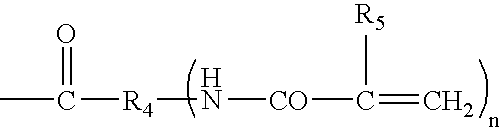Patents
Literature
42 results about "Spinal Disk Implant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
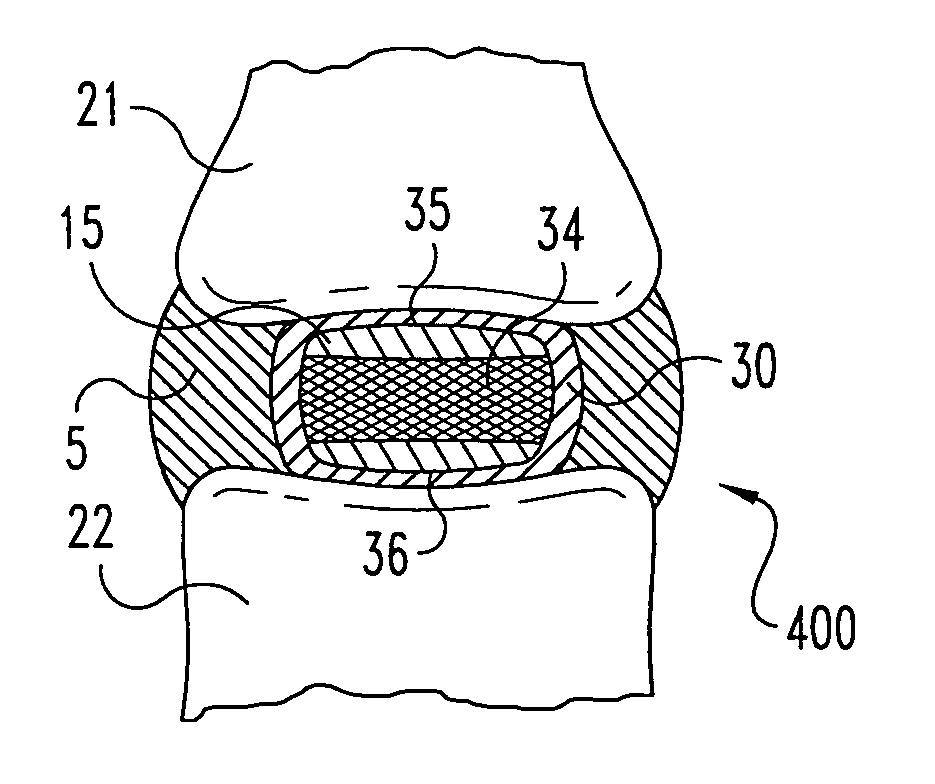
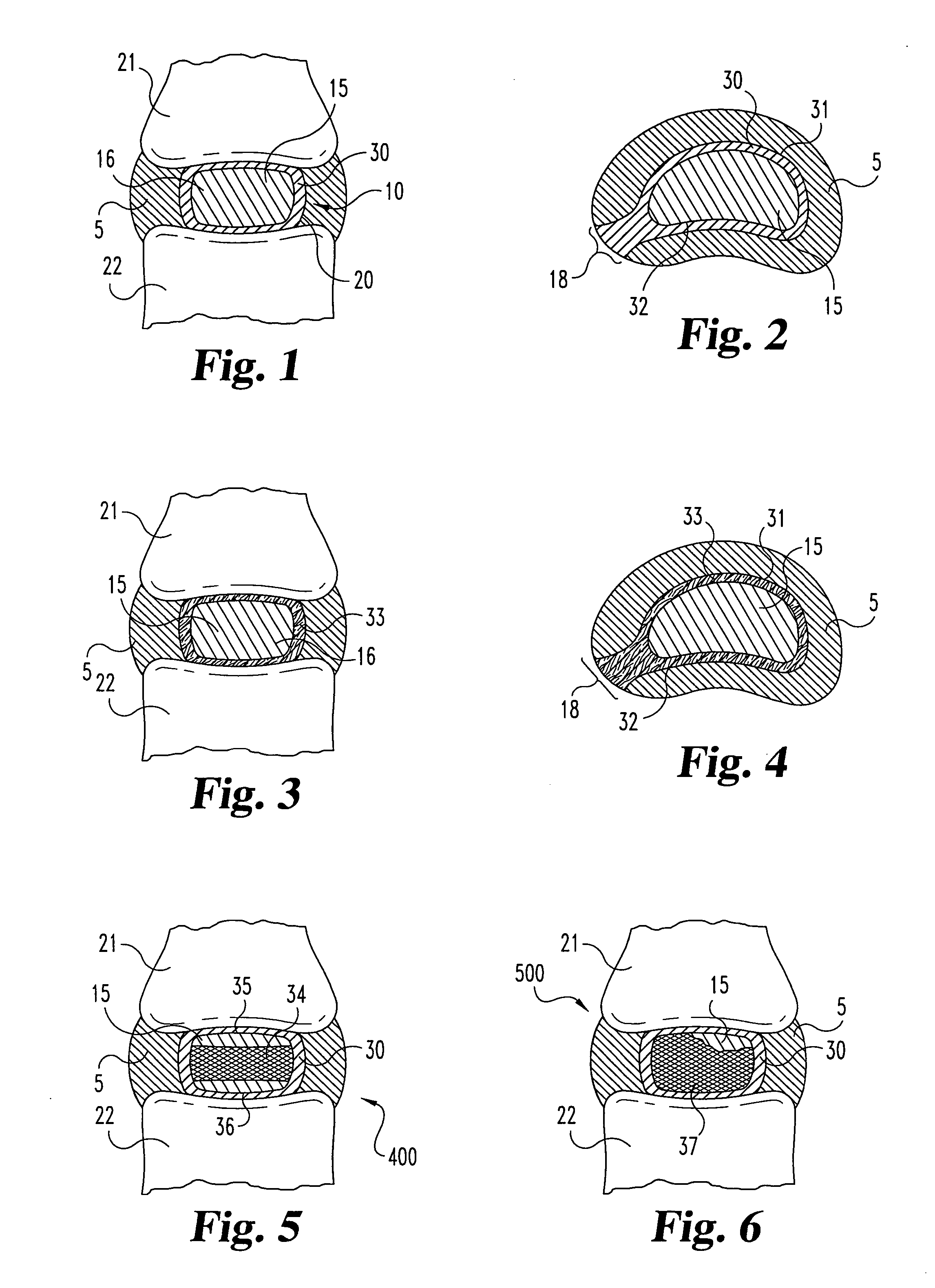
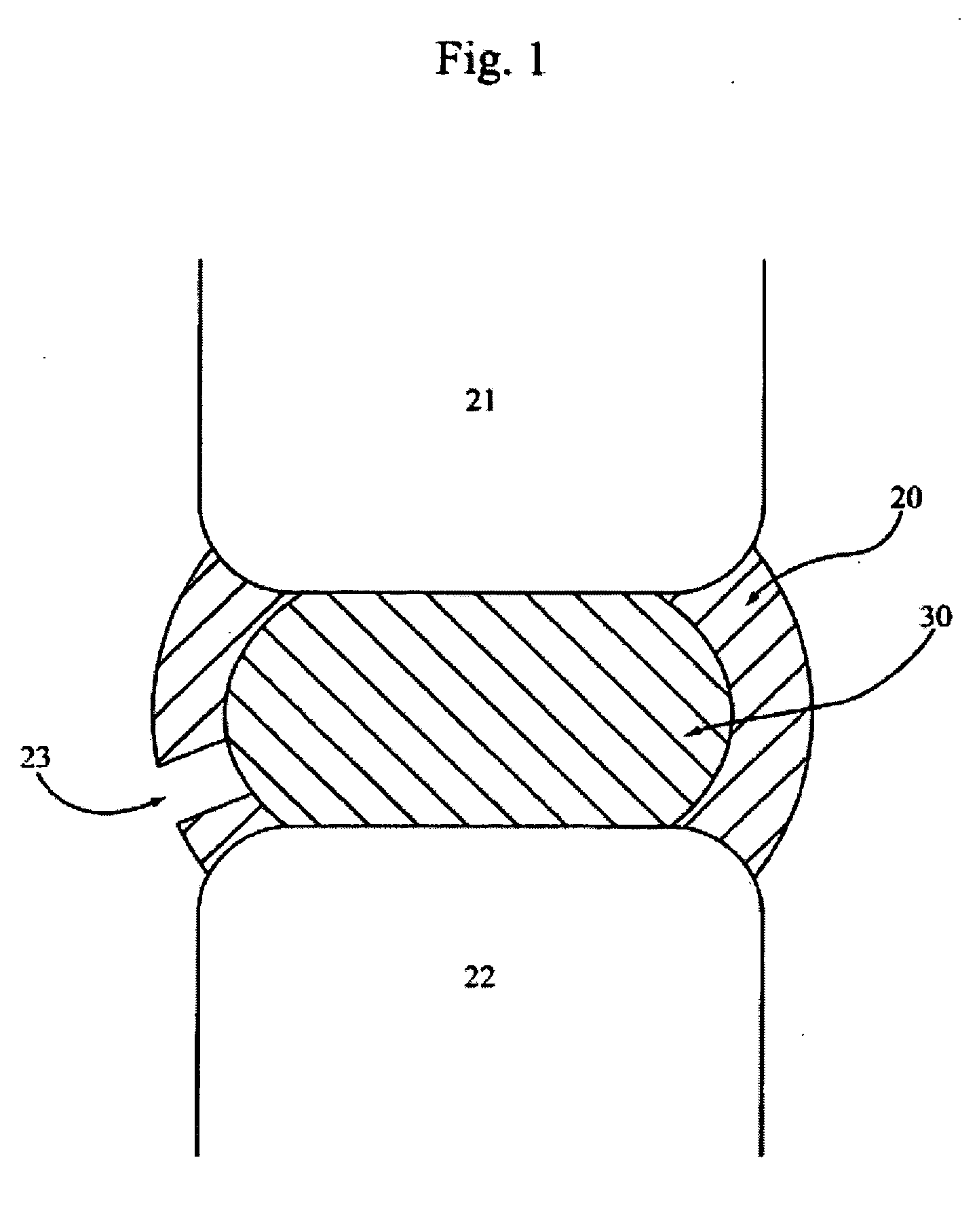
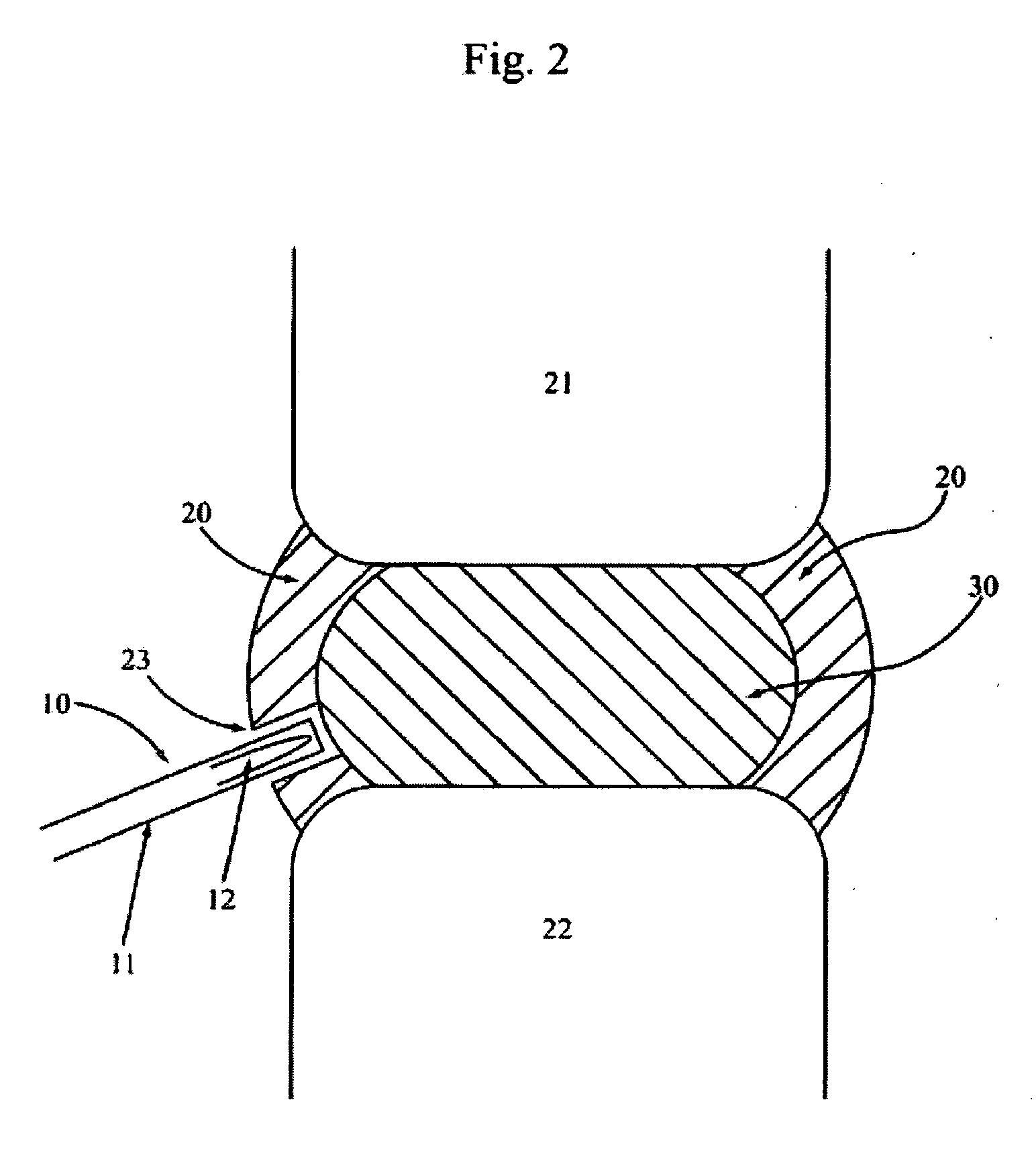
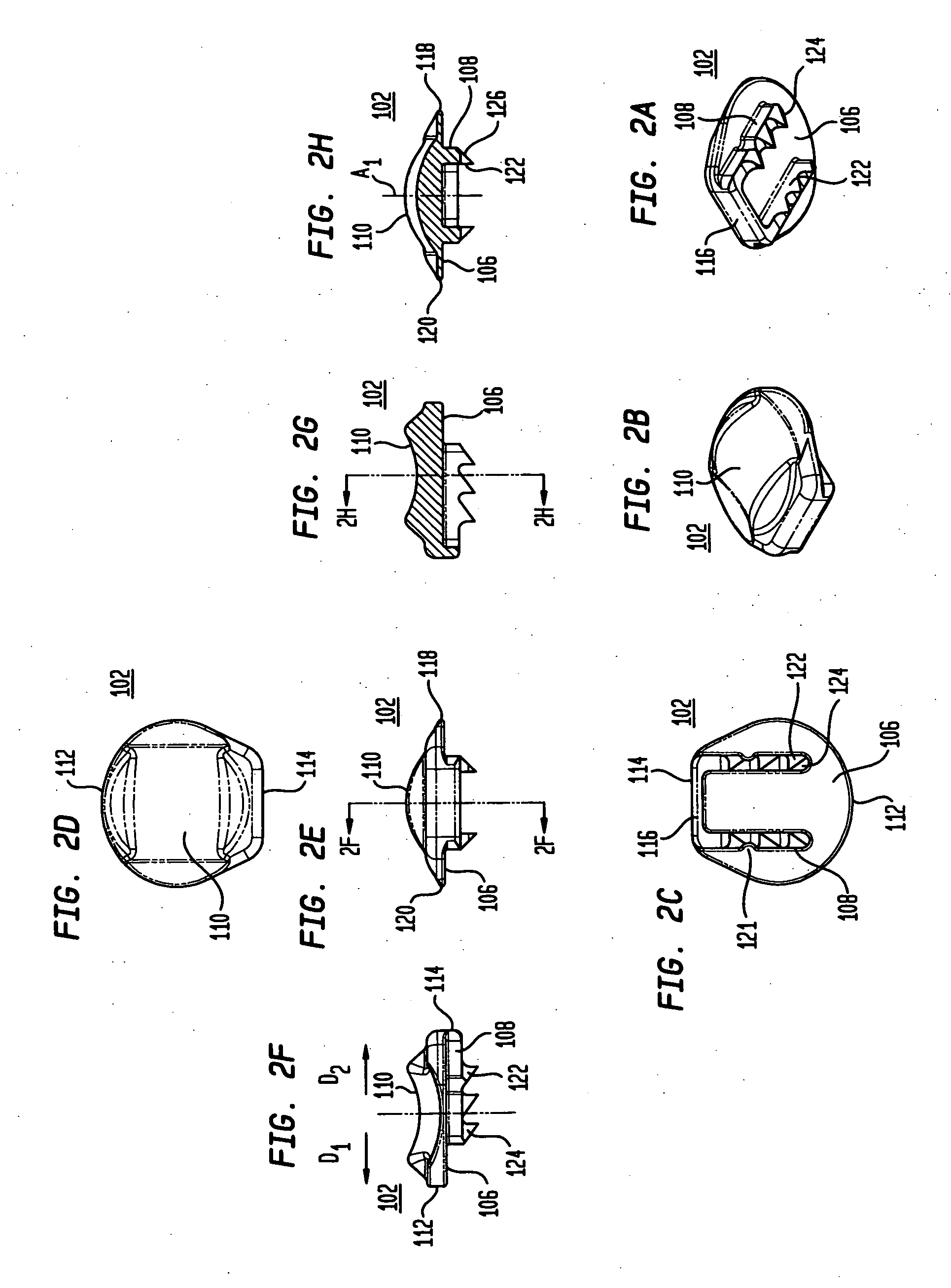
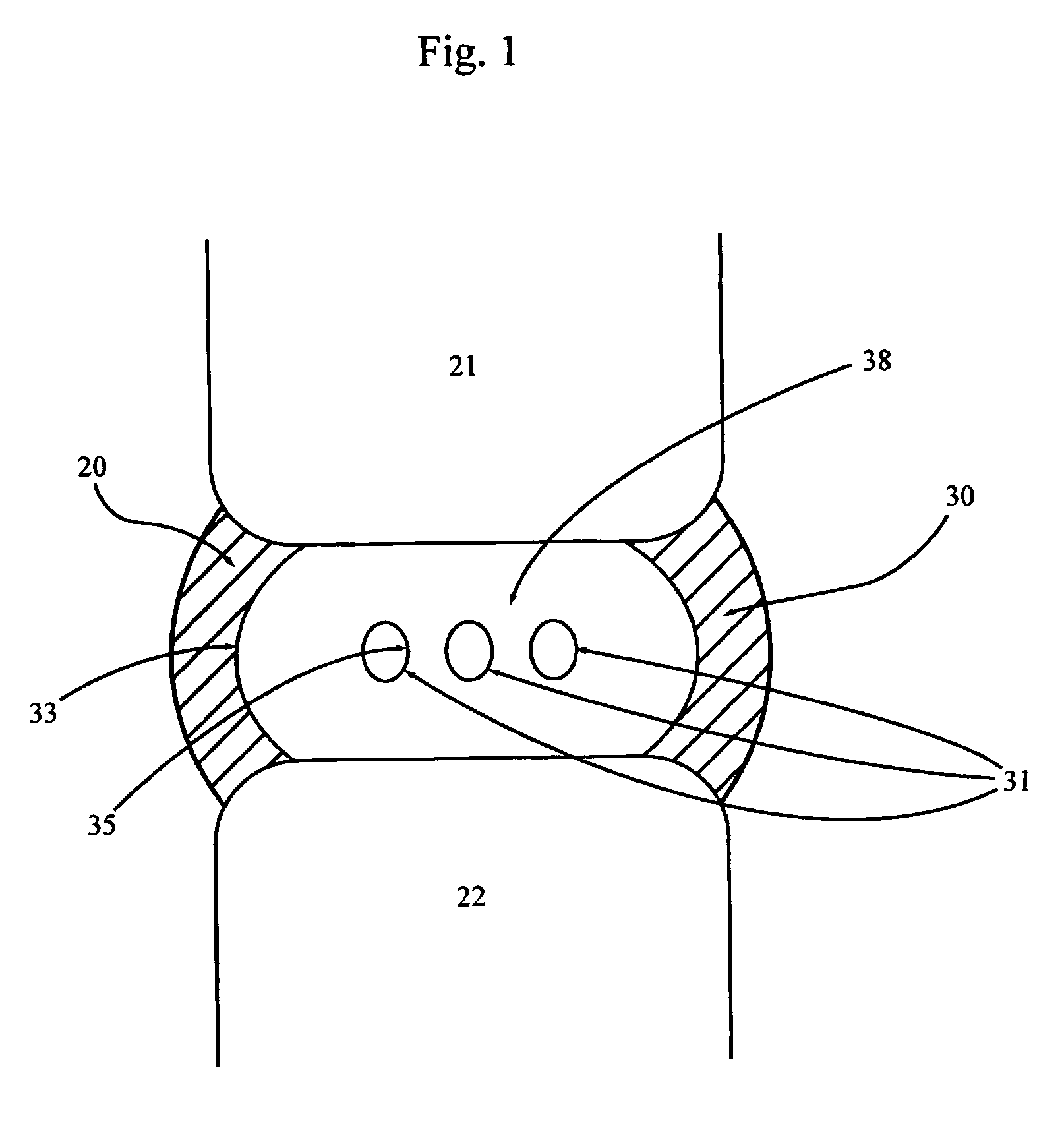
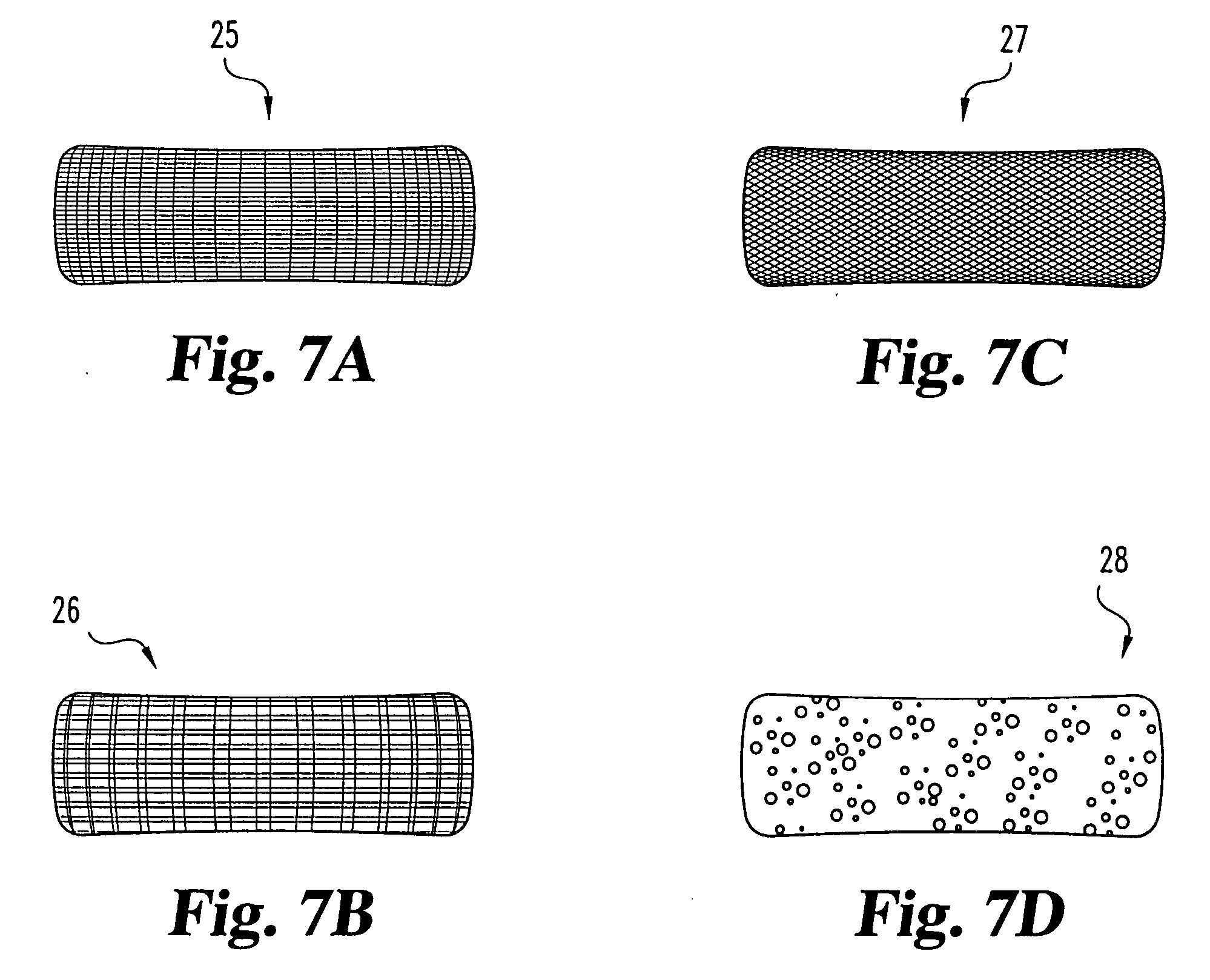
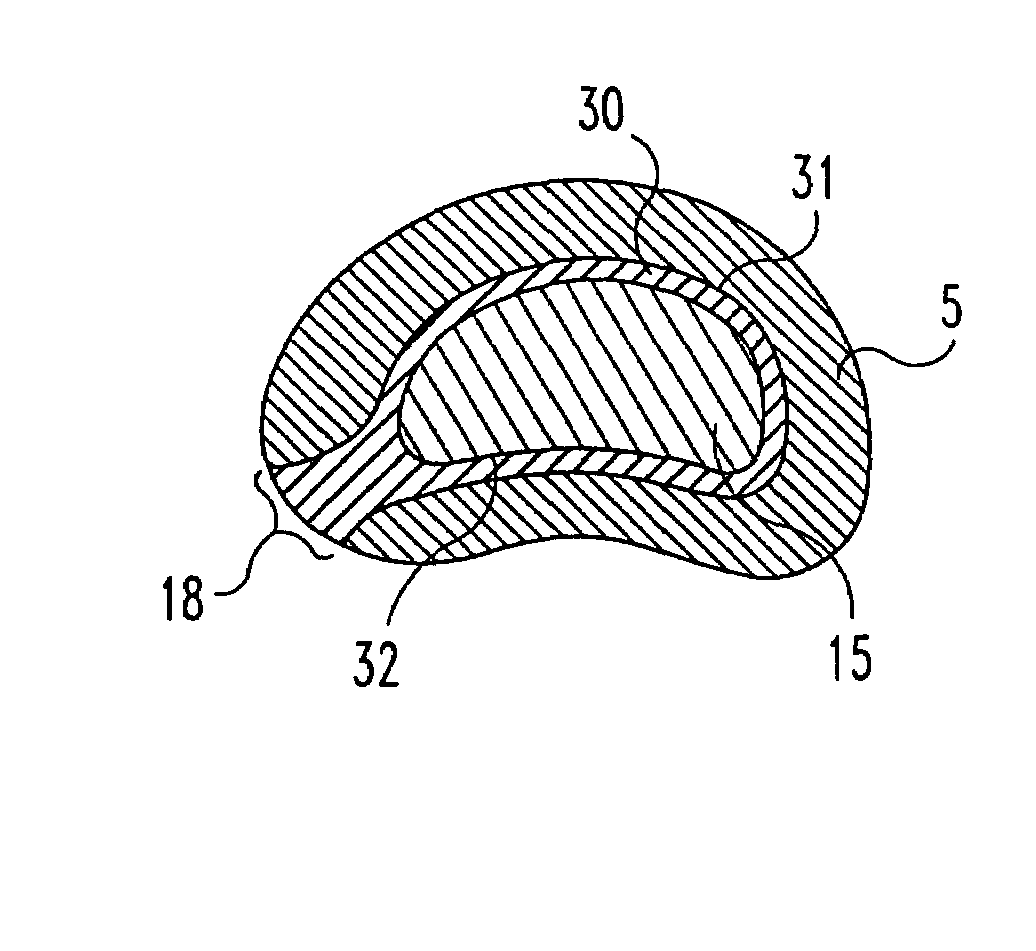
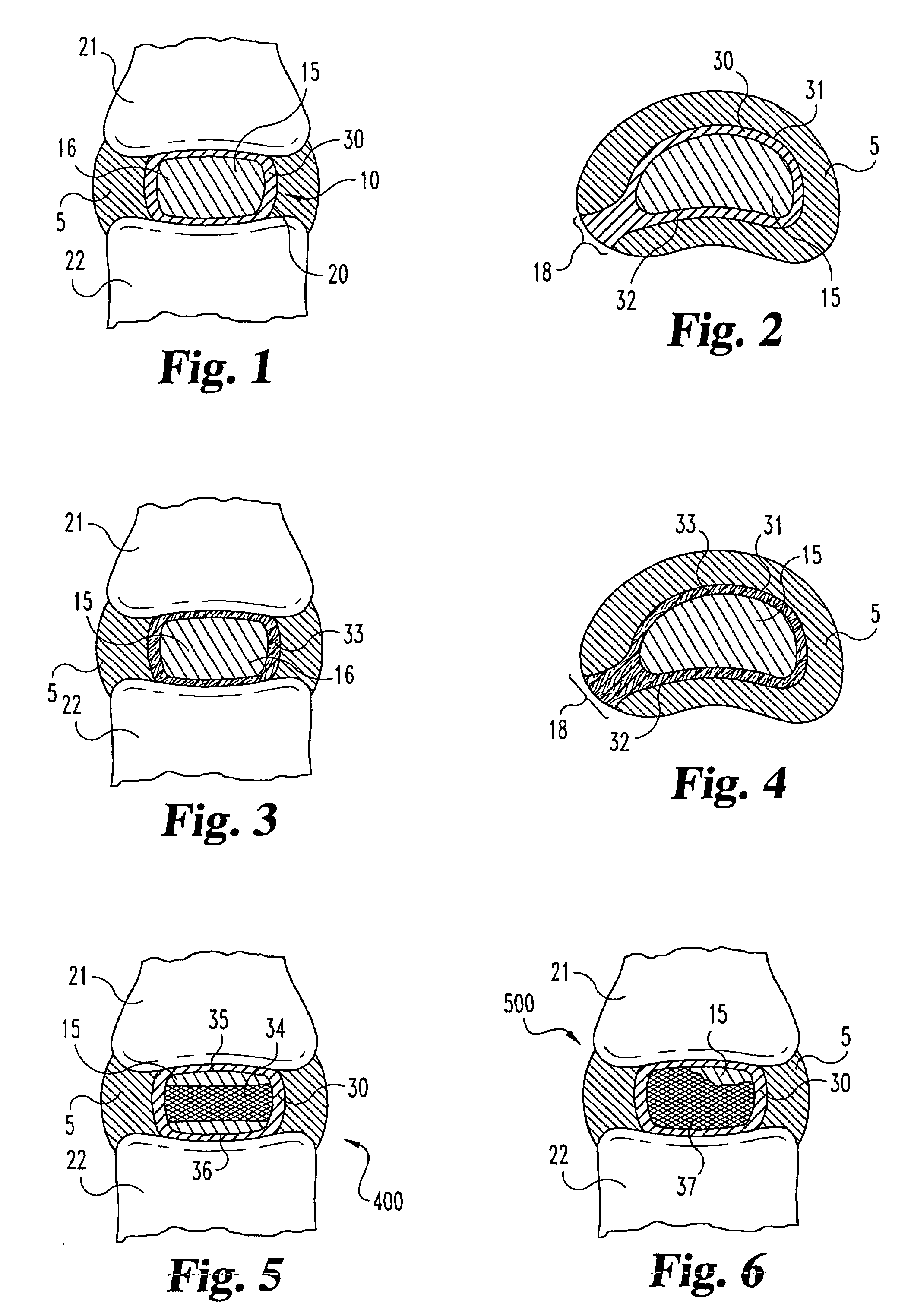
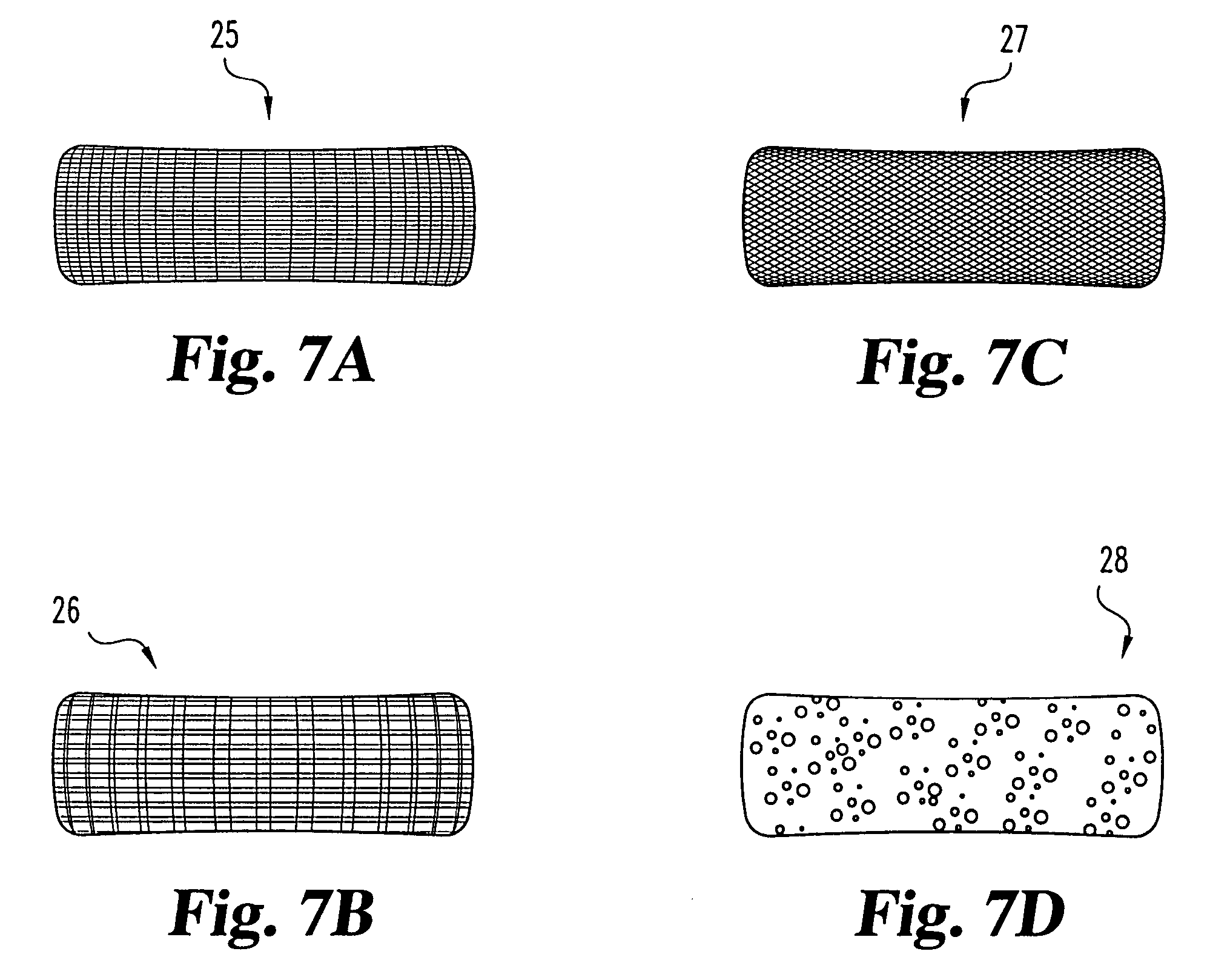
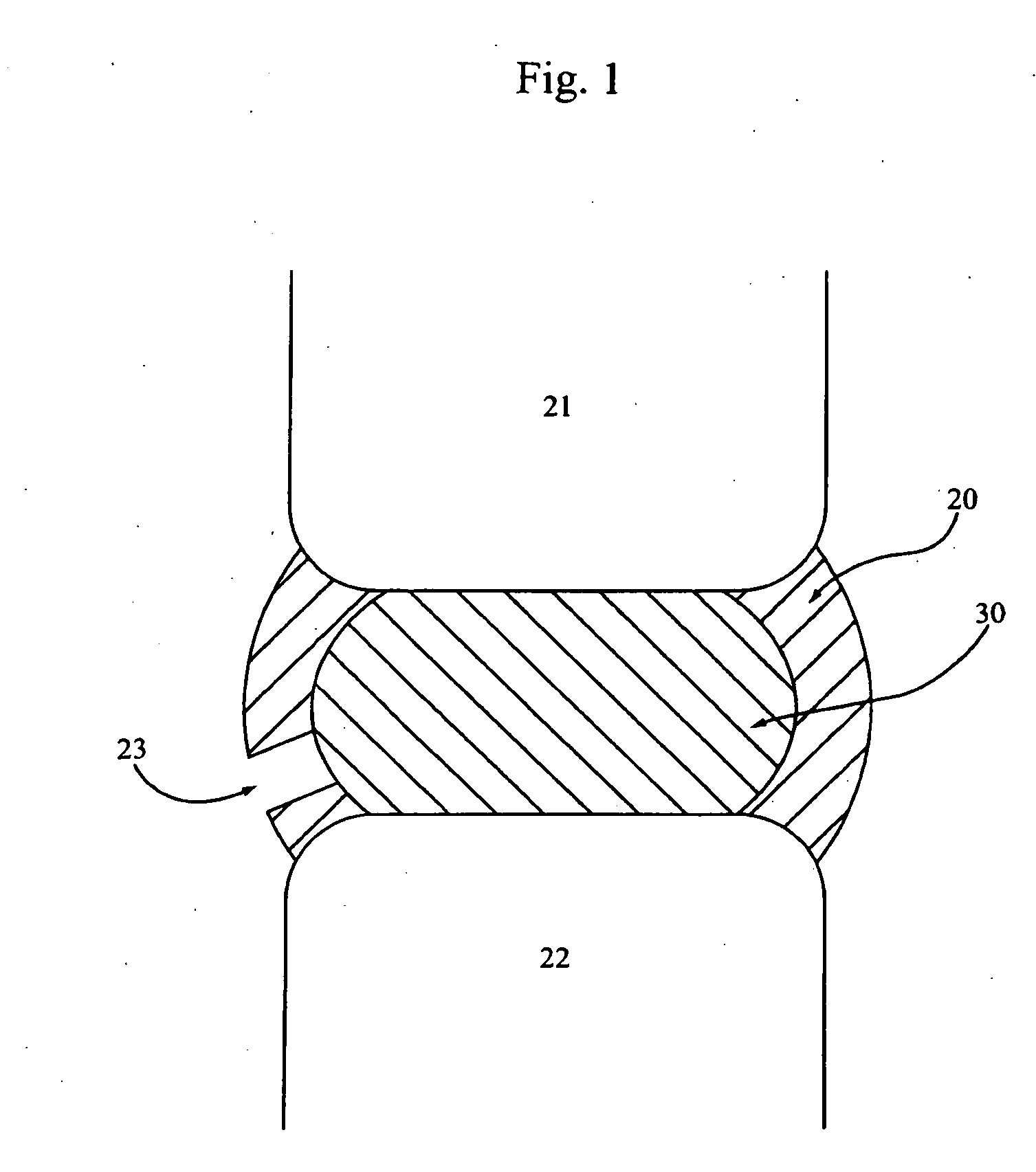
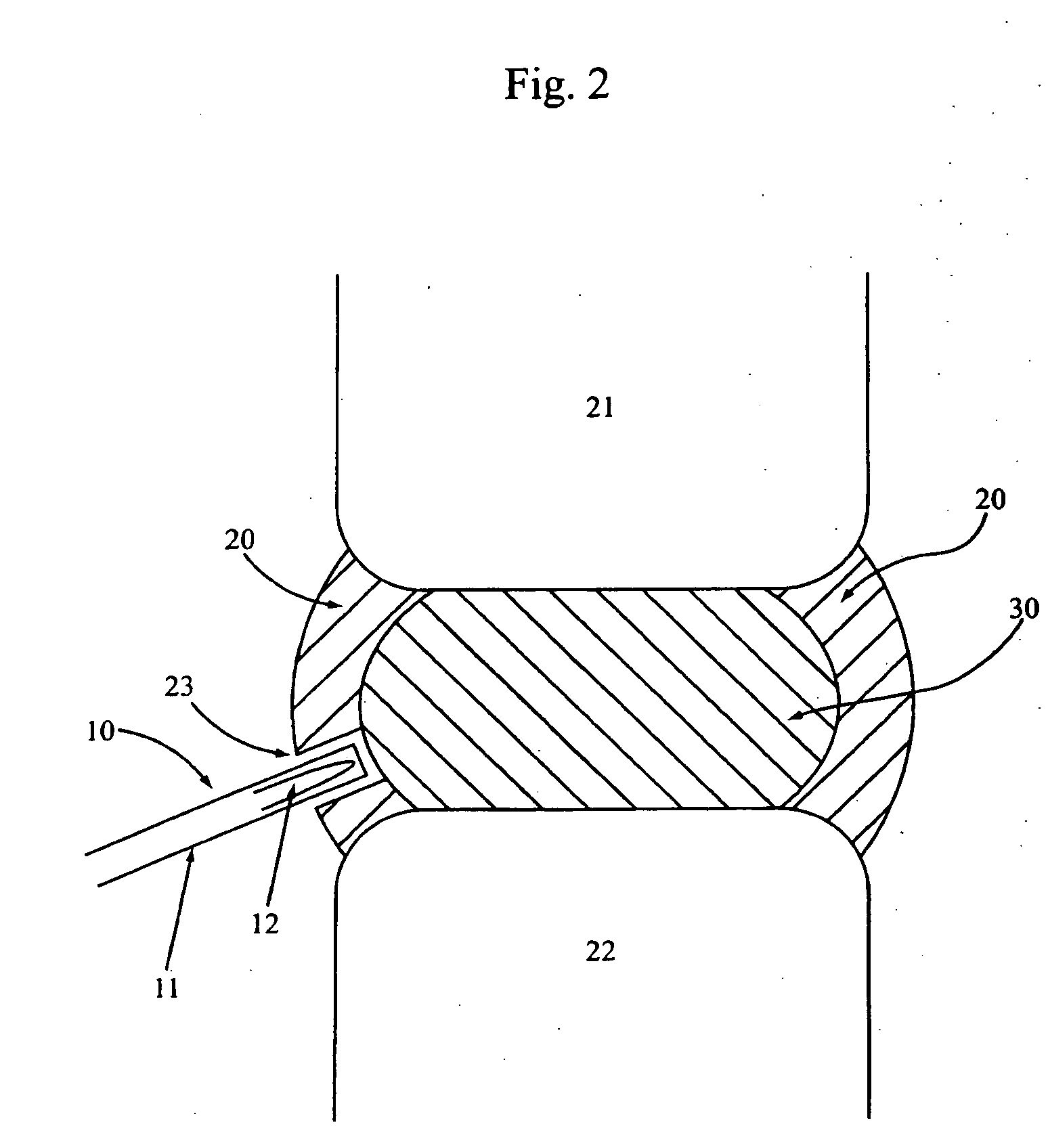
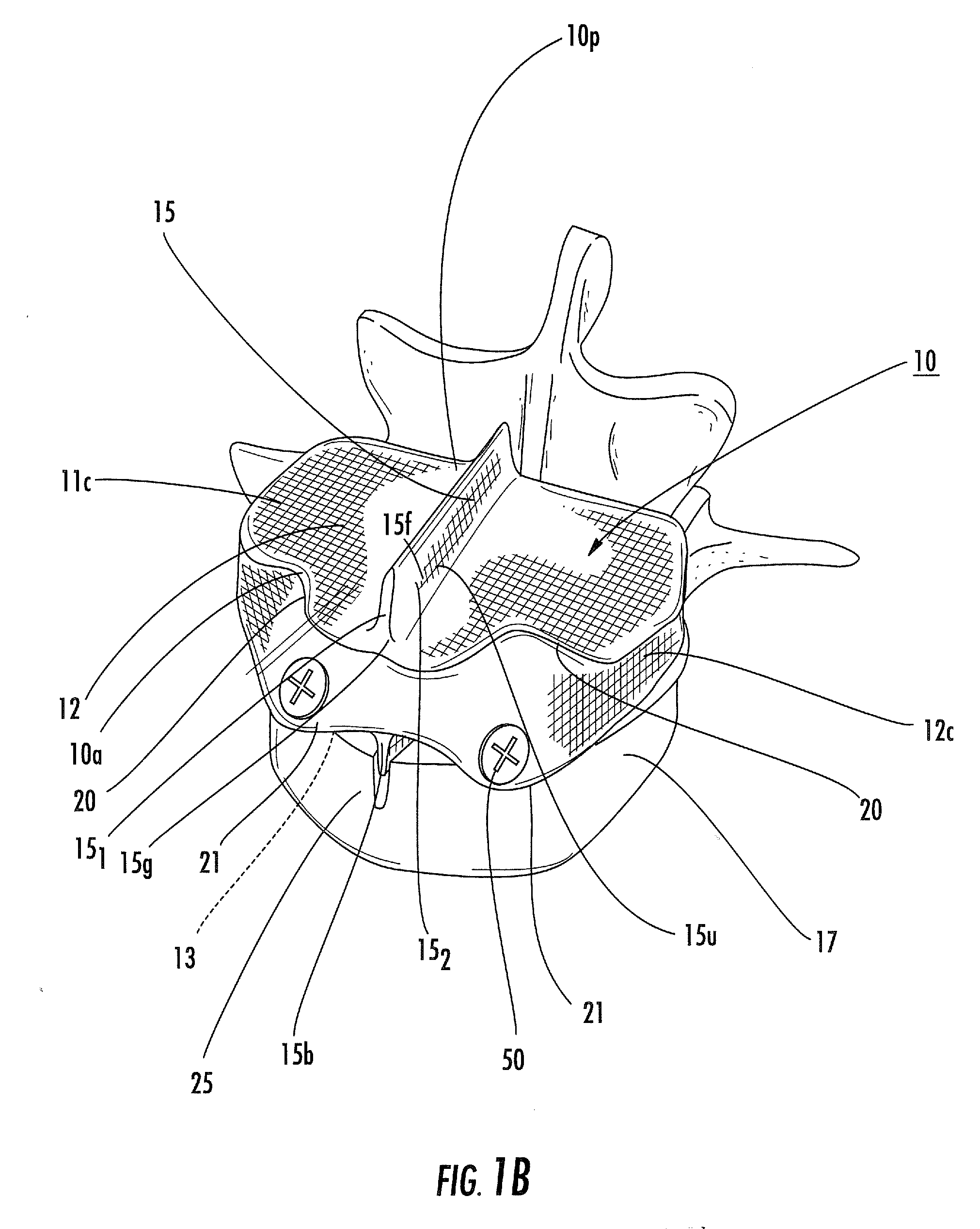
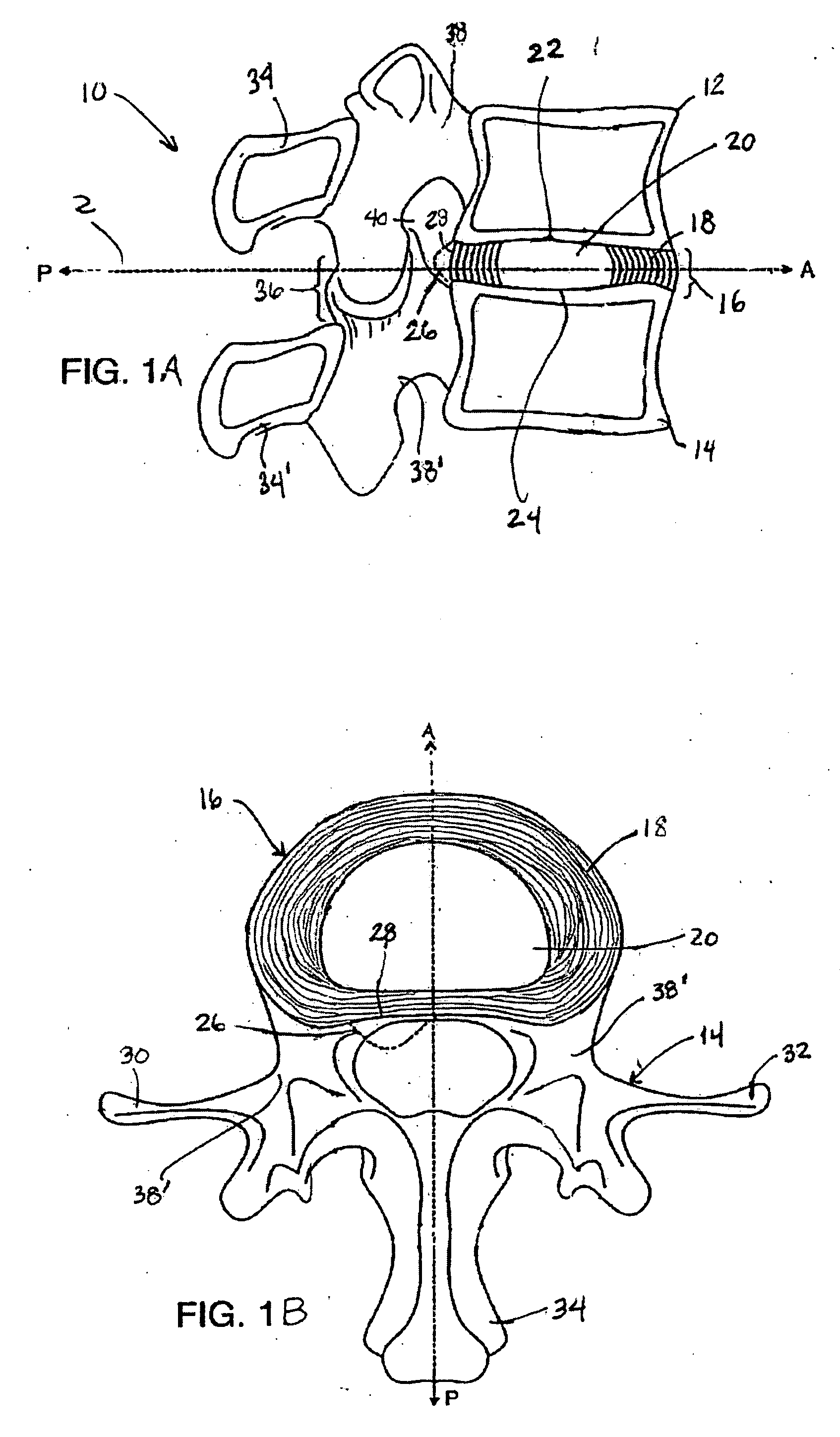
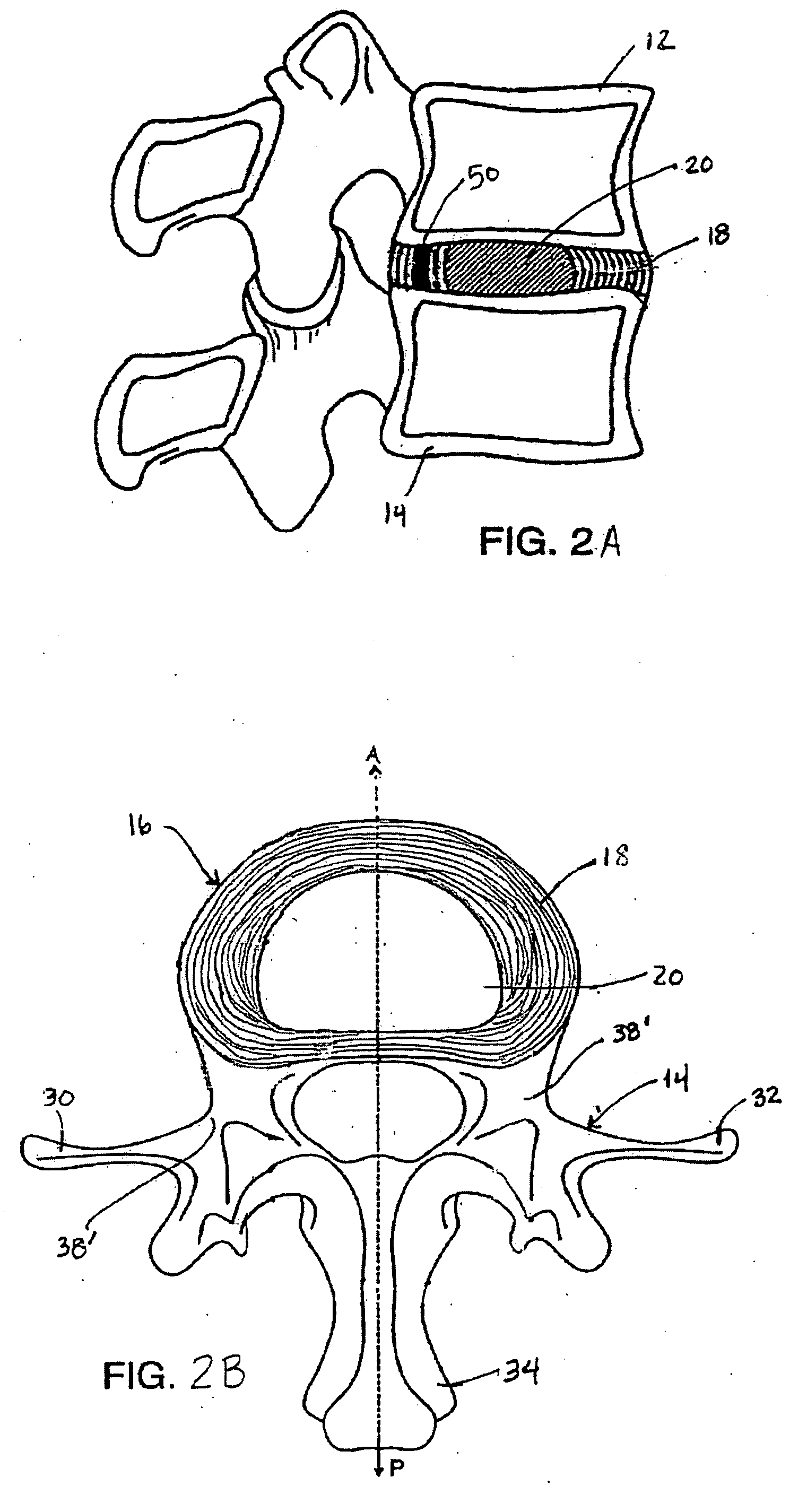
An interbody spinal implant of flat circular form for insertion at least in part across a disc space between adjacent vertebral bodies of a human spine as a part of surgical solution for degenerative disk disease or another morbid condition, which causes serious vertebral disk structure damage.
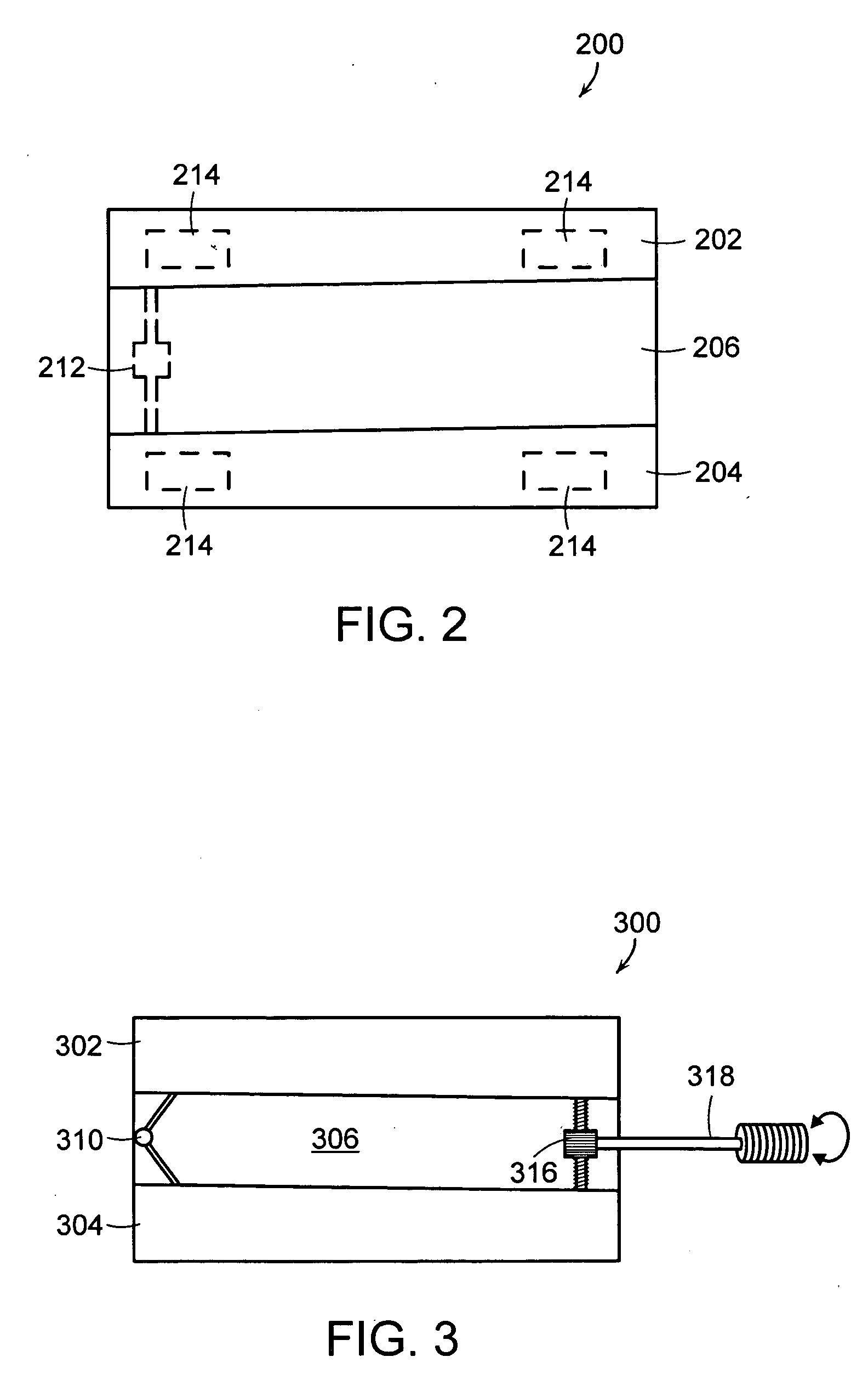
Intervertebral disc implant
InactiveUS6187048B1Speed up the flowReduce and eliminate any adverse effectJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral discProsthesis
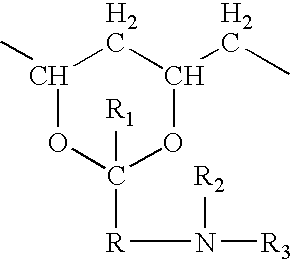
An implant for forming an intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus prosthesis includes a conformable material adapted to fill cavities within the disc and to at least partially polymerize in-situ to form a shaped, resiliently deformable prosthesis.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
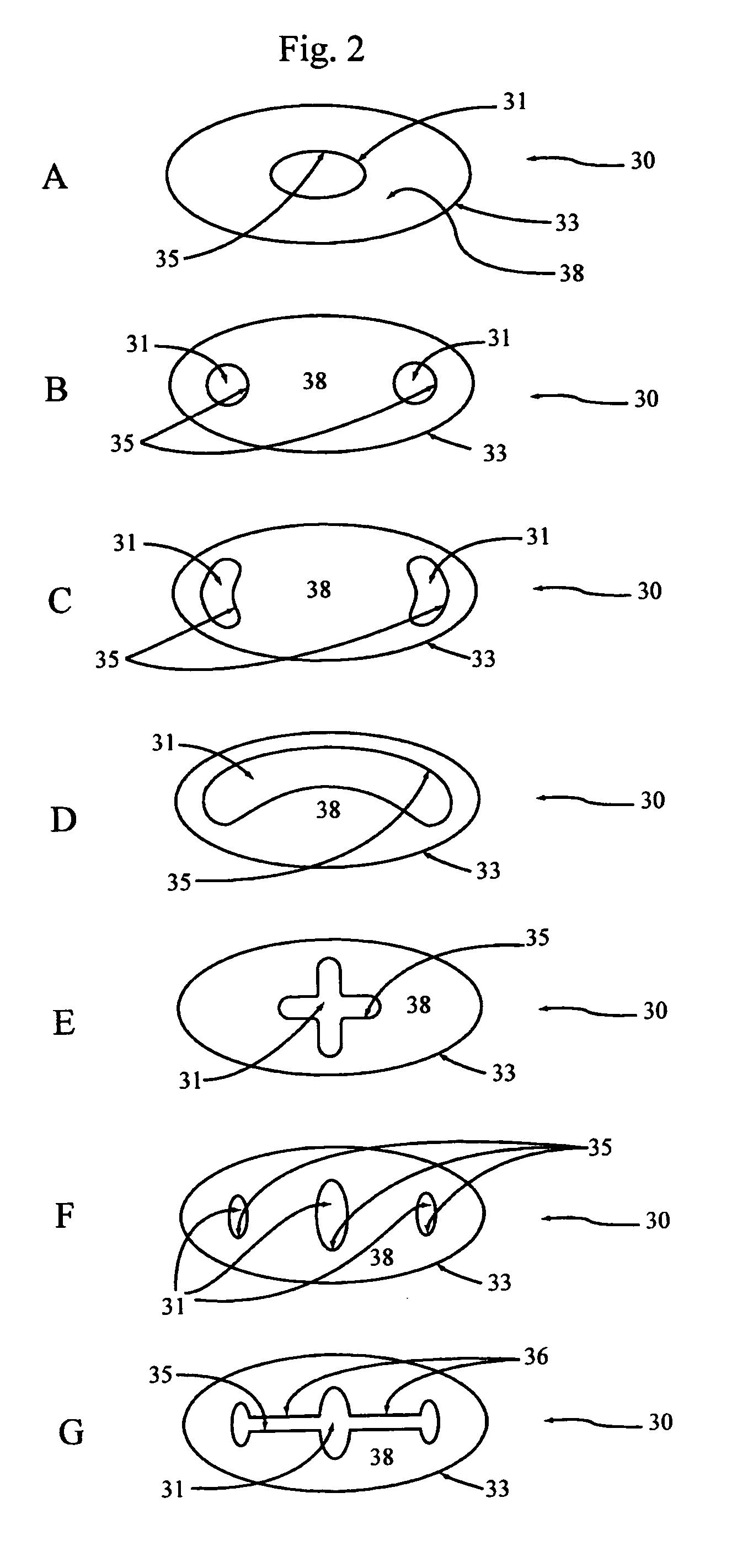
In situ formation of intervertebral disc implants
InactiveUS20060089719A1Improve bindingLarge deformationSkeletal disorderSpinal implantsSpinal Disk ImplantShort terms
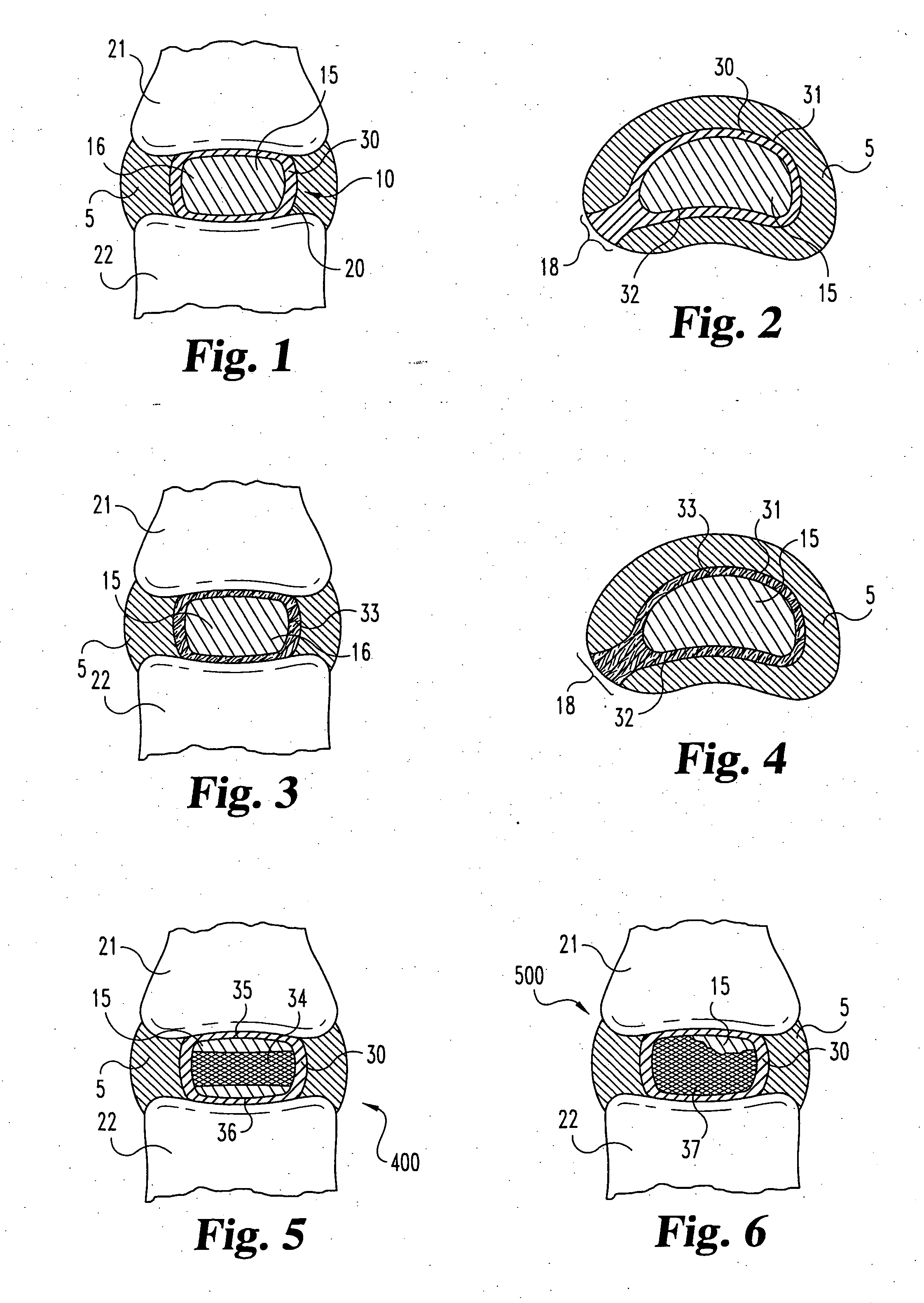
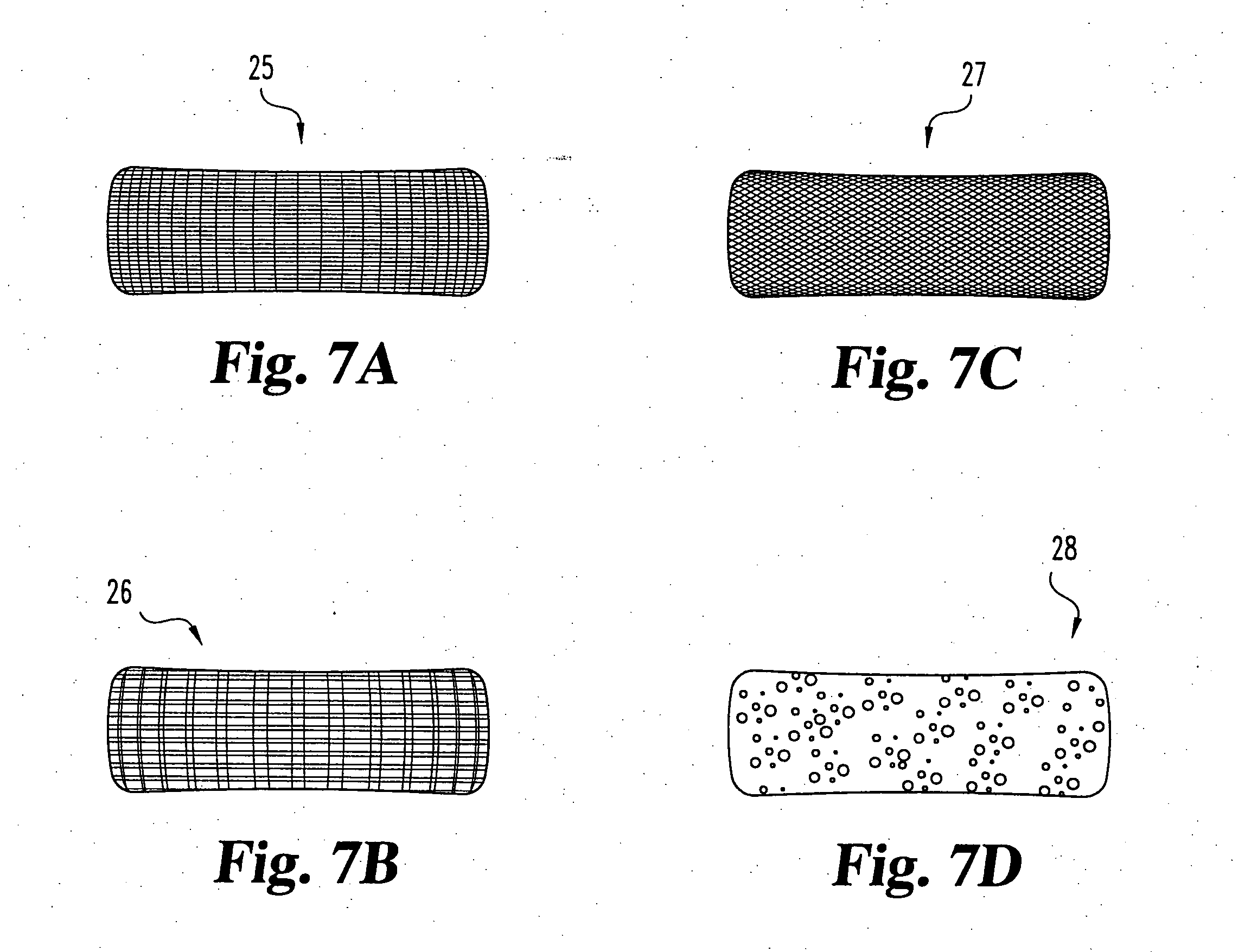
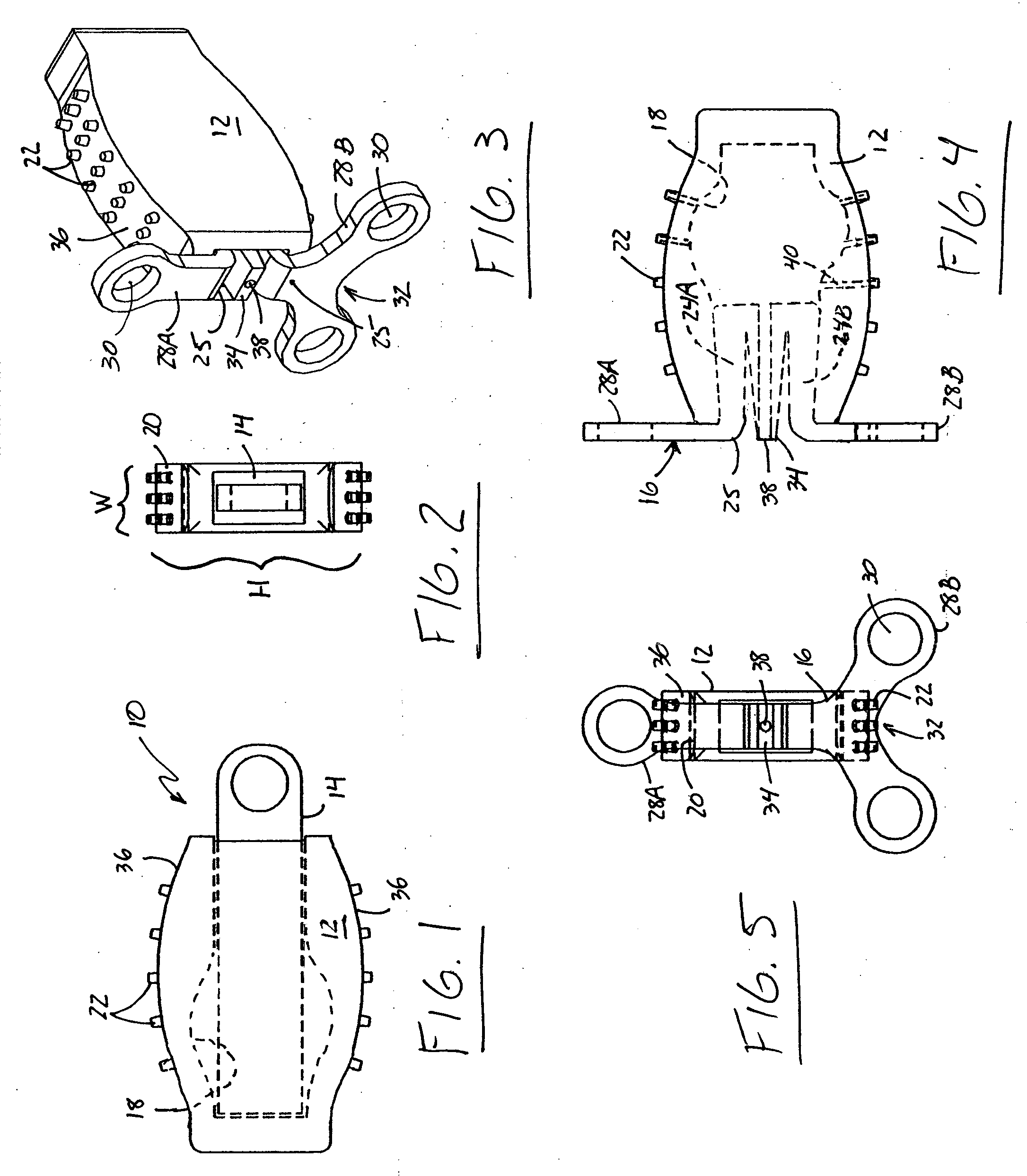
Nucleus pulposus implants that are resistant to migration in and / or expulsion from an intervertebral disc space are provided. In one form of the invention, an implant includes a load bearing elastic body surrounded in the disc space by an anchoring, preferably resorbable, biocompatible material which may be in the form of an outer shell. In certain forms of the invention, the elastic body is surrounded by a supporting member, such as a band or jacket, and the supporting member is surrounded by the outer shell. Kits for forming such implants are also provided. In another form of the invention, an implant is provided that has locking features and optional shape memory characteristics. In yet another aspect of the invention, nucleus pulposus implants are provided that have shape memory characteristics and are configured to allow short-term manual, or other deformation without permanent deformation, cracks, tears, breakage or other damage. Methods of forming and implanting the implants are also described, as are delivery devices and components thereof for delivering the implants.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
Devices and methods for explantation of intervertebral disc implants
Methods and devices are provided for the explantation of spinal implants. A cutting tool may be extended into the spinal implant. The spinal implant may be cut into pieces and the pieces removed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Trial disk implant
InactiveUS20060069436A1Minimize changesReduce dependencePerson identificationJoint implantsSpinal Disk ImplantIntervertebral disk
A trial intervertebral disk implant includes a first plate, a second plate, adjacent to the first plate, a conformable layer between the first and the second plates, and a pressure sensor within the conformable layer. The pressure sensor measures a distribution of compression force exerted by the first and the second plates on the conformable layer. The trial implant includes indicating means for indicating a position of the first and the second plates relative to each other, and locating means, for locating a position of the trial implant relative to the vertebrae between which said trial implant has been placed. The trial implant further includes at least one retractable member, connected to at least one of the first and the second plates. The retractable member can be extended or retracted through an aperture defined by a surface of the plate that is proximal to an abutting vertebra.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Intervertebral disc implant resistant to migration
InactiveUS20050033440A1Reduce long-term negative consequenceImprove leakageSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal Disk ImplantMedicine
Devices for implantation into an intervertebral disc can include a membrane support member to augment a disc having a defect. A defect in the anulus of a disc can be repaired using a prosthesis such as a barrier. The barrier can include a sealant and an enlarger. The barrier can be implanted into the disc using a delivery cannula, an advancer and at least one control filament to control the positioning of the barrier. A stiffening element can be included within the barrier to impart stiffness to the barrier. The support member can also be connected to an anchor.
Owner:INTRINSIC THERAPEUTICS
Methods and apparatuses for minimally invasive replacement of intervertebral discs
In one embodiment, an access device is inserted through an incision in skin of a patient. The access device is expanded from a first configuration to a second configuration, the second configuration having an enlarged cross-sectional area at a distal portion of said access device such that the distal portion extends across at least a portion of the interbody space. A prosthetic spinal disc implant is then delivered through the access device.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Instruments for delivery of intervertebral disc implants
InactiveUS20050131540A1Improve bindingLarge deformationBone implantJoint implantsSpinal Disk ImplantMedicine
Nucleus pulposus implants that are resistant to migration in and / or expulsion from an intervertebral disc space are provided. In one form of the invention, an implant includes a load bearing elastic body surrounded in s the disc space by an anchoring, preferably resorbable, outer shell. In certain forms of the invention, the elastic body is surrounded by a supporting member, such as a band or jacket, and the supporting member is surrounded by the outer shell. Kits for forming such implants are also provided. In another form of the invention, an implant is provided that has locking features and optional shape memory characteristics. In yet another aspect of the invention, nucleus pulposus implants are provided that have shape memory characteristics and are configured to allow short-term manual, or other deformation without permanent deformation, cracks, tears, breakage or other damage. Methods of forming and implanting the implants are also described, as are delivery devices and components thereof for delivering the implants.
Owner:TRIEU HAI H
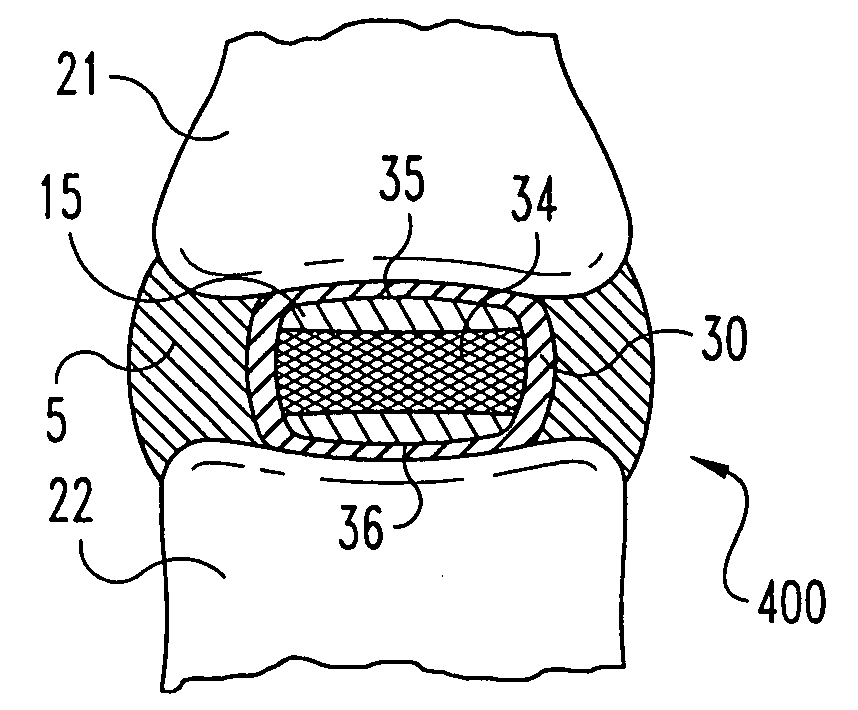
Intervertebral disc and insertion methods therefor
ActiveUS20070123985A1Good for long-term fixationPrevent over-insertionDiagnosticsSpinal implantsSpinal Disk ImplantIntervertebral disk
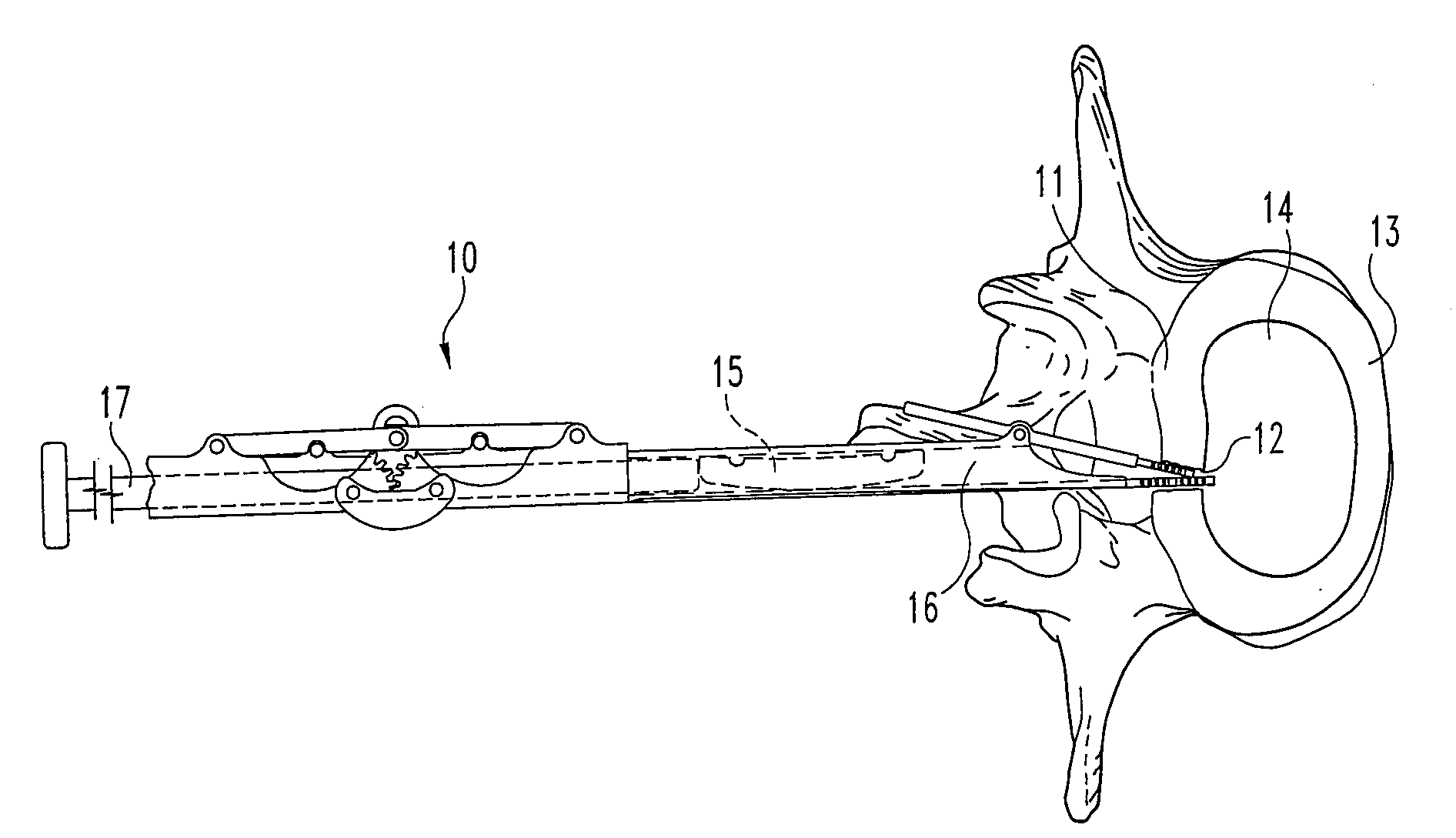
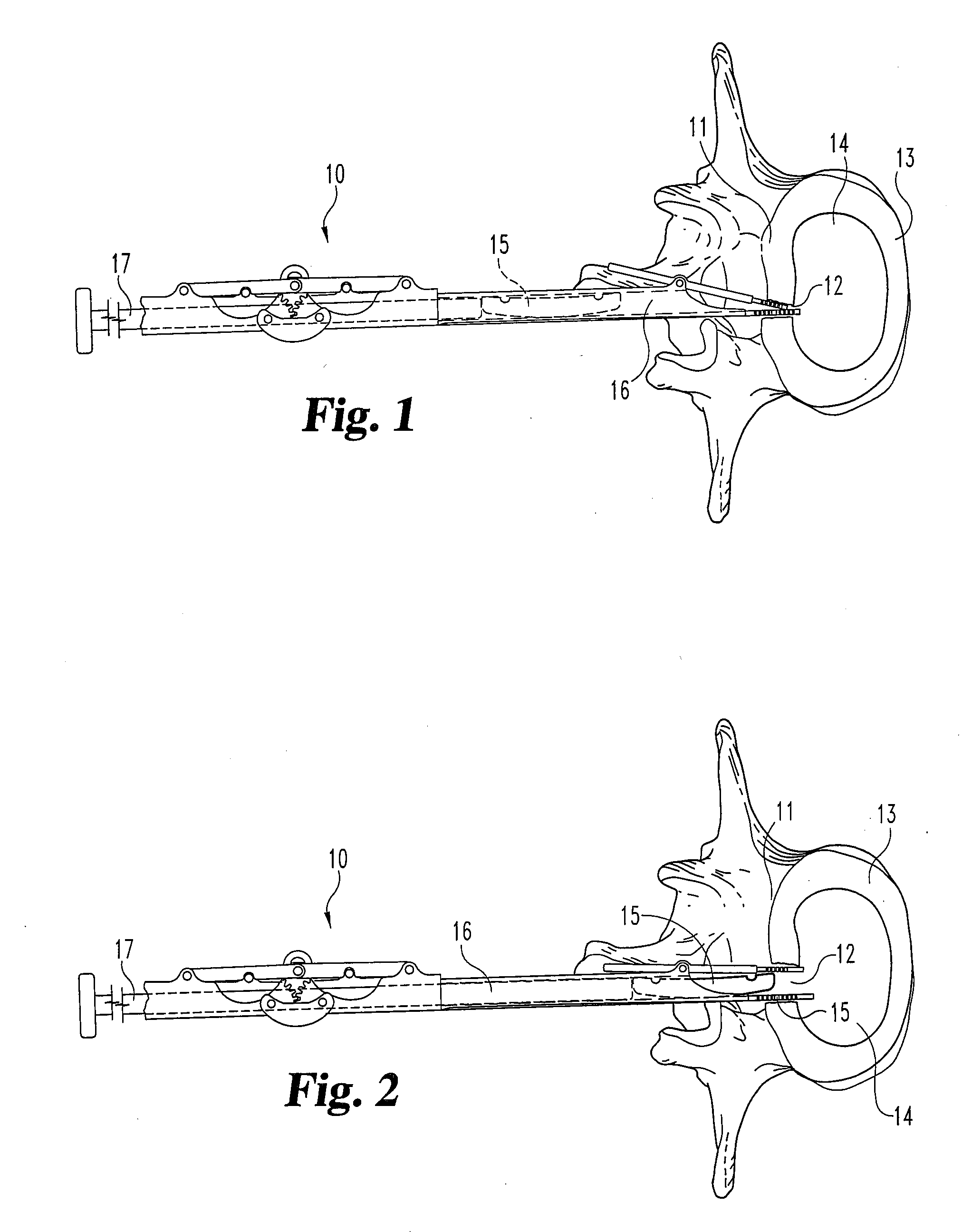
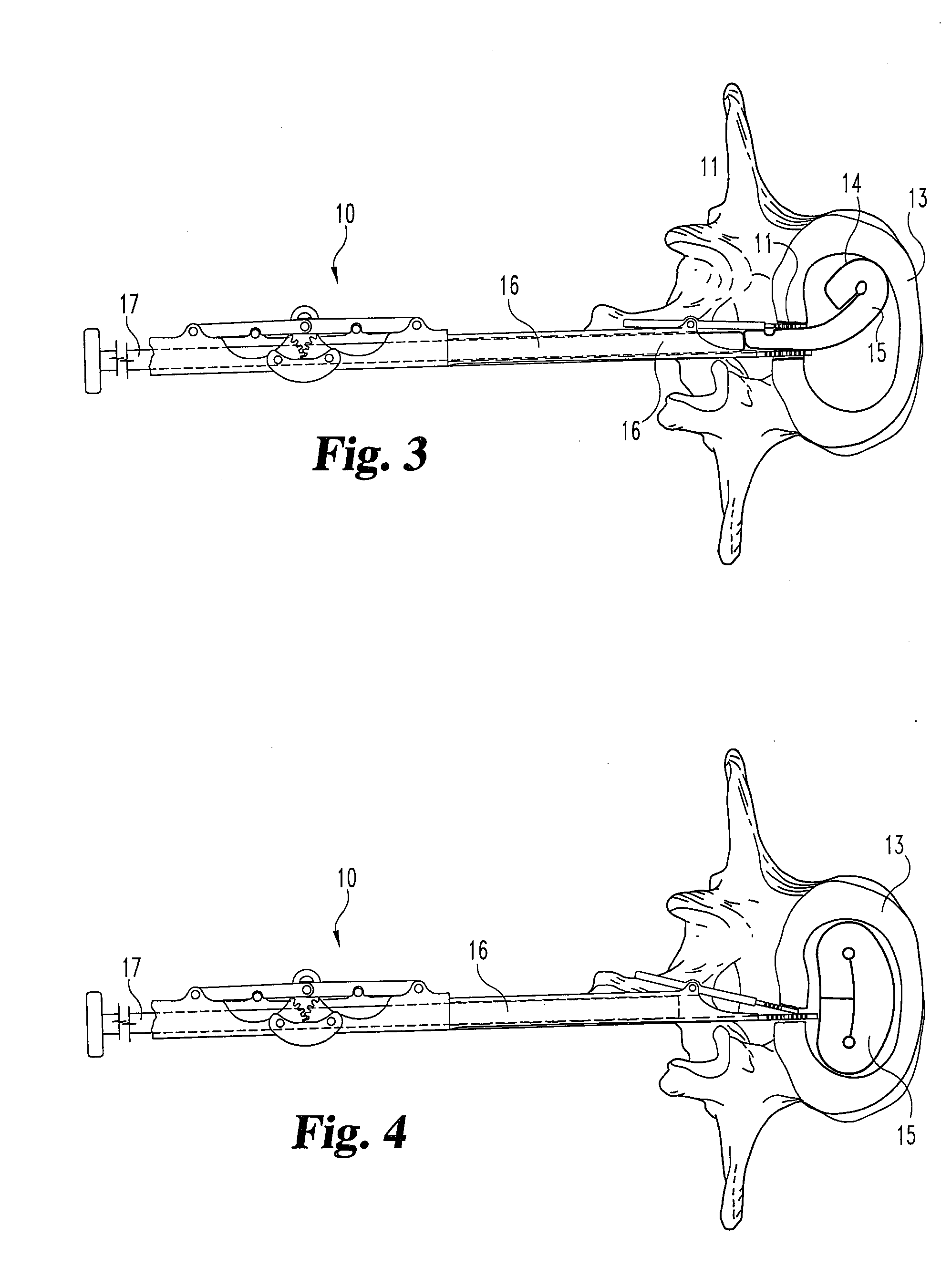
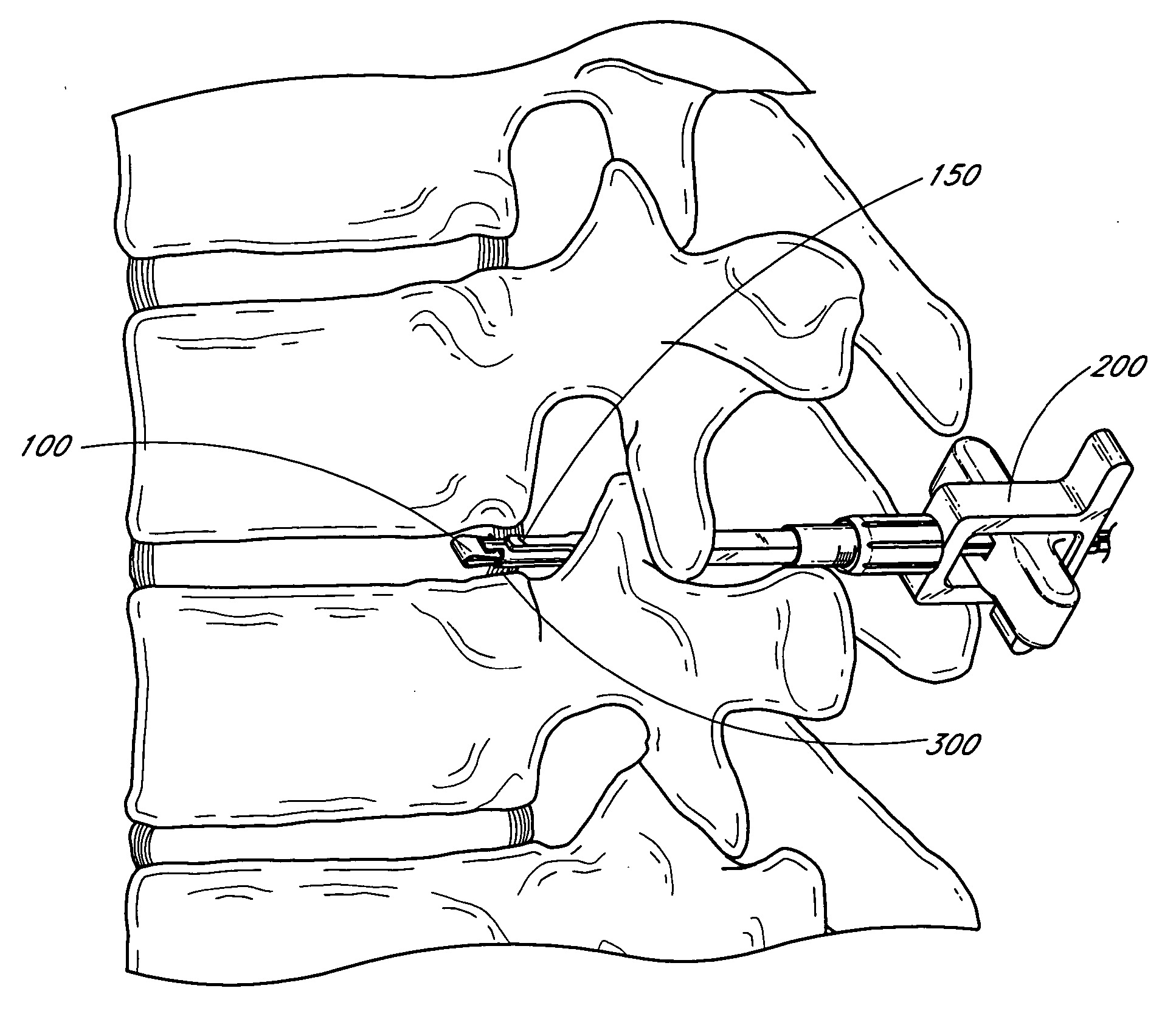
A method of inserting an intervertebral disc implant into a disc space includes accessing a spinal segment having a first vertebral body, a second vertebral body and a disc space between the first and second vertebral bodies. The method includes securing a first pin to the first vertebral body and a second pin to the second vertebral body, using the first and second pins for distracting the disc space, and providing an inserter holding the intervertebral disc implant. The method also desirably includes engaging the inserter with the first and second pins, and advancing the inserter toward the disc space for inserting the intervertebral disc implant into the disc space, whereby the first and second pins align and guide the inserter toward the disc space.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Composite intervertebral disc implants and methods for forming the same
InactiveUS20060064172A1Improve bindingLarge deformationBone implantSurgeryElastomerSpinal Disk Implant
Nucleus pulposus implants that are resistant to migration in and / or expulsion from an intervertebral disc space are provided. In one form of the invention, an implant includes a load bearing elastic body surrounded in the disc space by an anchoring, preferably resorbable, outer shell. In certain forms of the invention, the elastic body is surrounded by a supporting member, such as a band or jacket, and the supporting member is surrounded by the outer shell. Kits for forming such implants are also provided. In another form of the invention, an implant is provided that has locking features and optional shape memory characteristics. In yet another aspect of the invention, nucleus pulposus implants are provided that have shape memory characteristics and are configured to allow short-term manual, or other deformation without permanent deformation, cracks, tears, breakage or other damage. Methods of forming and implanting the implants are also described.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method and apparatus for delivering an intervertebral disc implant
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
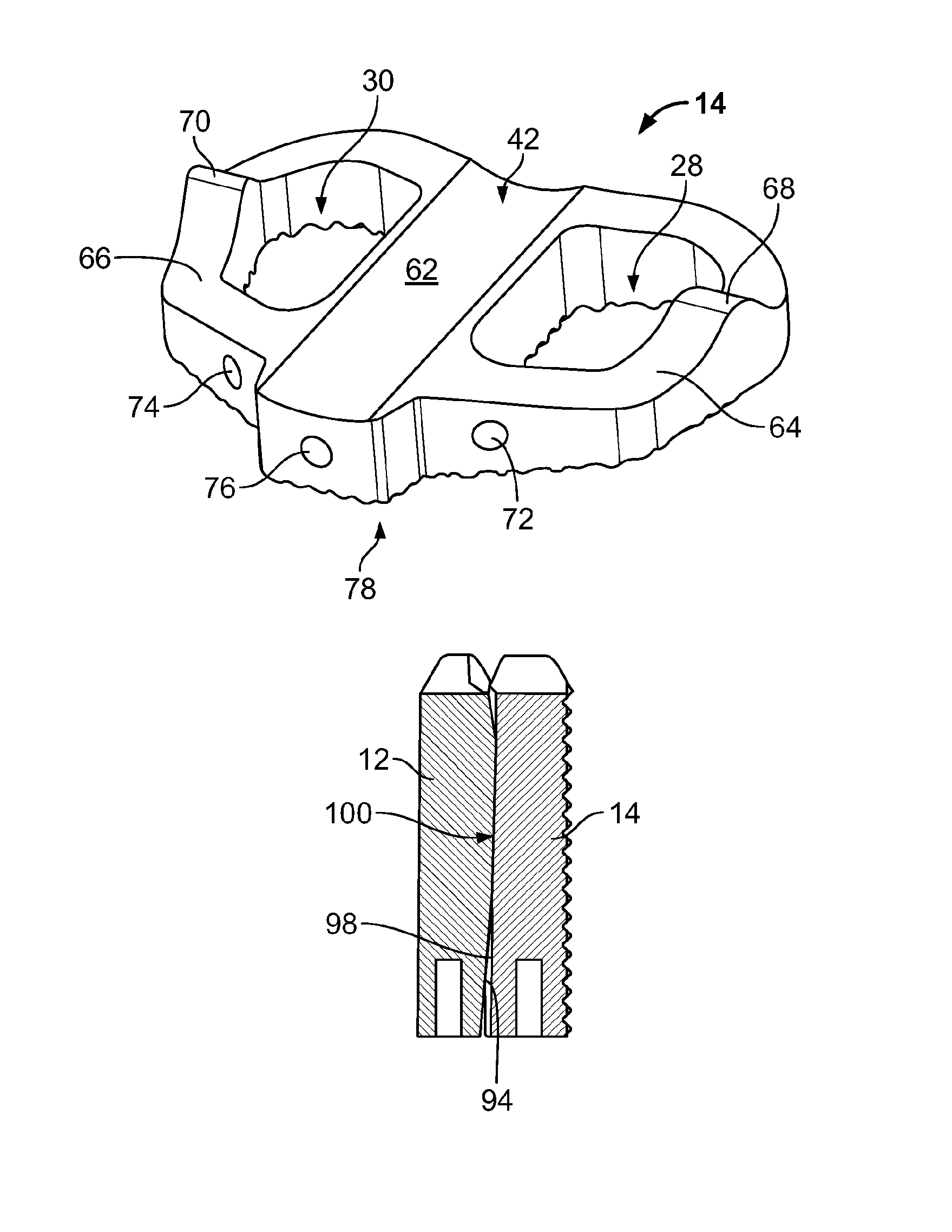
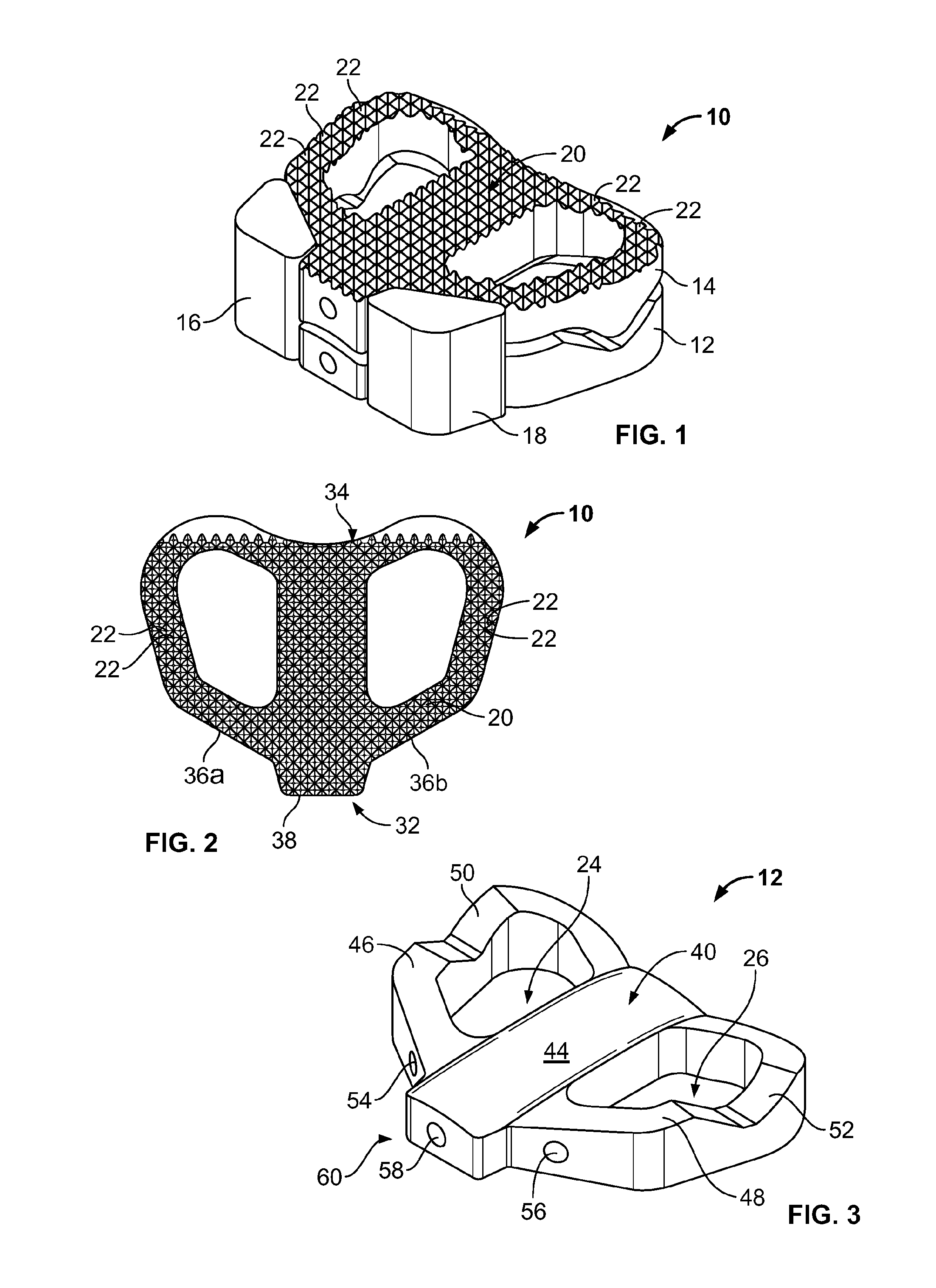
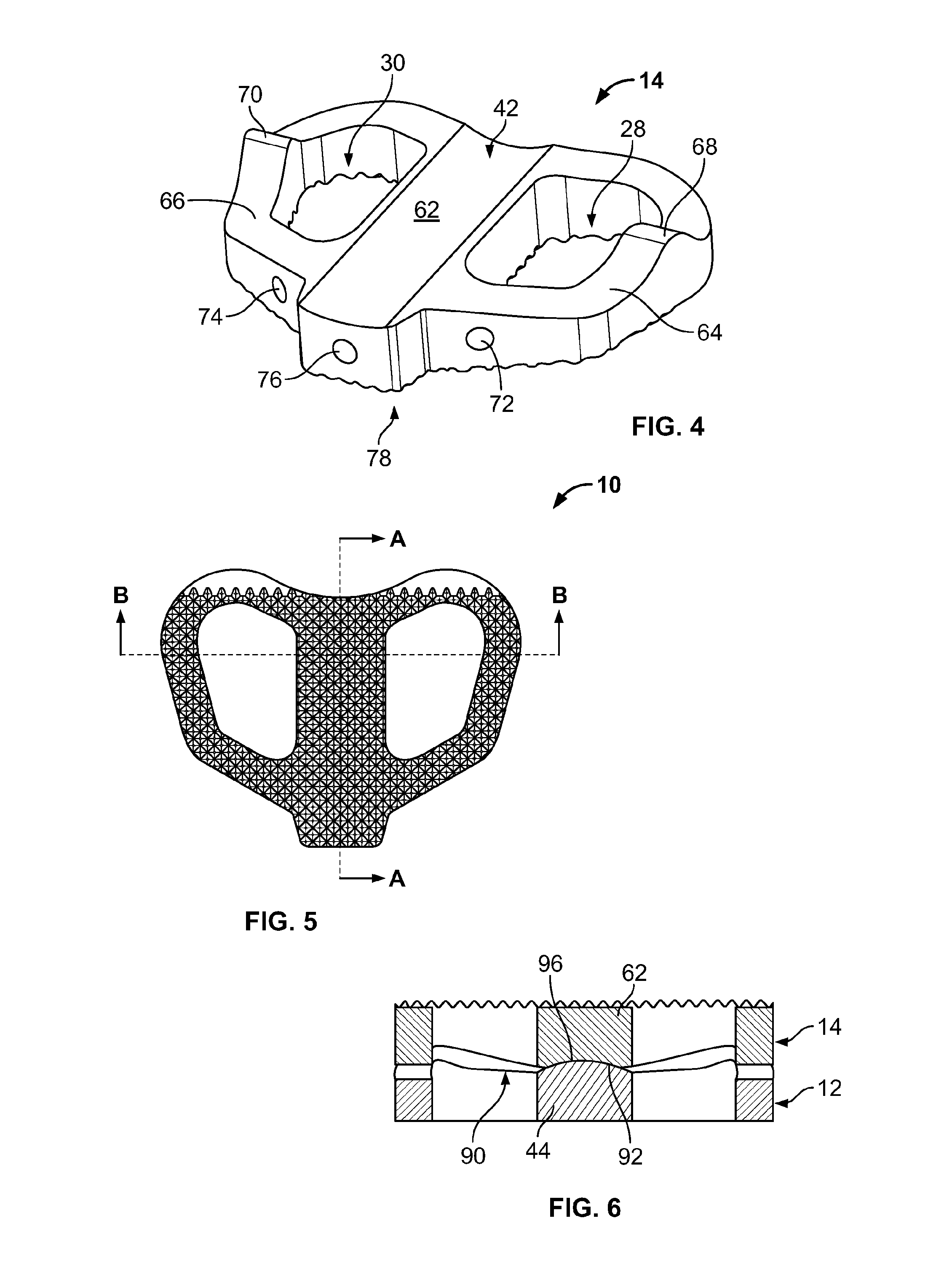
Spinal disc implants with reservoirs for delivery of therapeutic agents
Nucleus pulposus implants that contain reservoirs for receiving, holding, and releasing therapeutic agents are provided. In one form of the invention, a spinal implant is provided with reservoirs positioned at least partially beneath the external surface of the implant. The reservoirs are provided to receive, hold, and release therapeutic and / or pharmaceutical agents into the surrounding tissues.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Methods for forming and retaining intervertebral disc implants
Nucleus pulposus implants that are resistant to migration in and / or expulsion from an intervertebral disc space are provided. In one form of the invention, an implant includes a load bearing elastic body surrounded in the disc space by an anchoring, preferably resorbable, outer shell. In certain forms of the invention, the elastic body is surrounded by a supporting member, such as a band or jacket, and the supporting member is surrounded by the outer shell. Kits for forming such implants are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Methods for forming and retaining intervertebral disc implants
InactiveUS7503936B2Improve bindingLarge deformationBone implantSurgeryBiomedical engineeringIntervertebral disc space
Nucleus pulposus implants that are resistant to migration in and / or expulsion from an intervertebral disc space are provided. In one form of the invention, an implant includes a load bearing elastic body surrounded in the disc space by an anchoring, preferably resorbable, outer shell. In certain forms of the invention, the elastic body is surrounded by a supporting member, such as a band or jacket, and the supporting member is surrounded by the outer shell. Kits for forming such implants are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
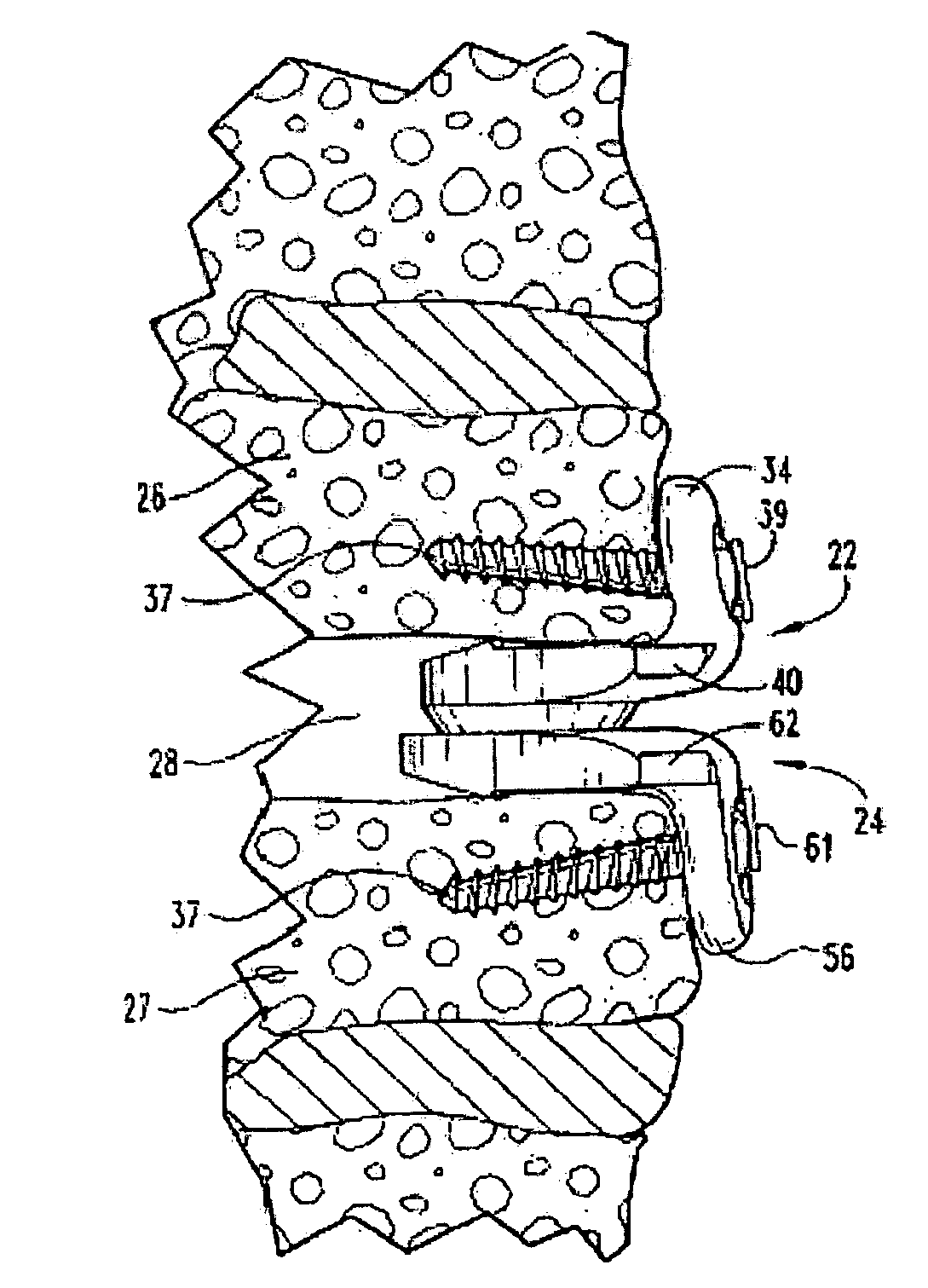
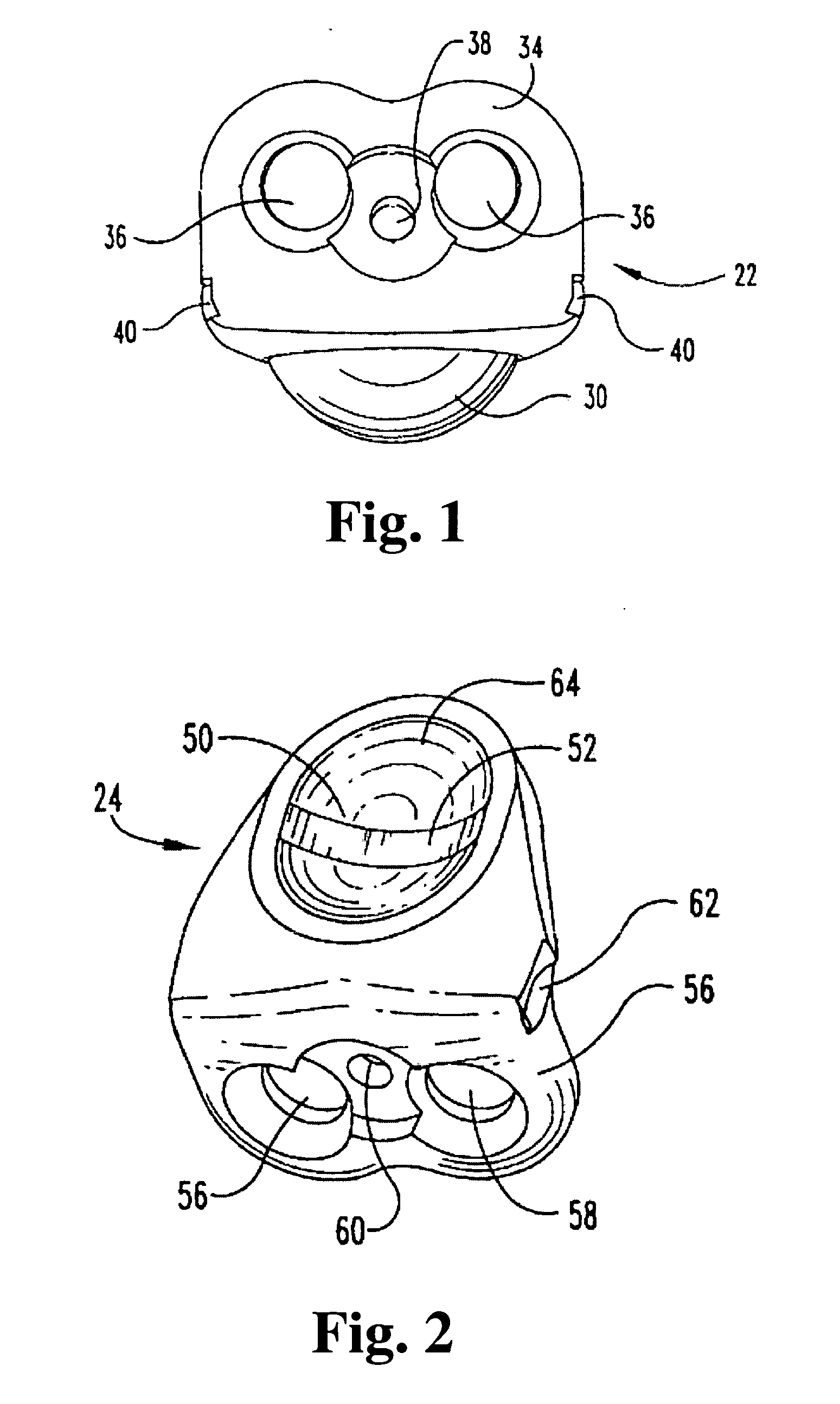
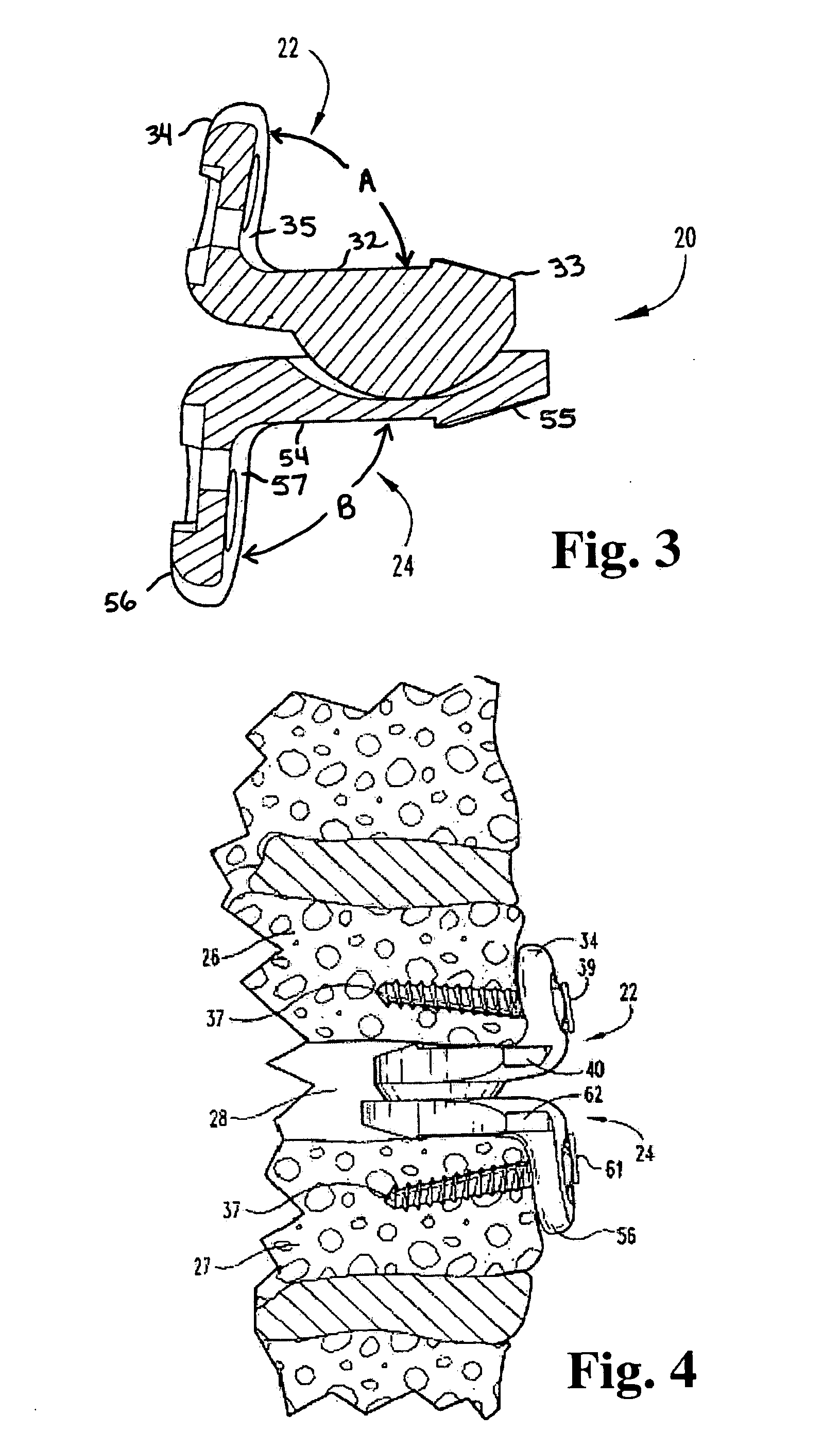
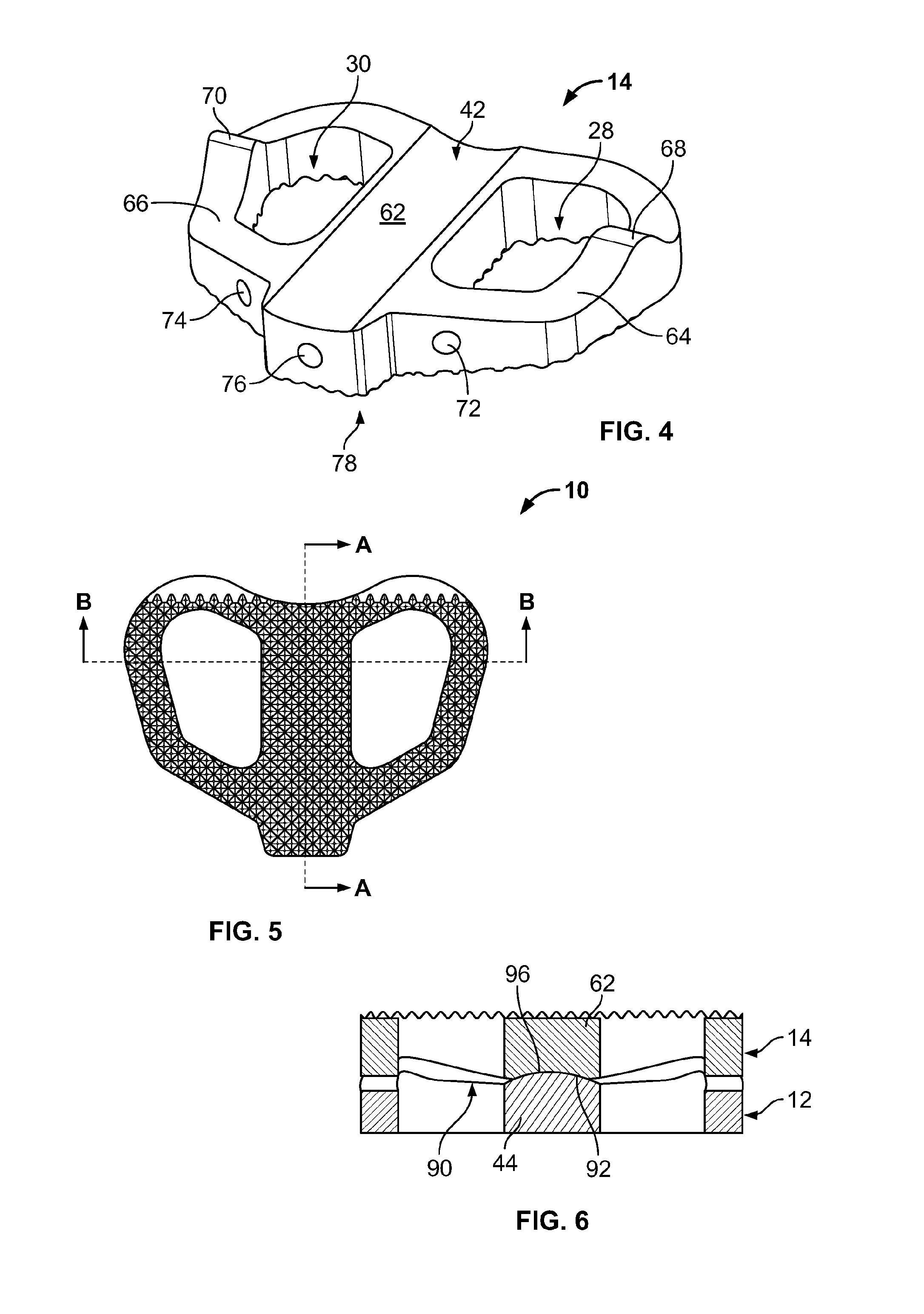
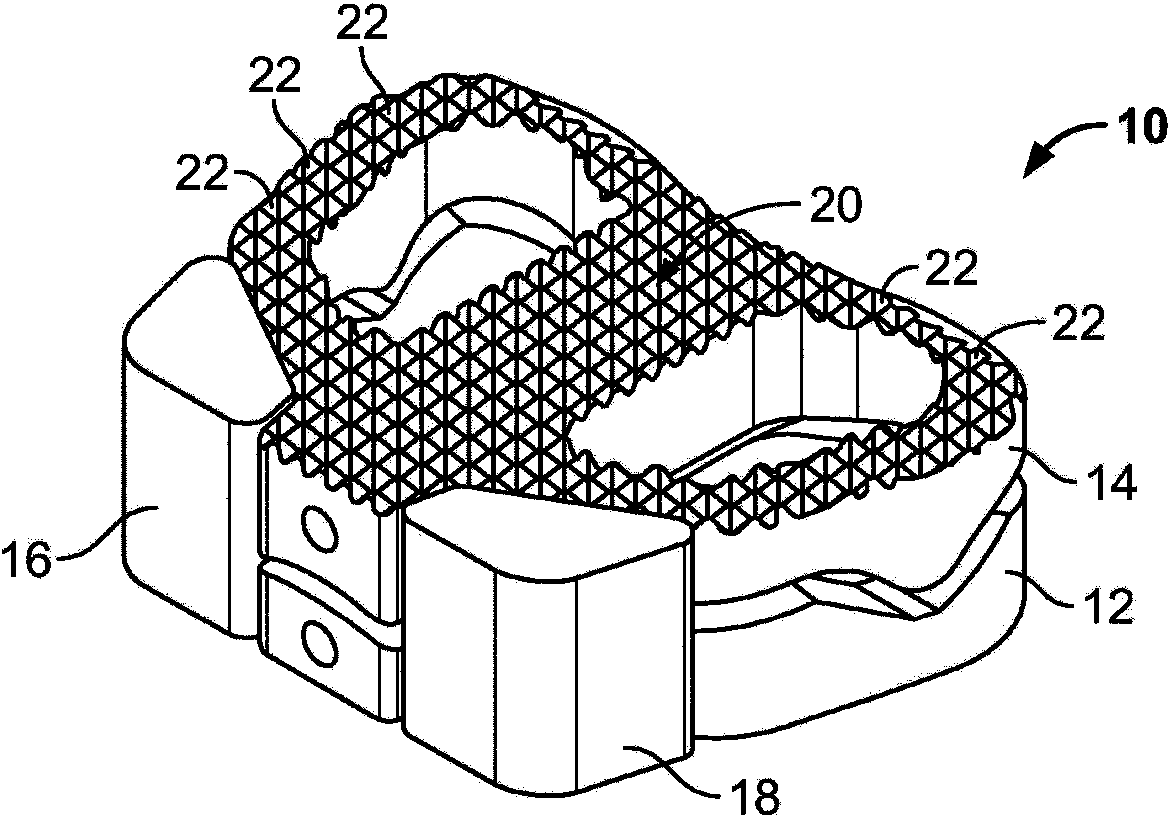
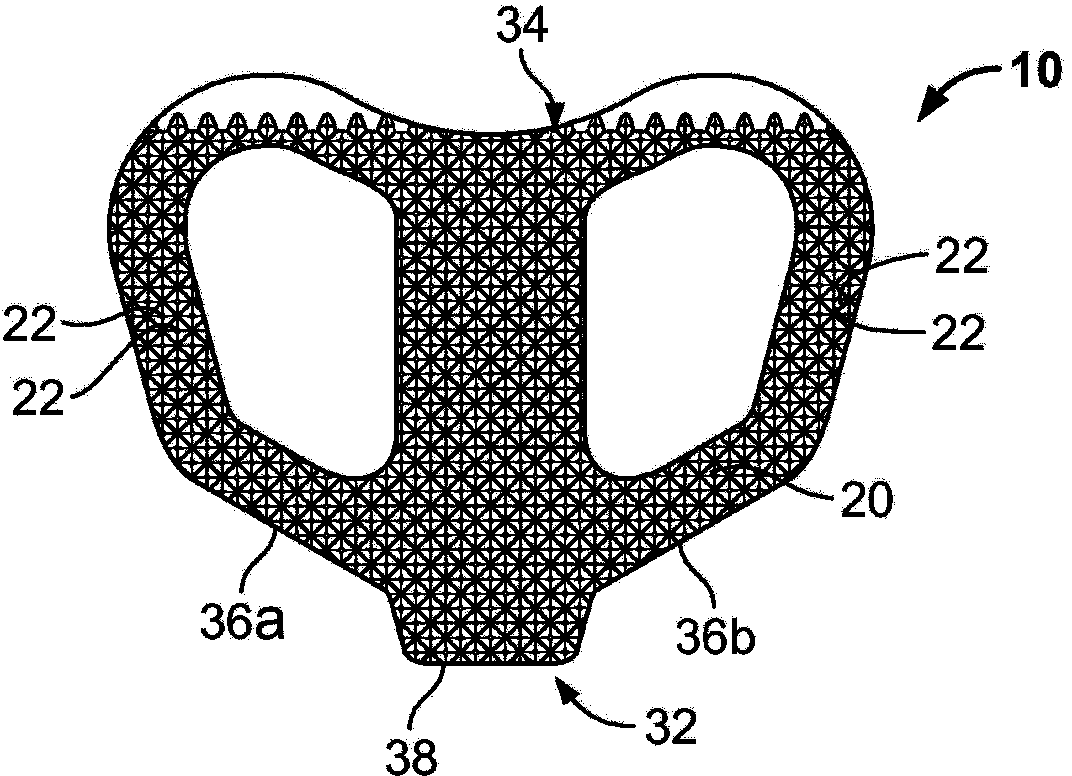
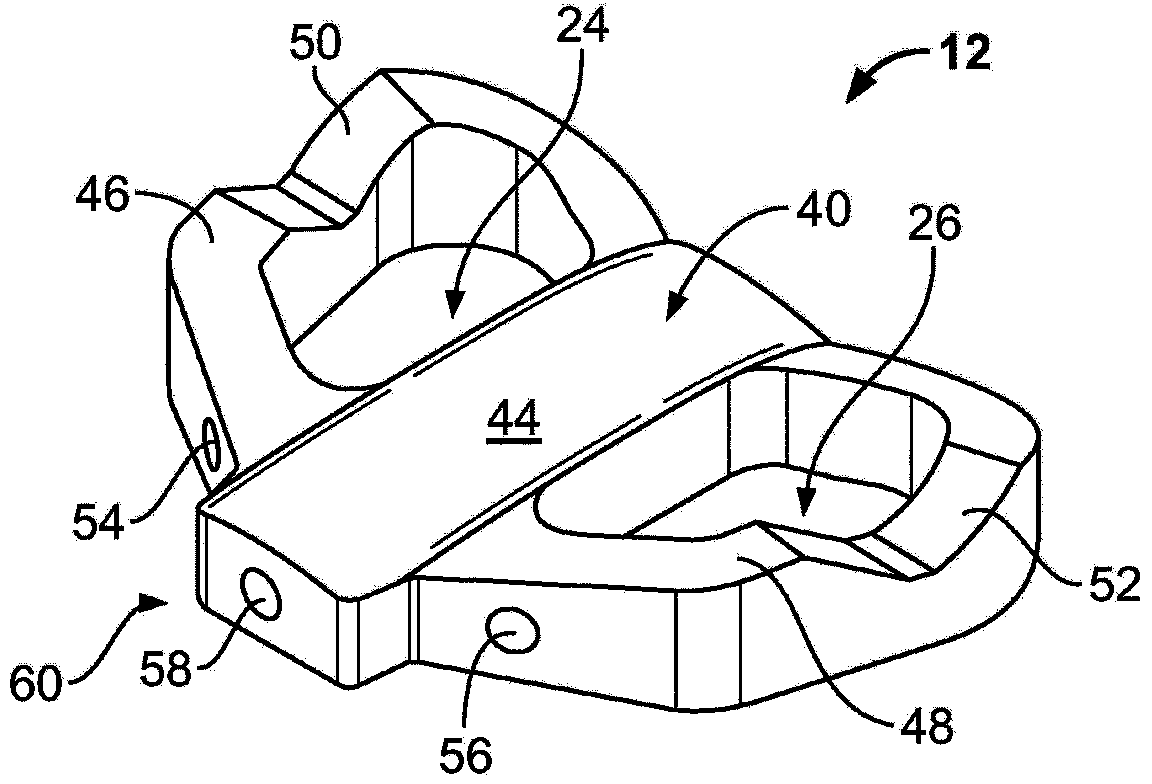
Total disc implant
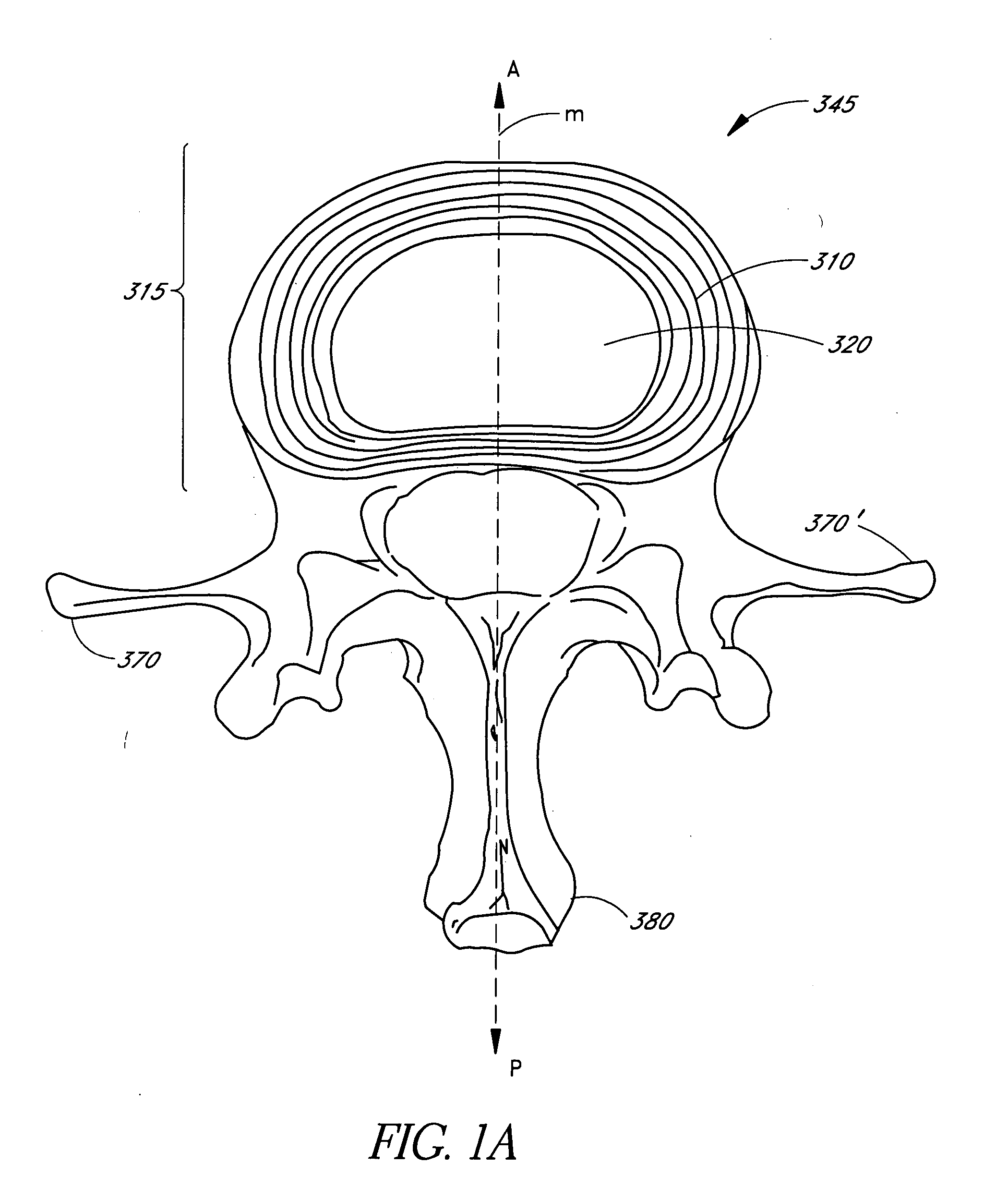
A total disc implant (TDI) is provided for total replacement of a spinal disc or discs in a human patient or other mammal, wherein the TDI is designed to maintain a substantially full range of natural motion (ROM) following implantation. The TDI generally comprises, in one preferred form, upper and lower end plates for affixation to adjacent vertebral bodies, with an intervening insert disposed therebetween. The end plates each include elongated part-cylindrical surfaces oriented generally perpendicular to each other, with one of said surfaces extending in an anterior-posterior direction and the other extending in a medial-lateral direction. The intervening insert defines concave upper and lower part-cylindrical seats oriented for respectively engaging these part-cylindrical surfaces, wherein these part-cylindrical seats are defined by offset radii to include a somewhat flattened central base region merging smoothly with upwardly curving radiused sides.
Owner:AMEDICA A DELAWARE
Methods for explantation of intervertebral disc implants
Methods and devices are provided for the explantation of spinal implants. A cutting tool may be extended into the spinal implant. The spinal implant may be disintegrated into pieces and the pieces removed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Articulating spinal disc implants with amorphous metal elements
Described are artificial disc implants for insertion between first and second adjacent vertebrae in a patient. The implants have a first member and a second member in articulating relationship. At least one member of the implant includes an amorphous metal element. Also described are related methods of making and using artificial disc implants.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Artificial spinal disc
The present invention relates to prostheses for treating spinal pathologies, and more specifically to an artificial disc implant. The implant includes an inferior implant for placement on an inferior vertebra and a superior implant for placement on a superior vertebra. The implant also includes an articulating interface that is generally saddle-shaped and ramped from the anterior of the vertebrae to the posterior of the vertebrae.
Owner:PAXSON ROBERT DAVID +2
Intervertebral disc implant
An intervertebral disc implant having a body with a greater height than width comprised of a resilient material and an elongate cavity for receiving a key to maintain the spacing between the vertebrae adjacent an intervertebral disc when implanted into the space from which a portion of the disc is removed. To distribute and cushion against compression loads, and to mimic the normal kinematics of the intact, healthy intervertebral disc, the key is removed after the body is implanted into the disc space and a frame that both provides resistance to compression and tension loads and translates the axis of rotation of the spinal column anteriorally and posteriorally as the patient bends and rotates is inserted into the cavity in the implant body. The frame does not extend all the way into the cavity in the body and the portion of the cavity into which the frame does not extend is filled with a hydrogel.
Owner:PERUMALA CORP
Minimally invasive method for delivery and positioning of intervertebral disc implants
Owner:INTRINSIC THERAPEUTICS
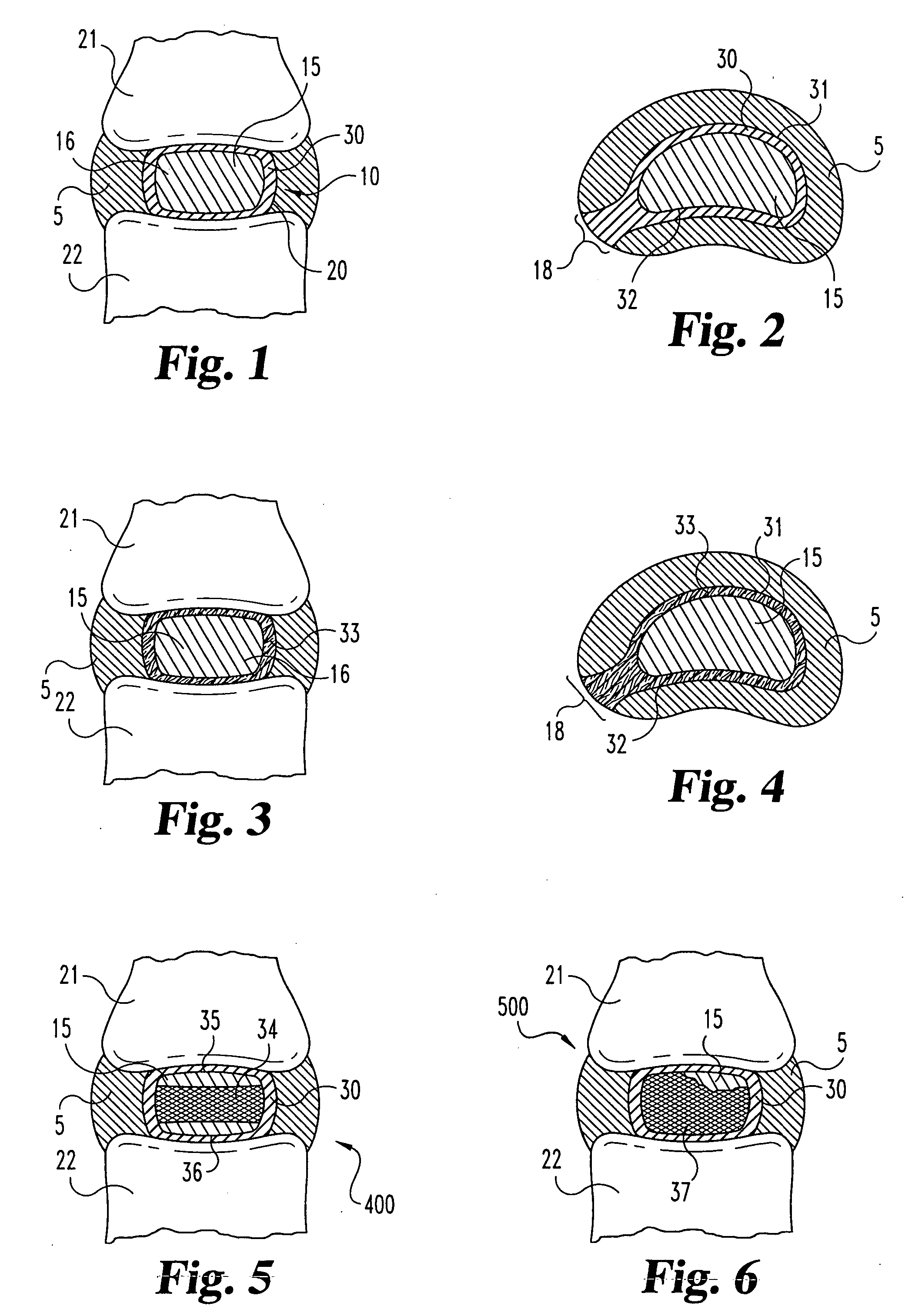
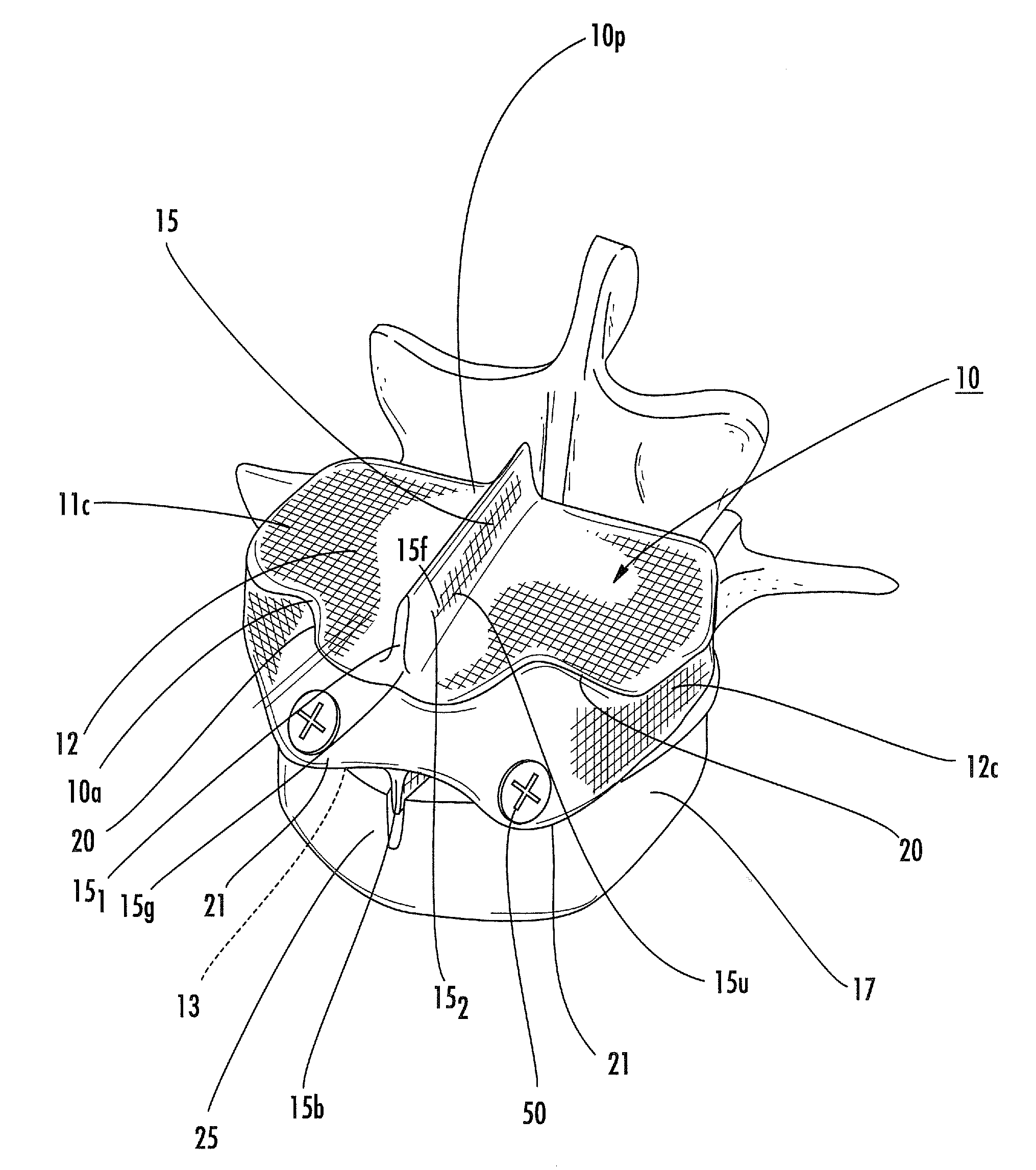
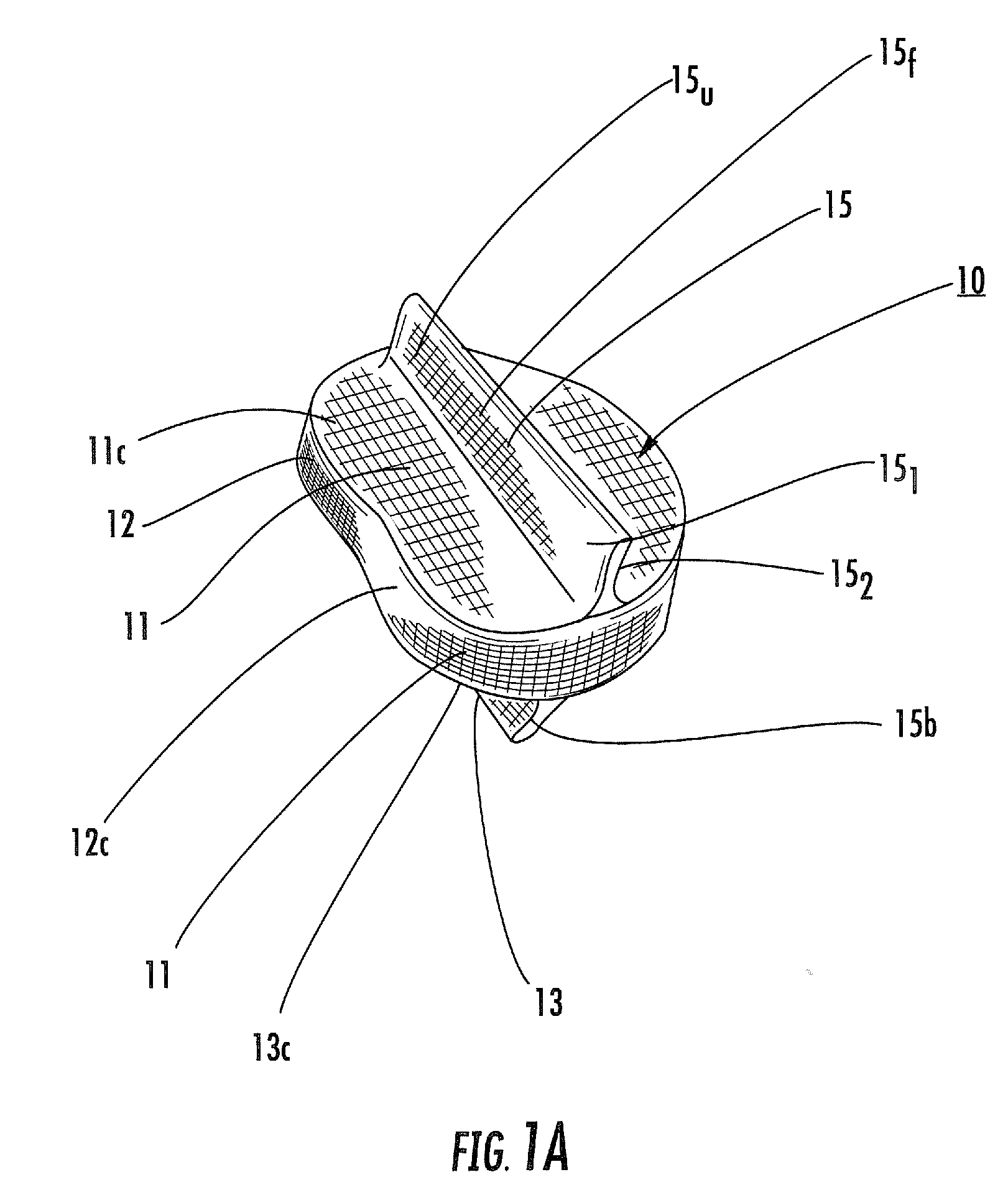
Spinal implant, instrument for preparation and method of use
ActiveUS8906095B2Raise the possibilityImprove stabilityBone implantSurgerySpinal columnSpinal Disk Implant
The present disclosure relates to the field of spine disc implants. Exemplary embodiments of the disclosed spinal disc implants advantageously and ultimately provide fusion with the body of the vertebra and stabilization of the spine in an anatomically correct position, e.g., in cervical, thoracic and / or lumbar regions. More particularly, the present disclosure is directed to a disc implant that addresses and overcomes the shortcomings of the prior implants by providing first and second inter-vertebral elements that are movably coupled relative to each other and are adapted to permit bone in-growth over time. Thus, the disclosed spinal disc implants permit relative movement between the first and second inter-vertebral elements upon implantation and after the patient is mobilized—thereby permitting the implant to assume a desired position based on the specific and unique spinal balance of the patient in an initial post-implantation period—but then the first and second inter-vertebral elements become fixed relative to each other (i.e., fused). The present disclosure also provides advantageous instrumentation and associated methods for positioning a spine disc implant in a desired anatomical location.
Owner:FBCDEVICE
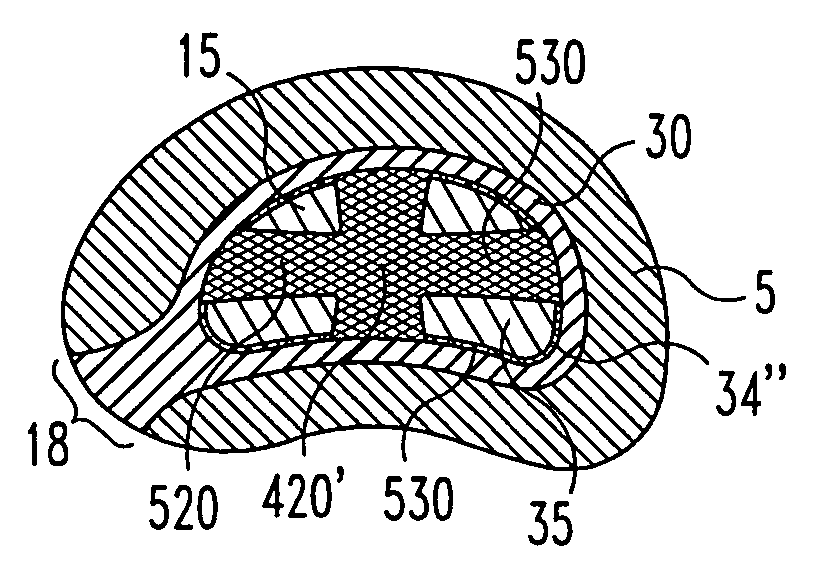
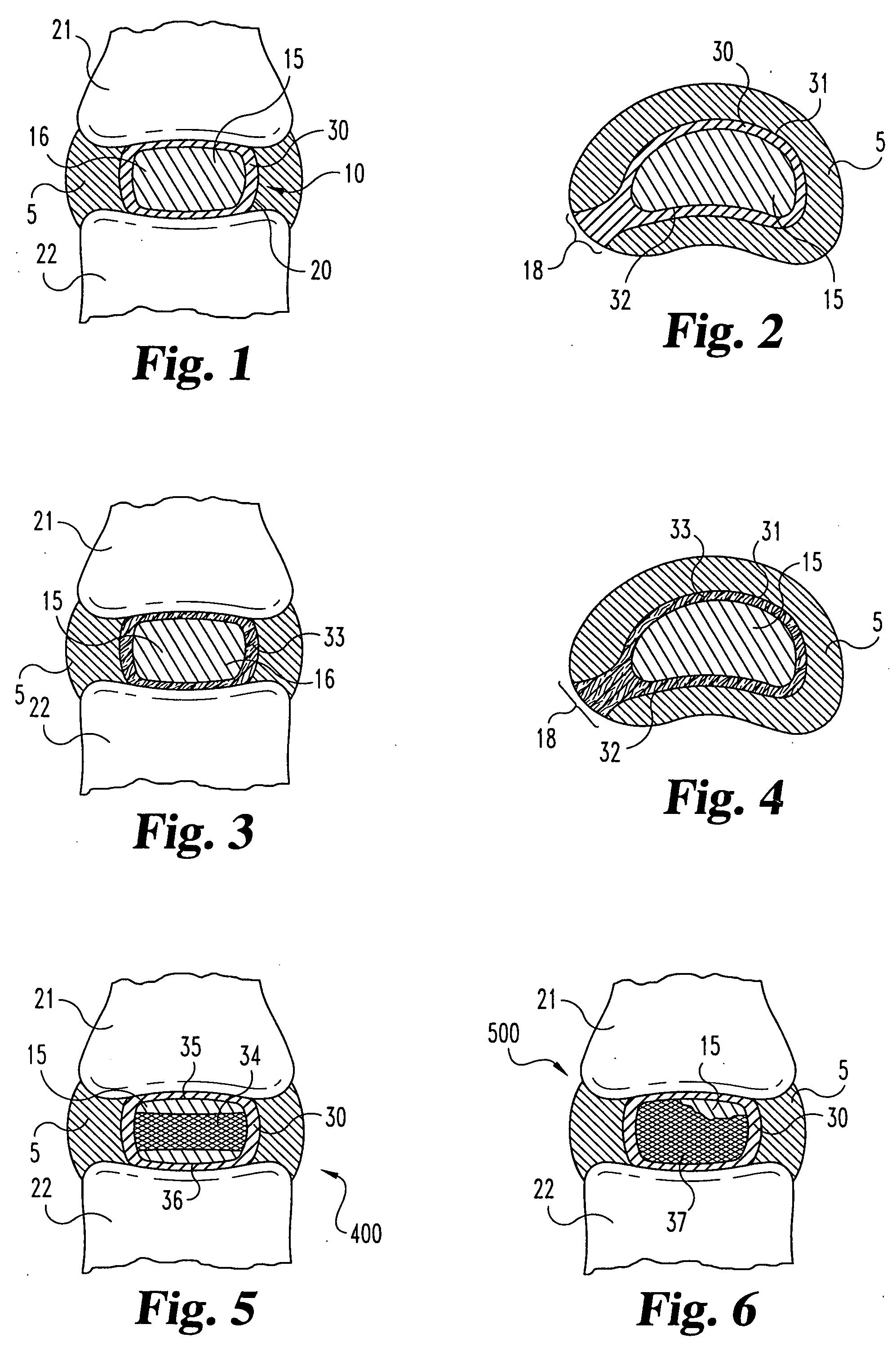
Spinal disc annulus augmentation
InactiveUS20060271196A1Augmenting intervertebral disc annulusSpinal implantsSpinal columnSpinal Disk Implant
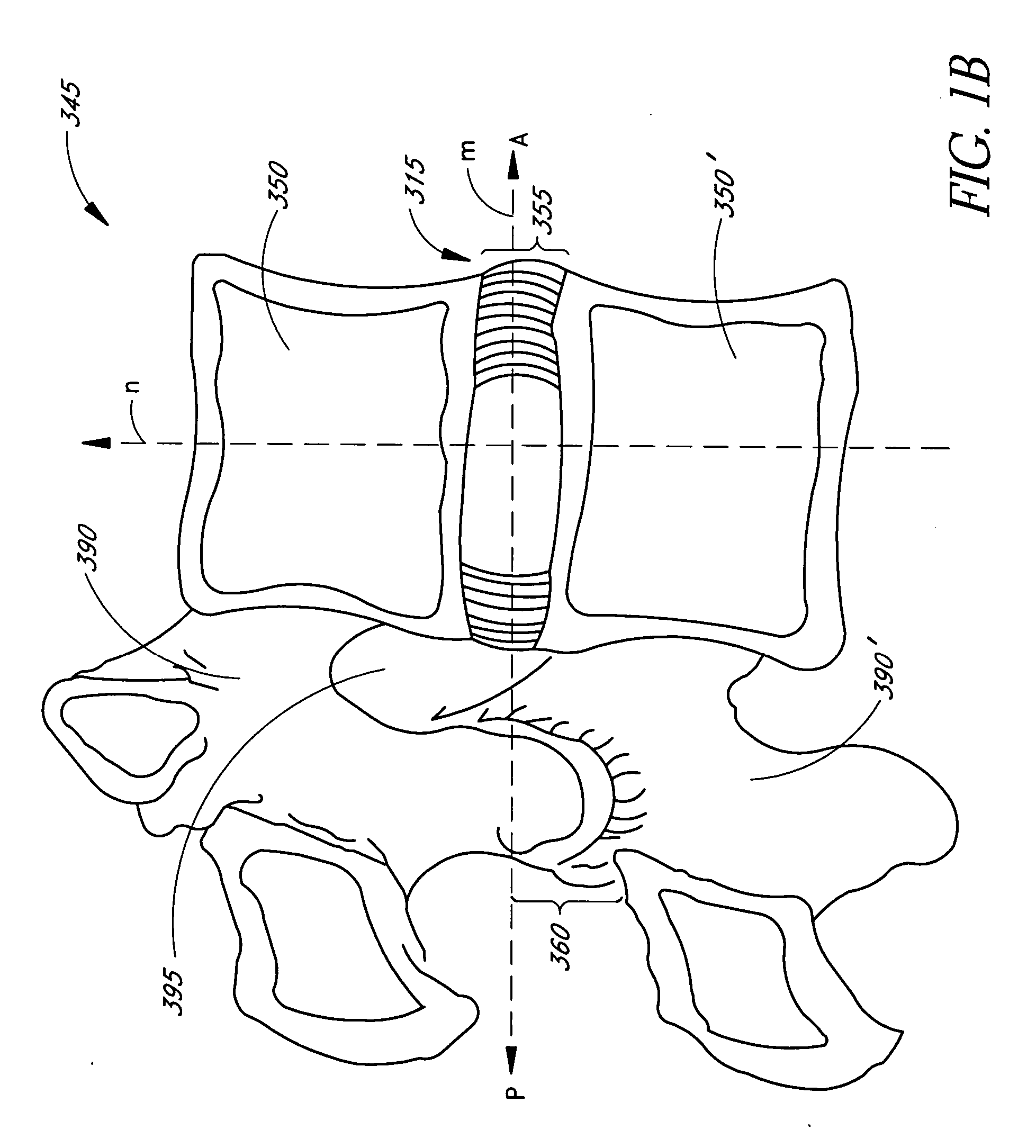
Intervertebral disc implants are provided for augmenting the annulus of the disc in a manner to bear at least part of the axial and / or torsional load on the annulus so that rents, fissures and subsequent herniation of the disc are prevented or substantially delayed. An aspect of the subject devices is that they have an operative height dimension that is equal to or less than the disc height of a normally functioning, healthy disc. Methods and tools are also provided for the minimally invasive implantation of the device within an intervertebral disc.
Owner:SAAL JEFFREY ALAN +1
Foam prosthesis for spinal disc
Disclosed herein are spinal disc implants comprising a foam adapted to completely or partially replace a nucleus pulposus within a spinal disc cavity, the foam being a nonabsorbable, closed cell and having a Poisson ratio of less than 0.5. Also disclosed are methods of implanting a foam, either as an in-situ curable material or as a preformed foam.
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
Artificial spinal disc implant
An artificial spinal disc implant is provided that may be implanted between adjacent vertebrae in the spine to replace, repair or augment a natural spinal disc. The spinal disc implant may be characterized by one or more biomechanical properties that approximate those of a natural spinal disc. The implant is also designed to be sufficiently secured to the vertebrae so that it may function in the body for long time periods.
Owner:RANIER LIMITED
Spinal disc annulus augmentation
Intervertebral disc implants are provided for augmenting the annulus of the disc in a manner to bear at least part of the axial and / or torsional load on the annulus so that rents, fissures and subsequent herniation of the disc are prevented or substantially delayed. An aspect of the subject devices is that they have an operative height dimension that is equal to or less than the disc height of a normally functioning, healthy disc. Methods and tools are also provided for the minimally invasive implantation of the device within an intervertebral disc.
Owner:SAAL JEFFREY ALAN +1
Instrument system for the insertion of intervertebral disk implants
InactiveUS20060085011A1Reliable functionHinder surgeonDiagnosticsJoint implantsSpinal Disk ImplantForceps
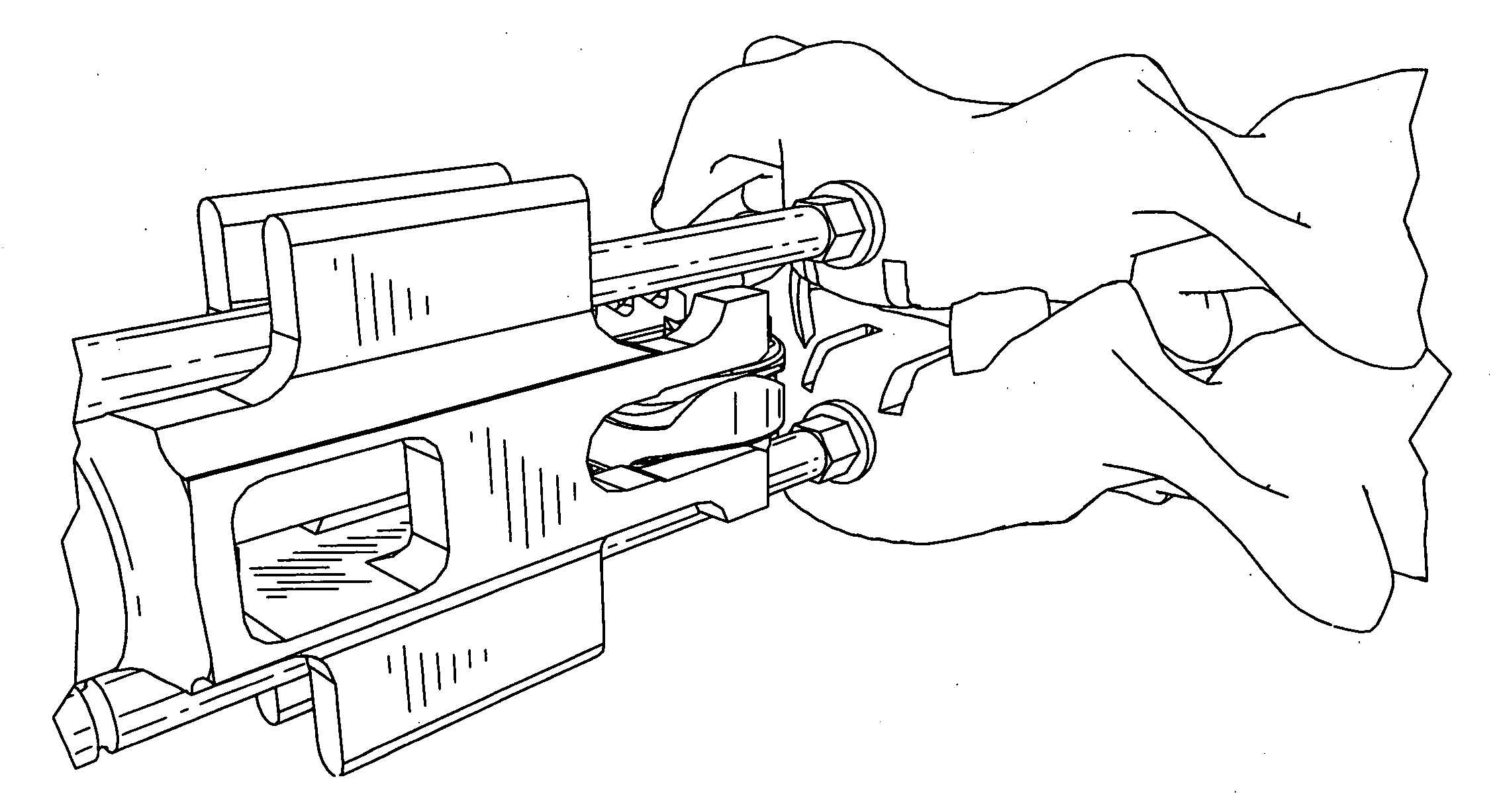
The invention relates to an instrument system for the insertion of intervertebral disk implants including two implant plates and one implant core comprising at least one trial unit including two trial elements of preferably plate shape for the determination of an implant suitable for the respective patient, at least one machining unit for the preparation of the surfaces of the bodies of the vertebra of the patient which includes operating elements having two sections of preferably forked shape and at least one holding unit which can be coupled to the implant plates for the insertion of the implant, with the trial unit, the machining unit and the holding unit each being able to be coupled to a traction instrument in particular in the manner of forceps for the pressing apart of the trial elements, the operating elements or the implant elements.
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
Spinal Implant, Instrument for Preparation and Method of Use
ActiveUS20140336652A1The relative position is appropriateProvide goodBone implantSurgerySpinal columnSpinal Disk Implant
The present disclosure relates to the field of spine disc implants. Exemplary embodiments of the disclosed spinal disc implants advantageously and ultimately provide fusion with the body of the vertebra and stabilization of the spine in an anatomically correct position, e.g., in cervical, thoracic and / or lumbar regions. More particularly, the present disclosure is directed to a disc implant that addresses and overcomes the shortcomings of the prior implants by providing first and second inter-vertebral elements that are movably coupled relative to each other and are adapted to permit bone in-growth over time. Thus, the disclosed spinal disc implants permit relative movement between the first and second inter-vertebral elements upon implantation and after the patient is mobilized—thereby permitting the implant to assume a desired position based on the specific and unique spinal balance of the patient in an initial post-implantation period—but then the first and second inter-vertebral elements become fixed relative to each other (i.e., fused). The present disclosure also provides advantageous instrumentation and associated methods for positioning a spine disc implant in a desired anatomical location.
Owner:FBCDEVICE
Spinal implant, instrument for preparation and method of use
The present disclosure relates to the field of spine disc implants. Exemplary embodiments of the disclosed spinal disc implants advantageously and ultimately provide fusion with the body of the vertebra and stabilization of the spine in an anatomically correct 5 position, e.g., in cervical, thoracic and / or lumbar regions. More particularly, the present disclosure is directed to a disc implant that addresses and overcomes the shortcomings of the prior implants by providing first and second inter-vertebral elements that are movably coupled relative to each other and are adapted to permit bone in-growth over time.
Owner:FBC EQUIP CO LTD
Spinal implant and cutting tool preparation accessory for mounting implant
InactiveCN1379645AEasy to integrateBest practiceBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnLamina terminalis
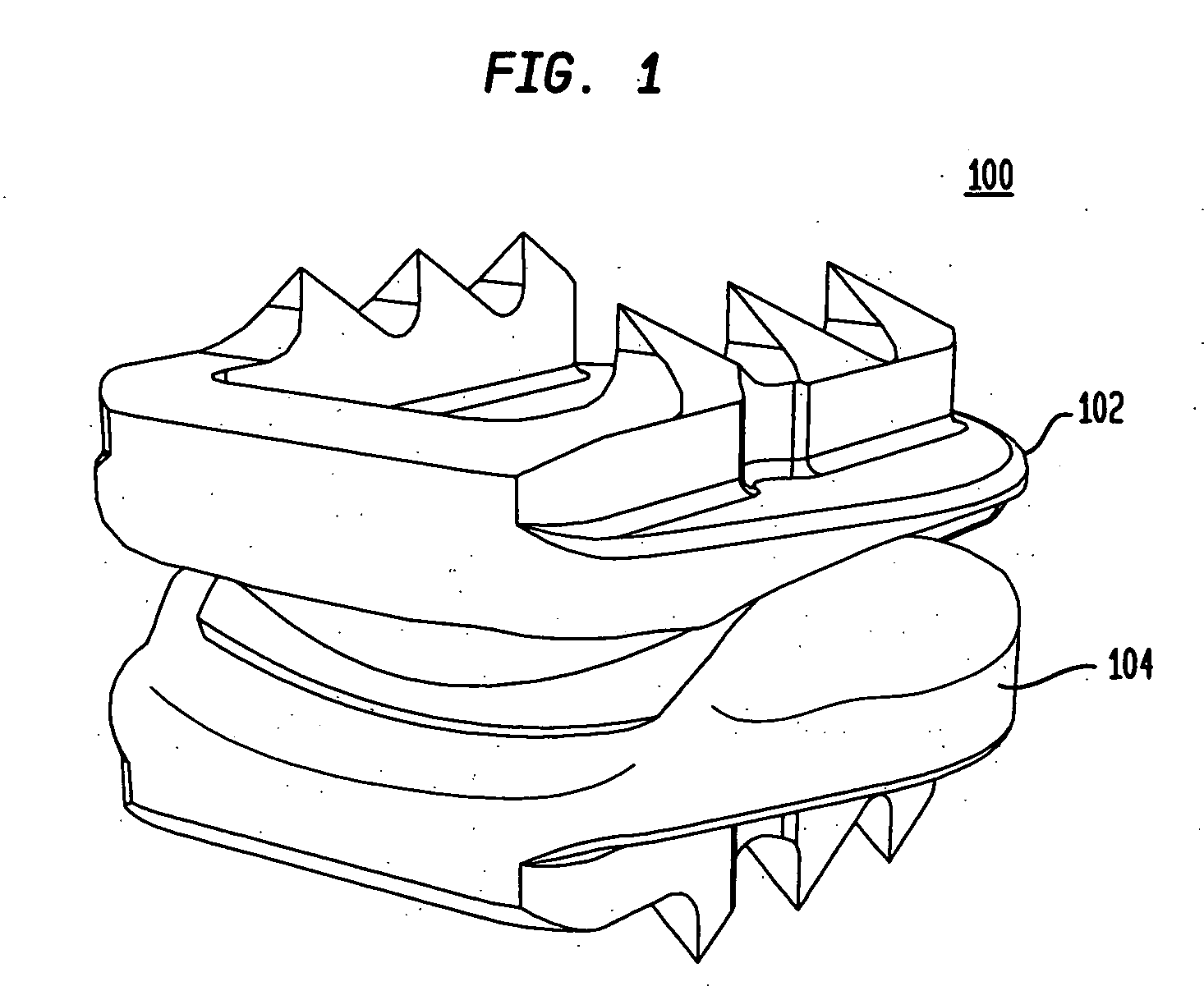
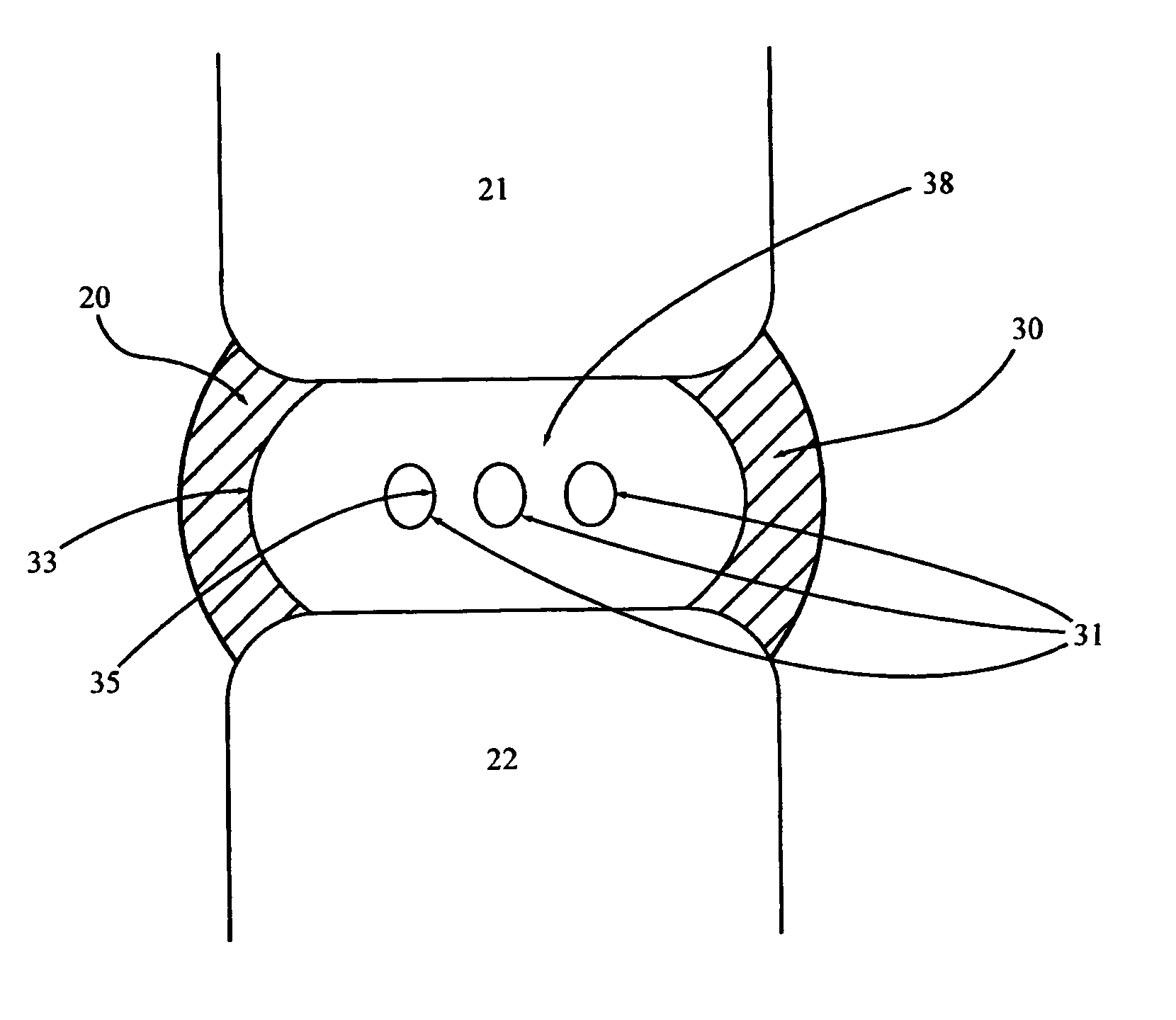
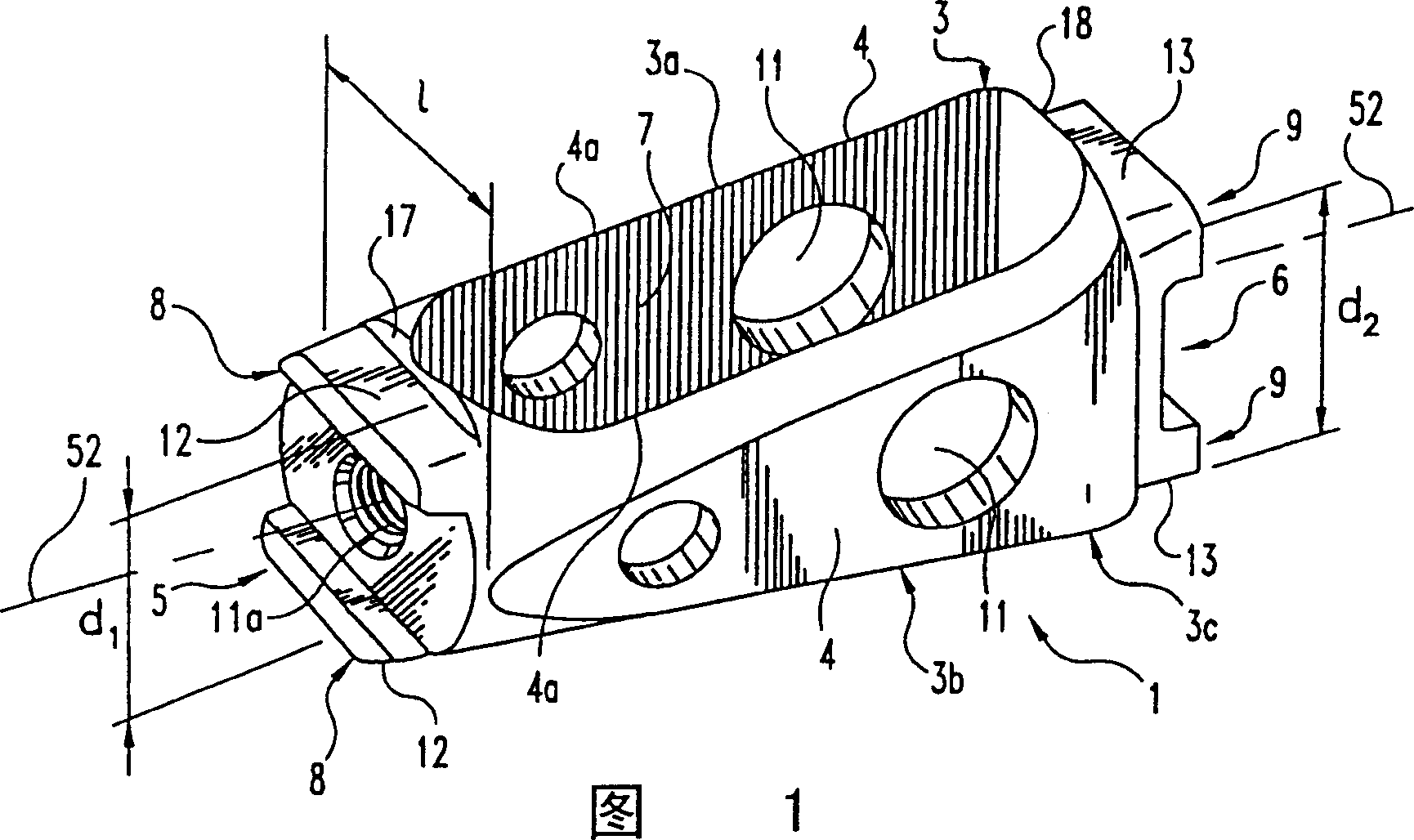
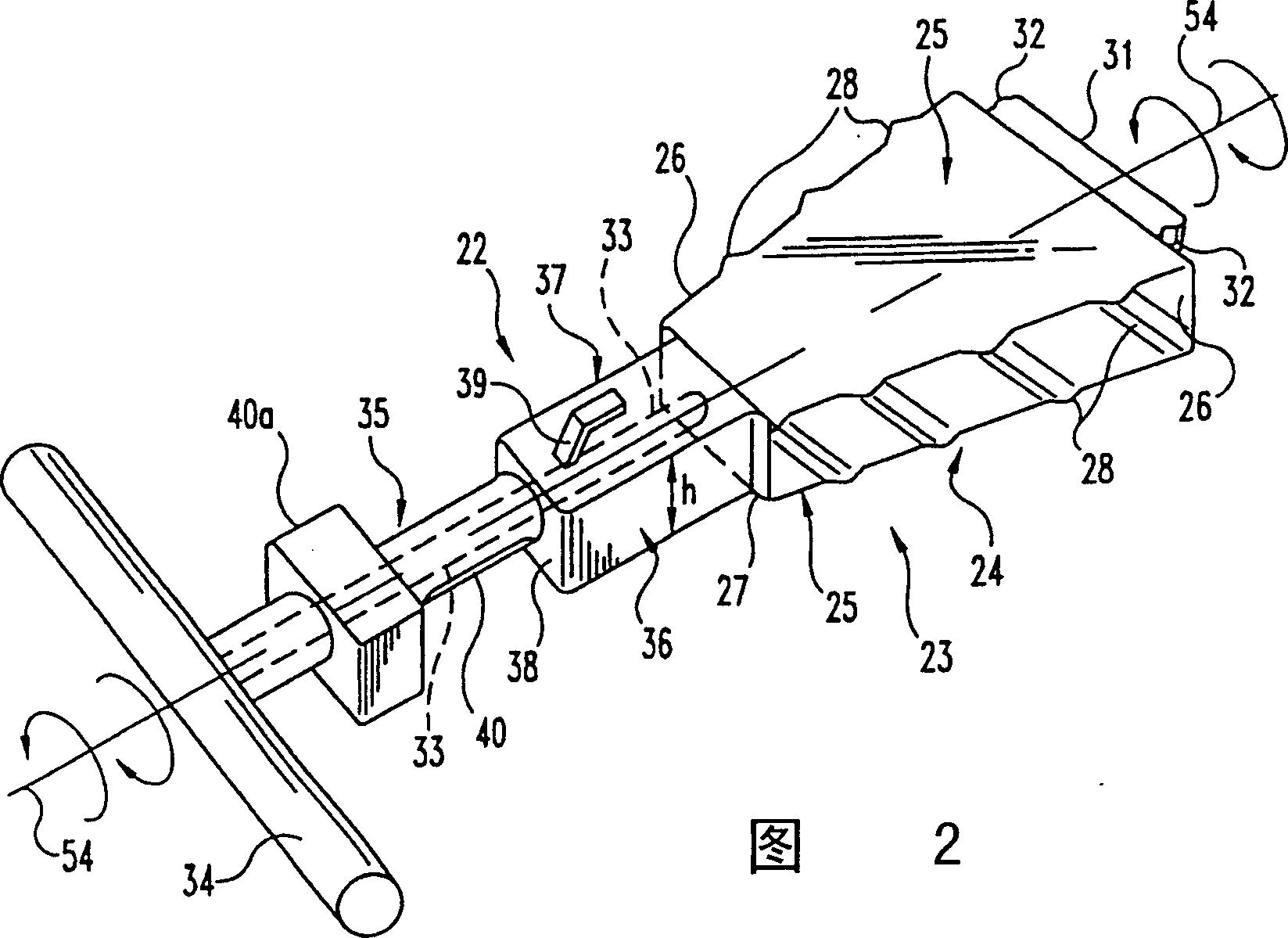
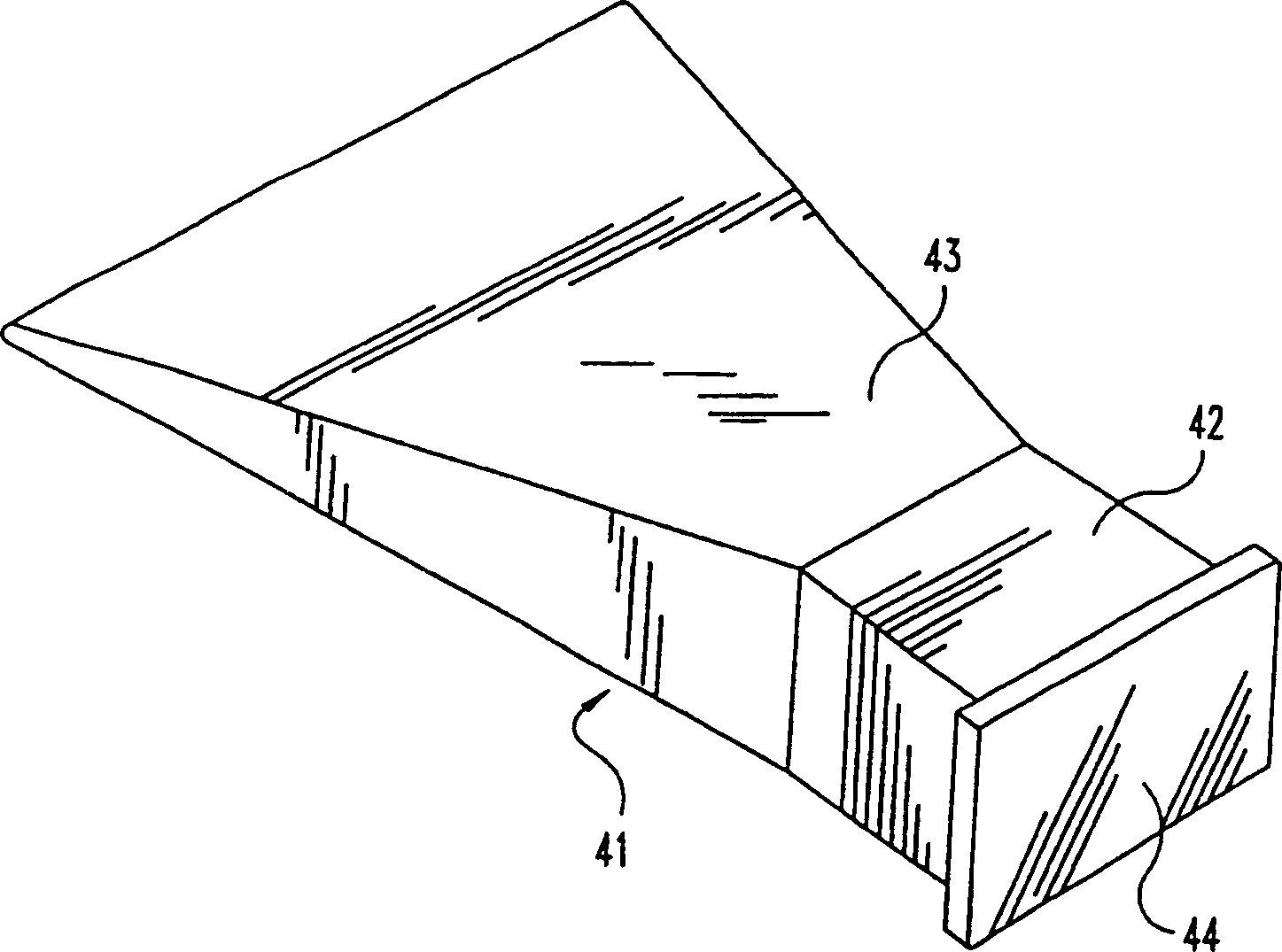
This invention relates to a spinal implant (110) for promoting fusion of adjacent vertebrae and restoration of normal disc height. The spinal implant includes an upper and lower surface (120, 122) adapted to engage cancellous bone tissue in the vertebral bodies. The spinal implant also includes at least two opposing bearing surfaces (138, 140) adapted to bear against cortical bone tissue in the endplates of adjacent vertebrae. This invention also provides an instrumentation to prepare the intervertebral space to receive the spinal implant and techniques for treating patients in need of corrective spinal surgery. <IMAGE>
Owner:SDGI HLDG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com