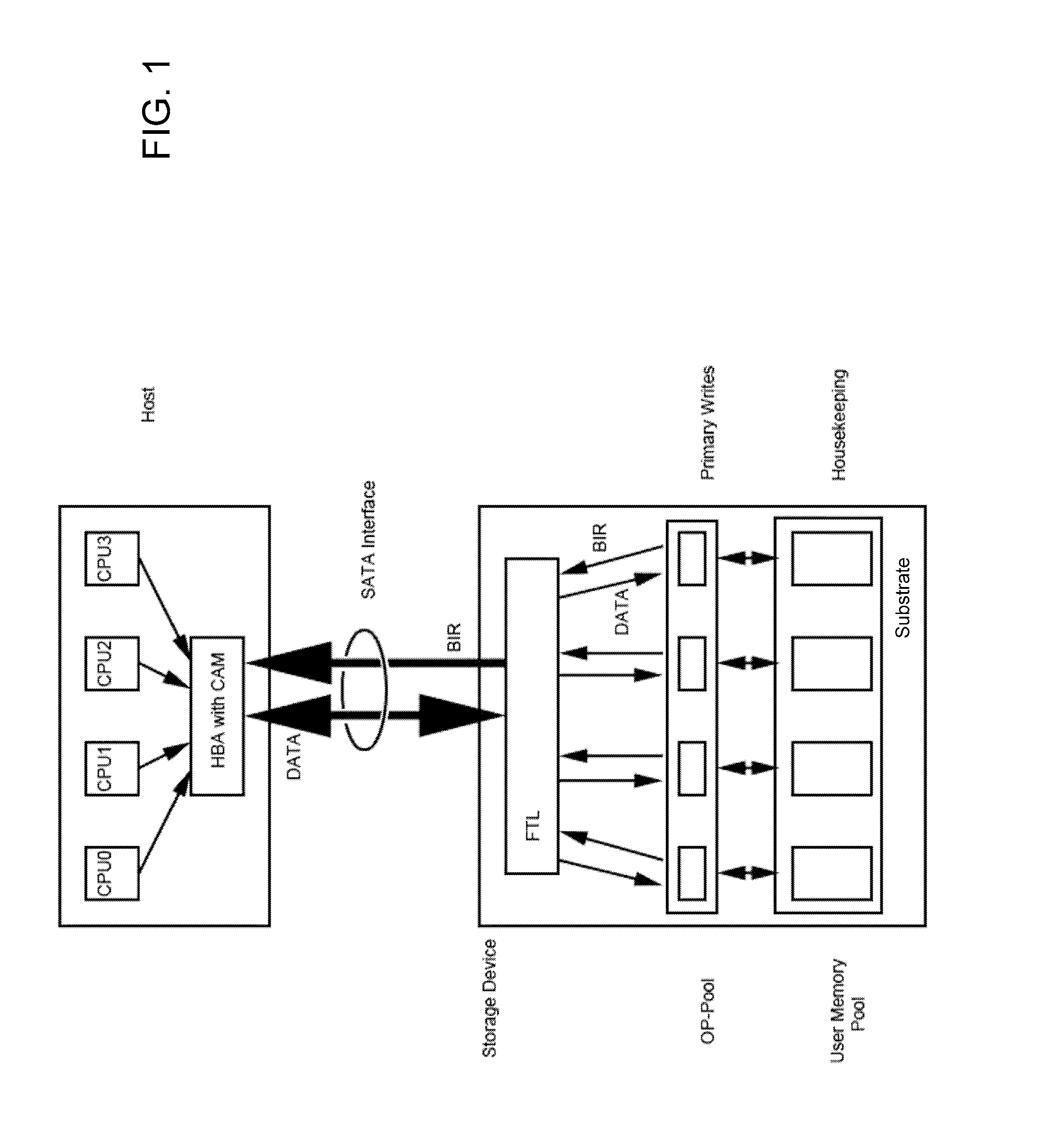
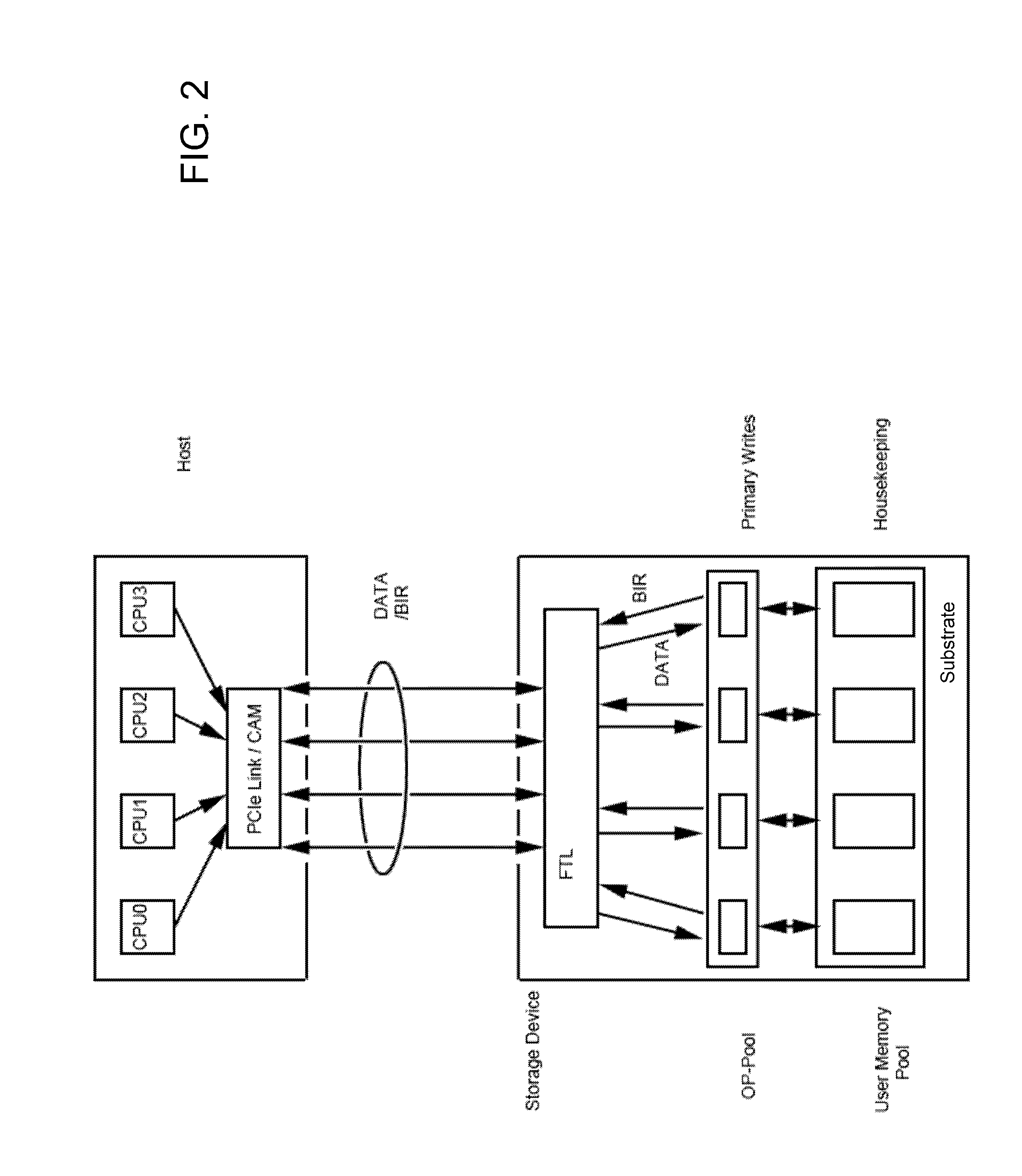
Non-volatile memory-based mass storage devices and methods for writing data thereto
ActiveUS20130067138A1Need for goodMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesMass storageComputer science
A non-volatile solid state memory-based mass storage device having at least one non-volatile memory component and methods of operating the storage device. In one aspect of the invention, the one or more memory components define a memory space partitioned into user memory and over-provisioning pools based on a P / E cycle count stored in a block information record. The storage device transfers the P / E cycle count of erased blocks to a host and the host stores the P / E cycle count in a content addressable memory. During a host write to the storage device, the host issues a low P / E cycle count number as a primary address to the content addressable memory, which returns available block addresses of blocks within the over-provisioning pool as a first dimension in a multidimensional address space. Changed files are preferably updated in append mode and the previous version can be maintained for version control.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
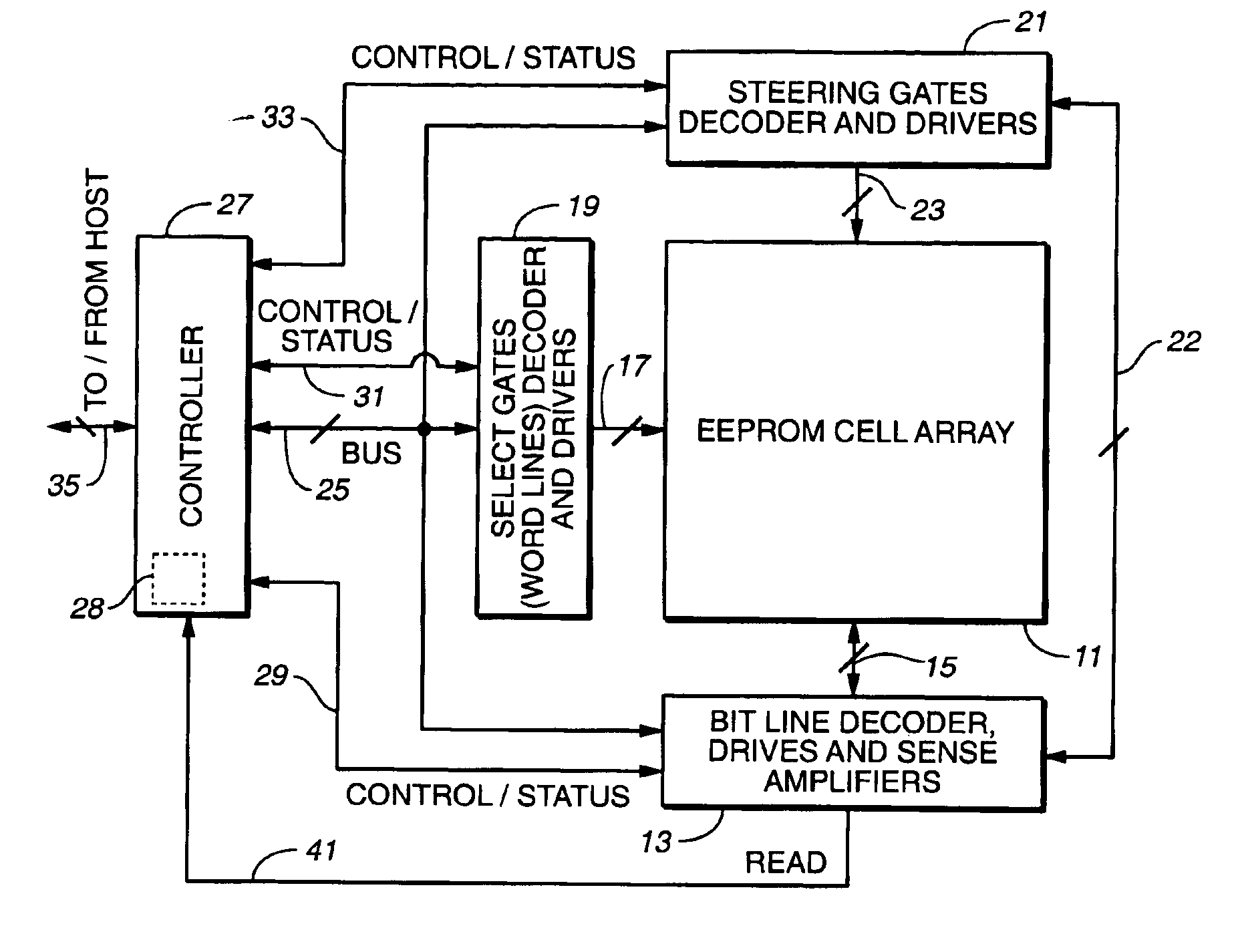
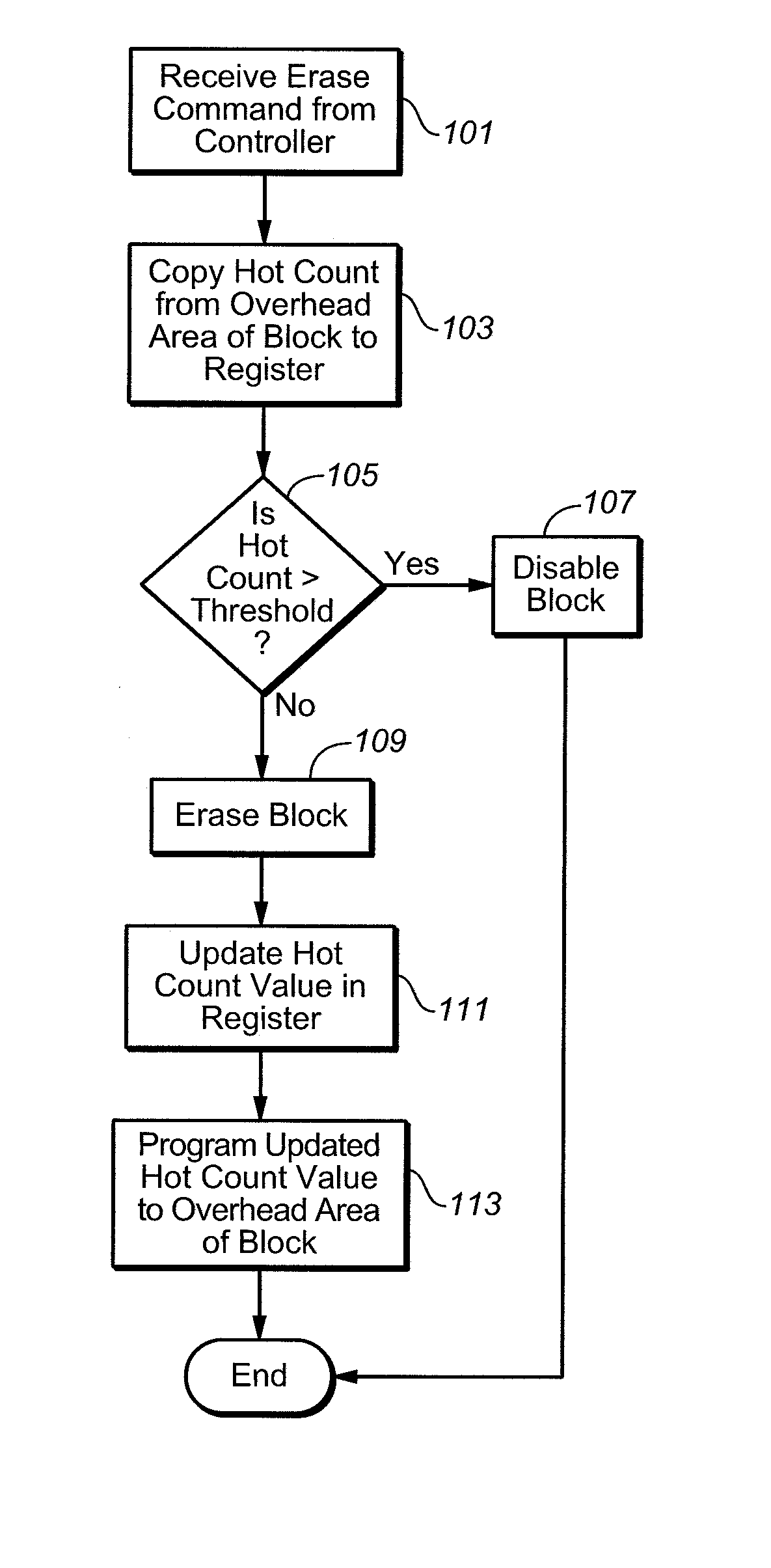
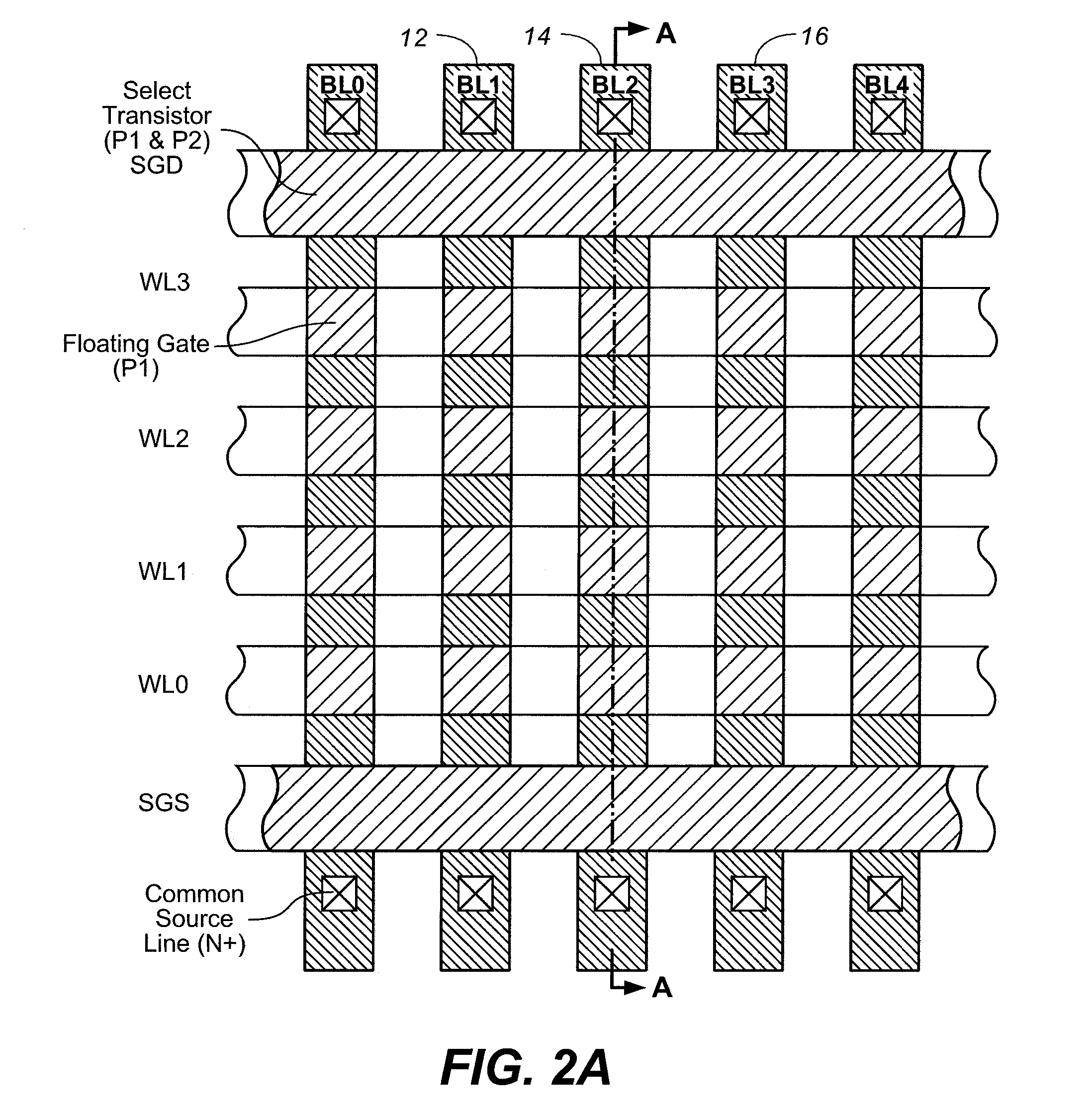
Non-volatile semiconductor memory with large erase blocks storing cycle counts
InactiveUS6944063B2Increase volumeReduce the amount of noiseError detection/correctionSolid-state devicesComputer scienceCorrection code
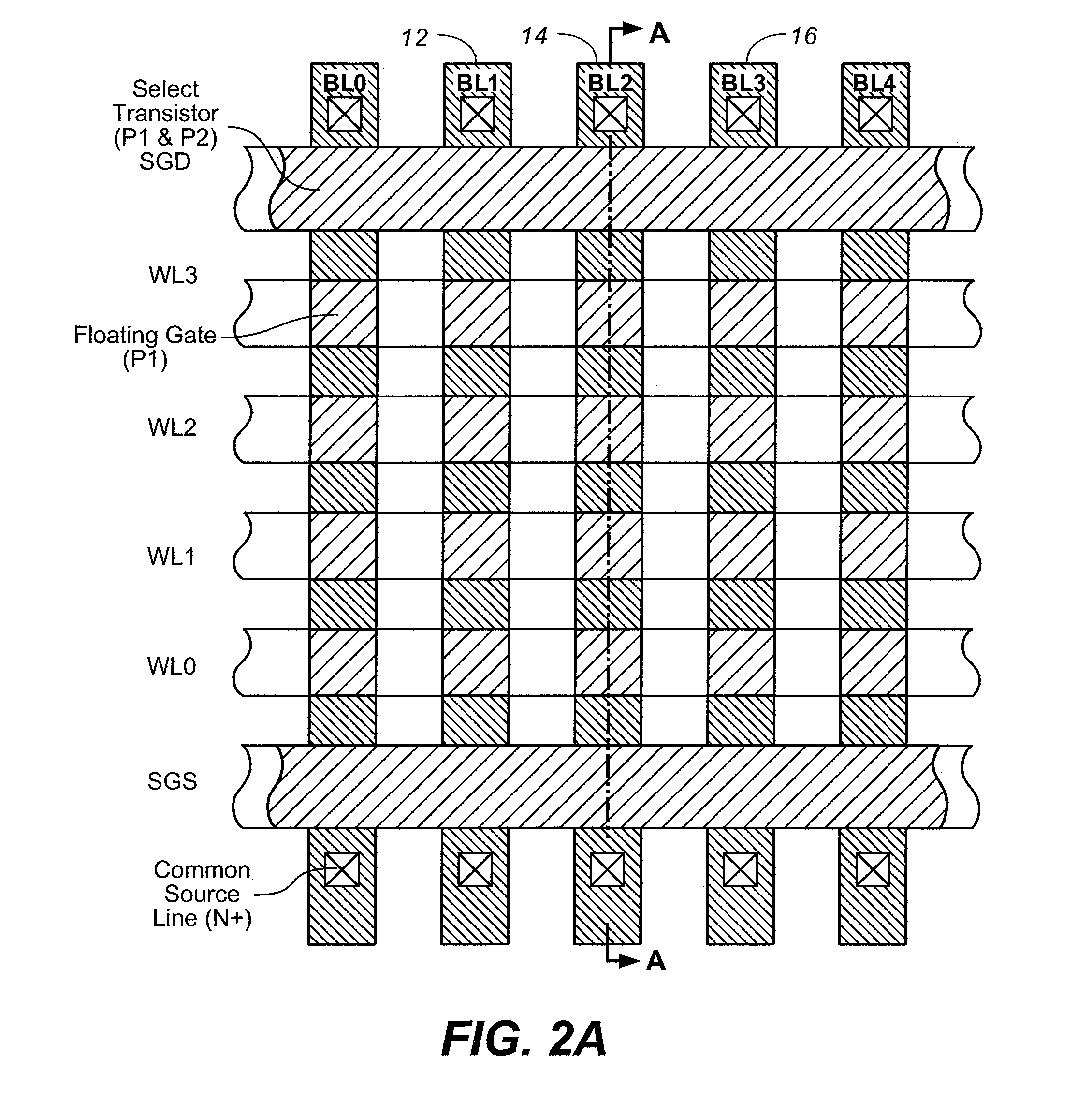
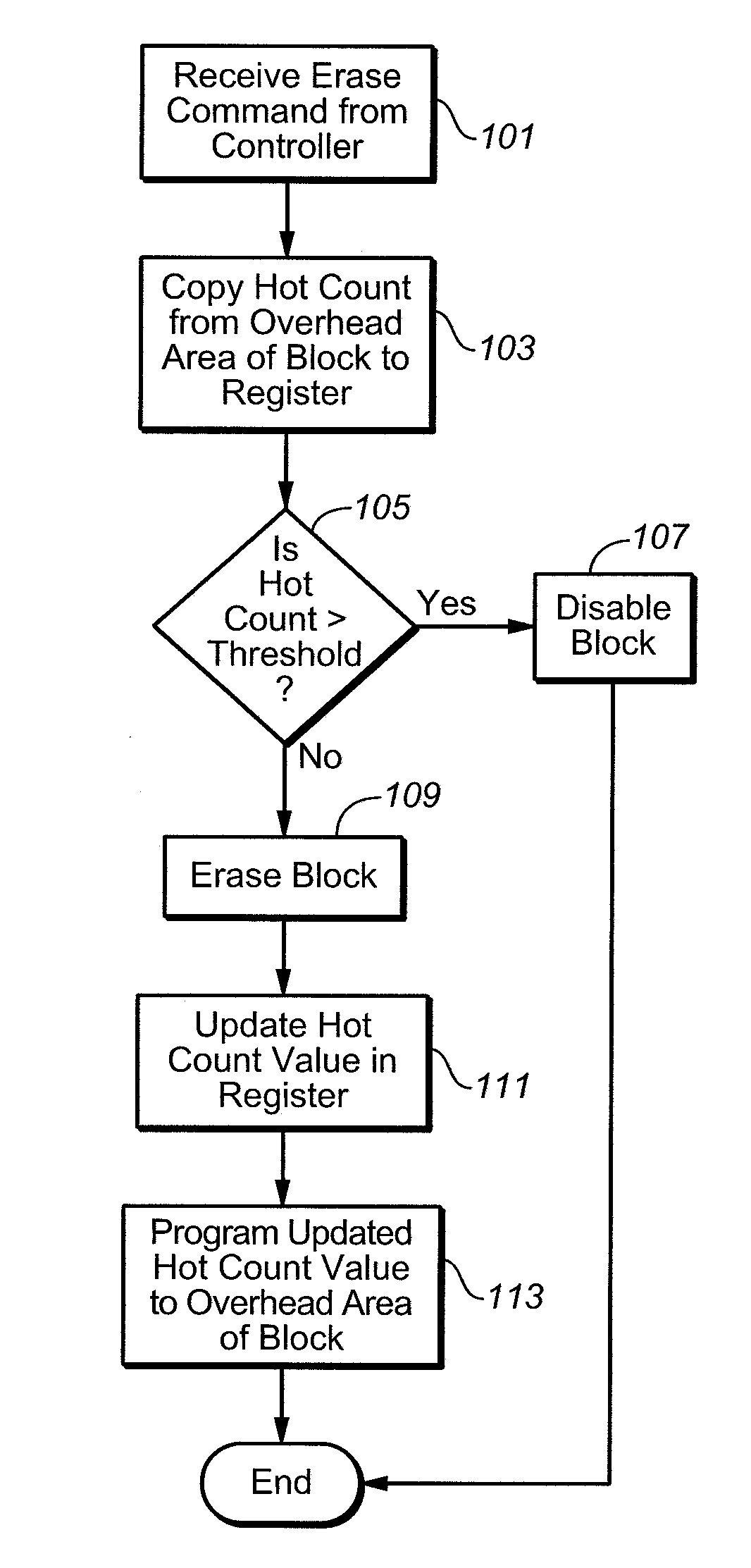
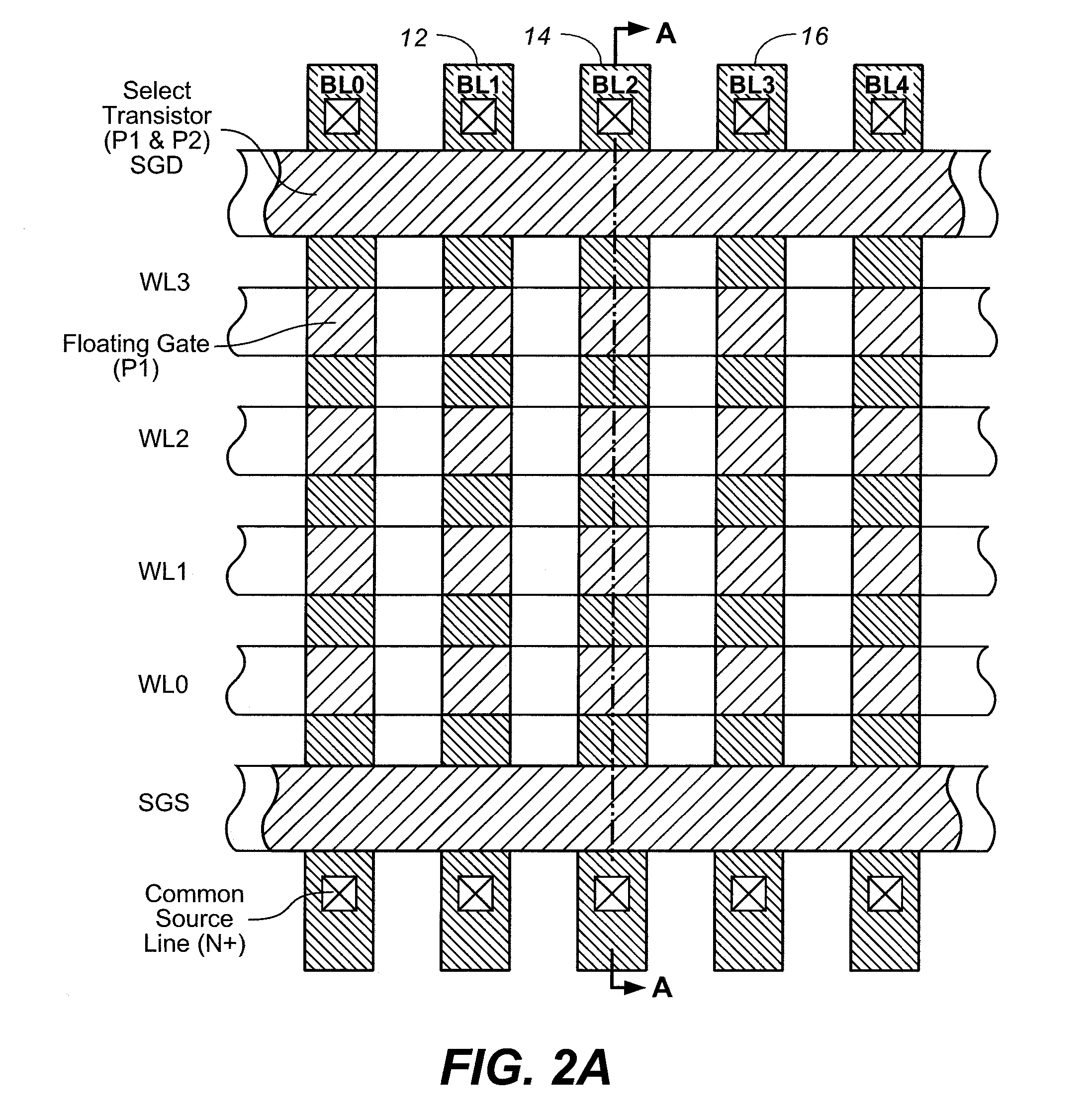
In a flash EEPROM system that is divided into separately erasable blocks of memory cells with multiple pages of user data being stored in each block, a count of the number of erase cycles that each block has endured is stored in one location within the block, such as in spare cells of only one page or distributed among header regions of multiple pages. The page or pages containing the block cycle count are initially read from each block that is being erased, the cycle count temporarily stored, the block erased and an updated cycle count is then written back into the block location. User data is then programmed into individual pages of the block as necessary. The user data is preferably stored in more than two states per memory cell storage element, in which case the cycle count can be stored in binary in a manner to speed up the erase process and reduce disturbing effects on the erased state that writing the updated cycle count can cause. An error correction code calculated from the cycle count may be stored with it, thereby allowing validation of the stored cycle count.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP +1
Flash memory module and method for programming a page of flash memory cells
A flash memory module and a method for programming a page of flash memory cells, the method includes: receiving a cycle count indication indicative of a number of program cycles of the page of memory cells; setting a value of a programming parameter of a programming operation based on the cycle count indication; and programming at least one flash memory cell of the page of flash memory cells by performing the programming operation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
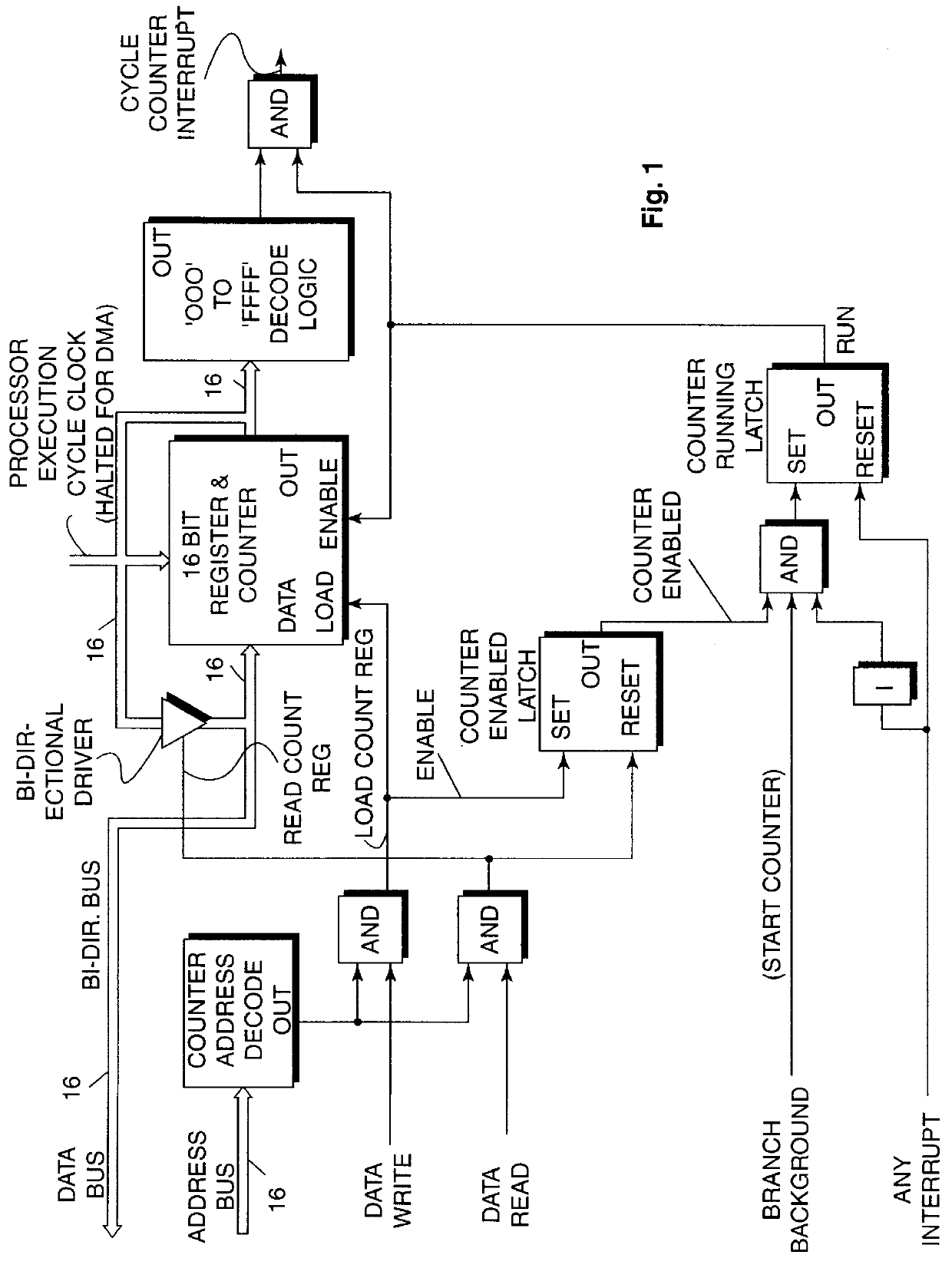
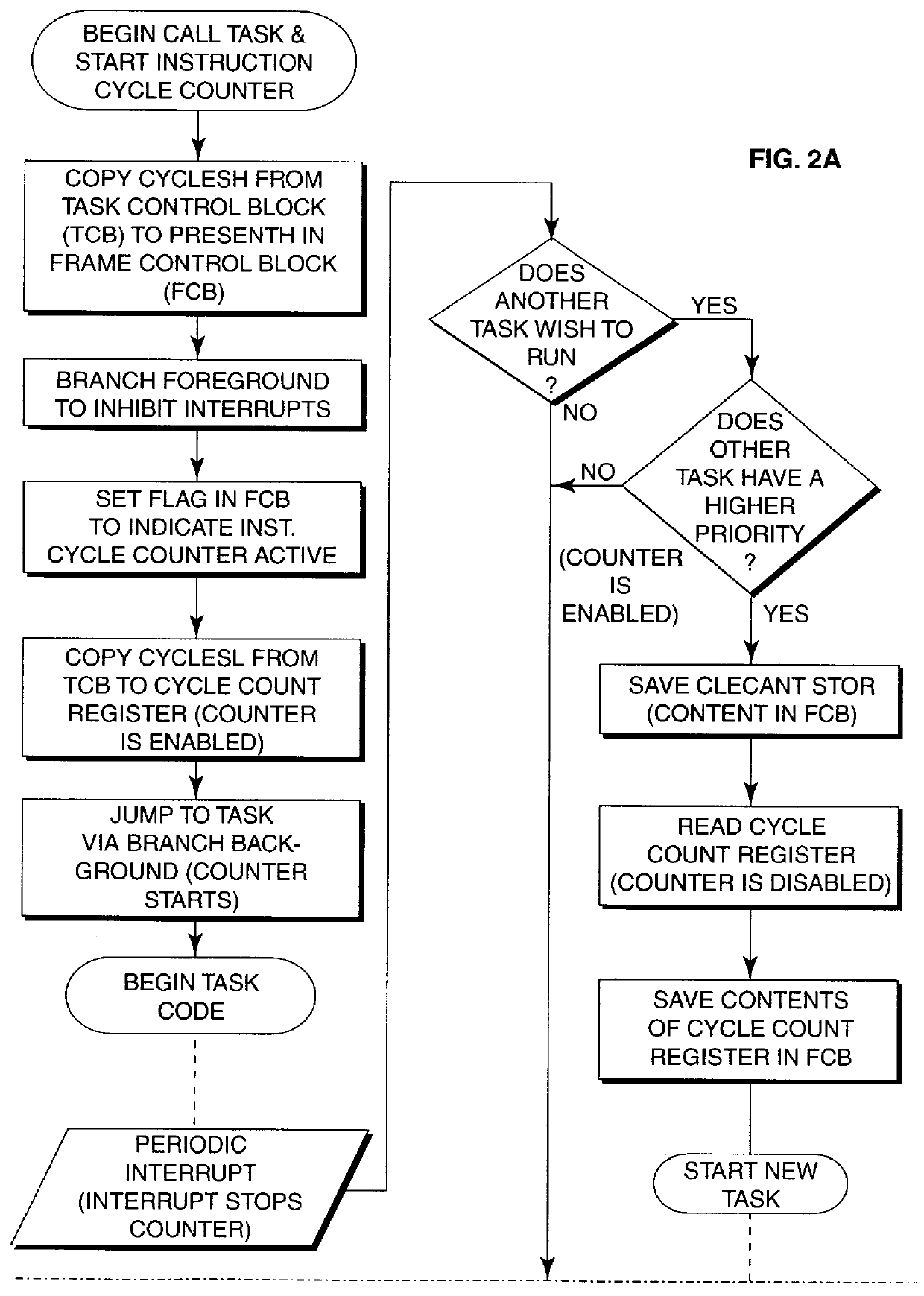
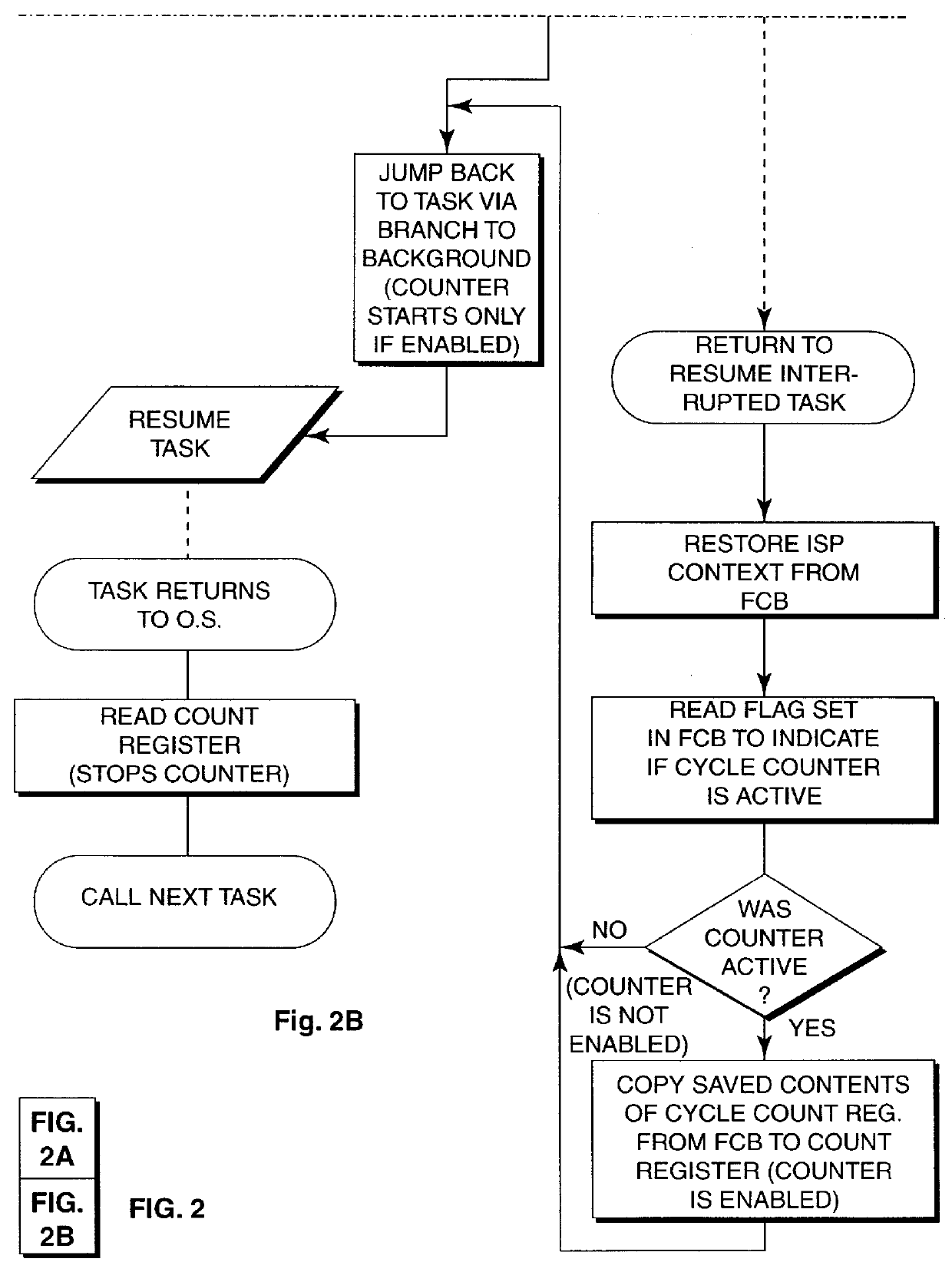
Monitoring processor execution cycles to prevent task overrun in multi-task, hard, real-time system
InactiveUS6085218AMinimal overheadIntegrity guaranteedDigital data processing detailsHardware monitoringEmbedded systemTime system
Hard, real-time, multi-tasking system is monitored by combined hardware and software and logic to detect overrun of any task beyond a declared maximum processor cycle limit for the task. Processor execution cycles utilized by DMA or interrupt processing and not related to the task being executed are not counted. Counter hardware and control logic reduces software overhead for monitoring execution cycle utilization by a task and provides capability not only of overrun detection, but programmed cycle usage alarm, consumed cycle count and overall processor loading or utilization measurements to be made.
Owner:IBM CORP
Write-erase endurance lifetime of memory storage devices
ActiveUS20110029715A1Improves the write-erase endurance lifetime of a flash-based SSDMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationManagement systemData structure
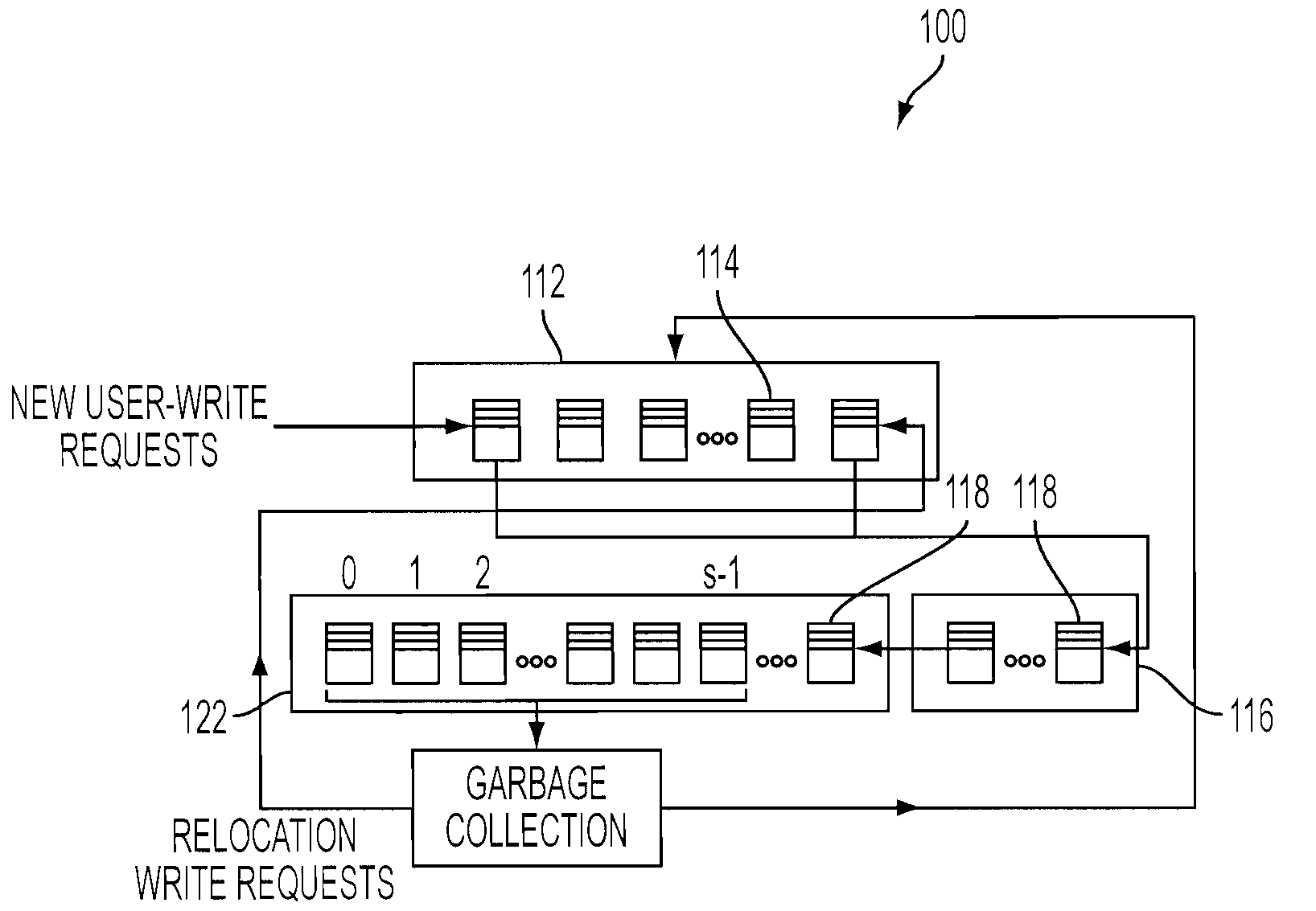
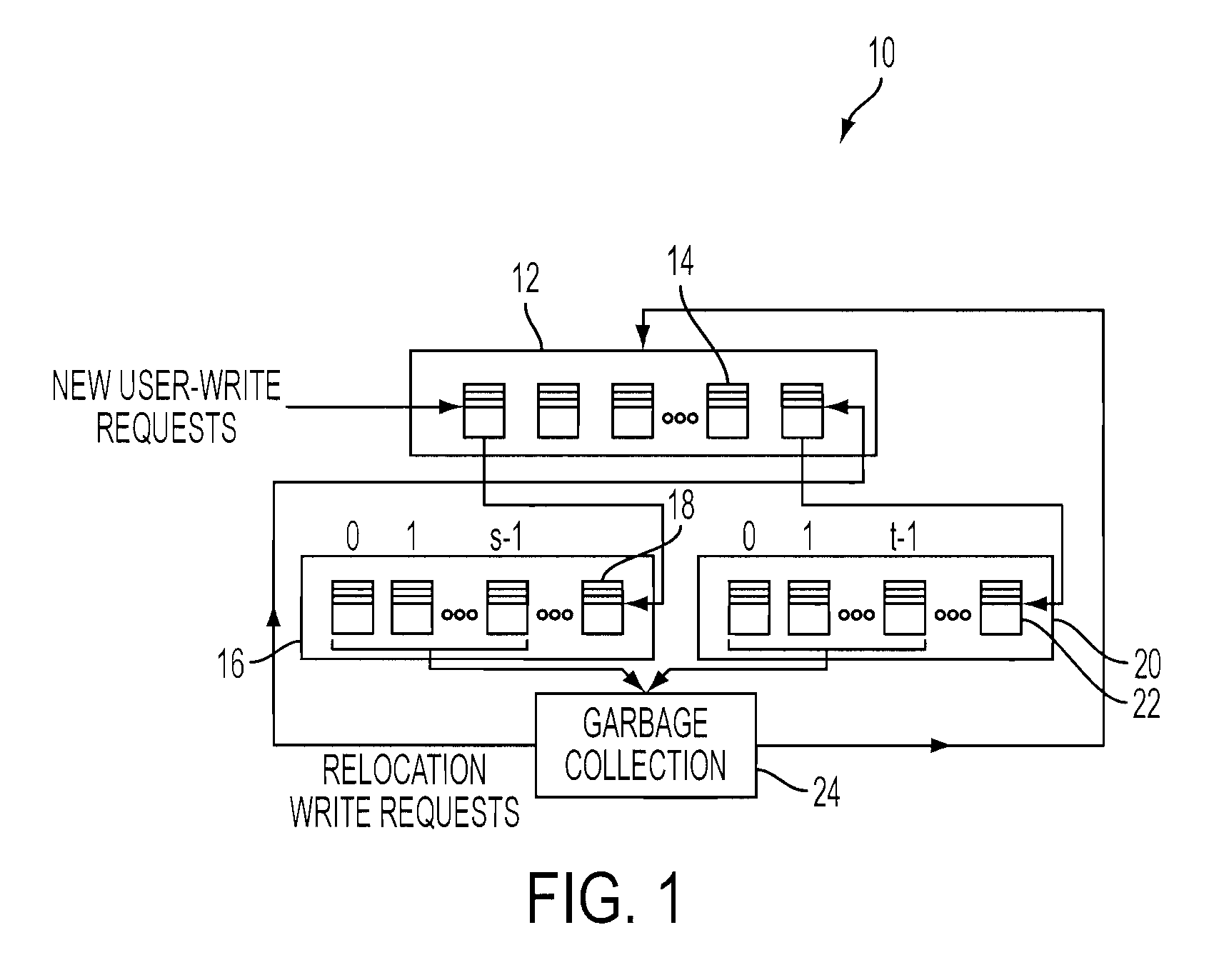
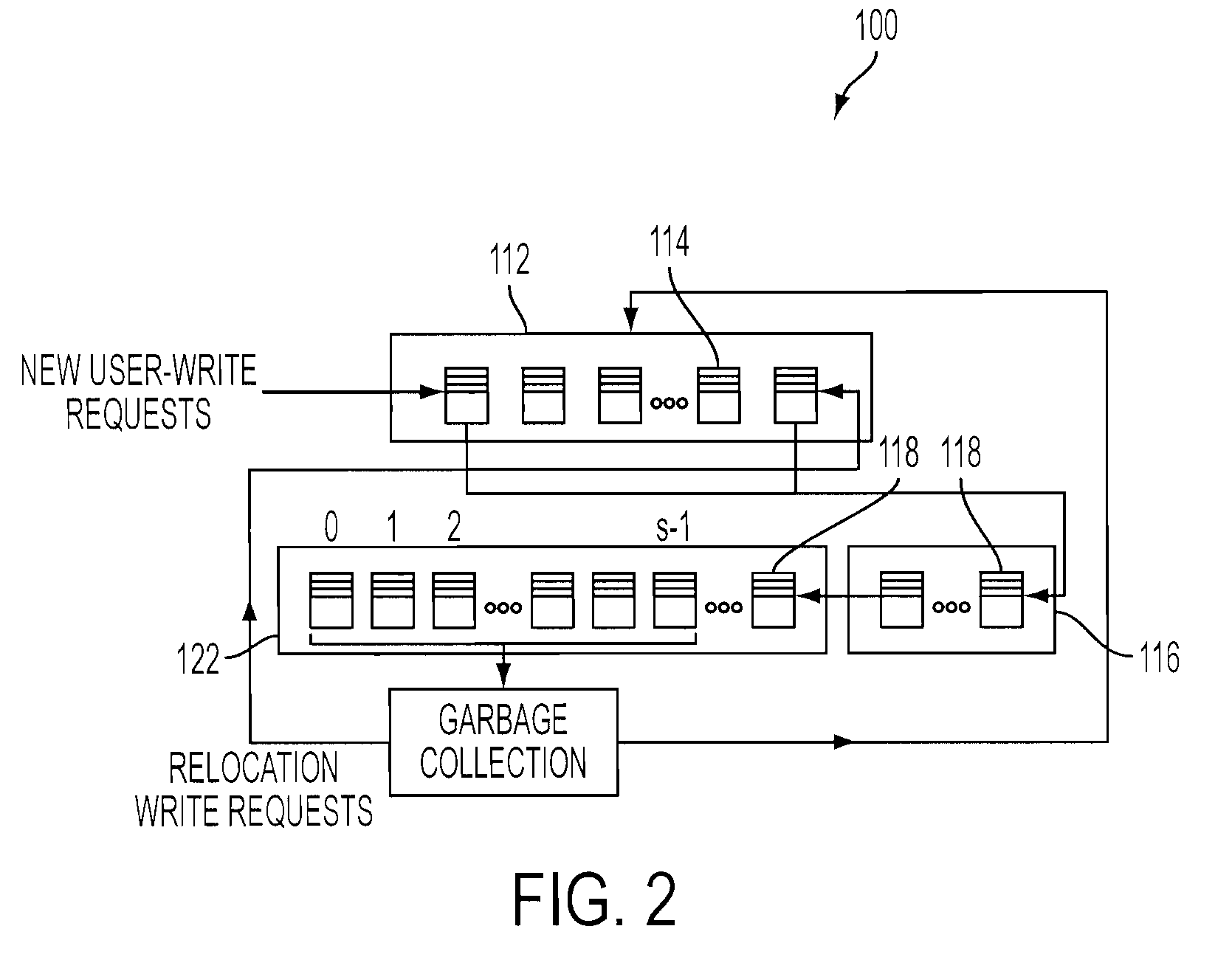
A memory management system and method for managing memory blocks of a memory device of a computer. The system includes a free block data structure including free memory blocks for writing, and sorting the free memory blocks in a predetermined order based on block write-erase endurance cycle count and receiving new user-write requests to update existing data and relocation write requests to relocate existing data separately, a user-write block pool for receiving youngest blocks holding user-write data (i.e., any page being updated frequently) from the free block data structure, a relocation block pool for receiving oldest blocks holding relocation data (i.e., any page being updated infrequently) from the free block data structure, and a garbage collection pool structure for selecting at least one of user-write blocks and relocation blocks for garbage collection, wherein the selected block is moved back to the free block data structure upon being relocated and erased.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
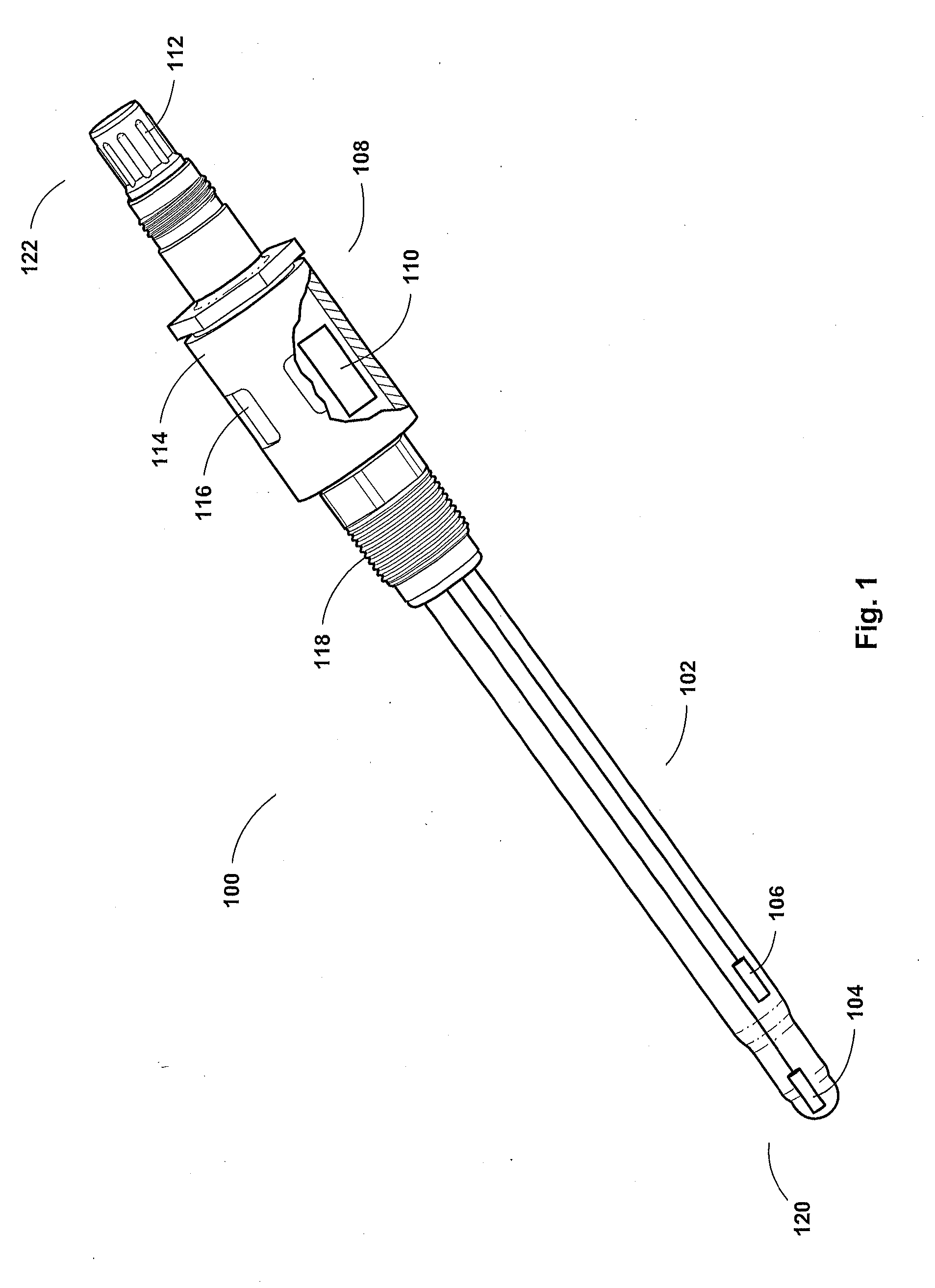
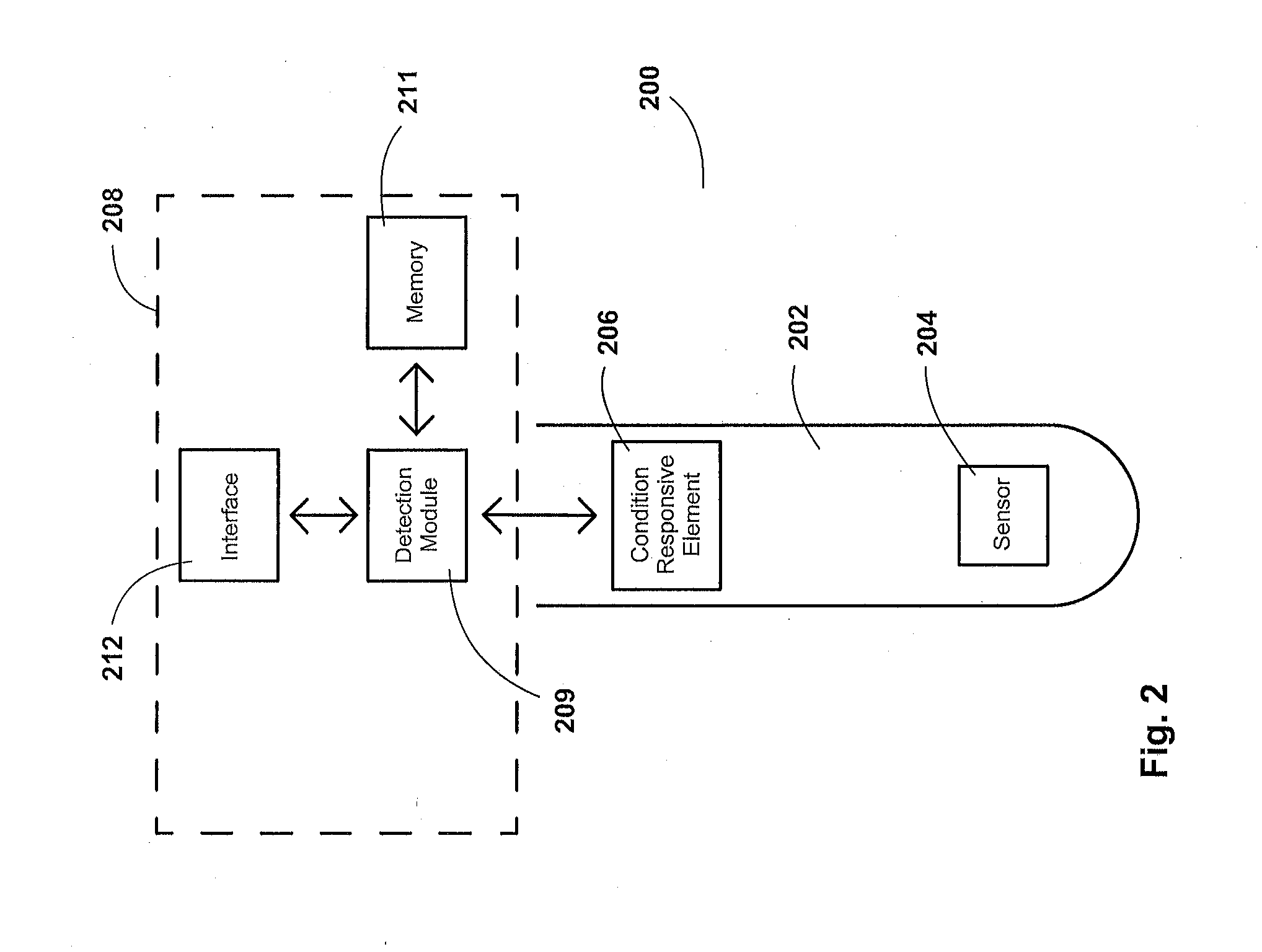
Measurement probe with heat cycle event counter
ActiveUS20160004956A1Protect the circuitSave powerBatteries circuit arrangementsRegistering/indicating working of machinesMeasurement deviceComputer module
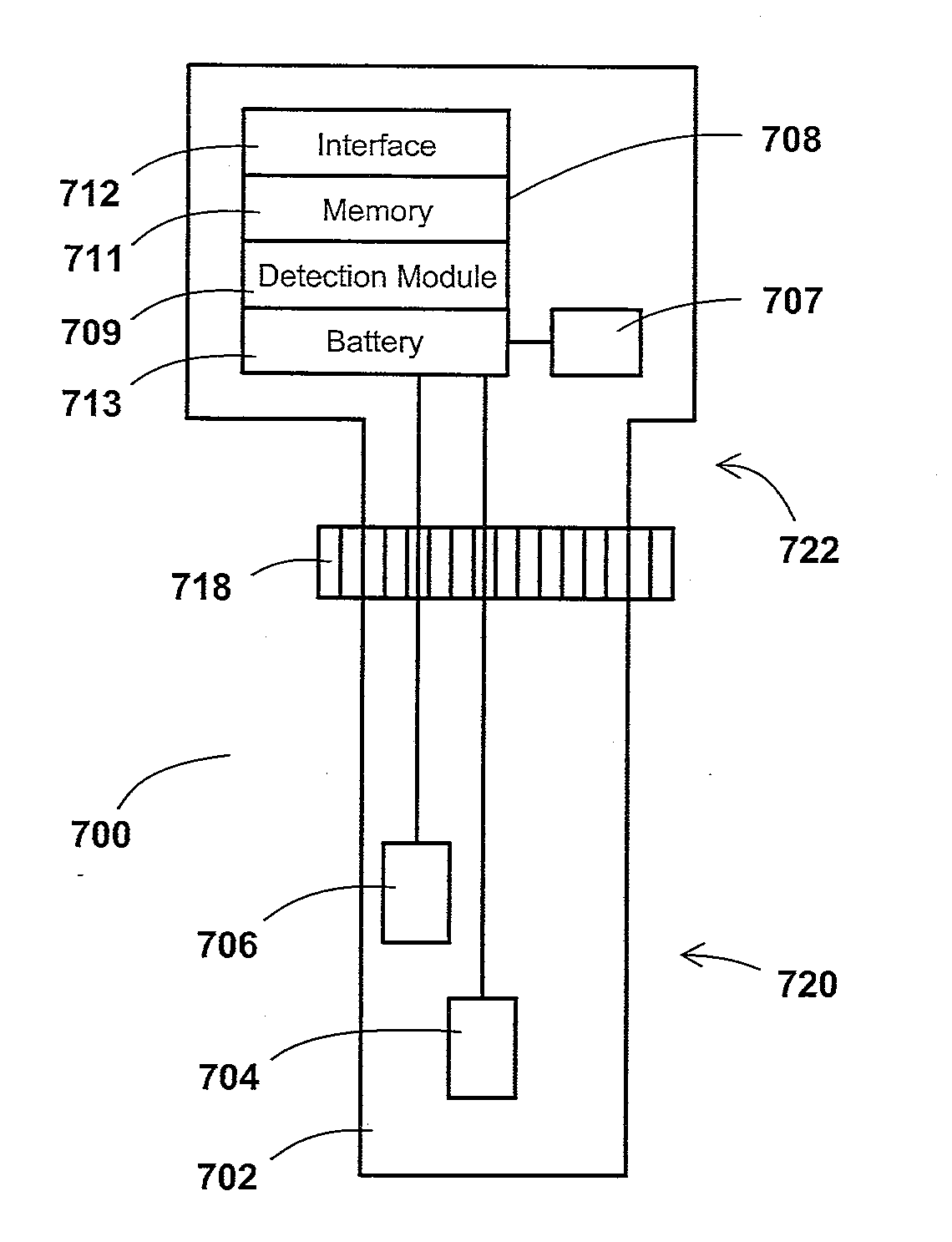
A system comprising a measurement device and a handheld device is disclosed, the system adapted to withstand, detect, record, and display heat cycle event counts. The measurement device comprises a sensor for measuring and a heat cycle detection unit. The heat cycle detection unit comprises a temperature or pressure responsive element, a detection module, data interface, and data memory. The handheld device comprises a screen, a button, a communication circuit, and a processing system. The communication circuit is configured to communicate with the measurement device and a computing device and the processing system is configured to receive non-measurement information from the measurement device, display the received information on the screen, and cycle the received information displayed on the screen based on an actuation of the button, wherein the handheld device is used to display a heat sterilization cycle count of the measurement device.
Owner:BROADLEY JAMES
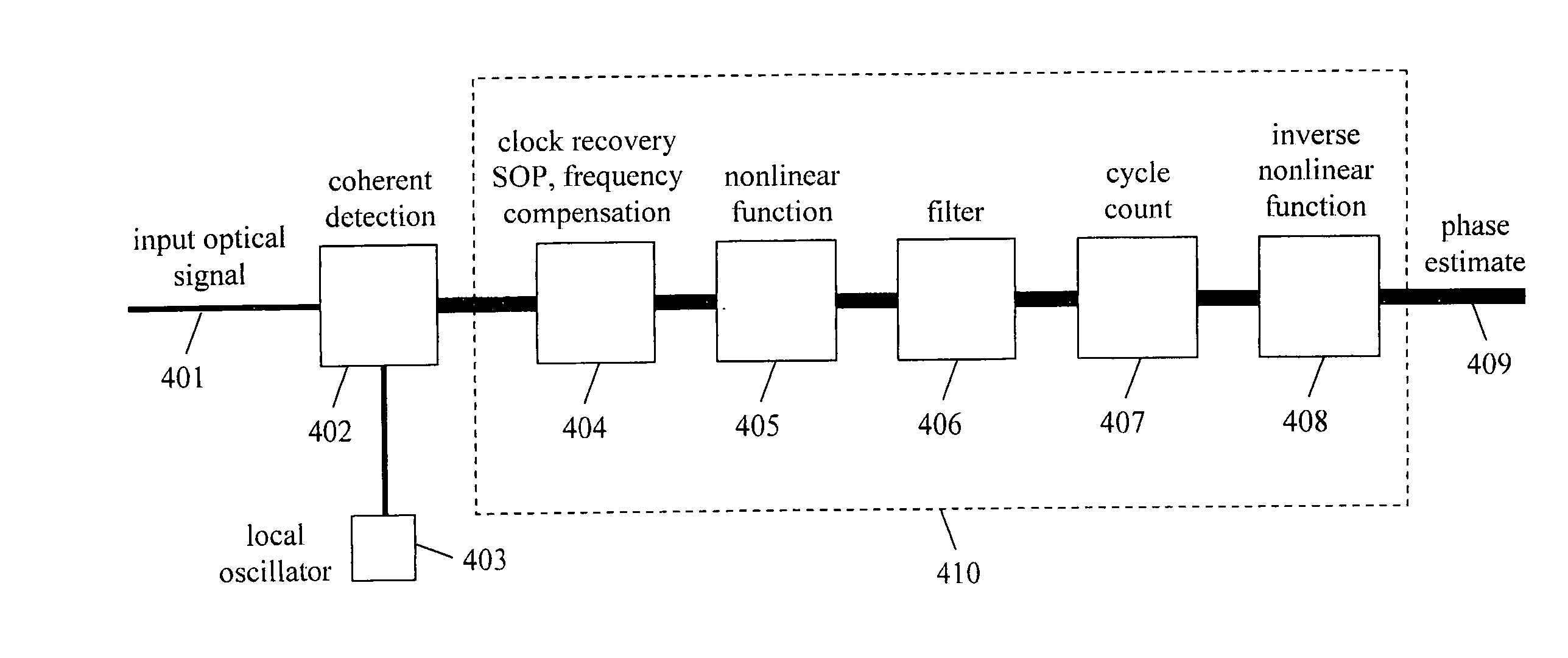
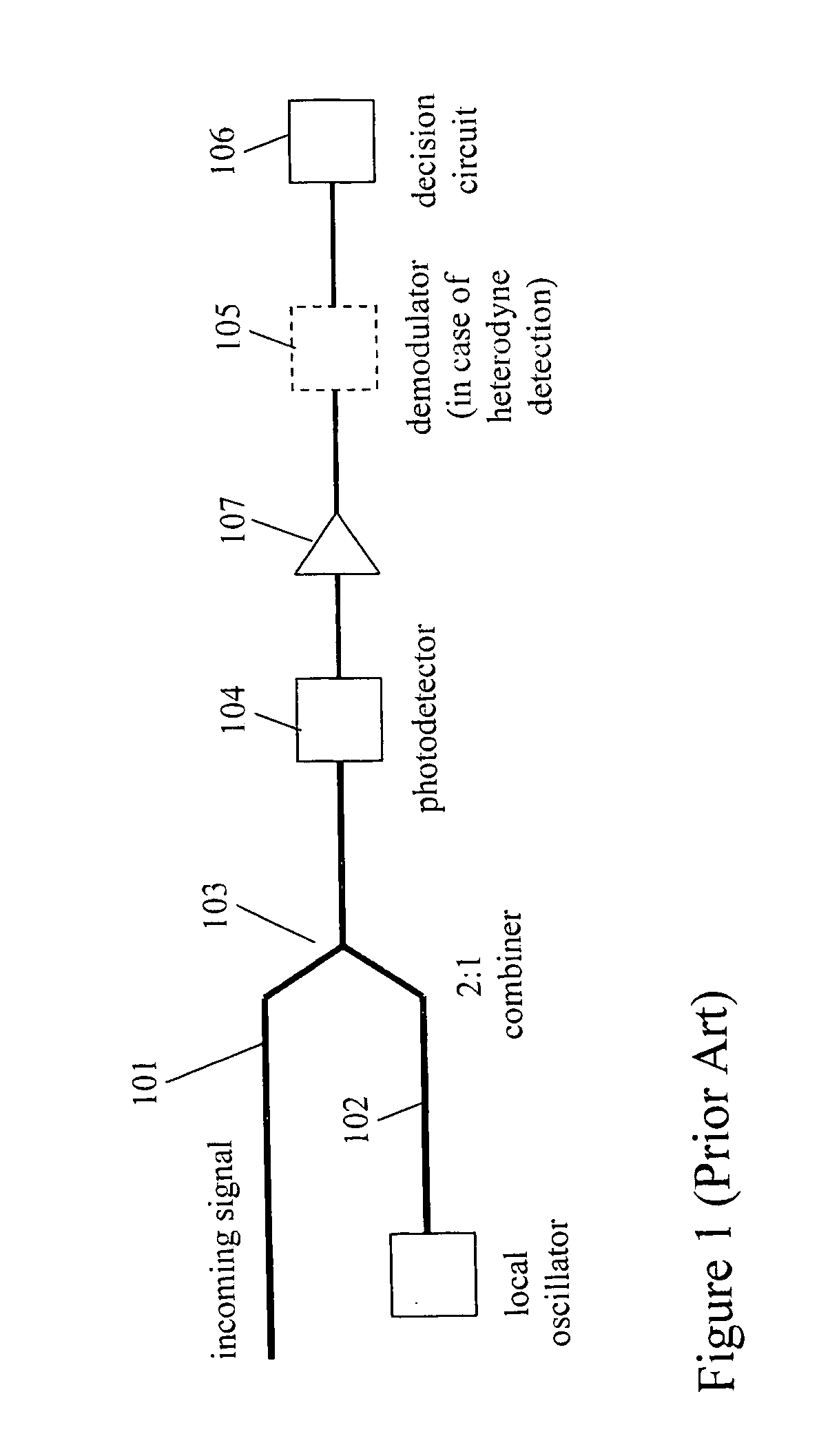
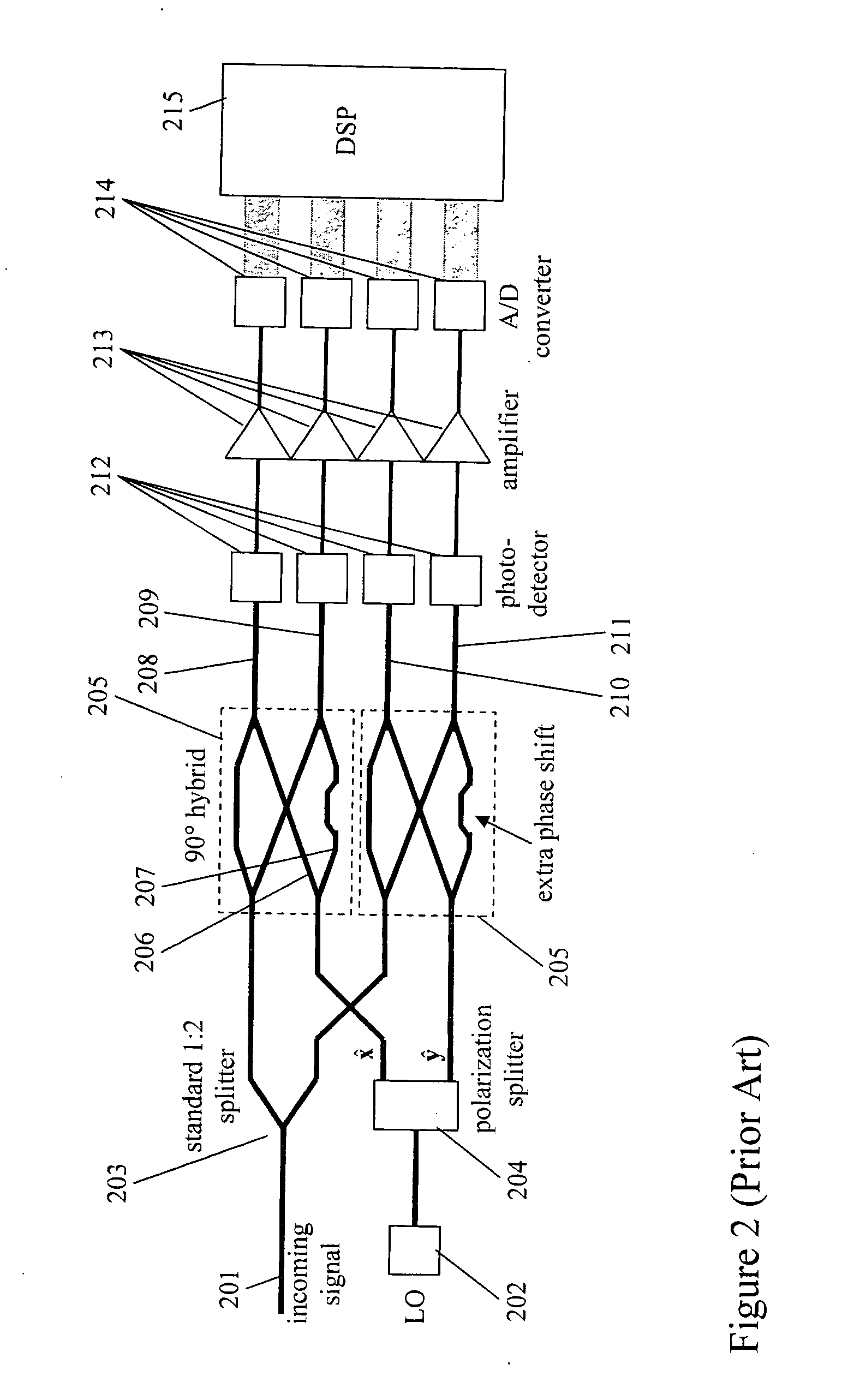
Phase estimation for coherent optical detection
InactiveUS20060245766A1Accurate transfer functionEliminate the effects ofElectromagnetic receiversEstimation methodsLocal oscillator
The present invention is a method and apparatus to make an estimate of the phase of a signal relative to the local oscillator in an optical coherent detection subsystem that employs a digital signal processor having a parallel architecture. The phase estimation method comprises operations that do not use feedback of recent results. The method includes a cycle count function so that the phase estimate leads to few cycle slips. The phase estimate of the present invention is approximately the same as the optimal phase estimate.
Owner:TAYLOR MICHAEL GEORGE
Perishable product electronic label including time and temperature measurement
ActiveUS20060061454A1Facilitate inter communication of dataFacilitates wireless radio frequency communicationStampsElectric signal transmission systemsCommunication interfaceInterface circuits
An electronic assembly may be contained in a label that performs time-temperature integration (TTI) and indicates that time and / or temperature levels have been reached that may compromise the quality, shelf life, or safety of the item to which the label is affixed. The label may be used on a wide variety of objects that require careful handling in terms of temperature and / or time elapsed before use. The labeling system includes circuitry that measures and calculates, and indictor(s) that signal that the time has come for discounted sale, and, later, that the time has come for disposal rather than sale. Optionally, the circuitry may act as an “over-temperature alarm” system, to measure, calculate, and indicate when a one-time temperature violation has occurred that is of such a magnitude that the item is immediately considered compromised or spoiled. The label may take the form of a flexible, disposable label that is typically powered by a small battery. Methods may include providing a temperature-variable oscillator or time-base, counting cycles of said oscillator within a logic circuit to determine when one or more preset total cycle counts is / are reached, and signaling when said total cycle count(s) is / are reached. Extra sensing, time-keeping, memory storage, and / or communication interface circuits may be incorporated to augment the electronic assembly's and method's capabilities.
Owner:COPELAND COLD CHAIN LP
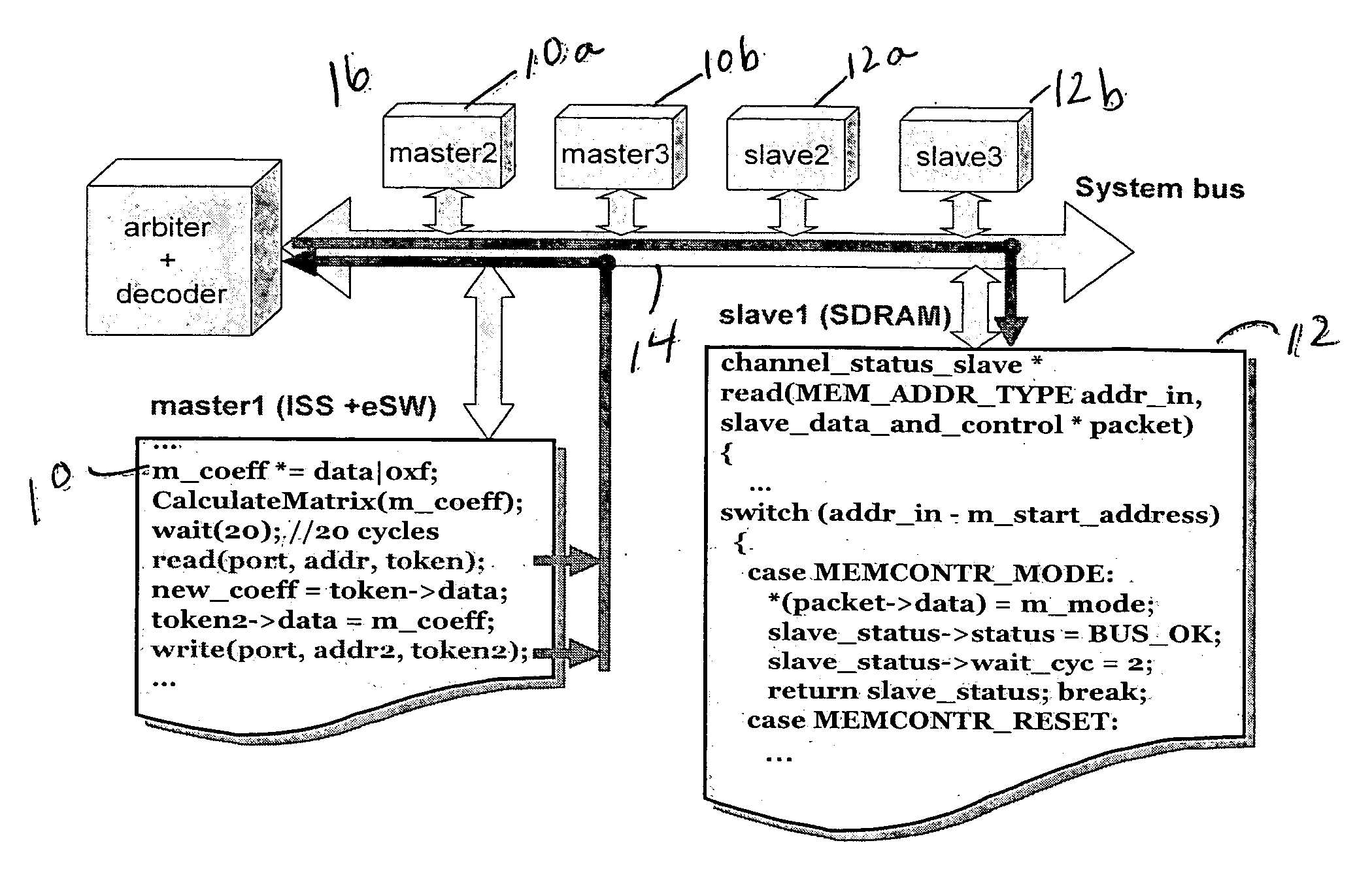
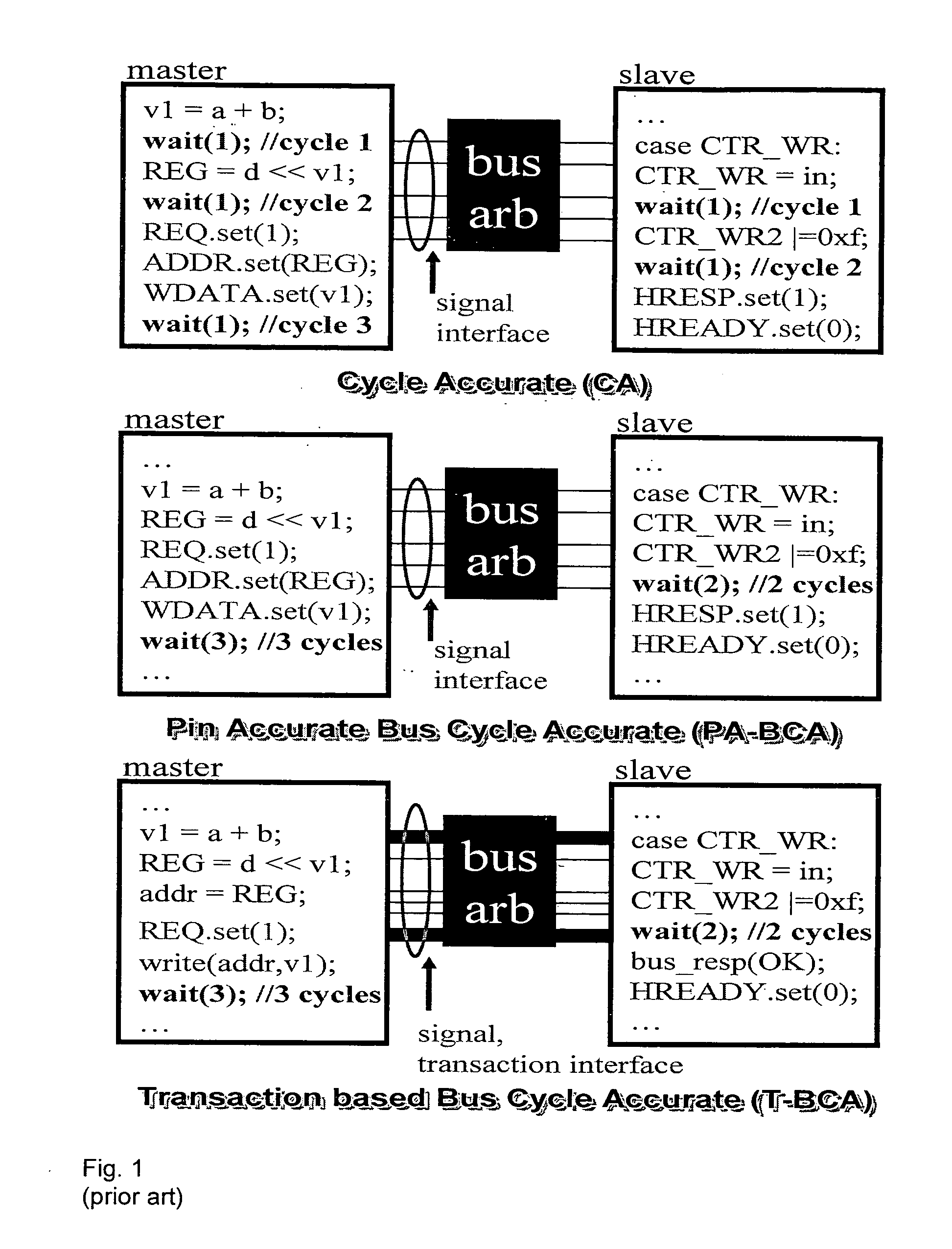
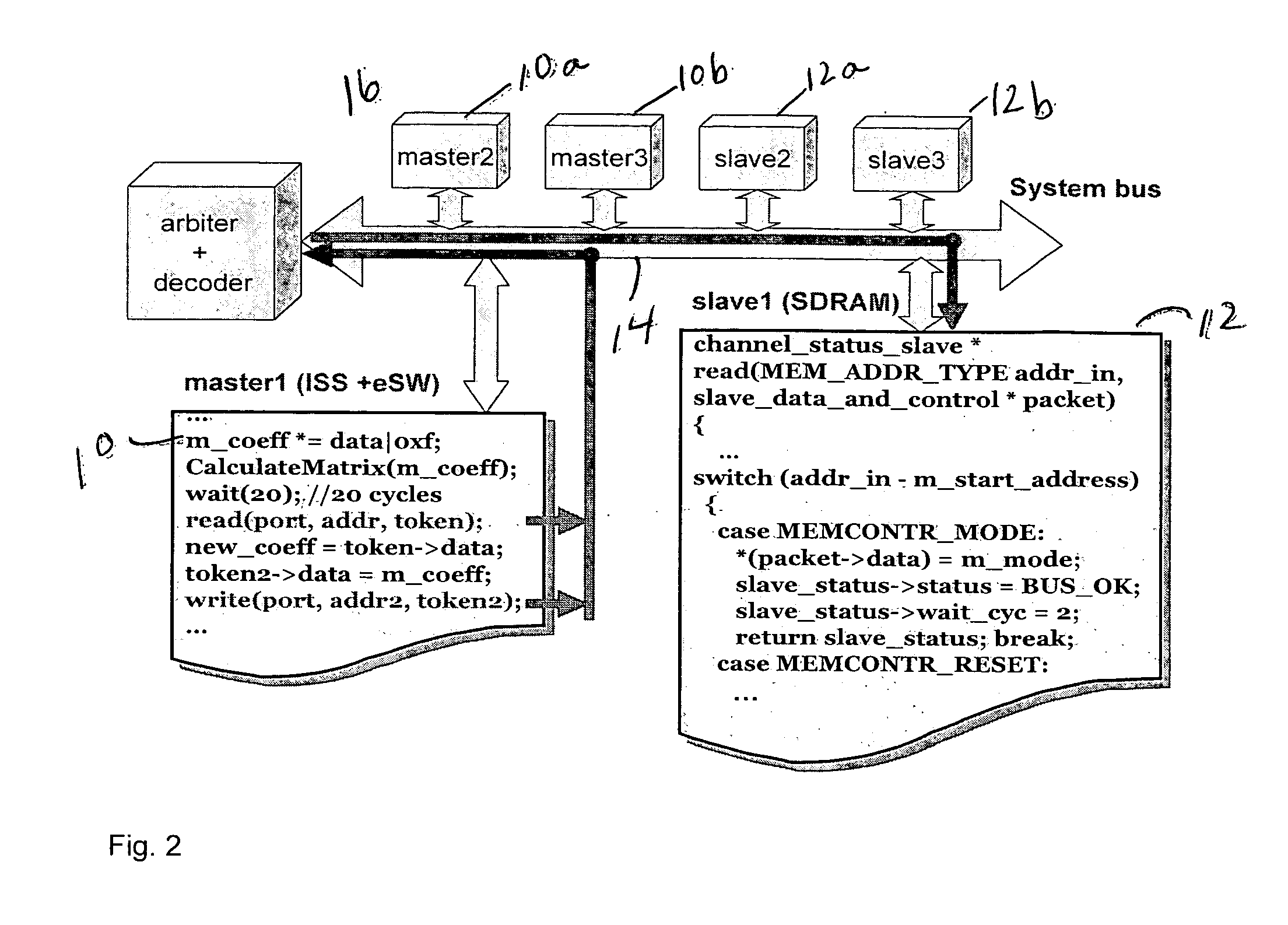
Method for the fast exploration of bus-based communication architectures at the cycle-count-accurate-at-transaction -boundaries (CCATB) abstraction
ActiveUS20060282233A1Speed up system prototypingMaintaining cycle count accuracyAnalogue computers for electric apparatusCAD circuit designComputer hardwareHardware architecture
A computer system simulation method starts with algorithmically implementing a specification model independently of hardware architecture. High level functional blocks representing hardware components are connected together using a bus architecture-independent generic channel. The bus architecture-independent generic channel is annotated with timing and protocol details to define an interface between the bus architecture-independent generic channel and functional blocks representing hardware components. The interface is refined to obtain a CCATB for communication space. The read( ) and write( ) interface calls are decomposed into several method calls which correspond to bus pins to obtain observable cycle accuracy for system debugging and validation and to obtain a cycle accurate model. The method calls are replaced by signals, and the functional blocks representing hardware components are further refined to obtain pin / cycle-accurate models which can be manually or automatically mapped to RTL, or be used to co-simulate with existing RTL components.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
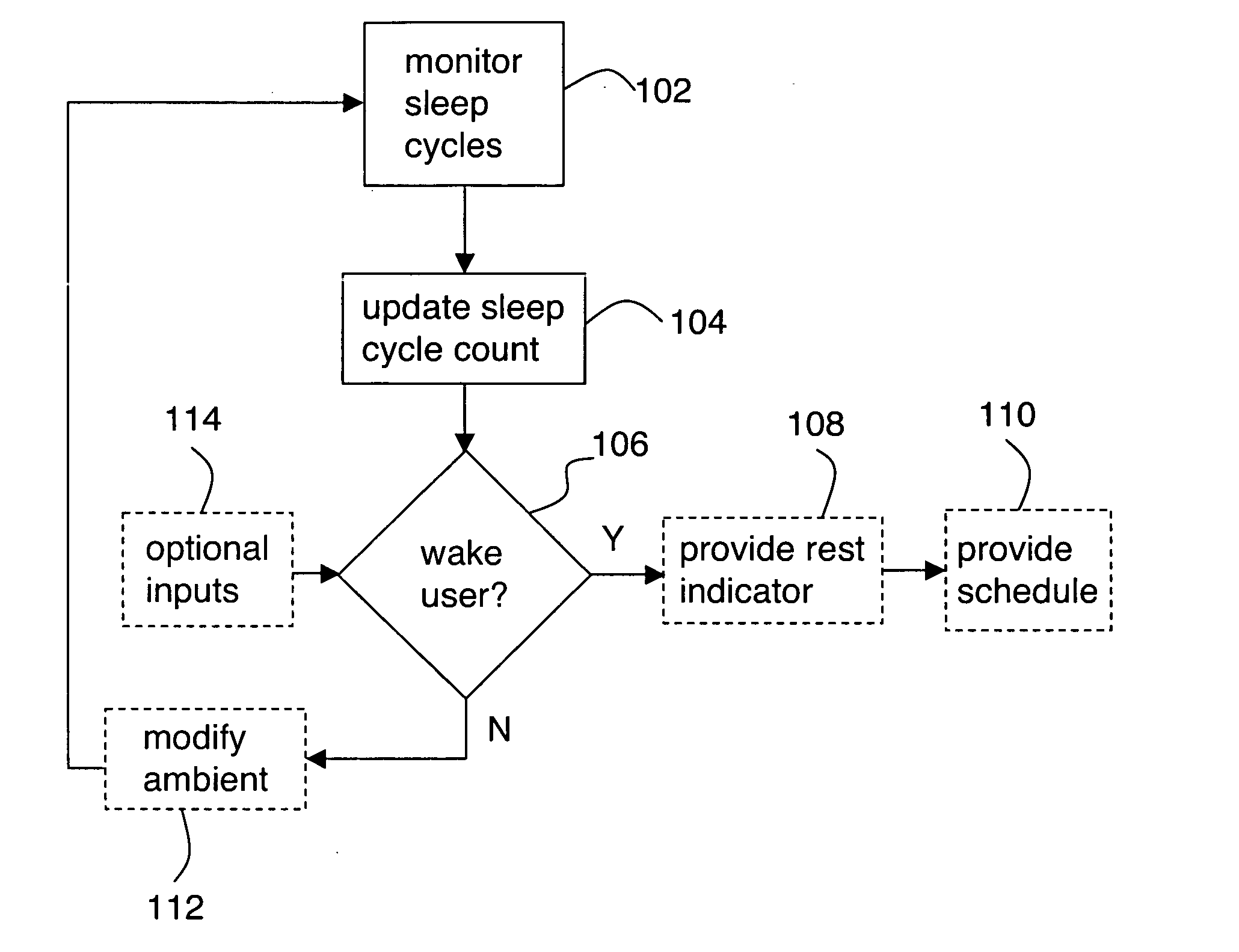
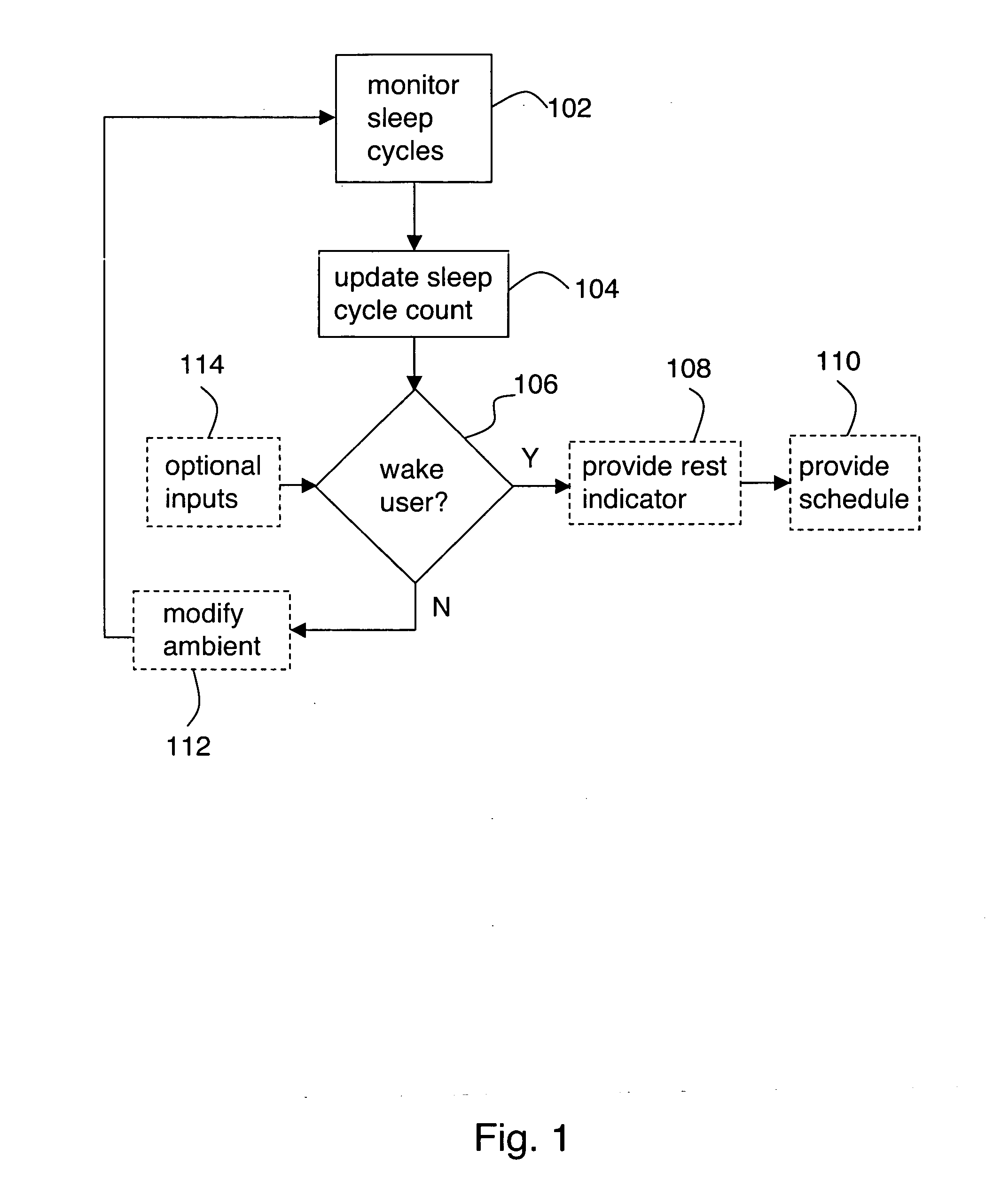
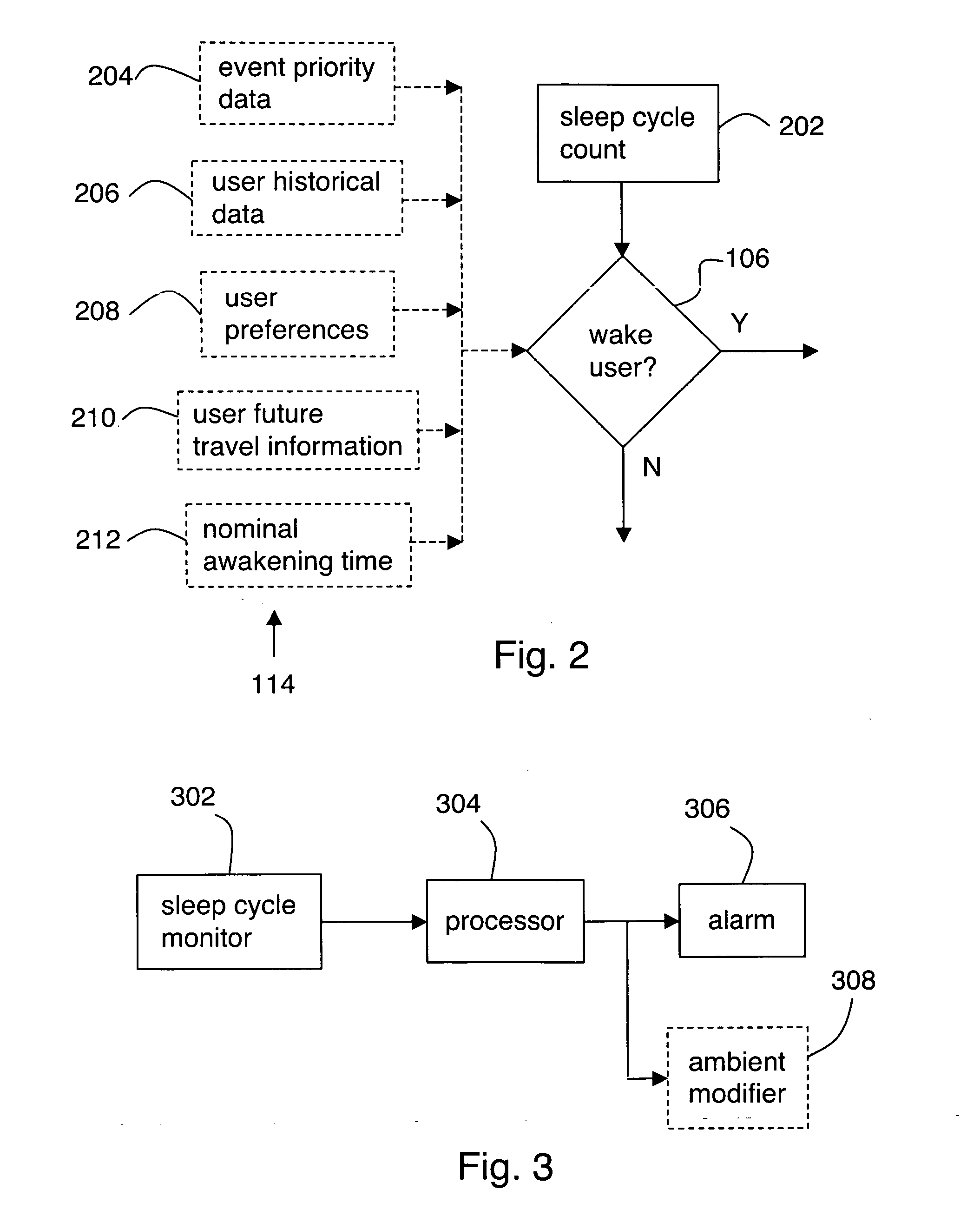
Monitoring and control of sleep cycles
InactiveUS20050012622A1Full controlProcess controlMedical devicesAlarmsMonitoring and controlGerontology
A system is provided including: a monitor for monitoring a user's sleep cycles; a processor which counts the sleep cycles to provide a sleep cycle count and which selects an awakening time according to a decision algorithm including the sleep cycle count as an input; and an alarm for awakening the user at the awakening time. Use of the sleep cycle count as an input to the decision algorithm advantageously enables a user to more fully control and optimize his or her personal sleeping behavior.
Owner:SUTTON WILLIAM R
Cycle count storage systems
ActiveUS7467253B2Improve performanceReduce riskMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesParallel computingCycle count
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Cycle count storage methods
ActiveUS20070245068A1Reduce riskImprove storage densityMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesParallel computingCycle count
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
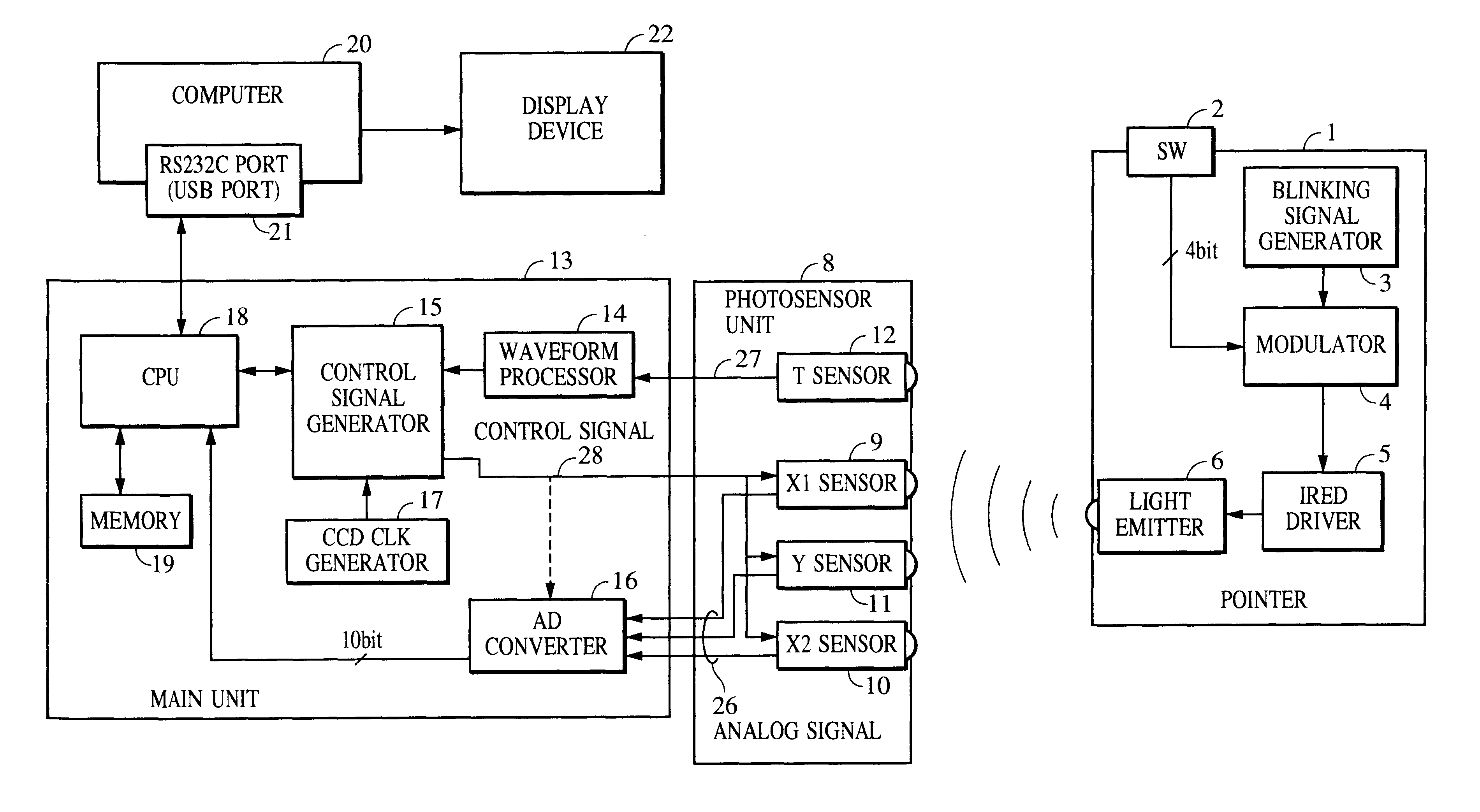
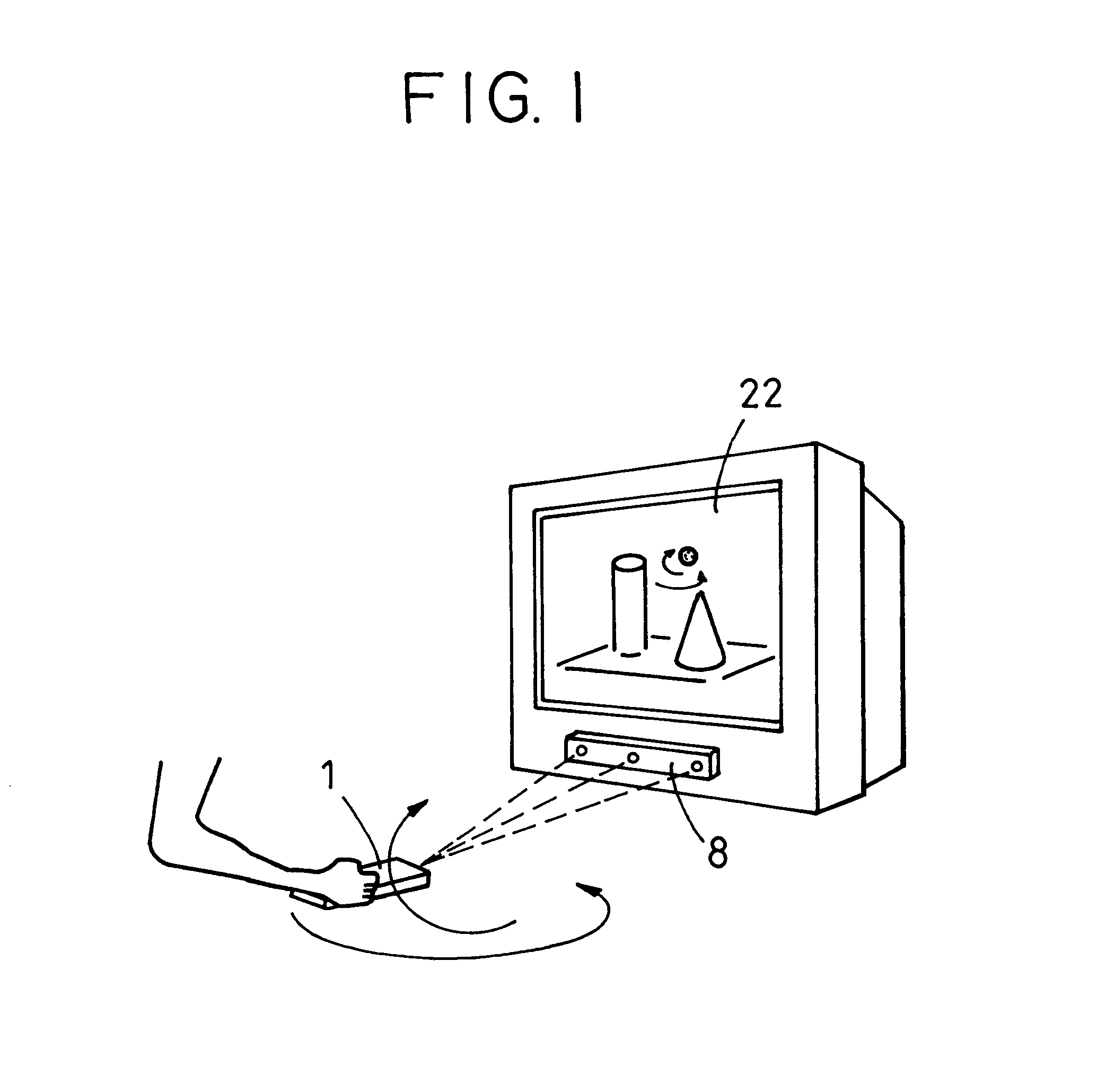
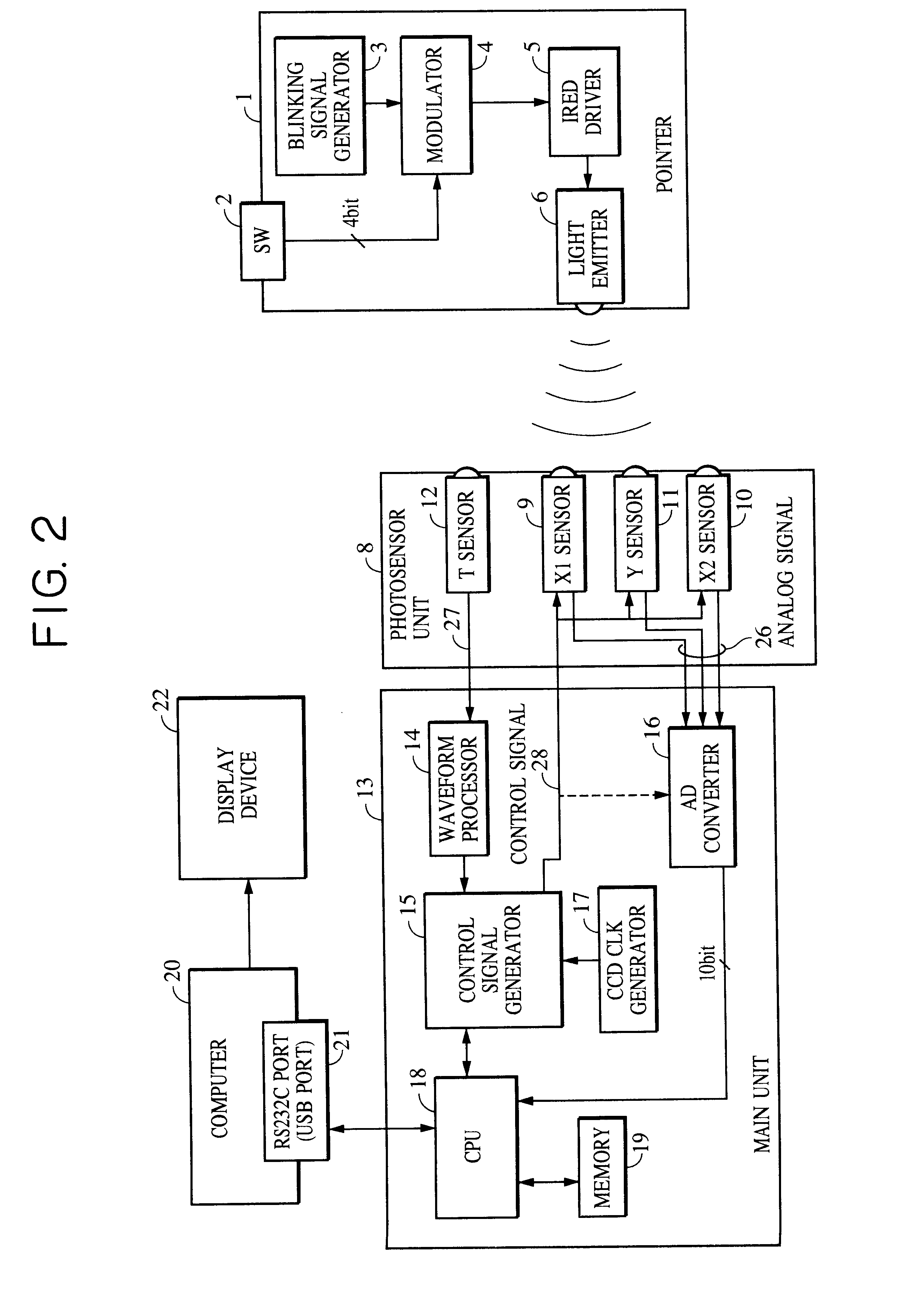
Photodetector, photosensing position detector, coordinate input device, coordinate input/output apparatus, and photodetection method
InactiveUS6740860B2Material analysis by optical meansCounting objects on conveyorsPhotovoltaic detectorsLight beam
A photodetector includes a photoreceiving unit which receives a light beam that blinks a plurality of times per detection period and converts the received light beam into an output signal. A signal processing and control unit controls the photoreceiving unit so that the output signal increases in strength as a blinking cycle count increases in each detection period.
Owner:CANON KK
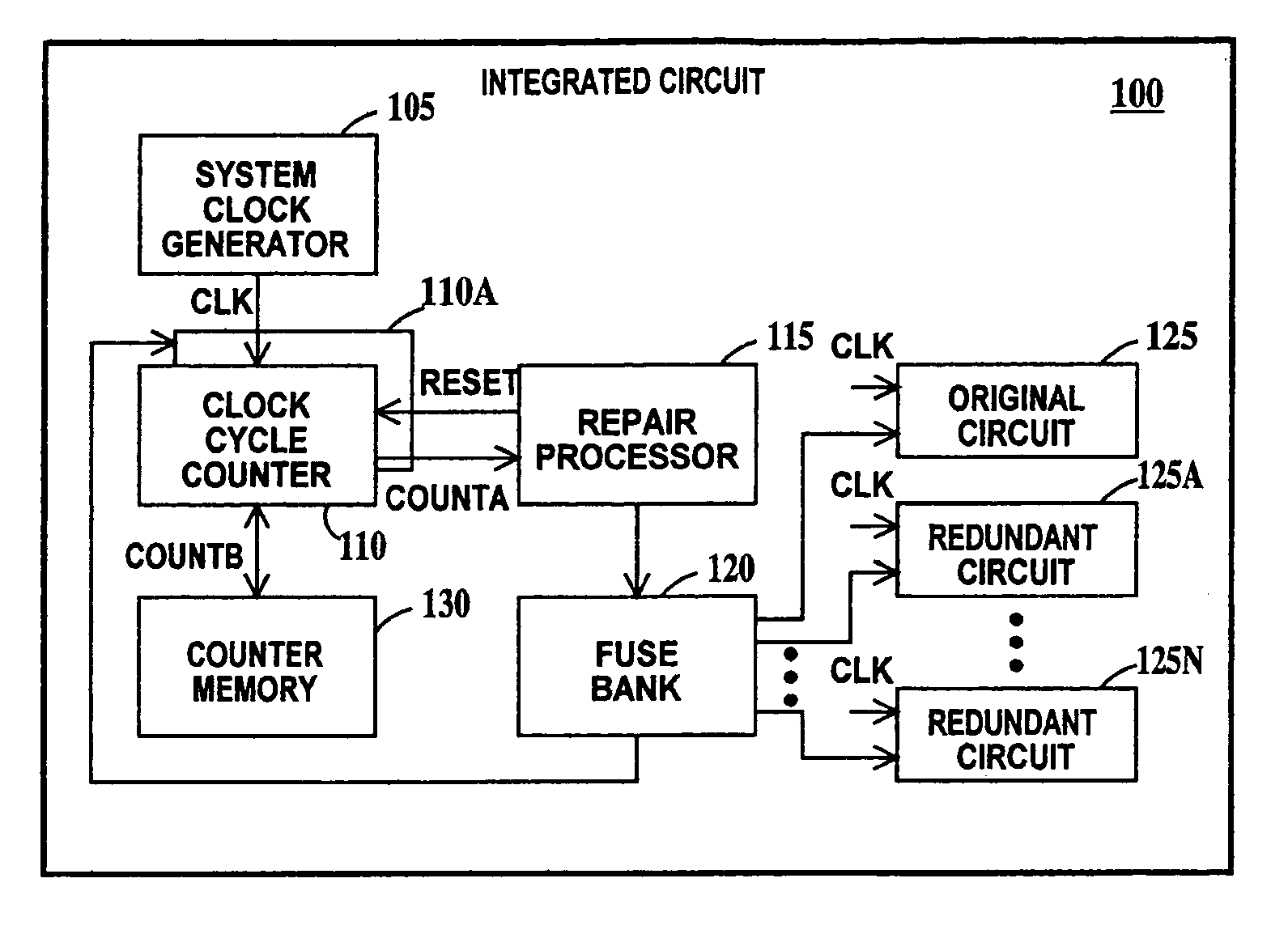
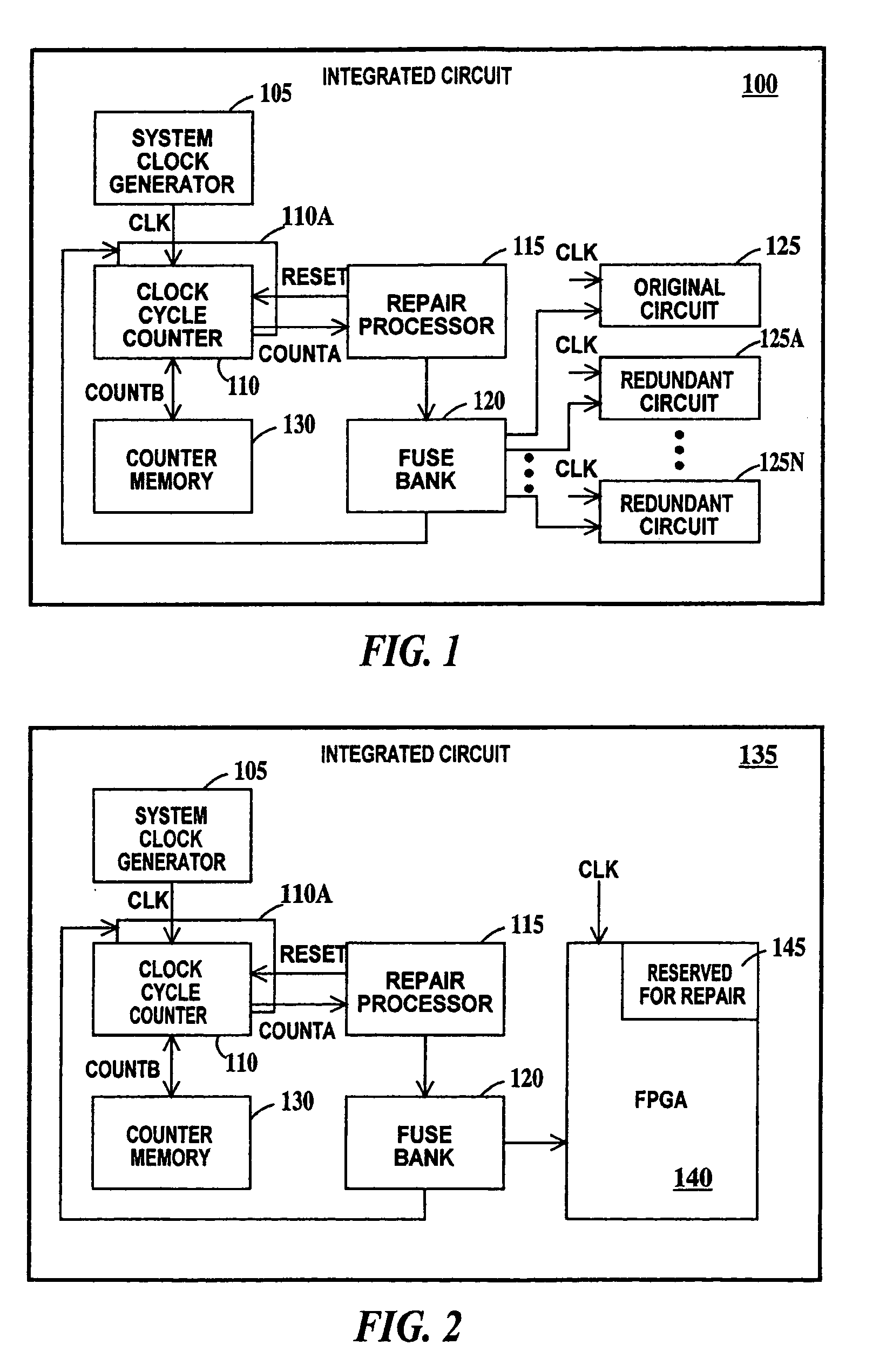
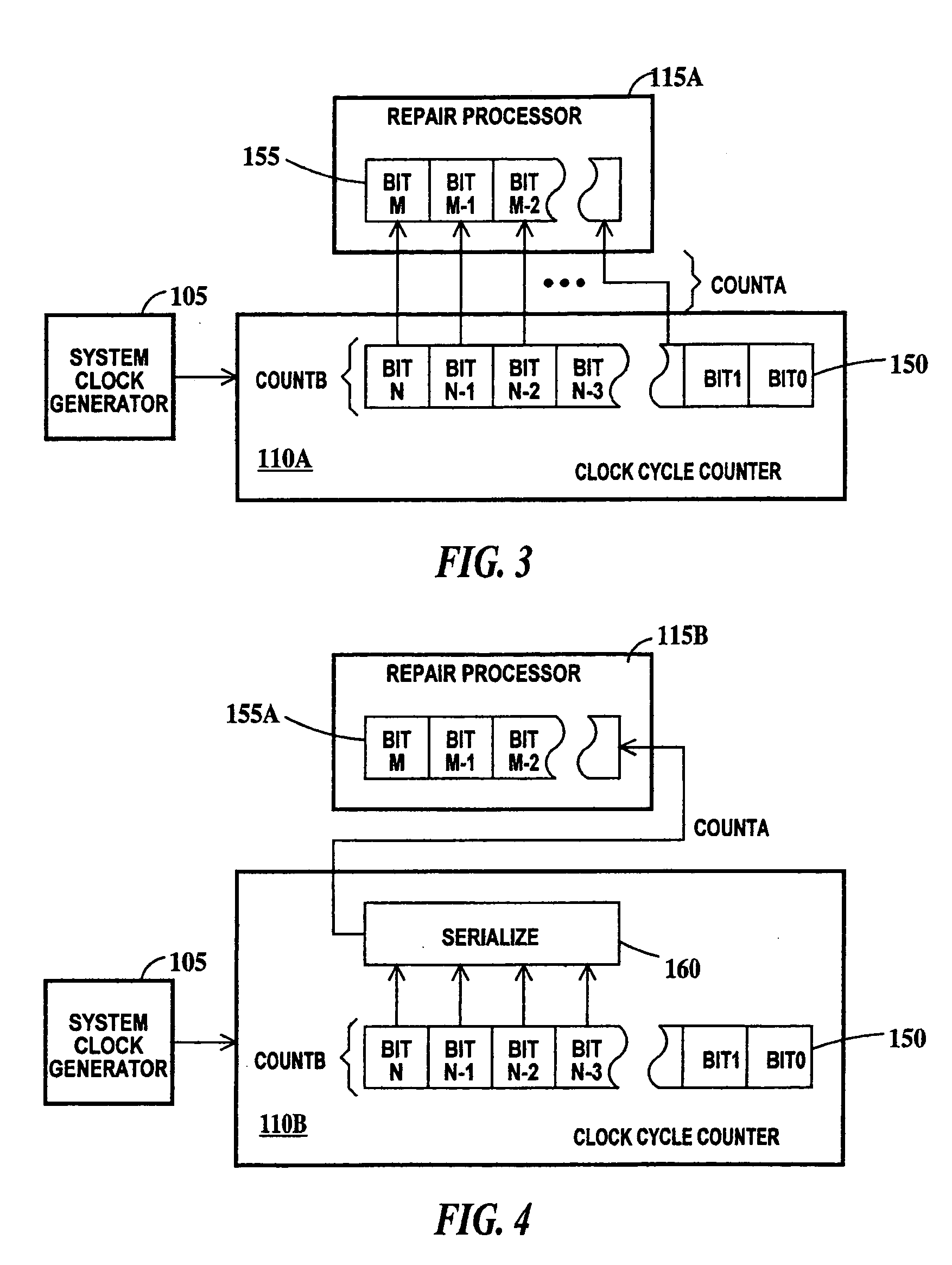
Digital reliability monitor having autonomic repair and notification capability
InactiveUS20050144524A1Avoid failureError detection/correctionGenerating/distributing signalsDependabilityIntegrated circuit
A method a circuit for preventing failure in an integrated circuit. The circuit including: an original circuit; one or more redundant circuits; and a repair processor, including a clock cycle counter adapted to count pulses of a pulsed signal, the repair processor adapted to (a) replace the original circuit with a first redundant circuit or (b) adapted to select another redundant circuit, the selection in sequence from a second redundant circuit to a last redundant circuit, and to replace a previously selected redundant circuit with the selected redundant circuit each time the cycle counter reaches a predetermined count of a set of predetermined cycle counts.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
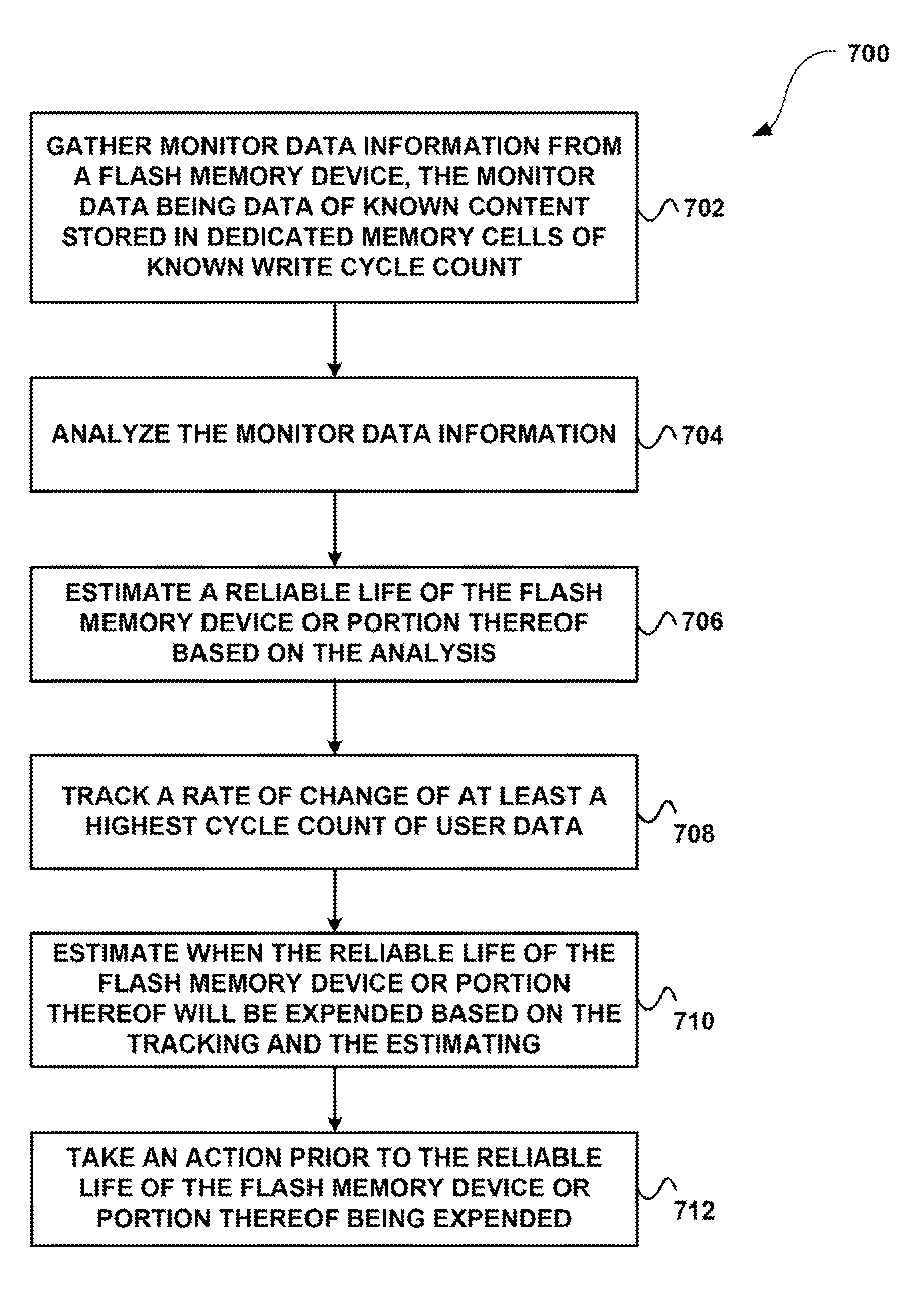
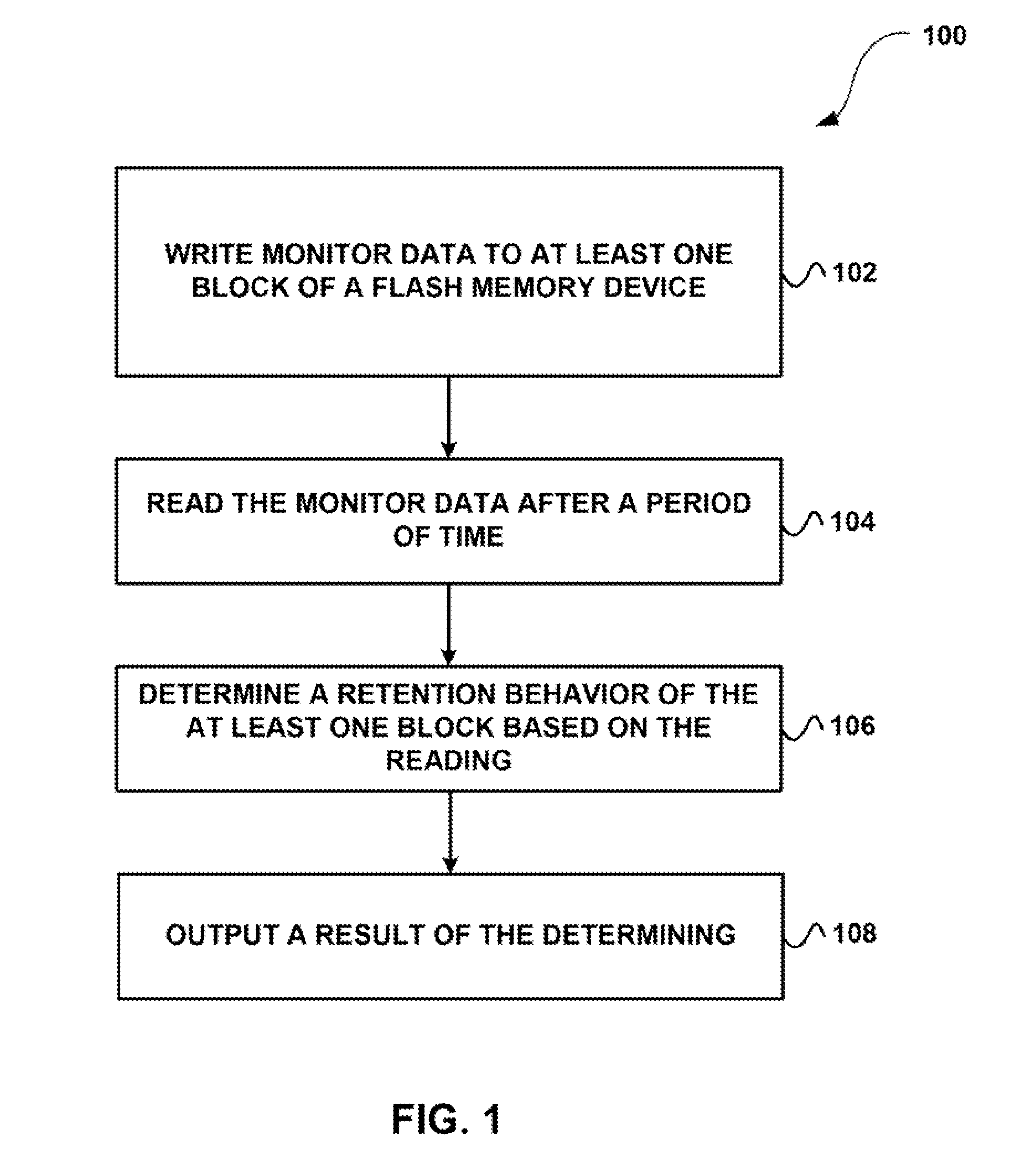
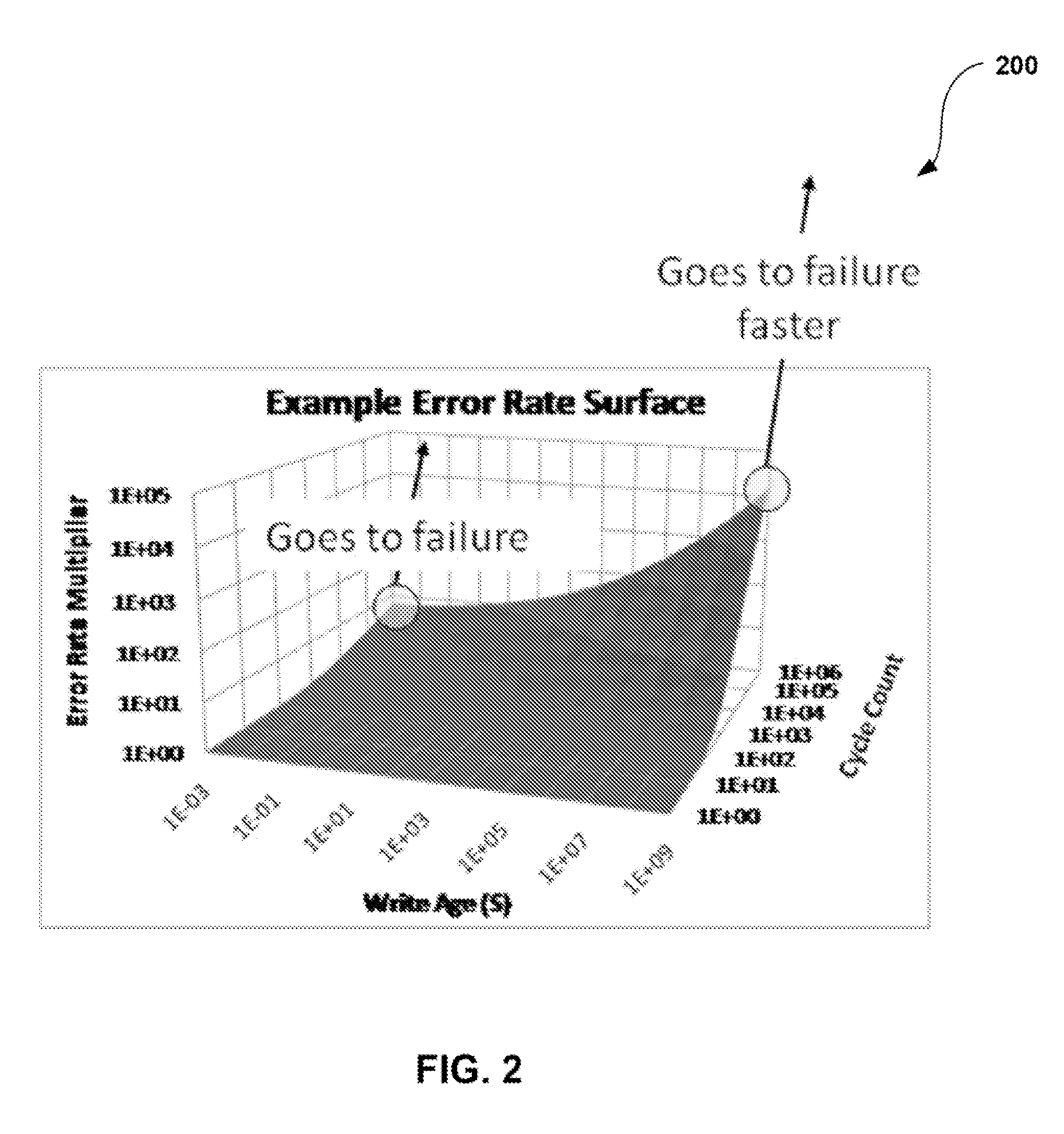
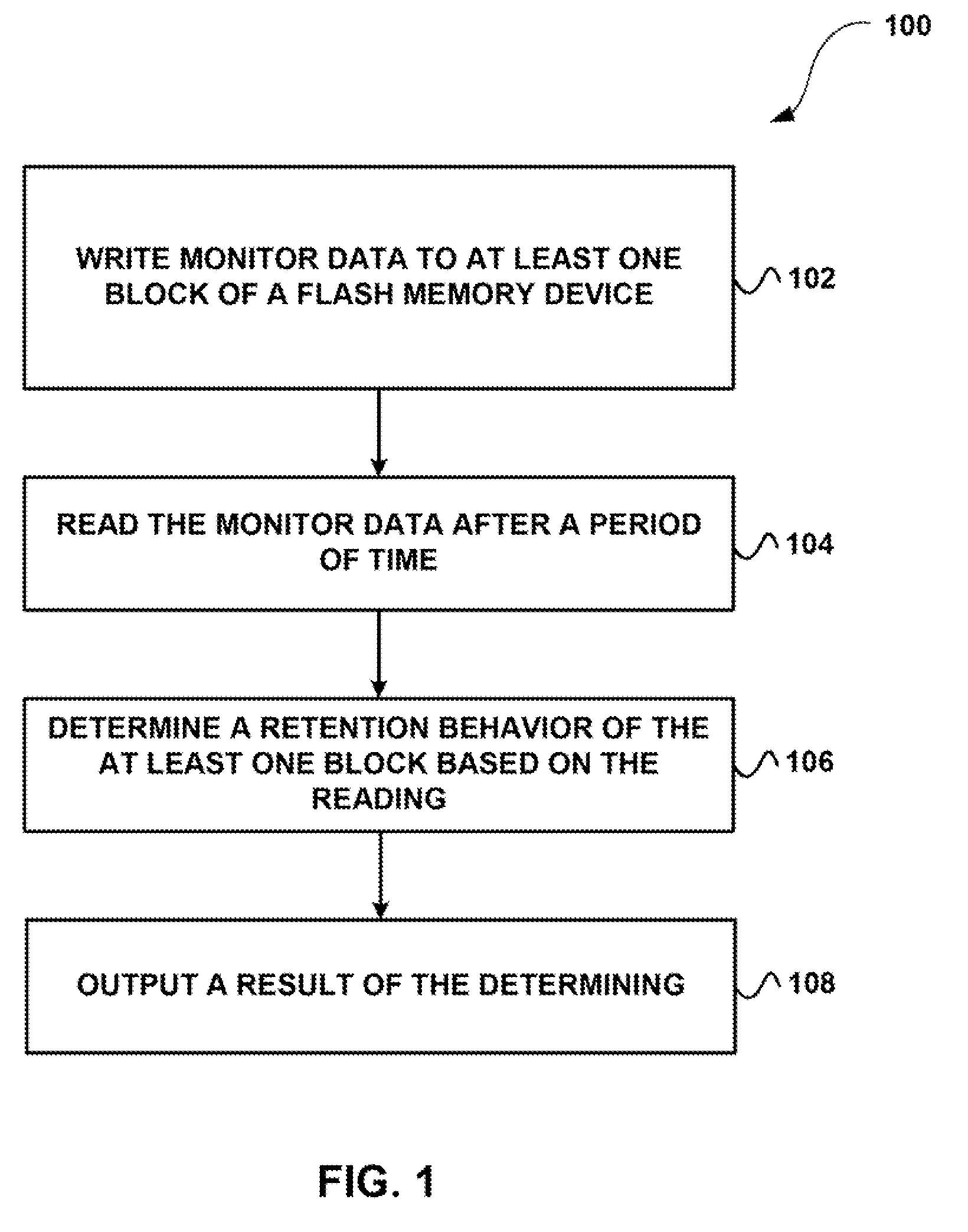
System, method, and computer program product for estimating when a reliable life of a memory device having finite endurance and/or retention, or portion thereof, will be expended
A method according to one embodiment includes gathering monitor data information from a memory device having finite endurance and / or retention, the monitor data being data of known content stored in dedicated memory cells of known write cycle count; analyzing the monitor data information; estimating a reliable life of the memory device or portion thereof based on the analysis; tracking a rate of change of at least a highest cycle count of user data; estimating when the reliable life of the memory device or portion thereof will be expended based on the tracking and the estimating; and taking an action prior to the reliable life of the memory device or portion thereof being expended. Additional systems, methods, and computer program products are also disclosed.
Owner:IBM CORP
System, method, and computer program product for analyzing monitor data information from a plurality of memory devices having finite endurance and/or retention
A method according to one embodiment includes gathering monitor data information from a plurality of memory devices having finite endurance and / or retention, the monitor data being data of known content stored in dedicated memory cells of known write cycle count; analyzing the monitor data information; and taking an action relating to at least one of the devices based on the analyzing. Additional systems, methods, and computer program products are also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
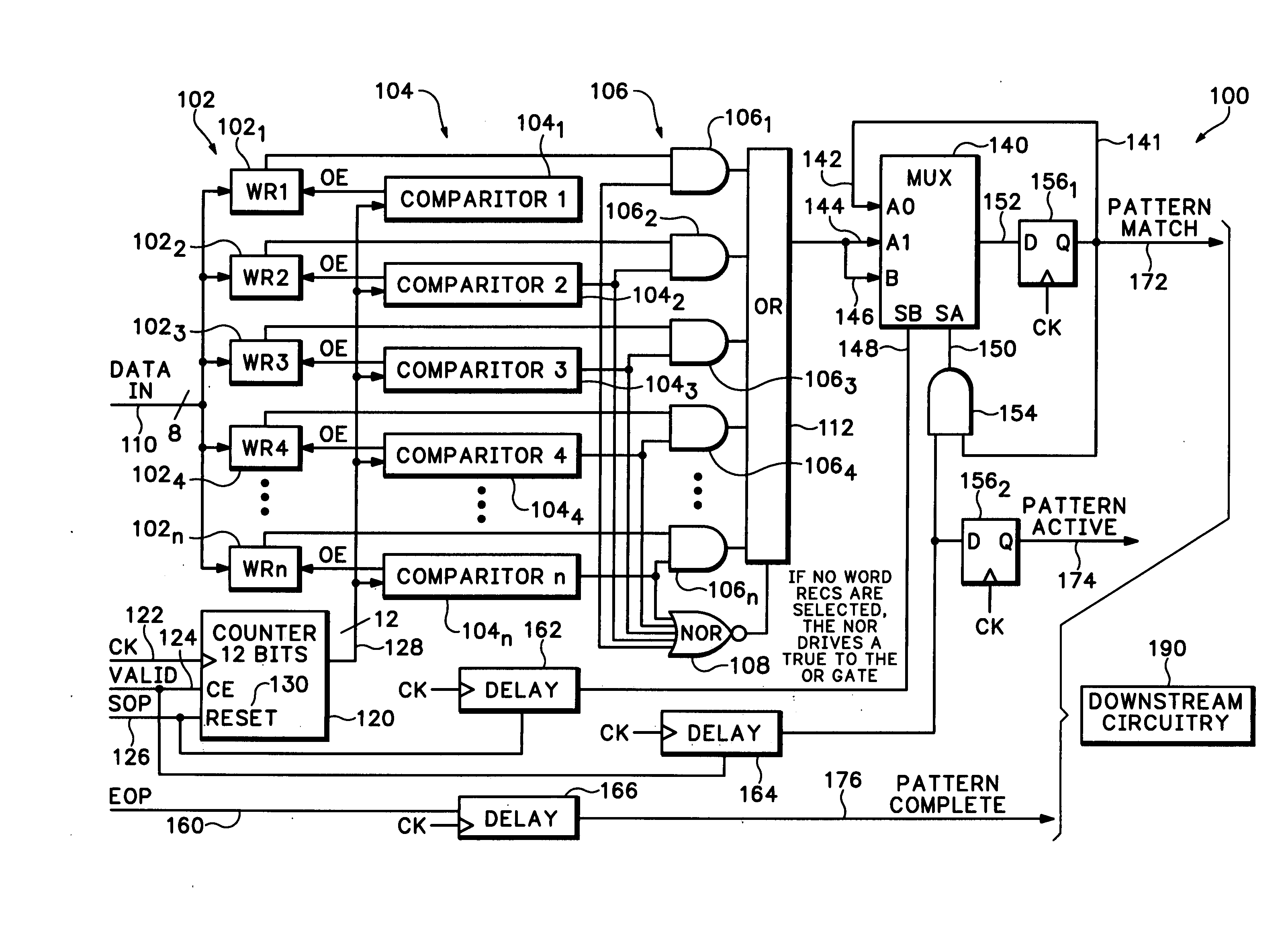
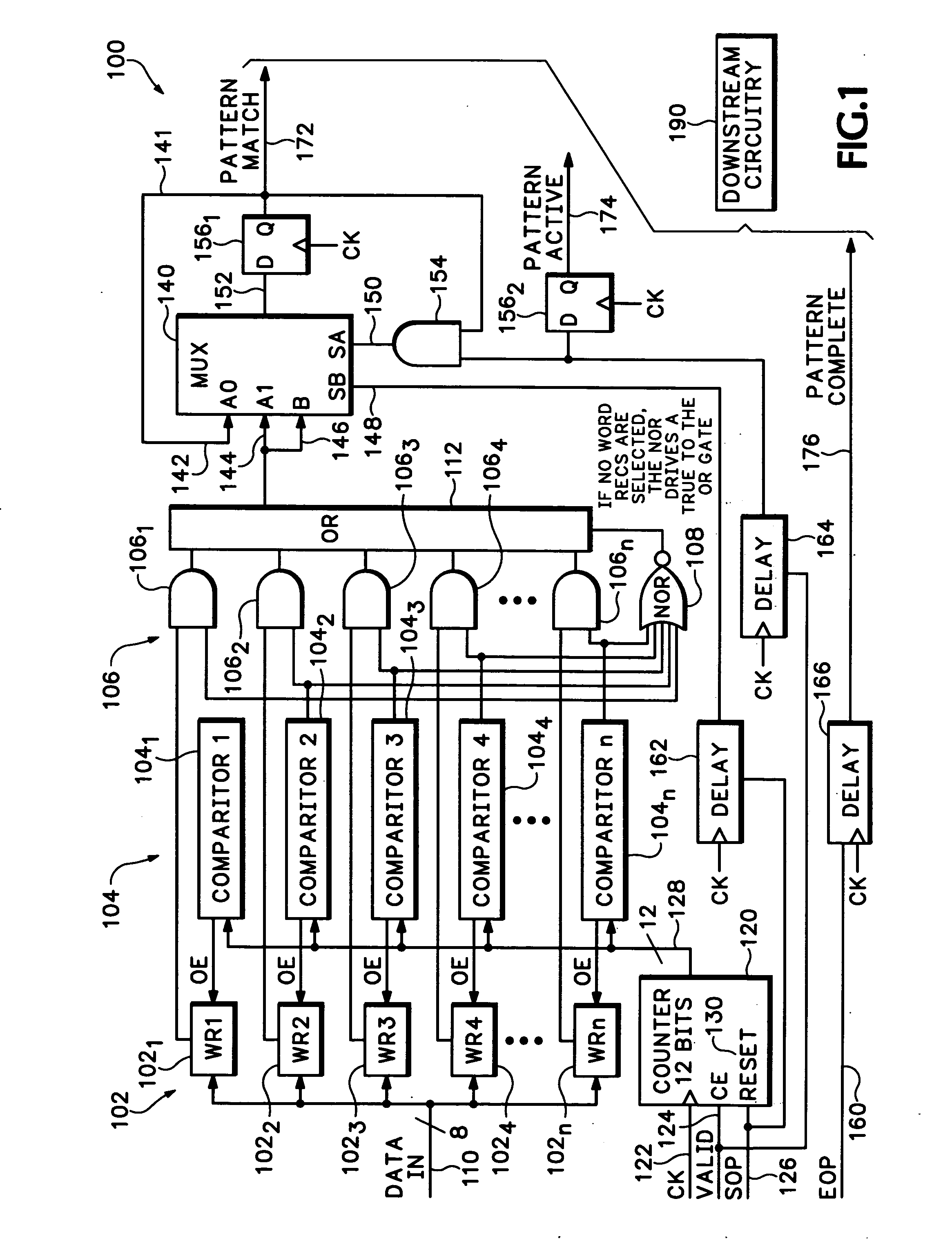
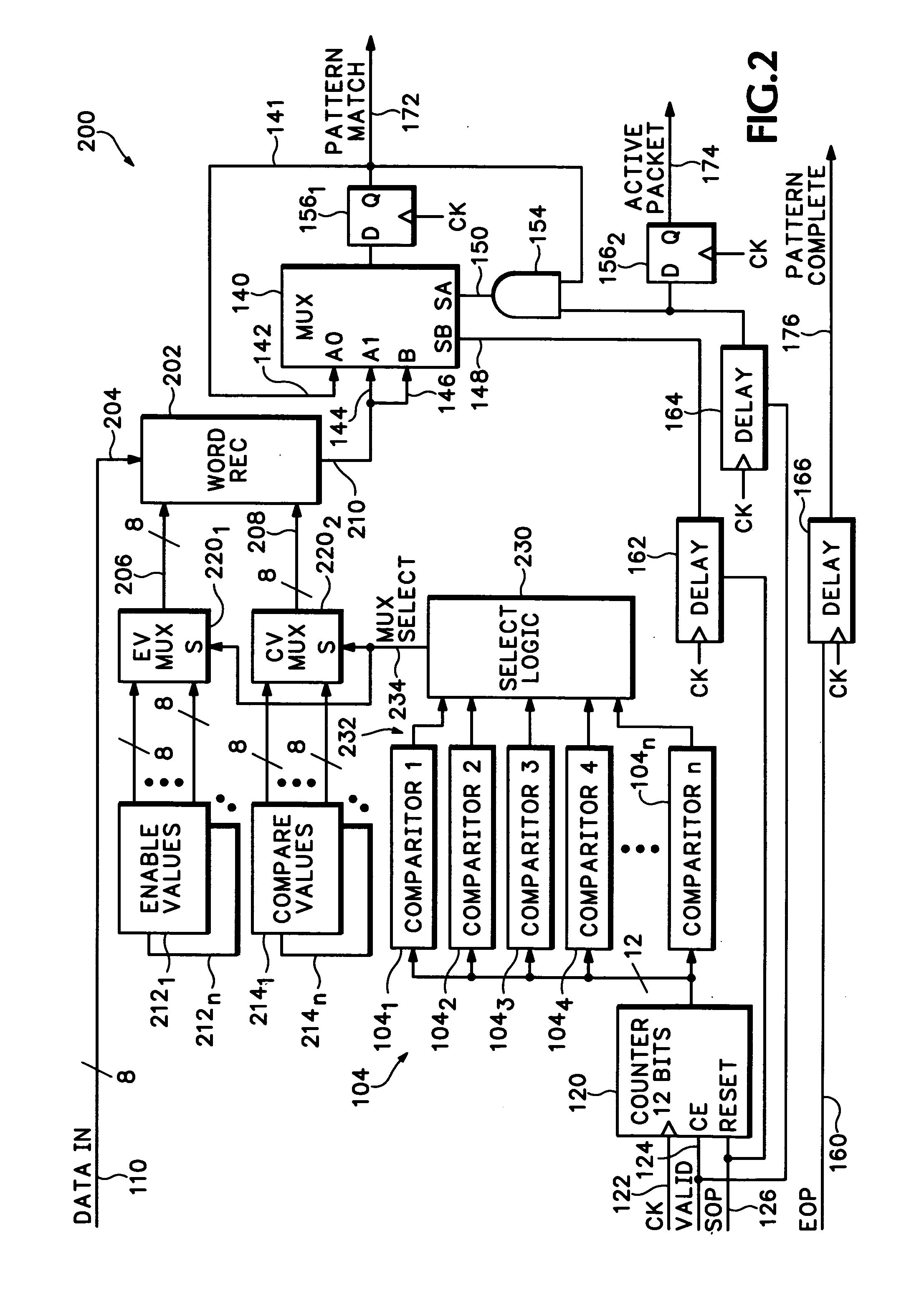
Apparatus and method of analyzing packetized data spanning over multiple clock cycles
A method and apparatus for processing packetized data spanning multiple clock cycles includes at least one comparator, for comparing a present clock cycle count to a reference clock cycle count, wherein the reference clock cycle values may be anywhere within the packet and may be non-contiguous with other reference clock cycle values. At least one word recognizer, compares a presently clocked word to a reference word, and an output circuit provides an indication of a favorable word comparison that occurred in response to a favorable clock cycle count comparison.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Cycle count storage methods
ActiveUS7451264B2Improve performanceReduce riskMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesParallel computingCycle count
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
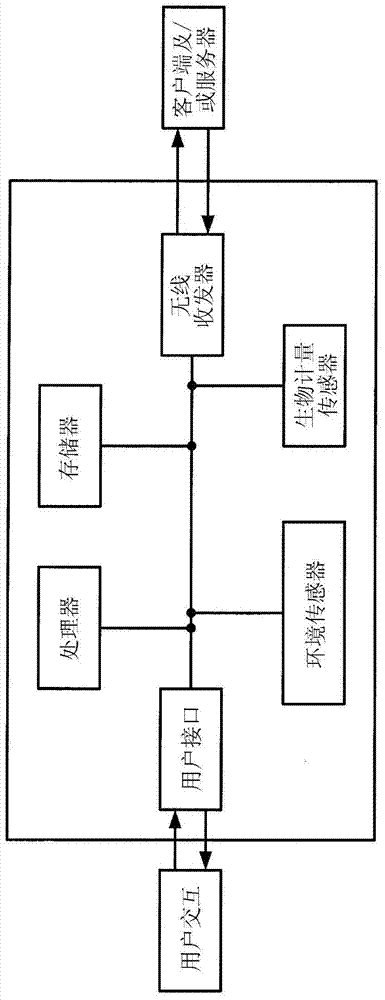
Use of gyroscopes in personal fitness tracking devices
The application relates to gyroscopes and use of other types of gyroscopes in personal fitness tracking devices. Biometric monitoring devices, including various technologies that may be implemented in such devices, are discussed herein. Additionally, techniques for utilizing gyroscopes in biometric monitoring devices are provided. Such techniques may, in some implementations, involve obtaining swimming metrics regarding stroke cycle count, lap count, and stroke type. Such techniques may also, in some implementations, involve obtaining performance metrics for bicycling activities.
Owner:FITBIT INC
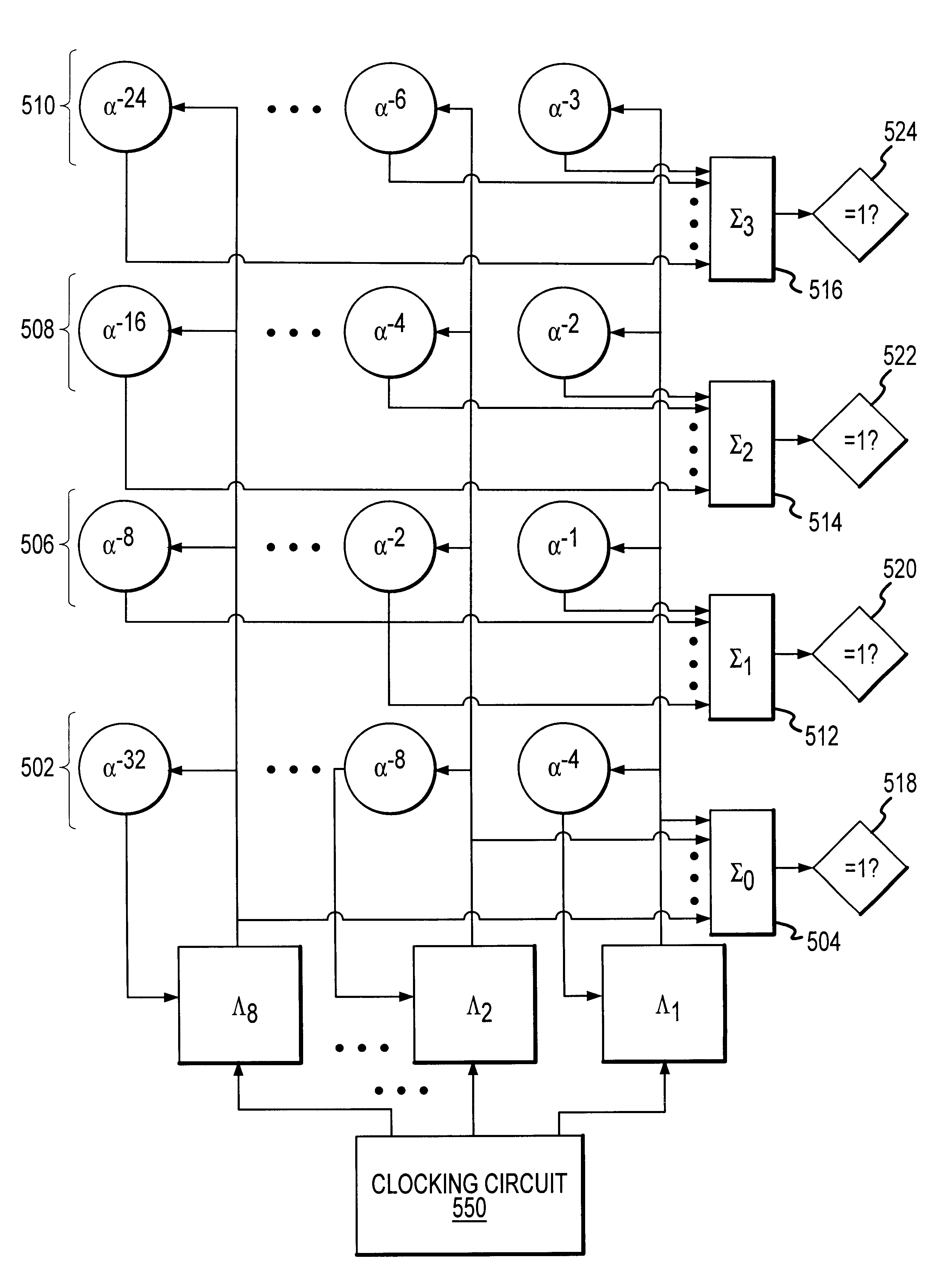
System and method for a storage-efficient parallel Chien Search
A system determines the root of a polynomial by employing a parallel structure that implements a Chien Search and minimizes the amount of storage required. The location of an error in a codeword can be derived from the root of an error locator polynomial. The performance of the Chien Search is enhanced by the parallel structure, and the location of the error can be easily determined using a simple calculation that preferably includes the cycle count, the parallelism, and the index of the multiplier / summer rank that indicates a root. Multiple ranks of multipliers receive data stored in a single array of data storage units. Multiplier values of each multiplier are based on the elements of a Galois Field. A method configures data storage units, multipliers, summers, and comparators, and performs a Chien Search. The location of an error in a codeword is determined using a simple calculation based on a determined root of an error locator polynomial.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
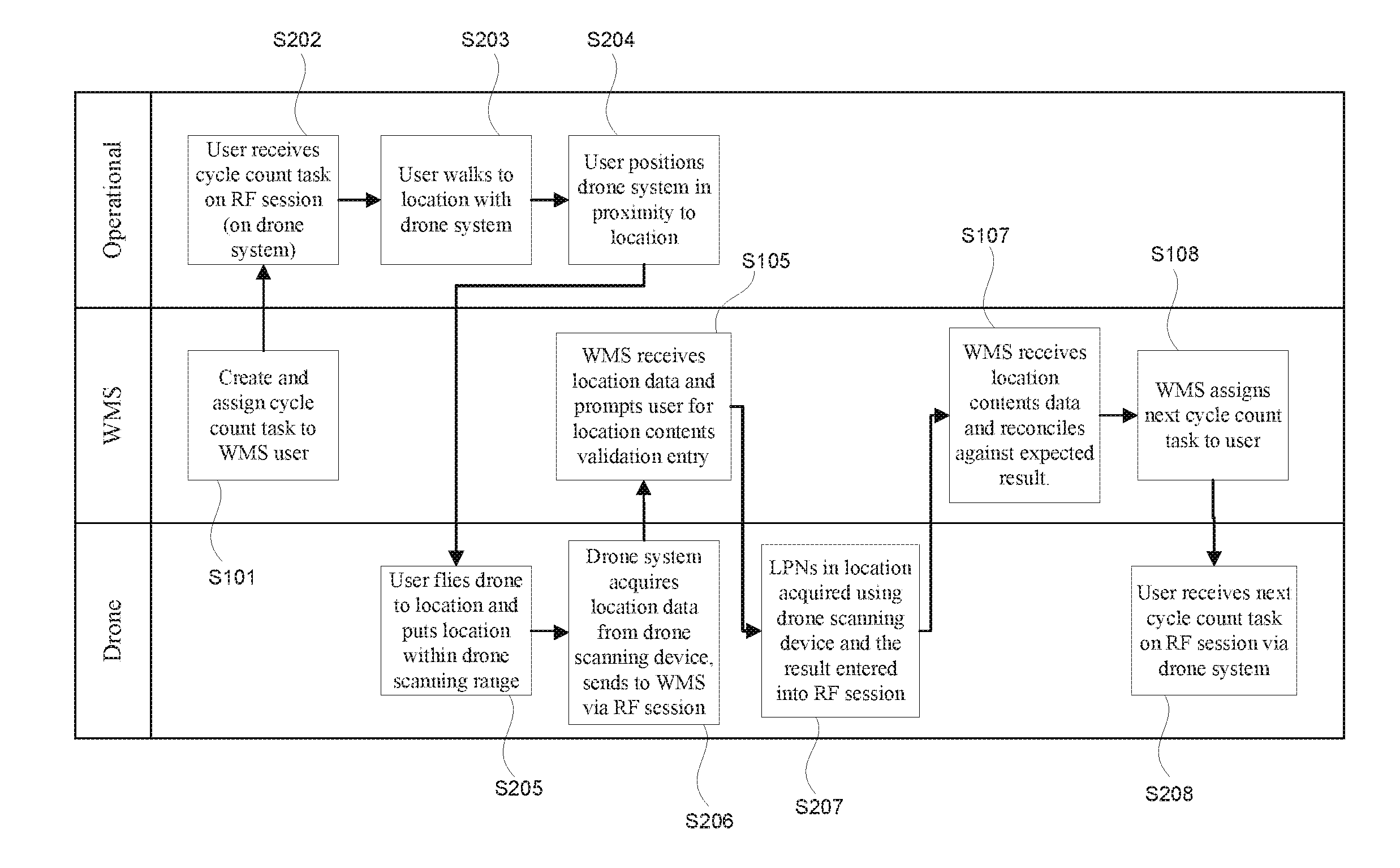
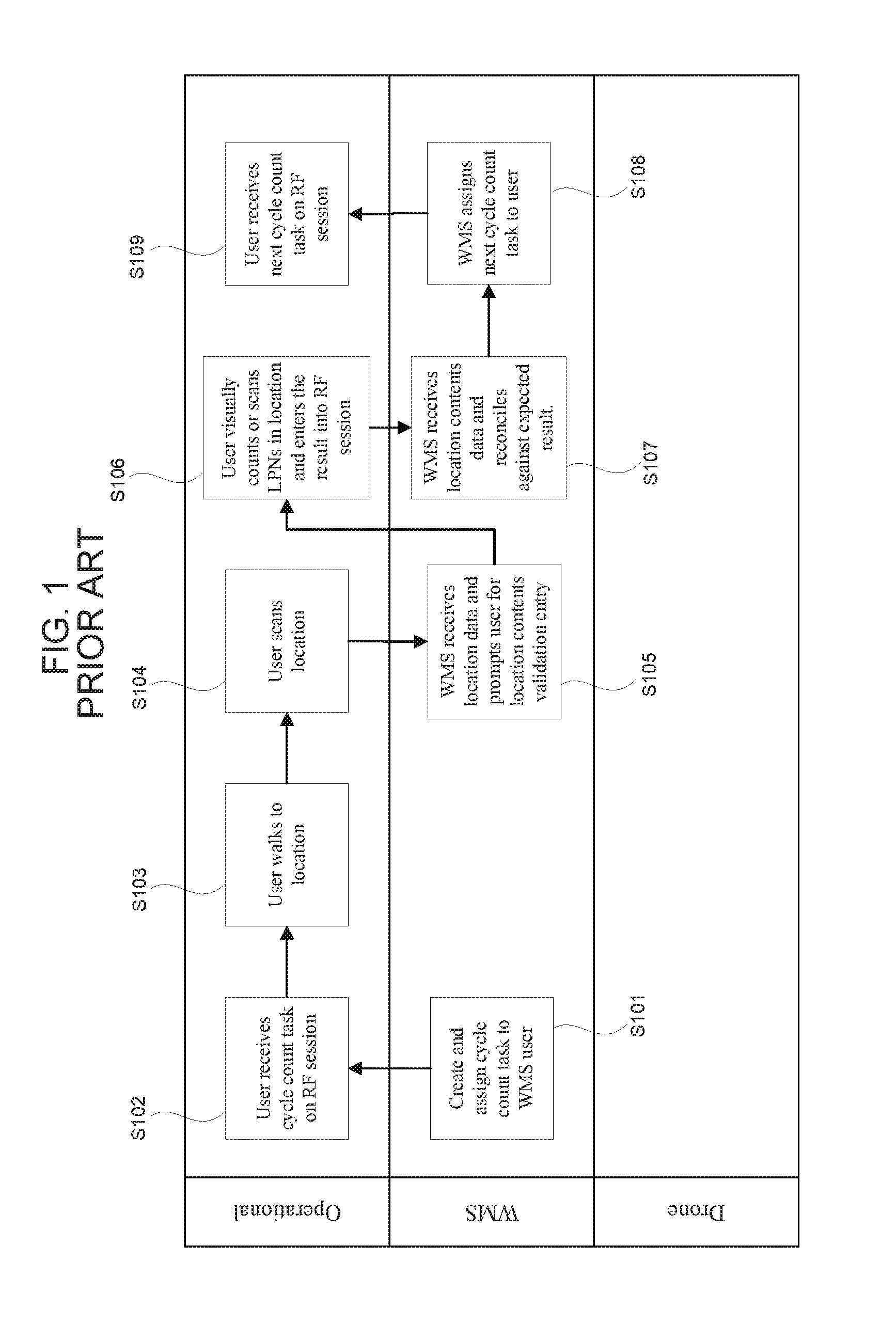
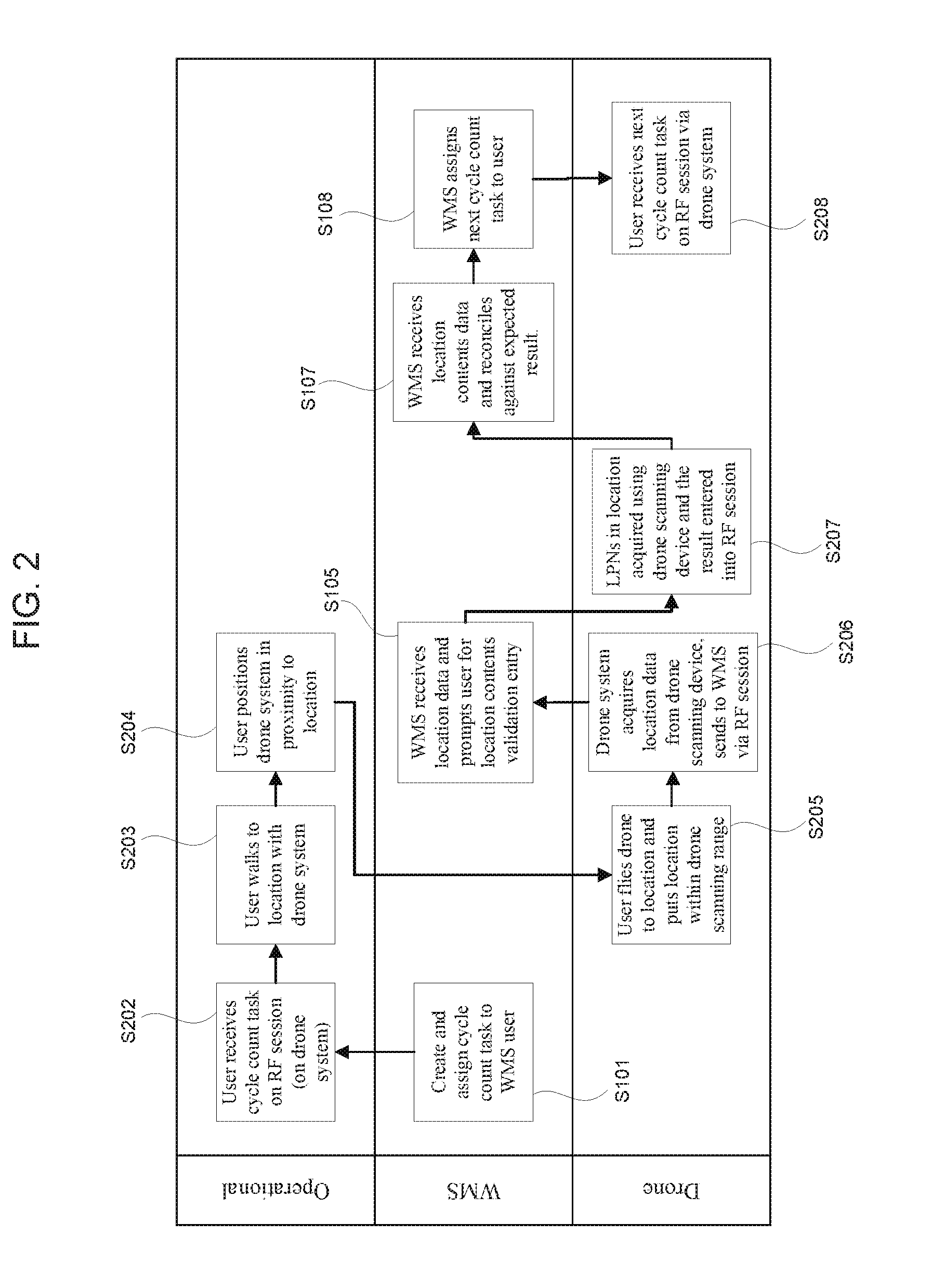
Method and apparatus for warehouse cycle counting using a drone
InactiveUS20160247116A1Reduce needShorten counting timeTelevision system detailsUnmanned aerial vehiclesManagement systemEmbedded system
A method for cycle counting warehouse inventory using a drone system with a drone carrying a scanning device and a computer with an RF session receiving cycle count tasks. The drone system is placed within a flight range of the drone to a cycle count location and flown to the cycle count location of the cycle count task. The drone acquires the inventory location data and sends it to a warehouse management system through the RF session. Then the drone acquires the inventory data and sends it to a warehouse management system through the RF session. If prompted by the warehouse management system, further data are acquiring such as SKU data, LPN attribute information, and / or quantity information.
Owner:OLIVO CRAIG +1
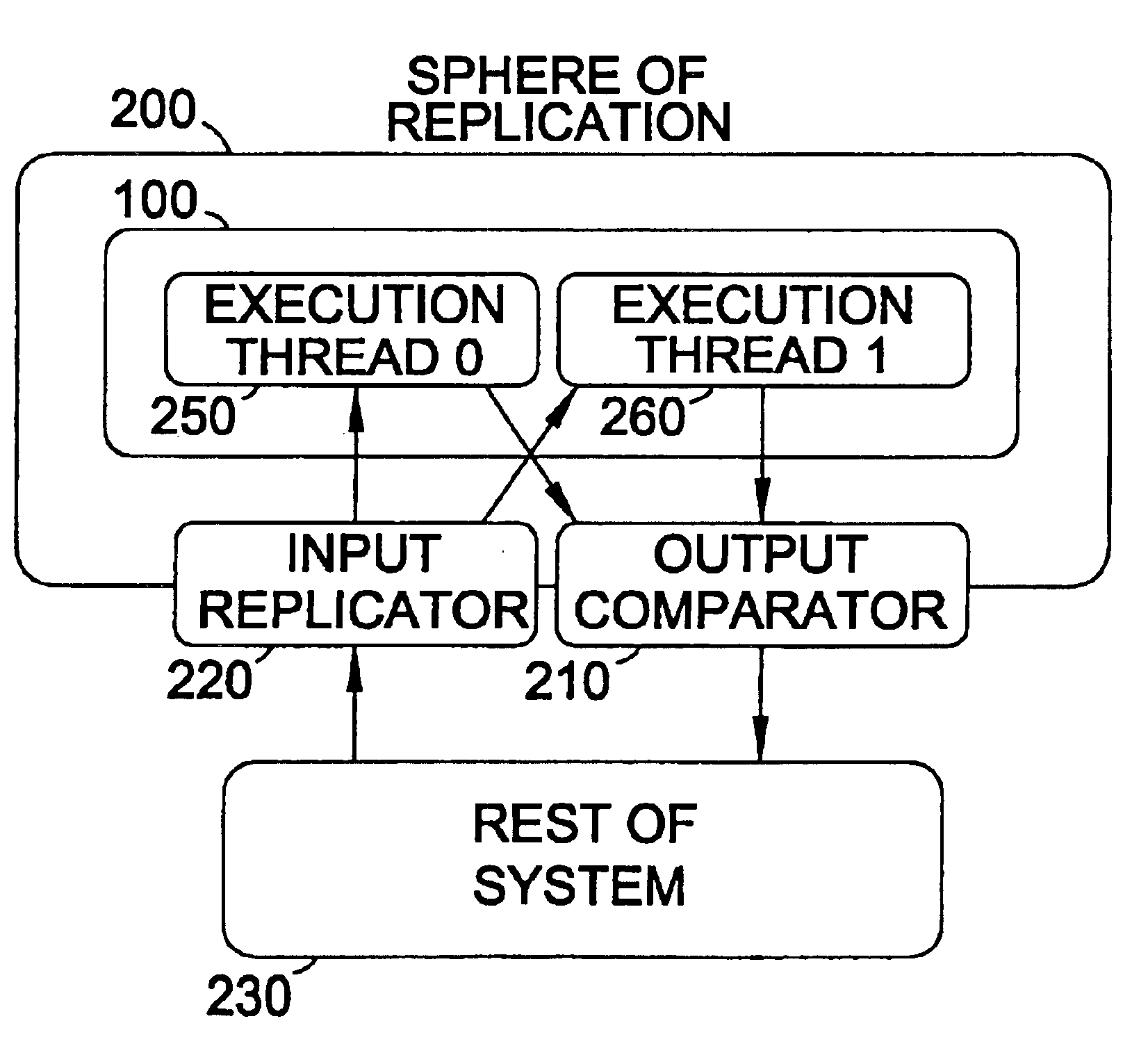
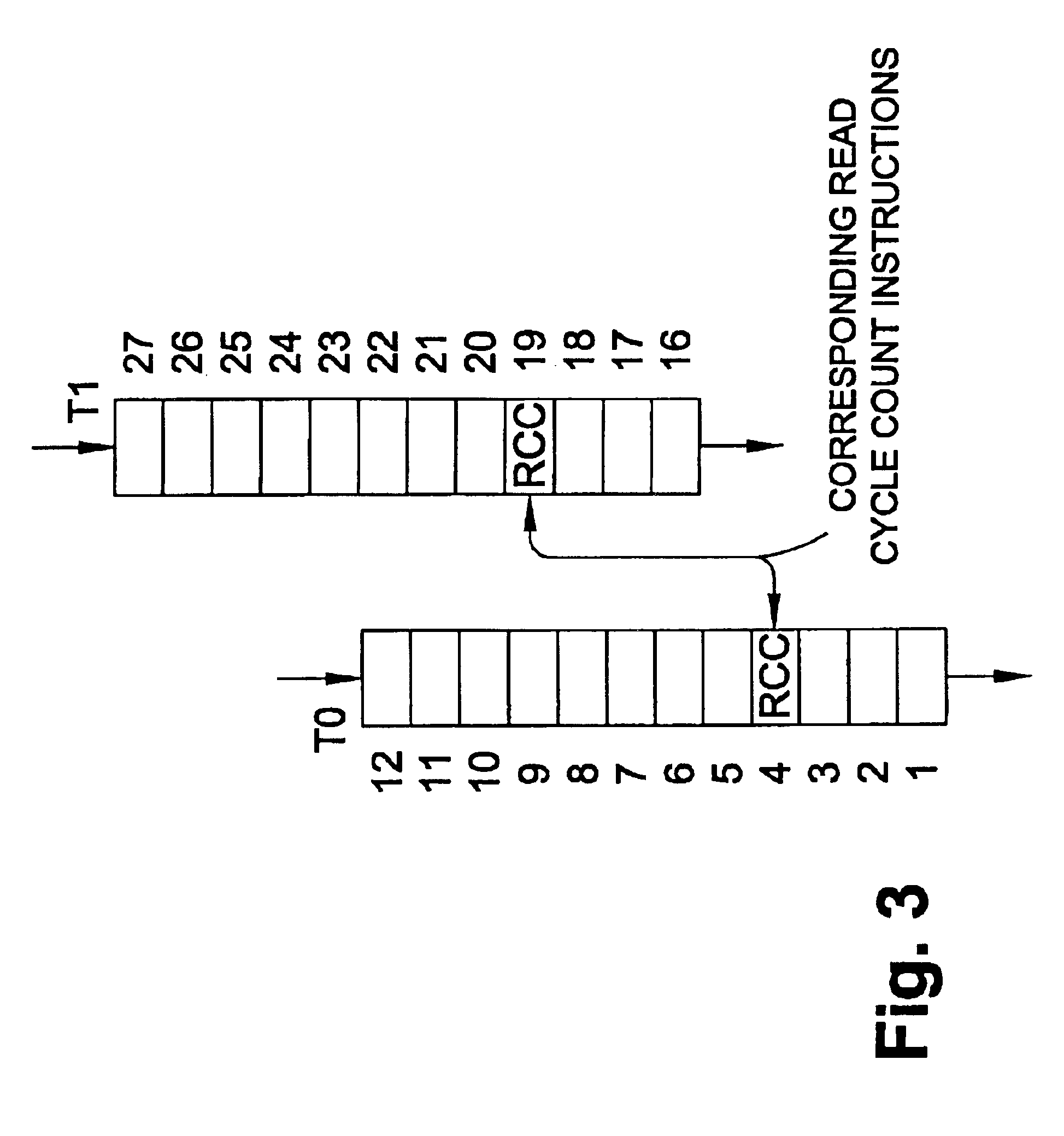
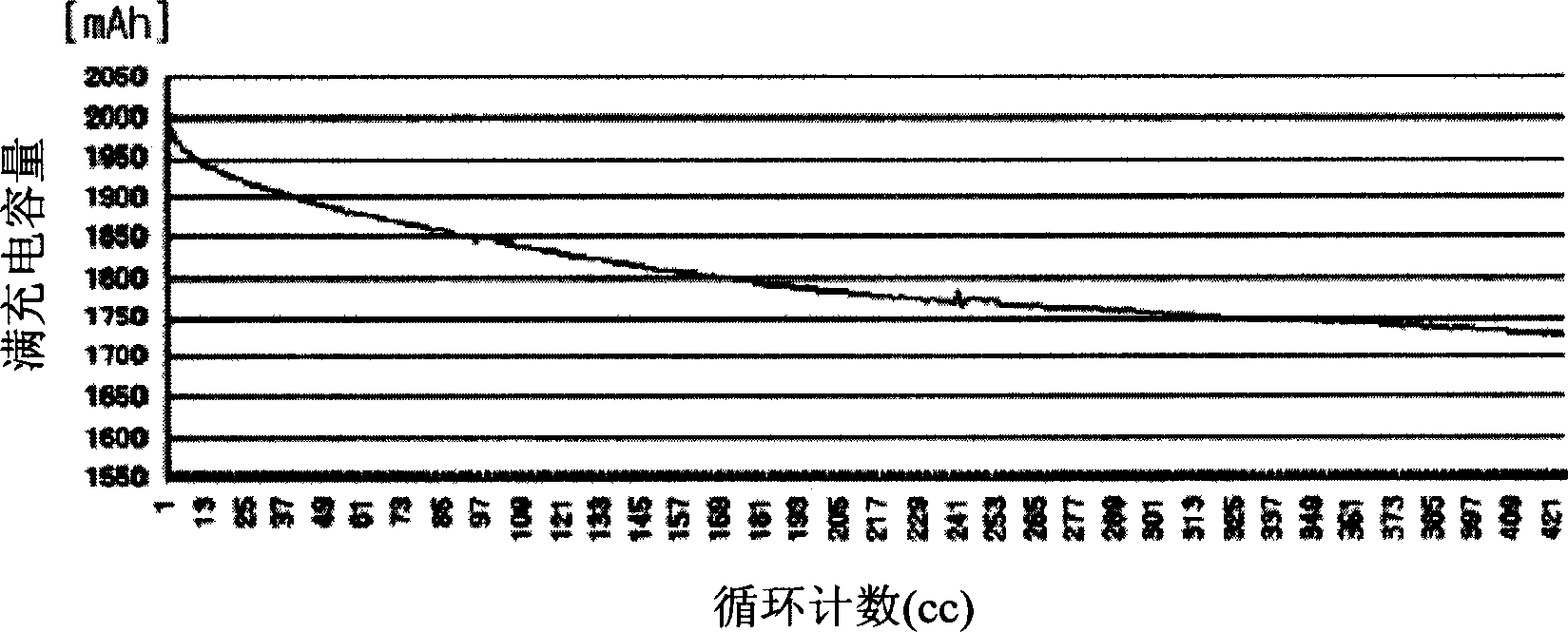
Cycle count replication in a simultaneous and redundantly threaded processor
InactiveUS6854051B2Improve performanceProviding fault toleranceInterprogram communicationDigital computer detailsProgram ThreadStorage cell
A pipelined, simultaneous and redundantly threaded (“SRT”) processor comprising, among other components, load / store units configured to perform load and store operations to or from data locations such as a data cache and data registers and a cycle counter configured to keep a running count of processor clock cycles. The processor is configured to detect transient faults during program execution by executing instructions in at least two redundant copies of a program thread and wherein false errors caused by incorrectly replicating cycle count values in the redundant program threads are avoided by implementing a cycle count queue for storing the actual values fetched by read cycle count instructions in the first program thread. The load / store units then access the cycle count queue and not the cycle counter to fetch cycle count values in response to read cycle count instructions in the second program thread.
Owner:SONRAI MEMORY LTD
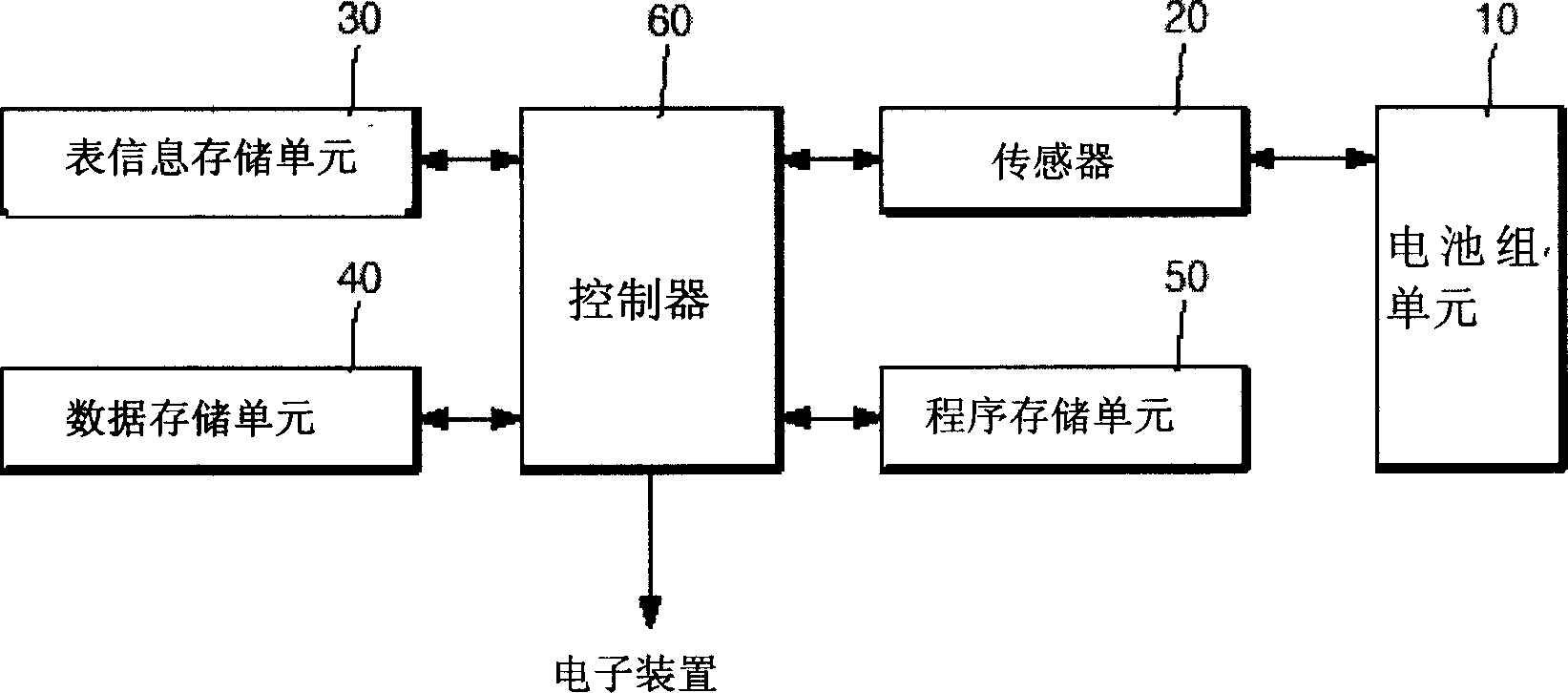
Method for caculating circulation type of intelligent battery, method and equipment for correcting full recharge capacity to intelligent battery using said method
InactiveCN1503000ARegardless of state of chargeHigh precisionElectrical testingComputational intelligenceLinearization
A method for counting cycle count of a smart battery, a method and device for correcting full charge capacity of a smart battery, which is used as reference capacity for indicating correct remaining capacity of the battery, are disclosed. The present invention increase cycle count that is a standard for updating FCC in gradual floating variables in consideration of SOC to obtain continuous cycle count. FCC information is updated when the battery has been fully charged or the integer of the cycle count increases 1 using a predetermined FCC correction table in which FCC correction values varying with the cycle count are linearized by sections. This improves reliability in actually corrected FCC information and increases accuracy in the remaining capacity indicated on the basis of the FCC information.
Owner:MTEQ SYST
Systems and methods to visualize component health and preventive maintenance needs for subsea control subsystem components
ActiveUS20150184505A1Easy to identifyImprove visualizationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyOcean bottomGraphics
Systems and methods to visualize component health and preventive maintenance needs for subsea control subsystem components are provided. Embodiments can include energizing one or more solenoids, detecting a solenoid firing event, detecting activity in blowout preventer components downchain from the solenoids, and incrementing a cycle count for the one or more solenoids and each downchain blowout preventer component activated. Embodiments can include projecting a replacement date for the solenoid or any of the downchain blowout preventer components based on the cycle count and user-defined thresholds. In embodiments, a user is provided with an interactive graphical representation of a blowout preventer including selectable blowout preventer components thereby to visualize component health and preventive maintenance needs.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
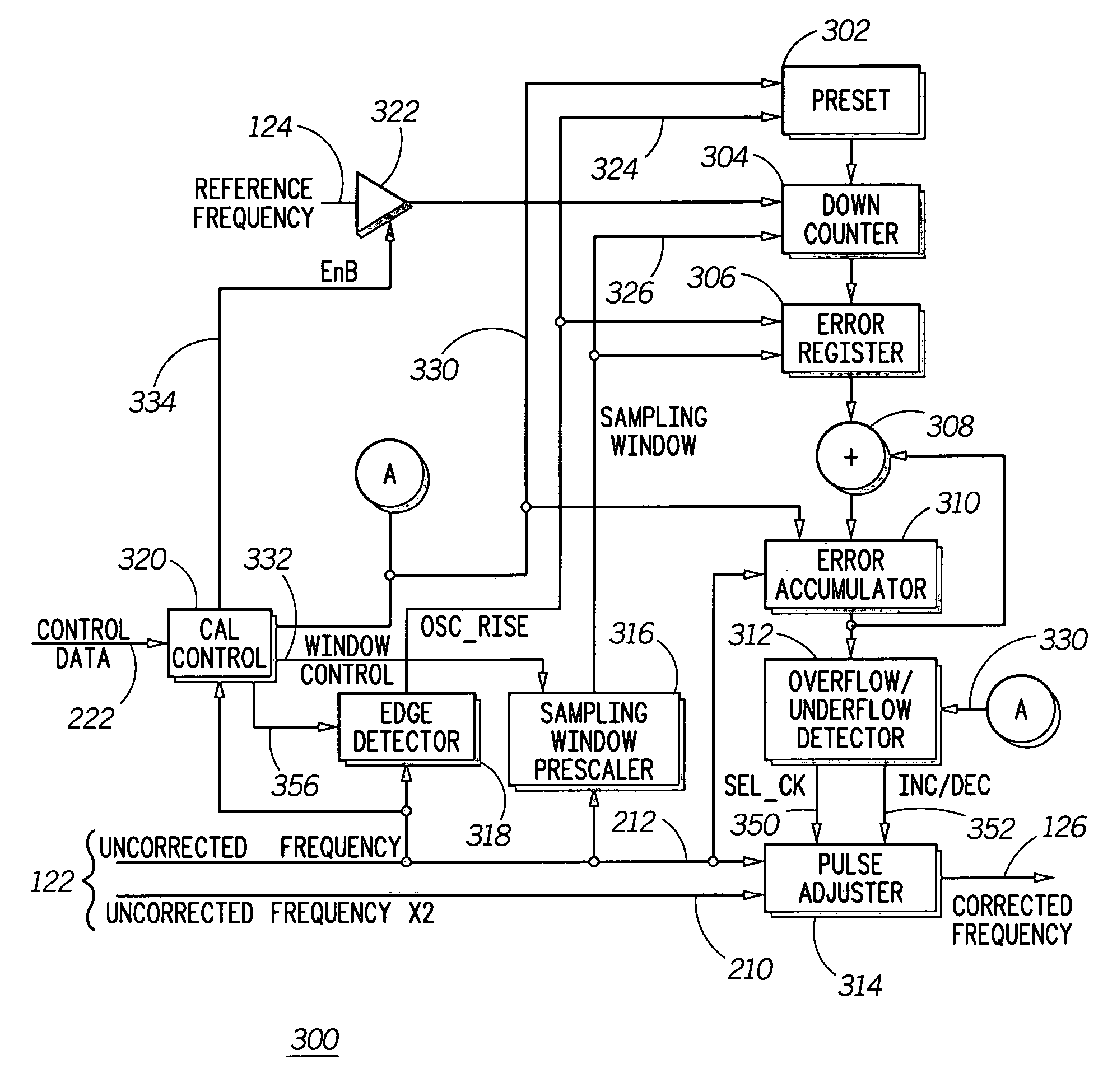
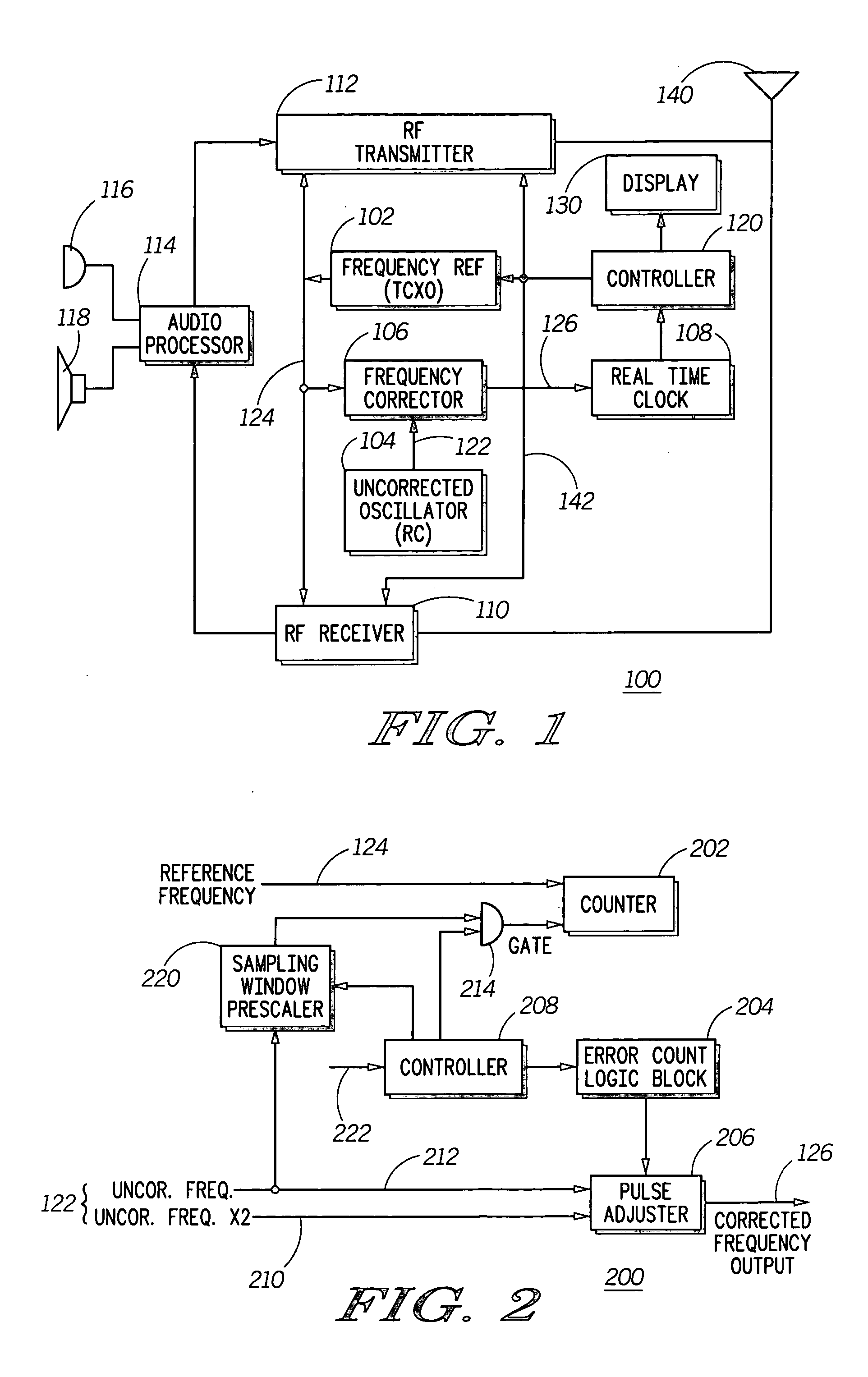
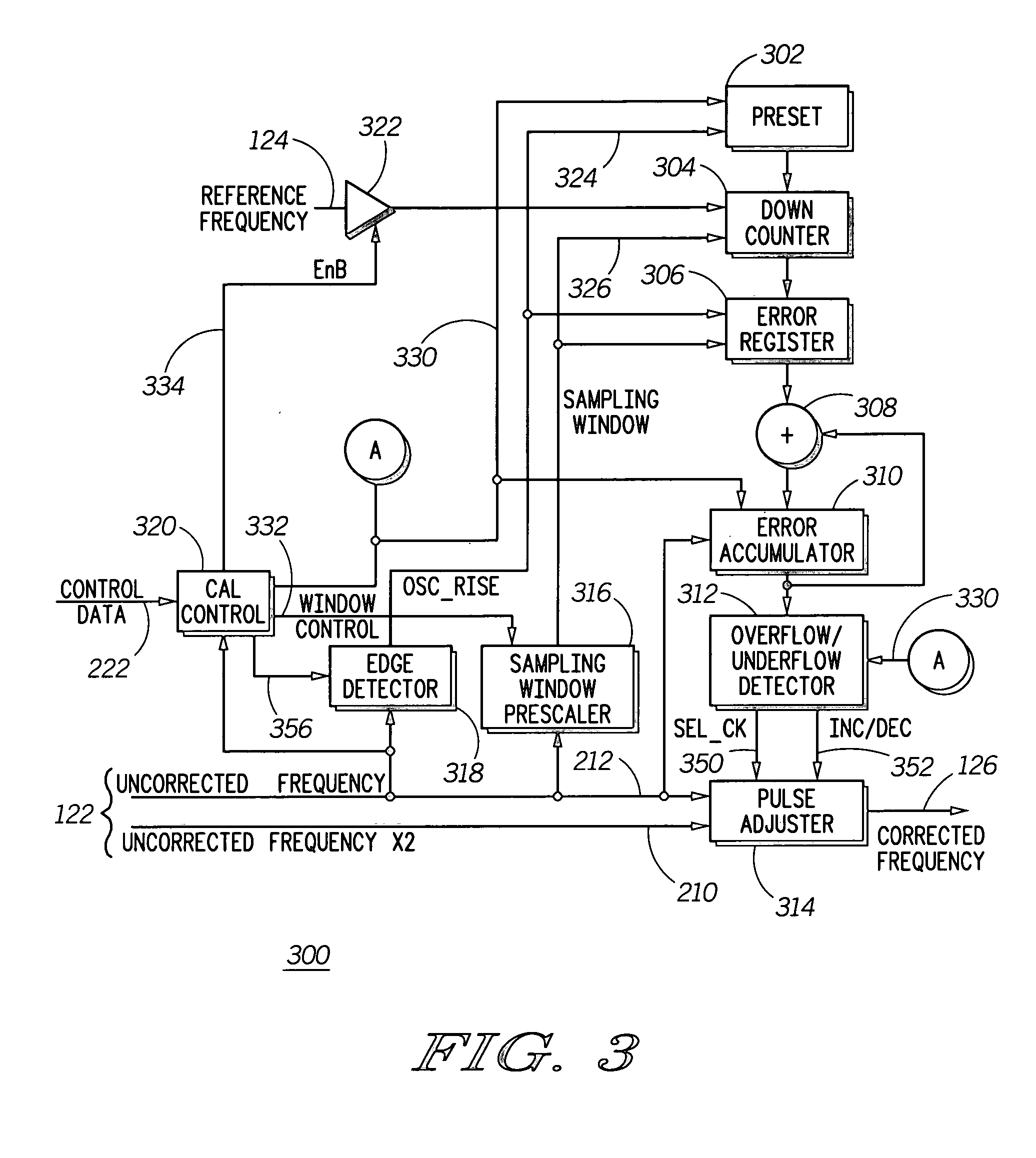
Method and apparatus for frequency correcting a periodic signal
InactiveUS20060045215A1Pulse automatic controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSignal generatorPhysics
A method and apparatus to correct a periodic signal, such as a frequency reference, based upon another frequency reference. A lower accuracy frequency signal generator (104) provides an uncorrected frequency reference signal (122) to a frequency corrector (106). Frequency corrector (106) counts cycles of a frequency reference signal (124), as generated by a higher accuracy reference generator (102) for a time period derived from the uncorrected frequency signal. Based upon the cycles counted, pulses are added or removed from the uncorrected frequency signal (122) to produce a corrected frequency signal (126). A ratio of pulses to be removed from the uncorrected frequency signal (122) is determined from the number of cycles counted and a counter arrangement is provided to automatically remove the required ratio of pulses from the uncorrected frequency signal (122).
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
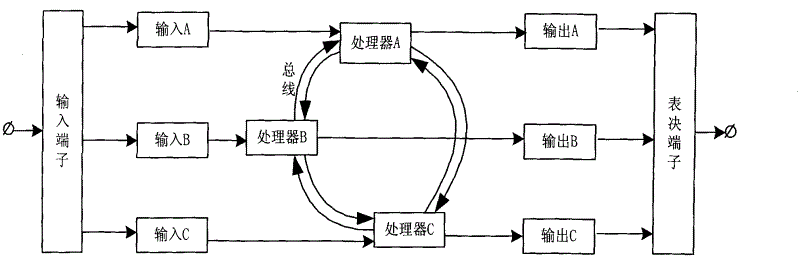
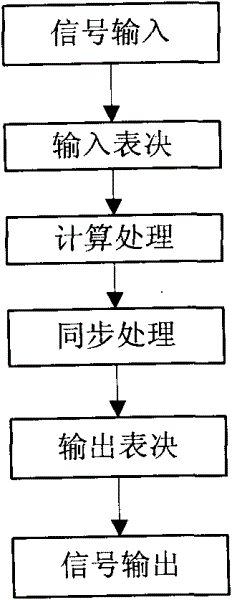
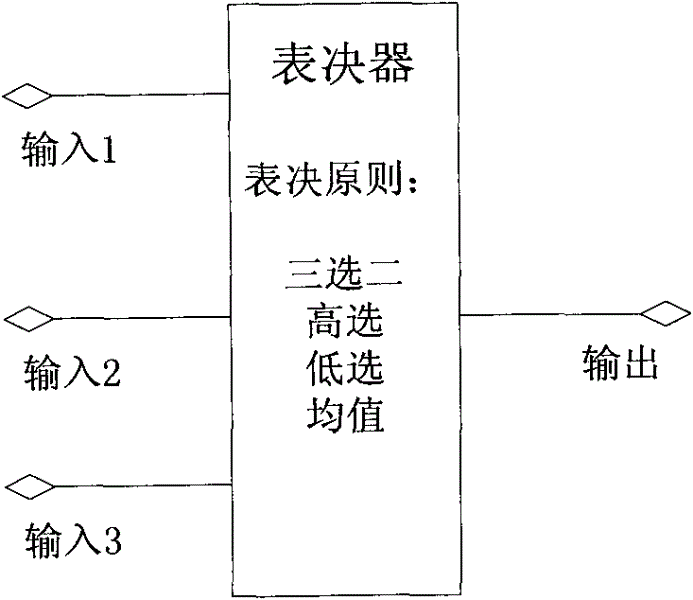
Triple redundancy control system in process control and method thereof
InactiveCN102621938AWork reliablyEnsure safetyTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlControl systemComputer module
The invention discloses a triple redundancy control system in process control and a method thereof. The system comprises three independent processors. The processors are connected with each other through a bus. The control system also comprises one output vote terminal which is connected with the three processors and is used to vote three processor output taken as voting input. Each processor comprises: one input voting module, which is used for the each processor to carry out input voting on the obtained three path input respectively; one calculation processing module, which is used for the each processor to carry out calculation according to a preset control logic respectively after the input voting, and adding 1 to respective cycle count after the calculation; one synchronous processing module, which is used for carrying out comparison taking a master processor as a reference, and sending the synchronization information to a slave processor after the main processor completes calculation. In the invention, by using a synchronization mechanism, a voting mechanism and a master-slave switching mechanism, high reliability and high security of the system can be guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINHUA CONTROL TECH GROUP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com