Patents
Literature
1873 results about "Blowout preventer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
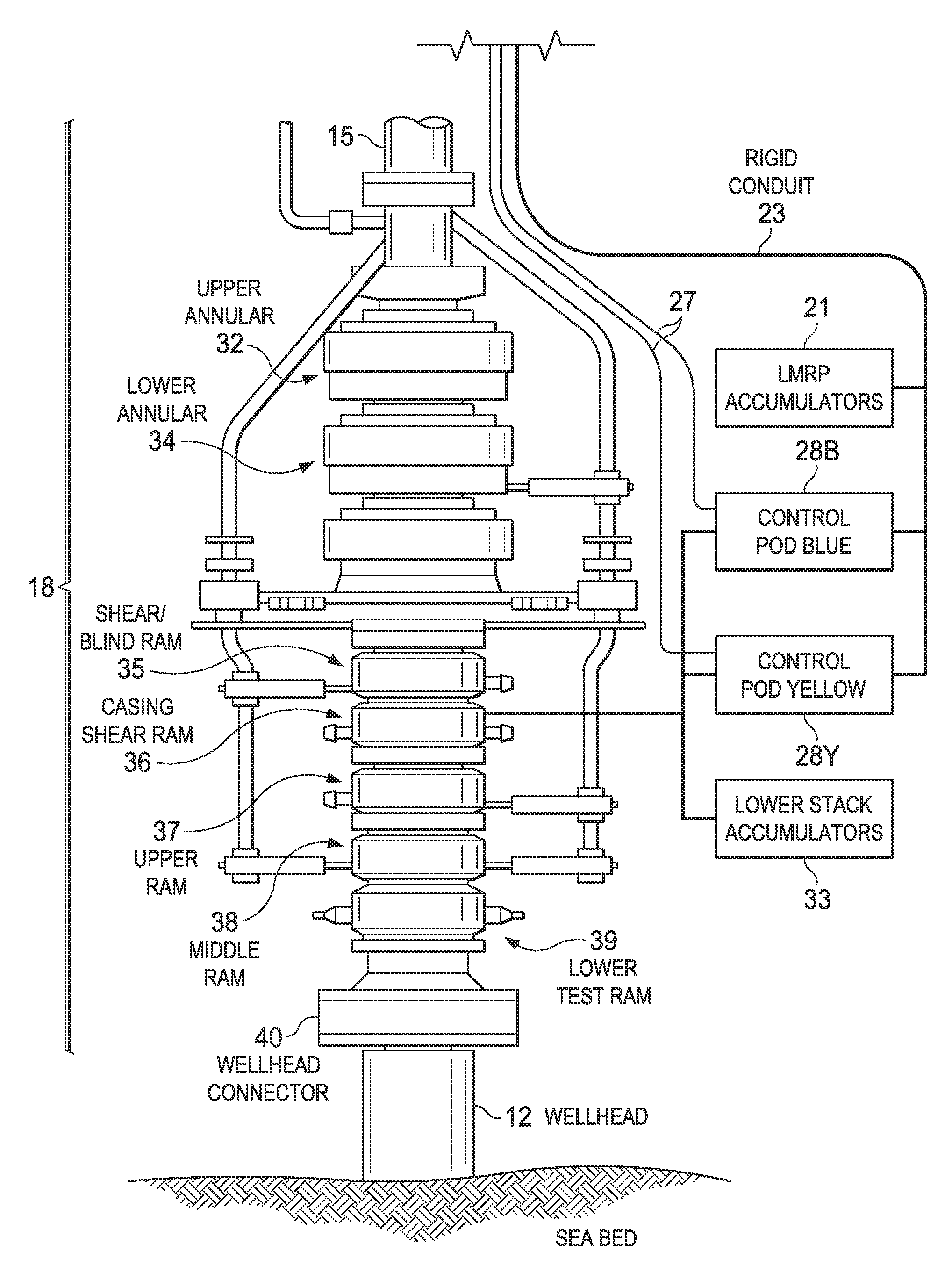
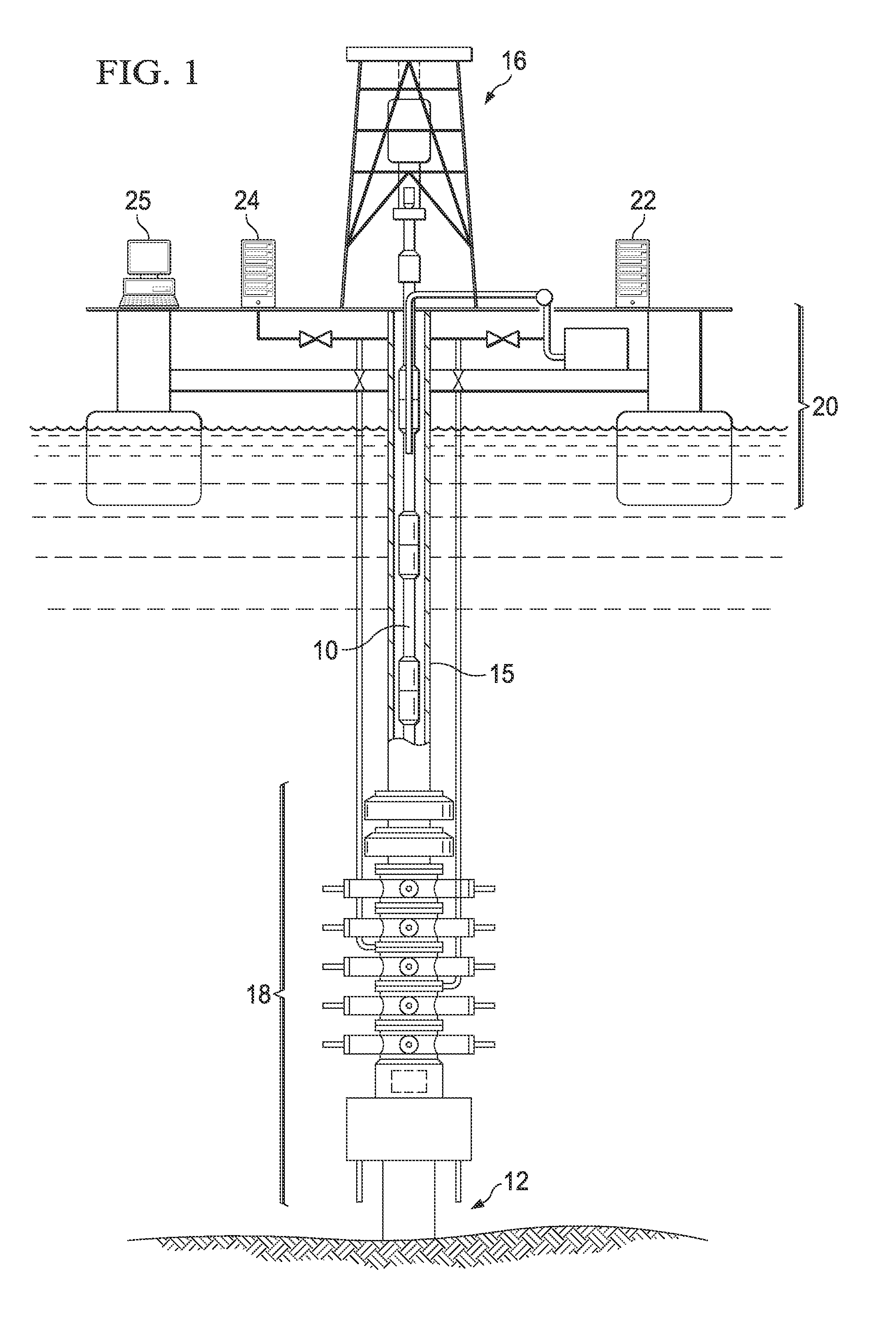
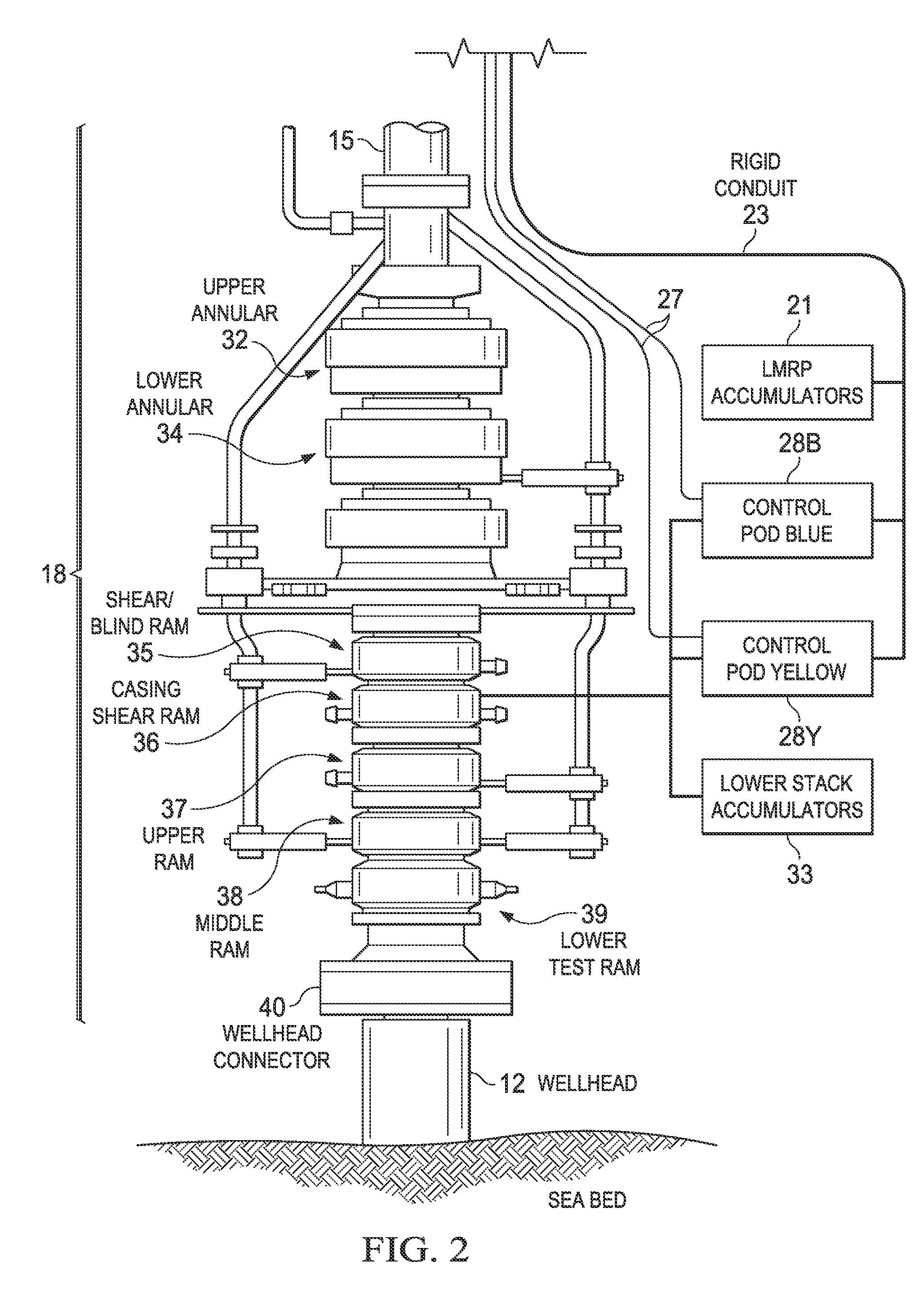
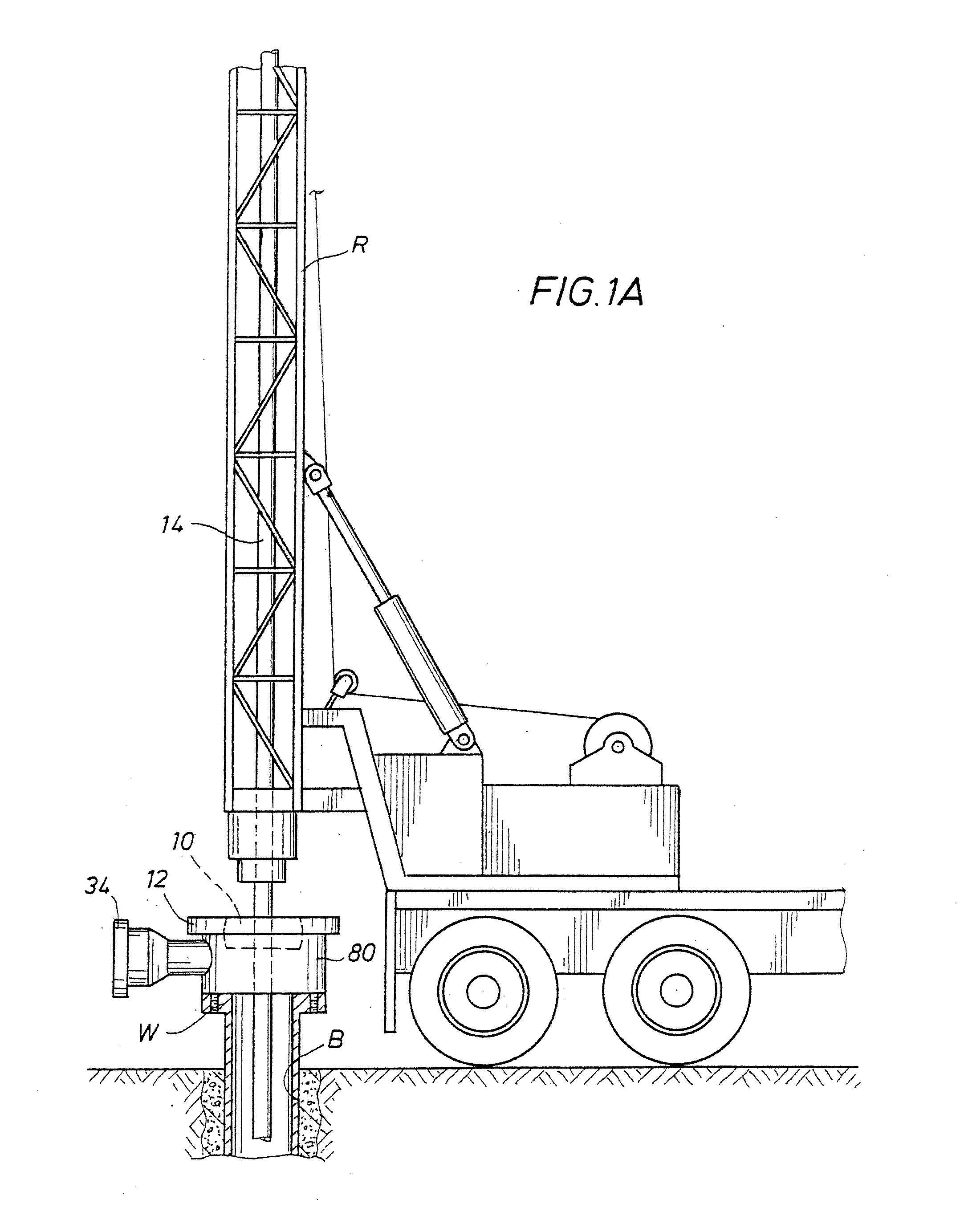
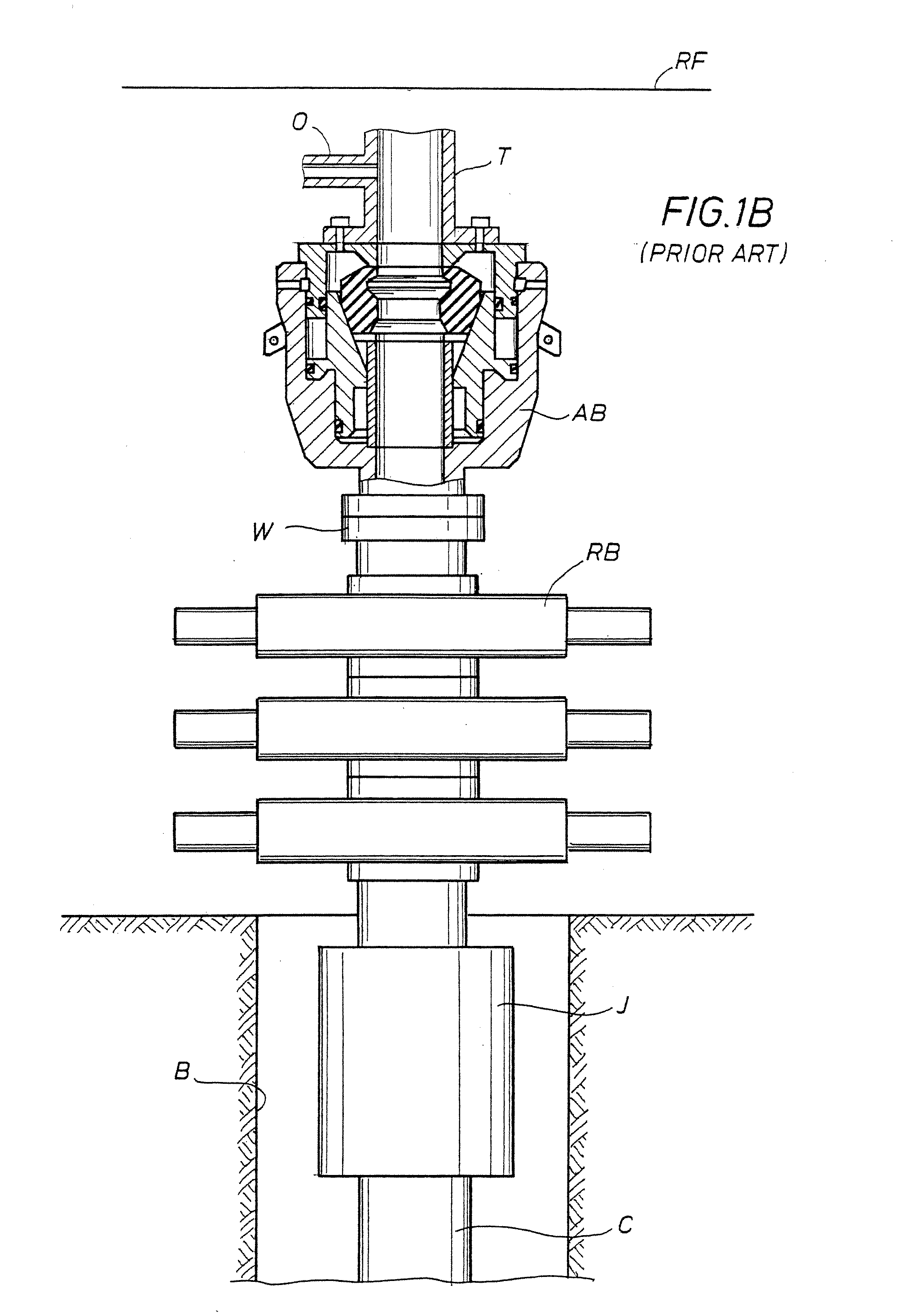
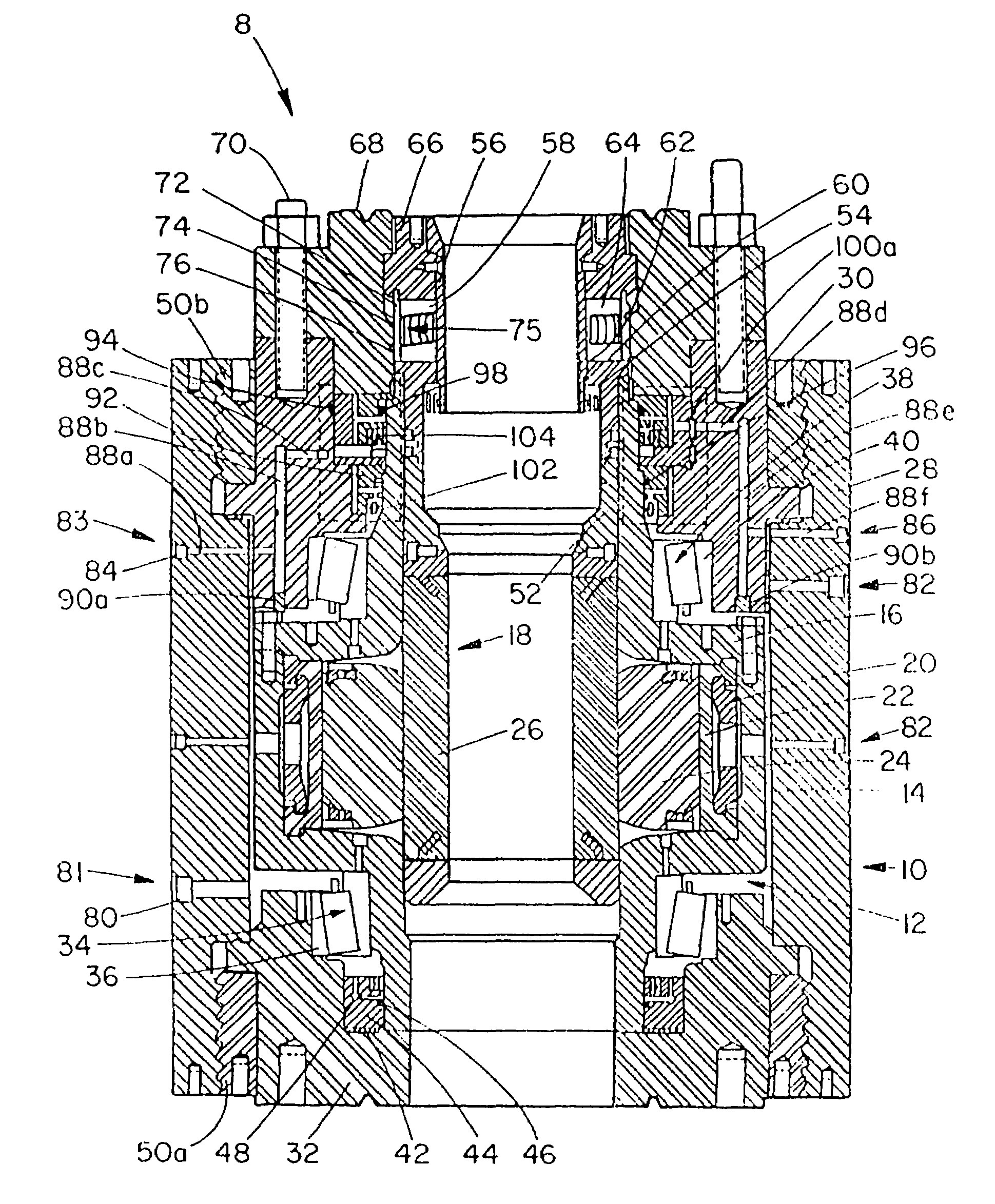
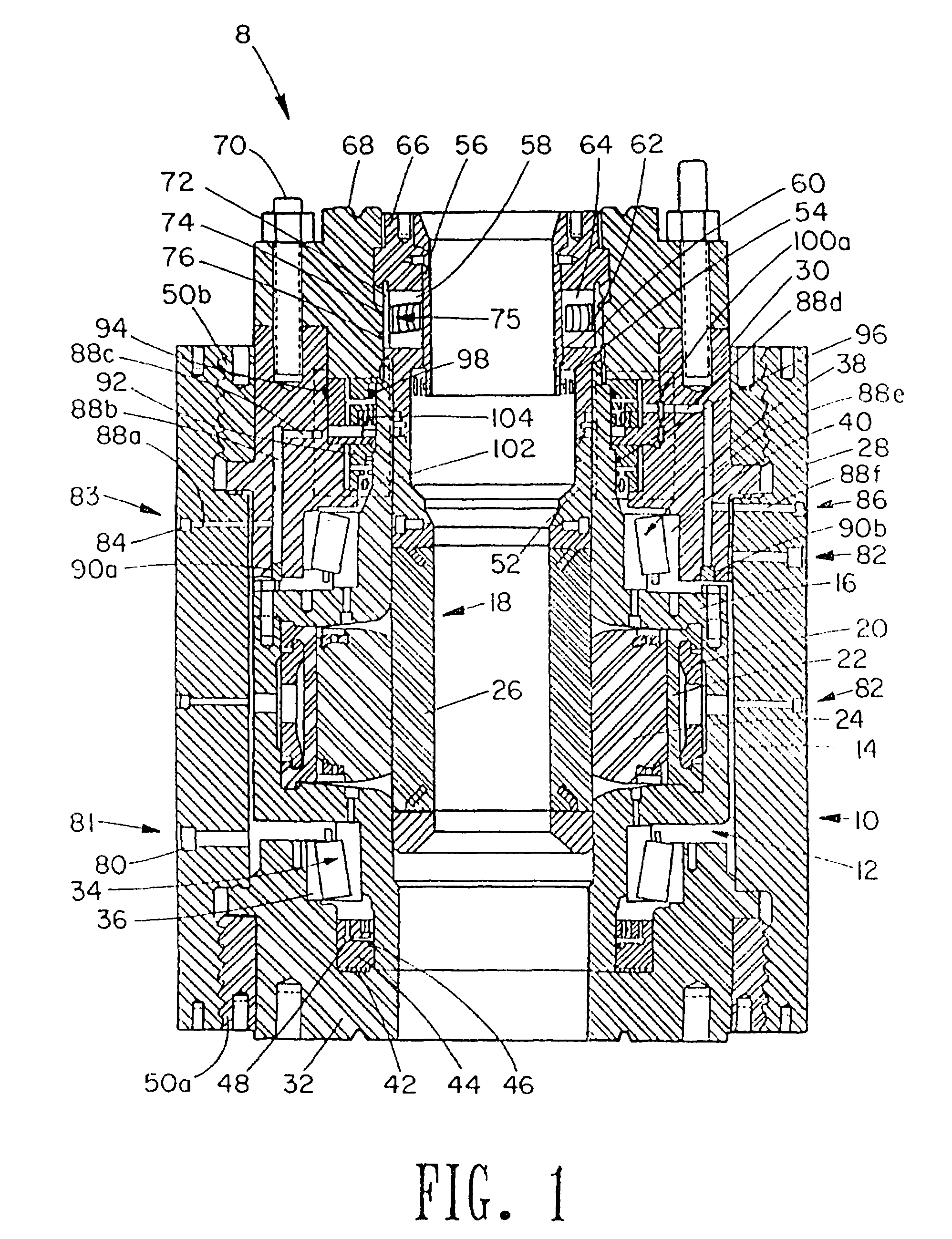
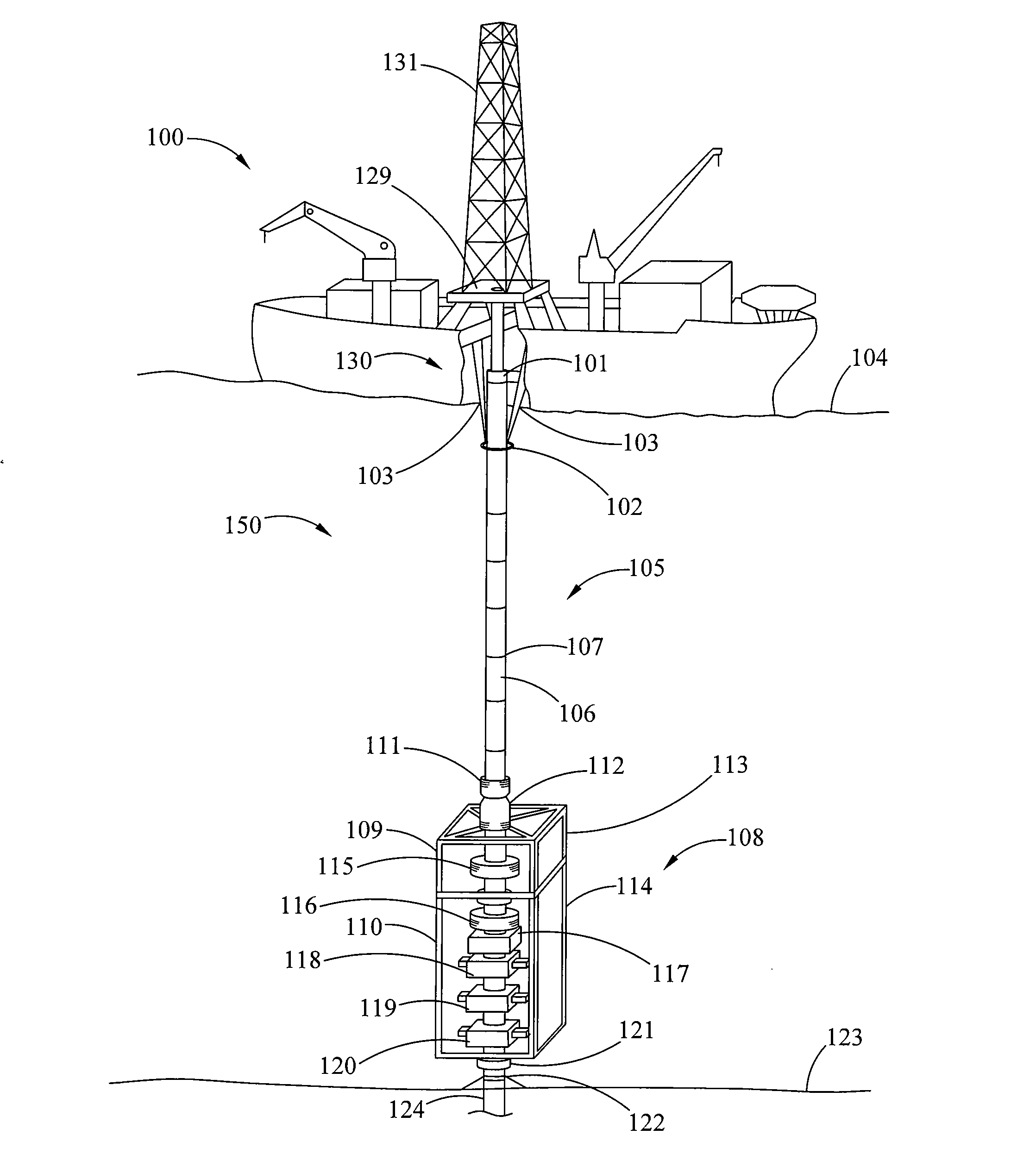
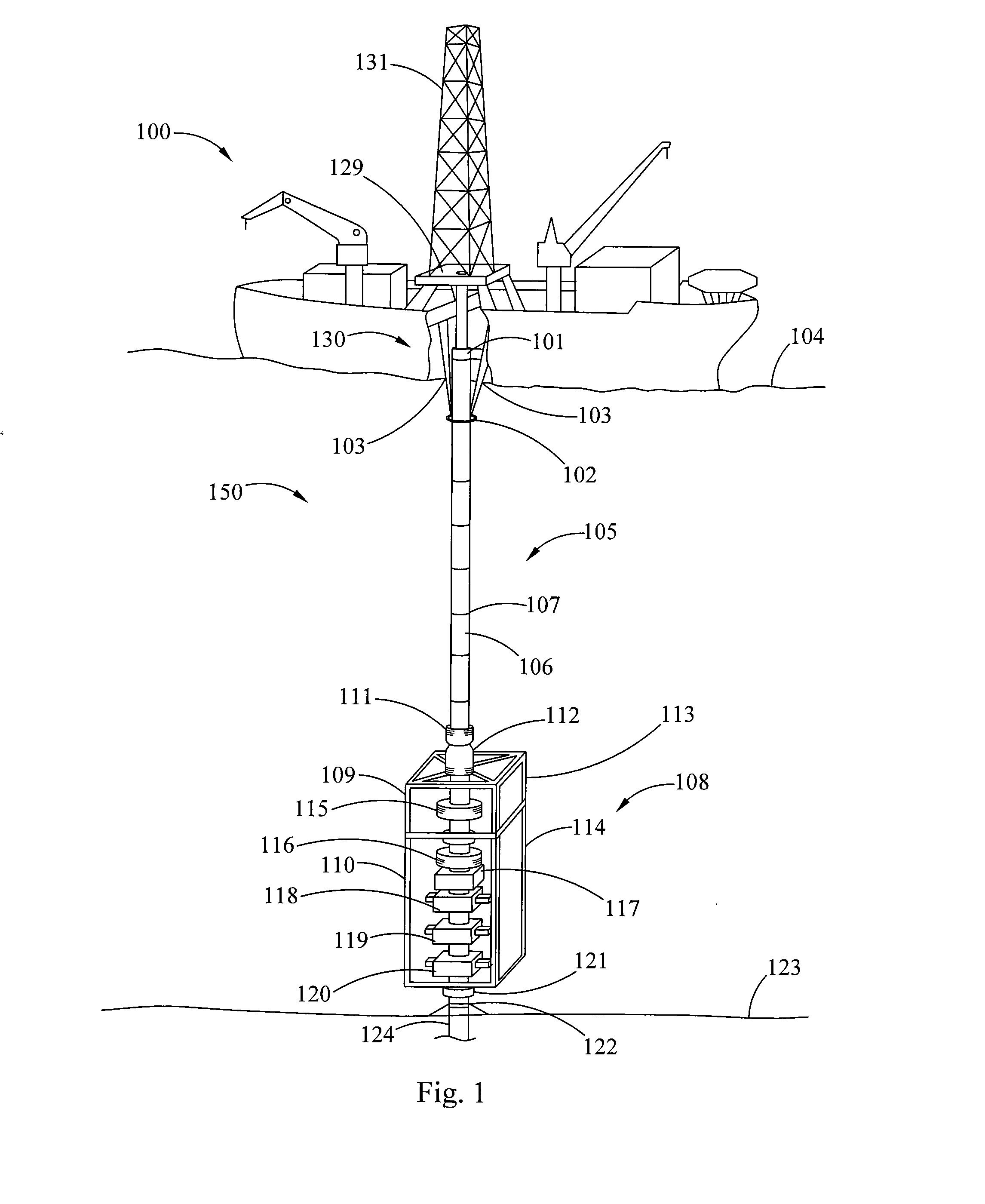
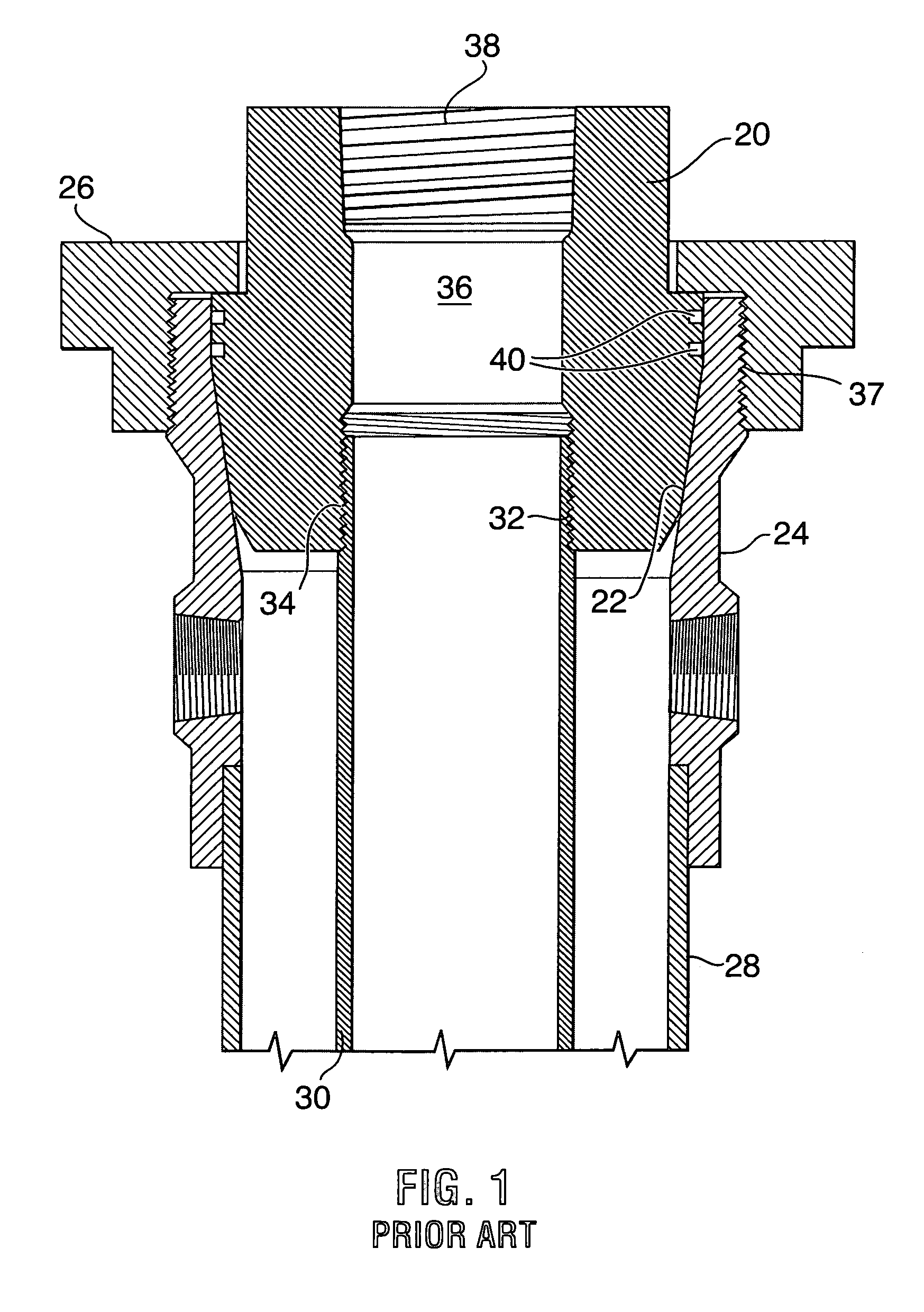
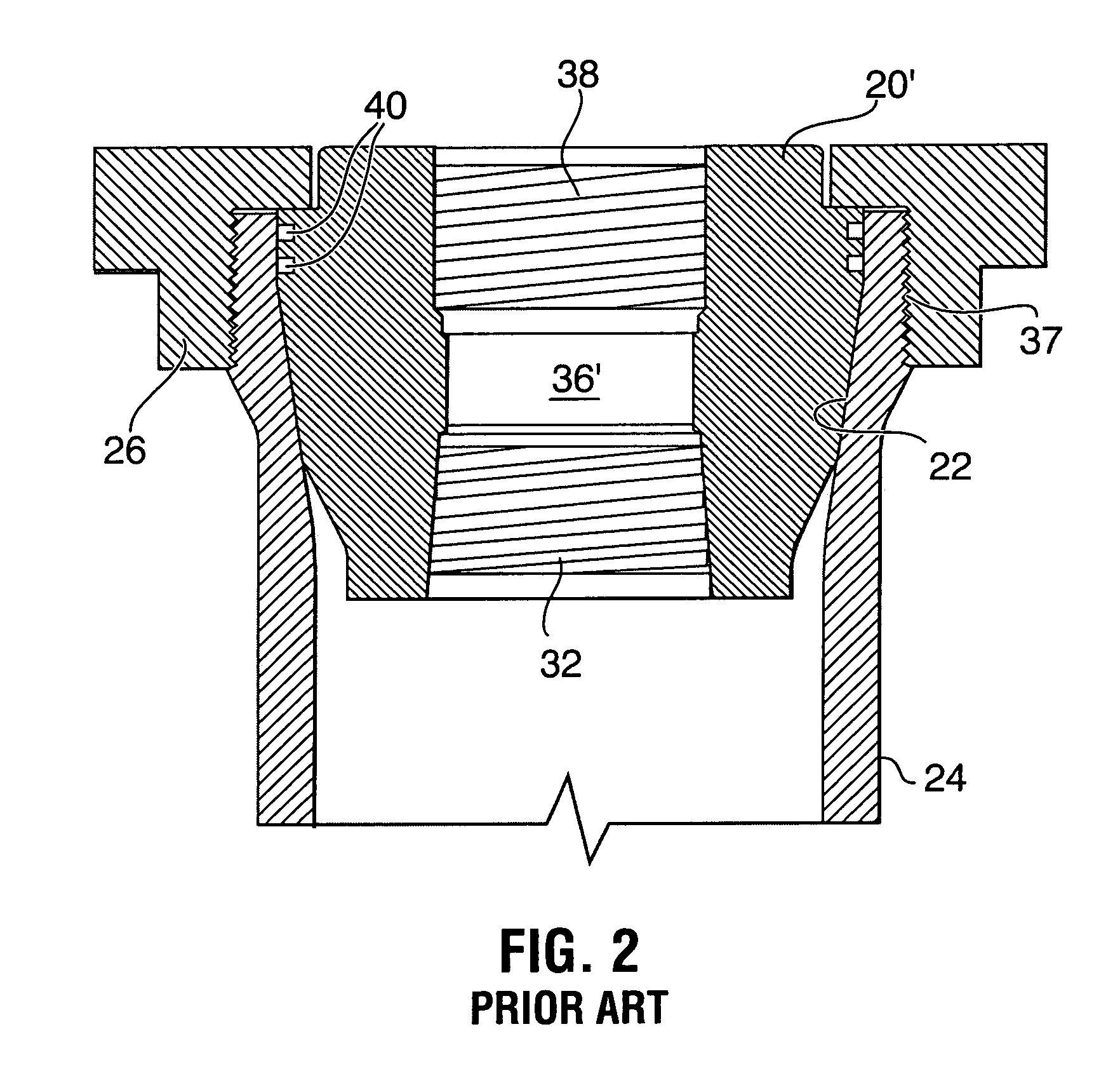
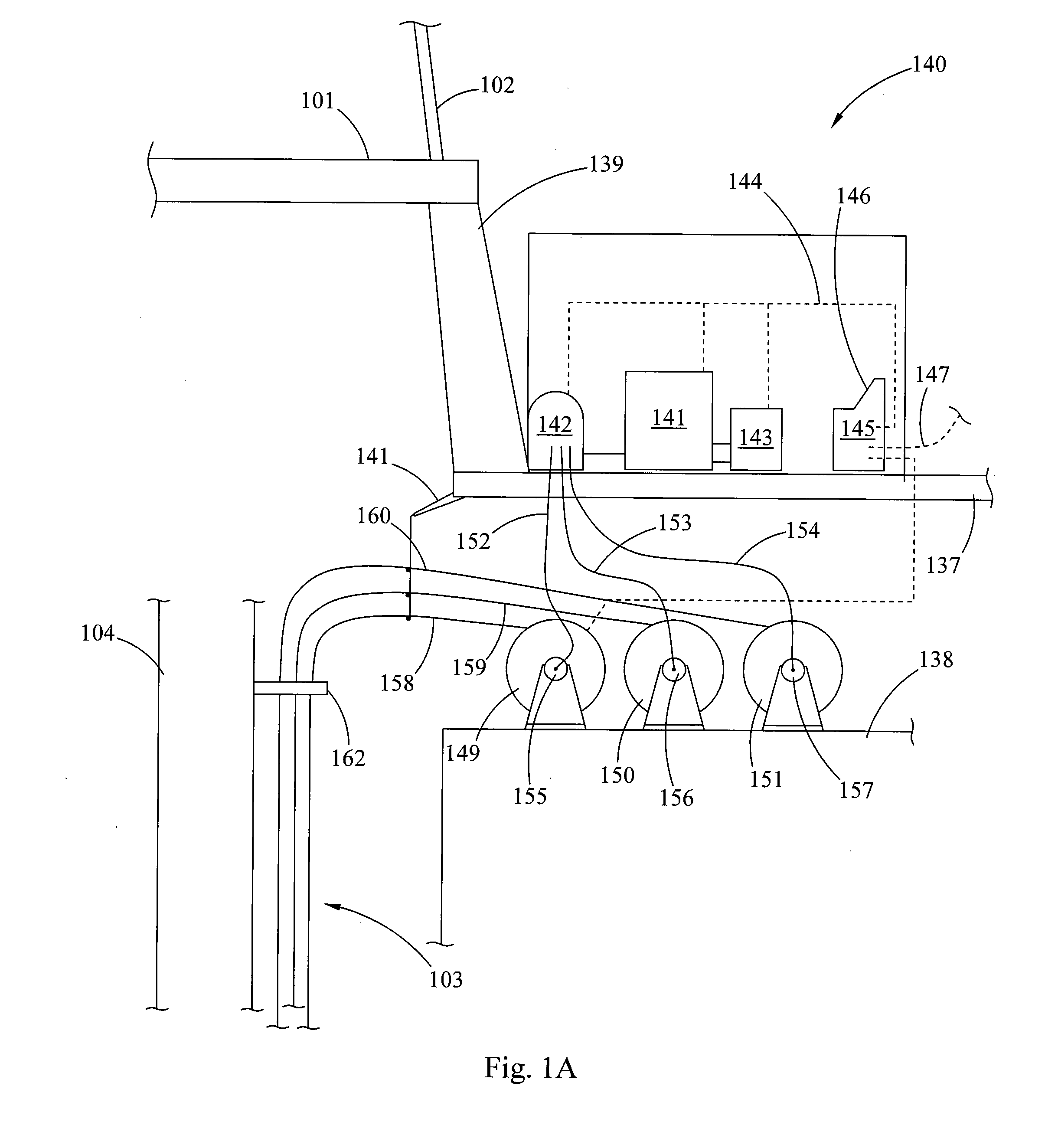
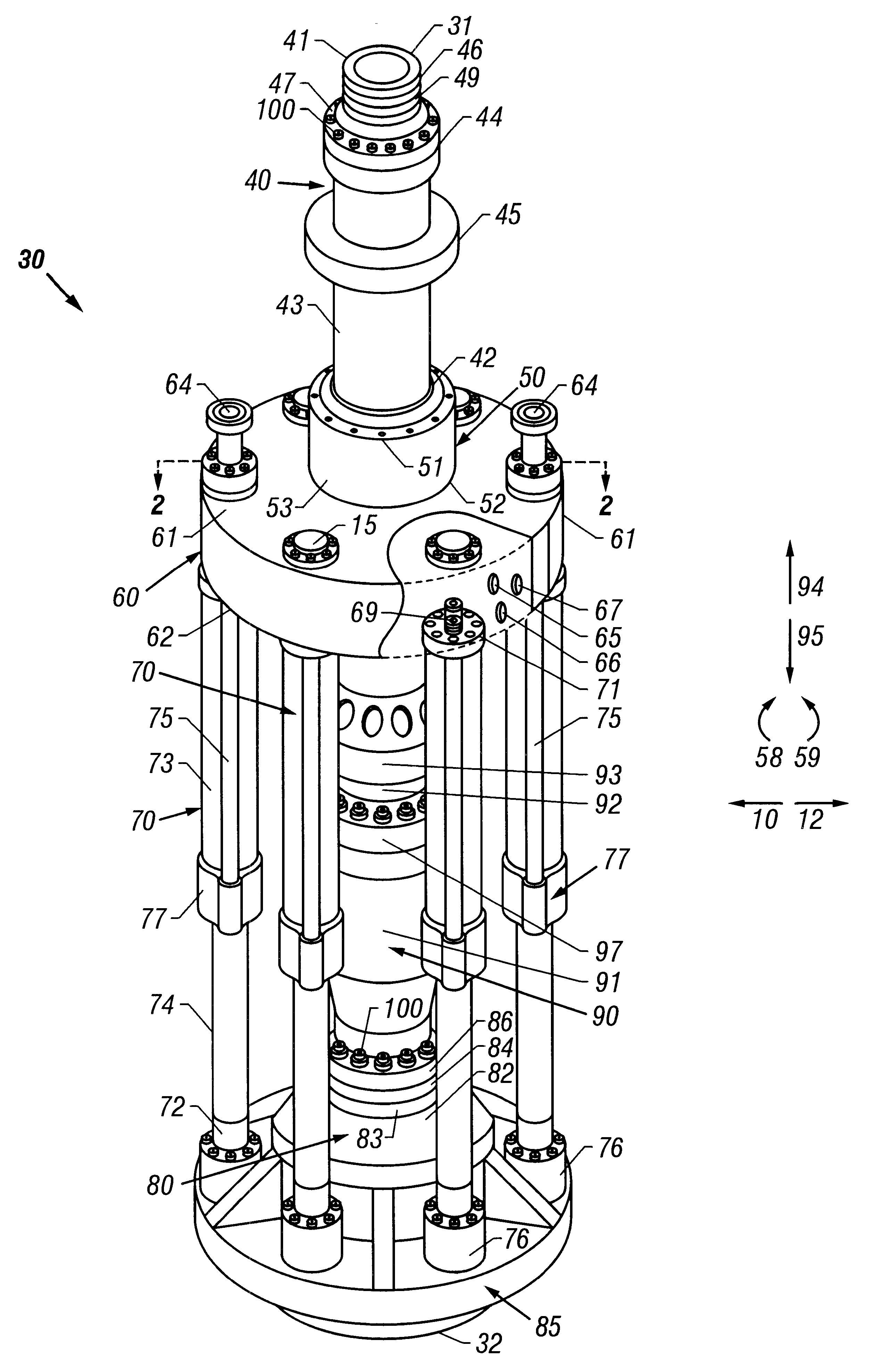
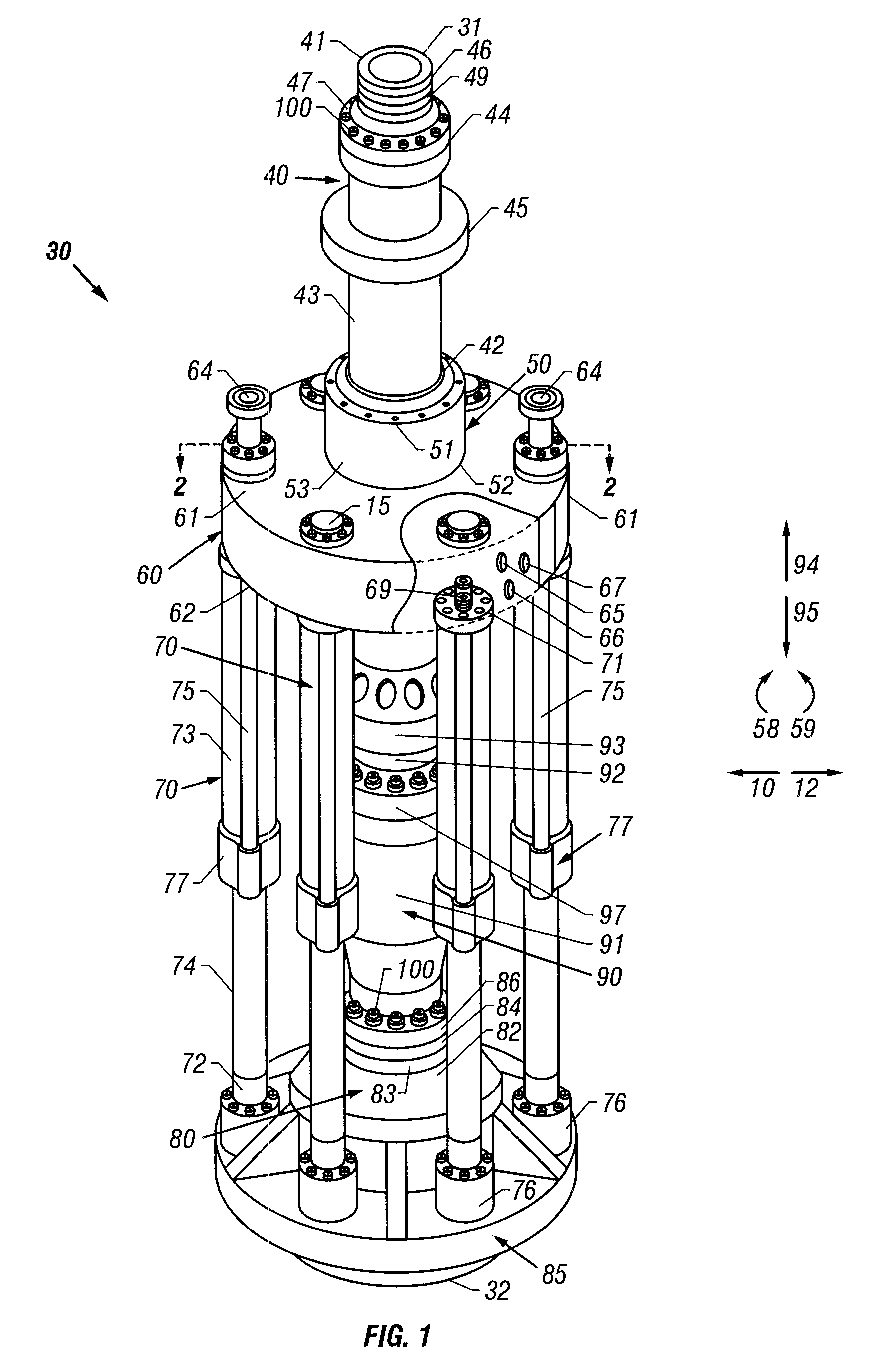
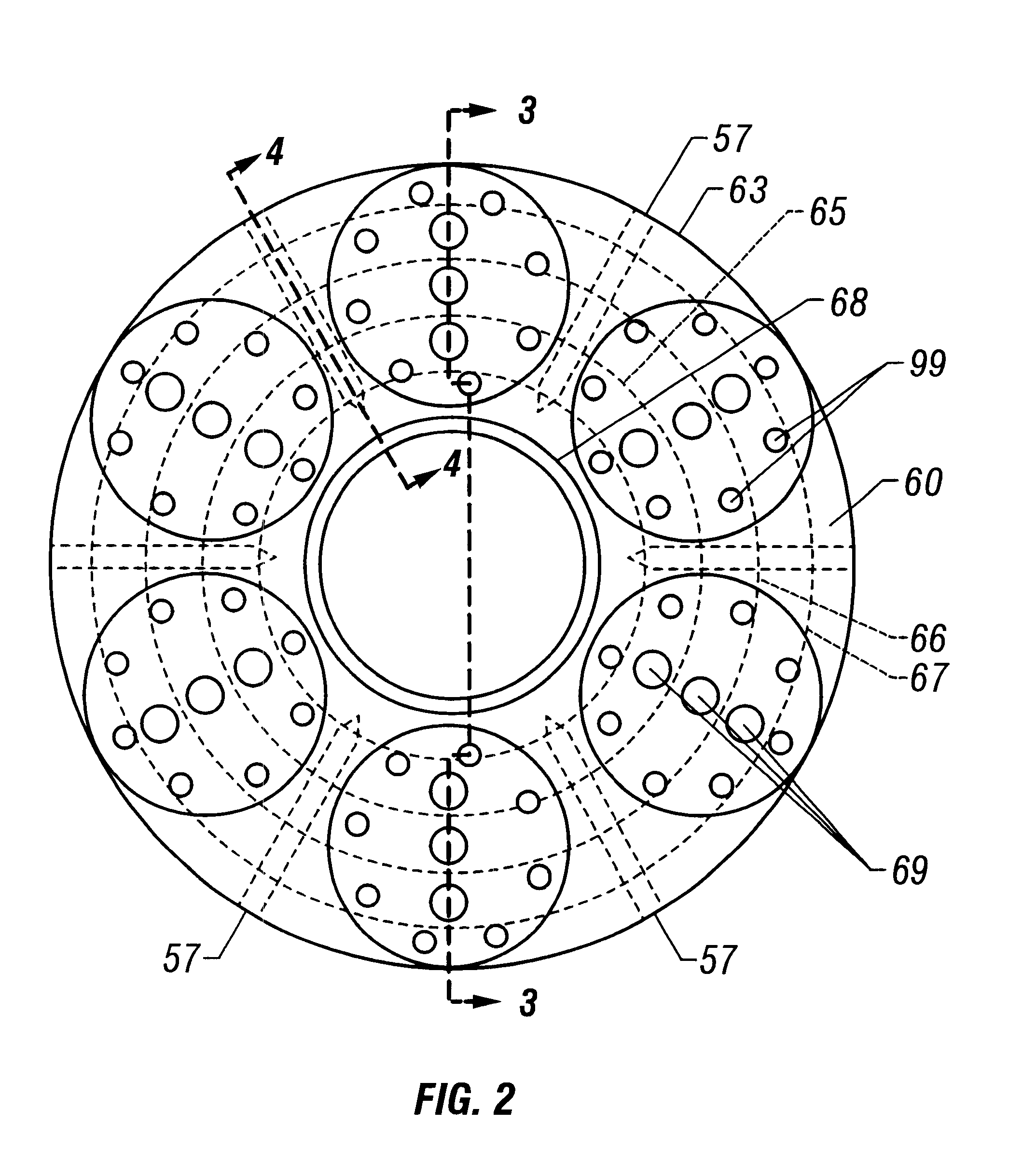
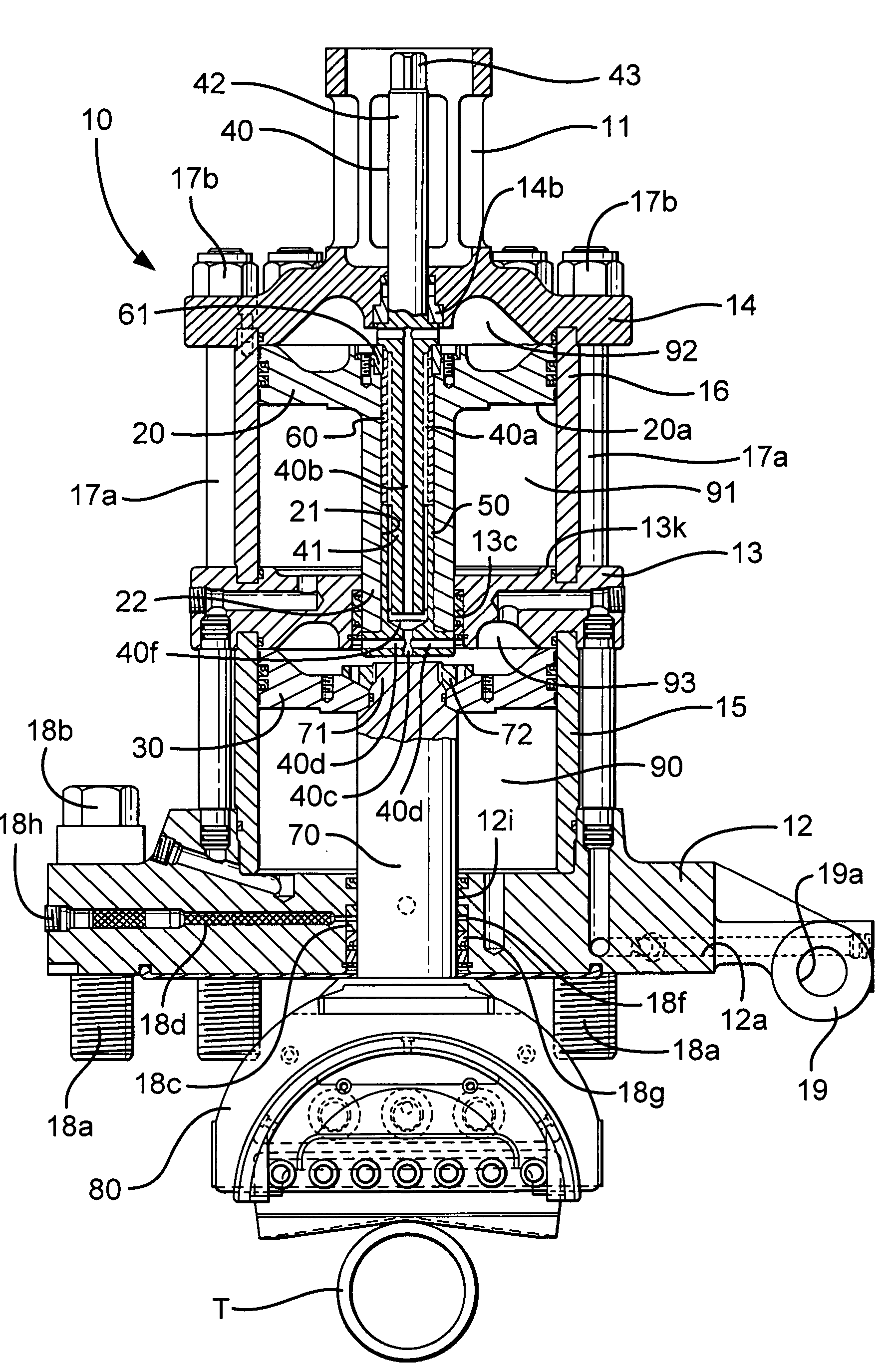
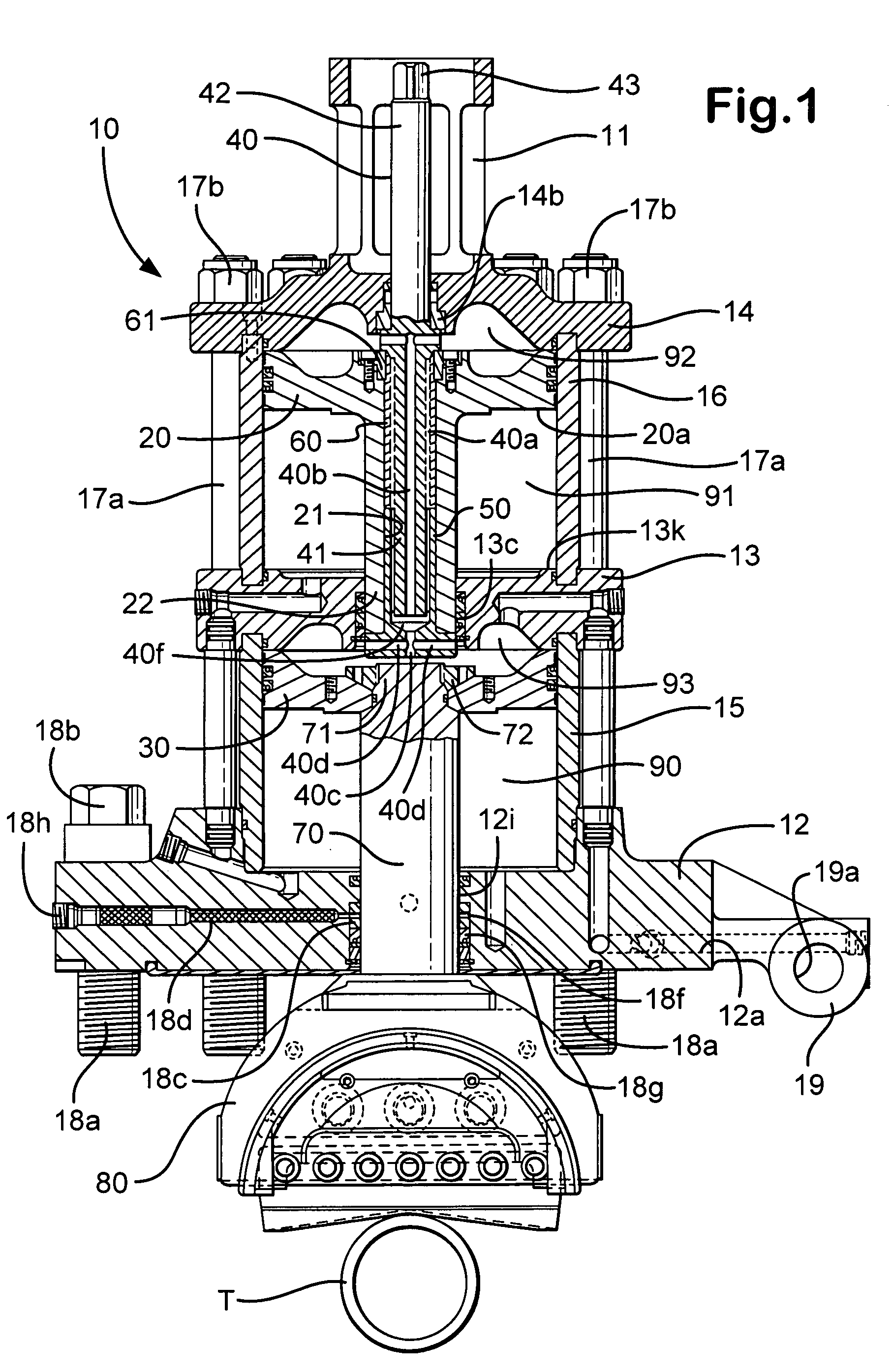
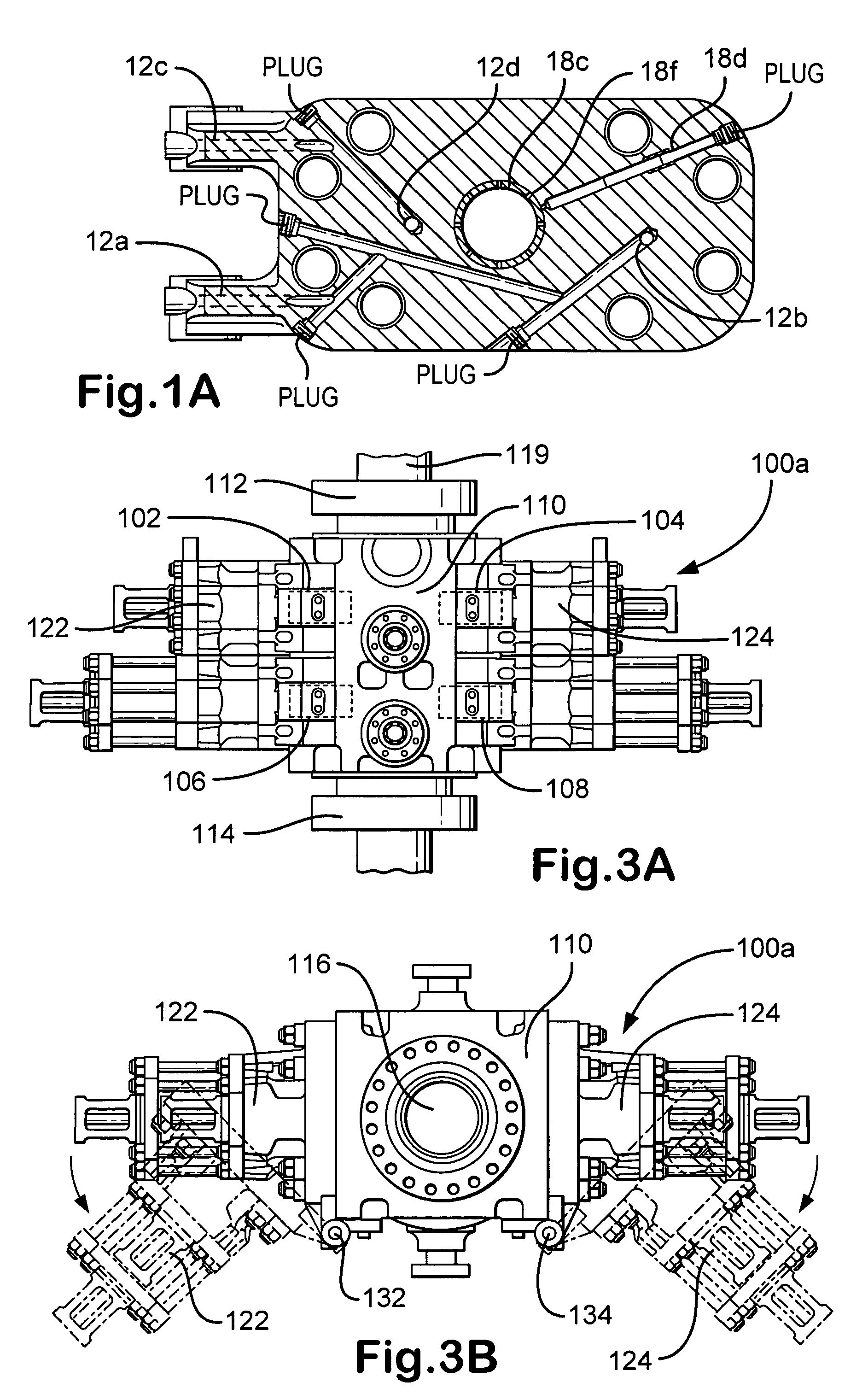
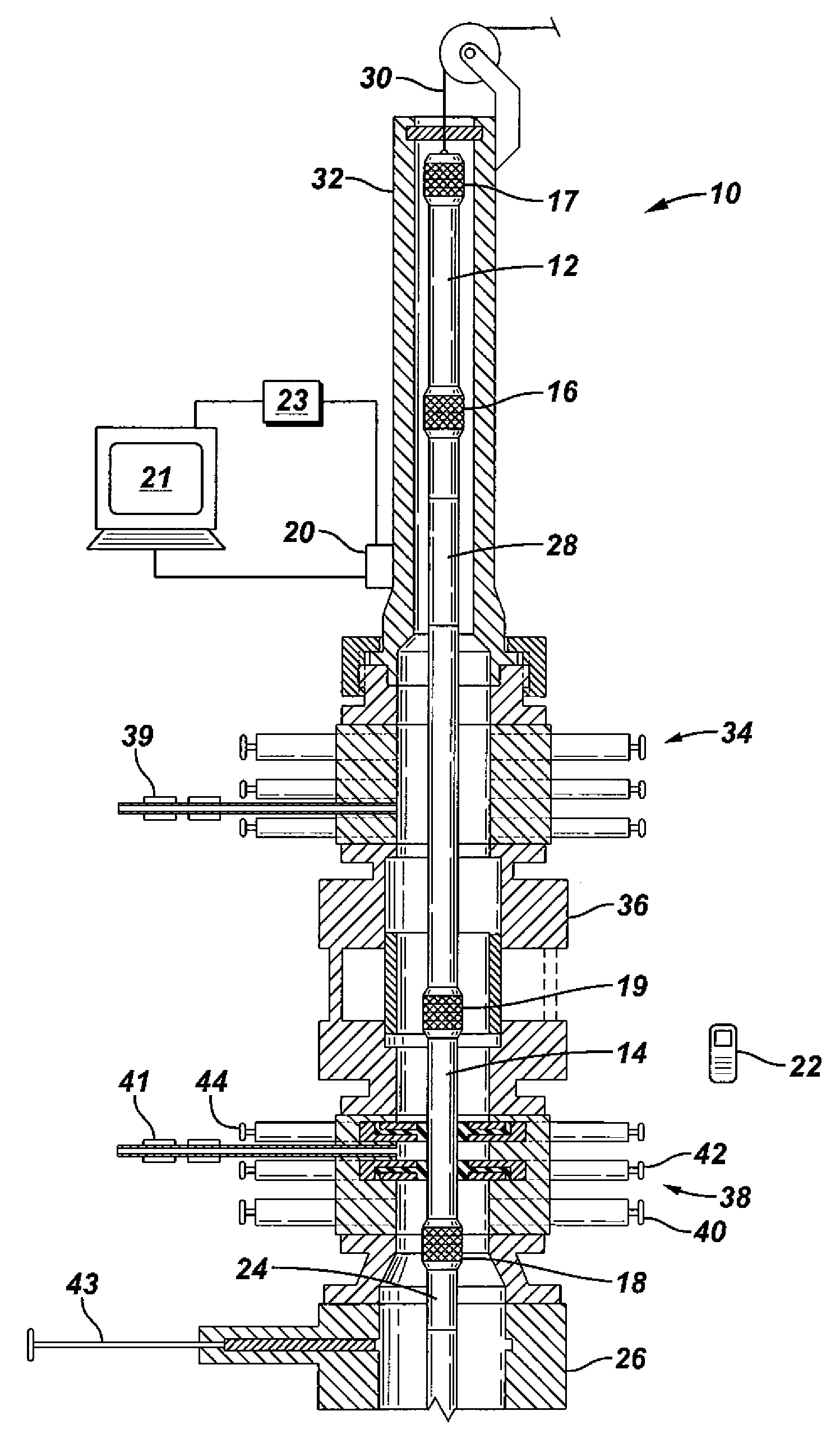
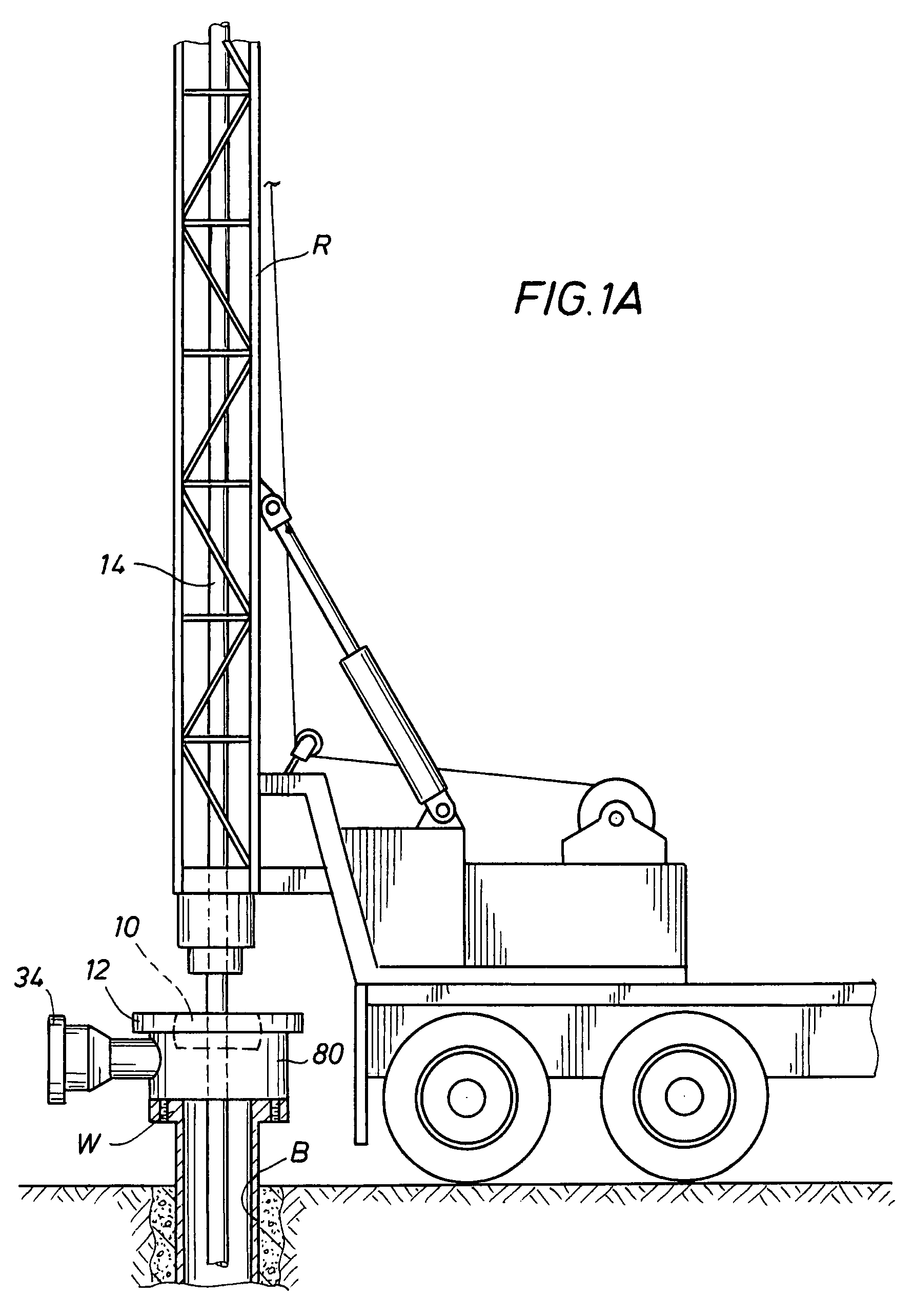
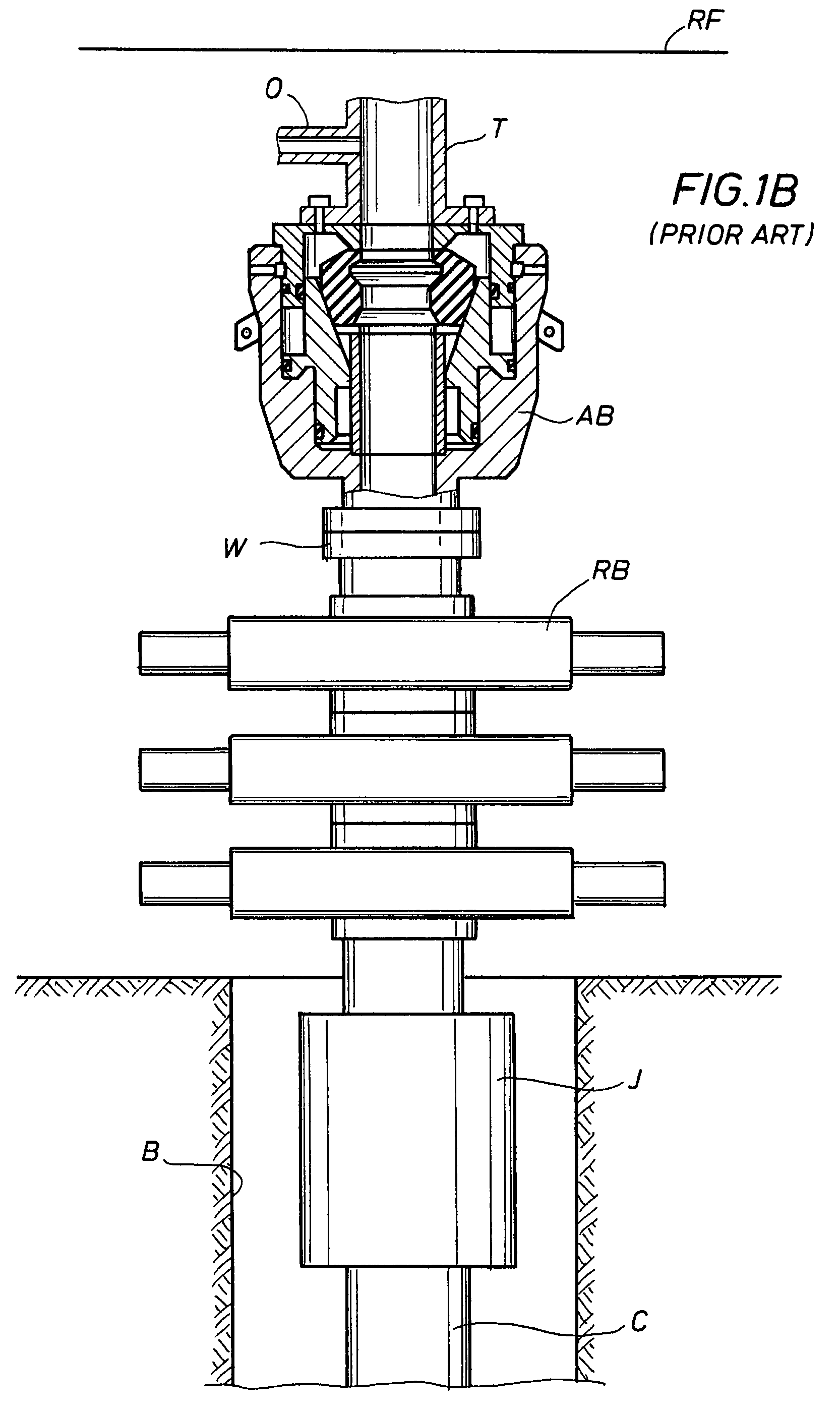
A blowout preventer (BOP) is a large, specialized valve or similar mechanical device, used to seal, control and monitor oil and gas wells to prevent blowouts, the uncontrolled release of crude oil and/or natural gas from a well. They are usually installed in stacks of other valves.
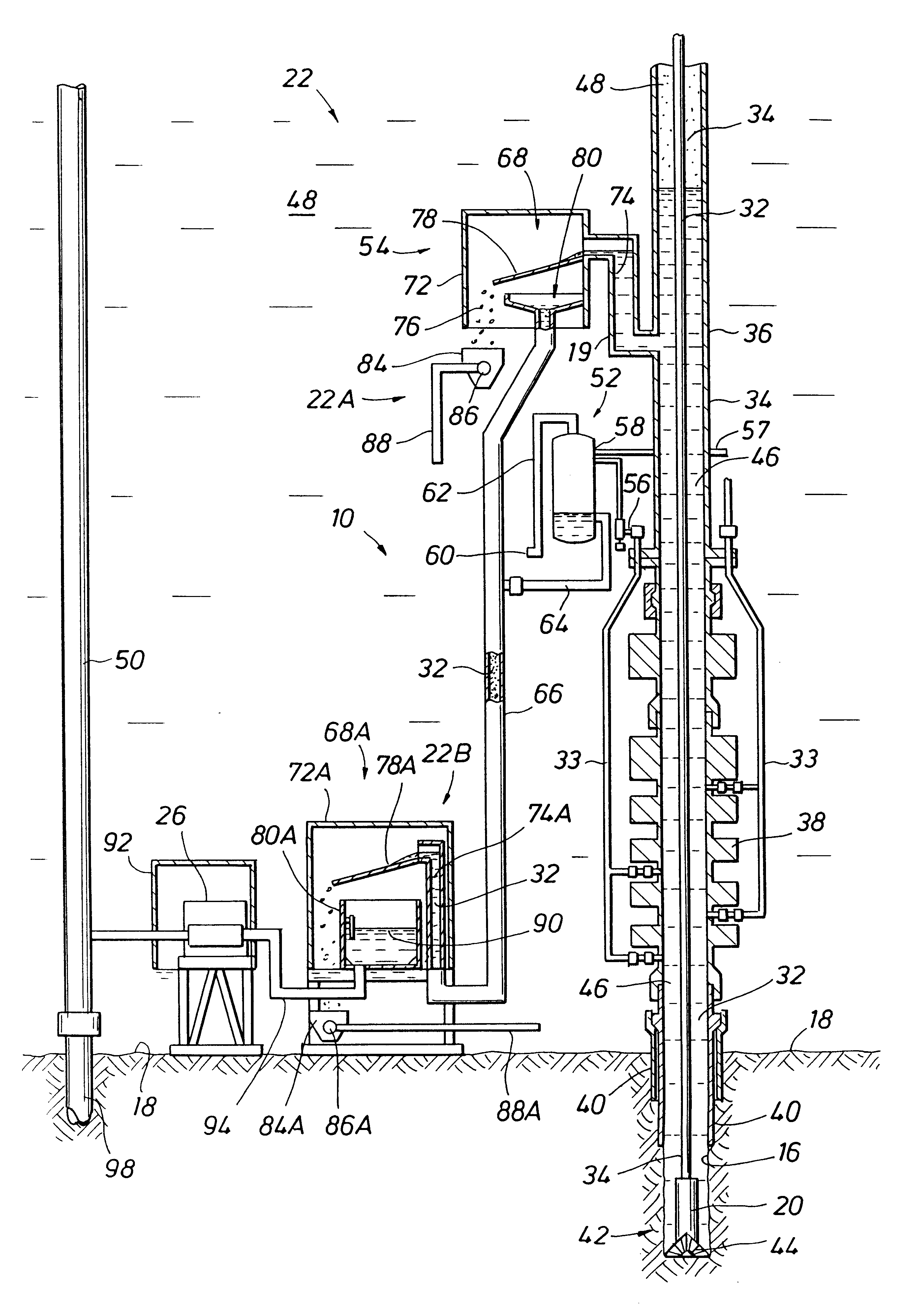
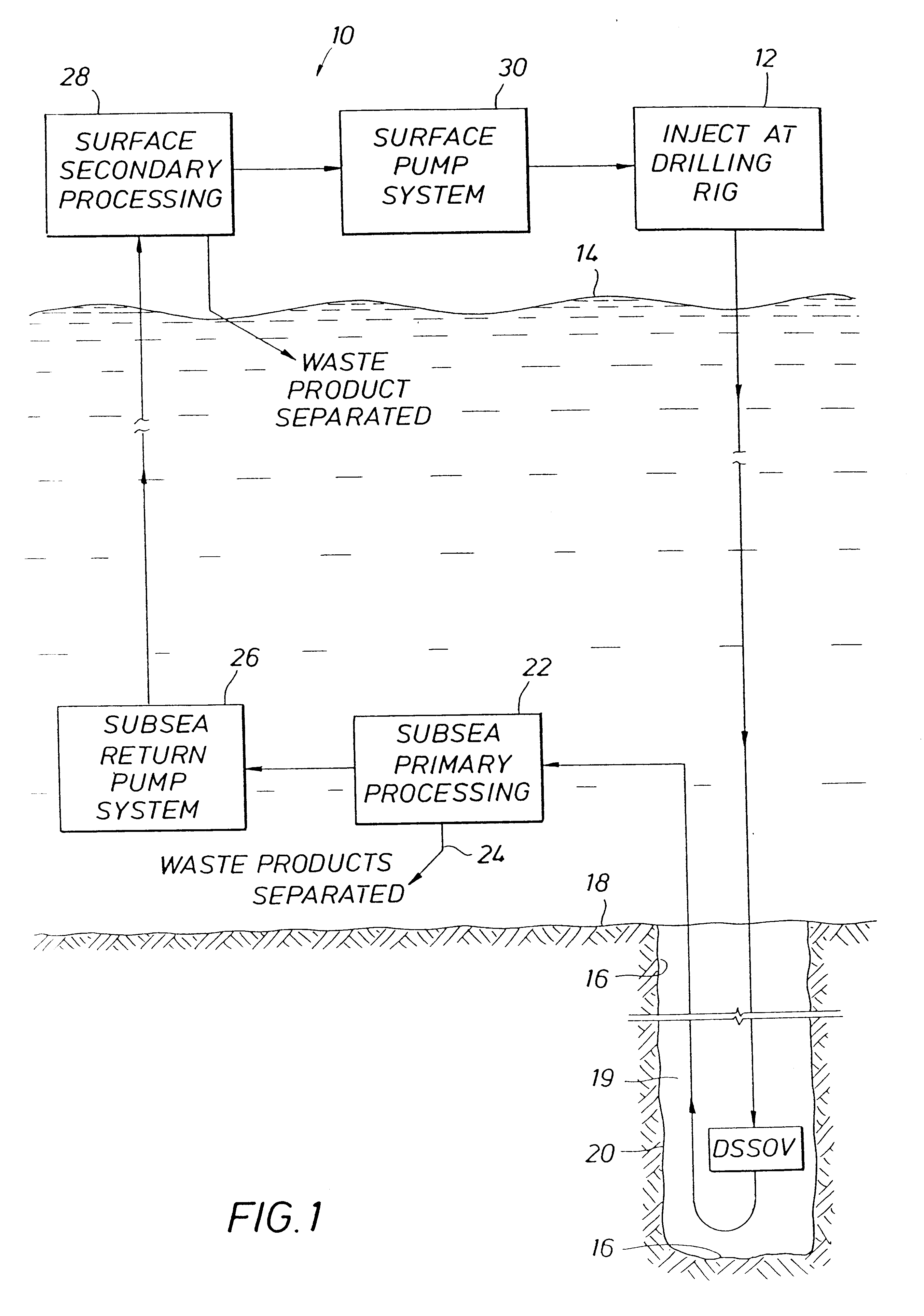
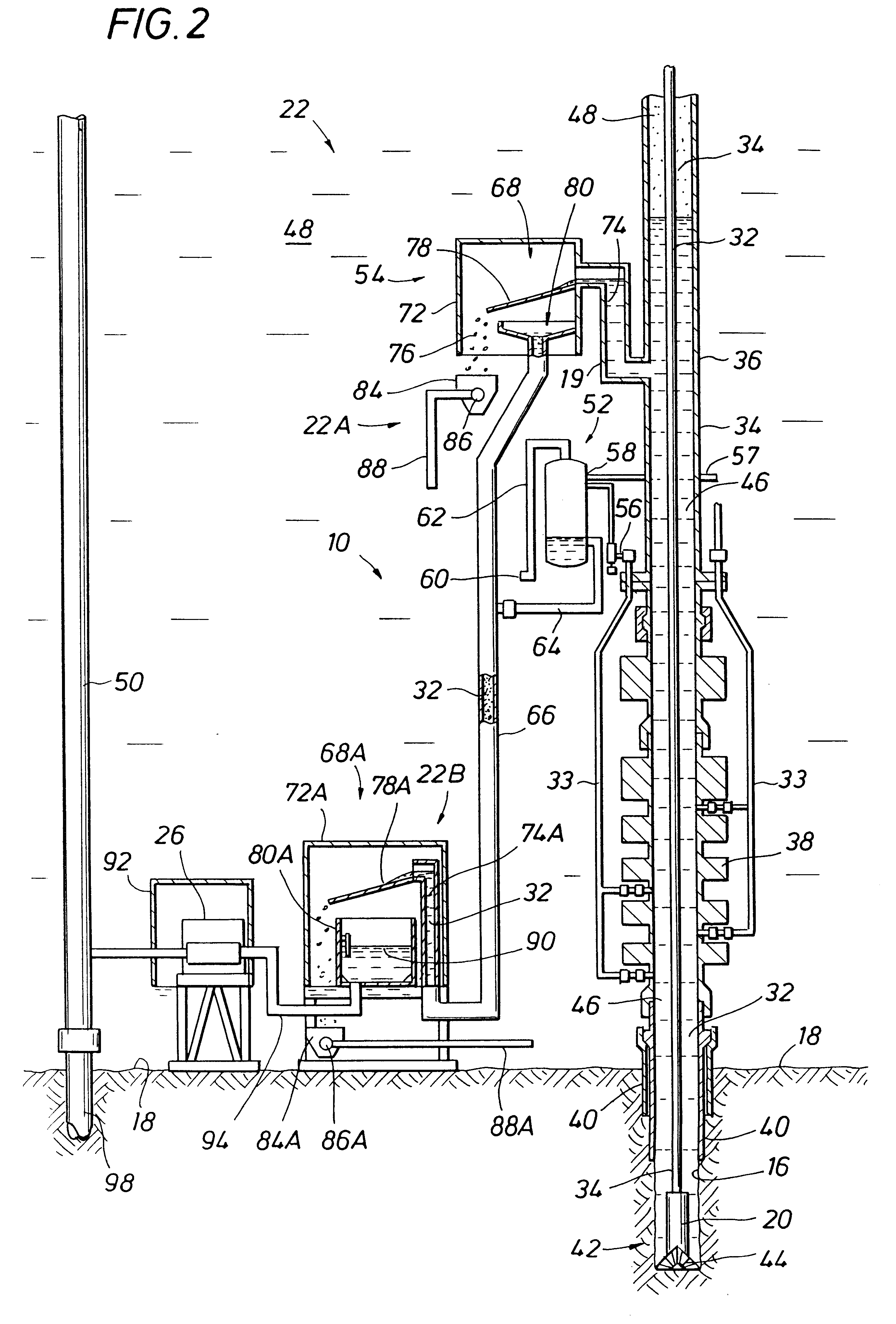
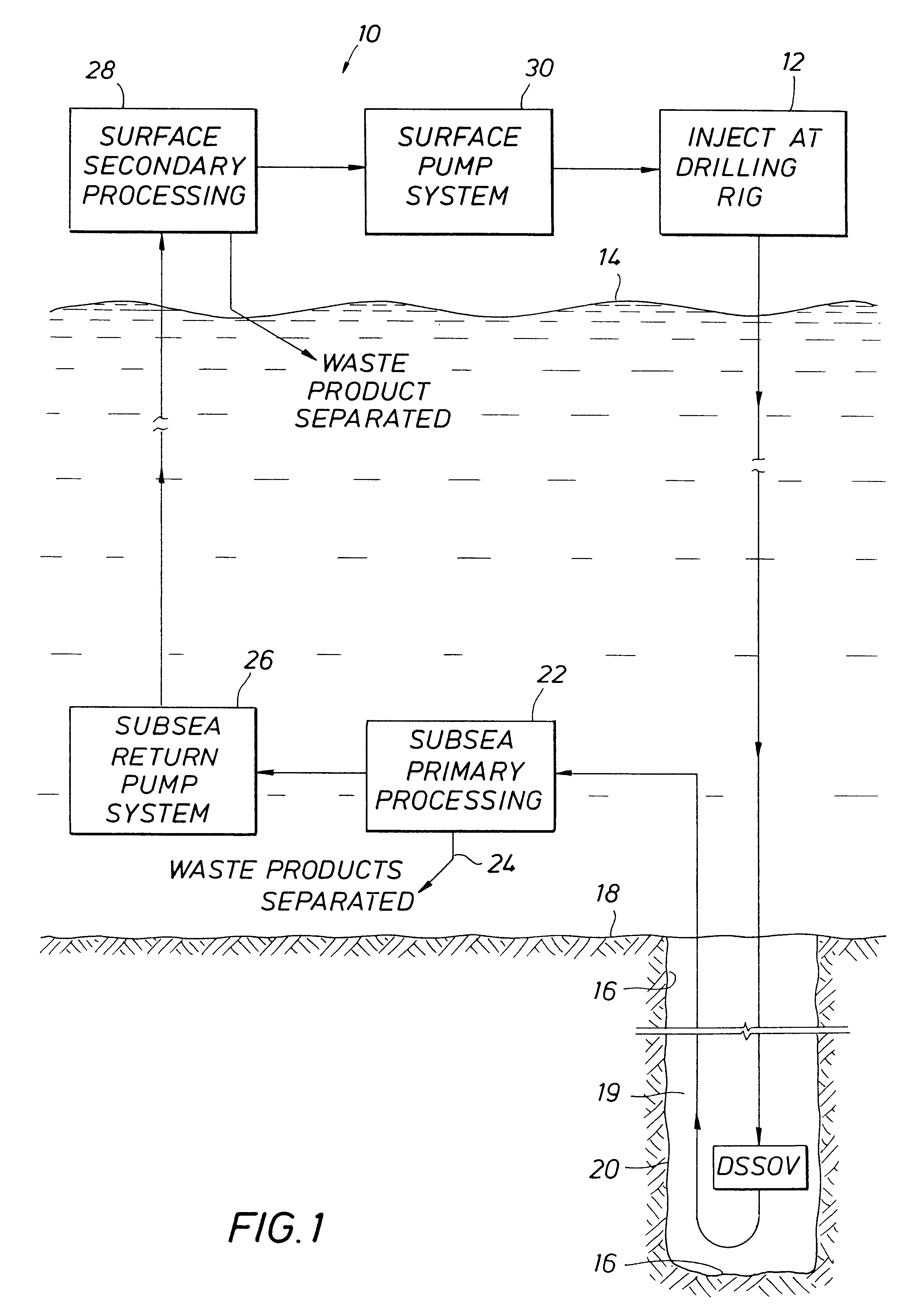
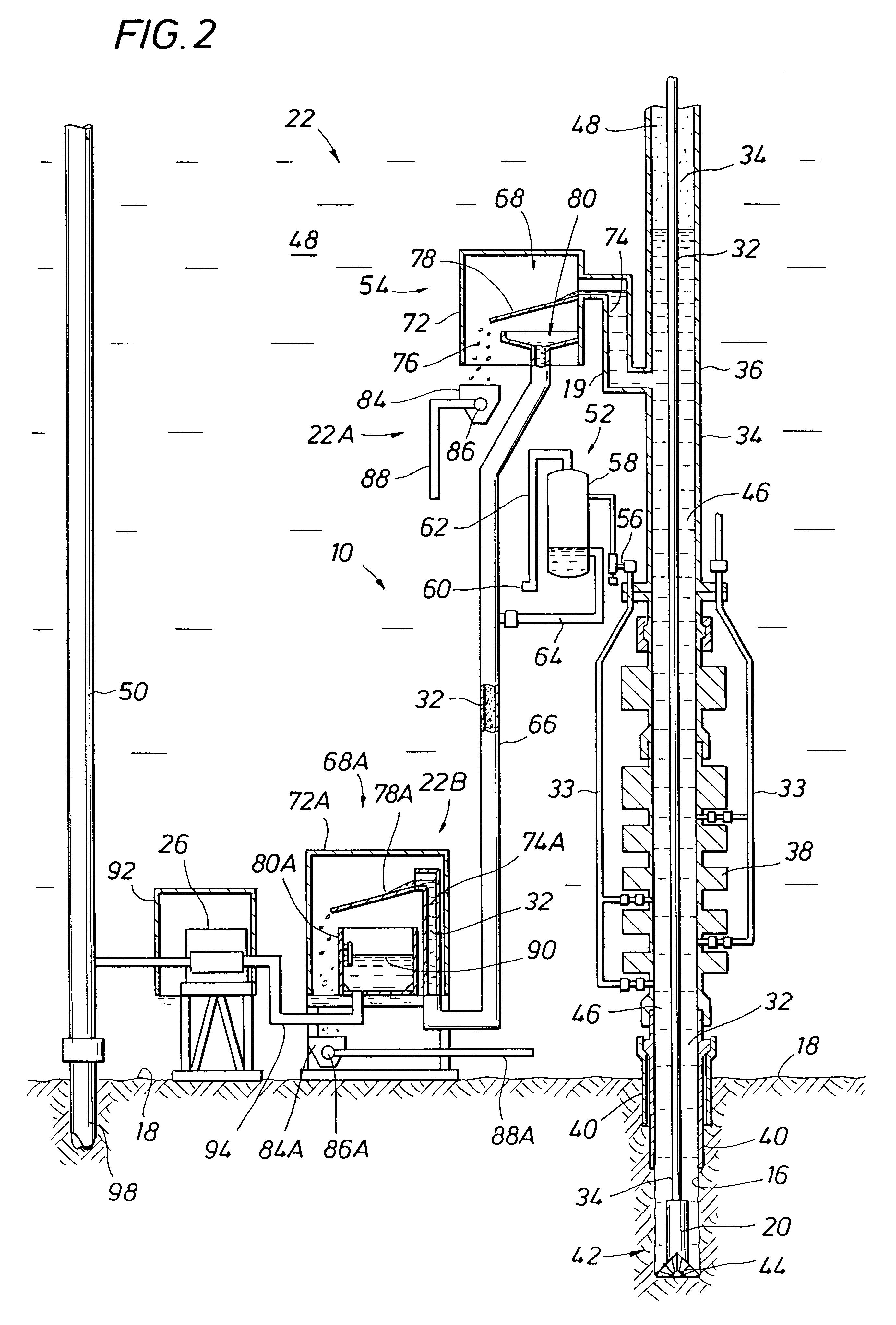
Subsea gas separation system and method for offshore drilling
A subsea gas separation system use in drilling an offshore well includes a subsea blowout preventor connected to the well and a gas separator connected to the blowout preventor near the seafloor. Gas released into the well bore during a well control event is removed at the separator and not returned with the drilling mud recirculated to the surface. A method offshore drilling includes a mud circulation circuit established leading down the drill string, through the drill bit, up the borehole, through a subsea pump, and to the surface through a return riser. The subsea pump is protected during critical well control events by removing gas released into the mud at a gas separator located upstream of the subsea pump and in communication with the blowout preventor.
Owner:SHELL OFFSHORE
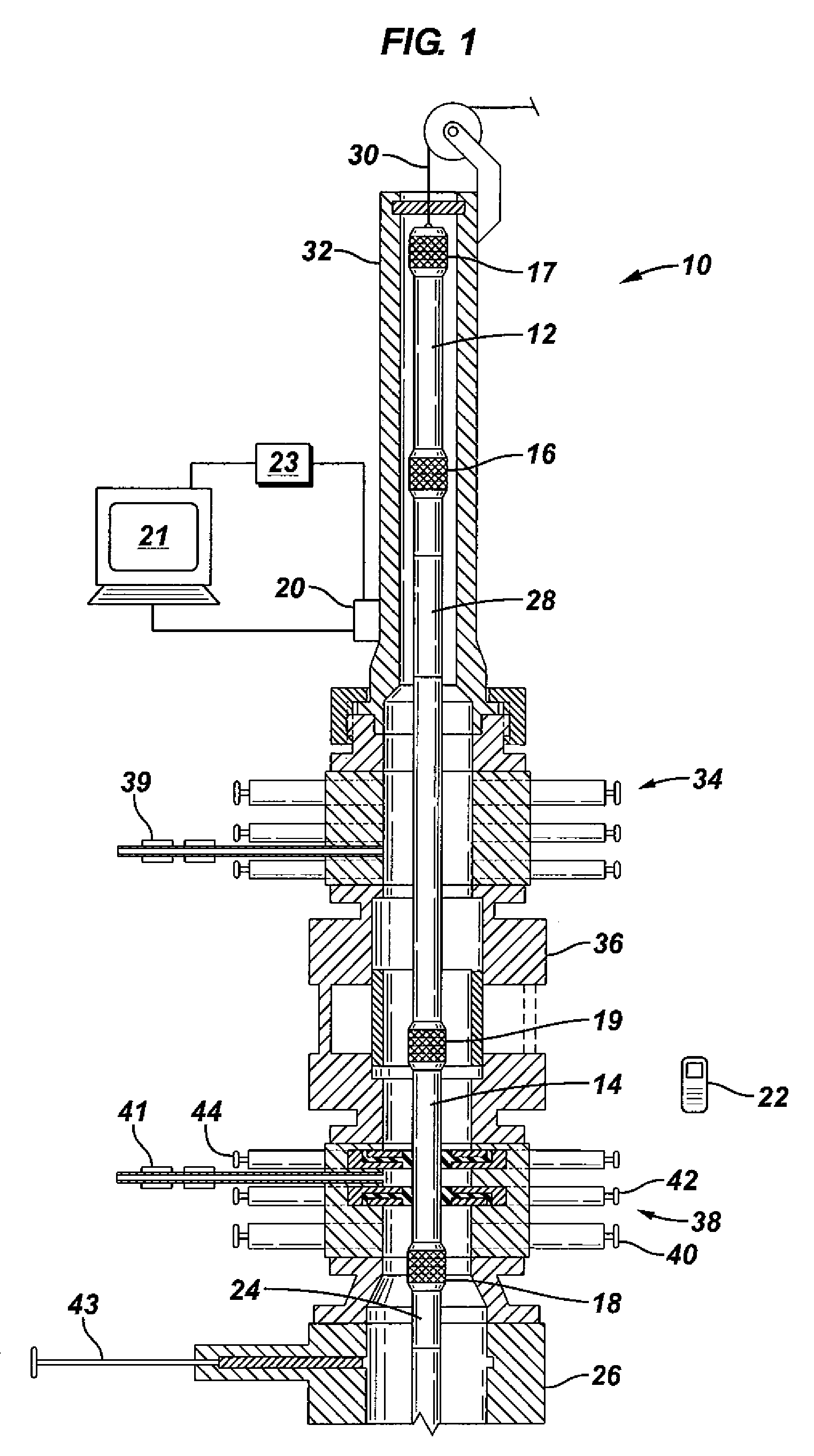
Monitoring the health of a blowout preventer
InactiveUS20120197527A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingFluid removalTraffic signalDisplay device
A computerized monitoring system and corresponding method of monitoring the status and health of a blowout preventer. The system includes a graphics display at which a graphical user interface (GUI) displays the health of various sealing elements and control systems by way of “traffic light” indicators. The health indicators are evaluated, by the monitoring system, based on a risk profile for each of the indicated elements and control systems. The risk profiles are evaluated based on inputs such as measurement inputs, feedback signals, mechanical positions, diagnostic results, drilling conditions, and other status information of the blowout preventer at a given time and based on levels of redundancy and levels of deviation from normal conditions. The GUI includes recent history of changes in operating condition, and alarm indications such as poor health, along with the times of those events.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Blowout preventers and methods of use
Methods and apparatuses for severing a wellbore tubular, the apparatus, in certain aspects, including: a first member movable toward a tubular to be severed; a second member with a second blade disposed opposite to the first member and movable toward the tubular; a first blade on the first member having a projection projecting from a center of a blade body with point structure on the projection for puncturing the tubular and cutting surfaces on the projection for cutting the tubular; and cutting surfaces, as needed, on the blade body adjacent the projection for cutting the tubular.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
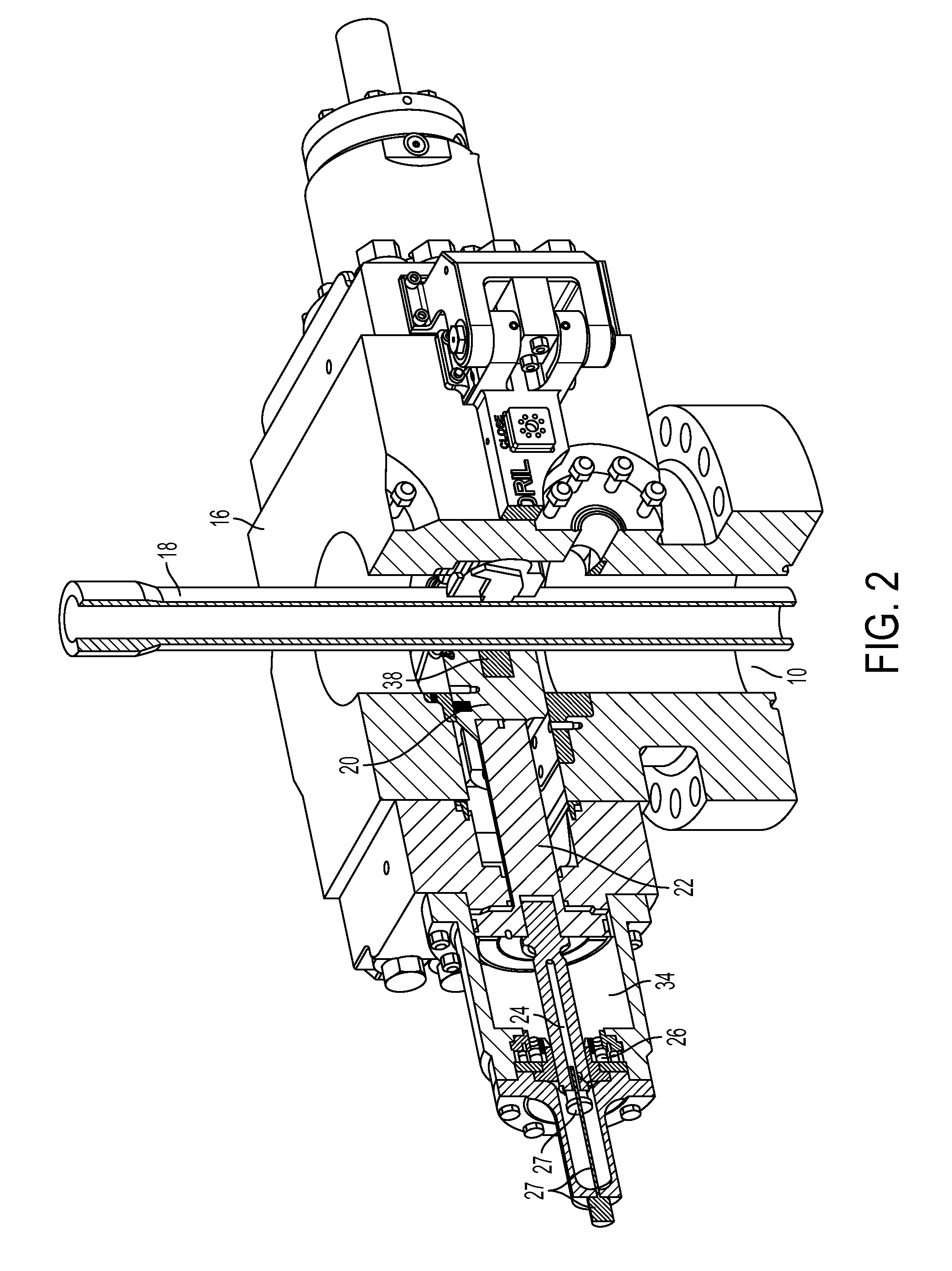
Ram BOP shear device
A ram-type blowout preventer may include a body, a first ram block positioned within the body and having a first shearing element and a first sealing element, and a second ram block positioned within the body and opposing the first ram block, the second ram block having a second shearing element and a second sealing element. The blowout preventer may also include a load intensifying member coupled to the first ram block, wherein the first ram block and the second ram block are configured to close together upon activation of the blowout preventer, and wherein the load intensifying member is positioned to engage with the second ram block when the first and second ram block close and force the first shearing element and the second shearing element together.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
Fully hydraulic intelligent workover rig
InactiveCN107476769ARealize grabbingRealize pipe deliveryDrilling rodsDrilling casingsBlowout preventerTruck
The invention belongs to the field of oil equipment, and particularly relates to a fully hydraulic intelligent workover rig. The fully hydraulic intelligent workover rig is characterized in that an engine 2 and a hydraulic pressure station 5 are installed on a chassis truck 1, in the conveying state, a walkway is folded automatically and stored, a wellhead assembly is fixed to the tail of the chassis truck, after the hydraulic workover rig is moved to a well site, a wellhead is subjected to initial positioning through a reverse image in a cab and positioning and ranging, and then accurate positioning is conducted by moving a rapid positioning device through a derrick; by conducting height adjusting and supporting on a vehicle carrying chassis through hydraulic adjusting landing legs and conducting mechanical locking, rapid positioning and locking of the wellhead are achieved; the automatic folding walkway is designed, and convenient and labor-saving installation is achieved; increasing and decreasing of pressure of a string in a well and setting and control of bit pressure and drilling speed parameters can be achieved automatically, full automatic operations such as tubing string gripping and conveying, automatic fastening and unfastening, automatic discharging and automatic detection are achieved; integrated transport of a blowout preventer is achieved, and separate disassembly and transport are not needed.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH PETROLEUM EQUIP & TECH CO LTD
High pressure system
An arrangement and method for integrating a high pressure riser sleeve from the upper end of a high pressure drilling and workover riser terminated by an upper BOP close to sea level in one end and by a sub-sea blowout preventer BOP or a low riser package LRP close to the seabed in the lower end. The high pressure riser sleeve being installed, connected and integrated to the high pressure drilling and workover riser and extending up to and above the drill floor, inside a low pressure drilling riser slip joint which is connected to the drilling and workover riser. This relates to offshore drilling and well activities preformed from a floating drilling or workover rig or vessel. Operations can be switched from drilling with jointed drillpipe in a conventional manner, into performing underbalanced wireline and / or coiled tubing activities with full well pressure, much more effectively than with prior art.
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
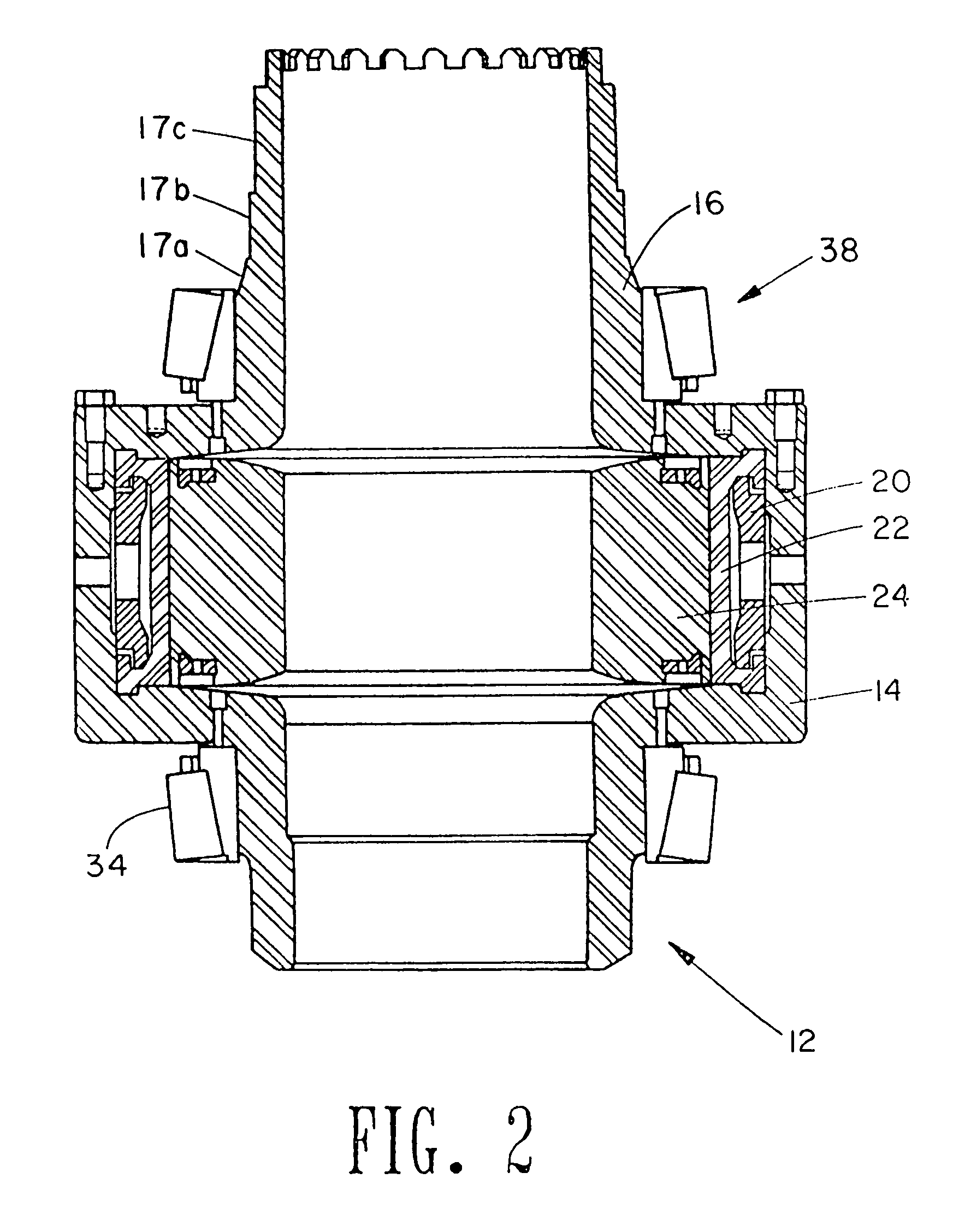
Blowout preventer monitoring system and method of using same
A blowout preventer for sealing a tubular of a wellbore is provided. The blowout preventer has a housing having a bore therethrough for receiving the tubular, at least one ram slidably positionable in the housing (each of the rams having a ram block for sealing engagement about the tubular), an actuator for selectively driving the ram block (the actuator comprising a piston slidably positionable in a cylinder), and a monitor for detecting the piston therein. The monitor has a visual indicator on an exterior of the cylinder. The visual indicator is operatively coupled to the piston for displaying a position of the piston as the piston travels within the cylinder whereby a position of the ram may be determined.
Owner:NAT OILWELL VARCO LP
Fast positioning device for derrick moving
InactiveCN107654196AReasonable structural designEasy to useDrilling rodsDerricks/mastsBlowout preventerPetroleum
The invention belongs to the field of petroleum equipment, and particularly relates to a fast positioning device for derrick moving. The fast positioning device for derrick moving is characterized inthat a derrick supporting seat can move in the transverse direction and the longitudinal direction of a chassis vehicle, and the derrick supporting seat integrates a blowout preventer group; and the blowout preventer group can lift, move and rotate around the center of the blowout preventer group, and a lifting cylinder of a derrick is supported on the derrick supporting seat, moves along with thesupporting seat and keeps unchanged relative to the position of the derrick. According to the fast positioning device for derrick moving, well opening aligning is conducted by adjusting the front, back, left and right positions of the derrick on a vehicle, fast and accurate positioning is achieved, in conclusion, a derrick supporting seat structure has the advantages of being reasonable in design, convenient and reliable to use, precise in positioning, automated in control and the like, the derrick can be fast aligned with a well opening, meanwhile, the well opening blowout preventer group isfixed to a fast positioning device, a telescopic liquid cylinder is collected during transported, the blowout preventer group is transported along with the vehicle, the efficiency of workover preparation work is improved, and the labor intensity of operators is reduced.
Owner:YANTAI JEREH PETROLEUM EQUIP & TECH CO LTD
Interlocking Low Profile Rotating Control Device
ActiveUS20110036638A1Reduce the overall heightEasy accessDrilling rodsConstructionsBlowout preventerScrew thread
A system and method is provided for a low profile rotating control device (LP-RCD) and its housing mounted on or integral with an annular blowout preventer seal, casing, or other housing. The LP-RCD and LP-RCD housing can fit within a limited space available on drilling rigs. An embodiment allows a LP-RCD to be removably disposed with a LP-RCD housing by rotating a bearing assembly rotating plate. A sealing element may be removably disposed with the LP-RCD bearing assembly by rotating a seal retainer ring. Alternatively, a sealing element may be removably disposed with the LP-RCD bearing assembly with a seal support member threadedly attached with the LP-RCD bearing assembly. The seal support member may be locked in position with a seal locking ring removably attached with threads with the LP-RCD bearing assembly over the seal support member. Spaced apart accumulators may be disposed radially outward of the bearings in the bearing assembly to provide self lubrication to the bearings.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
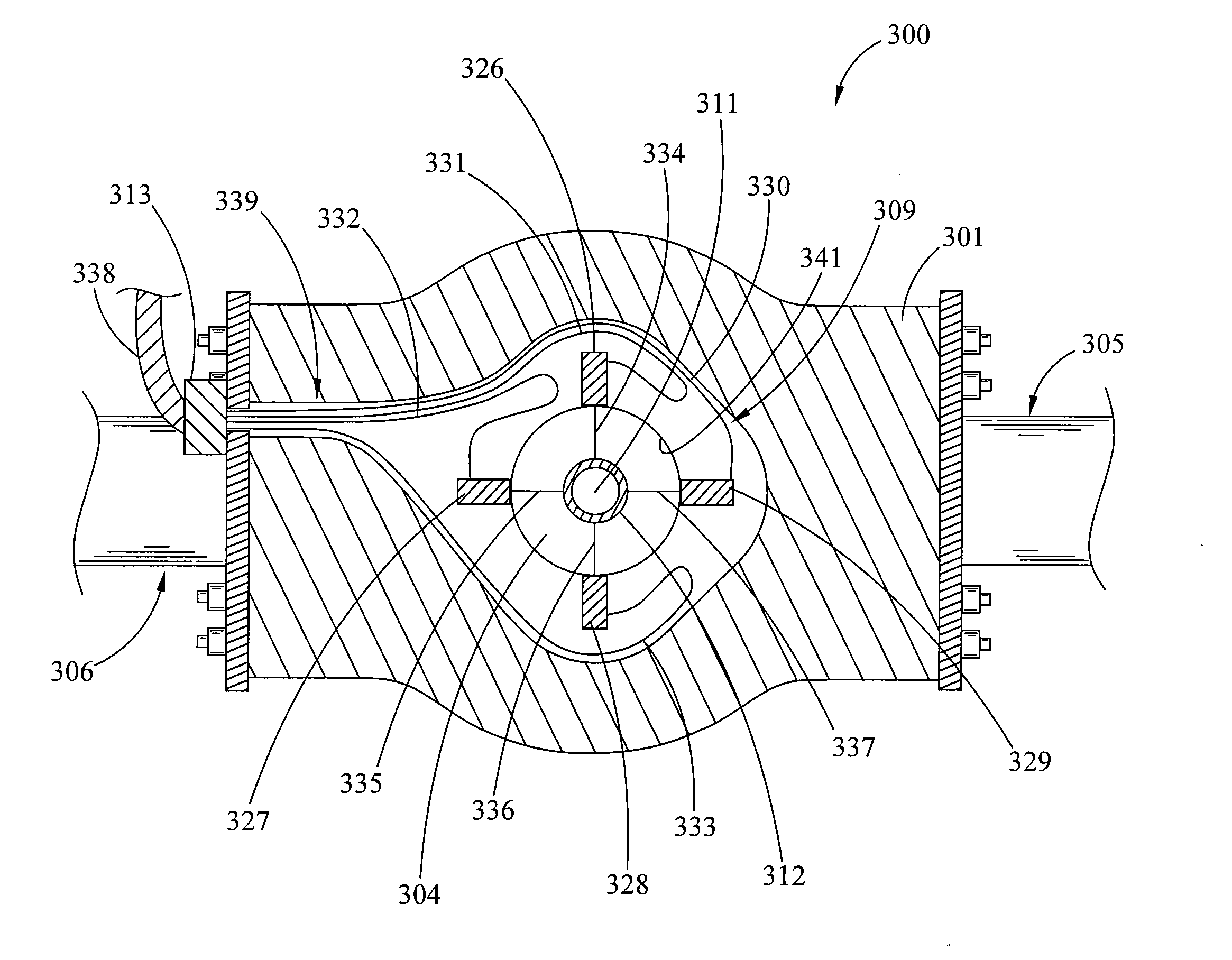
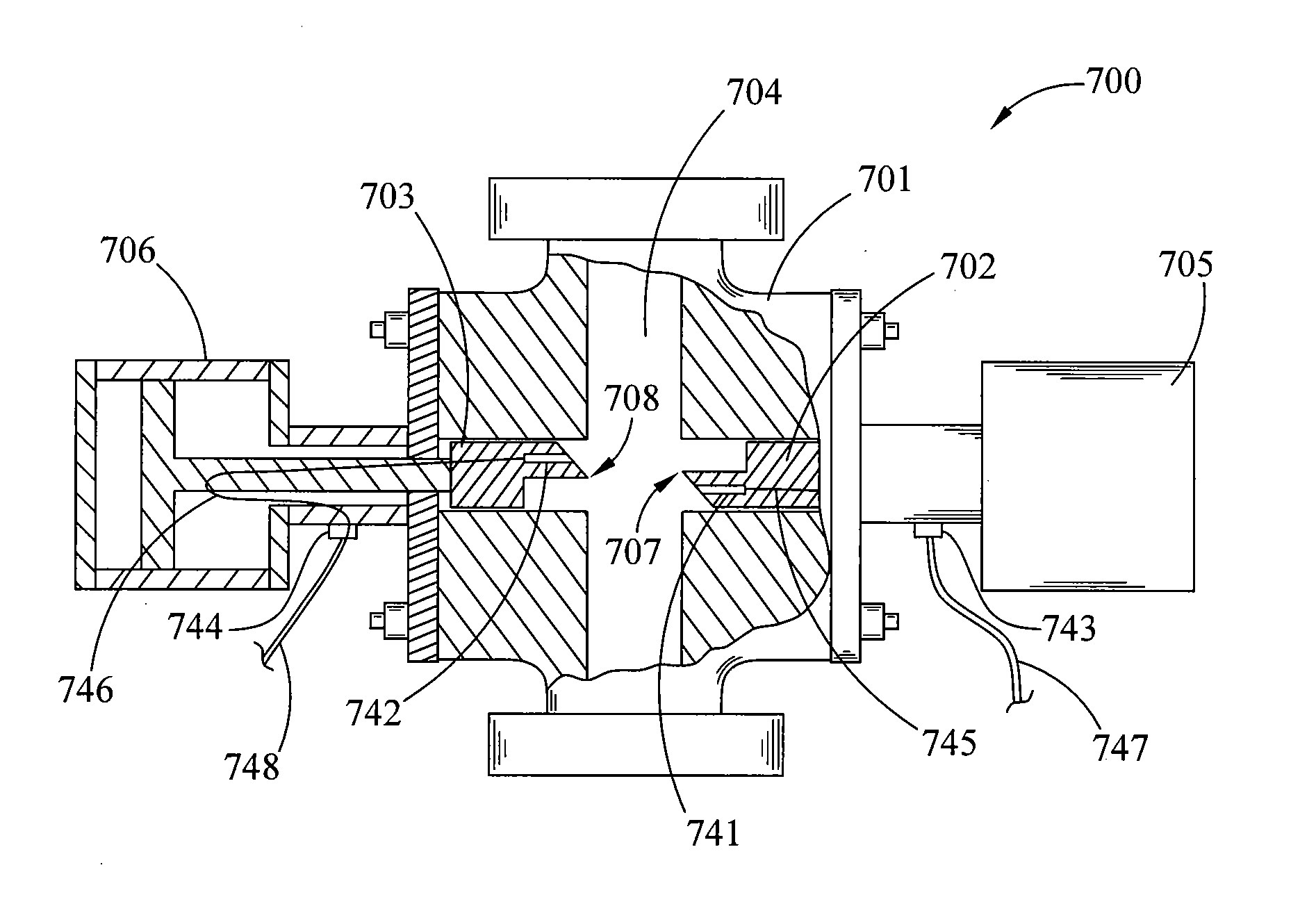
Rotating blowout preventer with independent cooling circuits and thrust bearing
A rotary blowout preventer has a first and a second fluid circuit. Each of the fluid circuits are defined into and out of a stationary body and between the stationary body, a rotating body, and two seals. The first fluid circuit is physically independent from the second fluid circuit although they share a seal interface. A fluid is introduced into the first fluid circuit at a pressure responsive to the well bore pressure. A fluid is introduced into the second fluid circuit at a pressure responsive to and lower than the pressure of the fluid in the first circuit. Adjustable orifices are connected to the outlet of the first and second fluid circuits to control such pressures within the circuits. Such pressures affect the wear rates of the seals. The system can therefore control the wear rate of one seal relative to another seal. A thrust bearing is added to share the load placed upon the upper bearings. The thrust bearing is connected between the top end of a packer sleeve and the stationary body.
Owner:WEATHERFORD CANADA PARTNERSHIP
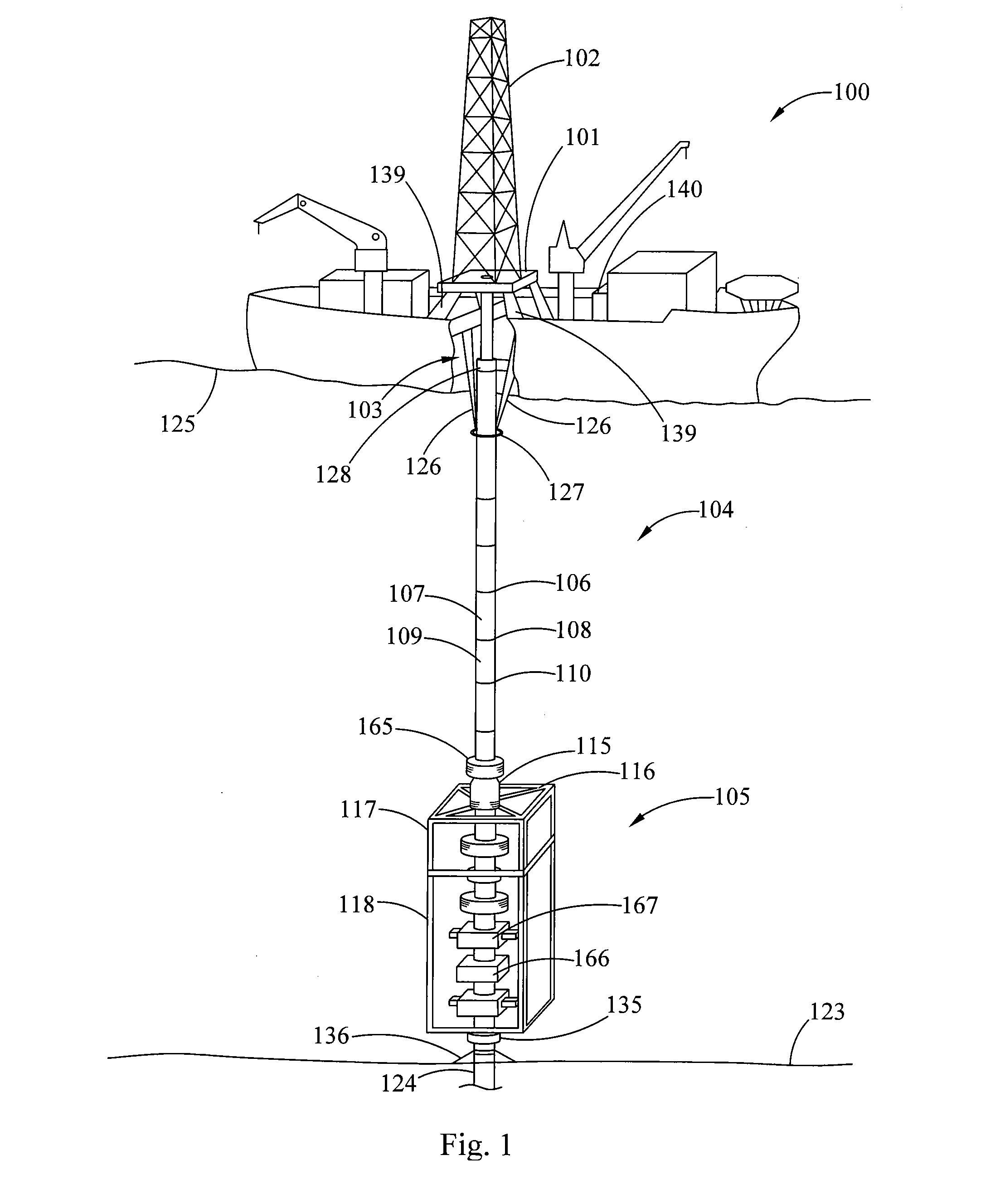
Self-supported riser system and method of installing same
InactiveUS20070044972A1Save rig timeReducing maneuvering stepCargo handling apparatusDrilling rodsBuoyPetroleum oil
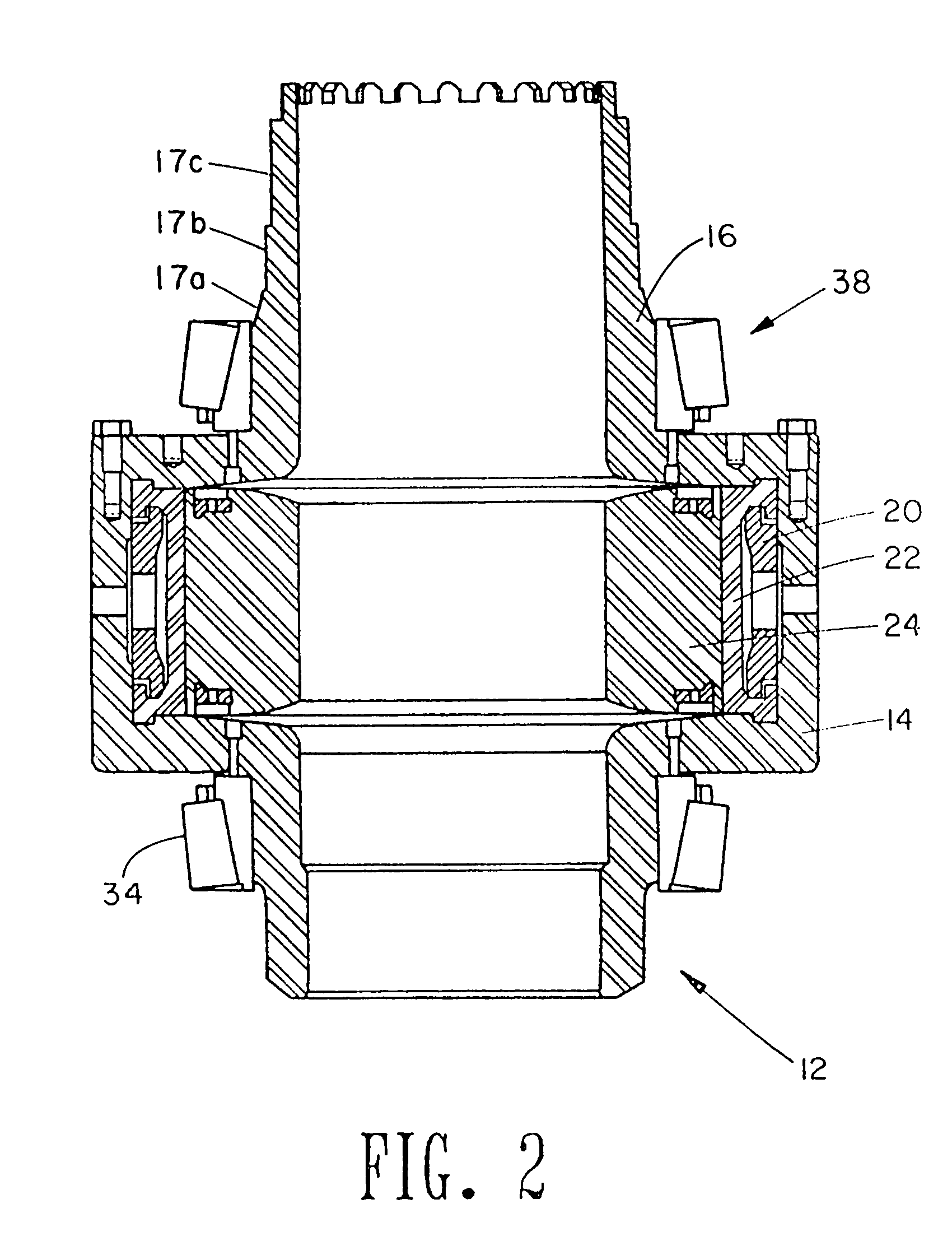
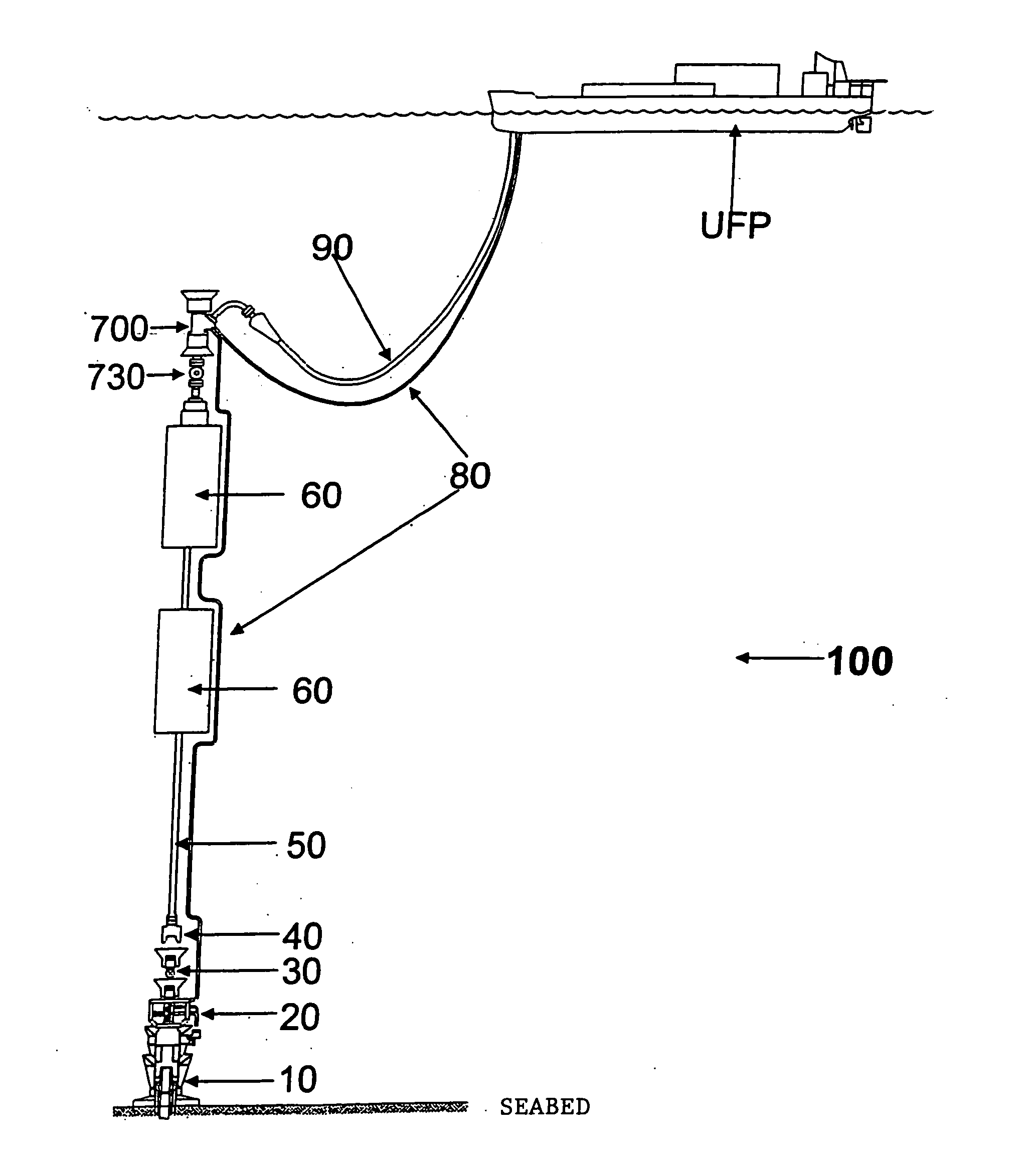
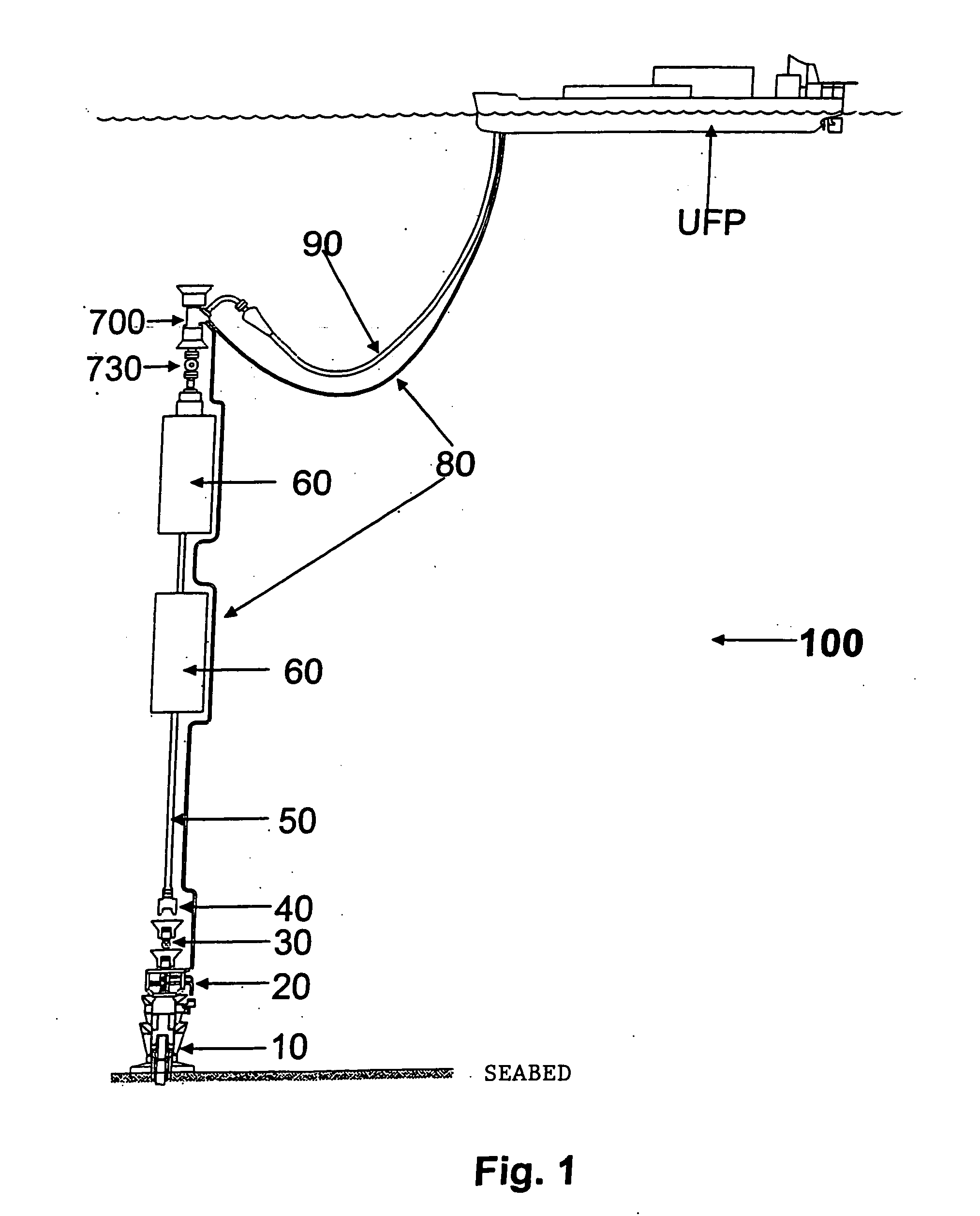
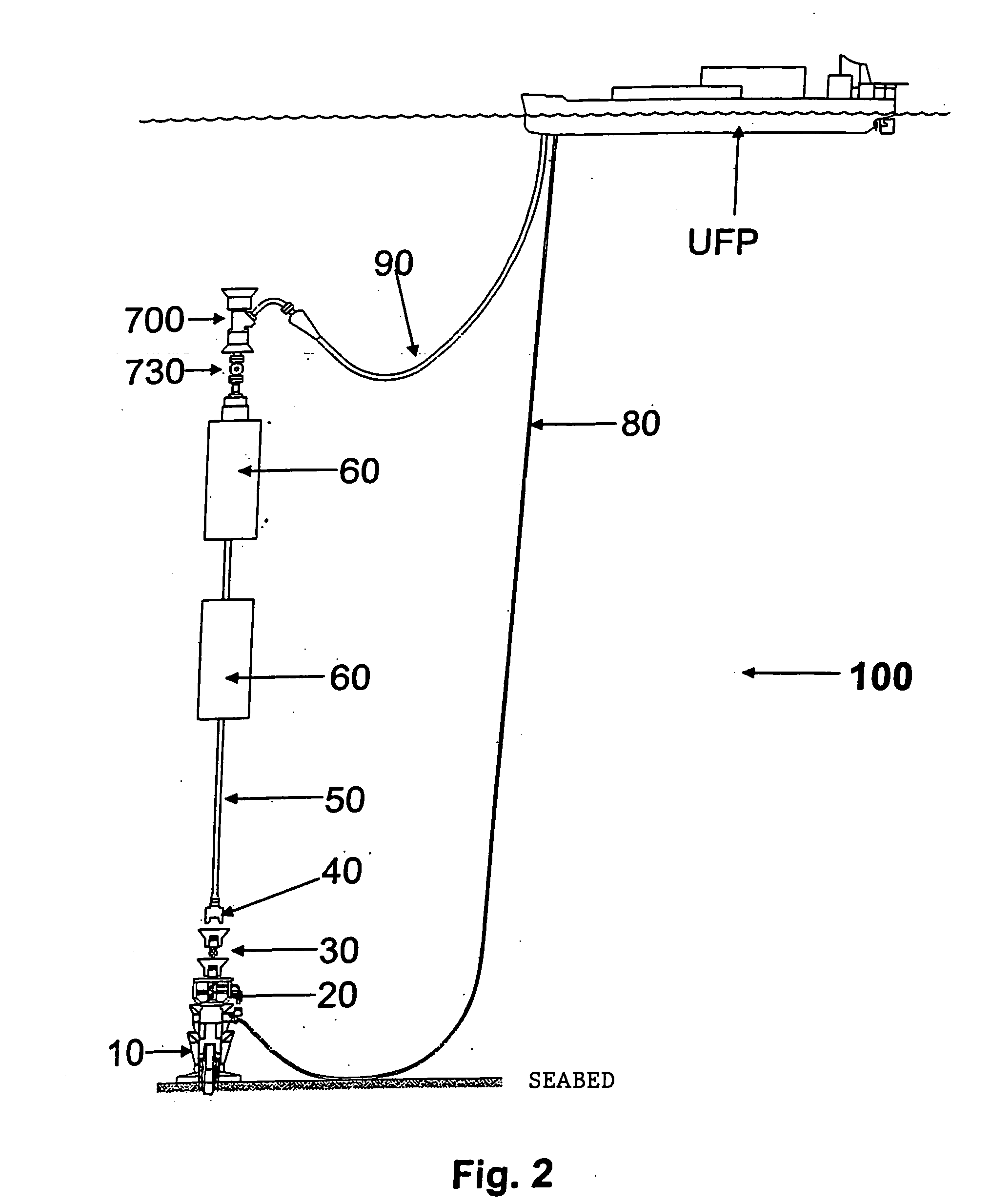
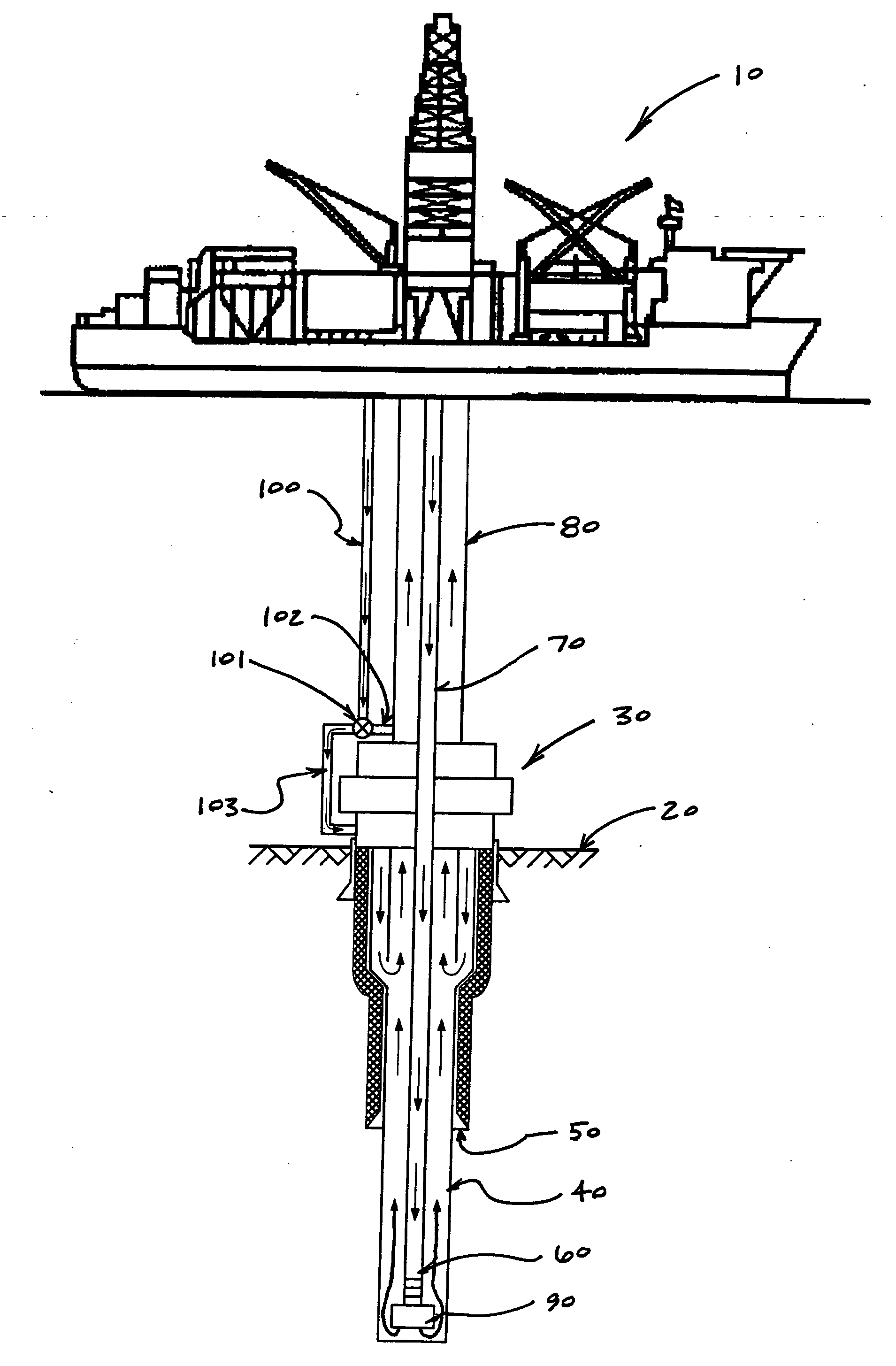
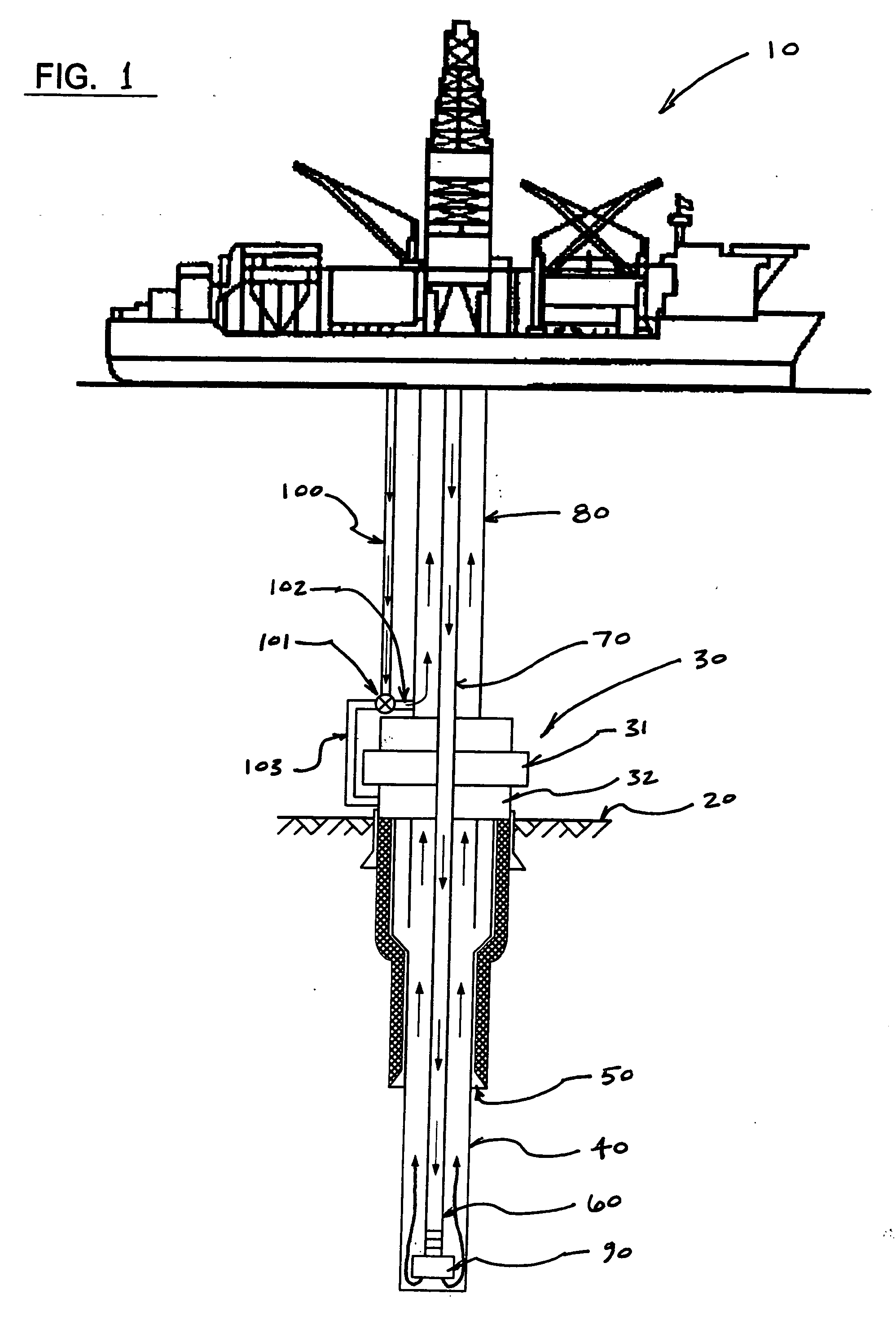
A self-supported riser system (100) for an Anticipated Production System (ASP) Test or a Long Duration Production (LDP) Test in a subsea petroleum production system, utilizing an ANM coupled to a wellhead and Floating Production Unit (FPU) is disclosed. The system includes a wellhead at the seabed, connected to an ANM (20) provided with a preventor (BOP of workover) (30). The preventor (30) is connected to a production riser (50) through a connection tool (40). The riser (50), mounted internally within a buoy assembly (60), is maintained under traction with the aid of a buoy assembly. The upper end of the riser (50) is provided with a Subsea Intervention Terminal (700), the Terminal being interlinked to the FPU by a flexible jumper (90) to carry the oil produced to the FPU. Two methods for installing the self-supported riser system (100) are also disclosed.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
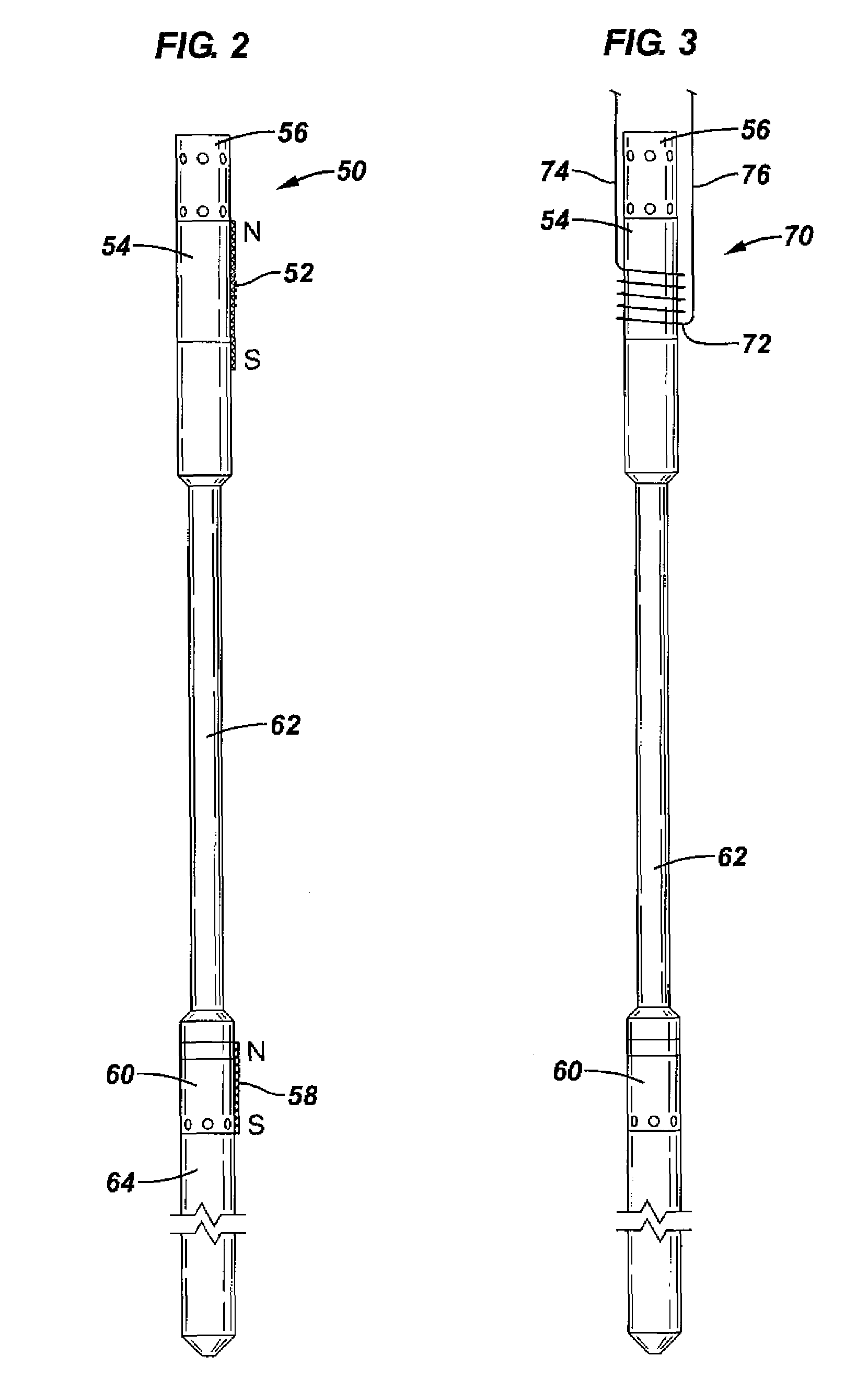
Shear laser module and method of retrofitting and use
There is provided a high power shear laser module, which can be readily included in a blowout preventer stack. The shear laser module as the capability of delivering high power laser energy to a tubular within a blowout preventer cavity, cutting the tubular and thus reducing the likelihood that the tubular will inhibit the ability of the blowout preventer to seal off a well.
Owner:FORO ENERGY
Modular, distributed, ROV retrievable subsea control system, associated deepwater subsea blowout preventer stack configuration, and methods of use
Owner:OCEANEERING INTERNATIONAL
System and method for safe well control operations
ActiveUS20110214882A1Facilitate well control operationFacilitates hands-on trainingDrilling rodsFluid removalLine tubingWell drilling
A system and method for safely controlling a well being drilled or that has been drilled into a subterranean formation in which a conventional blow-out preventer operates to close the well bore to atmosphere upon the detection of a fluid influx event. Fluid pressures as well as fluid flow rates into and out of the well bore are measured and monitored to more accurately and confidently determine the fracture pressure and pore pressure of the formation and perform well control operations in response to a fluid influx event. During a suspected fluid influx event, one or more of the fluid flow and pressure measurements are used to confirm the fluid influx event and to safely regain well control by circulating the fluid influx out of the well through a choke line while maintaining the pressure inside the well between specified, selected limits, such as between the fracture and pore pressures.
Owner:SAFEKICK AMERICAS LLC
Dual Gradient Drilling Method And Apparatus With An Adjustable Centrifuge
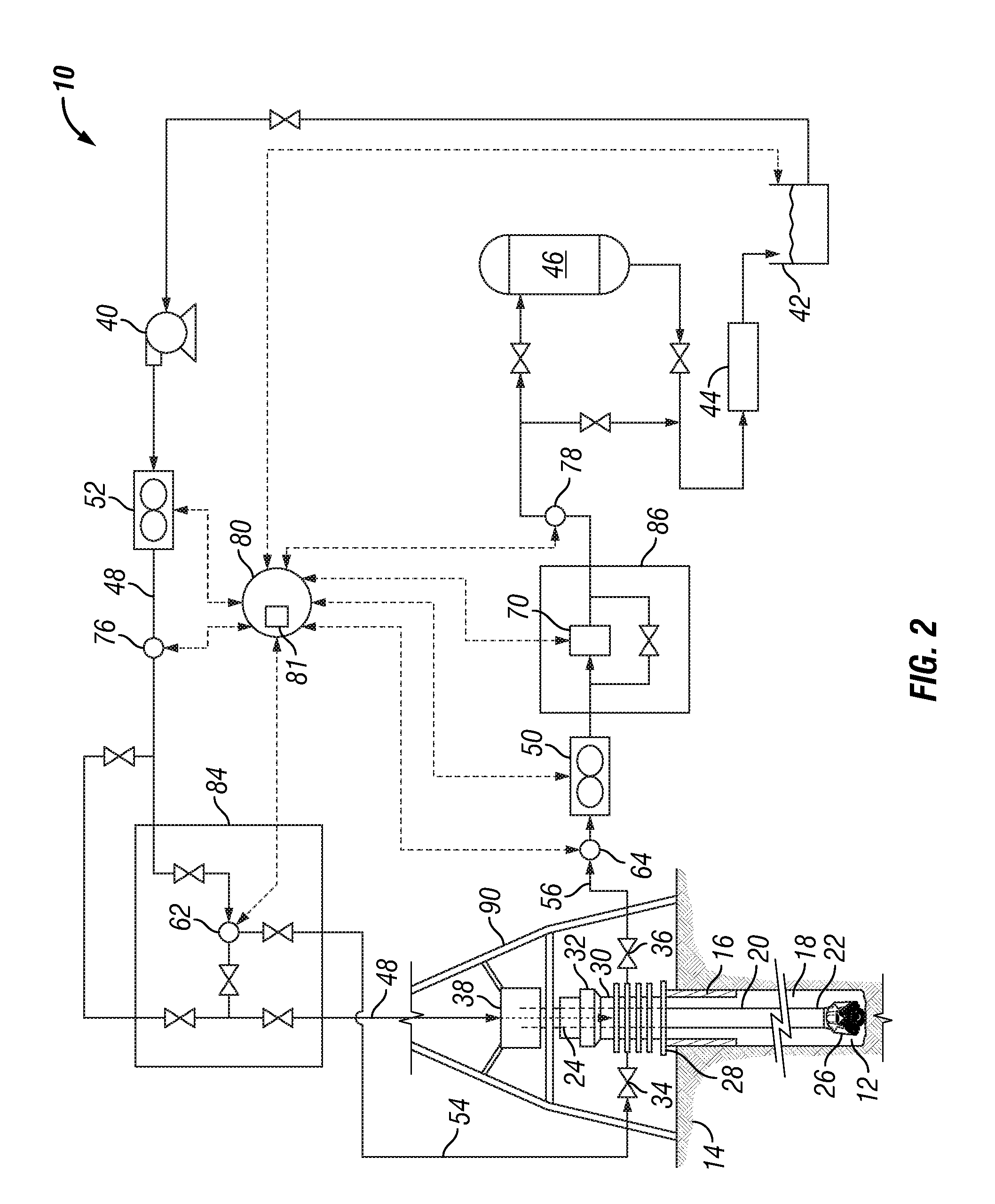
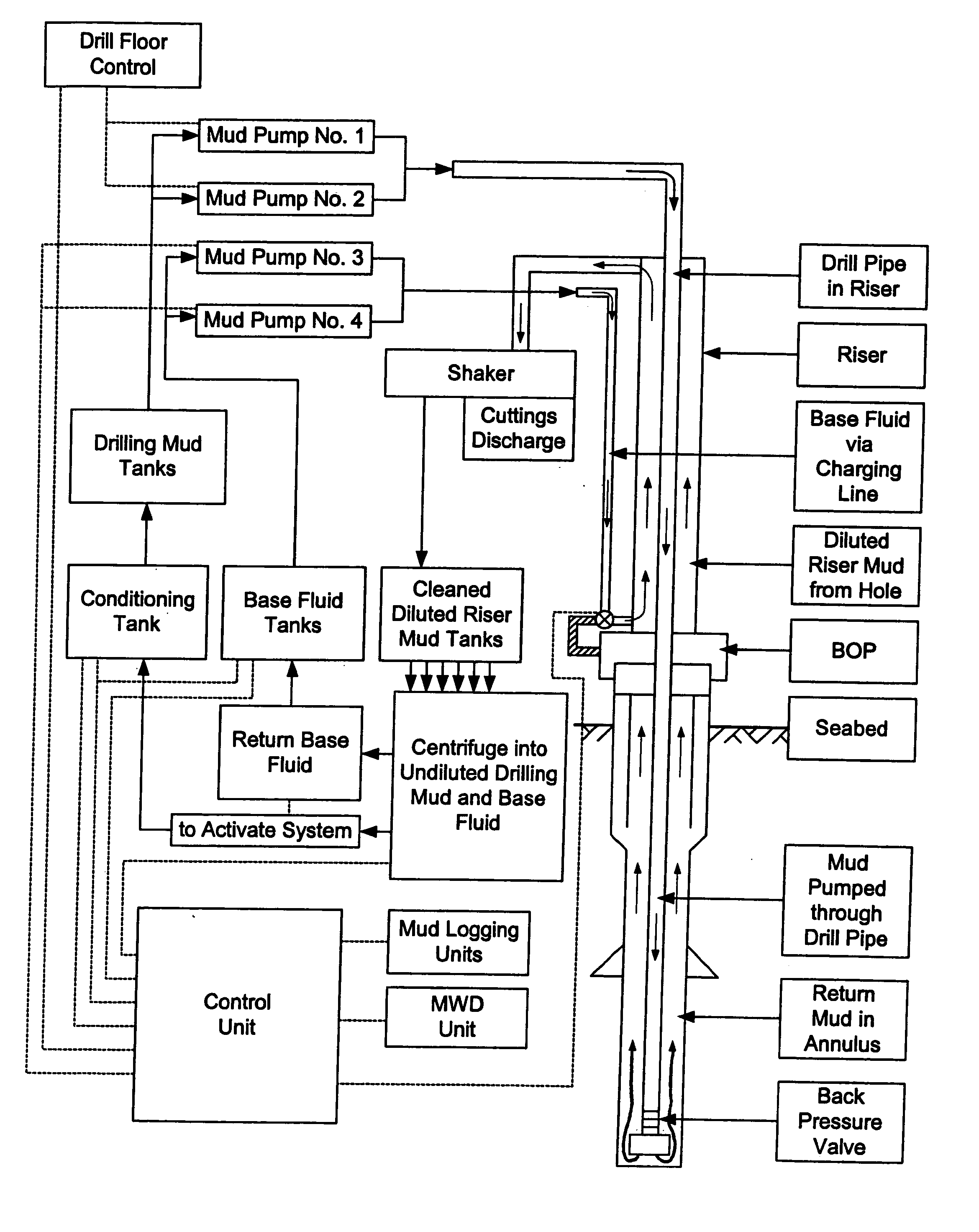
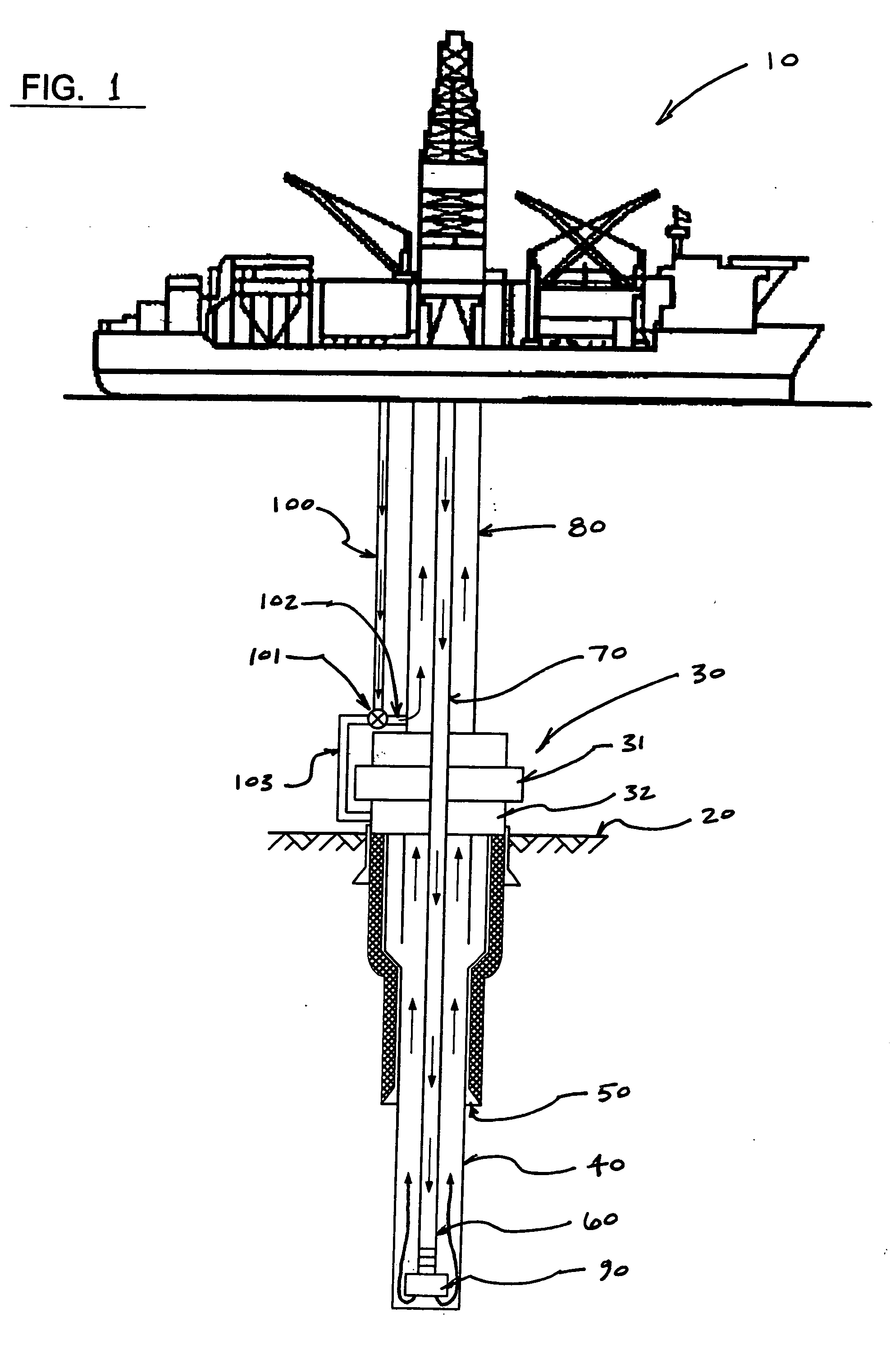
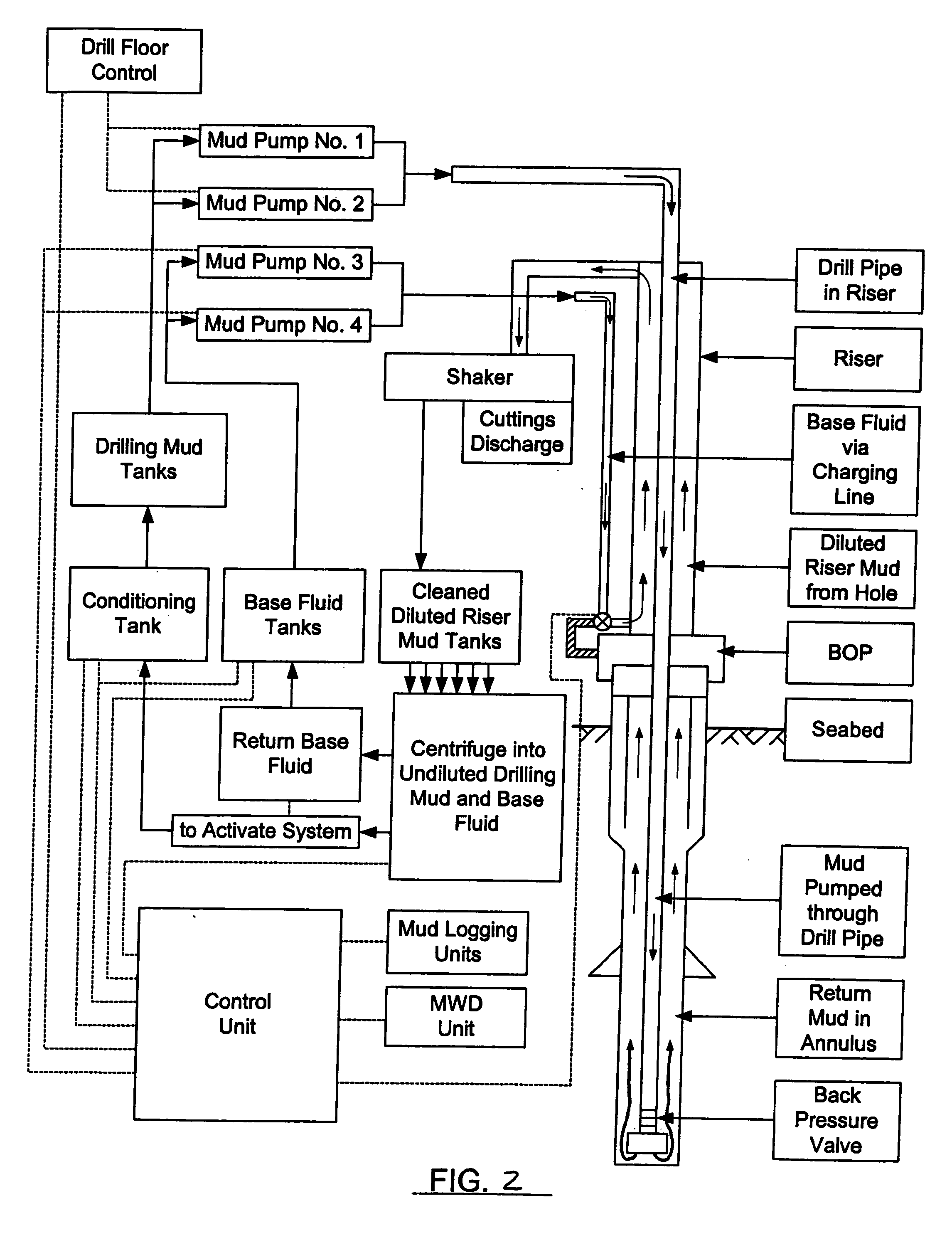
A method and system for controlling drilling mud density in drilling operations. The mud required at the wellhead is combined with a base fluid of a different density to produce diluted mud in the riser. By combining the appropriate quantities of drilling mud with base fluid, riser mud density at or near the density of seawater may be achieved, thereby permitting greater control over the pressure in the wellbore and various risers. Blowout preventers may also be used in combination with the process to control these pressures. Concentric risers are disclosed, wherein an annulus defined within one riser is utilized to carry the different density base fluid to the injection point for injection into the drilling mud, while an annulus defined within another riser is utilized to carry the combination fluid and cuttings back to the drilling rig. Cuttings are separated in the usual manner at the surface. The diluted mud is passed through a centrifuge system to separate drilling mud from the different density base fluid. The centrifuge system may also be utilized to separate the recovered drilling fluid into a substantially barite portion and a substantially drilling fluid portion, wherein the two portions are stored locally at the rig and recirculated during drilling operations.
Owner:DUAL GRADIENT SYST
Method for varying the density of drilling fluids in deep water oil and gas drilling applications
A method and system for controlling drilling mud density in drilling operations. The mud required at the wellhead is combined with a base fluid of a different density to produce diluted mud in the riser. By combining the appropriate quantities of drilling mud with base fluid, riser mud density at or near the density of seawater may be achieved, thereby permitting greater control over the pressure in the wellbore and various risers. Blowout preventers may also be used in combination with the process to control these pressures. Concentric risers are disclosed, wherein an annulus defined within one riser is utilized to carry the different density base fluid to the injection point for injection into the drilling mud, while an annulus defined within another riser is utilized to carry the combination fluid and cuttings back to the drilling rig. Cuttings are separated in the usual manner at the surface. The diluted mud is passed through a centrifuge system to separate drilling mud from the different density base fluid. The centrifuge system may also be utilized to separate the recovered drilling fluid into a substantially barite portion and a substantially drilling fluid portion, wherein the two portions are stored locally at the rig and recirculated during drilling operations.
Owner:DUAL GRADIENT SYST
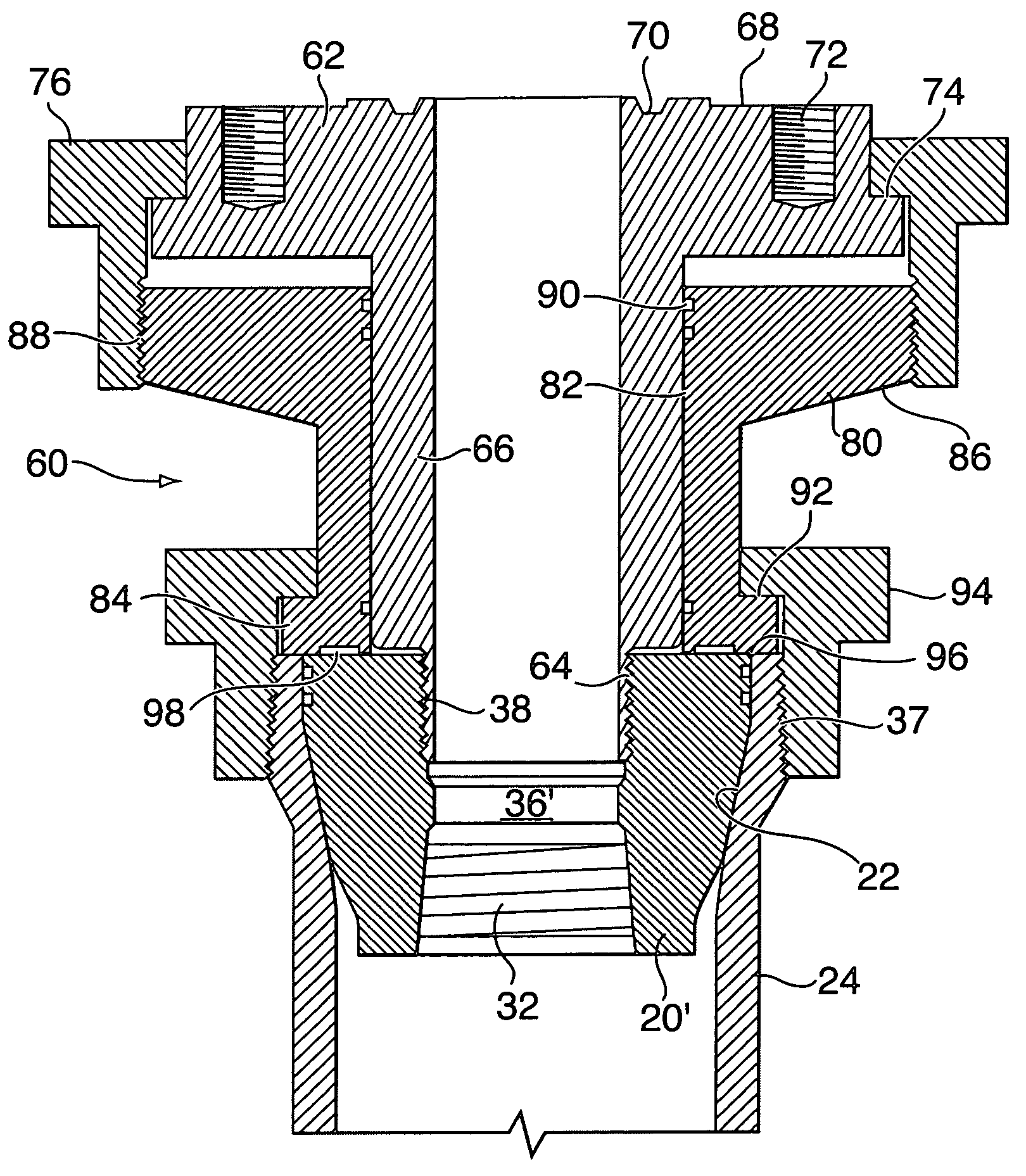
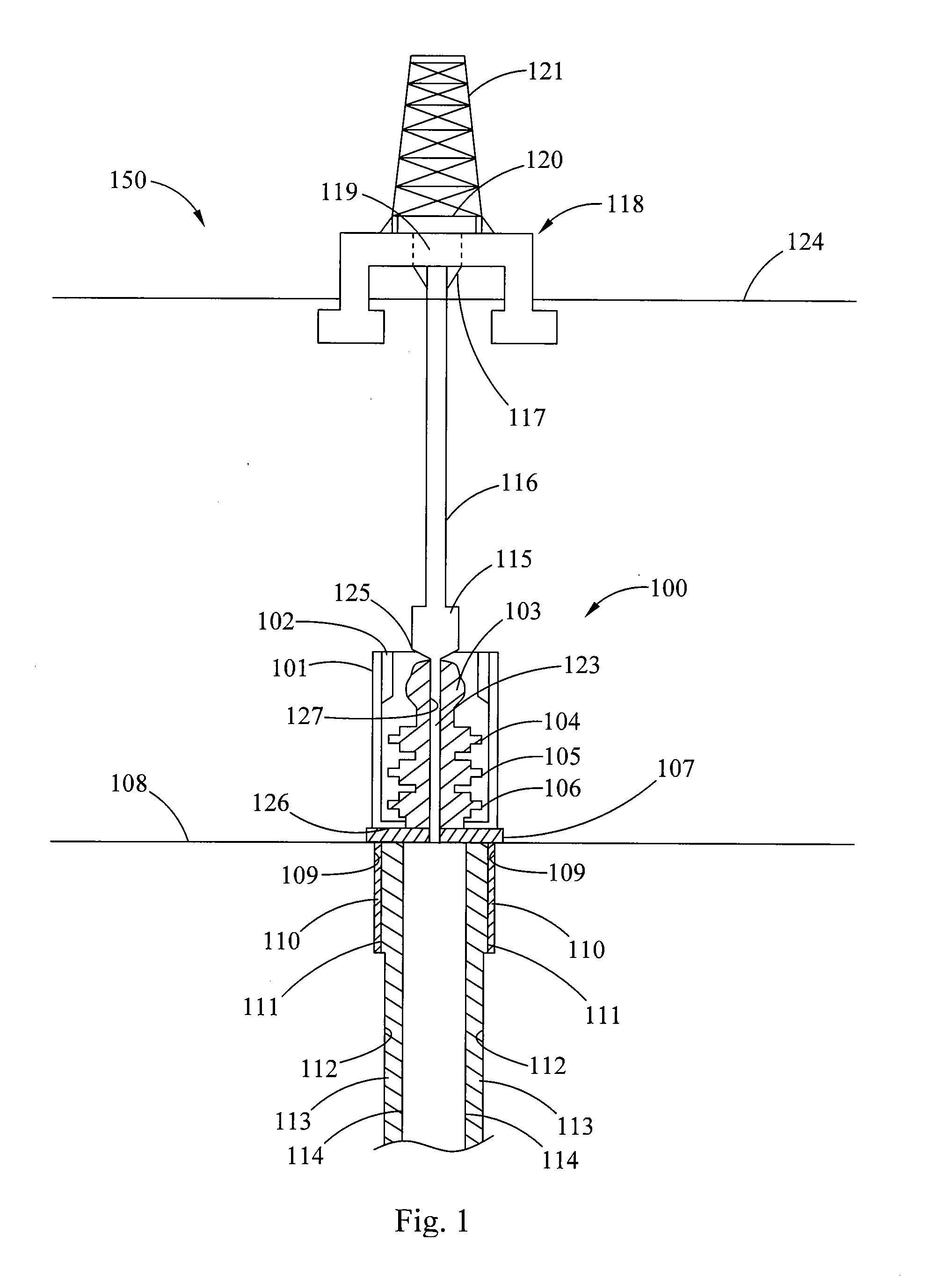
Multi-lock adapters for independent screwed wellheads and methods of using same
A lockdown flange for use with an independent screwed wellhead includes an annular body having a center passageway with an internal diameter at least as large as a passageway through the wellhead. The lock down flange may be used to construct a multi-lock adapter for connecting a high pressure valve, a blowout preventer or a well stimulation tool to the independent screwed wellhead. The lockdown flange ensures that stress on connection points to the screwed independent wellhead due to elevated fluid pressures used for well stimulation procedures does not exceed engineered specifications.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
Laser assisted system for controlling deep water drilling emergency situations
There is provided a high power laser riser blowout preventer system and controller for operation thereof. The system utilizes high power laser cutters that are associated with the riser and the blowout preventer to provided an integrated operation to quickly weaken or cut tubulars to address potential emergency and emergency situations that can arise during deep sea drilling.
Owner:FORO ENERGY
Tensioner/slip-joint assembly
A tensioner / slip-joint module for providing a conduit from a floating vessel at the surface of the ocean to the blowout preventer stack, or production tree, which is connected to the wellhead at the sea floor. The tensioner / slip-joint module compensates for vessel motion induced by wave action and heave and maintains a variable tension to the riser string alleviating the potential for compression and thus buckling or failure of the riser string. The tensioner / slip-joint module preferably includes at least one mandrel having at least one hang-off donut; at least one upper flexjoint swivel assembly, at least one radially ported manifold, at least one tensioning cylinder, and at least one slip-joint assembly combined in a single unit.
Owner:CONTROL FLOW
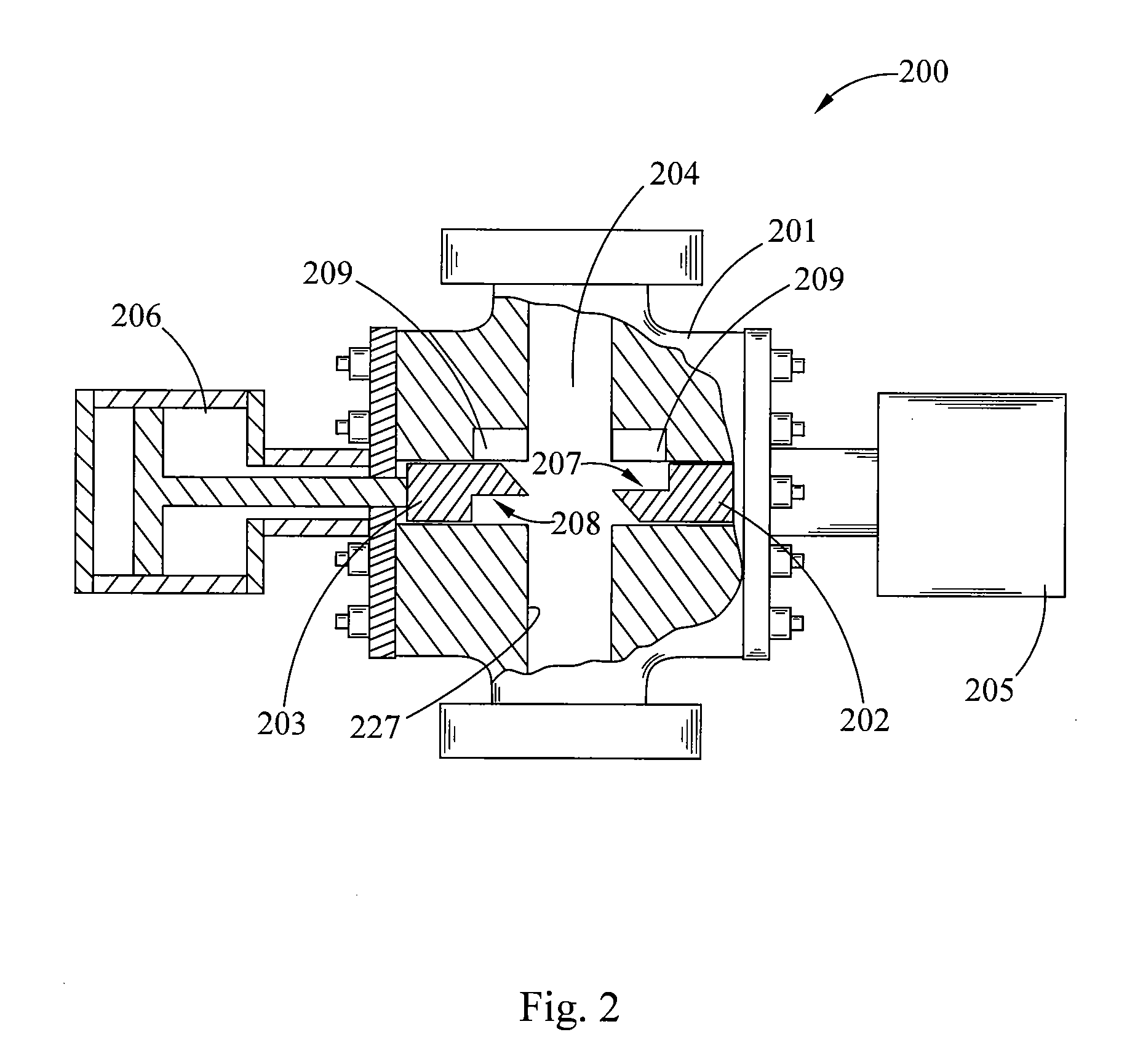
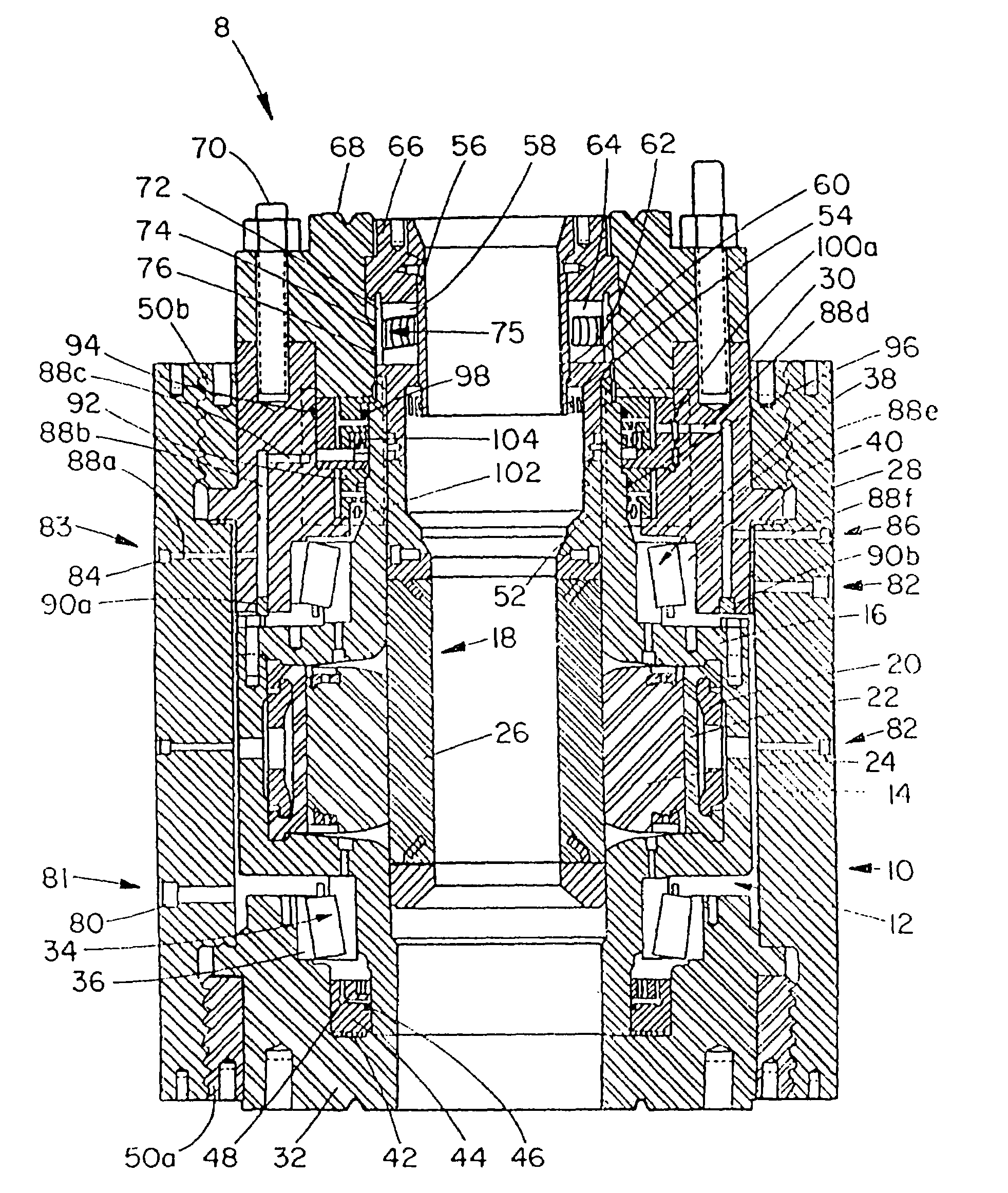
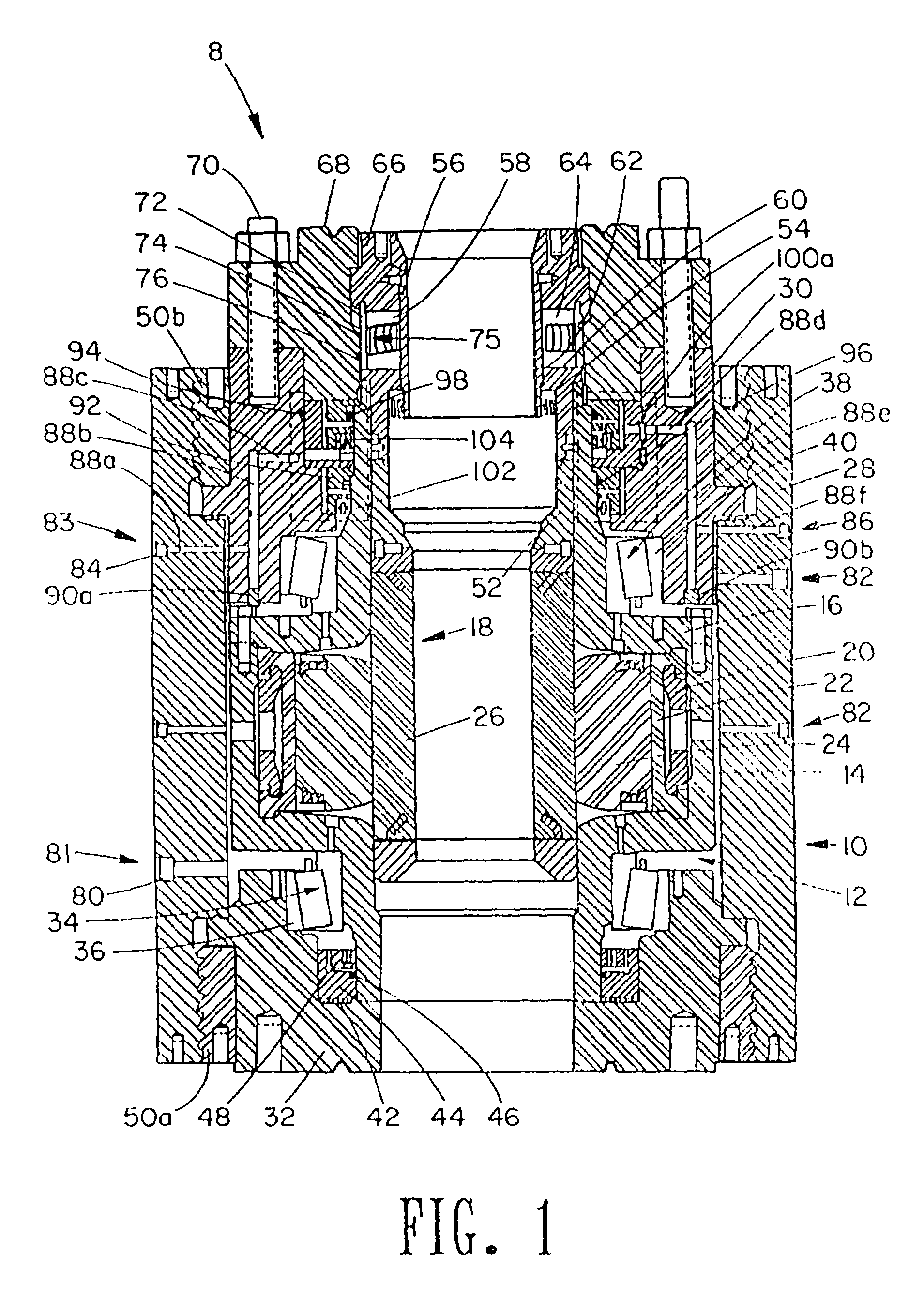
Blowout preventer and ram actuator
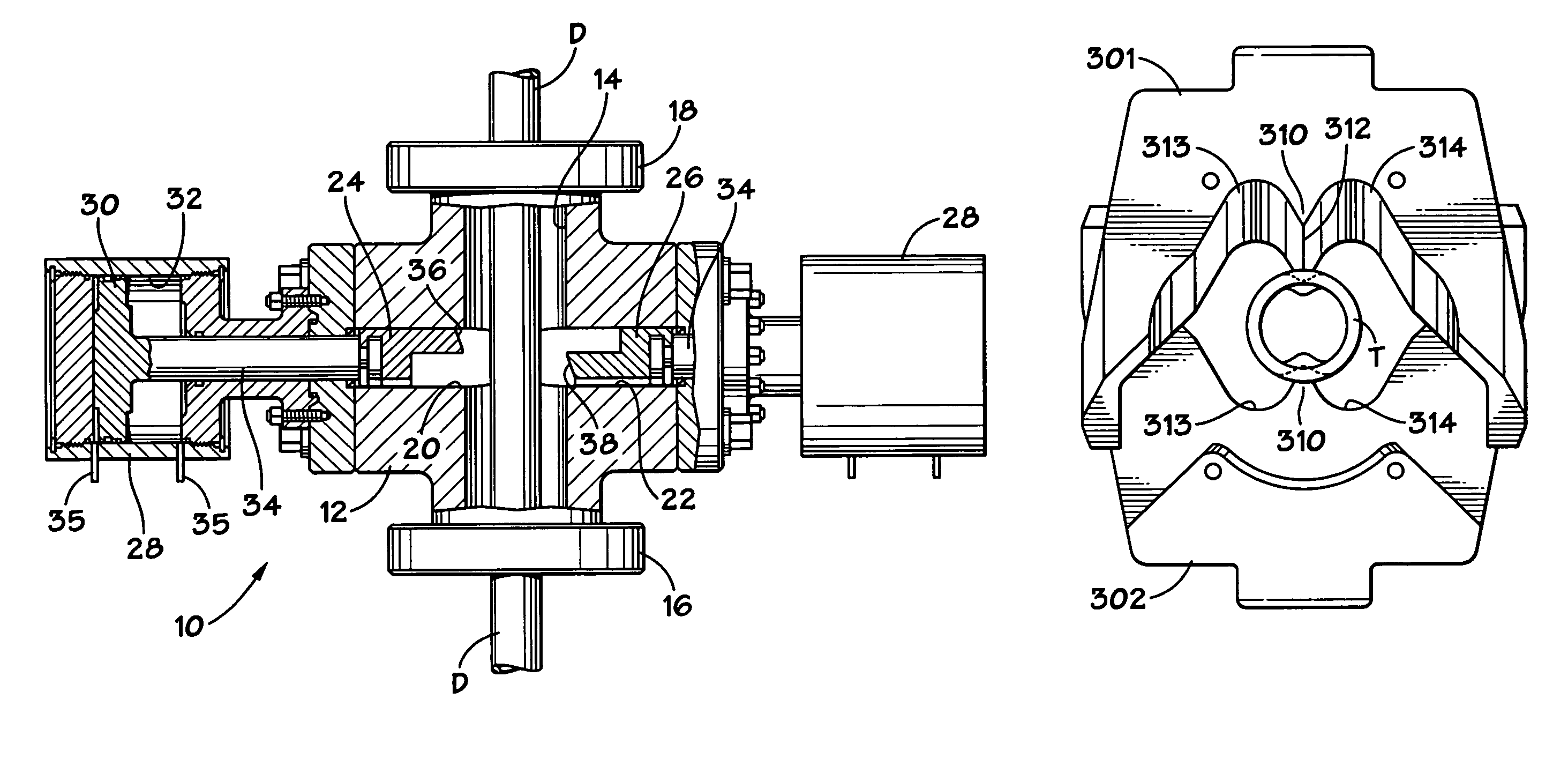
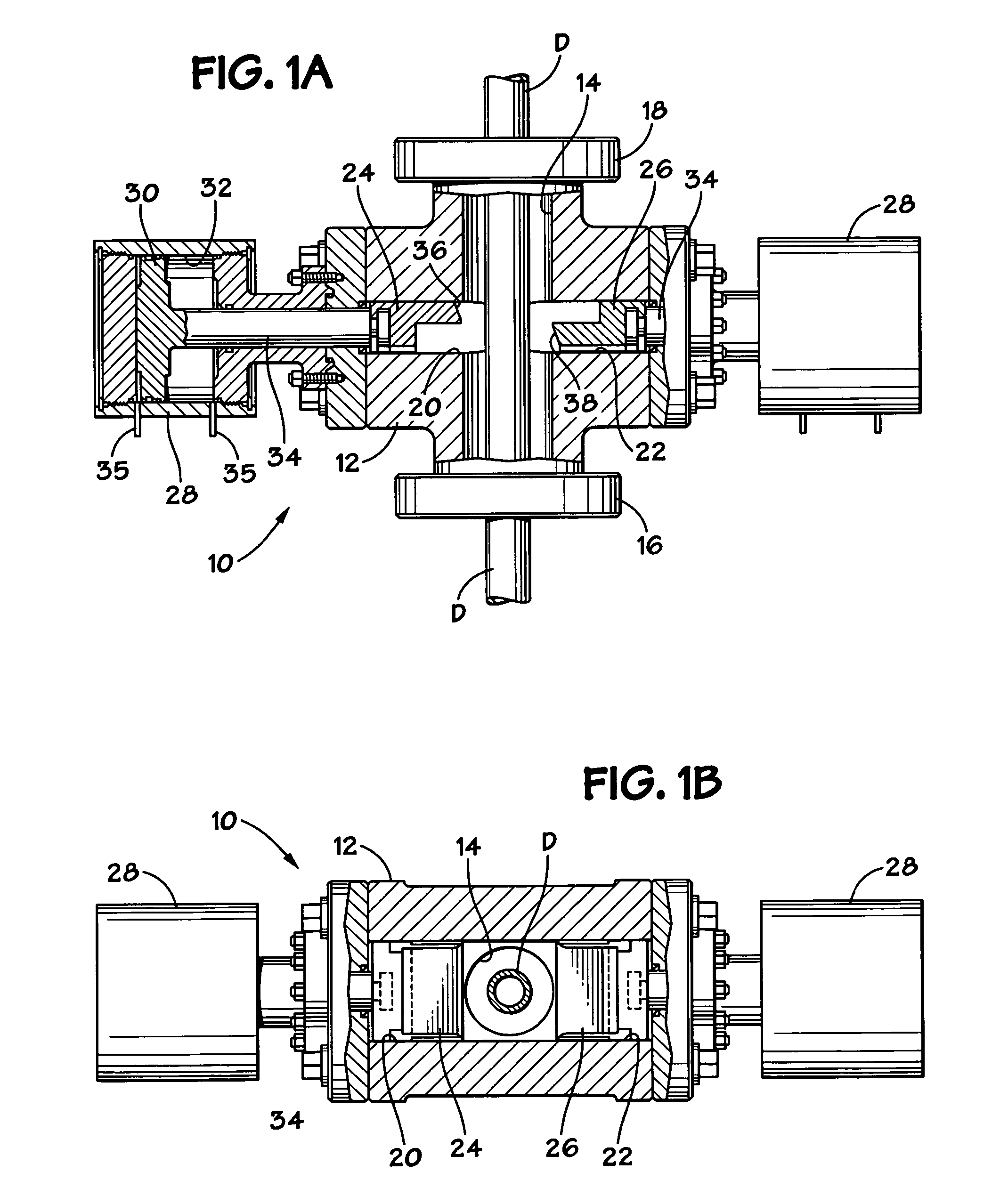
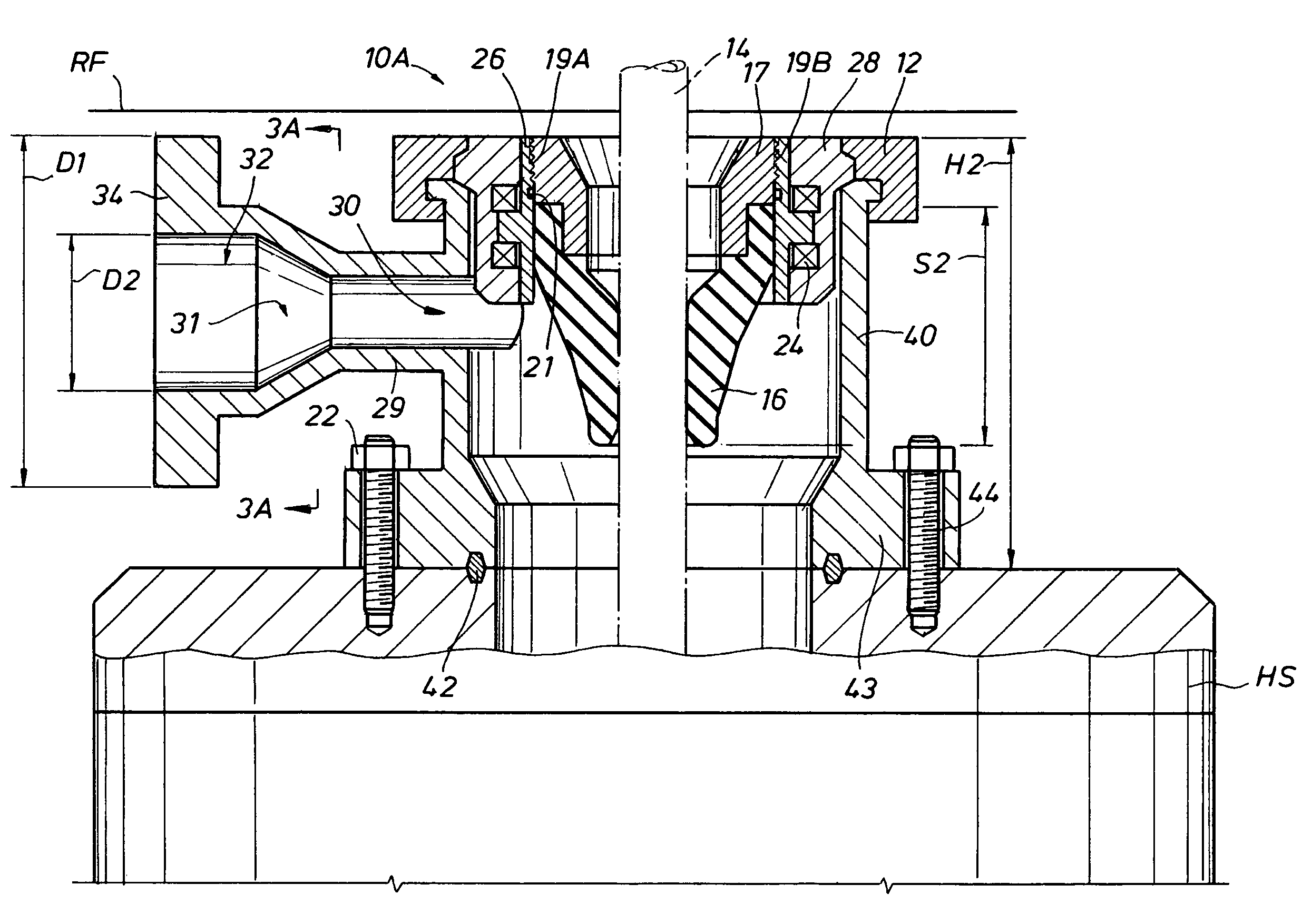
A blowout preventer with a main body; a base releasably connected to the main body, the base having a base space therein, the base having a ram shaft opening; a primary piston movably disposed within the base space; a ram shaft to which the primary piston is connected, the ram shaft including a ram end and a piston end; a ram connected to the ram end of the ram shaft; a housing connected to the base, the housing having a housing space therein, the housing including a middle member with a member opening; a booster piston movably disposed within the housing space and having a booster shaft projecting therefrom and a booster shaft space therein; the shaft including a push portion selectively movable to abut the ram shaft to prevent movement of the ram shaft and to transfer force of the booster piston to the primary piston; and power fluid apparatus for the primary piston and the booster piston.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
Magnetic locator systems and methods of use at a well site
Magnetic locator systems and methods of using same at a wellhead are described. The magnetic locator systems include a magnetic field generator on an oilfield tool component, such as a deployment bar, adapted to be moved through an oilfield pressure control component, such as a blow-out preventer, lubricator, riser pipe, or wellhead, and a magnetic field sensor located outside of the pressure control component adapted to detect the magnetic field and thus the position of the tool component in the pressure control component. The systems and methods of the invention provide safer and more efficient operation of oil and gas well pressure control systems. This abstract allows a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the disclosure. It will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. 37 CFR 1.72(b).
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Laser assisted blowout preventer and methods of use
ActiveUS20120217018A1Quick cutProtection from damageDrilling rodsDerricks/mastsHigh power lasersLaser assisted
There is provided a high power laser assisted blowout preventer and methods of use. In particular, there are provided systems and assemblies for utilizing high power laser energy within a blowout preventer to cut tubulars that are present within the bore of the blowout prevent, reducing the risk that such tubulars will inhibit the ability of the blowout preventer to seal a well.
Owner:FORO ENERGY
Dual purpose blow out preventer
An improved dual purpose blow out preventer (“BOP”) that provides both deployment and wellhead pressure containment functions. The dual purpose BOP may include four sets of rams including a set of seal / slip rams that provide bi-directional sealing being a first barrier to downhole pressure. The seal / slip rams may also grip a portion of a bottom hole assembly and create the bottom seal of an annular chamber. The BOP may include a set of seal rams that create the top seal of the annular chamber. The annular chamber may be pressurized through a port in the BOP, which may actuate a coiled tubing connector. The BOP may include a set of locate rams used to position a coiled tubing connector within the BOP stack. The BOP may also include a set of blind / shear rams that provide bi-directional sealing being a second barrier to wellhead pressure.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Rotating blowout preventer with independent cooling circuits and thrust bearing
A rotary blowout preventer has a first and a second fluid circuit. Each of the fluid circuits are defined into and out of a stationary body and between the stationary body, a rotating body, and two seals. The first fluid circuit is physically independent from the second fluid circuit although they share a seal interface. A fluid is introduced into the first fluid circuit at a pressure responsive to the well bore pressure. A fluid is introduced into the second fluid circuit at a pressure responsive to and lower than the pressure of the fluid in the first circuit. Adjustable orifices are connected to the outlet of the first and second fluid circuits to control such pressures within the circuits. Such pressures affect the wear rates of the seals. The system can therefore control the wear rate of one seal relative to another seal. A thrust bearing is added to share the load placed upon the upper bearings. The thrust bearing is connected between the top end of a packer sleeve and the stationary body.
Owner:WEATHERFORD CANADA PARTNERSHIP
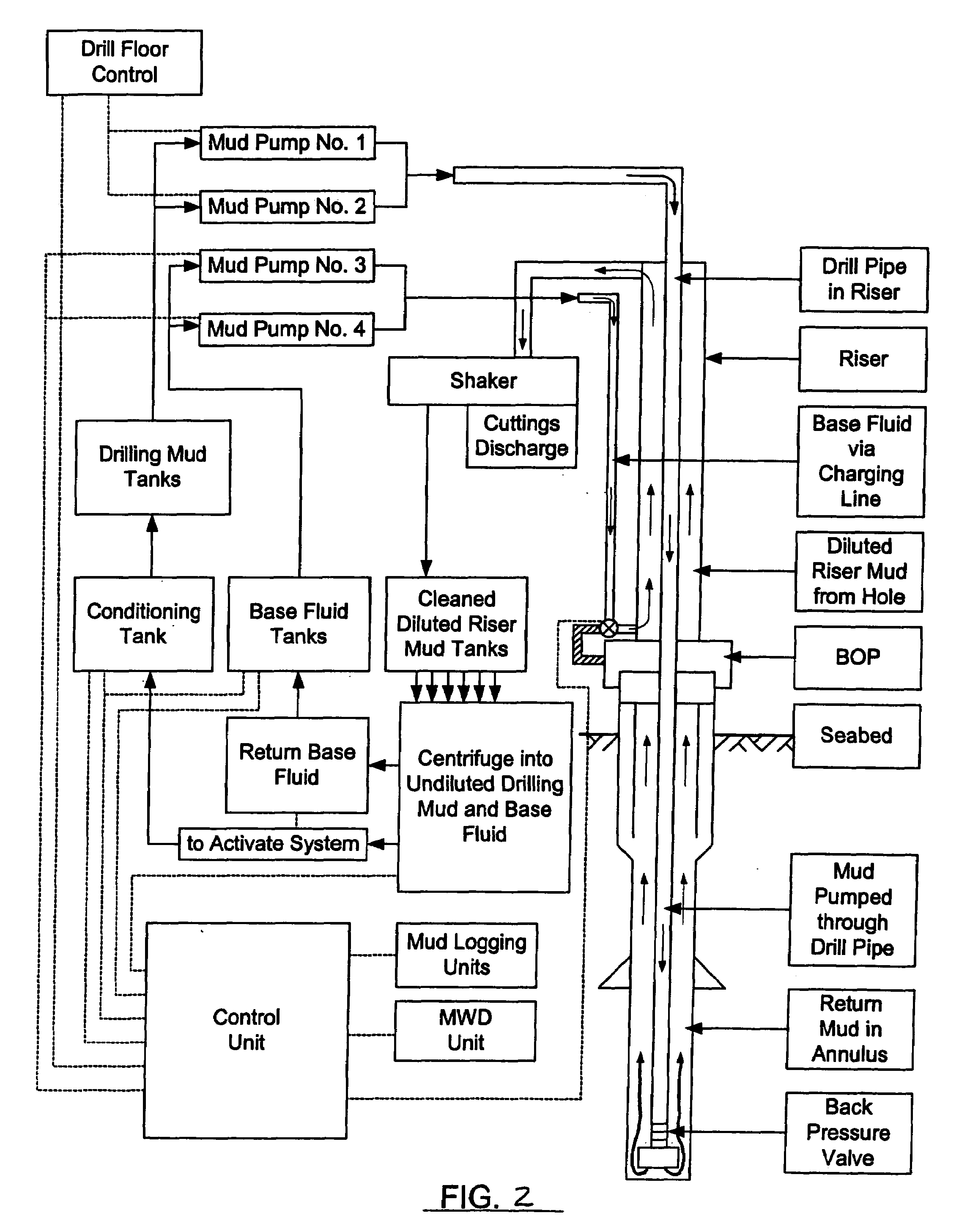
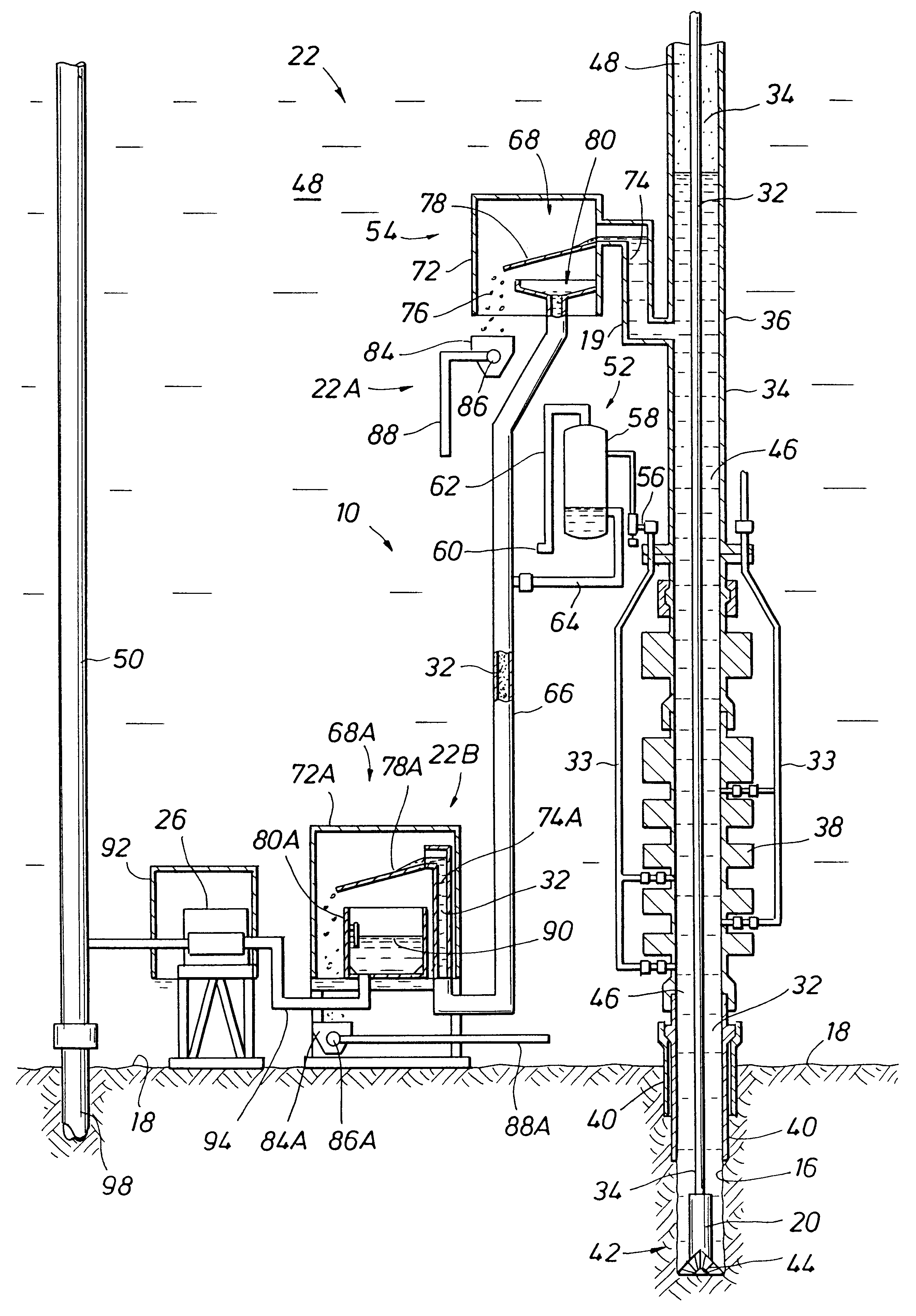
Deepwater drill string shut-off valve system and method for controlling mud circulation
A method is disclosed for controlling the mud circulation system for deepwater marine drilling operations in which a drill string is run from surface facilities, through a blowout preventor and into a borehole. Mud is injected into the drill string, up a borehole and through the blowout preventor adjacent the sea floor. There the mud is withdrawn from a mud exit return line near the blowout preventor and the hydrostatic head from the mud in the drill string is isolated from the relatively lesser ambient pressure at the sea floor seen at the mud exit return line with a pressure activated drill string shut-off valve when mud circulation is interrupted. A drill string shut-off valve system for controlling the mud circulation system for deepwater marine drilling operations is also disclosed. Further, a method of well control to overcome formation pressure in a well control event is disclosed.
Owner:SHELL OFFSHORE
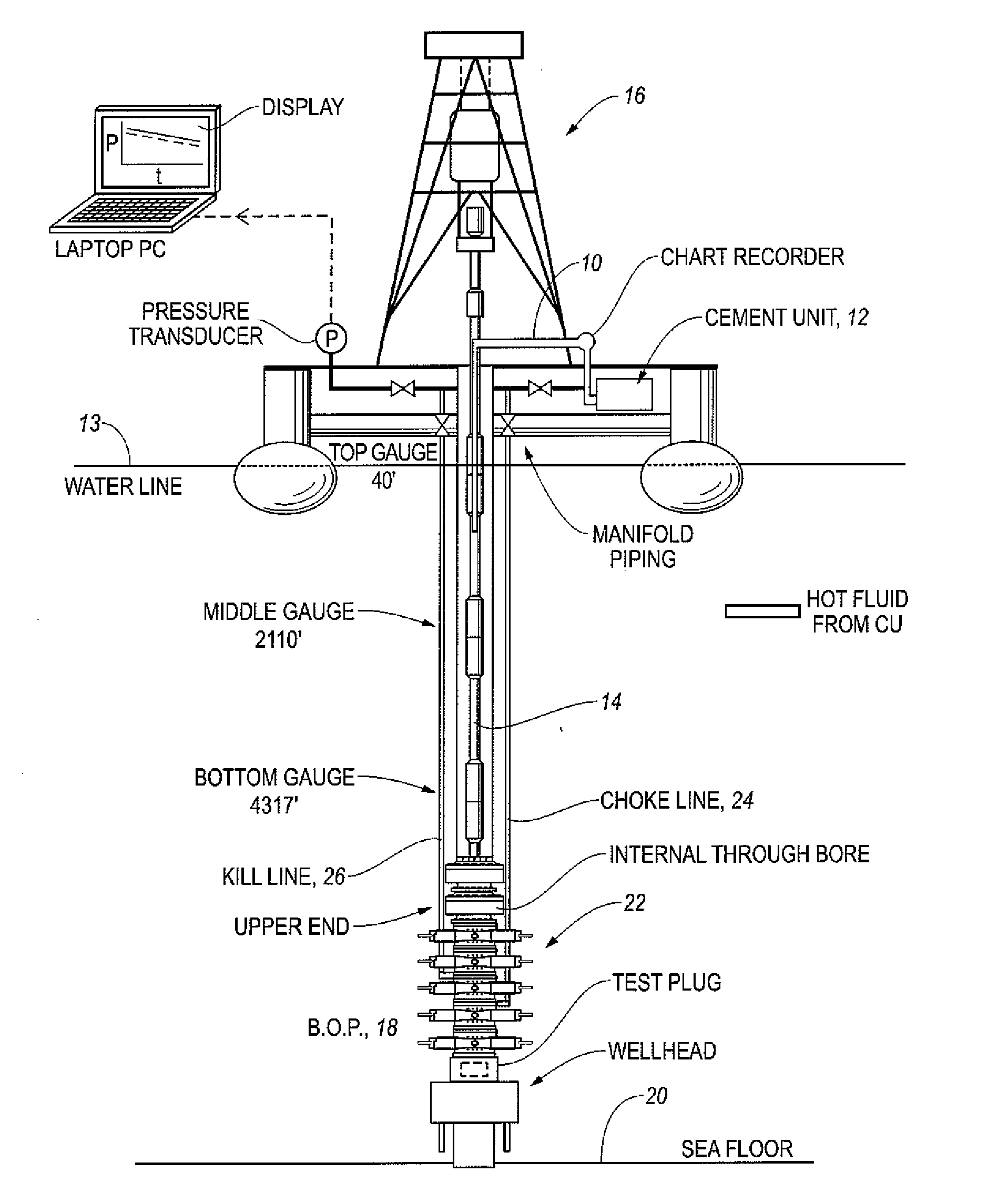
Blowout Preventer Testing System And Method
InactiveUS20080185143A1Slowing processing of dataImprove analysisElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSurveyEngineeringAutomaton
A method and apparatus for testing a blowout preventer (BOP) wherein a pressurization unit applies fluid to an isolated portion of the throughbore of the BOP. A signal that is representative of the actual pressure in the isolated portion of the throughbore over successive time points and a pre-determined non-deterministic finite state automaton are used to predict the pressure in the isolated portion of the throughbore as a function of time relative to a pre-determined acceptable leak rate and the time at which stability is achieved. In one embodiment stability is achieved when successive predicted pressures are within a predetermined difference over a predetermined interval of time. Visual indications are provided to depict the progress of testing.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Laser assisted riser disconnect and method of use
There is provided a high power laser-riser blowout preventer package and laser module for use with a subsea riser. The laser module and laser-riser package use high power laser energy to quickly cut the riser permitting an offshore drilling rig to quickly, and in a controlled manner disconnect from a blowout preventer.
Owner:FORO ENERGY
Low profile rotating control device
ActiveUS8286734B2Reduce the overall heightEasy accessDrilling rodsConstructionsEngineeringBlowout preventer
A system and method are provided for a low profile rotating control device (LP-RCD) and its housing mounted on or integral with an annular blowout preventer seal, casing, or other housing. The outer diameter of the lateral outlet flange may be substantially the same as the height of the LP-RCD housing and bearing assembly after the bearing assembly is positioned with the LP-RCD housing. The sealing element may be aligned with the lateral outlet, and may be replaced from above. Different embodiments of attachment members for attaching the LP-RCD housing with a lower housing allow the LP-RCD housing to be rotated to align the lateral outlet with the drilling rig's existing line to mud pits or other locations. In one embodiment, the LP-RCD bearings are positioned radially inside the LP-RCD housing. In another embodiment, the LP-RCD bearings are positioned radially outside the LP-RCD housing. One embodiment allows rotation of the inserted tubular about multiple planes. In still another embodiment, an annular BOP seal is integral with a RCD housing.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
Concentric type integrated test modification water injection technology and device
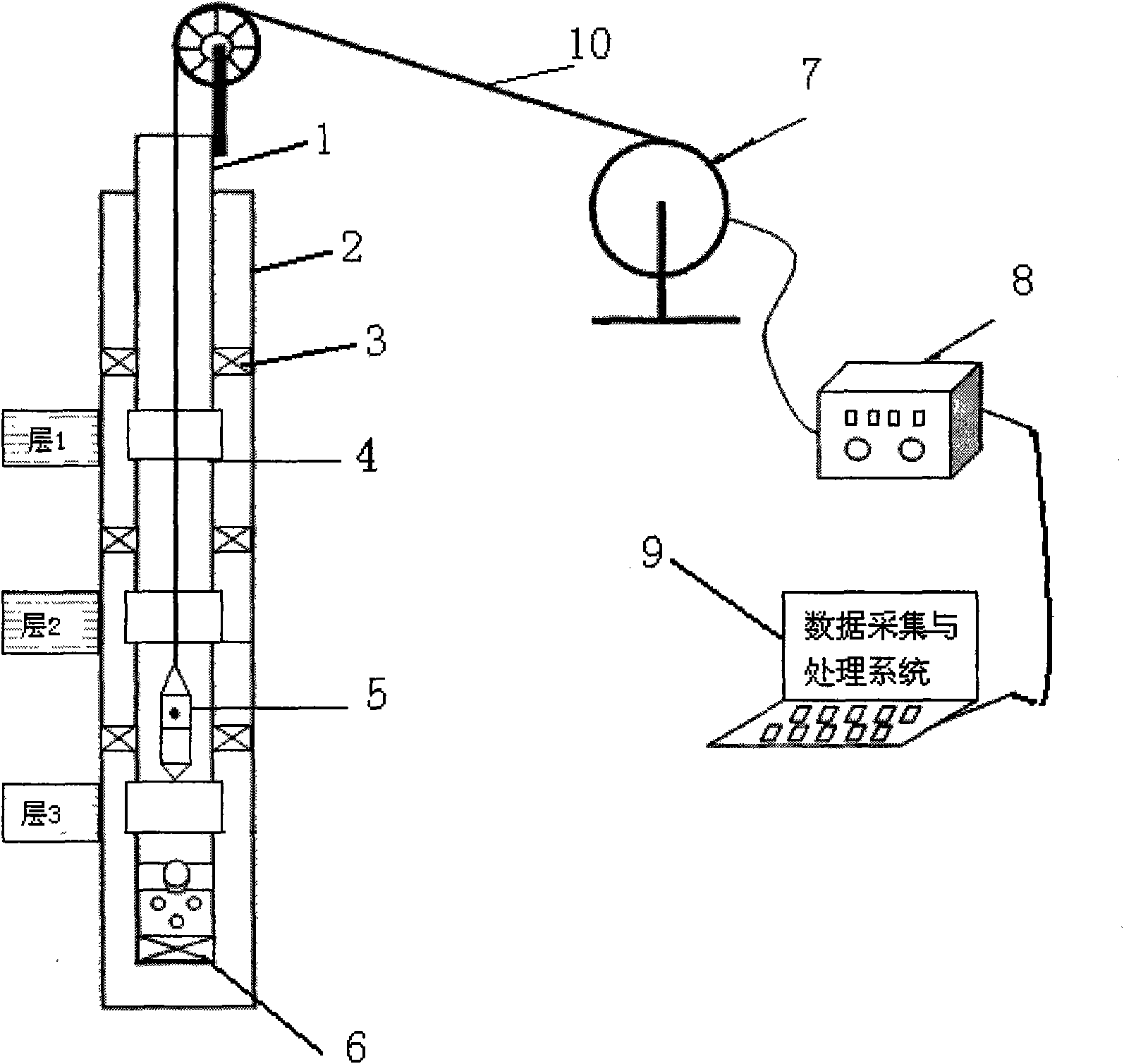
The invention provides a concentric type integrated test modification water injection technology and a device, wherein, the technology comprises the following steps: A. tripping in a test modificationwater injection technology pipe column; B. installing a wellhead blowout preventer; C. turning on the water injection flow to inject water normally; D. tripping in an integrated test modification instrument; E. tripping in the integrated test modification instrument in the test modification water distributor of the basecoat for location; F. starting the integrated test modification instrument totransmit the downhole temperature, pressure and flow to a ground data acquisition processing system; G. allocating the test modification water distributor; H. repeating the steps in F, G and H; I. repeating the steps in F-G after relocation; and J. closing the well and stopping injecting, and opening the well and injecting water after pulling out the integrated test modification instrument. The device comprises a sleeve and a test modification water injection technology pipe column, wherein, the pipe column comprises an oil pipe, the test modification water distributor thereon, a layered packer among the test modification water distributors and a screwed plug installed on the lower end. The integrated test modification instrument is tripped in the pipe column; a power cable, a winch, a ground control system and a data acquisition processing system are installed on the ground; and the power cable and the winch are in succession connected with the ground control system and the data acquisition processing system. The invention is mainly applied to oil water injection technology.
Owner:RES INST OF PETROLEUM ENG SHENGLI OIL FIELD SINOPEC
Position Data Based Method, Interface and Device for Blowout Preventer
Methods and devices for using position data of a piston connected to a ram block in a blowout preventer to determine a backlash of the ram block, and / or to record a position of the ram block, and / or to calculate an instant when a supplemental closing pressure is desired to be applied, and / or to determine when maintenance of a ram locking mechanism is due, and / or to determine when sealing elements are worn.
Owner:HYDRIL USA DISTRIBUTION LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com