Patents
Literature
12383 results about "Load bearing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
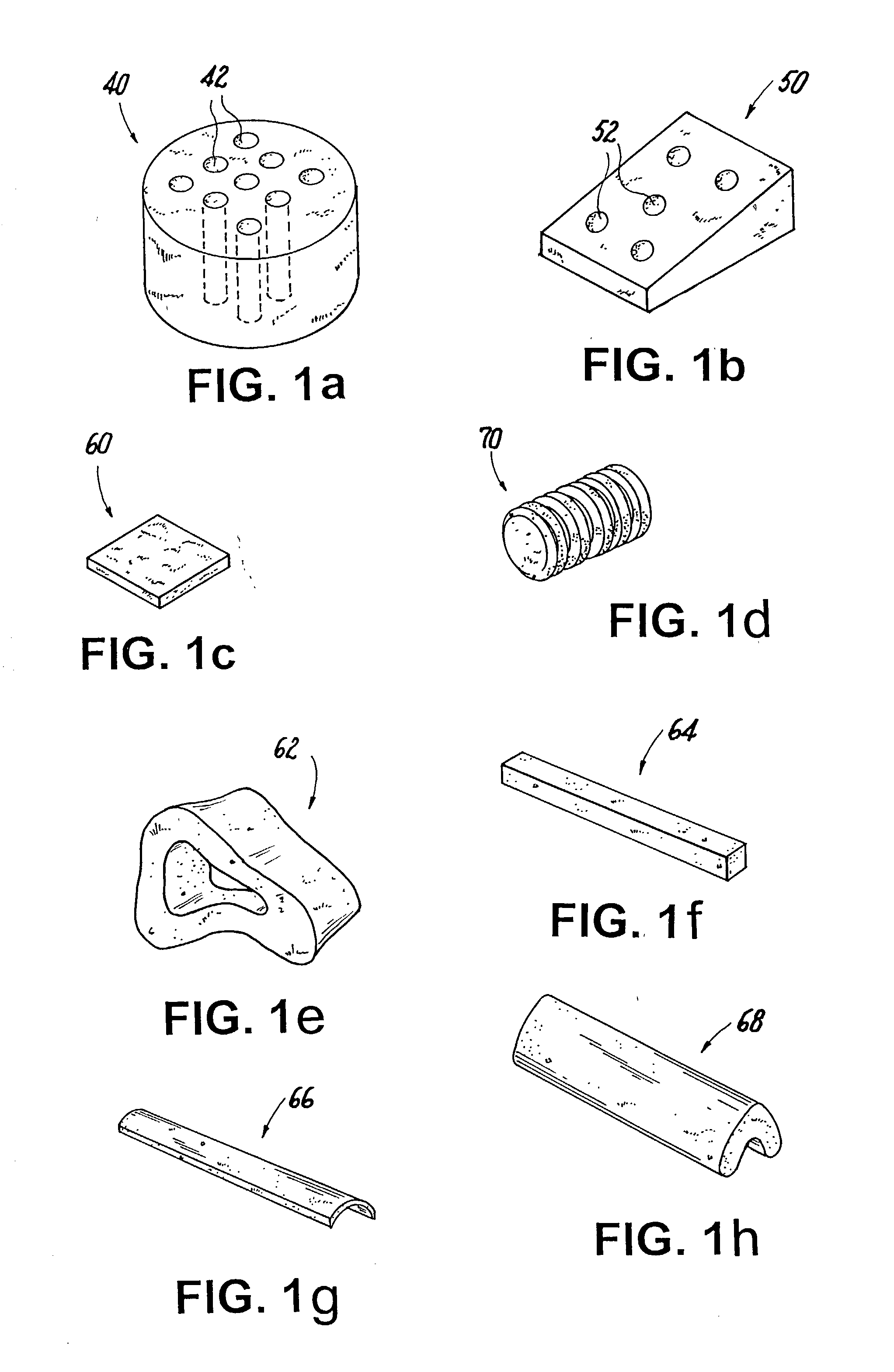
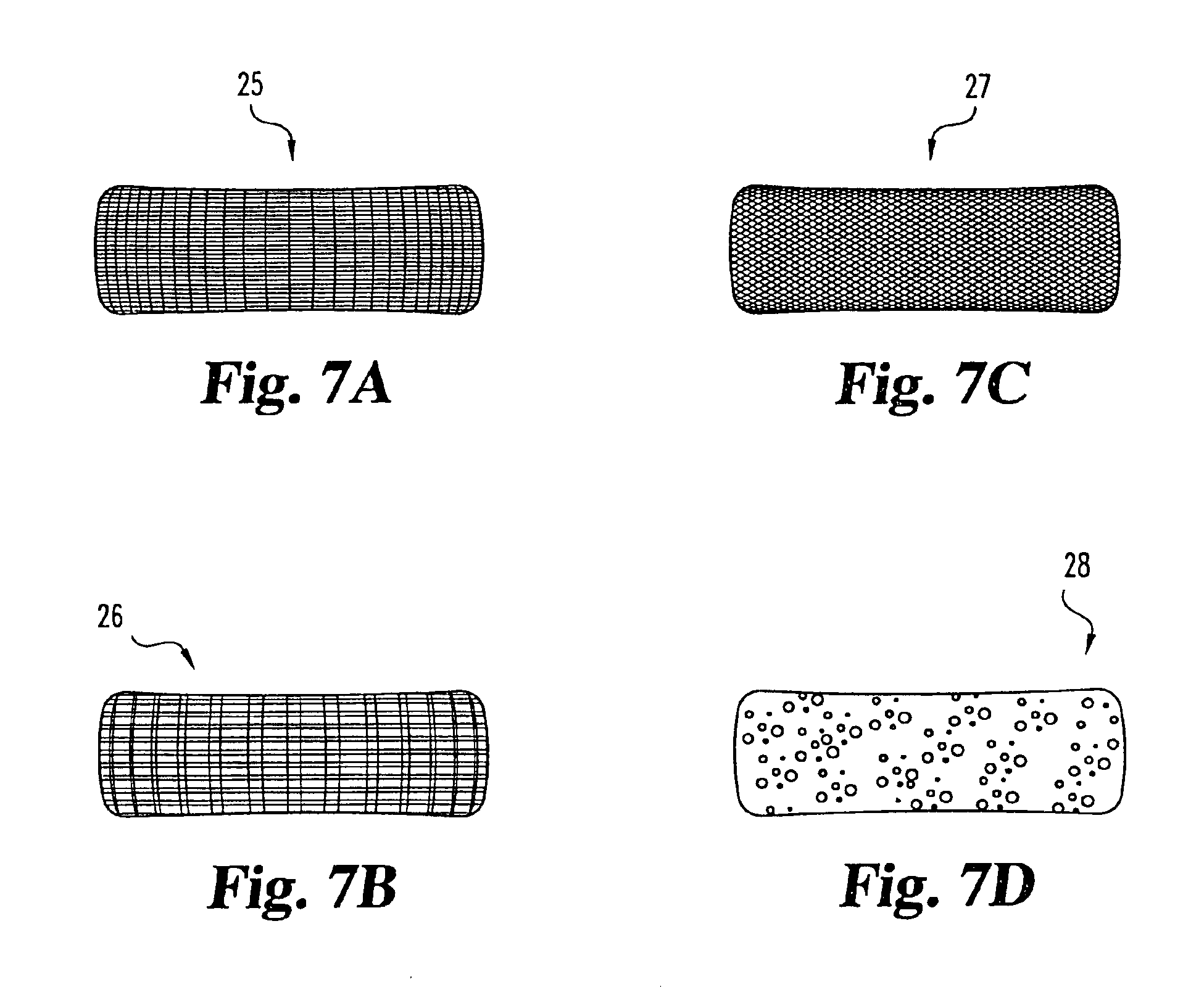
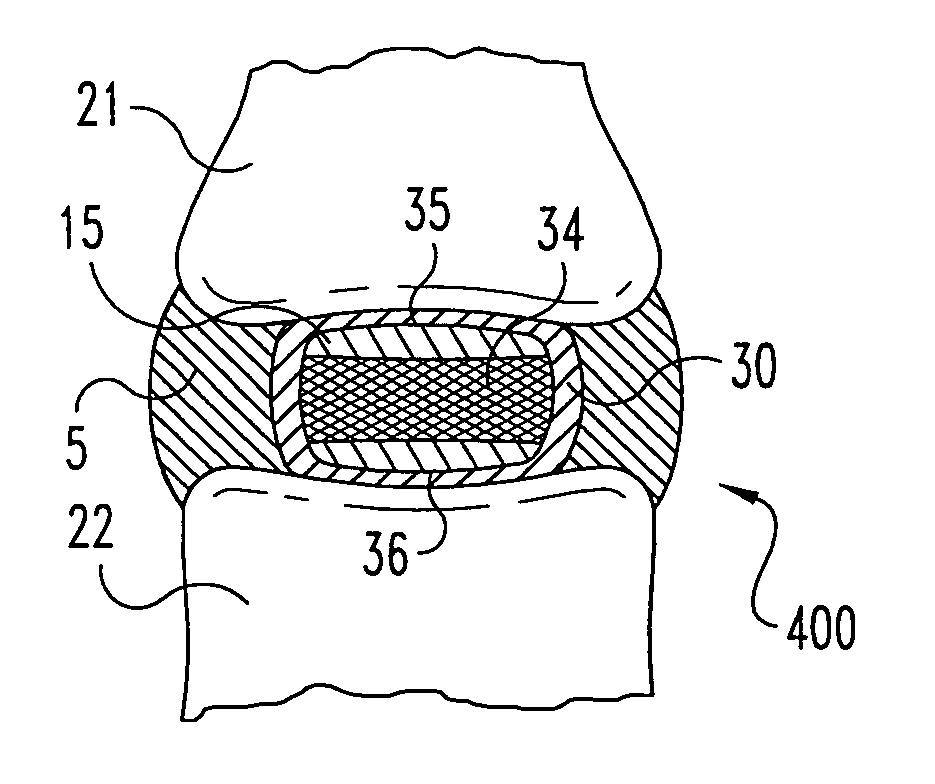
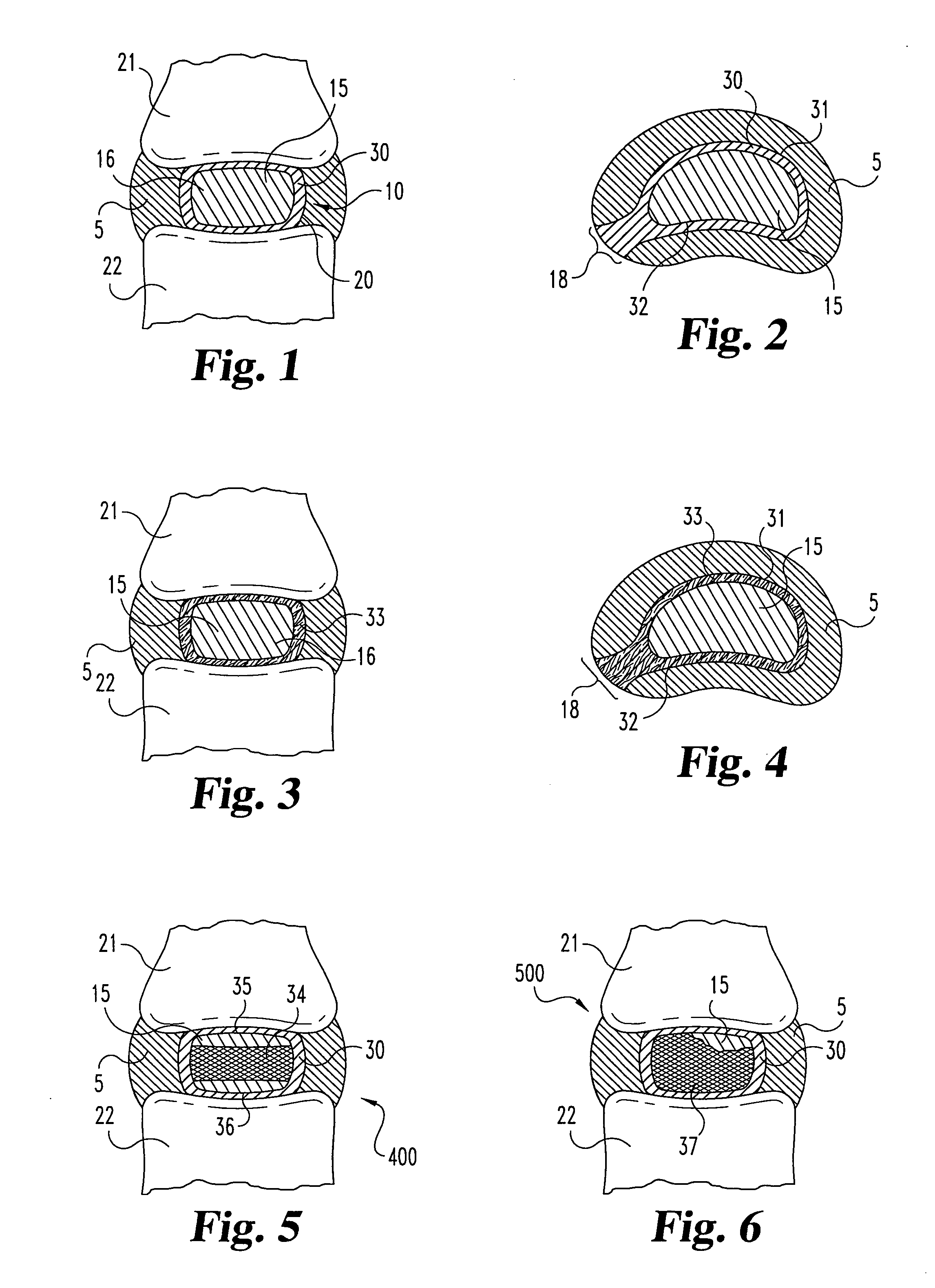
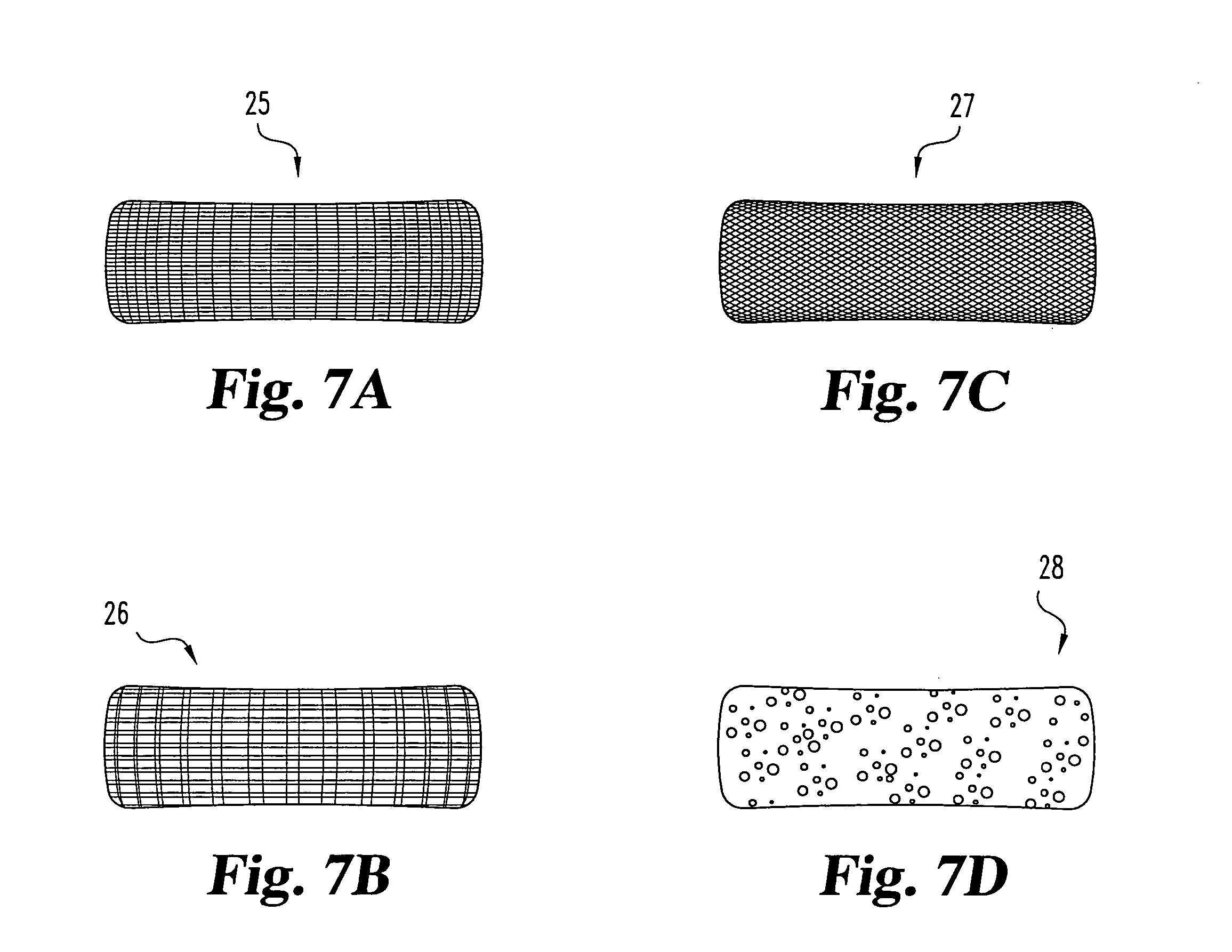
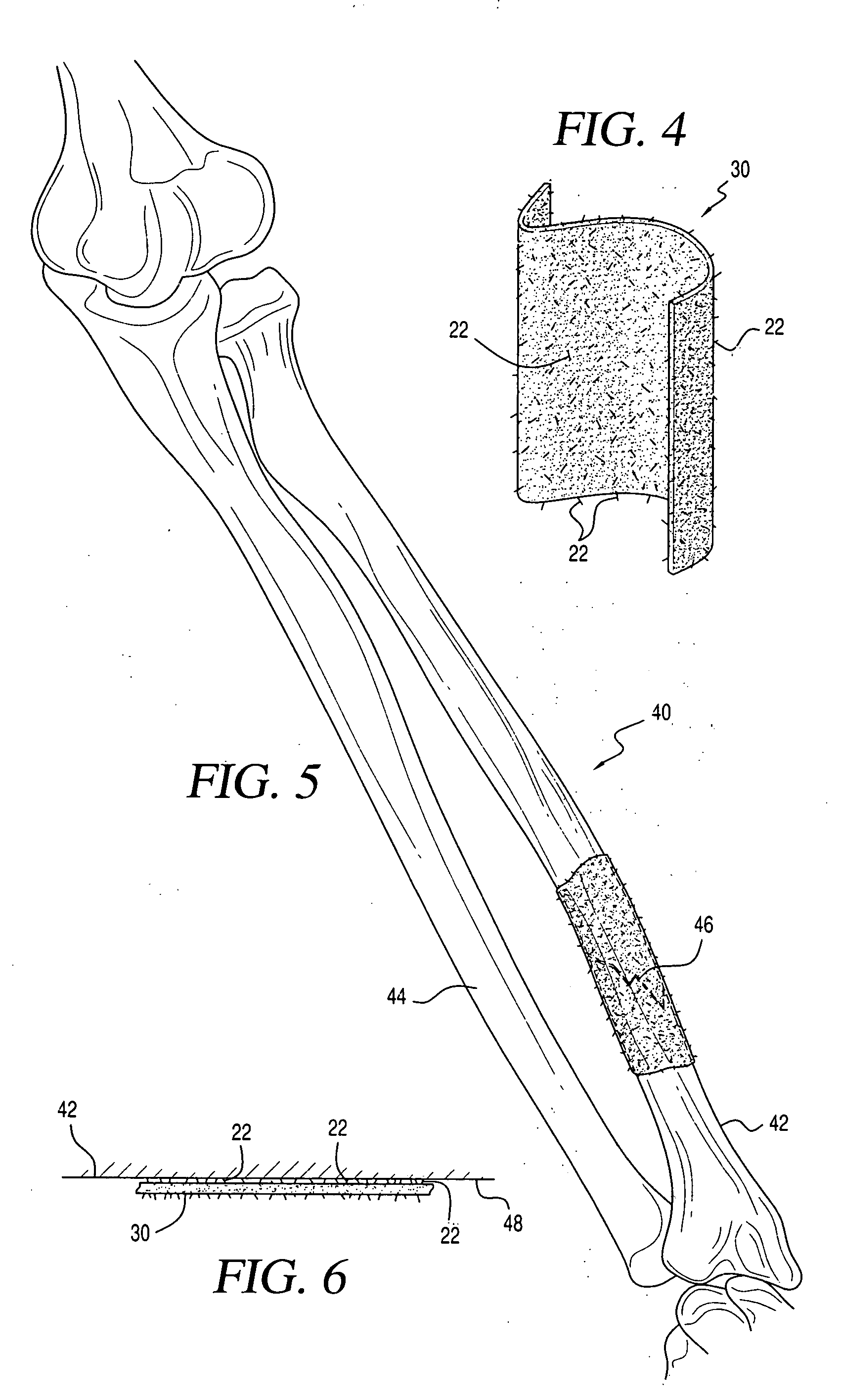
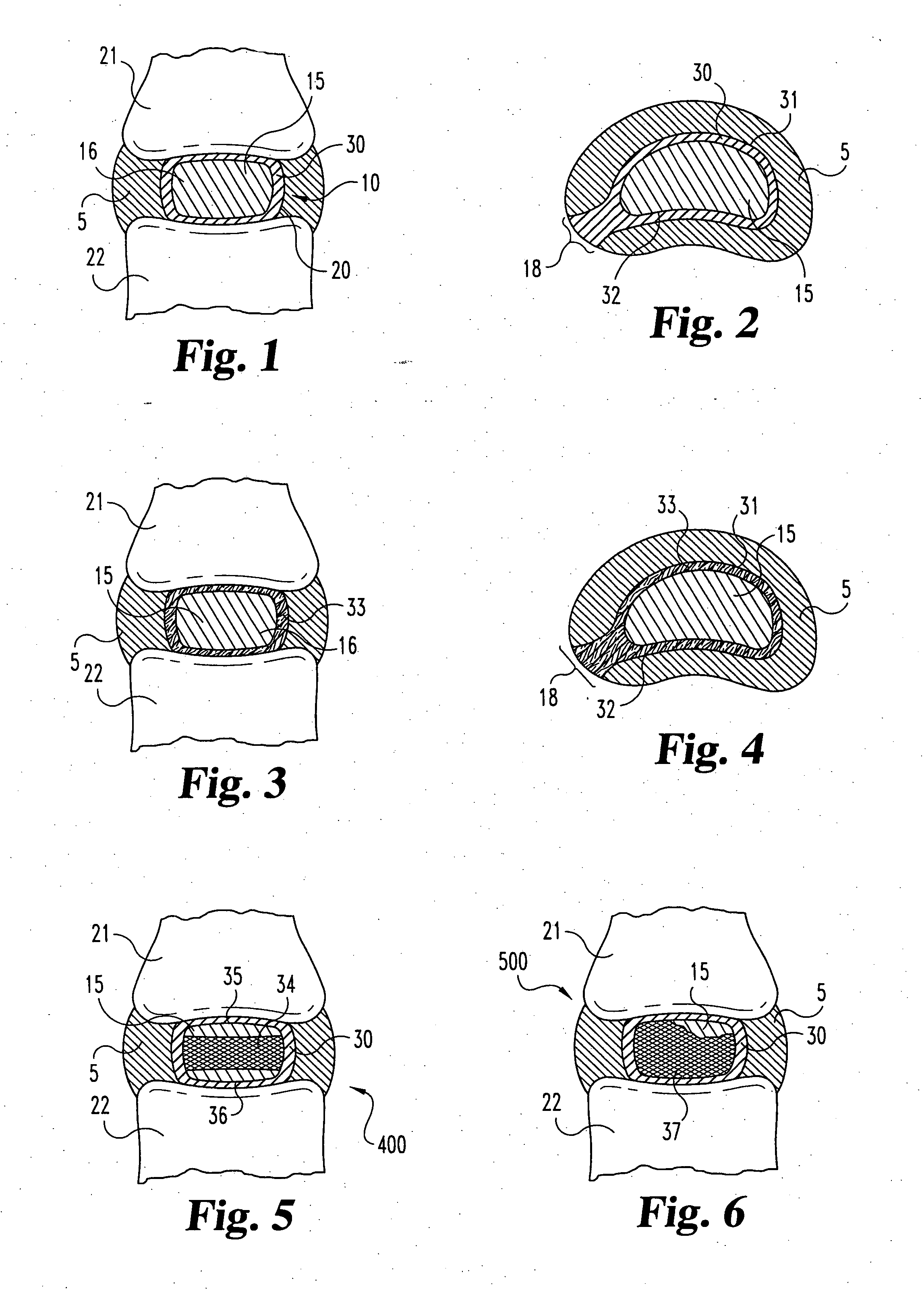
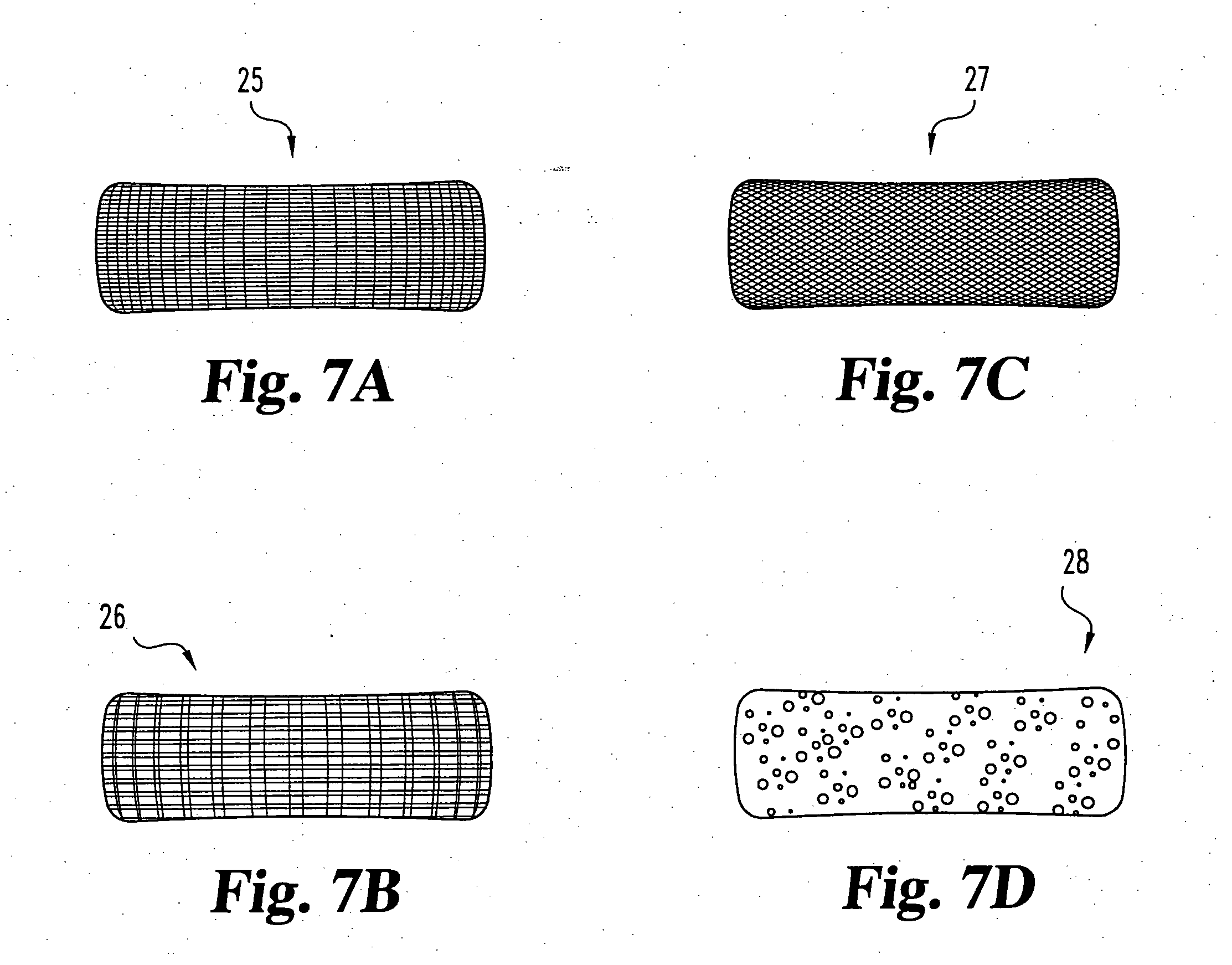
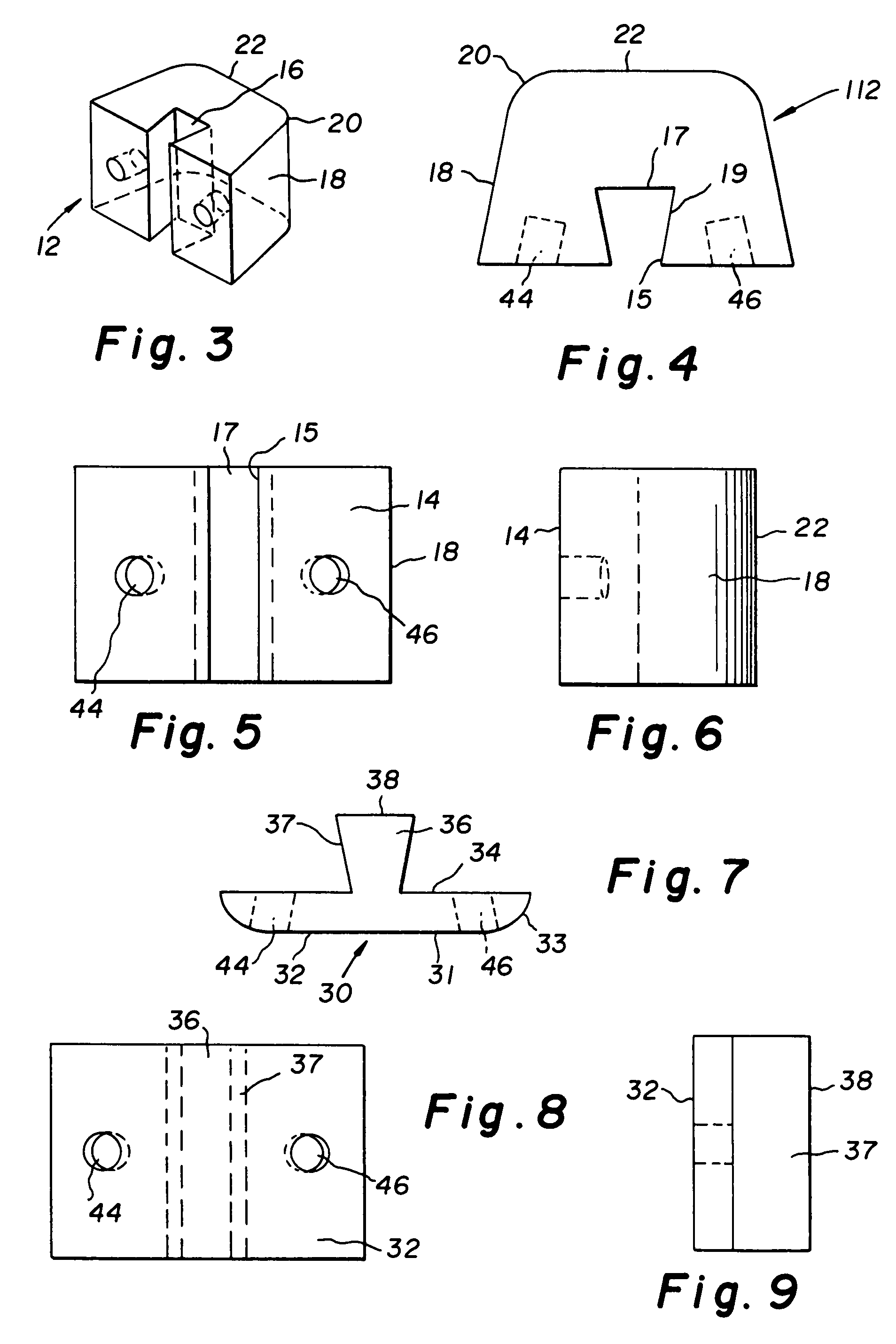
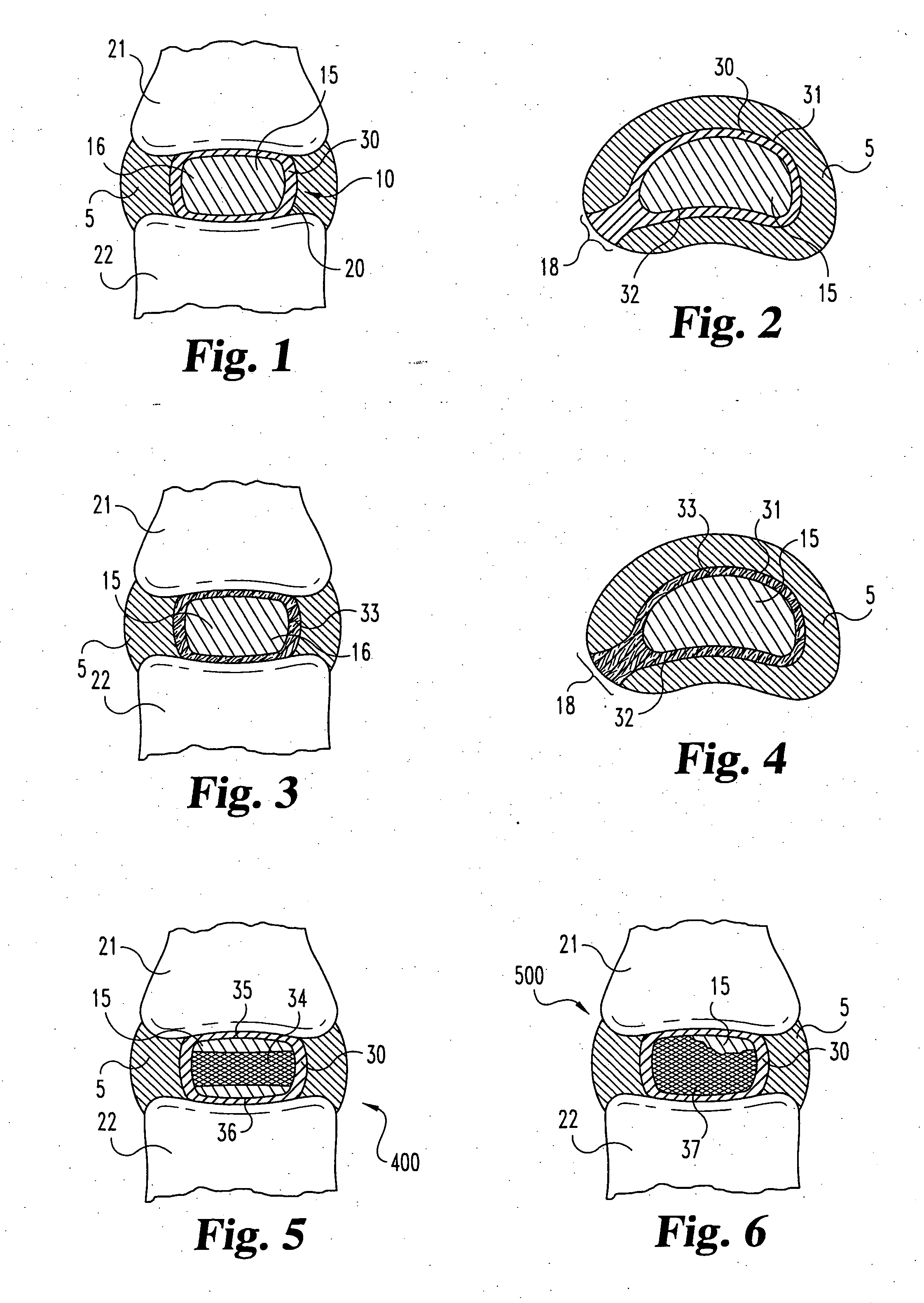
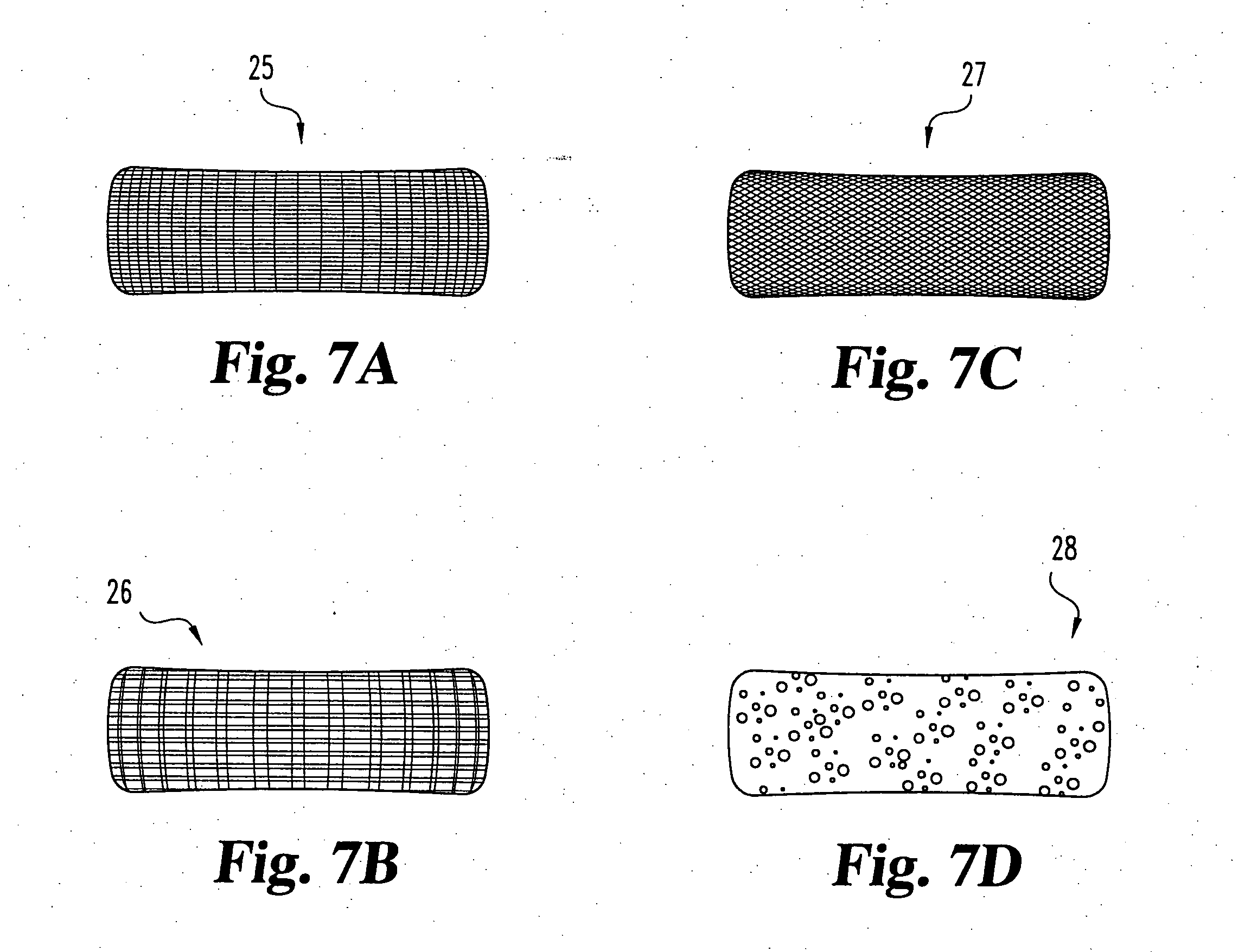
Porous medical device and method for its manufacture
ActiveUS7964206B2Thickness of device can be variedControllable porosityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsFiberBioceramic
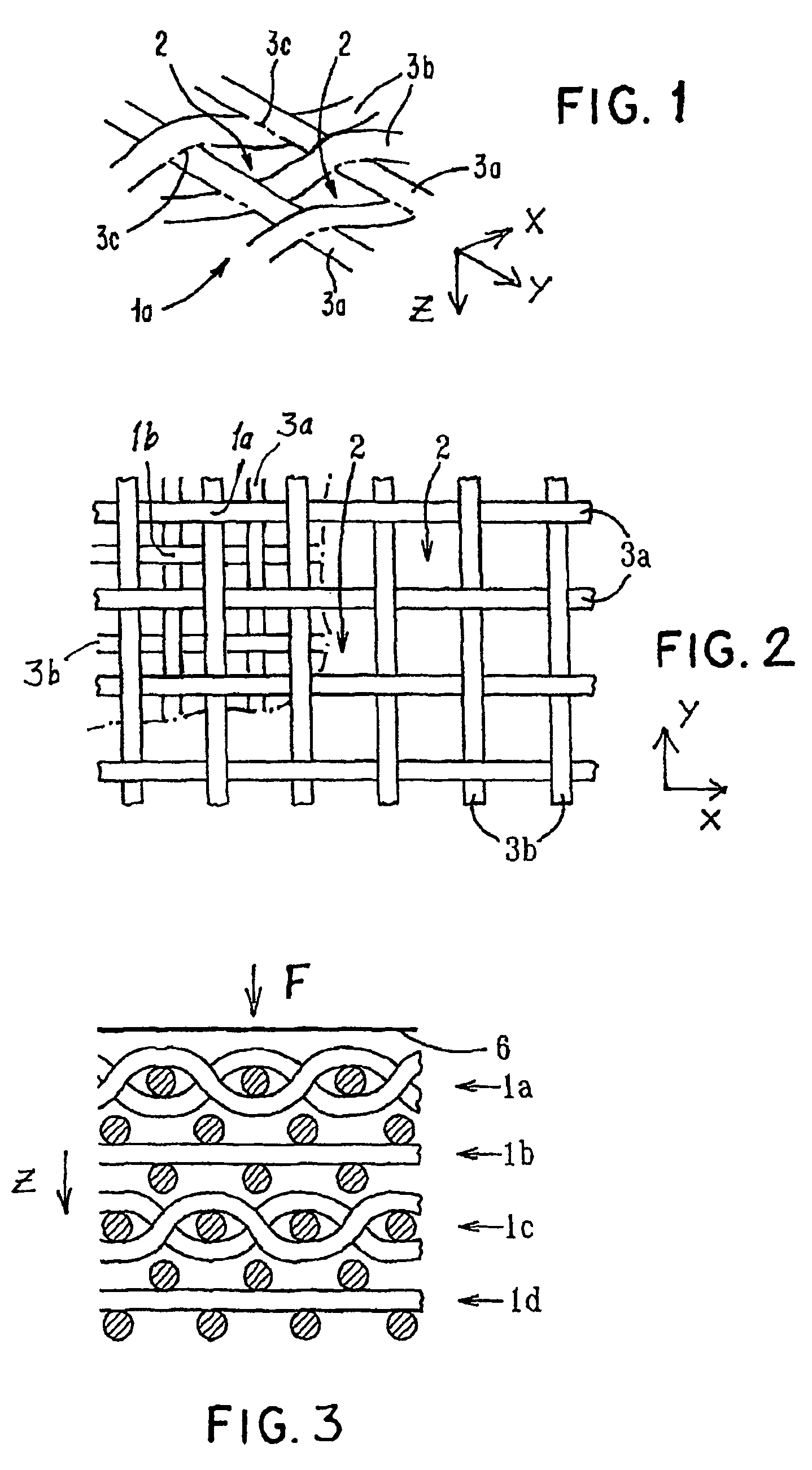
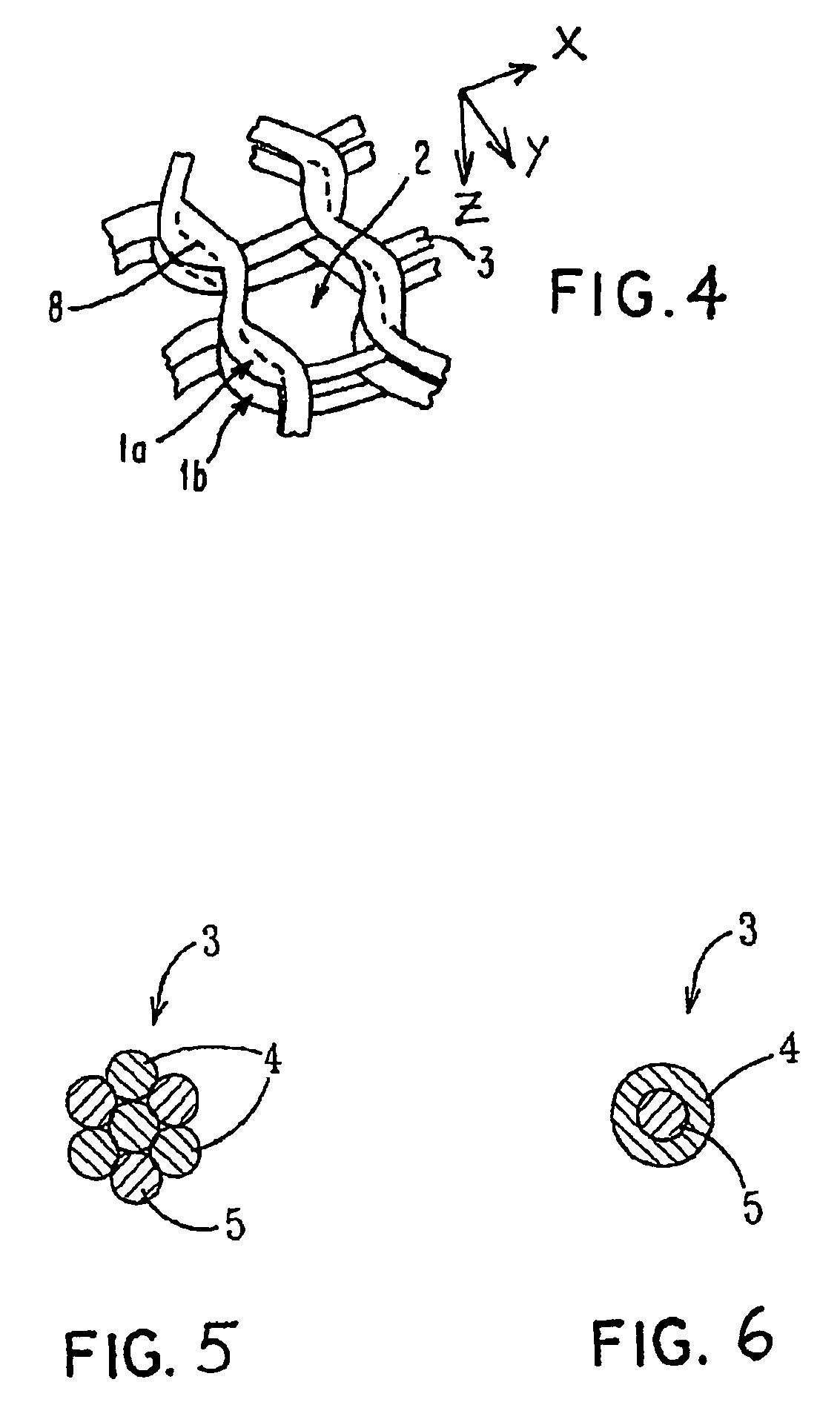
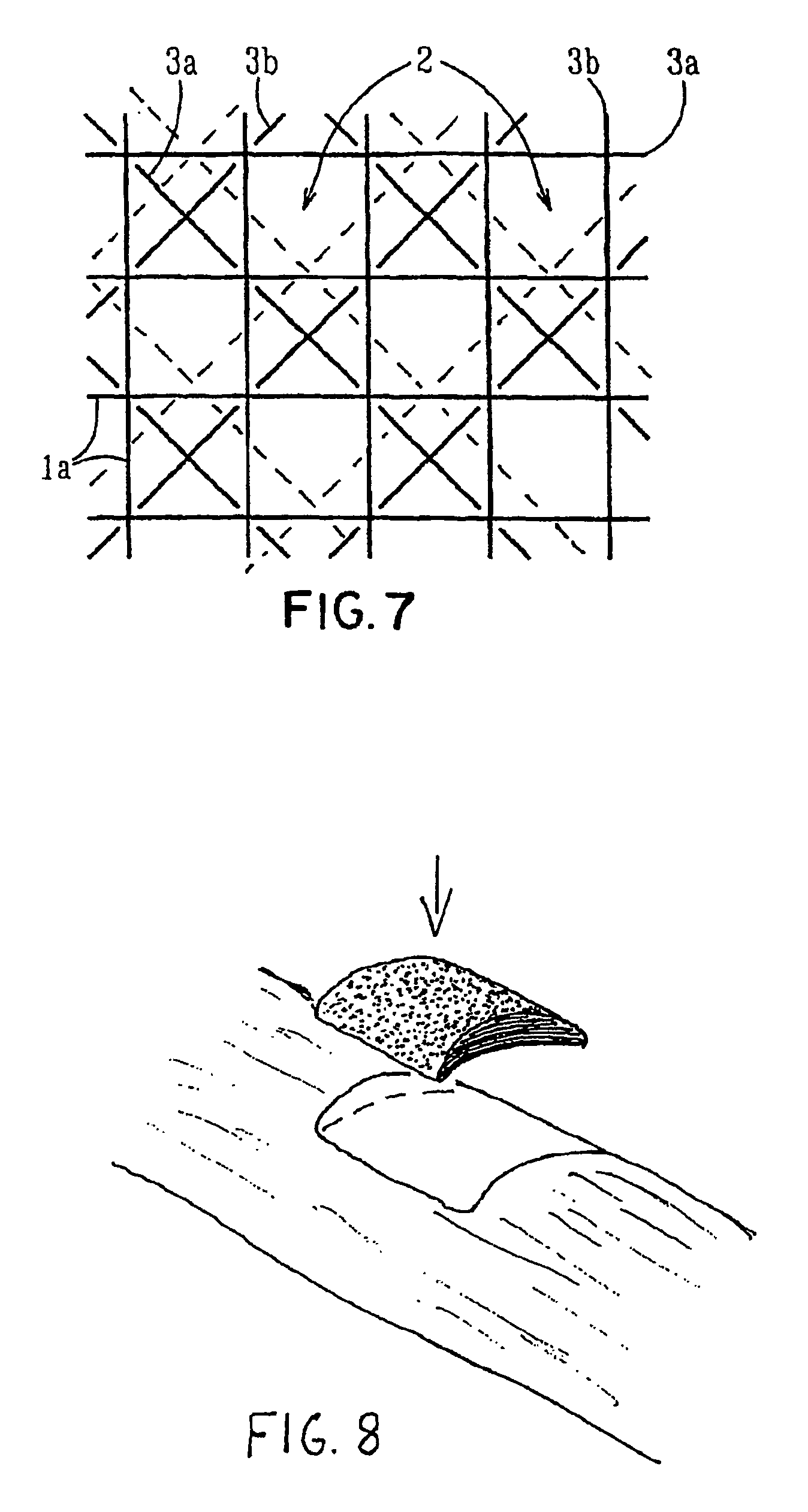
Porous bioabsorbable, bioactive and load-bearing composite medical device structure includes a plurality of regular textile planar layers (1a, 1b . . . ) formed of continuous bioabsorbable polymer matrix and bioceramic fibers acting as reinforcements, both included in continuous fibrous elements (3) forming the textile layers. The layers are placed on top of each other to form a structure having two dimensions (x, y) at right angles to each other according to the two dimensions of the textile layer and a third dimension (z) perpendicular to them and resulting from the piling of the layers. A plurality of passages extend through the layers as a result of the openings (2) defined by portions of the continuous fibrous elements (3) extending substantially in the direction of the plane. The continuous fibrous elements (3) comprise both bioactive ceramic reinforcing fibers which form a reinforcing structure and a bioabsorbable polymer matrix material which forms a matrix which binds the layers together and also binds the portions of continuous fibers defining the openings together, thereby forming the passages and stiffening the structure. This bioactive and bioabsorbable composite structure is suitable to be used as a basic structure in medical devices, especially in osteochondral applications where the load-bearing properties of implant are required.
Owner:BIORETEC
Selectively absorbable/biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs and applications thereof
A family of selectively absorbable / biodegradable, fibrous composite constructs includes different combinations of biostable and absorbable / biodegradable yarns assembled as initially interdependent, load-bearing components, transitioning to exhibit independent functional properties during in vivo end-use. The family of constructs consists of two groups, one group is made of fiber-reinforced composites of high compliance, absorbable matrices of segmented polyaxial copolyesters reinforced with multifilament yarn constructs, which are combinations of ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene fibers and at least one absorbable / biodegradable fiber selected from silk fibers and multifilament yarns made from linear segmented, l-lactide copolyesters and poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates, are useful in orthopedic, maxillofacial, urological, vascular, hernial repair and tissue engineering applications. The second group is made of coated and uncoated, warp-knitted mesh constructs for use in hernial, vascular, and urological tissue repair and tissue engineering.
Owner:POLY MED
Shaped load-bearing osteoimplant and methods of making same
InactiveUS20030039676A1Promotes new host bone tissue formationPermit of mechanical propertySuture equipmentsDental implantsMedicineHard tissue
A load-bearing osteoimplant, methods of making the osteoimplant and method for repairing hard tissue such as bone and teeth employing the osteoimplant are provided. The osteoimplant comprises a shaped, coherent mass of bone particles which may exhibit osteogenic properties. In addition, the osteoimplant may possess one or more optional components which modify its mechanical and / or bioactive properties, e.g., binders, fillers, reinforcing components, etc.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
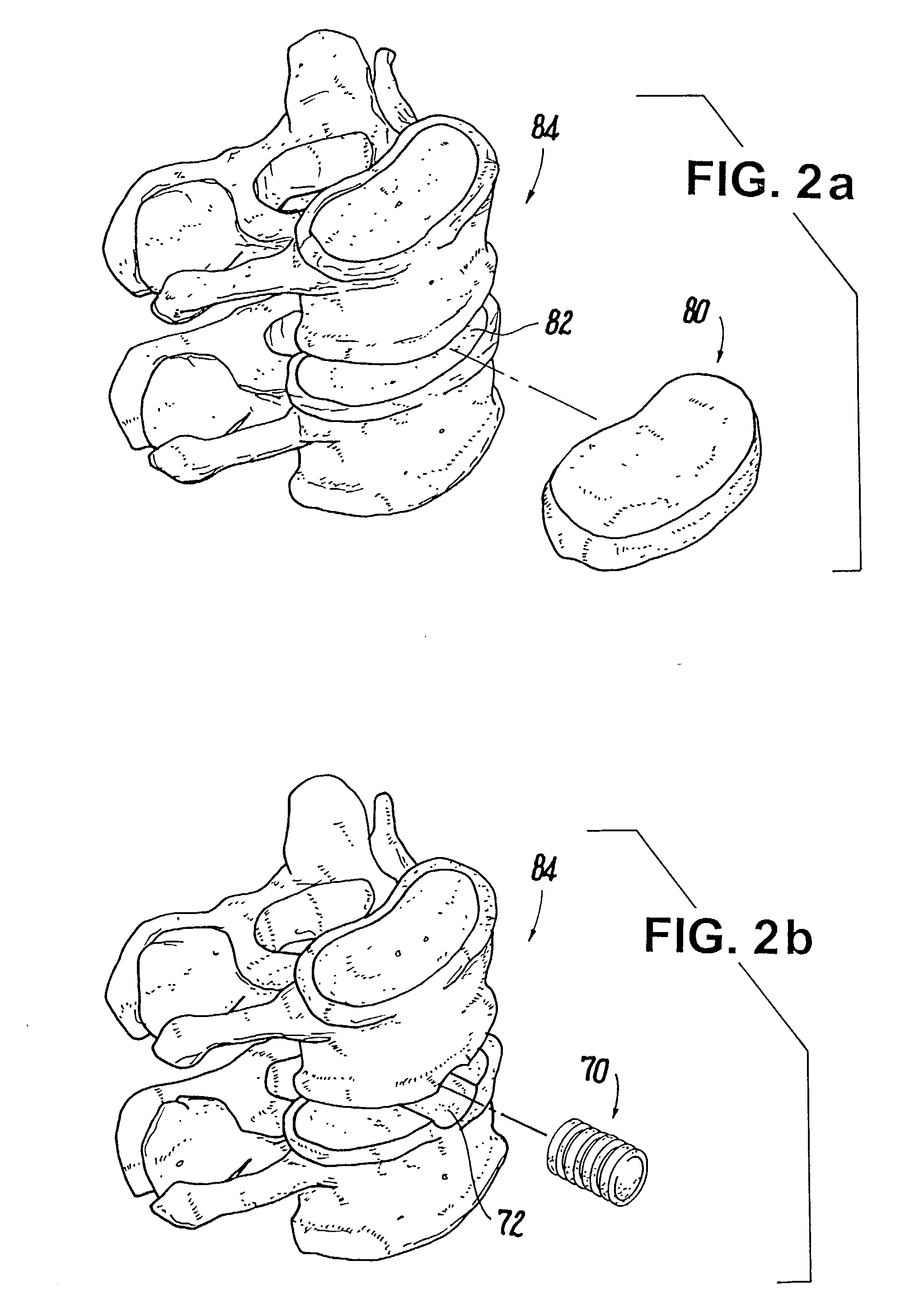
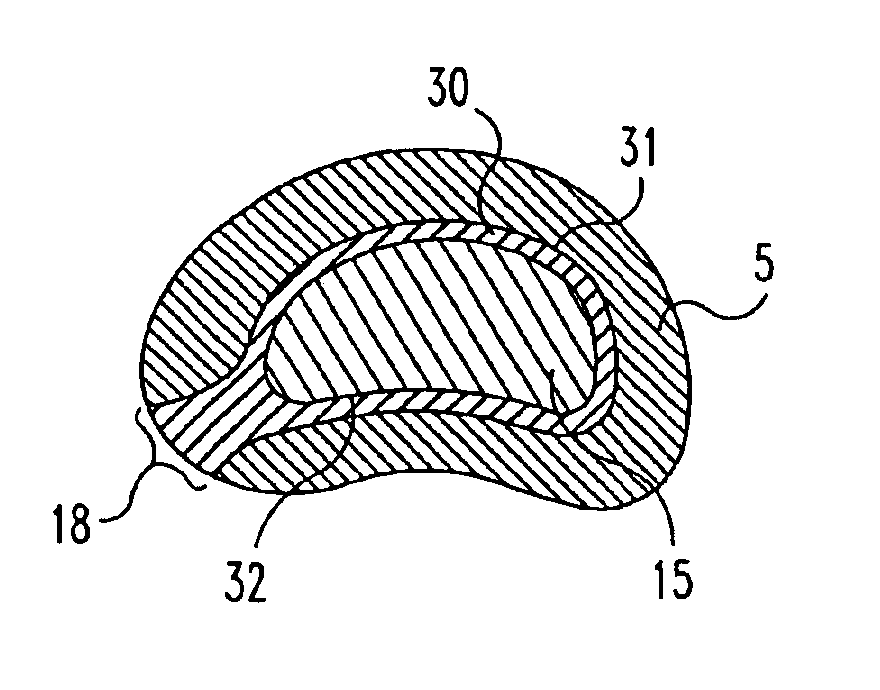
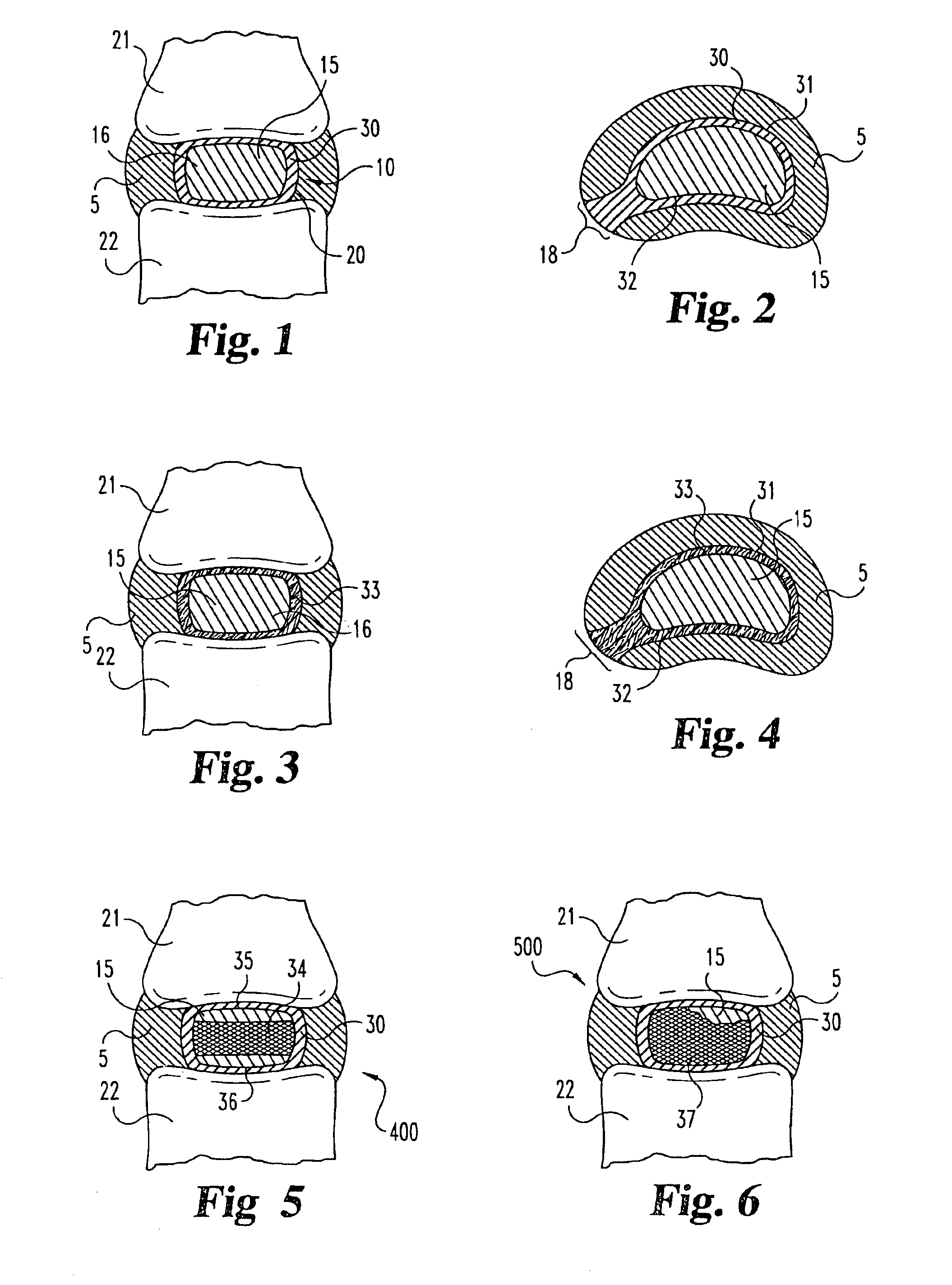
Intervertebral disc nucleus implants and methods
InactiveUS6893466B2Improve bindingLarge deformationBone implantSurgeryShort termsBiomedical engineering
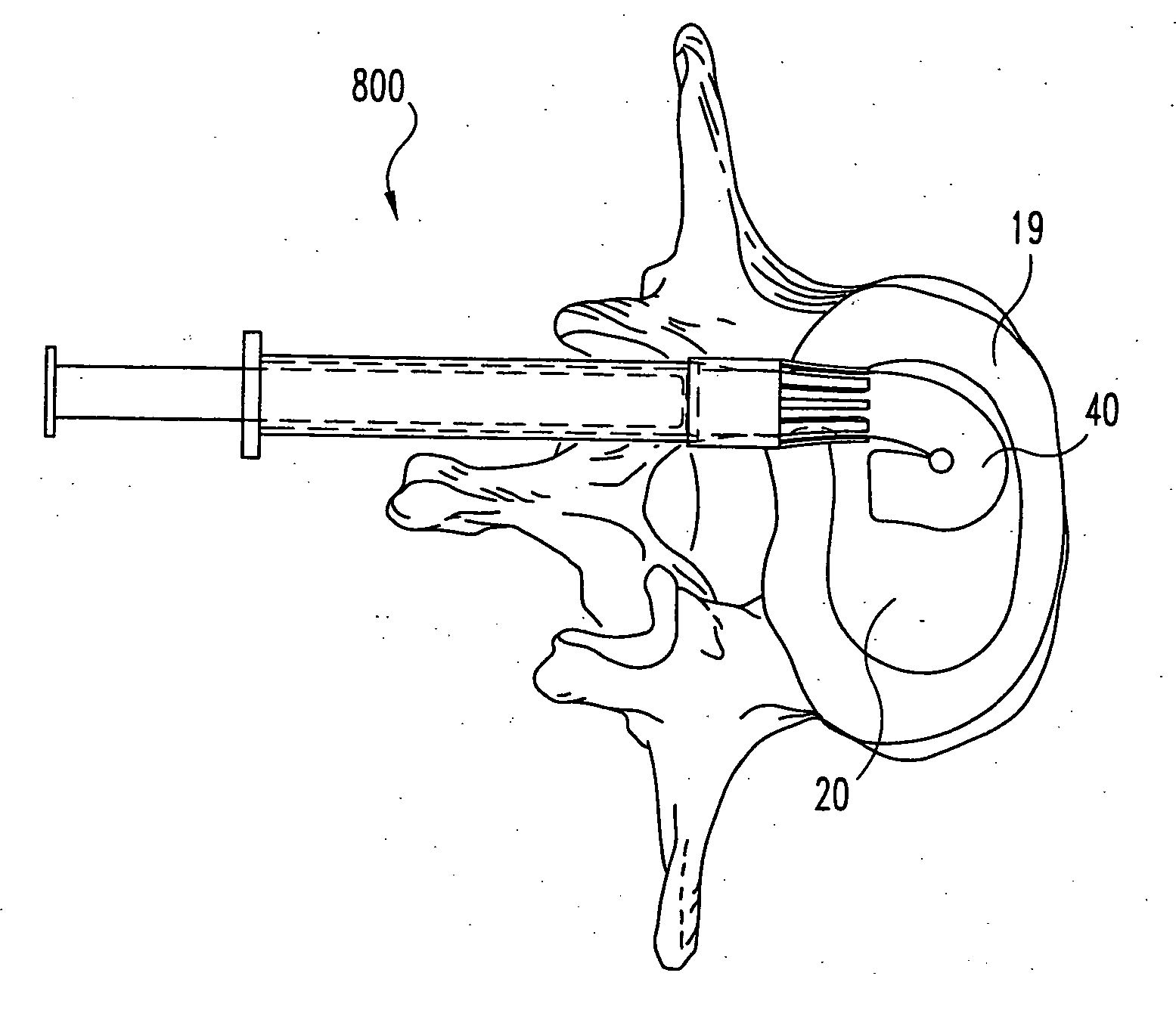
Nucleus pulposus implants that are resistant to migration in and / or expulsion from an intervertebral disc space are provided. In one form of the invention, an implant includes a load bearing elastic body surrounded in the disc space by an anchoring, preferably resorbable, outer shell. In certain forms of the invention, the elastic body is surrounded by a supporting member, such as a band or jacket, and the supporting member is surrounded by the outer shell. Kits for forming such implants are also provided. In another form of the invention, an implant is provided that has locking features and optional shape memory characteristics. In yet another aspect of the invention, nucleus pulposus implants are provided that have shape memory characteristics and are configured to allow short-term manual, or other deformation without permanent deformation, cracks, tears, breakage or other damage. Methods of forming and implanting the implants are also described.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
In situ formation of intervertebral disc implants
InactiveUS20060089719A1Improve bindingLarge deformationSkeletal disorderSpinal implantsSpinal Disk ImplantShort terms
Nucleus pulposus implants that are resistant to migration in and / or expulsion from an intervertebral disc space are provided. In one form of the invention, an implant includes a load bearing elastic body surrounded in the disc space by an anchoring, preferably resorbable, biocompatible material which may be in the form of an outer shell. In certain forms of the invention, the elastic body is surrounded by a supporting member, such as a band or jacket, and the supporting member is surrounded by the outer shell. Kits for forming such implants are also provided. In another form of the invention, an implant is provided that has locking features and optional shape memory characteristics. In yet another aspect of the invention, nucleus pulposus implants are provided that have shape memory characteristics and are configured to allow short-term manual, or other deformation without permanent deformation, cracks, tears, breakage or other damage. Methods of forming and implanting the implants are also described, as are delivery devices and components thereof for delivering the implants.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
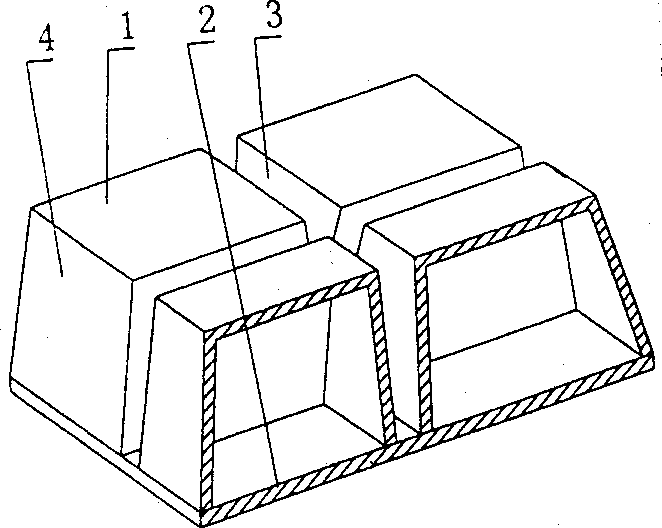
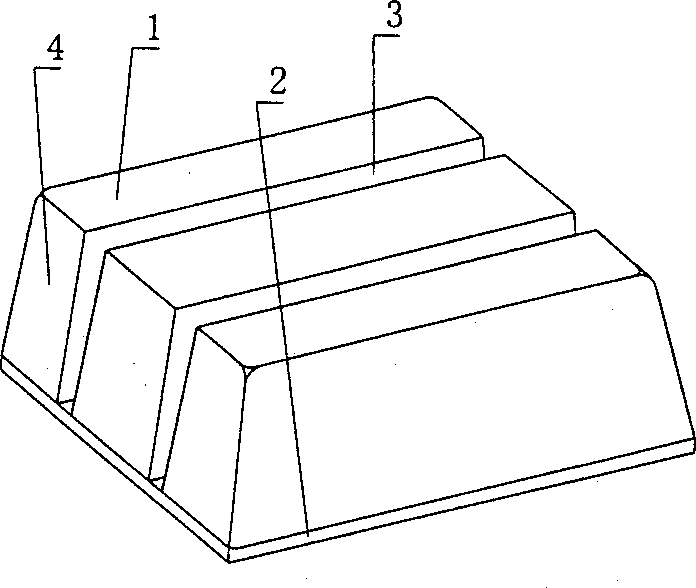
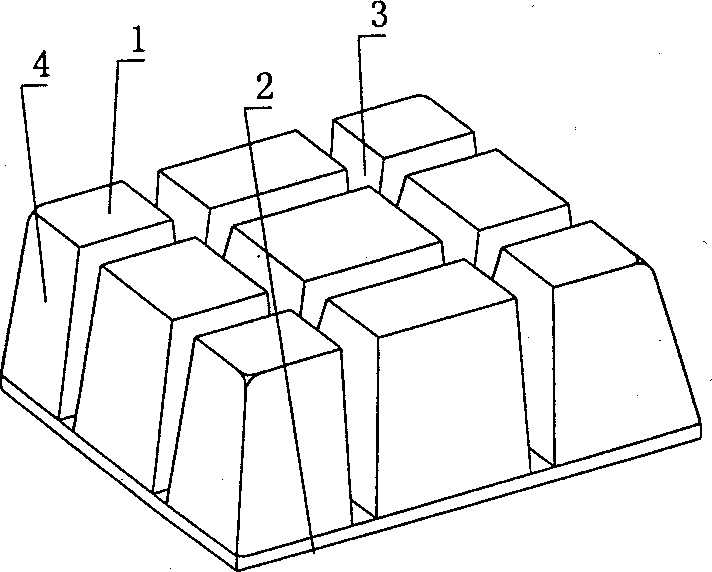
Comobined ribbed cavity member for spatial structure roof
A combined-rib cavity member for space-structure flooring includes cavity form and structure bottom plate, which are connected into one integral whole. It is characterized by that there are at least two cavity forms arranged alternate with each other on the structure bottom plate, its side forms with the structure bottle plate at least one subrit form cavity of casti-in-situ structure, and other other sides of the cavity form forms the side fromboard of main rib or beam or wall for cast-in-situ structure. By this, the subrib of cast-in-situ structure can be formed in the sub-rib form cavity on the structure battom plate, the sub-rib participates in load bearing of structural bottom slat, cast-in-situ main rib, cast-in-sita upper slab so to a load-bearing space structure, improved mechanical property, raise integrity and anti-shock property, decrease structural wt. lower cost and make construction be convenient.
Owner:湖南邱则有专利战略策划有限公司
Hydrogels and methods of making and using same
The invention is directed to methods of making novel porous and solid polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels. These hydrogels are particularly suited for use in the replacement and augmentation of soft tissue or non-load bearing bone of the face, head and cranium.
Owner:POREX CORP
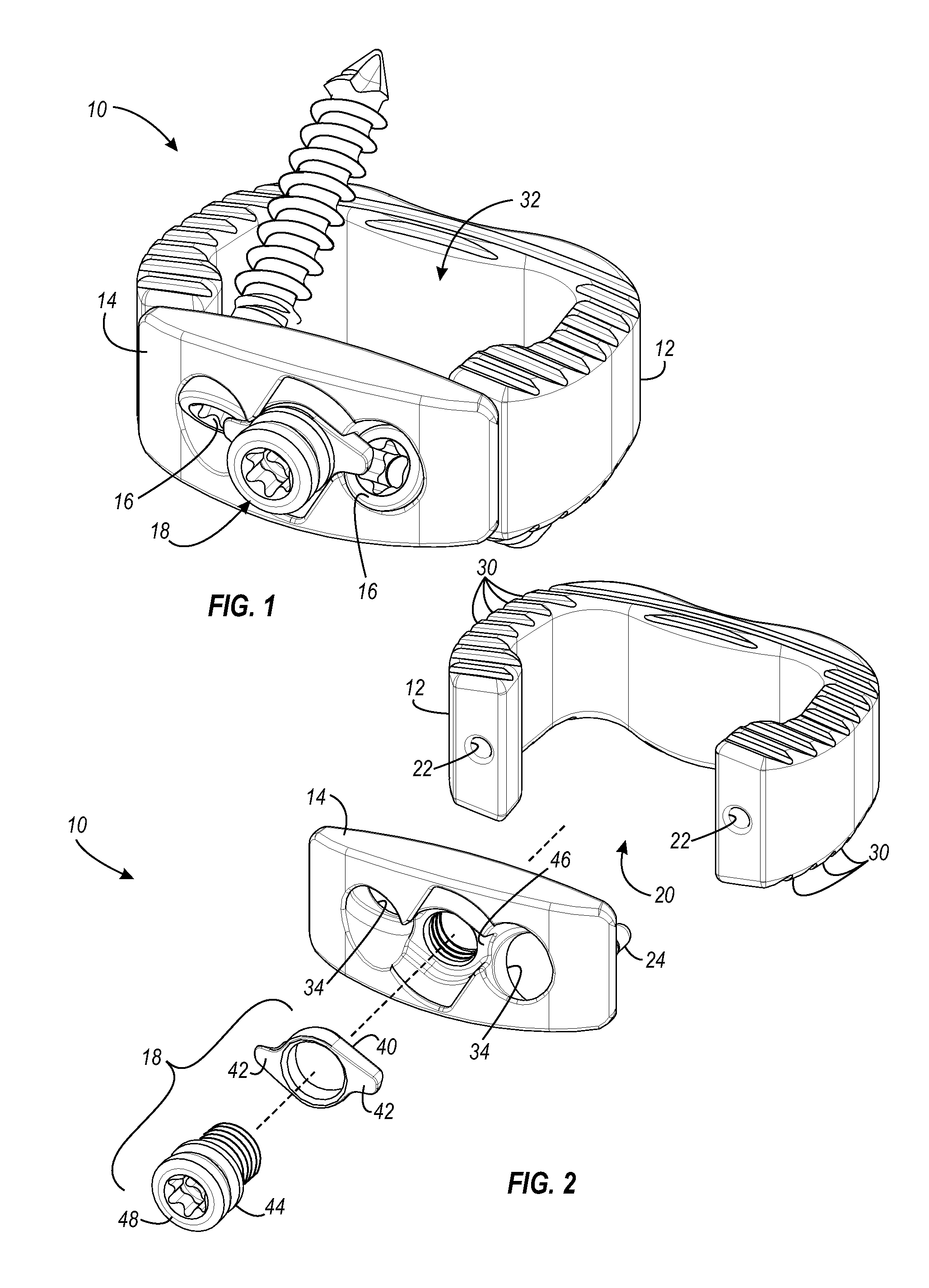
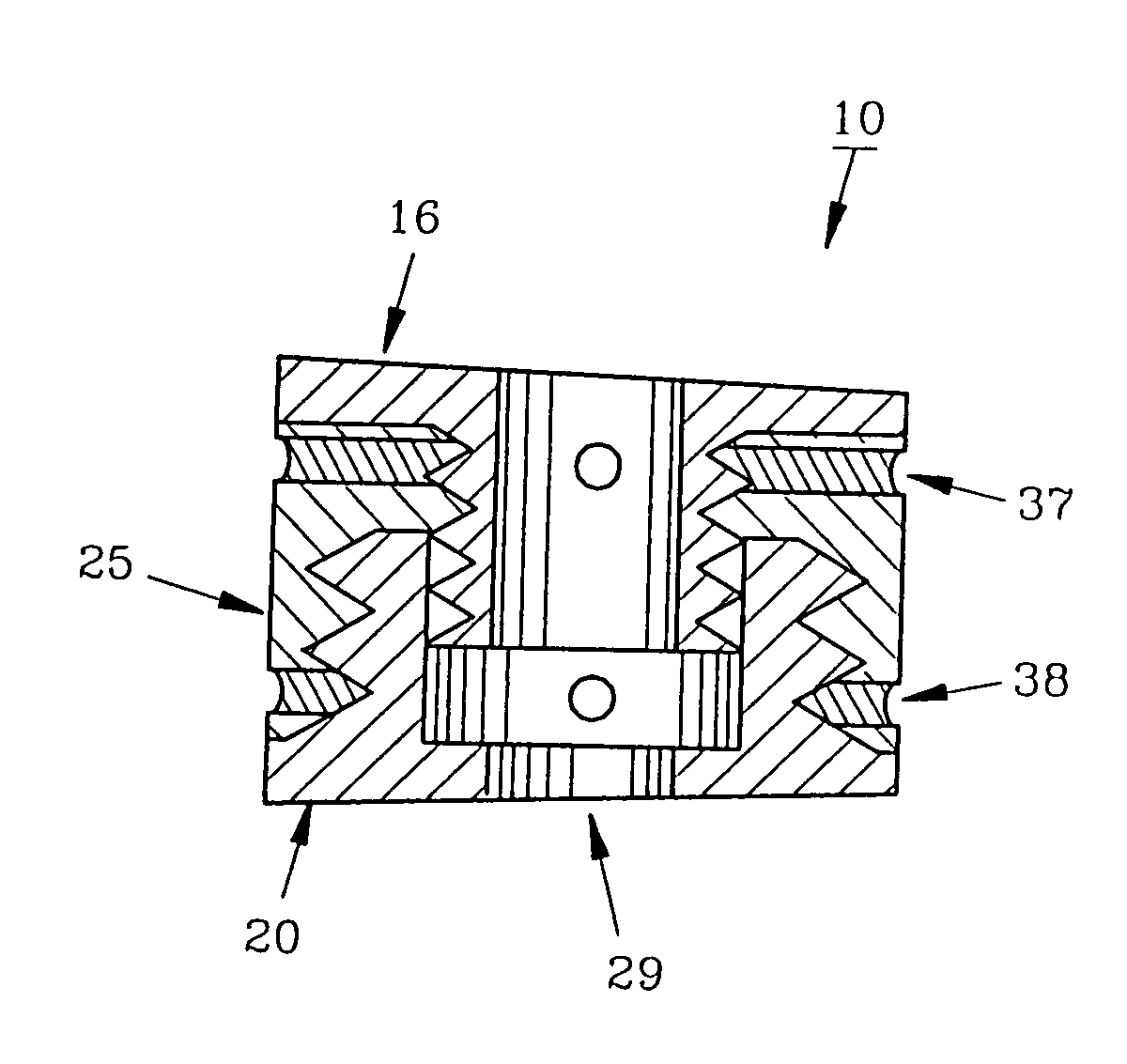
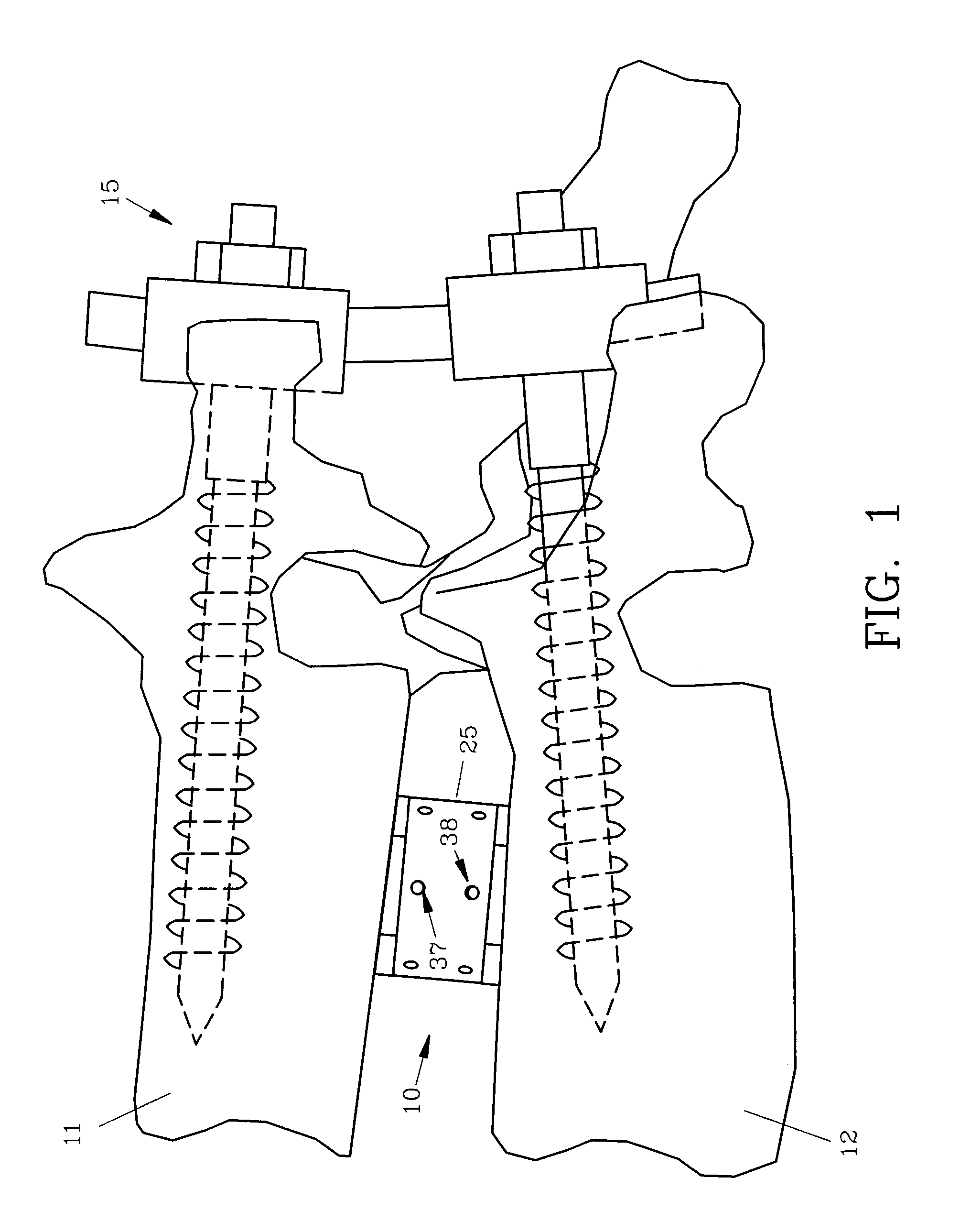
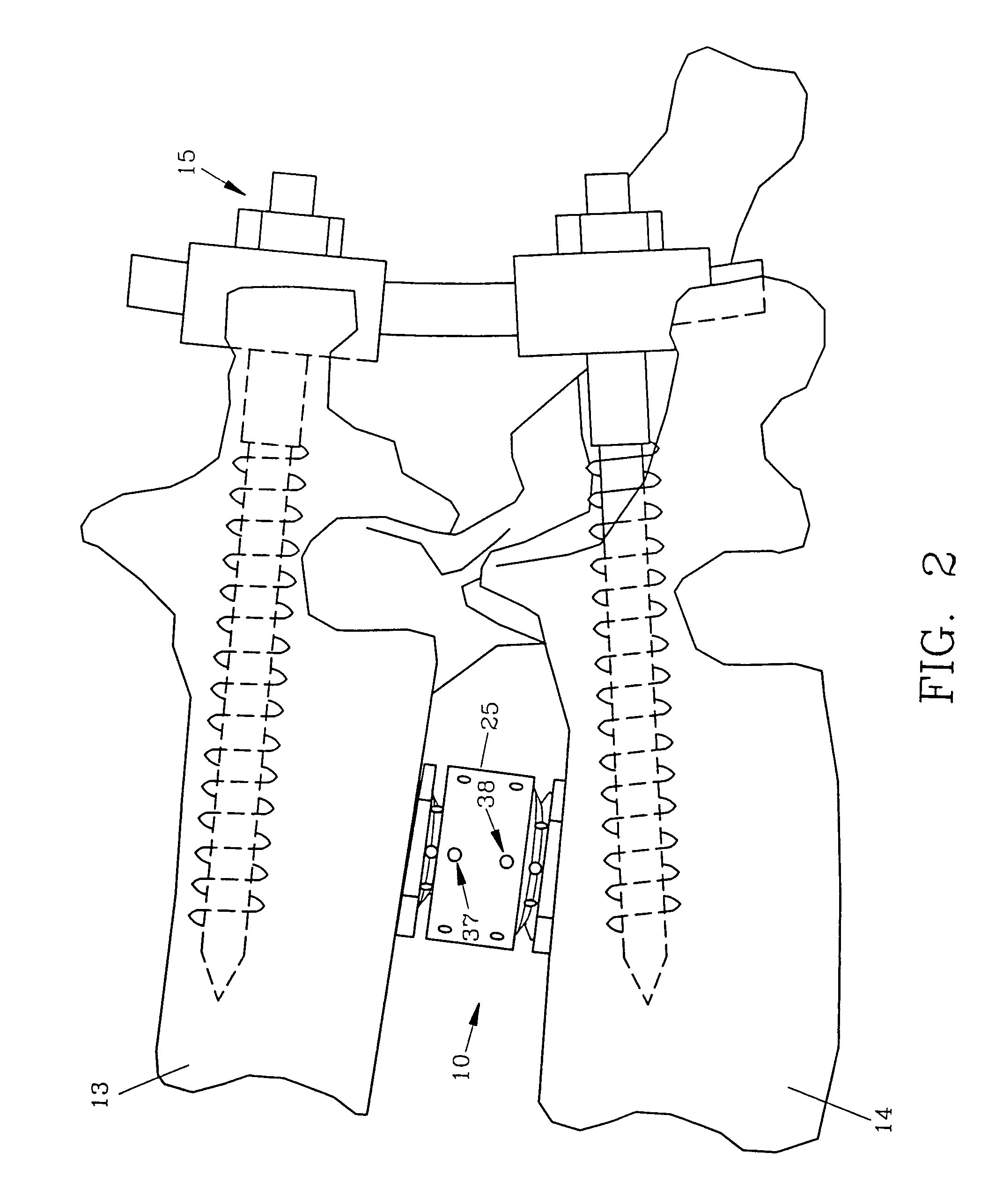
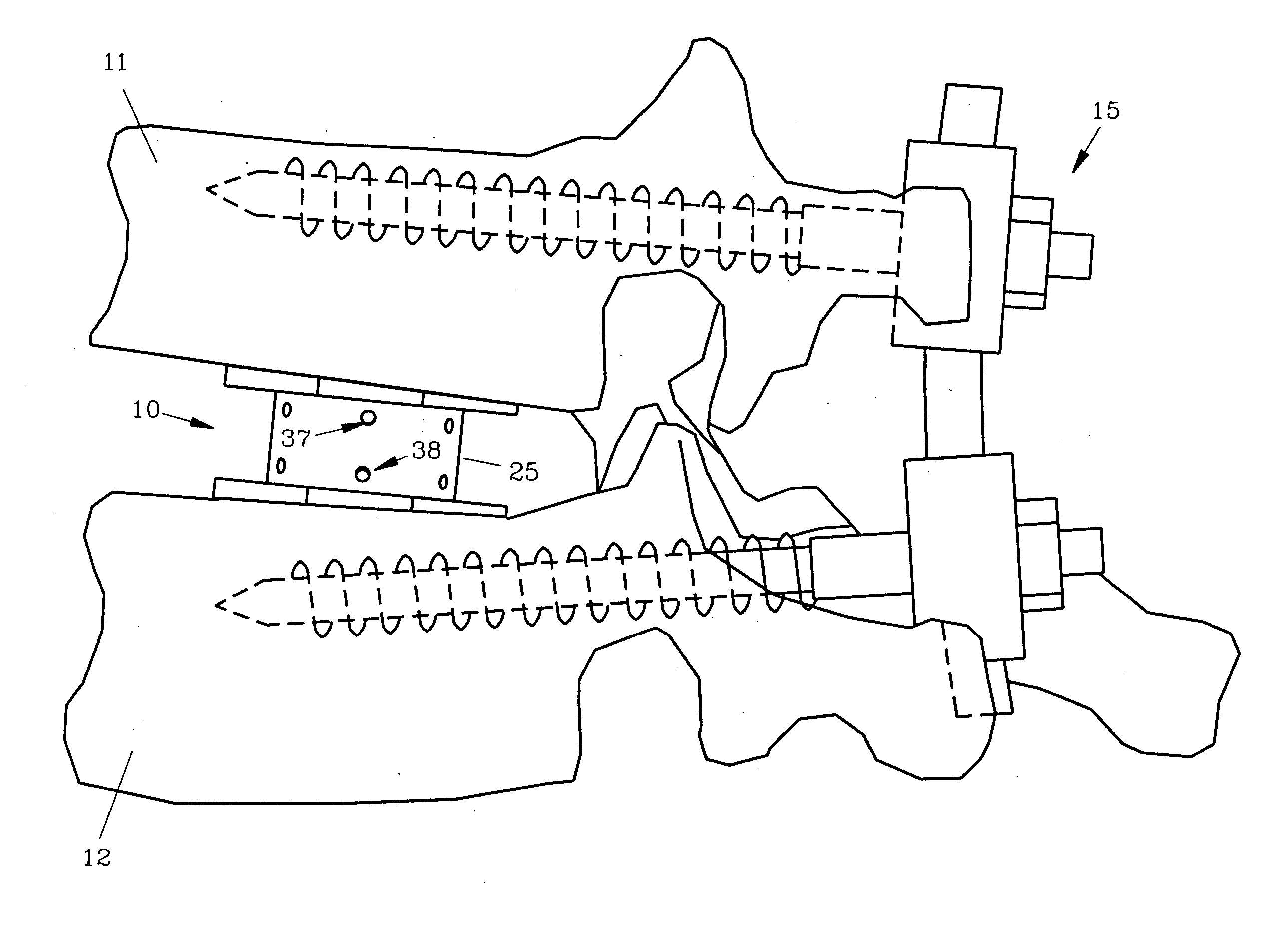
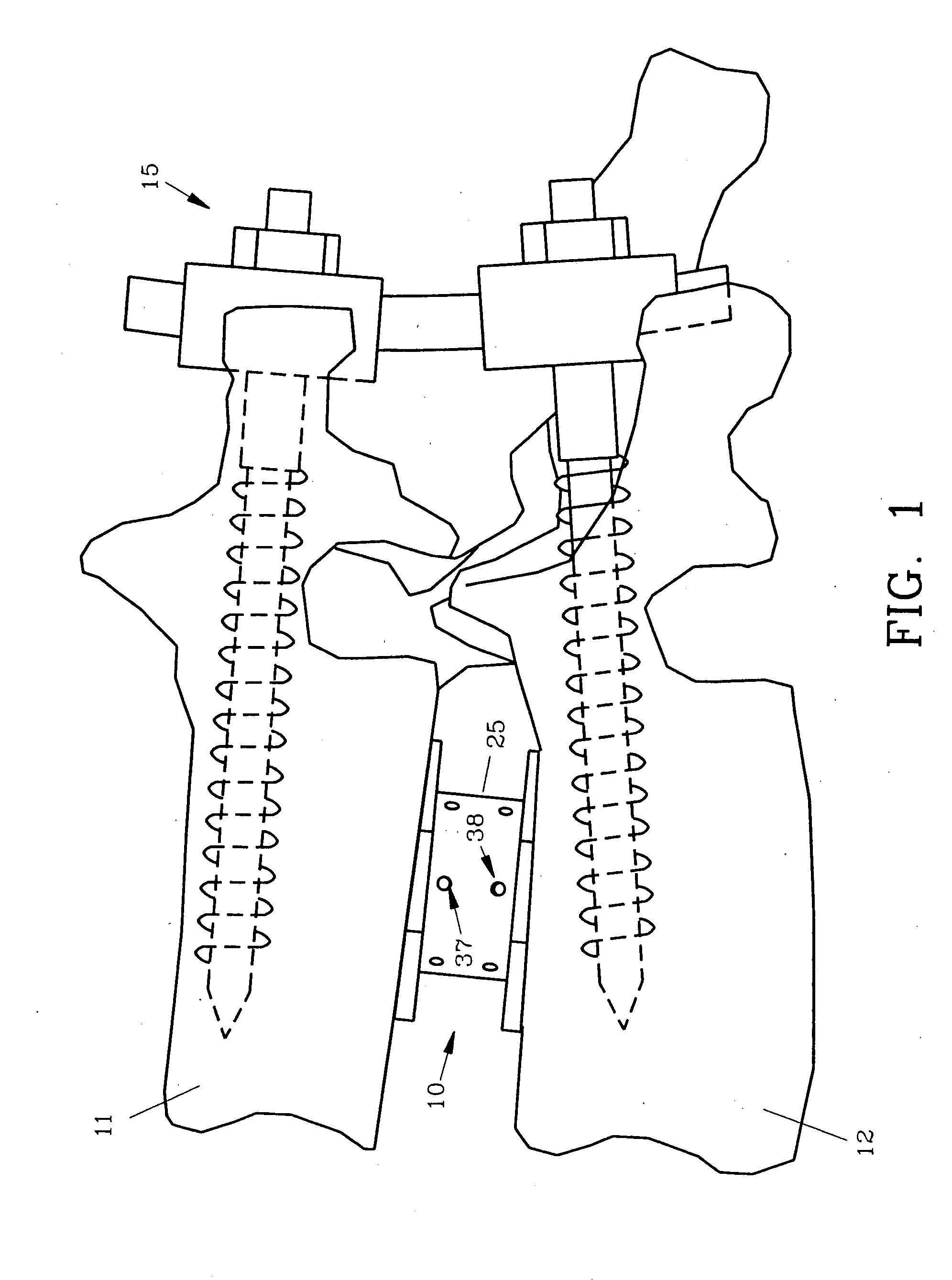
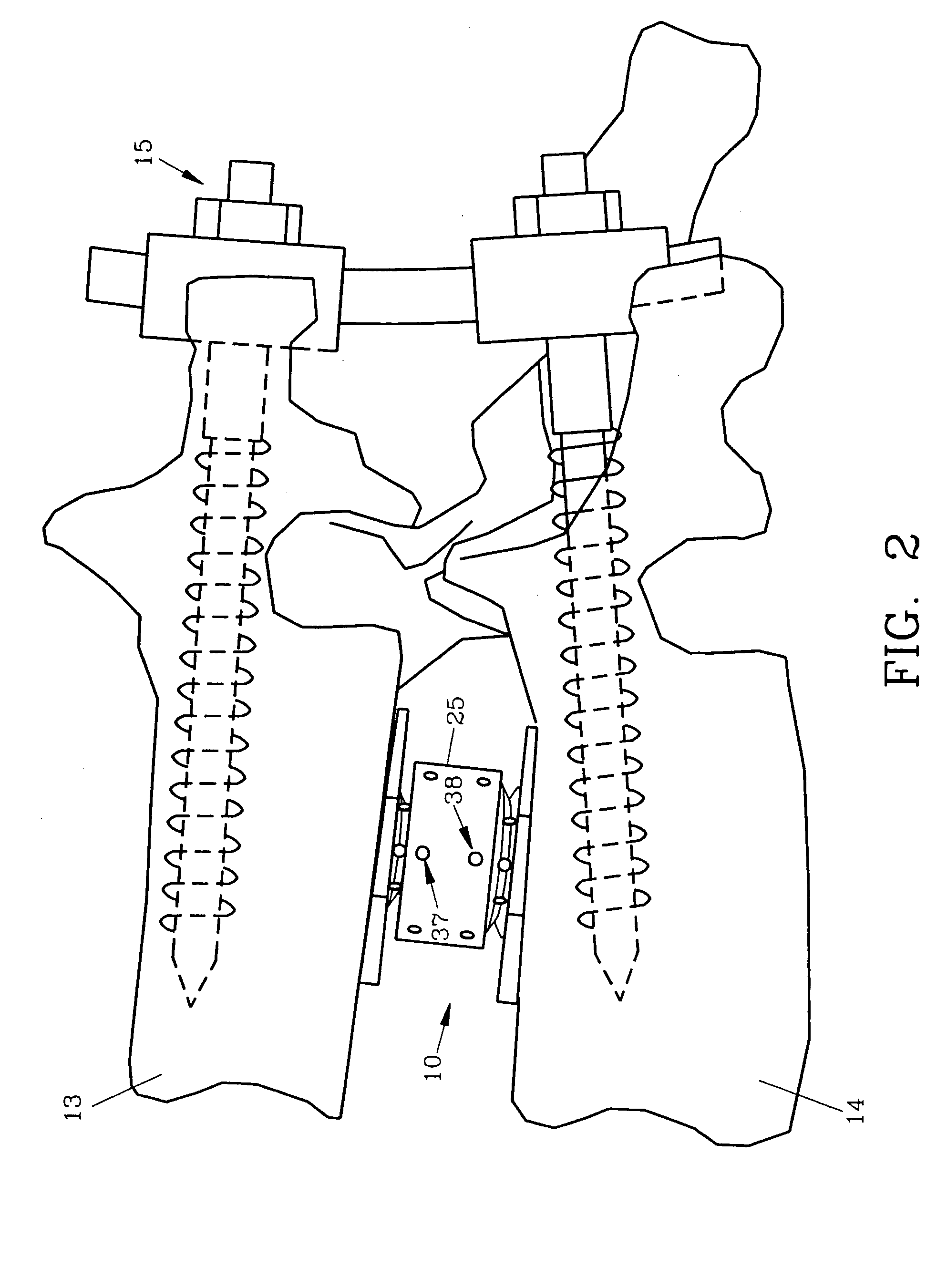
Interbody fusion device, integral retention device, and associated methods
A method and apparatus is provided for use in spinal fusion procedures. A one or two piece interbody fusion device has a fusion bearing component designed to bear the axial loading from the end plates of adjacent vertebrae. An optional retention piece prevents migration of the load bearing device. One or more fasteners secure the retention device to the vertebrae above and below the load bearing device. The fasteners cause the end plates of the vertebrae to compress the end plates to the load bearing device to facilitate proper fusion. An anti-backout mechanism prevents the fasteners backing out.
Owner:SPINESMITH PARTNERS
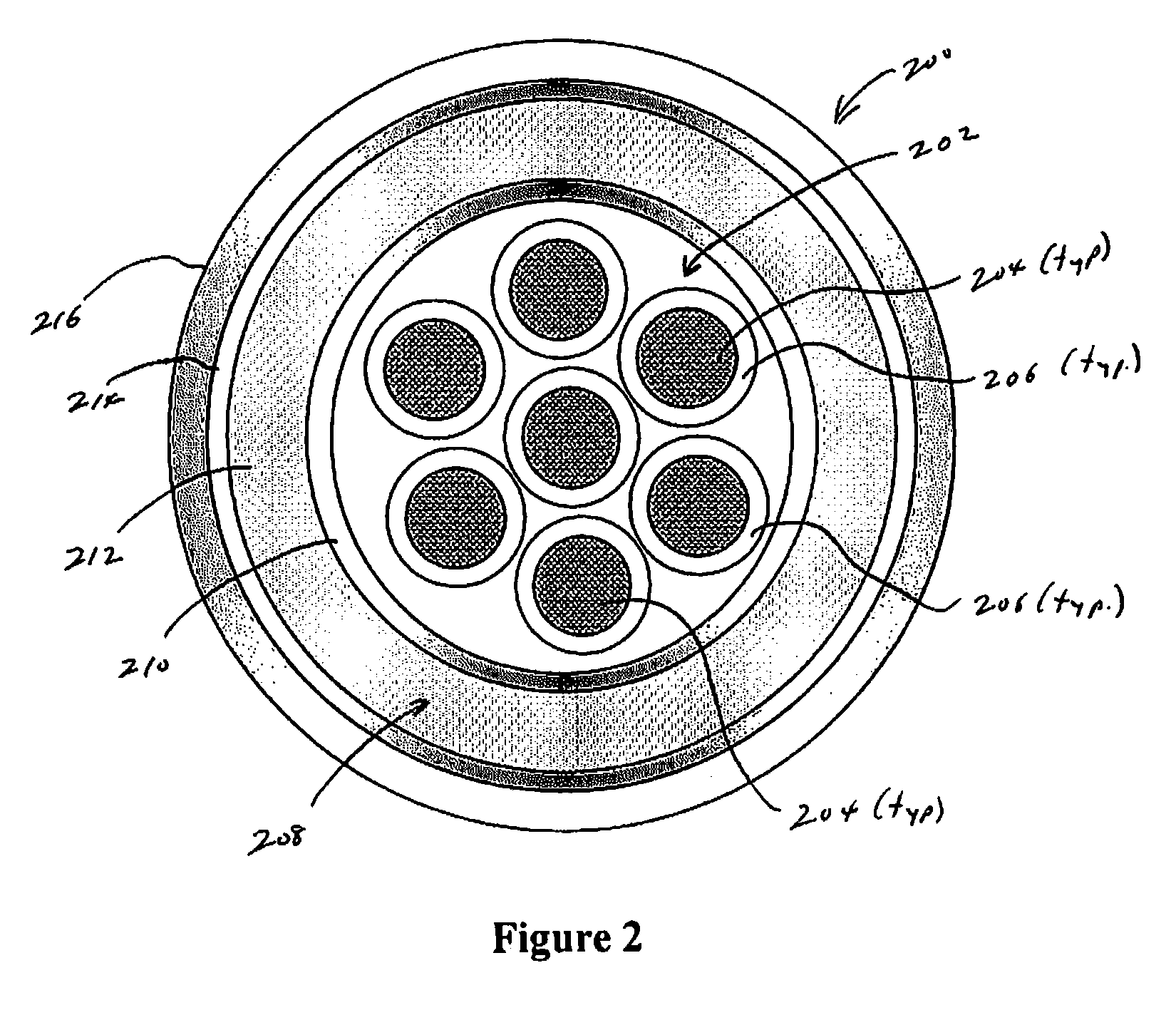
Downhole cable
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Spinal interbody fusion device and method
InactiveUS7022138B2Easy to copyAvoid injuryInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnIntervertebral disk
A disc replacement spinal interbody fusion device is provided having a central sleeve with oppositely left and right-hand threaded axial bores with different diameters. Circumferential threaded apertures are located on the sleeve and open into the sleeve bores. The device has two opposing plates which are oval-shaped and centrally, axially bored. Each plate has a perpendicular shaft with an axial bore which communicates with the plate bore. In situ, axial loading of the spinal column upon the fusion device creates a bending moment manifested by a flexing action of the plates to generate opposing axial directional forces which replicate the physiological function of shock absorption, load bearing and load transmission.
Owner:MASHBURN M LAINE
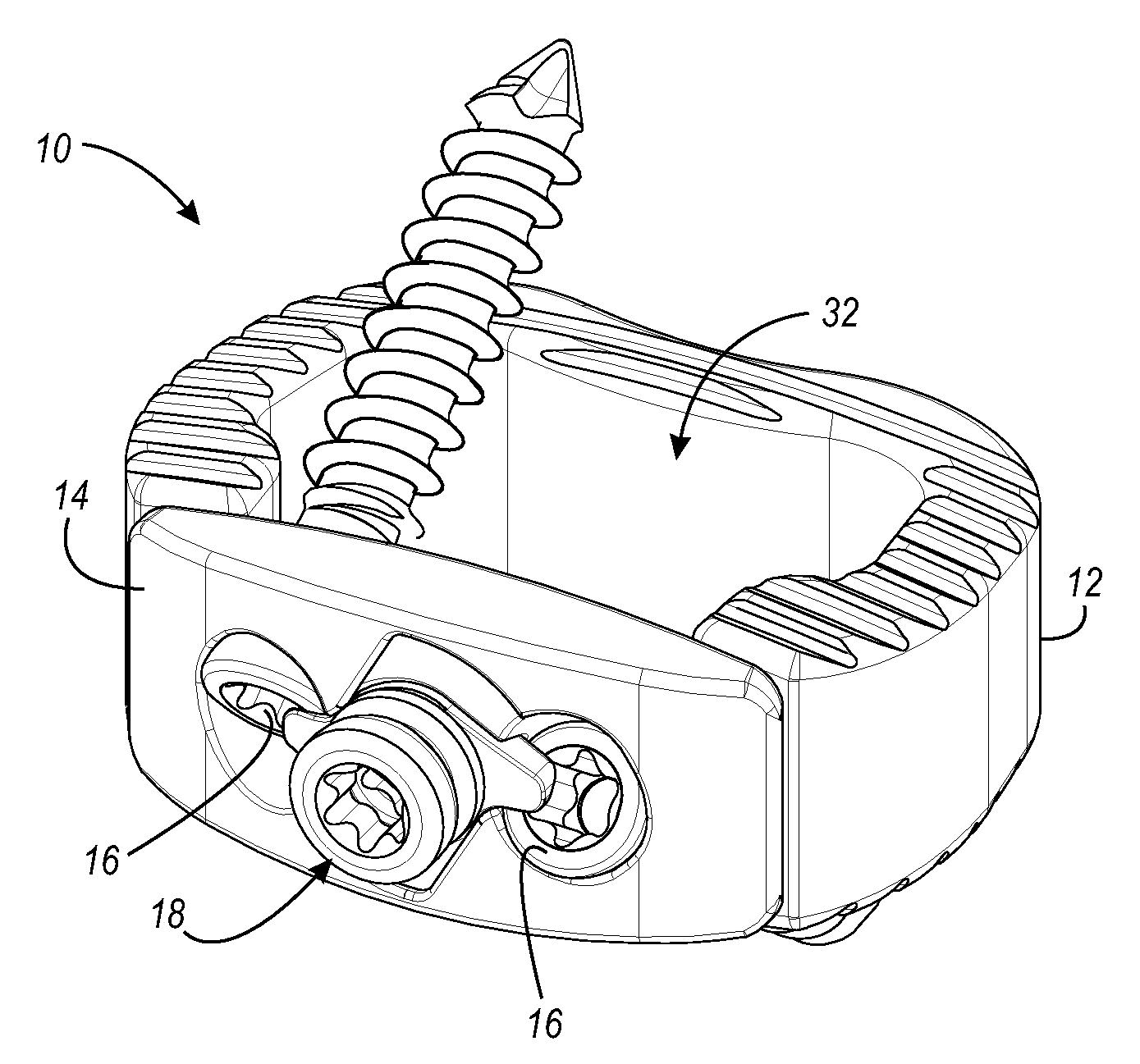
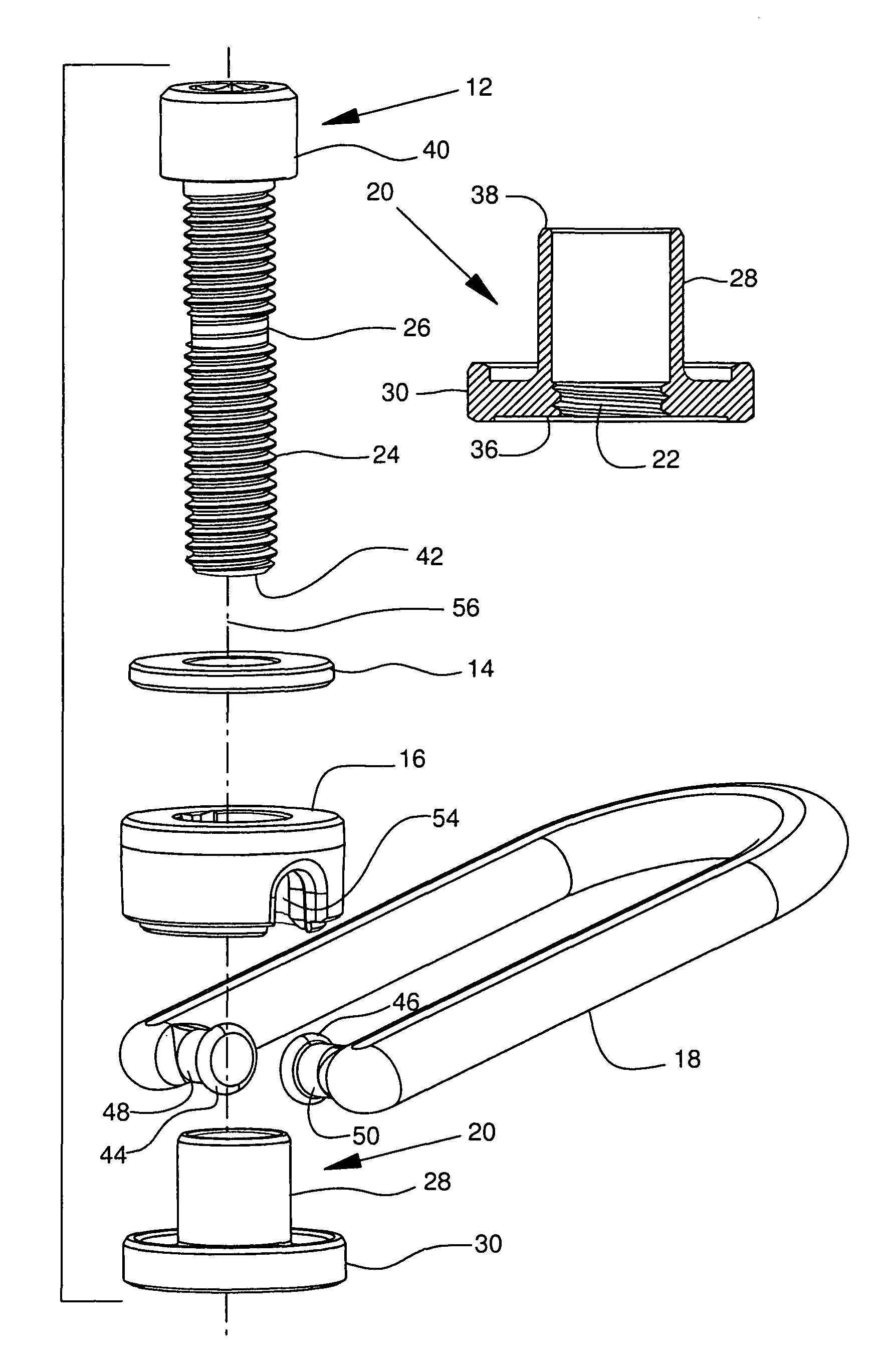
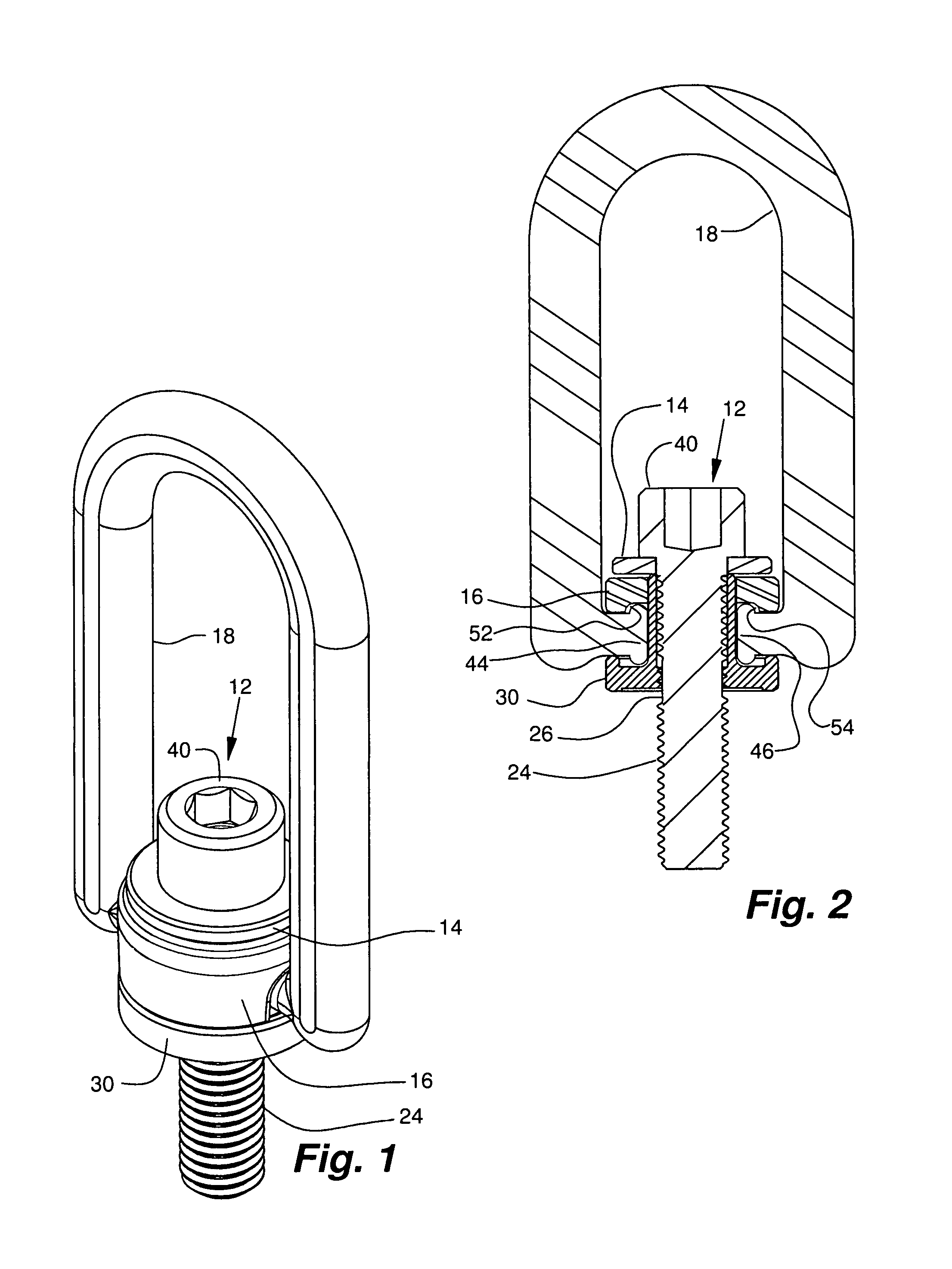
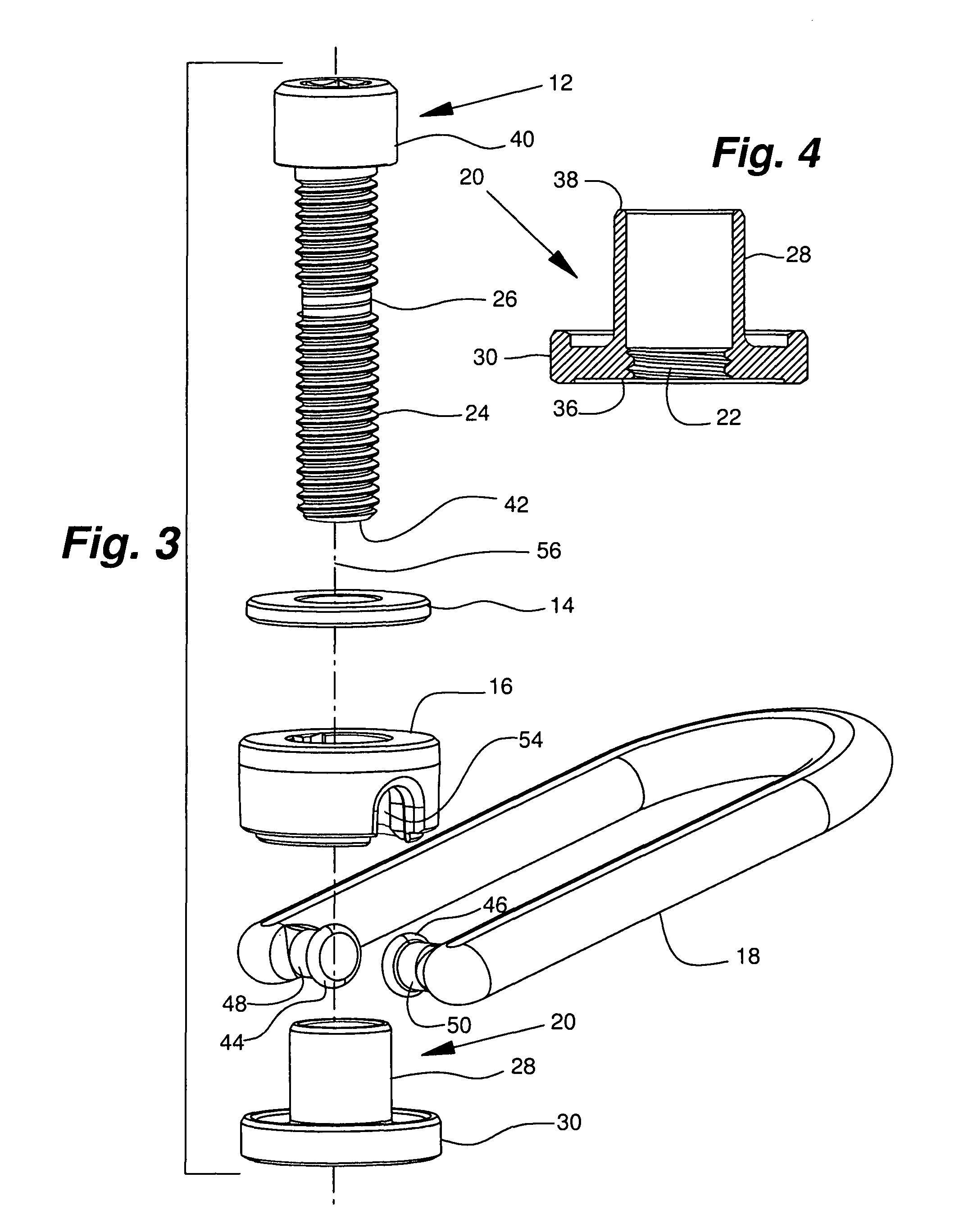
Threaded hoist ring screw retainer
An omni-positional hoist ring assembly including a bushing element that includes a sleeve with an axial length, a proximal end and a distal end. A load bearing flange is radially disposed about the proximal end of the sleeve. The sleeve has an internal thread extending at least part way of the axial length of the sleeve. A mounting screw element has a major axis, a head, and a shank disposed generally co-axially around the major axis. The shank includes a threaded shank portion and a bearing portion. The bearing portion is a generally cylindrical axially extending portion of the shank that has a diameter approximately equal to the minor diameter of the thread in the threaded shank portion. A thrust washer element is provided between the head and the distal end of the sleeve. A body element receives the in-turned opposed ends of the legs of a lifting loop element in sockets. The lifting loop is free to pivot. The body element is free to rotate about the sleeve, so the lifting loop will self align with a load that is applied to it from any direction within a hemisphere centered on the major axis of the mounting screw element. The elements of the hoist rig assembly are assembled by aligning them and inserting the mounting screw element into the sleeve and threadably advancing it until the bearing is aligned with the internal thread so further rotation of the mounting screw element does not threadably advance the mounting screw element relative to the sleeve.
Owner:MJT HLDG
Reconfigurable battery-operated vehicle system
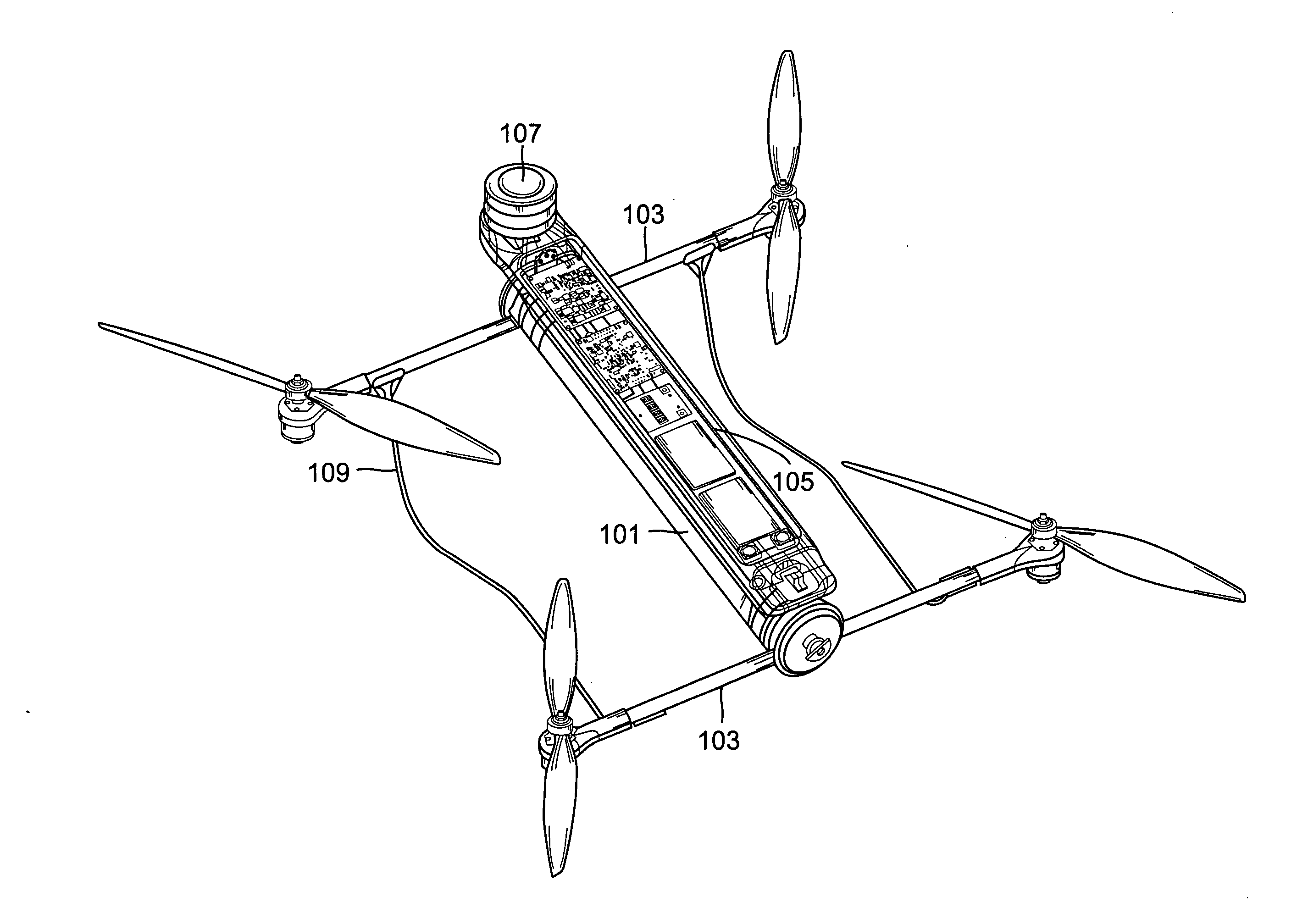
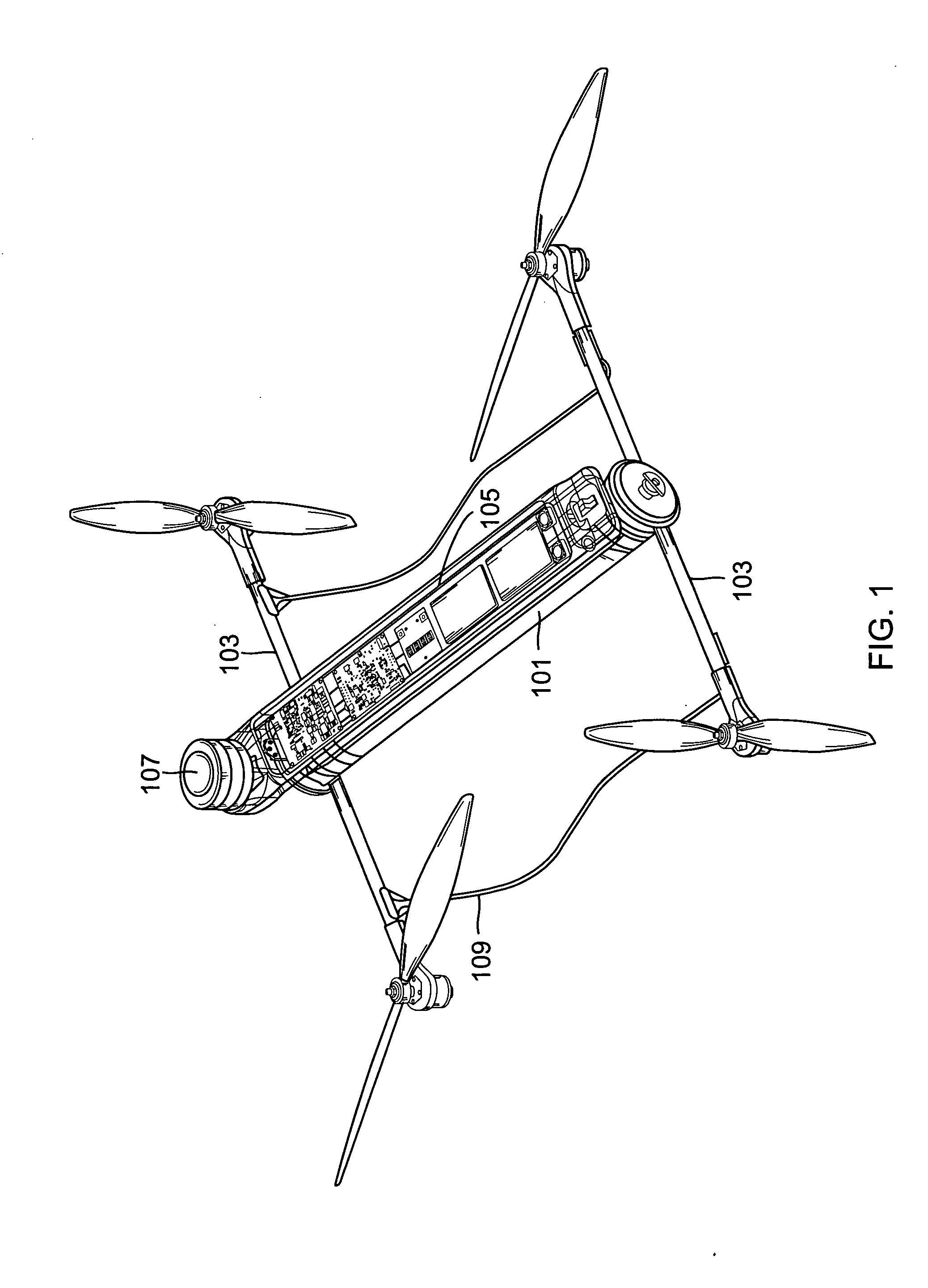
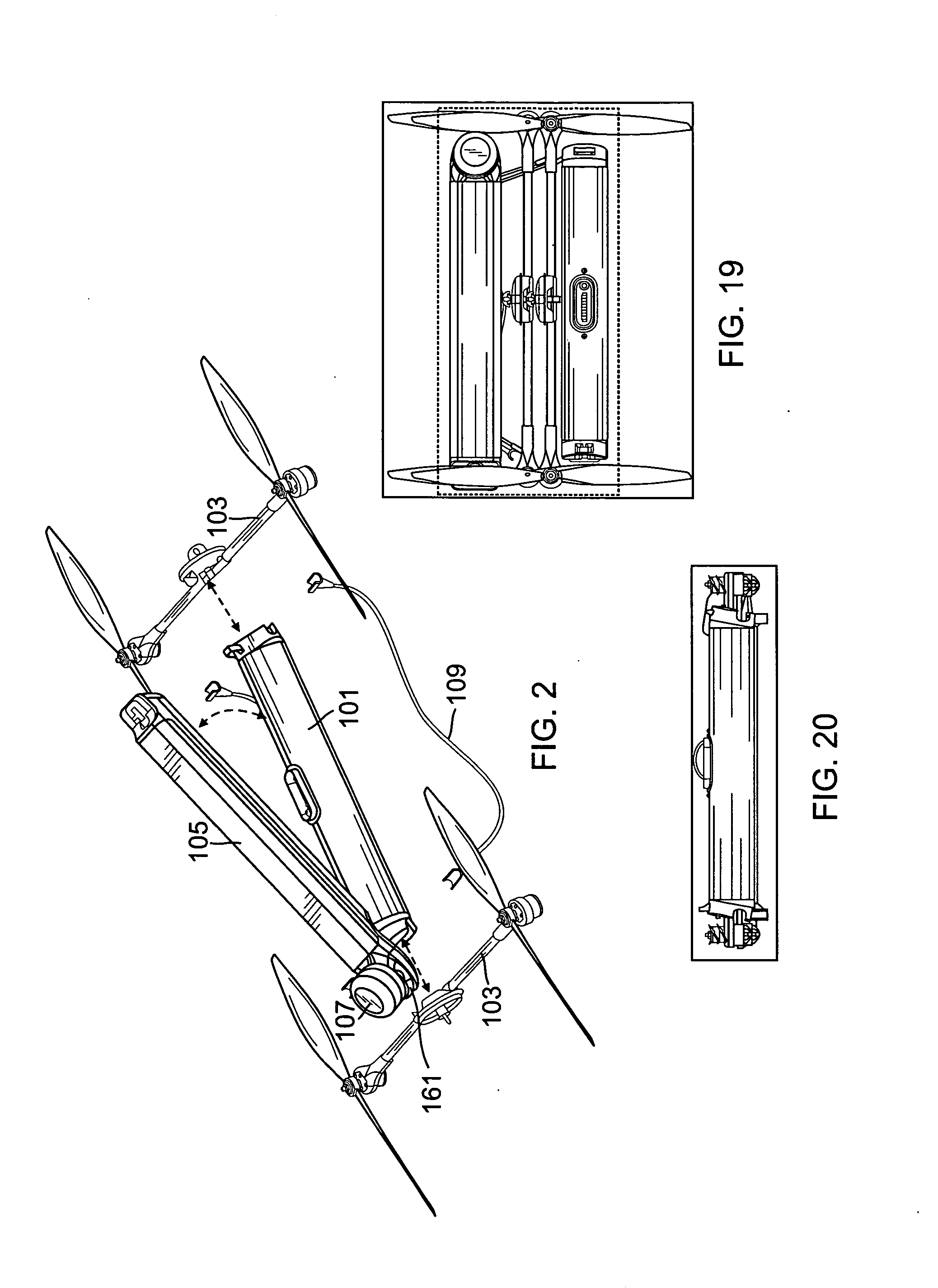
InactiveUS20140061376A1Reduce weightStable structureUnmanned surface vesselsRemote controlled aircraftReconfigurable antennaComputer module
A quadrotor UAV including ruggedized, integral-battery, load-bearing body, two arms on the load-bearing body, each arm having two rotors, a control module mounted on the load-bearing body, a payload module mounted on the control module, and skids configured as landing gear. The two arms are replaceable with arms having wheels for ground vehicle use, with arms having floats and props for water-surface use, and with arms having pitch-controlled props for underwater use. The control module is configured to operate as an unmanned aerial vehicle, an unmanned ground vehicle, an unmanned (water) surface vehicle, and an unmanned underwater vehicle, depending on the type of arms that are attached.
Owner:AEROVIRONMENT INC
Bone graft composition, method and implant
ActiveUS20070142916A1Simple compositionHigh mechanical strengthMaterial nanotechnologyBone implantFiberNanofiber
A bone regenerative composition includes a resorbable osteoconductive matrix and a multiplicity of substantially rigid nanofibers dispersed within structure of the matrix to impart structural integrity with nanofiber ends projecting out of a surface of the matrix to provide differential load bearing surface bristles.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
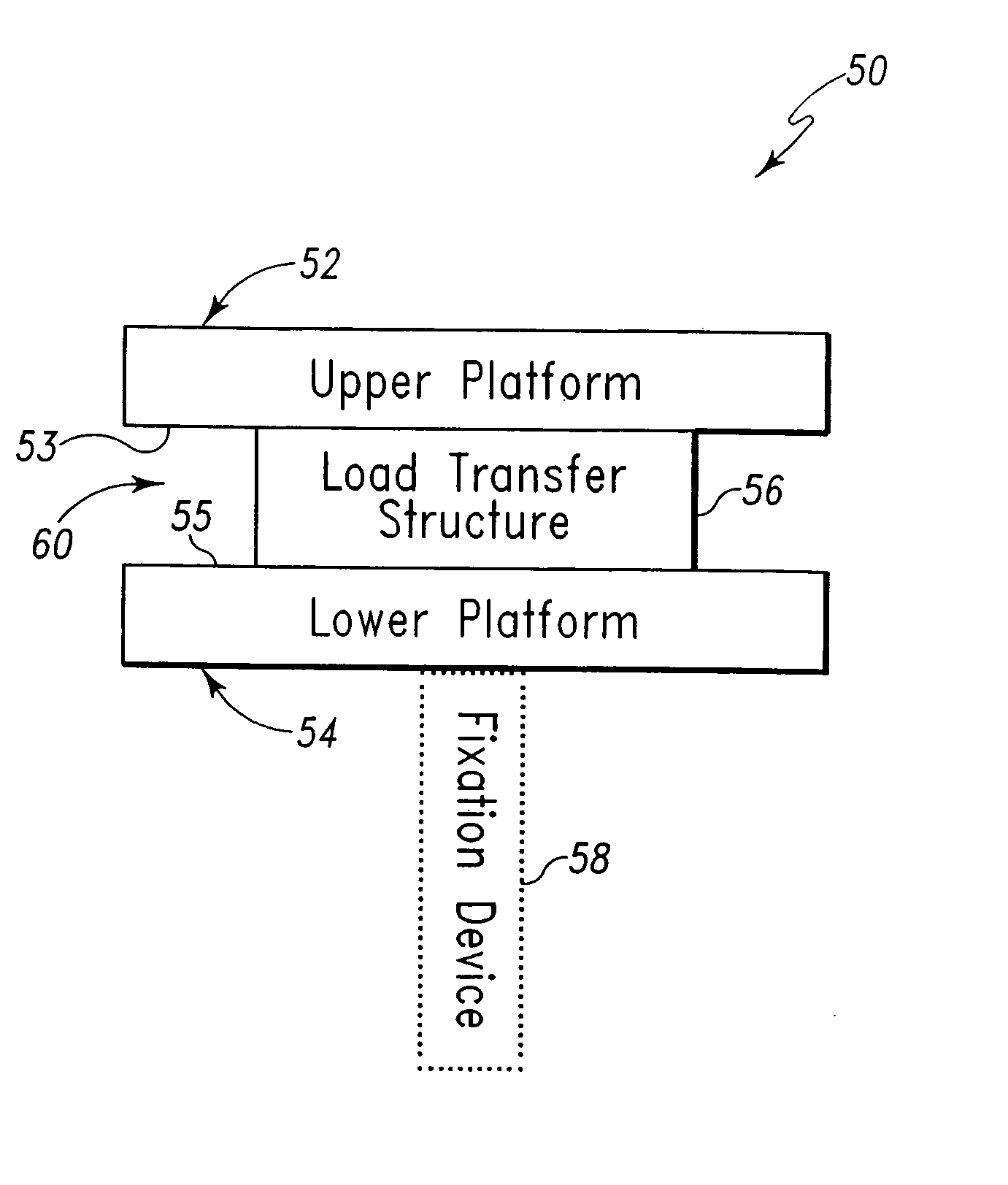
Implant device for cartilage regeneration in load bearing articulation regions
An implant device for cartilage regeneration in loading-bearing regions uses the osteochondral defect model. The implant is formed of resorbable polymeric materials. The implant is designed such that load is transmitted from the articulating surface of the bone platform through the implant to the entire area of subchondral bone of the bone platform. Application of load in this manner results in reduced subchondral bone resorption, leading to joint stabilization and maintenance of normal joint biomechanics. The implant allows for the incorporation therein of a resorbable scaffold or matrix material. The present implant solves the current inability to regenerate cartilage in load-bearing articulating surfaces using engineered scaffold devices.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Robotic total/partial knee arthroplastics
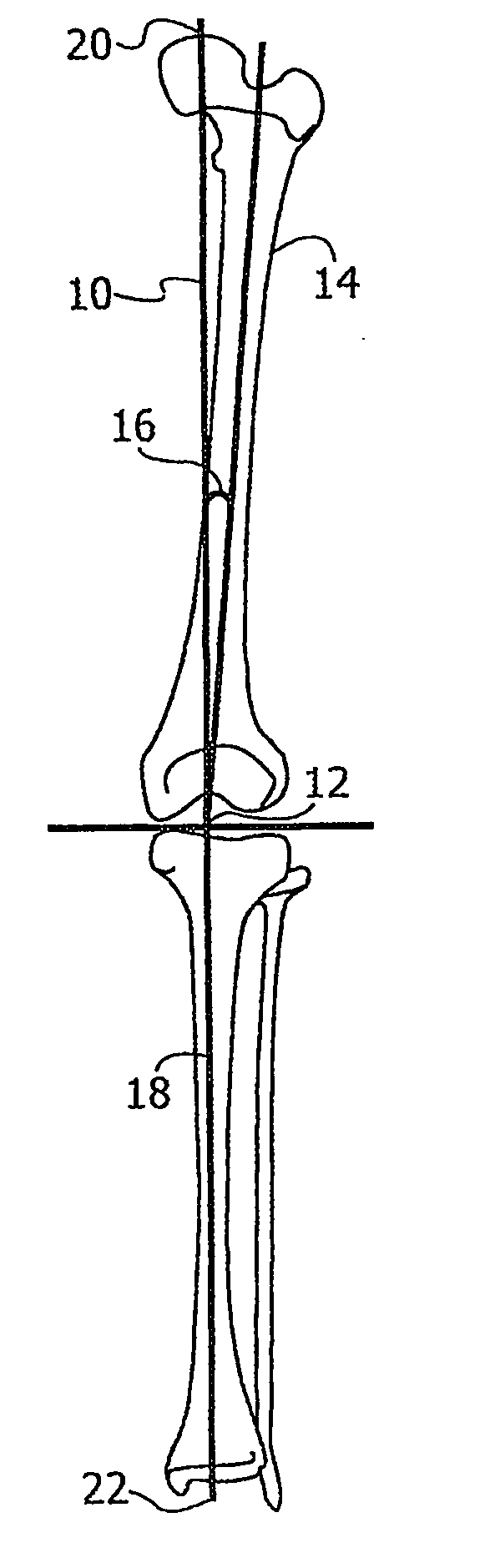
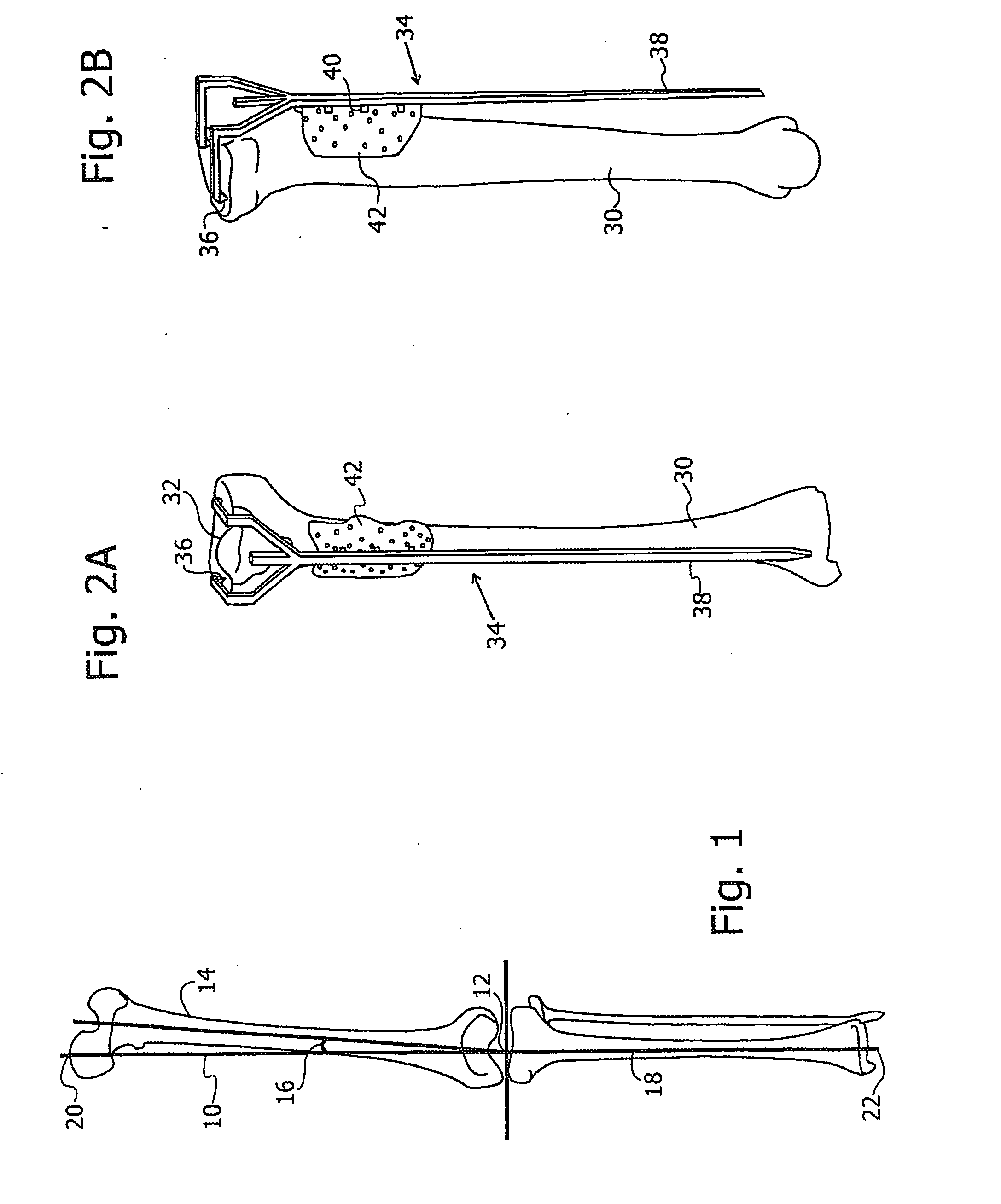
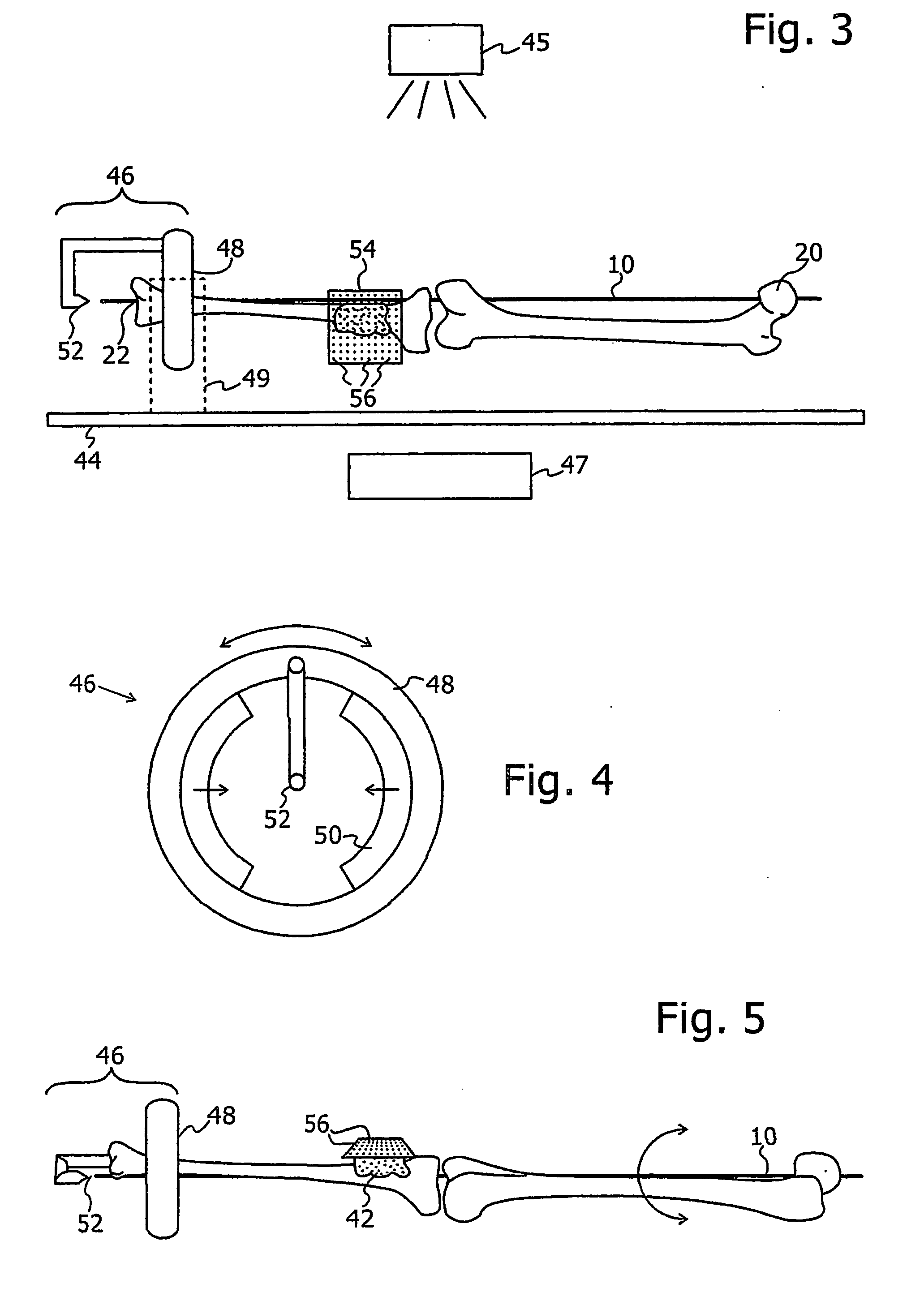
ActiveUS20070100258A1Improve accuracyReduce responsibilityPerson identificationMaterial analysis by optical meansTibiaSurgical robot
A system and method for knee arthroplasty procedures, using a novel leg rotation fixture to enable the leg mechanical axis, the tibia and the femur to be mutually disposed such that the load bearing, mechanical axis of the leg runs through the center of the knee joint. A measurement gauge is provided for mounting on the tibia and for aligning a baseplate in a known position on the tibia. This baseplate supports an X-ray target plate in a known position relative to the tibia, used in determining the mechanical axis, and an optional surgical robot, used to perform tibial and femoral cuts. The position of the femur relative to the robot may be determined from X-ray imaging of the pelvic region after attachment to the baseplate of an additional target extending to the pelvic region. The system enables improvement in the accuracy of knee arthroplasty procedures.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Intervertebral disc nucleus implants and methods
Nucleus pulposus implants that are resistant to migration in and / or expulsion from an intervertebral disc space are provided. In one form of the invention, an implant includes a load bearing elastic body surrounded in the disc space by an anchoring, preferably resorbable, outer shell. In certain forms of the invention, the elastic body is surrounded by a supporting member, such as a band or jacket, and the supporting member is surrounded by the outer shell. Kits for forming such implants are also provided. In another form of the invention, an implant is provided that has locking features and optional shape memory characteristics. In yet another aspect of the invention, nucleus pulposus implants are provided that have shape memory characteristics and are configured to allow short-term manual, or other deformation without permanent deformation, cracks, tears, breakage or other damage. Methods of forming and implanting the implants are also described, as are delivery devices and components thereof for delivering the implants.
Owner:SEMINIS VEGETABLE SEEDS
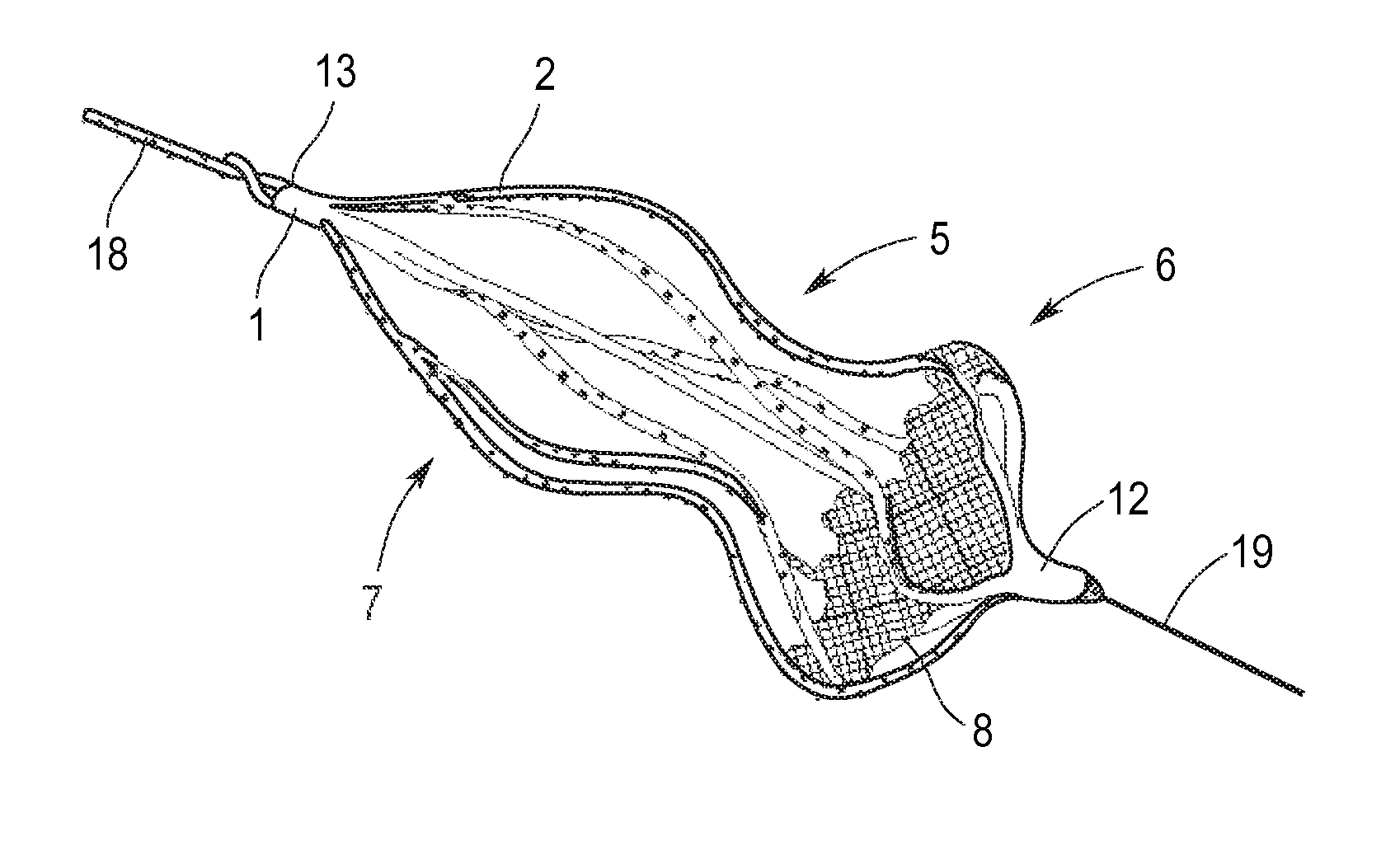
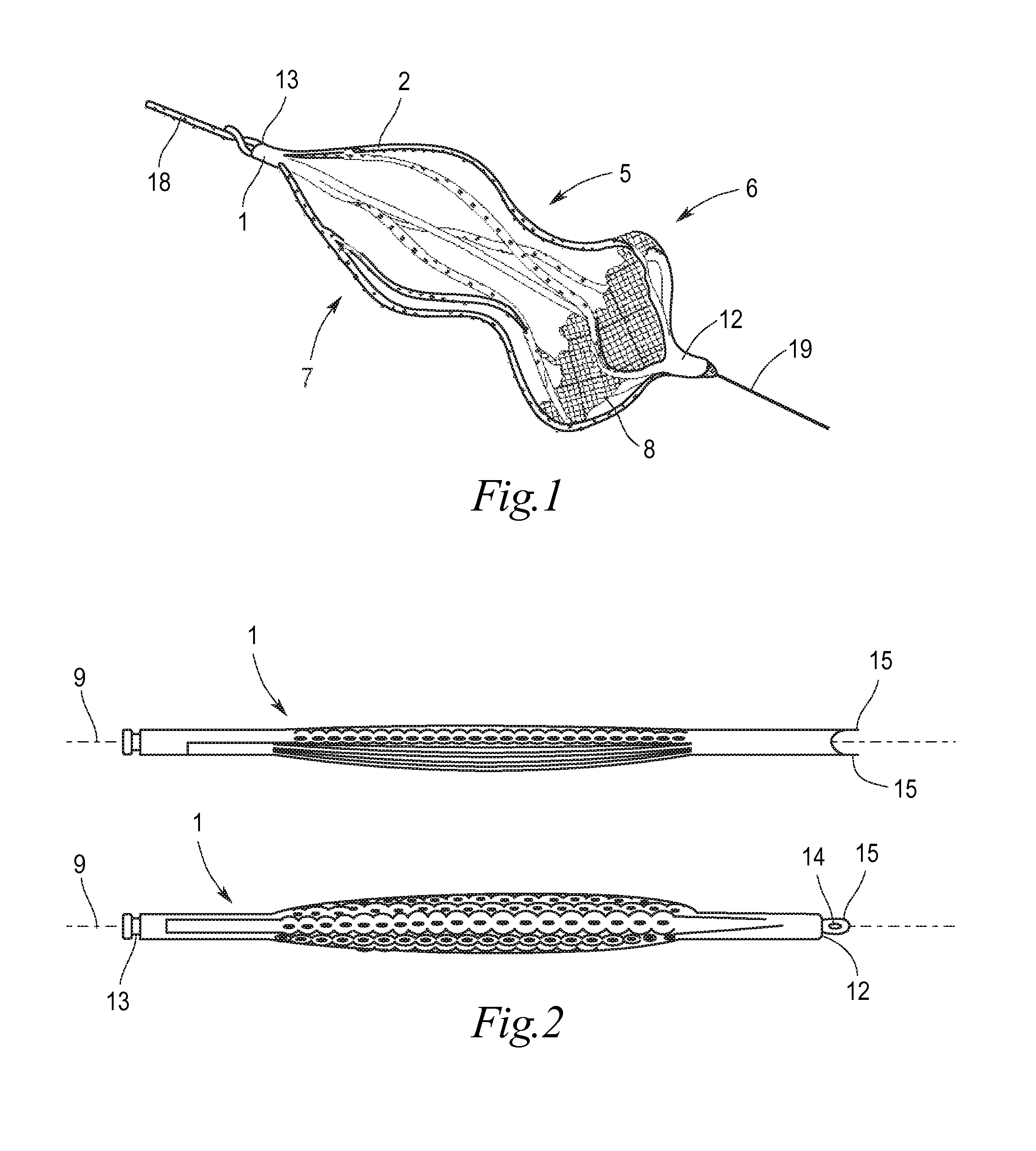
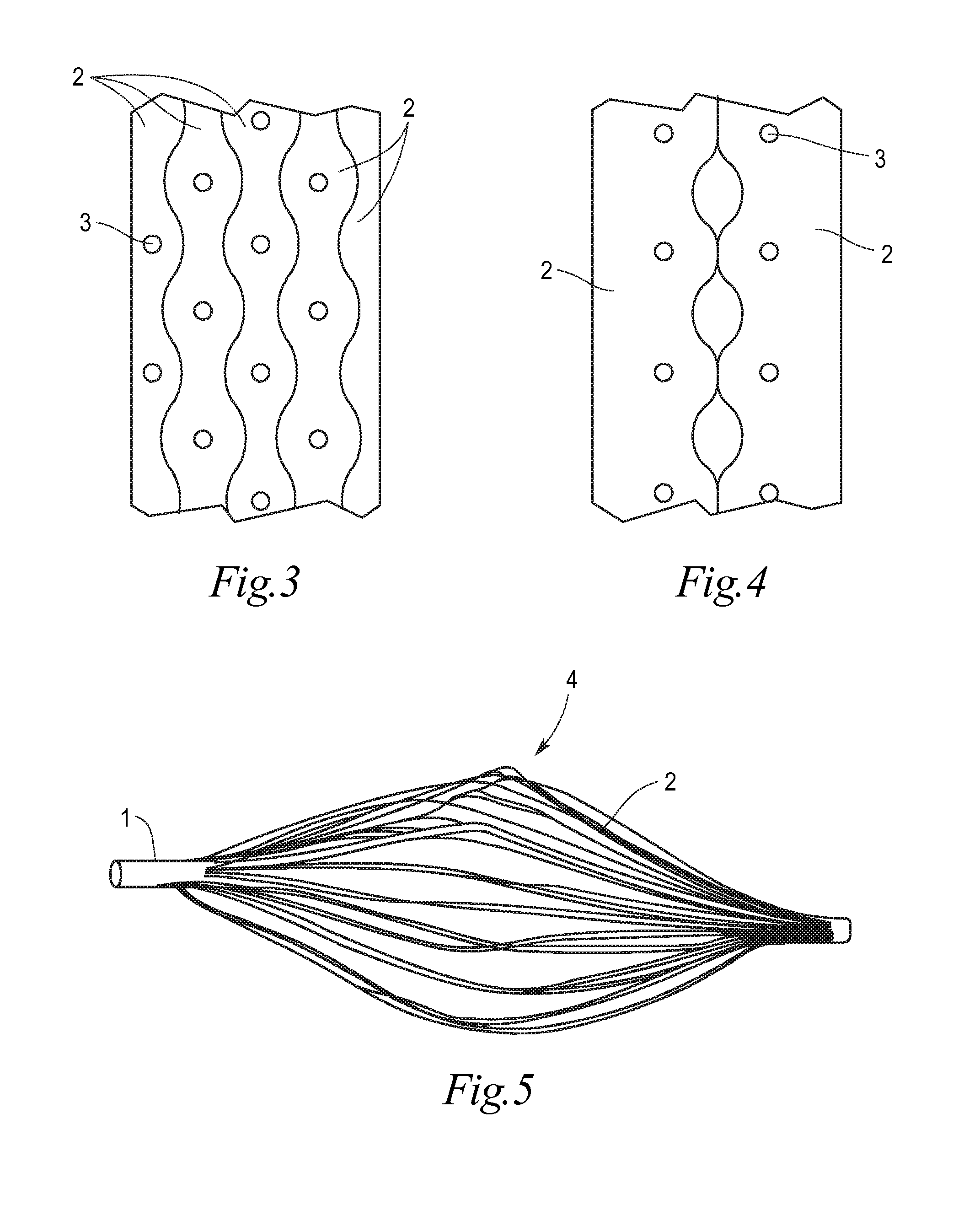
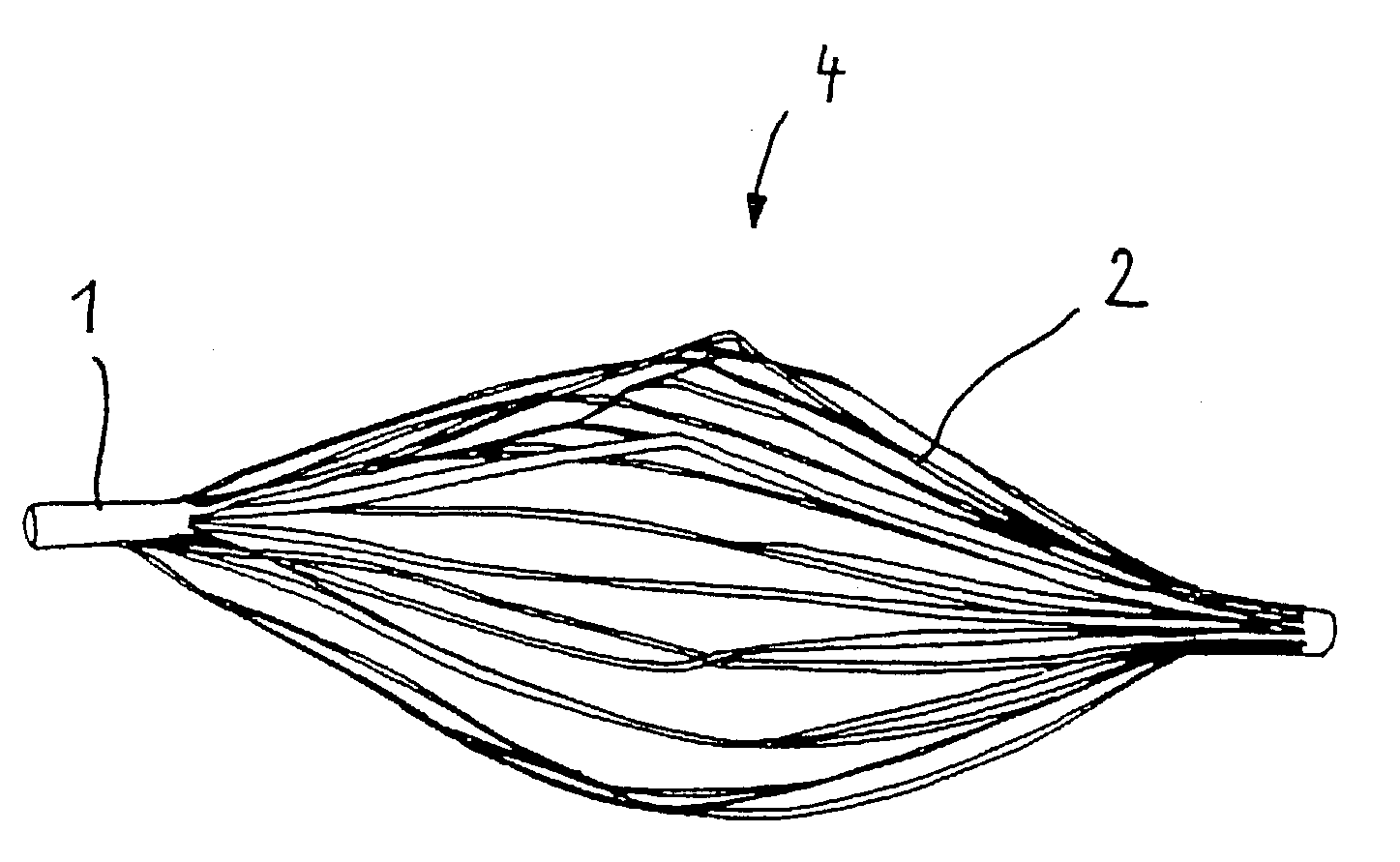
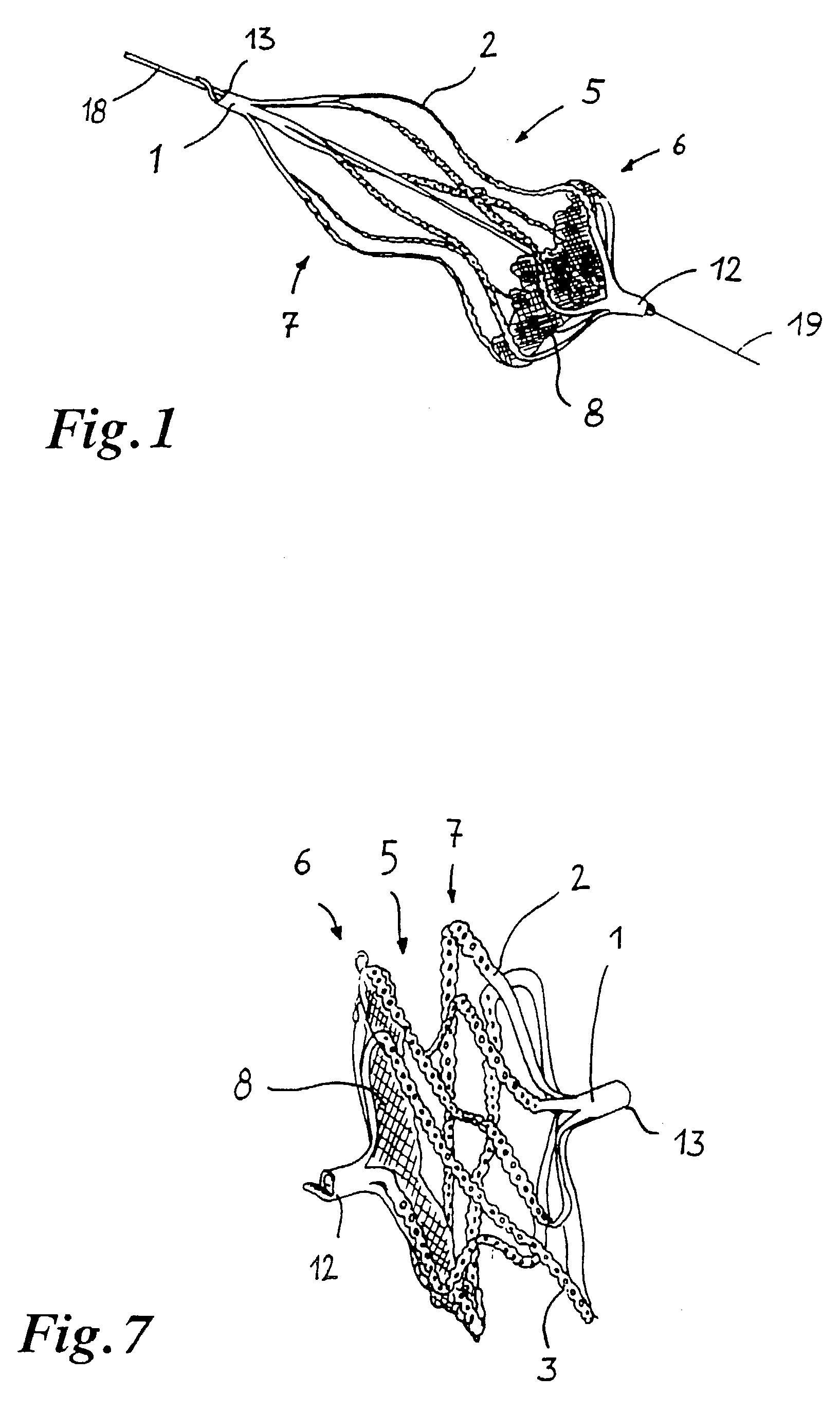
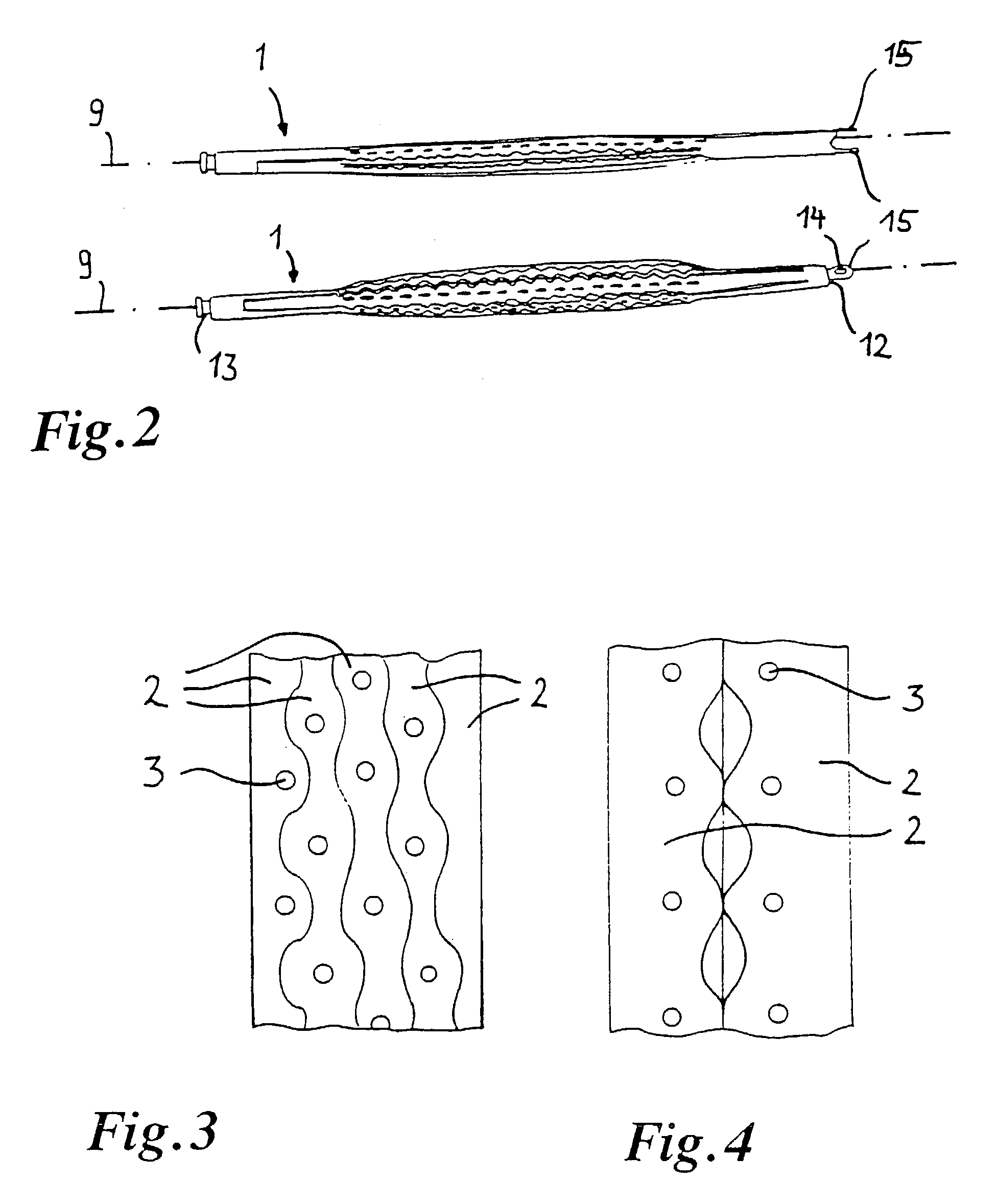
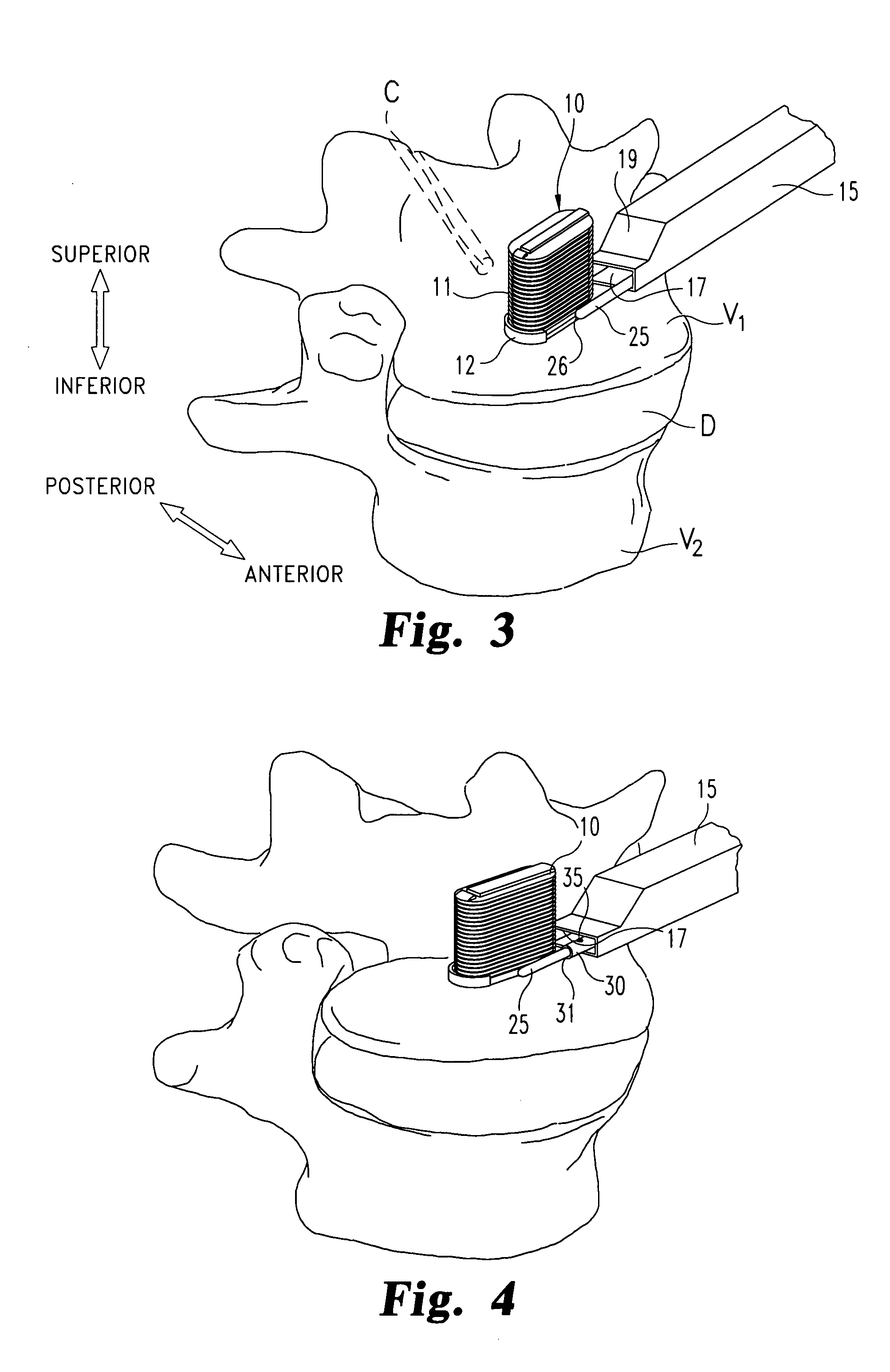
Implant for the closing of defect openings in the body of a human or animal and a system for the placement of such an implant
InactiveUS7097653B2Quick upgradeReduce effortDilatorsSurgical veterinaryExertionBiomedical engineering
An implant for the closing of defect openings in the body of a human or animal is proposed, with a load-bearing structure which, in a first operating state (primary form), has a great ratio of length to transverse extent along an axis (9) and, at least in a further operating state (secondary form), has a much smaller ratio of length to transverse extent along the axis (9), the load-bearing structure (1) being capable of being reversibly transformed from the secondary form into the primary form by exertion of a force against elastic material forces, the secondary form assuming approximately the form of a double disc with a proximal disc element (7) and a distal disc element (6) for receiving the surroundings of the defect opening between the disc elements, and the load-bearing structure (1) being formed essentially in one piece without joining connections, and a placement system.
Owner:PFM MEDICAL
Implant for the closing of defect openings in the body of a human or animal and a system for the placement of such an implant
InactiveUS20030171774A1Quick upgradeReduce effortDilatorsTubular organ implantsCircular discExertion
An implant for the closing of defect openings in the body of a human or animal is proposed, with a load-bearing structure which, in a first operating state (primary form), has a great ratio of length to transverse extent along an axis (9) and, at least in a further operating state (secondary form), has a much smaller ratio of length to transverse extent along the axis (9), the load-bearing structure (1) being capable of being reversibly transformed from the secondary form into the primary form by exertion of a force against elastic material forces, the secondary form assuming approximately the form of a double disc with a proximal disc element (7) and a distal disc element (6) for receiving the surroundings of the defect opening between the disc elements, and the load-bearing structure (1) being formed essentially in one piece without joining connections, and a placement system.
Owner:PFM MEDICAL
Radiopaque, coaxial orthopedic tether design and method
InactiveUS20050192581A1Good imaging propertiesInternal osteosythesisLigamentsFiberBiomedical engineering
This invention relates to orthopedic tethers and their use to treat orthopedic defects. The tethers of the present invention include a central or inner load bearing fiber or cable surrounded by one or more protective sheaths. Additionally the tethers of the present invention provide enhanced imaging characteristics and can include one or more a radiopaque elements that can readily observed under common diagnostic imaging techniques.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
In-situ intervertebral fusion device and method
ActiveUS20120310352A1Increase disc heightMinimally invasiveLuminescence/biological staining preparationBone implantIntervertebral spaceVertebral bone
An orthopedic device for implanting between adjacent vertebrae comprising: an arcuate balloon and a hardenable material within said balloon.In some embodiments, the balloon has a footprint that substantially corresponds to a perimeter of a vertebral endplate. An inflatable device is inserted through a cannula into an intervertebral space and oriented so that, upon expansion, a natural angle between vertebrae will be at least partially restored. At least one component selected from the group consisting of a load-bearing component and an osteobiologic component is directed into the inflatable device through a fluid communication means.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC +1
Cortical and cancellous allograft cervical fusion block
InactiveUS7323011B2Enhance healing processPromote new bone growthBone implantJoint implantsCervical fusionsBone Cortex
A sterile composite bone graft for use in implants comprising a T shaped cortical bone load bearing member mated to a cancellous member. The crosspiece of the T defines an inner planar surface and dove tail shaped mating member extends outward from the inner planar surface. The allograft cancellous bone member defines tapered side walls on the exterior surface of the body, a flat proximal end surface and a flat distal end surface. A dove tail shaped recess with the narrowest portion exiting the flat proximal end surface is cut into the interior of the cancellous member body. The dove tail shaped member and dove tail shaped recess are mated together to hold both component members together. Pins are mounted in both members to provide additional stability.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Spinal interbody fusion device and method
InactiveUS20050027359A1Resist translationalResist rotational movementInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnBending of plates
A disc replacement spinal interbody fusion device is provided having a central sleeve with oppositely left and right-hand threaded axial bores with different diameters. Circumferential threaded apertures are located on the sleeve and open into the sleeve bores. The device has two opposing plates which are oval-shaped and centrally, axially bored. Each plate has a perpendicular shaft with an axial bore which communicates with the shaft bore. The first shaft has external left-hand threads and the second shaft has external right-hand threads, each to mate with different bores of the sleeve. The outside diameter of the first shaft is smaller than the inside diameter of the second shaft, allowing the two shafts to axially engage. The spinal interbody fusion device operates like a turnbuckle, vertically expanding when the sleeve is rotated in one direction and retracting when the sleeve is rotated in the opposite direction. The assembled device defines an open channel axially. Once the fusion device is set at its proper height, set screws are threaded into circumferential apertures of the sleeve to compress against the shaft threads of each plate to maintain a fixed height. In situ, axial loading of the spinal column upon the fusion device creates a bending moment manifested by a flexing action of the plates to generate opposing axial directional forces which replicate the physiological function of shock absorption, load bearing and load transmission.
Owner:MASHBURN M LAINE
Devices and methods for protecting tissue at a surgical site
ActiveUS20050283050A1Minimize local loadingDissipate forceCannulasDiagnosticsWear resistantSurgical site
A tissue protector is adapted to be positioned on the skin surrounding an incision. The tissue protector provides a load bearing surface for surgical tools and instruments to prevent blunt force and pressure trauma to the skin and soft tissues within the incision. In one embodiment, the tissue protector is a sheet of wear-resistant material having an opening corresponding to the incision and expandable as the incision is retracted. In another embodiment, a tissue protector device includes a continuous expandable arrangement of interconnected L-shaped links. In still another embodiment, a one-piece tissue protector includes a flexible panel supported on the skin and a flexible sleeve extending into the incision. Yet another embodiment of the invention resides in a track that is supported about the incision. An instrument support platform is slidably mounted to the track to support a surgical tool relative to the incision.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Resorbable interposition arthroplasty implant
InactiveUS6017366AImprove permeabilityAvoid collisionFinger jointsWrist jointsTrapezium BoneSurgical department
A resorbable implant for interposition arthroplasty which is intended to fill a void between two adjacent bone ends, providing a cushion between the bone ends to prevent impingement of the bone ends while providing time for tissue to infiltrate into the space occupied by the implant. It has a protracted resorption time of preferably at least three months to allow time for the proliferation of load-bearing host fibrous tissue in place of the resorbed implant material. The implant preferably is porous with a pore size of greater than about 80 microns in order to enhance infiltration of fibrous tissue. The implant has a modulus in the range of 0.8 to 20 MPa which is soft enough to allow it to conform to surface irregularities of the adjacent bone surfaces while being hard enough to maintain a desired separation between those bones while tissue infiltration replaces the resorbable implant material. The implant may be preformed to the desired shape or alternatively may be formable by the surgeon by methods such as carving with a scalpel. A preferred application for the implant is as a trapezium bone replacement.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Apparatus and method for injecting fluent material at a distracted tissue site
A system and method is provided for distracting opposite surfaces from the interior of a bone, such as a vertebral body. A working channel cannula provides a working channel through which an inserter and an injection cannula can simultaneously pass. The inserter transports a plurality of wafers into the interior of the bone to form a load-bearing stack bearing against the opposite surfaces. The injection cannula is used to inject a fluent material into and / or around the stack. In certain embodiments, the fluent material is a load-bearing or hardenable material, such as bone cement. In other embodiments, the fluent material can be a BMP, HAP, or other osteo-inductive, osteo-conductive, or pharmaceutical compositions. A syringe containing the fluent material is engaged to the injection cannula and is operable to inject the fluent material into the vertebral body under controlled pressure.
Owner:SPINEWAVE
Implantable biomedical devices including biocompatible polyurethanes
Disclosed are implantable devices that include biocompatible polyurethane materials. In particular, the disclosed polyurethane materials can maintain desired elastomeric characteristics while exhibiting thermoset-like behavior and can exhibit improved characteristics so as to be suitable in load-bearing applications. For example, the disclosed polyurethane materials can be suitable for use in artificial joints, including total joint replacement applications. The disclosed polyurethane materials include biocompatible cross-linking agents as chain extenders, more particularly chain extenders comprising a terminal group capable of side reactions and further comprising an electron withdrawing group immediately adjacent the terminal group. In addition, the reaction materials and conditions can be selected to encourage intermediate levels of cross-linking without the use of traditional cross-linking trifunctional reagents. In addition, the chain extenders can also include substantially inflexible moieties so as to increase the rigidity of the product polyurethanes.
Owner:CLEMSON UNIVERSITY +1
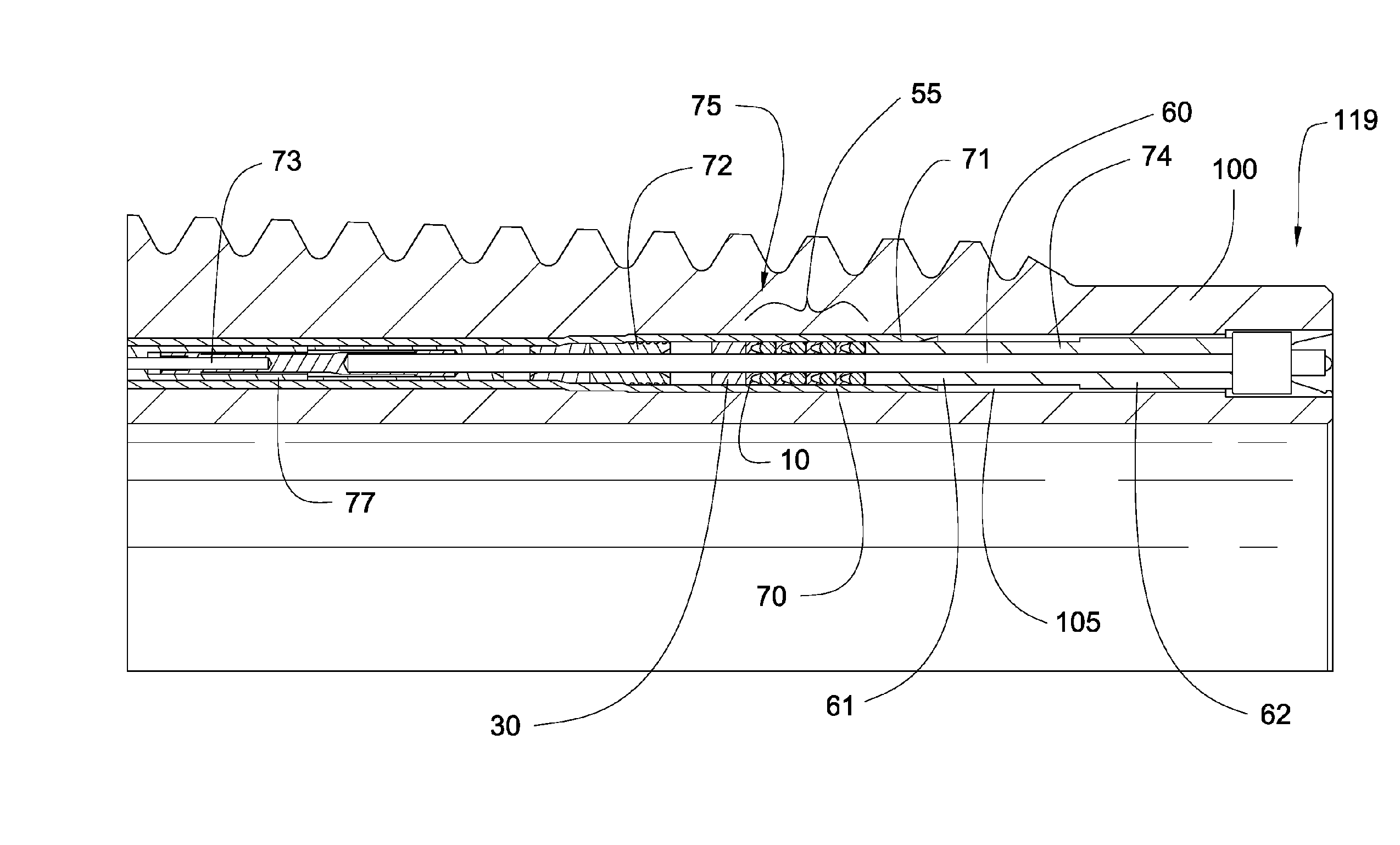
Internal coaxial cable seal system
The invention is a seal system for a coaxial cable and is placed within the coaxial cable and its constituent components. A series of seal stacks including load ring components and elastomeric rings are placed on load bearing members within the coaxial cable sealing the annular space between the coaxial cable and an electrical contact passing there through. The coaxial cable is disposed within drilling components to transmit electrical signals between drilling components within a drill string. The seal system can be used in a variety of downhole components, such as sections of pipe in a drill string, drill collars, heavy weight drill pipe, and jars.
Owner:INTELLISERV
System and method for joint resurface repair
An implant for installation into a portion of an articular surface includes a protrusion configured to cover an un-excised portion of articular surface proximate to the implant. Another implant may form a cavity to allow the un-excised portion of articular surface to remodel over a perimeter edge of the implant. The implant may also include indentations such as grooves to promote articular cartilage remodeling over a portion of the load bearing surface of the implant. An elongated or non-round implant is also provided having two opposing concentric arcuate shaped sides, as well as a method to seat such an implant in an articular surface. A method for seating an implant without cutting articular cartilage is also provided.
Owner:ARTHROSURFACE
Method of bending sheet metal to form three-dimensional structures
InactiveUS20020184936A1Bending stress to the metal is minimized and controlledMinimize distortionEngineeringMetal sheet
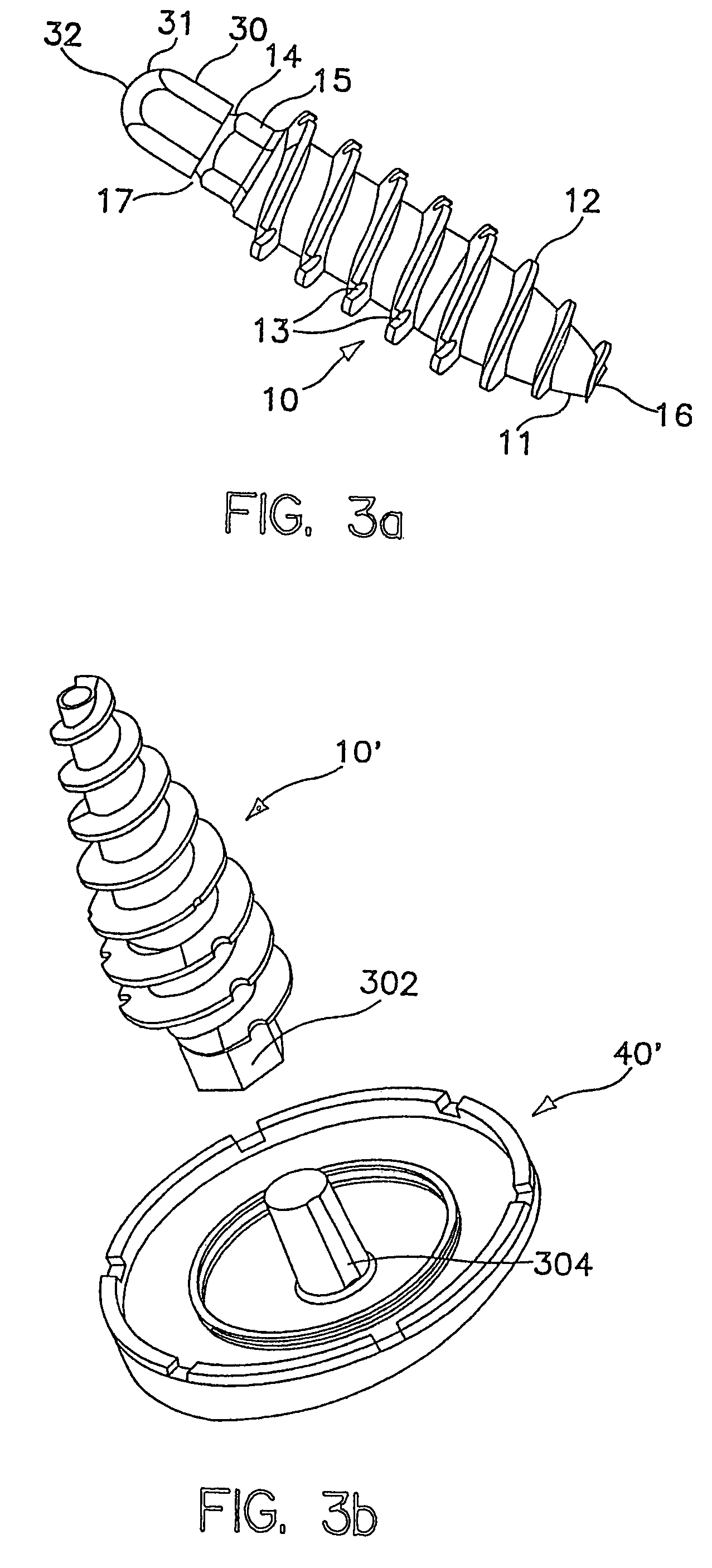
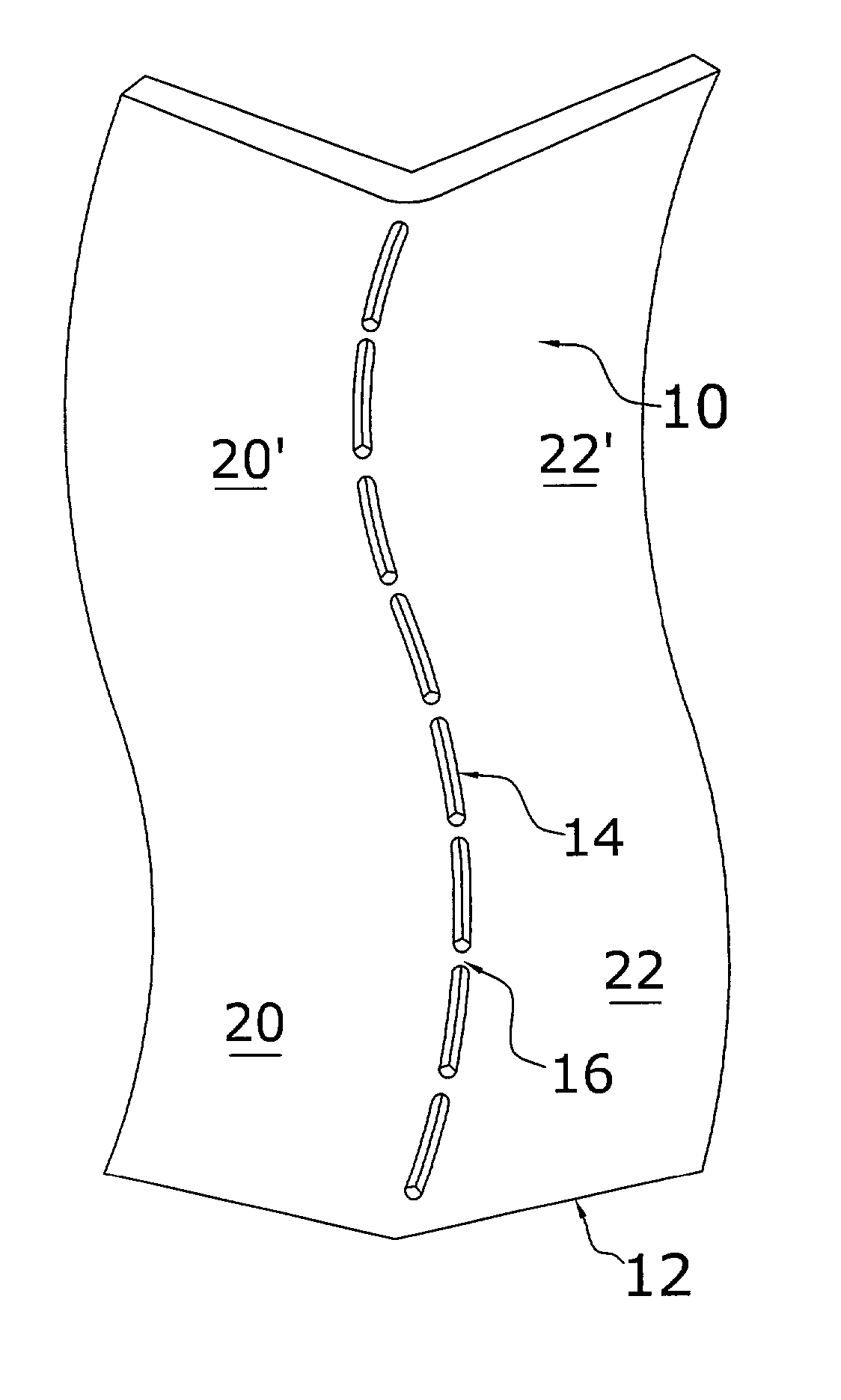
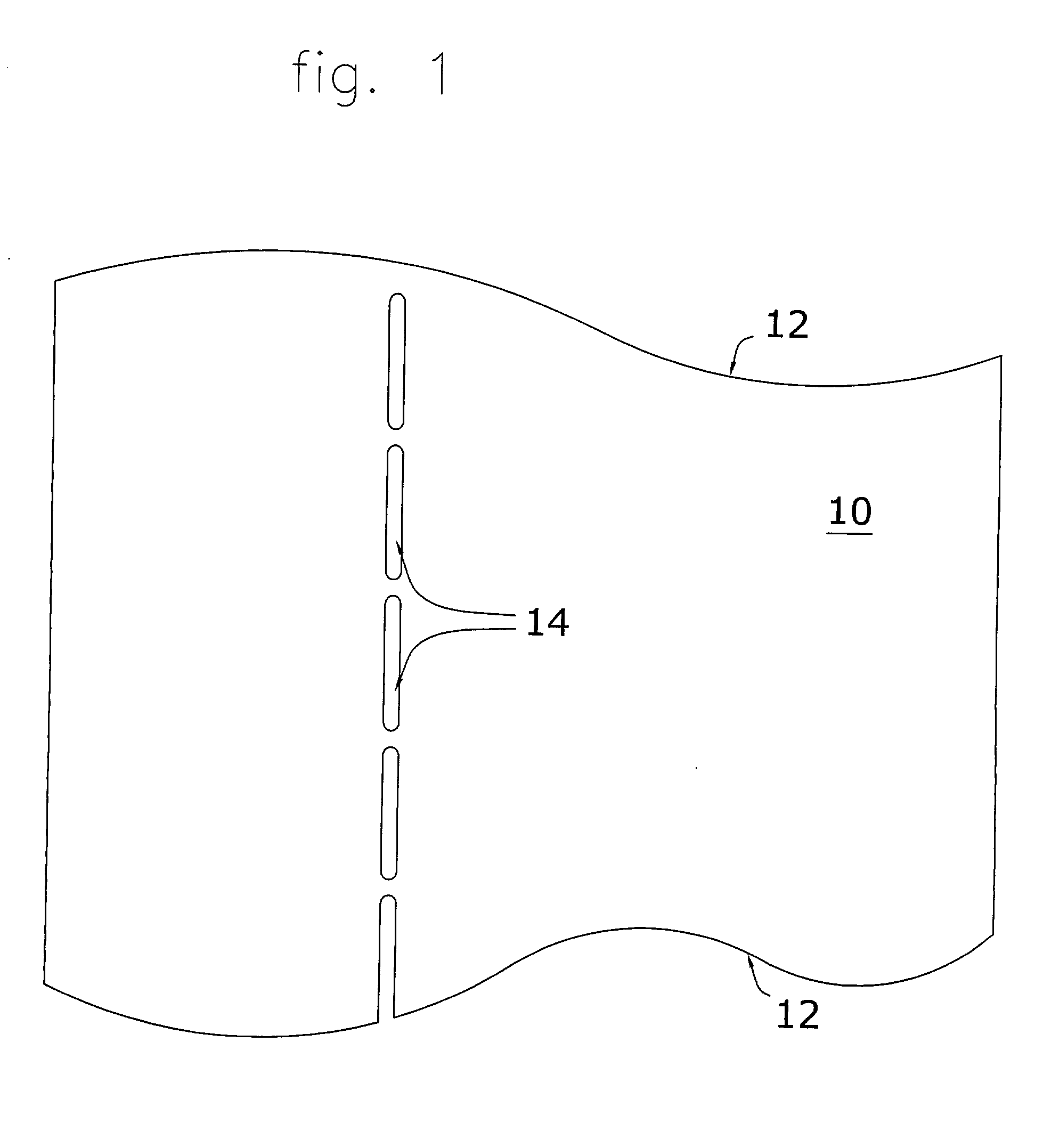
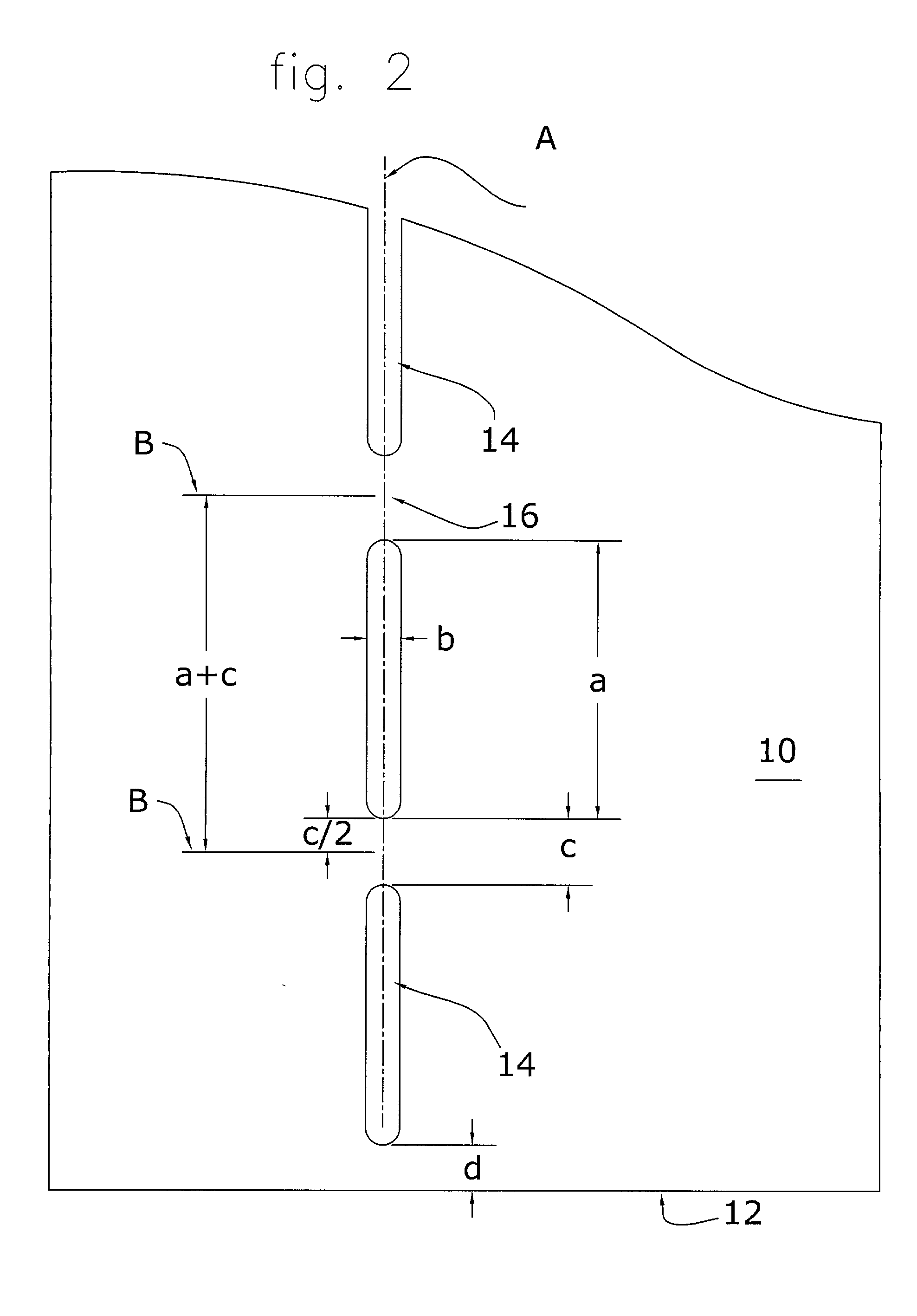
A method for bending sheet metal includes introducing to the sheet metal thinned regions which are positioned either along or immediately adjacent to a bending line. These thinned regions allow the metal to be easily bent along the bending line using conventional hand tools or non-specialized machines. The thinned regions may be shaped as slots having a specific width, length, end shape, spacing from each adjacent slot, and depth into the metal sheet. According to one embodiment of the invention, each slot is cut through the entire thickness of the metal sheet. Other related embodiments require that the slots be only partially cut or etched thereby having a depth that is less than the thickness of the metal sheet. The thinned regions may be any appropriate shape as controlled by the shape of the bend, the type of metal, the thickness of the metal, the ductility of the metal, the angle of the bend, and the application of the metal (e.g., load bearing, etc). According to a second embodiment, two generally parallel sets of thinned regions are formed adjacent and generally parallel to the bending line. In a preferred application, the two sets of thinned regions are slots (cutting through the metal) and are staggered or offset with respect to each other.
Owner:MILGO INDAL
Instruments for delivery of intervertebral disc implants
InactiveUS20050131540A1Improve bindingLarge deformationBone implantJoint implantsSpinal Disk ImplantMedicine
Nucleus pulposus implants that are resistant to migration in and / or expulsion from an intervertebral disc space are provided. In one form of the invention, an implant includes a load bearing elastic body surrounded in s the disc space by an anchoring, preferably resorbable, outer shell. In certain forms of the invention, the elastic body is surrounded by a supporting member, such as a band or jacket, and the supporting member is surrounded by the outer shell. Kits for forming such implants are also provided. In another form of the invention, an implant is provided that has locking features and optional shape memory characteristics. In yet another aspect of the invention, nucleus pulposus implants are provided that have shape memory characteristics and are configured to allow short-term manual, or other deformation without permanent deformation, cracks, tears, breakage or other damage. Methods of forming and implanting the implants are also described, as are delivery devices and components thereof for delivering the implants.
Owner:TRIEU HAI H
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com