Patents
Literature
1121 results about "Internal fixation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
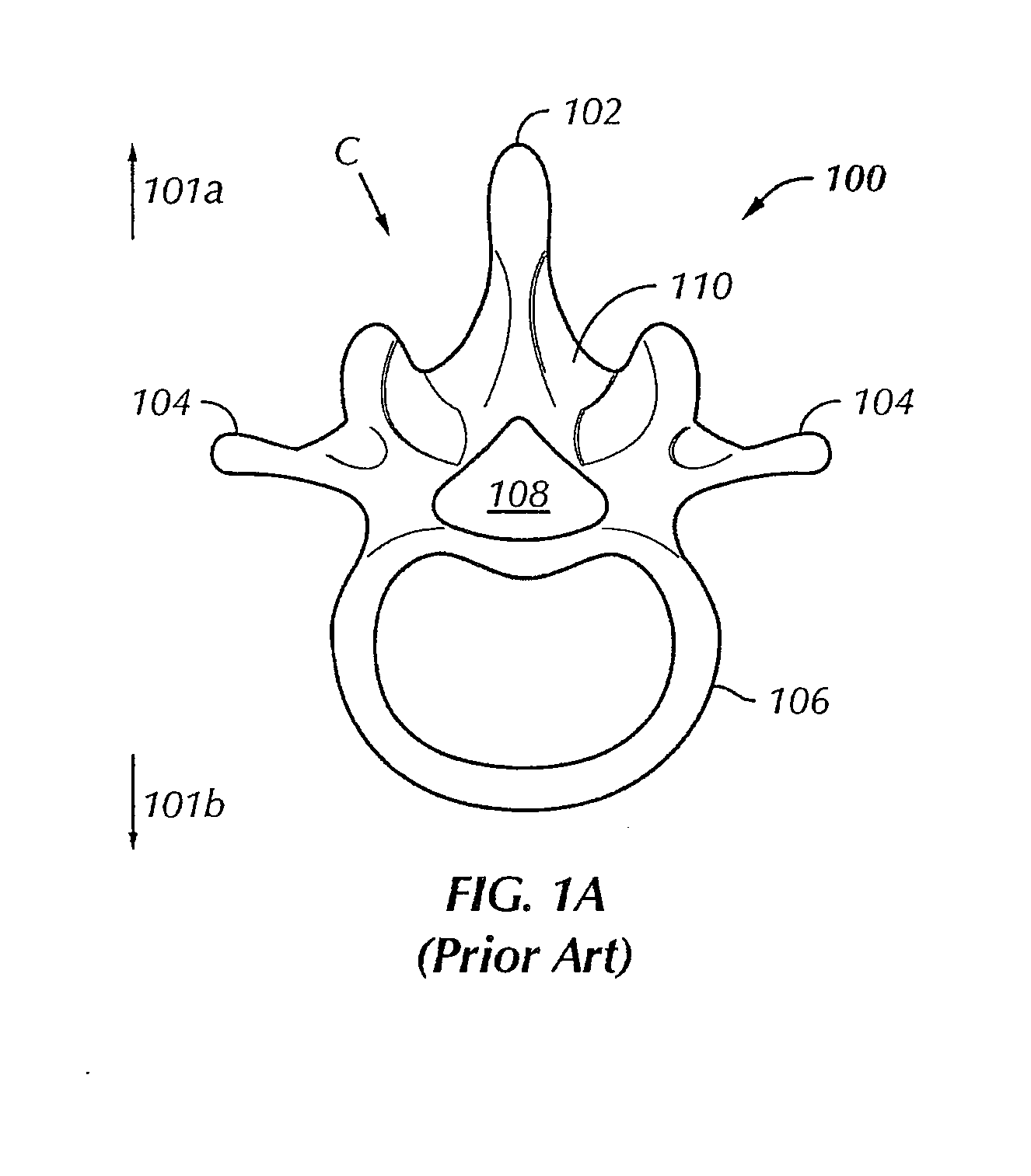
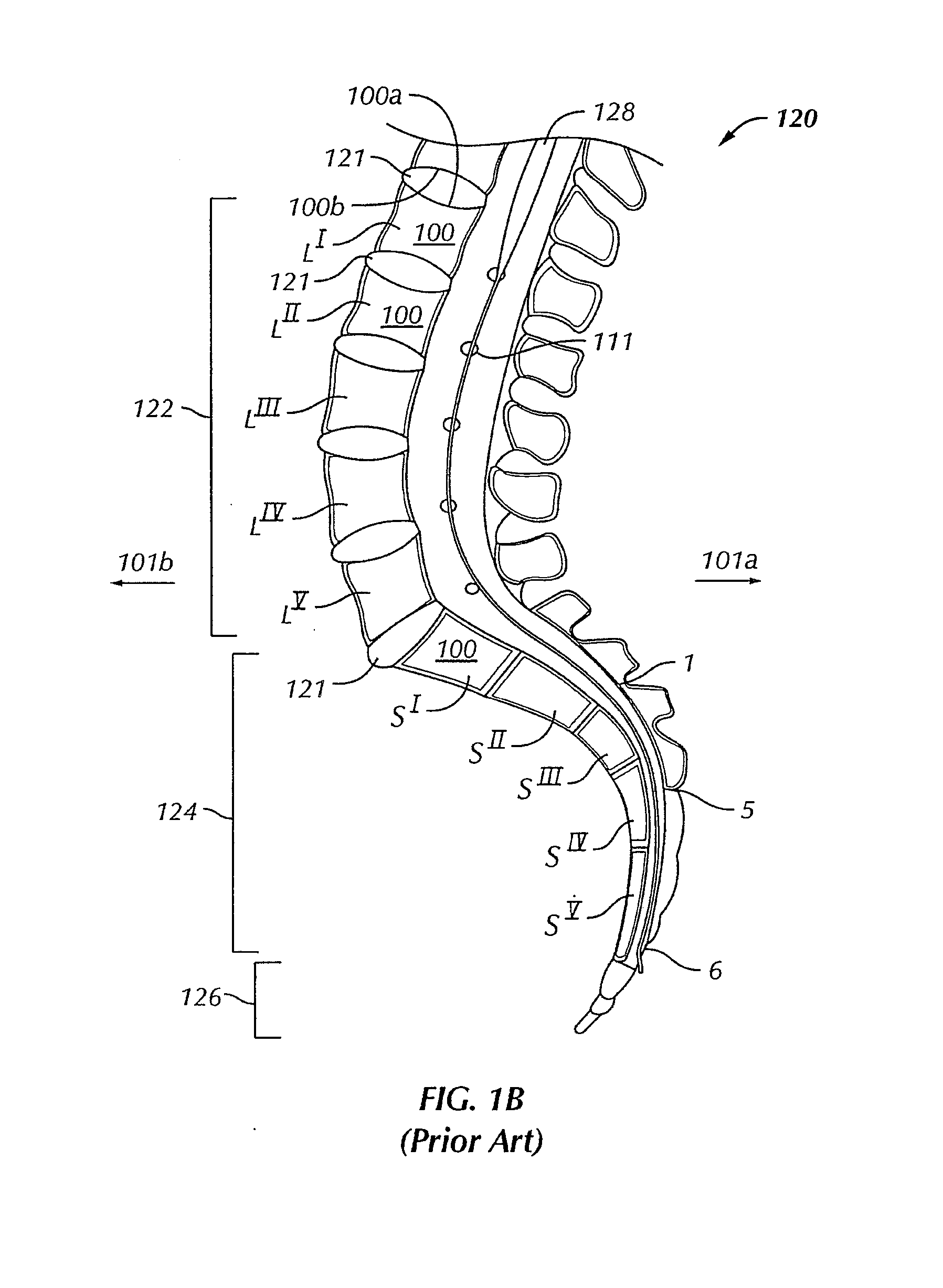
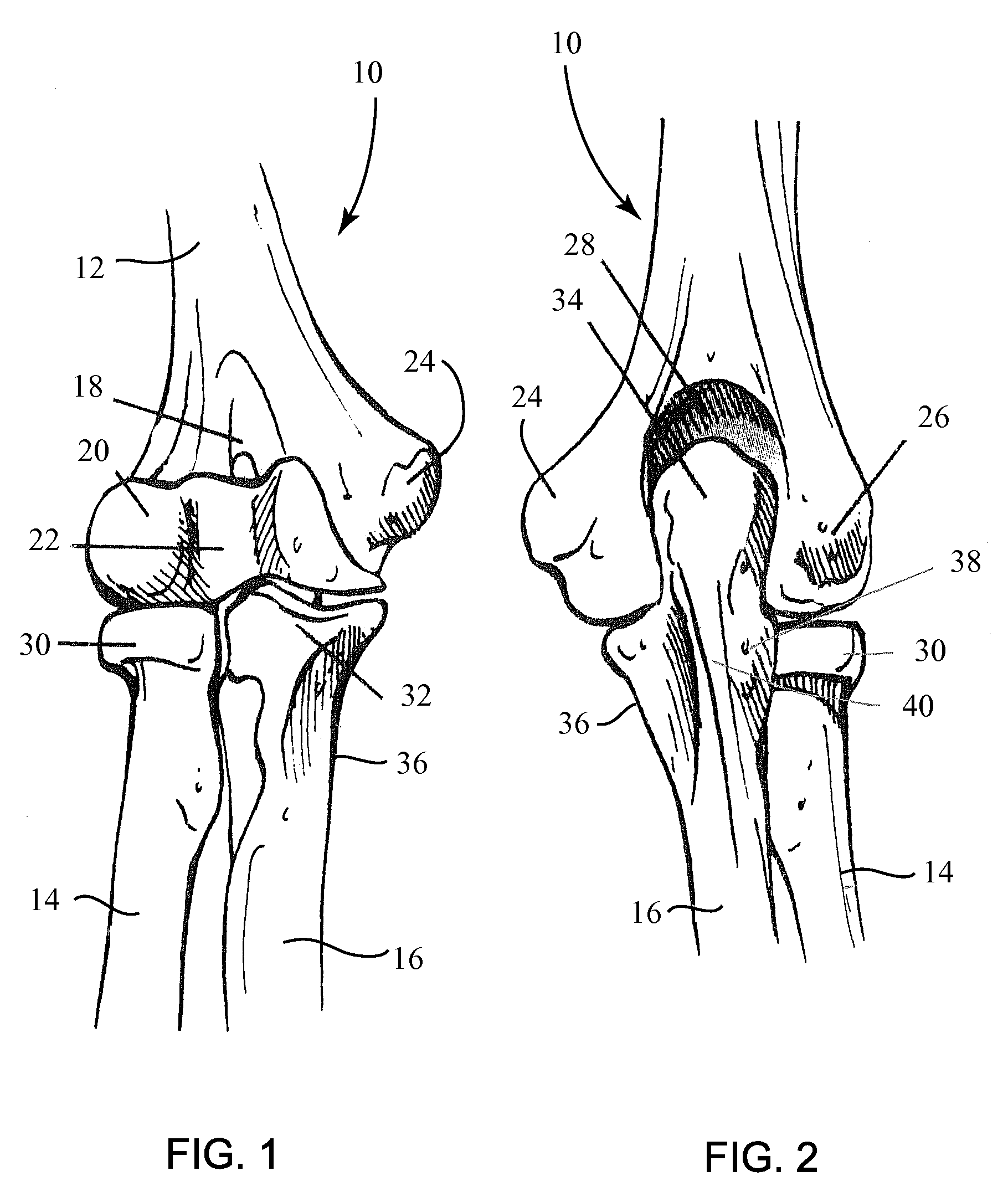
Internal fixation is an operation in orthopedics that involves the surgical implementation of implants for the purpose of repairing a bone, a concept that dates to the mid-nineteenth century and was made applicable for routine treatment in the mid-twentieth century. An internal fixator may be made of stainless steel, titanium alloy, or cobalt-chrome alloy.
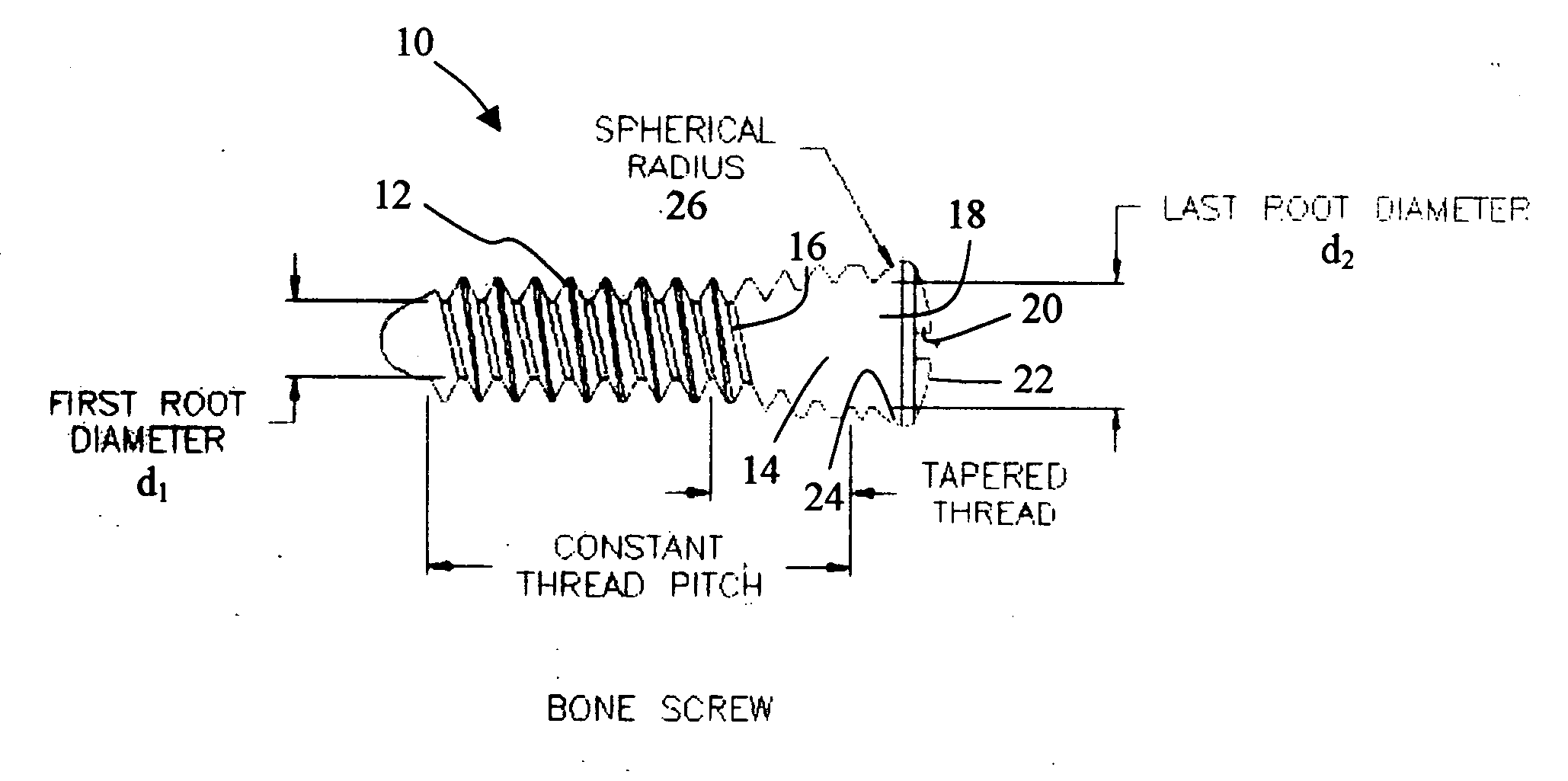
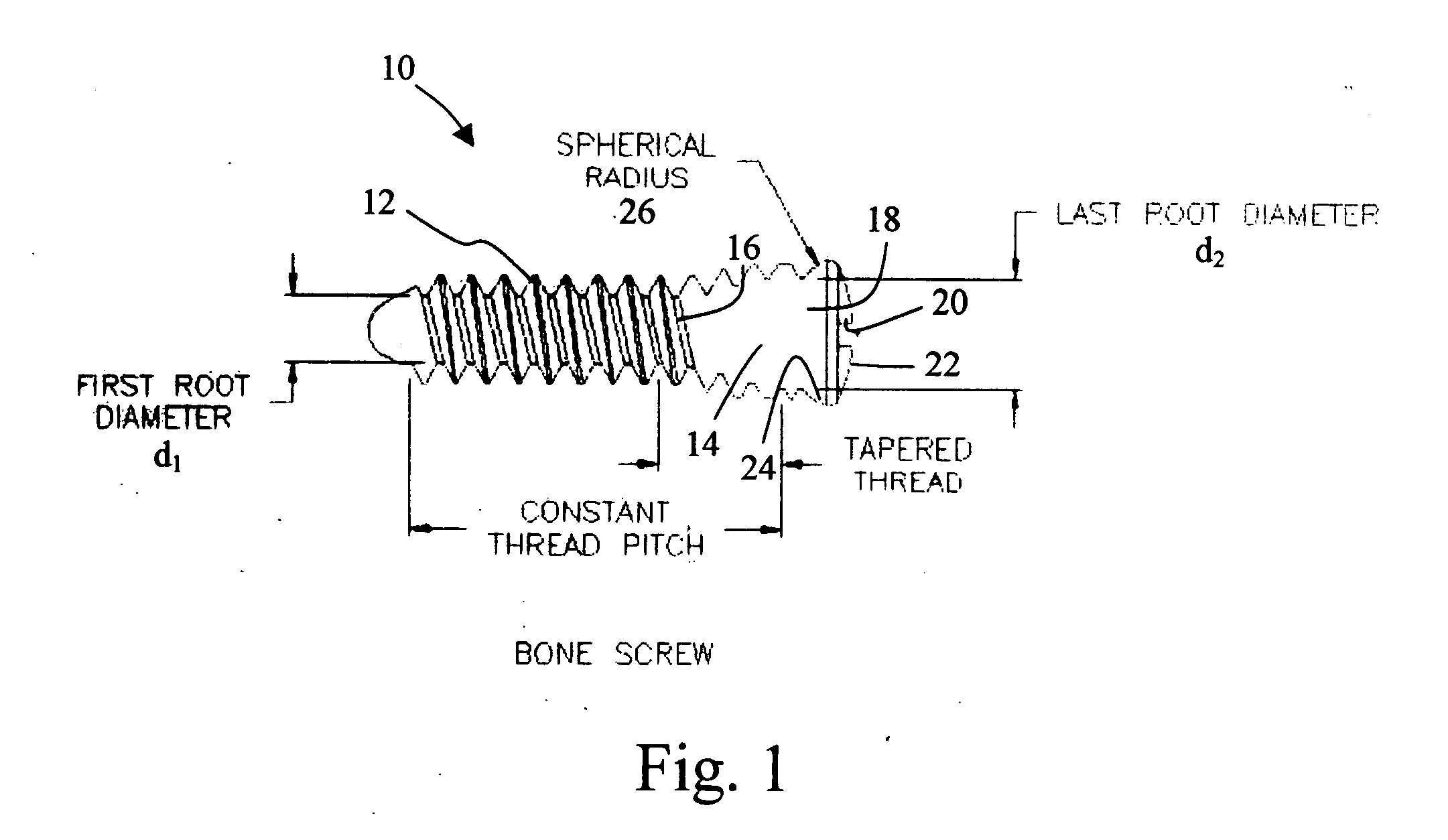
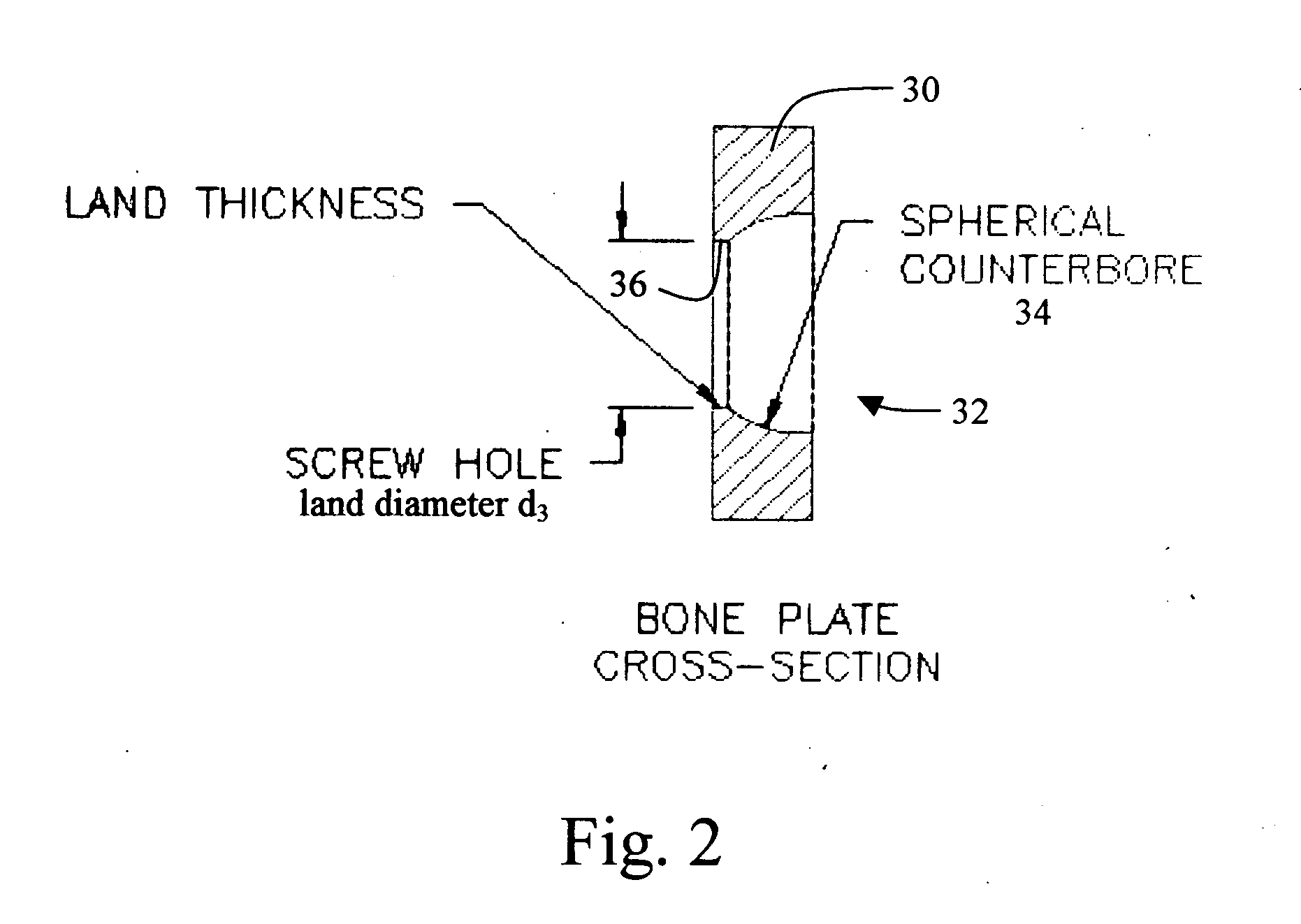
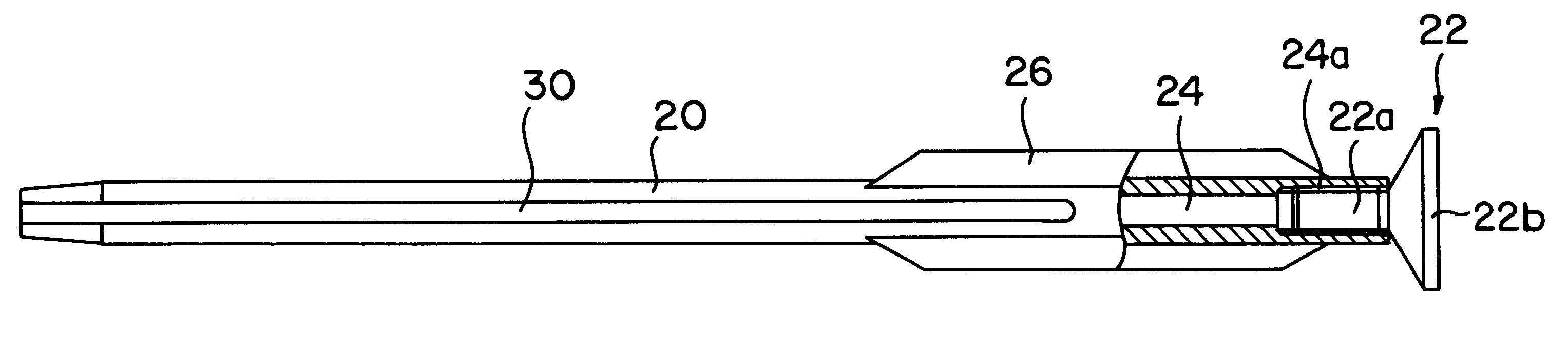
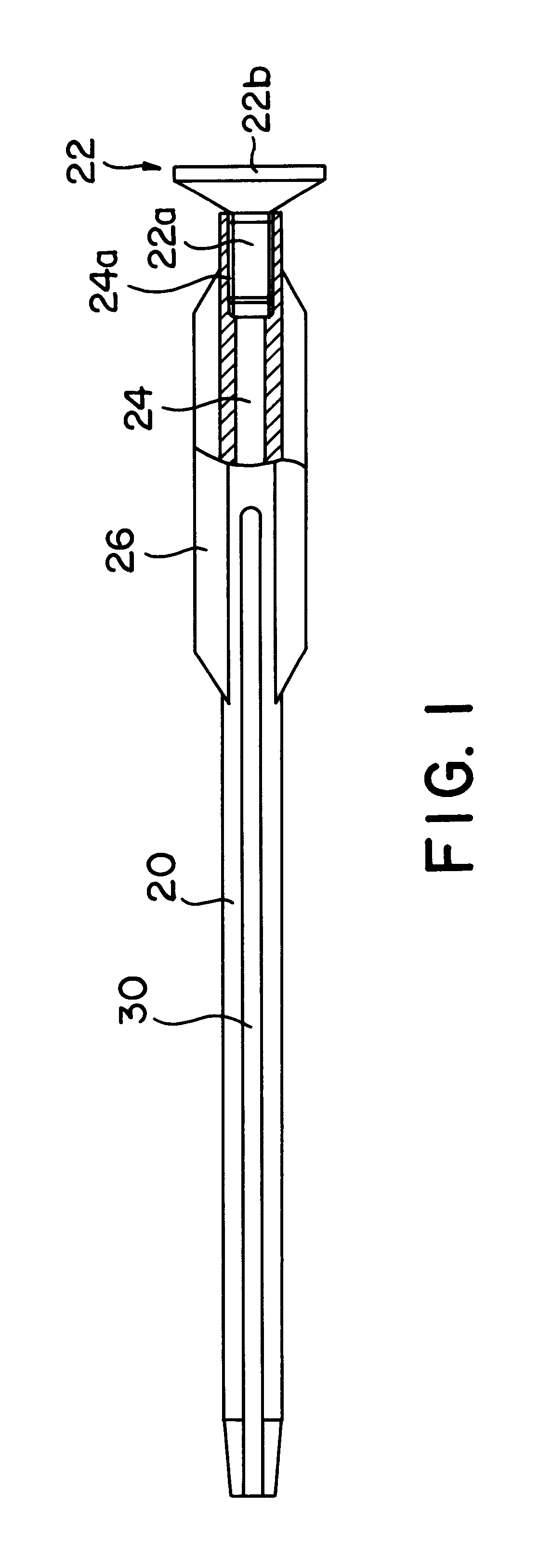
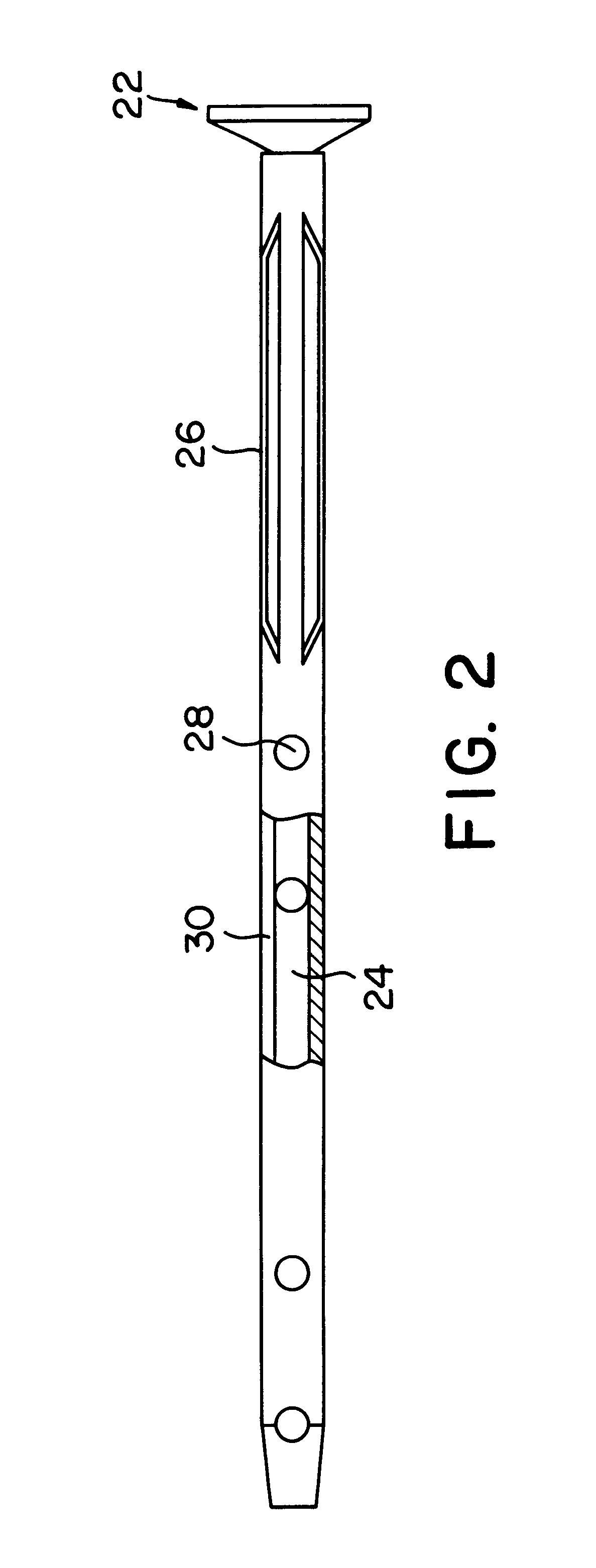
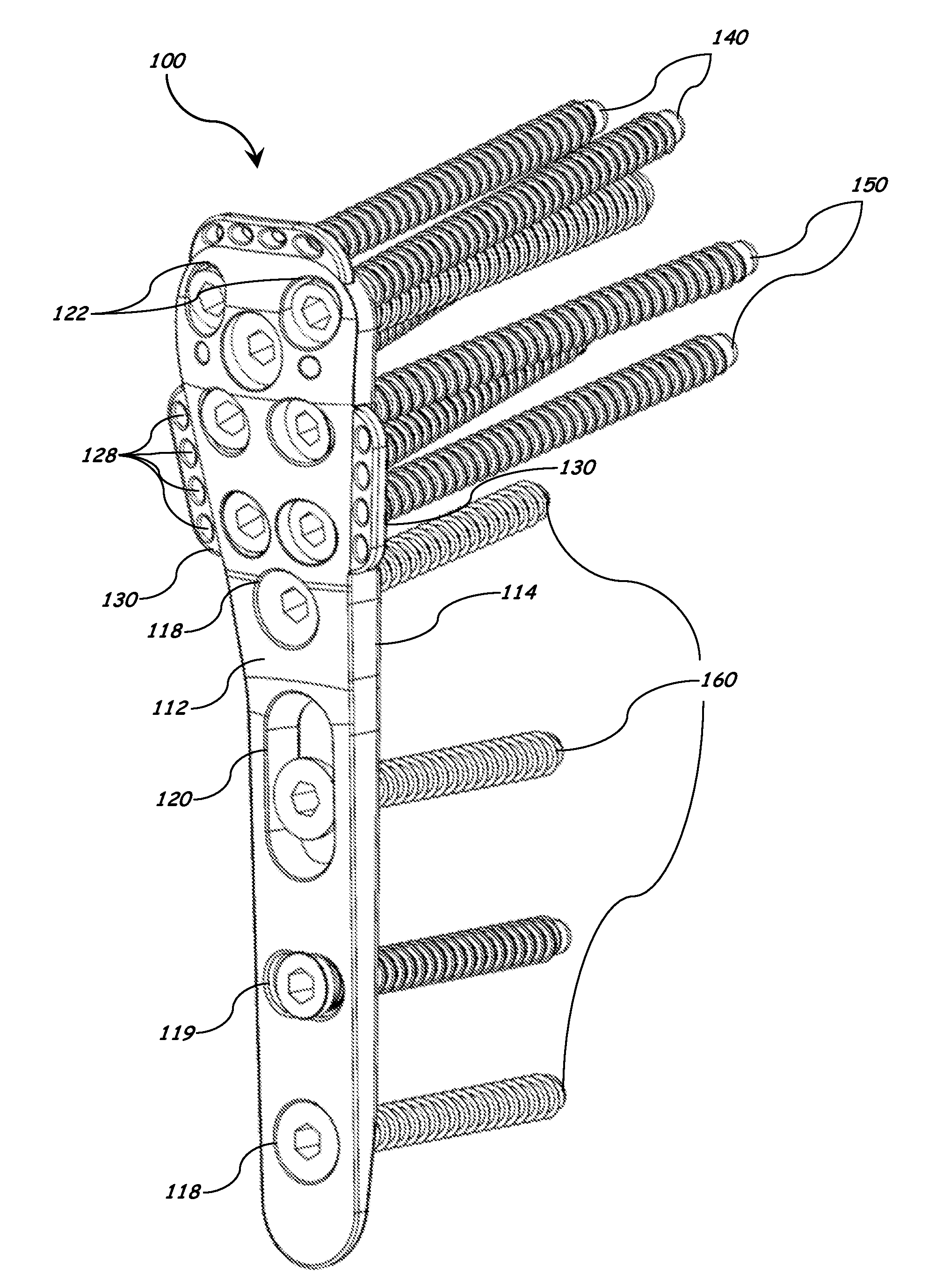
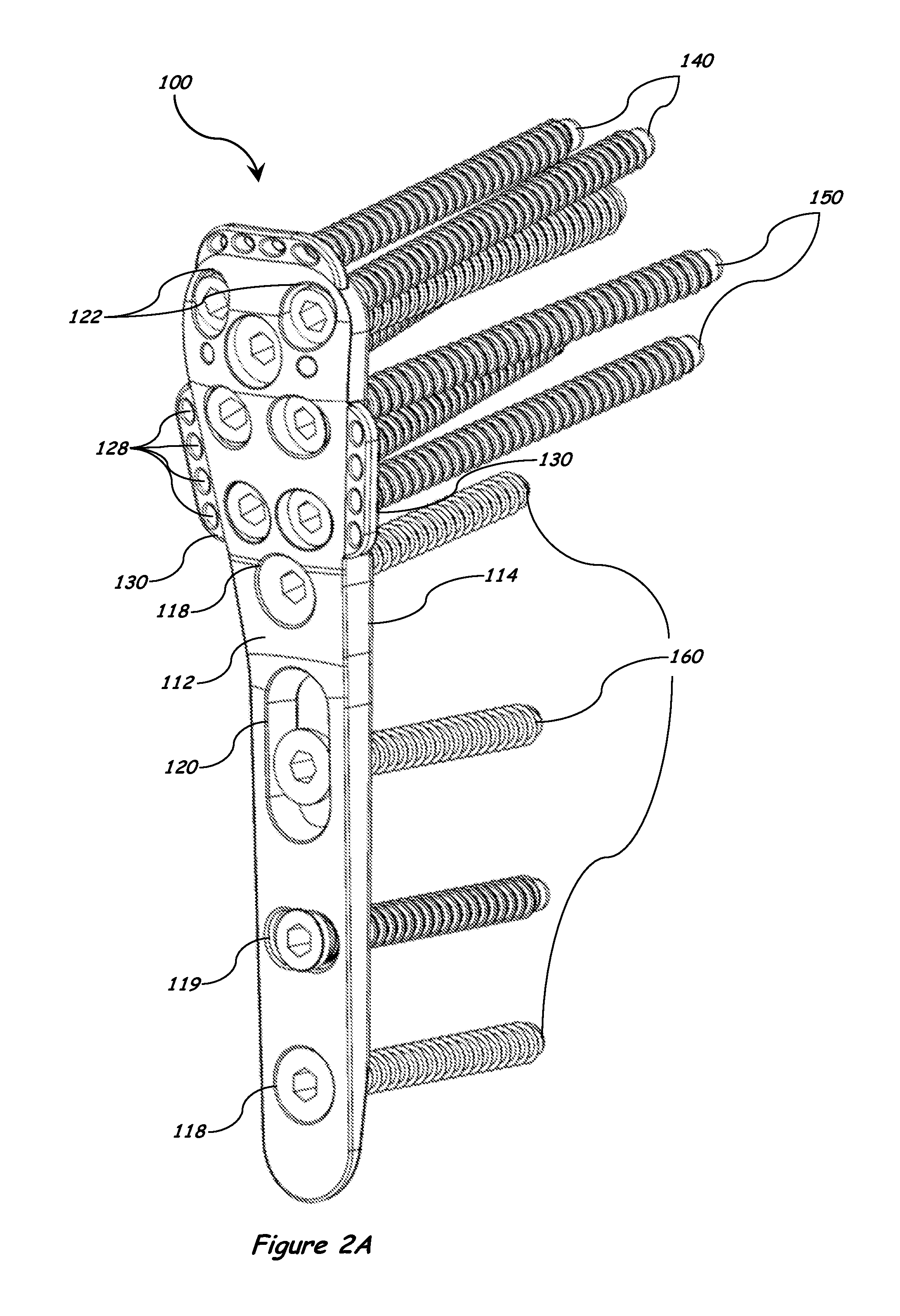
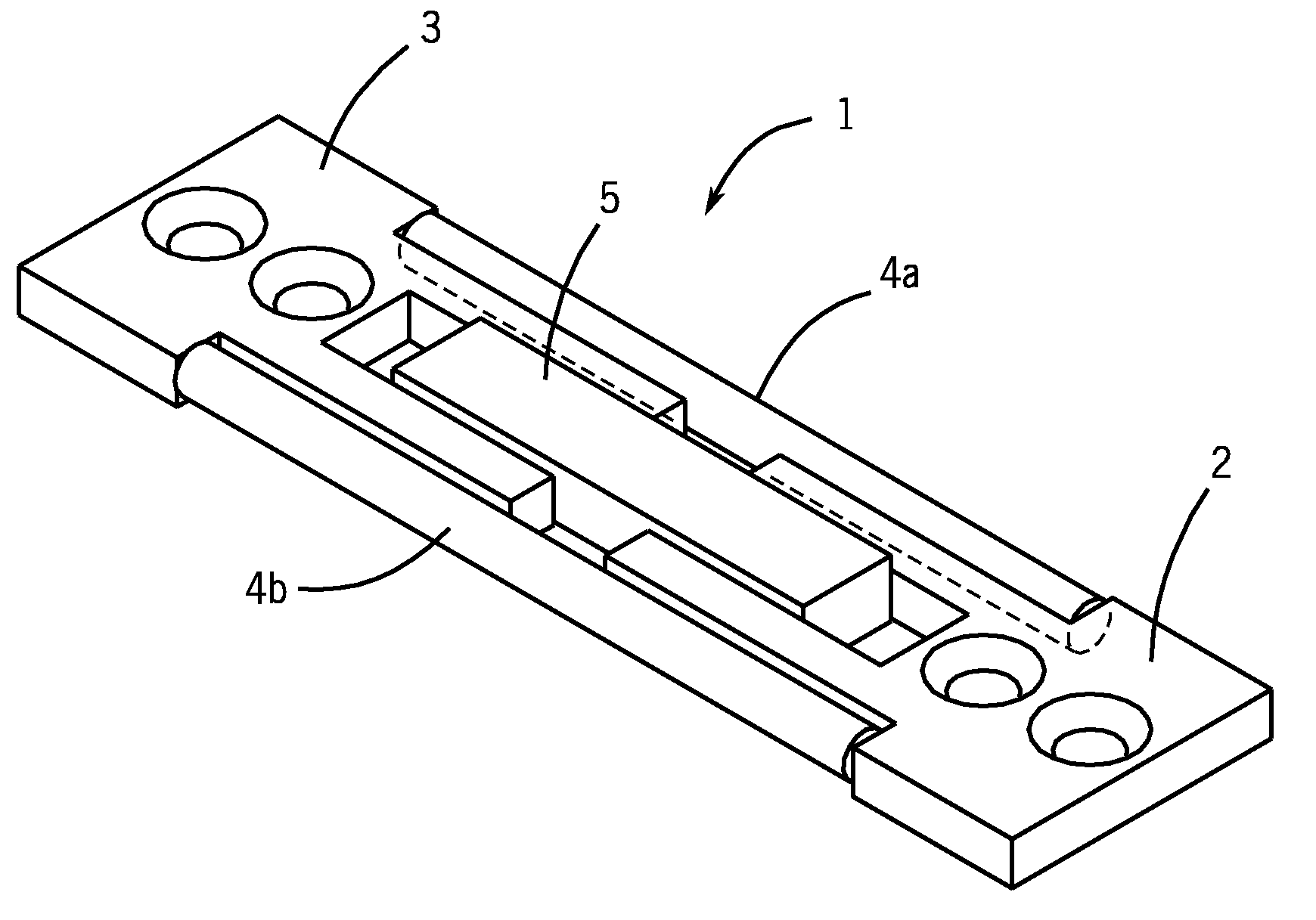
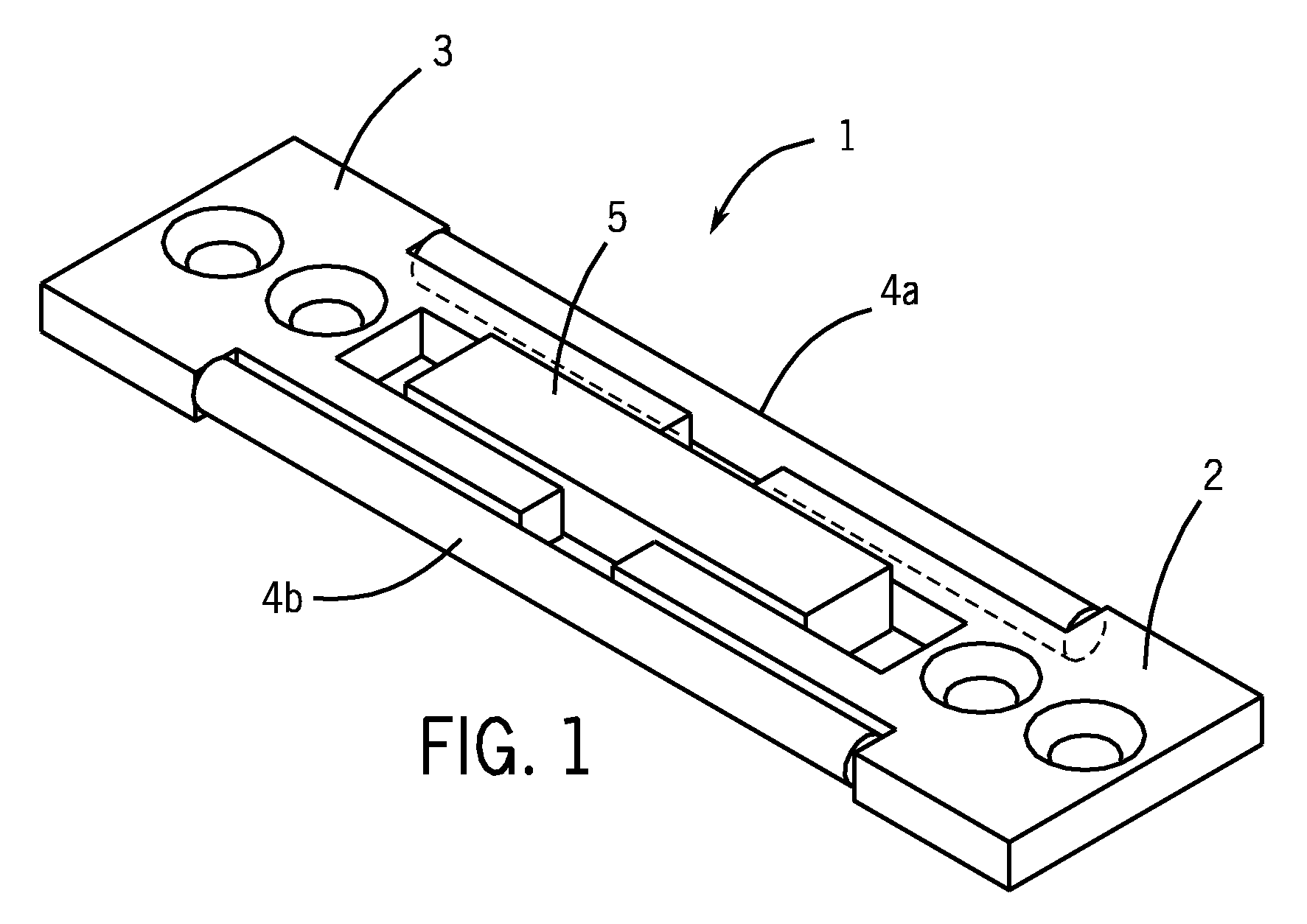
Bone plate with interference fit screw
InactiveUS20050131413A1Relieve painMinimally invasiveSuture equipmentsLigamentsInterference fitScrew system
Systems, including apparatus and methods, for internal fixation of a fractured or otherwise compromised bone. These systems may include and / or make use of bone plates, locking screws, and / or kits, among others.
Owner:ODRISCOLL SHAWN W +1
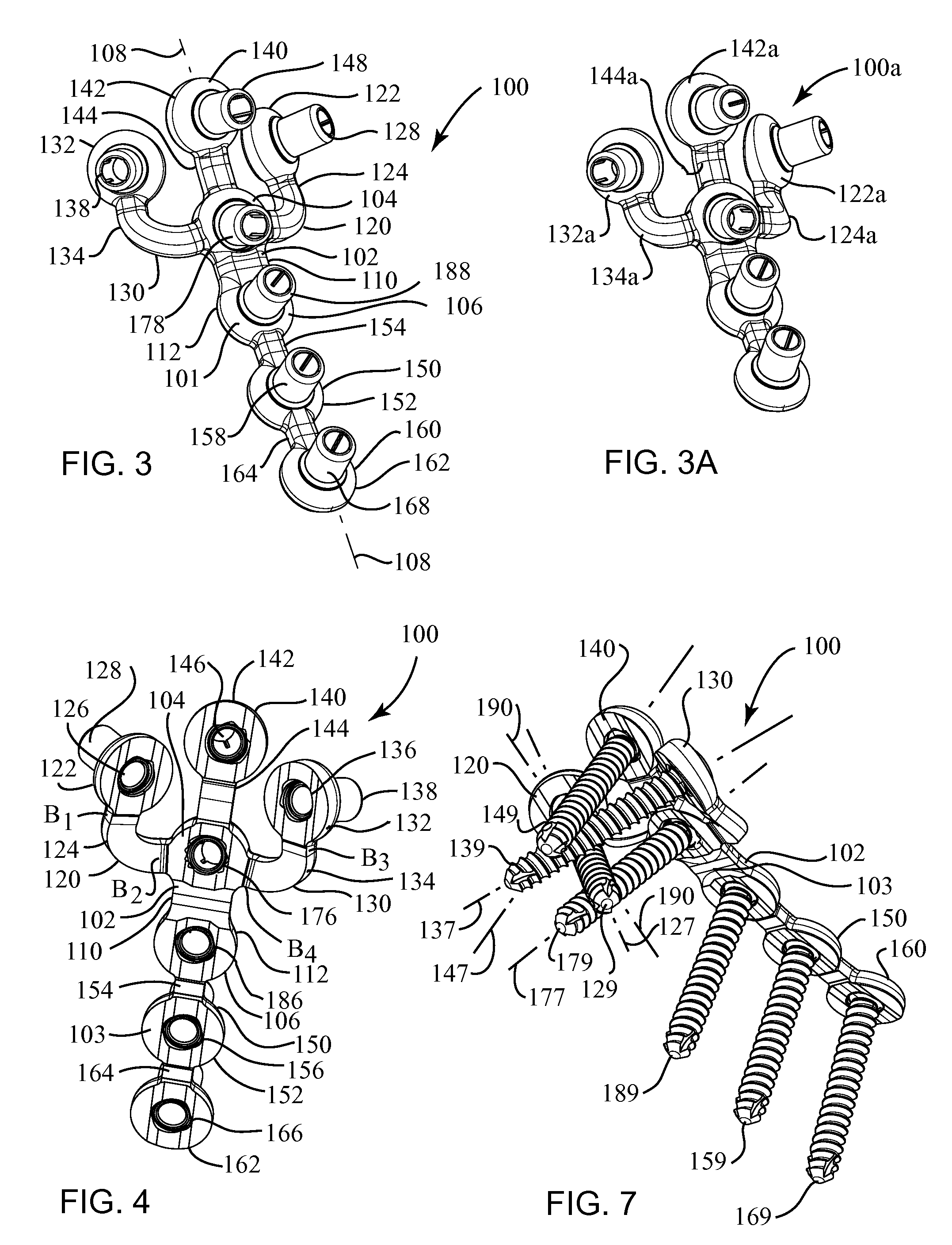
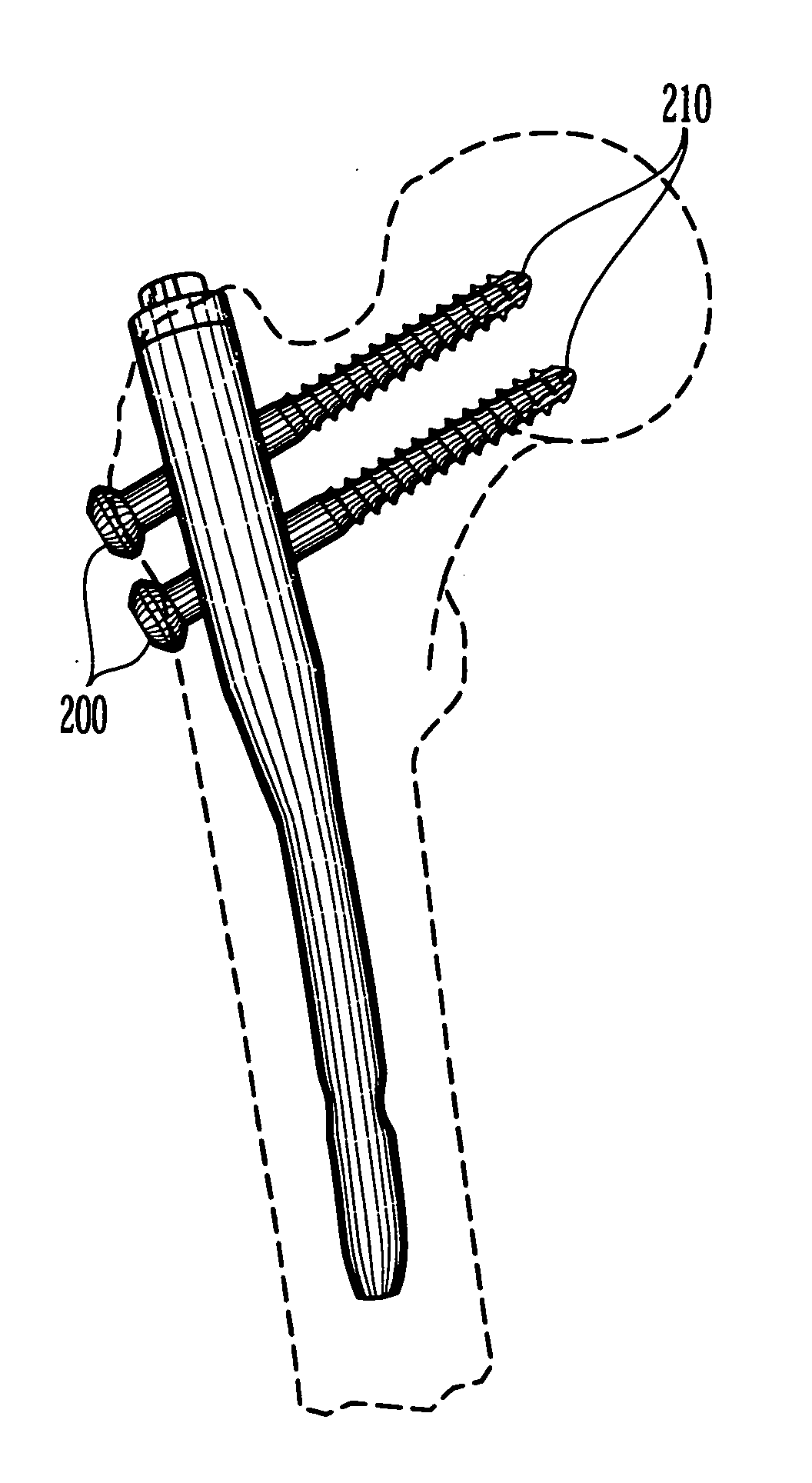
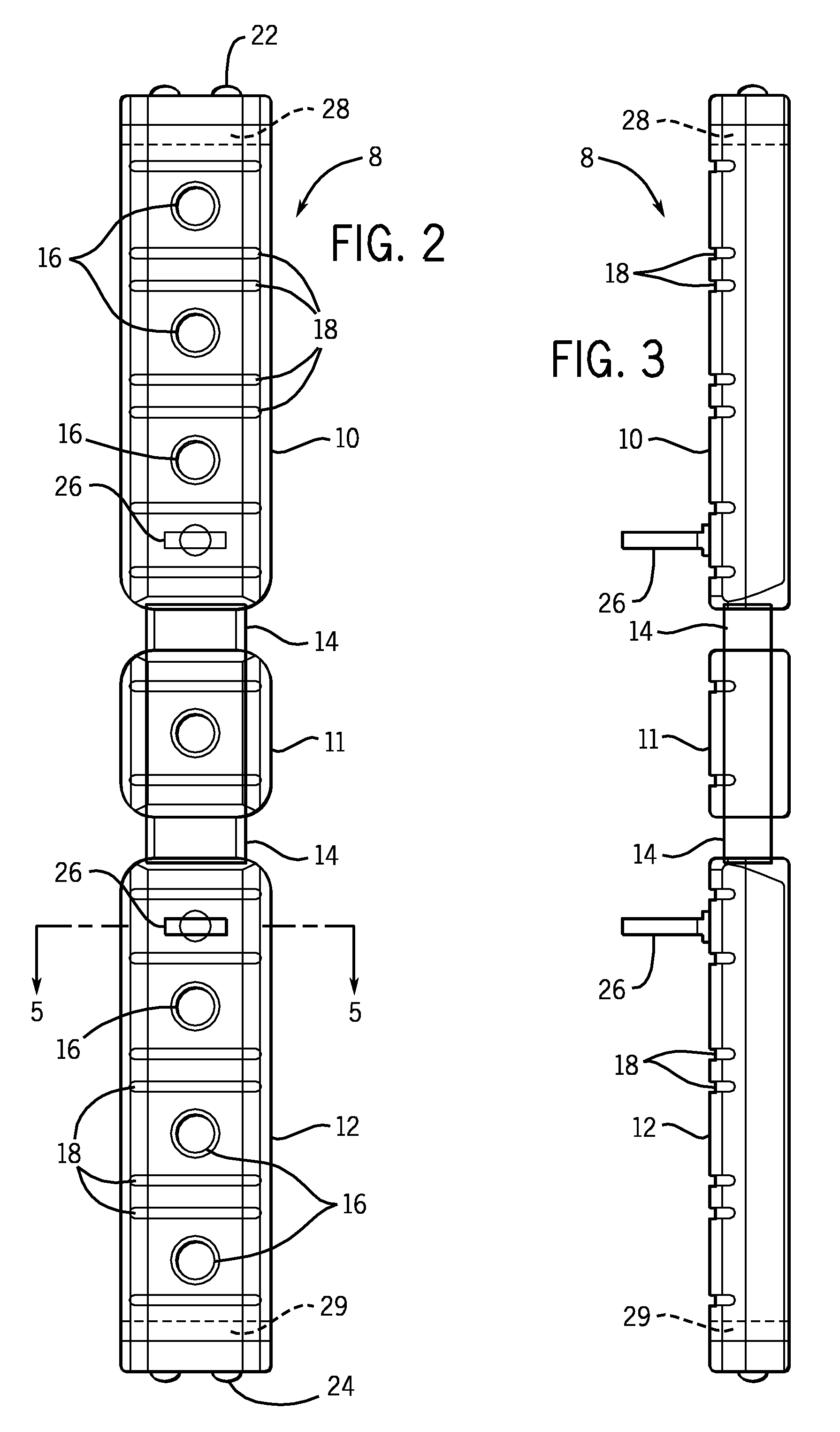
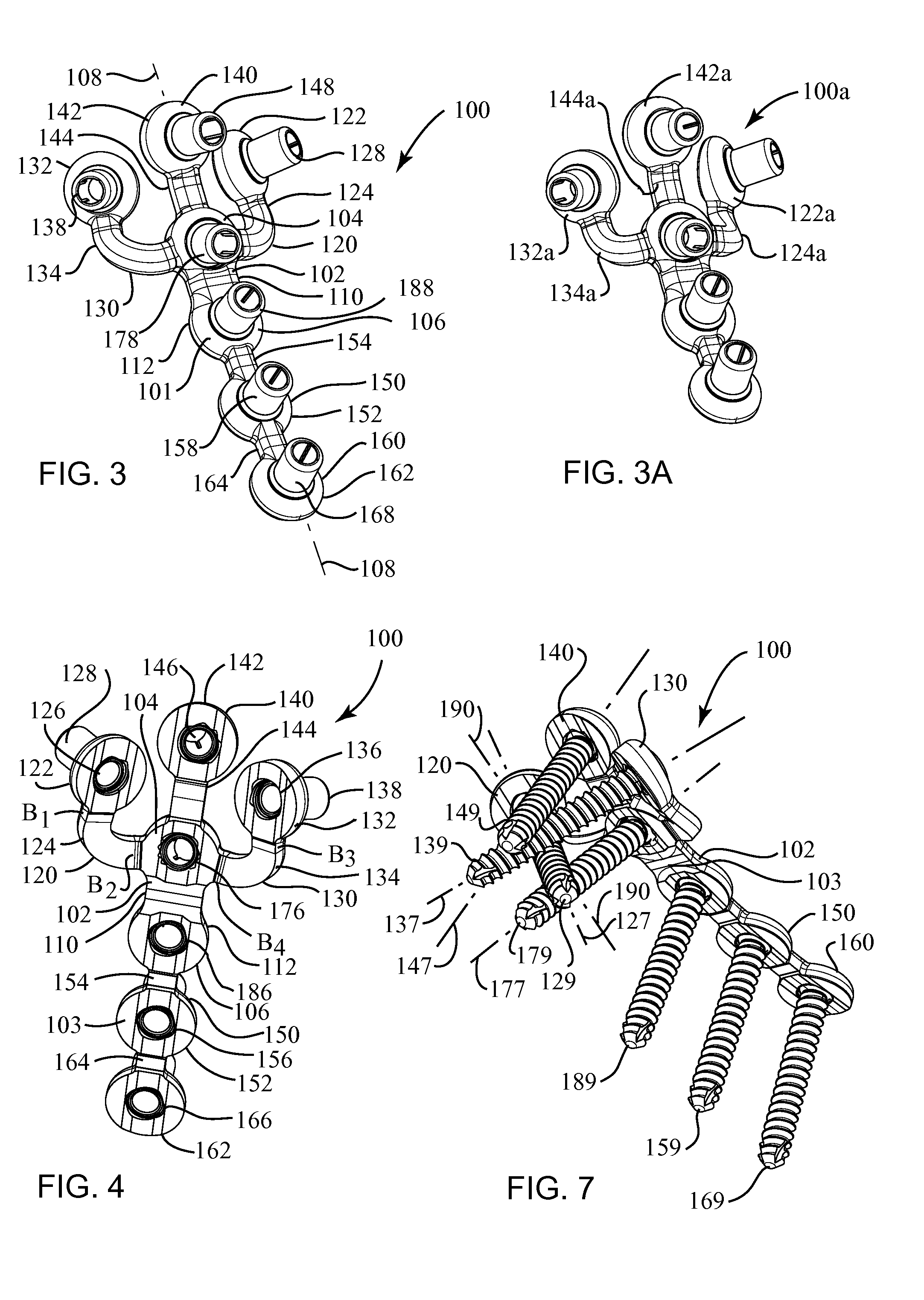
Highly-versatile variable-angle bone plate system
ActiveUS20080140130A1Improve versatilitySuture equipmentsThread cutting machinesEngineeringInternal fixation
A bone plate system for internal fixation of bone fractures includes a bone plate having a plurality of bone plate holes. The holes are constructed to receive either a non-locking, locking, or variable-angle locking bone screw. The holes have discrete columns of teeth or thread segments arranged around the inner surface of the hole for engaging threads on the heads of locking and variable-angle locking bone screws. Conventional locking bone screws engage the bone plate coaxially with the central axis of the bone plate hole. Variable-angle locking bone screws can engage the bone plate at a selectable angle within a range of selectable angles relative to the central axis of the bone plate hole. The head of the variable-angle locking screw is at least partially spherical, and the thread thereon has a profile that follows the arc-shaped radius of curvature of the spherical portion of the screwhead.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
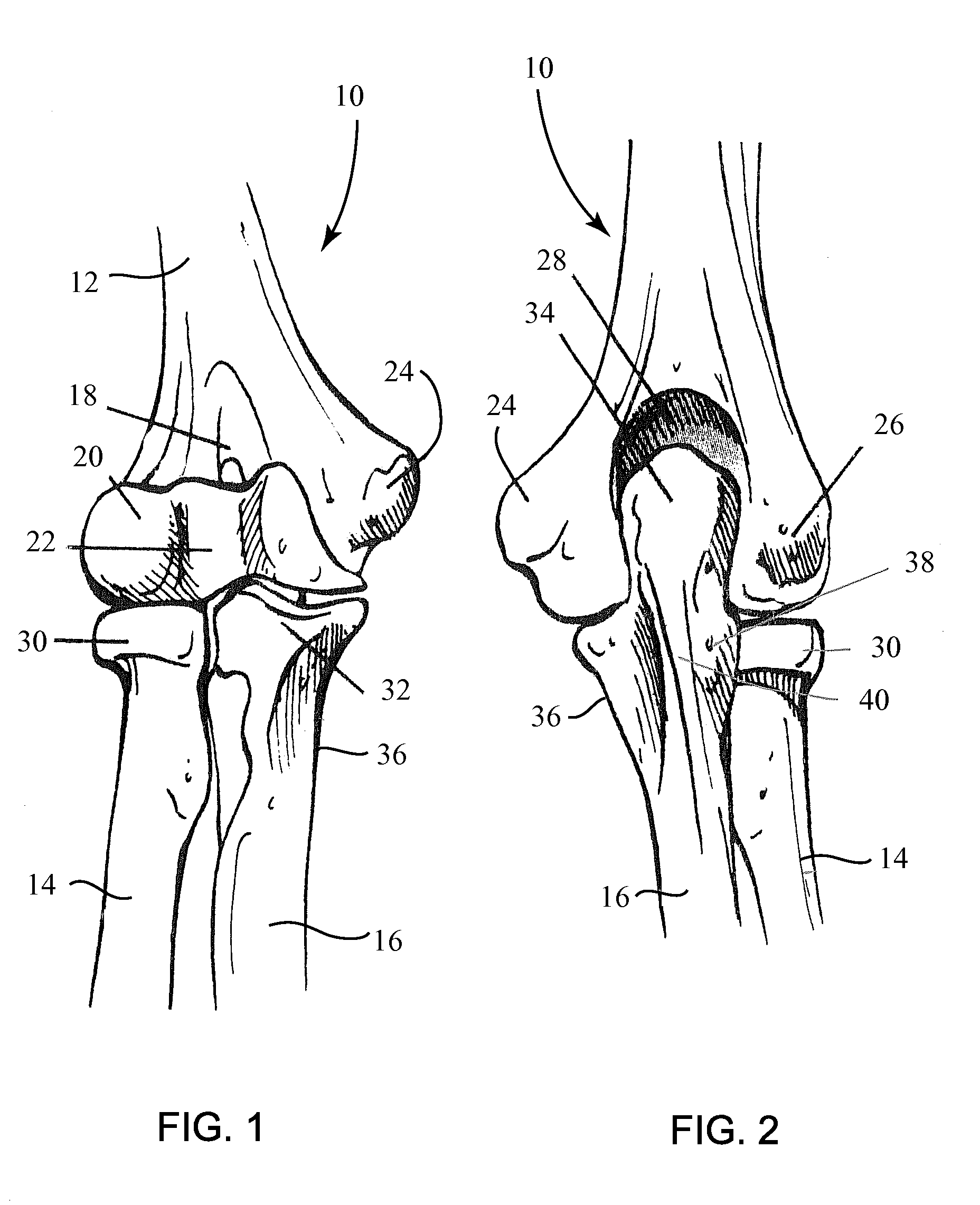
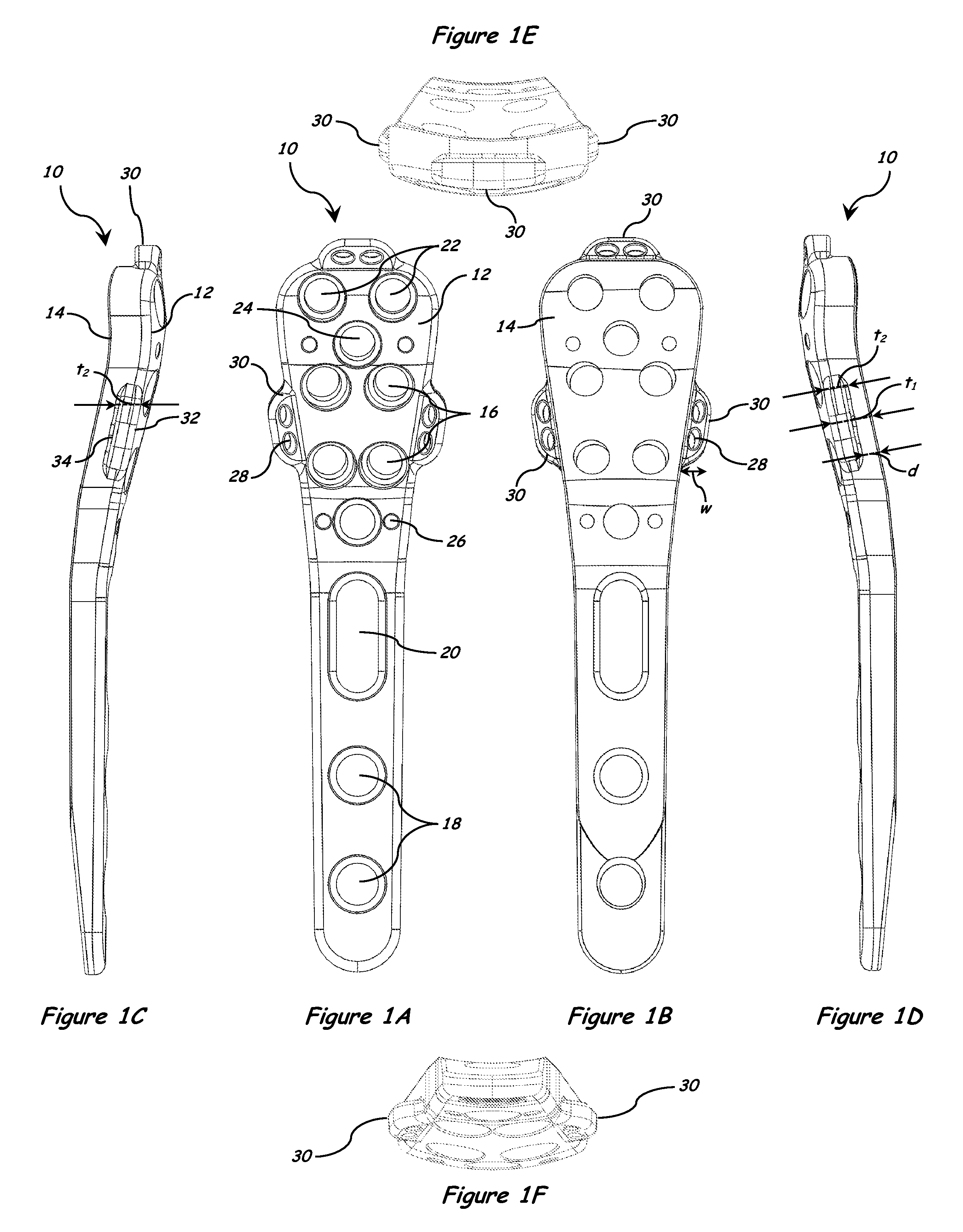
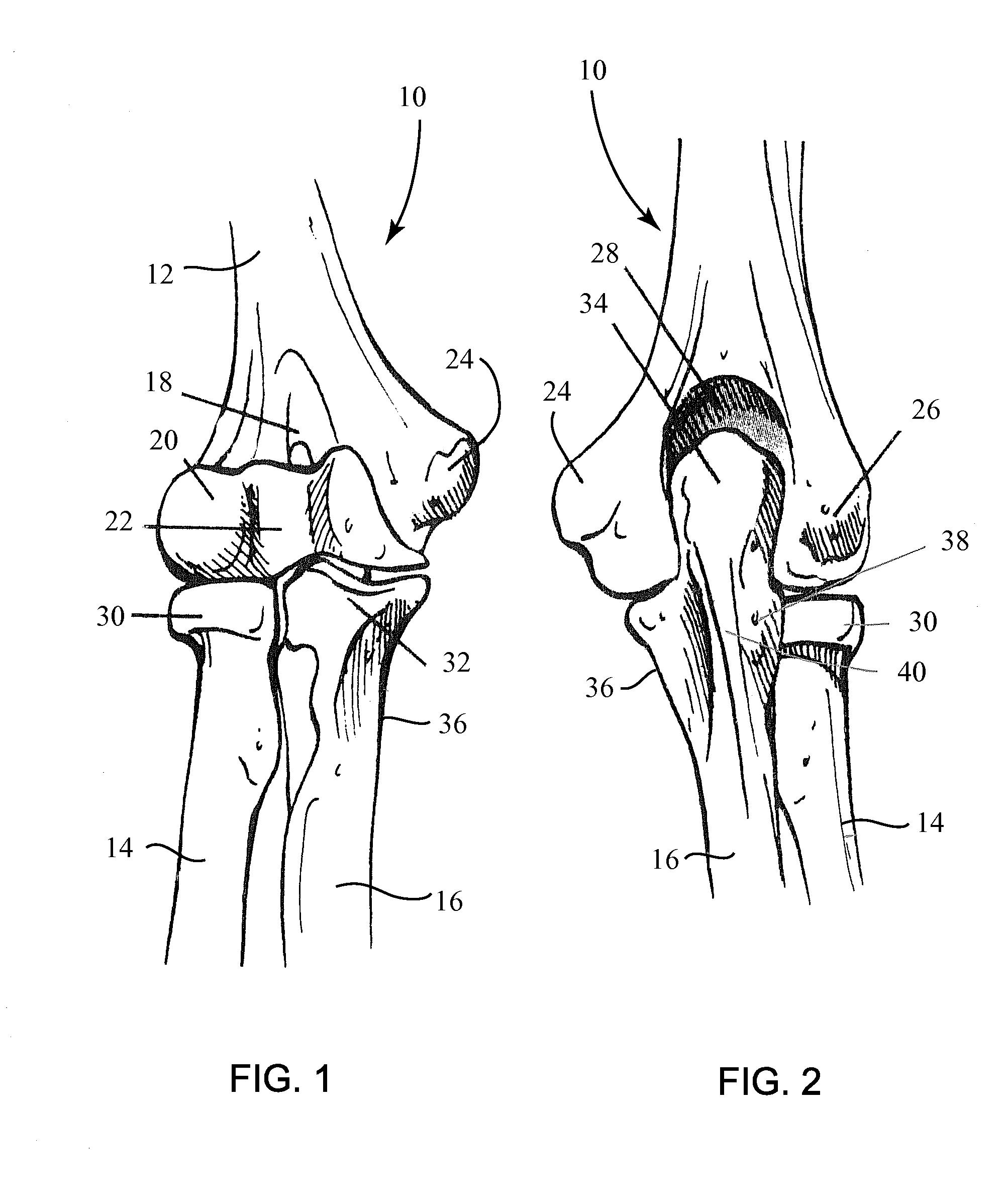
Fracture Fixation Plate for the Proximal Radius
ActiveUS20090118769A1Simple and safe processEasily and safely reconfiguredInternal osteosythesisMetal-working hand toolsProximal radiusInternal fixation
A system for the internal fixation of a fractured bone of an elbow joint of a patient includes at least one bone plate, each bone plate having a plurality of holes and generally configured to fit an anatomical surface of the fractured bone. The at least one plate is adapted to be customized to the shape of a patient's bone. The system also includes a plurality of fasteners including at least one locking fastener for attaching the bone plate to the bone. At least one of the holes is a threaded hole. Guides for plate benders, drills, and / or K-wires can be pre-assembled to the threaded holes, and the locking fastener can lock into any of the threaded holes after the guides are removed.
Owner:BIOMET CV
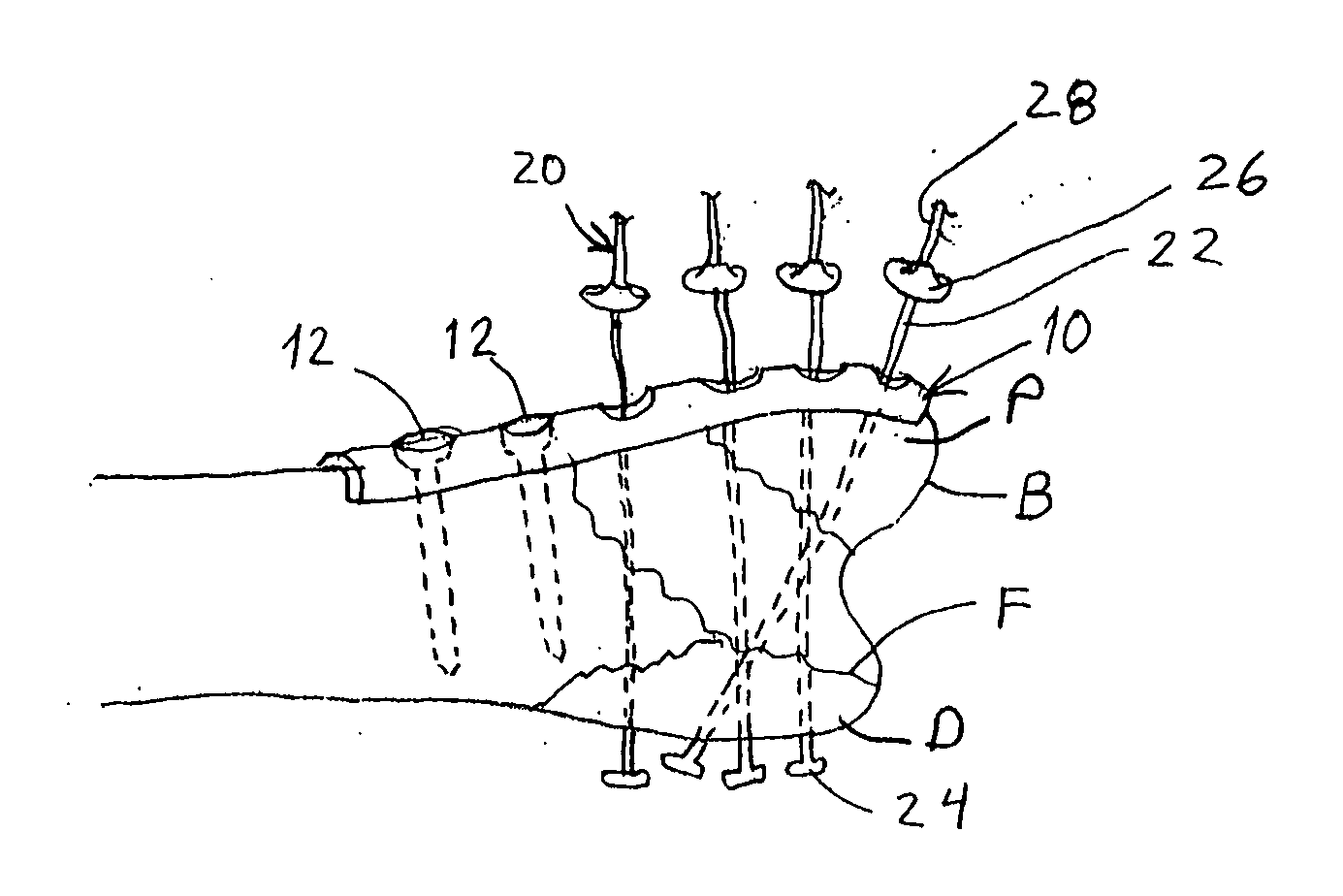
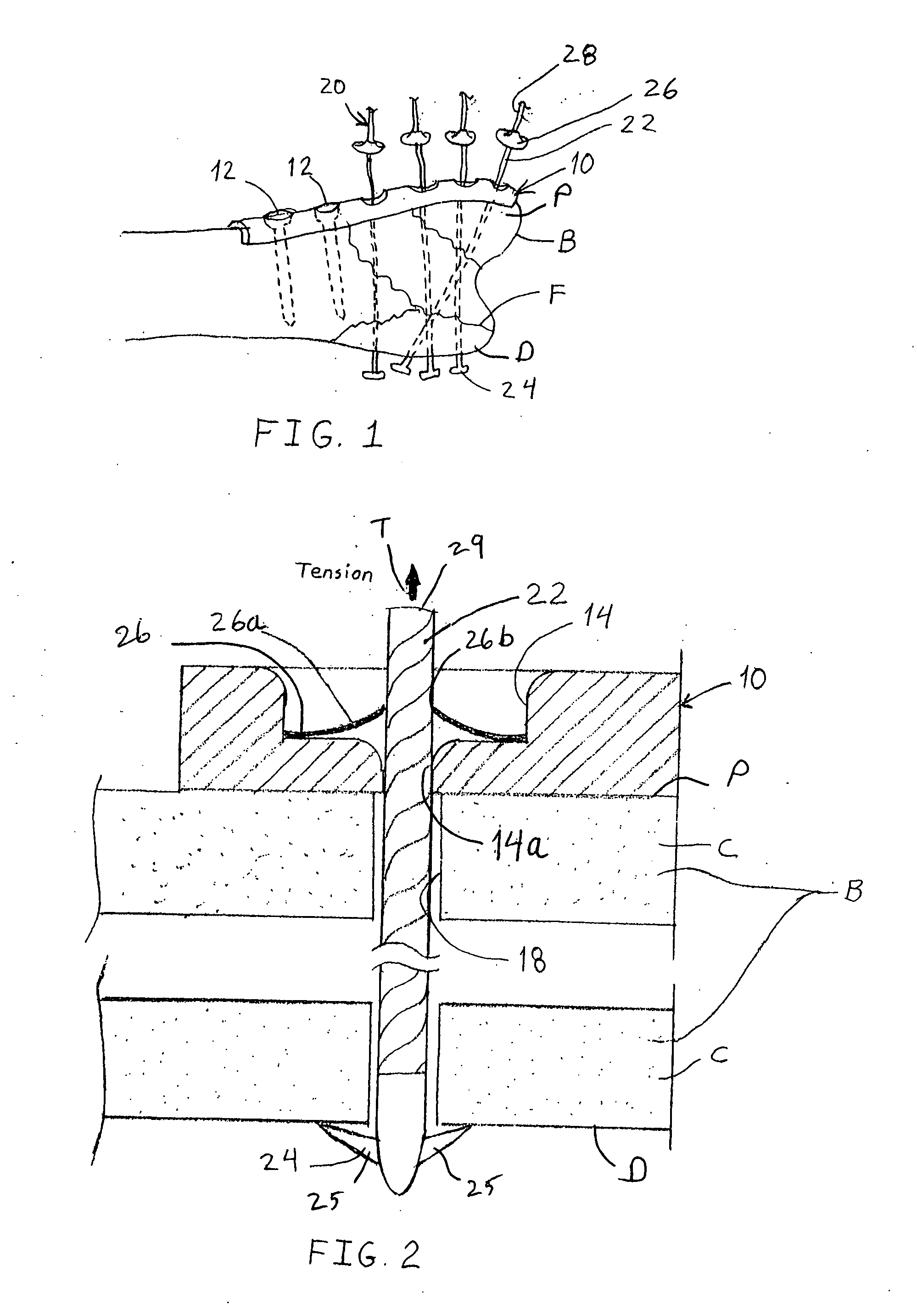
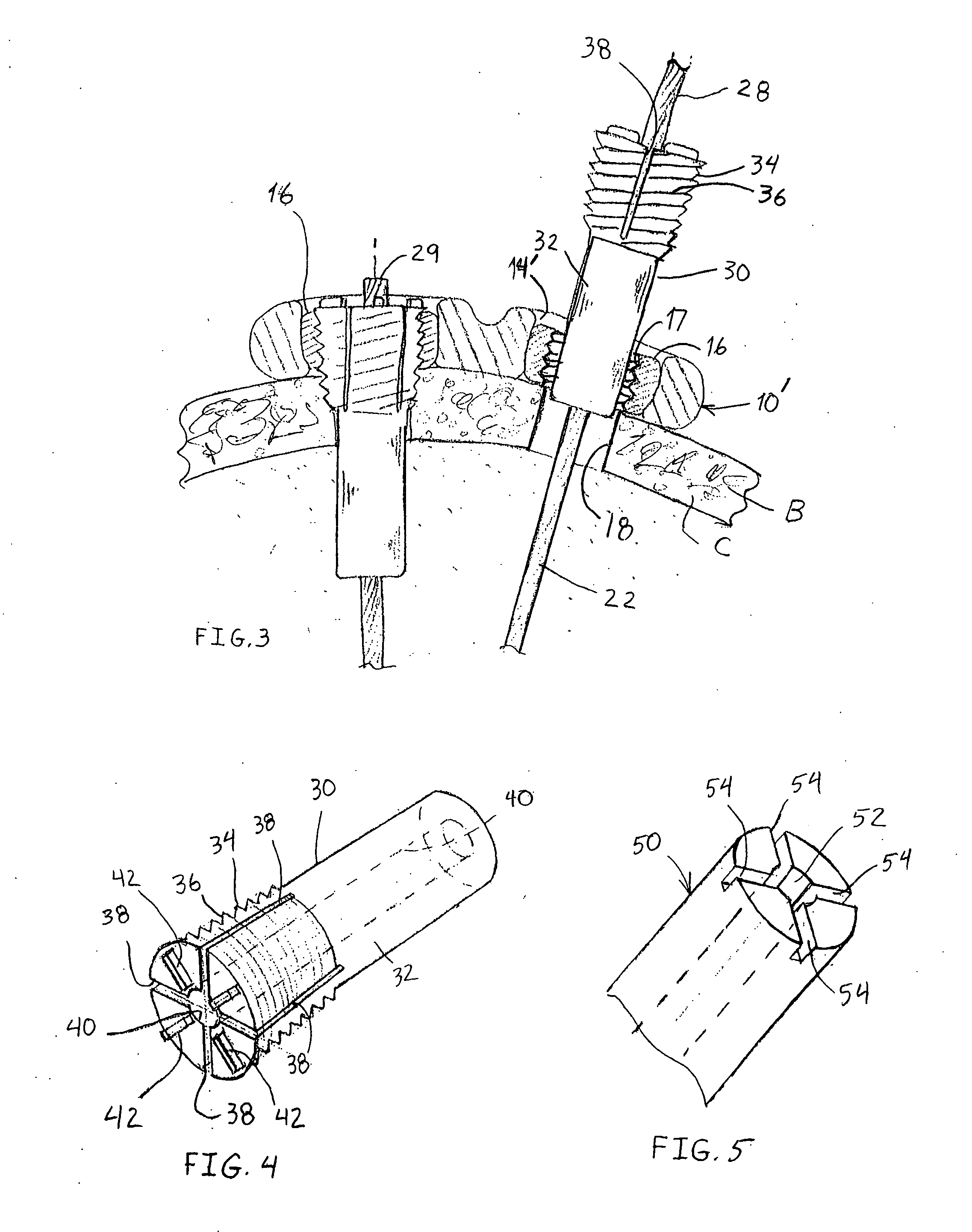
Fastening system for internal fixation
InactiveUS20070225715A1Maintain tensionEasy accessSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisInternal fixationBiomedical engineering
A bone fracture fixation system comprises a bone plate configured to bear against a proximal surface of the bone and a plurality of elongated tension elements, each sized to pass through an opening in the bone plate and through the bone from the proximal surface to a distal surface thereof. Each tension element is anchored to the bone and maintained in tension by a distal anchor attached to said tension element and configured to engage the distal surface of the bone and a proximal anchor engageable between the bone plate and the tension element.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Highly-versatile variable-angle bone plate system
A bone plate system for internal fixation of bone fractures includes a bone plate having a plurality of bone plate holes. The holes are constructed to receive either a non-locking, locking, or variable-angle locking bone screw. The holes have discrete columns of teeth or thread segments arranged around the inner surface of the hole for engaging threads on the heads of locking and variable-angle locking bone screws. Conventional locking bone screws engage the bone plate coaxially with the central axis of the bone plate hole. Variable-angle locking bone screws can engage the bone plate at a selectable angle within a range of selectable angles relative to the central axis of the bone plate hole. The head of the variable-angle locking screw is at least partially spherical, and the thread thereon has a profile that follows the arc-shaped radius of curvature of the spherical portion of the screwhead.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Elbow Fracture Fixation System
InactiveUS20090118768A1Simple and safe processEasily and safely reconfiguredSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisInternal fixationFractured bone
A system for the internal fixation of a fractured bone of an elbow joint of a patient includes at least one bone plate, each bone plate having a plurality of holes and generally configured to fit an anatomical surface of the fractured bone. The at least one plate is adapted to be customized to the shape of a patient's bone. The system also includes a plurality of fasteners including at least one locking fastener for attaching the bone plate to the bone. At least one of the holes is a threaded hole. Guides for plate benders, drills, and / or K-wires can be pre-assembled to the threaded holes, and the locking fastener can lock into any of the threaded holes after the guides are removed.
Owner:BIOMET CV
Orthopaedic universal appliance box
InactiveCN102038553AReasonably placedConvenient remote medical treatmentSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsEngineeringInternal fixation
The invention discloses an orthopaedic universal appliance box which comprises a box body and an upper cover, wherein the upper end of the bottom surface of the box body is uniformly fixed with a plurality of screw take-out device boxes; the left side of the leftmost screw take-out device box is provided with a vertical quick-change straight-handle groove; the left side of the lower end of the bottom surface of the box body is provided with a transverse A-shaped broken-screw take-out embedding groove, and the right side is provided with a transverse T-shaped quick-change handle groove; and the lower side of the A-shaped broken-screw take-out embedding groove and the T-shaped quick-change handle groove is provided with a transverse osteotome groove. The invention solves the problem that the standby tools of orthopaedic surgical appliances are not unified and not convenient to carry, which is common in the clinical work. The overall structure of the orthopaedic universal appliance box is compact. By reasonably putting a set of orthopaedic steel plates and surgical universal appliances of a nail-stick internal fixation system and a bracket external fixation system in the box body, the orthopaedic universal appliance box meets the use requirements during surgery.
Owner:中国人民解放军第一零五医院
Intramedullary nail
An intramedullary nail in which a plurality of fins (26) which protrude radially are formed on the outer circumference of the nail, providing firm internal fixation which makes the nail easy to operate.
Owner:FUJIMORI JUHRO +2
Intramedullary rod with spiraling flutes
ActiveUS20050277936A1Reduce usageLower potentialInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFluteIntramedullary rod
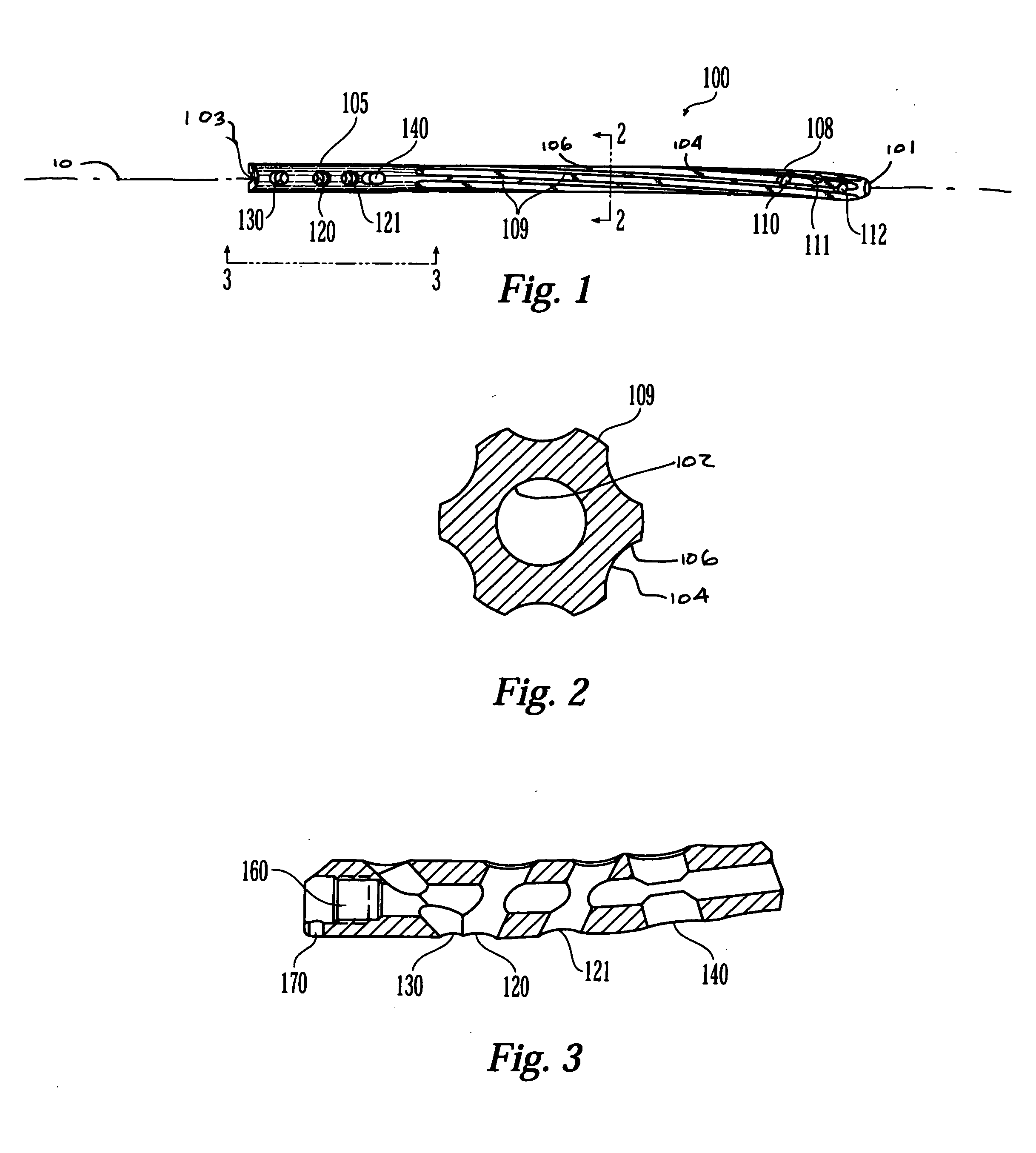
This invention relates generally to devices, systems and methods for the internal fixation of bone fractures, and particularly, to intramedullary fracture fixation devices such as those used in, for example, the treatment of long bone fractures. An IM rod preferably is provided with multiple curved sections in different planes preferably designed to conform with the long bones of a patient, both during insertion and in the rod's final position in the long bone. In addition, the overlap of portions of the curved sections results in a co-planar curvature of portions of the IM rod which assist in the insertion process by guiding the proper rotation of the IM rod as it is inserted into the bone. Spiraling flutes extending down the distal portion of the rod also assist in properly guiding and orienting the rod about its longitudinal axis during insertion such that the appropriate segment of the curved rod conforms with the appropriate portion of the long bone at the appropriate place.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
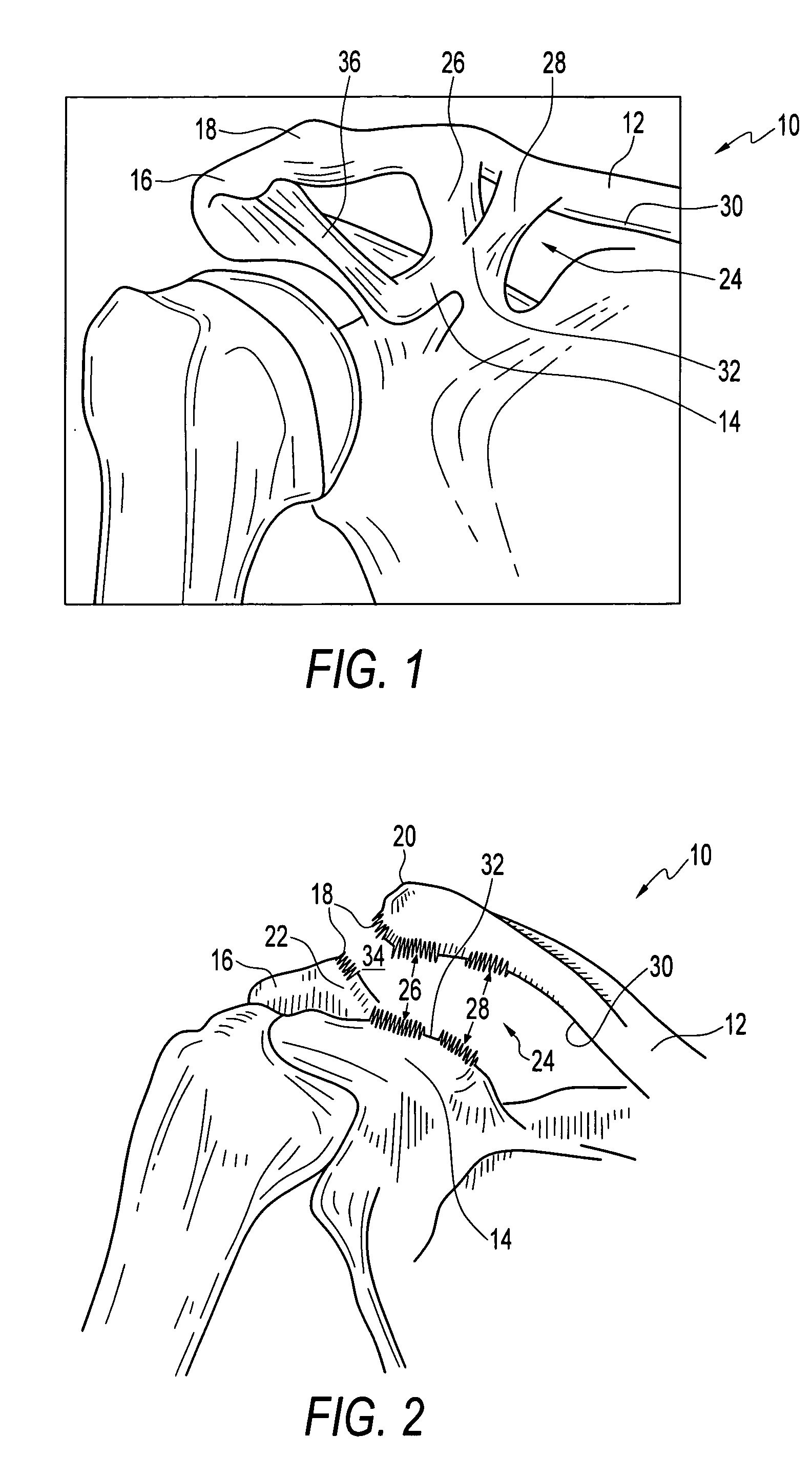
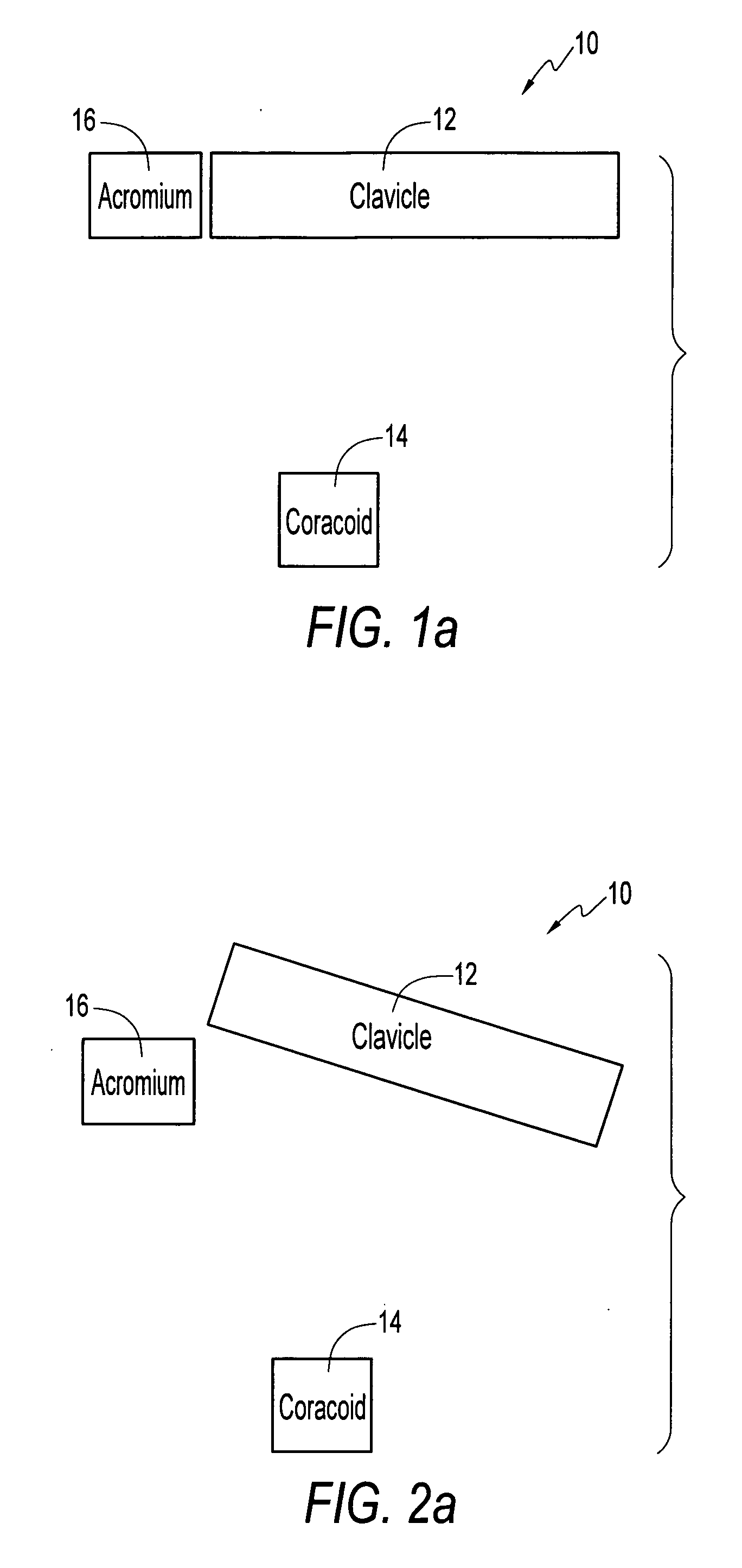
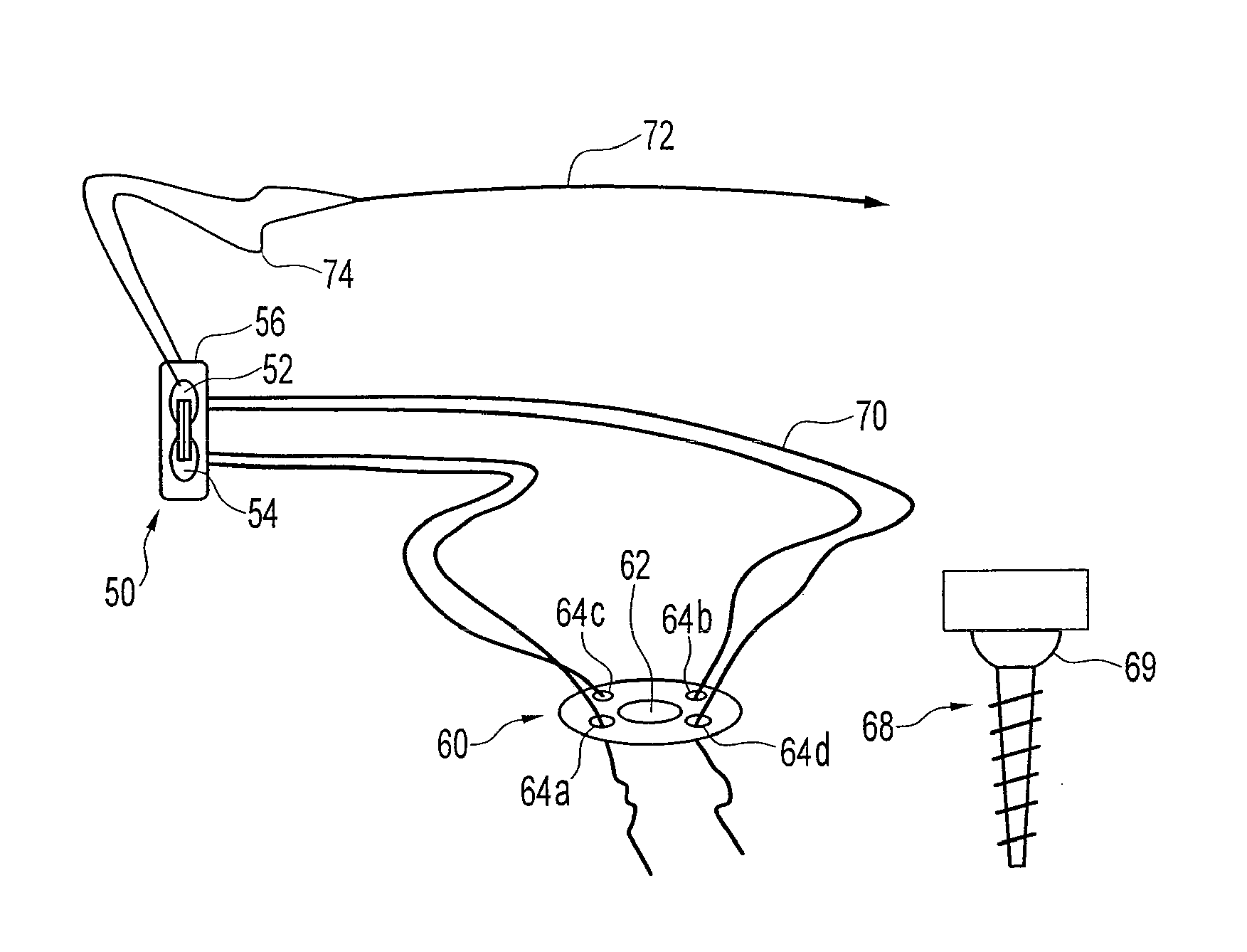
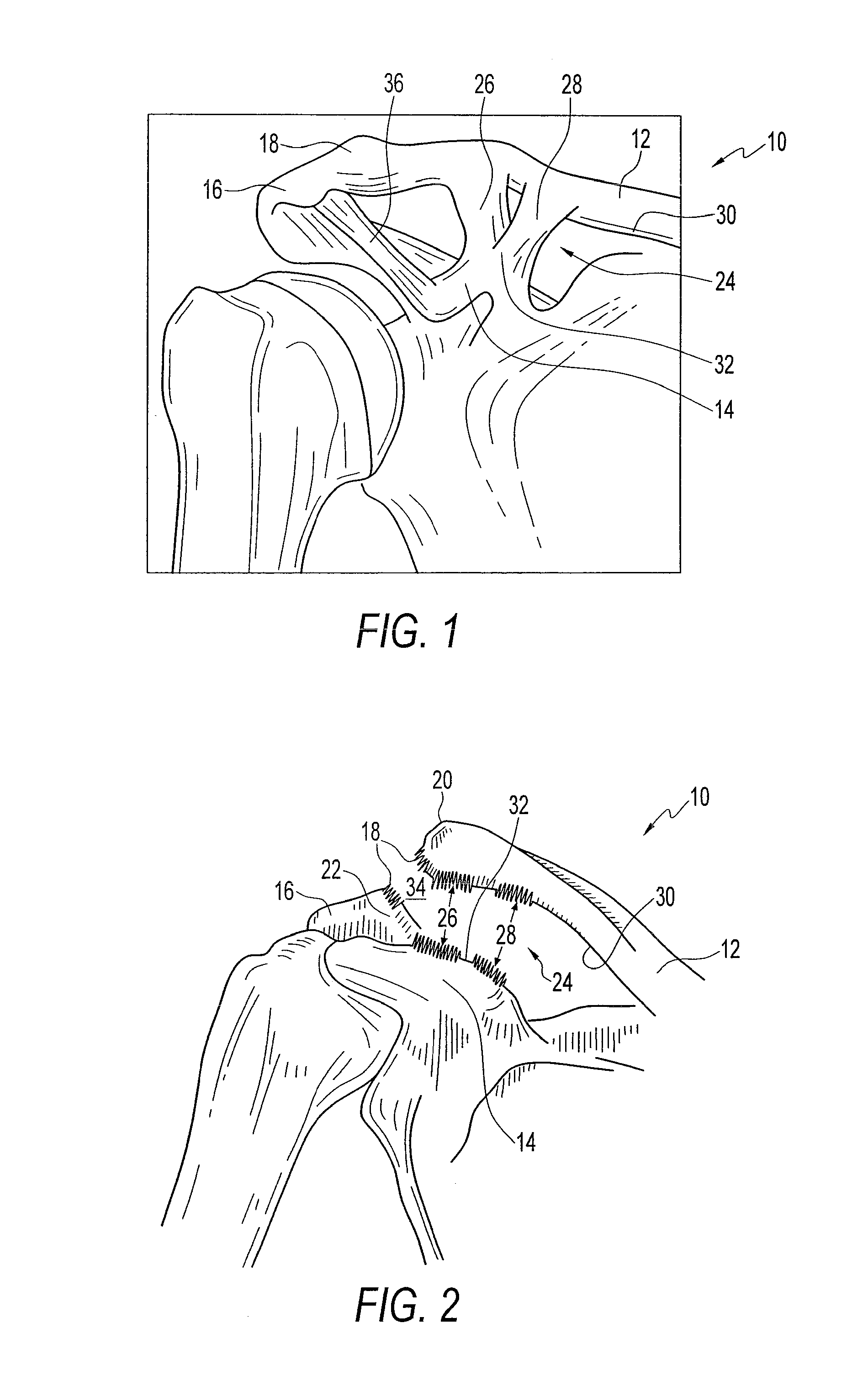
Method and apparatus for internal fixation of an acromioclavicular joint dislocation of the shoulder
ActiveUS8512376B2Reduce fixed distanceReduce distanceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisInternal fixationIliac screw
An apparatus and method for surgically reducing and internally fixing a shoulder acromioclavicular joint dislocation are disclosed. The apparatus preferably comprises a button and a washer, the washer being flexibly secured to the coracoid process of the scapula by means of a bone screw, the button and washer being secured together by means of a first suture. A second suture is provided secured between the button and a needle, such that the needle and associated button, may be advanced through a hole drilled through the clavicle, wherein the button and the washer may then be tightened, reducing the coracoclavicular distance, by means of the first suture connected therebetween, to reduce and hold a desired acromioclavicular joint dislocation.
Owner:ARTHREX
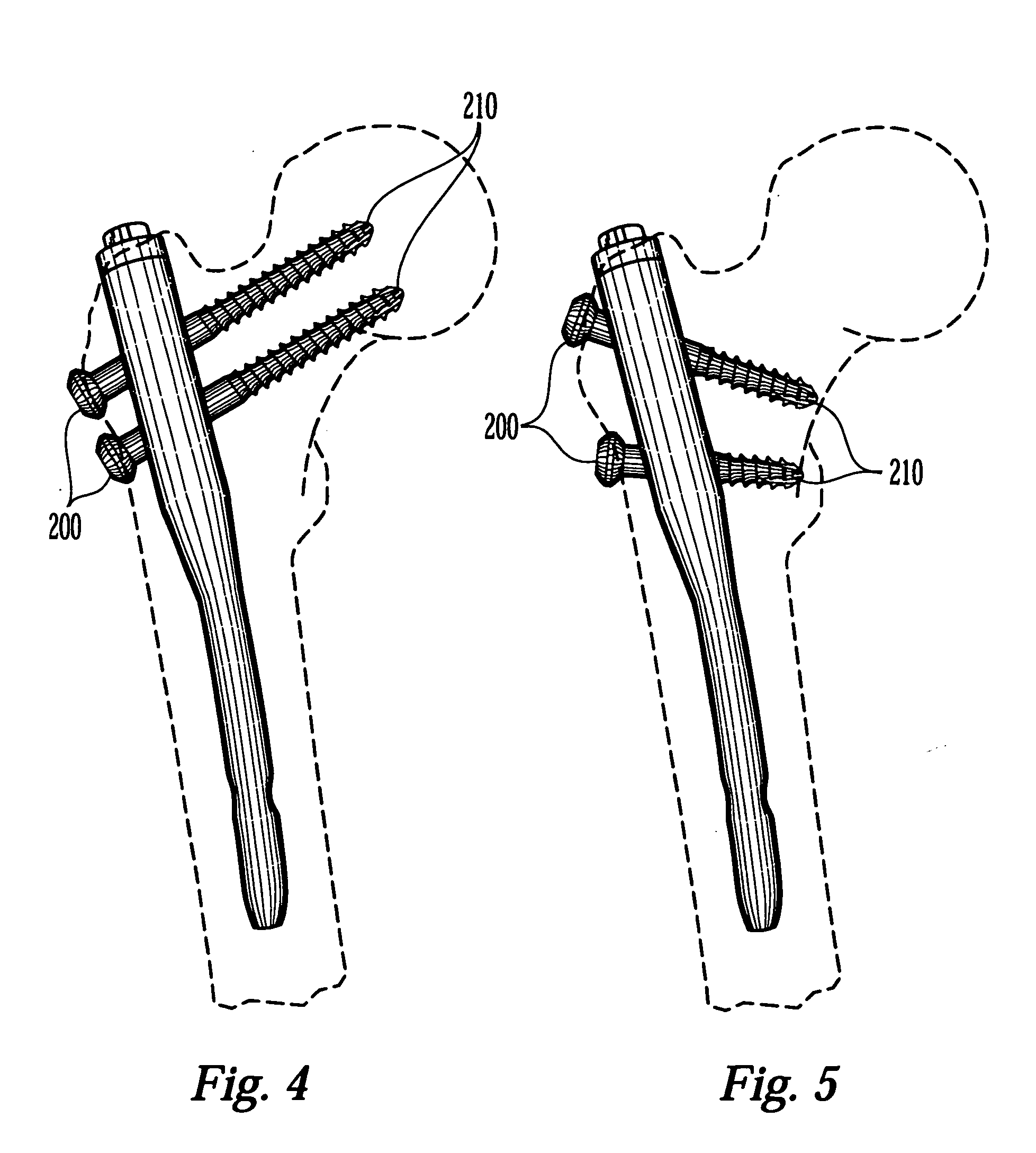
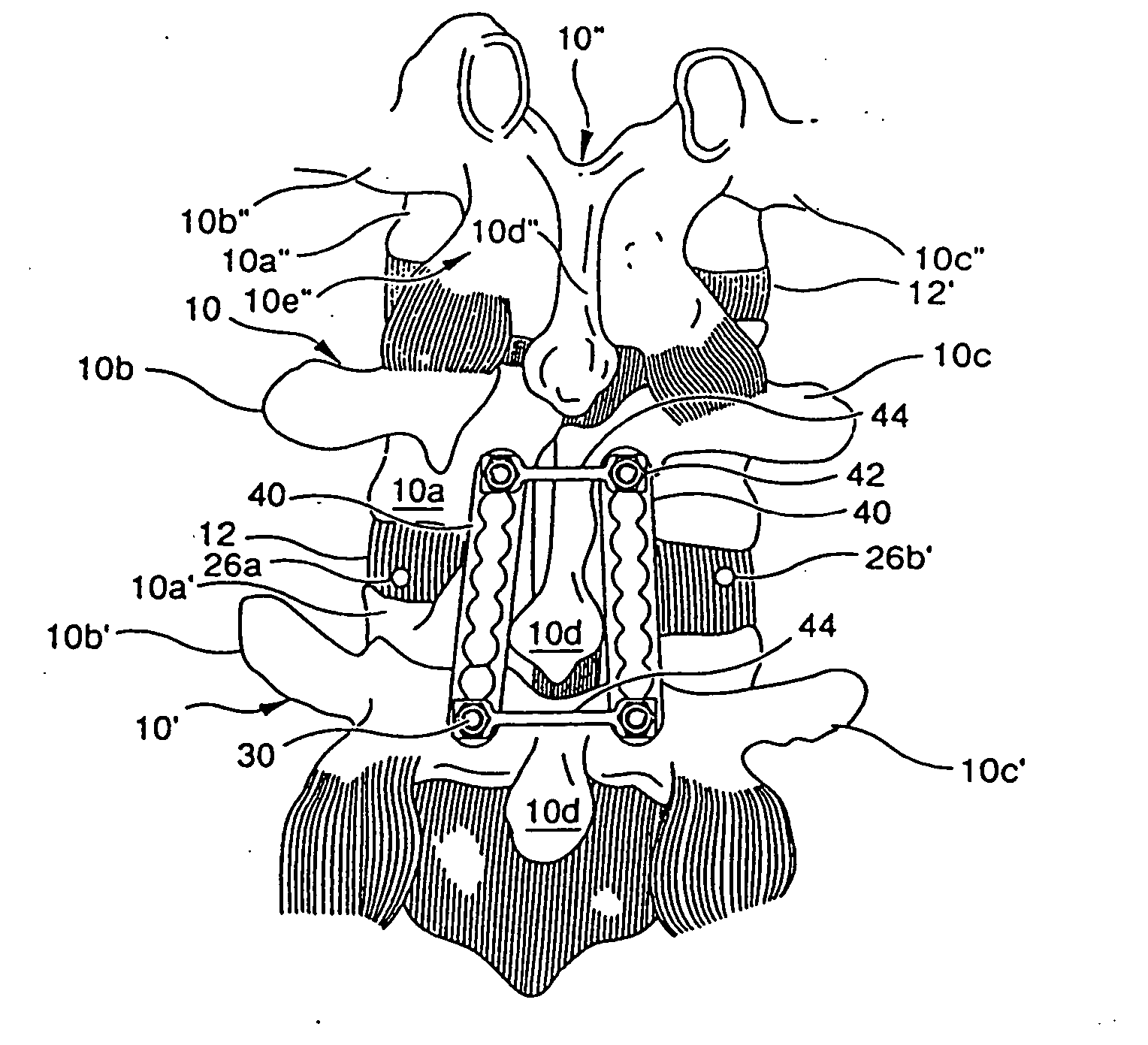
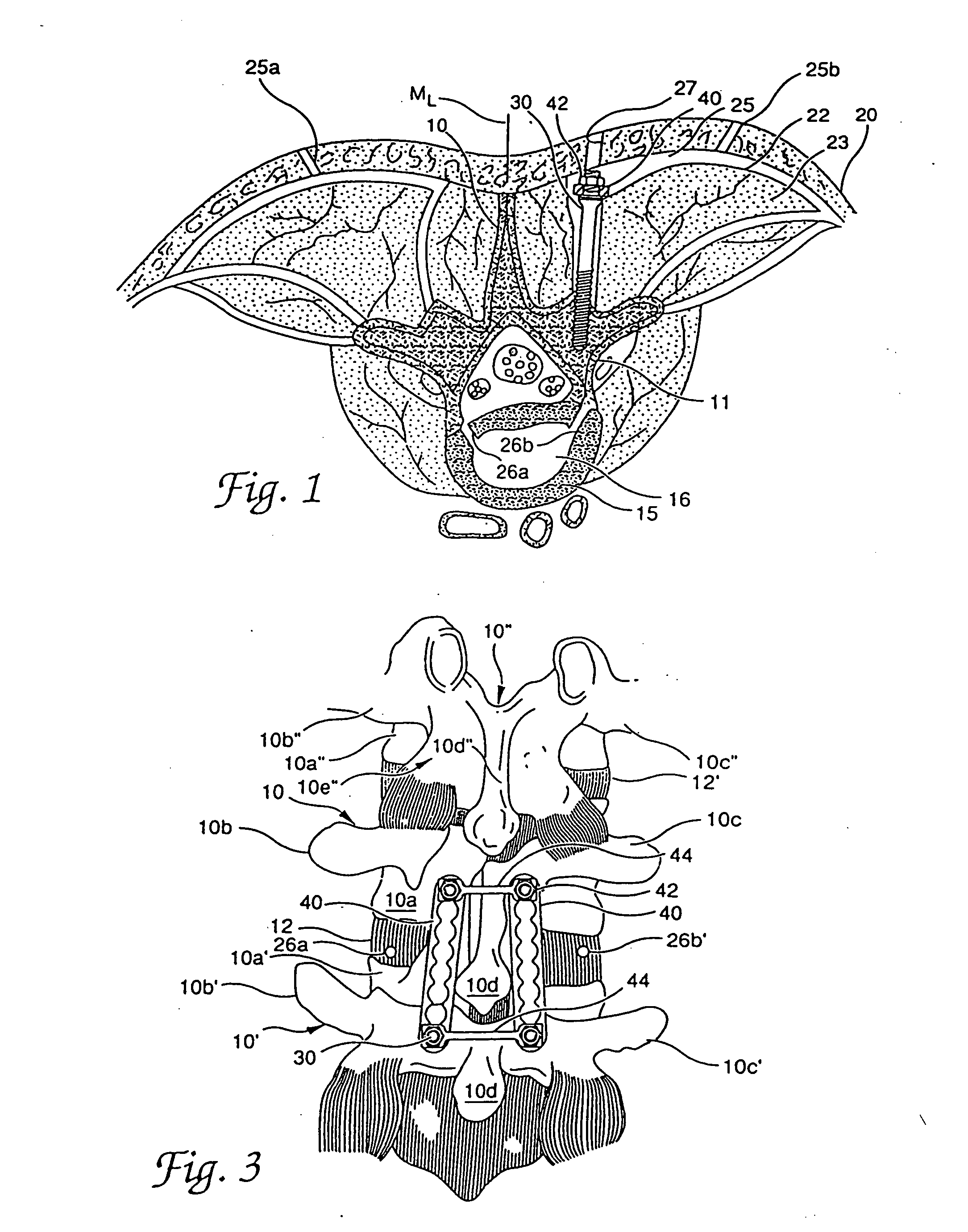
Systems and methods for fixation of adjacent vertebrae
InactiveUS20050038434A1Permit fusionReduce infectionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisMuscle tissueDilator
A method for internal fixation of vertebra of the spine to facilitate graft fusion includes steps for excising the nucleus of an affected disc, preparing a bone graft, instrumenting the vertebrae for fixation, and introducing the bone graft into the resected nuclear space. Disc resection is conducted through two portals through the annulus, with one portal supporting resection instruments and the other supporting a viewing device. The fixation hardware is inserted through small incisions aligned with each pedicle to be instrumented. The hardware includes bone screws, fixation plates, engagement nuts, and linking members. In an important aspect of the method, the fixation plates, engagement nuts and linking members are supported suprafascially but subcutaneously so that the fascia and muscle tissue are not damaged. The bone screw is configured to support the fixation hardware above the fascia. In a further aspect of the invention, a three component dilator system is provided for use during the bone screw implantation steps of the method.
Owner:MATHEWS HALLETT H
Highly-Versatile Variable-Angle Bone Plate System
A bone plate system for internal fixation of bone fractures includes a bone plate having a plurality of bone plate holes. The holes are constructed to receive either a non-locking, locking, or variable-angle locking bone screw. The holes have discrete columns of teeth or thread segments arranged around the inner surface of the hole for engaging threads on the heads of locking and variable-angle locking bone screws. Conventional locking bone screws engage the bone plate coaxially with the central axis of the bone plate hole. Variable-angle locking bone screws can engage the bone plate at a selectable angle within a range of selectable angles relative to the central axis of the bone plate hole. The head of the variable-angle locking screw is at least partially spherical, and the thread thereon has a profile that follows the arc-shaped radius of curvature of the spherical portion of the screwhead.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
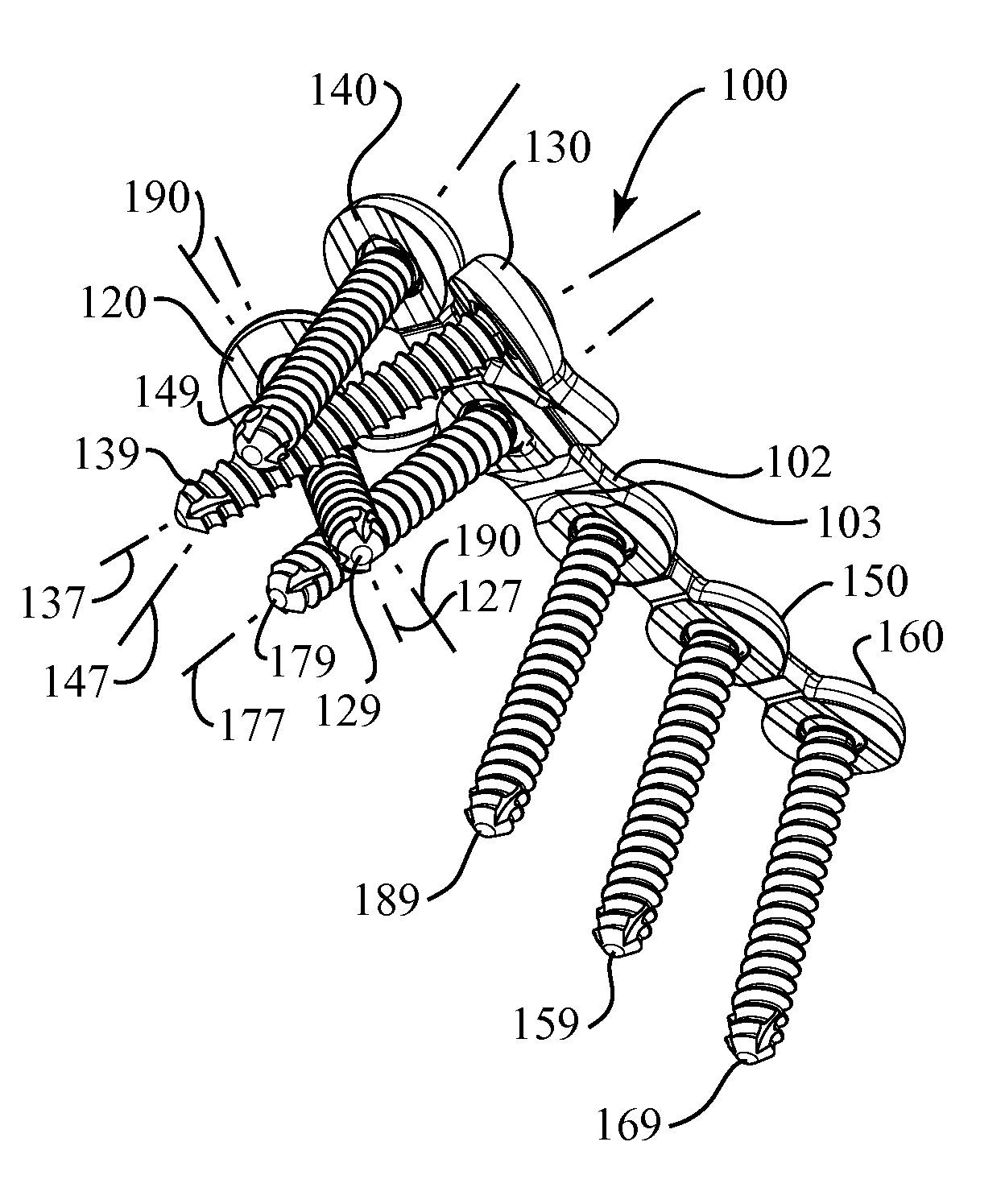
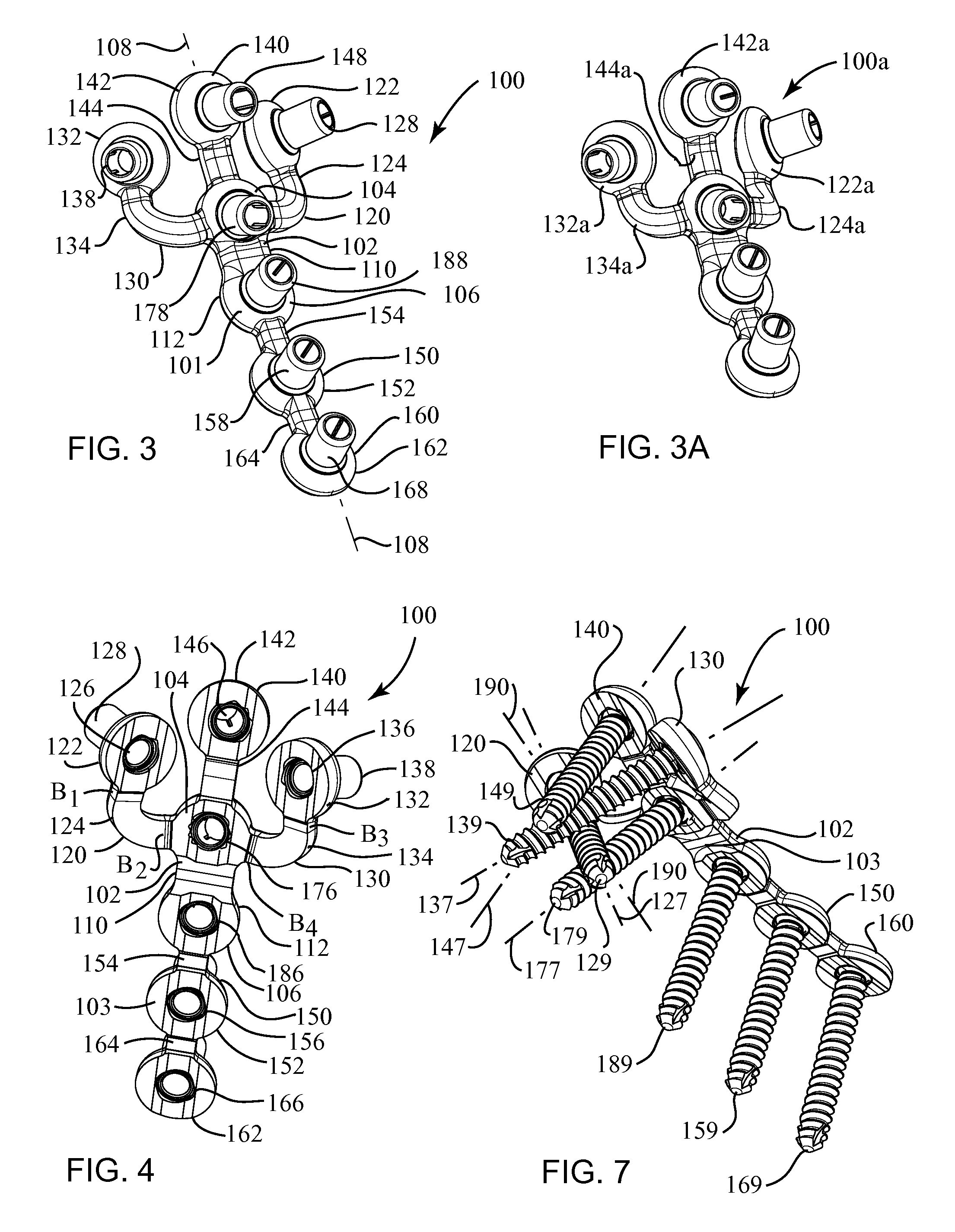
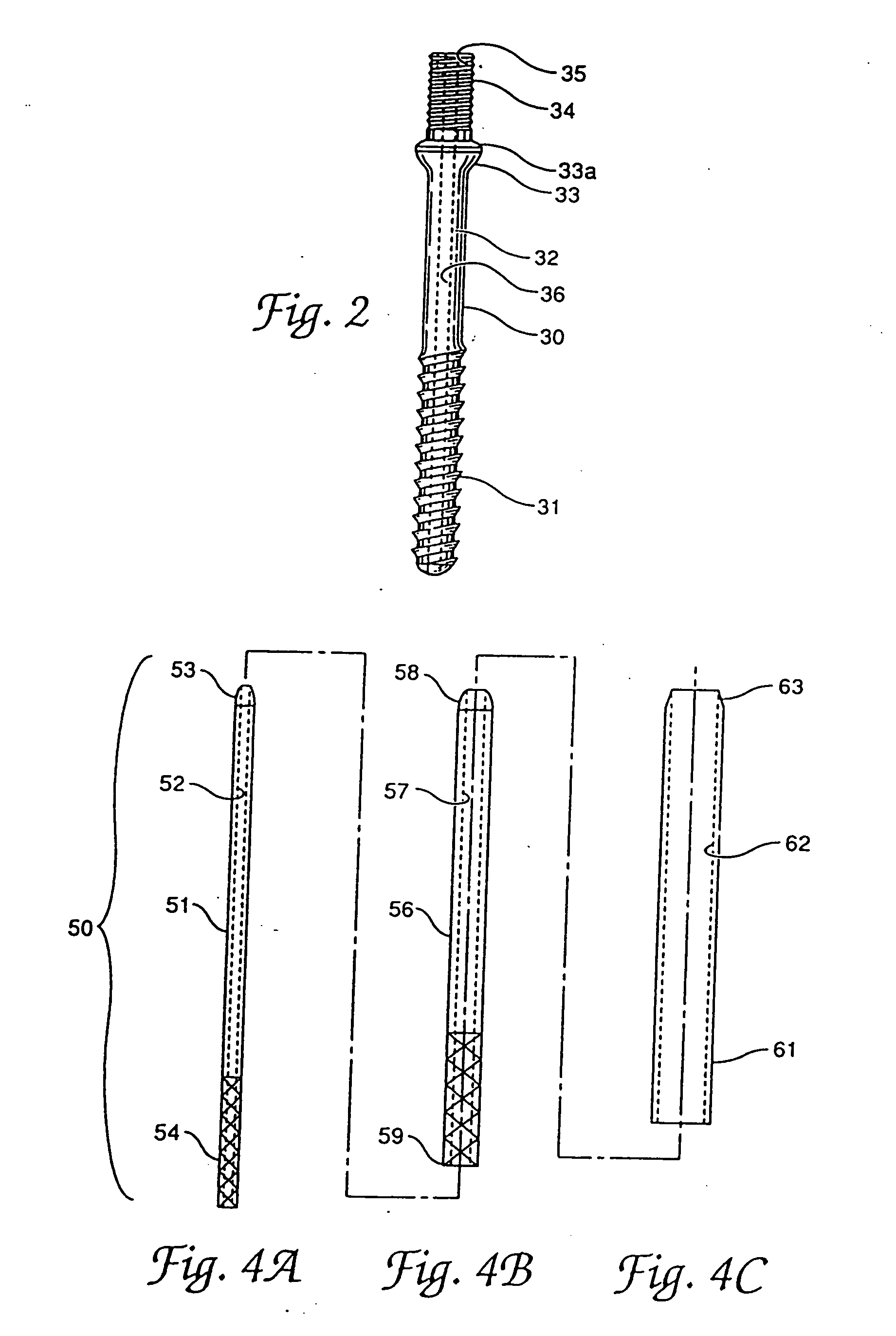
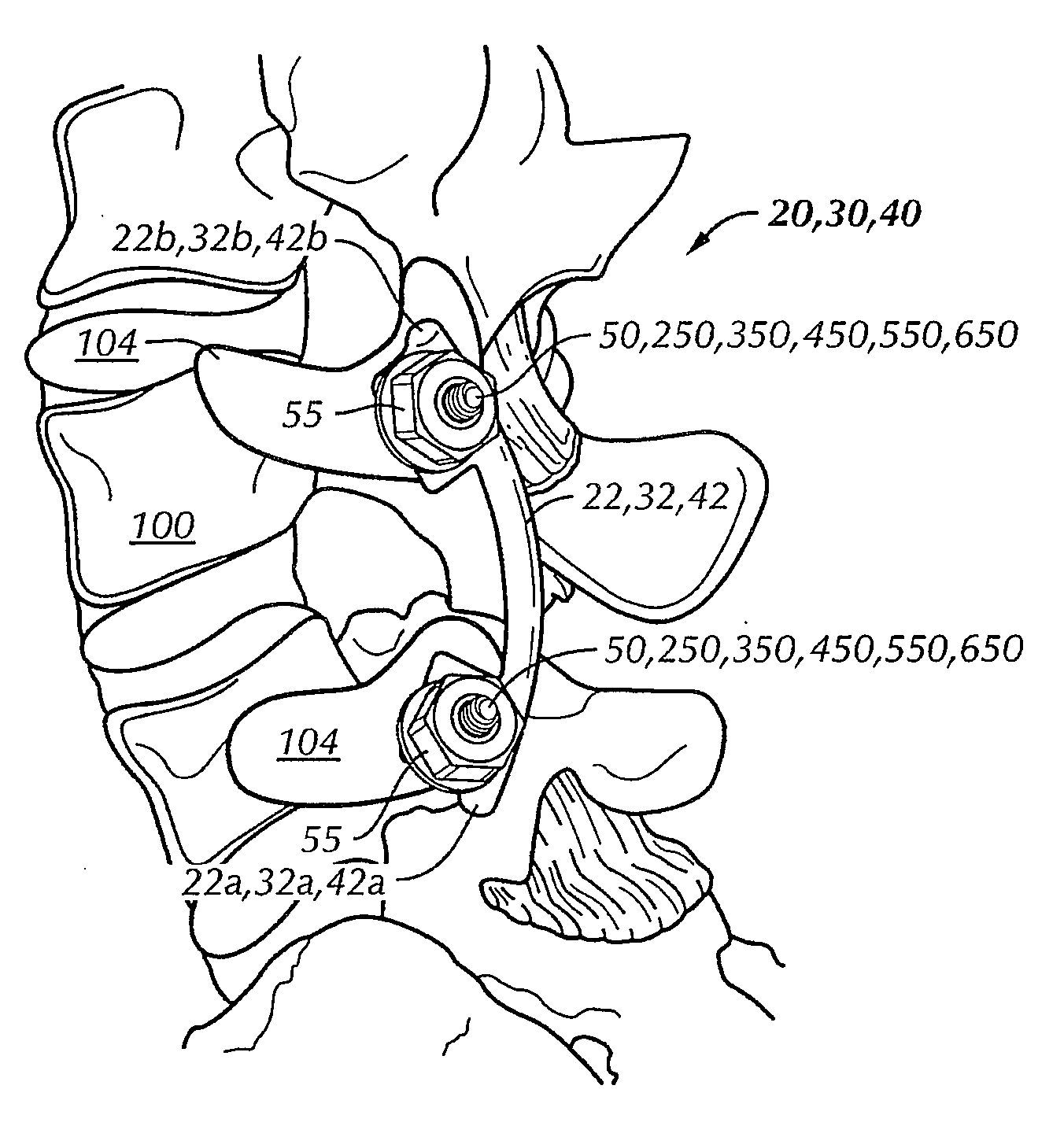
Internal fixation system for spine surgery
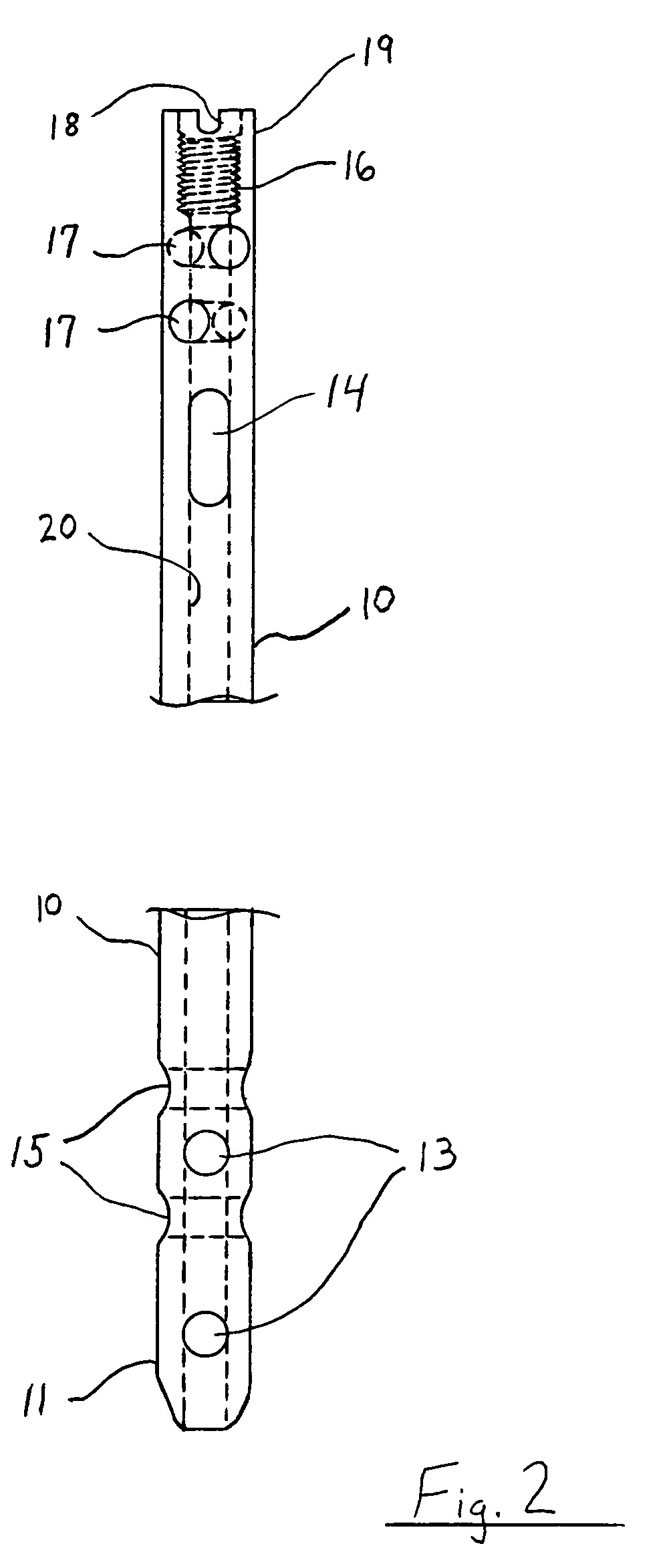
An internal fixation rod for spine surgery includes an elongate body, a first rod end, a second rod end, a first mounting member and a second mounting member. The first mounting member is disposed proximate the first rod end, and the second mounting member is disposed proximate the second rod end. The first mounting member and the second mounting member are smaller in cross-section than the elongate body.
Owner:CONCEPT MATRIX
Internal fixation element for hip acetabular shell
InactiveUS20050288793A1Reduced cross sectionImprove deformationJoint implantsAcetabular cupsCouplingProsthesis
An acetabular cup assembly for a prosthetic hip joint includes an outer shell for attachment to the acetabulum. The outer shell has an inner surface receiving a bearing insert portion. Complimentary coupling features are provided on the inner surface of the outer shell and the outer surface of the bearing insert for coupling the bearing insert to the outer shell. A plurality of adaptors are provided having an outer surface for engaging an inner surface of the outer shell and having an inner surface for receiving the bearing insert. Each adaptor has at least one radial extending strap or flange for engaging the bone surrounding the acetabulum. The straps or flanges may be of different sizes and shapes and may be at different locations on the adapter. The inner surface of the adaptor includes the same coupling features as the shell so as to be able to receive a bearing insert.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
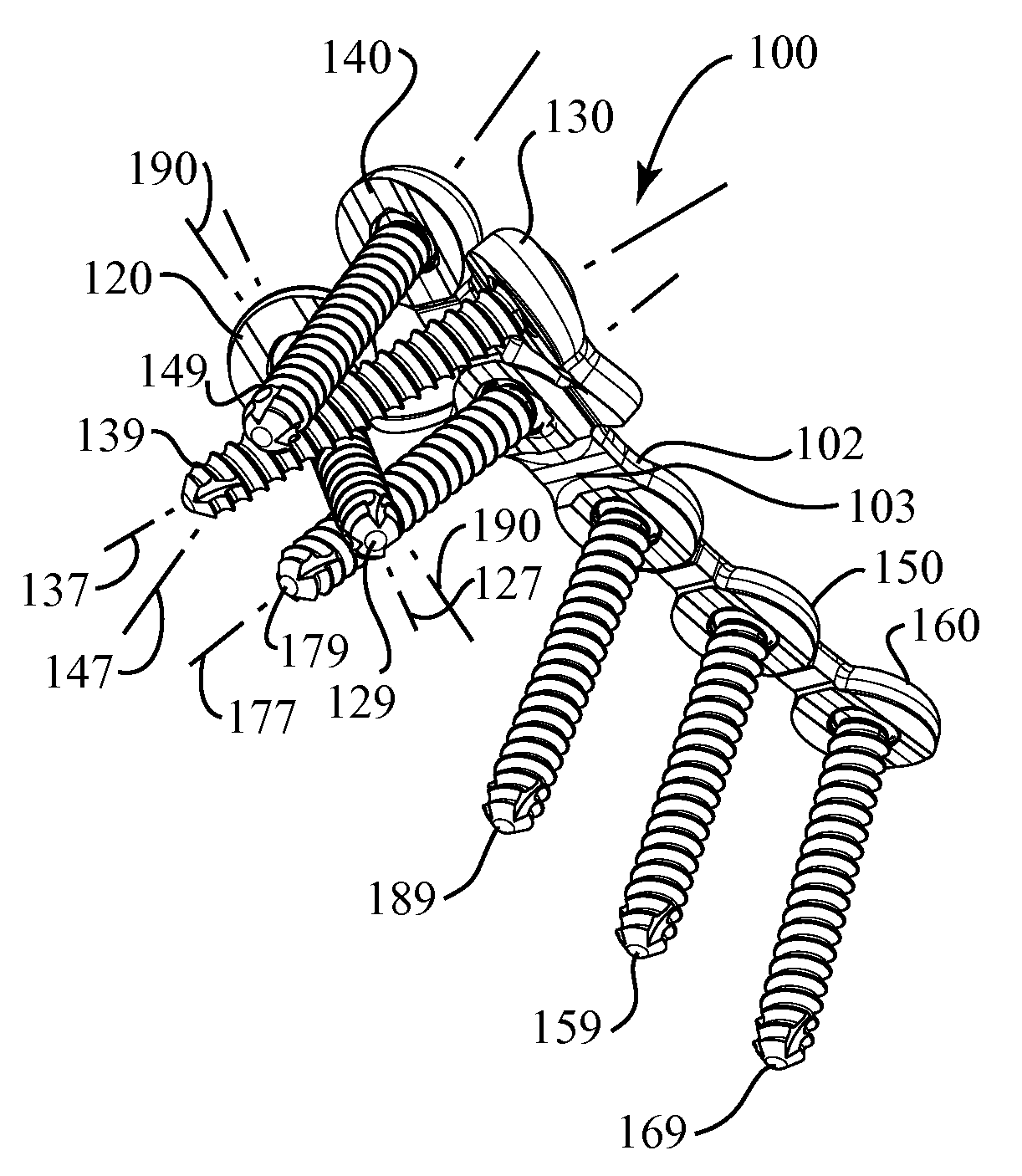
Pedicle screw system with offset stabilizer rod
InactiveUS20070233062A1Quick and easy drop-in placementLimit articulationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSet screwEngineering
An improved pedicle screw system is provided with an offset stabilizer rod for the internal fixation of the spine. The pedicle screw system includes at least two multi-angle pedicle screw units adapted for anchored securement to patient bone, and an elongated stabilizer rod extending therebetween. Each pedicle screw unit includes a bone screw associated with an anchor bracket defining a laterally offset and upwardly open channel or trough for receiving and supporting the stabilizer rod. A securement member such as a set screw is fastened to the anchor bracket for compressively retaining the stabilizer rod within the bracket channel or trough. The securement member may also bear against the associated bone screw for compressively retaining the screw in position relative to the anchor bracket.
Owner:AMEDICA A DELAWARE
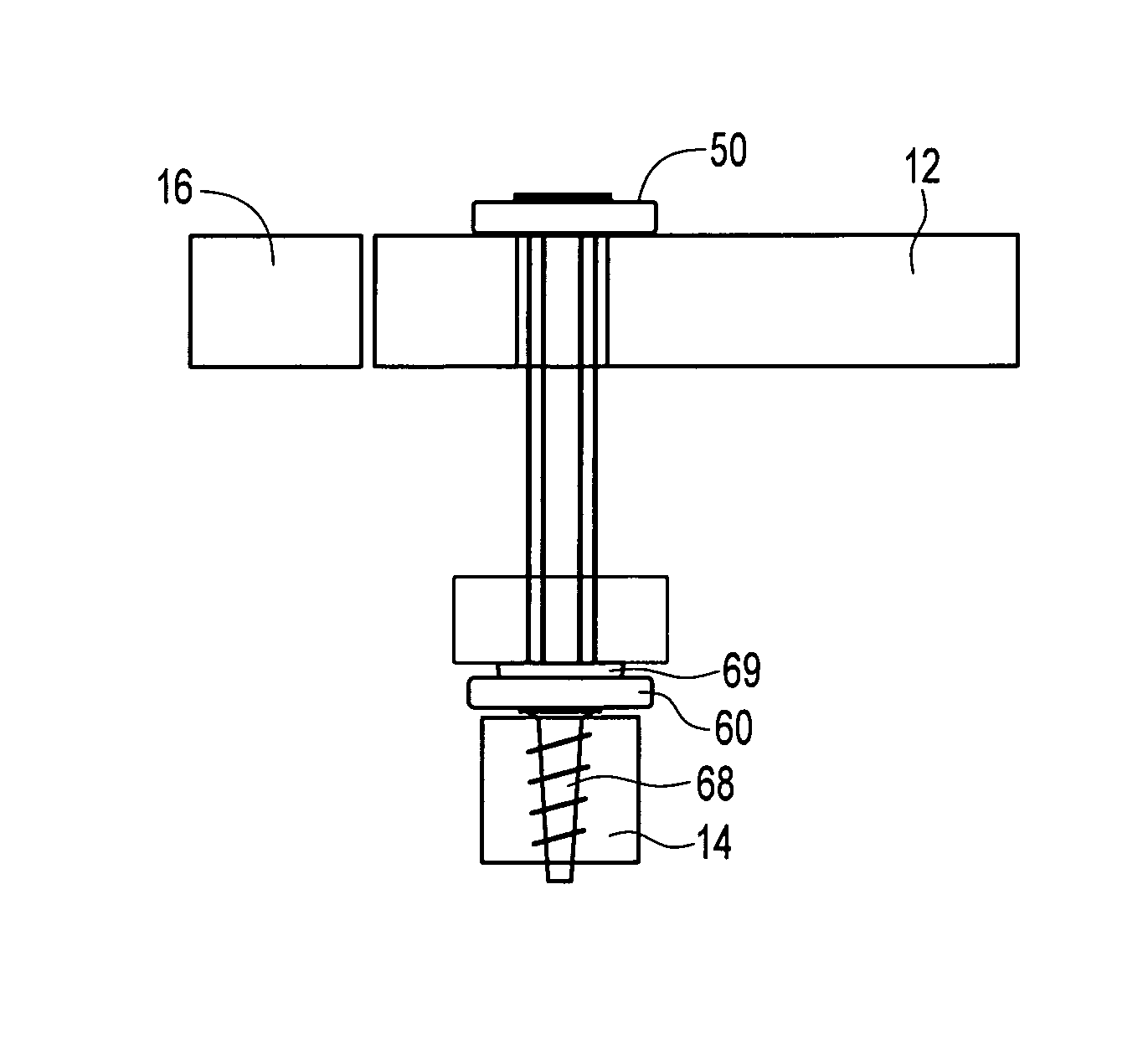
Bone plate with elevated suture hole structures
The present invention includes a bone fixation plate assembly comprising a bone plate and a plate compression device for internal fixation of bone and tissue. The bone plate includes a top surface and a bottom bone-facing surface, one or more fastener holes extending between the top surface and the bottom bone-facing surface for fasteners, and one or more suture cleats extending from at least a portion of a boundary of the bone plate and configured to have one or more sutures passed therethrough. In one embodiment, the bone plate has a suture cleat configured to be elevated above the bottom bone-facing surface of the bone plate by a distance of between about 1-5 mm for providing suturing clearance for a suturing instrument, for example.
Owner:EXTREMITY DESIGNS
Method and apparatus for internal fixation of an acromioclavicular joint dislocation of the shoulder
InactiveUS20130331886A1Reduce fixed distanceReduce distanceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisInternal fixationIliac screw
An apparatus for surgically reducing and internally fixing a shoulder acromioclavicular joint dislocation. The apparatus preferably comprises a button and a washer, the washer being flexibly secured to the coracoid process of the scapula by means of a bone screw, the button and washer being secured together by means of a first suture. A second suture is provided and secured between the button and a needle, such that the needle and associated button, may be advanced through a hole drilled through the clavicle. The button and the washer may then be tightened, reducing the coracoclavicular distance, by means of the first suture connected therebetween, to reduce and hold a desired acromioclavicular joint dislocation.
Owner:ARTHREX INC
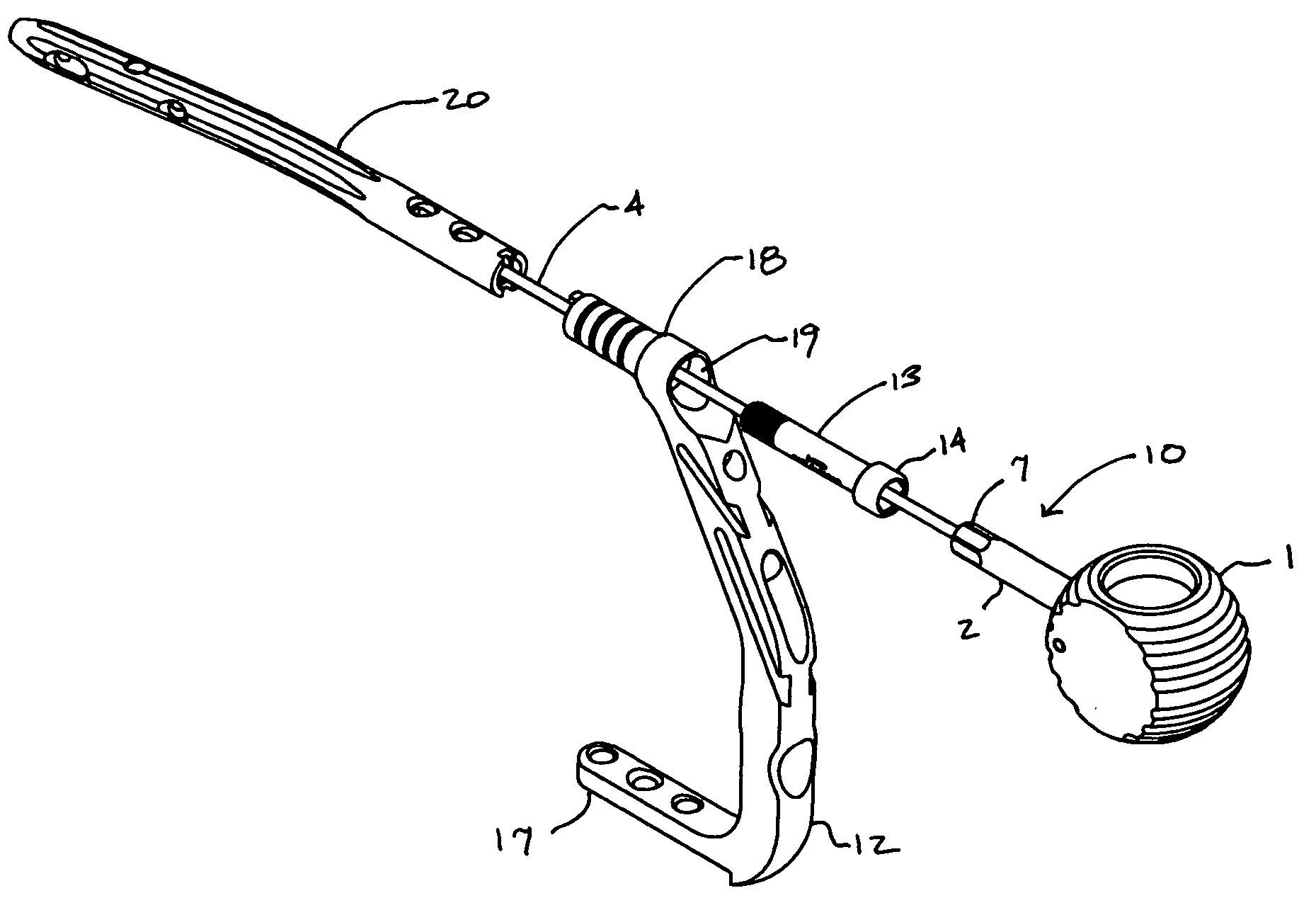
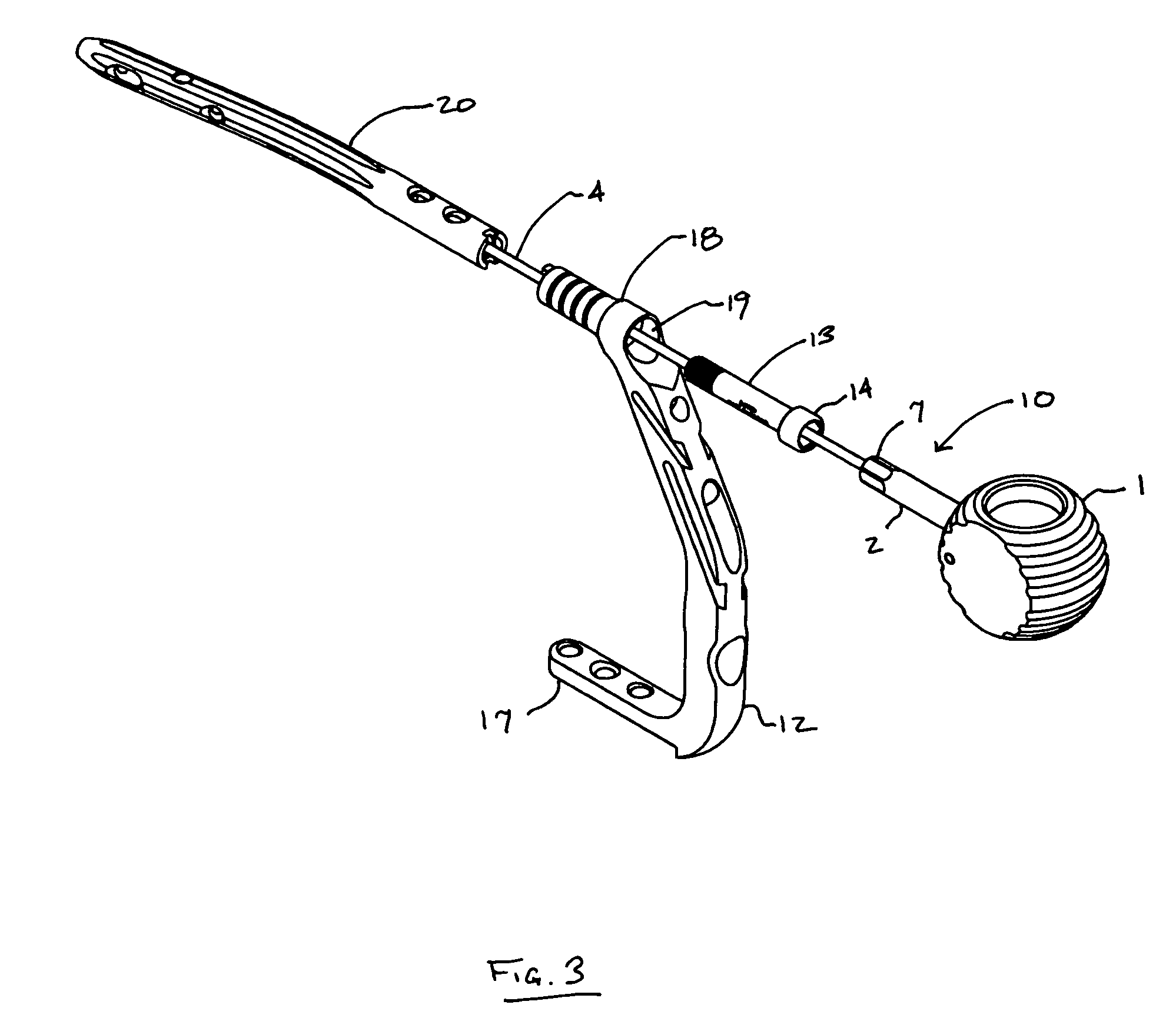
Implant assembly device
ActiveUS7033365B2Reduce measurement errorEasily and securely attachInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTibiaLONG BONE FRACTURE
This invention relates generally to systems for the internal fixation of bone fractures, and particularly, to equipment associated with the insertion of intramedullary fracture fixation devices such as those used in the treatment of long bone fractures, such as for example fractures of the femur, tibia, humerus, etc. An implant assembly device of the present invention may comprise a handle, a shaft with a first end and a second end, and an elongated rod extending from the shaft. The first end of the shaft is connected to the handle and the second end of the shaft is configured to engage the head of a connecting screw. The device can be held with one hand while the various components are placed one by one into their proper position onto the rod, leaving the other hand free to manipulate the other components.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Intramedullary rod with spiraling flutes
ActiveUS7771428B2Lower potentialReduce usageInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFluteIntramedullary rod
This invention relates generally to devices, systems and methods for the internal fixation of bone fractures, and particularly, to intramedullary fracture fixation devices such as those used in, for example, the treatment of long bone fractures. An IM rod preferably is provided with multiple curved sections in different planes preferably designed to conform with the long bones of a patient, both during insertion and in the rod's final position in the long bone. In addition, the overlap of portions of the curved sections results in a co-planar curvature of portions of the IM rod which assist in the insertion process by guiding the proper rotation of the IM rod as it is inserted into the bone. Spiraling flutes extending down the distal portion of the rod also assist in properly guiding and orienting the rod about its longitudinal axis during insertion such that the appropriate segment of the curved rod conforms with the appropriate portion of the long bone at the appropriate place.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
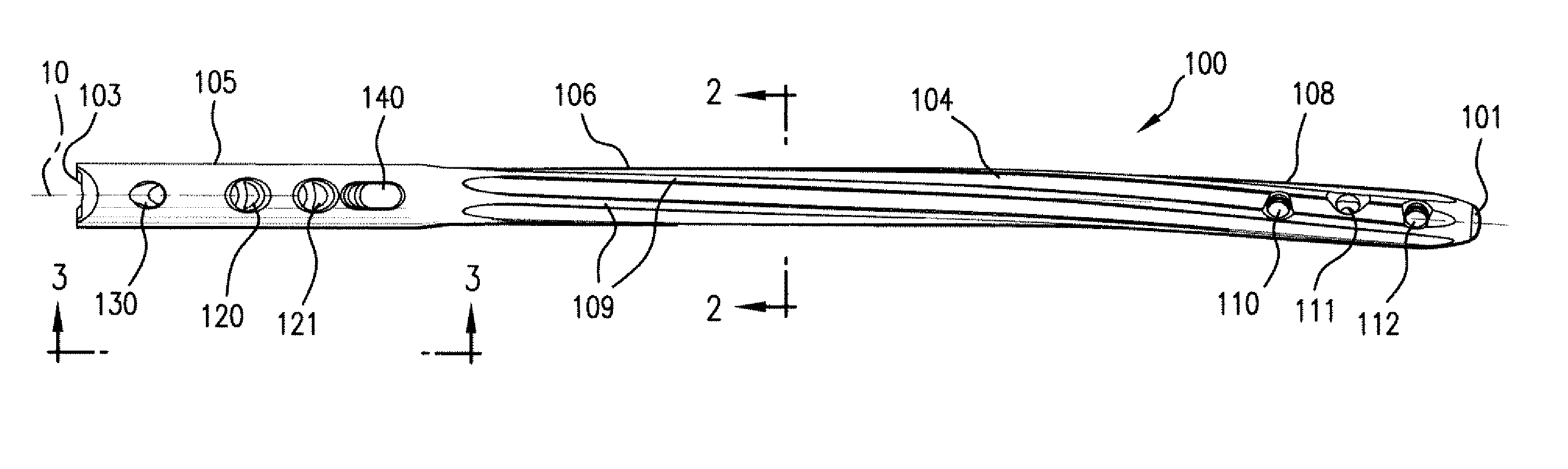
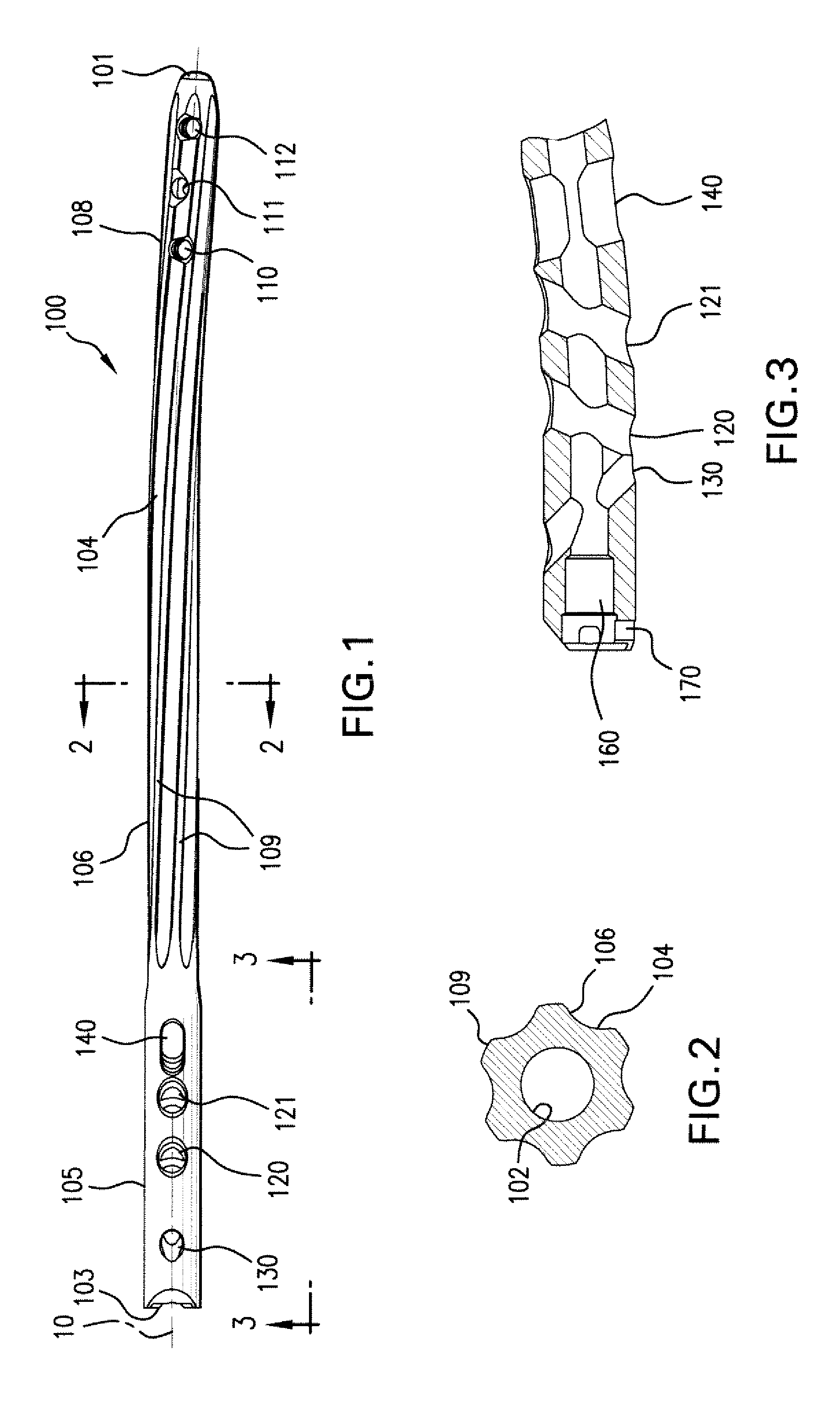
Device for internal fixation of the bone fragments in a radius fracture
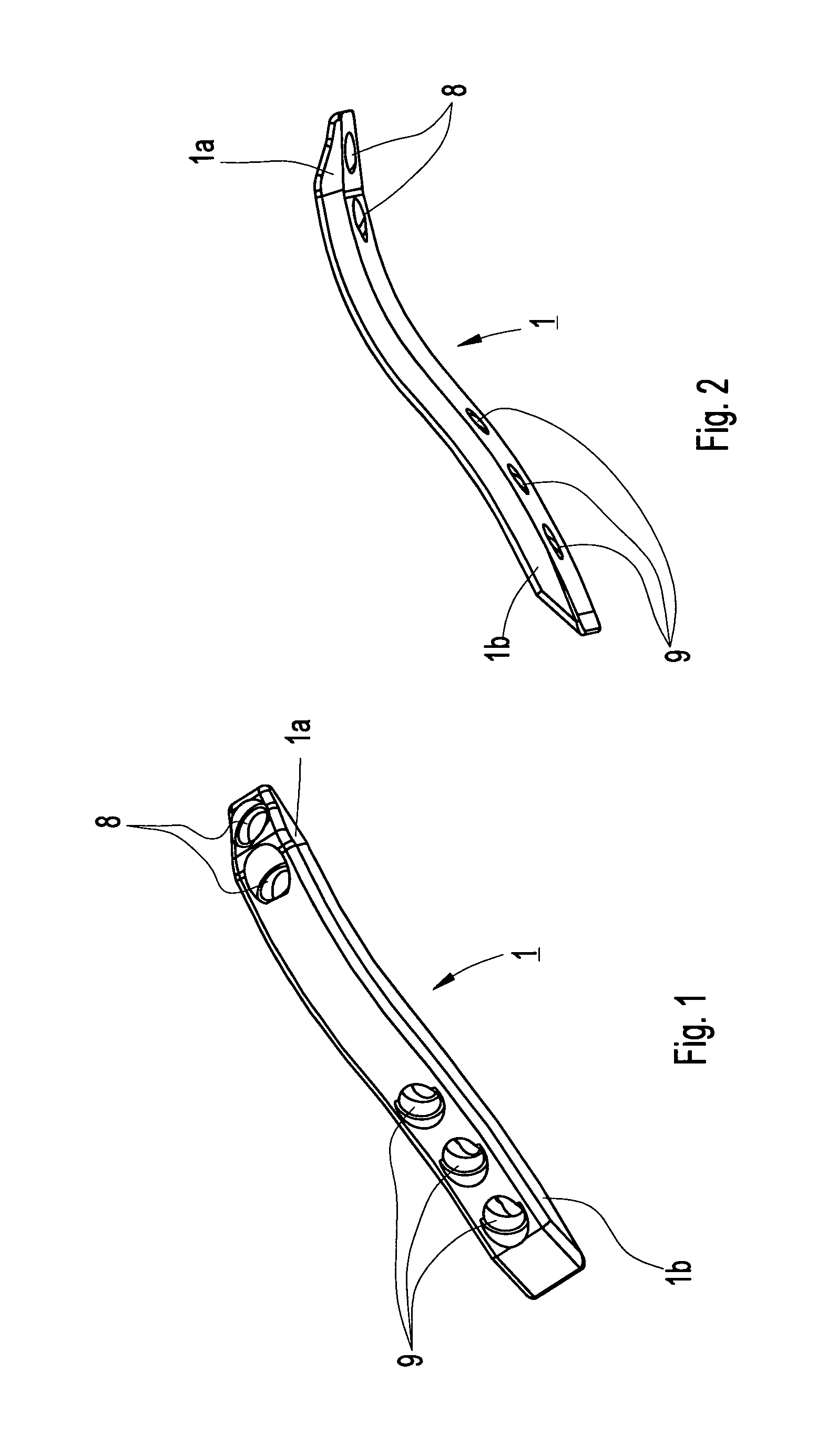
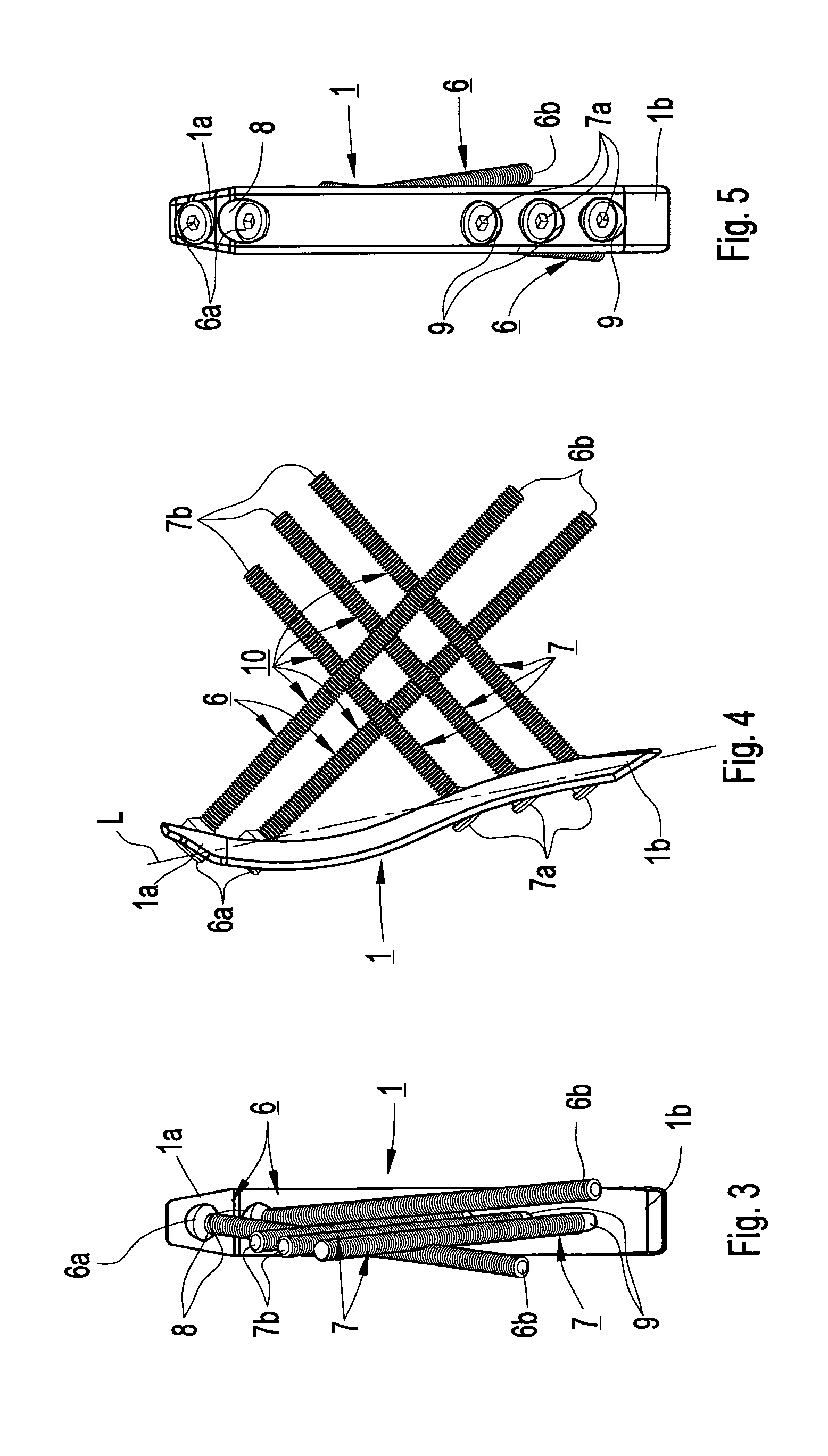
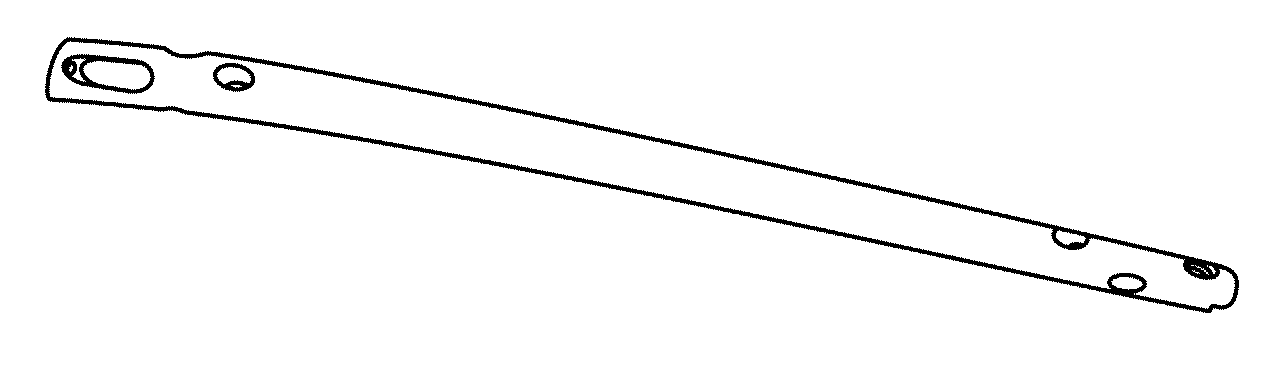
The present invention relates to a device for internal fixation of the bone fragments (2, 3) in a radius fracture (4). The device comprises at least one body (1) for abutment against the bone fragments (2, 3) in the radius fracture (4), and fixing elements (6, 7) which are intended to be locked to the body for fixation of said bone fragments. The body (1) itself has in a distal end portion (1a) at least two predrilled holes (8) for fixing elements (6), and in a proximal end portion (1b) at least two predrilled holes (9) for fixing elements (7). To allow effective optimum internal fixation of the bone fragments in the radius fracture, the predrilled holes (8, 9) run obliquely relative to a longitudinal axis (L) of the body (1) so that all of the fixing elements (6, 7) which, after the body has been caused to abut against the bone fragments (2, 3) in the radius fracture (4), are introduced into said bone fragments through holes (8, 9) in the body's distal end portion (1a) and proximal end portion (1b) cross the radius fracture (4) as viewed in the transverse direction of the body. Each fixing element (6, 7) has at least one fixing portion (10; 10a, 10b) for locking the fixing element in the bone fragments (2, 3) in the radius fracture (4) and for locking the fixing element to the body (1).
Owner:SWEMAC INNOVATION
Dmls orthopedic intramedullary device and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20170027624A1Add partsAdditive manufacturing apparatusInternal osteosythesisInternal fixationMachining
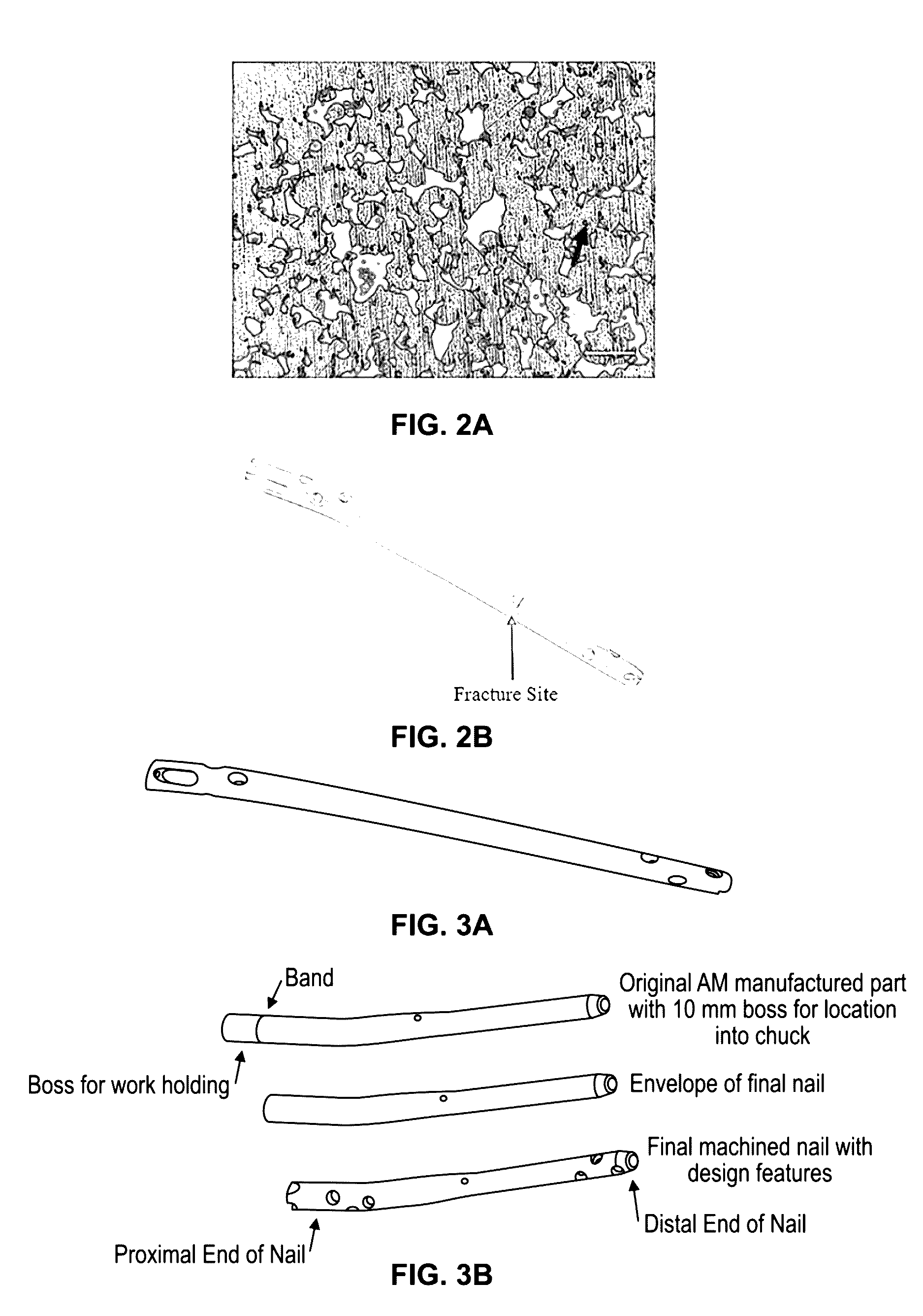
An orthopedic device, such as an intramedullary nail for internal fixation of a bone and a method of manufacturing the same. The orthopedic device may be formed from a medical grade powder via an additive manufacturing process. The forming process may include heat treating the additive manufactured component and machining the heat treated additive manufactured component to form the orthopedic device. Further, the orthopedic device may be formed to include an internal sensor probe channel that extends within at least a portion of the wall of the device, but which does not protrude through an outer portion of the wall. Embodiments further include a dynamizing intramedullary nail that accommodate adjustments in the relative axial positions of one or more sections of the orthopedic device. The devise may include features in an inner region of the orthopedic device that may alter an elastic modulus of the orthopedic device.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Method and system for securing an intramedullary nail
InactiveUS7727240B1Simple designSimple and efficient procedureInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsIntramedullary rodEngineering
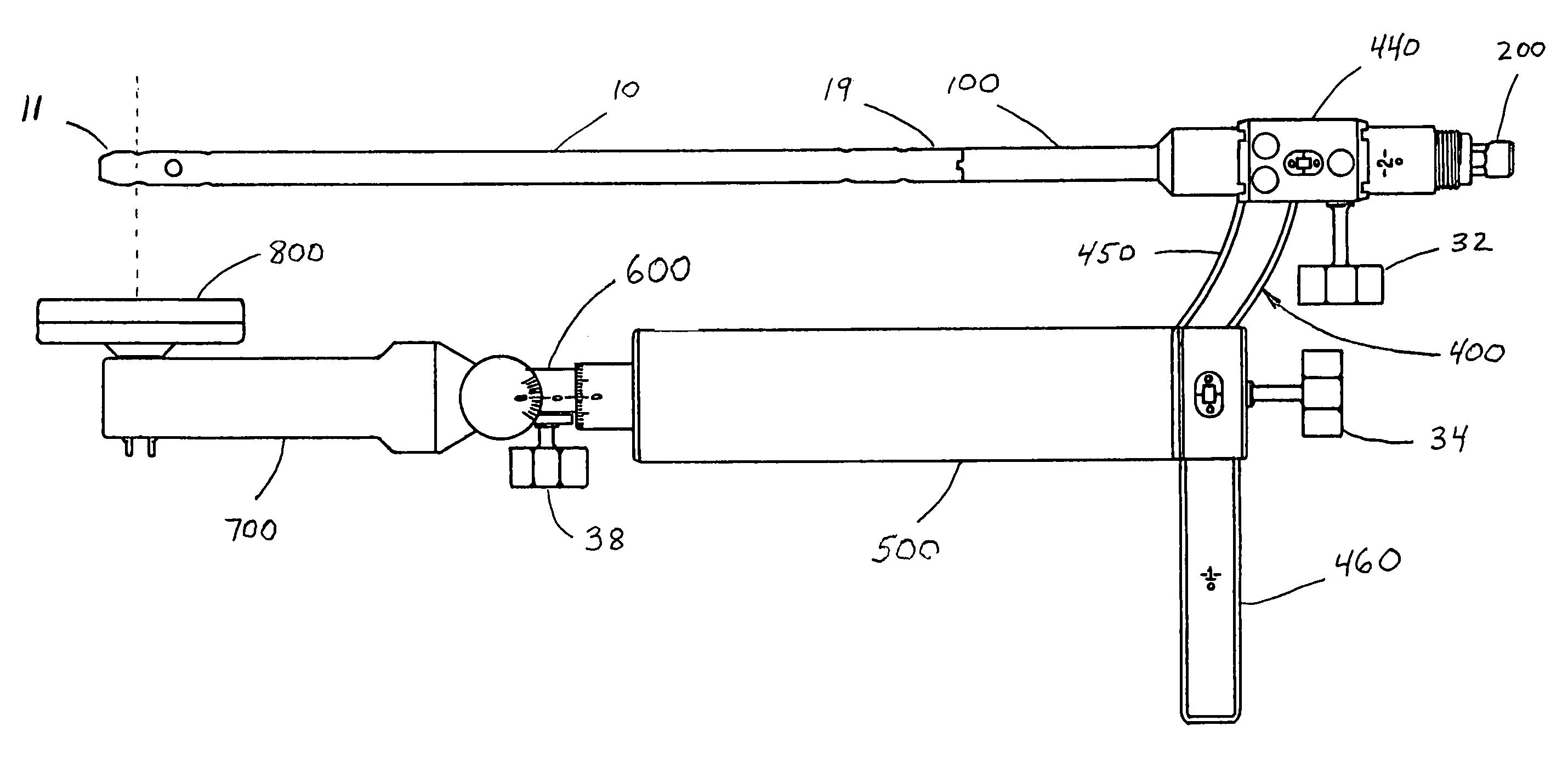
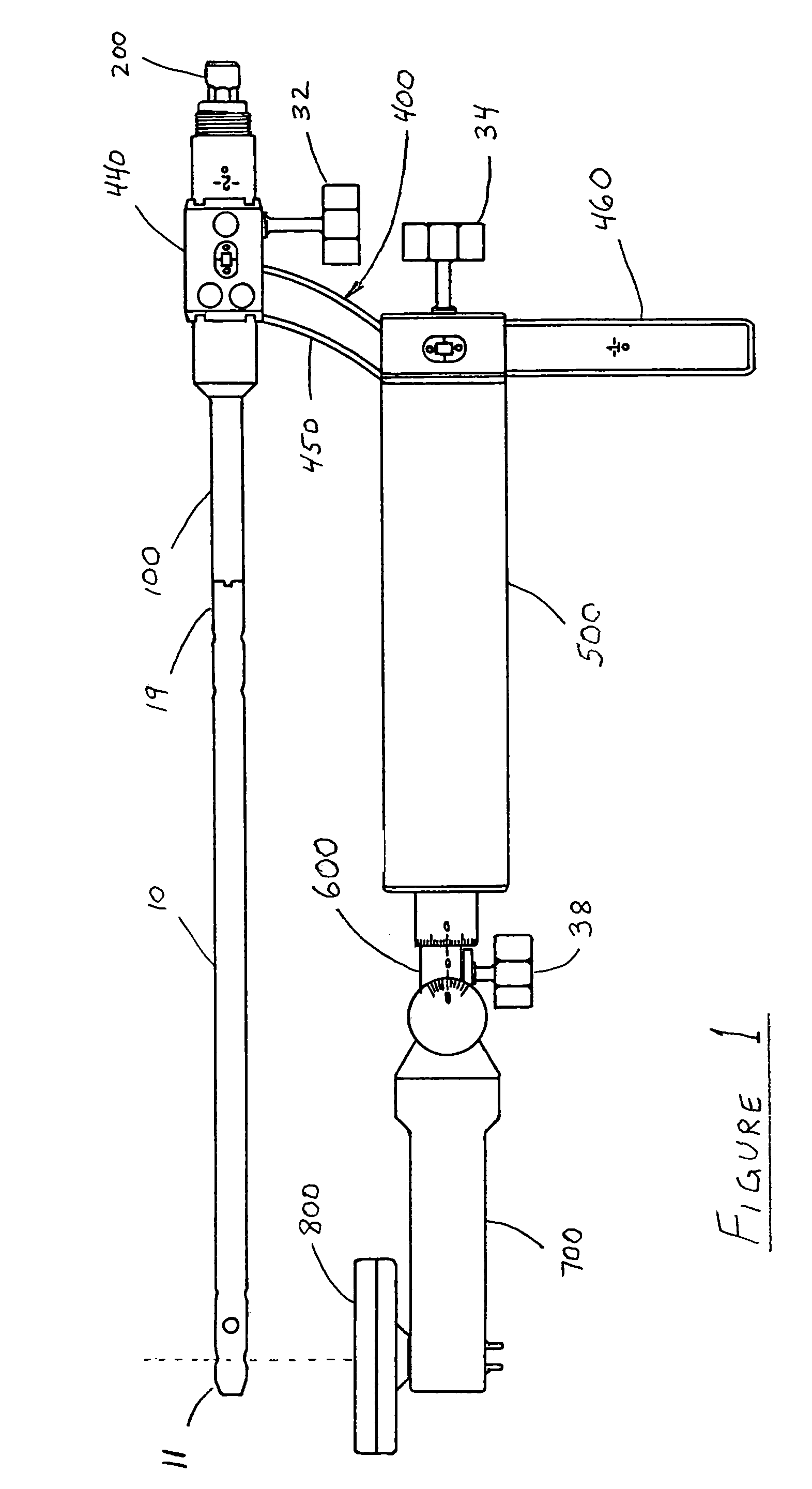
A device, method and system adapted to determine a targeting position on a surgically implantable nail adapted to be used in internal fixation of a bone, the nail comprising a distal end and a proximal end, the device including an extension rod comprising a longitudinal axis and adapted to be detachably coupled to the proximal end of the nail, a bridge member adjustably secured to the extension rod and extending radially from the longitudinal axis of the extension rod, a position of the bridge member on the extension rod being rotationally and longitudinally adjustable with respect to the longitudinal axis of the extension rod, and a targeting arm adjustably coupled to the bridge member and extending from the bridge member toward the distal end of the locking nail, the targeting arm comprising a drill guide.
Owner:BENTON BLAKE
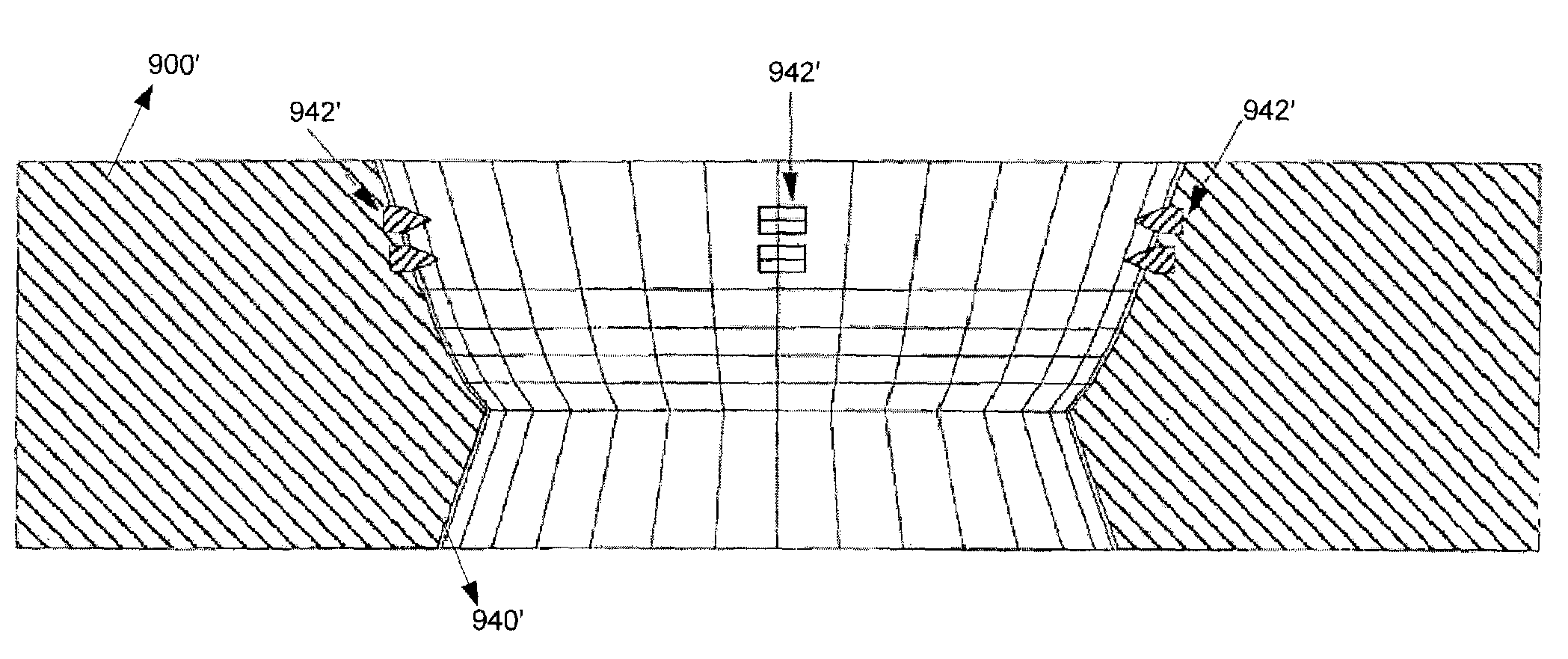
Bone plate system providing dynamic compression
An orthopedic bone plate, suitable for internally fixating and stabilizing fractured bones, includes: an elongated structure, capable of contraction in a longitudinal direction and having at least two ends, the structure having at least two fixation points adapted to be fixated to a fractured bone with the fixation points on opposing sides of a fracture. An elastic, polymer cable is longitudinally stretched and coupled in tension to the elongated structure, capable of causing the structure to contract in the longitudinal direction.
Owner:KINAMED
Internal fixation system for spine surgery
Provided is a spinal fixation system that includes a pedicle screw having a bone engagement thread at a first end of the pedicle screw and an intermediate shaft portion located between the bone engagement thread and a second end of the pedicle screw and having a substantially conical shaped flange. The system also includes a clamp that fits over the second end of the pedicle screw, a fixation rod that can be secured between the clamp and an external side of the pedicle screw, and a fastener that can be coupled to the second end of the pedicle screw. Coupling of the fastener to the second end of the pedicle screw provides a clamping force that presses the fixation rod against the intermediate shaft portion of the pedicle screw.
Owner:CONCEPT MATRIX
Fracture Fixation Plate for the Olecranon of the Proximal Ulna
ActiveUS20090118770A1Easily and safely reconfiguredIncreasing the thicknessSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPelvic fixationInternal fixation
A system for the internal fixation of a fractured bone of an elbow joint of a patient includes at least one bone plate, each bone plate having a plurality of holes and generally configured to fit an anatomical surface of the fractured bone. The at least one plate is adapted to be customized to the shape of a patient's bone. The system also includes a plurality of fasteners including at least one locking fastener for attaching the bone plate to the bone. At least one of the holes is a threaded hole. Guides for plate benders, drills, and / or K-wires can be pre-assembled to the threaded holes, and the locking fastener can lock into any of the threaded holes after the guides are removed.
Owner:BIOMET CV
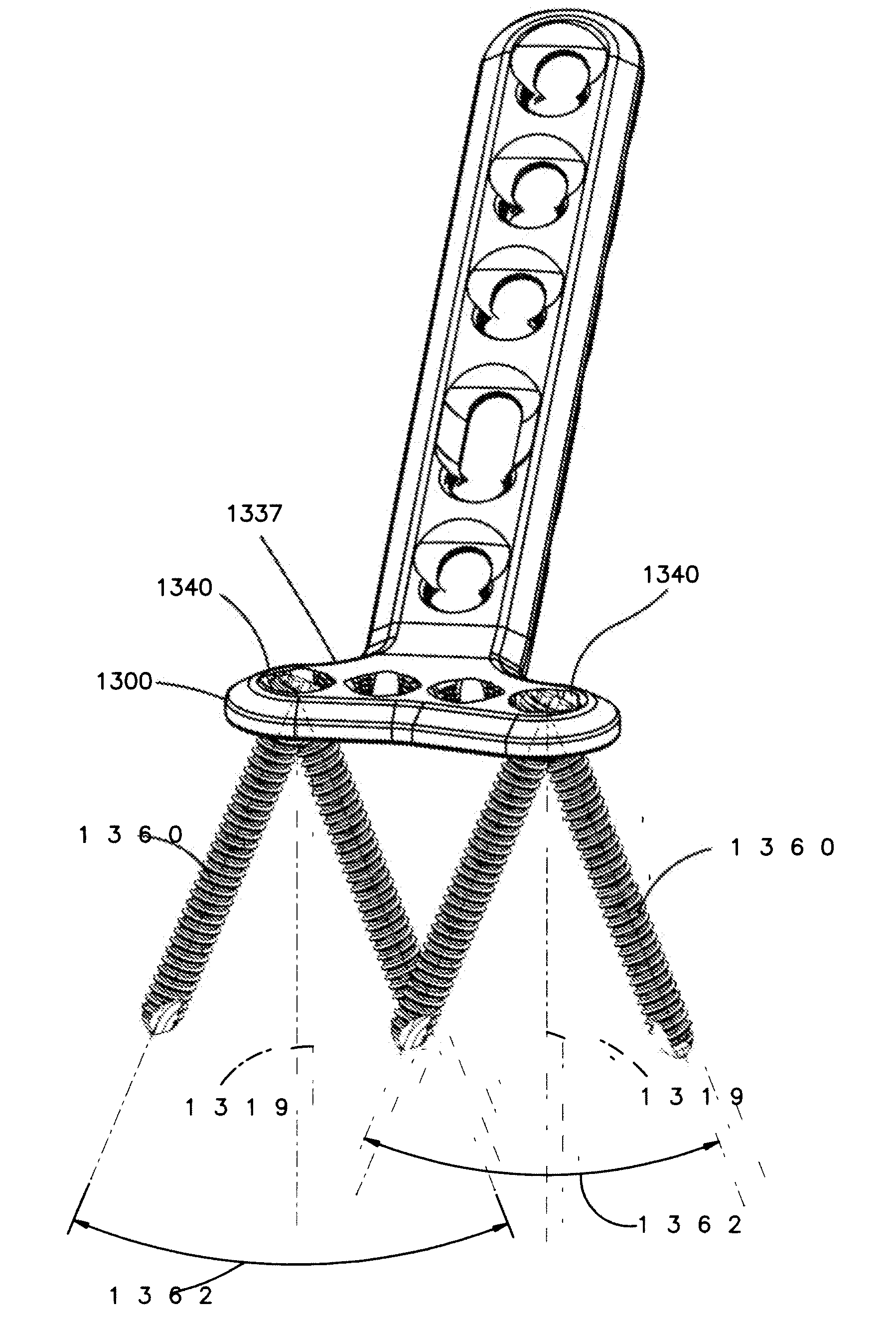
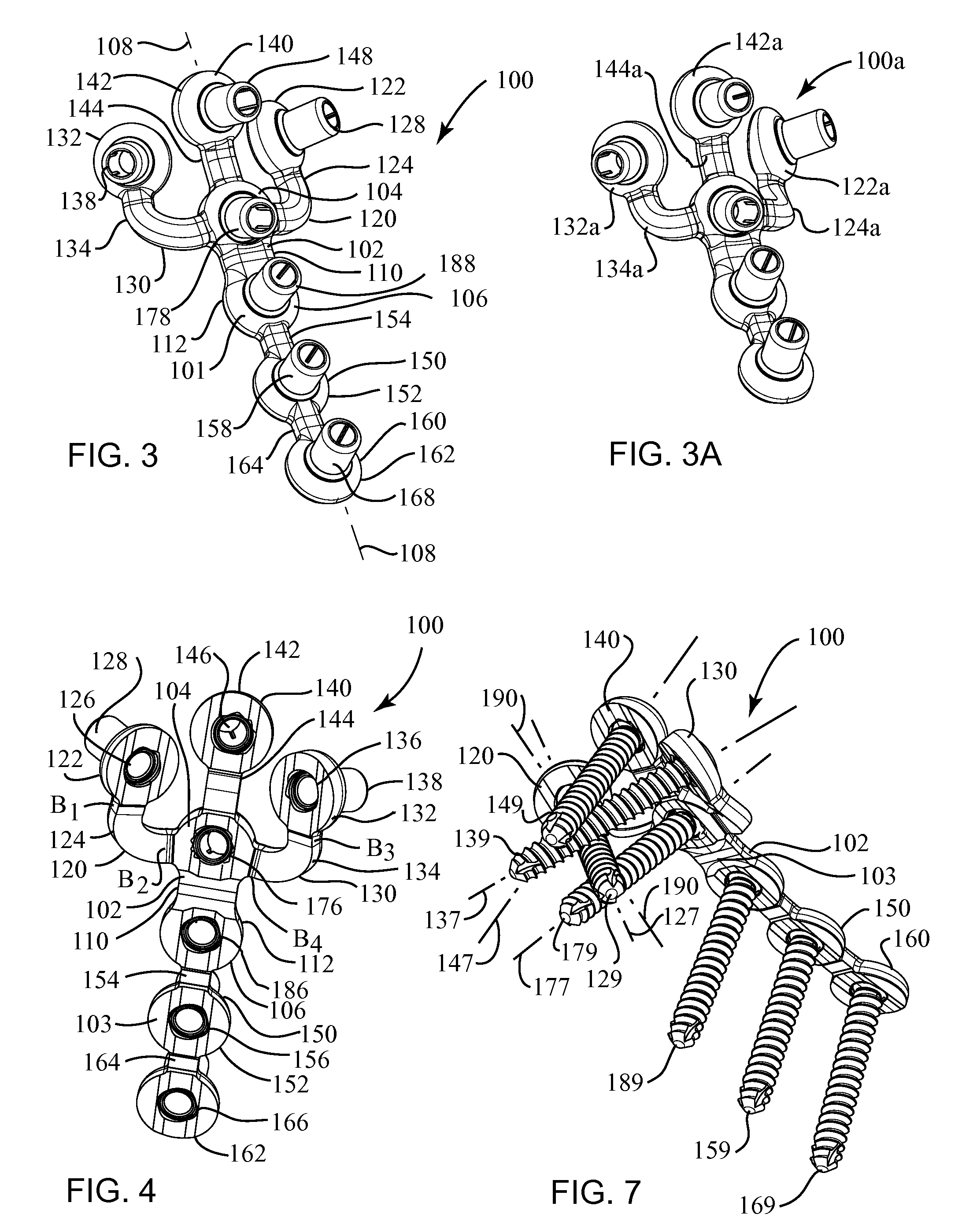
Interspinous Internal Fixation/Distraction Device
ActiveUS20100241166A1Improved interspinous fixationIncreased distractionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsElement spaceDistraction
Disclosed are an apparatus for an interspinous fixation and / or distraction of vertebrae and a methodology for minimally invasive implantation of the apparatus in the spine of a patient. The apparatus corresponds to a pair of teardrop shaped lateral wing elements spaced apart by a central core element that may be selectively sized during the implantation process. The wings and central core are held together by a single threaded bolt and locking nut configuration resulting in a simple structure that may be easily implanted with minimal patient discomfort.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Surgical device, system and method of use thereof
The present invention includes a surgically implantable compression staple, system, and method of use thereof for the internal fixation of bone fractures, fusions, and osteotomies. The staple has a grooved construction along the outside edge of each of its legs and cannulated tabs are aligned above the grooves. The grooves and cannulated tabs of the staple are sized to fit and align with guide wires. Once holes are drilled over the guide wires with a specialized cannulated drill, the appropriately sized staple can be inserted over the guide wires and the guide wires are subsequently removed. The compression feature of the staple is activated and the staple provides stability across the desired fractured site. The system and method allows for easy alignment and precise placement of surgically implantable staples.
Owner:MBRACE
Fracture Fixation Plate for the Coronoid of the Proximal Ulna
ActiveUS20090125070A1Easily and safely reconfiguredIncreasing the thicknessSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCoronoid process of the ulnaInternal fixation
A system for the internal fixation of a fractured bone of an elbow joint of a patient includes at least one bone plate, each bone plate having a plurality of holes and generally configured to fit an anatomical surface of the fractured bone. The at least one plate is adapted to be customized to the shape of a patient's bone. The system also includes a plurality of fasteners including at least one locking fastener for attaching the bone plate to the bone. At least one of the holes is a threaded hole. Guides for plate benders, drills, and / or K-wires can be pre-assembled to the threaded holes, and the locking fastener can lock into any of the threaded holes after the guides are removed.
Owner:BIOMET CV
Designing and forming method for anatomical bone plate of individuation bone model
InactiveCN105816232AReduce fatigue strengthEasy accessAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputer-aided planning/modellingData acquisitionComputer-aided
The invention discloses a method for designing and forming an anatomical bone plate of an individualized bone model, which includes the following steps: 1) Data collection: use a CT machine to scan both sides of the affected side and the healthy side of the patient, and collect image files in Dicom format file, imported into medical 3D reconstruction software for 3D reconstruction; 2) using medical 3D reconstruction software, the image is segmented according to CT scan data, and bone 3D model reconstruction is carried out, which is materialized and converted into a solid model format file in reverse engineering software; 3) Use computer-aided design CAD software to reconstruct the model according to the three-dimensional bone. The design and forming method of the anatomical bone plate of the individualized skeletal model of the present invention can quickly customize an individualized anatomical internal fixation plate with a high bone matching degree according to different patients, different parts, and different fracture characteristics, so that the internal fixation plate of the patient The fixing plates are fully individualized and provide optimum fixing performance.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
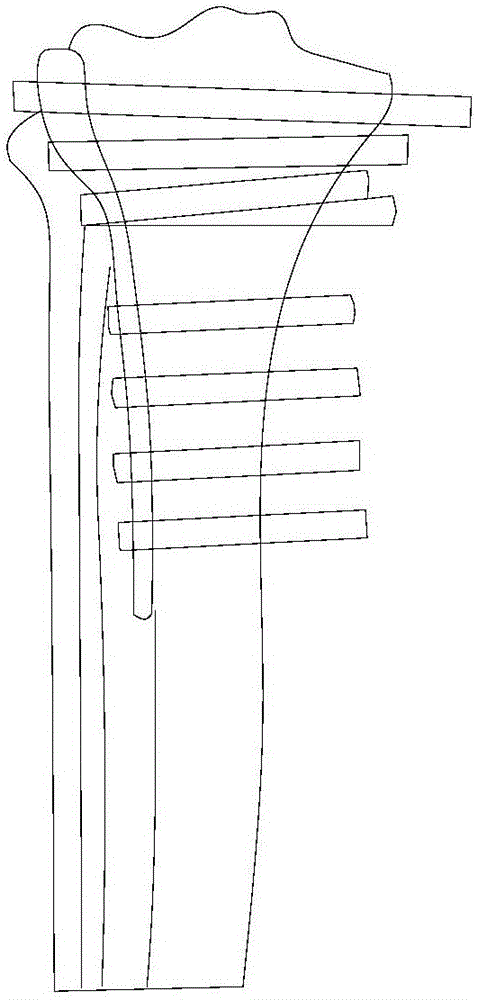
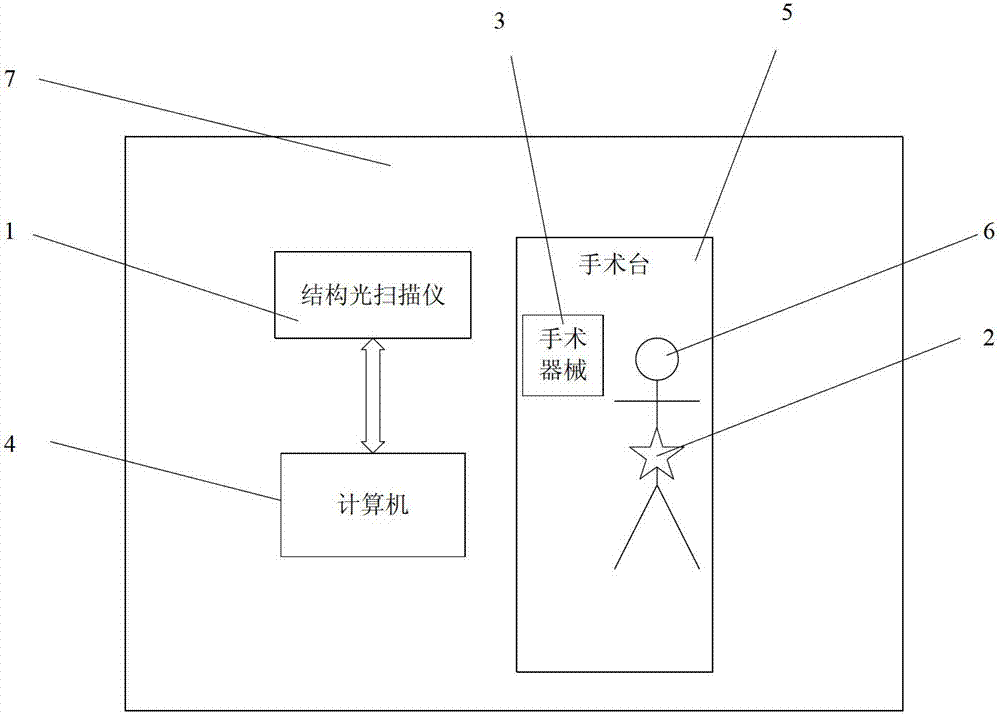
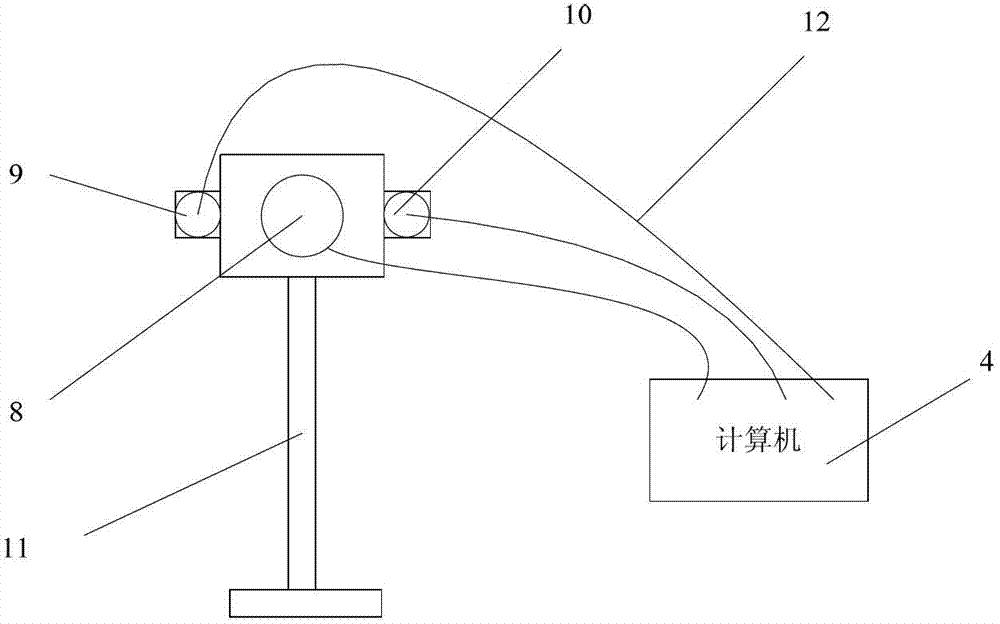
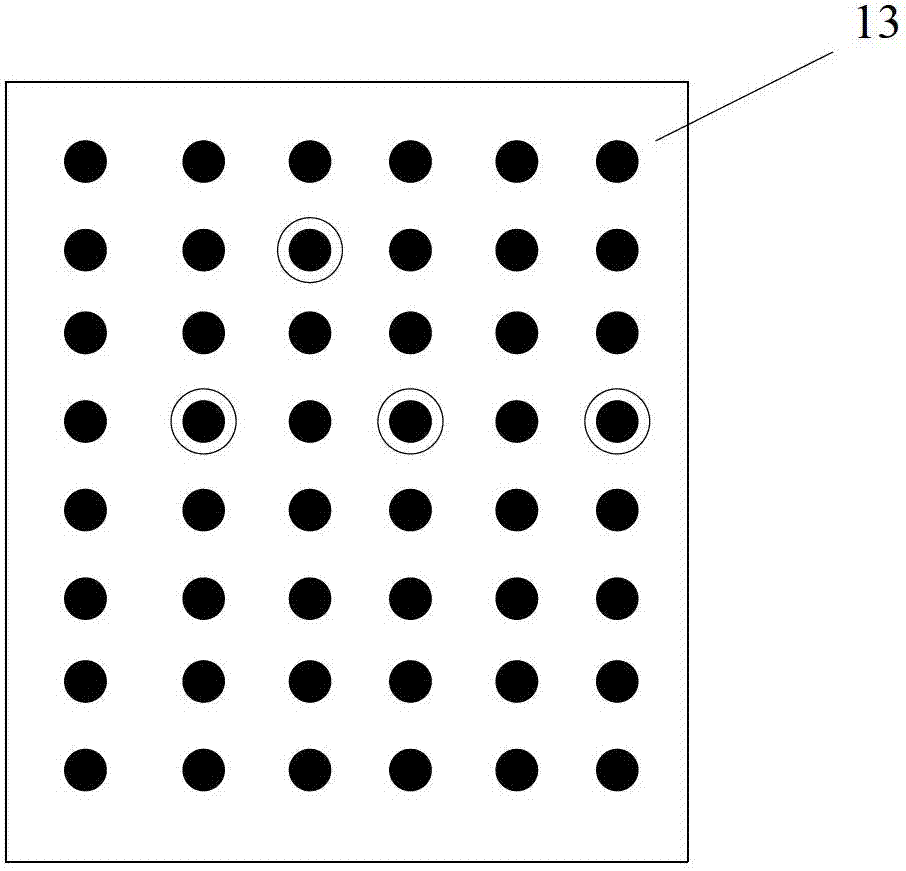
Pediculus arcus vertebrae internal fixation operation navigation system based on structured light scanning
ActiveCN102784003ASmall space requirementImprove reliabilitySurgeryNavigation systemInternal fixation
The invention provides a pediculus arcus vertebrae internal fixation operation navigation system based on structured light scanning. The system comprises a structured light scanner, a dynamic base, operation instruments and a computer provided with an operation navigation software and a sick bone CT (Computed Tomography) three-dimensional model, wherein during the operation, the dynamic base is fixedly arranged at a sick bone; the structured light scanner is utilized to scan the sick bone so as to obtain a structured light three-dimensional image and is subjected to surface rectification together with the sick bone CT three-dimensional model; a camera on the structured light scanner is utilized to track the operation instrument, so as to obtain the position relations of the operation instruments relative to the dynamic base and the sick bone three-dimensional model; and the position relations are displayed on the computer provided with the operation navigation software in real time, so as to realize operation navigation. Compared with similar systems, the operation navigation system provided by the invention does not require an infrared navigation position finder to participate in tracking during the operation, can be used for improving the navigational fixing precision, simplifying the operation navigation process, lowering the complexity and cost of the whole system and occupying less space of an operation room, and can be conveniently used by doctors.
Owner:李书纲
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com