Patents
Literature
3295results about "Gas handling applications" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
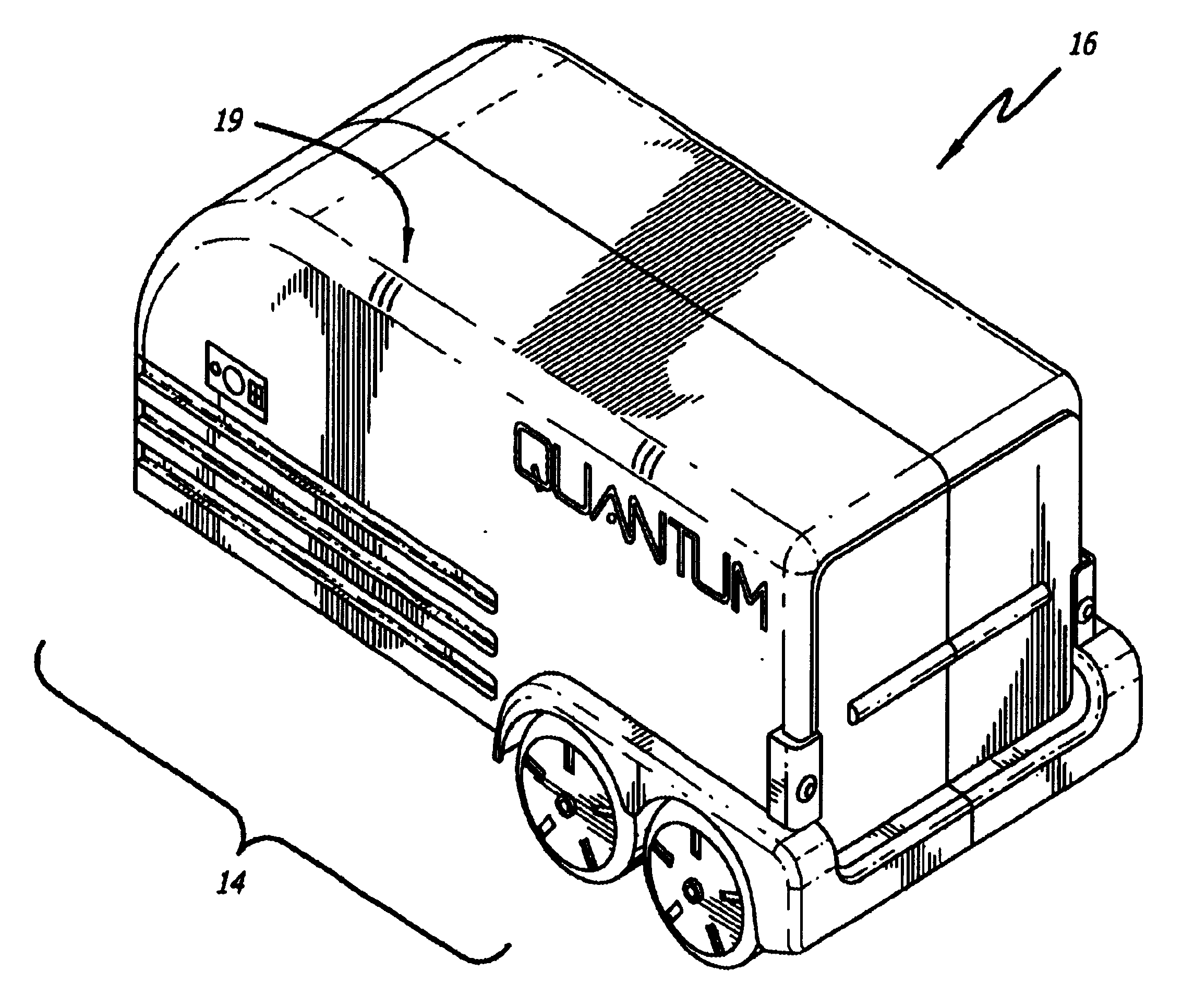
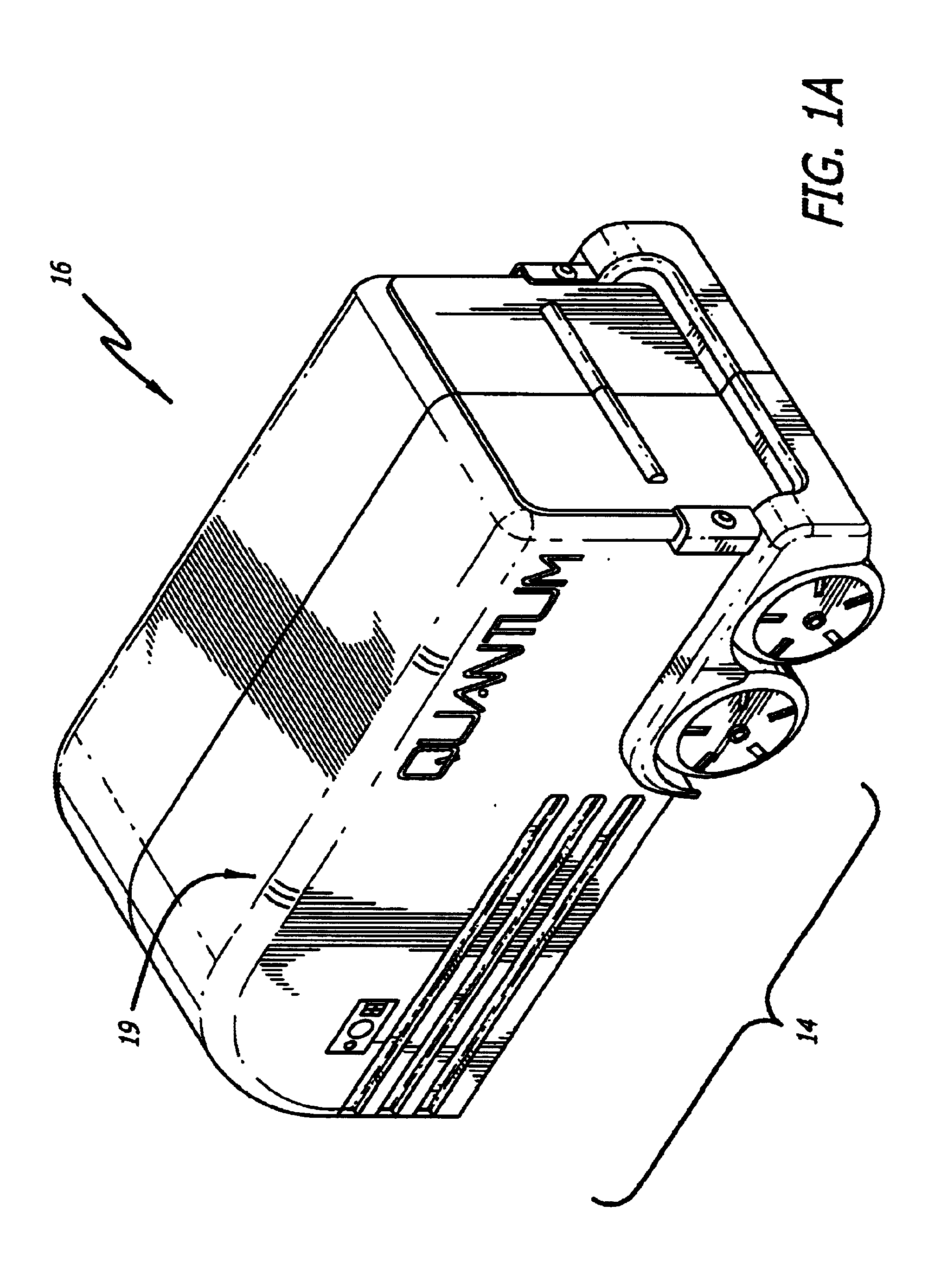
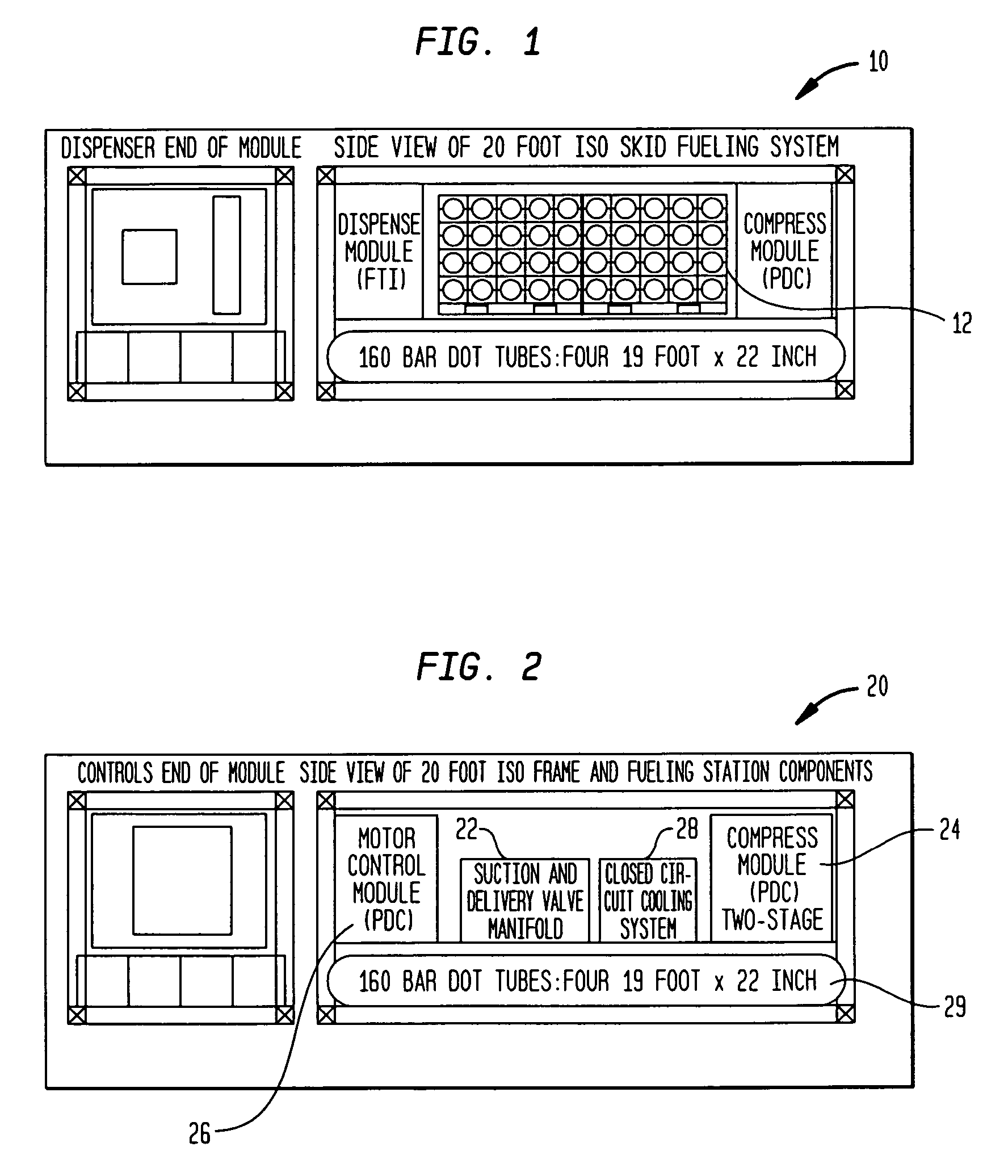
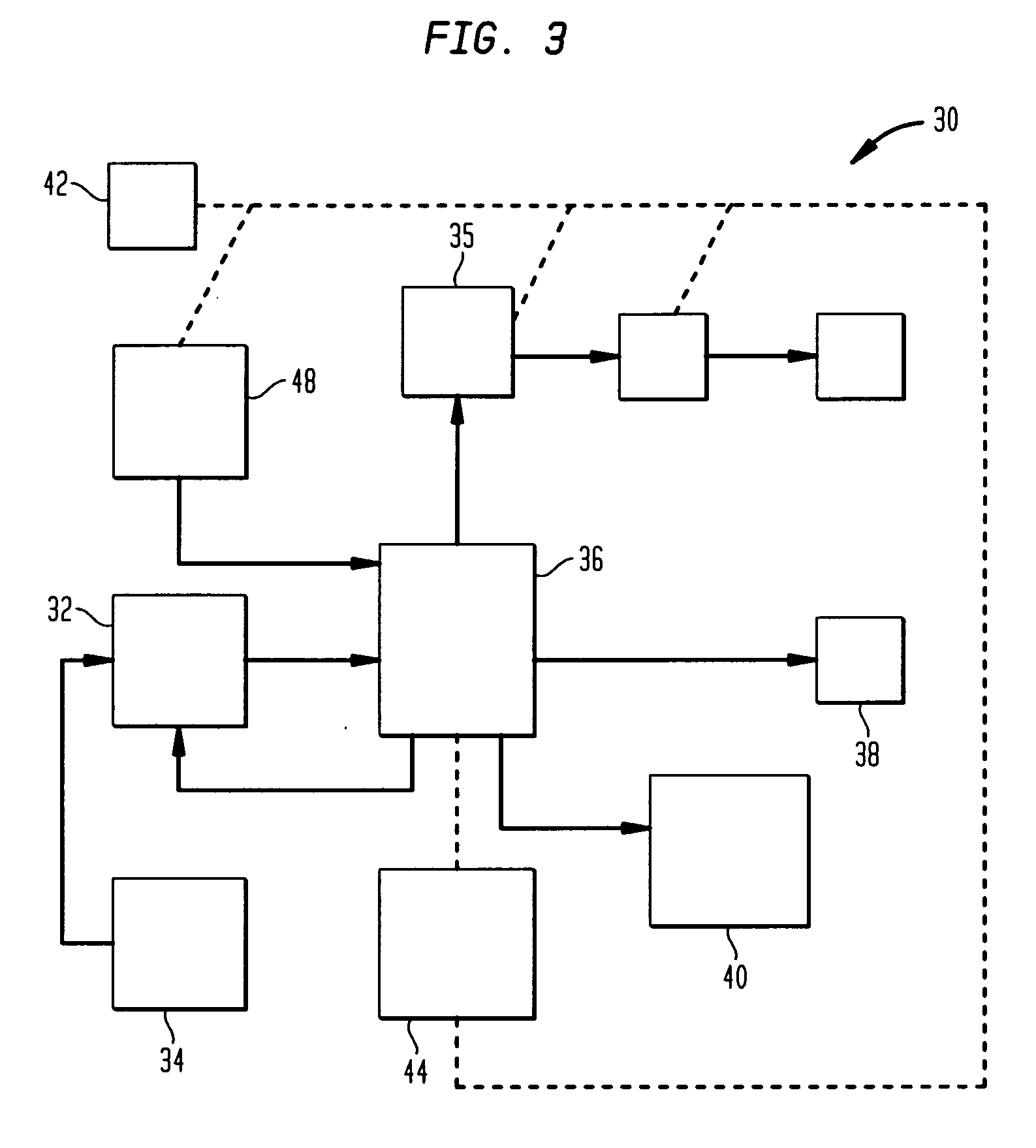
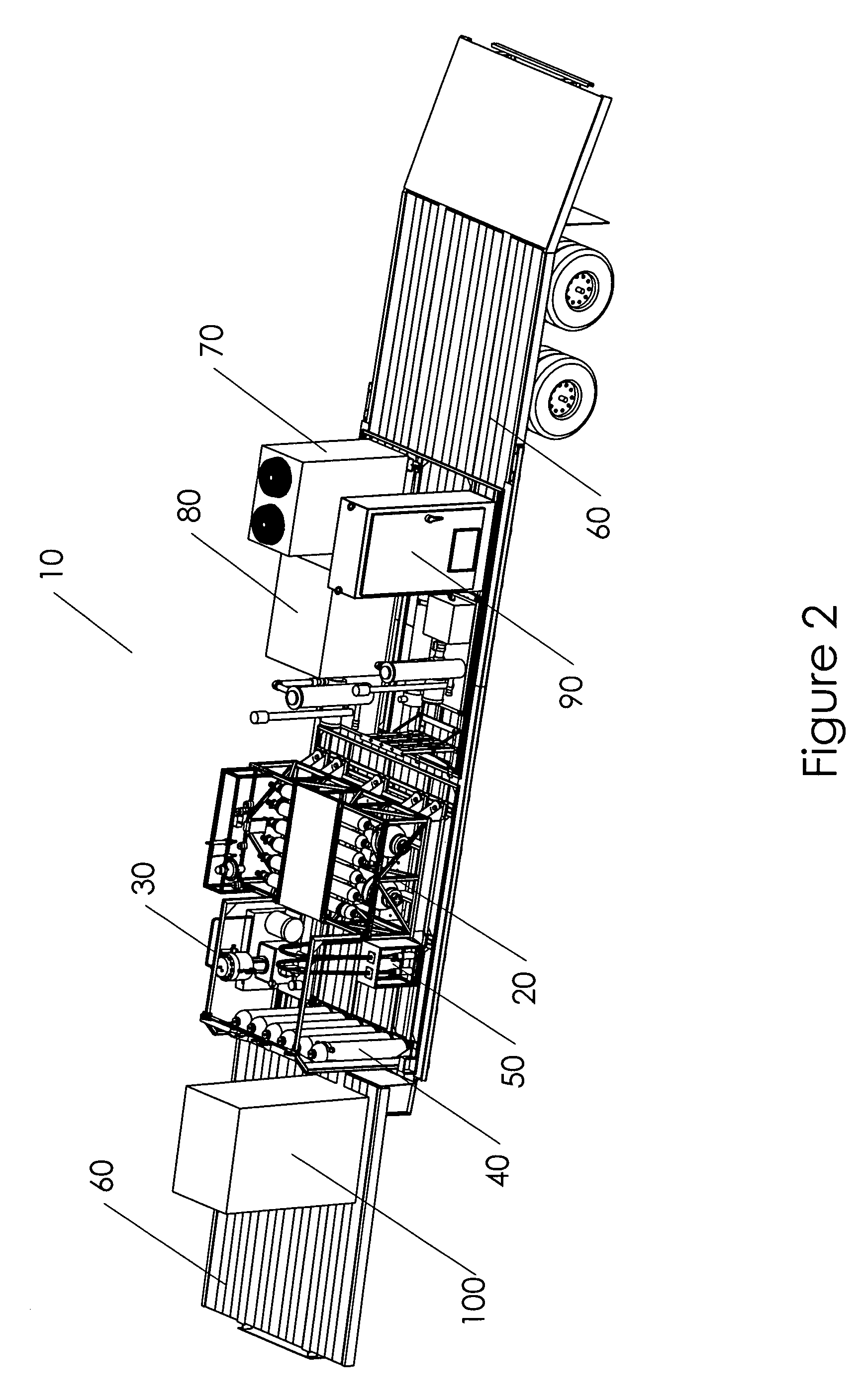
Transportable hydrogen refueling station
InactiveUS6755225B1Easy to monitorReduce riskTank vehiclesGas handling applicationsHigh pressureGaseous hydrogen
A portable hydrogen refueling stations which can dispense gaseous hydrogen from one or more internal high pressure tanks. The refueling station can be refilled with a lower pressure hydrogen gas feed and then compressed for storage within the refueling station.
Owner:QUANTUM FUEL SYST TECH WORLDWIDE INC
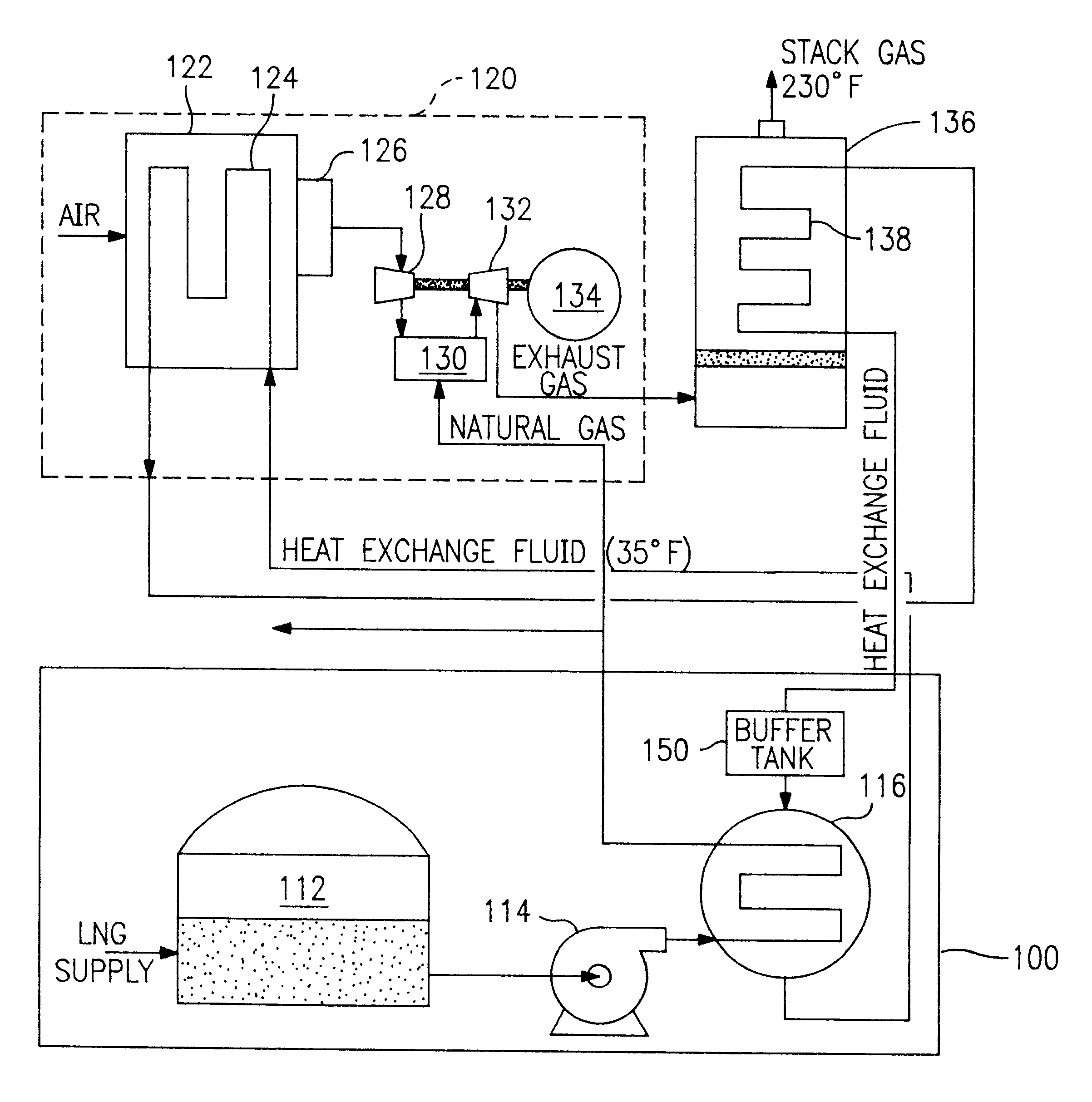
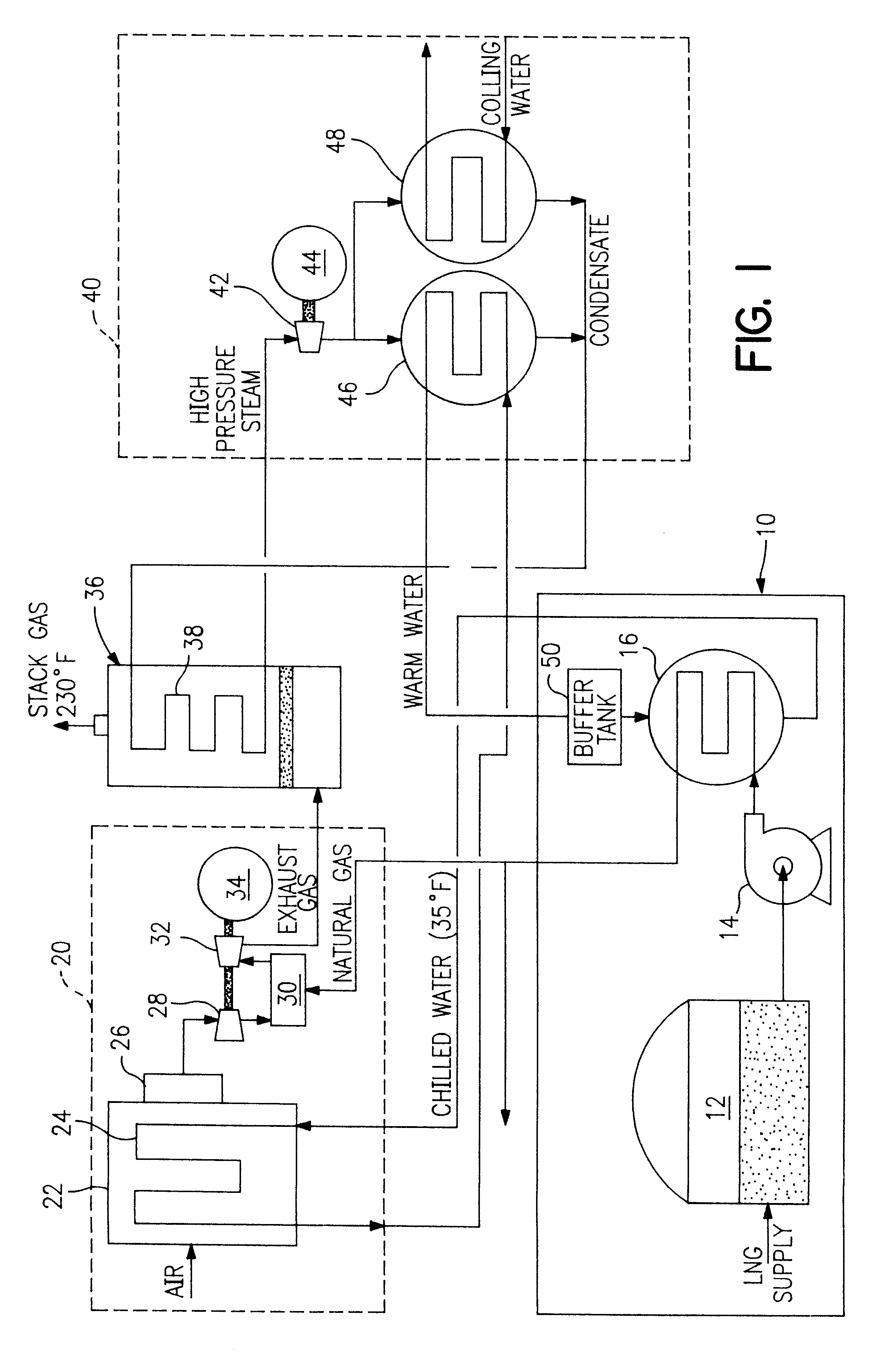
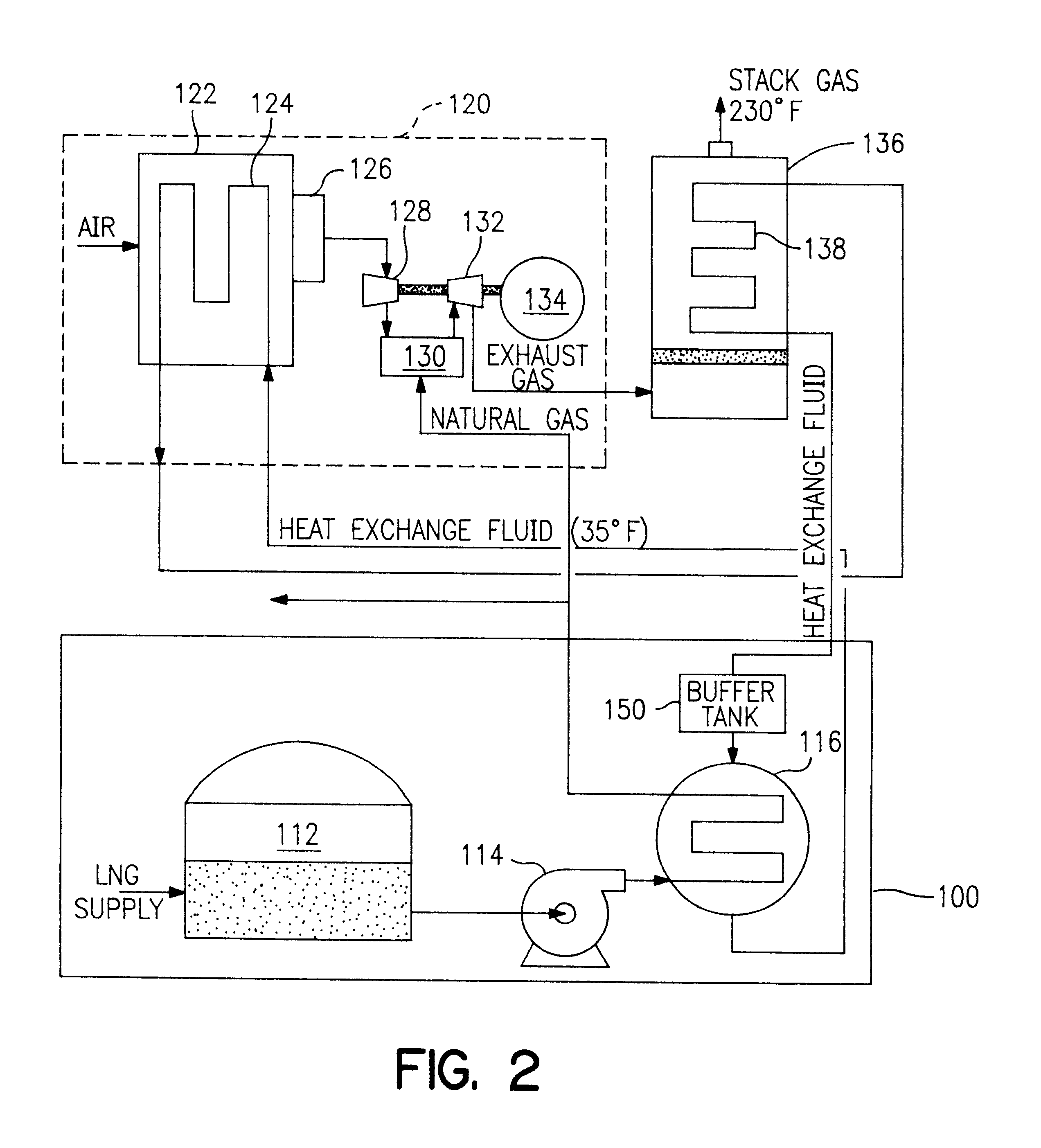
Liquified natural gas (LNG) fueled combined cycle power plant and a (LNG) fueled gas turbine plant
InactiveUS6374591B1Improve efficiencyParts are smallGas handling applicationsGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberPower station
A process and system which improves the capacity and efficiency of a power plant. A LNG supply system fuels the plant. Gasified LNG in a combustor mixes with the air from an air compressor to provide the hot combustion gas for a gas turbine. The expanding LNG is used to chill a heat exchange fluid, e.g. water, which heat exchange fluid cools and densifies the intake air for the air compressor. Subsequently, the heat exchange fluid is used in another heat exchange step and is then re-chilled and recycled to cool and densify the intake air.
Owner:SUEZ LNG NA
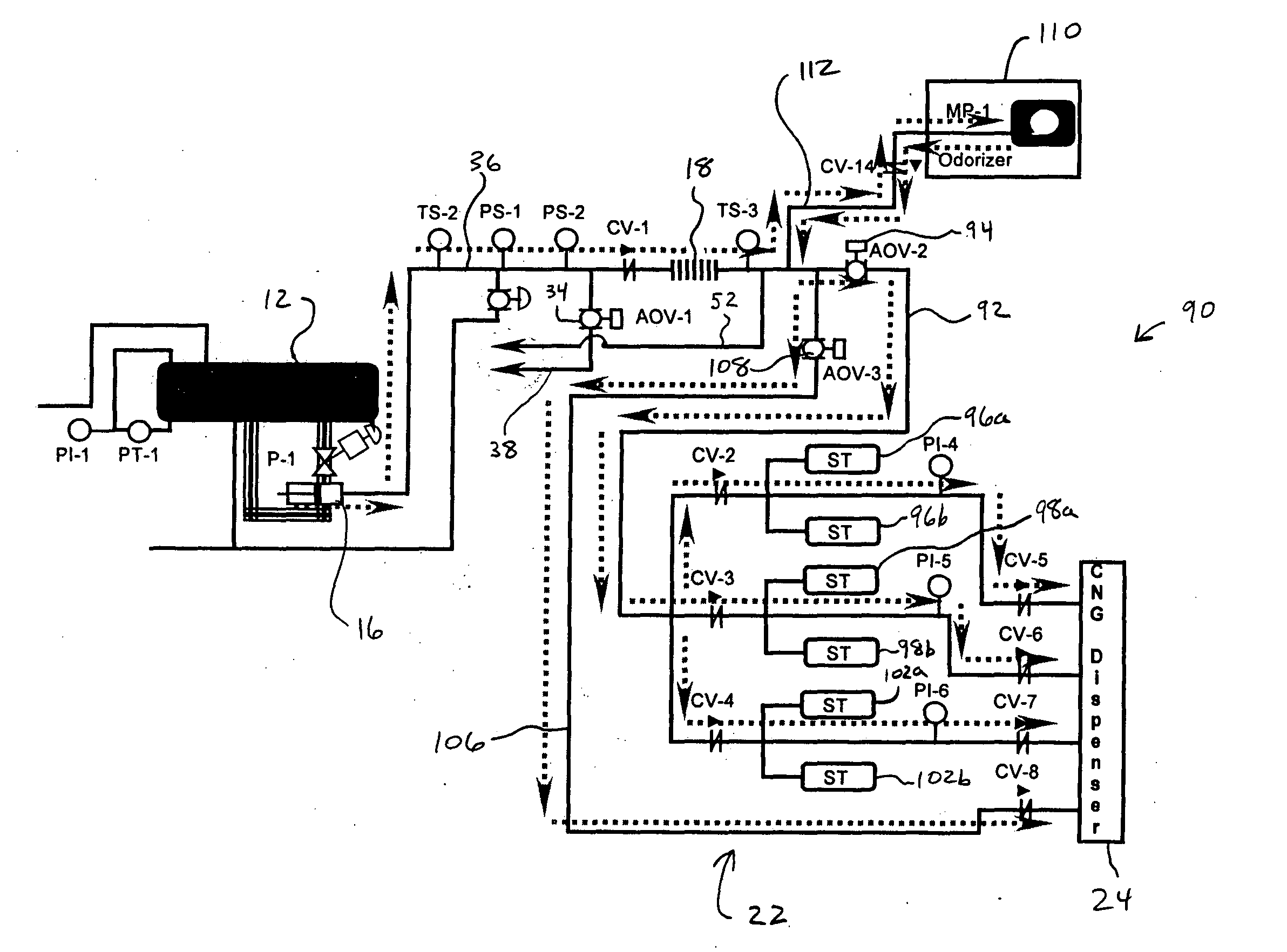
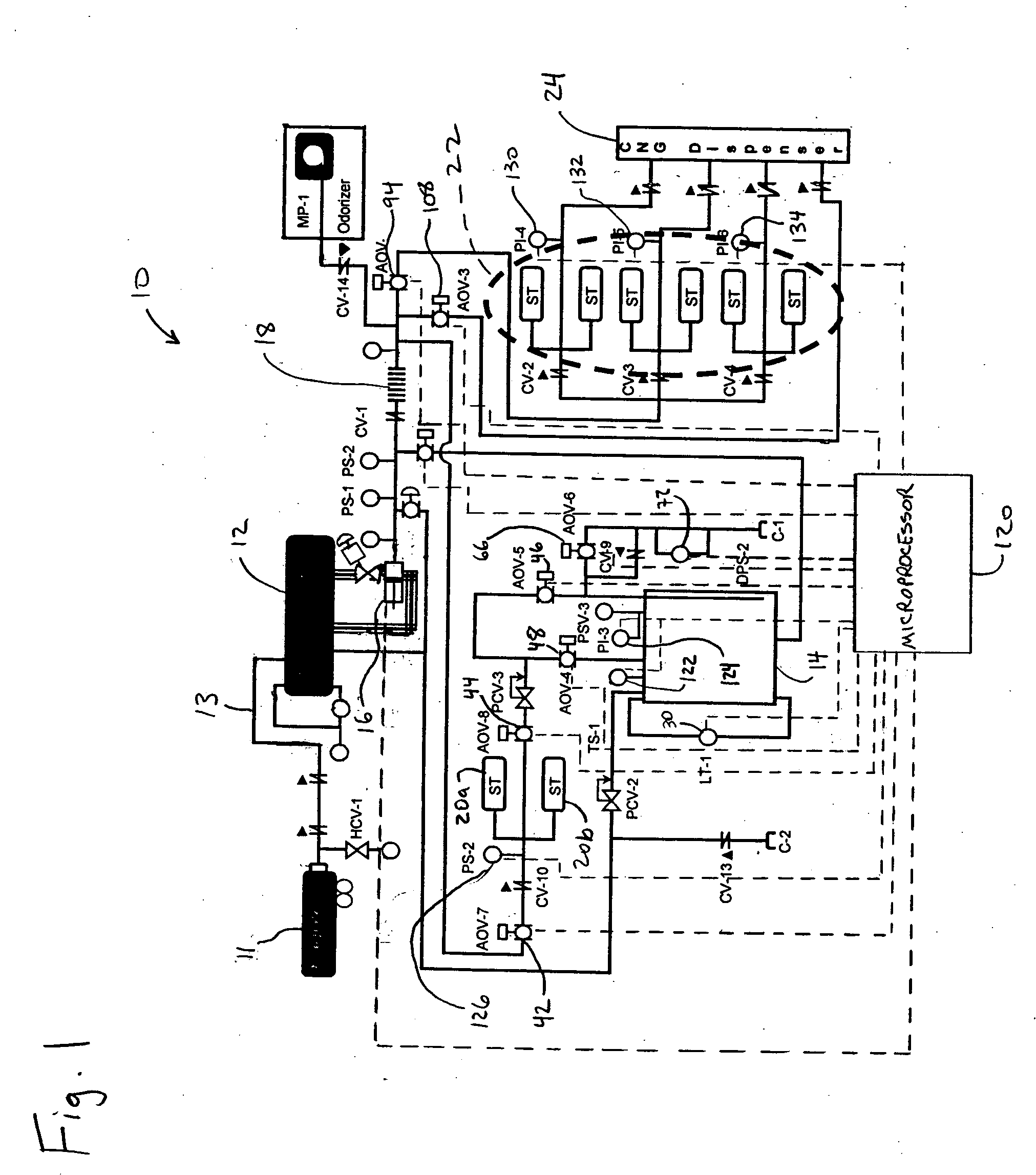
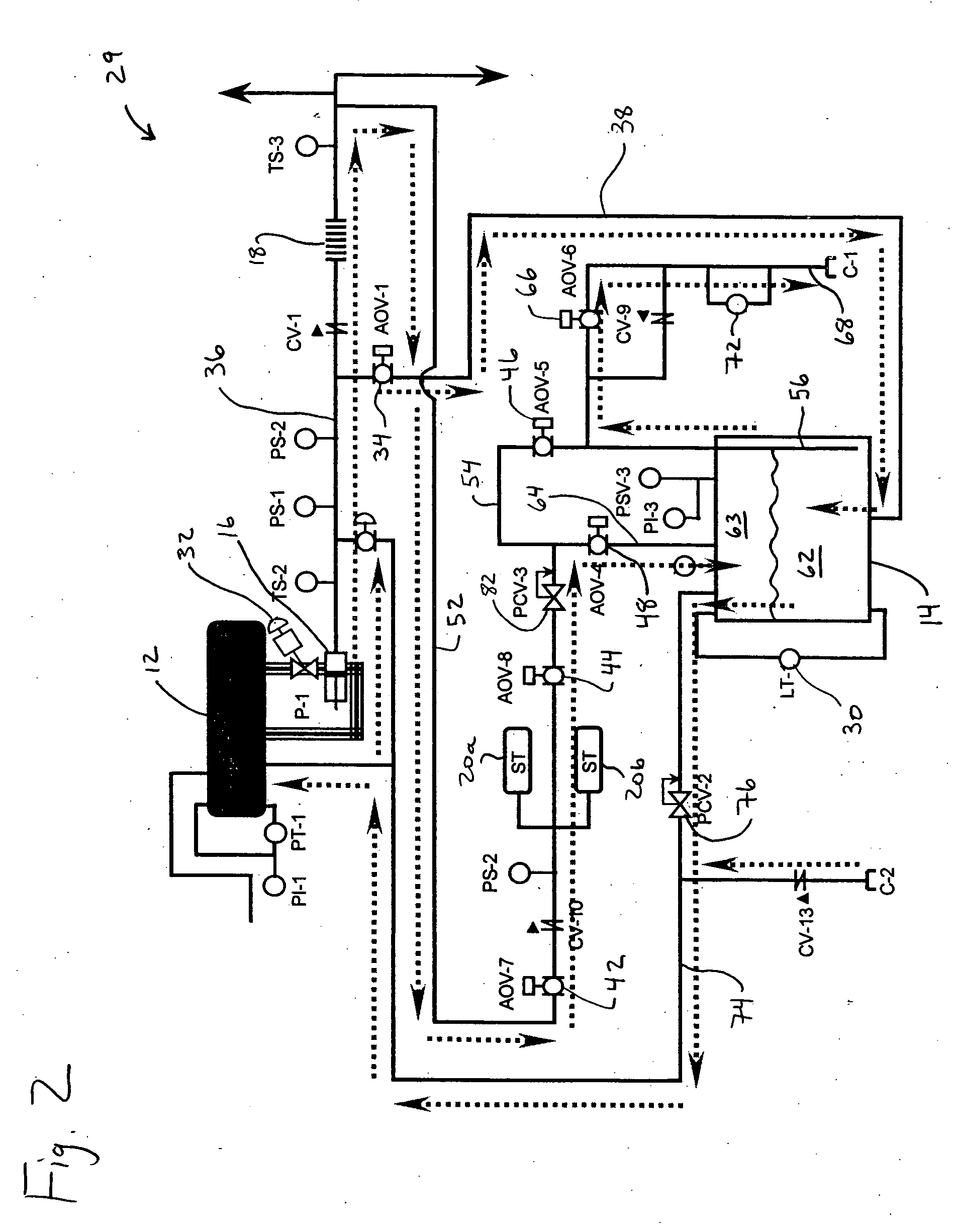
Hydrogen handling or dispensing system
InactiveUS20050000802A1Avoid burnsCheap manufacturingLiquid fillingGas handling applicationsHydrogenHuman life
Systems for handling and / or dispensing hydrogen or a mixture of fuels containing hydrogen gas including refueling stations for hydrogen-powered vehicles. Pure hydrogen or various mixtures ratios of hydrogen and CNG may be dispensed. Hydrogen handling equipment may include a hydrogen generator, a pressurizing apparatus or compressor, pressure vessels, piping, valves, vent pipes, and / or a dispenser. Substantially vertical orientation of pressure vessels may reduce the amount of land required and facilitate installation in urban environments. Pressurization may take place before hydrogen generation to reduce the power required for pressurization. Safety features include enclosures and surrounding walls that lean away from the equipment. Any leaking hydrogen, fires, or explosions may be contained and / or directed upward, protecting human life and property. Systems may be shop assembled and certified.
Owner:ARIZONA PUBLIC SERVICE
Configurations and methods for power generation with integrated LNG regasification
Owner:FLUOR TECH CORP
Liquefied natural gas floating storage regasification unit
InactiveUS20060156744A1Reduce the amount requiredProvide protectionGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsMooring systemMarine engineering
An offshore liquefied natural gas floating storage regasification unit that may receive, store, and process liquefied natural gas from carriers. A floating storage regasification unit may include transfer equipment to offload liquefied natural gas from a carrier, a first mooring system to provide for mooring of a floating storage regasification unit at a location in a body of water, a second mooring system to provide for mooring a carrier to the floating storage regasification unit, and combinations thereof. A portion of the floating storage regasification unit may be composed of a double-hull containment structure.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Apparatus and method for flowing compressed fluids into and out of containment
ActiveUS20080209916A1Adjustable temperatureGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsChemical compositionCompressed fluid
Methods for loading a compressed fluid, such as natural gas, into and discharging the compressed fluid out of containment are provided. The compressed fluid is injected into a bottom portion of a container system for storage and / or transport until a target pressure is reached after which gas is withdrawn from an upper portion of the container system at a rate to maintain the target pressure while the compressed fluid is injected in the bottom portion. The compressed fluid is cooled through an expansion valve and by refrigerated chillers or by injecting a cold liquid of the same chemical composition as the compressed fluid, such as liquid natural gas, into the compressed fluid prior to injection into the container system. Withdrawal or discharge from the container system to a receiving facility begins with blow down from the bottom portion of the container system without a displacement fluid and continues until pressure falls below an acceptable differential pressure. The discharge stream is passed through a separator and a light gas from the separator is pressurized and injected into an upper portion of the container system to drive the compressed fluid out the bottom. The light gas is pressurized using either a compressor or a heated tank system, where two vessels operate in parallel, trapping and heating the light gas and then discharging to the container system from one while filling the other and alternating the operation between the two.
Owner:WHITE CHARLES N +1
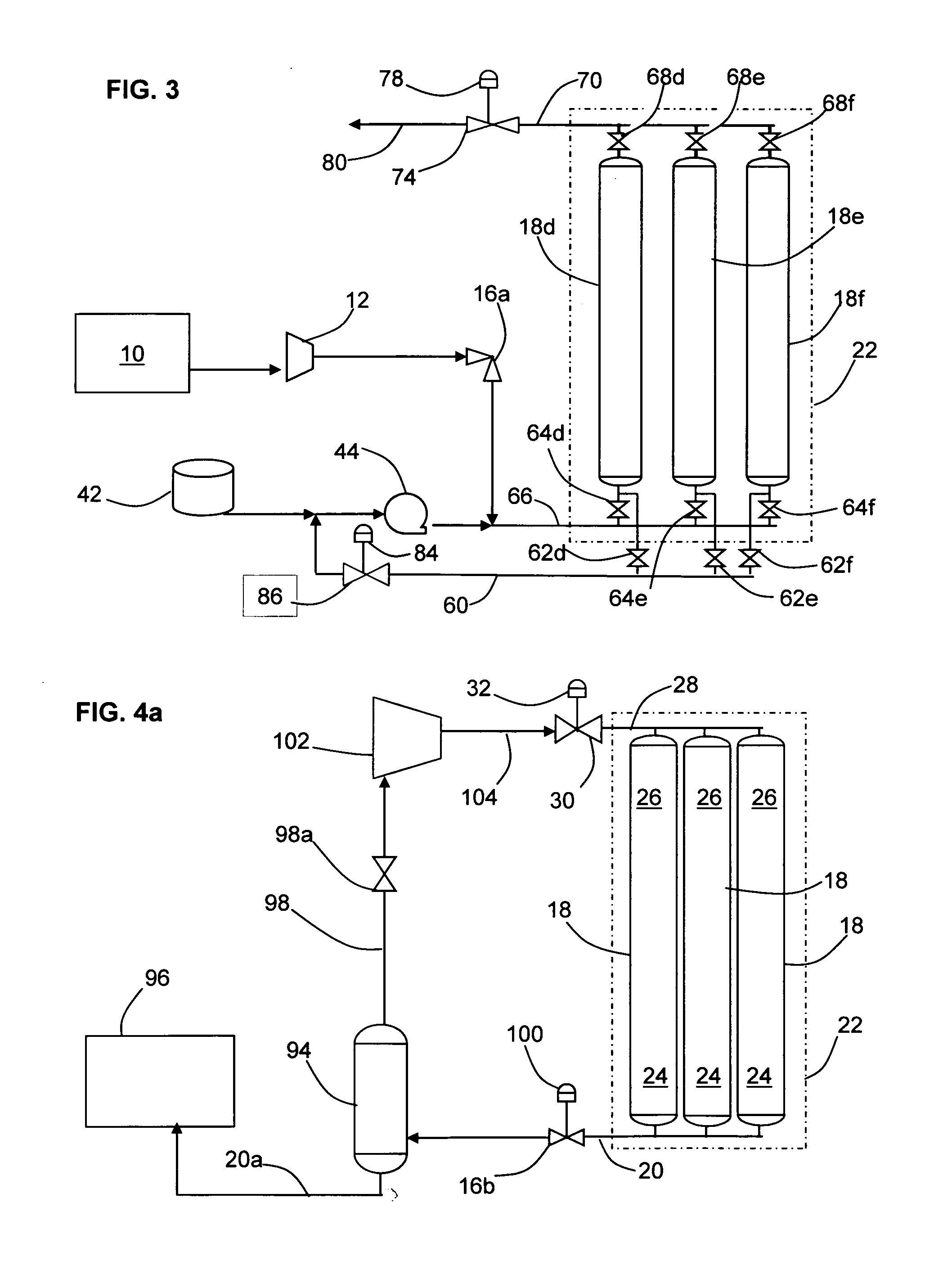
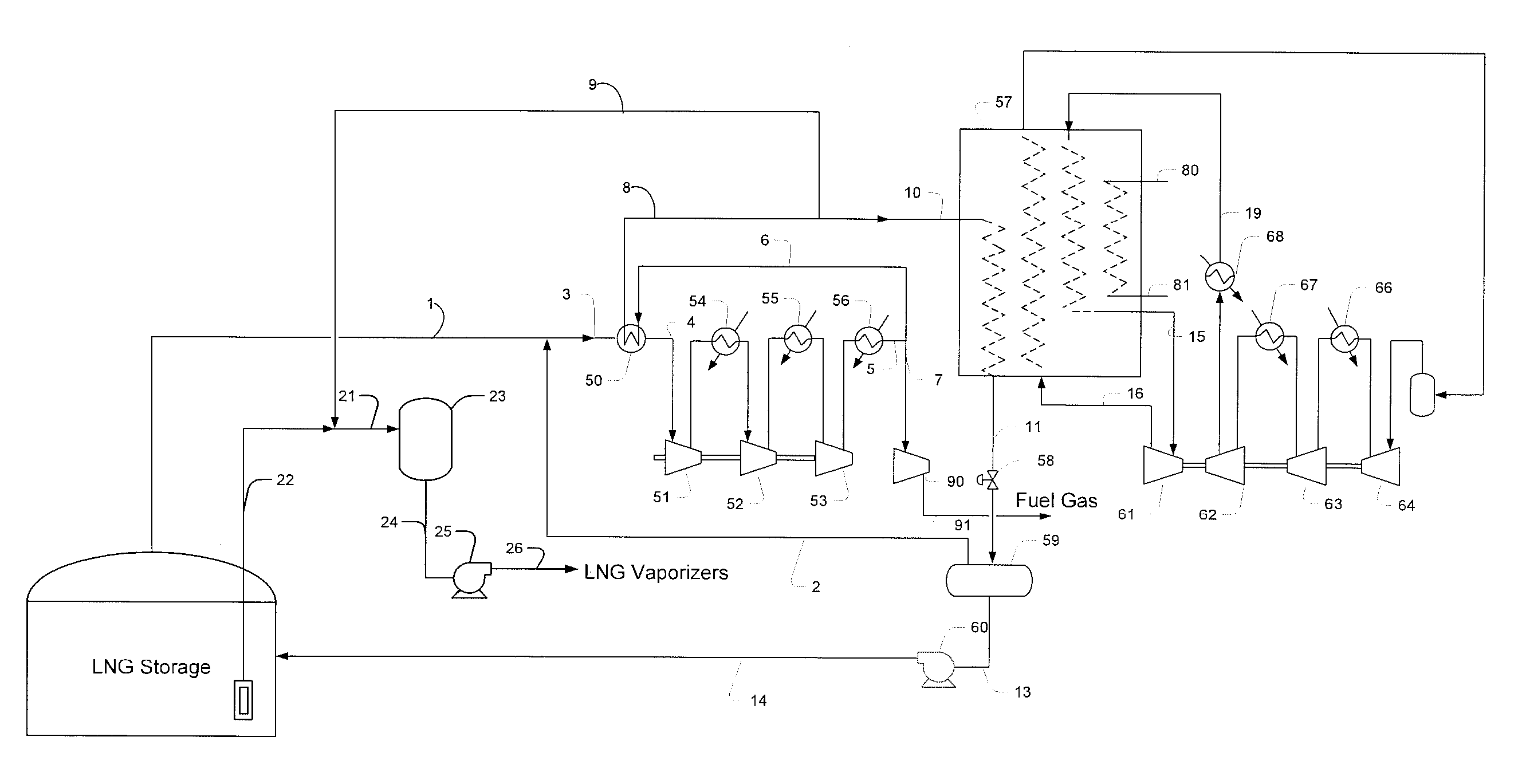
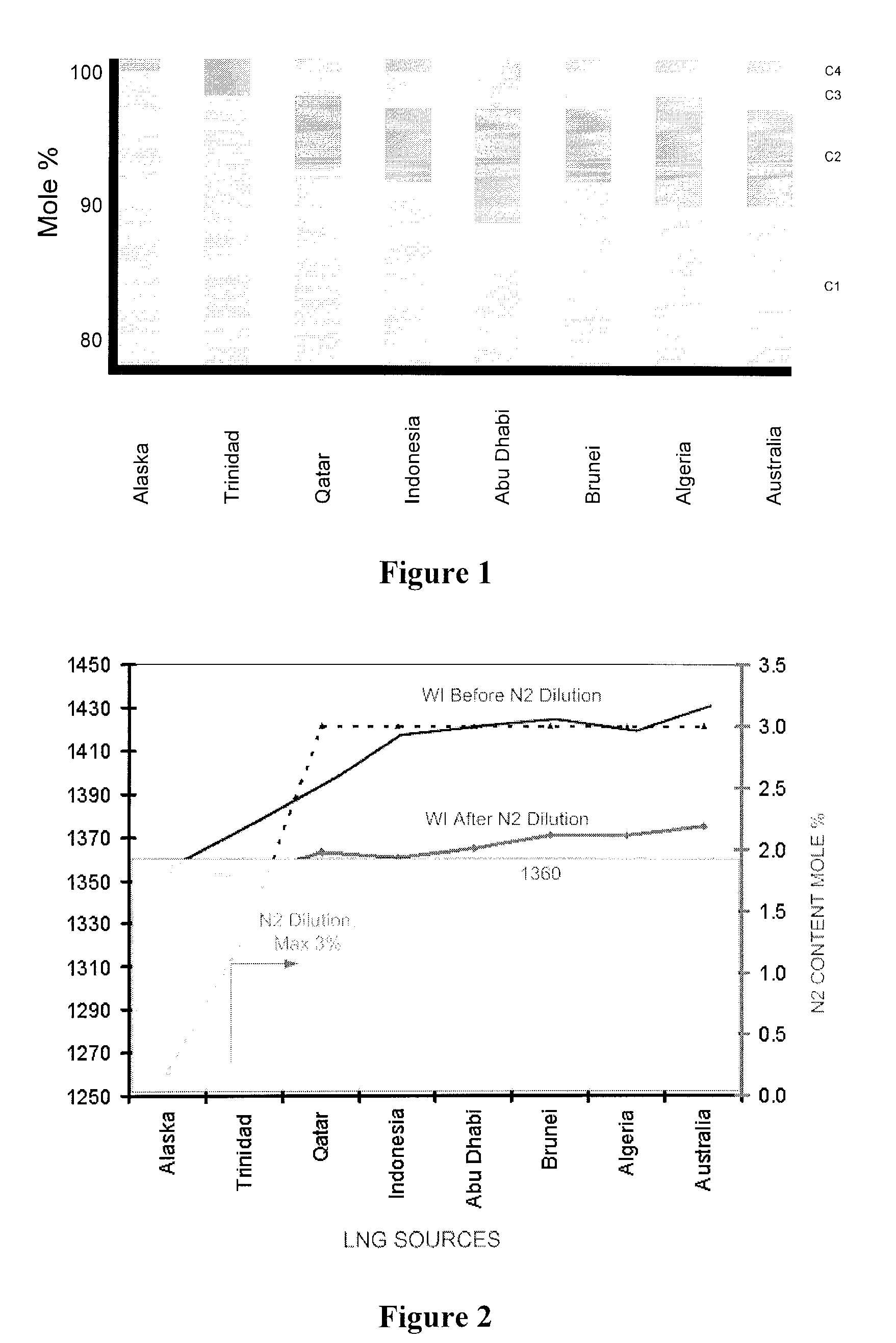
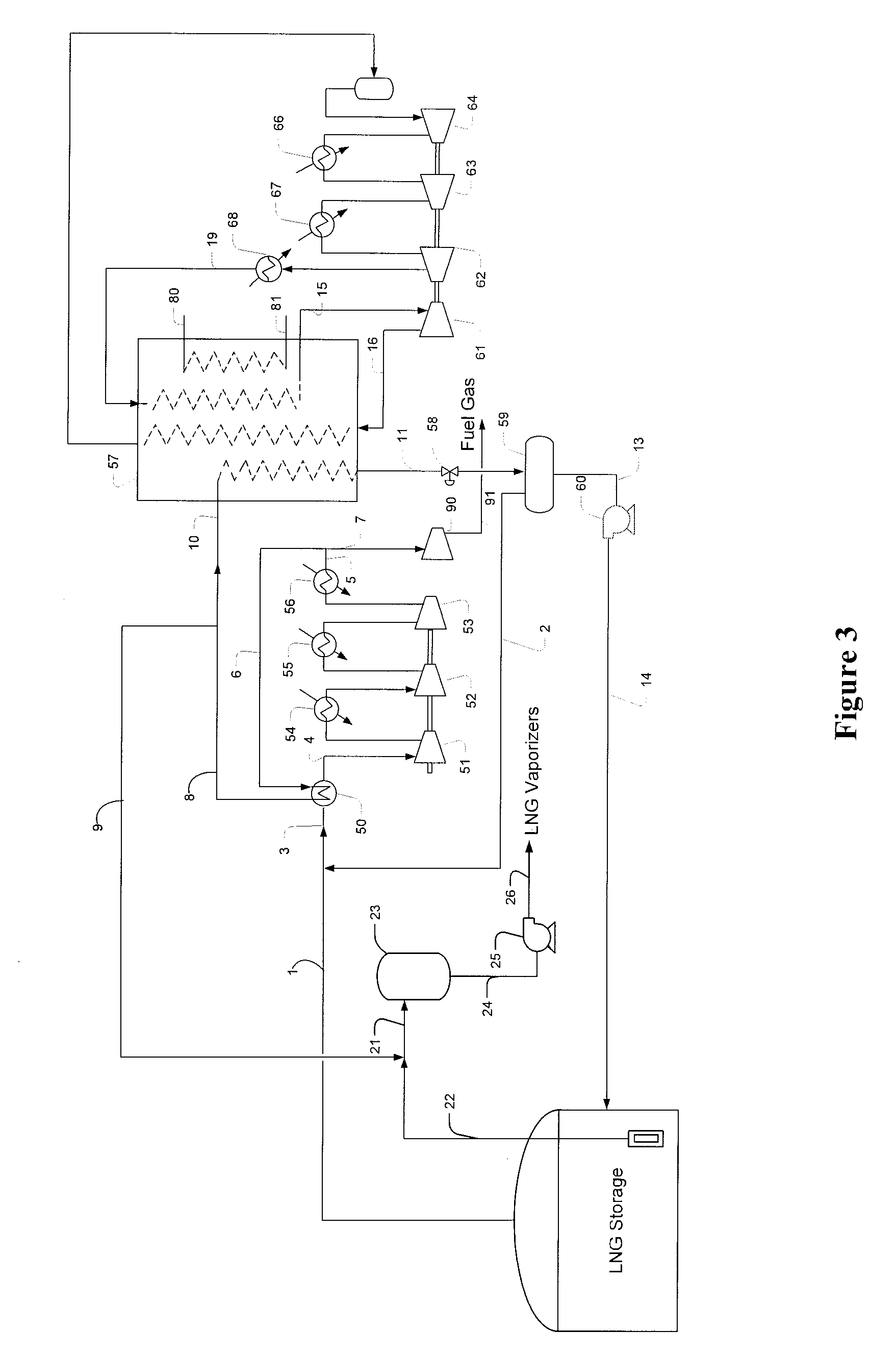
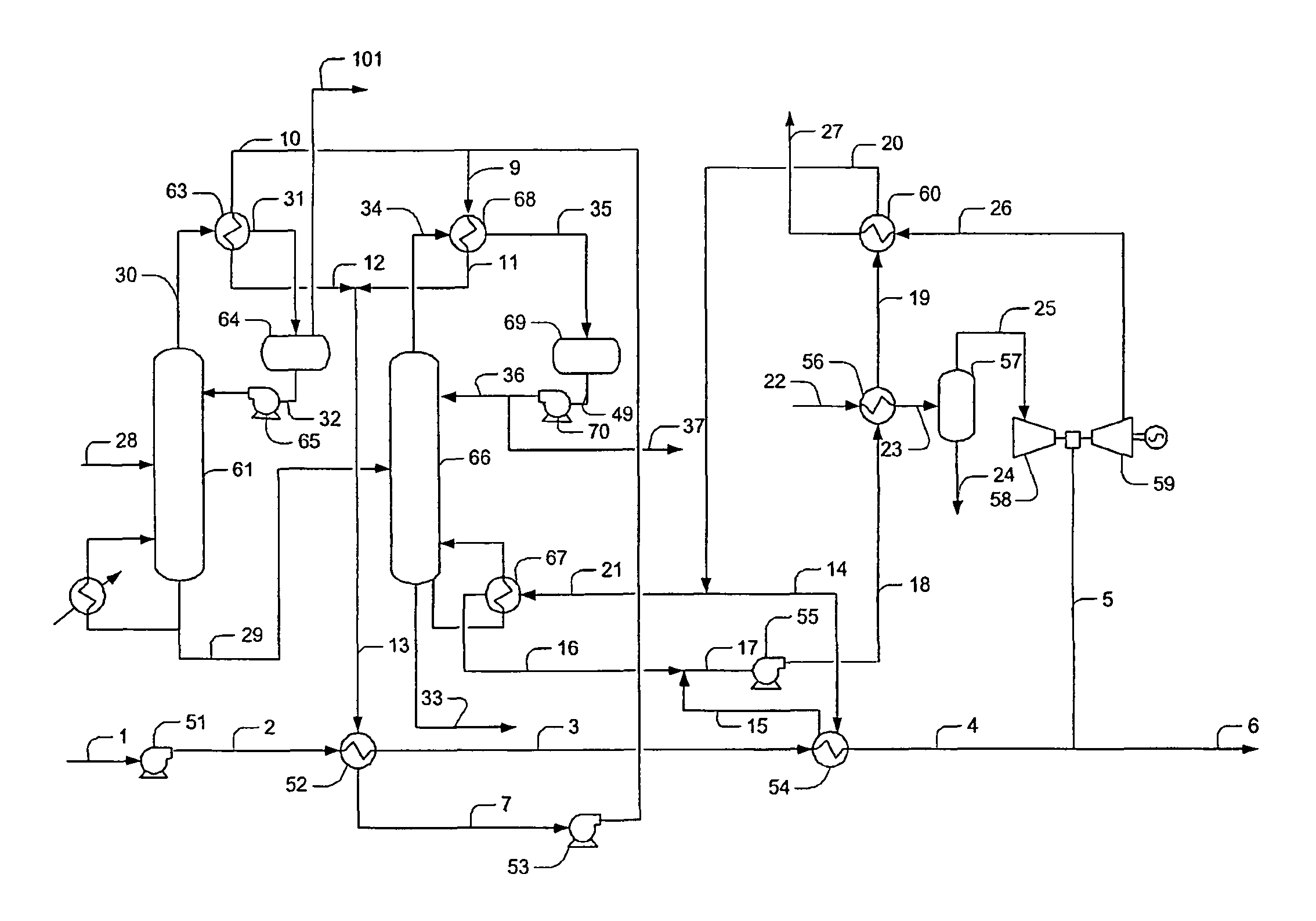
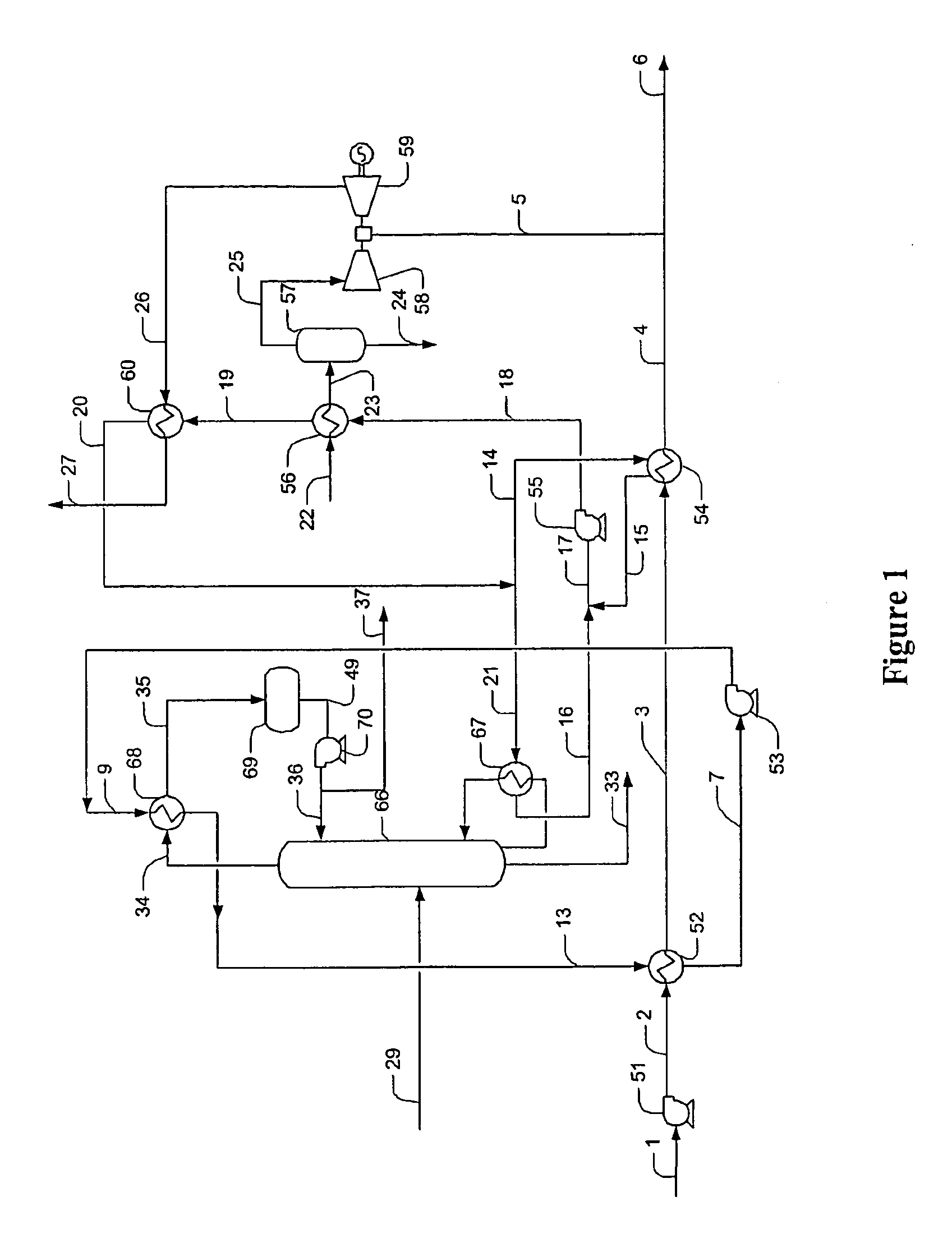
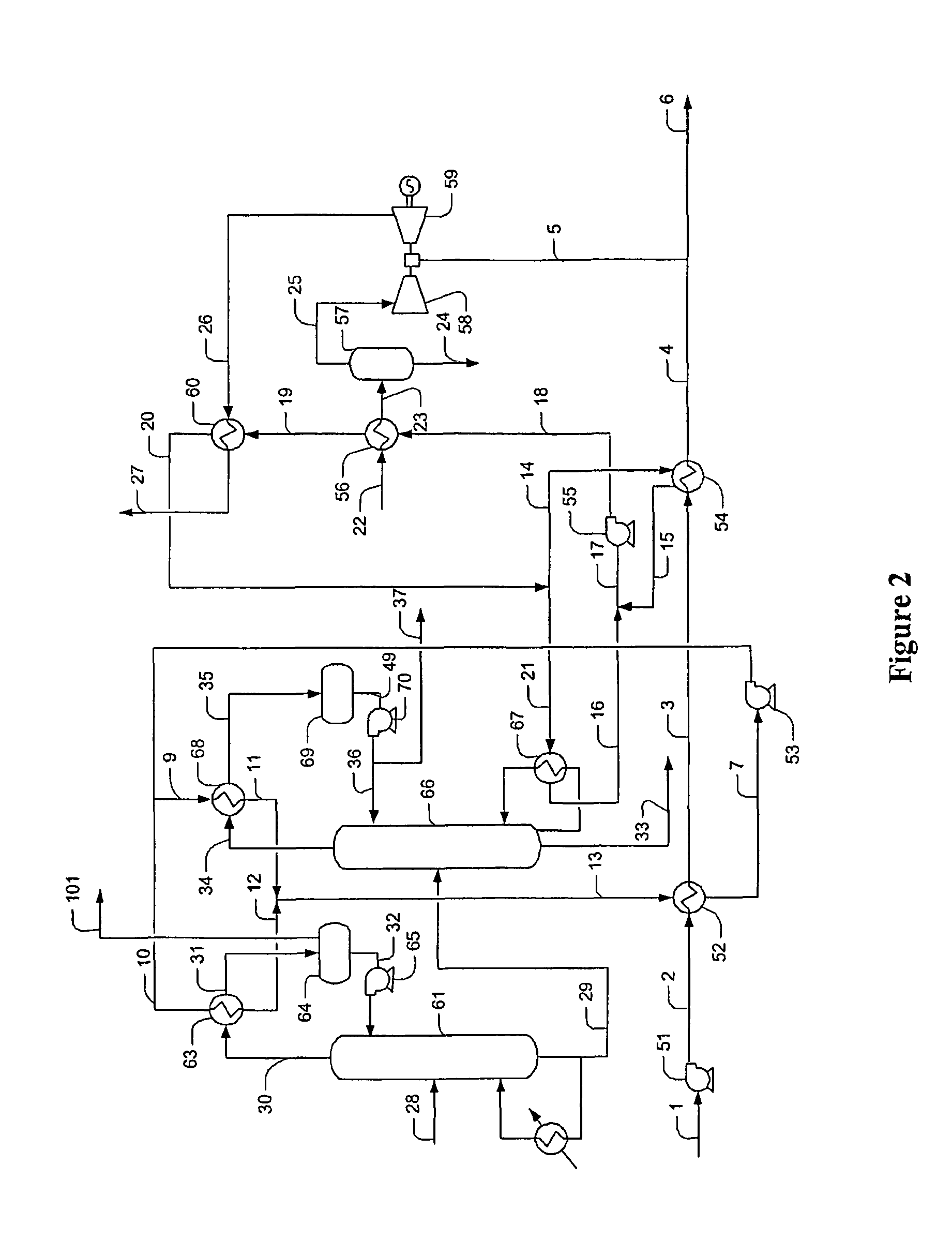
Methods and Configurations of Boil-off Gas Handling in LNG Regasification Terminals
InactiveUS20110056238A1Stable storage tank pressure controlStable controlSolidificationLiquefactionProcess engineeringWobbe index
A LNG storage and regasification plant includes a reliquefaction unit in which boil-off vapors from the storage tanks are re liquefied and recycled back to the LNG storage tanks for tank pressure and Wobbe index control. Preferably, LNG cold is used for reliquefaction and operational flexibility is achieved by feeding a portion of the pressurized boil-off gas to a fuel gas header and / or to be recondensed by the sendout LNG.
Owner:FLUOR TECH CORP
Liquid and compressed natural gas dispensing system
InactiveUS20050016185A1Distribute quicklyEliminate timeGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsCompressed natural gasProcess engineering
A system dispenses both liquid natural gas (LNG) and compressed natural gas (CNG). A bulk tank contains a supply of LNG which is pumped to a smaller storage tank. After the storage tank is refilled, LNG from the bulk tank is pumped to a vaporizer so that CNG is produced. The CNG may be routed to the LNG in the storage tank to condition it. It is also used to recharge a pressurizing cylinder that is placed in communication with the head space of the storage tank when it is desired to rapidly dispense LNG to a vehicle. A bank of cascaded storage cylinders alternatively may receive CNG from the vaporizer for later dispensing through the system CNG dispenser. The CNG from the vaporizer may also be dispensed directly via the system CNG dispenser.
Owner:CHART INC
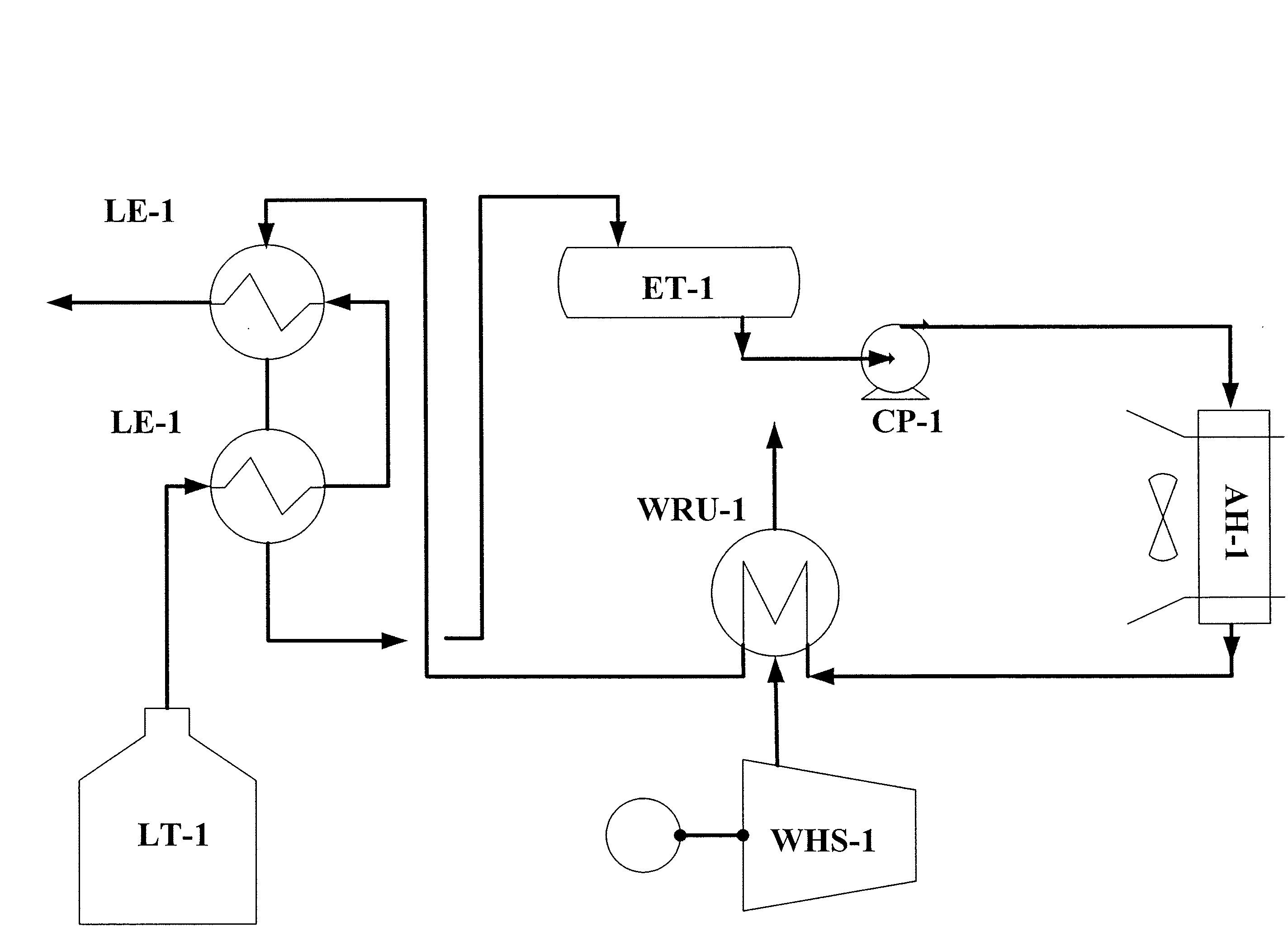
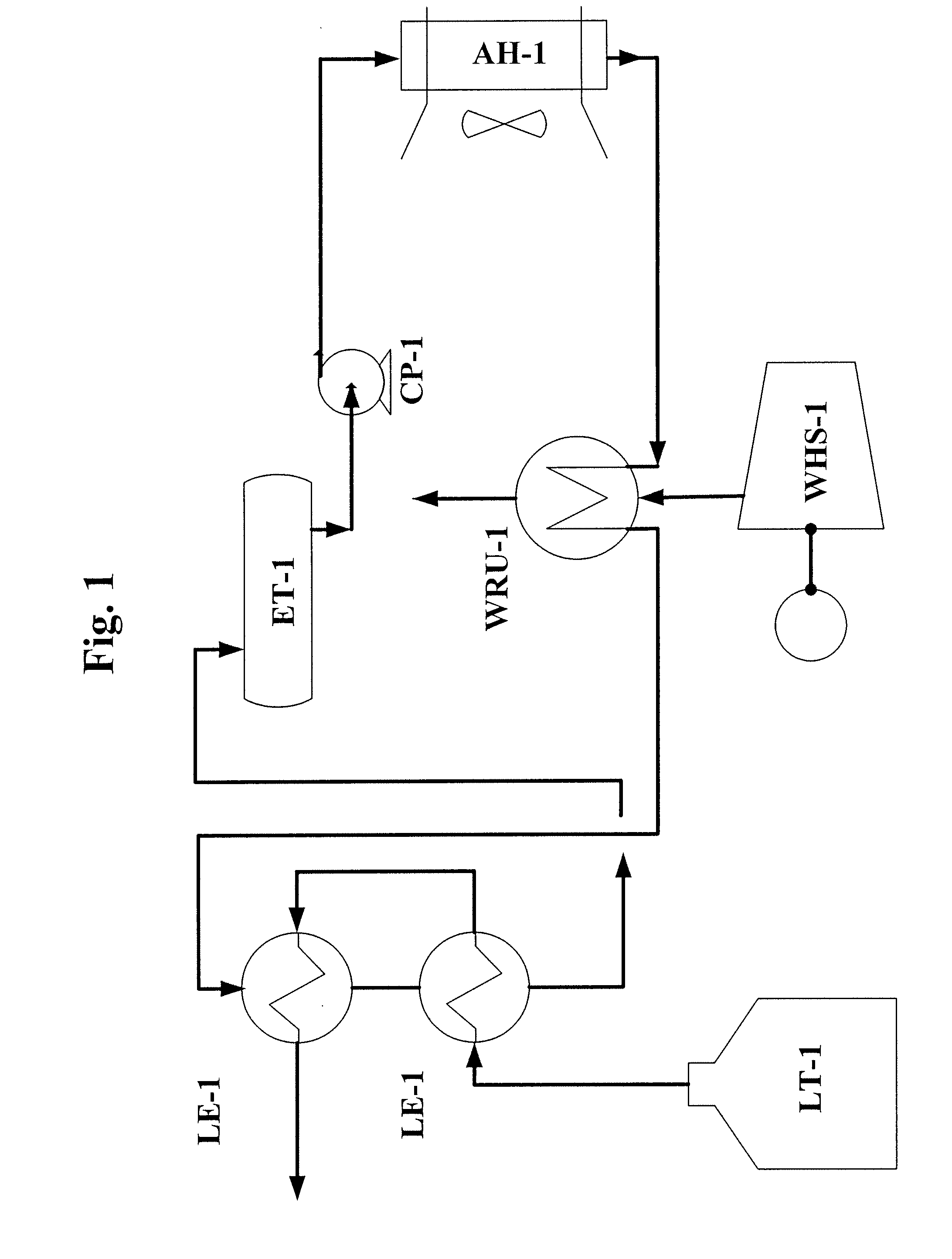
Ecological Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Vaporizer System
InactiveUS20080178611A1Gas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsProcess engineeringAmbient air
An approach is provided for vaporizing liquefied natural gas (LNG). A system utilizing closed circulation of a heat transfer medium heated by ambient air and waste heat from a waste heat source vaporizes the LNG.
Owner:AMEC FOSTER WHEELER USA CORP
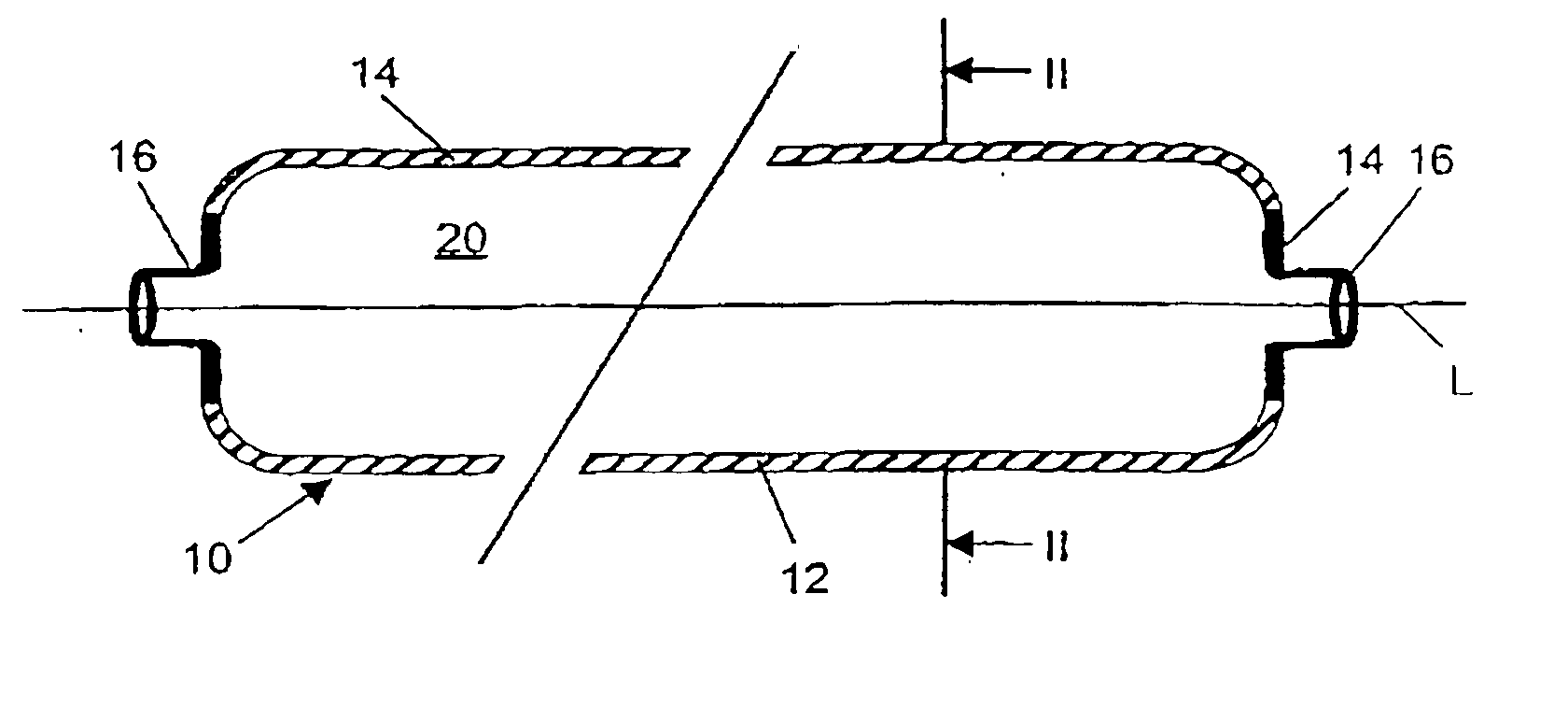
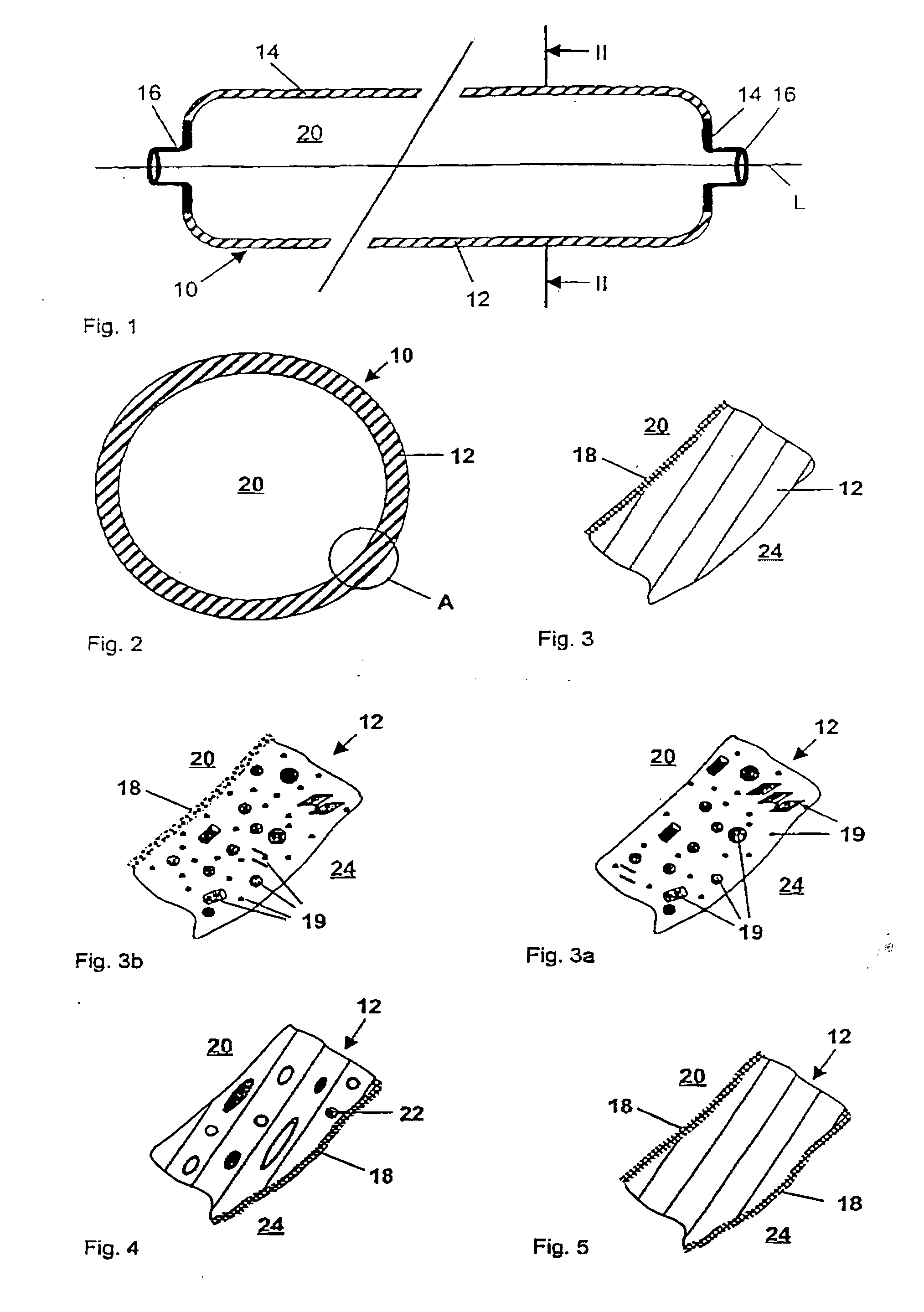
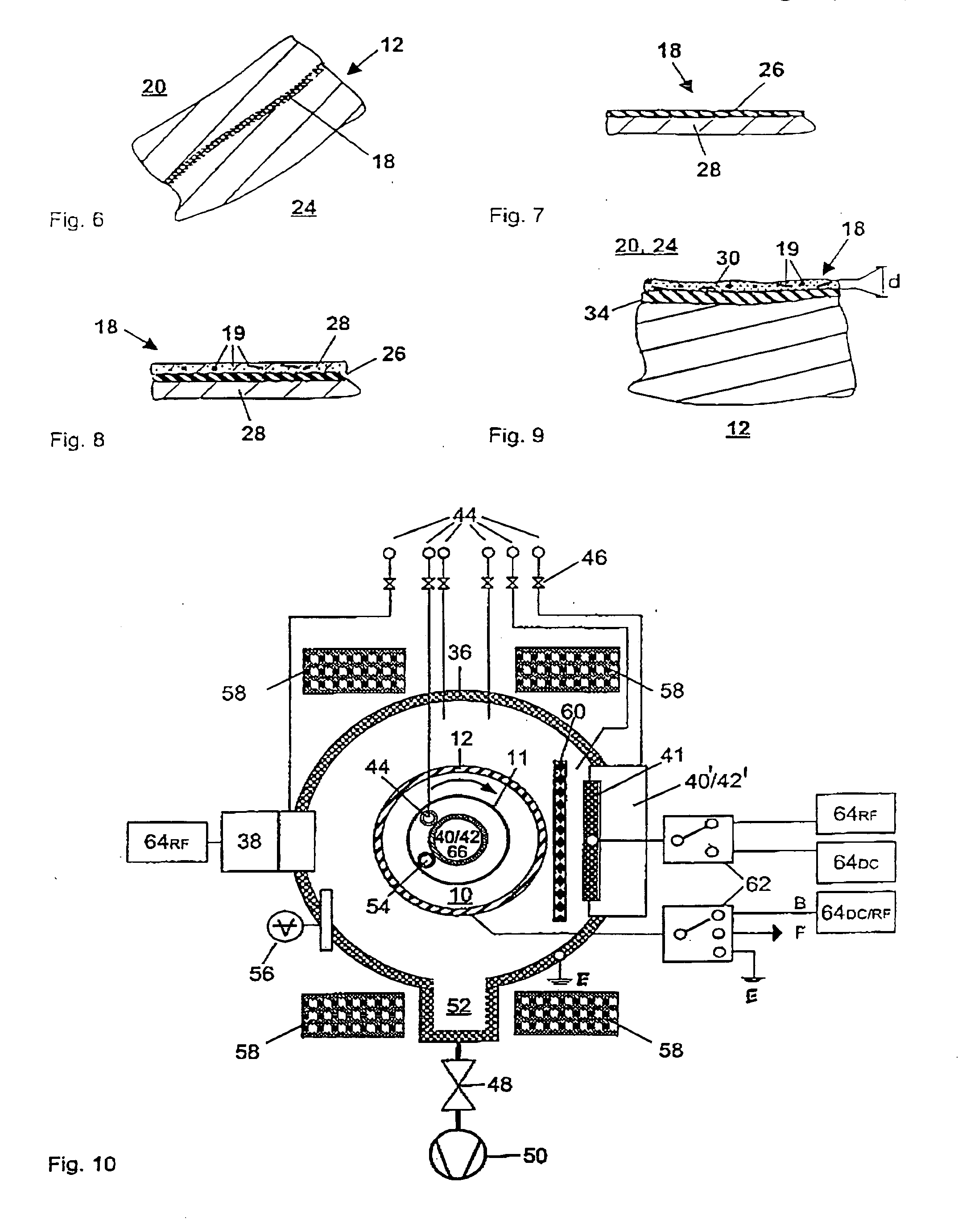
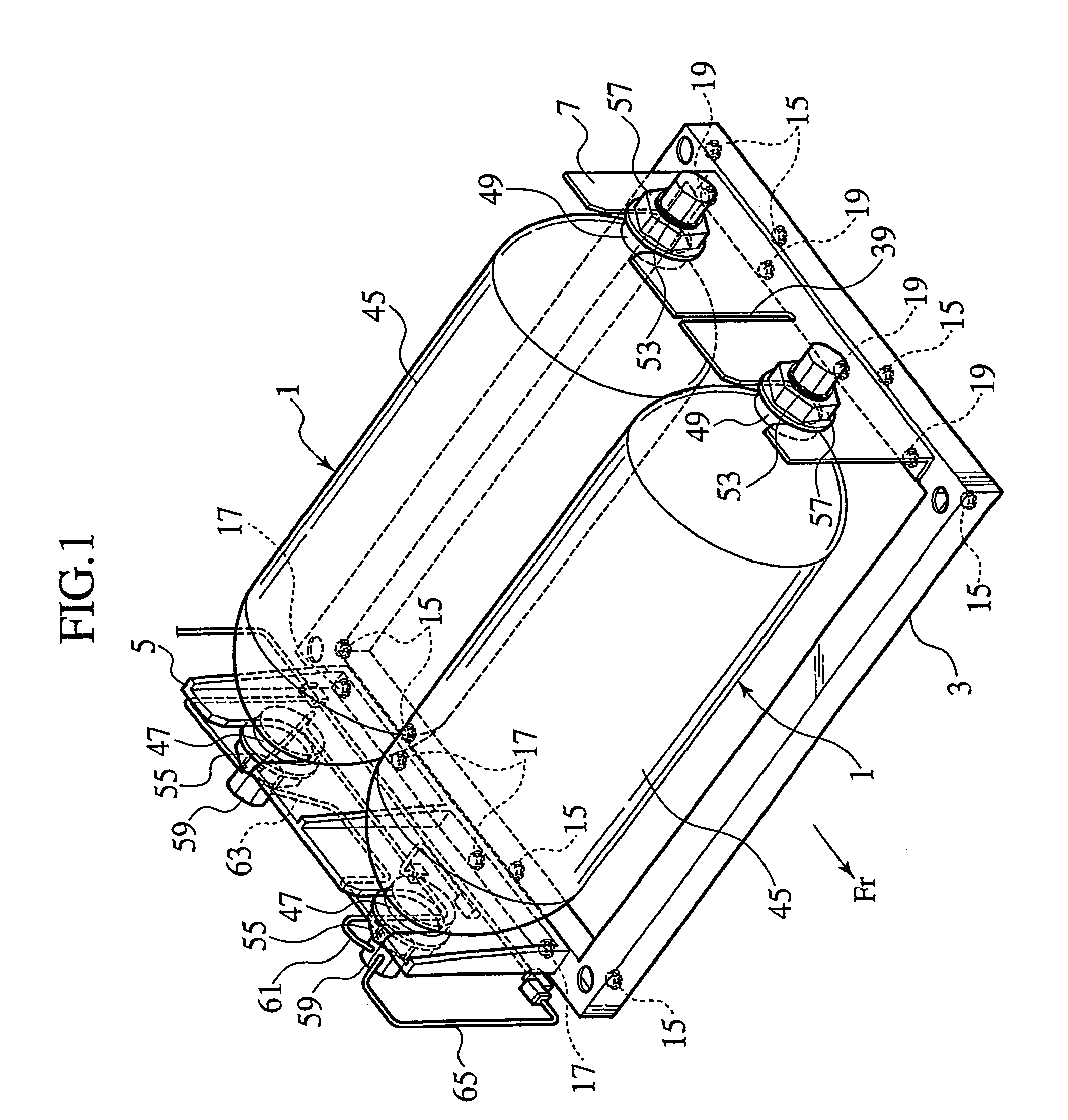
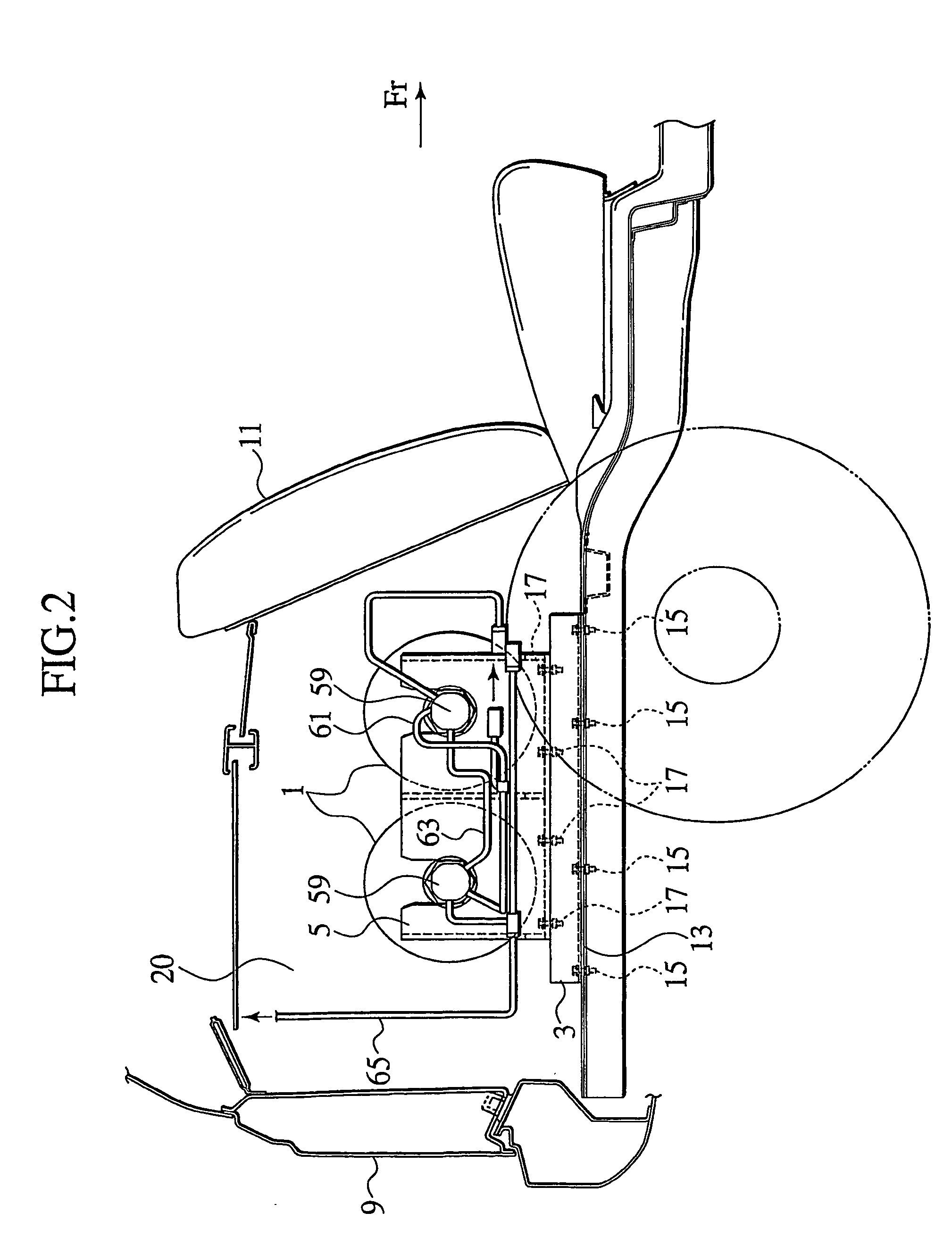
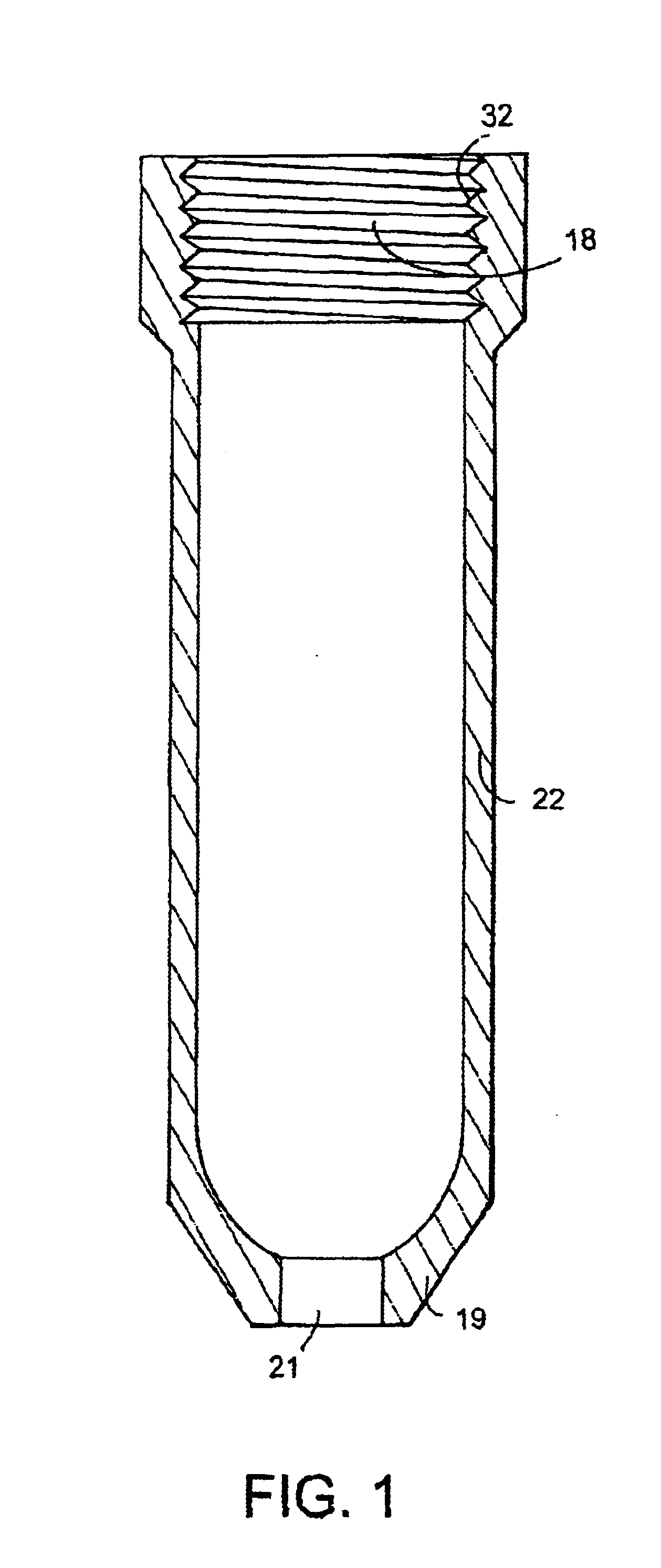
Gastight container
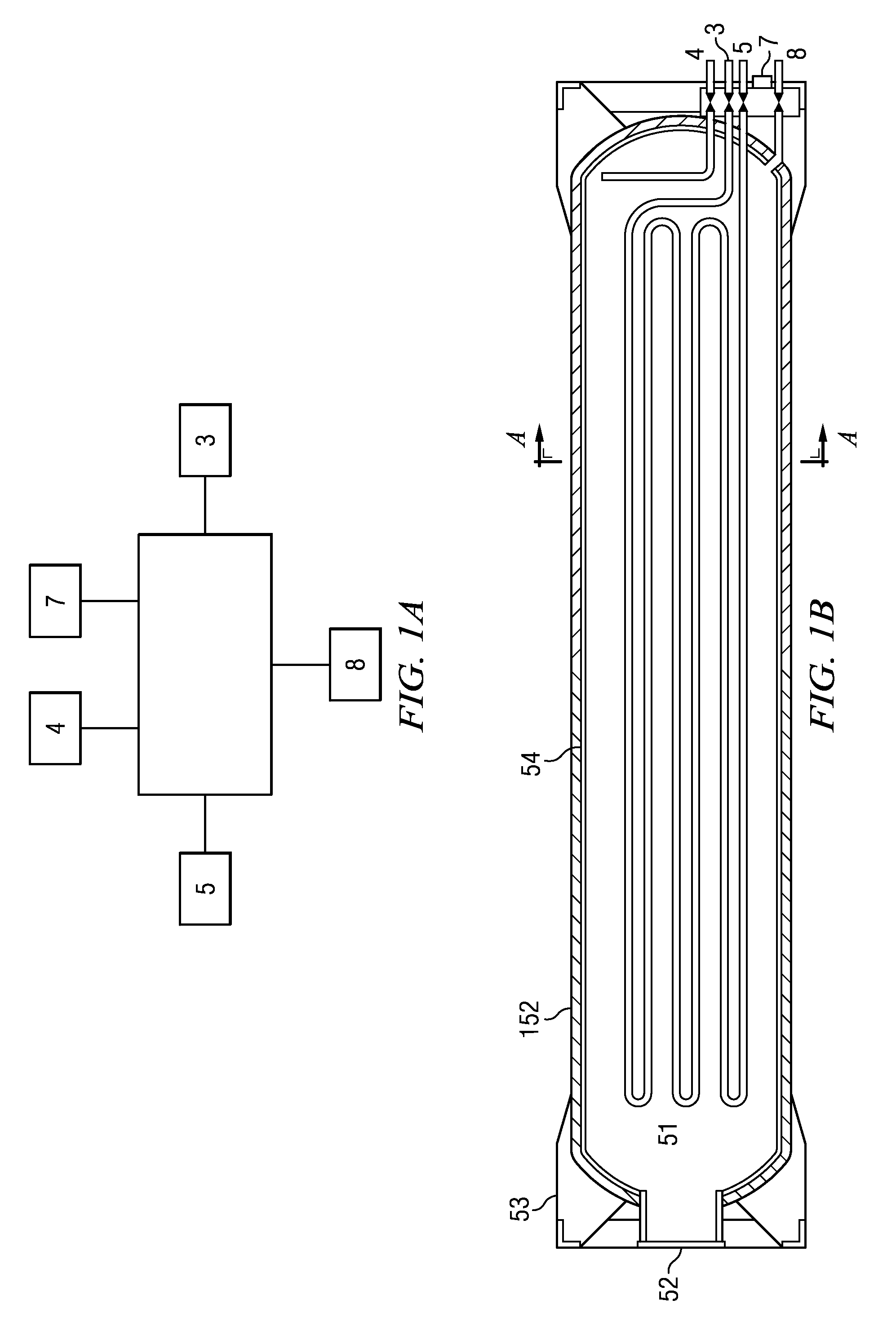
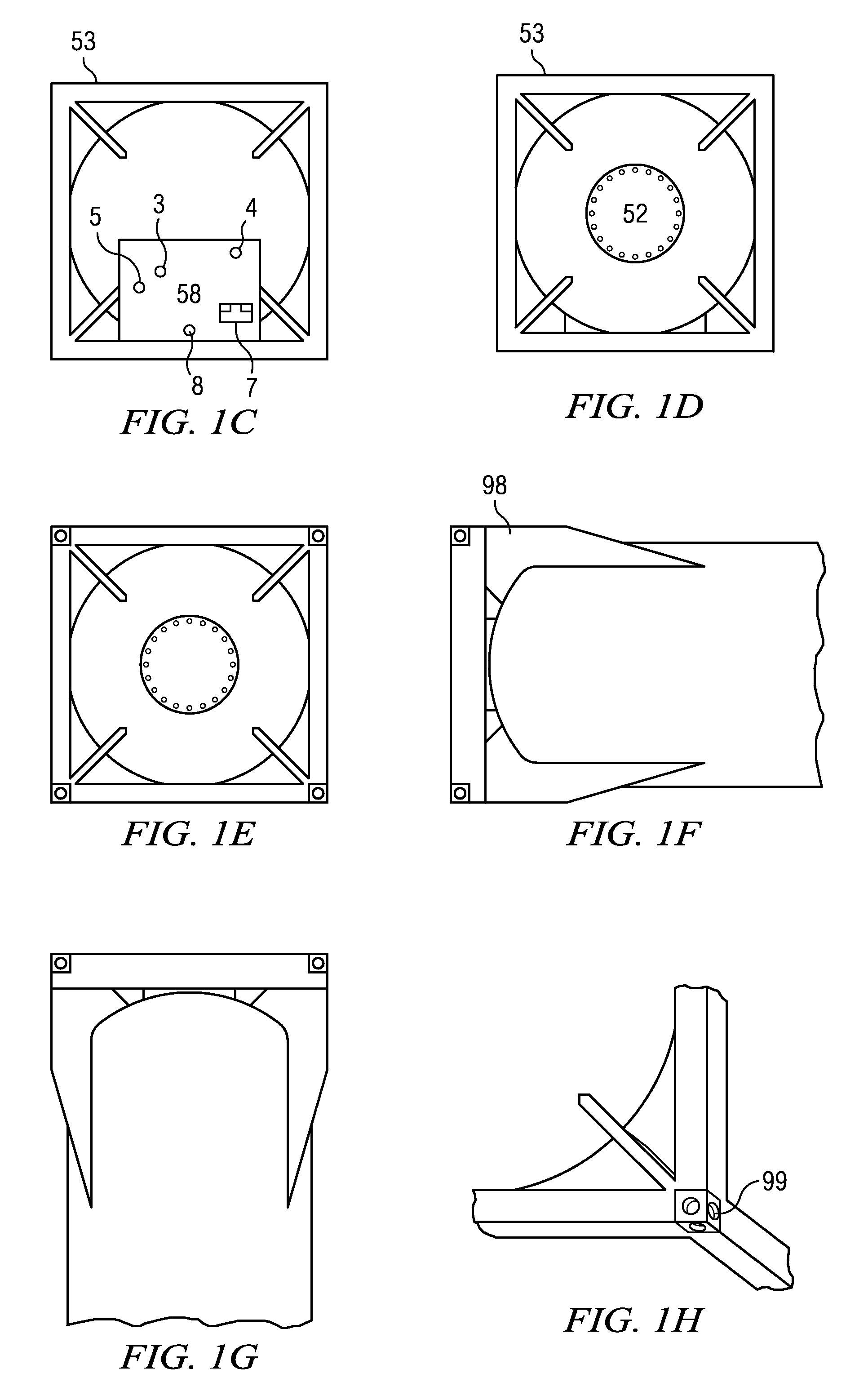
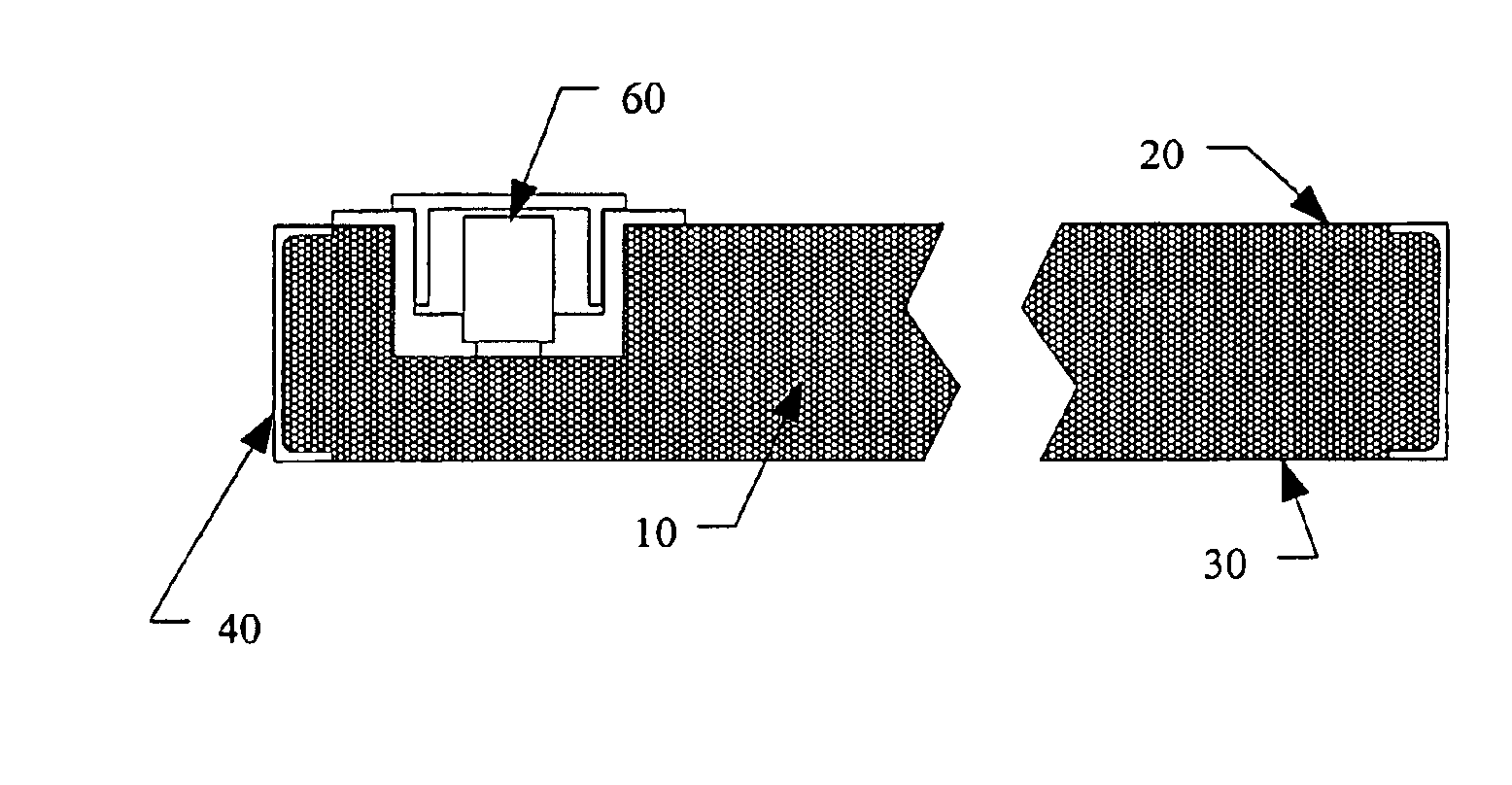
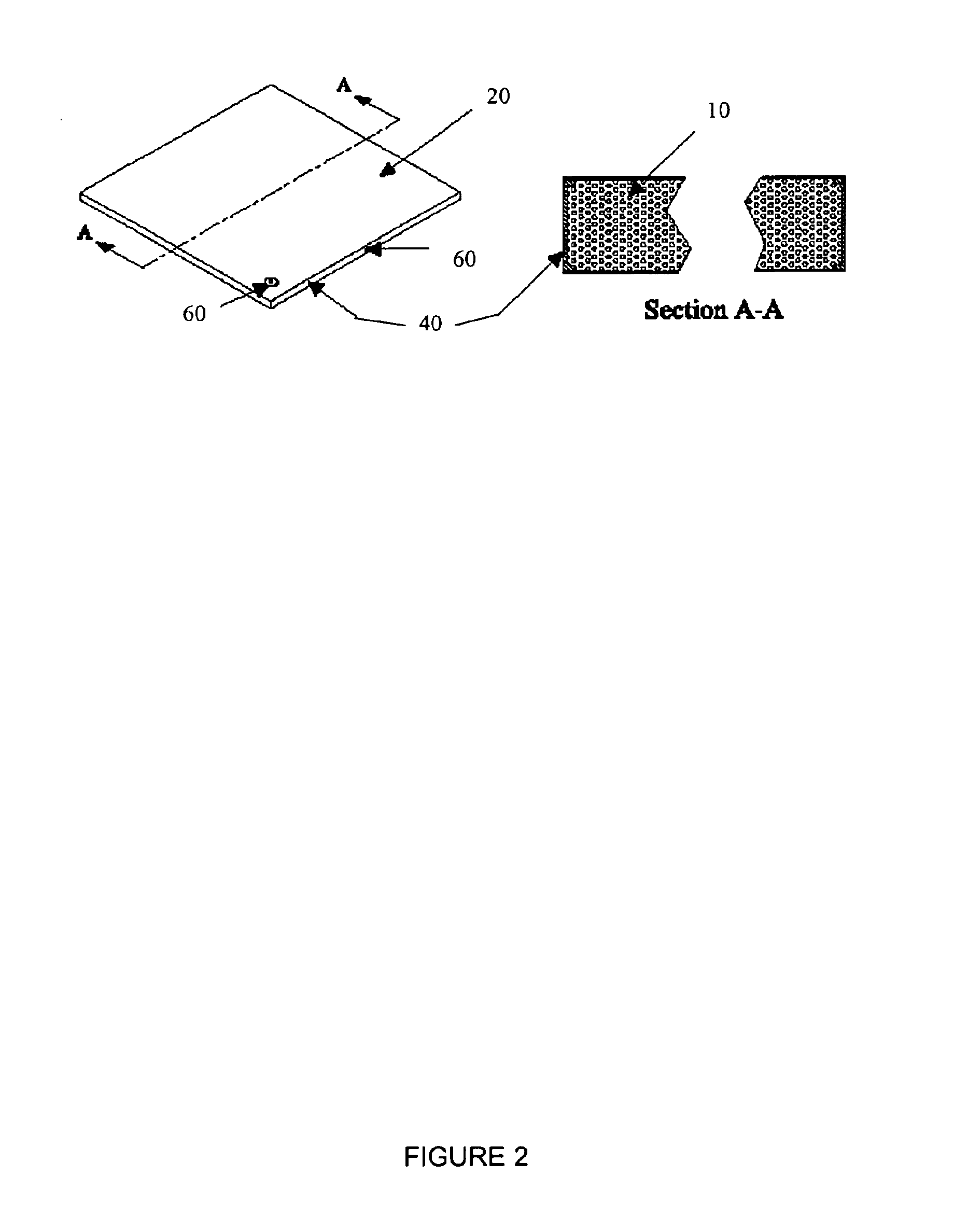
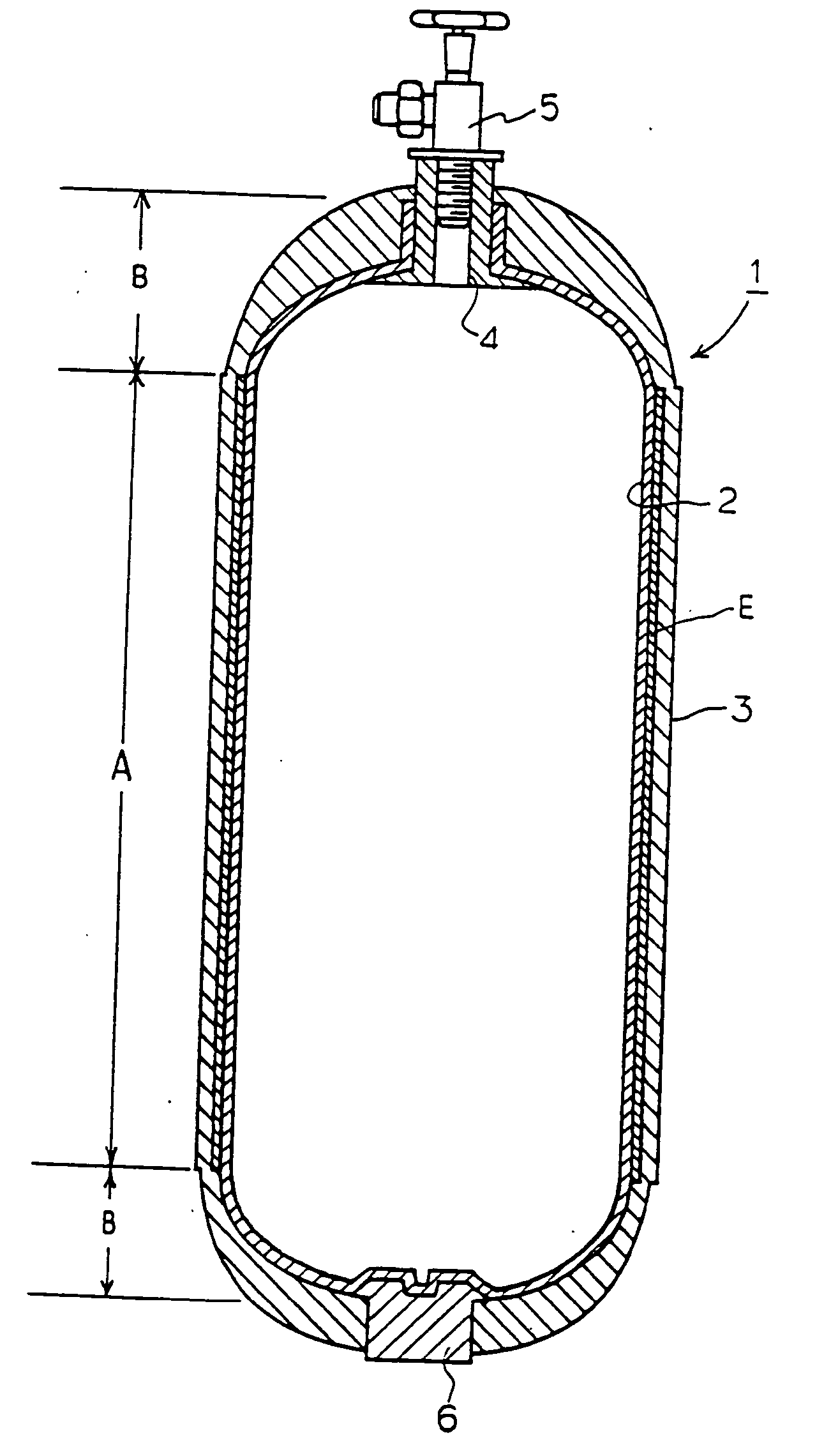
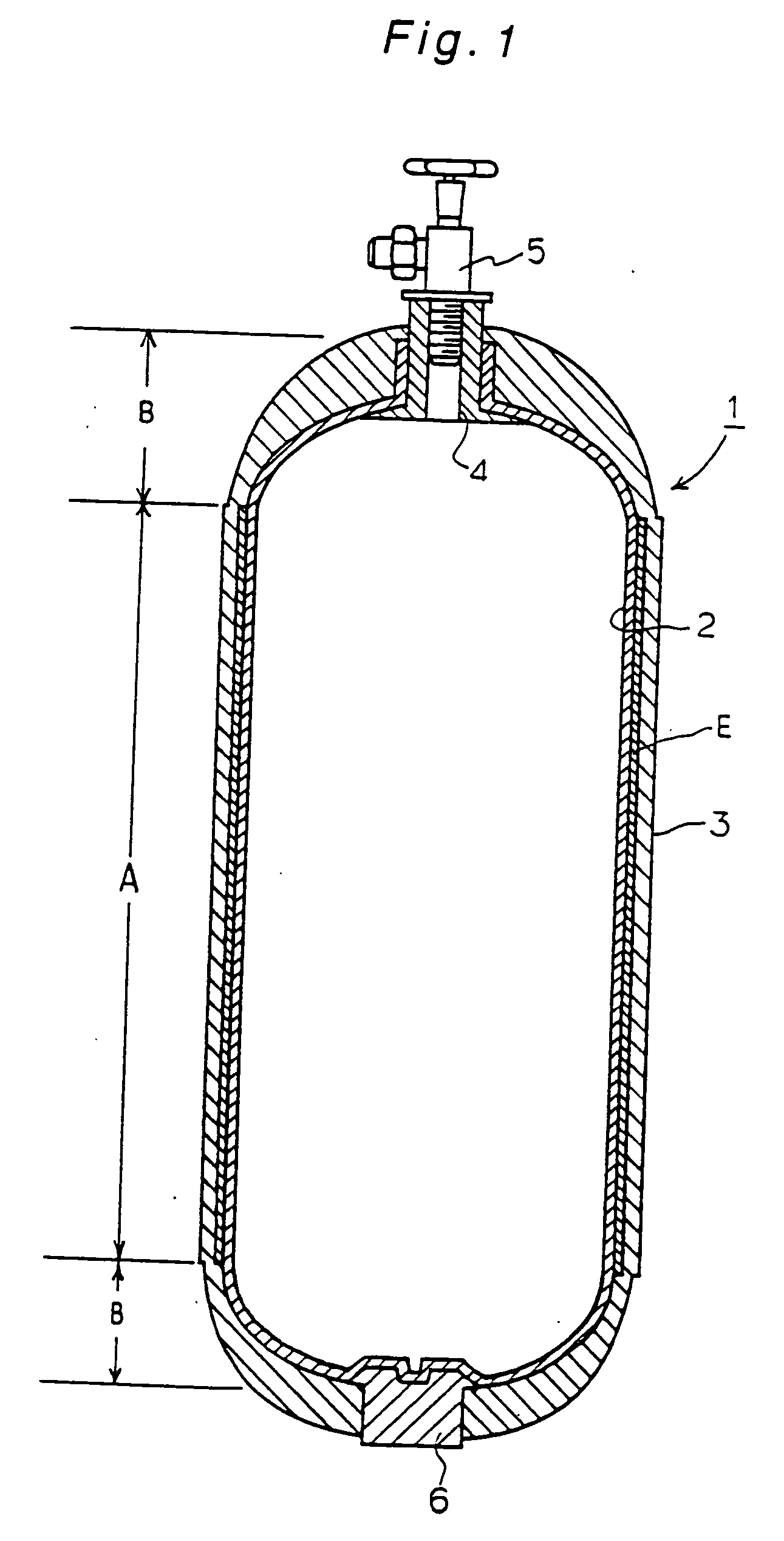
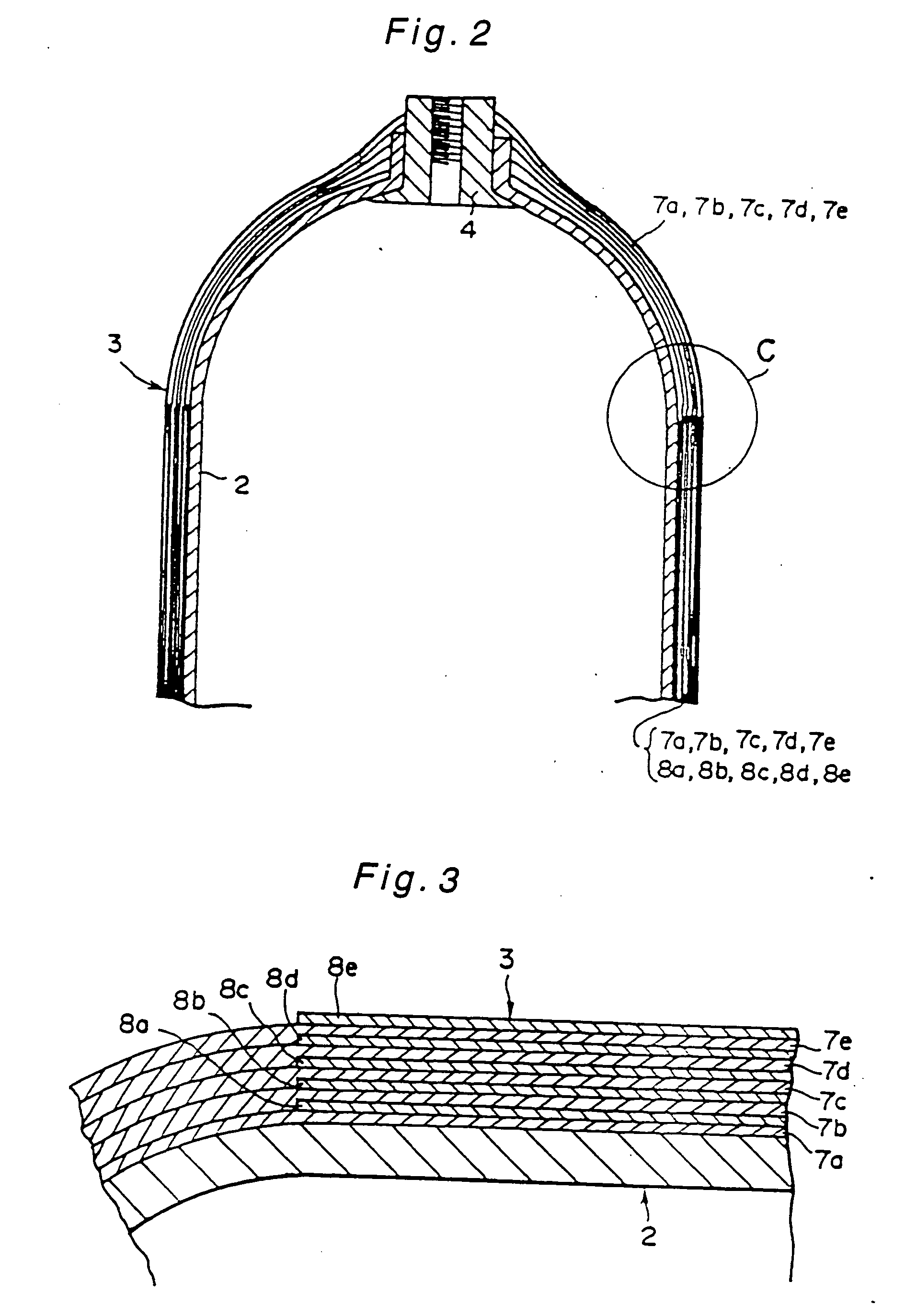
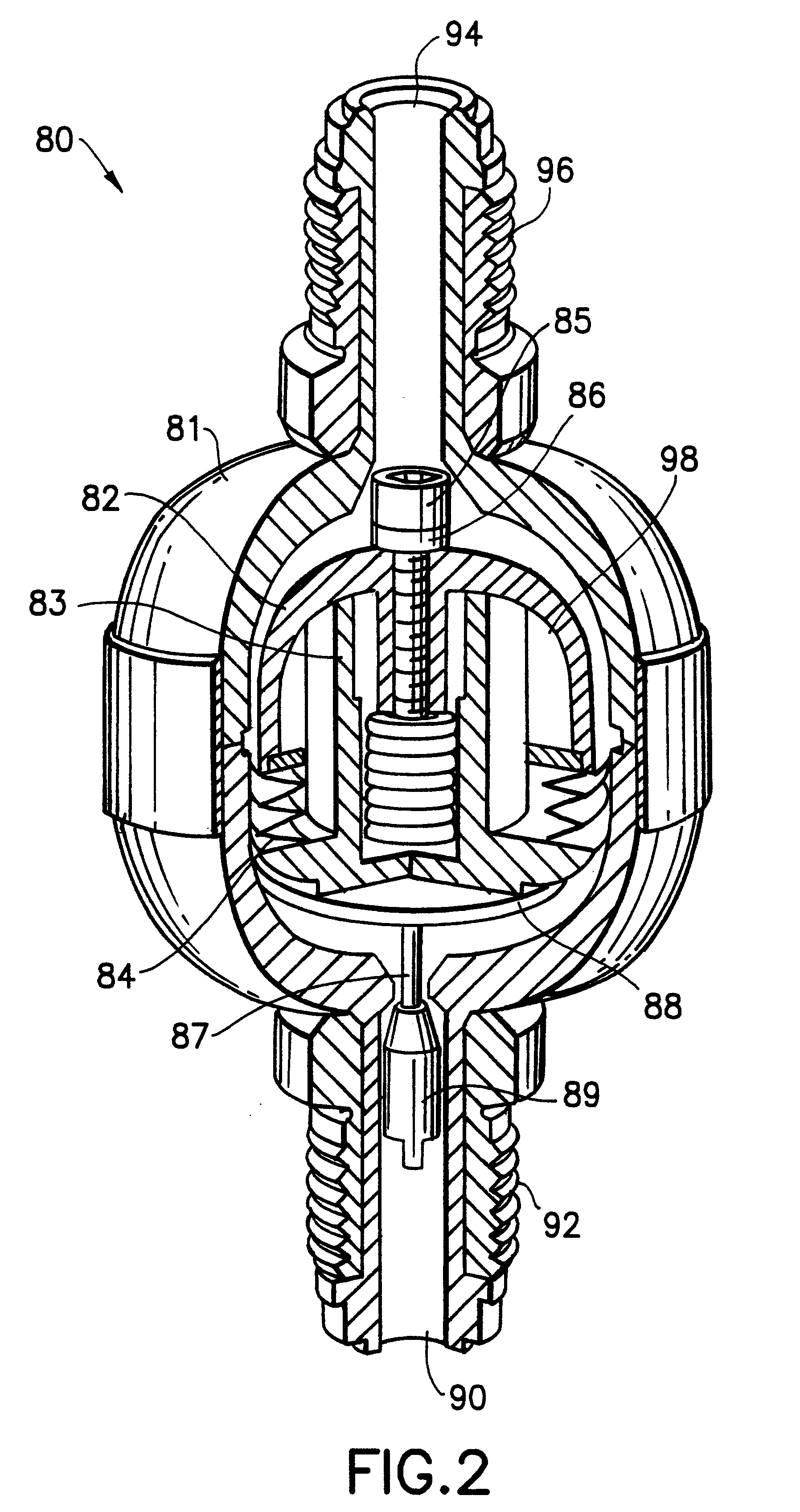
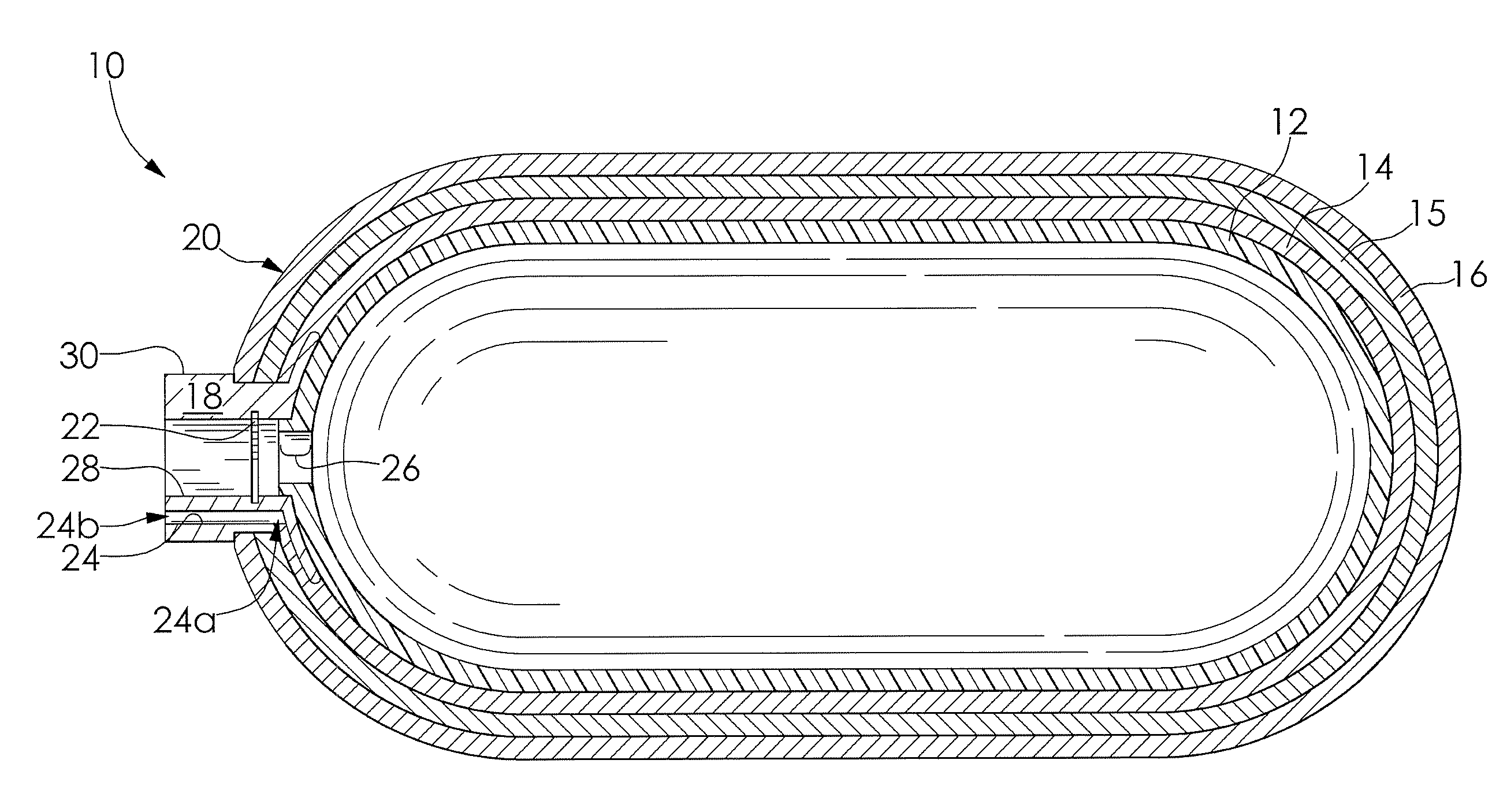
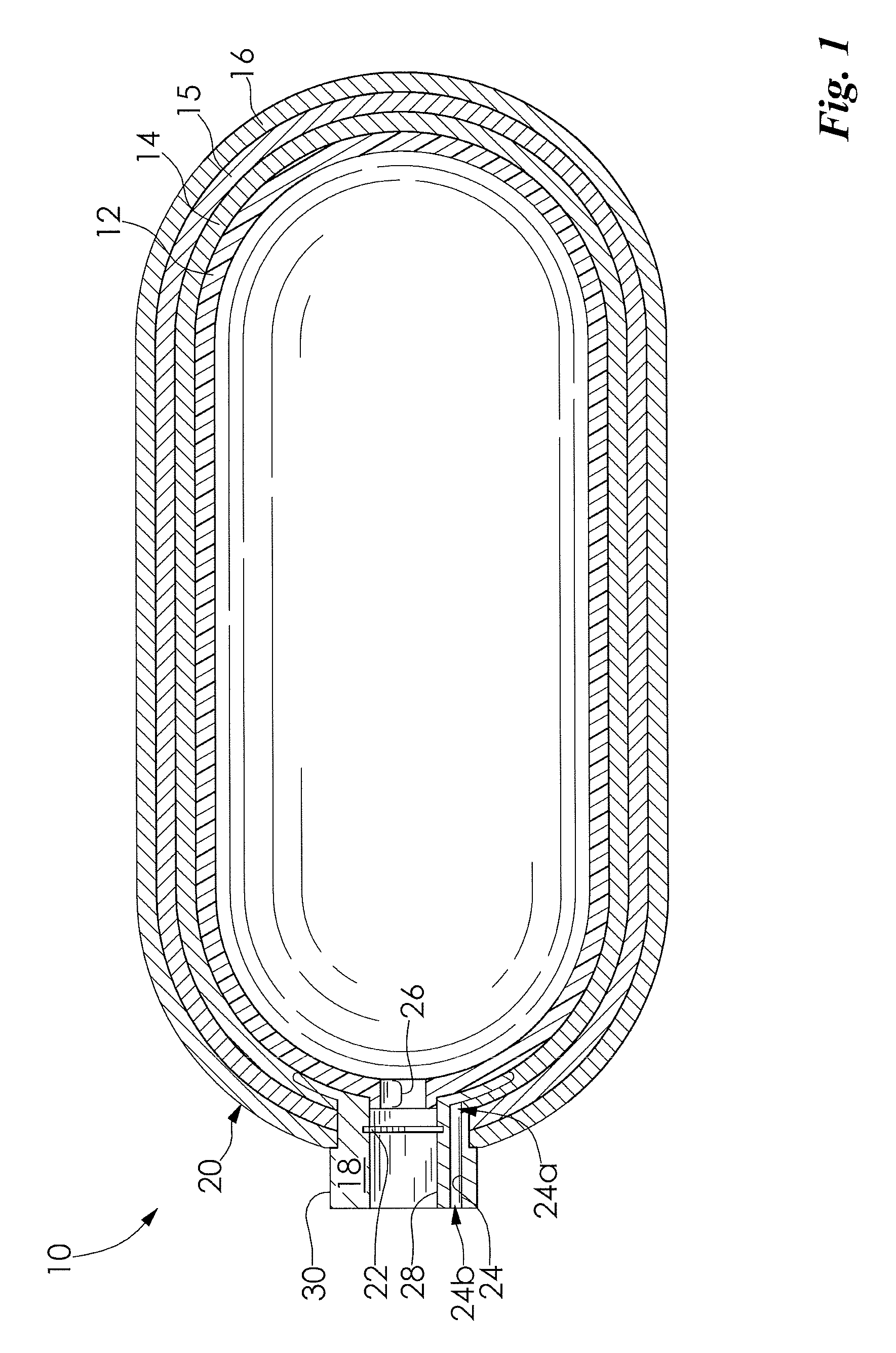
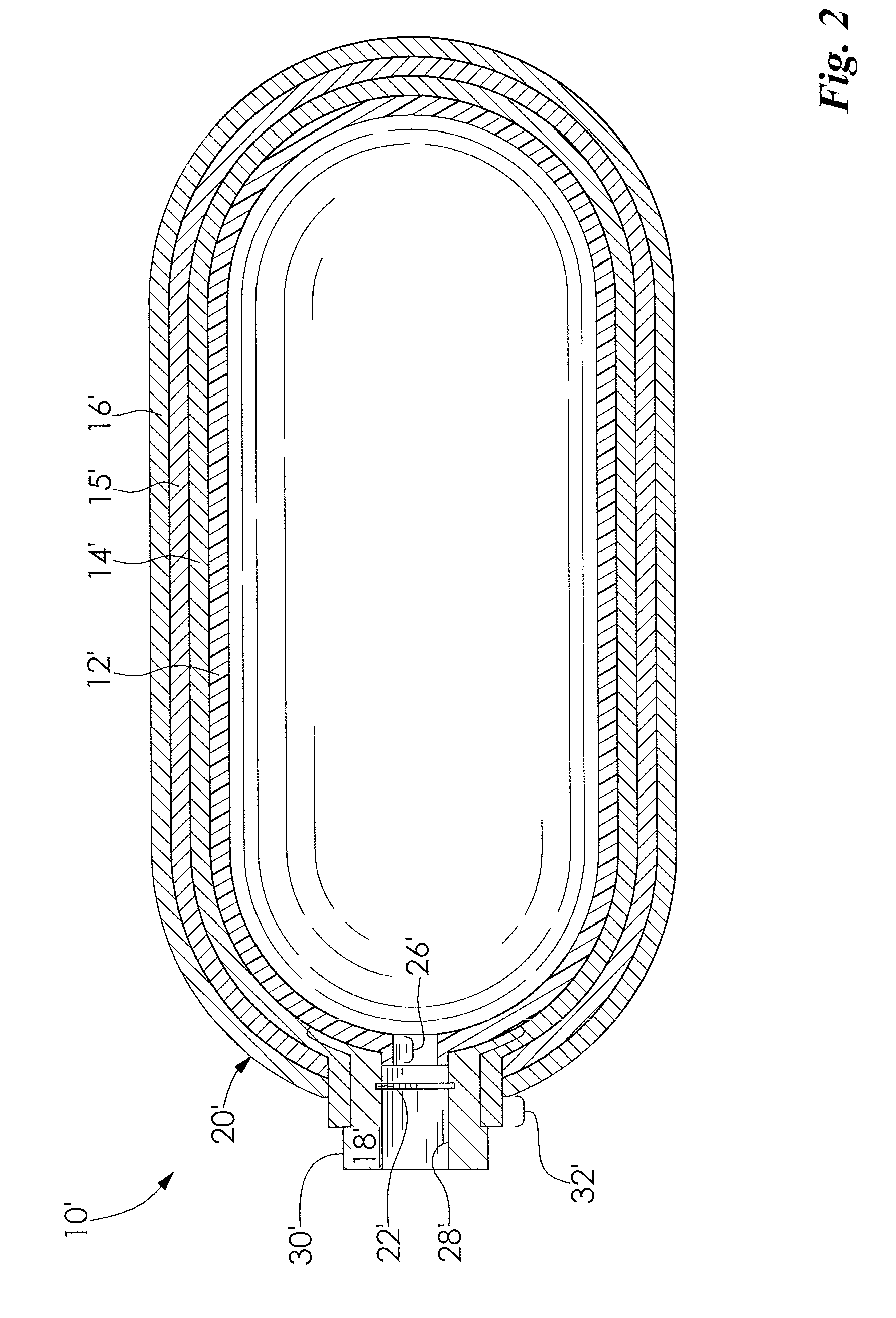
InactiveUS20040149759A1Reduce quality problemsNegligible in recyclingAircraft componentsVessel mounting detailsHydrogenComposite film
The invention relates to a gastight, pressure-resistant storage and / or transport container (10) for low-molecular, reactive filling media, especially for hydrogen, oxygen, air, methane and / or methanol. Said container has a high filling pressure and is embodied in an essentially rotationally symmetric manner, having at least one connector cap (15) with a sealing device (16). The wall (12) of the container is essentially comprised of a thermoplastic synthetic material having at least one diffusion barrier (18, 19) system and / or a diffusion barrier and anti-corrosion system (18, 19). In order to offer protection for hydrogen and oxygen containers, the diffusion barrier system can be embodied in the form of at least one compact layer and / or can contain finely dispersed, distributed reactive nanoparticles (18) in the wall (12) of the container, in at least one composite film (28) and / or in at least one diffusion barrier layer (18).
Owner:MOSER EVA MARIA +1
Clathrate hydrate modular storage, applications and utilization processes
Methods, apparatuses and systems directed to clathrate hydrate modular storage, applications and utilization processes. In one implementation, the present invention provides a method of creating scalable, easily deployable storage of natural gas and thermal energy by assembling an array of interconnecting, modular gas clathrate hydrate storage units.
Owner:SOLID GAS TECH
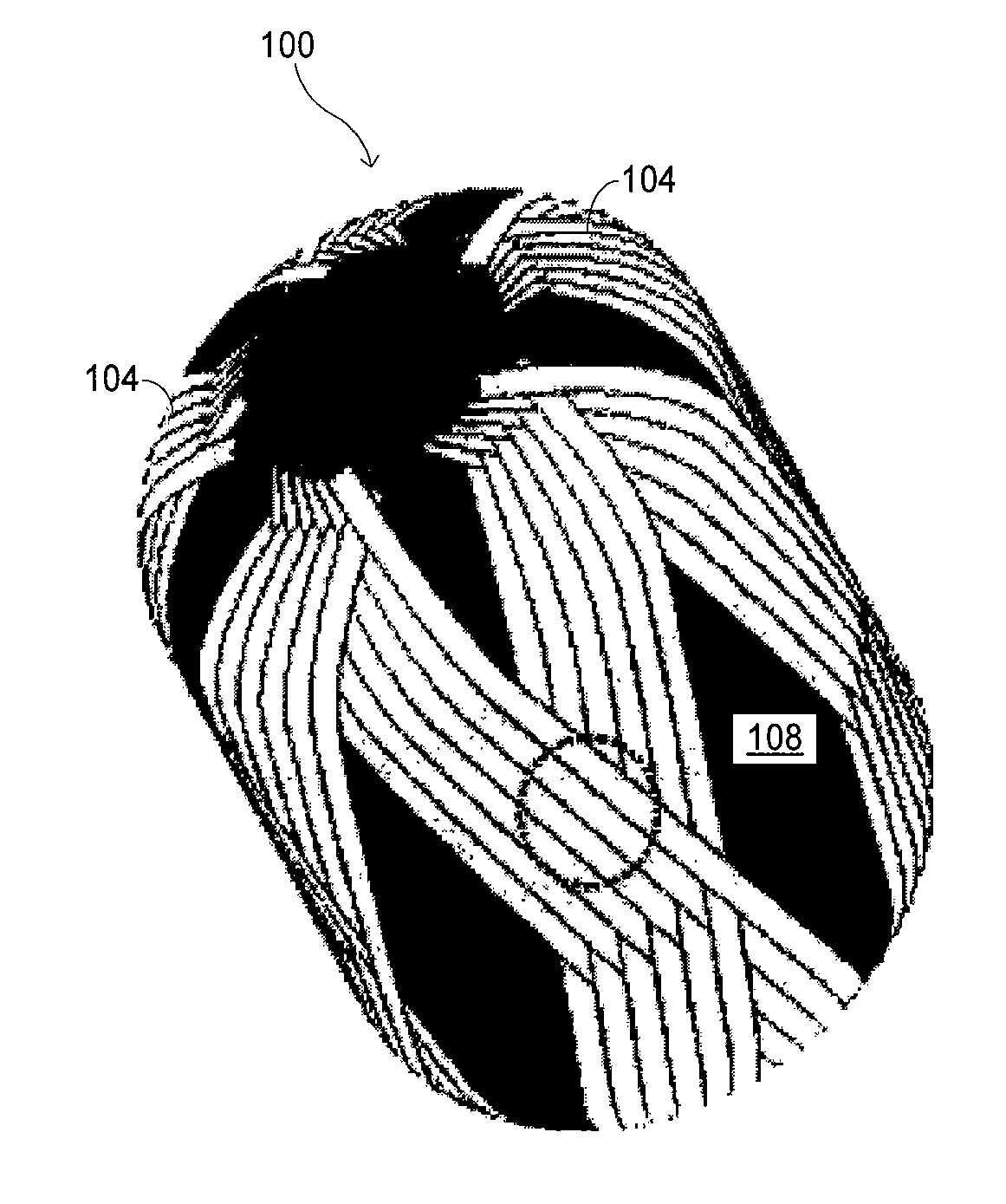
Damage and leakage barrier in all-composite pressure vessels and storage tanks
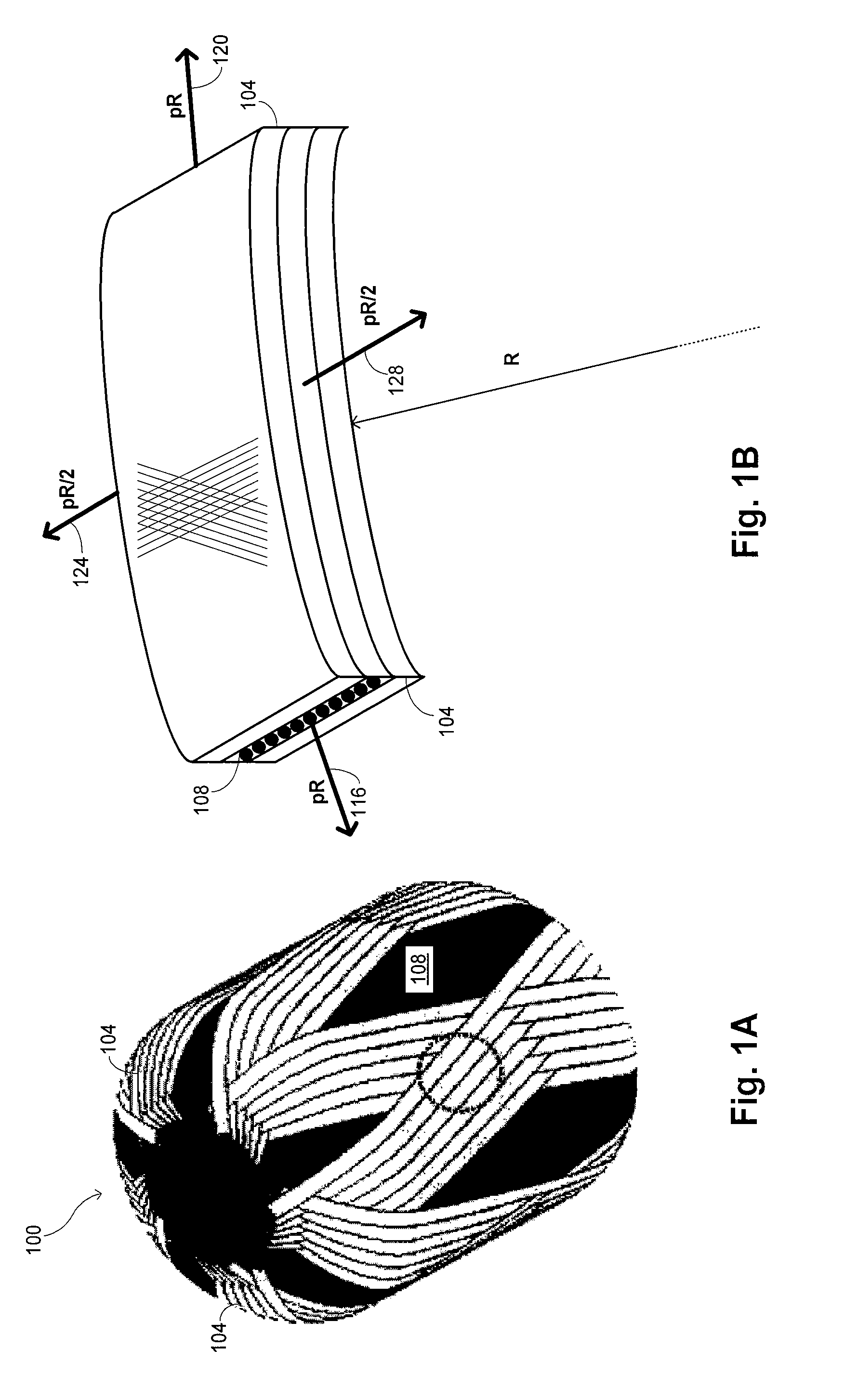
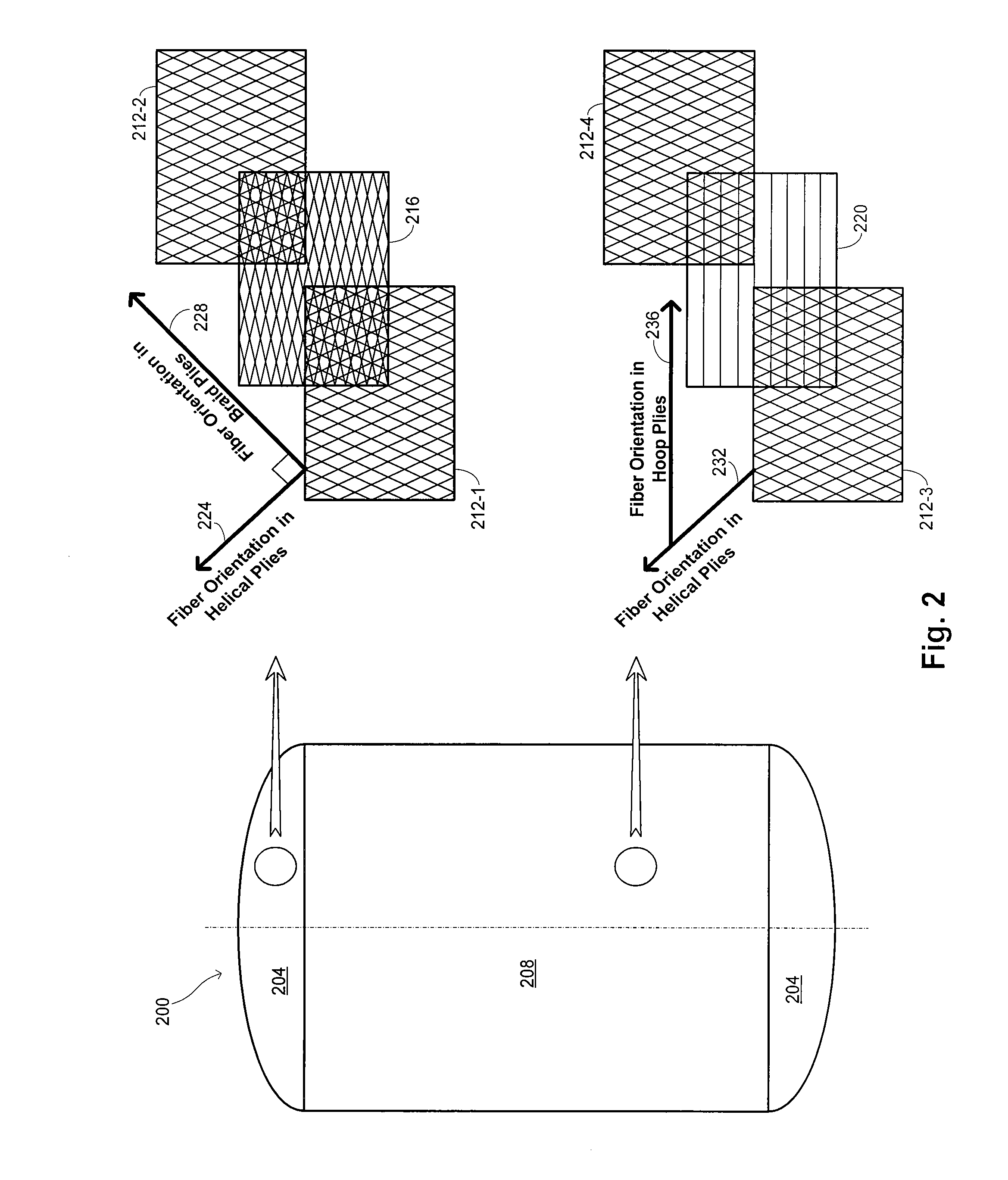
ActiveUS20090314785A1Superior barrier against leakageStrengthAdhesive processesGas handling applicationsFiberAxis of symmetry
A linerless tank structure has a body that defines an enclosed interior volume. The body has a cylindrical section having an axis of symmetry and a dome section coupled with the cylindrical section. The construction of the pressure vessel includes multiple fiber plies. At least one of the fiber plies is a helical ply having fibers traversing the dome helically about the axis of symmetry. At least a second of the fiber plies is a braided or woven ply.
Owner:COMPOSITE TECH DEV
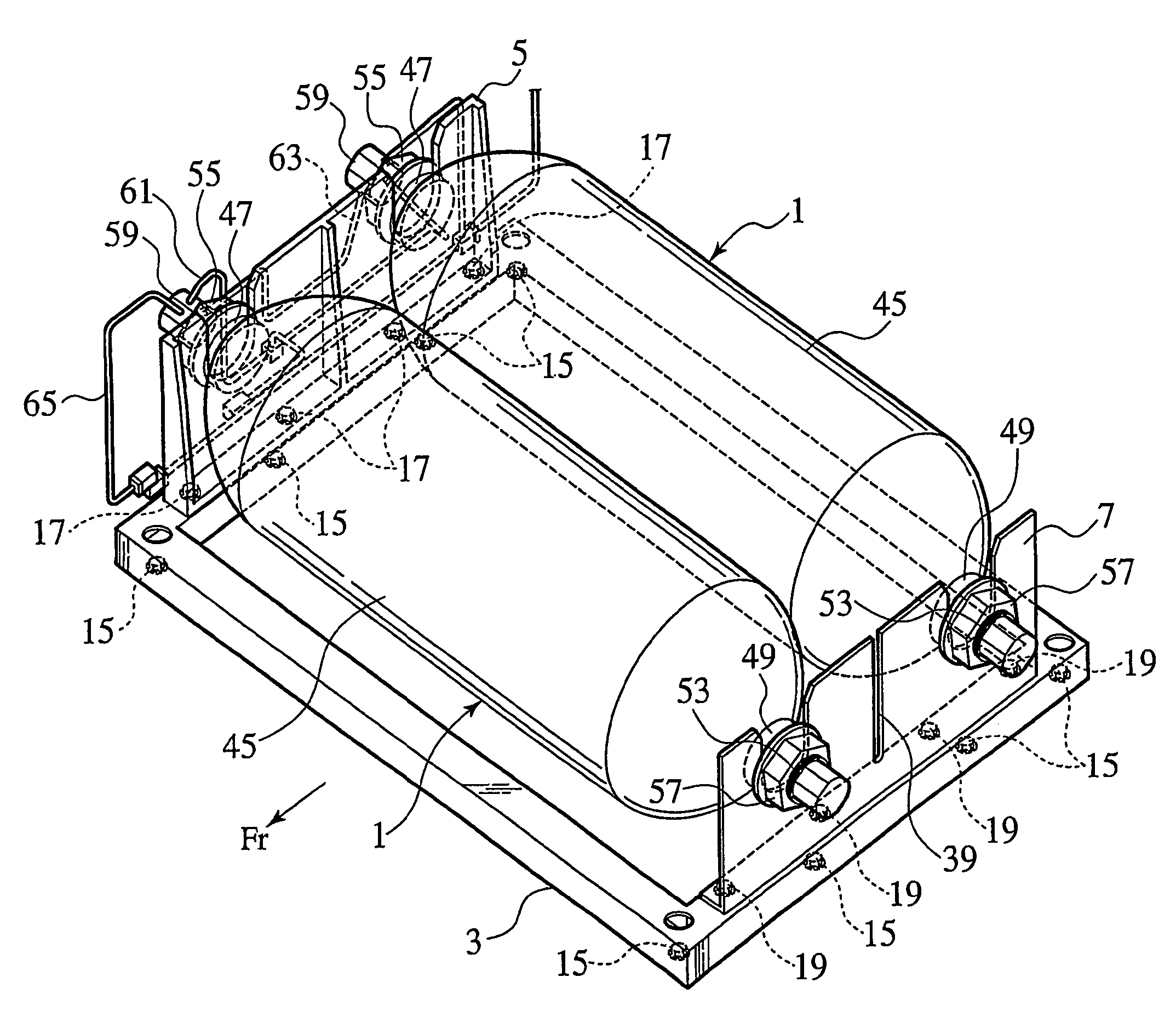
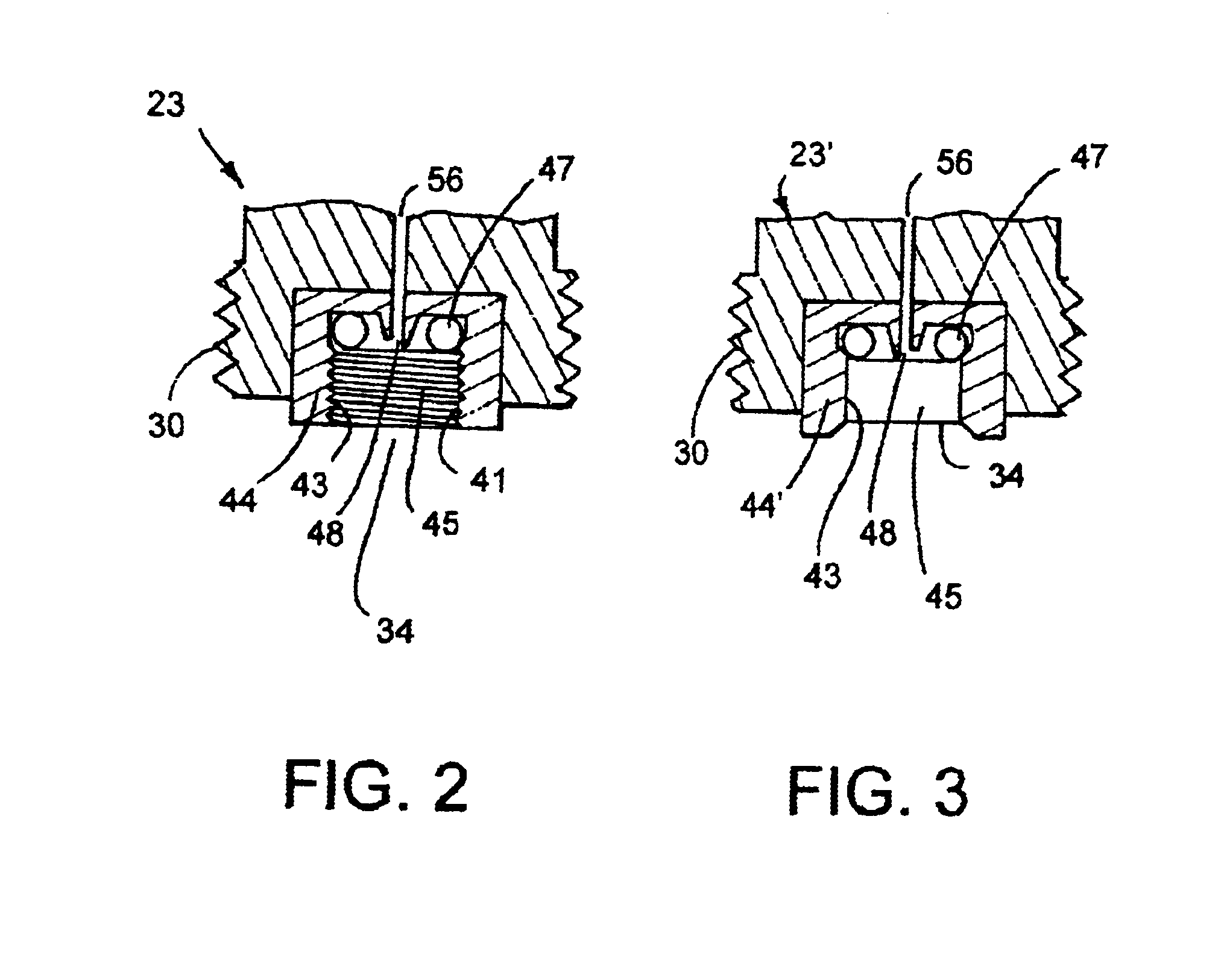
Pressure regulator adaptable to compressed gas cartridge
ActiveUS7334598B1Reduce manufacturing costImprove reliabilityContainer filling methodsGas handling applicationsEngineeringHigh pressure
This pressure regulator is specifically designed to operate with a portable compressed gas cartridge thus reducing the high vapor pressure found in compressed gas cartridges down to a substantially consistent outlet pressure. Due to the nature of the crowded regulator art, the soon to be embodied pressure regulator has been specifically embodied for use in the portable compressed gas cartridge harnessing art and this specific use is carried into the claims. Exemplified in the pressure regulator embodiments is a reduced amount of components over existing designs. Additionally, safety and reliability features have been integrated into the design and will shortly be taught in the following paragraphs. A burp-off feature in all embodiments will be exemplified that vents back-pressure spikes as well as a method of adjusting the burp-off back-pressure spikes independent of regulated pressure in some embodiments.
Owner:HOLLARS ANTHONY SCOTT
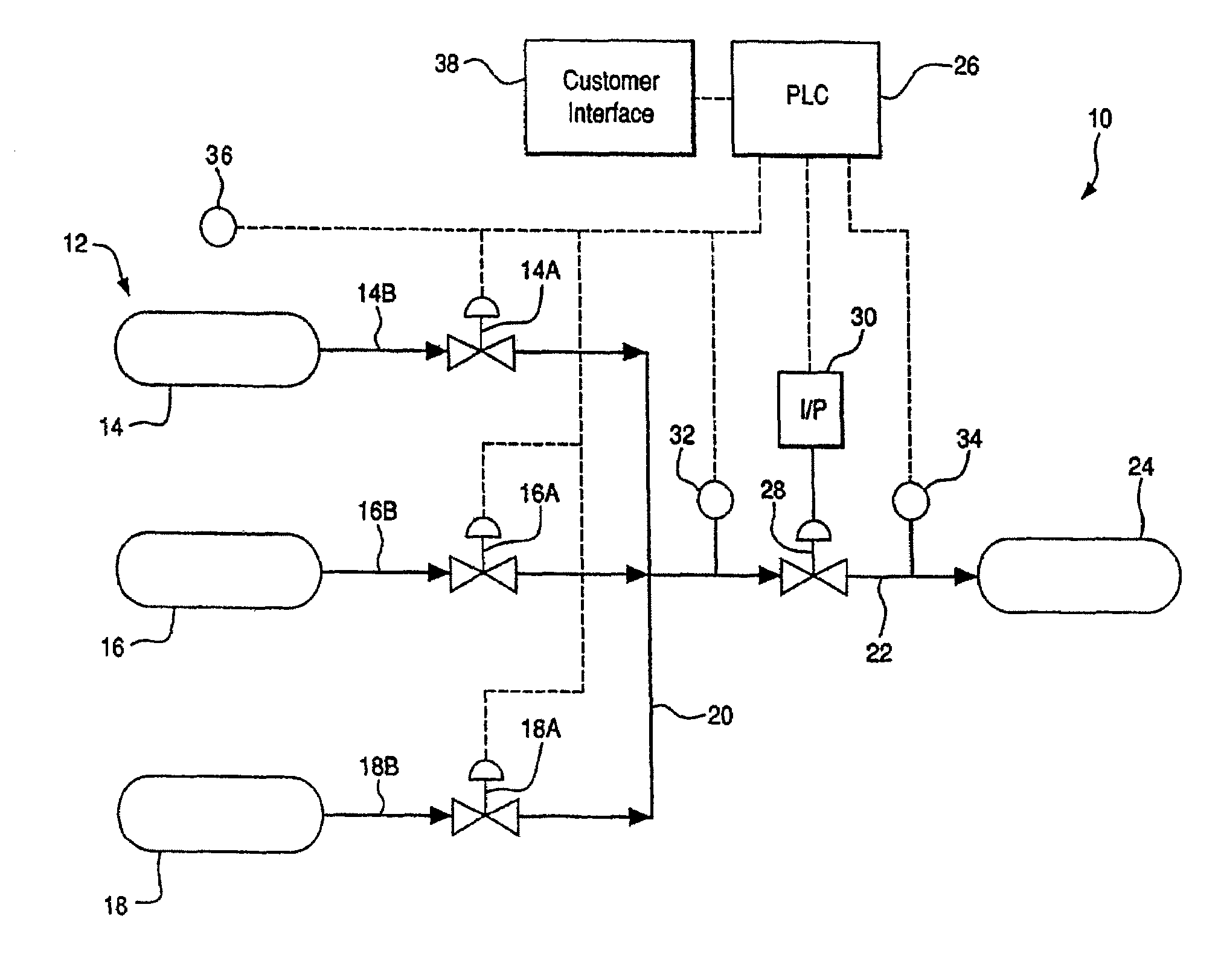
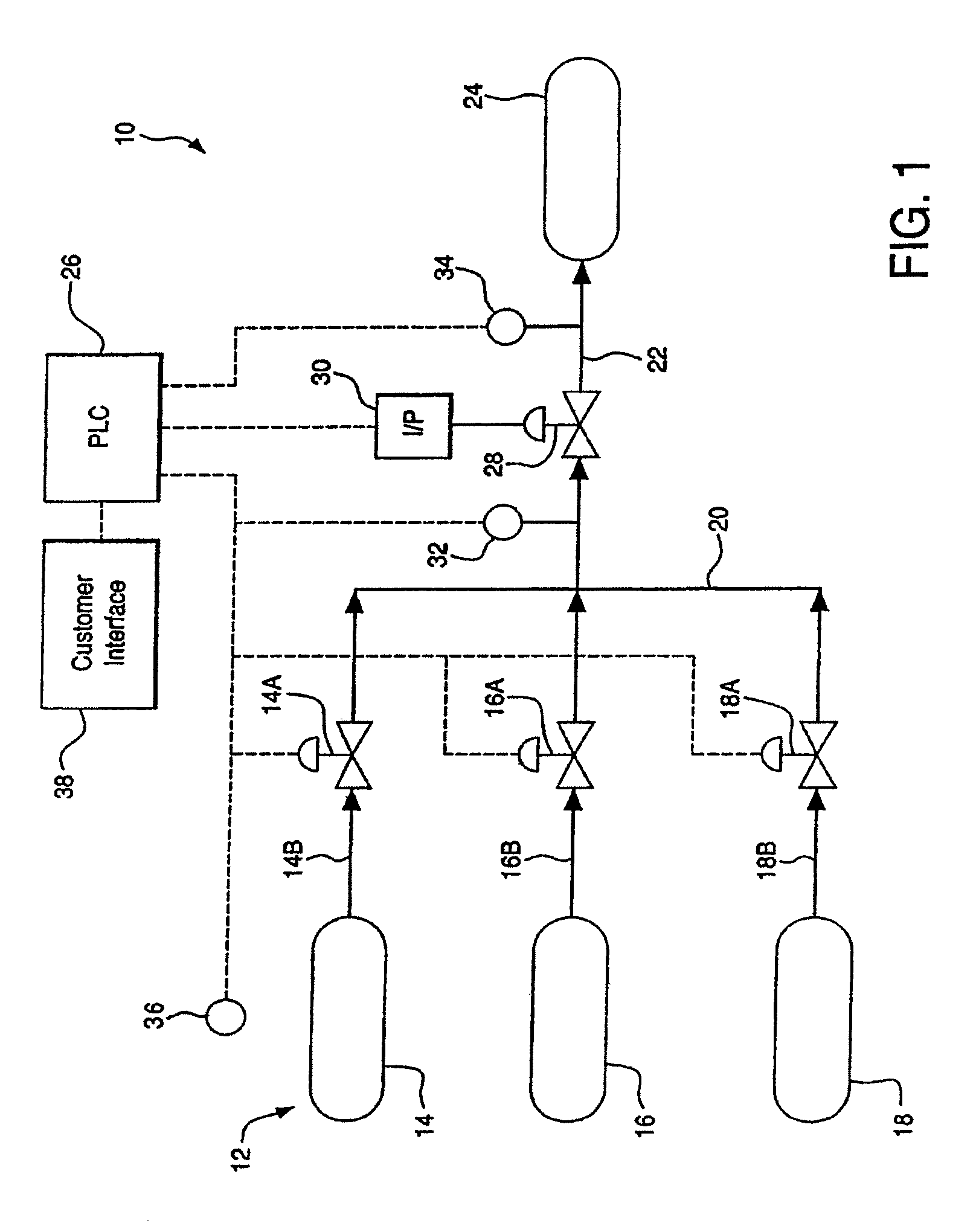
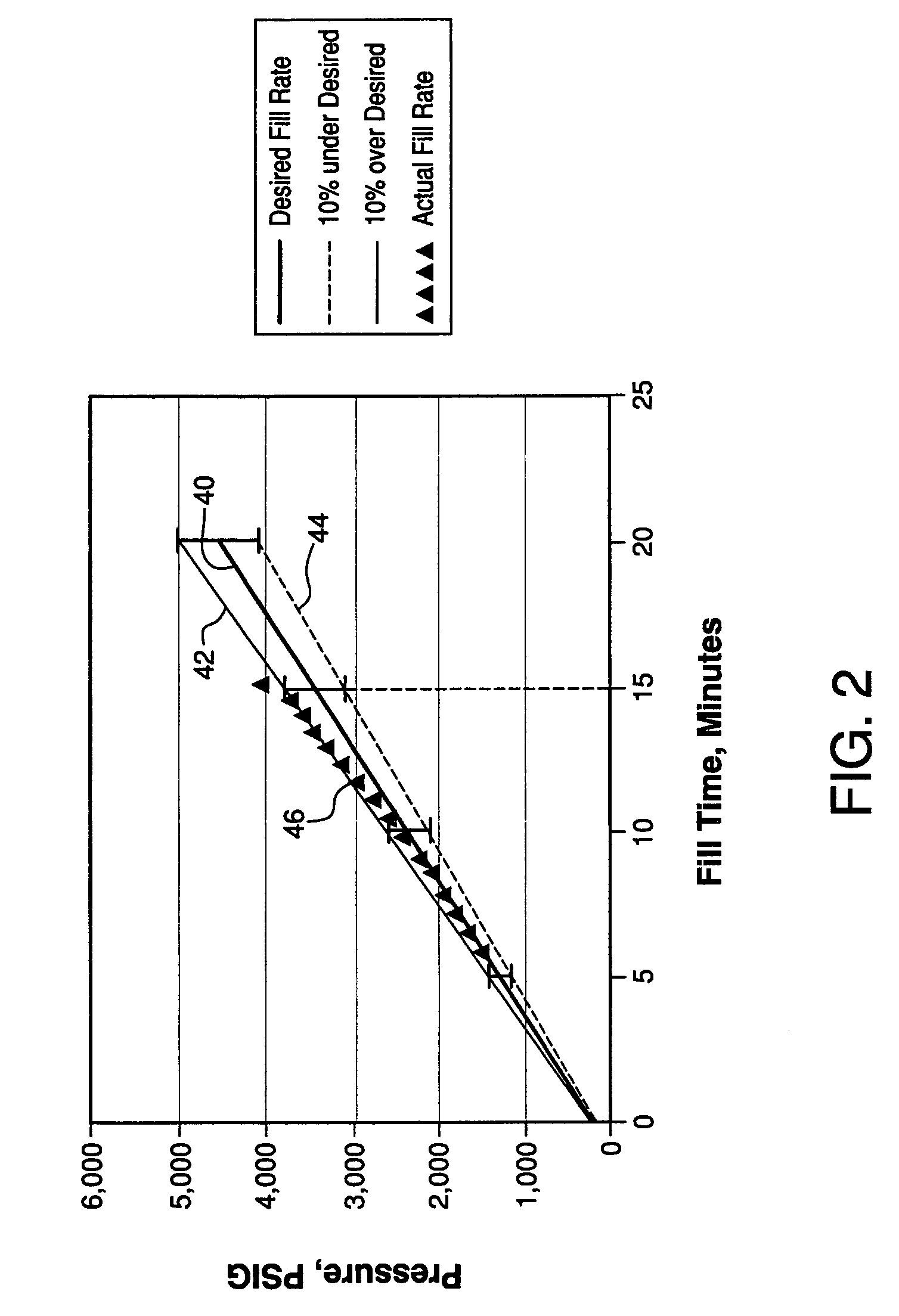
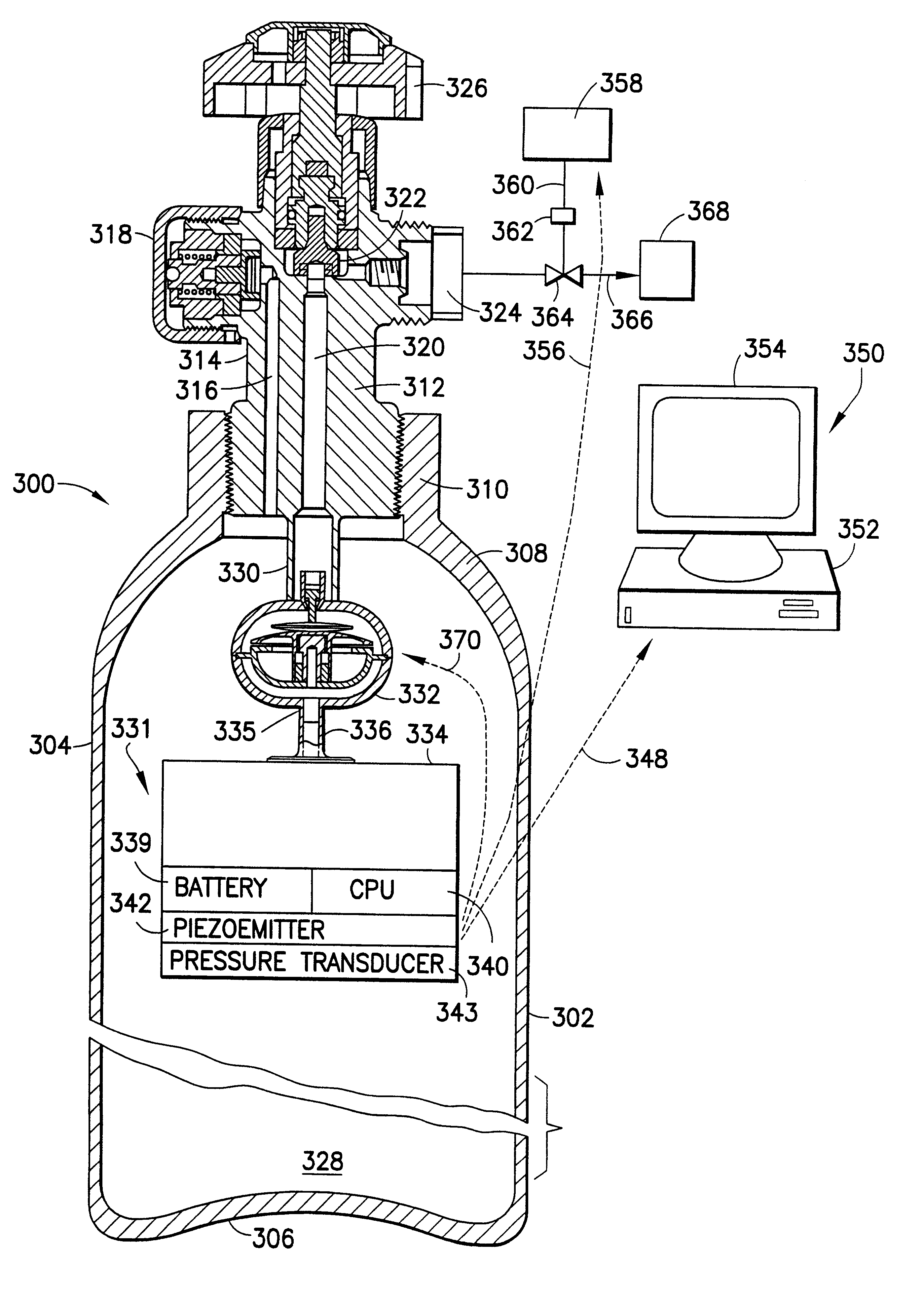
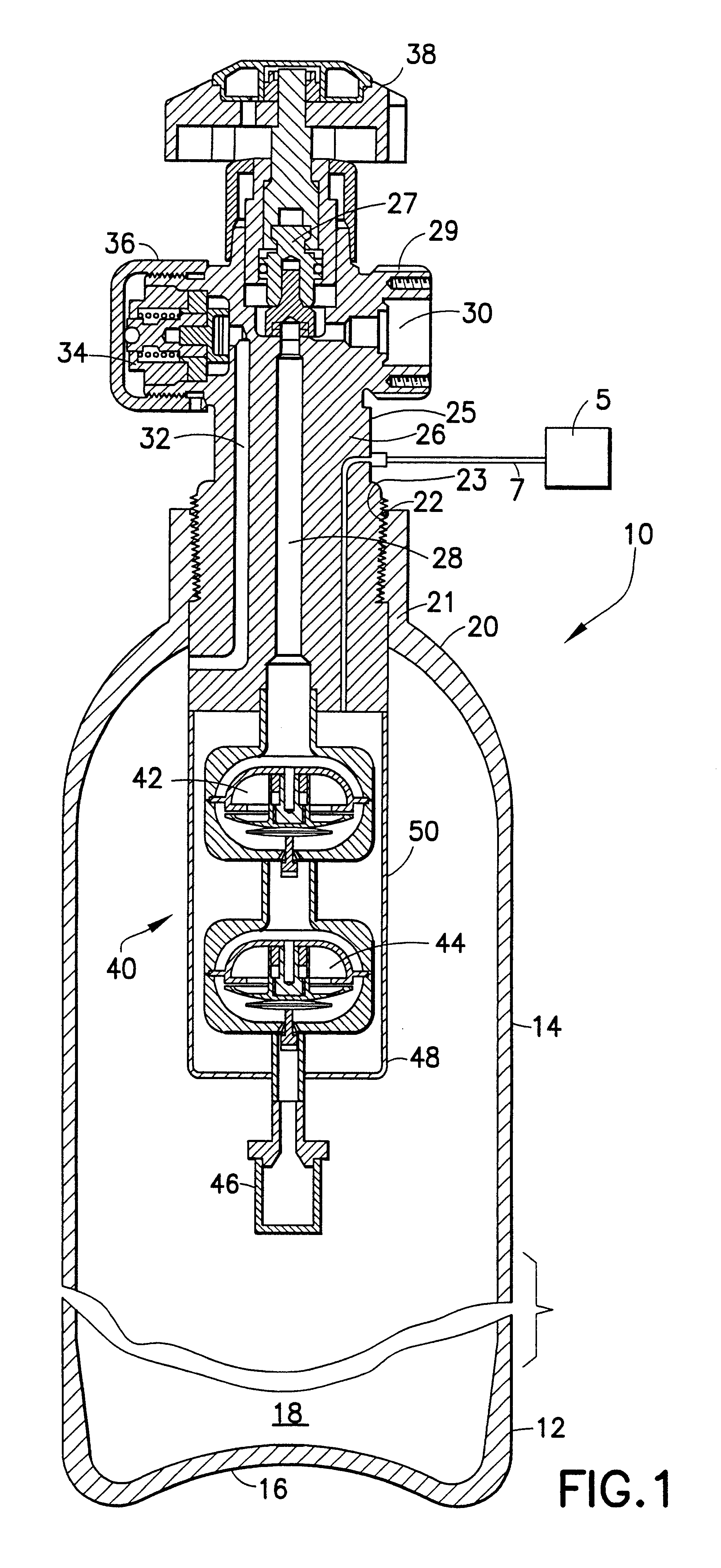
Diagnostic method and apparatus for a pressurized gas supply system
ActiveUS7568507B2Prevent excessive pressure risePreventing a potentially dangerous overheating problemLiquid fillingGas handling applicationsLine tubingEngineering
A diagnostic method for a gas supply system includes: determining a desired ramp rate for filling a vessel from a supply of compressed gas; monitoring the actual pressure of gas entering the vessel; and discontinuing the flow of gas into the vessel when the actual pressure deviates from the intended pressure at the desired ramp rate by an undesired amount. A system for carrying out the method includes a flow controller for controlling operation of the supply system to deliver compressed gas from a source to a vessel through a supply line at a desired ramp rate. The system employs a pressure monitor downstream of a control valve for measuring the pressure of gas directed into the vessel and transmitting pressure-related data to the flow controller, which closes the control valve to discontinue filling of the vessel if the actual pressure exceeds a permissible deviation from the intended pressure.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Microsphere insulation systems
InactiveUS6858280B2Reduce the impactIncreases insulation valueLayered productsContainer filling methodsMicrosphereEngineering
A new insulation system is provided that contains microspheres. This insulation system can be used to provide insulated panels and clamshells, and to insulate annular spaces around objects used to transfer, store, or transport cryogens and other temperature-sensitive materials. This insulation system provides better performance with reduced maintenance than current insulation systems.
Owner:TECH APPL
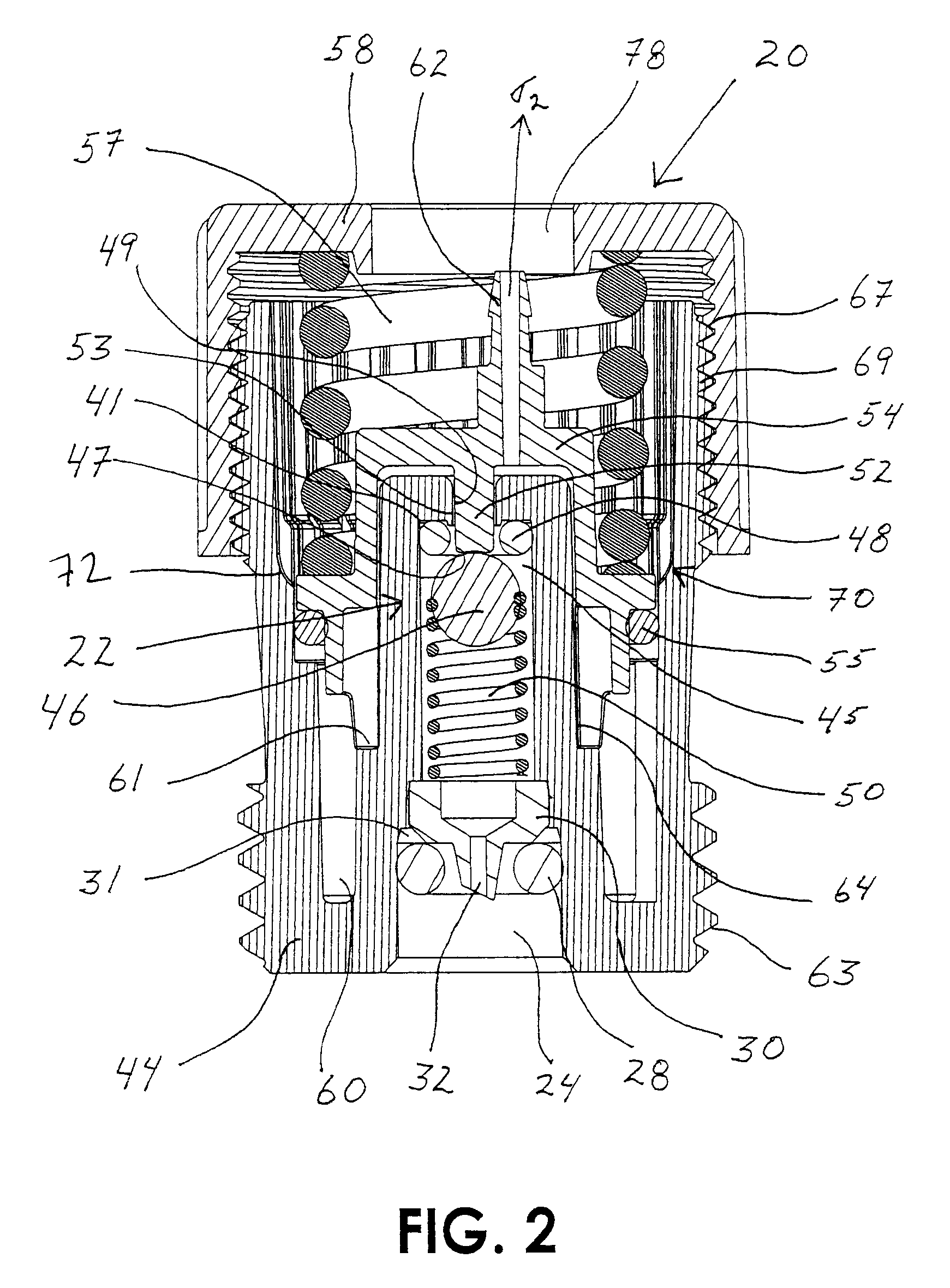
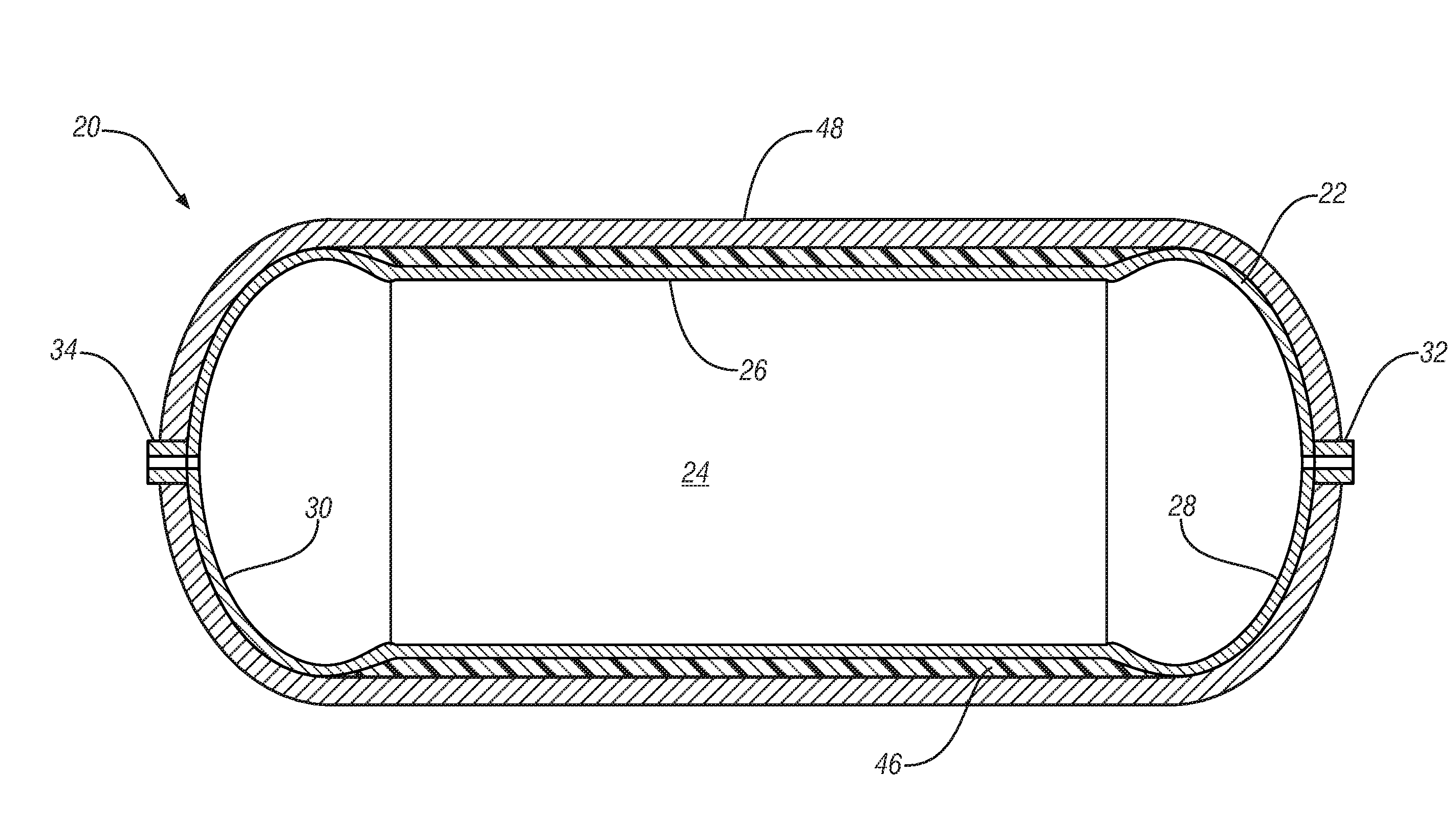
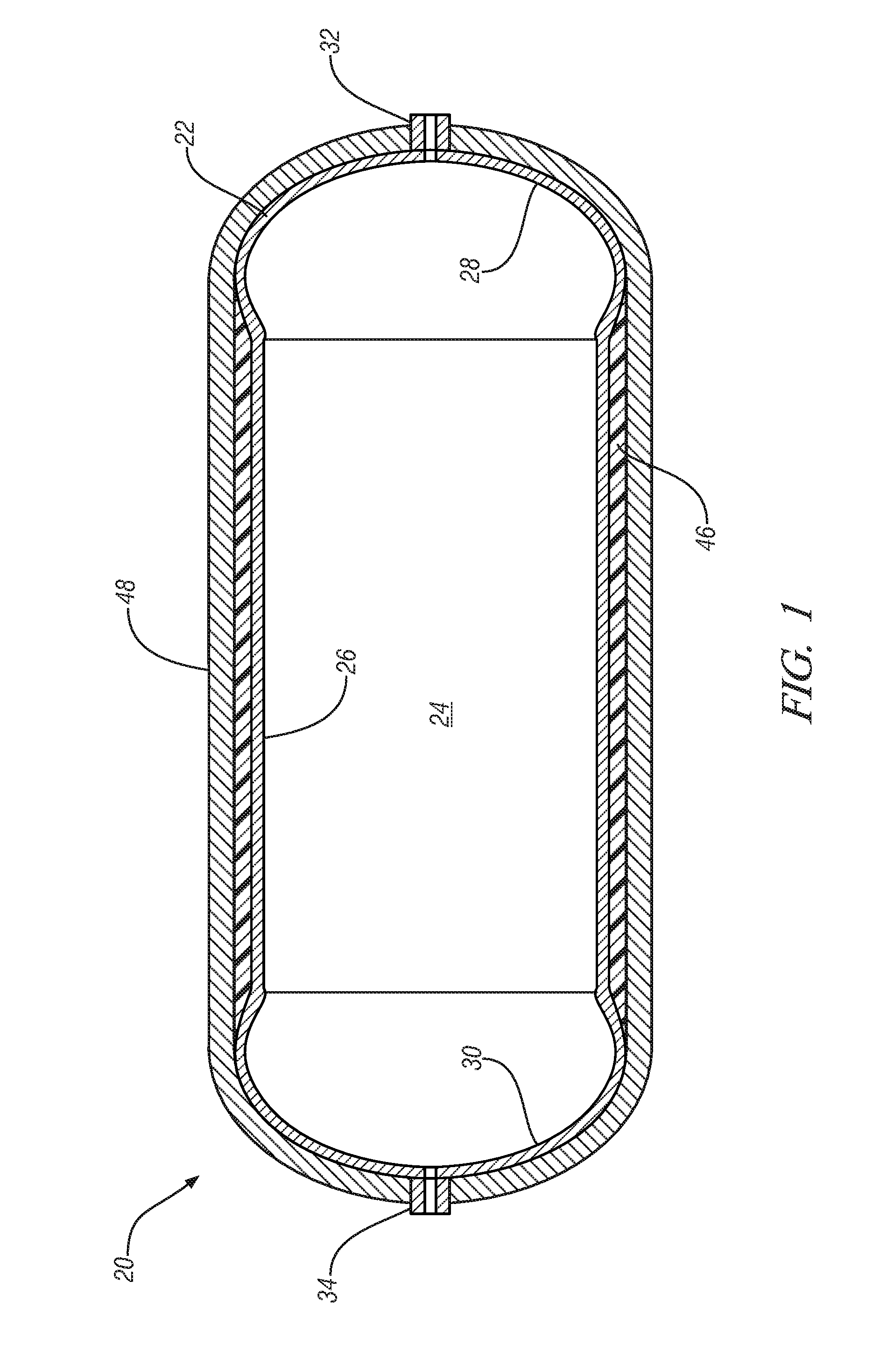
Storage vessel and method of forming
A storage vessel, such as vessels used in storing high pressure gas is provided. The storage vessel includes a liner having a center portion and a first and second end dome. A first composite layer is disposed circumferentially about the center portion. A second composite layer is disposed about said first composite layer and the first and second end dome. In some embodiments, the second composite layer is formed from a knitted or braided sleeve that is tightened over the liner and first composite layer by pulling the sleeve.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
System and method for delivering cryogenic fluid
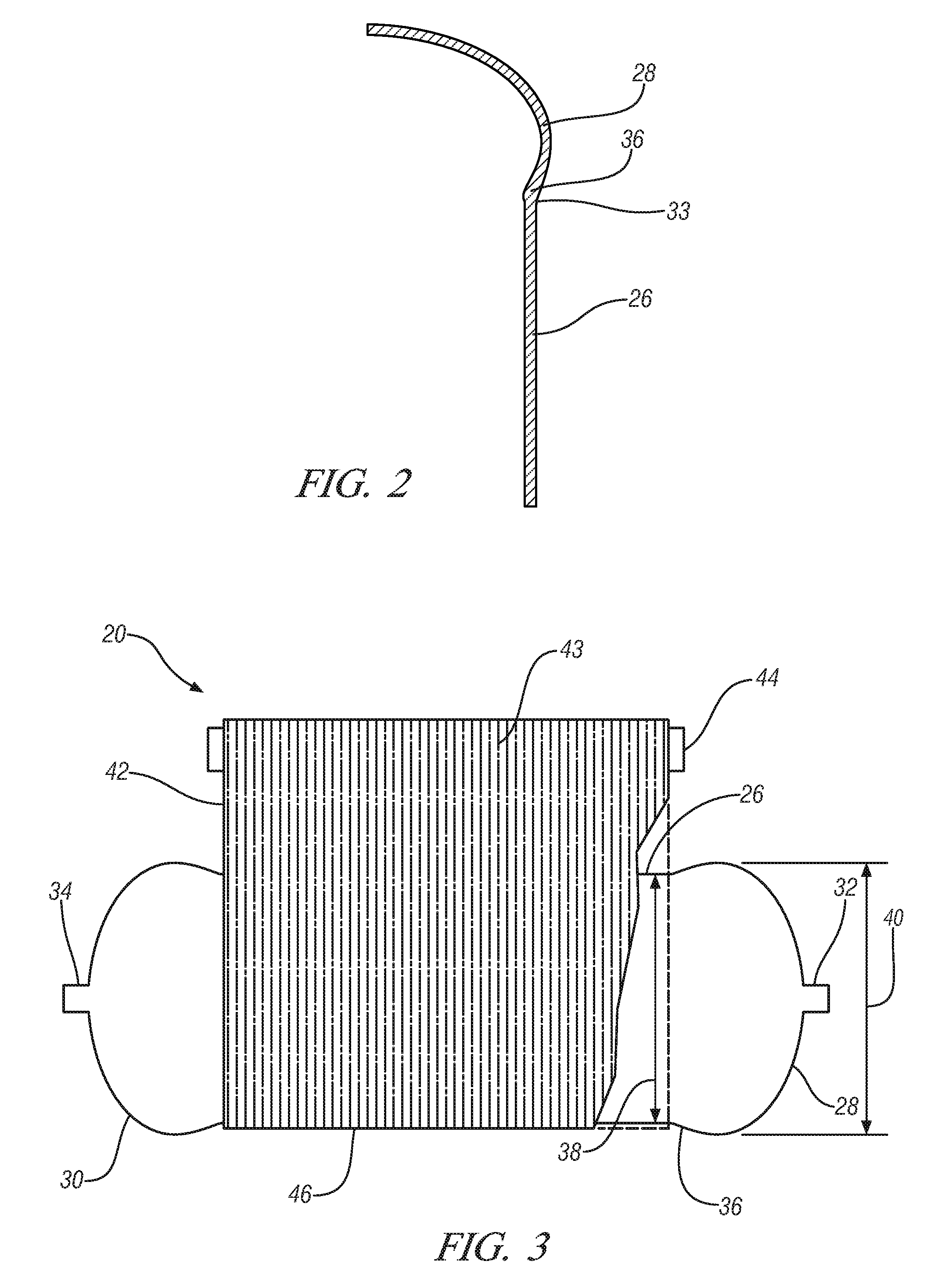
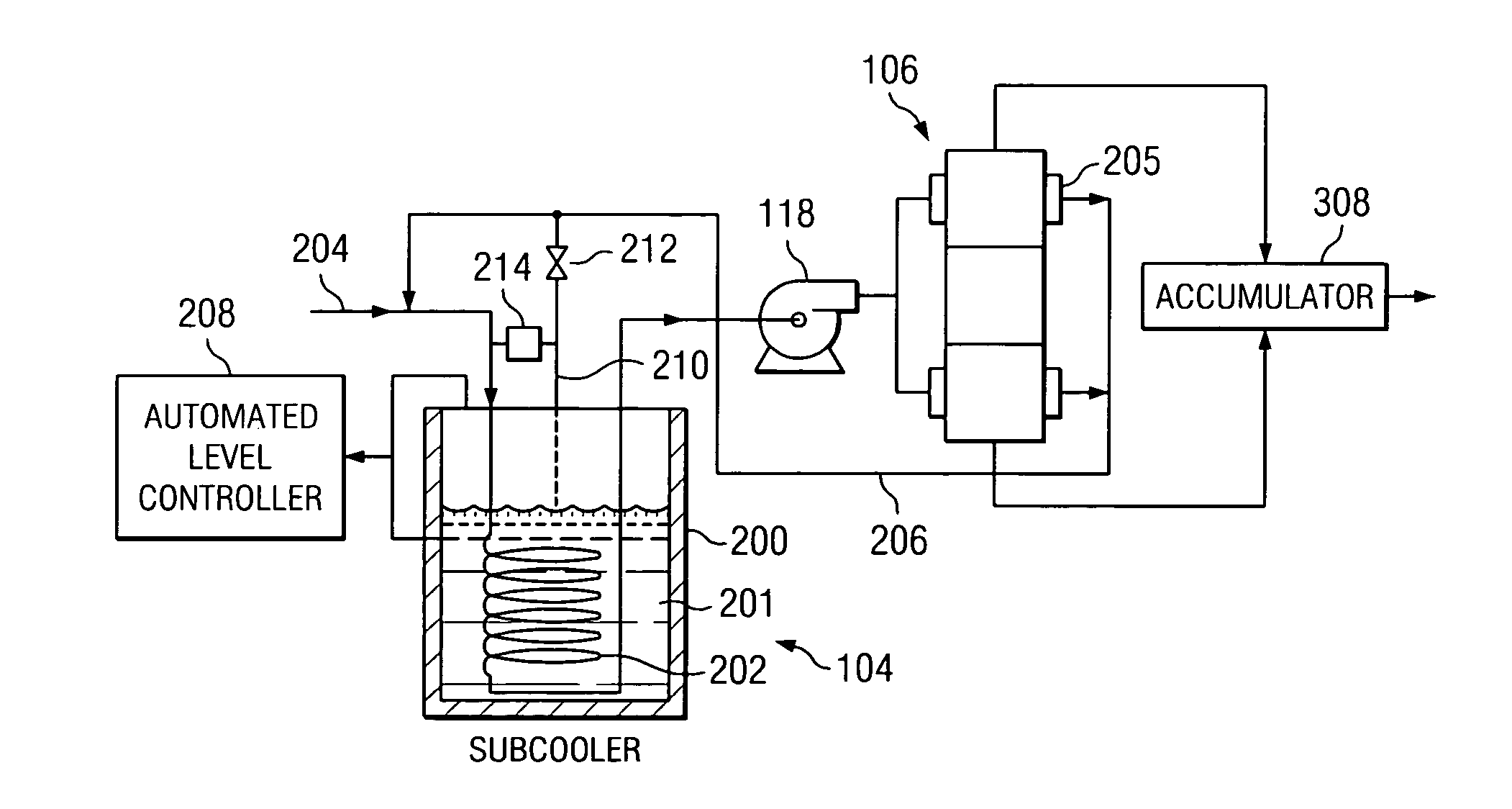
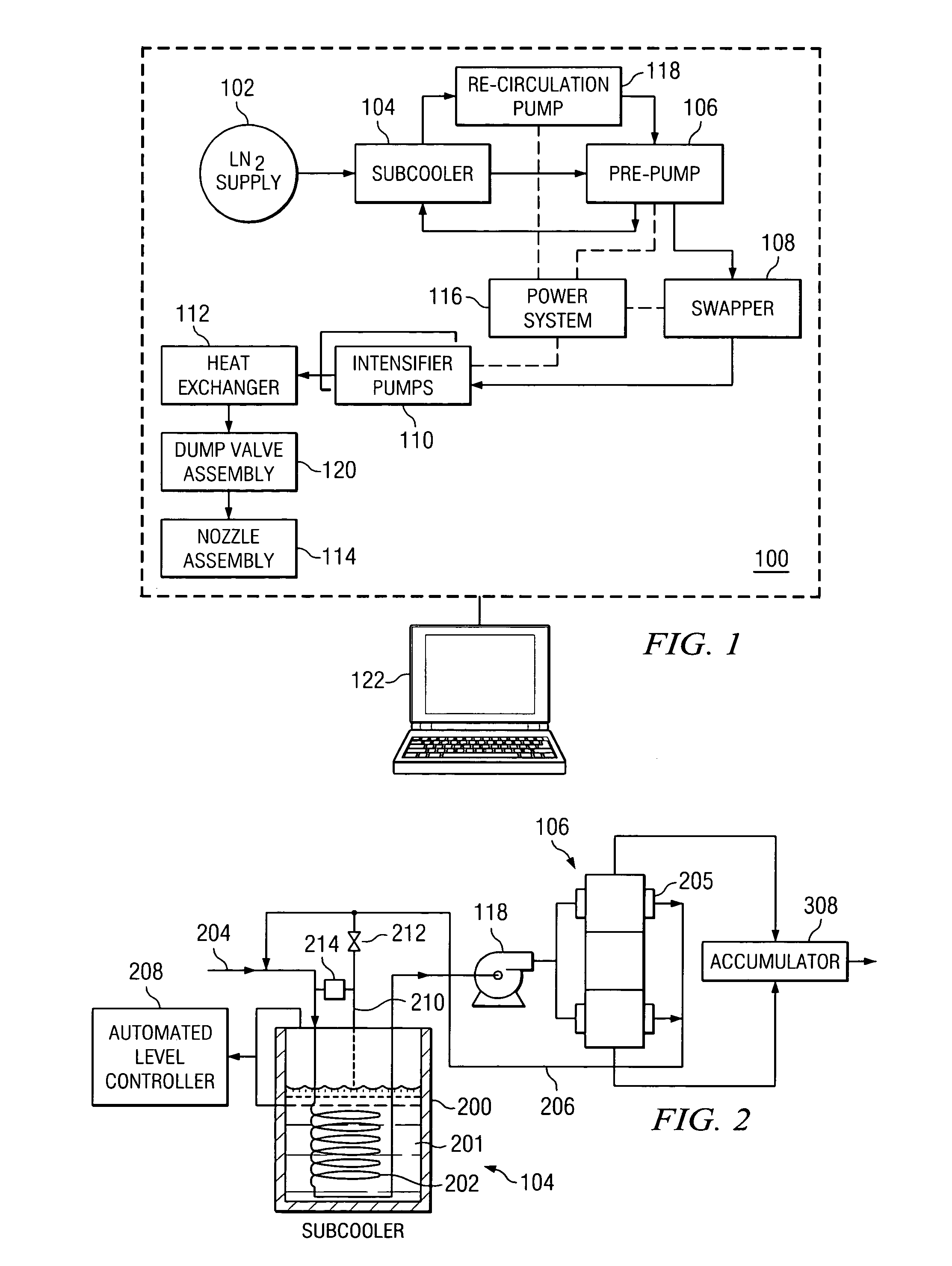
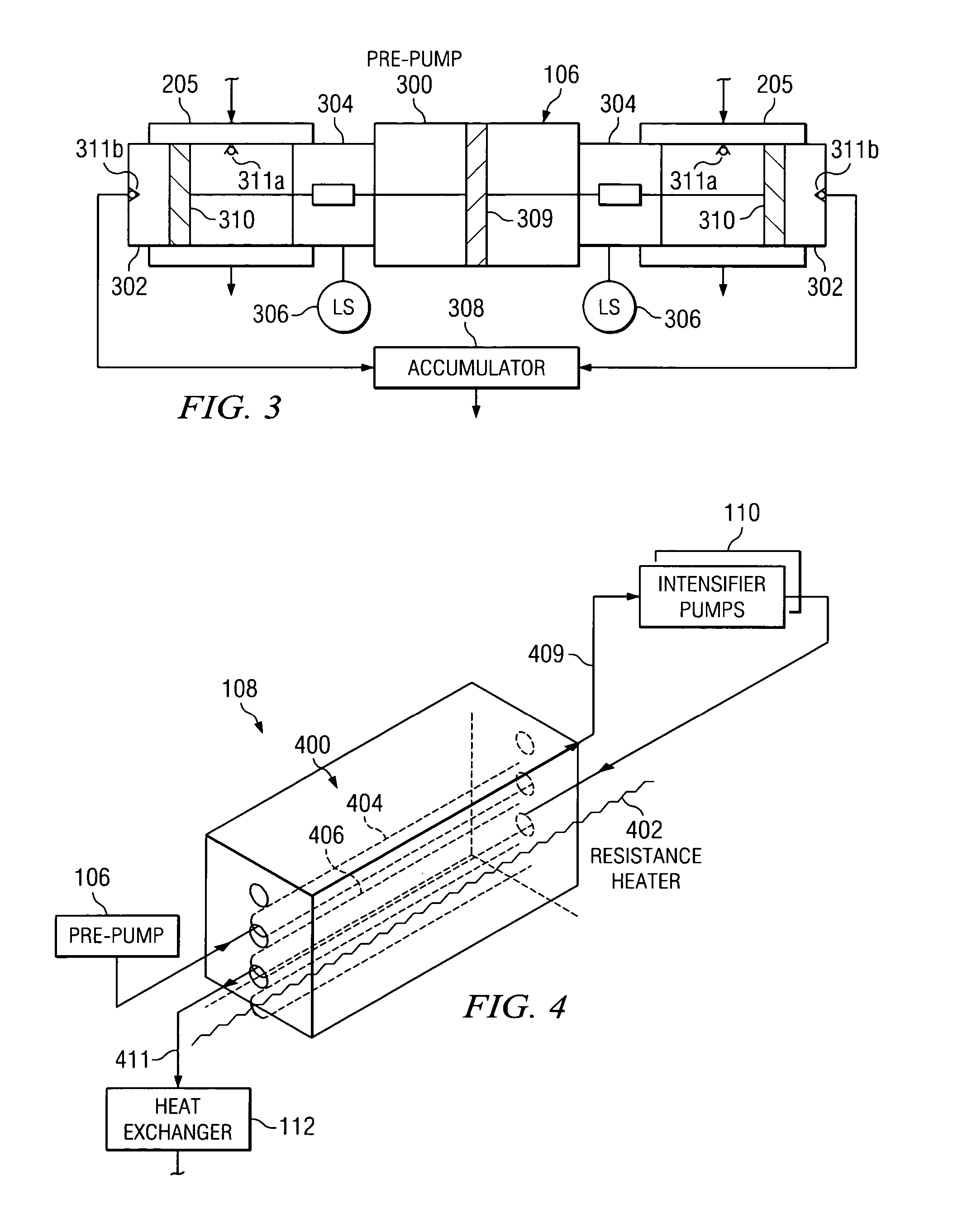
ActiveUS7310955B2Increase pressureIncrease speedContainer filling methodsGas handling applicationsProcess engineeringDelivery system
According to an embodiment of the present invention, a cryogenic fluid delivery system includes a vessel containing a cryogenic fluid at a first pressure and a first temperature, a first heat exchanger coupled to the vessel for receiving the cryogenic fluid and cooling the cryogenic fluid to a second temperature, a first pump coupled to the first heat exchanger for pressurizing the cryogenic fluid to a second pressure, a second pump for pressurizing the cryogenic fluid to a third pressure, a second heat exchanger coupled to the second pump for cooling the cryogenic fluid to a third temperature, and a nozzle coupled to the second heat exchanger for delivering a jet of the cryogenic fluid toward a target.
Owner:IHI CORP
Integration of LNG regasification with refinery and power generation
Contemplated plants thermally integrate operation of a refinery component, and most preferably of a hydrocarbon splitter with LNG regasification to provide refrigeration duty and with a power cycle to provide the reboiler duty of the component. It should be noted that such configurations advantageously allow operation of the splitter at a reduced temperature and at reduced pressure, thereby increasing separation efficiency, while the power output is boosted using air intake chilling. Most notably, such process advantages are achieved by satisfying the heating duty of LNG regasification.
Owner:FLUOR TECH CORP
Support structure of high pressure container
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
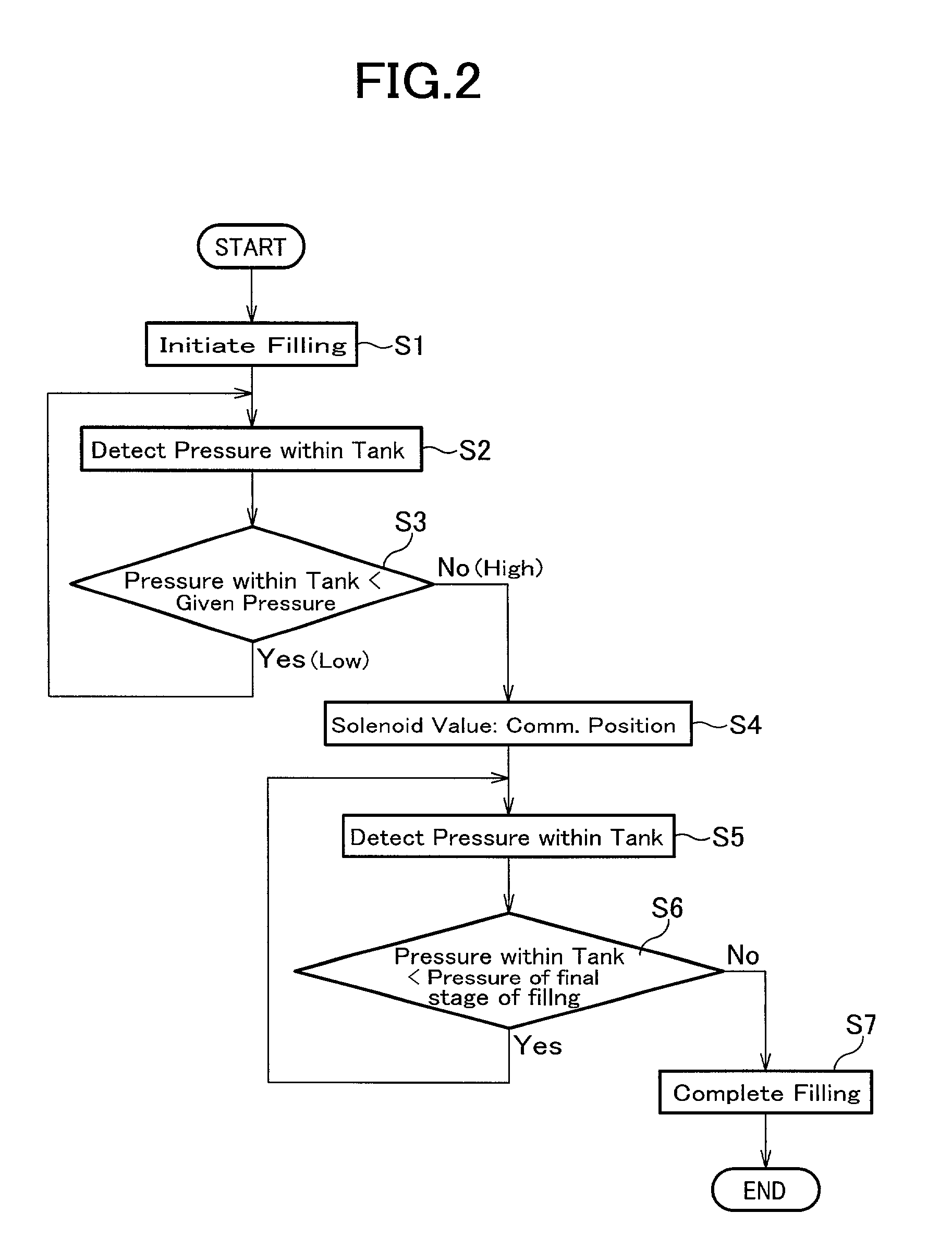
Apparatus and process for rapidly filling with hydrogen
InactiveUS20020014277A1Increase heatIncrease rangeLiquid fillingGas handling applicationsFilling rateDelayed time
An apparatus for rapidly filling a hydrogen tank with a hydrogen gas comprises a hydrogen source; a hydrogen tank; a passage which connects the hydrogen source and said hydrogen tank; and a mechanism for varying the hydrogen-filling rate. The mechanism for varying the hydrogen-filling rate changes the hydrogen-filling rate depending upon the pressure within said hydrogen tank. The apparatus can suppress heat generation at the initial filling stage where the temperature is easily increased. Also, even if it takes longer time for increasing the pressure within the hydrogen tank at the initial filling state, the delayed time can be caught up and, the apparatus and the process of the present invention can totally attain a rapidly filling with hydrogen.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Gas supply apparatus
InactiveUS20060246177A1Reduce supplyReduce pressureGas handling applicationsSpecial dispensing meansProcess engineeringGas holder
A gas supply apparatus including: a tank unit that includes a tank storing a gas and a discharge mechanism discharging the stored gas to the outside of the tank at a reduced pressure of the stored gas; a temperature detector that detects a temperature of the tank; and a supply regulator that regulates supply of the gas from the tank according to the detected tank temperature.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Pressure vessel and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20040206762A1Light weightIncrease pressureVessel mounting detailsVessel manufacturingInternal pressureEngineering
The pressure vessel of the present invention comprises an inner shell capable of serving as a gas barrier and a pressure resistant outer shell provided to cover the inner shell, said outer shell being made of an FRP comprising reinforcing fibers and a resin and is 35 GPa or more in tensile modulus and 1.5% or more in tensile breaking strain. The present invention can provide a pressure vessel not only light in weight,.but also excellent in retaining its internal pressure against repetitive impacts and also excellent in reliability. The process for producing a pressure vessel of the present invention comprises the step of forming a pressure resistant outer shell made of an FRP comprising reinforcing fibers and a resin and is 35 GPa or more in tensile modulus and 1.5% or more in tensile breaking strain, around an inner shell capable of serving as a gas barrier, by a filament winding method or a tape winding method. The present invention can produce a pressure vessel excellent in retaining its internal pressure, excellent in reliability, and light in weight at a low cost.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Compressed gas cartridge dispensing system allowing interchangeable use of different capacity compressed gas cartridges and novel storage feature
InactiveUS6843388B1Improve versatilityVessel mounting detailsVessel geometry/arrangement/sizeProcess engineeringMechanical engineering
A compressed gas cartridge dispensing system capable of dispensing at least two different capacities of non-threaded neck compressed gas cartridges as well as optionally dispensing all cartridges having a ⅜-24 neck thread. The standard 12-gram CO2 non-threaded neck compressed gas cartridge fits this dispenser. The same dispensing system is also capable of dispensing larger capacity cartridges having a neck dimensioned smaller than a ⅜-24 female thread minor diameter with a water capacity in the range of 16 to 50 ml. Obvious advantages to the dispensing system are added options offering increased versatility for harnessing compressed gas cartridges of differing capacities in a unique dispenser including a novel cartridge storage feature.
Owner:HOLLARS ANTHONY SCOTT
Fluid storage and dispensing system featuring externally adjustable regulator assembly for high flow dispensing
InactiveUS6360546B1CostPerformanceContainer filling methodsGas handling applicationsEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
A fluid storage and dispensing system including a fluid storage and dispensing vessel enclosing an interior volume for holding a fluid. The vessel includes a fluid discharge port for discharging fluid from the vessel. A pressure regulating element in the interior volume of the fluid storage and dispensing vessel is arranged to flow fluid therethrough to the fluid discharge port at a set pressure for dispensing thereof. A controller external of the fluid storage and dispensing vessel is arranged to transmit a control input into the vessel to cause the pressure regulating element to change the set pressure of the fluid flowed from the pressure regulating element to the fluid discharge port. By such arrangement, the respective storage and dispensing operations can have differing regulator set point pressures, as for example a subatmospheric pressure set point for storage and a super atmospheric pressure set point for dispensing.
Owner:ADVANCED TECH MATERIALS INC
Composite pressure tank and process for its manufacture
InactiveUS20070205201A1Reduce weightLow costVessel mounting detailsVessel manufacturingBody shapeMaterials science
A pressure vessel and method for producing a pressure vessel is disclosed. The pressure vessel comprises a liner shell fabricated from composite material applied to a soluble mandrel having a body shaped to pattern an interior of the pressure vessel, the liner shell having an opening, a boss having an aperture therethrough, the boss sealingly bonded to the liner shell with the aperture adjacent the opening, and an outer shell fabricated from plies of composite material filament impregnated with matrix material wound over the liner shell and the boss, but not over the aperture.
Owner:MICROCOSM INC
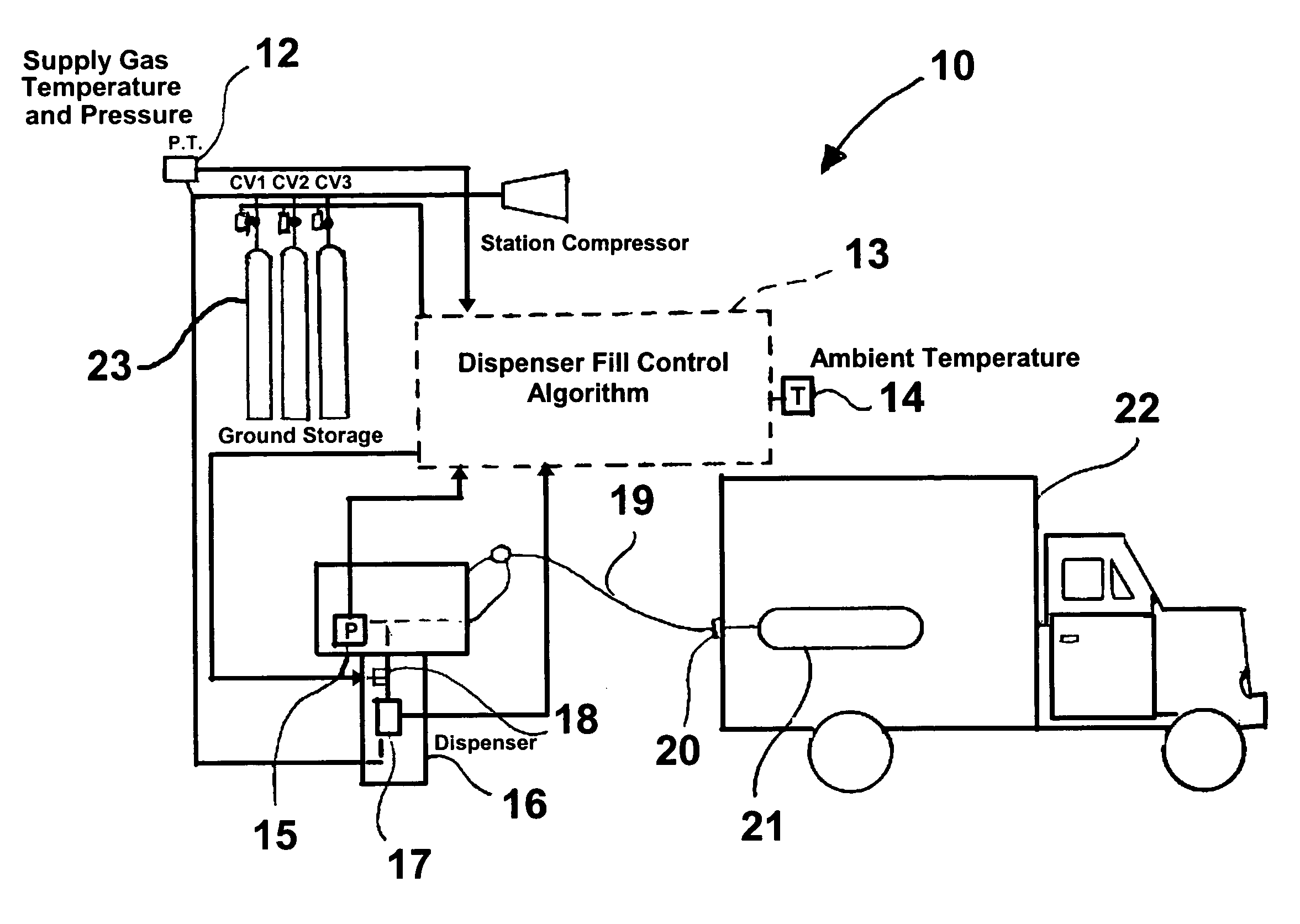
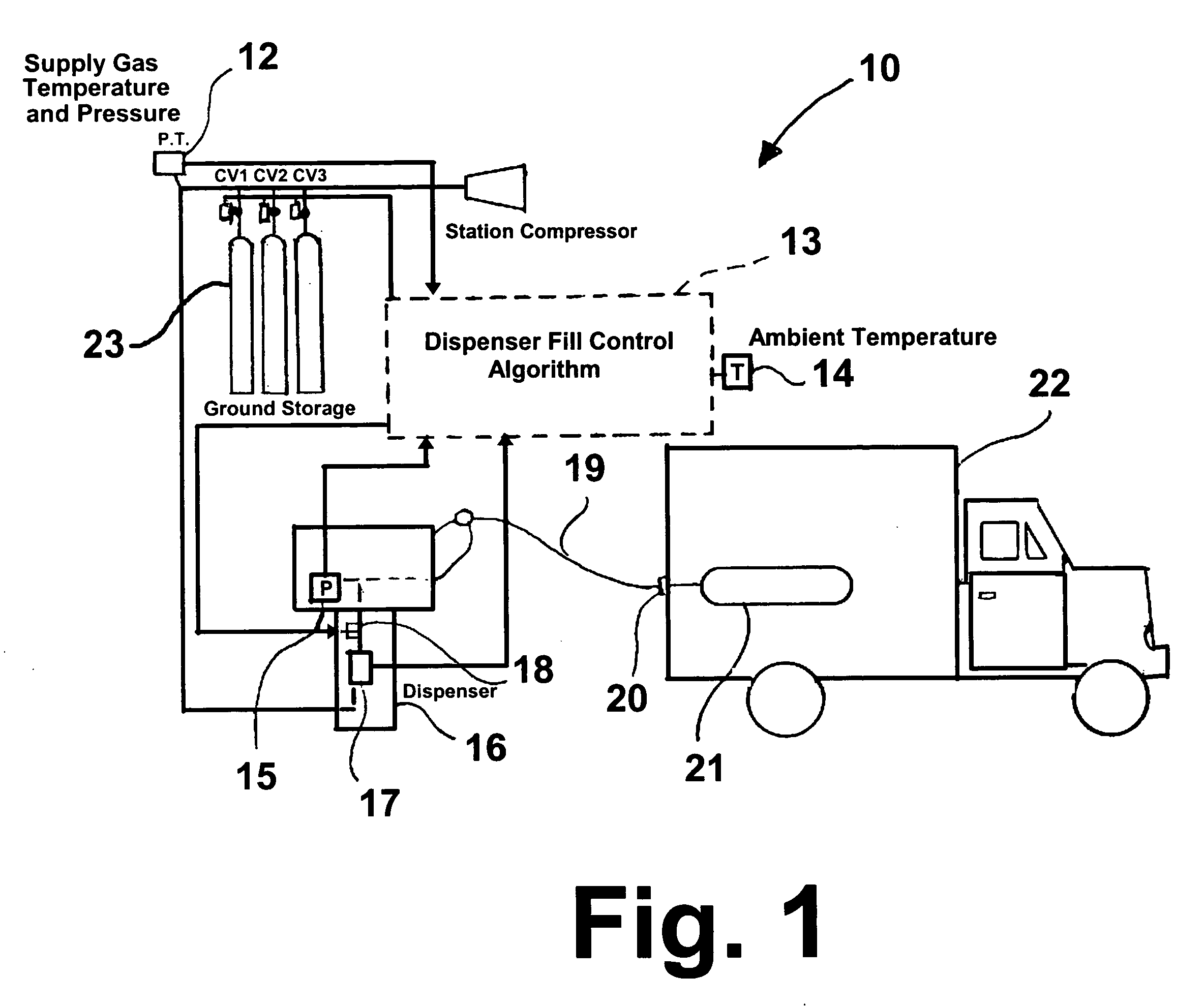
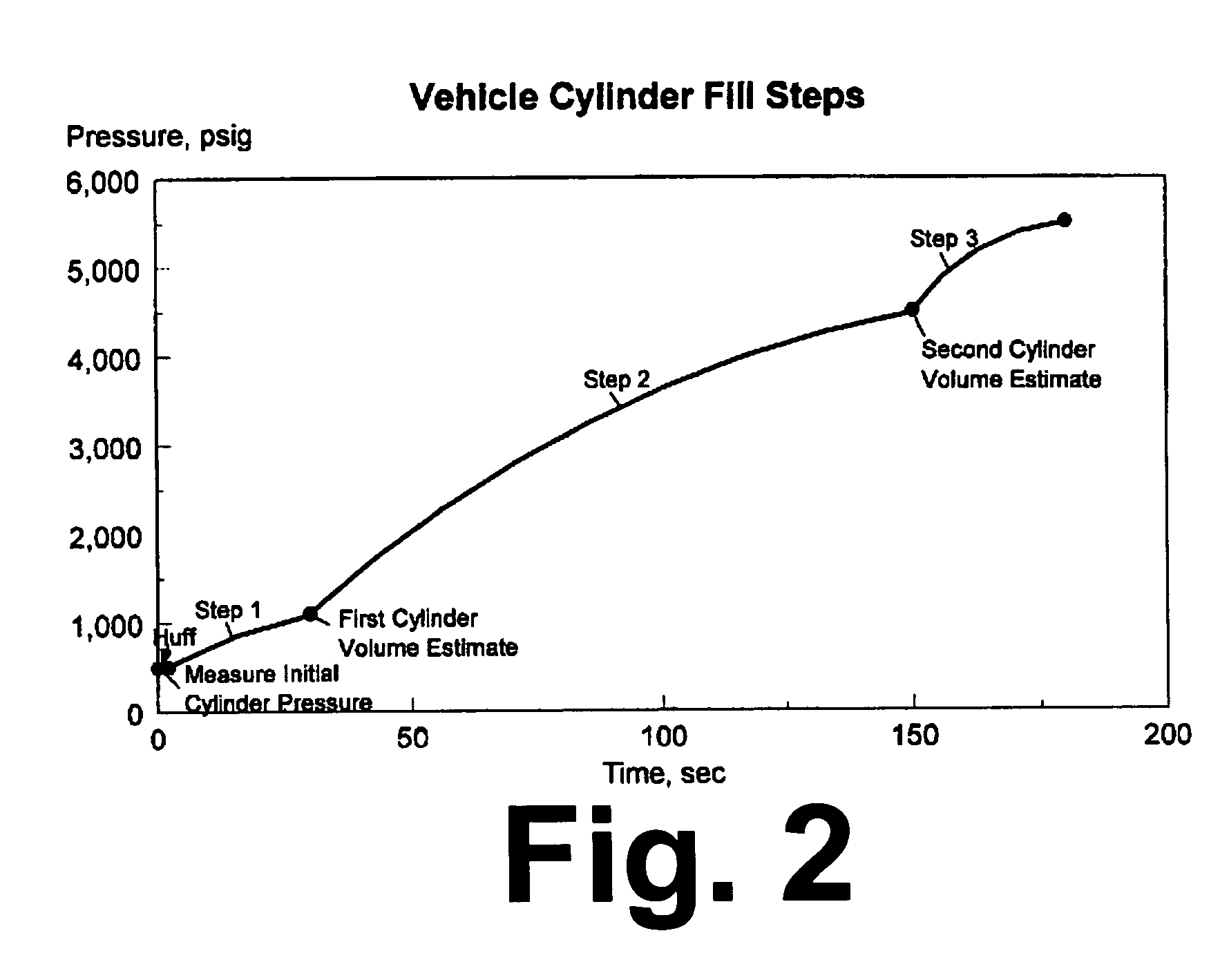
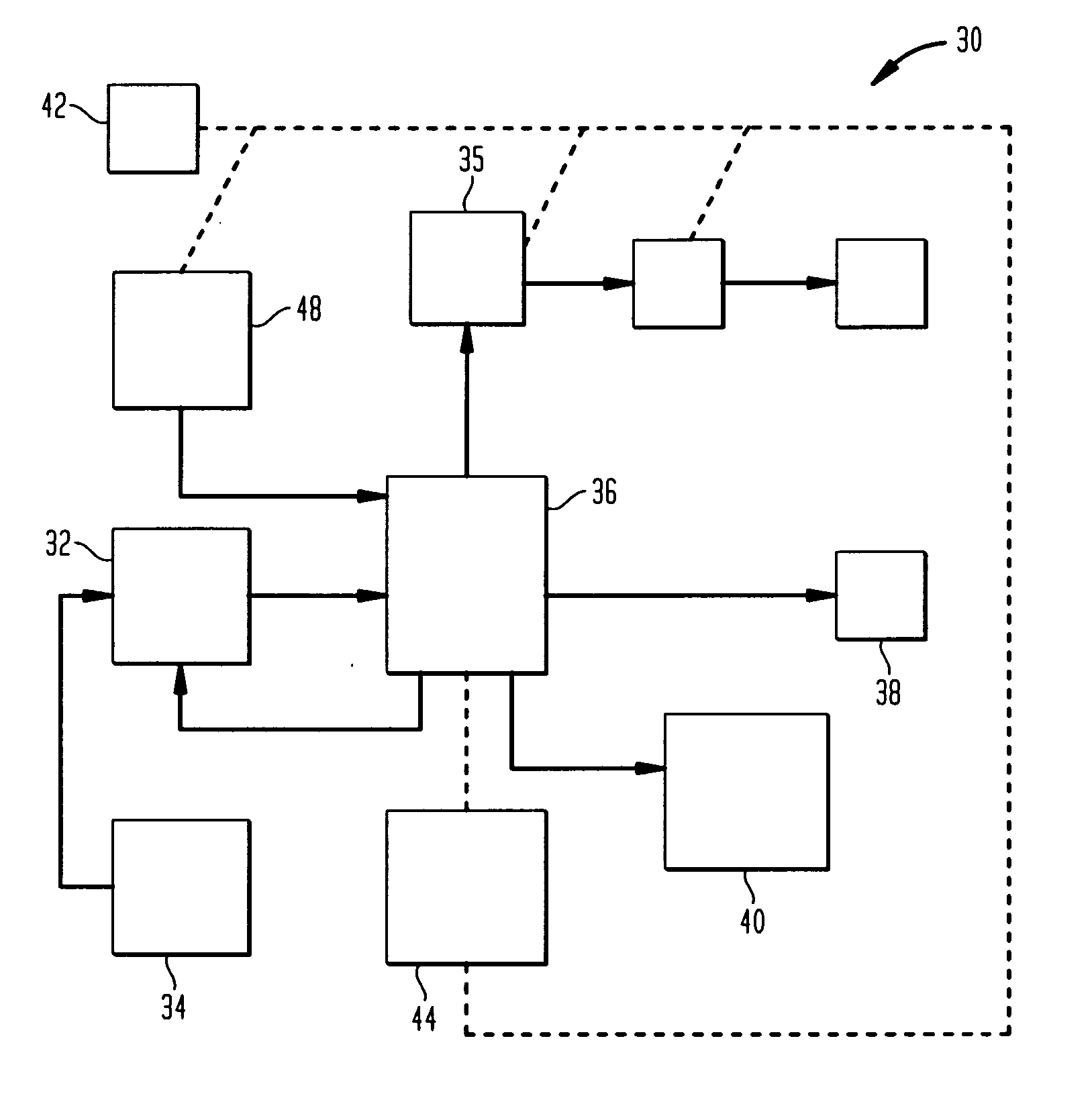
Control method for high-pressure hydrogen vehicle fueling station dispensers
InactiveUS7059364B2Reduces potential for underfillingFast fillGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsHigh pressure hydrogenHigh pressure
A method for quick filling a vehicle hydrogen storage vessel with hydrogen, the key component of which is an algorithm used to control the fill process, which interacts with the hydrogen dispensing apparatus to determine the vehicle hydrogen storage vessel capacity.
Owner:GAS TECH INST
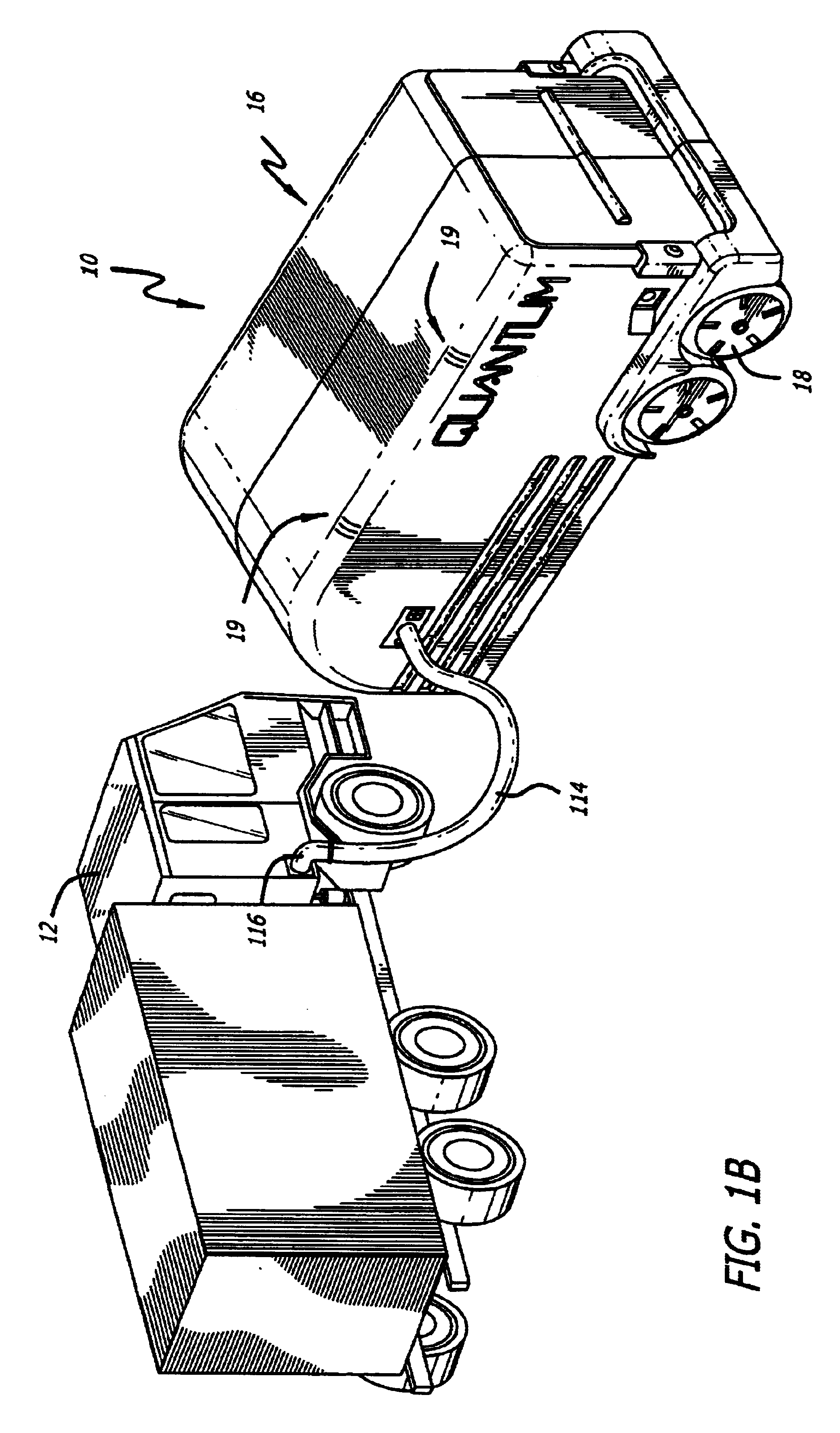
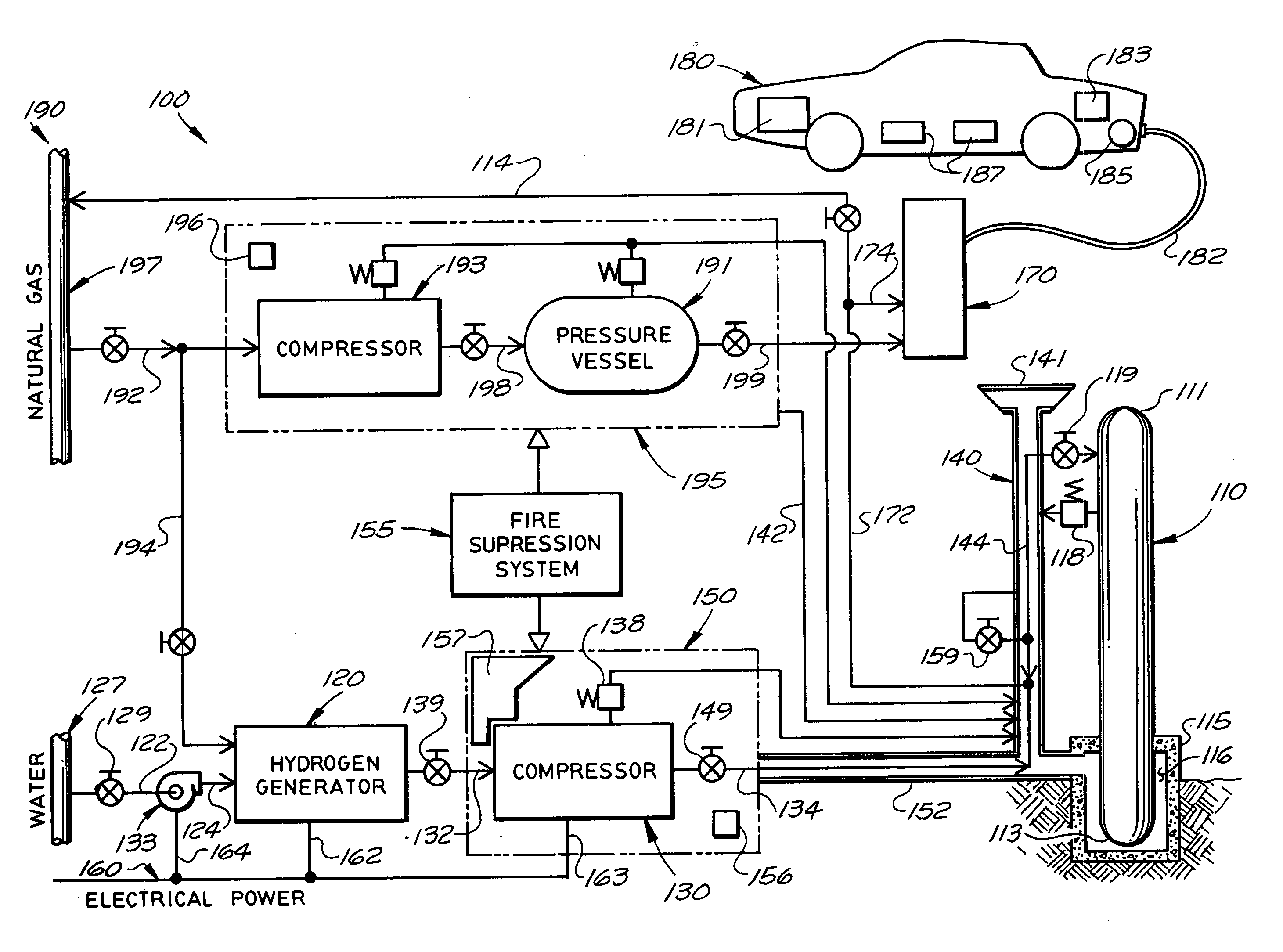
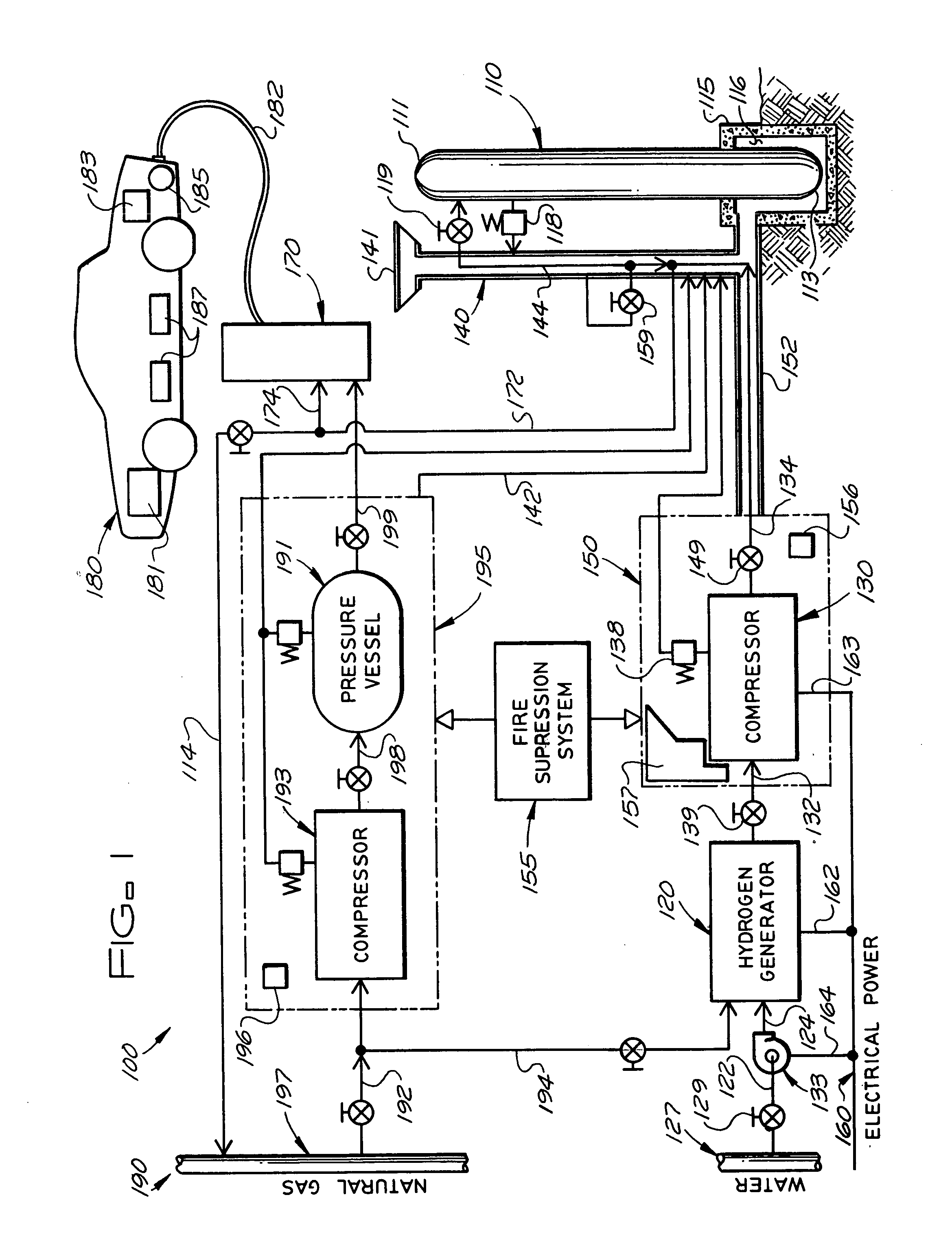
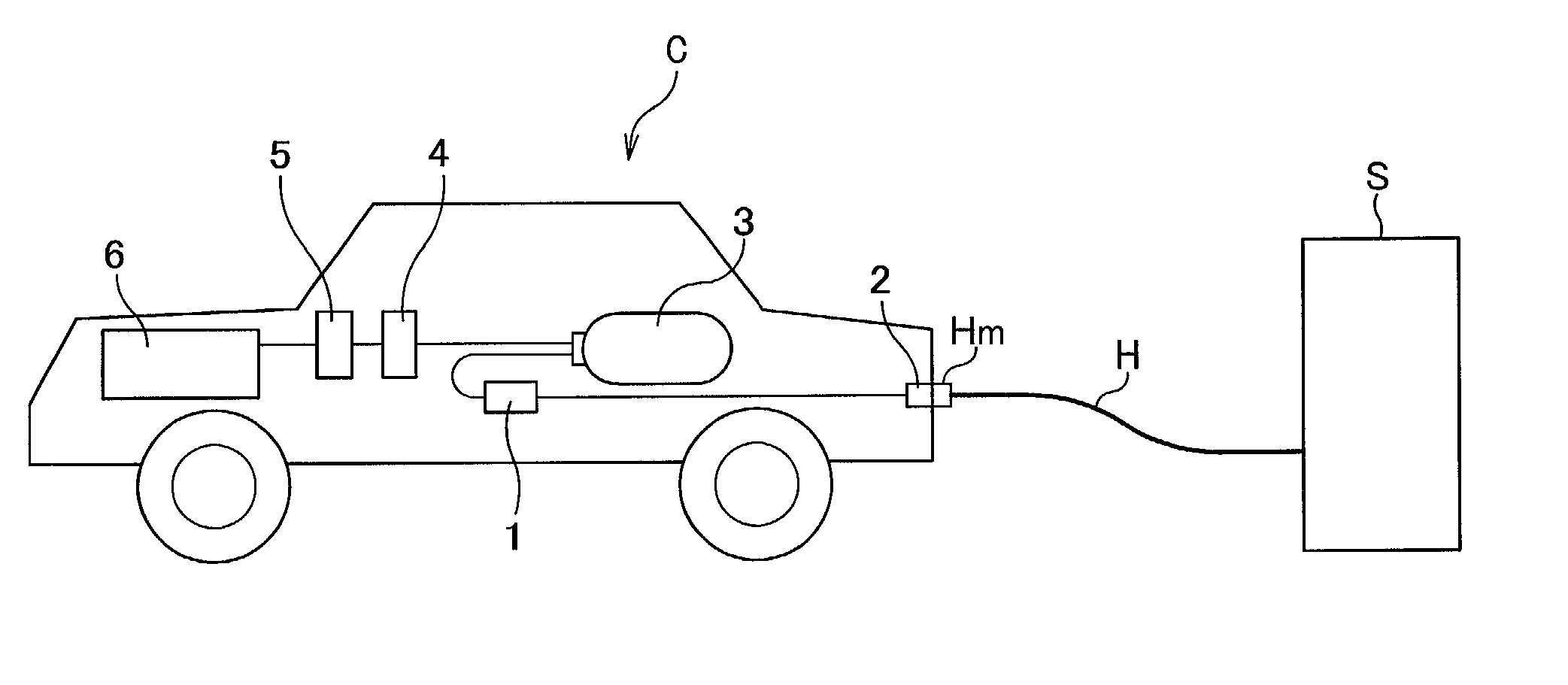
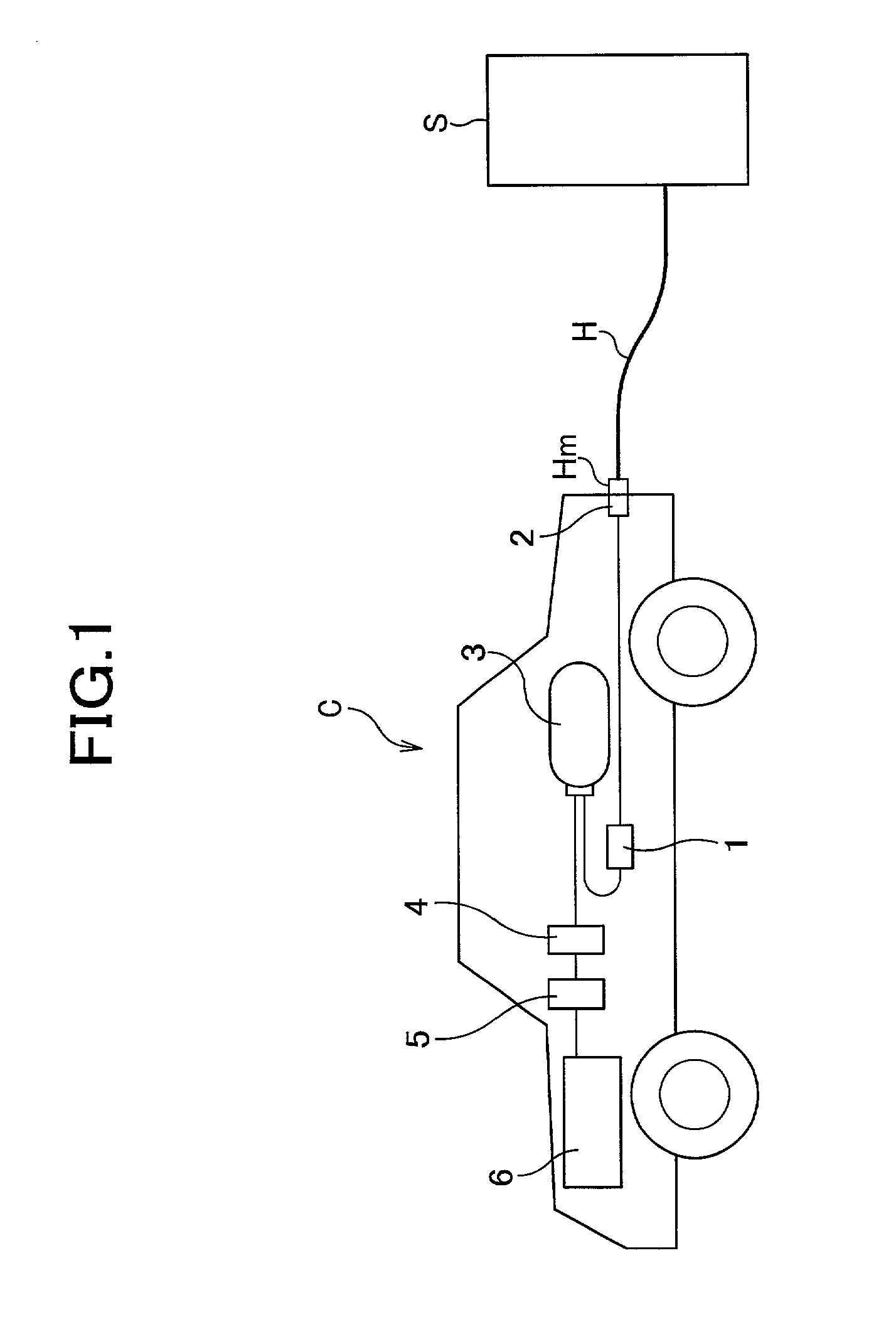
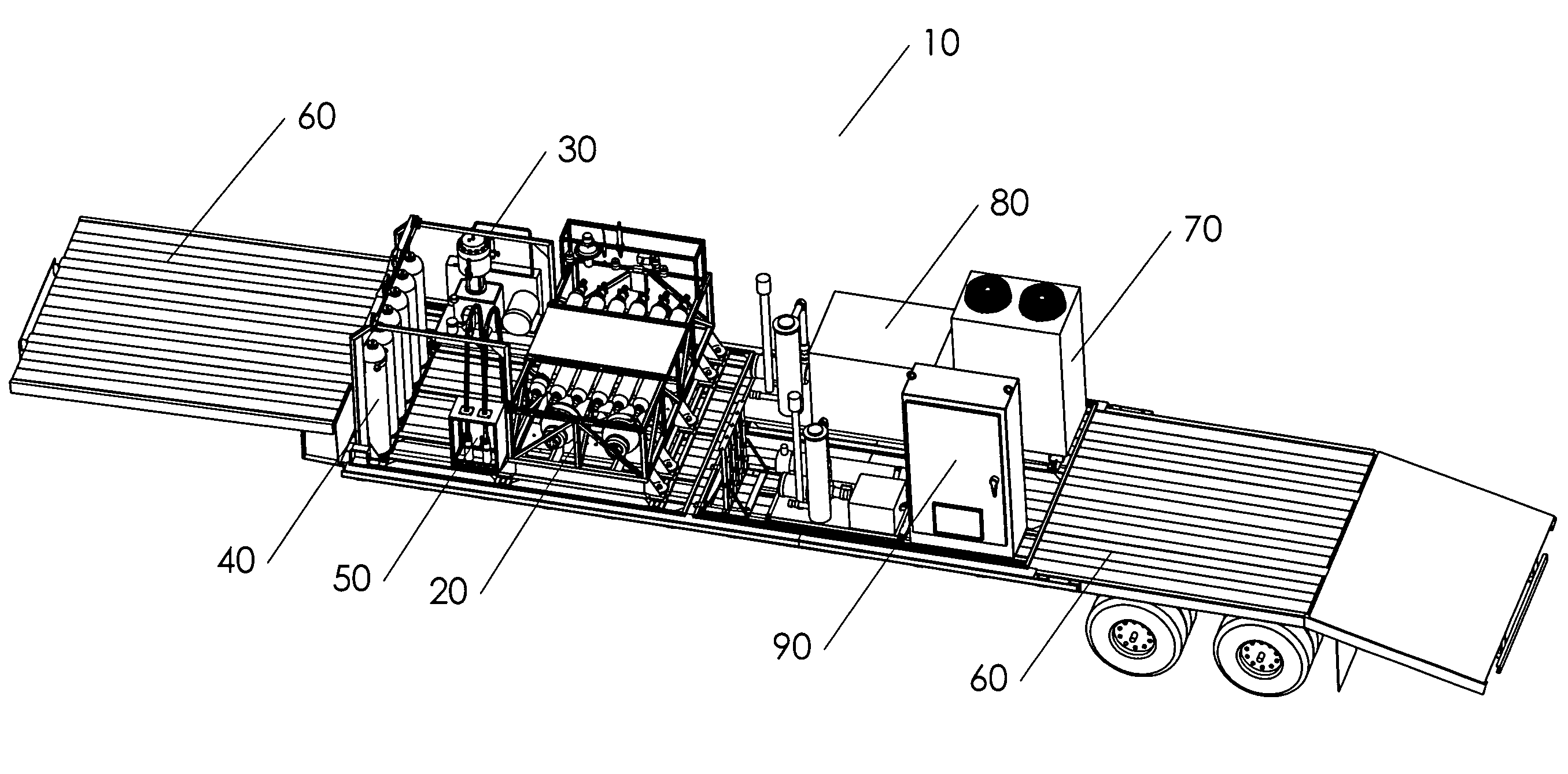
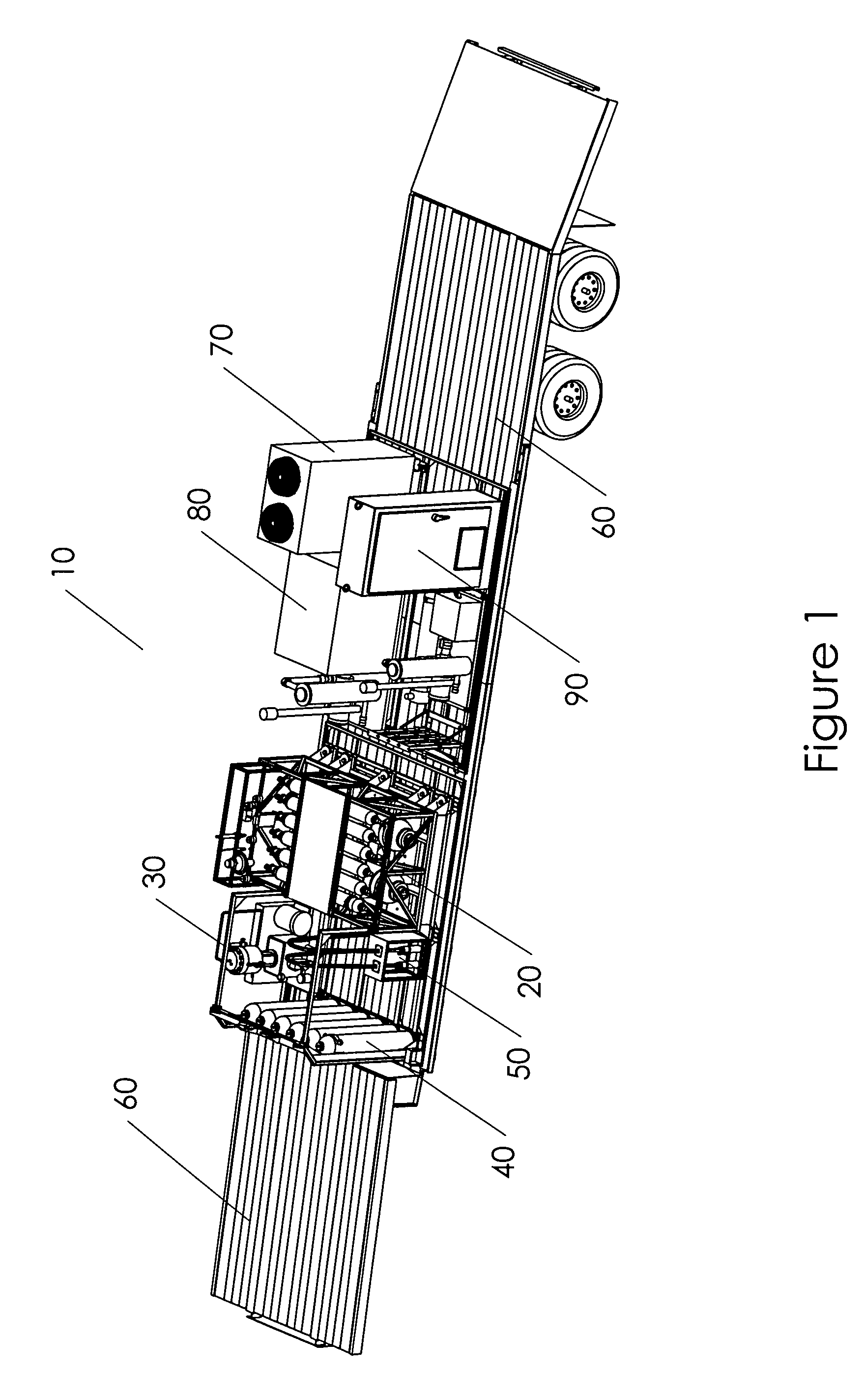
Mobile hydrogen delivery system
A mobile hydrogen delivery system for delivering a compressed stream of hydrogen at pressures up to 15000 psig. The mobile hydrogen delivery system includes a hydrogen compression system, a gaseous hydrogen storage system, and a delivery system for supplying hydrogen to end users. A mobile platform supports the hydrogen compression system, the gaseous hydrogen storage system, and the dispensing system. The mobile platform may be any platform, such as a trailer, capable of being pulled, pushed, or supported by any type of vehicle, such a truck, train, boat, tractor, etc.
Owner:HARNYSS IP LLC +1
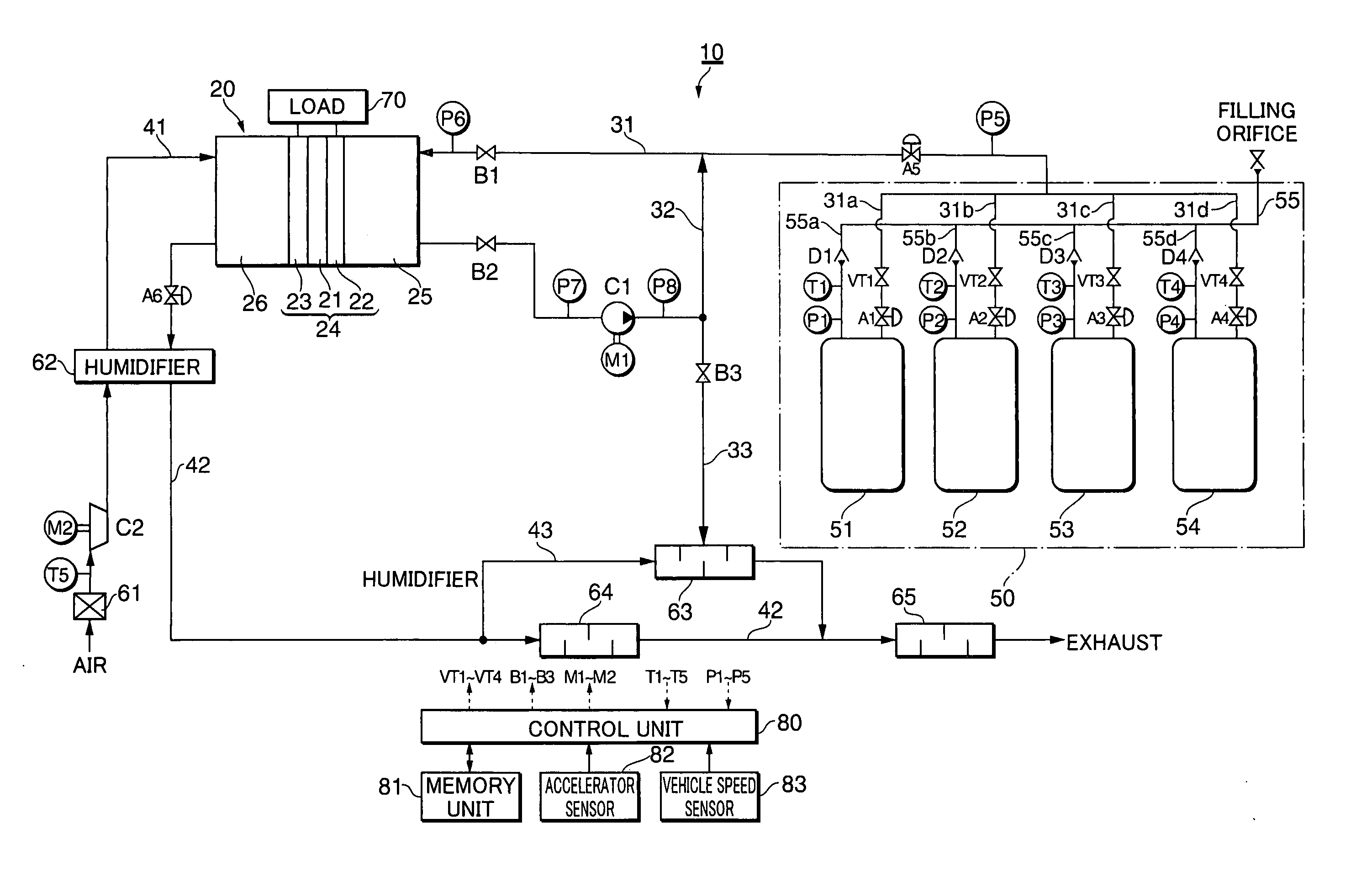
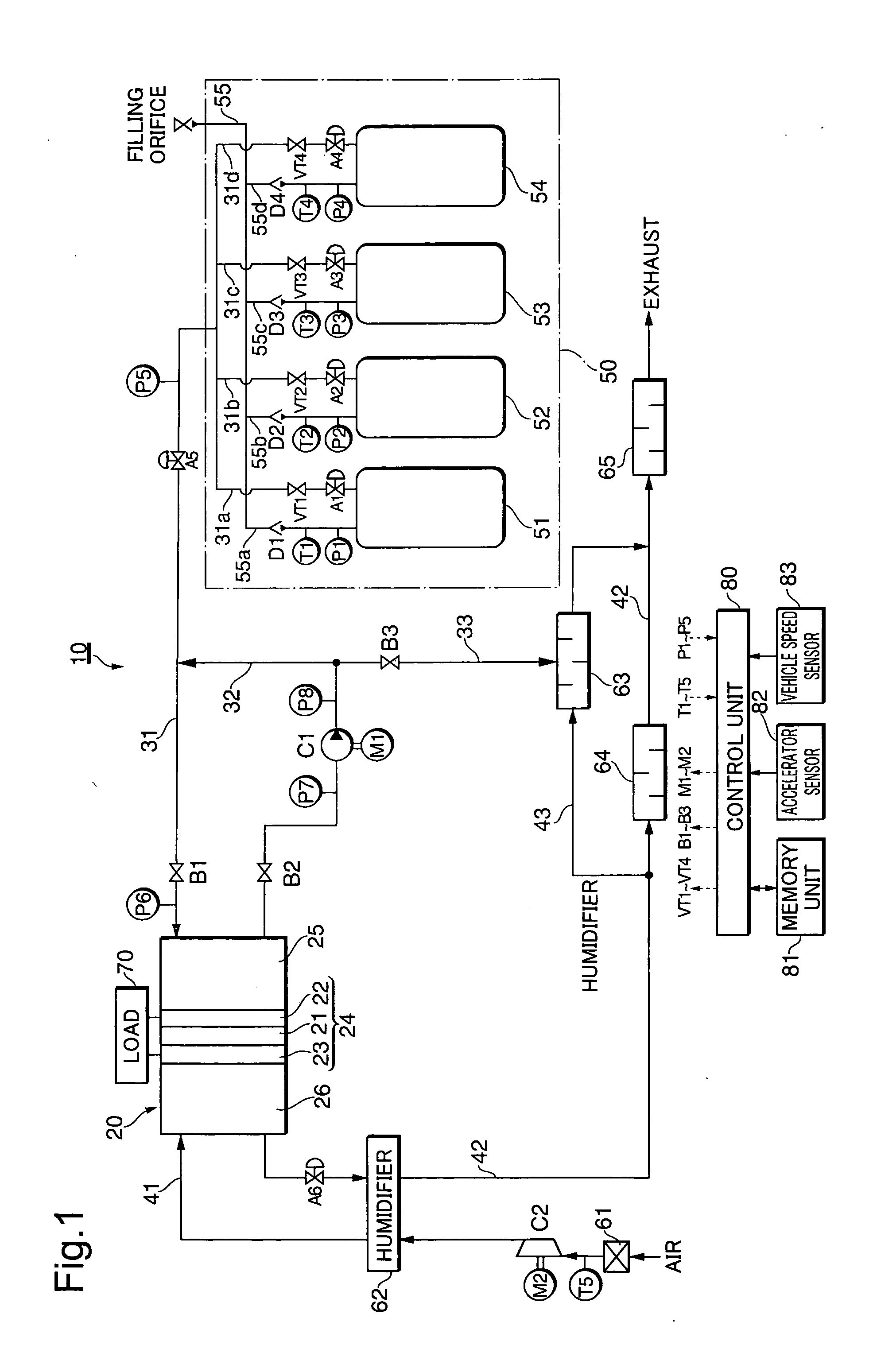
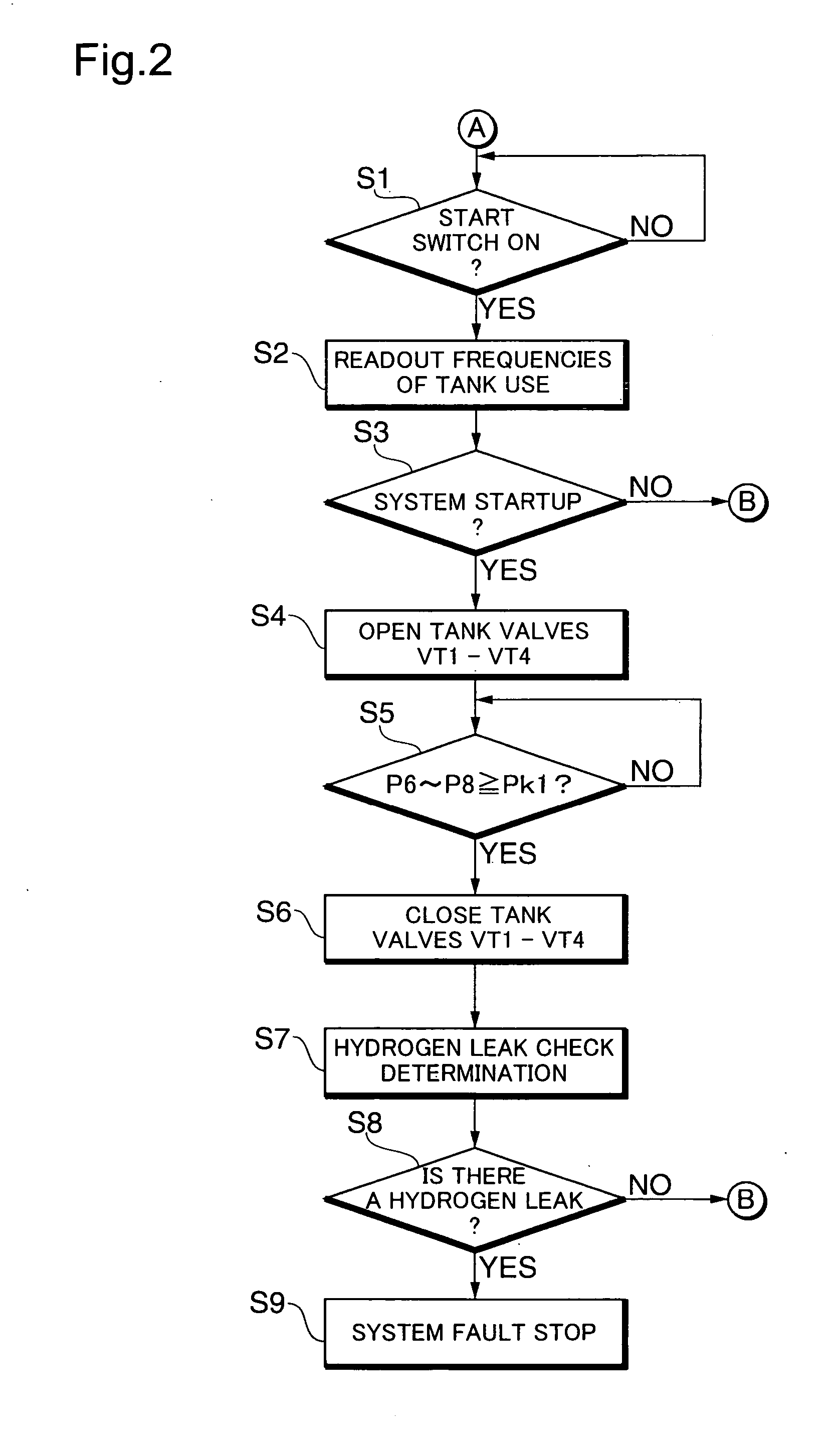
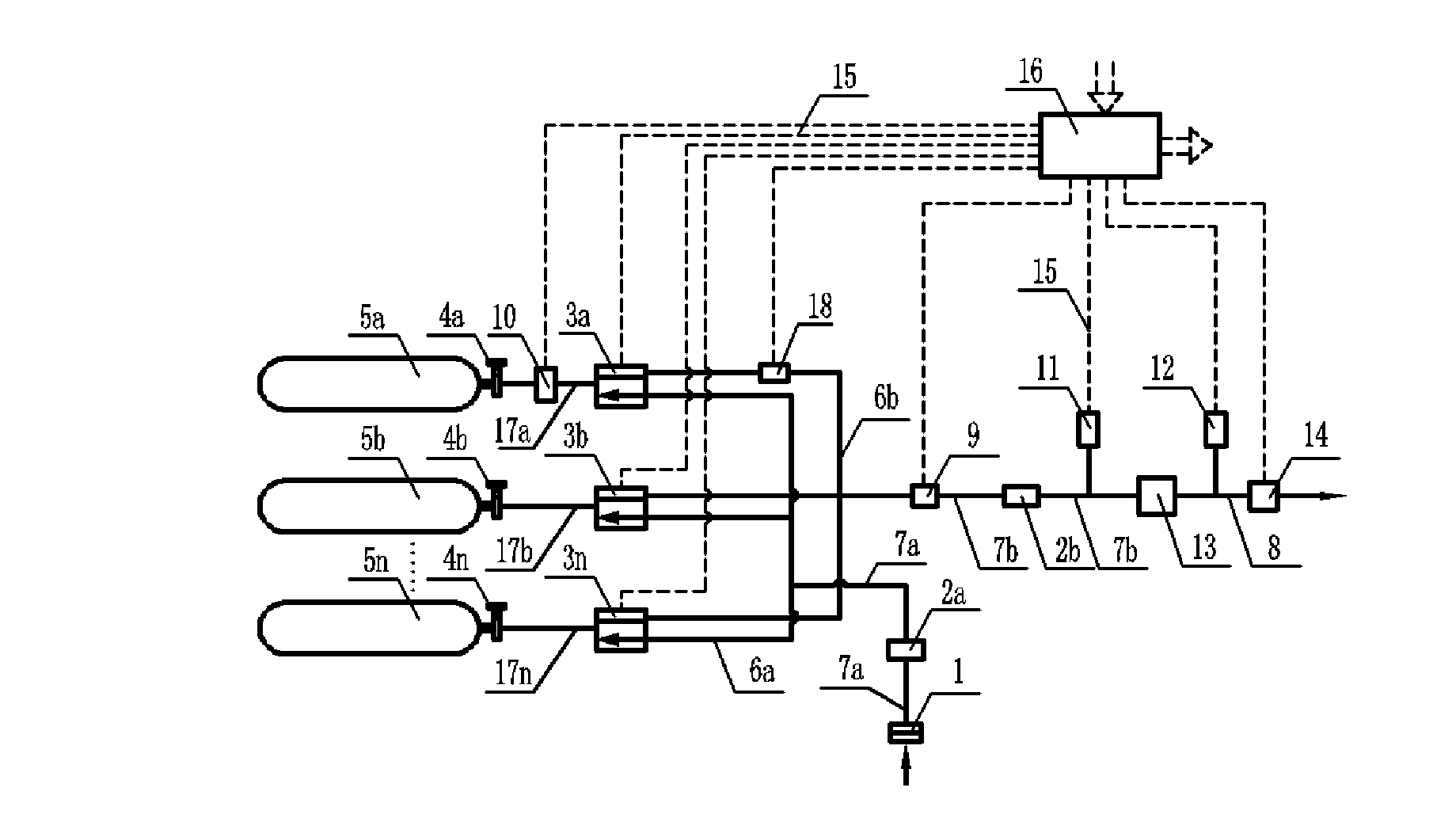
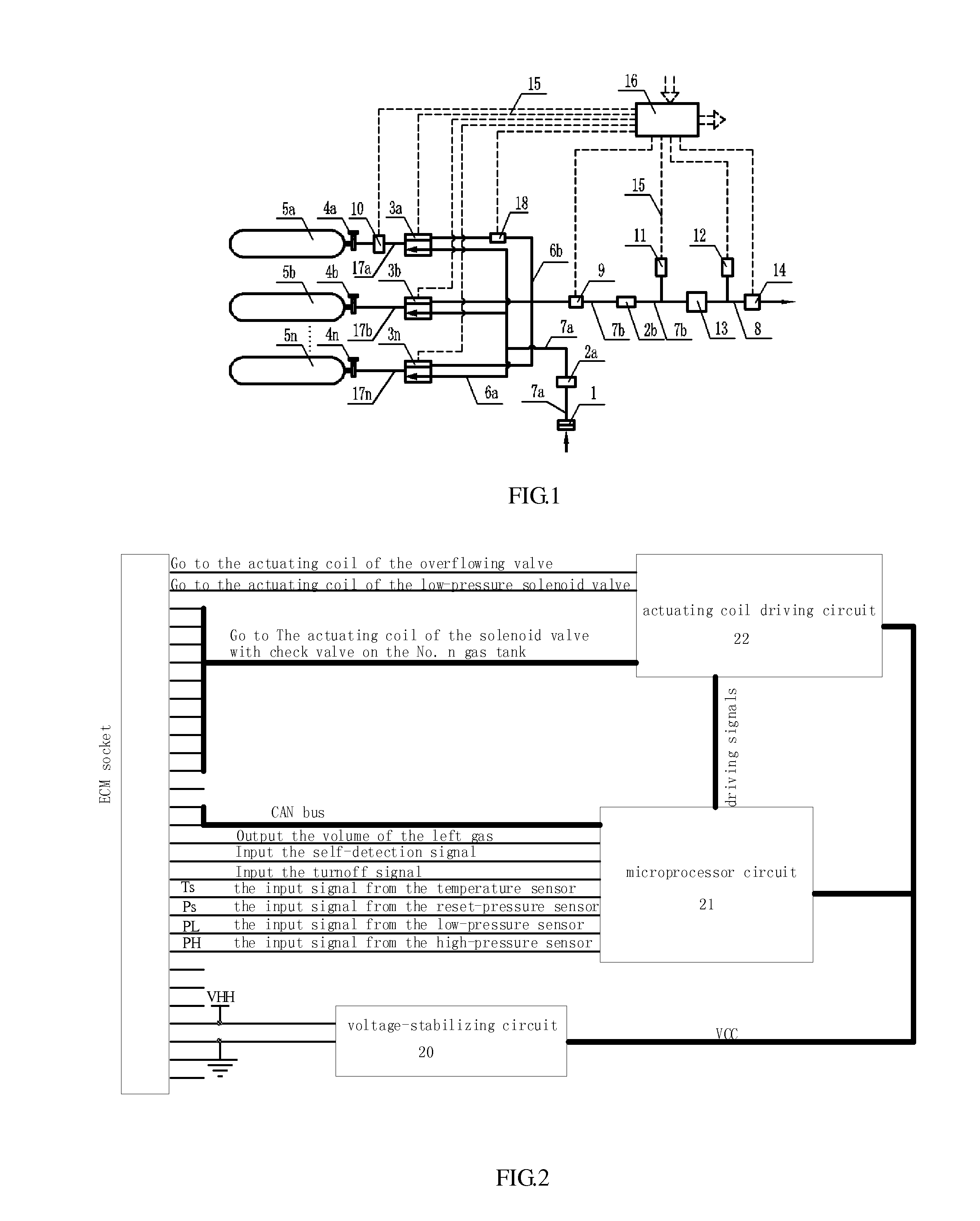
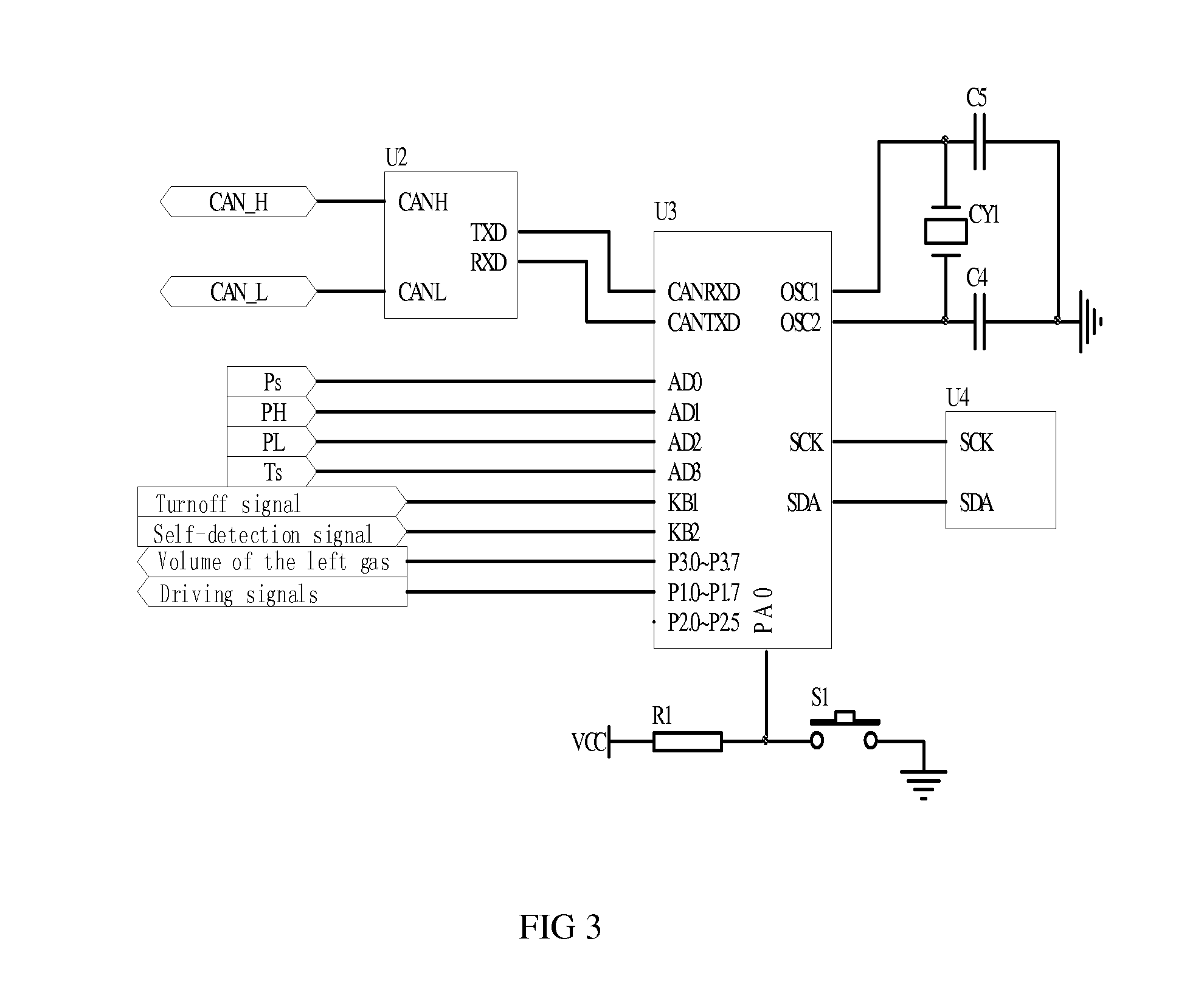
Low consumption and intelligent safe gas-supply system for gas tanks
ActiveUS20100193045A1Simple processImprove reliabilityGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsSolenoid valveHigh pressure hydrogen
A low consumption and intelligent safe gas-supply system for gas tanks comprises: at least two gas tanks and gas tank valves installed on them, charge valves with check valve, at least two gas-filled parallel unit pipes, high-pressure sensor, at least two gas-supply parallel unit pipes, gas-supply main conduit, reset pressure sensor, at least two solenoid valves with check valve, and electronic control module ECM. The invention has the characteristics such as the gas tanks supply gas in sequence, intelligent control, security and reliability for use, low consumption, high display precision for gas volume, decompression transfinite alarm and convenience for installing, use and maintenance etc., and it can be used in the vehicle hydrogen supply system in the fuel cell vehicles or the vehicle compressed natural gas-supply system in the natural gas vehicles, and also the high-pressure hydrogen or natural gas-supply system for gas tanks on the ground.
Owner:BEIJING BOLKEN EQUIP
Diffusion layer for pressure vessels
ActiveUS20090057319A1Improve fluid flowVessel mounting detailsVessel manufacturingEngineeringDiffusion layer
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com