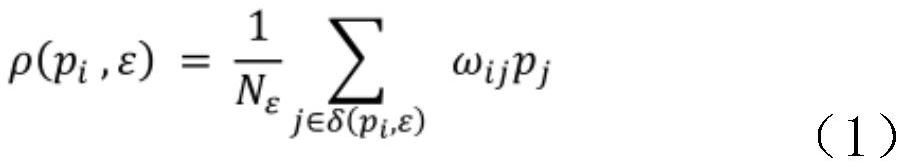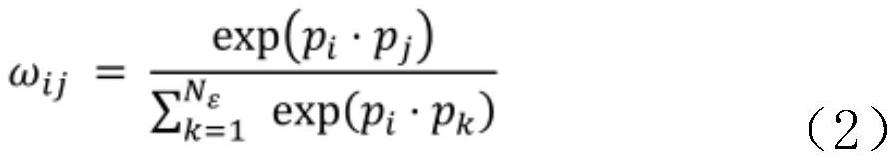Patents
Literature
71 results about "A vertebralis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Prosthesis for the replacement of a posterior element of a vertebra
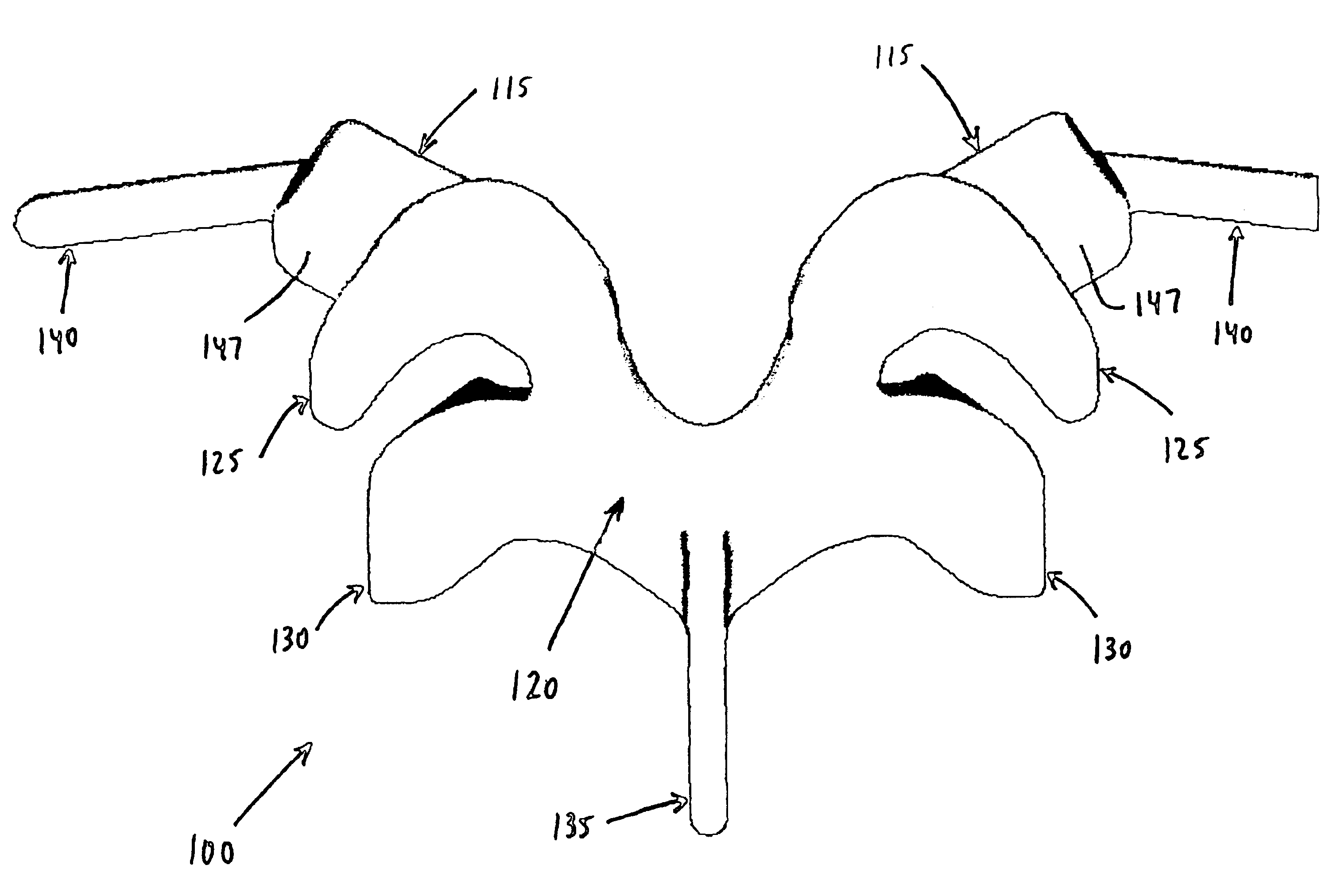
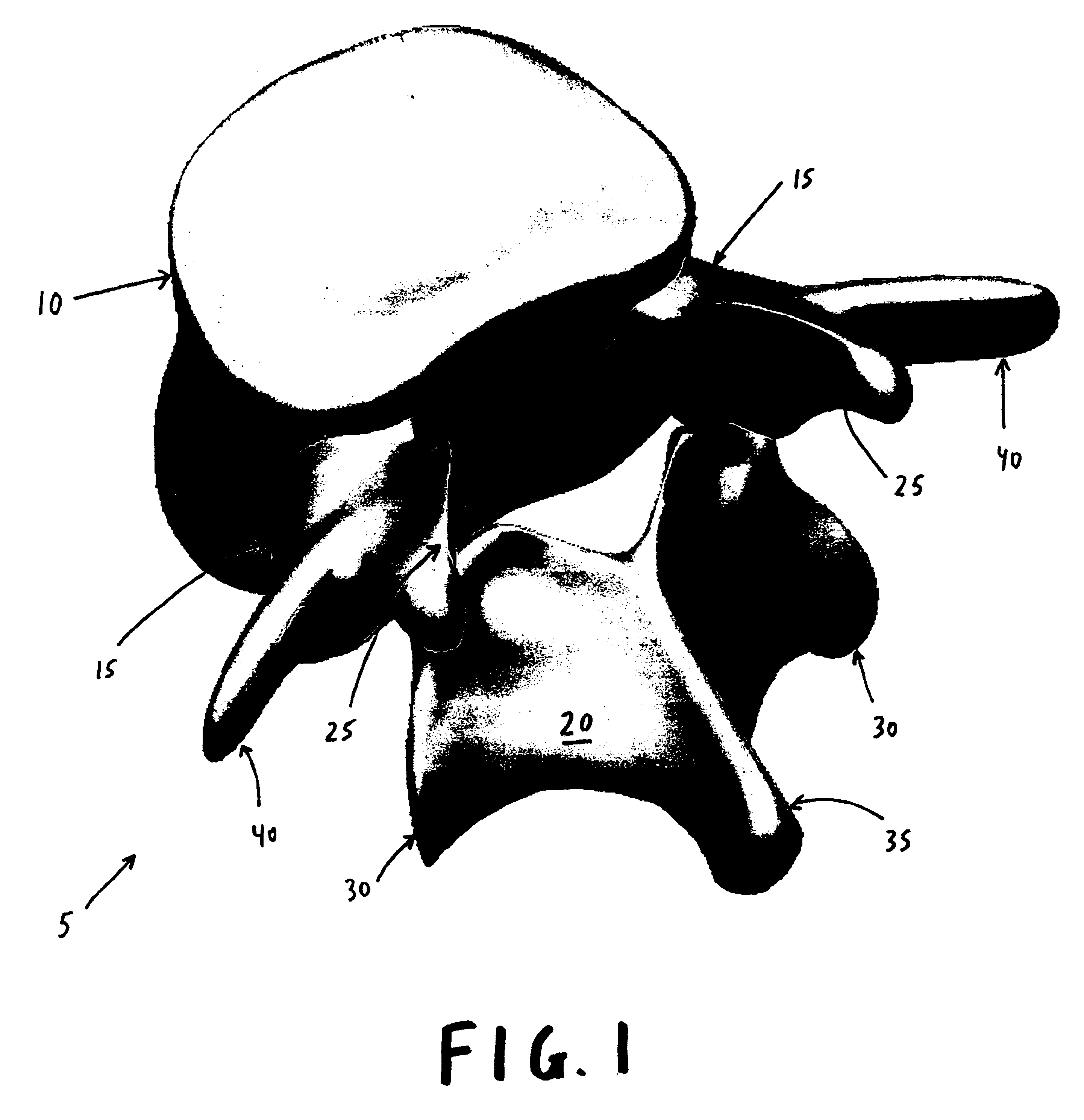
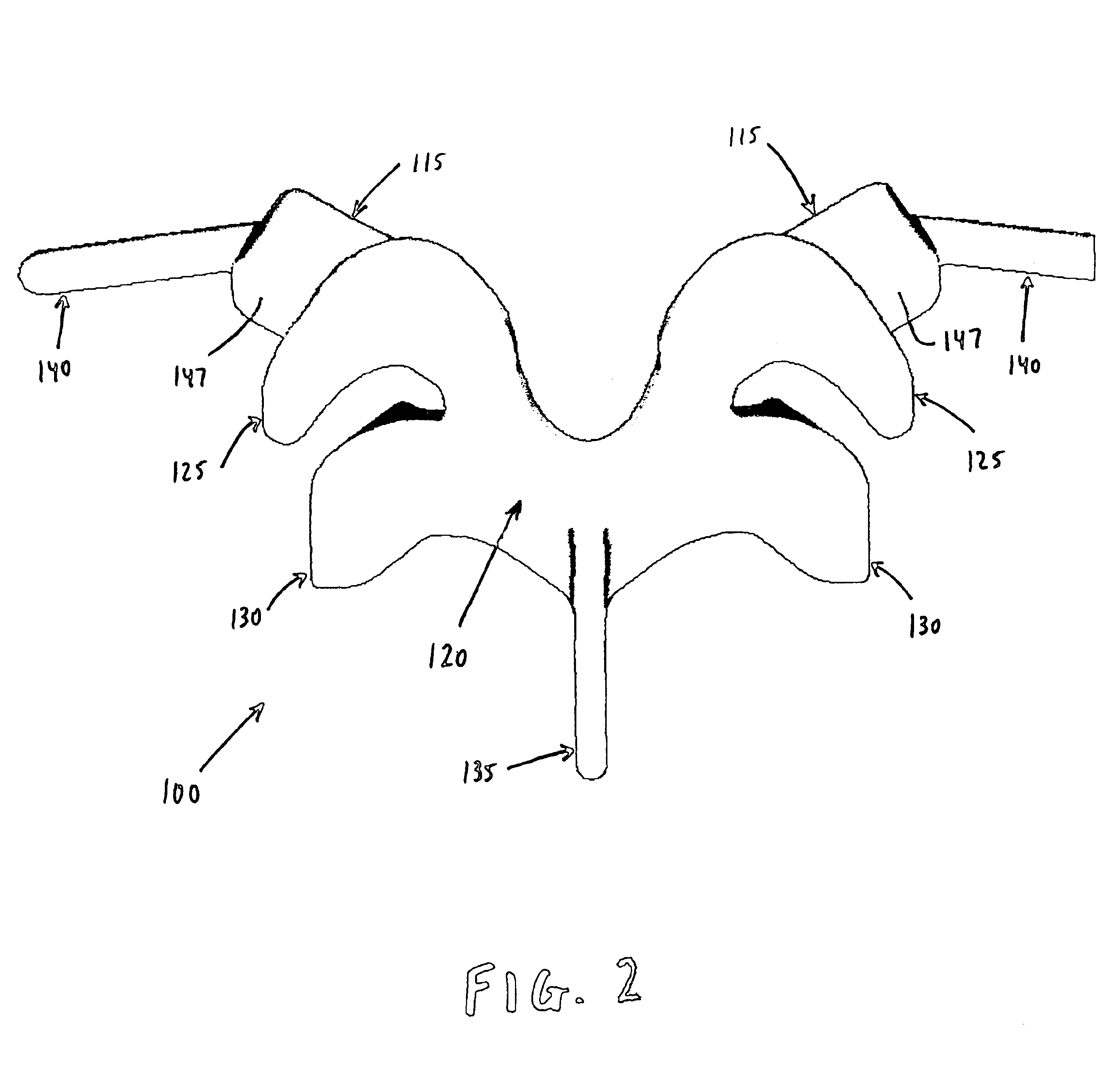
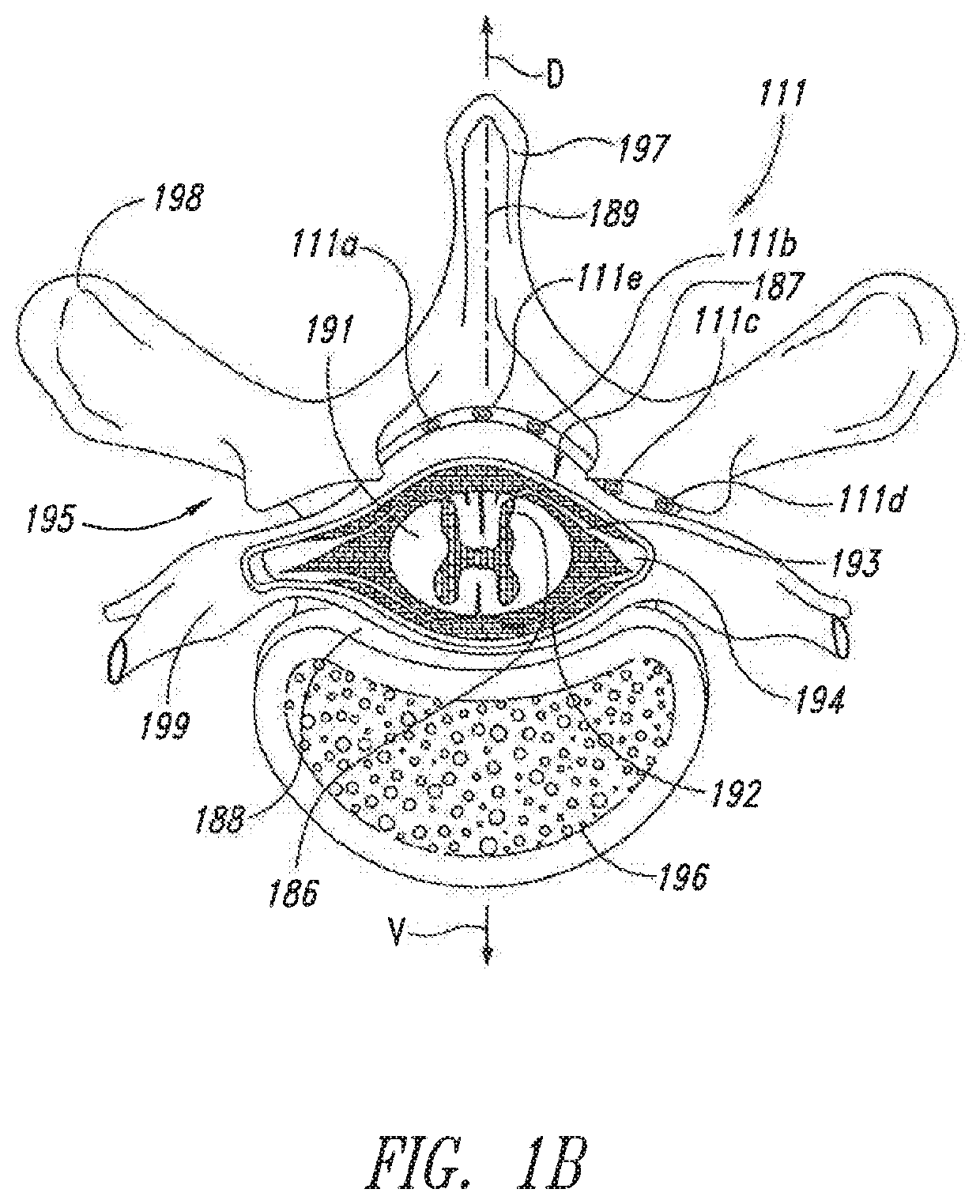
A prosthetic replacement for a posterior element of a vertebra comprising portions that replace the natural lamina and the four natural facets. The prosthetic replacement may also include portions that replace one or more of the natural spinous process and the two natural transverse processes. If desired, the prosthesis replacement may also replace the natural pedicles. A method for replacing a posterior element of a vertebra is also provided.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Spinal Surgical Implant and Related Methods
This invention relates generally to spine surgery and, in particular, to a surgical implant for separating adjacent spinal vertebrae.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Methods and systems for spinal radio frequency neurotomy
InactiveUS20110213356A1Increase the effective areaIncrease surface areaSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingAnatomical structuresProximate
Methods and systems for spinal radio frequency neurotomy. Systems include needles capable of applying RF energy to target volumes within a patient. Such target volumes may contain target medial branch nerves along vertebrae or rami proximate the sacrum. Such procedures may be used to ablate or cauterize a portion of the targeted nerve, thus blocking the ability of the nerve to transmit signals to the central nervous system. Disclosed needles may be operable to asymmetrically, relative to a central longitudinal axis of the needle, apply RF energy. Such asymmetry facilitates procedures where a tip of the needle is placed proximate to anatomical structures for location verification. Then RF energy may be applied in a selectable direction relative to the needle tip to ablate volumes that include the targeted medial branch nerves or rami, thus denervating facet joints or the sacroiliac joint, respectively, to relieve pain in a patient.
Owner:NIMBUS CONCEPTS
System that secures an electrode array to the spinal cord for treating back pain
ActiveUS20140371830A1Increase surface areaAvoid liftingSpinal electrodesMachines/enginesAnatomical structuresMedicine
This invention provides a device for implantation directly into the spinal cord for the purpose of treating back pain. Electrodes on a backing that conforms directly to the spinal cord are installed as a source of electrical stimulation and pain relief. The electrode array is maintained on the spinal cord at a chosen location by way of a spring or support structure that is anchored to an anatomical structure outside the spinal cord but near the site of implantation. Suitable anchoring structures include the vertebrae and the dura. Secured in this fashion, the support structure maintains a gentle pressure of the electrode array against the spinal cord so as to stay in electrical contact but minimize injury or inflammation. The device may accommodate and buffer movement of the spinal cord both laterally and in a caudal-rostral fashion so that the electrode array remains in place.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
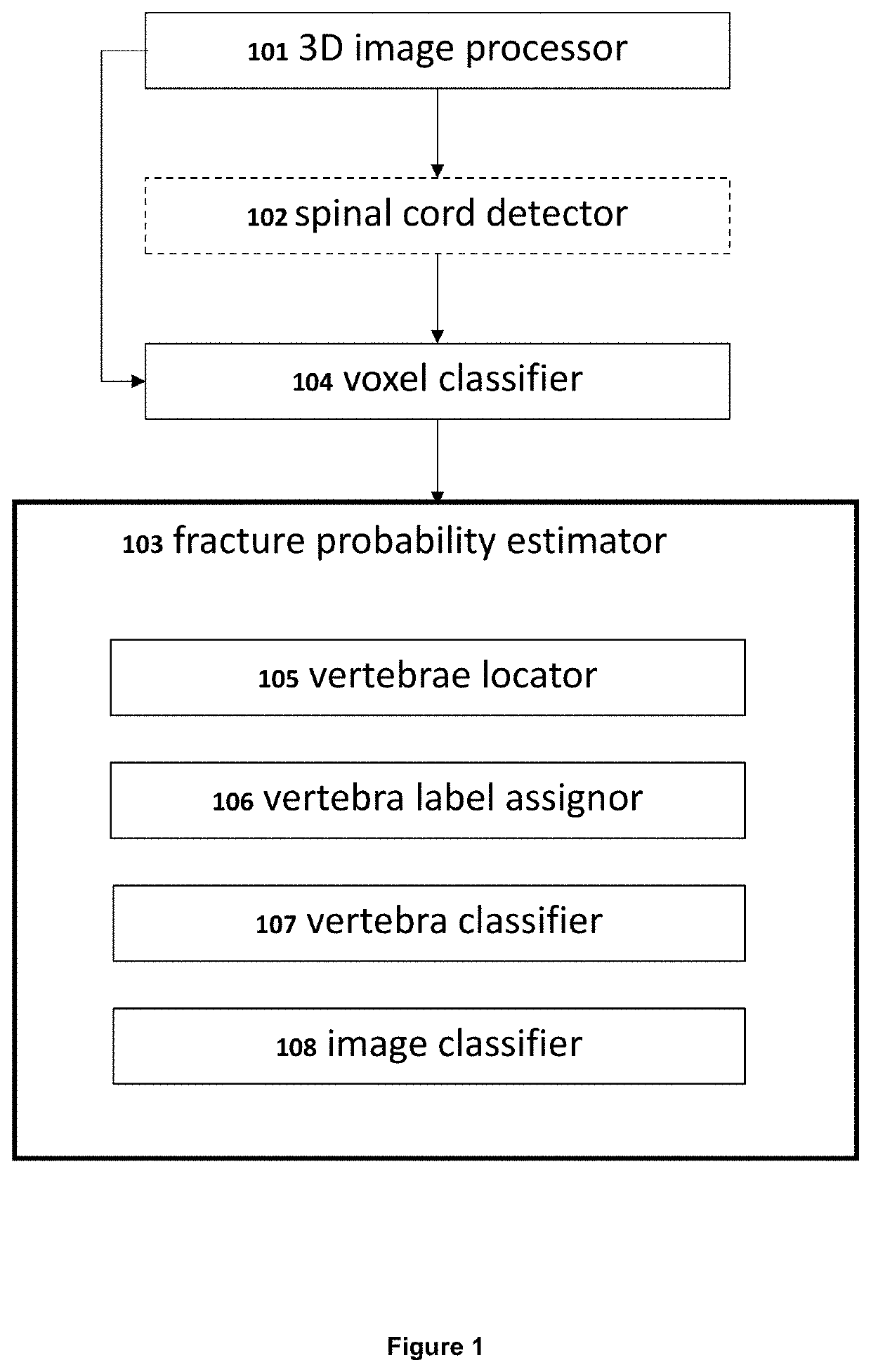
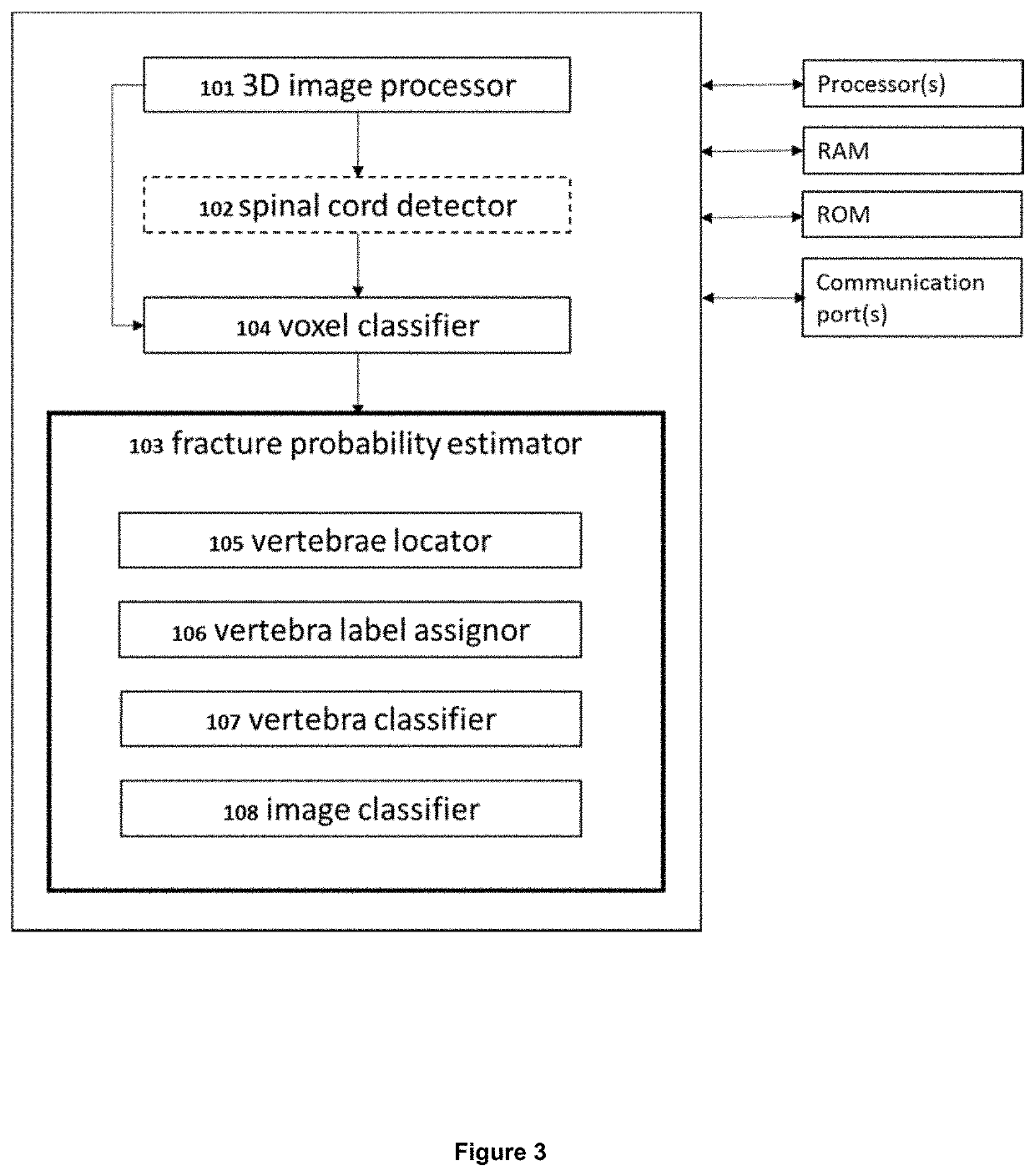
Three-dimensional medical image analysis method and system for identification of vertebral fractures
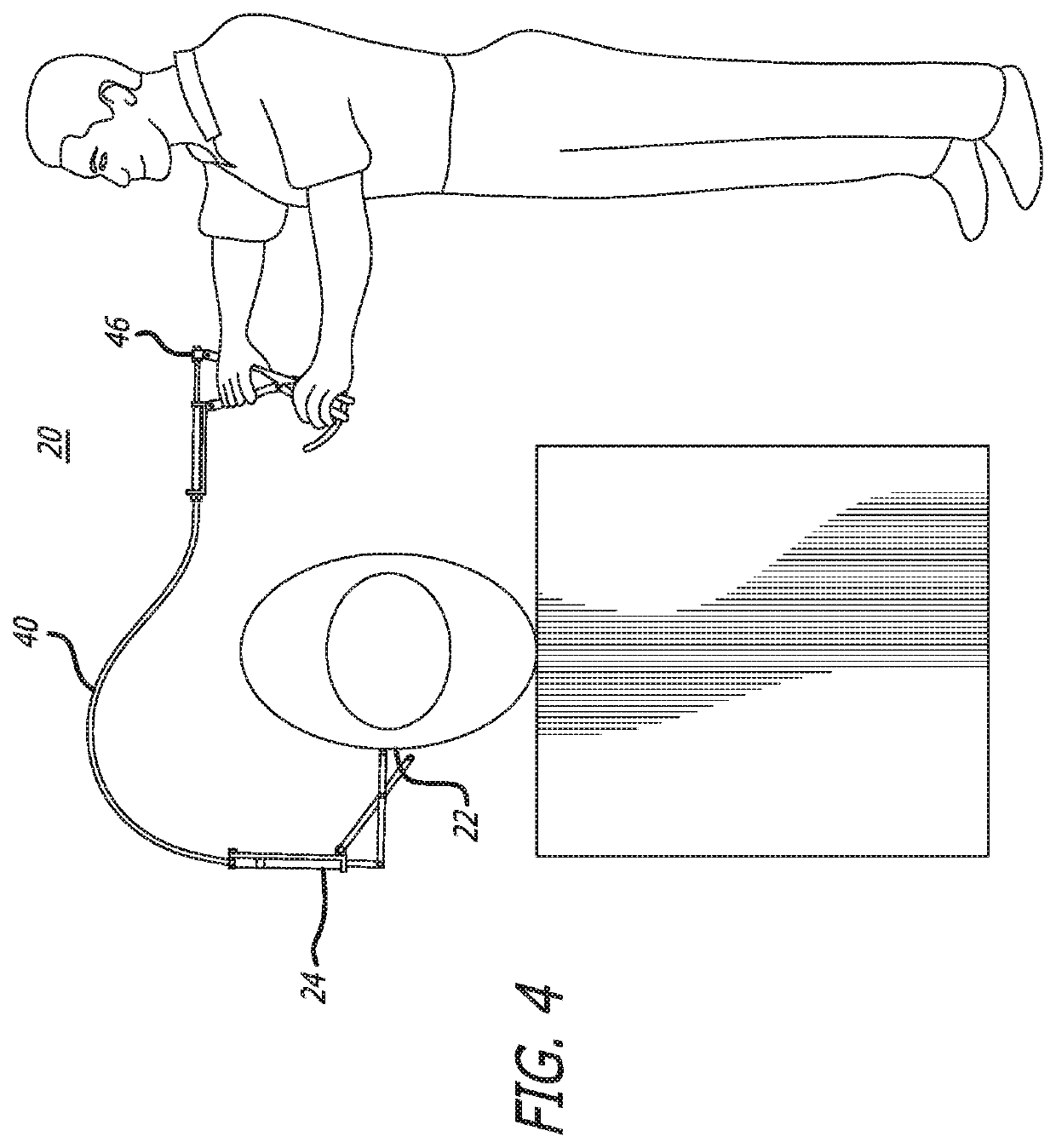
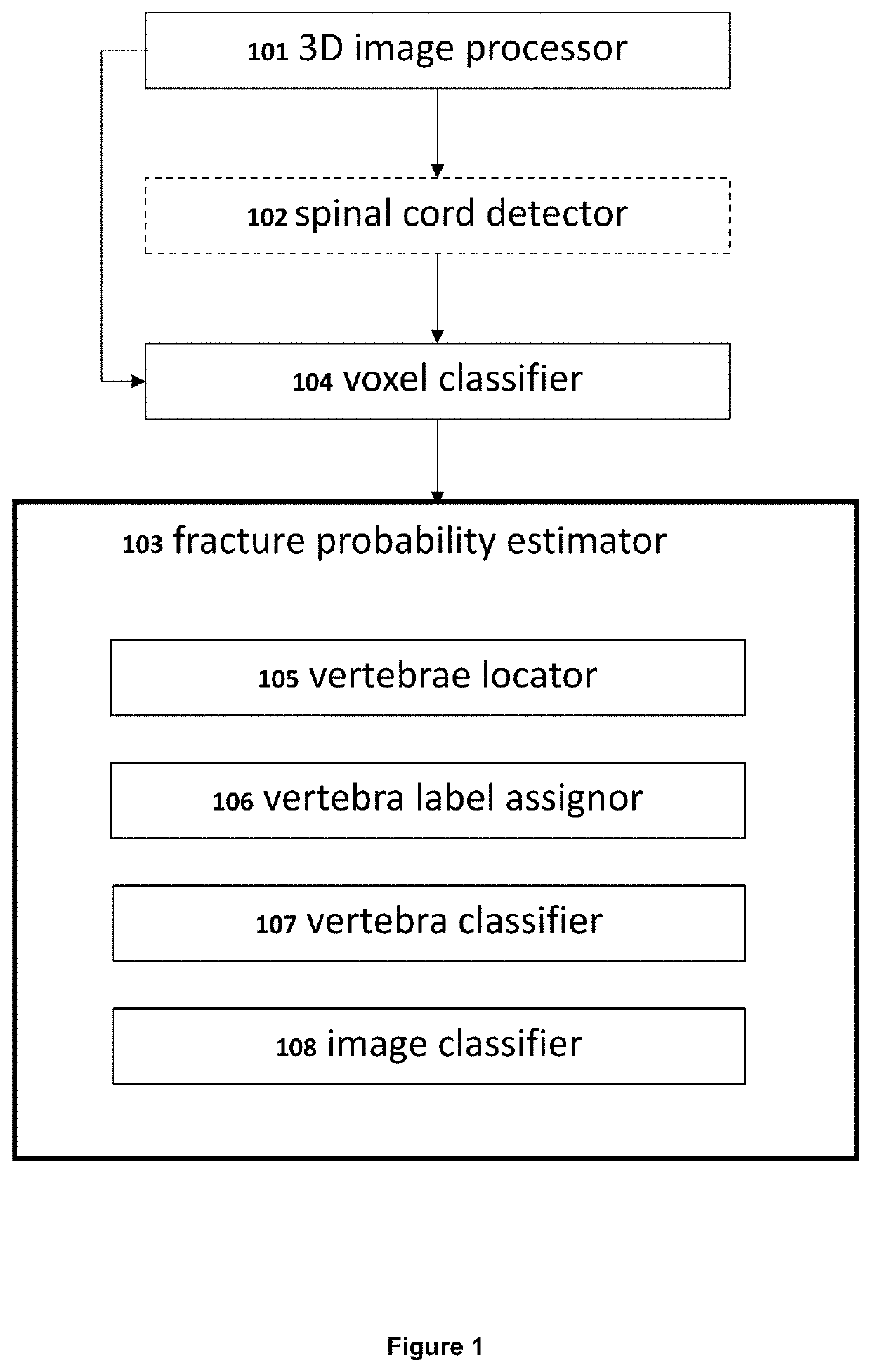
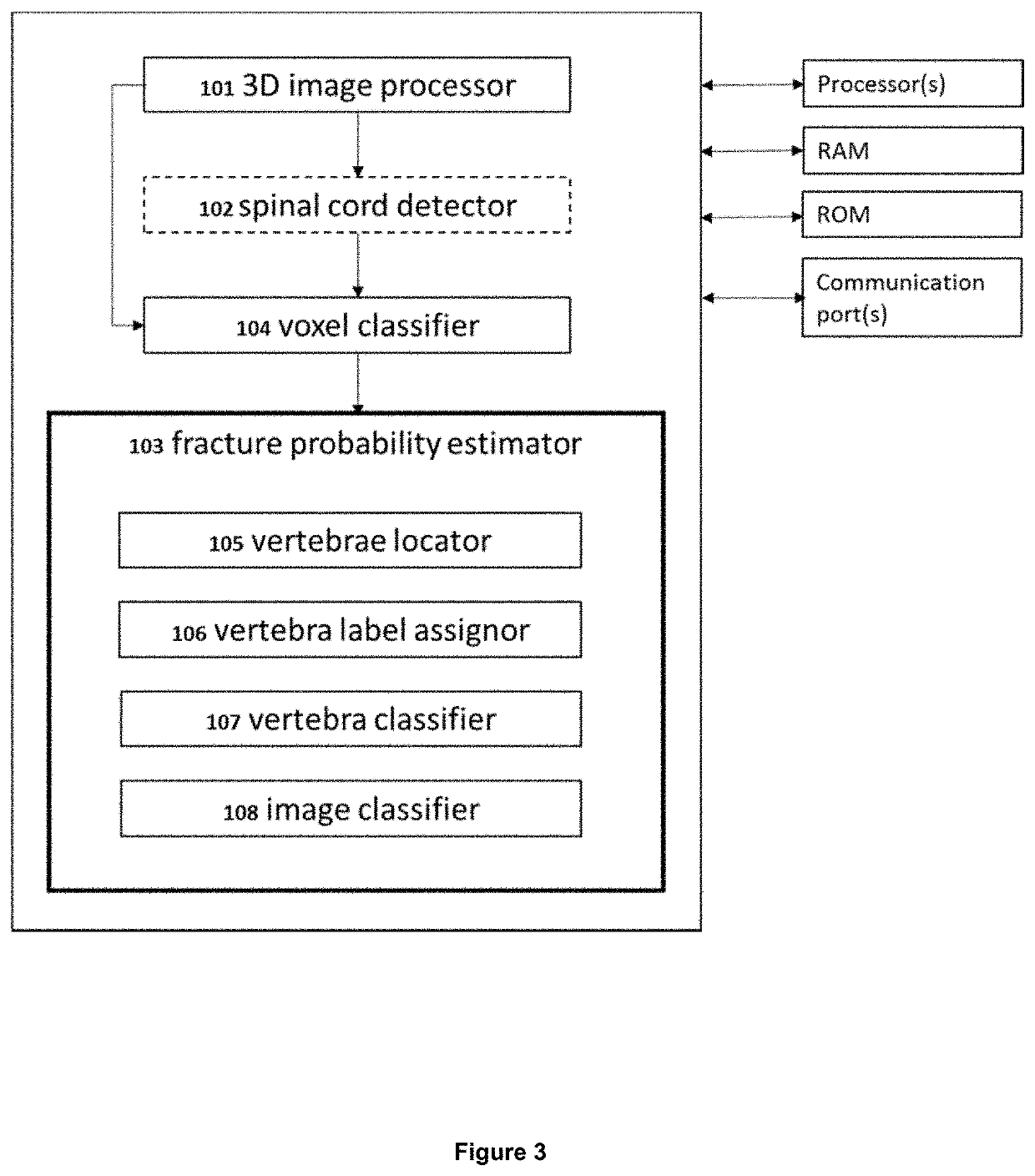
A machine-based learning method estimates a probability of bone fractures in a 3D image, more specifically vertebral fractures. The method and system utilizing such method utilize a data-driven computational model to learn 3D image features for classifying vertebra fractures. A three-dimensional medical image analysis system for predicting a presence of a vertebral fracture in a subject includes a 3D image processor for receiving and processing 3D image data of a 3D image of the subject, producing two or more sets of 3D voxels. Each of the sets of 3D voxels corresponds to an entirety of the 3D image and each of the sets of 3D voxels consists of equal 3D voxels of different dimensions. The system also includes a voxel classifier for assigning the 3D voxels one or more class probabilities each of the 3D voxels contains a fracture using a computational model, and a fracture probability estimator for estimating a probability of the presence of a vertebral fracture in the subject.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SRL
Computer simulation model for determining damage to the human central nervous system
ActiveUS6980922B2Improve practicalityImage enhancementImage analysisTwo-dimensional graphSpinal cord
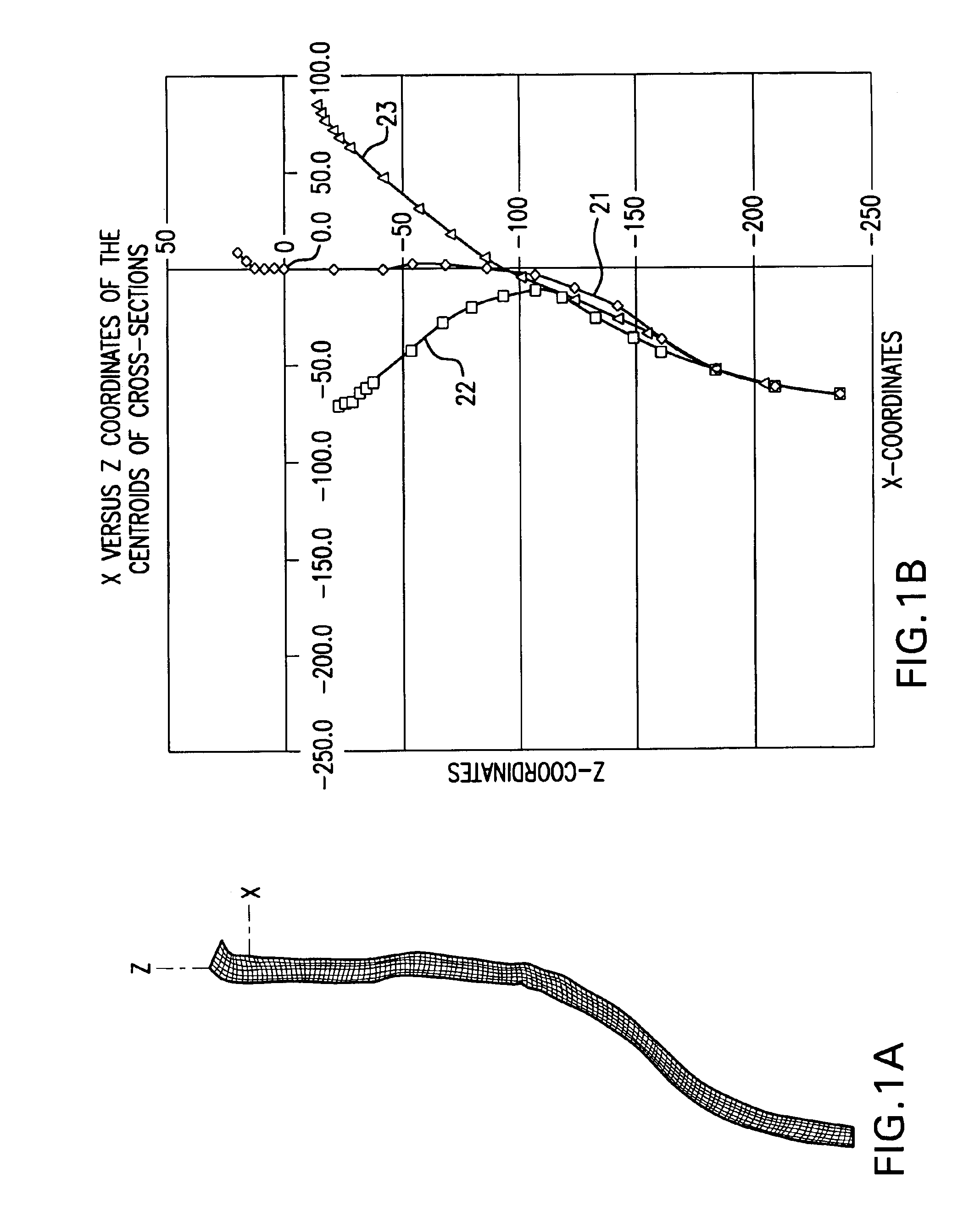
A computerized model simulates the human spinal cord and makes it possible to draw inferences about the probability of future injury or the likelihood that specific injuries occurred in the past. The spinal cord is modeled by a plurality of two-dimensional graphs formed of a large number of finite elements. The two-dimensional graphs are stacked in positions corresponding to the measured positions of the spinal cord at various vertebral levels of a patient. The stacked graphs yield a three-dimensional model, which may be compared with similar data taken from other patients. The model may include the simulation of stress, applied to all or part of the spinal cord, resulting in a perturbed three-dimensional model which may again be compared with similar data taken from patients having known injuries. The invention can therefore be used, among other things, to verify claims of spinal injury as a result of vehicular or sporting accidents.
Owner:COMPUTATIONAL BIODYNAMICS
Automated 3-D orthopedic assessments
Systems, methods, computer programs, and circuits can perform automated spinal assessments using a 3-D model and a 3-D patient image data set of the spine which do not rely on vertebral symmetry.
Owner:SECTRA
Automatic extraction method for the vertebra in MRI lumbar vertebra image
ActiveCN106780520ASolve the problem of automatic identification and extractionImprove diagnostic productivityImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseMedical imaging technology
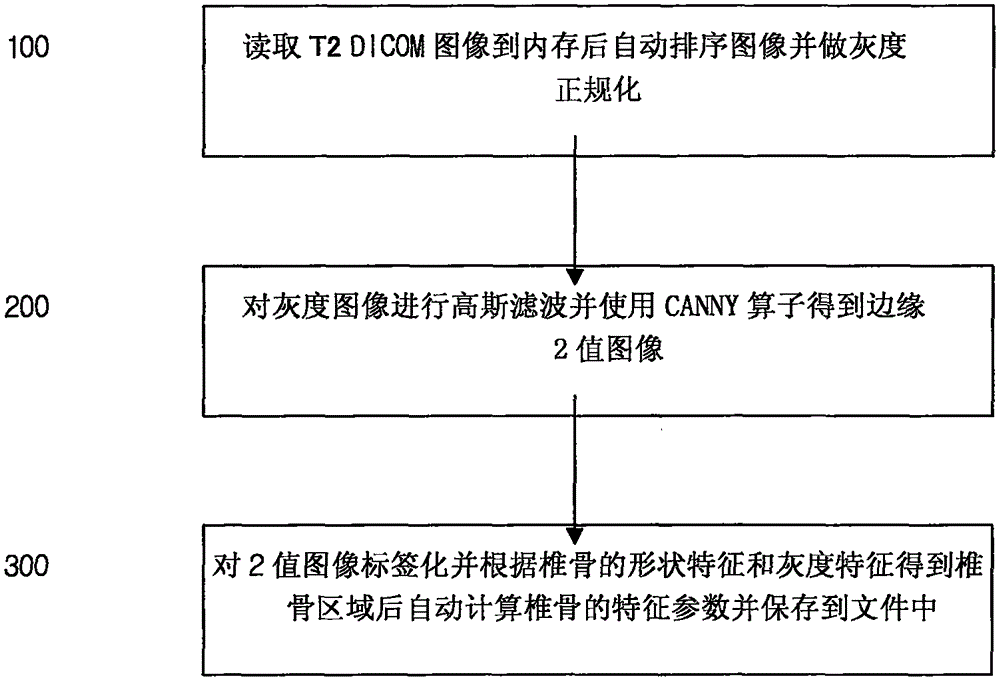
The invention provides an automatic extraction method for the vertebra in MRI lumbar vertebra image. The invention relates to the field of medical image processing technology and more particularly to an automatic extraction method for the vertebra in MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) lumbar vertebra image. With the progress in medical image technology, MRI has already become an important means for diagnosing lumbar vertebra troubles. Traditionally, it takes about ten minutes to locate a troubled vertebra of a patient through the use of a mouse, which directly influences the working efficiency of a doctor to diagnose. The invention solves the problem of automatic identification and extraction of vertebra in MRI lumbar vertebra image. Through the use of the MRI lumbar vertebra's T2 image, it is possible to automatically extract the vertebra and to automatically calculate the size, the width, the height and the average grayscale of the vertebra so as to realize quantitative diagnosis of vertebra troubles rapidly and to increase the diagnosing efficiency of vertebra diseases.
Owner:周兴祥 +2
Cervical vertebrae and lumbar vertebrae intelligent recovery device
InactiveCN103006427AReduce blood and oxygen supplyGood blood and oxygen supplyMassage combsMassage beltsEngineeringCervical vertebral body
The invention discloses a cervical vertebrae and lumbar vertebrae intelligent recovery device. The cervical vertebrae and lumbar vertebrae intelligent recovery device comprises a rectifier, a controller and a massage drug pillow. An automatic control device and a program are arranged in the controller, the controller is connected with the massage drug pillow through an air tube and a wire and controls three indexes of timing, air pressure and temperature in the massage drug pillow for program control, the massage drug pillow forms an arced surface after an airbag is inflated to match with a curve part of a human waist or neck, activity and elasticity of muscle are enhanced by multiple effects such as promoting blood circulation for sterilization by drugs, physiological curvature of vertebra is recovered gradually by physical jacking, jacking of the neck and the waist can be automatically relieved by controlling time, and normal blood supply of a brain is recovered. Sleep and cure of a person are integrated, and accordingly long-term persistence is convenient, a great amount of time can be saved, safety and reliability are achieved without any negative effect, operation is convenient, the person can sleep well and be cured by pressing gently before sleep, clinical practice shows that the cervical vertebrae and lumbar vertebrae intelligent recovery device is evidently effective in prevention and curing of neck and waist diseases caused by modern ways of act.
Owner:张雯逸
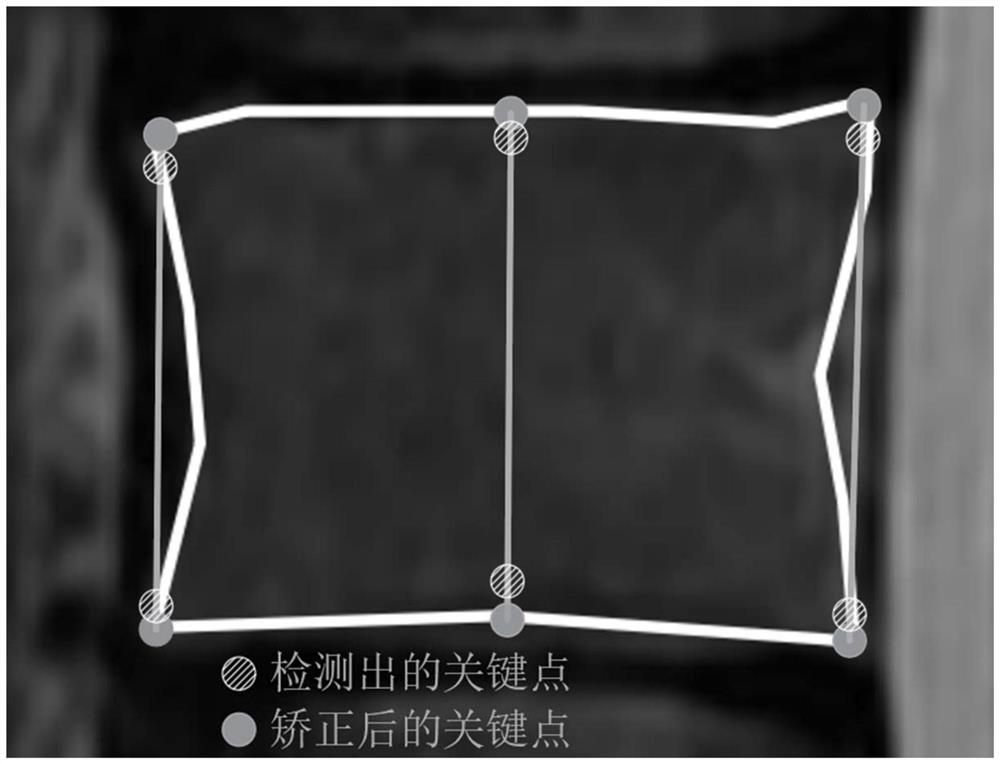
Spine MRI image key point detection method based on deep learning
ActiveCN112184617AAvoid the influence of subjective factorsReduce the burden onImage enhancementImage analysisSpine imagingBlock vertebrae
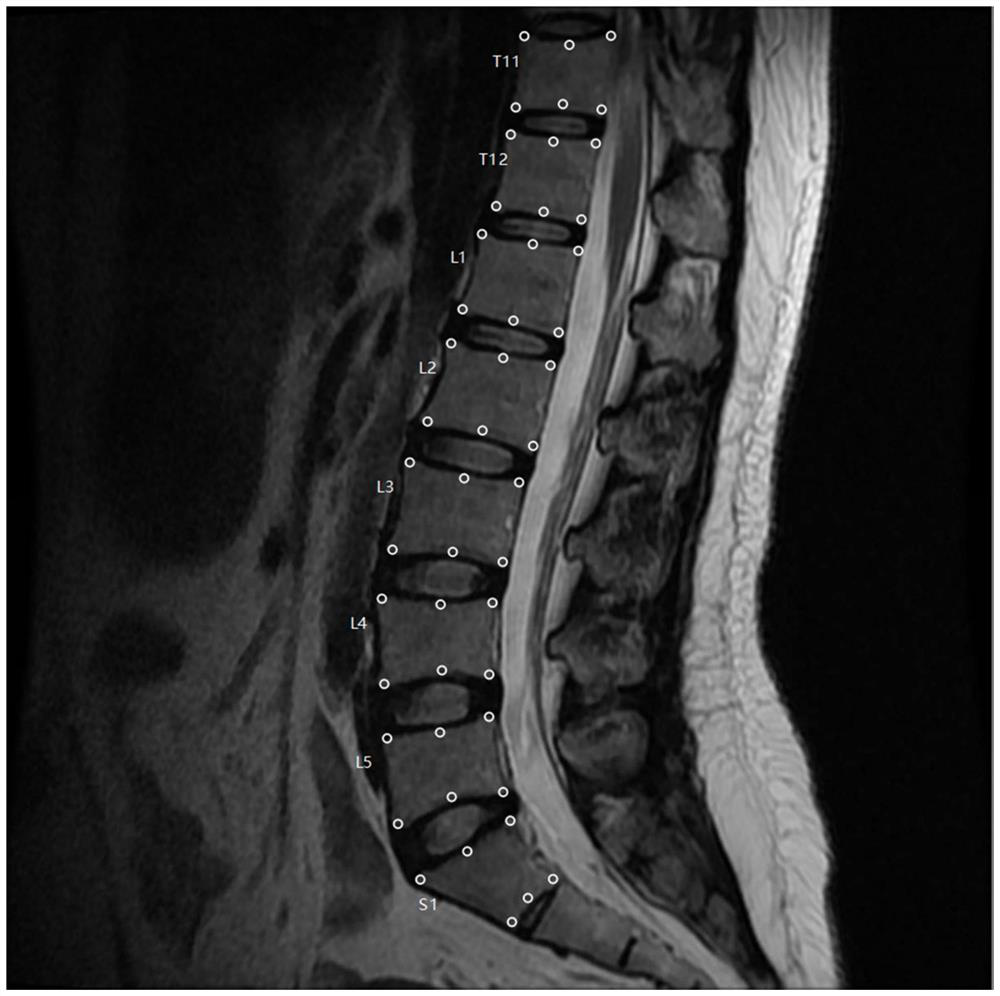
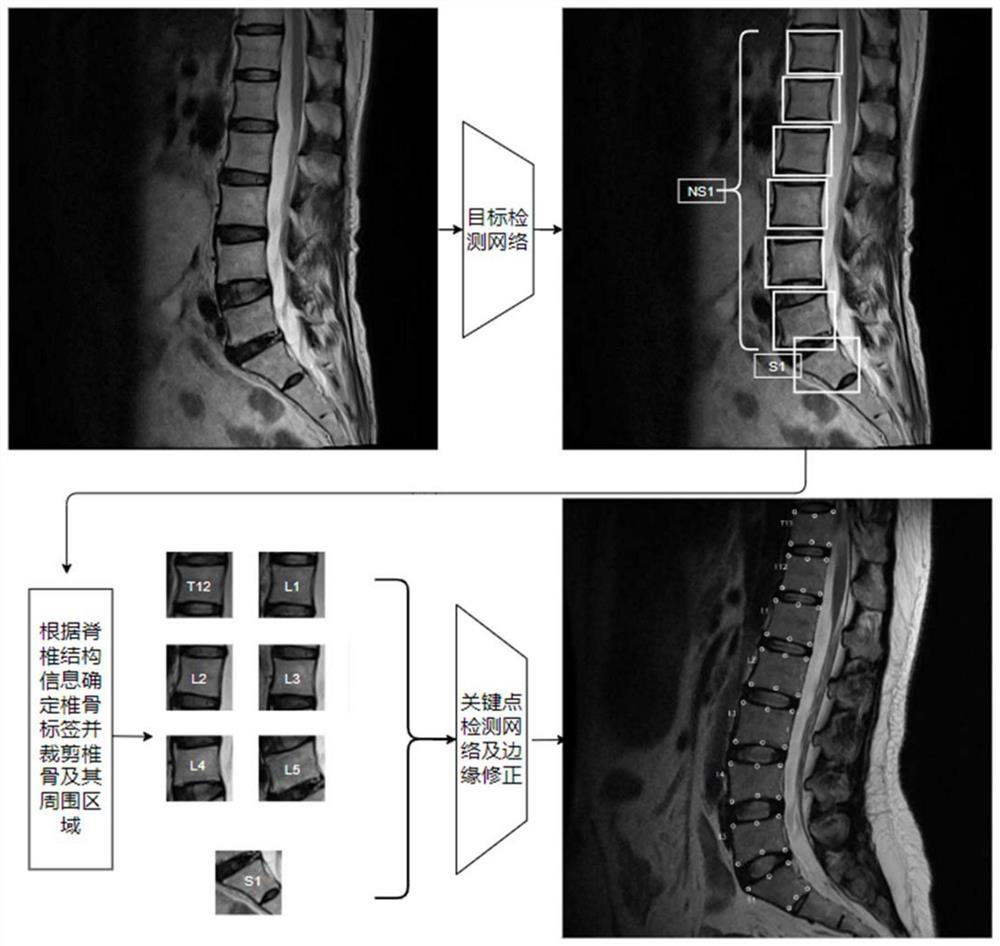
The invention provides a spine MRI image key point detection method based on deep learning. The invention discloses the spine MRI image key point detection method based on deep learning, and the method comprises the steps: firstly detecting and positioning vertebrae in a spine MRI image through a depth target detection network, recognizing S1 (sacral 1) as a positioning spine, filtering a false positive detection result through combining with the structural information of the spine, and judging the fine granularity label of each vertebra; using a key point detection network for detecting six key points including UA, UM, UP, LA, LM and LP of the upper boundary and the lower boundary of each vertebra, determining and correcting the key point positions of all the vertebrae in combination withedge information, and finally developing interactive visual MRI spine image key point automatic labeling software. Spine MRI image key points can be automatically extracted, and the spine MRI image key point extraction method has huge application value in the aspects of medical image analysis, auxiliary medical treatment and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Vertebra positioning and spine segmentation method based on deep learning in medical image
ActiveCN113506308AImprove perceptionHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisSpinal columnAutomatic segmentation
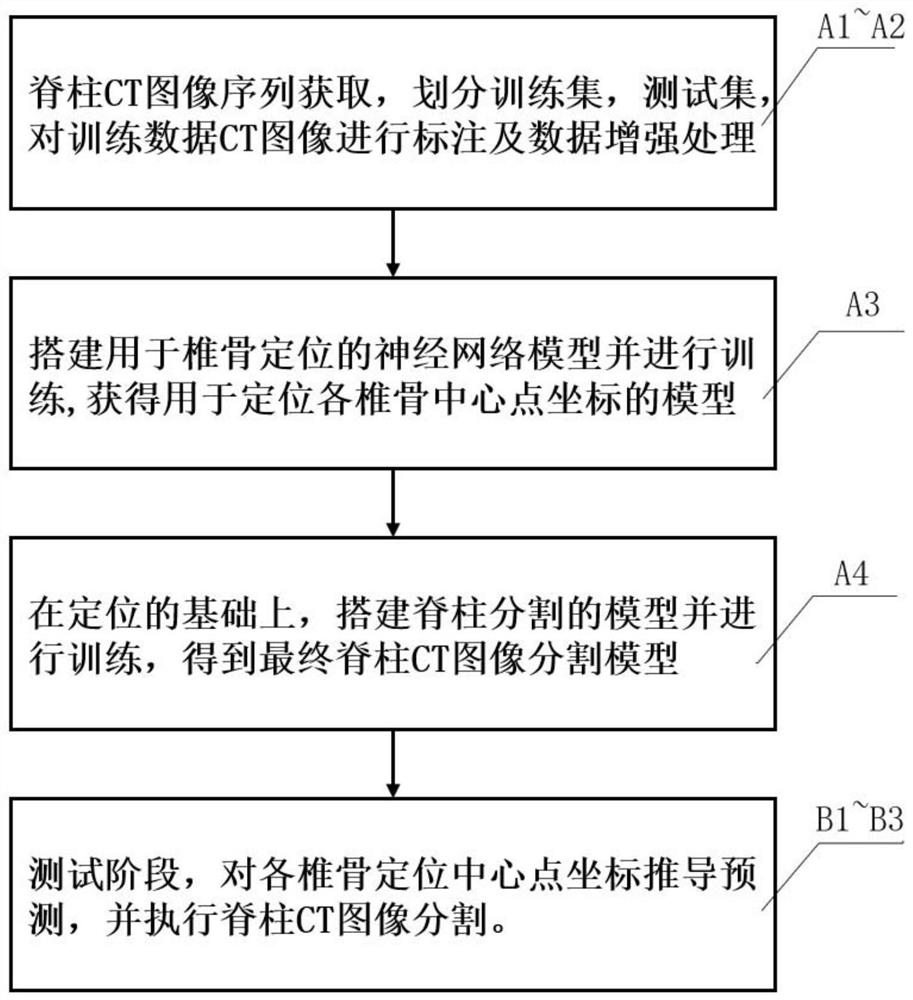
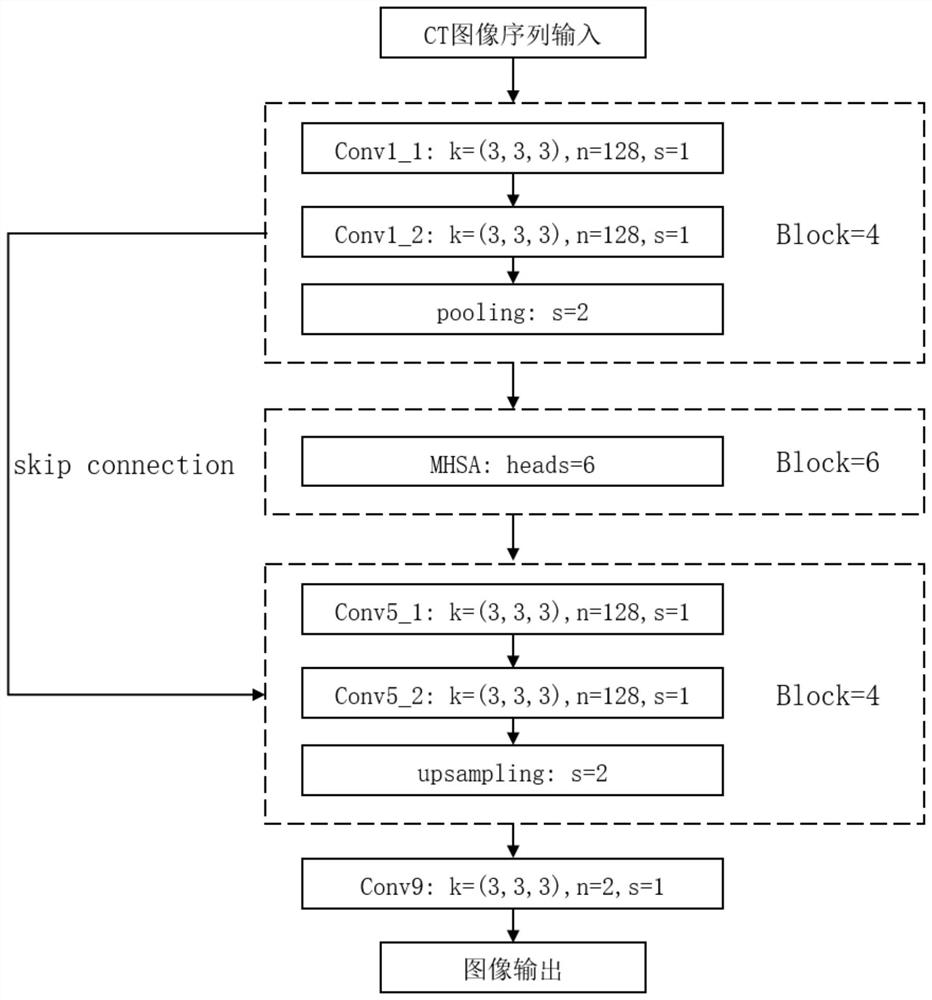
The invention relates to a vertebra positioning and spine segmentation method based on deep learning in a medical image, which comprises a training stage and a testing stage, and is characterized in that the training stage comprises the following steps: training data is acquired and marked; performing data enhancement processing on the training data; training a network model for vertebra positioning; on the basis of positioning, training a spine segmentation model. The test stage comprises the following steps: acquiring test data; deriving and predicting the coordinates of each vertebra positioning center point; executing spinal CT image segmentation, wherein the vertebra positioning network model and the spine segmentation model both adopt U-Net models in which a multi-head attention mechanism is introduced. Compared with the prior art, the spine CT image automatic segmentation and vertebra marking positioning are realized, the segmentation accuracy is improved by introducing a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and decision-making help is provided for subsequent complex medical diagnosis.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
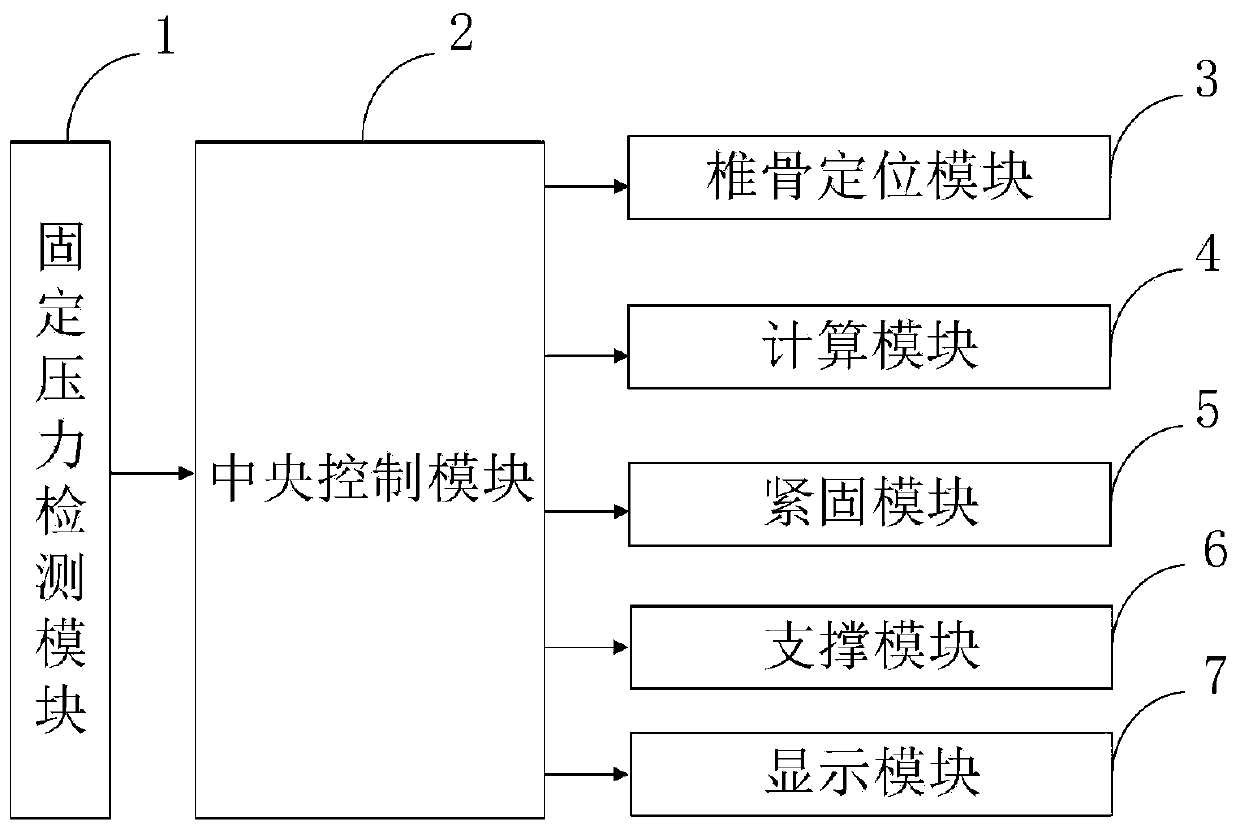
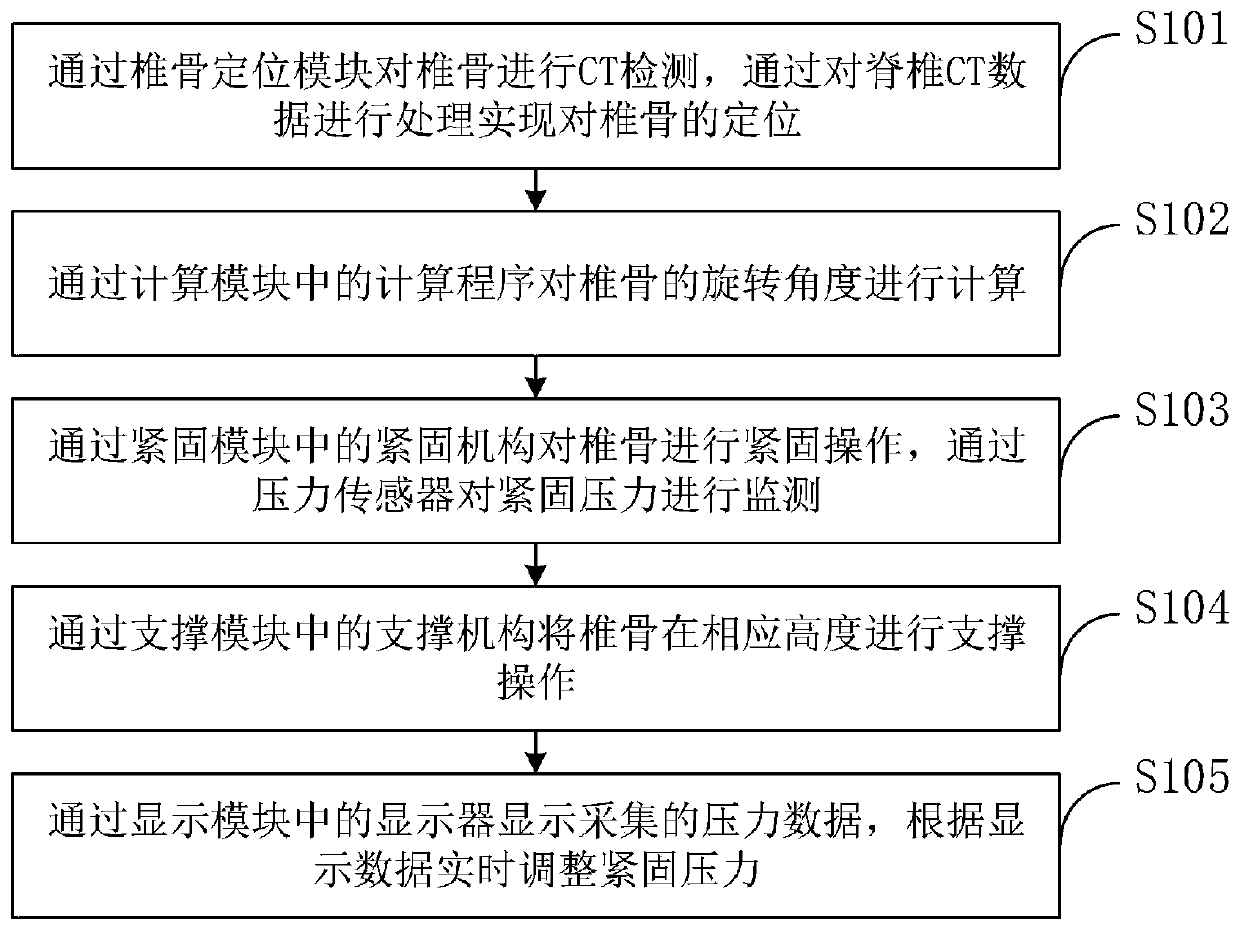
Vertebra stabilization system and method
PendingCN111317580AAccurate identificationAccurate measurementImage enhancementImage analysisSpinal columnPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention belongs to the technical field of vertebra stabilization, and discloses a vertebra stabilization system and method. The vertebra stabilization system and method comprises a fixed pressure detection module, a central control module, a vertebra positioning module, a calculation module, a fastening module, a supporting module and a display module. Through the vertebra positioning module, vertebra identification can be quickly carried out and is more accurate; a kernel density estimation method is used for refining the center of mass of the vertebra, and software is used for carryingout three-dimensional reconstruction so as to three-dimensionally show a whole segment of spine. Through a way of positioning after segmentation, a detection area is reduced, and accuracy is improved. Meanwhile, through the calculation module, on the basis of obtaining a back spine center line, a scoliosis calculation model and a spine center line and back spine center line deviation degree calculation model are constructed to realize the accurate measurement of a vertebra rotation angle, and the invention has a wide application value.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO WENZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
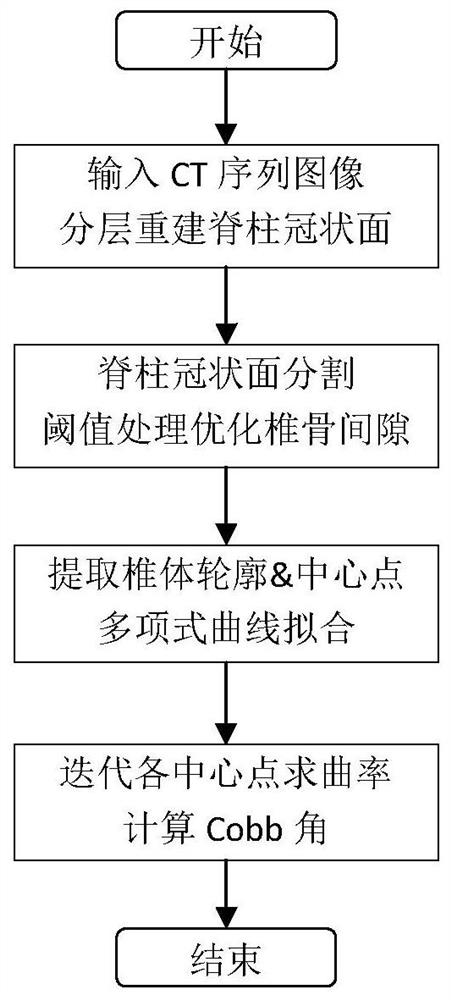
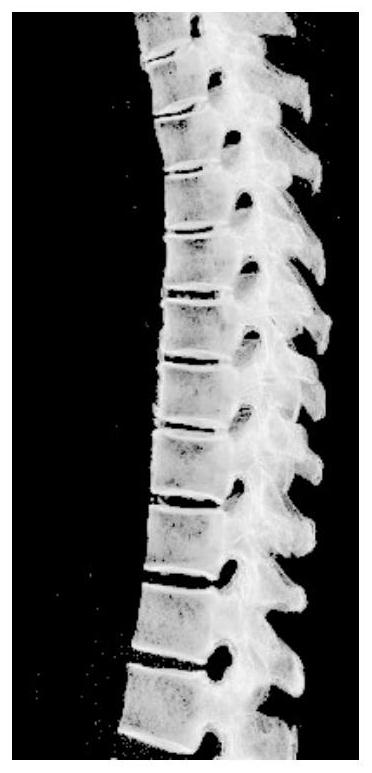
Automatic Cobb angle measurement method based on spine layered reconstruction
The invention discloses an automatic Cobb angle measurement method based on spine hierarchical reconstruction. The method comprises the following steps: (1) inputting a cross section CT sequence image, preprocessing DICOM original data, performing hierarchical reconstruction to obtain a superposed sagittal graph, selecting a sagittal range of a spine by adopting a template matching method, and then selecting a middle one-third position interval to reconstruct a skeleton coronal graph; (2) based on a deep learning network, training a vertebra segmentation model based on a skeleton coronal diagram, and adopting the model to perform detection segmentation on each section of vertebra of a spine and performing threshold processing to optimize a vertebra gap; (3) extracting a central point of each section of vertebra, and performing curve fitting on a central point set by using a hexatic polynomial to obtain a spine curve; and (4) iteratively solving the Cobb angle by calculating the curvature between the feature points in the spine curve.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Devices for and methods of measuring enhancing and facilitating correct spinal alignment
The title of the invention is devices for and methods of measuring, enhancing, and facilitating correct spinal alignment. The present invention provides a device for measuring, enhancing, and facilitating optimal spinal alignment using an Atlas bar with an Atlas pad inserted into an Atlas sheath configured to be placed on three distinct areas of the spine of a user when worn by the user, and a method thereof. The device comprises: (a) an Atlas pad at the center of the Atlas vertebra; (b) an Atlas sheath at the center of the thoracic region; and (c) a sacrum pad on the Atlas sheath at the center of the sacrum. The Atlas pad may be removed and replaced as the spinal alignment of a user improves. The device may be held in place on the body of the user by using a torso harness attached to a jacket or other wearable garments, or a backpack. When in use, the Atlas bar and the Atlas sheath simultaneously and physically come in contact with three areas of the spine of the user to provide the user with tactile feedback and create proprioceptive awareness representing improvement of spinal alignment over time.
Owner:A R 奥提基
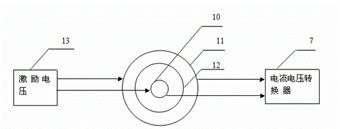
Opening navigator detection circuit for spinal surgery
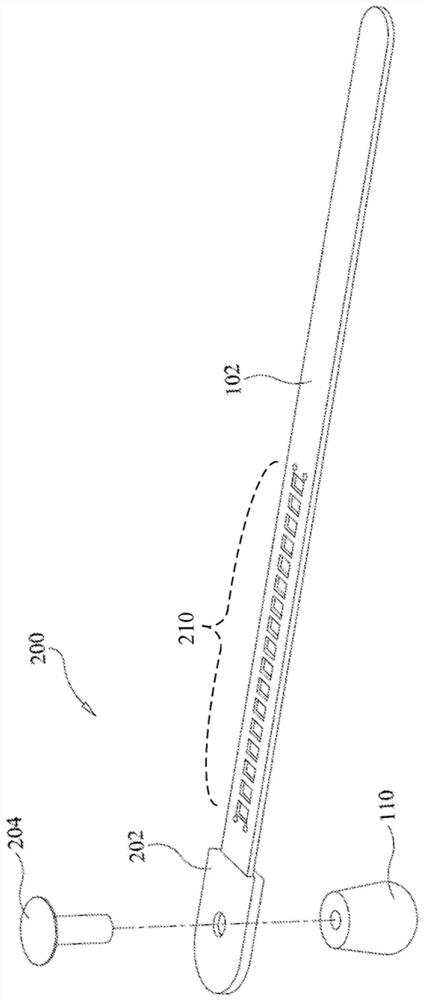
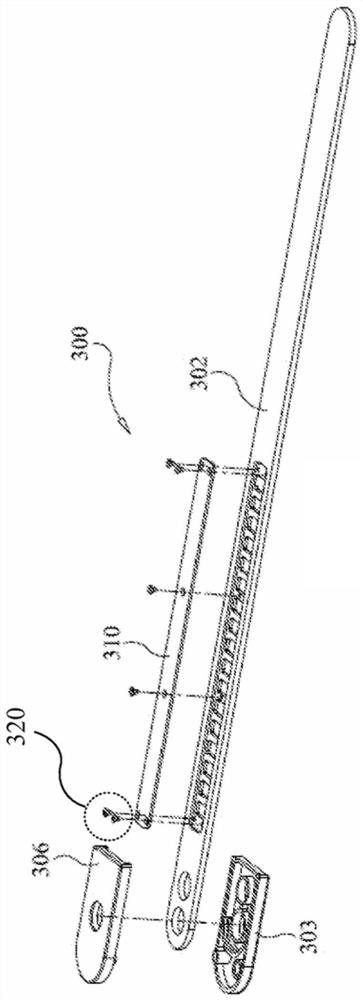
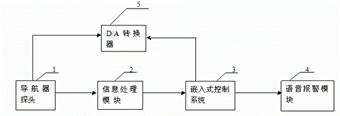
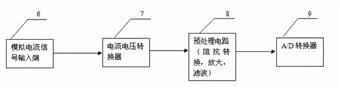
ActiveCN102670199AAvoid misplacementAvoid damageSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringSpinal columnConverters
The invention relates to an opening navigator detection circuit for a spinal surgery. The opening navigator detection circuit comprises a navigator probe, an excitation voltage module, an information processing module and an embedded control system, wherein the excitation voltage module outputs excitation voltage to act on two electrodes of the navigator probe; the two electrodes of the navigator probe output current signals and then output voltage signals through a current to voltage converter, and the voltage signals are processed through a preprocessing circuit, are then sampled through an analog to digital converter and are finally input to the embedded control system to be processed; and the embedded control system analyzes the size of input data and respectively compares the input data with pre-stored current value corresponding data of the navigator probe positioned in vertebra and spinal fluid, so that the position of the navigator probe is indicated. The opening navigator detection circuit navigates opening of the spinal surgery, and the injury caused by misplacement of vertebral screws is avoided. The invention also relates to an opening navigation method for the spinal surgery.
Owner:上海朗信医学科技有限公司
Endoscope and surgical robot
ActiveCN113854935AImprove sealingAvoid infectionEndoscopesSurgical robotsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationUniversal joint
The invention relates to the technical field of endoscopes, in particular to an endoscope and a surgical robot. The endoscope comprises a lens assembly, a universal joint, an abdomen entering assembly and an adjusting handle which are sequentially connected, wherein the universal joint comprises a vertebra joint and a first sealing piece, a first connecting end of the vertebra joint is connected with a first connecting part of the abdomen entering assembly, a second connecting end of the vertebra joint is connected with a third connecting part of the lens assembly, the first connecting part, the vertebra joint and the third connecting part are sequentially nested by the first sealing piece, and a second connecting part of the abdomen entering assembly is connected with a fourth connecting part. According to a structure of the endoscope, all the assemblies of the endoscope are connected in a sealed mode, and the sealing effect of connection between the lens assembly and the universal joint is better through the arrangement of the first sealing piece. The endoscope is applied to the surgical robot, the endoscope used by the surgical robot is good in sealing performance, and infection caused by using the endoscope in a surgical process can be effectively avoided.
Owner:APEIRON SURGICAL CO LTD
Device and method for assembling adjustable vertebra segment assembly and hose
InactiveCN113696500AIncrease inner diameterIncrease the cross sectionDomestic articlesEngineeringStructural engineering
The embodiment of the invention provides a device and method for assembling an adjustable vertebra segment assembly and a hose, and belongs to the technical field of medical instruments. The device comprises an air suction device and an assembly pipe with openings in the two ends, and a connection part is arranged on the side wall of the assembly pipe; the inner diameter of the assembly pipe is configured to be larger than the outer diameter of the hose, and an air suction channel is formed between the inner wall of the assembly pipe and the outer wall of the hose; and when the hose is located in the assembly pipe, the air suction device sucks air in the air suction channel through the connection part so as to enlarge the inner diameter of the hose. By means of the device and method for assembling the adjustable vertebra segment assembly and the hose, the air suction device can be used for sucking air in the air suction channel formed between the inner wall of the assembly pipe and the outer wall of the hose so as to uniformly enlarge the inner diameter of the hose, and then the difficulty in inserting the adjustable vertebra segment assembly into the hose is reduced for a worker.
Owner:APEIRON SURGICAL (BEIJING) CO LTD
Device and method for treatment of spinal deformity
ActiveUS20170273721A1Shorten the lengthDevice degradationInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present invention generally relates to methods and devices for treatment of spinal deformity, and in particular to the utilization of at least one implant to either maintain the position of at least one vertebra of a patient to prevent increase in abnormal spinal curvature, to slow progression of abnormal curvature, or to impose at least one corrective displacement and / or rotation on at least one vertebra of a patient so as to incrementally correct abnormal spinal curvature.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Methods for molding interbody devices in situ
InactiveUS20090001622A1Low costReduce riskBone implantSpinal implantsBiocompatibility TestingUltimate tensile strength
A method is provided for producing and inserting a cervical interbody mold device (CIMD). The CIMD produces an interbody device that is formed in situ and that possesses suitable strength and biocompatibility so as to provide sufficient vertebral support while providing optimal ease of use and insertion for the surgeon.
Owner:NADER REMI +1
Rapid registration method and device for a robot-assisted spinal operation
PendingCN111728701AImprove adaptabilityImprove registration accuracySurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingSpinal columnRadiation exposure
The invention discloses a rapid registration method and device for a robot-assisted spinal operation. The method comprises the steps: carrying out the Boolean operation of a three-dimensional model ofa registration device and a spinous process part of a vertebral three-dimensional model of an operation object, and exporting a registration matrix; exporting the registration device three-dimensional model after Boolean operation, and carrying out rapid prototyping processing; and in the operation process, enabling the registration device object to be installed and fixed on the spinous process part of the operation object, and completing registration. The method is simple in interactive operation, short in learning period, light in registration device, easy to carry to disinfect and high inregistration speed, X-ray radiation exposure is avoided, and the operation environment is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Anatomic chiropractic training mannequin with network of pressure sensors
Chiropractic training apparatus includes an anatomic mannequin incorporating a network of electronic sensors providing feedback to a user related to applied pressure. The mannequin may include a simulated human head and pelvic region with simulated articulating spinal vertebrae embedded in pliable silicone skin and gel materials. Electronic circuitry determines when pressure is applied to any of the plurality of pressure sensors during the palpation of the model, and output an electronic signal representative of the applied pressure. A mechanism may be provided to facilitate adjustment of relative joint stiffness. A computer display in communication with the model may show information indicative of vertebral level and / or color gradients associated with the pressure applied by a user. The physical model may only include portions of a simulated human spine (i.e., lumbar only). However, the model is preferably life-sized, and may be configured for prone positioning on a table or other work surface.
Owner:OWENS JR EDWARD F
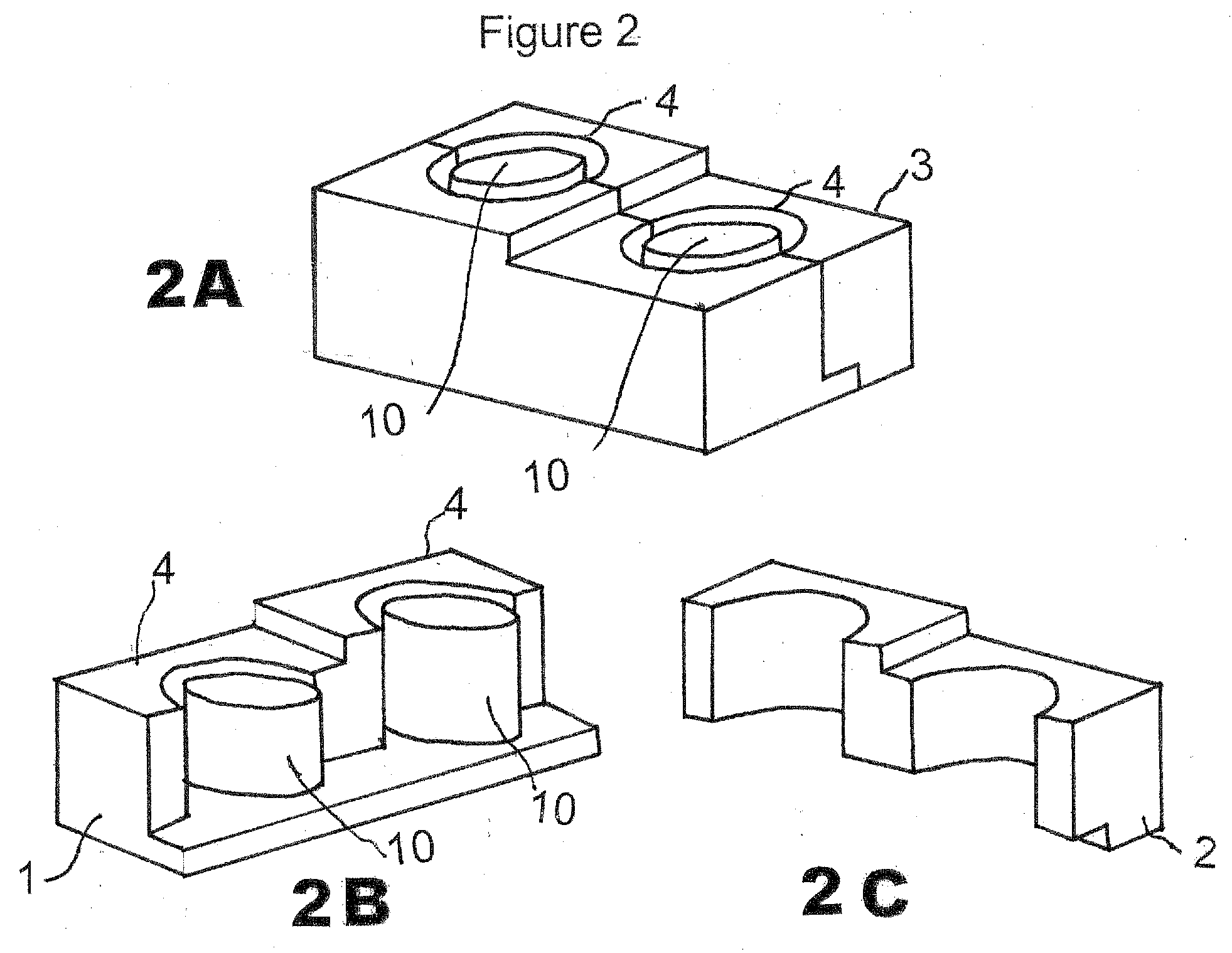
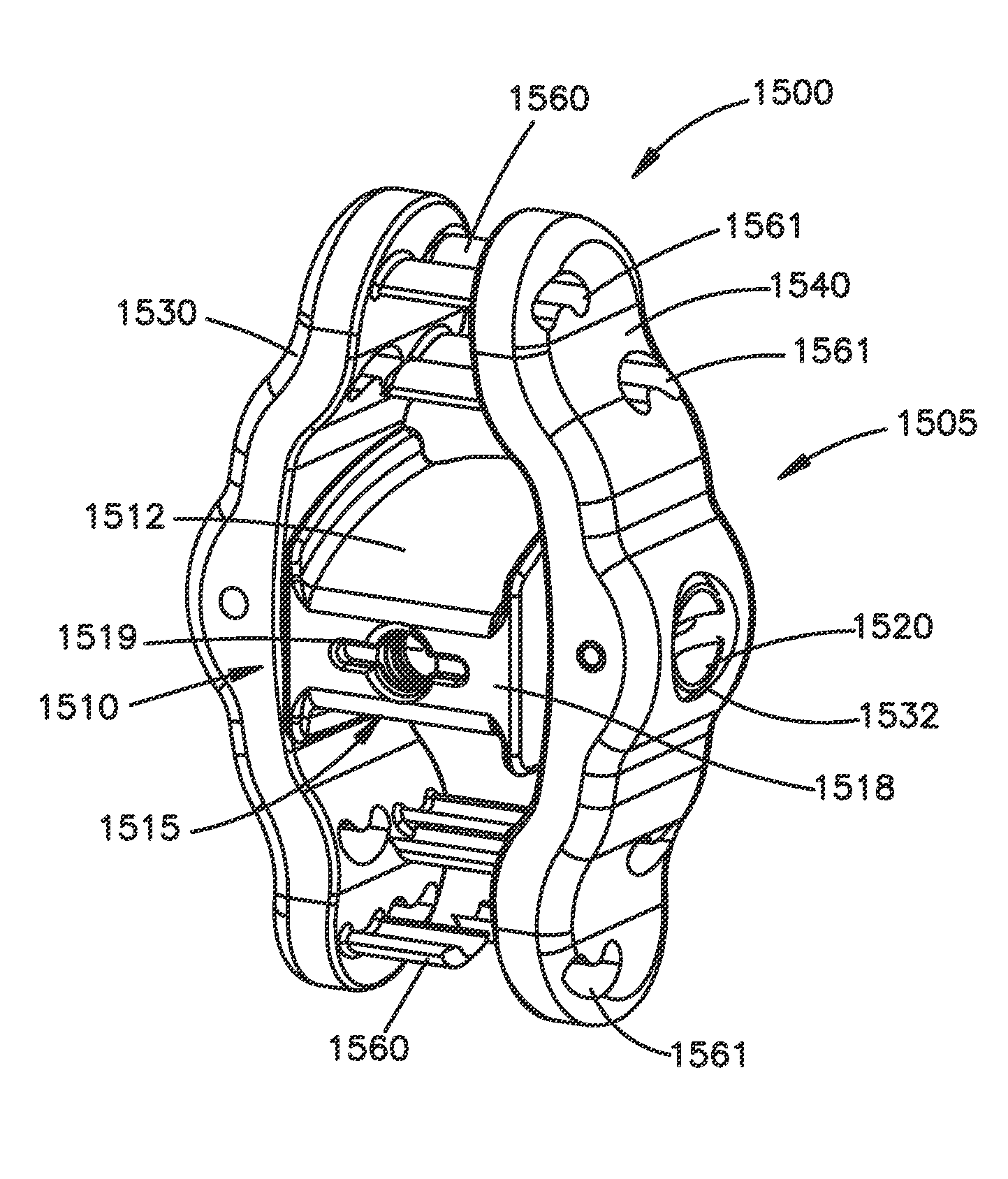
Vertebral implant, device for vertebral attachment of the implant and instrumentation for implantation thereof
ActiveUS10702391B2Easy to implantGuaranteed fit sizeJoint implantsSpinal implantsBone implantEngineering
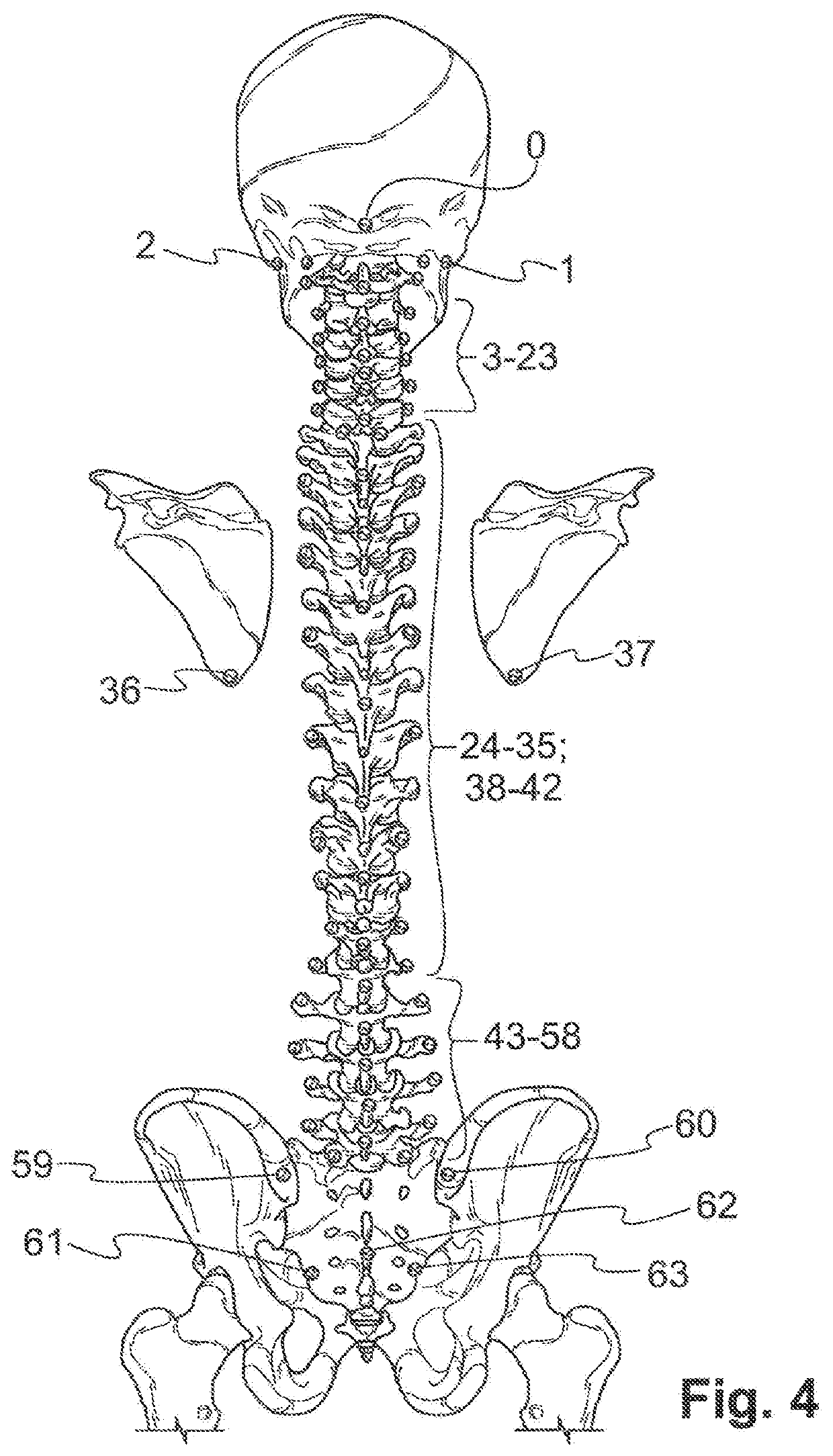
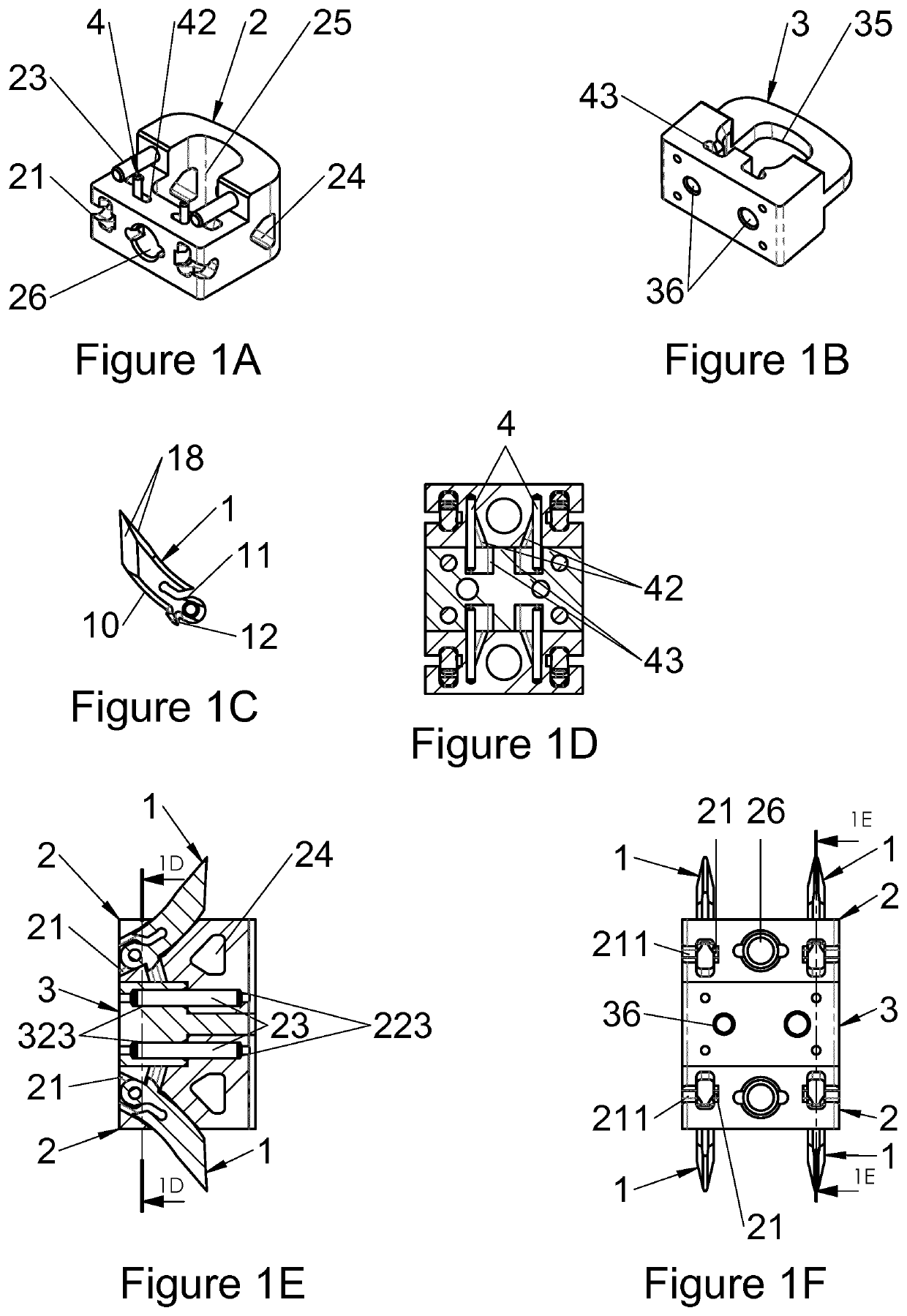
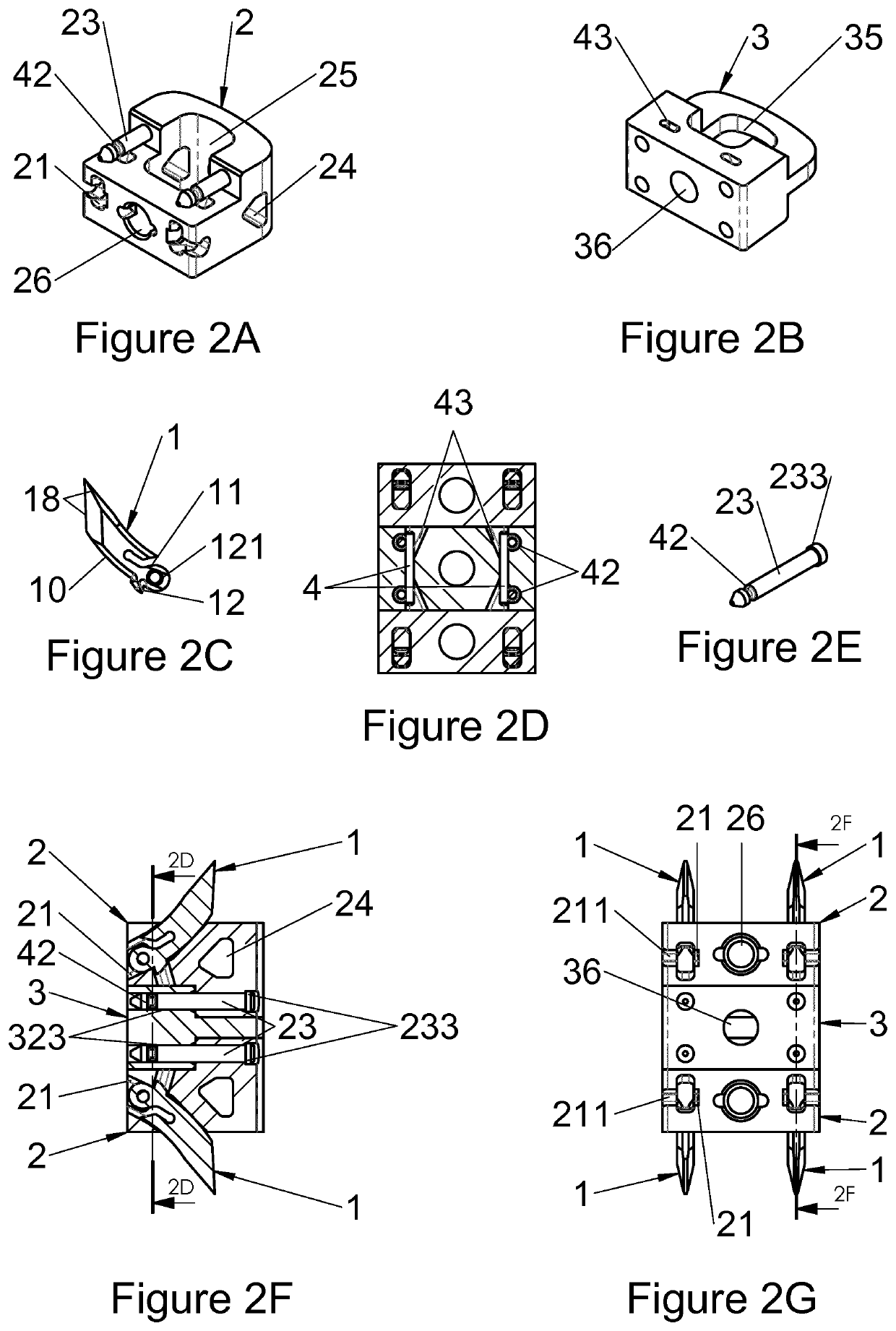
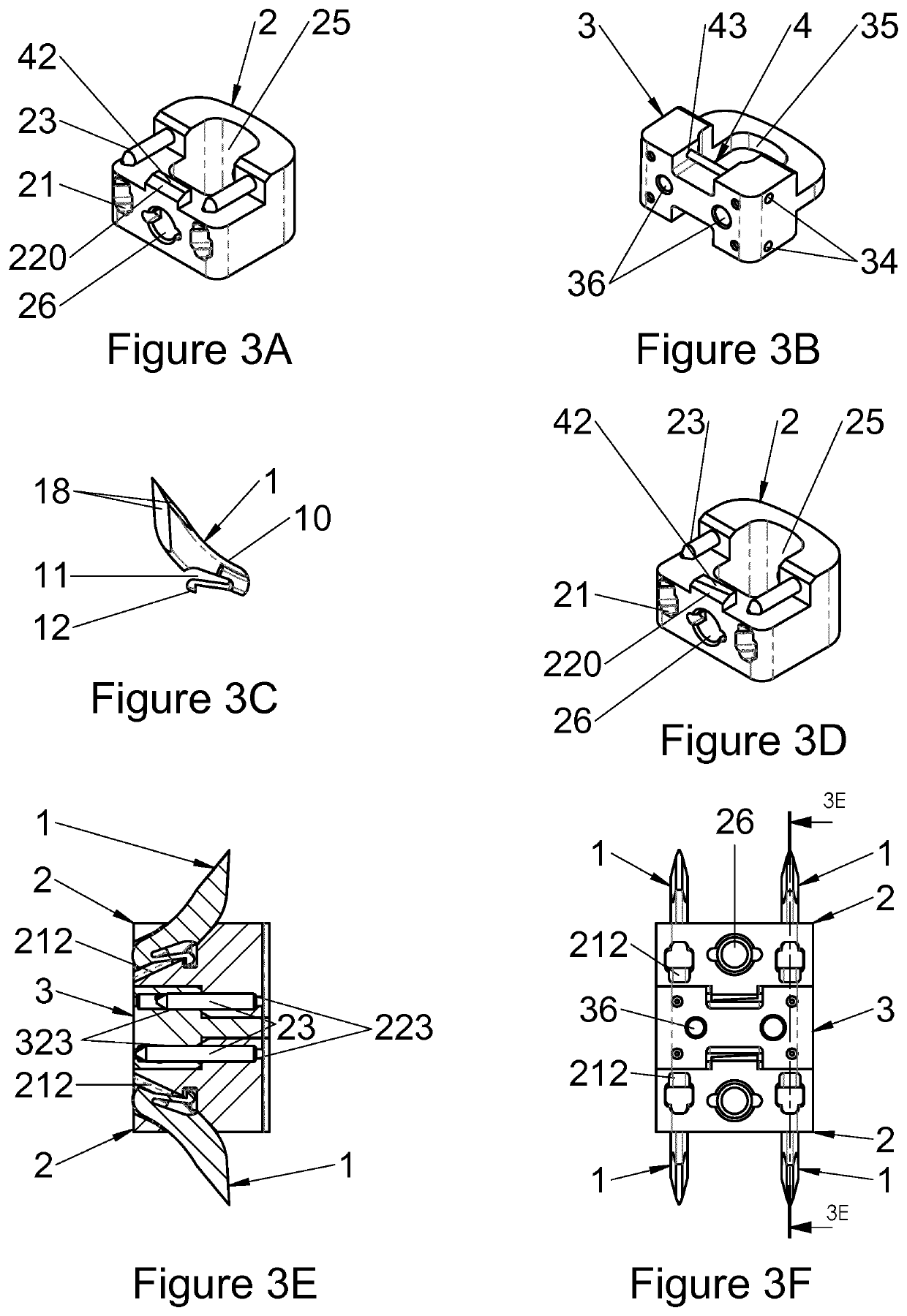
The present invention relates to a vertebral implant, in particular for corpectomy, to a device for attaching a vertebral implant and to implantation instrumentation, the implant including at least one first body (2) and at least one second body (3) each having at least one face having shapes and dimensions mating those of at least one face of another body (3, 2) and forming mutual fitting means, in order to allow assembling of said bodies (2, 3) by sliding along a sliding axis and, on the other hand, at least one locking means (4) retained in at least one of the bodies (2, 3) and at least one abutment portion of which is laid out for passing from a so-called open position, allowing sliding for the assembling of said bodies (2, 3), to a so-called closed position, locking said bodies (2, 3) assembled together by the contact between at least said abutment portion and at least one abutment (42, 43) of at least one of said bodies (2, 3), said abutment (42, 43) being oriented not parallel to the sliding axis and said abutment portion passing from the open position to the closed position elastically by flexure or torsion.
Owner:LDR MEDICAL SAS
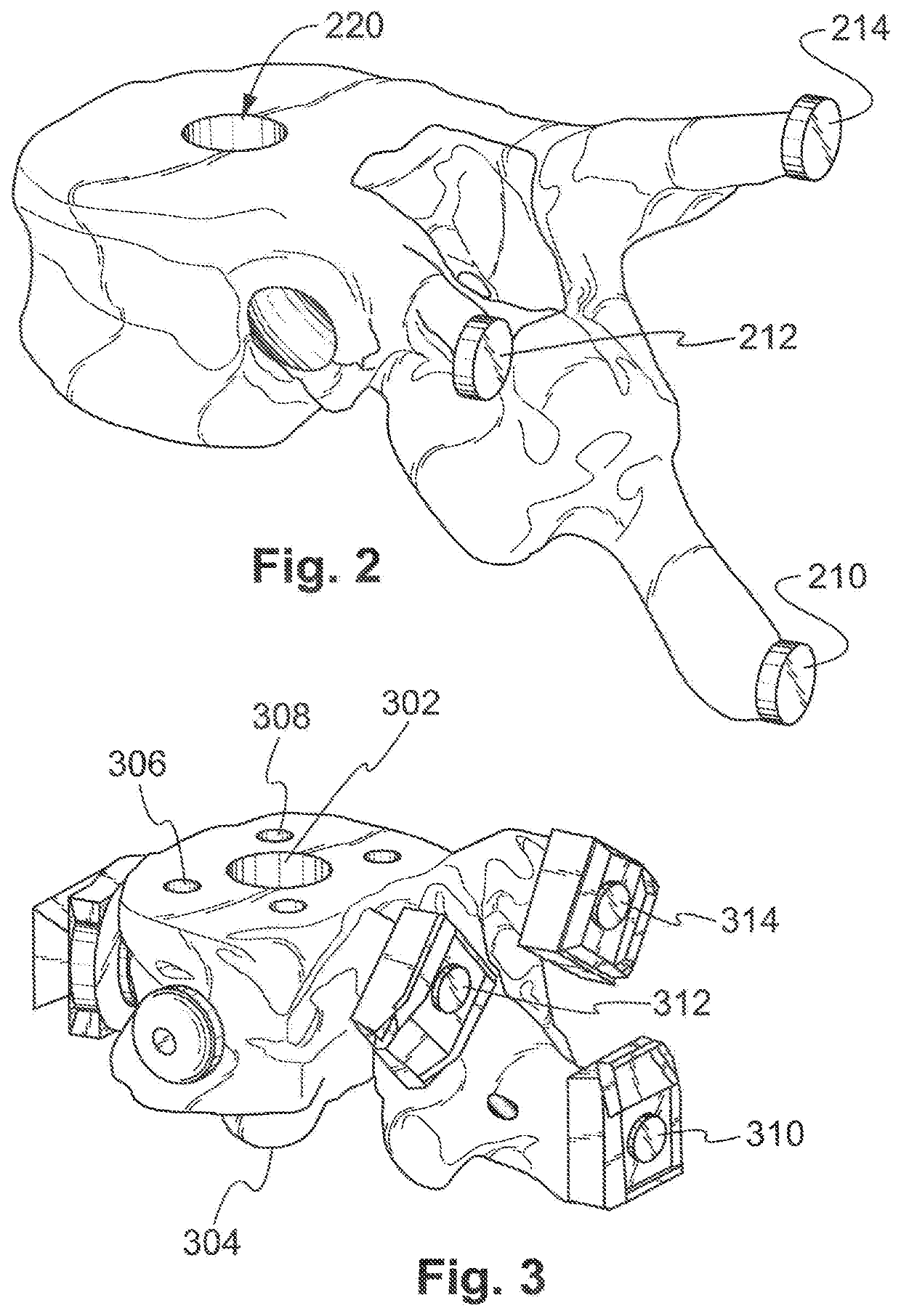
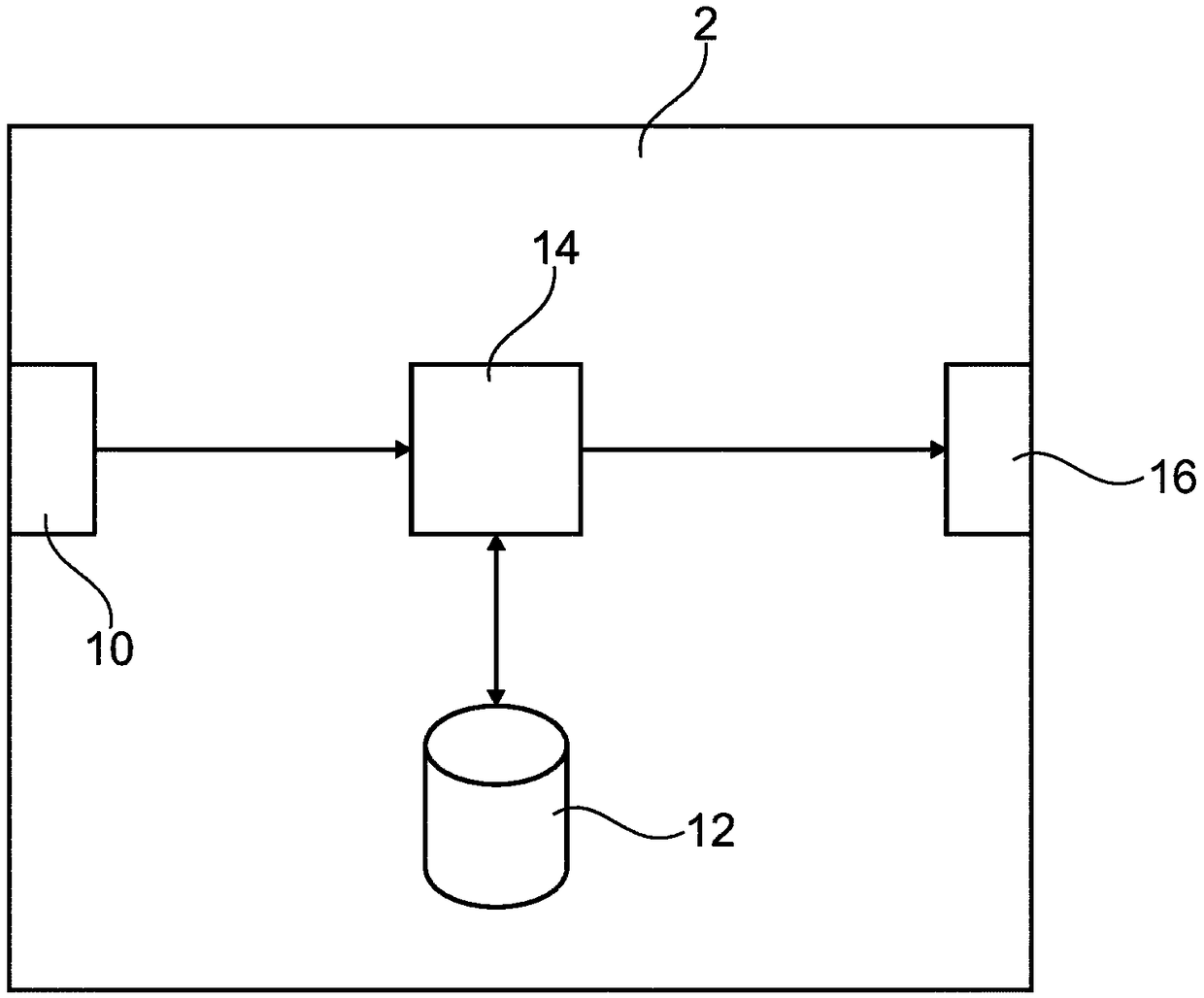
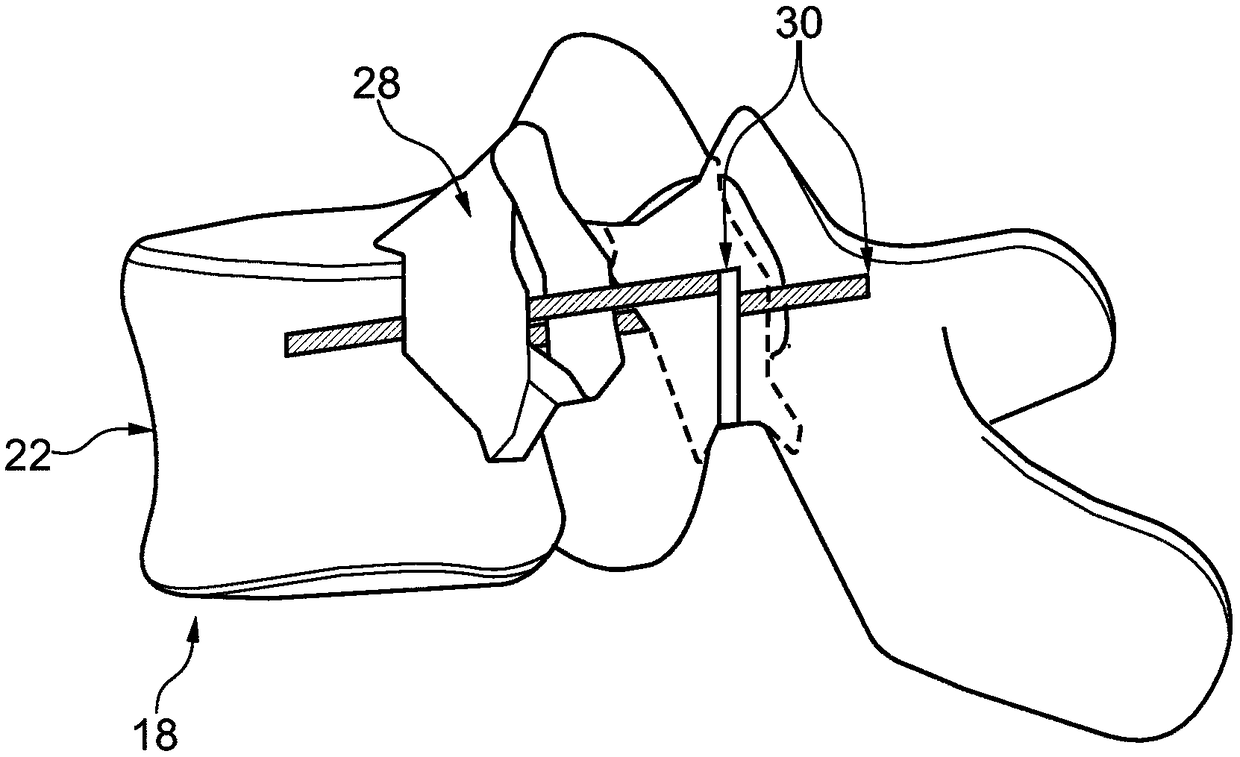
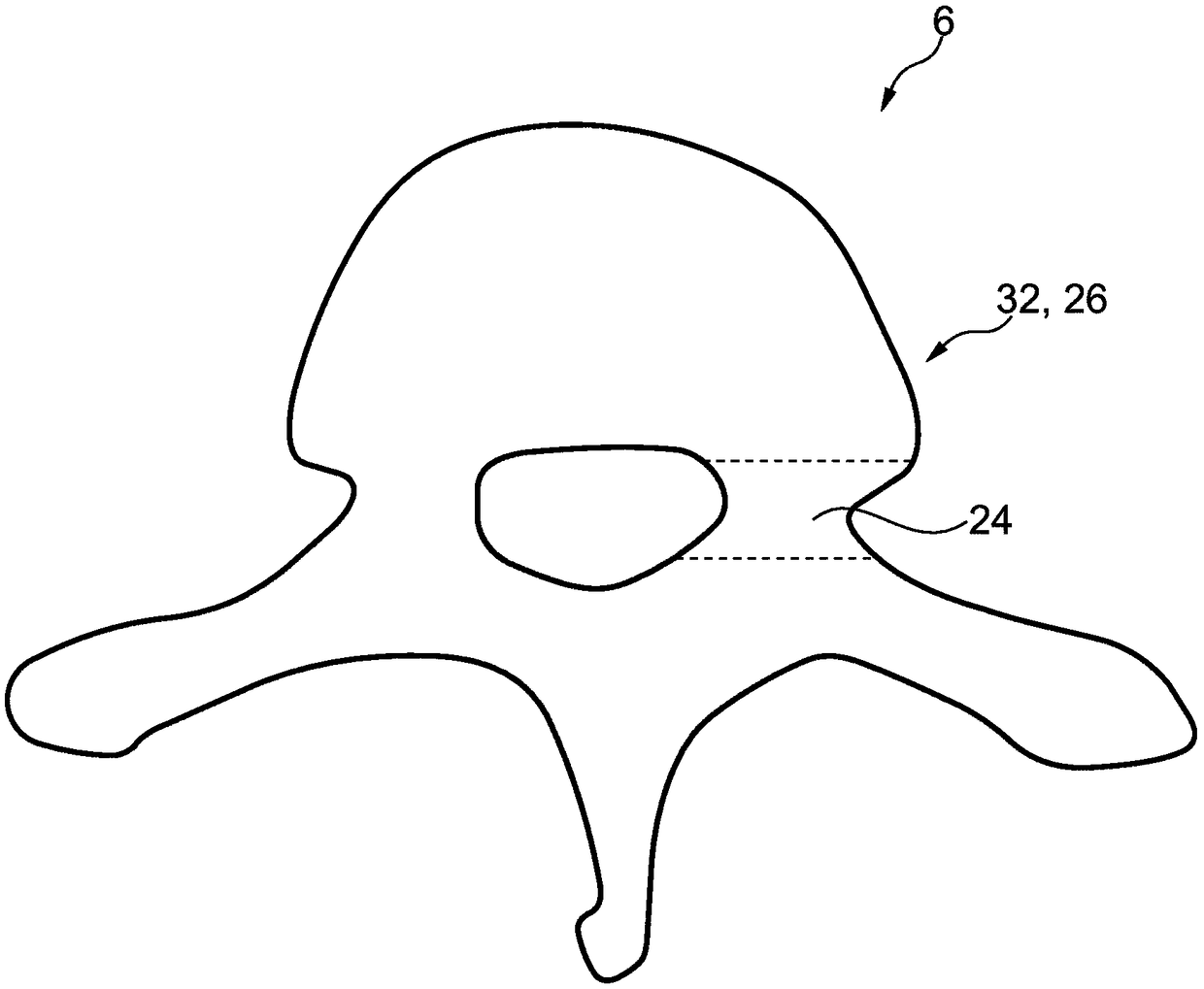
Determining an optimal placement of a pedicle screw
The present invention relates to a device (2) for determining an optimal placement of a pedicle screw (4). The device comprises a processing unit (14), wherein the processing unit is configured to receive a model data set representing a model surface (22) of a human vertebra model (18) and a pedicle screw model (30) being optimally placed in a span of a pedicle section (28) of the model surface; the processing unit is configured to receive 5 image data representing a surface image (26) of at least one human vertebra (6); the processing unit is configured to adapt the model data set for each ofa number of the at least one human vertebra, such that an adapted model data set representing a correspondingly adapted model surface (36), which fits to the surface image of the respective human vertebra, is provided for each of the number of the at least one human vertebra; and each of the 10 adapted model data sets also represents a correspondingly adapted pedicle screw model (38). The presentinvention further relates to a corresponding method, a corresponding computer program element and a corresponding computer readable medium.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS NV
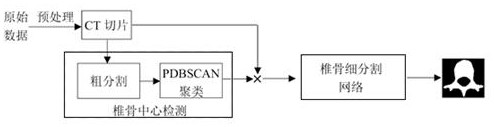
Segmented vertebra CT image segmentation method based on deep learning
ActiveCN113313717AEffective detection of deformitiesEffectively detect damageImage enhancementImage analysisImage segmentationComputer vision
The invention discloses a segmented vertebra CT image segmentation method based on deep learning, and relates to the technical field of image segmentation. The segmentation method comprises the following steps: step 1, preprocessing a spine CT image; step 2, performing vertebra center detection; step 3, segmenting the vertebra CT image. According to the invention, all visible vertebra centers in a current image are automatically detected in a deep learning mode, and high-resolution segmentation is performed on the vertebra centers through a segmentation network; doctors are helped to effectively find vertebra deformity and injury in an early stage, so that prevention and treatment can be performed in time.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus for acupressure based self-massage
PendingUS20220226185A1Reduce manufacturing costDevices for pressing relfex pointsChiropractic devicesAcupressurePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
An apparatus for self-massage of the vertebra includes a board and a frame. The board can be mounted onto the frame and the frame can be placed on ground. The board have several spherical balls protruding outwards from the top surface of the board and the spherical balls can freely rotate. A user can lie down on the board and push himself back and forth on the board wherein the spherical balls rub against the vertebra of the user.
Owner:RAMDASS SUMEET
Tri spine model
PendingUS20220198960A1Realistic sizeRealistic positionEducational modelsSpinal columnAnatomical structures
A model mimicking an anatomical formation, such as a spine, can be used for teaching and practice to students and practitioners. The model includes a number of segments in the form of spinal vertebrae, which are connected to one to mimic the movement of human vertebra. The rotational movement between the segments can be adjusted frictionally to mimic human spines of varying conditions. A cavitation member is included between at least two adjacent segments to mimic a manipulation of the spinal members and to provide feedback to the user. The model can improve manual mobilization and manipulation skills within the academic or clinical setting.
Owner:DRAKE UNIVERSITY
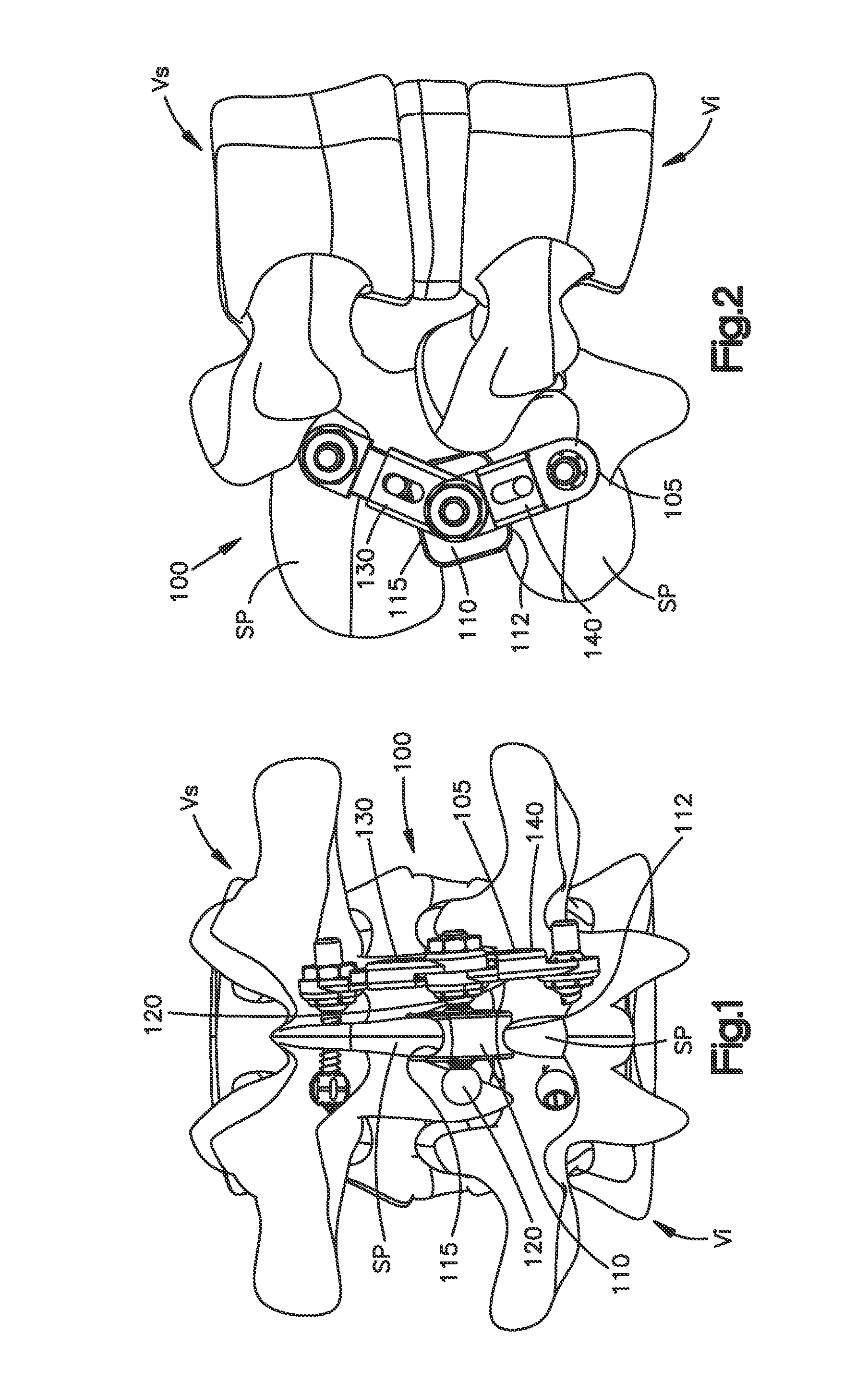
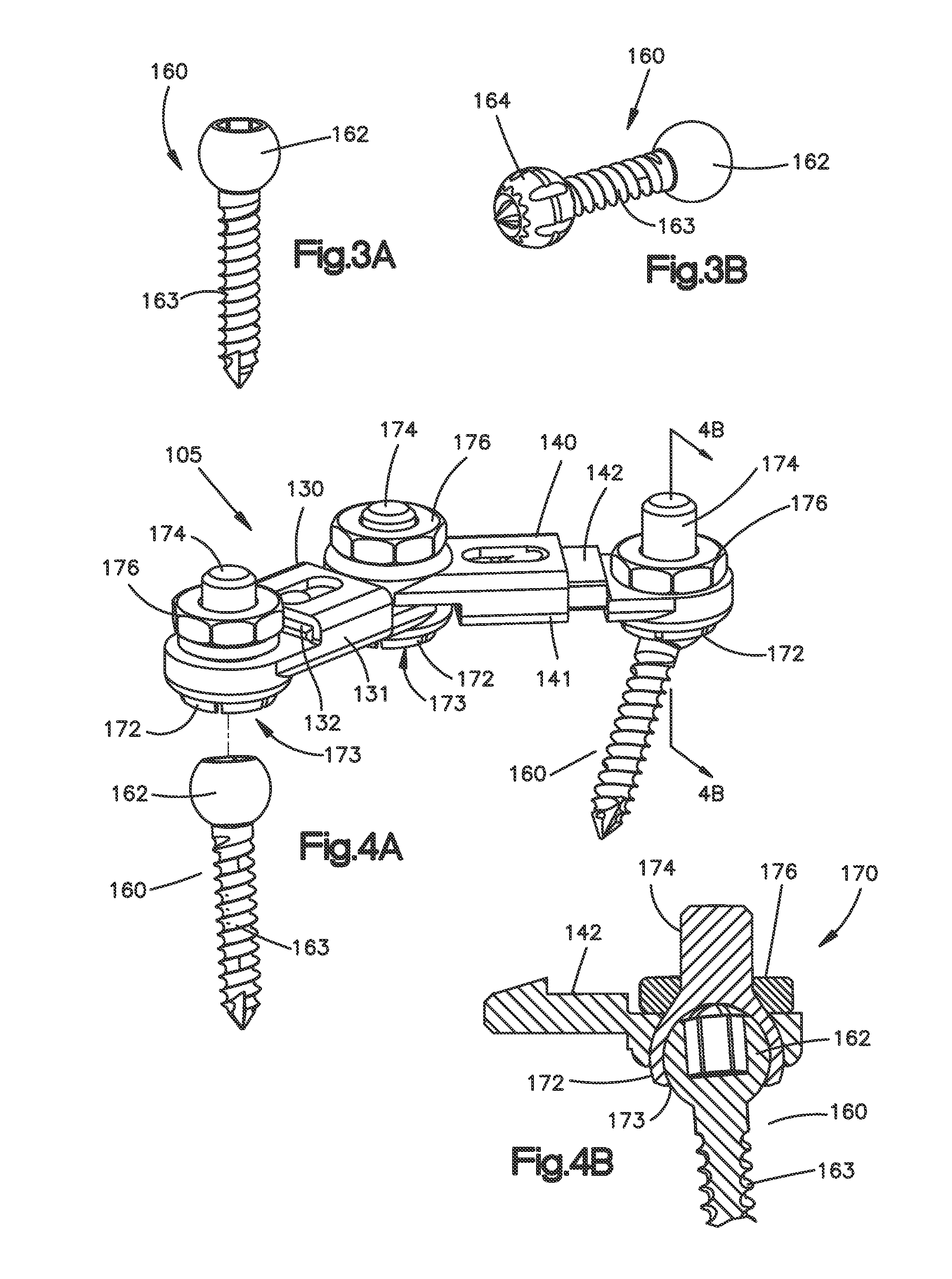
Interspinous spacer assembly
ActiveUS9402655B2Inhibit migrationInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsEngineeringBiomedical engineering
An interspinous spacer assembly (100) for insertion and / or implantation between spinous processes of adjacent superior and inferior vertebrae includes an interspinous spacer member (110) sized and configured for insertion into the interspinous space located between adjacent spinous processes and an engagement mechanism (105) for operatively coupling the spacer member to the adjacent spinous processes and for preventing migration of the assembly once implanted. The interspinous spacer assembly is adjustable to conform to the individual anatomy of a patient's spine.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
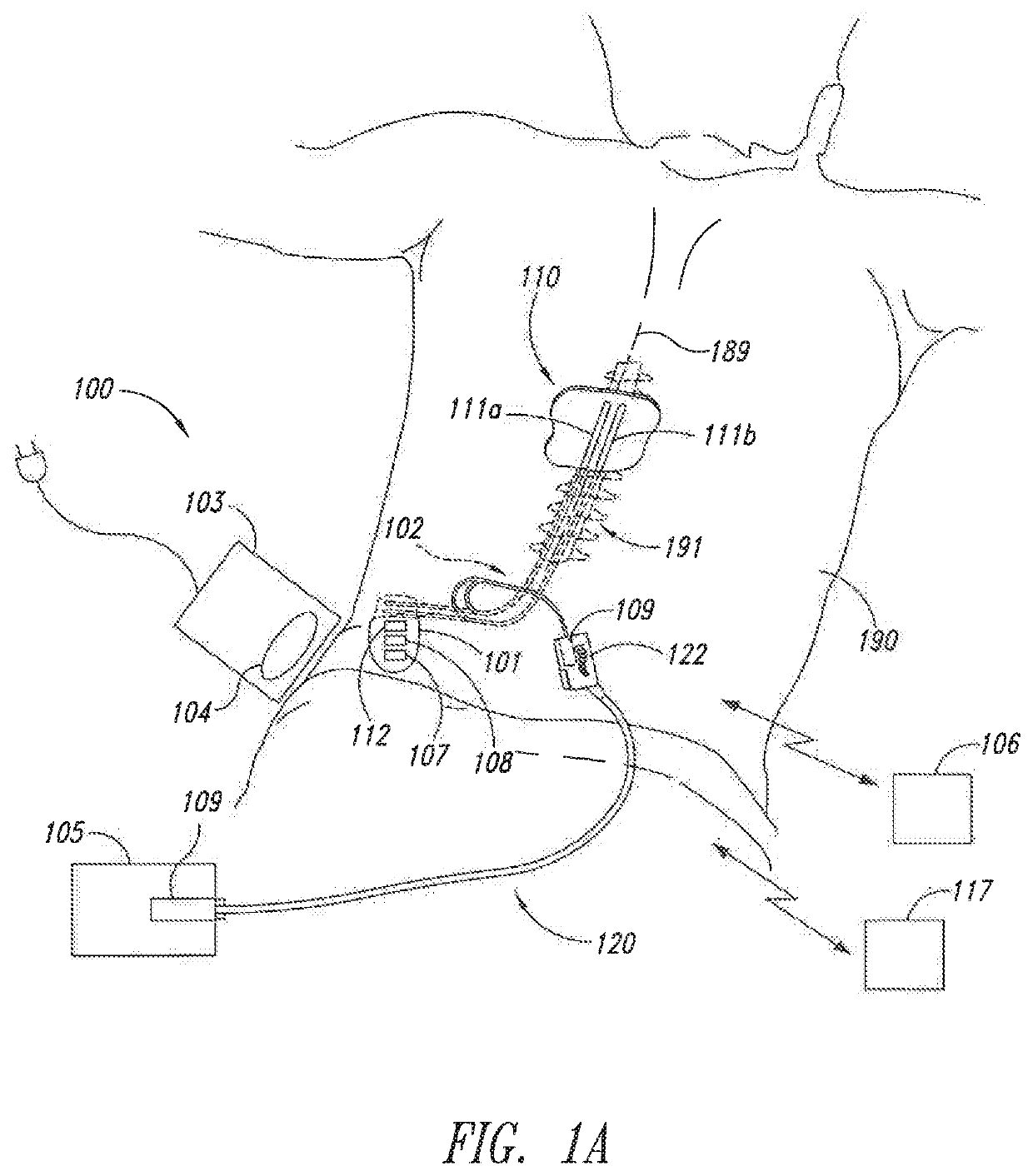
Therapeutic modulation to treat acute decompensated heart failure, and associated systems and methods
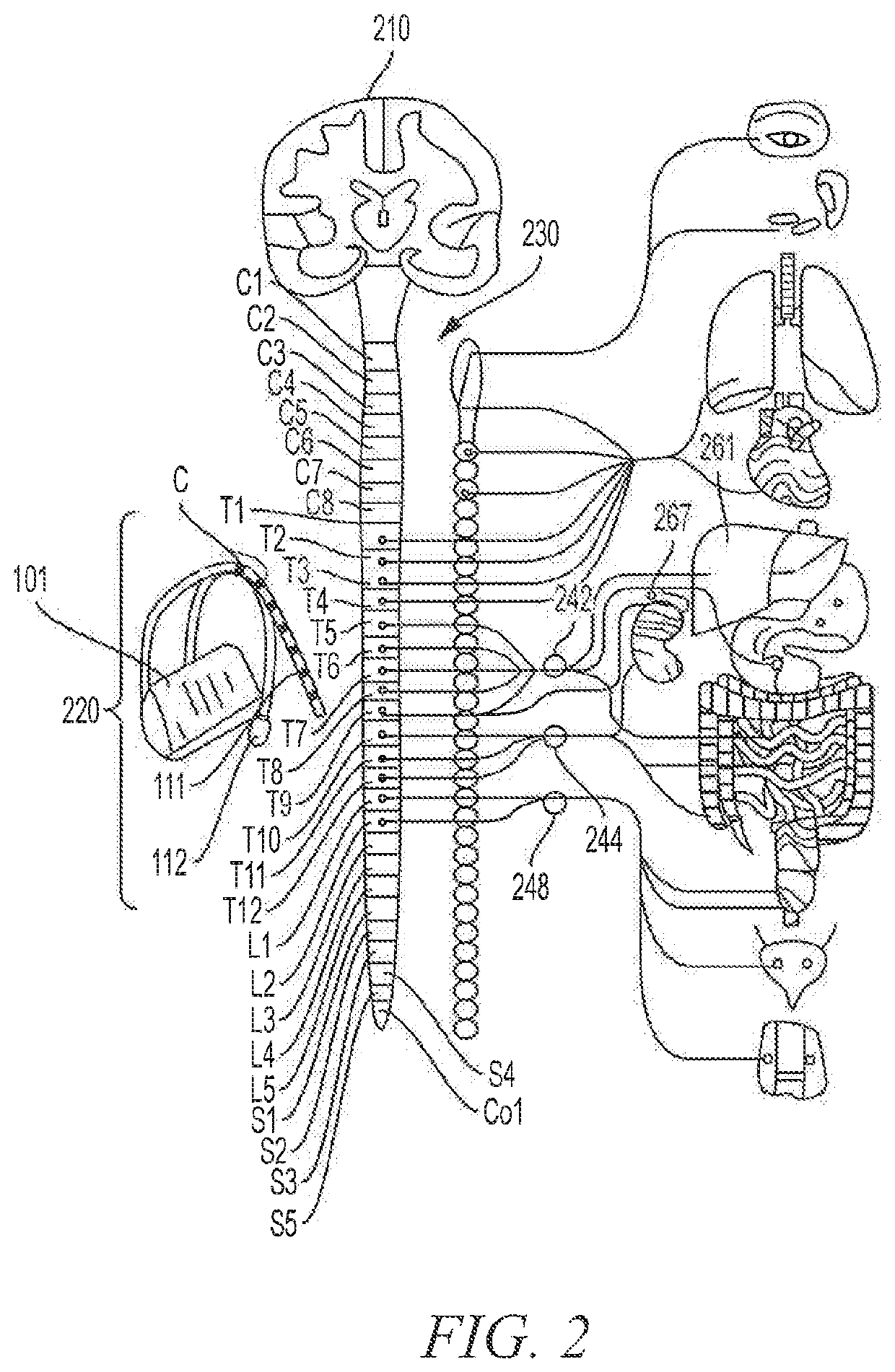
Systems and methods for treating a patient having acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) using electrical stimulation are disclosed. A representative method for treating a patient includes positioning an implantable signal delivery device proximate to a target location at or near the patient's spinal cord within a vertebral range of about T1 to about T12, directing an electrical therapy signal to the target location via the implantable signal delivery device, wherein the electrical signal has a frequency in a frequency range of from 1.2 kHz to 100 kHz to modulate one or more of the patient's sympathetic nerves and treat the patient's ADHF.
Owner:NEVRO CORP
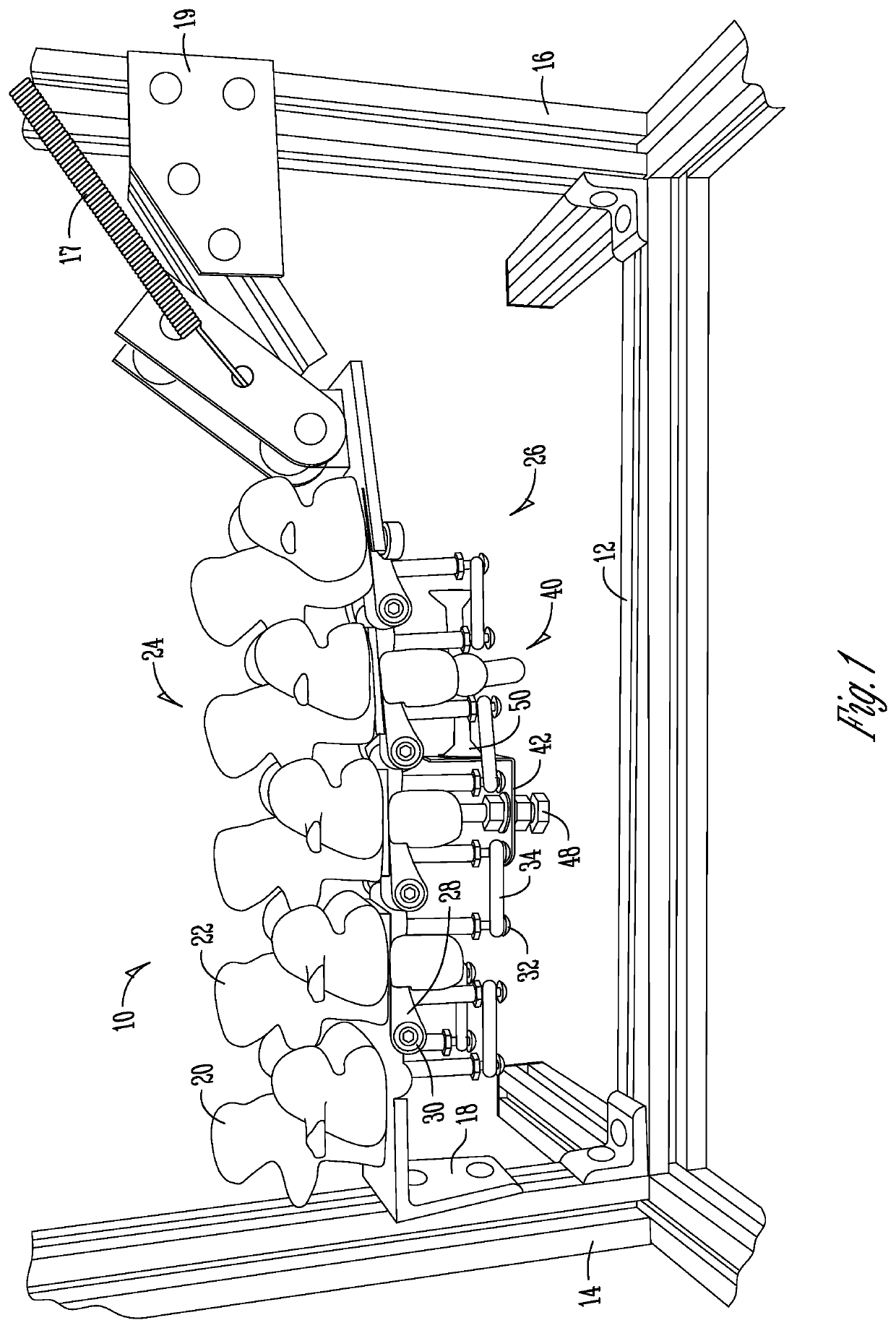
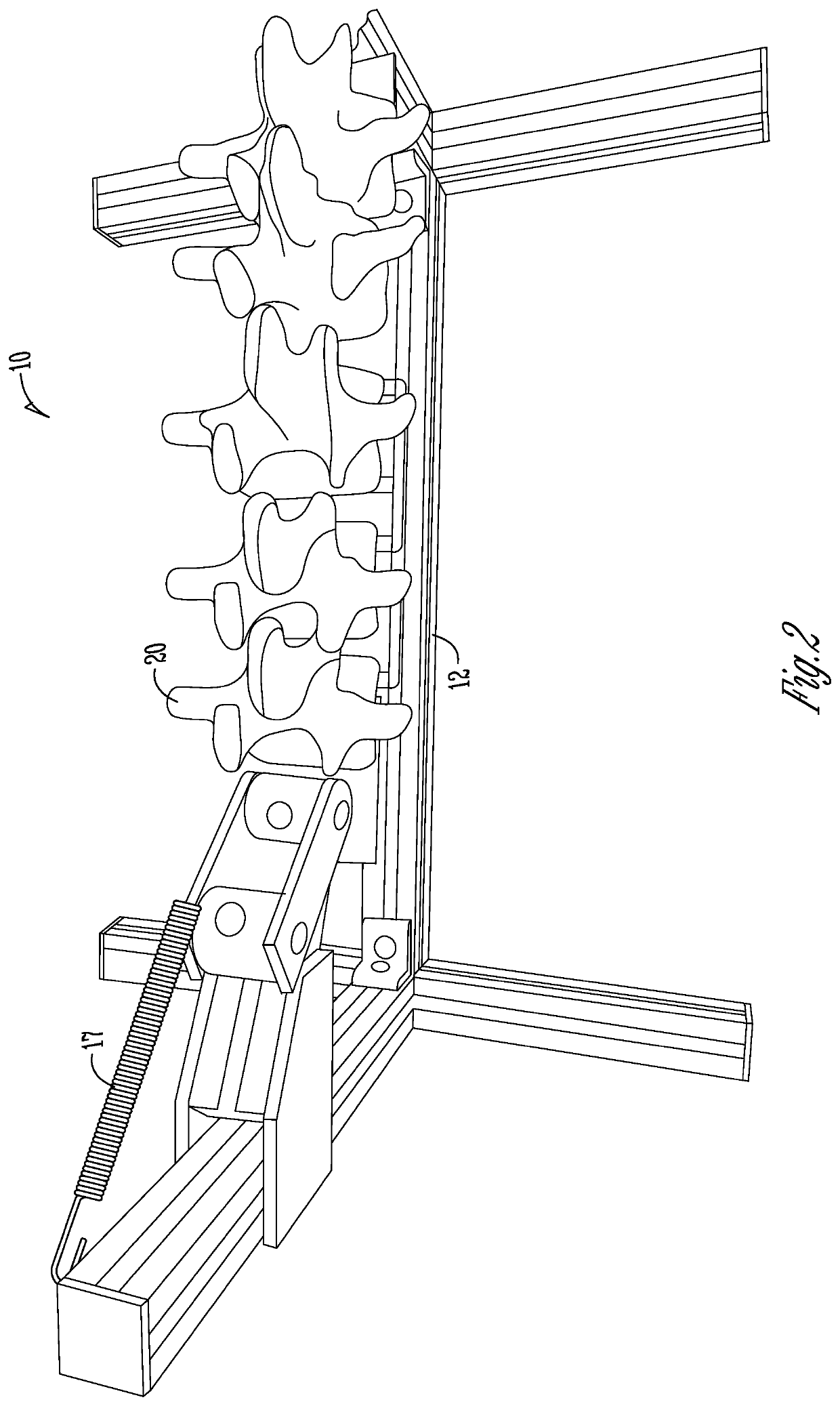
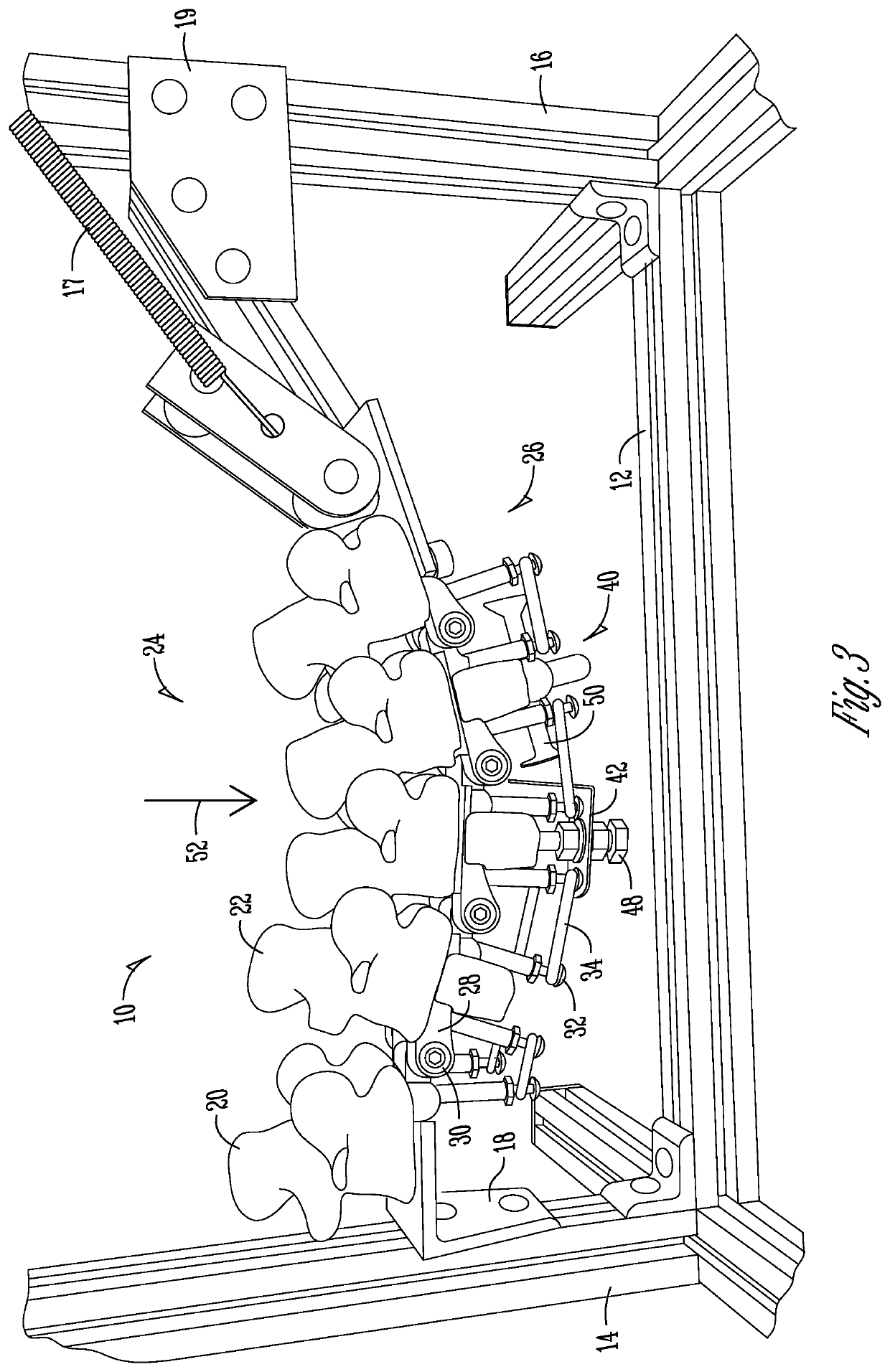
Remote spinal manipulating assembly and method for remote spinal manipulation
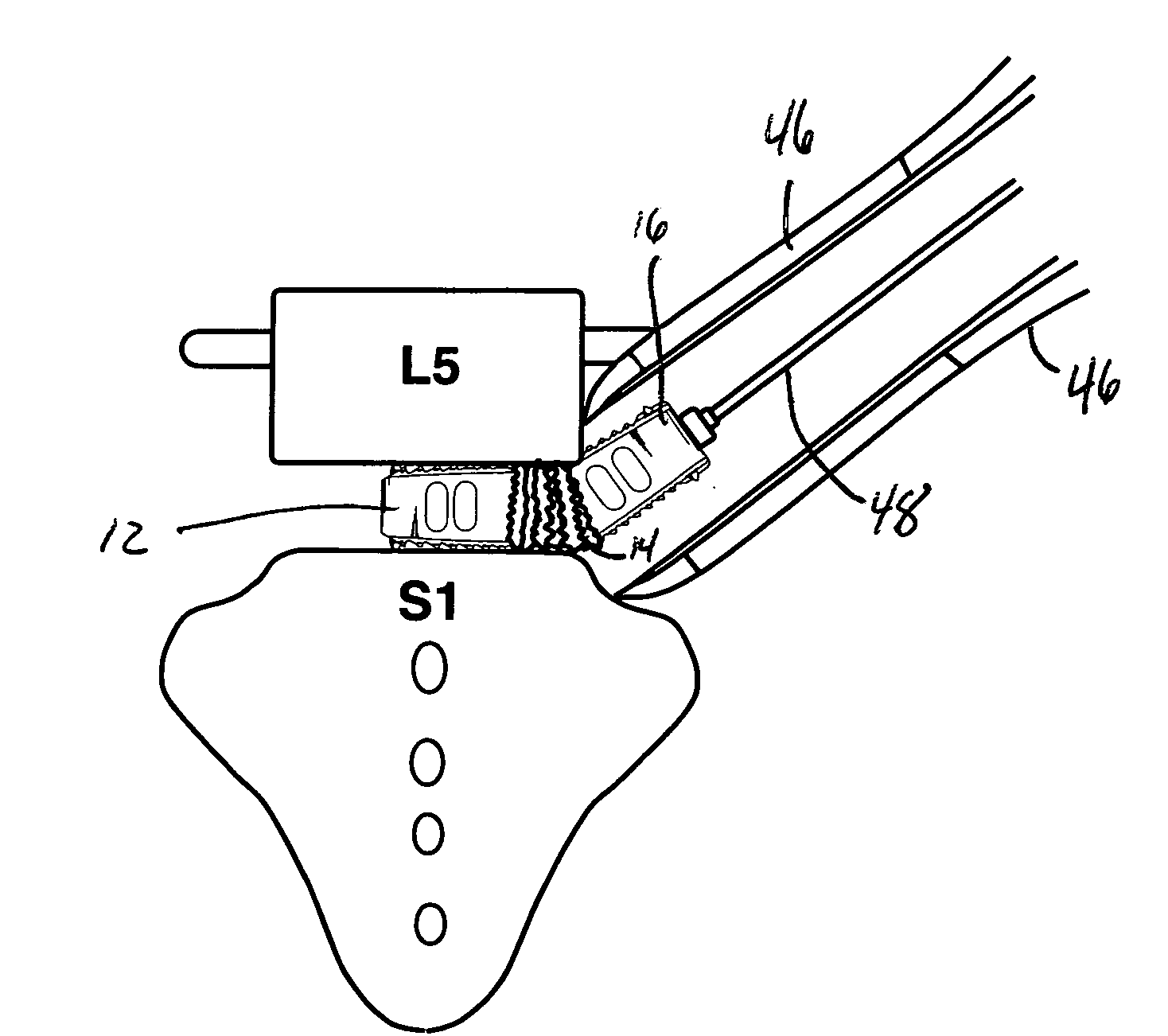
An assembly for remotely manipulating a patient's spine. A compressor / distractor mechanism attaches to spinal anatomy or vertebral screws on adjacent vertebrae at a spinal surgical site on a patient's spine. A flexible cable is operatively connected to the compressor / distractor mechanism and to a control mechanism. The control mechanism manipulates the flexible cable, controlling the compressor / distractor mechanism to compress or distract the vertebrae. A rotatable surgical table with a remote control can be used in place of the compressor / distractor mechanism and the control mechanism. The rotatable surgical table can rotate the patient to place the spinal surgical site in a desired compressed or distracted position, and to place the patient in a desired orientation with respect to a horizontal reference plane. The assembly permits manipulation of the spine at the surgical site via a posterior approach, while the surgeon can also manipulate the spine at the surgical site via an anterior, lateral or oblique approach.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Three-dimensional medical image analysis method and system for identification of vertebral fractures
A machine-based learning method estimates a probability of bone fractures in a 3D image, more specifically vertebral fractures. The method and system utilizing such method utilize a data-driven computational model to learn 3D image features for classifying vertebra fractures. A three-dimensional medical image analysis system for predicting a presence of a vertebral fracture in a subject includes a 3D image processor for receiving and processing 3D image data of a 3D image of the subject, producing two or more sets of 3D voxels. Each of the sets of 3D voxels corresponds to an entirety of the 3D image and each of the sets of 3D voxels consists of equal 3D voxels of different dimensions. The system also includes a voxel classifier for assigning the 3D voxels one or more class probabilities each of the 3D voxels contains a fracture using a computational model, and a fracture probability estimator for estimating a probability of the presence of a vertebral fracture in the subject.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SRL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com