Patents
Literature
123 results about "Anatomical configuration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
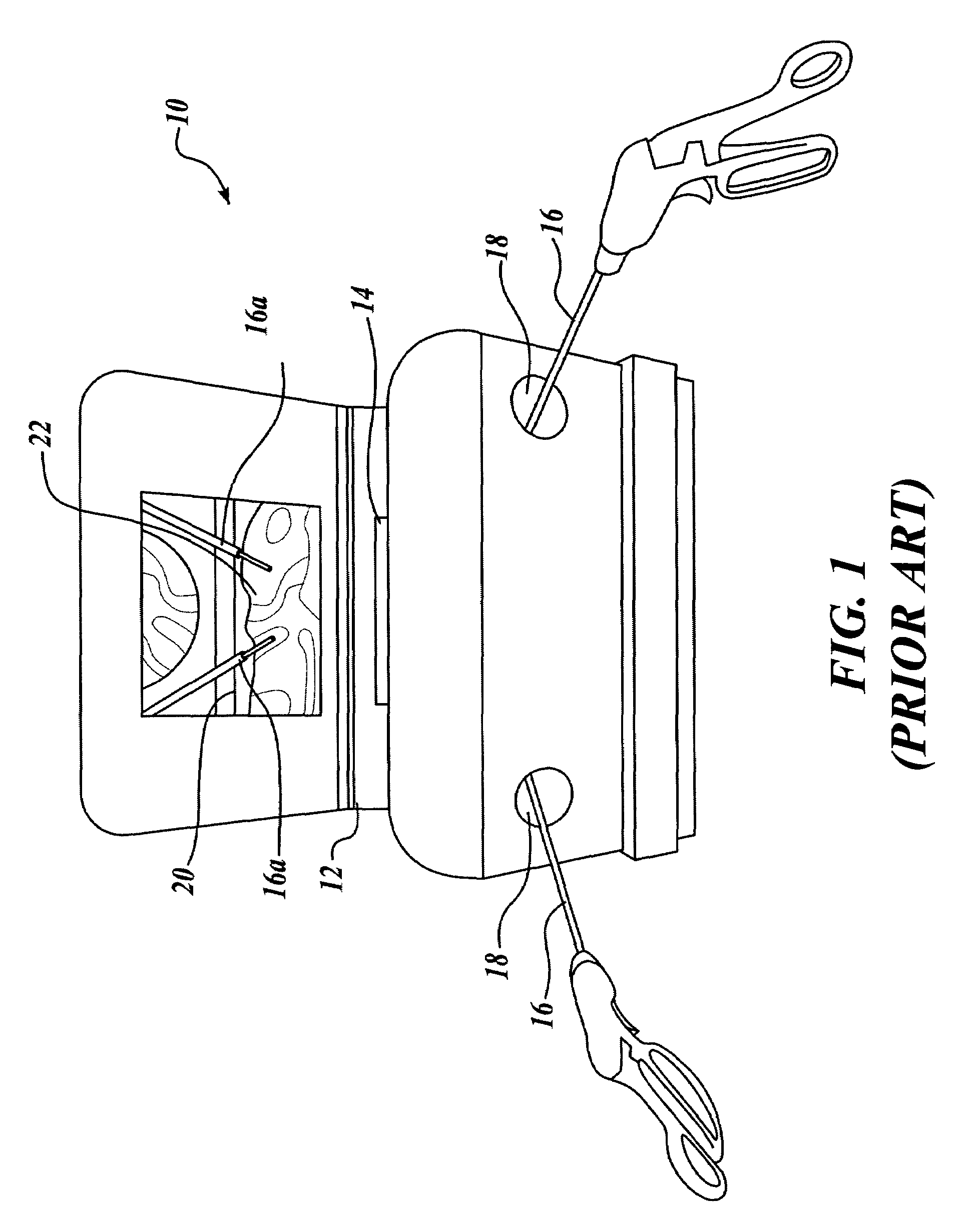
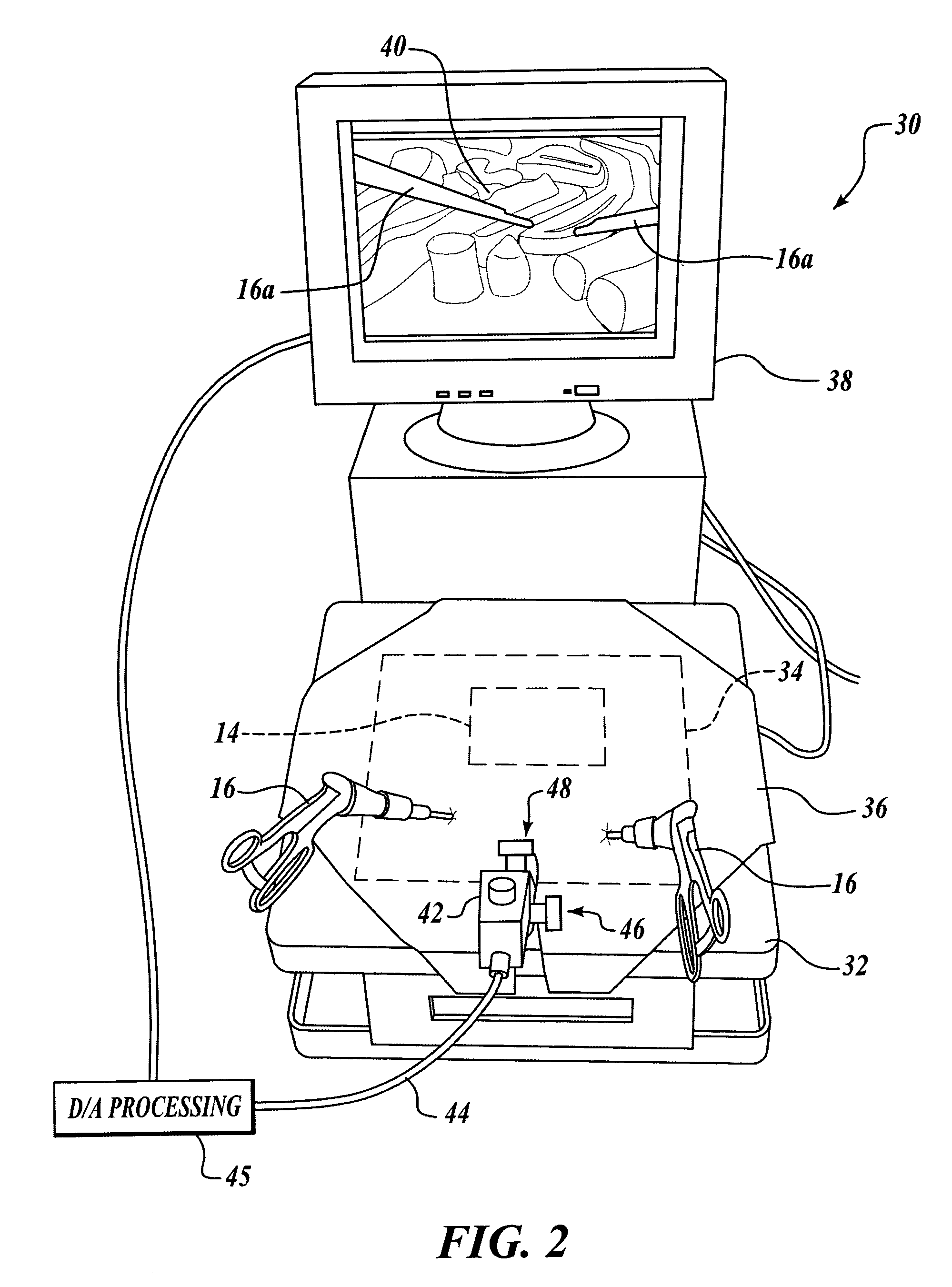
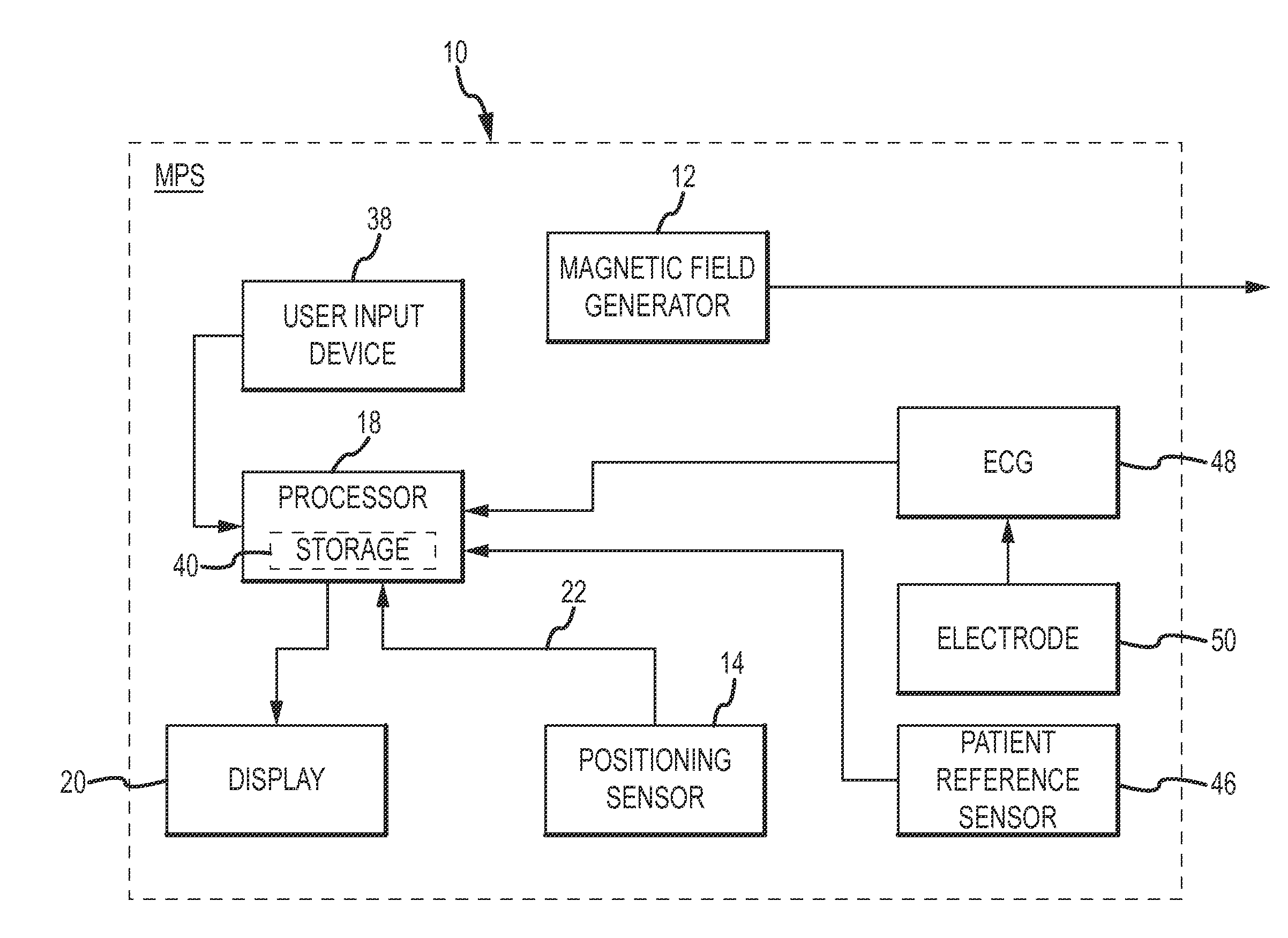
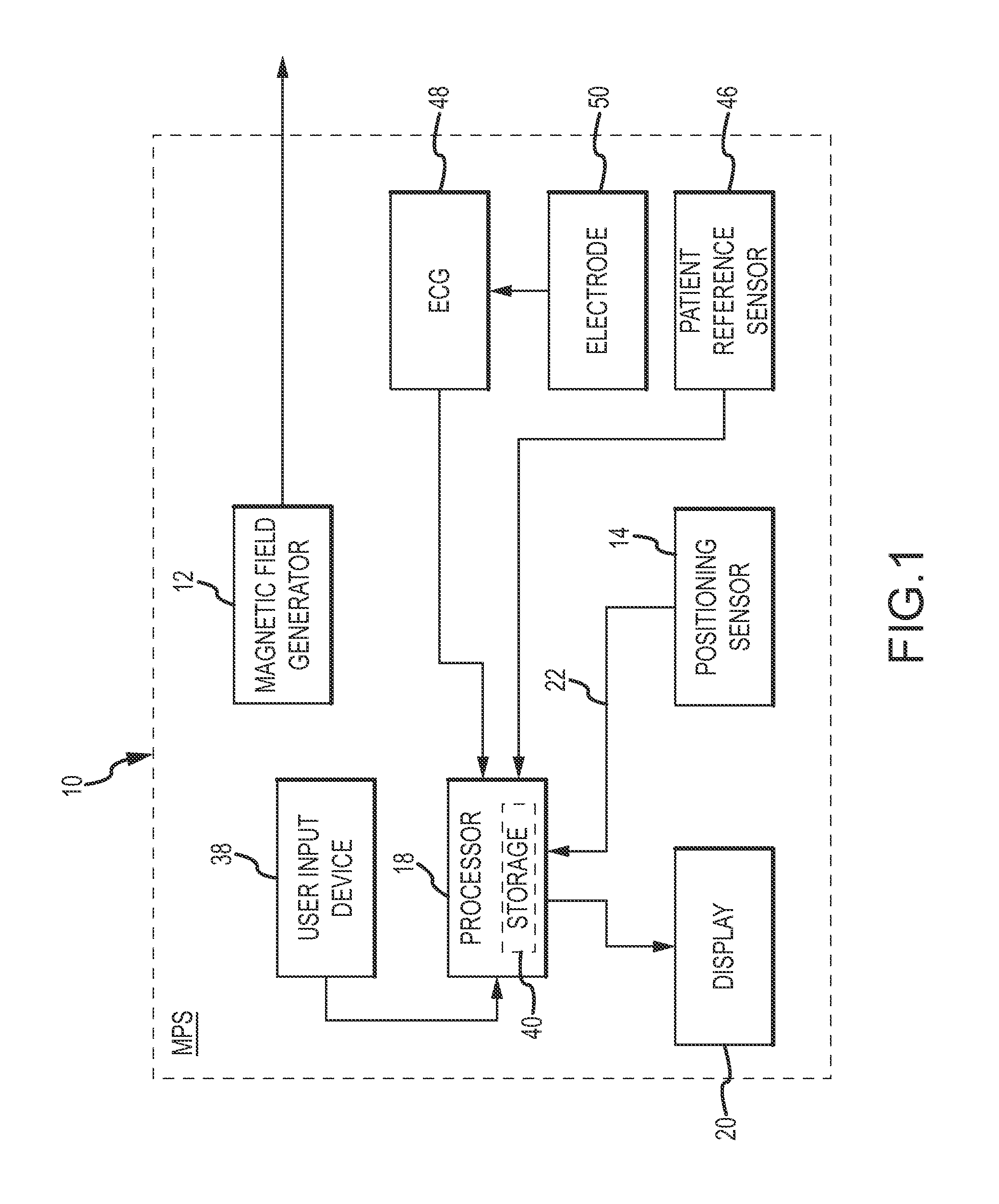
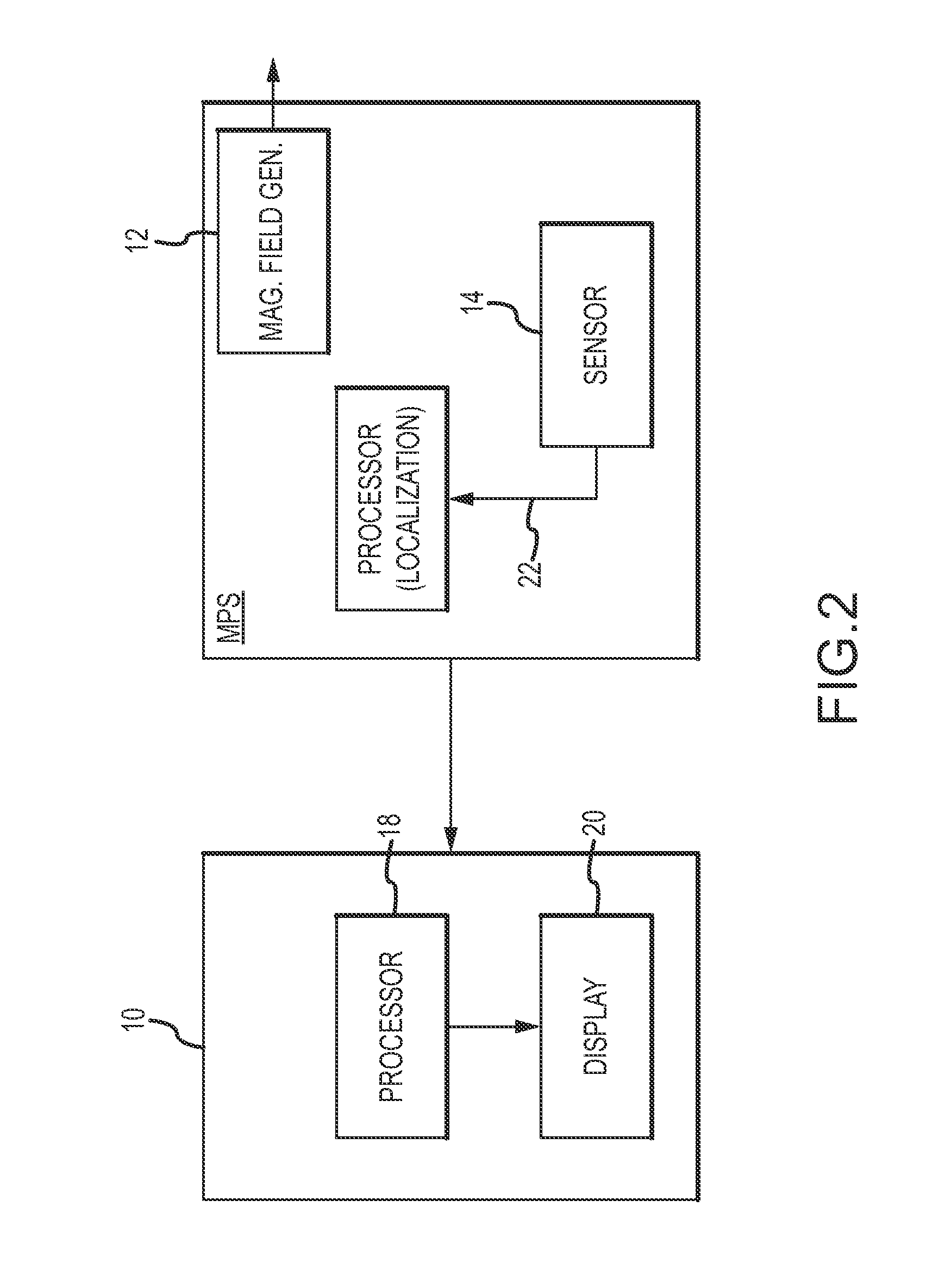
Surgical navigation with overlay on anatomical images
ActiveUS20060079745A1Enhance displayed imagePrecise positioningMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayDisplay device
A system and method are provided for control of a navigation system for deploying a medical device within a subject, and for enhancement of a display image of anatomical features for viewing the projected location and movement of medical devices, and projected locations of a variety of anatomical features and other spatial markers in the operating region. The display of the X-ray imaging system information is augmented in a manner such that a physician can more easily become oriented in three dimensions with the use of a single-plane X-ray display. The projection of points and geometrical shapes within the subject body onto a known imaging plane can be obtained using associated imaging parameters and projective geometry.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
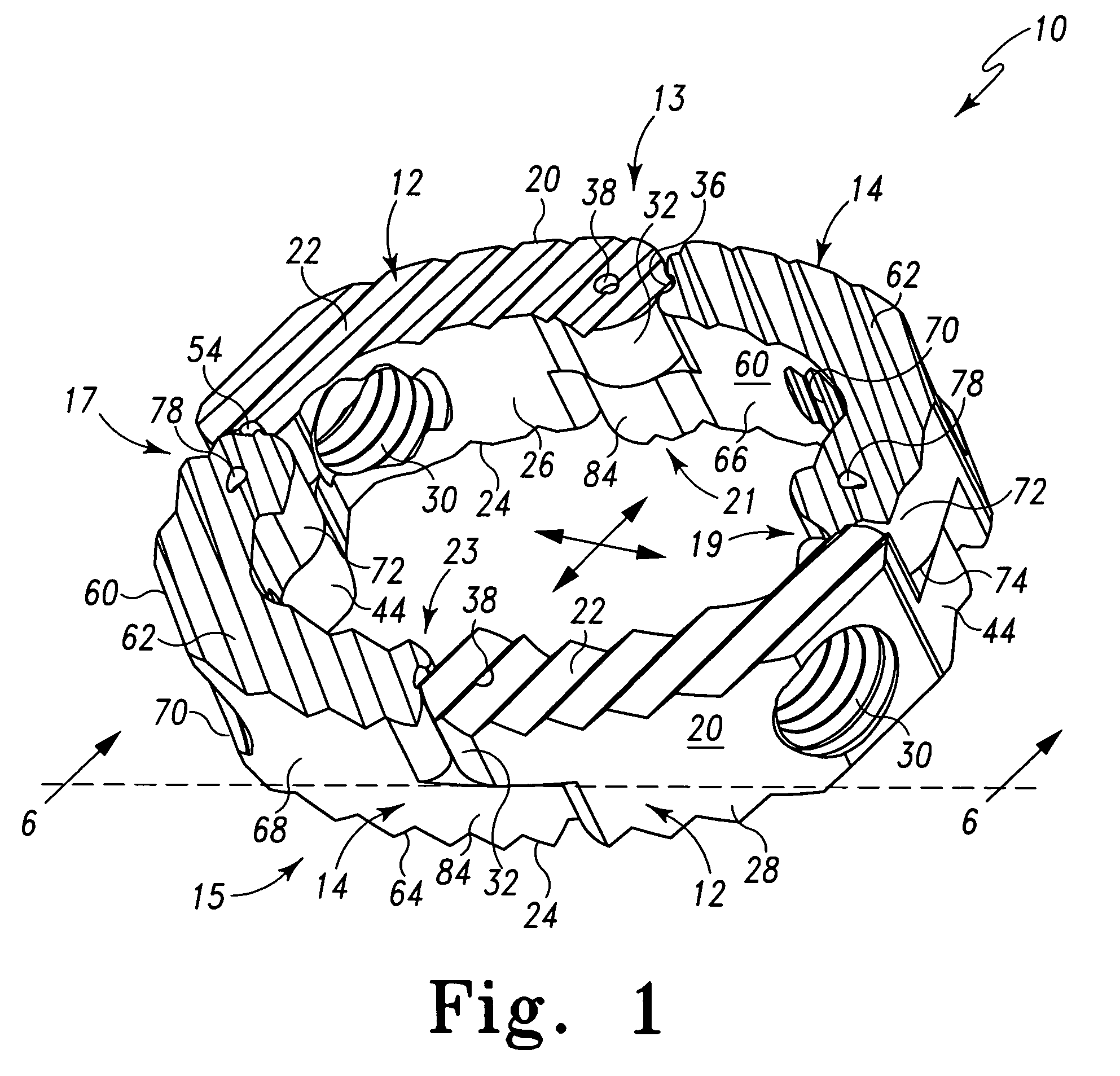
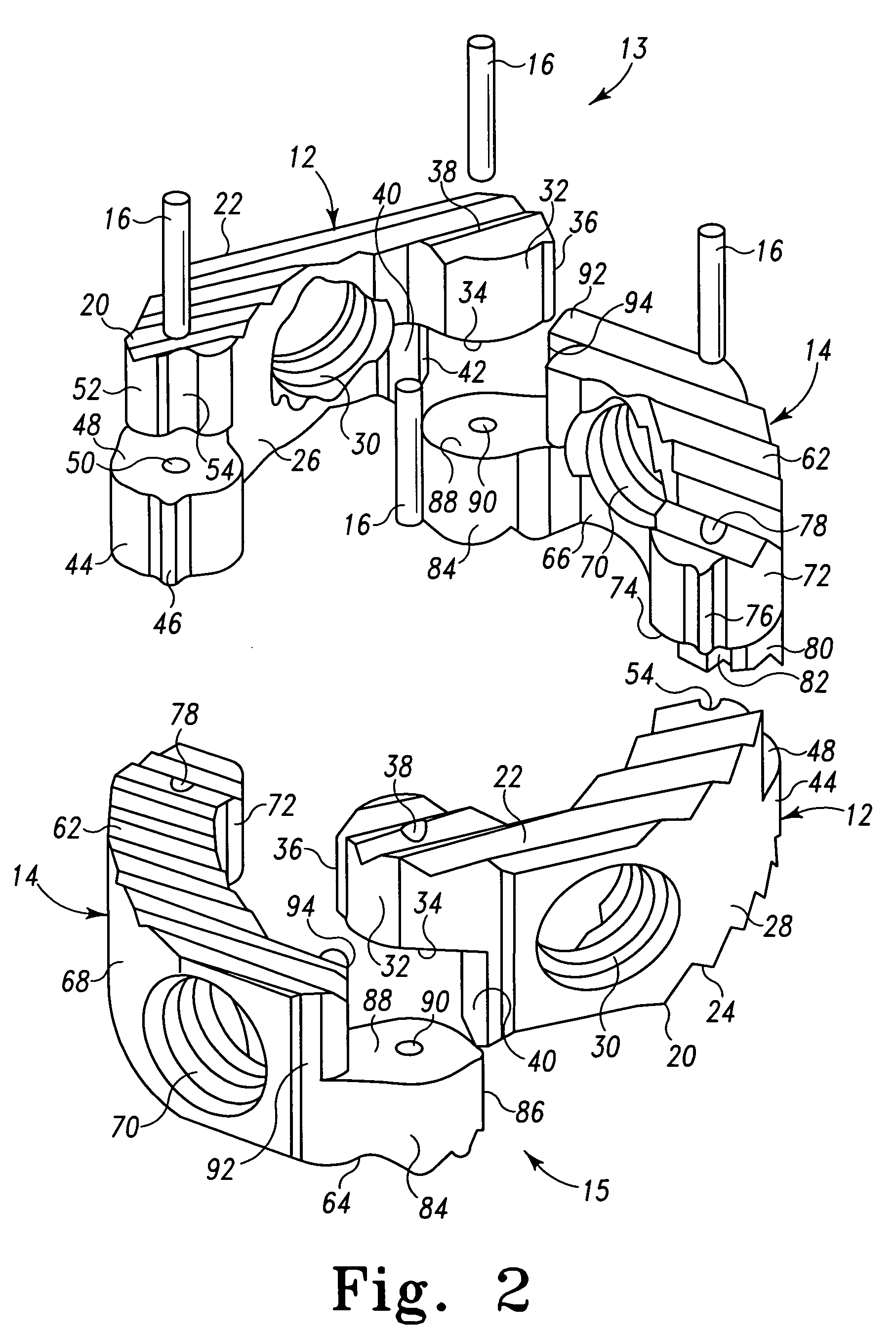
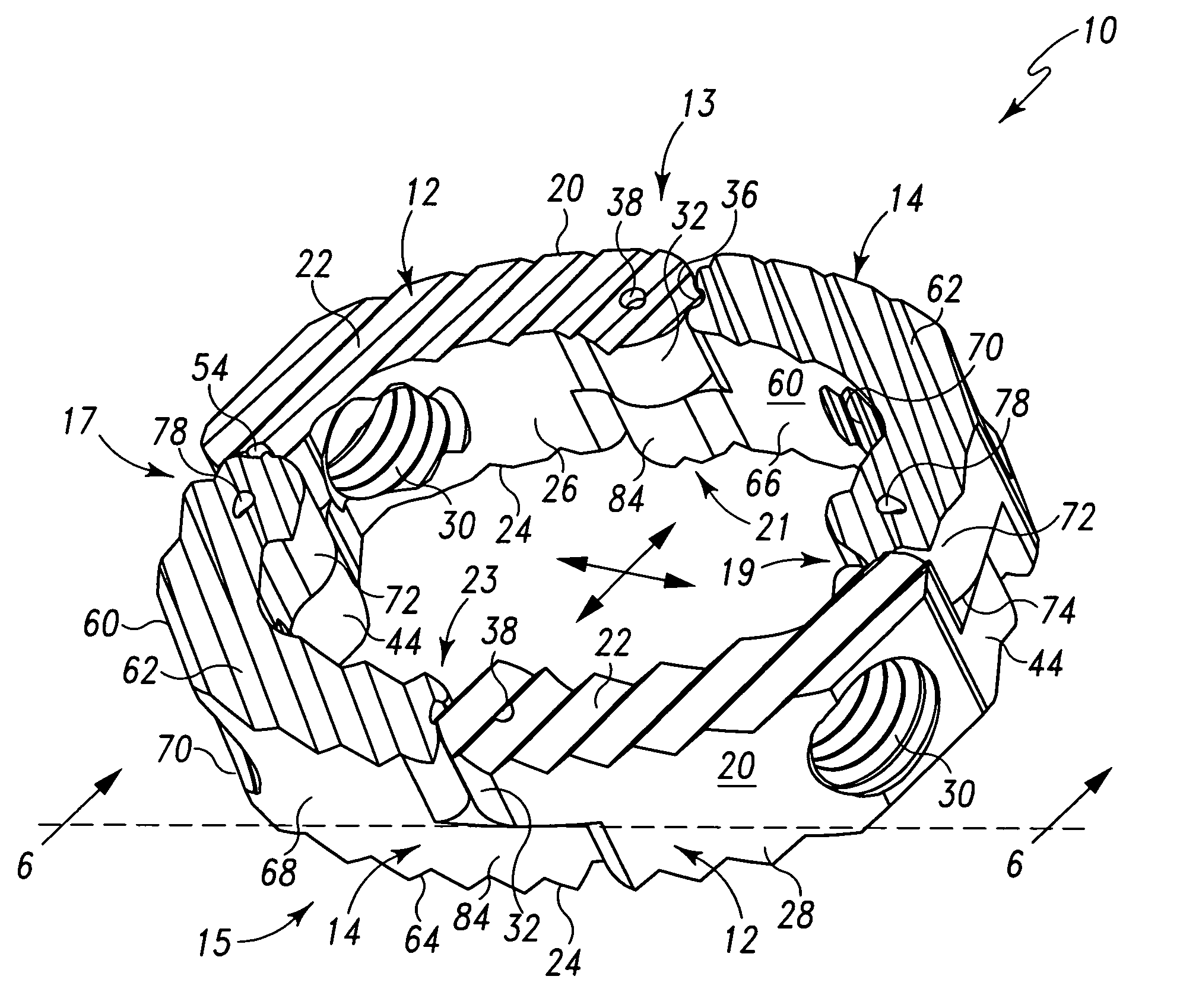
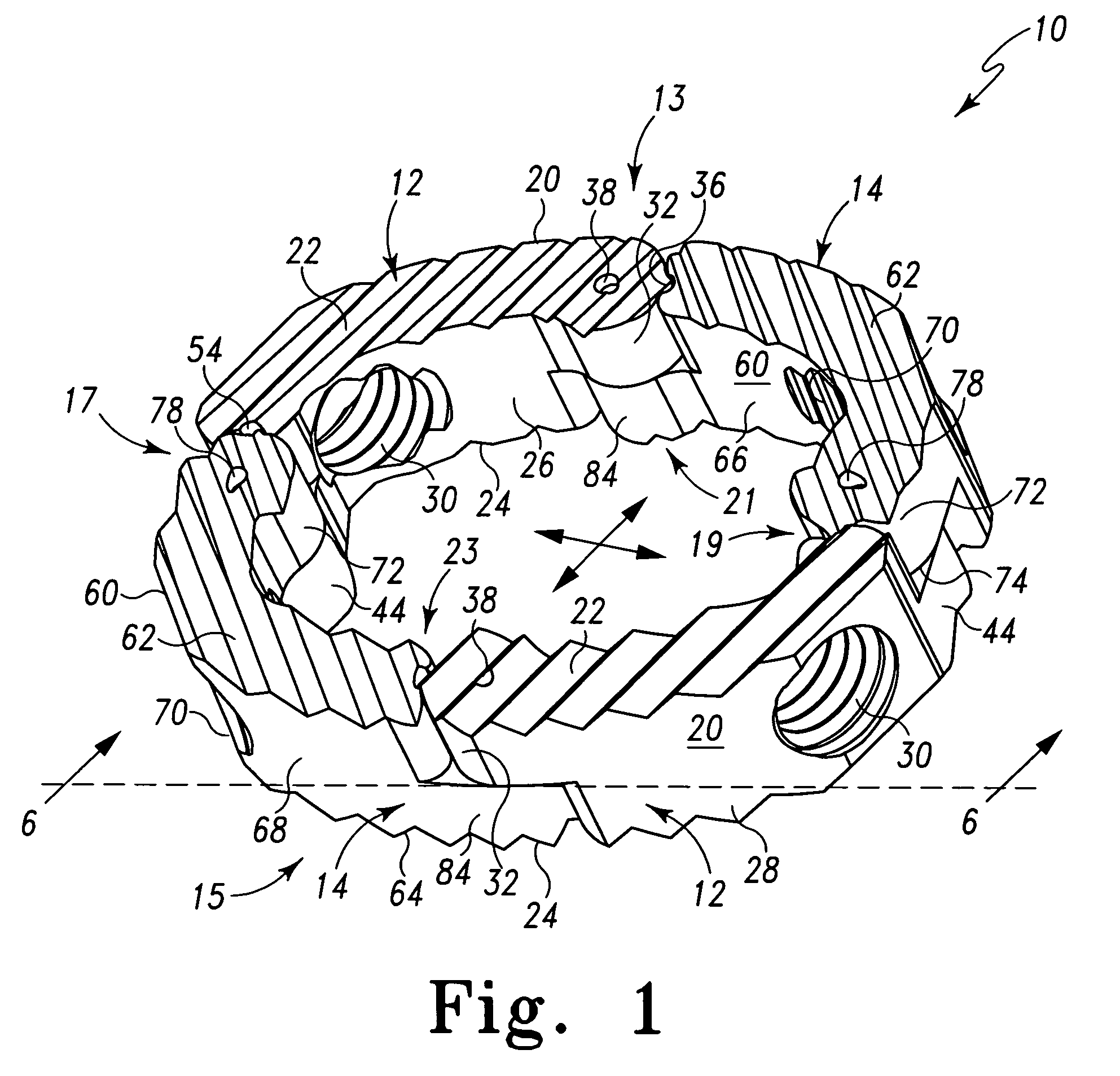
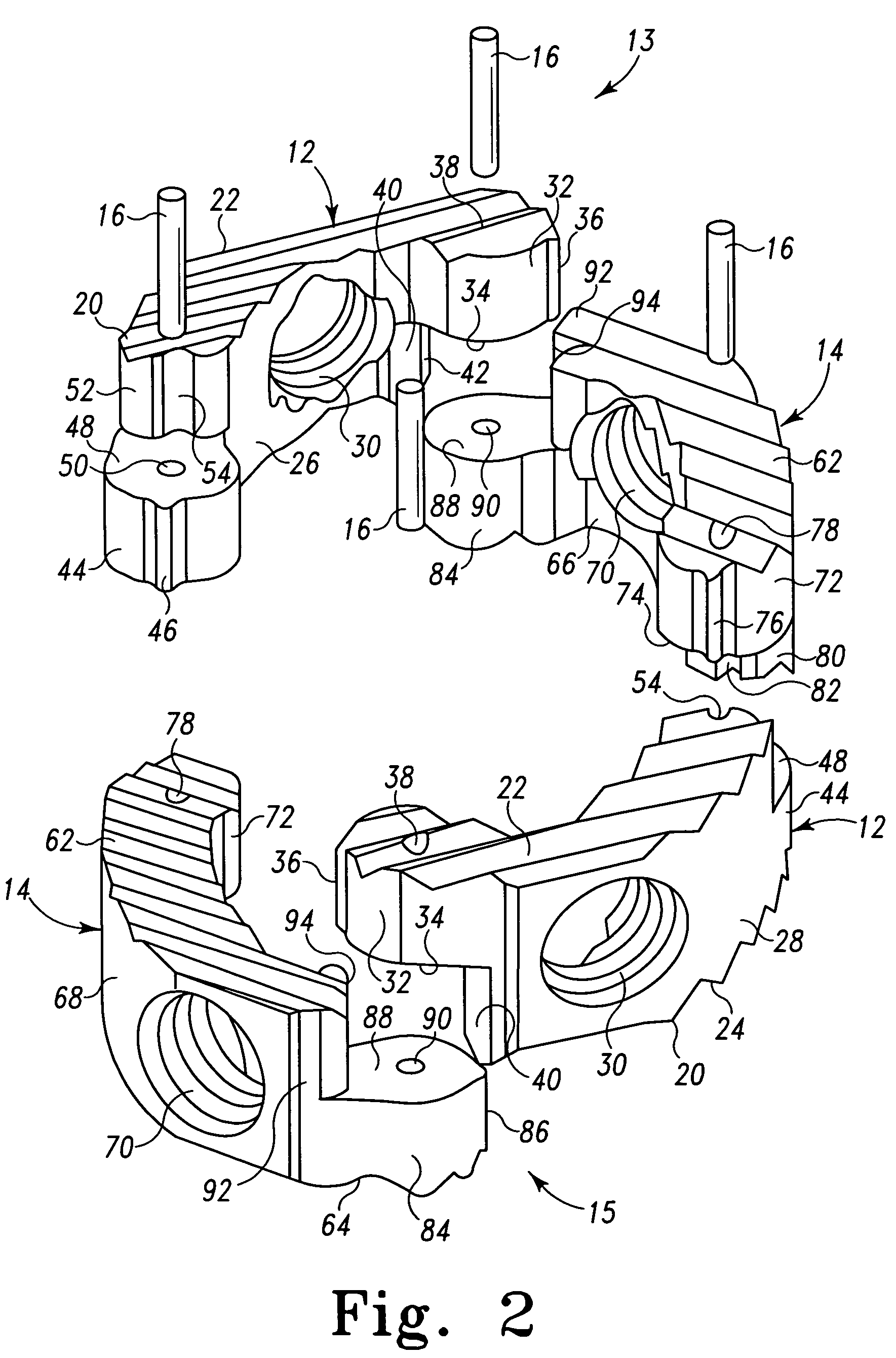
Radially expandable spinal interbody device and implantation tool
ActiveUS20080243255A1Inhibit and prevent overextensionBone implantSpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceImplantation Site
A radially expandable spinal interbody device for implantation between adjacent vertebrae of a spine is deliverable to an implant area in a radially collapsed state having minimum radial dimensions and once positioned is then radially expandable through and up to maximum radial dimensions. The expanded radially expandable spinal interbody device is configured to closely mimic the anatomical configuration of a vertebral face. The radially expandable spinal interbody device is formed of arced, pivoting linkages that allow transfiguration from the radially collapsed minimum radial dimensions through and up to the radially expanded maximum radial dimensions once deployed at the implant site (i.e. between adjacent vertebrae). The pivoting linkages have ends with locking features that inhibit or prevent overextension of the linkages. In one form of the locking features, one end of the linkage includes lobes that form a pocket while the other end of the linkage includes a projection that is adapted to be received in the pocket of the lobes of an adjacent linkage. A kit is also provided including a tool for the implantation and deployment of the spinal interbody device into an intervertebral space.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
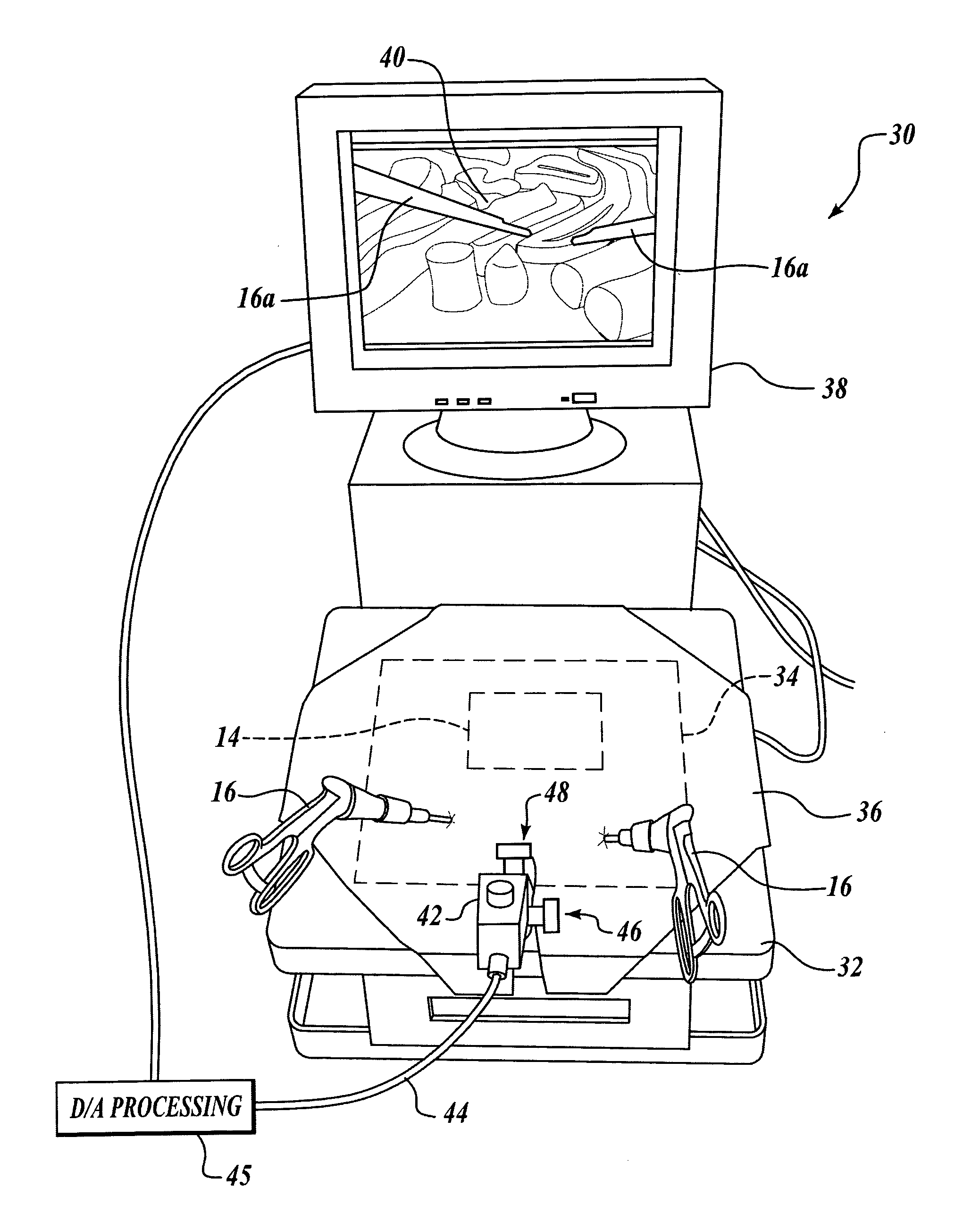
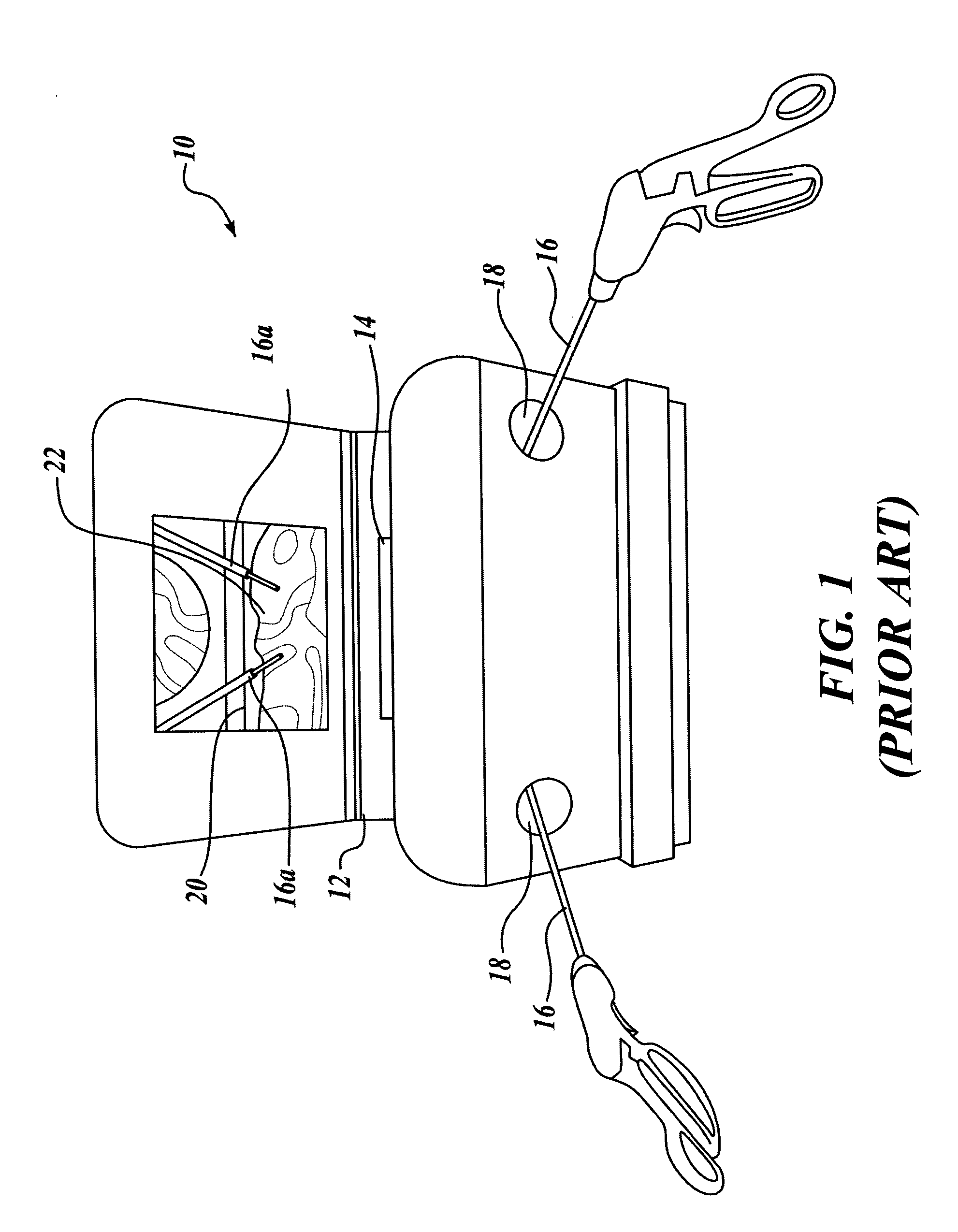
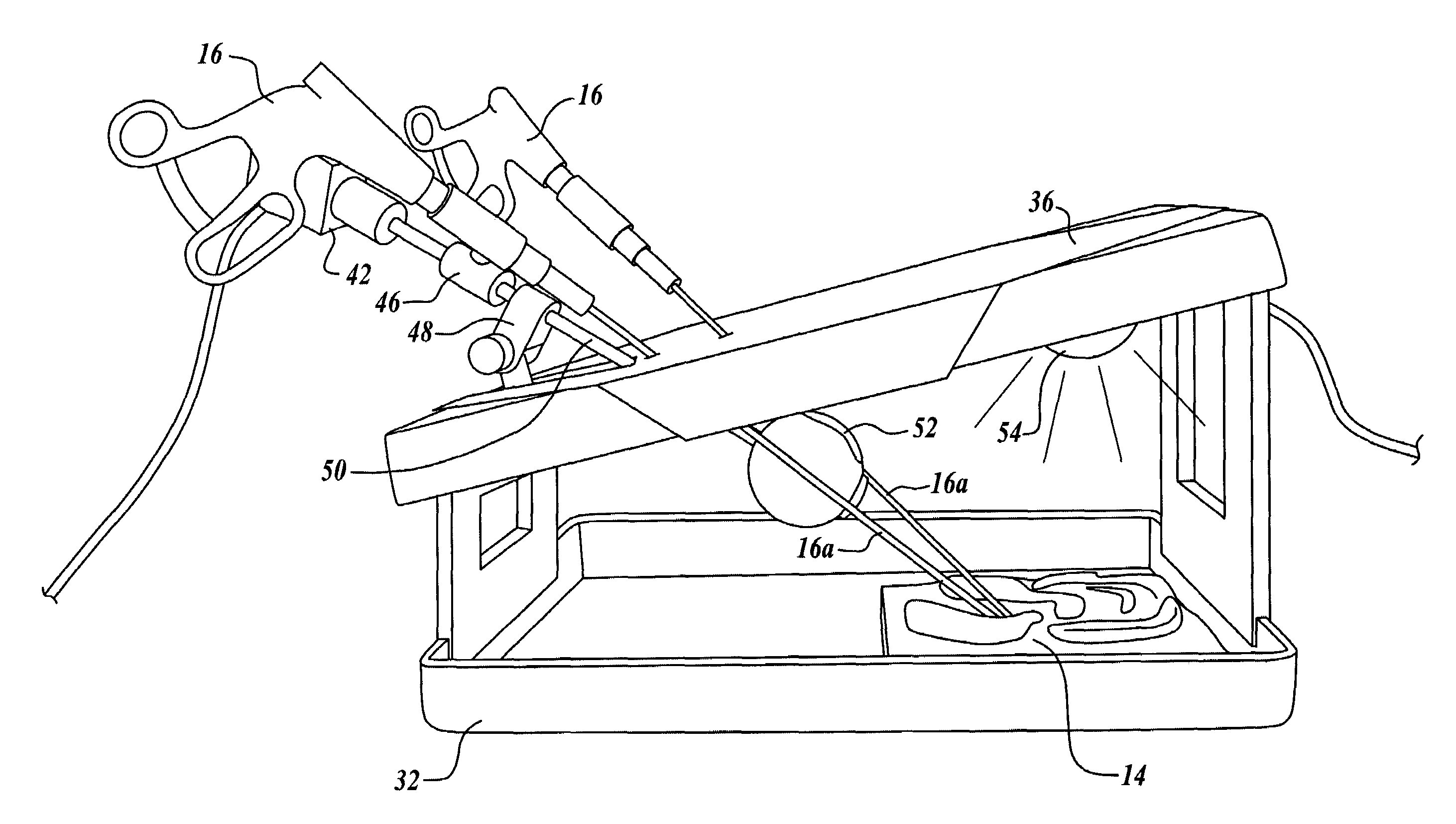
Laparoscopic and endoscopic trainer including a digital camera
ActiveUS20050064378A1Enhance endoscopic skill trainingEasy to trainSurgeryEducational modelsDigital videoAnatomical structures
A videoendoscopic surgery training system includes a housing defining a practice volume in which a simulated anatomical structure is disposed. Openings in the housing enable surgical instruments inserted into the practice volume to access the anatomical structure. A digital video camera is disposed within the housing to image the anatomical structure on a display. The position of the digital video camera can be fixed within the housing, or the digital video camera can be positionable within the housing to capture images of different portions of the practice volume. In one embodiment the digital video camera is coupled to a boom, a proximal end of which extends outside the housing to enable positioning the digital video camera. The housing preferably includes a light source configured to illuminate the anatomical structure. One or more reflectors can be used to direct an image of the anatomical structure to the digital video camera.
Owner:TOLY CHRISTOPHER C
Shoulder joint prosthetic system
InactiveUS20070156246A1Easy to adjustStabilising prosthesisJoint implantsCoatingsArticular surfacesShoulder hemiarthroplasty
In a first aspect the present invention provides a glenoid prosthesis assembly for use in shoulder joint arthroplasty to address conditions where deterioration of the rotator cuff mechanism of the shoulder joint is severe, the assembly comprising a first shell component to be affixed to a scapula by fixing means, and a smaller second component adapted to nest within the first component and having an articulation surface for articulating with a humeral head, the first component being over-sized relative to the glenoid surface of a scapula whereby the first component may be first affixed to at least two of the glenoid, acromion and coracoid processes of the scapula in use by the fixing means and the second component may be cemented in place within the first component allowing initial adjustability in the poise of the second component relative to the first component. Amongst other aspects the invention also provides a modular proximal humeral prosthesis system for use in shoulder joint arthroplasty which enables the proximal humeral prosthesis to be changed between anatomical and reverse of anatomical configurations to address differing degrees of shoulder joint deterioration.
Owner:STANMORE IMPLANTS WORLDWIDE
Radially expandable spinal interbody device and implantation tool
ActiveUS8241358B2Inhibit and prevent overextensionBone implantSpinal implantsIntervertebral spacesBiomedical engineering
A radially expandable spinal interbody device for implantation between adjacent vertebrae of a spine is deliverable to an implant area in a radially collapsed state having minimum radial dimensions and once positioned is then radially expandable through and up to maximum radial dimensions. The expanded radially expandable spinal interbody device is configured to closely mimic the anatomical configuration of a vertebral face. The radially expandable spinal interbody device is formed of arced, pivoting linkages that allow transfiguration from the radially collapsed minimum radial dimensions through and up to the radially expanded maximum radial dimensions once deployed at the implant site (i.e. between adjacent vertebrae). The pivoting linkages have ends with locking features that inhibit or prevent overextension of the linkages. In one form of the locking features, one end of the linkage includes lobes that form a pocket while the other end of the linkage includes a projection that is adapted to be received in the pocket of the lobes of an adjacent linkage. A kit is also provided including a tool for the implantation and deployment of the spinal interbody device into an intervertebral space.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
Laparoscopic and endoscopic trainer including a digital camera
ActiveUS7594815B2Easy to trainWide field of viewSurgeryEducational modelsAnatomical structuresDigital video
Owner:TOLY CHRISTOPHER C
system and method for real-time surface and volume mapping of anatomical structures
A method and system for mapping a volume of an anatomical structure includes a processor for computing a contour of a medical device as a function of positional and / or a shape constraints, and to translate the contour into known and virtual 3D positions. The processor is configured to determine a spatial volume based on a virtual position, and to render a 3D representation of the spatial volume. A method and system of mapping a surface of an anatomical structure includes a processor configured to obtain an image of the structure. The processor is further configured to receive a signal indicative of a medical device contacting the surface of the anatomical structure, and to determine a position of the device upon when contact has been made. The processor is configured to superimpose marks on the image indicative of a contact points between the device and the structure.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL INT HLDG SARL
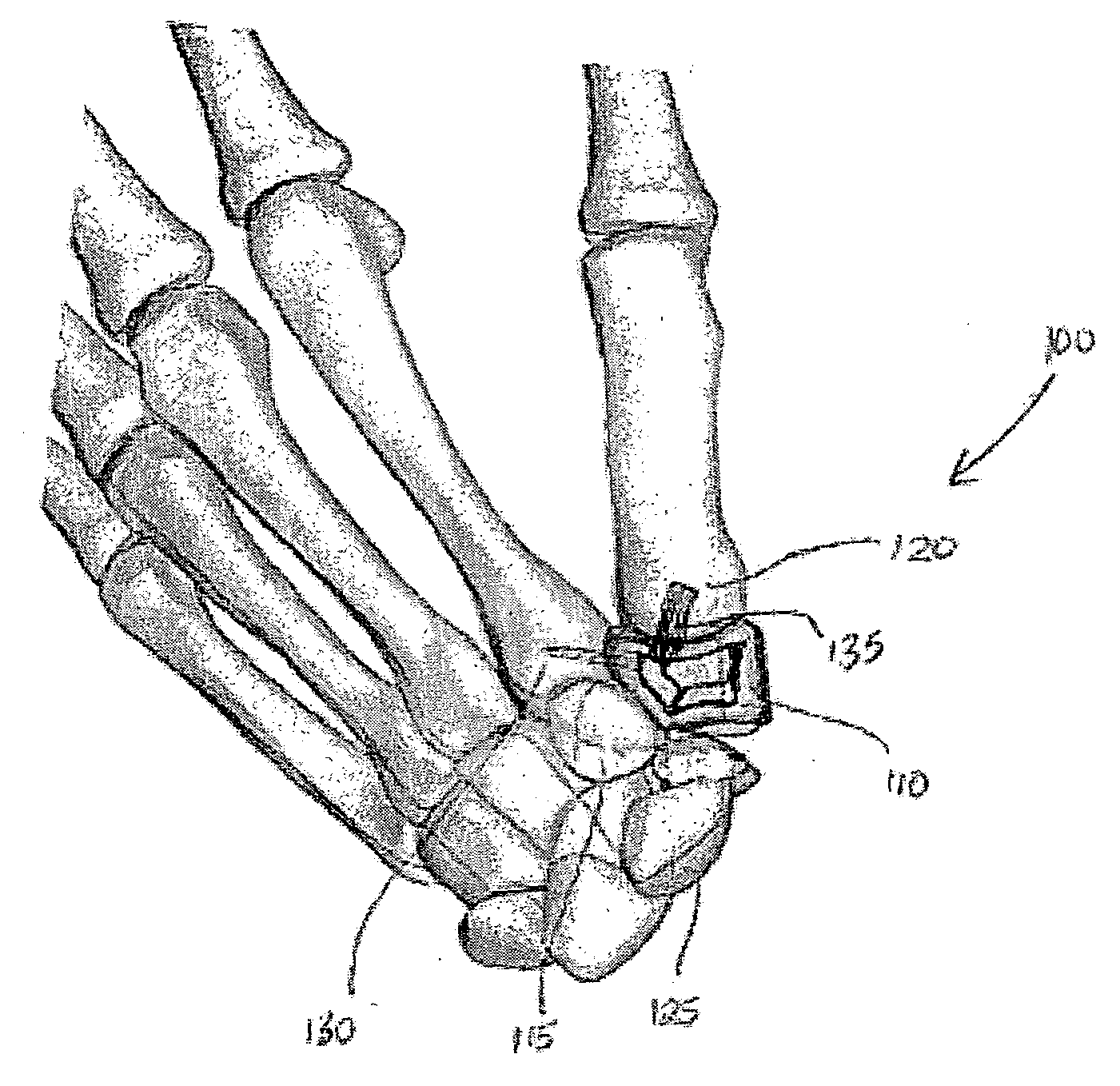
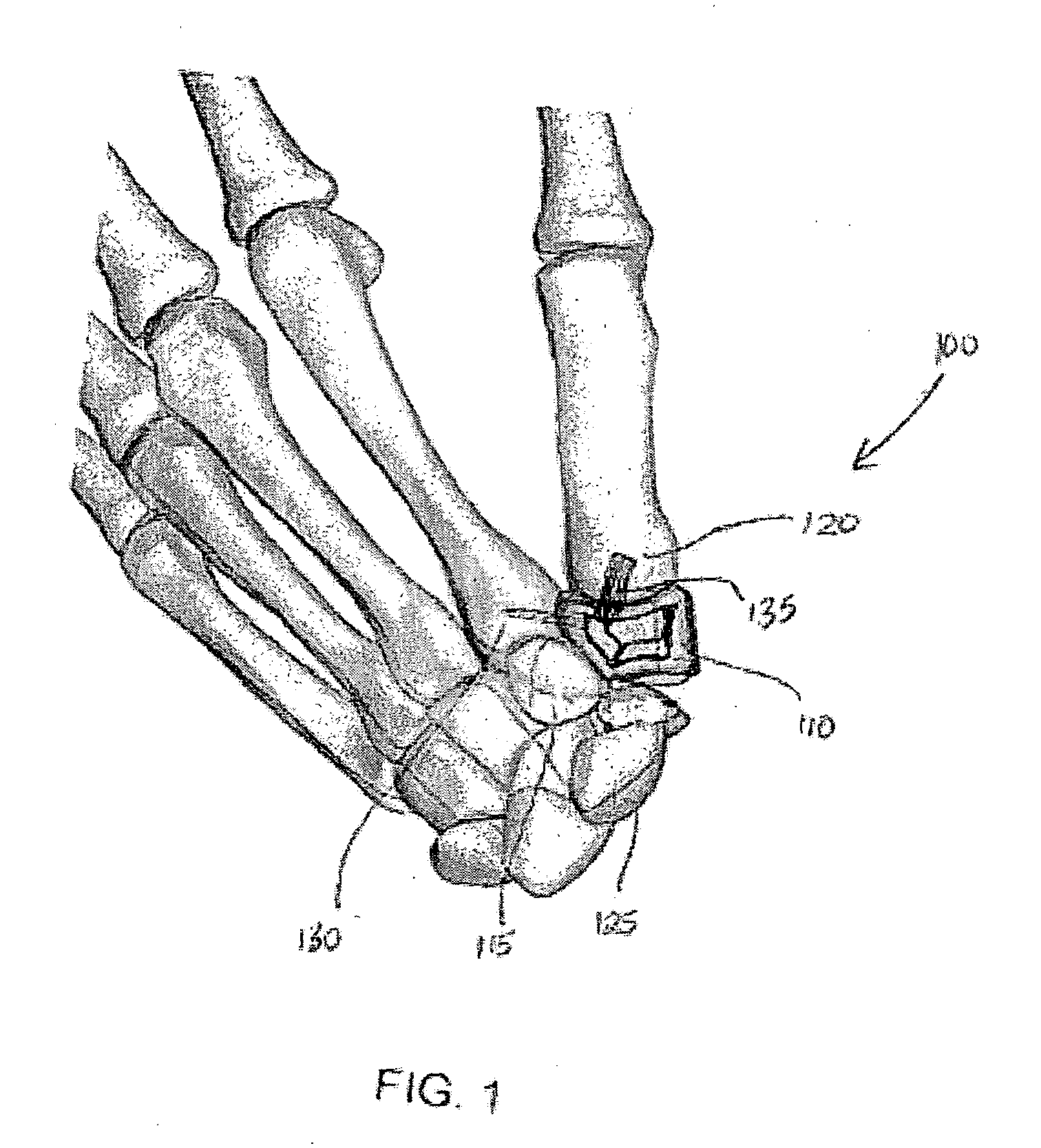
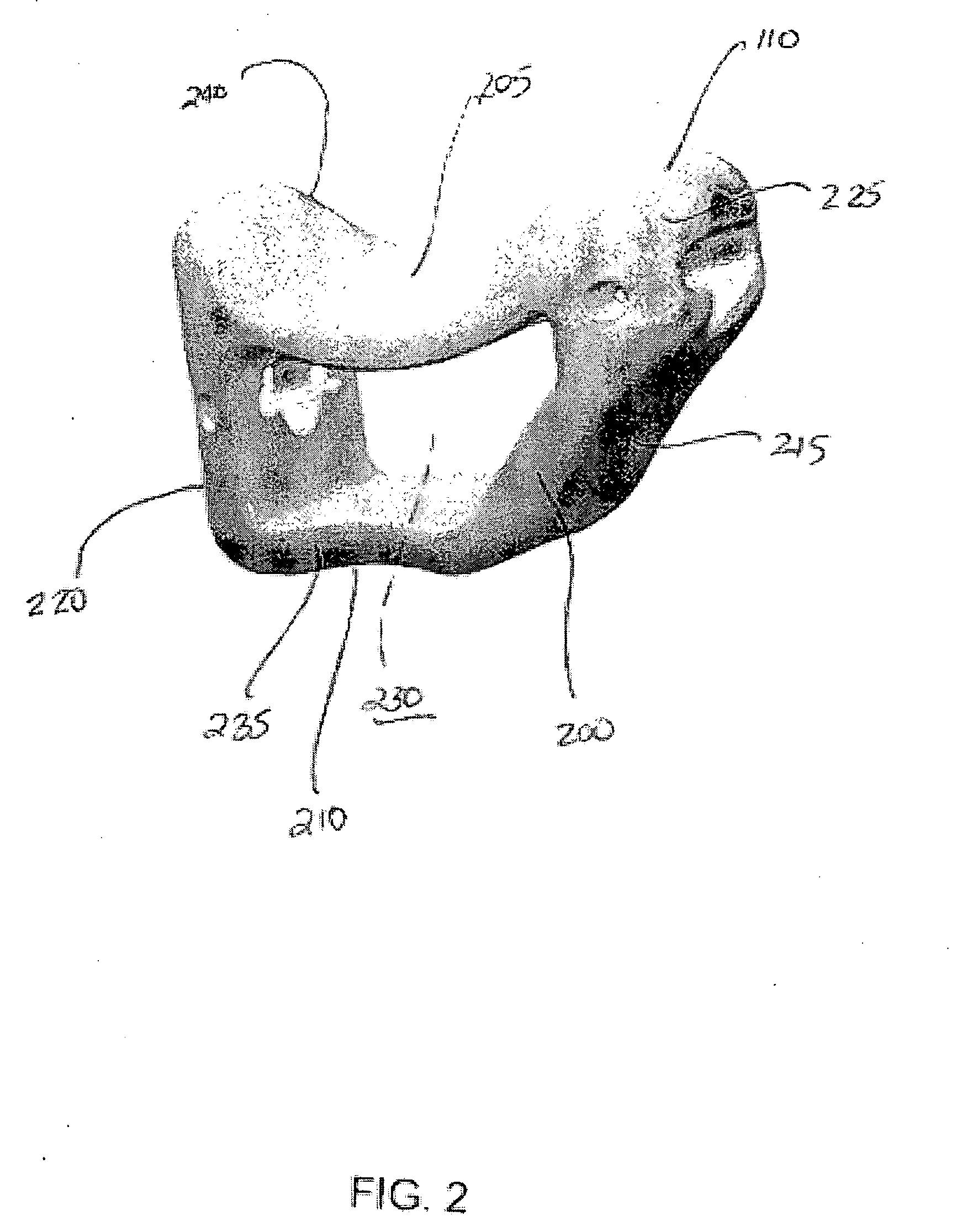
System and method for trapezium bone replacement
ActiveUS20090254190A1Efficiently distribute forceEffective forceSuture equipmentsFinger jointsTrapezium BoneProsthesis
A carpometacarpal joint replacement system for replacing the trapezium bone in the hand is provided. The system includes a trapezial implant for the carpometacarpal joint resulting in replacement of the carpal trapezium bone with a prosthesis having the same anatomical configuration as the trapezium bone. The implant device comprises a plurality of concave surfaces, with the plurality of concave surfaces articulating with the carpal and metacarpal bones.
Owner:EXTREMITY MEDICAL
Apparatus and method for targeting for surgical procedures
InactiveUS20050203490A1Reduce manufacturing costEasy to manufactureDiagnostic markersBone drill guidesAnatomical structuresSurgical site
A targeting instrument that consists of an indicating surface that is a planar body that can be placed so as to lie on the skin of a patient or placed in a cavity in the patient where an operation is being performed by a surgeon, so as to align the operation site with the target being operated on by the surgeon. The targeting instrument can be dimensioned to match the size and shape of the cannula or the desired size of the surgical exposure and can include a stencil configuration to allow the surgeon to inscribe the target area on the skin of the patient. The targeting instrument may include a handle. The method of use is to insert the targeting instrument in the location where the target of the operation is and to hone in on the target with the use of an imaging device. In one method of use this will align the target, select the entry incision and allowing the surgeon to make an accurate and minimally sized incision. In other methods of use, the targeting instrument can be placed in proximity to the skin or thereon of the patient for locating anatomical targets, for localizing bony anatomy.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
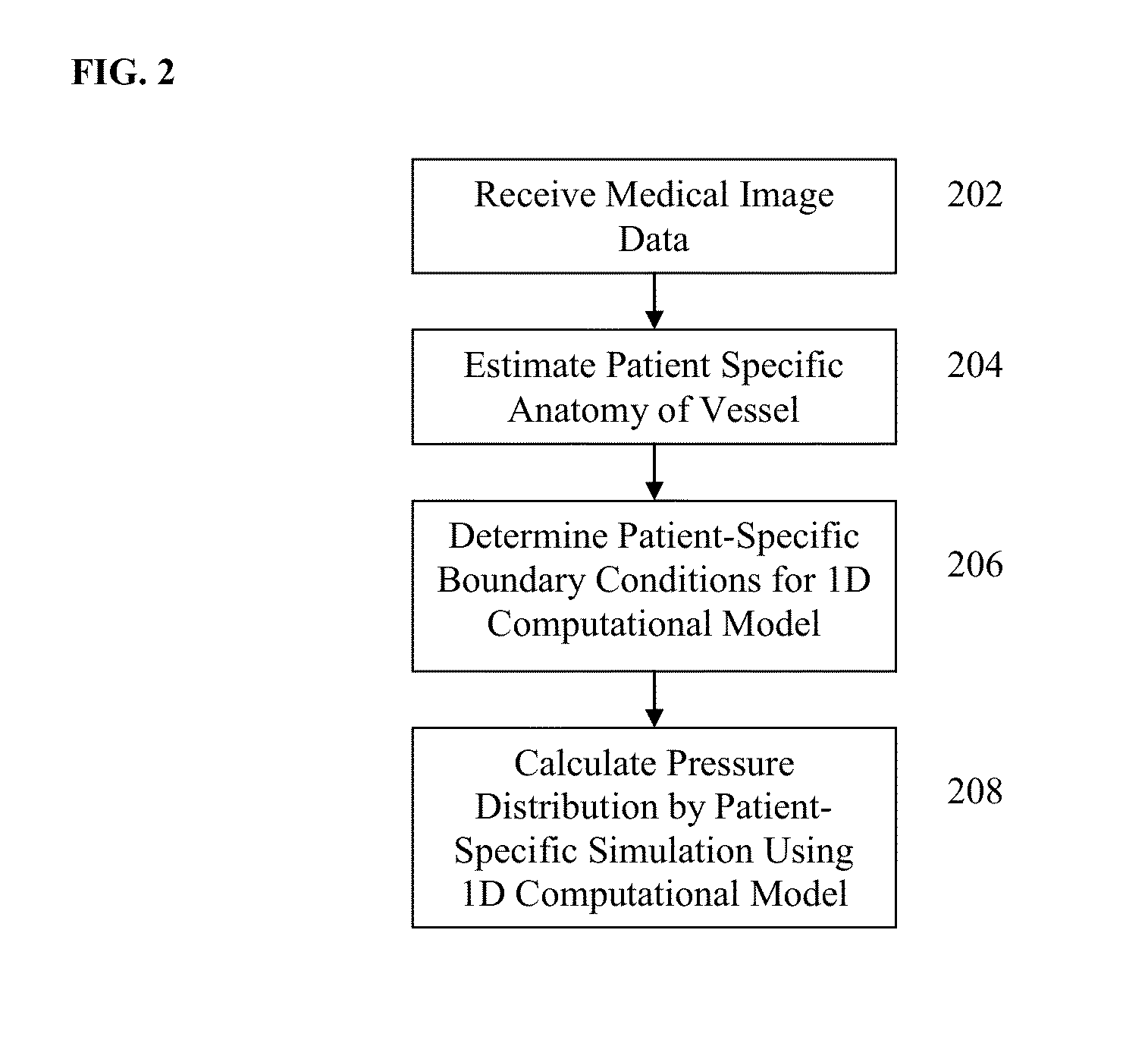
Method and System for Hemodynamic Assessment of Aortic Coarctation from Medical Image Data
A method and system for non-invasive hemodynamic assessment of aortic coarctation from medical image data, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data is disclosed. Patient-specific lumen anatomy of the aorta and supra-aortic arteries is estimated from medical image data of a patient, such as contrast enhanced MRI. Patient-specific aortic blood flow rates are estimated from the medical image data of the patient, such as velocity encoded phase-contrasted MRI cine images. Patient-specific inlet and outlet boundary conditions for a computational model of aortic blood flow are calculated based on the patient-specific lumen anatomy, the patient-specific aortic blood flow rates, and non-invasive clinical measurements of the patient. Aortic blood flow and pressure are computed over the patient-specific lumen anatomy using the computational model of aortic blood flow and the patient-specific inlet and outlet boundary conditions.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
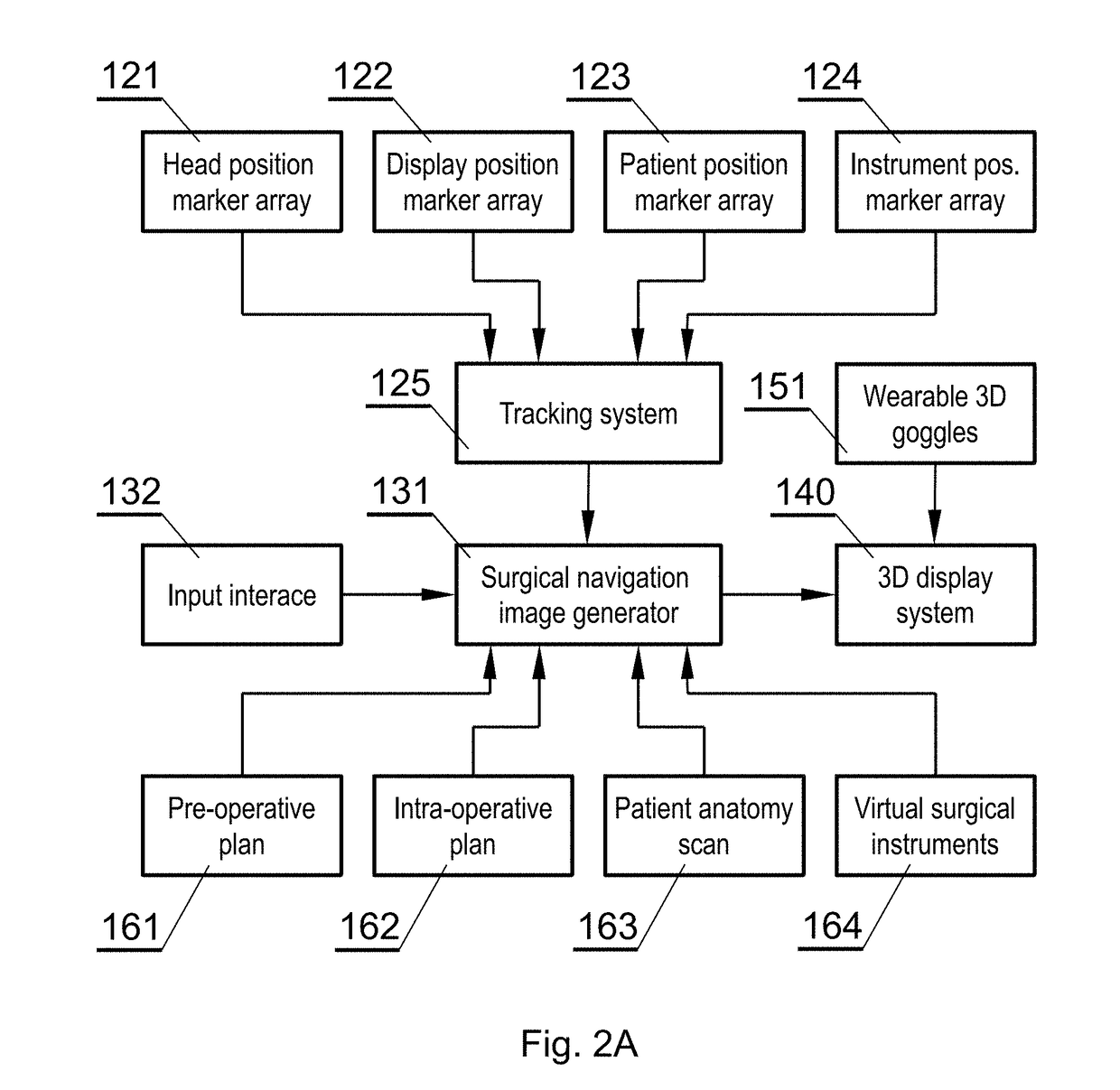
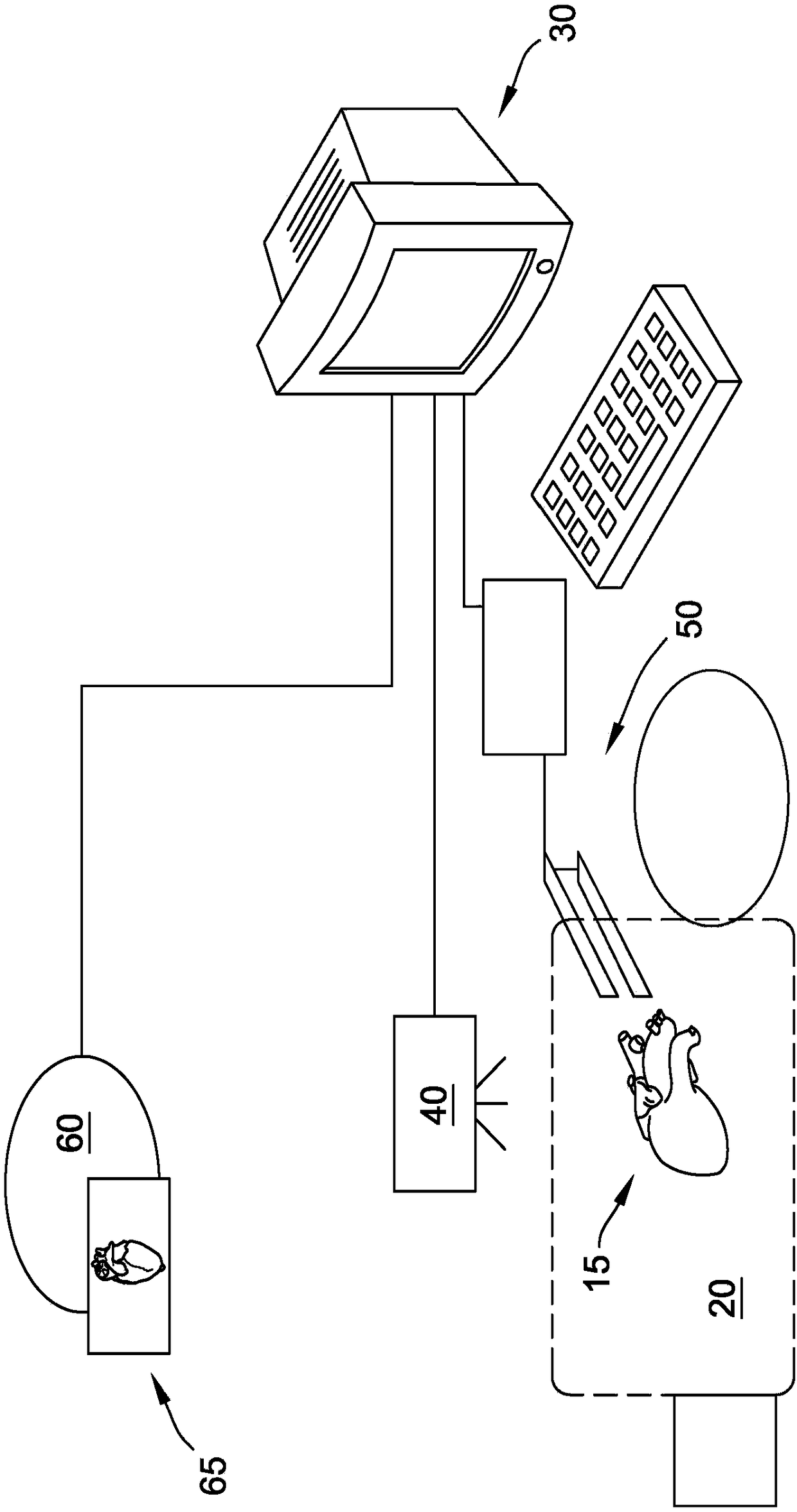
Surgical navigation system and method for providing an augmented reality image during operation
PendingUS20190053851A1Improve planning accuracyEasy to identifyImage analysisSurgical navigation systemsDisplay deviceNavigation system
A surgical navigation system includes: a 3D display with a see-through mirror that is partially transparent and partially reflective; a tracking system comprising means for real-time tracking of: a surgeon's head, the see-through mirror and a patient anatomy to provide current position and orientation data; a source of a patient anatomy data; a surgical navigation image for generating a surgical navigation image comprising at least the patient anatomy data, in accordance with the current position and orientation data provided by the tracking system based on the current relative position and orientation of the surgeon's head, the see-through mirror and the patient anatomy; the 3D display configured to emit the surgical navigation image towards the see-through mirror, such that an augmented reality image collocated with the patient anatomy in the surgical field underneath the see-through mirror is visible to a viewer looking from above the see-through mirror towards the surgical field.
Owner:HOLO SURGICAL INC
Patient reference device
ActiveUS20180193097A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceSurgical operationOutput device
Methods and devices to track patient anatomy during a surgical operation. A patient reference device is attached to an anatomical feature of a patient and it includes an attachment base and an optically-trackable array detectable by an optical navigation system and having a longitudinally-extending arm to space apart the fixed geometric pattern from the anatomical feature. The arm includes a connector to be detachably secured to the attachment base. An inertial measurement unit within the attachment base enables determining, based on comparing a threshold level to a motion signal, that the attachment base has changed position, wherein the motion signal represents the change in position and its magnitude. Based on determining that the attachment base has changed position an alarm signal is generated an and an output device in the attachment base outputs an alarm in response to the alarm signal.
Owner:SYNAPTIVE MEDICAL INC
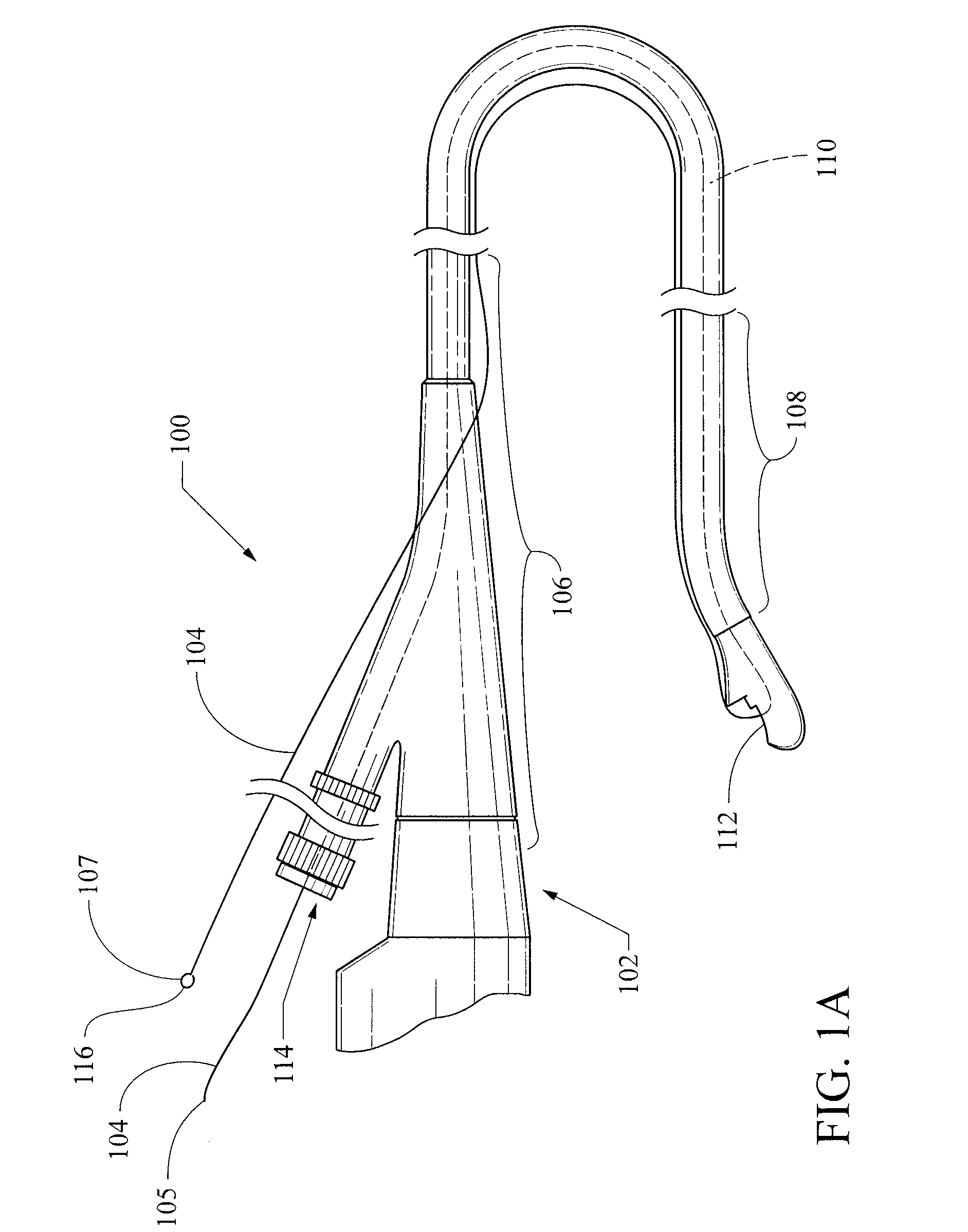
Advancing system and method of use thereof
A system is provided for advancing medical devices along an endoscope to a selected target anatomy in a patient. The advancing system includes a tether having a first portion disposed through a working channel of an endoscope and a second portion disposed external the endoscope. The advancing system may include a guiding device configured to advance a medical device beyond a distal portion of the endoscope to a selected target anatomy.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC
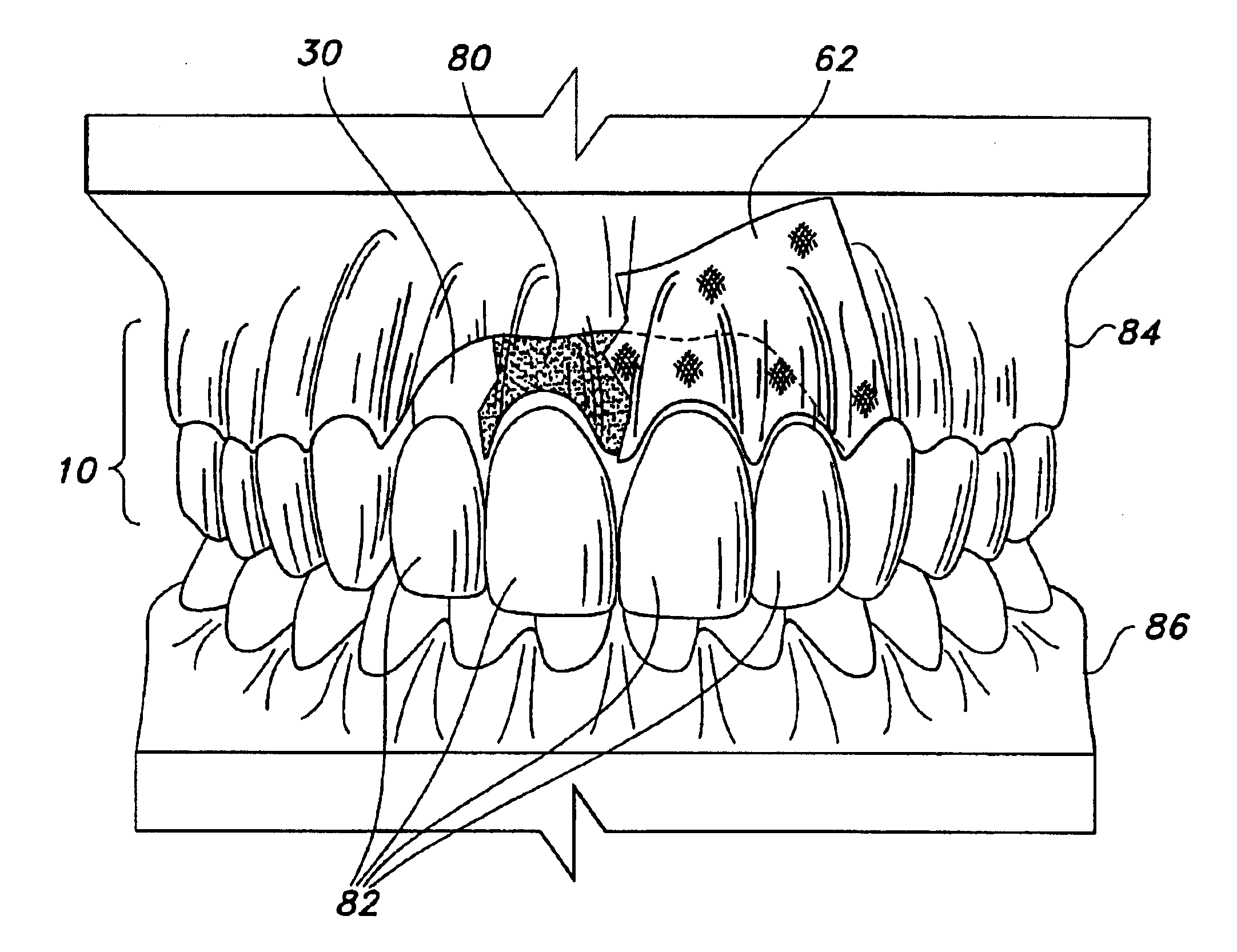
Biocompatible form and method of fabrication
InactiveUS6911046B2Avoiding “ black hole ” problemAccurate placementDental implantsBone implantFiberMylohyoid Ridge
A biocompatible form and a method for fabricating the implant are provided. The biocompatible form may be used to support bone graft material such as that used to reconstruct missing bone in a patient's oral cavity. The implant is fabricated from a biocompatible mesh, which may be made of titanium, a titanium alloy or fiber and is permanently implantable in the patient's oral cavity. The biocompatible form has an anatomical configuration which includes one or more portions conforming substantially to various alveolar bone contours which may include predetermined, human interproximal bone contours, root prominence bone contours and mylohyoid ridge bone contours. The biocompatible form may include a palatal section. The biocompatible form may also include one or more apertures for receiving a corresponding number of dental prostheses therethrough.
Owner:CAGENIX TECH
System and method for flattened anatomy for interactive segmentation and measurement
ActiveUS7643662B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementVoxelComputer science
Systems and methods are provided for accessing three dimensional representation of an anatomical surface and flattening the anatomical surface so as to produce a two dimensional representation of an anatomical surface. The two dimensional surface can be augmented with computed properties such as thickness, curvature, thickness and curvature, or user defined properties. The rendered two dimensional representation of an anatomical surface can be interacted by user so as to deriving quantitative measurements such as diameter, area, volume, and number of voxels.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Methods and systems for user defined distributed learning models for medical imaging
Systems and methods are provided for user defined distributed learning models grouped based on user clusters for configuring settings of a medical diagnostic imaging system. The systems and methods are configured to maintain models with predetermined settings for at least one of system settings, image presentation settings, or anatomical structures. The systems and methods are configured to calculate a data value representing select user preferences for a first user, identifying a first cluster based on the data value, and assigning a first model from the models to the first user based on the first cluster. The systems and methods are configured to monitor use of the first model by the first user during a medical diagnostic application to determine whether the first model is updated by the first user or automatically during the medical diagnostic application by changing at least one of system settings, image presentation settings, or anatomical structures.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
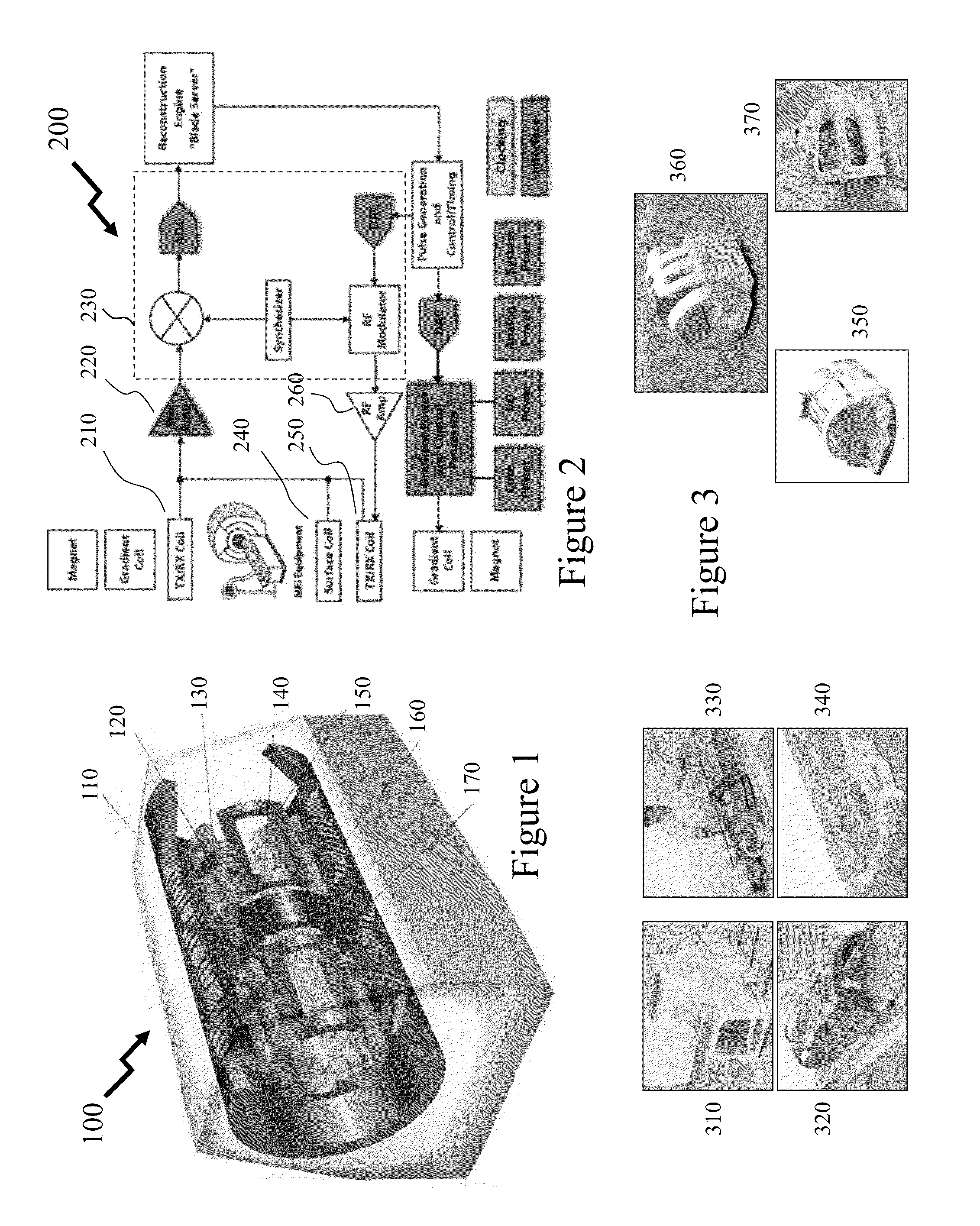
Methods and systems relating to high resolution magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveUS20160018489A1Easy to assembleImprove usabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsShape optimizationSingle shot
The inventors have established design principles for phased-array MRI coils from the considerations of the target region of the anatomy being evaluated and physical anatomy of the patients. Accordingly, the inventors have demonstrated shape-optimized phased array coils with dense packing of 32 channels for posterior-head imaging exhibiting the SNR gains required to realize not only sub-millimeter fMRI BOLD imaging but also allowing single-shot Gradient Echo-EPI imaging to be performed upon general 3 T MRI instruments. At the same time the design techniques address ergonomic considerations of the patient and designing shape-optimized phased-array MRI coils and patient supports that account for variations within the human population arising from factors such as race, gender, etc.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
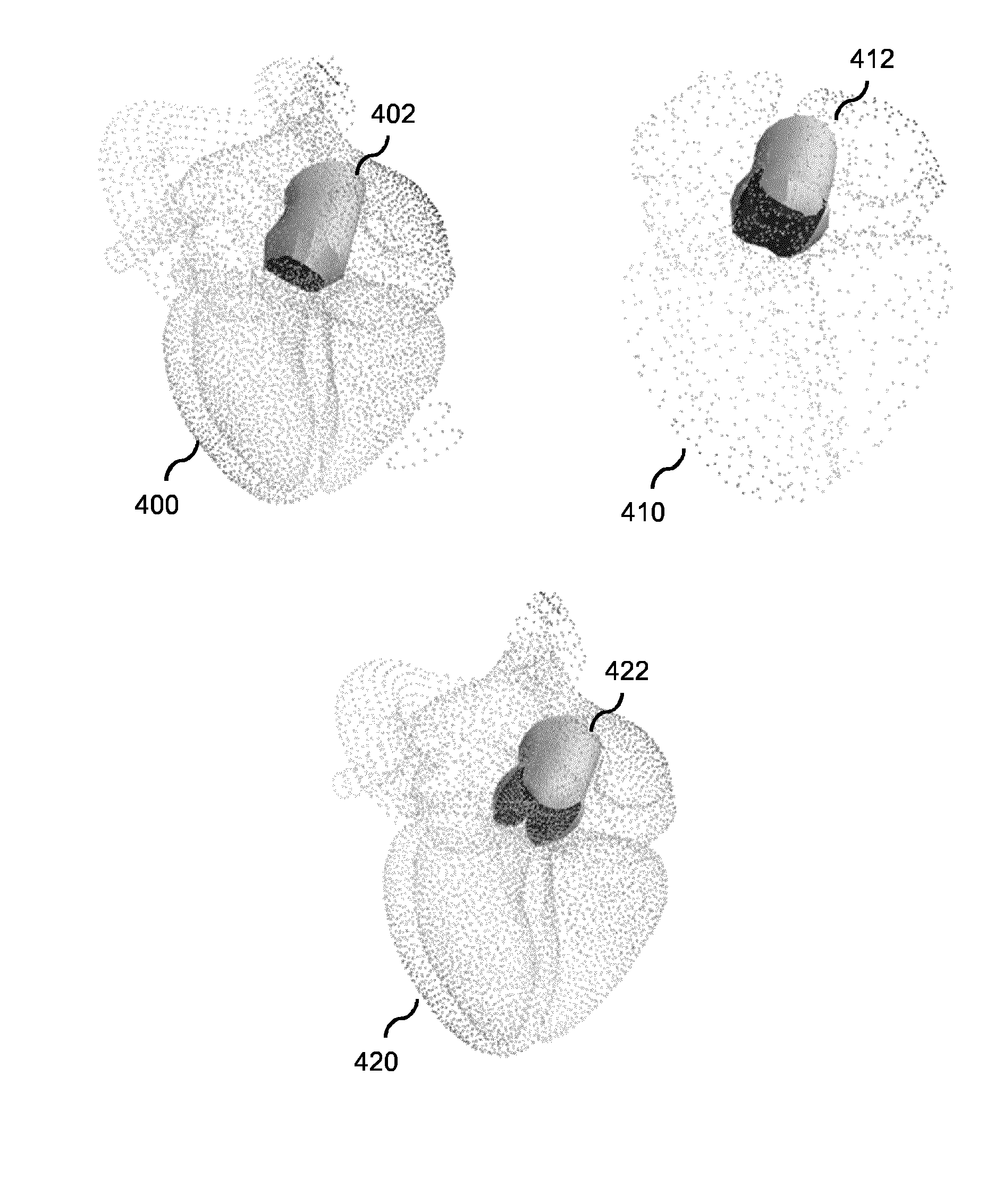
Model-based segmentation of an anatomical structure
ActiveUS20160307331A1Reduce cognitive loadComprehensive understandingImage enhancementImage analysisDiagnostic Radiology ModalityAnatomical structures
A system and method is provided which obtains different medical images (210) showing an anatomical structure of a patient and having been acquired by different medical imaging modalities and / or different medical imaging protocols. The system is configured for fitting a first deformable model to the anatomical structure in the first medical image (220A), fitting a second deformable model to the anatomical structure in the second medical image (220B), mutually aligning the first fitted model and the second fitted model (230), and subsequently fusing the first fitted model and the second fitted model to obtain a fused model (240) by augmenting the first fitted model with a part of the second fitted model which is missing in the first fitted model; or adjusting or replacing a part of the first fitted model based on a corresponding part of the second fitted model having obtained a better fit. The fused model represents a multimodal / multi-protocol segmentation of the anatomical structure, and provides a user with a more comprehensive understanding of the anatomical structure than known models.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
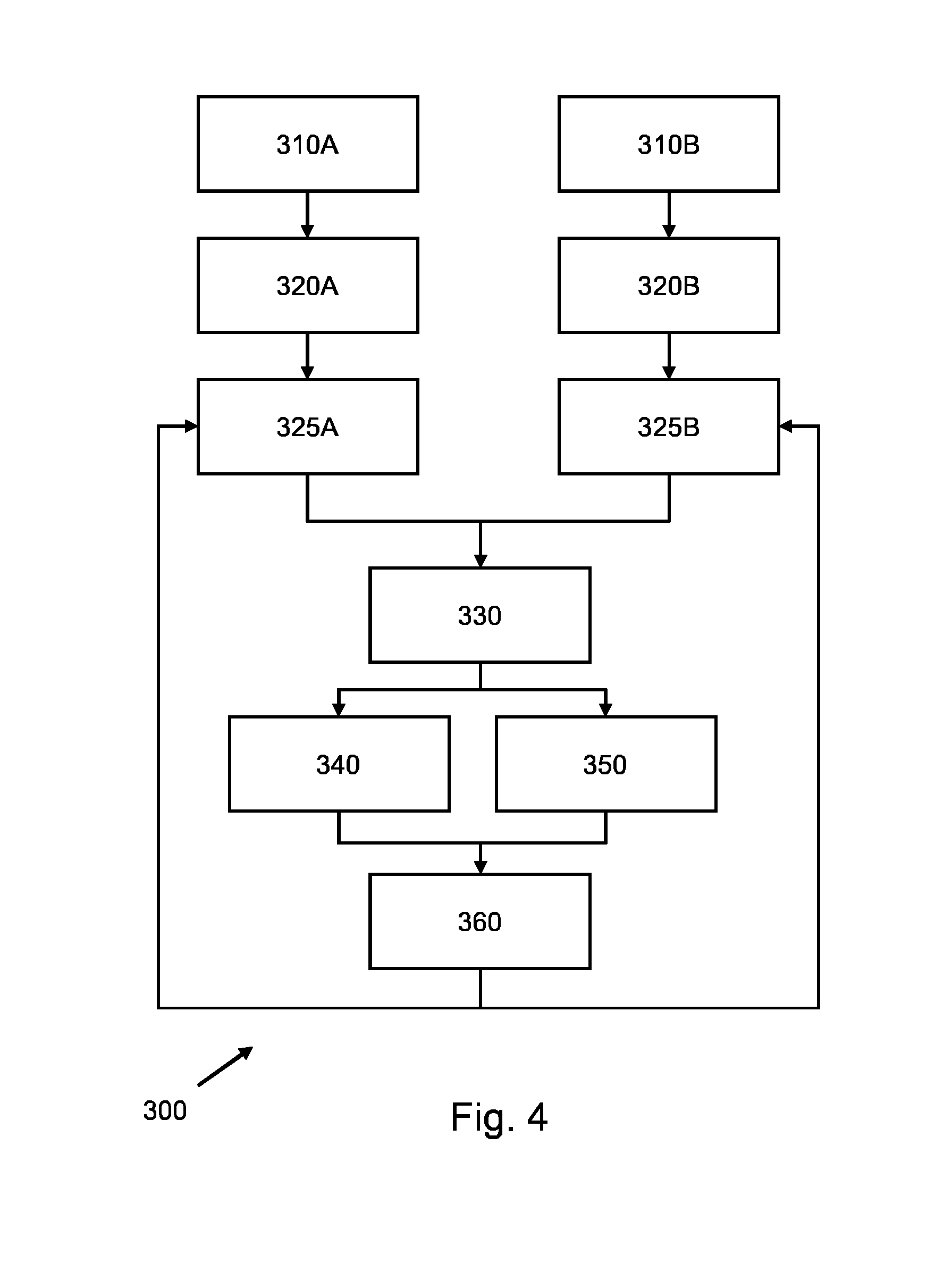
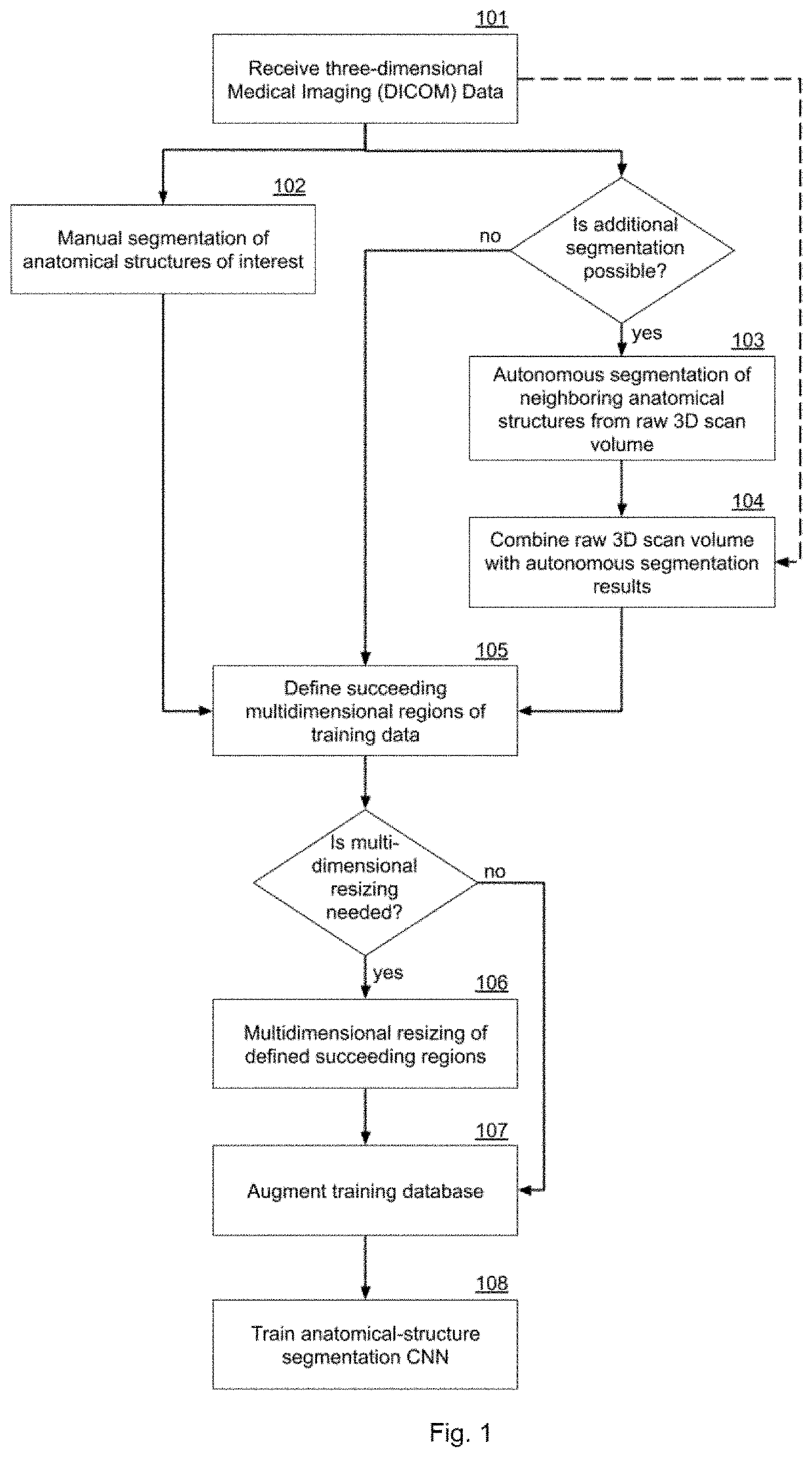
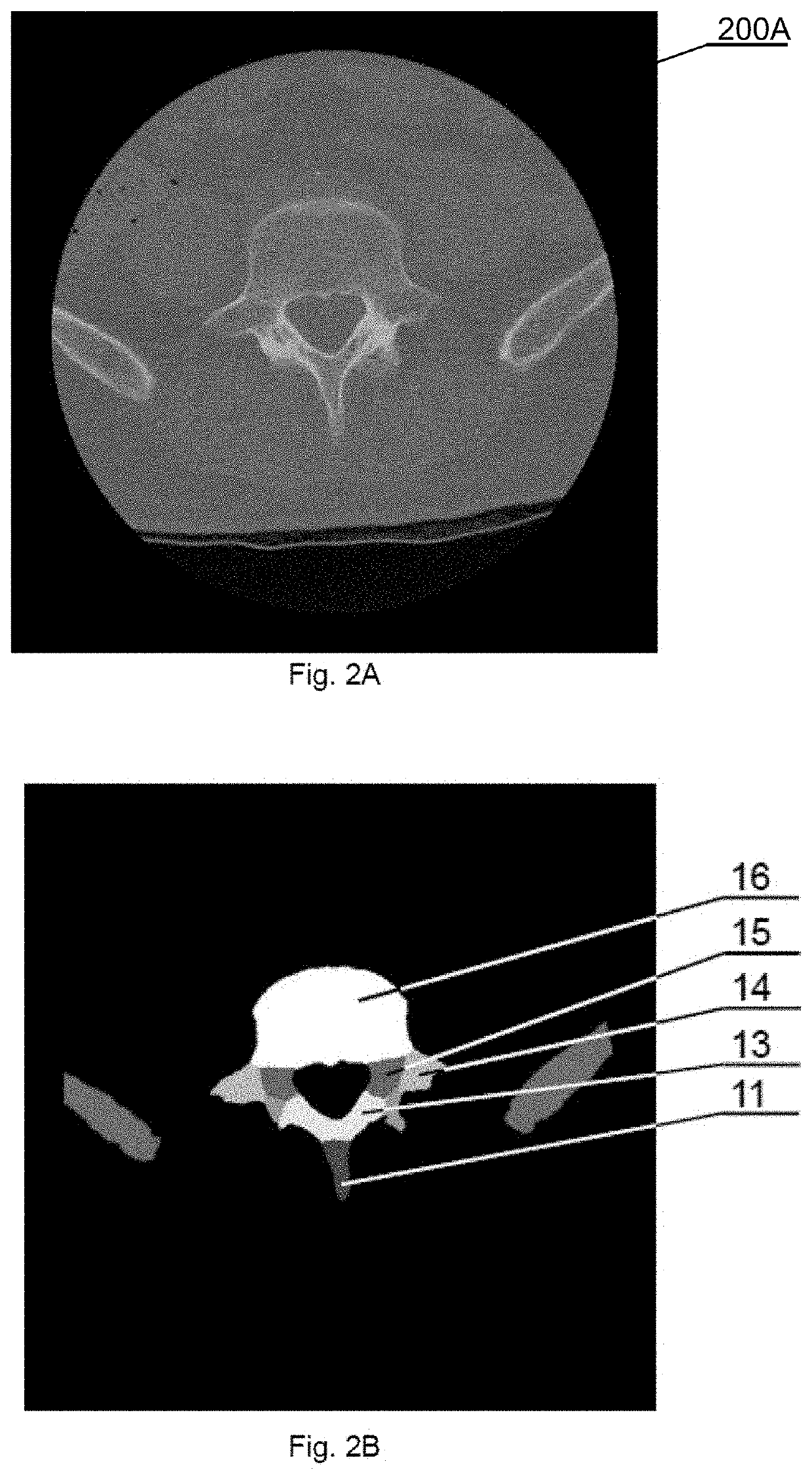
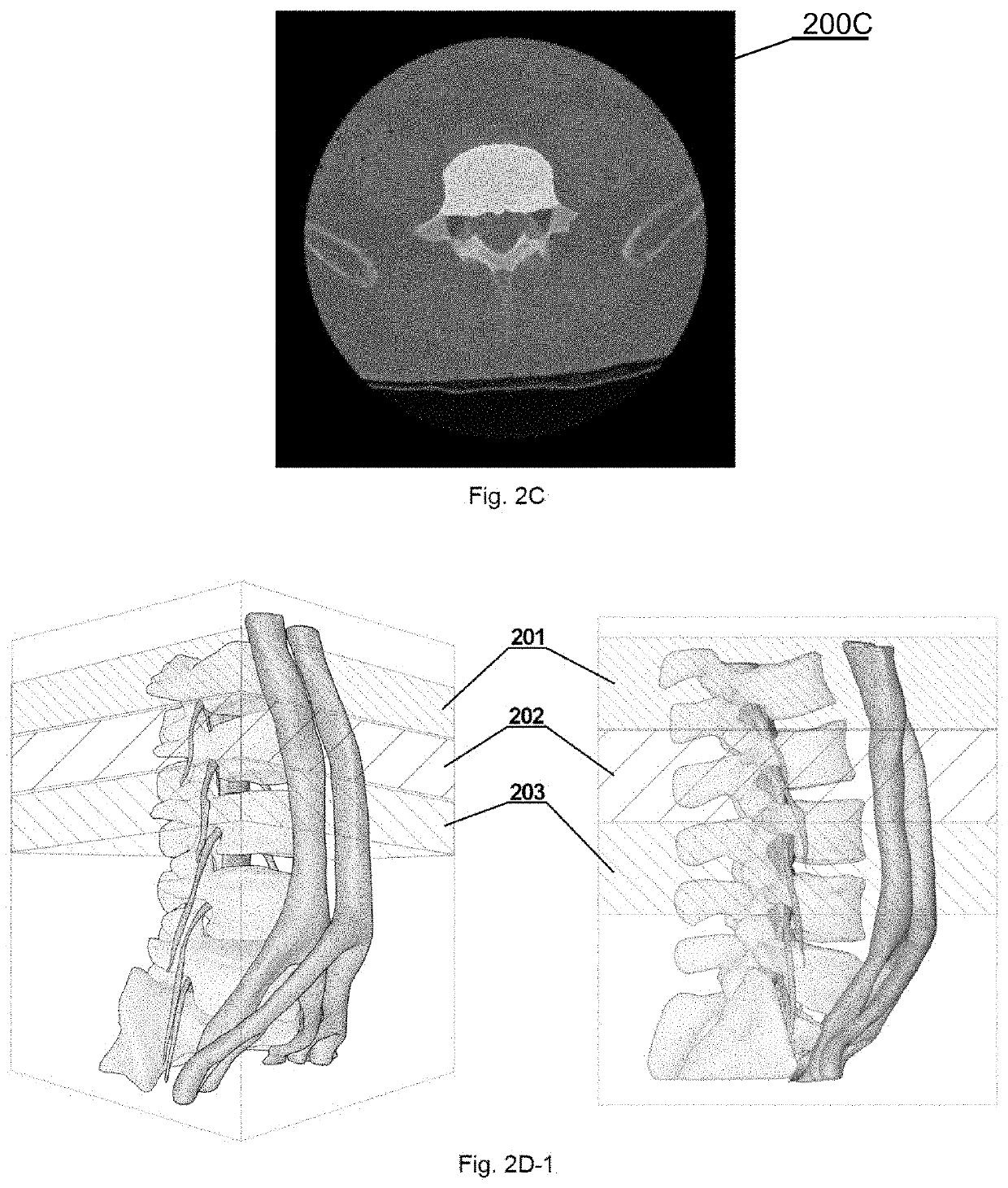
Autonomous multidimensional segmentation of anatomical structures on three-dimensional medical imaging
PendingUS20200410687A1Increasing input data dimensionalityEnhance segmentation CNN performanceImage enhancementImage analysis3d shapesVoxel
A method for autonomous multidimensional segmentation of anatomical structures from 3D scan volumes including receiving the 3D scan volume including a set of medical scan images comprising the anatomical structures; automatically defining succeeding multidimensional regions of input data used for further processing; autonomously processing), by means of a pre-trained segmentation convolutional neural network, the defined multidimensional regions to determine weak segmentation results that define a probable 3D shape, location, and size of the anatomical structures; automatically combining multiple weak segmentation results by determining segmented voxels that overlap on the weak segmentation results, to obtain raw strong segmentation results with improved accuracy of the segmentation; autonomously filtering the raw strong segmentation results with a predefined set of filters and parameters for enhancing shape, location, size and continuity of the anatomical structures to obtain filtered strong segmentation results; and autonomously identifying classes of the anatomical structures from the filtered strong segmentation results.
Owner:AUGMEDICS INC
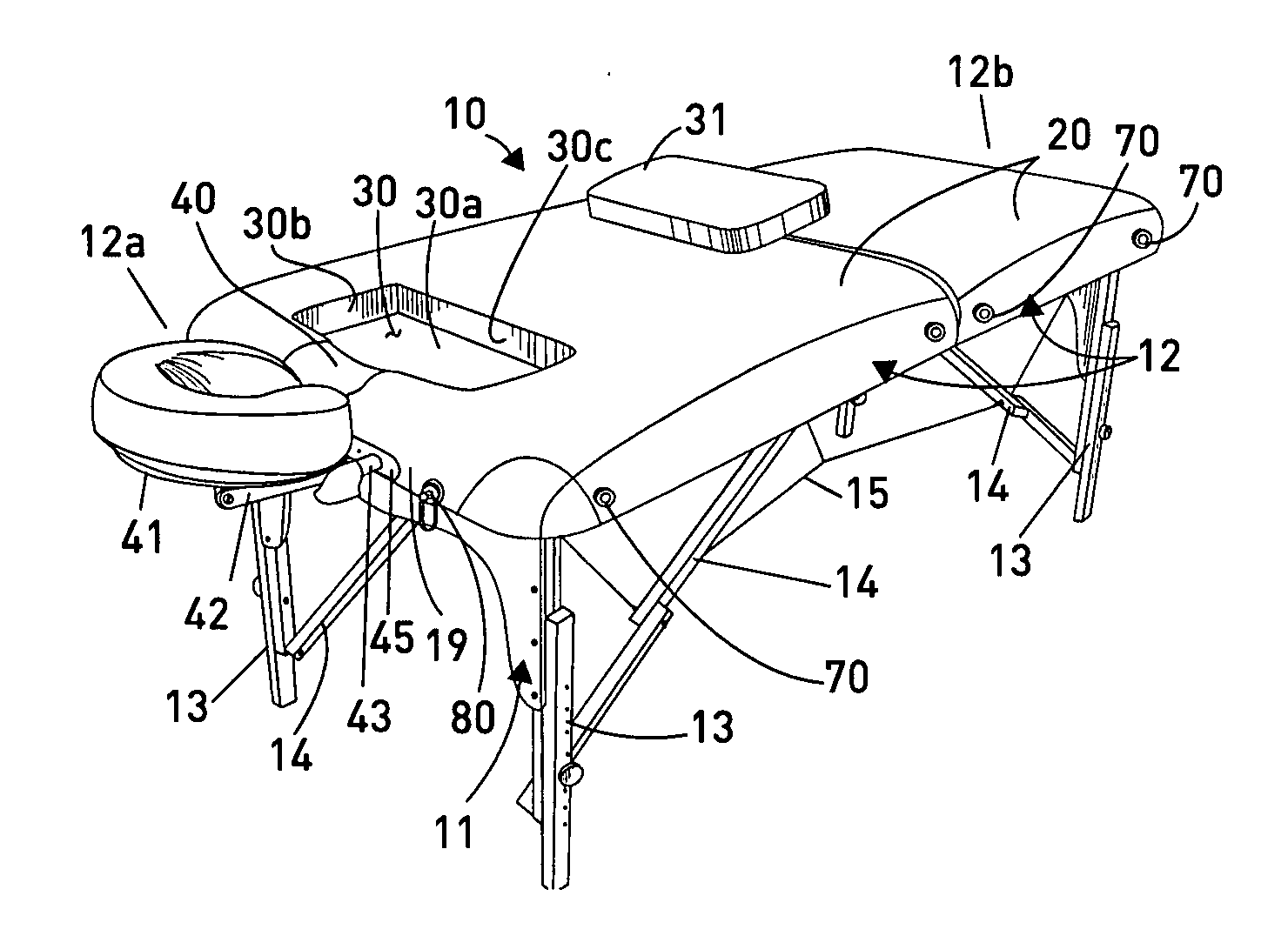
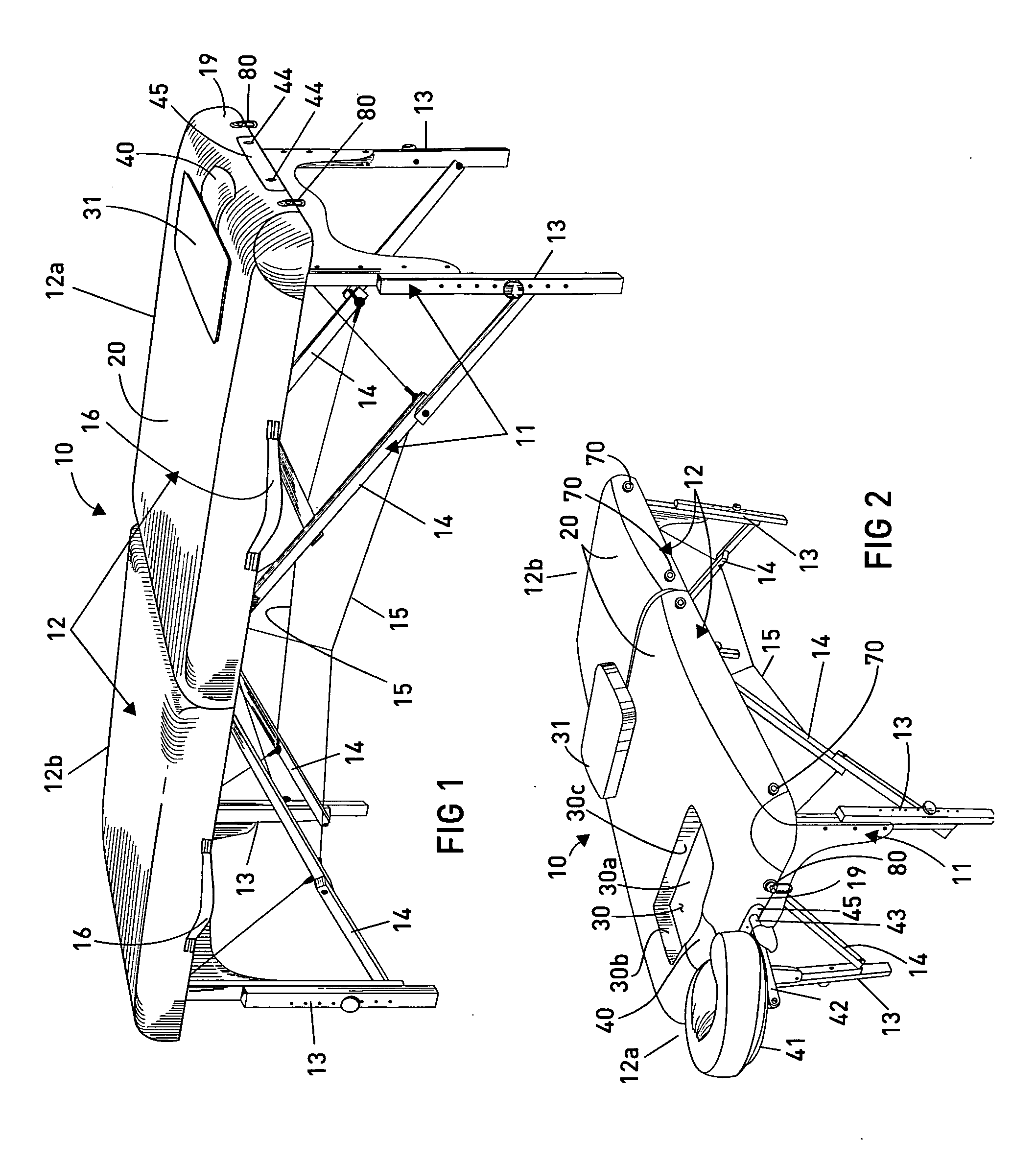
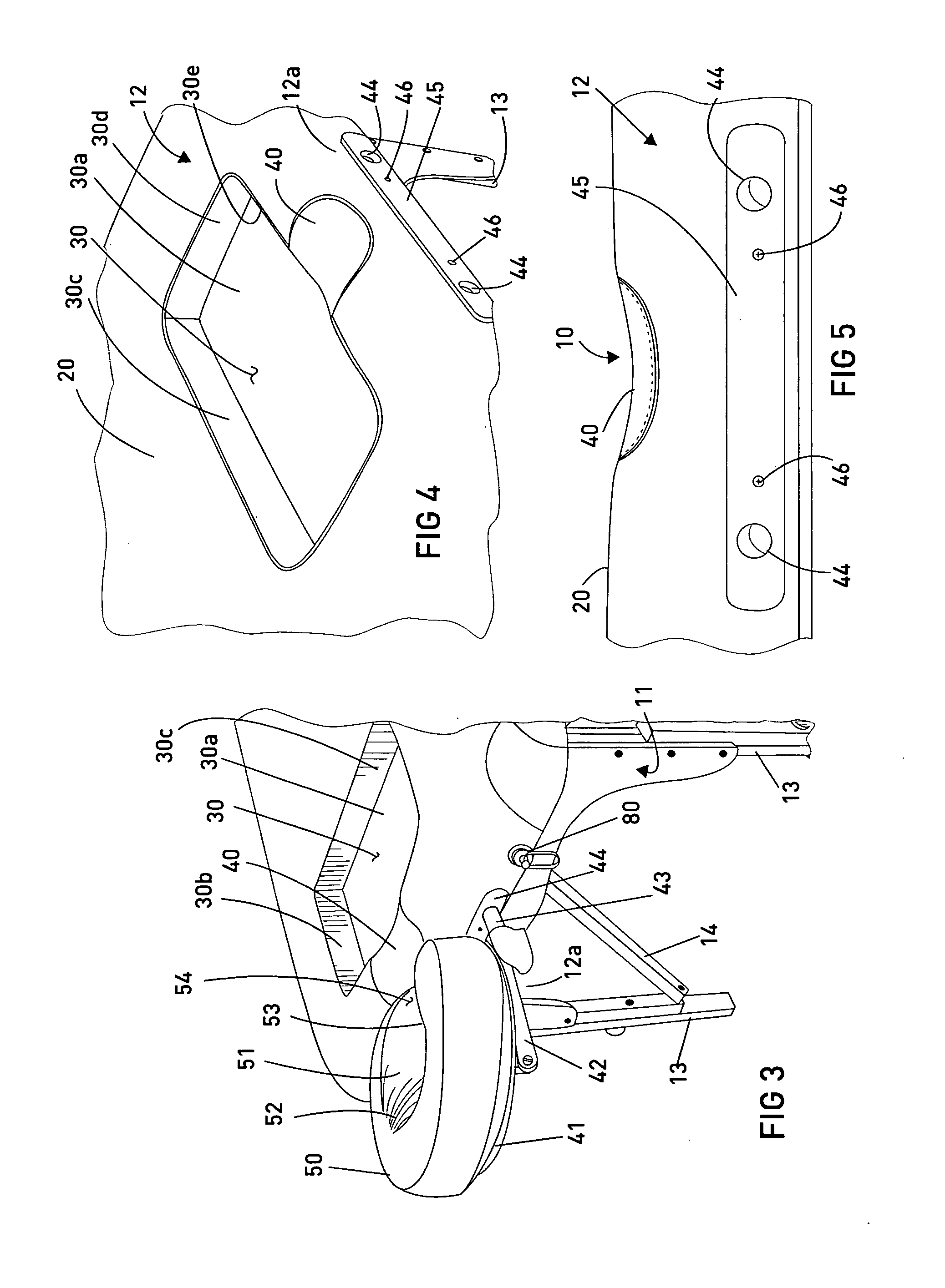
Massage table with comfort feature
A massage and chiropractic table having a supporting frame and a surface supported on the frame, and having one or more comfort features, including a recess formed in the surface of the table for accommodating a person's anatomical configuration, such as a woman's breasts, a removable recess insert that may be removed and replaced to expose the recess as desired, a neck recess for facilitating supporting a user's neck in a comfortable position, and a head rest that is configured to reduce or eliminate pressure on a user's face when the user is lying face down on the table. The massage table may be foldable and may have a handle so that it may be readily stored and transported, or, according to other embodiments may be stationary.
Owner:BODY THERAPY ASSOC LLC
Augmented reality navigation systems for use with robotic surgical systems and methods of their use
ActiveCN110169822AMedical simulationMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgical siteDisplay device
The present disclosure is directed to augmented reality navigation systems and methods of their use that, address the need for systems and methods of robotic surgical system navigation with reduced distraction to surgeons. Augmented reality navigation systems disclosed herein enable a surgeon to maintain focus on a surgical site and / or surgical tool being used in a surgical procedure while obtaining a wide range of navigational information relevant to the procedure. Navigational information can appear in the augmented reality navigation system as being presented on virtual displays that sit ina natural field of view of a surgeon during a procedure. Navigational information can also appear to be overlaid over a patient's anatomy. Augmented reality navigation systems comprise a head mounteddisplay comprising an at least partially transparent display screen, at least one detector connected to the head mounted display for identifying real-world features, and a computer subsystem.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Skeleton registration method and system and storage medium
ActiveCN112991409ASurgical precisionImage enhancementImage analysisSingular value decompositionEngineering
The invention provides a skeleton registration method and system for a surgical navigation system and a storage medium, which are used for determining a transformation relation between a preoperative coordinate system and an intra-operative coordinate system, and the method comprises the following steps: obtaining a source point cloud SPC by using preoperative skeleton image data; obtaining a target point cloud TPC by using point data collected from an actual skeleton surface; selecting four groups of corresponding point pairs from the source two point clouds, and performing initial registration; performing accurate registration through different initial transformation matrices, wherein the initial registration is based on an affine transformation method of singular value decomposition, producing a 4 * 4 dimensional matrix, thereby mapping points of the 3D virtual model to an approximation of patient bone coordinates in an intra-operative coordinate system. According to the invention, the anatomical structures of the patient before and during the operation can accurately correspond to each other, so that a doctor can clearly know the anatomical positions of the surgical instrument and the patient, and the surgical tool can be accurately controlled to reach the required part.
Owner:杭州素问九州医疗科技有限公司
Oblique stent
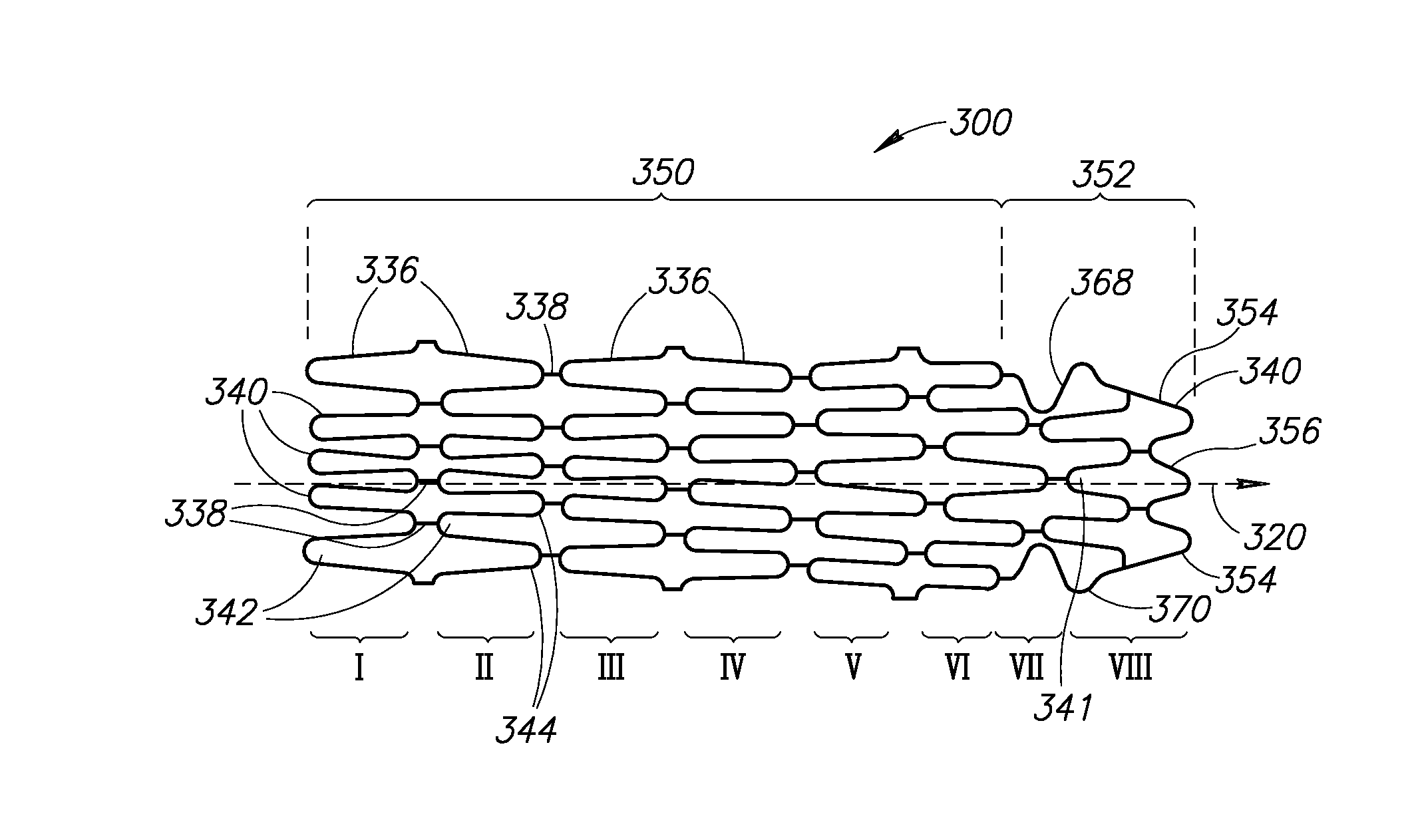
A stent having a main body with a proximal end and a distal end section having proximal and distal openings used for treatment of lesions in blood vessels and hollow organs, particularly at the ostium of side branches. The stent adapts to the anatomical configuration of a vessel branch by having at least one oblique end section in at least its expanded state. Truncated versions of the oblique end section are described as well.
Owner:CURAVAS GMBH
Thoracic and lumbar vertebral posterior prosthesis
InactiveCN101327153ASolve the problem of iatrogenic instabilityRebuild stabilitySpinal implantsSpinal columnNon fusion
The present invention relates to a thoracolumbar vertebrae posterior false body which comprises a manual spinous process and a manual vertebral lamina. The manual spinous process is connected with the manual vertebral lamina, and the connection is shape as the connection of the spinous prcess and the vertebral lamina of human body pyramid. Compared with the prior art, the thoracolumbar vertebrae posterior false body can reconstruct the stability of thoracolumbar vertebrae and recover the physical structure and the physical function of thoracolumbar vertebrae posterior column, and can reconstruct the normal anatomical configuration and the function of vertebral canal, and can effectively avoid the possibility of the iatrogenic injury caused by vertebral canal content during operation; the thoracolumbar vertebrae posterior false body integrates spine fusion and non-fusion fixation functions as a whole, the fusion and non-fusion fixation functions are selected and used freely according to the requirement of the operation, and the operation is simple.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV AFFILIATED SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL +1
Massage table with comfort feature
A massage and chiropractic table having a supporting frame and a surface supported on the frame, and having one or more comfort features, including a recess formed in the surface of the table for accommodating a person's anatomical configuration, such as a woman's breasts, a removable recess insert that may be removed and replaced to expose the recess as desired, a neck recess for facilitating supporting a user's neck in a comfortable position, and a head rest that is configured to reduce or eliminate pressure on a user's face when the user is lying face down on the table. The massage table may be foldable and may have a handle so that it may be readily stored and transported, or, according to other embodiments may be stationary.
Owner:BODY THERAPY ASSOC LLC
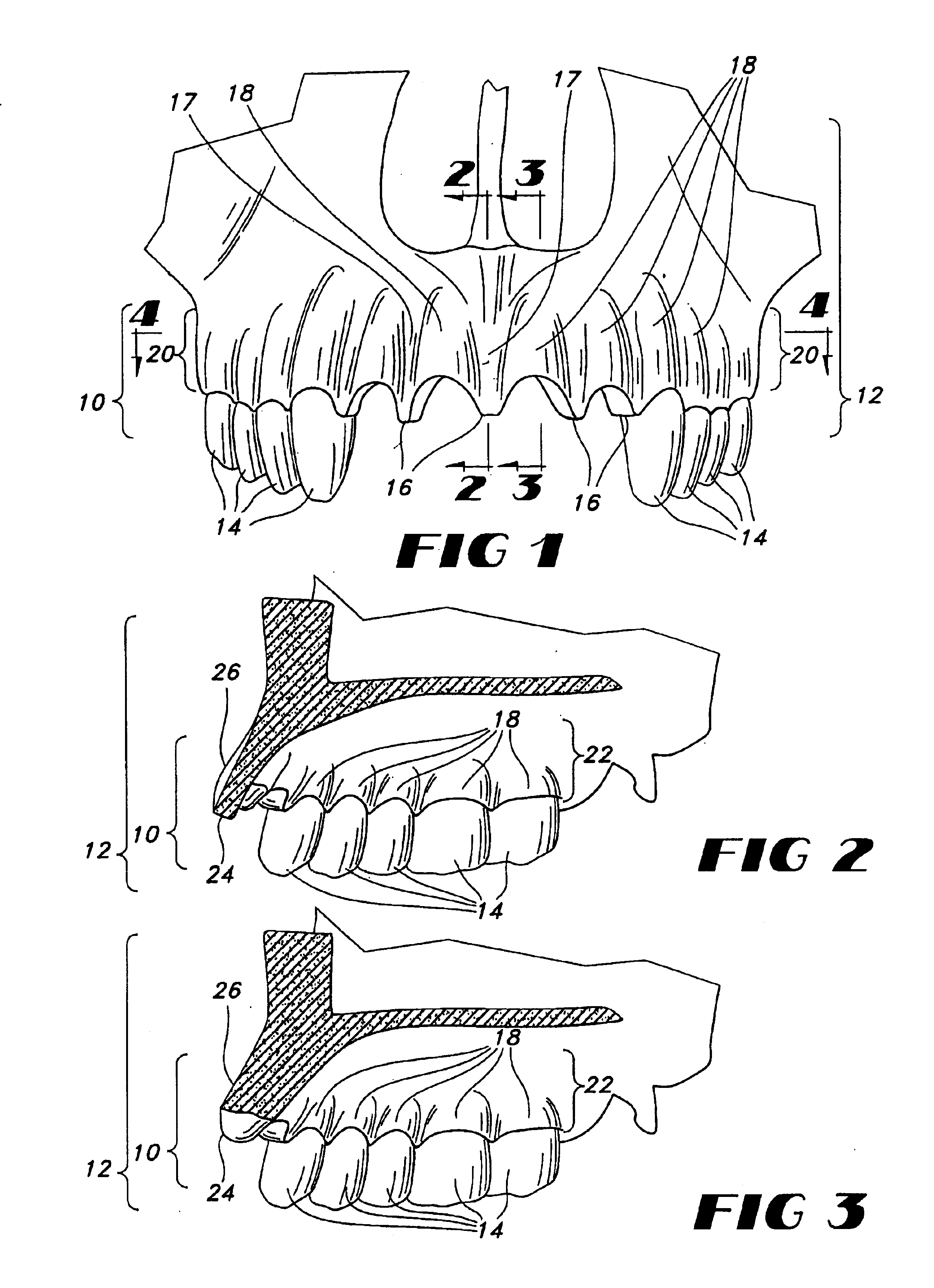
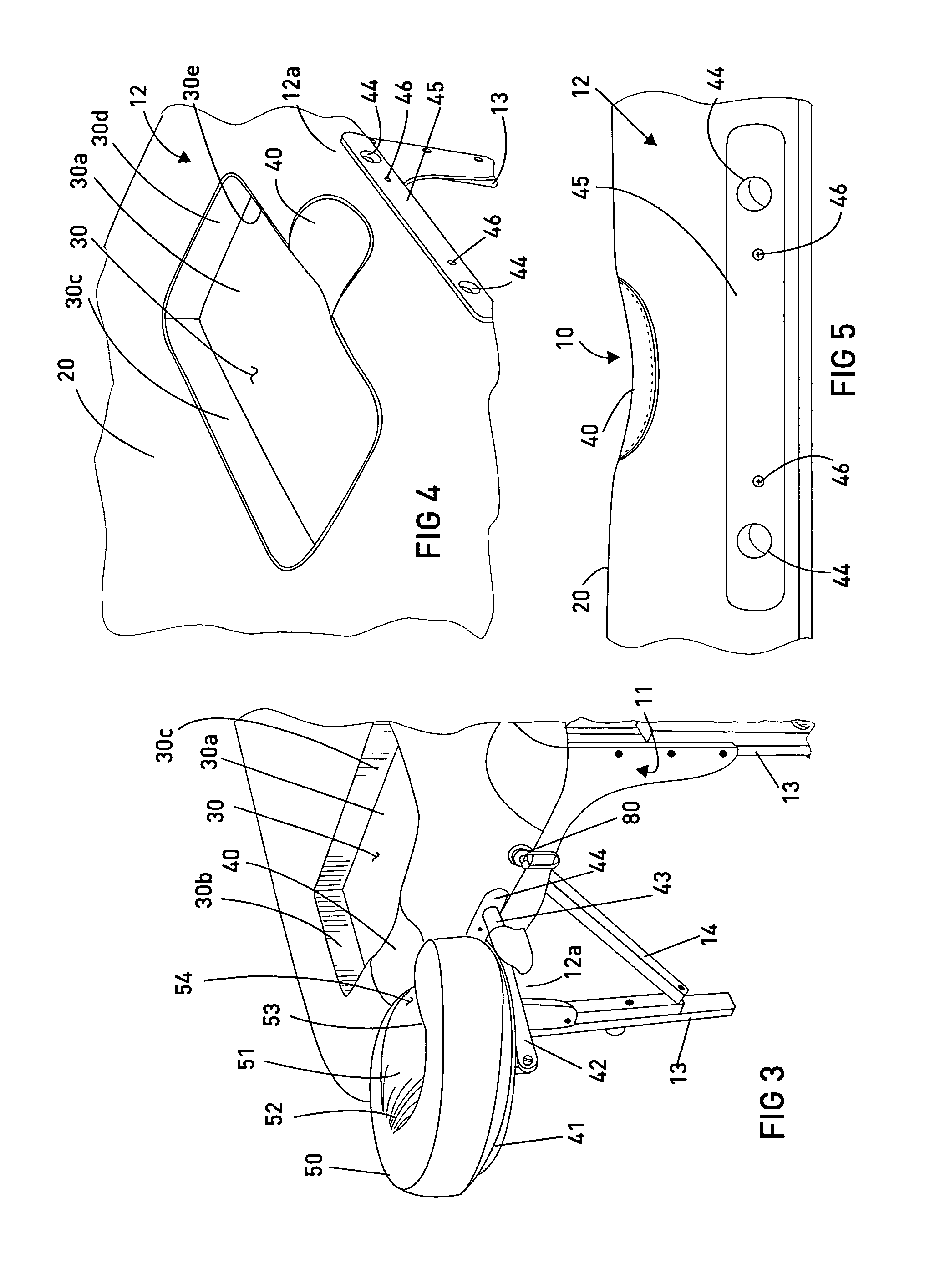
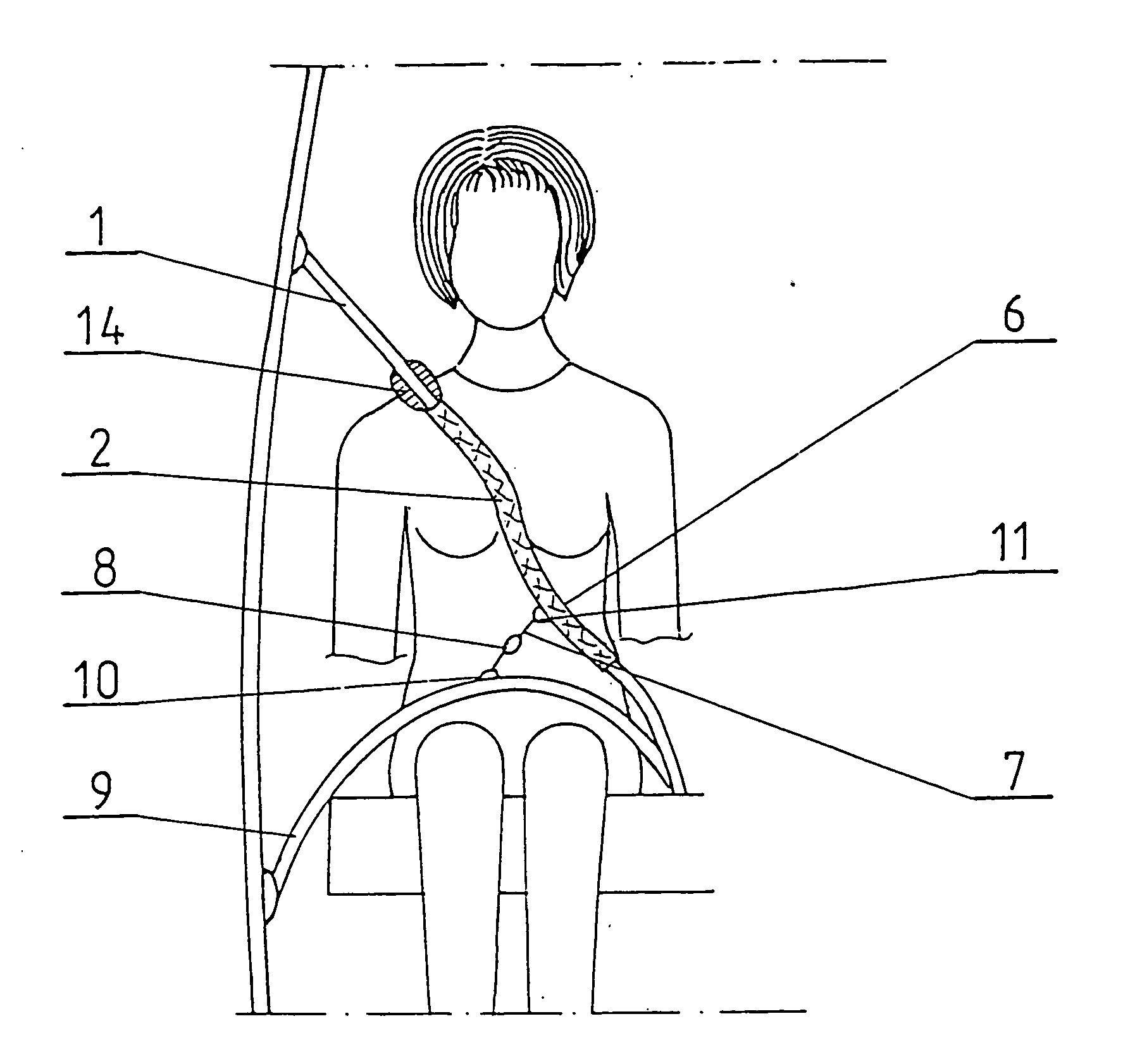
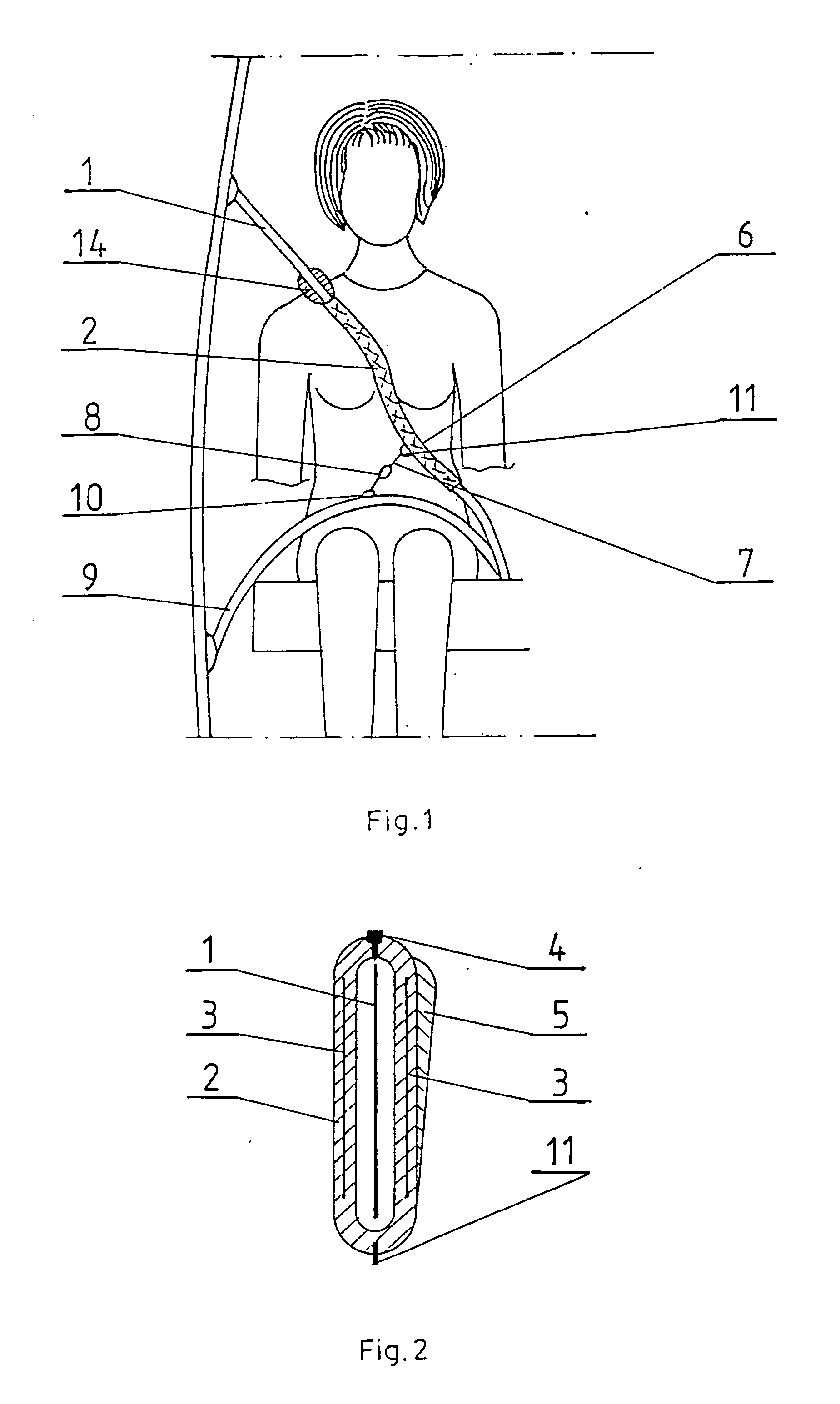
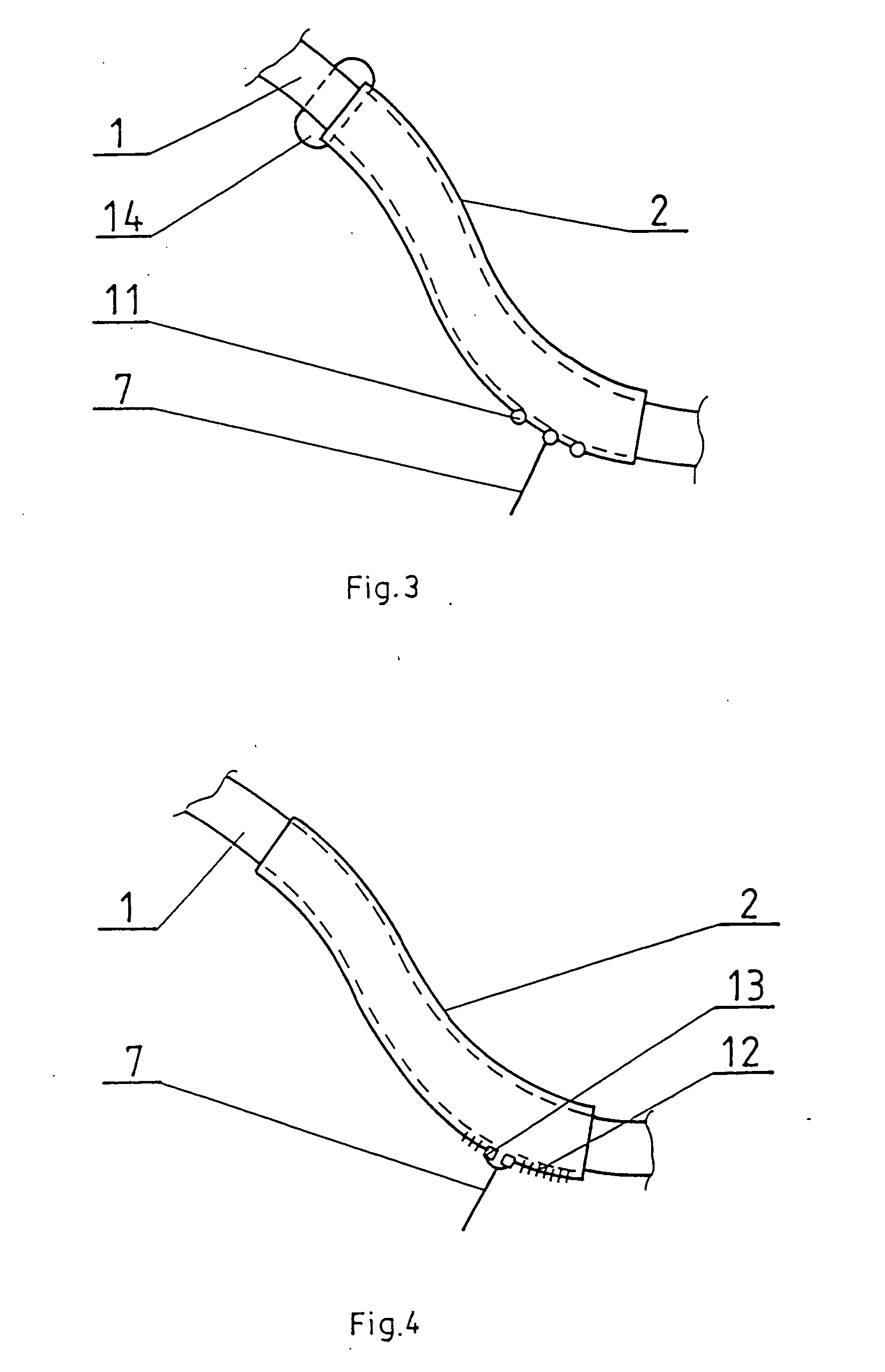
Anatomical configuration of safety belts in cars and accessories for its implementation
InactiveUS20060125227A1Reduce distortionStress minimizationSafety beltsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementPull forceSubject matter
The subject matter of the invention is a way of shaping anatomically the safety belts of cars, particularly for the use of women, and the devices required for its realization. The essence of this anatomical shaping of a safety belt consists in providing such a form of the belt that it looks like an elongated S, passing between the breasts as well as above and under the bust. For its purpose a safety belt is provided with a shaping strip, which is a flat sleeve made of elastic plastic material in the form of an elongated S, with a rigid material lining, open on the side and closed by means of any kind of fastener, for example a zipper or Velcro. On the upper part of the strip there is a pad protecting the collar-bone and neck against pressure and rubbing. The strip is put on the safety belt, so that it takes the required shape without affecting the structure of the safety belt. The strip can be shifted along the safety belt, adapting it to the height of the passenger. It is practically stable on the safety belt because of its shape, but it can be additionally stabilized by means of a tension pull, the length of which can be adjusted according to the needs of the wearer. The pull can be provided with a clasp, attached to the outer bottom part of the edge of the abdomen part of the safety belt, e.g. by using a clip. Due to different constitutions of the human body there are several hooks for adjusting the position. The tension pull preferably is run perpendicularly to a tangential line of the lower edge of the strip.
Owner:BECZKOWSKI ANDRZEJ
Biocompatible form and method of fabrication
A biocompatible form and a method for fabricating the implant are provided. The biocompatible form may be used to support bone graft material such as that used to reconstruct missing bone in a patient's oral cavity. The implant is fabricated from a biocompatible mesh, which may be made of titanium, a titanium alloy or fiber and is permanently implantable in the patient's oral cavity. The biocompatible form has an anatomical configuration which includes one or more portions conforming substantially to various alveolar bone contours which may include predetermined, human interproximal bone contours, root prominence bone contours and mylohyoid ridge bone contours. The biocompatible form may include a palatal section. The biocompatible form may also include one or more apertures for receiving a corresponding number of dental prostheses therethrough.
Owner:CAGENIX
Virtual reality or augmented reality visualization of 3D medical images
Systems and methods for virtual reality or augmented reality (VR / AR) visualization of 3D medical images using a VR / AR visualization system are disclosed. The VR / AR visualization system includes a computing device operatively coupled to a VR / AR device, and the VR / AR device includes a holographic display and at least one sensor. The holographic display is configured to display a holographic image toan operator. The computing device is configured to receive at least one stored 3D image of a subject's anatomy and at least one real-time 3D position of at least one surgical instrument. The computing device is further configured to register the at least one real-time 3D position of the at least one surgical instrument to correspond to the at least one 3D image of the subject's anatomy, and to generate the holographic image comprising the at least one real-time position of the at least one surgical instrument overlaid on the at least one 3D image of the subject's anatomy.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
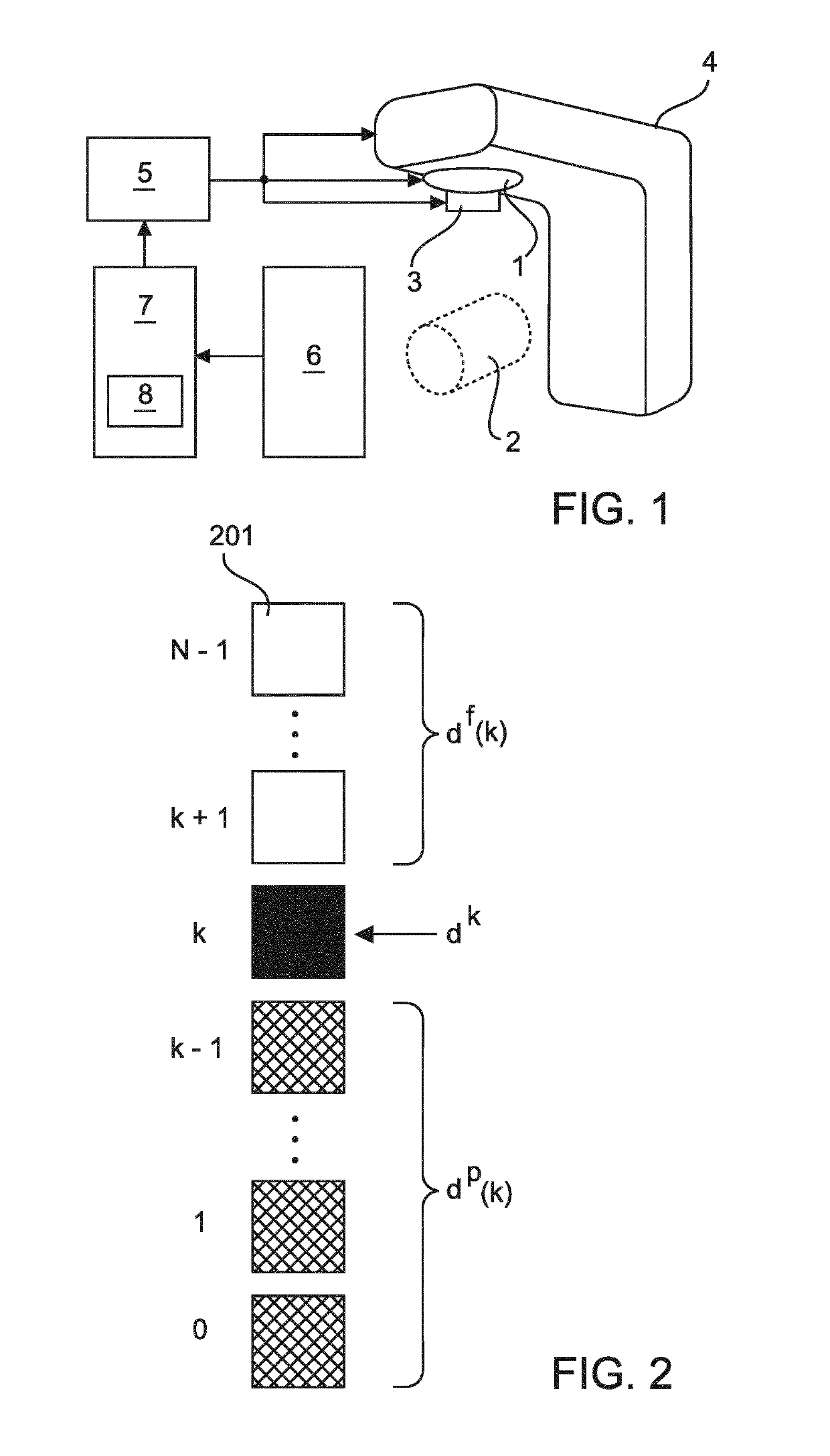
Adaptive radiation therapy planning
ActiveUS20190099620A1Less complexReduce complexityX-ray/gamma-ray/particle-irradiation therapyTherapy planningAdaptive radiation therapy
The invention relates to system and a method for adapting a radiotherapy treatment plan for treating a target structure within a target region of a patient body, where a planning unit (7) adapts the treatment plan on the basis of a set of influence parameters quantifying an influence of the radiation on the target region per unity intensity emission in accordance with an anatomical configuration of the target region. In a storage (8), a plurality of sets of influence parameters is stored, each set being associated with an image of the body region representing a particular anatomical configuration of the target region and the planning unit (7) is configured to select the set of influence parameters from the stored sets on the basis of a comparison between a captured image of the body region and at least one of the images associated with the sets of influence parameters.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
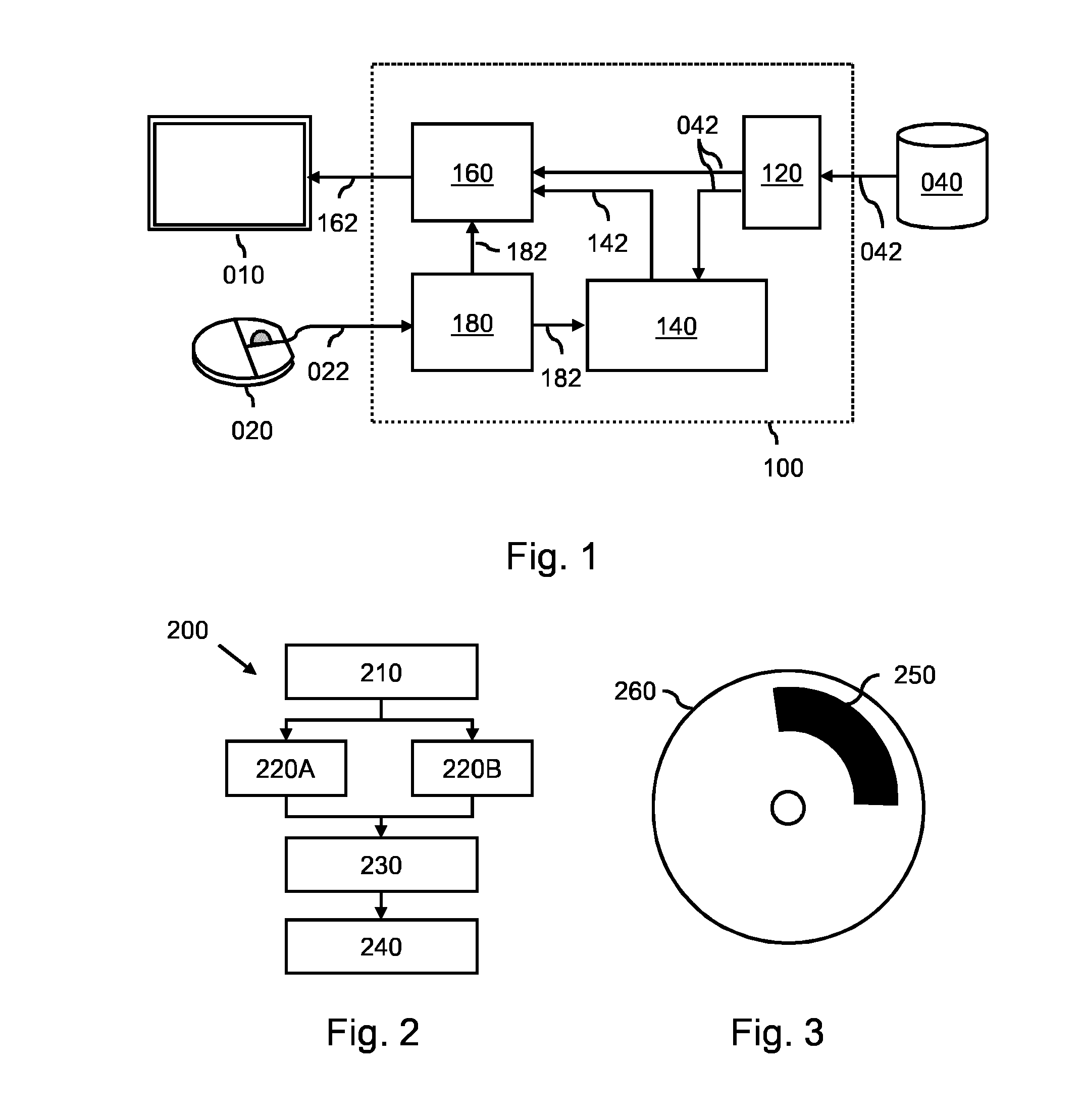
Medical image editing
ActiveUS20180005455A1Easy to optimizeFacilitate the processImage generationDetails involving graphical user interfaceVisual presentationAnatomical structures
The present invention relates to medical image editing. In order to facilitate the medical image editing process, a medical image editing device (50) is provided that comprises a processor unit (52), an output unit (54), and an interface unit (56). The processor unit (52) is configured to provide a 3D surface model of an anatomical structure of an object of interest. The 3D surface model comprises a plurality of surface sub-portions. The surface sub-portions each comprise a number of vertices, and each vertex is assigned by a ranking value. The processor unit (52) is further configured to identify at least one vertex of vertices adjacent to the determined point of interest as an intended vertex. The identification is based on a function of a detected proximity distance to the point of interest and the assigned ranking value. The output unit (54) is configured to provide a visual presentation of the 3D surface model. The interface unit (56) is configured to determine a point of interest in the visual presentation of the 3D surface model by interaction of a user. The interface unit 56 is further configured to modify the 3D surface model by displacing the intended vertex by manual user interaction. In an example, the output unit (54) is a display configured to display the 3D surface model directly to the user (58).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com