Patents
Literature
207 results about "Osteotome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
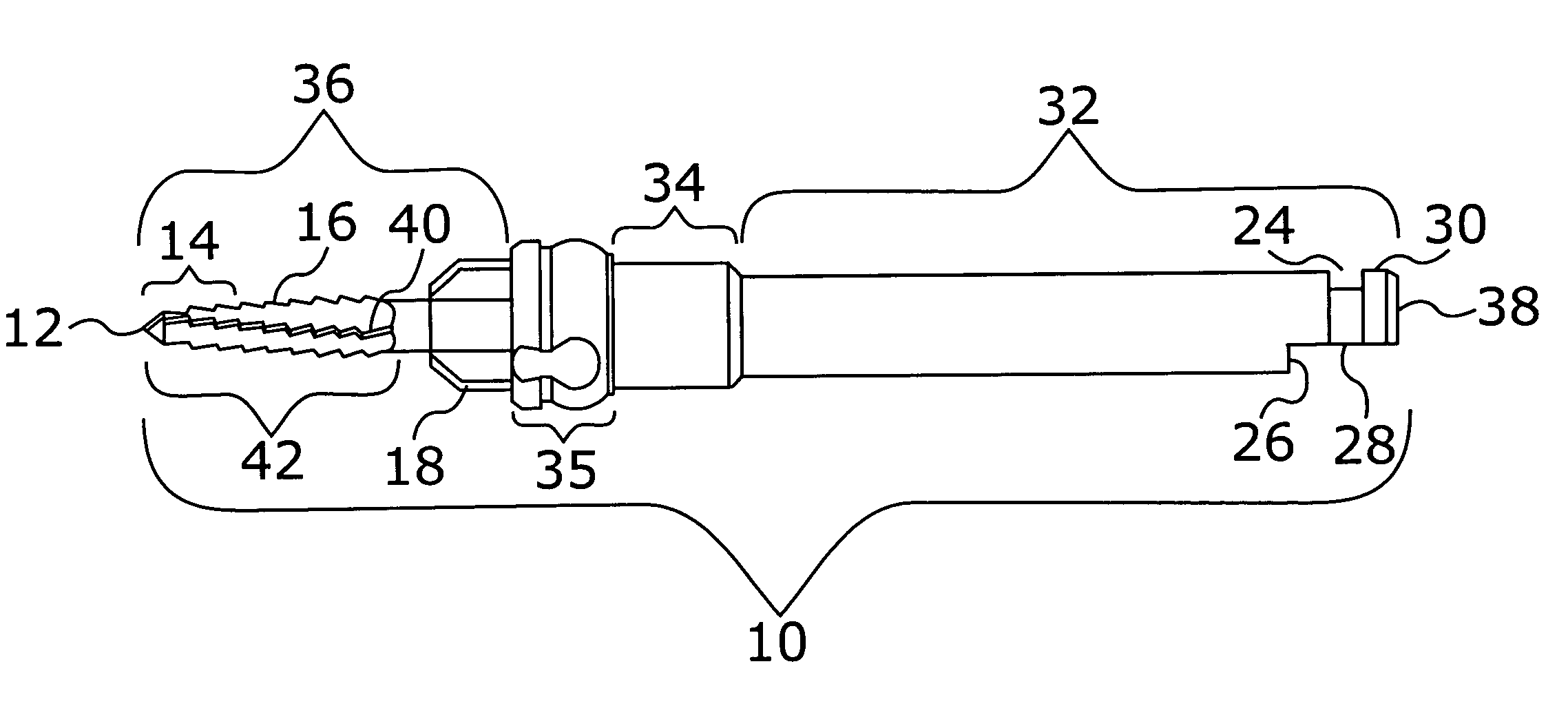
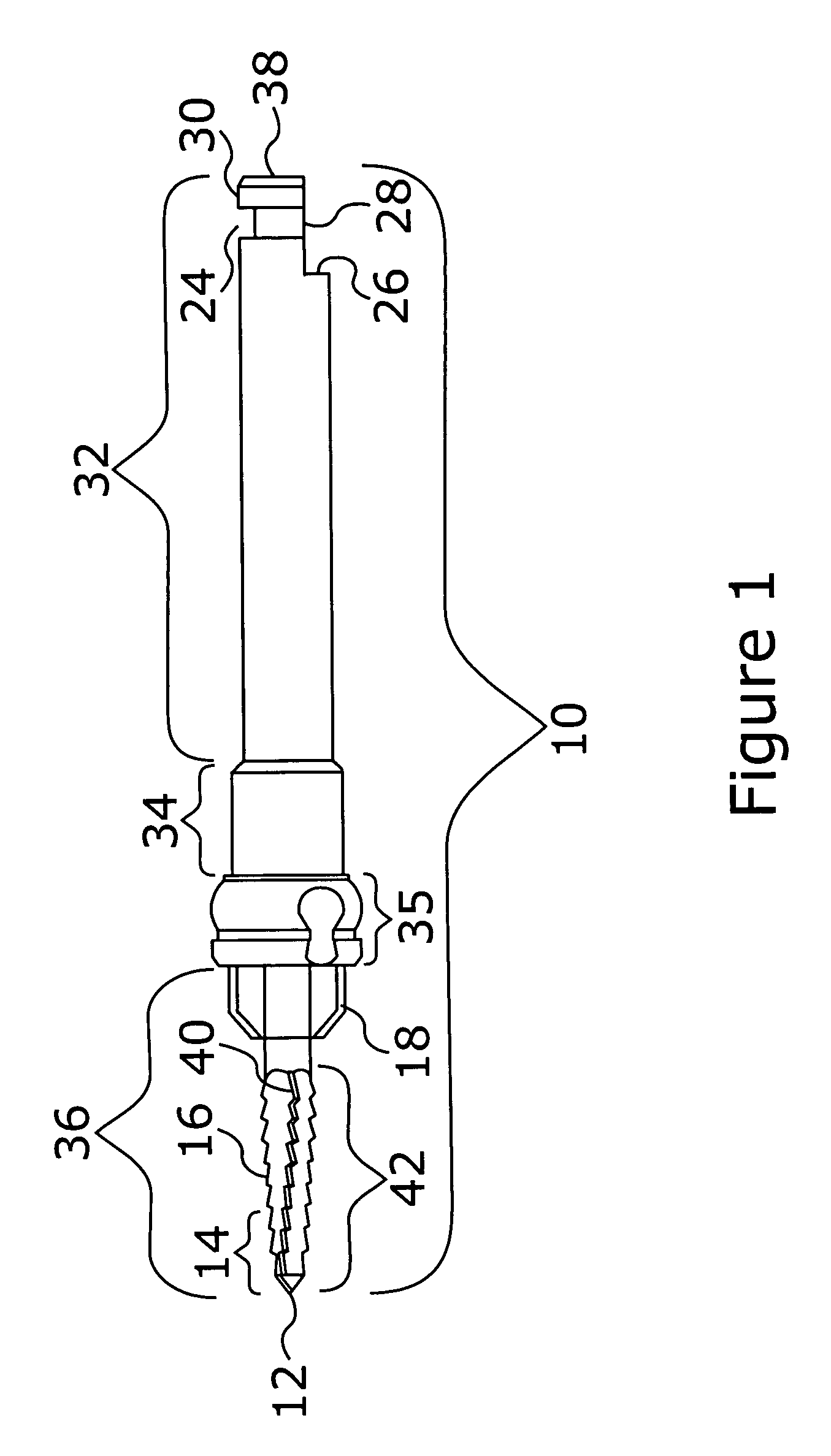
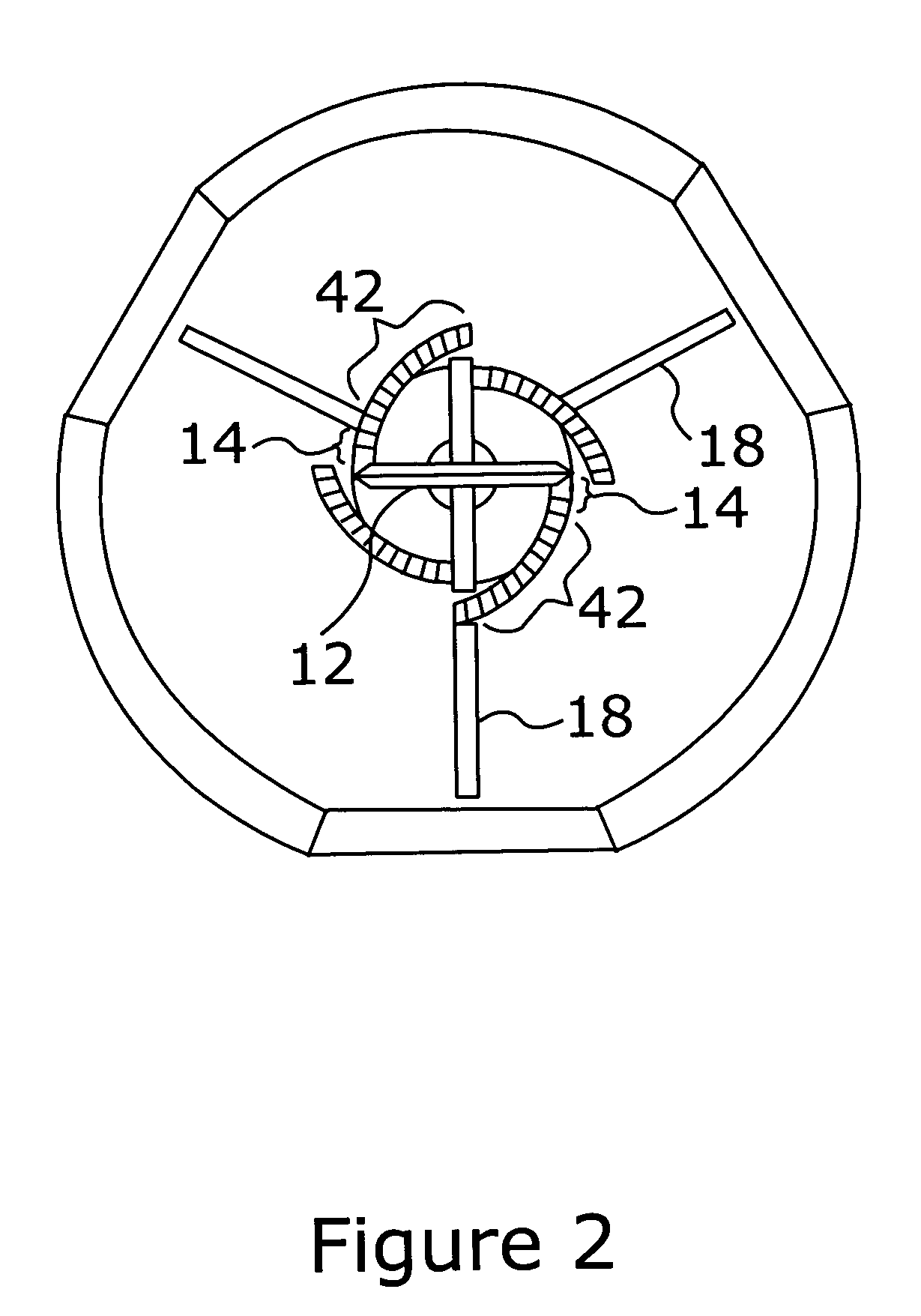
Patent Status
Application Year
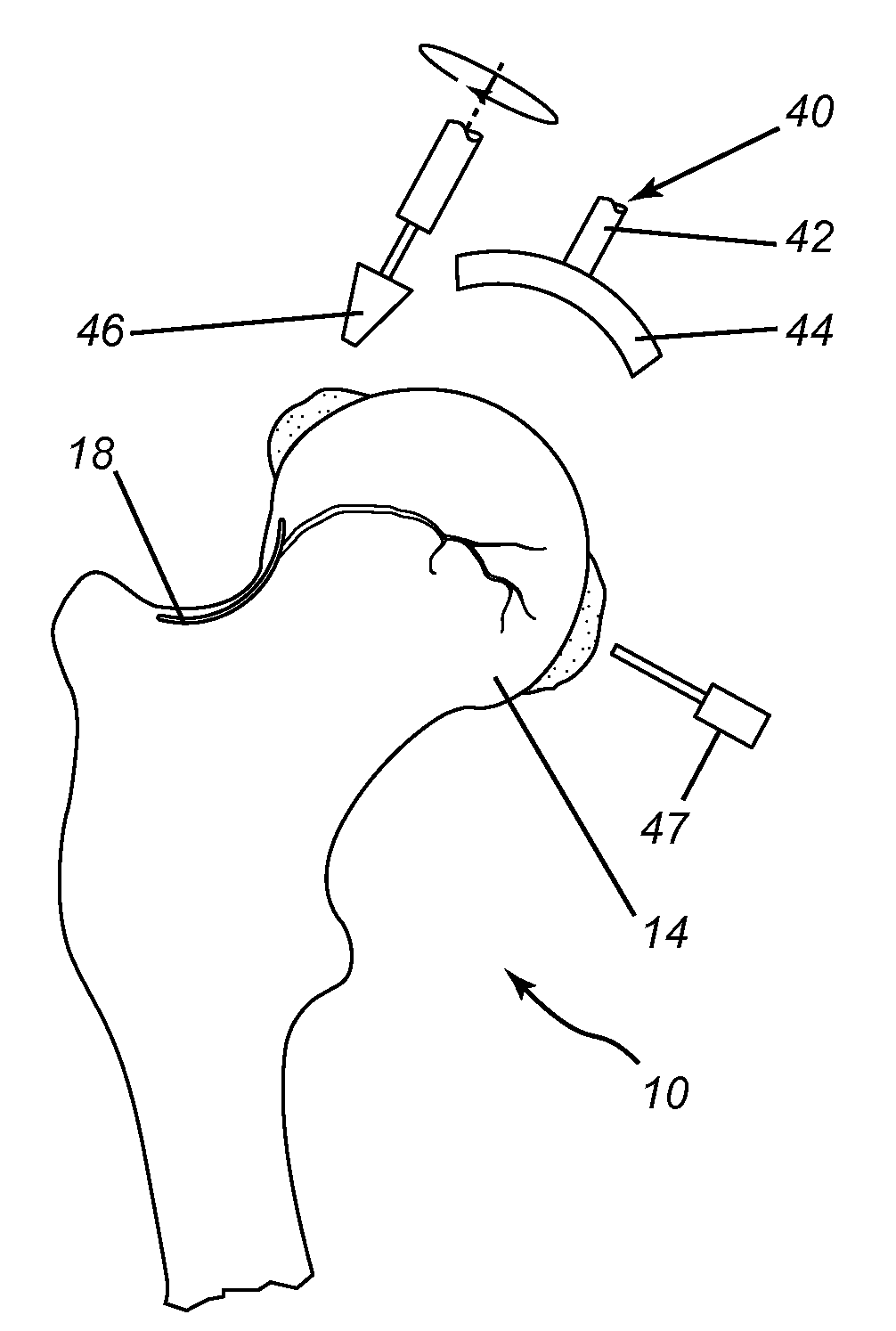
Inventor
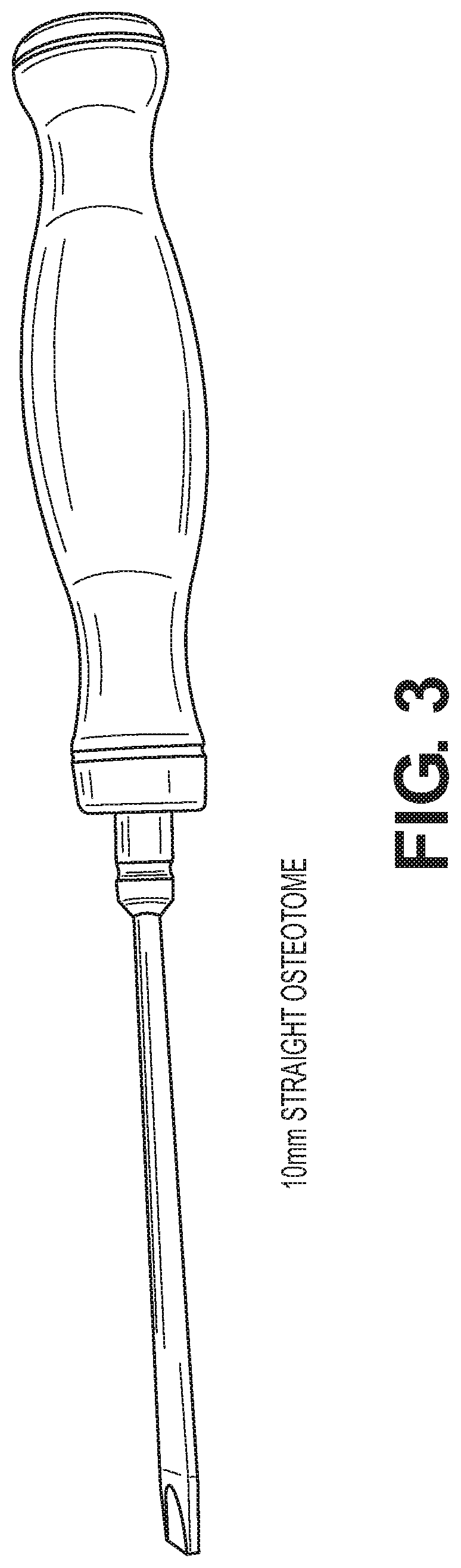
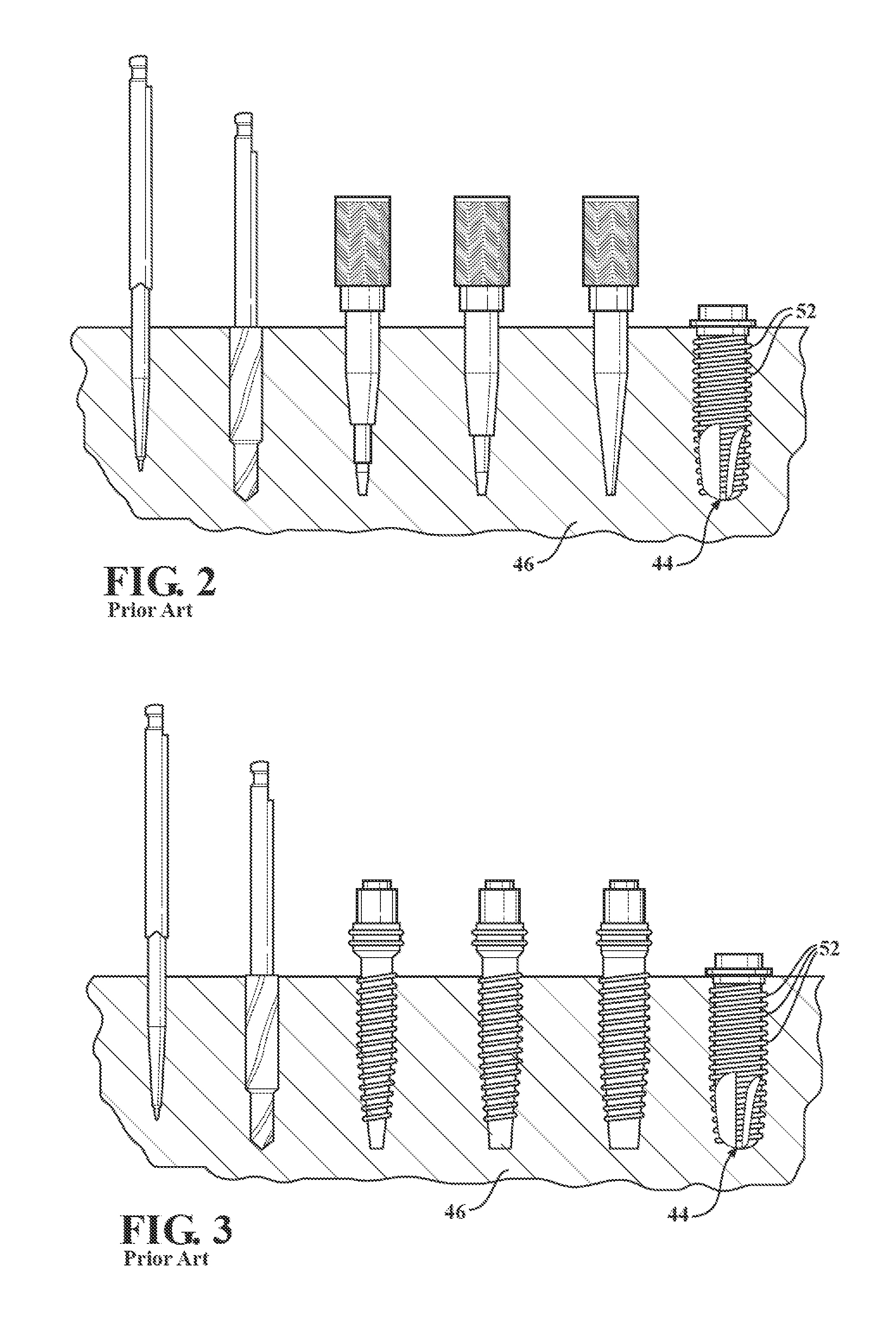
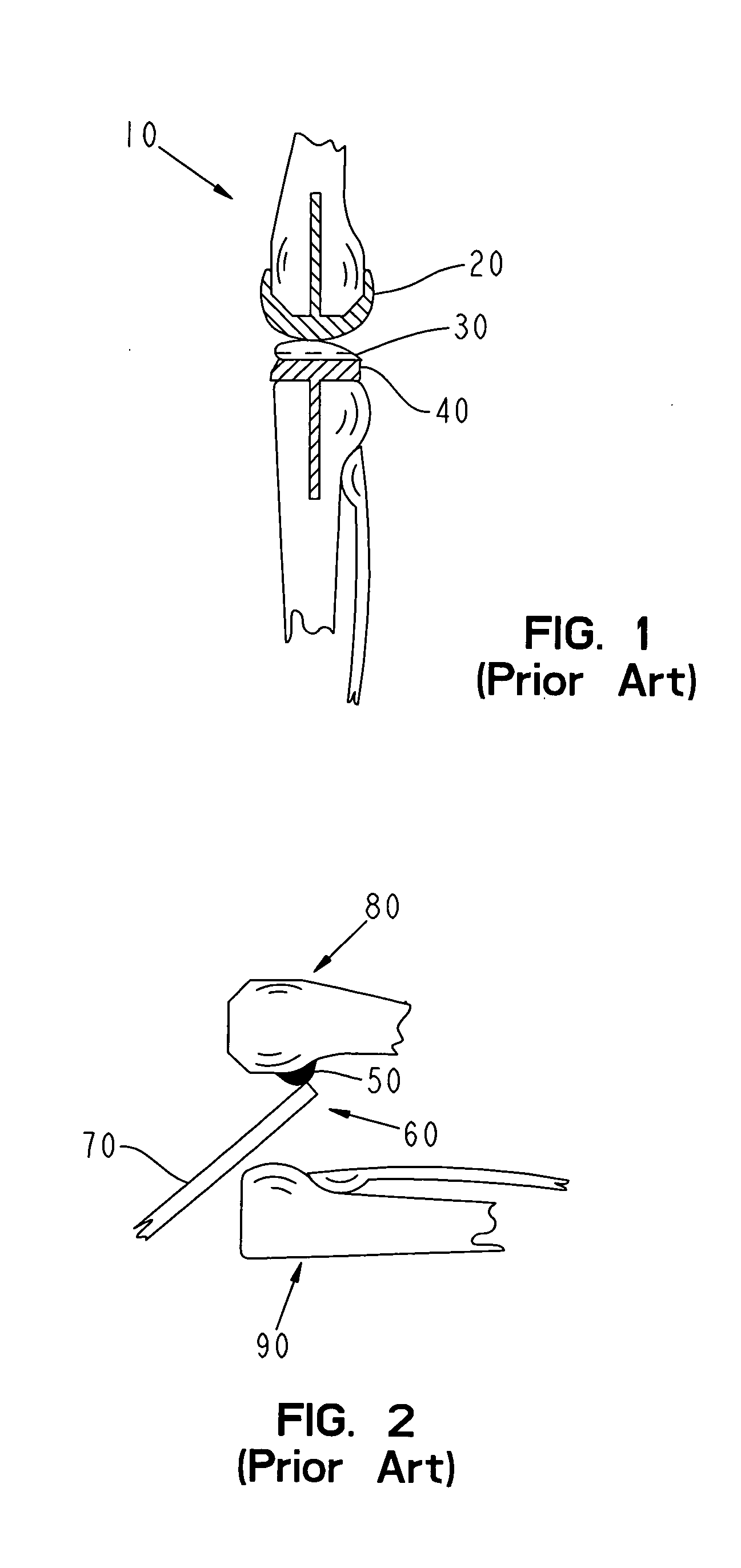
An osteotome is an instrument used for cutting or preparing bone. Osteotomes are similar to a chisel but bevelled on both sides. They are used today in plastic surgery, orthopedic surgery and dental implantation.
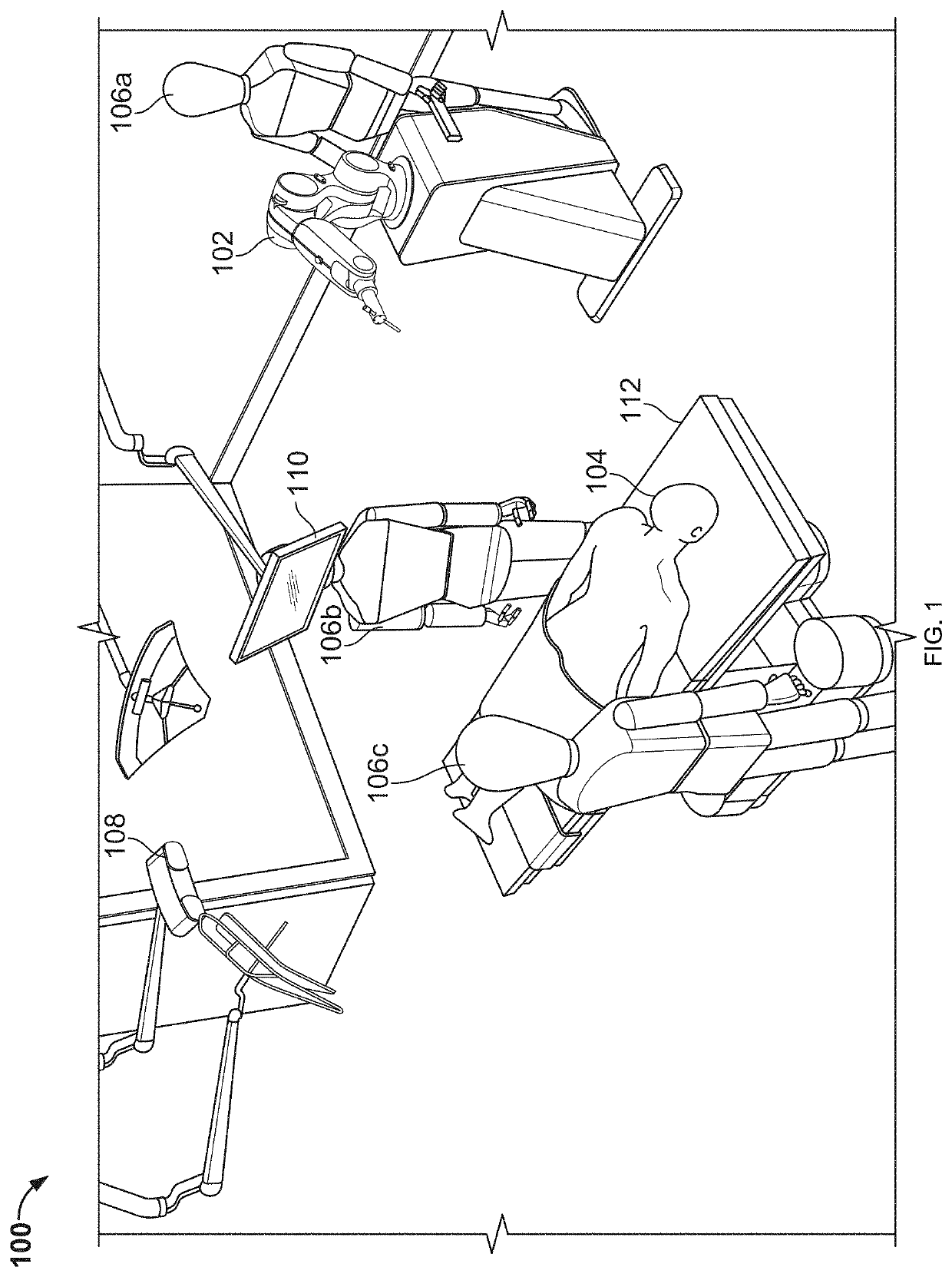
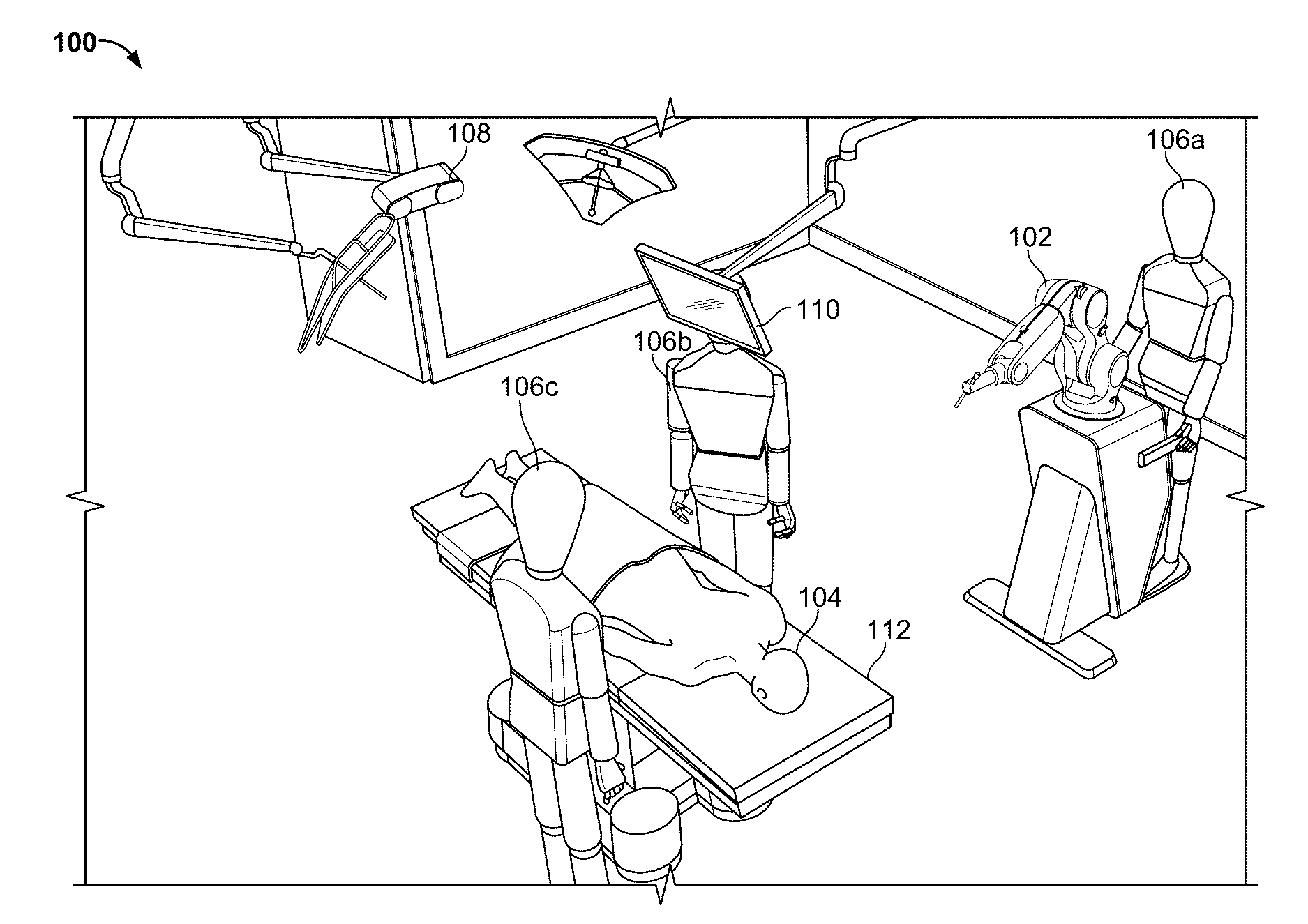
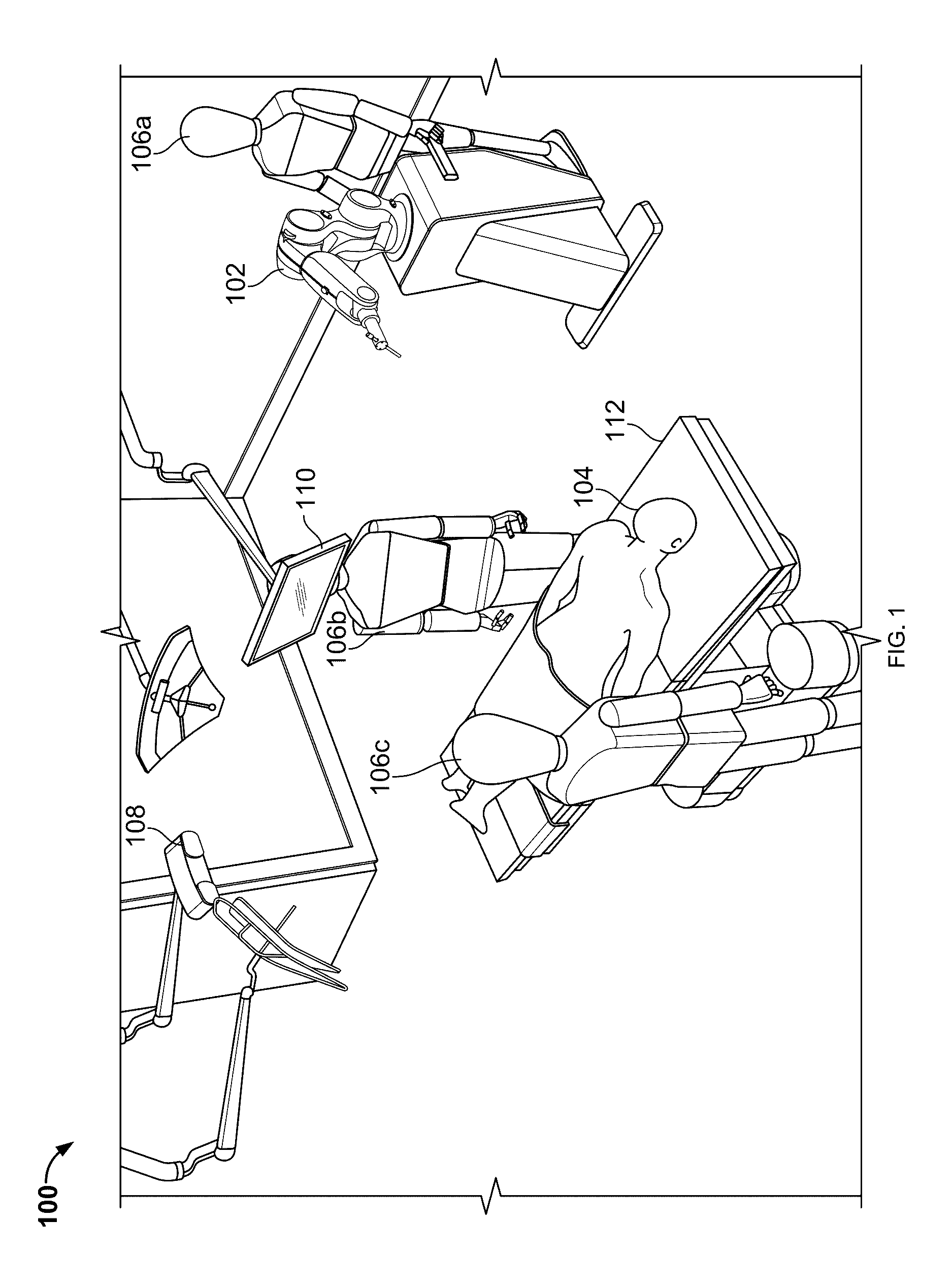
Robotic surgical systems and methods
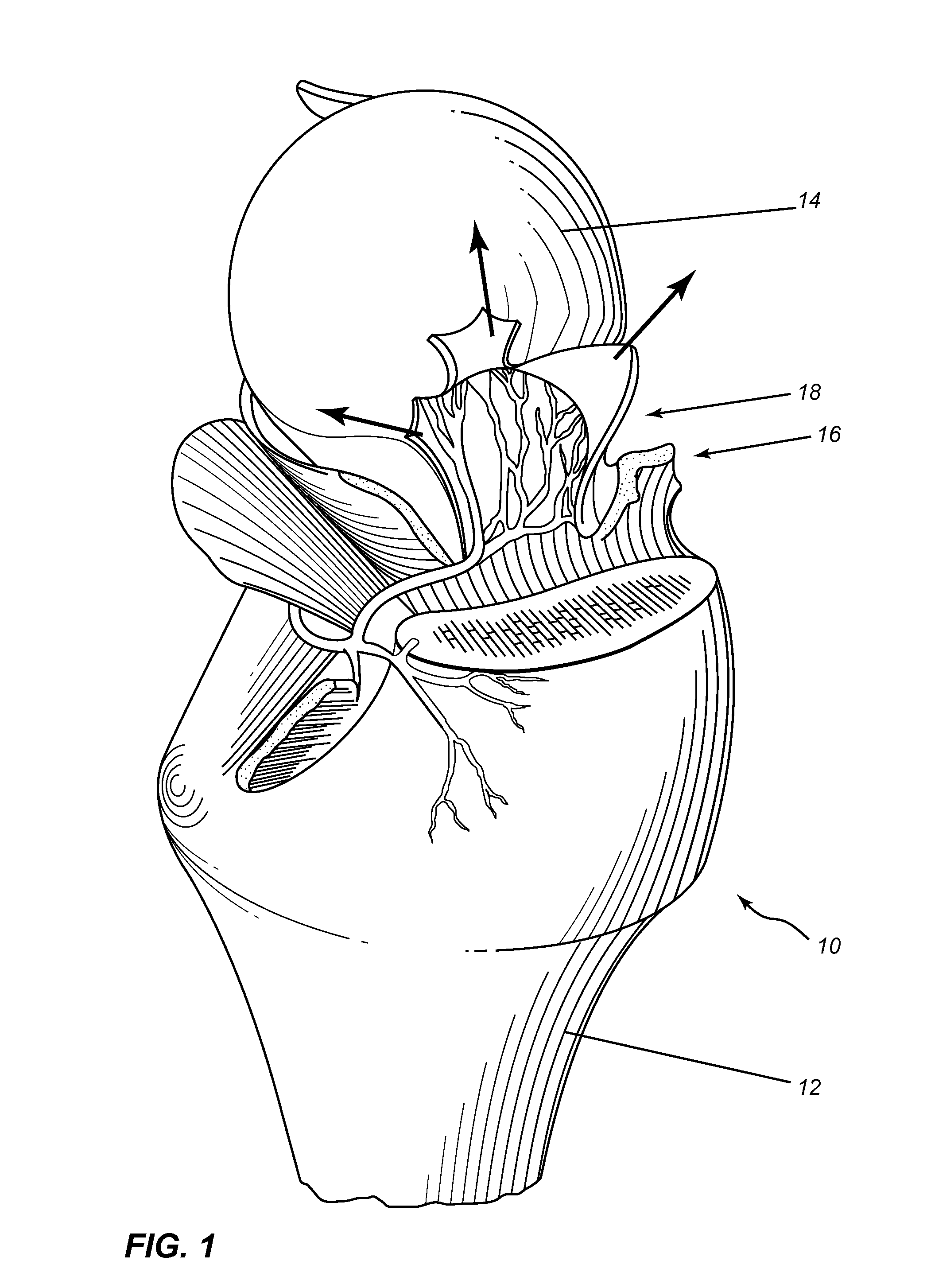
ActiveUS10687905B2Avoid damageMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgical instrument detailsSurgical operationBone structure
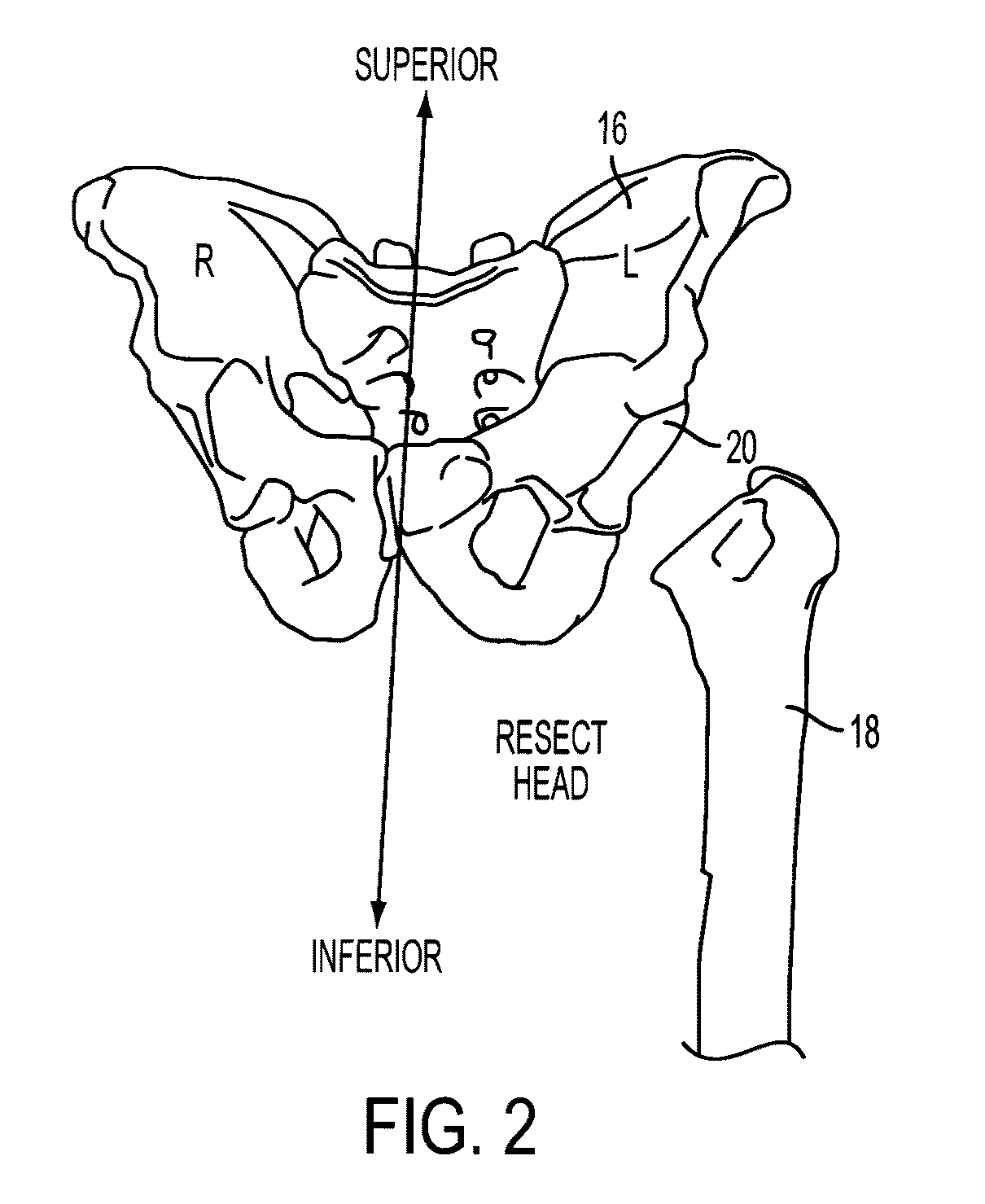
The disclosed technology relates to robotic surgical systems for improving surgical procedures. In certain embodiments, the disclosed technology relates to robotic surgical systems for use in osteotomy procedures in which bone is cut to shorten, lengthen, or change alignment of a bone structure. The osteotome, an instrument for removing parts of the vertabra, is guided by the surgical instrument guide which is held by the robot. In certain embodiments, the robot moves only in the “locked” plane (one of the two which create the wedge—i.e., the portion of the bone resected during the osteotomy). In certain embodiments, the robot shall prevent the osteotome (or other surgical instrument) from getting too deep / beyond the tip of the wedge. In certain embodiments, the robotic surgical system is integrated with neuromonitoring to prevent damage to the nervous system.
Owner:KB MEDICAL SA
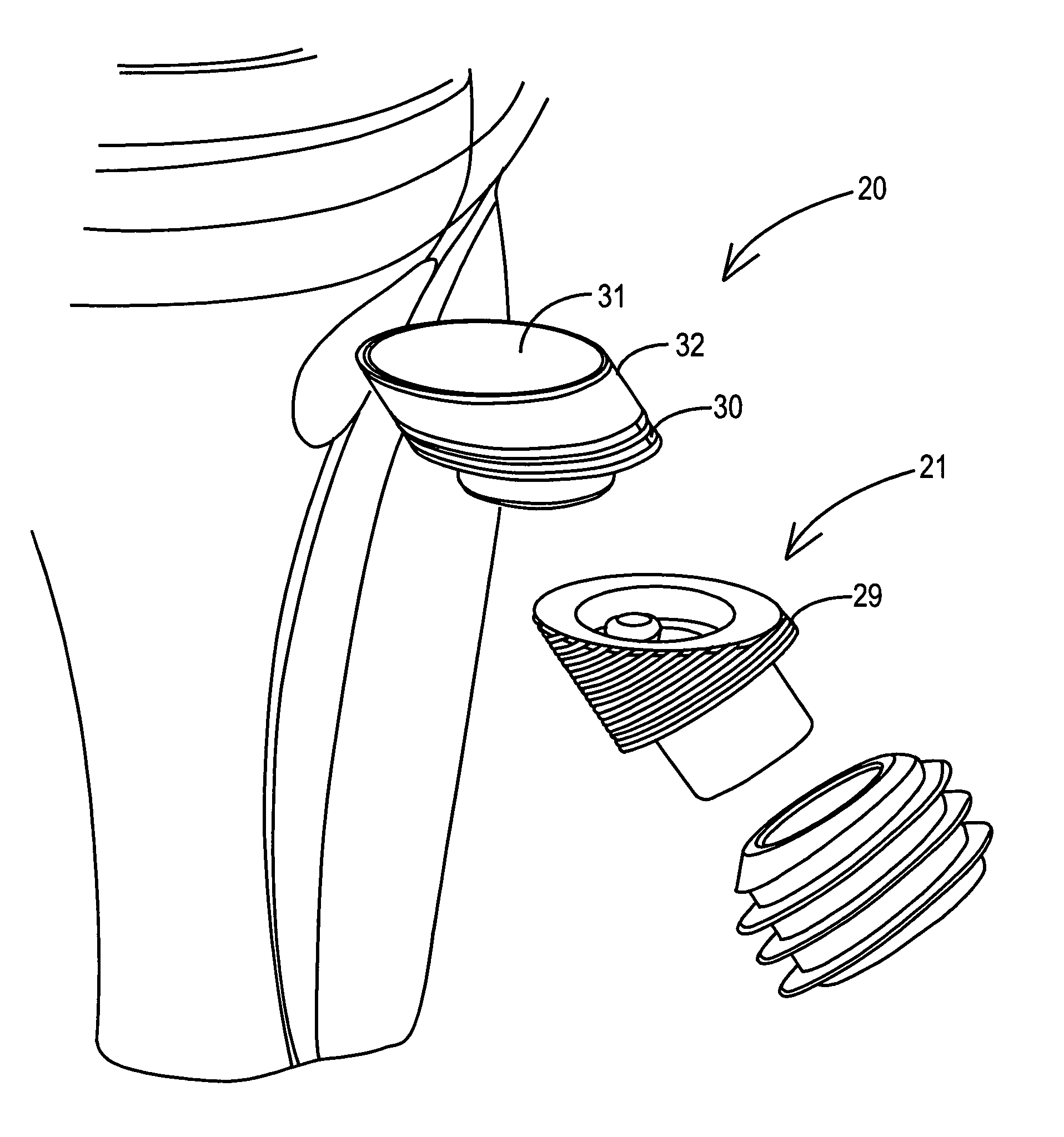
Tibial resurfacing system
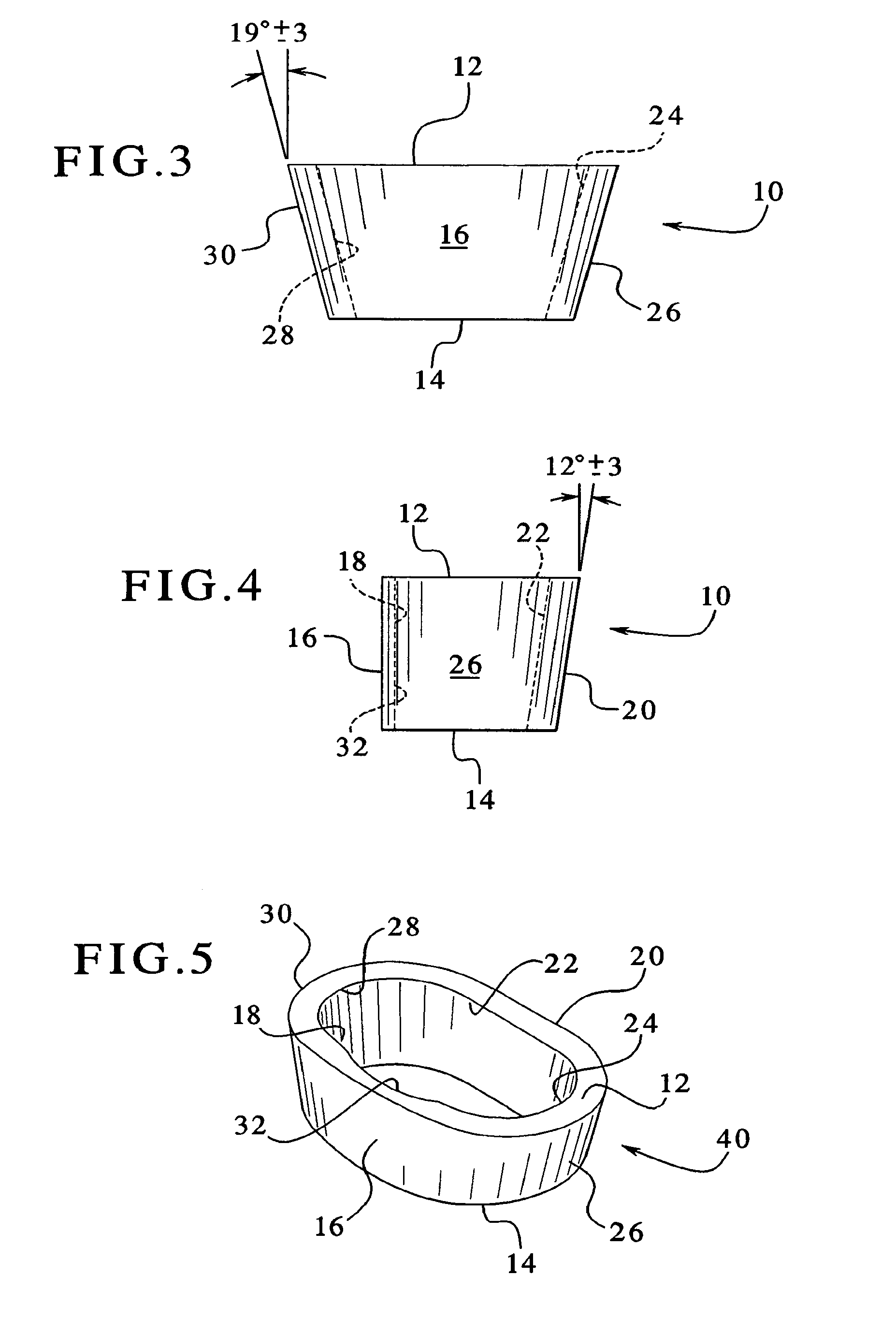
A tibial resurfacing system is provided that includes a drill guide, bone chisel and implant. In one aspect, the system includes a drill guide that includes a targeting ring that is shaped to be placed on the superior tibial surface and a bore section that is connected to the ring to create an axis through the tibia to the superior tibial surface in the vicinity of the targeting ring. The drill guide permits a drill pin and / or drill to be advanced through the tibia to the superior tibial surface. In another aspect, a bone chisel is provided that includes an elongated tubular structure having a first end and a bone-cutting end, and the bone-cutting end is terminated in a transverse angle thereby creating an elliptical bone-cutting face. In another aspect, an implant is provided that includes an angled bearing element formed of a cylindrical member having a first end and a second end. The first end is formed at an angle that creates an elliptical face of the first end, and the first end defines a load-bearing surface of an articular surface.
Owner:ARTHROSURFACE
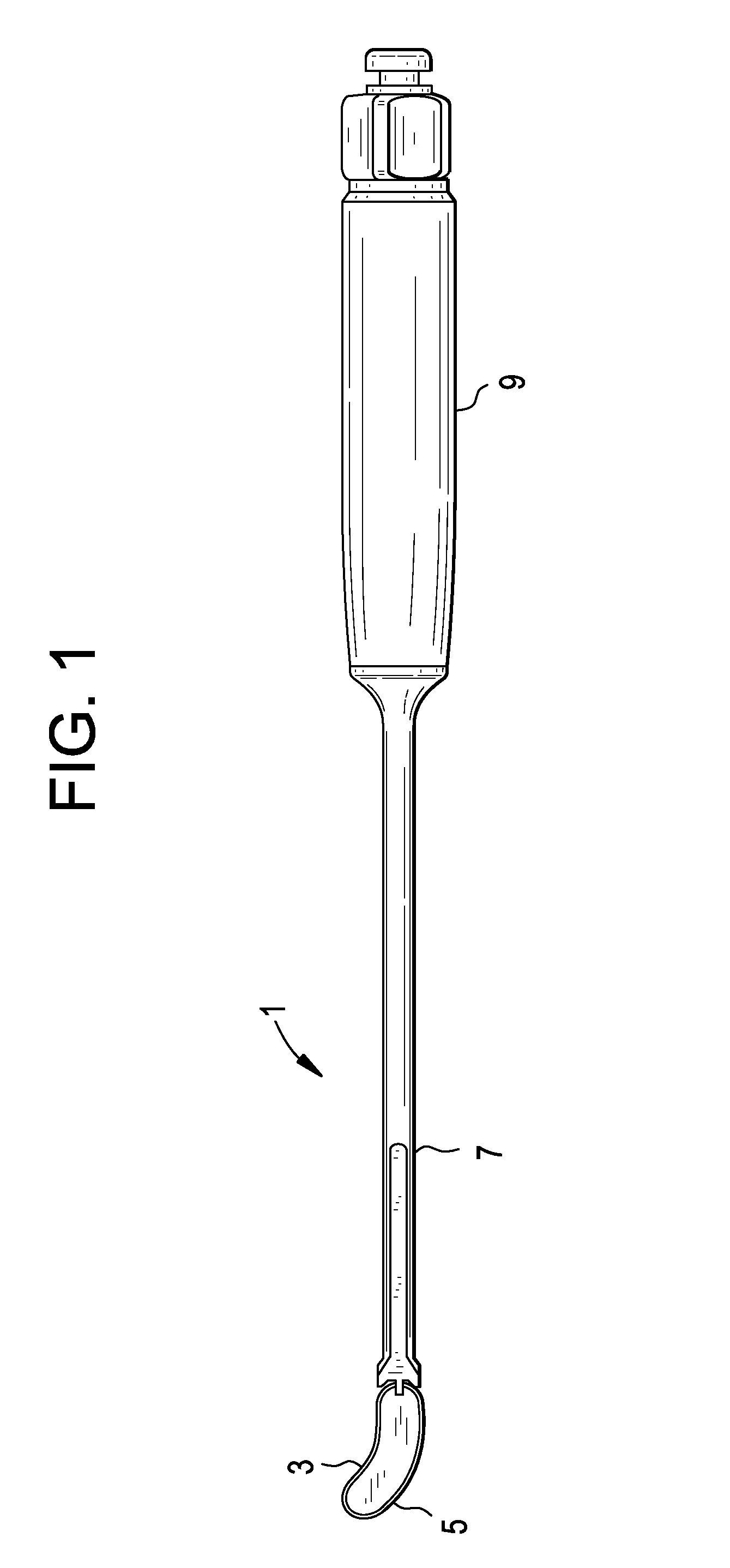
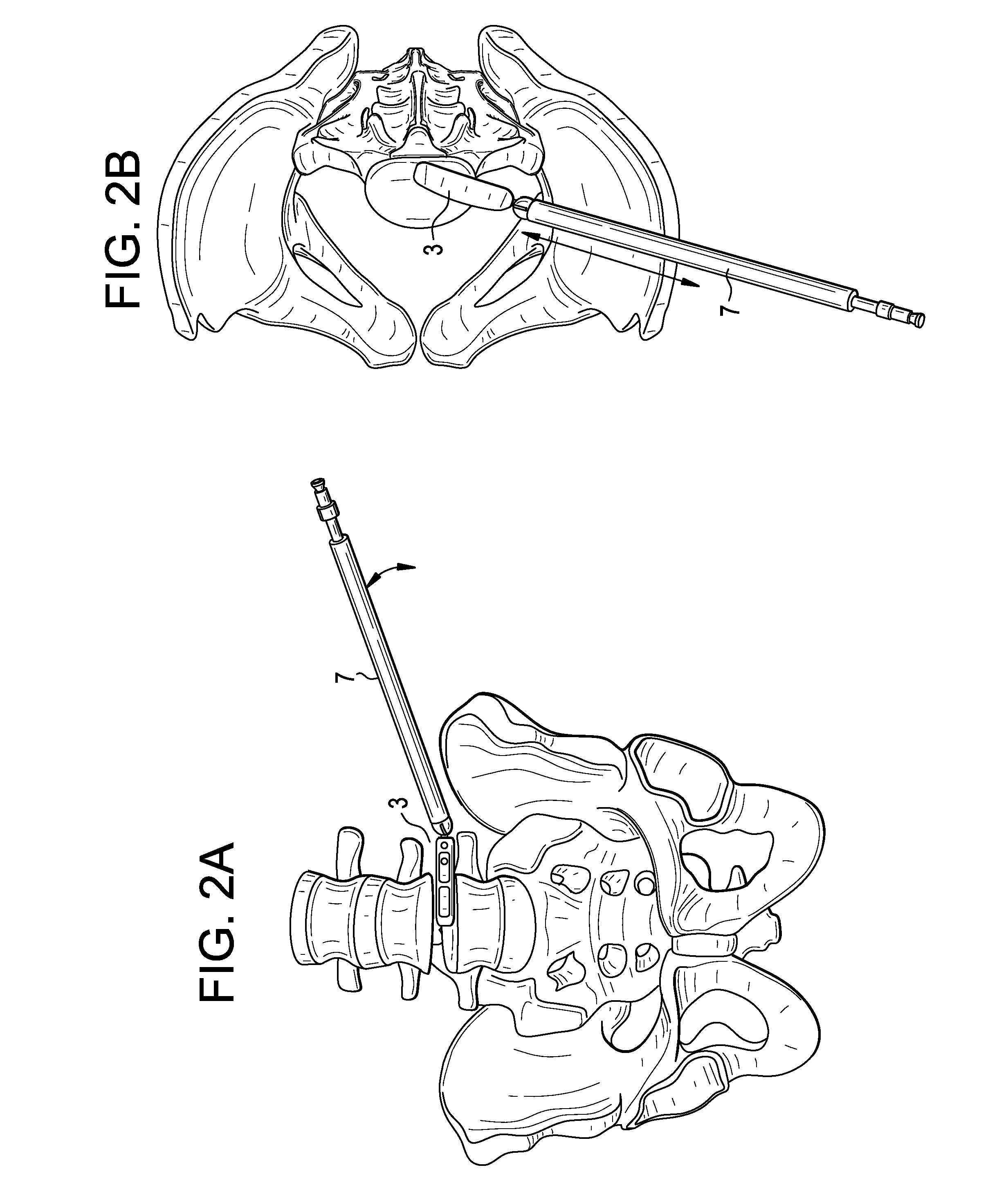
System and method for modular navigated osteotome
InactiveUS20060271056A1Process economySurgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceComputer-assisted surgeryEngineering
An osteotome instrument for use in computer assisted surgery is disclosed. The instrument includes a shaft, a connector, a handle, and a cutter component. The handle has a proximal end portion and a distal end portion. The cutter component is connected to the handle at the distal end portion. The connector is releasably connected to the handle at the proximal end portion, and the connector is adapted to rotate about the shaft relative to the handle. A fiducial for tracking is connected to the connector.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Tibial resurfacing system
A tibial resurfacing system is provided that includes a drill guide, bone chisel and implant. In one aspect, the system includes a drill guide that includes a targeting ring and a bore section for creating an axis through the tibia to the superior tibial surface in the vicinity of the targeting ring. In another aspect, a bone chisel is provided that includes a bone-cutting end, having a transverse angle creating an elliptical bone-cutting face. In another aspect, an implant is provided that includes an angled bearing element formed of a cylindrical member having a first end defining a load-bearing surface, and a second end. The first end is formed at an angle that creates an elliptical face of the first end.
Owner:ARTHROSURFACE
Spinal bone chisels
InactiveUS20050090829A1Enlarge groovePrevent slippingEndoscopic cutting instrumentsChiselEngineering
A chisel with distal cutting edges, used to form channels in adjacent vertebrae, includes a shank having a longitudinal axis and a cutting head coupled to the distal end of the shank. The cutting head includes distal cutting edges, which may be linear, arcuate, or V-shaped, and a guide member, which may be hollow or formed as two spaced members, to guide the chisel into the disc space to uniformly chisel both adjacent vertebrae simultaneously to partially form a channel in the vertebrae. The guide member and cutting head may have openings for distributing cut debris to the top and bottom surfaces of the head. The guide member may also include distal transverse, longitudinal side and / or vertical cutting edges, some of which may be in stepped relationship, for further cutting the endplates and removing disc material from between adjacent vertebrae, and for scraping of endplates. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:OSTEOTECH INC
Orthopaedic universal appliance box
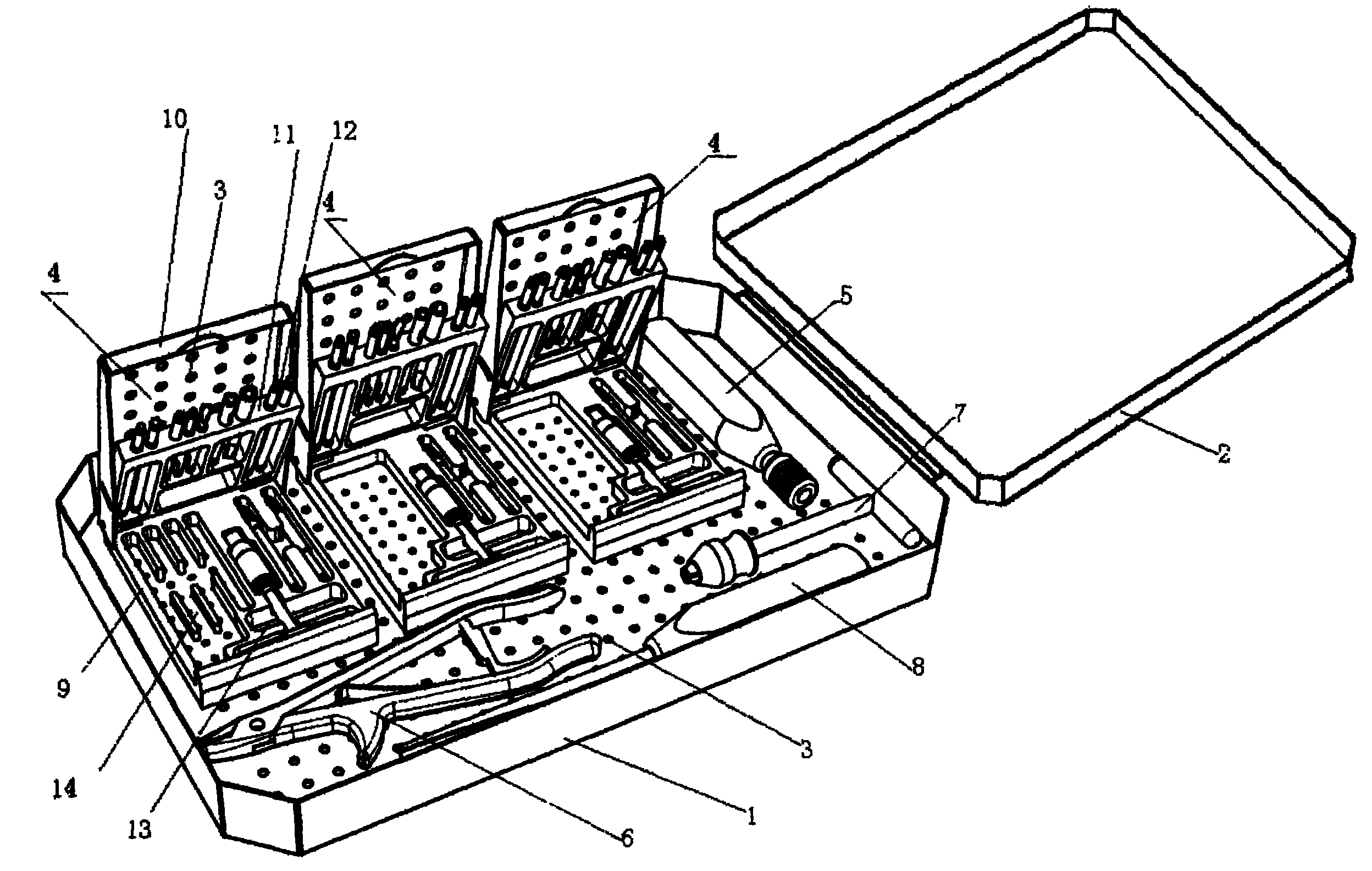
InactiveCN102038553AReasonably placedConvenient remote medical treatmentSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsEngineeringInternal fixation
The invention discloses an orthopaedic universal appliance box which comprises a box body and an upper cover, wherein the upper end of the bottom surface of the box body is uniformly fixed with a plurality of screw take-out device boxes; the left side of the leftmost screw take-out device box is provided with a vertical quick-change straight-handle groove; the left side of the lower end of the bottom surface of the box body is provided with a transverse A-shaped broken-screw take-out embedding groove, and the right side is provided with a transverse T-shaped quick-change handle groove; and the lower side of the A-shaped broken-screw take-out embedding groove and the T-shaped quick-change handle groove is provided with a transverse osteotome groove. The invention solves the problem that the standby tools of orthopaedic surgical appliances are not unified and not convenient to carry, which is common in the clinical work. The overall structure of the orthopaedic universal appliance box is compact. By reasonably putting a set of orthopaedic steel plates and surgical universal appliances of a nail-stick internal fixation system and a bracket external fixation system in the box body, the orthopaedic universal appliance box meets the use requirements during surgery.
Owner:中国人民解放军第一零五医院
Femoral implant revision tool
ActiveUS9198776B2Direct contact guaranteeJoint implantsFemoral headsUltrasonic vibrationPlastic surgery
An osteotome suitable for cutting through cancellous bone that is holding an orthopaedic implant requiring revision within a cavity of a bone, includes a cylindrical waveguide connectable to a source of ultrasonic vibrations at its proximal end and a blade having a hollow part-cylindrical cross-section and a cutting edge at its distal tip. The respective longitudinal axes of the waveguide and the blade cross at an angle of about 30°, and the waveguide and blade taper and curve smoothly together where they meet. The osteotome is dimensioned such that a first antinode of the ultrasonic vibrations is located at a proximal end of the waveguide, a second antinode is located at the distal tip of the blade and a node is located where the waveguide and blade meet. The osteotome cuts readily through cancellous bone when ultrasonically energized.
Owner:ORTHOFIX SRL
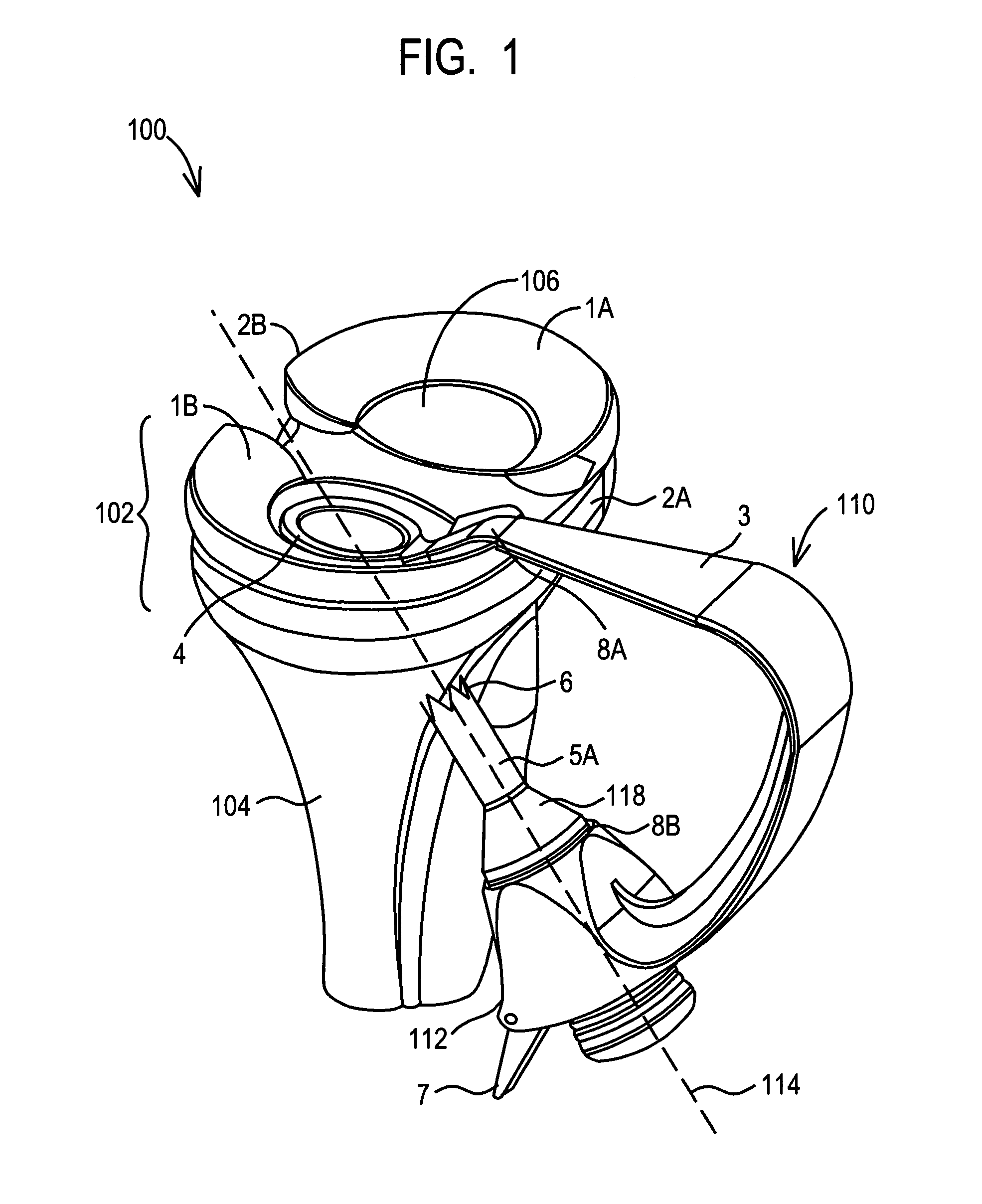
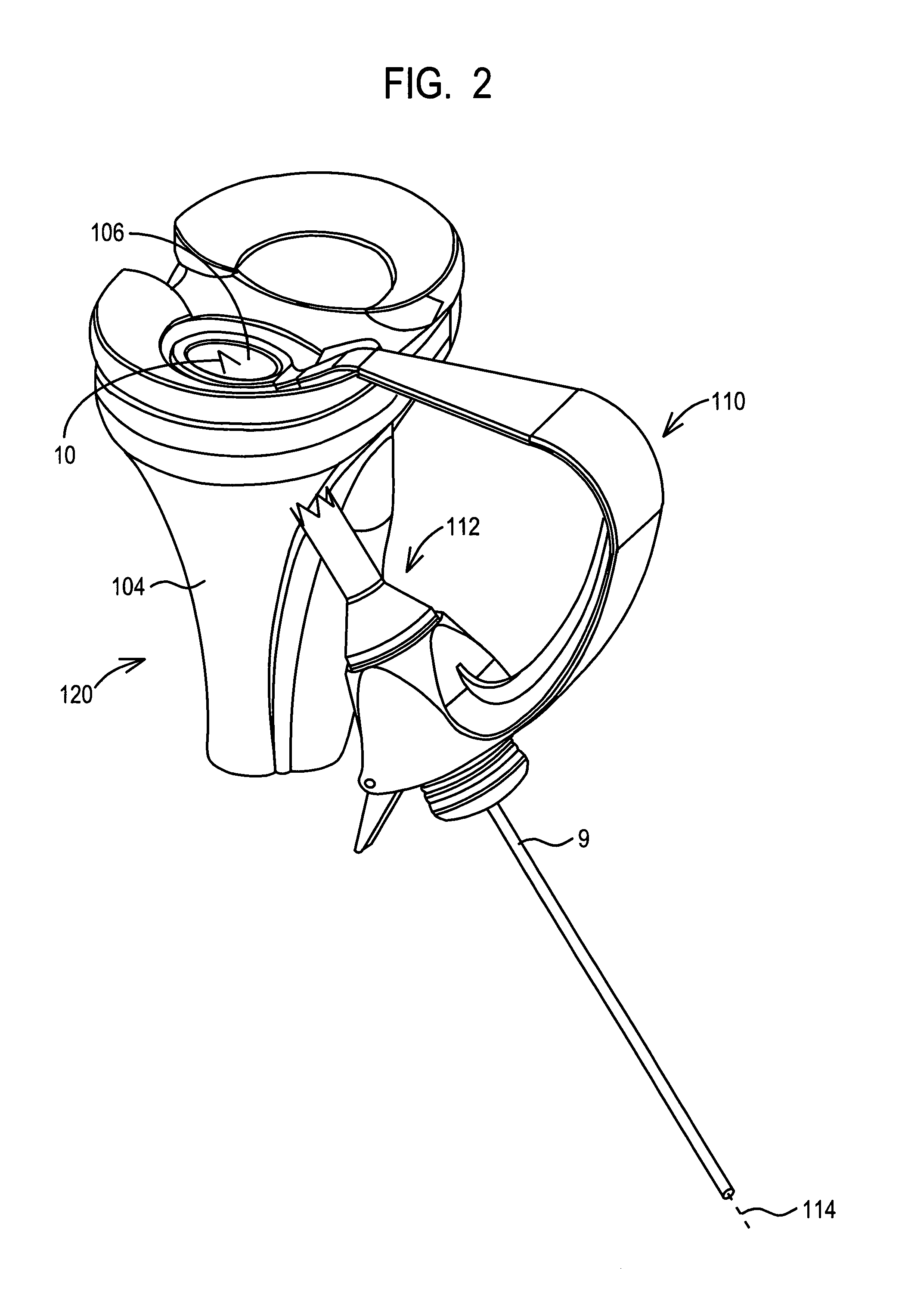
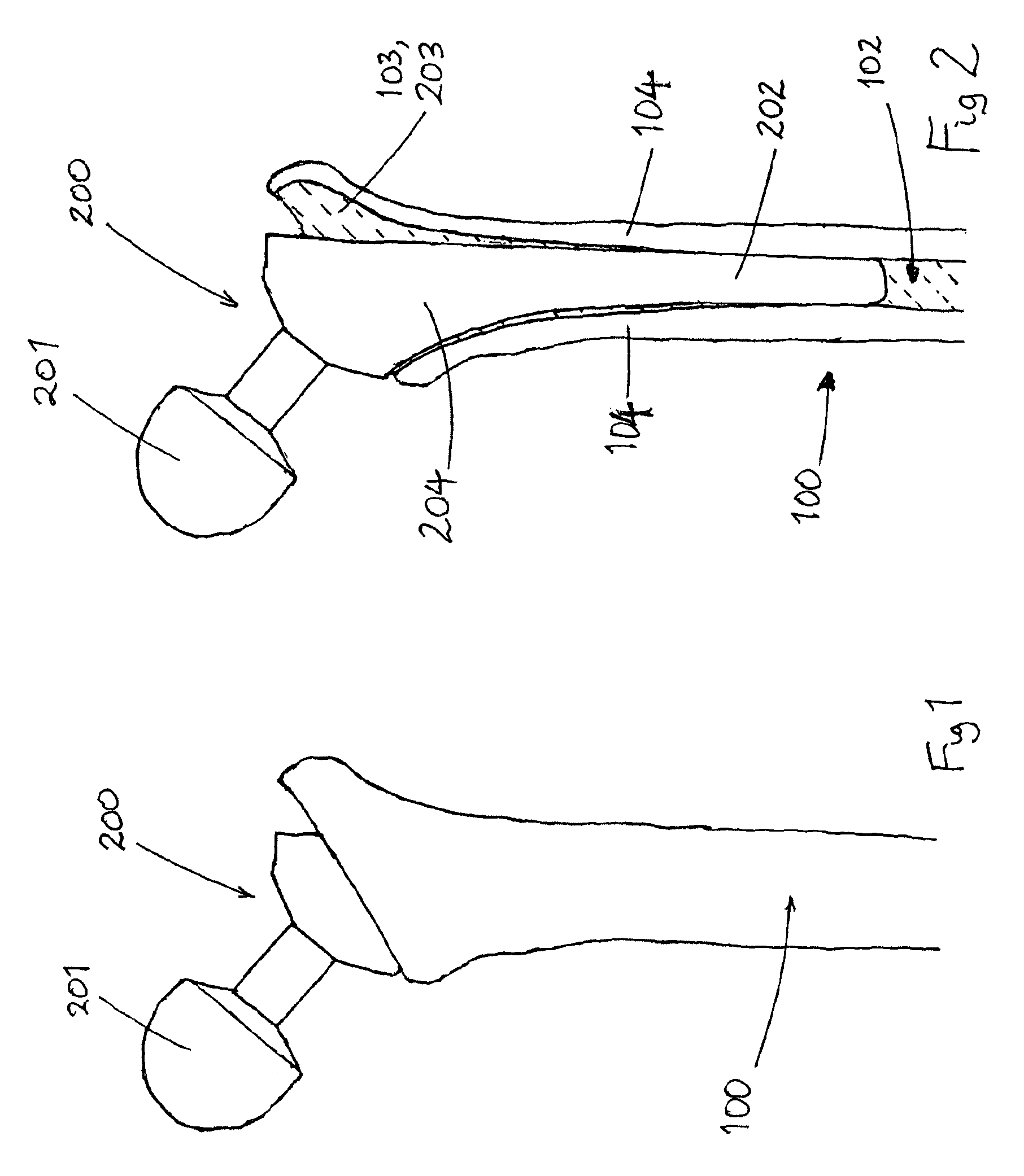
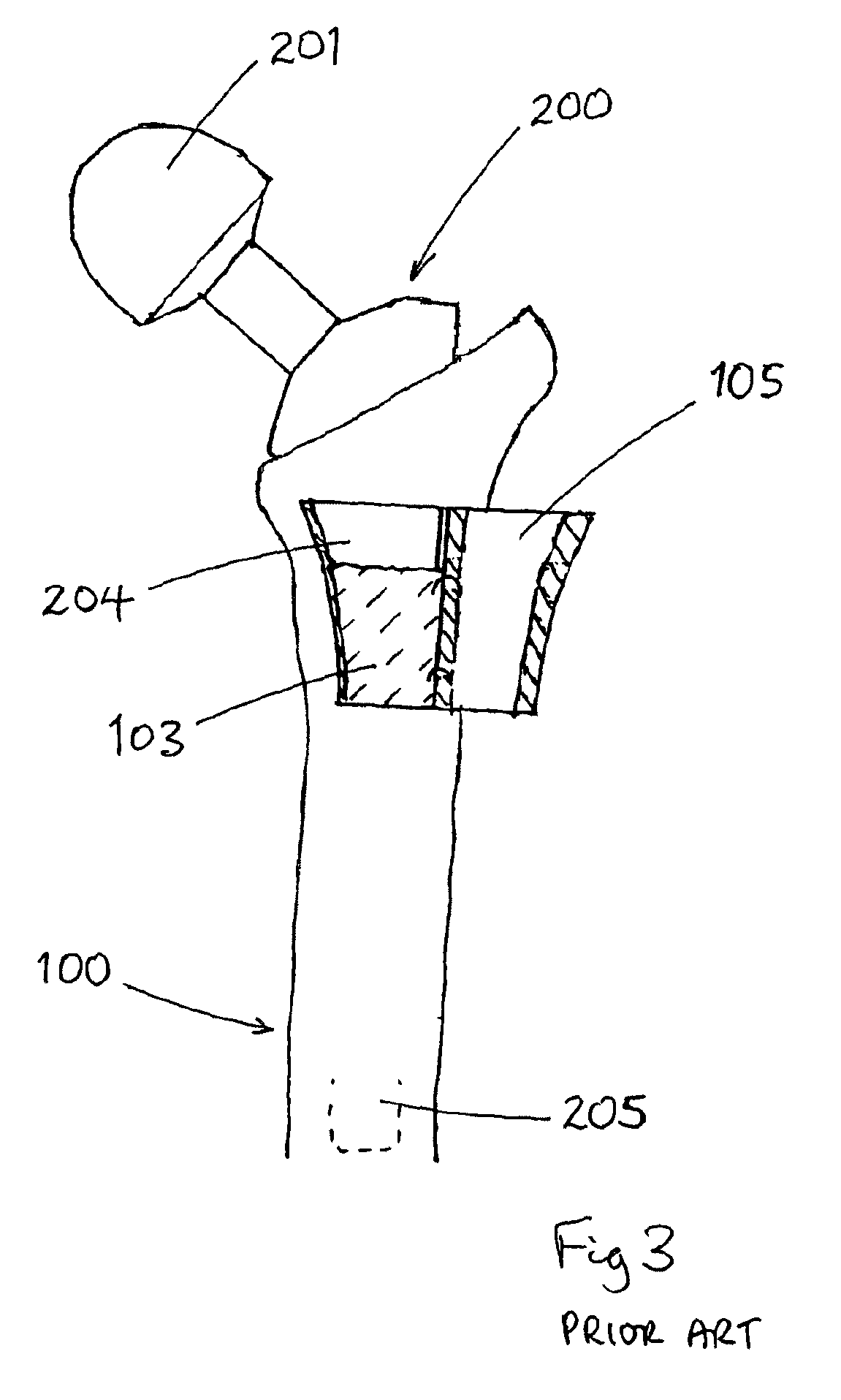
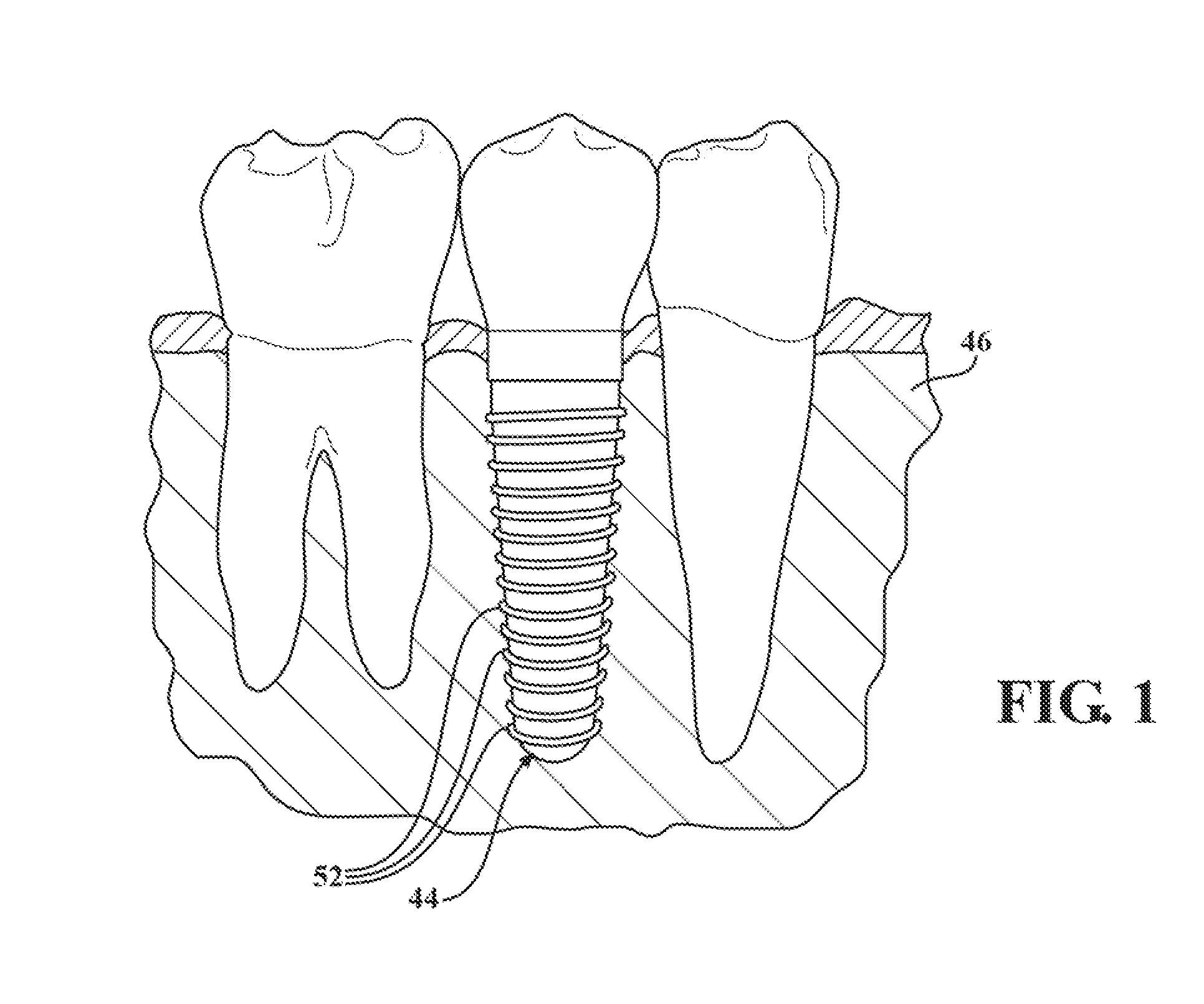
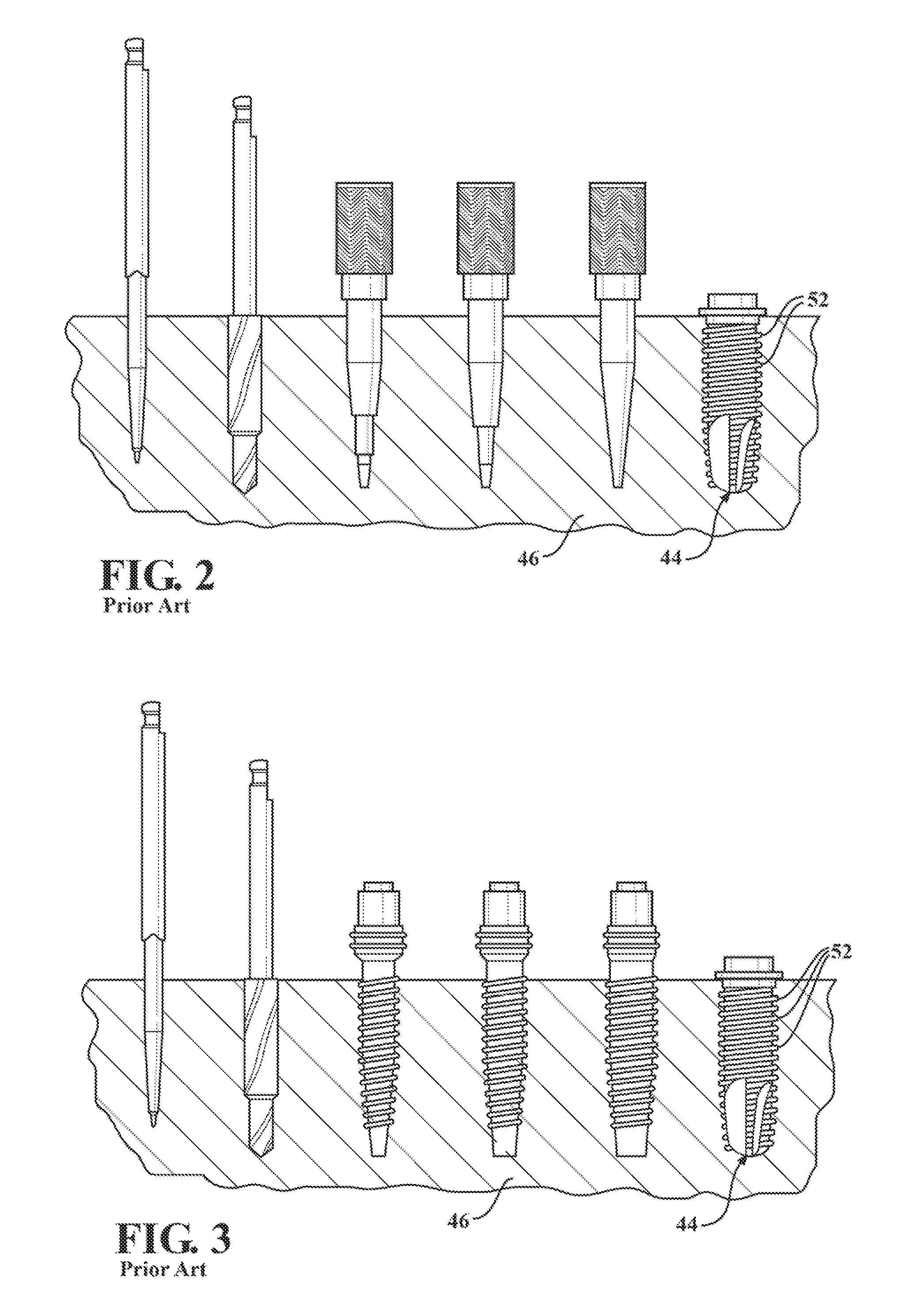
Spinal vertebral implant and methods of insertion
InactiveUS6843804B2Promote bone growthPrevent implantationInternal osteosythesisBone implantNoseIntervertebral space
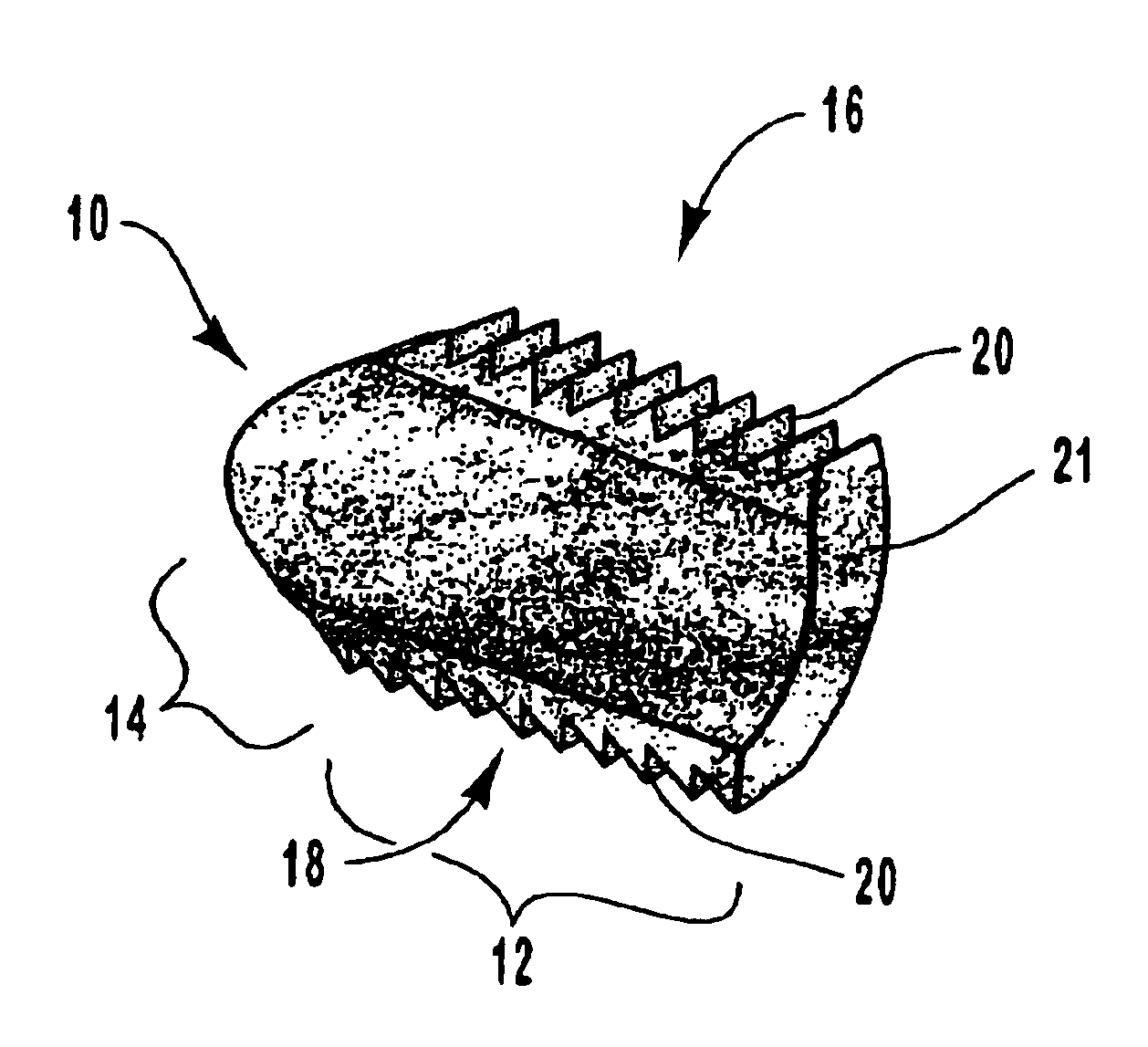
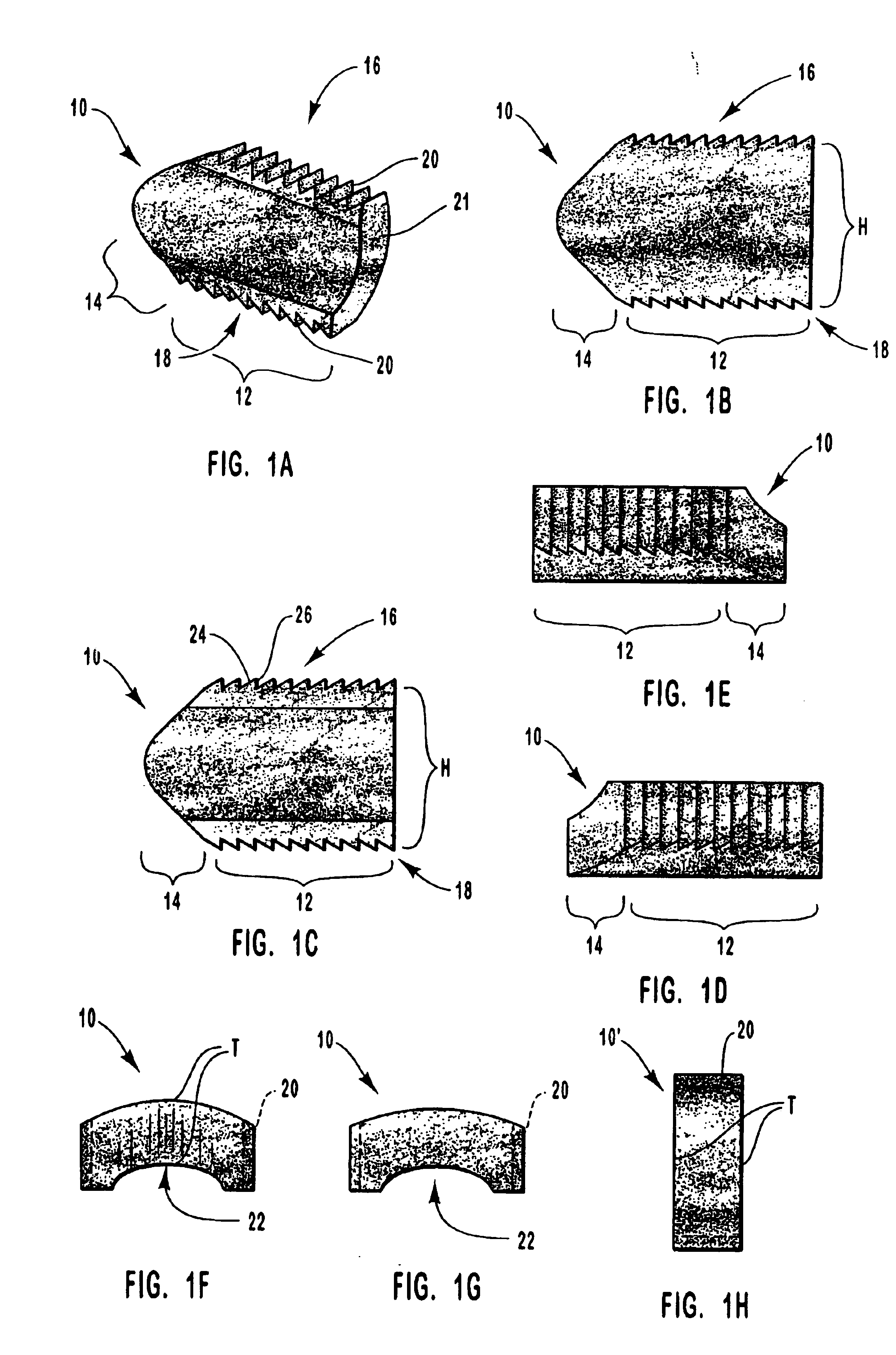
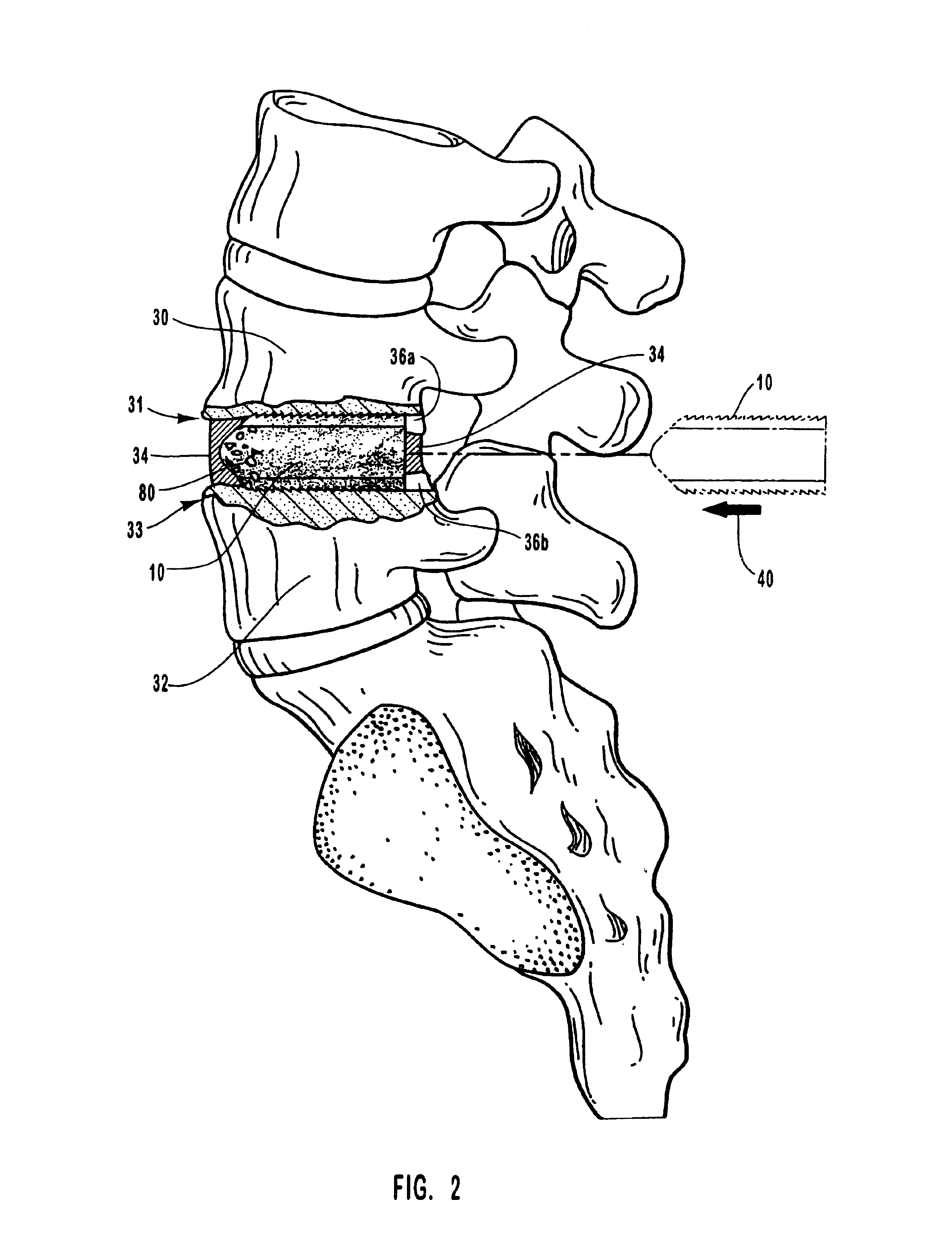
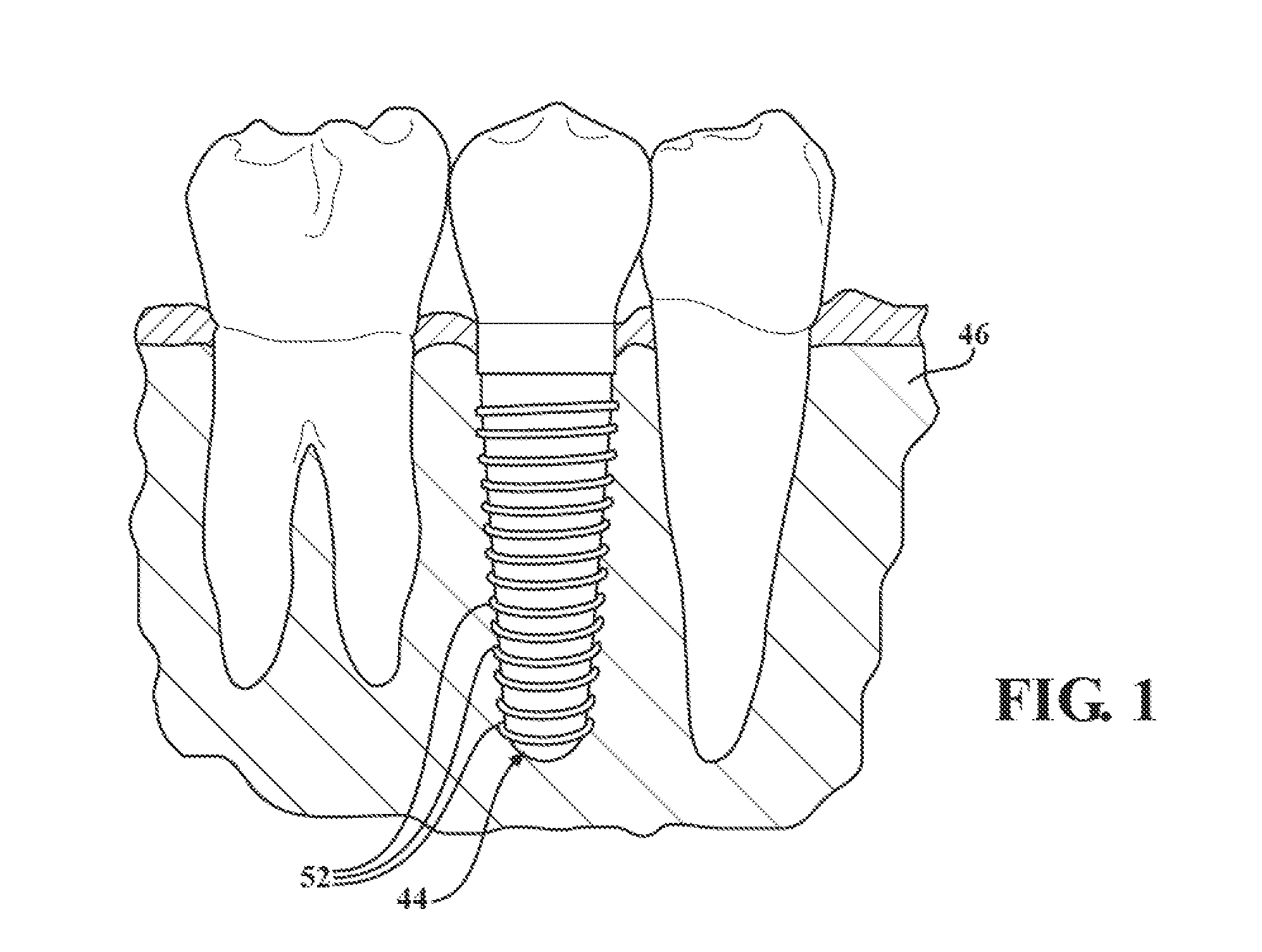
A spinal vertebral implant includes a substantially rectangular shaped base section made from a solid piece of bone. A nose section extends integrally from the substantially rectangularly shaped base section and preferably has a generally tapering shape to foster entry between adjacent vertebrae. The nose section tapers distally and inwardly from the base section to form a generally pointed or rounded distal tip portion and comprises a solid piece of bone. Serrated sides assist the implant in gripping adjacent upper and lower vertebrae and in being maintained therebetween. The serrated sides are angled in a manner that encourages the implant to be placed between the vertebrae and locked therebetween upon such placement. First and second implants may be placed into respective left and right sides of an intervertebral space. A method for placing one or more implants between the adjacent vertebrae comprises forming a slot configured to receive an implant and inserting the implant into the slot. Each slot is preferably formed from an upper slot portion and a lower slot portion in the posterior portion of adjacent upper and lower vertebrae, respectively. Instruments for performing the method include osteotomes, impactors, and spacers.
Owner:BRYAN DONALD W
Polyaxial Articulating Instrument
ActiveUS20140172105A1Less flouroscopy scatterAccurate assessmentInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRaspCurette
A polyaxial instrument suitable for preparing the intervertebral disc space of a patient through an anterior, posterior, transforaminal or anterolateral approach. The trial can be partially inserted into a disc space and then its angle adjusted to ease its further insertion into the disc space. The trial work tip can be interchangeable with the working tip of another type of instrument such as a curette, a rasp, a spreader, a shaver, a cobb elevator, a penfield, a woodson, a chisel and an osteotome.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Tibial augments for use with knee joint prostheses
Owner:ZIMMER INC
Betts Osteotome
InactiveUS20100249785A1Disrupt volumeExcision instrumentsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsEngineeringMedical device
A medical device and method of using the device to reinforce and stabilize a compressed tissue is disclosed. The medical device comprises a shaft with a single blade that is biased with a bend, but is elastic enough to be straightened. The end of a cannula is inserted into a tissue, and the blade and shaft are then inserted into a cannula to straightens the blade and direct it to the tissue site. When the blade reaches the tissue site, the blade naturally returns to its bent biased state, and the shaft and blade are then rotated to pulp a volume of tissue. A binding material is then injected into the pulped tissue without removing the tissue.
Owner:BETTS ANDRES
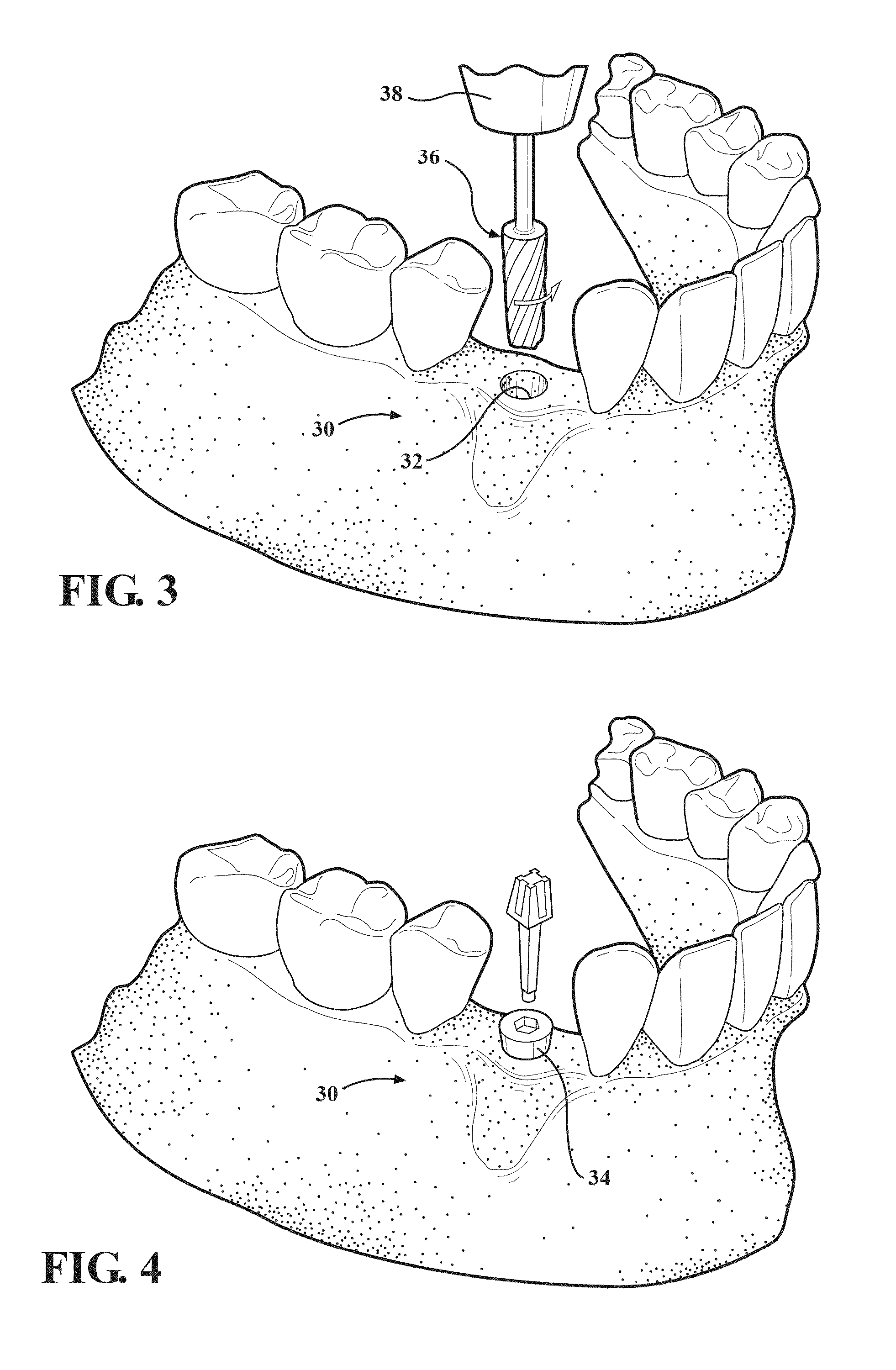
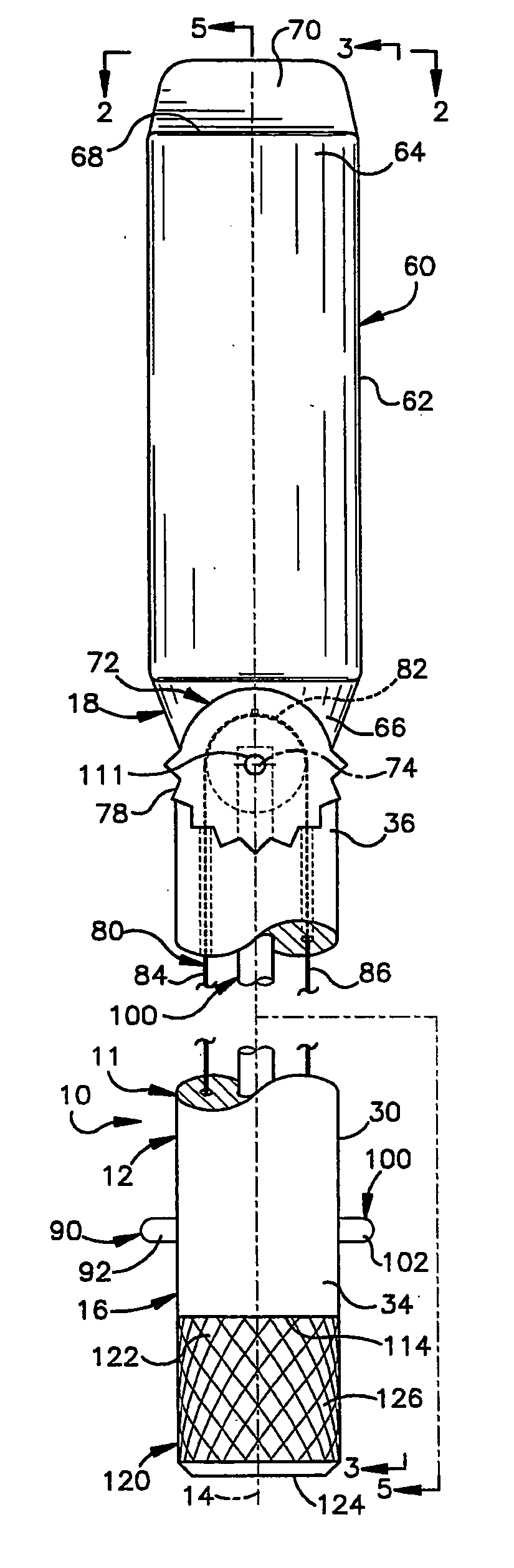
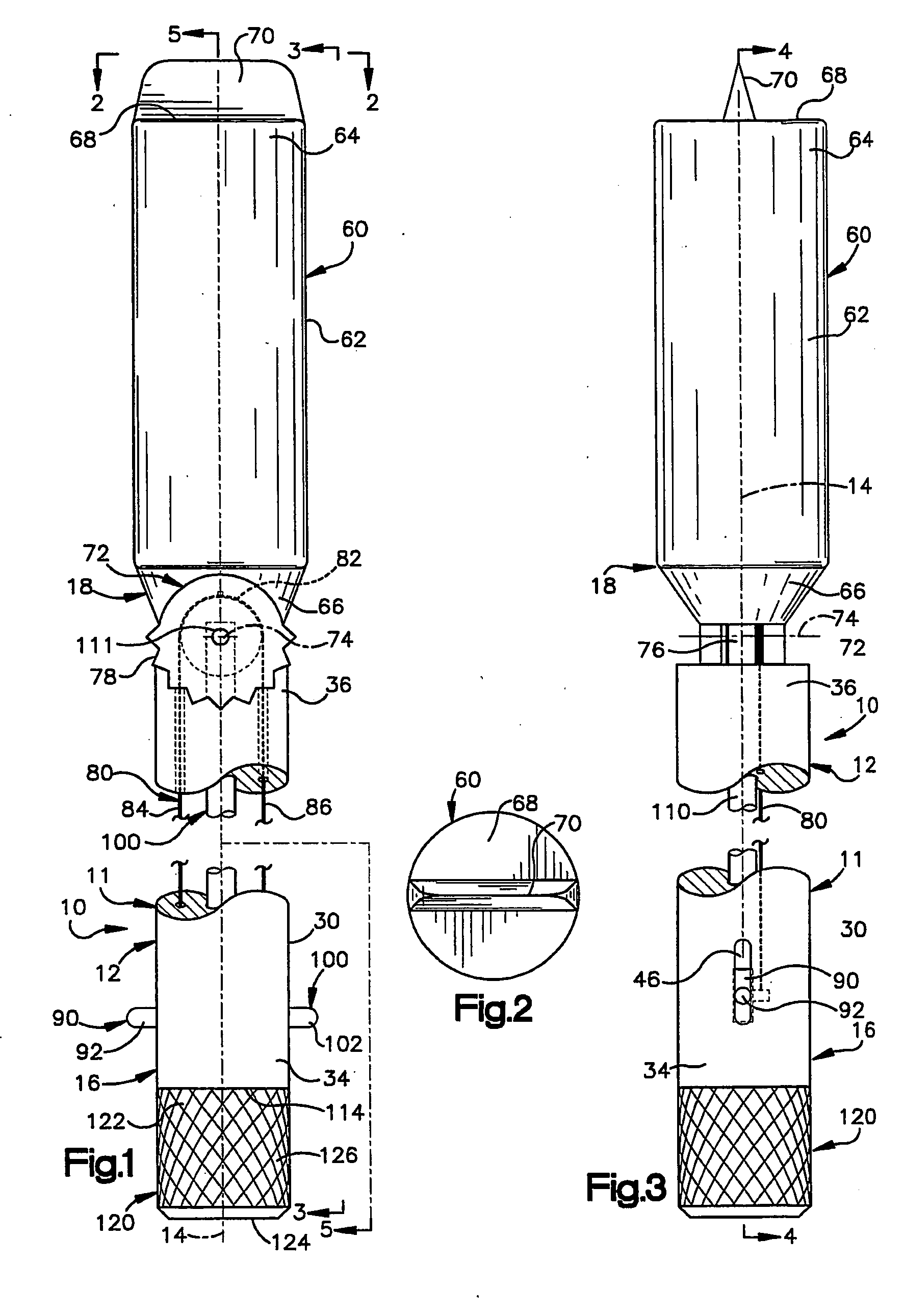
Bone cutting osteotome tool and method for preparing a surgical sinus-lift osteotomy
InactiveUS20060172255A1Minimize the risk of damageRisk minimizationDental implantsTeeth fillingNasal cavitySurgical operation
A surgical tool (5) used for preparing a surgical sinus-lift osteotomy has a defined thread geometry in series with an osteotome tip to cut, crack and push bone from the sinus floor upward into the sinus cavity in a tactual, gentle and controlled motion. The apical osteotome tip is driven into a pre-drilled pilot osteotomy after the cutting threads are engaged and rotated until the sinus floor is cracked free. Once the bony sinus floor is cracked free, a fluid passageway can be pressurized with a sterile fluid at a defined pressure to release and push the sinus membrane upward into the sinus cavity to create a desired apical cavity for grafting. The invention solves the problems for preparing a sinus-lift surgical osteotomy and desired cavity space while minimizing the risk of compromising or tearing the sinus membrane. The invention allows the physician to easily form the desired sinus cavity to allow for grafting and to receive a screw formed dental implant while minimizing the risk of certain undesired surgical conditions.
Owner:ACE SURGICAL SUPPLY
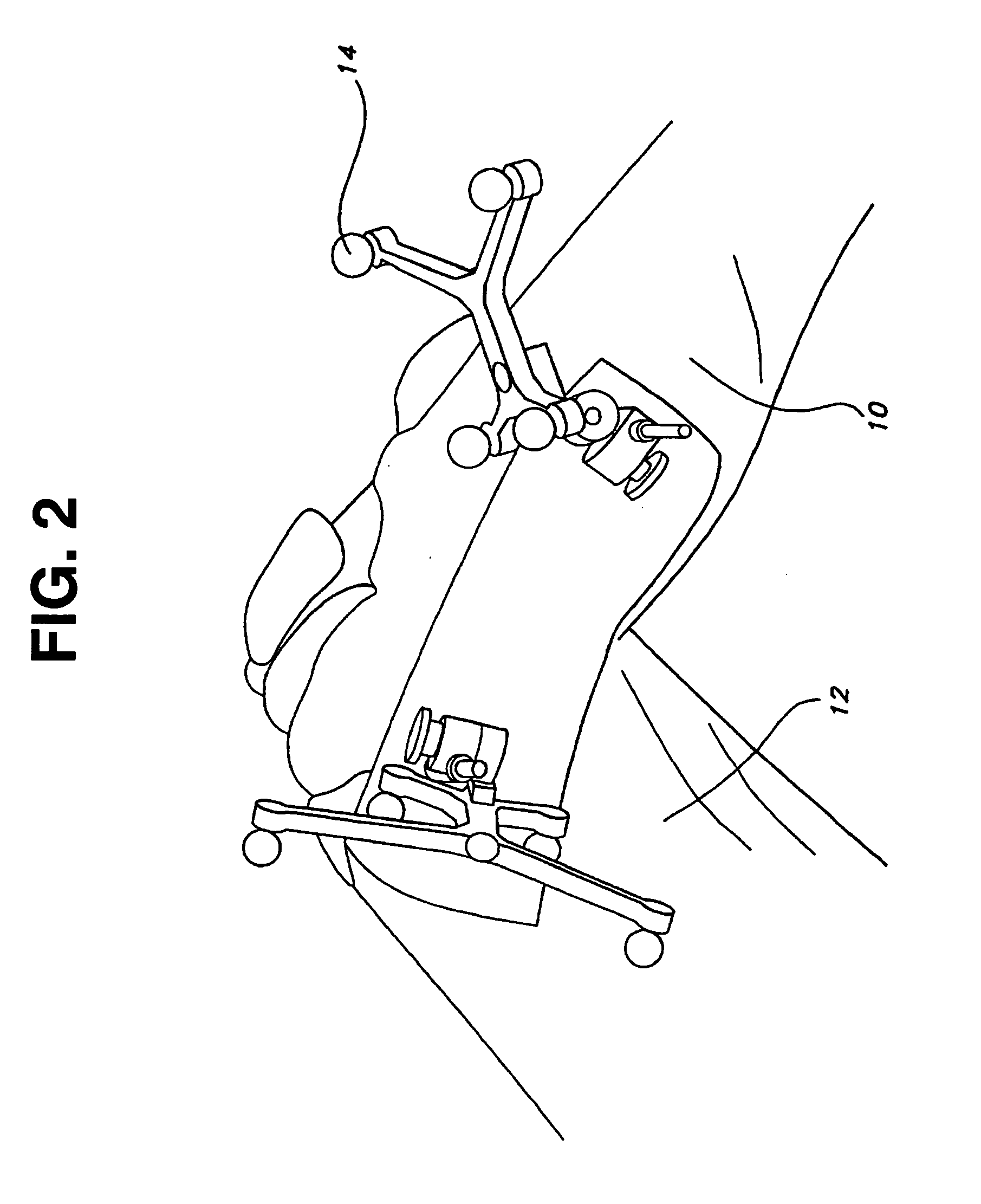
Universal double offset surgical instrument
Instruments for use in anterior approach total hip arthroplasty. Instruments according to certain embodiments of the invention connect to a shaping member such as a broach, reamer or osteotome that is used to prepare the intramedullary canal of a desired femur or other bone for total hip arthroplasty. Such an instrument according to such embodiments can be configurable to allow operation on either the left or right leg, and in doing so to provide lateral offset and anterior offset of the instrument handle relative to the shaping member so that the patient's gut, musculature or other bodily portions may be avoided while still providing desired leverage and control over the shaping member to prepare the intramedullary canal.
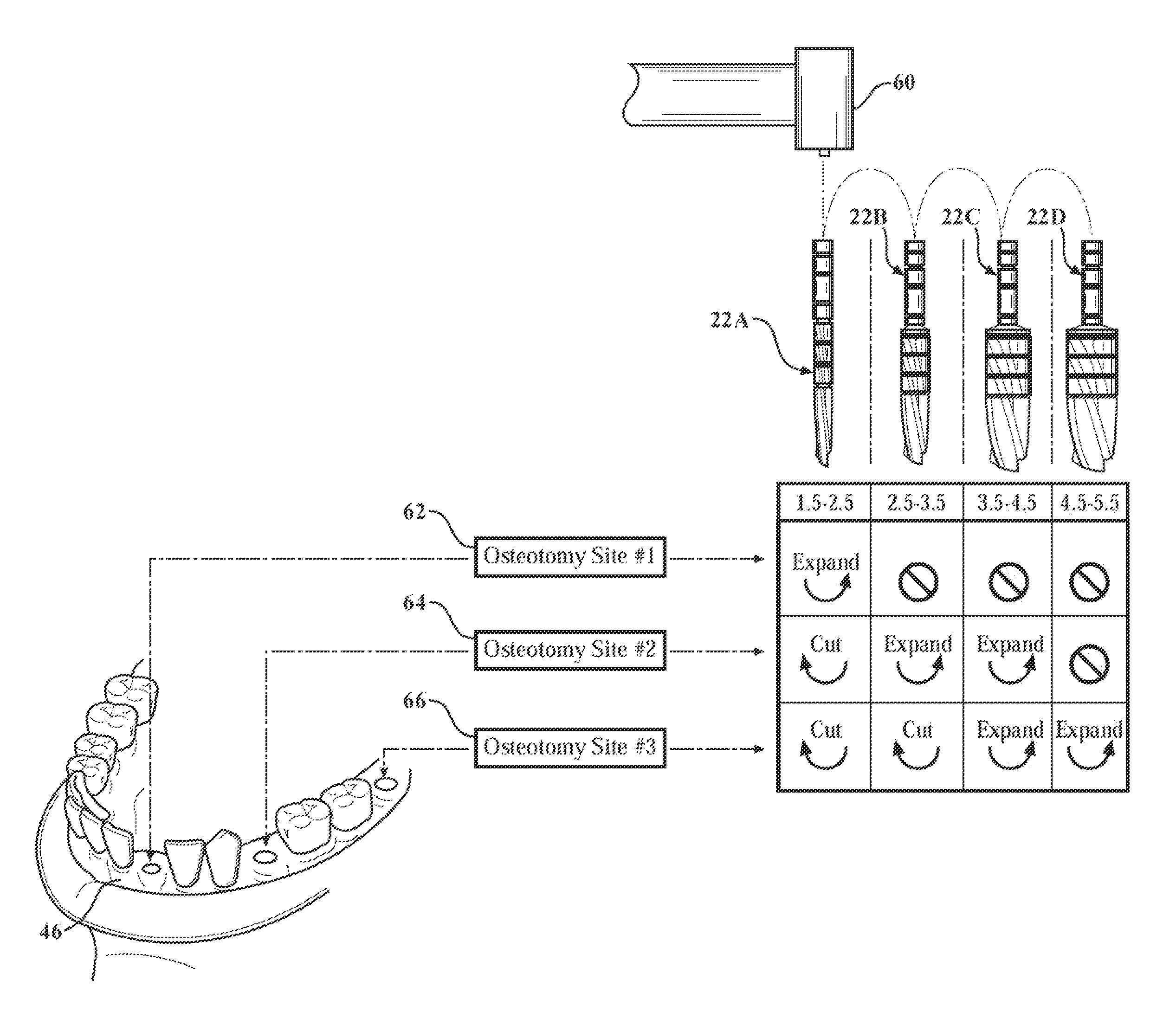
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Tibial augments for use with knee joint prostheses, method of implanting the tibial augment, and associated tools
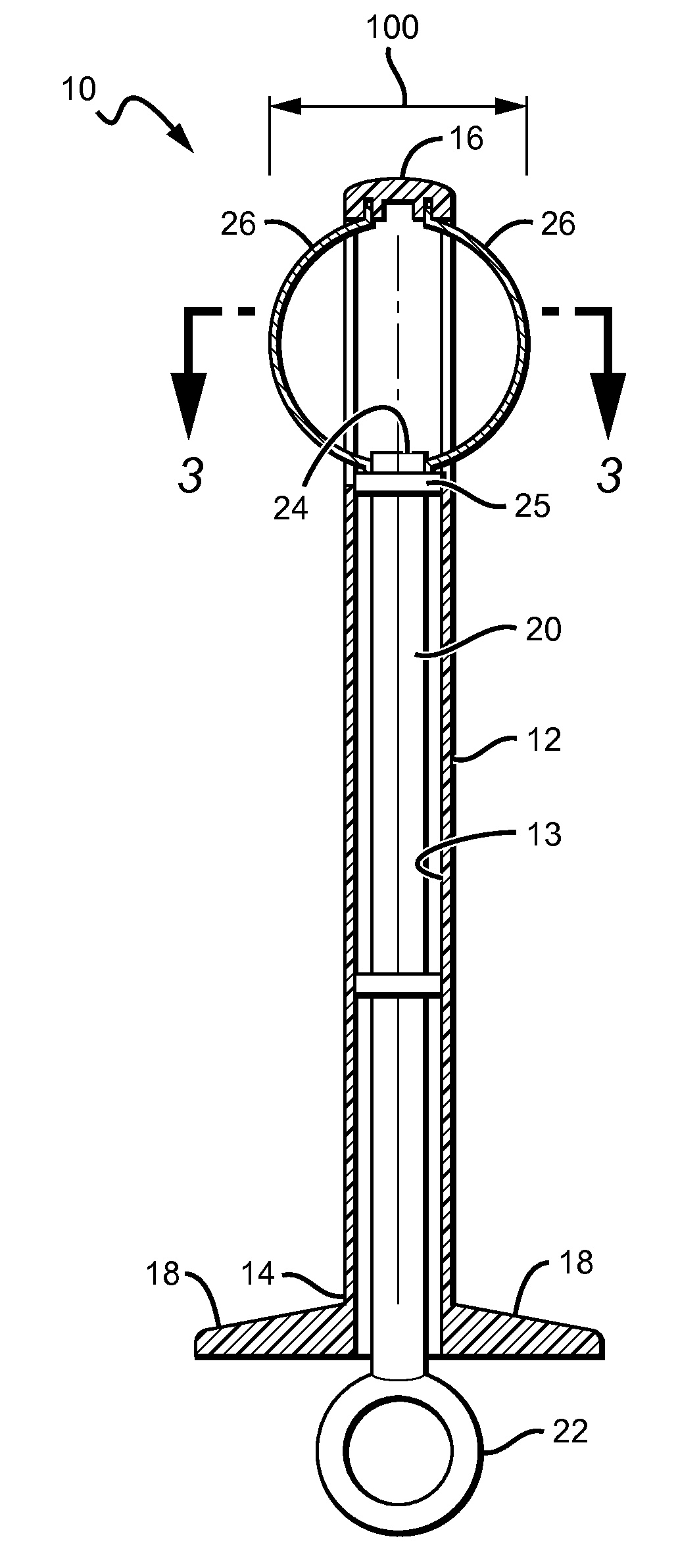
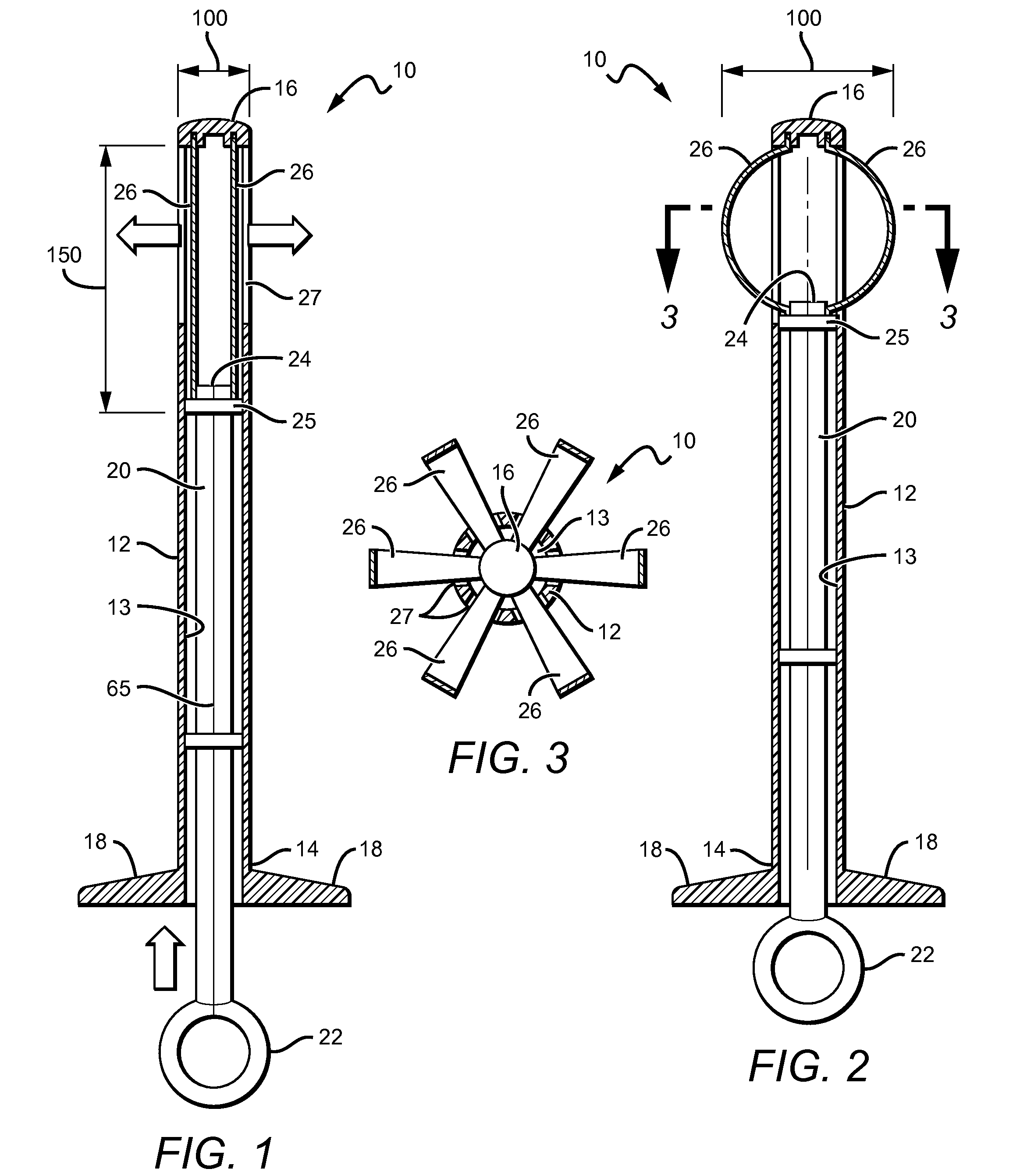
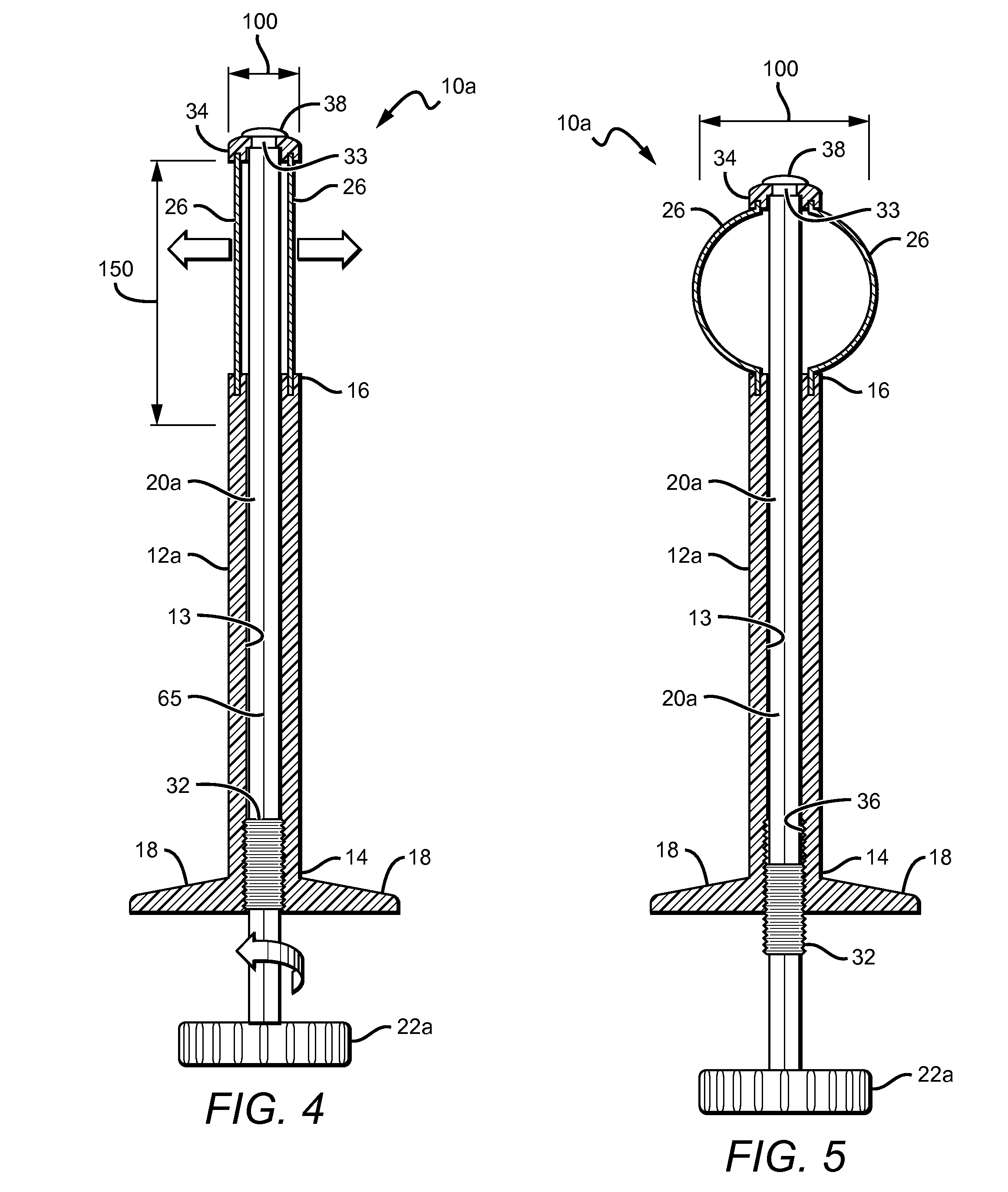
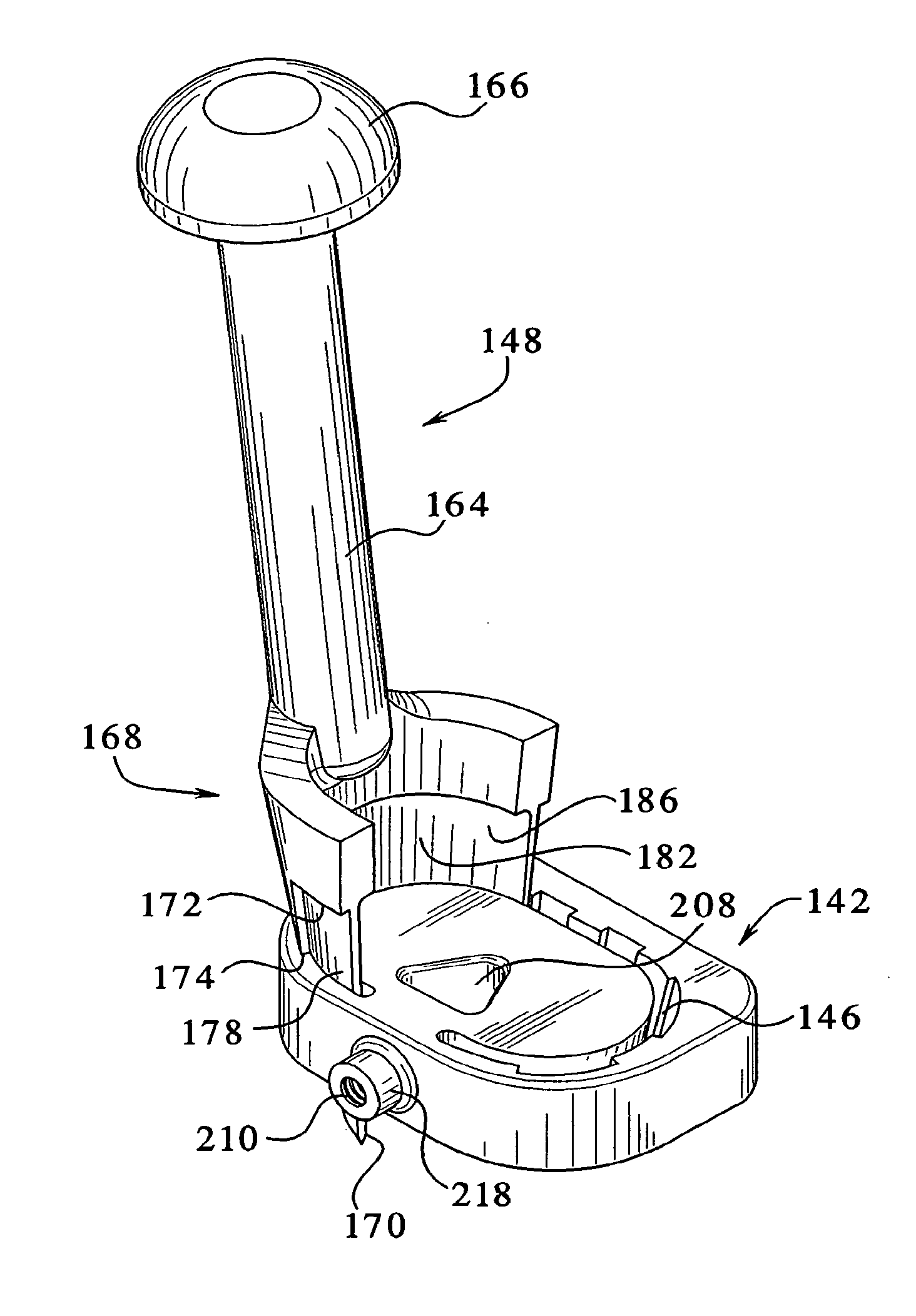
A tibial augment for use with a knee joint prosthesis, composed of annular members of different stock sizes, each size being configured to fit within a cavity formed in a human tibia. The augment may include a stepped distal surface. A provisional (temporary) tibial augment used to ensure a proper fit for the permanent augment is also provided. The provisional may include grooves configured to cooperate with a set of ribs on a tong-like holder used for removing the provisional from the cavity. A pusher for use implanting the tibial augment is also provided. In addition, a system for creating a cavity in a human tibia is also described. The system preferably includes a guide with a slot therein and a set of osteotomes that are inserted within different portions of the slot. Methods for using the tools and / or implanting the prosthetic devices discussed above are also described.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
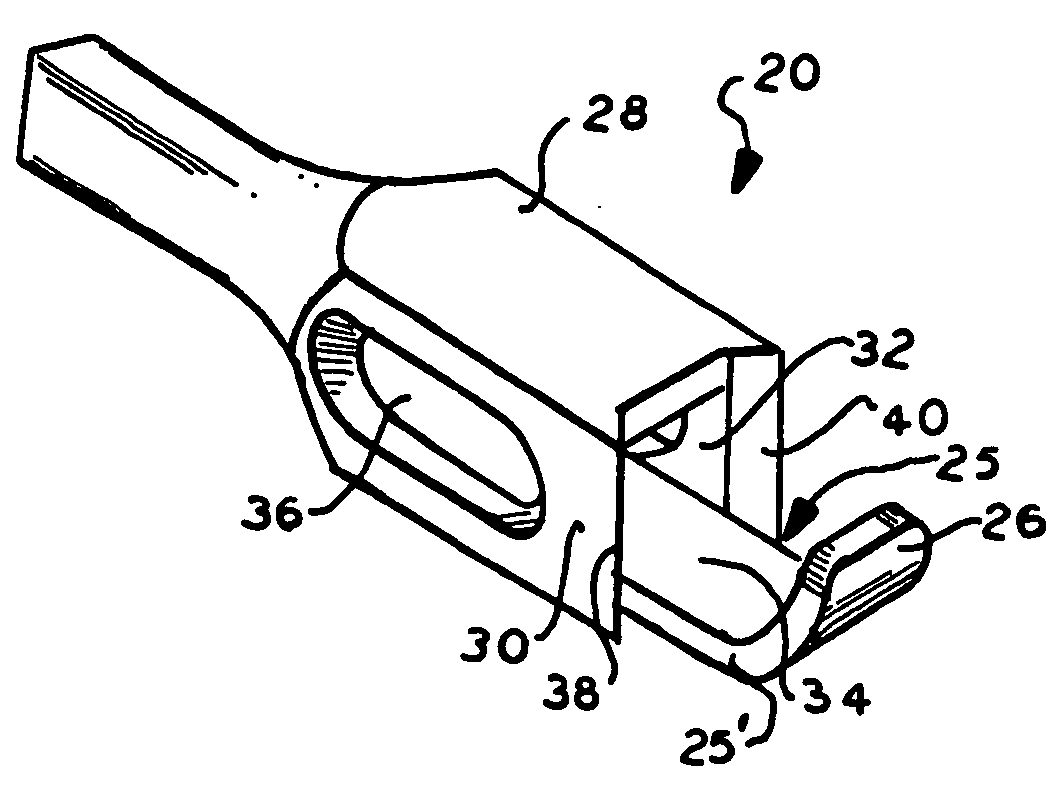
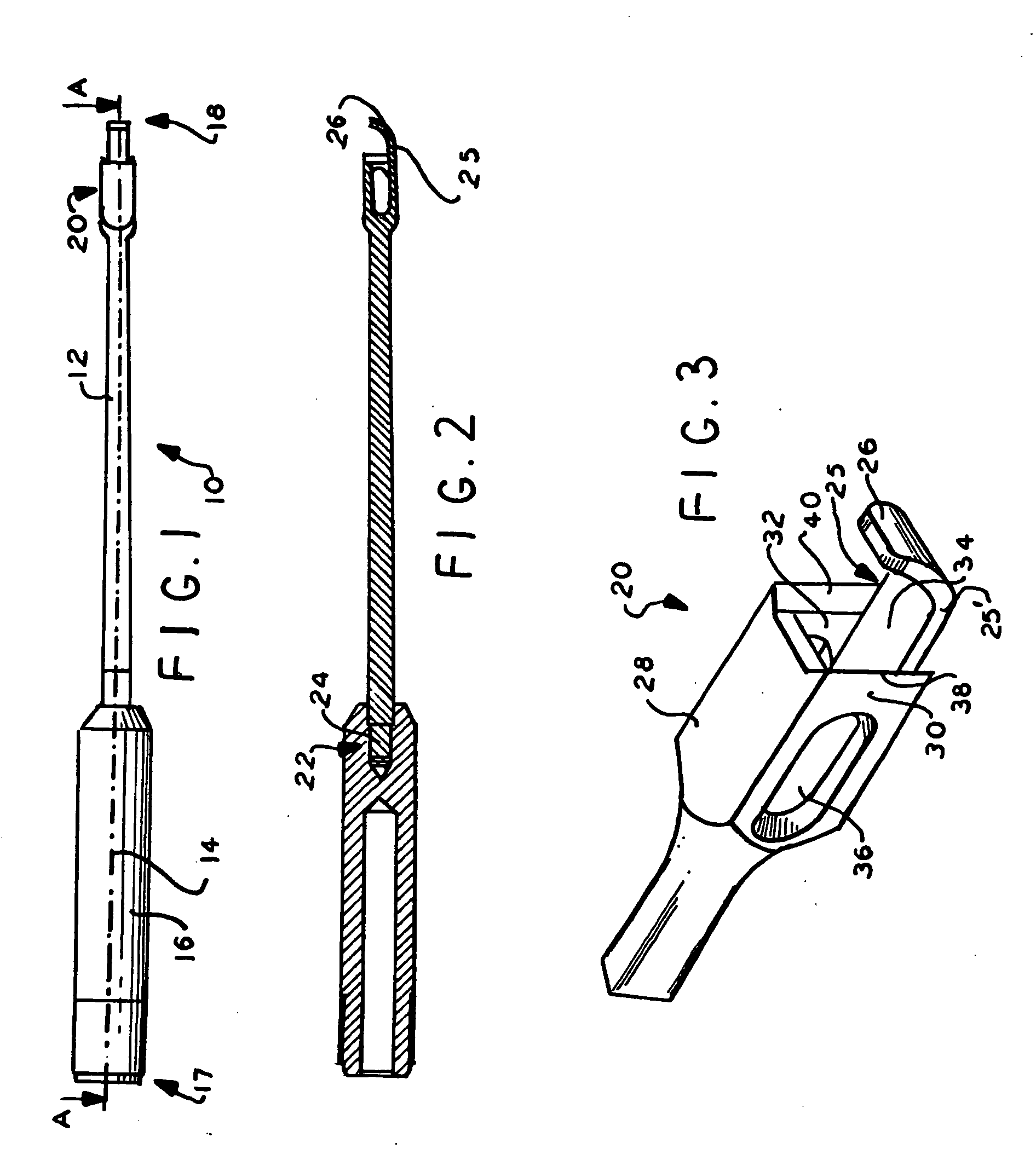
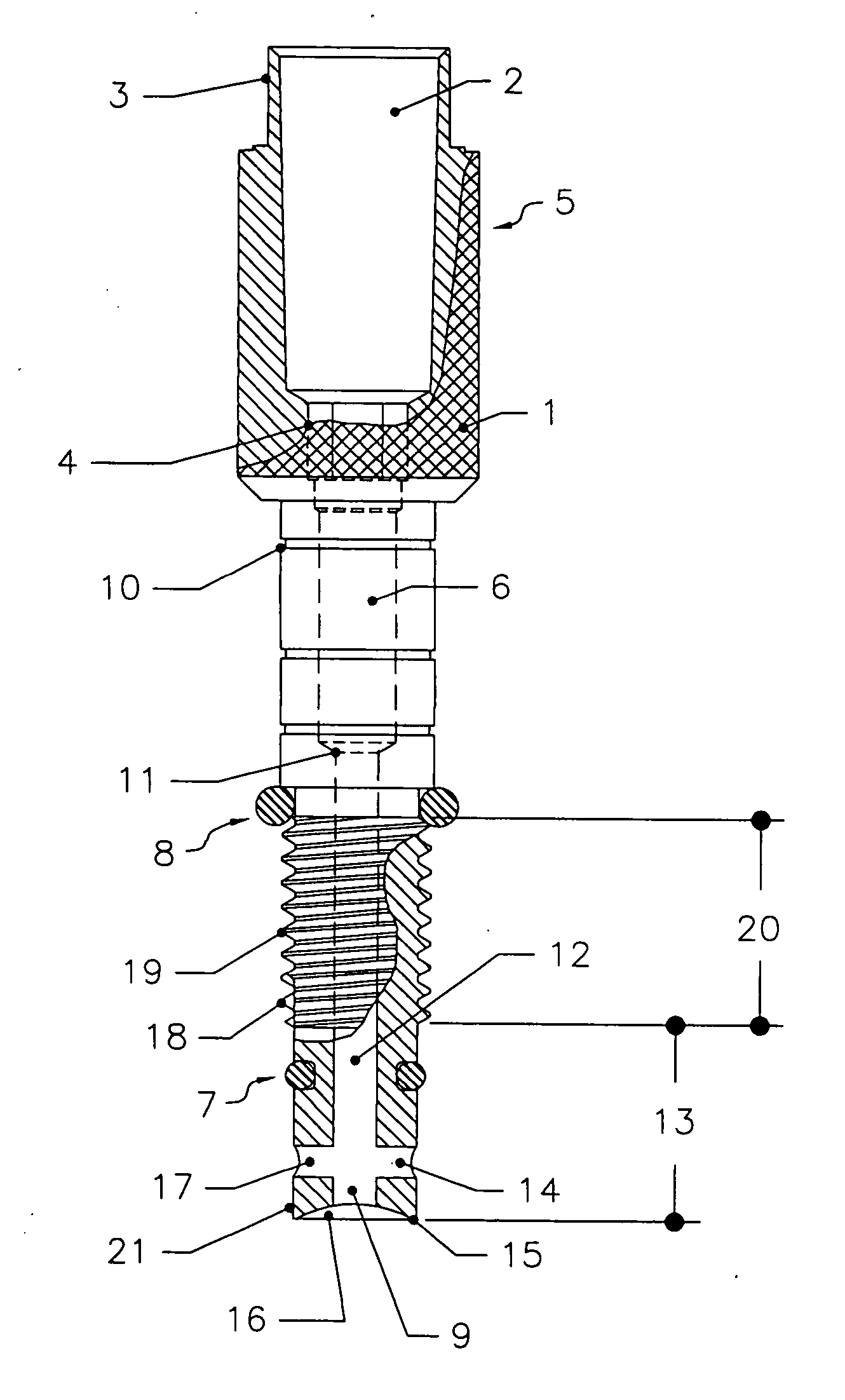
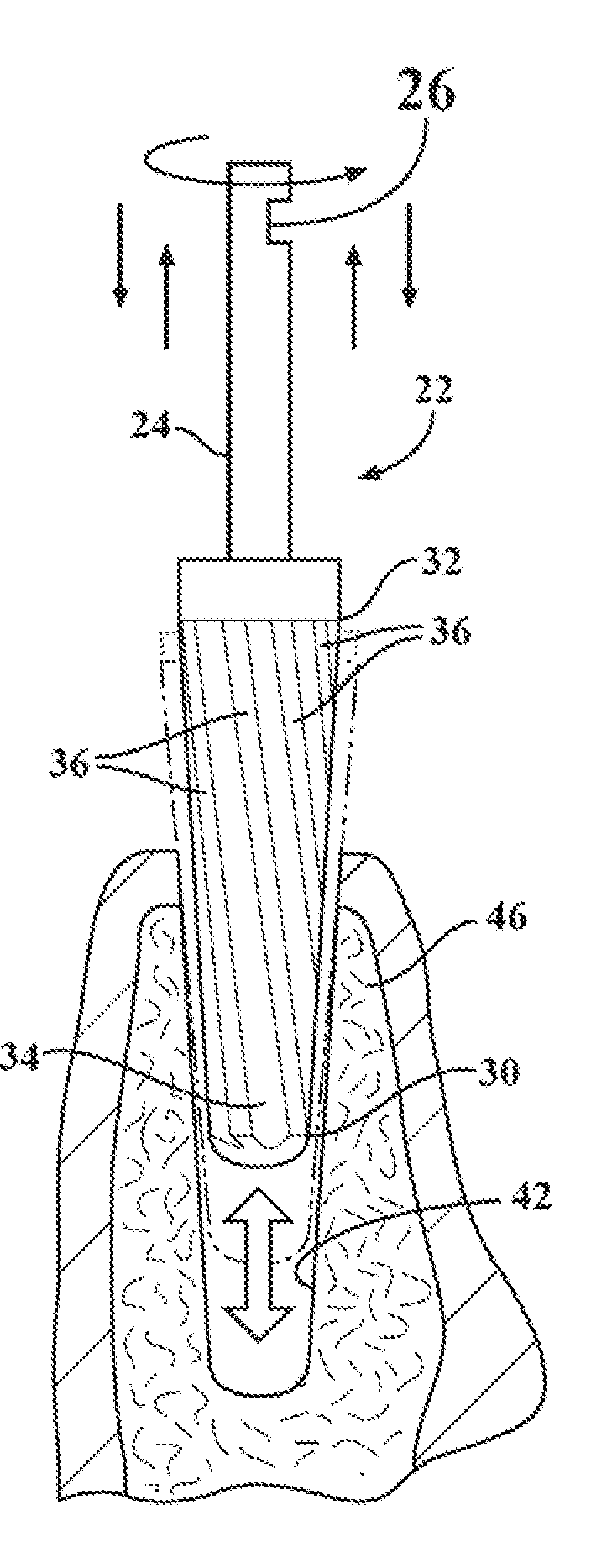
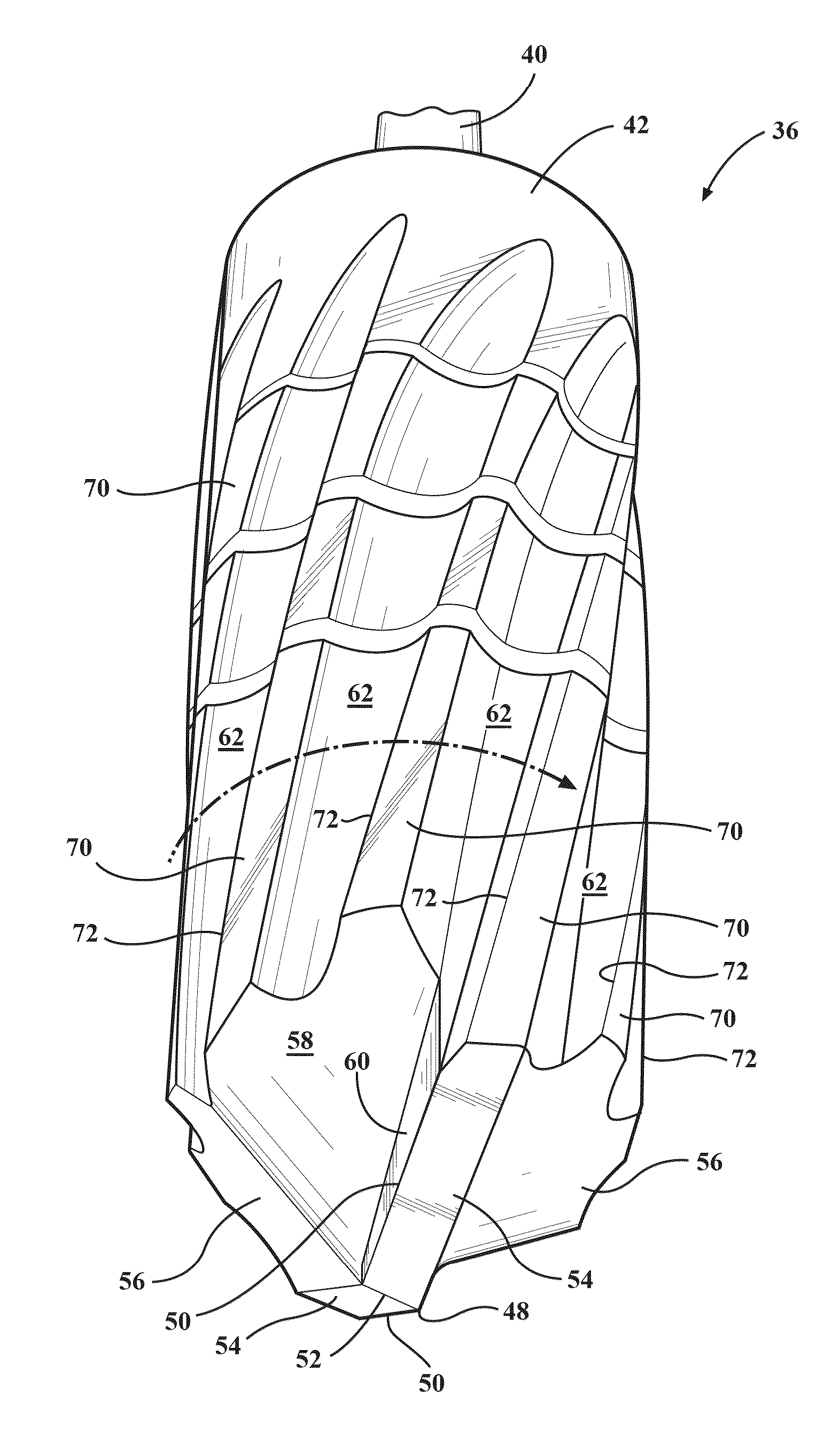
Fluted osteotome and surgical method for use
ActiveUS20120244497A1Effective expansionEasy to controlDental implantsDental toolsEngineeringNo removal
A surgical method and tool for expanding an initial osteotomy (42) to receive a dental implant (44). An osteotome (22) having a tapered working end (28) is inserted into the initial osteotomy (42). The initial osteotomy (42) is enlarged by simultaneously rotating and pushing the working end (28) of the tapered osteotome (22) into the osteotomy (42). One or more burnishing edges (40) concentrate the pushing and rotational force in outward normal and tangential component forces against the interior surface of the osteotomy (42) to incrementally expand the osteotomy (42) with little to no removal of bone material (46). The inserting and enlarging steps are repeated, as needed, with progressively larger tapered osteotomes (22) until an osteotomy (42) of predetermined size is achieved. Finally, a fixture portion of a dental implant (44) is installed into the expanded osteotomy (42).
Owner:HUWAIS IP HLDG
Robotic surgical systems and methods
ActiveUS20170056116A1Avoid damageMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgical navigation systemsBone structureNervous system
The disclosed technology relates to robotic surgical systems for improving surgical procedures. In certain embodiments, the disclosed technology relates to robotic surgical systems for use in osteotomy procedures in which bone is cut to shorten, lengthen, or change alignment of a bone structure. The osteotome, an instrument for removing parts of the vertabra, is guided by the surgical instrument guide which is held by the robot. In certain embodiments, the robot moves only in the “locked” plane (one of the two which create the wedge—i.e., the portion of the bone resected during the osteotomy). In certain embodiments, the robot shall prevent the osteotome (or other surgical instrument) from getting too deep / beyond the tip of the wedge. In certain embodiments, the robotic surgical system is integrated with neuromonitoring to prevent damage to the nervous system.
Owner:KB MEDICAL SA
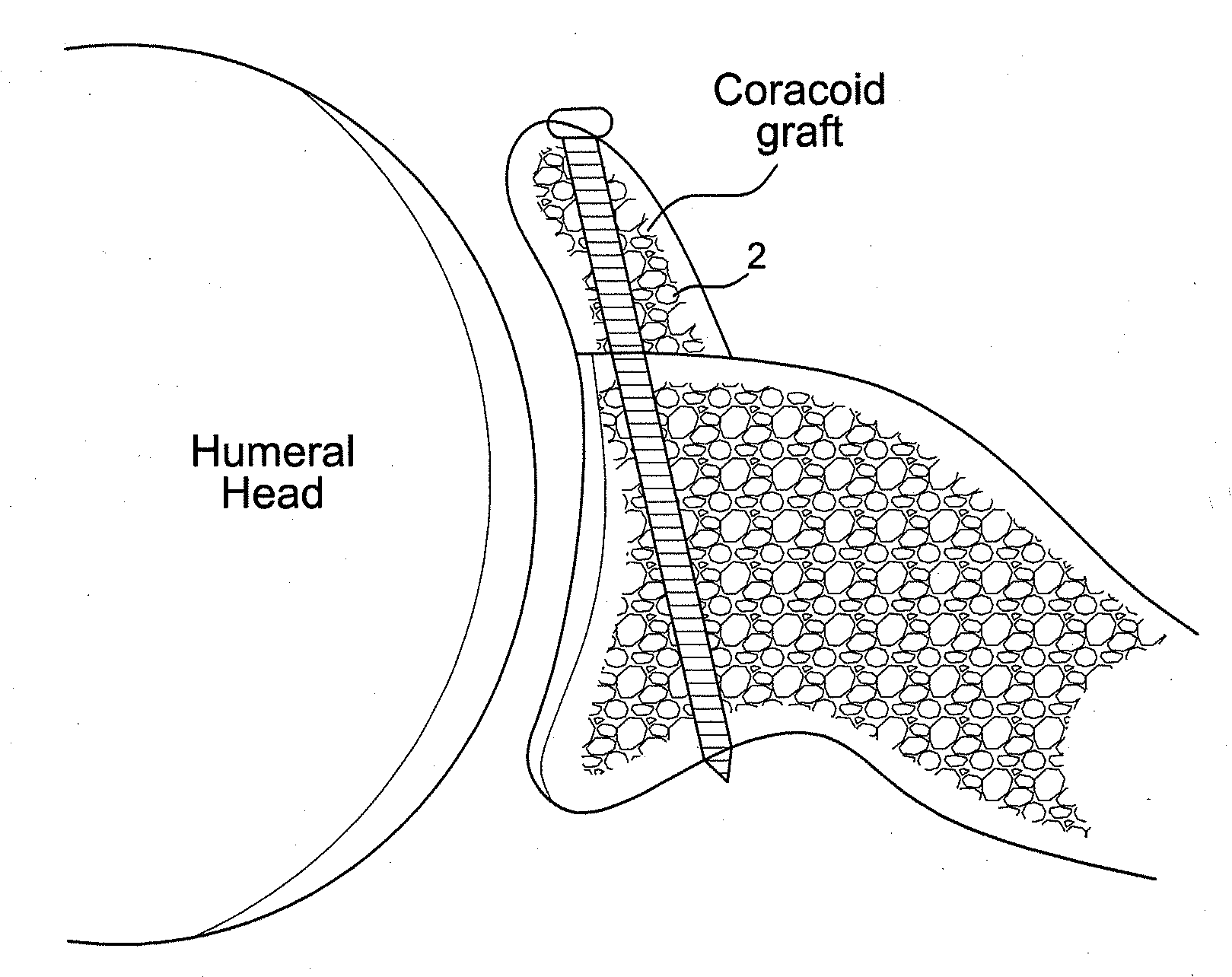
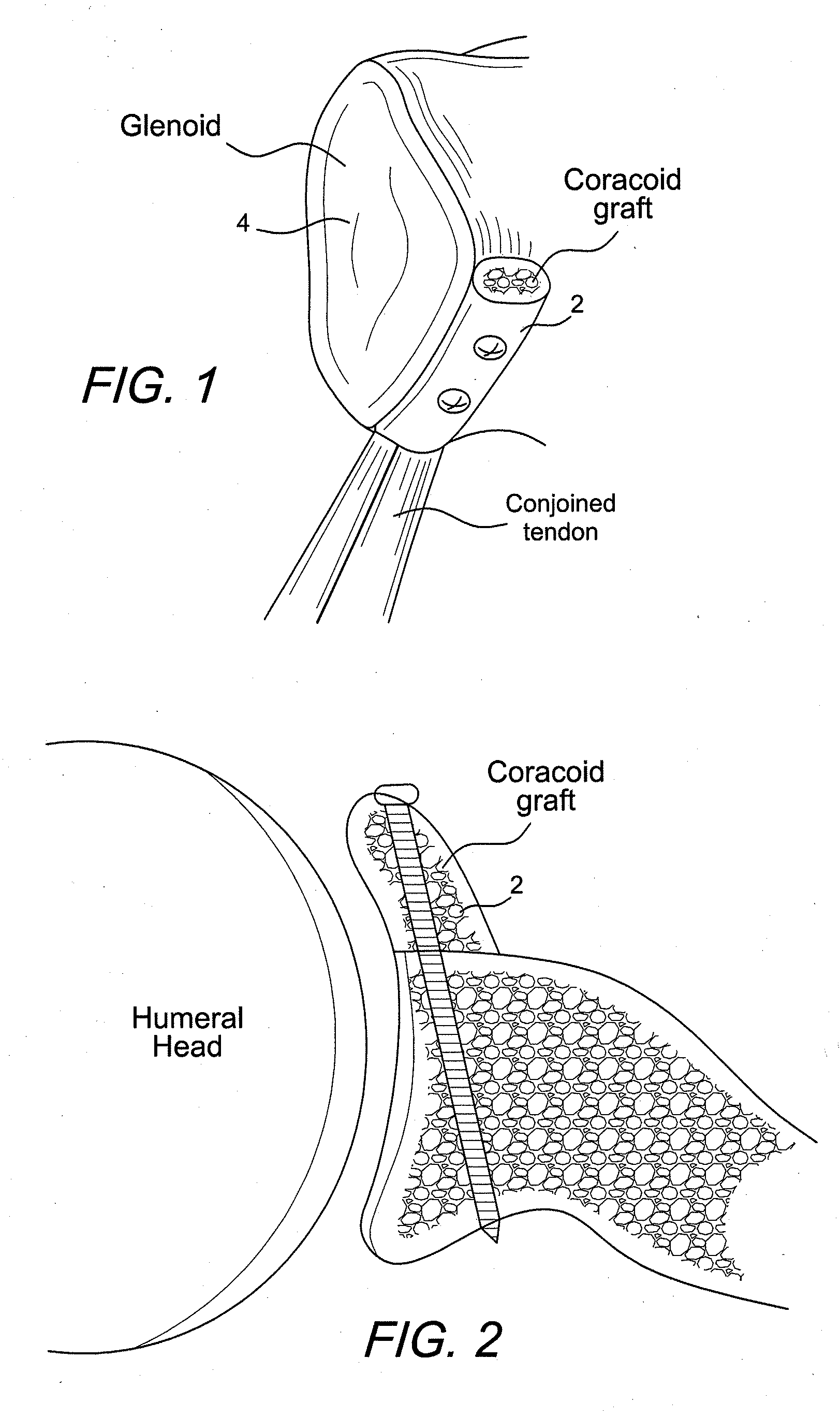
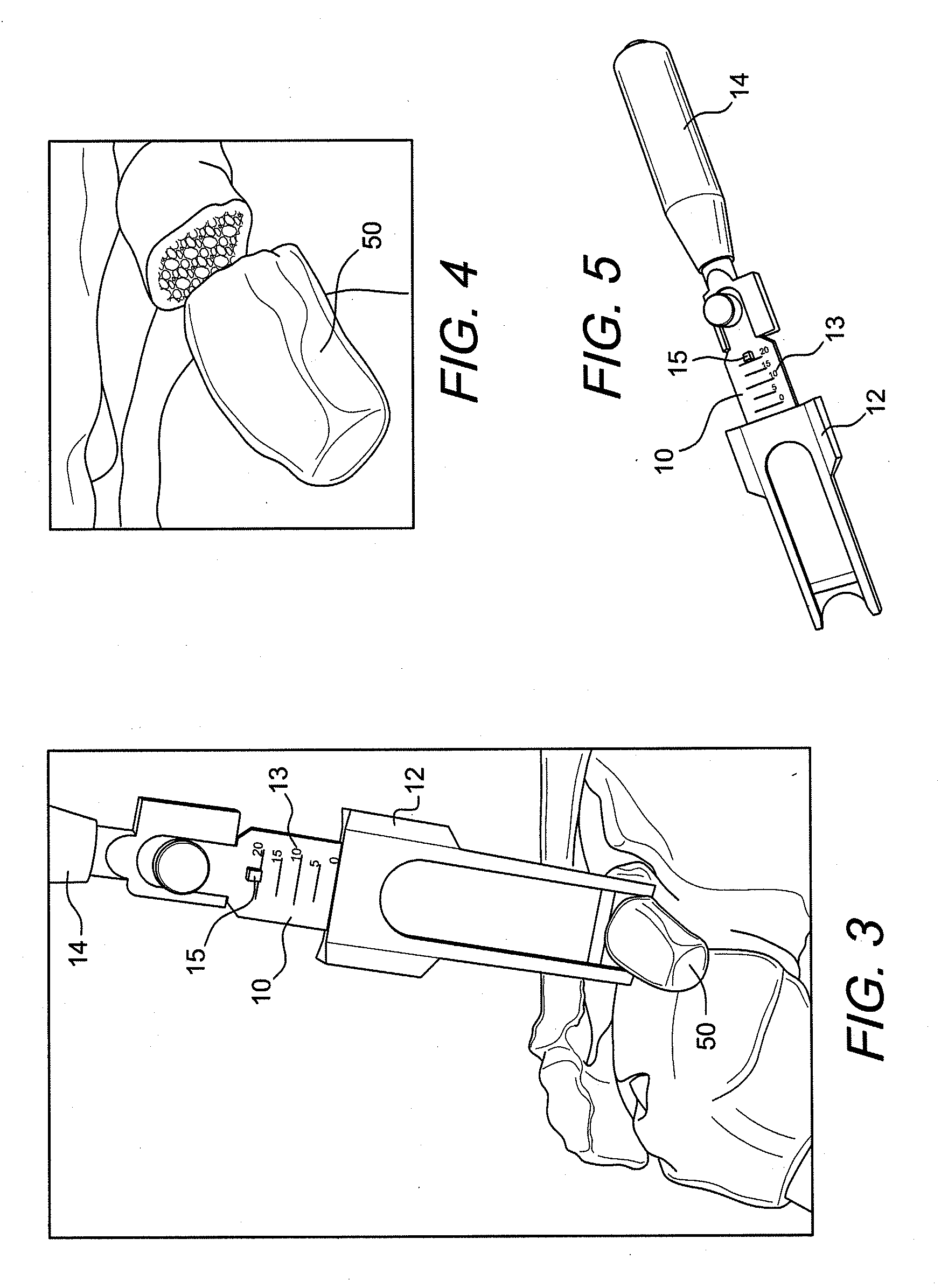
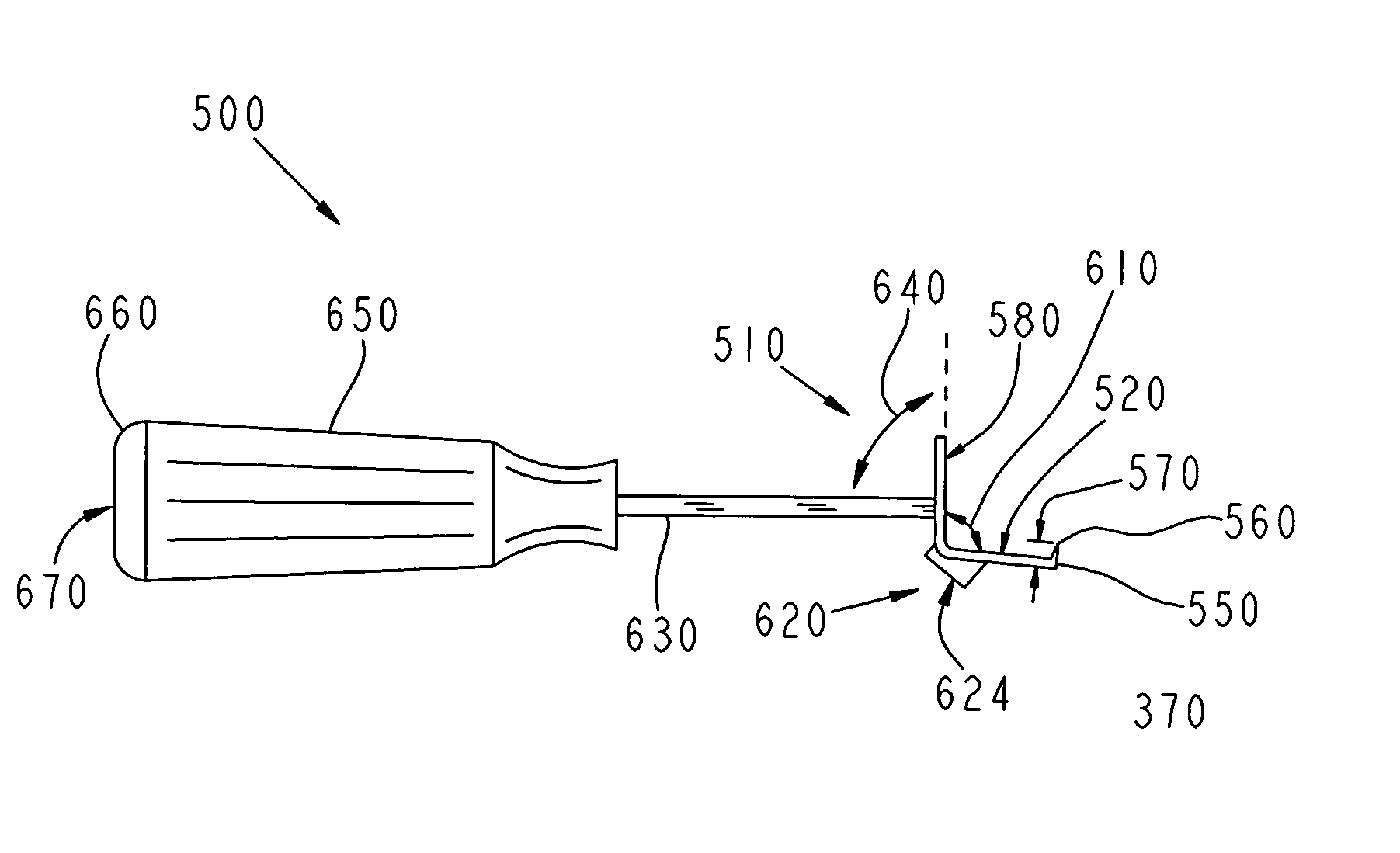
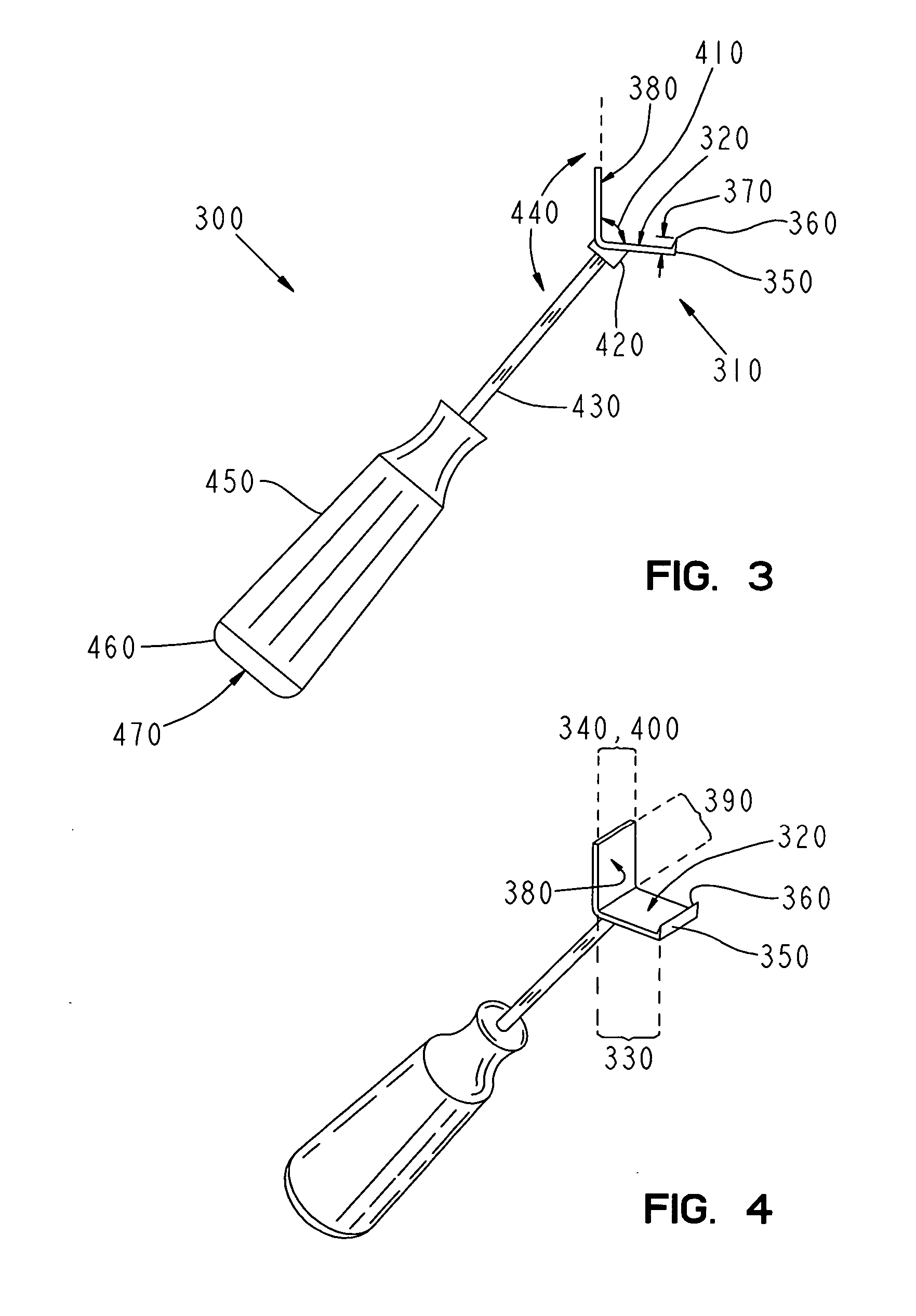
Latarjet instrumentation and method
ActiveUS20090318923A1Control graft handlingAdditional instrumentationDiagnosticsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSurgical instrumentationEngineering
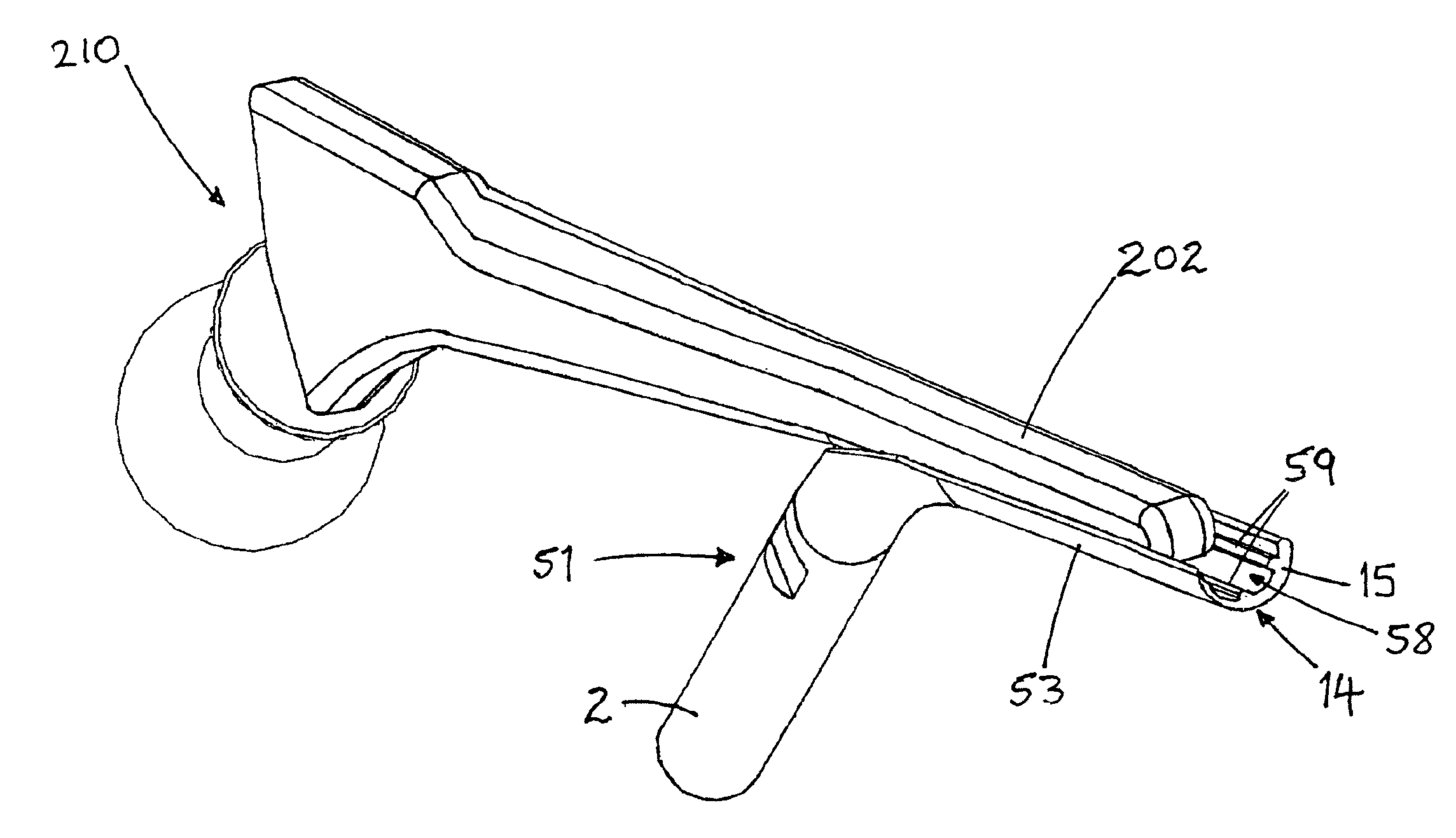
Instrumentation for an open or arthroscopic Latarjet procedure that allows more control graft handling during the formation of the hole and proper positioning parallel to the articulating bone surface. The surgical instrumentation of the present invention includes an osteotome with a plurality of markings and a depth stop, a drill guide with jaws configured to securely engage an outer surface of the graft, and an offset guide to position the graft to the bone.
Owner:ARTHREX
Methods and instruments for forming non-circular cartilage grafts
Techniques and instruments for knee replacement surgery that allow for the removal of an oval oblong-shaped allograft bone and cartilage plug from a donor distal femur. The instruments include (i) sizing guides to match the recipient's femoral size and curvature to that of a donor femur (the sizing guides also acting as a wide pin placement template for the donor distal femur); (ii) osteotomes that cut the curved and straight portions of the implant shape (these may be disposable or reusable); and (iii) templates that fit over the guide pins and have openings to allow the osteotomes to cut the donor femur plug to the correct size, shape and depth. The instruments allow for a non-circular shape to be extracted from a donor femur for use in a bone-saving osteoarthritis distal femur resurfacing procedure.
Owner:ARTHREX
Instrumentation for repair of meniscus tissue
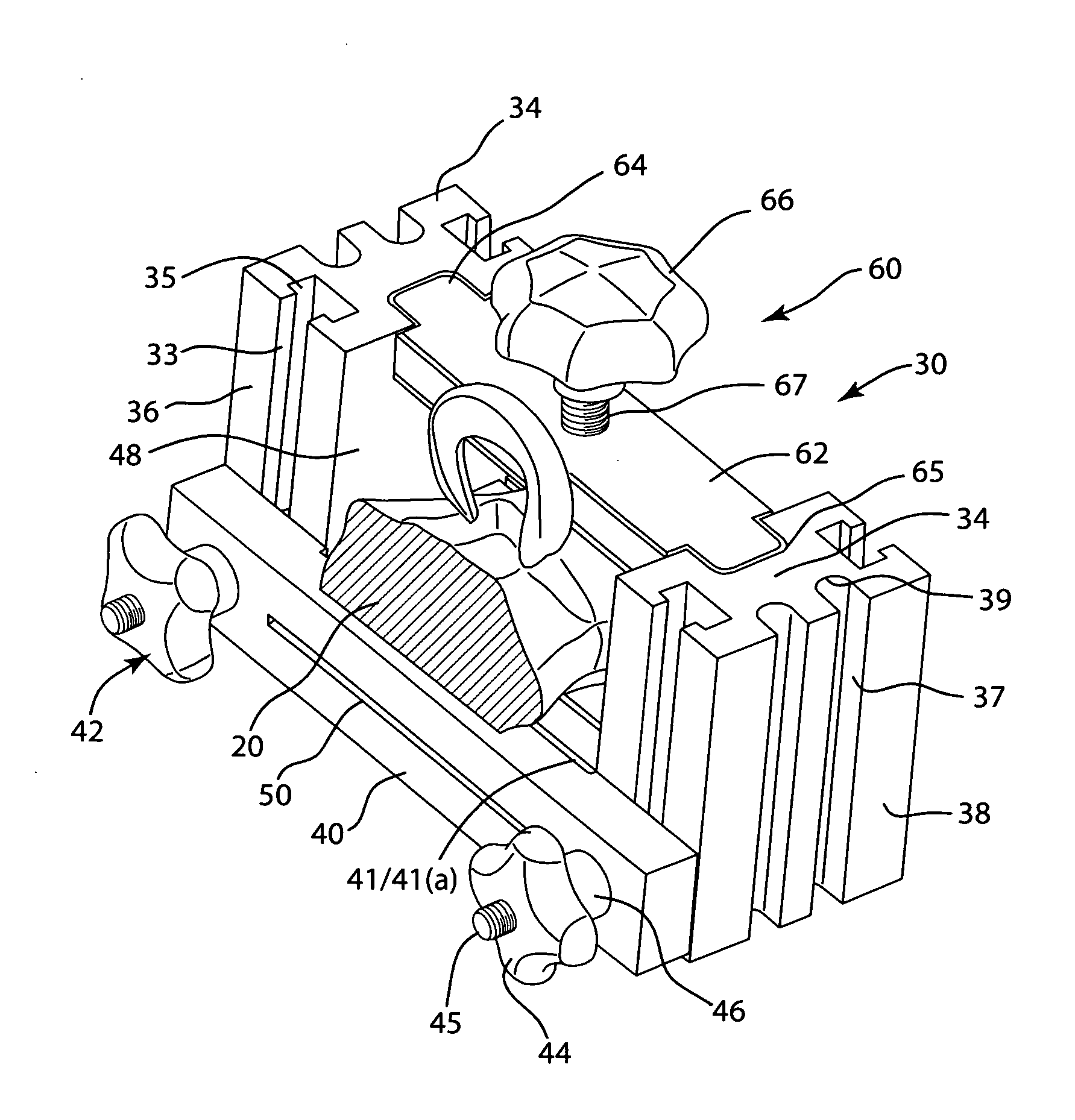
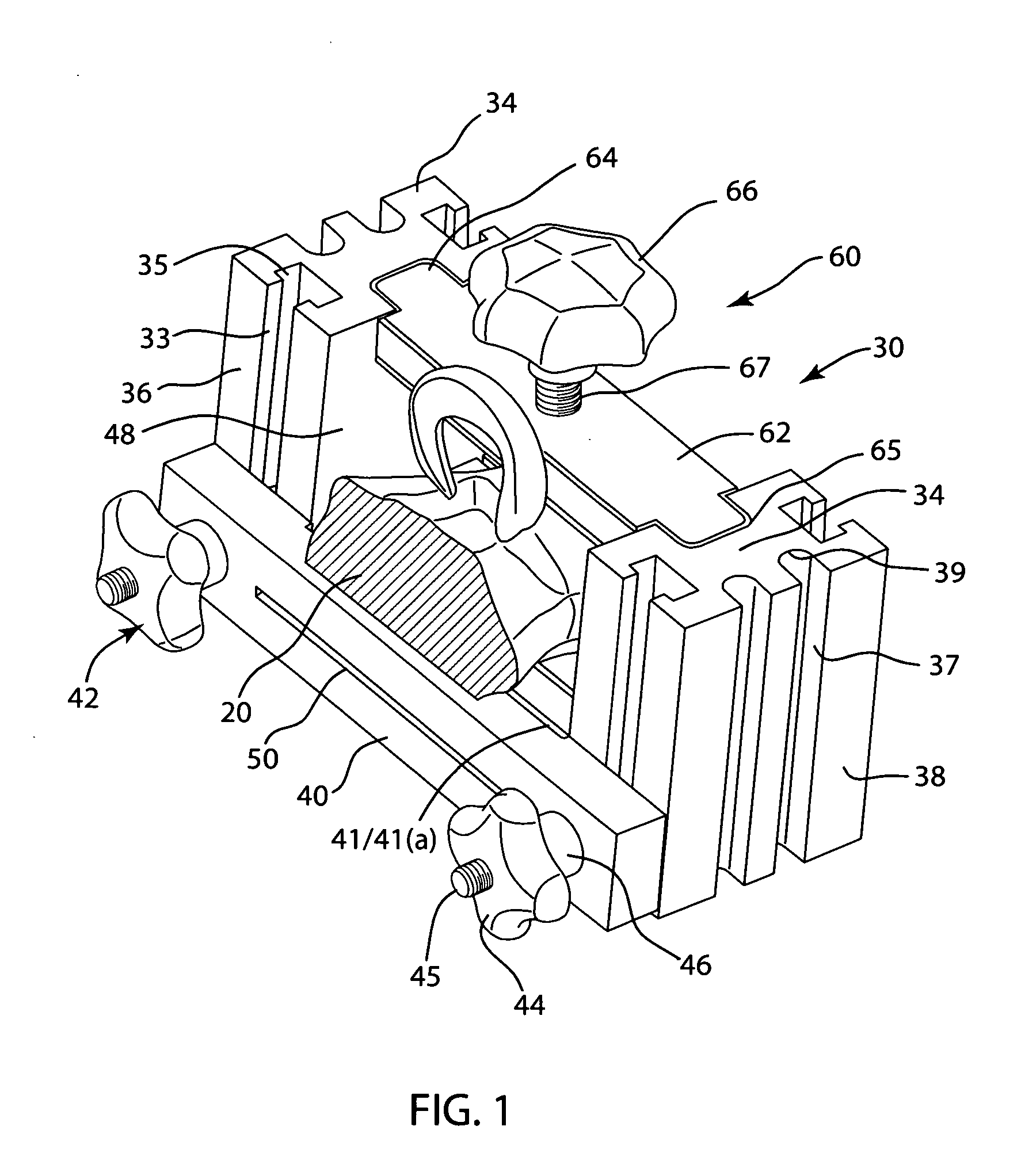
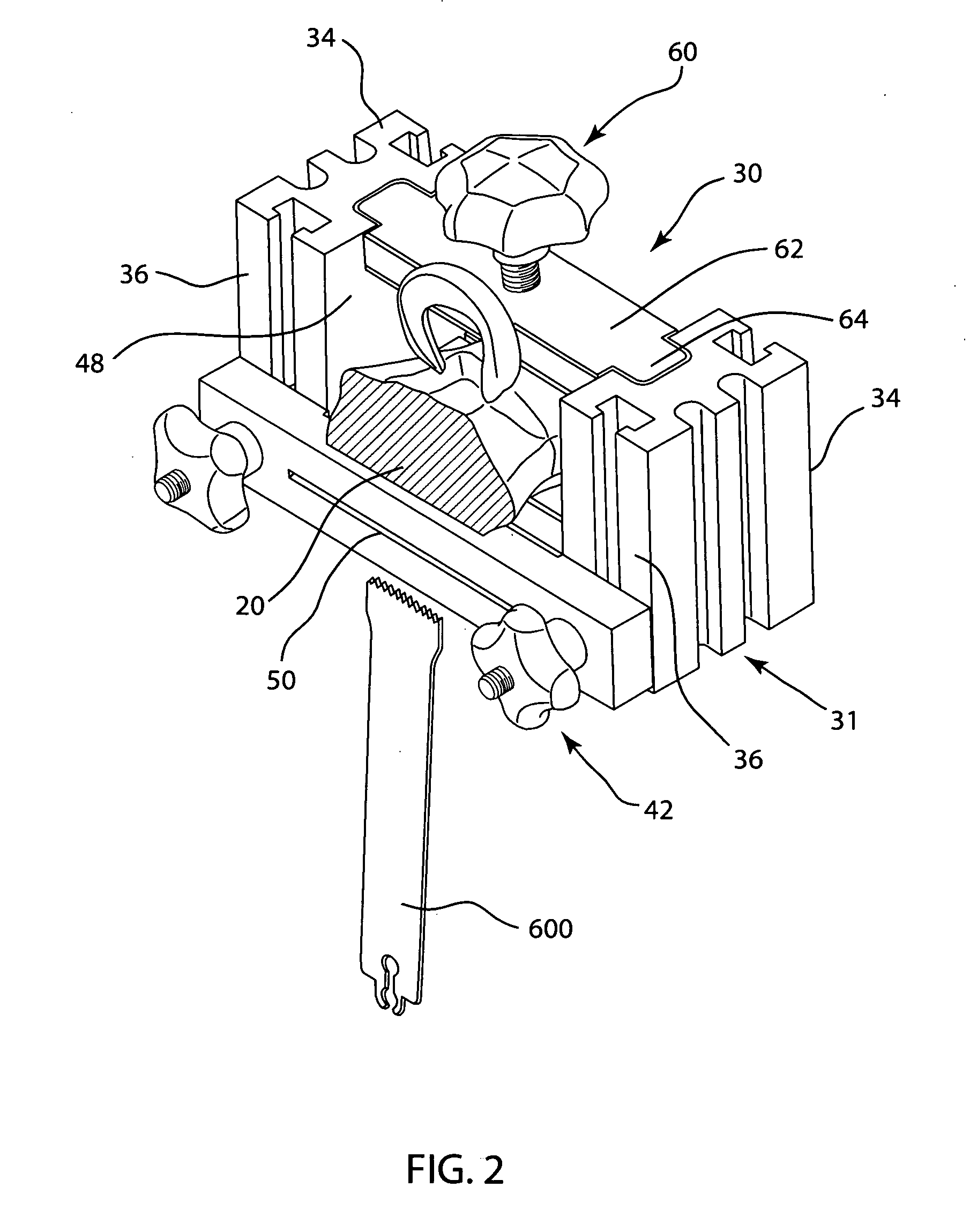
The invention is directed toward an instrumentation kit used to replace a damaged human knee joint meniscus with an allograft meniscus implant. The kit includes a workstation having a base and upright end sections with a clamping assembly is mounted on the end sections and a movable cutting guide mounted to a side wall of each end section. The tibia is then drilled with a drill to a desired depth and length and a groove is formed in the tibia with an osteotome so that the width is the same as the width of the bone base of the meniscus implant which has been trimmed in the workstation.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Methods and instruments for forming non-circular cartilage grafts
Techniques and instruments for knee replacement surgery that allow for the removal of an oval oblong-shaped allograft bone and cartilage plug from a donor distal femur. The instruments include (i) sizing guides to match the recipient's femoral size and curvature to that of a donor femur (the sizing guides also acting as a wide pin placement template for the donor distal femur); (ii) osteotomes that cut the curved and straight portions of the implant shape (these may be disposable or reusable); and (iii) templates that fit over the guide pins and have openings to allow the osteotomes to cut the donor femur plug to the correct size, shape and depth. The instruments allow for a non-circular shape to be extracted from a donor femur for use in a bone-saving osteoarthritis distal femur resurfacing procedure.
Owner:ARTHREX
Carlo-computer assisted and robot guided laser-osteotome
ActiveUS20120220992A1High osteotomic precisionImprove securityDiagnosticsControlling energy of instrumentPhotoablationRobotic arm
A Computer Assisted and Robot-Guided Laser Osteotome (CARLO) medical device (1) for perforating hard tissue, having a photoablation laser source (31) mounted in a robotic arm (2), and optical system (37) for focusing a laser beam in a target plane of the ostetomy line featuring an autotracking navigation system (8).
Owner:ADVANCED OSTEOTOMY TOOLS - AOT
Universal, multifunctional, single unit, rotary osteotome
InactiveUS7547210B1Precise positioningReduce crestal bone heightDental implantsTeeth fillingSurgical dentistrySurgical department
A multifunctional surgical rotary instrument with a corrosion resistant wear reducing hard coating, to be used in a surgical dental motor driven handpiece for preparing an osteotomy for implant insertion, combining the functions of six surgical instruments is described. The multifunctional surgical rotary instrument has structural features that provide the functions of a crestal bone height reducer, an osteotomy locator, an osteotomy lateral redirector, osteotomy drill, tapered countersink, and an osteocompressor. These structural features include a dual-lobed single plane tip that remains where the drilling is initiated without wandering, and facilitates the precise location of the osseous implant site. Advantageously, the instrument can save time and cost in the implant procedure.
Owner:IMPLADENT
Surgical instrument tray, hip resurfacing kit, and method of resurfacing a femoral head to preserve femoral head vascularity
InactiveUS20070260256A1Avoid attenuationIncreased vascularityDiagnosticsProsthesisRight femoral headLeft femoral head
A method of resurfacing a femoral head involves using a chamfered reamer to ream only a top portion of the femoral head above an anterior lateral portion of the femoral head where the retinacular vessels supply blood to the femoral head. As no cylindrical reaming is performed on the lateral portions of the femoral head, damage to the retinacular vessels is avoided. The method thereby preserves femoral head vascularity. A surgical instrument tray for enabling a surgeon to perform this method includes both a reamer and a spherometer for assessing the sphericity of the femoral head to determine whether osteophyte growth on the femoral head is likely to cause femoro acetabular impingement. The instrument tray can also include a tool, such as a bone chisel or burr, for removing the osteophytes to restore the sphericity of the femoral head, rather than removing the osteophytes using a cylindrical reamer.
Owner:BEAULE PAUL E
Autografting osteotome
ActiveUS9326778B2Promote osseointegrationEnlarge osteotomyDental implantsAbrasive surgical cuttersFluteGrafts bone
A fluted osteotome is rotated in one direction to enlarge an osteotomy by burnishing, and by cutting / drilling when turned in an opposite direction. A conically tapered body has an apical end with lips. The lips are set to grind bone when rotated in the burnishing direction and cut bone when turned in the cutting / drilling direction. Helical flutes and interposed lands are disposed about the body. The flutes each have a working edge that burnishes bone when rotated in the burnishing direction and cuts bone when turned in the cutting / drilling direction. The lips and lands generate an opposing axial reaction force that improves surgical control. The osteotome auto-grafts bone by reapplying ground particles in a compacted manner along the entire depth of the osteotomy, particularly at the bottom.
Owner:HUWAIS IP HLDG
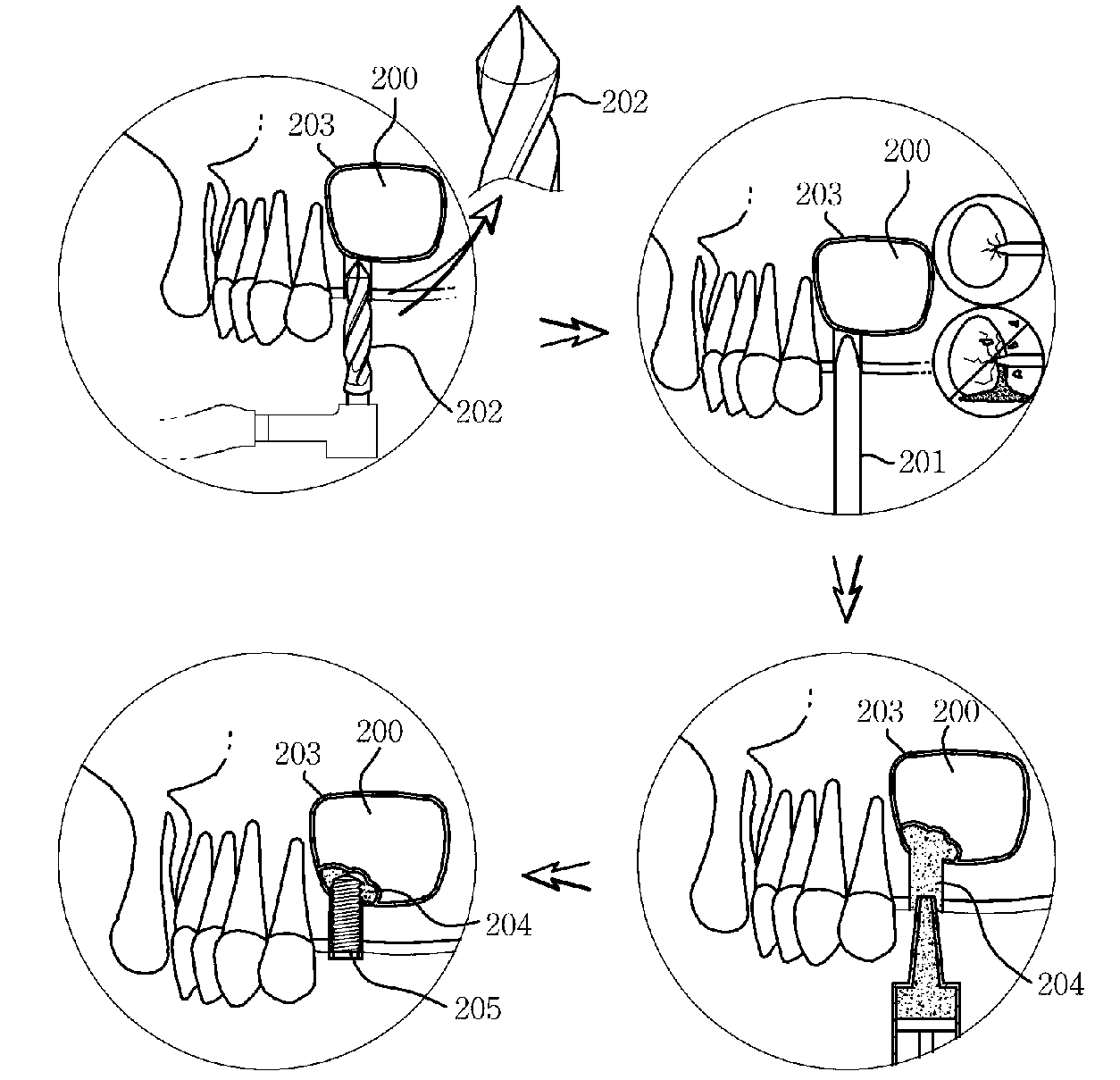
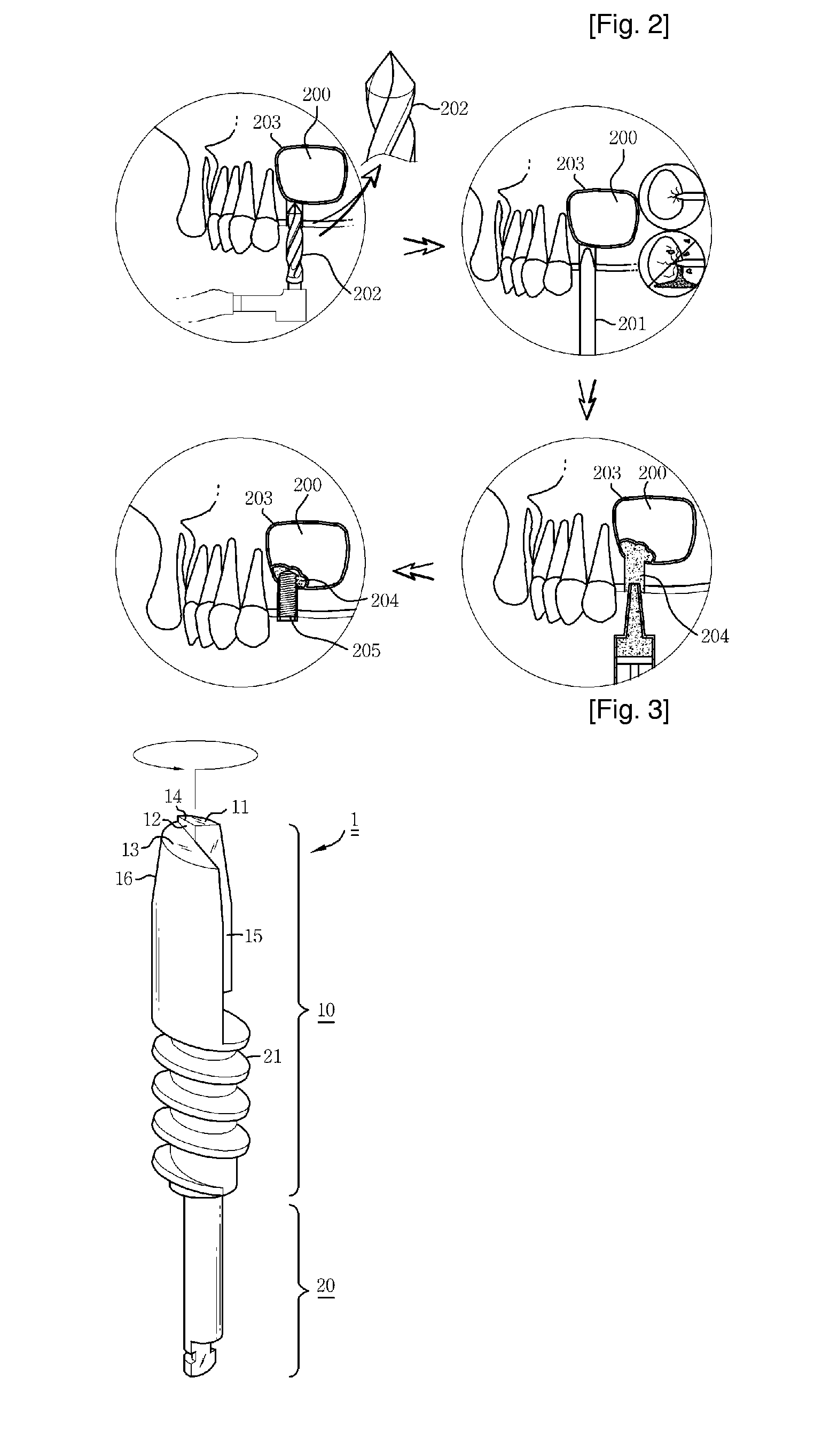
Reamer for Operating Implant
InactiveUS20090259227A1Simple and safe processPerformed safely and easilyDental implantsSurgeryReamerClockwise
Disclosed therein is a reamer for operating implant, which can very usefully apply an implant operation to a patient who is short of bone quantity to the maxillary sinus, which is easier and safer than a conventional hammering method using a drill and an osteotome or a conventional operation method for transplanting a bone or planting an implant after forming a bone window on a maxillary sinus side wall, and which can reduce a treatment time period and treatment costs by minimizing the patient's pain occurring before and after the operation of the implant. A cutting part of the reamer includes: a protruding face formed on the top surface thereof in such a manner as to upwardly upheave a partial surface including an outer circumference of the cutting part of the entire top surface of the cutting part to form a stepped jaw; a depressed face formed on the top surface thereof in such a manner as to depress a partial surface of the entire top surface of the cutting part to be opposite to the protruding face according to the formation of the protruding face, the depressed face having a reverse inclination in a clockwise direction; a cut edge horizontally formed on a connected portion between the stepped jaw and the protruding face so that the cut edge evenly disperses a force while being in horizontal line contact with the mucosa even though the cut edge is in contact with the mucosa of the maxillary sinus so as to allow a dentist to perform a cutting work safely without damaging a mucosa of a maxillary sinus; and a discharge path longitudinally formed on the cutting part in such a manner as to cut an area ranging from a partial surface of the top surface of the cutting part, i.e., a predetermined portion between the protruding face and the depressed face to a portion which is slightly shorter than the lower end of the cutting part.
Owner:AHN IN
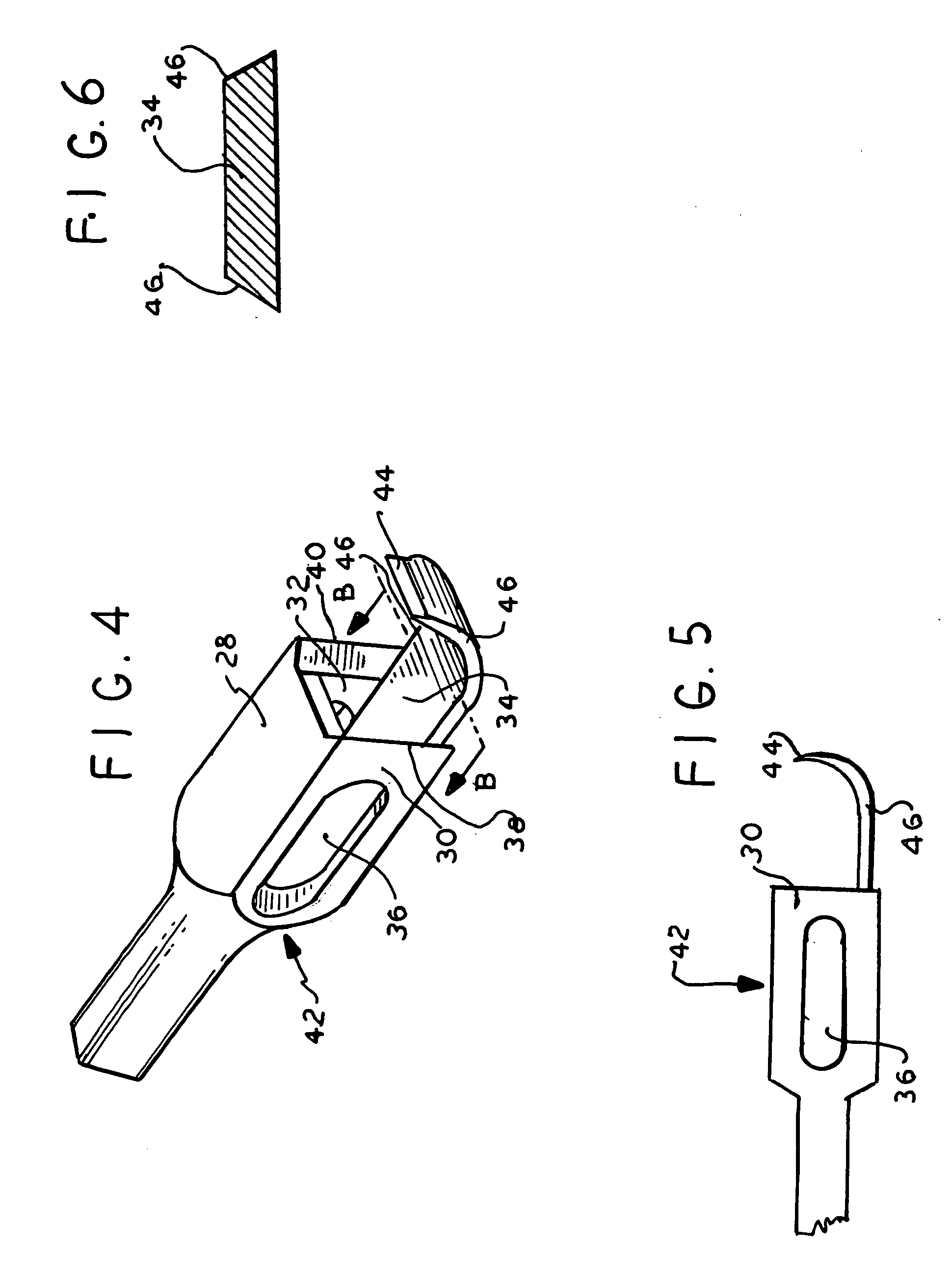
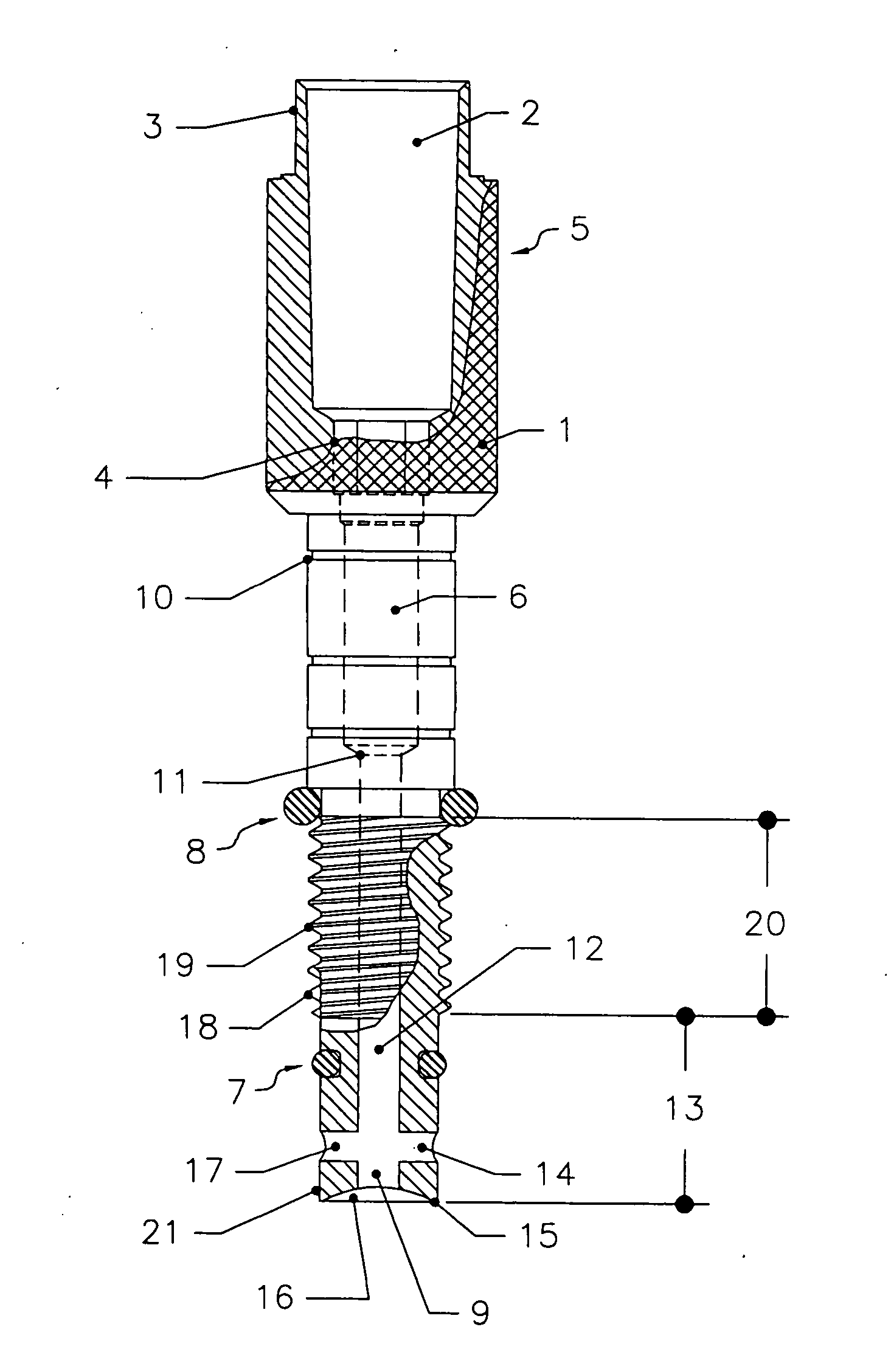
Fluted osteotome and surgical method for use
ActiveUS20130004918A1Effective expansionEasy to controlDental implantsOsteosynthesis devicesSurgical approachEngineering
A surgical method and tool for expanding an initial osteotomy (42) to receive a bone implant (44). An osteotome (22) having a tapered working end (28) is inserted into the initial osteotomy (42). The initial osteotomy (42) is enlarged by simultaneously rotating and pushing the working end (28) of the tapered osteotome (22) into the osteotomy (42). When rotated in one direction the burnishing edges (40) concentrate the pushing and rotational force in outward normal and tangential component forces against the interior surface of the osteotomy (42) to incrementally expand the osteotomy (42) with little to no removal of bone material (46). When rotated in the opposite direction the burnishing edges cut the interior surface of the osteotomy. Progressively larger tapered osteotomes (22) are used until an osteotomy (42) of predetermined size is achieved.
Owner:HUWAIS IP HLDG
Betts osteotome
InactiveUS8480675B2Disrupt volumeExcision instrumentsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsEngineeringMedical device
A medical device and method of using the device to reinforce and stabilize a compressed tissue is disclosed. The medical device comprises a shaft with a single blade that is biased with a bend, but is elastic enough to be straightened. The end of a cannula is inserted into a tissue, and the blade and shaft are then inserted into a cannula to straightens the blade and direct it to the tissue site. When the blade reaches the tissue site, the blade naturally returns to its bent biased state, and the shaft and blade are then rotated to pulp a volume of tissue. A binding material is then injected into the pulped tissue without removing the tissue.
Owner:BETTS ANDRES
Articulatable apparatus for cutting bone
InactiveUS20060074427A1Prevent the cutting edge from undesirably engaging other tissue or boneMinimally invasiveSurgeryEngineeringSurgical procedures
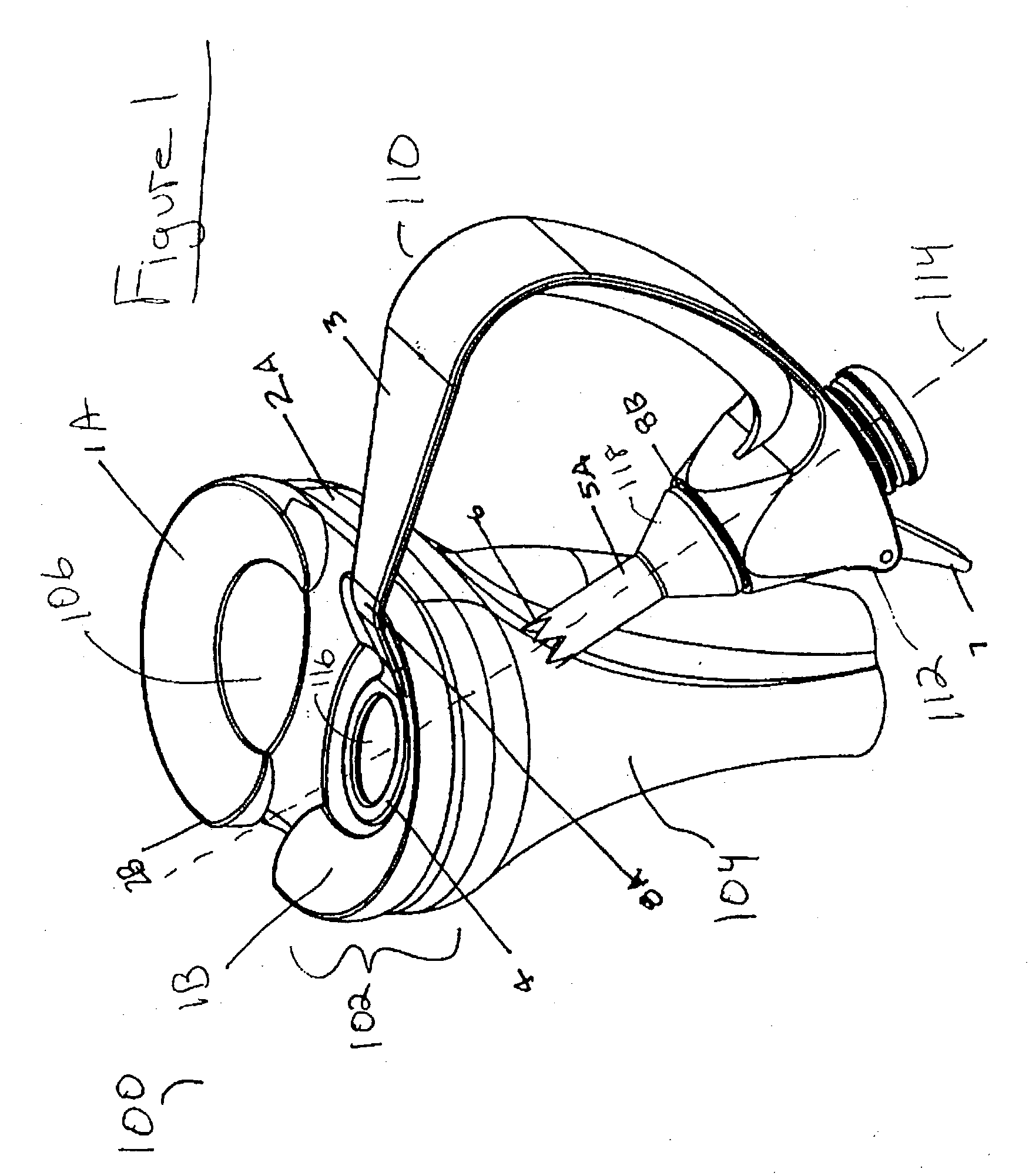
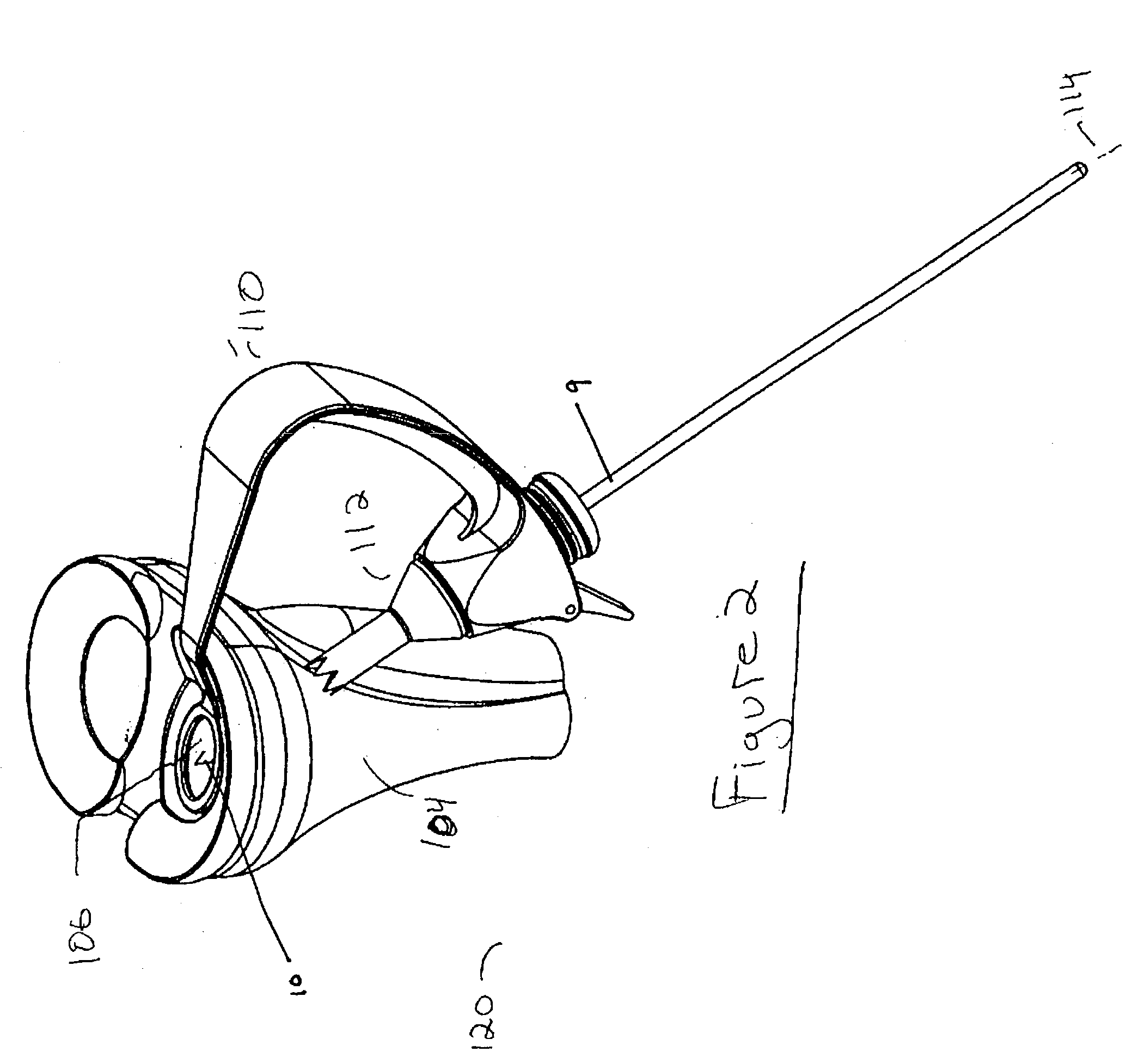
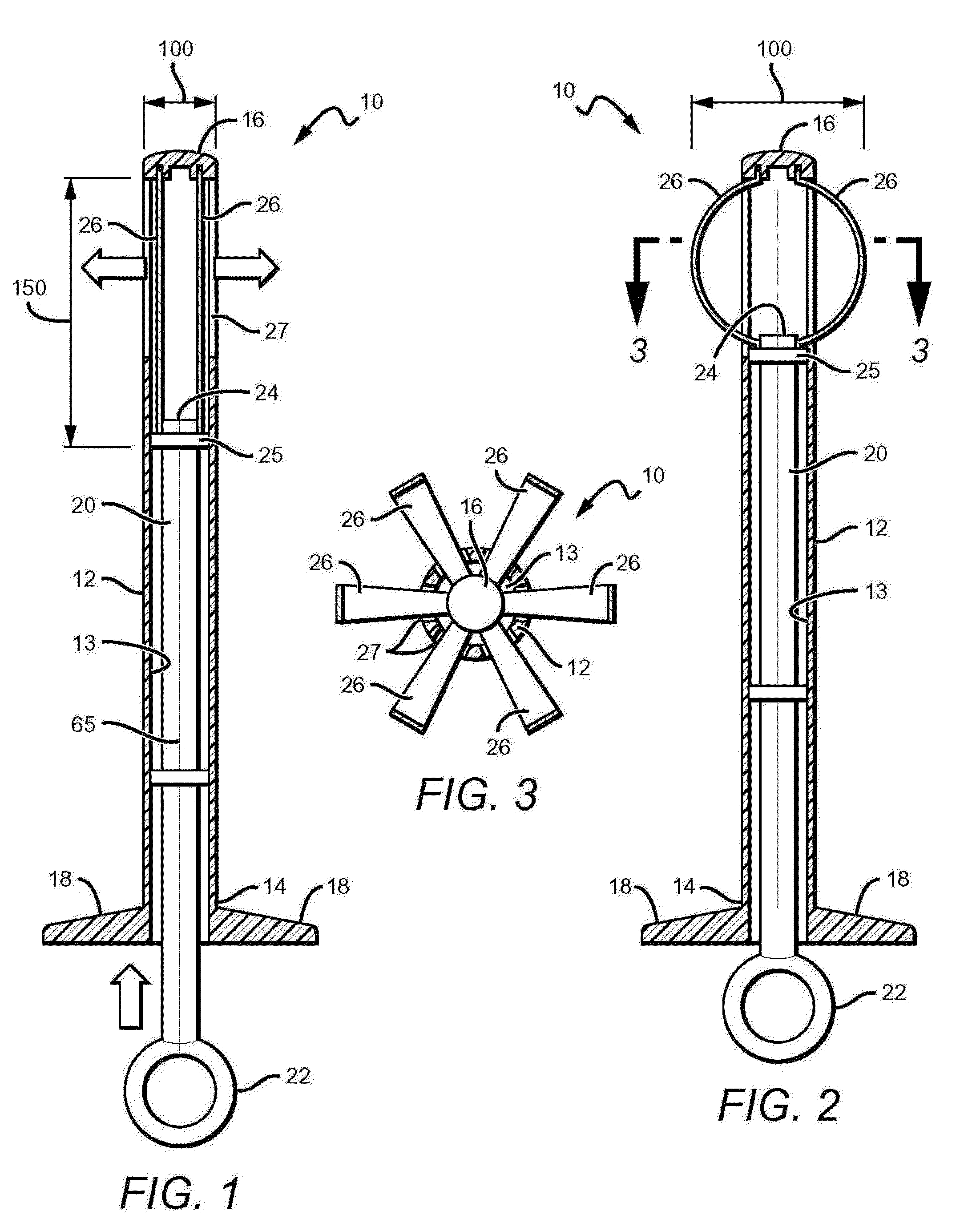
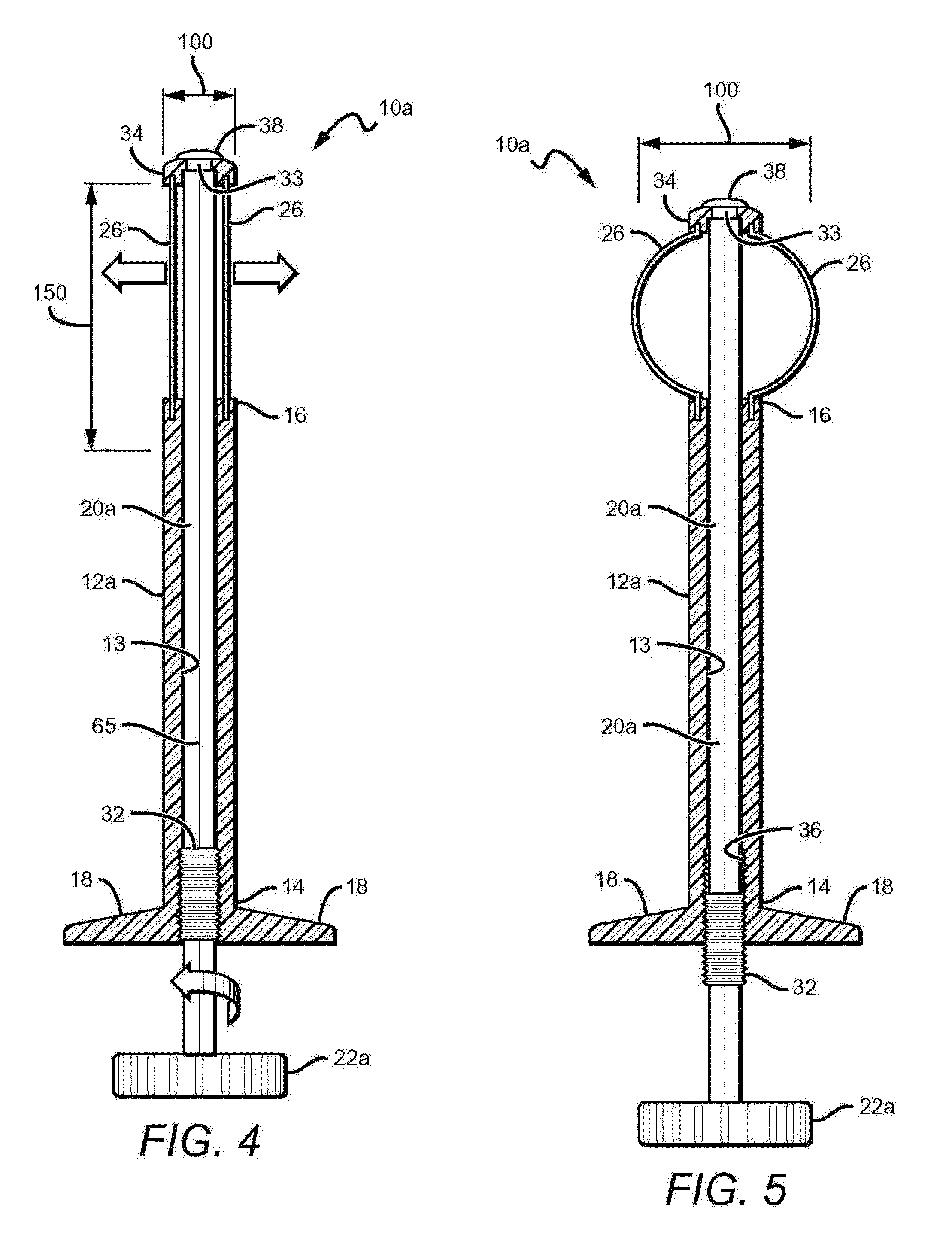
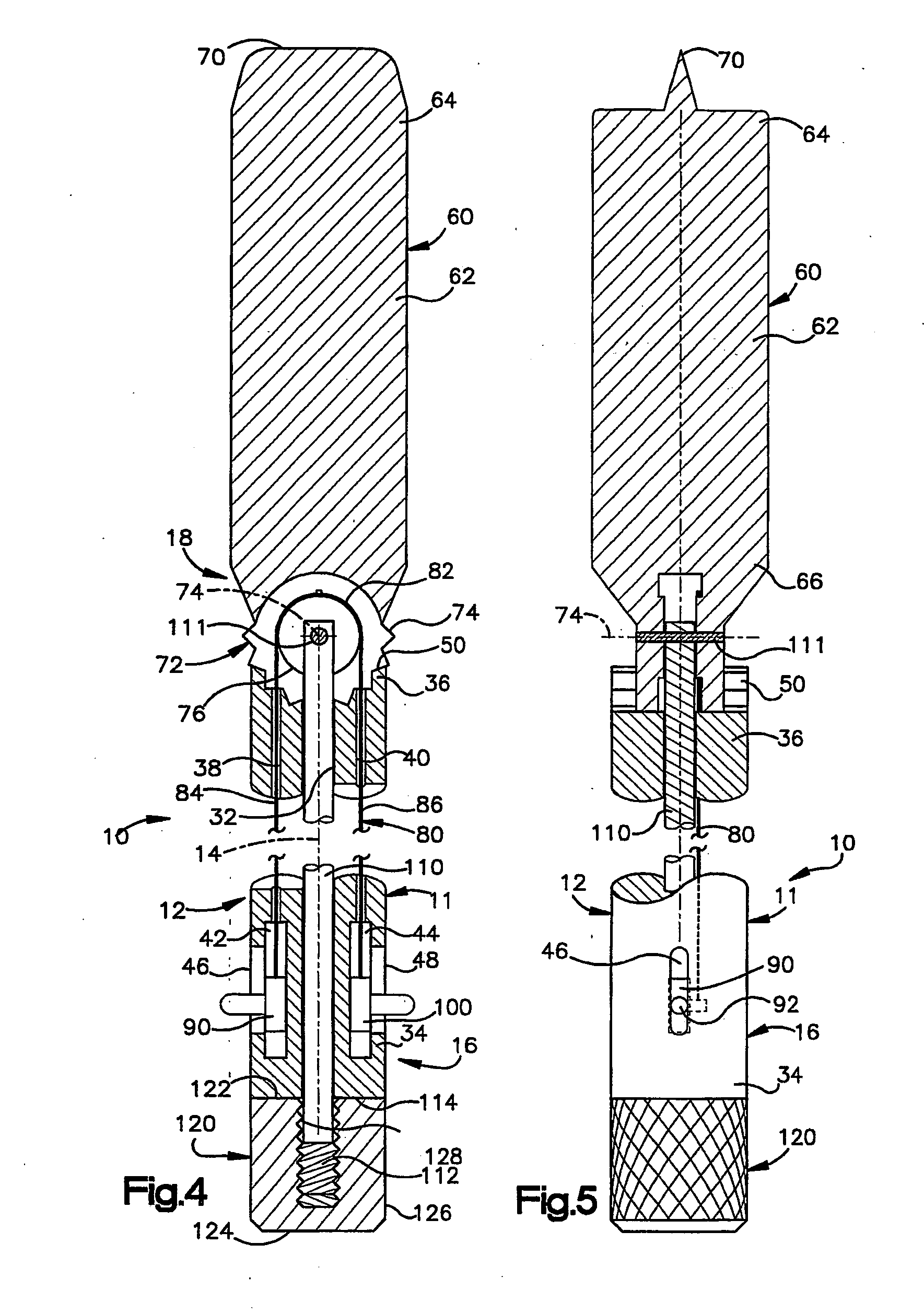
An apparatus for cutting bone includes an elongate member (11) having a central axis. The elongate member includes a tubular portion (12) that extends between a proximal end portion and a distal end portion. The distal end portion includes an articulatable head section with a stop surface and a cutting edge (70) projecting from the stop surface. The head section is articulatable about a pivot axis (74) that extends transverse to the central axis. The apparatus further includes a mechanism (90, 100) for articulating the head section relative to the tubular portion. The apparatus is a form of an osteotome that is particularly useful for certain spine-related surgical procedures.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
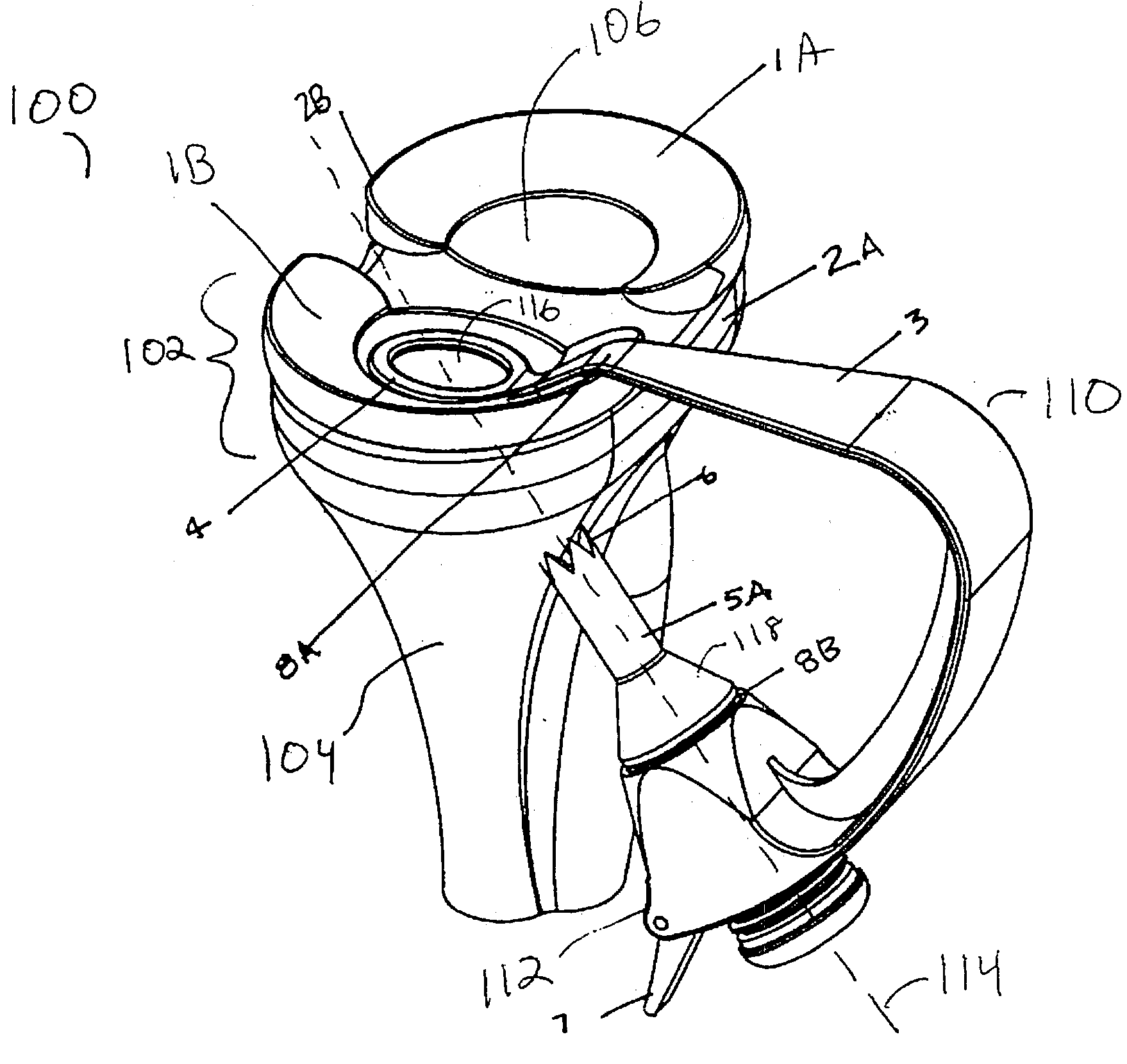
Guided osteotomes
An osteotome including a head portion is provided. The head portion includes a first substantially planar surface and a second substantially planar surface extending obtusely from the first substantially planar surface. The osteotome further includes a bone cutter extending from the first substantially planar surface, and an elongated portion extending from the head portion. The first substantially planar surface and the second substantially planar surface face away from the elongated portion.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
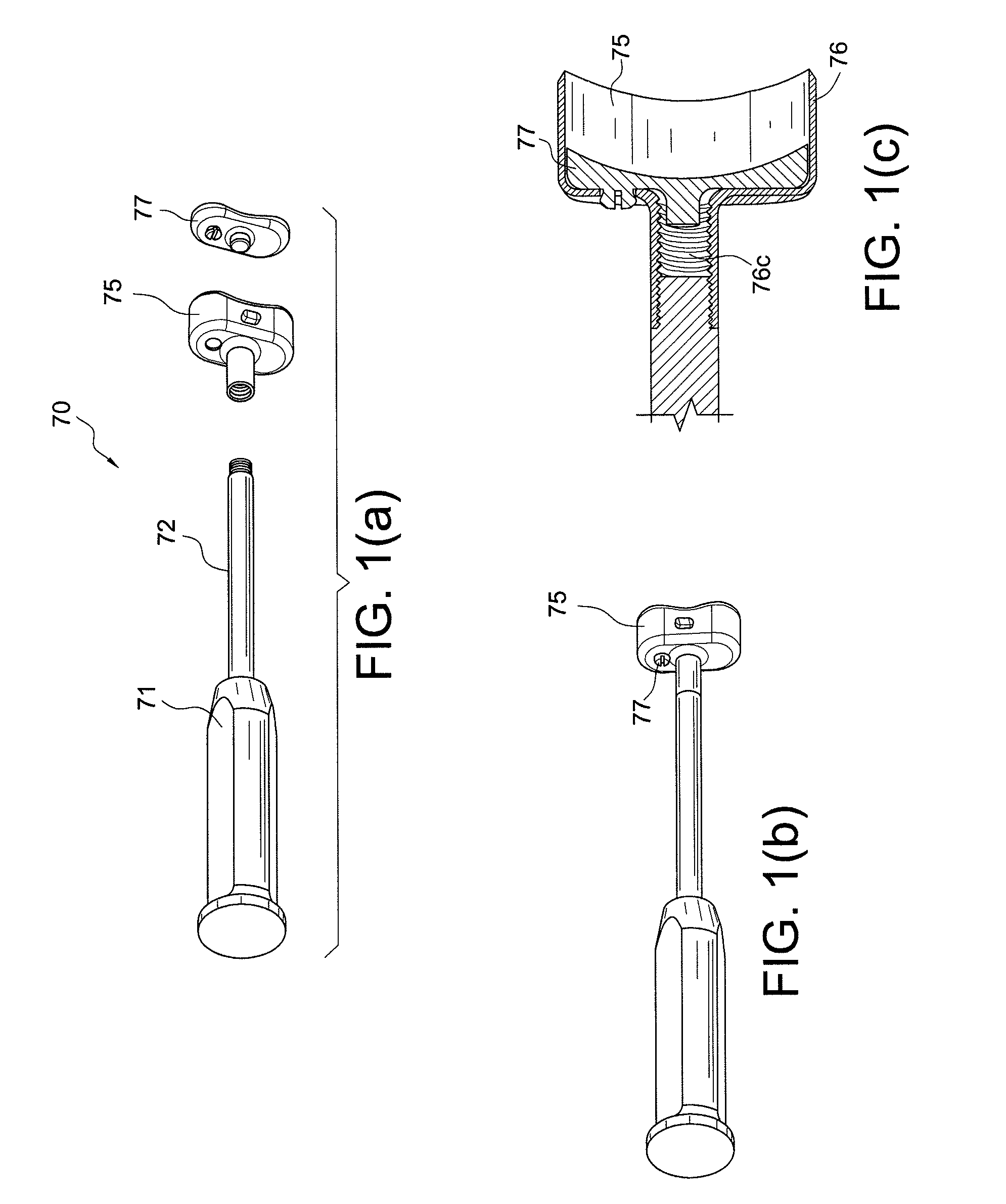
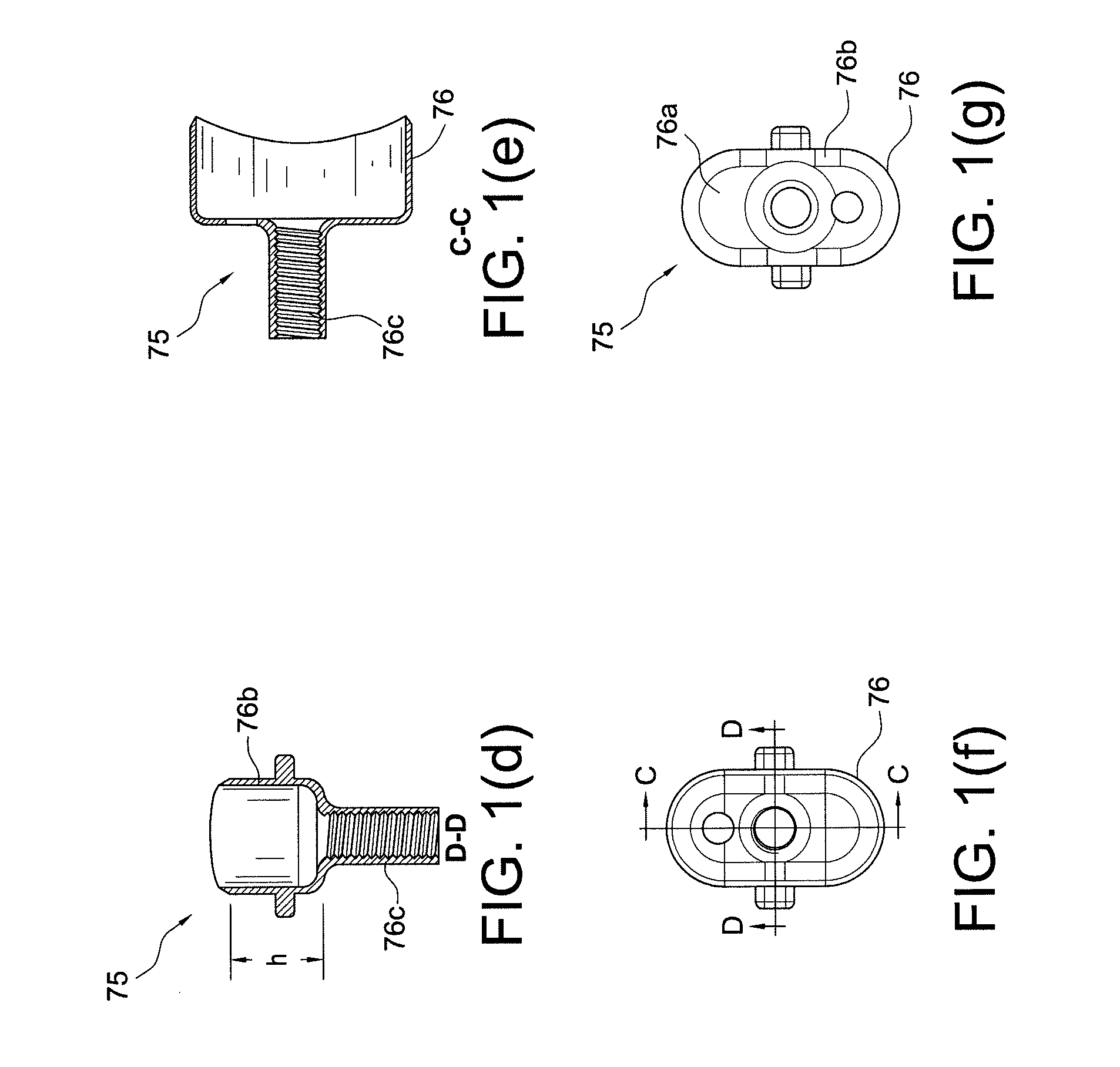
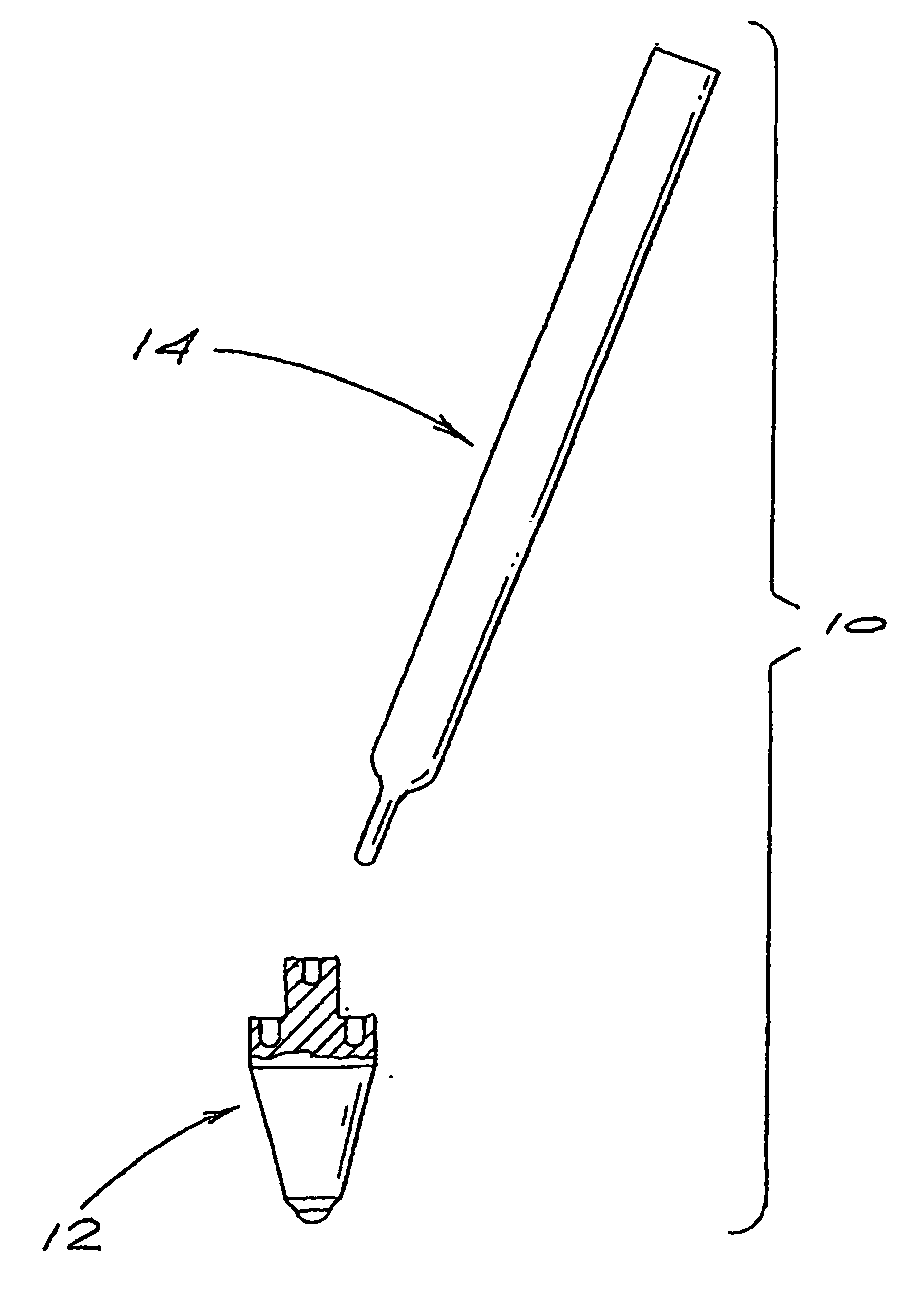
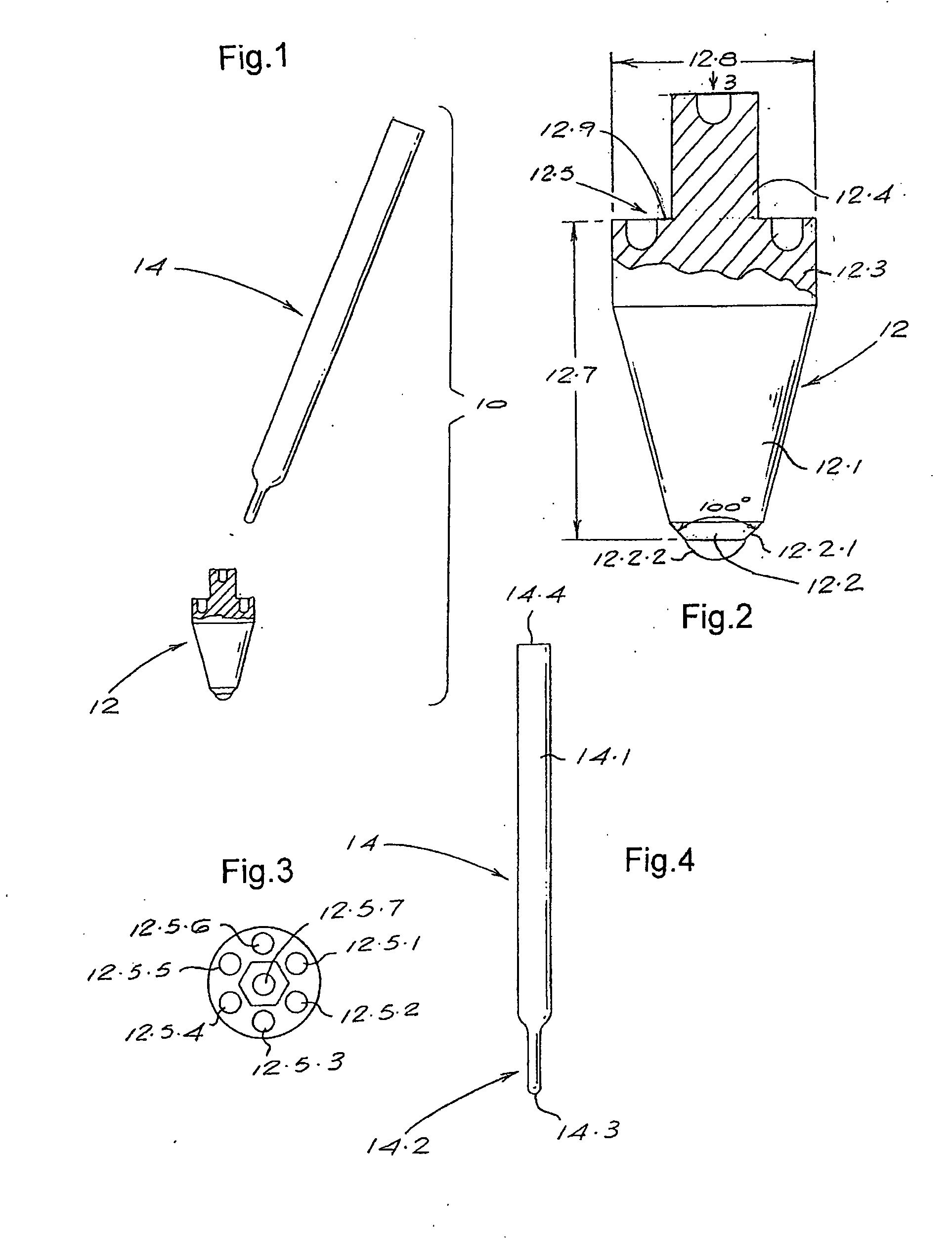
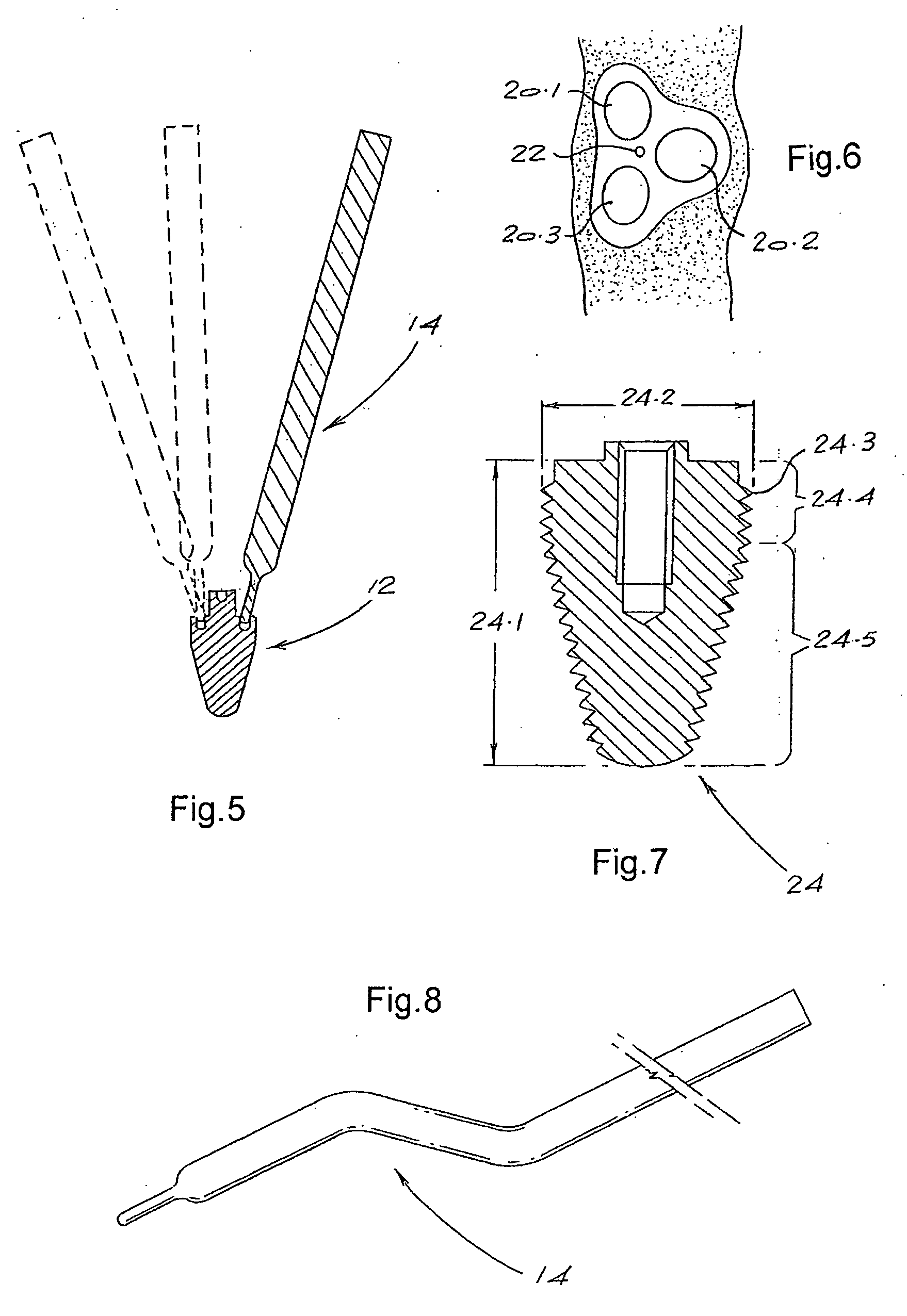
Osteotome and components thereof
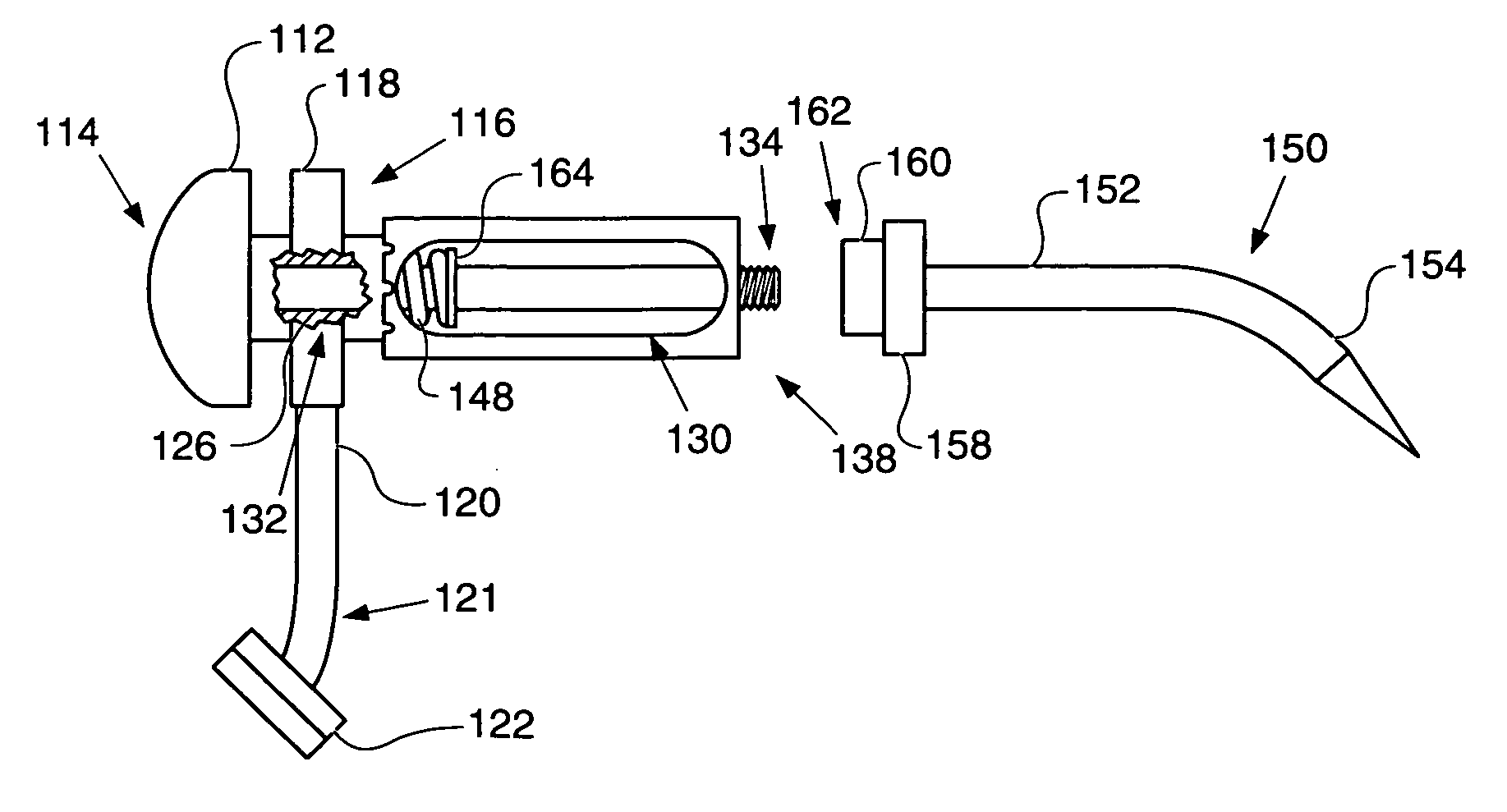
An osteotome includes a penetration tool which is to be driven into a bone and a separate, elongate driving tool for use in driving the penetration tool into the bone. The penetration tool has a tapered penetration end and an opposite end including at least one curved formation. The driving tool has an operative end including another curved formation which is shaped to engage the curved formation at the said opposite end of the penetration tool. With the curved formation at the operative end of the driving tool engaged with the curved formation at the said opposite end of the penetration tool, the driving tool can be used to transmit a driving force to the penetration tool to drive the penetration tool into the bone. The complemental curvatures of the formations enable the driving tool to be applied to the penetration tool at different angles, facilitating access to different regions of the mouth. The invention encompasses the penetration tool and the driving tool per se.
Owner:SOUTHERN IMPLATS (PTY) LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com