Patents
Literature
140 results about "Vertebral lamina" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
1. a thin, flat plate or stratum of a composite structure; called also layer. 2. vertebral lamina. basal lamina (lamina basa´lis) the layer of the basement membrane lying next to the basal surface of the adjoining cell layer composed of an electron-dense lamina densa and an electron-lucent lamina lucida.
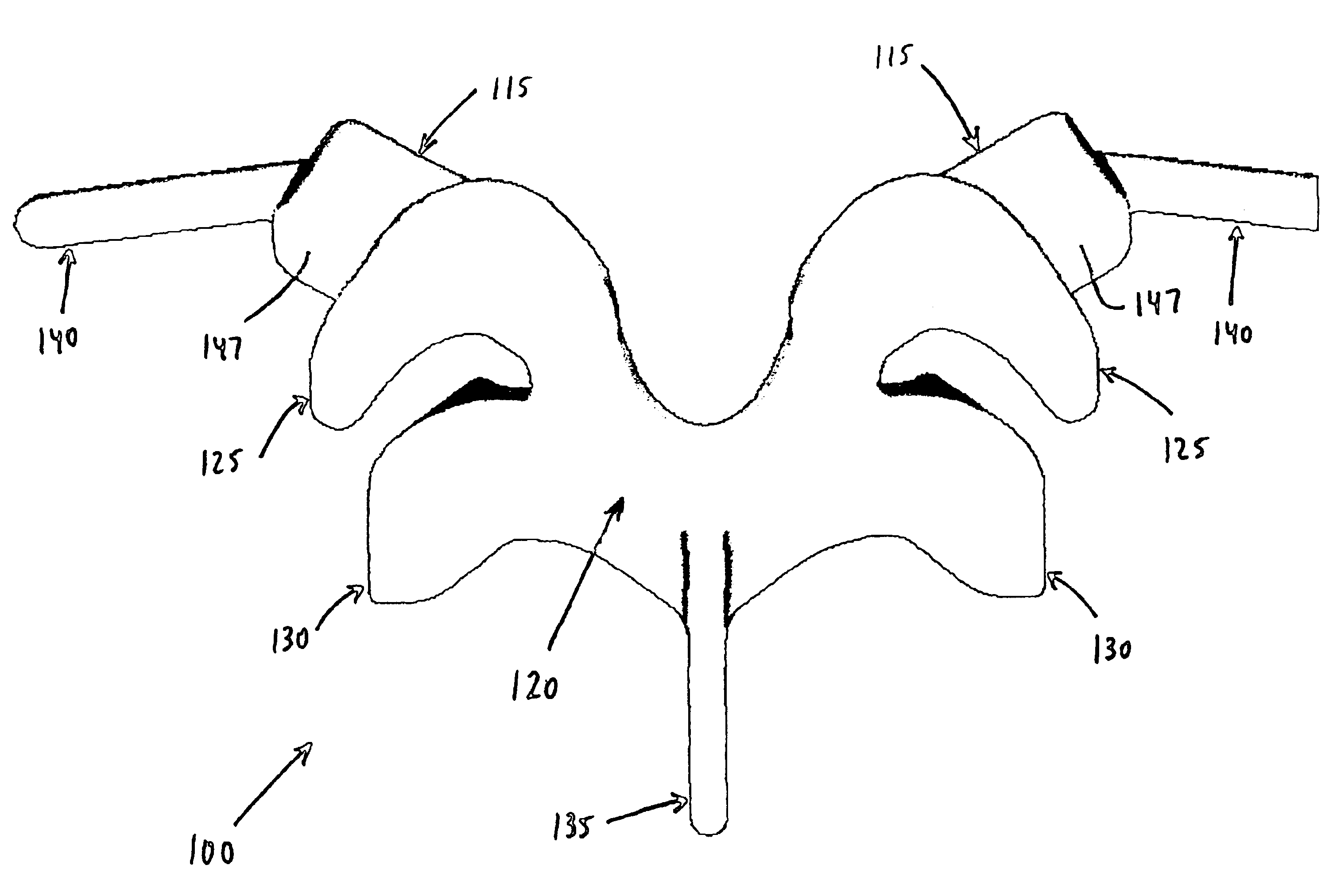
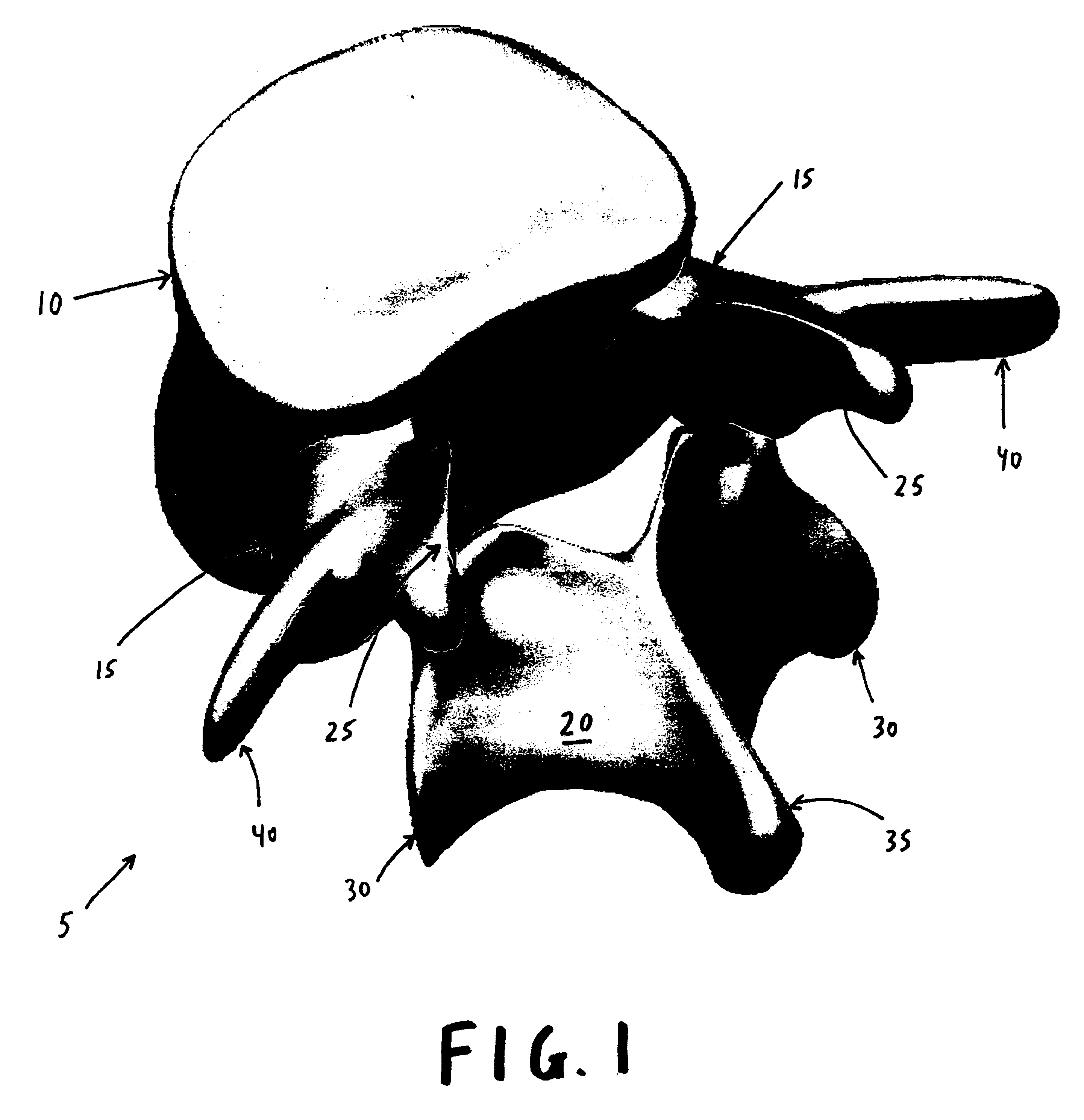
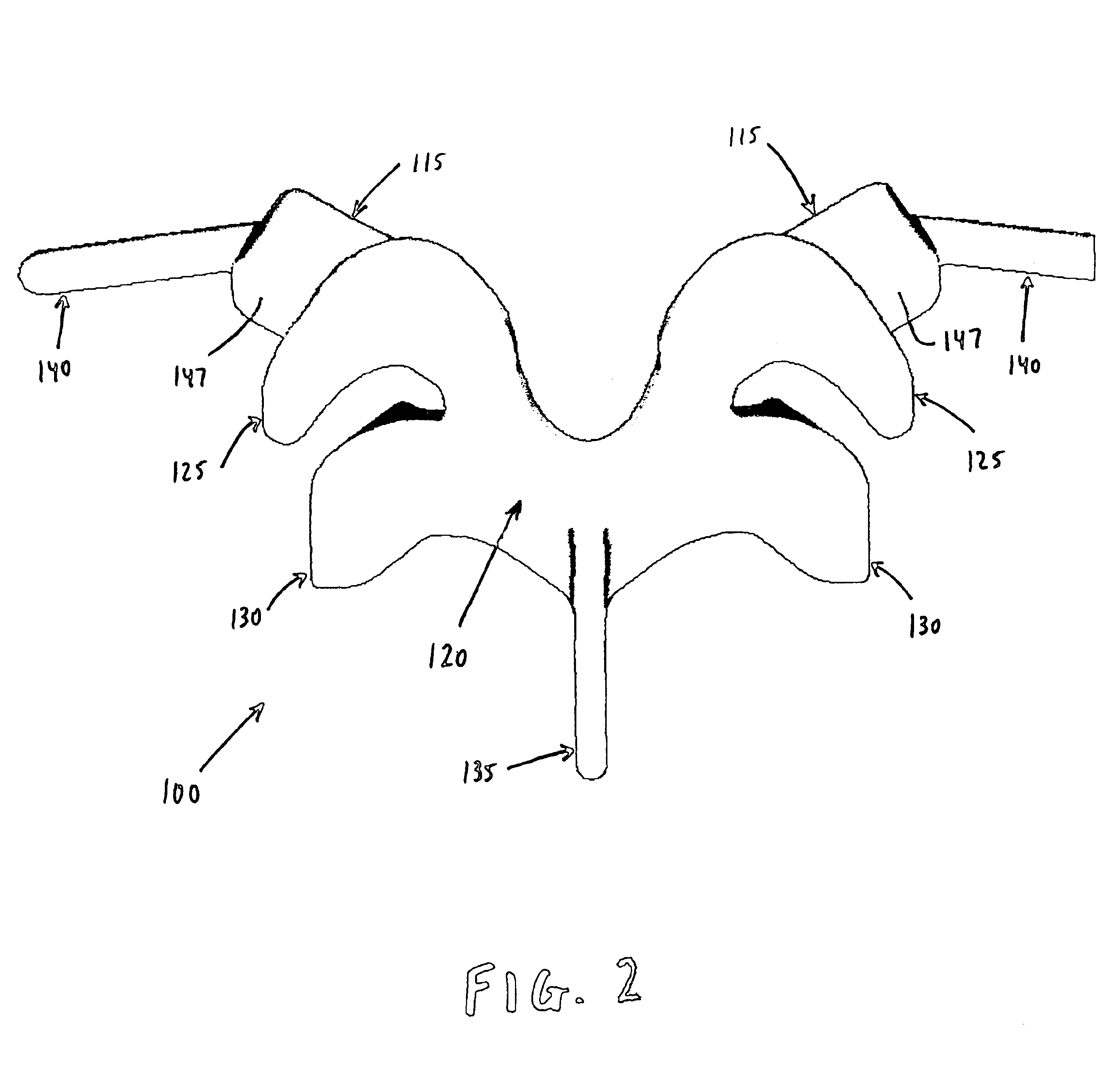
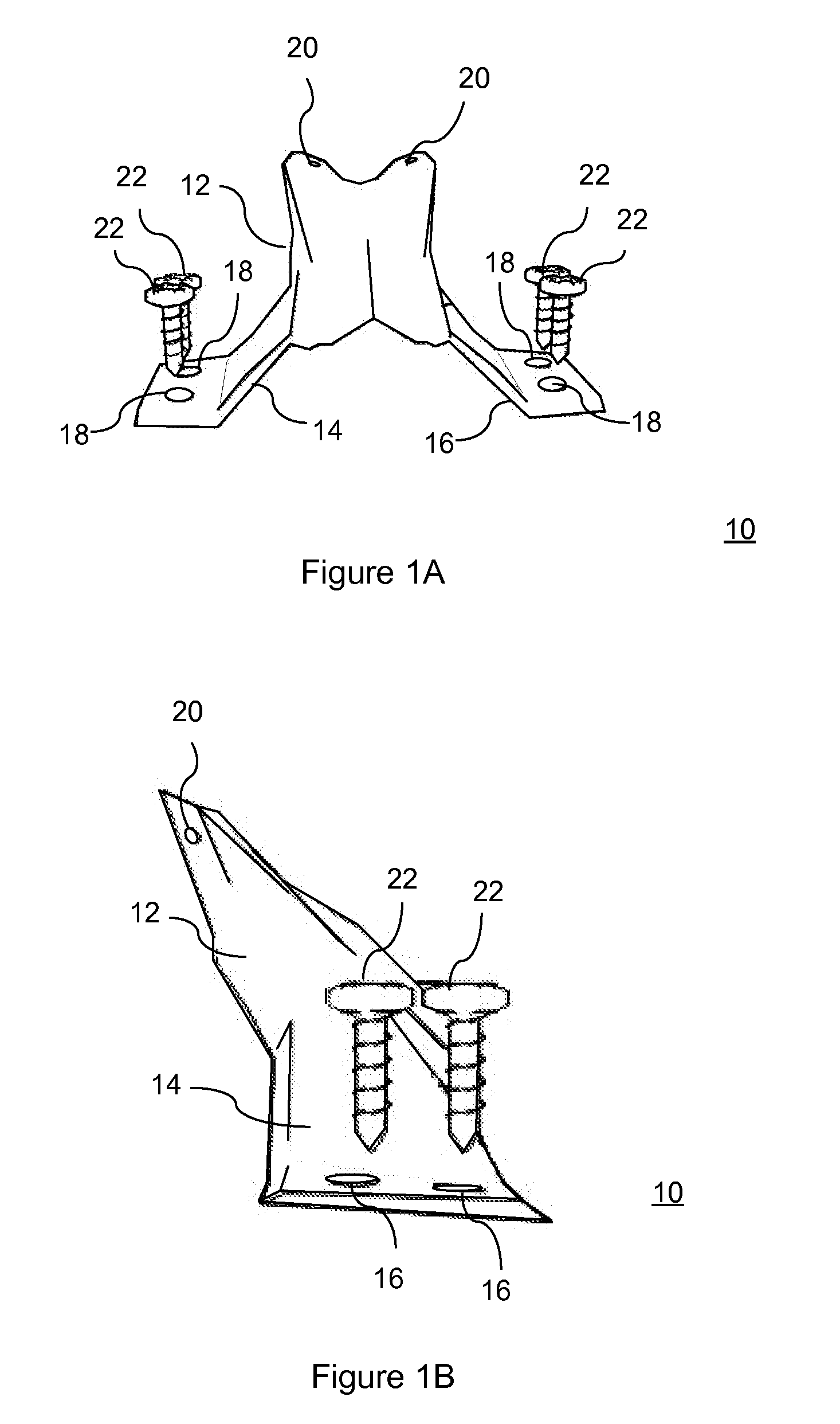
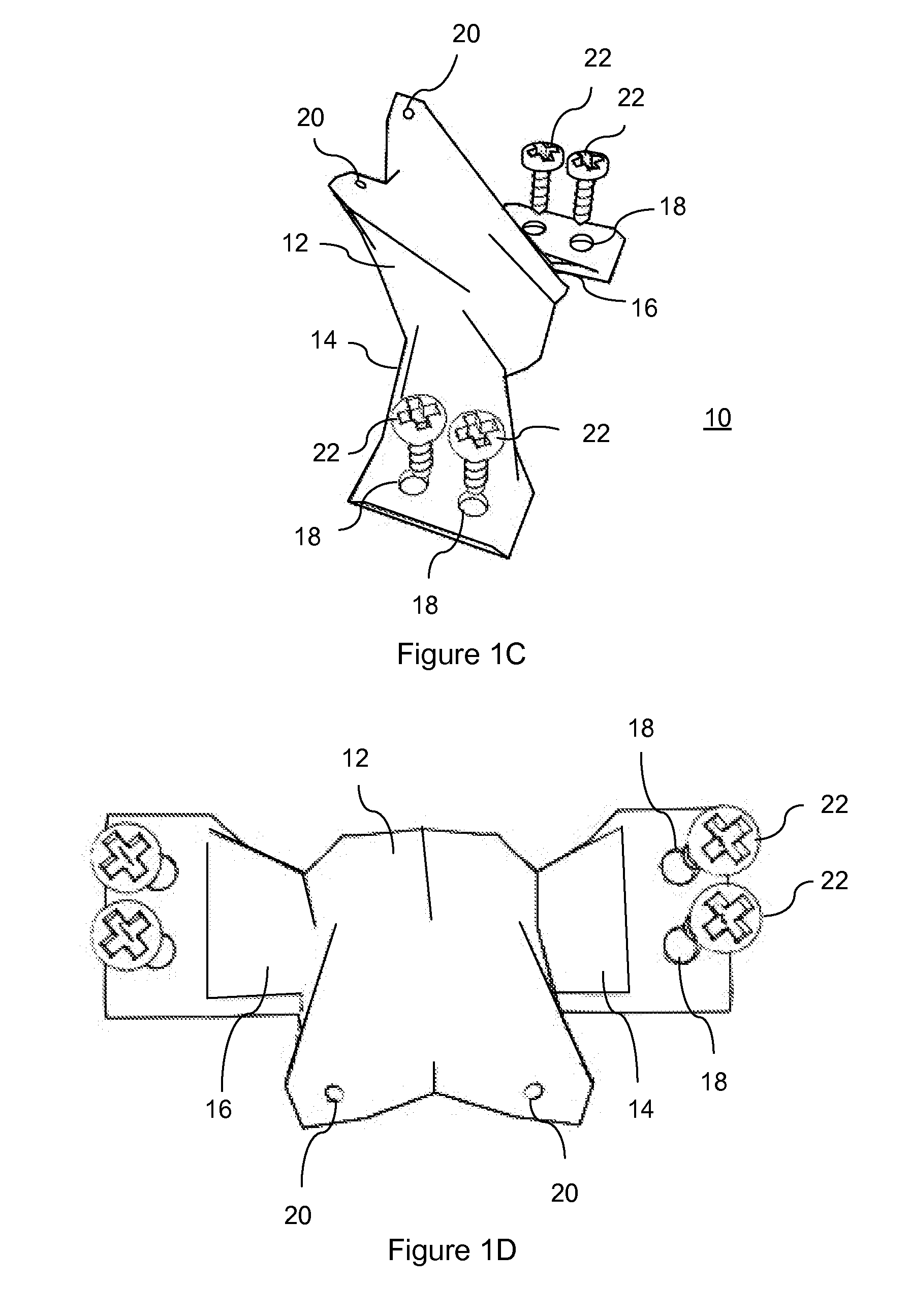
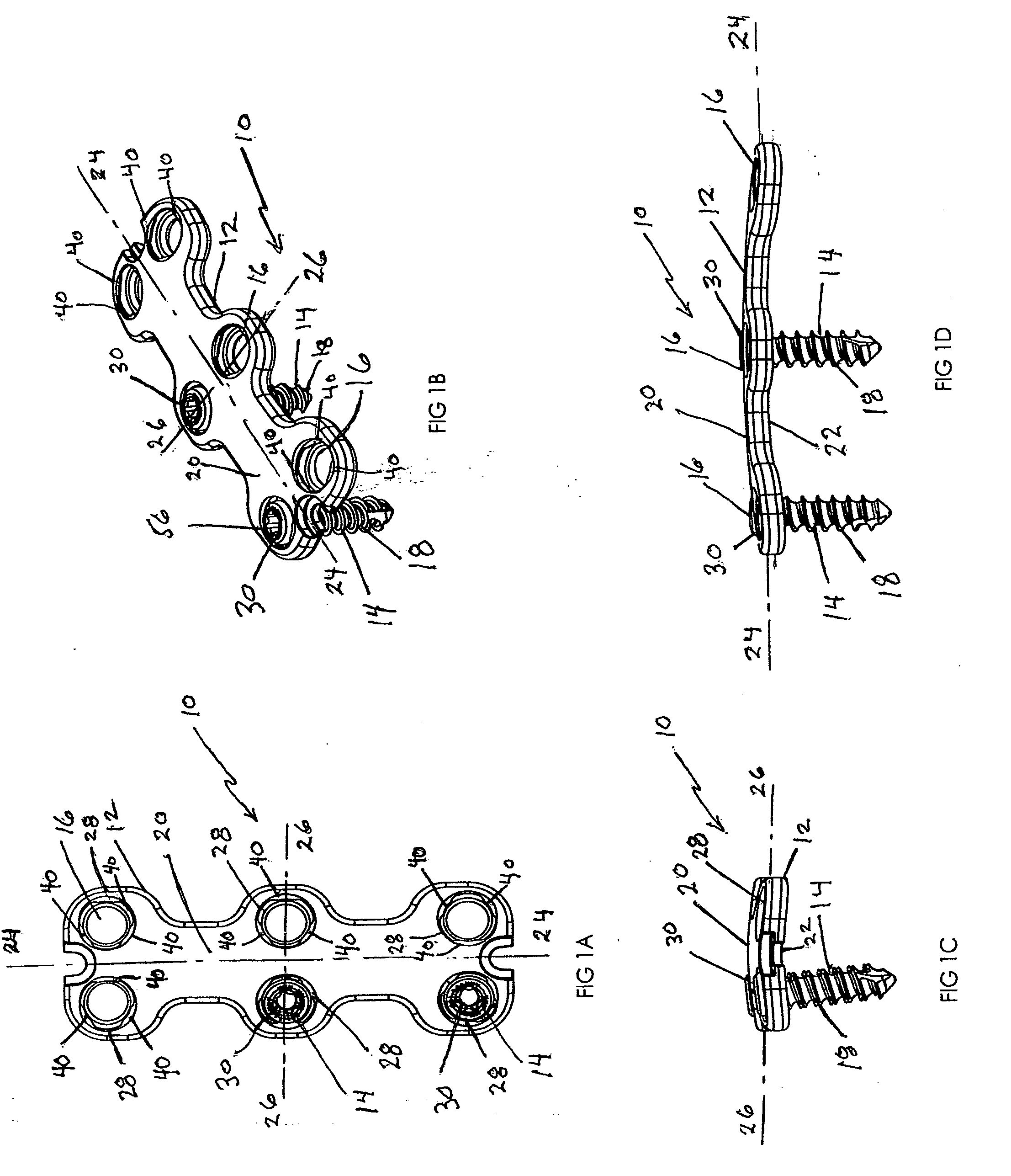
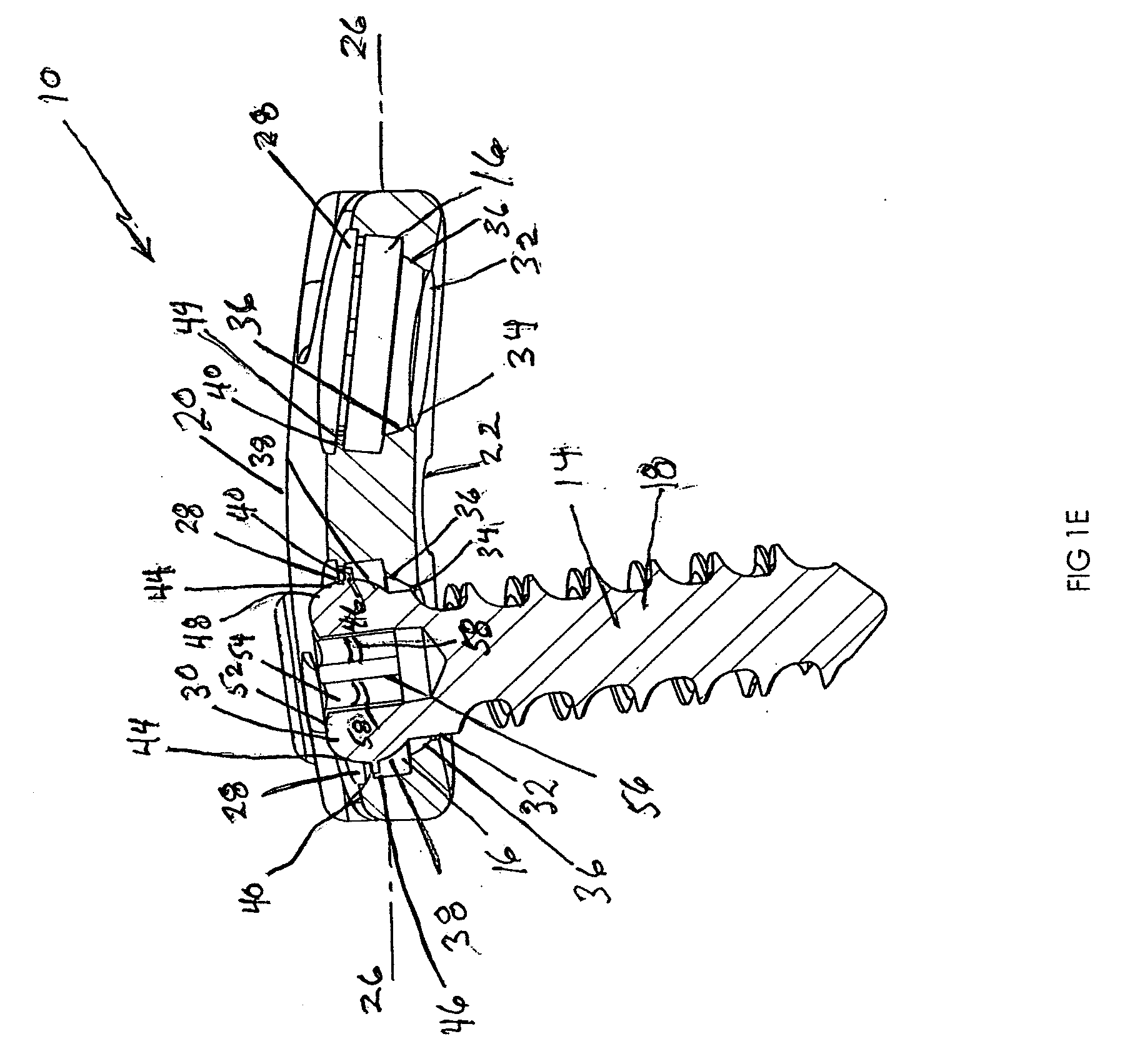
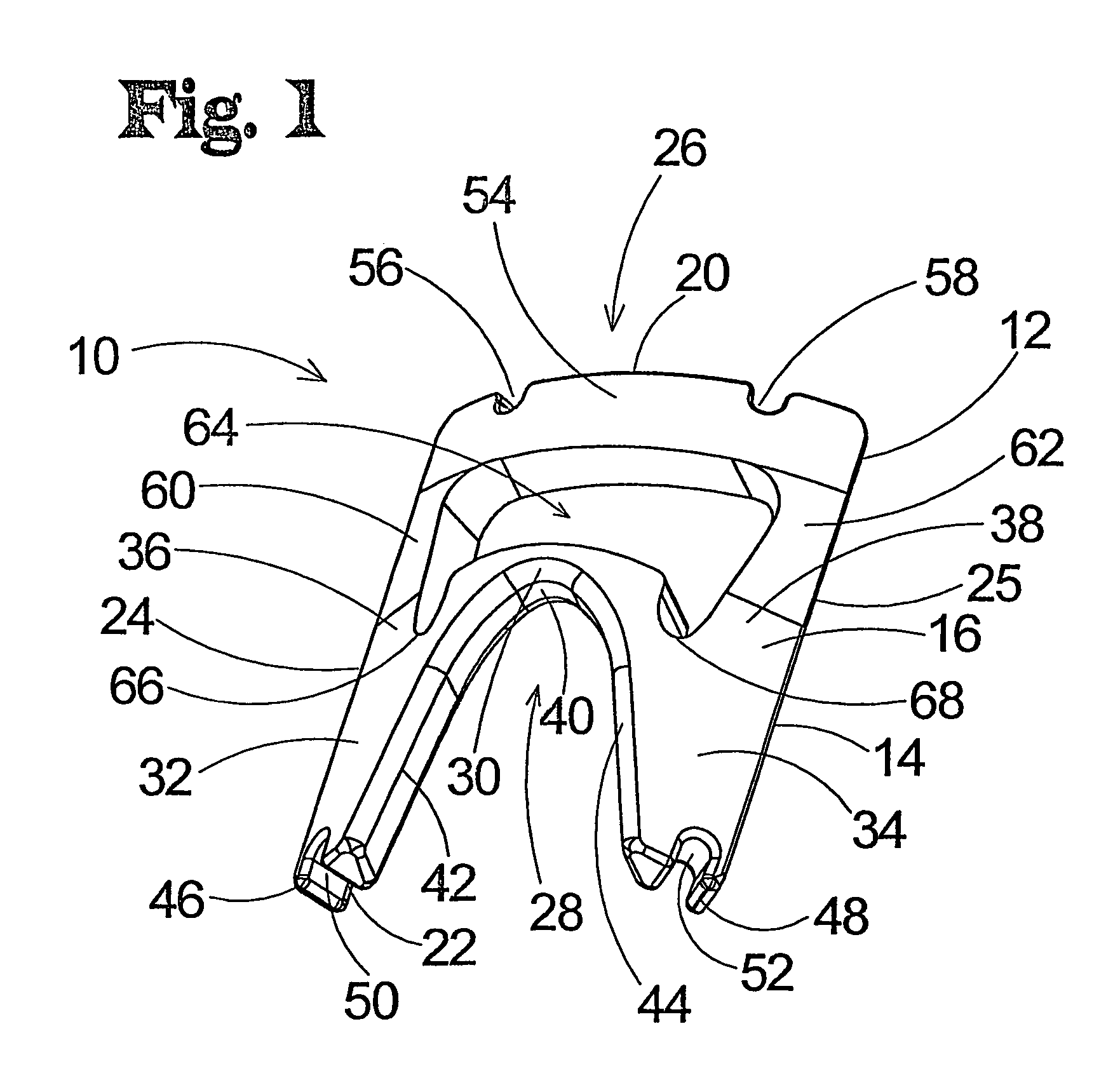
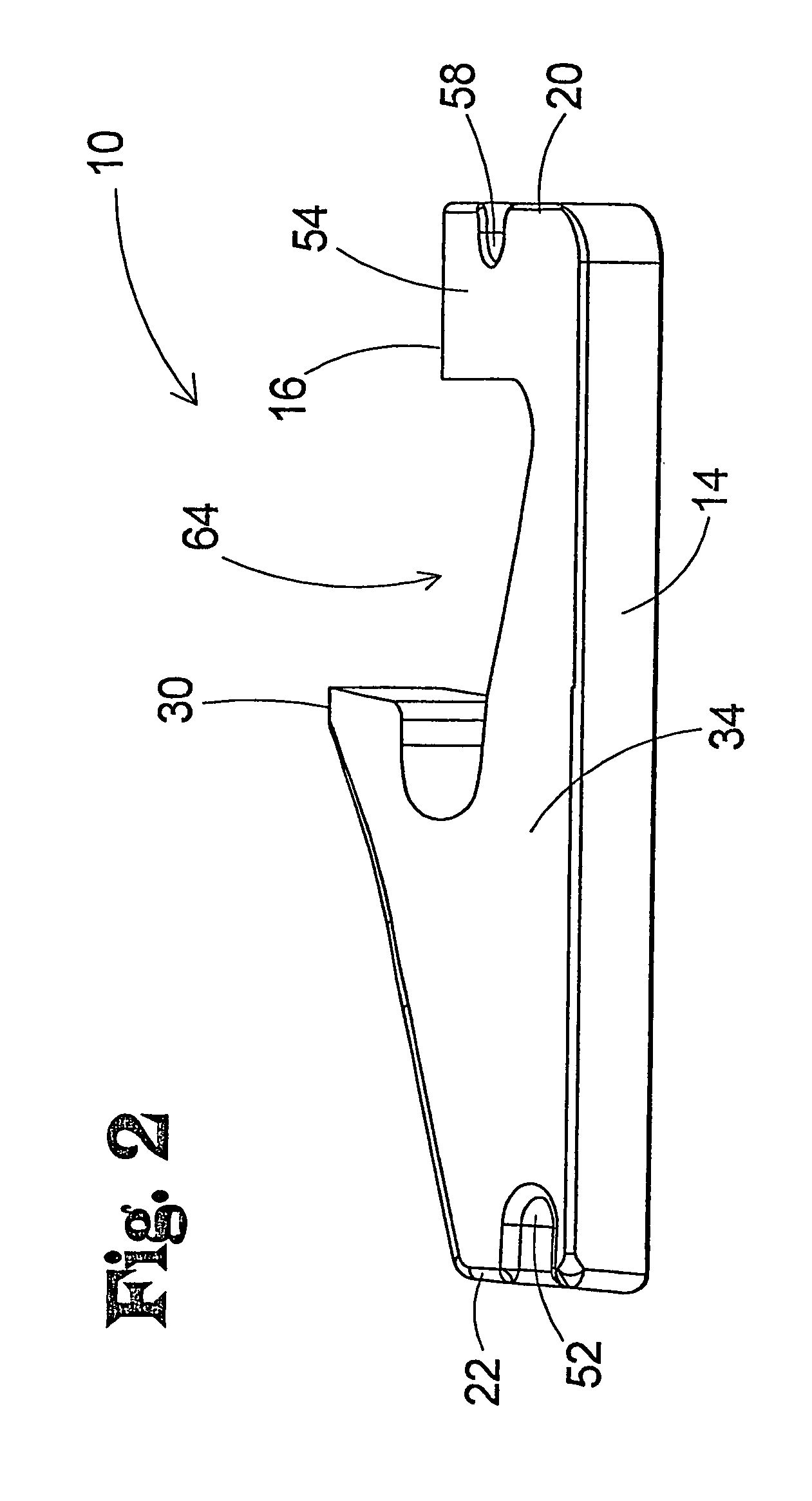
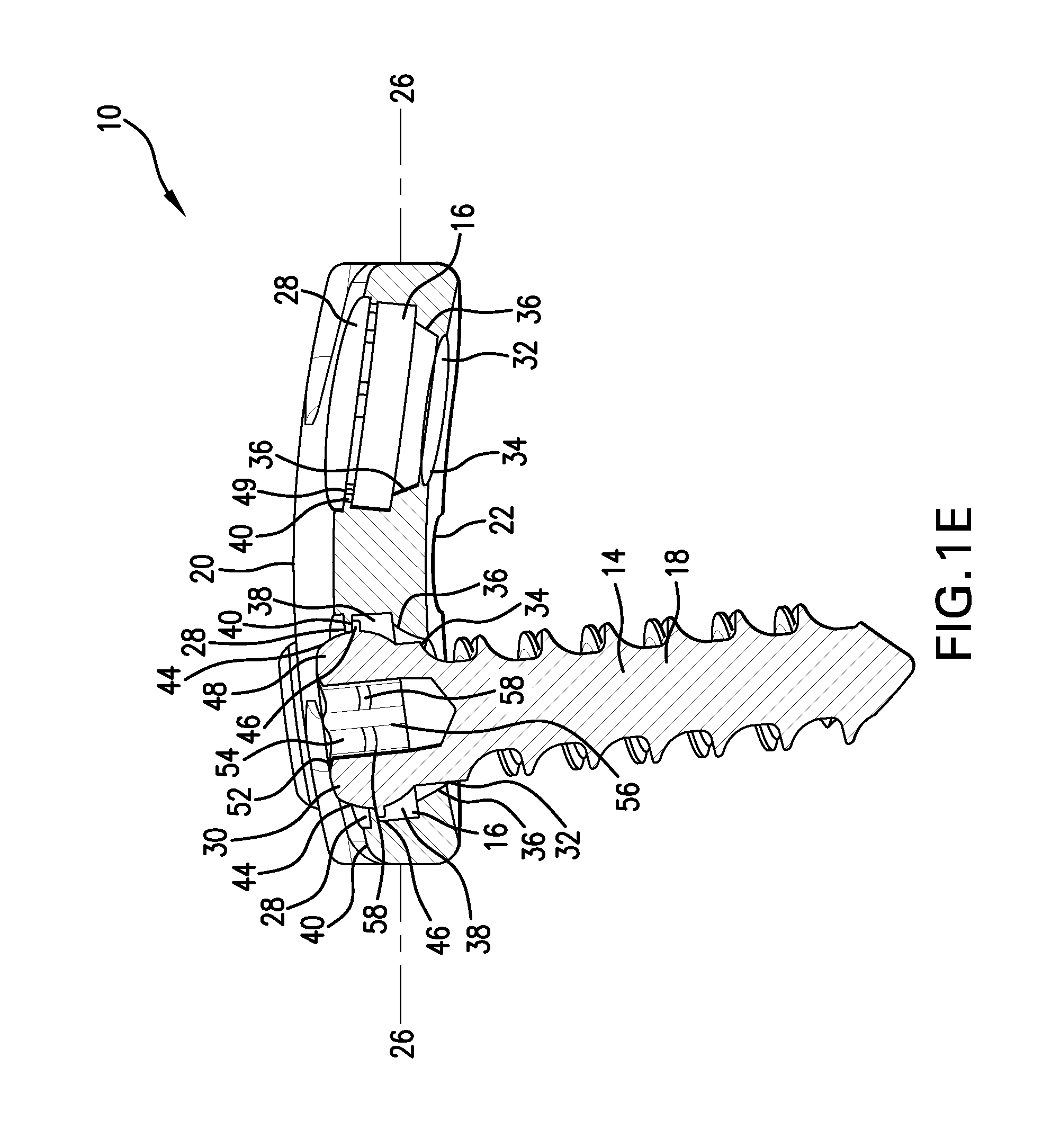
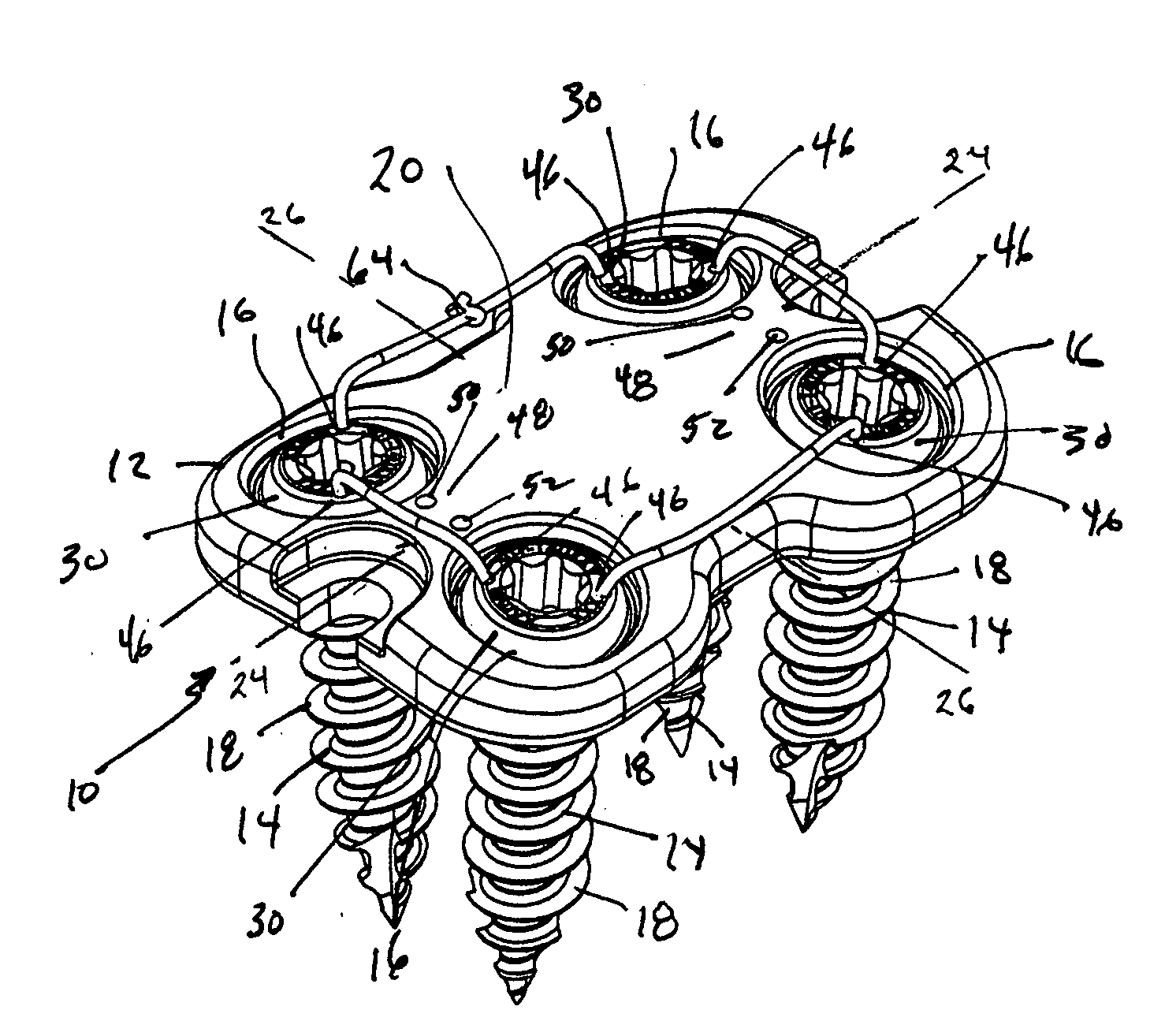
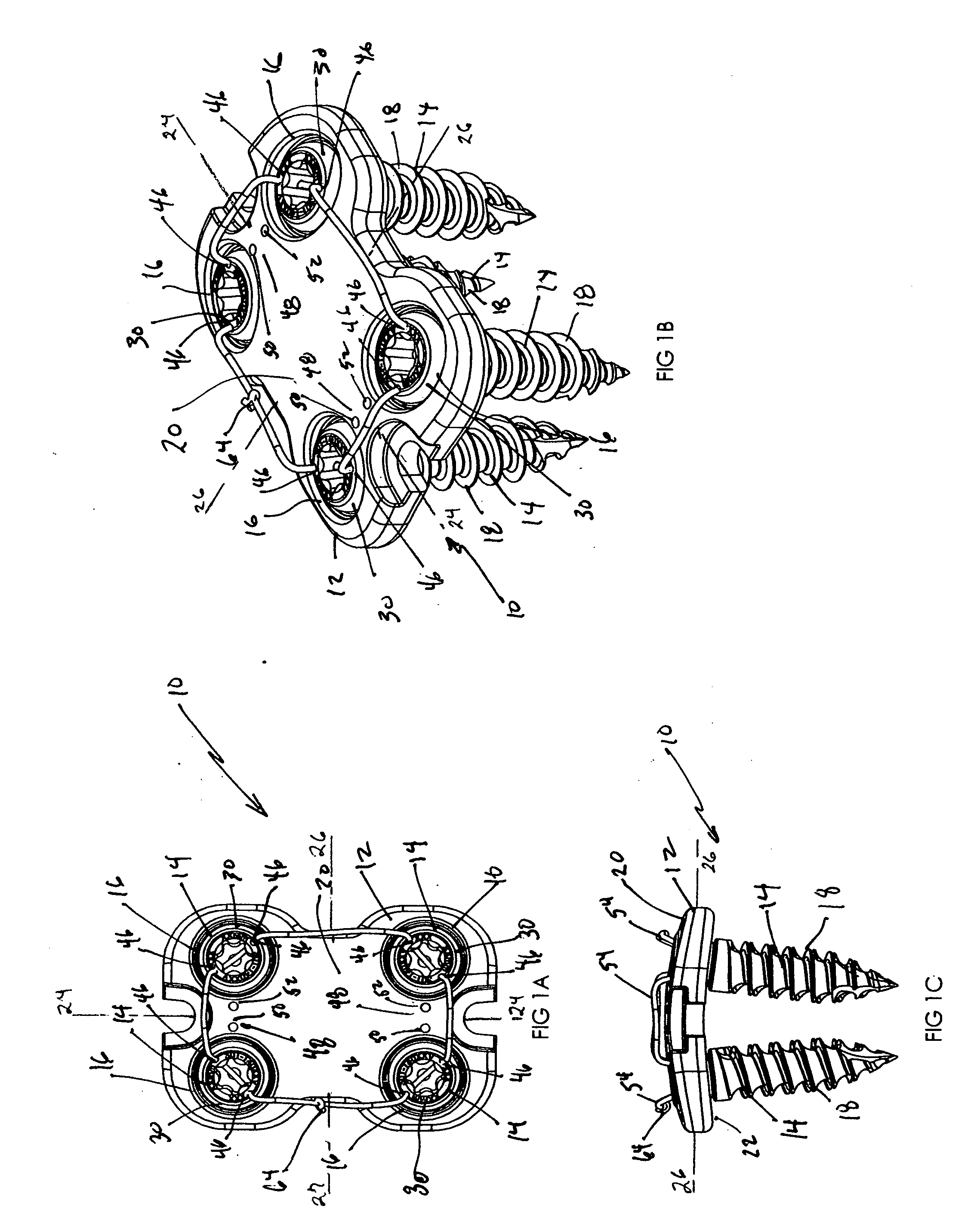
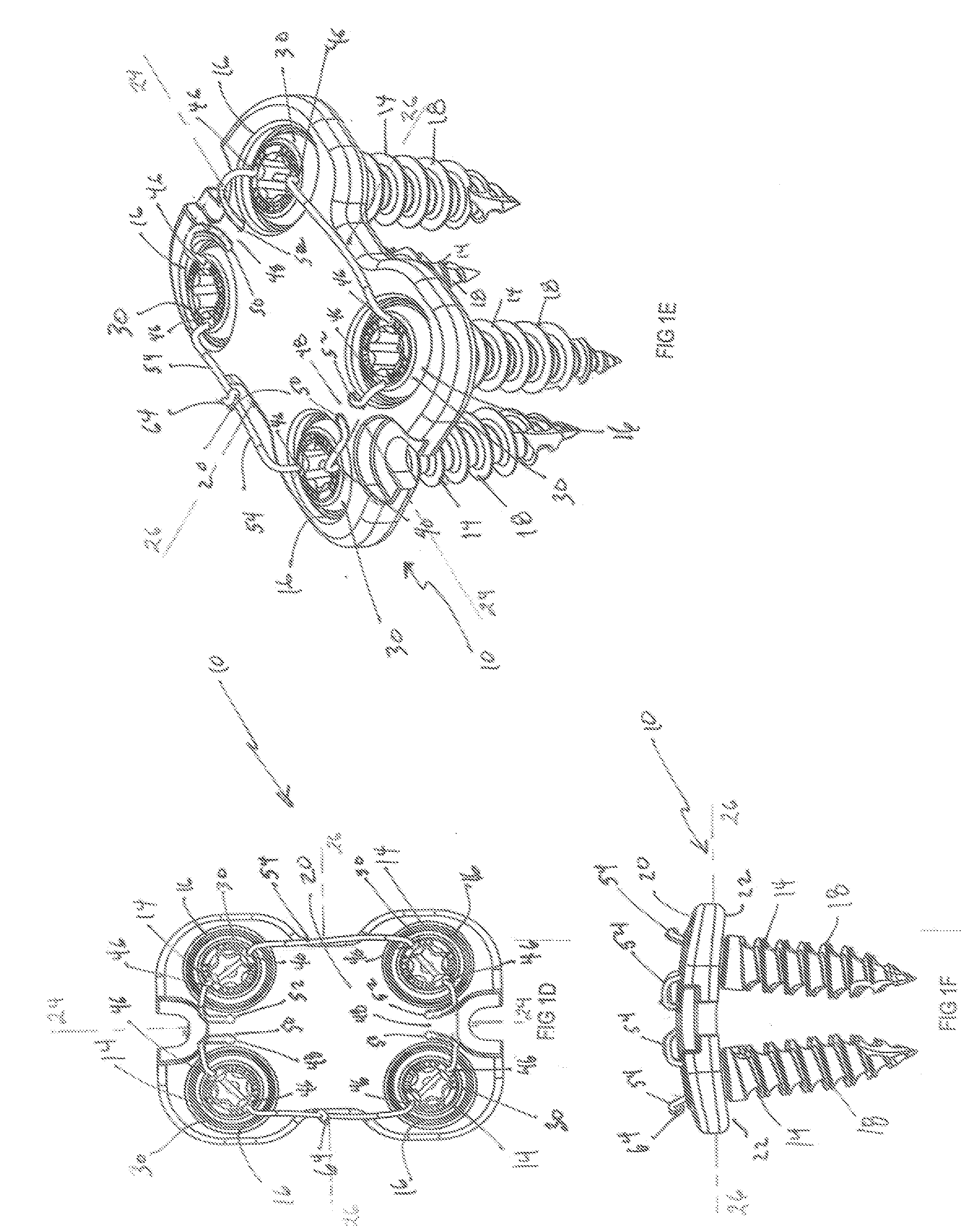
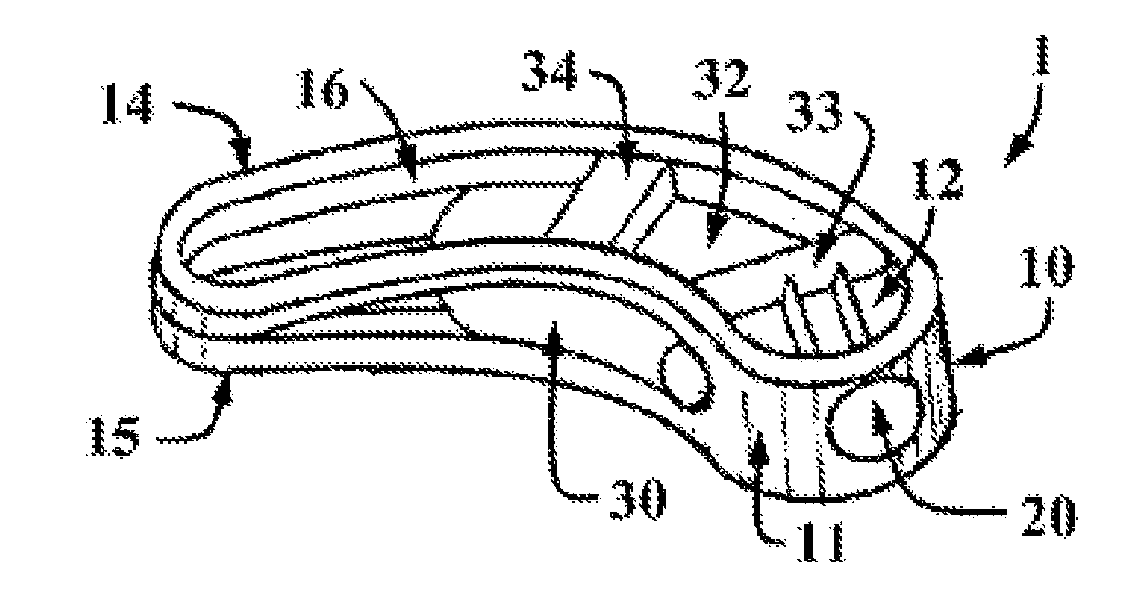
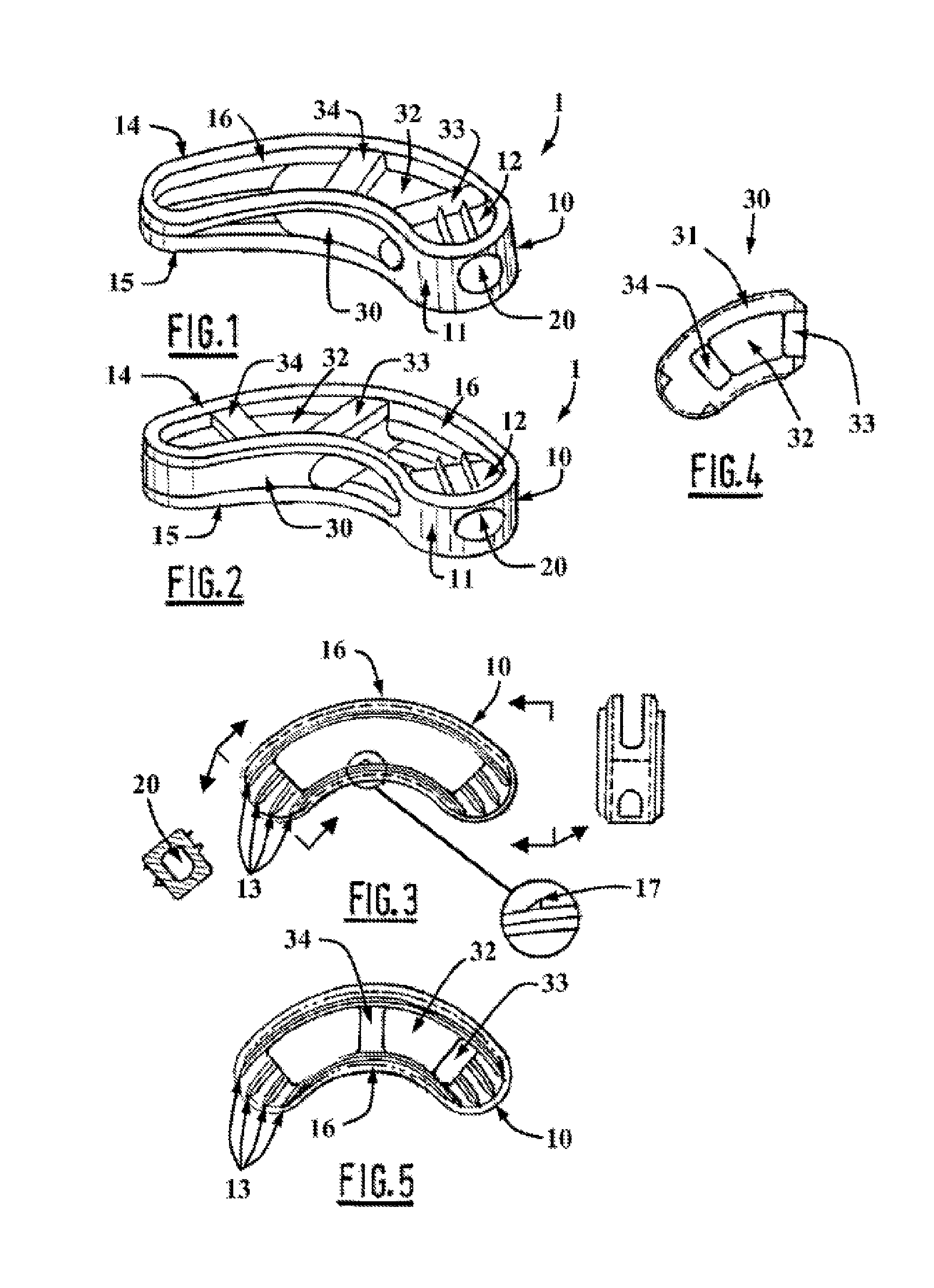
Prosthesis for the replacement of a posterior element of a vertebra
A prosthetic replacement for a posterior element of a vertebra comprising portions that replace the natural lamina and the four natural facets. The prosthetic replacement may also include portions that replace one or more of the natural spinous process and the two natural transverse processes. If desired, the prosthesis replacement may also replace the natural pedicles. A method for replacing a posterior element of a vertebra is also provided.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Minimally Invasive Spine Restoration Systems, Devices, Methods and Kits
InactiveUS20070088358A1Restore qualityRestore stateInternal osteosythesisBone implantArticular surfacesRestoration device
The invention discloses methods and devices for repairing, replacing and / or augmenting natural facet joint surfaces and / or facet capsules. A facet joint restoration device of the invention for use in a restoring a facet joint surface comprises: a cephalad facet joint element comprising a flexible member adapted to engage a first vertebrae and an artificial cephalad joint; and a caudad facet joint element comprising a connector adapted for fixation to a second vertebrae and an artificial caudad joint adapted to engage the cephalad facet joint. In another embodiment, the invention discloses a facet joint replacement device for use in replacing all or a portion of a natural facet joint between a first vertebrae and a second vertebrae comprising: a first cephalad facet joint element having a fixation member adapted to engage a lamina or spinous process of the first vertebrae and a first caudad facet joint element, the first caudad facet joint element comprising a first caudad connector adapted to fixate to the second vertebral body and an artificial caudad facet surface adapted to engage with the cephalad facet joint element.
Owner:FACET SOLUTIONS
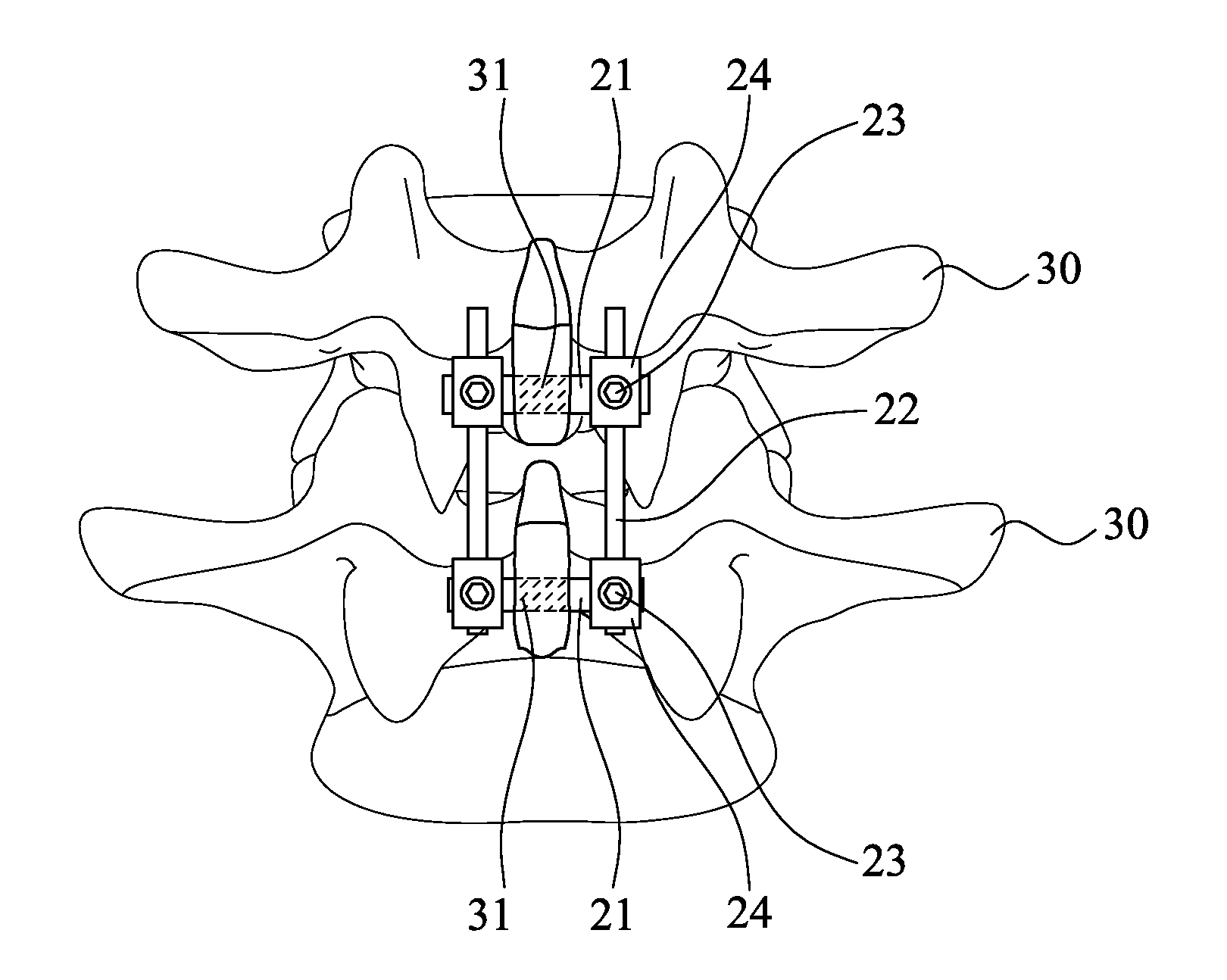
Minimally invasive method and apparatus for placing facet screws and fusing adjacent vertebrae
InactiveUS20060079908A1Minimally invasiveInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSacroiliac jointIliac screw
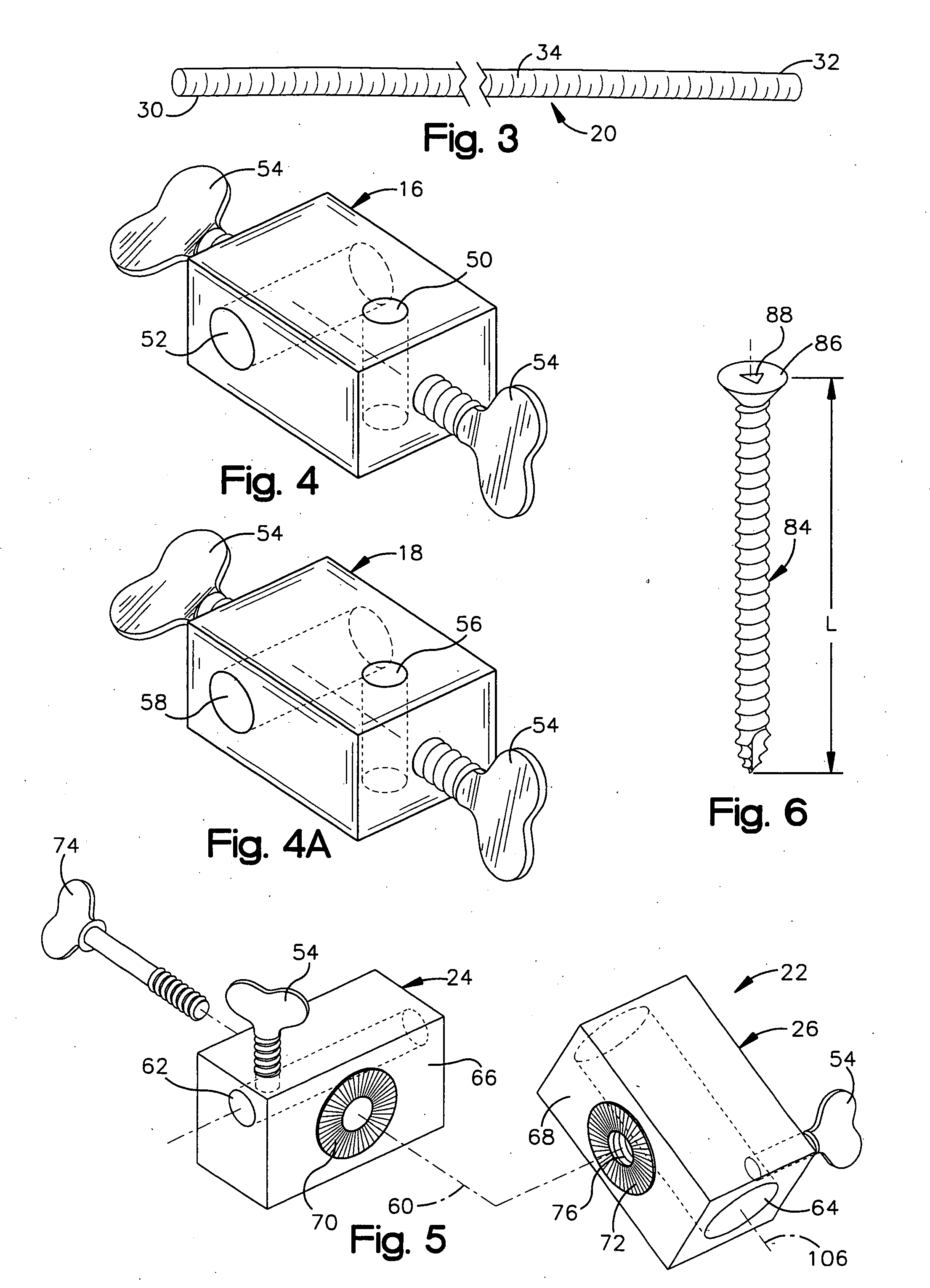
An example apparatus places translaminar screws across a facet joint between adjacent first and second vertebrae in a minimally invasive surgical procedure. The apparatus includes a first K-wire, a second K-wire, a first fixation block, a second fixation block, a support block, a first rod member, a second rod member, and a cannula. The first K-wire is inserted into the spinous process of the first vertebrae. The second K-wire is inserted into a transverse process of the second vertebrae. The first fixation block has perpendicularly extending first and second passages. The first K-wire extends into the first passage in the first fixation block. The second fixation block has perpendicularly extending first and second passages. The second K-wire extends into the first passage in the second fixation block. The support block has perpendicularly extending first and second passages. The first K-wire extends into the first passage in the support block. The first rod member extends through the second passage in the first fixation block and the second passage in the second fixation block. The second rod member further secures the first and second fixation blocks to the first and second vertebrae. The second rod member extends through the second passage in the support block. The cannula enables implantation of the translaminar screws across a facet joint between the first and second vertebrae.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Trans-Vertebral and Intra-Vertebral Plate and Fusion Cage Device for Spinal Interbody Fusion and Method of Operation
InactiveUS20100004747A1Limiting intervertebral movementEasy to integrateSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnCage device
A trans-vertebral and intra-vertebral plate and a rectangular cage with a slot for the plate of spinal fixation device are for neutralizing intervertebral movement for the spinal interbody fusion. The rectangular cage with a vertical or oblique slot is inserted into the intervertebral space from the lateral or anterior side of the spinal column and then the plate is inserted through the slot of the cage and hammered into and buried inside two adjacent vertebral bodies, to achieve three-dimensional intervertebral fixation.
Owner:LIN JIN FU +1
Production method of navigation template for positioning the pediculus arcus vertebrae
InactiveCN101390773ARelieve painSolve the slow scanning speedSurgerySpecial data processing applicationsOriginal dataRadiology
The invention relates to a method for fabricating a navigation templet used in pedicle positioning, including the following steps: firstly, collecting the original data and building up a three-dimensional vertebra model; wherein focusing on the location of a pedicle (1); then, conducting three-dimensional analysis to a screw entry passage of the pedicle and building up a virtual screw entry templet(3) which includes the screw entry passage(2); wherein the screw entry templet(3) is a reverse navigation templet which matches with the outline of the rear part of a vertebral lamina; and then, fabricating the reverse navigation templet through quick molding technique. The increases of CT or MRI scanning velocity and precision provide a precise sectional image for acquiring a three-dimensional model in reverse engineering, and the necessary organs can be quickly reconstructed through a three-dimensional reconstruction software and can be transformed and bored freely on the virtual model so as to figure out an optimal pedicle screw entry route. On the basis of the virtual model, the pedicle screw entry direction and depth can be guided by using the reverse navigation templet fabricated through quick molding technique during an operation so as to quickly and accurately finish the operation.
Owner:陆声
Total artificial spino-laminar prosthetic replacement
ActiveUS20110125269A1Reconstitute strength and structural integritySimple direct attachmentInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsMedicineProsthesis
A total artificial spinous process (spino)-laminar prosthesis (TASP-LP) including a body having a portion forming a spinous process extending away from the body, a first lamina portion extending from a first side of the body, and a second lamina portion extending from a second side of the body, wherein the first lamina portion and the second lamina portion are disposed on opposite sides of the spinous process.
Owner:MOSKOWITZ FAMILY LLC
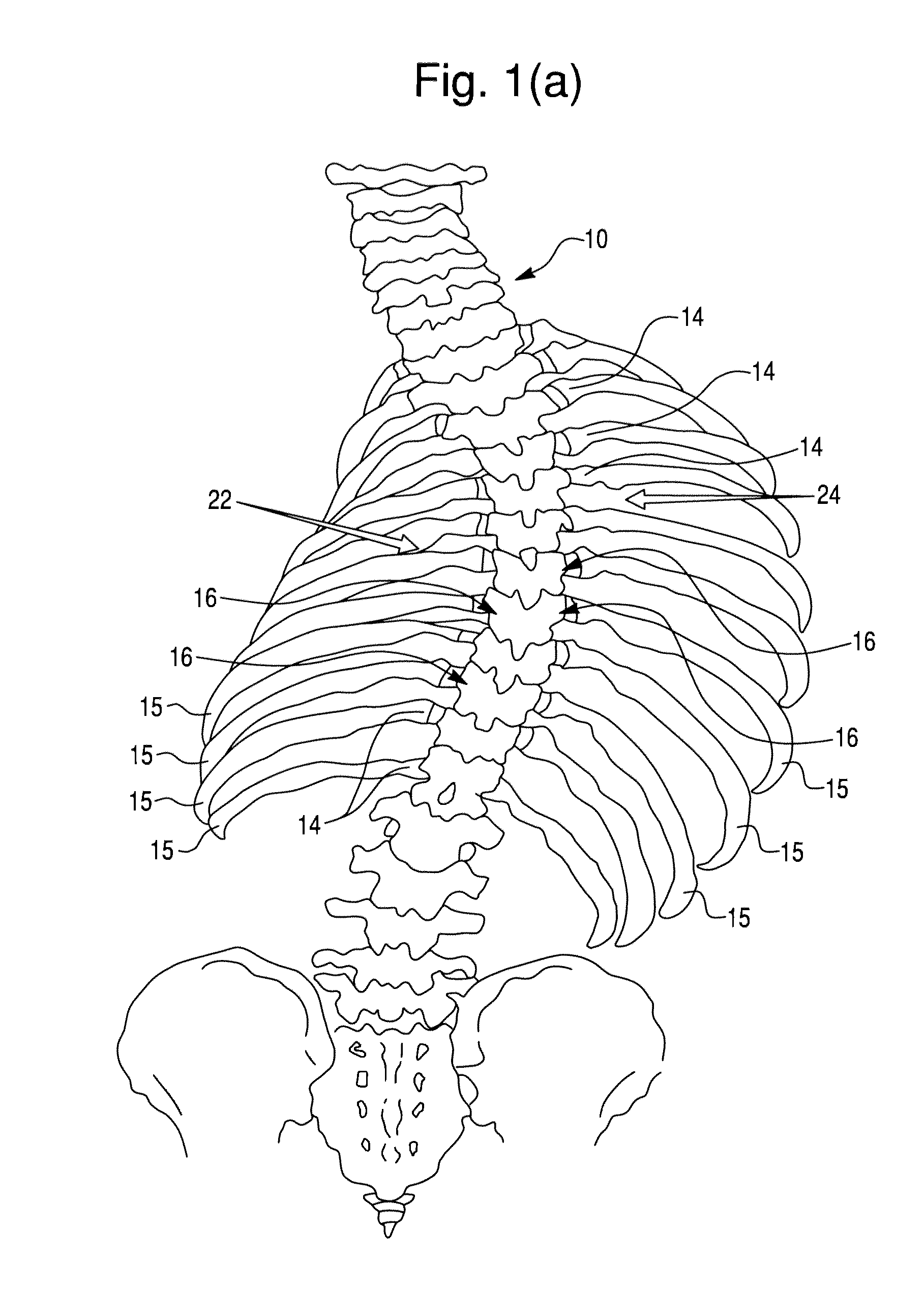
Segmental orthopedic device for spinal elongation and for treatment of scoliosis
ActiveUS20110137353A1Prevent movementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisOrthopaedic deviceDistraction
An orthopaedic device to realign bone segments comprises first and second attachment members and a strut or spacer member. The first attachment member is attached to a first rib bone or first transverse process or first lamina of a vertebra. The second attachment member is attached to a second rib bone or second transverse process or second lamina of a vertebra. The strut is positioned between the first and second attachment members. The strut is fixedly or releasably connected to the first and second attachment members to couple the first attachment member to the second attachment member. The strut provides distraction between the first and second rib bones or transverse processes to realign the rib bones. The attachment members comprise a clamp and screw combination.
Owner:DYNAMIC SPINE
Expandable cage for vertebral surgery involving lumbar intersomatic fusion by a transforaminal posterior approach
An implant of the intersomatic cage type, for fusion of vertebral bodies by a transforaminal approach, is disclosed that comprises a body with a curved profile that is designed to be implanted between the vertebral plates of two adjacent vertebrae. According to the invention, said body of curved profile comprises a posterior maneuvering part and an anterior attack part, said anterior attack part being composed of a lower tongue and of an upper tongue that are designed to receive between them a spacer element that can slide between a position of introduction, in which it is situated near said posterior maneuvering part, and a spacing position, in which it is situated near the end of said anterior attack part, thus increasing the thickness of the latter by spreading the tongues apart, said spacer element comprising a receiving seat that is open at the top and bottom.
Owner:SCHAUMBURG GERALD +1
Anterior vertebral plate with quick lock screw
Provided is a novel system that includes a low profile anterior vertebral body plate and quick lock screws for the fixation and stabilization of the cervical spine, the quick lock screw having an integral novel screw locking mechanism of a locking thread disposed on at least a portion of the side of the screw head, which engages an inwardly directed screw hole flange and thus attaches to the plate so as to lock the screw into the plate Also provided is a method of stabilizing cervical vertebrae using the disclosed system.
Owner:K2M
Prosthesis for the replacement of a posterior element of a vertebra
A prosthetic replacement for a posterior element of a vertebra comprising portions that replace the natural lamina and the four natural facets. The prosthetic replacement may also include portions that replace one or more of the natural spinous process and the two natural transverse processes. If desired, the prosthesis replacement may also replace the natural pedicles. A method for replacing a posterior element of a vertebra is also provided.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
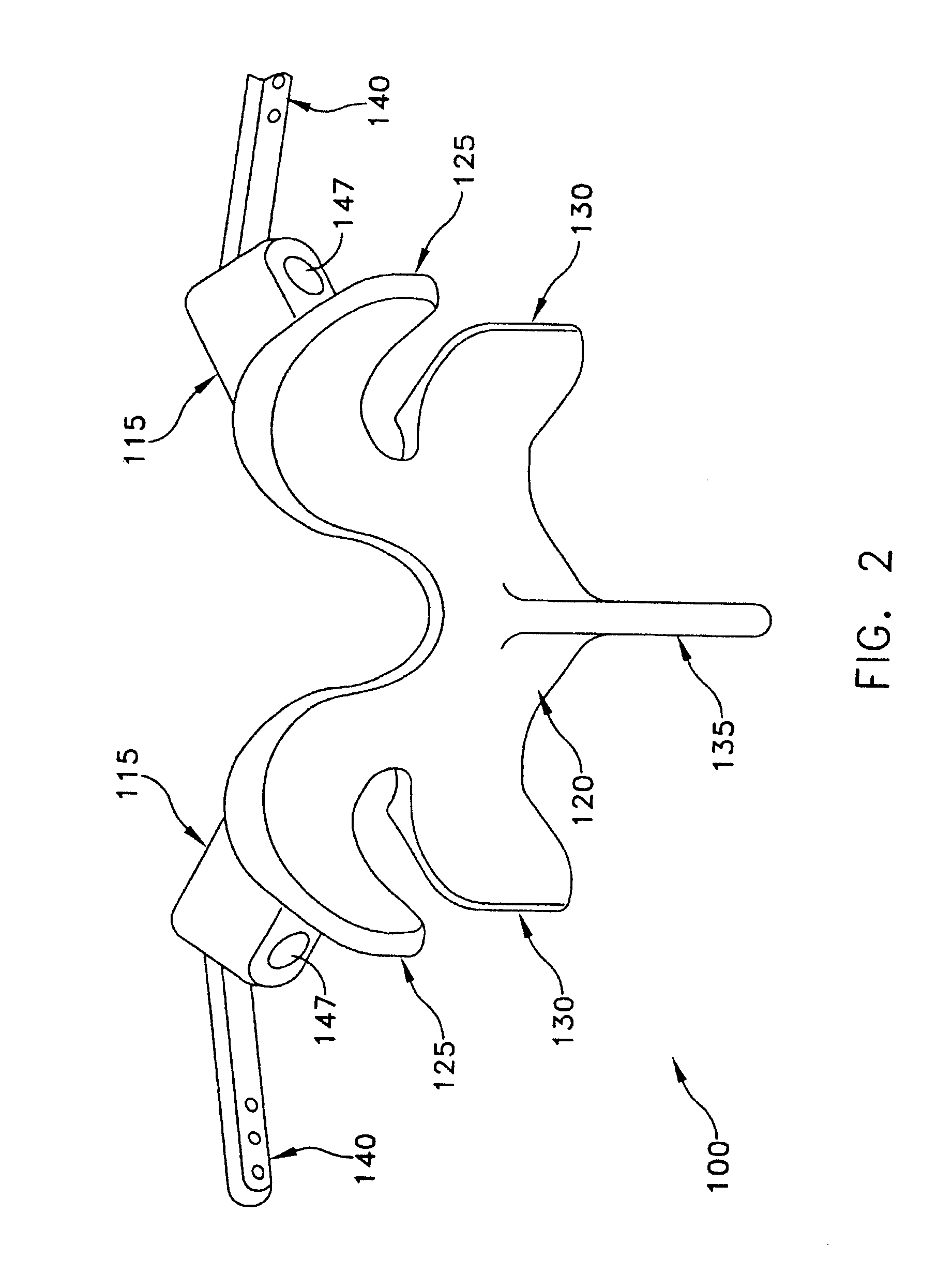
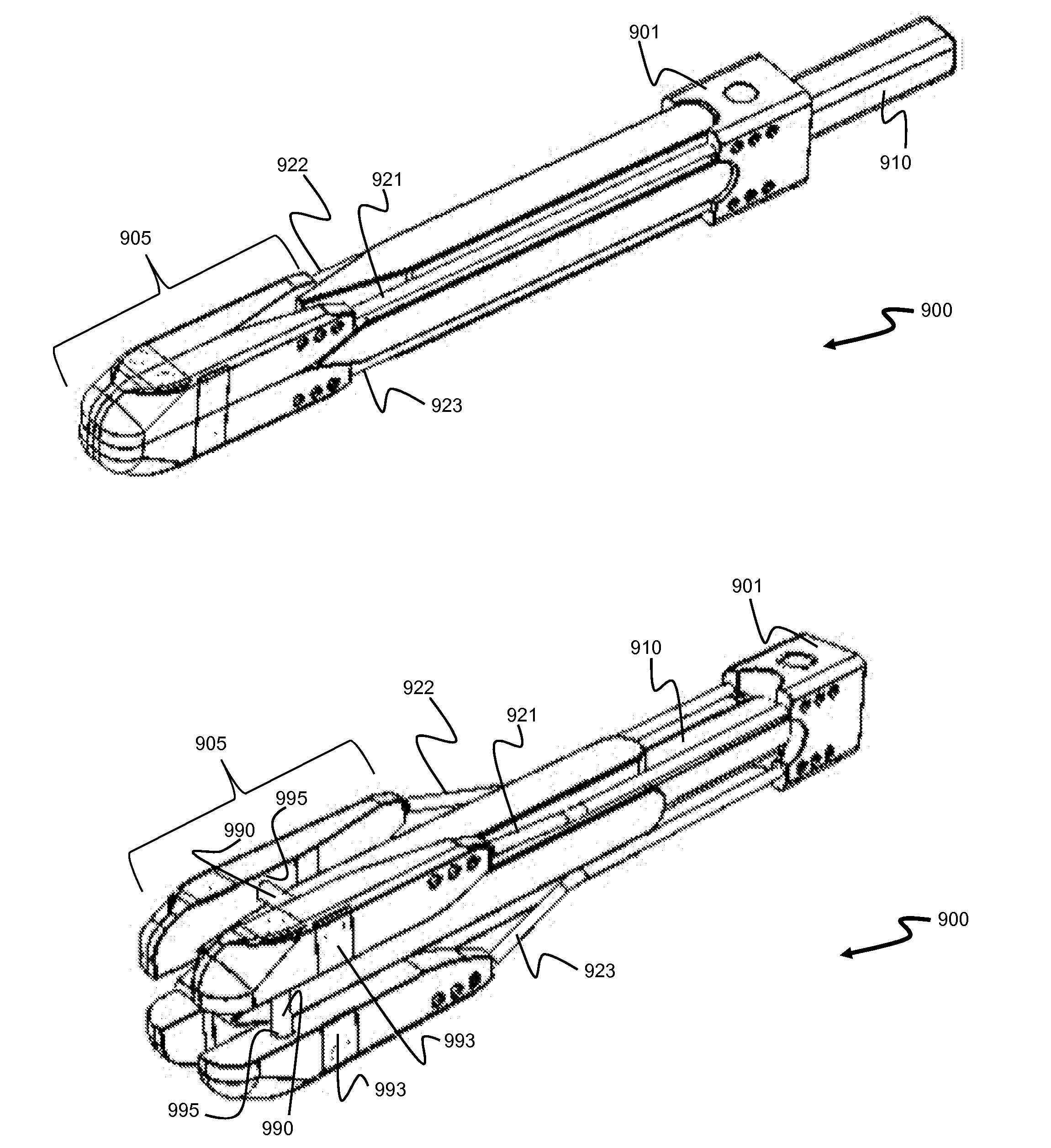
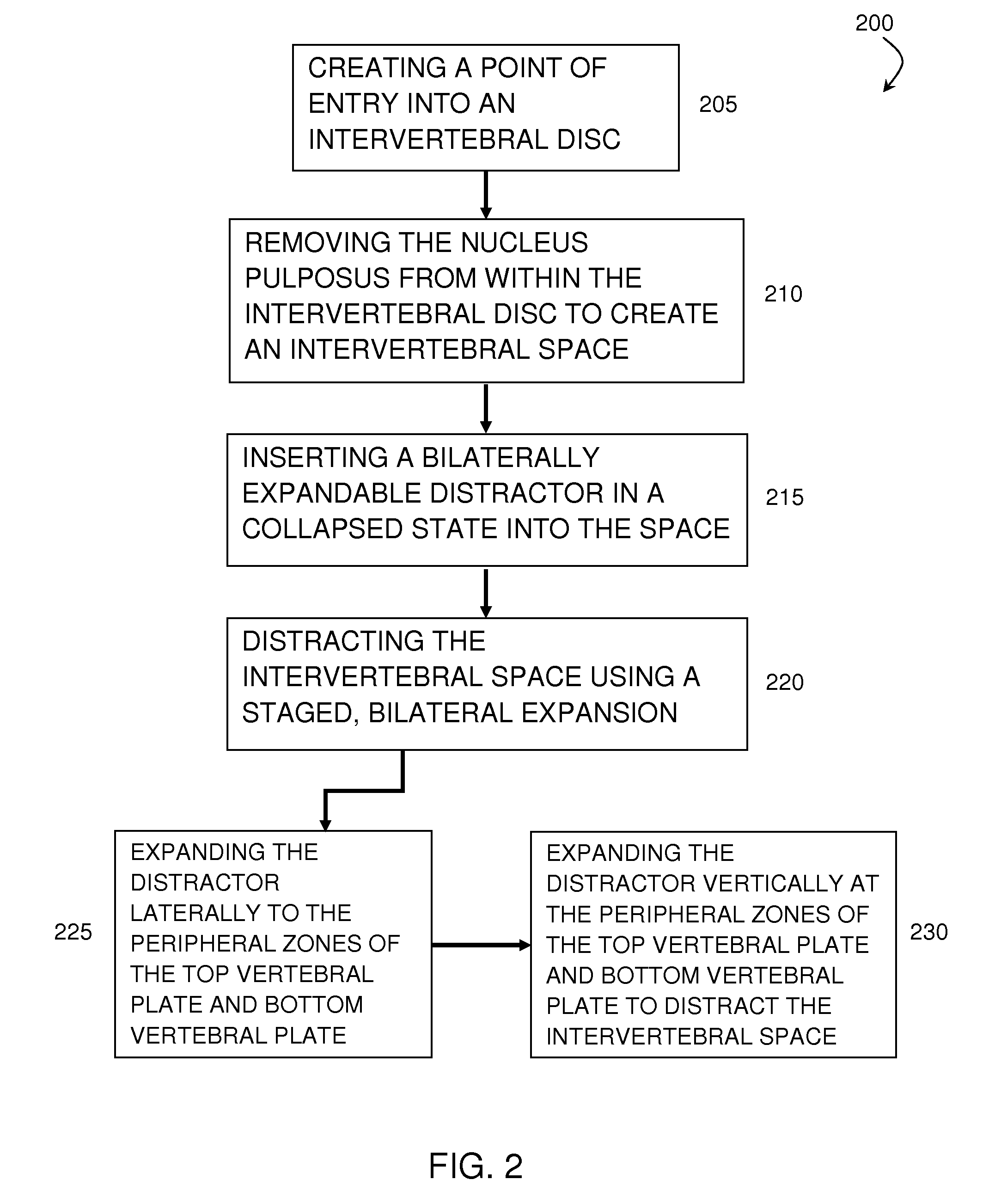
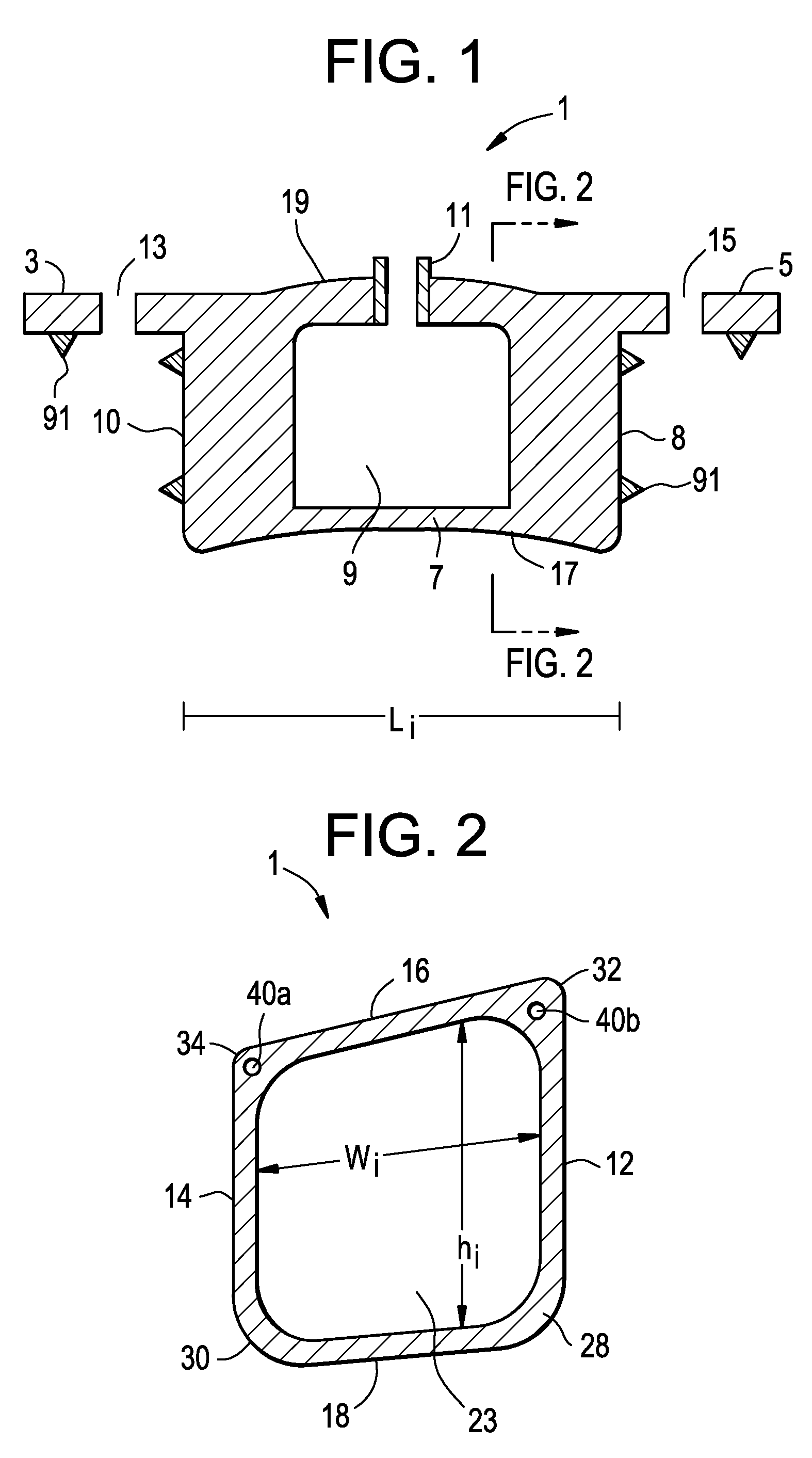
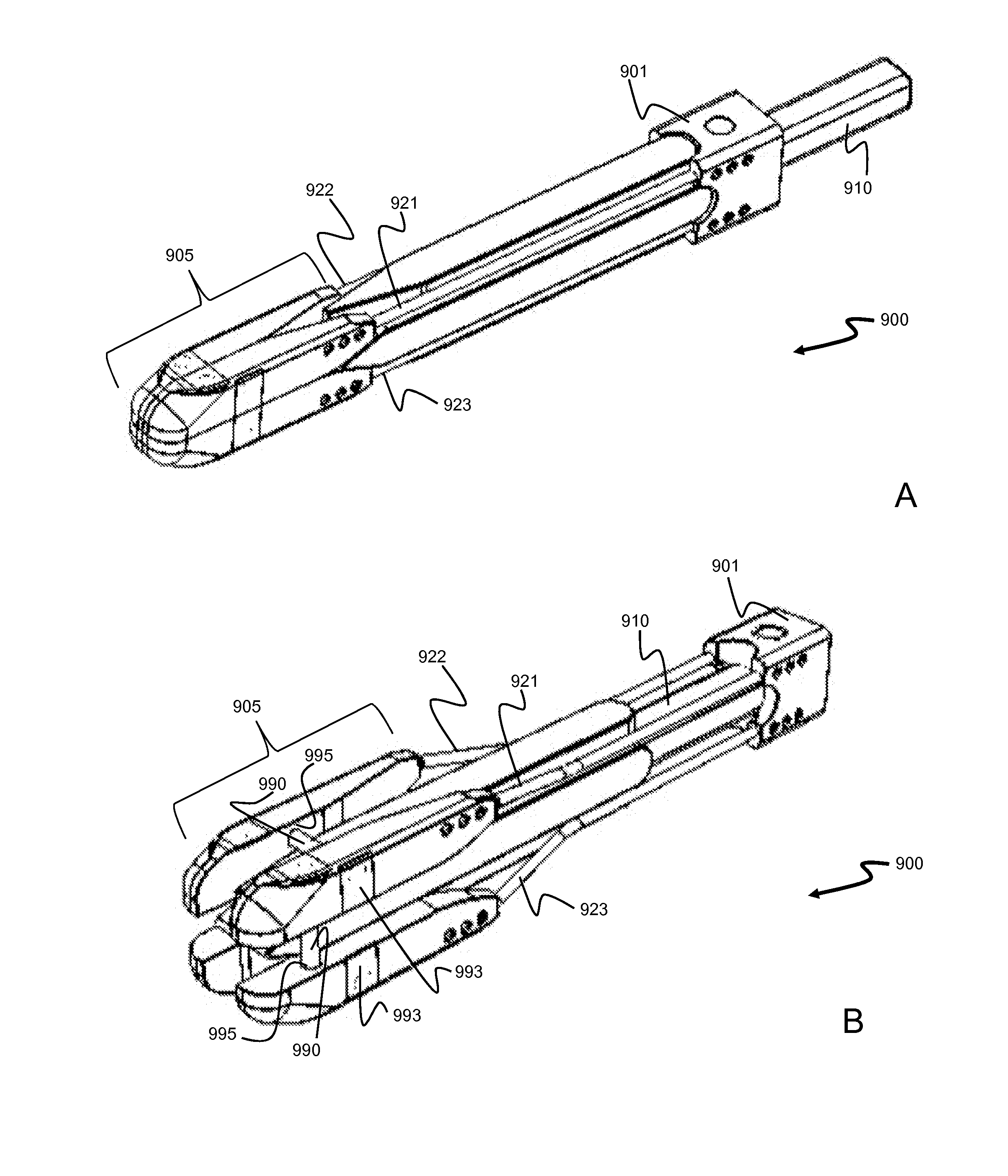
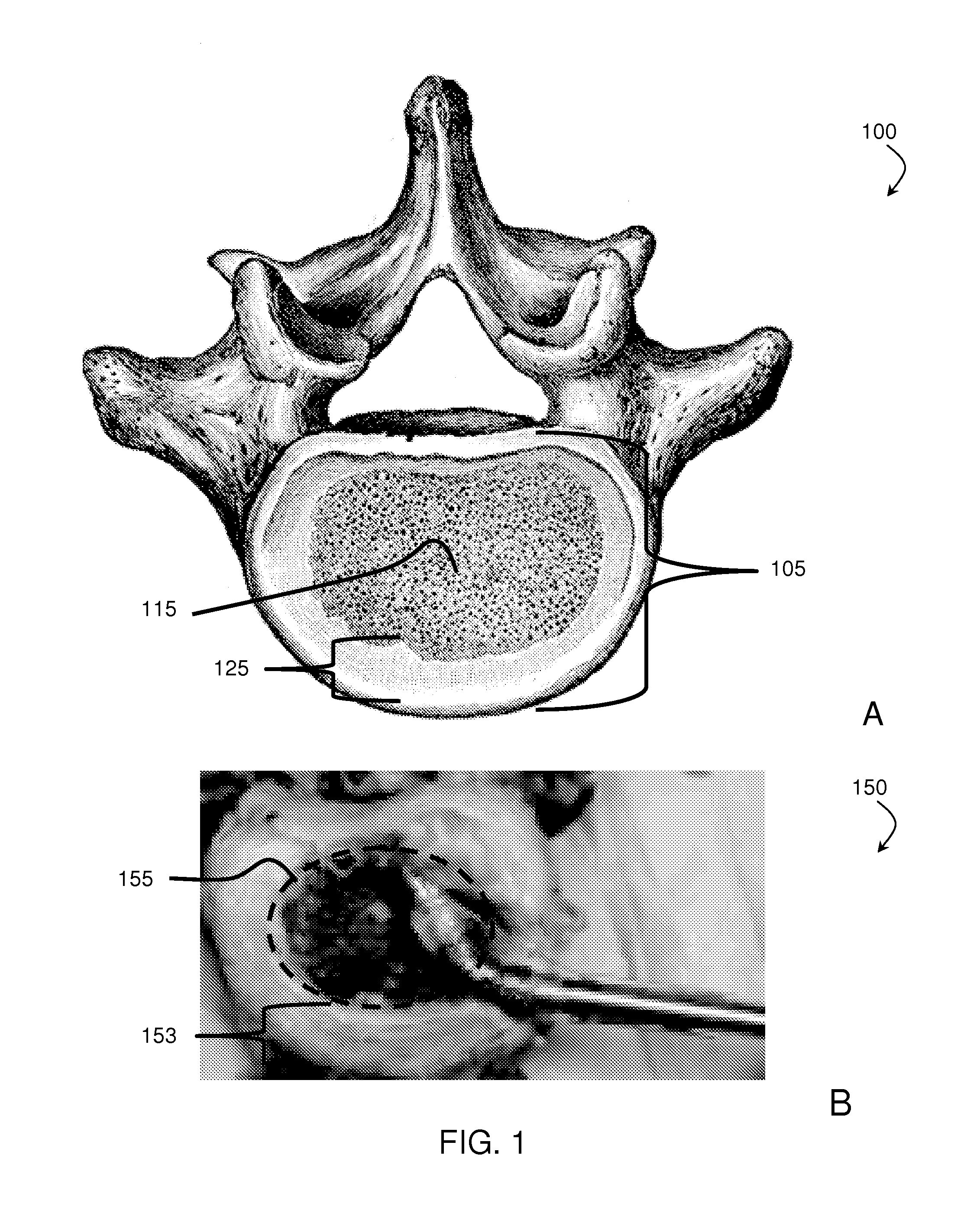
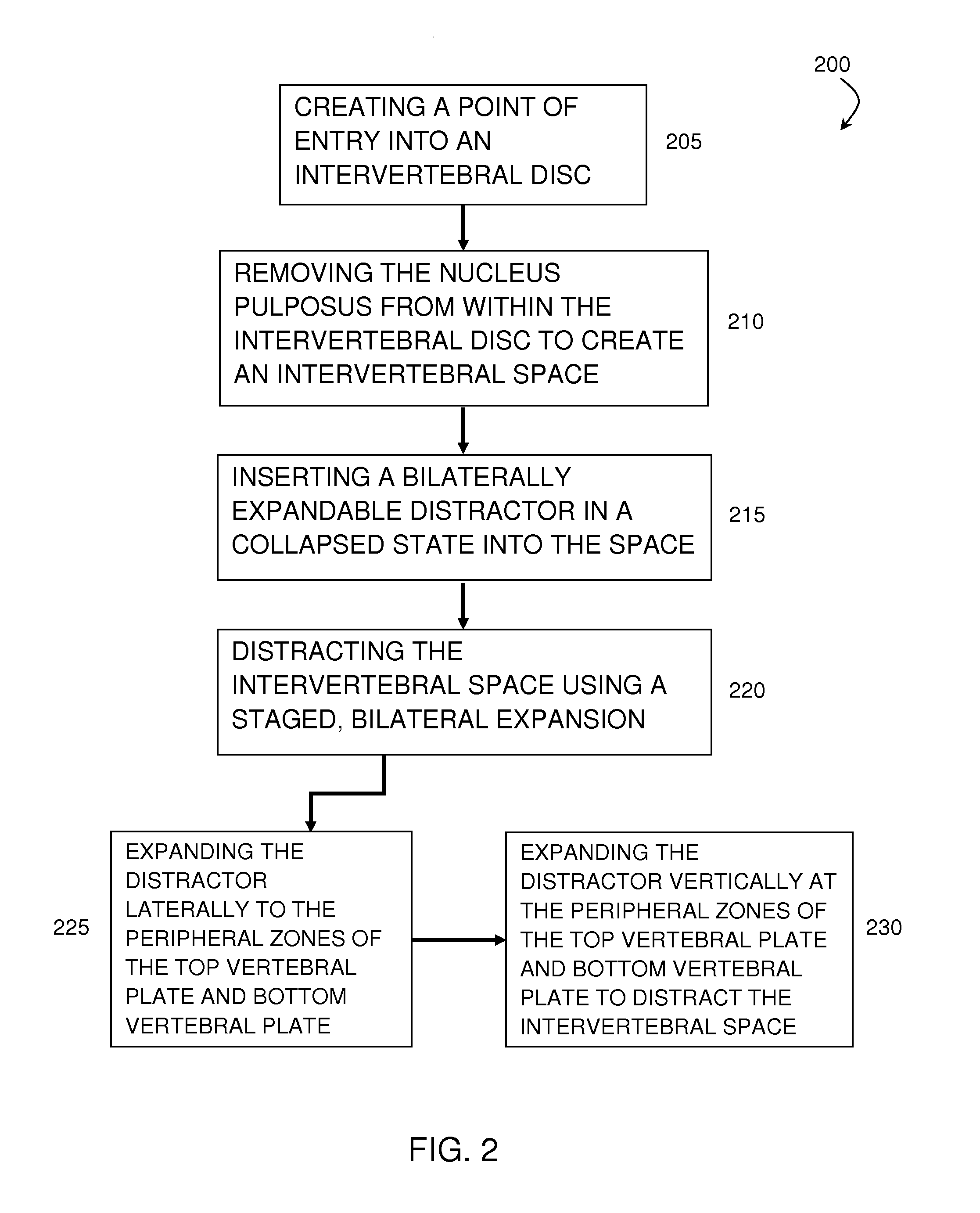
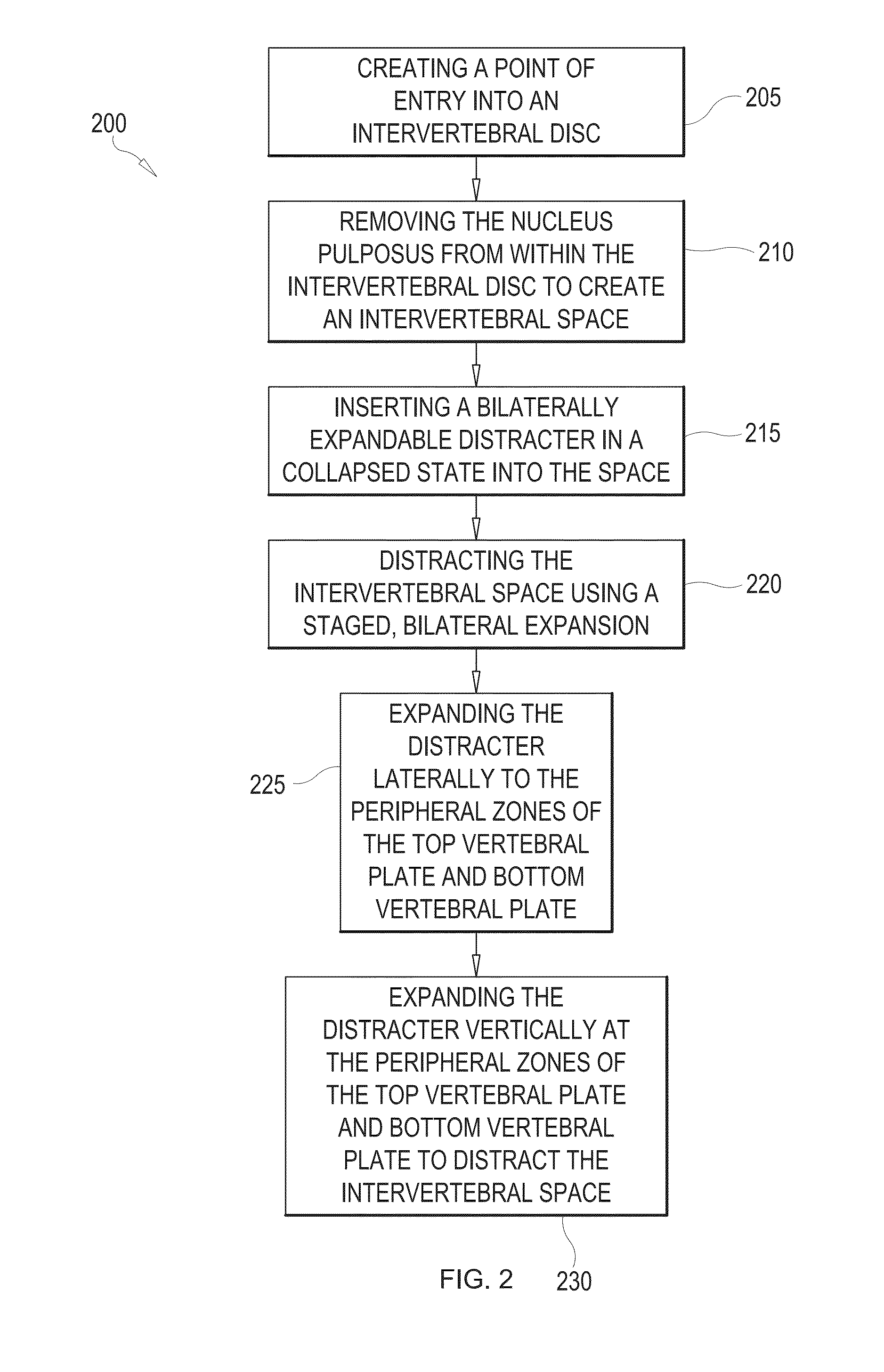
Staged, bilaterally expandable trial
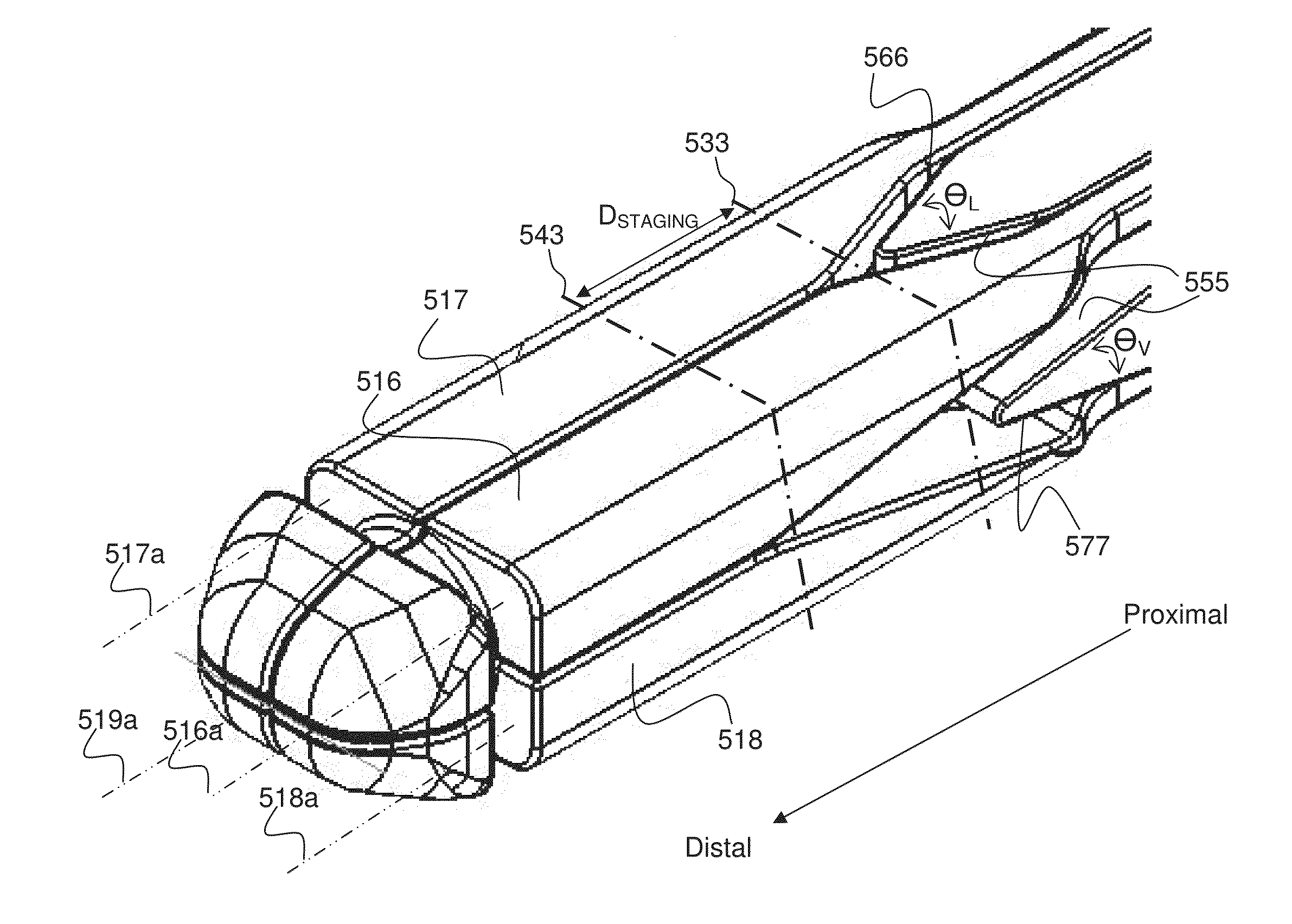
InactiveUS20150073552A1Easy to insertFacilitate horizontal expansionSurgerySpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceVertebral lamina
Systems and methods for distracting an intervertebral disc space are provided. The systems use a staged, bilaterally expandable trial. The systems and methods of distracting an intervertebral space are provided in a manner that addresses the problem of subsidence. The method includes inserting the trial into the intervertebral space in a collapsed state and, once inserted, the trial is then used for distracting the intervertebral space using an expansion that includes a first stage and a second stage. The first stage includes expanding the trial laterally toward the peripheral zones of the top vertebral plate and the bottom vertebral plate, and the second stage includes expanding the trial vertically to distract the intervertebral space.
Owner:INTEGRITY IMPLANTS INC
Segmental orthopedic device for spinal elongation and for treatment of scoliosis
ActiveUS9204908B2Prevent movementSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisOrthopaedic deviceSpinal column
An orthopaedic device to realign bone segments comprises first and second attachment members and a strut or spacer member. The first attachment member is attached to a first rib bone or first transverse process or first lamina of a vertebra. The second attachment member is attached to a second rib bone or second transverse process or second lamina of a vertebra. The strut is positioned between the first and second attachment members. The strut is fixedly or releasably connected to the first and second attachment members to couple the first attachment member to the second attachment member. The strut provides distraction between the first and second rib bones or transverse processes to realign the rib bones. The attachment members comprise a clamp and screw combination.
Owner:DYNAMIC SPINE
Posterior cervical vertebral stabilizing system
ActiveUS7666208B1Raise the possibilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnVertebral bone
A posterior cervical vertebral stabilizing system is disclosed. The system includes a device comprising an upper portion for positioning adjacent to a relatively superior vertebra of a patient's spine and a lower portion for positioning adjacent to a relatively inferior vertebra of the patient's spine. The upper portion forms a support for abutting the posterior surface of the superior vertebra and the lower portion forms a saddle for engaging a spinous process of the inferior vertebra. The device has an anterior face that, at each of the upper and lower portions, has a radius of curvature about an axis. The system includes a method of affixing the device to a spine of a patient by positioning the device posteriorly of the relatively superior and relatively inferior vertebrae, and looping cable about the device and the lamina of the vertebrae. The method may also include promoting fusion of the vertebrae together.
Owner:ASFORA IP
Methods and Devices for Expanding A Spinal Canal Using Balloons
ActiveUS20100152854A1Minimally invasive procedureAvoiding permanenceInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsVertebral laminaBiomedical engineering
An in-situ formed laminoplasty implant comprising an expandable bag containing a flowable, hardenable composition, wherein the implant may be shaped to act as a laminoplasty strut and be rigidly connected to a prepared lamina space.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
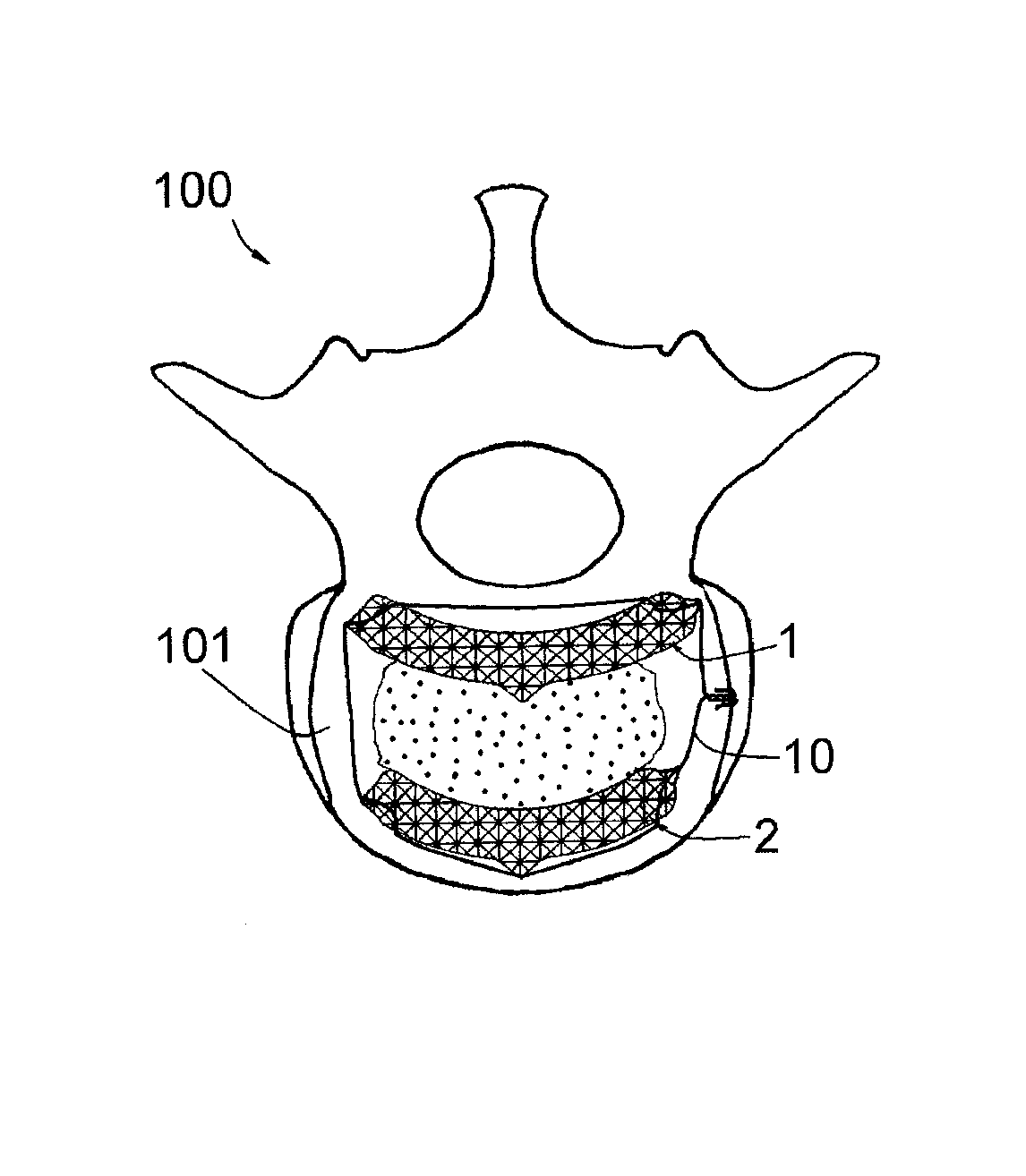
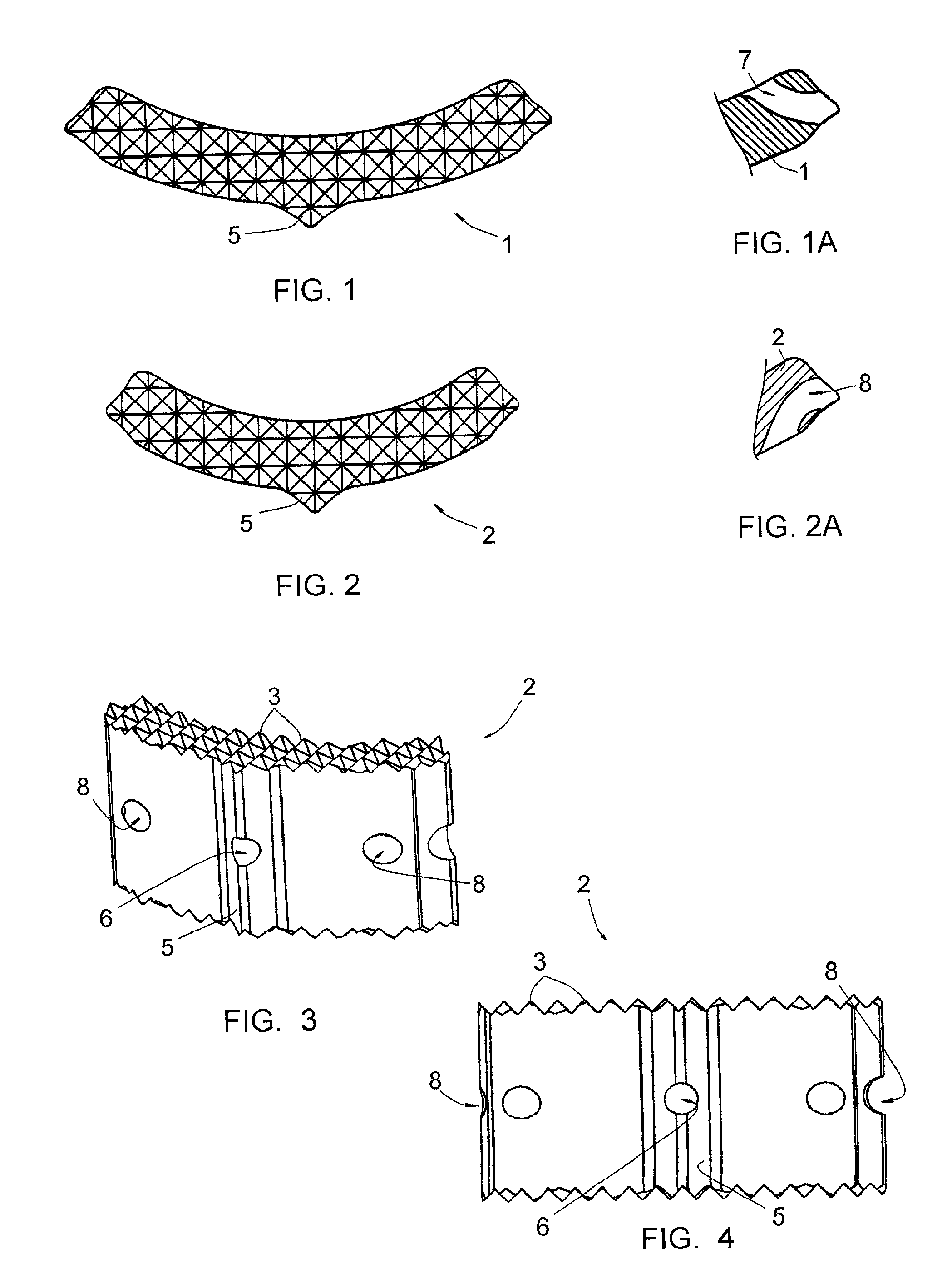
Intervertebral implant to immobilize one vertebra relative to another
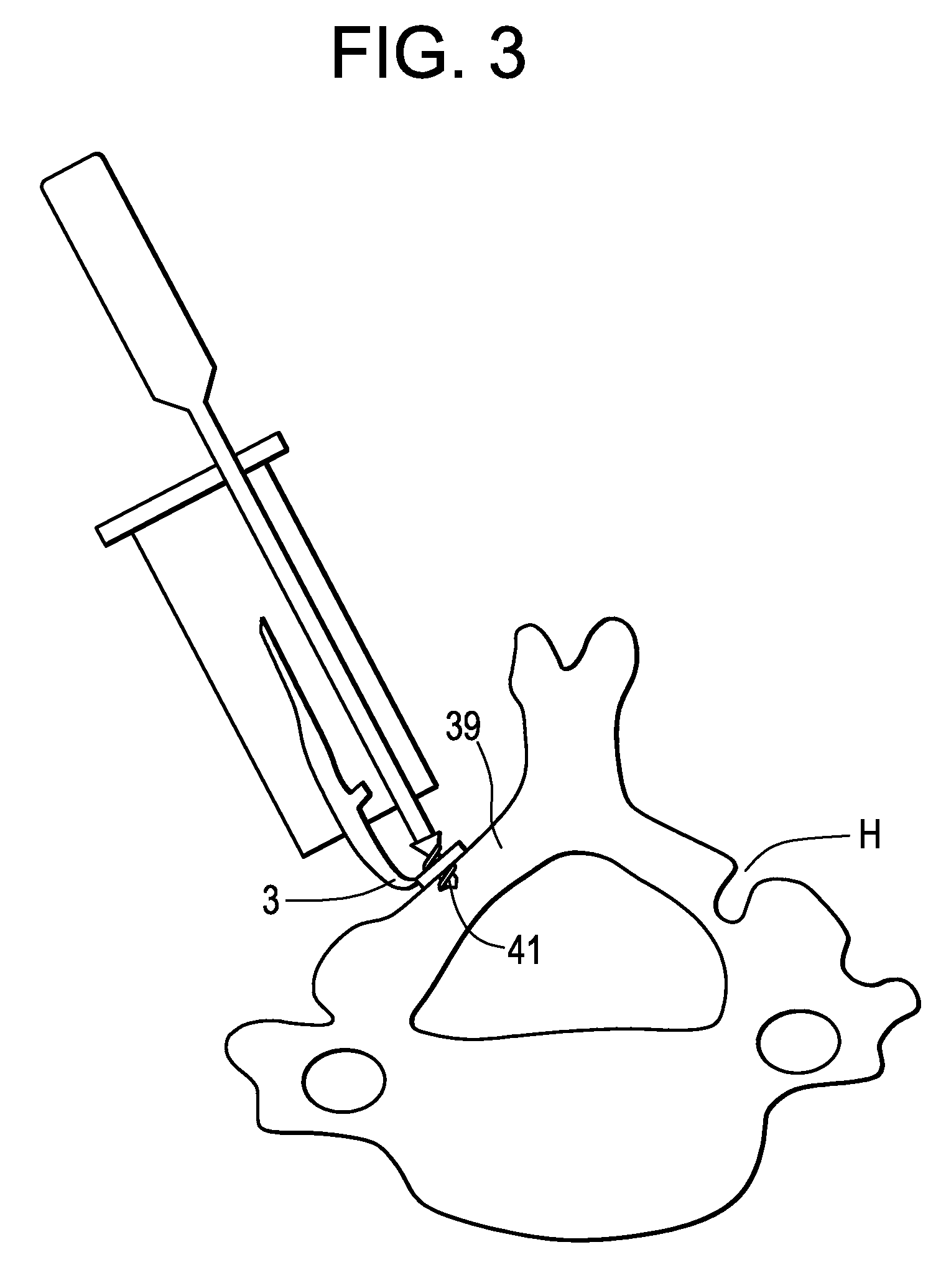
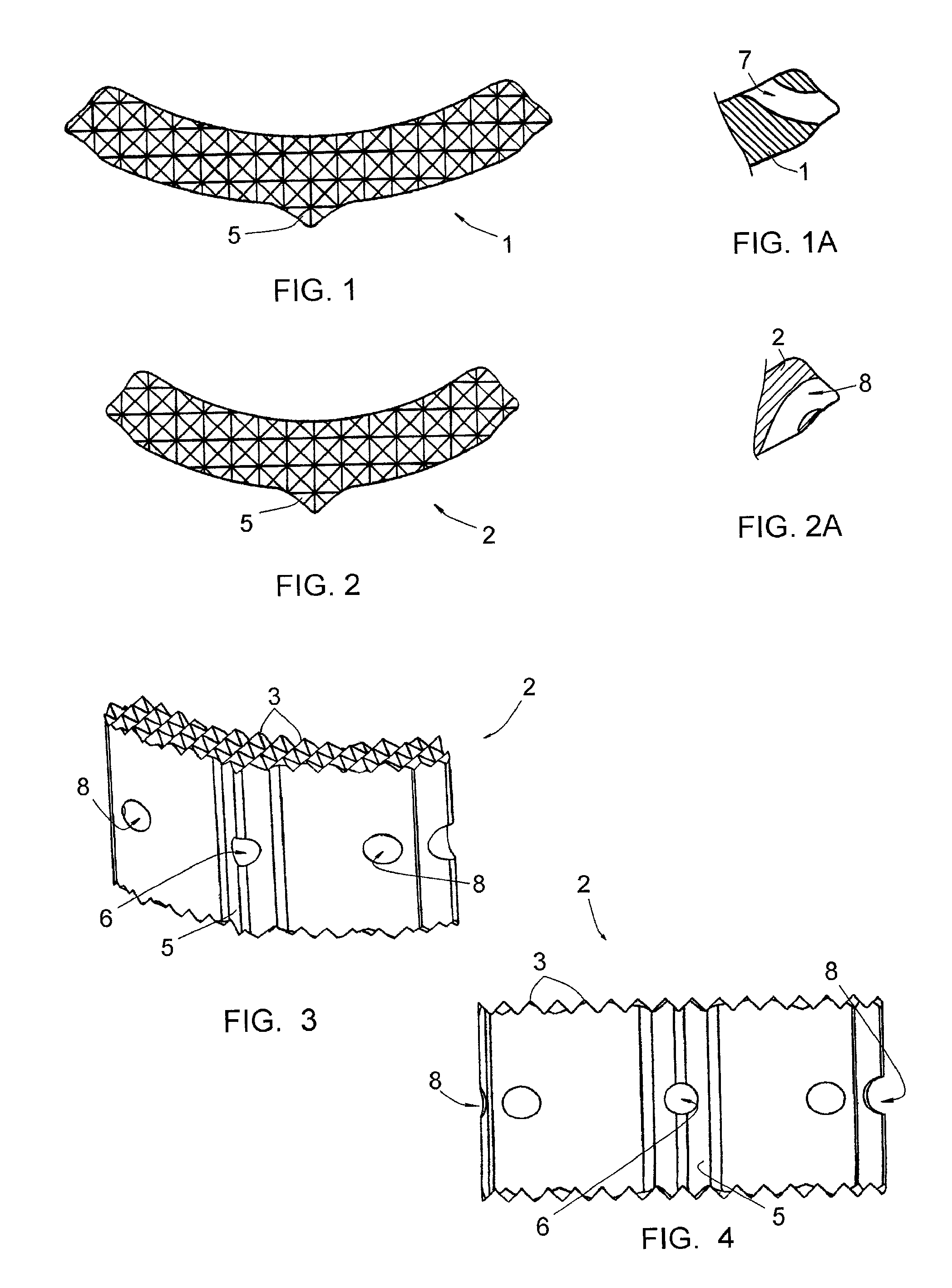
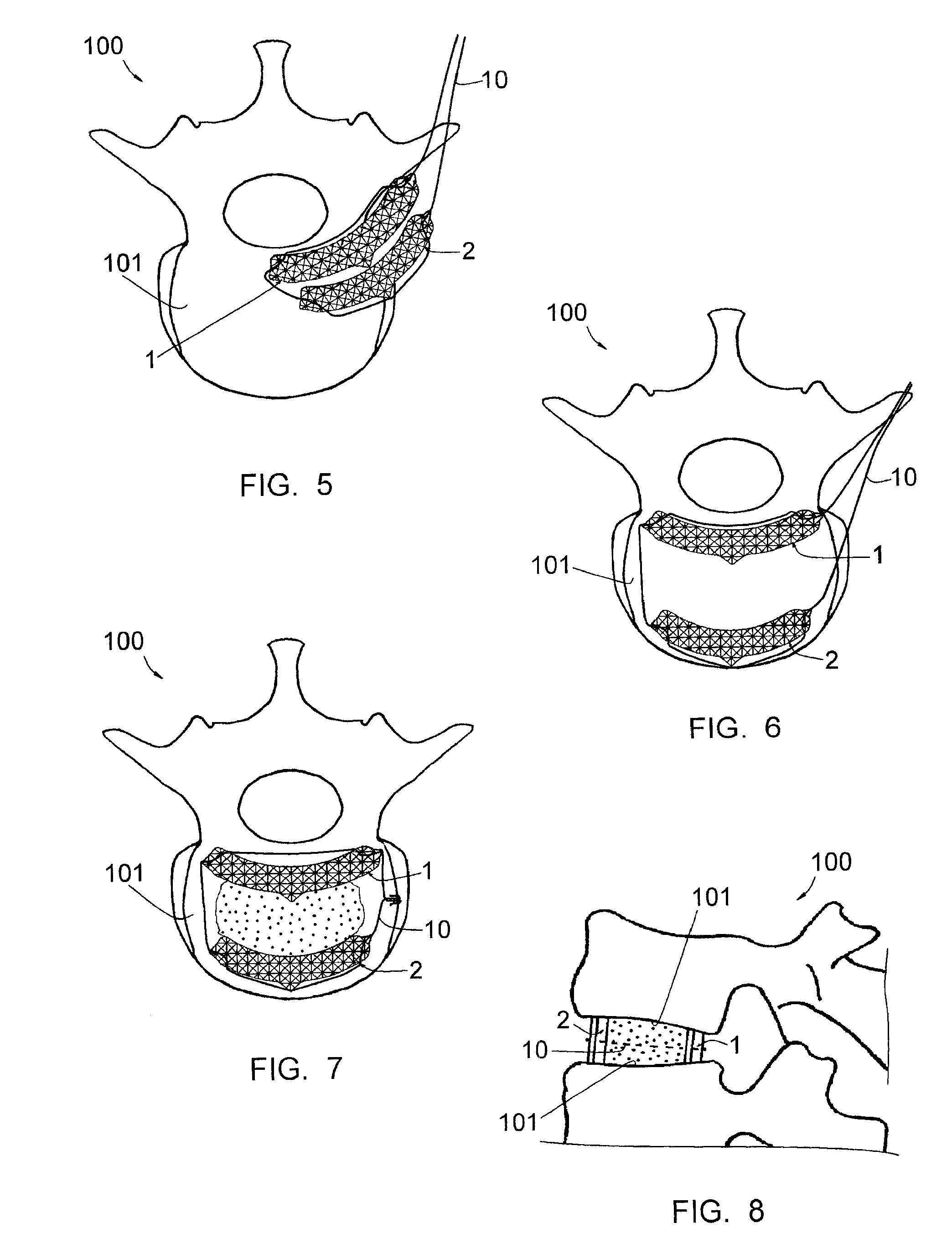
InactiveUS20100262248A1Easy to introduceConvenient ArrangementJoint implantsSpinal implantsCurve shapeVertebral lamina
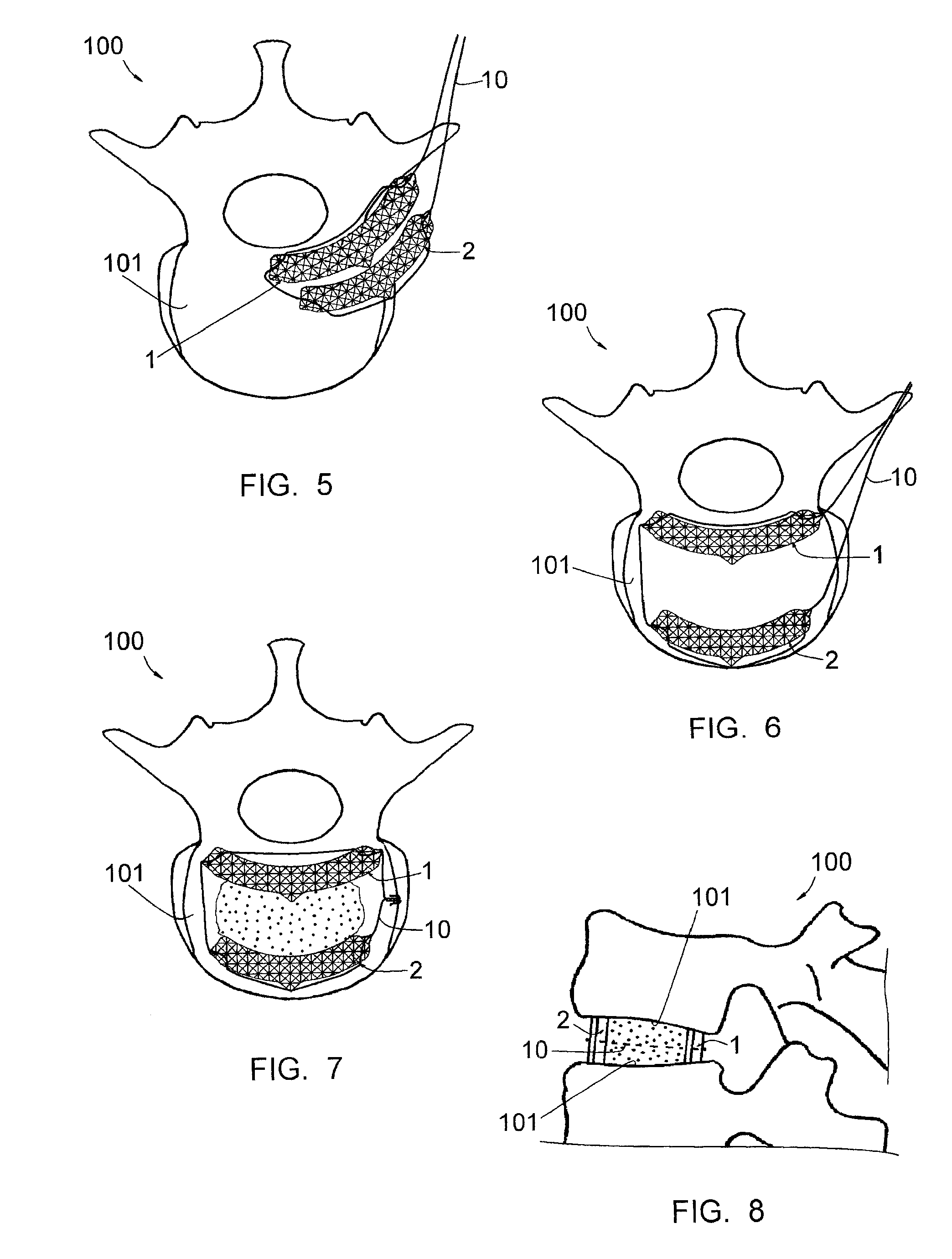
This implant includes two elongated elements (1, 2) of reduced width, defining, at their edges, two longitudinal surfaces opposite each other. These elements (1, 2) being intended to be positioned between the vertebral plates (101) of the vertebrae, apart from each other, with their longitudinal surfaces in contact with the vertebral plates (101. Elements (1, 2) have curved shapes, having substantially the same curvature from one element (1, 2) to the other, and one of the elements (2) has a length smaller than that of the other element (1), the element (2) with the smaller length being intended to be placed in the anterior position on a vertebral plate (101) while the element (1) with the larger length is intended to be placed in the posterior position on this same vertebral plate (101).
Owner:MEDICREA INT SA
3D-printed cervical vertebra pedicle screw guide and implantation plate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104739501AFit closelyQuick fitAdditive manufacturing apparatusInternal osteosythesisMedicineCervical vertebral pedicle
The invention relates to a 3D-printed cervical vertebra pedicle screw (cervical spine 2-7) guide and implantation plate and a preparation method thereof. The implantation plate is printed through the 3D printing technology and comprises one or more guide plates, one or more cervical vertebra pedicle screw guide screw ways and one or more spinous process holes where spinous processes are inserted, wherein the cervical vertebra pedicle screw guide screw ways and the spinous process holes are formed in the guide plates, a plane is arranged on the upper portion of each guide plate, a curve surface is arranged on the bottom of each guide plate and consistent with the vertebral plate reversely, and the plane on the upper portion of each guide plate extends to a screw inlet way and extends for 2-5 mm on the outlet of the plane on the upper portion. When many guide plates are provided, connectors are arranged between the guide plates. Several fixing pins are arranged on the guide plates in order to guarantee stability of the guide and implantation plate, and fixing clamps are arranged near the spinous process holes. The 3D-printed cervical vertebra pedicle screw guide and implantation plate is simple and reasonable in structure, convenient to use and capable of effectively providing individual screw inlet guide hole ways for cervical vertebra pedicle screws, guaranteeing screw inlet accuracy, reducing operation difficulty and operation risks.
Owner:BEIJING FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
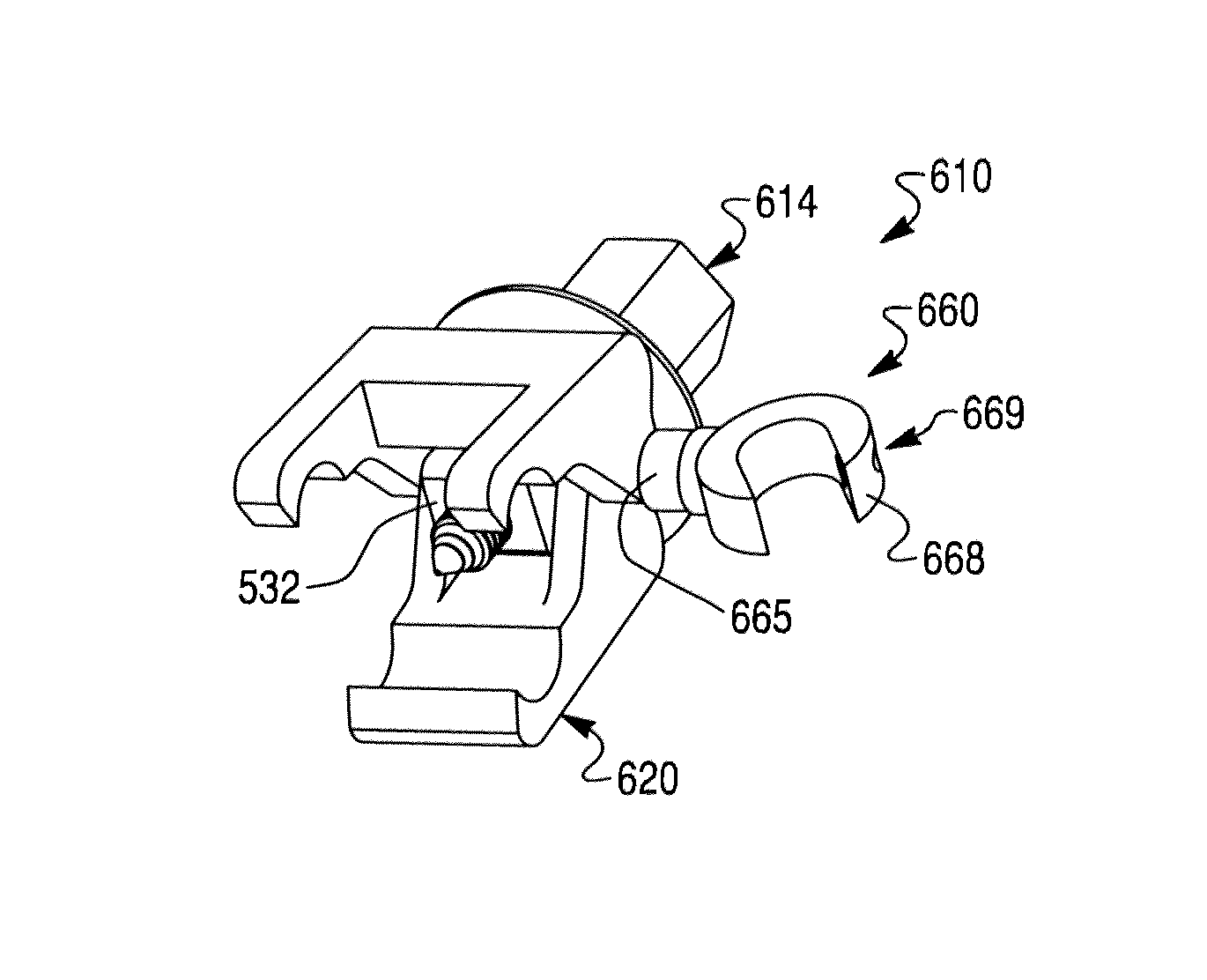
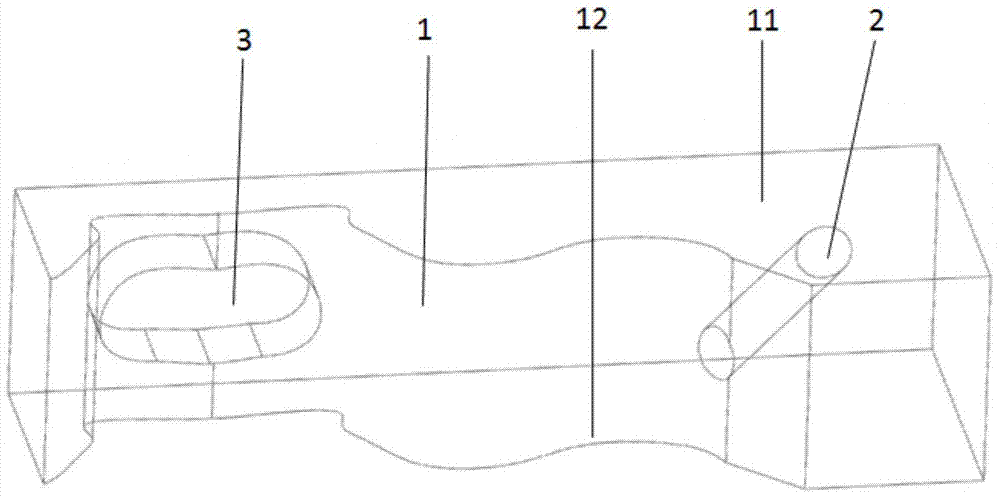
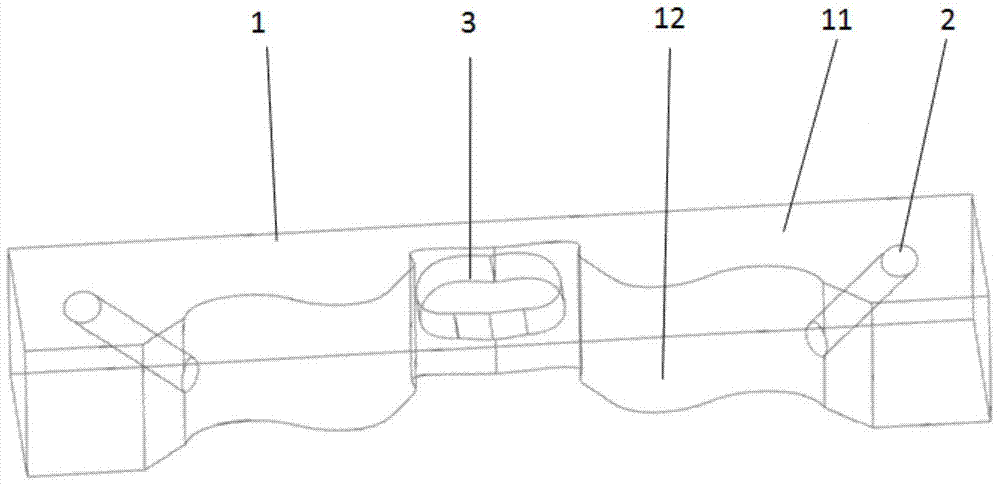
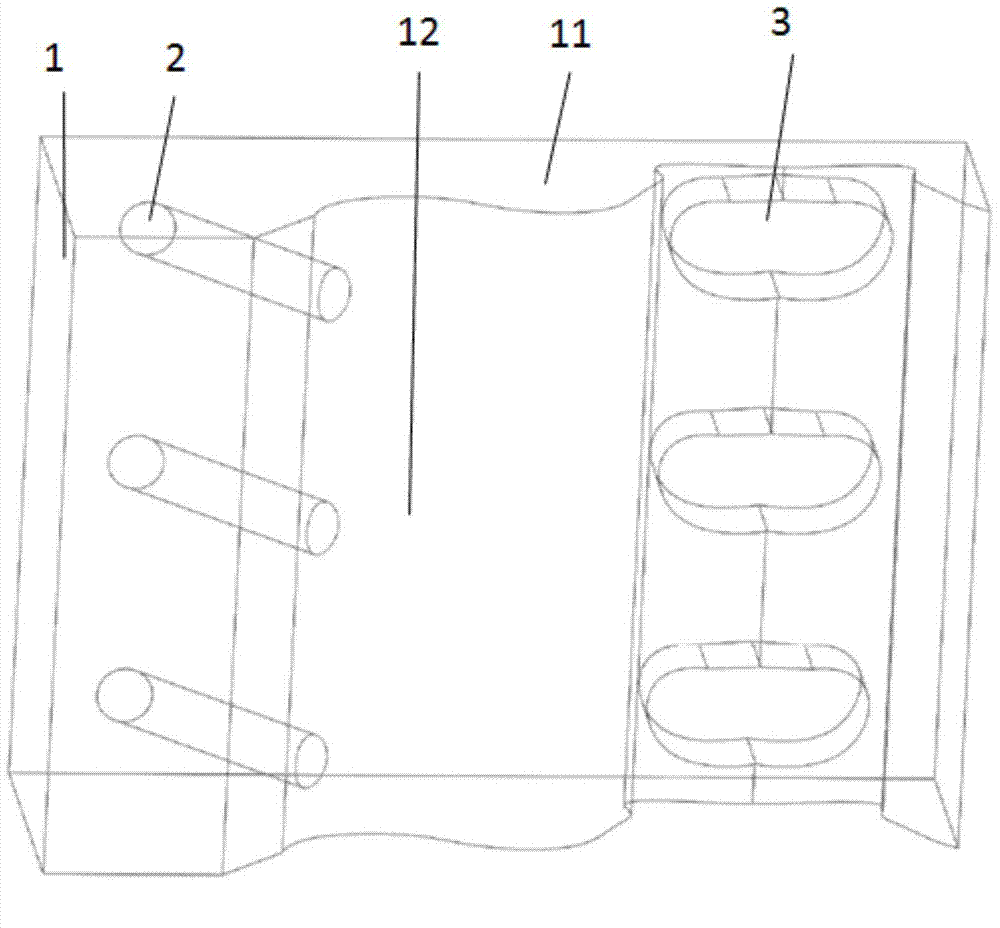
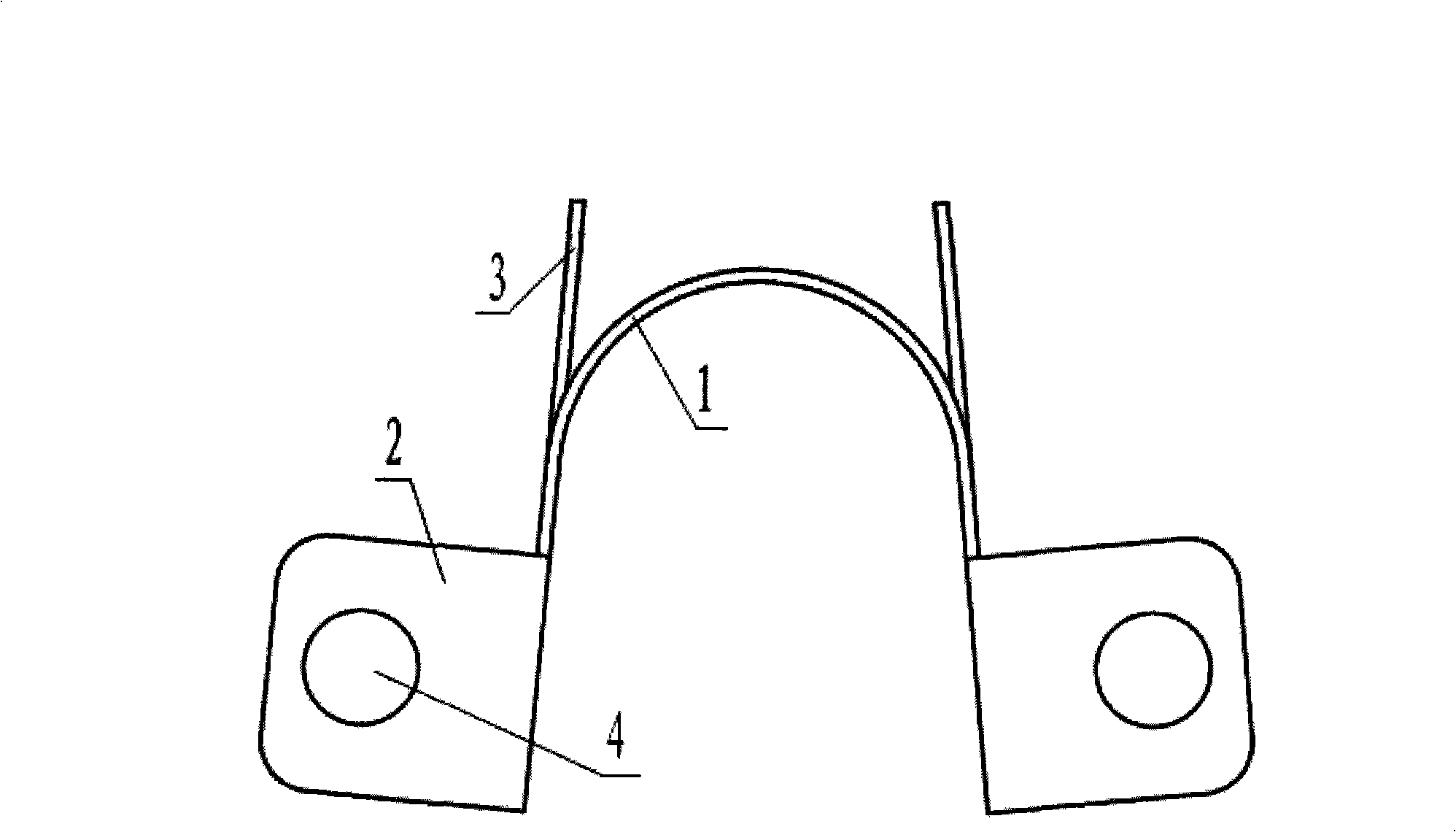
Spinal crest elastic internal fixation device
The invention discloses an inner elastic fixer of vertebral spinous process. The fixer comprises a U-shaped elastic strip (1) and a U-shaped clip (2) arranged at both sides of the U-shaped elastic strip. The invention is characterized in that lateral wings (3) are arranged at both sides of the bottom of the U-shaped elastic strip (1) respectively, the lateral wings (3) extend along the negative direction of a U-shaped opening and a tapping screw hole (5) is arranged on each lateral wing (3). The invention fastens a fixed bolt on the upper spinous process and the lower spinous process by the U-shaped clip and adopts the tapping screw hole to fix the lateral wing on a vertebral lamina at the root of the spinous process, thus greatly reducing force acting on the spinous process so as to improve the stability of fixing and effectively prevent the fracture and incision of the spinous process.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Anterior vertebral plate with quick lock screw
Provided is a novel system that includes a low profile anterior vertebral body plate and quick lock screws for the fixation and stabilization of the cervical spine, the quick lock screw having an integral novel screw locking mechanism of a locking thread disposed on at least a portion of the side of the screw head, which engages an inwardly directed screw hole flange and thus attaches to the plate so as to lock the screw into the plate Also provided is a method of stabilizing cervical vertebrae using the disclosed system.
Owner:K2M
Laminoplasty devices and methods
InactiveCN1678248AIncrease the cross-sectional areaInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsMedicineVertebral lamina
Laminoplasty plates are engageable to at least one portion of a divided lamina to maintain a desired spacing relative to the spinal canal. The laminoplasty plates include a spacer portion having a first end and a second end that spans a gap formed by at least one of a divided lamina portion. The laminoplasty plates can include a lamina engagement portion at one end for engagement with the divided lamina portion.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Anterior vertebral plate with suture lock
Provided is a novel system that includes an anterior vertebral body plate, suture lock bone screws, and an elongated suture lock to provide an interconnection for said bone screws, such that said system can be used for the fixation and stabilization of the cervical spine, the suture lock bone screws being connected one to the other by the elongated suture lock are prevented from unintentionally backing out of said plate. Also provided is a method of stabilizing cervical vertebrae using the disclosed system.
Owner:K2M
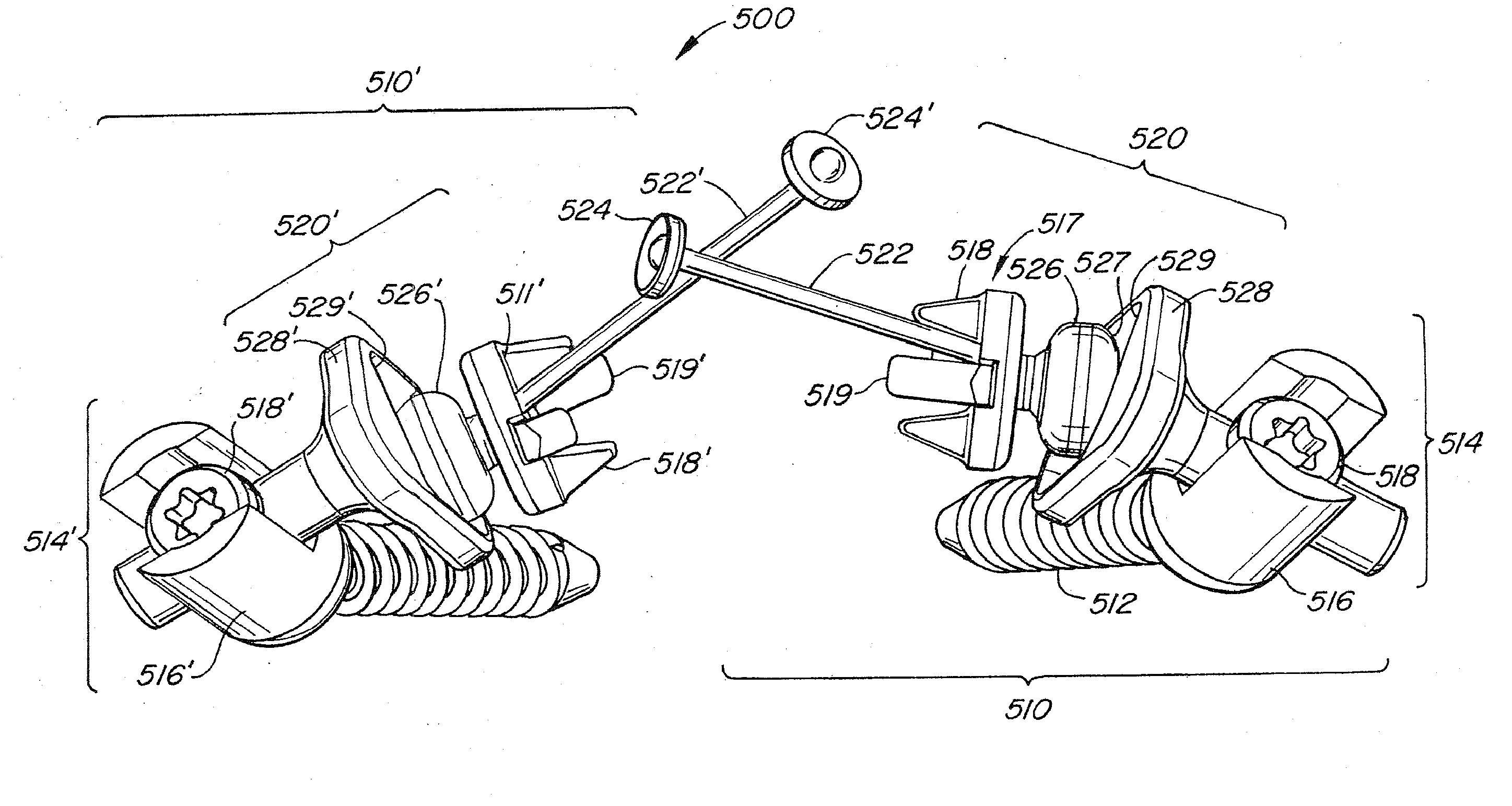
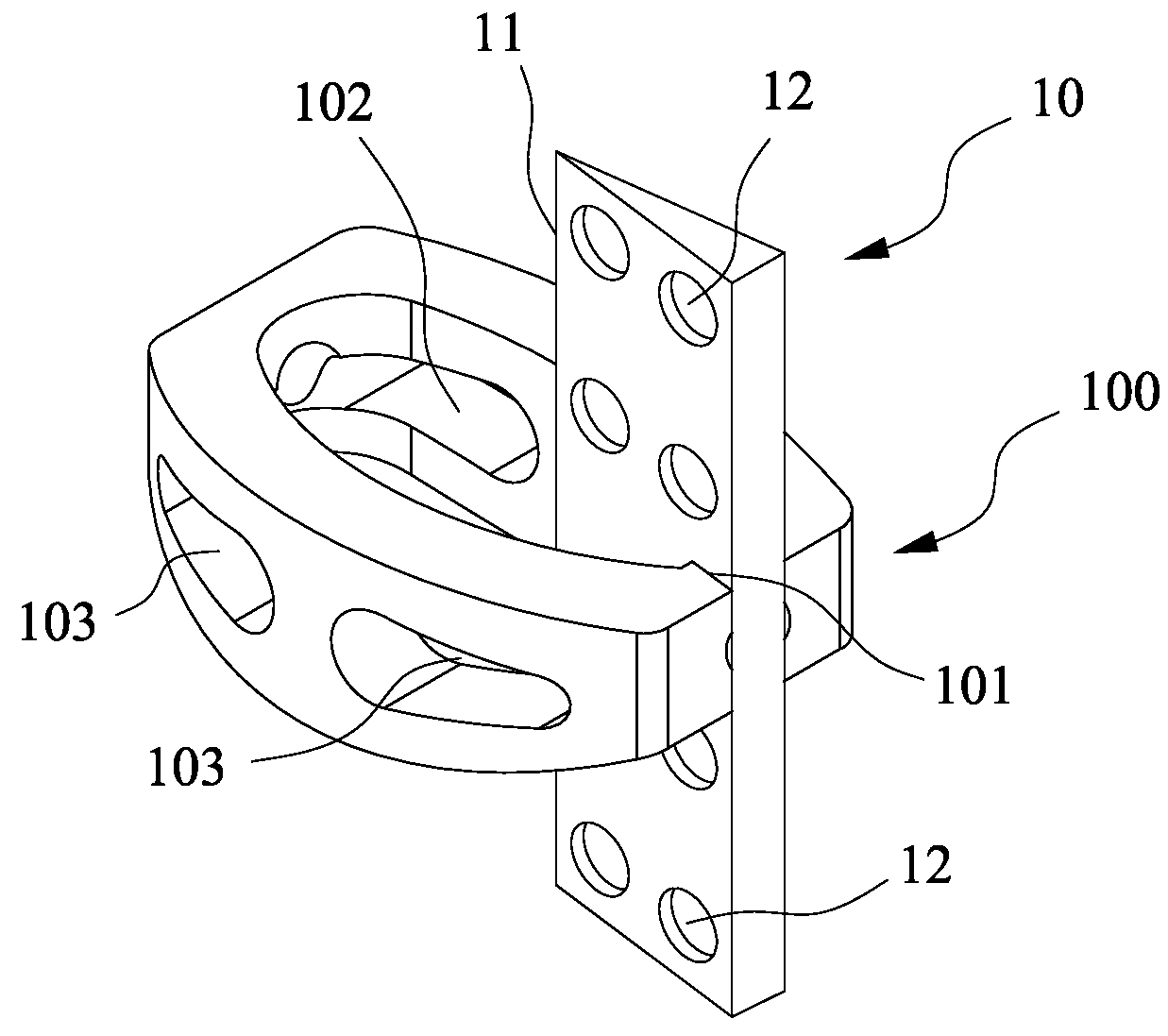
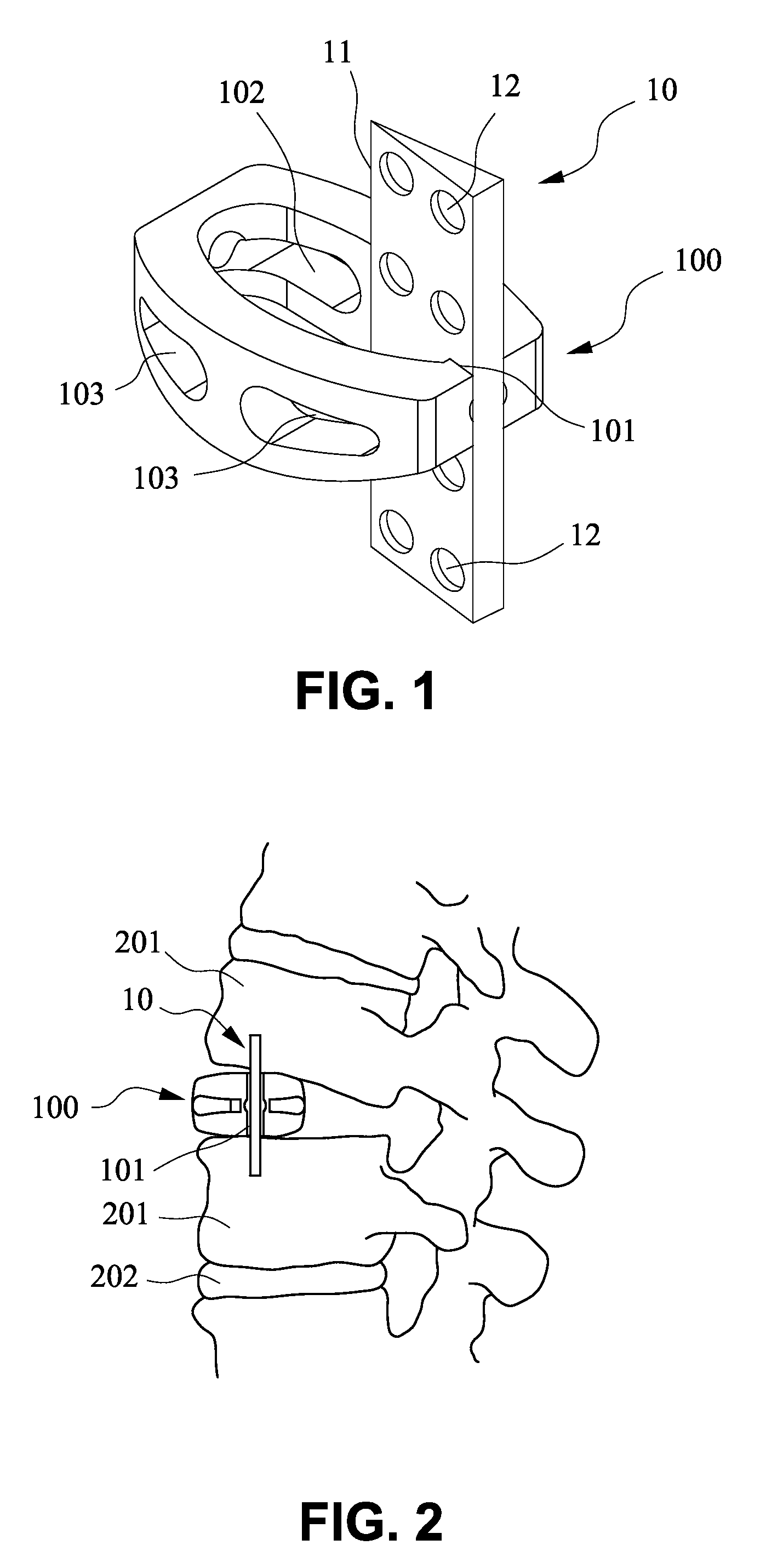
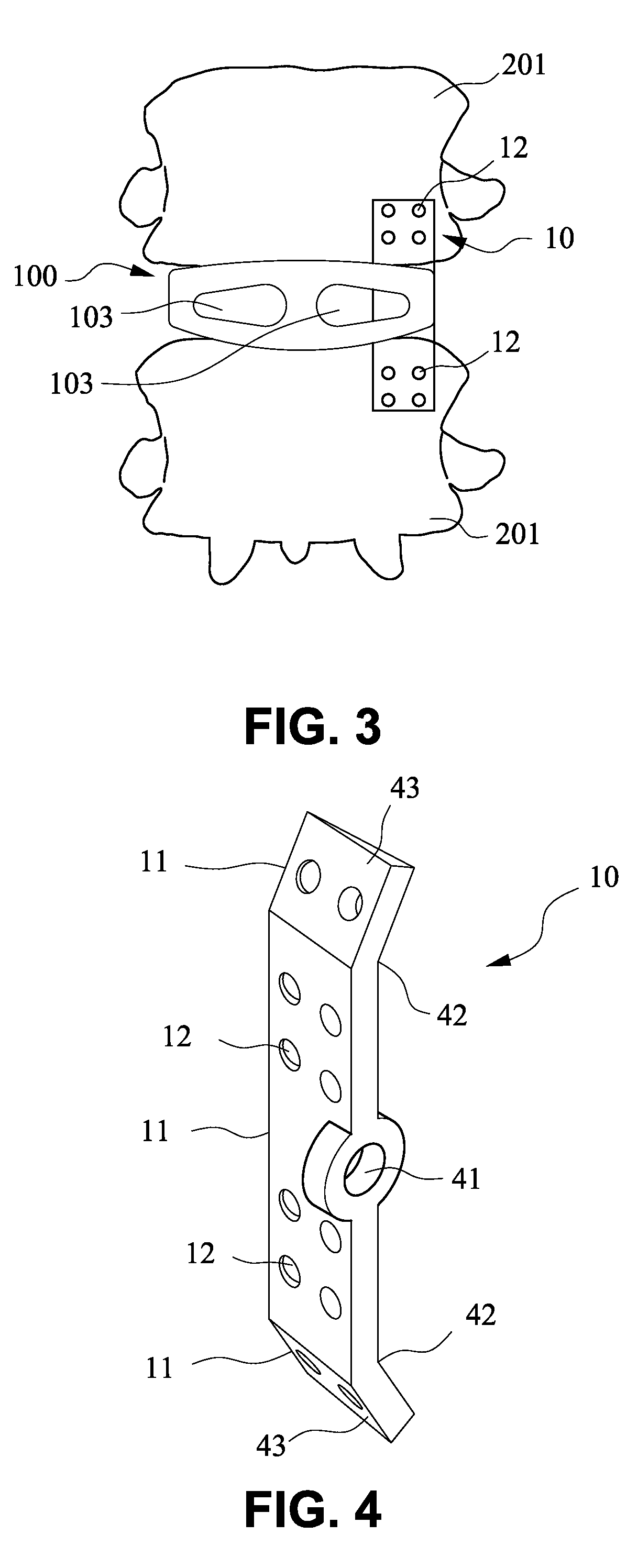
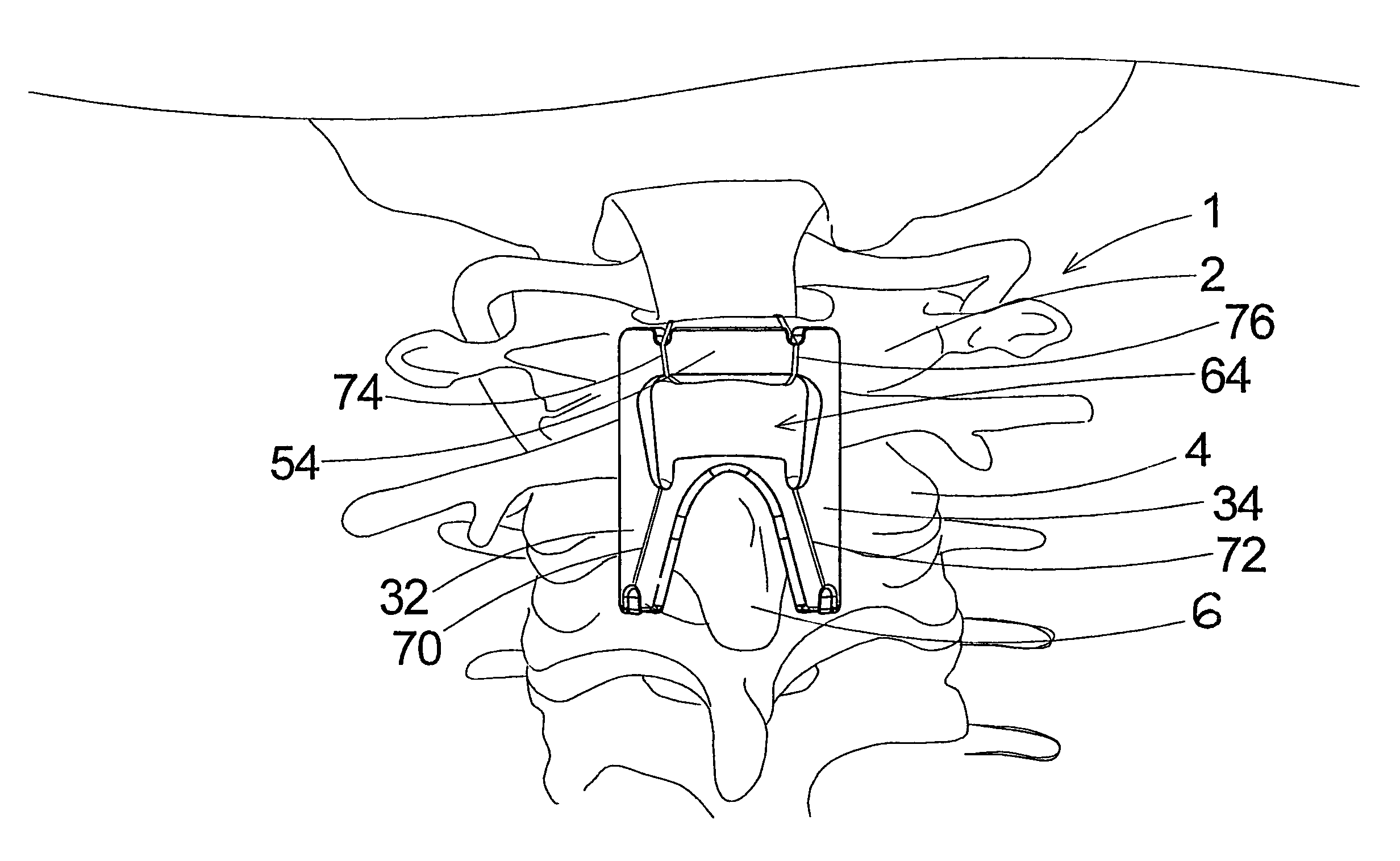
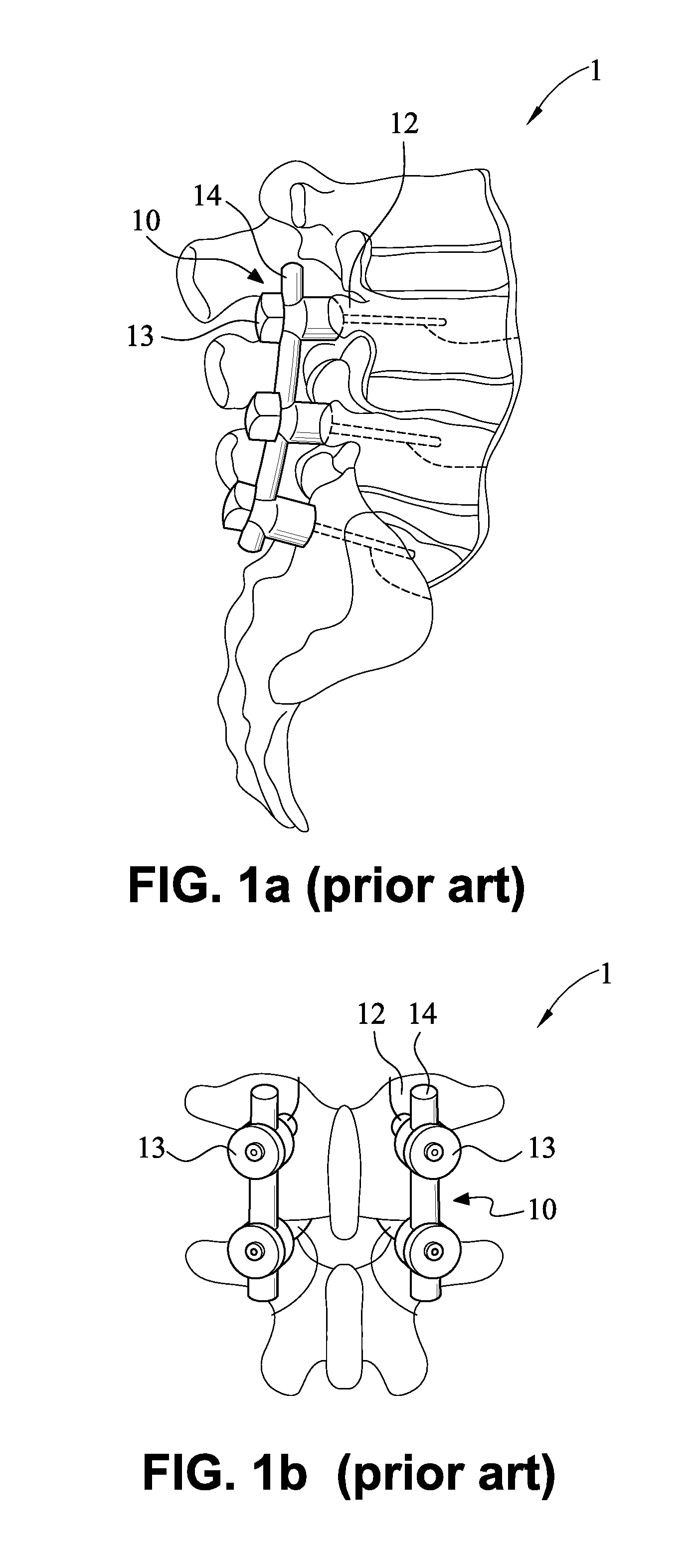
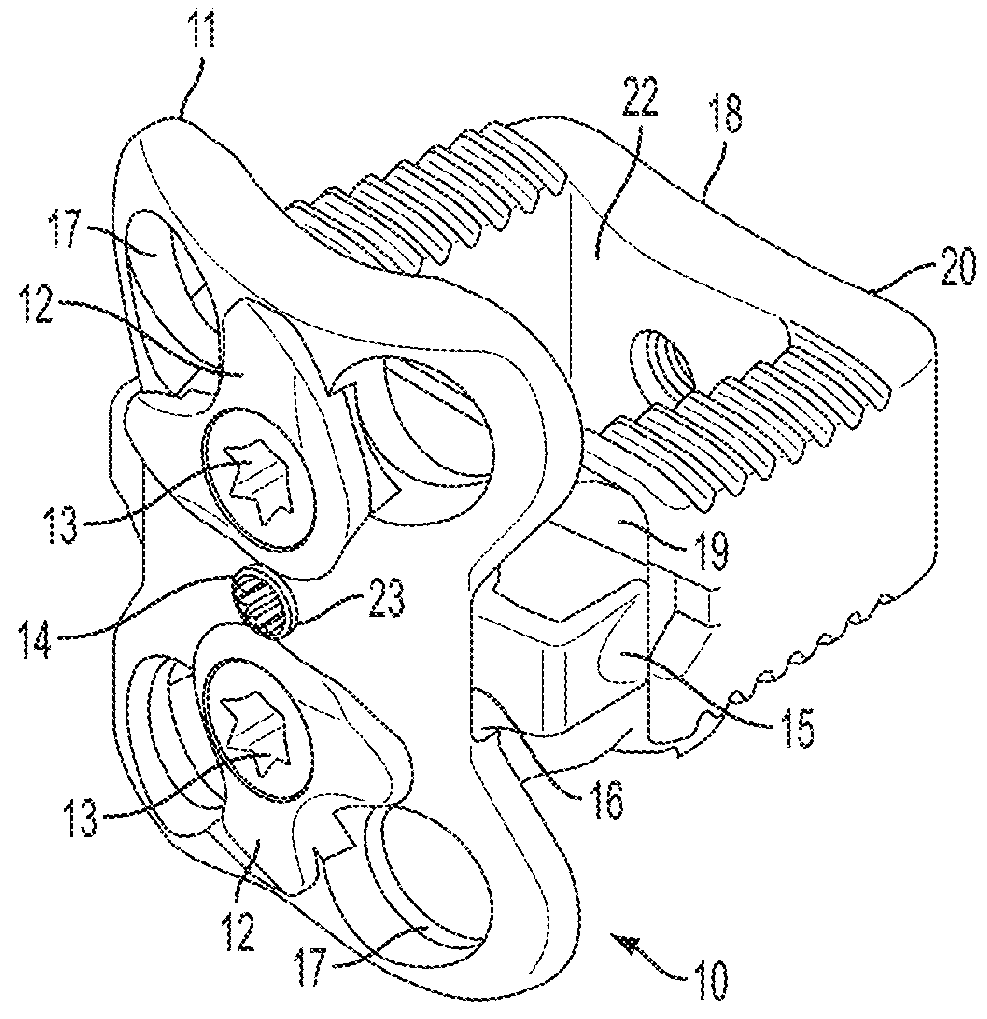
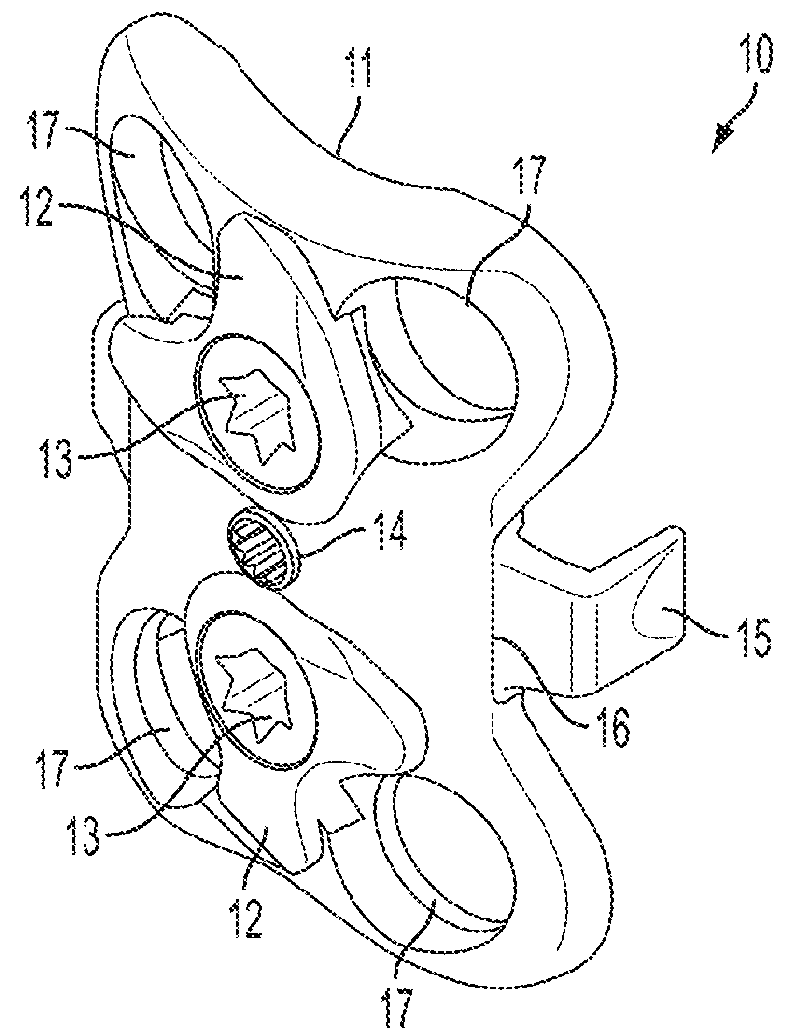
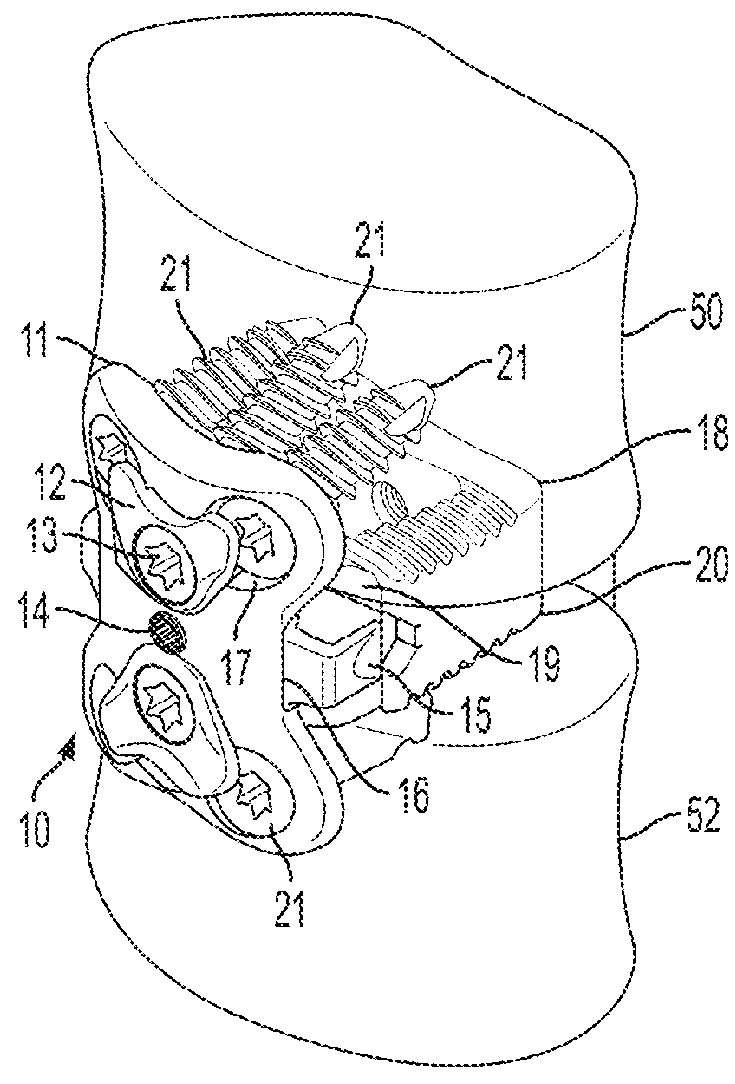
Device for connecting transverse beam at triangular position of vertebral lamina
InactiveUS20120283778A1Increase heightStrengthens patients with unstable spinal structure the stabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringVertebral lamina
A fixing device for securing vertebral lamina includes a transverse rod, a vertical rod having a length longer than that of the transverse rod and a joint having a vertical hole to securely receive therein a portion of the vertical rod and a cutout communicating with the vertical rod to receive therein a portion of the transverse rod.
Owner:YEH CHUNG CHUN
Intervertebral implant to immobilize one vertebra relative to another
InactiveUS8377137B2Convenient ArrangementSimpler and less-costly to manufactureJoint implantsSpinal implantsCurve shapeVertebral lamina
This implant includes two elongated elements (1, 2) of reduced width, defining, at their edges, two longitudinal surfaces opposite each other. These elements (1, 2) being intended to be positioned between the vertebral plates (101) of the vertebrae, apart from each other, with their longitudinal surfaces in contact with the vertebral plates (101. Elements (1, 2) have curved shapes, having substantially the same curvature from one element (1, 2) to the other, and one of the elements (2) has a length smaller than that of the other element (1), the element (2) with the smaller length being intended to be placed in the anterior position on a vertebral plate (101) while the element (1) with the larger length is intended to be placed in the posterior position on this same vertebral plate (101).
Owner:MEDICREA INT SA
Universal omni-posterior-double lateral mass bridging board for cervical vertebra
InactiveCN102247207AImprove stabilityReach physiologicalInternal osteosythesisBone platesBiomechanicsLateral mass
The invention discloses a universal omni-posterior-double lateral mass bridging board for cervical vertebra. The bridging board is in an arched whole made of a narrow and long metal plate, and comprises two lateral mass fixing plates, two vertebral lamina fixing plates, a spinous platform fixing plate and a bone grafting fixing plate. The bridging board is mainly used for reconstructing a vertebral canal structure after posterior expansive laminoplasty of cervical spine, can simultaneously fulfill fixation of open door side and hinge side in the expansive laminoplasty, the length of each fixing plate and angles among the fixing plates are in accordance with the characteristics of human cervical vertebra dissection; the bridging board has strong biological attachment and can furthest resist posterior pressure, so that the expansive laminoplasty failure caused by crack reclosing at the vertebral open door side and hinge fracture is avoided; the whole structure adapts to the posterior anatomy structure of human cervical vertebra and the characteristics of biological mechanics; and the bridging board can be pre-bent properly in use. The universal omni-posterior-double lateral mass bridging board for cervical vertebra is expected to replace the conventional posterior cervical single open door fixing plate to become a clinical standard postoperative physiology and stability reconstructing method after the posterior cervical single open door expansive laminoplasty.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Staged, bilaterally expandable trial
ActiveUS20150073555A1Facilitate insertionEasy to insertSurgeryJoint implantsPeripheral zoneIntervertebral spaces
Systems and methods for distracting an intervertebral disc space are provided. The systems use a staged, bilaterally expandable trial. The systems and methods of distracting an intervertebral space are provided in a manner that addresses the problem of subsidence. The method includes inserting the trial into the intervertebral space in a collapsed state and, once inserted, the trial is then used for distracting the intervertebral space using an expansion that includes a first stage and a second stage. The first stage includes expanding the trial laterally toward the peripheral zones of the top vertebral plate and the bottom vertebral plate, and the second stage includes expanding the trial vertically to distract the intervertebral space.
Owner:INTEGRITY IMPLANTS INC
Bone fracture plate formed by a vertebral plate
InactiveCN101584601APromote reconstructionEnough bone graftInternal osteosythesisBone platesBone graftingLateral mass
A bone fracture plate formed by a vertebral plate comprises a reticular frame for holding a bone grafting material. The reticular frame comprises a bottom surface facing to the inner cavity of a vertebral canal, an upper side face and a lower side face. The top surface of the reticular frame is used for implanting and tamping the opening of the bone grafting material. The inner side face of the reticular frame is provided with an inner opening used for the connection of the broken ends of the vertebral plate and the bone grafting material inside the reticular frame. The outer side face of the reticular frame is provided with an outer opening used for the connection of the broken ends of a lateral mass of a cervical vertebra and the bone grafting material inside the reticular frame. The inner side on the top surface of the reticular frame is provided with a first mounting plate fixedly connected with the broken ends of the vertebral plate and the outer side on the top surface of the reticular frame is provided with a second mounting plate fixedly connected with the broken ends of the lateral mass. The invention has the advantages that the invention is capable of effectively and adequately grafting bone, preventing grafted bone piece from falling into the vertebral canal after surgery, and also preventing a callus from proliferating and protruding towards the vertebral canal.
Owner:陈哲
Thoracic and lumbar vertebral posterior prosthesis
InactiveCN101327153ASolve the problem of iatrogenic instabilityRebuild stabilitySpinal implantsSpinal columnNon fusion
The present invention relates to a thoracolumbar vertebrae posterior false body which comprises a manual spinous process and a manual vertebral lamina. The manual spinous process is connected with the manual vertebral lamina, and the connection is shape as the connection of the spinous prcess and the vertebral lamina of human body pyramid. Compared with the prior art, the thoracolumbar vertebrae posterior false body can reconstruct the stability of thoracolumbar vertebrae and recover the physical structure and the physical function of thoracolumbar vertebrae posterior column, and can reconstruct the normal anatomical configuration and the function of vertebral canal, and can effectively avoid the possibility of the iatrogenic injury caused by vertebral canal content during operation; the thoracolumbar vertebrae posterior false body integrates spine fusion and non-fusion fixation functions as a whole, the fusion and non-fusion fixation functions are selected and used freely according to the requirement of the operation, and the operation is simple.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV AFFILIATED SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL +1
Vertebral disc prosthesis, notably for cervical vertebrae
ActiveUS20100256763A1Easy to engageFirmly attachedSpinal implantsArticular surfacesArticular surface
The present invention relates to a prosthesis including a first component that delimits a single central housing, including a bottom forming a first articular surface, a peripheral wall and, at a distance from the bottom, an edge extending inwards, a peripheral supporting surface, and on the side turned towards said bottom a second articular surface; and a second component including a plate intended to come into contact with the vertebral plate of the relevant vertebra and a single central pin with a widened head.
Owner:MEDICREA INT SA
Expandable cage for vertebral surgery involving lumbar intersomatic fusion by a transforaminal posterior approach
An implant of the intersomatic cage type, for fusion of vertebral bodies by a transforaminal approach, is disclosed that comprises a body with a curved profile that is designed to be implanted between the vertebral plates of two adjacent vertebrae. According to the invention, said body of curved profile comprises a posterior maneuvering part and an anterior attack part, said anterior attack part being composed of a lower tongue and of an upper tongue that are designed to receive between them a spacer element that can slide between a position of introduction, in which it is situated near said posterior maneuvering part, and a spacing position, in which it is situated near the end of said anterior attack part, thus increasing the thickness of the latter by spreading the tongues apart, said spacer element comprising a receiving seat that is open at the top and bottom.
Owner:SCHAUMBURG GERALD +1
Method of distracting an intervertebral space
ActiveUS20150157464A1Easy to insertFacilitate horizontal expansionSurgerySpinal implantsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationIntervertebral space
Systems and methods for distracting an intervertebral disc space are provided. The systems use a staged, bilaterally expandable trial. The systems and methods of distracting an intervertebral space are provided in a manner that addresses the problem of subsidence. The method includes inserting the trial into the intervertebral space in a collapsed state and, once inserted, the trial is then used for distracting the intervertebral space using an expansion that includes a first stage and a second stage. The first stage includes expanding the trial laterally toward the peripheral zones of the top vertebral plate and the bottom vertebral plate, and the second stage includes expanding the trial vertically to distract the intervertebral space.
Owner:INTEGRITY IMPLANTS INC
Cervical implant with exterior face plate
Owner:SPINESMITH PARTNERS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com