Patents
Literature
78 results about "Hydrostatic head" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
When generating hydropower, the head is the distance that a given water source has to fall before the point where power is generated. Ultimately the force responsible for hydropower is gravity, so a hydroelectricity plant with a tall/high head can produce more power than a similar plant with a short/low head. In short, for a given water flow, a larger head will be converted into greater kinetic energy. That energy is then harnessed by a water wheel or water turbine to create usable hydropower.
Liquid water resistant and water vapor permeable garments
A water resistant garment is disclosed having regions of high MVTR while maintaining water resistance. The garment has a fabric layer adjacent one major surface of a nanofiber layer. The surface of the nanofibers are coated with a coating containing a fluorocarbon polymeric moiety and a resin binder or extender which is soluble in water and / or other solvents. The coated nanofiber layer has a contact angle of greater than 145°. The garment optionally includes a second fabric layer adjacent the other major surface of the nanofiber layer. The garment has regions having a Frazier air permeability of between about 0.5 m3 / min / m2 and about 8 m3 / min / m2, an MVTR of greater than about 500 g / m2 / day and a hydrostatic head of at least about 50 cmwc.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
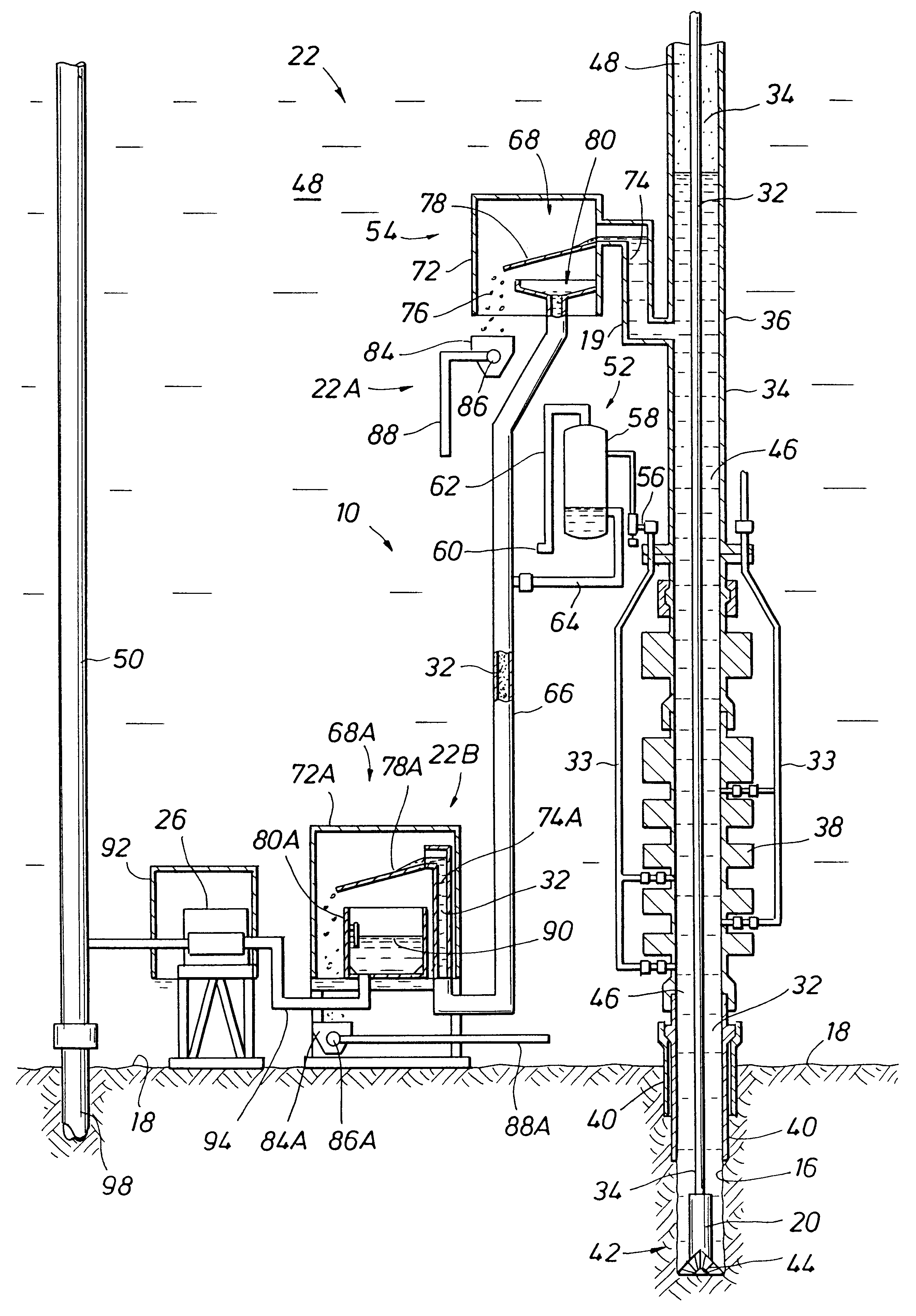
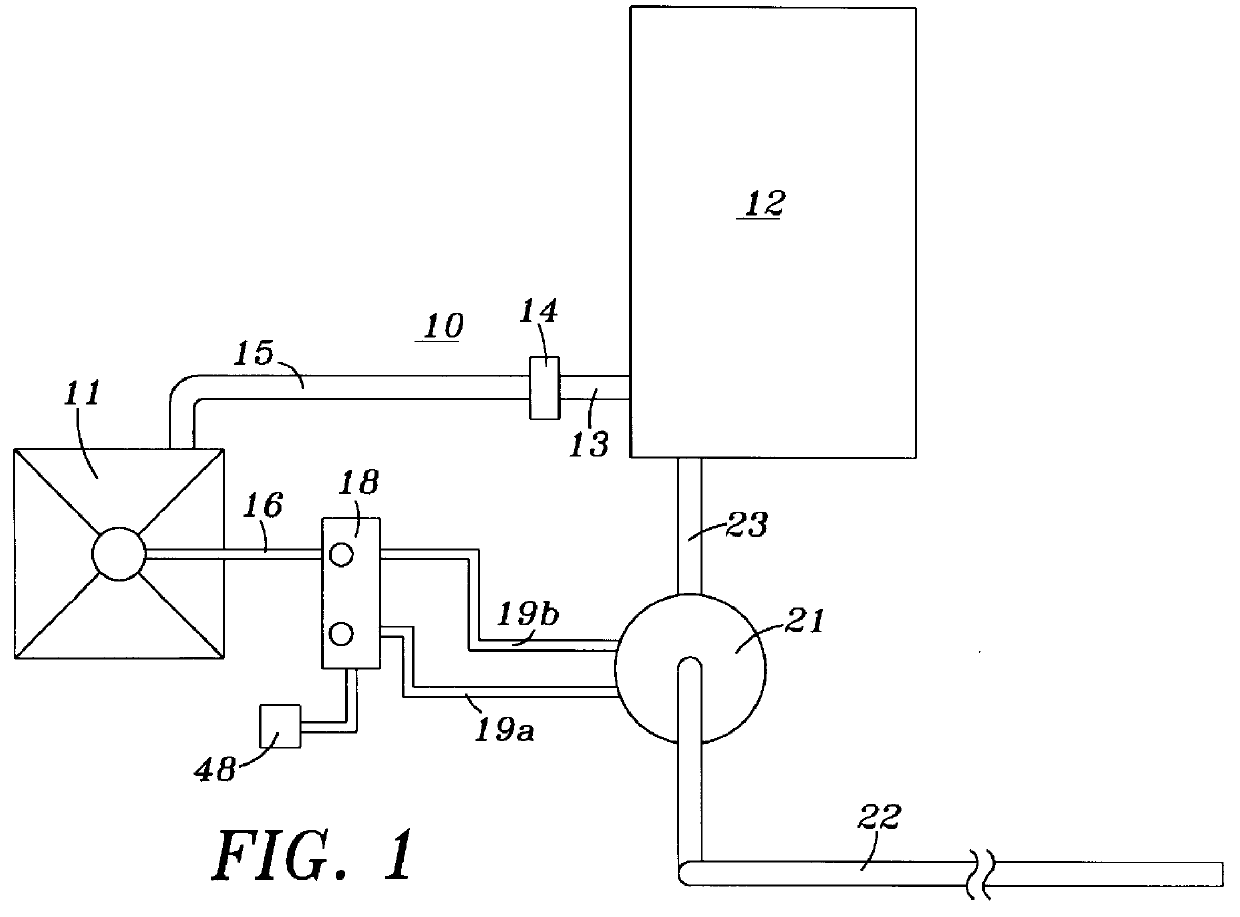
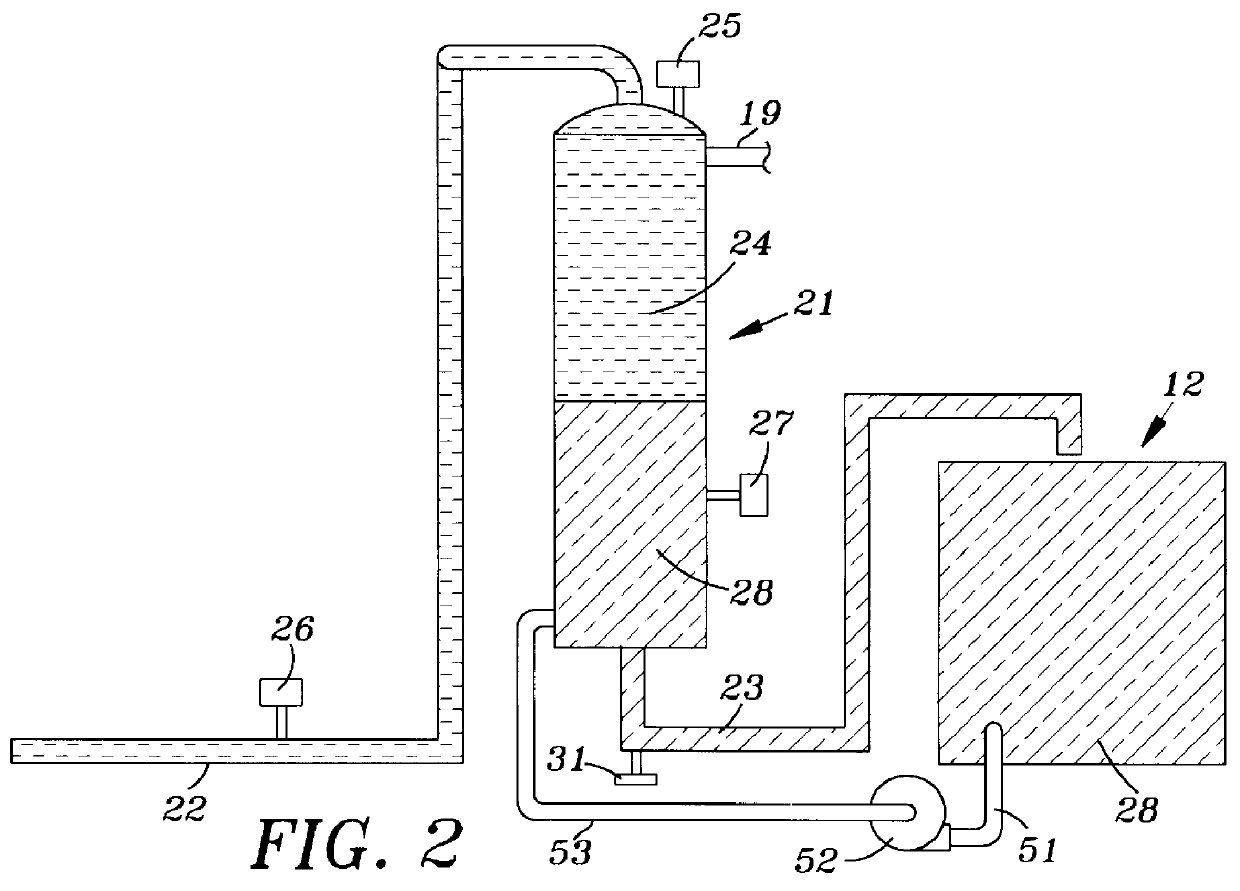
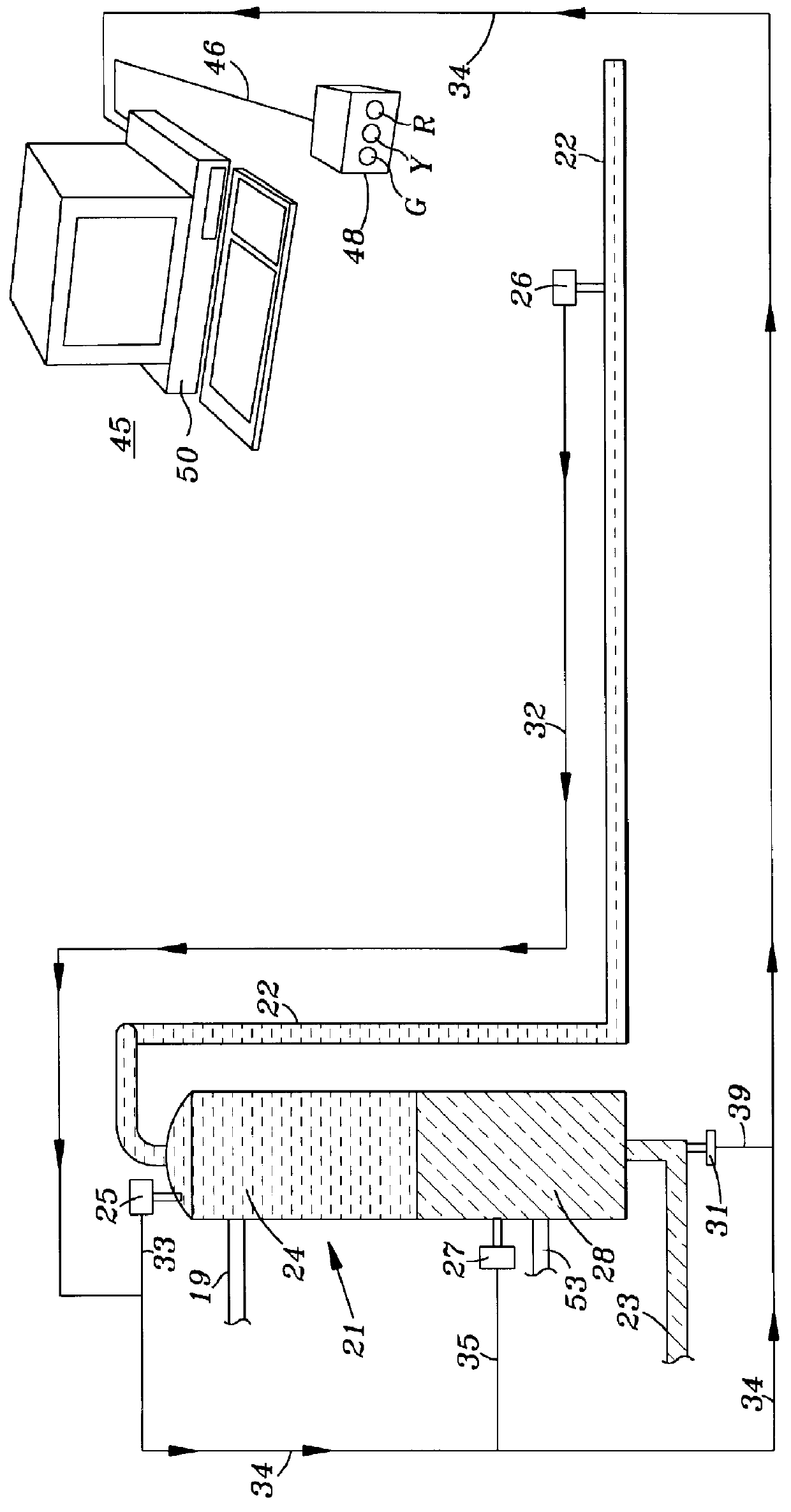
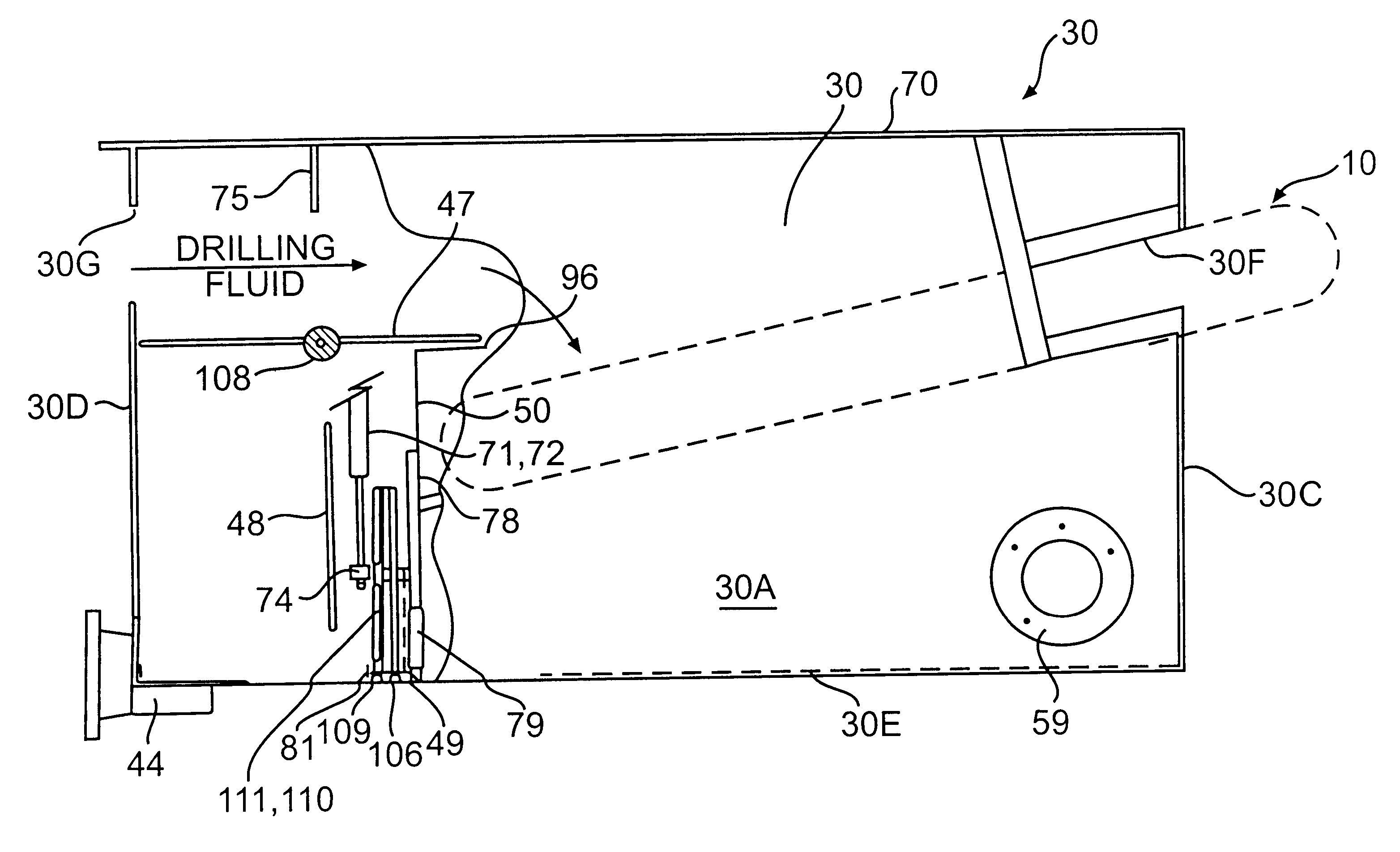
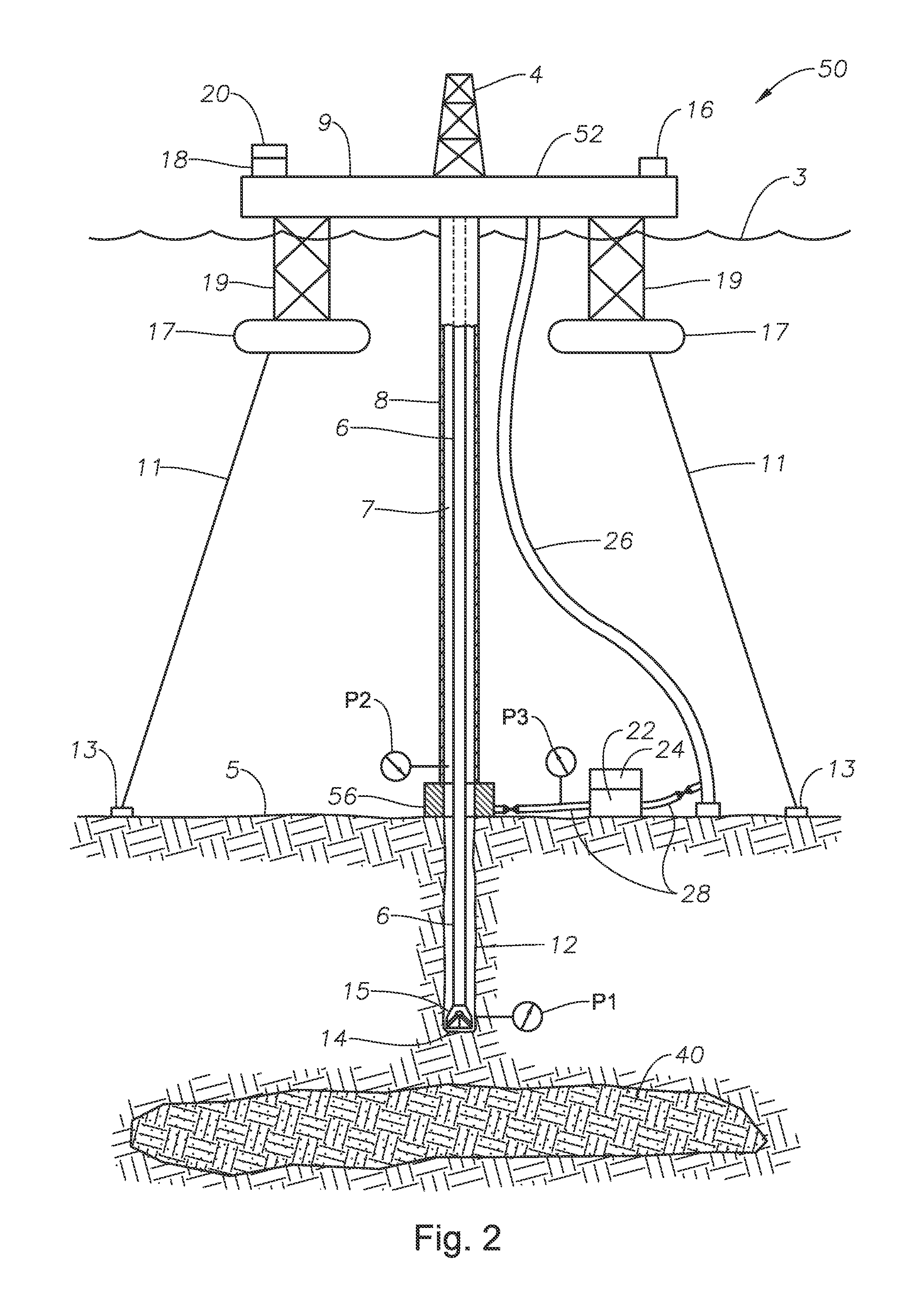
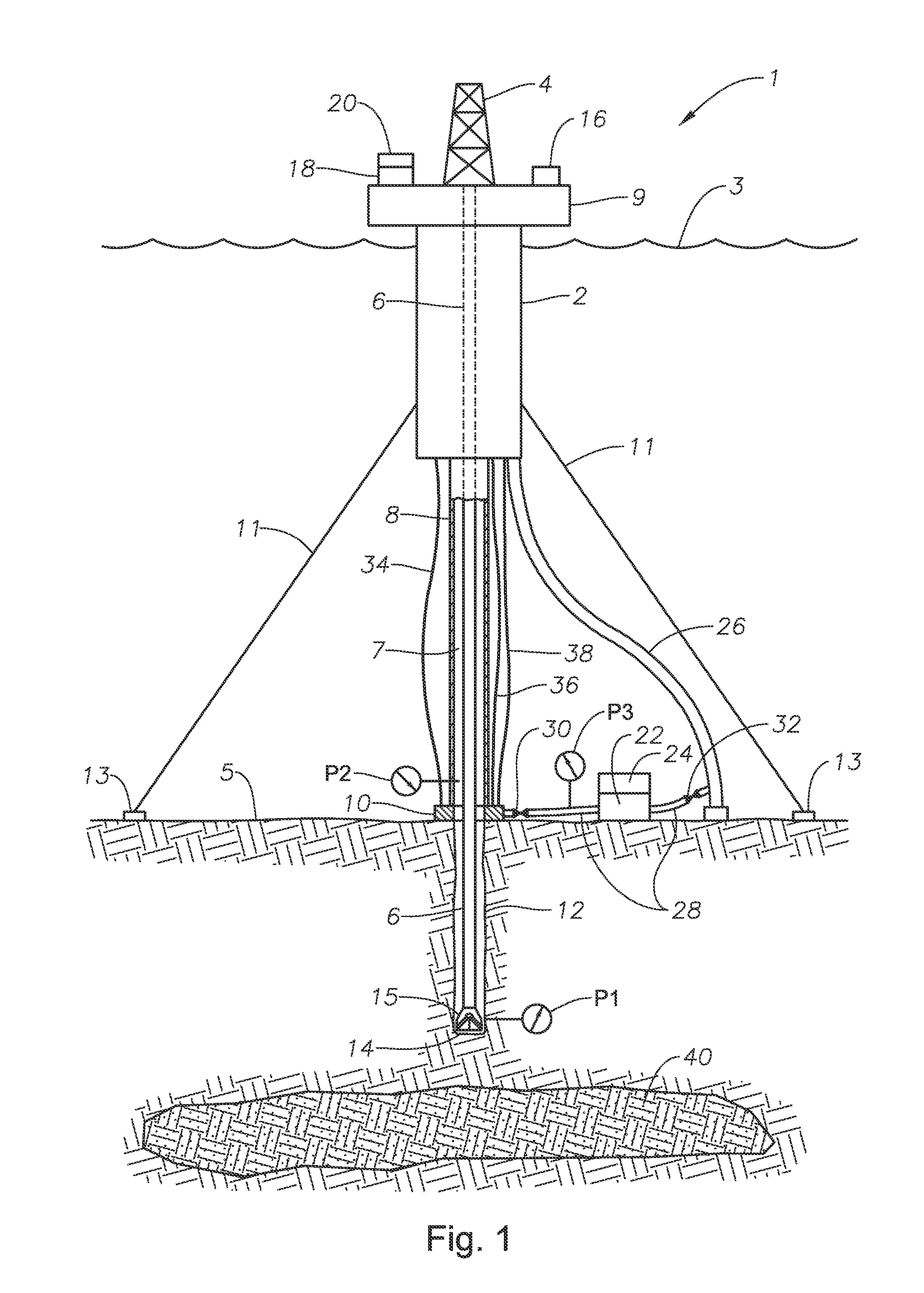
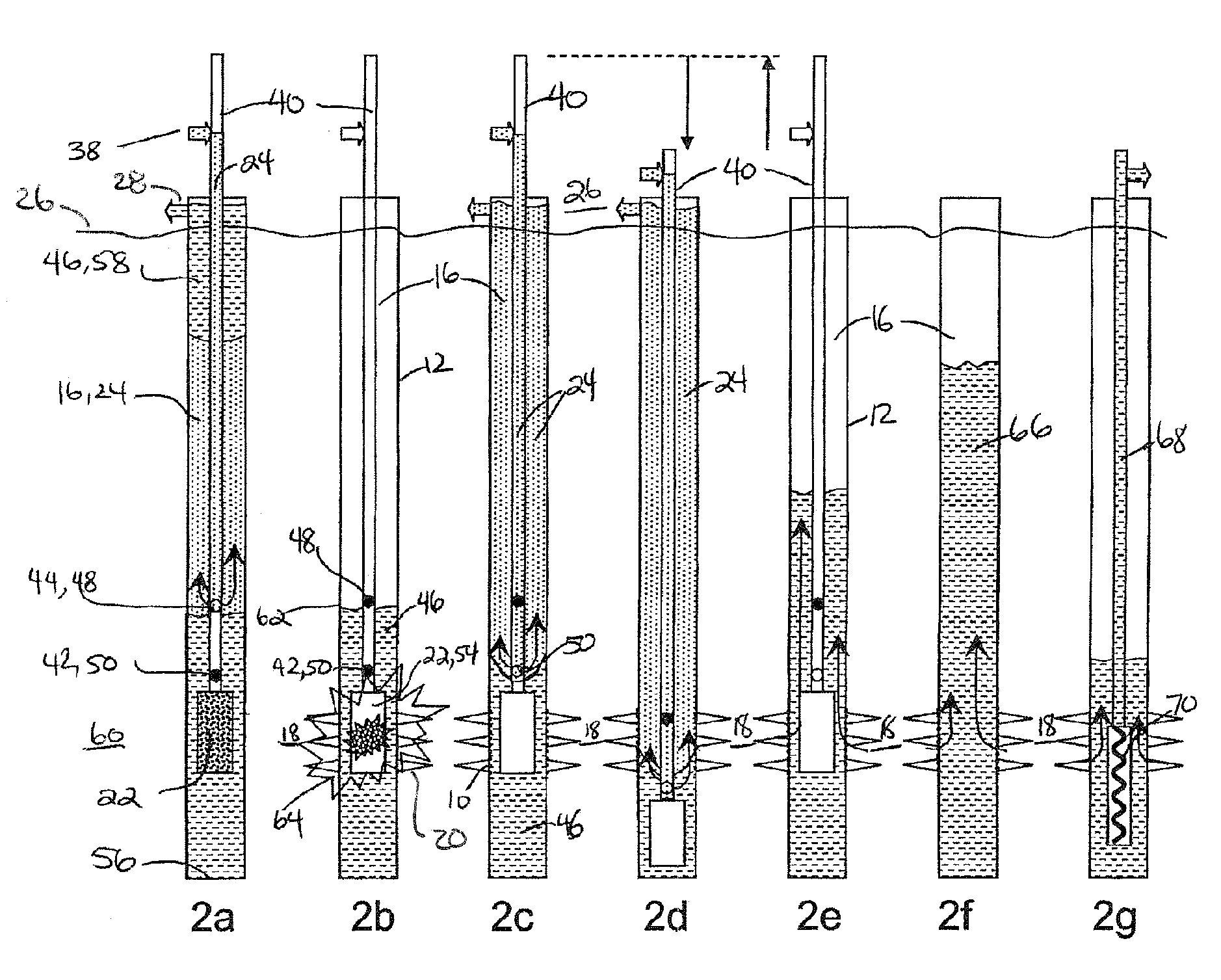
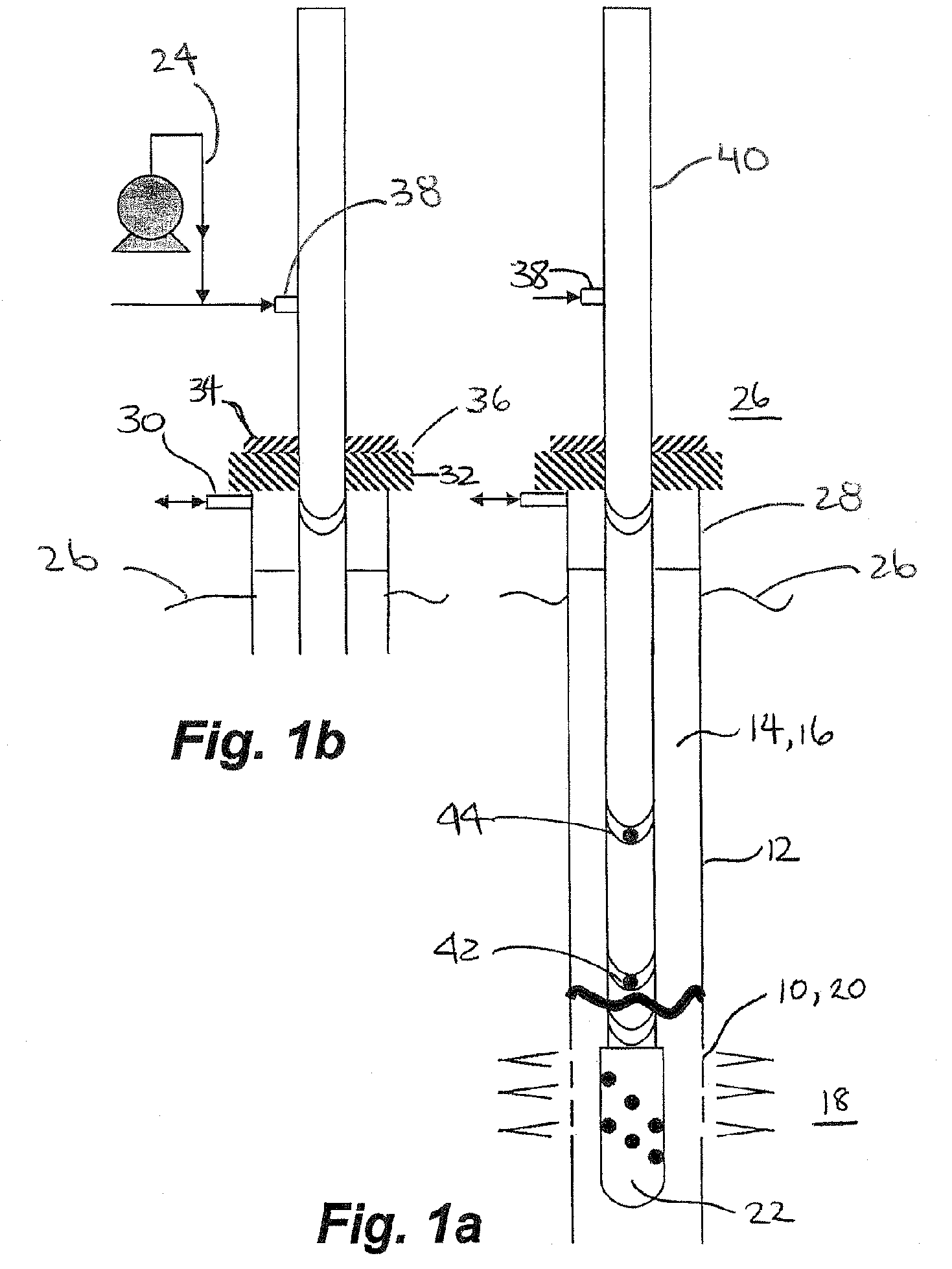
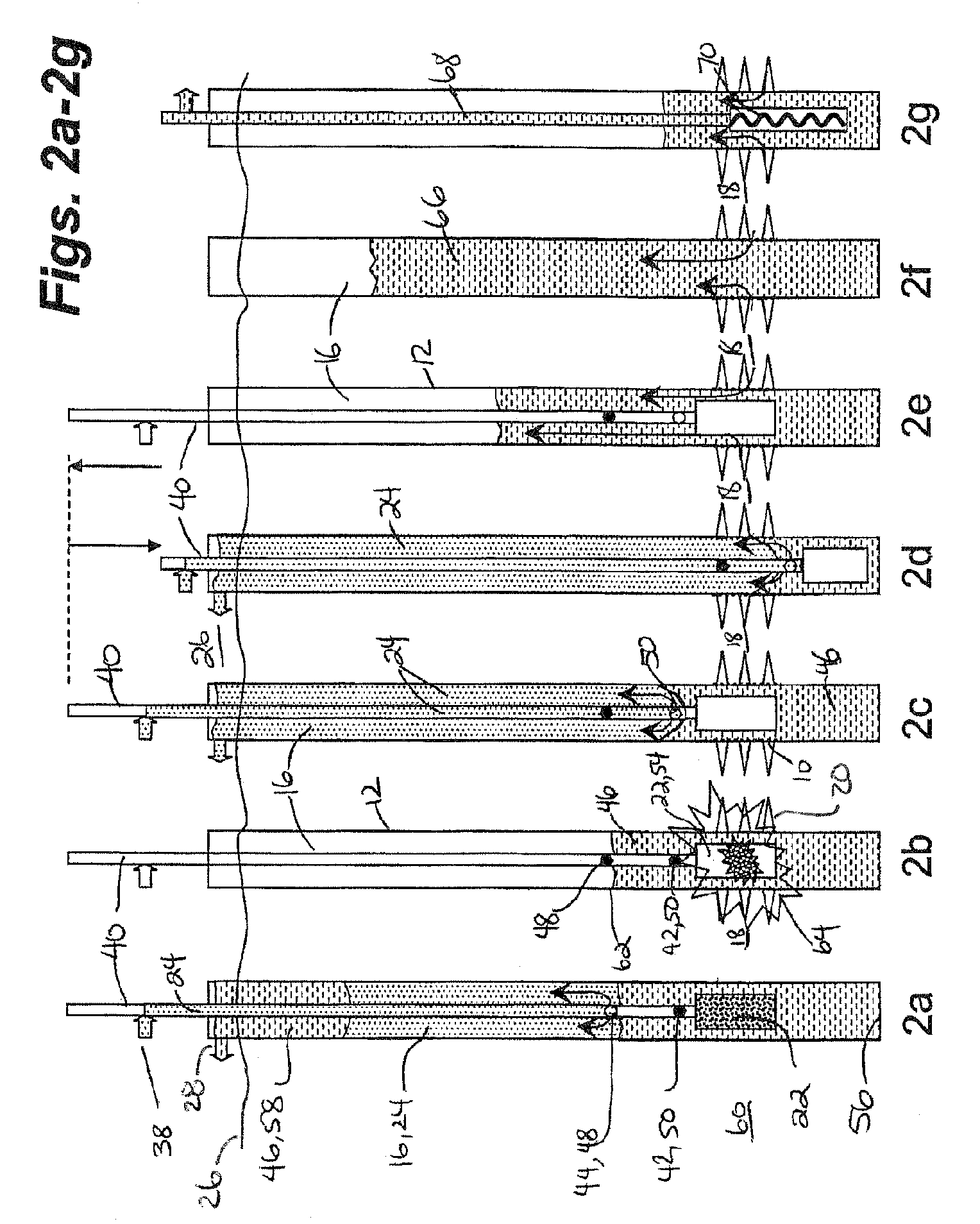
Deepwater drill string shut-off valve system and method for controlling mud circulation
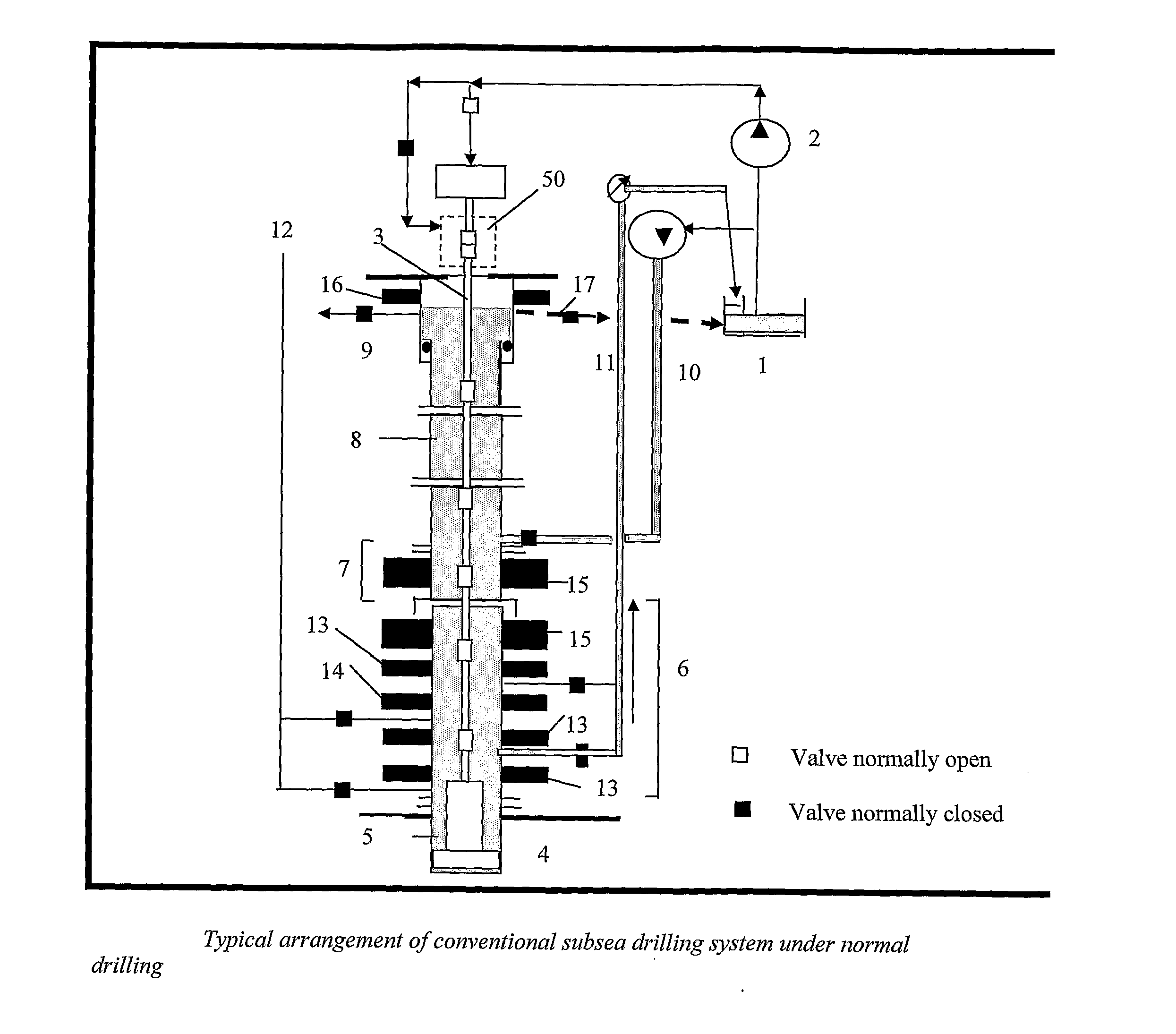
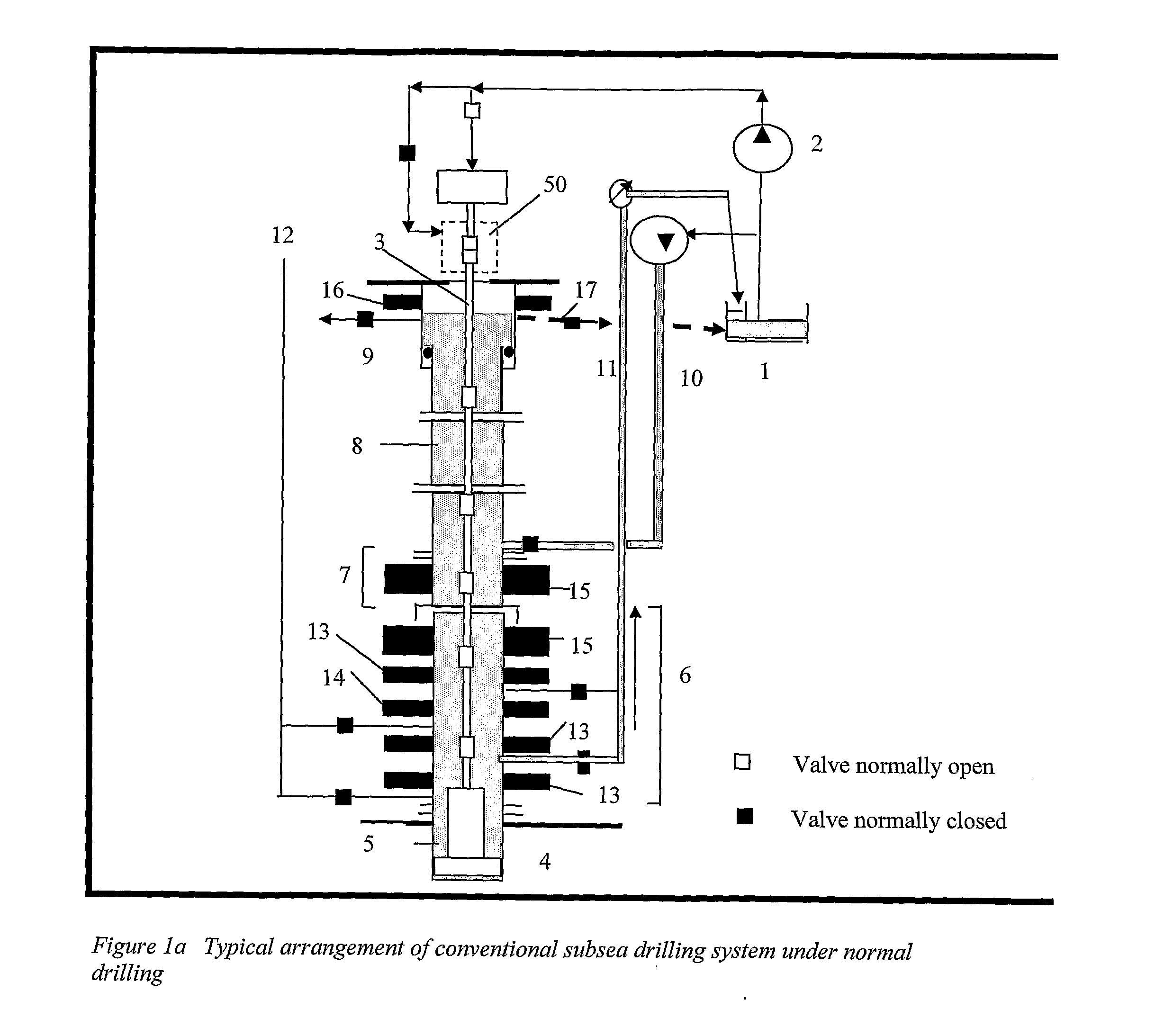
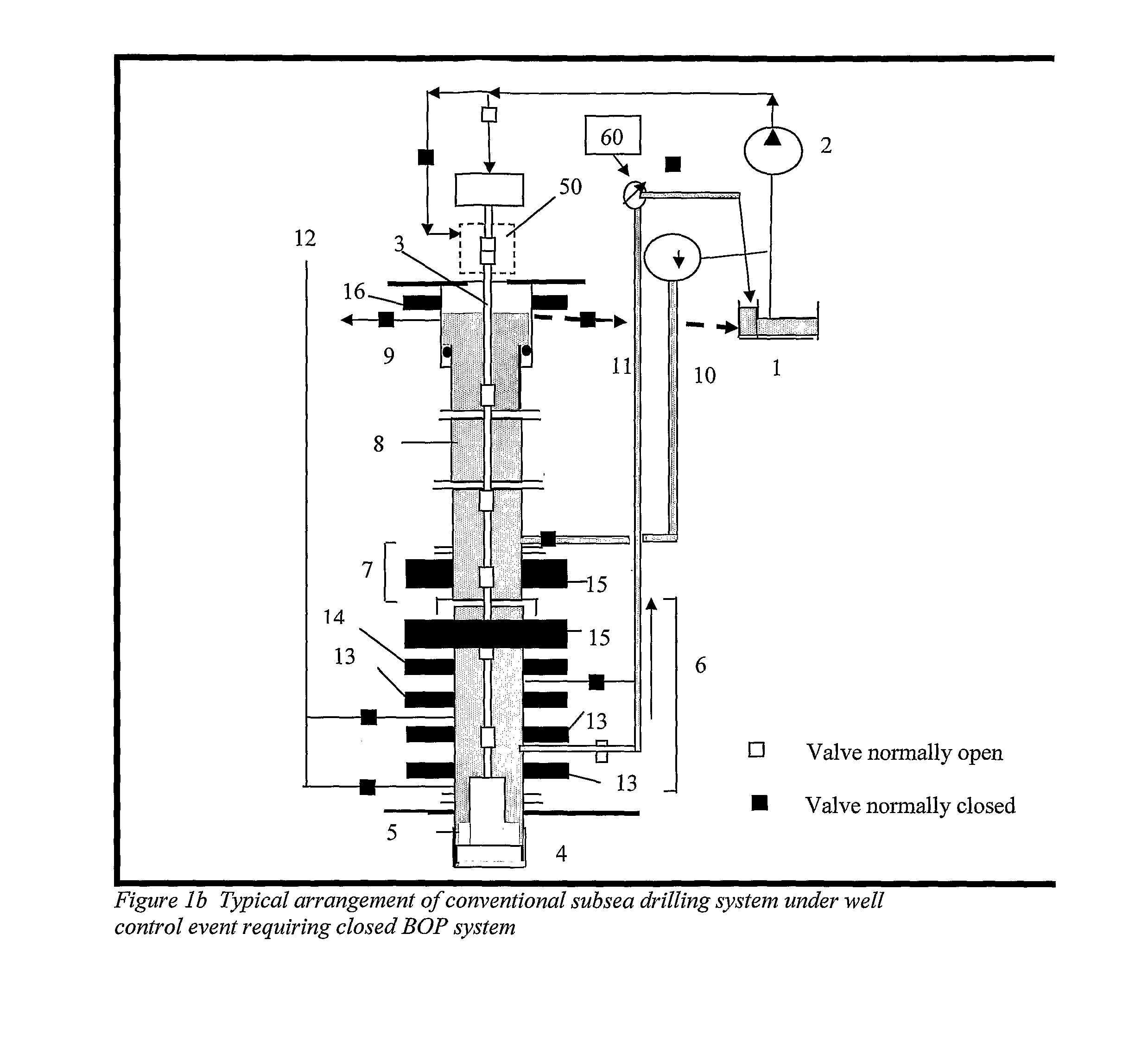
A method is disclosed for controlling the mud circulation system for deepwater marine drilling operations in which a drill string is run from surface facilities, through a blowout preventor and into a borehole. Mud is injected into the drill string, up a borehole and through the blowout preventor adjacent the sea floor. There the mud is withdrawn from a mud exit return line near the blowout preventor and the hydrostatic head from the mud in the drill string is isolated from the relatively lesser ambient pressure at the sea floor seen at the mud exit return line with a pressure activated drill string shut-off valve when mud circulation is interrupted. A drill string shut-off valve system for controlling the mud circulation system for deepwater marine drilling operations is also disclosed. Further, a method of well control to overcome formation pressure in a well control event is disclosed.
Owner:SHELL OFFSHORE
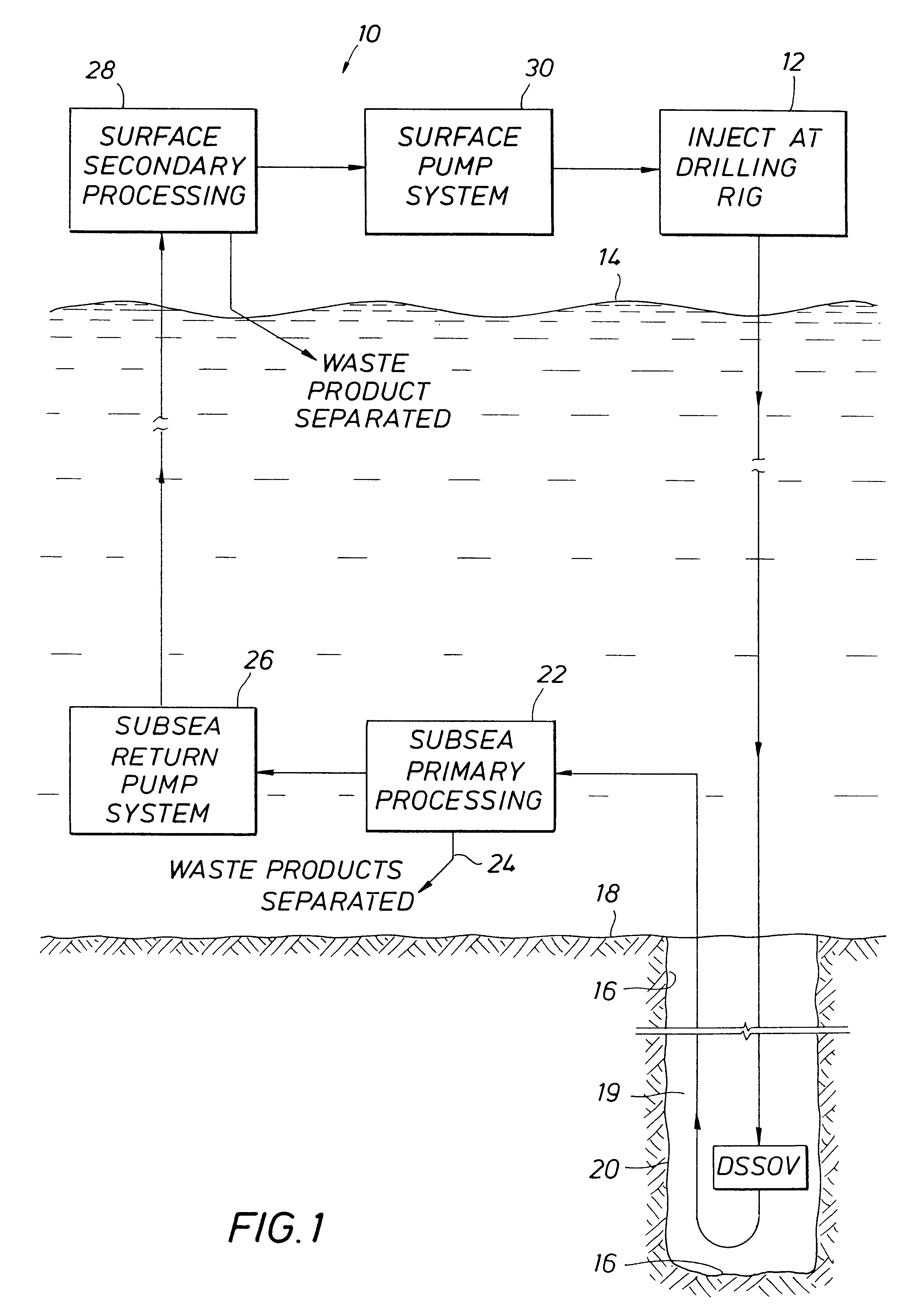
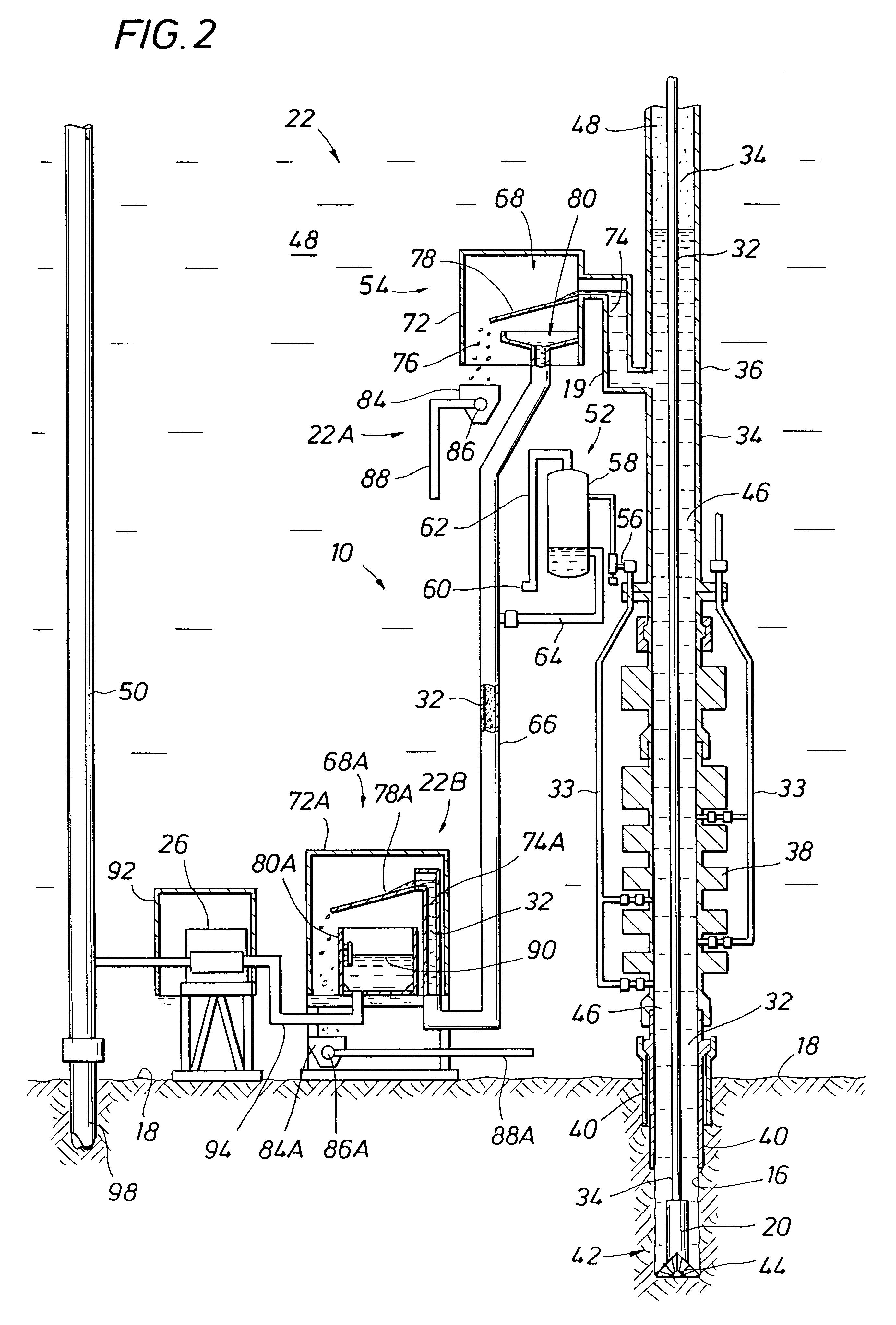
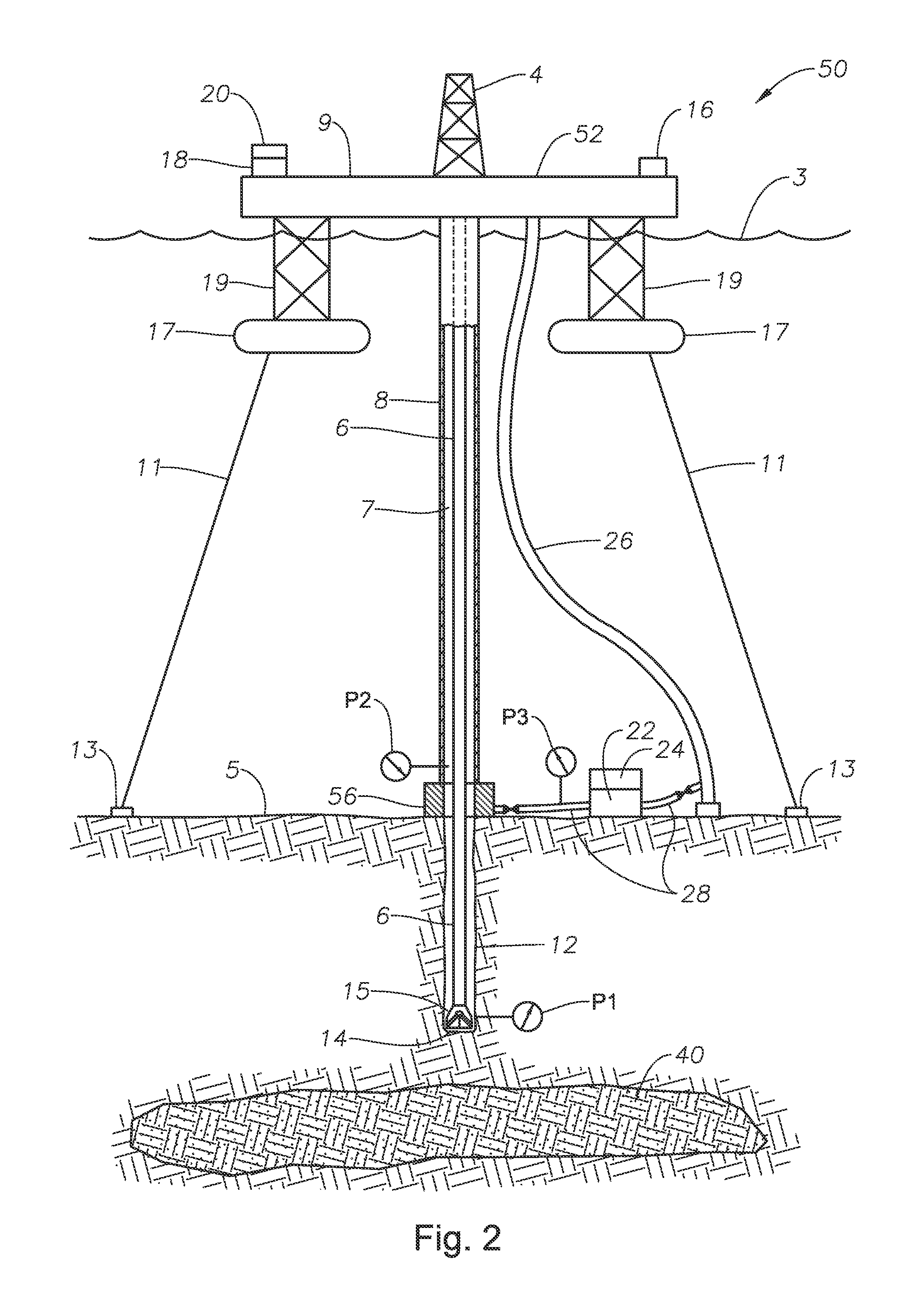
Systems and methods for subsea drilling
ActiveUS20110100710A1Improve securityReduce pressure requirementsDrilling rodsDerricks/mastsWell drillingHydrostatic head
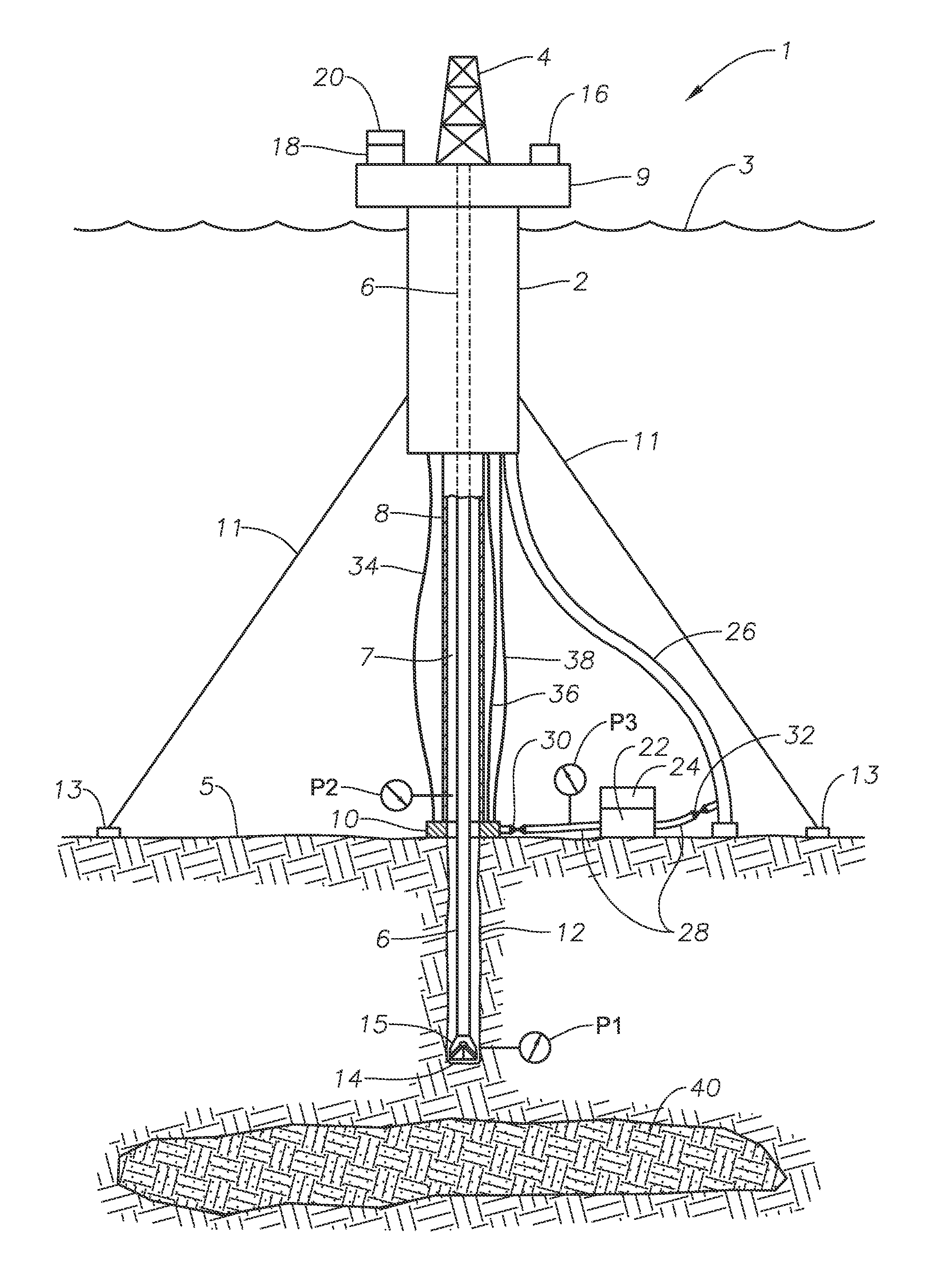
A subsea drilling method and system for controlling the drilling fluid pressure, where drilling fluid is pumped down into the borehole through a drill string and returned back through the annulus between the drill string and the well bore. The drilling fluid pressure is controlled by draining drilling fluid out of the drilling riser (8) or BOP (6) at a level between the seabed and the sea water in order to adjust the hydrostatic head of drilling fluid. The drained drilling fluid and gas is separated in a subsea separator (28) where the gas is vented to surface through a vent line (39), and the fluid is pumped to surface via pump (40).
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
Mud separator monitoring system
A mud separator monitoring system utilizing electronic transducers positioned in various locations in the mud separator and the lines leading from the mud separator to the mud return pit and gas discharge flare for obtaining data during drilling operations to calculate the volume of gas retained in the drilling fluid, the hydrostatic head of the drilling fluid and gas pressure in the separator on a continuing basis and informing field personnel of conditions in the mud separator indicating potential hazard. The system further monitors continuously the volume of injected gases and hydrocarbon gases circulated during drilling operations for making adjustments to the volume of injected gases required to sustain the drilling operations.
Owner:MCGUIRE FISHING & RENTAL TOOLS
Weir box for drilling mud separation unit
InactiveUS6244362B1Settling tanks feed/dischargeLoose filtering material filtersLithologyShale shakers
A weir box disposed upstream from conventional solids control equipment of a mud system of a drilling rig contains a drilling mud separation unit having a continuous-loop scalper screen that is driven in a continuous loop to separate, convey and discharge large amounts of gumbo, heavy clays and drill solids at the end of the separation unit. The flow divider box is a box-like housing with a diverter plate, weir baffle plates and a sliding gate that allows drilling fluid or drilling mud to be selectively directed to the mud separation unit to be separated prior to passing to the conventional downstream solids control equipment or allows the fluid to bypass the separation unit and flow directly to the conventional solids control equipment. The sliding gate is adjustable to selectively control or meter the flow rate and to create a hydrostatic head upstream from the conventional solids control equipment. The weir box baffle plates, sliding gate, and selective utilization of the mud separation unit allows the operator to produce an increased hydrostatic head, which enables high flow rates to be easily processed by shale shakers and other conventional downstream solids control equipment of the mud system and to compliment the drilling operation with respect to changes in the lithology, geological formations, or loss of returns in relation to the gallons pumped or volume of drilling fluid or drilling mud entering the weir box.
Owner:WILLIAMS J TERRELL
Systems and methods for circulating out a well bore influx in a dual gradient environment
Methods and systems for drilling subsea wells bores with dual-gradient mud systems include drilling the subsea well bore while employing a subsea pumping system, a subsea choke manifold and one or more mud return risers to implement the dual gradient mud system. When a well bore influx is detected, the well bore is shut in, and components determine if pressure control may be used to circulate the influx out of the well bore, the size of the influx, and how much the mud system weight will need to be reduced to match the dual gradient hydrostatic head before the influx reaches the subsea pump take point. The subsea pumping system, subsea choke manifold, and mud risers are isolated while the influx is circulated up one or more fluid passages in the drilling riser package using the surface pump, through the wellhead, and out the surface choke manifold.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
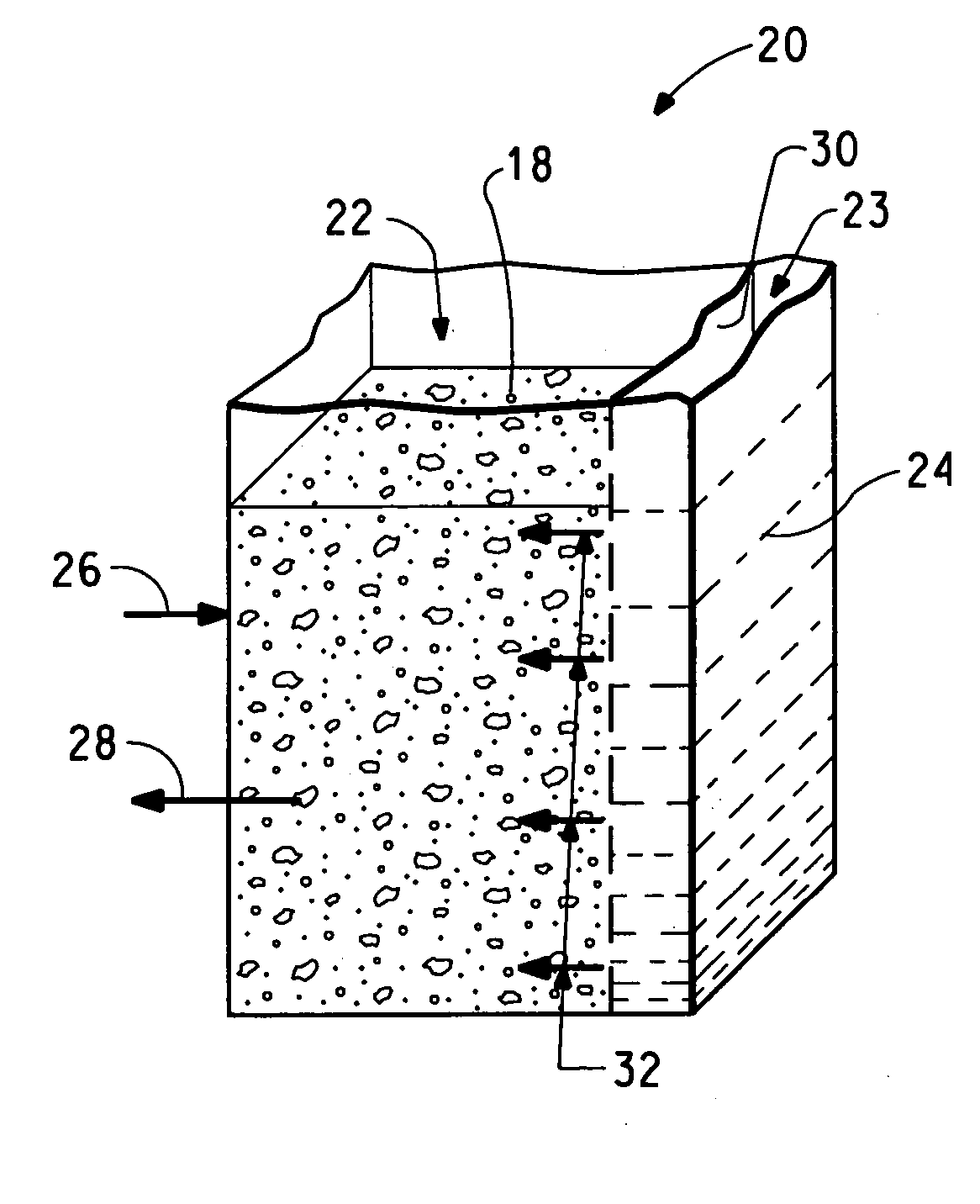
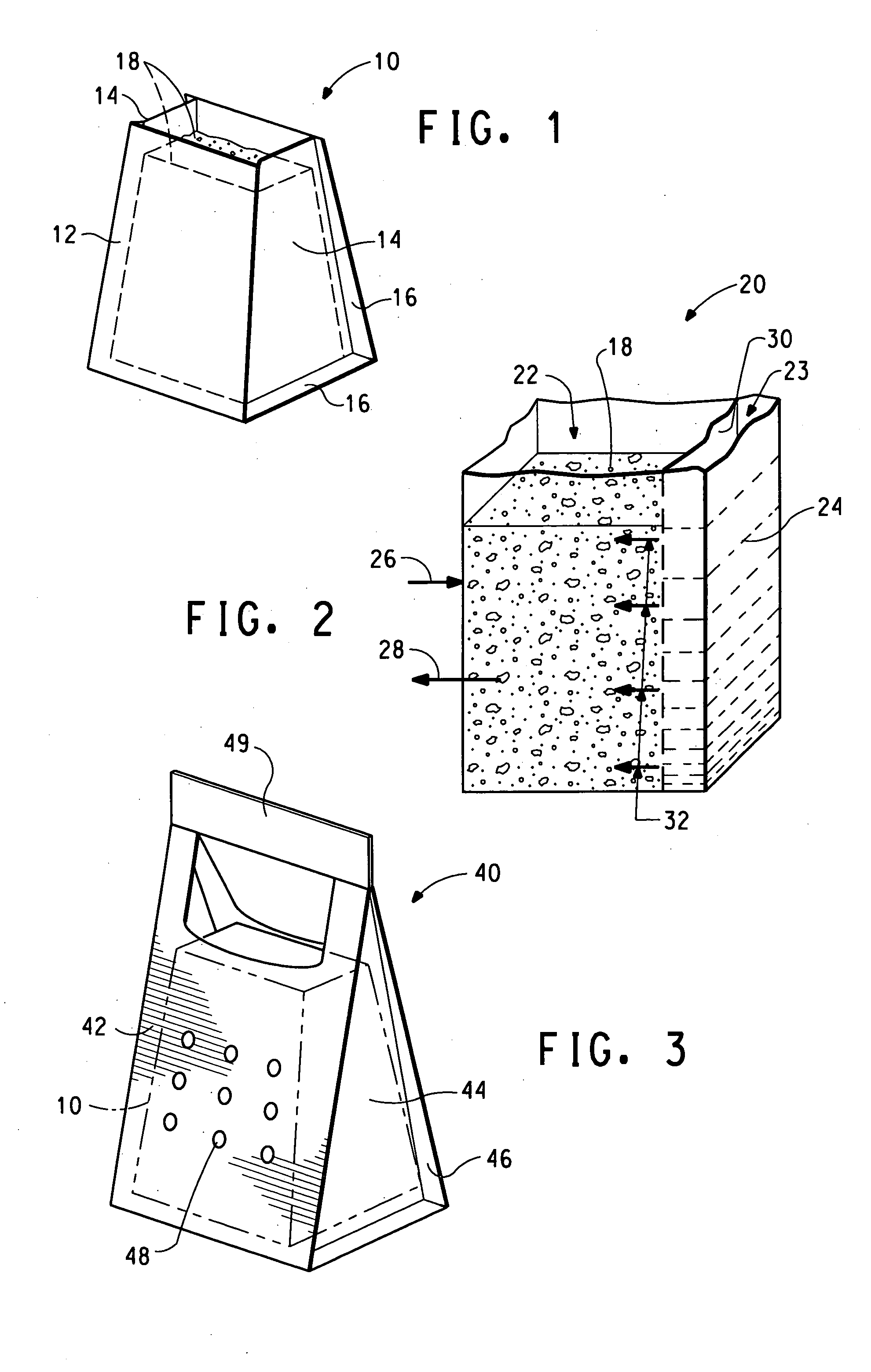
Breathable plant container
InactiveUS20050166451A1Easy to controlHigh tensile strengthFlower holdersAgriculture gas emission reductionPorosityHydrostatic head
A breathable plant container is provided that includes a hollow vessel having an opening through which planting soil can be inserted into the hollow portion of the vessel and through which a plant growing in the soil can grow out of the vessel. The hollow vessel has a wall comprised of a synthetic microporous sheet material selected from the group of flash-spun plexifilamentary fabrics, spunbonded / meltblown / spunbonded (“SMS”) fabrics, and microporous film laminates. The wall of the hollow vessel preferably has an air porosity less than 200 seconds / 100 cm3, a moisture vapor transmission rate of at least 300 g / m2 / day, and a hydrostatic head of at least 20 cm. The hollow vessel may have a first compartment separated from a second compartment by a synthetic, moisture vapor permeable membrane that resists the passage of water such that water added to the second compartment can keep moist soil added to the first compartment.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Liquid water resistant and water vapor permeable garments
A water resistant garment is disclosed having regions of high MVTR while maintaining water resistance. The garment has a fabric layer adjacent one major surface of a nanofiber layer. The surface of the nanofibers are coated with a coating containing a fluorocarbon polymeric moiety and a resin binder or extender which is soluble in water and / or other solvents. The coated nanofiber layer has a contact angle of greater than 145°. The garment optionally includes a second fabric layer adjacent the other major surface of the nanofiber layer. The garment has regions having a Frazier air permeability of between about 0.5 m3 / min / m2 and about 8 m3 / min / m2, an MVTR of greater than about 500 g / m2 / day and a hydrostatic head of at least about 50 cmwc.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Microporous composite sheet material
InactiveUS7972981B2High strengthImprove barrier propertiesFilament/thread formingMonocomponent polypropylene artificial filamentPolymer sciencePolyolefin
A moisture vapor permeable, water impermeable composite sheet material is provided which is suitable for use as a housewrap material, and is also useful for other applications such as tarpaulins, or as covers for automobile, boats, patio furniture or the like. The composite sheet material includes a nonwoven substrate and an extrusion-coated polyolefin film layer overlying one surface of the substrate. The nonwoven substrate is comprised of polymeric fibers randomly disposed and bonded to one another to form a high tenacity nonwoven web. The nonwoven substrate has a grab tensile strength of at least 178 Newtons (40 pounds) in at least one of the machine direction (MD) or the cross-machine direction (CD). The extrusion coated polyolefin film layer is intimately bonded to the nonwoven substrate. The film layer has micropores formed therein to impart to the composite sheet material a moisture vapor transmission rate (MVTR) of at least 35 g / m2 / 24 hr. at 50% relative humidity and 23° C. and a hydrostatic head of at least 55 cm. In one embodiment, the nonwoven substrate comprises a spunbonded nonwoven fabric formed of randomly disposed substantially continuous polypropylene filaments. The spunbonded nonwoven fabric is an area bonded fabric in which the filaments are bonded to one another throughout the fabric at locations where the randomly disposed filaments overlie or cross one another.
Owner:FIBERWEB LLC
Moisture transmissive laminate
InactiveUS20060089073A1Exceptional strength characteristicExceptional aestheticCovering/liningsRoofingHydrostatic headMoisture permeability
A laminate having high moisture vapor permeability includes a moisture vapor transmissive monolithic film layer and a water permeable support layer. The laminate has a moisture permeability of at least about 25 perms as measured by the Water Method and a Hydrostatic Head of at least about 20 cm.
Owner:OMNOVA SOLUTIONS INC
Systems and methods for circulating out a well bore influx in a dual gradient environment
Methods and systems for drilling subsea wells bores with dual-gradient mud systems include drilling the subsea well bore while employing a subsea pumping system, a subsea choke manifold and one or more mud return risers to implement the dual gradient mud system. When a well bore influx is detected, the well bore is shut in, and components determine if pressure control may be used to circulate the influx out of the well bore, the size of the influx, and how much the mud system weight will need to be reduced to match the dual gradient hydrostatic head before the influx reaches the subsea pump take point. The subsea pumping system, subsea choke manifold, and mud risers are isolated while the influx is circulated up one or more fluid passages in the drilling riser package using the surface pump, through the wellhead, and out the surface choke manifold.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
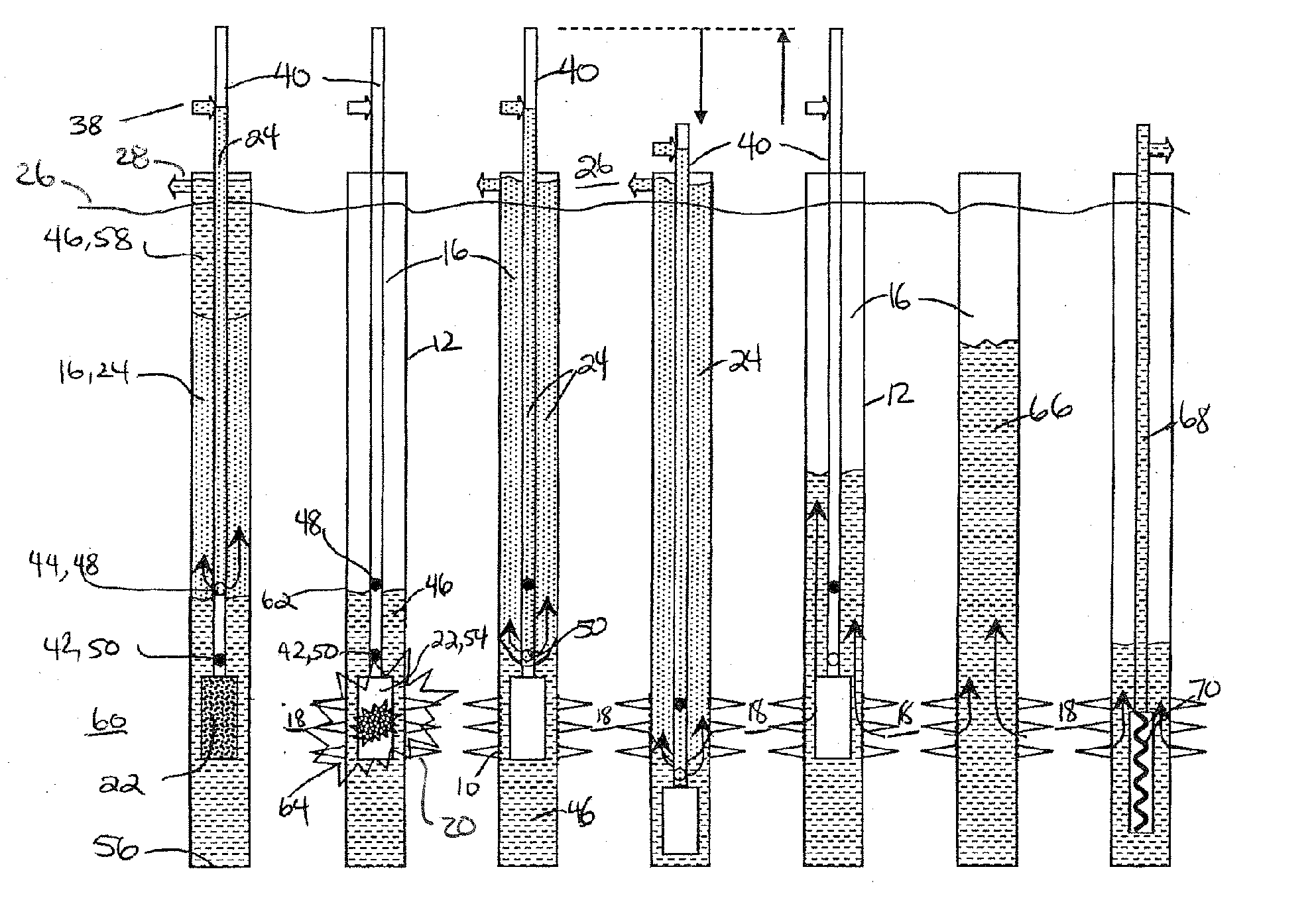
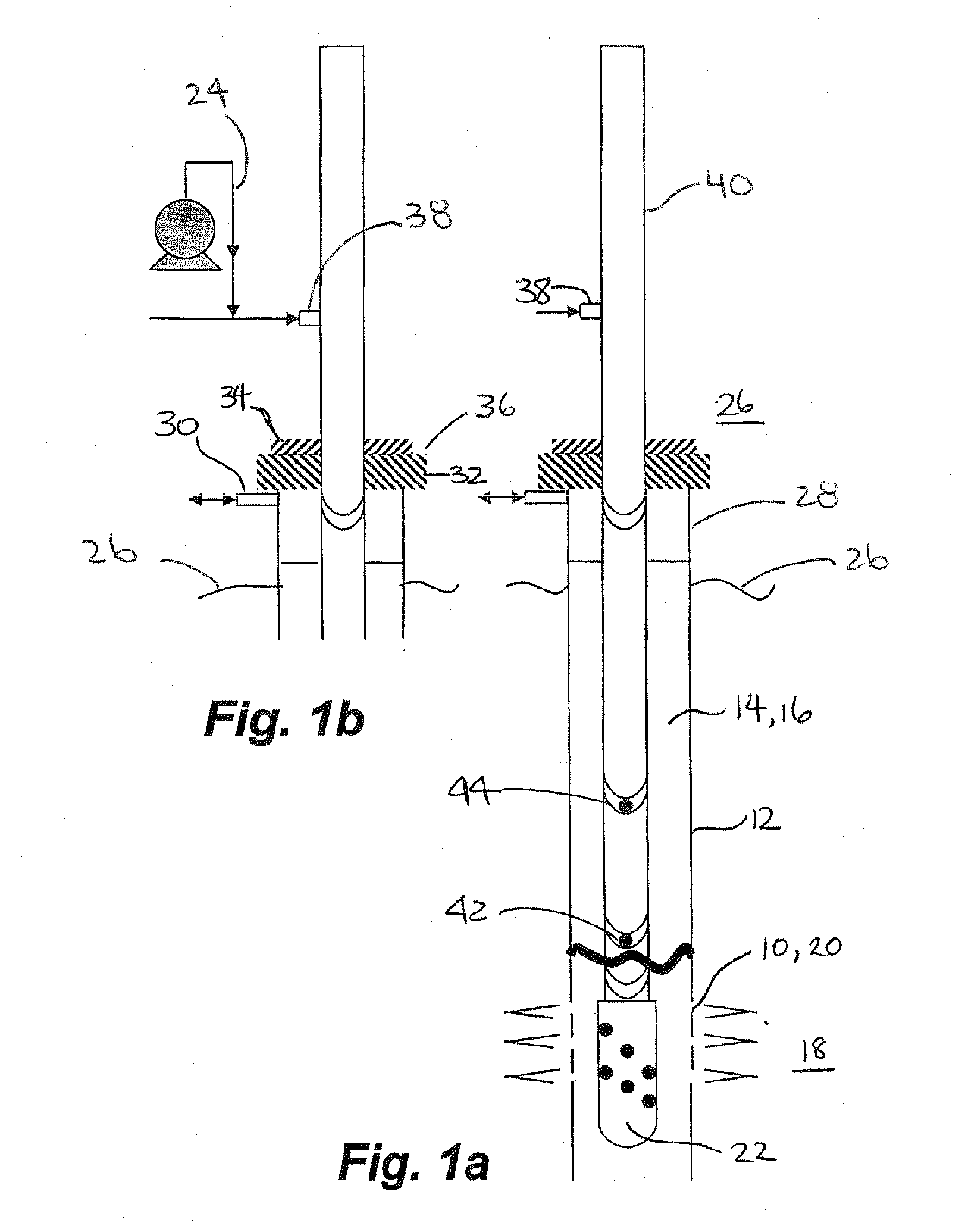
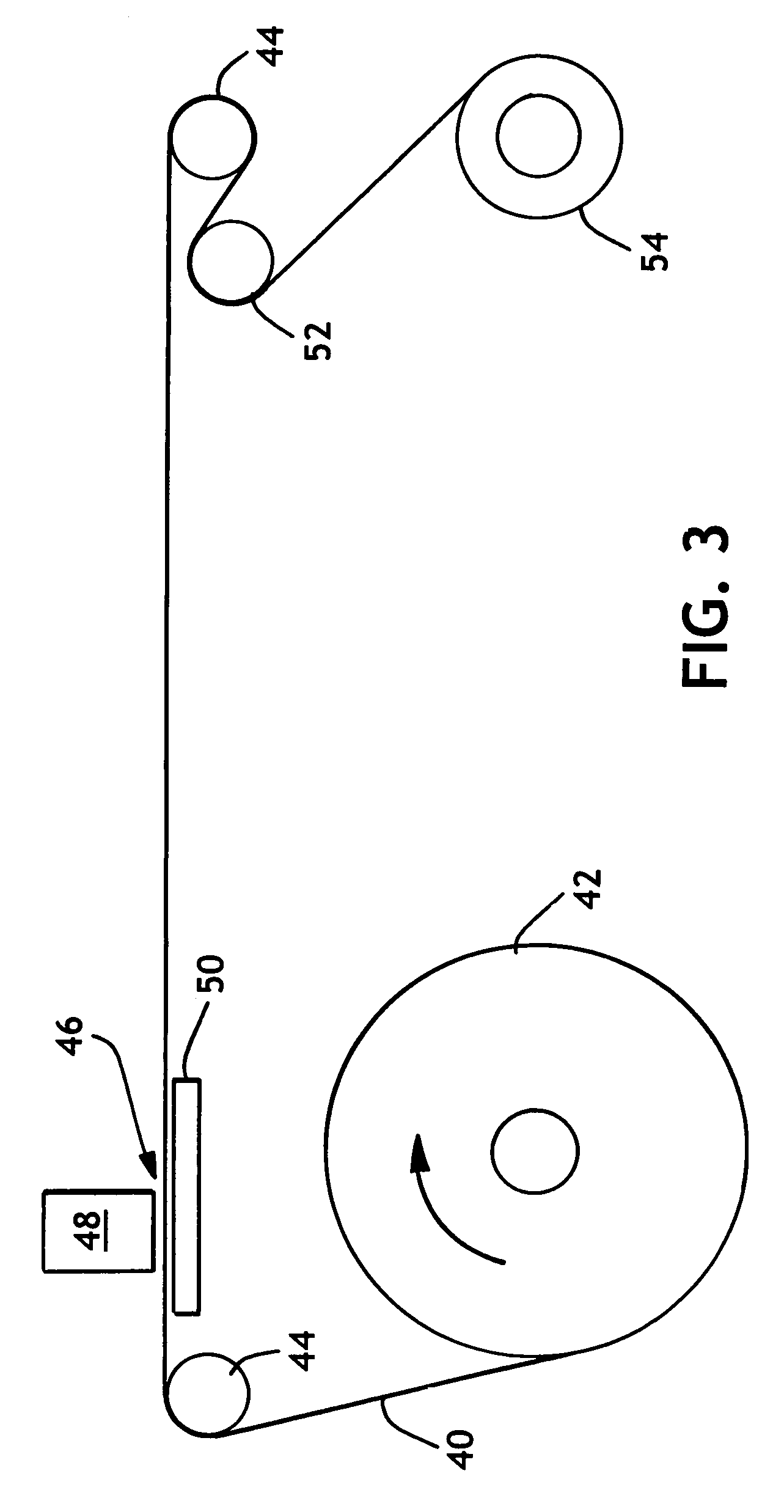
Pressure-actuated perforation with automatic fluid circulation for immediate production and removal of debris
InactiveUS20050217854A1Improve debris removalGood removal effectCleaning apparatusFluid removalInjection portHydrostatic head
Openings are created between a wellbore and a formation by firing a perforating gun adjacent to a zone in the formation and the production fluids are produced along with any formation debris. A tubing string extending to the formation is pressurized to actuate the perforating gun and simultaneously to actuate a downhole injection port. Substantially immediately thereafter fluids are injected into the wellbore near the openings and circulated to the surface for the removal of debris and the production of the formation fluids. An optional and uphole injection port can be used to adjust the hydrostatic head above the perforating gun with the removal or addition of fluid prior to actuation. The tubing string extends sufficiently above the wellbore at surface to enable lowering of the downhole injection port below the openings during fluid circulation for enhanced removal of debris.
Owner:VERTEX RESOURCE GRP LTD +1
Anti-gas lock valve for a reciprocating downhole pump
ActiveUS20150376996A1Increase productionReduce maintenanceFluid parameterConstructionsPump chamberHydrostatic head
Method and apparatus overcoming gas-lock in reciprocating downhole pumps. On the downstroke of a plunger in a barrel, gassy fluid is compressed in the pump chamber between standing and travelling valves. Downhole plunger movement drags a sleeve over a mandrel for opening a chamber valve to a staging chamber located at a downhole end of the travelling valve for receiving at least a portion of the compressed and gassy fluid therein. On the upstroke, the chamber valve is dragged closed for sealably retaining the compressed gassy fluid therein while drawing an additional increment of fluid through the standing valve into the pump chamber. Continued downstroke and upstroke cycles increases pressure of the compressed gassy fluid in the pump chamber until it exceeds the hydrostatic head above the travelling valve for resumption of normal fluid pumping.
Owner:INNOVATIVE OILFIELD CONSULTANTS
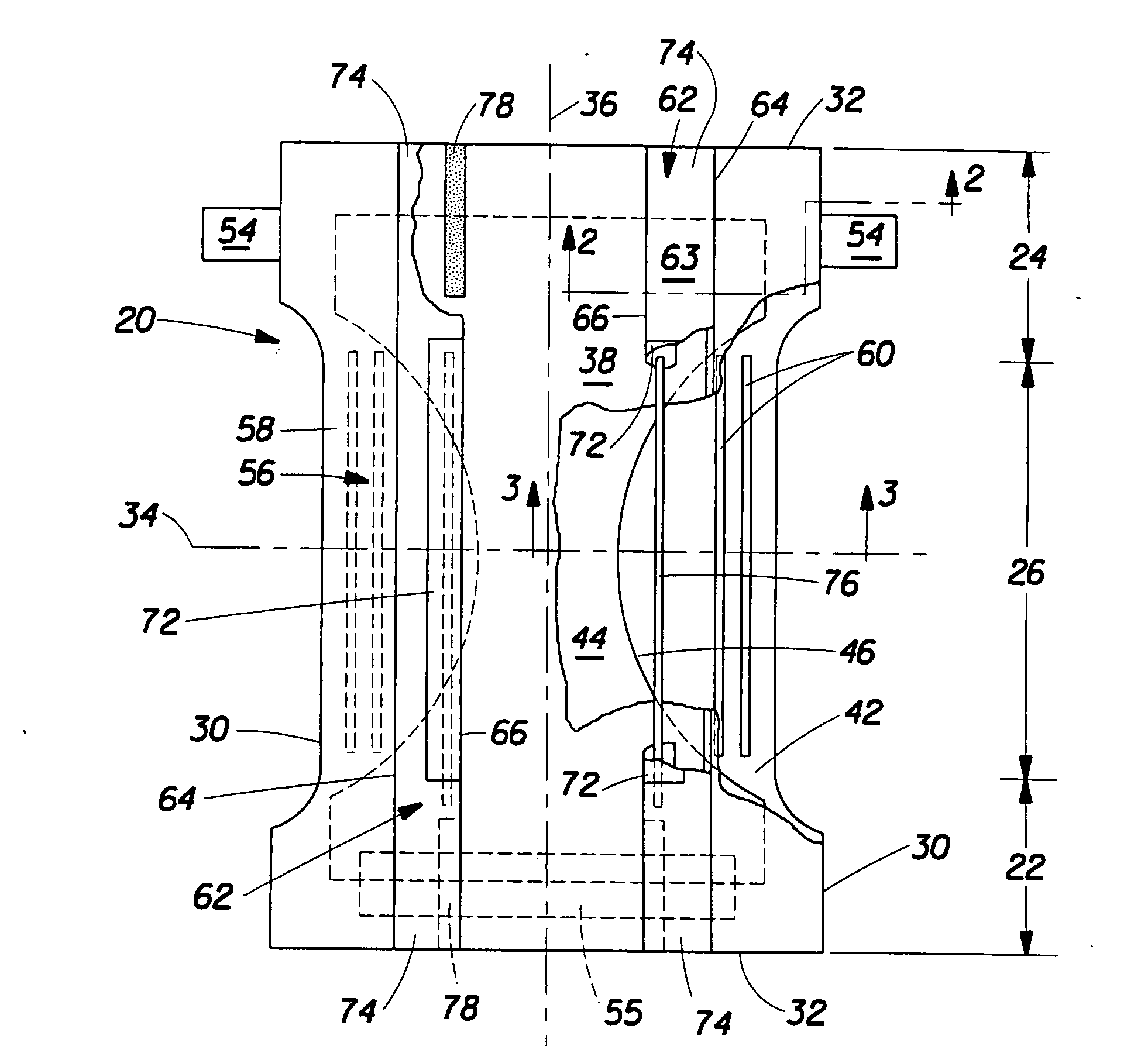
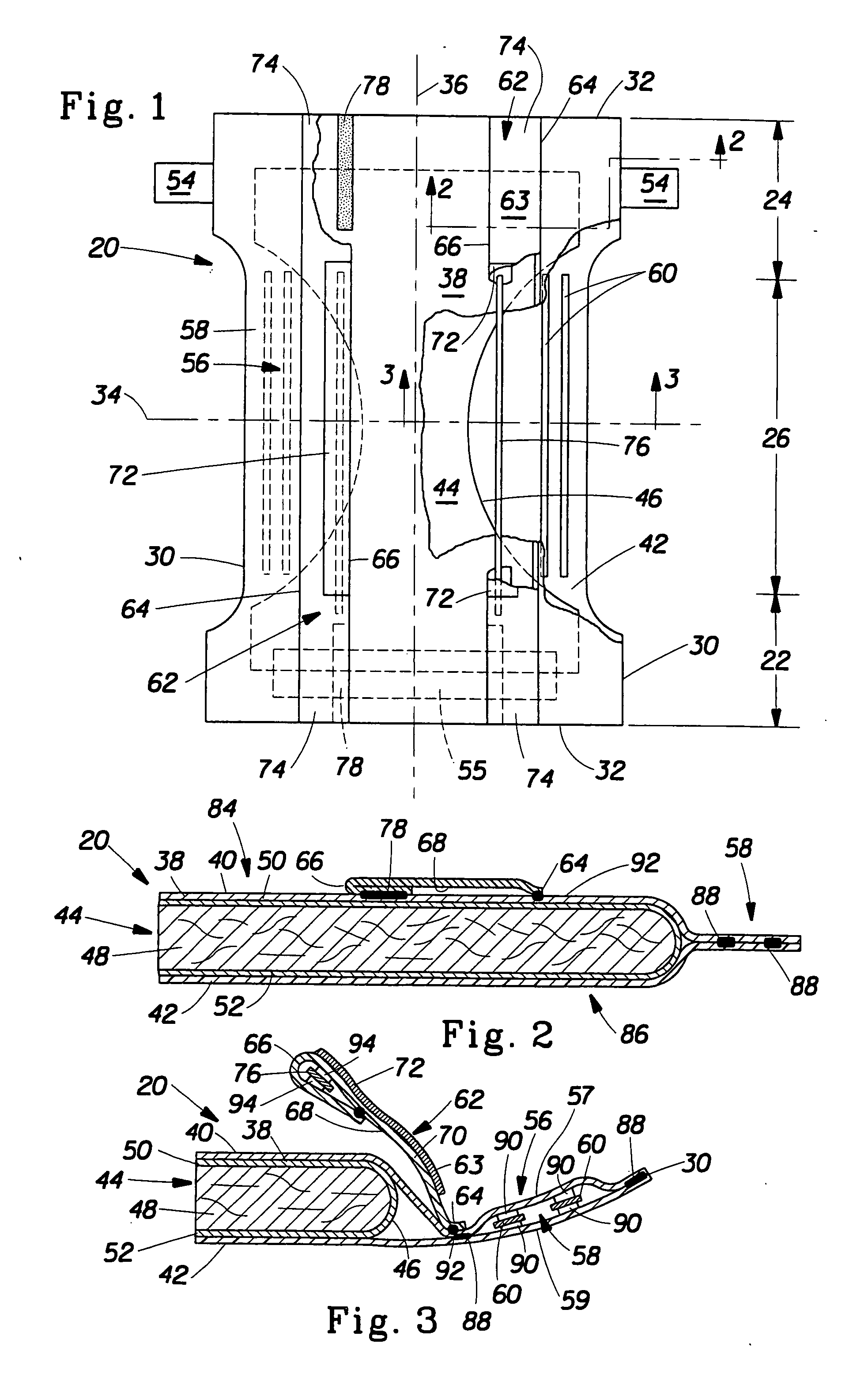
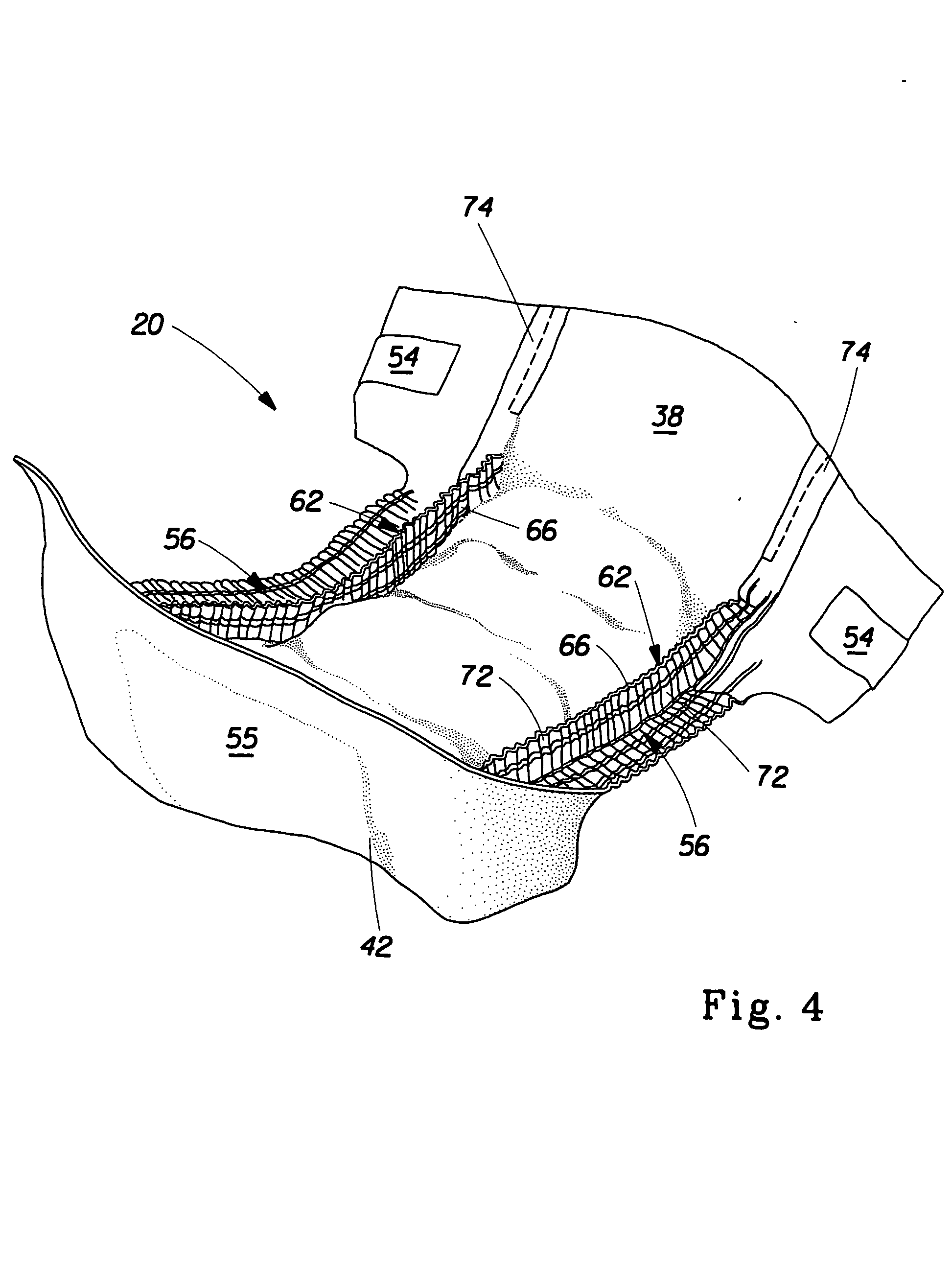
Absorbent article having a multifunctional containment member
An absorbent article such as a diaper, training pant, and the like comprises a containment member that has a central zone and a barrier zone. The central zone has greater air flow according to the Air Permeability Test than the barrier zone. The barrier zone a greater hydrohead according to the Hydrostatic Head Pressure Test than the central zone. The containment member may be used for absorbent core formation and may have portions configured to serve as barrier leg cuffs for the finished absorbent article.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Systems and methods for subsea drilling
ActiveUS8640778B2Improve securityReduce pressure requirementsDrilling rodsDerricks/mastsWell drillingHydrostatic head
A subsea drilling method and system for controlling the drilling fluid pressure, where drilling fluid is pumped down into the borehole through a drill string and returned back through the annulus between the drill string and the well bore. The drilling fluid pressure is controlled by draining drilling fluid out of the drilling riser (8) or BOP (6) at a level between the seabed and the sea water in order to adjust the hydrostatic head of drilling fluid. The drained drilling fluid and gas is separated in a subsea separator (28) where the gas is vented to surface through a vent line (39), and the fluid is pumped to surface via pump (40).
Owner:ENHANCED DRILLING
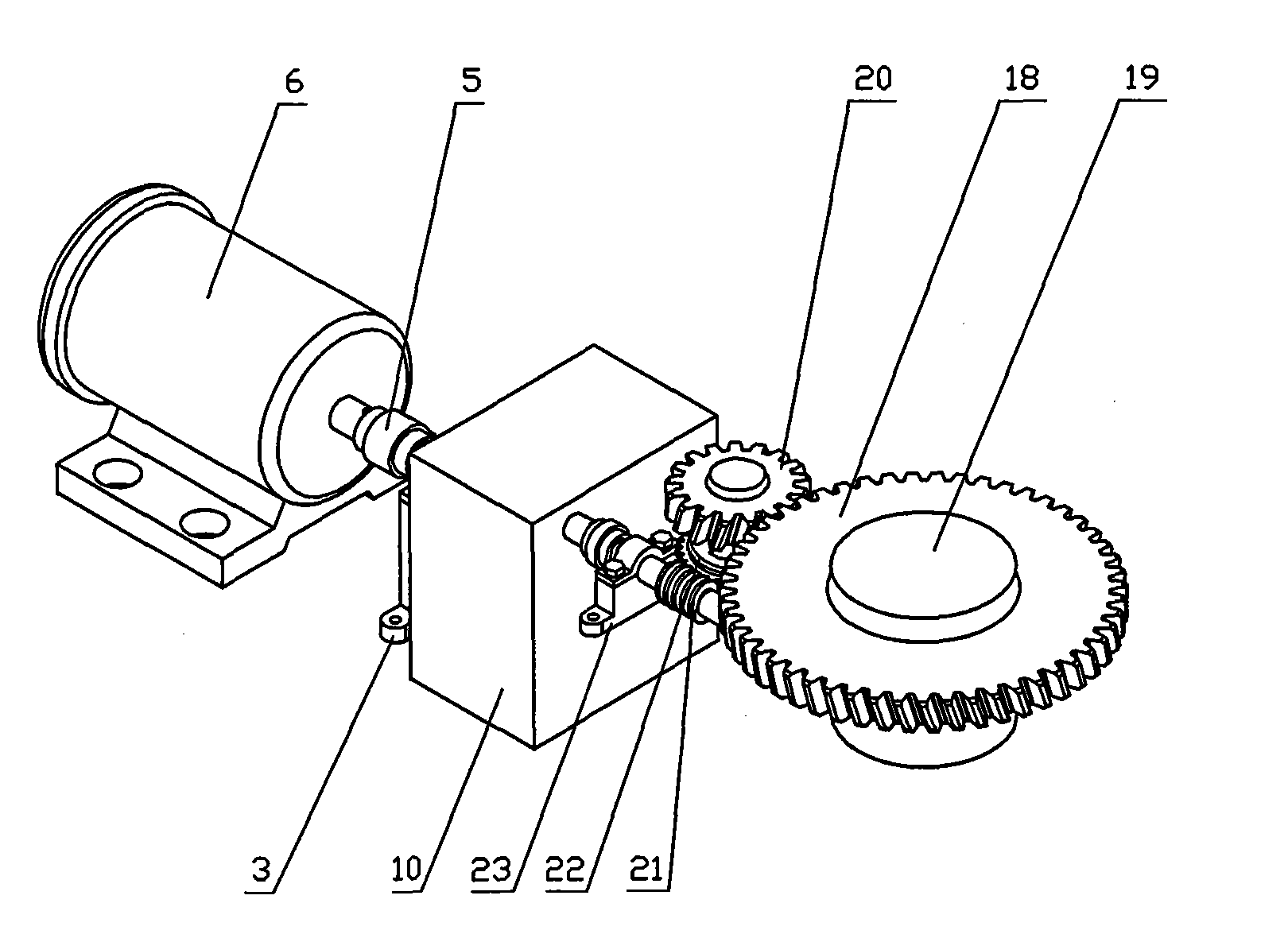
Bidirectional composite deflection tilting gravity casting method and device thereof
InactiveCN101658919AMeet the casting process requirementsImprove casting qualityThree-dimensional spaceHydrostatic head
The invention discloses a bidirectional composite deflection tilting gravity casting method and a device thereof. A casting mold and a pouring cup fixed on the casting mold both controllably perform bidirectional composite three-dimensional space movement of tilting and swinging on a casting machine workbench; the pouring cup rotates towards the above of the casting mold from the position horizontal to the casting mold or the position forming certain tilting angle with the casting mold, and the pouring cup pours metal liquid into the casting mold in the movement process. The invention also provides a device capable of realizing composite three-dimensional space movement of tilting and swinging. The casting method and the casting device of the invention can cause the resultant movement of vertical rotation and horizontal swinging of the casting mold; the height of the metal hydrostatic head gradually increases to adjust casting position, direction and metal liquid casting speed in the pouring process in real time and satisfy the casting technological requirements of complex allotype castings, such as magnesium alloy intake manifolds and the like; in addition, the invention also realizes stable filling, reduces defects of air holes, mixing and poor pouring, improves feeding state and improves the casting quality of complex allotype castings.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Waterborne hydrophobic barrier coatings derived from copolymers of higher vinyl esters
InactiveUS7332450B2Eliminate needSynthetic resin layered productsOrganic dyesParaffin waxHydrostatic head
A blend comprising a paraffin wax emulsion and a polymer emulsion, wherein the polymer contains polymerized units of one or more C1-12 ester of acrylic or methacrylic acid and a vinyl ester of a C8-13 neo-acid. When the blend is applied as a coating to a substrate, such as a nonwoven web, a nonwoven absorbent pad, a nonwoven textile, or a textile fabric, and dried, it has a hydrostatic head barrier sufficient to prevent passage of aqueous fluids but allow passage of water vapor through it. A multi-layer material comprising at least one layer of a nonwoven web, an absorbent pad, or a textile, and at least one layer of the above described blend.
Owner:ASHLAND LICENSING & INTPROP LLC
Absorbent articles having cuffs with skin care composition disposed thereon
InactiveUS20080249491A1Less red markingLess erythemaCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsHydrostatic headSkin protection
An absorbent article, such as a diaper, containing cuffs with a skin care composition disposed thereon. In one embodiment the cuff is a nonwoven leg cuff comprising spunbonded nonwoven material and characterized by the lack of a meltblown component, the nonwoven material having a basis weight of about 17 gsm and a hydrostatic head of at least about 95 mm. The spunbonded material comprises metallocene polypropylene fibers having a denier of less than about 1.3. In another embodiment, small amounts of meltblown fibers, for example, up to about 10% by weight, can be added to the metallocene polypropylene spunbonded material to increase production rates of the nonwoven material, without an unacceptable decrease in skin health benefits. The skin care composition disposed on the cuffs is transferable to the wearer's skin by normal contact and / or wearer motion and / or body heat. The skin care compositions disclosed in the present invention are selected to maintain and / or improve the skin health of the wearer upon transfer during use, for example, to provide a skin protective barrier or a therapeutic benefit; to minimize the abrasion between the cuffs and skin in the area where the cuffs contact the wearer's skin, resulting in less skin irritation; to improve BM clean up on the skin, or to improve the barrier properties of the cuffs.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
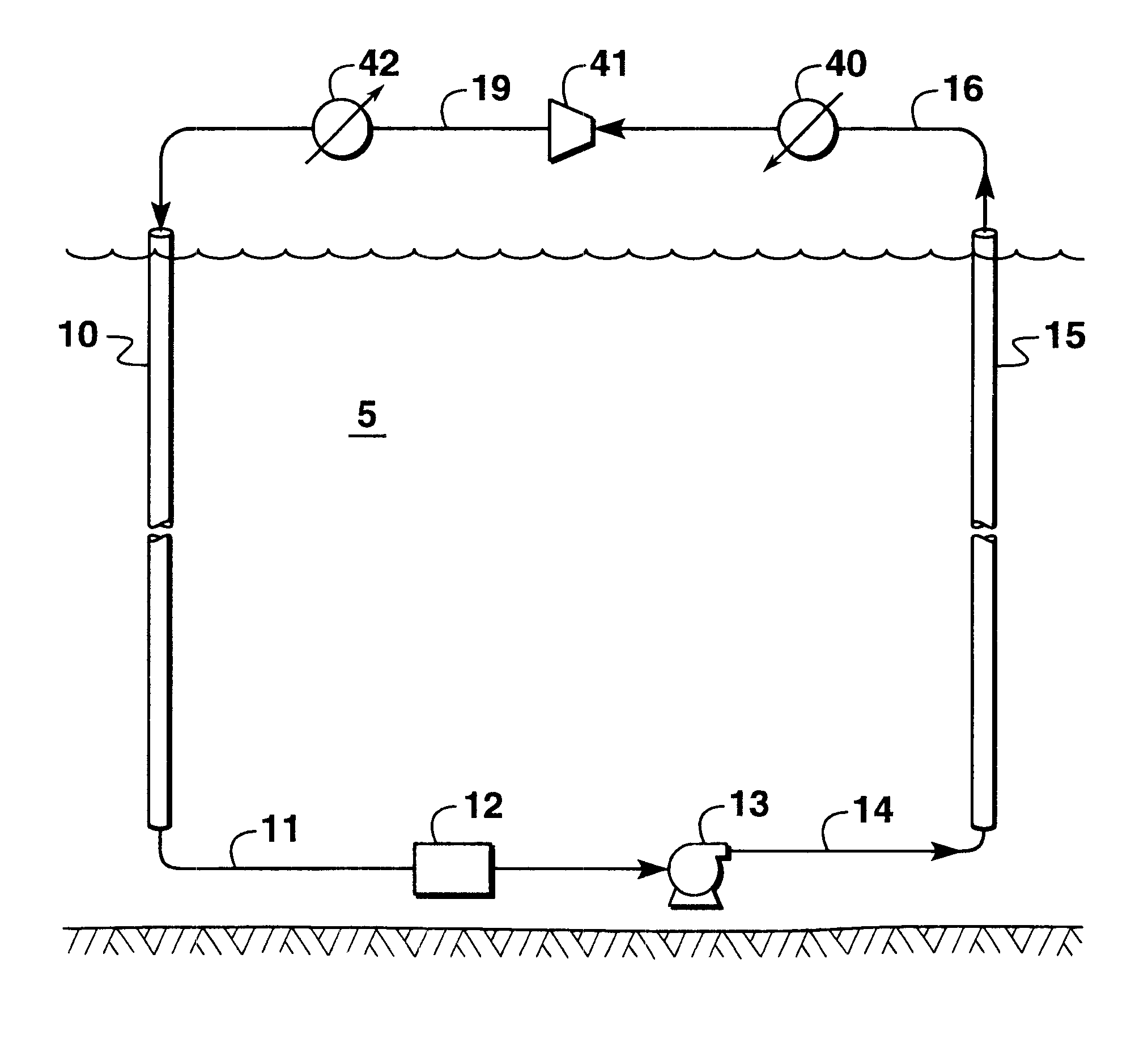
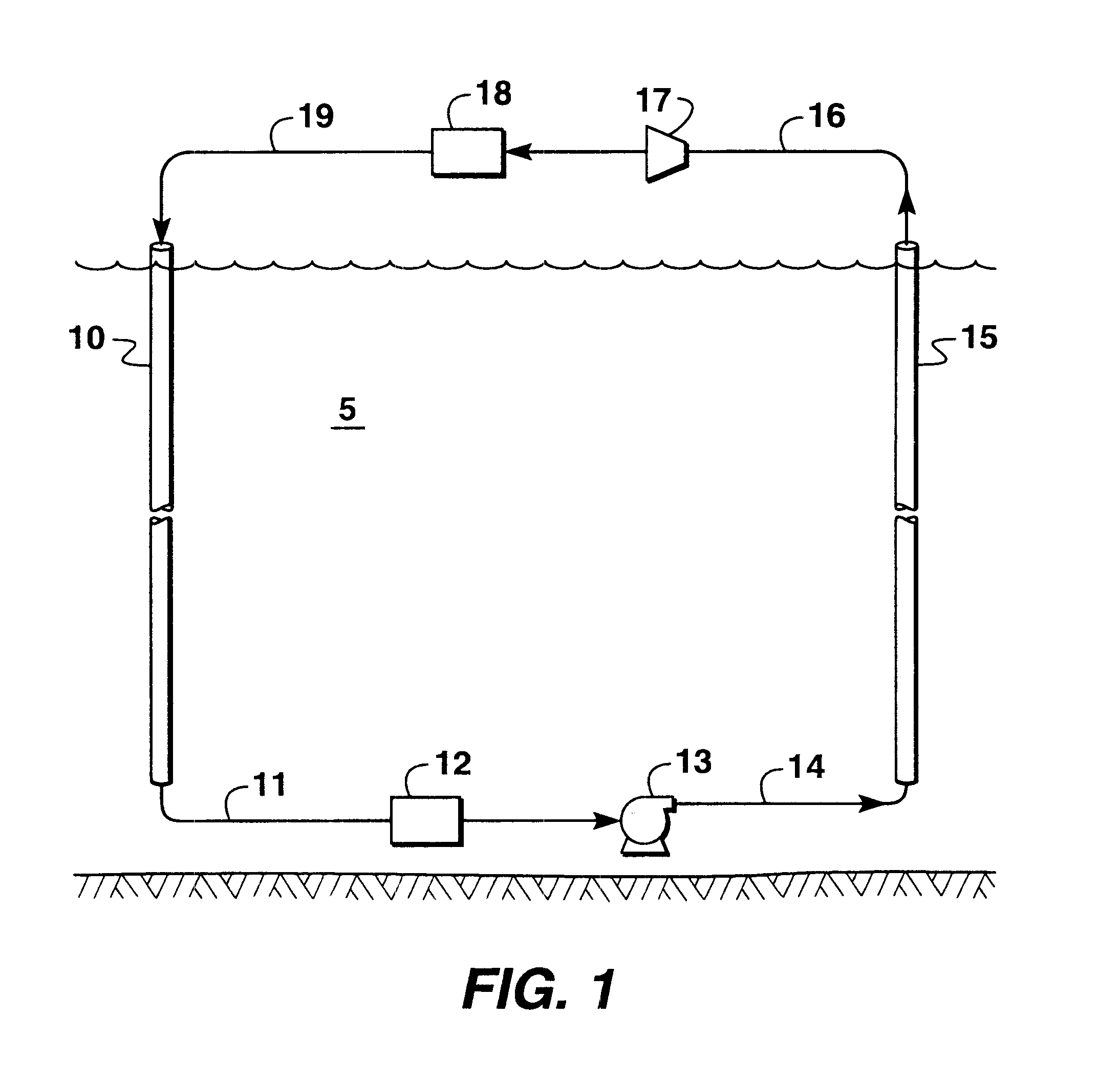
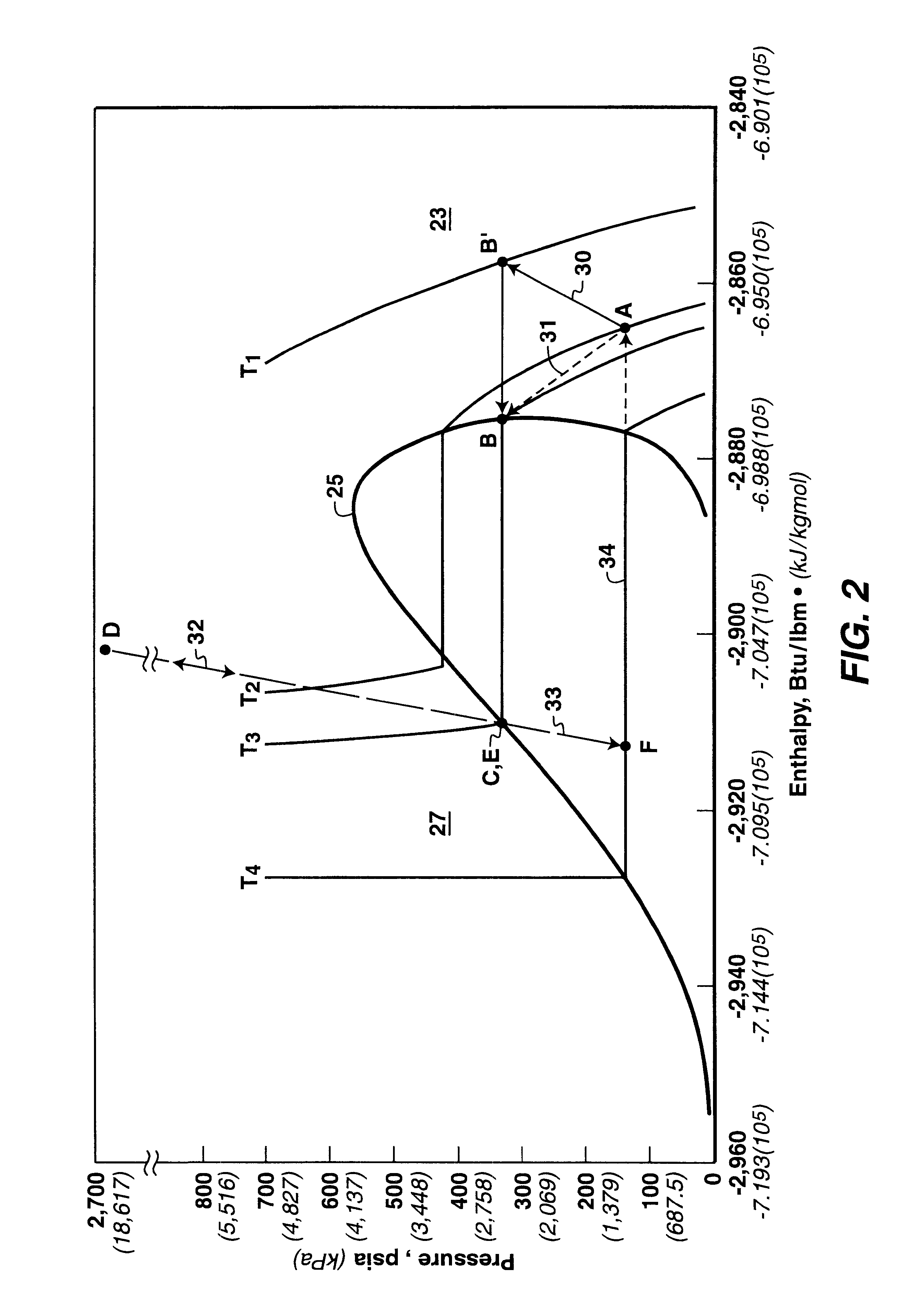
Thermodynamic cycle using hydrostatic head for compression
InactiveUS6494251B2Low costEliminate needDomestic cooling apparatusOther heat production devicesHydrostatic headRefrigeration
A thermodynamic cycle is disclosed that uses compression and expansion to generate refrigeration or power in which at least some of the compression is effected by hydrostatic head of the heat-exchange medium used in the cycle. In a refrigeration cycle, the head of a heat-exchange medium in the refrigeration cycle is used to compress the heat-exchange medium. A vaporous heat-exchange medium is introduced into the upper end of a down riser that extends downwardly through a heat sink. The vaporous heat-exchange medium descends through the down riser and the head of the heat-exchange medium compresses the heat-exchange medium. The heat generated by the compression is transferred to the heat sink. The heat-exchange medium is then pumped up through a return riser and passed through a pressure expansion means and evaporator. From the evaporator the heat-exchange medium is returned to the upper end of the down riser for recycling.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method of treating substrates with ionic fluoropolymers
ActiveUS20050112969A1Minimize impactImproving the alcohol repellency of a nonwoven substrateDiagnosticsFibre treatmentAntistatic agentAlcohol
The present invention provides a method of treating a substrate to improve the alcohol repellency of the substrate while minimizing the effect on the hydrostatic head value of the substrate that includes contacting a substrate with a treatment solution that includes an ionic fluoropolymer, a monovalent salt, and essentially no antistatic agent or less than 0.05 weight percent by weight of an antistatic agent.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Waterborne hydrophobic barrier coatings
A waterborne hydrophobic barrier coating formulation comprising a blend of a vinyl acetate-ethylene (VAE) polymer emulsion and a paraffin wax emulsion, wherein a dried coating of the blend on a substrate, such as a nonwoven web, an absorbent pad, or a textile, and dried, has a hydrostatic head barrier sufficient to prevent passage of fluids but allow passage of water vapor through it. A multi-layer material comprising at least one layer of a nonwoven web, an absorbent pad, or a textile, and at least one layer of a blend of a VAE polymer emulsion and paraffin wax emulsion.
Owner:WACKER CHEM CORP
Solution distribution arrangement for a cleaning machine
Owner:HEALTHY GAIN INVESTMENTS
Liquid water resistant and water vapor permeable garments comprising hydrophobic treated nonwoven made from nanofibers
A water resistant garment is disclosed having regions of high MVTR while maintaining water resistance. The garment has a fabric layer adjacent one major surface of a nanofiber layer. The surface of the nanofibers are coated with a coating containing a fluorocarbon polymeric moiety and a resin binder or extender which is soluble in water and / or other solvents. The coated nanofiber layer has a contact angle of greater than 145 DEG . The garment optionally includes a second fabric layer adjacent the other major surface of the nanofiber layer. The garment has regions having a Frazier air permeability of between about 0.5 m<3> / min / m<2 >and about 8 m<3> / min / m<2>, an MVTR of greater than about 500 g / m<2> / day and a hydrostatic head of at least about 50 cmwc.
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Method of treating substrates with ionic fluoropolymers
ActiveUS7931944B2Improving the alcohol repellency of a nonwoven substrateDecrease in levelDiagnosticsFibre treatmentAlcoholAntistatic agent
The present invention provides a method of treating a substrate to improve the alcohol repellency of the substrate while minimizing the effect on the hydrostatic head value of the substrate that includes contacting a substrate with a treatment solution that includes an ionic fluoropolymer, a monovalent salt, and essentially no antistatic agent or less than 0.05 weight percent by weight of an antistatic agent.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Pressure-actuated perforation with automatic fluid circulation for immediate production and removal of debris
Openings are created between a wellbore and a formation by firing a perforating gun adjacent to a zone in the formation and the production fluids are produced along with any formation debris. A tubing string extending to the formation is pressurized to actuate the perforating gun and simultaneously to actuate a downhole injection port. Substantially immediately thereafter fluids are injected into the wellbore near the openings and circulated to the surface for the removal of debris and the production of the formation fluids. An optional and uphole injection port can be used to adjust the hydrostatic head above the perforating gun with the removal or addition of fluid prior to actuation. The tubing string extends sufficiently above the wellbore at surface to enable lowering of the downhole injection port below the openings during fluid circulation for enhanced removal of debris.
Owner:VERTEX RESOURCE GRP LTD +1
Bulk material cargo container liner with internal restraint system for preventing the outward bulging of the liner
ActiveUS20050052047A1Simple structureEconomically viable to constructLarge containersMonocoque constructionsBulk cargoHydrostatic head
A bulk container liner assembly for use in conjunction with a bulk material cargo container comprises structure incorporated therein such that restraint forces are impressed upon or transmitted to the back or rear wall member of the bulk material cargo container liner, along linearly seamed loci, so as to effectively prevent the back or rear wall member of the bulk material cargo container liner from experiencing or undergoing any outward bulging thereof under the influence of the hydrostatic head load forces generated internally within the bulk material cargo container liner as a result of the charging of bulk cargo material into the interior portion of the bulk material cargo container liner.
Owner:SIGNODE IND GRP
Pressure-actuated perforation with continuous removal of debris
ActiveUS20050217853A1Improve debris removalGood removal effectCleaning apparatusFluid removalInjection portHydrostatic head
Openings are created between a wellbore and a formation by firing a perforating gun adjacent a perforating zone in the formation and debris is removed. A tubing string extending to the formation is pressurized to a first pressure to actuate the perforating gun. A second higher pressure is applied to activate a downhole injection port. Substantially immediately thereafter fluids are injected into the wellbore near the openings and circulated to the surface for the removal of debris. An optional and uphole injection port can be used to adjust the hydrostatic head above the perforating gun with the removal or addition of fluid. The tubing string extends sufficiently above the wellbore at surface to enable lowering of the downhole injection port below the openings during fluid circulation for enhanced removal of debris.
Owner:HURRICANE IND CORP +1
Waterborne hydrophobic barrier coatings
InactiveUS20060122313A1Eliminate needWax coatingsSynthetic resin layered productsParaffin waxWater vapor
A waterborne hydrophobic barrier coating formulation comprising a blend of a vinyl acetate-ethylene (VAE) polymer emulsion and a paraffin wax emulsion, wherein a dried coating of the blend on a substrate, such as a nonwoven web, an absorbent pad, or a textile, and dried, has a hydrostatic head barrier sufficient to prevent passage of fluids but allow passage of water vapor through it. A multi-layer material comprising at least one layer of a nonwoven web, an absorbent pad, or a textile, and at least one layer of a blend of a VAE polymer emulsion and paraffin wax emulsion.
Owner:WACKER CHEM CORP
Bulk material cargo container liner with internal restraint system for preventing the outward bulging of the liner
InactiveUS20070024078A1Prevent movementEffective maintenanceLarge containersMonocoque constructionsBulk cargoHydrostatic head
A bulk container liner assembly for use in conjunction with a bulk material cargo container comprises structure incorporated therein such that restraint forces are impressed upon or transmitted to the back or rear wall member of the bulk material cargo container liner, along linearly seamed loci, so as to effectively prevent the back or rear wall member of the bulk material cargo container liner from experiencing or undergoing any outward bulging thereof under the influence of the hydrostatic head load forces generated internally within the bulk material cargo container liner as a result of the charging of bulk cargo material into the interior portion of the bulk material cargo container liner.
Owner:MINO OSWALDO +3
Solution distribution arrangement for a cleaning machine
A portable cleaning apparatus for cleaning a surface is provided and includes a housing. A distributor is operatively connected to the housing for distributing solution to the surface. A first solution container is mounted to the housing and contains a first solution. The first solution container has a bottom portion with an outlet portion fluidly connected to the distributor for supplying a flow of a first solution to the distributor. A second solution container with an outlet is provided in the first solution container and contains a second solution. The outlet of the second solution container is fluidly connected to the distributor for supplying a flow of a second solution to the distributor. In at least one aspect of the invention, the second solution container is design and constructed to transfer the weight of the first solution above the second solution container to the second solution in the second solution container to produce substantially the same hydrostatic head at both the outlet of the first solution container and the outlet of the second solution container.
Owner:HEALTHY GAIN INVESTMENTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com