Patents
Literature
518 results about "Hydrogen tank" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Hydrogen tank (other names- cartridge or canister) is used for hydrogen storage. The first type IV hydrogen tanks for compressed hydrogen at 700 bars (70 MPa; 10,000 psi) were demonstrated in 2001, the first fuel cell vehicles on the road with type IV tanks are the Toyota FCHV, Mercedes-Benz F-Cell and the GM HydroGen4.
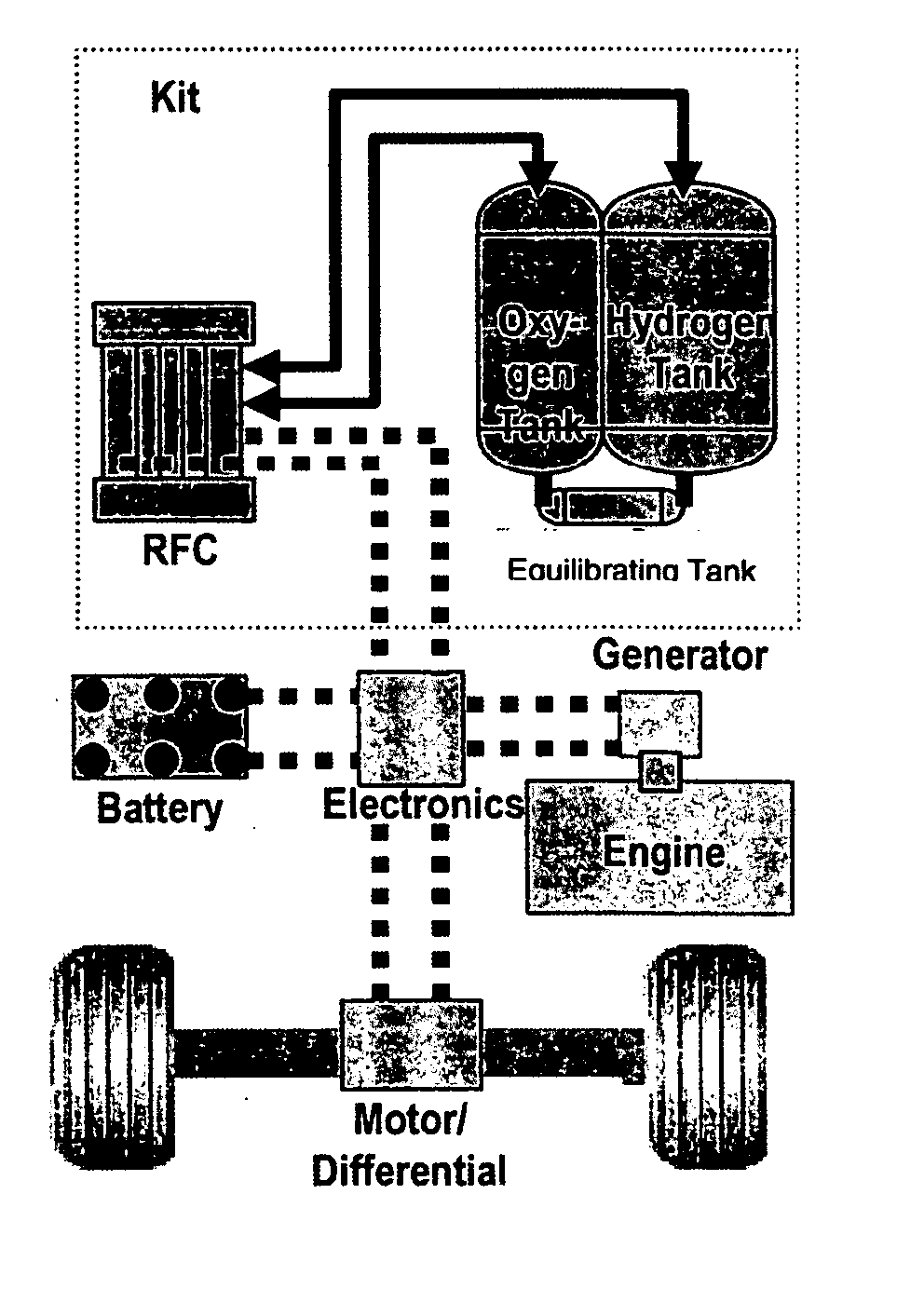
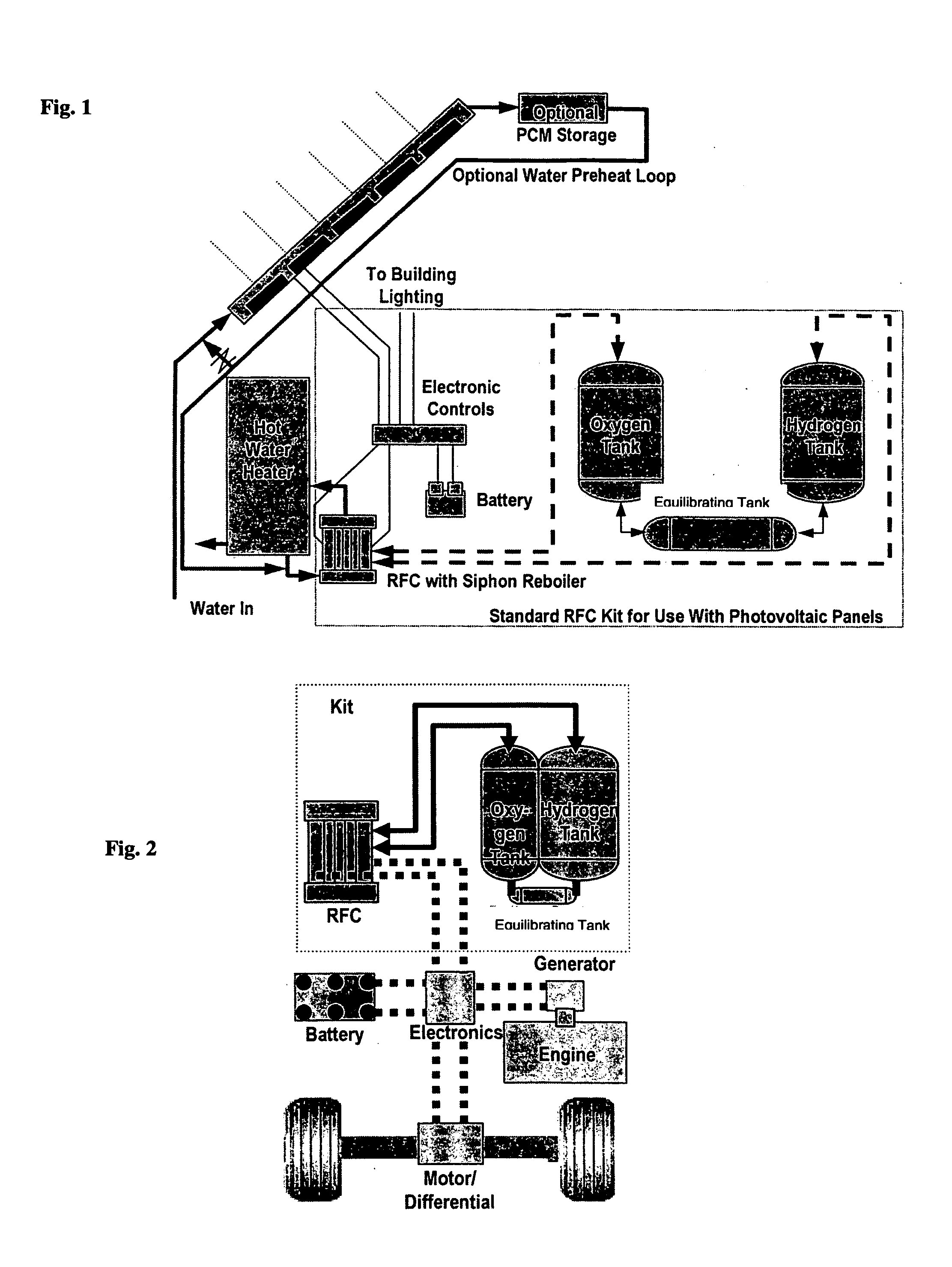
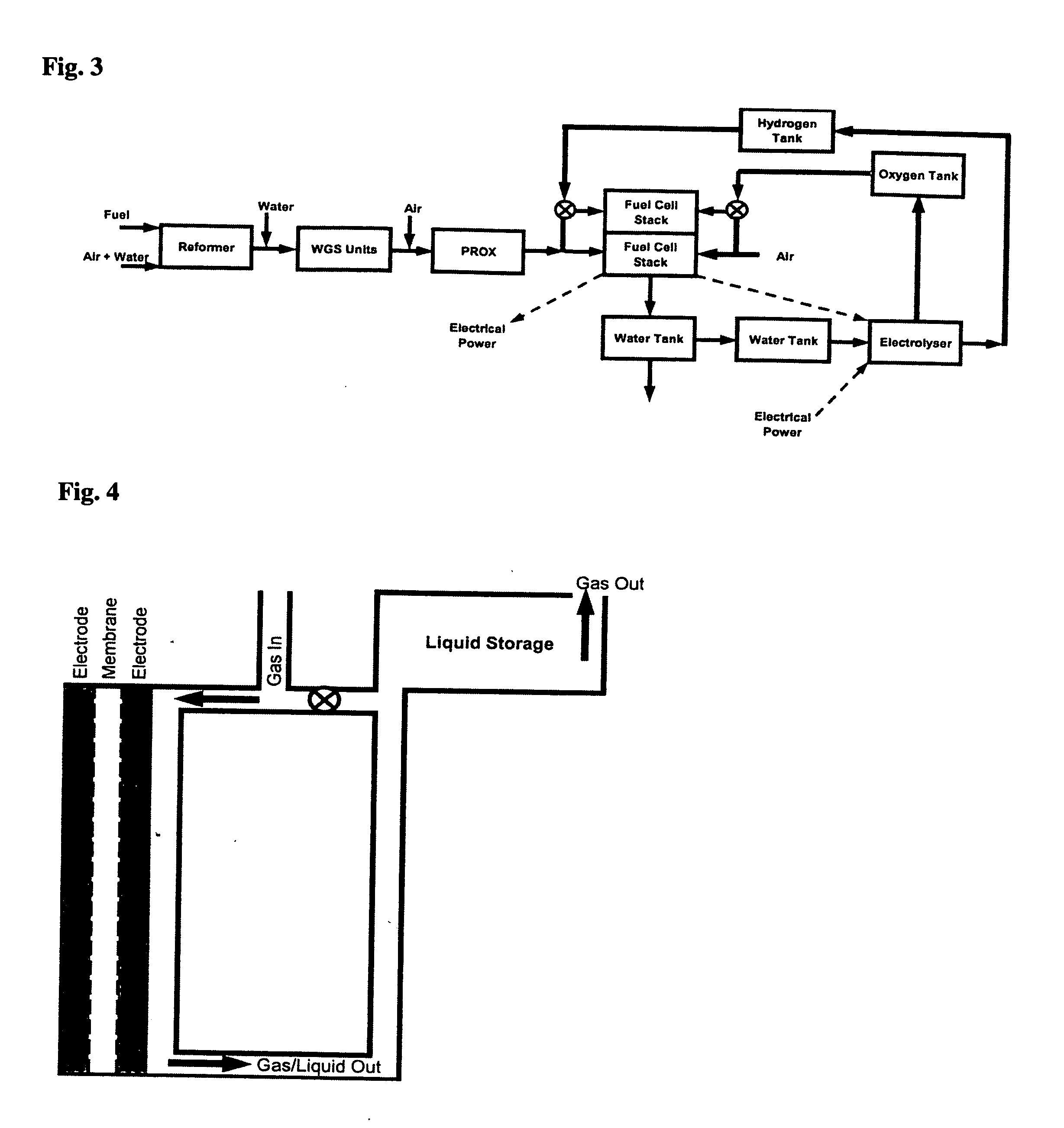
Regenerative fuel cell technology
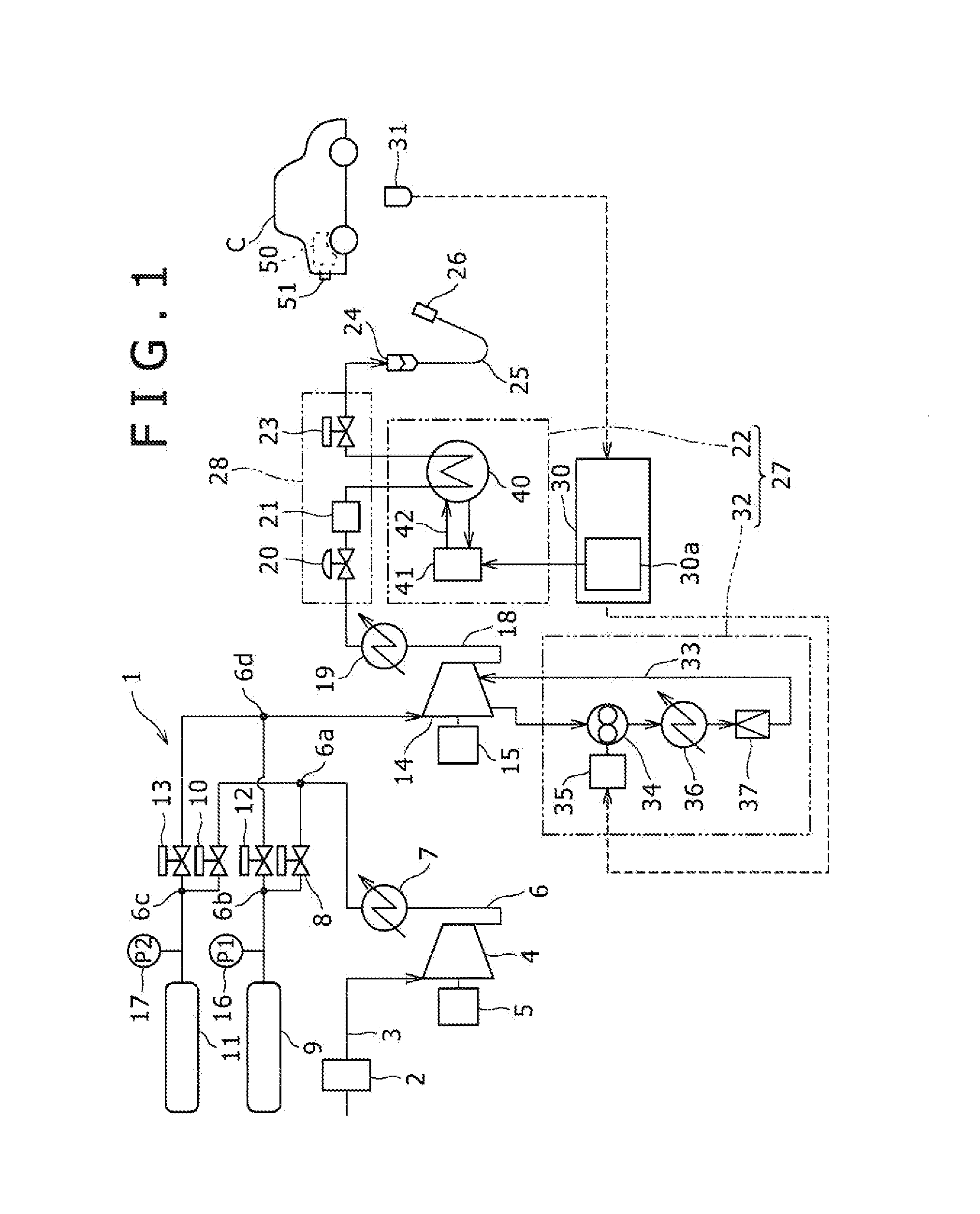
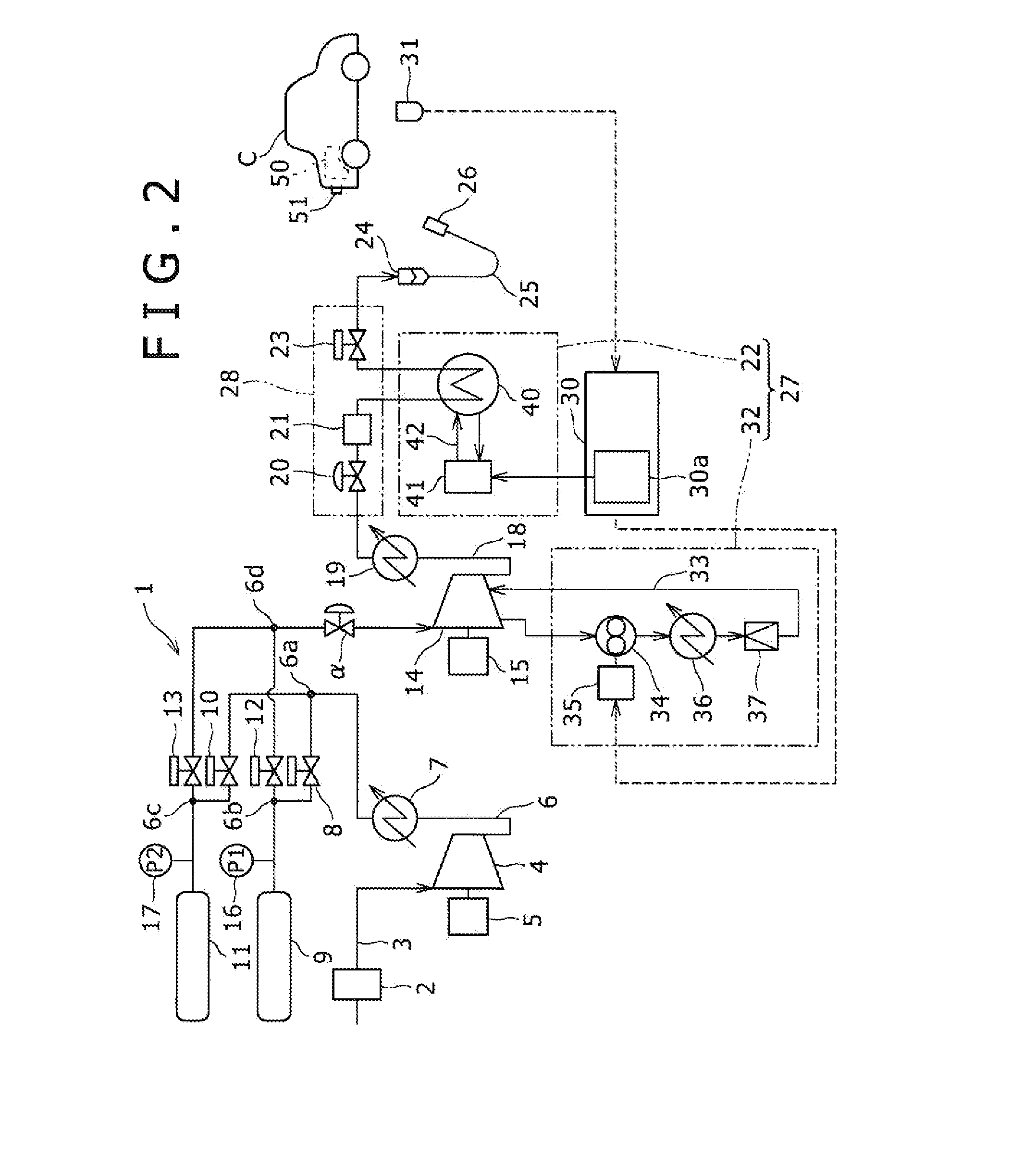
InactiveUS20050008904A1Constant gainSmall fuel cellBatteries circuit arrangementsRegenerative fuel cellsElectrolysisOxygen
For a mobile fuel cell system a narrow-gap modular approach allows reforming to be performed in the same architecture as the fuel cell. A regenerative fuel cell operates much like a battery using electrical power to produce hydrogen and oxygen. The preferred mode of using the regenerative fuel cell is as a battery charger since this application is able to use a much smaller fuel cell than is required to power the vehicle. A novel equilibrating tank between the electrolysis oxygen and hydrogen tanks allows pressurized oxygen and hydrogen to be used without mechanical compression equipment.
Owner:SUPPES GALEN J
Apparatus and process for rapidly filling with hydrogen
InactiveUS20020014277A1Increase heatIncrease rangeLiquid fillingGas handling applicationsFilling rateDelayed time
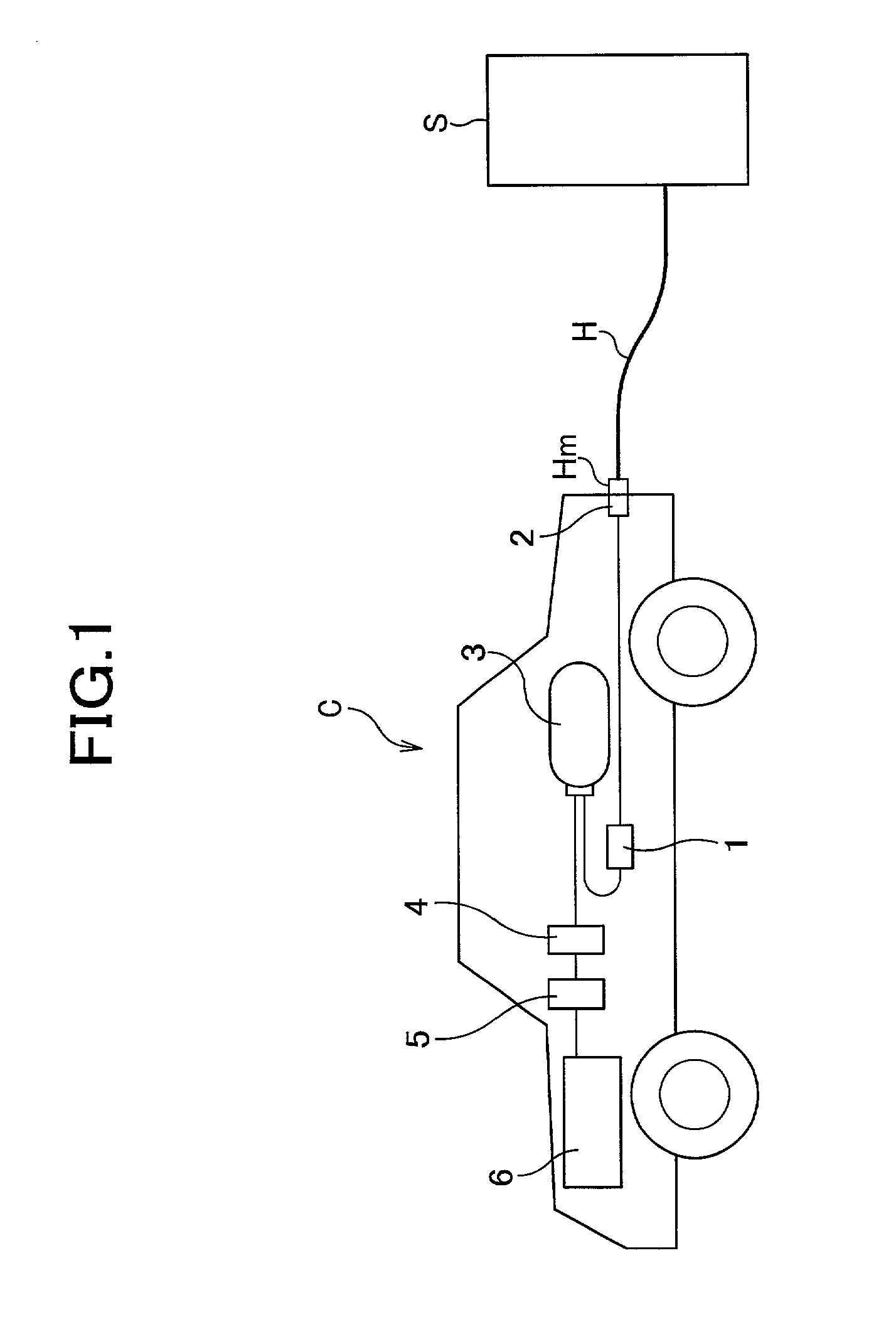
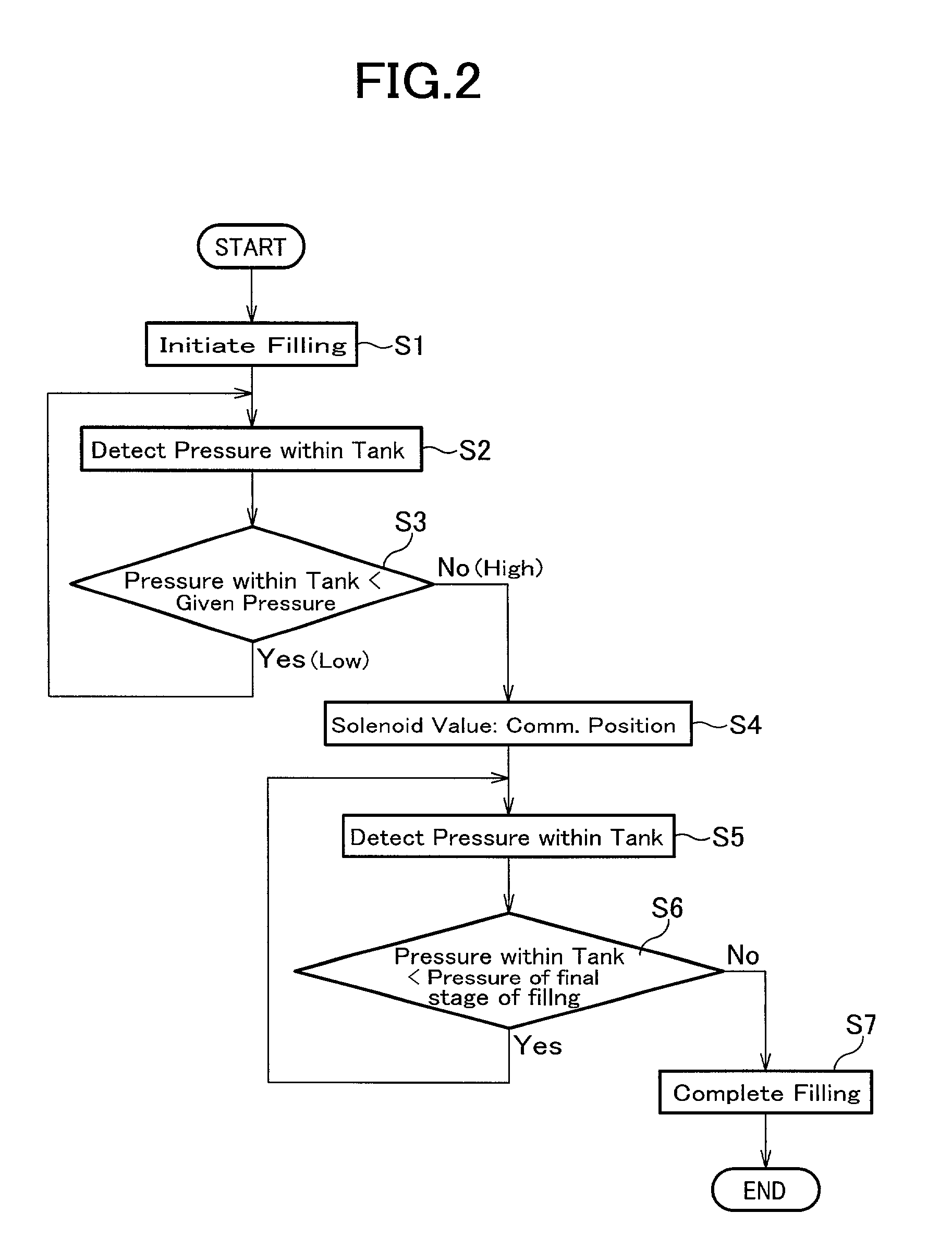
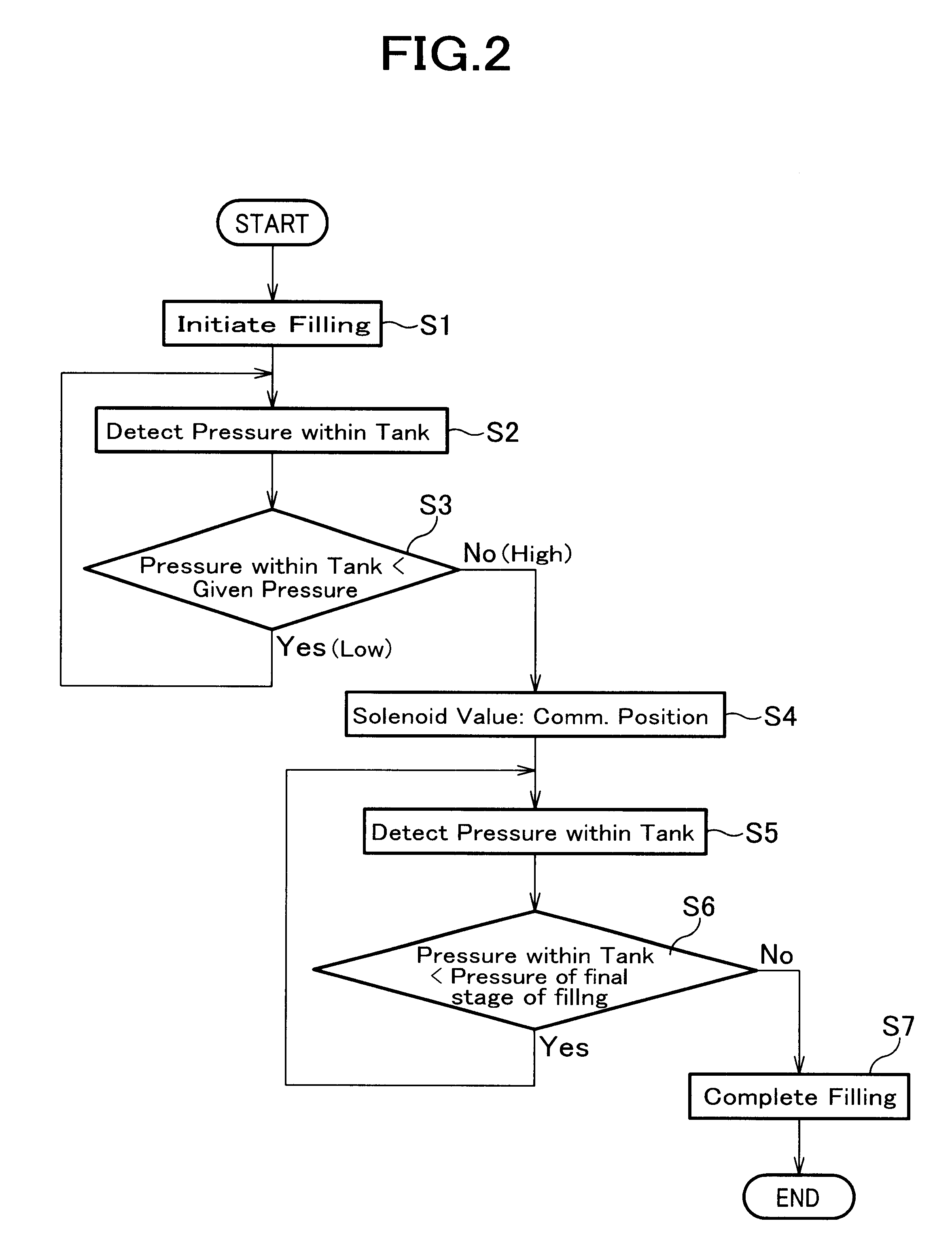
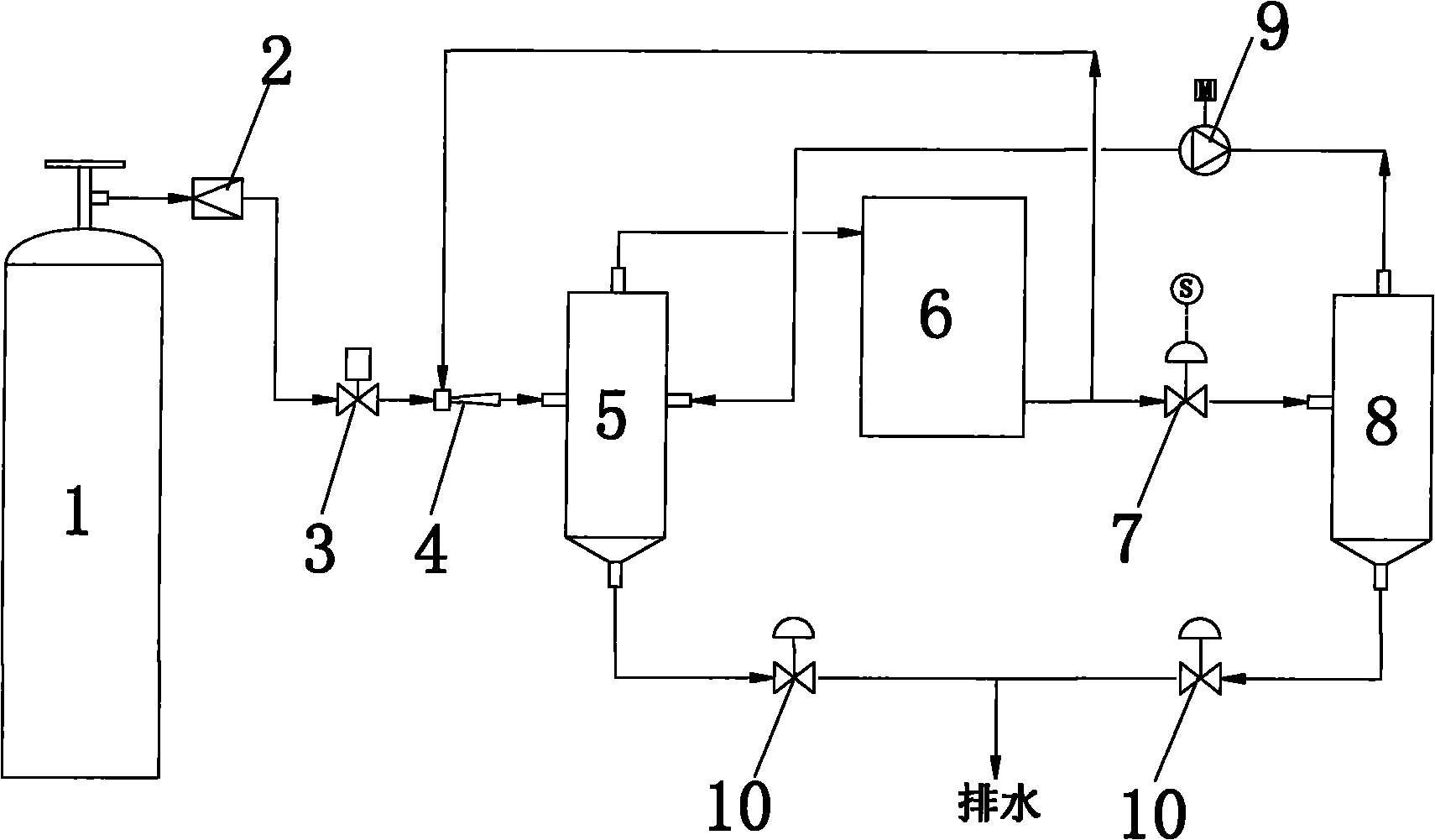
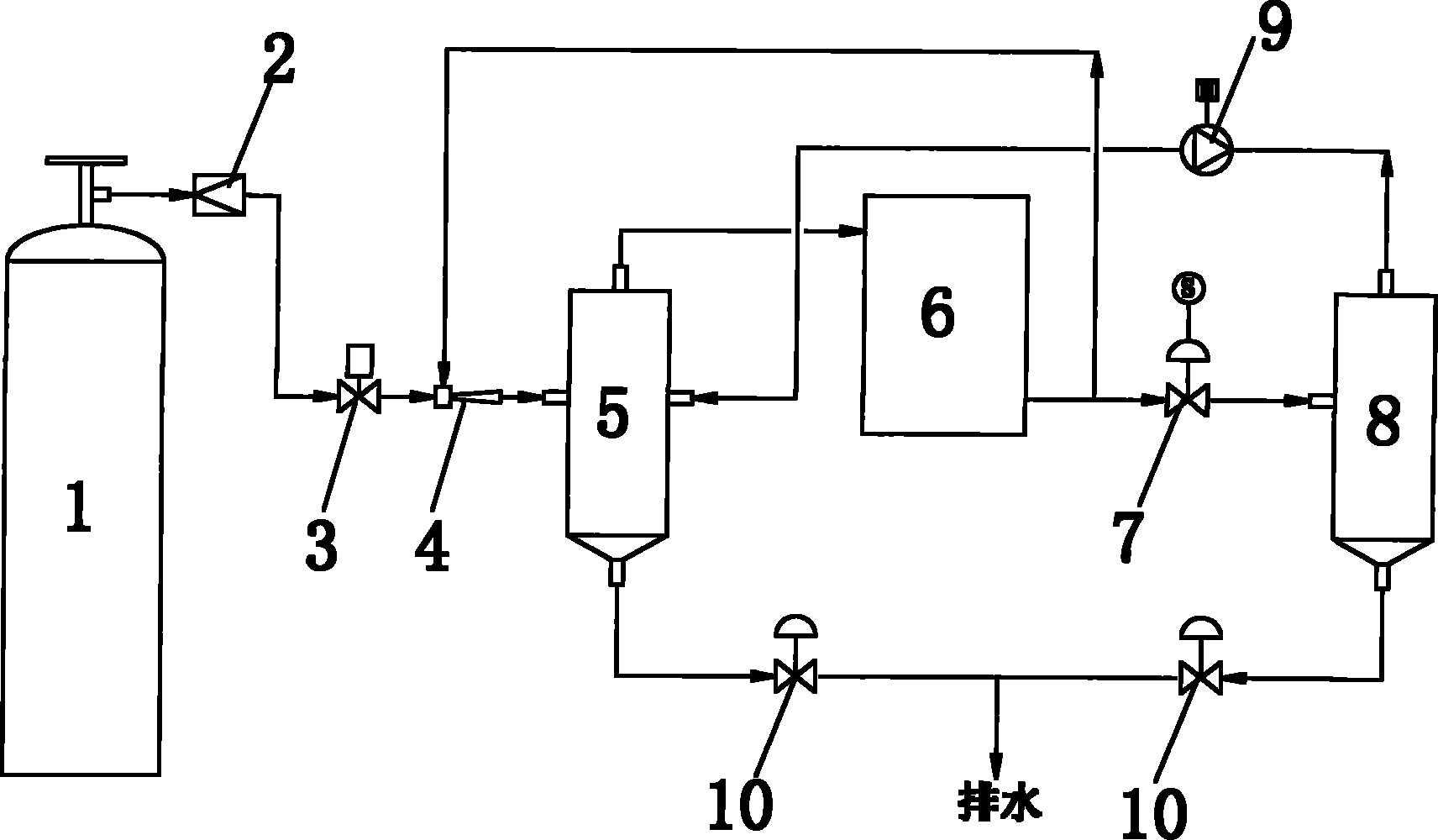
An apparatus for rapidly filling a hydrogen tank with a hydrogen gas comprises a hydrogen source; a hydrogen tank; a passage which connects the hydrogen source and said hydrogen tank; and a mechanism for varying the hydrogen-filling rate. The mechanism for varying the hydrogen-filling rate changes the hydrogen-filling rate depending upon the pressure within said hydrogen tank. The apparatus can suppress heat generation at the initial filling stage where the temperature is easily increased. Also, even if it takes longer time for increasing the pressure within the hydrogen tank at the initial filling state, the delayed time can be caught up and, the apparatus and the process of the present invention can totally attain a rapidly filling with hydrogen.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
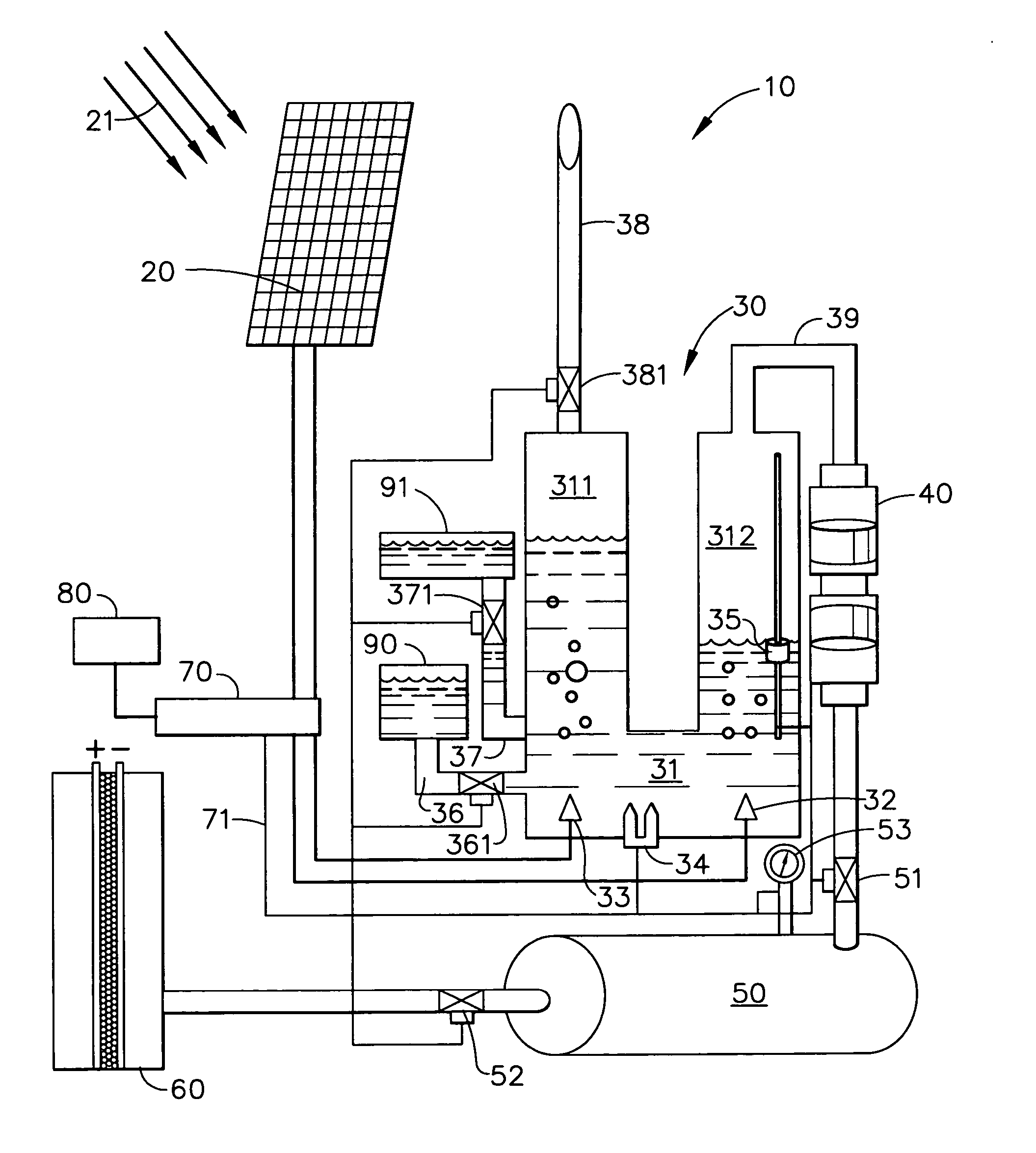
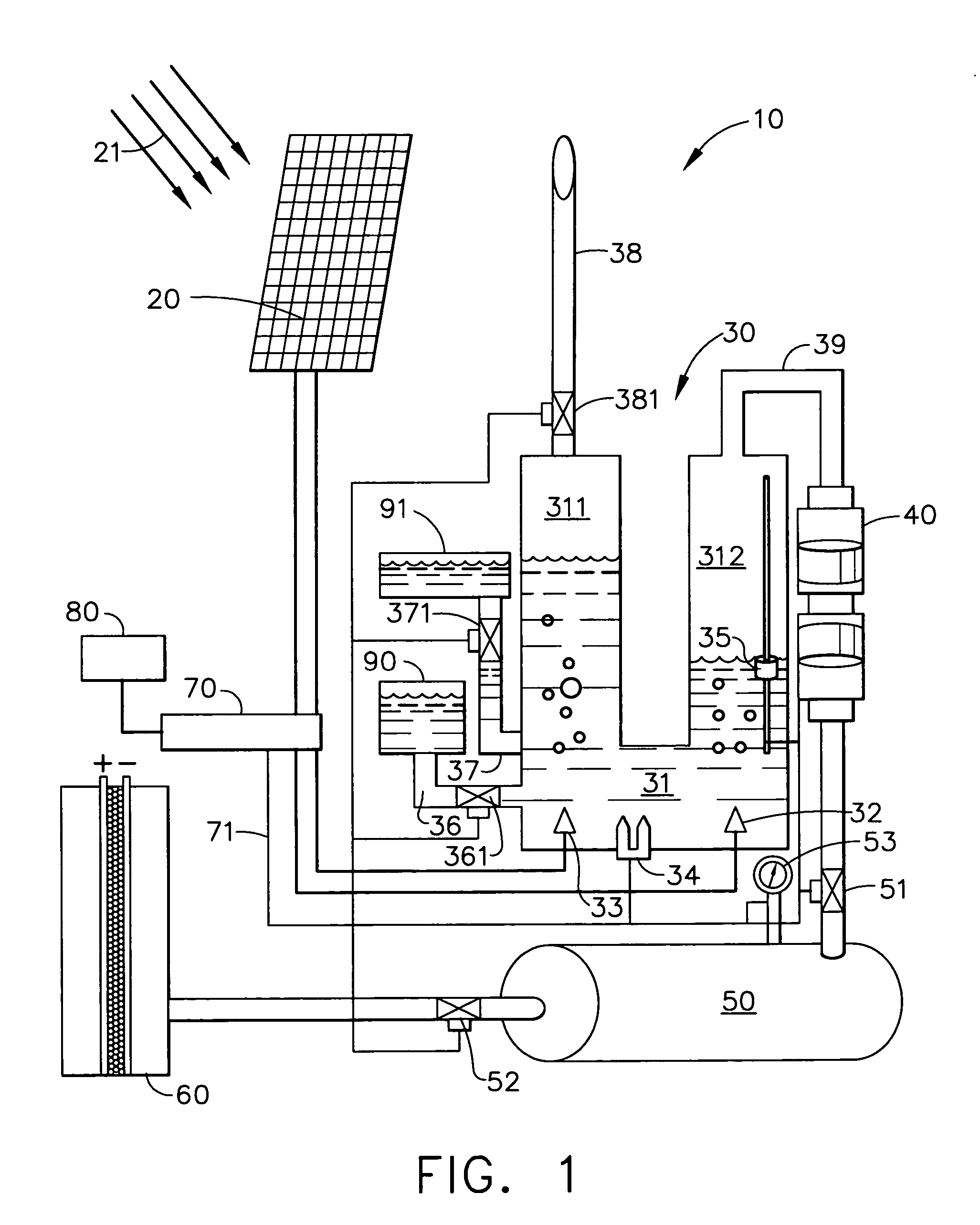
Solar electrolysis power co-generation system
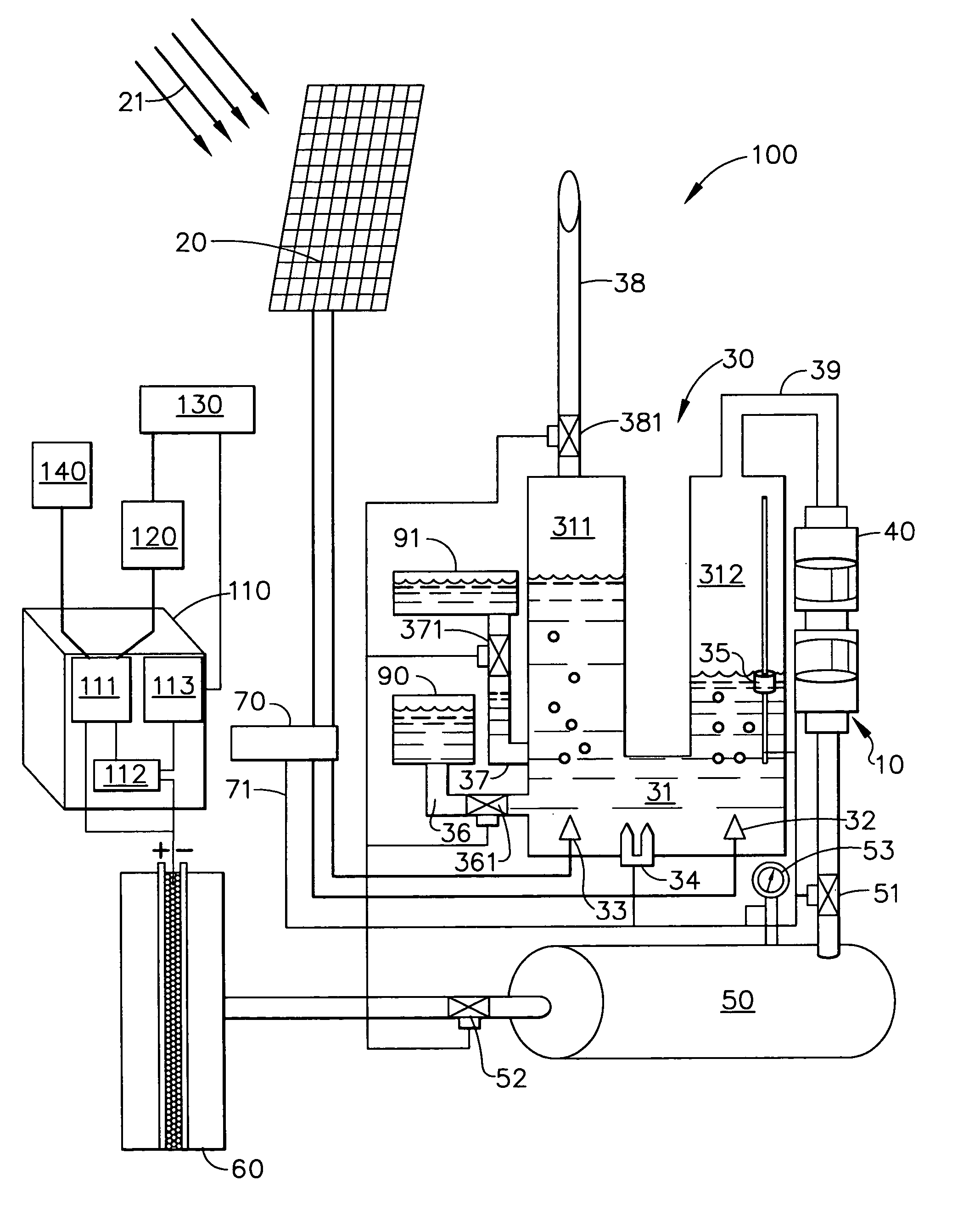
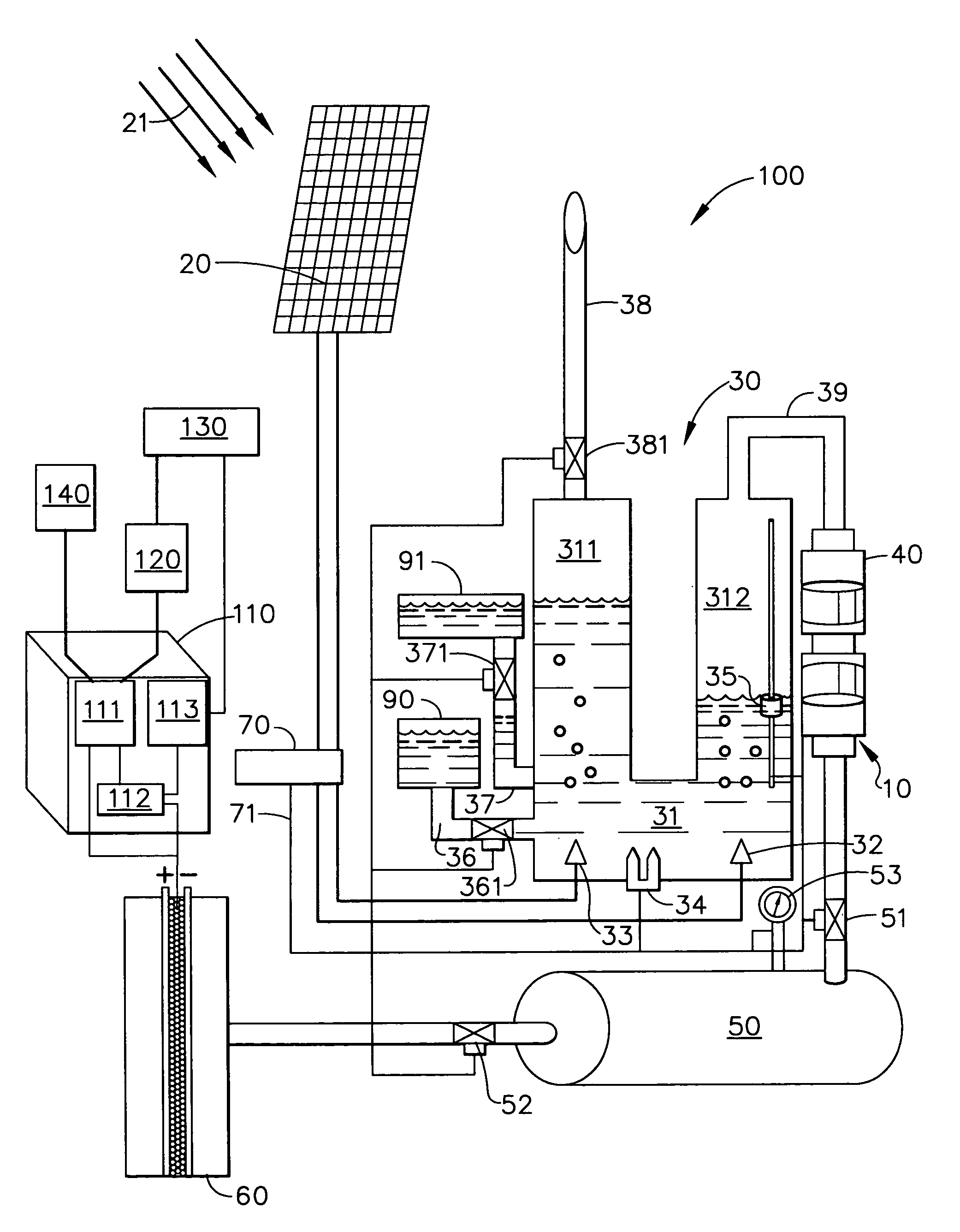
A solar electrolysis power co-generation system includes a solar electrolysis source and a control unit. The solar electrolysis source includes a solar panel, an electrolysis unit, a hermetically sealed compressor, a hydrogen tank, and a hydrogen-powered fuel cell and produces, compresses, and stores hydrogen gas that is used to fuel the fuel cell. The control unit includes an inverter, a microprocessor, and a modem. The control unit connects the solar electrolysis power source with a power grid and with an individual consumer having an electrical load. The power co-generation system utilizes the electrolysis of water and solar energy to power a fuel cell. The energy produced with the fuel cell may be provided to an existing power gird as well as to an individual consumer. Further a method for decentralized power co-generation includes the step of providing a plurality of solar electrolysis power co-generation systems.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
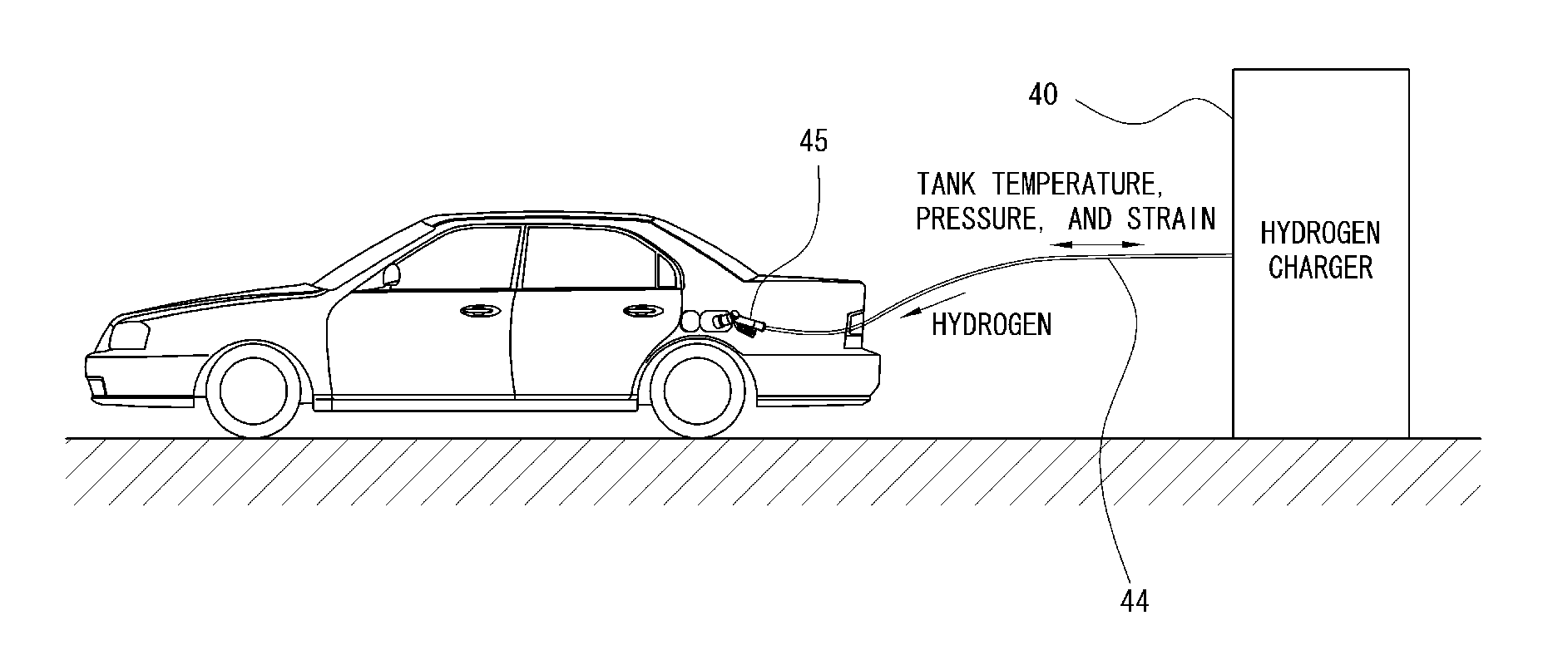
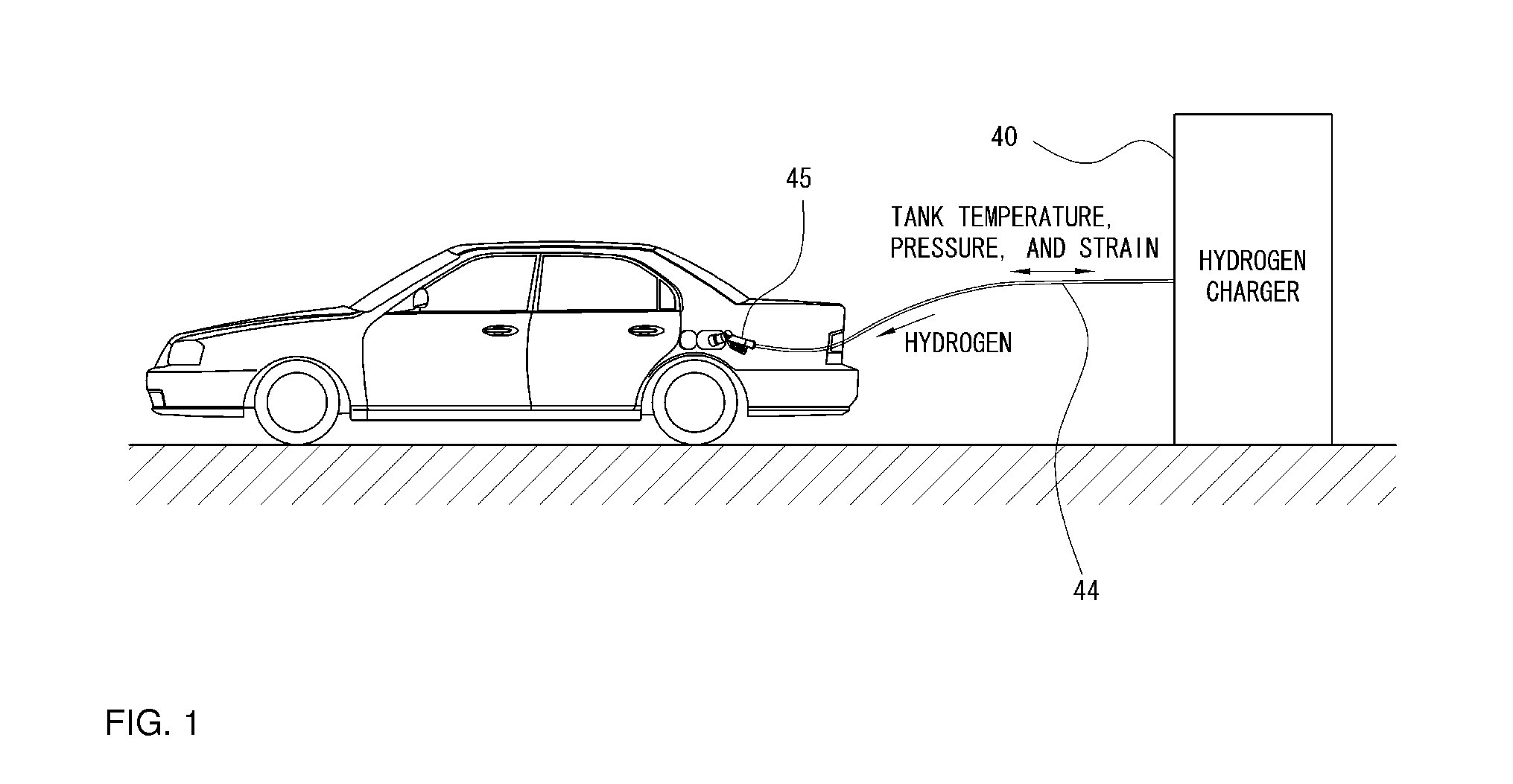
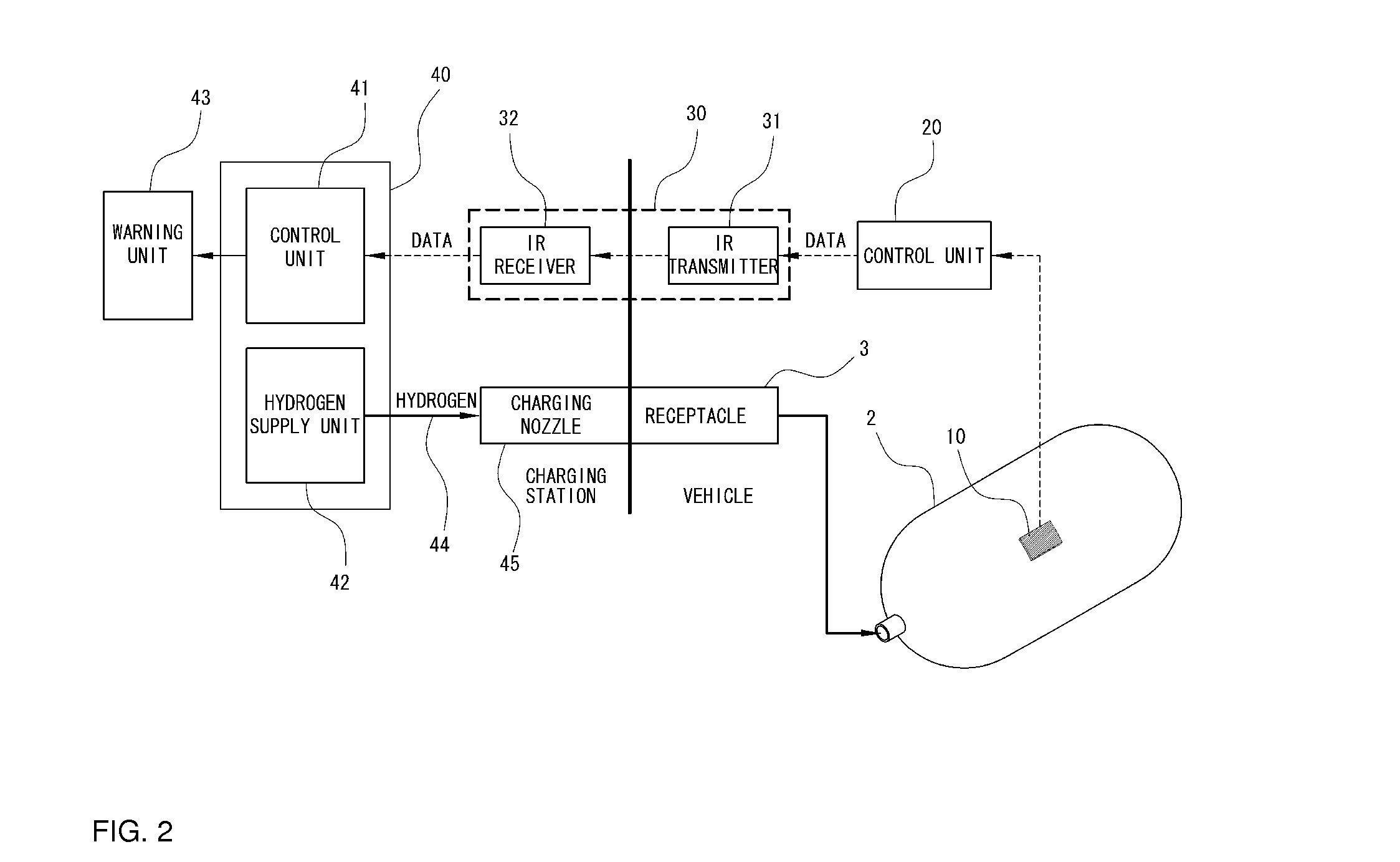
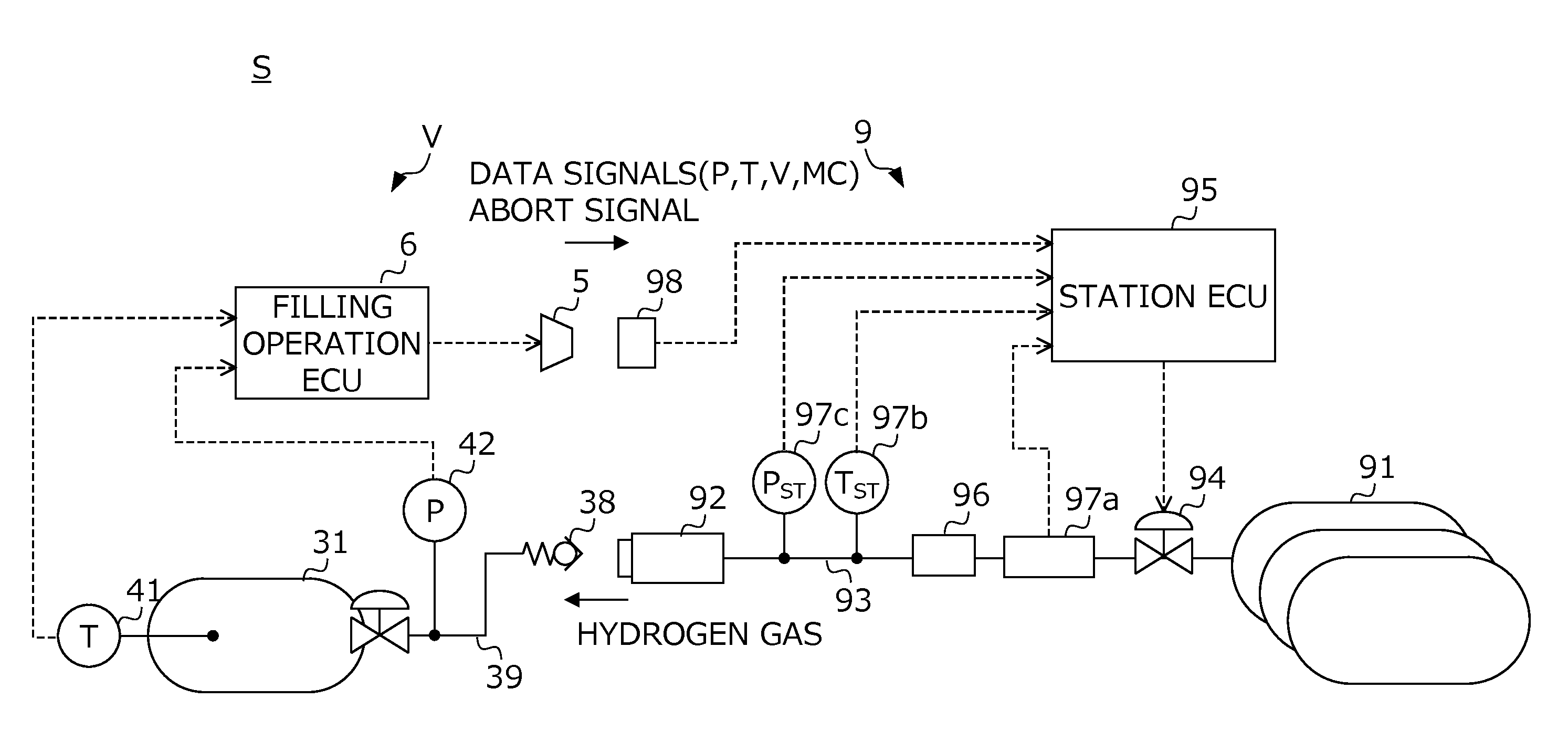
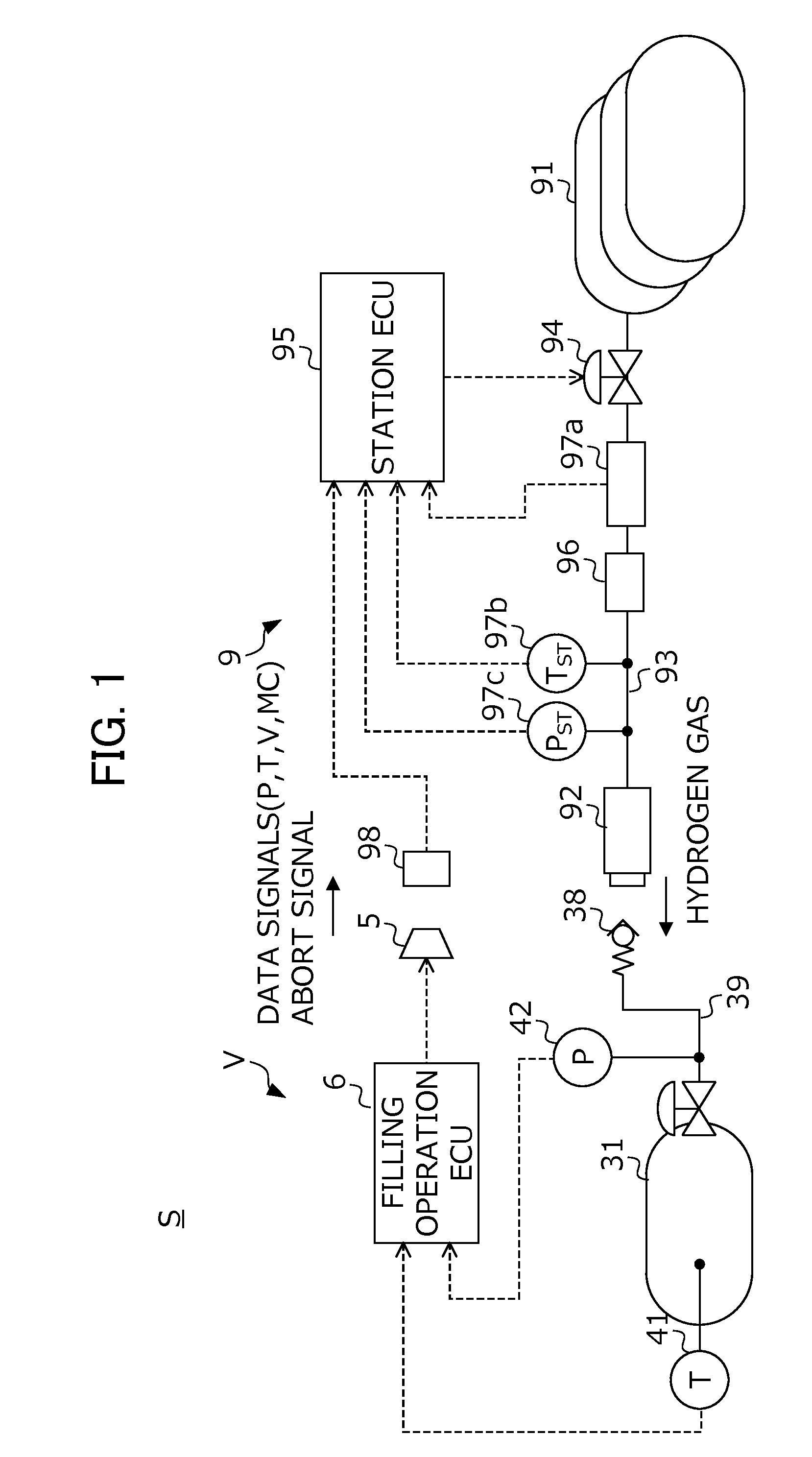
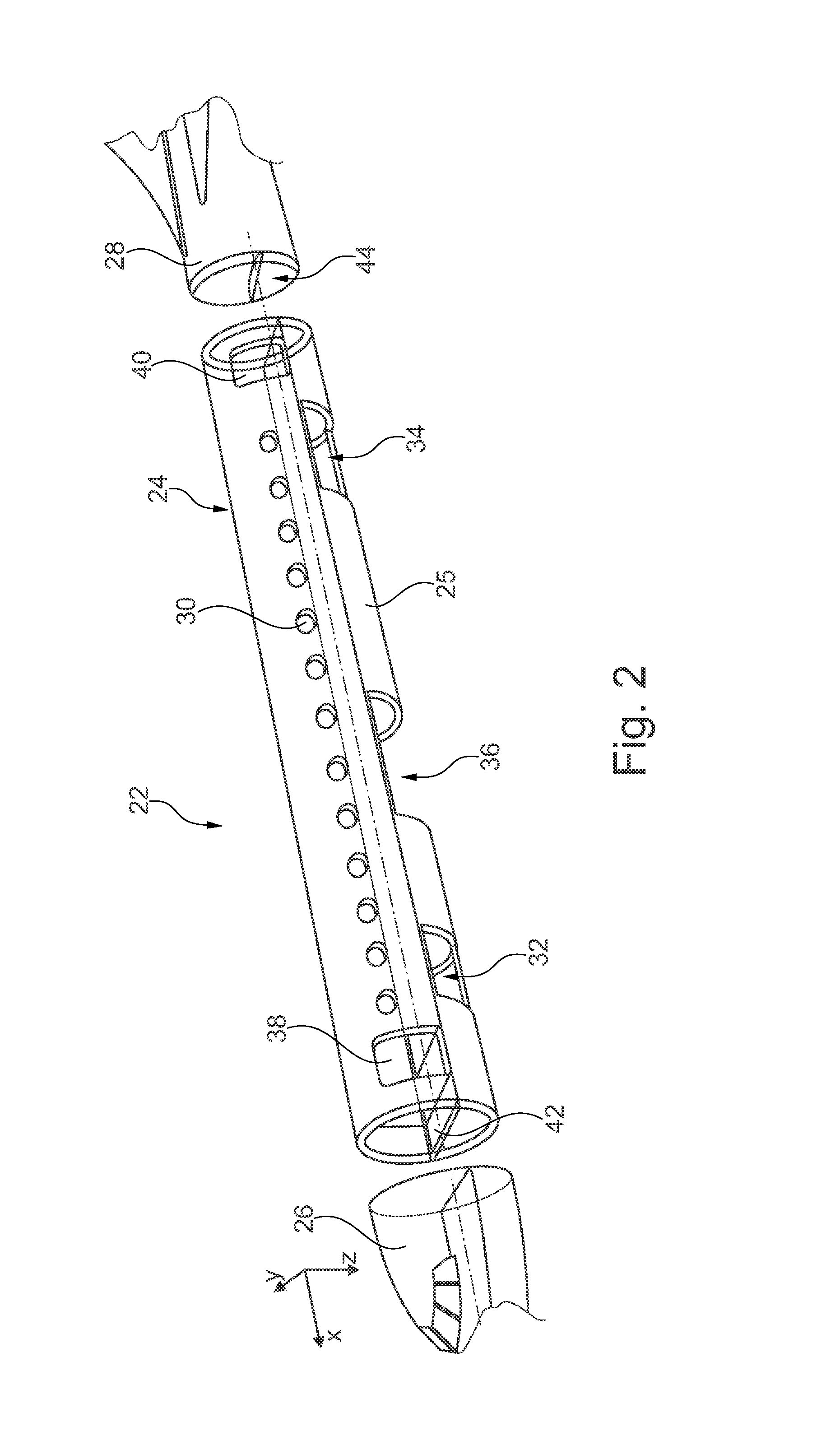
Real-time system for monitoring hydrogen tank expansion and a method for using same
InactiveUS20130139897A1Safely replenishingGas handling applicationsService pipe systemsCommunication unitWireless data
The present disclosure provides a system and method for safely charging hydrogen using real-time hydrogen tank expansion data. The system includes an expansion measurement unit, a vehicle-side control unit, a charging station-side control unit, and a wireless communication unit. The expansion measurement unit is disposed on a hydrogen tank of the vehicle, and measures the degree of expansion of the hydrogen tank and generates a corresponding output signal. The vehicle-side control unit converts the output signal into data wireless output signal. The charging station-side control unit stops hydrogen replenishment by a hydrogen charger when the wireless output signal indicates an unsafe degree of tank expansion based. The wireless communication unit is provided to perform wireless data communication between the vehicle-side control unit and the charging-side control unit.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +1
Hydrogen tank liner material and hydrogen tank liner
ActiveUS20090203845A1Improve impact resistanceSuitable for useVessel mounting detailsVessel manufacturingAlpha-olefinHydrogen tank
A hydrogen tank liner material comprises a polyamide resin composition which comprises (A) a polyamide resin at 85-40 wt %, (B) a copolyamide at 5-30 wt % and (C) an impact-resistant material at 10-30 wt % with respect to the total weight of the polyamide resin composition. Preferably, the (B) copolyamide is PA6 / 66 and the (C) impact-resistant material is an acid-modified ethylene / α-olefin-based copolymer. A hydrogen tank liner material with excellent gas barrier properties and superior impact resistance even at low temperatures is obtained.
Owner:UBE CORP +1
Apparatus and process for rapidly filling with hydrogen
InactiveUS6598624B2Increase heatIncrease rangeLiquid fillingGas handling applicationsFilling rateDelayed time
An apparatus for rapidly filling a hydrogen tank with a hydrogen gas comprises a hydrogen source; a hydrogen tank; a passage which connects the hydrogen source and said hydrogen tank; and a mechanism for varying the hydrogen-filling rate. The mechanism for varying the hydrogen-filling rate changes the hydrogen-filling rate depending upon the pressure within said hydrogen tank. The apparatus can suppress heat generation at the initial filling stage where the temperature is easily increased. Also, even if it takes longer time for increasing the pressure within the hydrogen tank at the initial filling state, the delayed time can be caught up and, the apparatus and the process of the present invention can totally attain a rapidly filling with hydrogen.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
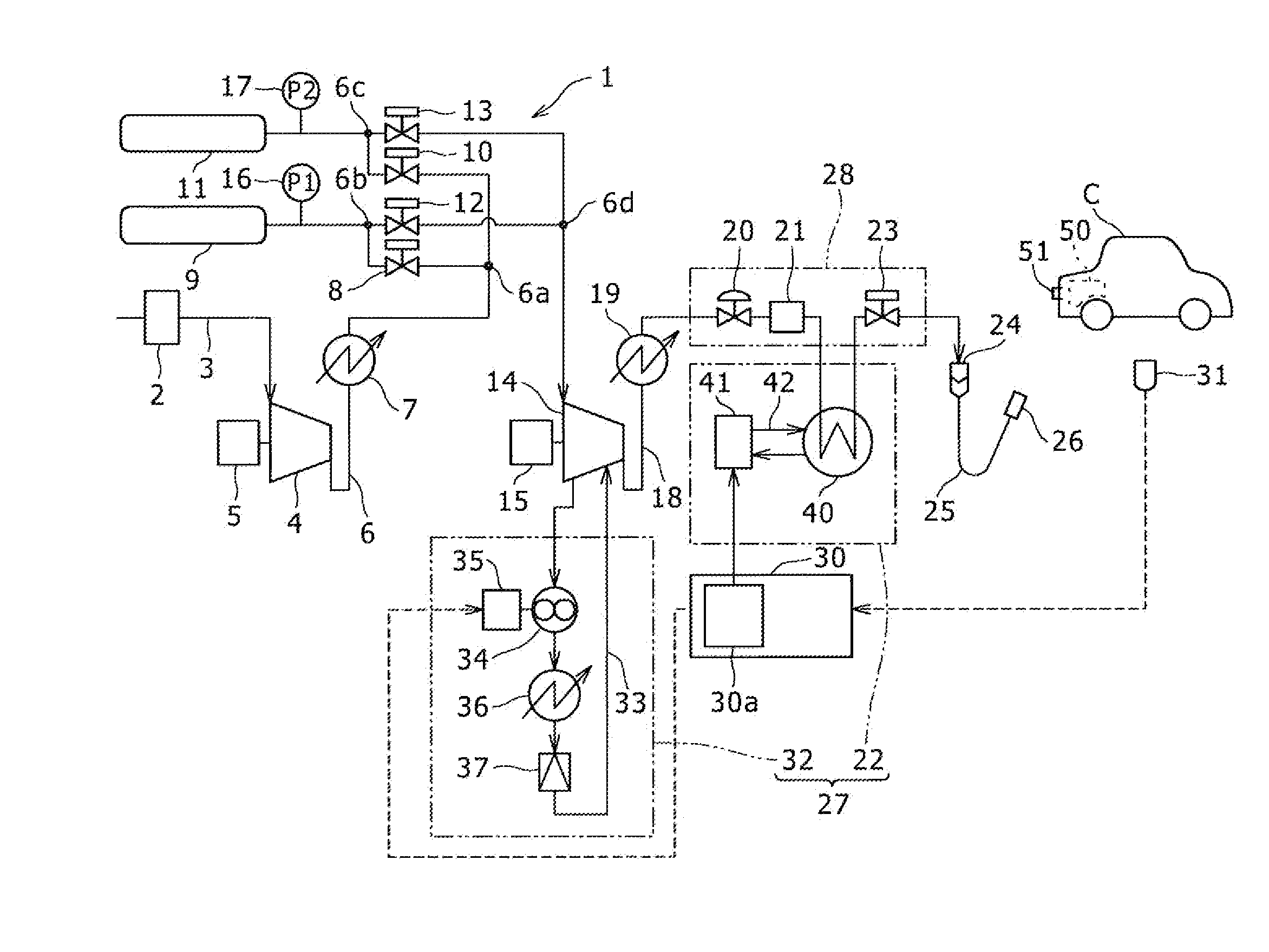
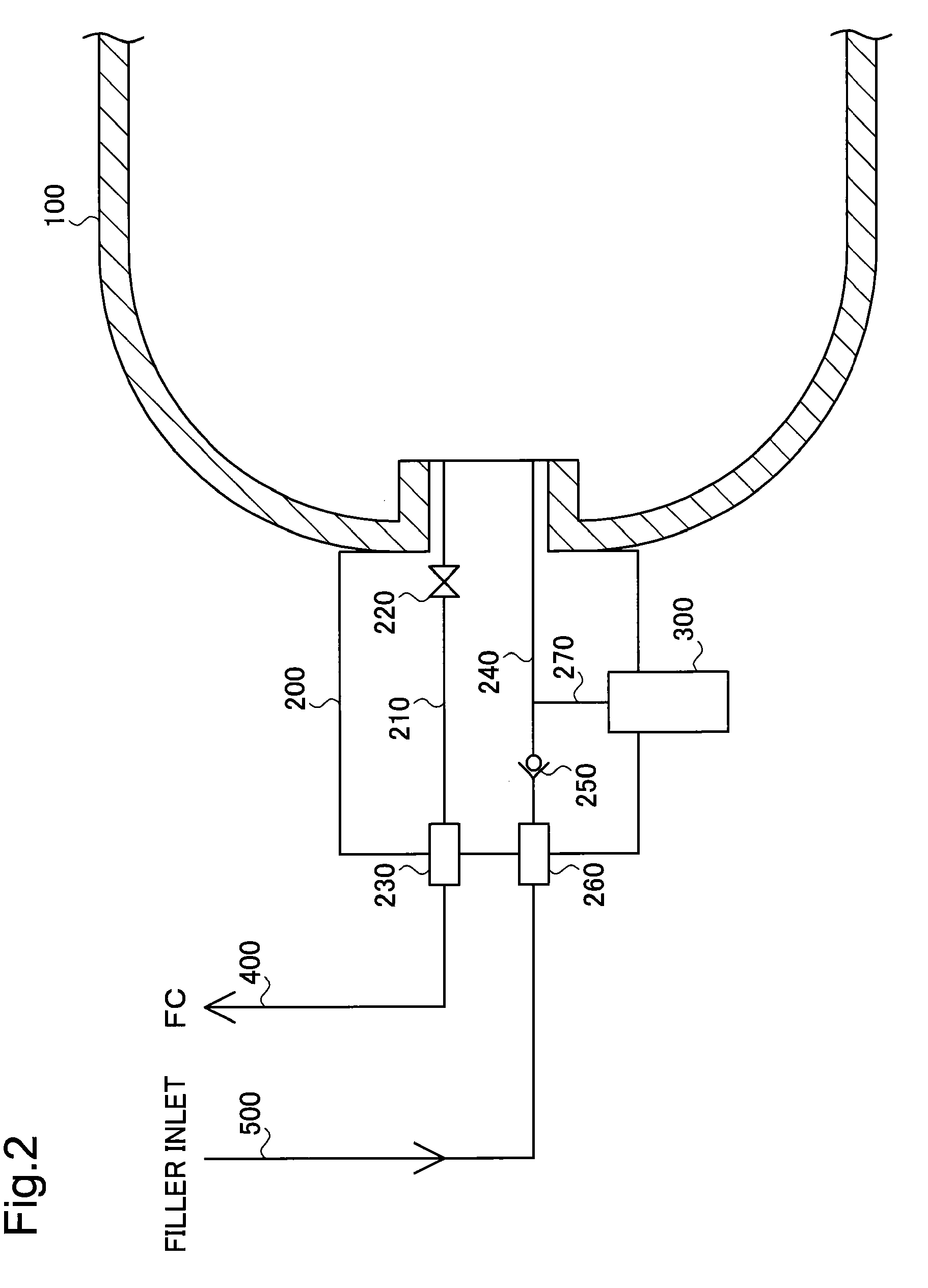
Method and System for Tank Refilling
ActiveUS20110259469A1Improve performanceLow costCapsCap application using vaccuumAnalytical equationsEngineering
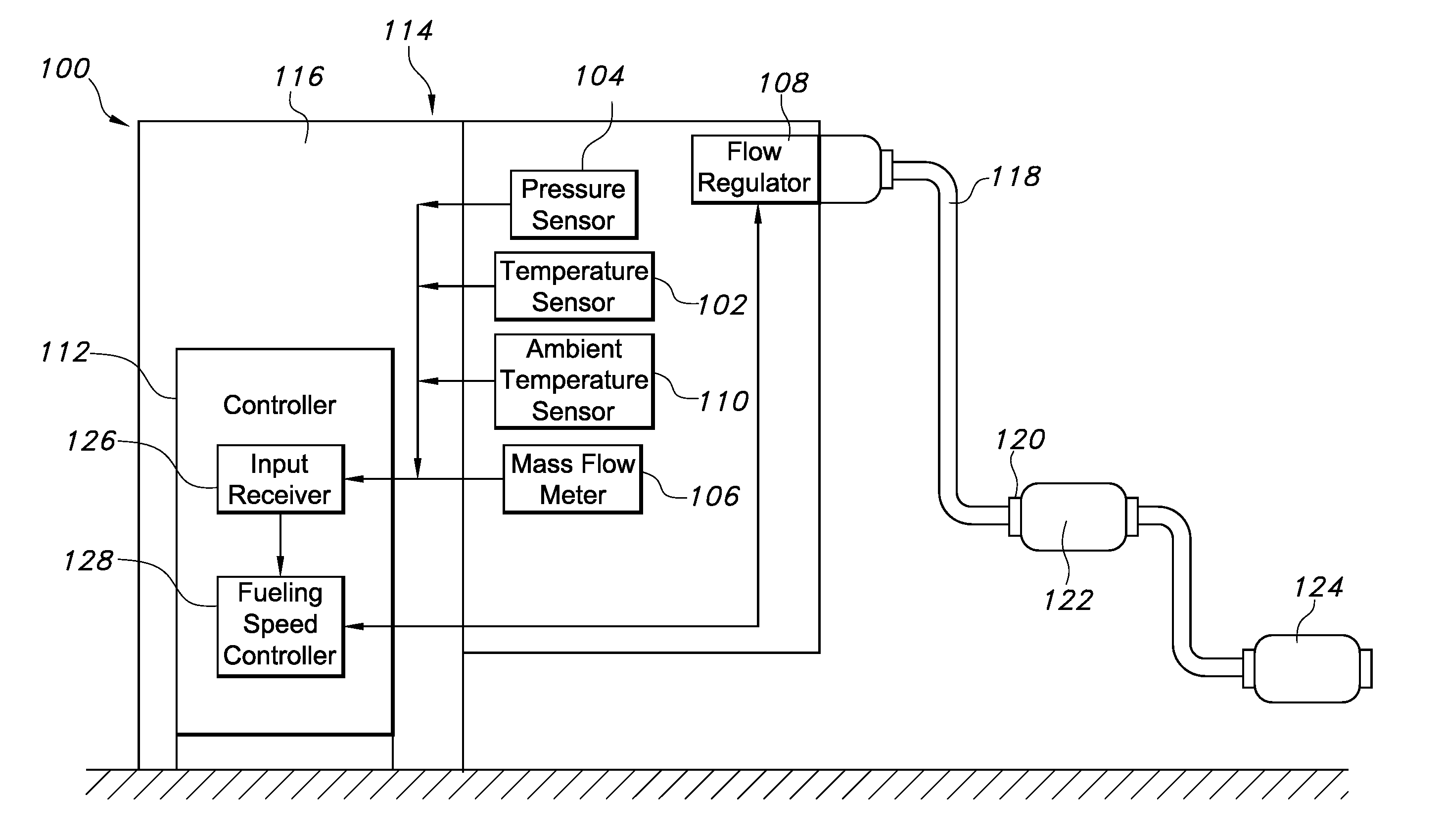
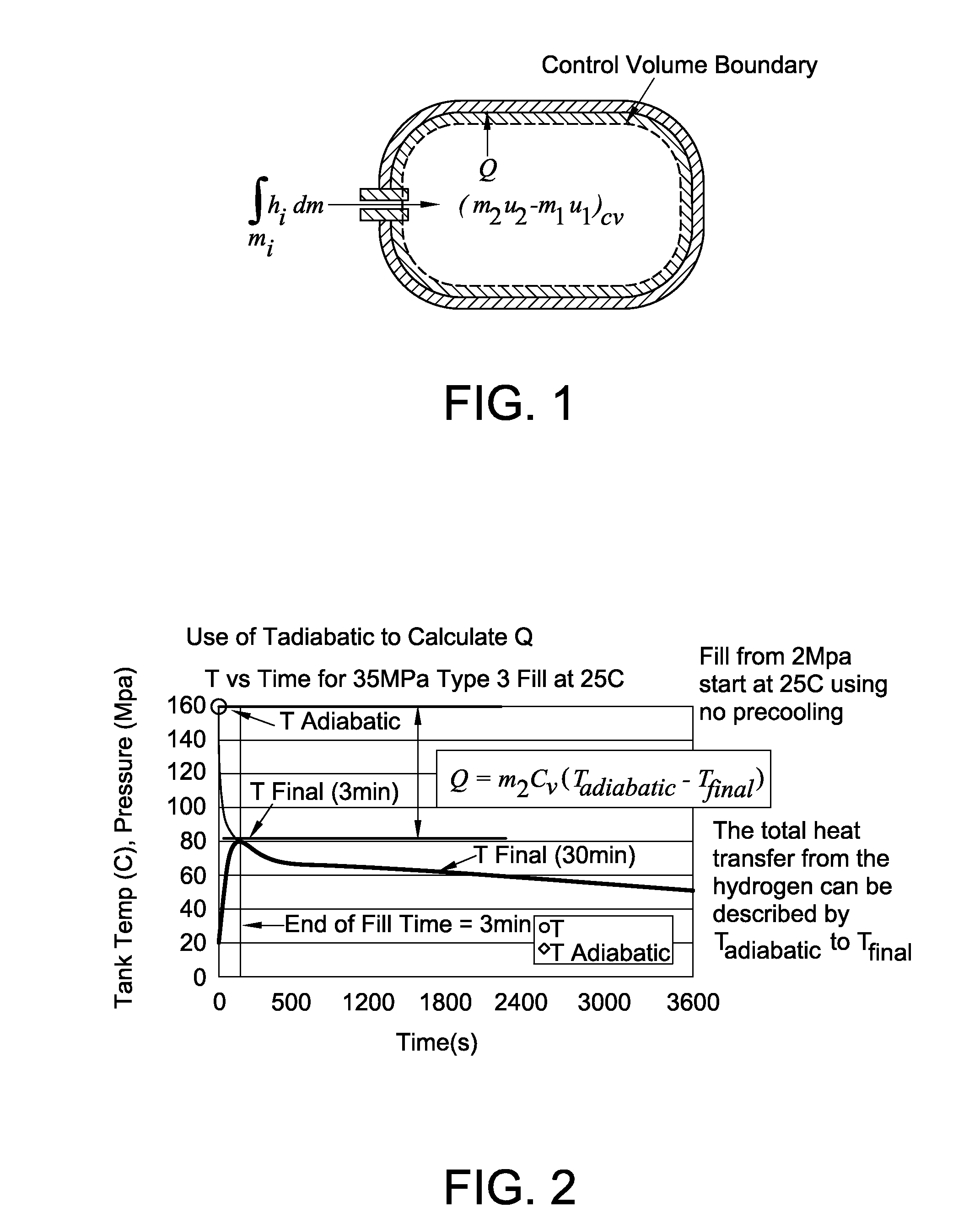
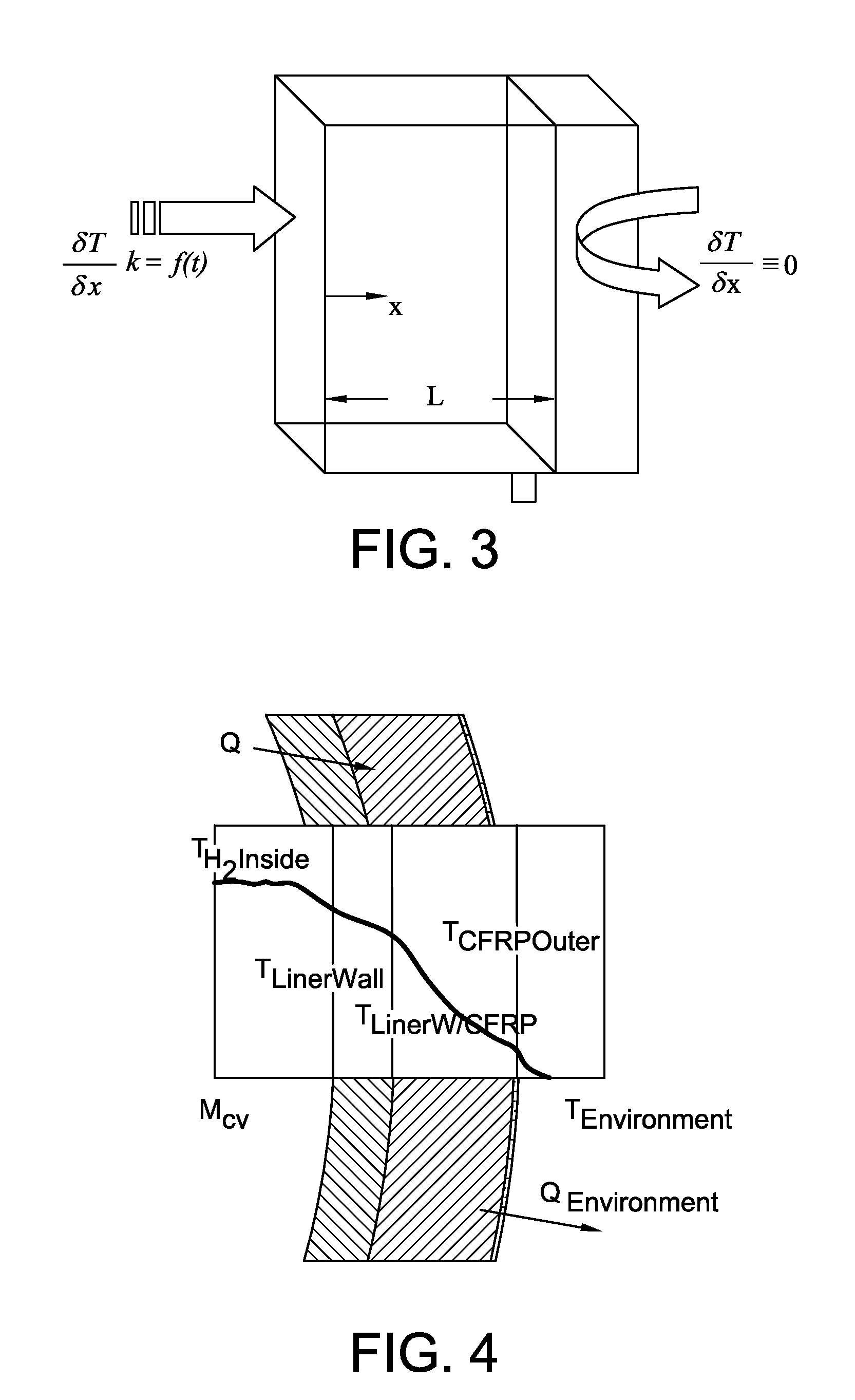
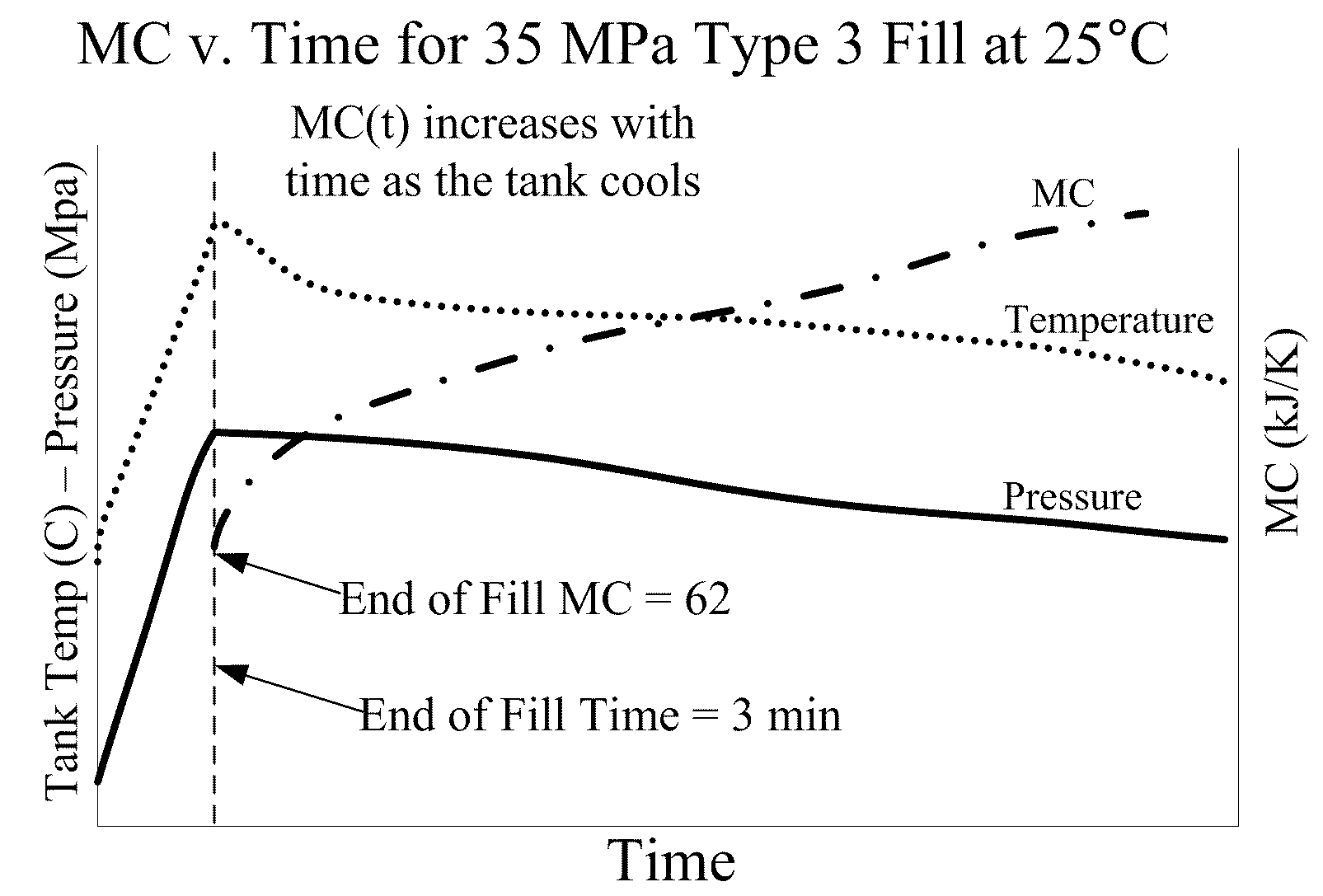
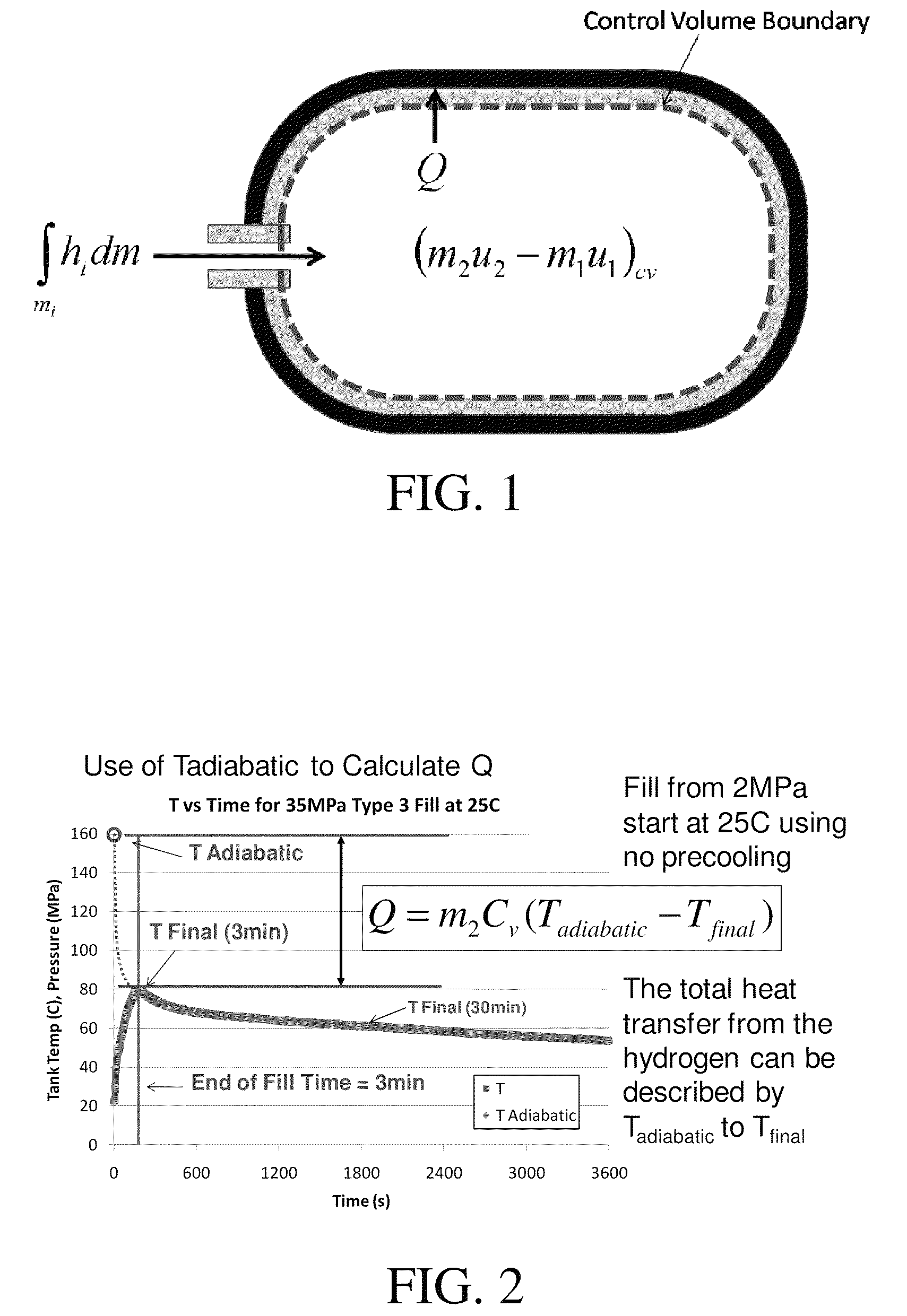
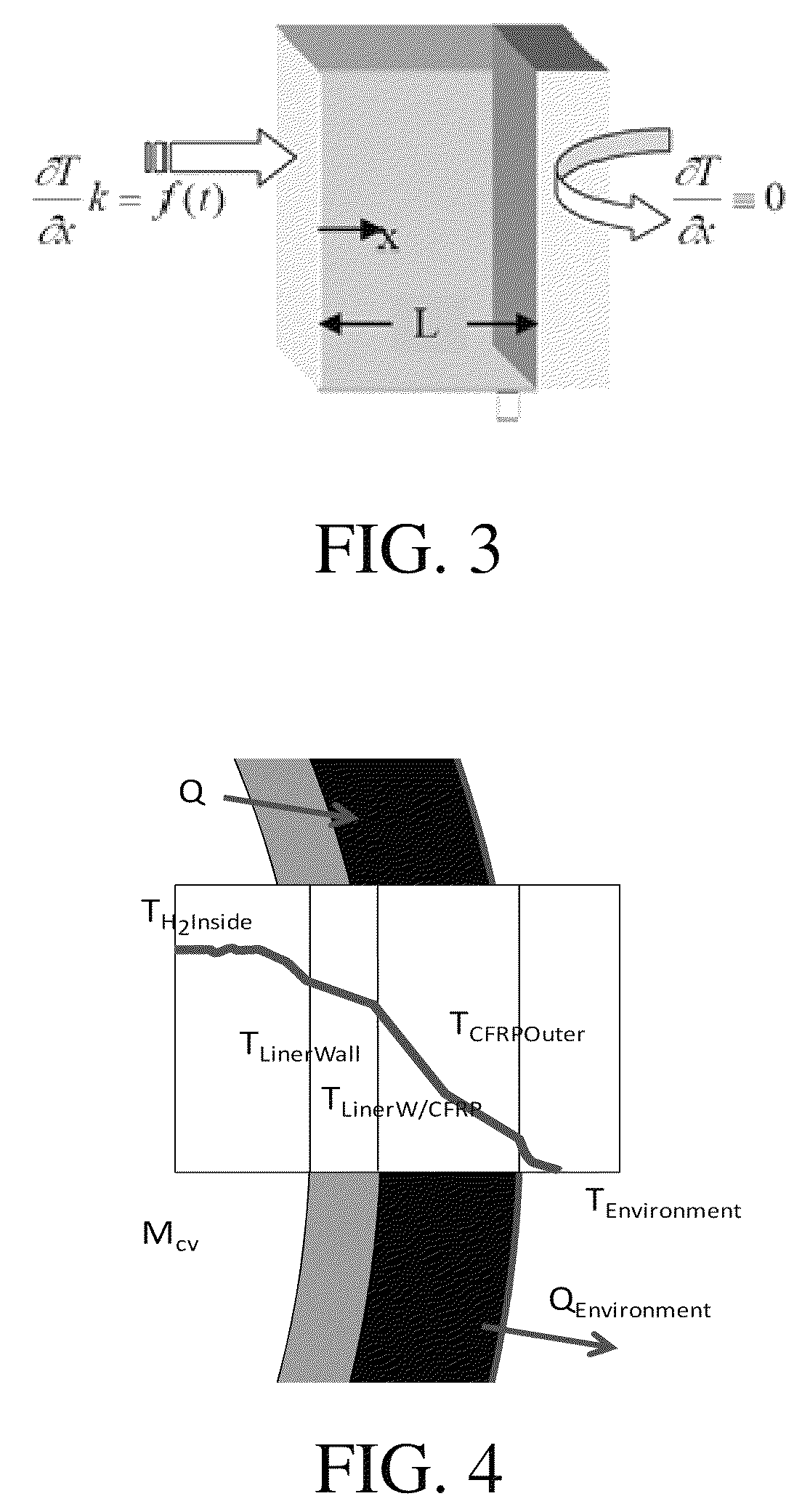
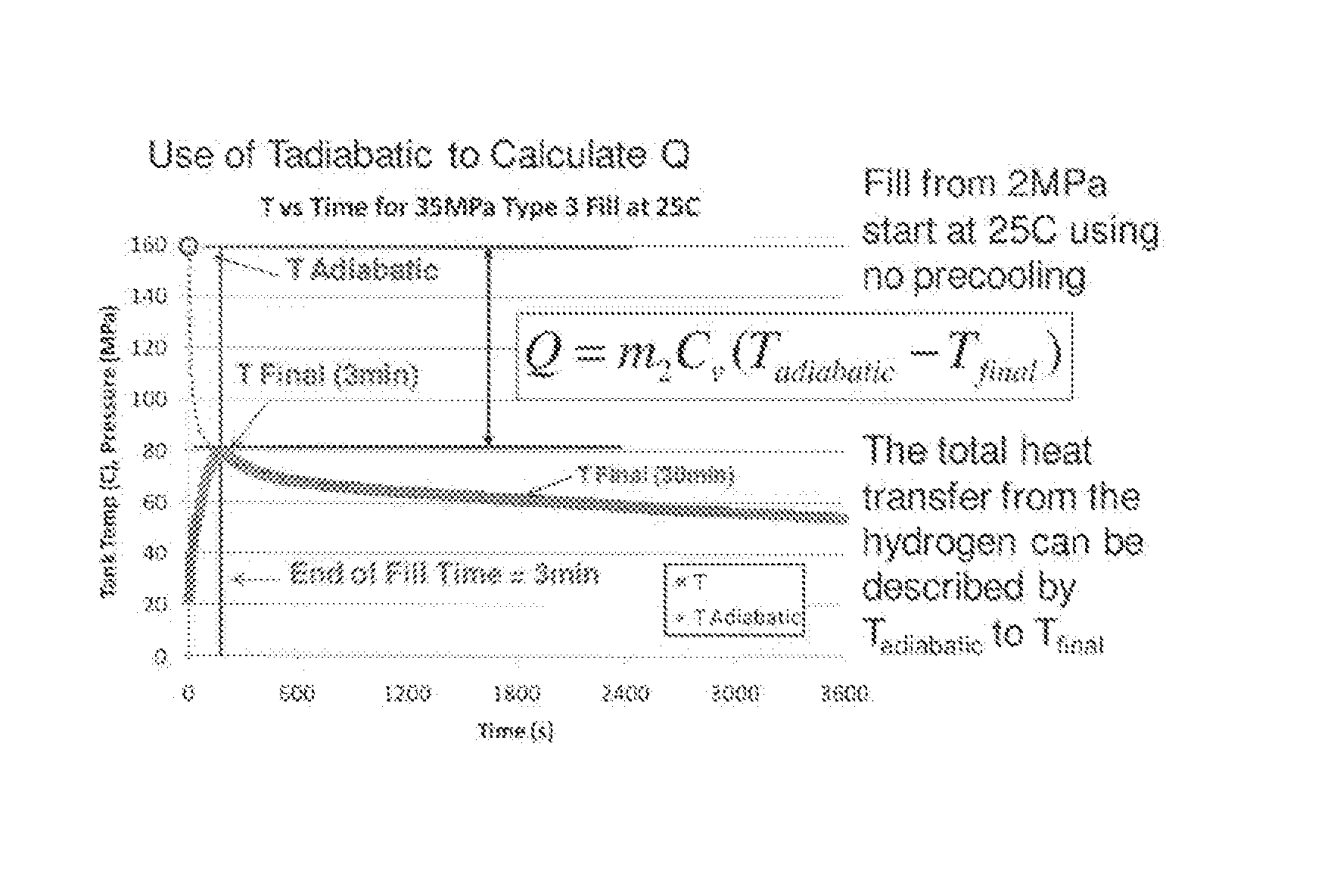
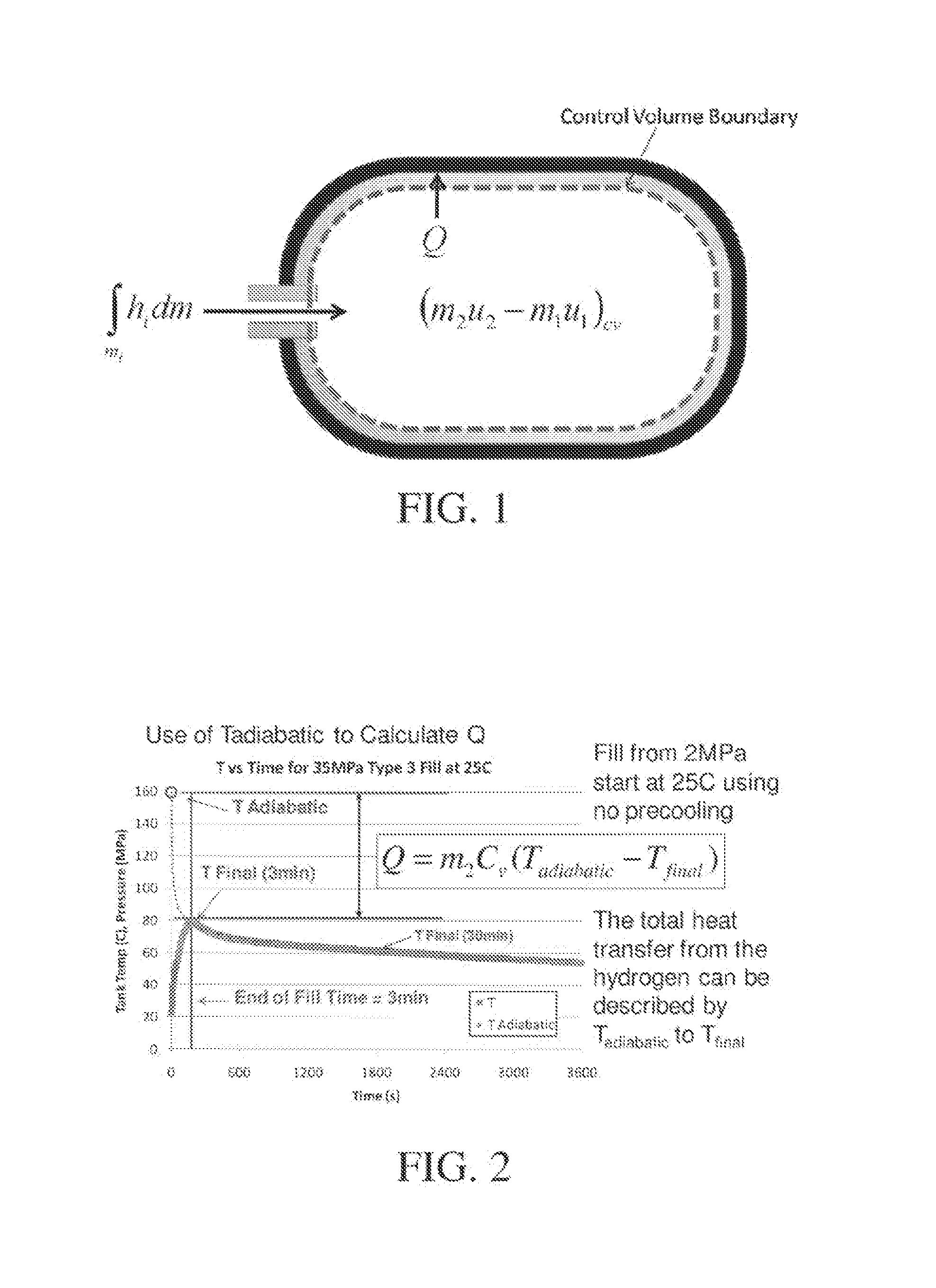
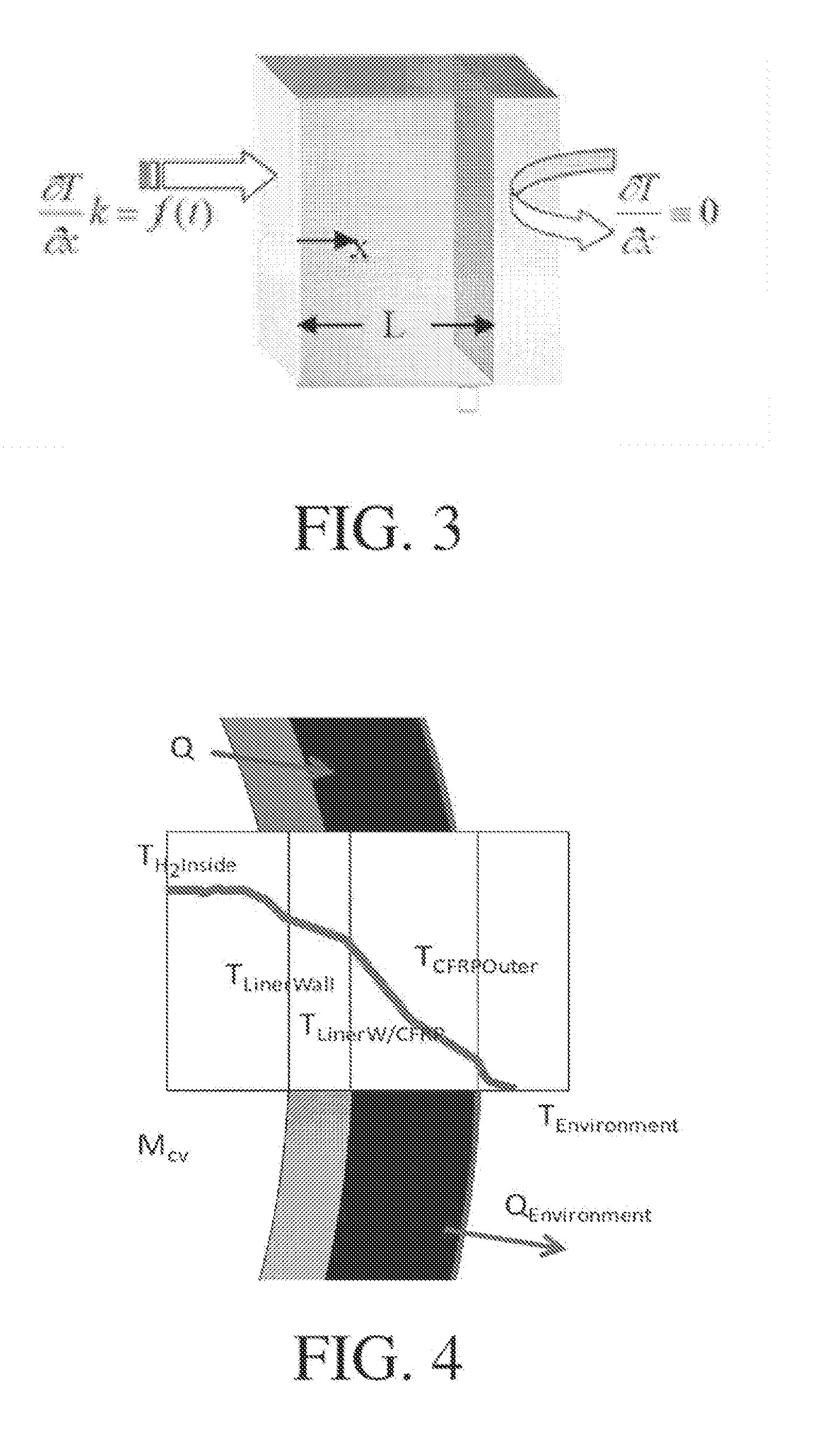
Disclosed is a simple, analytical method that can be utilized by hydrogen filling stations for directly and accurately calculating the end-of-fill temperature in a hydrogen tank that, in turn, allows for improvements in the fill quantity while tending to reduce refueling time. The calculations involve calculation of a composite heat capacity value, MC, from a set of thermodynamic parameters drawn from both the tank system receiving the gas and the station supplying the gas. These thermodynamic parameters are utilized in a series of simple analytical equations to define a multi-step process by which target fill times, final temperatures and final pressures can be determined. The parameters can be communicated to the station directly from the vehicle or retrieved from a database accessible by the station. Because the method is based on direct measurements of actual thermodynamic conditions and quantified thermodynamic behavior, significantly improved tank filling results can be achieved.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Hydrogen station
ActiveUS20140196814A1Easy to controlSuppresses internal temperature riseVessel mounting detailsGas handling applicationsEngineeringHydrogen supply
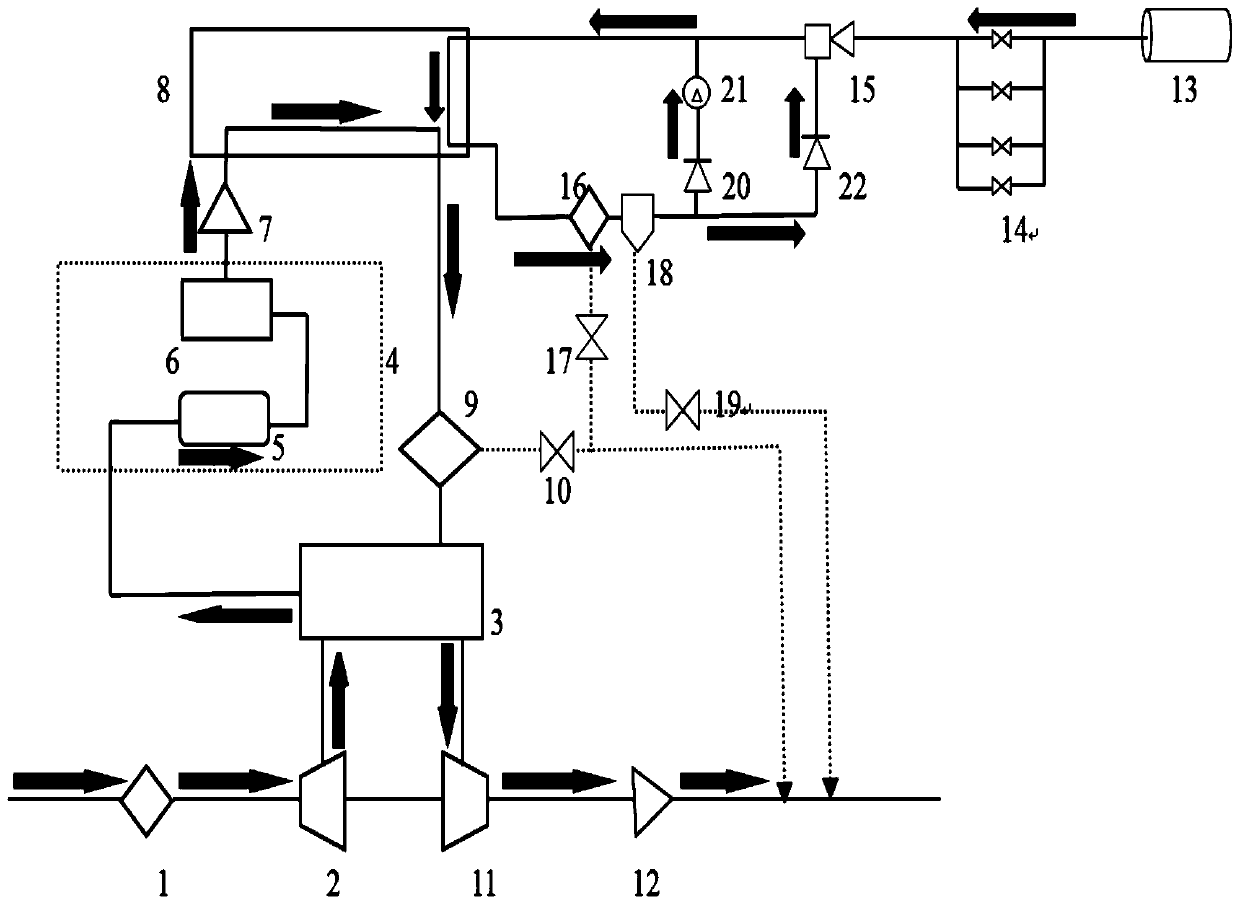
Provided is a hydrogen station that supplies hydrogen to an external hydrogen tank, the hydrogen station including: a reciprocating compressor that is driven by a driver of which revolution is controllable; a cooling device that is capable of cooling hydrogen supplied from the reciprocating compressor to the hydrogen tank; a temperature sensor that detects an internal temperature of the hydrogen tank or a temperature of the hydrogen supplied to the hydrogen tank; and a control unit that controls the revolution of the driver based on the temperature detected by the temperature sensor.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
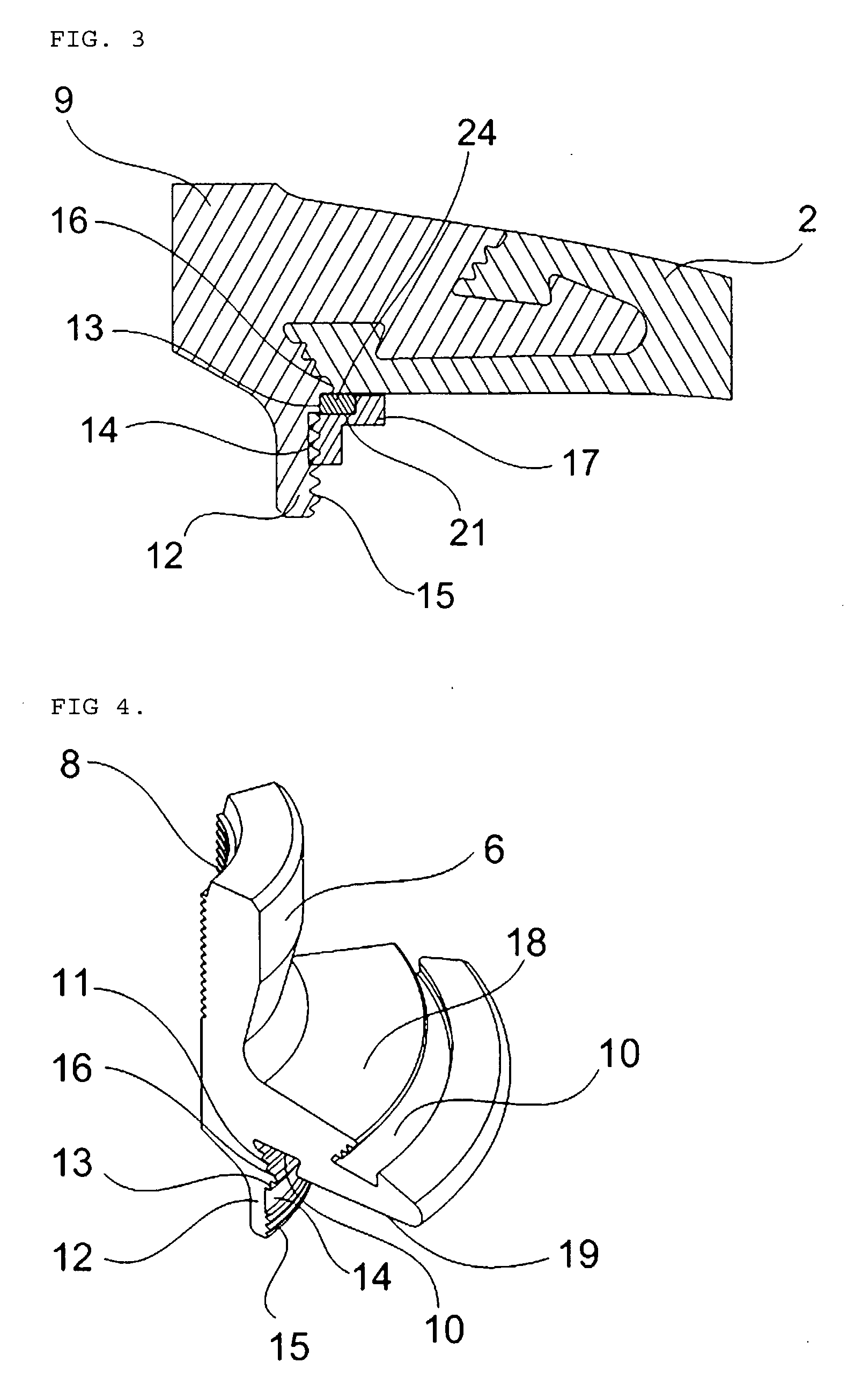
High gas-tightened metallic nozzle-boss for a high pressure composite vessel
InactiveUS20070164561A1Prevent leakageVessel mounting detailsVessel manufacturingFuel cellsFuel tank
The present invention relates to a metal nozzle boss provided with a sealing device, which has highly improved tightness and is combined with a plastic liner of a composite vessel used as a high-pressure vessel. The metal nozzle boss uses an elastic seal ring and a tightening piece in the plastic liner, so that the nozzle boss reliably seals the junction of the nozzle boss and the liner and prevents gas leakage from the vessel. The blade part of the nozzle boss has a dovetail-shaped locking groove, with locking ridges formed in the locking groove. Thus, when the plastic liner is produced by injecting molten resin into the locking groove, the plastic liner is securely combined with the metal nozzle boss. The composite vessel having the metal nozzle boss can be used as a fuel tank for natural gas vehicles or a hydrogen tank for fuel cell vehicles.
Owner:ILJIN COMPOSITES CO LTD
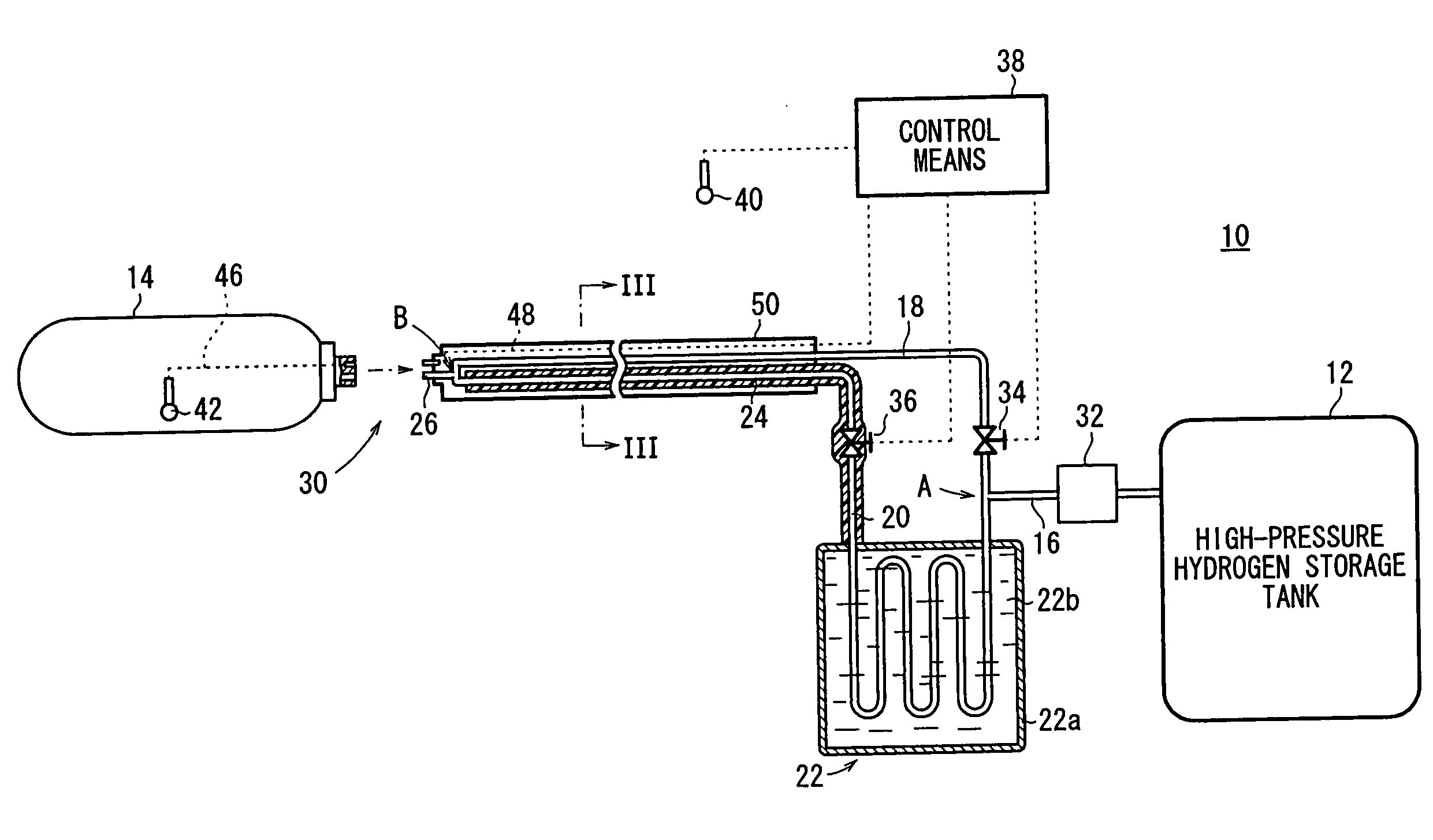
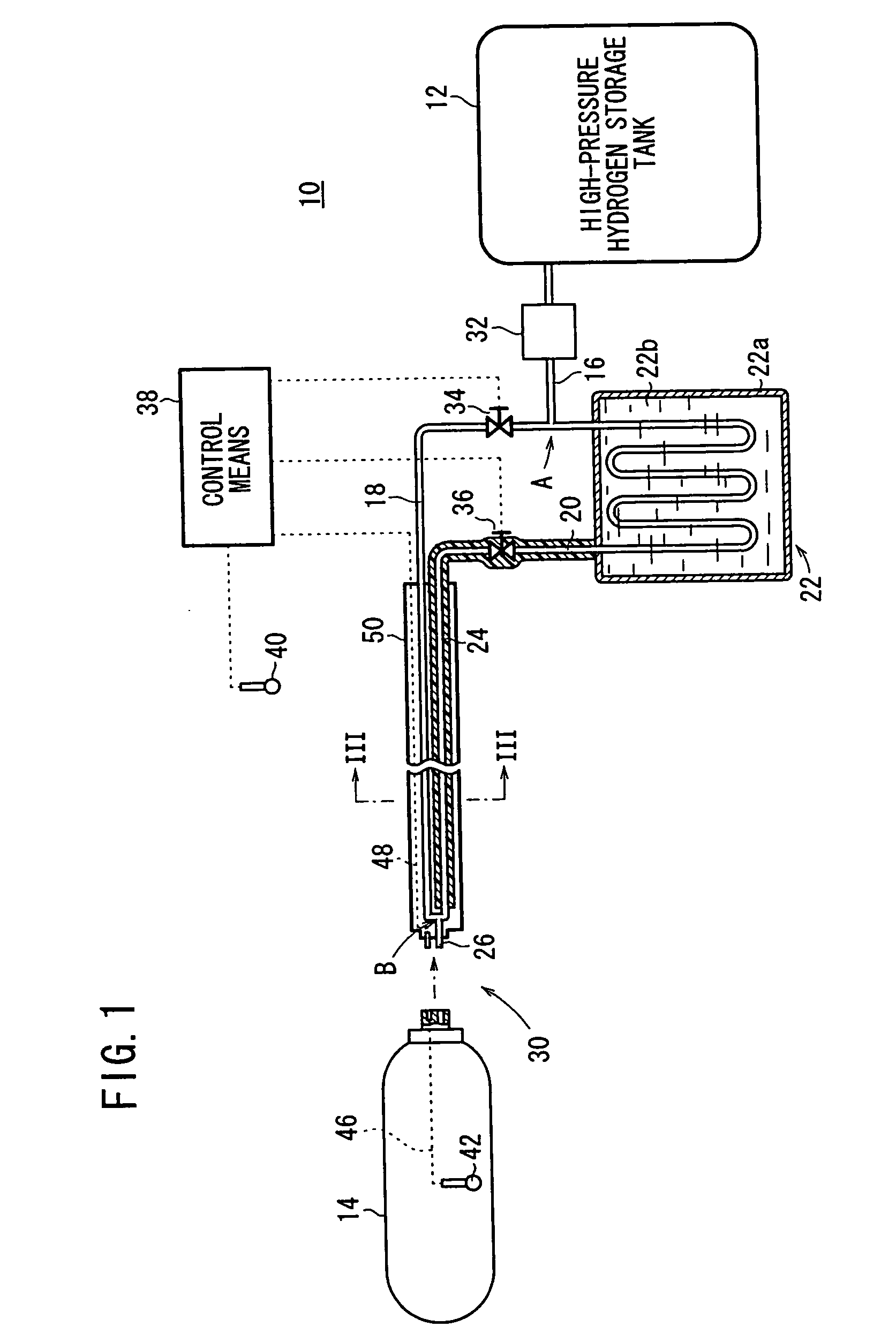
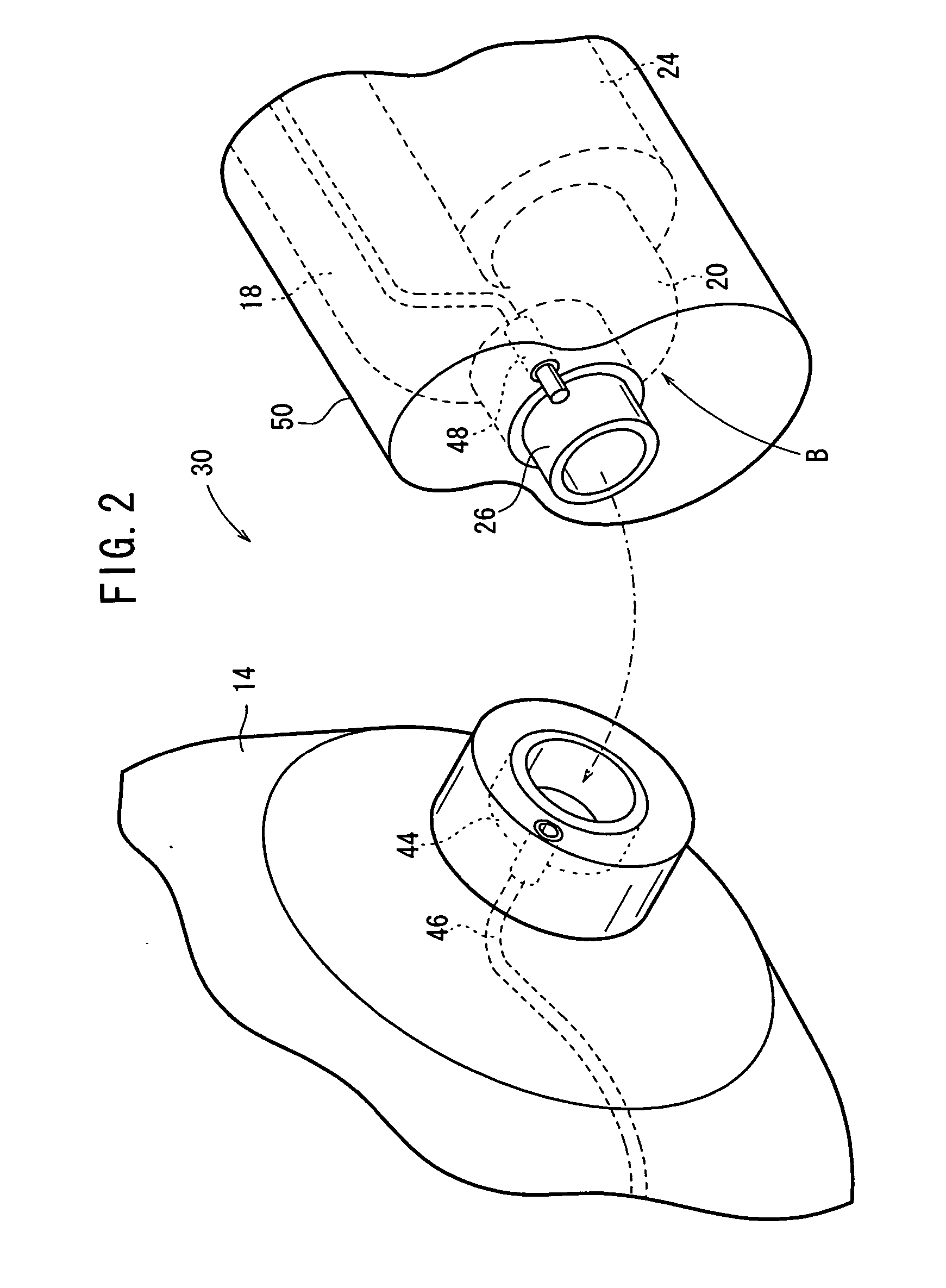
Apparatus for and method of filling hydrogen tank with hydrogen
InactiveUS20070257043A1Fast fillSuppresses temperature changesLarge containersGas handling/storage effectsHigh pressure hydrogenAtmospheric temperature
An hydrogen tank filling apparatus includes a first hydrogen supply pipe for supplying hydrogen substantially at an atmospheric temperature from a high-pressure hydrogen storage tank to a hydrogen tank, a second hydrogen supply pipe for supplying cooled hydrogen from the high-pressure hydrogen storage tank to the hydrogen tank, and an internal tank temperature measuring unit for measuring the temperature inside the hydrogen tank. The first hydrogen supply pipe and the second hydrogen supply pipe are selectively switched by a control unit, depending on changes in the temperature inside the hydrogen tank.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Gas tank
ActiveUS20110180551A1Reduce gas pressureIncrease gas pressureDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringProduct gas
There is provided a gas tank that suppresses an increase in pressure of a gas filled therein. A hydrogen tank comprises a tank main body filled with hydrogen, a thermofoamable heat-insulating layer provided on the external surface of the tank main body, a relief valve which is provided at the left end of the tank main body and which reduces the pressure in the tank main body by releasing the hydrogen in the tank main body, and a liner which extends from the relief valve toward the right end and which detects an increase in temperature. The relief valve is thermally connected to the liner, and is actuated based on heat transferred from the liner in order to release the hydrogen in the tank main body, thereby reducing the pressure in the tank main body.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
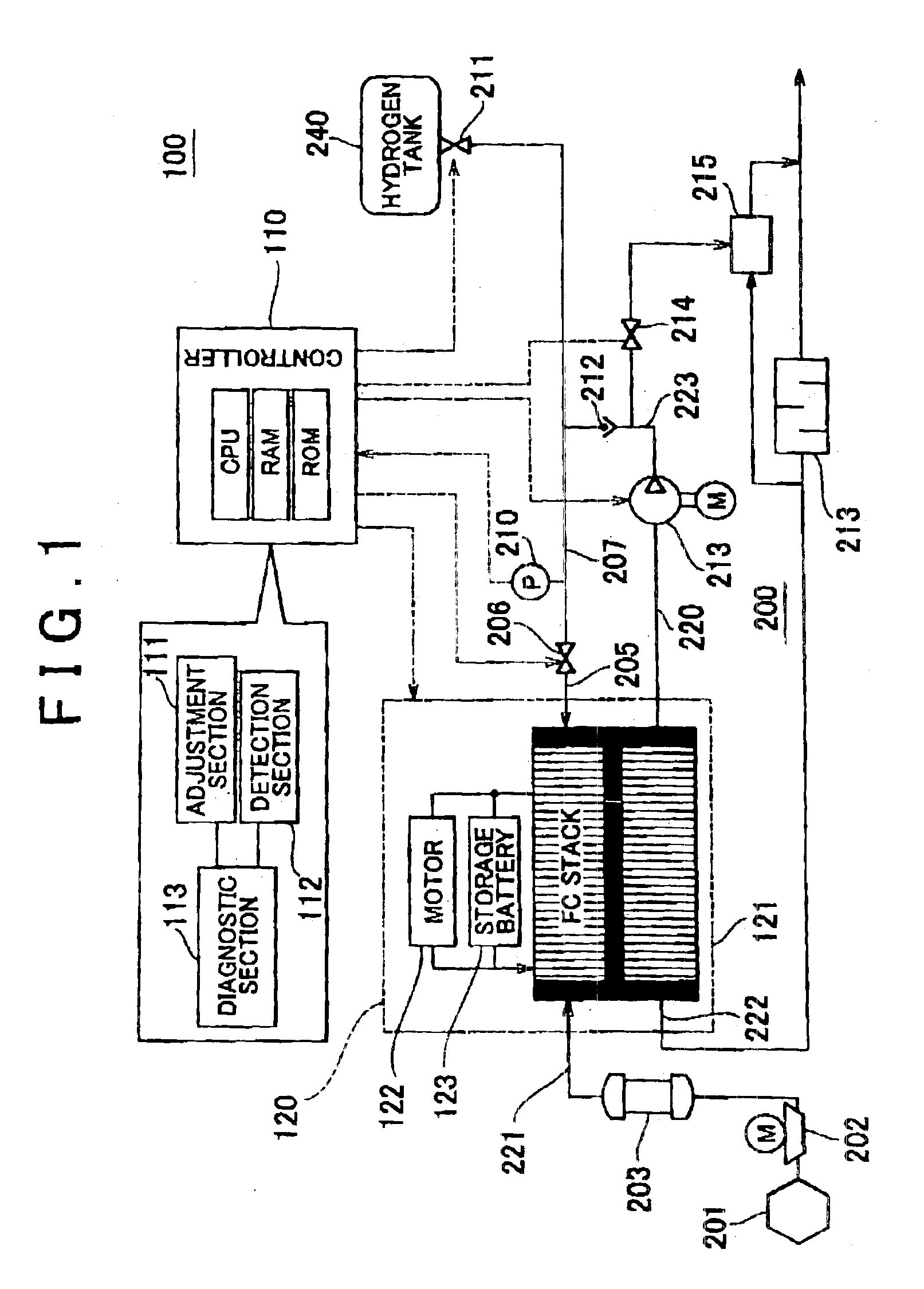
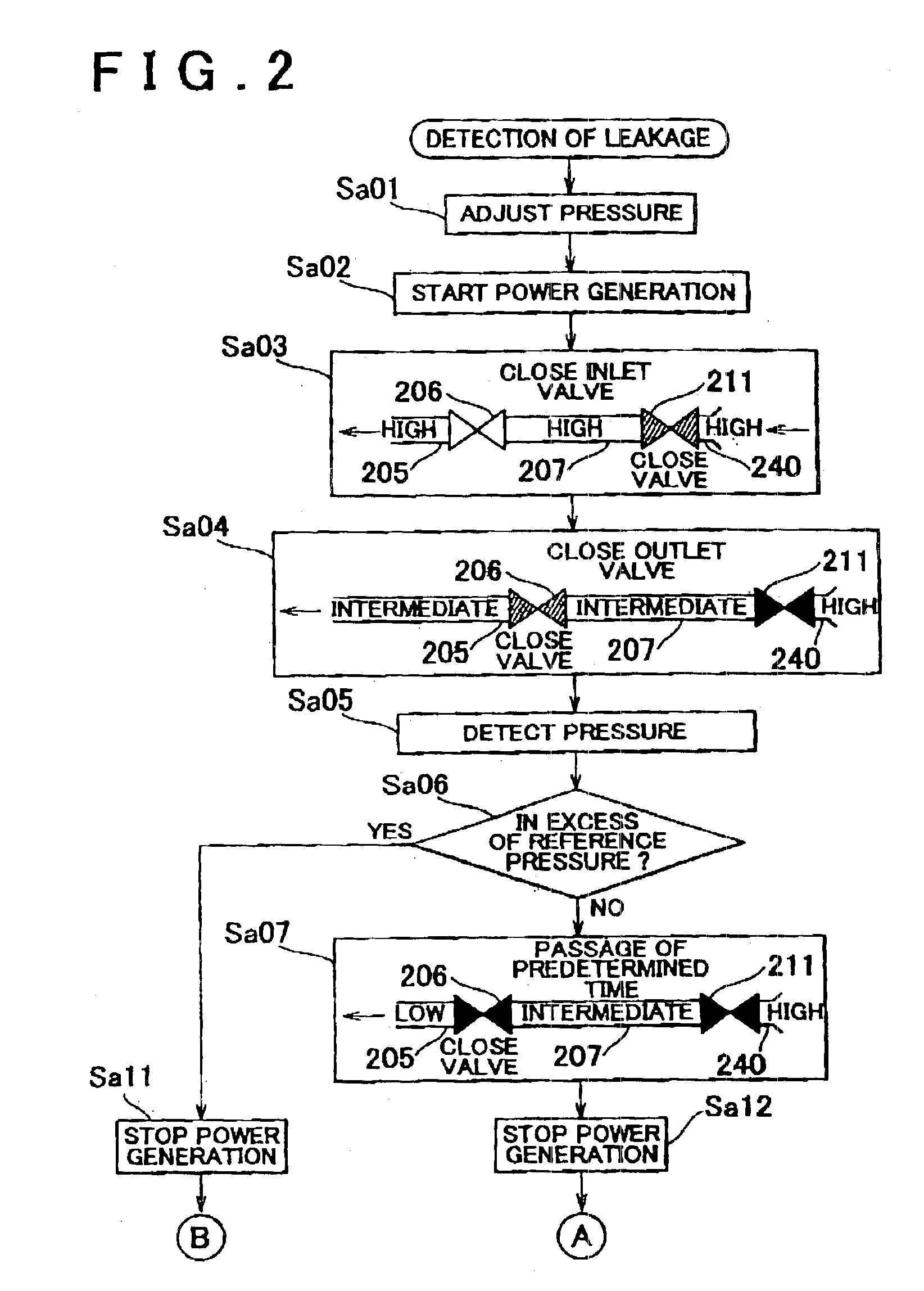
Fluid leakage detection apparatus and fluid leakage detection method
ActiveUS6851298B2Detects leakageEnsure correct executionDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateInlet valveEngineering
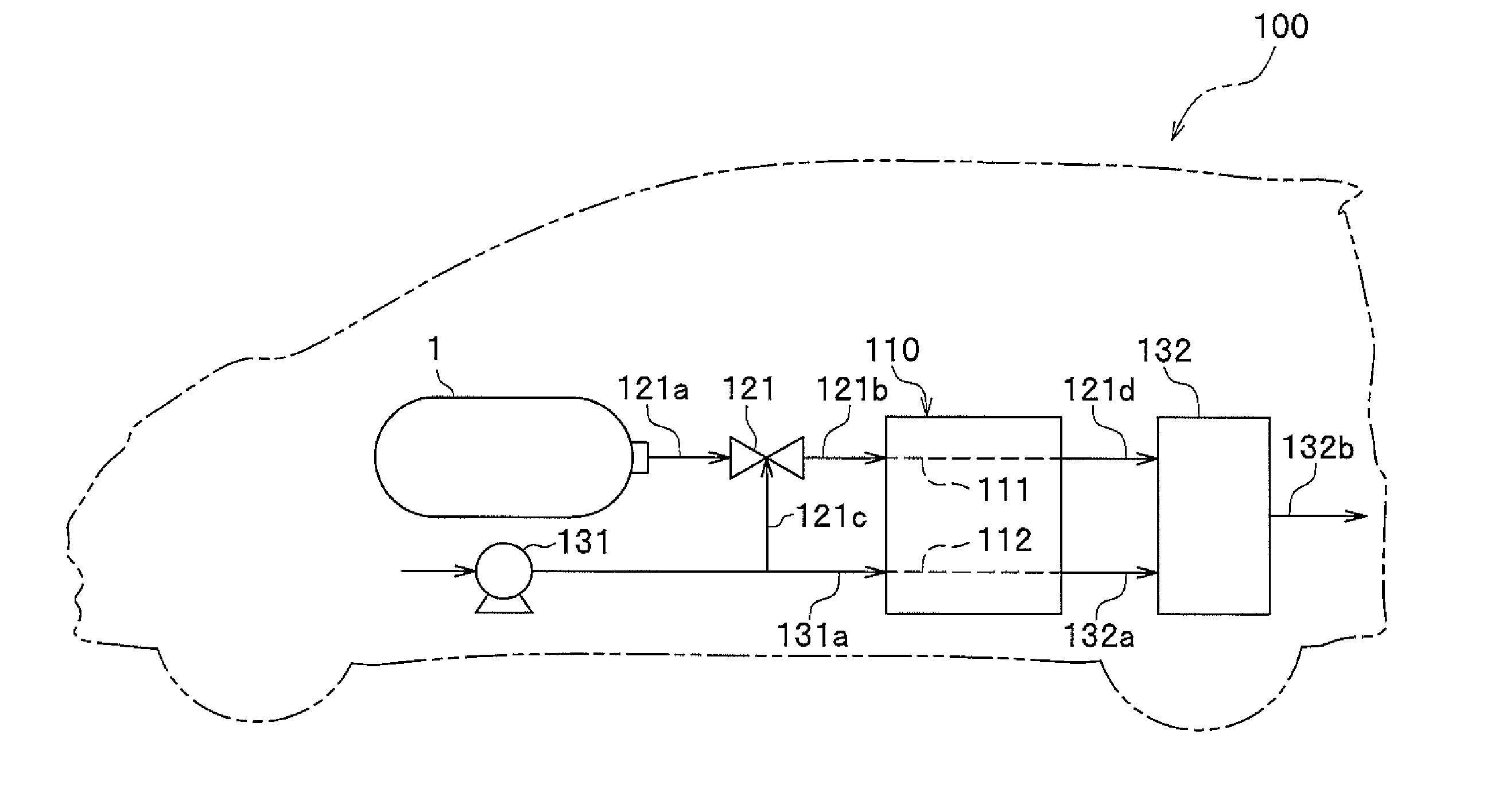
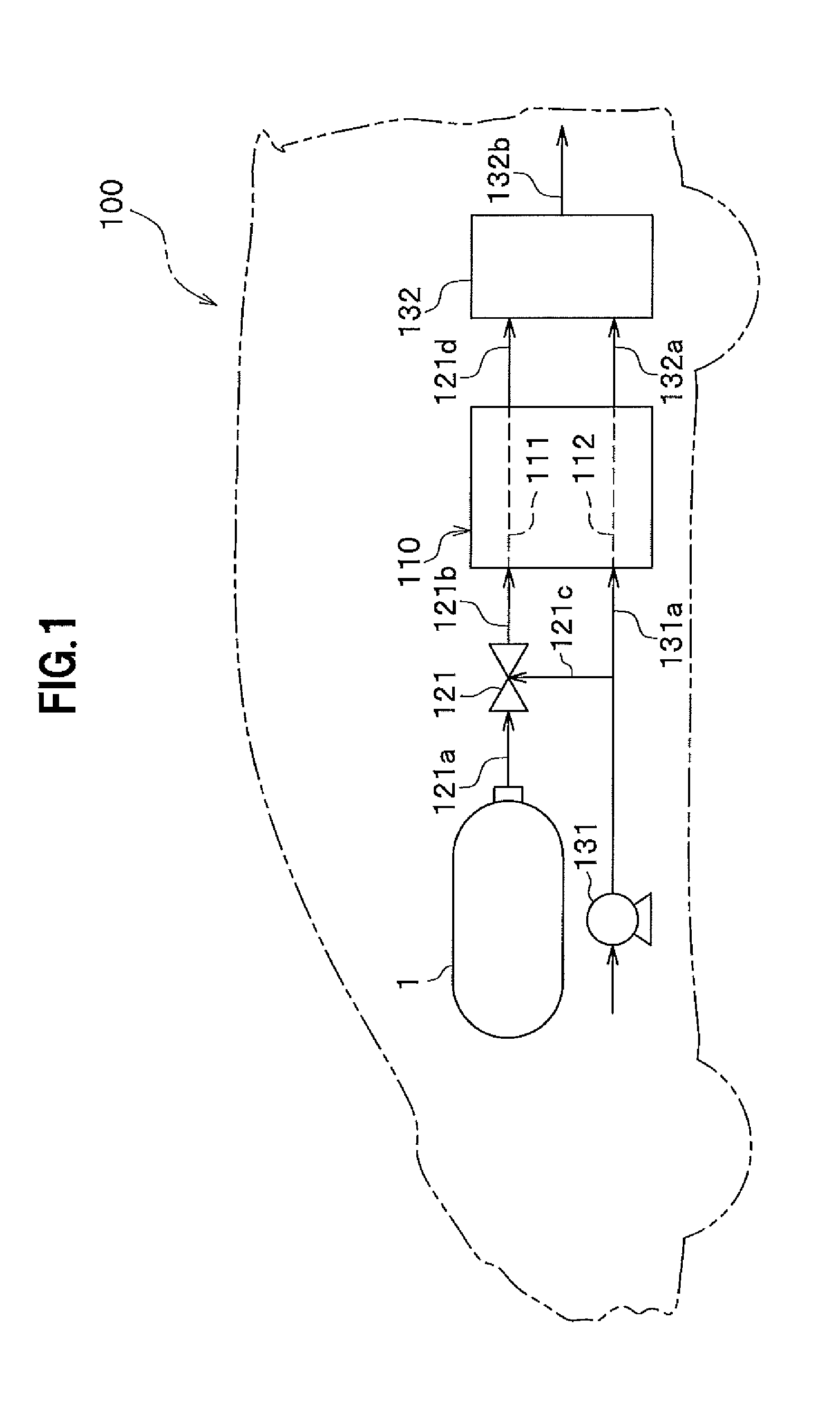
In a fluid leakage detection apparatus, hydrogen is supplied from a hydrogen tank to an FC stack of a fuel cell via first and second pipes. An inlet valve is provided between the hydrogen tank and the first pipe, and an outlet valve is provided between the first pipe and the second pipe. A controller serves to control valve opening a valve closing operation of the inlet and outlet valves, respectively. Those valves are closed in a state where the pressure within the hydrogen tank is made lower than the pressure within the first pipe, and the pressure within the second pipe is made lower than the pressure within the first pipe by operating those valves. Thereafter, the increase or decrease in the pressure within the first pipe is detected by a pressure gauge such that the leakage in the inlet valve or the outlet valve is determined. This makes it possible to detect the leakage both in the inlet valve and the outlet valve at the same time.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
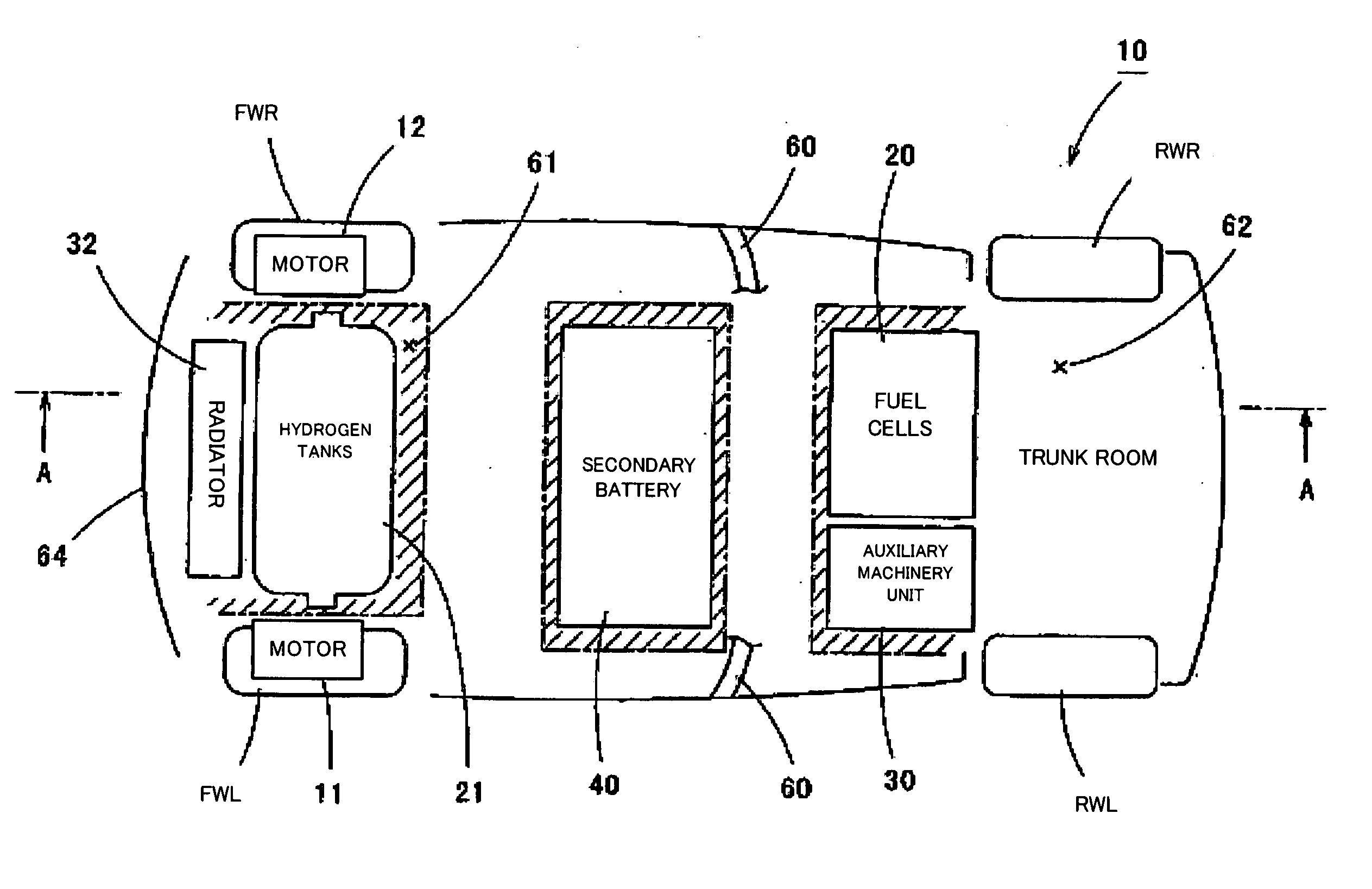
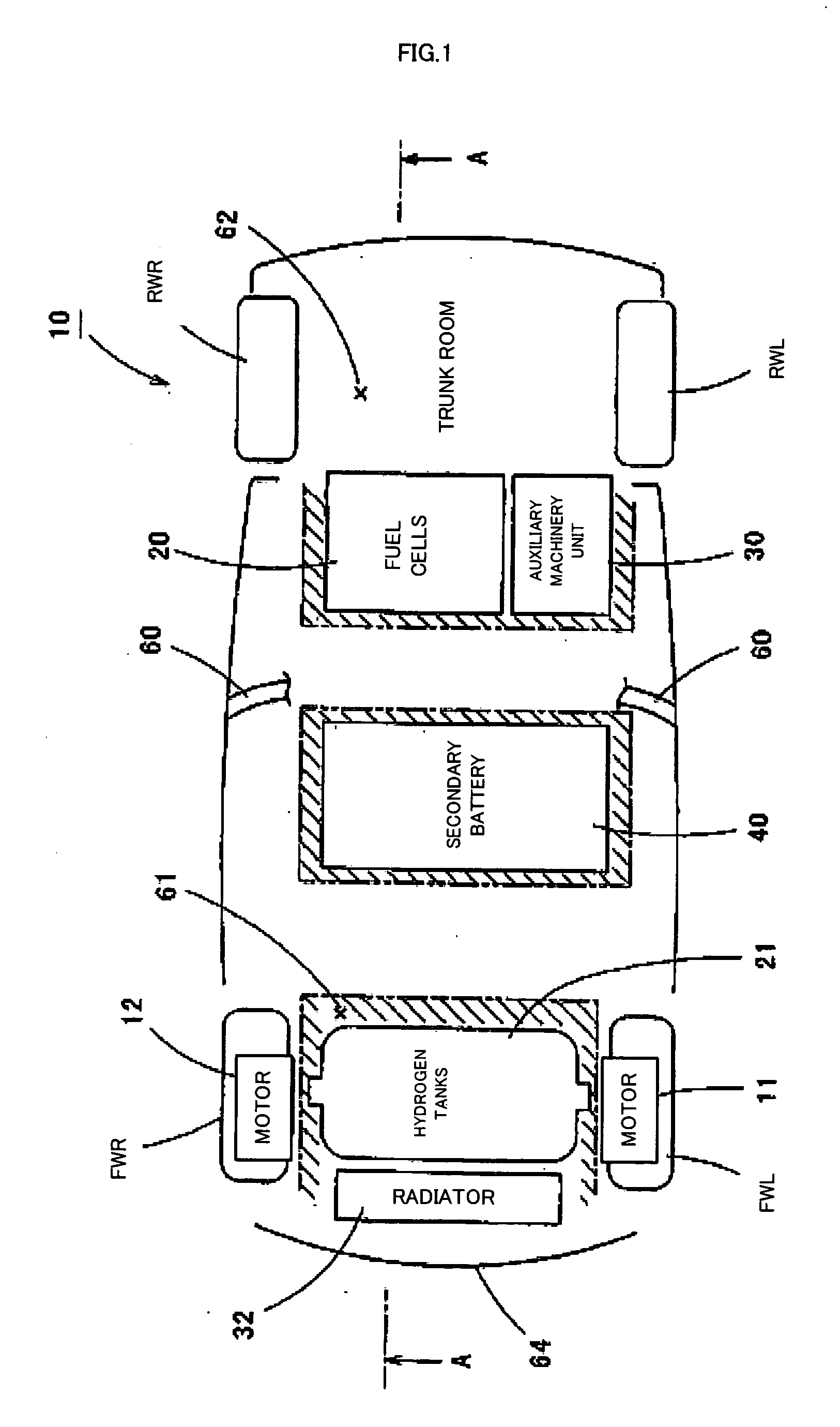
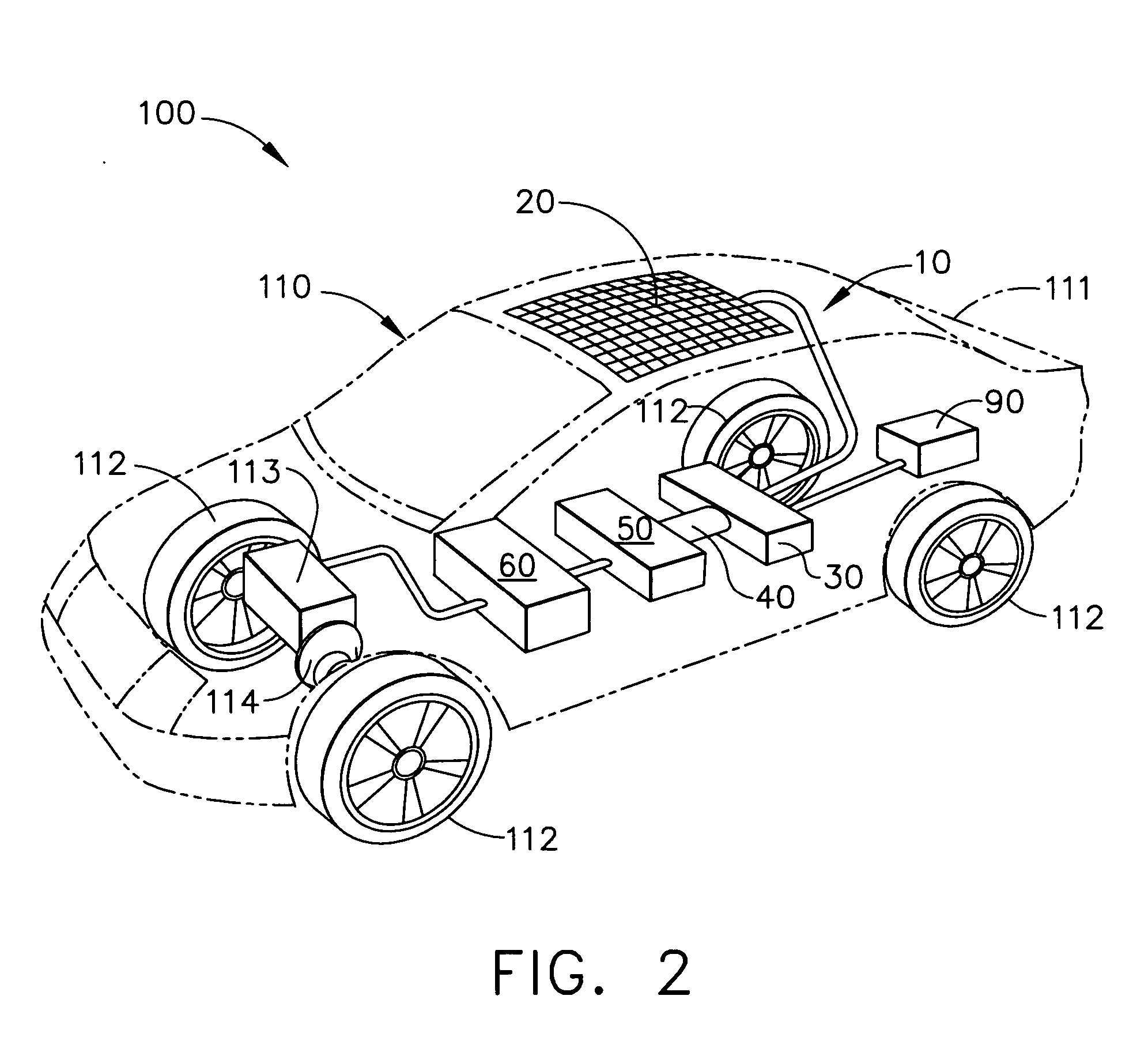
Motor vehicle
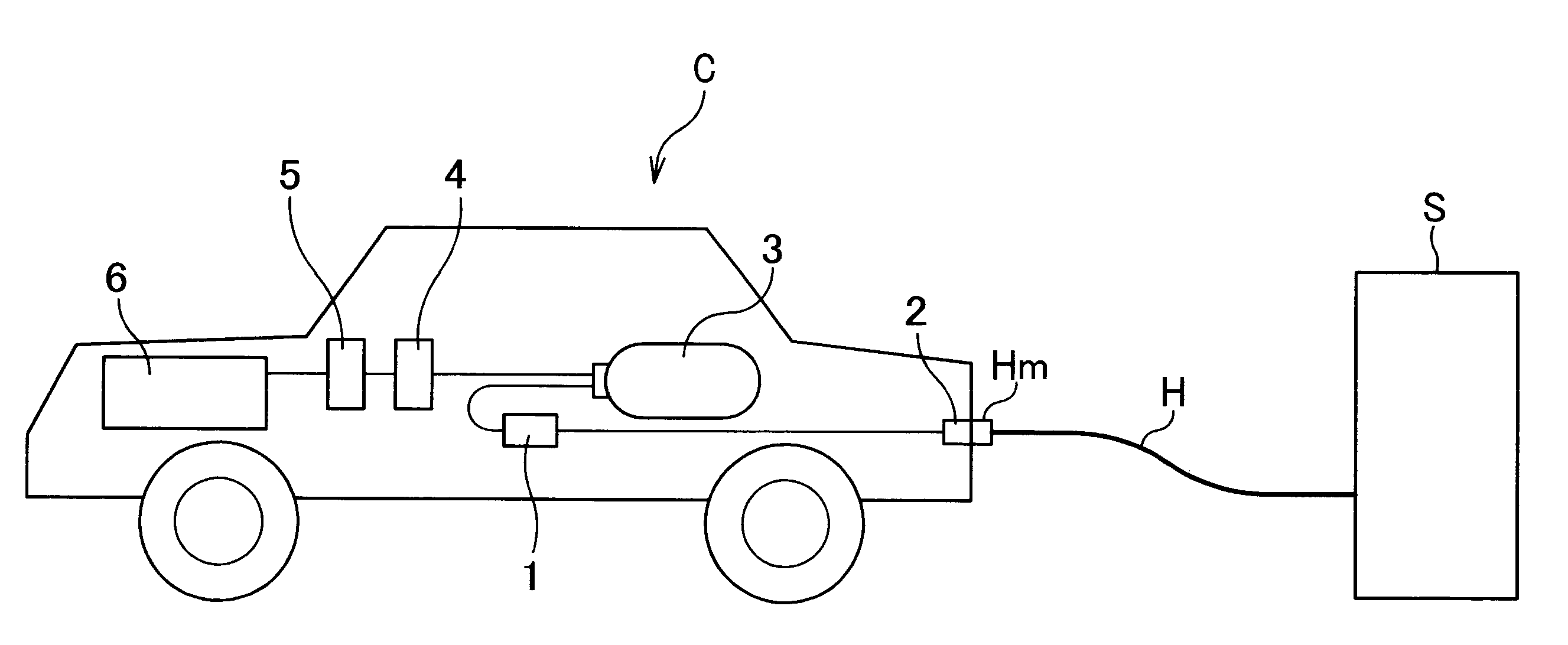
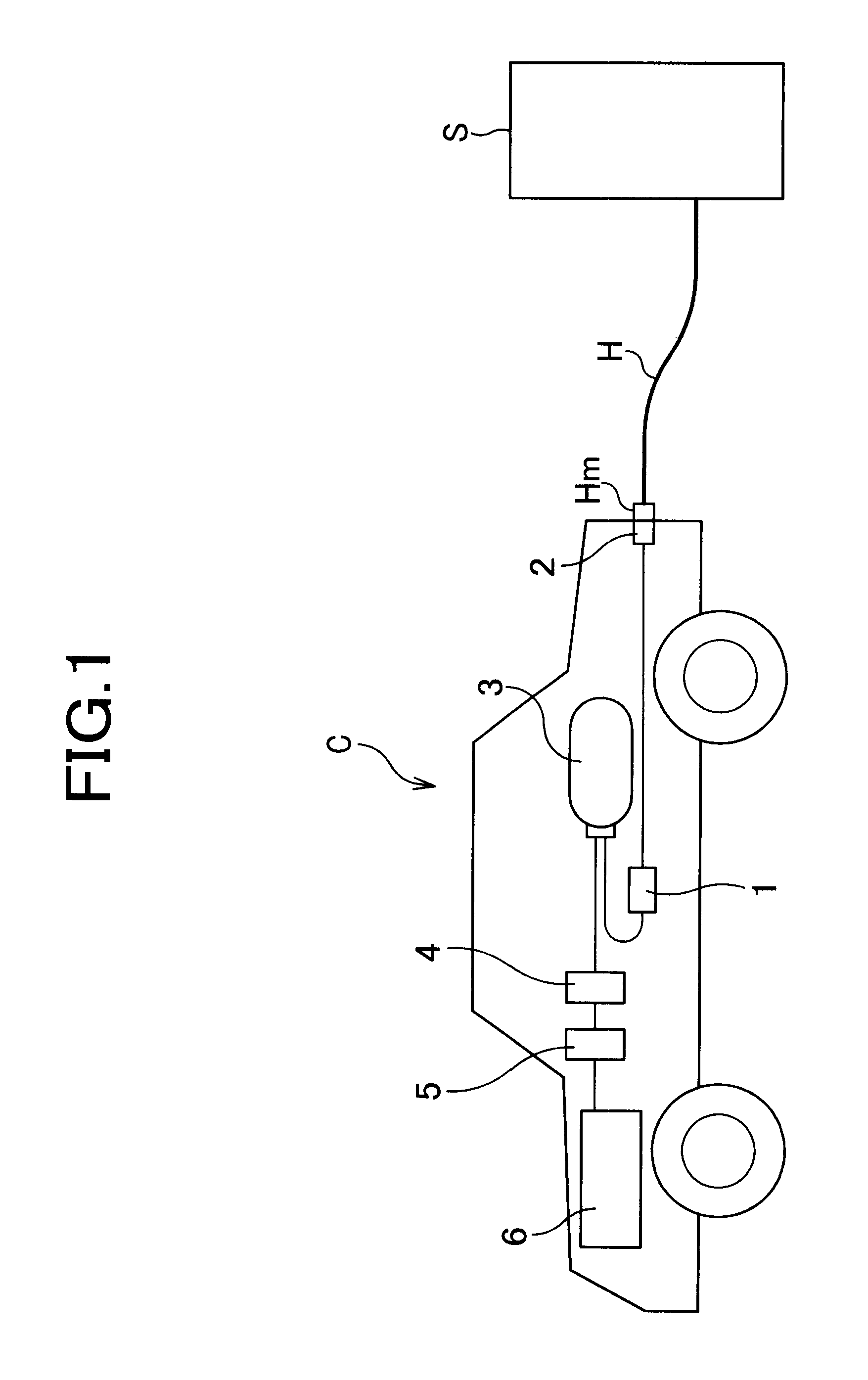
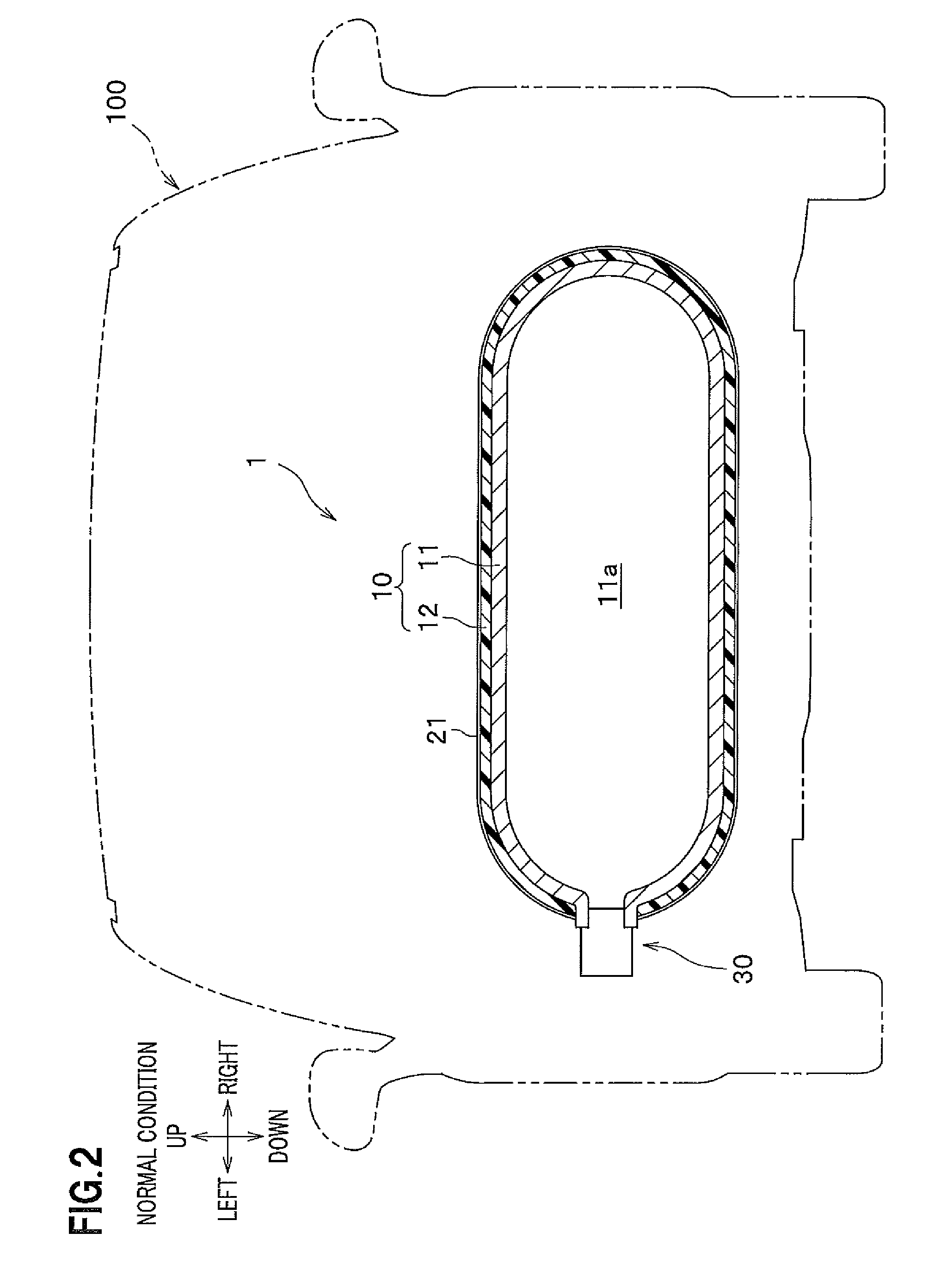
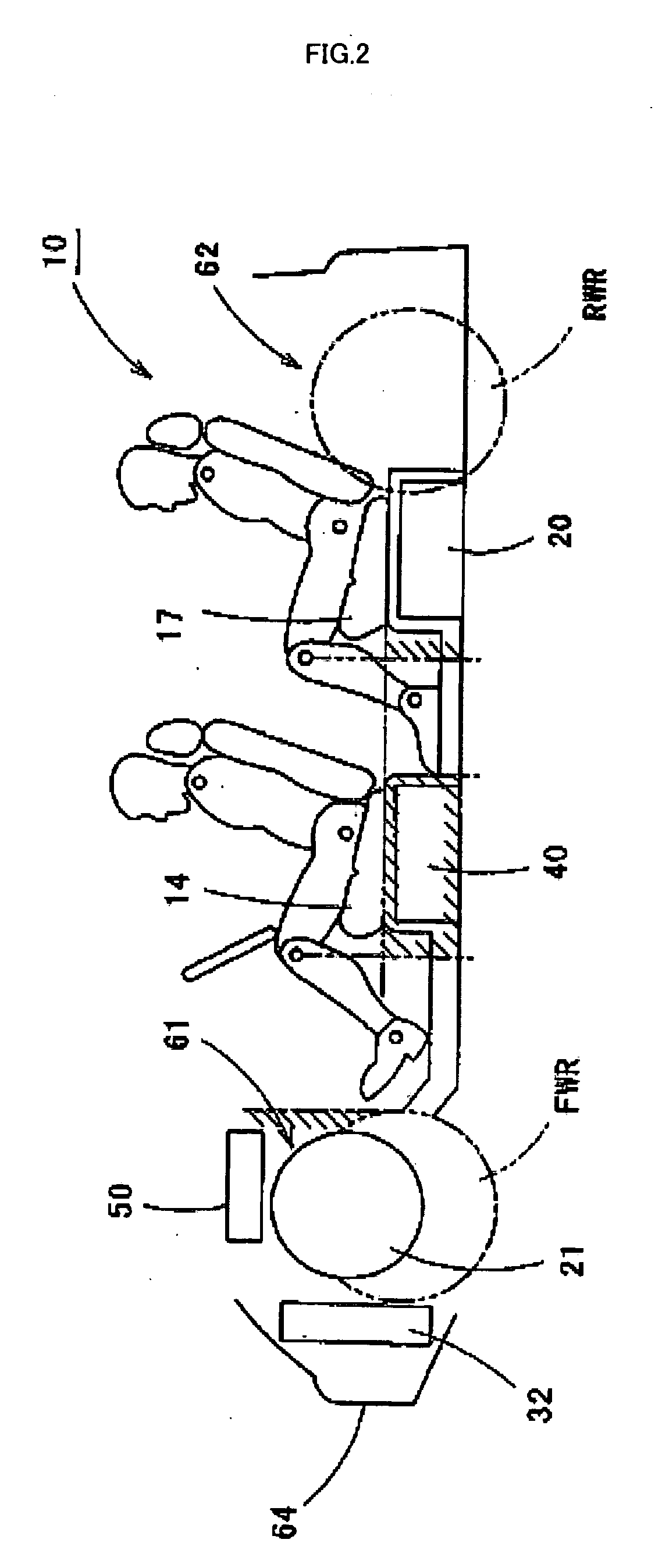
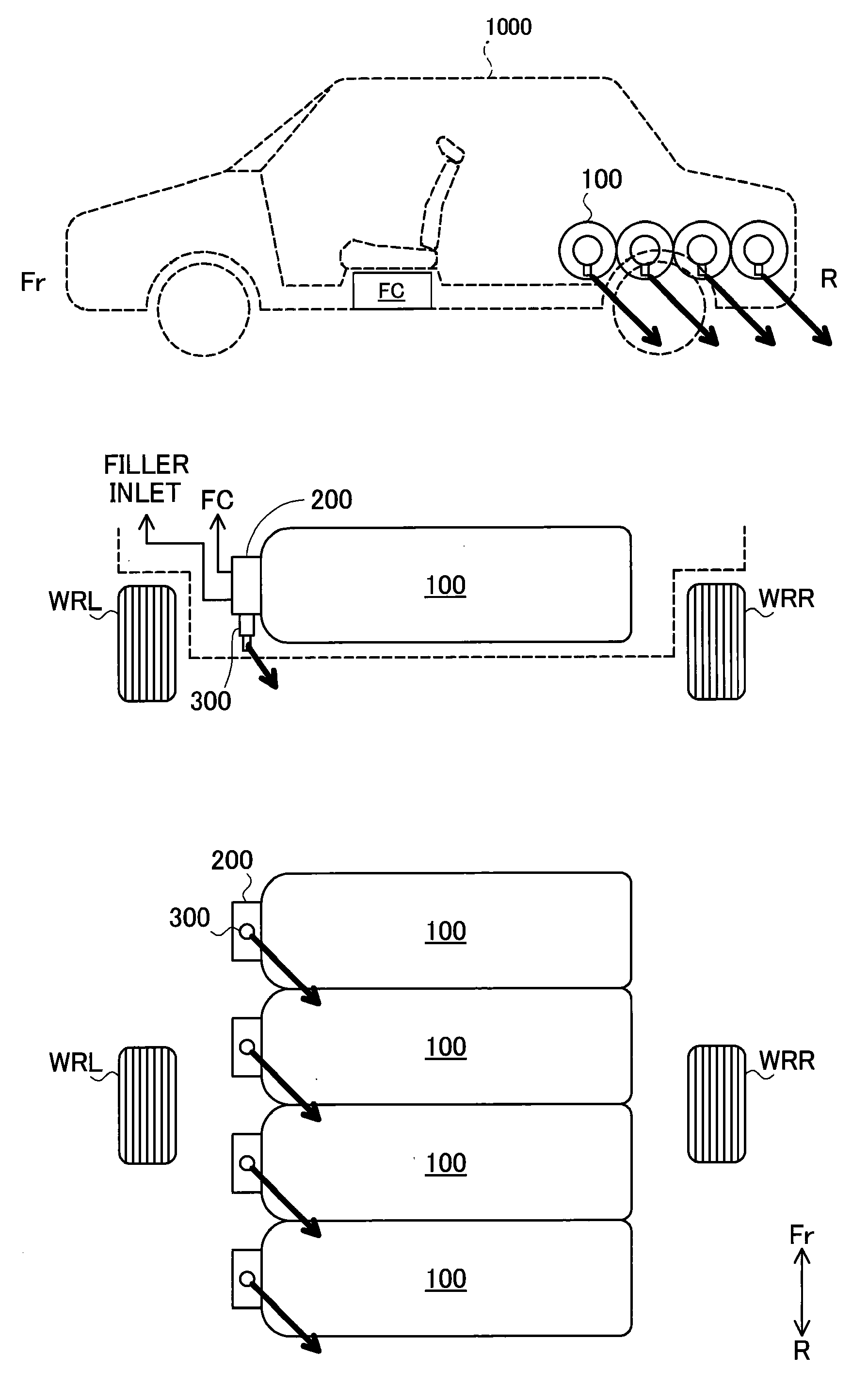
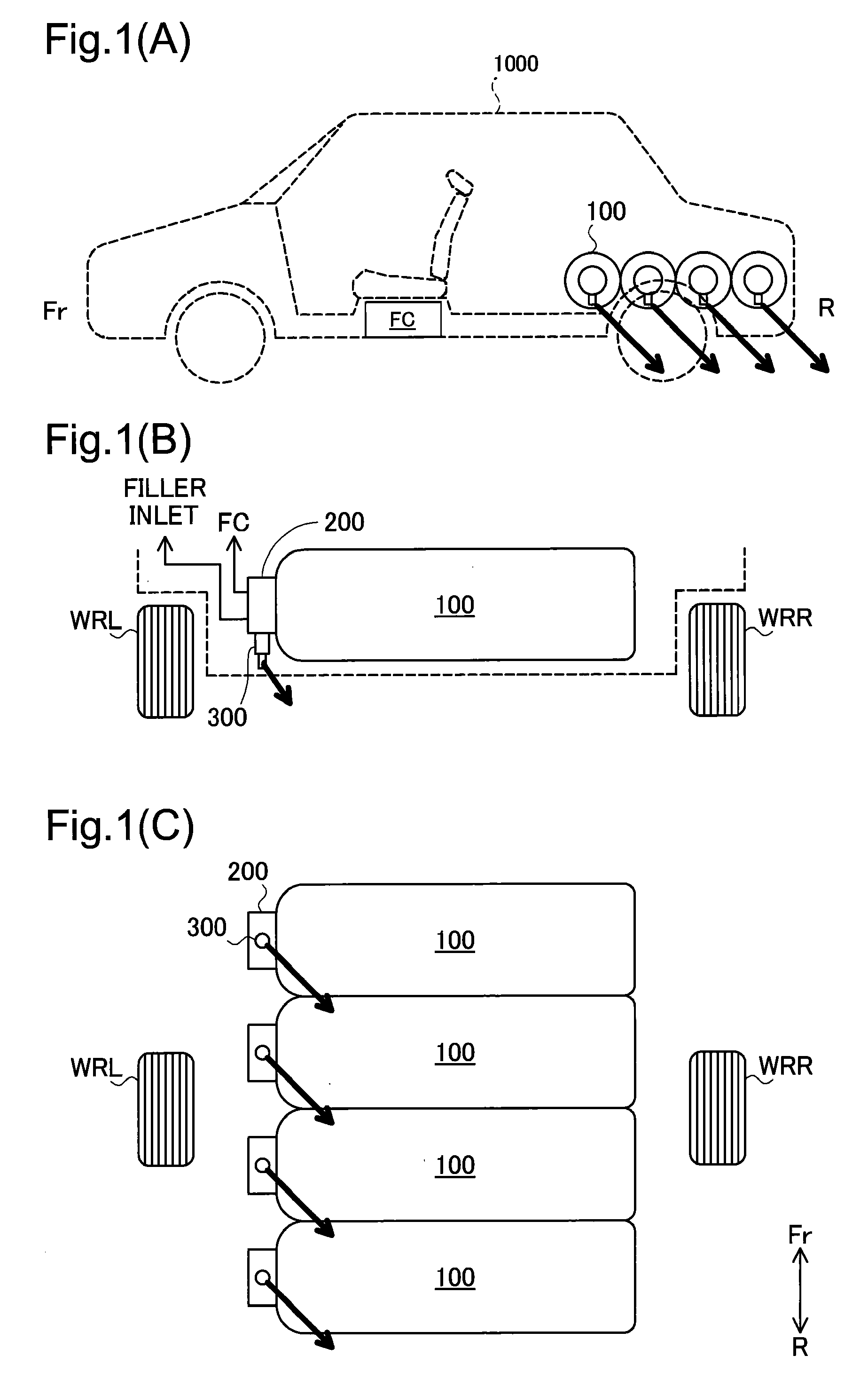
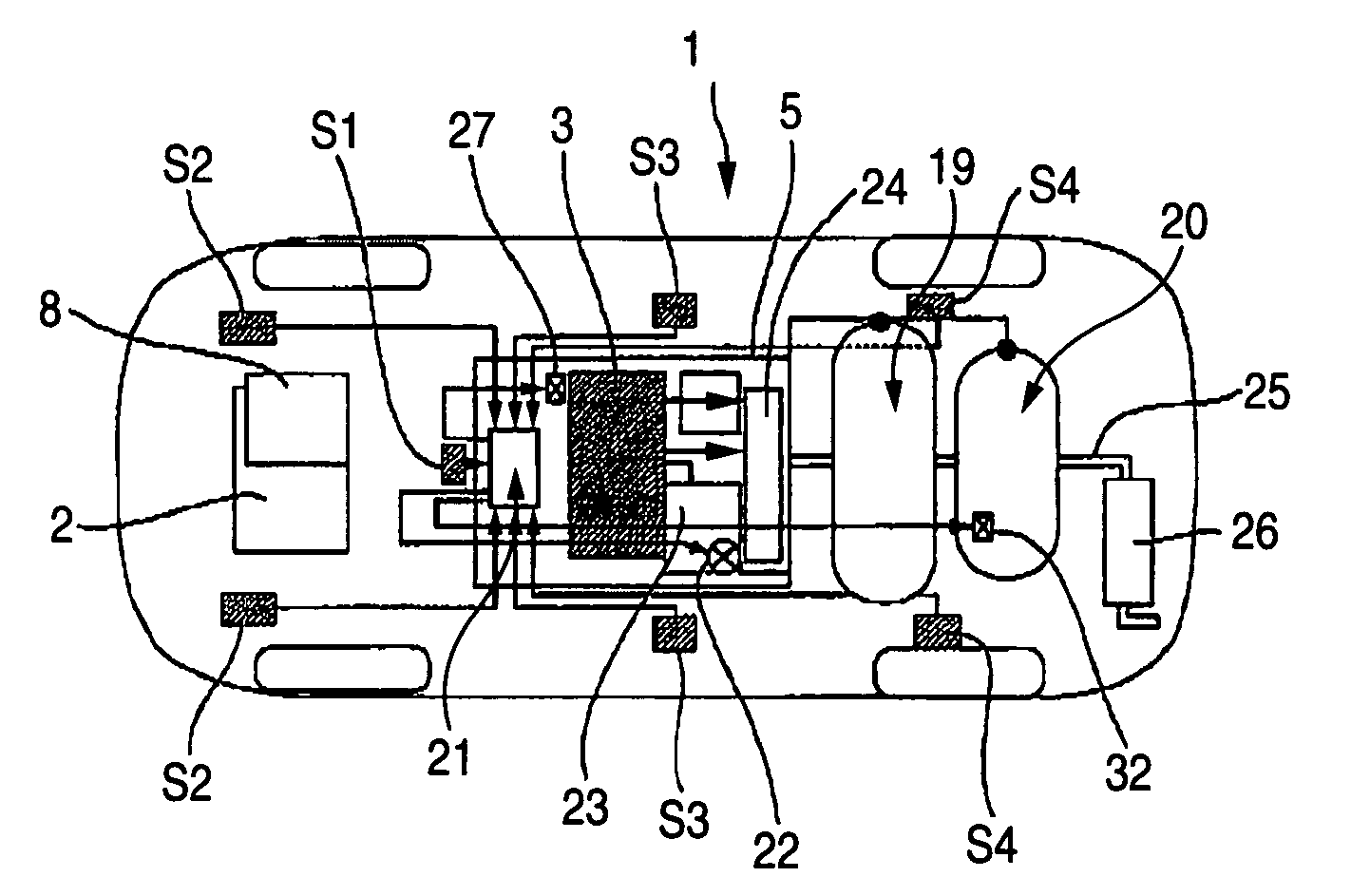
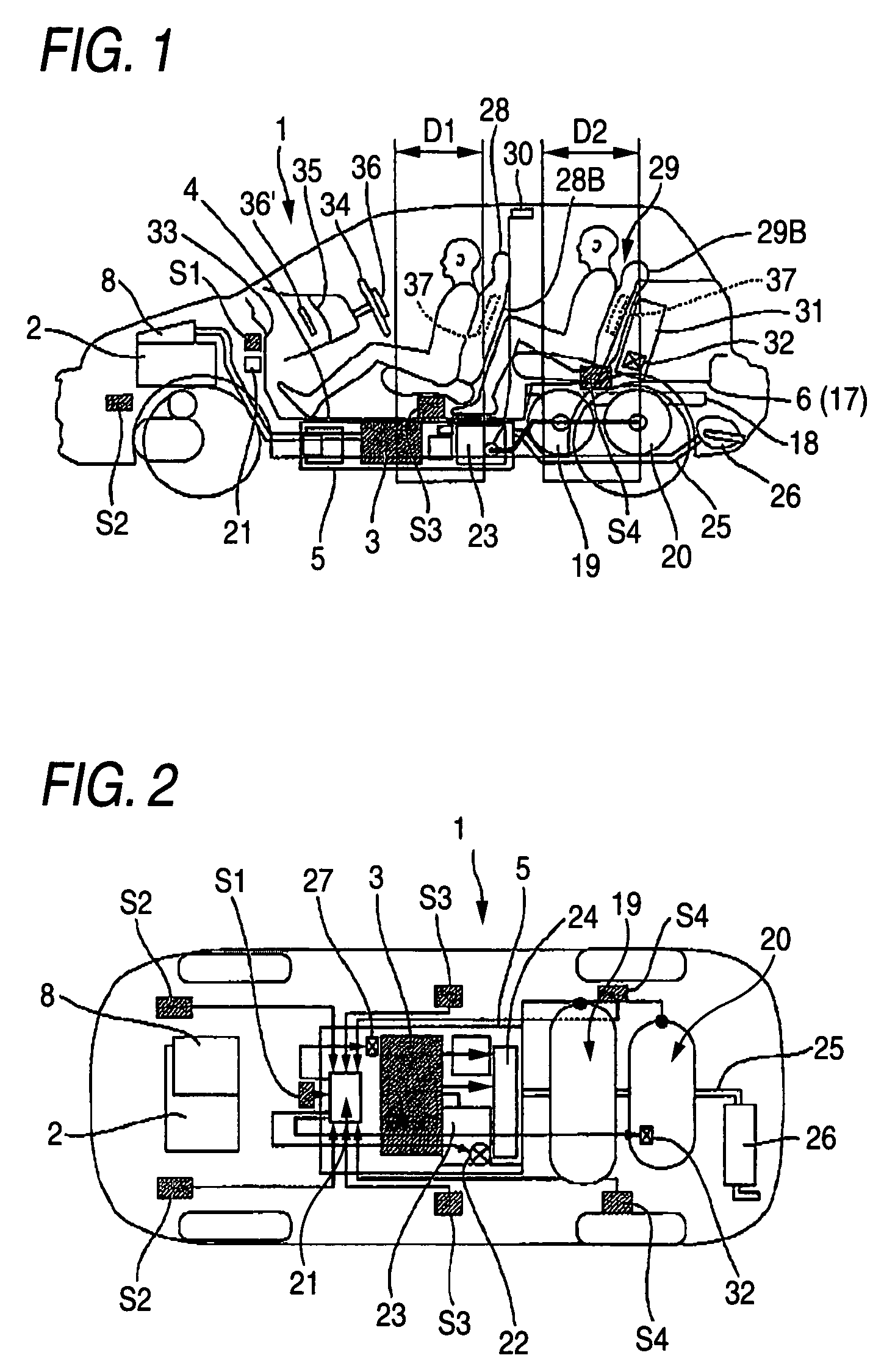
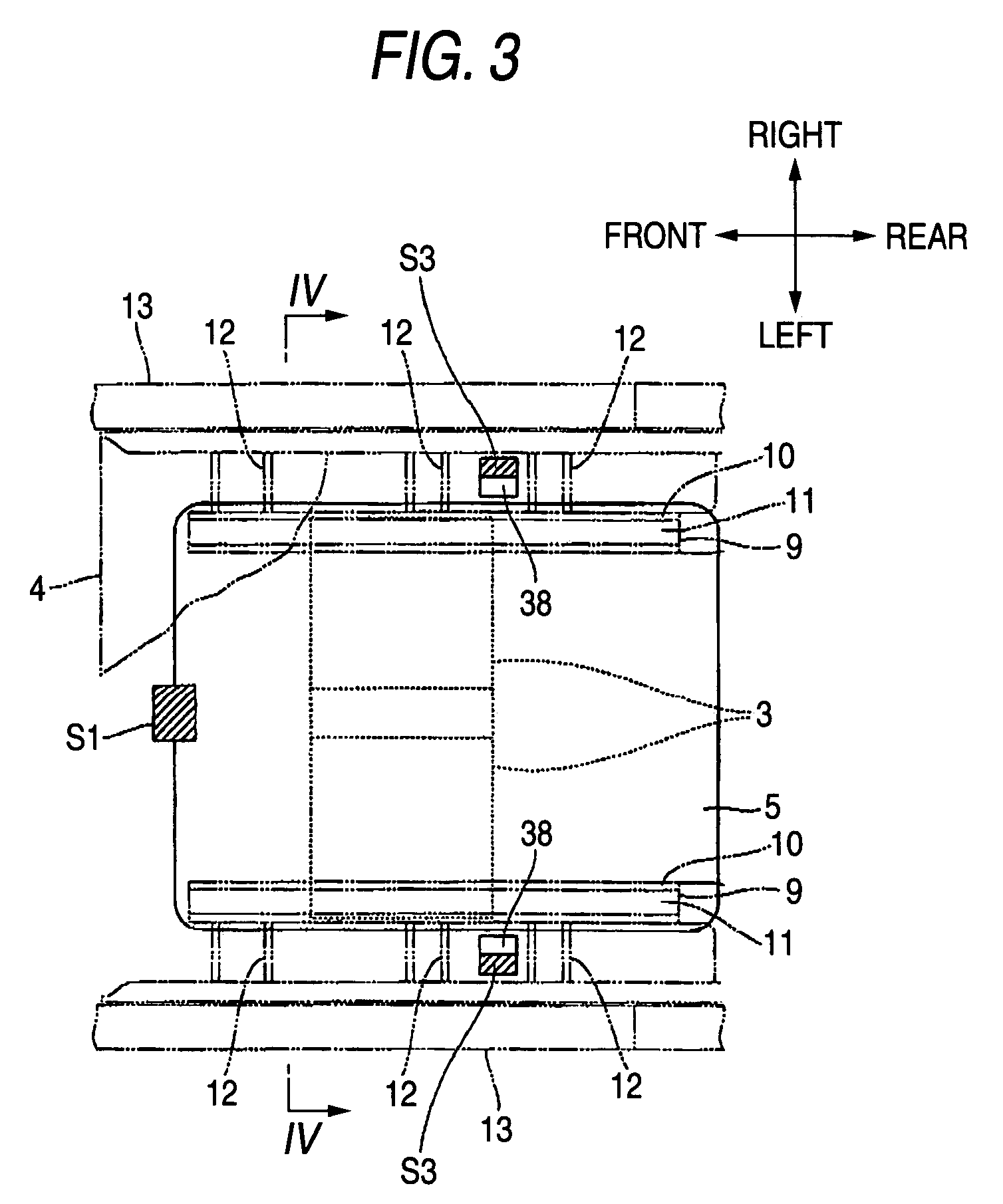
InactiveUS20050224265A1Improve load balancingSolve the lack of spaceTank vehiclesLarge containersMobile vehicleMotor vehicle part
Hydrogen tanks 21 are located in the vicinity of a front axle of a left front wheel FWL and a right front wheel FWR in a front space 61 of a motor vehicle and are arranged to have their longitudinal axis along a width of the vehicle. The hydrogen tanks 21 are positioned at a height substantially the same as a mounting height of a front bumper 64. This layout desirably ensures sufficient spaces in a trunk room 62 on the rear side of the vehicle and in a passenger compartment of the vehicle. This layout also enables the load of the hydrogen tanks 21 to be directly applied to the left and right front wheels FWL and FWR, while ensuring the good weight balance over the width of the vehicle. The positioning of the hydrogen tanks 21 at substantially the same height as the mounting height of the front bumper 64 effectively reduces a potential shock to the hydrogen tanks 21 in the event of a vehicle collision.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and system for tank refilling using active fueling speed control
ActiveUS20140290790A1Improve performanceImprove fuel performanceLiquid fillingGas handling applicationsAnalytical equationsFuel tank
Disclosed is an improved analytical method that can be utilized by hydrogen filling stations for directly and accurately calculating the end-of-fill temperature in a hydrogen tank that, in turn, allows for improvements in the fill quantity while tending to reduce refueling time. The calculations involve calculation of a composite heat capacity value, MC, from a set of thermodynamic parameters drawn from both the tank system receiving the gas and the station supplying the gas. These thermodynamic parameters are utilized in a series of simple analytical equations to define a multi-step process by which target fill times, final temperatures and final pressures can be determined. The parameters can be communicated to the station directly from the vehicle or retrieved from a database accessible by the station. Because the method is based on direct measurements of actual thermodynamic conditions and quantified thermodynamic behavior, significantly improved tank filling results can be achieved.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Solar electrolysis power source
A solar electrolysis power source includes a solar panel, an electrolysis unit, a hermetically sealed compressor, a hydrogen tank, and a fuel cell. By utilizing the electrolysis of water powered by solar energy, the solar electrolysis power source enables a safe, environmentally benign, and cost-effective method of power generation. Furthermore, by combining the production, the compression, the storage of hydrogen, as well as the delivery of the hydrogen to the fuel cell in one hermetically sealed unit currently existing problems with the production, storage delivery, and refueling of hydrogen can be eliminated. The solar electrolysis power source uses hydrogen gas that is hermetically sealed from production to use.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Hydrogen station
ActiveUS20140102587A1Reduce the necessary timeIncrease power consumptionReactant parameters controlSecondary cellsProcess engineeringHydrogen tank
Provided is a hydrogen station that is used to charge hydrogen to a hydrogen tank mounted on a vehicle, the hydrogen station including: a compressor that compresses hydrogen; a lubricant cooling unit that cools the lubricant of the compressor while circulating the lubricant; a hydrogen cooling unit that is capable of cooling hydrogen which is not charged to the hydrogen tank mounted on the vehicle yet and is compressed by the compressor; a sensor that detects whether the vehicle approaches or reaches the hydrogen station; and a startup unit that starts up at least one of the lubricant cooling unit and the hydrogen cooling unit by a signal from the sensor.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Safety valve device, valve apparatus, high-pressure gas tank, and vehicle
ActiveUS20100276024A1Facilitated DiffusionImprove performanceFunctional valve typesPipe elementsHydrogen tankProduct gas
A safety valve device has a safety valve body configured to include a valve mechanism opened at a temperature of or over a preset reference temperature. The safety valve device also includes a gas flow path arranged to make a flow of hydrogen flowing out of a hydrogen tank via the safety valve body in a valve open position of the valve mechanism, and a discharge pipe configured to have a hydrogen discharge opening and arranged to discharge the hydrogen flowing through the gas flow path to the outside. The hydrogen discharge opening of the discharge pipe is formed to discharge the hydrogen in an oblique direction relative to a direction of an axial center of the gas flow path. The discharge pipe also has a groove formed to apply an input rotational force to the discharge pipe and thereby rotate the discharge pipe around the axial center of the gas flow path. In a typical application of a high-pressure gas tank with such a safety valve device mounted on a vehicle, this arrangement of the safety valve device enables the discharge direction of the high-pressure gas that is discharged from the safety valve device to be readily adjusted.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
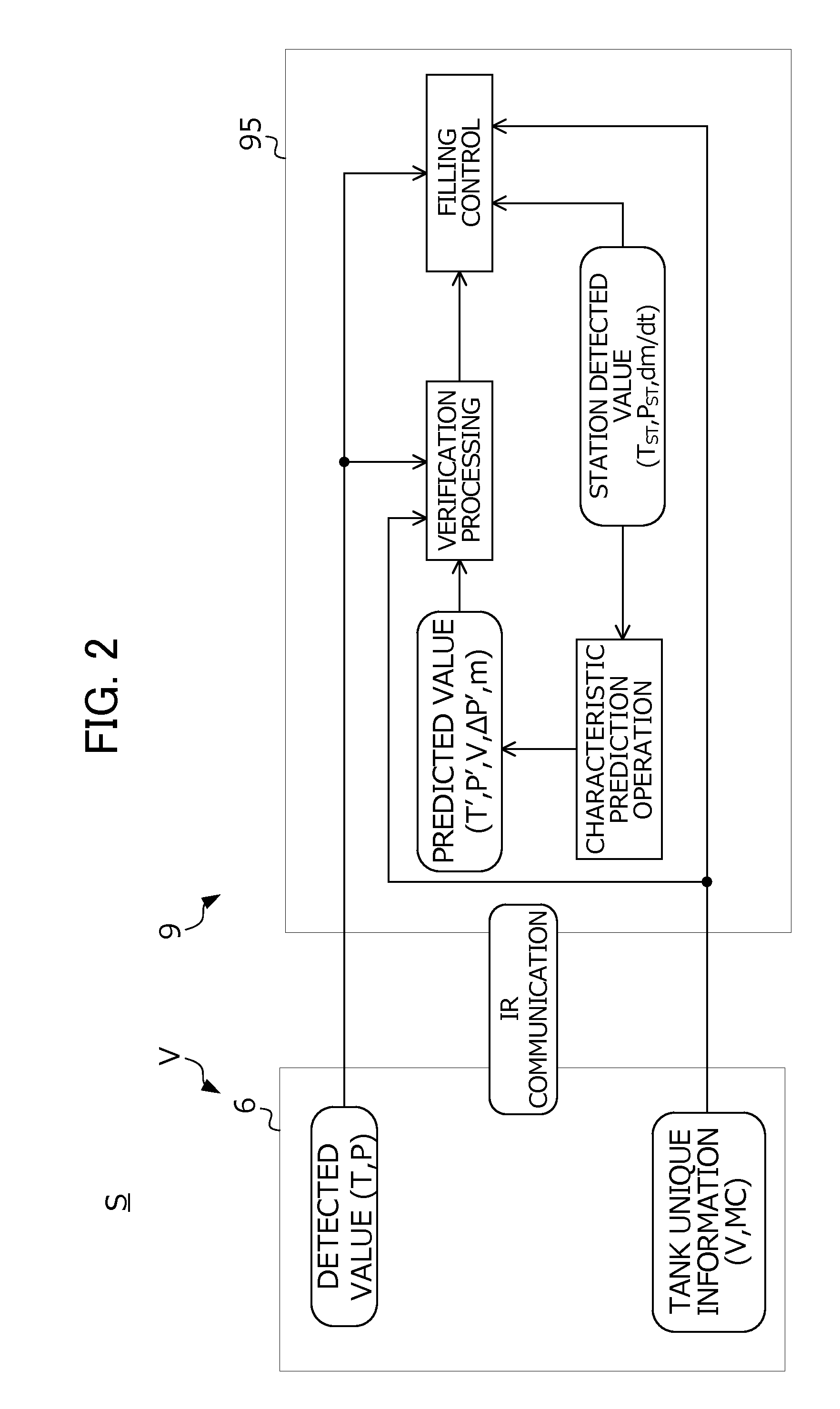
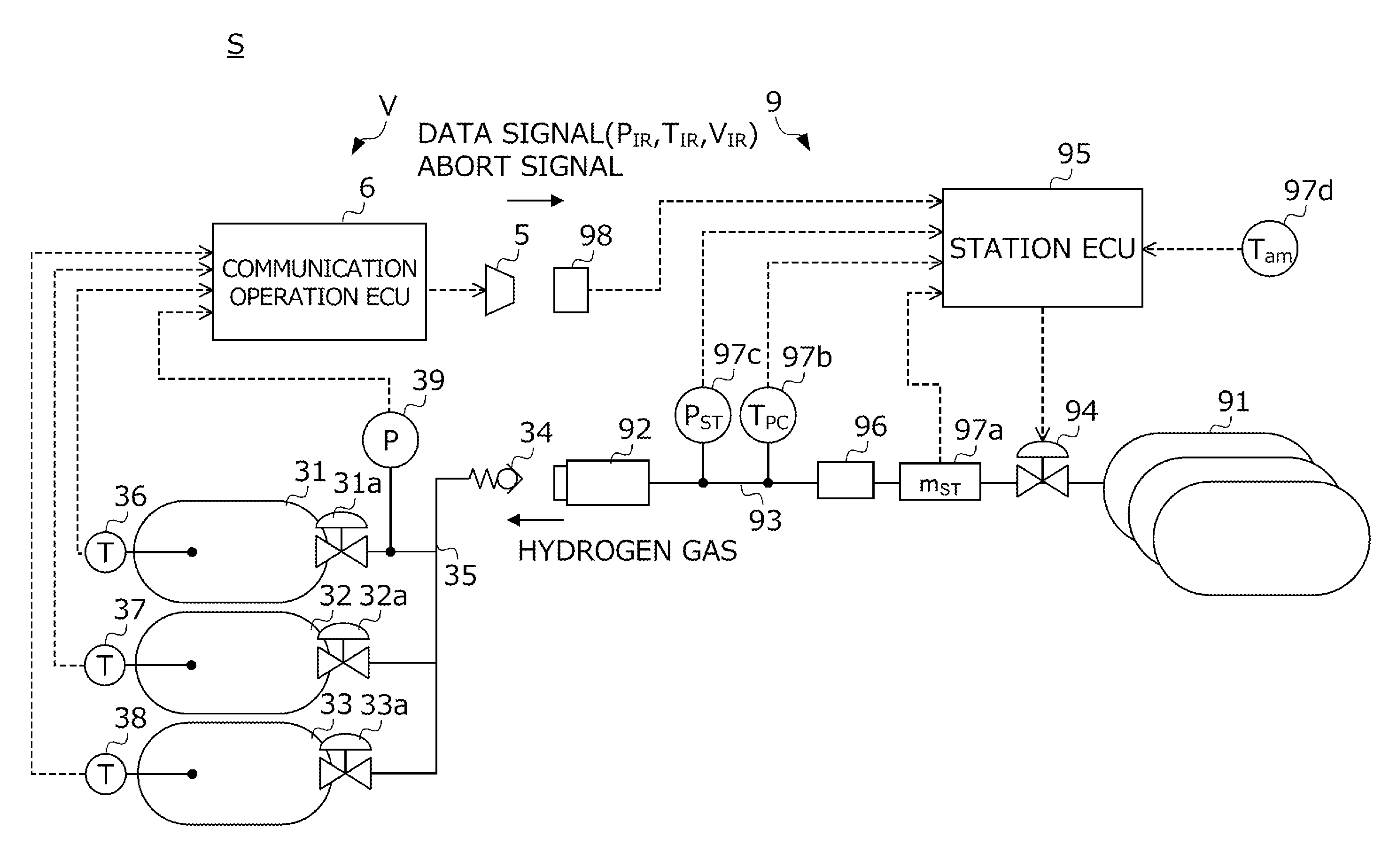
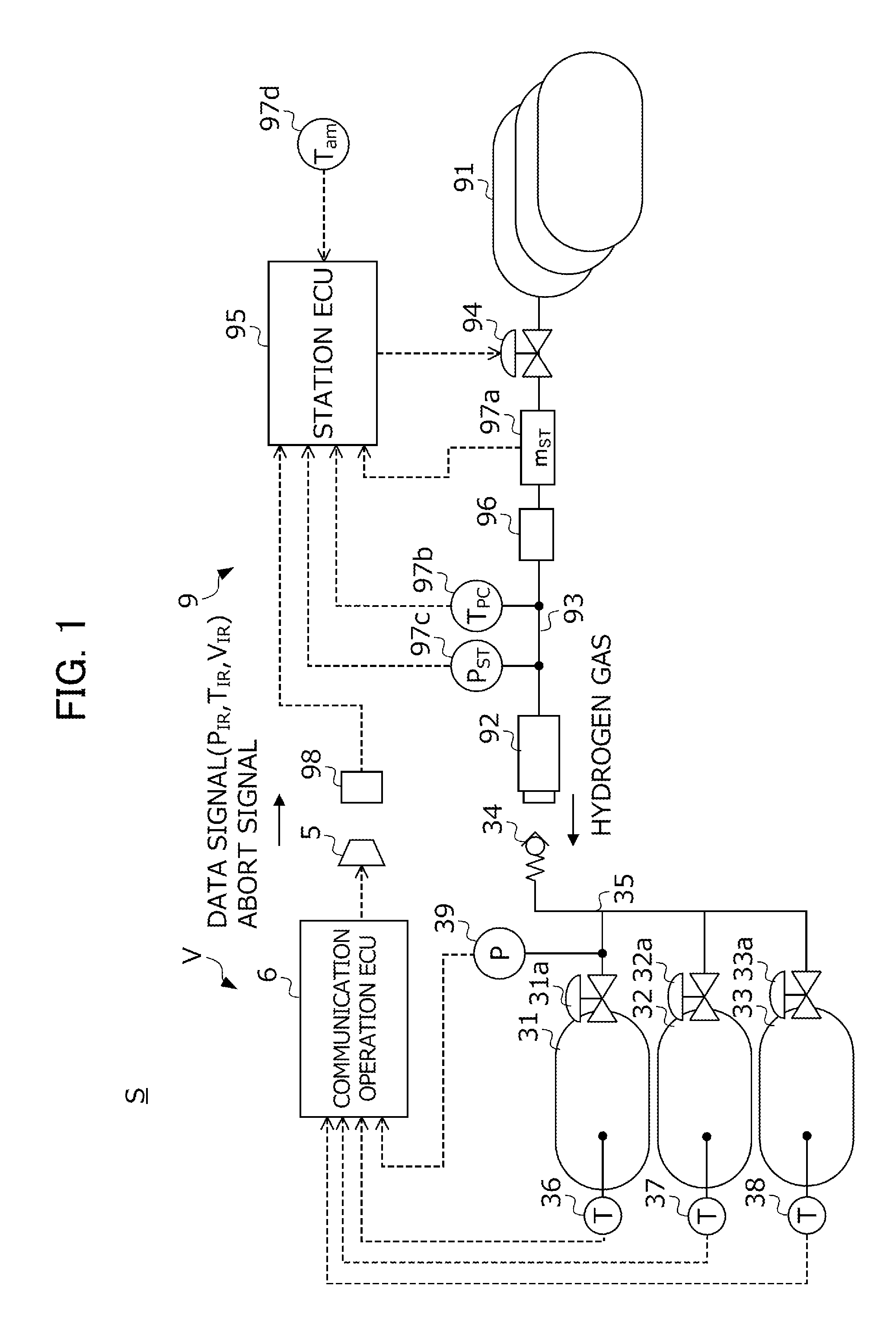
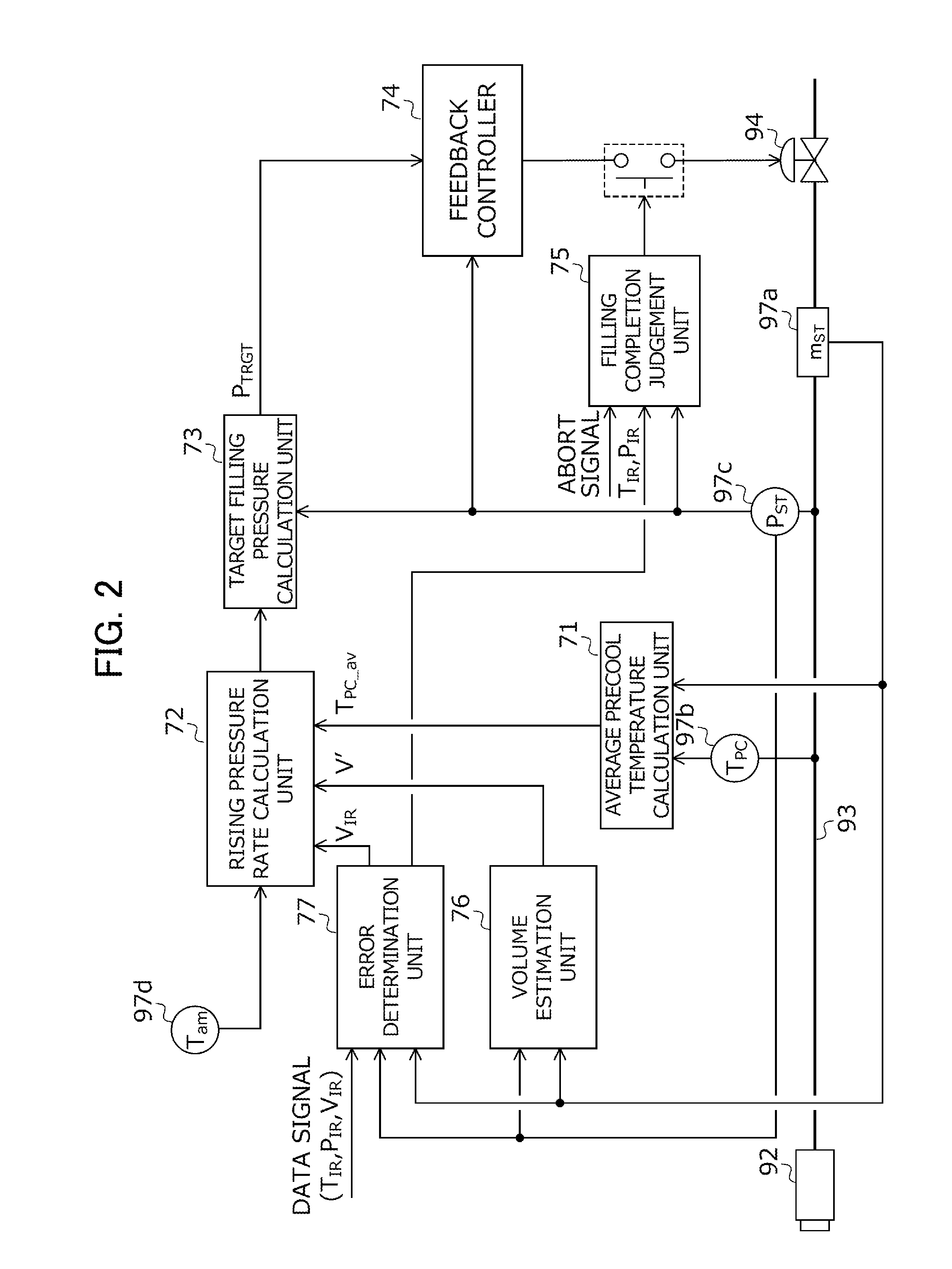
Control method for fuel filling system
ActiveUS20150184804A1Accurately calculate predicted valueImprove forecast accuracyGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsEngineeringProcess engineering
A control method for a hydrogen filling system is provided. A hydrogen filling system (S) includes a vehicle (V) that sends unique information (V, MC) of the hydrogen tank and detected values (T, P) of sensors, and a station (9) that determines a filling mode based on this information (V, MC, P, T), and fills hydrogen to the tank in this determined mode. A station ECU (95) calculates predicted values (T′, P′) of the temperature and pressure inside of the hydrogen tank during filling of hydrogen based on the unique information (V, MC), continuously confirms whether the detected values (T, P) of the sensors and the predicted values (T′, P′) match while filling fuel, and in the case of an inconsistency between the detected values and predicted values being confirmed, interrupts filling of fuel in the filling mode determined based on the unique information.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Fuel cell emergency power system
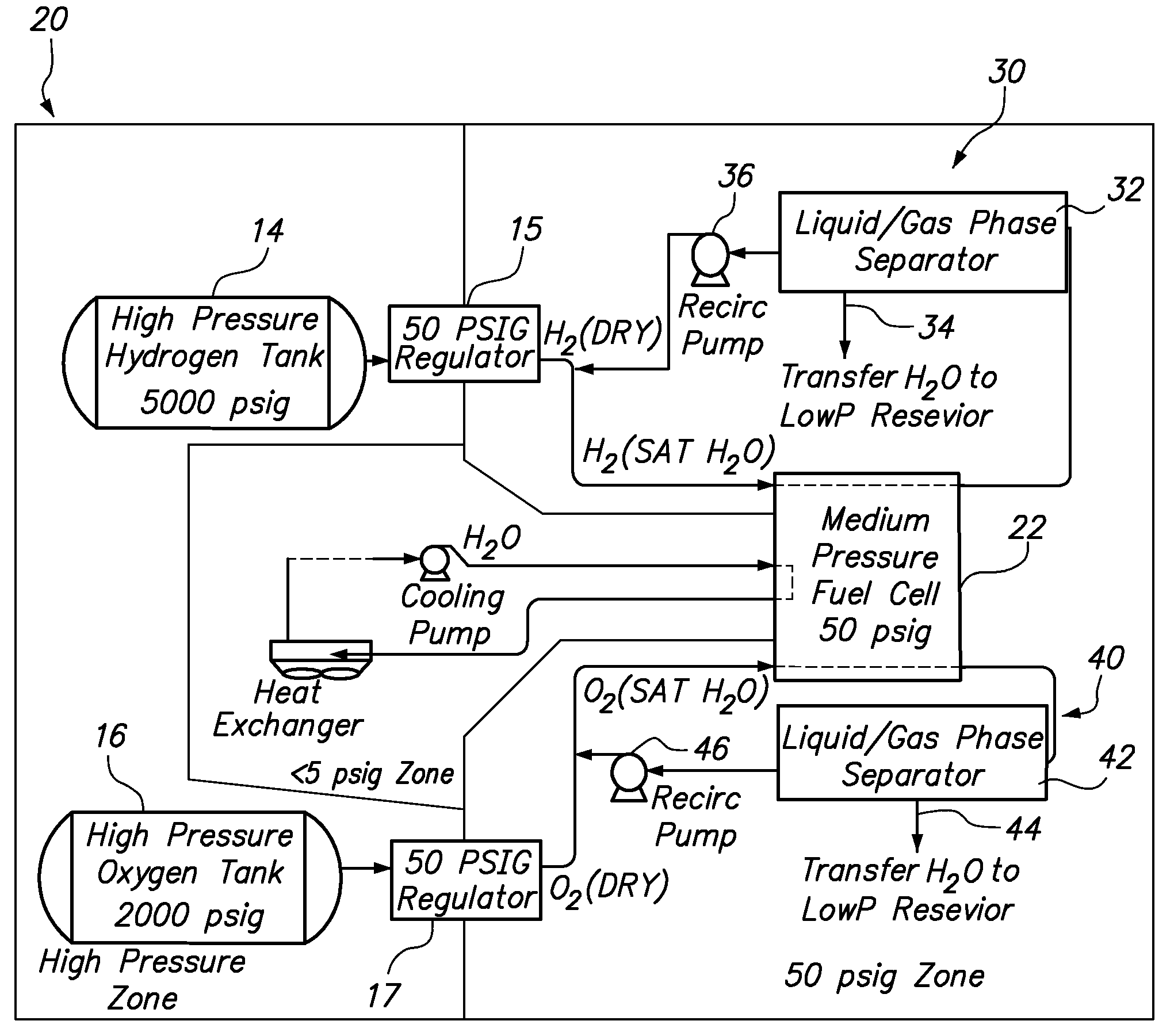
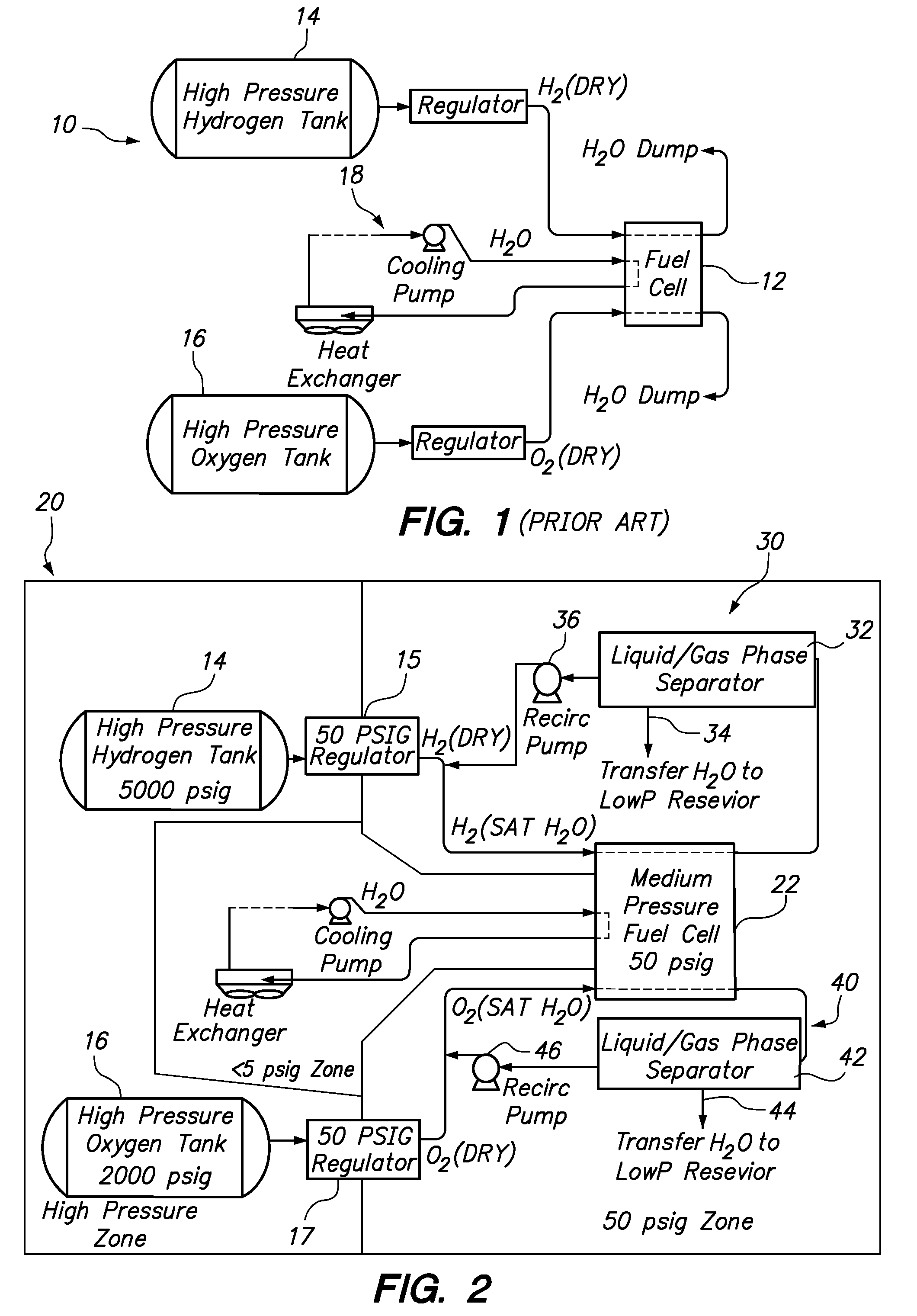
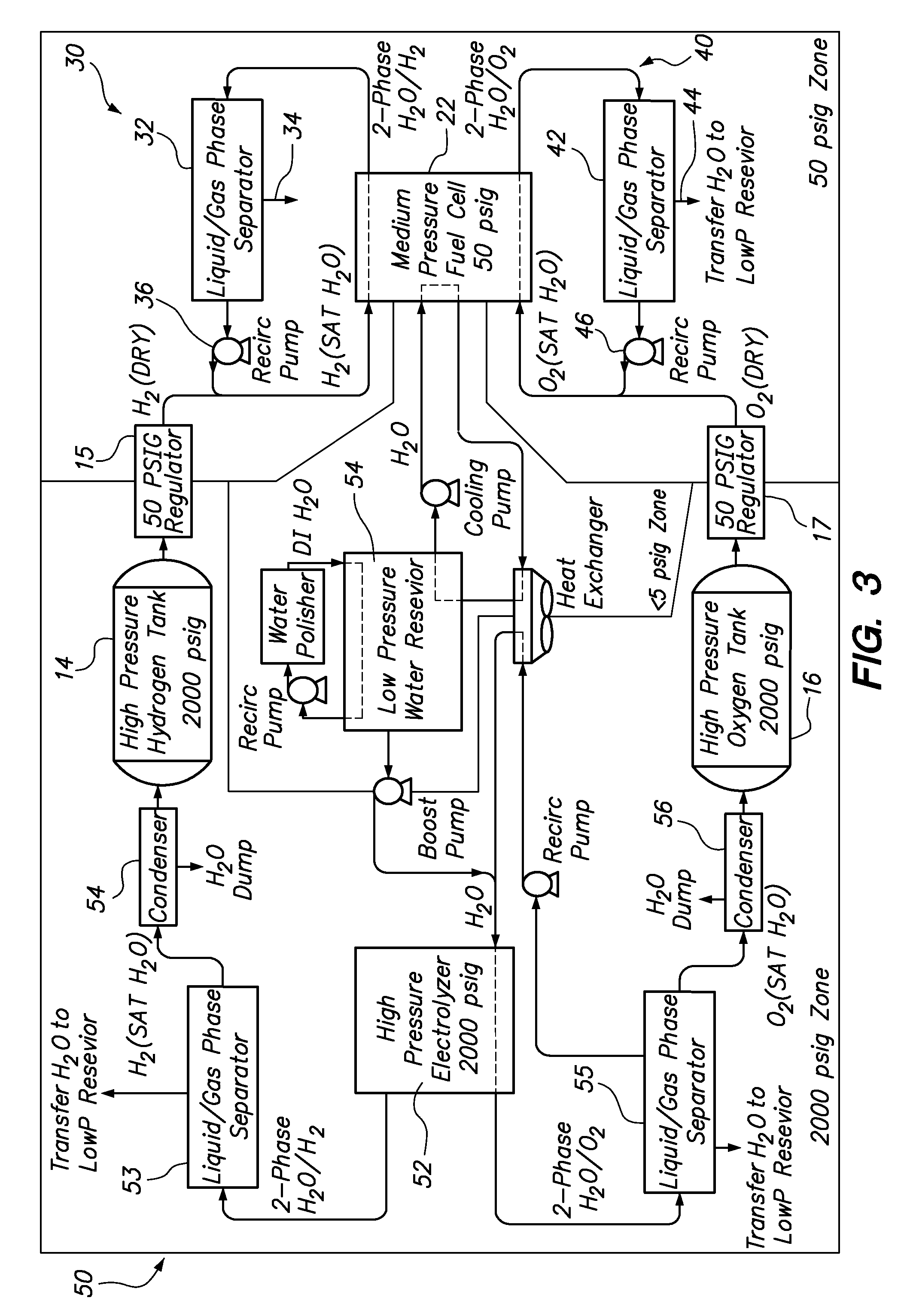
Fuel cell emergency power systems comprising a fuel cell having an anode and a cathode, a power distribution unit for selectively directing electrical current from the fuel cell to one or more consuming device, a hydrogen gas control system and an oxygen gas control system. The hydrogen gas control system includes a pressurized hydrogen tank providing hydrogen gas in selective fluid communication to the anode, a hydrogen gas-liquid water phase separator in downstream fluid communication with the anode, and a hydrogen recirculation pump for recirculating substantially liquid water-free hydrogen from the hydrogen gas-liquid water phase separator to the anode. Similarly, the oxygen gas control system includes a pressurized oxygen tank providing oxygen gas in selective fluid communication to the anode, an oxygen gas-liquid water phase separator in downstream fluid communication with the anode, and an oxygen recirculation pump for recirculating substantially liquid water-free oxygen from the oxygen gas-liquid water phase separator to the anode.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Operation control of fuel cell system
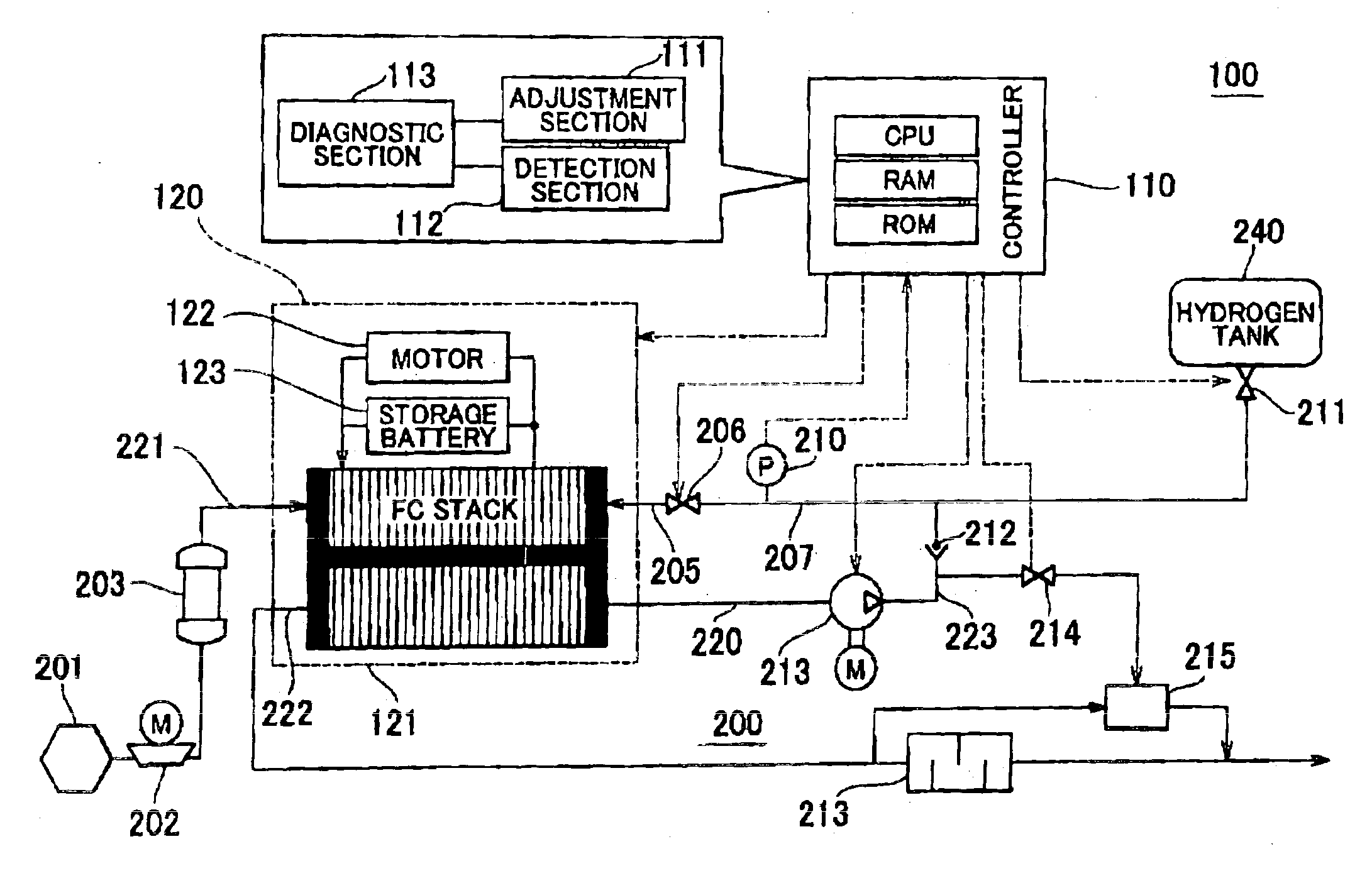
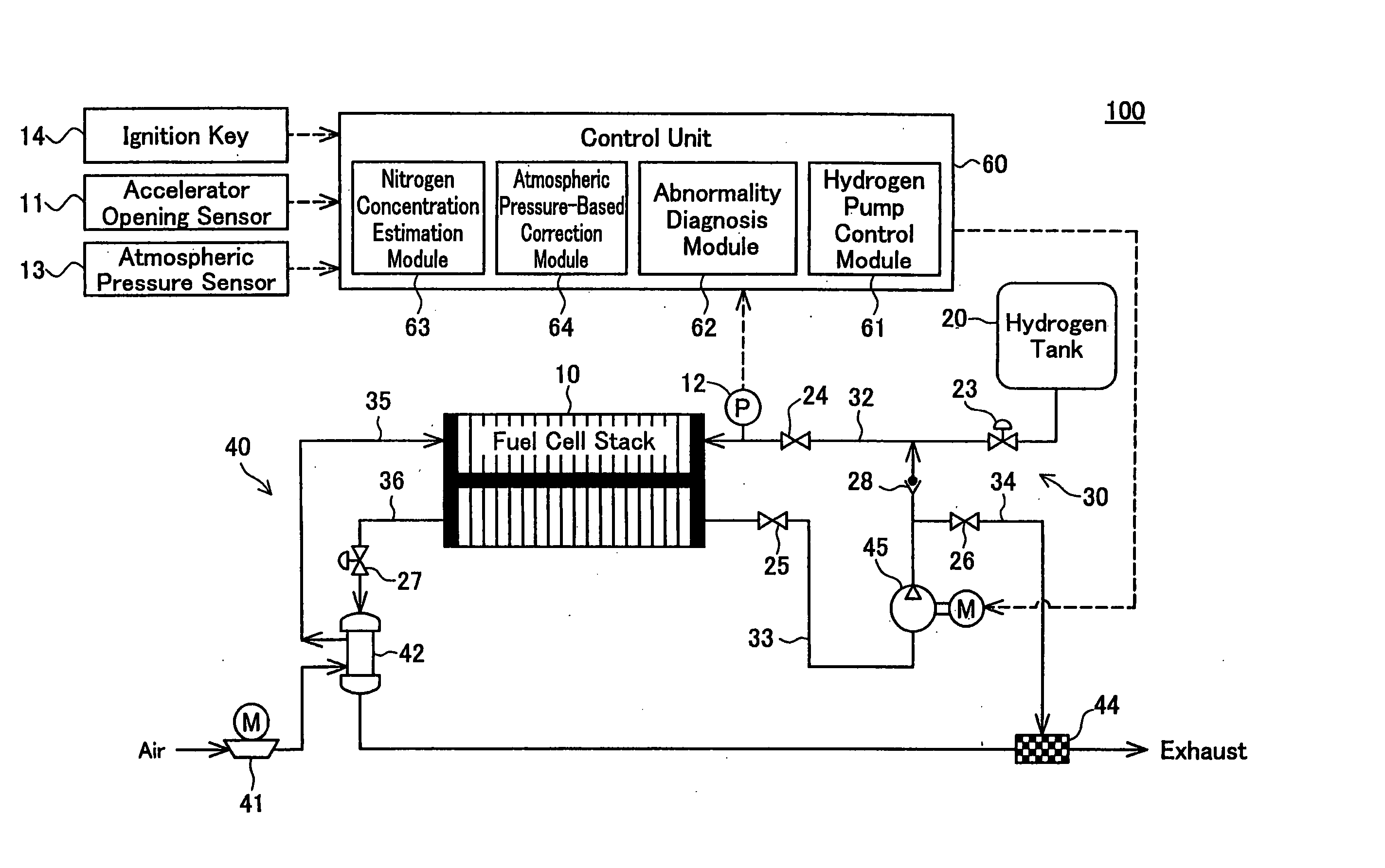
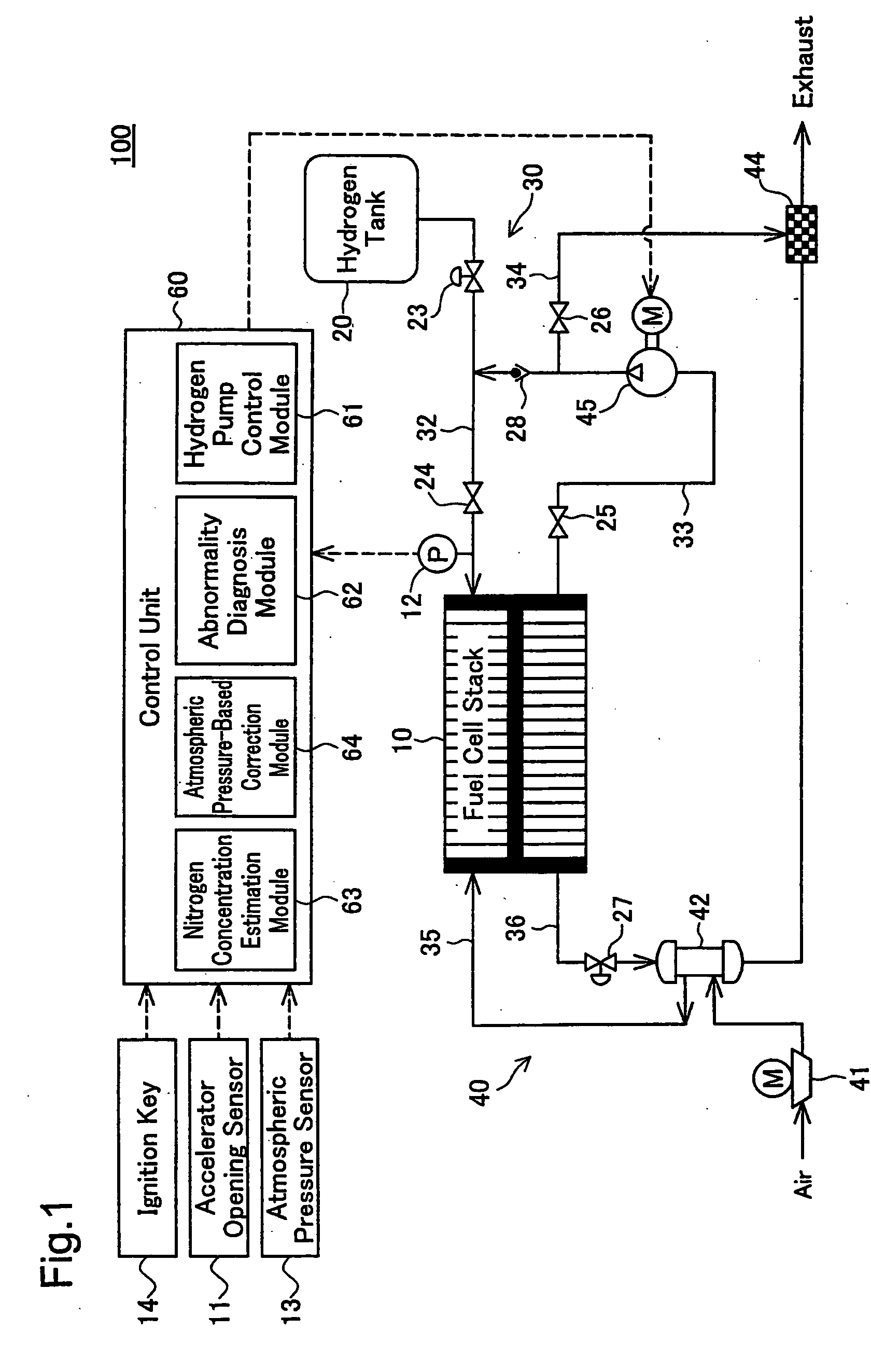
InactiveUS20060110640A1Reducing pressure of hydrogenPotent effectFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesElectric forceEngineering
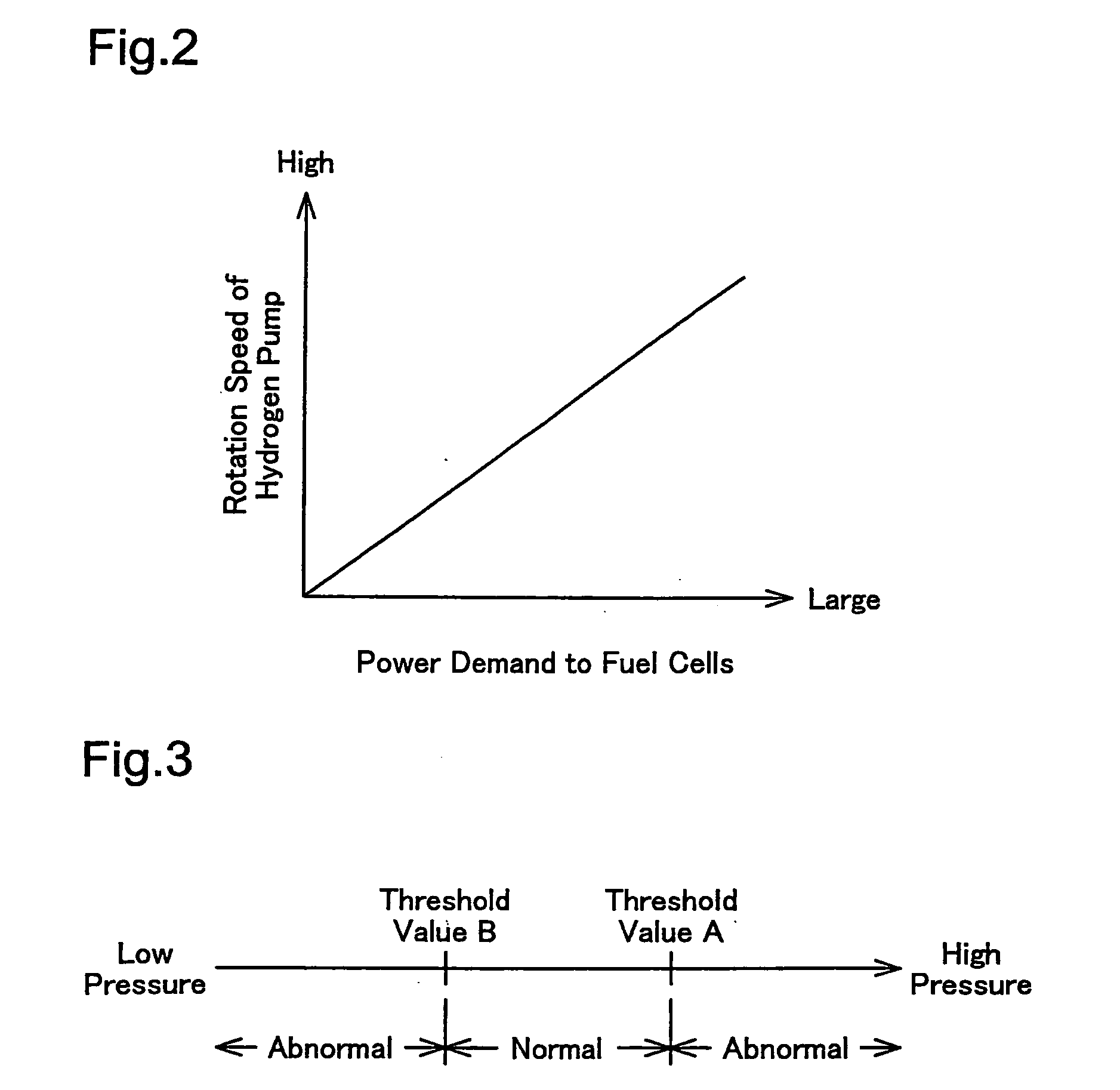
In a fuel cell system of the invention, a pressure regulator is provided in the pathway of a hydrogen supply conduit that connects a hydrogen tank to a fuel cell stack. An anode off gas discharged from the fuel cell stack is recirculated through a recirculation pipe into the hydrogen supply conduit. A hydrogen pump is provided in the pathway of the recirculation pipe to increase the pressure of the anode off gas. A control unit of the fuel cell system includes a hydrogen pump control module, an abnormality diagnosis module, and an atmospheric pressure-based correction module. The hydrogen pump control module regulates the rotation speed of the hydrogen pump corresponding to a power demand to be output from the fuel cell system. The abnormality diagnosis module detects an abnormal state, based on a result of determination of whether the pressure of the hydrogen supply measured by a pressure sensor is within a certain range defined by two preset threshold values. The atmospheric pressure-based correction module corrects the rotation speed of the hydrogen pump and the threshold values used for abnormality diagnosis according to the atmospheric pressure measured by an atmospheric pressure sensor. Even in the state of unstable output of the pressure regulator with a variation of the atmospheric pressure, such correction compensates for the varying flow rate of the hydrogen supply to the fuel cell stack and thus effectively prevents misjudgment of abnormality diagnosis. Namely the technique of the invention reduces the potential effect of the varying pressure of the hydrogen supply to the fuel cell system with a variation of the atmospheric pressure.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
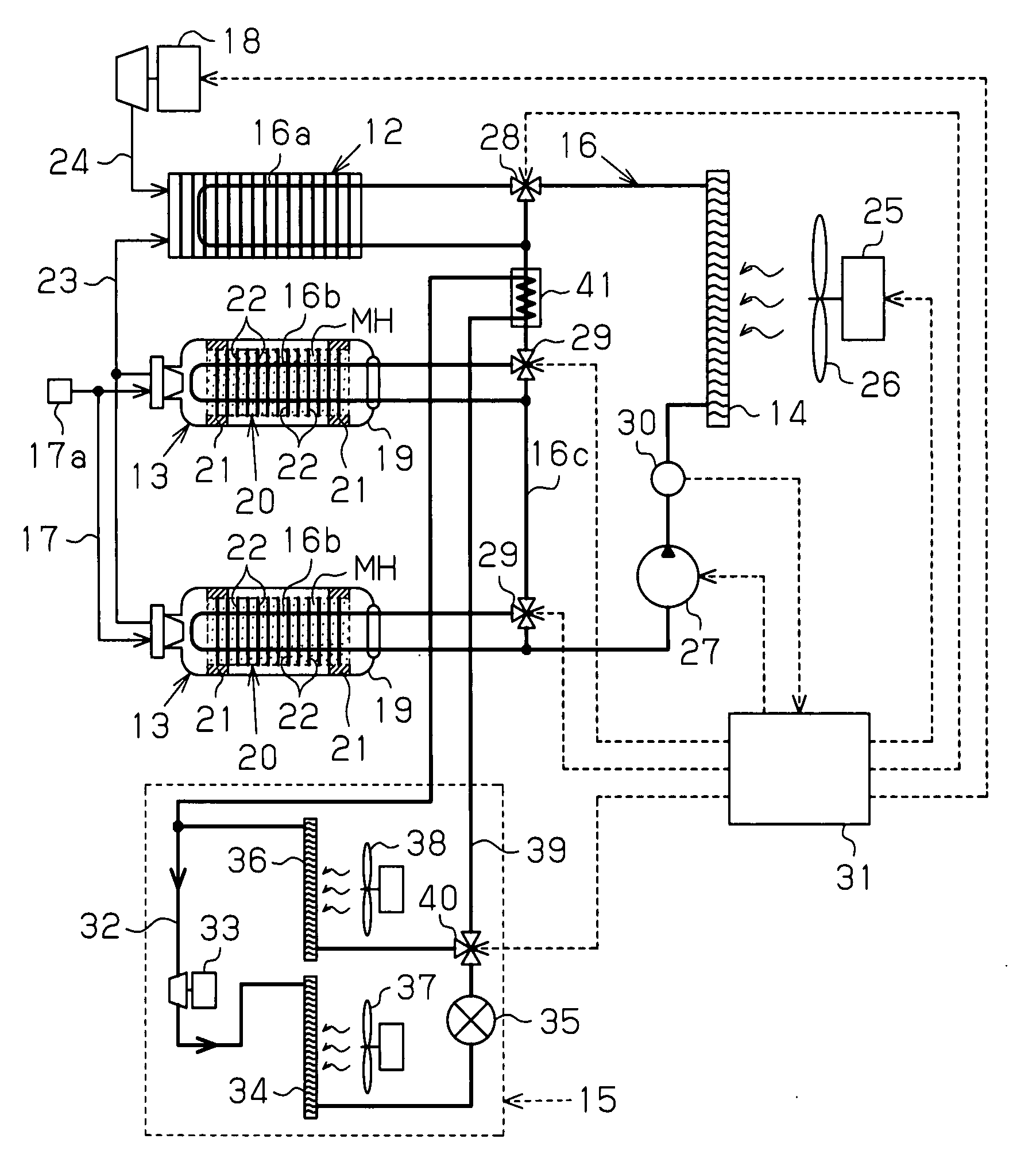
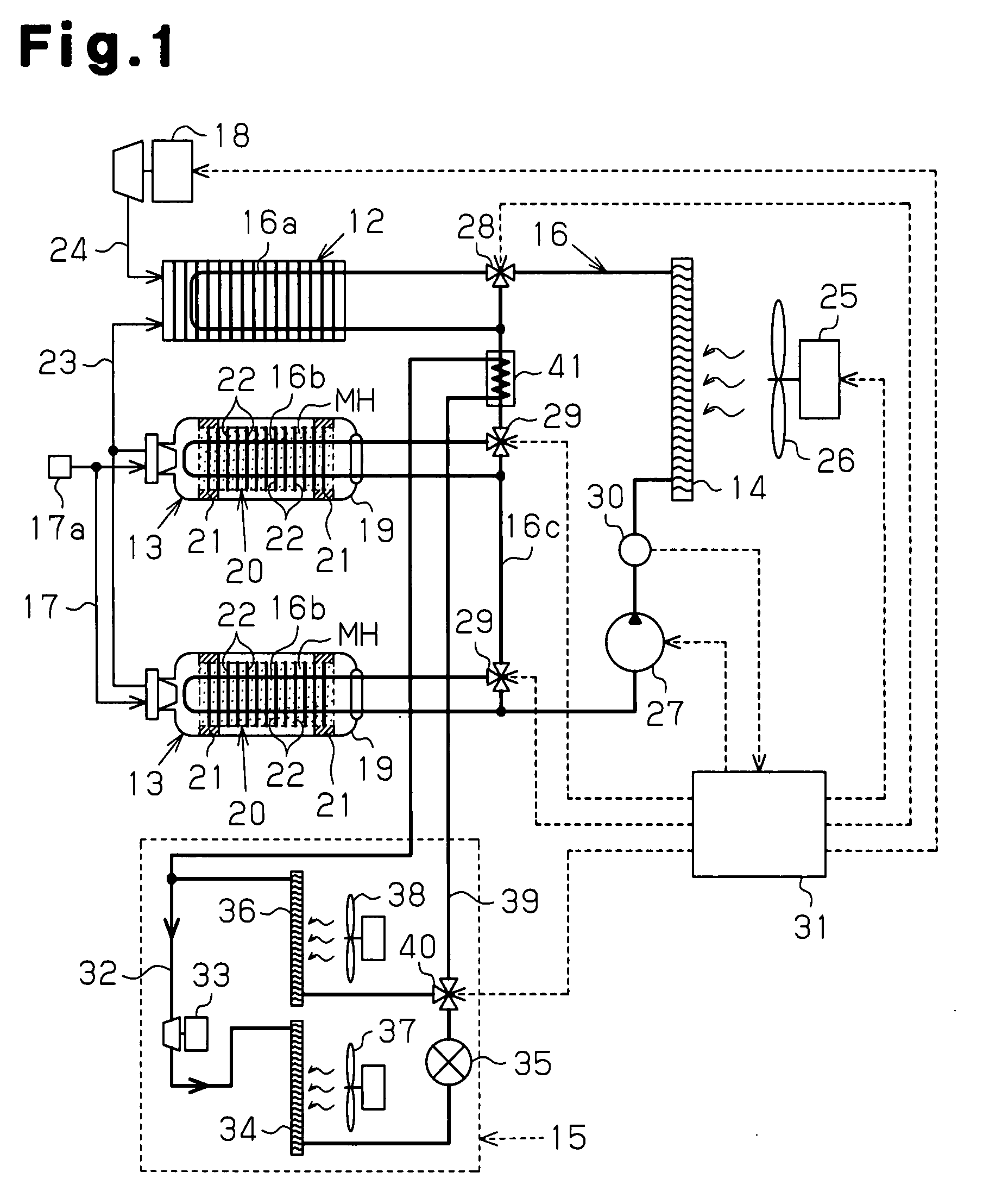
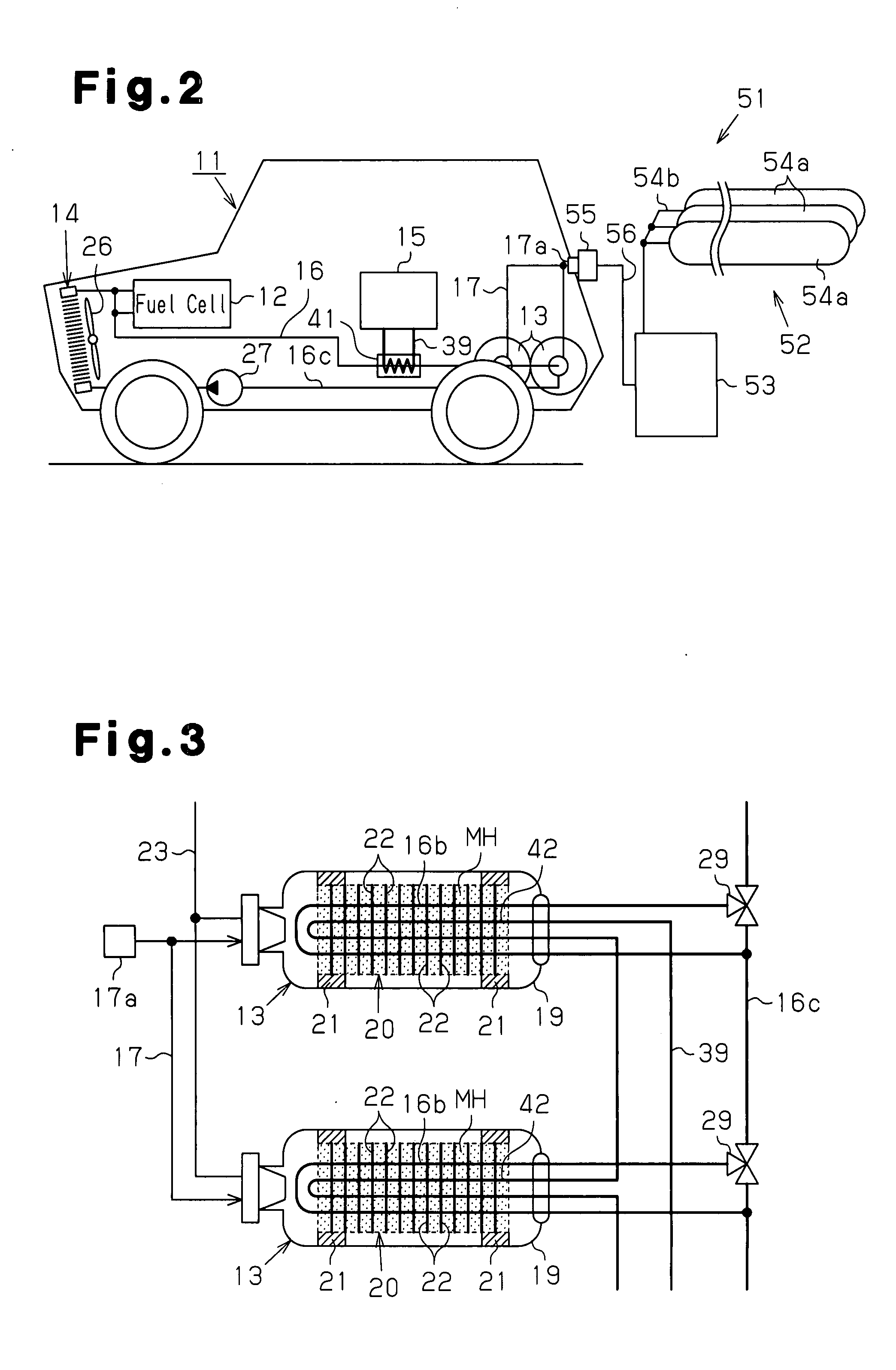
Hydrogen Tank Cooling Device and Cooling Method in Hydrogen Fuel Automobile, and Hydrogen Fuel Automobile
InactiveUS20080250804A1Reduce decreaseShort timeGas handling applicationsStationary tubular conduit assembliesHydrogen fuelProduct gas
A hydrogen fuel automobile has a heat medium passage through which a heat medium which can exchange heat with a drive portion and can be supplied to a heat medium pipe for a hydrogen tank flows. An air cooling apparatus has a compressor for compressing a refrigerant gas, a condenser, an evaporator and a refrigerant circuit. The hydrogen fuel automobile is provided with a bypass passage which branches from the refrigerant circuit so that expanded refrigerant liquid detours the evaporator so as to be drawn into the compressor. A switch portion can switch between a state where the refrigerant liquid passes through the evaporator so as to be drawn into the compressor and a state where the refrigerant liquid detours the evaporator so as to flow through the bypass passage. The hydrogen storage material cooling portion cools the hydrogen storage material in the hydrogen tank using the refrigerant liquid that flows through the bypass passage. Accordingly, the time for filling the tank with hydrogen can be made short in comparison with a case where the radiator and the fan mounted in the automobile are used to cool the hydrogen tank when the tank is being filled with hydrogen.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP +1
Method and system for tank refilling
ActiveUS8783303B2Improve performanceLow costCapsCap application using vaccuumAnalytical equationsEngineering
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Hydrogen closed circulation system used for fuel cell
ActiveCN101887981AImprove recycling ratesReduce the required powerFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesWater vaporSolenoid valve
The invention relates to a hydrogen closed circulation system used for a fuel cell. The system comprises a hydrogen tank, a pressure-reducing valve, a ratio switch solenoid valve, an ejector pump, a fuel cell stack, a hydrogen discharging solenoid valve, a hydrogen circulation pump and voltage-regulation tanks (A,B), wherein the hydrogen tank is connected to the hydrogen inlet of the fuel cell stack through the pressure-reducing valve, the ratio switch solenoid valve and the ejector pump sequentially; the hydrogen outlet of the fuel cell stack is connected with the hydrogen discharging solenoid valve; the voltage-regulation tank A is arranged between the ejector pump and the hydrogen inlet of the fuel cell stack; the voltage-regulation tank B is connected with the hydrogen discharging solenoid valve; the hydrogen circulation pump is connected with the voltage-regulation tanks (A,B) respectively; hydrogen enters the voltage-regulation tank A for water vapor separation and then enters the fuel cell stack for reaction; excessive hydrogen is discharged to the voltage-regulation tank B by the hydrogen discharging solenoid valve; and the hydrogen in the voltage-regulation tank B is returned to the voltage-regulation tank A by the hydrogen circulation pump. Compared with the prior art, the hydrogen closed circulation system has the advantages of small self-consuming power, high hydrogen utilization ratio and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Fuel cell-powered motorcycle
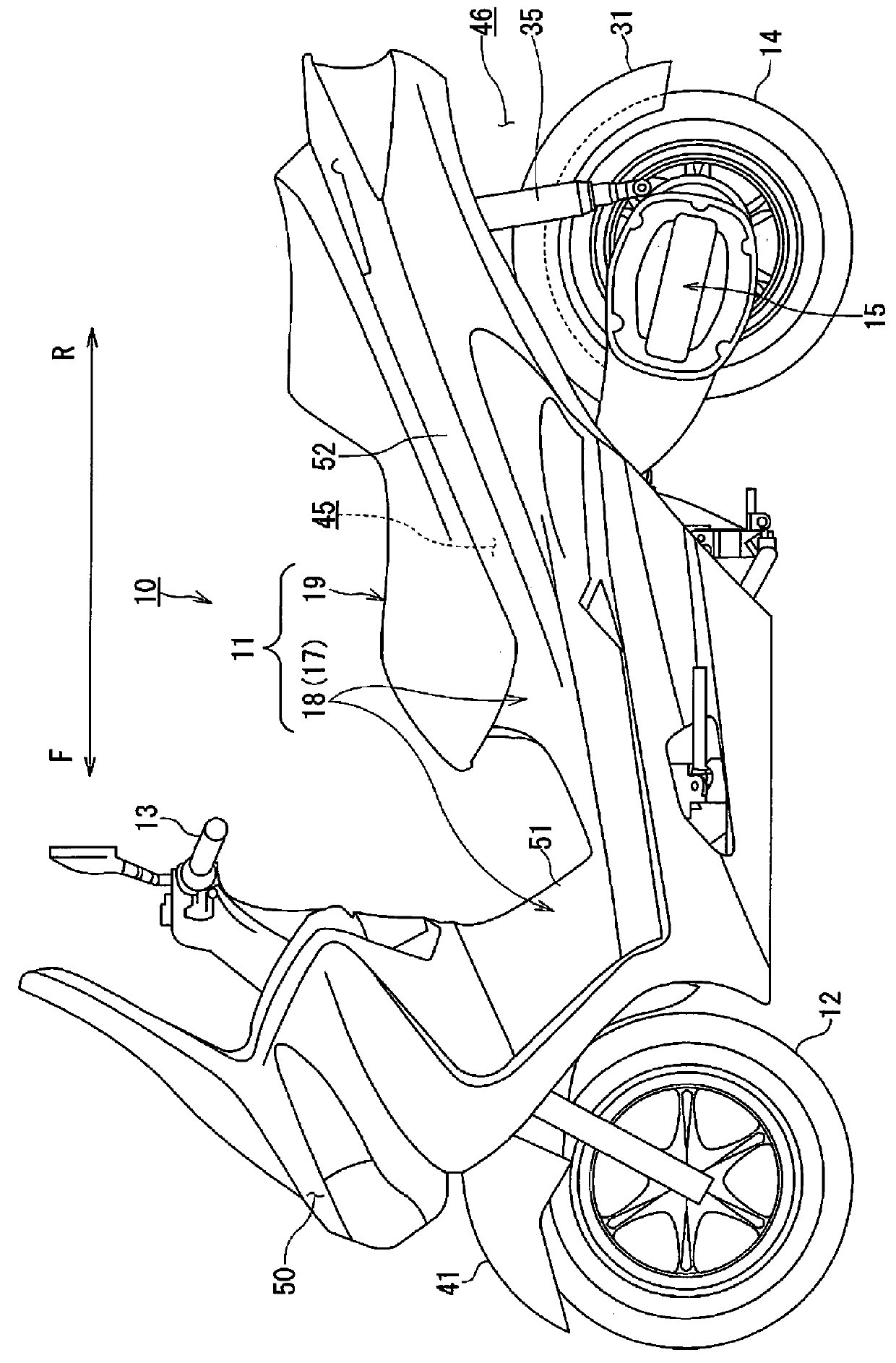
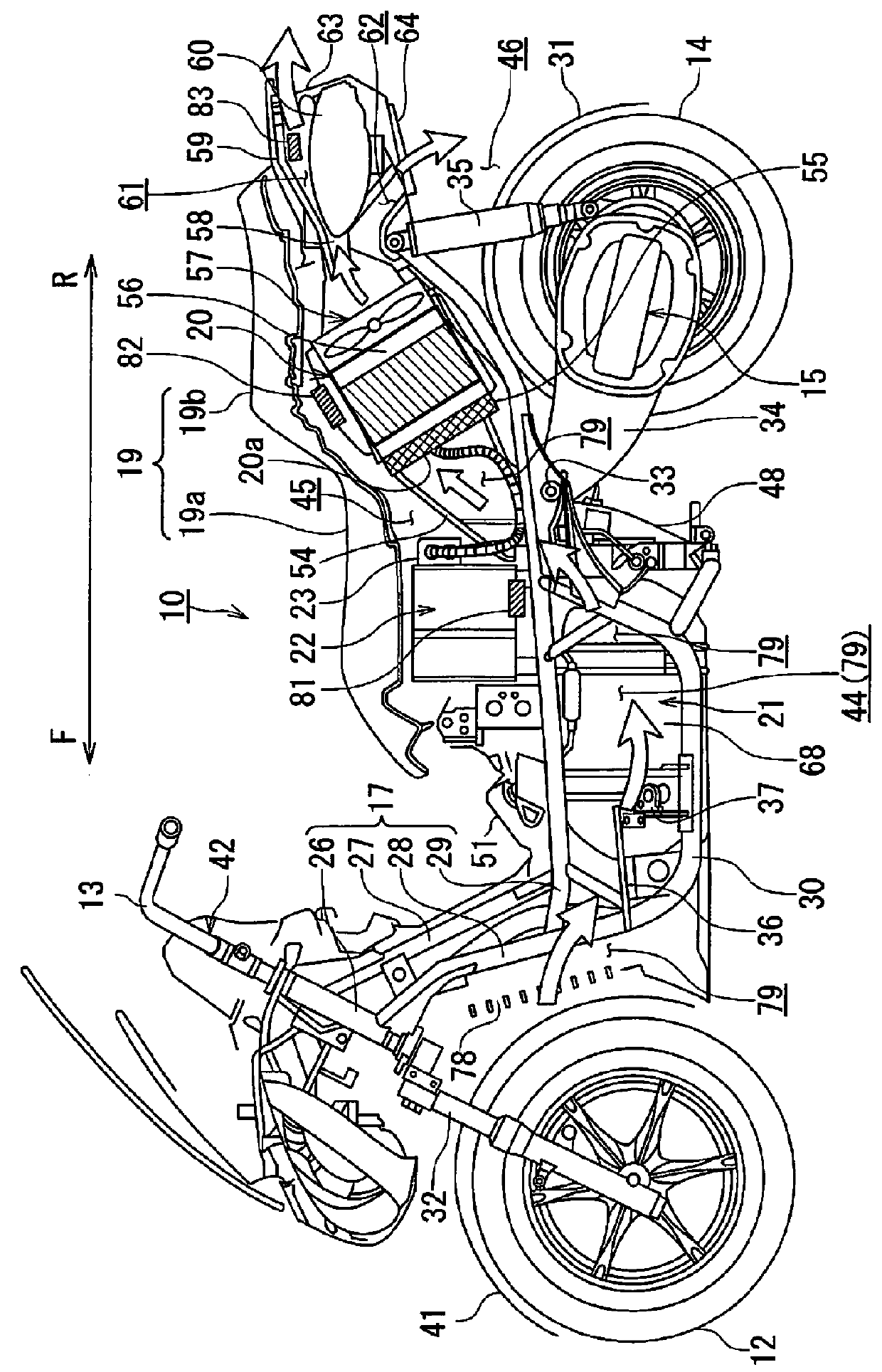
ActiveUS20160056482A1Early detectionAvoid failureFuel cell heat exchangeReactant parameters controlDrive wheelHydrogen tank
An air-cooled fuel cell-powered motorcycle allowing early detection of a malfunction in a fuel cell stack. The fuel cell-powered motorcycle includes a vehicle body; an electric motor for driving a driving wheel, an air-cooled fuel cell for supplying electric power to the electric motor and a hydrogen tank for storing a fuel gas supplied to the fuel cell, respectively housed in the vehicle body; a fan for supplying air as a reactant and a coolant to the fuel cell; and an exhaust duct for discharging the air having cooled the fuel cell out of a rear end of the vehicle body, the exhaust duct having an inlet connected to a rear end portion of the fuel cell.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
Arrangement structure of component parts for fuel cell vehicle
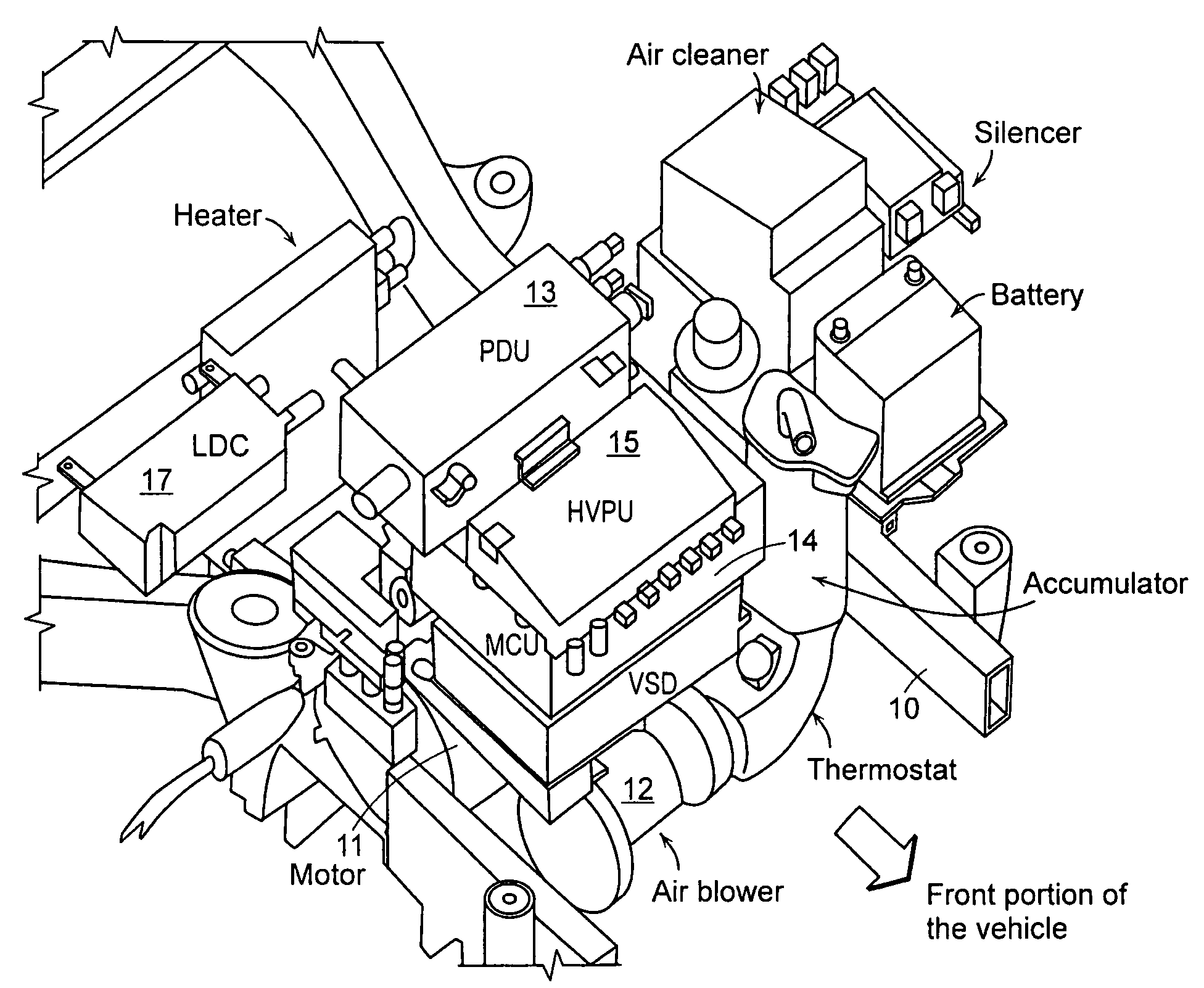
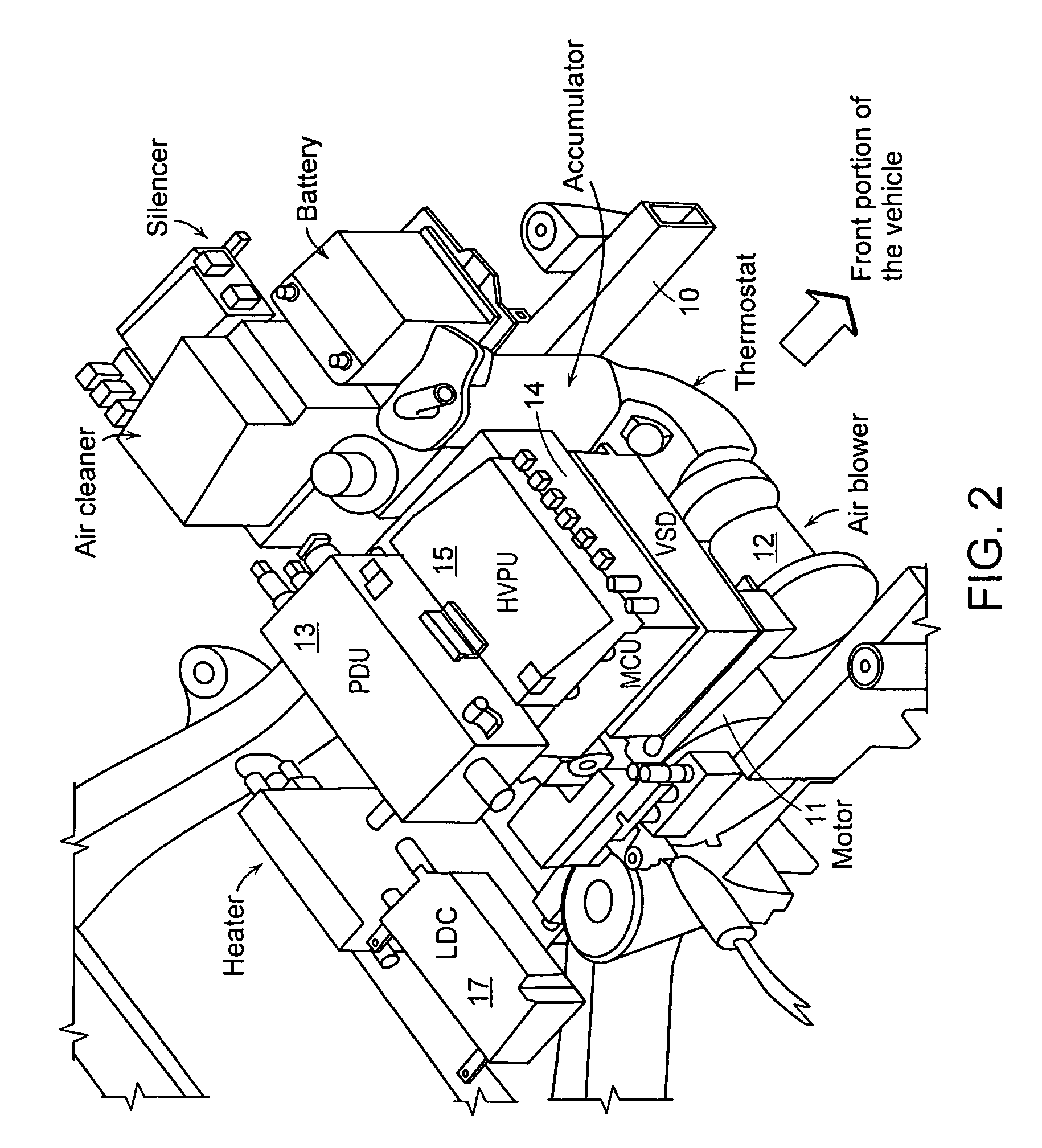
InactiveUS20080149410A1Improved weight distributionReduce noiseReactant parameters controlPlural diverse prime-mover propulsion mountingAir blowerRear-end collision
The present invention provides an arrangement structure of component parts for a fuel cell vehicle that efficiently arranges various component parts of a fuel cell system, a hydrogen supply system and an electric driving system to make the best use of interior space, improve weight distribution of the vehicle, reduce noise, and provide security against a rear-end collision.The arrangement structure of the present invention includes an engine room, in which a motor 11 and an air blower 12 are mounted on an upper portion of a frame 10, and component parts of an electrical system and a fuel cell system are arranged on an upper portion of the motor 11; an under-floor 20, on which a humidifier 21, a stack 22, a fuel processing system (FPS) box 23, and a hydrogen tank 40 are mounted; seats 29, beneath which electronic parts are arranged on the under-floor 20; and a trunk room, in which a super-capacitor and an initial charging device are mounted.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
New energy automobile fuel cell system, working method, hydrogen inlet flow calculation method and efficiency evaluation method
The invention discloses a new energy automobile fuel cell system, a working method, a hydrogen inlet flow calculation method and an efficiency evaluation method, Belongs to the technical field of newenergy. Keys points of the new energy automobile fuel cell system are that the new energy automobile fuel cell system comprises an air supply system, a hydrogen supply system and a fuel cell stack, wherein the air supply system provides fresh air for the fuel cell stack, and the system comprises an air filter, a centrifugal air compressor, a gas heat exchanger, a humidifying and intercooling assembly, a throttle valve, a water segregator, a drain valve, a turbine and a back pressure valve; the hydrogen supply system provides fresh hydrogen for the fuel cell stack and comprises a hydrogen tank,a pressure reducing valve, an ejector, a water distributor, a water distribution valve, a nitrogen discharger, a nitrogen discharge valve, a first one-way valve, a circulating pump and a second one-way valve; and the fuel cell stack is a place where hydrogen and air react, and chemical energy is converted into electric energy to provide kinetic energy for accessory mechanisms and loads. The invention aims to provide the new energy automobile fuel cell system, the working method, the hydrogen inlet flow calculation method and the efficiency evaluation method, the stability of the fuel cell isimproved, and the efficiency of the fuel cell is conveniently calculated and evaluated.
Owner:擎能动力科技(苏州)有限公司
Method and system for tank refilling using active fueling speed control
ActiveUS20140202584A1Improve performanceLow costGas handling applicationsGas handling/storage effectsAnalytical equationsFuel tank
Disclosed is an improved analytical method that can be utilized by hydrogen filling stations for directly and accurately calculating the end-of-fill temperature in a hydrogen tank that, in turn, allows for improvements in the fill quantity while tending to reduce refueling time. The calculations involve calculation of a composite heat capacity value, MC, from a set of thermodynamic parameters drawn from both the tank system receiving the gas and the station supplying the gas. These thermodynamic parameters are utilized in a series of simple analytical equations to define a multi-step process by which target fill times, final temperatures and final pressures can be determined. The parameters can be communicated to the station directly from the vehicle or retrieved from a database accessible by the station. Because the method is based on direct measurements of actual thermodynamic conditions and quantified thermodynamic behavior, significantly improved tank filling results can be achieved.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
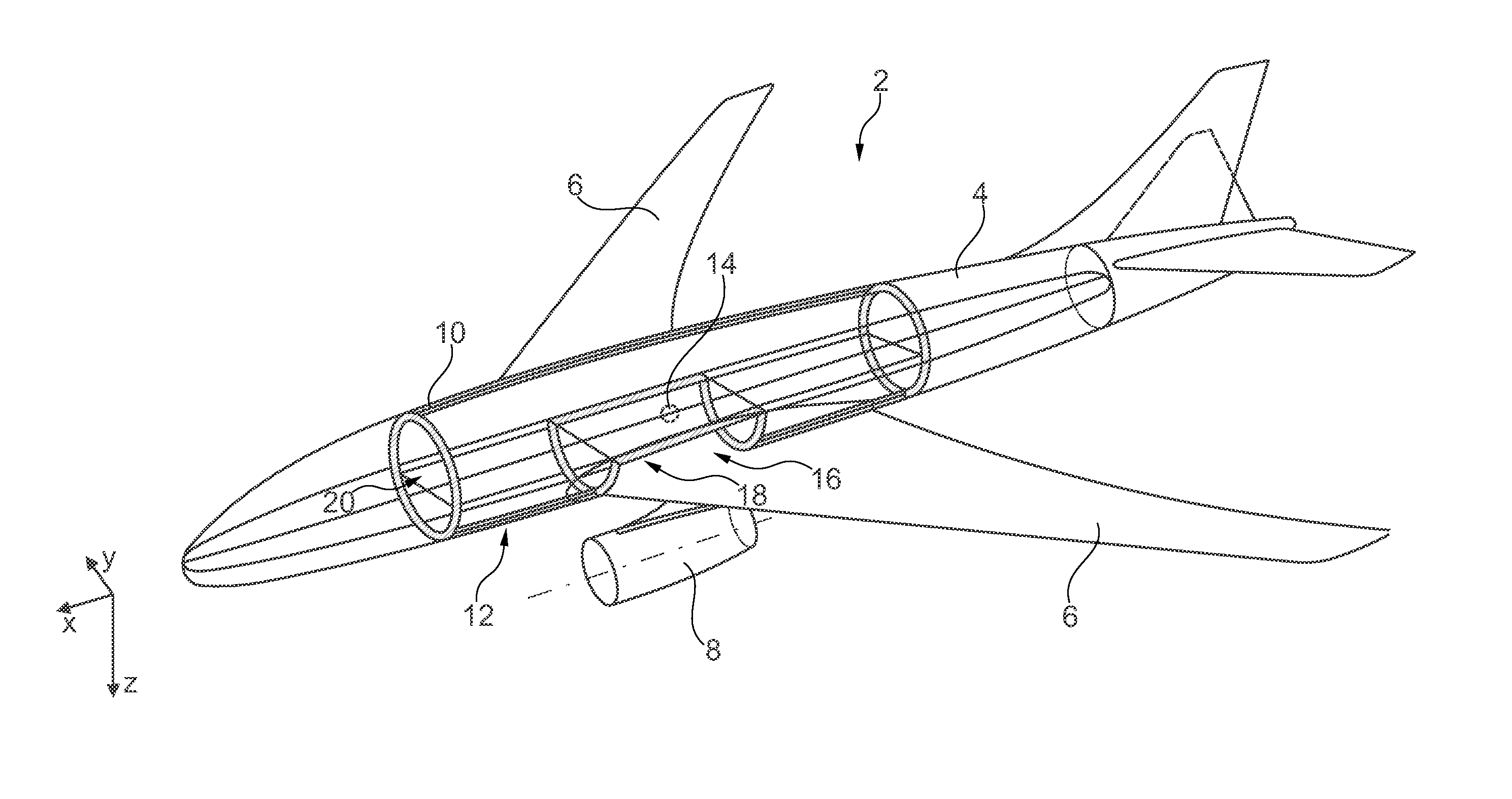
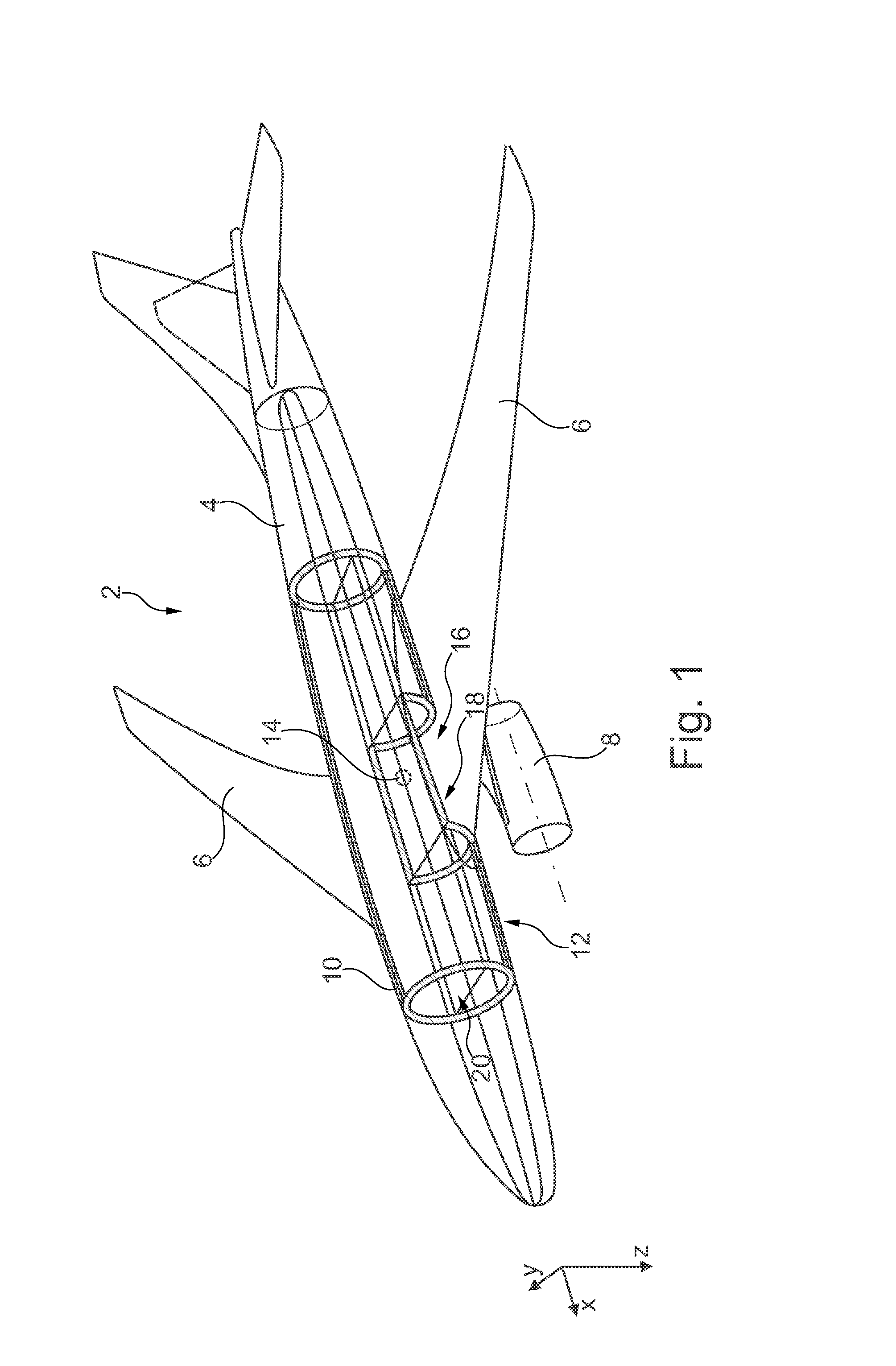
Tank System For The Cryogenic Storage Of Hydrogen, And Aircraft With A Tank System For The Cryogenic Storage Of Hydrogen
InactiveUS20150336680A1Offset the pressureHigh strengthPower plant fuel tanksVessel geometry/arrangement/sizeLiquid hydrogenHydrogen tank
A tank system for the cryogenic storage of hydrogen includes a tank structure with at least one hollow body for accommodating liquid hydrogen and at least one insulating means, which encloses the tank structure, for insulating the at least one hollow body. The tank structure has an exterior shape that is integrateable in a load-bearing primary structure of an aircraft. The tank structure is load bearing and is designed to at least partially absorb a load introduced into the primary structure. This makes it possible to achieve a particularly efficient design of an aircraft in which the fuselage of the aircraft is not divided into two parts by the hydrogen tank integrated therein, can be arranged near the center of gravity, and essentially does not increase the additional weight of the aircraft.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Fuel filling system and fuel filling method thereof
ActiveUS20160305611A1Improve accuracyReduce misjudgmentVessel mounting detailsSecondary cellsProcess engineeringHydrogen tank
The present invention provides a fuel filling system and a fuel filling method thereof that can determine the validity of information transmitted from a vehicle side while filling fuel with high accuracy. A hydrogen gas filling method of a hydrogen filling system includes: a step of filling hydrogen gas from a hydrogen station to a hydrogen tank under a predetermined filling control law (S2); and a determination step of determining whether a measurement error parameter corresponding to a difference between a filling amount of hydrogen gas calculated using information transmitted from the vehicle side and a filling amount of hydrogen gas calculated using a mass flow meter is within a predetermined permissible range (S9). In the filling step, the filling control law is changed after starting the filling of hydrogen gas, according to a determination result obtained in the determination step (S13 and S16).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Fuel cell vehicle
InactiveUS7363997B2Low production costAvoid collisionHybrid vehiclesAuxillary drivesElectrochemical responseOxygen
The fuel cell vehicle includes a fuel cell for generating electric power by electrochemical reaction of hydrogen and oxygen, and a hydrogen tank which stores pressurized hydrogen to supply hydrogen to the fuel cell, the fuel cell and the hydrogen tank being arranged at an underfloor region of the vehicle. Based on the detection results in a side G sensor arranged on the side of the fuel cell and a rear G sensor arranged on the side of the hydrogen tank, a side air bag device is made expandable and a cut-off valve and a contactor are operated to cut off.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com