Patents
Literature
158 results about "Intervertebral spaces" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
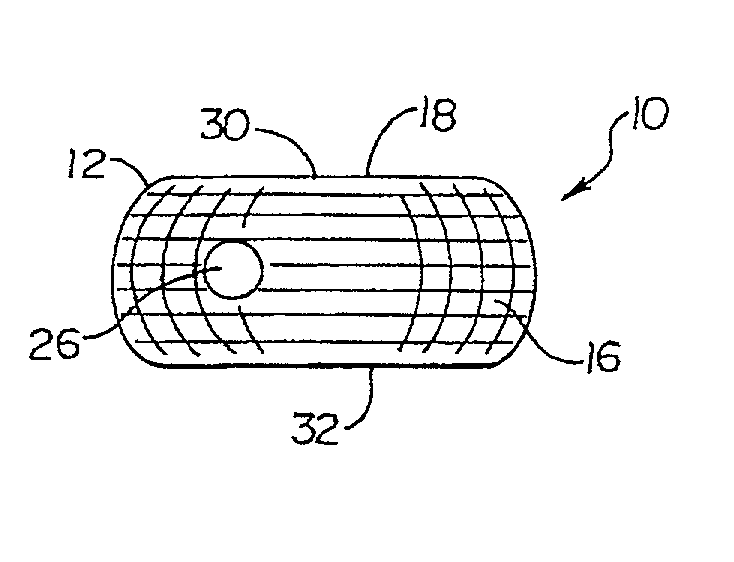
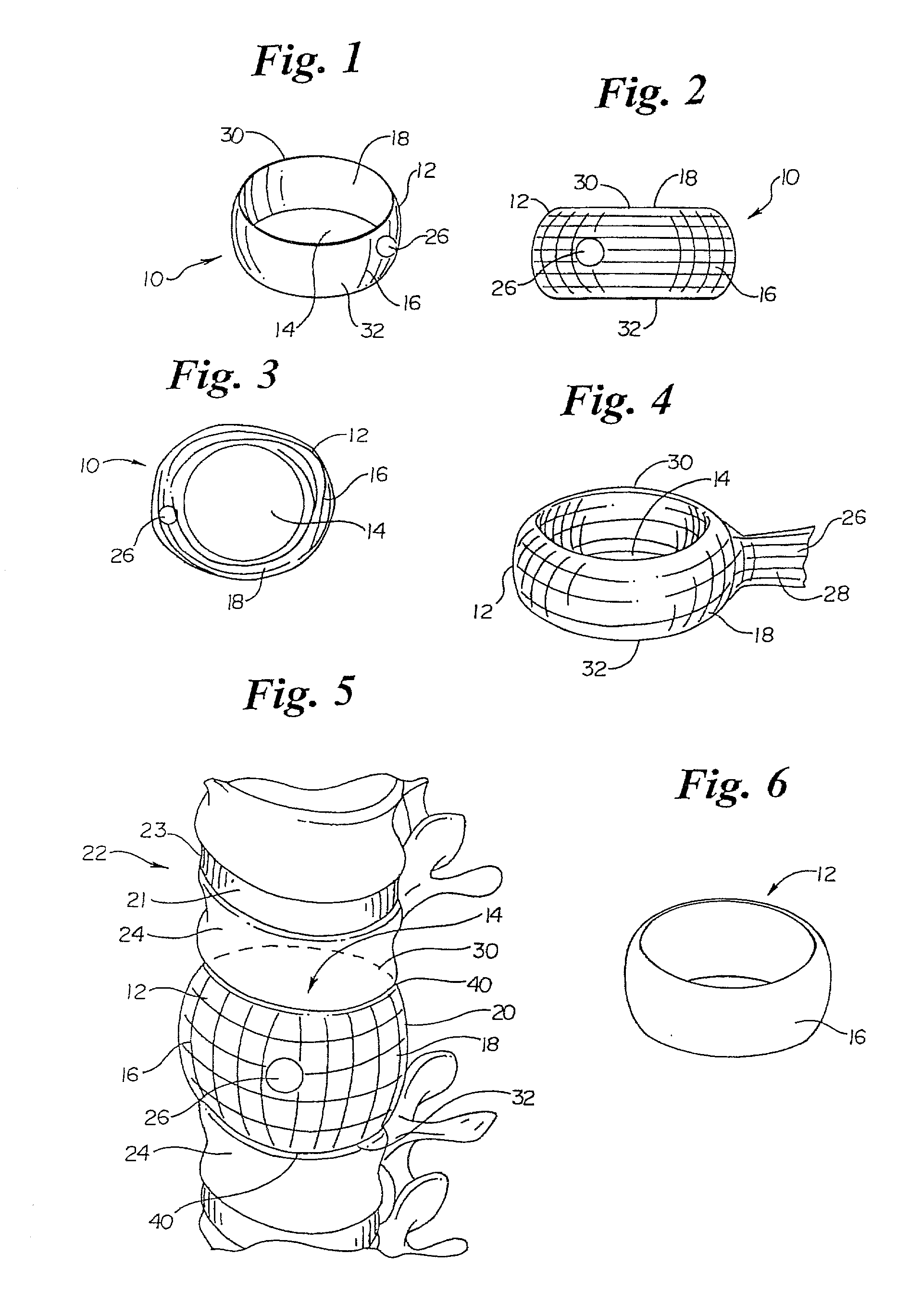
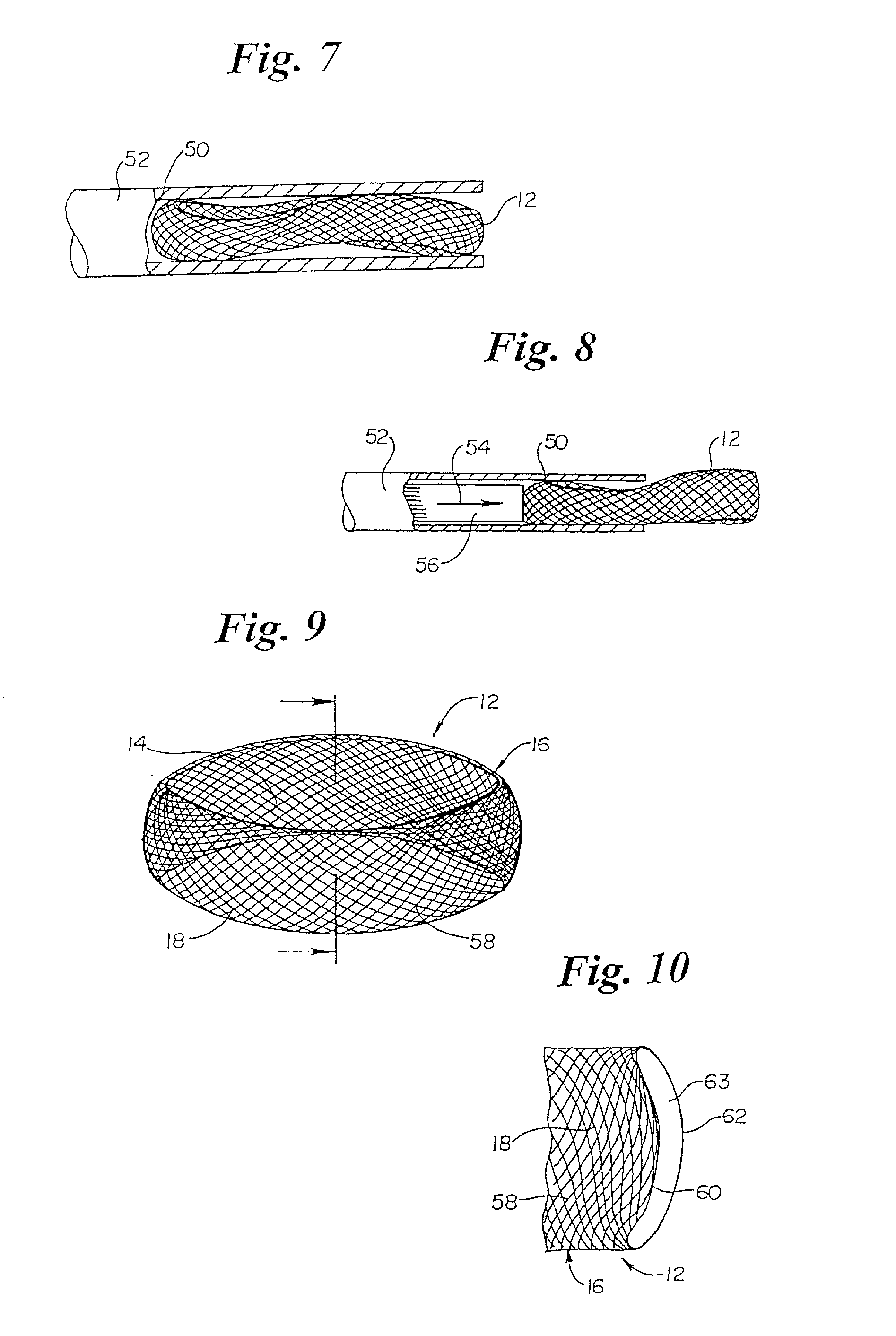
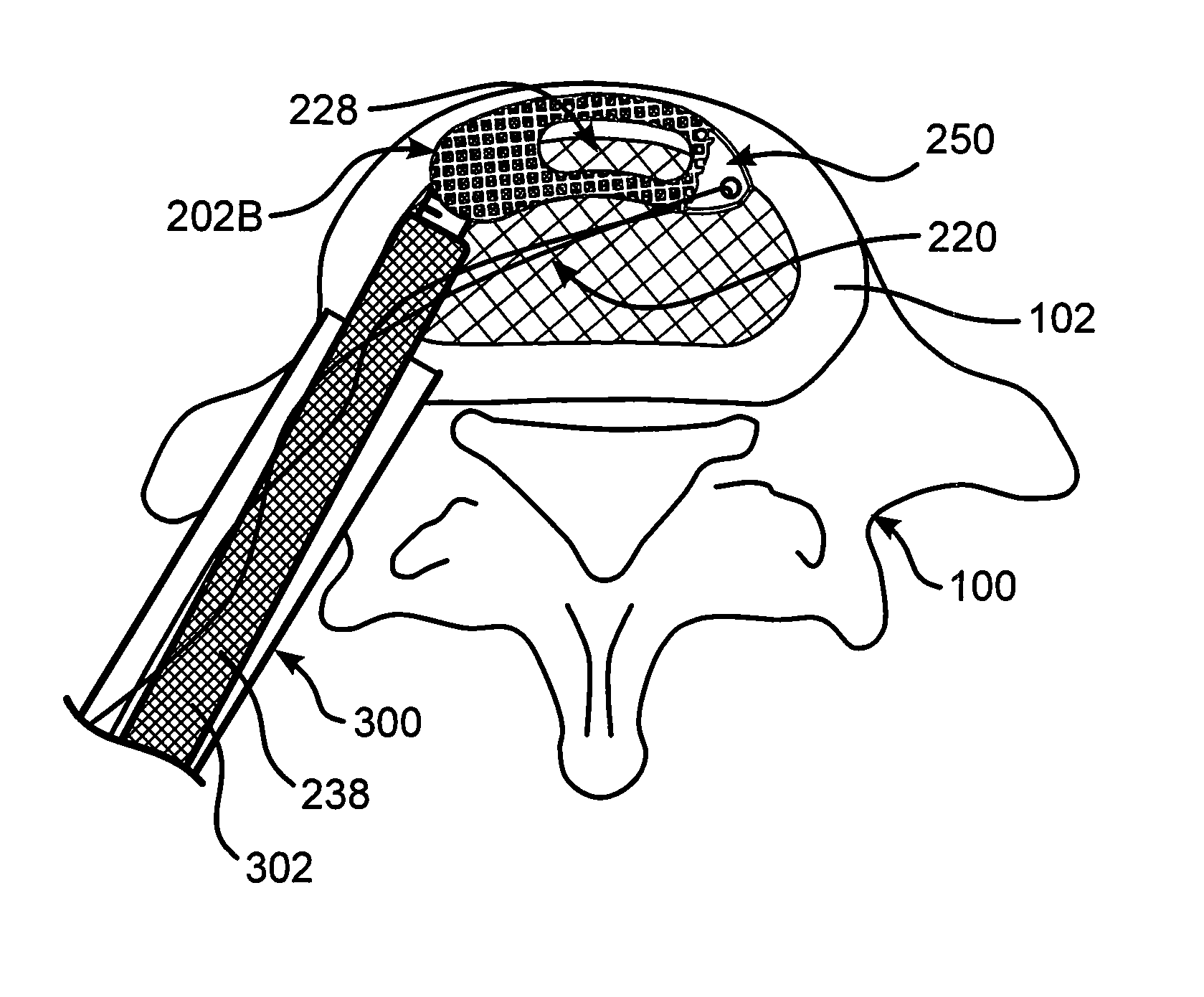
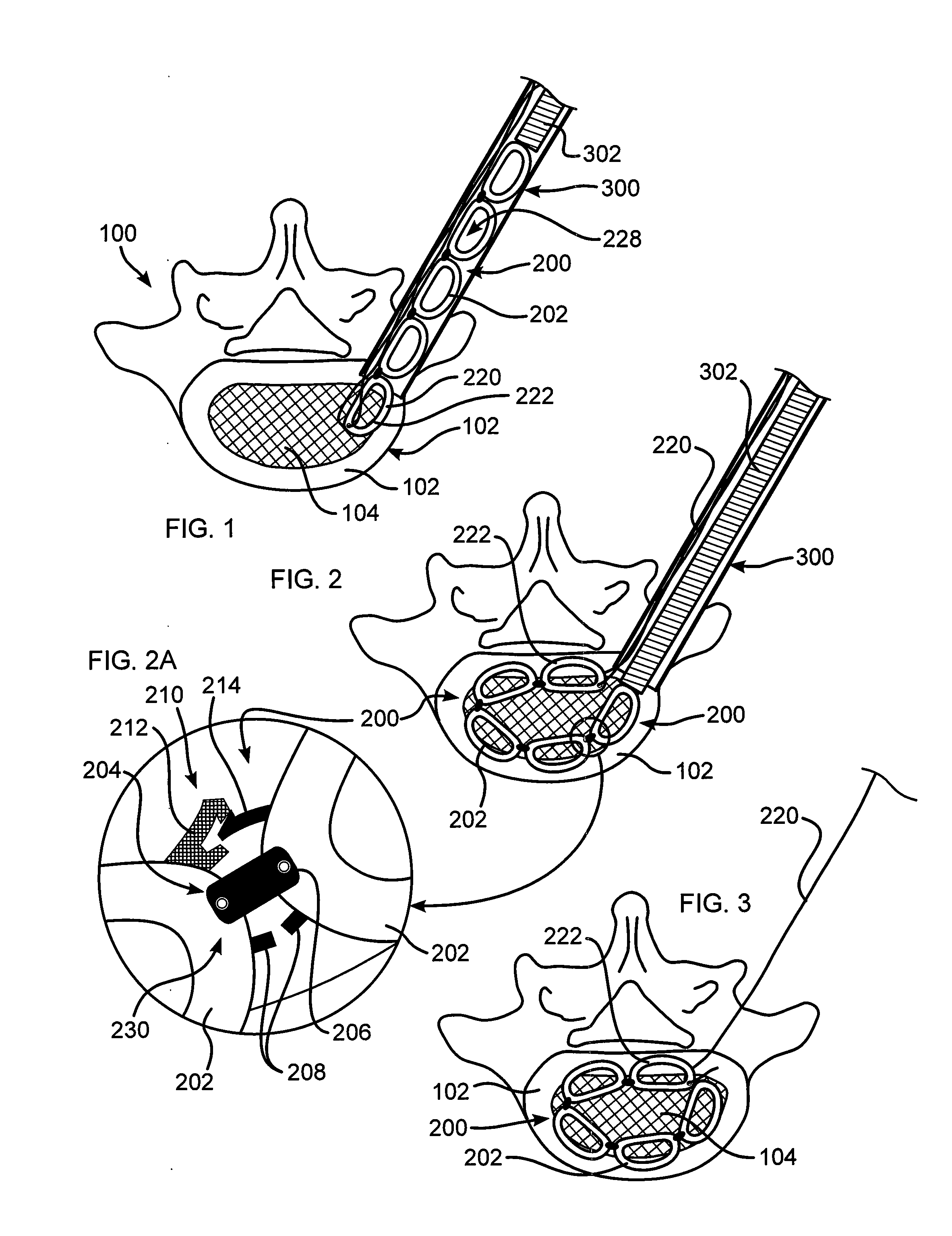
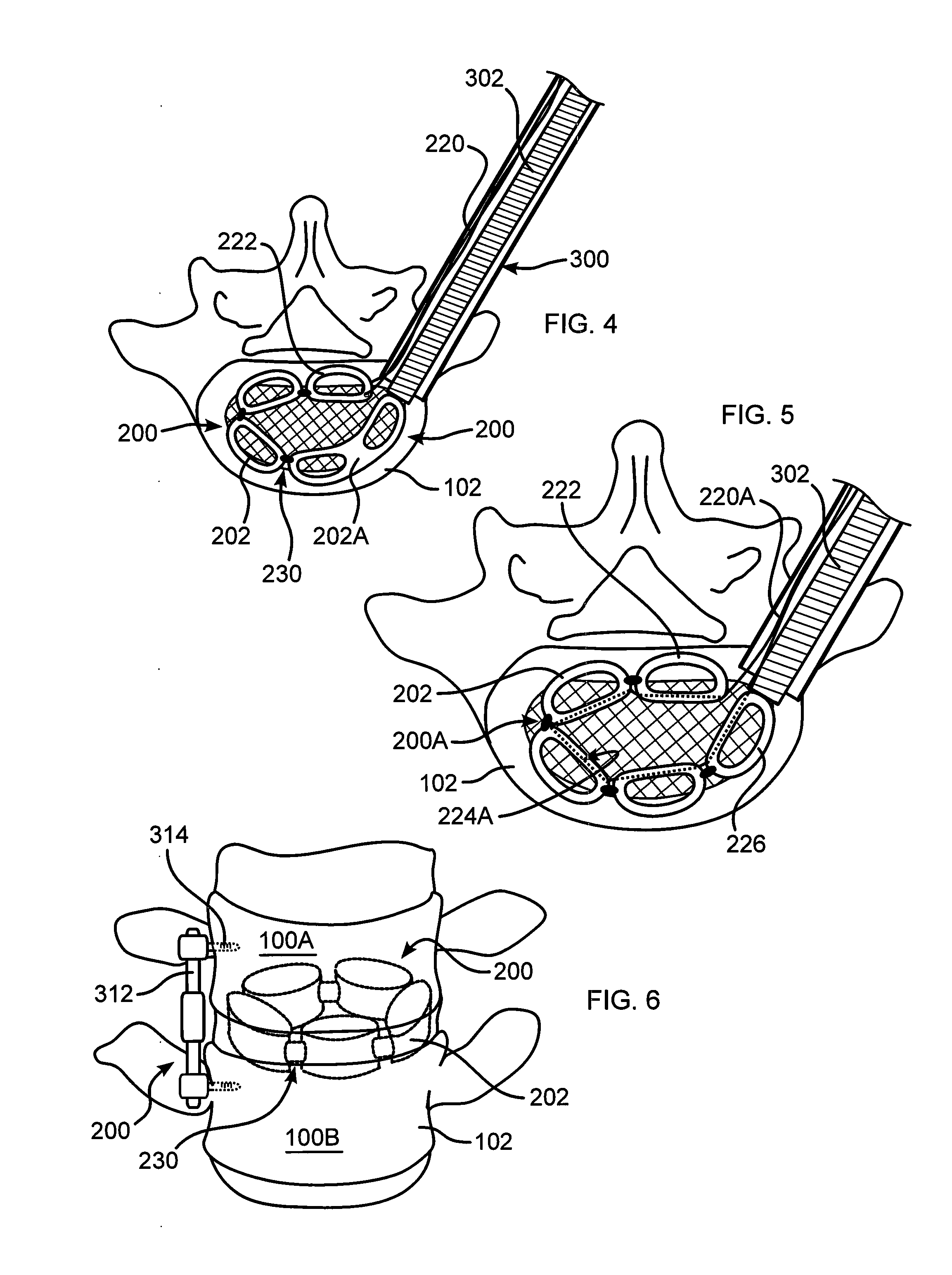
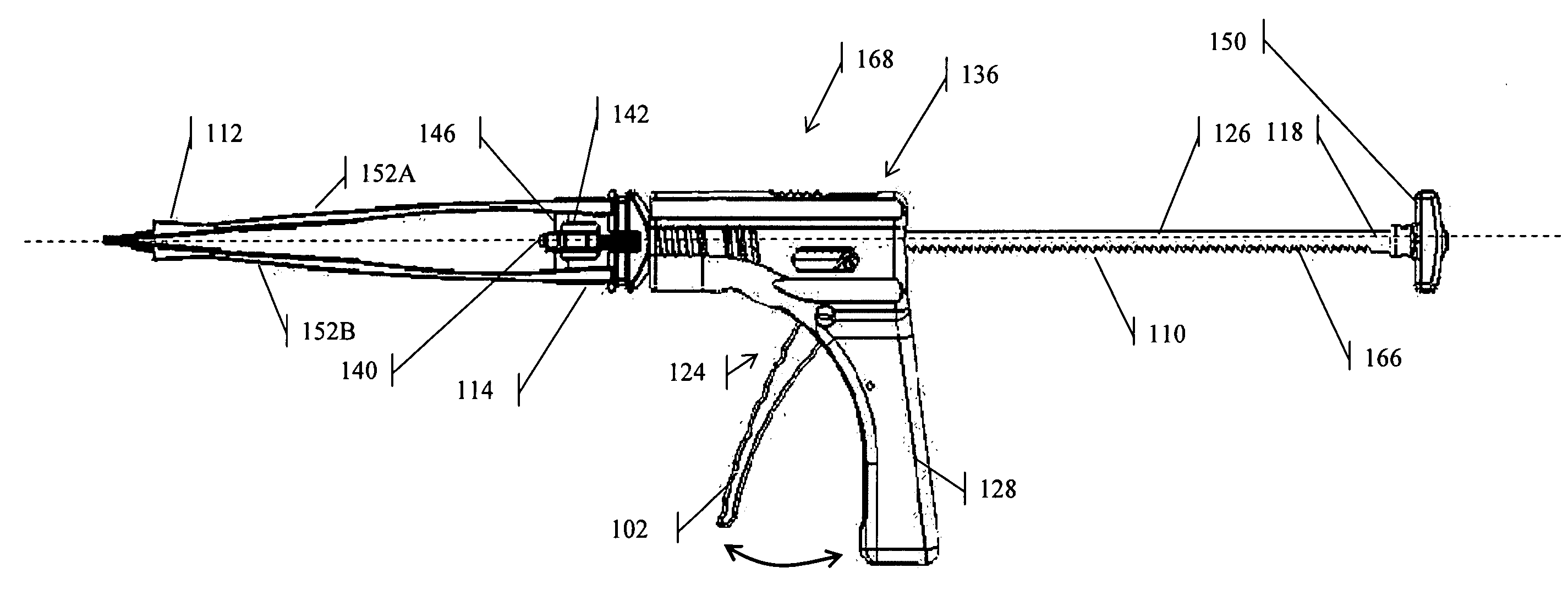
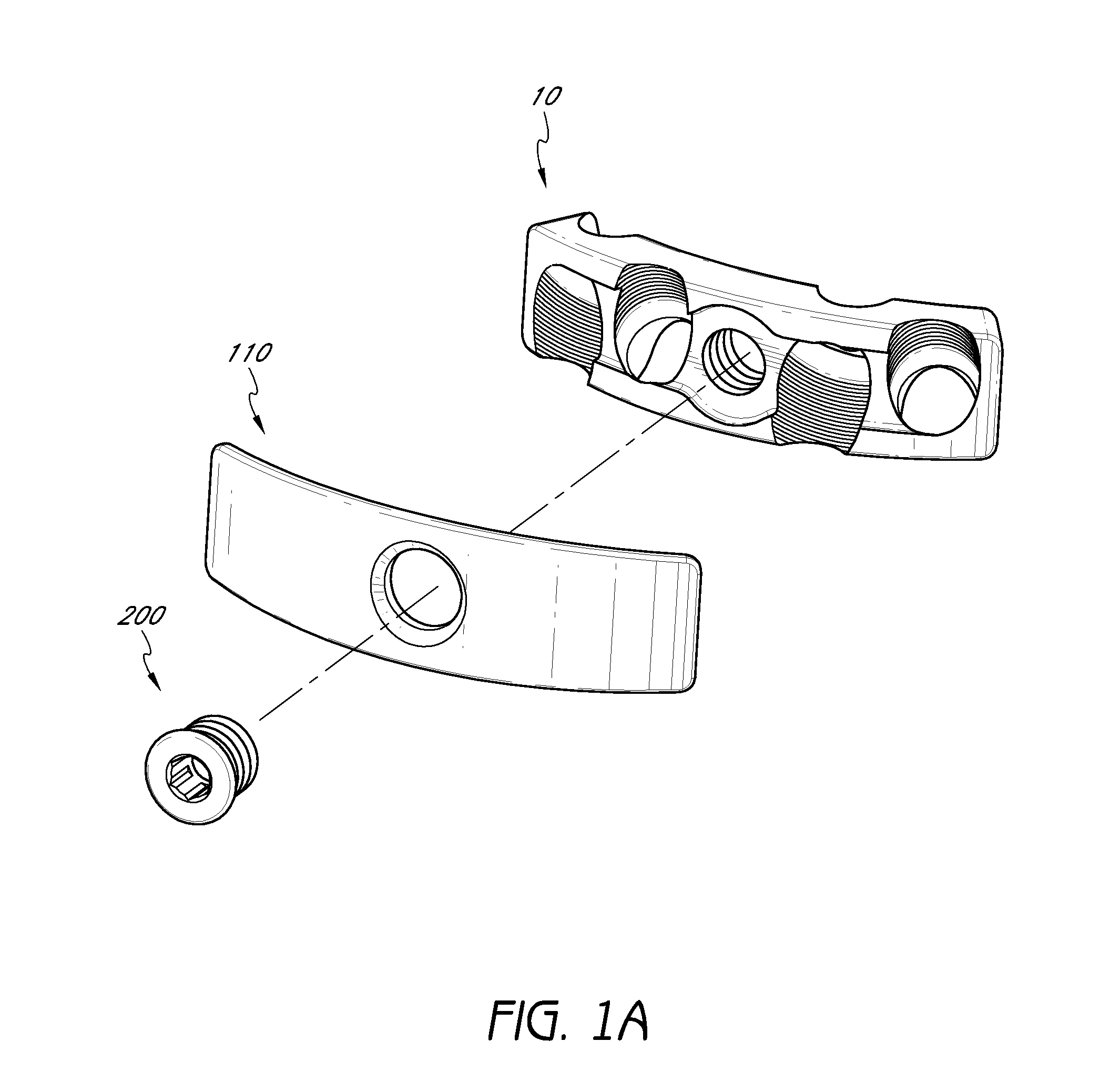
Annulus-reinforcing band
InactiveUS20020077701A1Easily and more effectivelySafely treat degenerative disc diseaseElectrotherapyInternal osteosythesisEngineeringBiomedical engineering
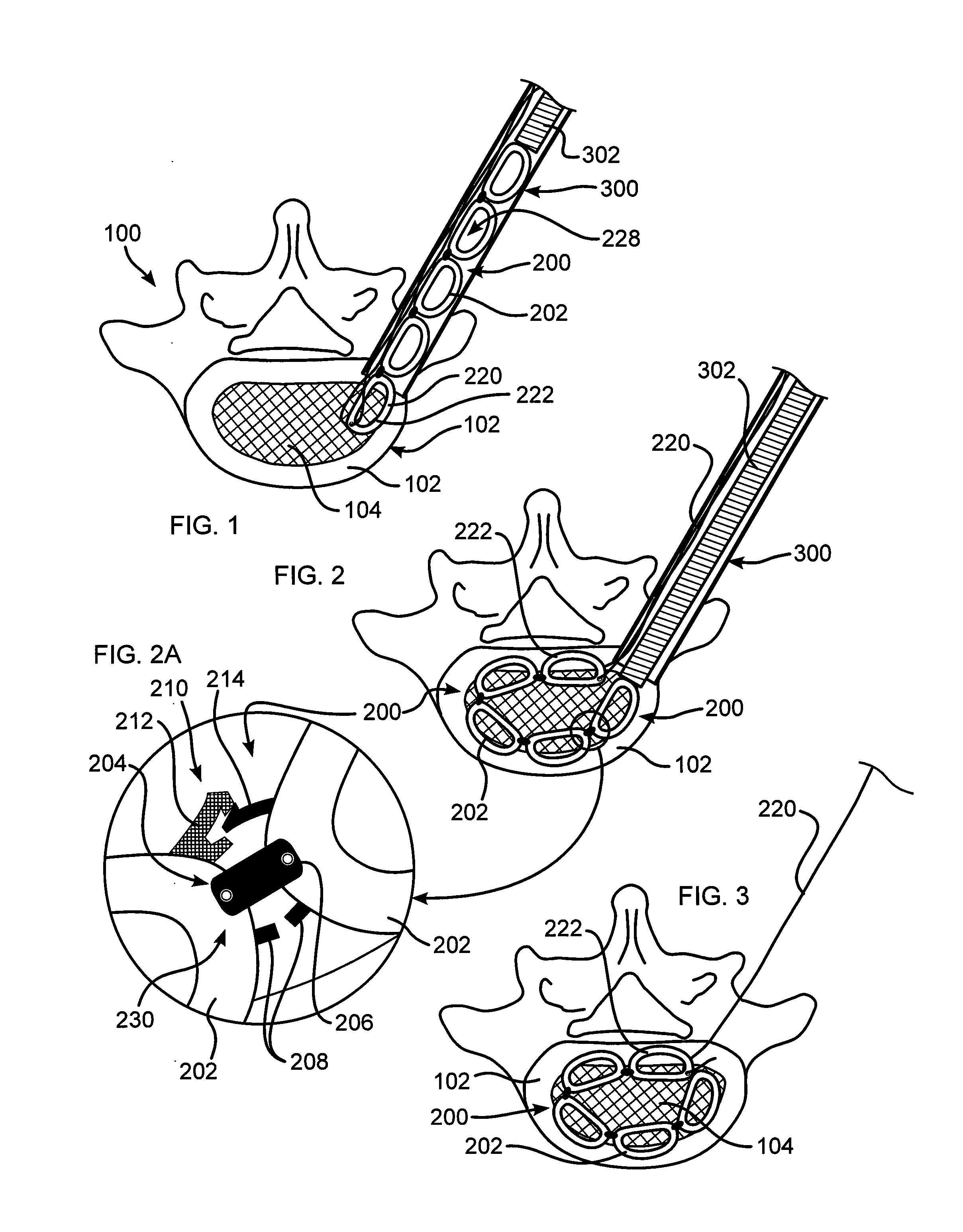
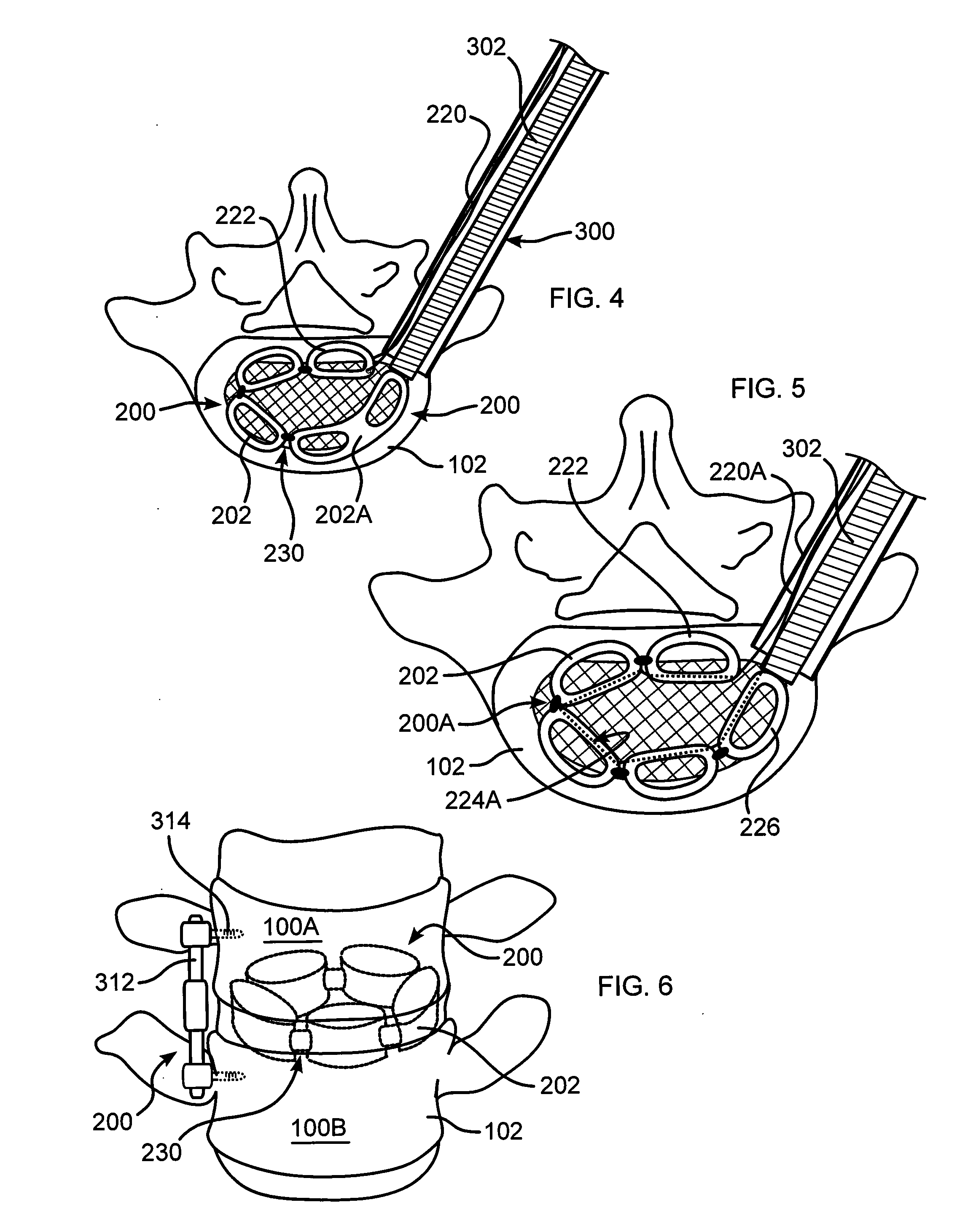
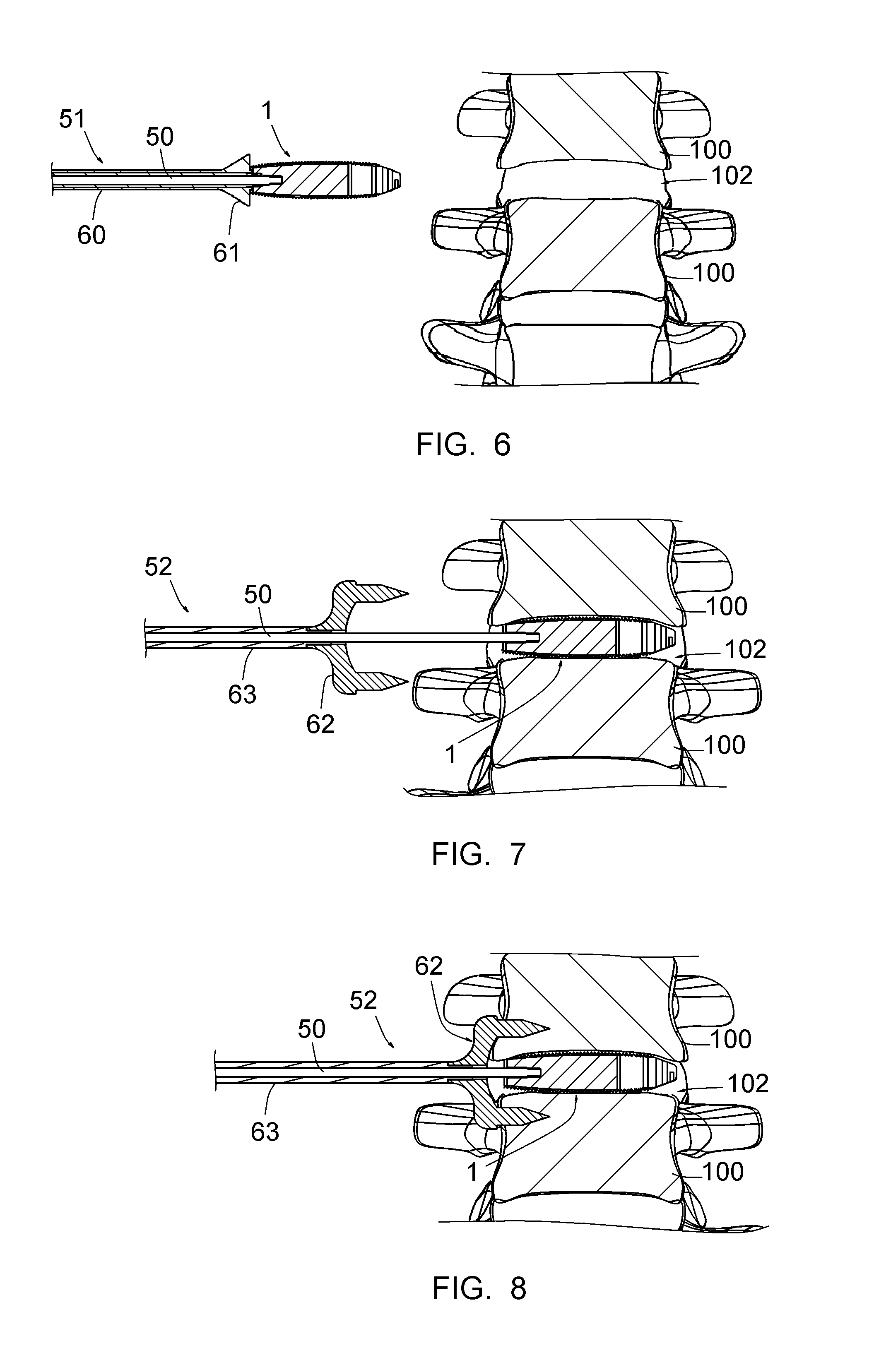
A pliable band or hoop that is flexible to normal handling, but cannot stretch circumferentially once it has reached the limits of its circumferential length. The band may have a structural portal to be used for filling, or it may simply be constructed of a fabric-like material that allows a fill tube to perforate its walls to allow for filling. In the latter case, the perforated wall tends to self-seal once the fill tube is withdrawn. The band may be flat or tubular in cross-section. However, unlike a balloon, the band does not require either a bottom or a top, as we found that a top and bottom are unnecessary when using a band or hoop to enclose material injected into a reamed out intervertebral space.
Owner:SPINEOLOGY
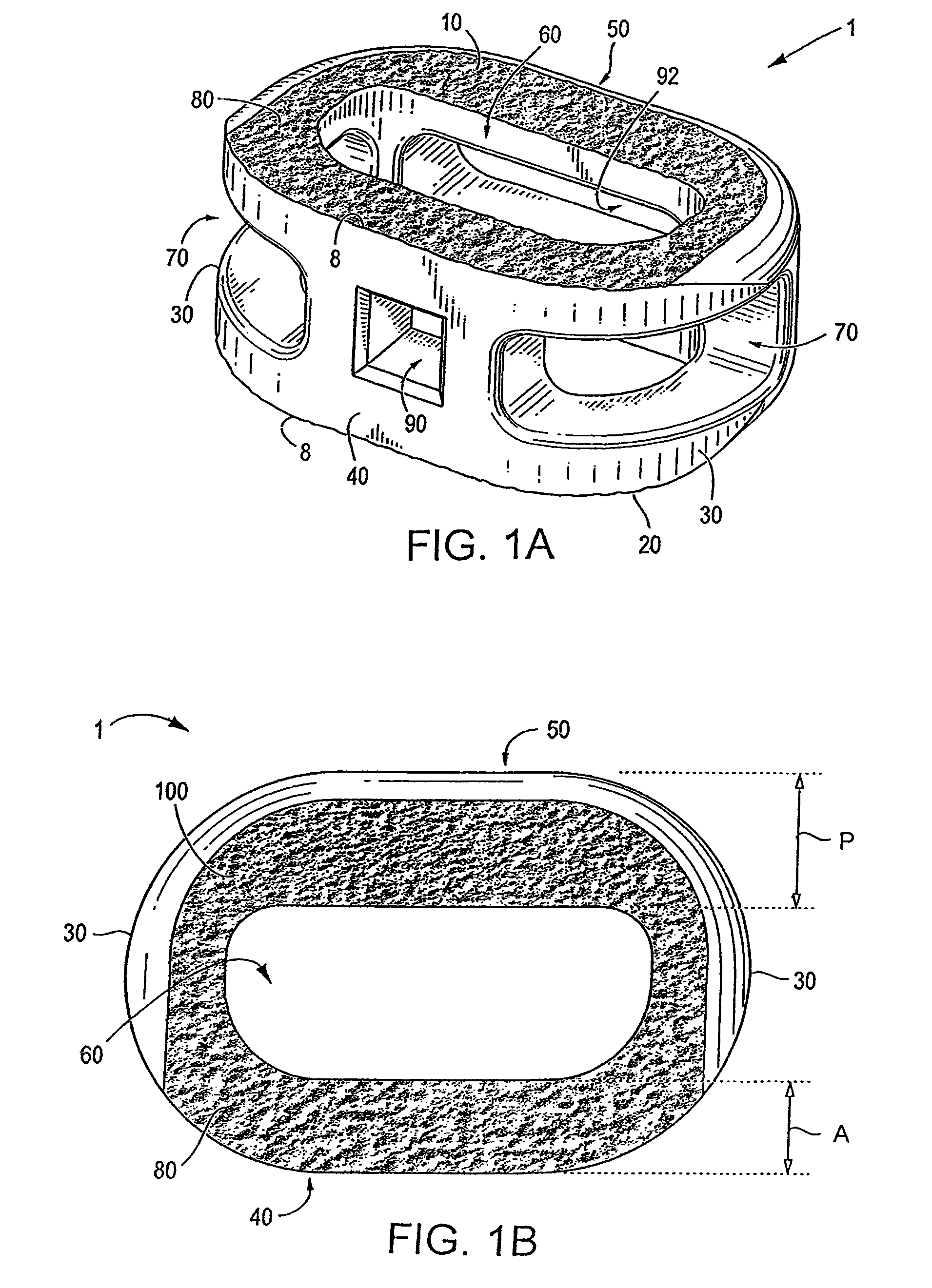
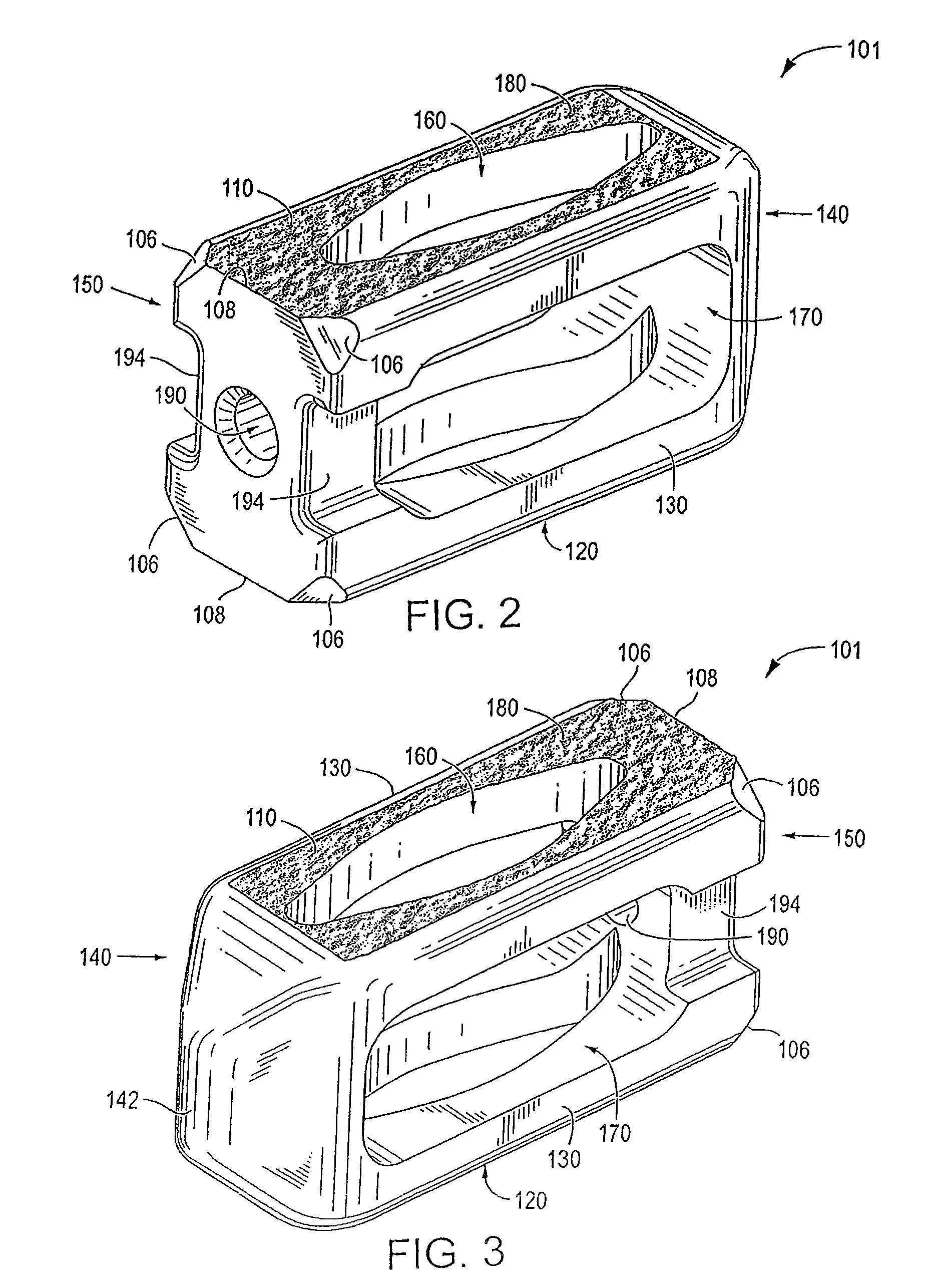
Intervertebral Implant
ActiveUS20140058513A1Different shapesLimited extentBone implantSpinal implantsIntervertebral spacesAngular orientation
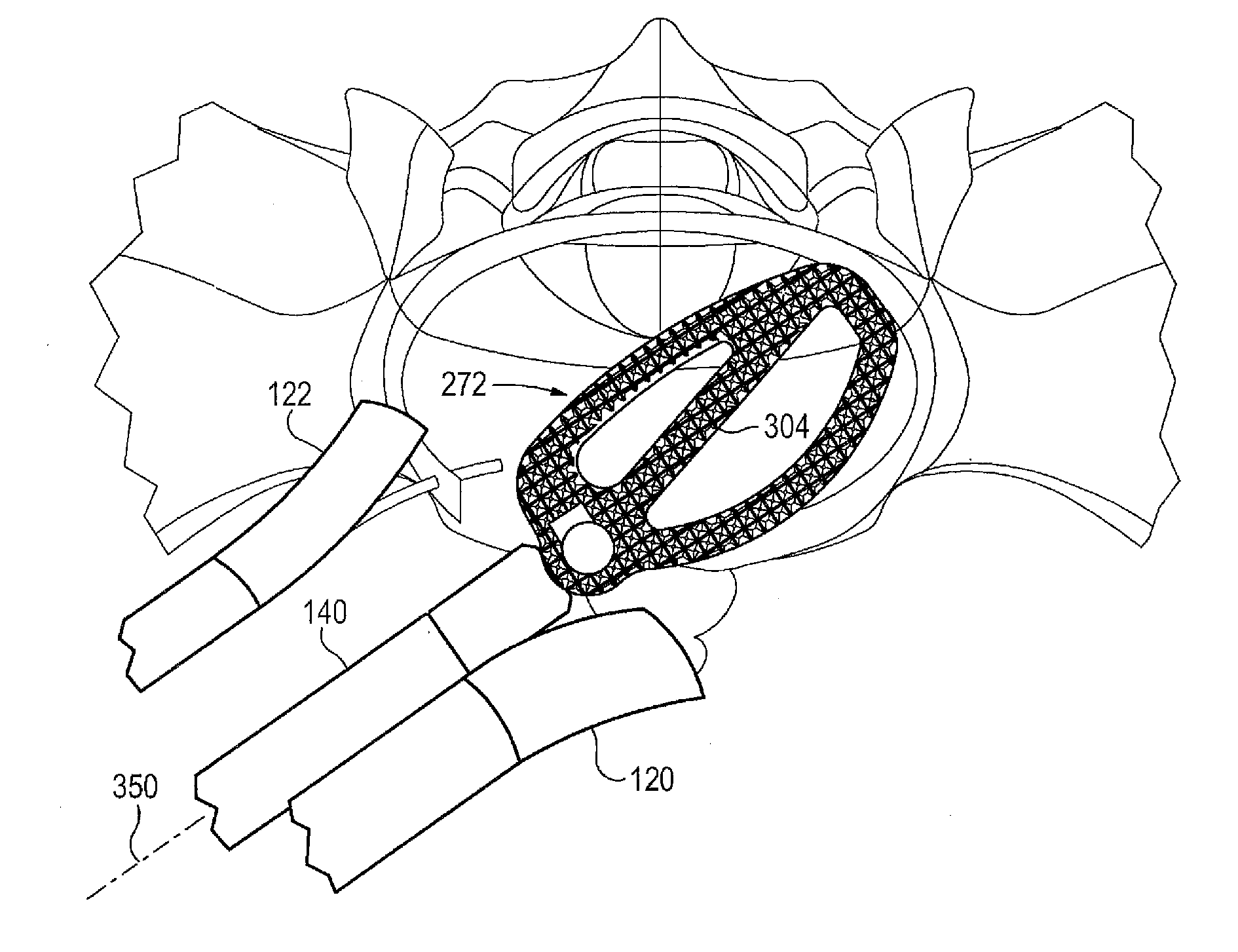
An intervertebral spacer for therapeutic treatment of a patient includes at least one link sized and dimensioned to fit within an intervertebral space in the patient, and is configured to maintain a separation of two adjacent vertebrae for a period of time. A rigid guiding object, which may be a tool or a successive link, is insertable into the patient, to guide other links into the patient using an MIS approach. A pivot is connected between successive links, or between a guide tool and a link, configured to limit a relative range of angular orientation between the link and the guiding tool, or successive links. Multiple links are so joined to form a chain pushable by the last link, and pullable by the first link, to form a chain which may be formed into a curved configuration corresponding to the patient's intervertebral space.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Adjustable distraction cage with linked locking mechanisms
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Deployable segmented tlif device
A segmented intervertebral body fusion support includes a plurality of segments, the segments including an initial segment, a final segment and at least one intermediate segment. The intermediate segment has a generally trapezoidal configuration and the initial and final segments include tapered side walls providing triangular gaps between adjacent segments. A draw wire is fixed to the first segment and passes through the remaining segments. By pulling the draw wire relative to the segments, the segments are drawn together in a generally arcuate configuration. The draw wire includes an enlargement that passes through the final segment and engages a plurality of fingers on the final segment, which prevents the draw wire from retracting, maintaining the arcuate configuration. The segmented device can be inserted through a laparoscopic device into the intervertebral space and can be subsequently drawn into the arcuate configuration to establish the desired intervertebral spacing.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Intervertebral Device Having Expandable Endplates
ActiveUS20080243251A1Small shapeIncrease the footprintJoint implantsSpinal implantsLamina terminalisMedicine
An intervertebral implant having an endplate that can be slidably expanded following its placement in the intervertebral space.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Radially expandable spinal interbody device and implantation tool
ActiveUS8241358B2Inhibit and prevent overextensionBone implantSpinal implantsIntervertebral spacesBiomedical engineering
A radially expandable spinal interbody device for implantation between adjacent vertebrae of a spine is deliverable to an implant area in a radially collapsed state having minimum radial dimensions and once positioned is then radially expandable through and up to maximum radial dimensions. The expanded radially expandable spinal interbody device is configured to closely mimic the anatomical configuration of a vertebral face. The radially expandable spinal interbody device is formed of arced, pivoting linkages that allow transfiguration from the radially collapsed minimum radial dimensions through and up to the radially expanded maximum radial dimensions once deployed at the implant site (i.e. between adjacent vertebrae). The pivoting linkages have ends with locking features that inhibit or prevent overextension of the linkages. In one form of the locking features, one end of the linkage includes lobes that form a pocket while the other end of the linkage includes a projection that is adapted to be received in the pocket of the lobes of an adjacent linkage. A kit is also provided including a tool for the implantation and deployment of the spinal interbody device into an intervertebral space.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Expandable intervertebral implant
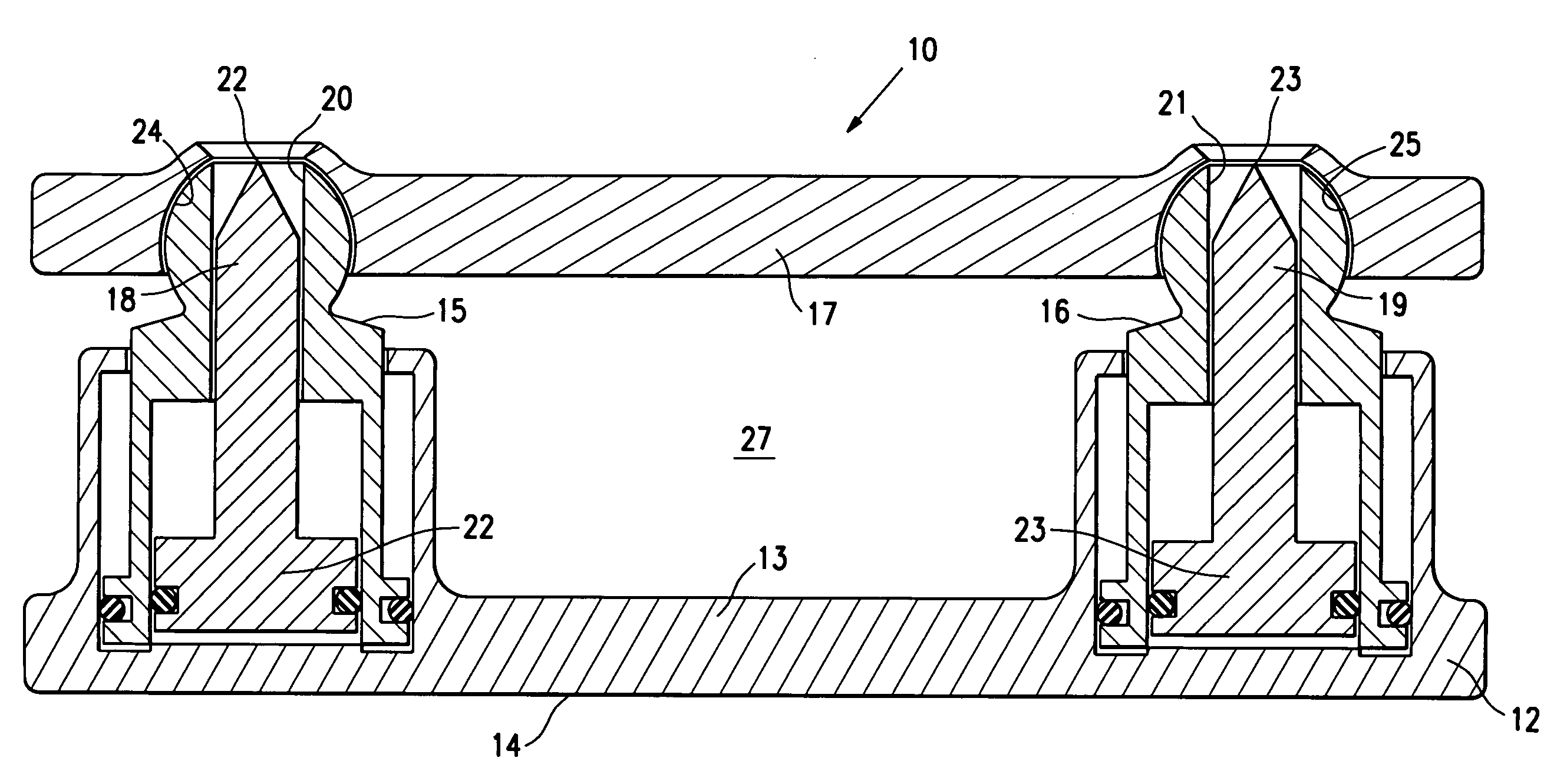
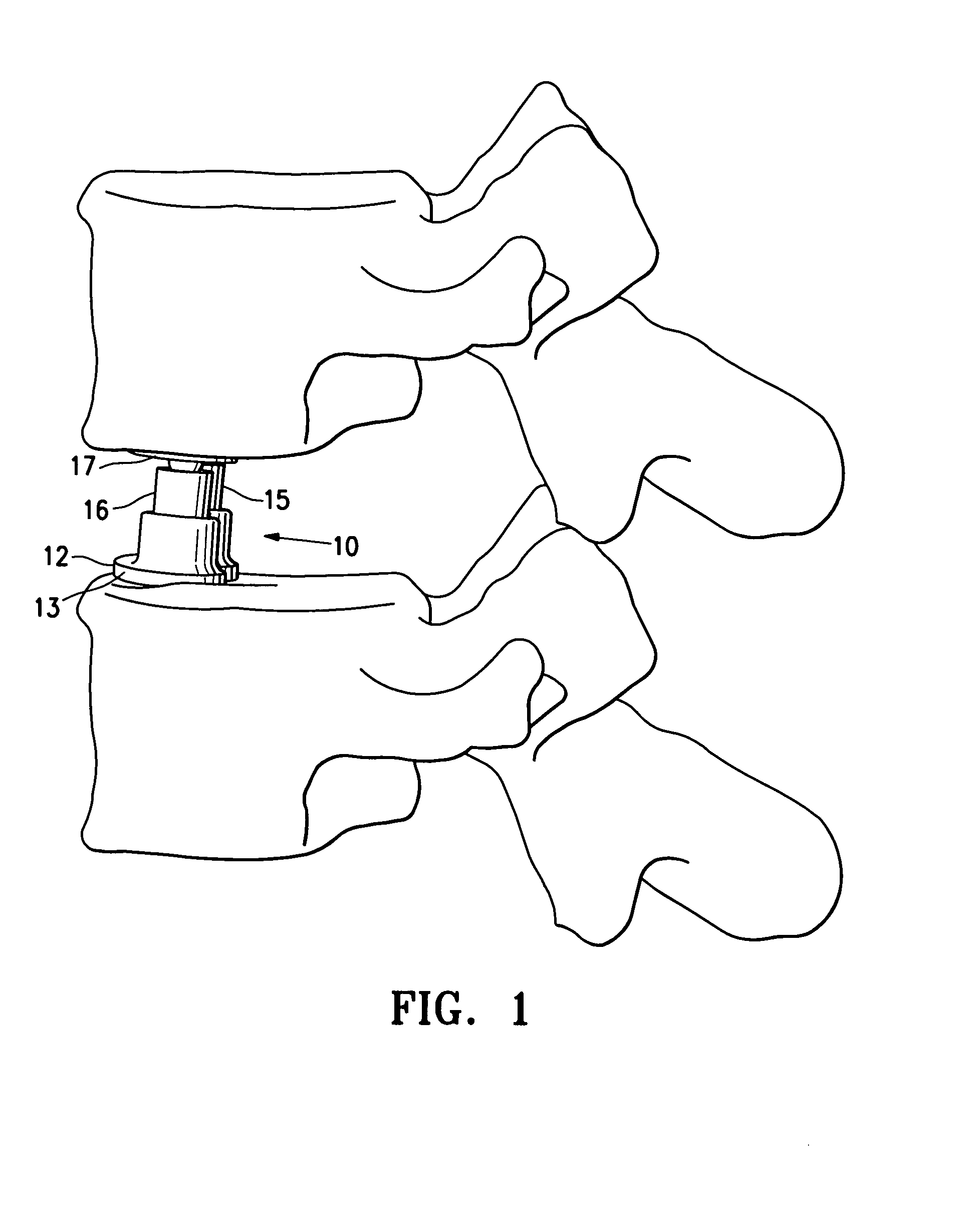
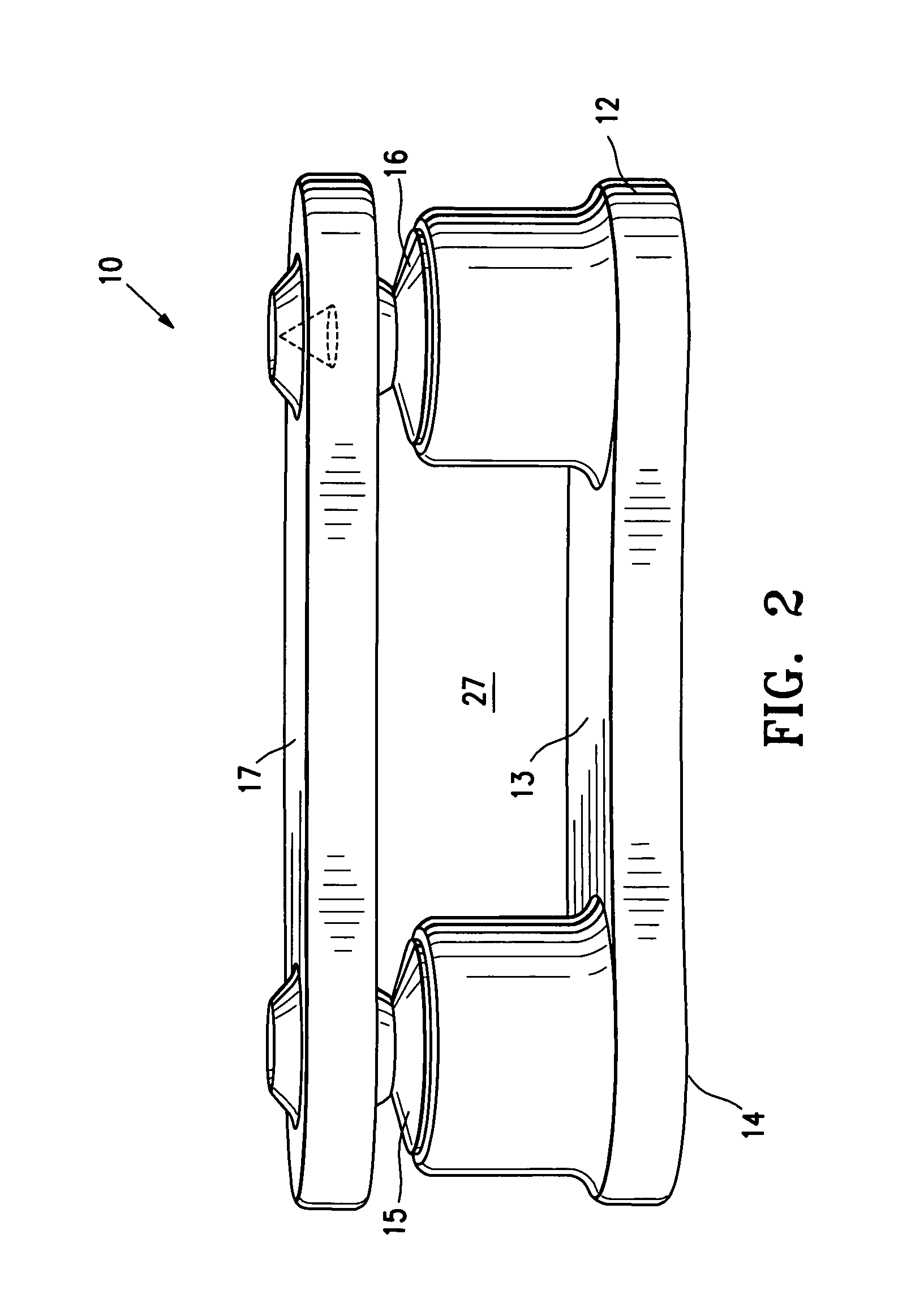
An expandable intervertebral implant (20) is provided for insertion into an intervertebral space defined by adjacent vertebrae. The expandable intervertebral implant includes a pair of outer sleeve portions (30A, 30B) and an inner core (50) disposed between the outer sleeve portions. Movement of the inner core relative to the outer sleeve portions causes the outers sleeve portions to deflect away from each other, thereby engaging the expandable intervertebral implant with the vertebrae and adjusting the height of the intervertebral space.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Segmented insert for intervertebral support
ActiveUS8328852B2Reduce loadImprove stabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsIntervertebral spacesEngineering
A spinal intervertebral support implant, for fusion or for dynamic stabilization purposes. A rod, preferably in the form of a screw, is inserted obliquely from the pedicle of an inferior vertebra into the body of a neighboring superior vertebra, through the disc space. The rod can be anchored into the body of the superior vertebra by means of a force fit or a screw thread. A pile of elements is disposed on the rod in the disc space like a pile of washers, so that the compression load between vertebrae is carried partly by these elements. These elements can be inserted through the bore through which the rod was inserted in a tightly folded configuration, and deployed into their washer-like form only when in position in the intervertebral space, such that there is no need for any additional incisions.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Adjustable Distraction Cage With Linked Locking Mechanisms
ActiveUS20130253650A1Increase hydraulic pressureSmall sizeSpinal implantsDistractionIntervertebral spaces
A spinal implant which is configured to be deployed between adjacent vertebral bodies. The implant has at least one extendable support element with a retracted configuration to facilitate deployment of the implant and an extended configuration so as to expand the implant and effectively distract the disc space, stabilize the motion segments and eliminate pathologic spine motion. The implant has a minimal dimension in its unexpanded state that is smaller than the dimensions of the neuroforamen through which it typically passes to be deployed within the intervertebral space. The implant is provided with a locking system having a plurality of linked locking elements that work in unison to lock the implant in an extended configuration. Bone engaging anchors also may be provided to ensure secure positioning.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Segmented insert for intervertebral support
ActiveUS20110054538A1Lateral dimension be relatively largeReduce loadInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsIntervertebral spacesEngineering
A spinal intervertebral support implant, for fusion or for dynamic stabilization purposes. A rod, preferably in the form of a screw, is inserted obliquely from the pedicle of an inferior vertebra into the body of a neighboring superior vertebra, through the disc space. The rod can be anchored into the body of the superior vertebra by means of a force fit or a screw thread. A pile of elements is disposed on the rod in the disc space like a pile of washers, so that the compression load between vertebrae is carried partly by these elements. These elements can be inserted through the bore through which the rod was inserted in a tightly folded configuration, and deployed into their washer-like form only when in position in the intervertebral space, such that there is no need for any additional incisions.
Owner:MAZOR ROBOTICS
Dynamic Spacer Device and Method for Spanning a Space Formed upon Removal of an Intervertebral Disc
A compliant intervertebral spacer according to the present invention replaces a damage intervertebral disc and functions to maintain disc height and prevent subsidence with a large surface area while substantially reducing patient recovery time. The compliant intervertebral spacer for spanning a space formed by upon removal of an intervertebral disc includes two end plates sized and shaped to fit within an intervertebral space and a compliant connector interconnecting the inner surfaces of the two end plates in a manner which limits motion between the plates to less than a total of 5 degrees of motion in any direction. The intervertebral spacer is configured to permanently maintain the disc space between the two adjacent discs without the use of bridging bone.
Owner:SIMPLIFY MEDICAL PTY LTD
Maximum support TLIF implant
A transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) implant to be placed in an intervertebral space includes a front member and a back member. The front member includes a first end having a hinge, a second end, a pair of lateral portions, a top wall and a bottom wall, an opening configured through the pair of lateral portions and a plurality of openings in each of the top wall and the bottom wall. The back member includes a first end having an arcuately-shaped attachment head comprising a receptor dimensioned and configured to accommodate the hinge of the front member, a second end, a pair of lateral portions, a top wall, a bottom wall and an opening configured through the pair of lateral portions. The top wall and the bottom wall of the back member further comprise a plurality of openings.
Owner:CUSTOM SPINE INC
Intevertebral Implant
An intervertebral spacer for therapeutic treatment of a patient includes at least one link sized and dimensioned to fit within an intervertebral space in the patient, and is configured to maintain a separation of two adjacent vertebrae for a period of time. A rigid guiding object, which may be a tool or a successive link, is insertable into the patient, to guide other links into the patient using an MIS approach. A pivot is connected between successive links, or between a guide tool and a link, configured to limit a relative range of angular orientation between the link and the guiding tool, or successive links. Multiple links are so joined to form a chain pushable by the last link, and pullable by the first link, to form a chain which may be formed into a curved configuration corresponding to the patient's intervertebral space.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Spinal implant distractor/inserter
ActiveUS20090005784A1Distracting vertebraInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsIntervertebral spaceEngineering
A method for distracting a pair of adjacent vertebrae and inserting an implant within the intervertebral space between the adjacent vertebrae using a posterior angle is described. The method employs a vertebral distractor-inserter comprising a housing, a pair of opposing arms in mechanical communication with the housing, a driving rod extending through at least a portion of the housing and between the arms, wherein the driving rod comprises an axis and a surface with a plurality of angled ratchet teeth on at least a portion of the surface, and a ratchet drive mechanism in mechanical communication with the driving rod.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
Intervertebral plate system
Devices and methods are provided for assisting in spinal stabilization. An improved intervertebral plate system is provided that includes an intervertebral spacer, a curvilinear plate, a plurality of bone screws, a curvilinear cover element and a cover screw. The curvilinear plate is configured and arranged to at least inhibit the intervertebral spacer from backing out when positioned between the two vertebrae of a patient. The plate can be secured to one or more intervertebral bodies via a plurality of bone screws. The curvilinear cover element, which can have a smooth and uniform surface, can be attached to the plate. The cover element is configured to inhibit the plurality of bone screws from inadvertently backing out of the plate. The plate and / or the cover element can be substantially recessed within the intervertebral space, thereby reducing the risk of damage to tissue.
Owner:SPINAL USA
Intervertebral disc space sizing tools and methods
ActiveUS20090182343A1Reduces time amount of timeShorten surgery timeSpinal implantsOsteosynthesis devicesDistractionSize measurement
A method and apparatus for making a size measurement within an intervertebral space by placing an expandable and contractible device into the intervertebral space, expanding the device, measuring a size characteristic of the space, contracting the device and then removing it. The measurement may be accomplished by an external x-ray or other imaging device imaging the expanded device in situ or by mechanically operated devices. An expansion and contraction mechanism such as fluid containing bladder or mechanically shifted members expands the device which later contracts in a controlled manner to the contracted size. An apparatus and method is provided for the measuring of the intervertebral space at a controlled distraction force. The apparatus includes an expandable device for providing a measurement within the intervertebral space and facilitating the measurement of the angulations of the lordotic curve of the intervertebral space.
Owner:PIONEER SURGICAL TECH INC
Retractor for use during retroperitoneal lateral insertion of spinal implants
InactiveUS20120010472A1Realize distributionMinimize traumaSurgerySpinal implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral spaces
A method is disclosed for introducing a spinal disc implant into an intervertebral space of a subject. The subject is placed in a lateral position, and the anterior face of the spinal disc intervertebral space is accessed, between the L5 and S1 vertebrae, from an anterior and lateral retroperitoneal approach. An operative corridor to the anterior face of the spinal disc space is established by introducing a retractor instrument anterolaterally to the spinal disc space between the anterior superior iliac spine and the anterior inferior iliac spine. The damaged spinal disc contents are removed from the intervertebral space through the operative corridor, and the implant is advanced into the intervertebral space at an oblique angle and pivoted to position the implant substantially laterally within the intervertebral space. Elongated retractor and insertion instruments, as well as a modified disc implant, are also disclosed for carrying out the method.
Owner:SPANN SCOTT
Minimally-invasive retroperitoneal lateral approach for spinal surgery
InactiveUS20120035730A1Realize distributionMinimize traumaSurgerySpinal implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral spaces
A method is disclosed for introducing a spinal disc implant into an intervertebral space of a subject. The subject is placed in a lateral position, and the anterior face of the spinal disc intervertebral space is accessed, between the L5 and S1 vertebrae, from an anterior and lateral retroperitoneal approach. An operative corridor to the anterior face of the spinal disc space is established by introducing a retractor instrument anterolaterally to the spinal disc space between the anterior superior iliac spine and the anterior inferior iliac spine. The damaged spinal disc contents are removed from the intervertebral space through the operative corridor, and the implant is advanced into the intervertebral space at an oblique angle and pivoted to position the implant substantially laterally within the intervertebral space. Elongated retractor and insertion instruments, as well as a modified disc implant, are also disclosed for carrying out the method.
Owner:PANTHEON SPINAL
Method of preparing a poorly crystalline calcium phosphate and methods of its use
InactiveUS7517539B1Readily injectableHigh strengthBiocideSurgical adhesivesOsteoporotic boneIntervertebral spaces
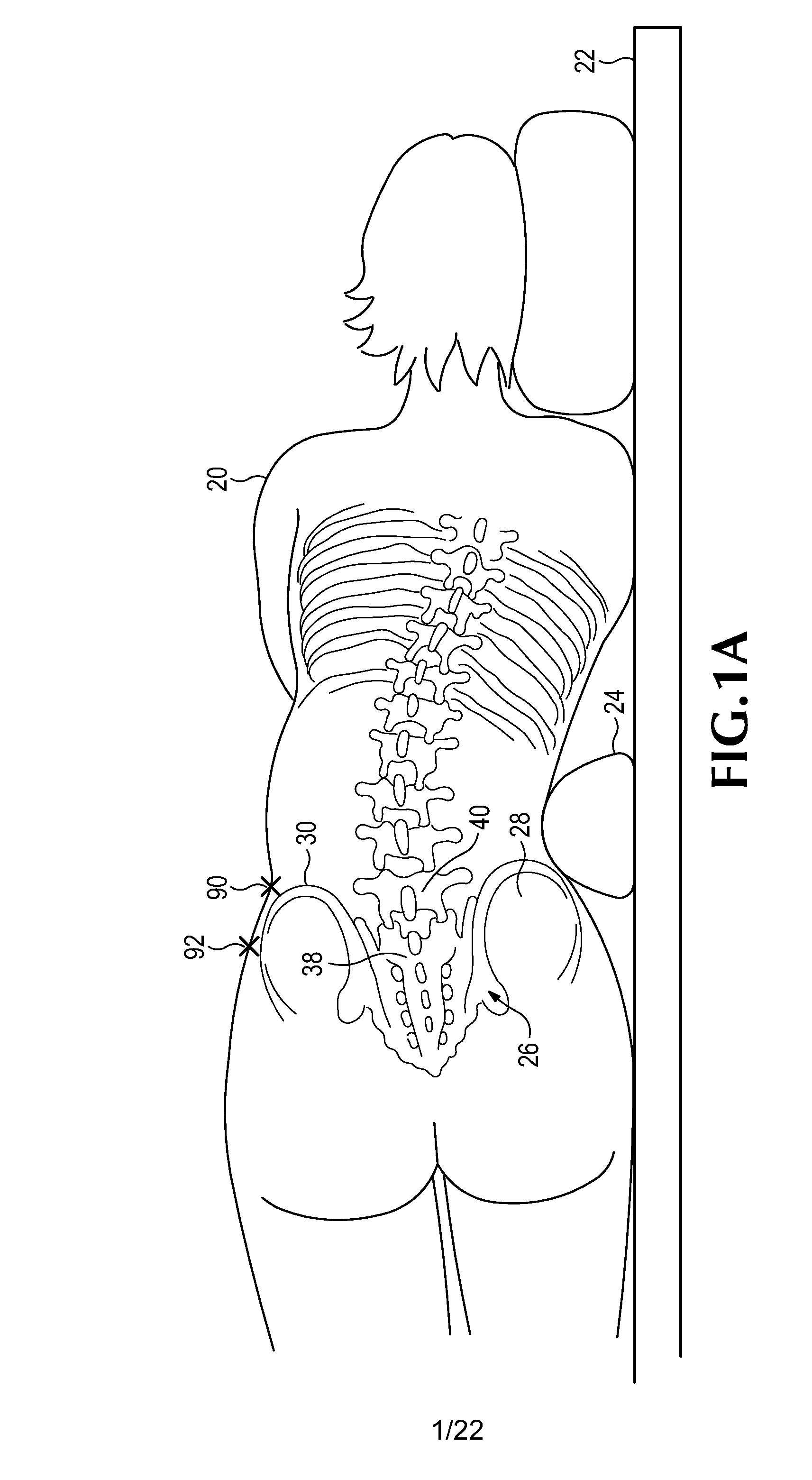
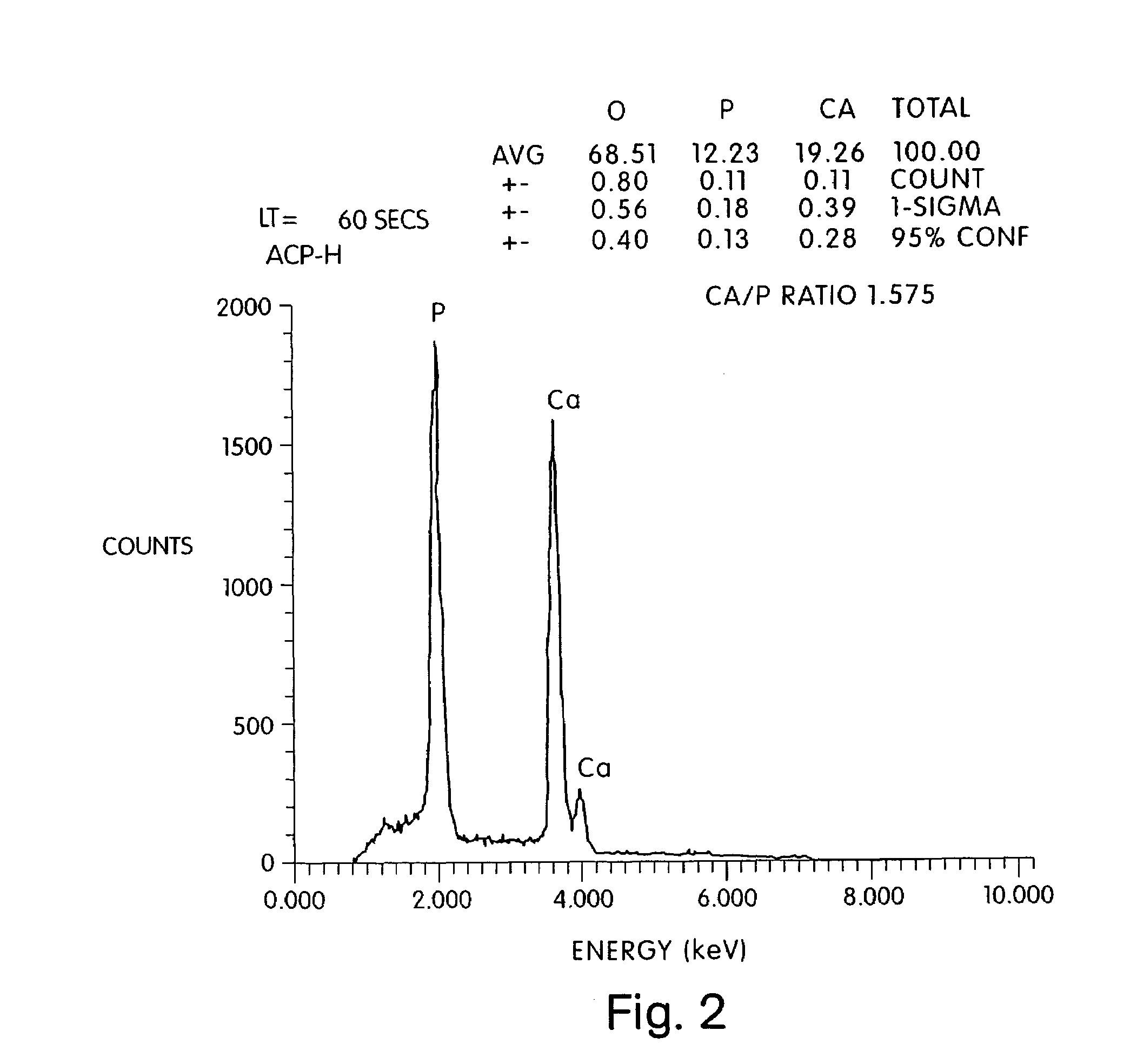
The present invention provides a novel process for producing a calcium phosphate cement or filler which hardens in a temperature dependent fashion in association with an endothermic reaction. In the reaction a limited amount of water is mixed with dry calcium phosphate precursors to produce a hydrated precursor paste. Hardening of the paste occurs rapidly at body temperature and is accompanied by the conversion of one or more of the reactants to poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate. The hardened cements, fillers, growth matrices, orthopedic and delivery devices of the invention are rapidly resorbable and stimulate hard tissue growth and healing. A composite material is provided including a strongly bioresorbable, poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate composite and a supplementary material. The supplementary material is in intimate contact with the hydroxyapatite material in an amount effective to impart a selected characteristic to the composite. The supplemental material may be biocompatible, bioresorbable or non-resorbable. A method for treating a bone defect also is provided by identifying a bone site suitable for receiving an implant, and introducing a strongly resorbable, poorly crystalline apatitic calcium phosphate at the implant site, whereby bone is formed at the implant site. The implant site may be a variety of sites, such as a tooth socket, non-union bone, bone prosthesis, an osteoporotic bone, an intervertebral space, an alveolar ridge or a bone fracture.
Owner:LIFE SCI ENTERPRISES
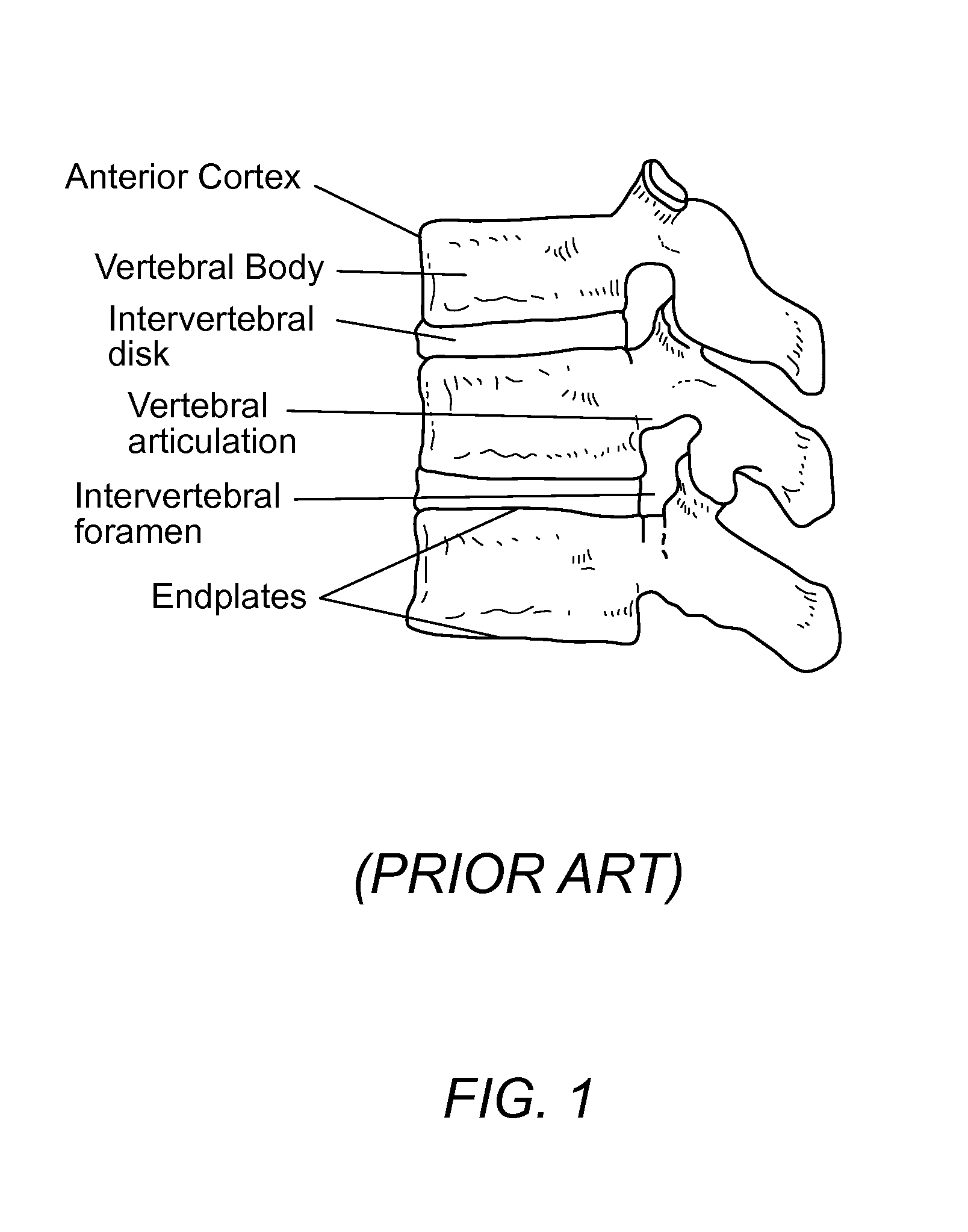
Anterior intervertebral spacer and integrated plate assembly and methods of use
InactiveUS8932358B1Easy to fuseImprove stabilityBone implantSpinal implantsAnterior cortexIntervertebral spaces
A precisely size matched intervertebral plate and spacer assembly for ensuring a tight fit within a disc space to promote spinal fusion, comprising: a “U-shaped” spacer configured to fit within the intervertebral space; and, a matching countersunk low profile “H-shaped” anterior plate joined perpendicularly to the spacer. The plate further comprises: a plurality of anchor members configured to attach to the junctions of the anterior cortex faces and the endplates; and, channels individually traversing through the anchor members for inserting screws into the vertebral bodies' cortical bone. The spacer comprises a hollow three-sided U-shaped member, comprising two opposing parallel side walls, and a perpendicular posterior wall, while lacking a superior, inferior, and anterior wall. The exterior walls of the plate and spacer are planar, while the interior walls of the spacer are curved to house a precisely fitting cylindrical graft, or other insert such as DBM, bone dust, bone paste, bone dowel with direct contact to the endplates to promote fusion.
Owner:NEHLS DANIEL
Spinal implant and integration plate for optimizing vertebral endplate contact load-bearing edges
An interbody spinal implant including a body and an integration plate having a top surface, a bottom surface, opposing lateral sides, opposing anterior and posterior portions, and a substantially hollow center in communication with a vertical aperture. The body is recessed in a way that portions of the integration plate protrude above the top and / or bottom surface of the body to enhance the resistance of the implant to expulsion from the intervertebral space.
Owner:TITAN SPINE
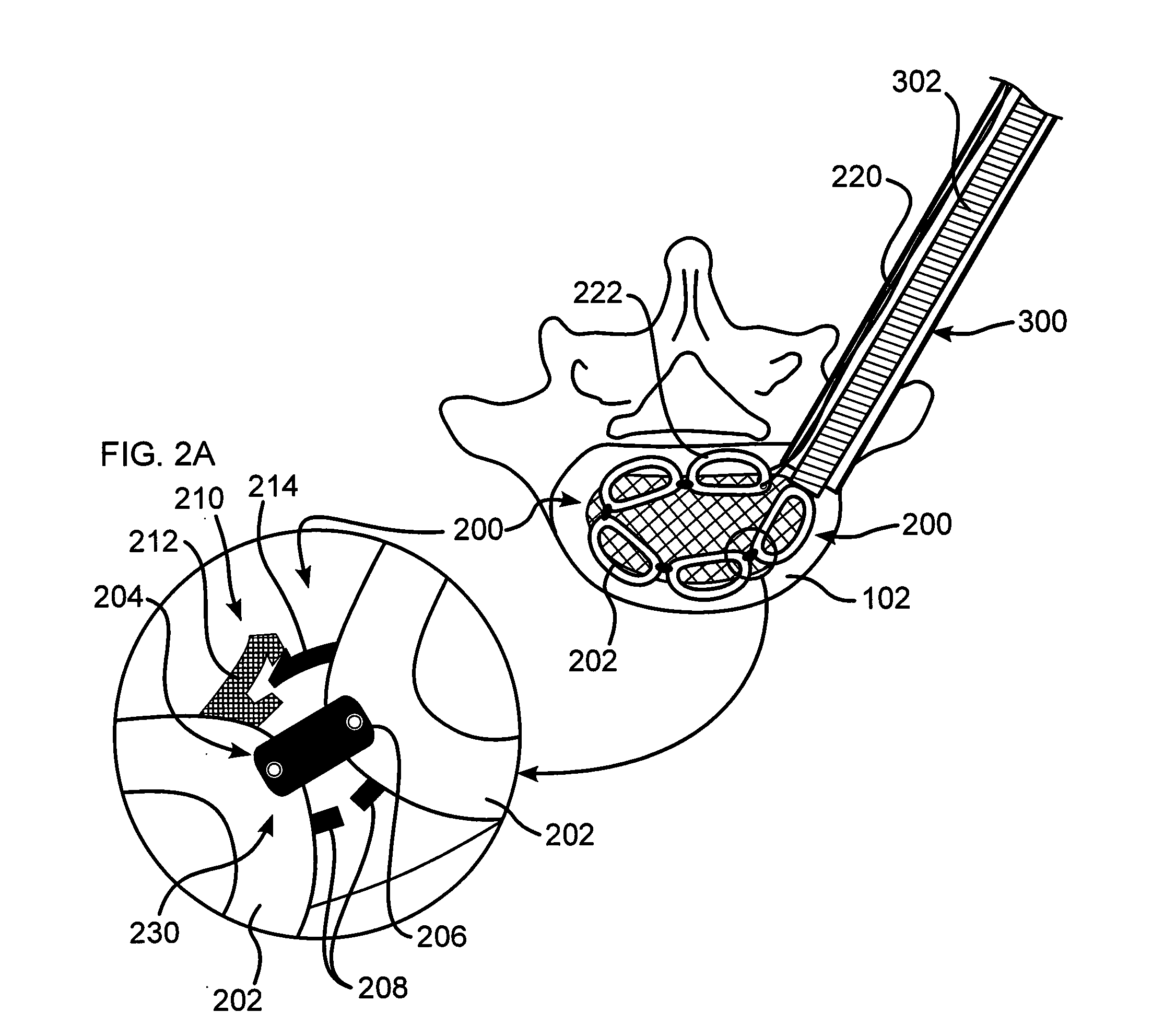
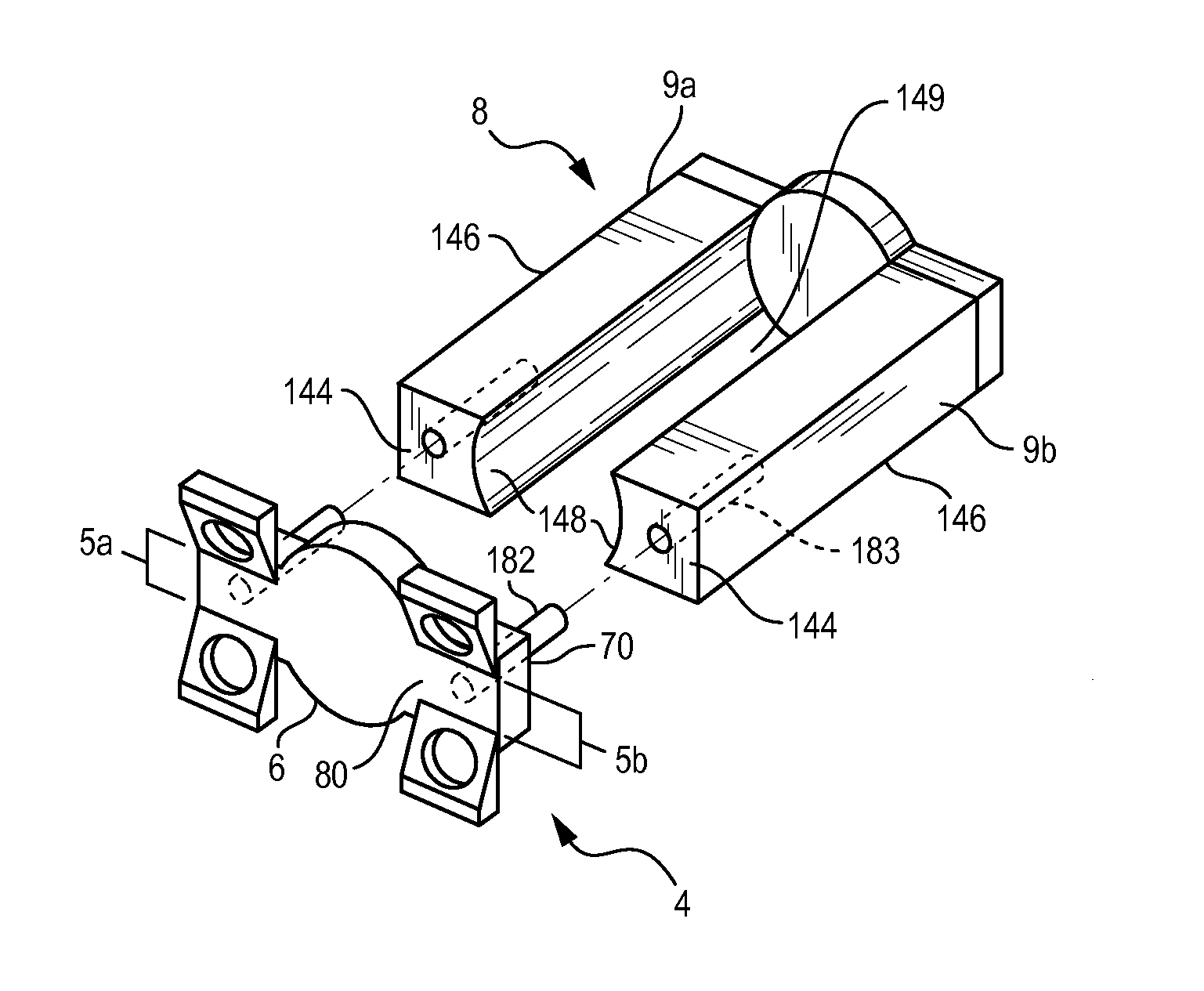
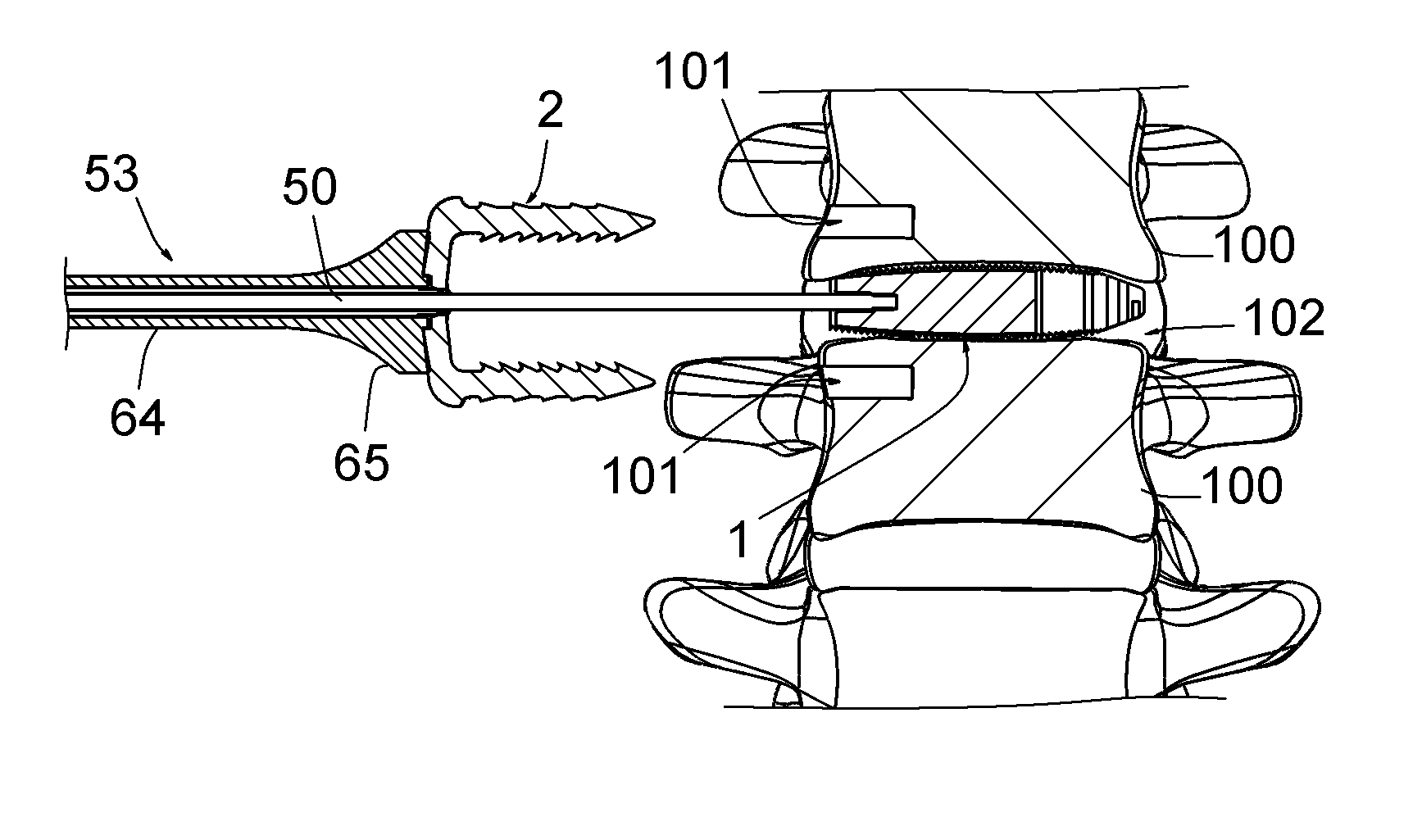
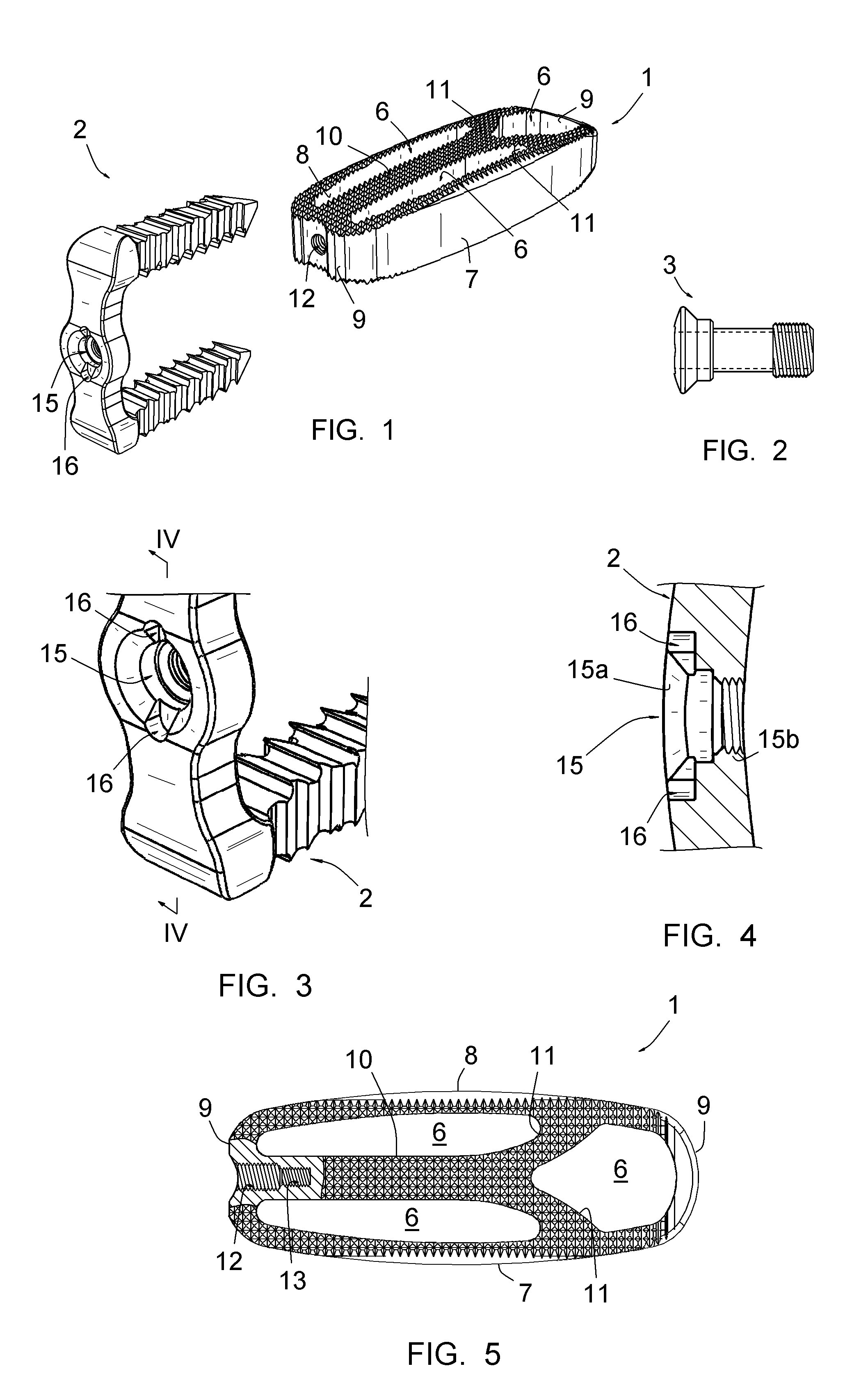
Vertebral osteosynthetis equipment
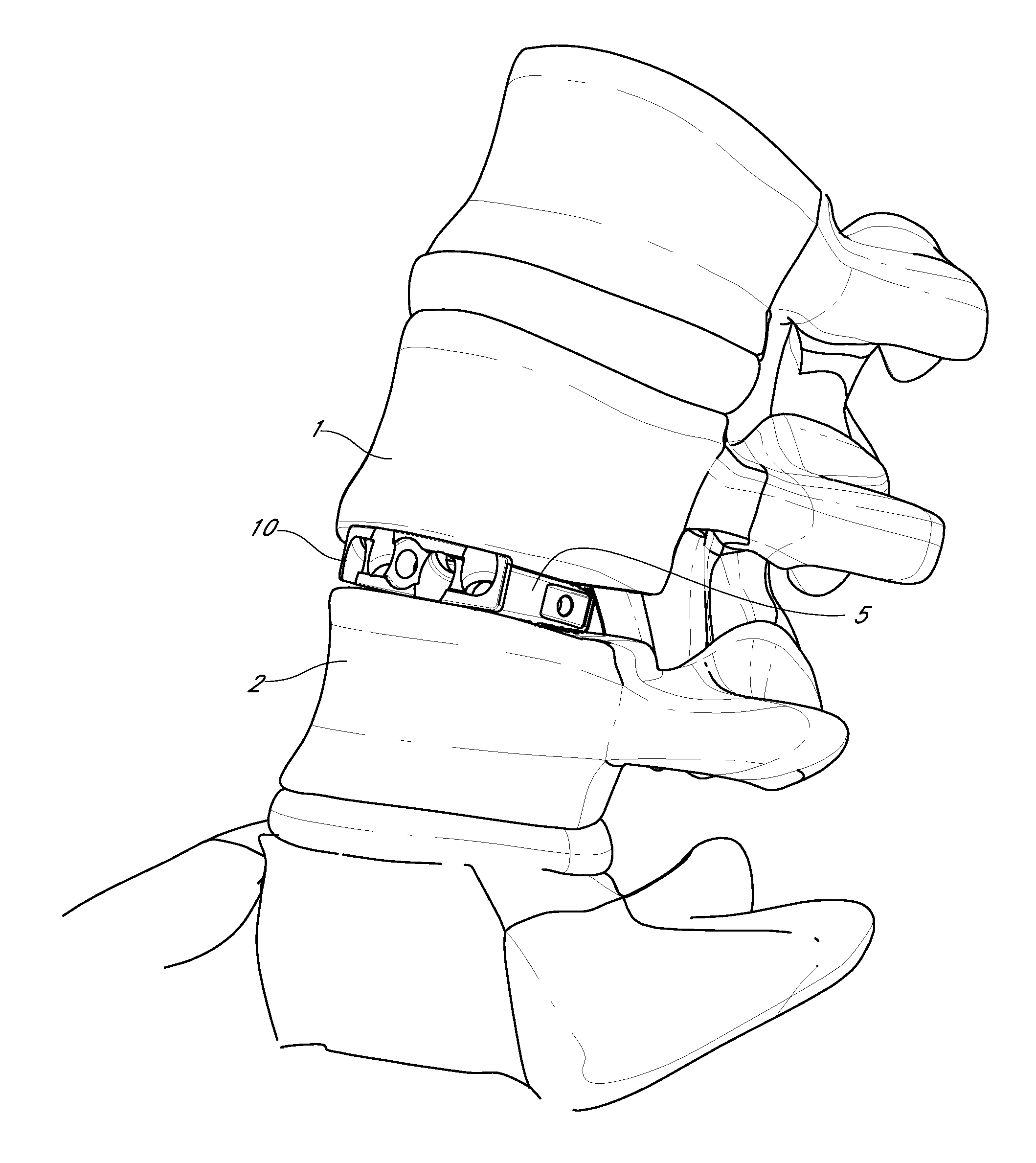
ActiveUS8956416B2Avoid insufficient thicknessInternal osteosythesisBone implantIntervertebral discDistal portion
A vertebral osteosynthesis equipemnt including an intervertebral implant (1); a member (2) for connecting vertebral bodies (100) of both treated vertebrae intended to be assembled to the intervertebral implant (1); and a member (3) for assembling the connecting member (2) to the intervertebral implant (1). The intervertebral implant (1) includes on its proximal side relatively to the direction of its introduction into the intervertebral space (102), a hole comprising two coaxial portions, i.e. a proximal portion of larger section and a distal portion of smaller section, these proximal and distal portions comprising respective connecting means. The connecting member (2) includes a hole which allows it to be engaged onto a guiding rod (50) intended to be inserted into said distal portion (13) of the hole of the implant (1), and the assembling member (3) comprises a conduit on this guiding rod (50).
Owner:MEDICREA INT SA
Method of retroperitoneal lateral insertion of spinal implants
ActiveUS20120010715A1Realize distributionMinimize traumaSurgerySpinal implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral spaces
A method is disclosed for introducing a spinal disc implant into an intervertebral space of a subject. The subject is placed in a lateral position, and the anterior face of the spinal disc intervertebral space is accessed, between the L5 and S1 vertebrae, from an anterior and lateral retroperitoneal approach. An operative corridor to the anterior face of the spinal disc space is established by introducing a retractor instrument anterolaterally to the spinal disc space between the anterior superior iliac spine and the anterior inferior iliac spine. The damaged spinal disc contents are removed from the intervertebral space through the operative corridor, and the implant is advanced into the intervertebral space at an oblique angle and pivoted to position the implant substantially laterally within the intervertebral space. Elongated retractor and insertion instruments, as well as a modified disc implant, are also disclosed for carrying out the method.
Owner:PANTHEON SPINAL
Device for Stabilizing a Vertebral Joint and Method for Anterior Insertion Thereof
ActiveUS20110190891A1Control freedomWear minimizationSuture equipmentsLigamentsIntervertebral spacesProsthesis
A prosthetic device can be used as a prosthesis following a discectomy or a corpectomy. The prosthetic device includes two endplates with staggered motion limiting members. The device can be configured to allow six degrees of motion when comparing one endplate relative to the other. The endplates can be configured to fix the joint by changing the body held within the device and by adding a locking plate and fasteners. A method teaches how to insert a device to an intervertebral space via an anterior incision.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Expandable intervertebral implants
Interbody spacers are expandable horizontally and vertically by an application of axial force, and lockable in an expanded configuration. The spacers include support members interconnected to end bodies by pivotable link members. The spacers are introduced between vertebral bodies in a compressed configuration and expanded to fill the intervertebral space and provide support and selective lordotic correction. Graft material may be introduced into the expanded spacer. Provisional and / or supplementary locking means lock the spacers in the expanded configuration. Embodiments of the spacers include symmetrically and asymmetrically configured spacers. Methods of expansion include symmetric expansion or asymmetric expansion along each of two directions.
Owner:AMPLIFY SURGICAL INC
Reinforced carbon fiber/carbon foam intervertebral spine fusion device
An intervertebral implant for placement in the intervertebral space between two adjacent vertebral bodies is provided. The implant comprises a hollow cage and a porous core received within the cage. The cage comprises a superior surface configured to contact a first vertebral body, an inferior surface configured to contact a second vertebral body, and an outer wall extending between the superior surface and inferior surface. The outer wall comprises an exterior surface defining the outer perimeter of the implant, and an interior surface defining an inner (hollow) space or void. The porous core is received within the inner space or void, and preferably fills the void. The core comprises a carbonaceous matrix comprising a continuous phase having a surface and defining a plurality of open spaces throughout said matrix. Suitable carbonaceous matrices are selected from the group consisting of carbon foam, graphite foam, and combinations thereof. Methods of making and using the same, along with kits to facilitate such use are also provided.
Owner:WICHITA STATE UNIVERSITY
Laterally expandable intervertebral fusion implant
InactiveUS20140188224A1Add supportSmall sectionBone implantSpinal implantsIntervertebral spacesInsertion stent
The invention relates to an intervertebral fusion implant for fusing two adjacent vertebrae, comprising an adjustable support body, the base surface and cover surface of which are configured to bear on end plates of the adjacent vertebrae, wherein provision is made for a side bracket, which can be pivoted laterally about a hinge and the base and cover of which have a planar design, and provision is made for an actuator for pivoting out the side bracket into a position (working position) spread from the support body. As a result, the implant has particularly small dimensions and can, after assembly at the envisaged implantation site, be actuated in such a way that it becomes larger and thereby affords a larger support surface for support in the intervertebral space. Thus, even comparatively large-area defects can be treated by minimally invasive surgery.
Owner:FACET LINK
Spinal implant with expandable fixation
ActiveUS8932355B2Easy to installMinimizing chanceBone implantJoint implantsIntervertebral spacesSpinal implant
A spinal implant which is configured to be deployed between adjacent vertebral bodies. The implant has at least one fixation element with a retracted configuration to facilitate deployment of the implant and an extended configuration so as to engage a surface of an adjacent vertebral body and secure the implant between two vertebral bodies. Preferably, the implant is expandable and has a minimal dimension in its unexpanded state that is smaller than the dimensions of the neuroforamen through which it must pass to be deployed within the intervertebral space. Once within the space between vertebral bodies, the implant can be expanded so as to engage the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae to effectively distract the anterior disc space, stabilize the motion segments and eliminate pathologic spine motion. Angular deformities can be corrected, and natural curvatures restored and maintained.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Systems, devices and apparatuses for bony fixation and disk repair and replacement methods related thereto
InactiveUS8486078B2Internal osteosythesisNon-surgical orthopedic devicesIntervertebral spacesReplacement method
Owner:K2M
Method of retroperitoneal lateral insertion of spinal implants
ActiveUS9451940B2Realize distributionMinimize traumaSurgeryJoint implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral spaces
A method is disclosed for introducing a spinal disc implant into an intervertebral space of a subject. The subject is placed in a lateral position, and the anterior face of the spinal disc intervertebral space is accessed, between the L5 and S1 vertebrae, from an anterior and lateral retroperitoneal approach. An operative corridor to the anterior face of the spinal disc space is established by introducing a retractor instrument anterolaterally to the spinal disc space between the anterior superior iliac spine and the anterior inferior iliac spine. The damaged spinal disc contents are removed from the intervertebral space through the operative corridor, and the implant is advanced into the intervertebral space at an oblique angle and pivoted to position the implant substantially laterally within the intervertebral space. Elongated retractor and insertion instruments, as well as a modified disc implant, are also disclosed for carrying out the method.
Owner:PANTHEON SPINAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com