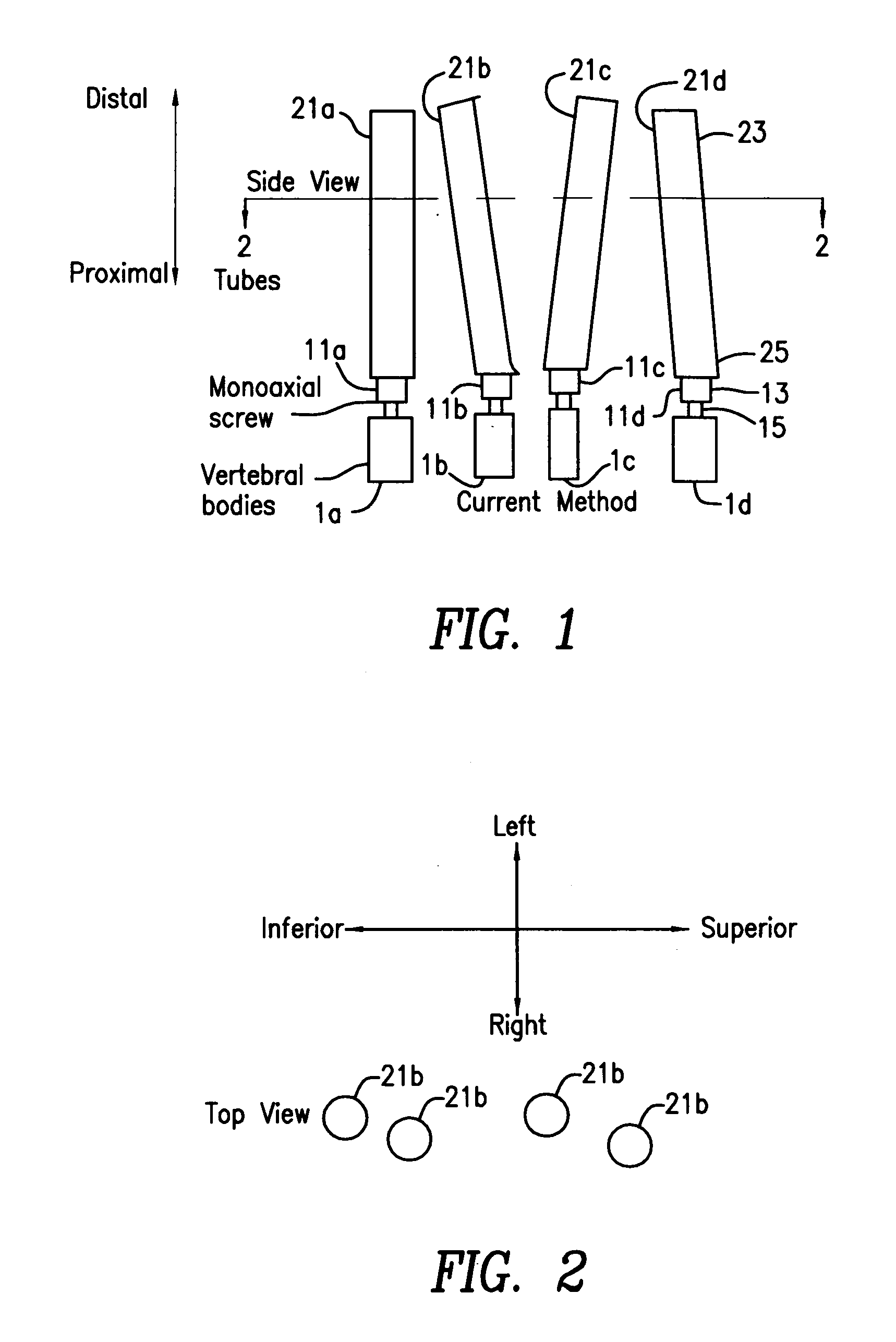
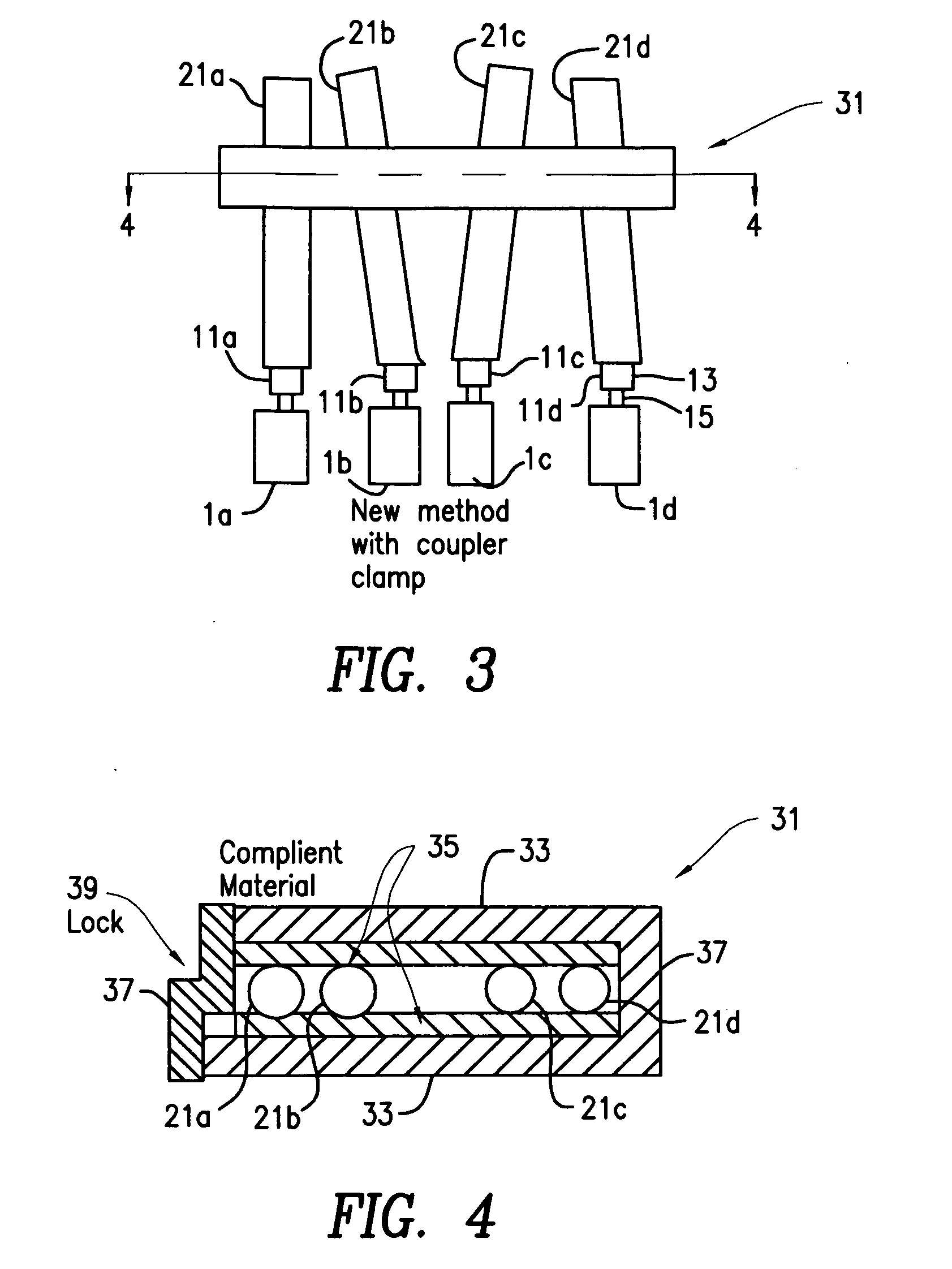
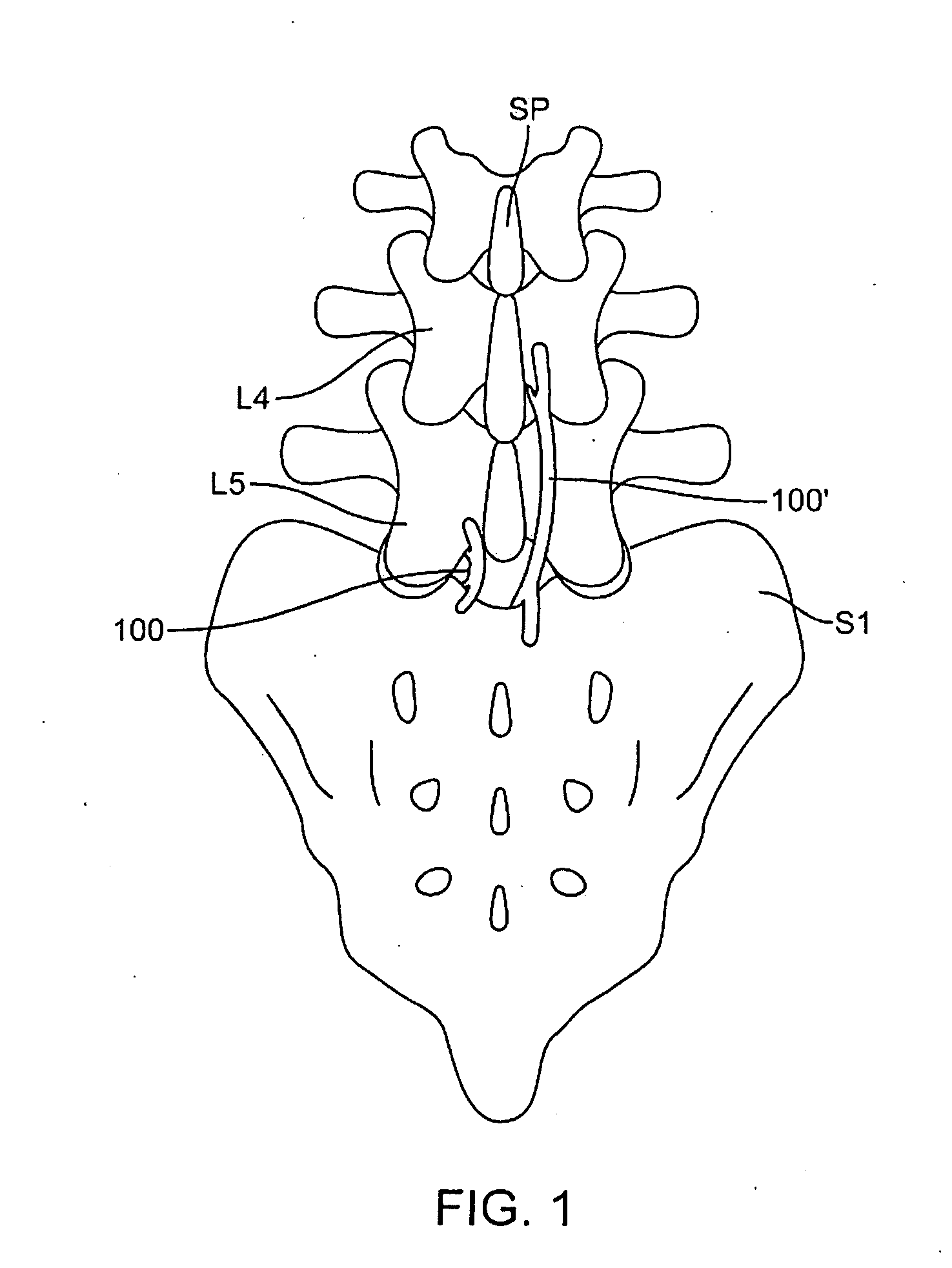
Patents
Literature
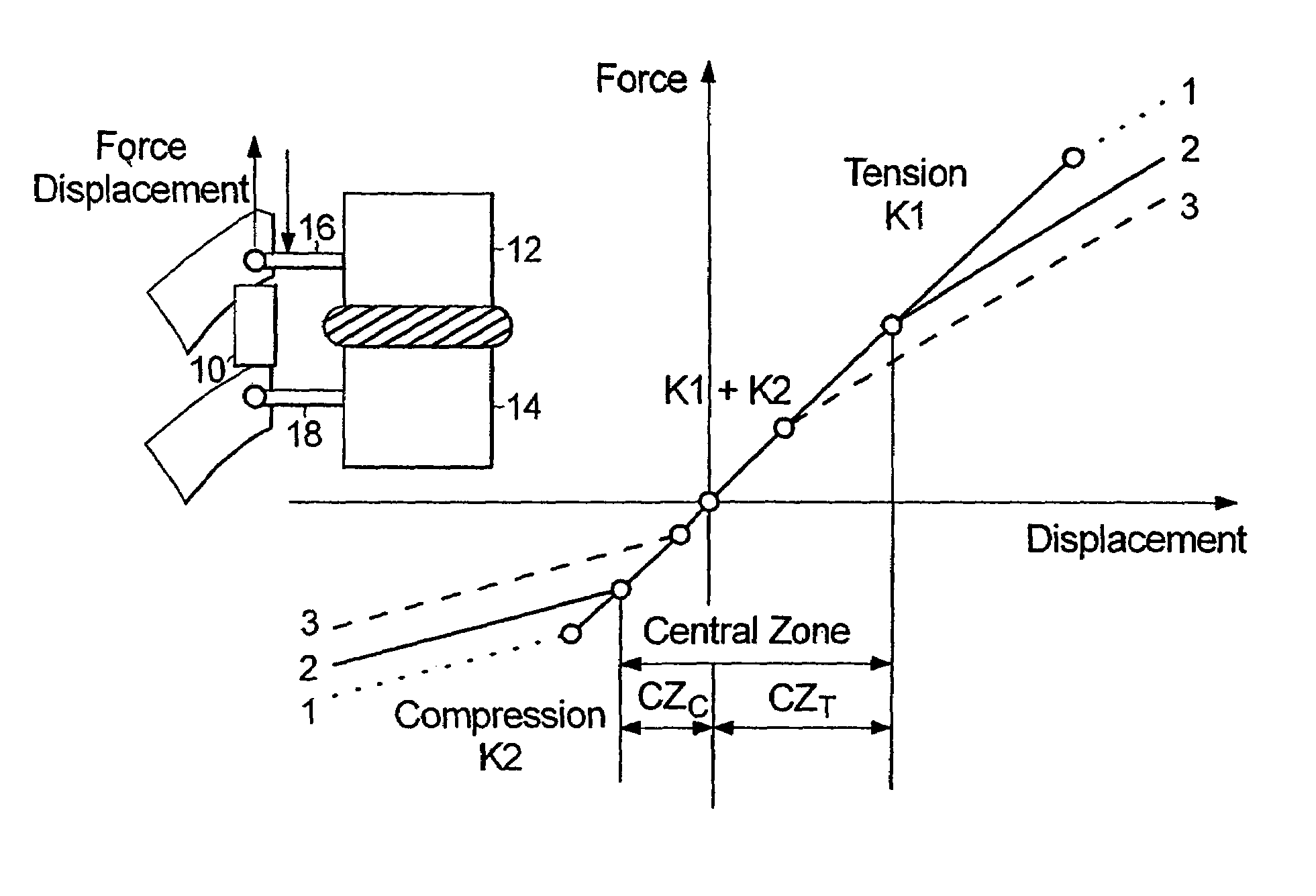
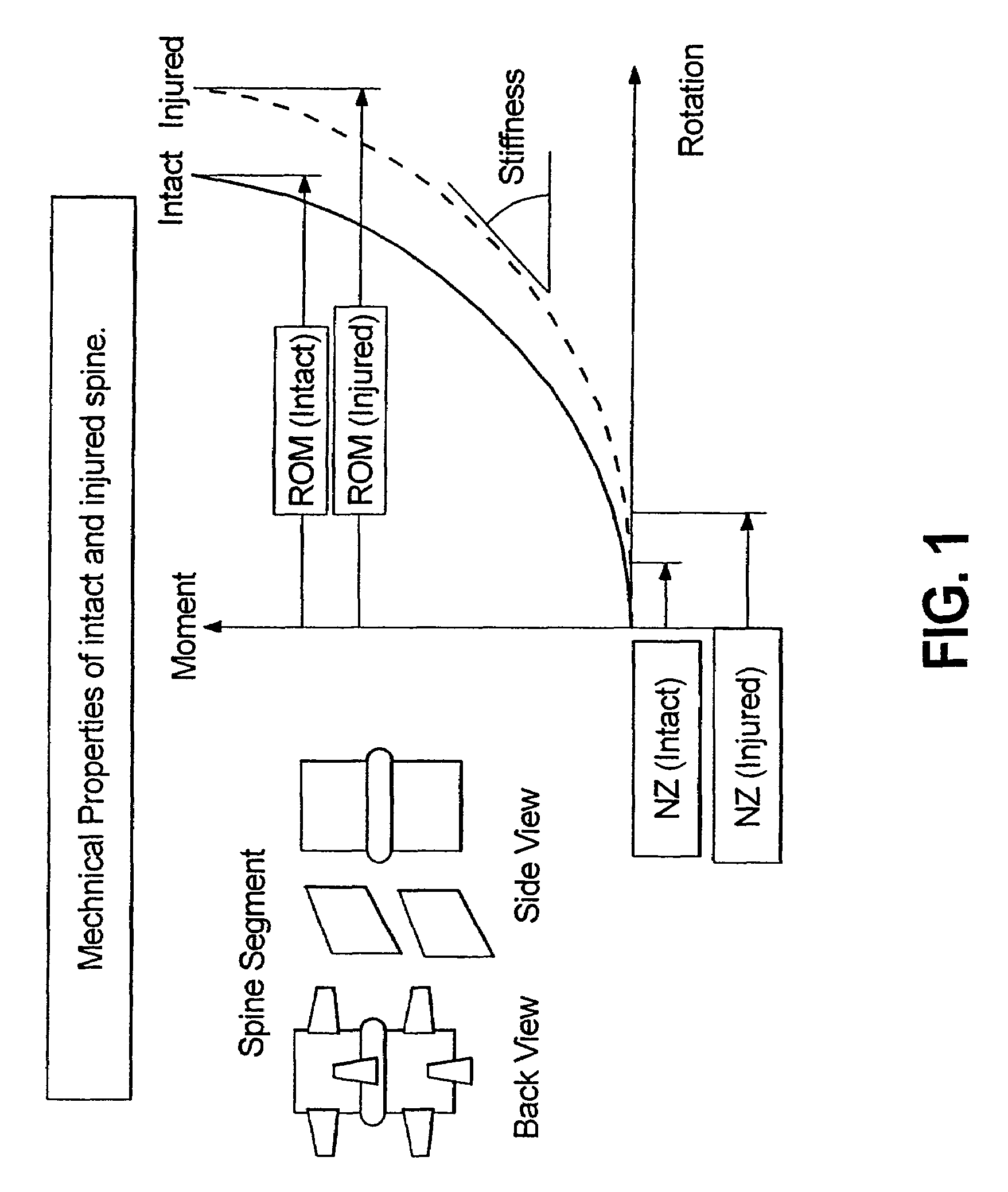
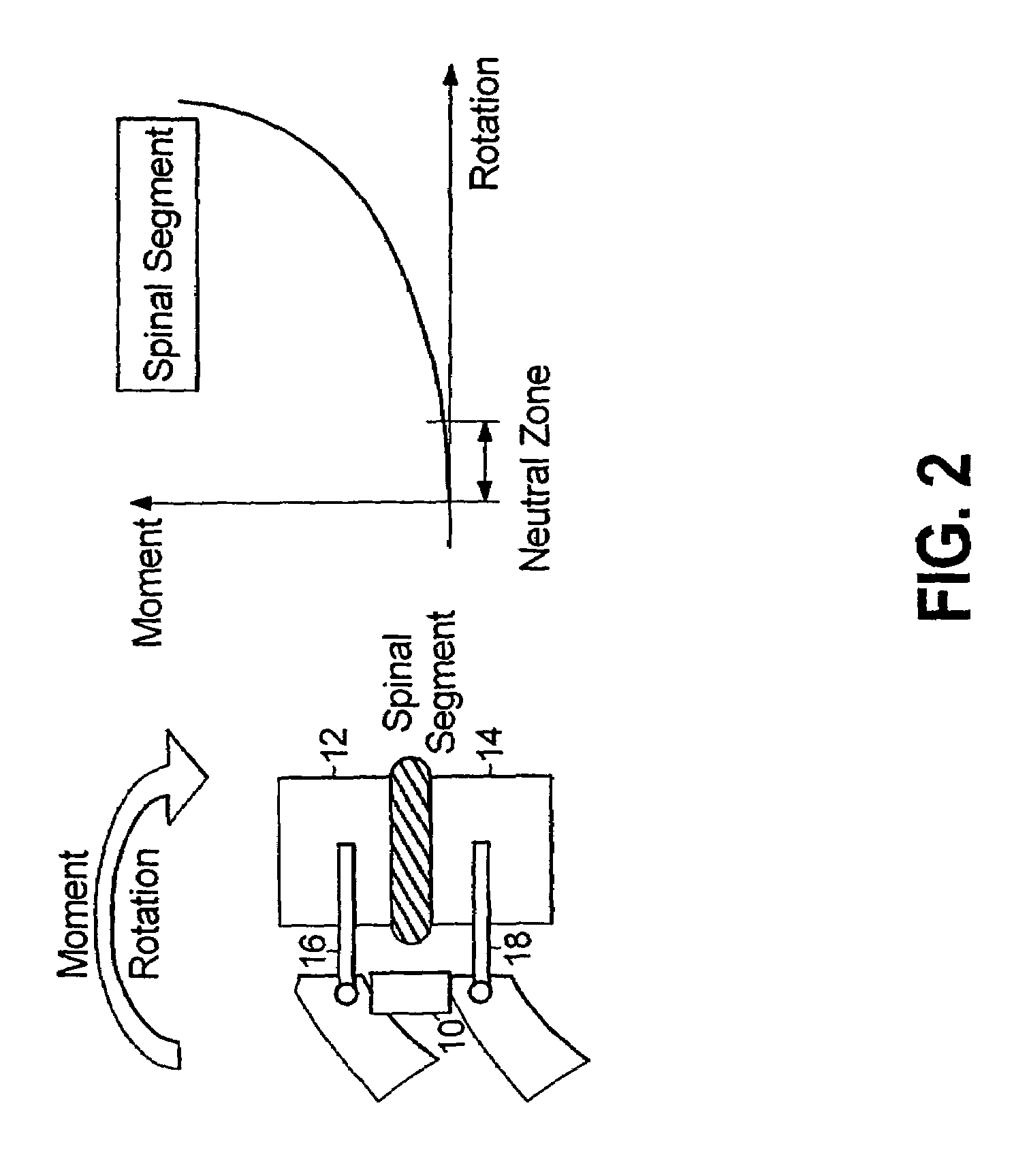
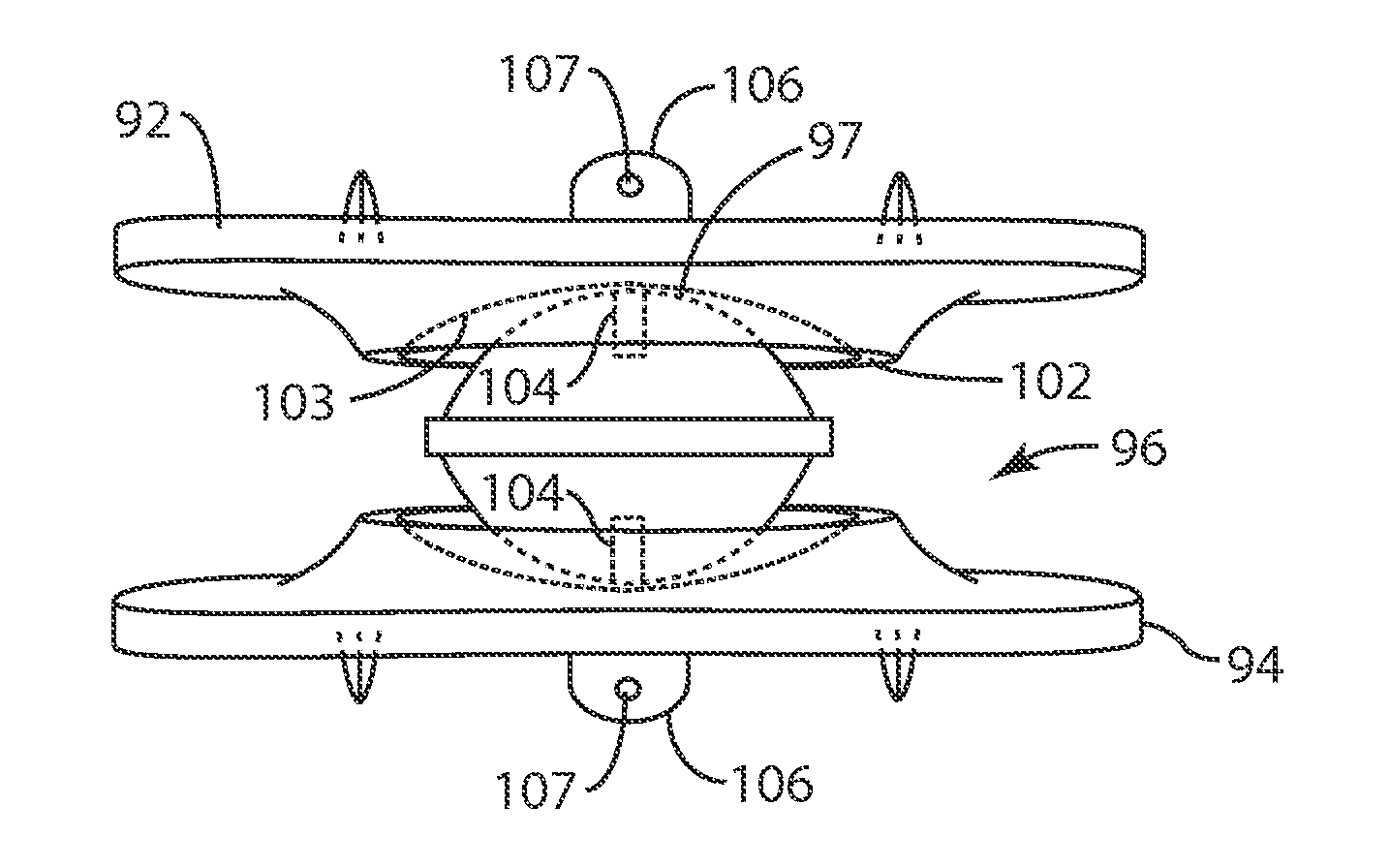
85 results about "Spinal segment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
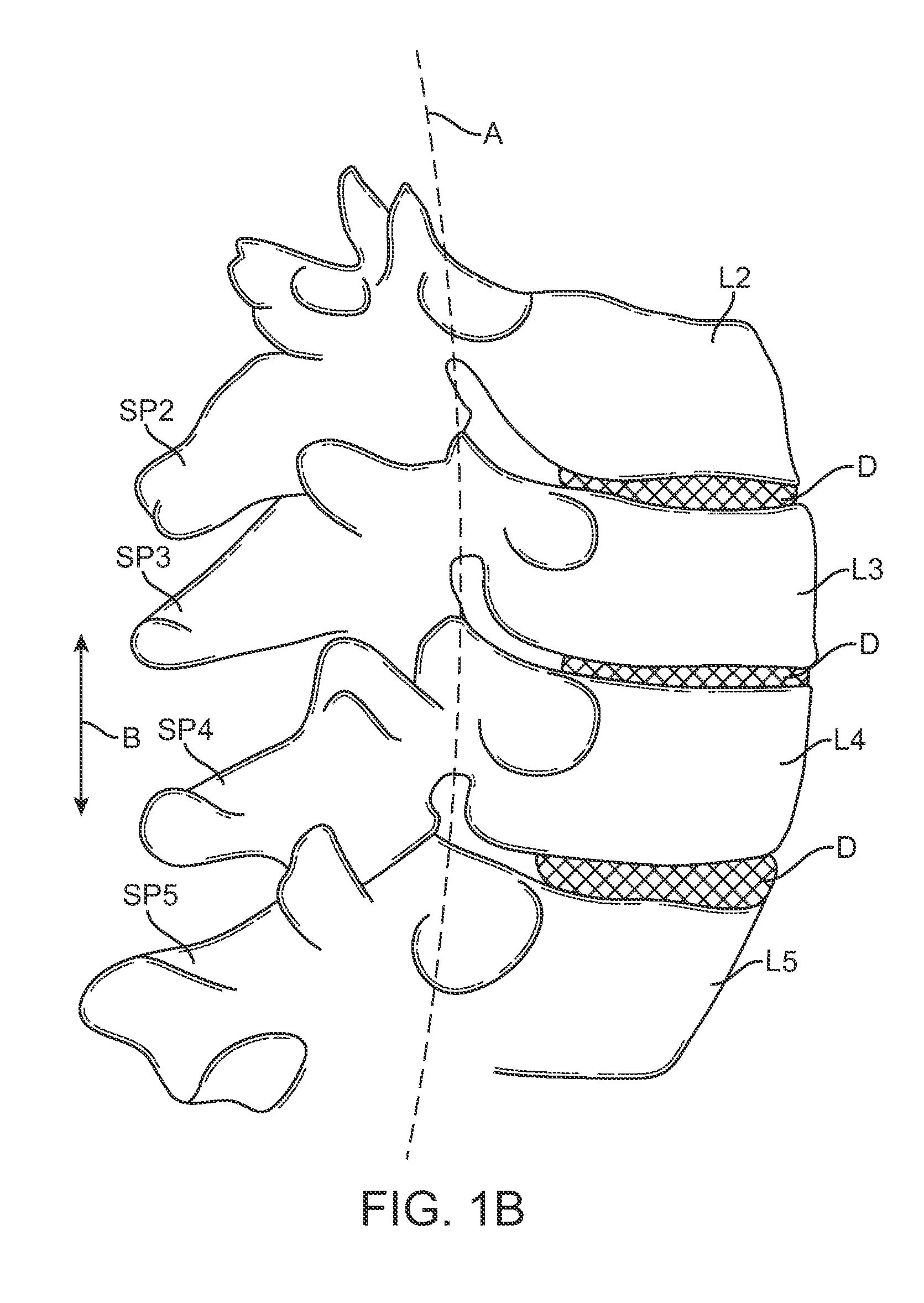
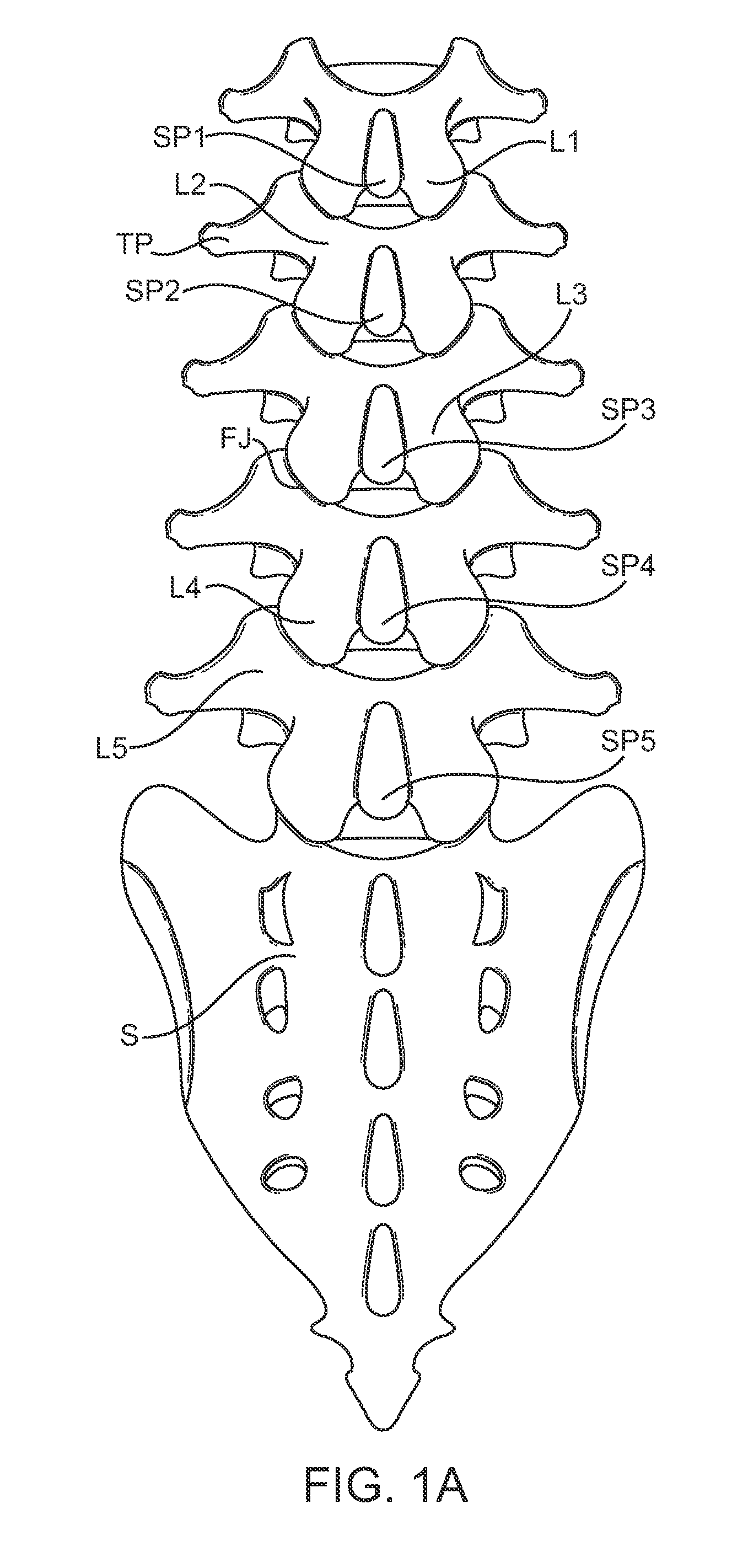
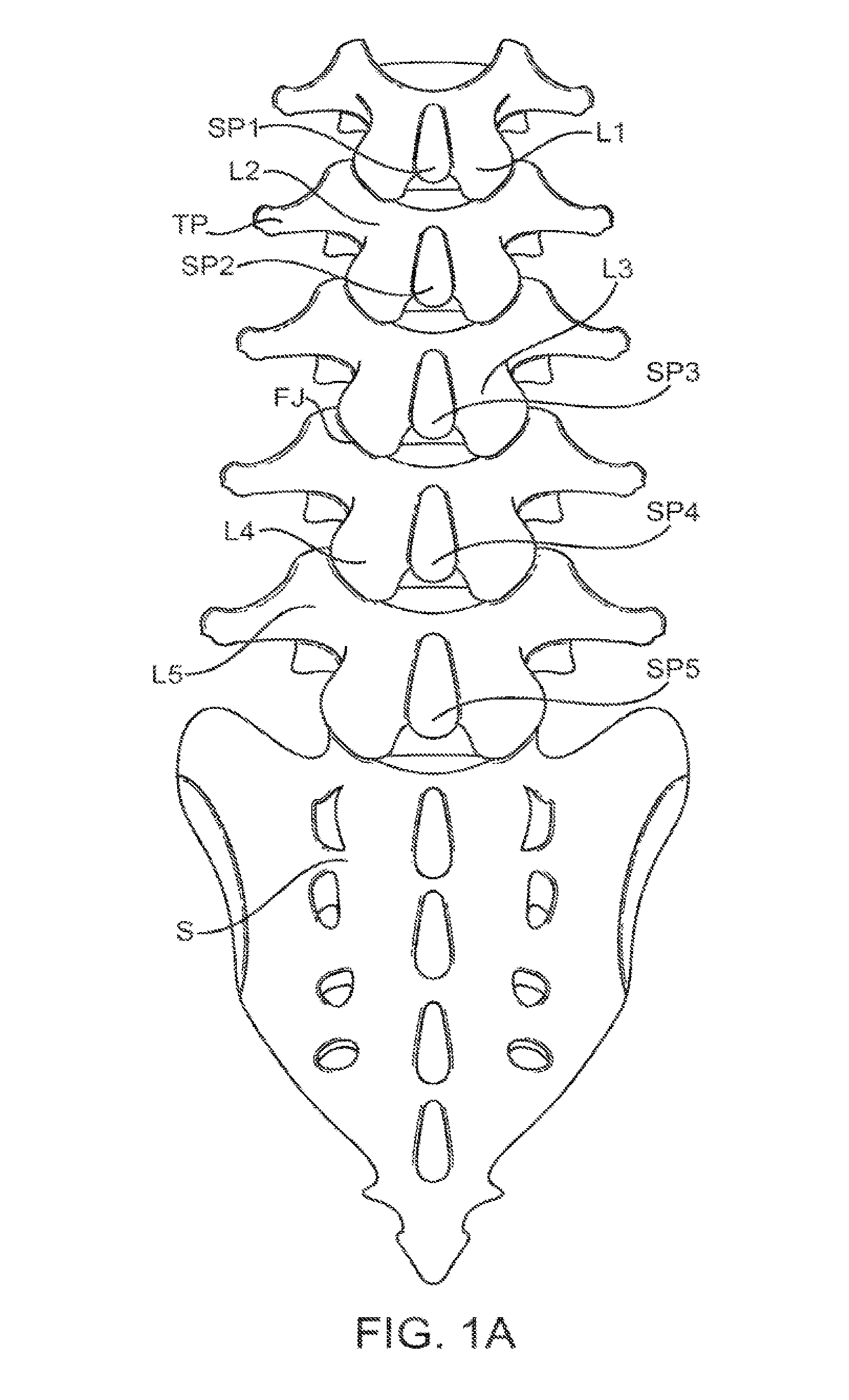
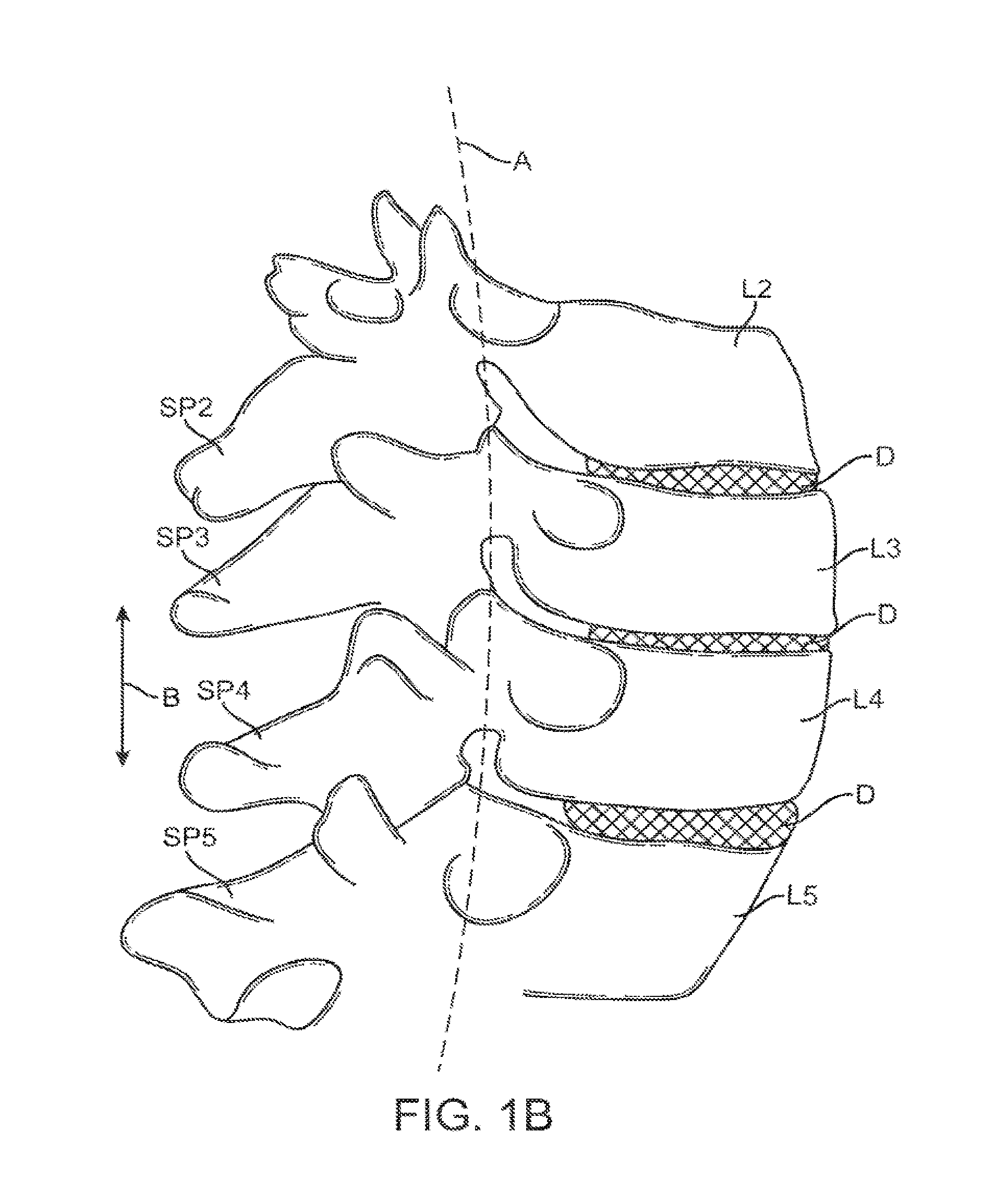
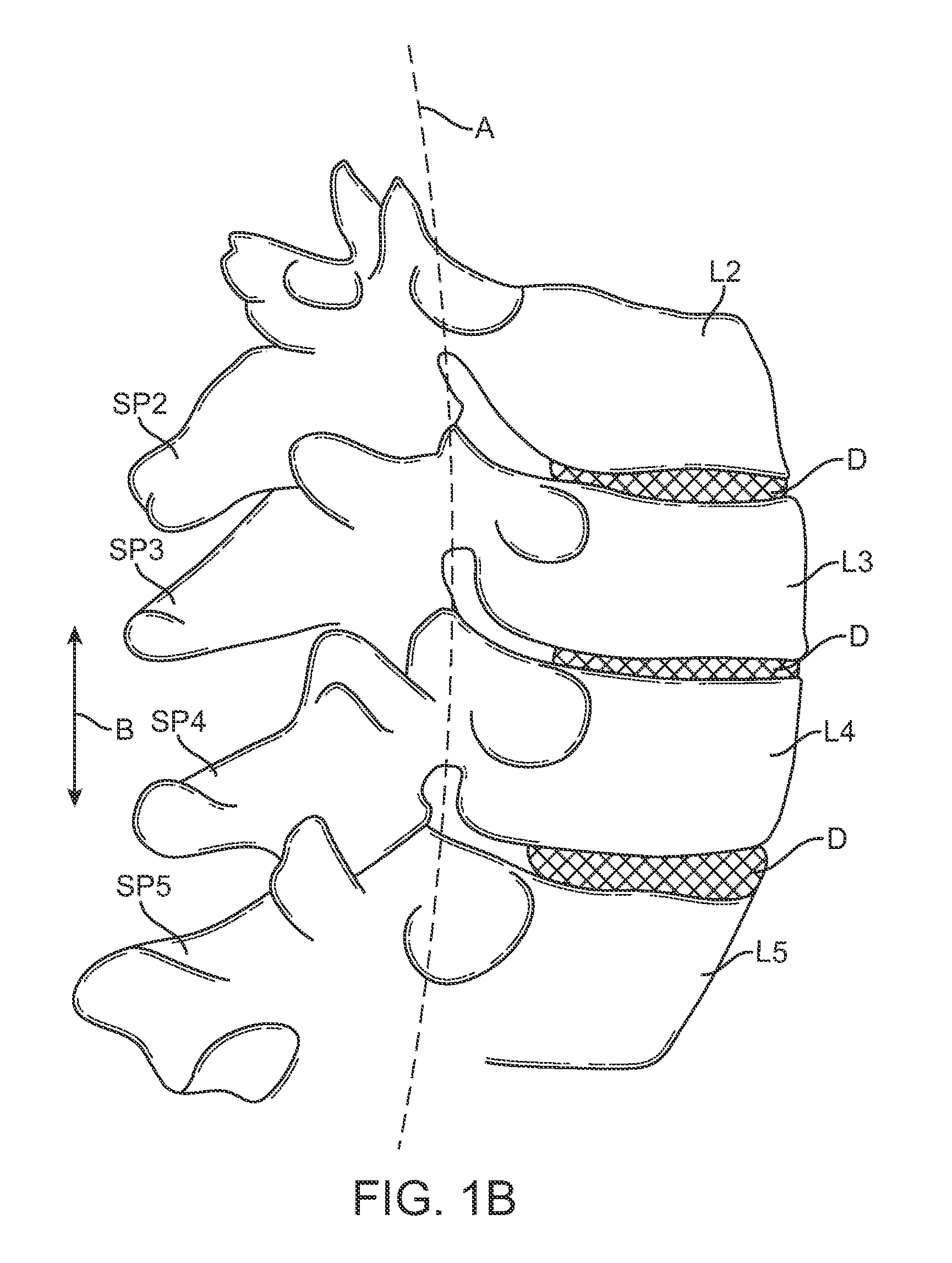
Medical Definition of spinal segment. : a segment of the spinal cord including a single pair of spinal nerves and representing the spinal innervation of a single primitive metamere.
Linearly expanding spine cage for enhanced spinal fusion
ActiveUS7819921B2Diameter minimizationEffectively distractBone implantSpinal implantsSpinal columnVertical axis
A linearly expanding spine cage has a minimized diameter in its unexpanded state that is equal to the diameter of an insertion groove cut into adjacent vertebral bodies. The cage conformably engages between the endplates of adjacent vertebrae to effectively distract the disc space, widen neuroforamina, stabilize the motion segments and eliminate pathologic spine motion. Angular deformities can be corrected, and natural curvatures maintained. The cage enhances spinal arthrodesis by creating a rigid spine segment. Expanding linearly (vertically, along the vertical axis of the adjacent spine) rather than uniformly, the cage height increases and holds the vertebrae with fixation forces greater than adjacent bone and soft tissue failure forces. Stability is thus achieved immediately, enabling patient function by eliminating painful motion. The cage width remains stable, so as to decrease impingement upon a second cage, or upon soft tissue structures in the immediate vicinity, including neural or vascular elements.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
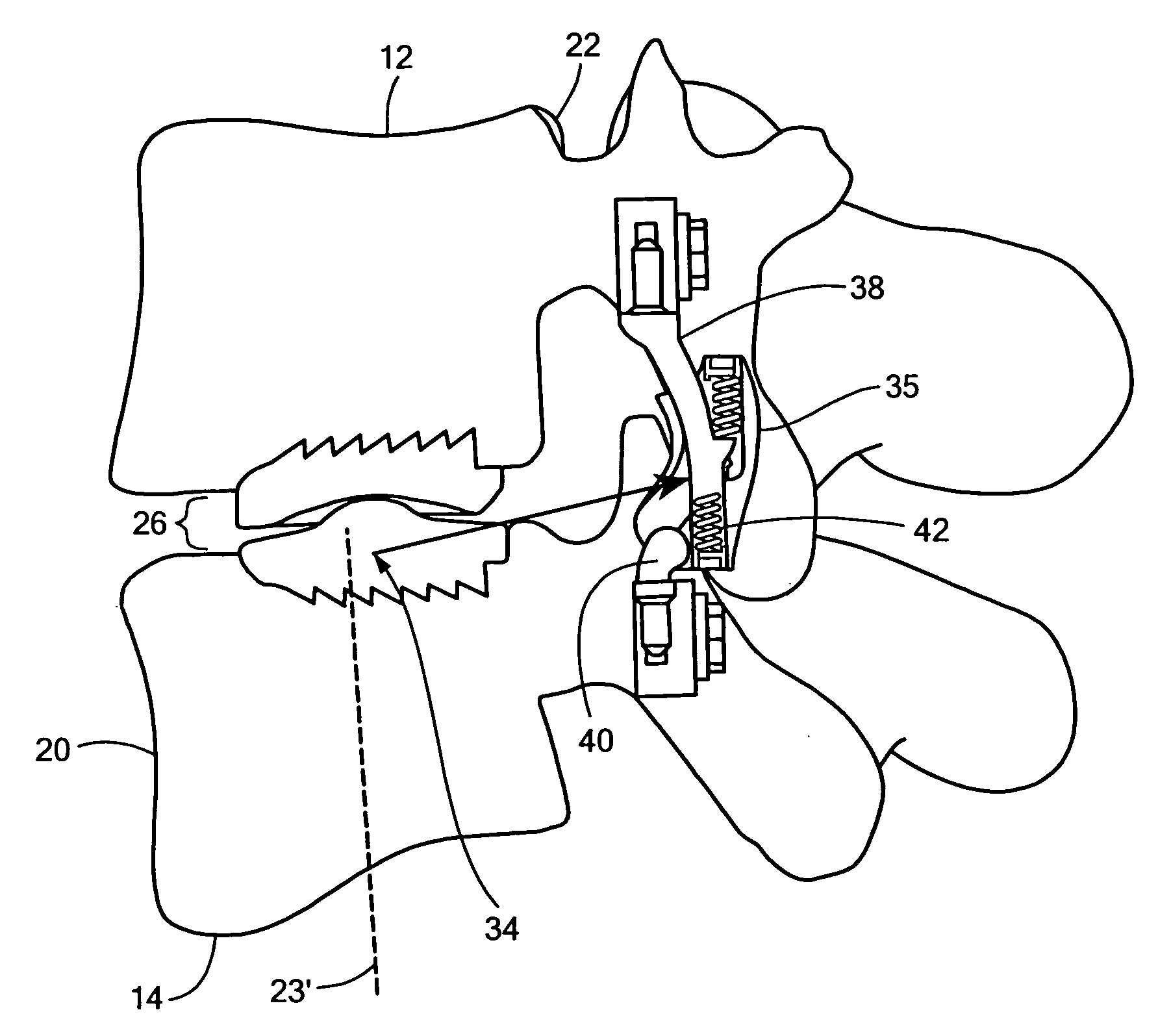
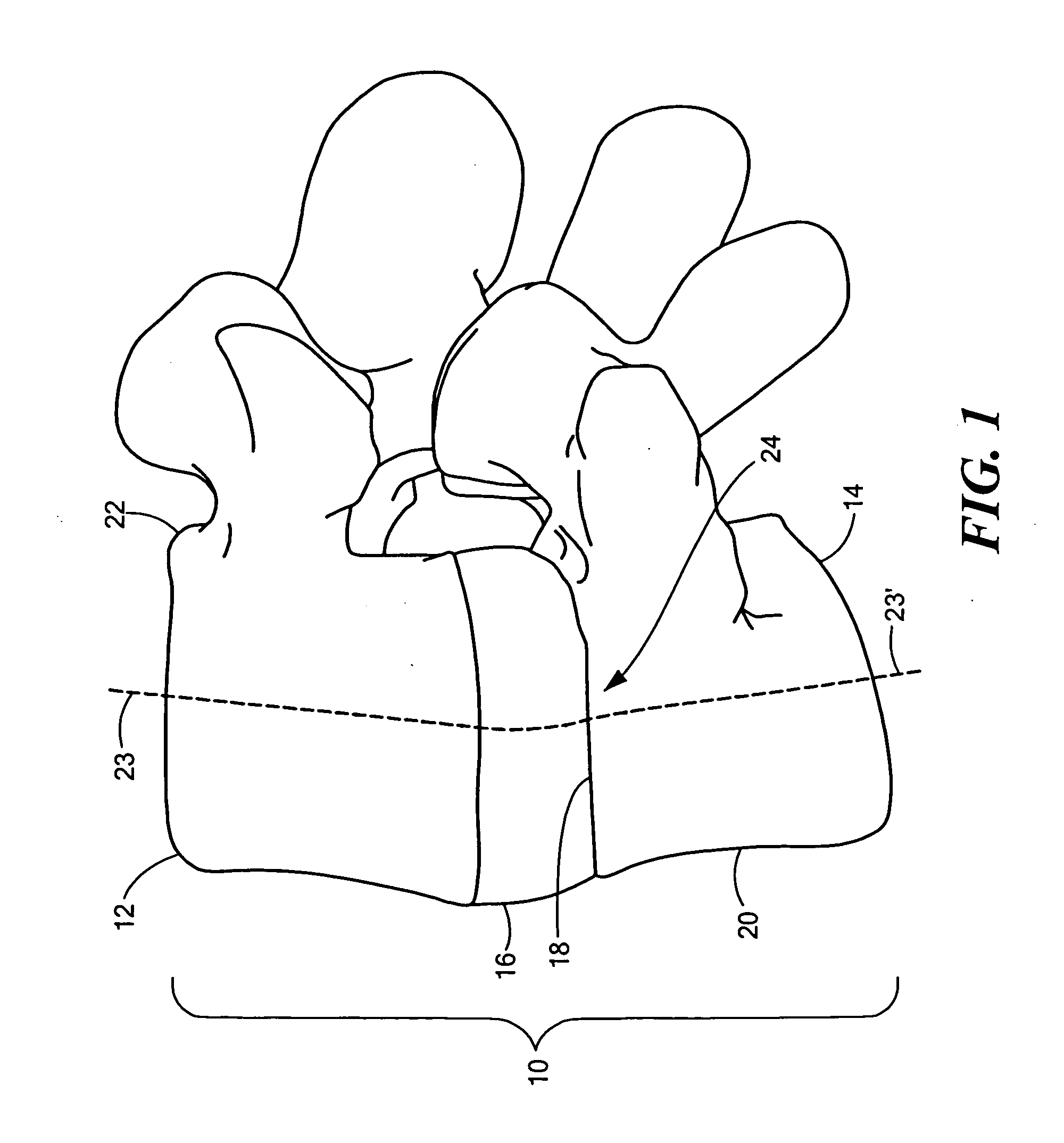
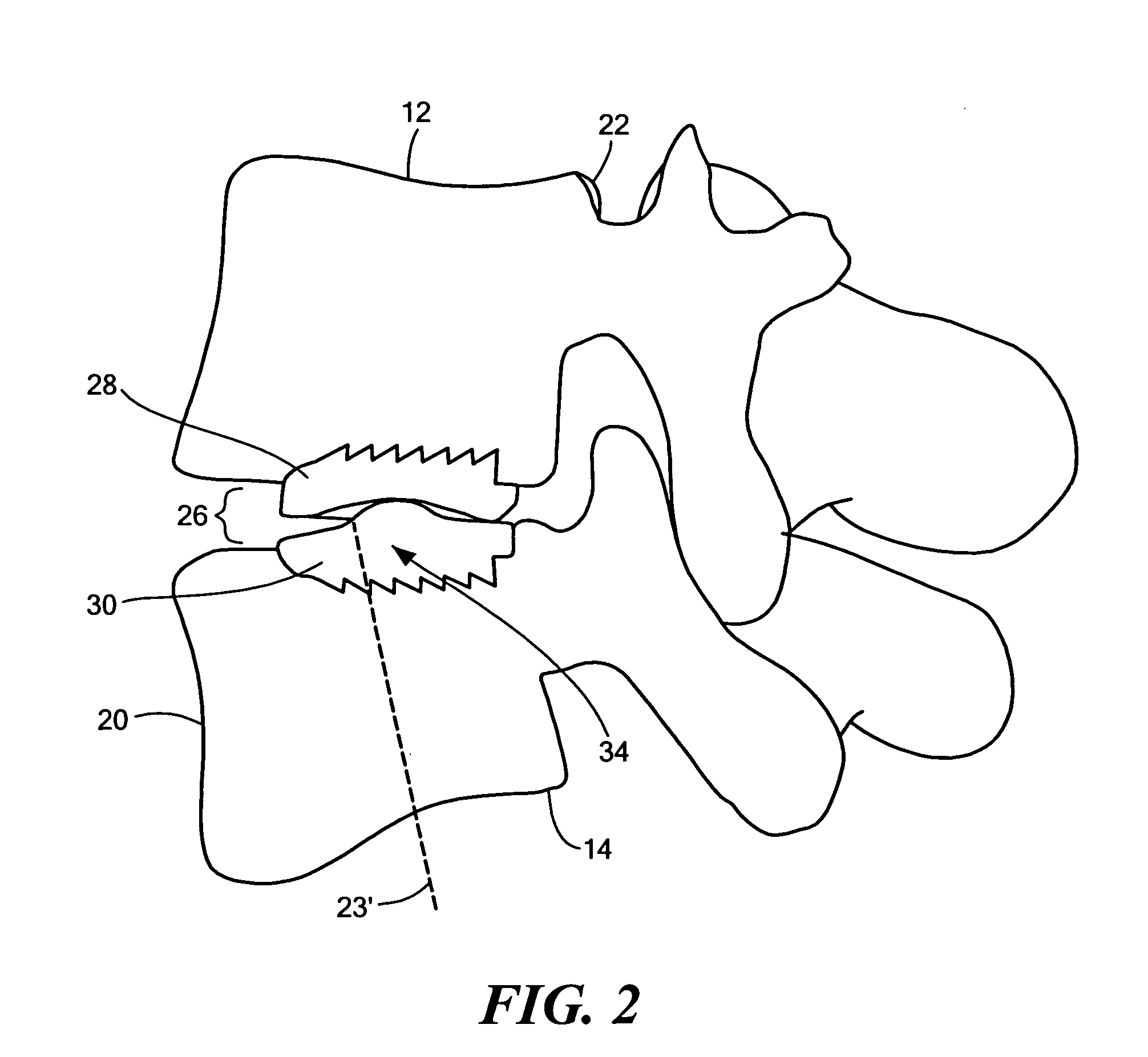
Spinal implant and method for restricting spinal flexion
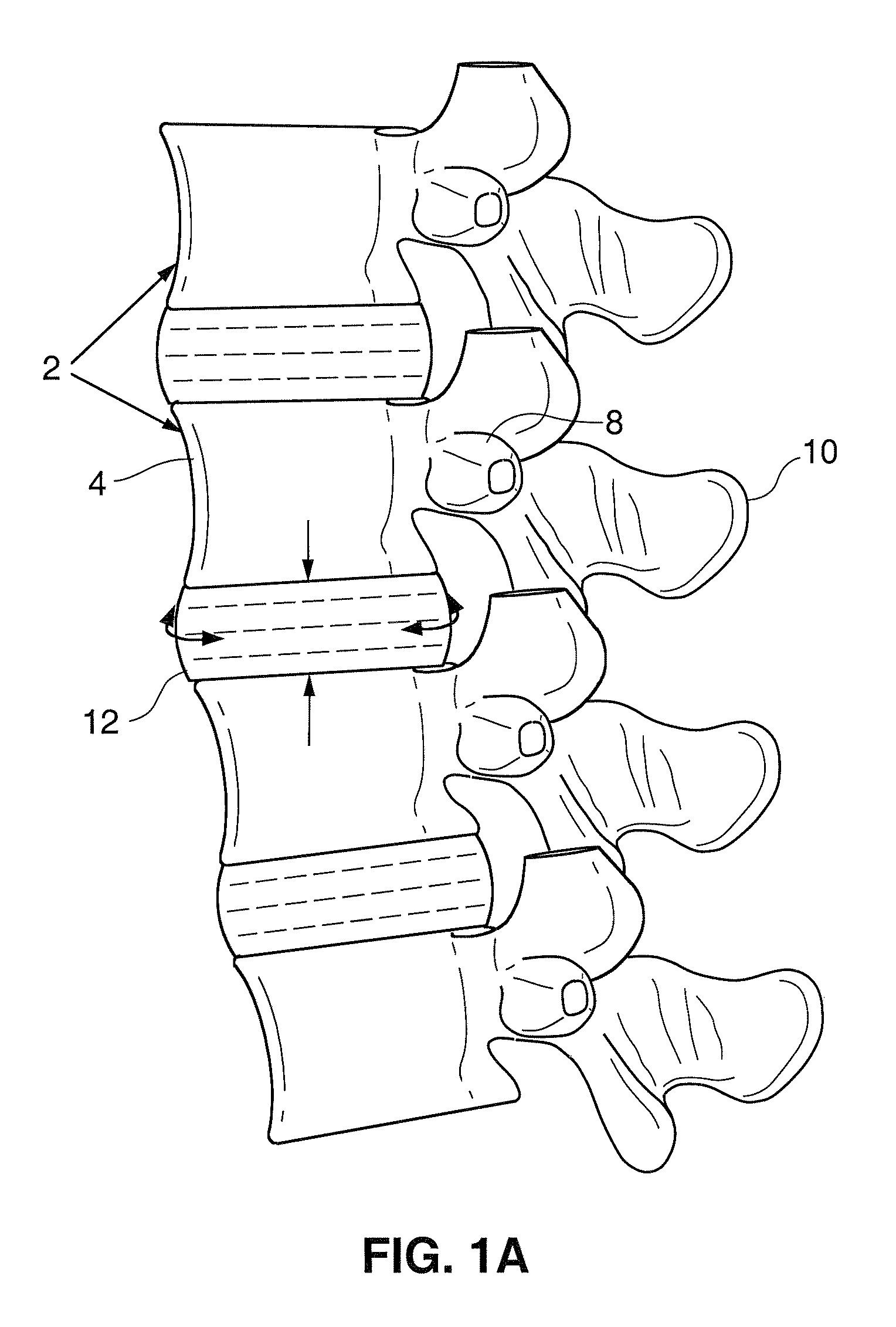
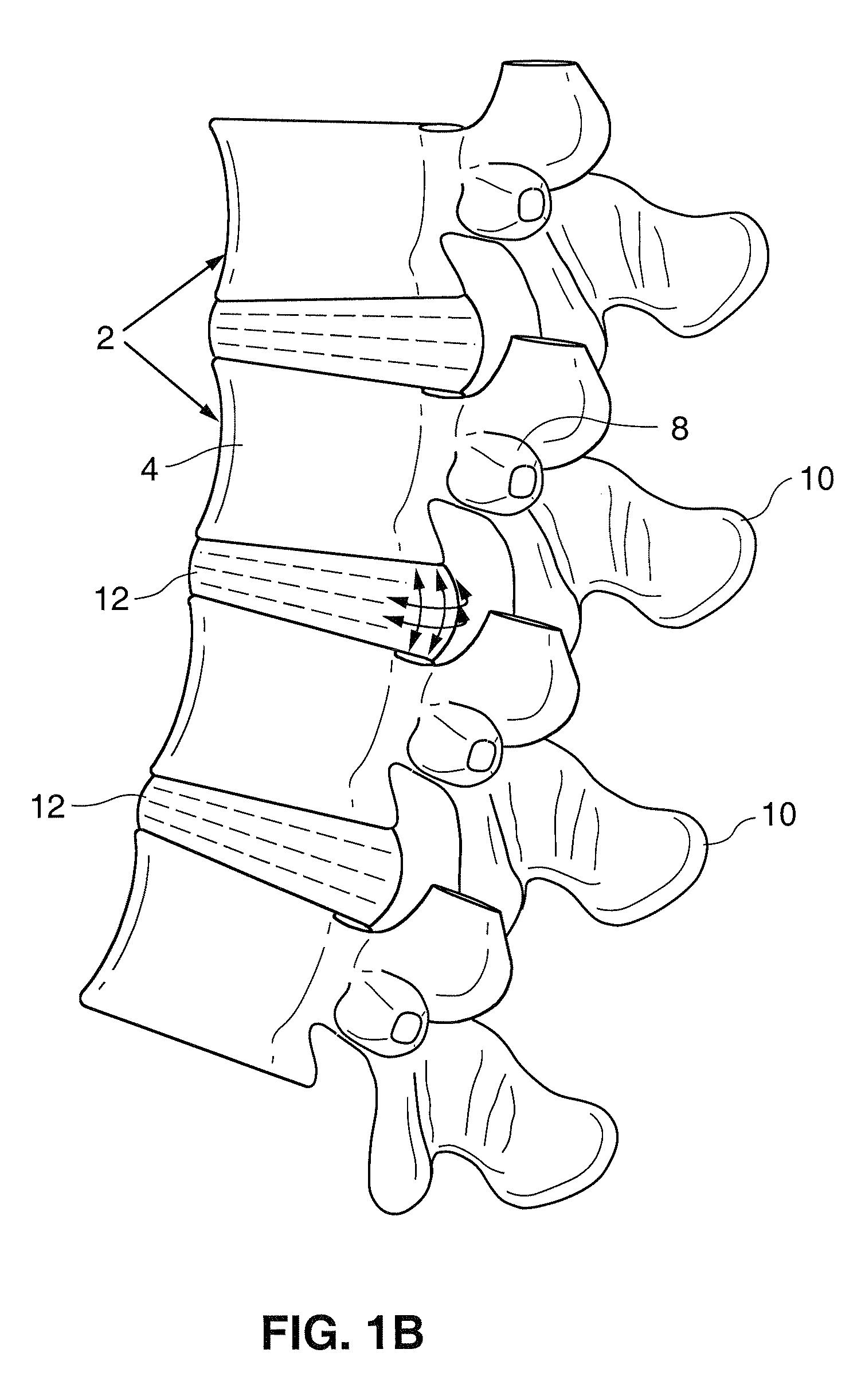
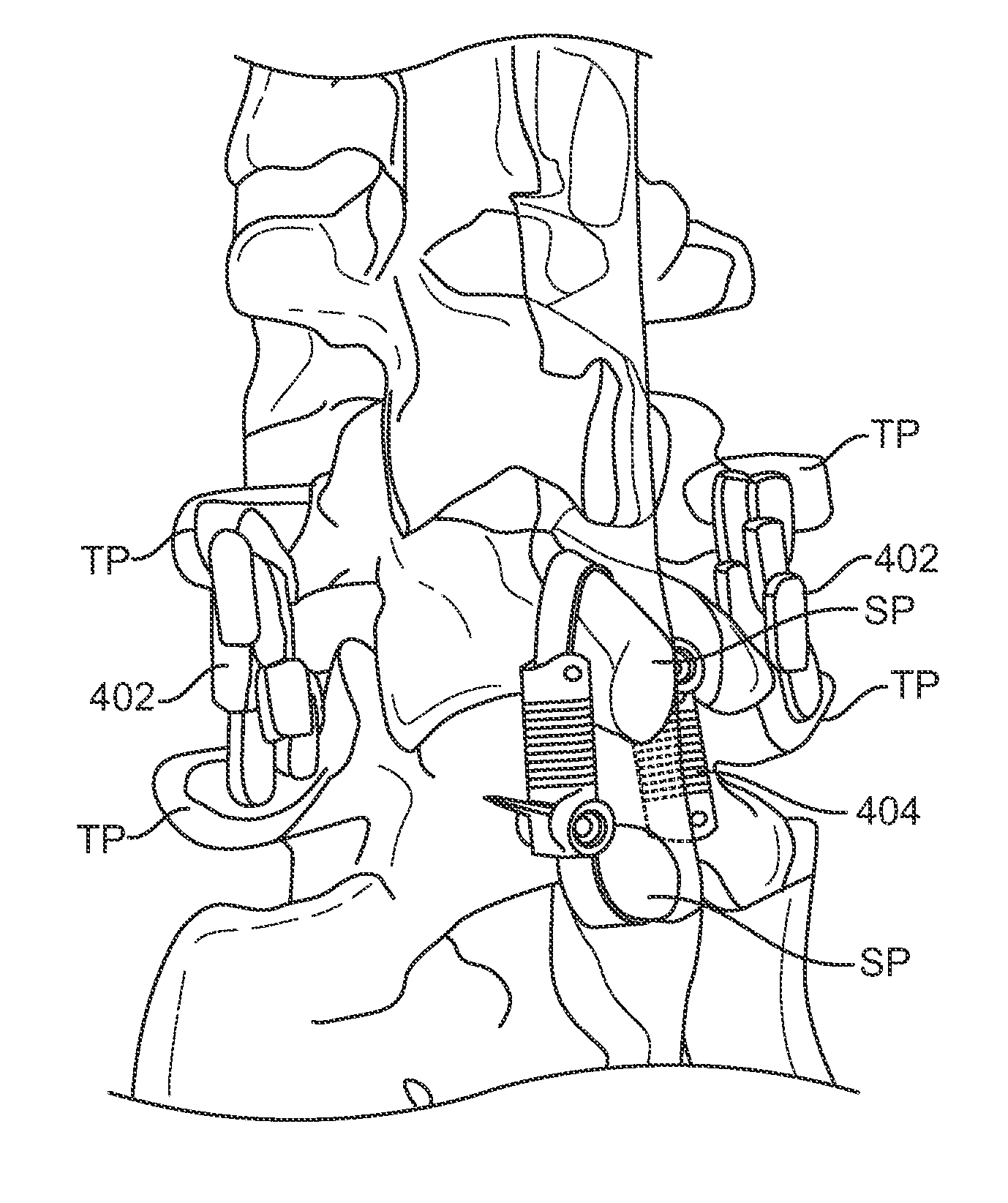
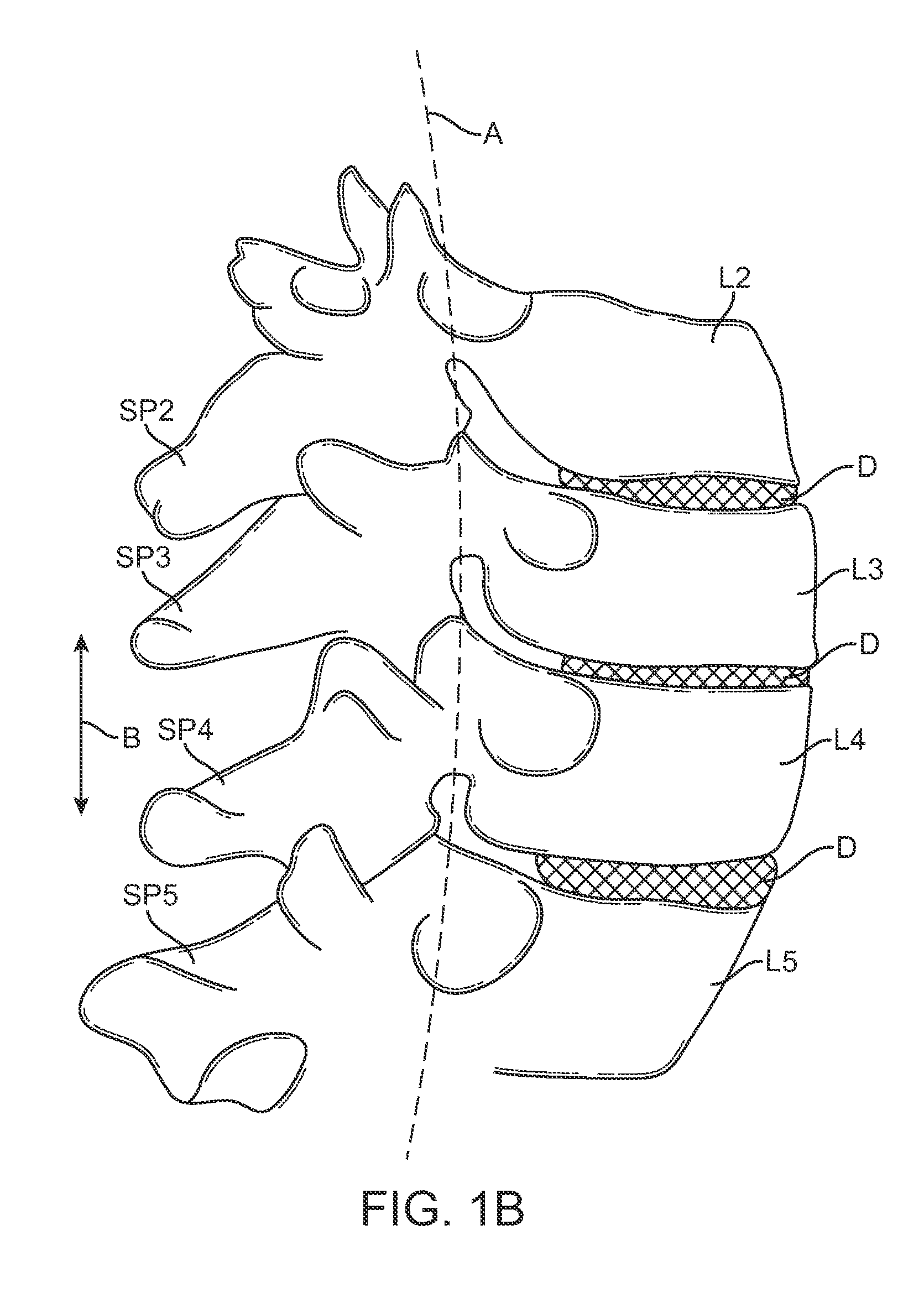
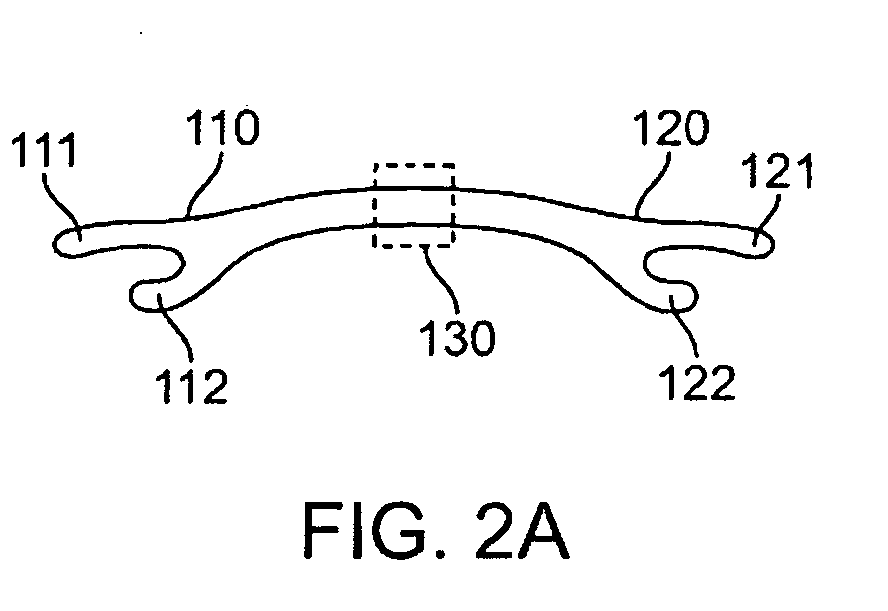
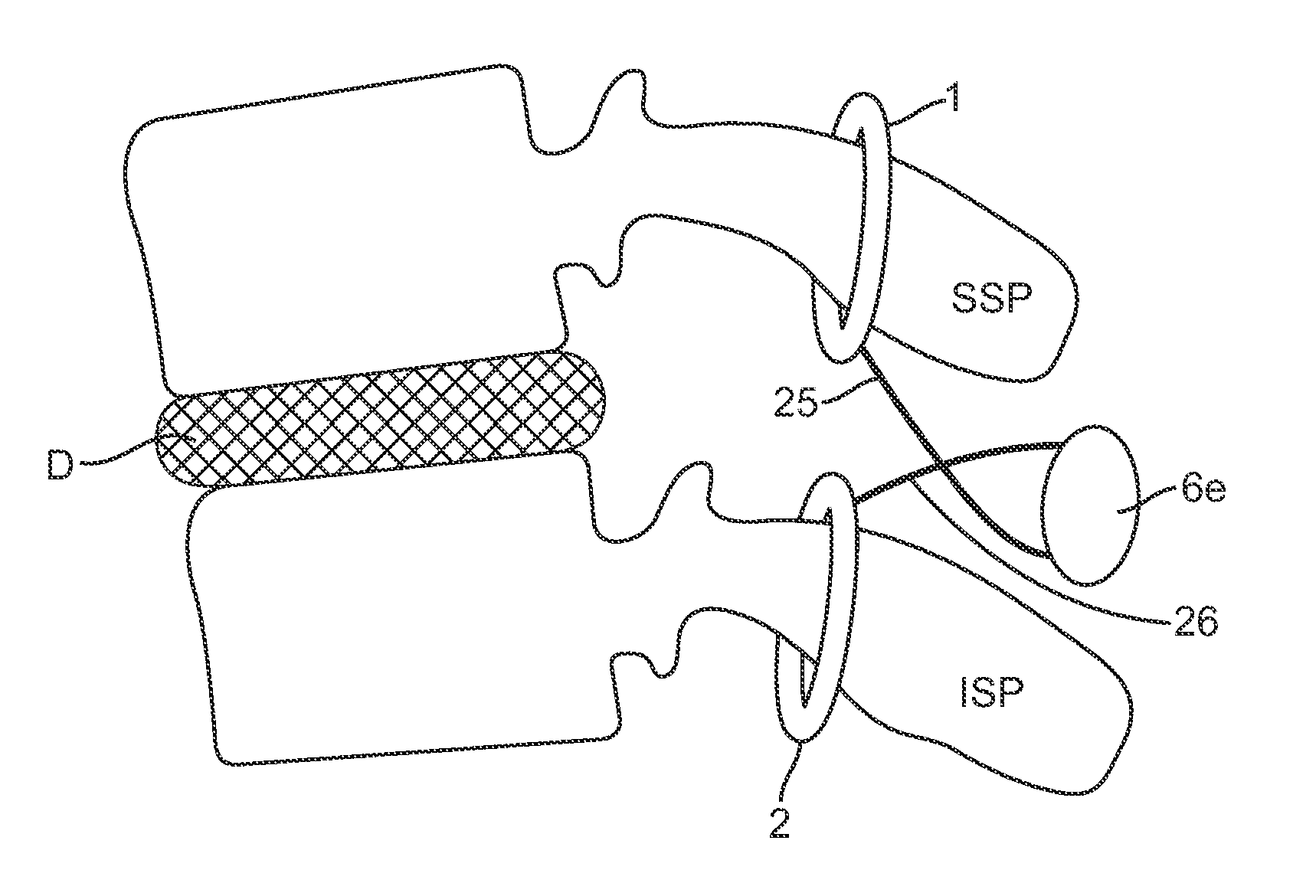
A spinal implant system for restricting flexion of a spine includes an elongate band proportioned to engage at least two spinous processes. During use, the band is positioned engaging the spinous processes at a spinal segment of interest, where it restricts flexion at the segment. The length and tension of the band may be adjustable following to implantation using percutaneous or transcutaneous means.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
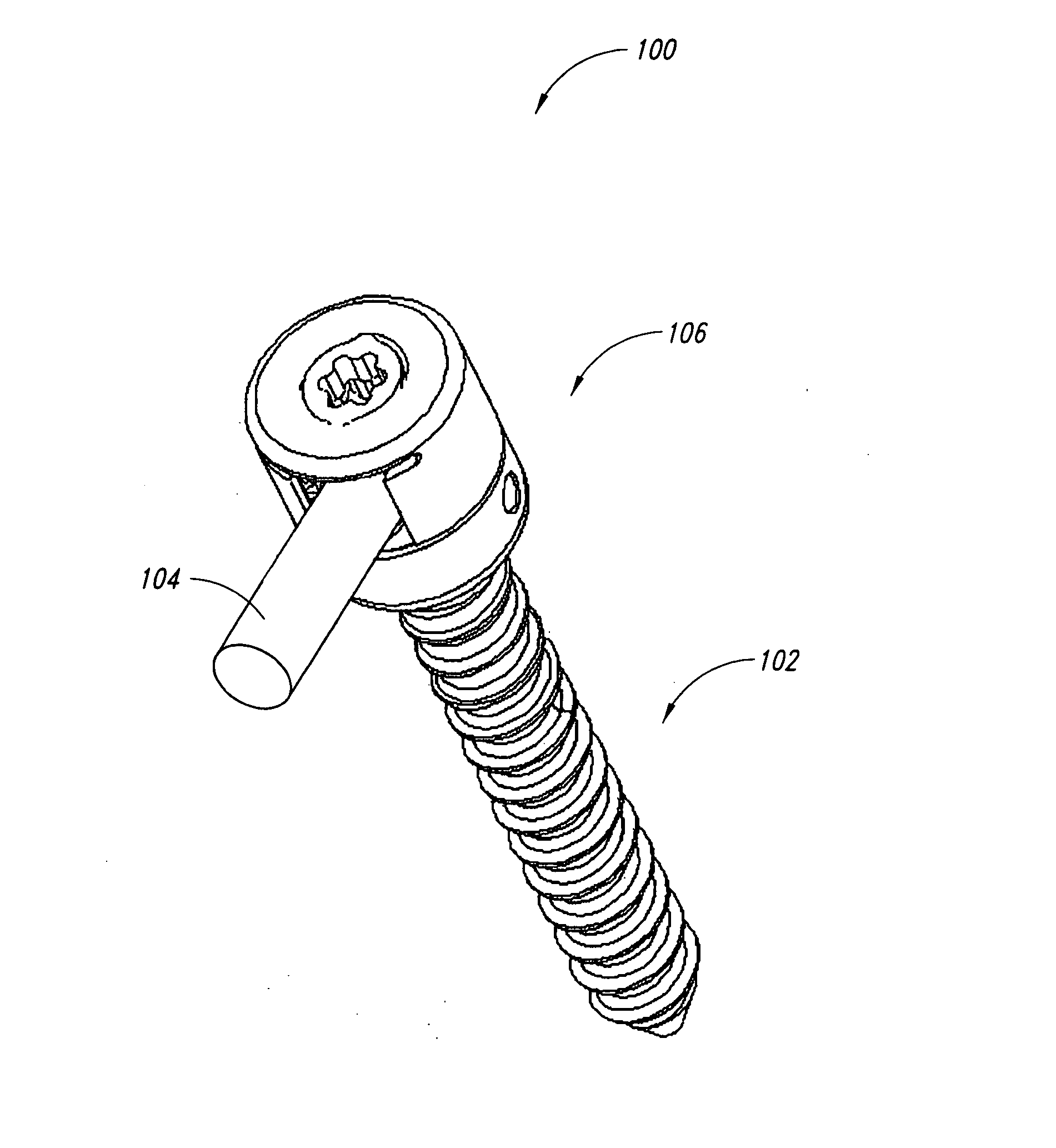
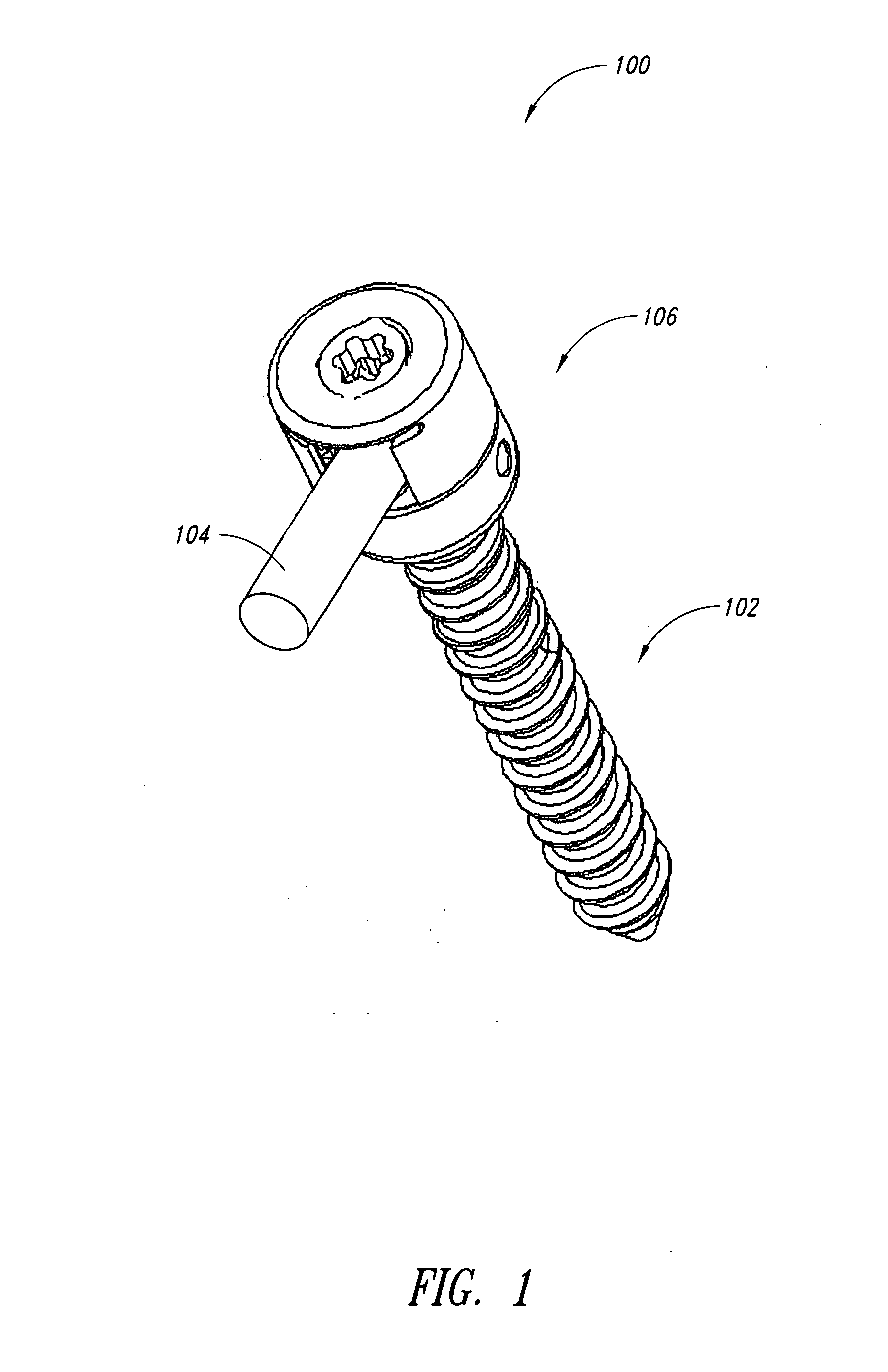
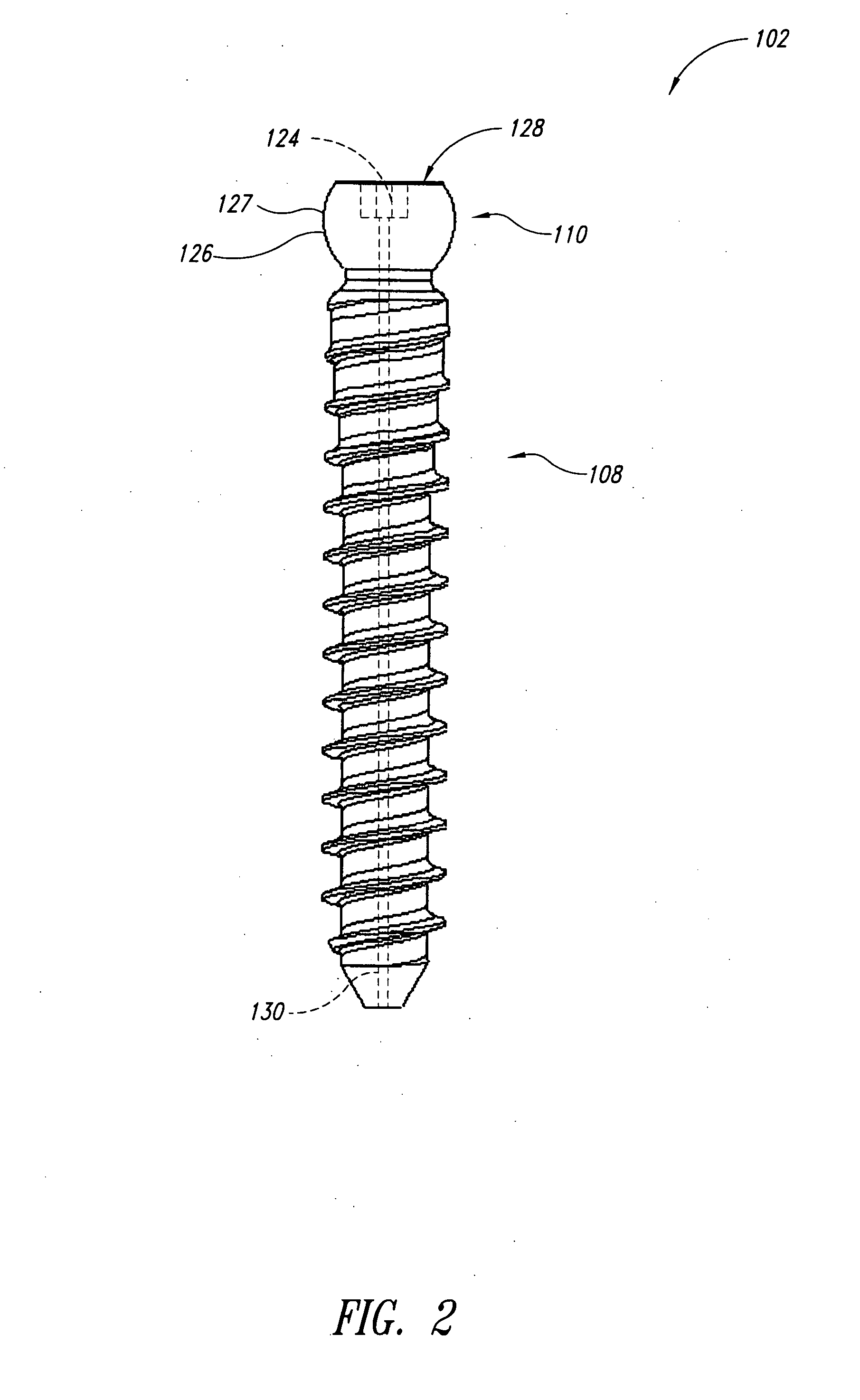
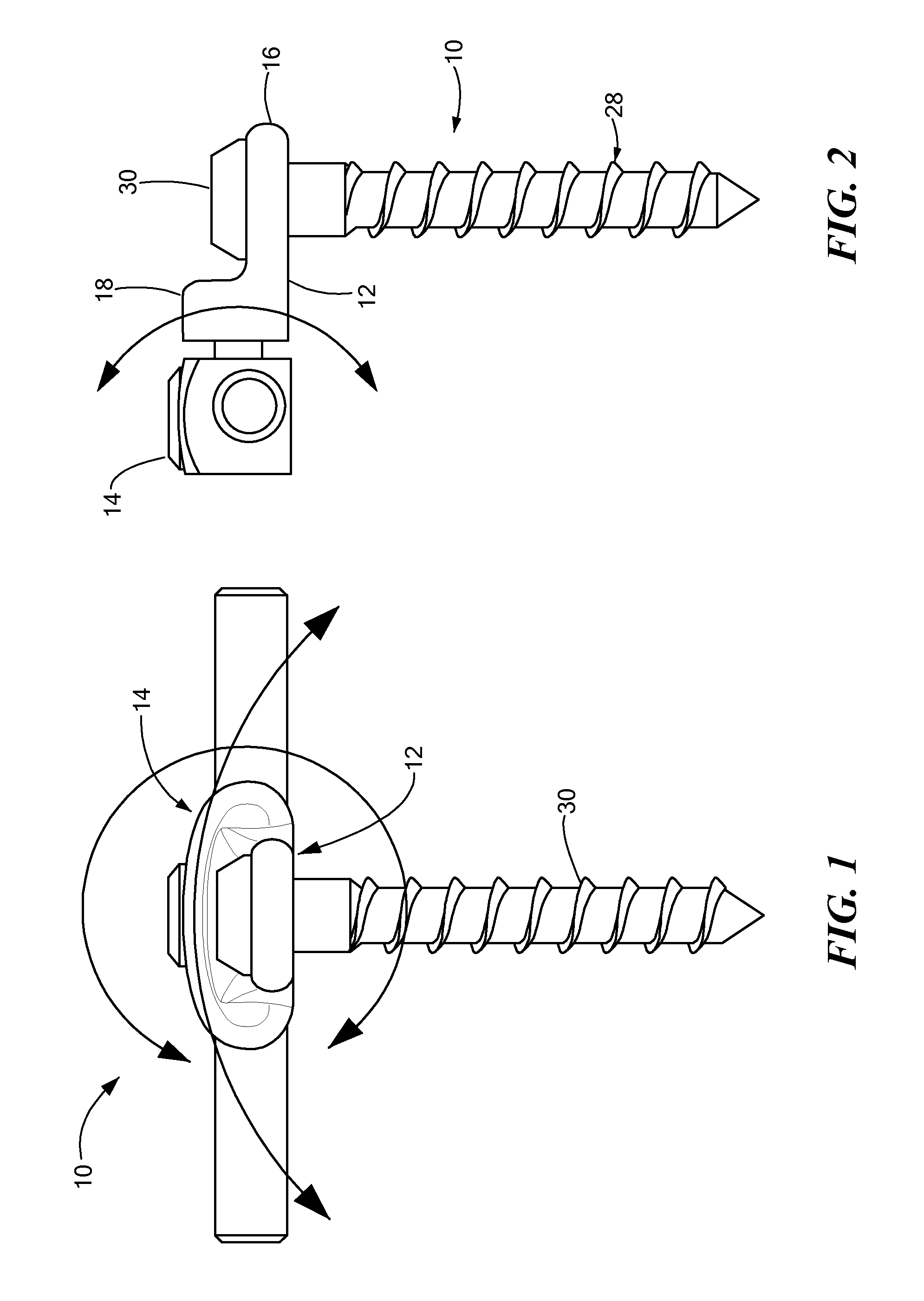
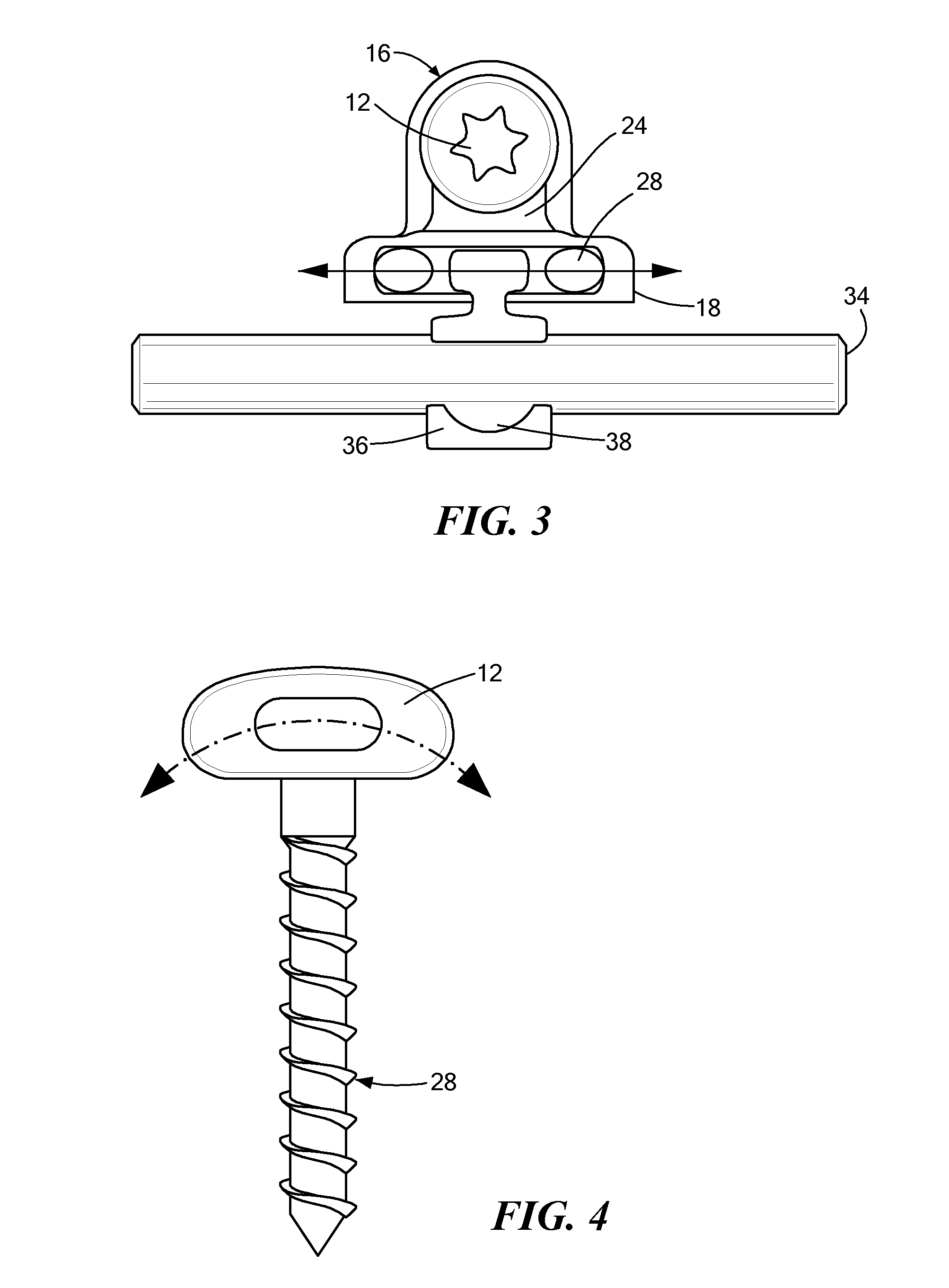
Pedicle screw systems and methods of assembling/installing the same
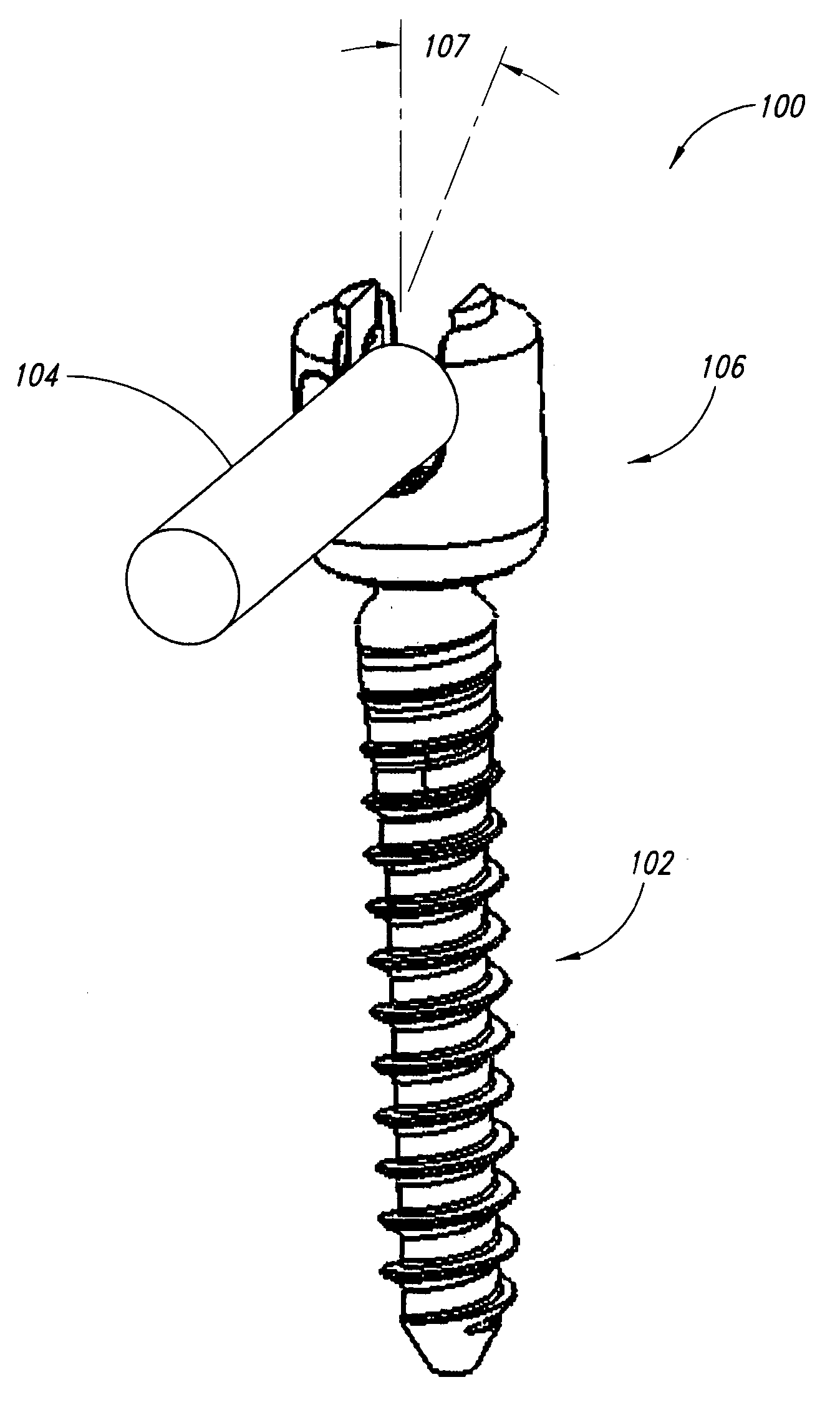
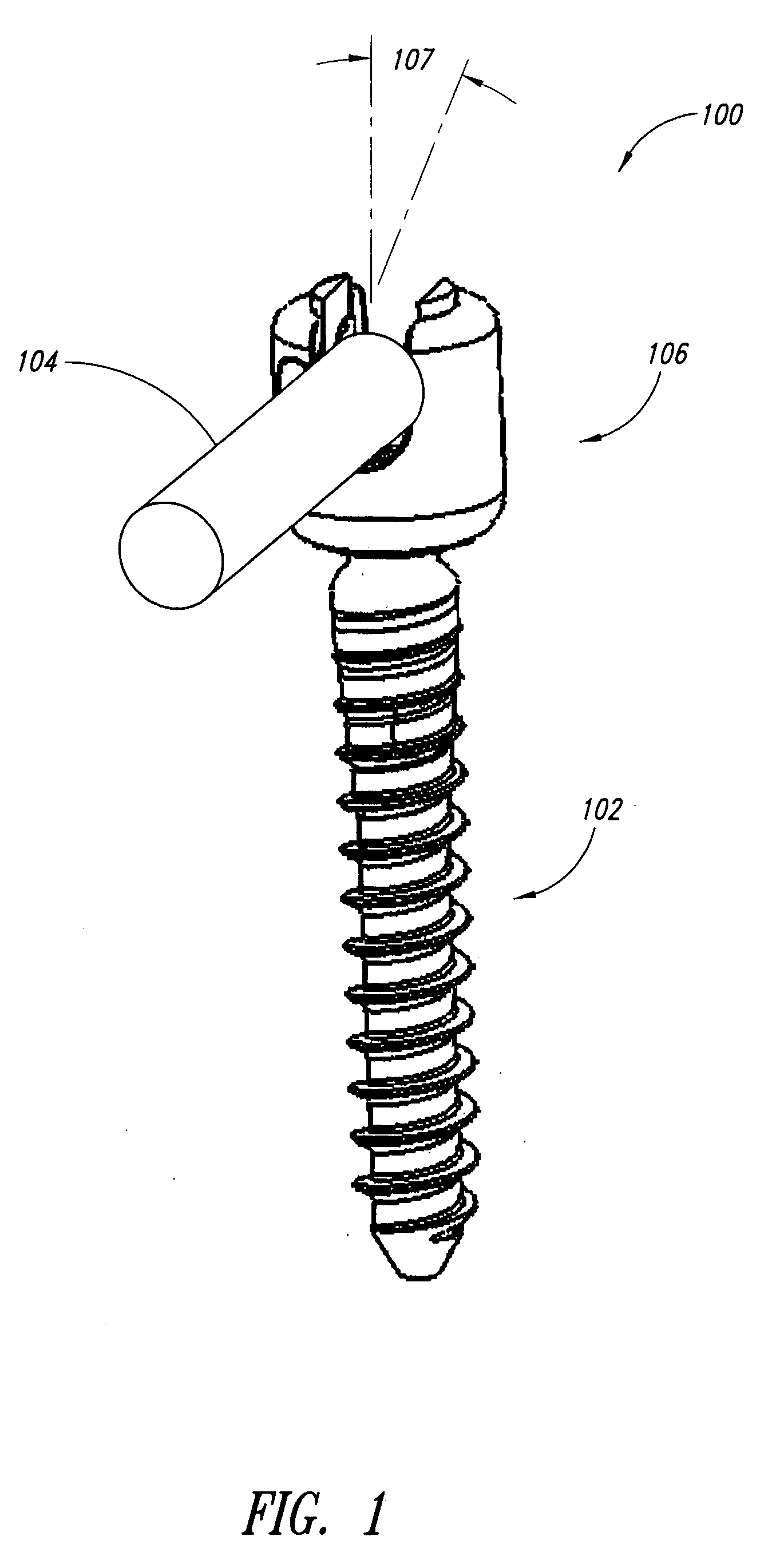
The pedicle screw system may be used for fixation of spinal segments and may be advantageous when minimally invasive surgery (MIS) techniques are employed. The pedicle screw system includes a tulip assembly comprising of a tulip body, a inner member, and an expansion member. Installation of the pedicle screw system into pedicles of the spine, for example, includes inserting the pedicle screw into a portion of the spine and then coupling the tulip assembly to the pedicle screw. The tulip assembly may be locked onto the pedicle screw before a distraction rod is placed in the tulip assembly. After the rod is placed in the tulip assembly, the tulip body and the inner member can be rotated relative to one another to lock the rod into the tulip assembly. In addition, the relative rotation may also provide additional locking of the tulip assembly to the pedicle screw.
Owner:X SPINE SYST
Artificial Spinal Disc
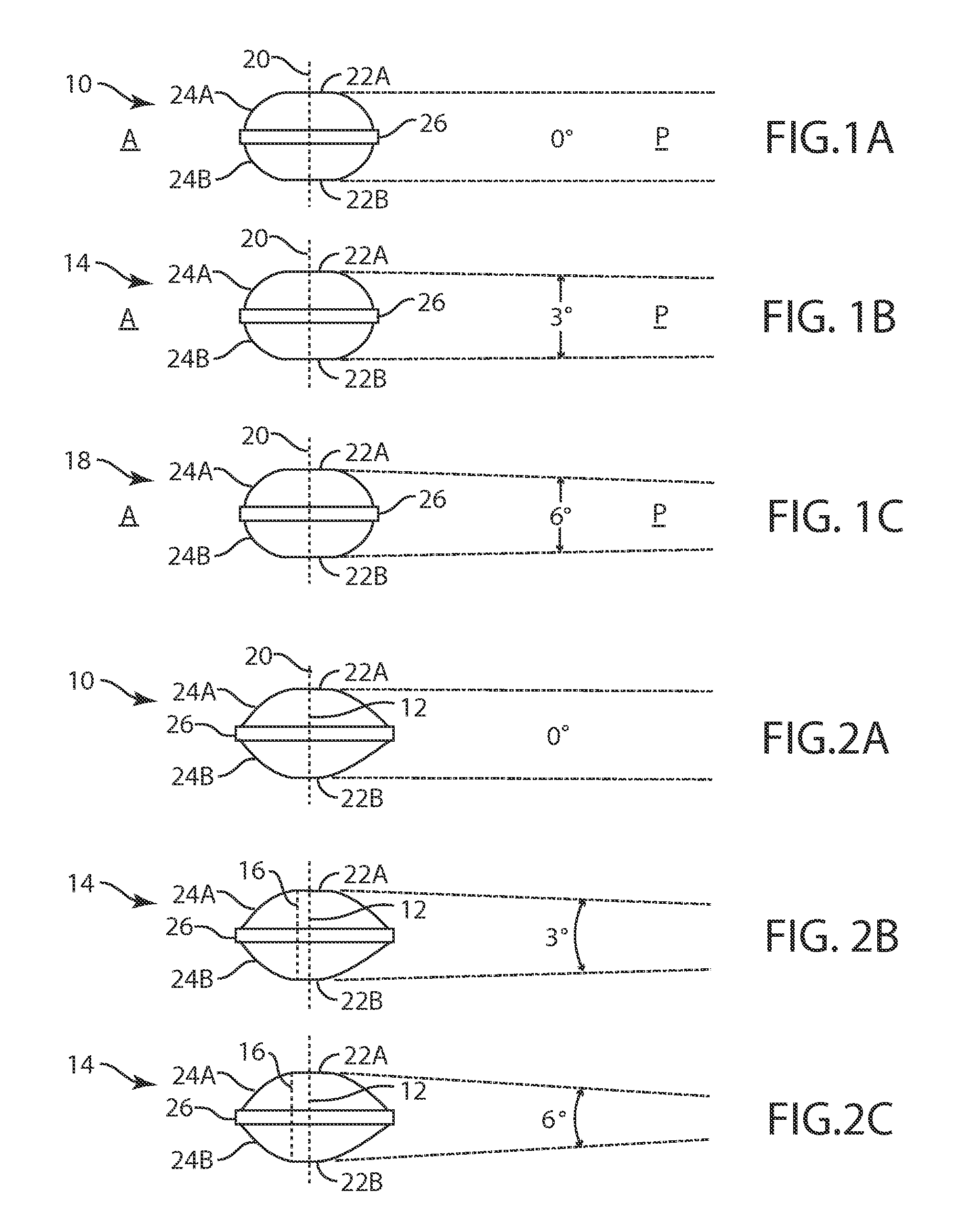
An artificial disc prosthesis is provided. The prosthesis of the present invention enables spinal segment alignment by having a variable height across its surface. The variable height is achieved by an asymmetric artificial nucleus or by at least one variable height end plate.
Owner:SYNERGY SPINE SOLUTIONS INC
Pedicle screw systems and methods of assembling/installing the same
The pedicle screw system may be used for fixation of spinal segments and may be advantageous when minimally invasive surgery (MIS) techniques are employed. The pedicle screw system includes a tulip assembly comprising a tulip body, a inner member, an expansion member, and a cap assembly. Installation of the pedicle screw system into pedicles of the spine, for example, includes inserting the pedicle screw into a portion of the spine, coupling a partial assembly comprising the tulip body, inner member, and expansion member to the pedicle screw, placing a rod in the tulip assembly, and then coupling the cap assembly to the tulip body. Coupling the cap assembly to the tulip body includes initially locking the tulip assembly to the pedicle screw and then locking the rod in the tulip assembly.
Owner:ALPINESPINE
Spinal implant and method for restricting spinal flexion
A spinal implant system for restricting flexion of a spine includes an elongate band proportioned to engage at least two spinous processes. During use, the band is positioned engaging the spinous processes at a spinal segment of interest, where it restricts flexion at the segment. The length and tension of the band may be adjustable following to implantation using percutaneous or transcutaneous means.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Spinal implant
InactiveUS20060241764A1Improve stabilityStabilize the adjacent vertebraeBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral disk
A spinal implant is disclosed which when placed within the spinal disc space stabilizes the spinal segment.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Pedicle Screw Systems and Methods of Assembling/Installing the Same
Owner:X SPINE SYST
Intervertebral disc and insertion methods therefor
ActiveUS20070123985A1Good for long-term fixationPrevent over-insertionDiagnosticsSpinal implantsSpinal Disk ImplantIntervertebral disk
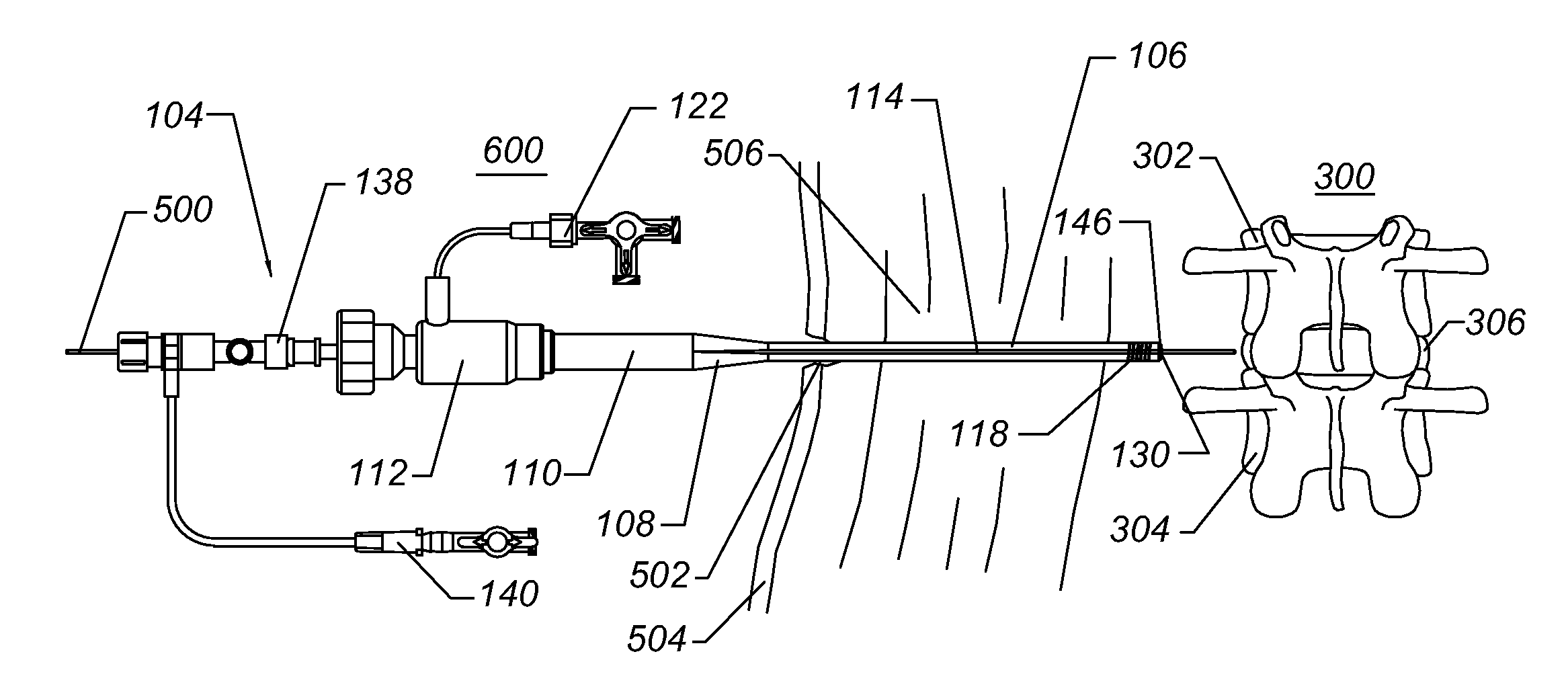
A method of inserting an intervertebral disc implant into a disc space includes accessing a spinal segment having a first vertebral body, a second vertebral body and a disc space between the first and second vertebral bodies. The method includes securing a first pin to the first vertebral body and a second pin to the second vertebral body, using the first and second pins for distracting the disc space, and providing an inserter holding the intervertebral disc implant. The method also desirably includes engaging the inserter with the first and second pins, and advancing the inserter toward the disc space for inserting the intervertebral disc implant into the disc space, whereby the first and second pins align and guide the inserter toward the disc space.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Spine treatment devices and methods
InactiveUS20070288014A1Easy to deployInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpine disorderLateral bending
The invention relates generally to implant systems and methods for treating spine disorders, and more particularly to least invasive implant systems configured for re-distributing loads on a spine segment while still allowing spine flexion, extension, lateral bending and torsion. The implant system can include implants configured for spanning bi-lateral intercostal locations that can be introduced and implanted via posterior access to the spine through small bilateral incisions.
Owner:DFINE INC
Flexible spine components
ActiveUS20080221620A1Increase flexibilityReduced flexibilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisElastomerDeformity
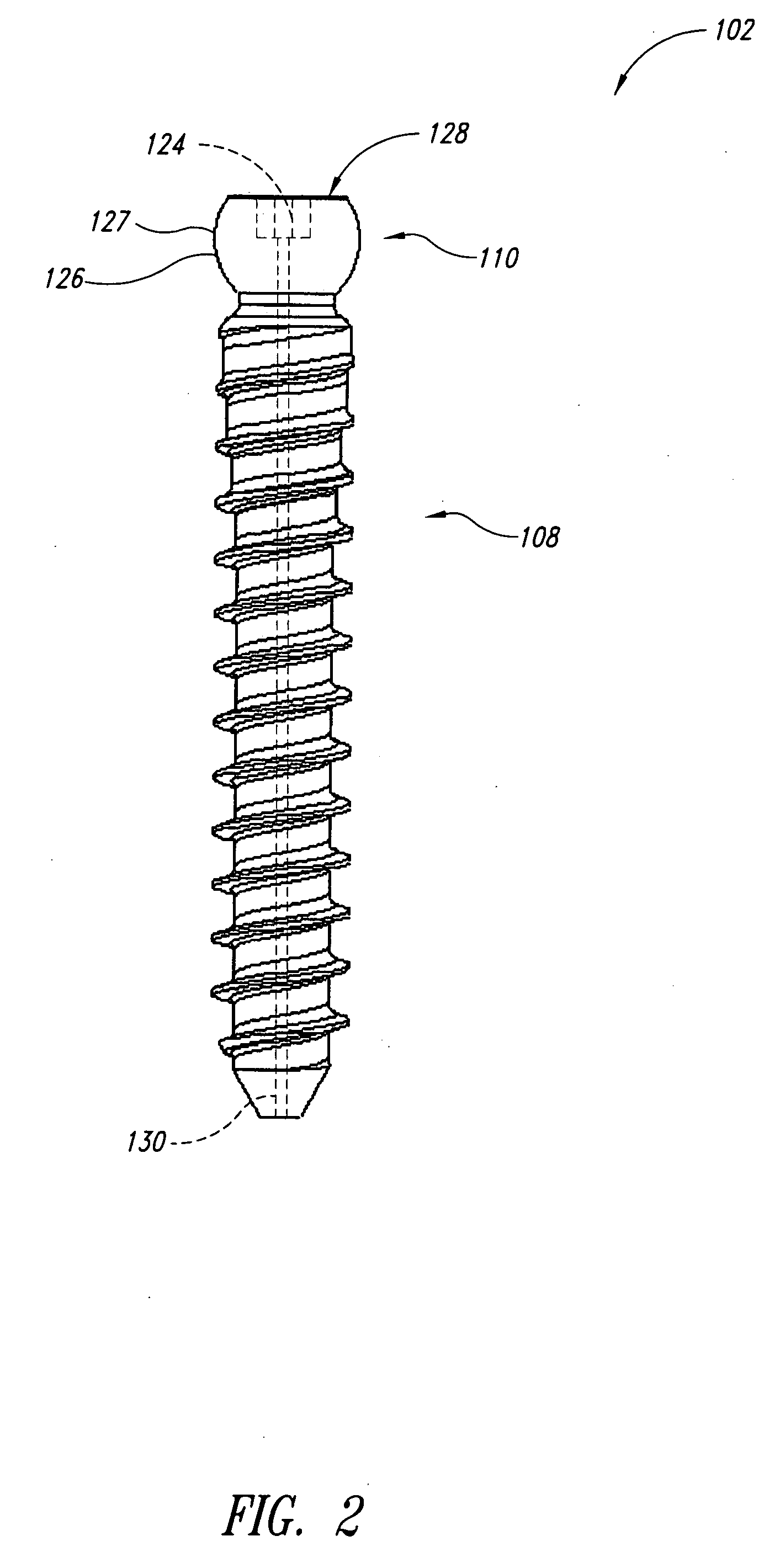
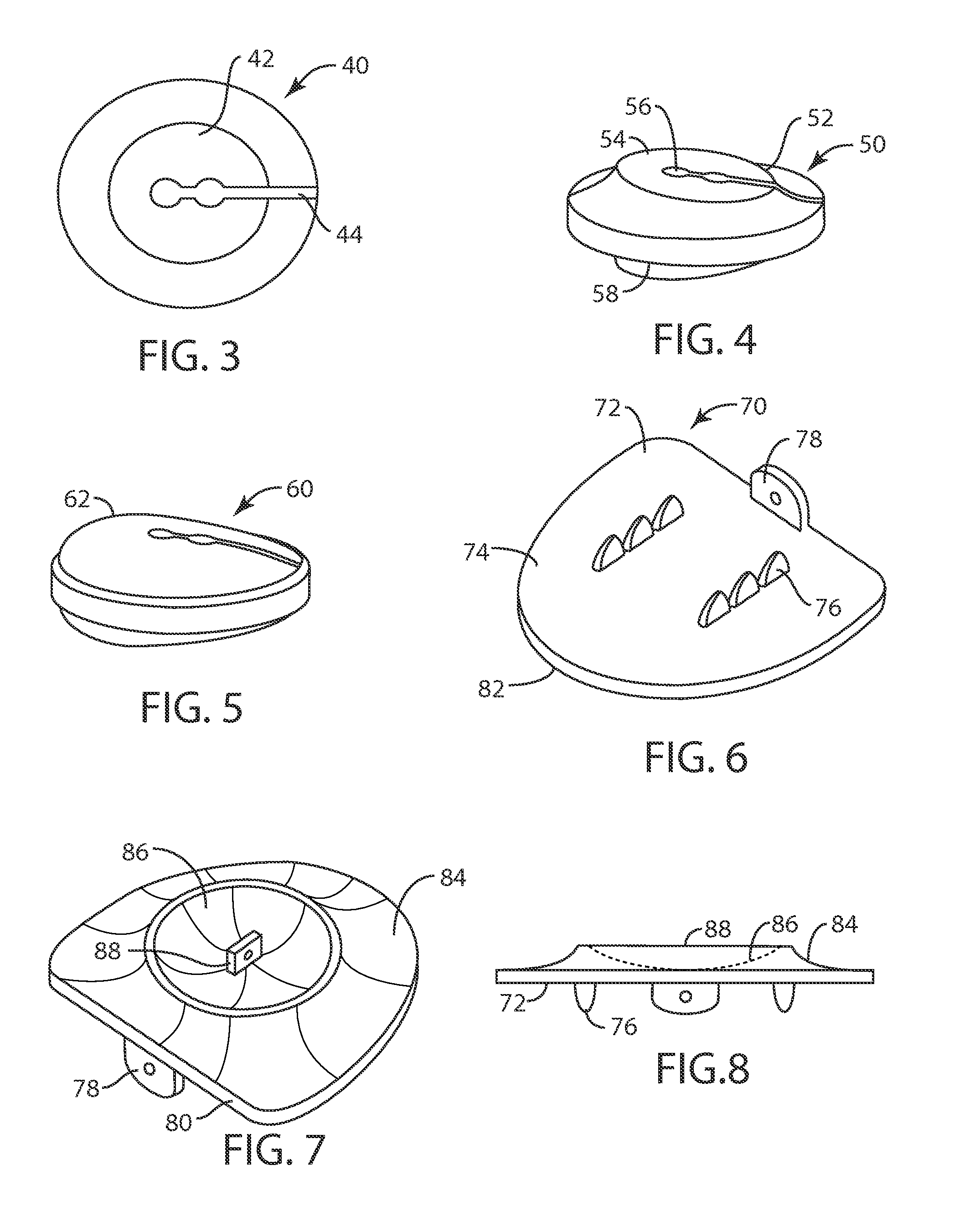
An improved flexible component used for dynamic stabilization of spinal segments for the treatment of vertebrae deformities and injuries and for the replacement of a complete or segment of the body of a vertebra in the spine is described. The flexible component is comprised of a solid, suitable implant material with a longitudinal bore the entire length and an appropriately formed slot which extends spirally around the shaft either continuously or segmentally. The flexible component may be encapsulated, fully or partially, in a suitable implant grade elastomeric resilient material. When used for a dynamic stabilization device, the component is attached to the vertebral bodies by pedicle screws know to those in the art. When used as a vertebral replacement device, attached to the component's opposite ends are members for attachment to the adjacent vertebra that allow for height and angular adjustment.
Owner:FLEX TECH
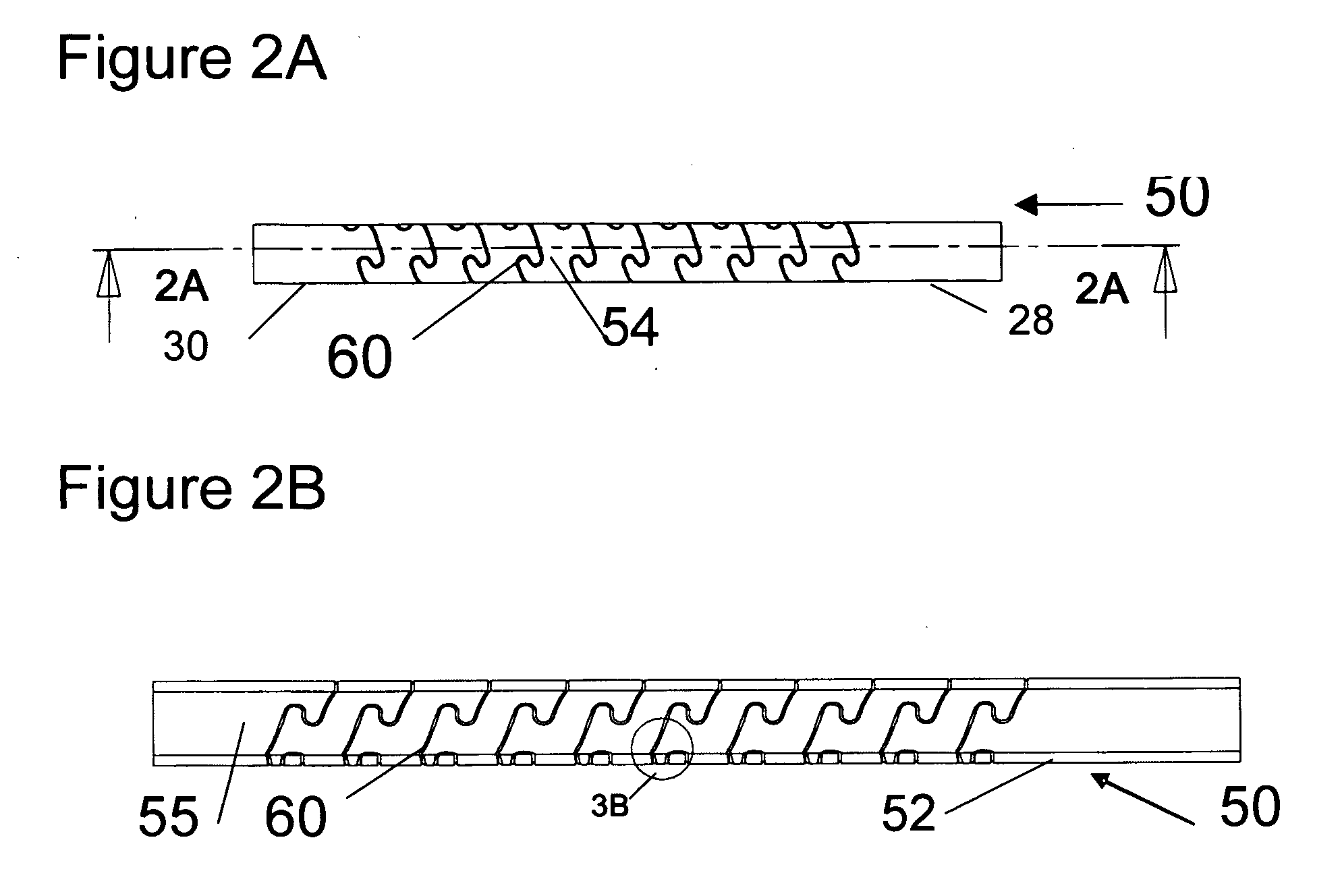
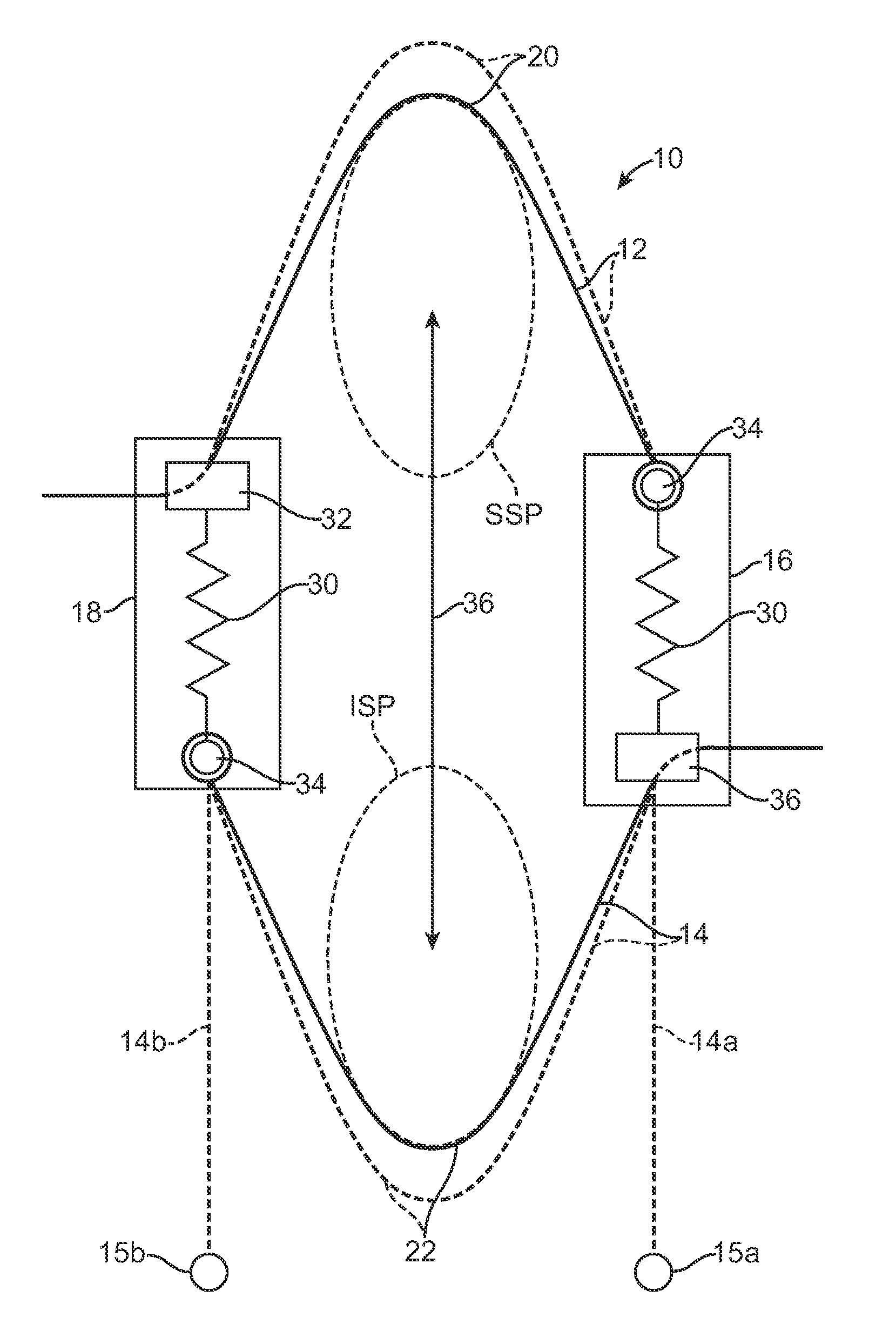
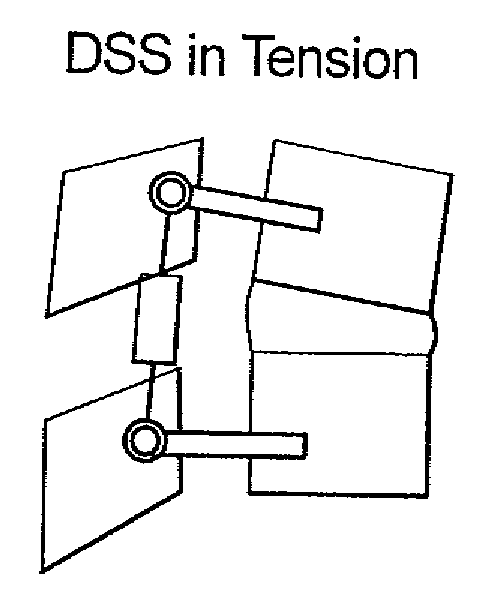
Methods and systems for increasing the bending stiffness and constraining the spreading of a spinal segment
InactiveUS20100036424A1Increased bending stiffnessRelieve instabilityInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsMedicineTension member
A system for restricting spinal flexion includes superior and inferior tether structures joined by a pair of compliance members. Compliance members comprise tension members which apply a relatively low elastic tension on the tether structures. By placing the tether structures on or over adjacent spinous processes, flexion of a spinal segment can be controlled in order to reduce pain.
Owner:SIMPIRICA SPINE
Dynamic spine stabilizer
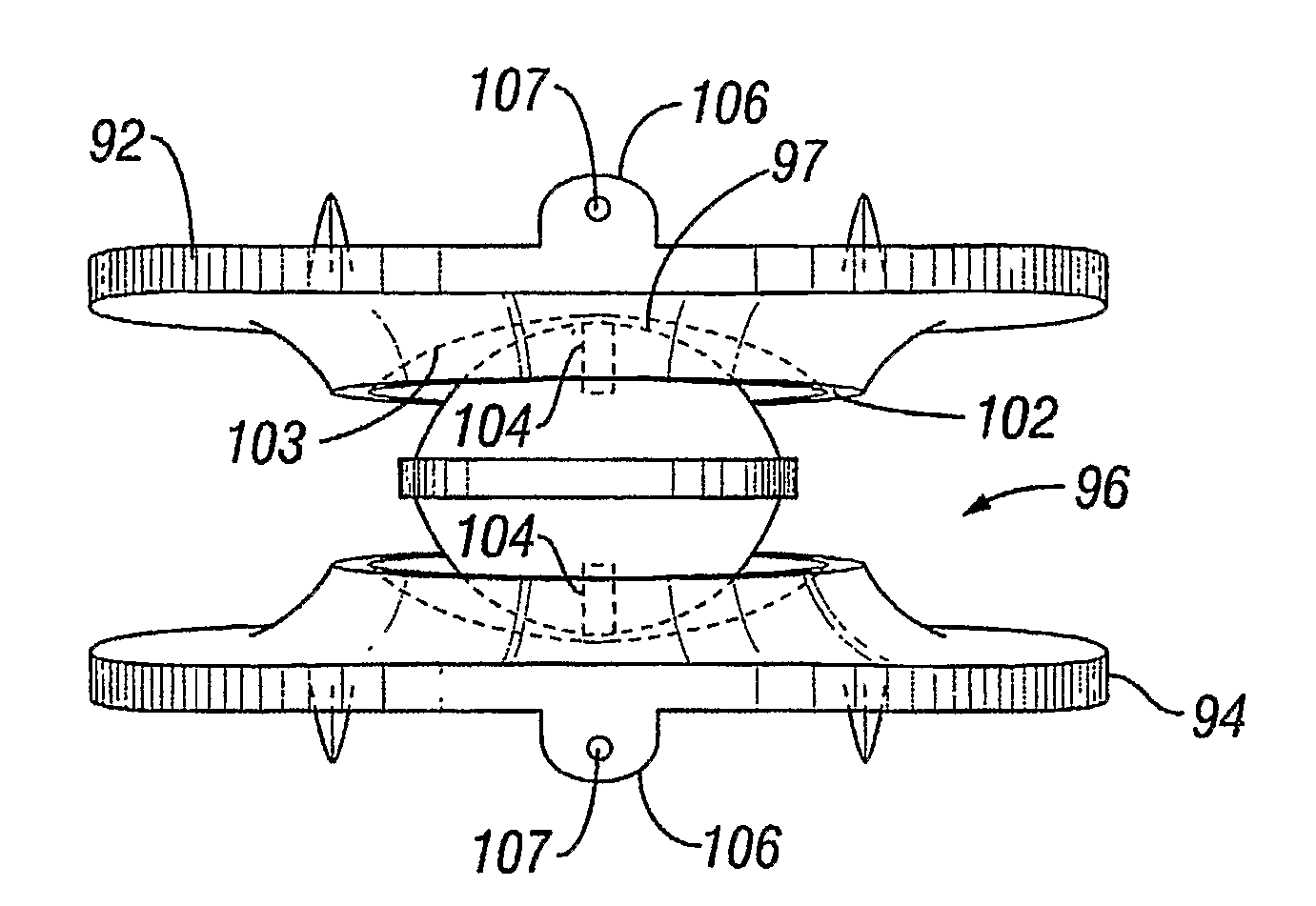
InactiveUS7713287B2Unrestricted angular motion of the spineImprove machineryInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRange of motionEngineering
A dynamic spine stabilization device is provided that includes at least one force imparting member, e.g., a spring. The force imparting member is adapted to deliver a force of between about 150 lb / inch and 450 lbs / inch, and restrict the relative travel distance between said first and second pedicles to a distance of between about 1.5 mm and 5 mm. The spinal stabilization devices also have a minimal impact on the location of the center of rotation for the spinal segment being treated. By providing resistance in the noted range and restricting the travel distance to the noted range, it has been found that the stabilization device provides a desired level of stabilization, as reflected by range of motion values that closely approximate pre-injury range of motion levels. In addition, the resistance levels are not so high as to alter the location of the center of rotation of the treated spinal segment from its normal anatomical location to levels previously obtained, thereby permitting substantially unimpeded angular motion despite the posterior presence of a stabilization device.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Artificial Spinal Disc
An artificial disc prosthesis is provided. The prosthesis of the present invention enables spinal segment alignment by having a variable height across its surface. The variable height is achieved by an asymmetric artificial nucleus or by at least one variable height end plate.
Owner:SYNERGY SPINE SOLUTIONS INC
Surgical tether apparatus and methods of use
ActiveUS20100234894A1Reduce loadReduce wearInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSurgical department
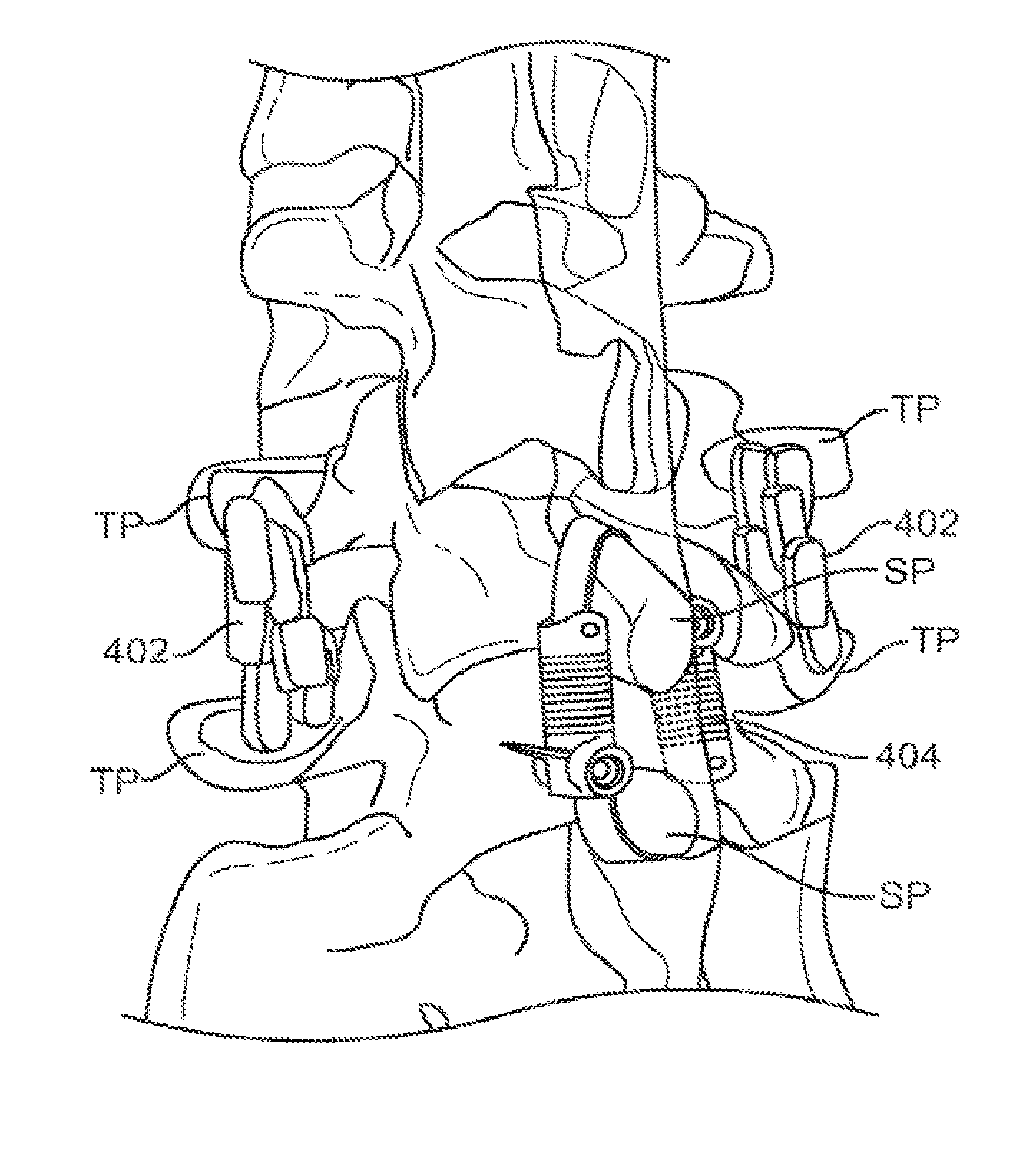
Methods and apparatus for controlling flexion in a spinal segment of a patient include performing a spinal fusion procedure on a pair of adjacent vertebrae in the spinal segment and implanting a constraint device into the patient. Adjusting length or tension in the constraint device allows the constraint device to provide a force a force resistant to flexion of the spinal segment undergoing fusion. The constraint device also modulates loads borne by the spinal segment undergoing fusion or tissue adjacent thereto.
Owner:SIMPIRICA SPINE
Surgical tether apparatus and methods of use
ActiveUS8529606B2Reduced load and wearModulating loadingInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSurgical department
Owner:SIMPIRICA SPINE
System and method for lumbar arthroplasty
InactiveUS20070288094A1Add supportLimit range of motionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRange of motionIntervertebral disc
The present invention provides a system and method for lumbar arthroplasty in a spinal segment having first and second vertebral bodies, where a intervertebral disc prosthesis may be provided and positioned between the first and second vertebral bodies such that a center of rotation of movement of the vertebral bodies about the prosthesis is located substantially proximate to the upper endplate of the second vertebral body and substantially proximate to the posterior one-third portion of the second vertebral body. In addition, a stabilization element may be affixed to the first and second vertebral bodies such that a range of motion of the stabilization device defines a center of rotation substantially proximate to that of the intervertebral disc prosthesis.
Owner:SPINADYNE
Expandable spinal sheath and method of use
ActiveUS20100145267A1Reduce wall thicknessLittle and spring propertyBalloon catheterInternal osteosythesisPlastic surgeryStructural element
Disclosed is an expandable percutaneous sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration by a removable tubular restraint or by structural elements built into the wall of the expandable portion of the sheath. In one application, the sheath is utilized to introduce a formed in place orthopedic fixation rod such as for use in spinal fixation procedures, preparation of a spinal segment, or placement of a vertebral body spacer. The sheath can further comprise structural elements to permit re-collapse of the sheath under fluid pressure following completion of the procedure and prior to removal from the patient.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Expandable spinal sheath and method of use
ActiveUS7951110B2Easy to insertEasy to installBalloon catheterInternal osteosythesisPlastic surgeryStructural element
Disclosed is an expandable percutaneous sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration by a removable tubular restraint or by structural elements built into the wall of the expandable portion of the sheath. In one application, the sheath is utilized to introduce a formed in place orthopedic fixation rod such as for use in spinal fixation procedures, preparation of a spinal segment, or placement of a vertebral body spacer. The sheath can further comprise structural elements to permit re-collapse of the sheath under fluid pressure following completion of the procedure and prior to removal from the patient.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Expandable, angularly adjustable intervertebral cages
ActiveUS20170367843A1Easy to insertStabilize spineJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceReduced size
The embodiments provide various interbody fusion spacers, or cages, for insertion between adjacent vertebrae. These intervertebral cages can restore and maintain intervertebral height of the spinal segment to be treated, and stabilize the spine by restoring sagittal balance and alignment. The cages may have a first, insertion configuration characterized by a reduced size at each of their insertion ends to facilitate insertion through a narrow access passage and into the intervertebral space. The cages may be expanded to a second, expanded size once implanted. In their second configuration, the cages are able to maintain the proper disc height and stabilize the spine by restoring sagittal balance and alignment. The intervertebral cages are configured to be able to adjust the angle of lordosis, and can accommodate larger lodortic angles in their second, expanded configuration. Further, these cages may promote fusion to further enhance spine stability by immobilizing the adjacent vertebral bodies.
Owner:EIT EMERGING IMPLANT TECH GMBH
Selectively expanding spine cage, hydraulically controllable in three dimensions for vertebral body replacement
ActiveUS8480741B2Deterioration of over timeStrong implantInternal osteosythesisBone implantDistractionSpinal locomotion
A selectively expanding spine cage has a minimized diameter in its unexpanded state that is smaller than the diameter of the neuroforamen through which it passes in the distracted spine. The cage conformably engages between the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae to effectively distract the anterior disc space, stabilize the motion segments and eliminate pathologic spine motion. The cage enhances spinal arthrodesis by creating a rigid spine segment. Expanding selectively, the cage height increases and holds the vertebrae with fixation forces greater than adjacent bone and soft tissue failure forces in natural lordosis. Stability is thus achieved immediately, enabling patient function by eliminating painful motion. Greater distraction height is achieved without an increase in implant size through the use of interfitted stages.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Apparatus and method for direct vertebral rotation
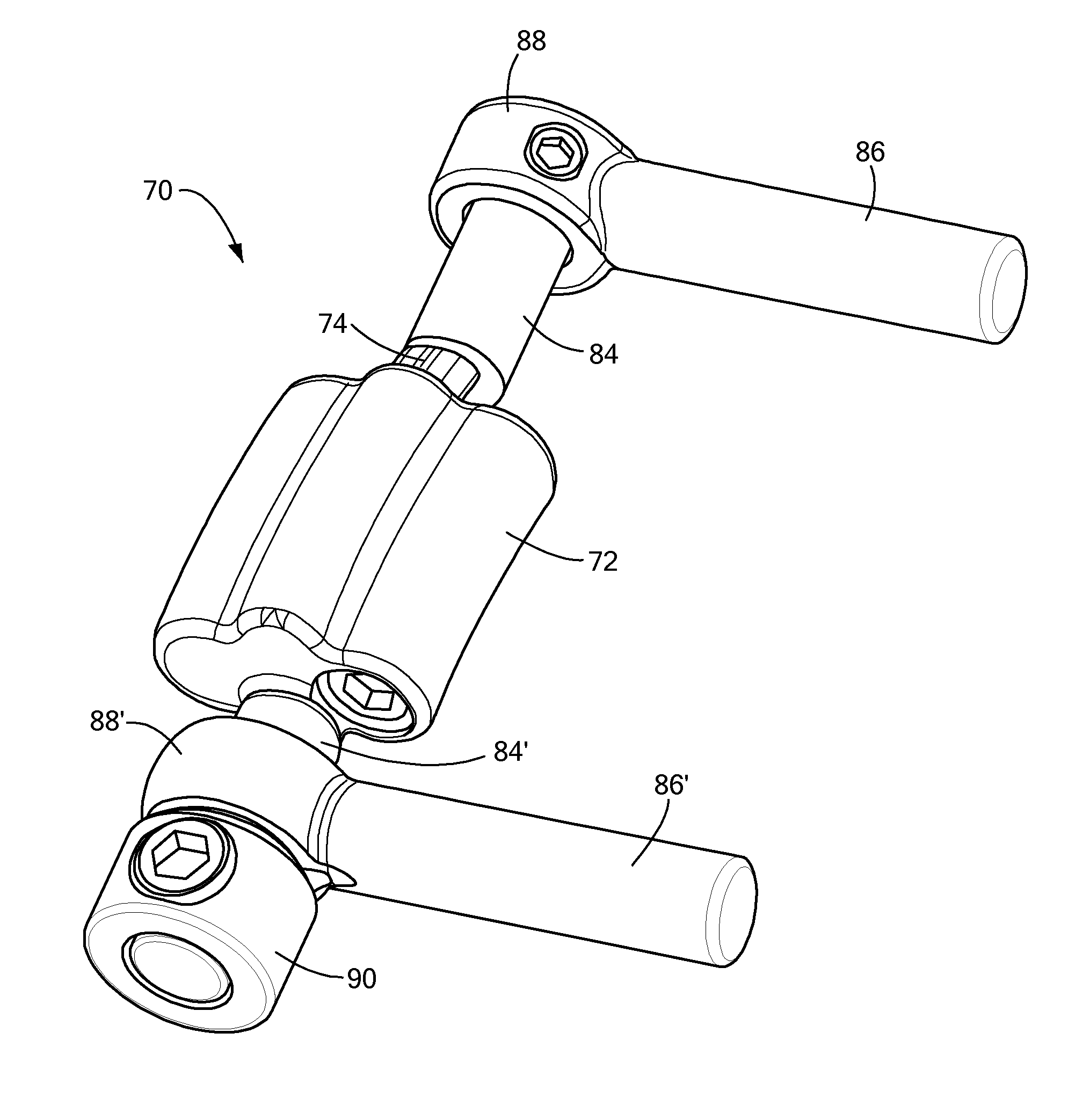
ActiveUS20080294206A1Easy to holdSmooth rotationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringPedicle screw
An instrument for spinal rotation that aligns and holds direct vertebral rotation (DVR) lever arms relative to each other to achieve an initial axial alignment of a segment of vertebrae and allows the final DVR rotation by rotating the instrument and lever arms together. A method of direct vertebral rotation that allows rotating the vertebrae to be aligned relative to each other, and collectively rotating the vertebrae to be aligned relative to adjacent spinal segments by rotating the direct vertebral rotation instrument. A system for direct vertebral rotation having at least two pedicle screws. The system also includes at least two levers attachable to the pedicle screws and a clamping instrument configured to clamp the levers.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Surgical method and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis and stabilization of vertebrae
InactiveUS20100121381A1Distracting and stabilizingRelieve painInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSpinal stenosis
Disclosed is a prosthetic device for distracting spinal column segments in the lumbar and the lumbar-sacral regions comprising a first engagement arm, a second engagement arm, a coupling mechanism and a locking mechanism. The first and the second engagement arms are configured to receive a lamina portion of the spinal column segment. The coupling mechanism is disposed between the first and the second engagement arms and is configured to allow the device to transition from an unextended configuration to an extended configuration in order to distract the spinal column segment. The locking mechanism is configured to maintain the extended configuration of the device.
Owner:SPRINGBACK
Surgical tether apparatus and methods of use
InactiveUS20140039558A1Reduced load and wearModulating loadingInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSurgical department
Methods and apparatus for controlling flexion in a spinal segment of a patient include performing a spinal fusion procedure on a pair of adjacent vertebrae in the spinal segment and implanting a constraint device into the patient. Adjusting length or tension in the constraint device allows the constraint device to provide a force a force resistant to flexion of the spinal segment undergoing fusion. The constraint device also modulates loads borne by the spinal segment undergoing fusion or tissue adjacent thereto.
Owner:SIMPIRICA SPINE
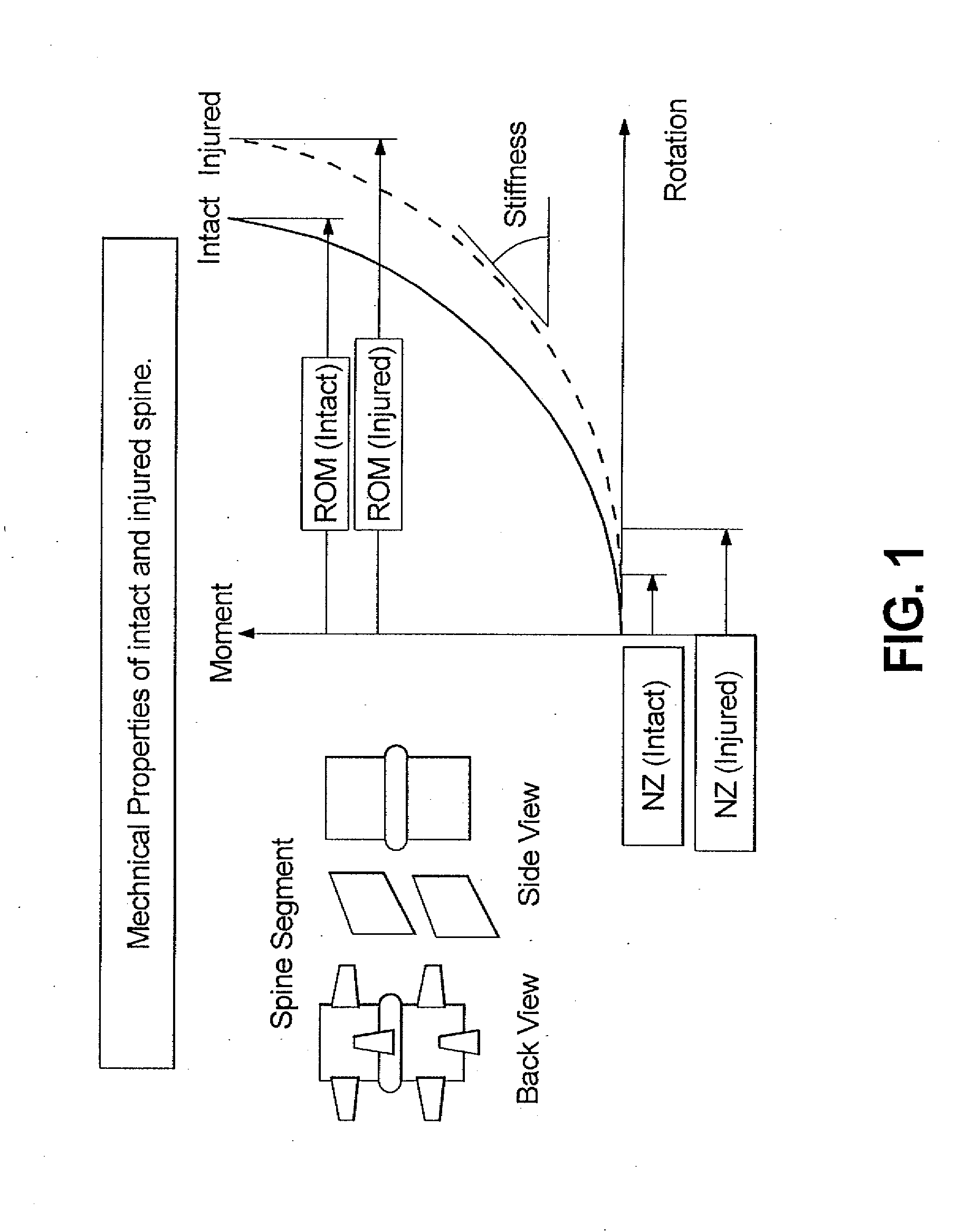
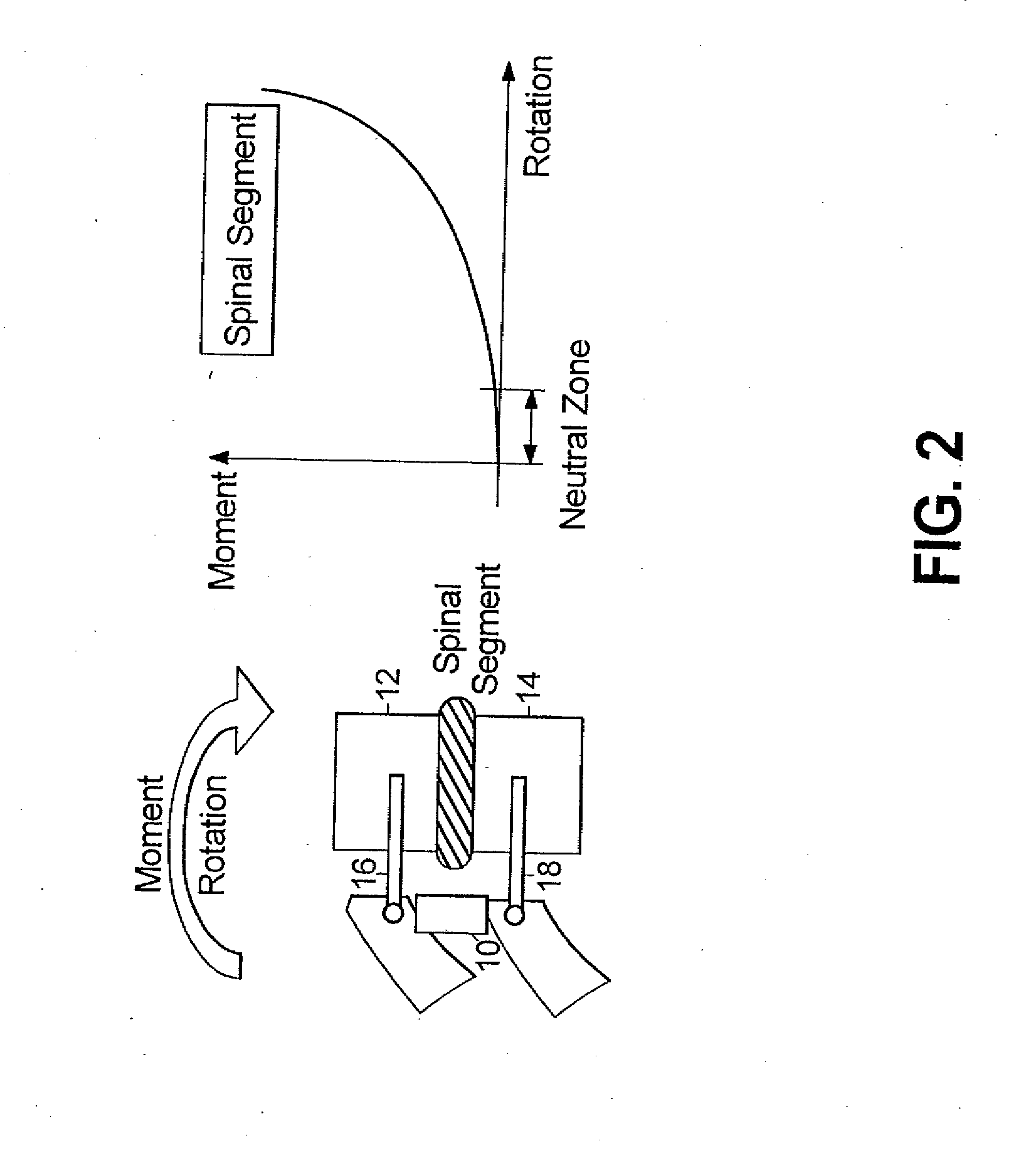
Method for stabilizing a spinal segment
ActiveUS20120253404A1The result is validEase of installation and in applicationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsAnatomical structuresSpinal column
A surgical implant is provided that includes first and second abutment surfaces between which are positioned a force imparting mechanism. A sheath is positioned between the first and second abutment surfaces, and surrounds the force imparting mechanism. The sheath is fabricated from a material that accommodates relative movement of the abutment members, while exhibiting substantially inert behavior relative to surrounding anatomical structures. The sheath is generally fabricated from expanded polytetrafluoroethylene, ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene, a copolymer of polycarbonate and a urethane, or a blend of a polycarbonate and a urethane. The force imparting member may include one or more springs, e.g., a pair of nested springs. The surgical implant may be a dynamic spine stabilizing member that is advantageously incorporated into a spine stabilization system to offer clinically efficacious results.
Owner:RACHIOTEK
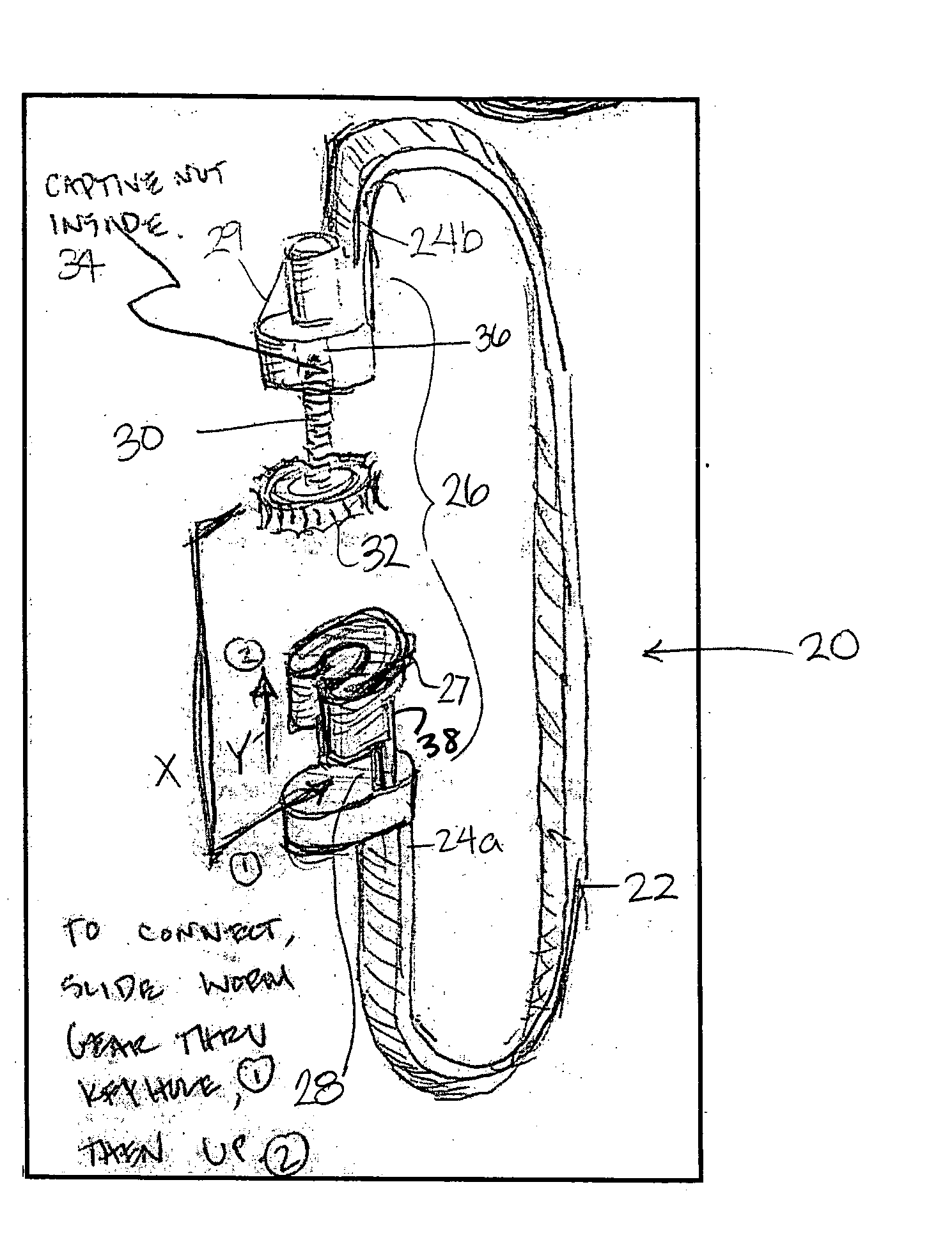
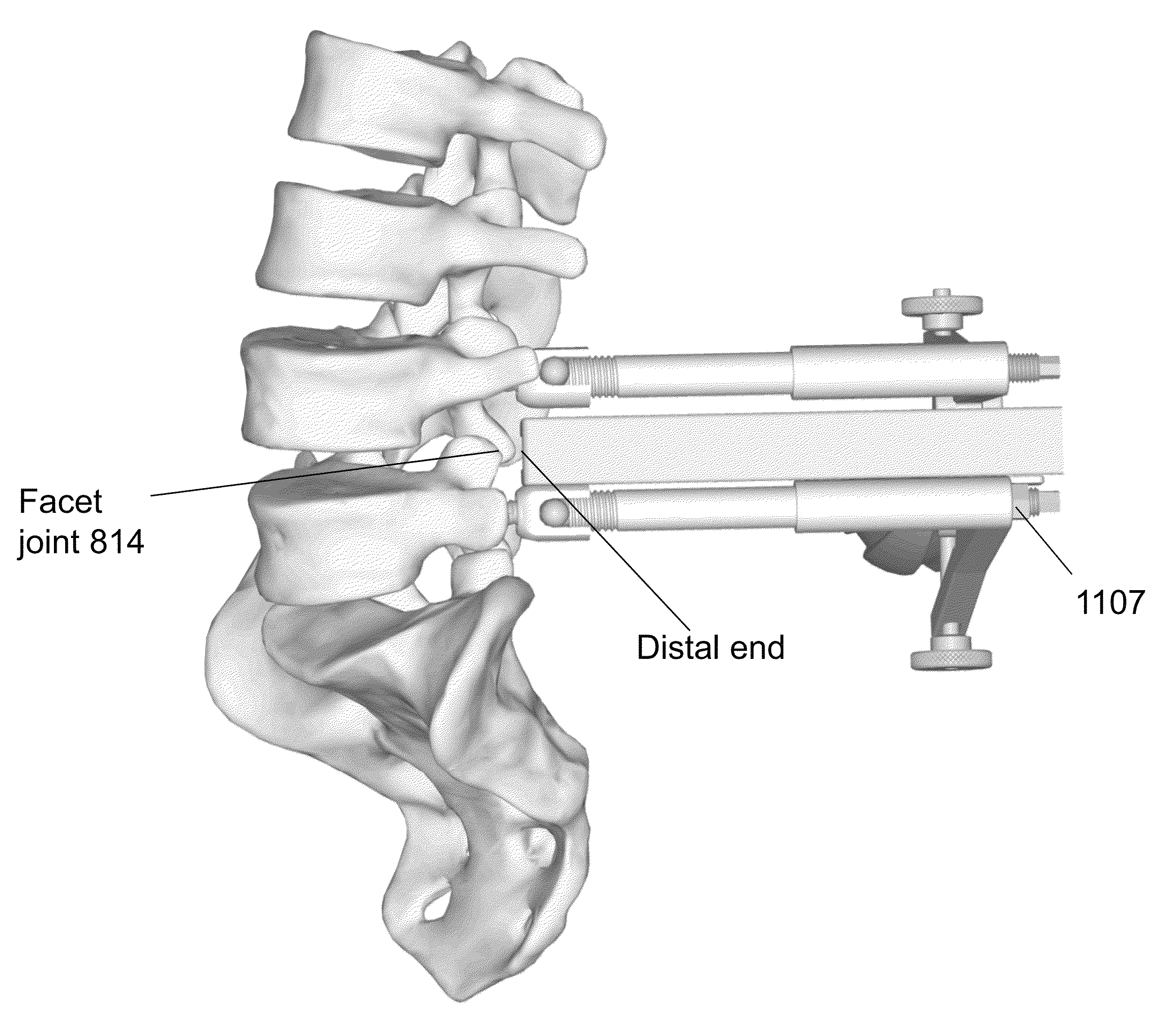
Devices and methods for minimally invasive spinal stablization and instrumentation
Described herein are devices and methods for fusion of adjacent vertebral bones using distractor platforms for exposure and resection of at least a portion of the facet joint, such as in performance of a TLiF procedure. In one embodiment, the distractor platform contains at least a first receptacle and / or extension adapted to couple to the implanted screw / bone marker and the method includes advancing a threaded segment of a bone fastener assembly into the identified first pedicle of the first vertebral bone, the first bone fastener assembly further comprises a second segment adapted to couple with a distraction platform adapted to concurrently attach onto at least one tissue retention blade and adapted to retain the tissue retention blade in the displaced position. Stabilization of a spinal segment is also provided by advancing a substantially concave orthopedic implant through an opening made in a posterior aspect of a disc space.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
Methods and devices for restricting flexion and extension of a spinal segment
InactiveUS20120109200A1Minimize risk of damageIncrease flexibilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSacrumPhysical therapy
Methods and devices for restricting movement of a spinal segment by providing an adjustable constraining device that includes a tether and a compliance member coupled together. The tether is coupled to a superior spinous process and an inferior spinous process or a sacrum so that the construct of the compliance member and tethers provides a force resistant to flexion and a force resistant to extension of a spinal segment. In some embodiments, the construct of the compliance member and tethers may provide only a force resistant to extension.
Owner:SIMPIRICA SPINE
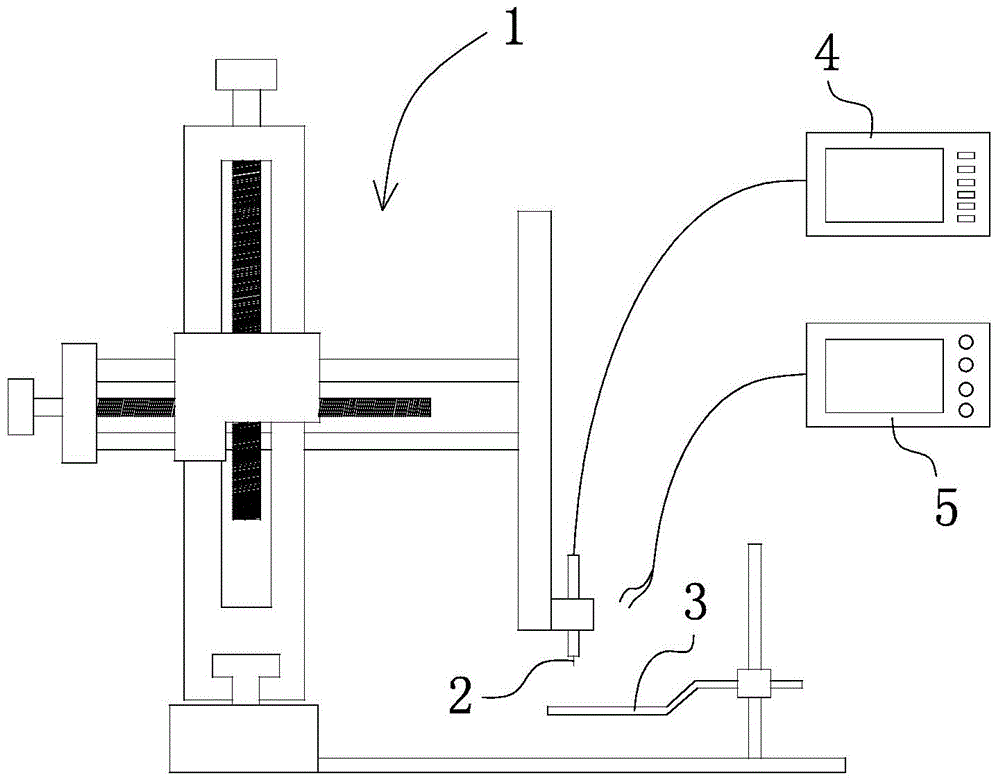
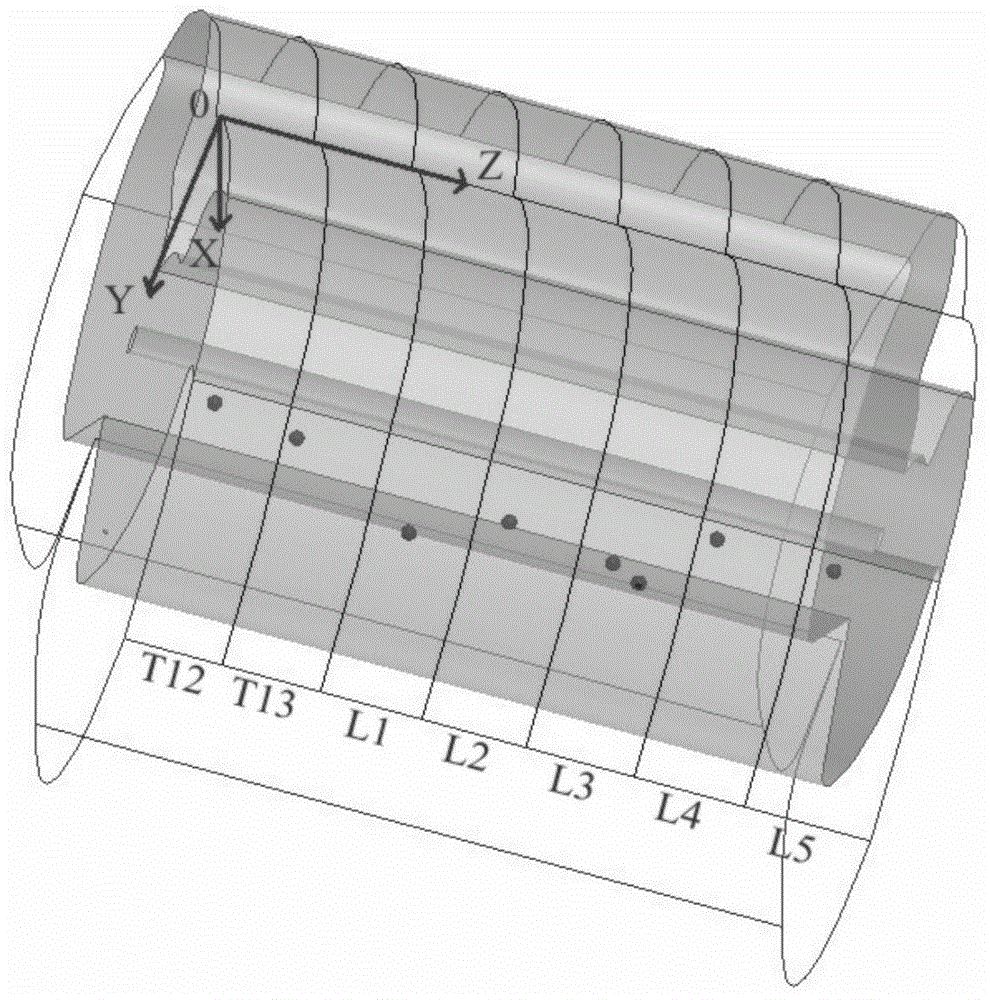
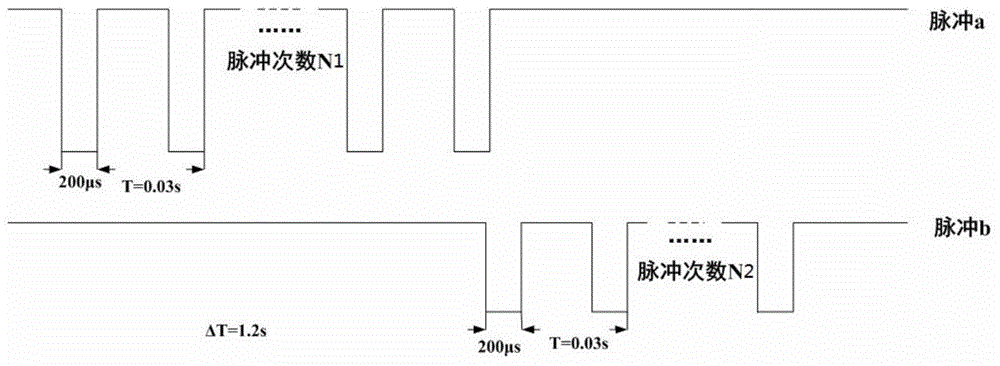
Rat leg motion reconstruction test method based on spinal nerve function electrical stimulation
InactiveCN104306066AUnderstanding the Process of Electrical ActuationAchieve stretching and coherent movementSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricitySpinal nerve
The invention relates to a rat leg motion reconstruction test method based on spinal nerve function electrical stimulation. Corresponded three-dimensional coordinates based on spinal segments are established while rat spinal cord is focused, a tester can find out an electrode implanting position rapidly and accurately, and the success rate of tests is increased; excitation pulses are transmitted to two electrodes inserted into the rat spinal cord alternately, coherent stretching motions of the rat leg can be implemented, and the tester can grasp the process of rat spinal cord electrical stimulation more directly; meanwhile, the electromyographic signals of rat leg muscles can be collected through an electromyographic monitor and are used for comparison and analysis. By the aid of test method, the rat leg stretching motion reconstruction based on the spinal nerve function electrical stimulation can be completed, and important significance is provided for the fields of scientific research and teach; the operating ability of the tester is improved, the tester can grasp complex spinal cord stimulation tests which are difficult to grasp more easily, and the further academic research of the tester can be benefited.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Posterior stabilizer
InactiveUS20110040331A1Improve stabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRange of motionIntervertebral space
A dynamic hybrid stabilization system having a plurality of affixation elements coupled to a spinal segment having at least two intervertebral spaces, each affixation element having a medially extending connector element. A plurality of dynamic stabilization devices having an adjustable range of motion and being spaced medially from the affixation elements is included, each dynamic stabilization device being coupled to at least one of the connector elements and including an attachment element spanning at least one intervertebral space, such that each dynamic stabilization device and the connector element when coupled together span at least two intervertebral spaces.
Owner:SPINADYNE
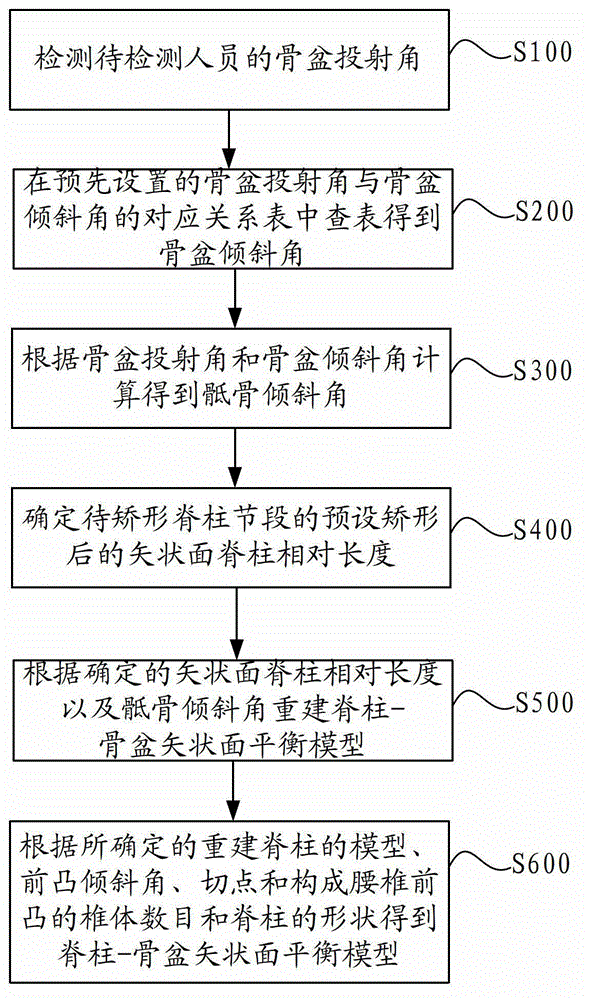
Vertebral column digital reconstruction method and system
InactiveCN102743158AEffective guidanceGood curative effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSacrumCurative effect
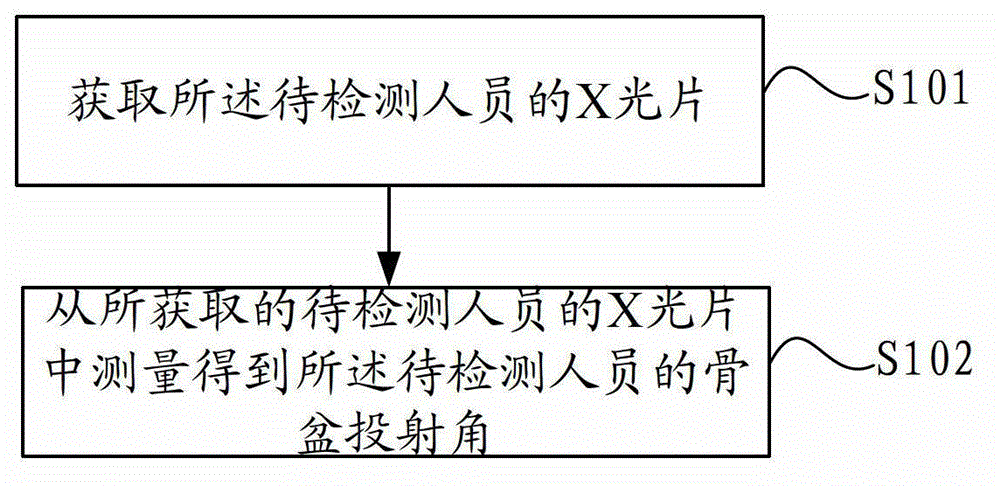
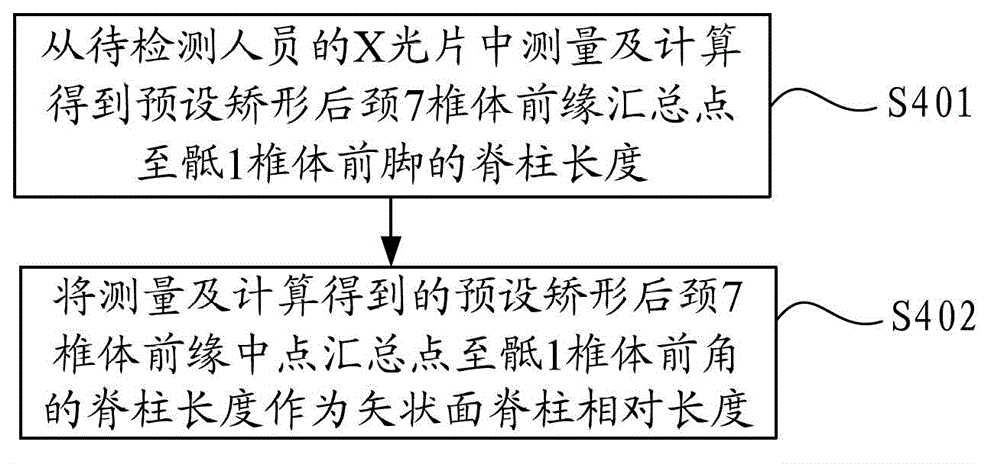
The invention discloses a vertebral column digital reconstruction method and a vertebral column digital reconstruction system. The method comprises the following steps of: detecting a pelvis projection angle of a person to be detected; checking in a preset table of the corresponding relationship between the pelvis projection angle and a pelvis inclination angle so as to obtain the pelvis inclination angle; calculating according to the pelvis projection angle and the pelvis inclination angle so as to obtain a sacrum inclination angle; determining the relative length of a sagittal plane vertebral column of an orthopedic vertebral column fragment after the preset orthopedic; and reconstructing a vertebral column-pelvis sagittal plane balance model according to the determined relative length of the sagittal plane vertebral column and the sacrum inclination angle. According to the method, on the basis of the pelvis projection angle of a patient, the balance of vertebral column-pelvis sagittal plane can be reconstructed through a series of calculation and drawing; and in comparison with the prior art, a stable vertebral column-pelvis sagittal plane can be reconstructed by the method, so that the vertebral column orthopedic operation can be instructed effectively, and the curative effect after the operation is improved.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com