Patents
Literature
668 results about "Subsea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
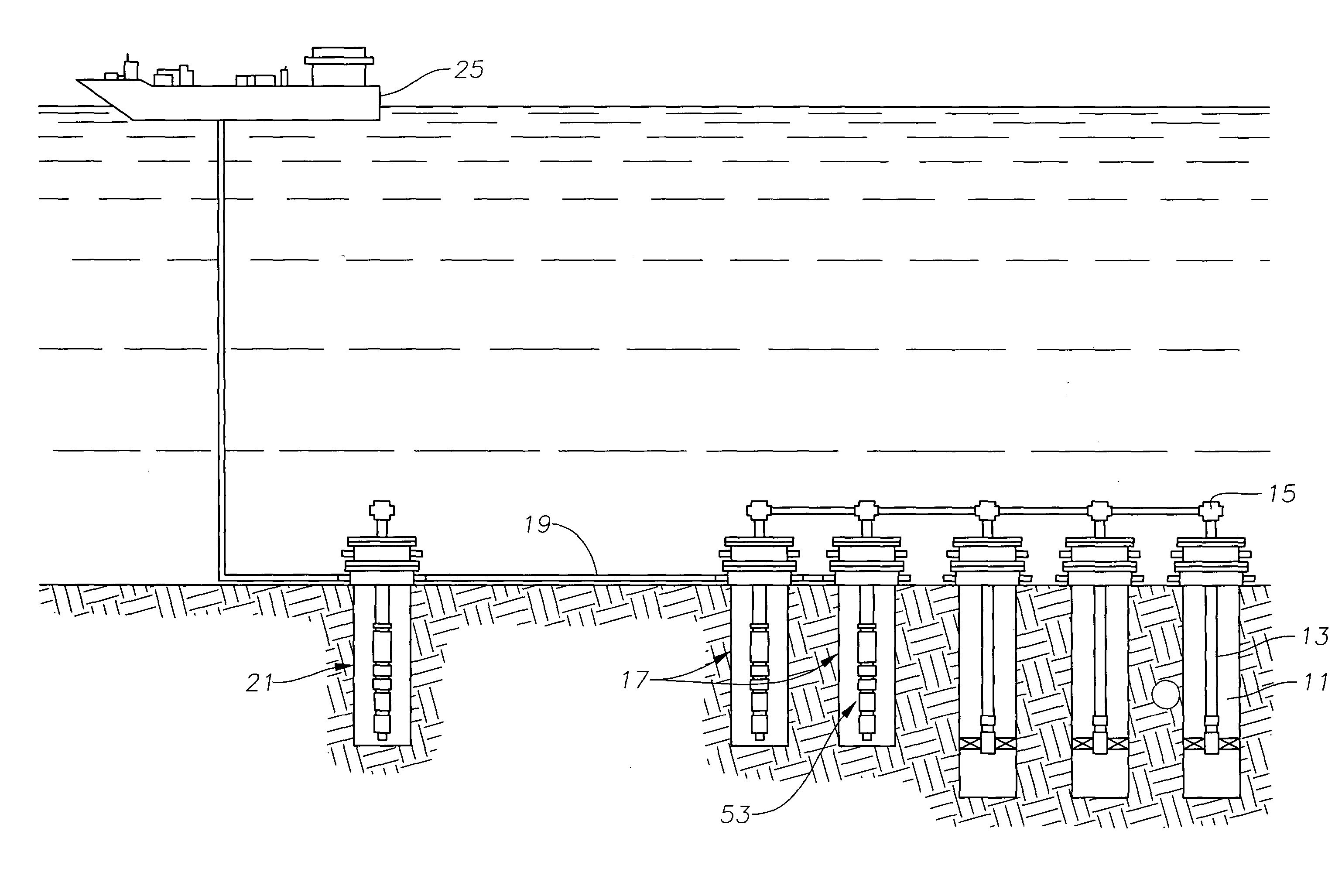
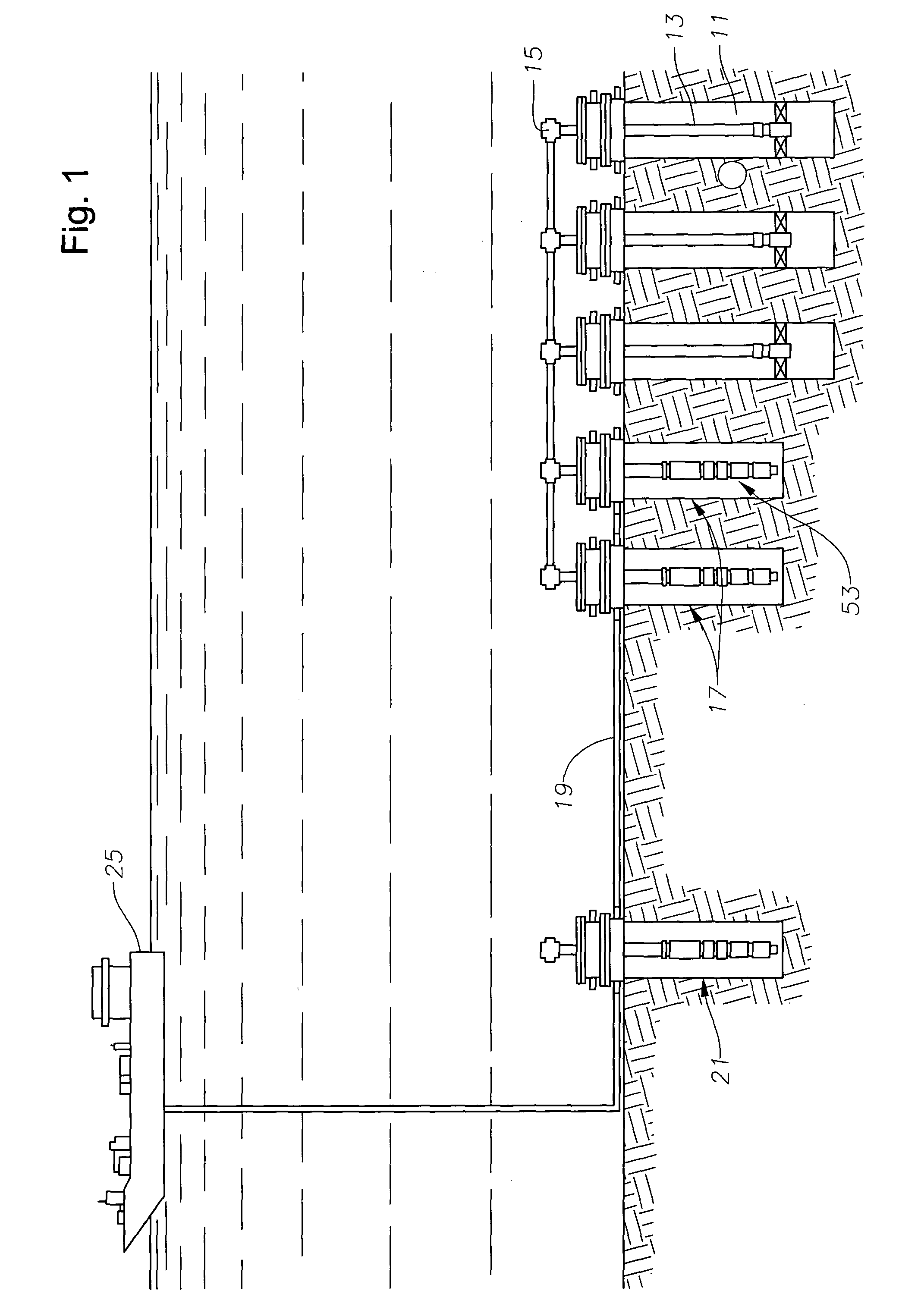
Subsea is fully submerged ocean equipment, operations or applications, especially when some distance offshore, in deep ocean waters, or on the seabed. The term is frequently used in connection with oceanography, marine or ocean engineering, ocean exploration, remotely operated vehicle (ROVs) autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), submarine communications or power cables, seafloor mineral mining, oil and gas, and offshore wind power.
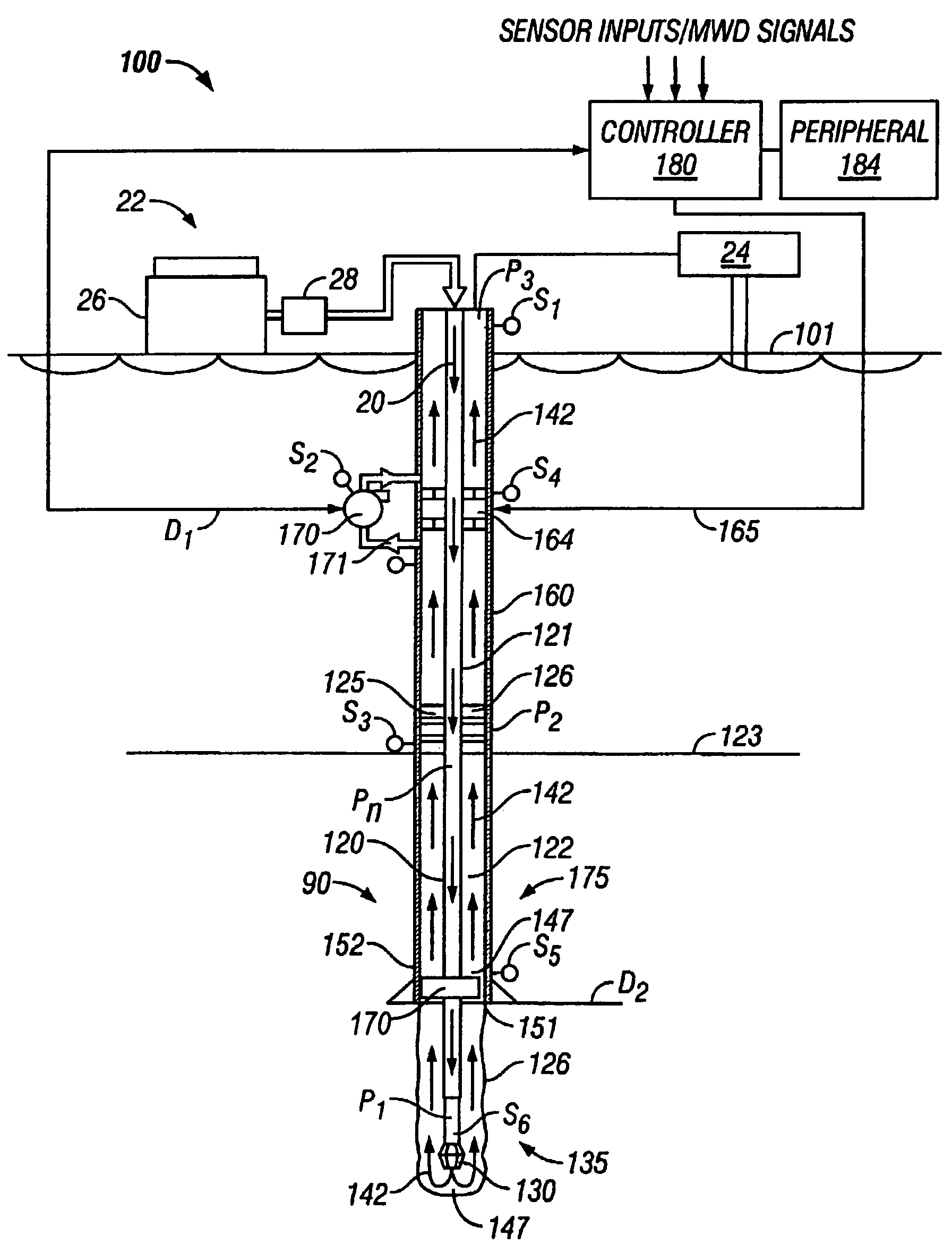
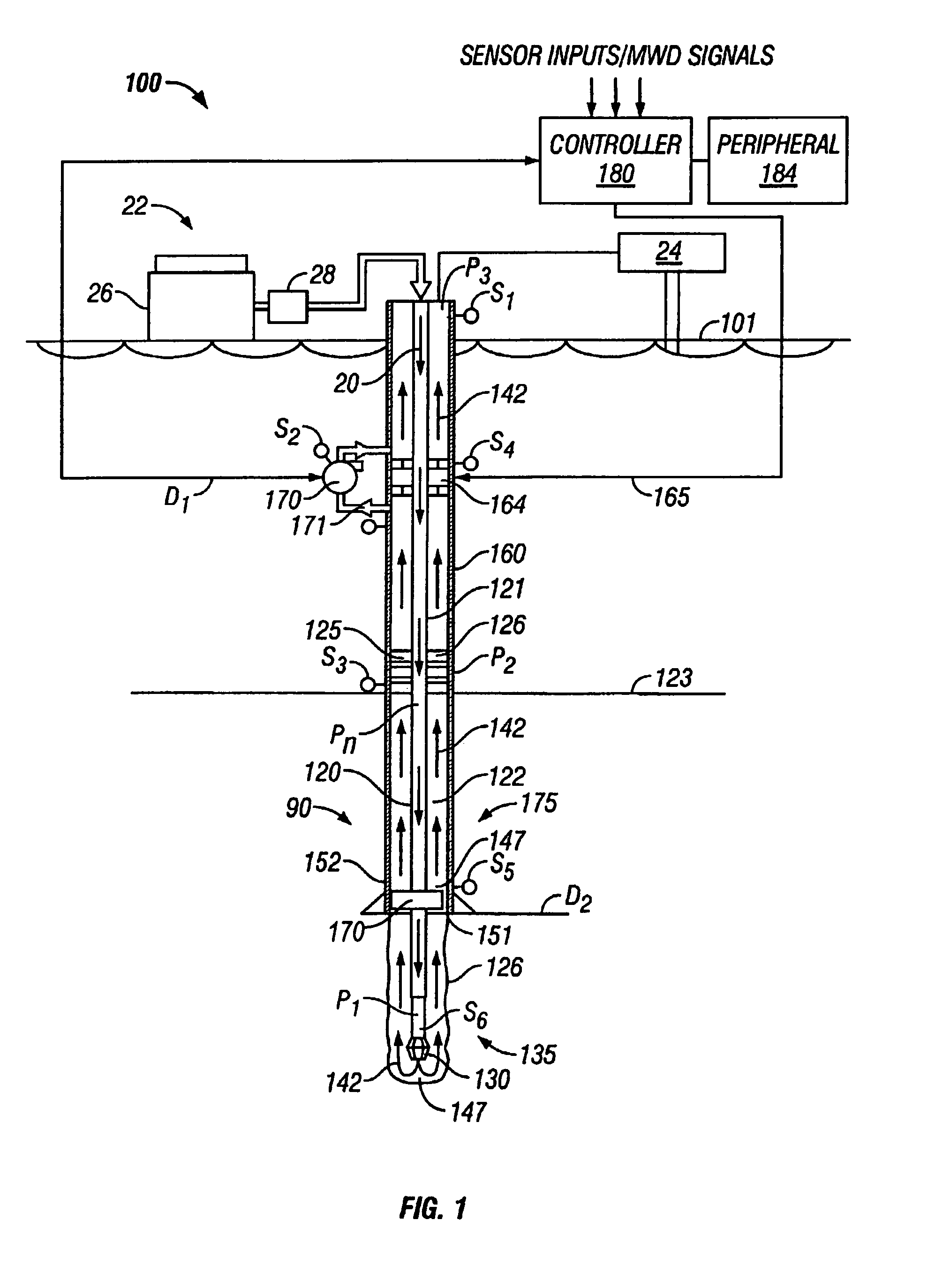
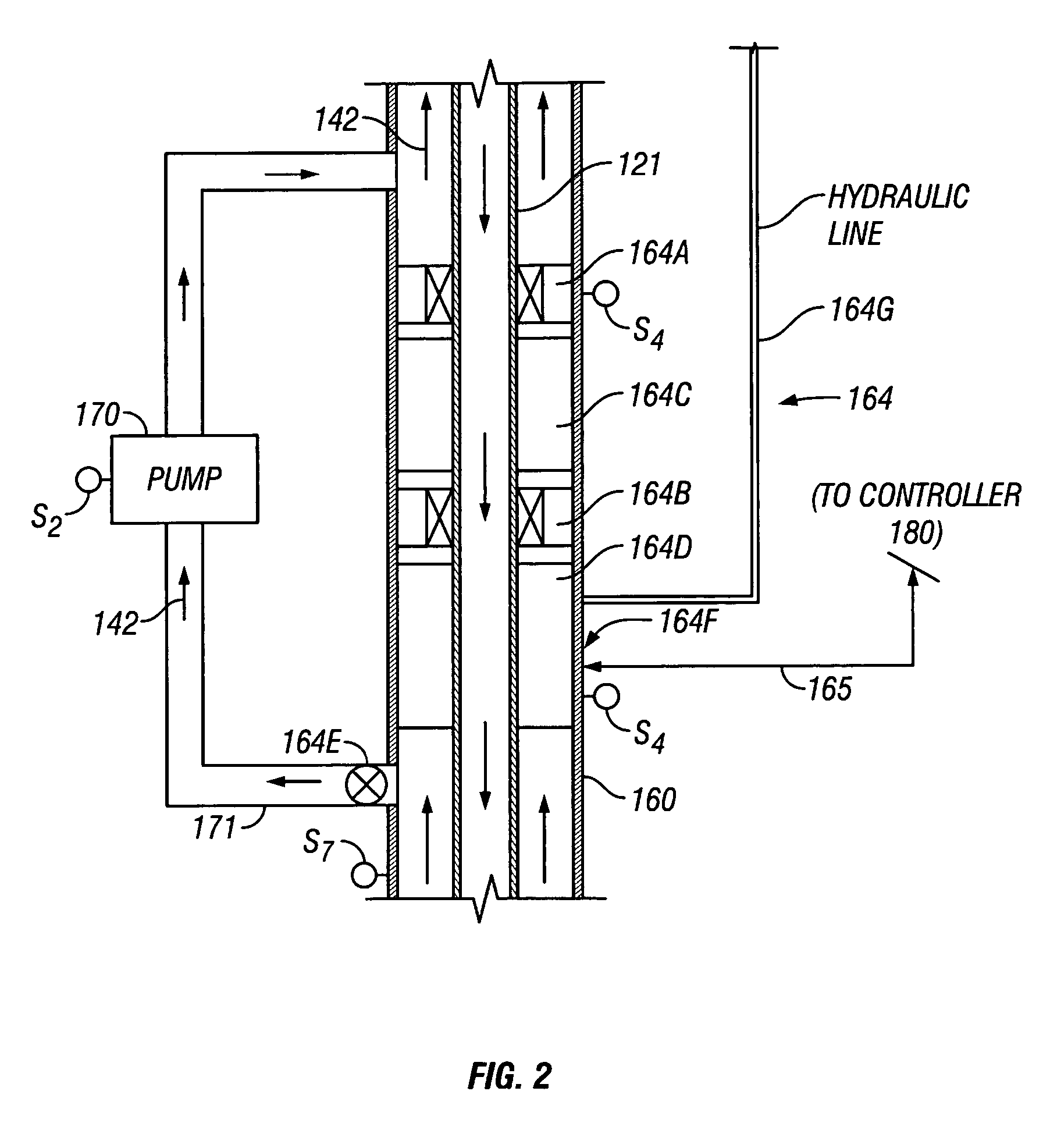
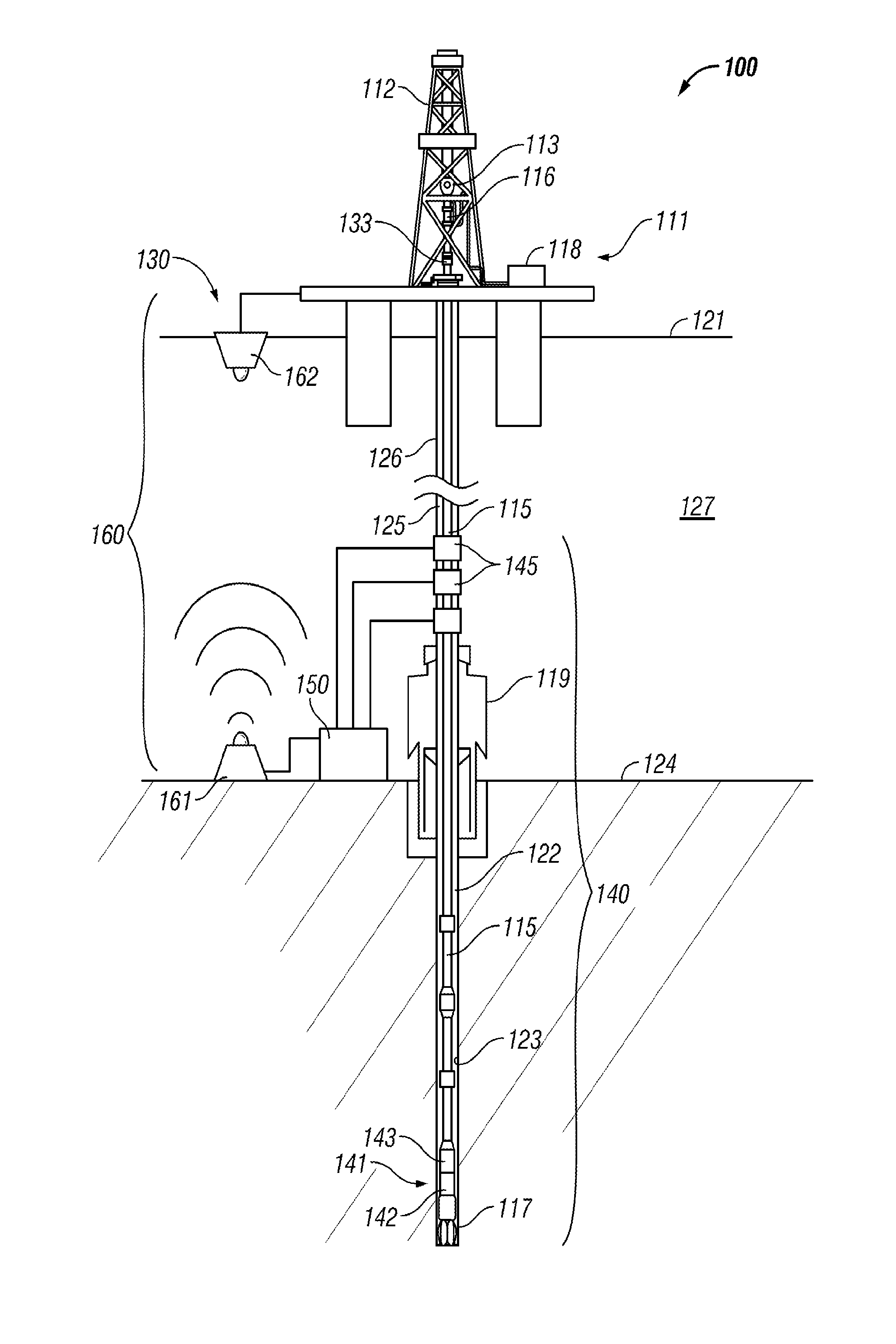
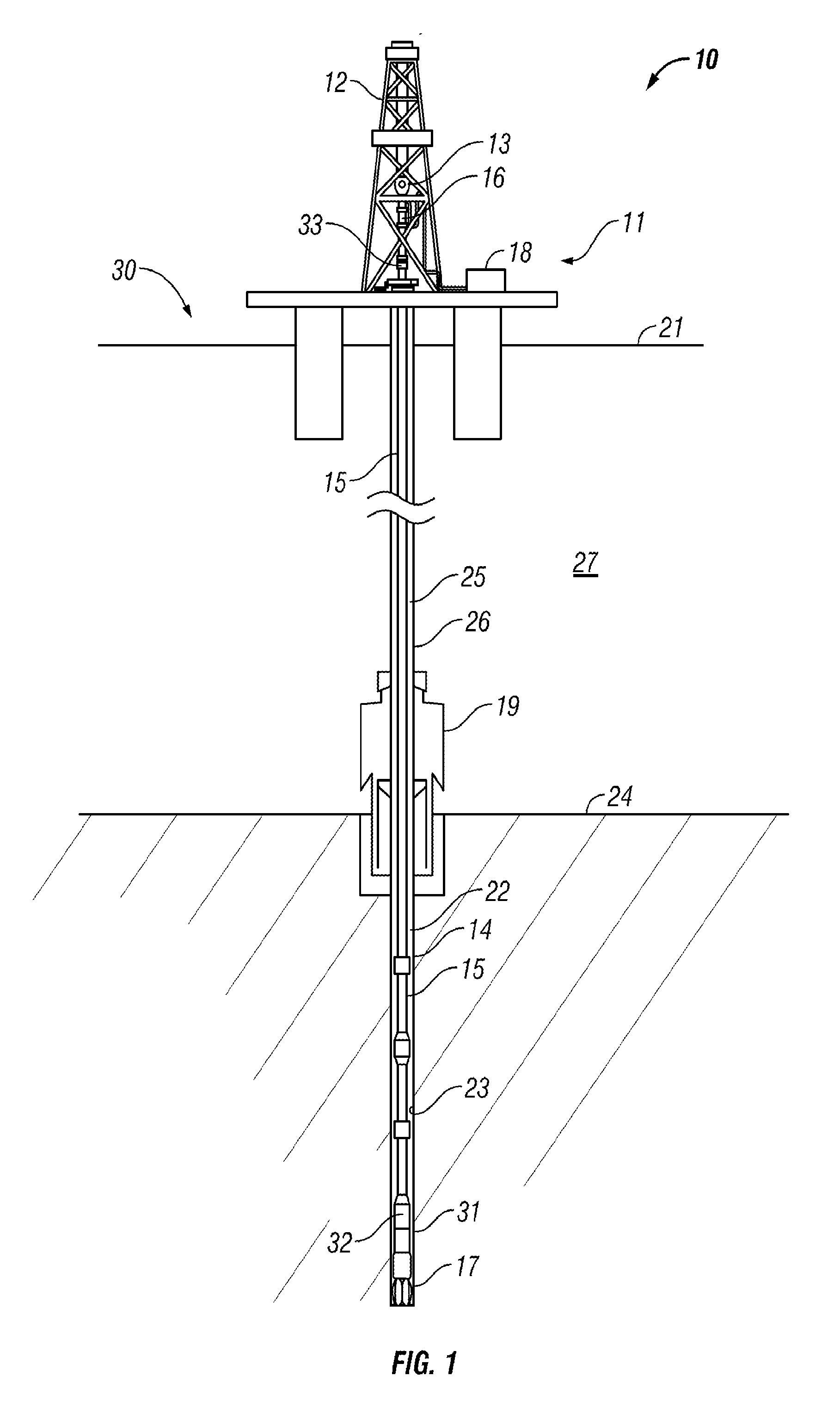
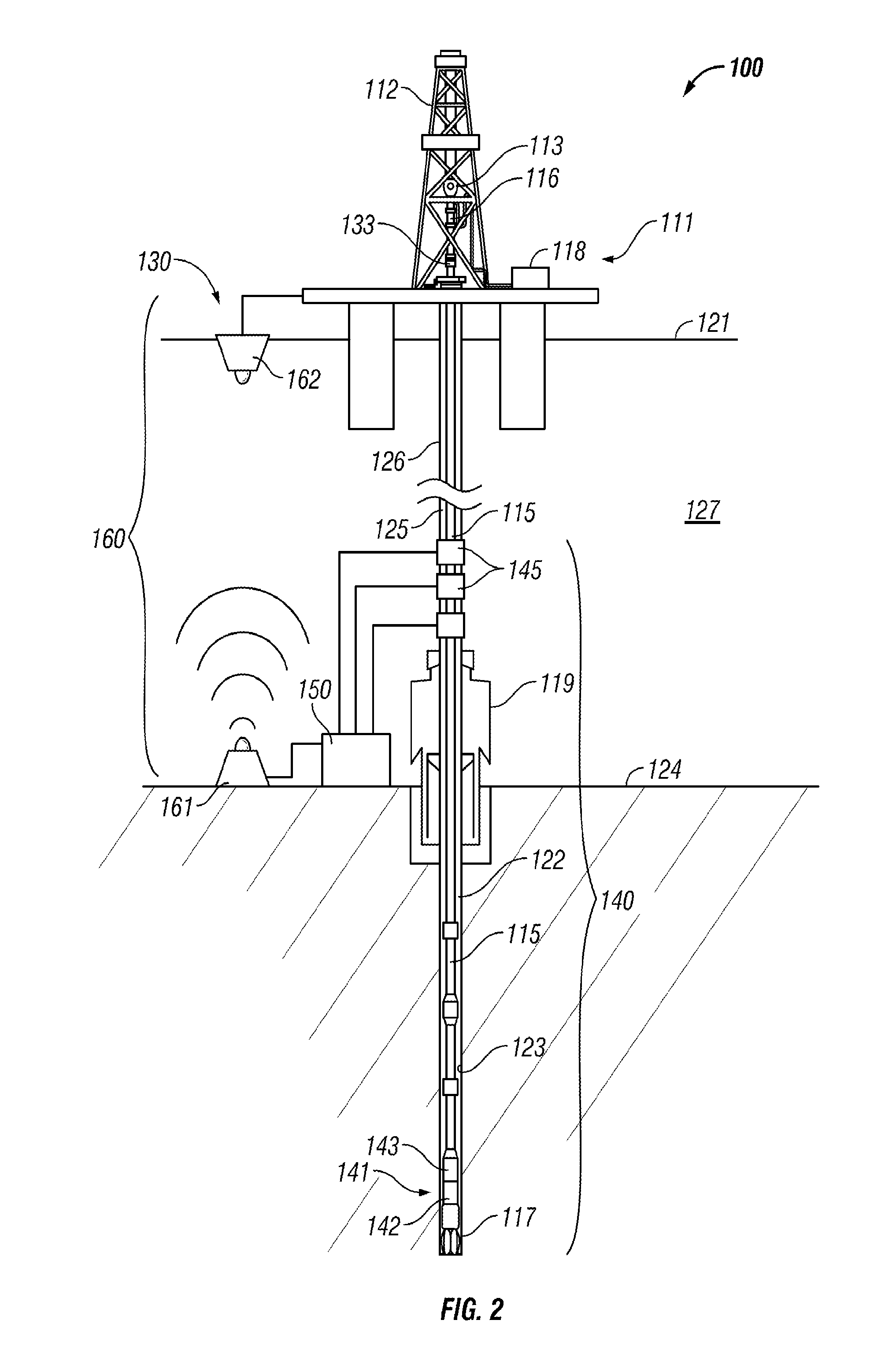
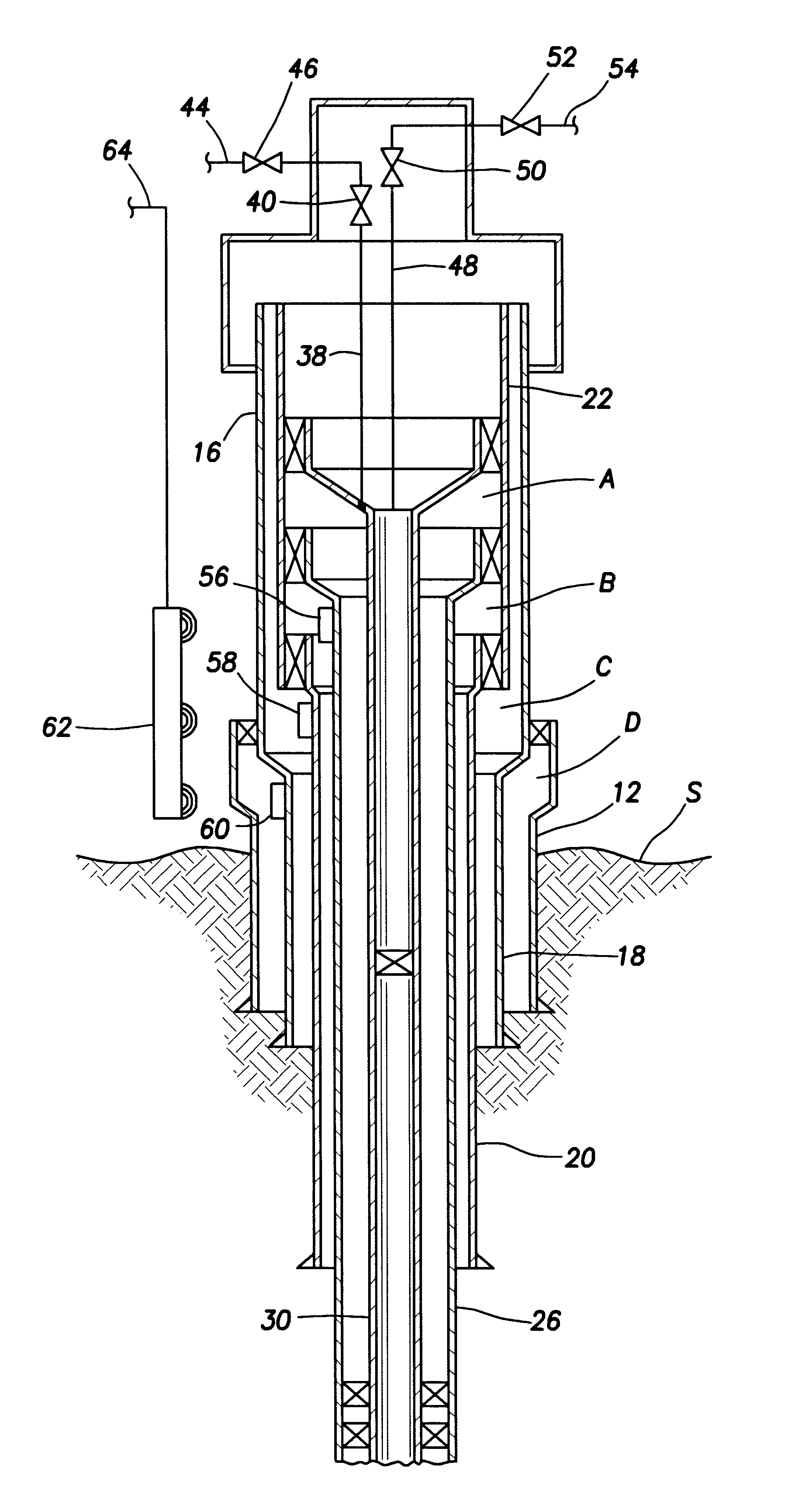
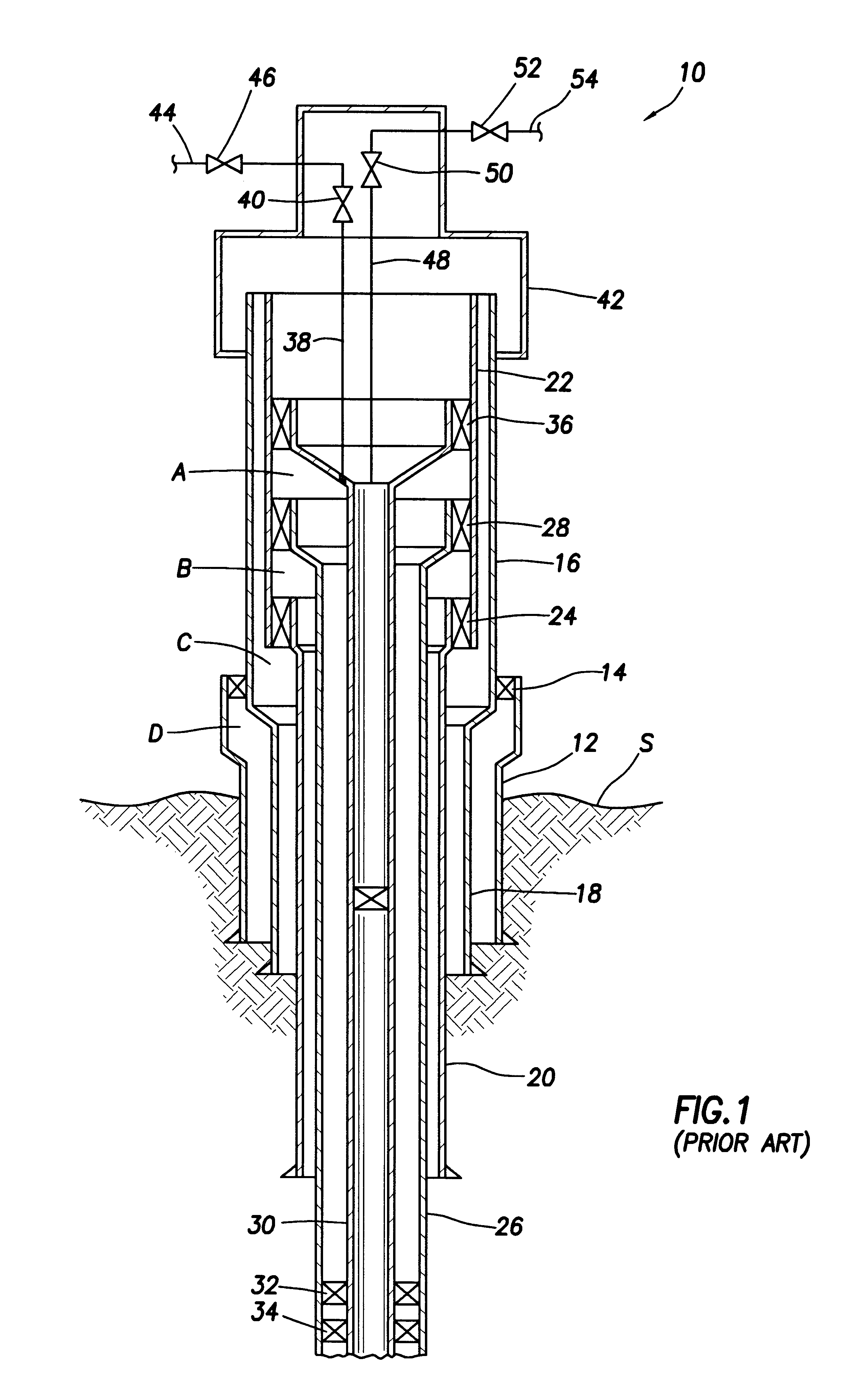
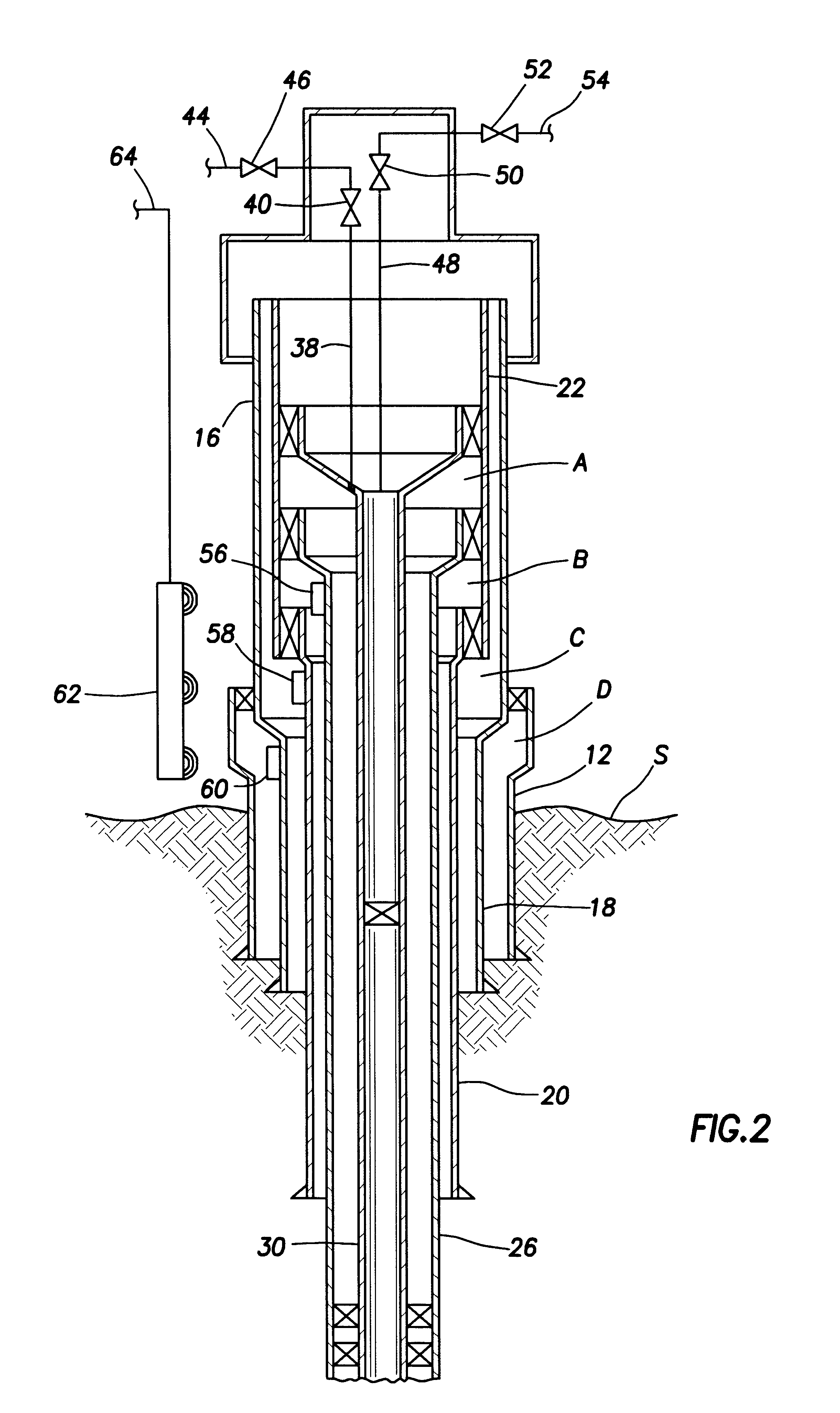
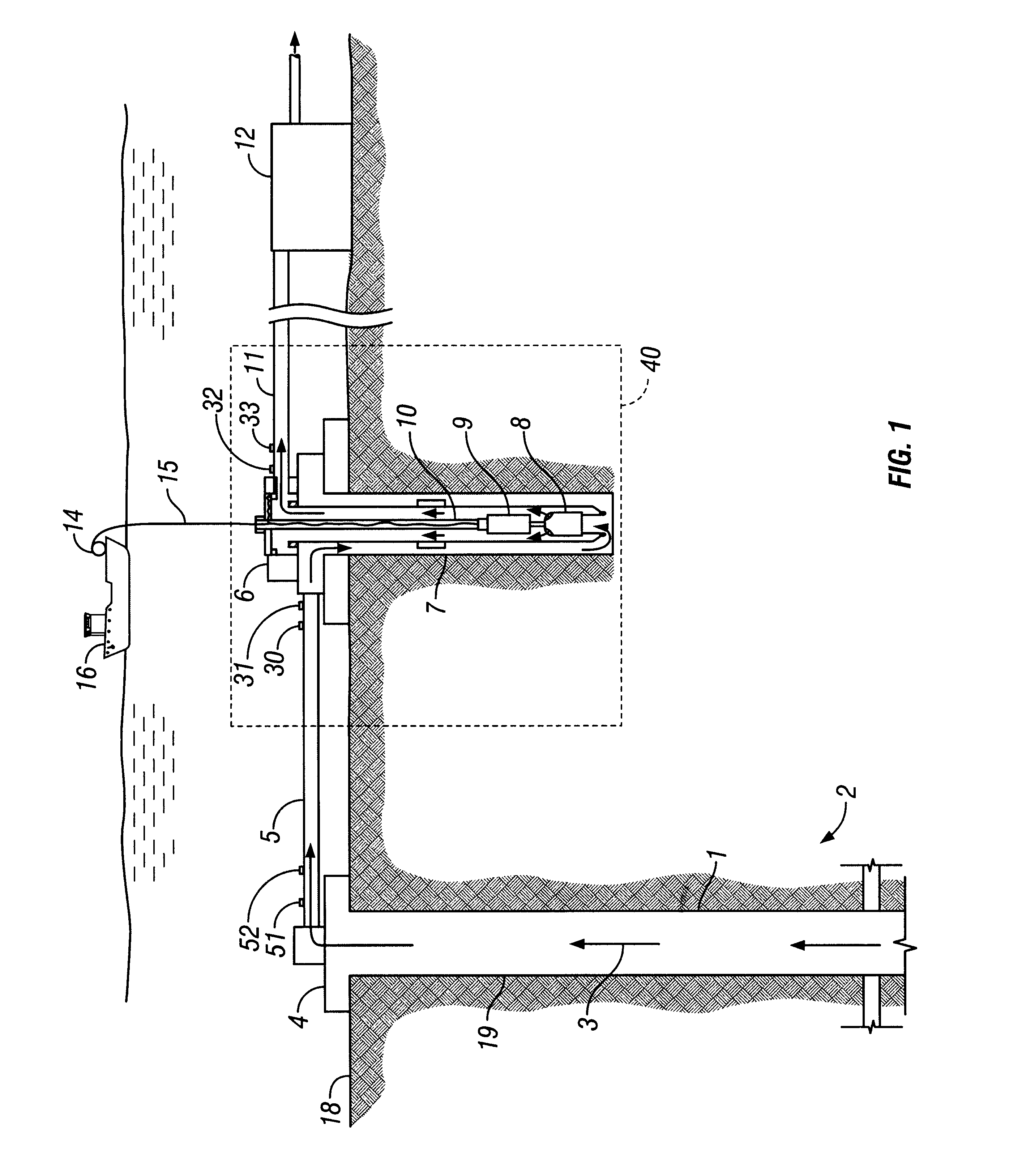
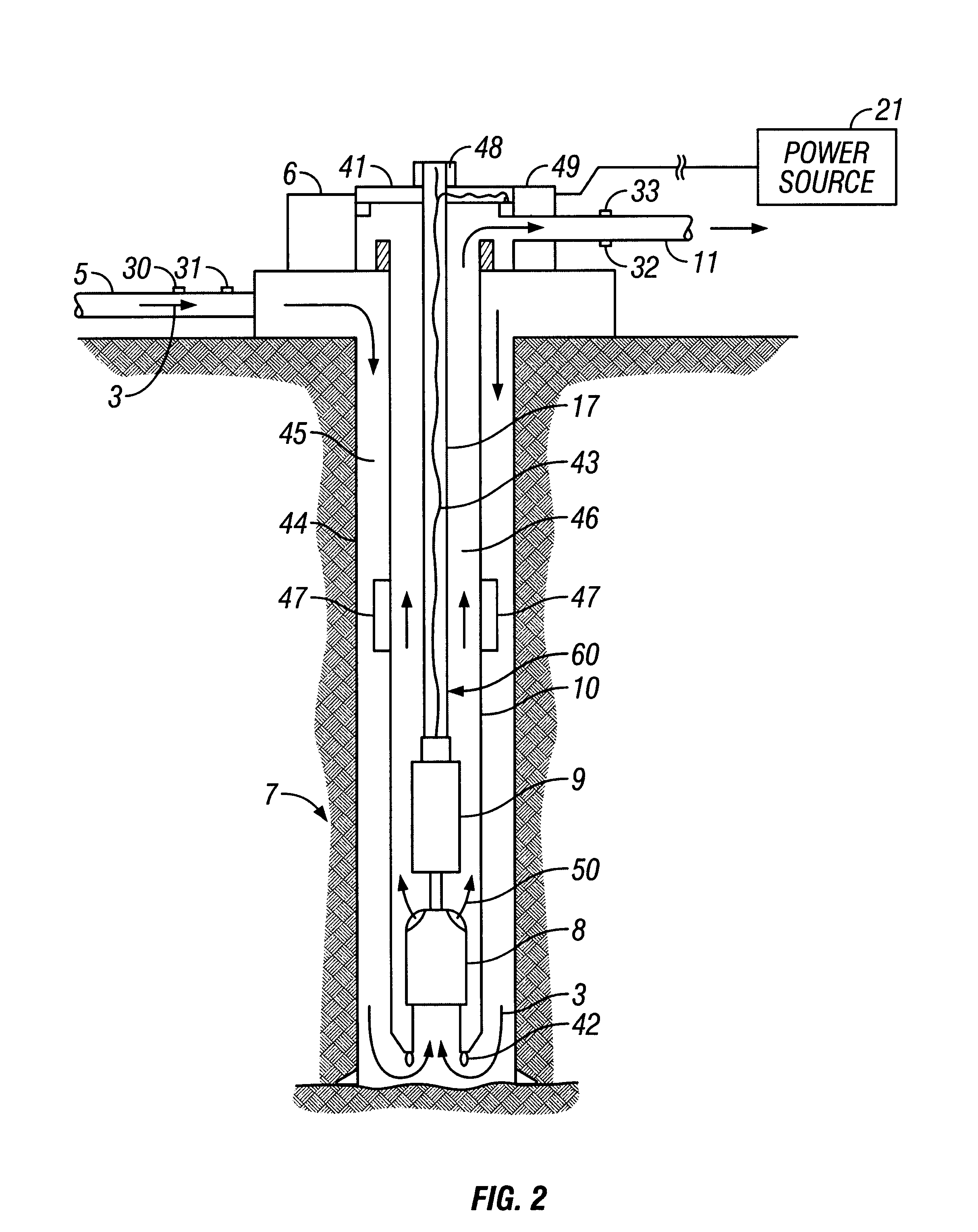
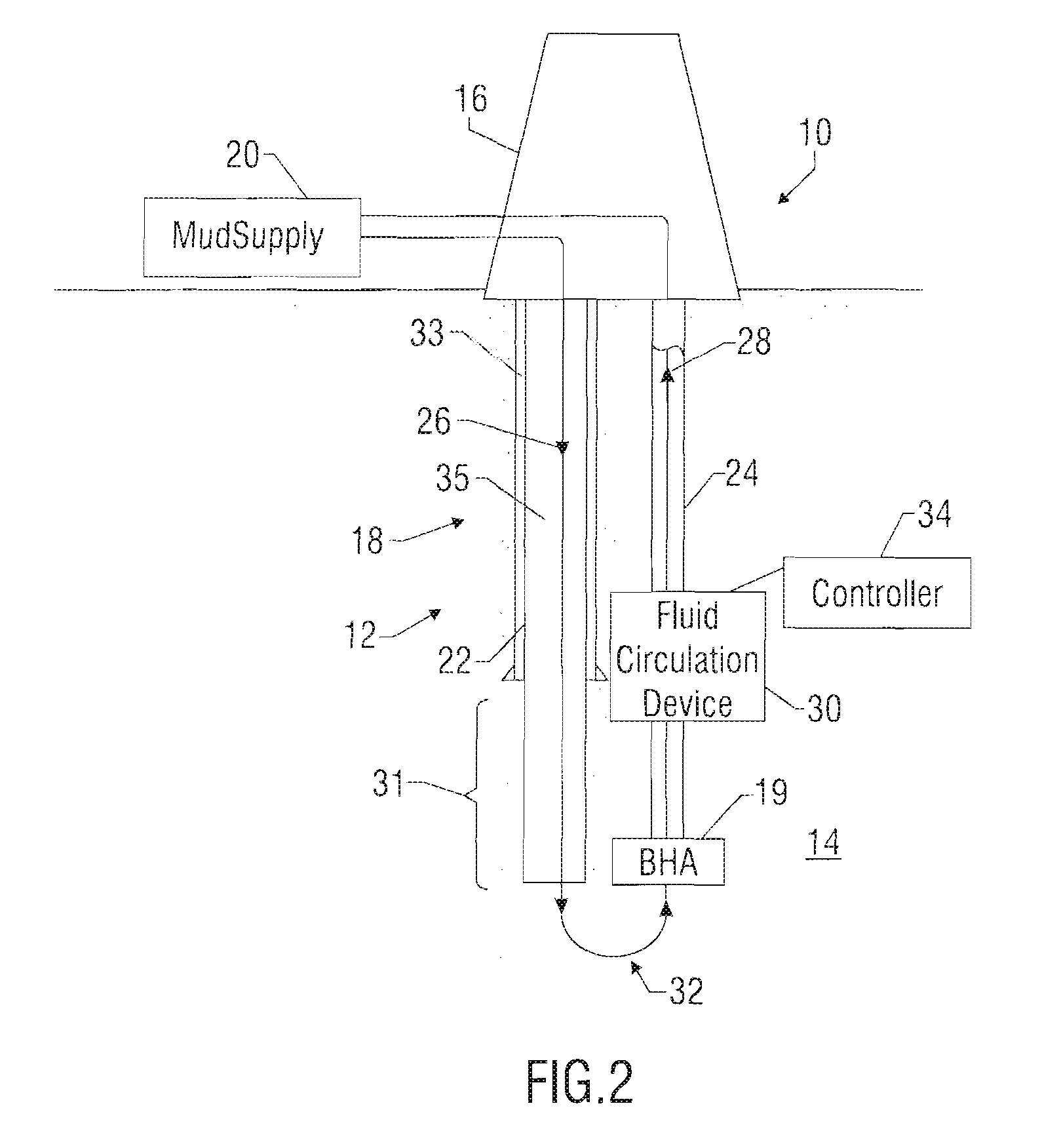
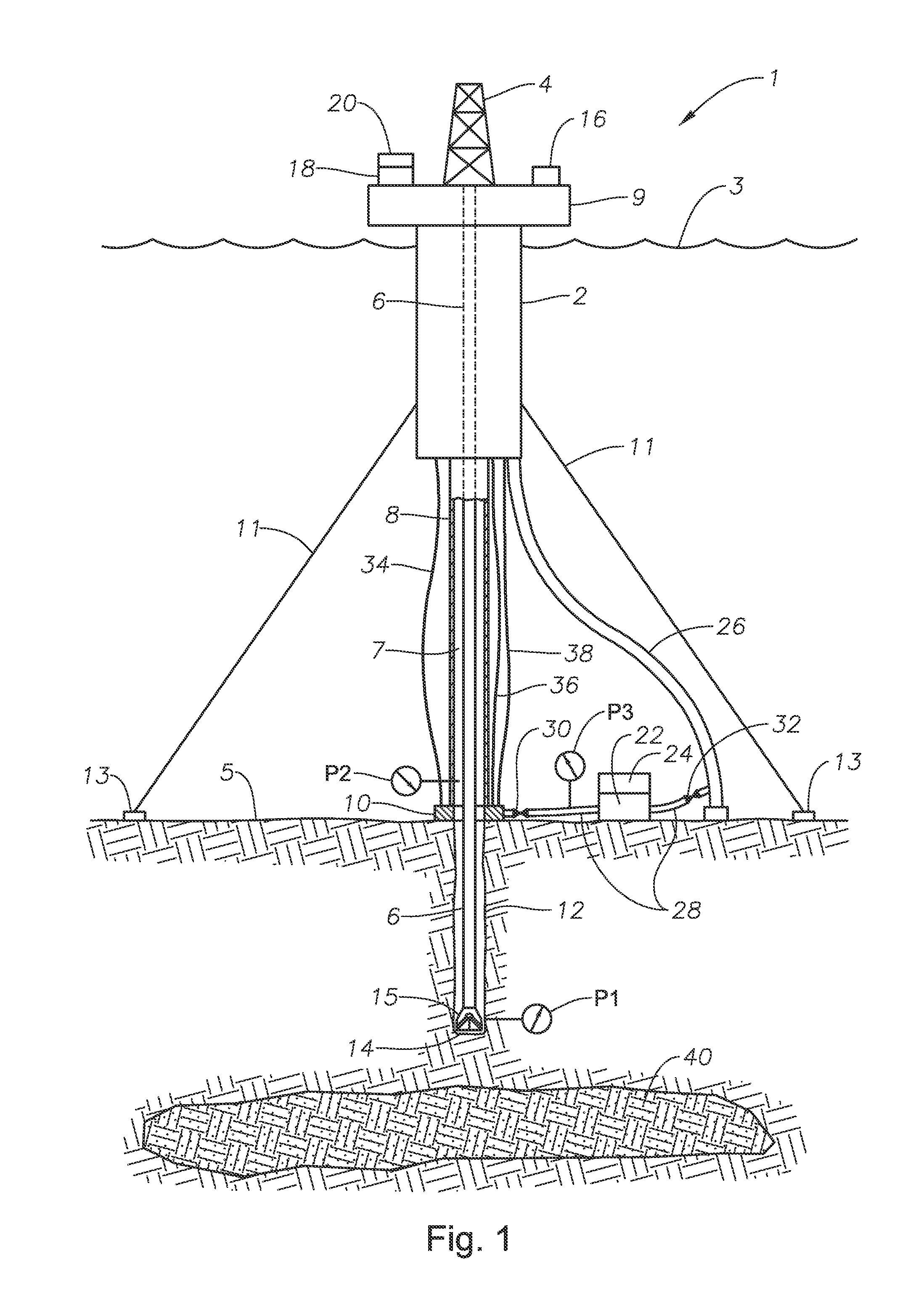
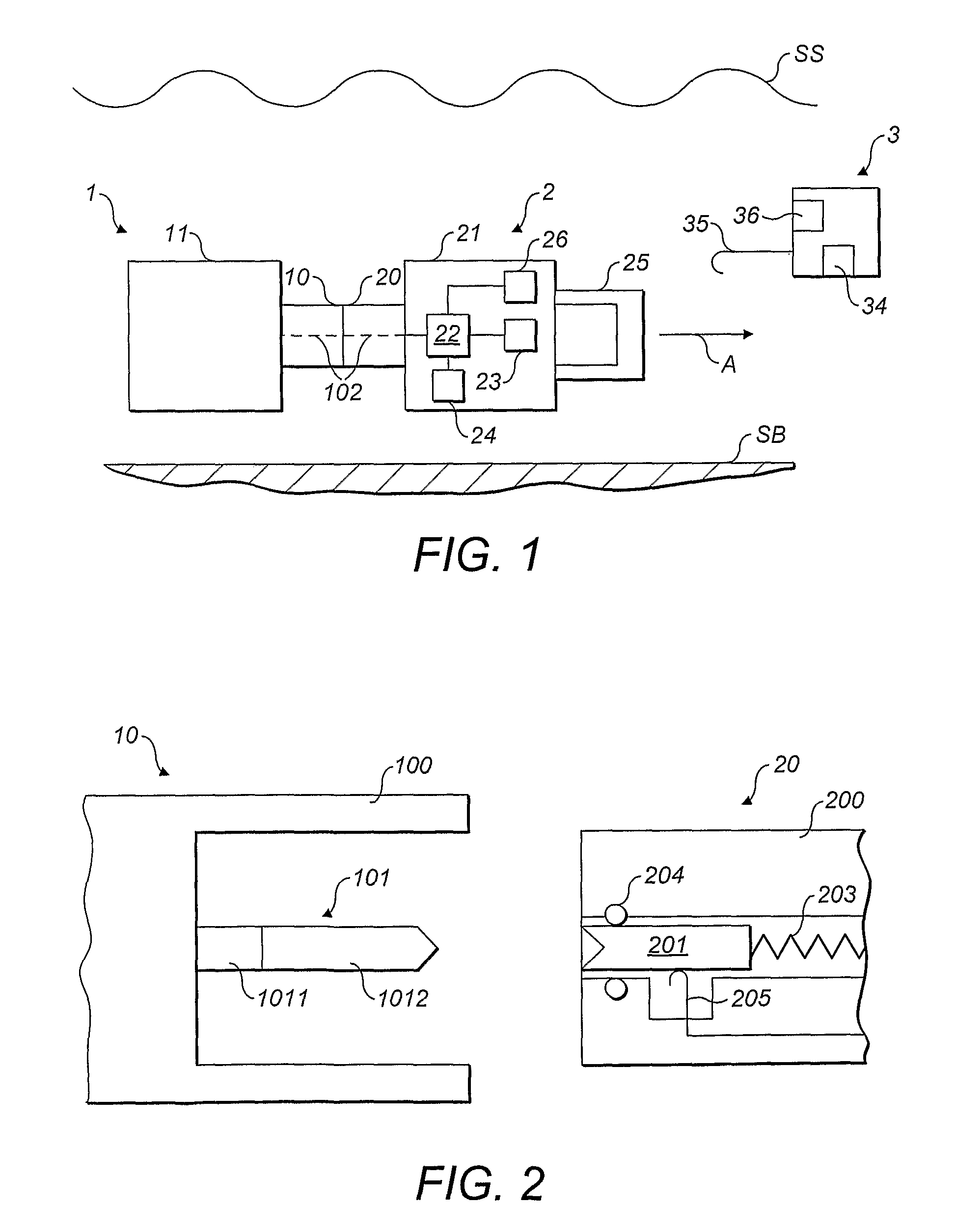
Drilling system and method for controlling equivalent circulating density during drilling of wellbores
A drilling system for drilling subsea wellbores includes a tubing-conveyed drill bit that passes through a subsea wellhead. Surface supplied drilling fluid flows through the tubing, discharges at the drill bit, returns to the wellhead through a wellbore annulus, and flows to the surface via a riser extending from the wellhead. A flow restriction device positioned in the riser restricts the flow of the returning fluid while an active fluid device controllably discharges fluid from a location below to just above the flow restriction device in the riser, thereby controlling bottomhole pressure and equivalent circulating density (“ECD”). Alternatively, the fluid is discharged into a separate return line thereby providing dual gradient drilling while controlling bottomhole pressure and ECD. A controller controls the energy and thus the speed of the pump in response to downhole measurement(s) to maintain the ECD at a predetermined value or within a predetermined range.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
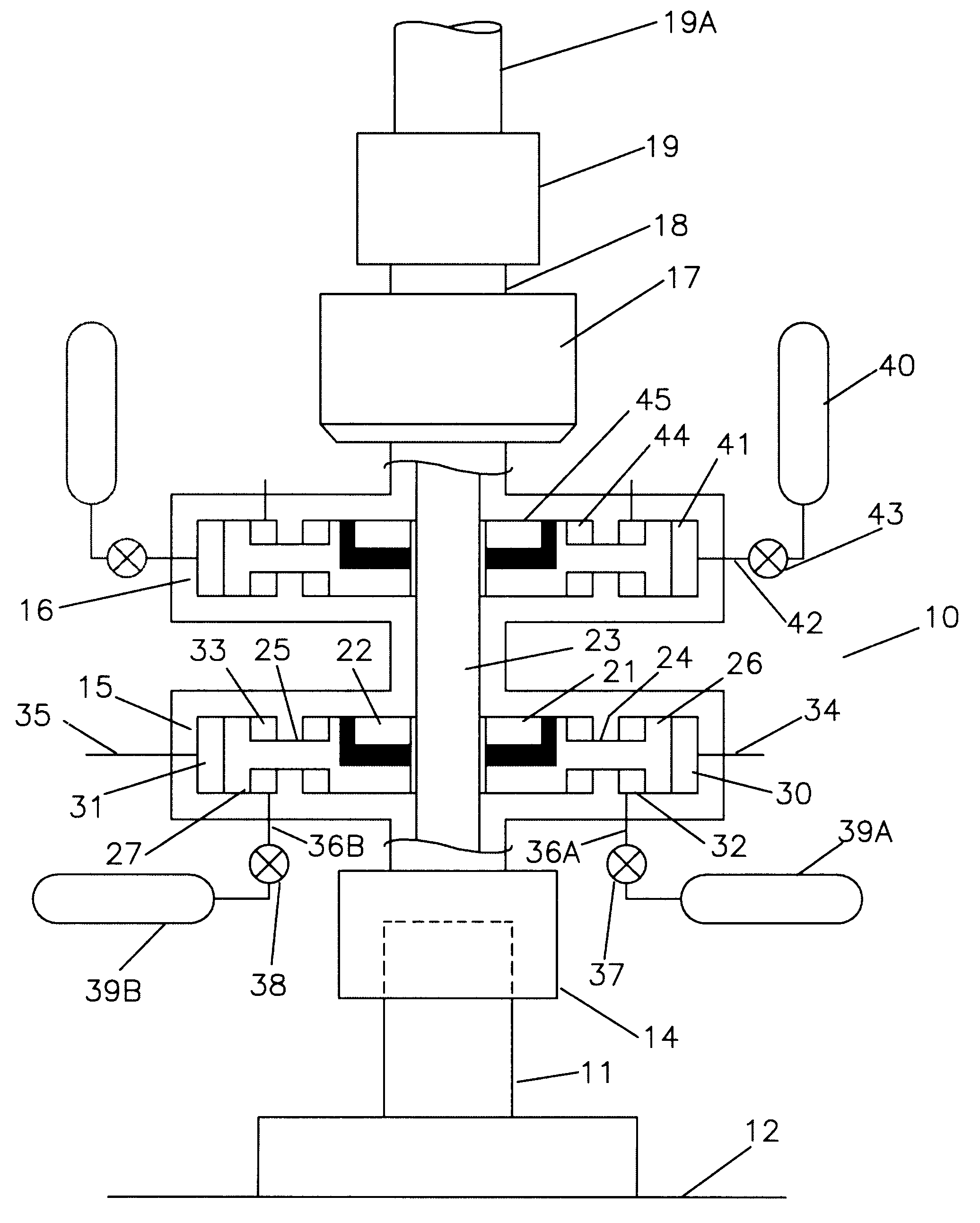
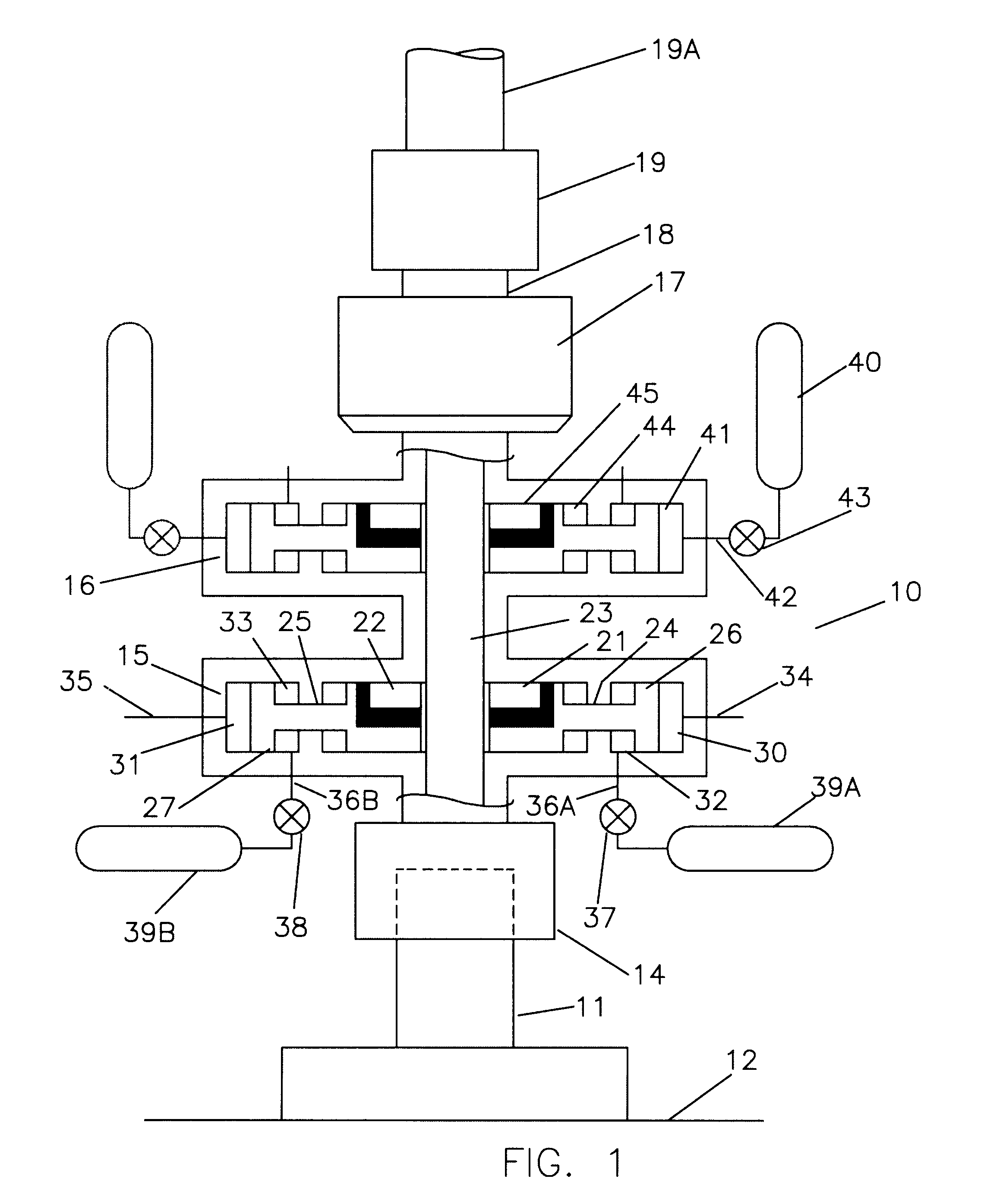
Subsea accumulator and method of operation of same
An accumulator for use in deepwater operational and control systems which uses a differential between a high pressure ambient pressure source such as sea water pressure and a low pressure source such as a chamber holding vacuum or atmospheric pressure to provide storage and delivery of hydraulic power for operation of equipment.
Owner:BAUGH BENTON F
Exploitation Of Sea Floor Rig Structures To Enhance Measurement While Drilling Telemetry Data
ActiveUS20120126992A1Readily apparentWell/borehole valve arrangementsTransmissionOcean bottomCommunications system
A method for communicating data in an offshore data communication system comprises measuring L / MWD data with a sensor disposed in a bottomhole assembly positioned in a subsea borehole. The bottomhole assembly is disposed along a drillstring extending through the subsea borehole. In addition, the method comprises communicating the L / MWD data from the bottomhole assembly to the seafloor with a telemetry signal. Further, the method comprises receiving the telemetry signal with at least one telemetry transducer positioned proximal the sea floor. Still further, the method comprises processing the telemetry signal at the seafloor to produce a processed signal. Moreover, the method comprises transmitting the processed signal from the sea floor to the sea surface.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Drilling system and method for controlling equivalent circulating density during drilling of wellbores
A drilling system for drilling subsea wellbores includes a tubing-conveyed drill bit that passes through a subsea wellhead. Surface supplied drilling fluid flows through the tubing, discharges at the drill bit, returns to the wellhead through a wellbore annulus, and flows to the surface via a riser extending from the wellhead. A flow restriction device positioned in the riser restricts the flow of the returning fluid while an active fluid device controllably discharges fluid from a location below to just above the flow restriction device in the riser, thereby controlling bottomhole pressure and equivalent circulating density (“ECD”). Alternatively, the fluid is discharged into a separate return line thereby providing dual gradient drilling while controlling bottomhole pressure and ECD. A controller controls the energy and thus the speed of the pump in response to downhole measurement(s) to maintain the ECD at a predetermined value or within a predetermined range.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
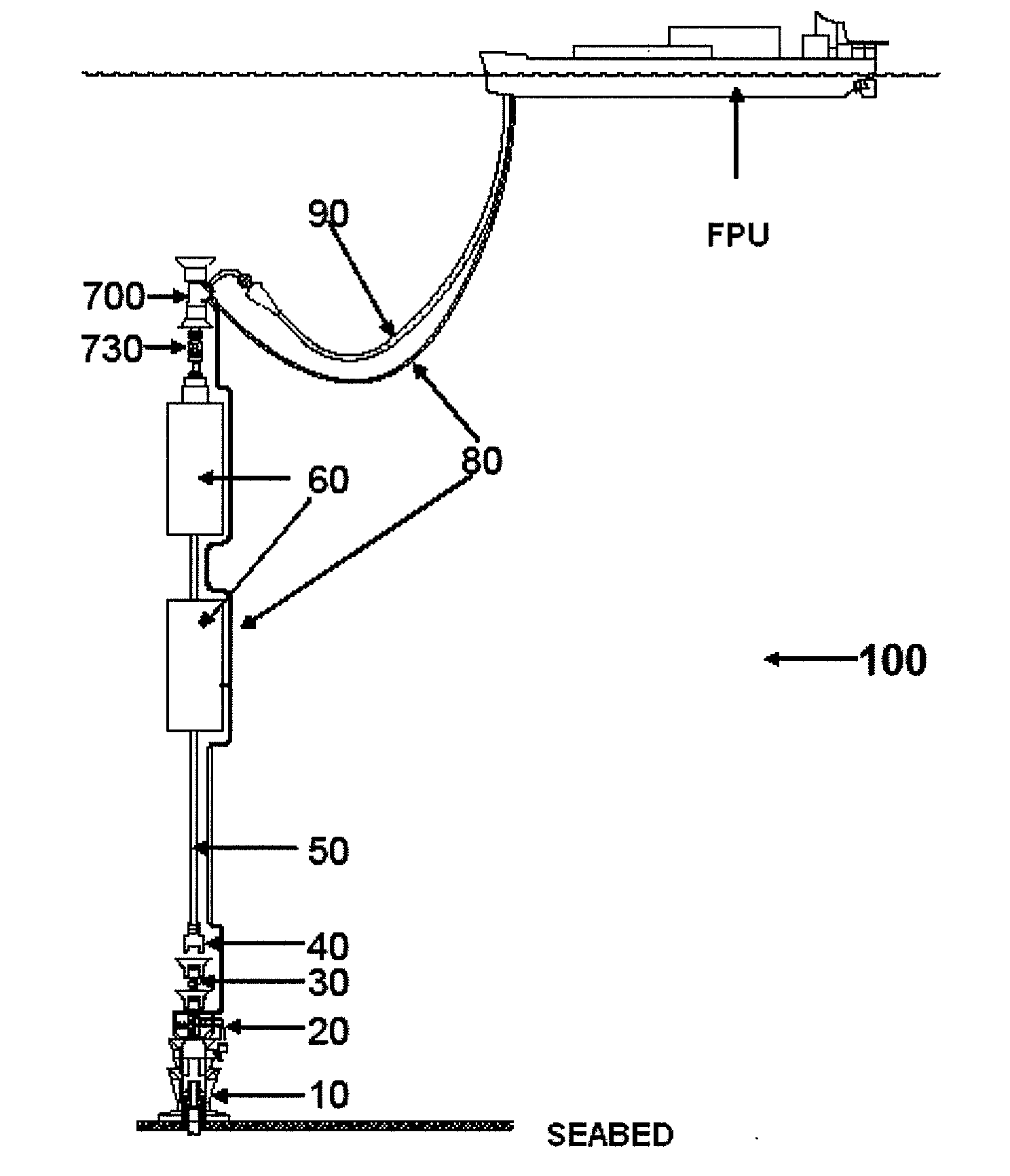
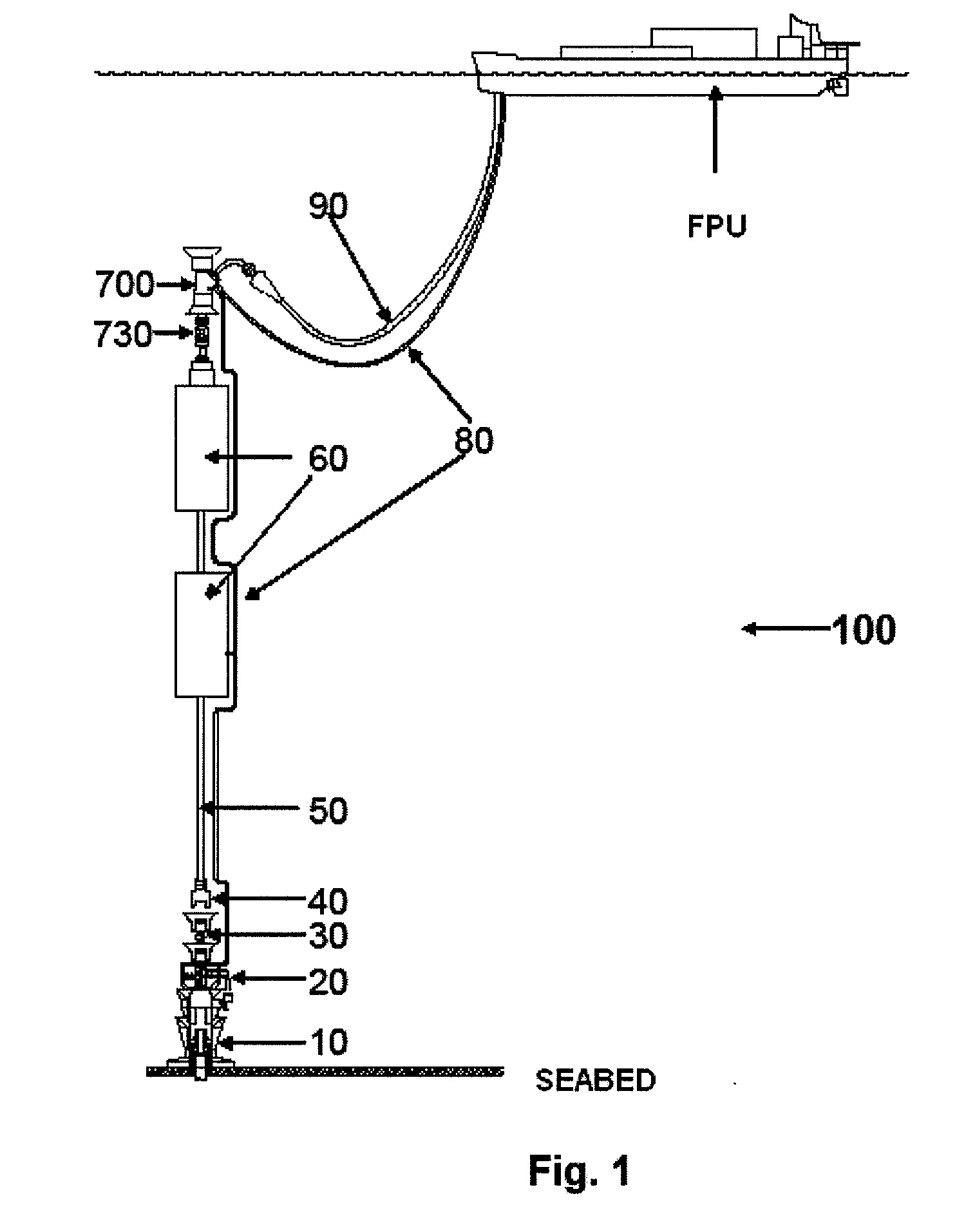
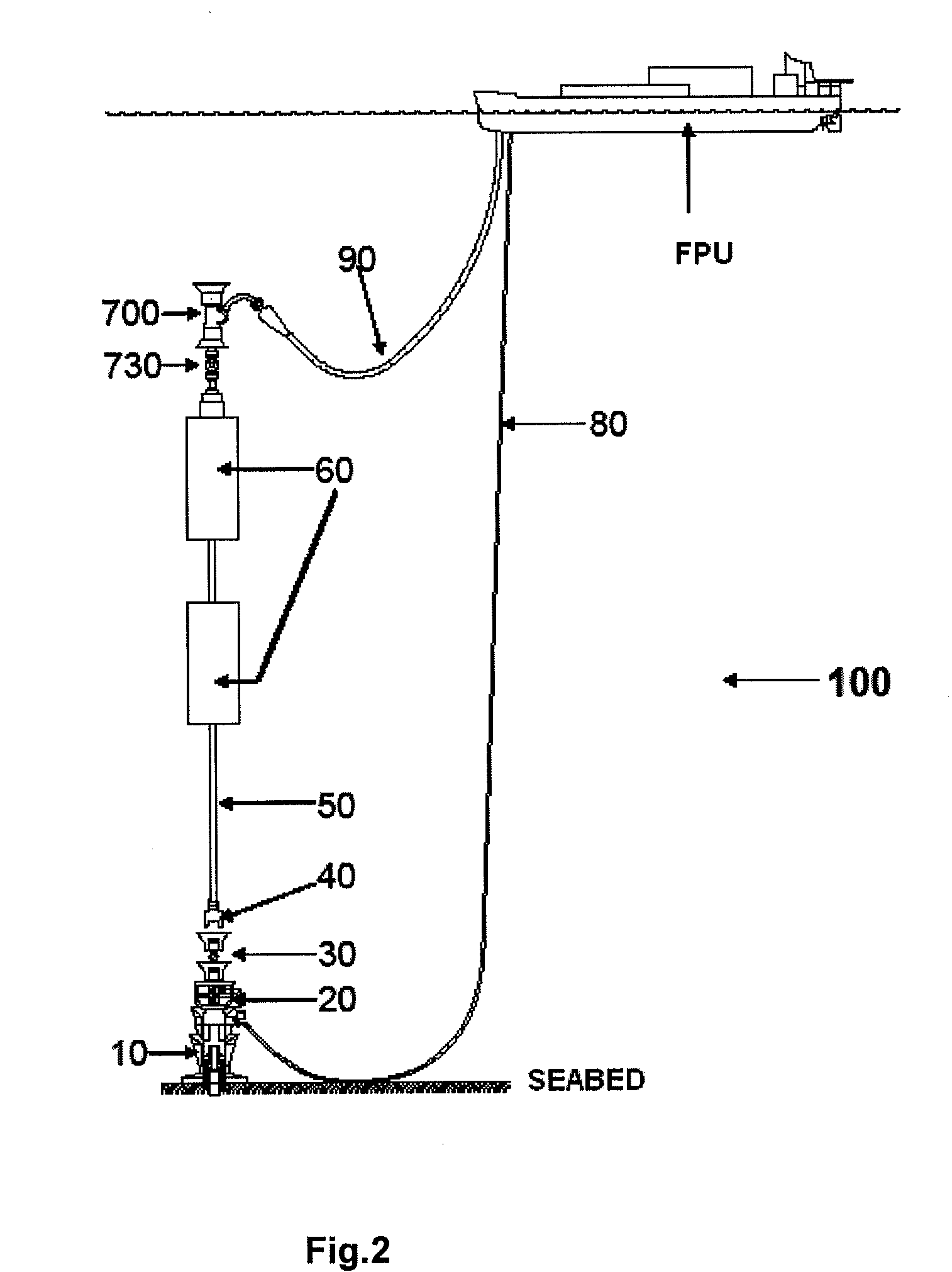
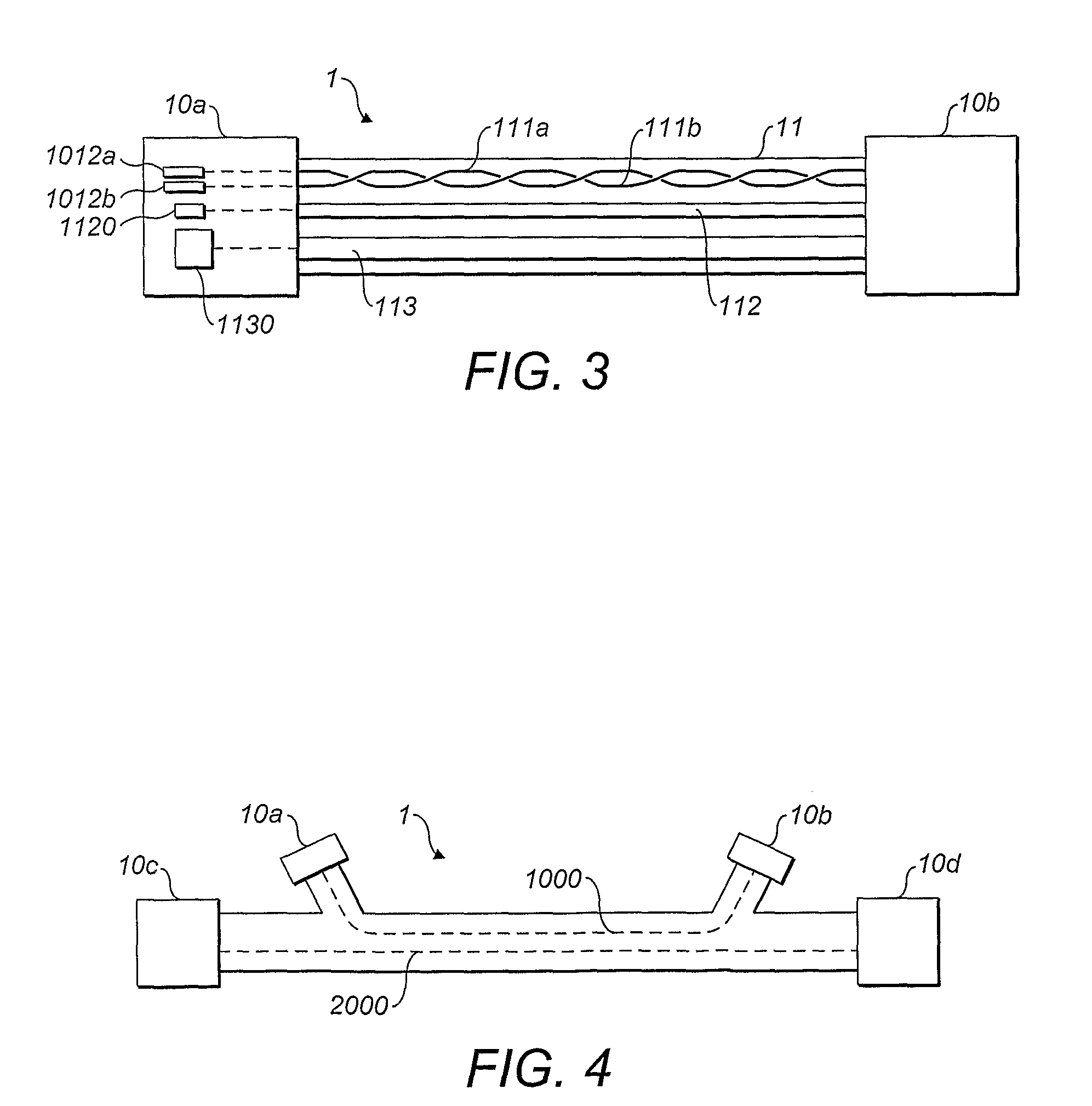
Self-supported riser system and method of installing same
InactiveUS20070044972A1Save rig timeReducing maneuvering stepCargo handling apparatusDrilling rodsBuoyPetroleum oil
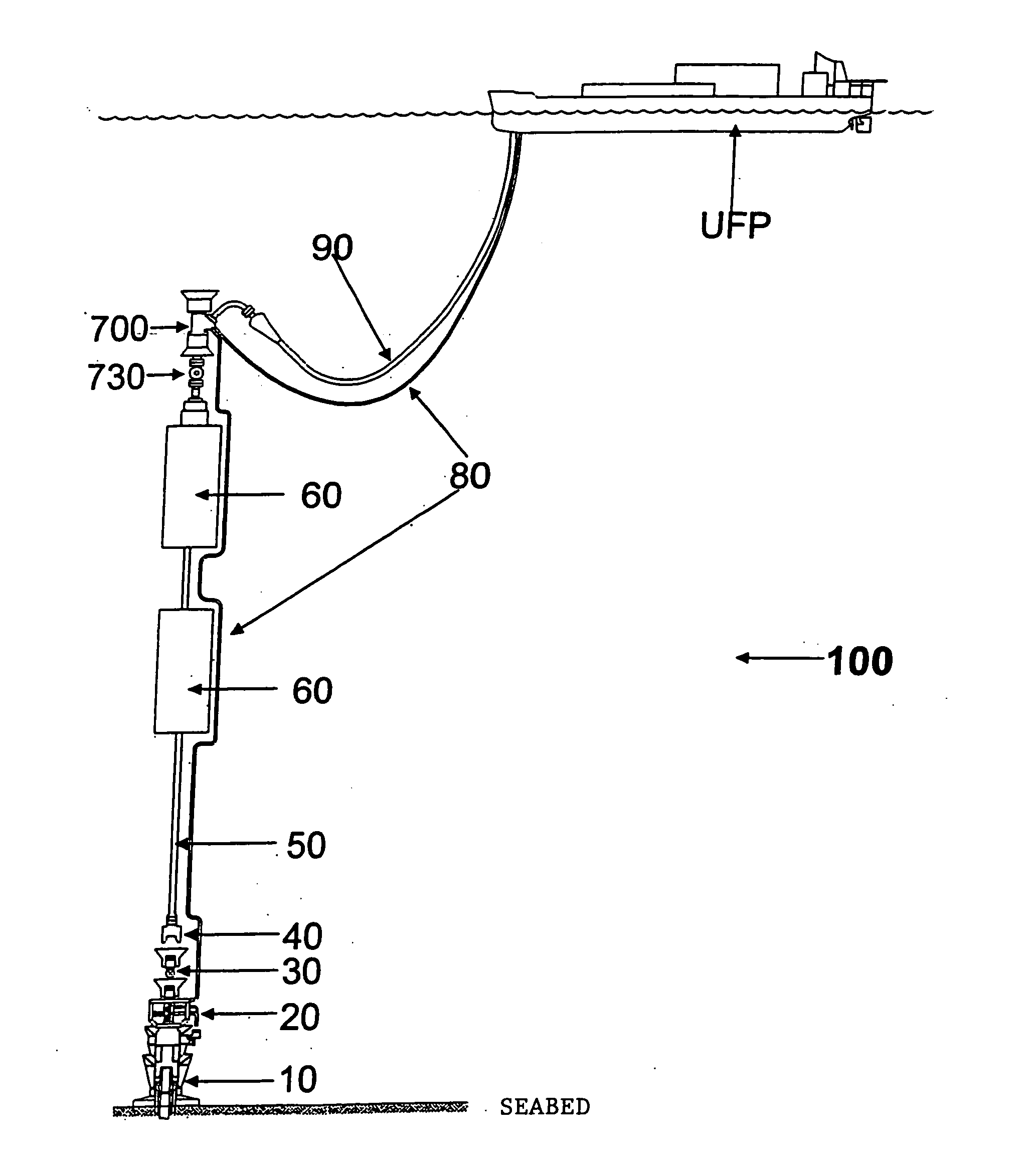
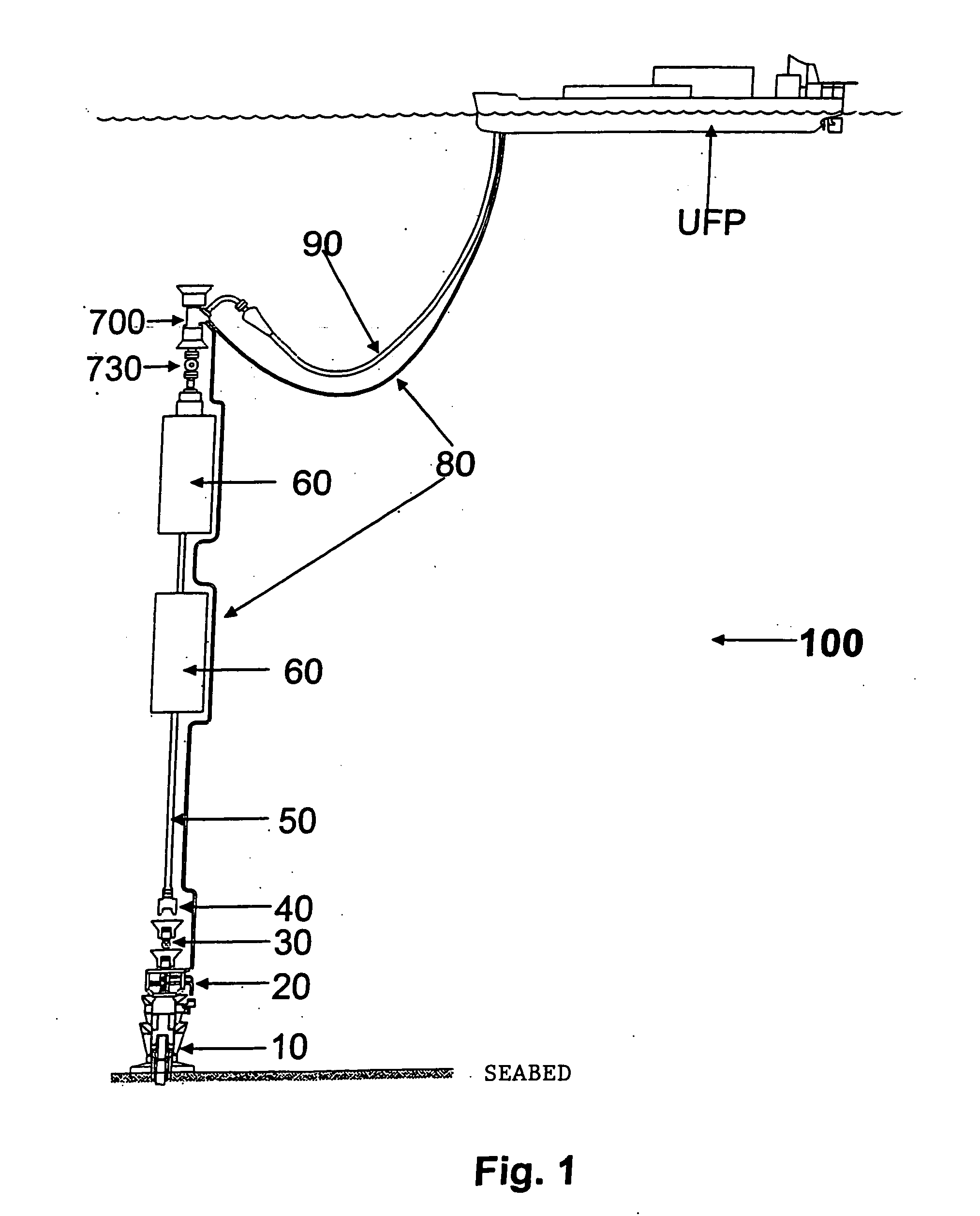
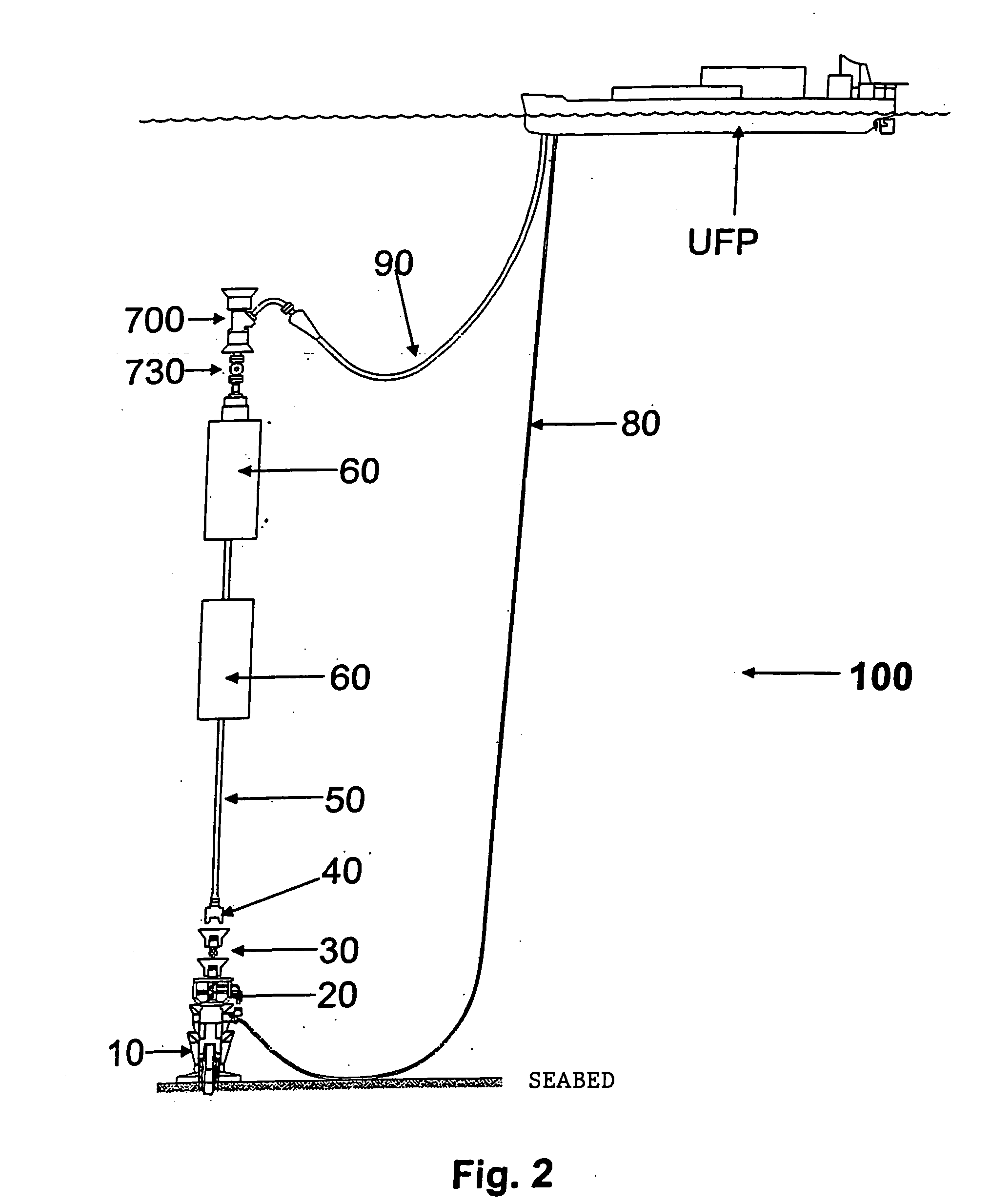
A self-supported riser system (100) for an Anticipated Production System (ASP) Test or a Long Duration Production (LDP) Test in a subsea petroleum production system, utilizing an ANM coupled to a wellhead and Floating Production Unit (FPU) is disclosed. The system includes a wellhead at the seabed, connected to an ANM (20) provided with a preventor (BOP of workover) (30). The preventor (30) is connected to a production riser (50) through a connection tool (40). The riser (50), mounted internally within a buoy assembly (60), is maintained under traction with the aid of a buoy assembly. The upper end of the riser (50) is provided with a Subsea Intervention Terminal (700), the Terminal being interlinked to the FPU by a flexible jumper (90) to carry the oil produced to the FPU. Two methods for installing the self-supported riser system (100) are also disclosed.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
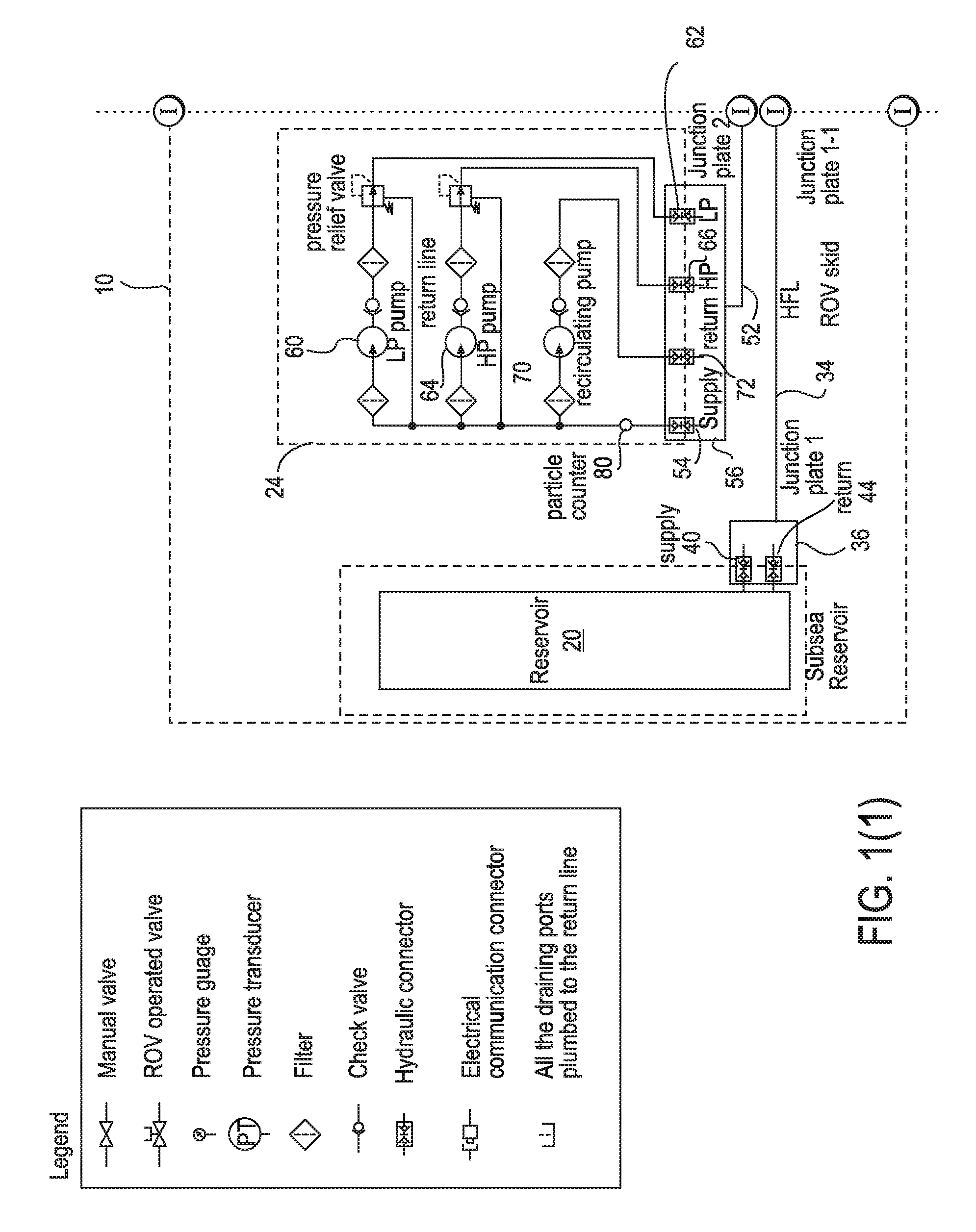
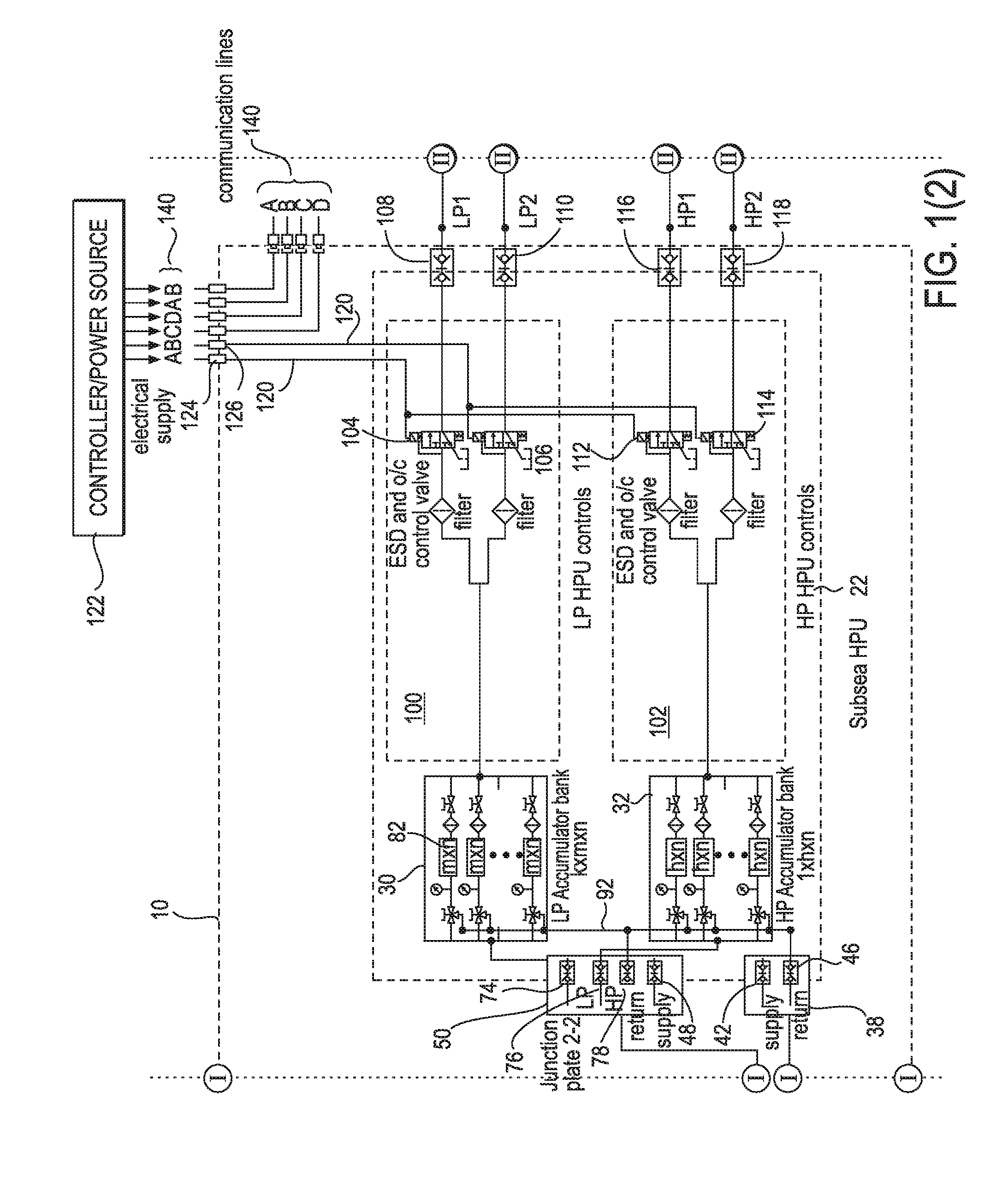
Apparatus and method for providing a controllable supply of fluid to subsea well equipment
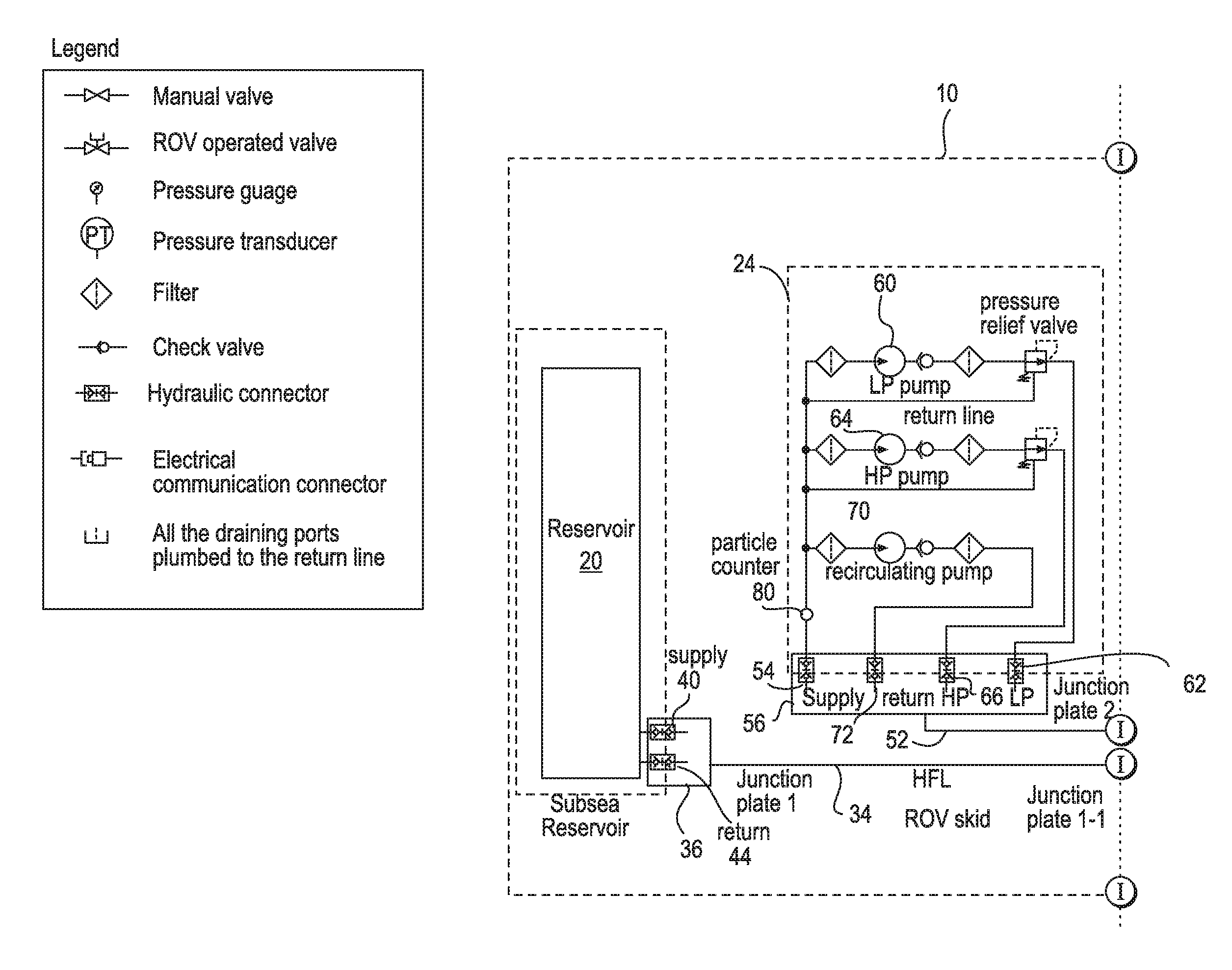
An apparatus and method for providing a controllable supply of fluid, and optionally power and / or communication signals, to a subsea equipment are provided. The fluid may be a water-based fluid, oil-based fluid, or chemicals. The apparatus includes a reservoir disposed on a seabed for storing a supply of fluid for delivery to the subsea well equipment. A subsea pumping device is configured to receive the fluid from the reservoir, pressurize the fluid, and deliver the pressurized fluid to an accumulator of a hydraulic power unit disposed on the seabed. The hydraulic power unit can store the pressurized fluid and control an output of the pressurized fluid to the subsea well equipment, thereby providing a subsea fluid source for the subsea equipment.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
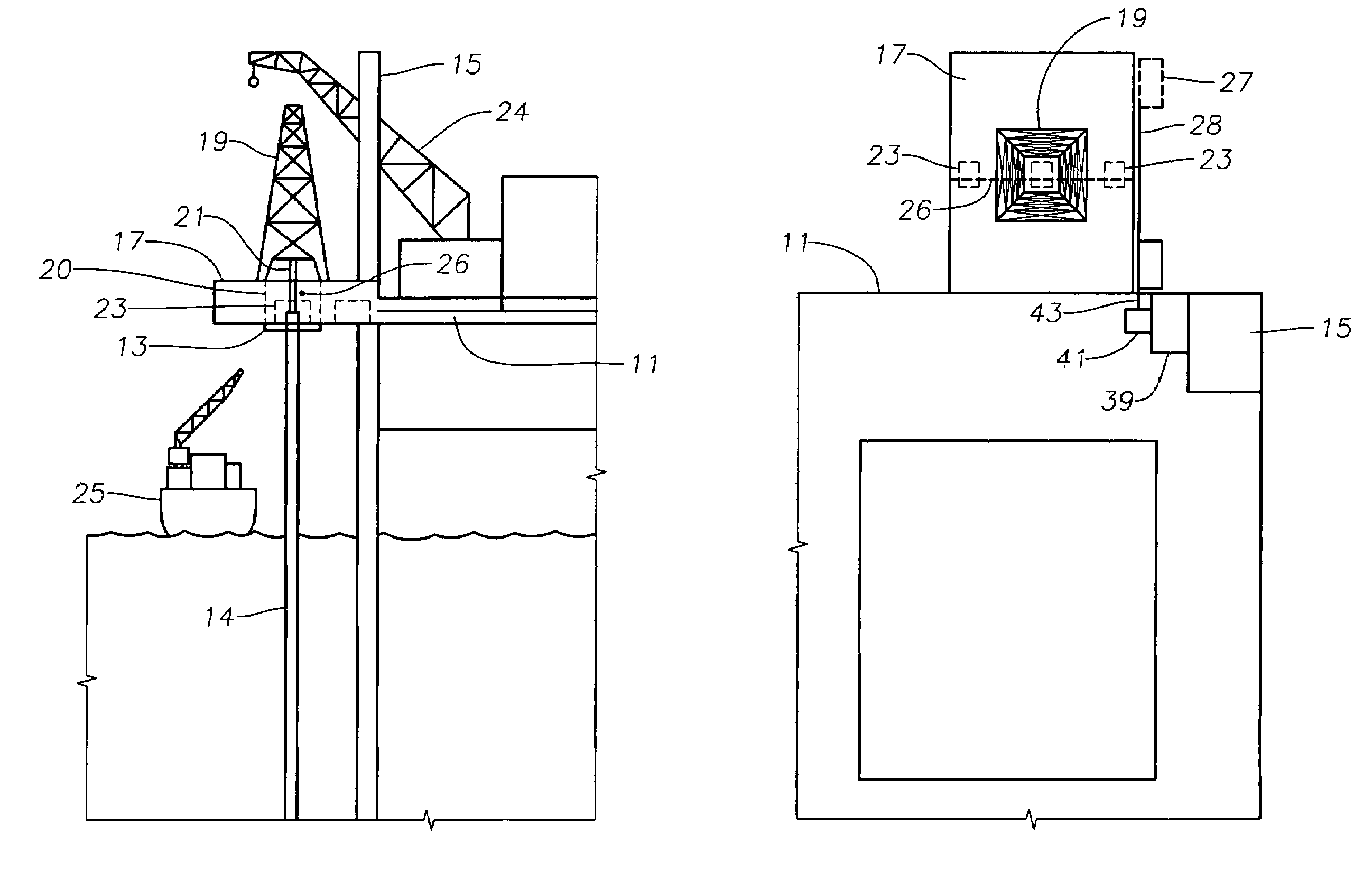
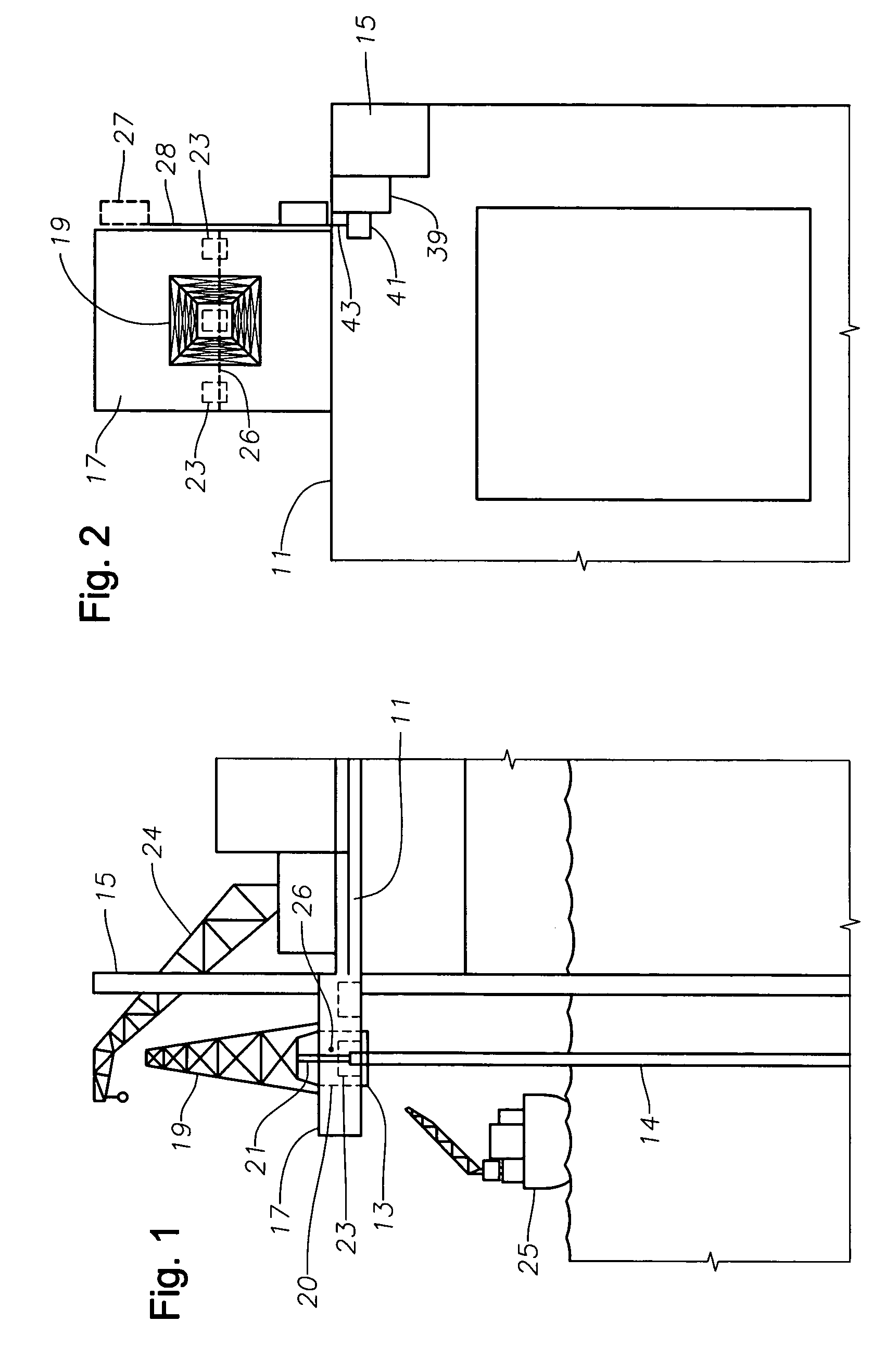
Modular, distributed, ROV retrievable subsea control system, associated deepwater subsea blowout preventer stack configuration, and methods of use
Owner:OCEANEERING INTERNATIONAL
Open water running tool and lockdown sleeve assembly
ActiveUS7028777B2Reduce manufacturing costImprove reliabilityDrilling rodsConstructionsOcean bottomEngineering
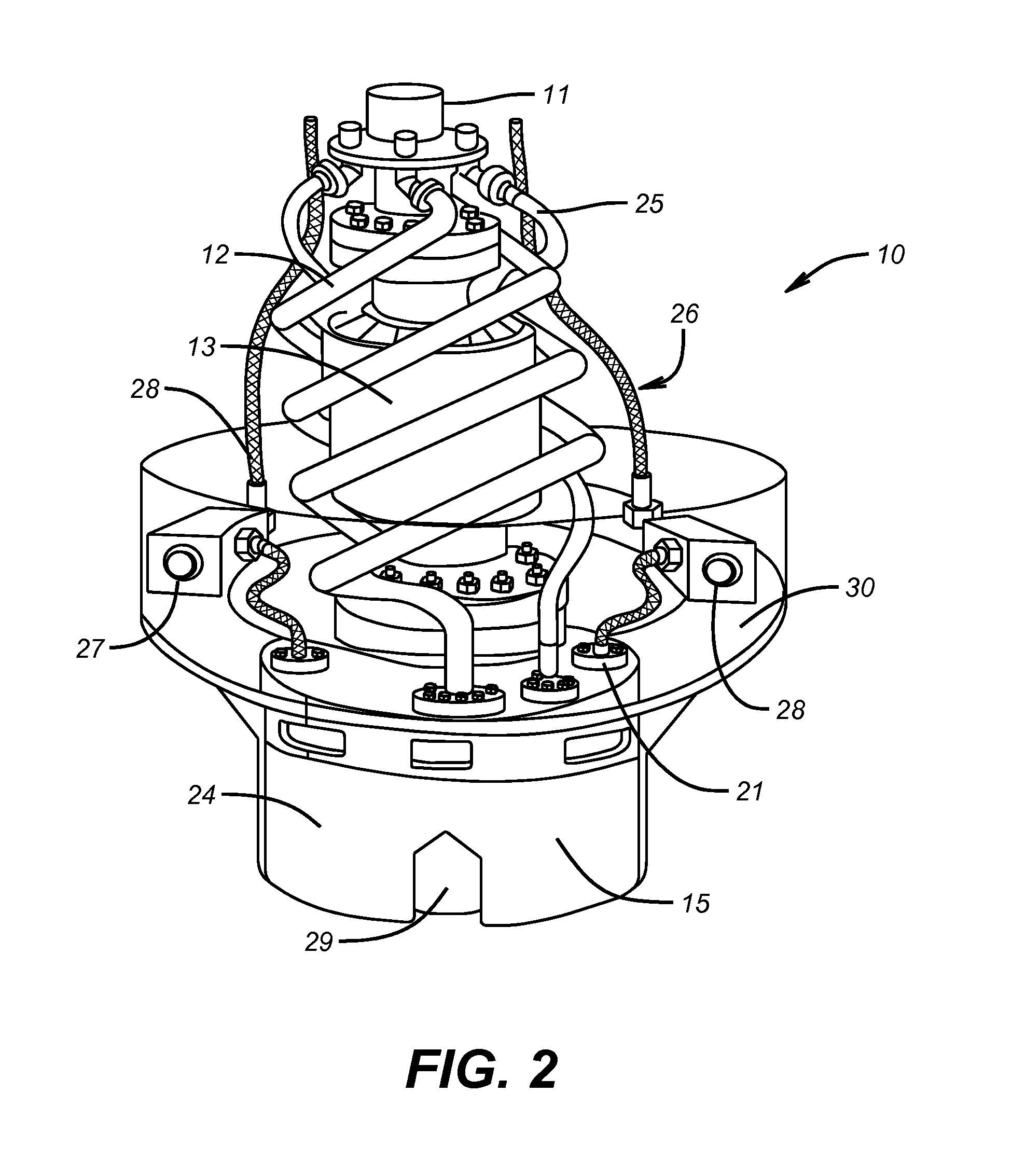
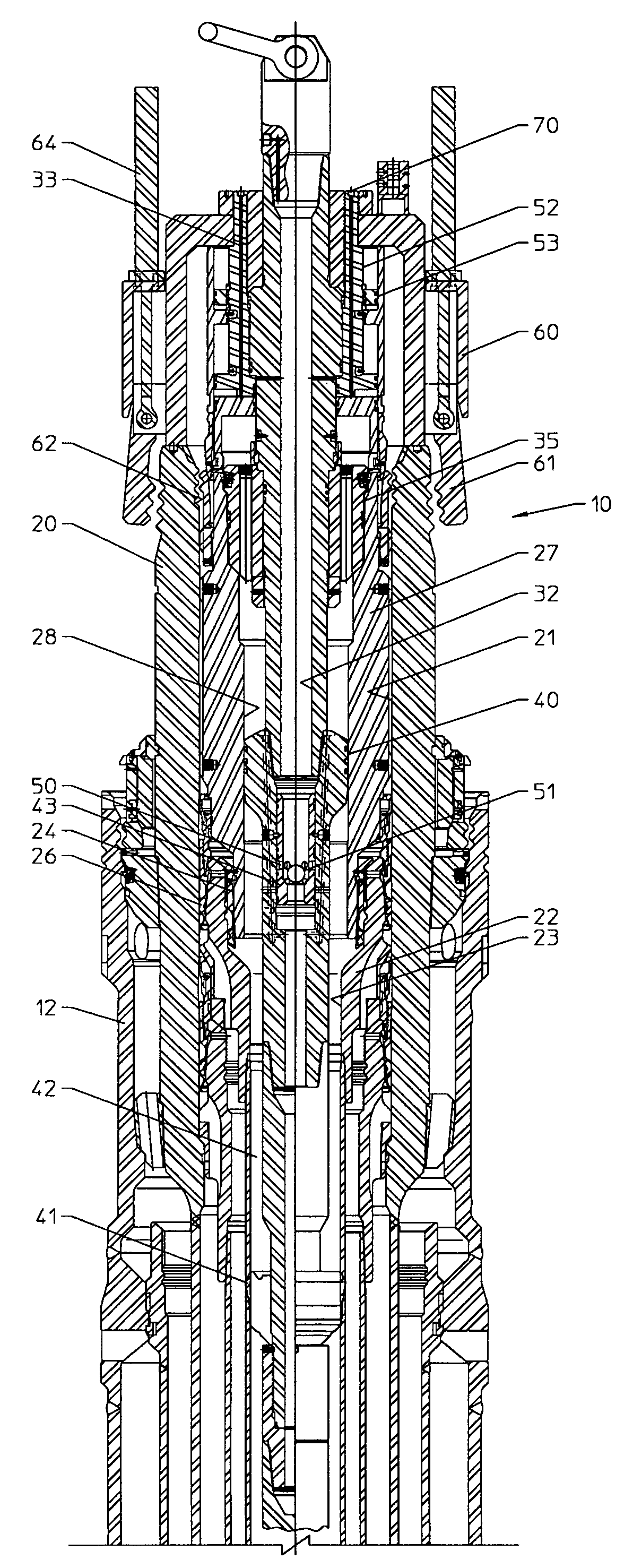
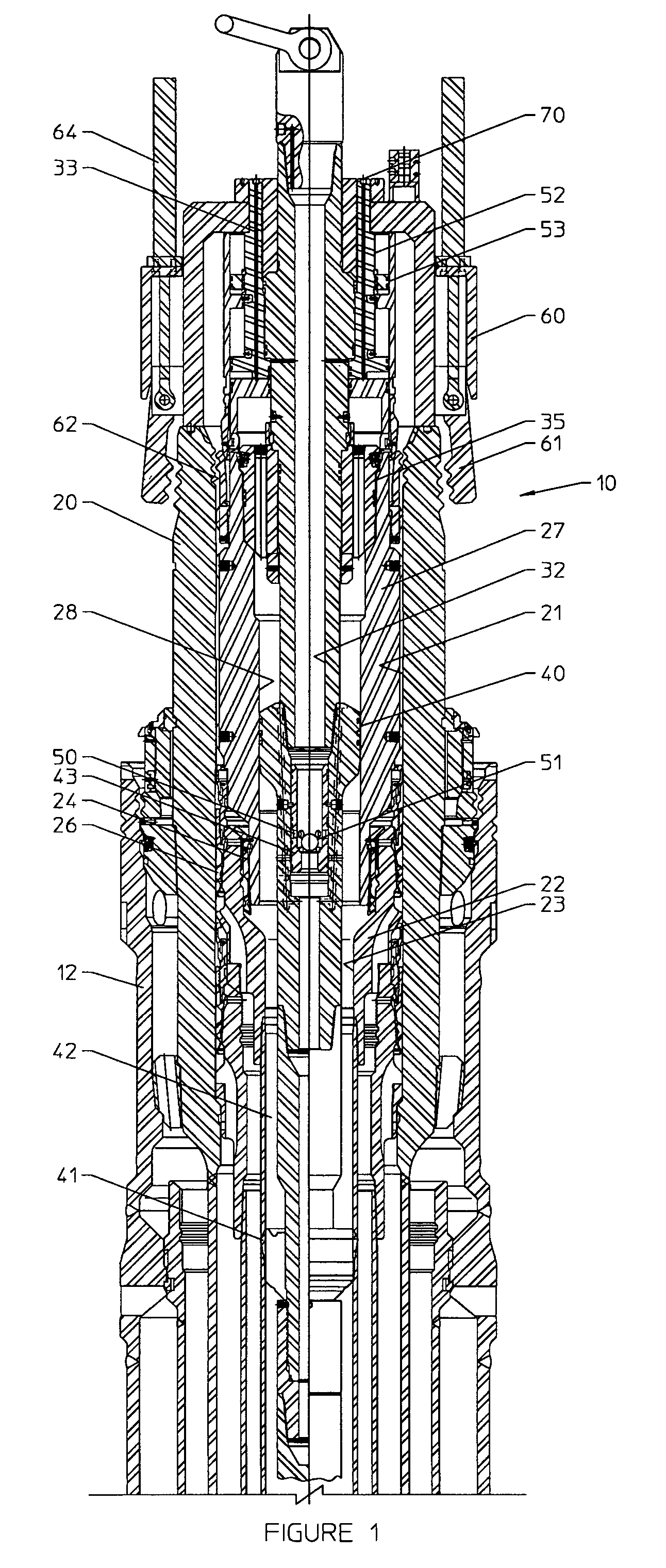
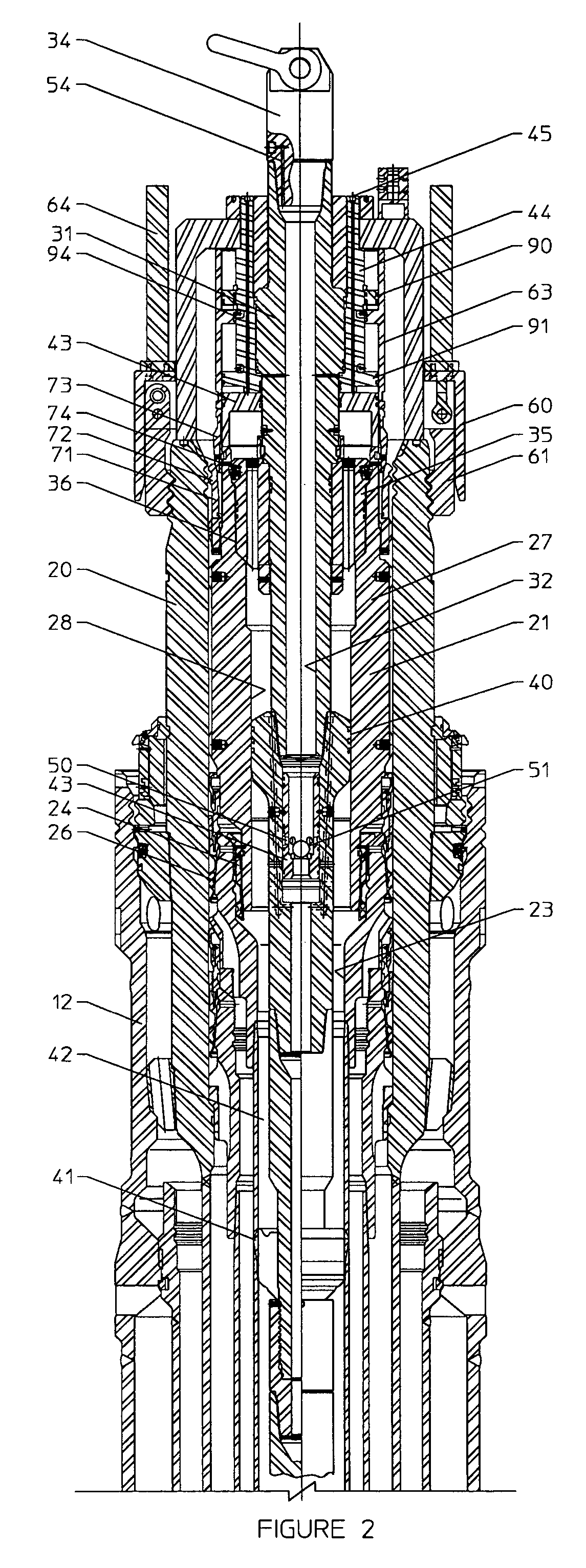
A running tool 10, a lockdown sleeve 27, and a seal ring 24 are provided for axially fixing upward movement of a tubular hanger with respect to a subsea wellhead. The running tool 10 includes a tool latching and unlatching mechanism 51 for axially connecting the running tool to the subsea wellhead housing, a tool force applicator 64 for exerting a downward setting force, and a sleeve latching mechanism 73 for securing the lockdown sleeve to the subsea wellhead housing 20. The seal 24 is provided between the lockdown sleeve and one of the tubular hanger and the wellhead housing. The method of the invention includes running the tool and sleeve in open water to the subsea wellhead housing, locking the tool to the housing, setting the seal, locking the sleeve to the housing, then retrieving the tool in open water.
Owner:DRIL QUIP
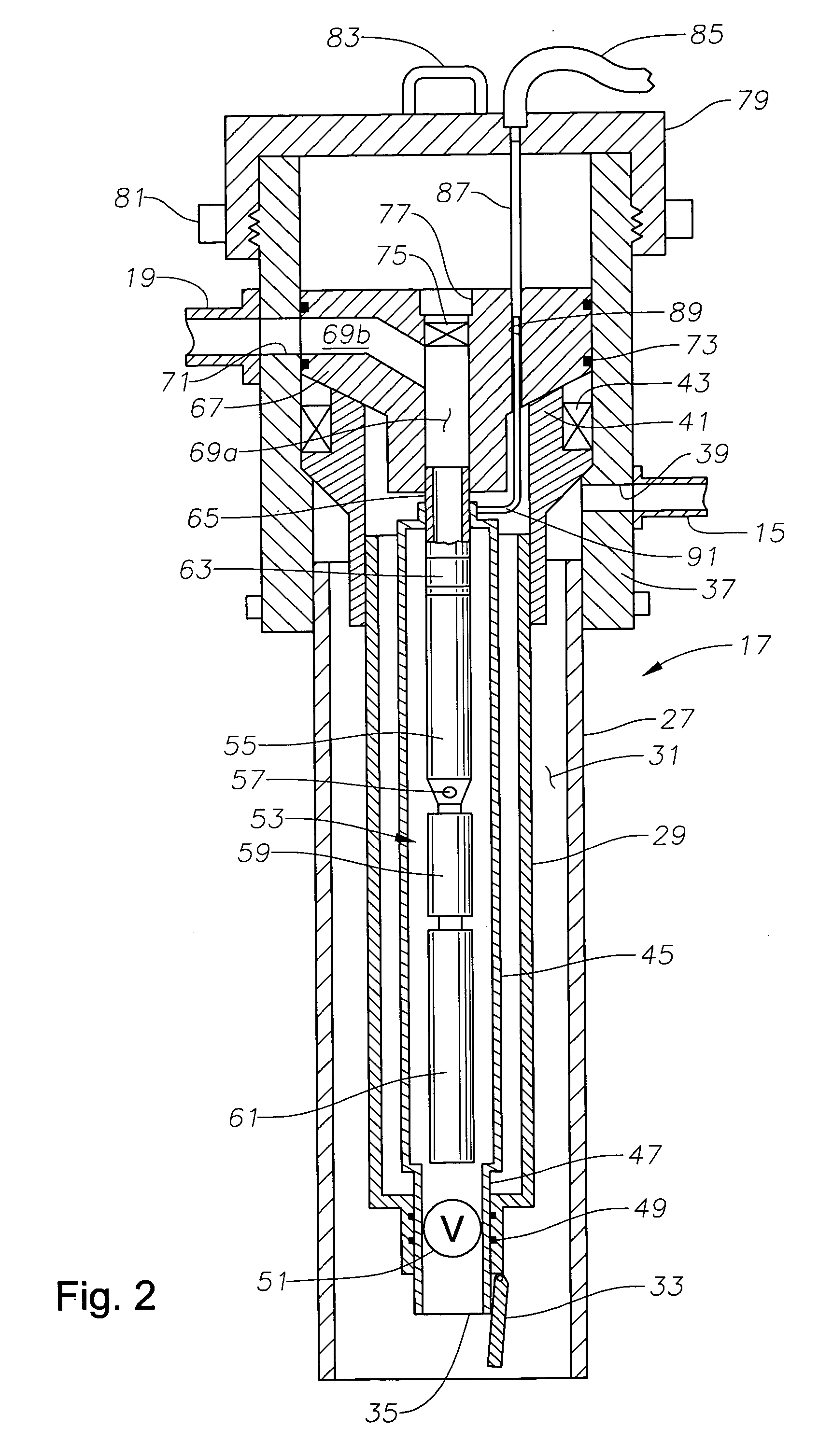
Non-intrusive pressure measurement device for subsea well casing annuli
InactiveUS6513596B2Preserve integrityMaximize safetySurveyConstructionsEngineeringIntelligent sensor
A well data monitoring system which enables annulus pressure and other well parameters to be monitored in the outer annuli of the well casing program without adding any pressure containing penetrations to the well system. This non-intrusive approach to monitoring pressure and other well parameters in the annuli preserves the pressure integrity of the well and maximizes the safety of the well. In the preferred embodiment an intelligent sensor interrogation system which can be located externally or internally of the pressure containing housing of the wellhead is capable of interrogating and receiving data signals from intelligent well data sensors which are exposed to well parameters within the various annuli of the well and wellhead program.
Owner:FMC TECH INC
System and method for flow/pressure boosting in a subsea environment
A system for producing hydrocarbon fluids from a subsea formation includes at least one producing well penetrating the formation for producing hydrocarbon fluids. At least one dummy well is hydraulically connected to the at least one producing well for routing the hydrocarbon fluids from the producing well to the dummy well. At least one pump is disposed in the at least one dummy well. The pump takes suction flow from the dummy well and boosts the flow energy of the discharge flow of hydrocarbon fluids.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
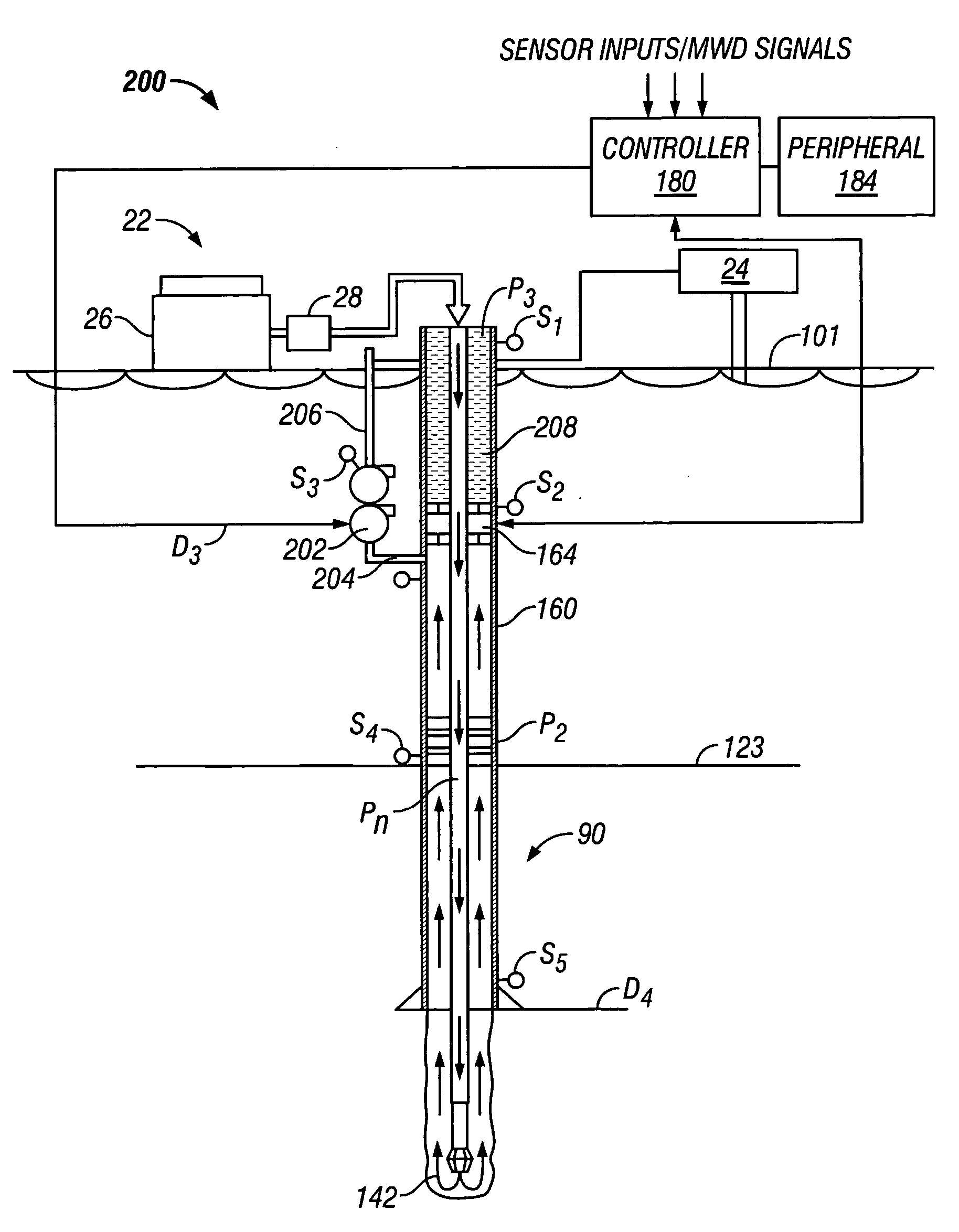
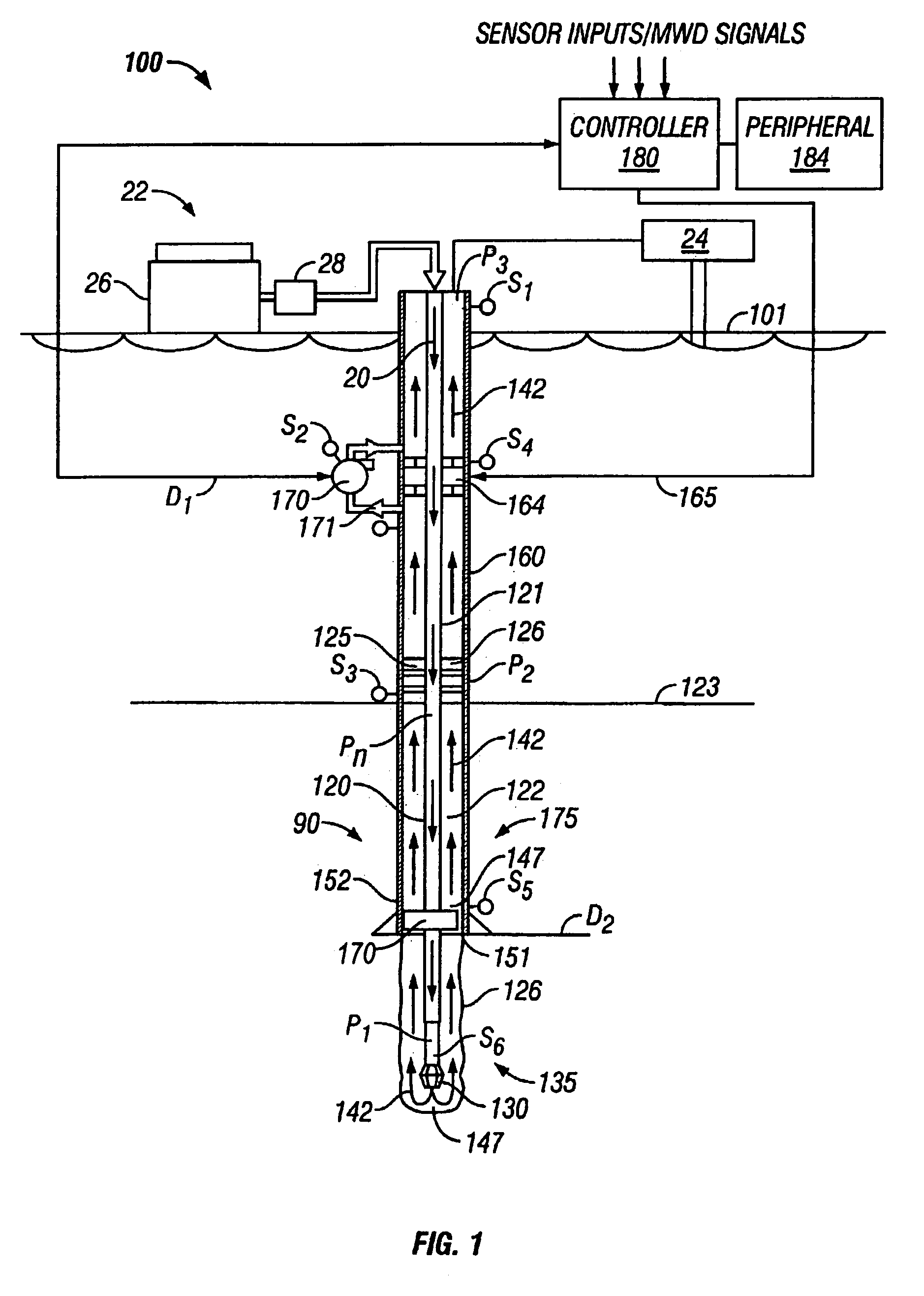
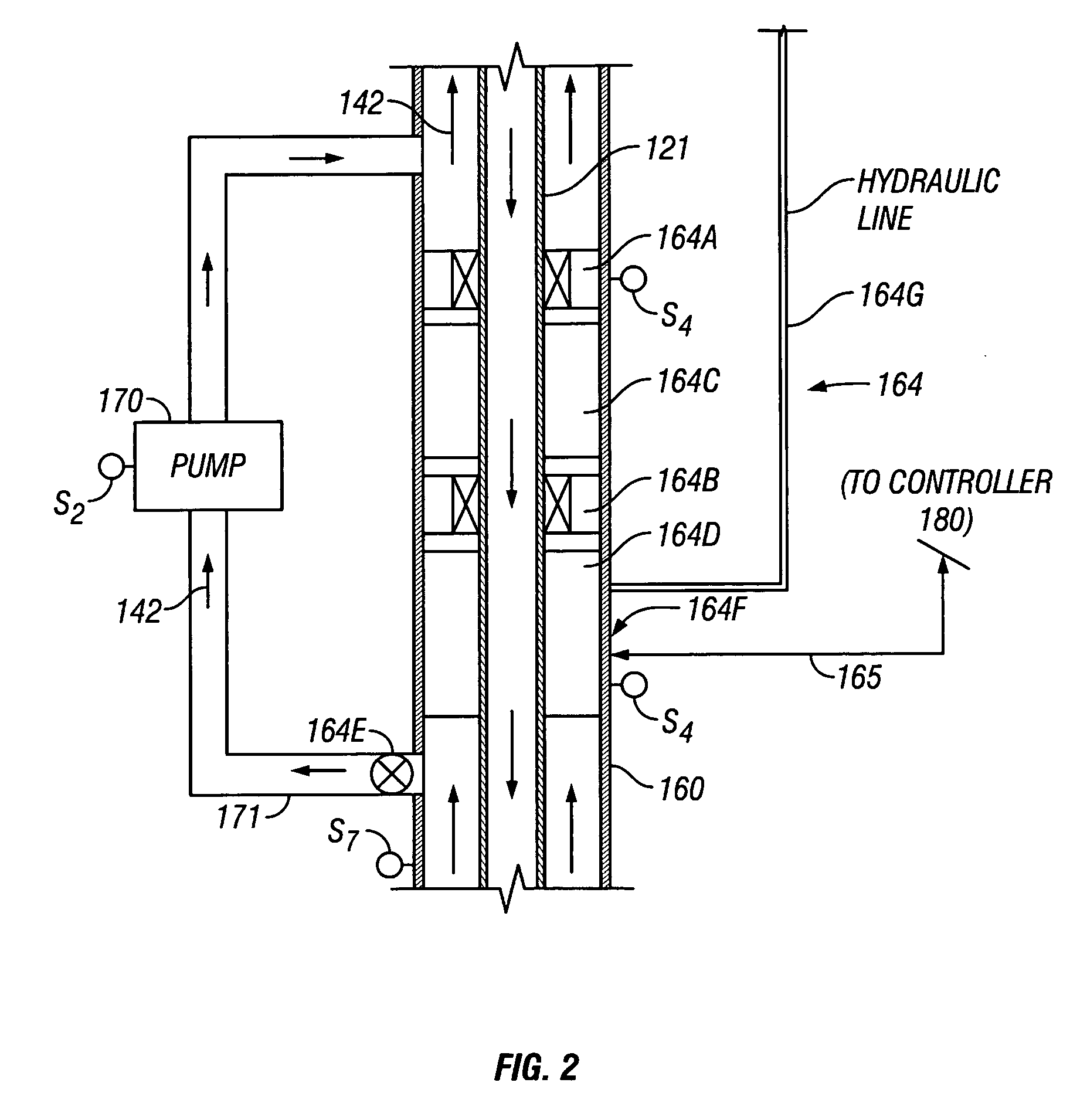
Reverse Circulation Pressure Control Method and System
A system for reverse circulation in a wellbore include equipment for supplying drilling fluid into the wellbore bit via at least an annulus of the wellbore and returning the drilling fluid to a surface location via at least a bore of a wellbore tubular. The system also includes devices for controlling the annulus pressure associated with this reverse circulation. In one embodiment, an active pressure differential device increases the pressure wellbore annulus to at least partially offset a circulating pressure loss. In other embodiments, the system includes devices for decreasing the pressure in the annulus of the wellbore. For offshore application, annulus pressure is decreased to accommodate the pore and fracture pressures of a subsea formation. In still other embodiments, annulus pressure is decreased to cause an underbalanced condition in the well.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
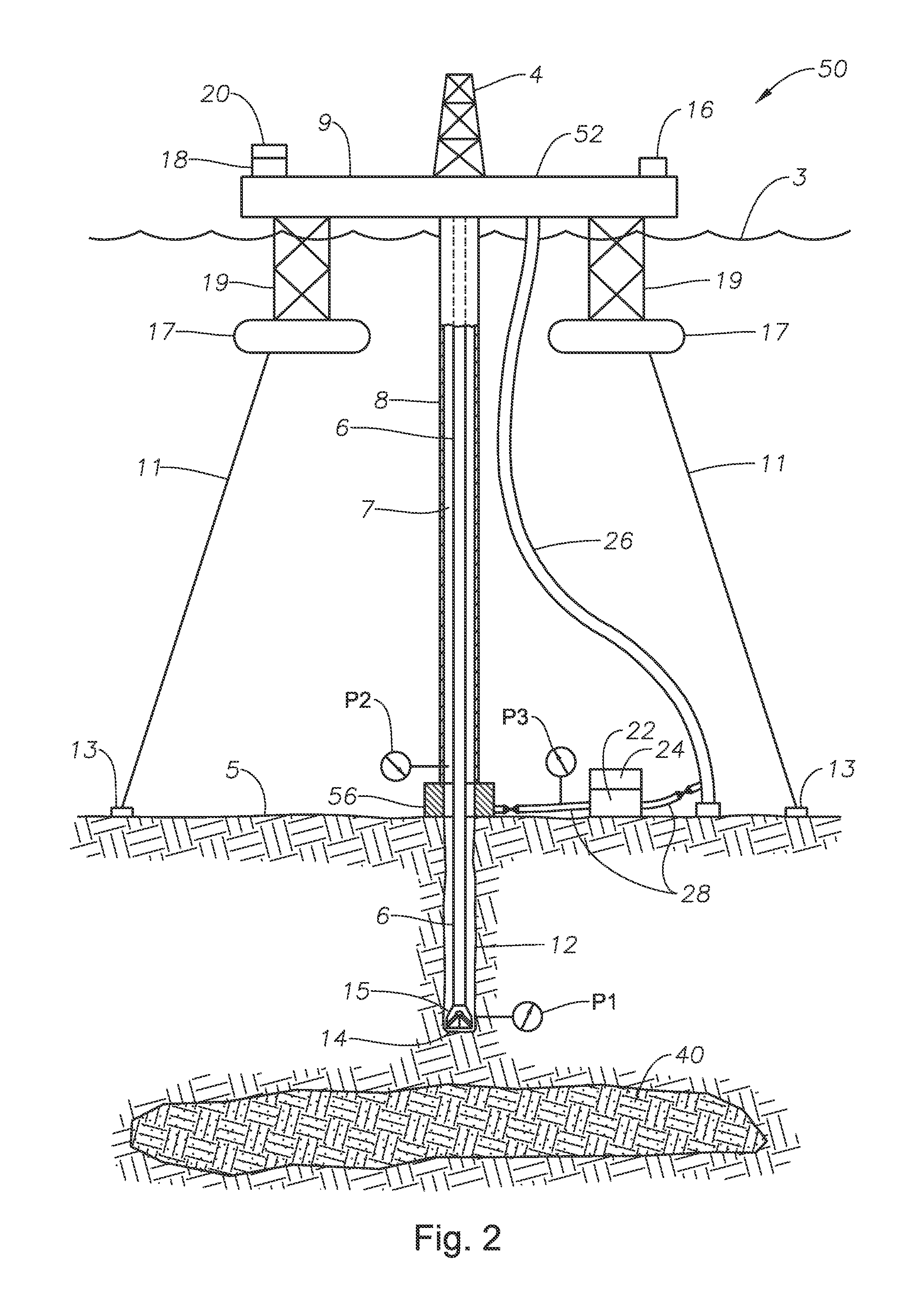
Free standing riser system and method of installing same
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
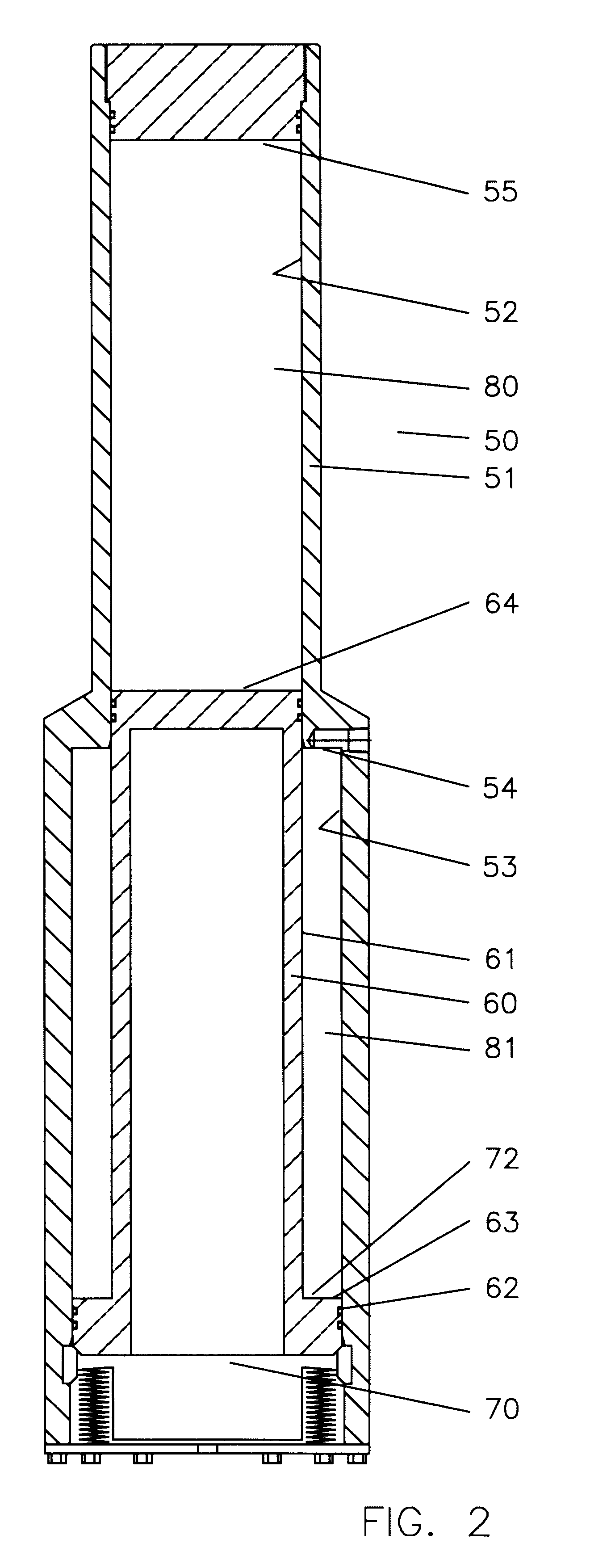
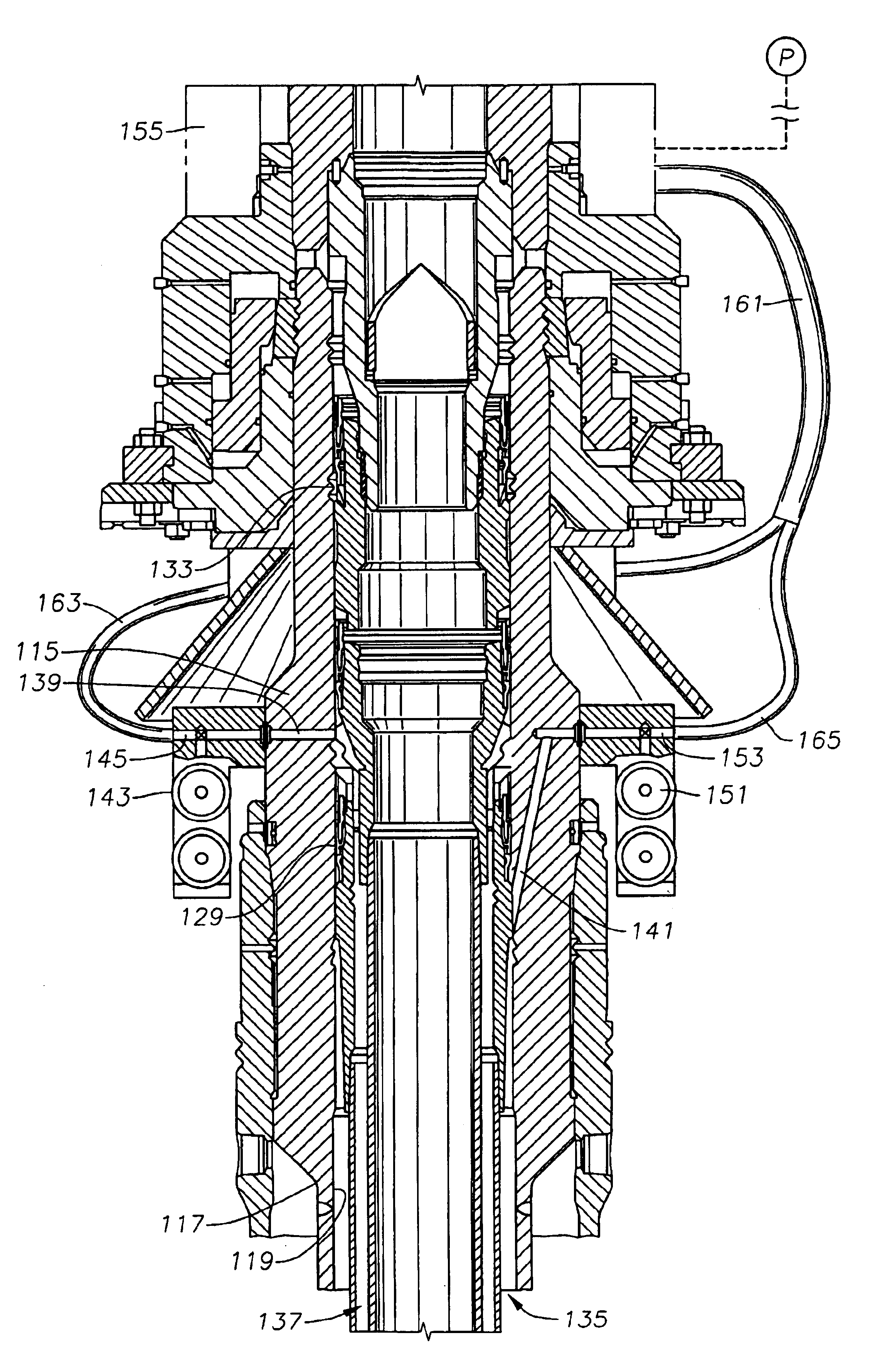
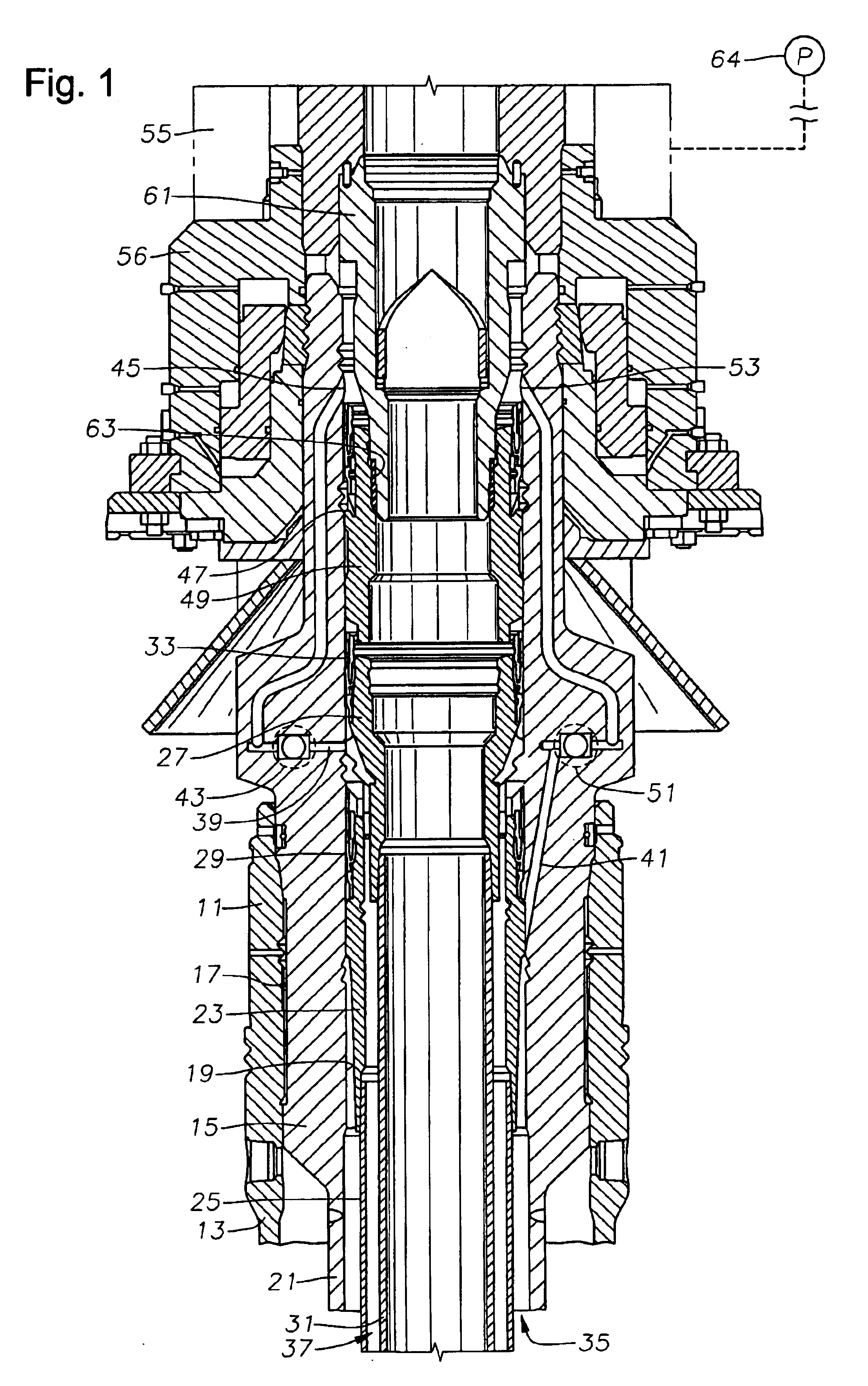
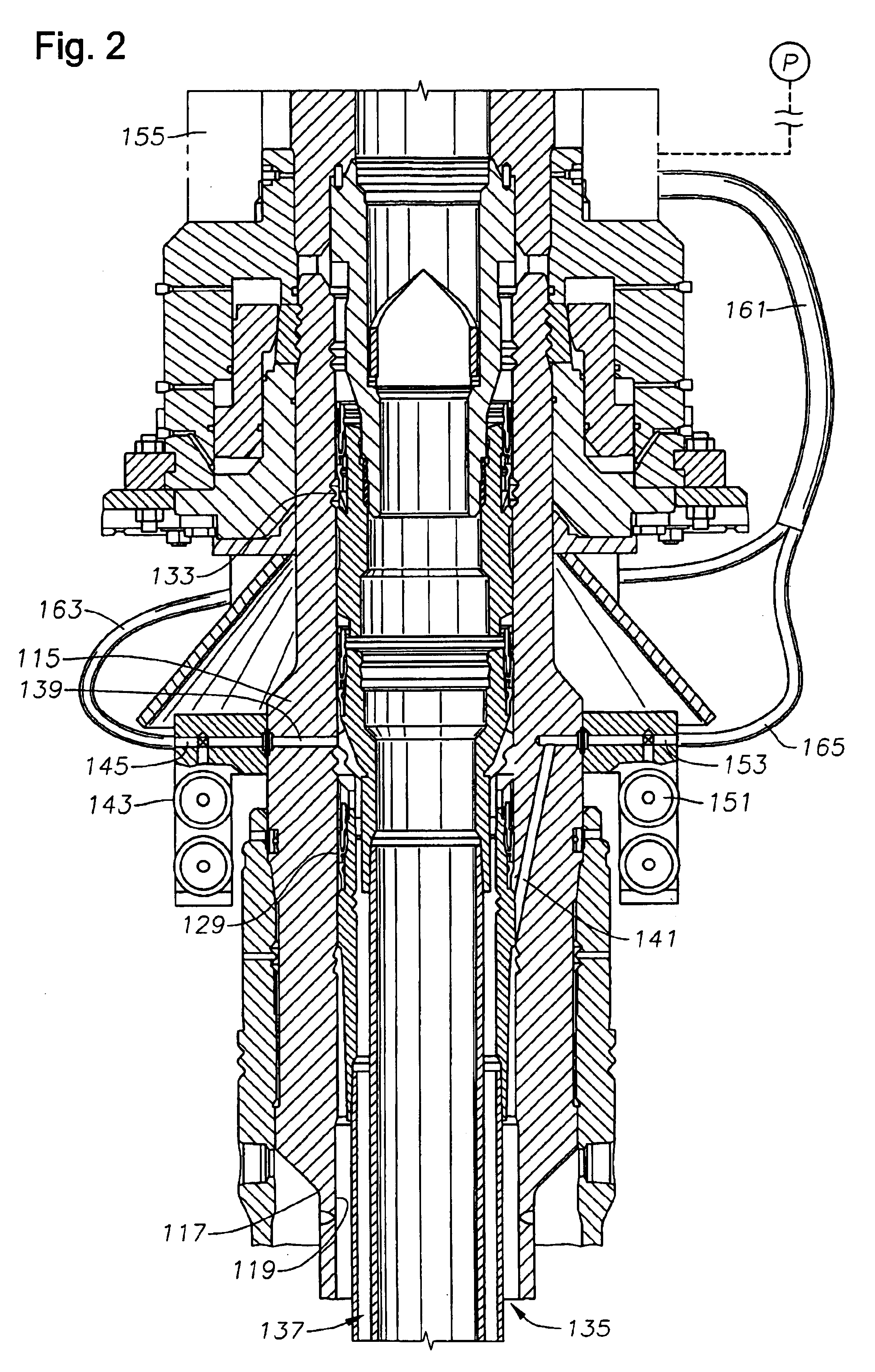
Ported subsea wellhead
A susbsea well has communication passages to enable annulus pressure surrounding inner and intermediate strings of casings to be monitored at the surface. The passages both have outlets that allow communication to the tree assembly for monitoring. In one embodiment, the passage outlets are located in the bore of the high pressure well head housing and communicates to the tree assembly along an isolation sleeve. In another embodiment, the passage outlets are located on the exterior of the high pressure wellhead housing and communicate through a flying lead coming down from the tree. In another embodiment, the passage outlets are located on the exterior of the high pressure wellhead housing and communicate to an upward facing connection which is stabbed with a downward facing connection coming down from the tree.
Owner:ABB VETCOGRAY
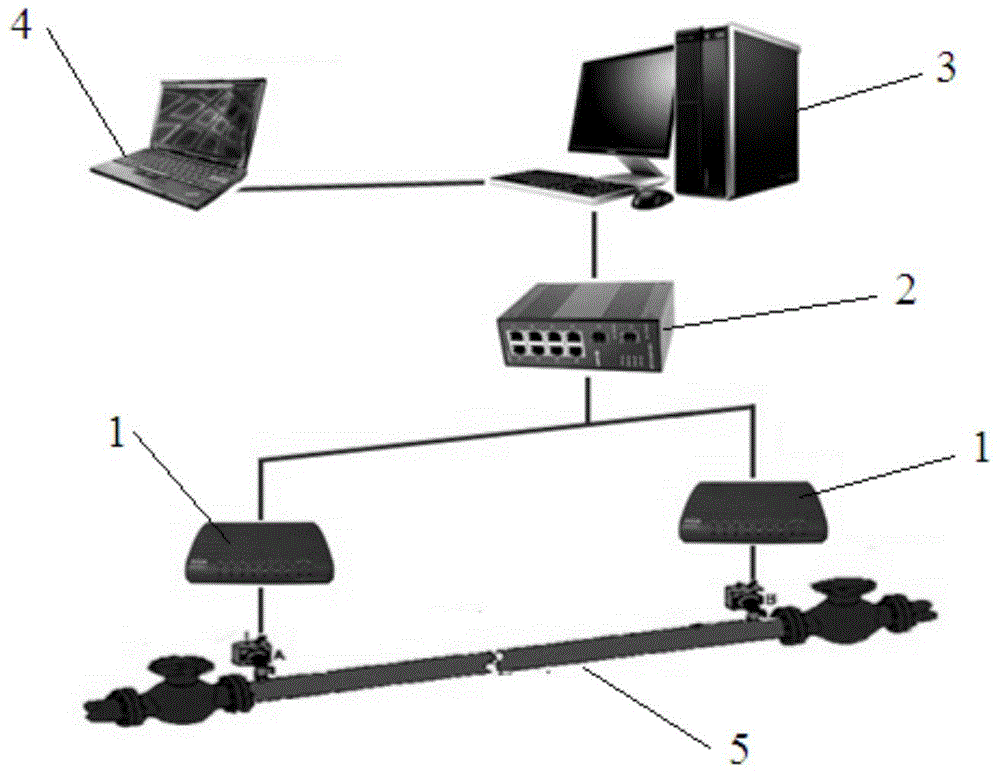
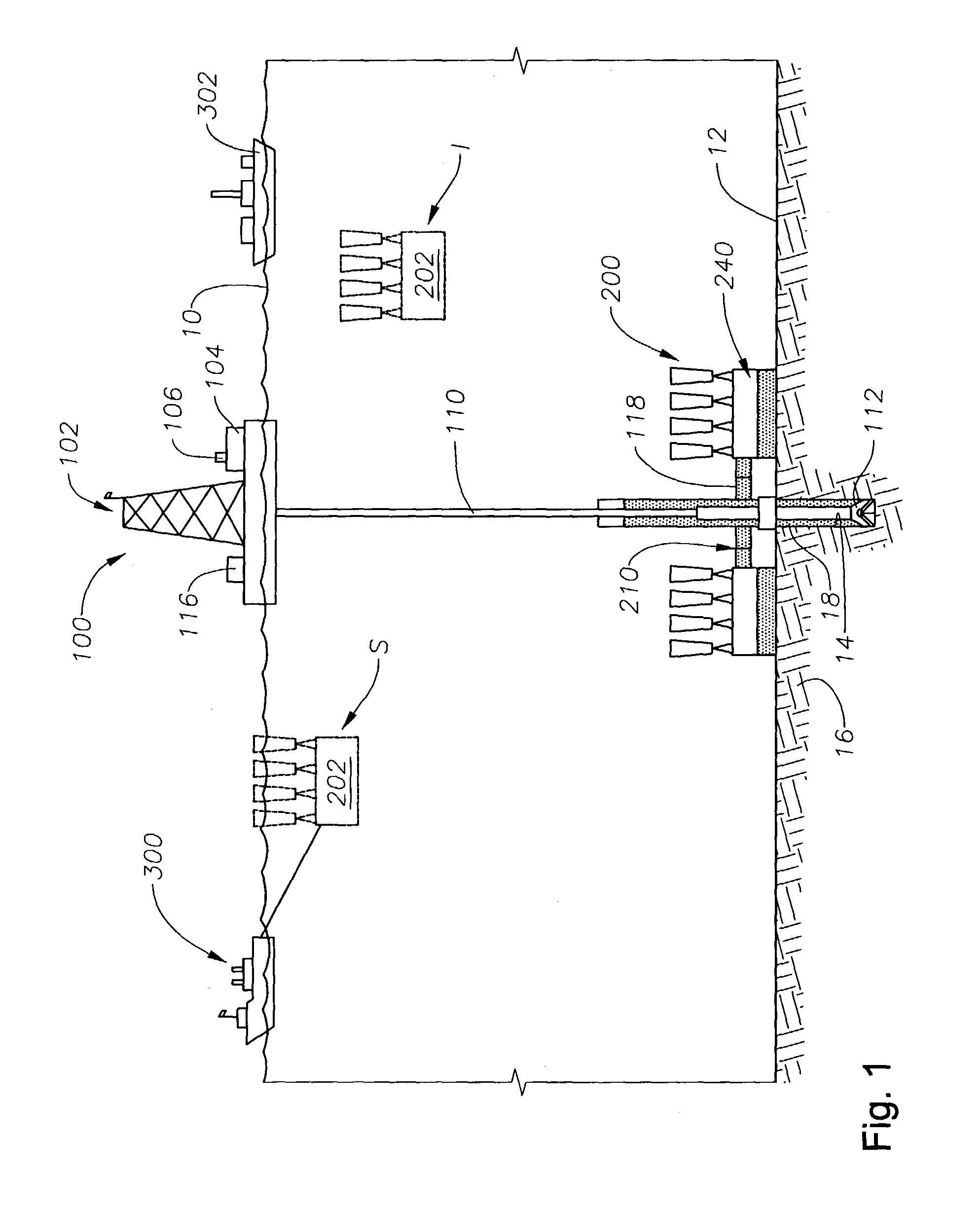
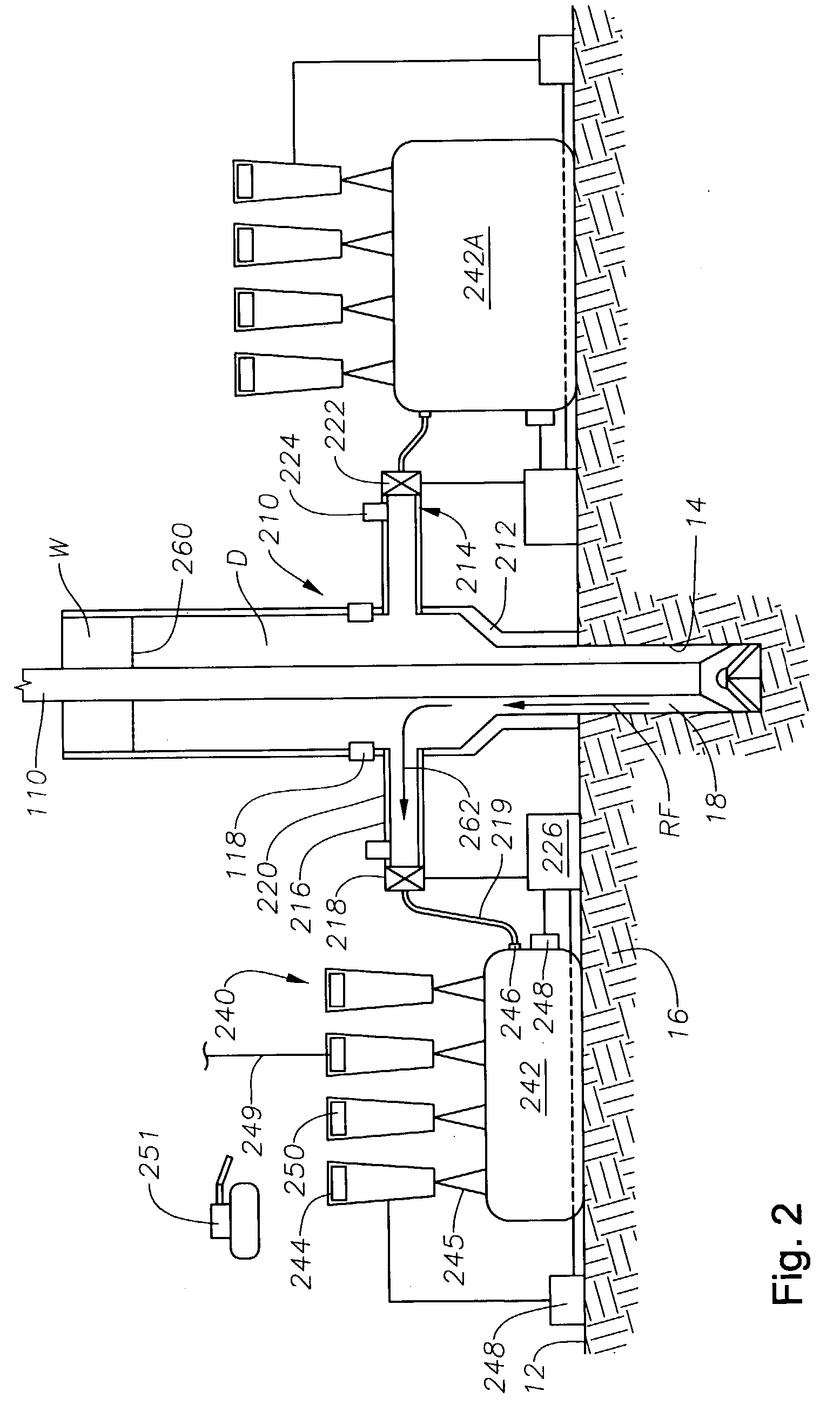
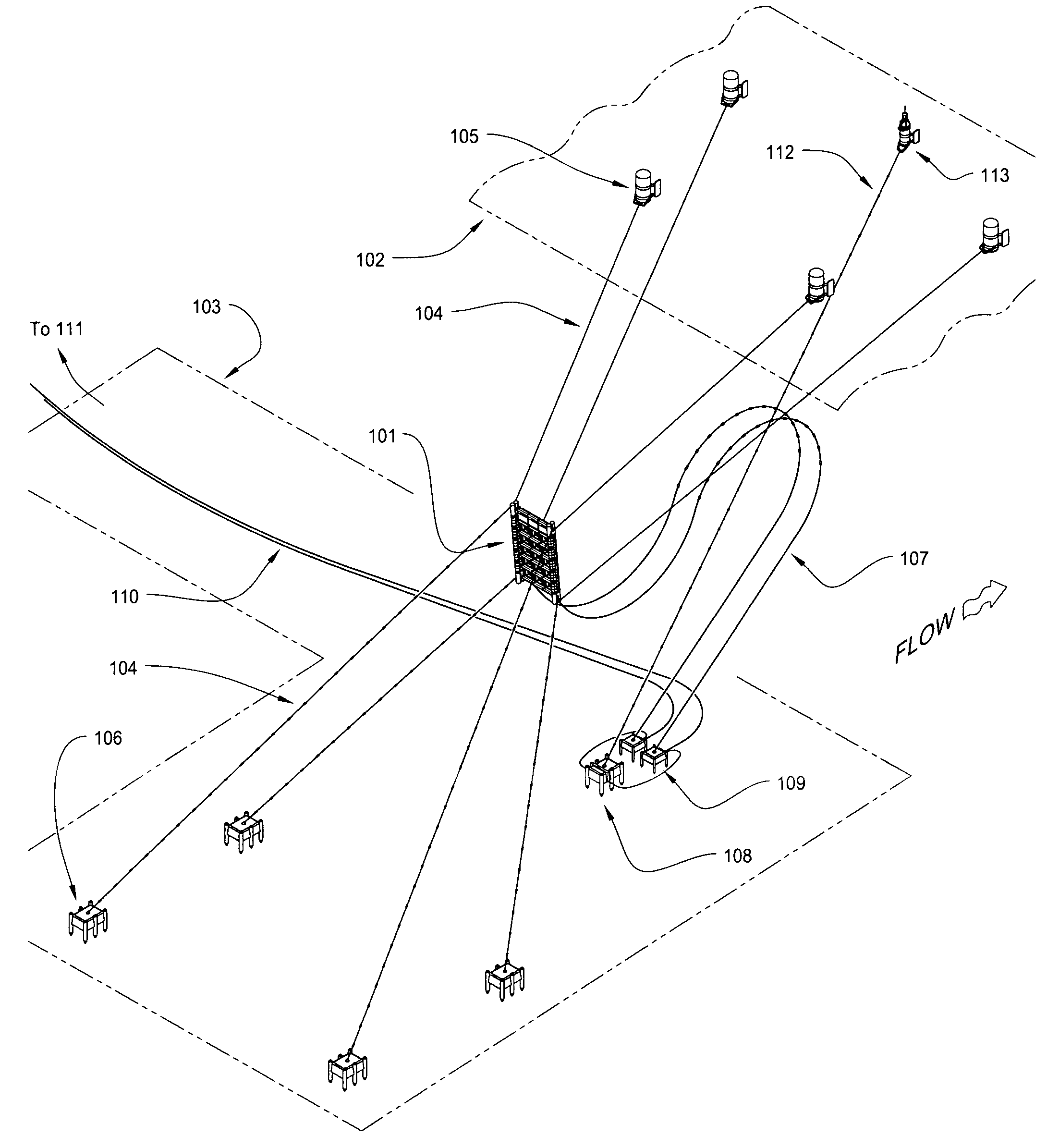
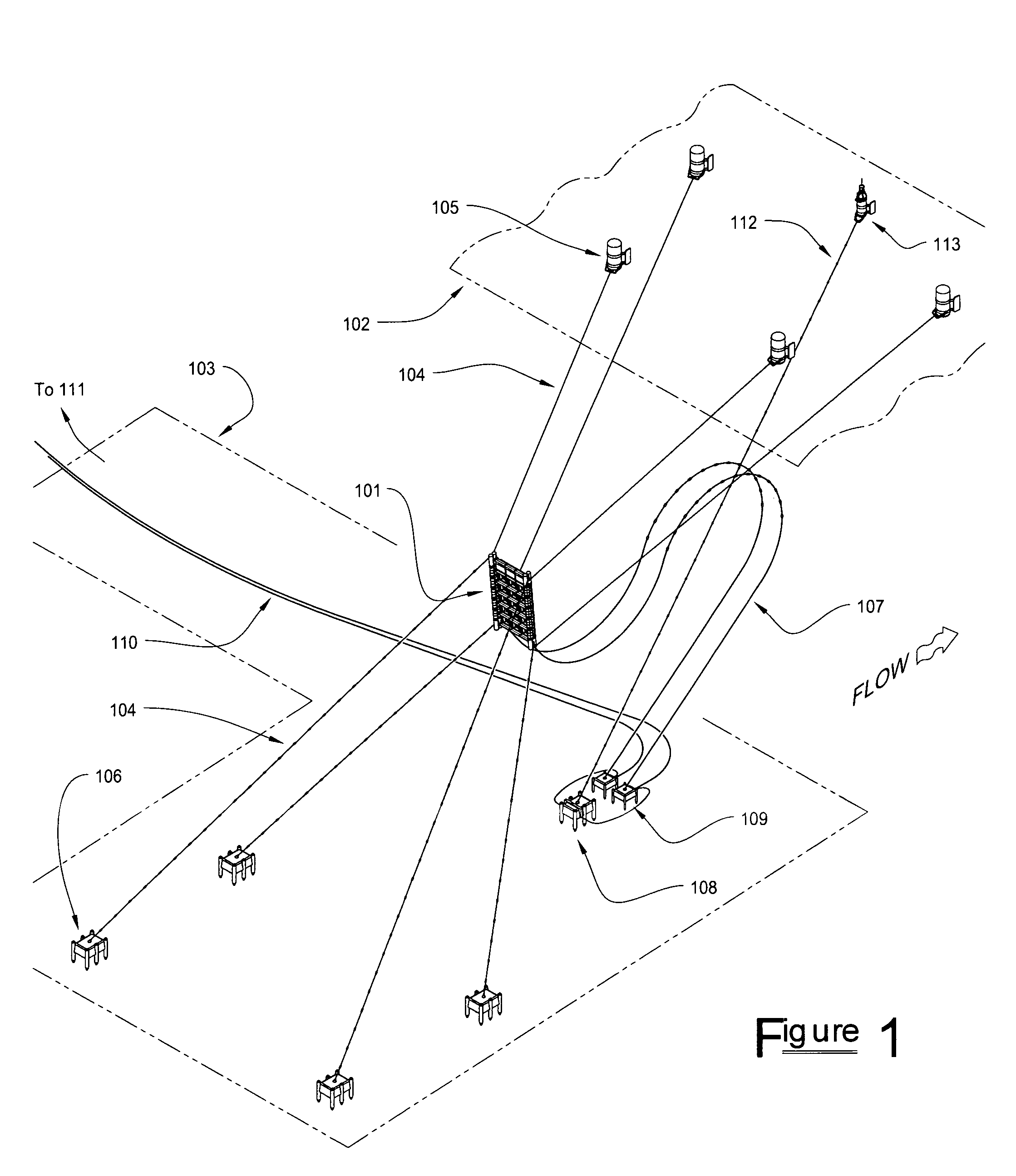
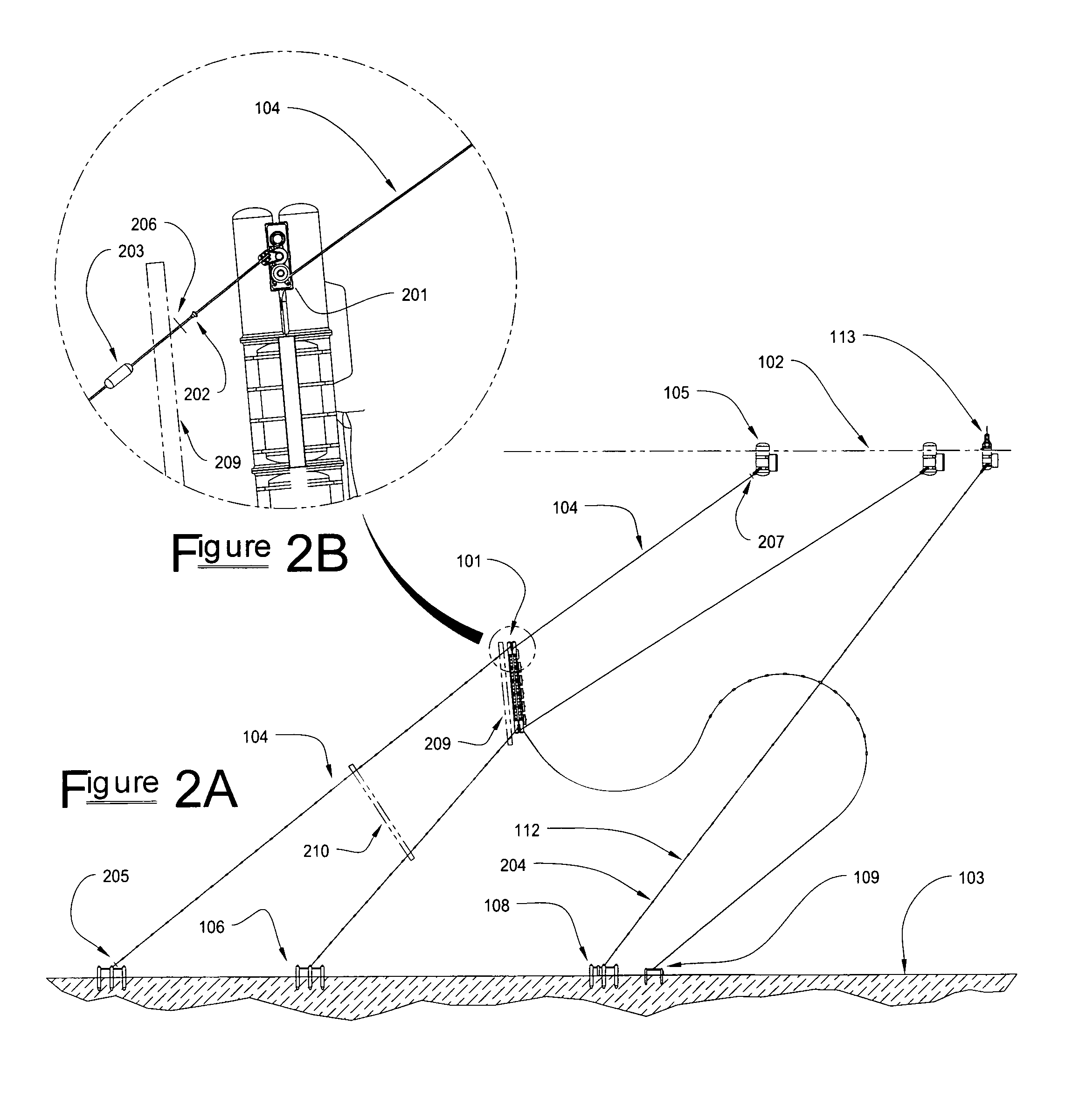
Subsea pipeline leakage monitoring system
The invention relates to a subsea pipeline leakage monitoring system. The subsea pipeline leakage monitoring system comprises controllers, flow sensors, pressure sensors, temperature sensors and a center host computer. The inlet end and the outlet end of a pipeline to be monitored are each provided with one flow sensor, one pressure sensor and one temperature sensor. The flow sensor, the pressure sensor and the temperature sensor at the inlet end collect the flow, pressure and temperature signals of the inlet end in real time and send the flow, pressure and temperature signals to the first controller. The flow sensor, the pressure sensor and the temperature sensor at the outlet end collect the flow, pressure and temperature signals of the outlet end in real time and send the flow, pressure and temperature signals to the second controller. The controllers send the signals to the center host computer through an Ethernet switch, the leakage monitoring system inside the center host computer displays the information in real time and judges where the pipeline to be monitored is leaked or not, a leakage alarm is given out when leakage happens, and the leakage amount and leakage position are worked out and displayed. The center host computer sends the received signals and the judgment result to remote monitoring devices.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +1
Subsea gang connector system
ActiveUS20060079107A1Easy to participatePipe laying and repairPipe elementsGeometric propertyEngineering
A subsea connector system is used to connect internally mounted couplers to provide sealed conduits for subsea operations. The system has a removable (outboard) connector and a fixed (inboard) connector each with a housing having special geometric properties that facilitate alignment and connection of the couplers. The latching mechanism has a latch pin in the fixed connector and a latch sleeve in the removable connector for receiving and latching to the latch pin. The couplers (male and female) and the latching mechanism are located within the housings of the fixed and removable connectors to provide protection for the components from damage during storage, handling, transport and installation operations.
Owner:OCEANWORKS INT
ROV retrievable sea floor pump
A subsea pumping assembly locates on a seafloor for pumping well fluid from subsea wells to the level. The pumping assembly has a tubular outer housing that is at least partially embedded in the seafloor. A tubular primary housing locates in the outer housing and has a lower end with a receptacle. An annular space surrounds the primary housing within the outer housing for delivering fluid to a receptacle at the lower end of the primary housing. A capsule is lowered in and retrieved from the primary housing. The capsule sealingly engages the receptacle for receiving well fluid from the annular space. A submersible pump is located inside the capsule. The pump has an intake that receives well fluid and a discharge that discharges the well fluid exterior of this capsule. The capsule has a valve in its inlet that when closed prevents leakage of well fluid from the capsule. The capsule may be retrieved through open sea without a riser.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
System and method for recovering return fluid from subsea wellbores
InactiveUS7185705B2Recovery system and method be enhanceImprove methodDerricks/mastsFluid removalCritical path methodEngineering
A subsea return fluid recovery system for recovering drilling fluid and cuttings (“return fluid”) from a subsea wellbore in one embodiment includes a hub at the opening of the subsea wellbore that directs fluid into a transport device. In one embodiment, the hub includes a stand pipe that forms a return fluid column, the hydrostatic pressure of which causes return fluid to flow into the transport device rather than up the stand pipe. One or more buoyant members attached to the transport device convey the transport device toward the surface. A preferred recovery method includes collecting return fluid at the seabed, passively transporting the collected fluid to the surface, and processing the collected fluid at a local (offshore) or land based treatment facility. The retrieval and processing of the return fluid is done outside the critical path of the drilling activities at an offshore platform.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
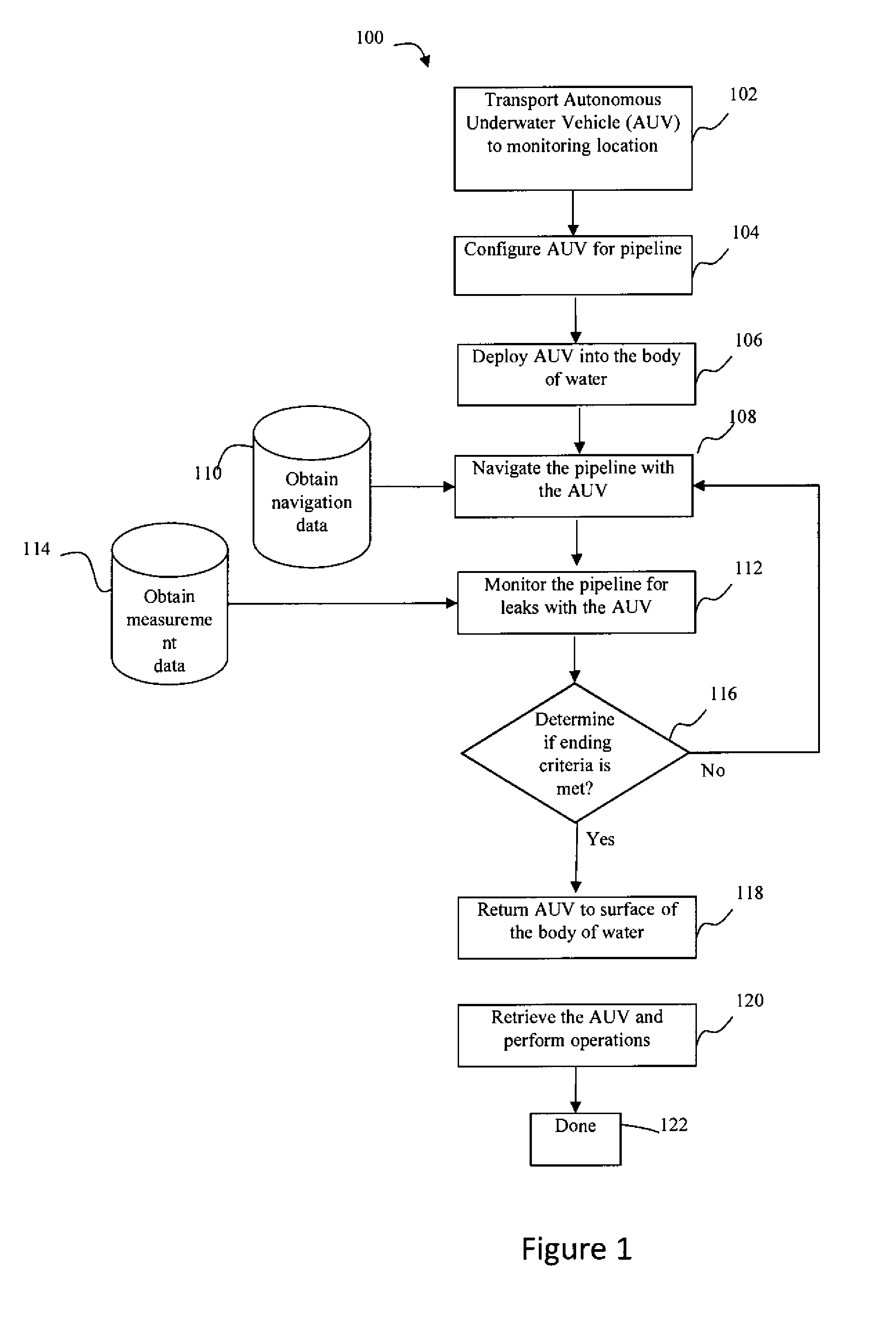
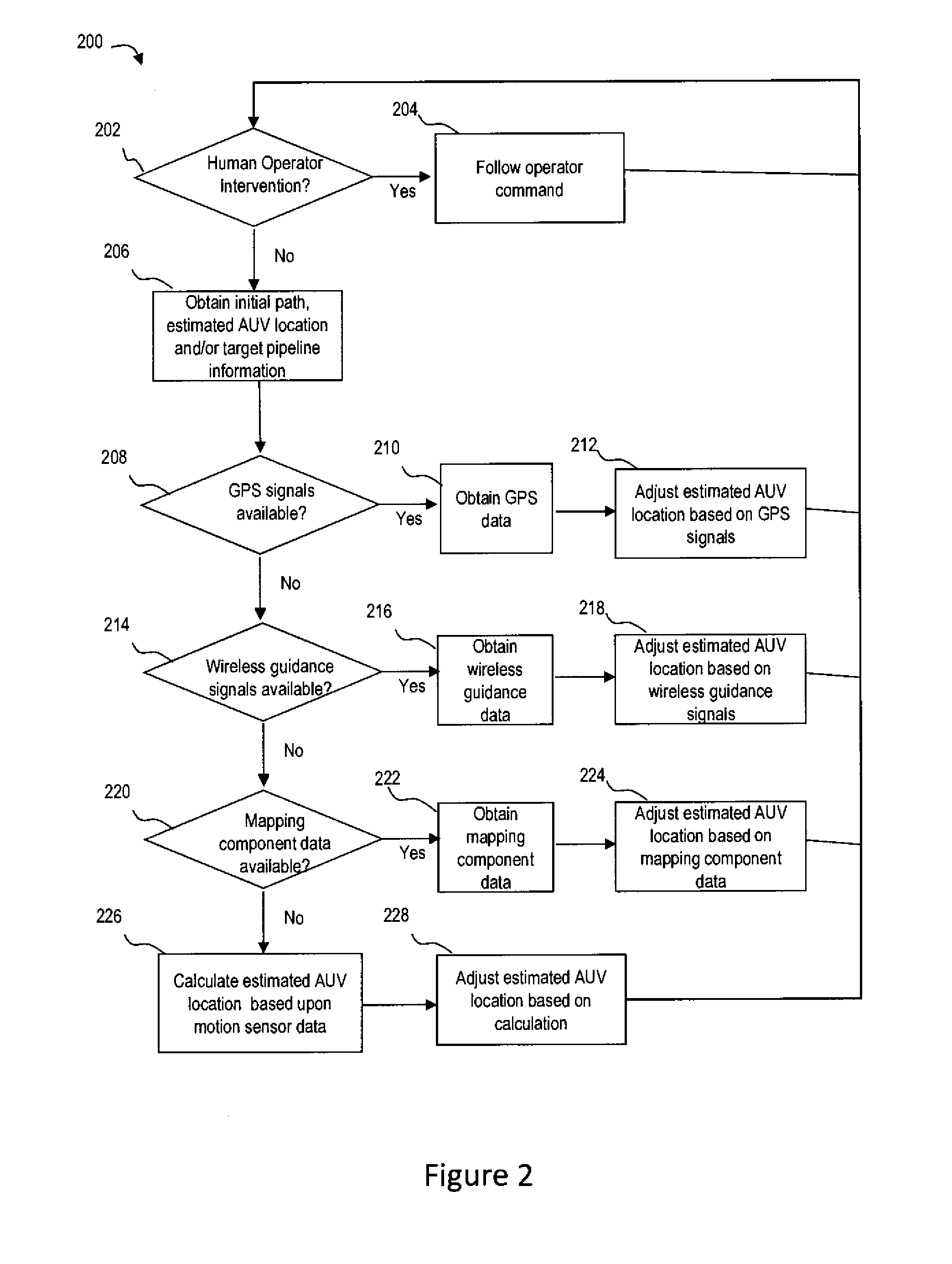
Method and System for Subsea Leak Detection Using Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV)
ActiveUS20150192488A1Television system detailsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesOcean bottomMarine engineering
Method and system is described for enhanced subsea leak detection by using autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) that is equipment with measurement components and navigation components. The method and system may include a one or more wireless communication components for navigation. Also, the method and system may include one or more sensors to detect leakage from a pipeline.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Submersible tethered platform for undersea electrical power generation
InactiveUS7470086B2Eliminate needEasy to separateWater-power plantsMachines/enginesElectric cablesSubmarine
A submersible and remotely-operable platform system for carrying out repeated operations in a submarine position, and producing electrical energy as either a primary or secondary purpose by means of one or more energy-conversion payload devices installed thereon. The platform and payload devices may be periodically brought to the surface and thence, if necessary, to a shore-based facility for maintenance or refit. In deployment, the platform is preferably engaged to its mooring lines and electrical cables while still on the surface. Simultaneous with controlled flooding of certain of its volumes, the platform is guided to an operational depth and attitude by the action of its winch assemblies upon their engaged mooring lines. Subsea currents energize the platform's payload of energy conversion devices, the electrical output being preferably conveyed via one or more surface-attached cables to an off-board facility for further processing, distribution, or consumption.
Owner:JENNINGS CLIFFORD ALLEN +1
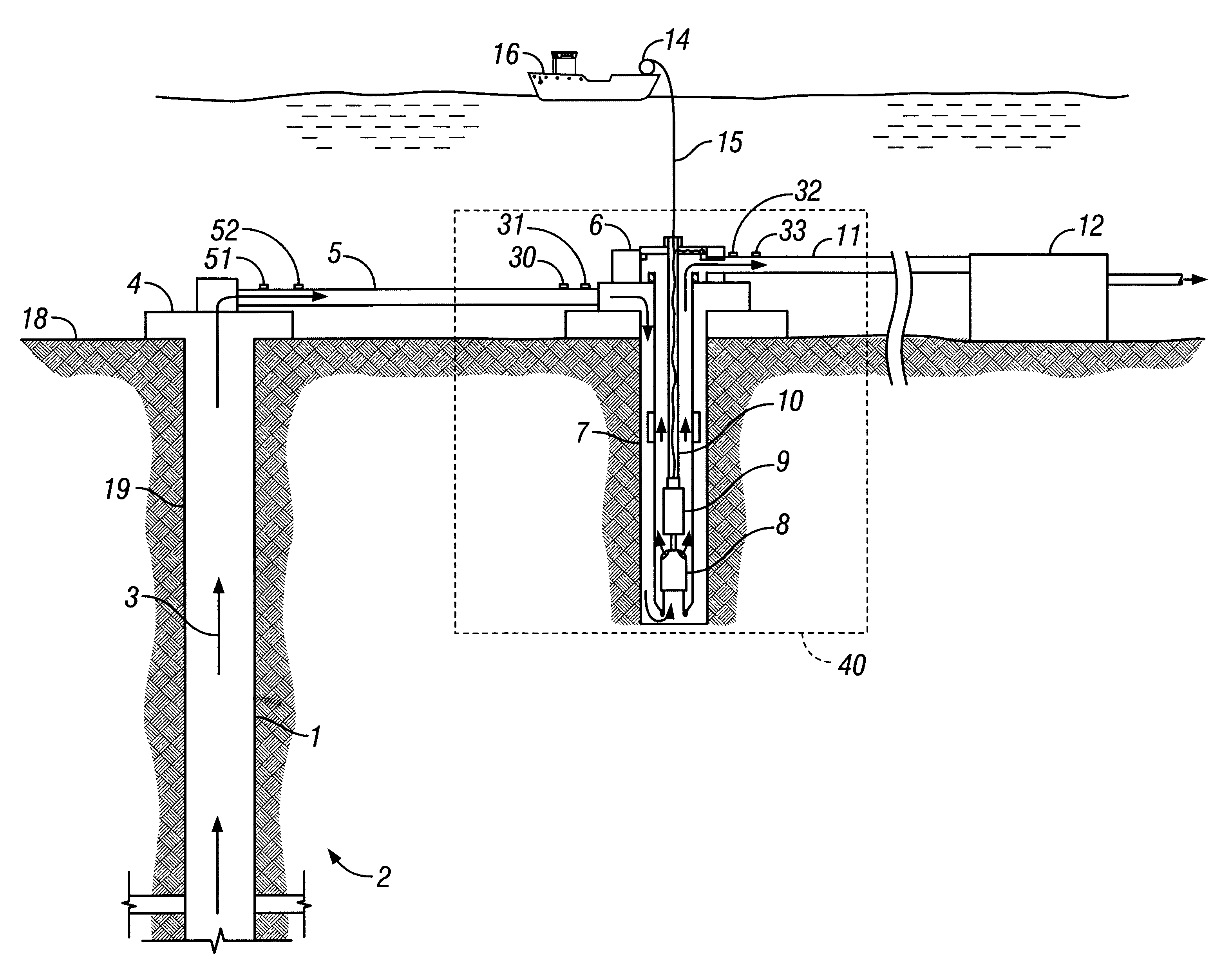
Subsea petroleum production system method of installation and use of the same
ActiveUS20060118310A1Long transportLow costFluid removalUnderwater drillingProduction lineOcean bottom
A subsea production system for producing petroleum by artificial elevation, assisted by submersible centrifugal pumps (SCPs) upstream of the WCT and installed on the seabed, includes a pumping module having one of more SCPs, installed in series or in parallel, with an inclination of up to 85 degrees in relation to the vertical, the module being connectible to a flow base to permit the “bypass” of production and wherein the pumping module and the flow base may be linked to installation and recovery by cable. A production line is connected upstream to the pumping module upstream and another production line is connected downstream to the pumping module. A method of installing the system in a new wellhead is described, as well as a method for installing the system in an existing wellhead. The uses of the subsea production system for boosting multiphase flow, injection of water in an injector well and the transfer of oil between two points of collection are also described.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
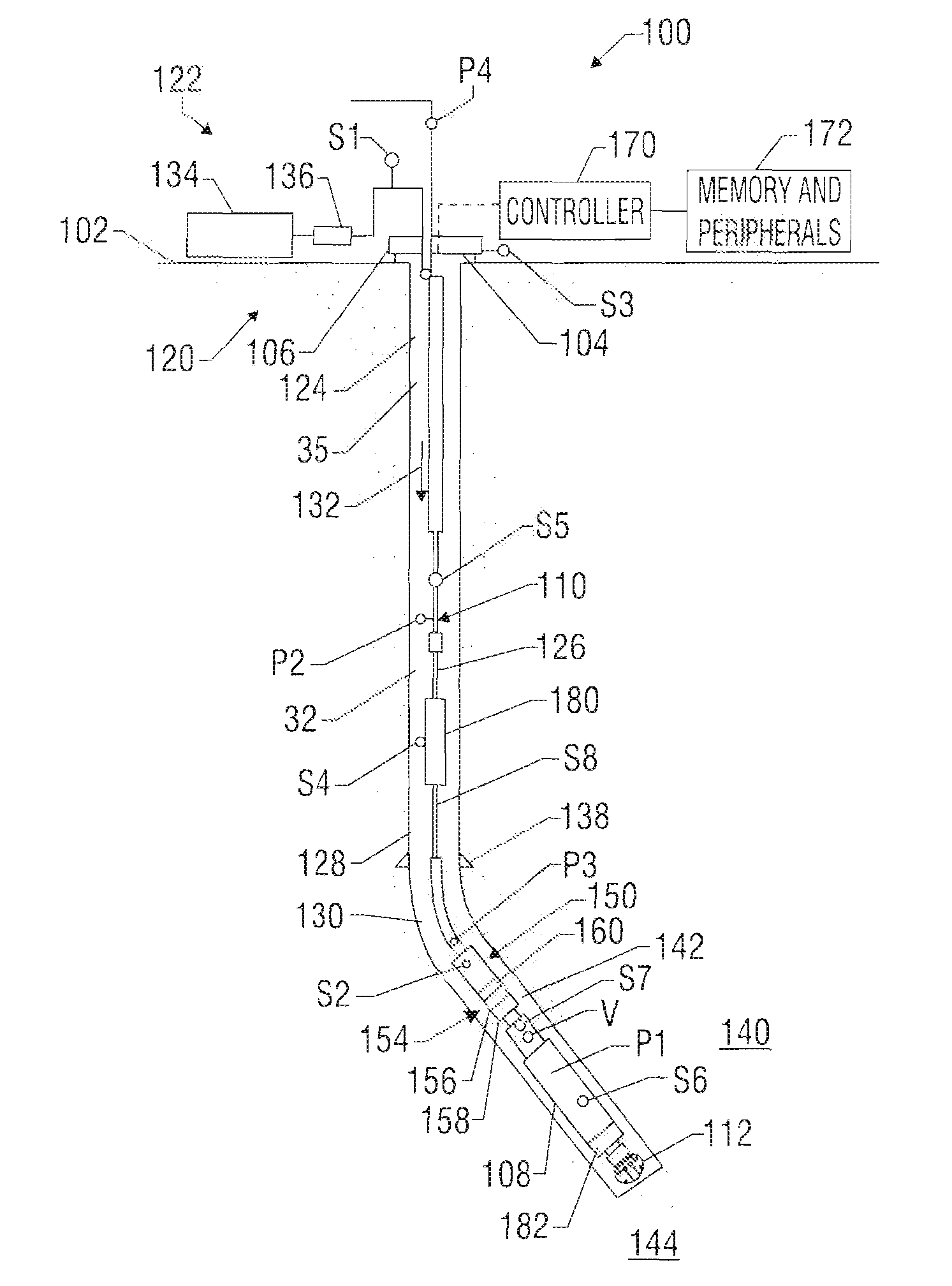
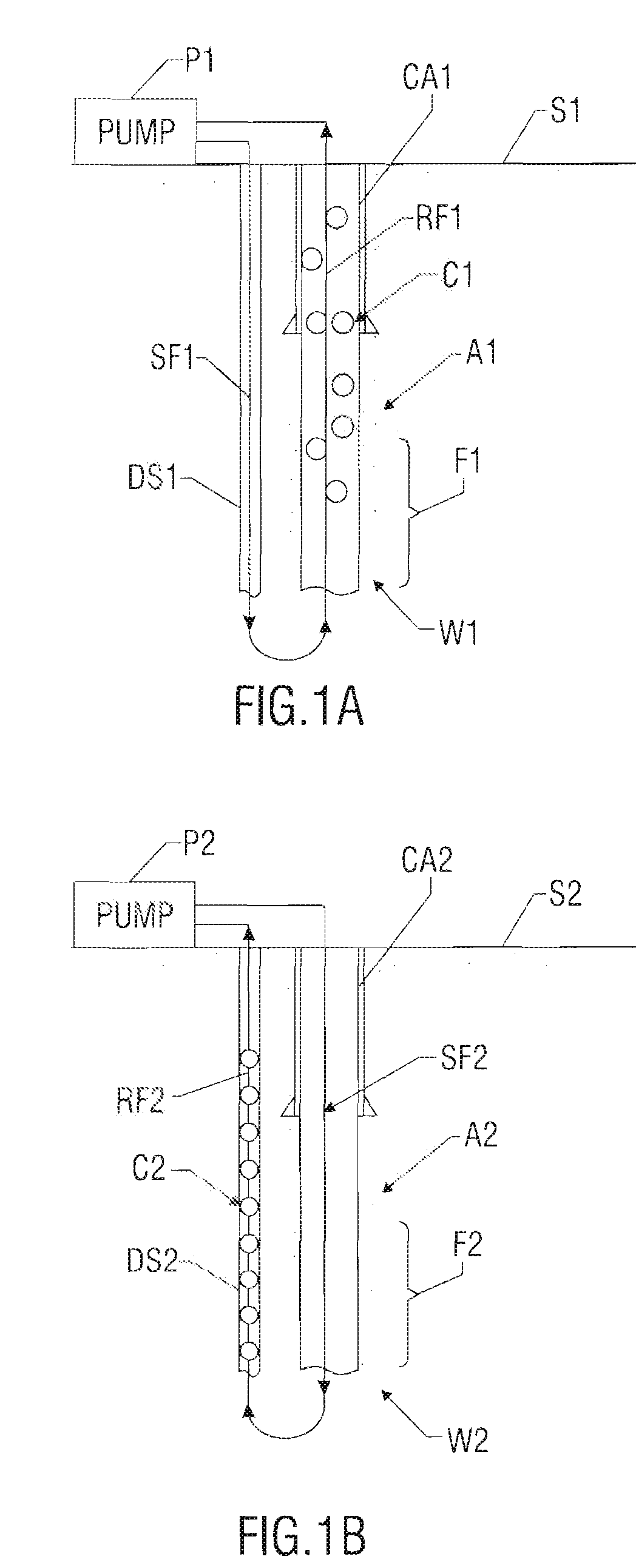
Systems and methods for circulating out a well bore influx in a dual gradient environment
Methods and systems for drilling subsea wells bores with dual-gradient mud systems include drilling the subsea well bore while employing a subsea pumping system, a subsea choke manifold and one or more mud return risers to implement the dual gradient mud system. When a well bore influx is detected, the well bore is shut in, and components determine if pressure control may be used to circulate the influx out of the well bore, the size of the influx, and how much the mud system weight will need to be reduced to match the dual gradient hydrostatic head before the influx reaches the subsea pump take point. The subsea pumping system, subsea choke manifold, and mud risers are isolated while the influx is circulated up one or more fluid passages in the drilling riser package using the surface pump, through the wellhead, and out the surface choke manifold.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
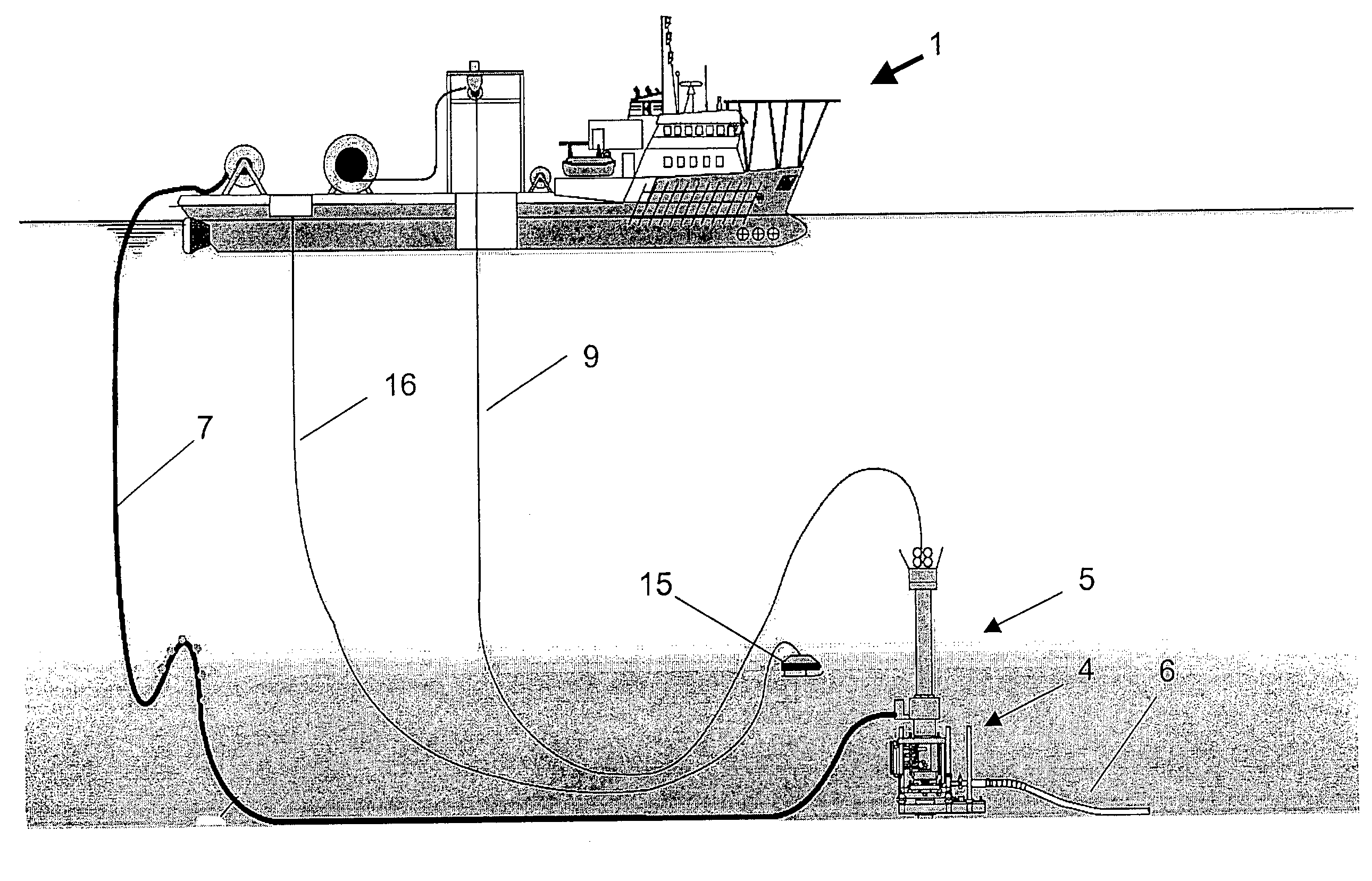
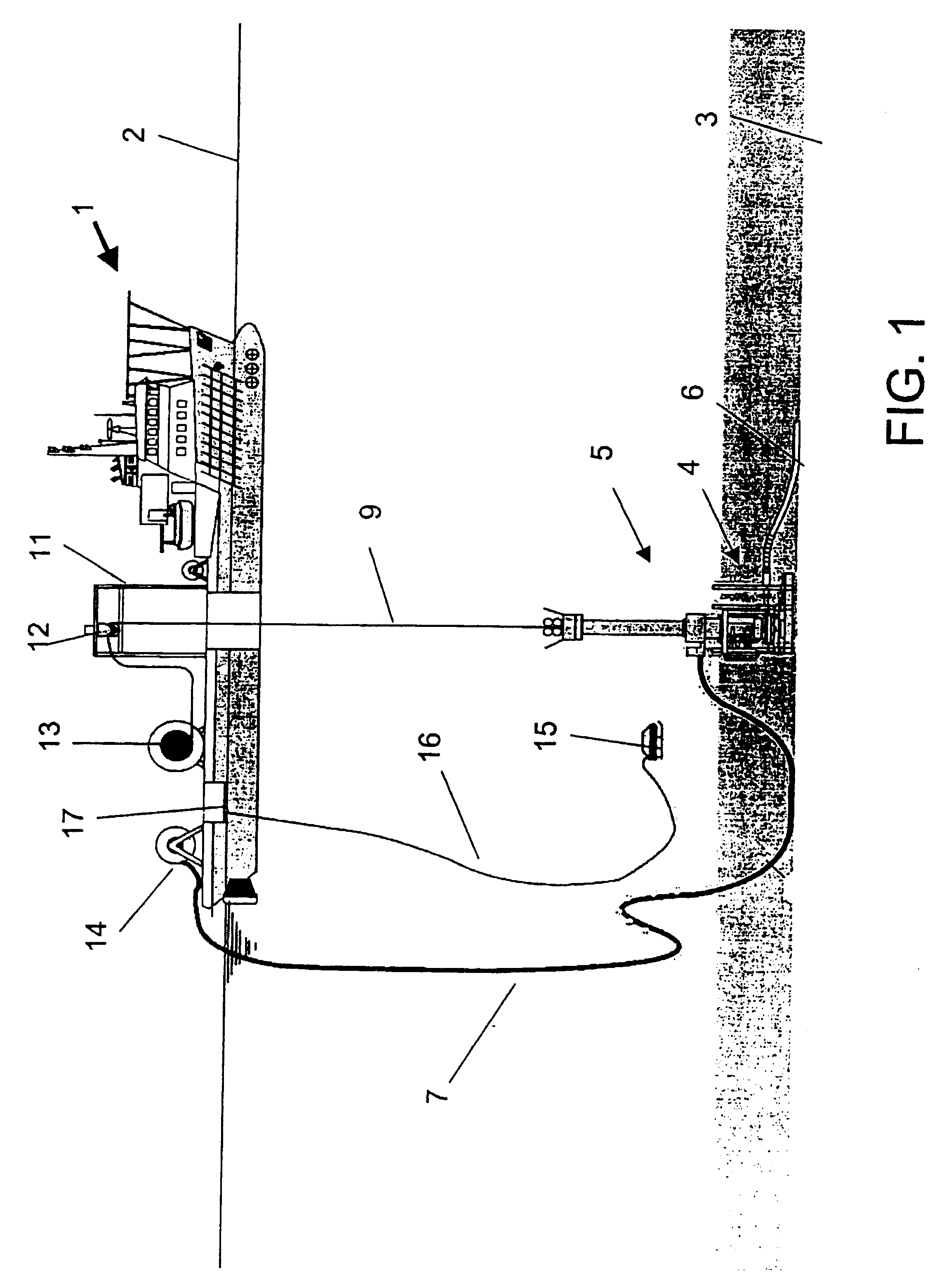
Intervention device for a subsea well, and method and cable for use with the device
InactiveUS20030155127A1Different lengthEnough timeDrilling rodsFluid removalEngineeringElectric cables
A device for intervention of a subsea oil and / or gas well by means of a tool (8) suspended by a cable (9), fed from or withdrawn to a vessel (1) and driven by a drive mechanism (12) located on the vessel. The device comprises a lubricator (5) having a tool housing for the insertion of the tool into the well, and a stuffing box (40) sealing around the cable after the tool is inserted into the well. According to the invention an injector which drives the cable in the well is located on the lubricator, and is controllable independently of the drive mechanism for the cable located on the vessel. The drive mechanism and the injector may be synchronized in a manner, among others, providing that the cable is hanging in a predetermined arc during the intervention, whereby the vessel may be moved from the well. Moreover, the invention relates to a method and a cable used together with the device.
Owner:FMC KONGSBERG SUS
Methods and apparatus for installation of VIV suppression during installation of marine pipeline
InactiveUS20050254903A1Reduce resistanceReducing vortex-induced-vibrationsPipe laying and repairProtective foundationOcean bottomEngineering
Methods and apparatus for the installation of VIV suppression during the S-Lay installation of a subsea pipeline. A locking member will be interposed between a pipe and a fairing rotatably mounted on the pipe, sufficient to bias the fairing against rotating. Upon marine application, the locking member will degrade, thereby releasing the fairing.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
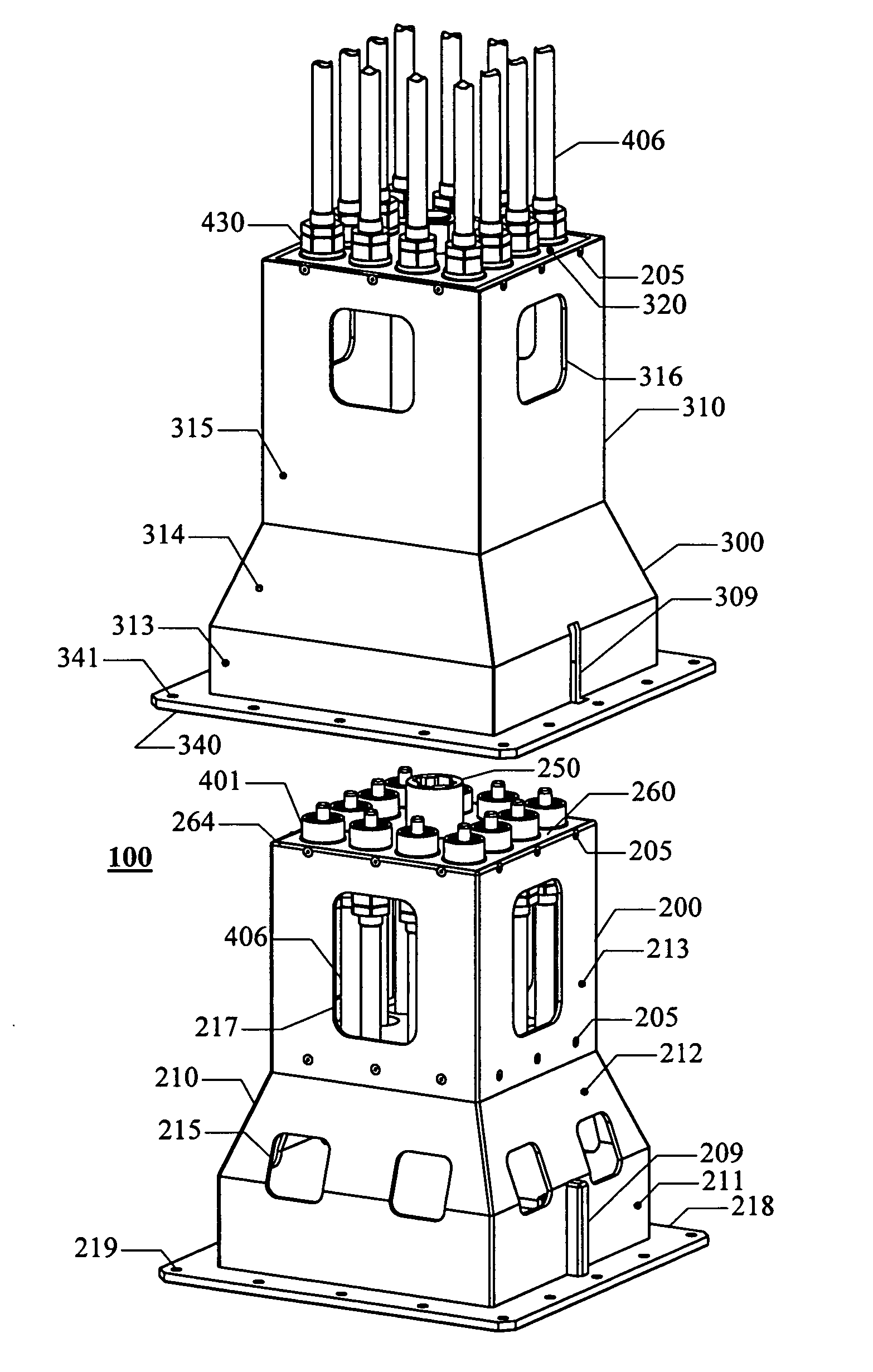
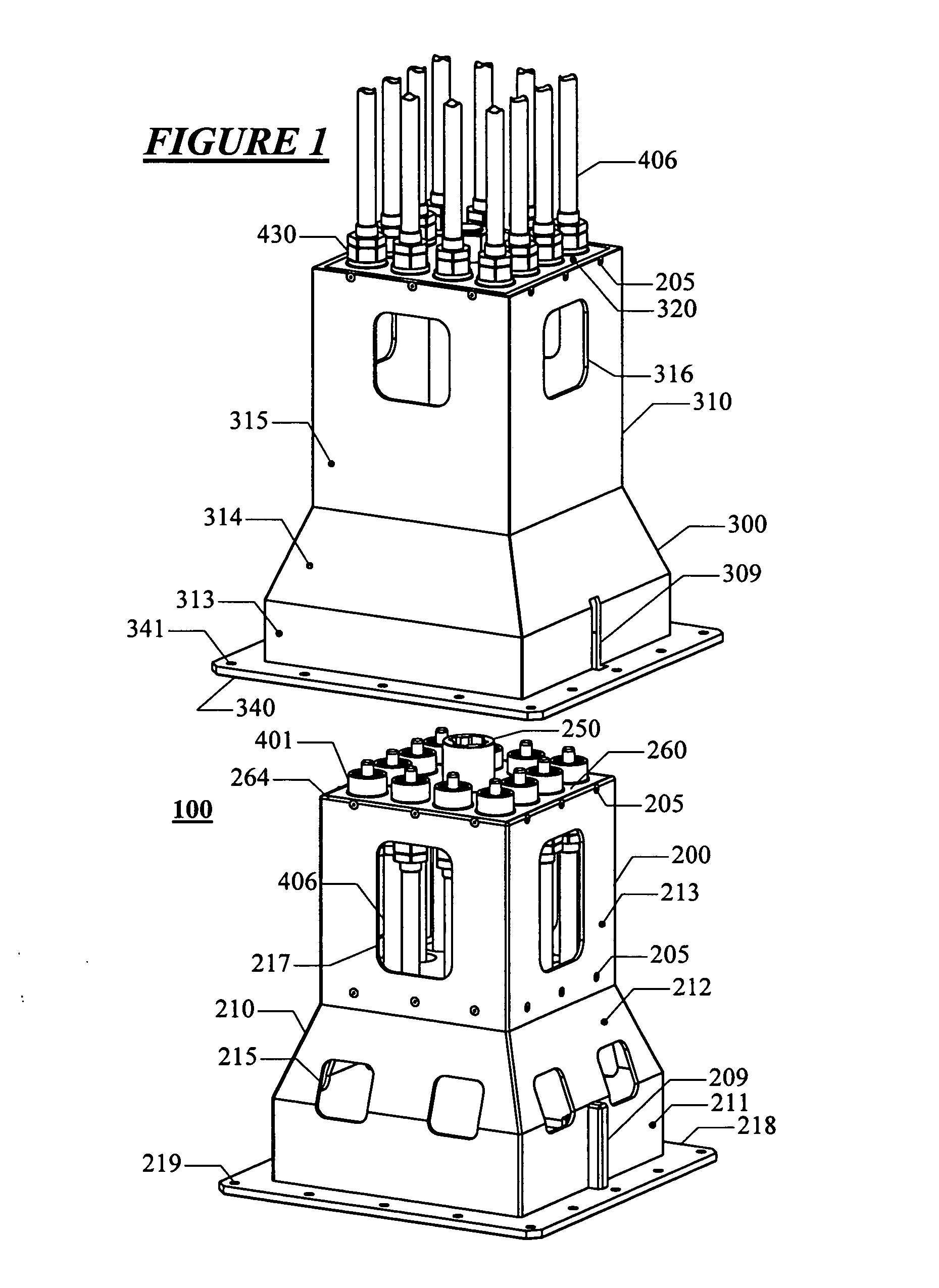
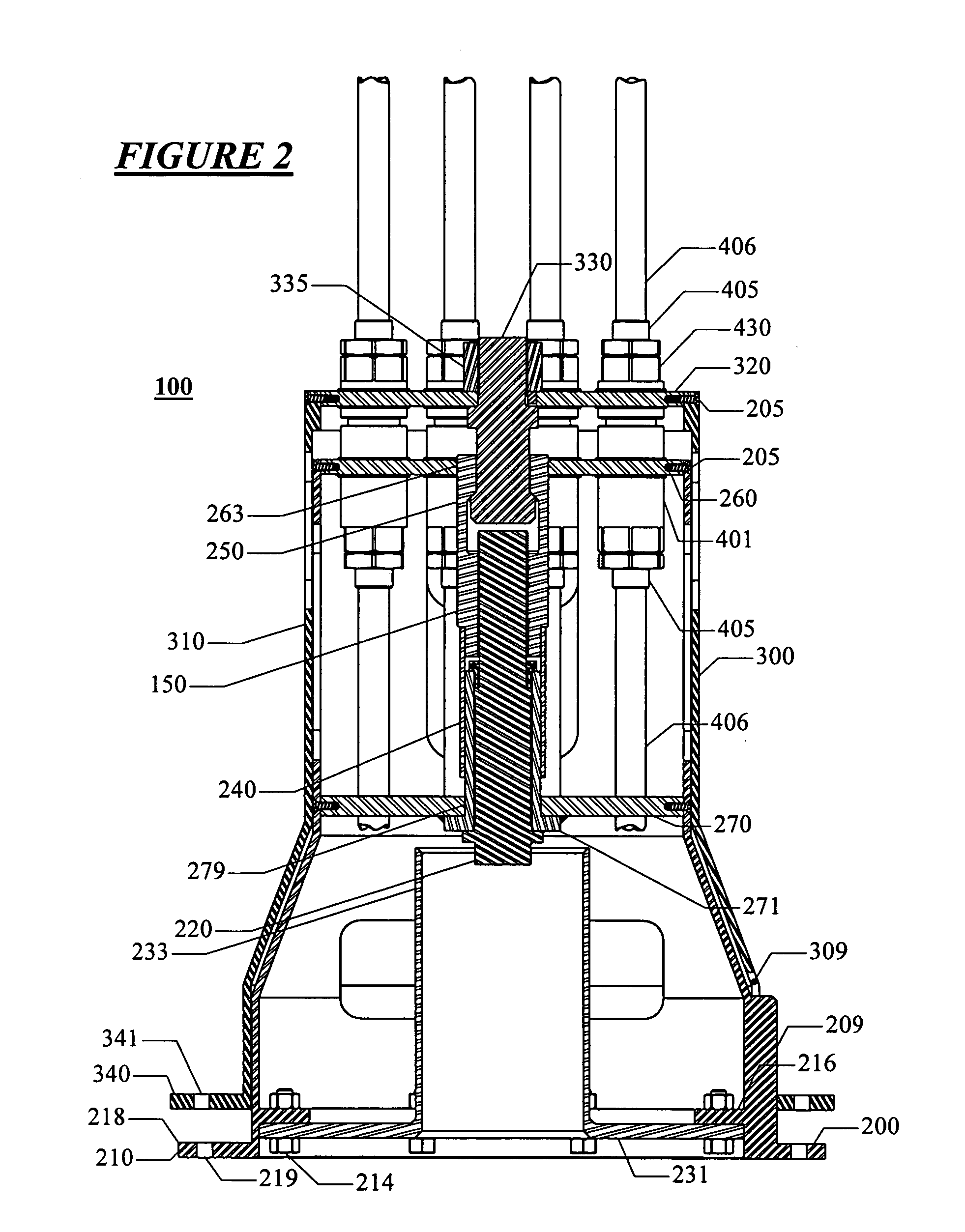
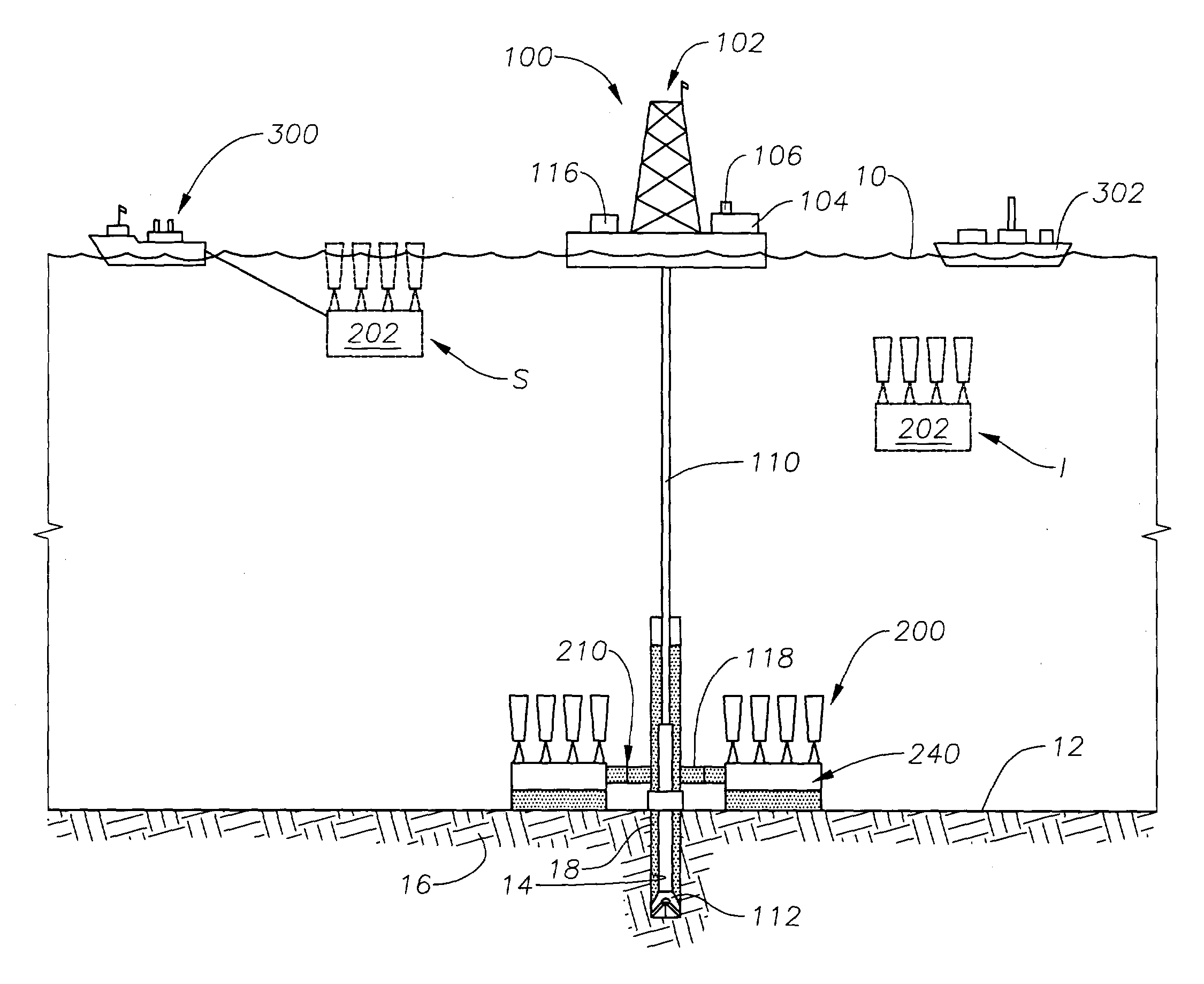
System for direct vertical connection between contiguous subsea equipment and method of installation of said connection
ActiveUS20060231266A1Promote exchangeLow costDrilling rodsFluid removalHydrocotyle bowlesioidesEngineering
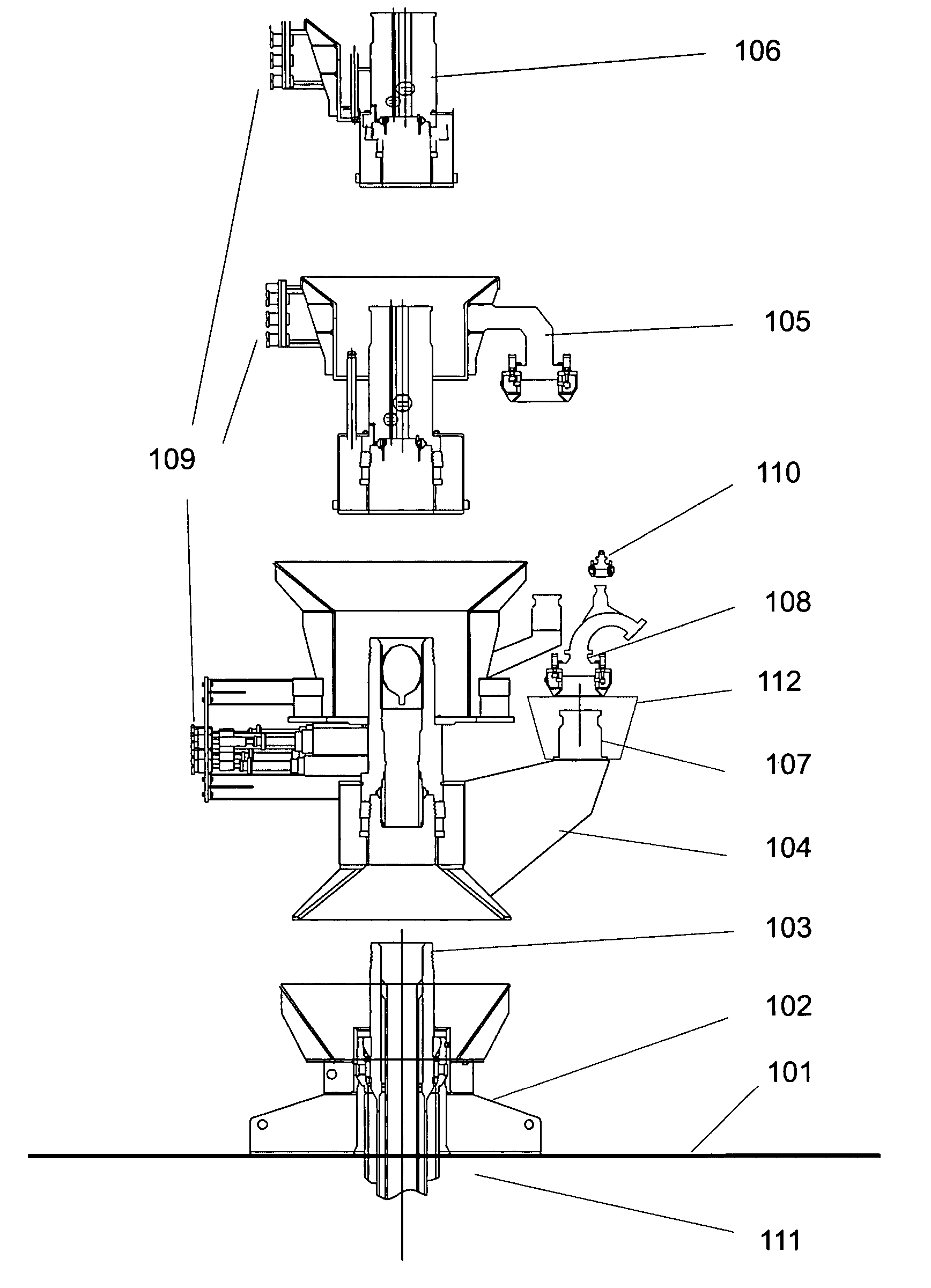
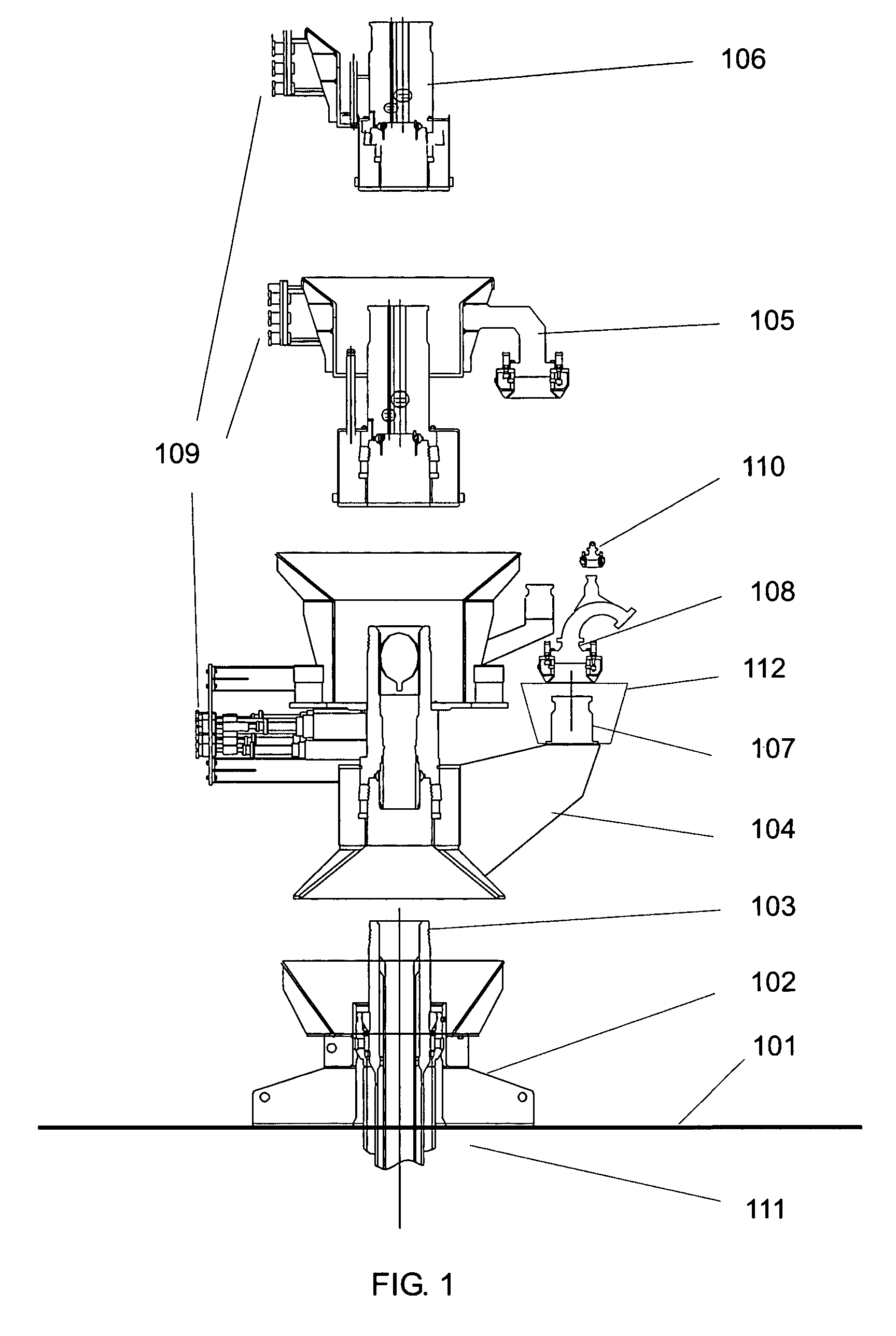
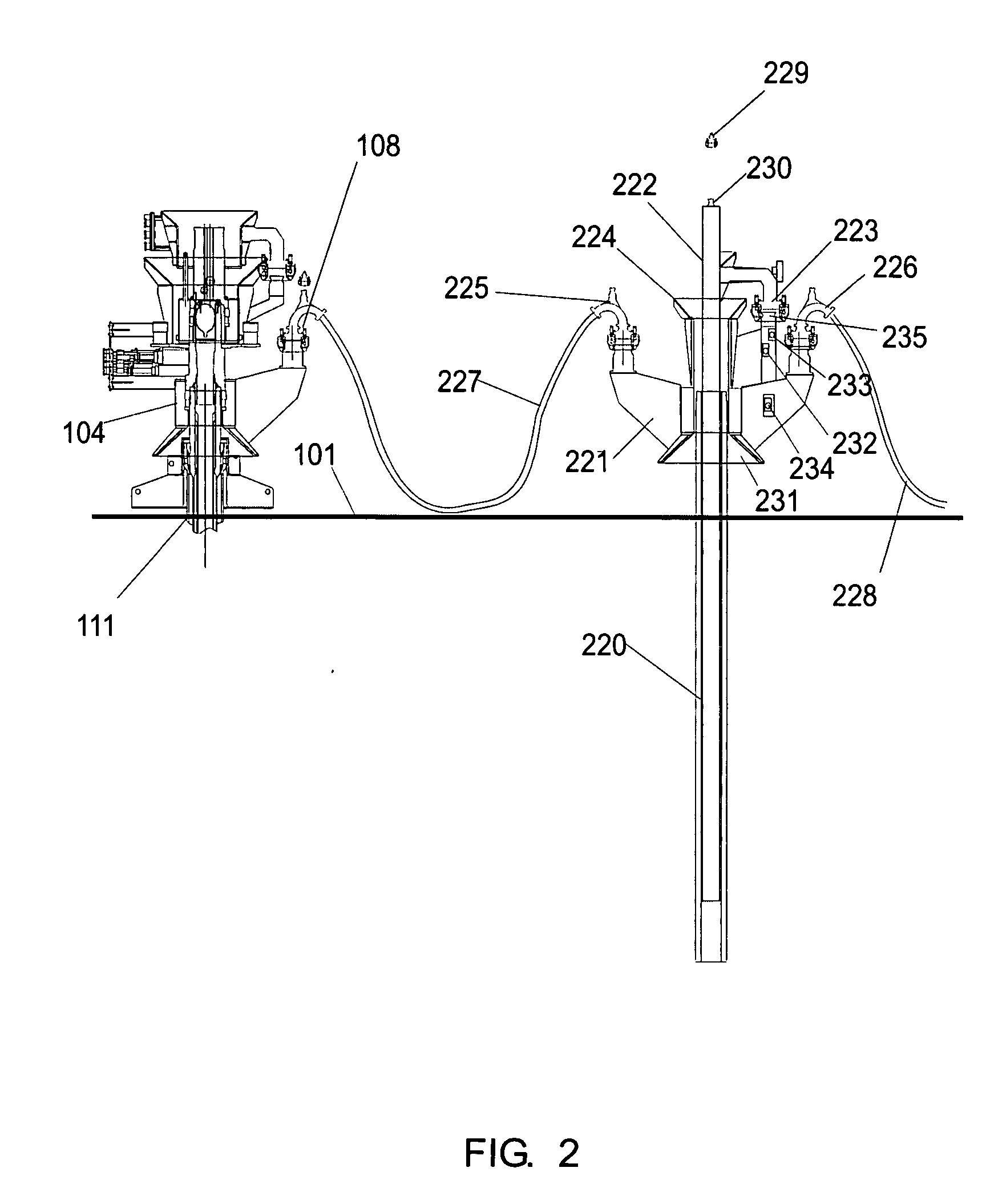
A system for the direct vertical connection between contiguous sub sea equipment is described, having one or more hydrocarbon flow and / or control interconnection between same, so as to dispense with the use of connecting jumpers. One mode of said system comprises a PuAB 221 vertically and directly connected to a PrAB 104. Equipment is directly fixed through the PuAB connector 251 with a PrAB 104-production mandrel 107, said mandrel being fitted with a funnel guide 112. PuAB 221 is fitted with a funnel 224 so as to guide the drilling of a cased borehole 220 in the marine soil 101, close to well 111. Once the cased borehole 220 is ready, PuAB 221 will be locked to the casing of said borehole 220 by means of a locking system, so as to complete the mechanical and hydraulic connection between the two devices, PuAB and PrAB or HWCT. Two modes of the method for installation of said system are also described.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Subsea oil and gas pipeline detecting and locating apparatus and process
InactiveCN101046466ARealize real-time detectionThe recognition effect is accurateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationOcean bottomLine tubing
The present invention discloses subsea oil and gas pipeline detecting and locating apparatus and process. The subsea oil and gas pipeline detecting and locating apparatus consists of an electrically driven creeping device, a creeping device controller, a high energy power source, an intelligent controller, a real-time locater, an ultrasonic acquiring processor, and an ultrasonic eddy flow detector connected through shaft couplings. The operation process includes the following steps: hose sweeping the pipeline and throwing the apparatus into the pipeline, moving the apparatus with the electrically driven creeping device under the control of the intelligent controller, detecting and locating the fault to be repaired, etc.
Owner:SHENGLI PETROLEUM ADMINISTRATION BUREAU DRILLING TECH ACAD SINOPEC
Apparatus for and method of installing subsea components
InactiveUS20020129755A1Lower potentialReduce the impactCargo handling apparatusAnchor handling/lashingWire rodControl theory
Owner:AKER MARINE CONTRACTORS
Subsea test apparatus, assembly and method
ActiveUS20110000677A1Reduce adverse effectsPrevents measuring meanSurveyDrilling rodsPower settingTest fixture
Subsea test apparatus comprises: a connector for mating with a corresponding connector of subsea apparatus to provide at least one of electrical, optical, and fluid connection between the test apparatus and the subsea apparatus; measuring means connected to the test apparatus's connector and operable underwater in a measurement mode; a power supply arranged to power the measuring means; and disconnection means for disconnecting the test apparatus's connector from a mated subsea apparatus's connector. The measuring means, in said measurement mode, is arranged to perform at least one measurement, via the mated connectors, on connected subsea apparatus, and the test apparatus further comprises indicating means operable underwater and arranged to provide an indication of a result of the or each measurement.
Owner:ZETECHTICS
Blow out preventer transfer platform
An offshore well drilling assembly includes a drilling facility or support platform for location at sea. A drilling platform connects to the support platform so the drilling platform is cantilevered from the support platform. The drilling platform extends from the support platform, for positioning over a subsea well. The well drilling assembly includes a staging platform for use in loading and unloading of wellhead equipment. The staging platform is mounted to the drilling platform. The staging platform moves along a side of the drilling platform in directions toward and away from the support platform to a distance over the sea. A method of conveying wellhead equipment uses the staging platform for conveying wellhead equipment between the support platform and a distance over the sea by moving the staging platform along the drilling platform.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
System using a catenary flexible conduit for transferring a cryogenic fluid
InactiveUS20070074786A1Improve securityMinimize changesGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsEngineeringTransfer operation
A system and a process are provided for transferring a cryogenic fluid such as liquefied natural gas between a floating transport vessel and a storage vessel. The fluid is transferred through at least one submerged / subsea / subsurface catenary flexible conduit, the conduits being configured to avoid damage from waves and abrasion or contact with the other conduits, the vessels, or other objects. A conduit transfer vessel is provided for storing the conduit in the water, delivering the conduit to each transport vessel, but standing off from the transport vessel during cryogenic fluid transfer, and then retrieving the conduit from the transport vessel, which greatly improves the safety of the cryogenic fluid transfer operations.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
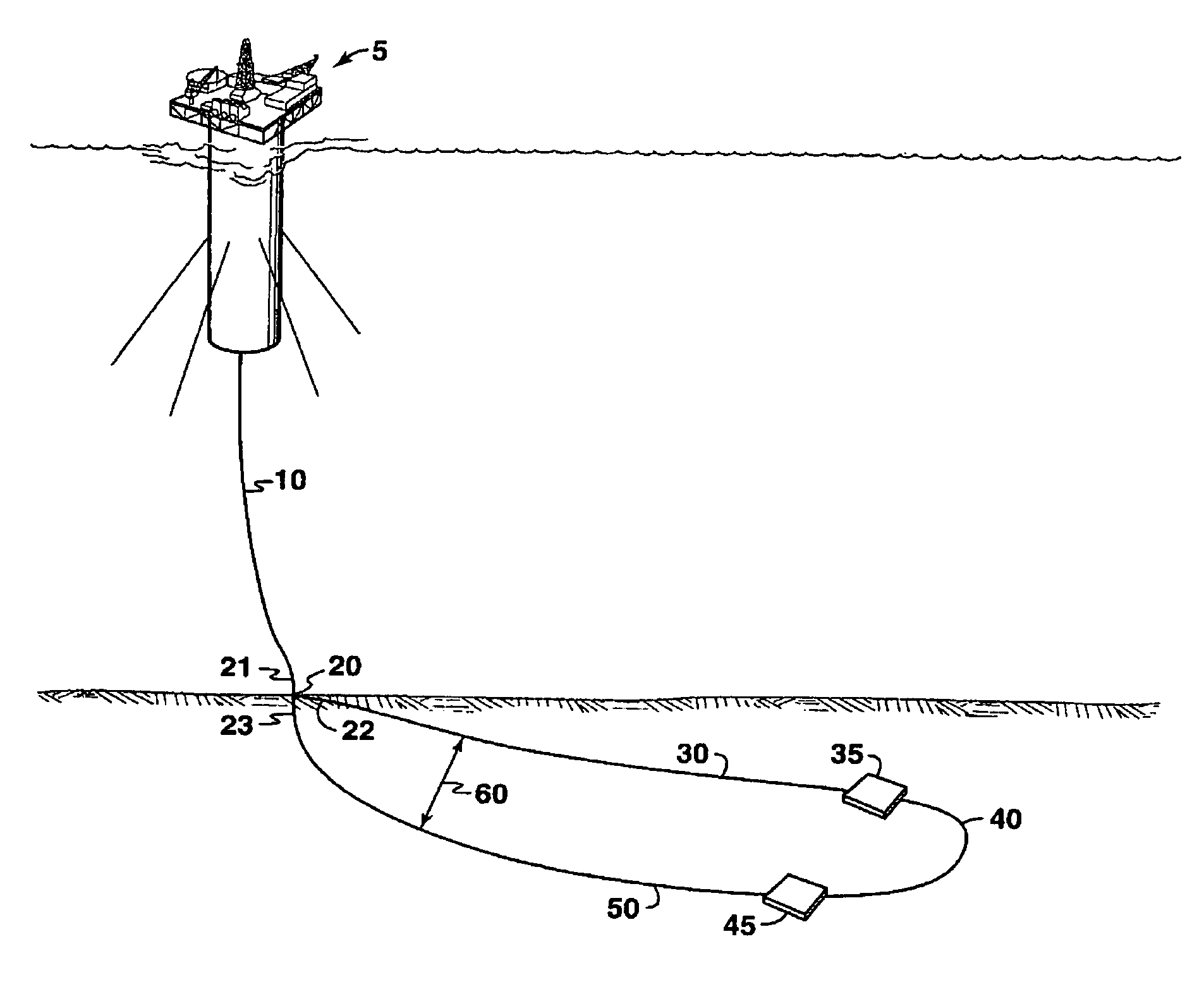
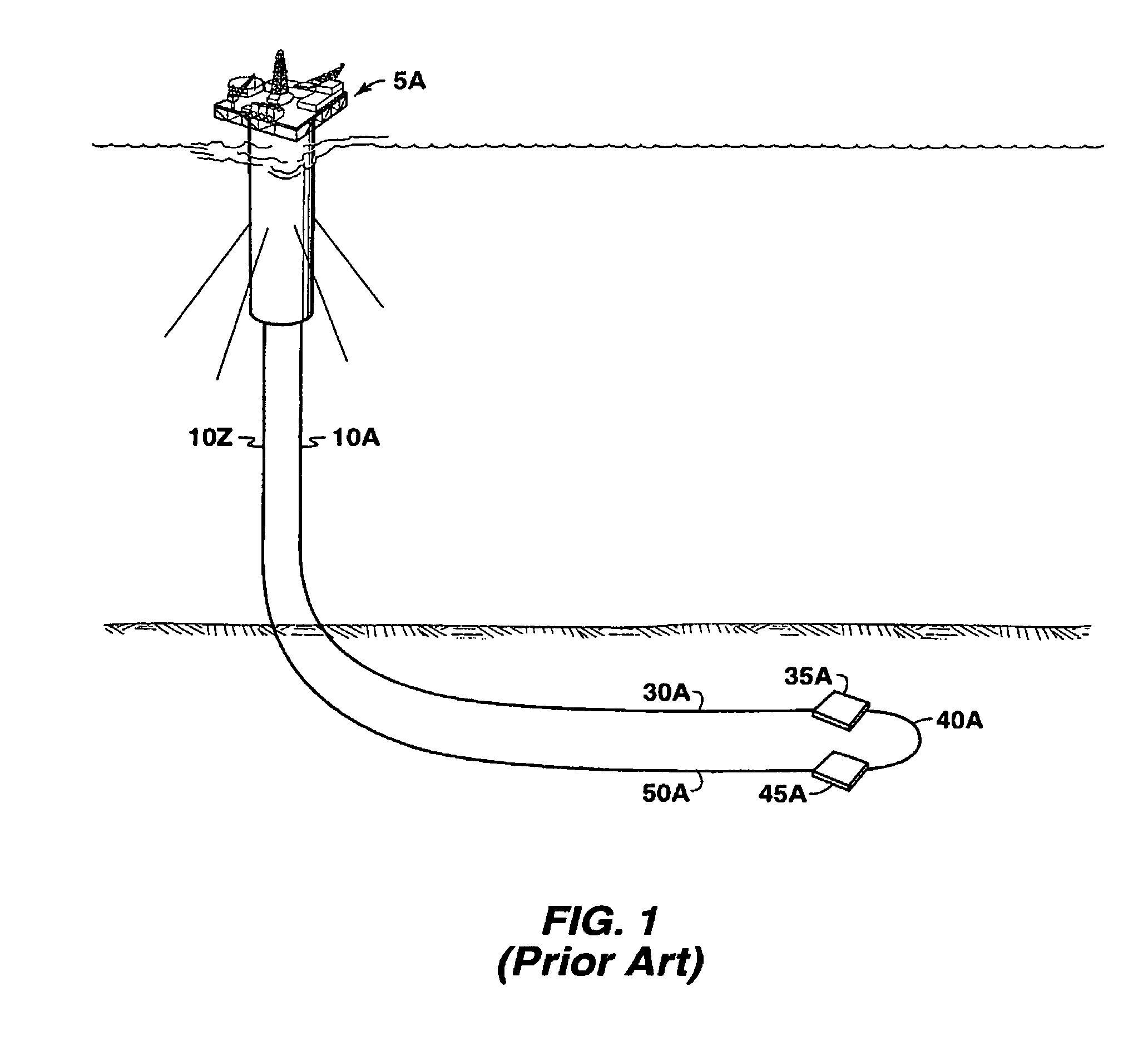
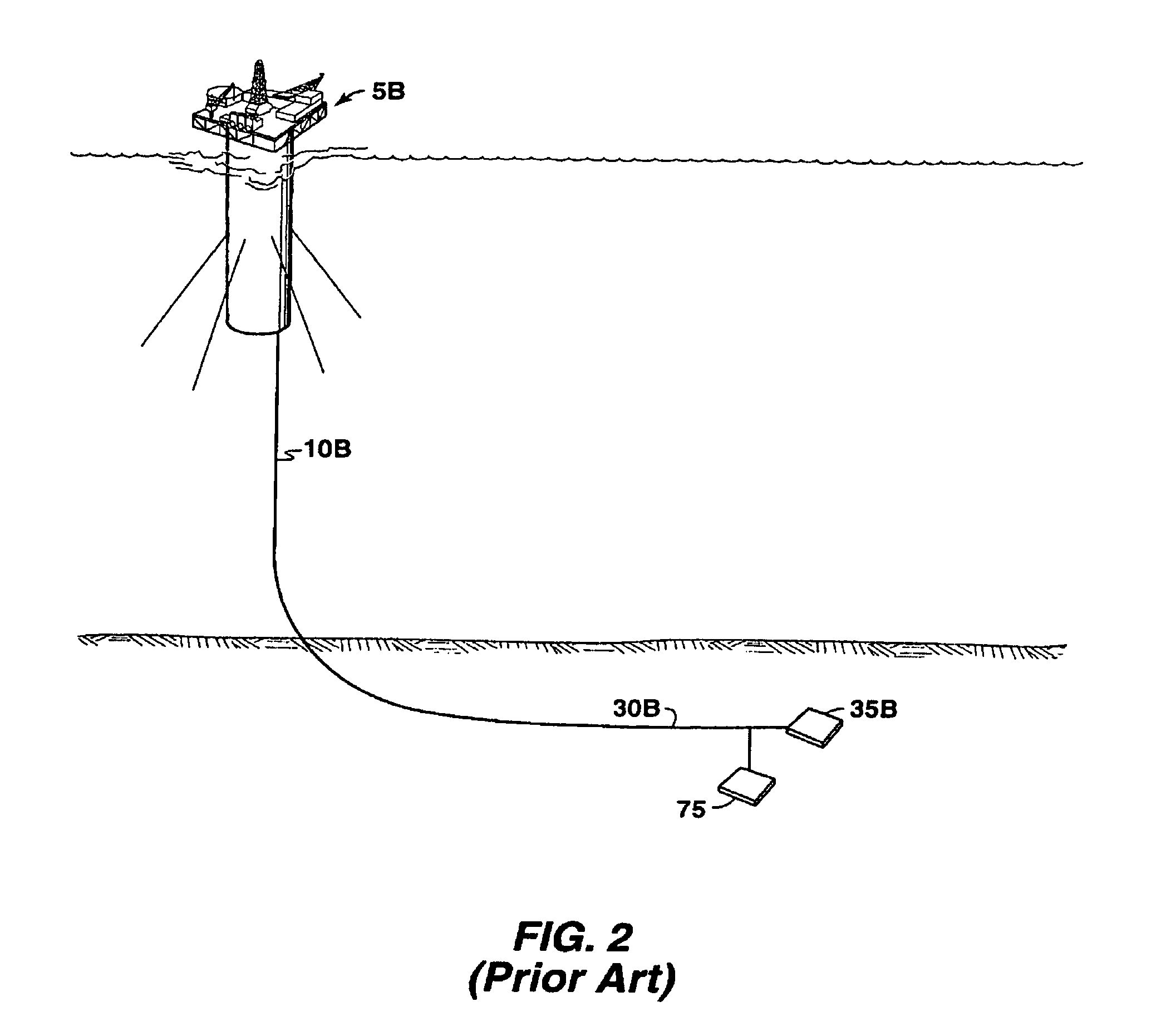
Piggable flowline-riser system
This invention relates to a flowline-riser production system for the recovery of hydrocarbons from offshore wells, and a method for pigging the interior surfaces of the riser and flowlines. More particularly, this invention is a piggable flowline-riser system in which a pig is launched from or near a host production facility, down a riser into a looped flowline and returned up through the same riser. According to one embodiment of the invention, there is a piggable flowline-riser system for producing hydrocarbons comprising a riser, a “Y” joint and a looped flowline, wherein the looped flowline is in fluid communication with at least one subsea well.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com