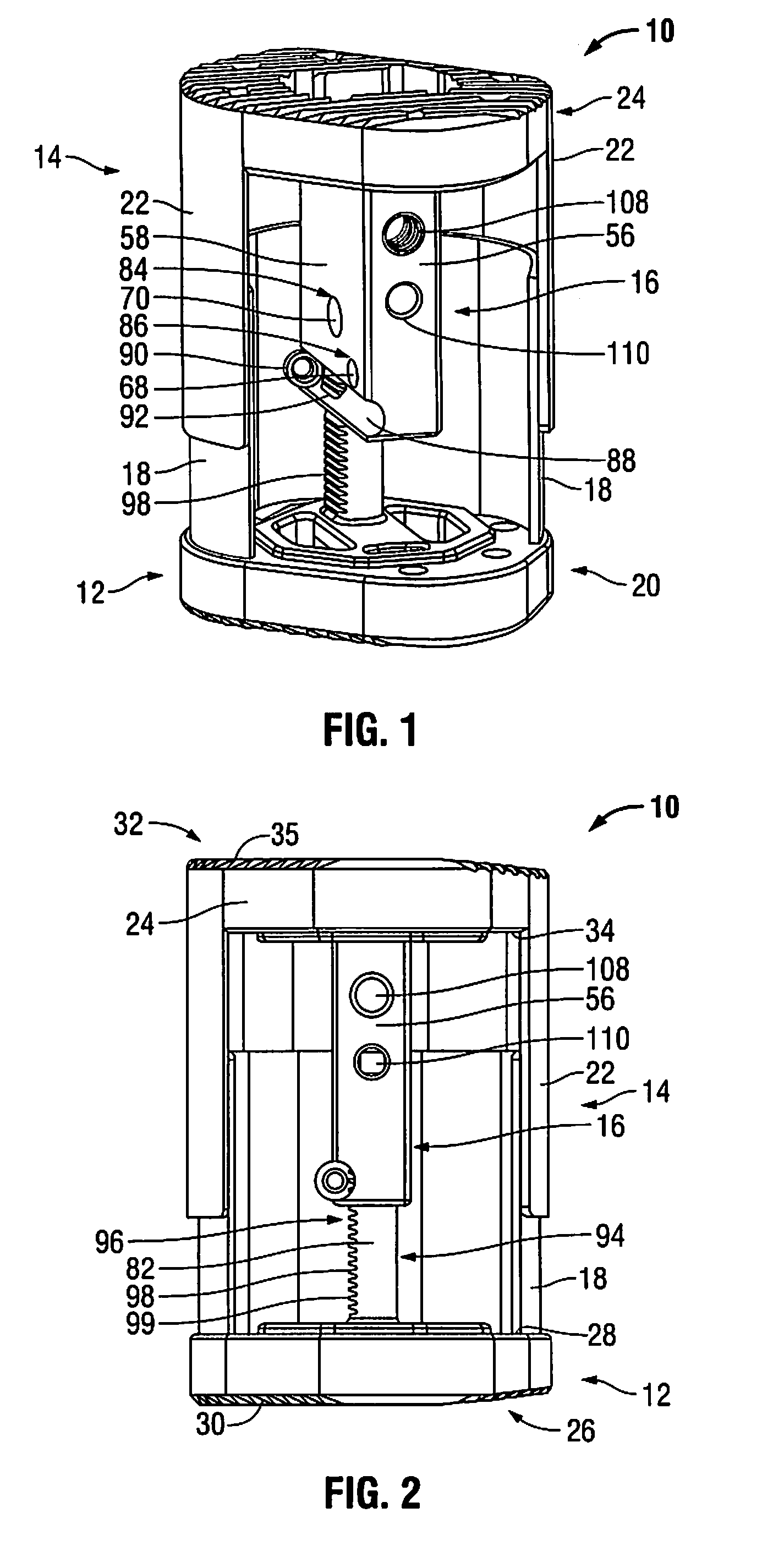
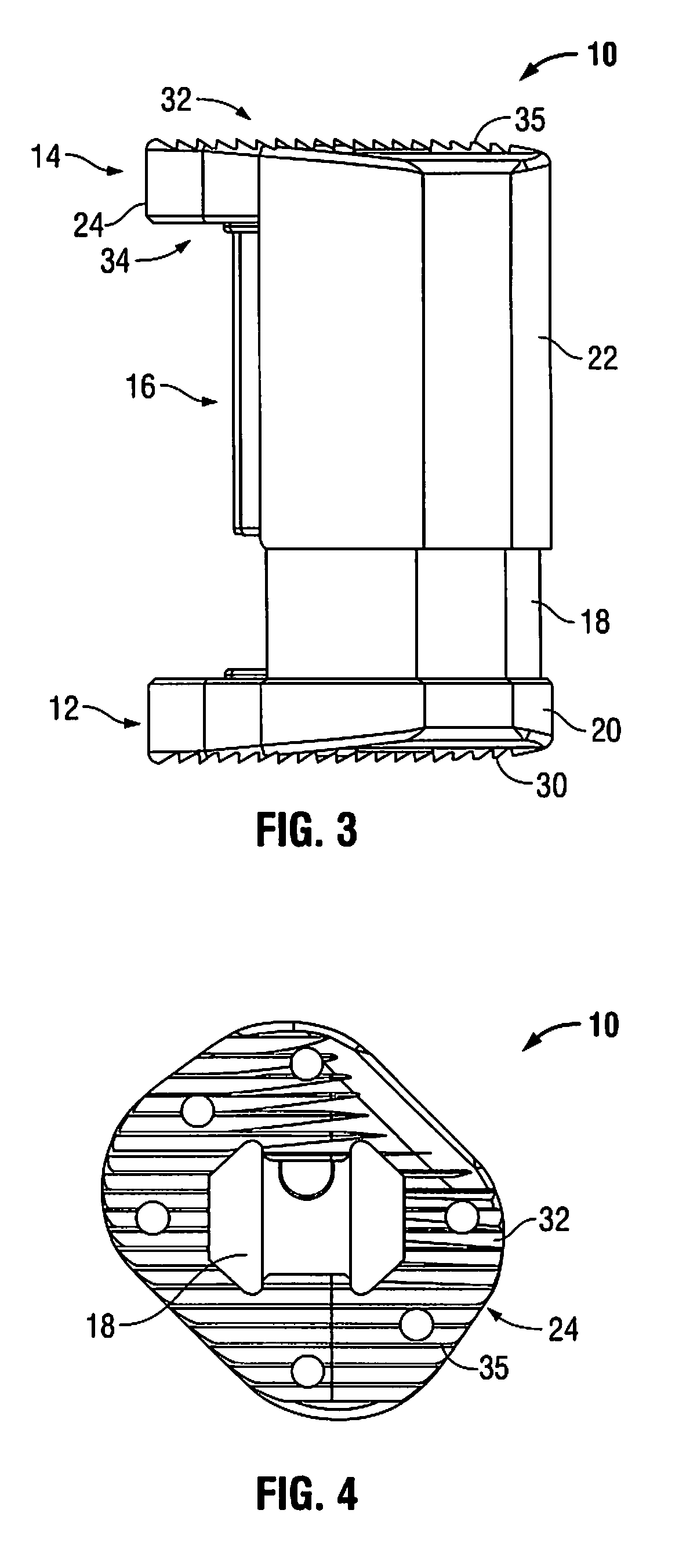
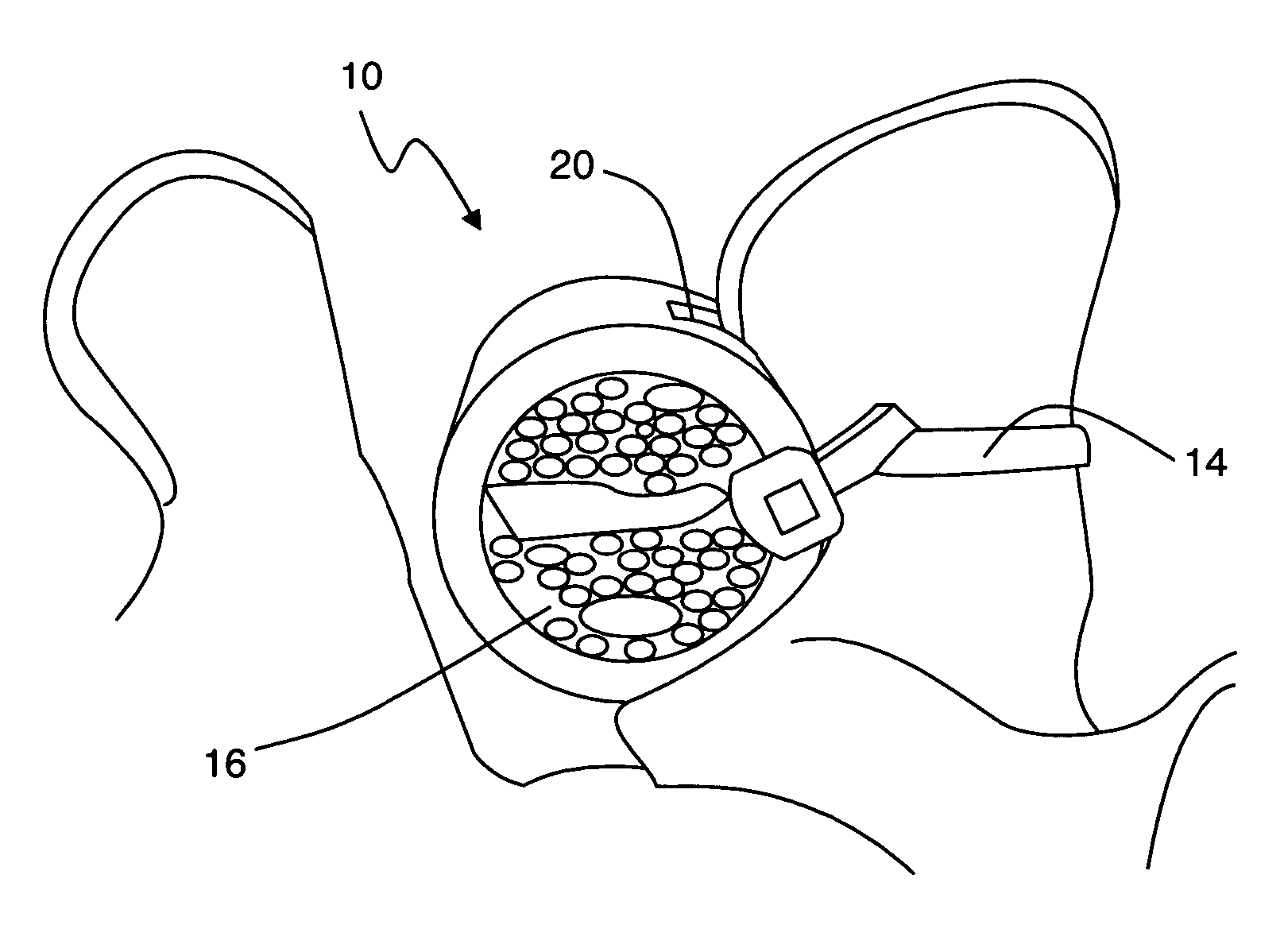
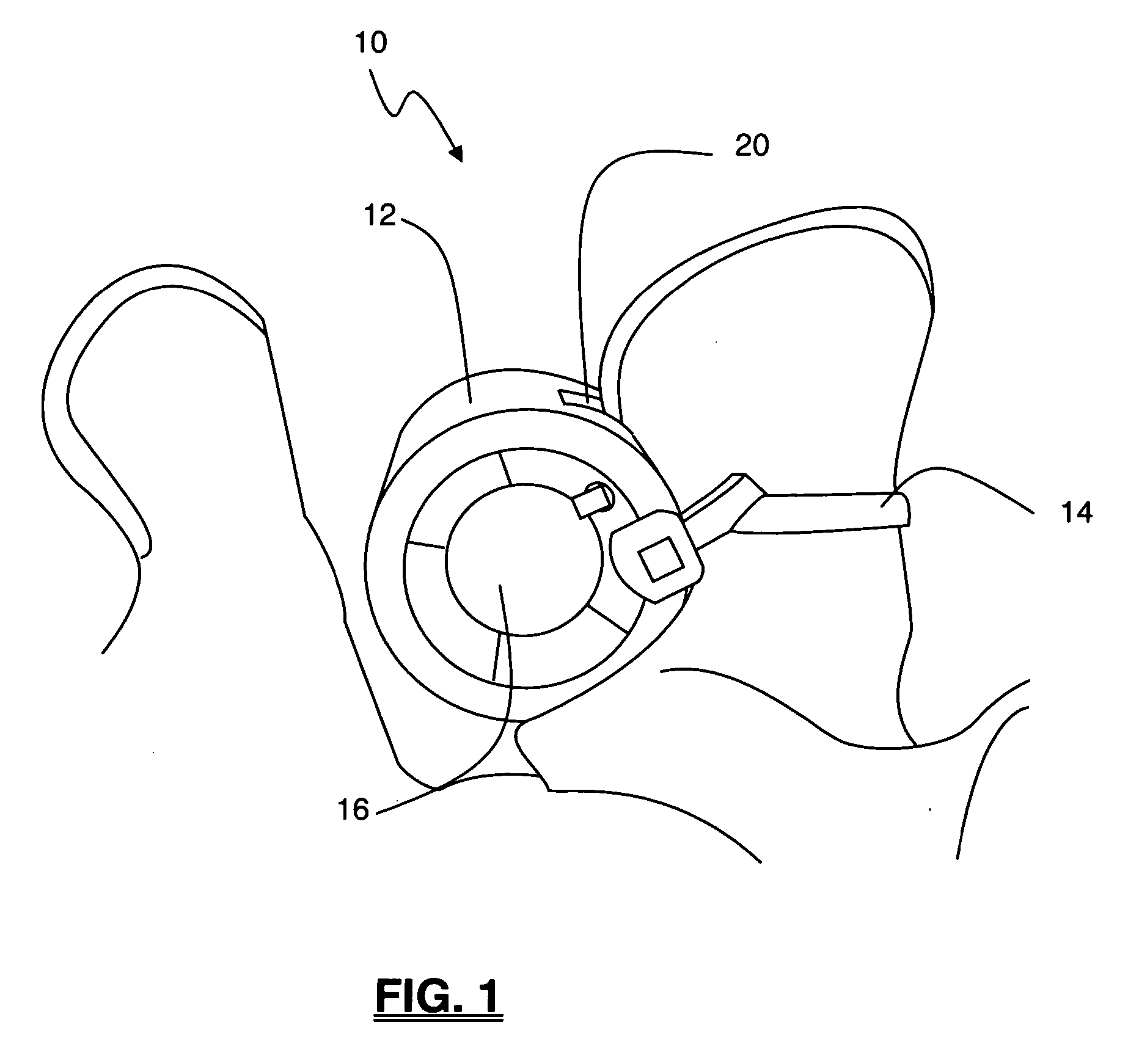
Patents
Literature
274 results about "Spine surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
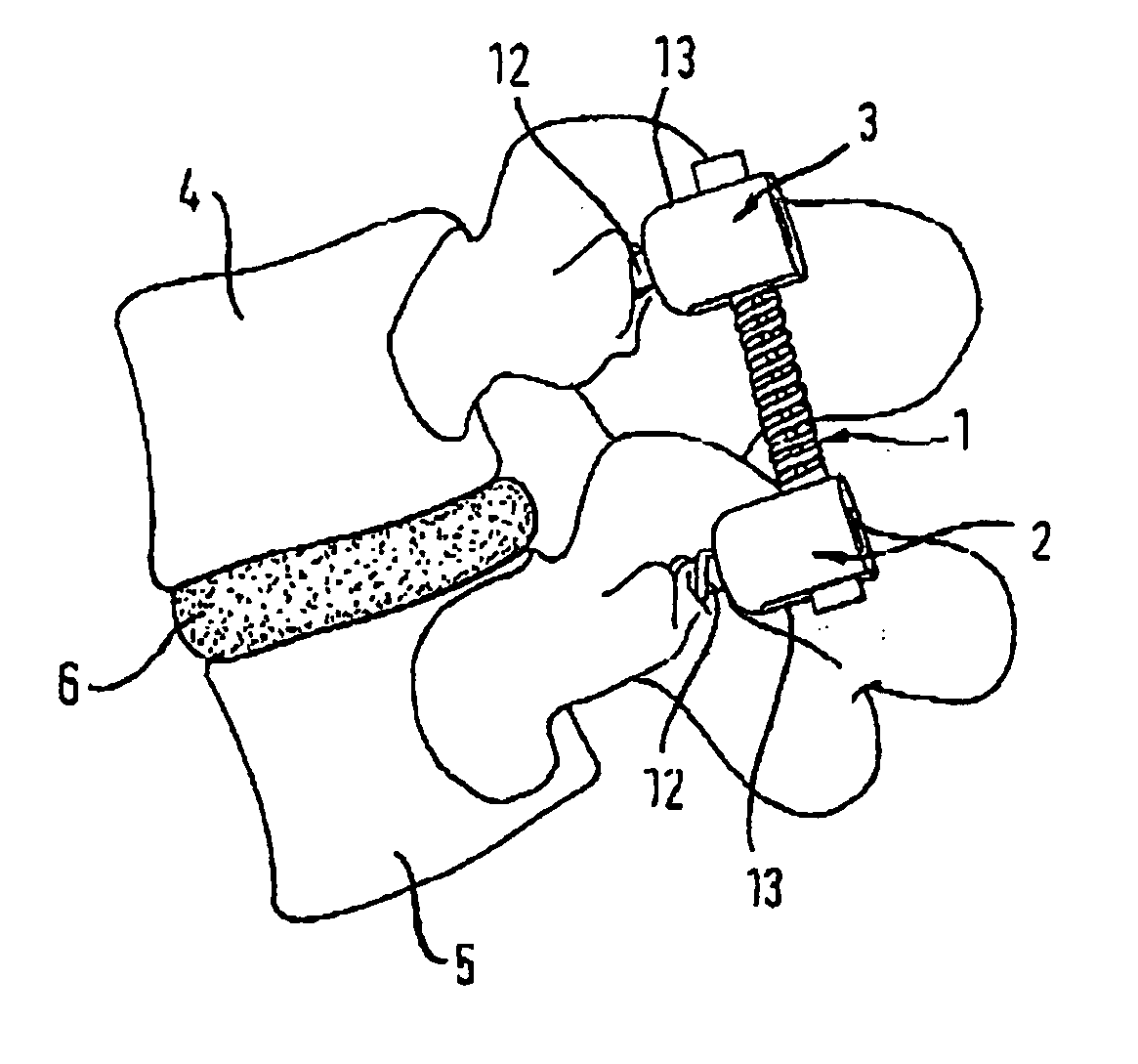
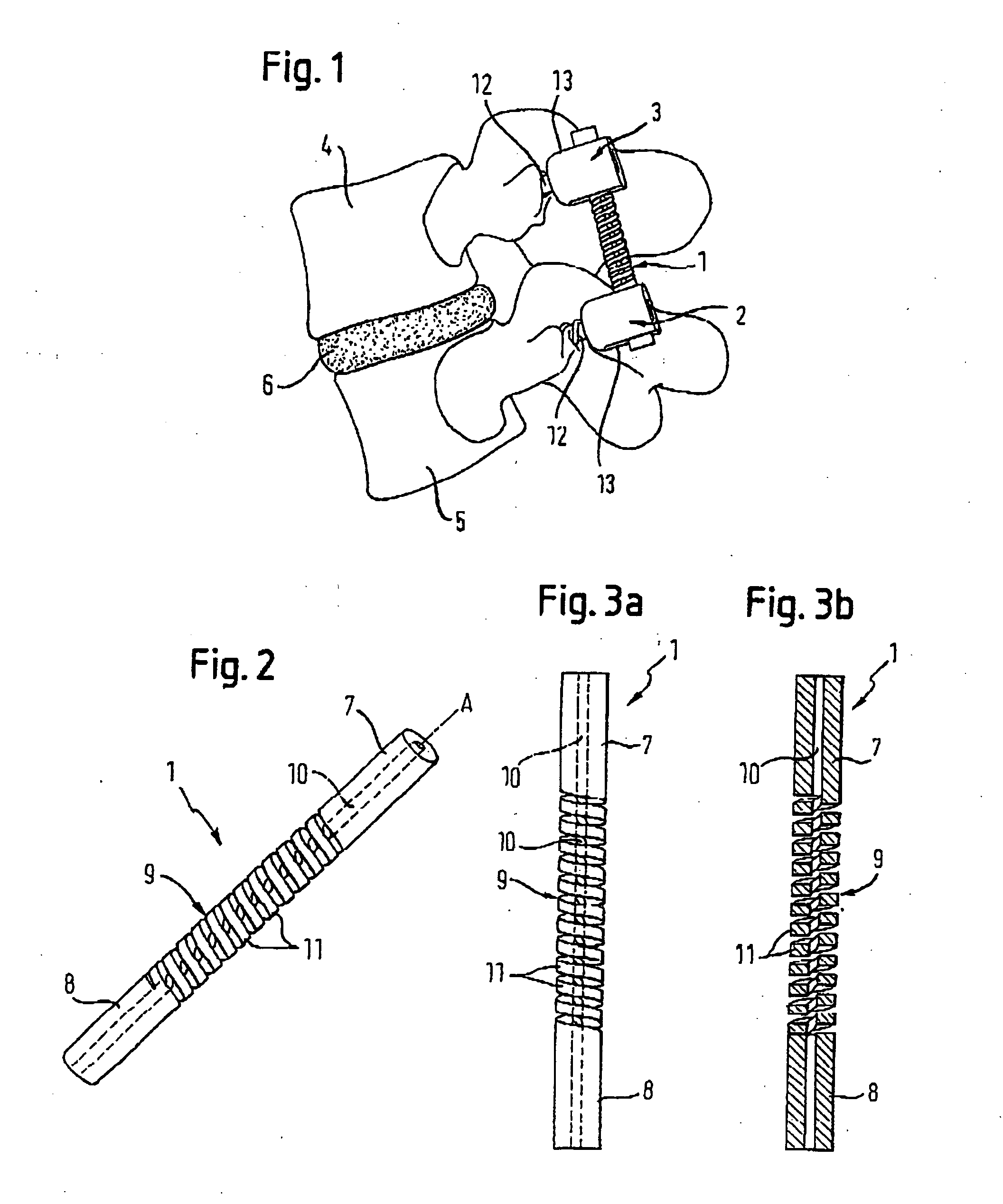
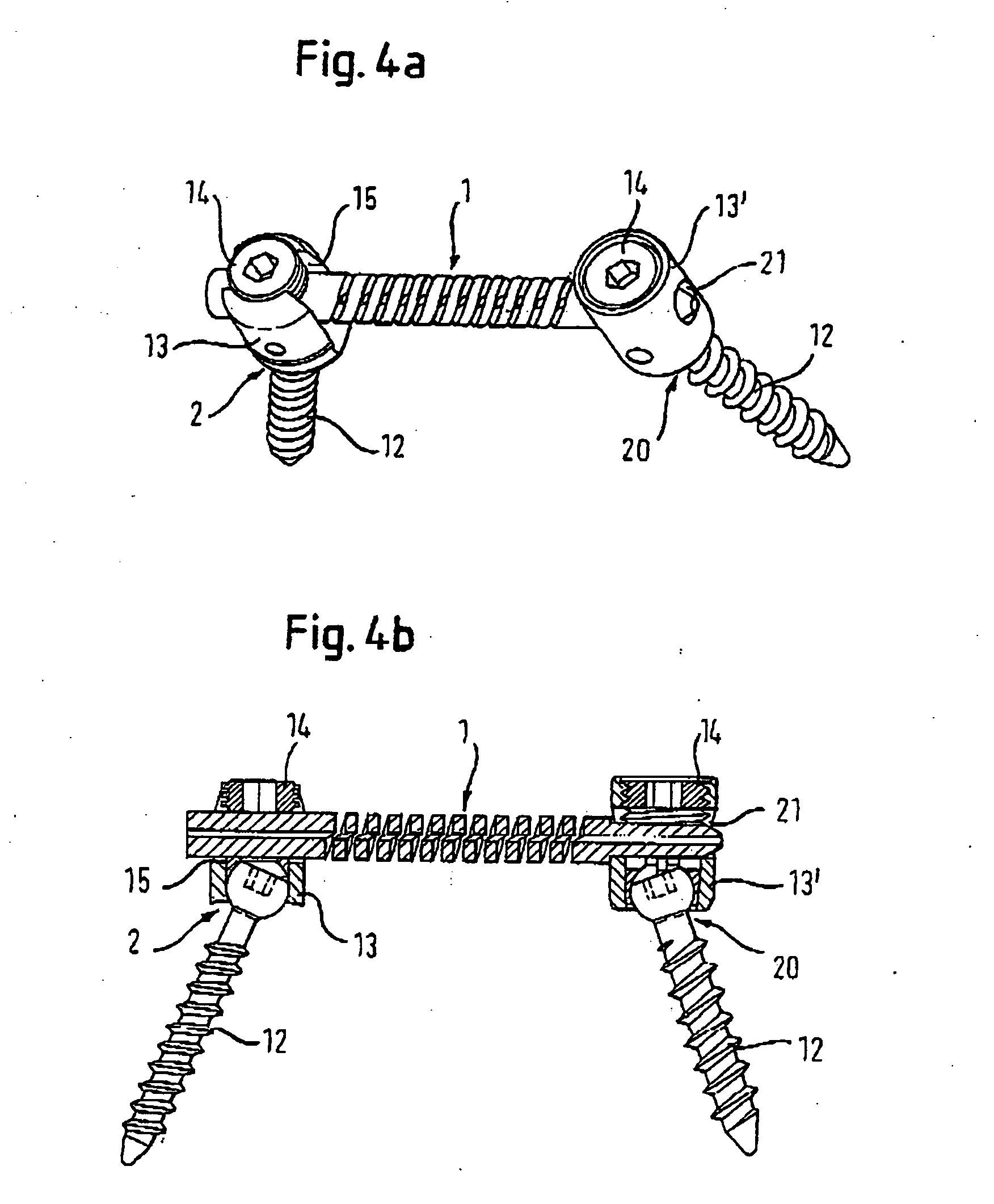
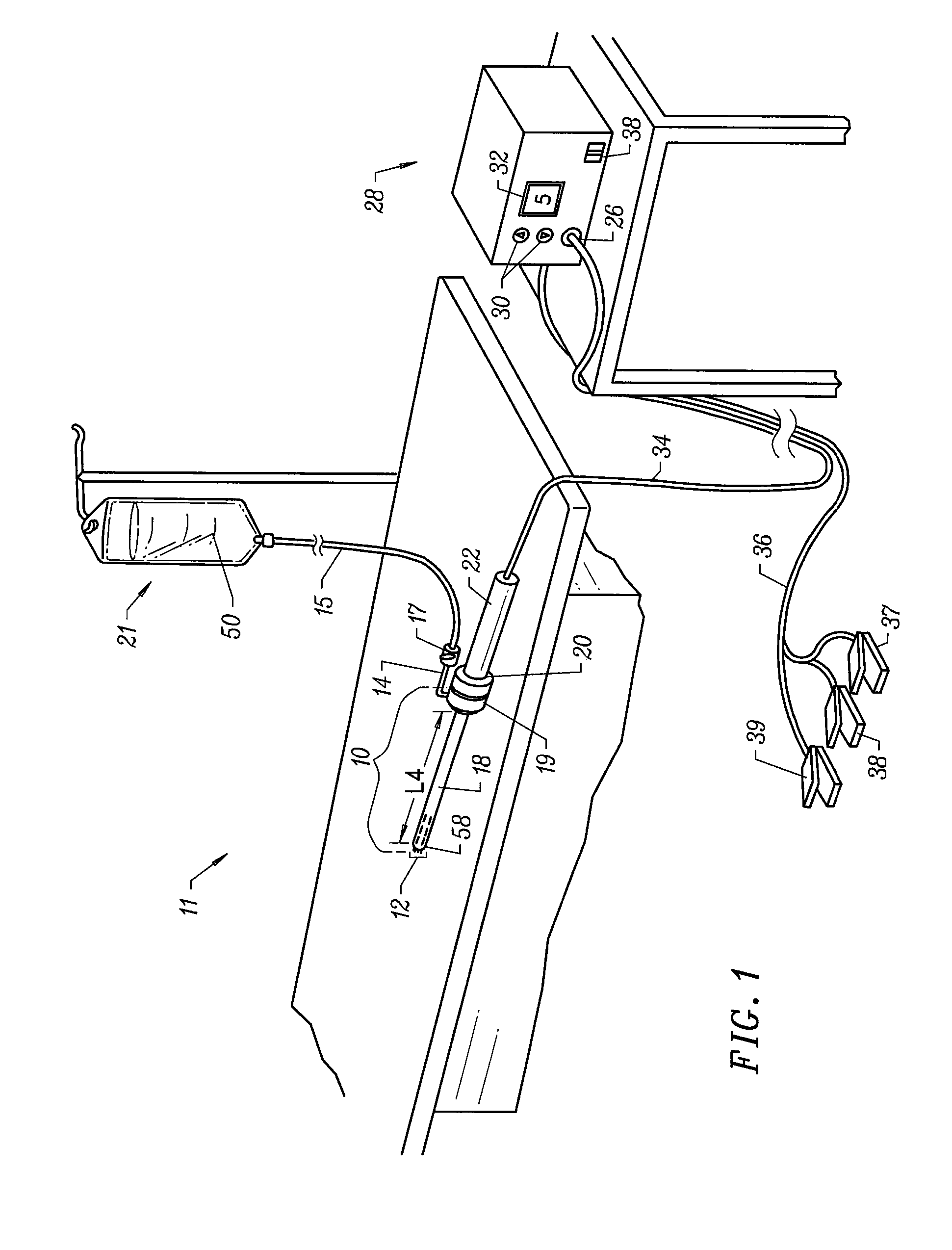
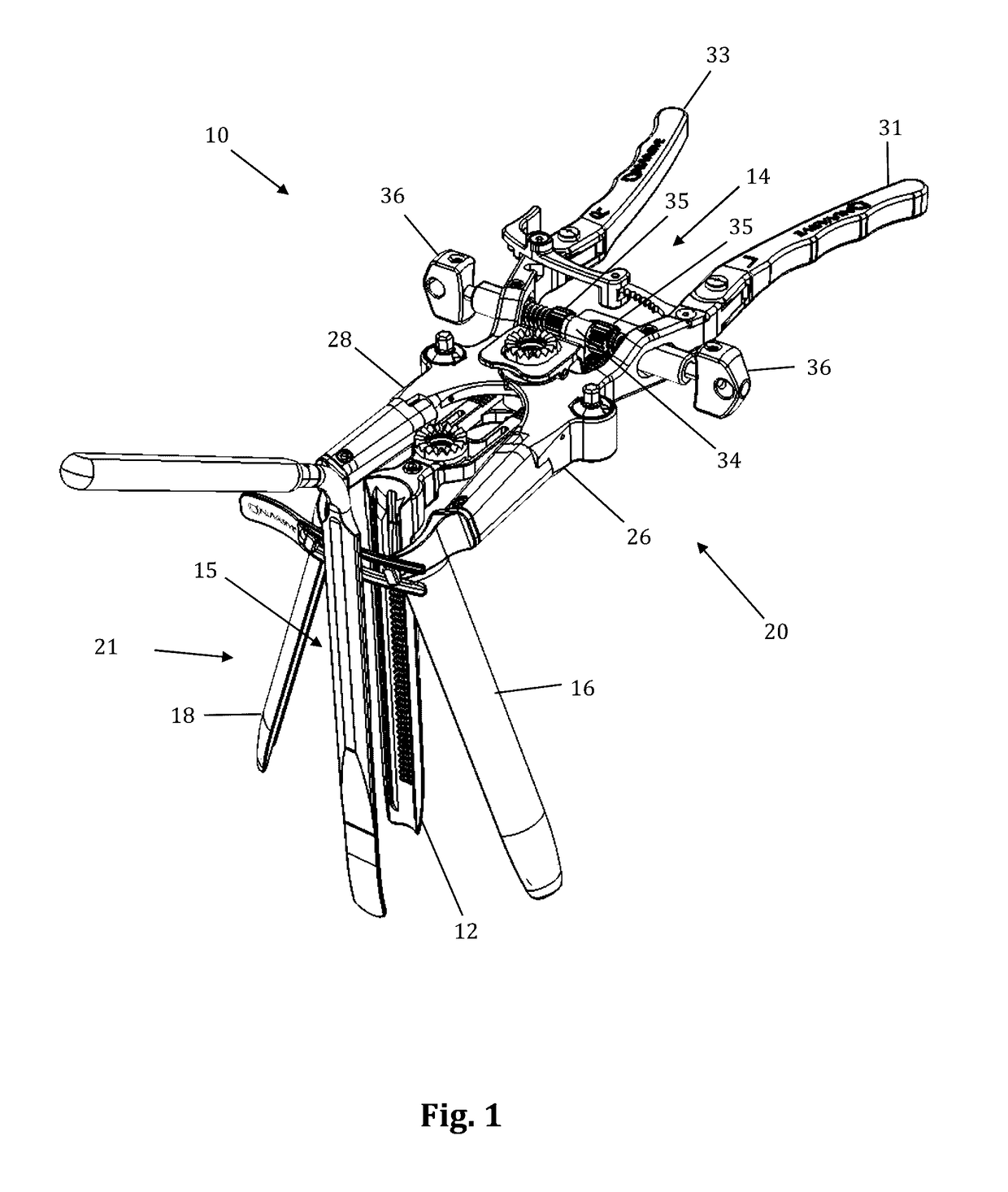
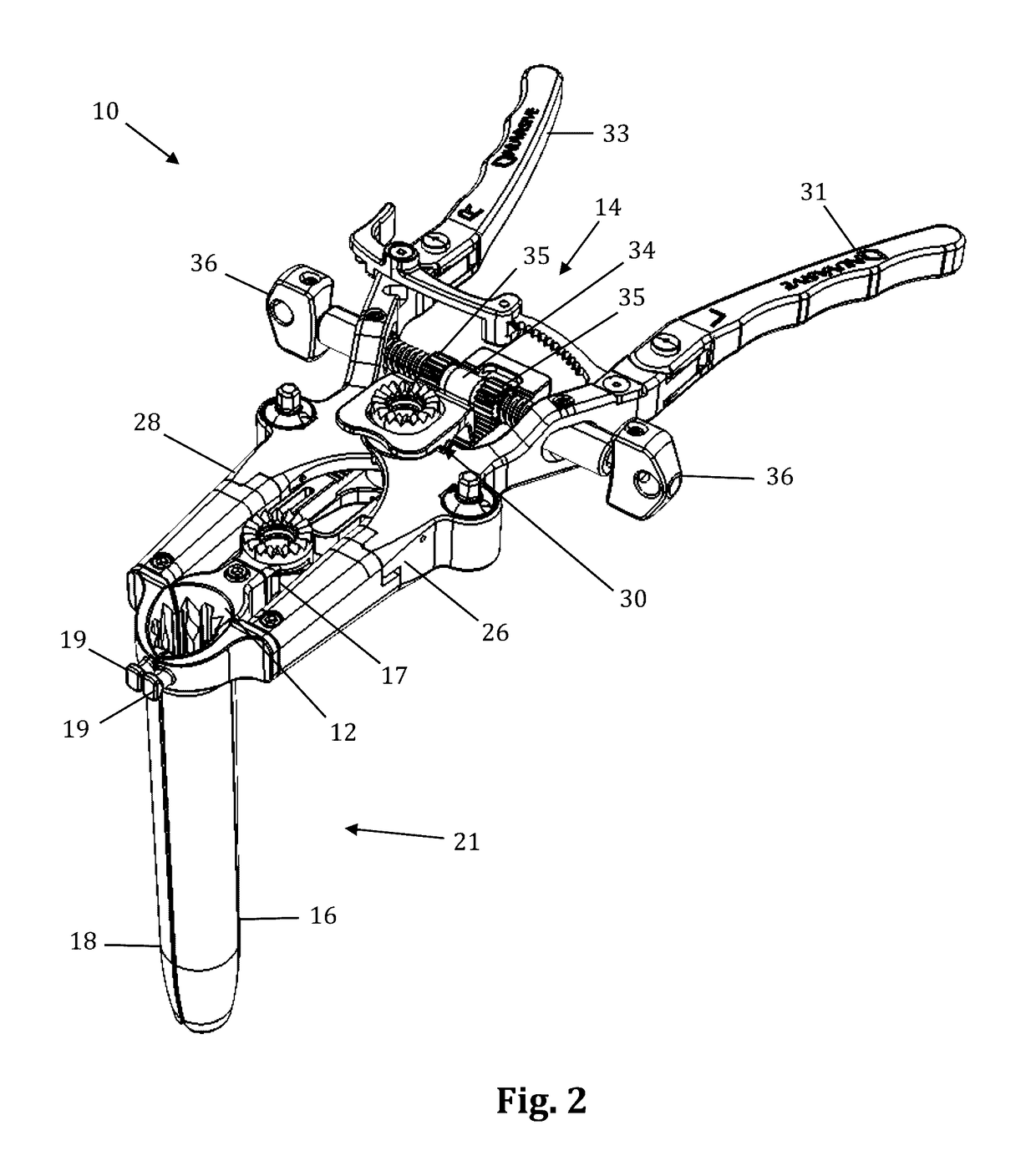
Rod-shaped implant element for application in spine surgery or trauma surgery, stabilization apparatus comprising said rod-shaped implant element, and production method for the rod-shaped implant element
ActiveUS20050085815A1Reliable fixed positioningEasily realizedSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisTrauma surgeryBone anchor
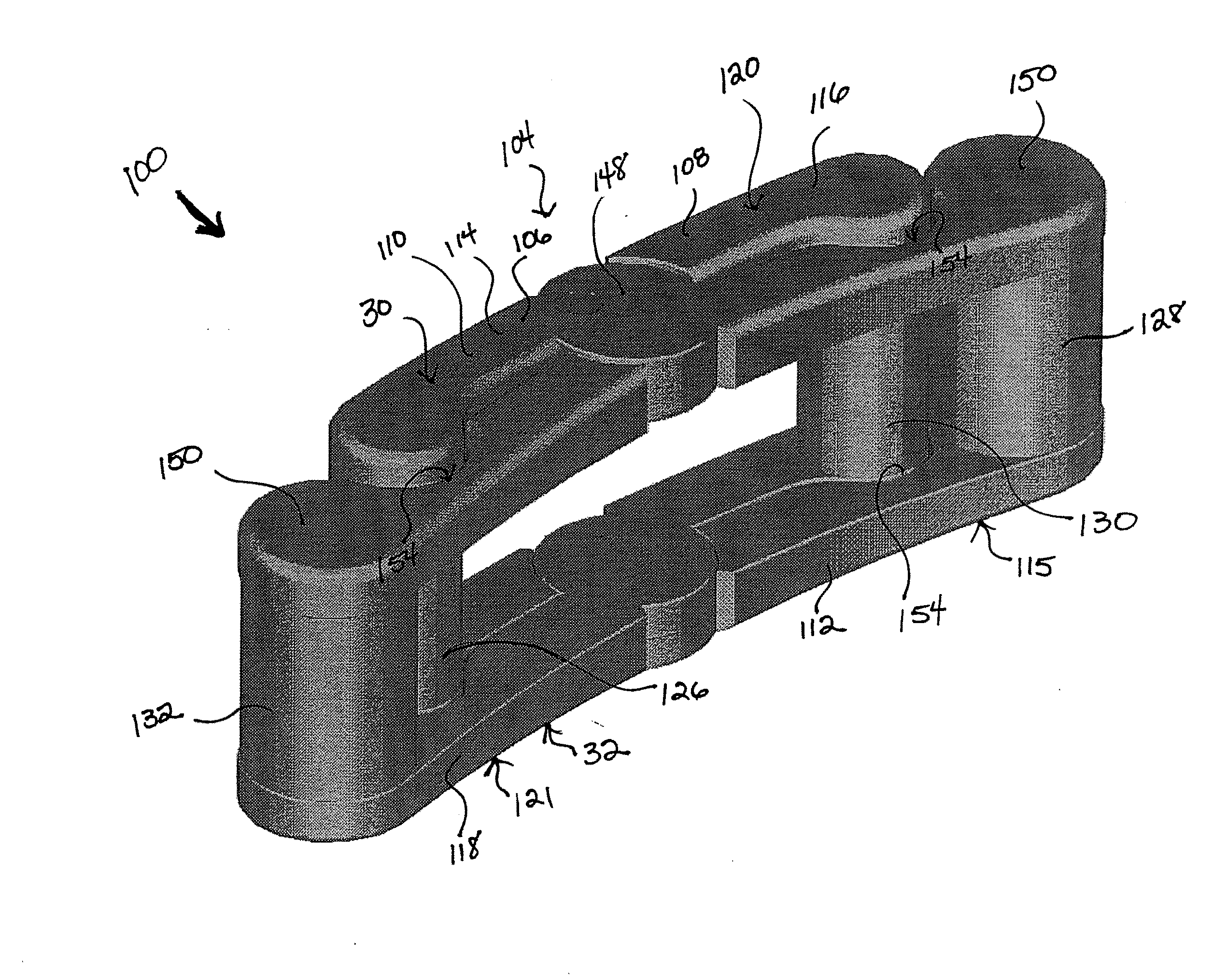
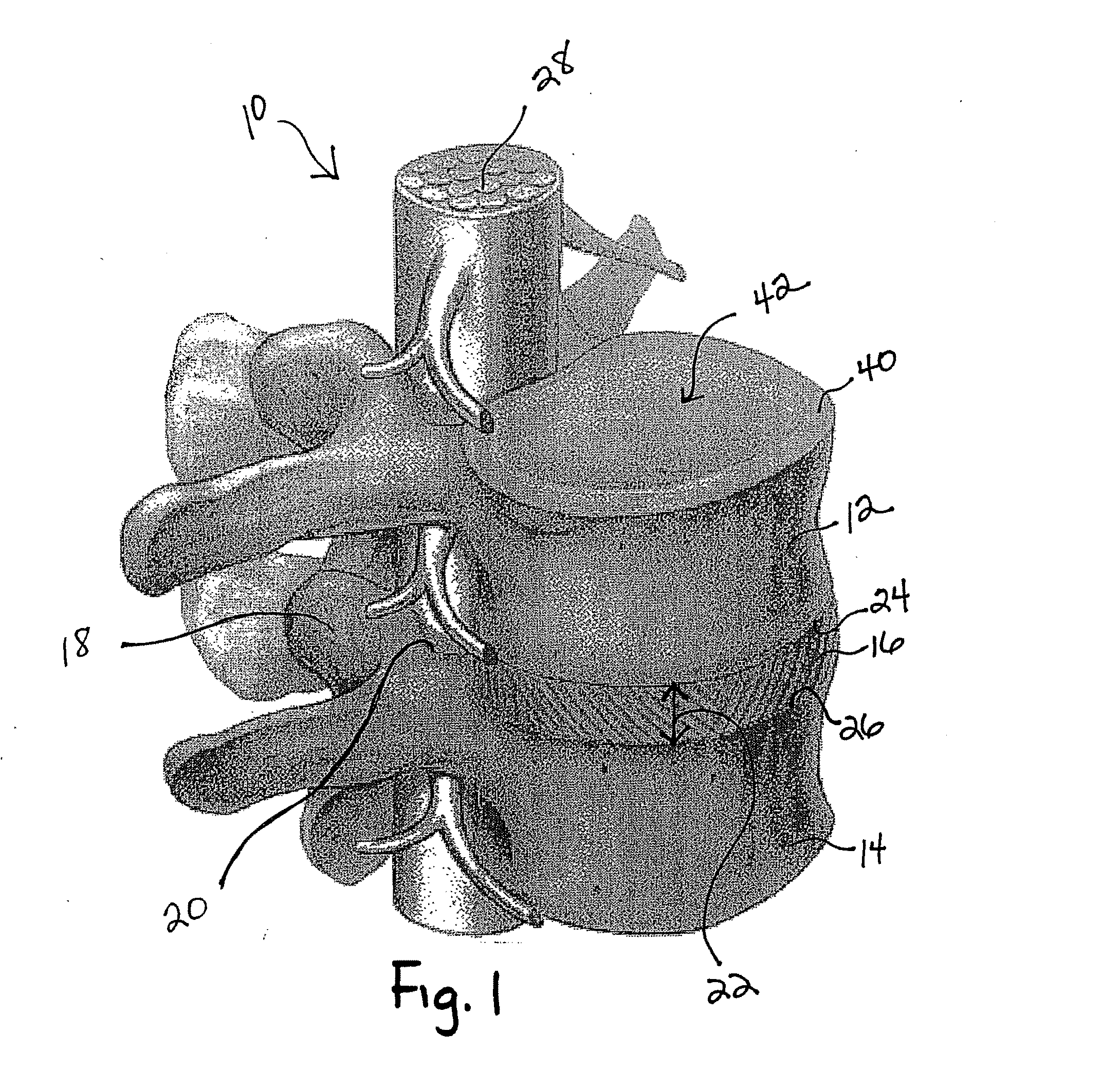
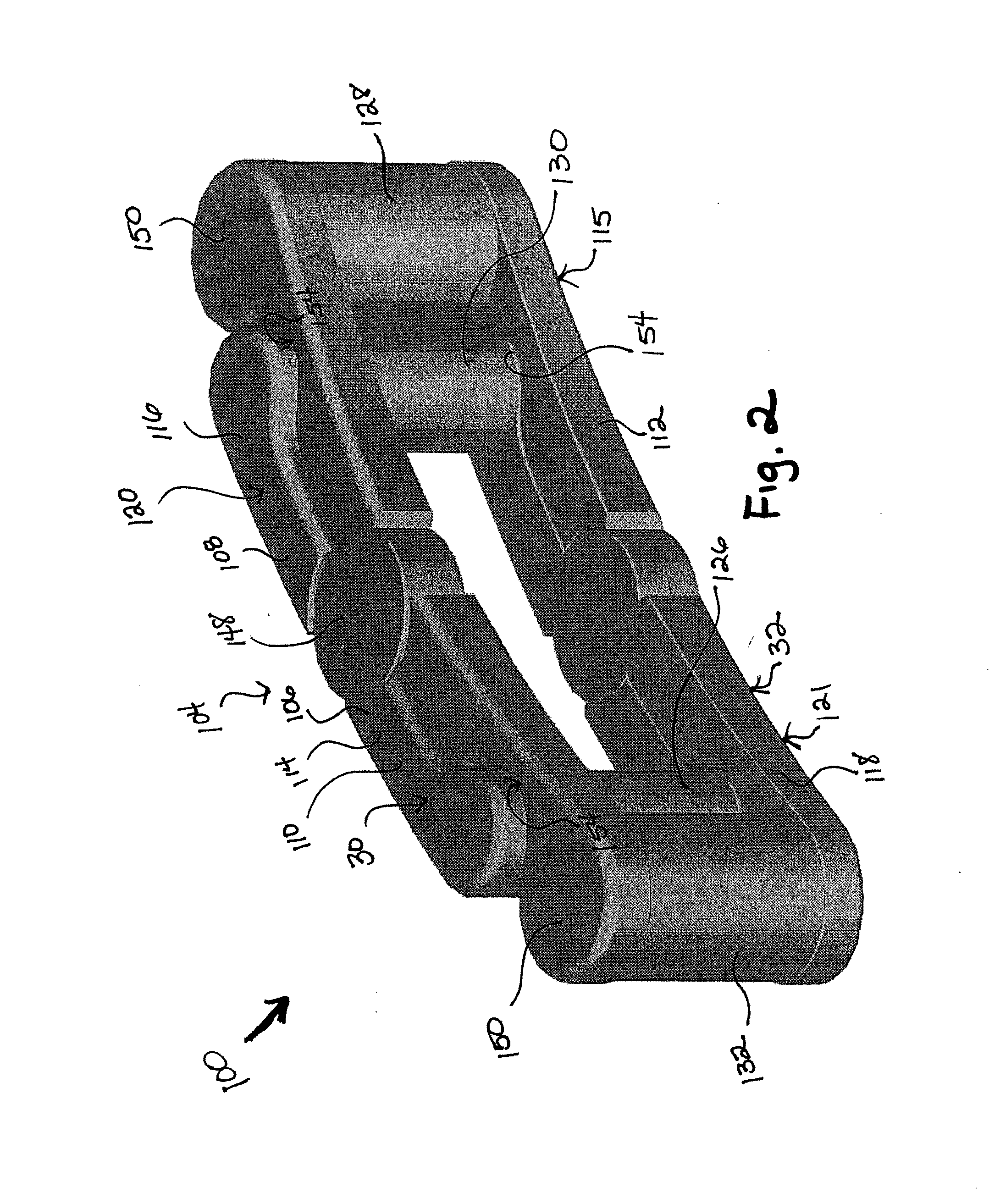
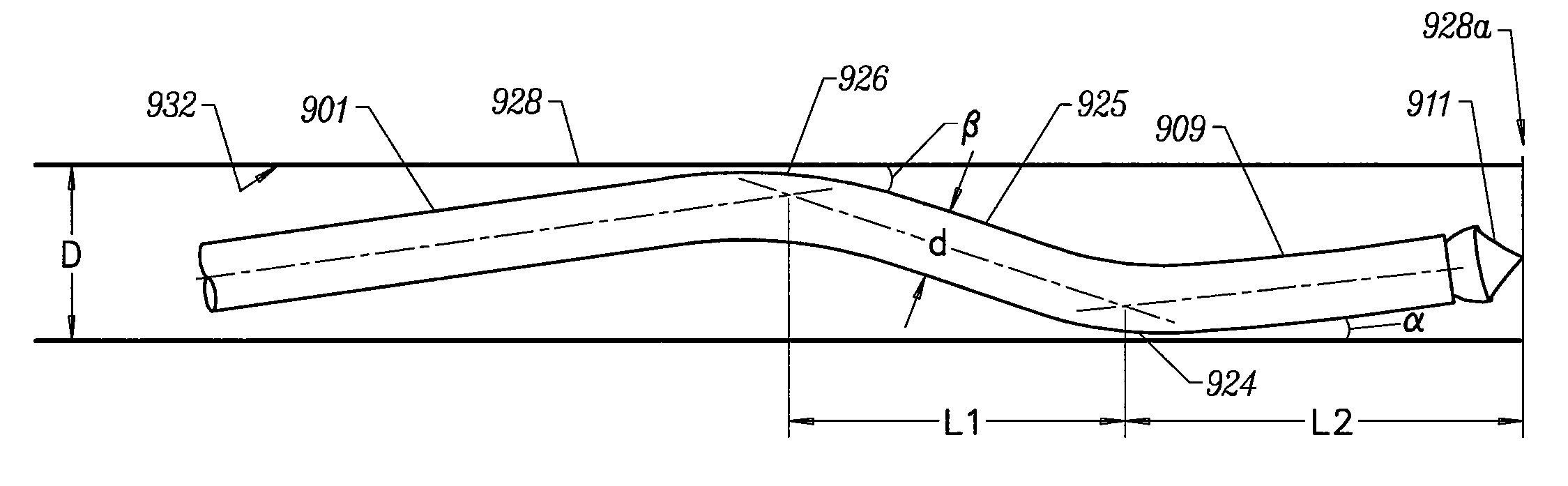
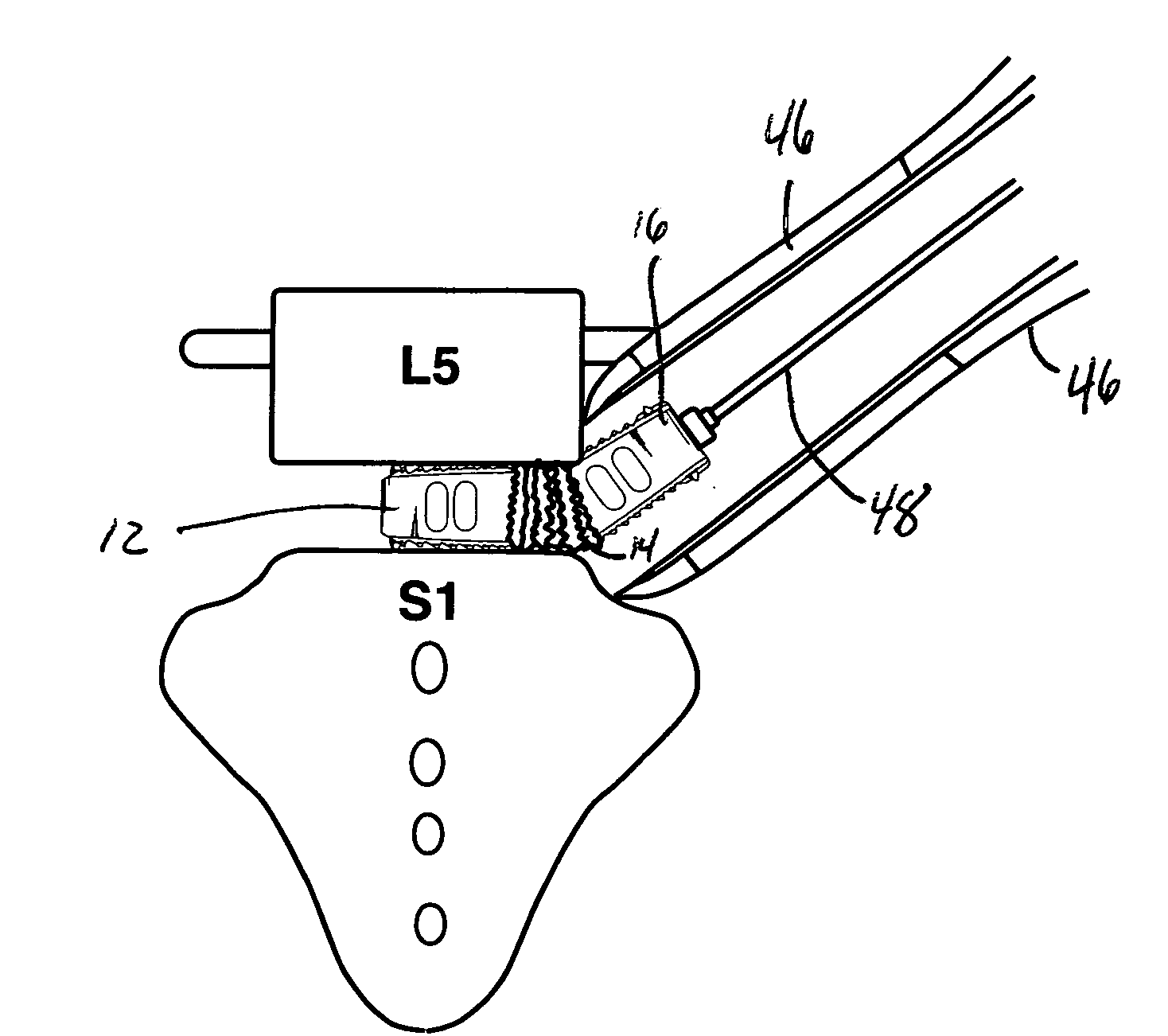
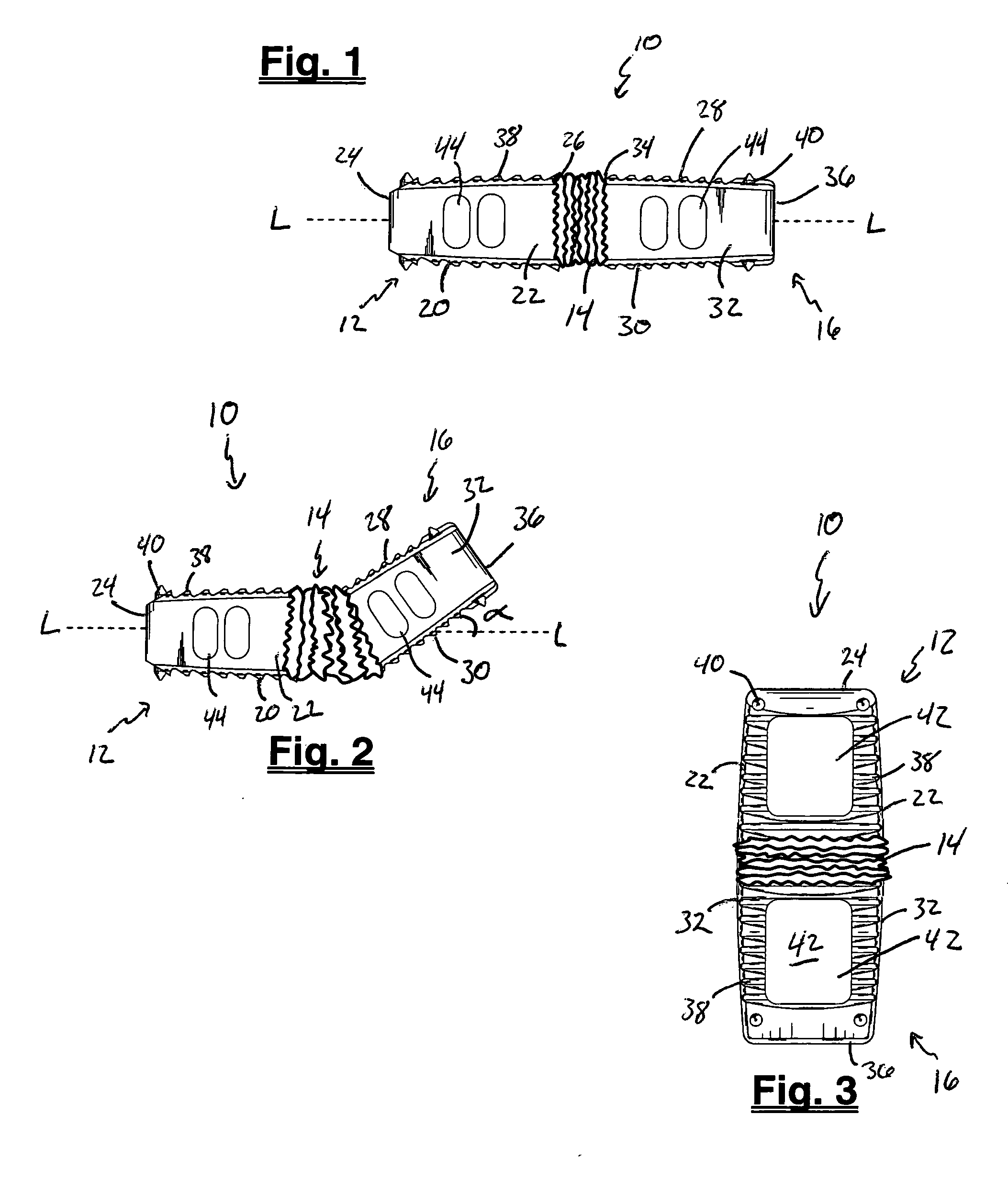
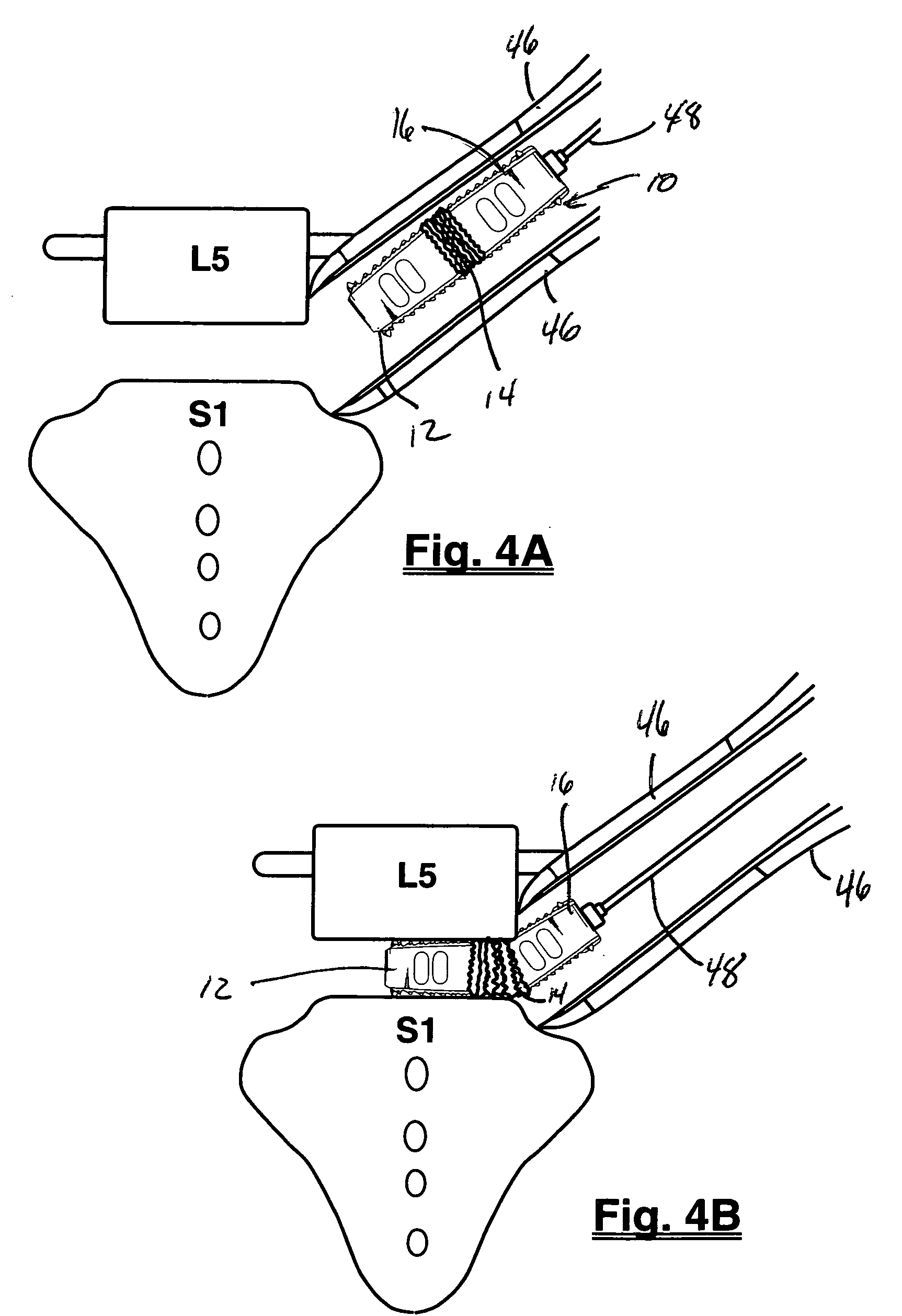
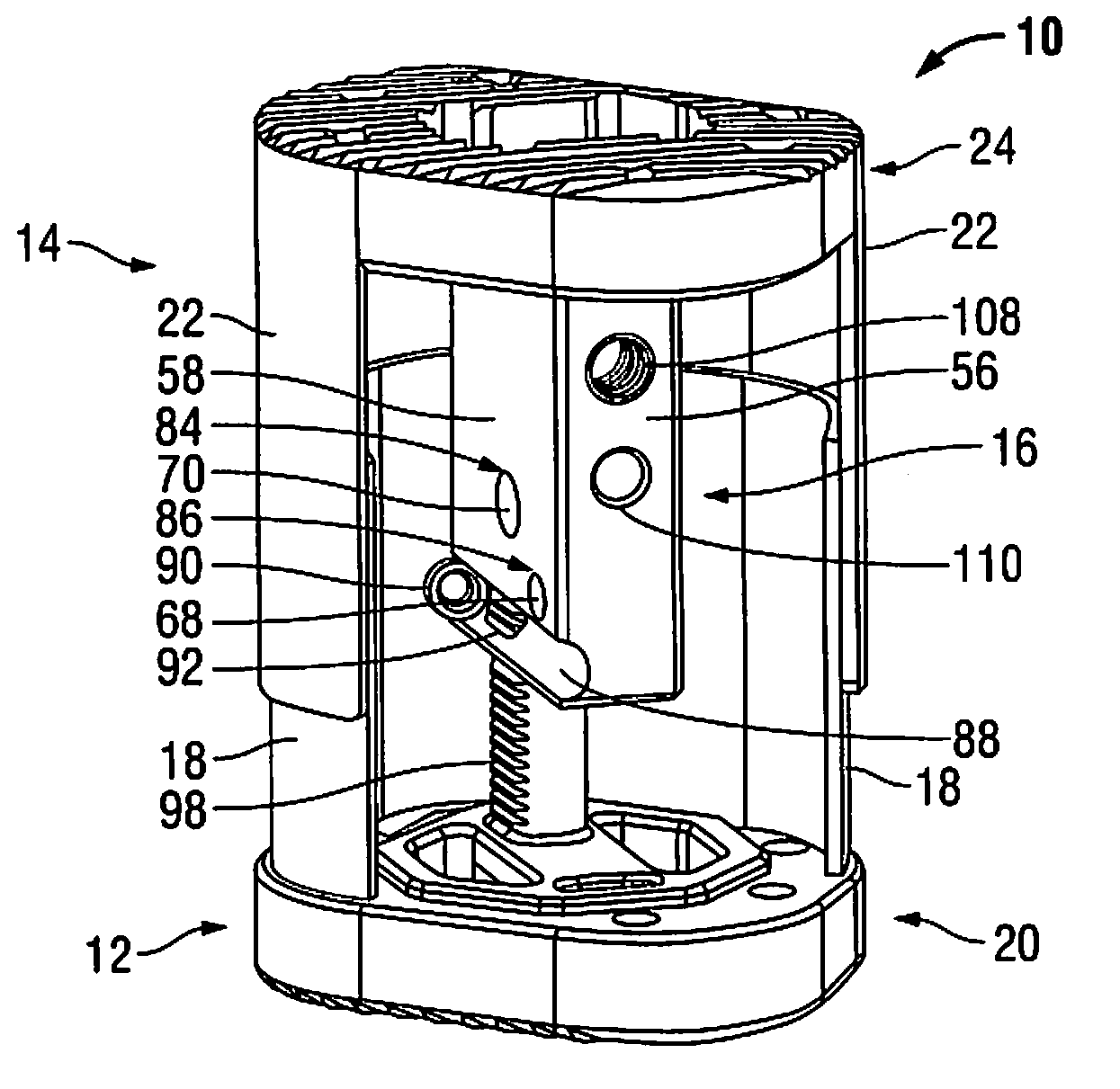
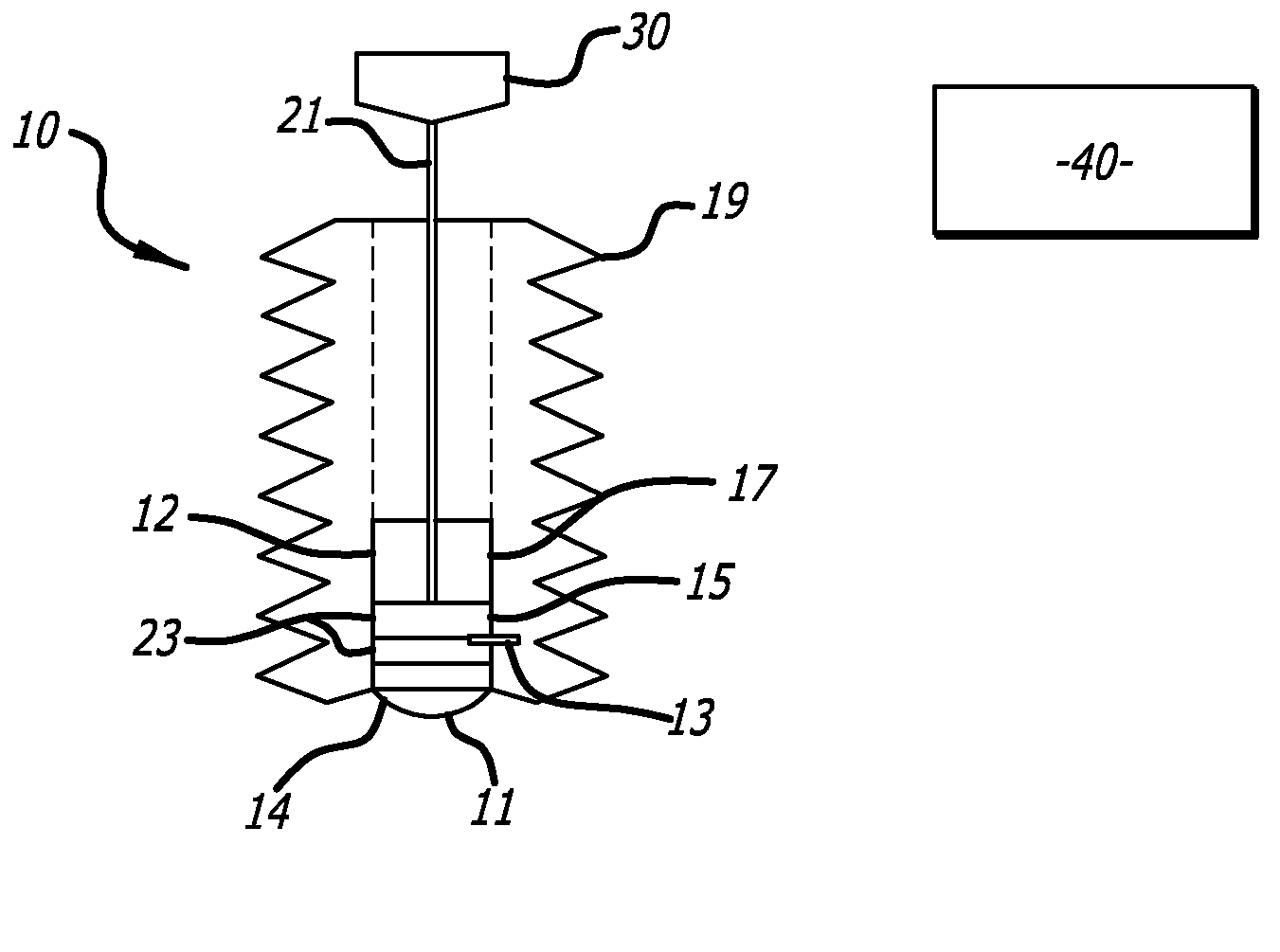
A rod-shaped implant element (1, 100, 101, 102, 300) is disclosed for the connection of bone anchoring elements, Each bone anchoring element has an anchoring section (12) to be anchored in the bone and a receiver member (13) to be connected to the rod-shaped implant element The rod-shaped implant element has at least one rigid section (7, 8) that is configured to be placed in the receiver member (13). It also has a flexible section (9, 90, 900, 902) that is adjacent to the rigid section. The flexible section and the rigid section are formed in one piece. Also disclosed is a stabilization apparatus using a rod-shaped implant element and at least two of the bone anchoring elements. The stabilization apparatus can limit the movement of two vertebrae or parts of a bone in relation to each other in a defined manner.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Methods for electrosurgical treatment of spinal tissue
InactiveUS20050004634A1Stiffening the interspinous tissue structureStabilizing the vertebral columnEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesThermal energySpinal ligaments
Systems, apparatus, and methods for treating spinal tissue and other body structures in open and endoscopic spine surgery to relieve symptoms, such as neck or back pain. In particular, the present invention provides methods for the controlled heating of various tissues in or around the vertebral column, including various interspinous tissues, such that spinal ligaments and cartilage surrounding the vertebrae and the facet joints are shrunk or tightened to stabilize the vertebral column of a patient. Thermal energy is applied to the target tissue in a subablation mode of an electrosurgical system to cause shrinkage of the tissue, thereby stiffening the interspinous tissue and stabilizing the vertebral column. In an exemplary embodiment, a high frequency RF voltage can be applied between one or more active electrode(s) and one or more return electrode(s) to heat a target interspinous tissue to within a temperature range at which irreversible shrinkage of the tissue occurs.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
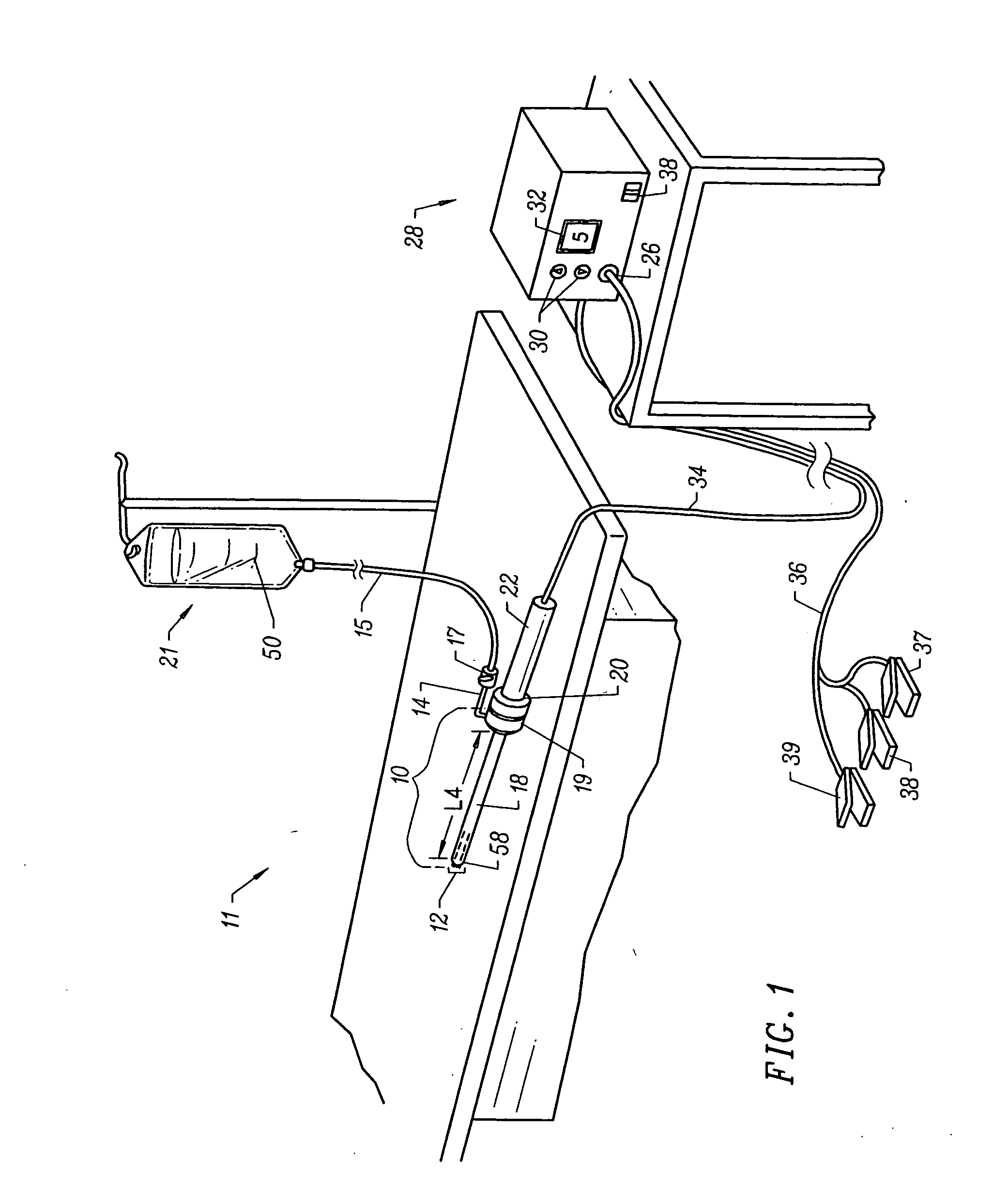
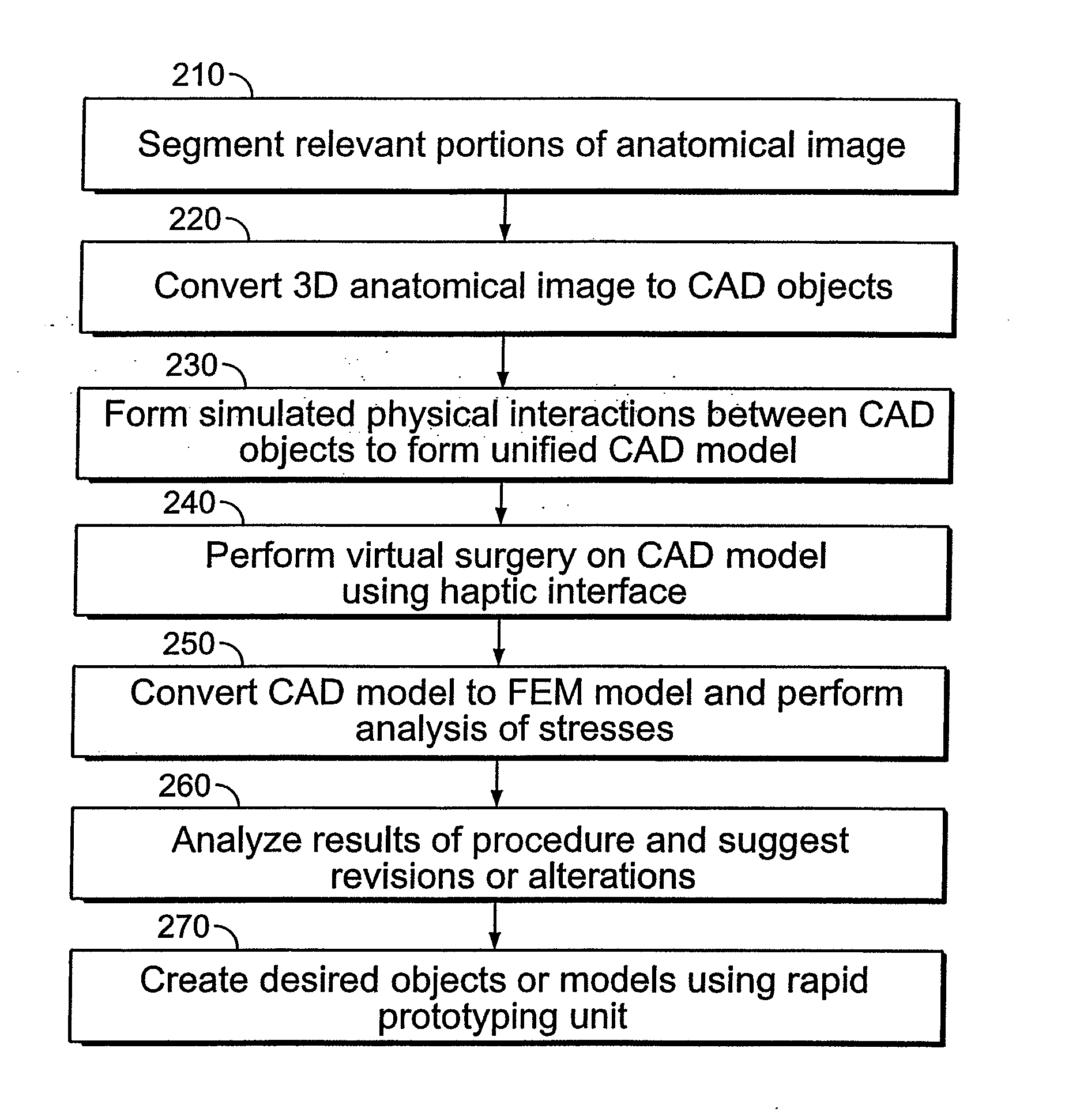
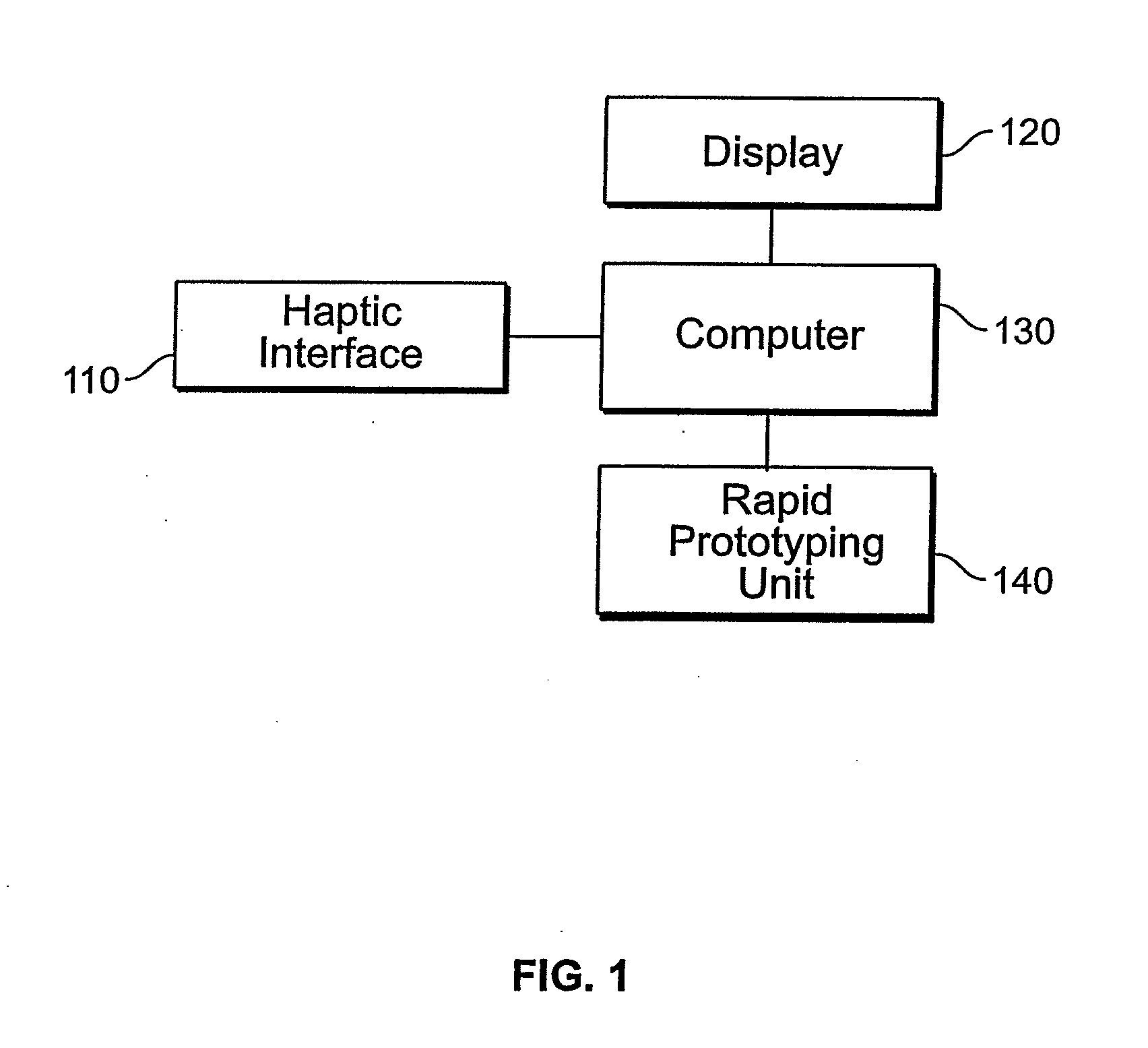
Computerized Planning Tool For Spine Surgery and Method and Device for Creating a Customized Guide for Implantations
InactiveUS20100217336A1Minimal effortMaximize accuracyMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusTouch PerceptionFinite element software
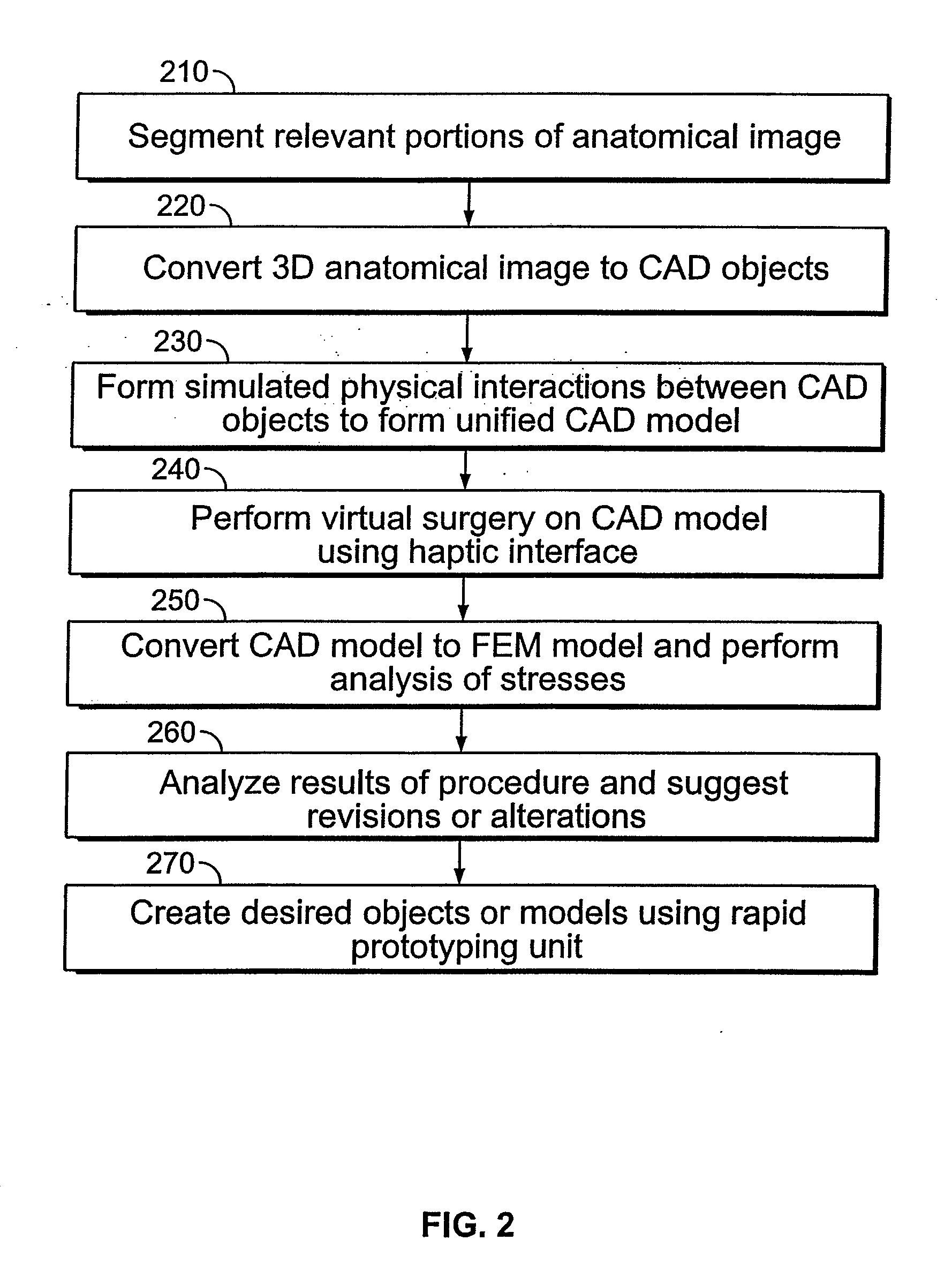
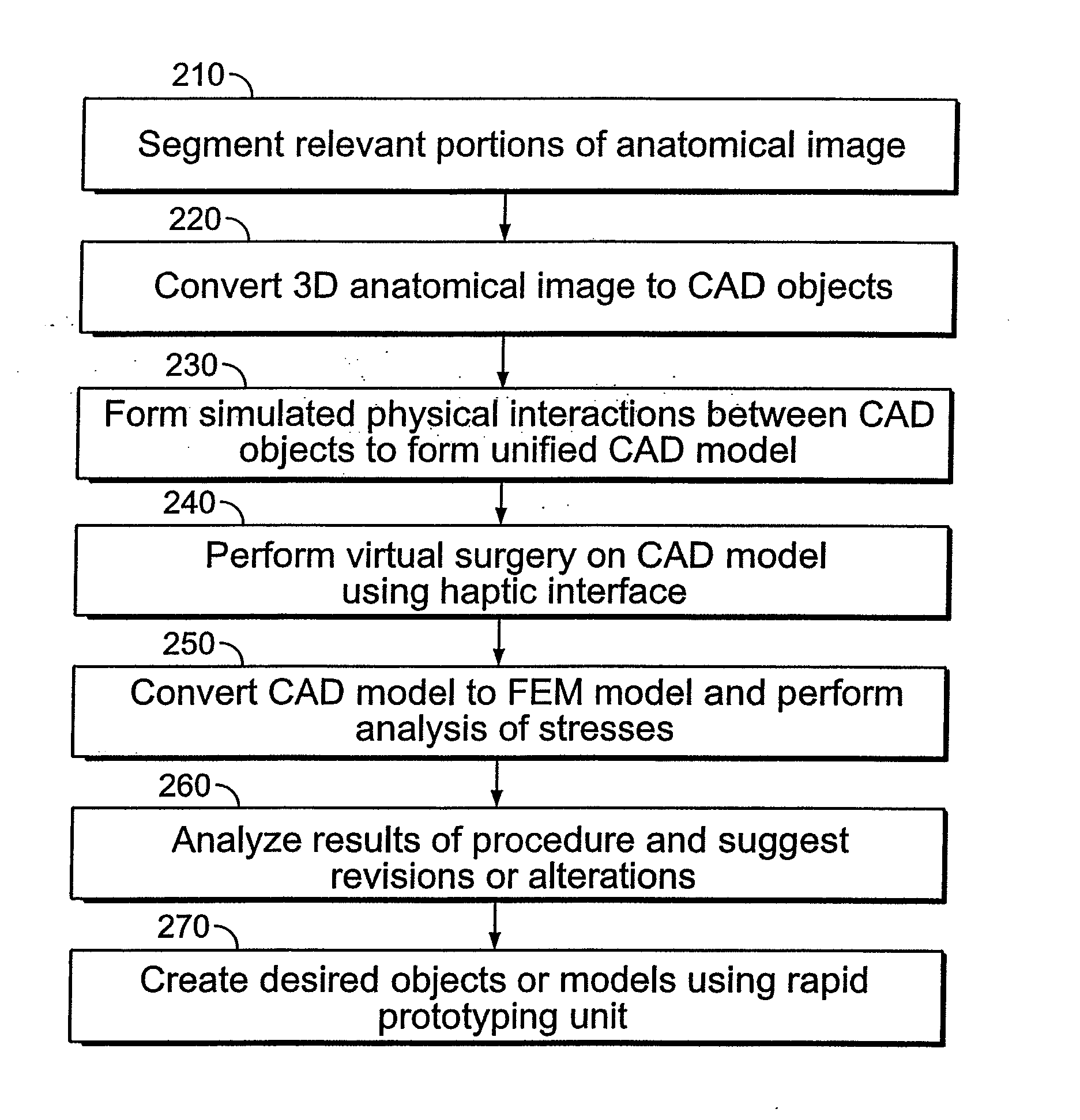
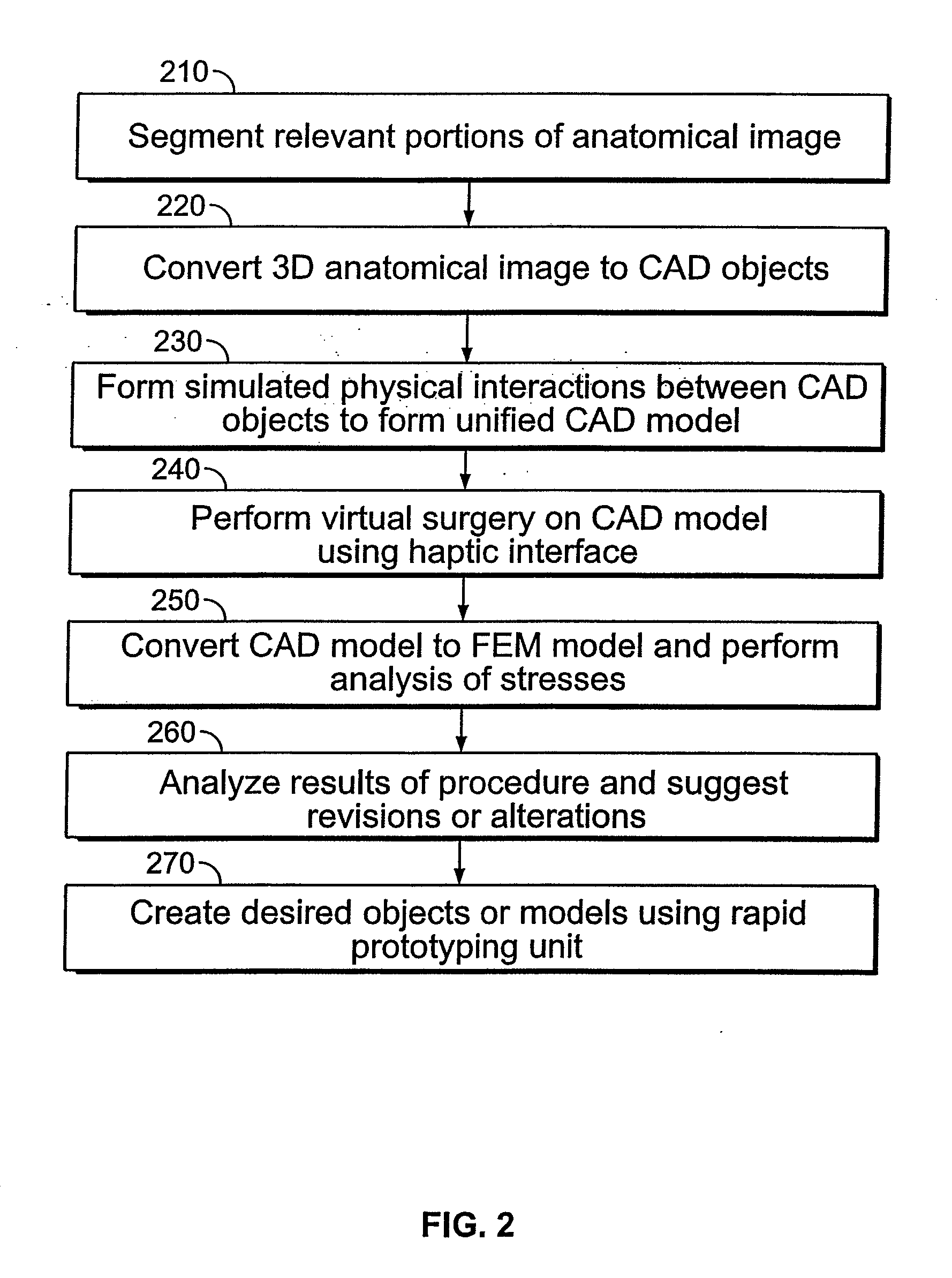
A system for planning a spine surgery, comprising a haptic interface capable of providing force feedback to the user and a computer adapted to simulate a surgical procedure by responding to inputs from the haptic interface and outputting haptic feedback to the haptic interface is provided.The system further comprising a rapid prototyping unit including a unit that is adapted to create models of the anatomical region where the surgical procedure will be performed in its current unoperated condition and in the predicted postoperative condition. Further the rapid prototyping unit is adapted to create a three dimensional guide to be used in the surgical procedure as well as suggest revisions to the surgical procedure. The system further comprises a computer that simulates loading of the spine and planned implanted hardware using finite element software.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
Spine microsurgery techniques, training aids and implants
InactiveUS7452369B2Improve securityWide range of usesInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsAnatomical structuresArticular facet
Owner:BARRY RICHARD J
Expandable vertebral device with cam lock
An expandable cage supports adjacent vertebra in spine surgery. The expandable cage includes a first supporting member configured to engage tissue and a second supporting member operatively associated with the first supporting member. The first and second supporting members are movable relative to each other. The expandable cage further includes a cam lock mechanism configured to maintain the first and second supporting members in a fixed relative position. In another embodiment, the expandable cage includes a ring plate lock mechanism in lieu of the cam lock mechanism. The ring plate lock mechanism is adapted to maintain the first and second supporting members in a fixed relative position.
Owner:K2M
Spine surgery method and implant
ActiveUS20070073398A1Large effective footprint areaMinimal requirementBone implantSpinal implantsLamina terminalisIntervertebral disk
An implant has a first contact surface to contact a first vertebral body endplate and a second contact surface to contact a second vertebral body endplate adjacent the first vertebral body. The implant is deployable, when positioned within an intradiscal space between the first and second vertebral bodies, from a first non-expanded condition where the first contact surface has a first effective footprint area A1 to a second expanded condition where the first contact surface has a second effective footprint area A2. The ratio A2 / A1 is at least 1.05.
Owner:VERTEBRATION
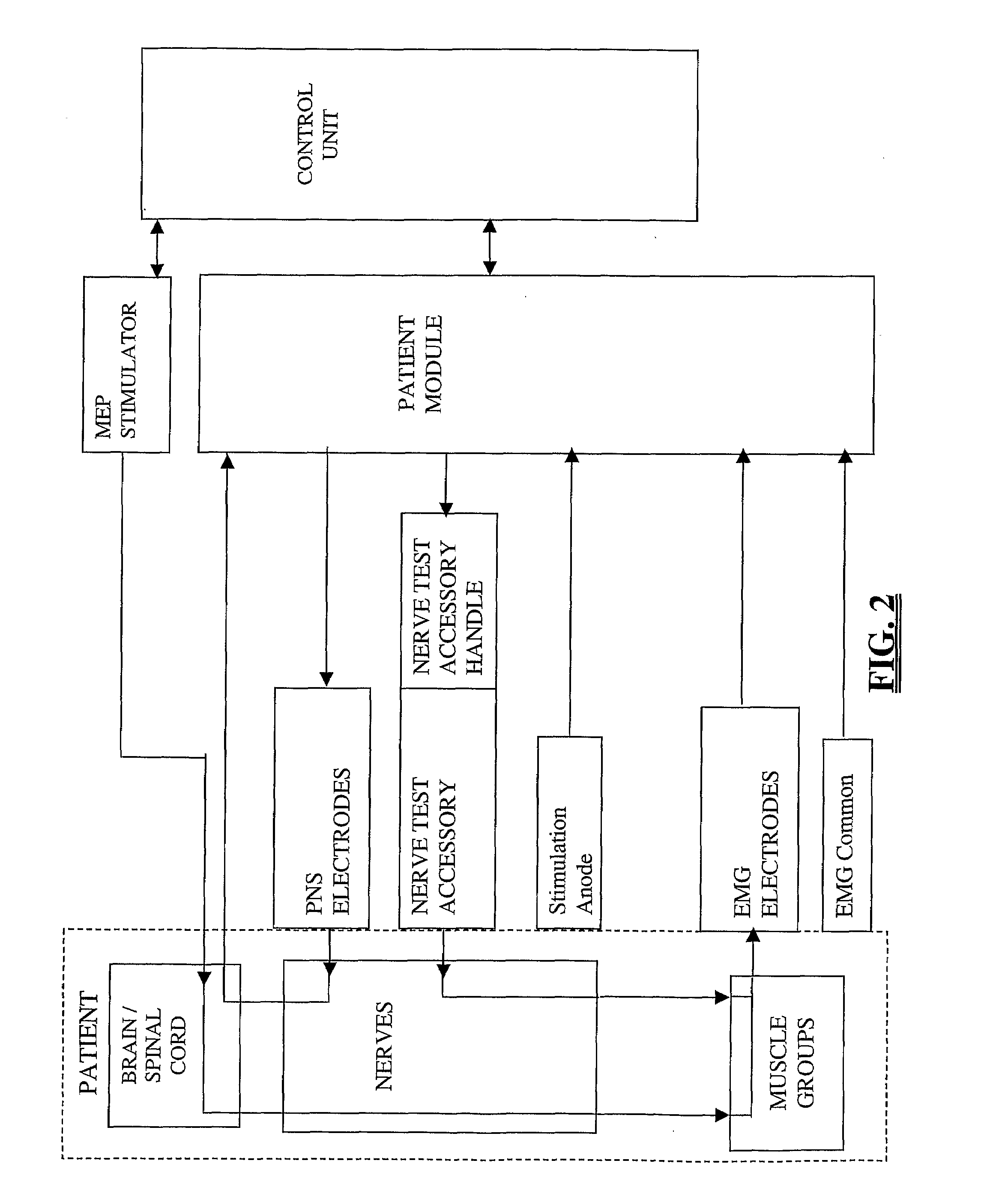
System and Methods for Performing Neurophysiologic Assessments During Spine Surgery
The present invention relates generally to an algorithm aimed at neurophysiology monitoring, and more particularly to an algorithm capable of quickly finding stimulation thresholds over multiple channels of a neurophysiology monitoring system.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Methods for electrosurgical treatment of spinal tissue
InactiveUS20060095026A1Stiffening the interspinous tissue structureStabilizing the vertebral columnEnemata/irrigatorsHeart valvesSpinal ligamentsSpinal column
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Spine surgery method and implant
ActiveUS20130310939A1Maximizing boney ingrowth surface areaMaximizing bone graft-host contactBone implantSpinal implantsBiomedical engineeringSpine surgery
An implant has a first contact surface to contact a first vertebral body endplate and a second contact surface to contact a second vertebral body endplate adjacent the first vertebral body. The implant is deployable, when positioned within an intradiscal space between the first and second vertebral bodies, from a first non-expanded condition where the first contact surface has a first effective footprint area A1 to a second expanded condition where the first contact surface has a second effective footprint area A2. The ratio A2 / A1 is at least 1.05.
Owner:FABIAN HENRY F +1
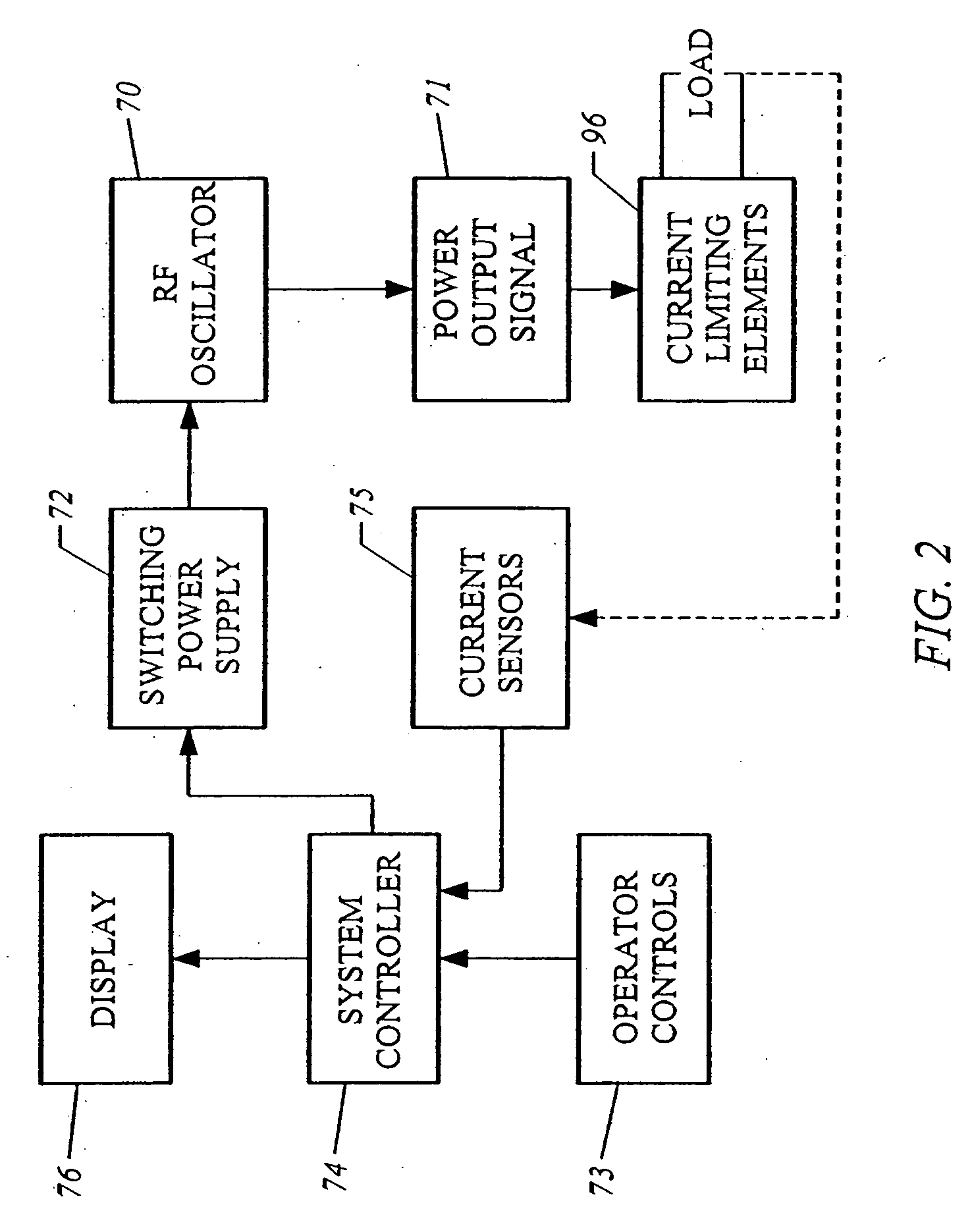
Systems and methods for electrosurgical spine surgery
InactiveUS7462178B2Lower the volumeUse performanceSurgical needlesEndoscopesSpinal cordSurgical department
Methods and apparatus for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the spine. In a method of the invention high frequency (RF) electrical energy is applied to one or more active electrodes on an electrosurgical probe in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to remove, contract or otherwise modify the structure of tissue targeted for treatment. In one aspect, a dura mater and spinal cord are insulated from the electrical energy by an insulator positioned on a non-active side of the probe. In another aspect, a plasma is aggressively formed in the electrically conductive fluid by delivering a conductive fluid to a distal end portion of the probe and aspirating the fluid from a location proximal of the return electrode. In another aspect, a distal end of an electrosurgical probe having at least one electrode on a biased, curved, bent, or steerable shaft is guided or steered to a target site within an intervertebral disc having a disc defect for treatment of tissue to be treated at the target site by the selective application of electrical energy thereto.
Owner:AOL LLC A DELAWARE LLC +1
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
This invention relates generally to spine surgery and, in particular, to methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Systems and methods for electrosurgical spine surgery
InactiveUS20080004615A1Lower the volumeUse performanceSurgical needlesEndoscopesSpinal cordSurgical department
Owner:AOL LLC A DELAWARE LLC +1
Spinal Surgical Implant and Related Methods
This invention relates generally to spine surgery and, in particular, to a surgical implant for separating adjacent spinal vertebrae.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Expandable vertebral device with cam lock
An expandable cage supports adjacent vertebra in spine surgery. The expandable cage includes a first supporting member configured to engage tissue and a second supporting member operatively associated with the first supporting member. The first and second supporting members are movable relative to each other. The expandable cage further includes a cam lock mechanism configured to maintain the first and second supporting members in a fixed relative position. In another embodiment, the expandable cage includes a ring plate lock mechanism in lieu of the cam lock mechanism. The ring plate lock mechanism is adapted to maintain the first and second supporting members in a fixed relative position.
Owner:K2M
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
ActiveUS20070093825A1Prevents and minimizes riskOvercomes drawbackInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal stenosisRadiology
This invention relates generally to spine surgery and, in particular, to methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis.
Owner:NUVASIVE
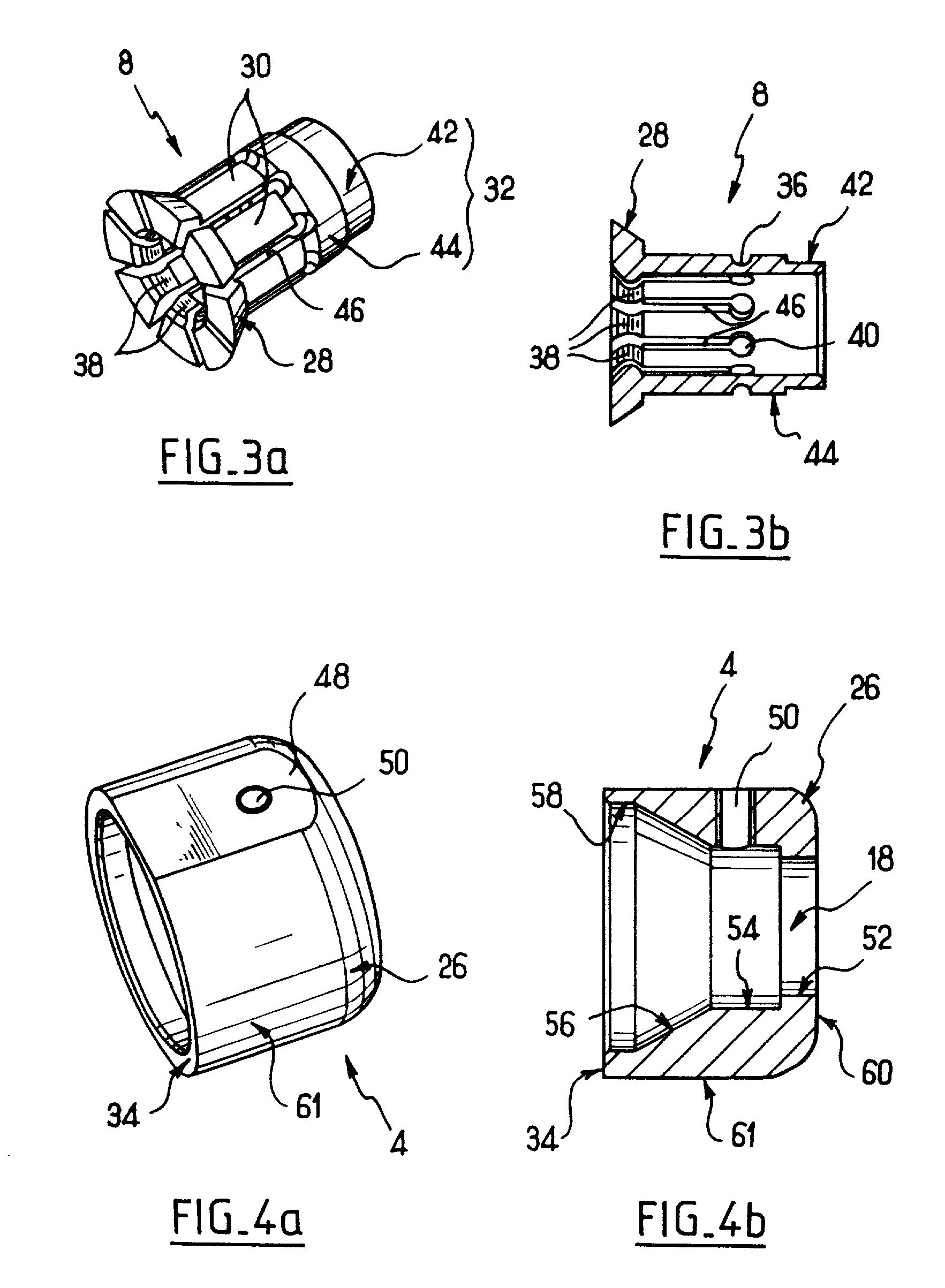
Spine cutter
ActiveUS20100292700A1Avoid disadvantagesDurable and resistantOsteosynthesis devicesBiomedical engineeringSpine surgery
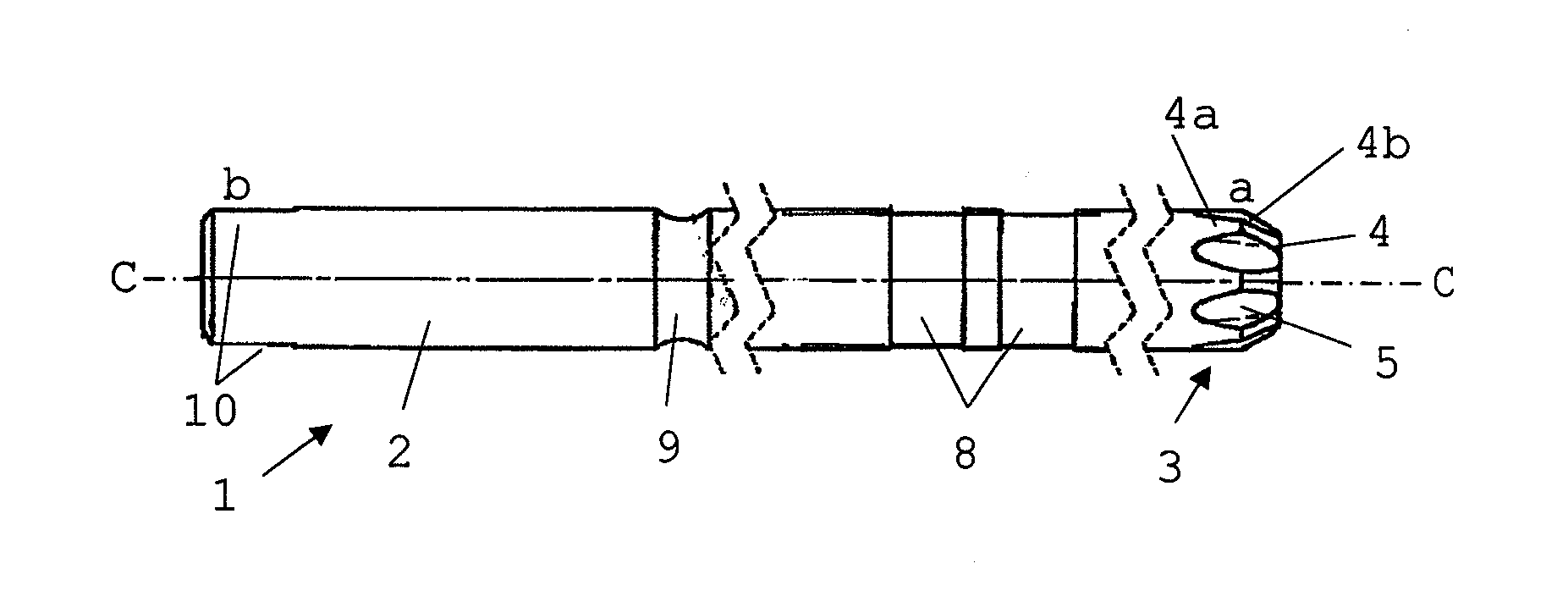
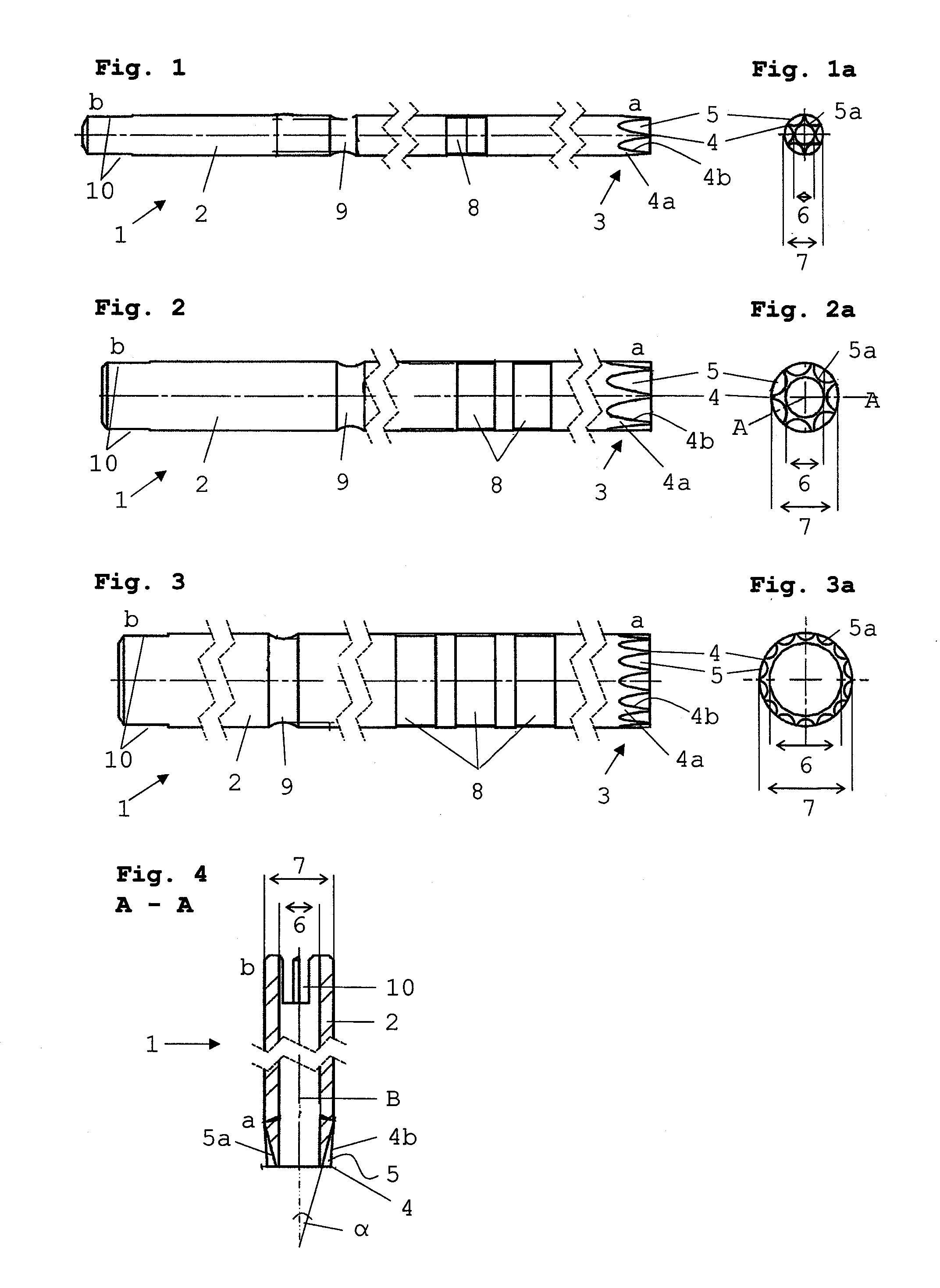
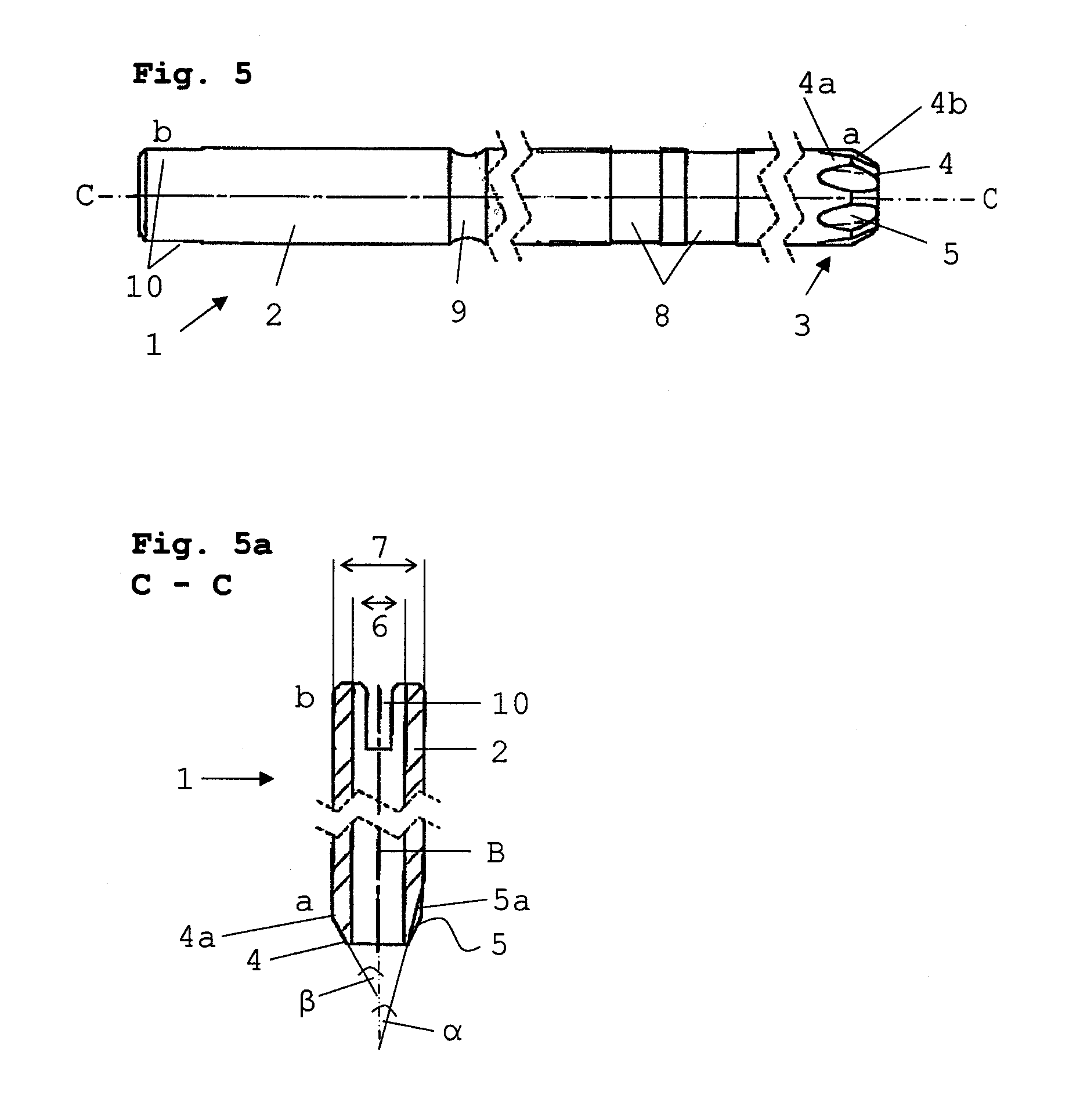
A cutter for spine surgery is provided, especially for use in the area of the delicate cervical spine. The cutter includes a cylindrical cutter shank with cutter teeth formed at the distal end thereof. The cutter teeth at the distal end of the cutter shank are formed by grooves in the wall of the cutter shank. The grooves become deeper and expand from the outer radius of the cutter shank towards the distal end such that teeth narrowing towards the distal end with increasing height are formed between them. This guarantees especially gentle cutting in the area of the cervical spine, without surrounding delicate tissue being additionally jeopardized.
Owner:JOIMAX GMBH
Computerized Planning Tool For Spine Surgery and Method and Device for Creating a Customized Guide for Implantations
InactiveUS20120150243A9Minimal effortMaximize accuracyMedical simulationAdditive manufacturing apparatusTouch PerceptionFinite element software
A system for planning a spine surgery, comprising a haptic interface capable of providing force feedback to the user and a computer adapted to simulate a surgical procedure by responding to inputs from the haptic interface and outputting haptic feedback to the haptic interface is provided.The system further comprising a rapid prototyping unit including a unit that is adapted to create models of the anatomical region where the surgical procedure will be performed in its current unoperated condition and in the predicted postoperative condition. Further the rapid prototyping unit is adapted to create a three dimensional guide to be used in the surgical procedure as well as suggest revisions to the surgical procedure. The system further comprises a computer that simulates loading of the spine and planned implanted hardware using finite element software.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
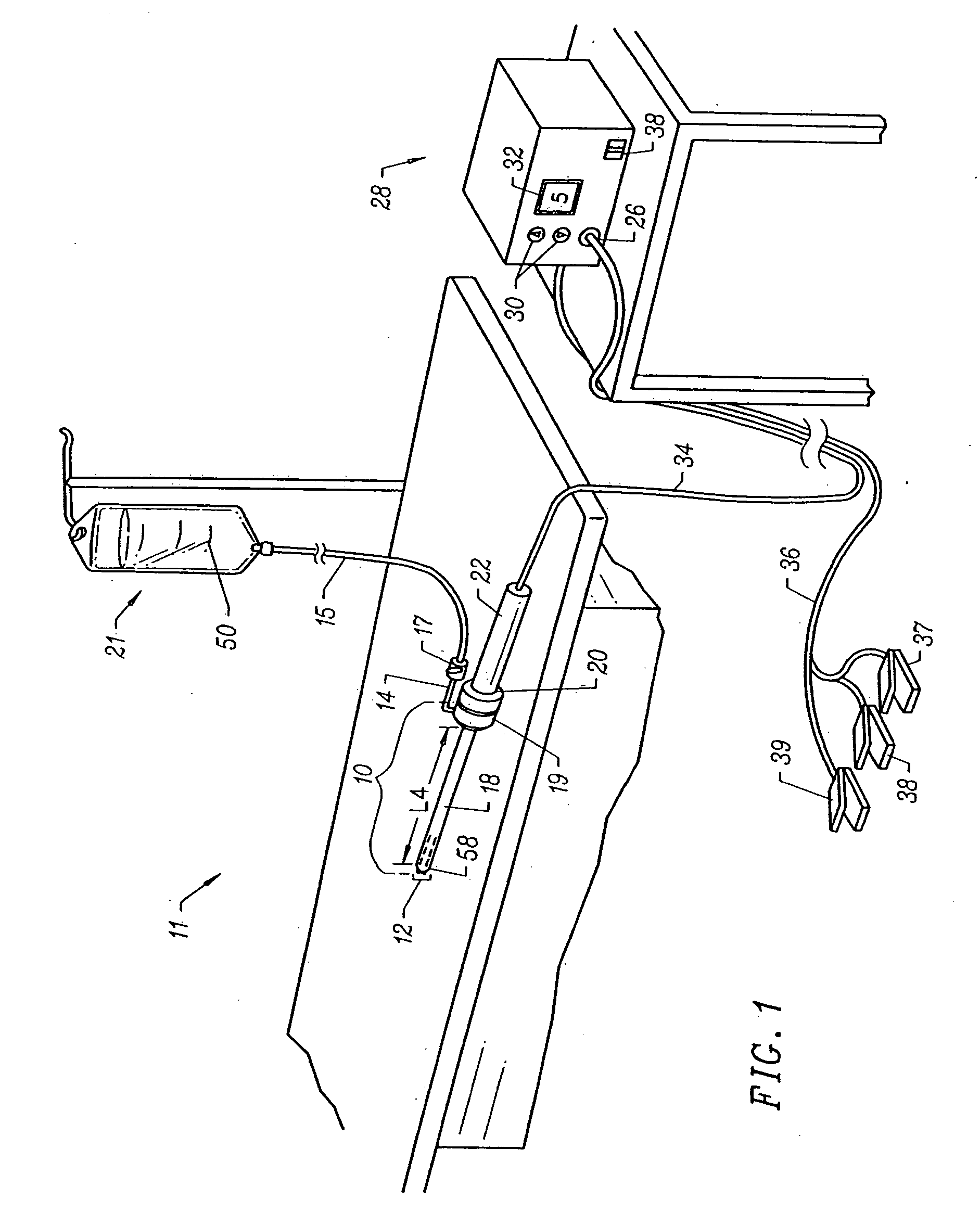
One step entry pedicular preparation device and disc access system
ActiveUS8236006B2Limit distanceQuicker procedureSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone structureIntervertebral disc
A one step entry pedicular preparation device works well with Minimal Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS) to facilitating such approach. A related intervertebral disc access system and pedicle screw compatible with the systems is also illustrated. The systems include a manipulator having a bar handle and main body with main barrel bore a pedicle dart having a proximal tip end and a second distal open end selectably attachable to the manipulator using a variety of interconnect configurations, both of which work in conjunction with a guide pin. The pedicle darts can be made of any material, disposable or re-usable and can be utilized for a variety of purposes, including bone structure formation for faster conventional pedicle screw insertion with precision and vertebra fixation.
Owner:LIFE SPINE INC
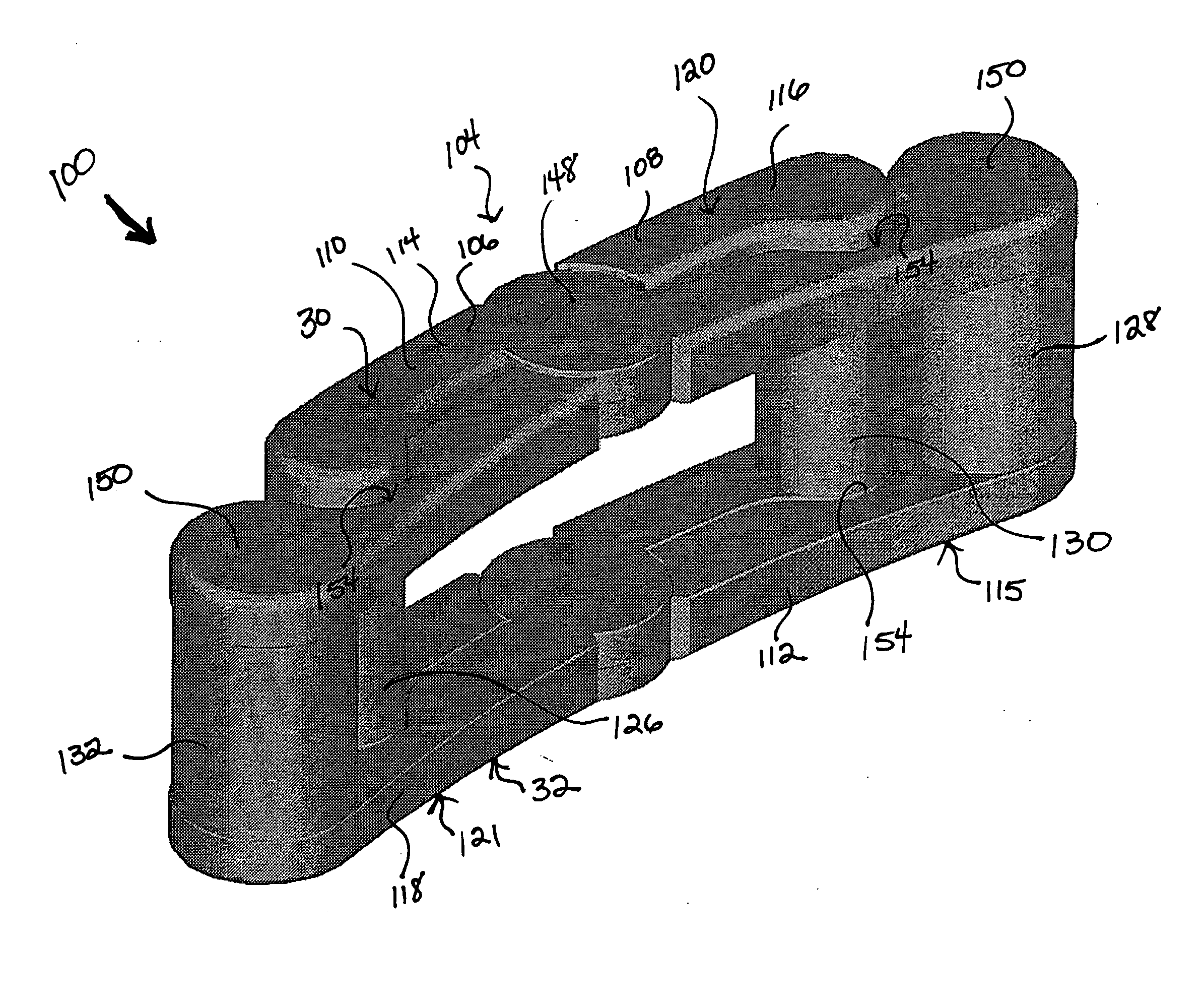
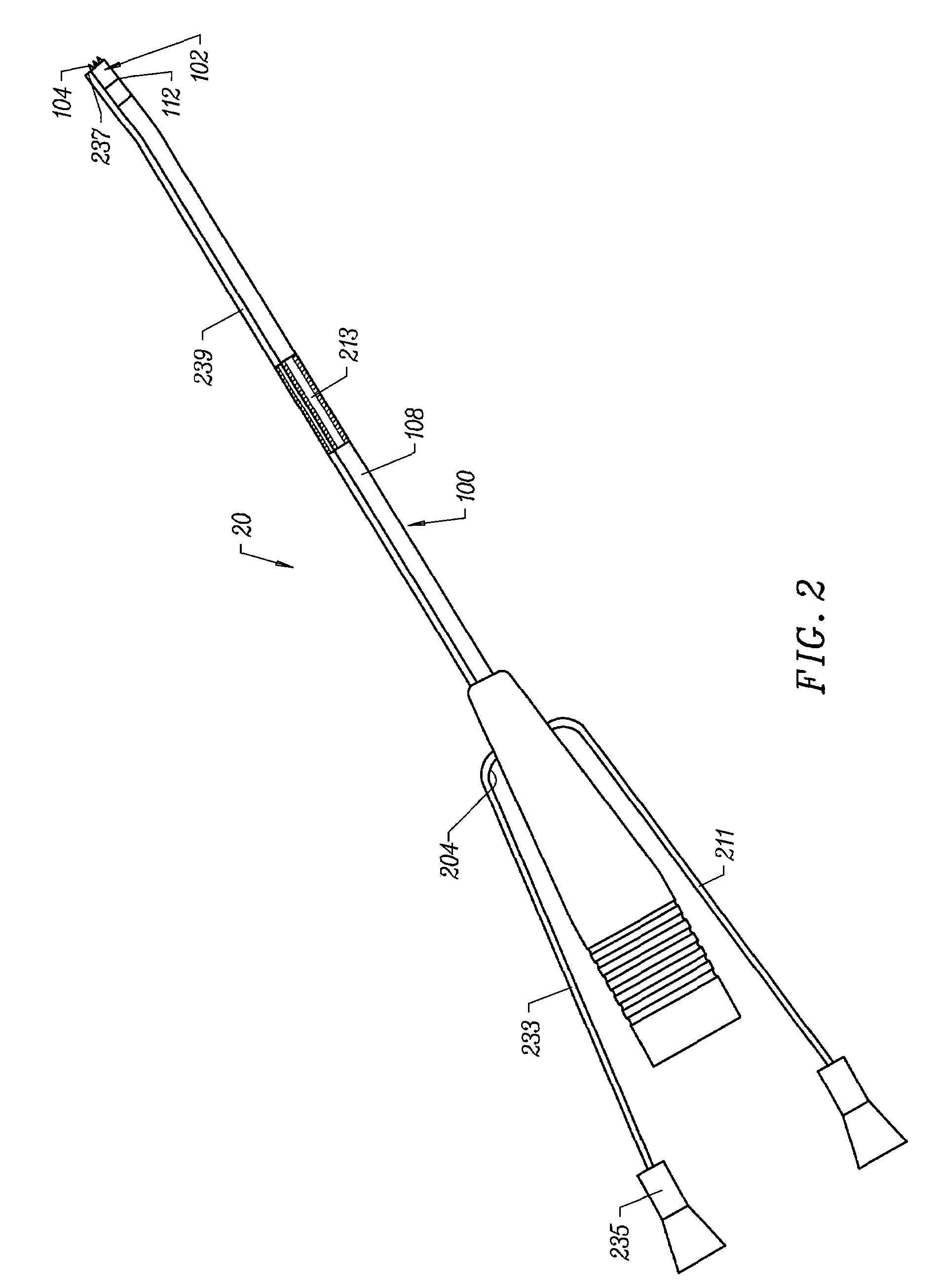
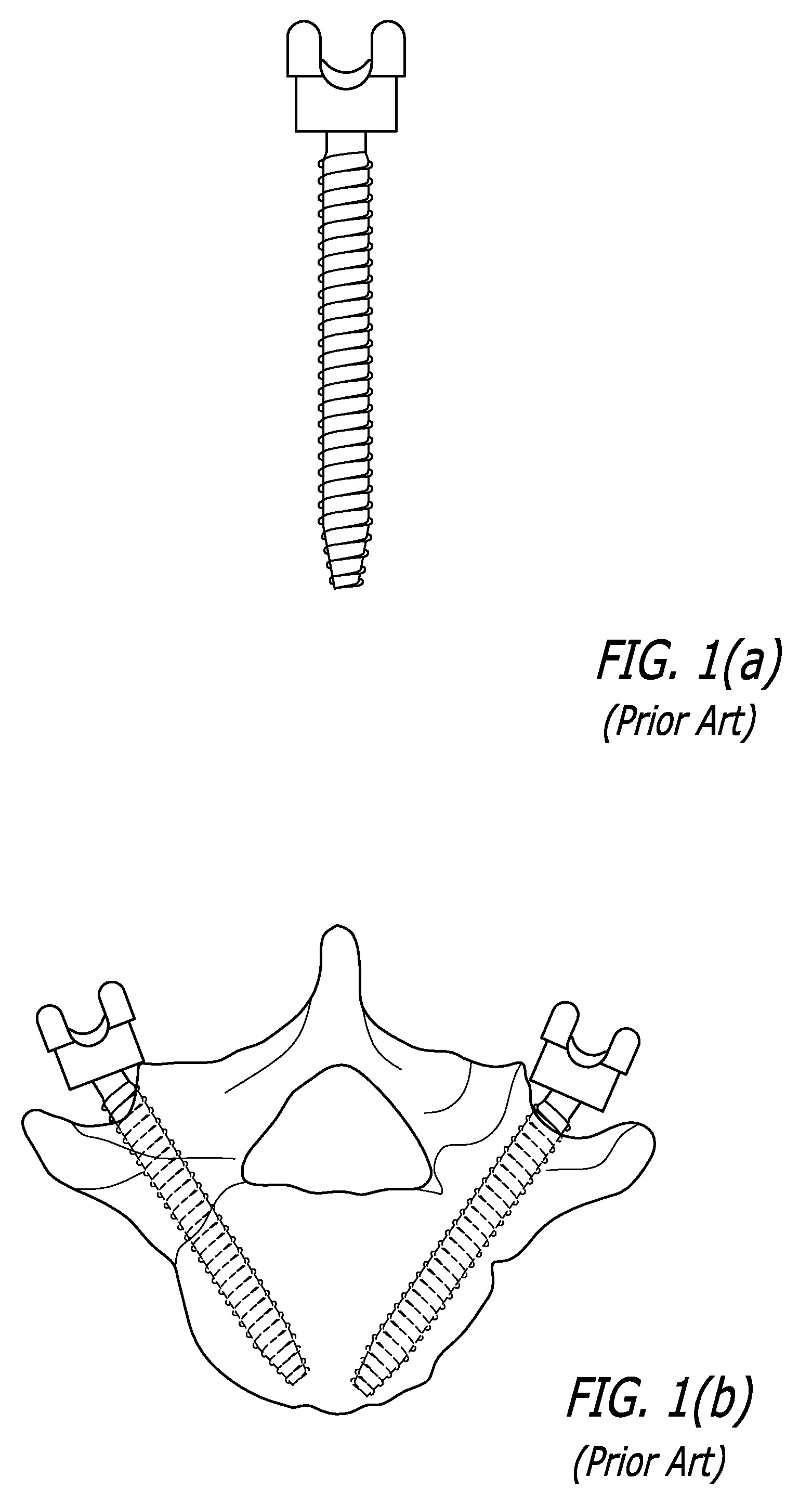
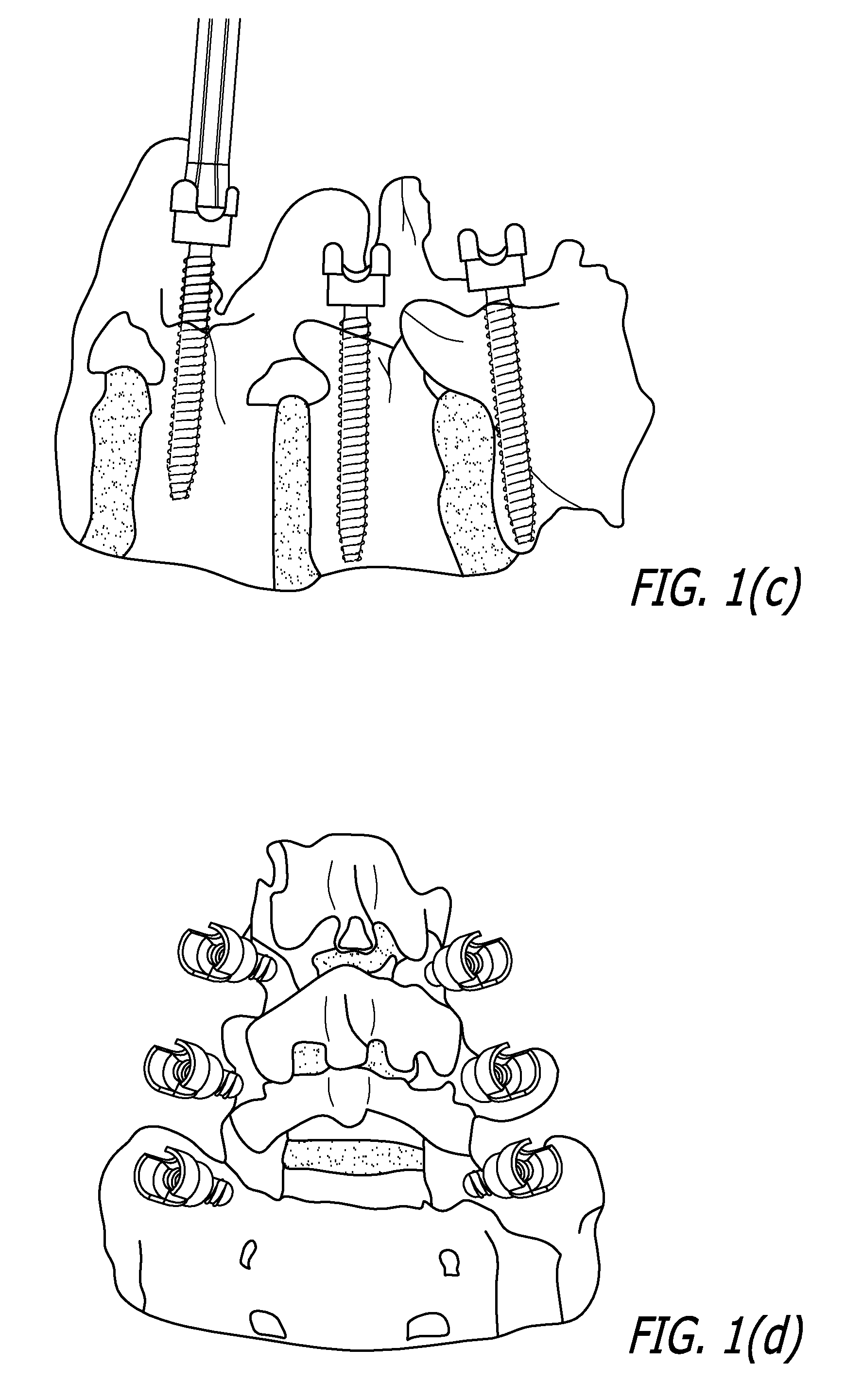
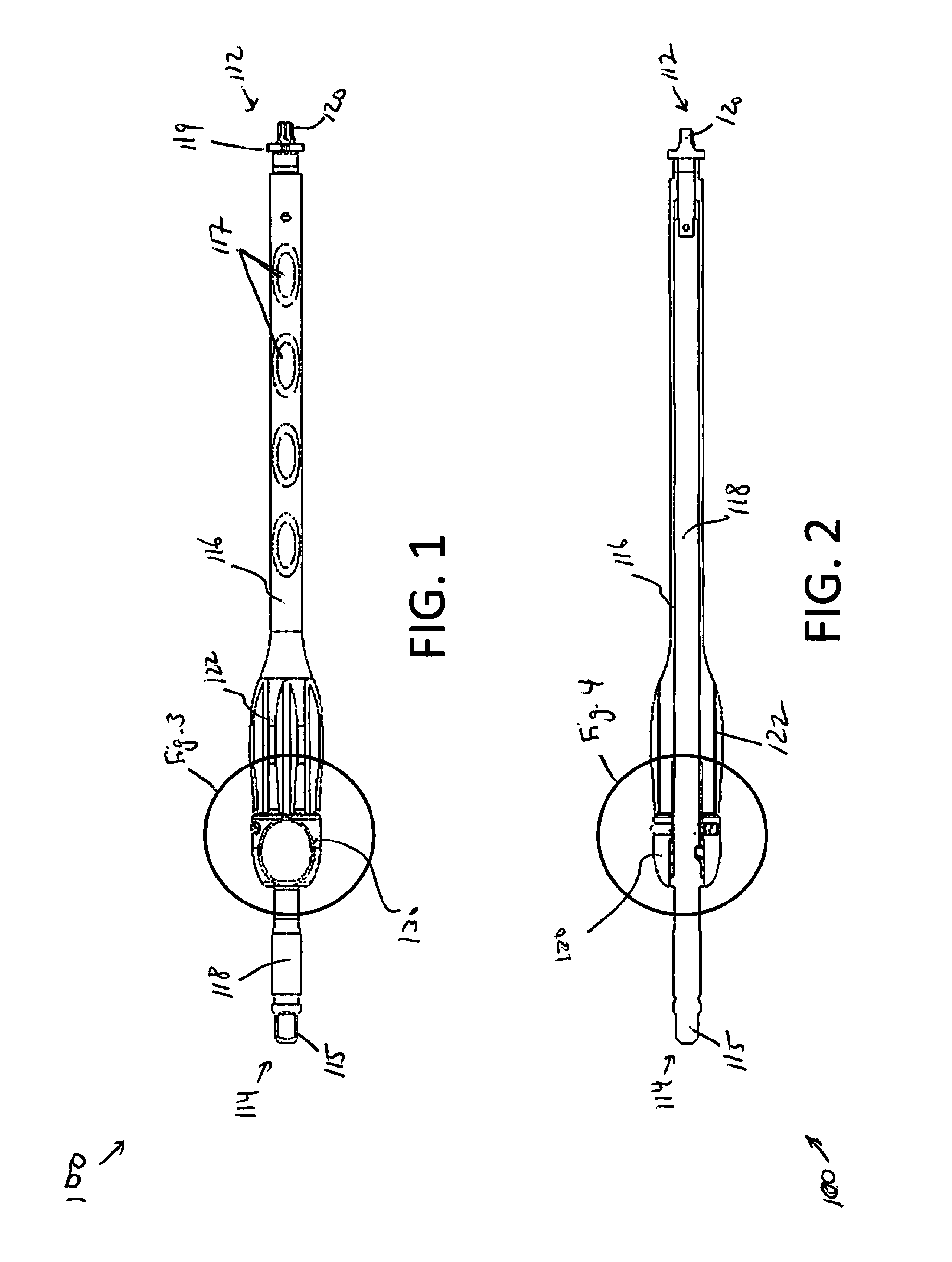
Internal fixation system for spine surgery
An internal fixation rod for spine surgery includes an elongate body, a first rod end, a second rod end, a first mounting member and a second mounting member. The first mounting member is disposed proximate the first rod end, and the second mounting member is disposed proximate the second rod end. The first mounting member and the second mounting member are smaller in cross-section than the elongate body.
Owner:CONCEPT MATRIX
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
This invention relates generally to spine surgery and, in particular, to methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Spine surgery method and motion preserving implant
ActiveUS20090048676A1Area maximizationMaximizing contactBone implantSpinal implantsSpinal implantBiomedical engineering
A spinal implant may be deployable, when positioned within a vertebral space between a pair of vertebral bodies, from a first laterally non-expanded condition to a second laterally expanded condition. The spinal implant may include top beams and bottom beams separated by at least one post that is, in one embodiment, length variable in response to a load put on the implant after deployment of the implant. In an alternate embodiment, at least one post is laterally variable in response to a load put on the implant. In another embodiment, one of the posts may be centrally located.
Owner:FABIAN JR HENRY F
Methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis
ActiveUS8167915B2Prevents and minimizes riskOvercomes drawbackInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal stenosisRadiology
This invention relates generally to spine surgery and, in particular, to methods and apparatus for treating spinal stenosis. The methods comprising gaining access to an interspinous space, abrading a portion of the superior spinous process, inserting an implant into the interspinous process space, verifying the position of the implant by observing the position of three radio-opaque markers embedded in the implant, and coupling the implant to the superior spinous process.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Spine surgery method and instrumentation
ActiveUS20080300601A1Easily and securely attachedEasy to moveSpinal implantsOptical signallingSurgical instrumentationInterconnection
Surgical instrumentation for use in placing an implant into a disc space between a pair of spinal vertebrae may include: (a) a distractor having a distal end that may be placed into the disc space between the pair of spinal vertebrae; (b) an inserter for use in moving the implant toward the disc space between the pair of spinal vertebrae; and, (c) a distractor / inserter rail / groove interconnection that interconnects the distractor and the inserter for relative movement thereby.
Owner:VERTEBRATION
Systems and methods for performing neurophysiologic monitoring during spine surgery
PendingUS20150230749A1Facilitate initiationElectromyographySurgeryNeurophysiologySurgical procedures
The present invention relates a system and related methods for performing neurophysiologic assessments during surgical procedures.
Owner:NUVASIVE
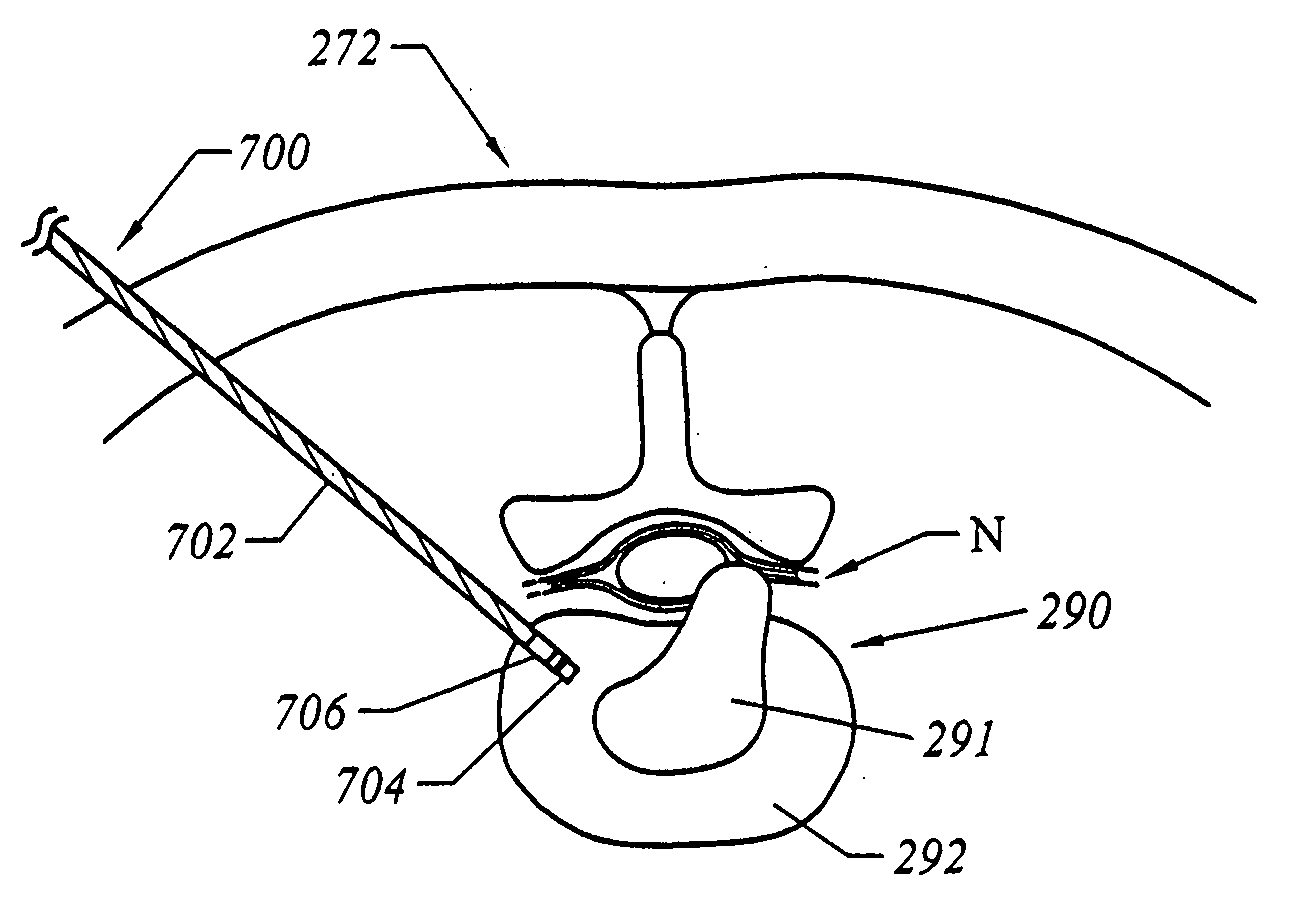
Acoustic Back-Scattering Sensing Screw for Preventing Spine Surgery Complications
InactiveUS20080228231A1Improve securitySatisfies FDA strength and nontoxicity requirementSuture equipmentsElectrotherapyBone tissueTransducer
A medical device having an implantable instrument configured to be implanted in bone tissue, the implantable instrument having an internal chamber configured to house at least one transducer; a transducer located within the internal chamber of the implantable instrument, the transducer configured to transmit a signal and to receive one or more reflections of that signal; and a signal processing system configured to process the signals transmitted and received by the transducer so as to provide information indicative of the acoustic impedance of matter in the vicinity of the implantable instrument after it is implanted into the bone tissue based on the signals transmitted and received by the transducer.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Systems and methods for performing spine surgery
ActiveUS9386971B1Stable positionReduce pressure pointInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsPosterior fixationSpinal column
This application describes surgical instruments and implants for building a posterior fixation construct across one or more segments of the spinal column during a medialized posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) procedure.
Owner:NUVASIVE
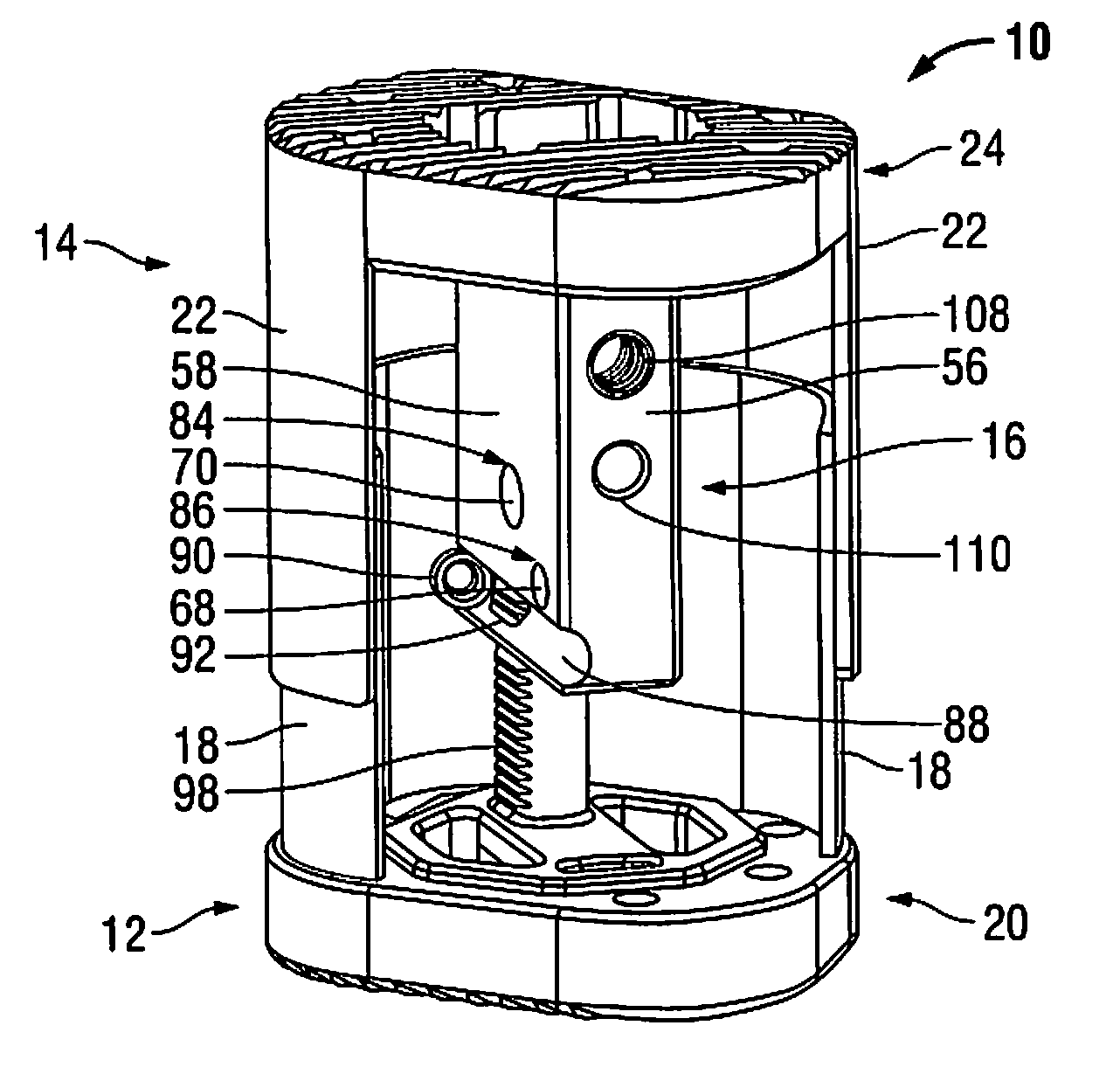
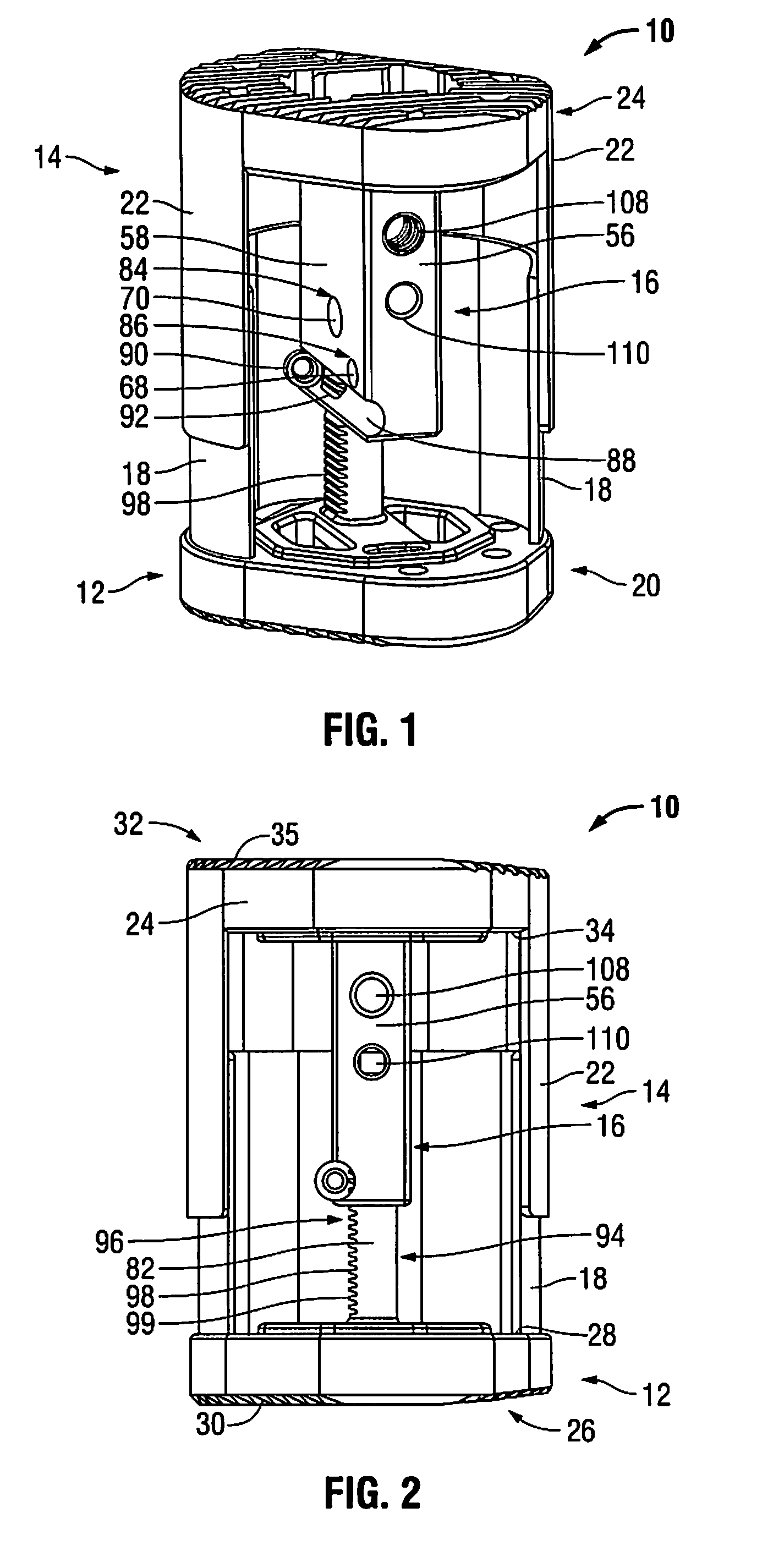
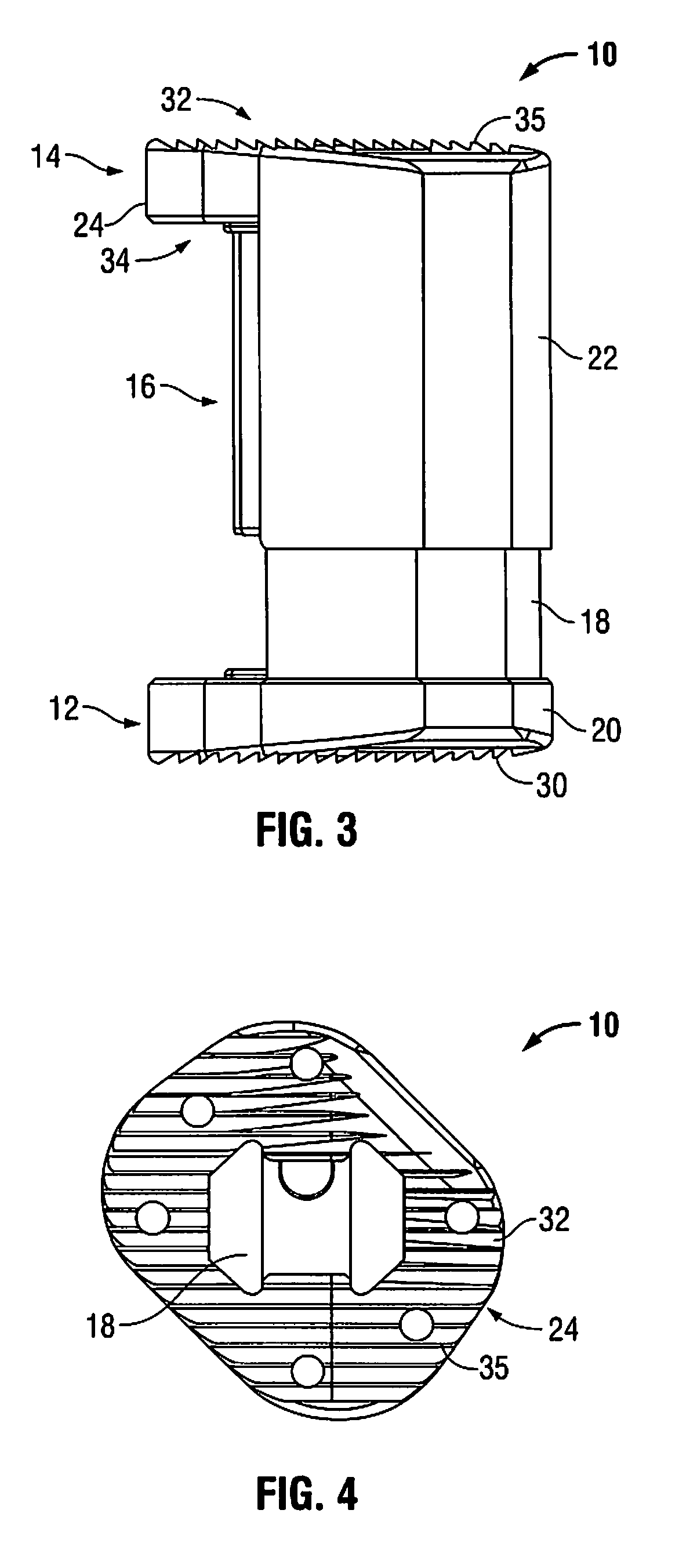
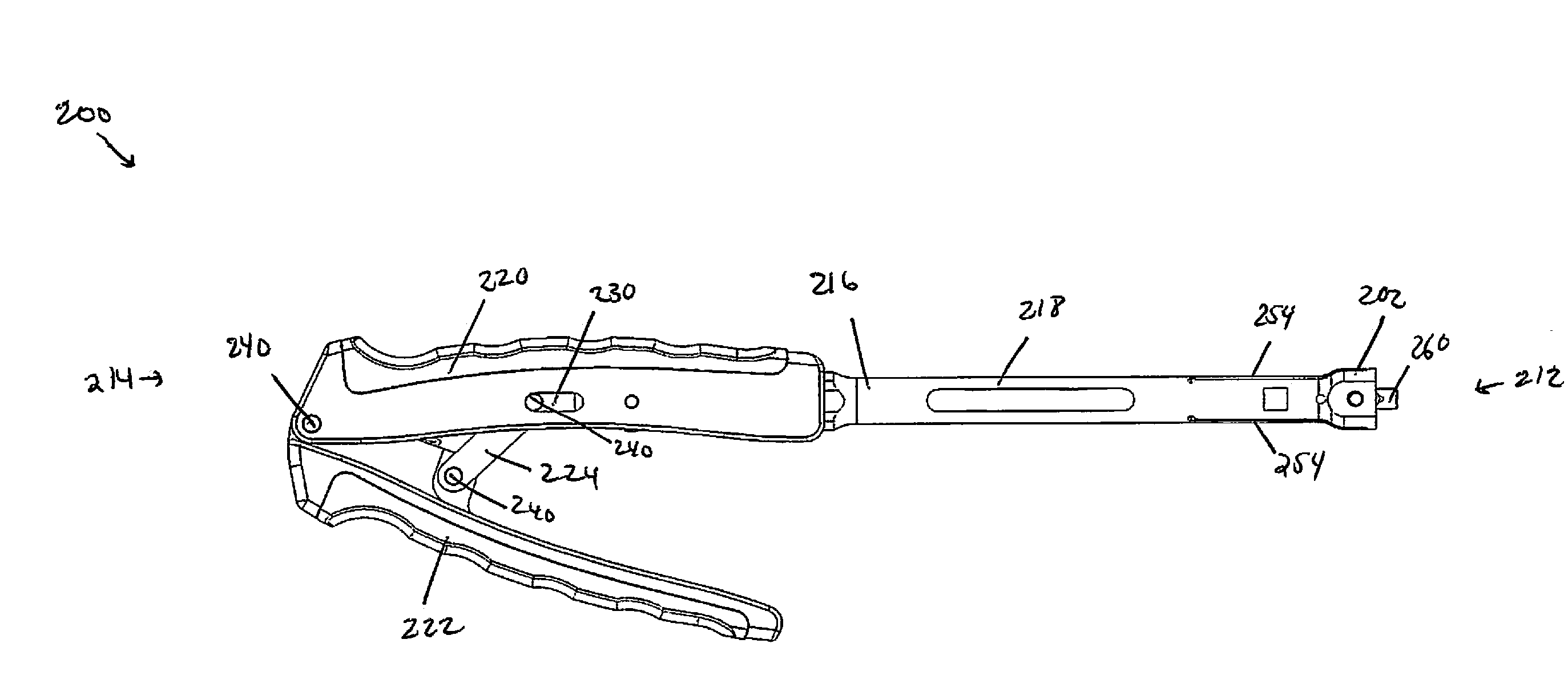
Position-adjustment system for an instrument for surgery of the spine
InactiveUS20020111627A1Prevent slidingInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringSurgical department
The position-adjustment system for a surgical instrument, in particular for surgery of the spine, the system comprises an elongate member suitable for being connected to a first element of the instrument, a body suitable for being fastened to the elongate member and for being connected to a second element of the instrument, and connection means for connecting the elongate member to the body and arranged to have an unlocked state in which they allow the elongate member to slide relative to the body and a locked state in which they prevent the elongate member from sliding relative to the body.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
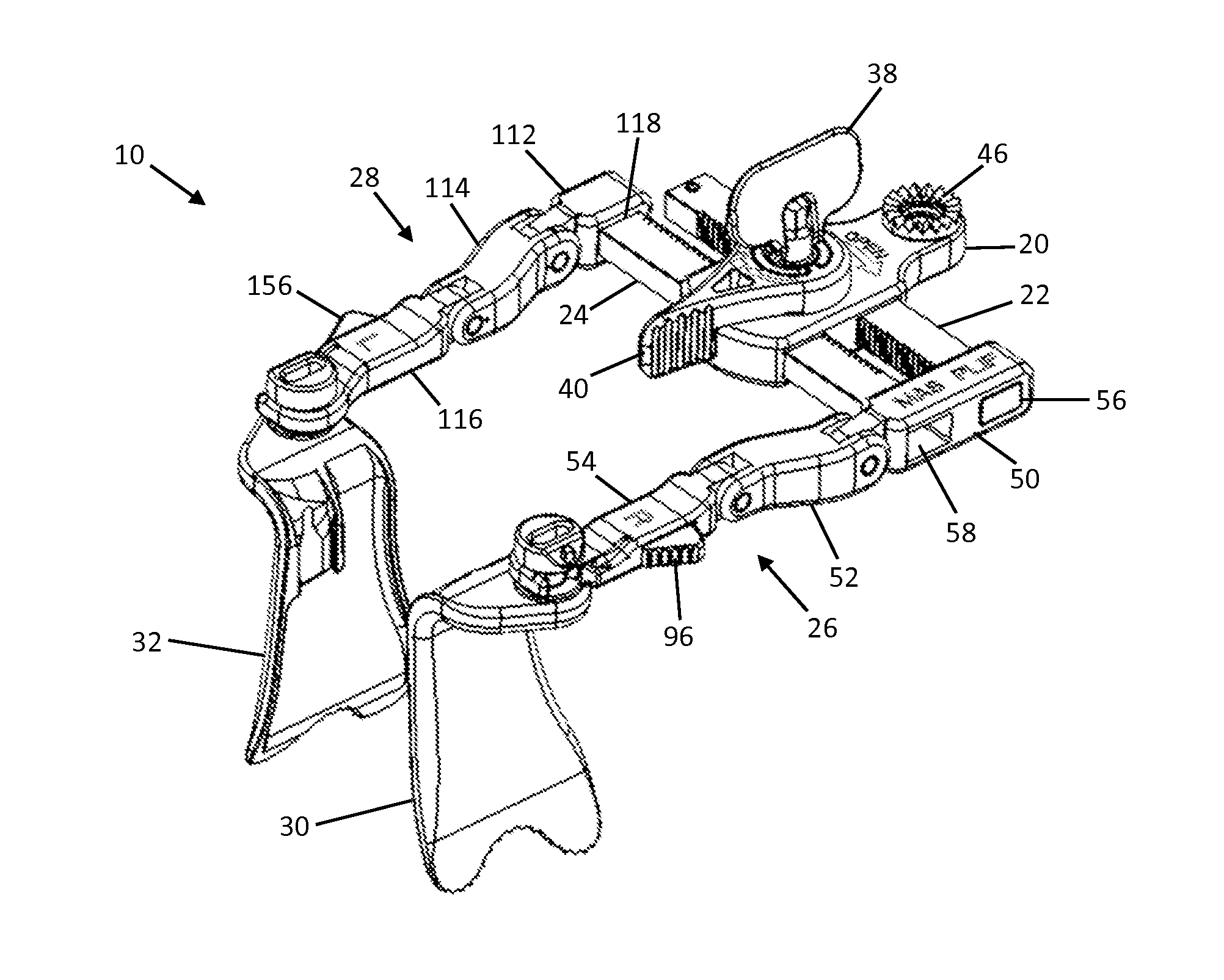
Instruments for Use During Spine Surgery
ActiveUS20140276896A1Improve safety and functionalityInternal osteosythesisSpannersSystems designGear system
Surgical instruments and devices including drivers, inserters, and reducers. The driver includes a ratcheting mechanism configured to provide uni-directional motion when engaged. The inserter includes a rack, pinion, and cam system designed to secure an implant and release an implant in-situ. The reducer includes a geared system for persuading together surgical components and aligning misaligned vertebrae.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Spine surgery method and instrumentation
ActiveUS8070754B2Easy to placeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical instrumentationIntervertebral disc
Surgical instrumentation for use in placing an implant into a disc space between a pair of spinal vertebrae may include: (a) a distractor having a distal end that may be placed into the disc space between the pair of spinal vertebrae; (b) an inserter for use in moving the implant toward the disc space between the pair of spinal vertebrae; and, (c) a distractor / inserter rail / groove interconnection that interconnects the distractor and the inserter for relative movement thereby.
Owner:VERTEBRATION
Systems and methods for performing neurophysiologic monitoring during spine surgery
ActiveUS9655505B1Easy to rotate manuallyImprove structural stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNeurophysiologyBiomedical engineering
A surgical access system comprising a tissue retraction assembly equipped with two or more electrodes for use in monitoring the status of nearby neural structures, including the localized depth of neural structures relative to one or more components of the tissue retraction assembly. Additional neurological testing may be performed to monitor the health and status of the neural structures during the portions of the surgical procedure in which the tissue retraction assembly is used to maintain the operative corridor.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com