Patents
Literature
33 results about "Tibial surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
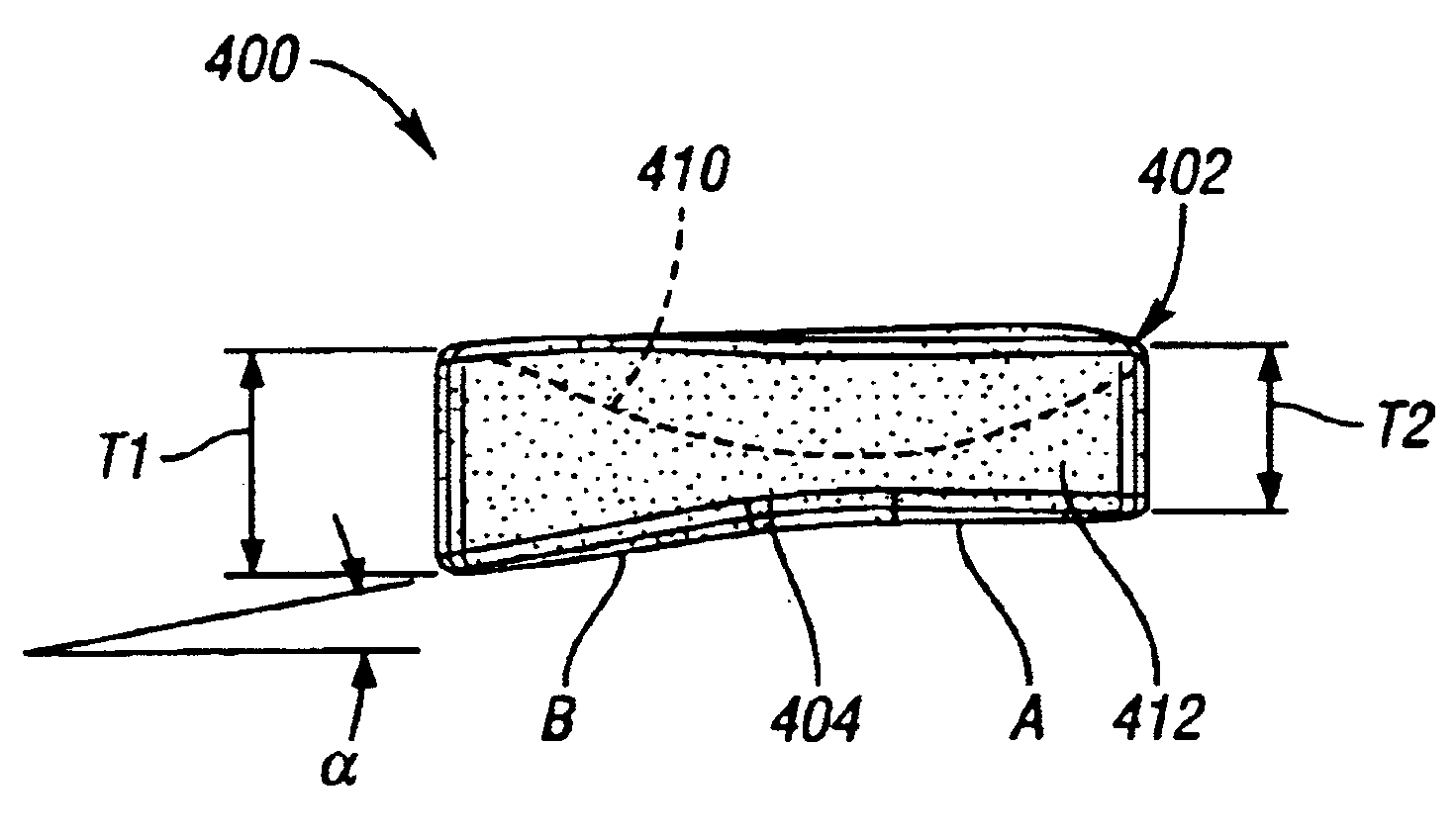
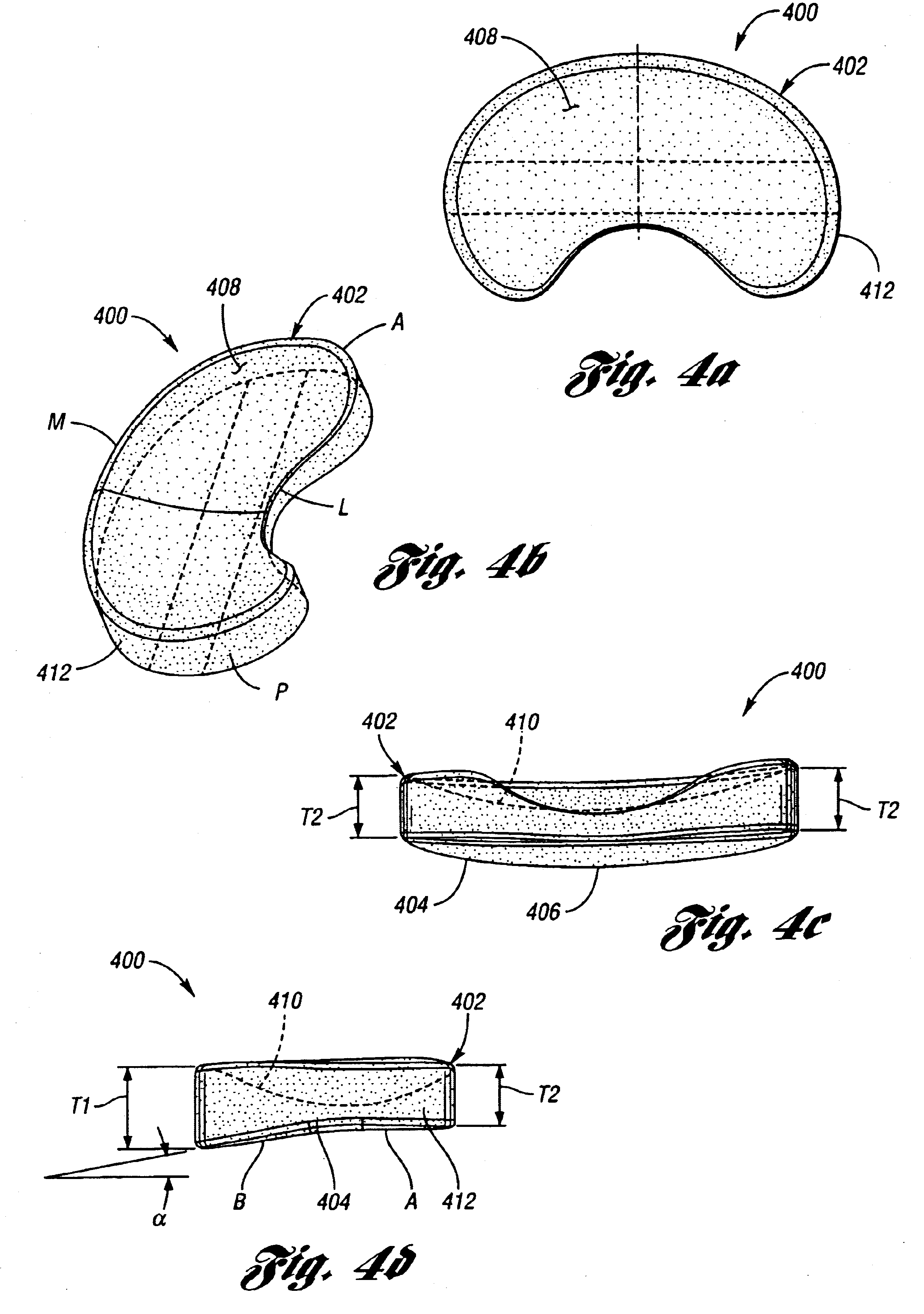
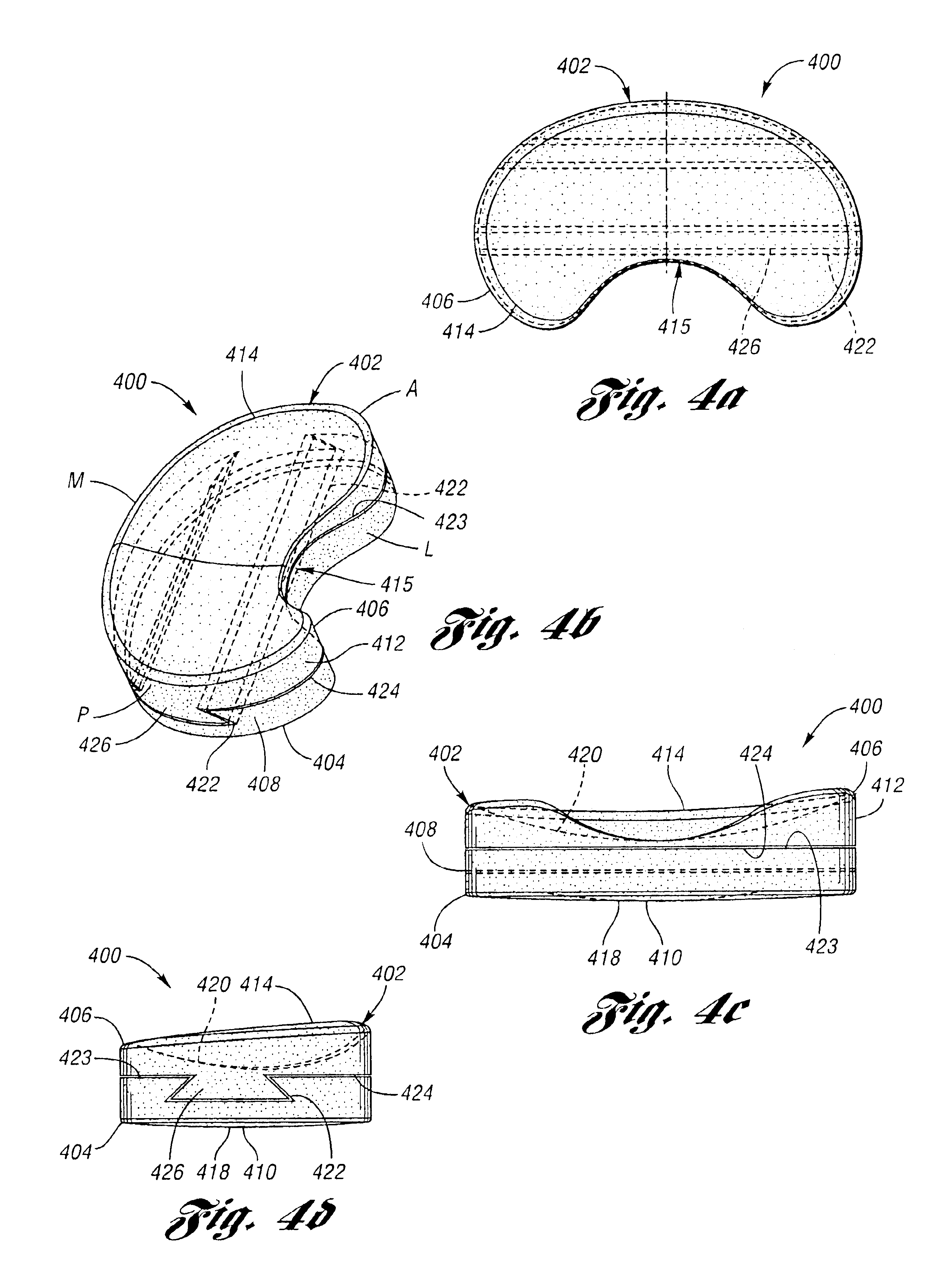
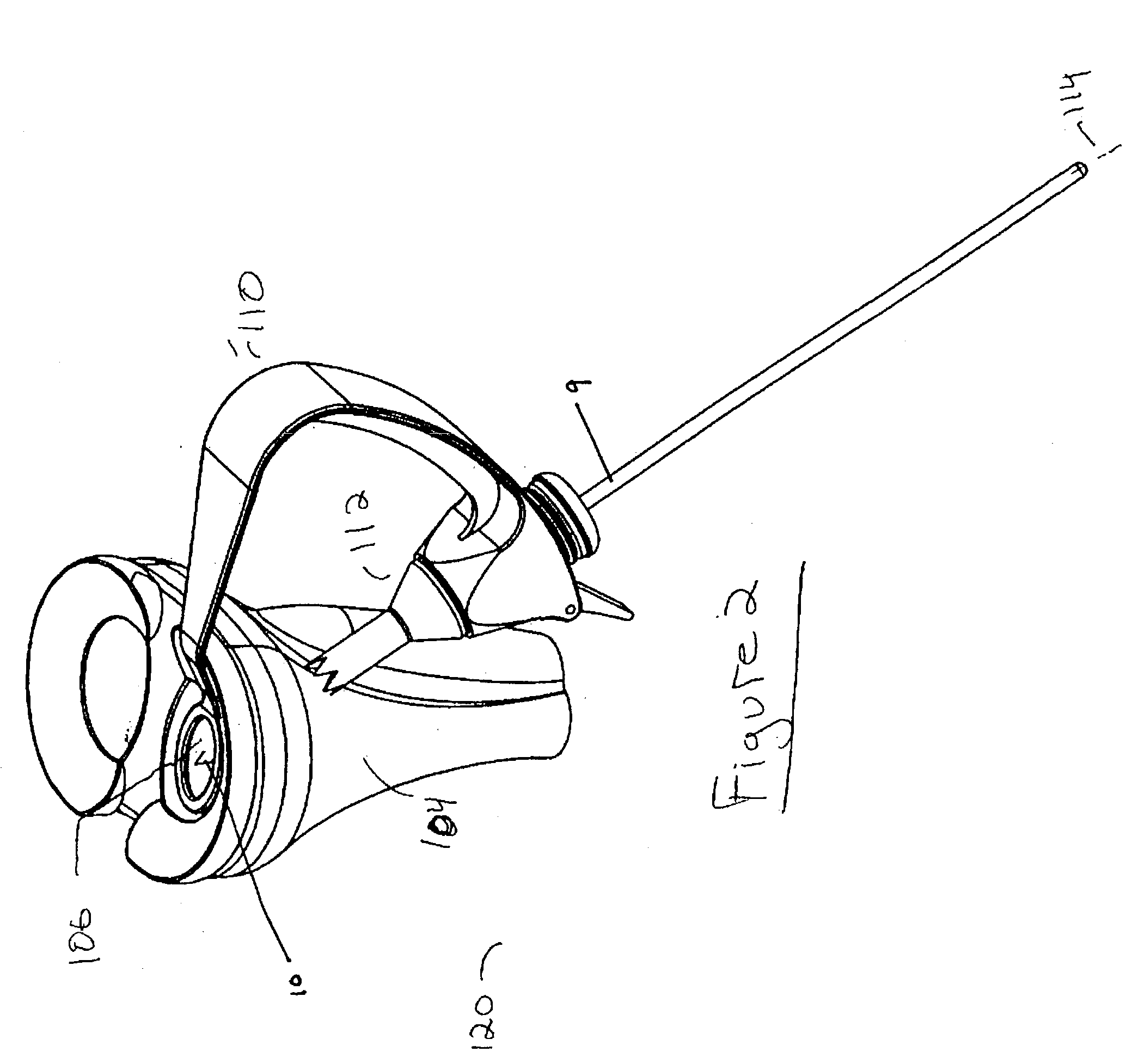
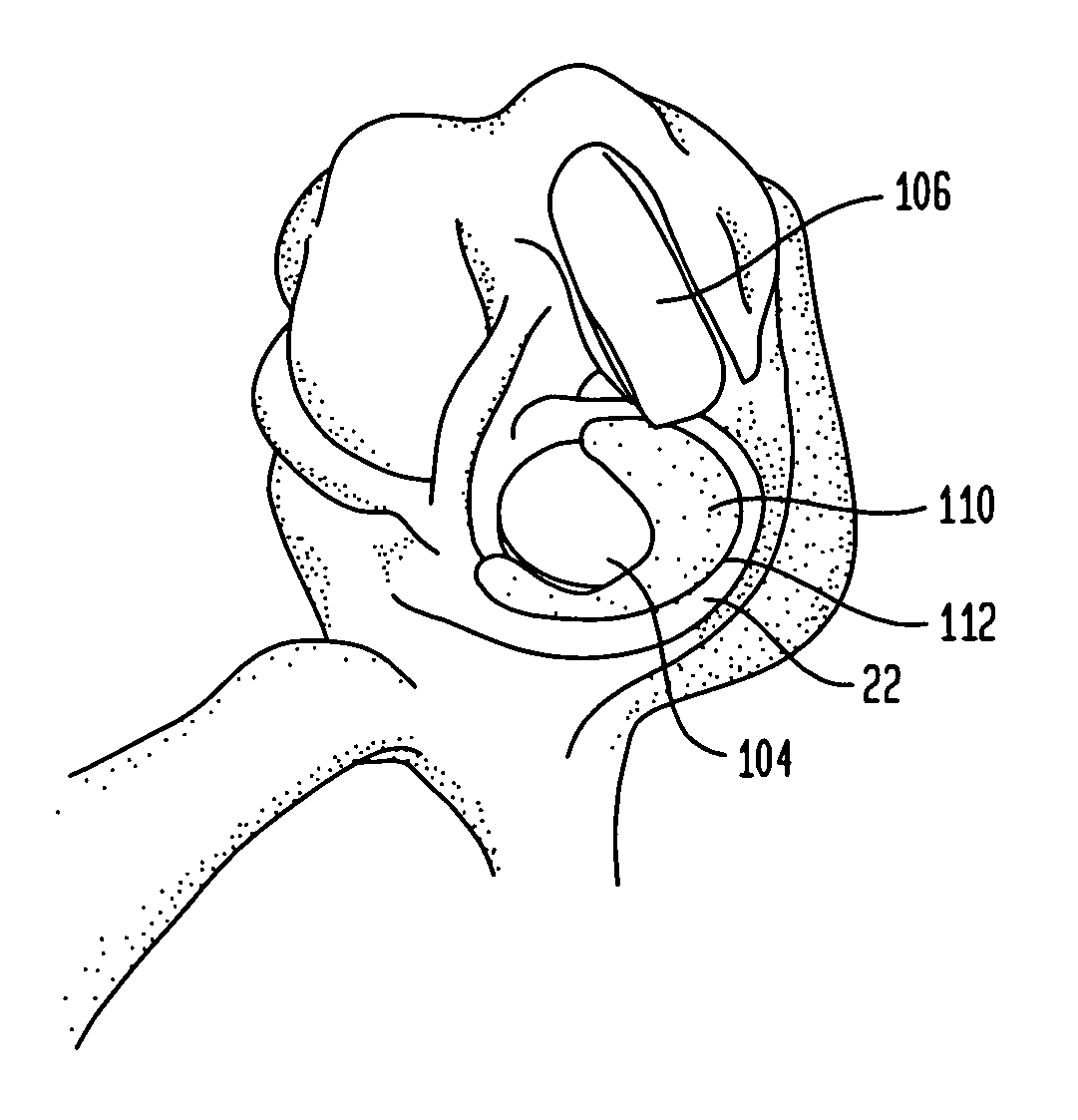
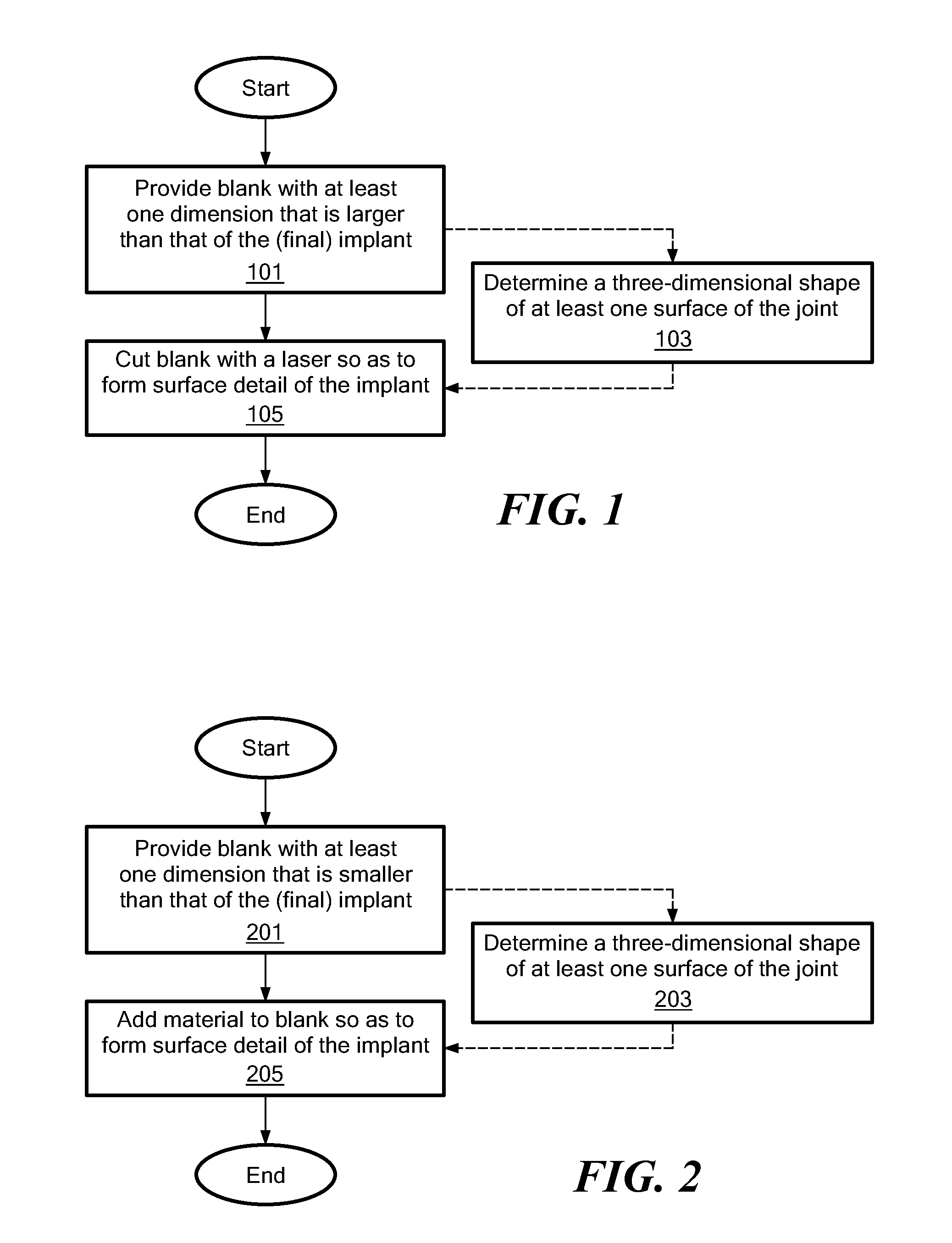
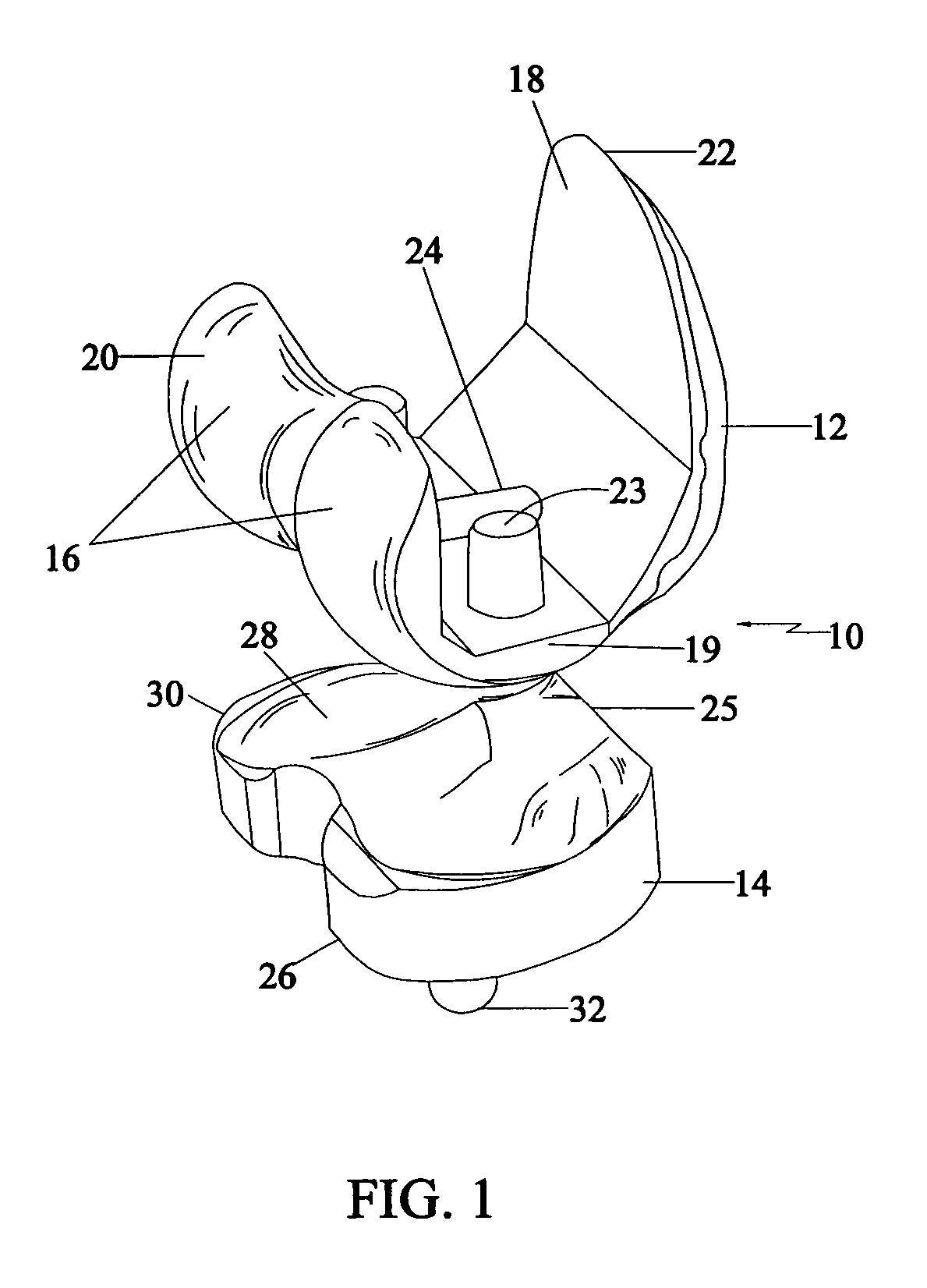
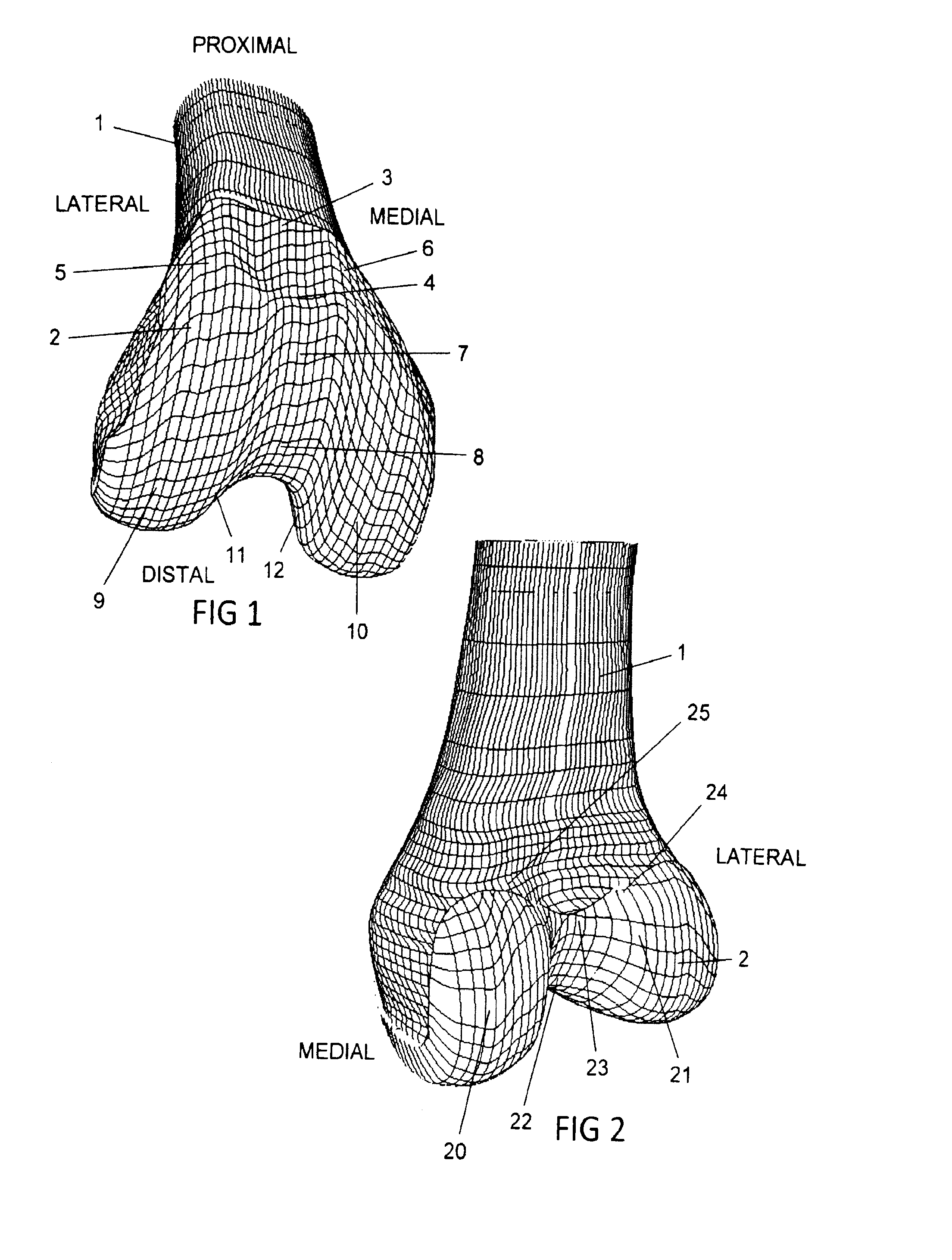
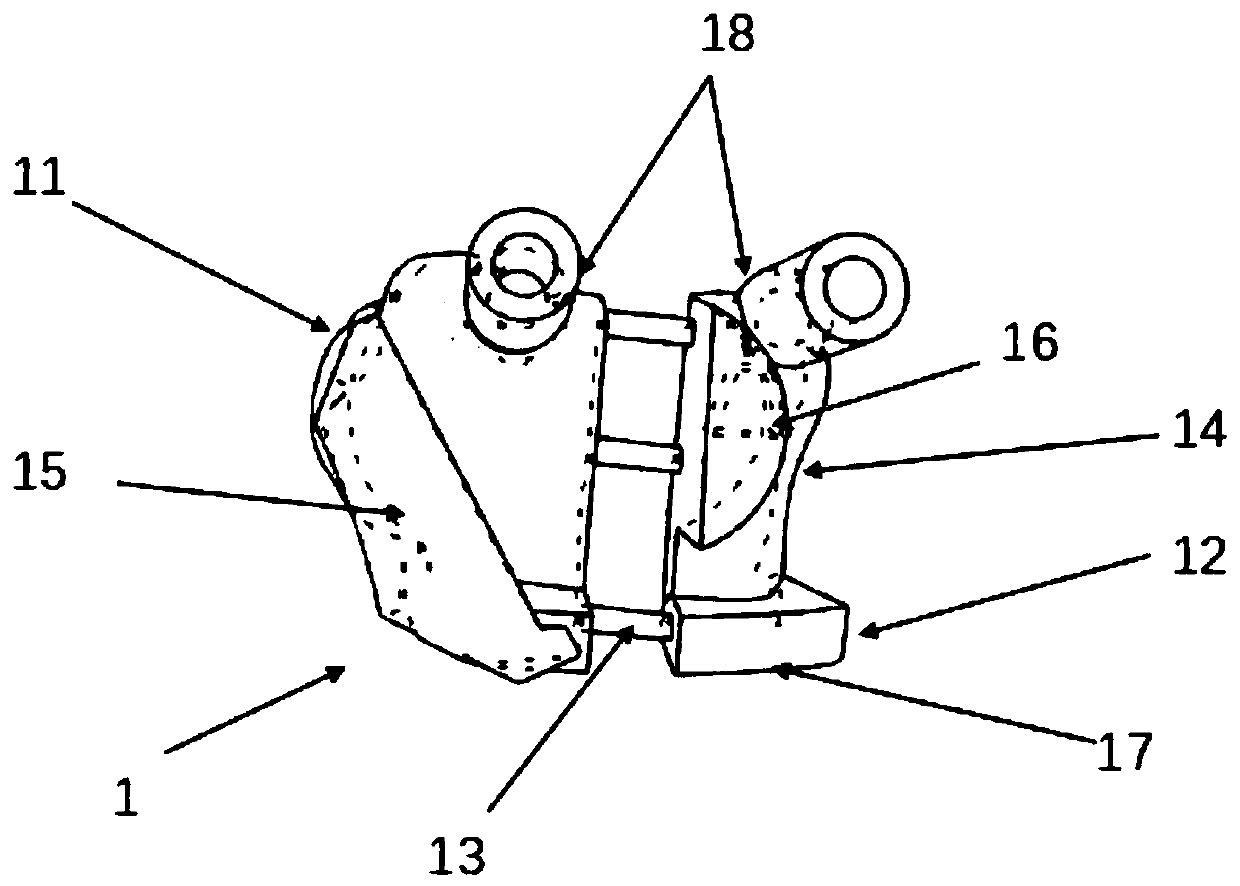
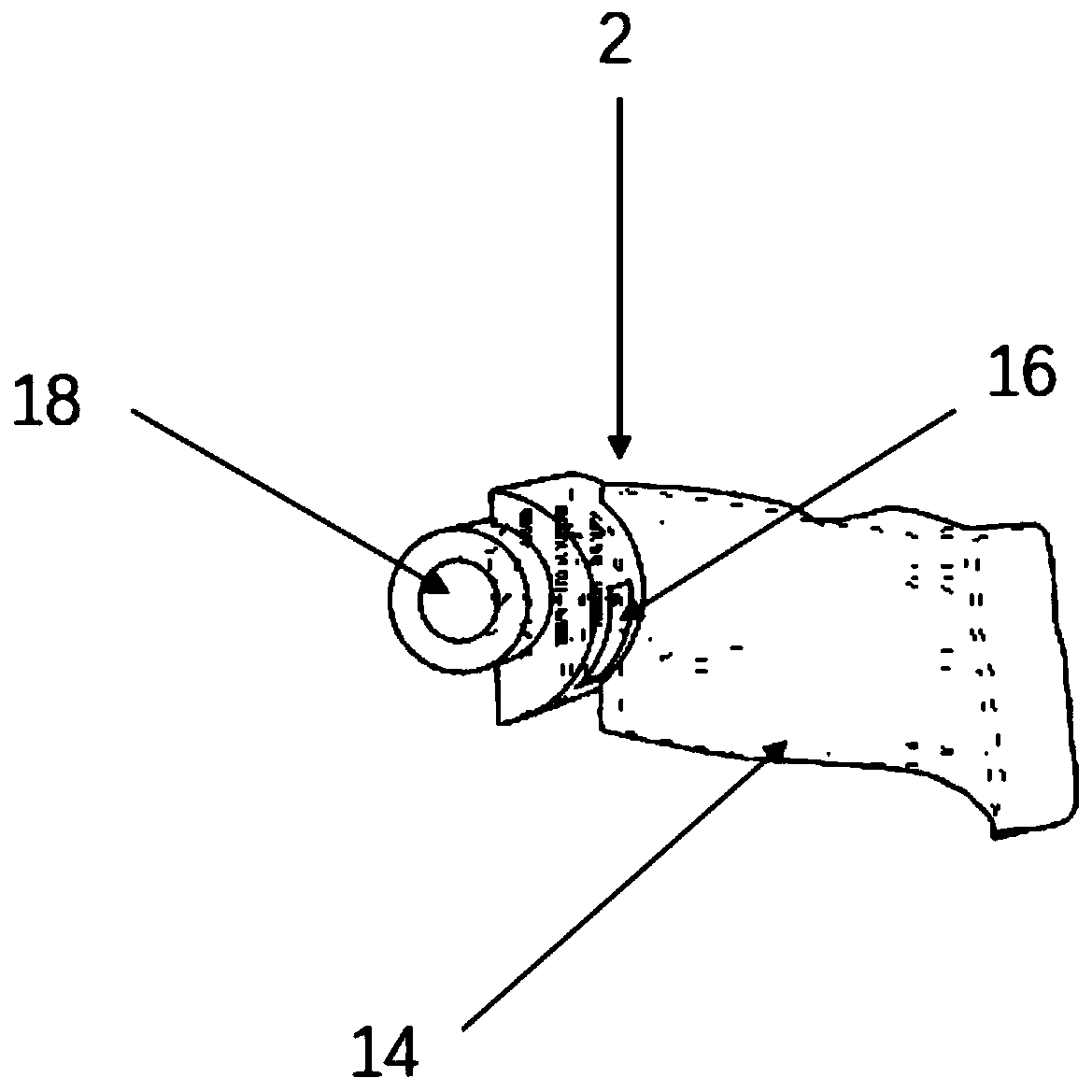
Interpositional Joint Implant
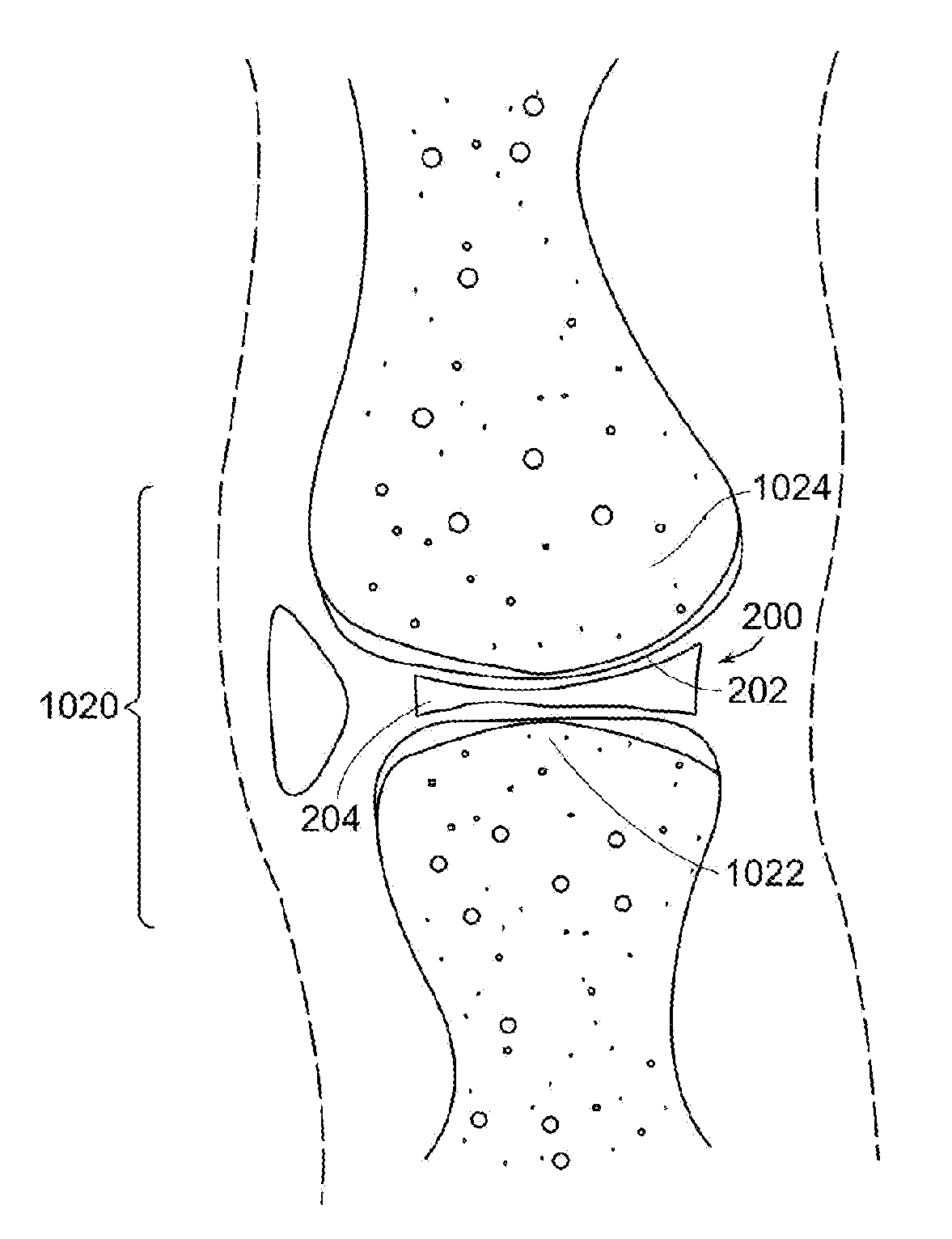
InactiveUS20070233269A1Improve anatomic functionalityPromote resultsJoint implantsDiagnostic recording/measuringTibiaTibial surface
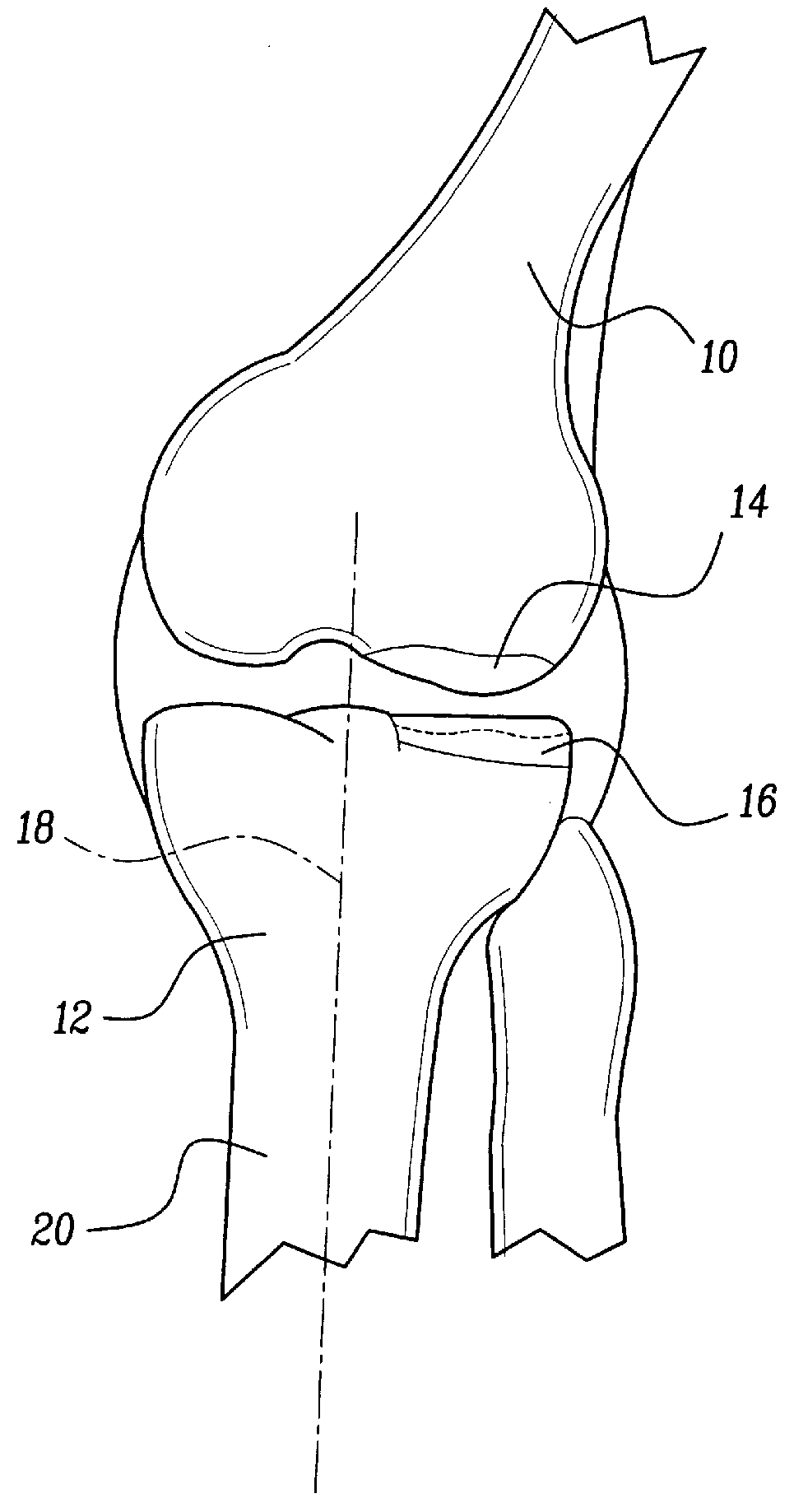
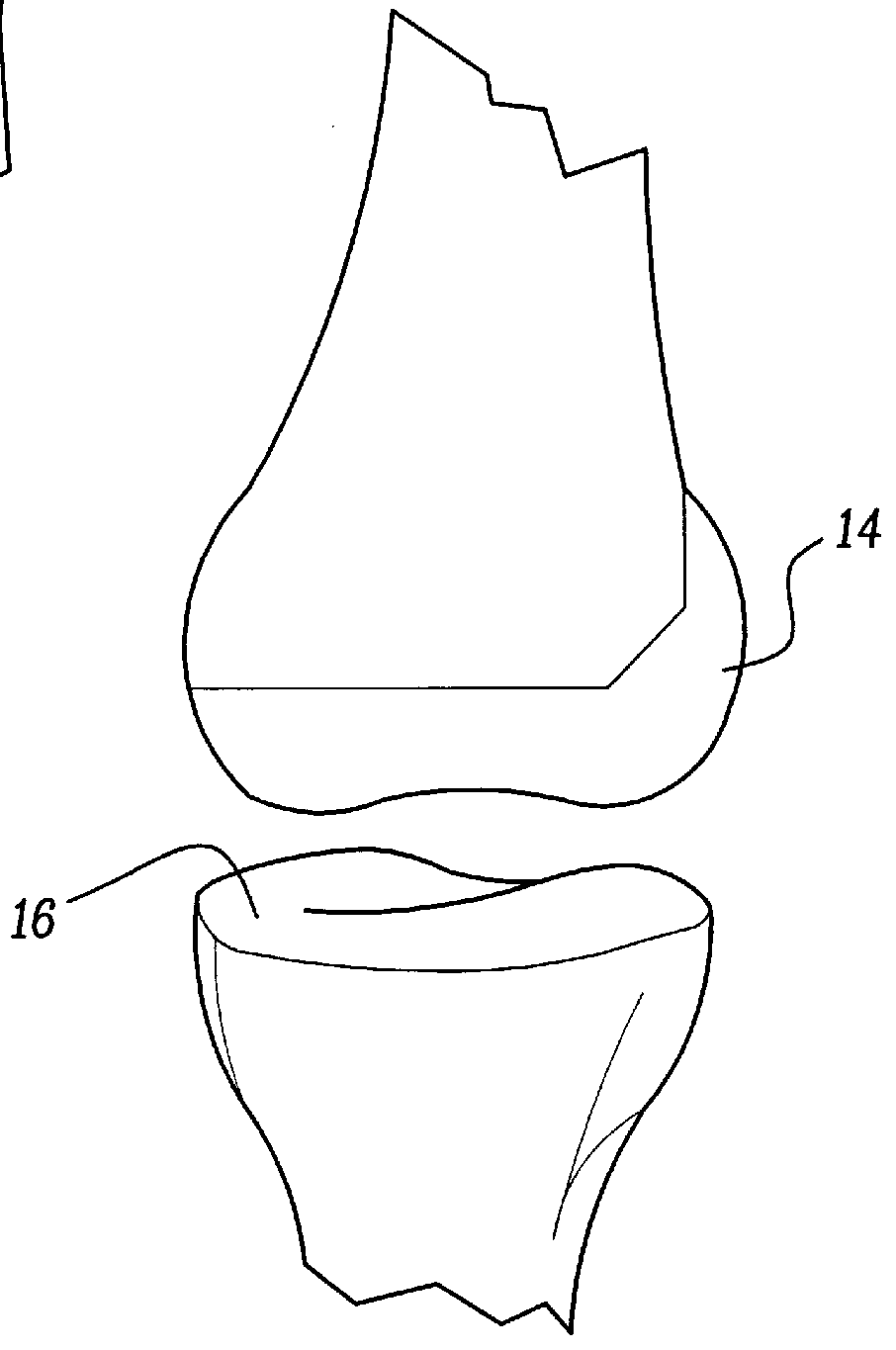
A method of preparing an interpositional implant suitable for a knee. The method includes determining a three-dimensional shape of a tibial surface of the knee. An implant is produced having a superior surface and an inferior surface, with the superior surface adapted to be positioned against a femoral condyle of the knee, and the inferior surface adapted to be positioned upon the tibial surface of the knee, The inferior surface conforms to the three-dimensional shape of the tibial surface. The implant may be inserted into the knee without making surgical cuts on the tibial surface. The tibial surface may include cartilage, or cartilage and bone.
Owner:CONFORMIS
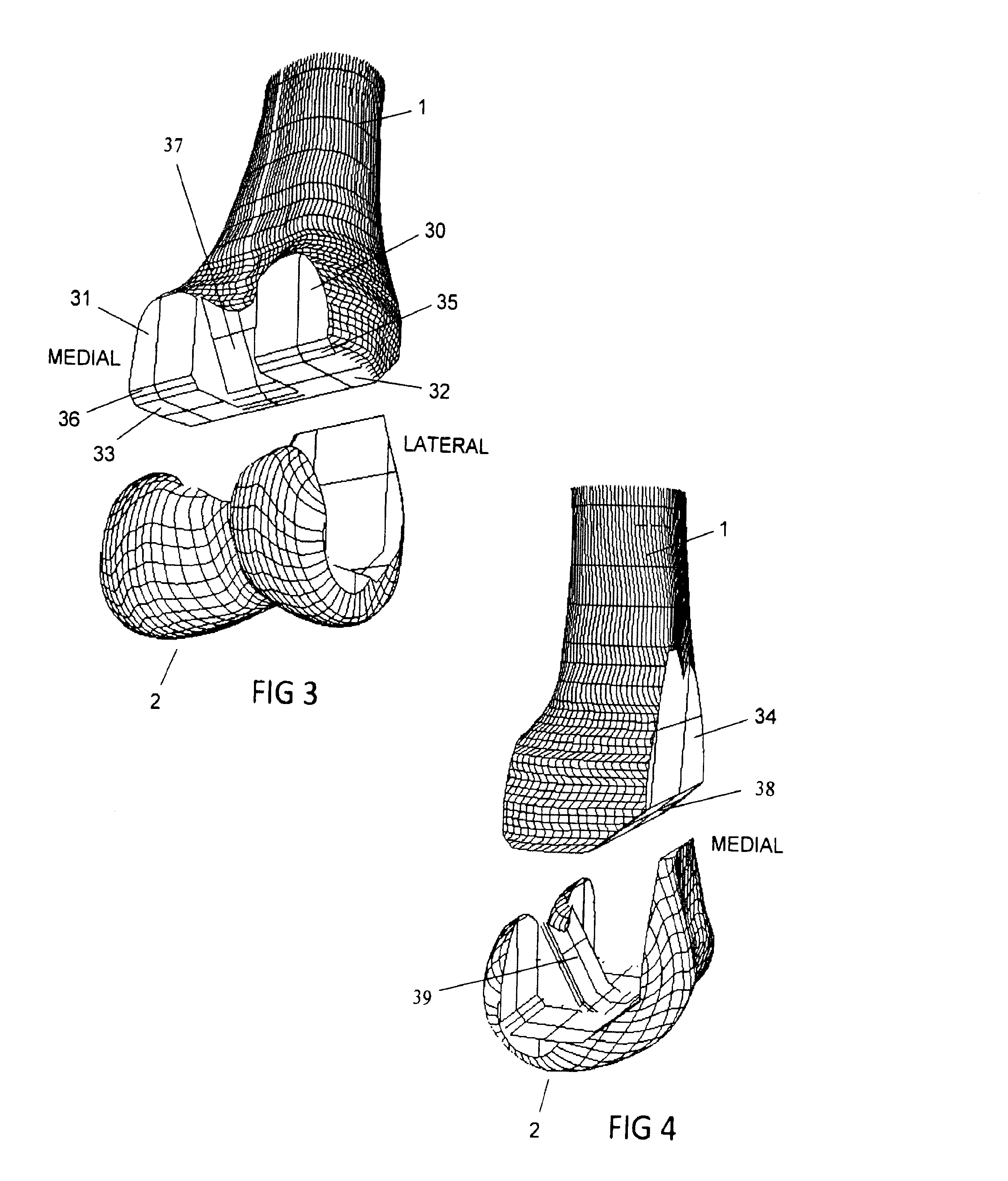
Implant Device and Method for Manufacture
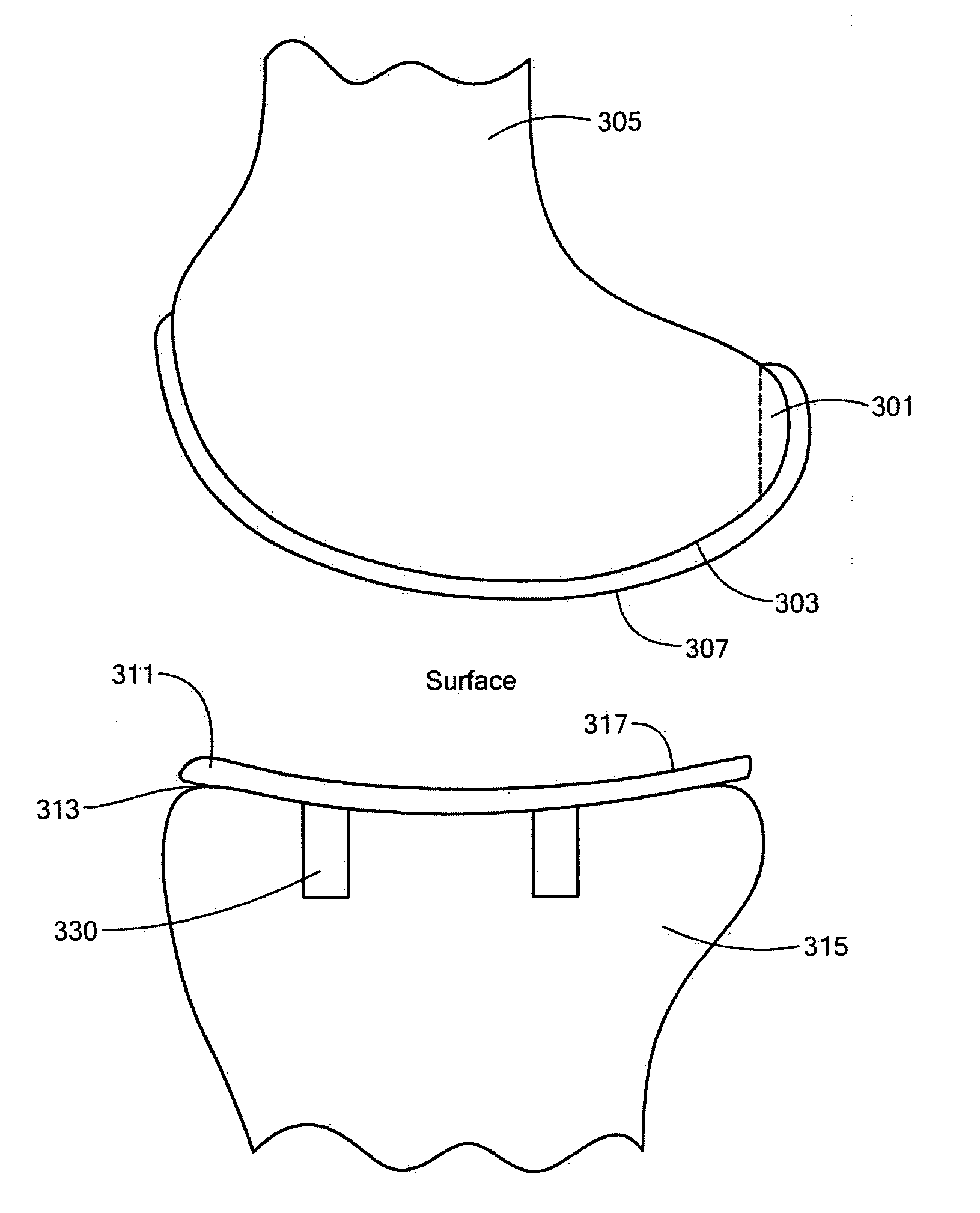
A knee implant includes a femoral component having first and second femoral component surfaces. The first femoral component surface is for securing to a surgically prepared compartment of a distal end of a femur. The second femoral component surface is configured to replicate the femoral condyle. The knee implant further includes a tibial component having first and second tibial component surfaces. The first tibial component surface is for contacting a proximal surface of the tibia that is substantially uncut subchondral bone. At least a portion of the first tibial component surface is a mirror image of the proximal tibial surface. The second tibial component surface articulates with the second femoral component surface.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Method of implanting a uni-condylar knee prosthesis
The invention relates generally to a method for implanting a uni-condylar knee prosthesis. The method includes steps for preparing the bone surfaces of both the femoral and tibial effected compartments. The femoral compartment is prepared by making a distal cut, a posterior cuts and a posterior chamfer cut. Holes that correspond to posts on the femoral component are also prepared. The tibial compartment is prepared using a cutting guide and following the sclerotic bone formation on the proximal tibia. At least one hole is prepared in the sloped cut tibial surface to use for alignment when cementing the tibial component that has an alignment peg.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
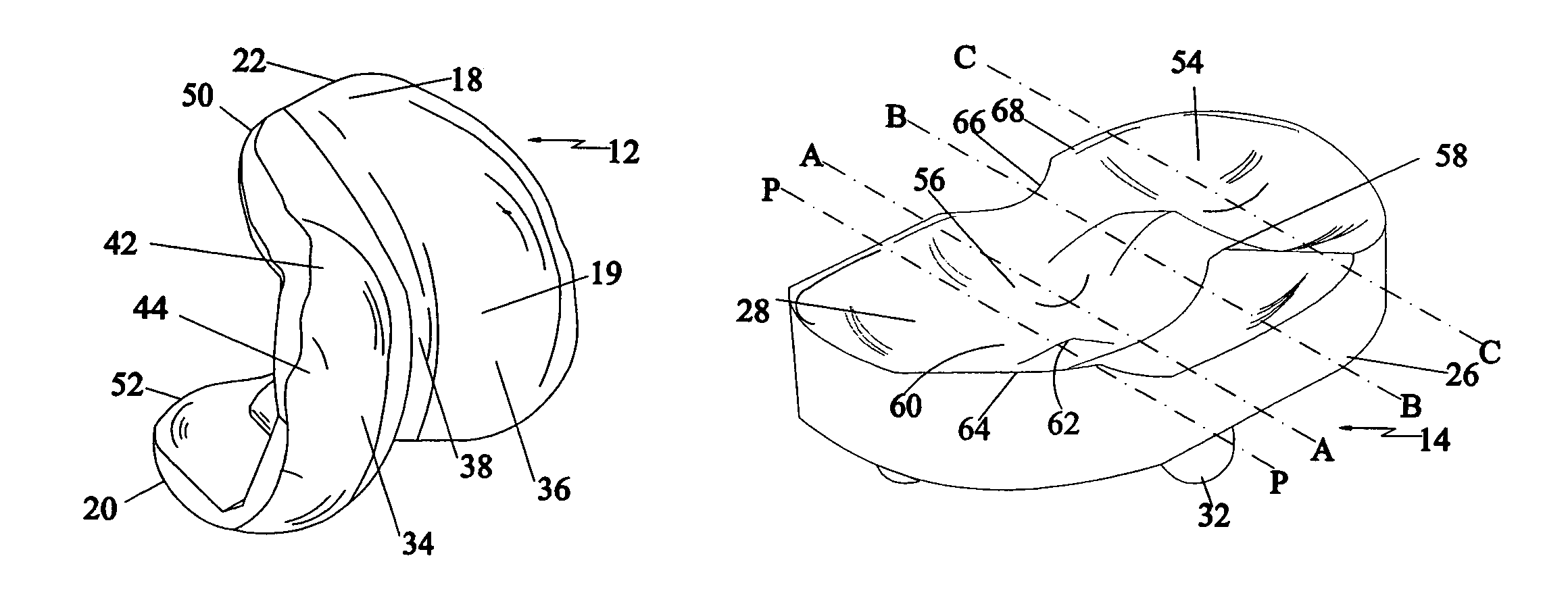
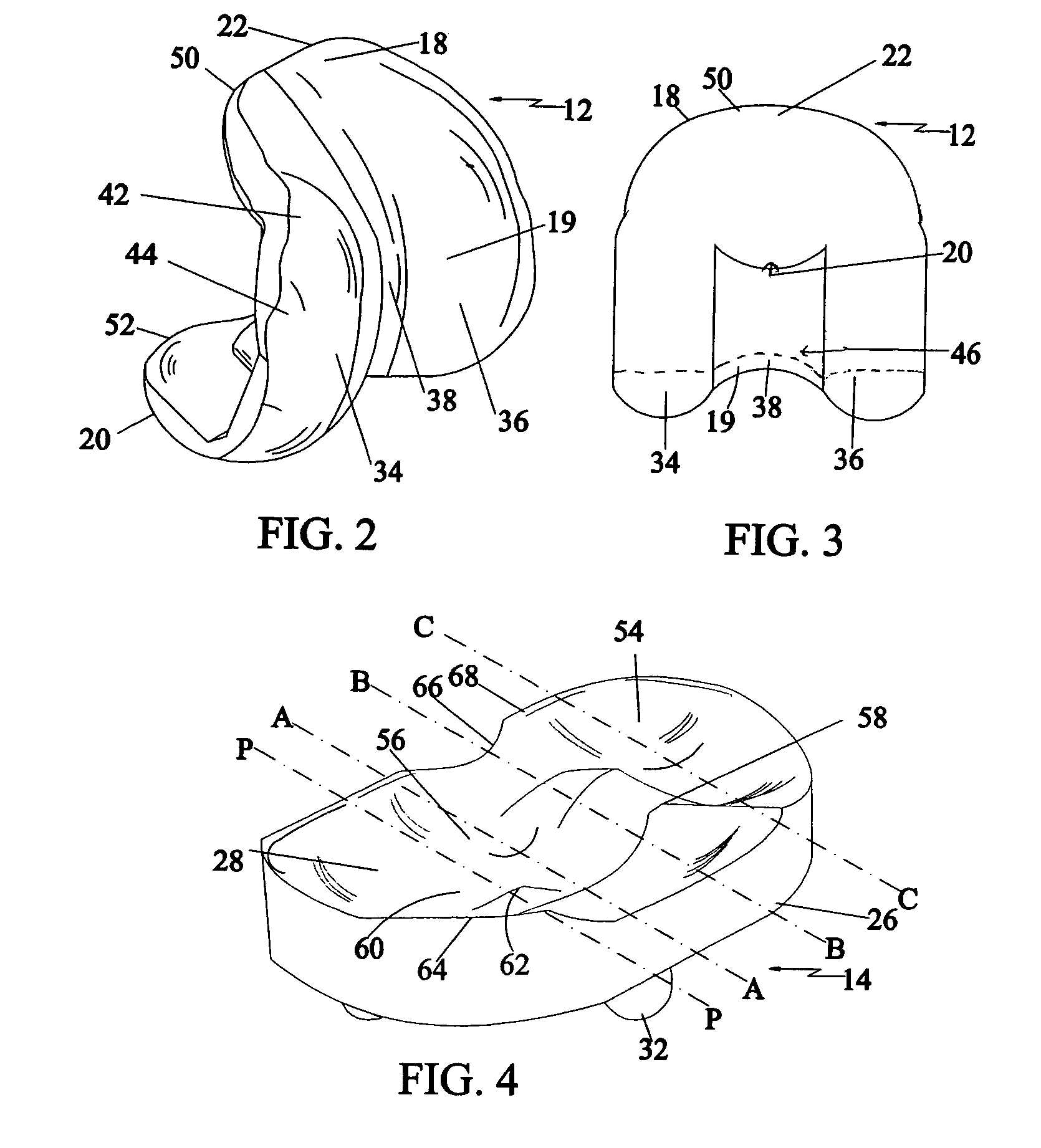
Surface guided knee replacement
ActiveUS20070135926A1Increase contact areaIncrease flexibilityJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaTibial surface
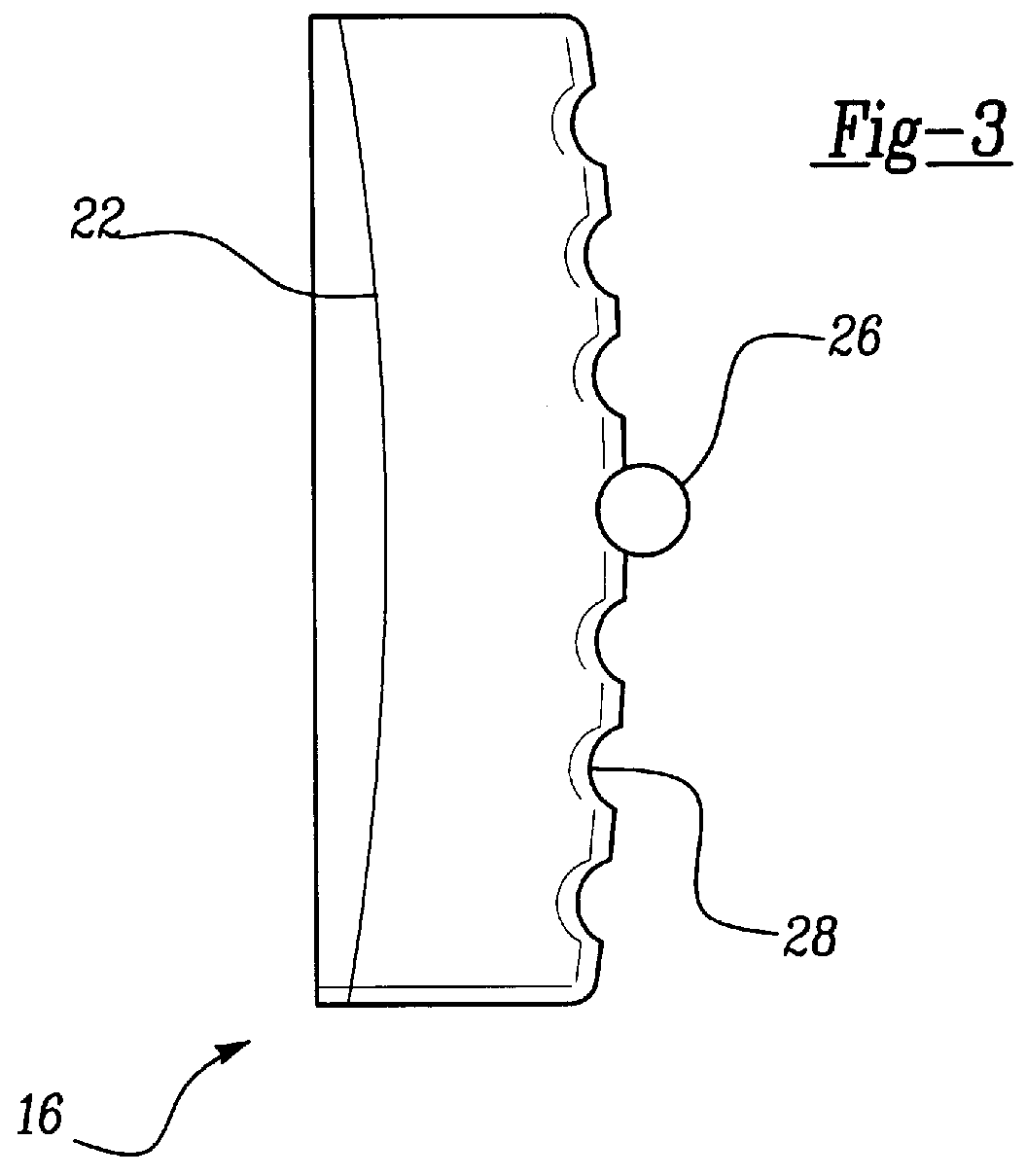
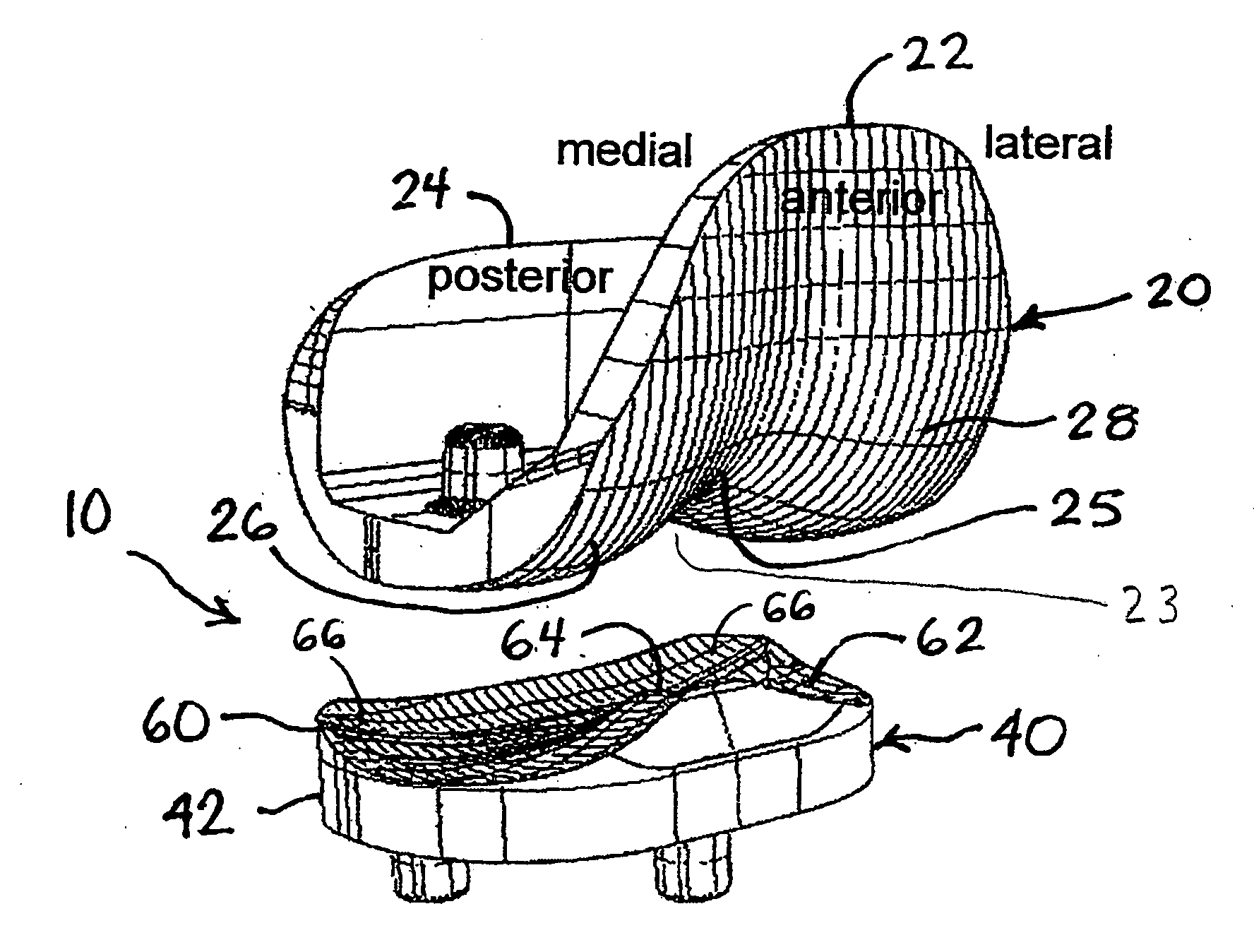
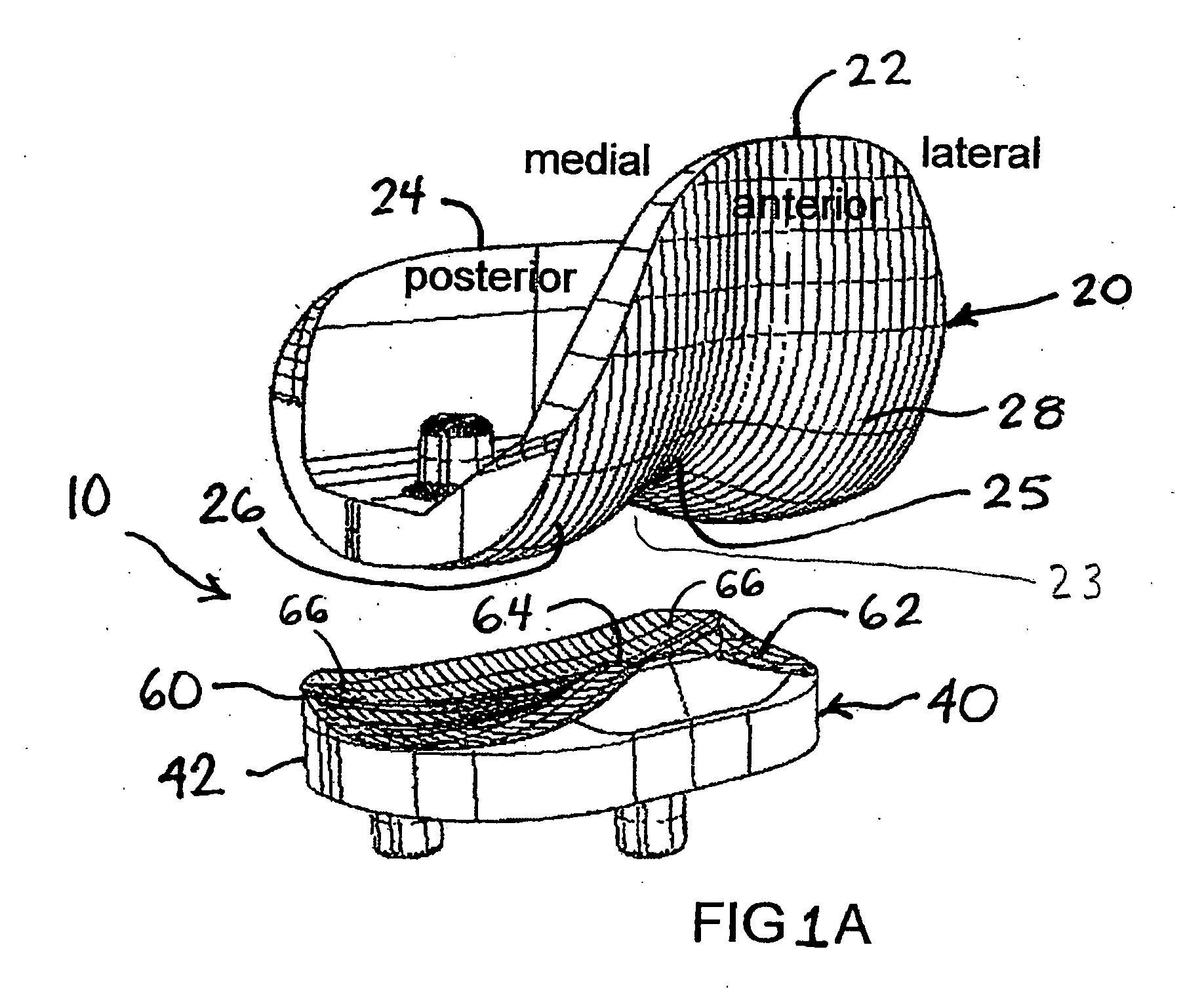
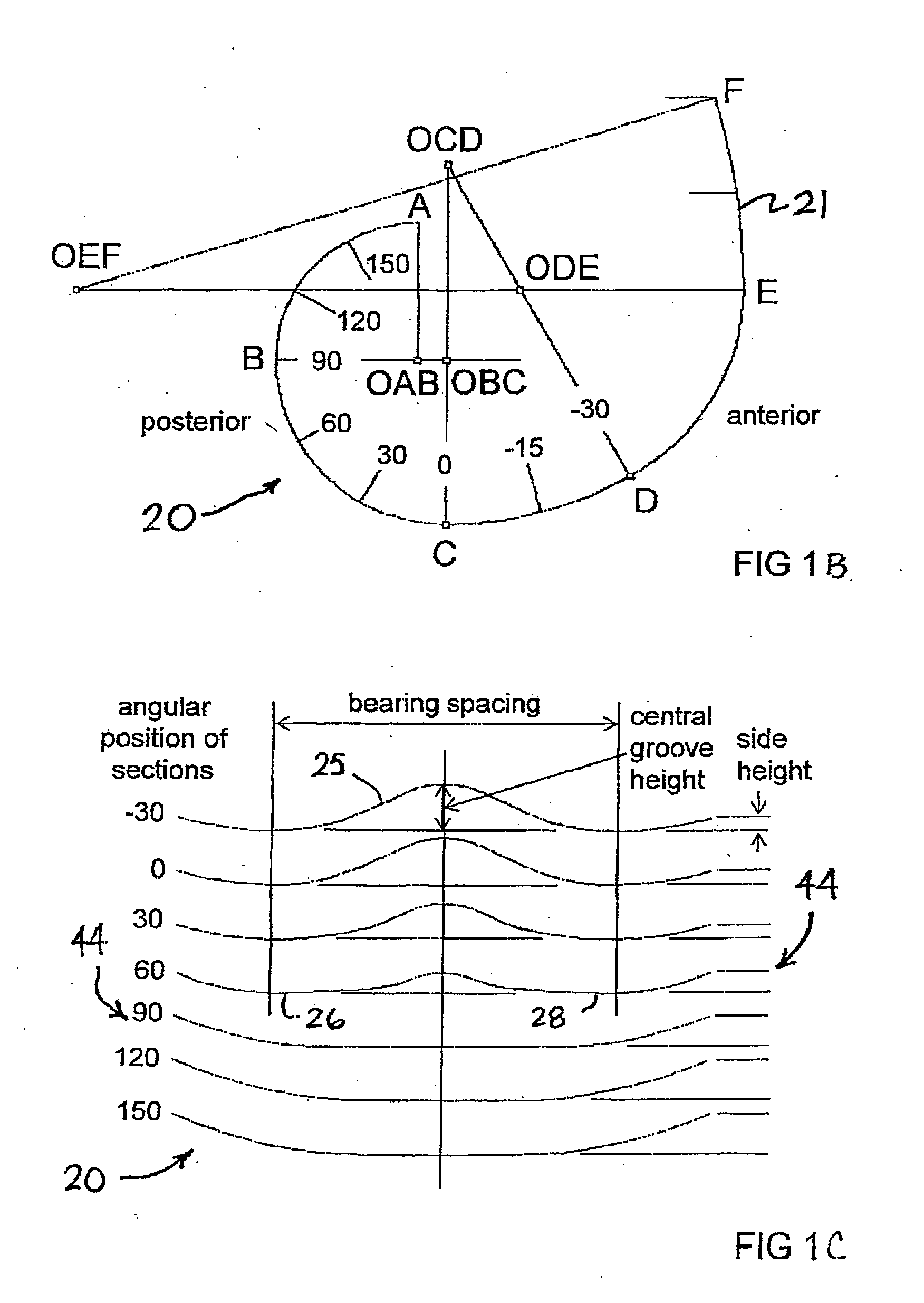
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the required motion and stability characteristics. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, by an amount similar to that in the anatomic knee. This is accomplished primarily by the depth and width of the femoral trochlea diminishing as the femoral component is flexed from zero to maximum, together with a ramp on the center of the tibial surface. The opposite motion, roll forward of the femur from a fully flexed to a more extended position, is accomplished by varying the outward radii of the lateral and medial femoral bearing surfaces, together with a ramp on the postero-lateral and postero-medial regions of the tibial surfaces. A variation of this is to generate a tibial surface which provides for a progressive internal rotation of the tibia as flexion proceeds.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
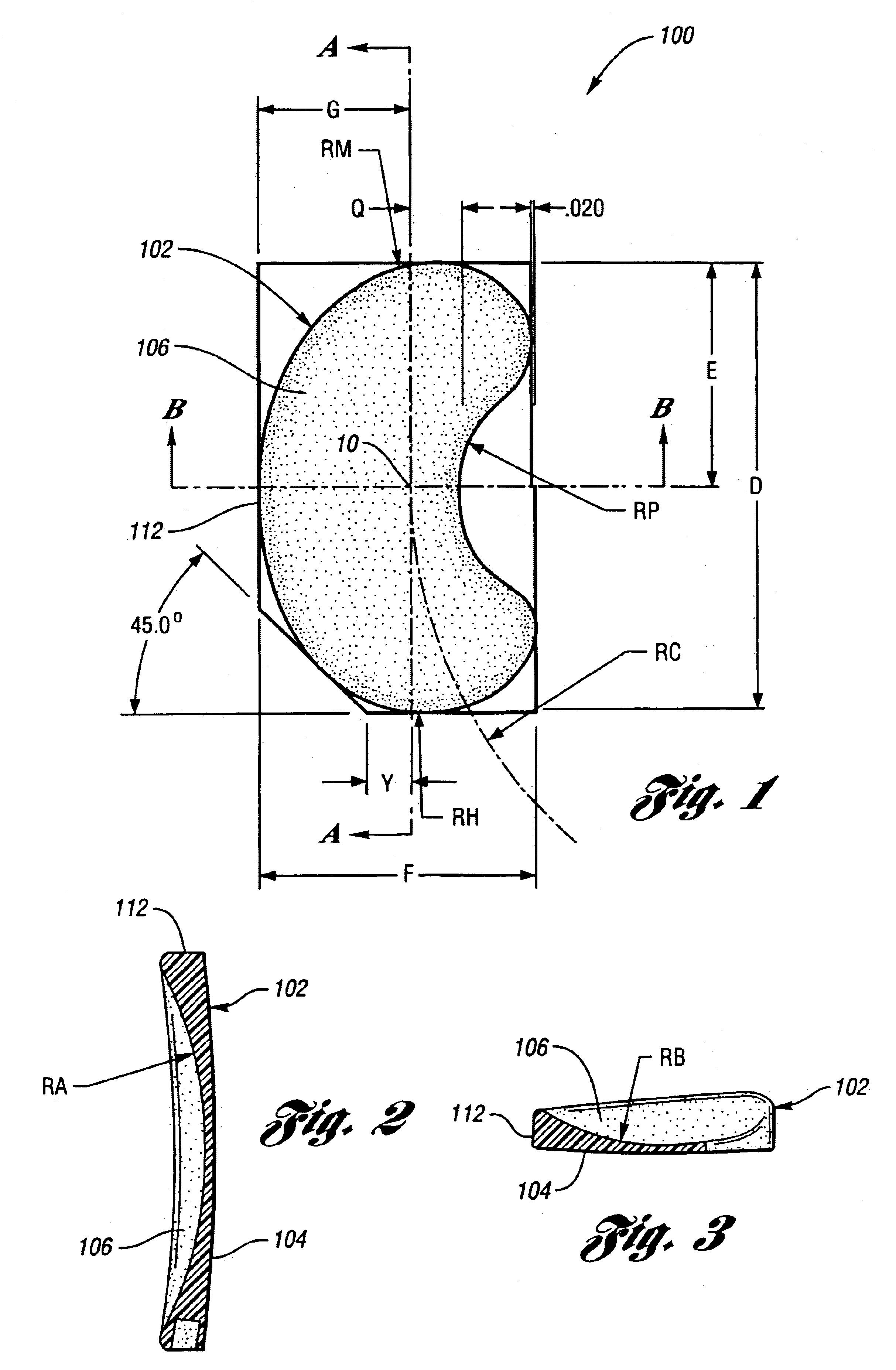
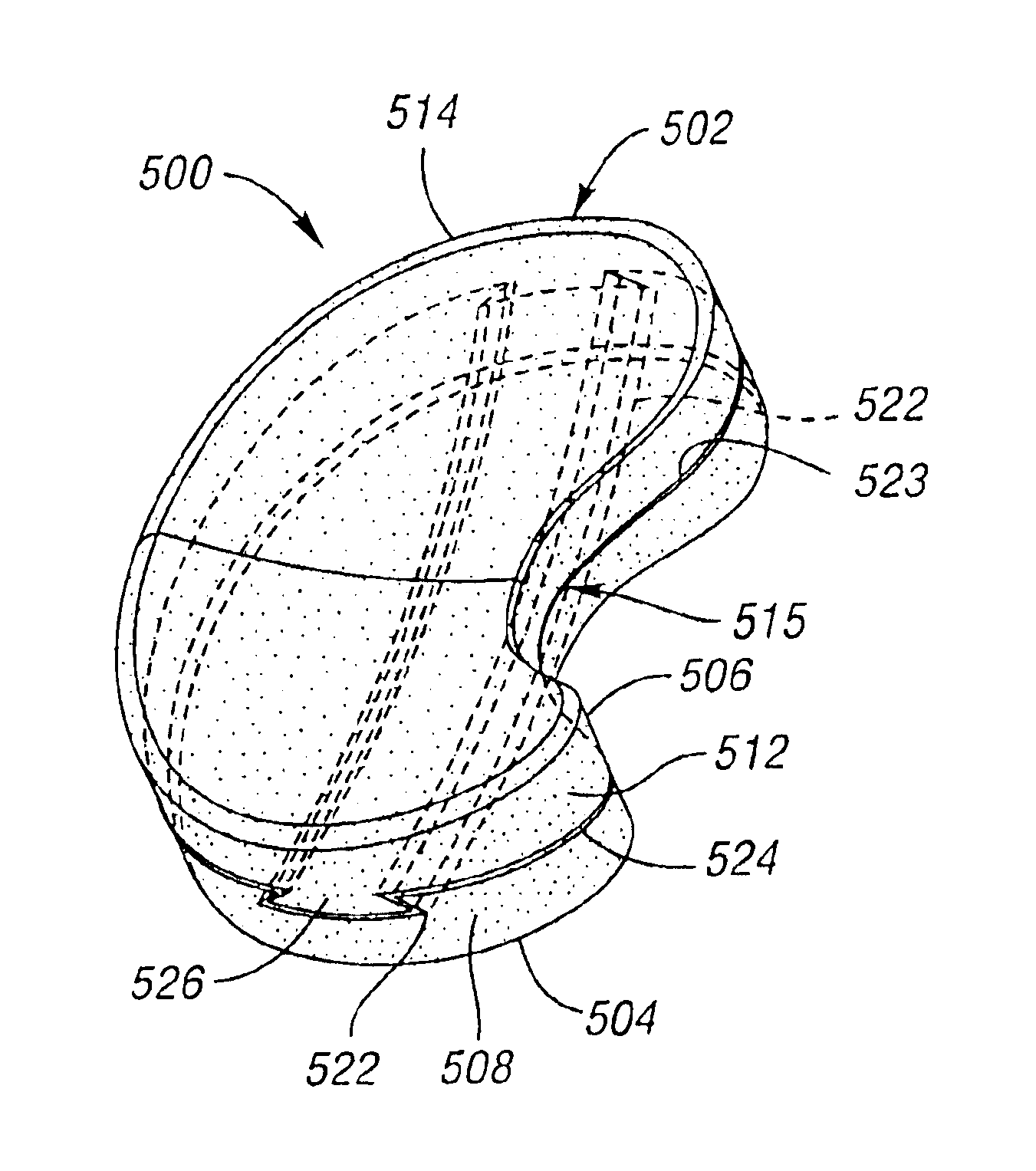
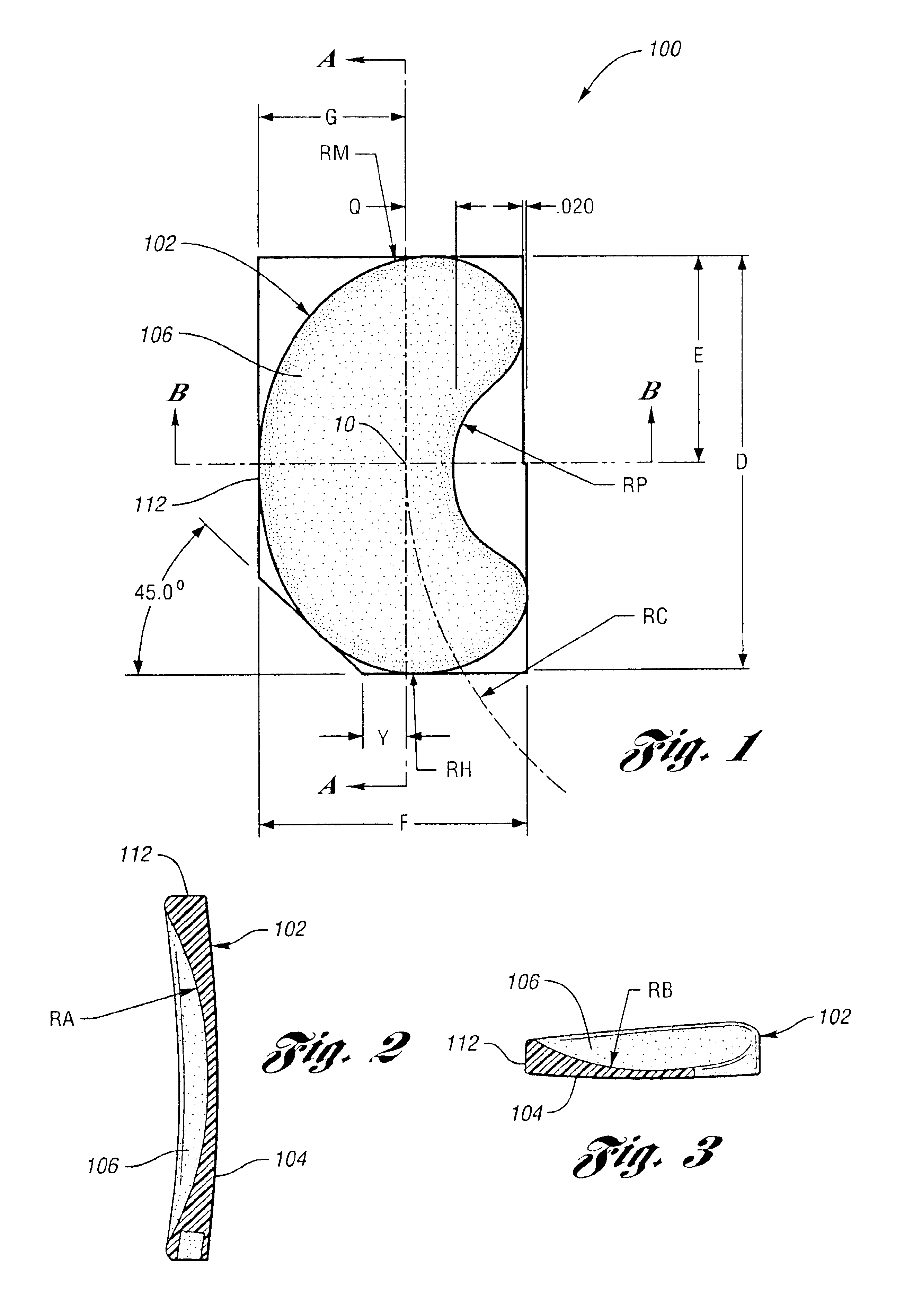
Surgically implantable knee prosthesis having medially shifted tibial surface
An implantable knee prosthesis includes a body having a substantially elliptical shape in plan and a pair of opposed faces. A peripheral edge of variable thickness extends between the faces and includes a first side, a second side opposite the first side, a first end and a second end opposite the first end. The thickness of the peripheral edge at the first side is greater than the thickness of the peripheral edge at the second side, the first end and the second end.
Owner:CENTPULSE ORTHOPEDICS
Surgically implantable knee prosthesis having two-piece keyed components
An implantable knee prosthesis includes a two-piece body having a substantially elliptical shape in plan and including a first piece and a second piece. The first piece is a tibial piece including a tibial surface. The second piece is a femoral piece including a femoral surface. The first piece and the second piece are mutually slidably engagable and separable.
Owner:CENTPULSE ORTHOPEDICS
Tibial resurfacing system
A tibial resurfacing system is provided that includes a drill guide, bone chisel and implant. In one aspect, the system includes a drill guide that includes a targeting ring that is shaped to be placed on the superior tibial surface and a bore section that is connected to the ring to create an axis through the tibia to the superior tibial surface in the vicinity of the targeting ring. The drill guide permits a drill pin and / or drill to be advanced through the tibia to the superior tibial surface. In another aspect, a bone chisel is provided that includes an elongated tubular structure having a first end and a bone-cutting end, and the bone-cutting end is terminated in a transverse angle thereby creating an elliptical bone-cutting face. In another aspect, an implant is provided that includes an angled bearing element formed of a cylindrical member having a first end and a second end. The first end is formed at an angle that creates an elliptical face of the first end, and the first end defines a load-bearing surface of an articular surface.
Owner:ARTHROSURFACE
Meniscal and tibial implants
InactiveUS6994730B2Highly mobile but stable jointSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsArticular surfacesTibia
Instrumentation and a method for resurfacing a joint capsule having cartilage and meniscal surfaces such as a knee joint includes resecting a central portion of the joint cartilage on one joint member such as the tibia while leaving a meniscal rim attached to the peripheral joint capsule. A cavity is then formed in the bone underlying the central portion of the joint surface such as the lateral tibial surface. A resurfacing implant is then coupled, by cementing for example, to the cavity. A soft prosthetic meniscal implant is then coupled to the remaining meniscal ring such as by suturing.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Tibial resurfacing system
A tibial resurfacing system is provided that includes a drill guide, bone chisel and implant. In one aspect, the system includes a drill guide that includes a targeting ring and a bore section for creating an axis through the tibia to the superior tibial surface in the vicinity of the targeting ring. In another aspect, a bone chisel is provided that includes a bone-cutting end, having a transverse angle creating an elliptical bone-cutting face. In another aspect, an implant is provided that includes an angled bearing element formed of a cylindrical member having a first end defining a load-bearing surface, and a second end. The first end is formed at an angle that creates an elliptical face of the first end.
Owner:ARTHROSURFACE
Implant device and method for manufacture
A knee implant includes a femoral component having first and second femoral component surfaces. The first femoral component surface is for securing to a surgically prepared compartment of a distal end of a femur. The second femoral component surface is configured to replicate the femoral condyle. The knee implant further includes a tibial component having first and second tibial component surfaces. The first tibial component surface is for contacting a proximal surface of the tibia that is substantially uncut subchondral bone. At least a portion of the first tibial component surface is a mirror image of the proximal tibial surface. The second tibial component surface articulates with the second femoral component surface.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Surface guided knee replacement
InactiveUS20070135925A1Reduce consistencyAvoid large displacementJoint implantsKnee jointsGonial angleTibial surface
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the motion and stability characteristics of the anatomic knee. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, more so on the lateral side than on the medial side. This is accomplished by the interaction of a projecting tibial post inside a cupola in the center of the femoral component, and by the saggital radius on the medial side being smaller than that on the lateral side. The prevention of anterior sliding of the femur on the tibia in early flexion is accomplished by the interaction between a distal-anterior recess on the medial side of the femur and an apposing raised pad on the tibial surface. Rotational laxity at all angles is allowed by the presence of only one recess pad and by non-conforming femoral-tibial surfaces on the lateral side.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Surface guided knee replacement
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Knee joint with a ramp
InactiveUS20090204221A1Minimize wear and deformationIncrease the areaJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaTibial surface
An artificial knee joint is described that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the required motion and stability characteristics. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, by an amount similar to that in the anatomic knee. The opposite motion, roll forward of the femur from a fully flexed to a more extended position, is accomplished by varying the outward radii of the lateral and medial femoral bearing surfaces, together with a ramp on the postero-lateral and postero-medial regions of the tibial surfaces.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
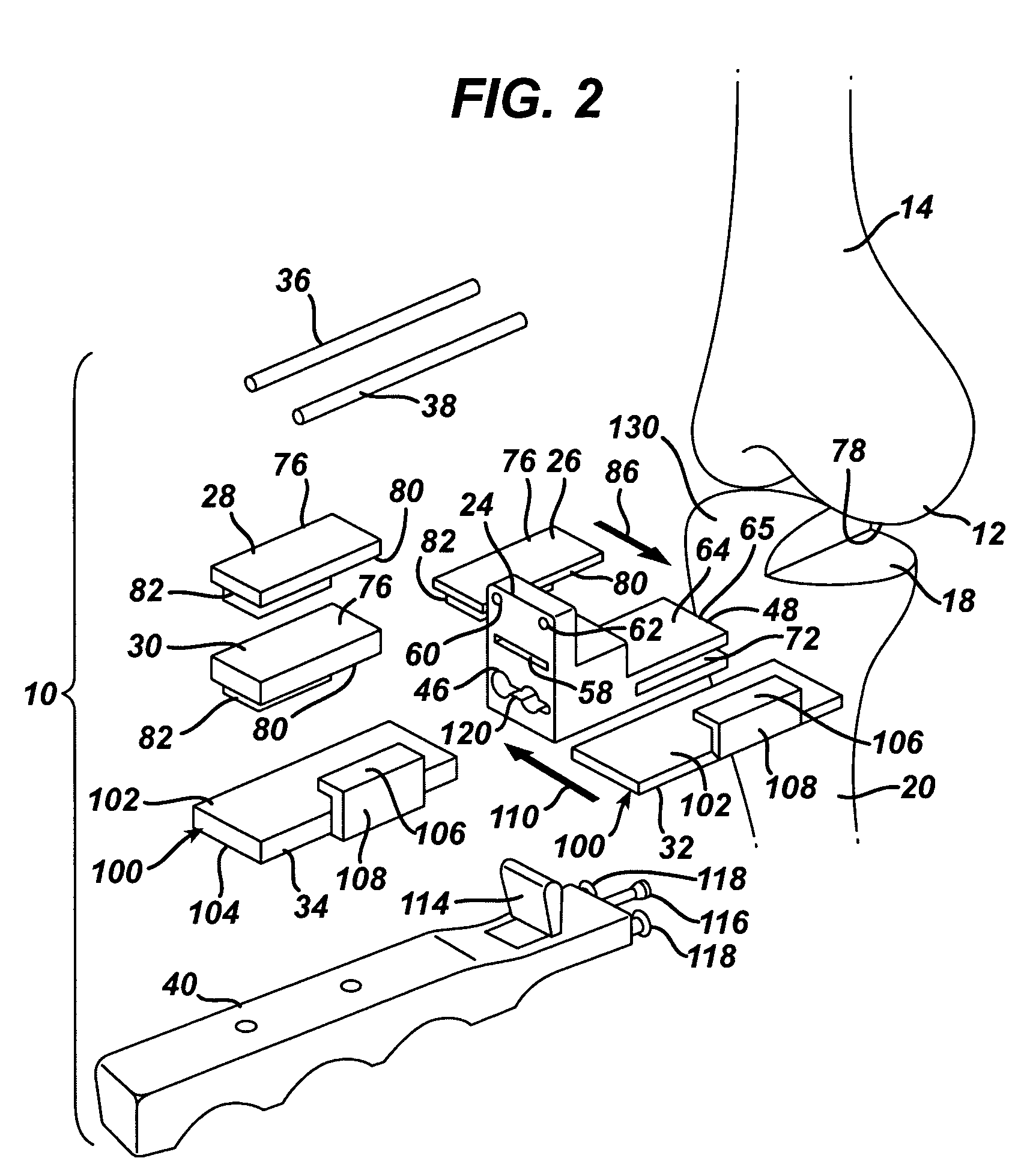
Kit, guide and method for locating distal femoral resection plane
A combination cutting and spacer guide has a cutting block portion and a guide arm portion. The cutting block portion has a cutting guide slot and holes to receive pins or drills for mounting the combination cutting and spacer guide to the femur. The cutting guide portion also has a cutting guide slot defining the distal femoral resection plane. The guide arm portion has a planar femoral and tibial surfaces and an elongate slot between the surfaces. A shim has a shim arm with contact surfaces for contacting part of the guide arm and part of one of the bones of the knee and a mounting member connected to the shim arm. The shim arm mounting member is receivable in the elongate slot of the guide arm to mount the shim to the guide arm to adjust the level of the femoral resection plane.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Kit, guide and method for locating distal femoral resection plane
A combination cutting and spacer guide has a cutting block portion and a guide arm portion. The cutting block portion has a cutting guide slot and holes to receive pins or drills for mounting the combination cutting and spacer guide to the femur. The cutting guide portion also has a cutting guide slot defining the distal femoral resection plane. The guide arm portion has a planar femoral and tibial surfaces and an elongate slot between the surfaces. A shim has a shim arm with contact surfaces for contacting part of the guide arm and part of one of the bones of the knee and a mounting member connected to the shim arm. The shim arm mounting member is receivable in the elongate slot of the guide arm to mount the shim to the guide arm to adjust the level of the femoral resection plane.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Knee joint with a ramp
InactiveUS8292965B2Minimize wear and deformationIncrease the areaJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaTibial surface
An artificial knee joint is described that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the required motion and stability characteristics. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, by an amount similar to that in the anatomic knee. The opposite motion, roll forward of the femur from a fully flexed to a more extended position, is accomplished by varying the outward radii of the lateral and medial femoral bearing surfaces, together with a ramp on the postero-lateral and postero-medial regions of the tibial surfaces.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Surface guided knee replacement
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the motion and stability characteristics of the anatomic knee. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, more so on the lateral side than on the medial side. This is accomplished by the interaction of a projecting tibial post inside a cupola in the center of the femoral component, and by the saggital radius on the medial side being smaller than that on the lateral side. The prevention of anterior sliding of the femur on the tibia in early flexion is accomplished by the interaction between a distal-anterior recess on the medial side of the femur and an apposing raised pad on the tibial surface. Rotational laxity at all angles is allowed by the presence of only one recess pad and by non-conforming femoral-tibial surfaces on the lateral side.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
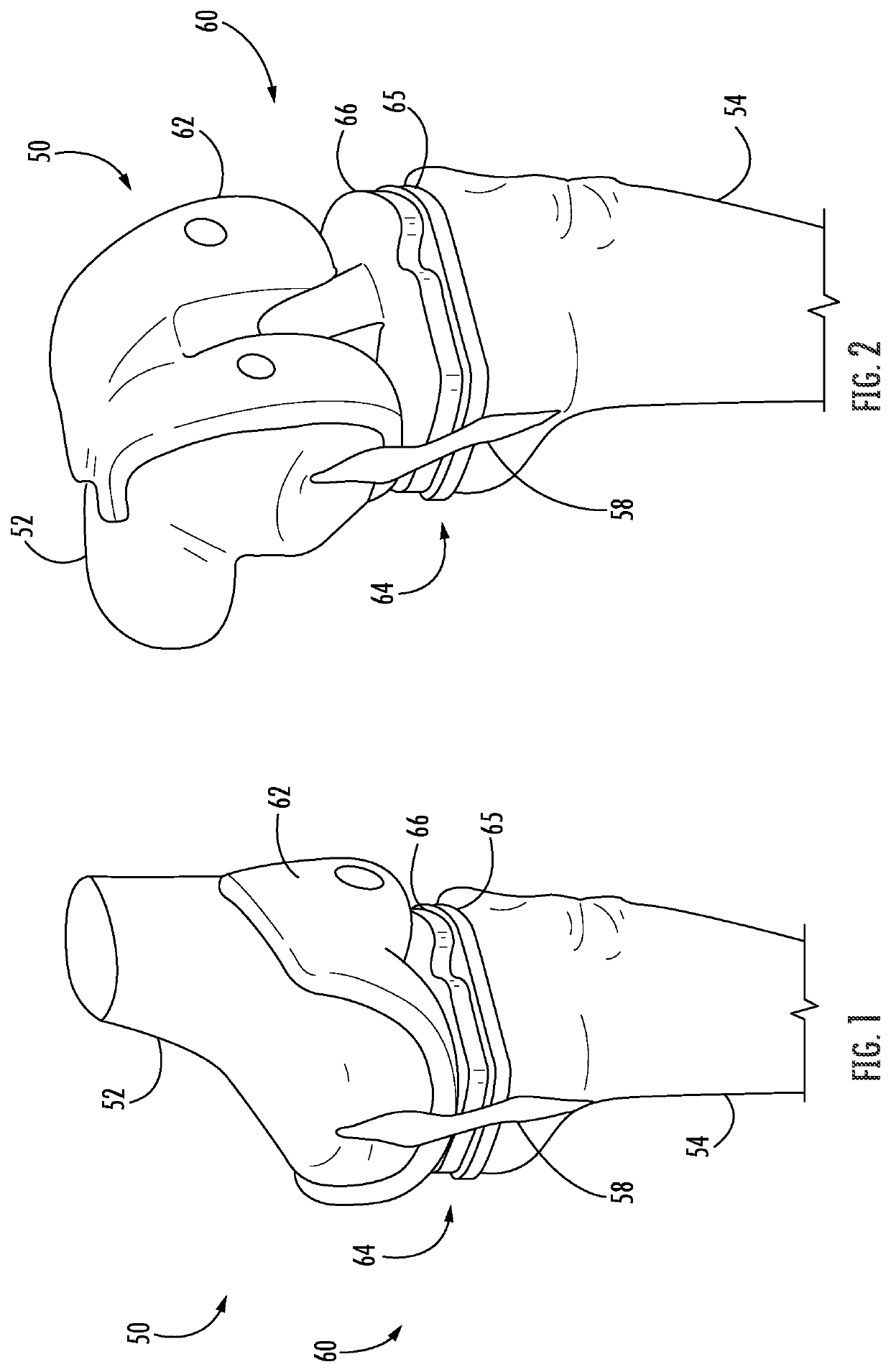
Total Knee Replacement Implant Based on Normal Anatomy and Kinematics
A total knee replacement prosthesis is presented whose bearing surfaces are derived from an anatomically representative femur and a modified baseline tibial surface. The contacting femoral and tibial bearing surfaces comprise the inter-condylar as well as condylar regions.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Interpositional Joint Implant
InactiveUS20170367828A1Improve functionalityPromote resultsJoint implantsDiagnostic recording/measuringTibial surfaceThree dimensional shape
A method of preparing an interpositional implant suitable for a knee. The method includes determining a three-dimensional shape of a tibial surface of the knee. An implant is produced having a superior surface and an inferior surface, with the superior surface adapted to be positioned against a femoral condyle of the knee, and the inferior surface adapted to be positioned upon the tibial surface of the knee. The inferior surface conforms to the three-dimensional shape of the tibial surface. The implant may be inserted into the knee without making surgical cuts on the tibial surface. The tibial surface may include cartilage, or cartilage and bone.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Instruments and method for arthroscopic arthroplasty of the knee
InactiveUS20080132895A1Small sizeReduce the amount requiredInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTibiaTibial surface
Instruments and method for the arthroscopy arthroplasty of a knee joint, including instruments and method for the use of the instruments in the resection of tibial and femoral surfaces and the implantation of tibial and femoral components. In resecting the femur, a femoral cutting mill is attached to the tibial surface with the knee in a flexed position. With the cutting mill activated, the knee is extended causing the cutting surface of the femoral cutting mill to engage the femoral surface and form a trough in the femoral surface for receipt of the femoral component. A network of channels formed within the prosthetic components is used for the delivery of bone cement to the component bone interface.
Owner:CLARK RON
Device for high tibial osteotomy
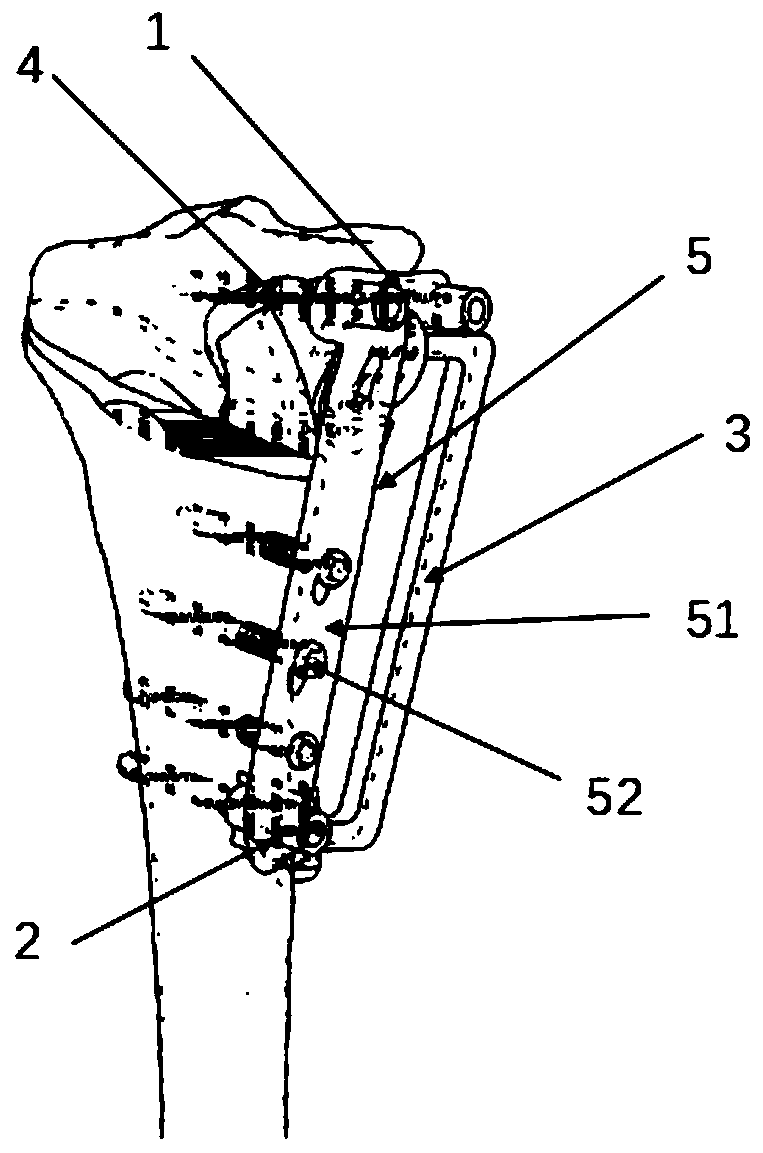
PendingCN111329583AProtect surrounding tissueInstallation does not hinderComputer-aided planning/modellingBone drill guidesArthritisProximal tibia
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments, in particular to a device for high tibial osteotomy. The device comprises a near-end component, a far-end component, a connecting bridge component, Kirschner wires, a fixing component and a calibration force line component, wherein the near-end component and the far-end component are located at the two ends of the connecting bridge component respectively and fixed to a tibia through Kirschner wires; the calibration force line component is connected with the near-end component through a bolt; and the fixing component is attached to thesurface of the tibia having undergone force line correction and connected with the near end and the far end of the tibia through Kirschner wire hole sites. According to the invention, the design of bony wainscots for the near end and the far end of the tibia is adopted, so the area of a tibia incision near an osteotomy line can be reduced, an operative wound is narrowed, and tissue around the osteotomy line is better protected; the device integrates three functions of osteotomy, force line correction and temporary immobilization and steel plate installation in a high tibial osteotomy operation; operation steps are simplified, operation time is shortened, operation risks are reduced, and the effect of treating knee osteoarthritis through the high tibial osteotomy operation can be better promoted.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Lateral and medial pivoting knee prosthesis
PendingUS20200085583A1Improve efficiencyEasy to moveJoint implantsKnee jointsArthritisKnee joint movement
The present invention comprises an implantable knee prosthesis for the arthritic, aging, ligament-deficient knee having a femoral component, a tibial component and patella component forming three interactive knee compartments mainly the lateral, medial, and femoral patellar compartments articulating together with a variable axial pivot type of knee motion. This novel design accomplishes this motion pattern with four femoral component radii coacting with four reciprocal proximal tibial surface recesses. This occurs in a laterally congruent axial pivot fashion during the first half of knee flexion creating efficient external femoral rotation to align the femoral-patellar groove with the patella / quadriceps muscle complex.
Owner:HODGE WILLIAM ANDREW
Tibia bone fracture plate of medical equipment for orthopedic surgery
InactiveCN104840242AGood biocompatibilityHigh strengthPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatingsSurgical operationMedical equipment
The invention discloses a tibia bone fracture plate of medical equipment for an orthopedic surgery. The tibia bone fracture plate comprises a bone plate body which is in the shape of Y, wherein the bone plate body comprises an attachment surface contacting with the surface of the tibia bone, and a bone plate body installation surface opposite to the attachment surface; installing through holes are formed in the bone fracture plate, the attachment surface is a titanium nitride ceramic material layer, and the installation surface is a titanium oxide ceramic material layer, and the surface treatment process of pickling and passivation is performed on the titanium alloy of the ingredient, and thus dark spots on any surface are avoided from occurrence and the prepared surface is clean and tidy; chemical agents composed of a specific pickling solution and a passivation solution are used, so that the period of surface treatment can be greatly saved and the surface treatment effect is very good.
Owner:刘乐
Total ankle replacement with anatomically fitted talar component
An anatomically fitted talar component for use in an ankle replacement system having a body including a talar surface having a portion contoured to approximately or exactly fit with a surface portion of a three dimensional rendering of bone of a talar dome; and a tibial surface configured for forming a joint with a second component of the ankle replacement system. A method of forming the talar component by: (i) obtaining image data of the talar dome, (ii) using the data to create a three-dimensional model of the talar dome, and (iii) forming a body having a talar surface that approximately or exactly fits with a portion of the surface of the three-dimensional model.
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
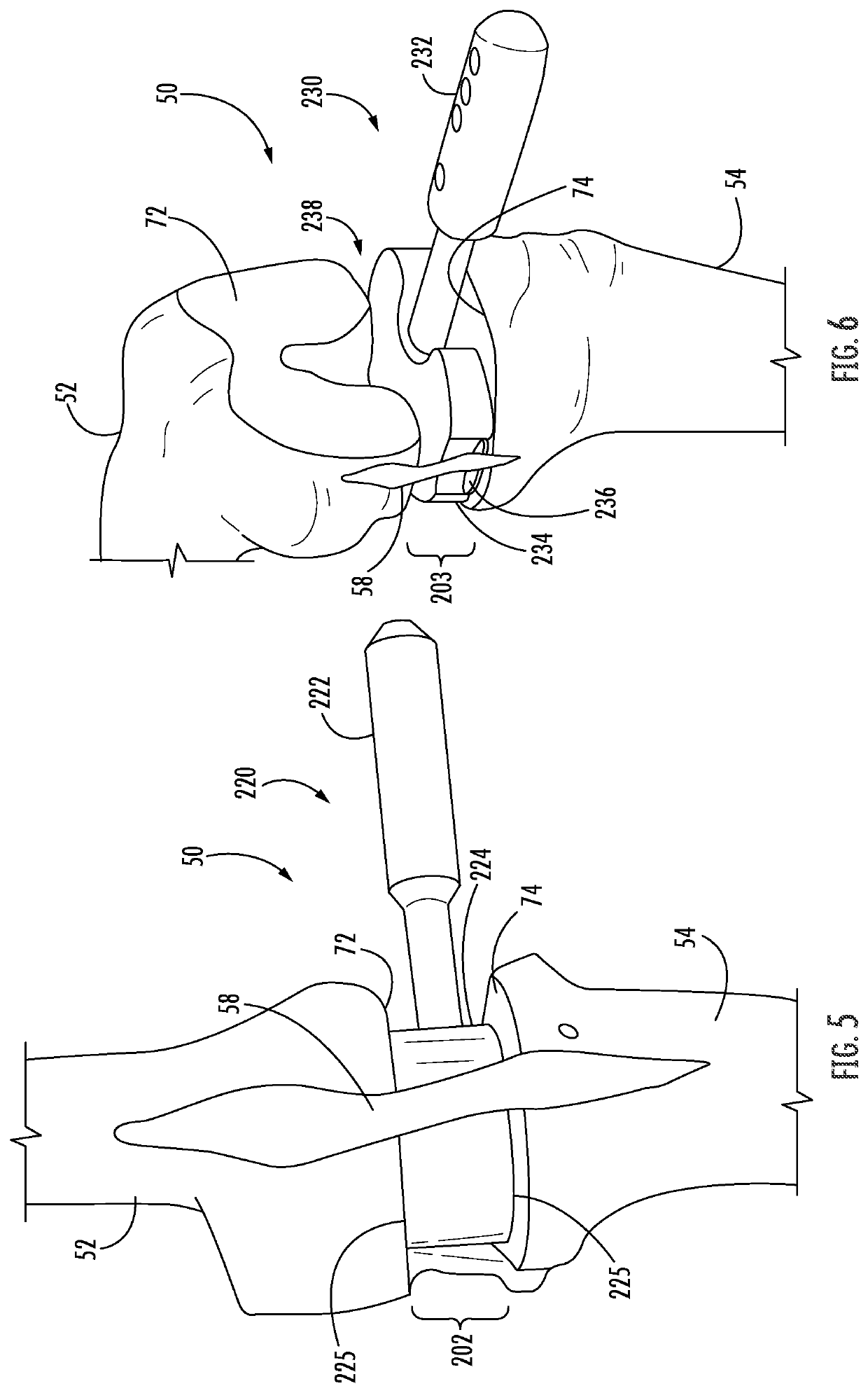
Methods and instrumentation for balancing of ligaments in flexion
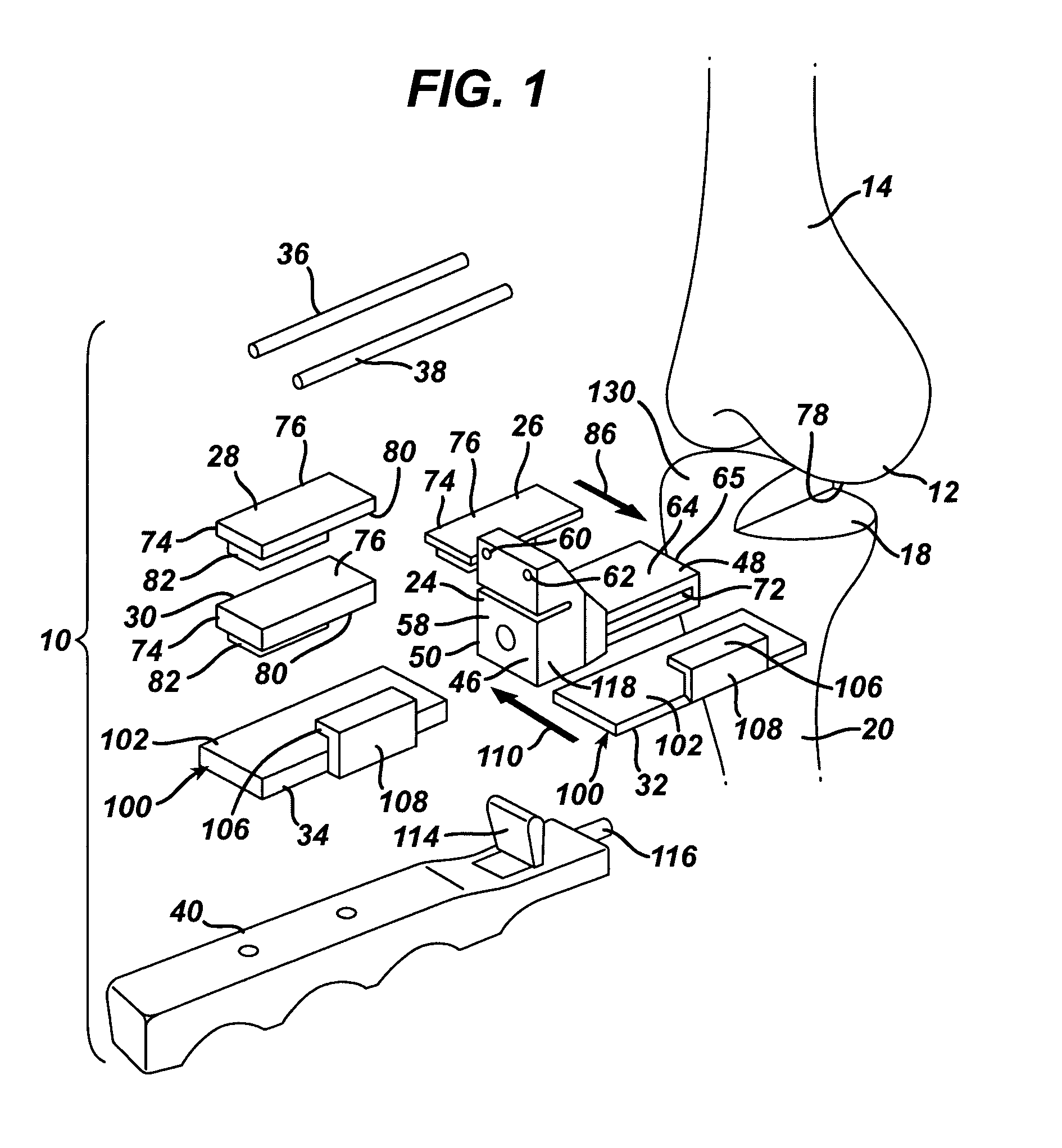
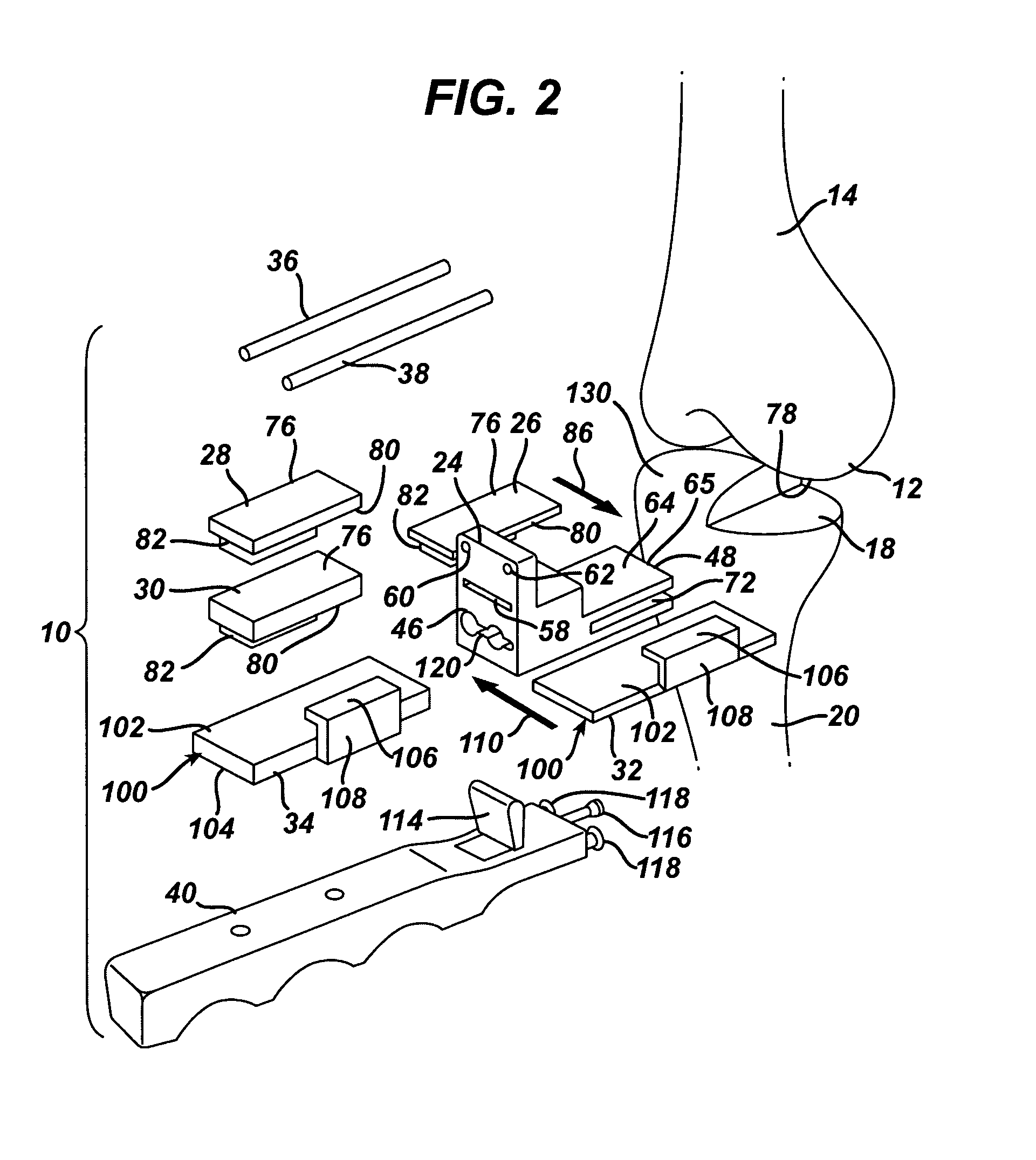
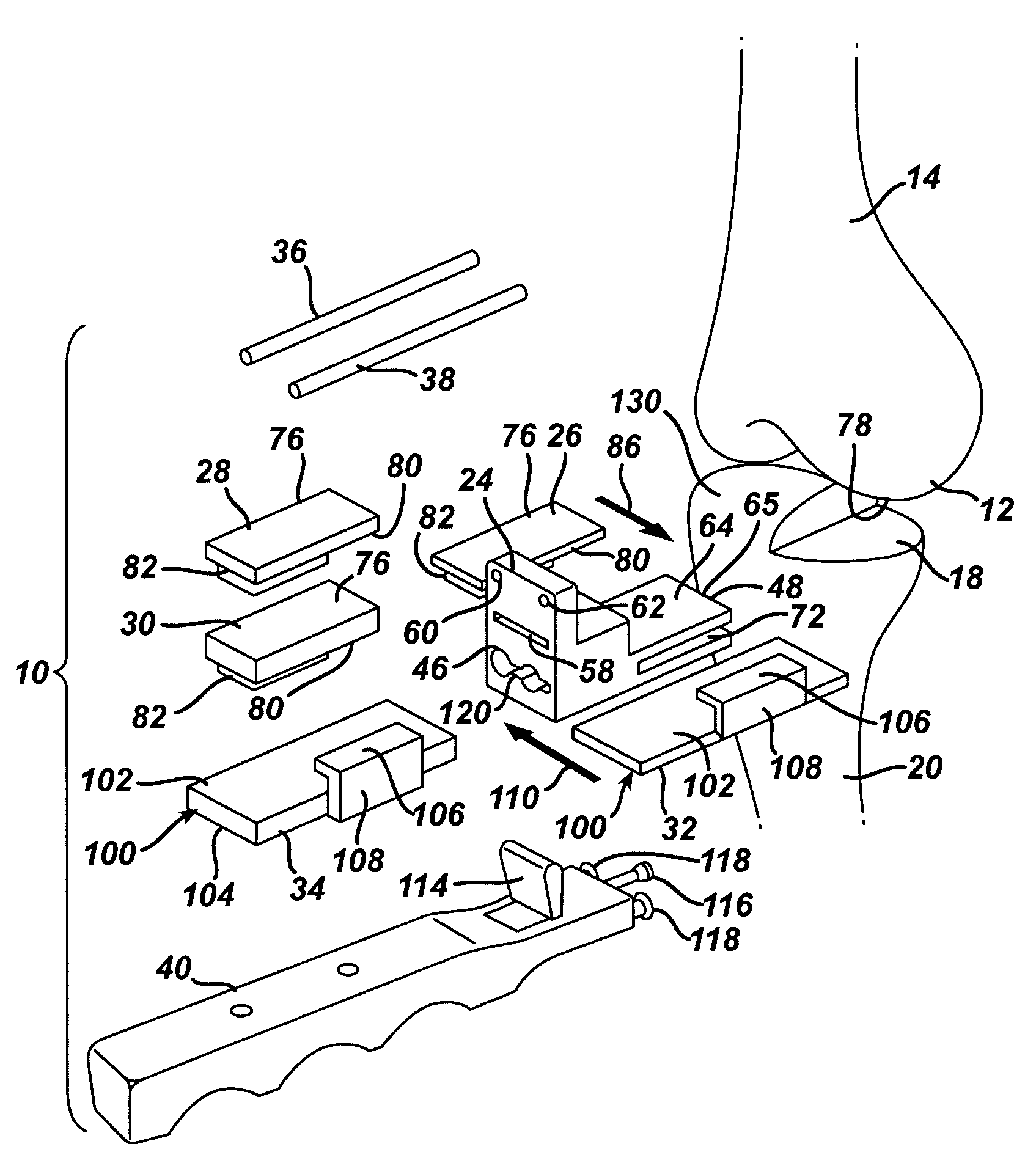
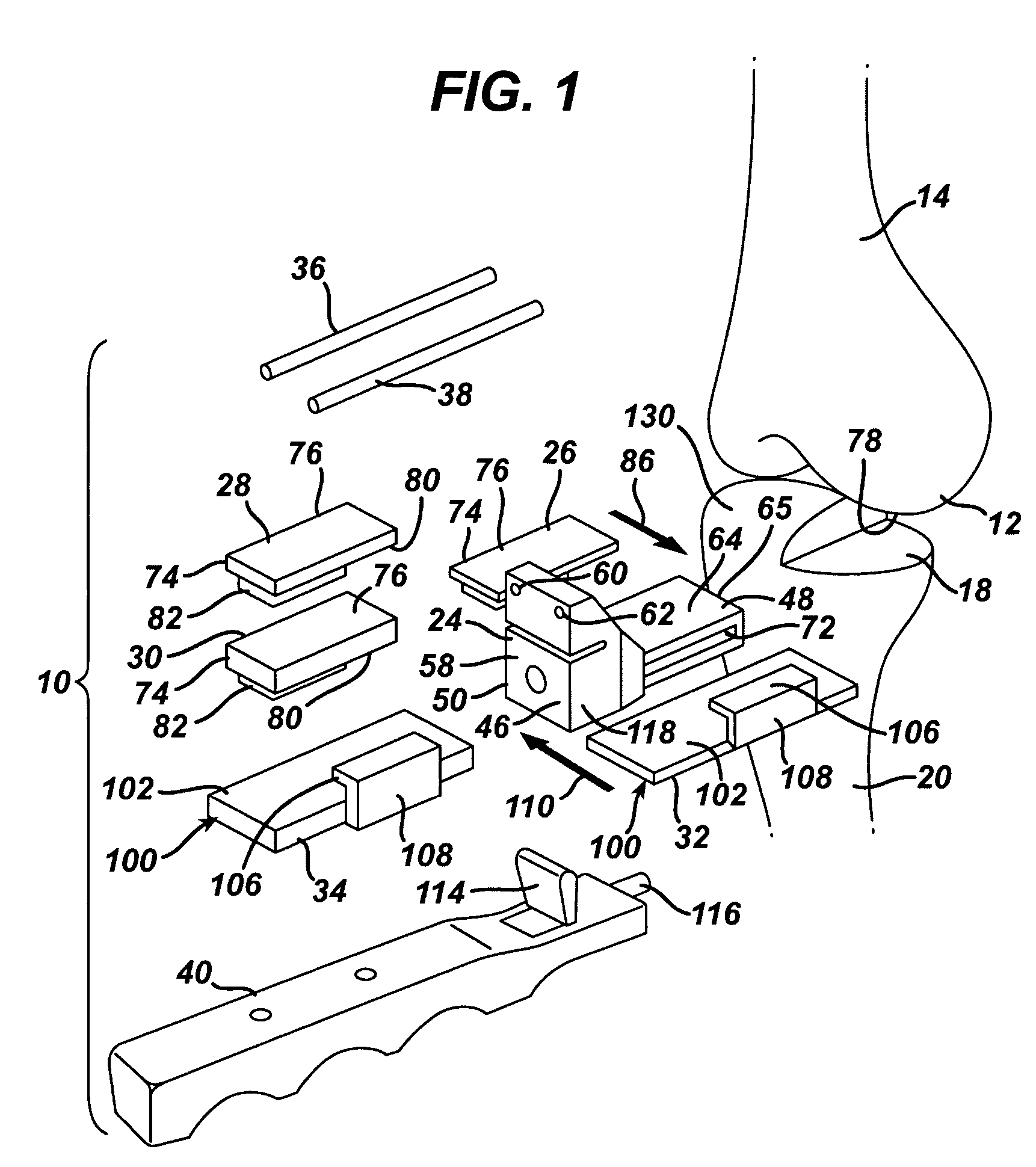
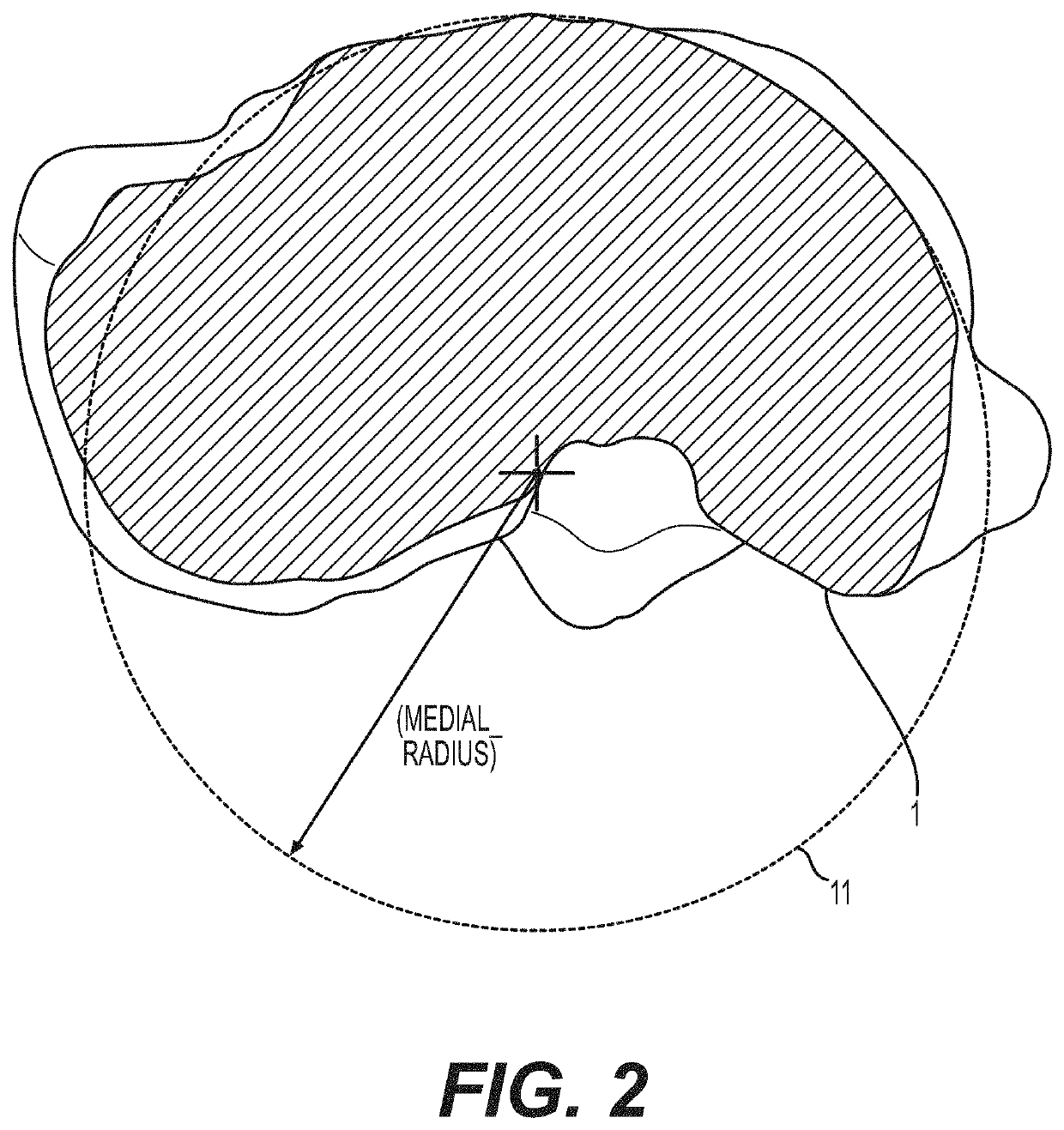
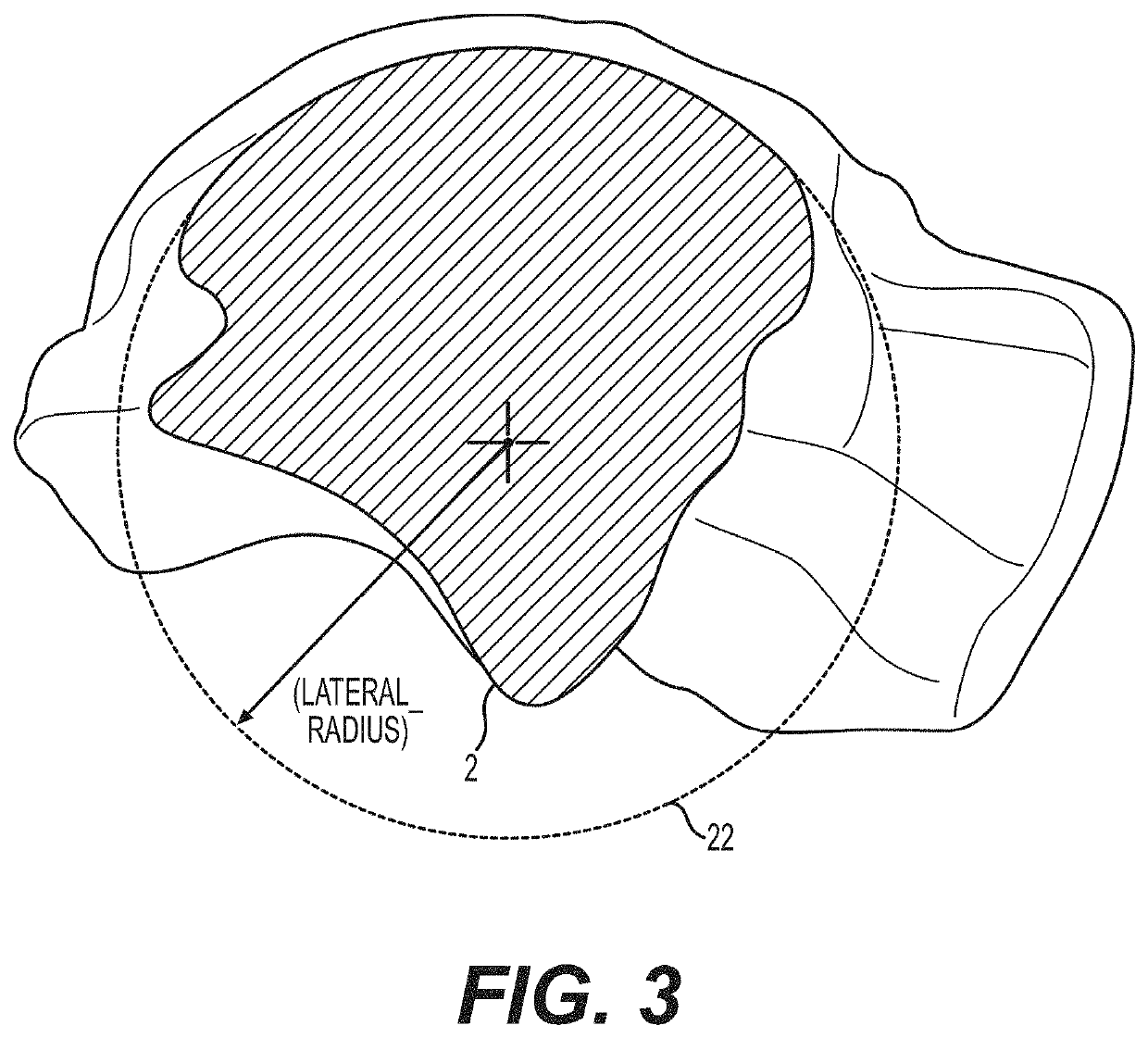
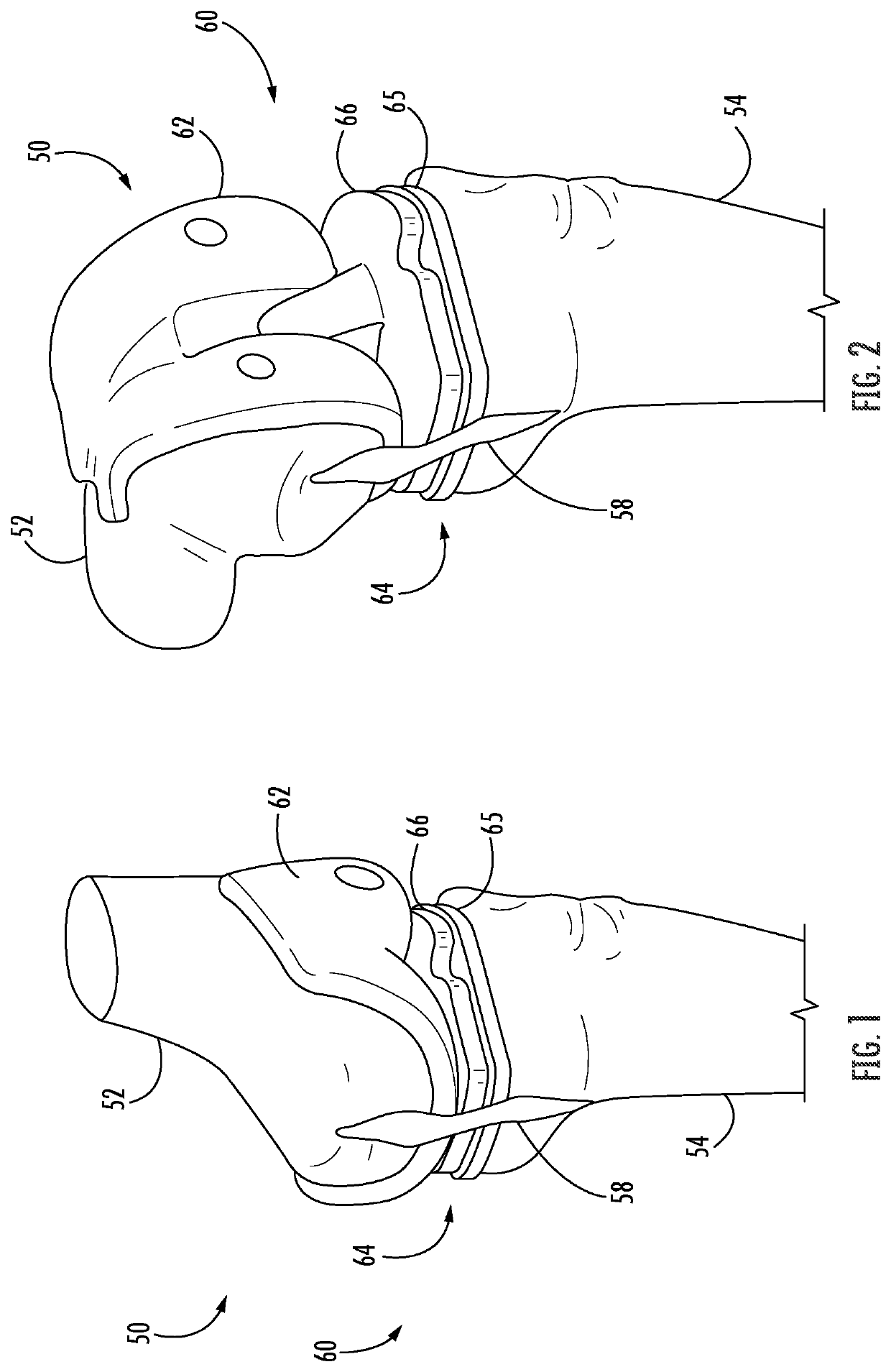
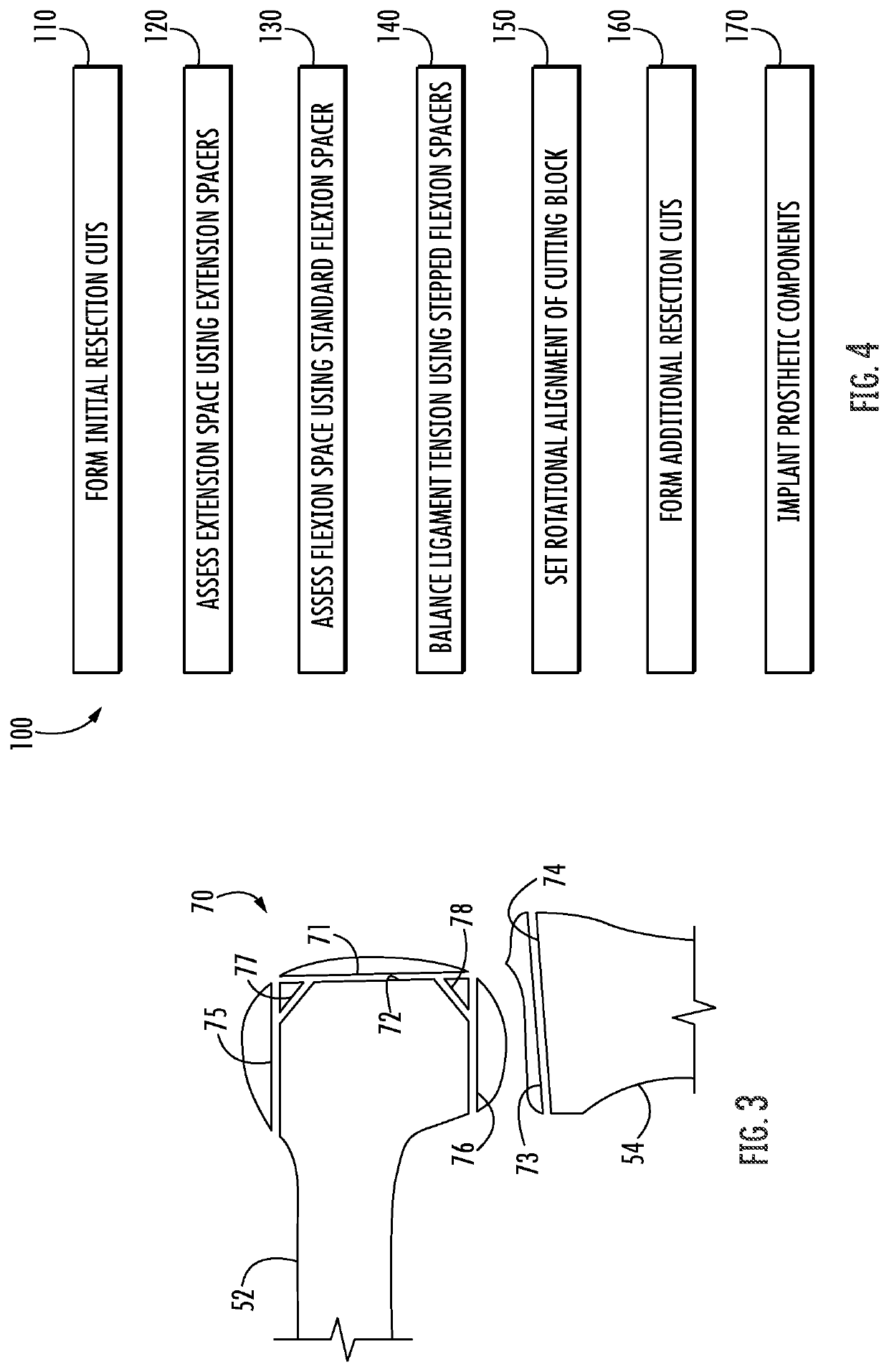
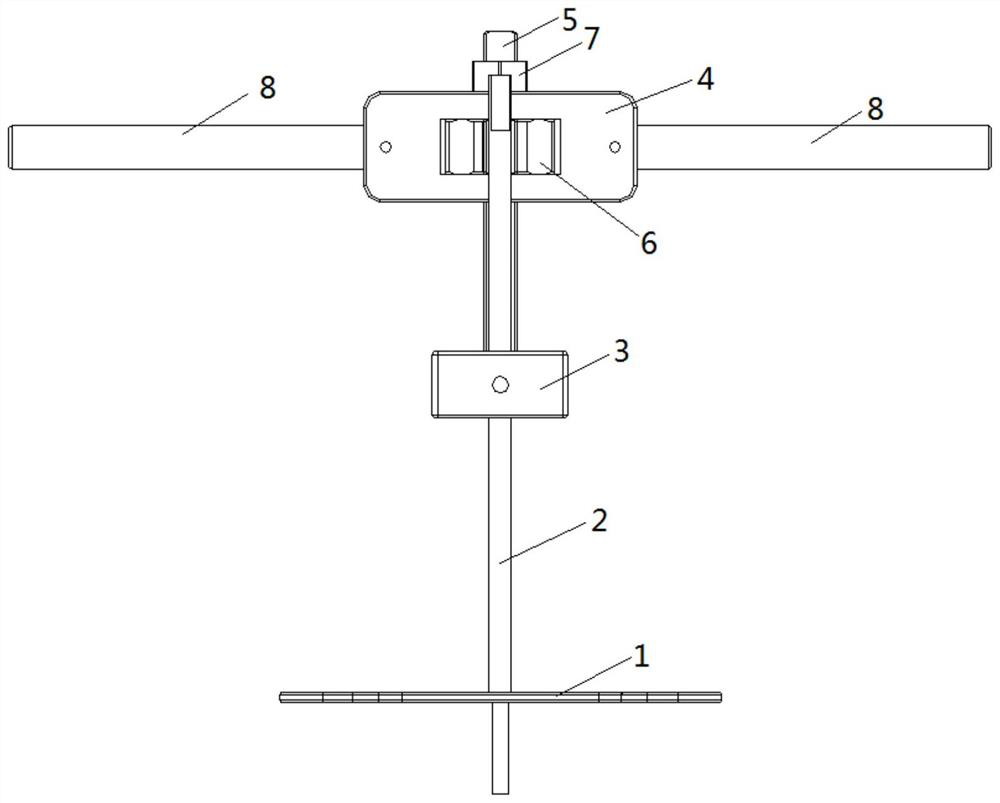
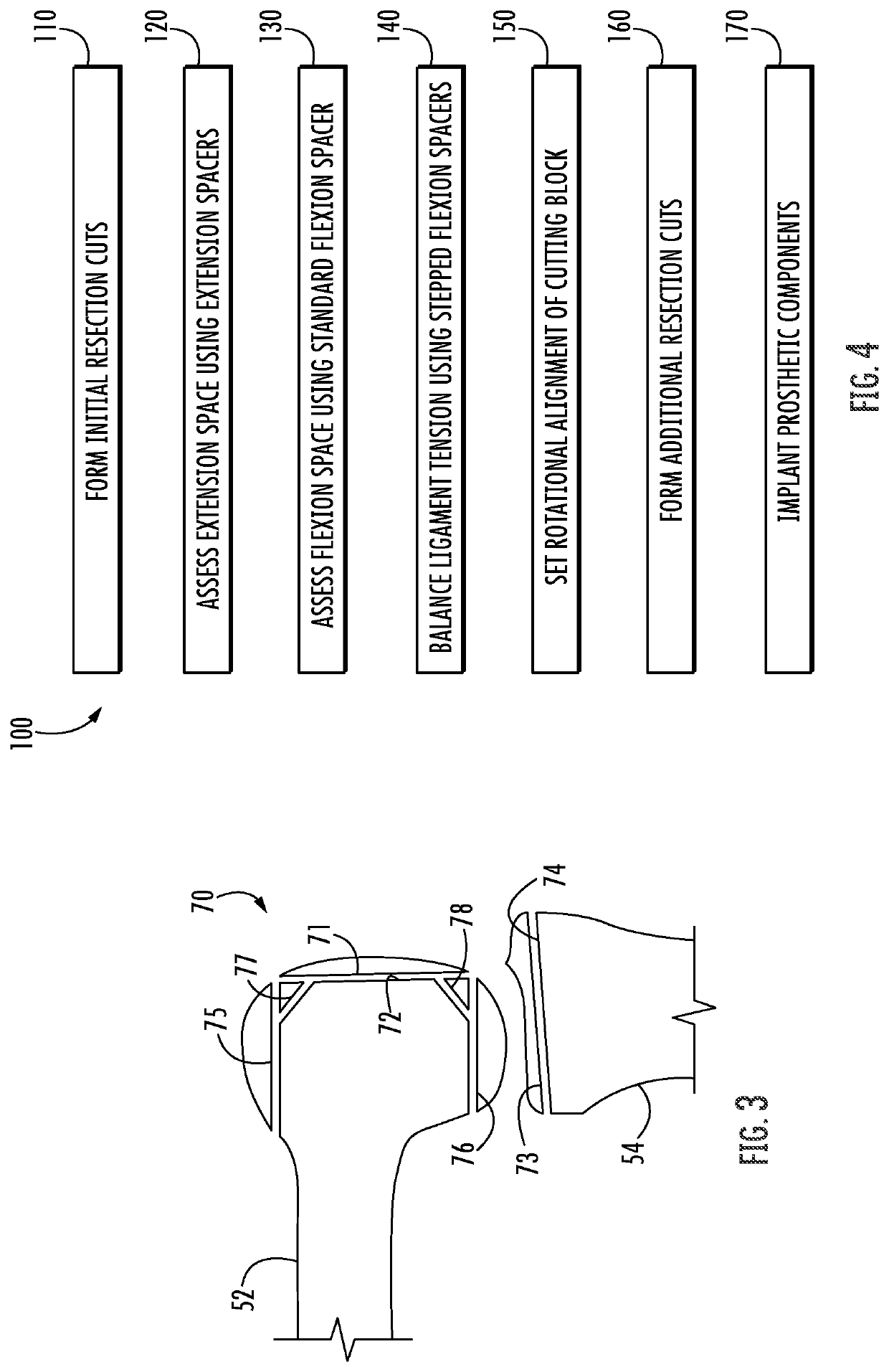
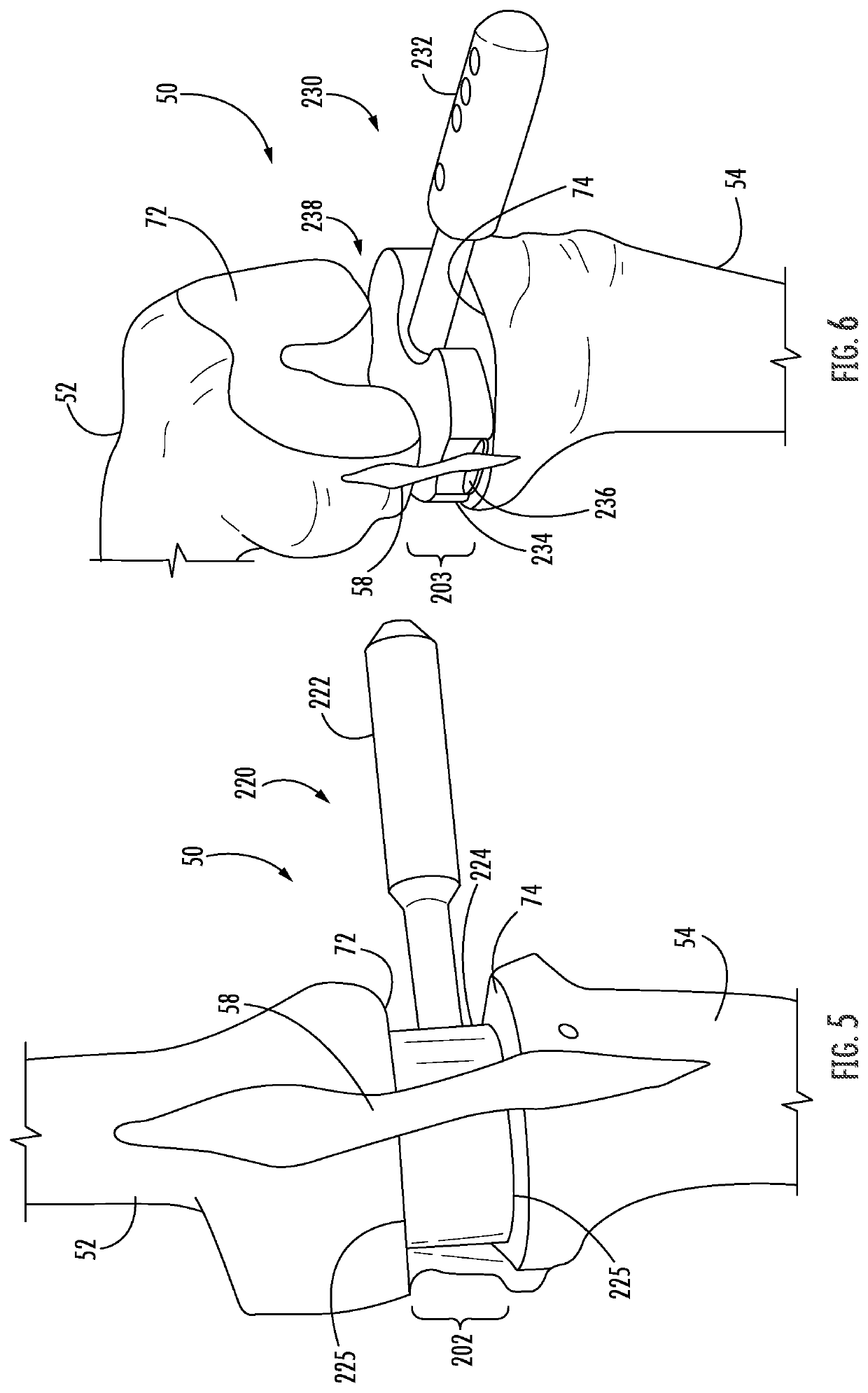
ActiveUS11344421B2Reduce tensionSmooth rotationDiagnosticsJoint implantsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFemoral condyles
An exemplary method, and corresponding instrumentation, of balancing the ligaments of a knee during flexion is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes forming initial resection cuts in a patient' femur and tibia, and subsequently placing the knee in flexion to form a flexion space between the posterior femoral condyles and the resected tibial surface. The method may further include sequentially inserting one or more flexion spacers into the flexion space, and selecting the flexion spacer that provides the ligaments with equal tension. The flexion spacers may include a medial platform and a lateral platform wherein, for at least one of the flexion spacers, the lateral platform has a greater thickness than the medial platform. The method may further include engaging an alignment sizing tool with the selected flexion spacer, forming a pair of pin holes in the femur, and mounting a cutting block to the femur using the pin holes.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC +2
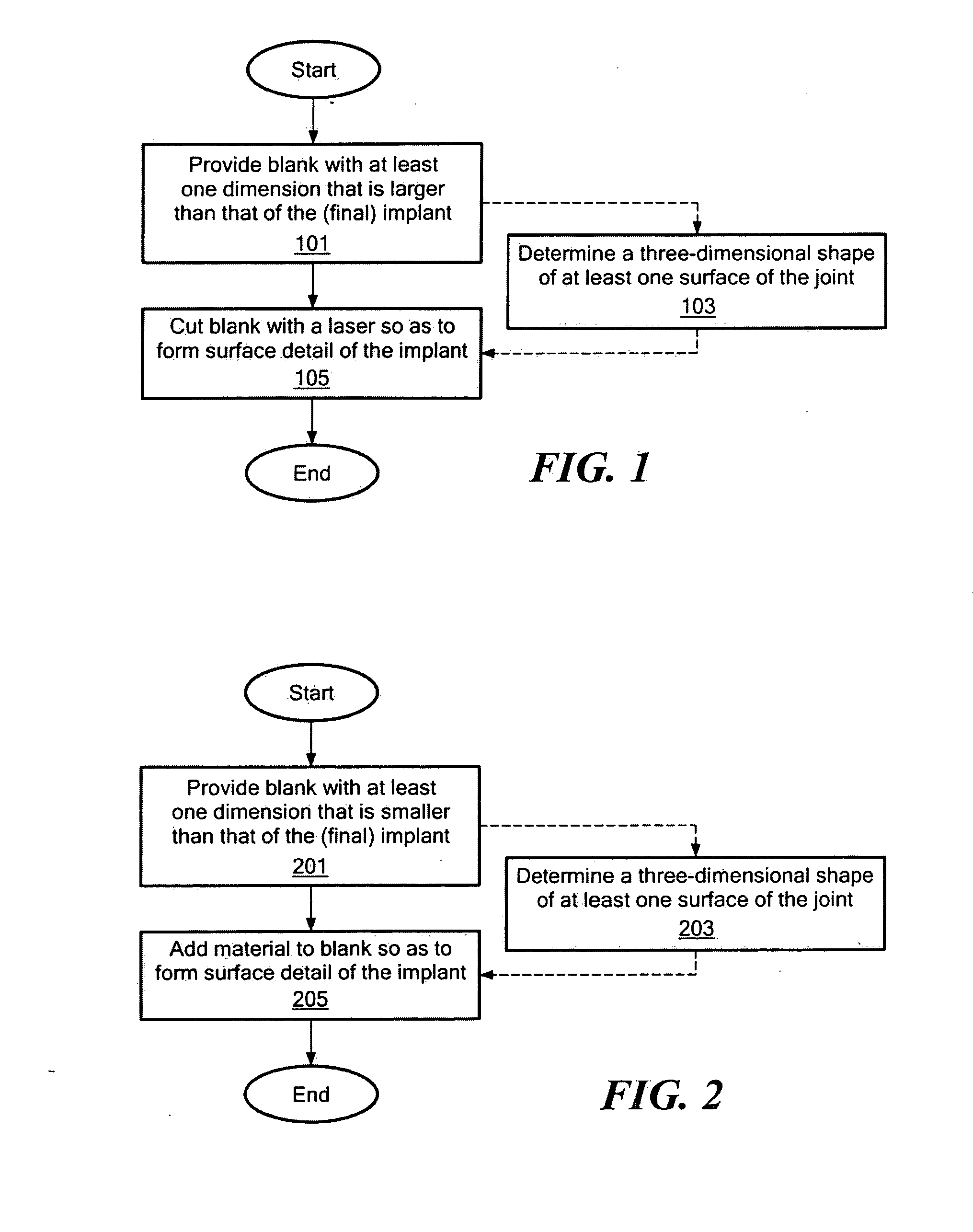
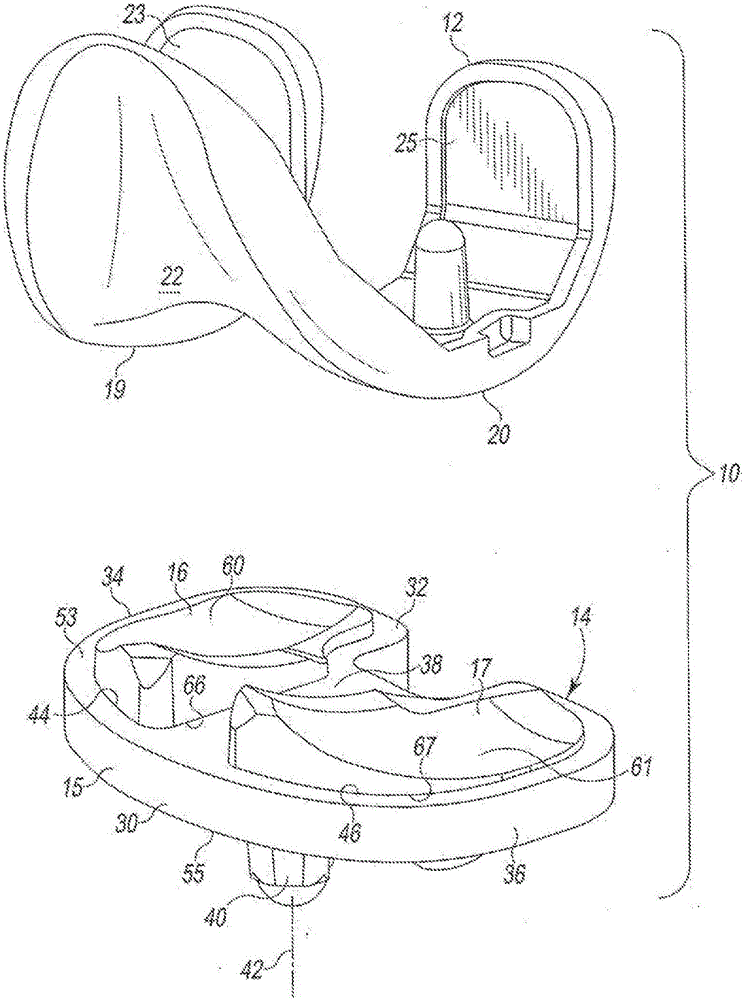
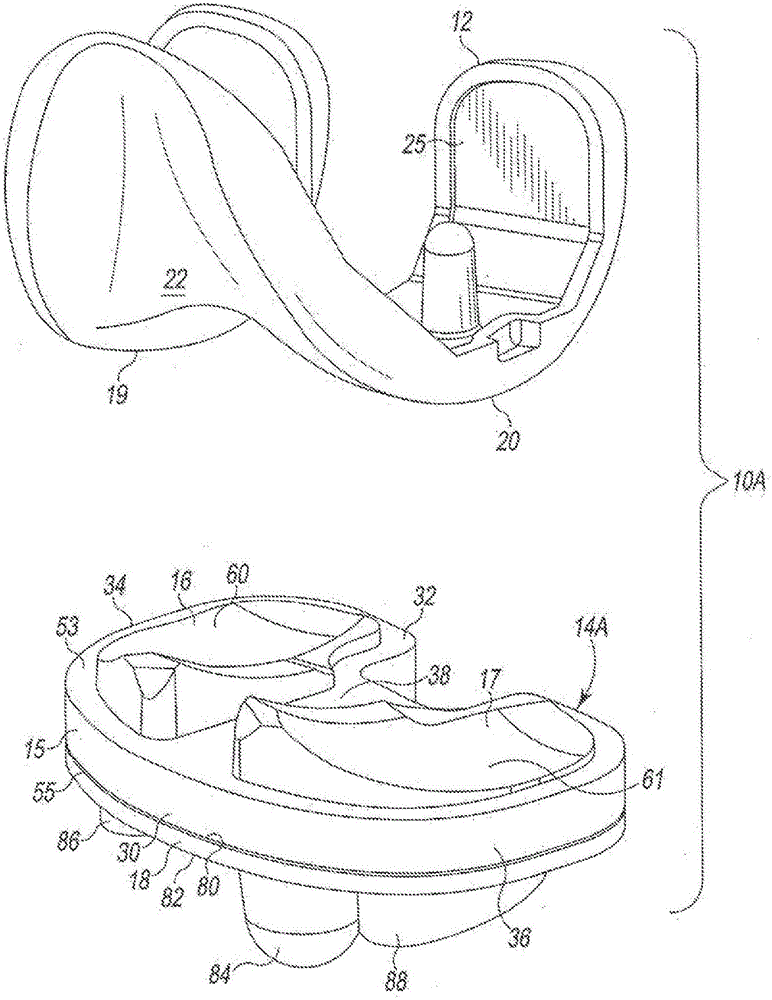
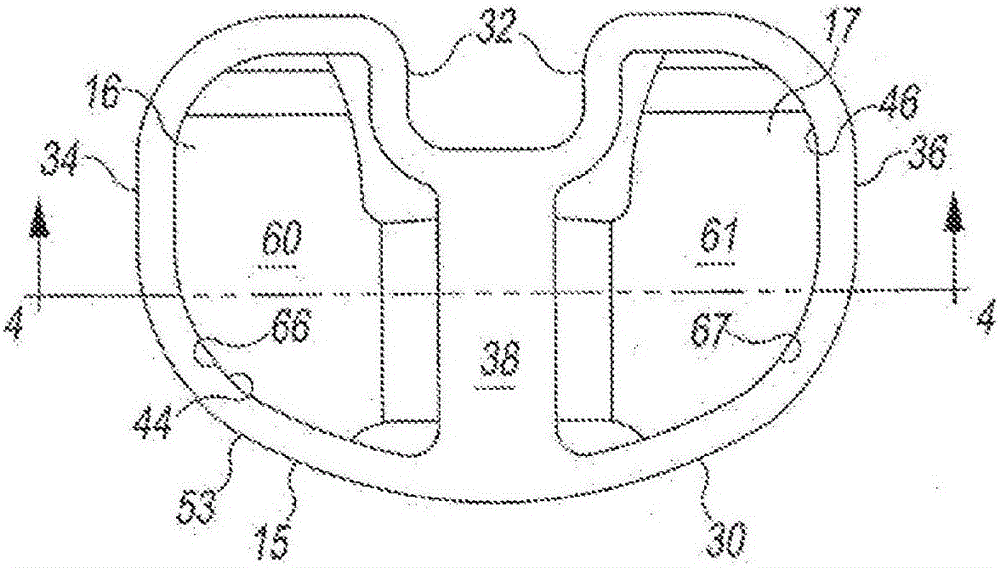
Low profile mobile/fixed prosthetic knee systems
A knee prosthesis system has a tibial component with frame with medial and lateral openings to receive the medial and lateral bearing components. The bearing components have distal surfaces that are exposed when assembled with the frame and pegs extending distally from the distal surfaces. The system optionally includes a tibial base plate with elongated curved receptacles to receive the pegs and allow the frame and bearing component assembly to rotate when mounted on the base plate. Different thicknesses of bearing components can be selectively locked onto the frame. Different sizes of tibial components have commonly sized, shaped and positioned elements so that multiple sizes of tibial components can be mounted on the same prepared tibial surface.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
Total knee replacement implant based on normal anatomy and kinematics
A total knee replacement whose bearing surfaces are derived from an anatomically representative femur and a modified baseline tibial surface. The contacting femoral and tibial bearing surfaces comprise the inter-codylar as well as condylar regions.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Thin Active/Fixed Prosthetic Knee System
InactiveCN106163454BSimple designJoint implantsKnee jointsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTibial surface
The present invention provides a knee prosthesis system having a tibial component with a frame having a medial opening and a lateral opening to receive a medial bearing member and a lateral bearing member. The support member has a distal surface that is exposed when assembled with the frame and a peg extending distally from the distal surface. The system optionally includes a tibial base plate having an elongated curved receptacle to receive the pegs and allow the frame and bearing assembly to rotate when mounted to the base plate. Support members of different thicknesses can be selectively locked to the frame. The different sized tibial components have elements of common size, shape, and positioning, enabling multiple sized tibial components to fit on the same prepared tibial surface.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
External fixing frame
The invention discloses an external fixing frame. The external fixing frame comprises a traction plate and a traction needle fixedly connected with the traction plate, and further comprises a thread transmission mechanism which is fixedly connected with the traction needle and drives the traction needle to move in the axial direction. When the external fixing frame is used, a periosteum is stripped under a tibia tuberosity of a patient, a small bone block is cut out, the periosteum on the surface of a tibia is protected, firstly, the traction plate is arranged between the cut tibia bone block and the periosteum on the surface of the tibia, then, the traction needle is connected with the traction plate and the bone block, finally, the thread transmission mechanism drives the traction needle to move in the axial direction of the traction needle. Therefore, by driving the traction needle and the traction plate to move, the periosteum is pulled while the bone block is pulled, so that vasculature neogenesis at a shank part can be promoted, neovasculature can be established, nutrient blood at the shank part can be increased, and then natural healing of a diabetic foot wound surface is promoted.
Owner:THE FIRST HOSPITAL OF HUNAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE (CLINICAL RES INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE)
Methods and instrumentation for balancing of ligaments in flexion
ActiveUS20200046509A1Reduce and eliminate needReduce tensionDiagnosticsJoint implantsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFemoral condyles
An exemplary method, and corresponding instrumentation, of balancing the ligaments of a knee during flexion is disclosed. In one embodiment, the method includes forming initial resection cuts in a patient' femur and tibia, and subsequently placing the knee in flexion to form a flexion space between the posterior femoral condyles and the resected tibial surface. The method may further include sequentially inserting one or more flexion spacers into the flexion space, and selecting the flexion spacer that provides the ligaments with equal tension. The flexion spacers may include a medial platform and a lateral platform wherein, for at least one of the flexion spacers, the lateral platform has a greater thickness than the medial platform. The method may further include engaging an alignment sizing tool with the selected flexion spacer, forming a pair of pin holes in the femur, and mounting a cutting block to the femur using the pin holes.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com