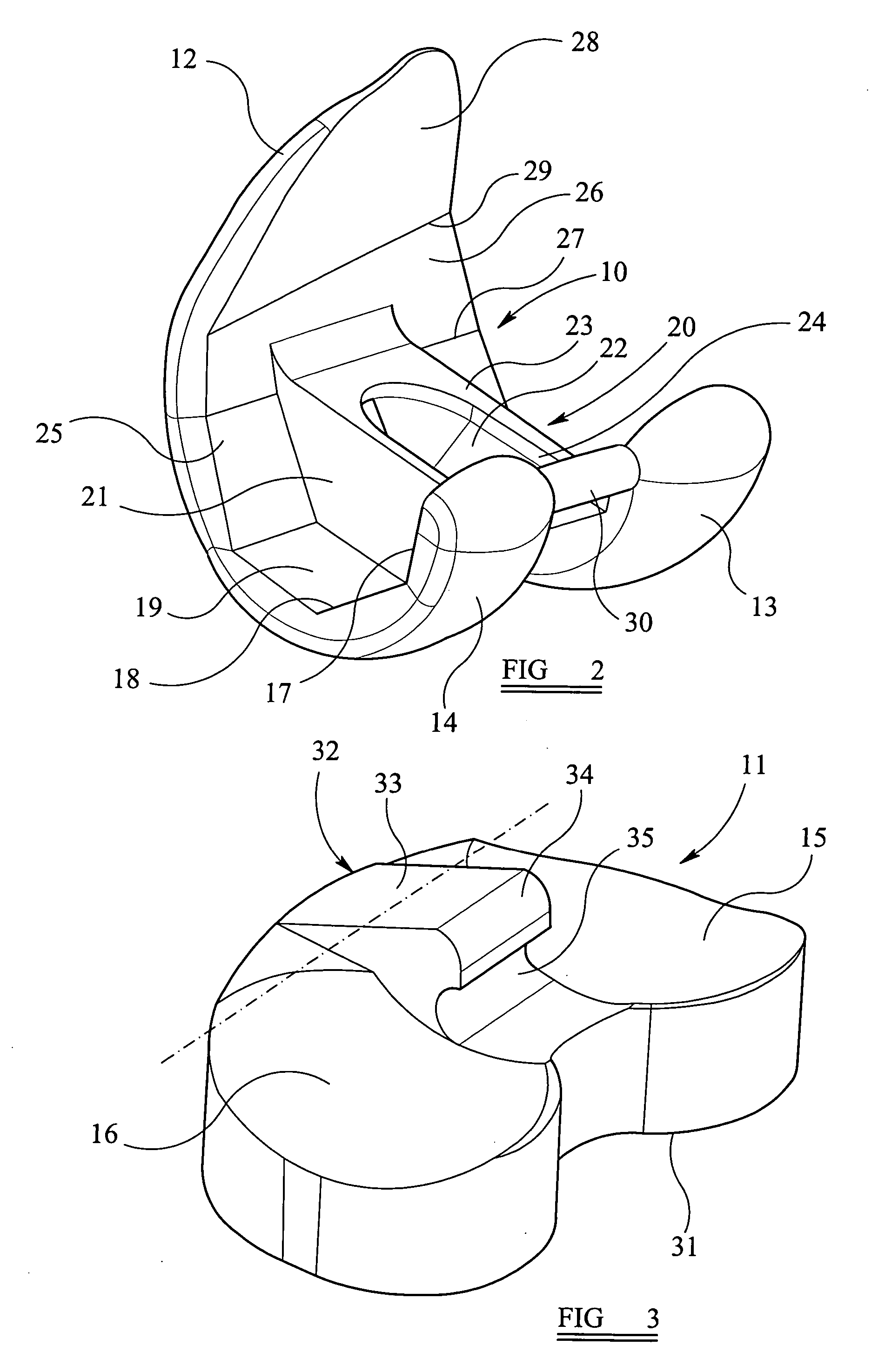
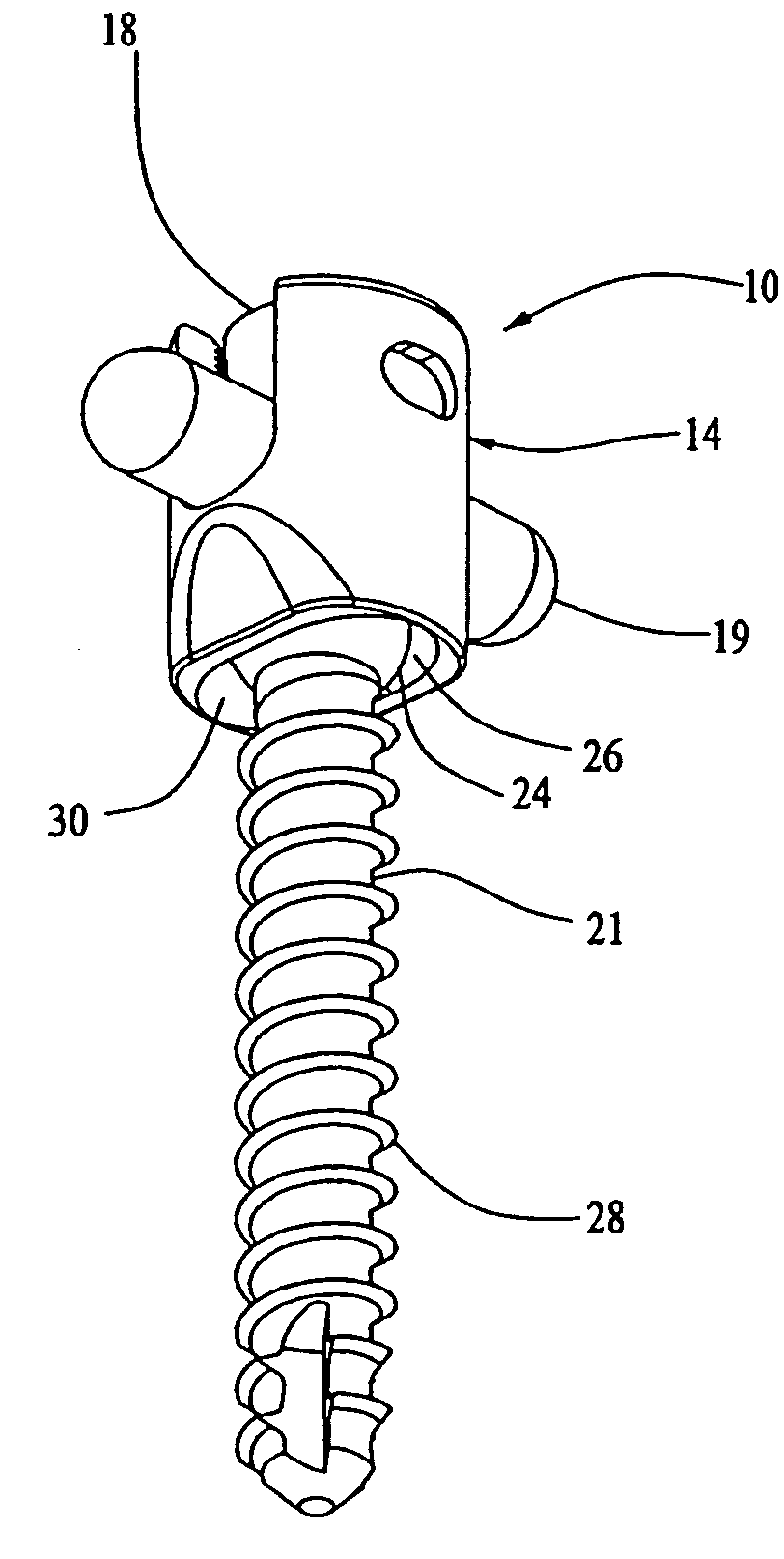
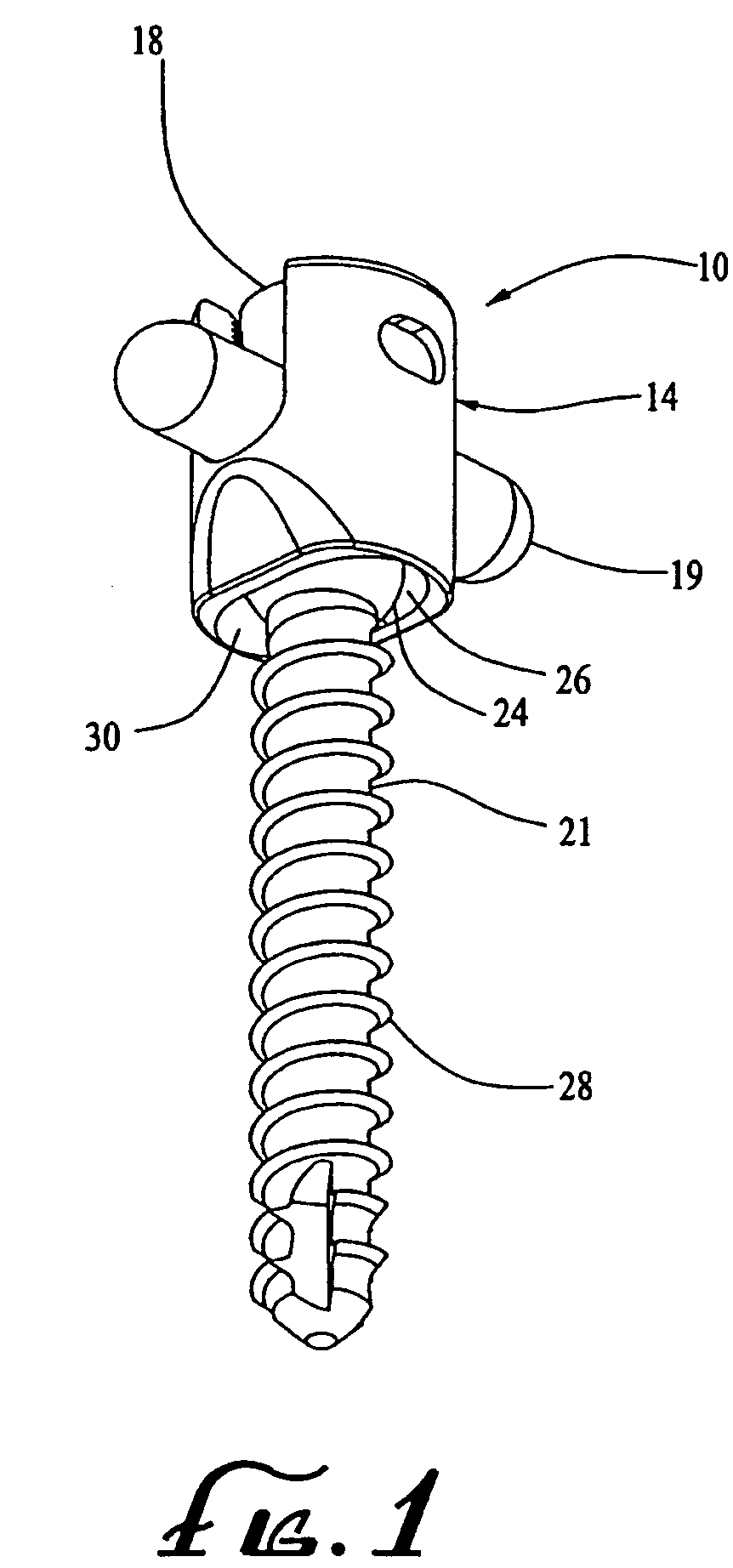
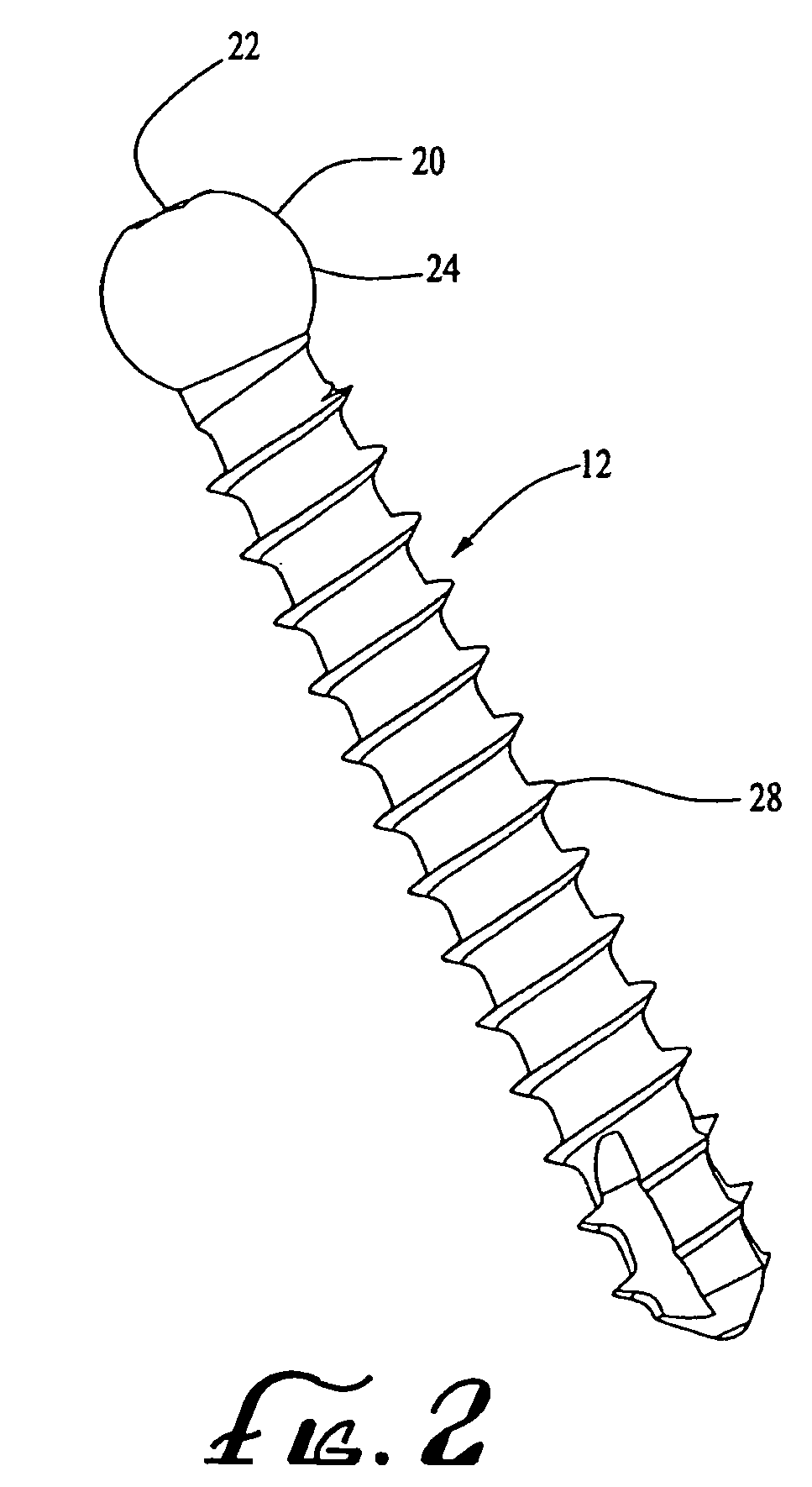
Patents
Literature
1343 results about "Gonial angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
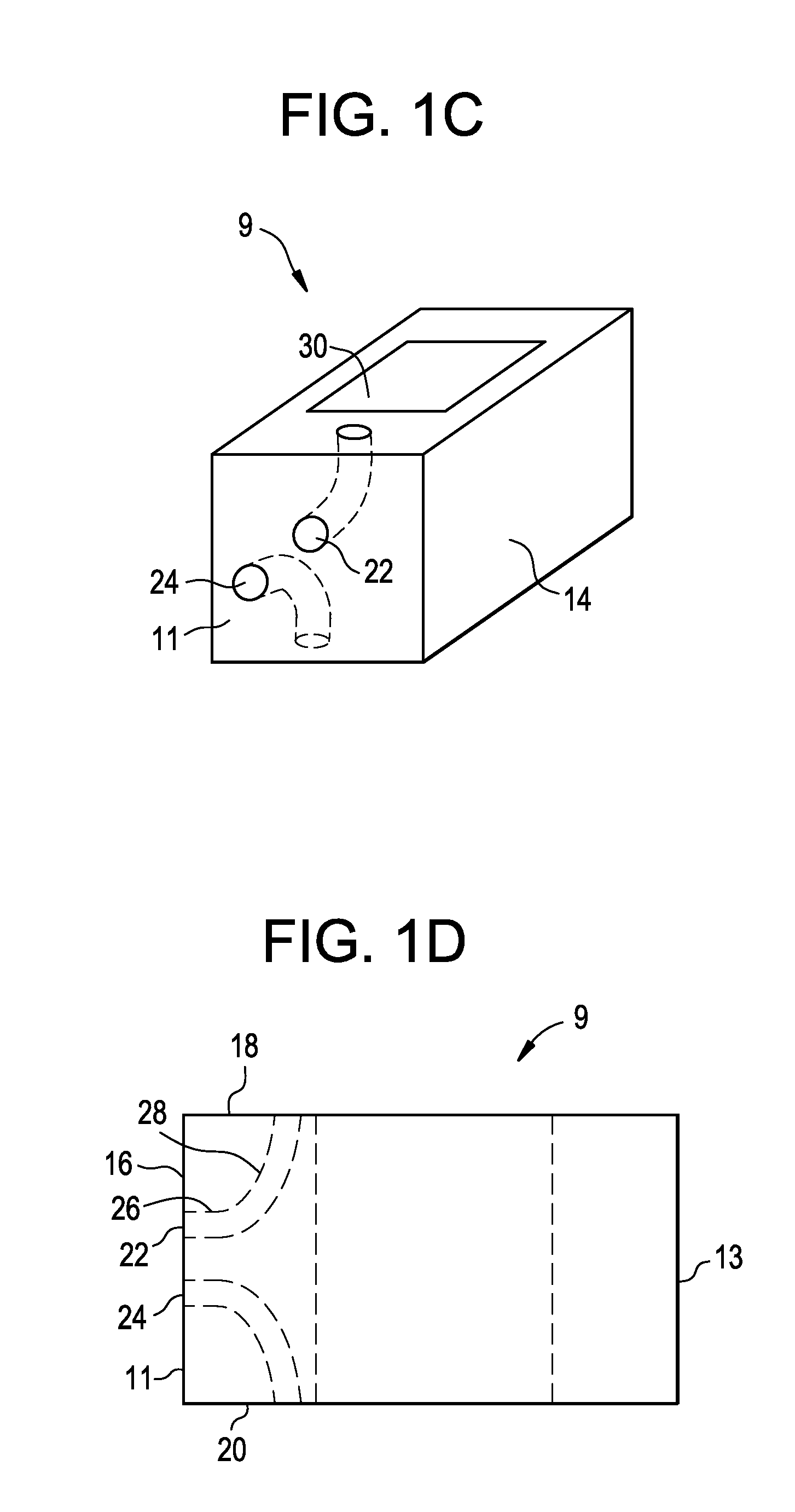
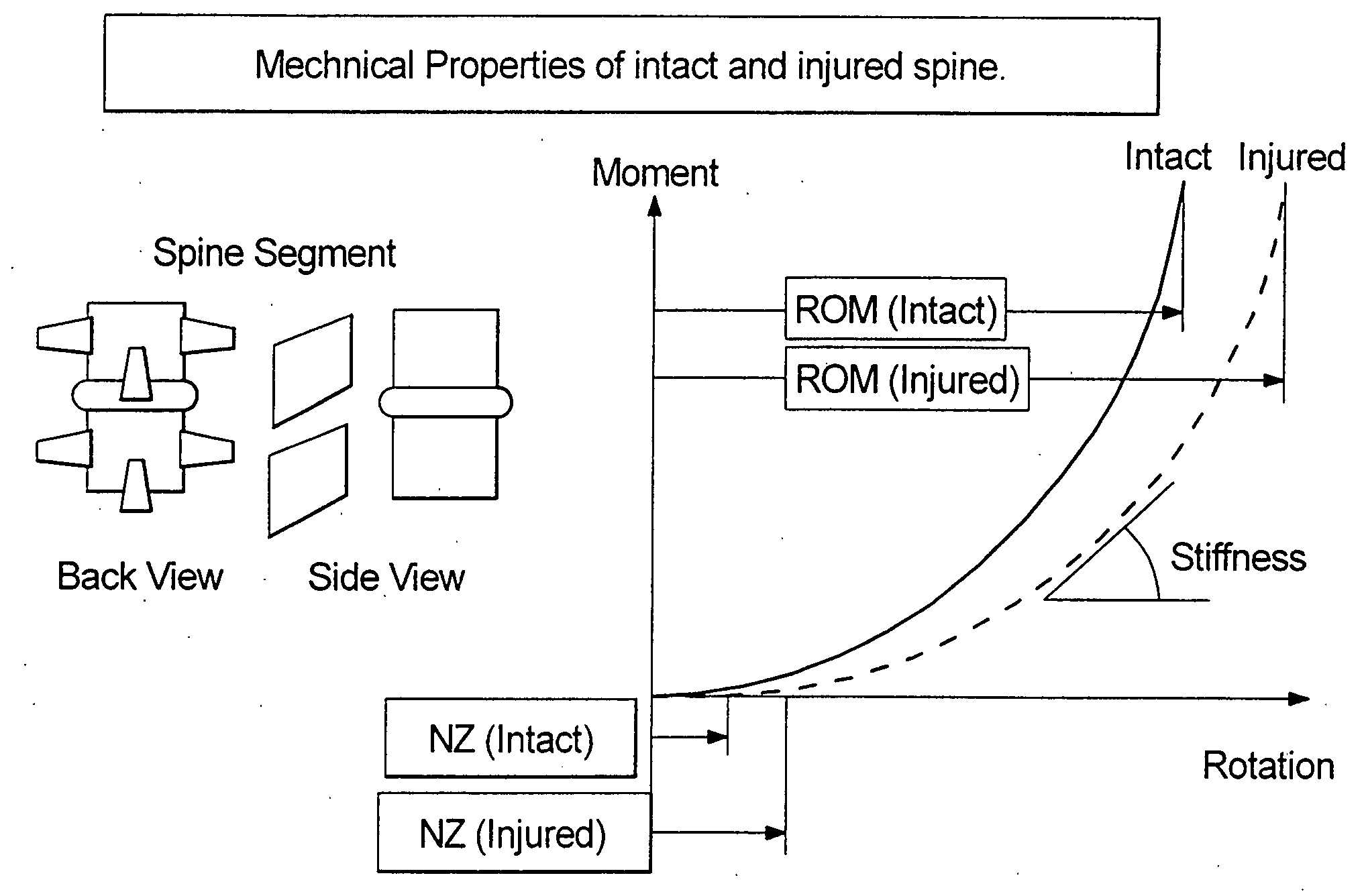
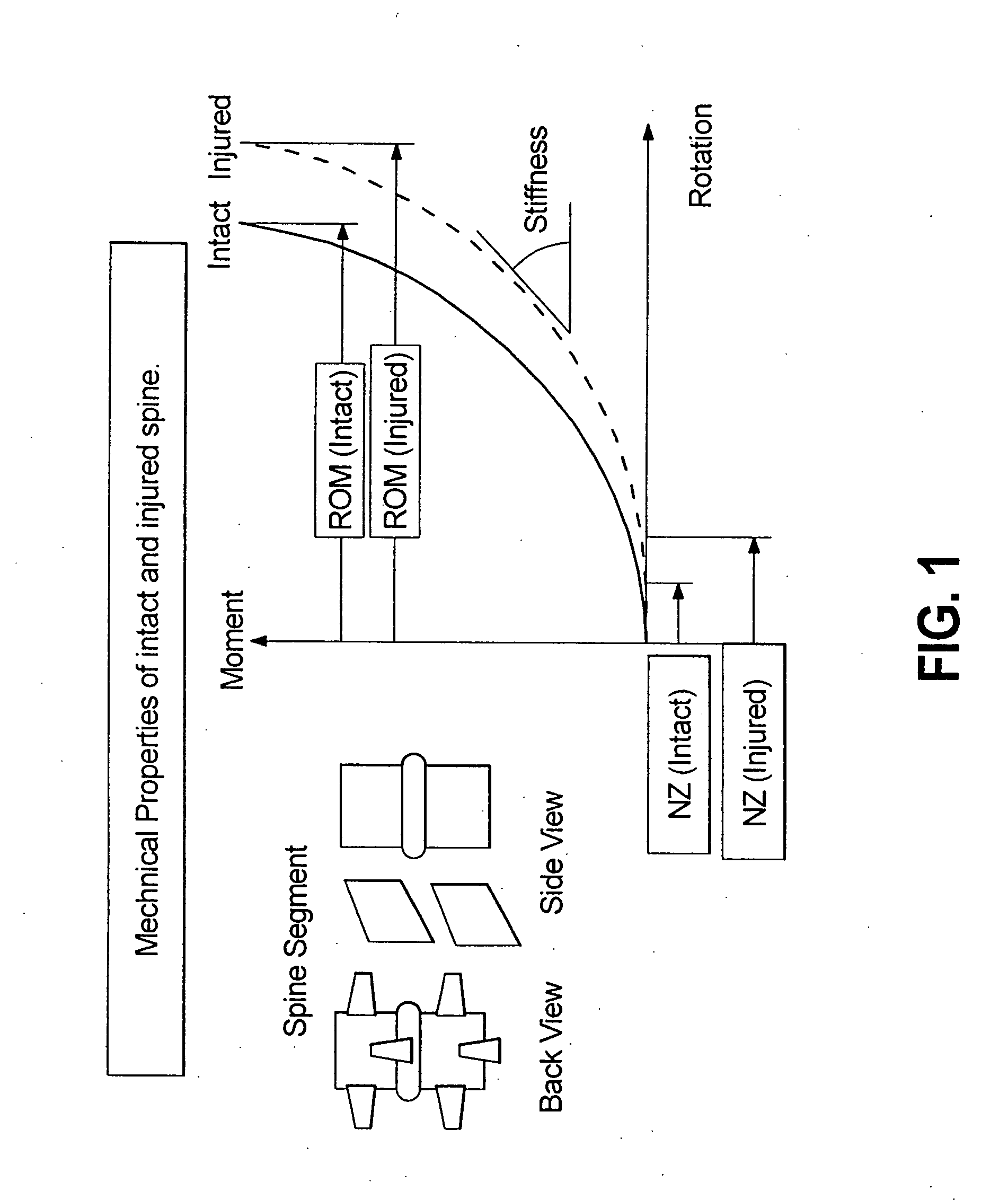
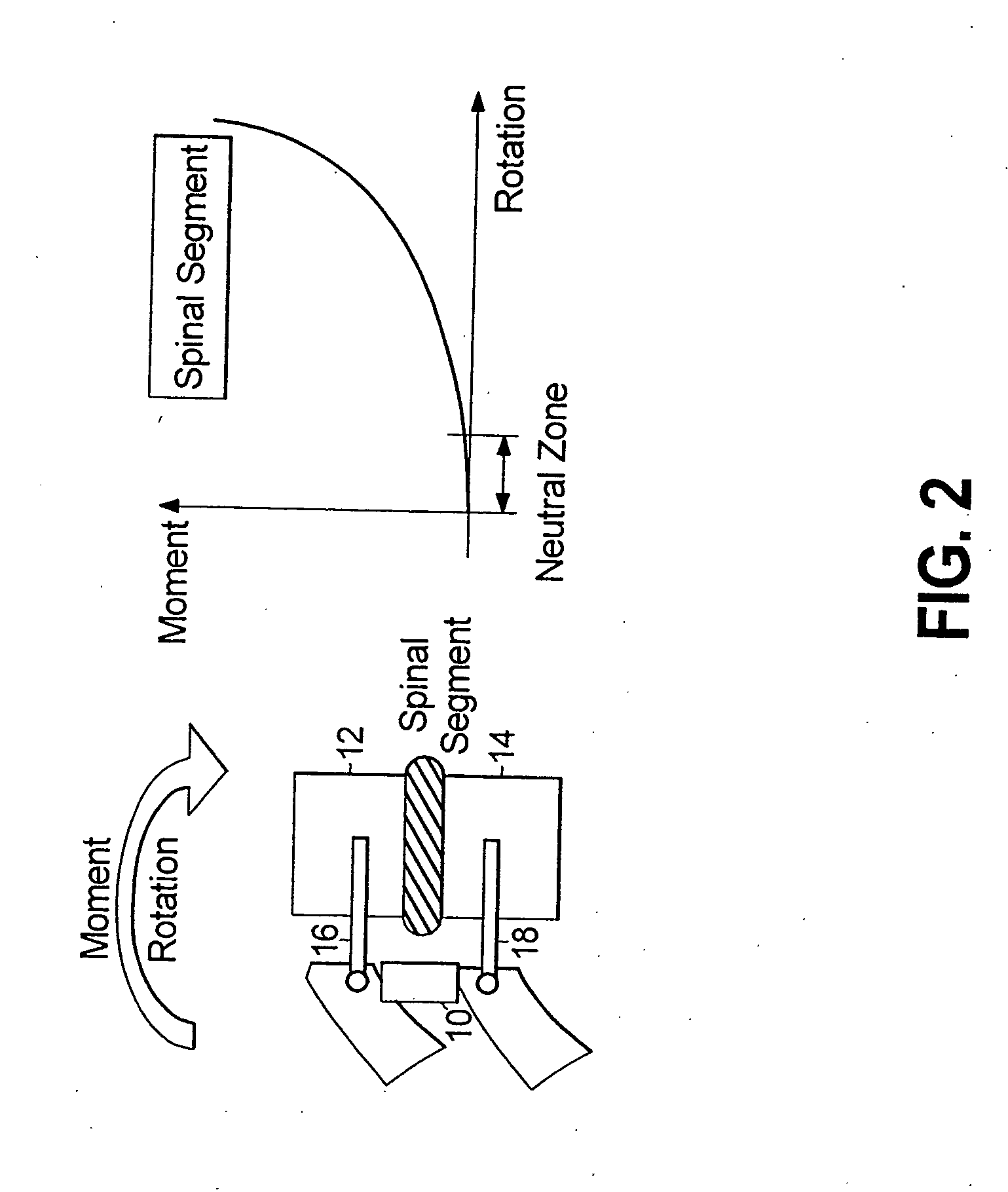
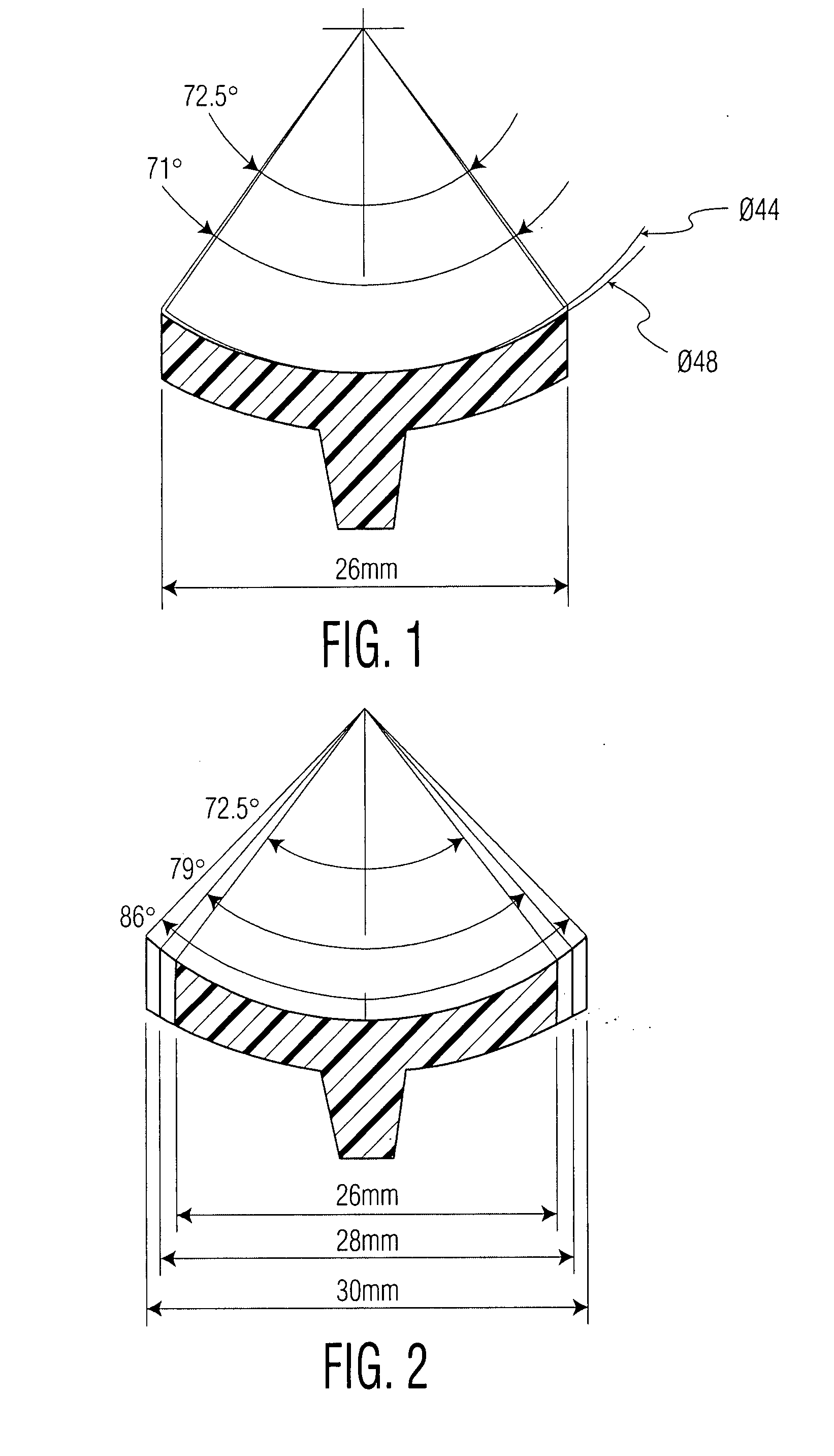
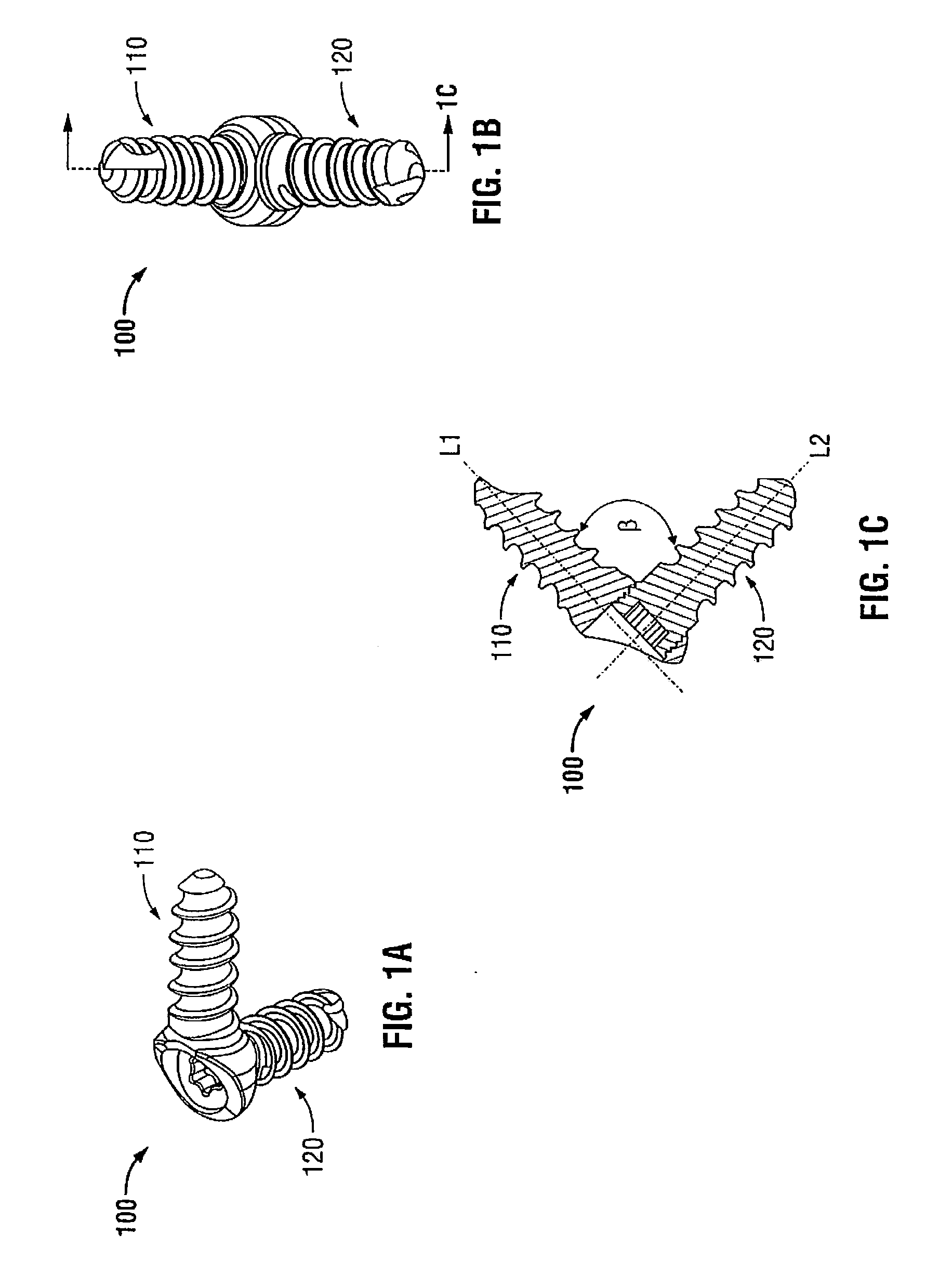
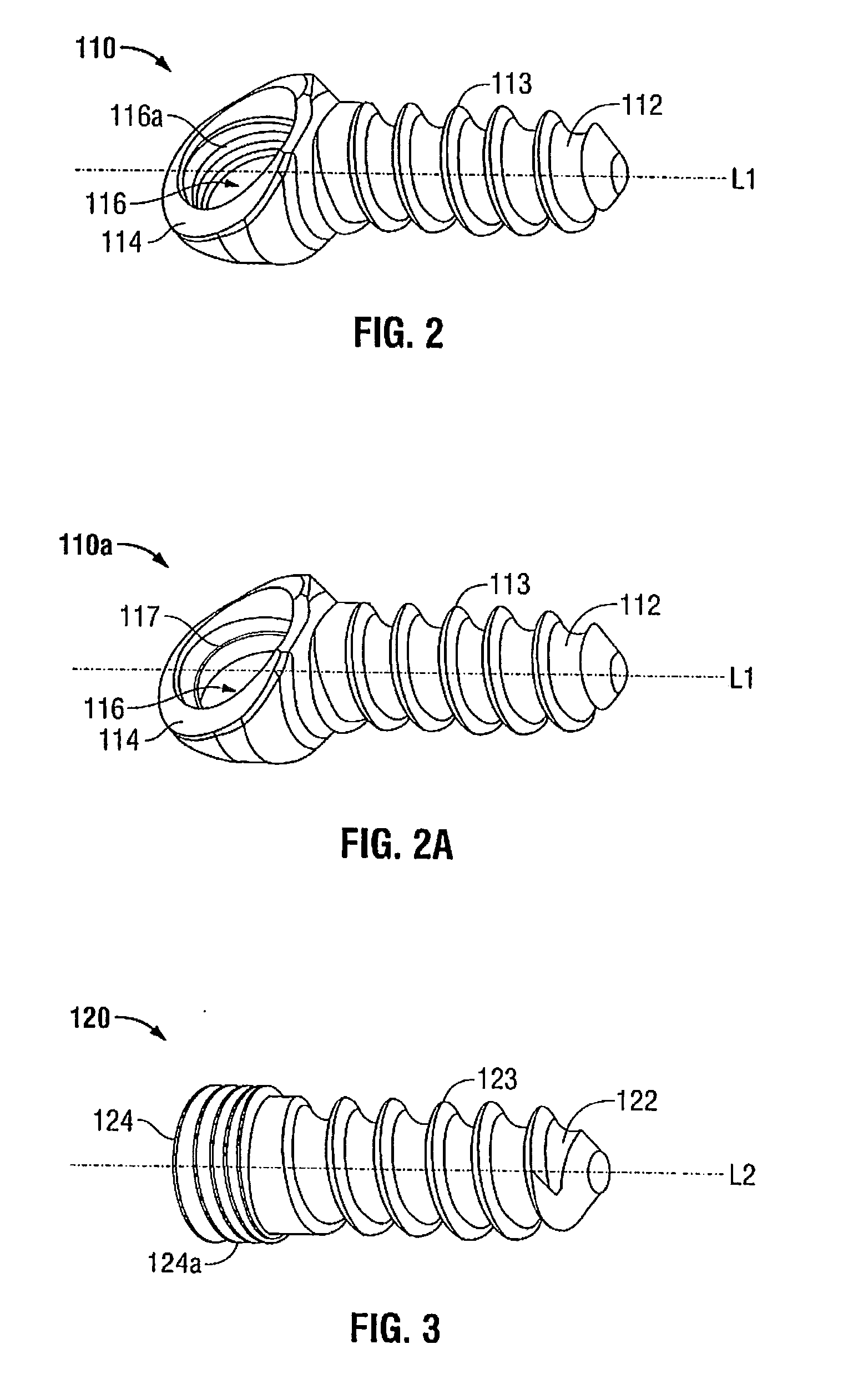
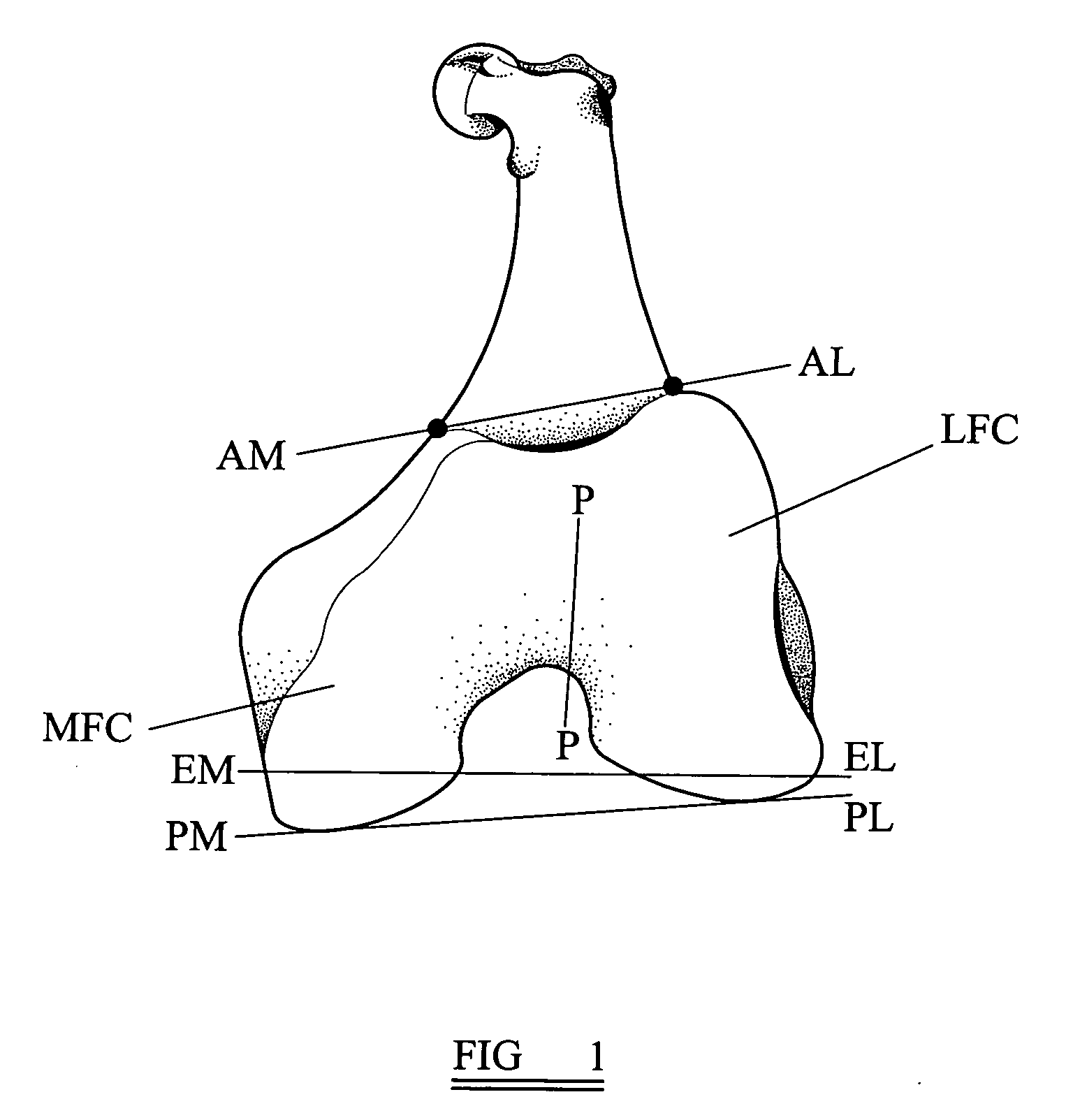
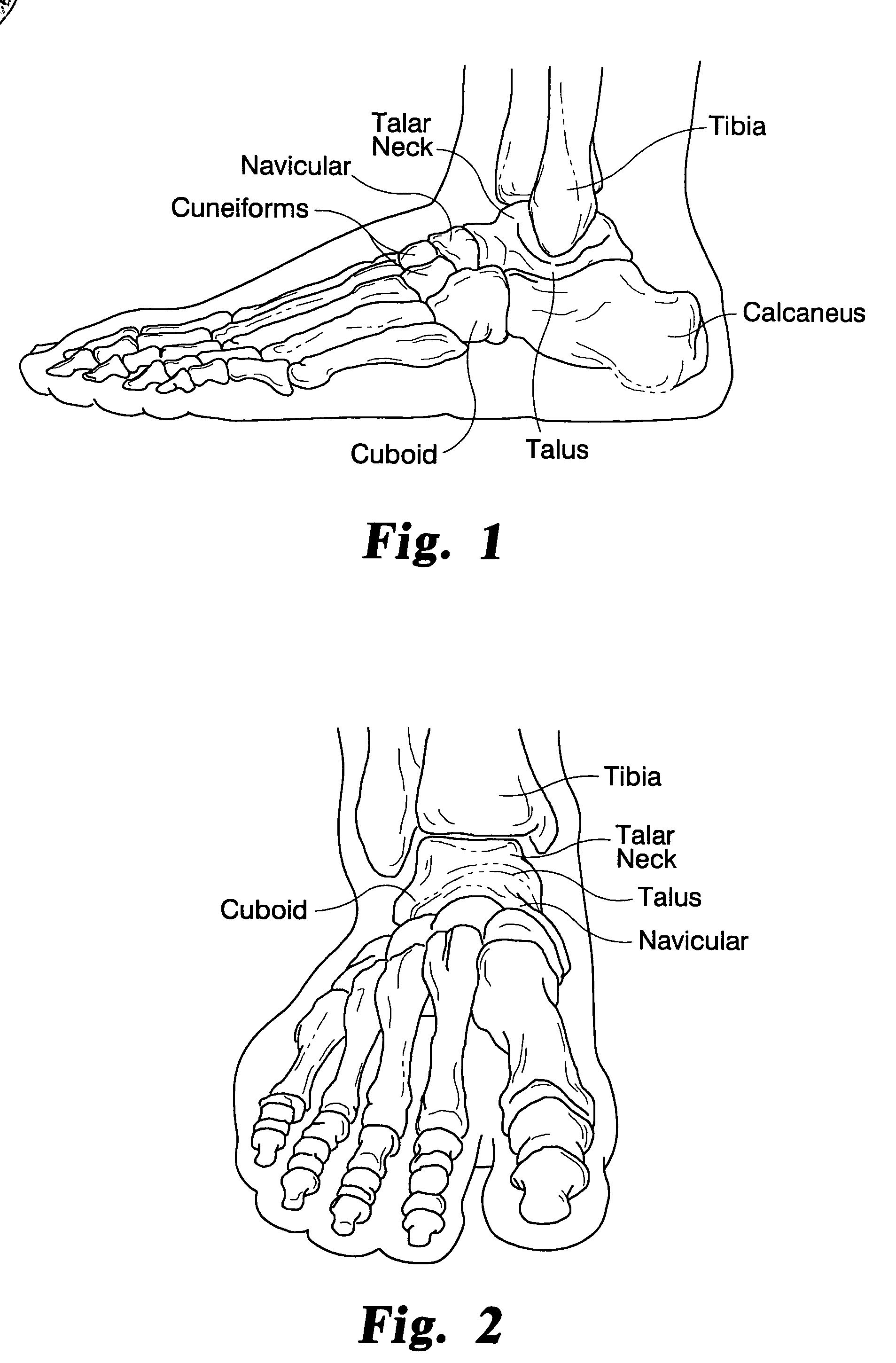
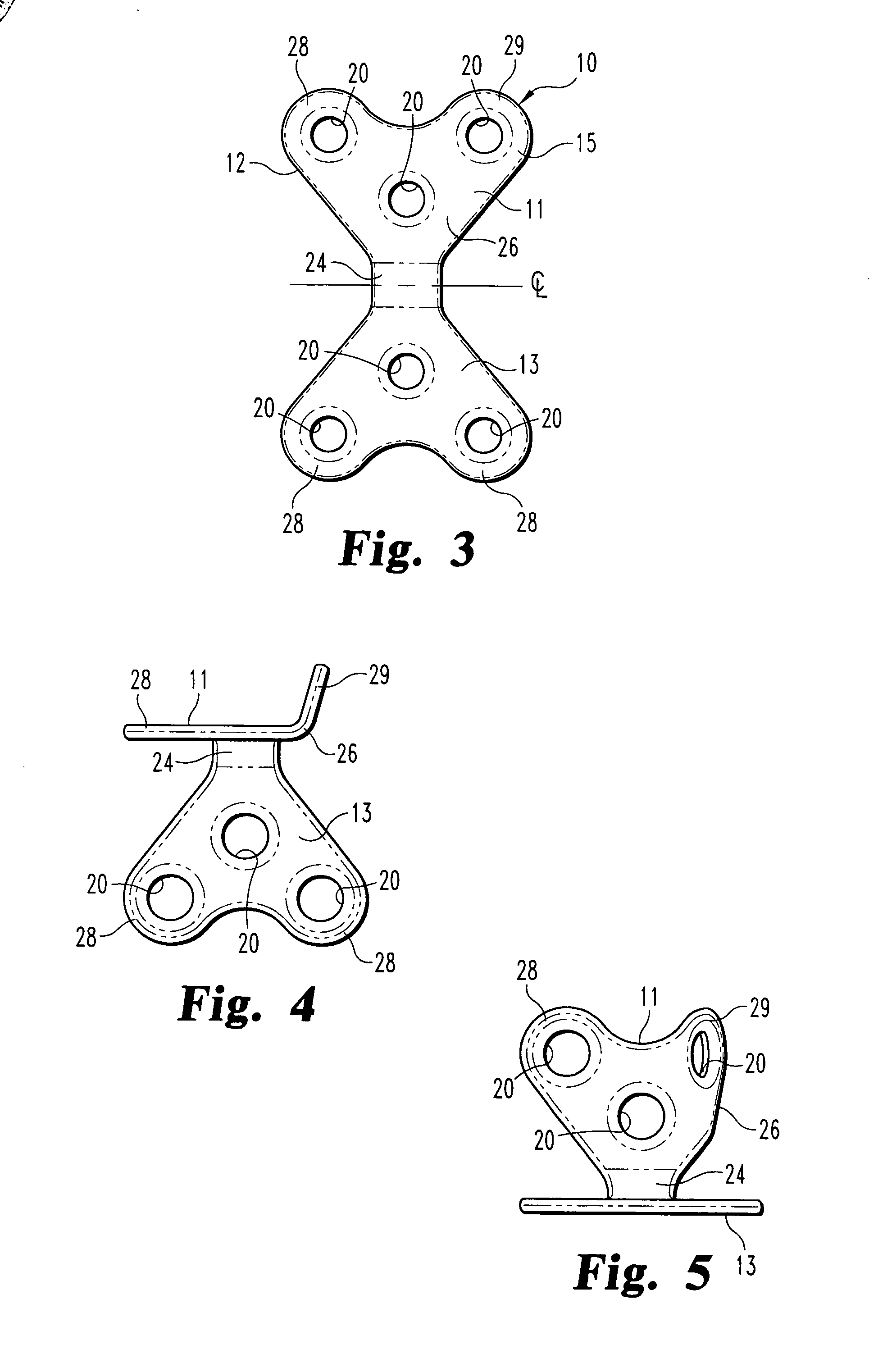
Angle formed by the junction of the posterior and lower borders of the lower jaw.
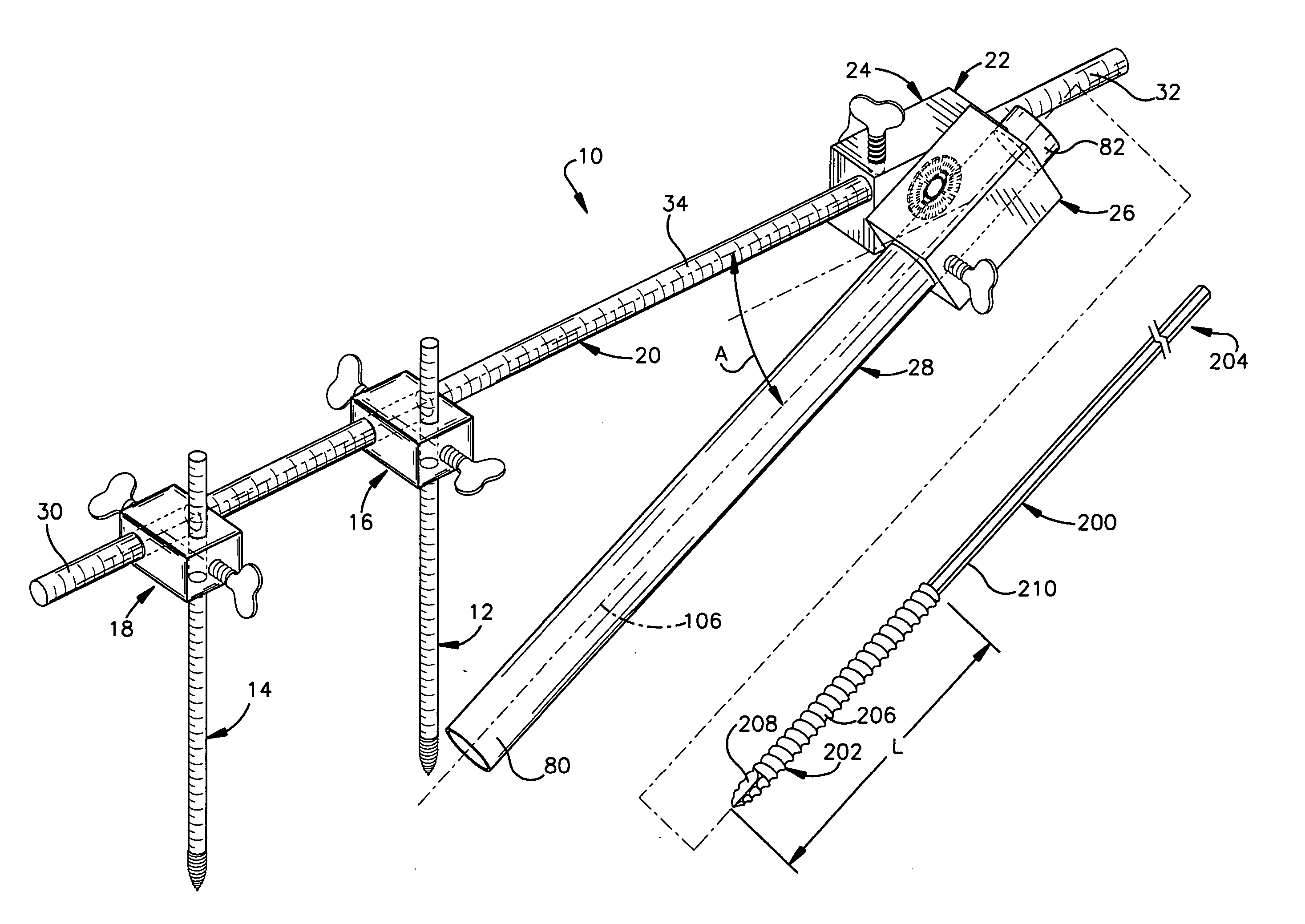
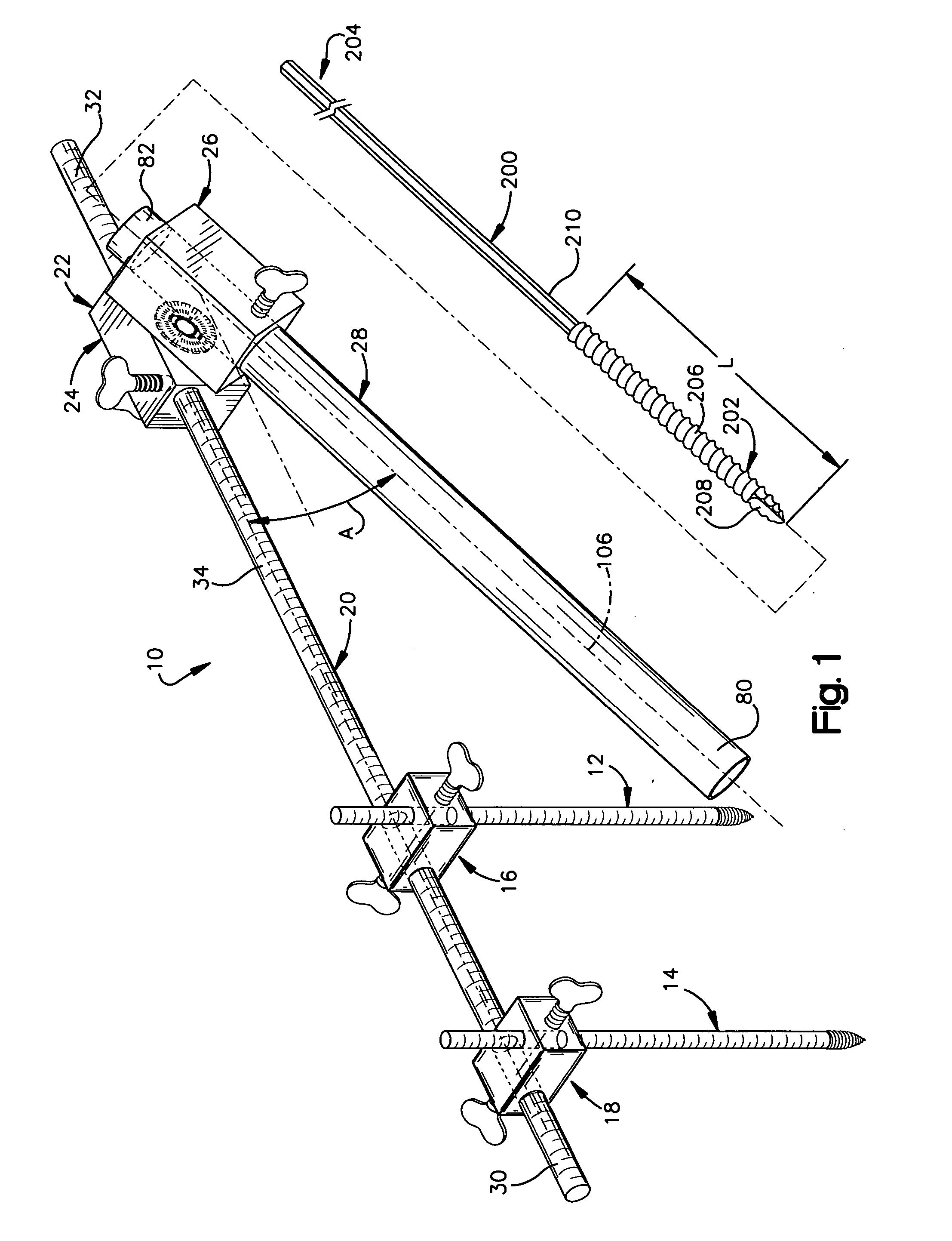
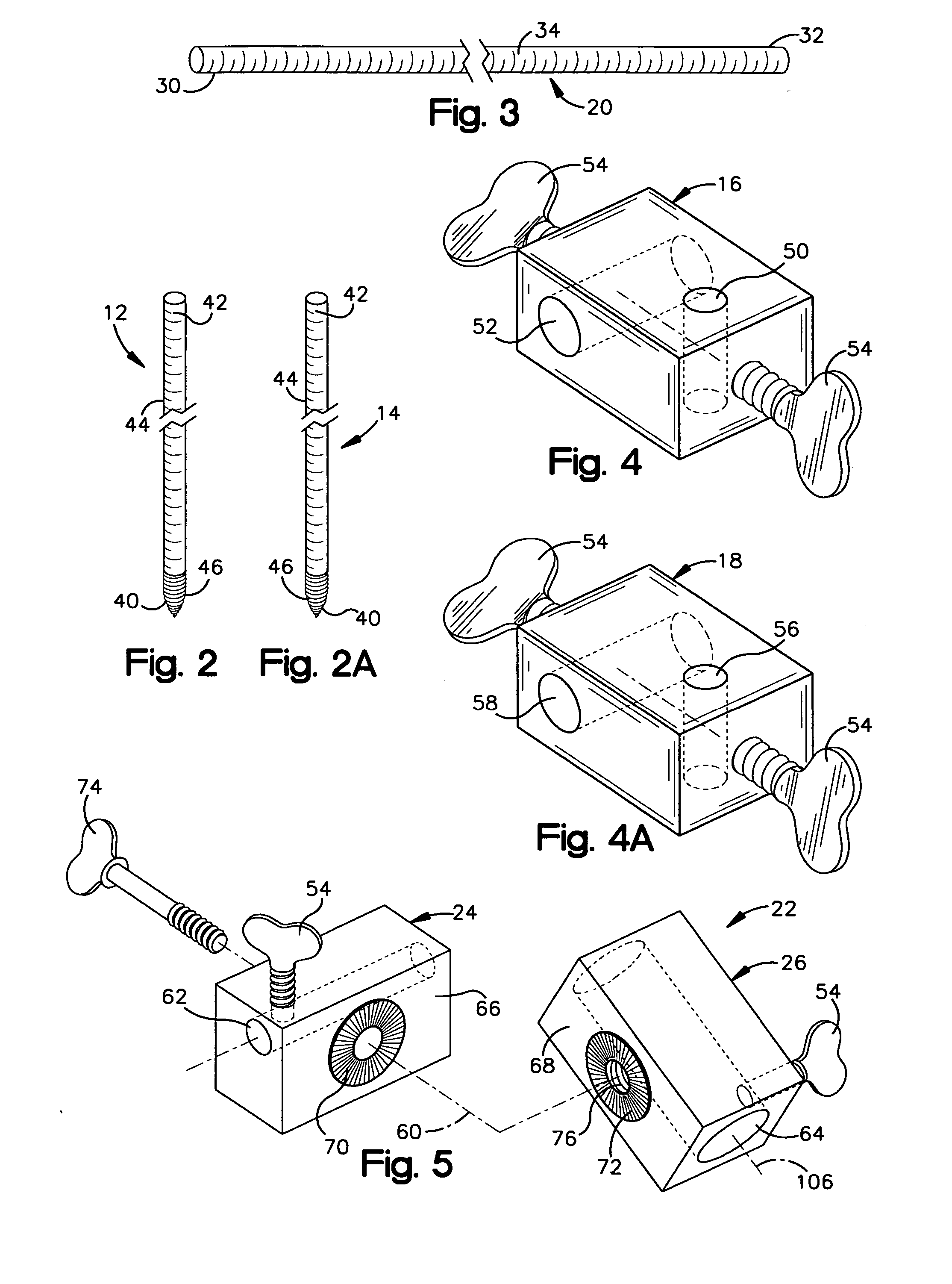
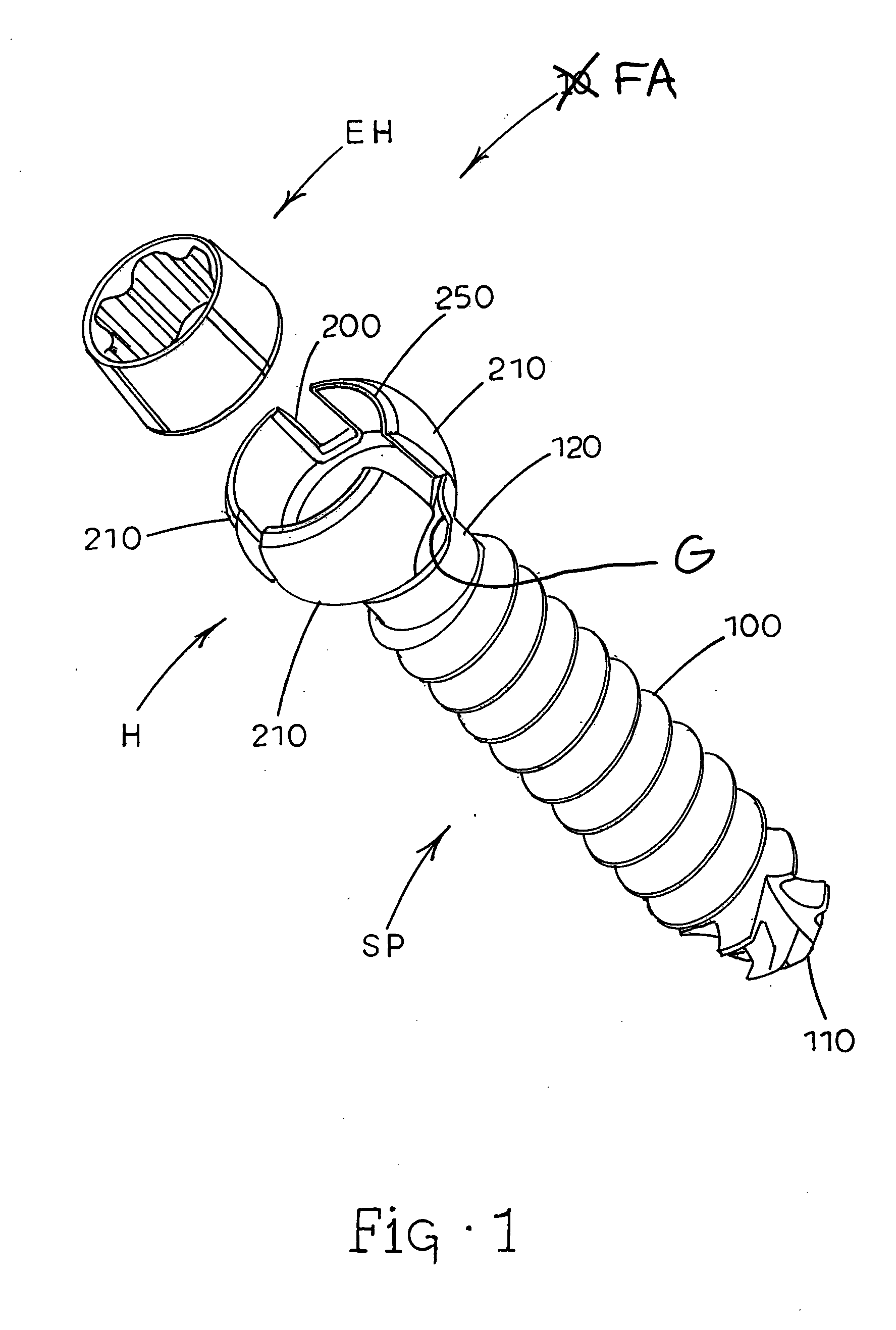
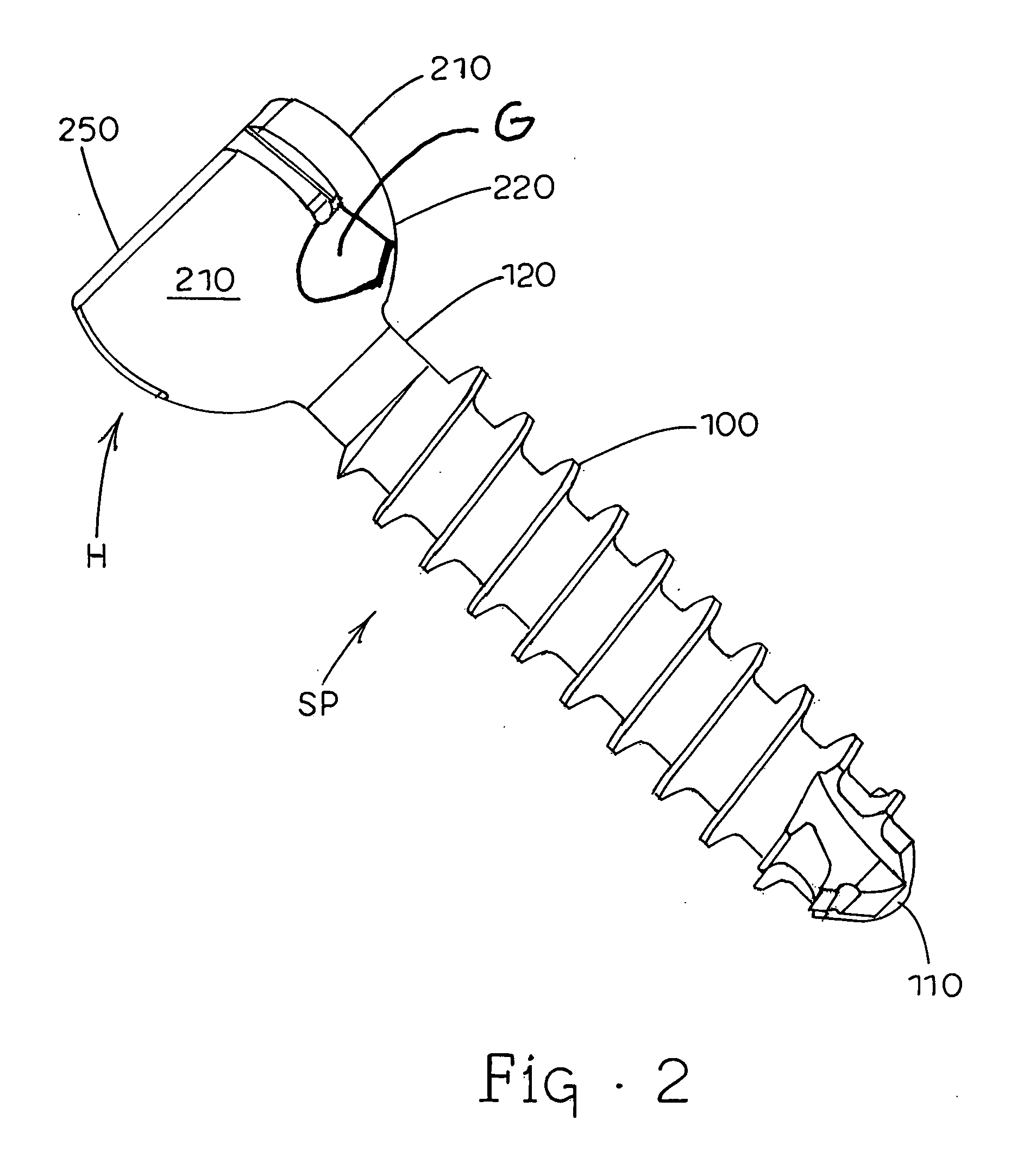
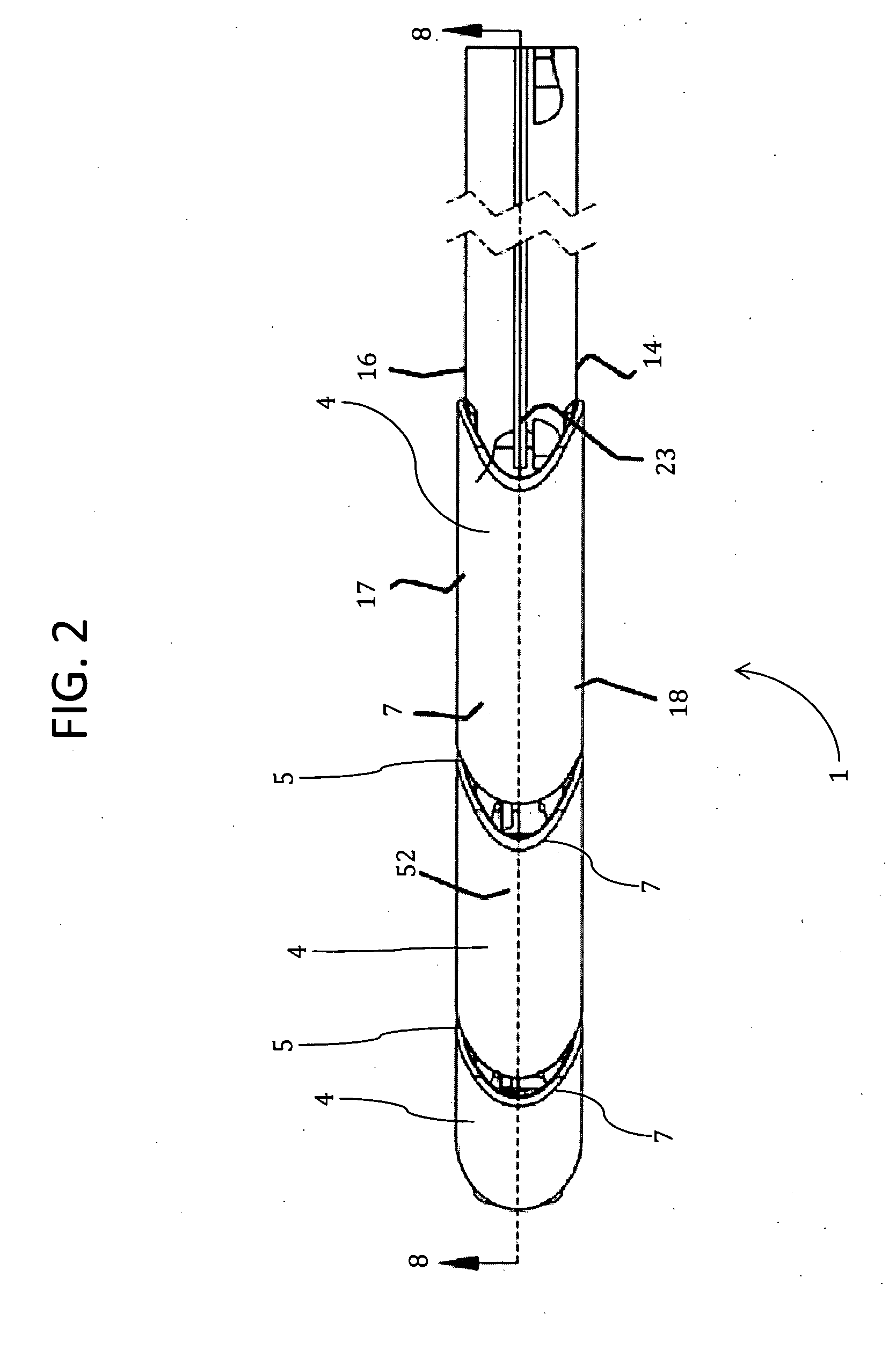
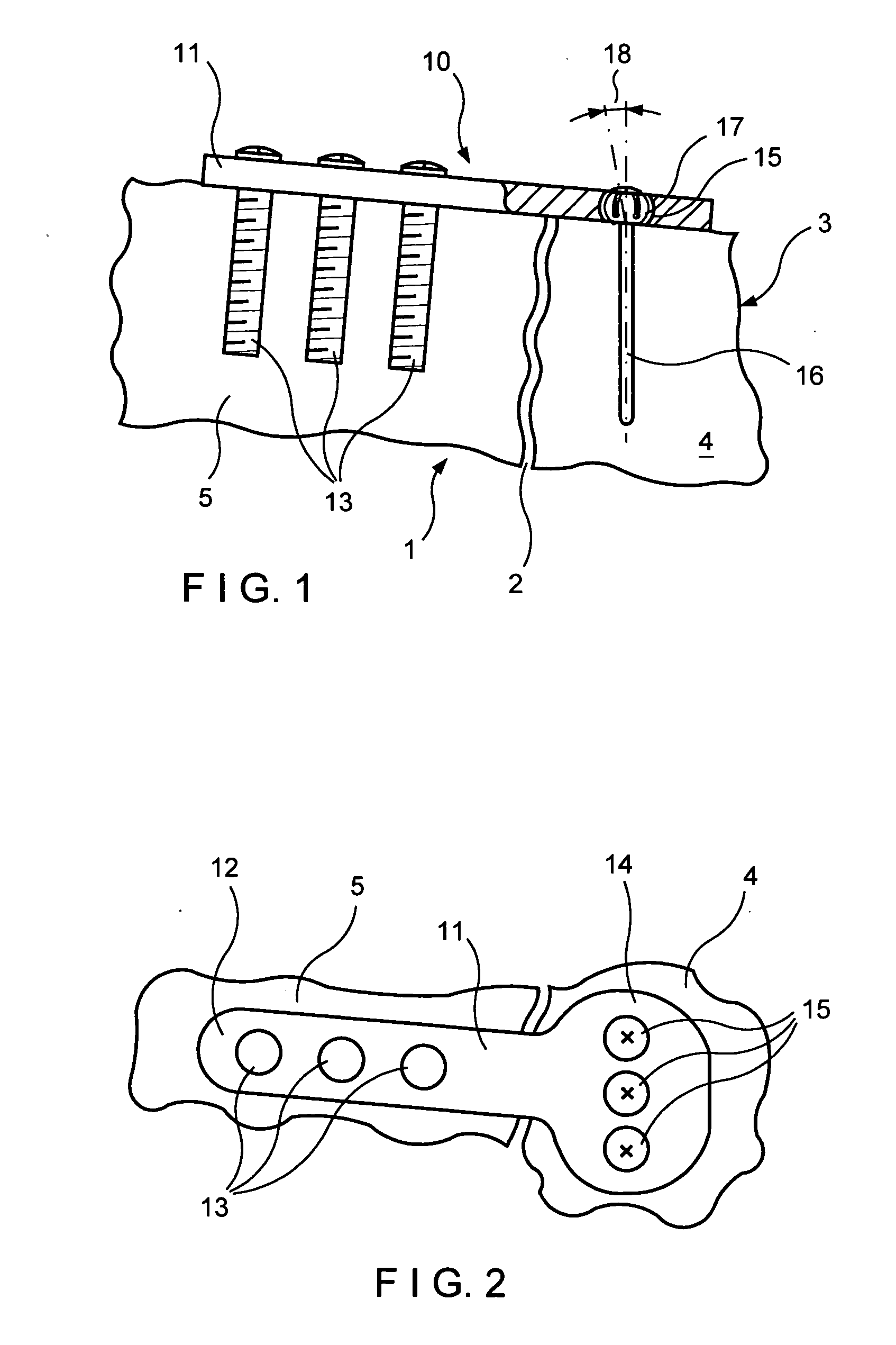
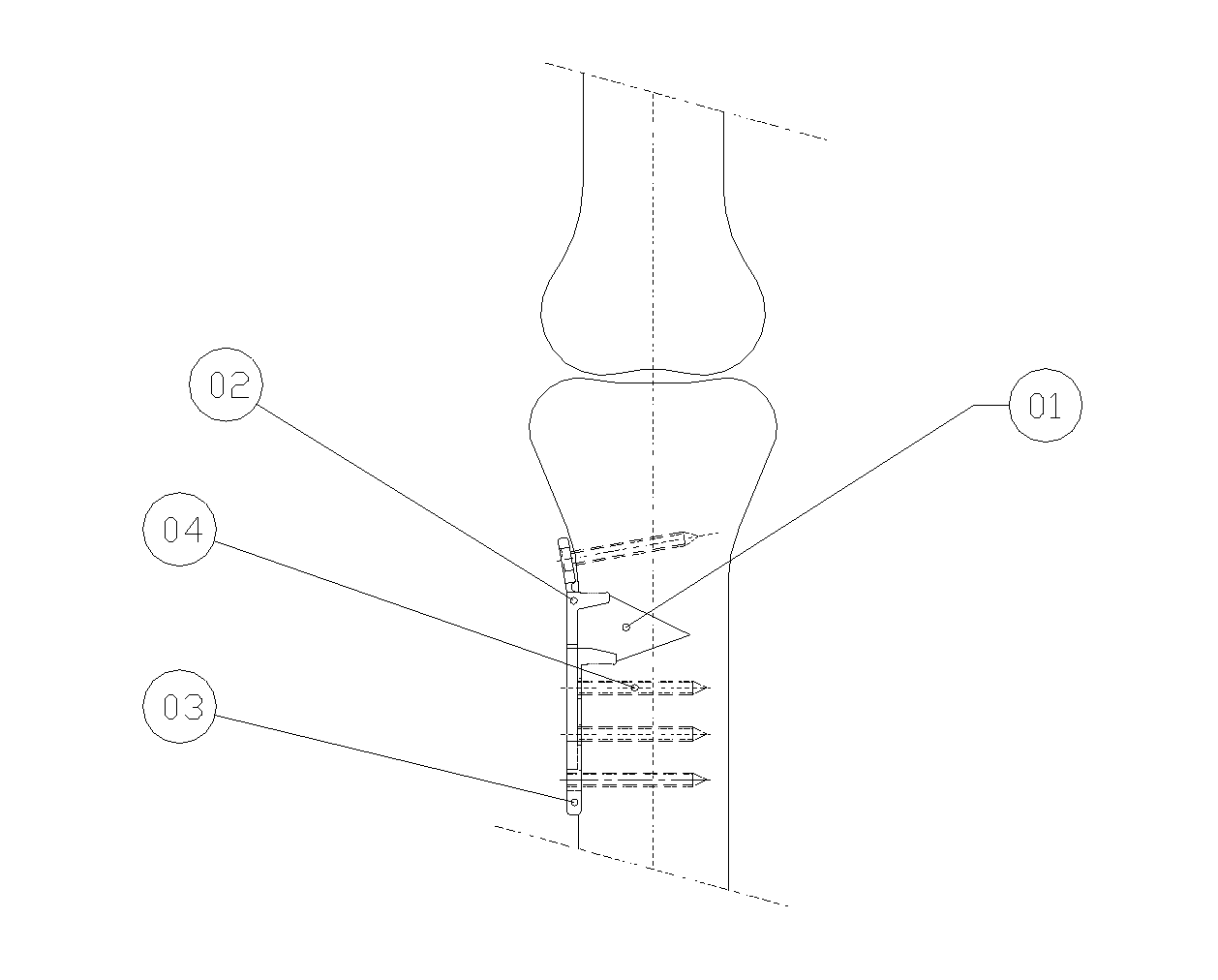
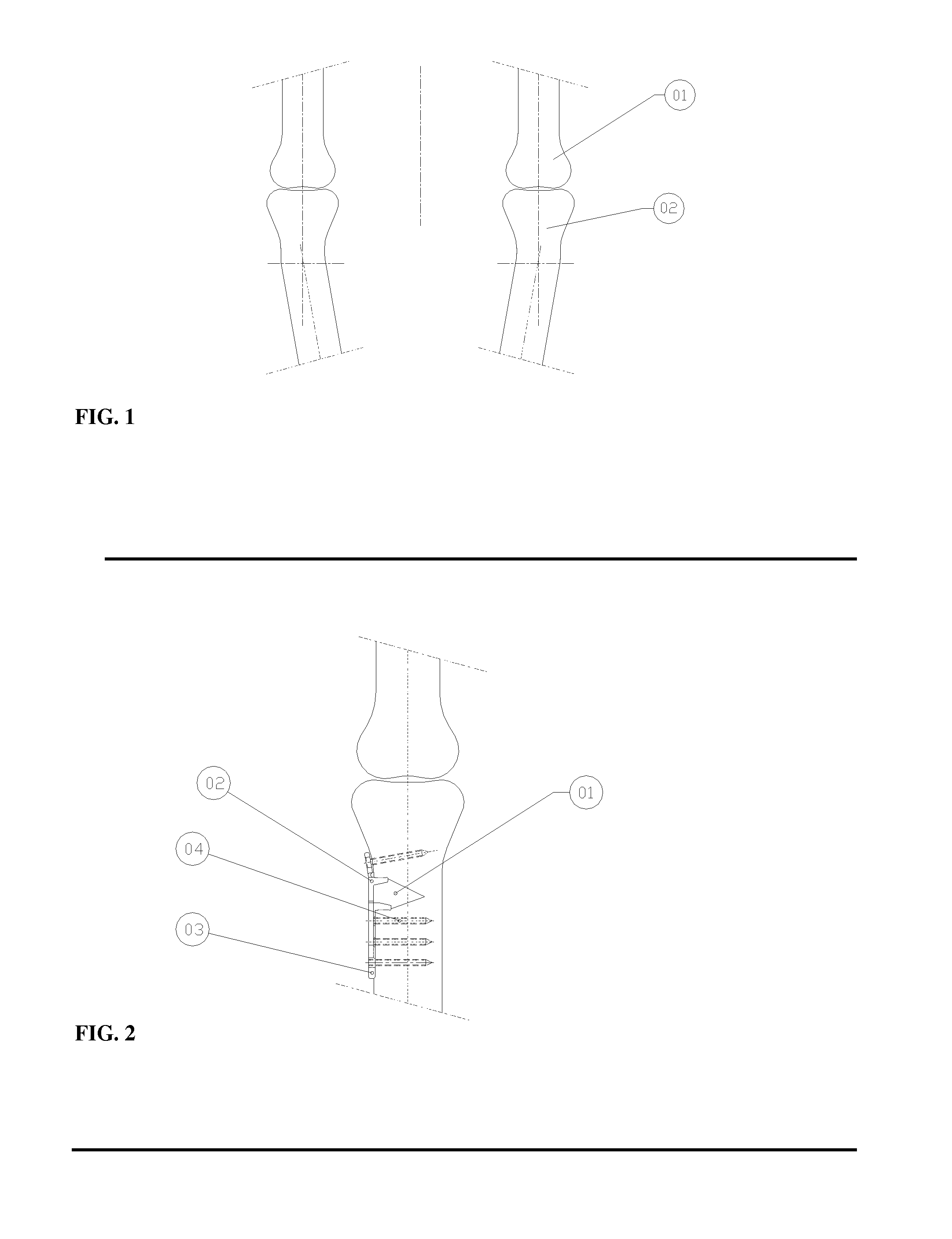
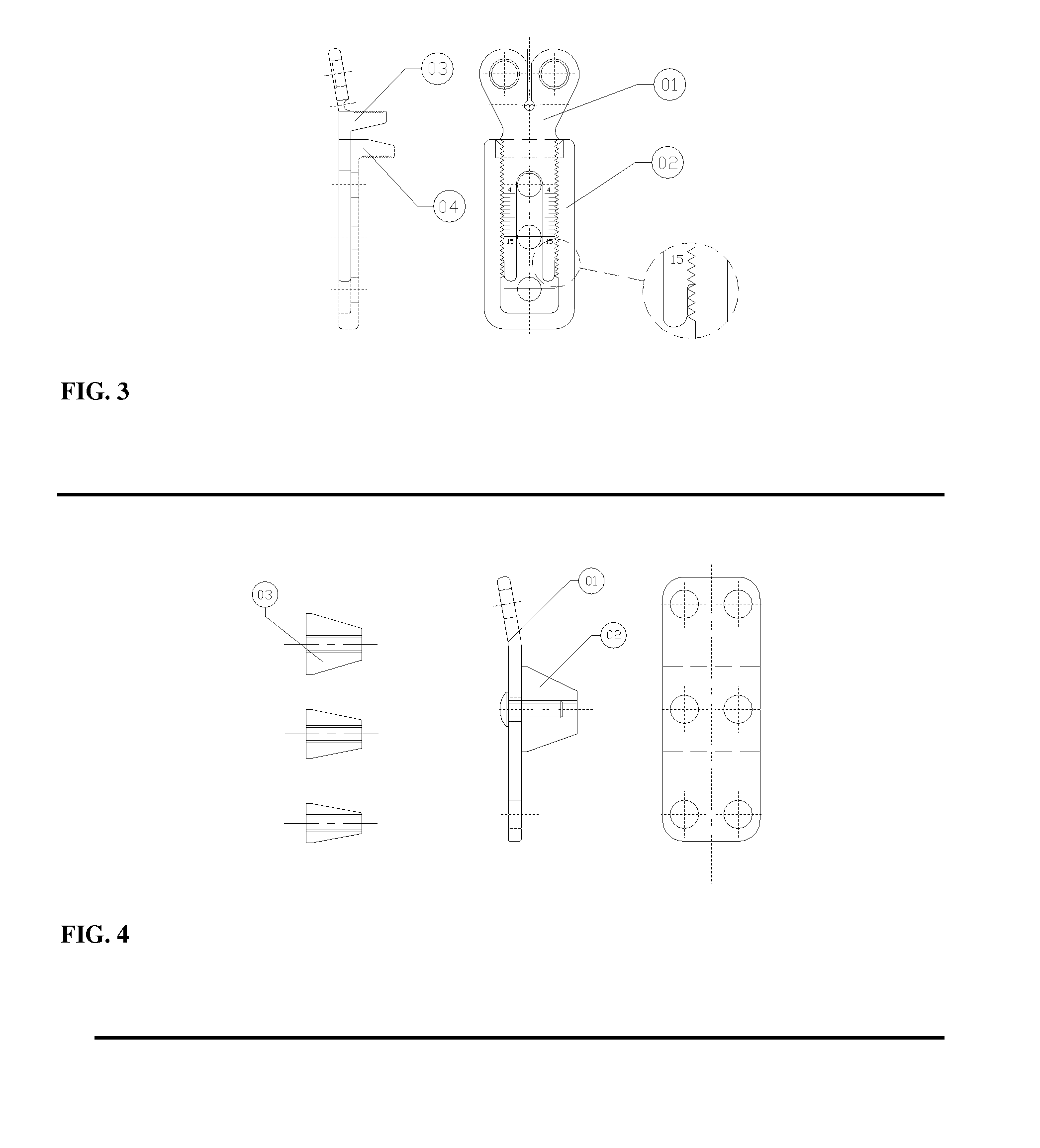
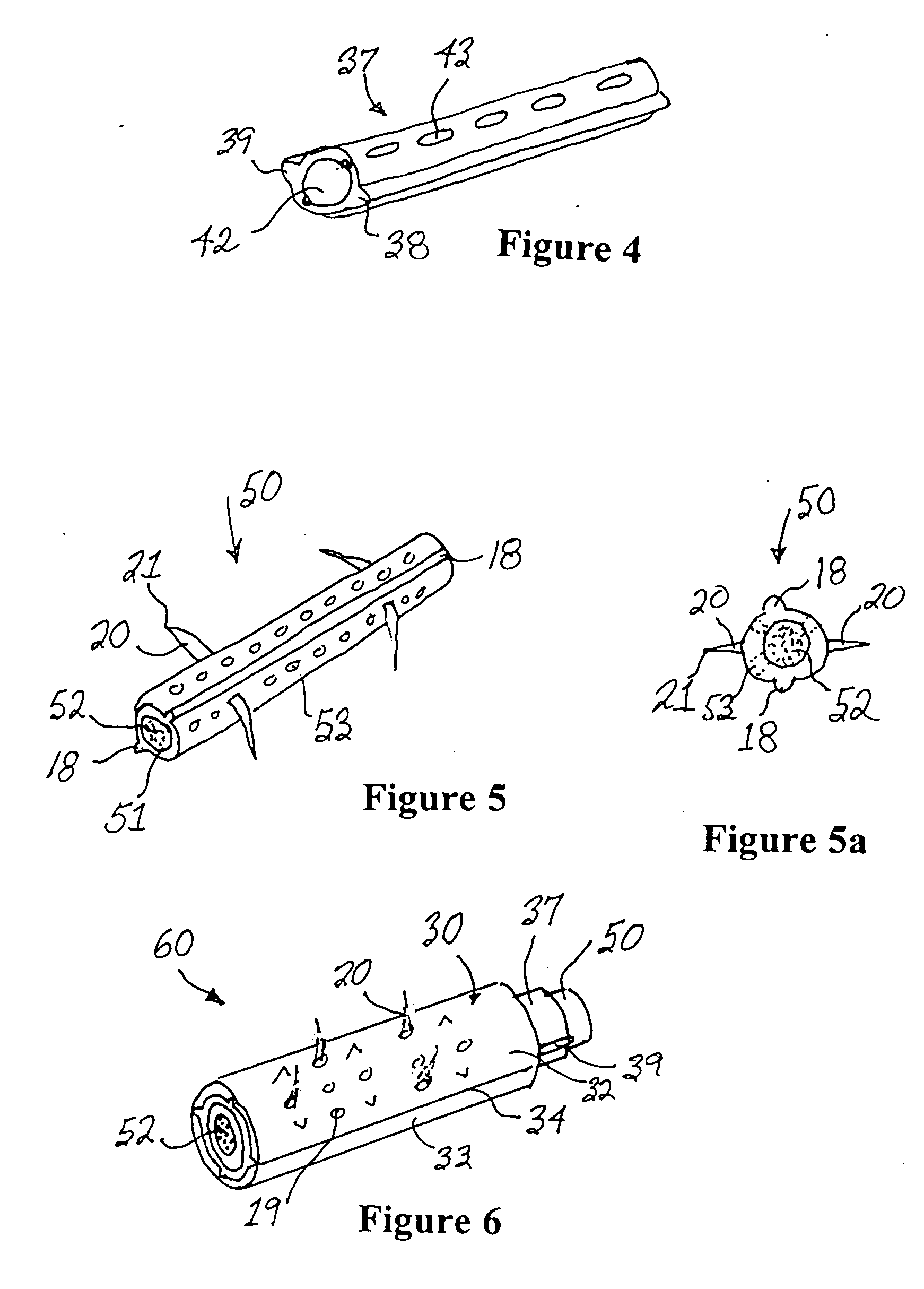
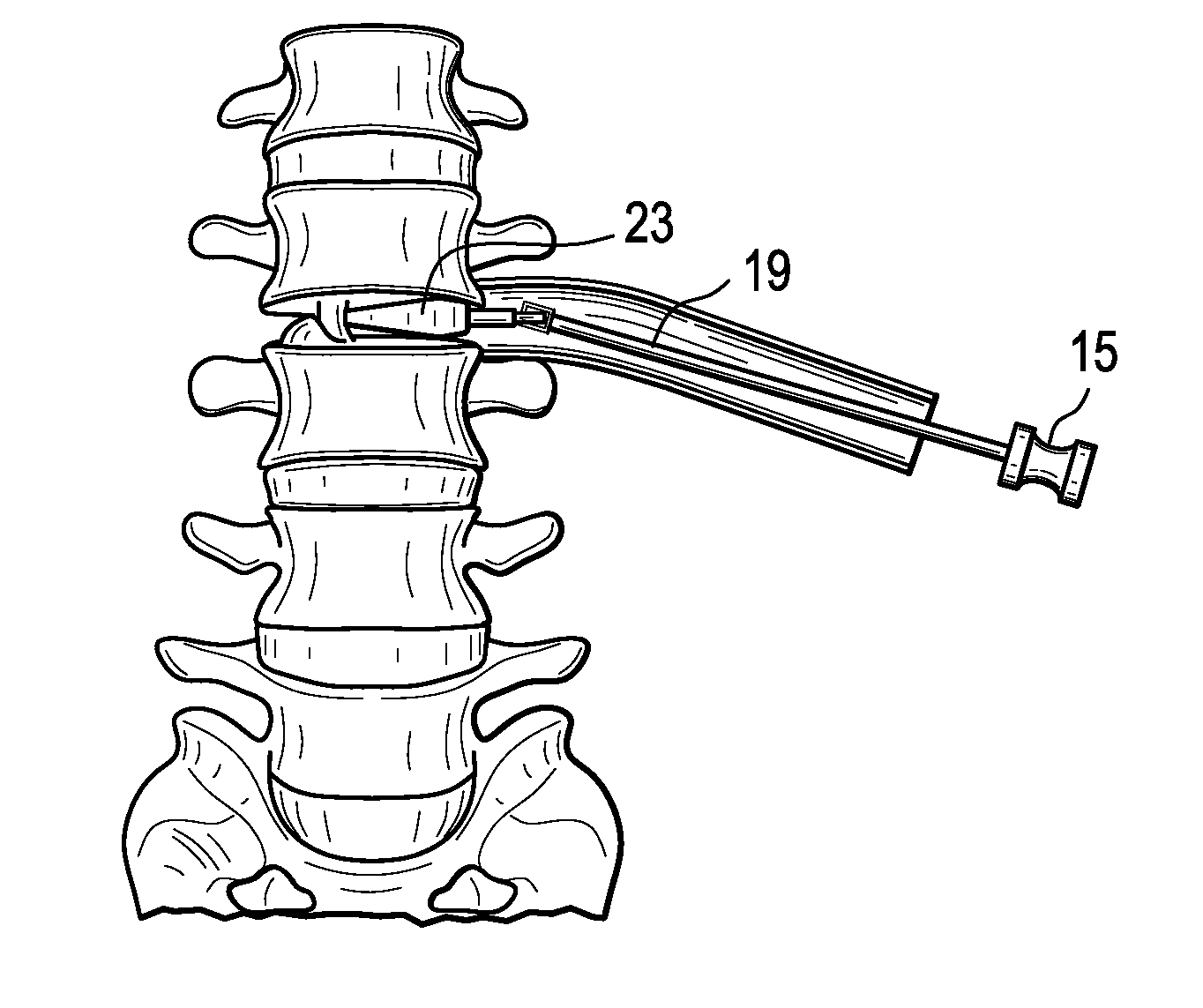
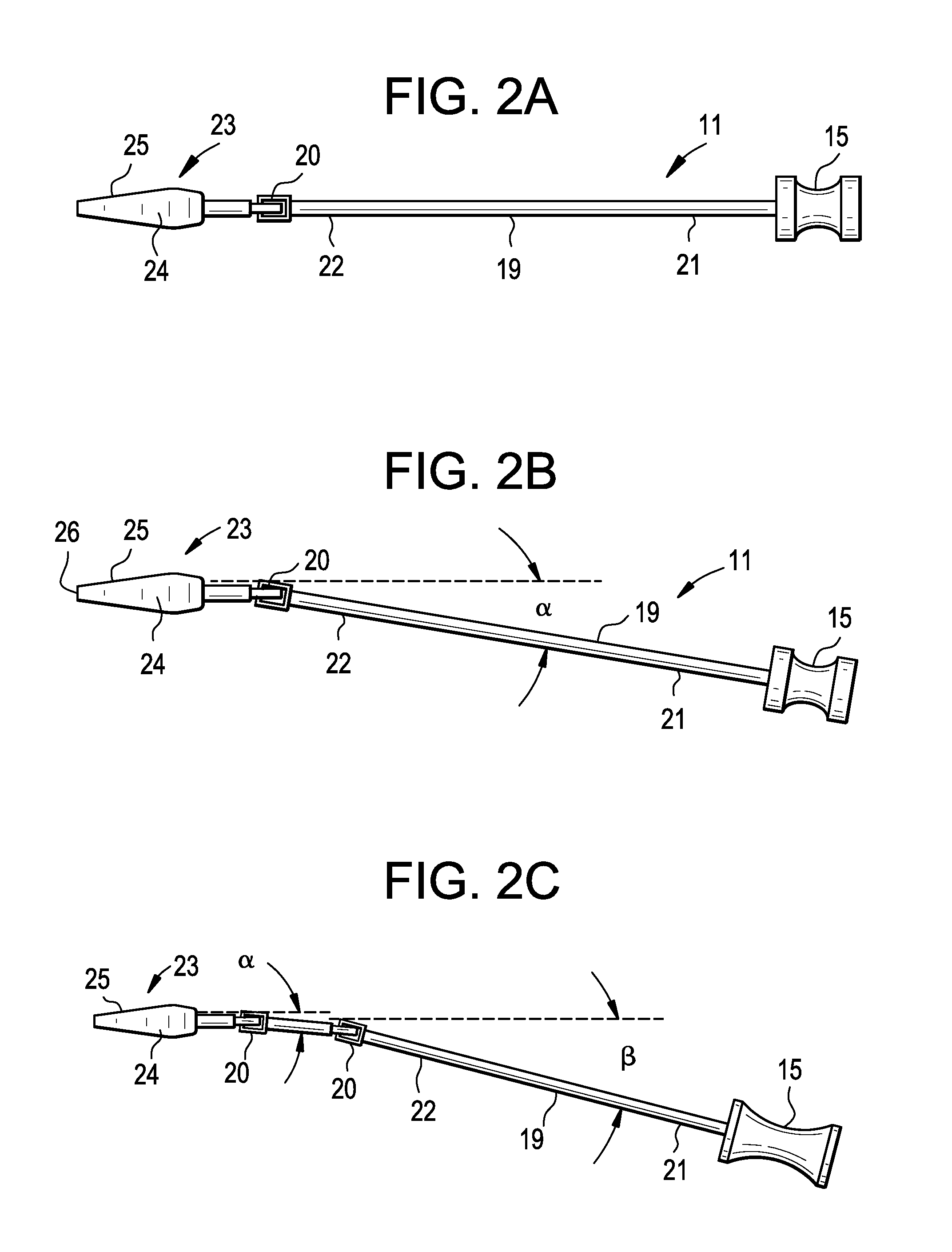
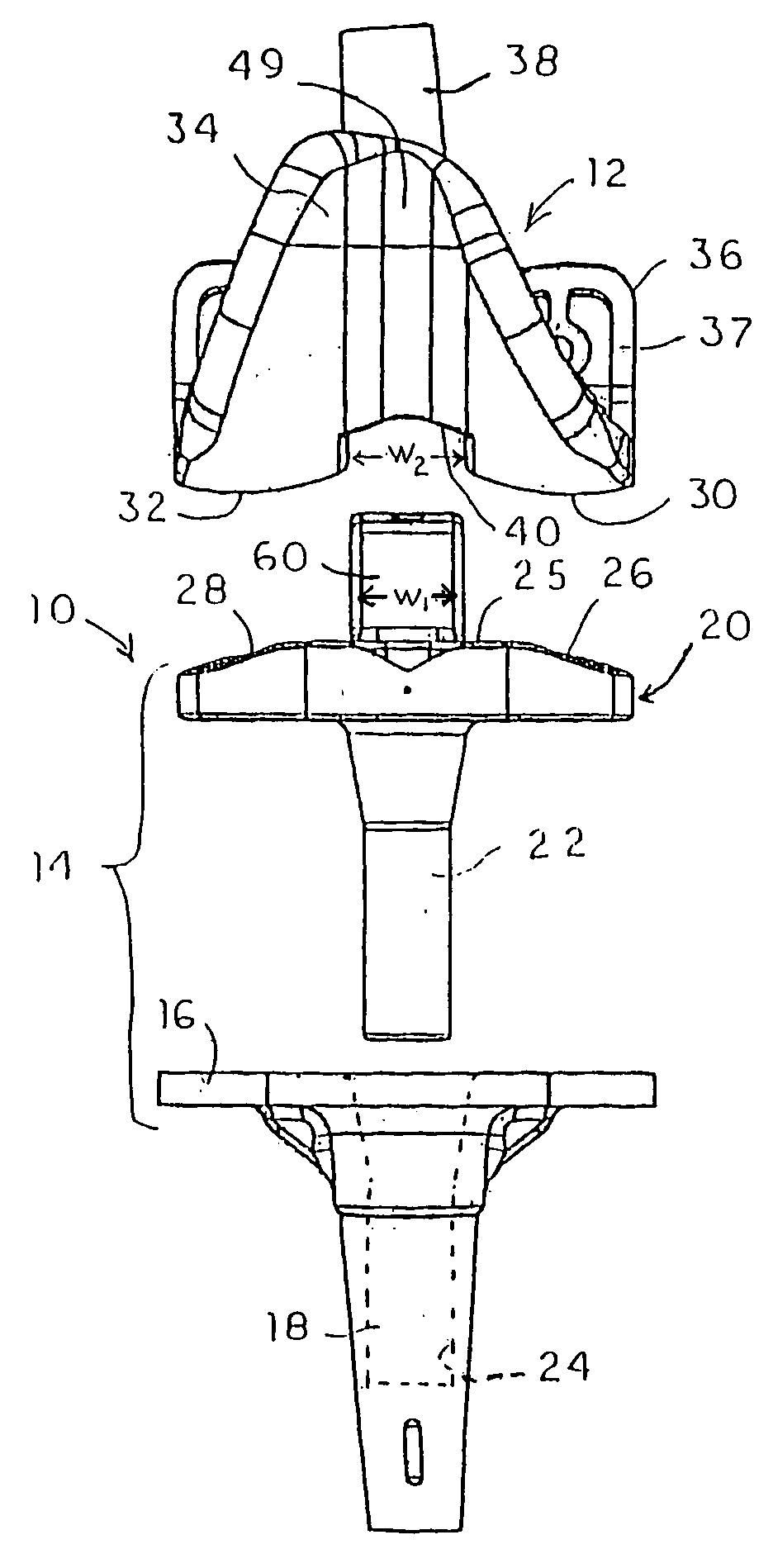
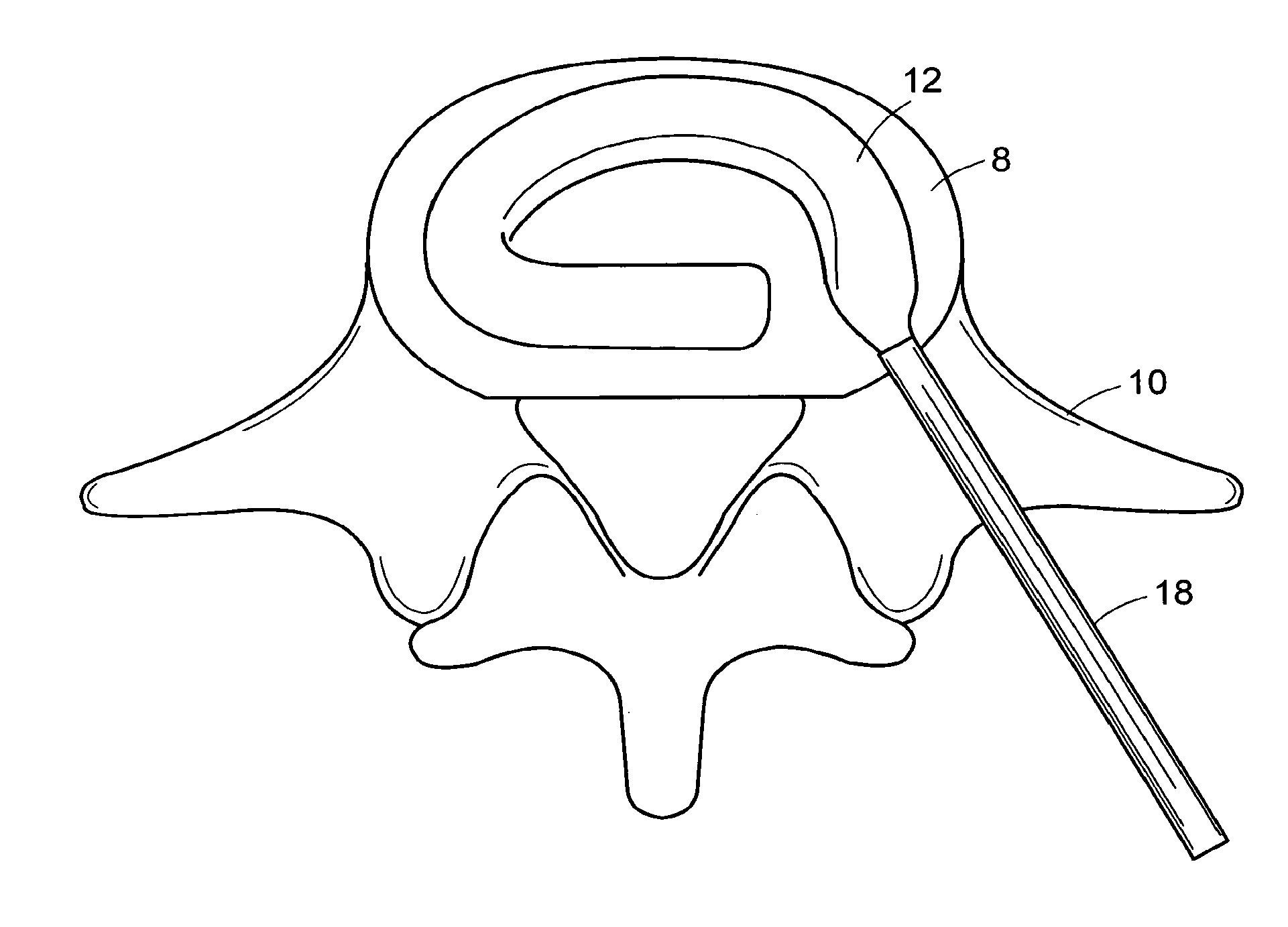
Minimally invasive method and apparatus for fusing adjacent vertebrae
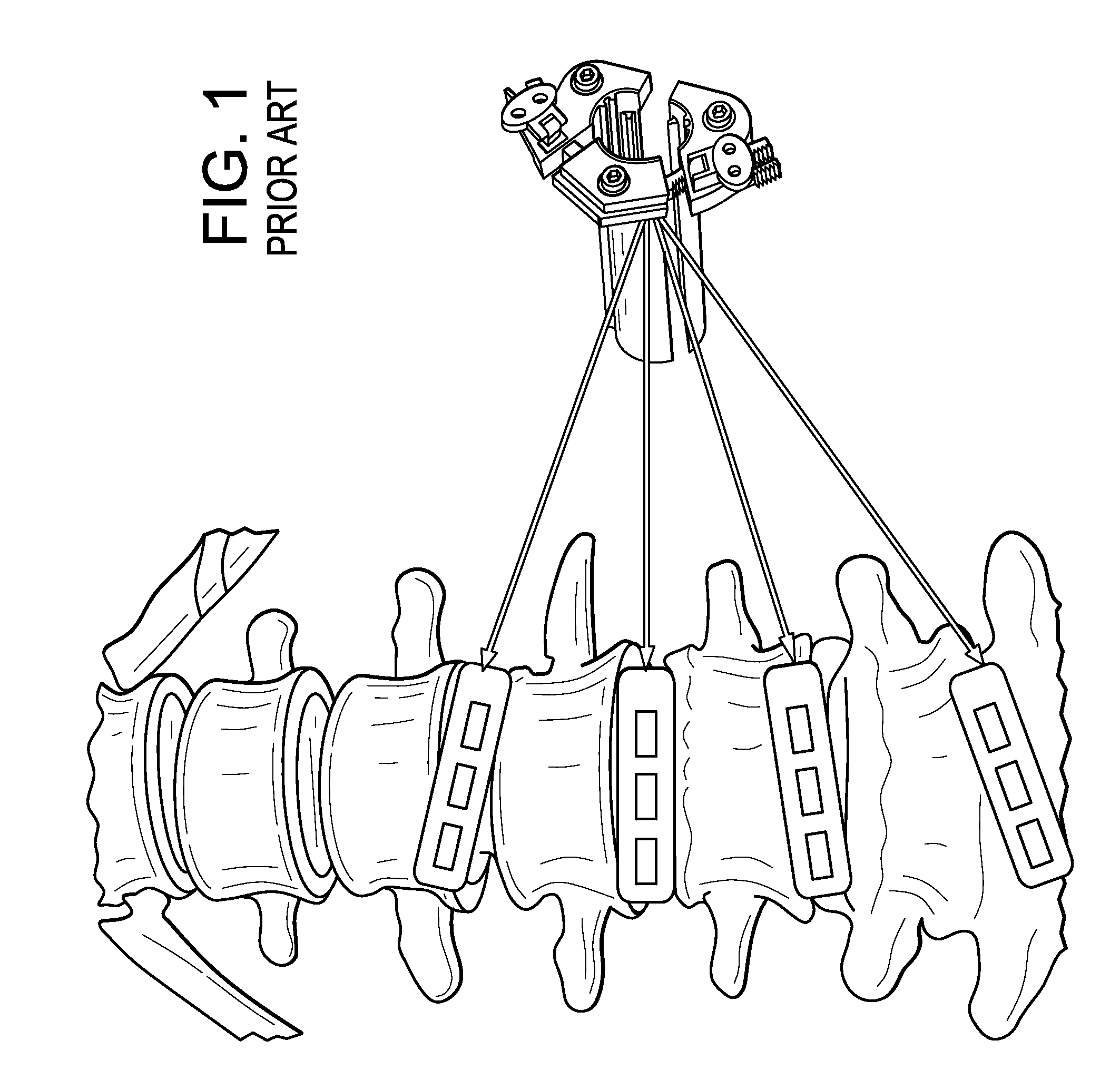
The present invention is a minimally invasive surgical method for fusing adjacent vertebrae. A first K-wire is inserted into the spinous process of an upper vertebrae. A second K-wire is inserted into a transverse process of a lower vertebrae. A first fixation block is secured to the first K-wire and a second fixation block is secured to the second K-wire. A rod member extends across the K-wires. A swivel block assembly is secured to achieve a desired angle for a first axis along which a first screw will be implanted into a facet joint. The swivel block assembly is secured at a desired axial position on the rod member. Percutaneous access to the upper vertebrae along the first axis is then obtained via a cannula. A removable screw having a threaded section for implantation across the facet joint and an elongated shank section that is shearable subcutaneously is inserted through the cannula. The threaded section is implanted along the first axis across the facet joint to attach the upper and lower vertebrae. A shearing tool is inserted percutaneously over the shank section and the shank section is sheared off immediately above the lamina.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
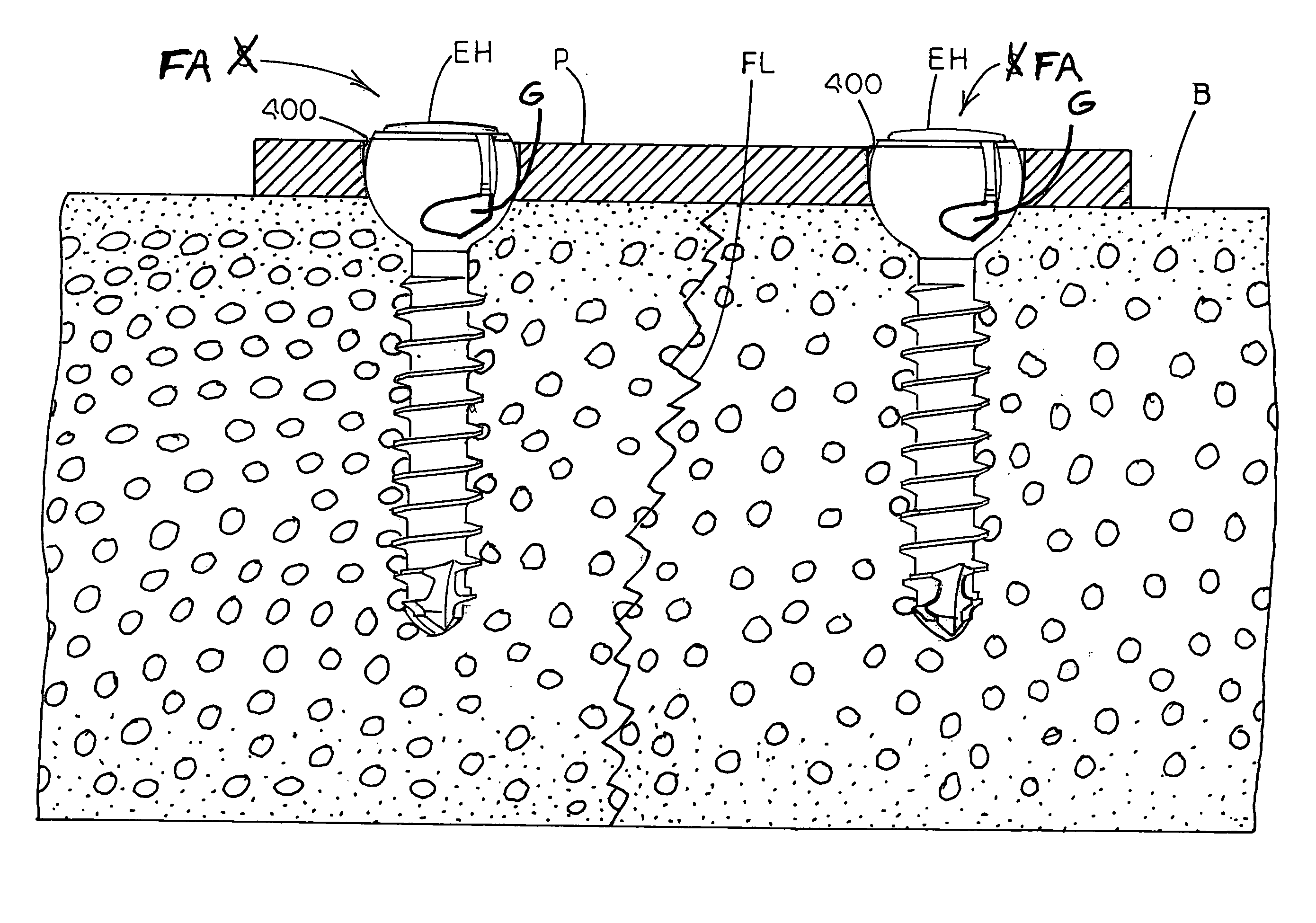
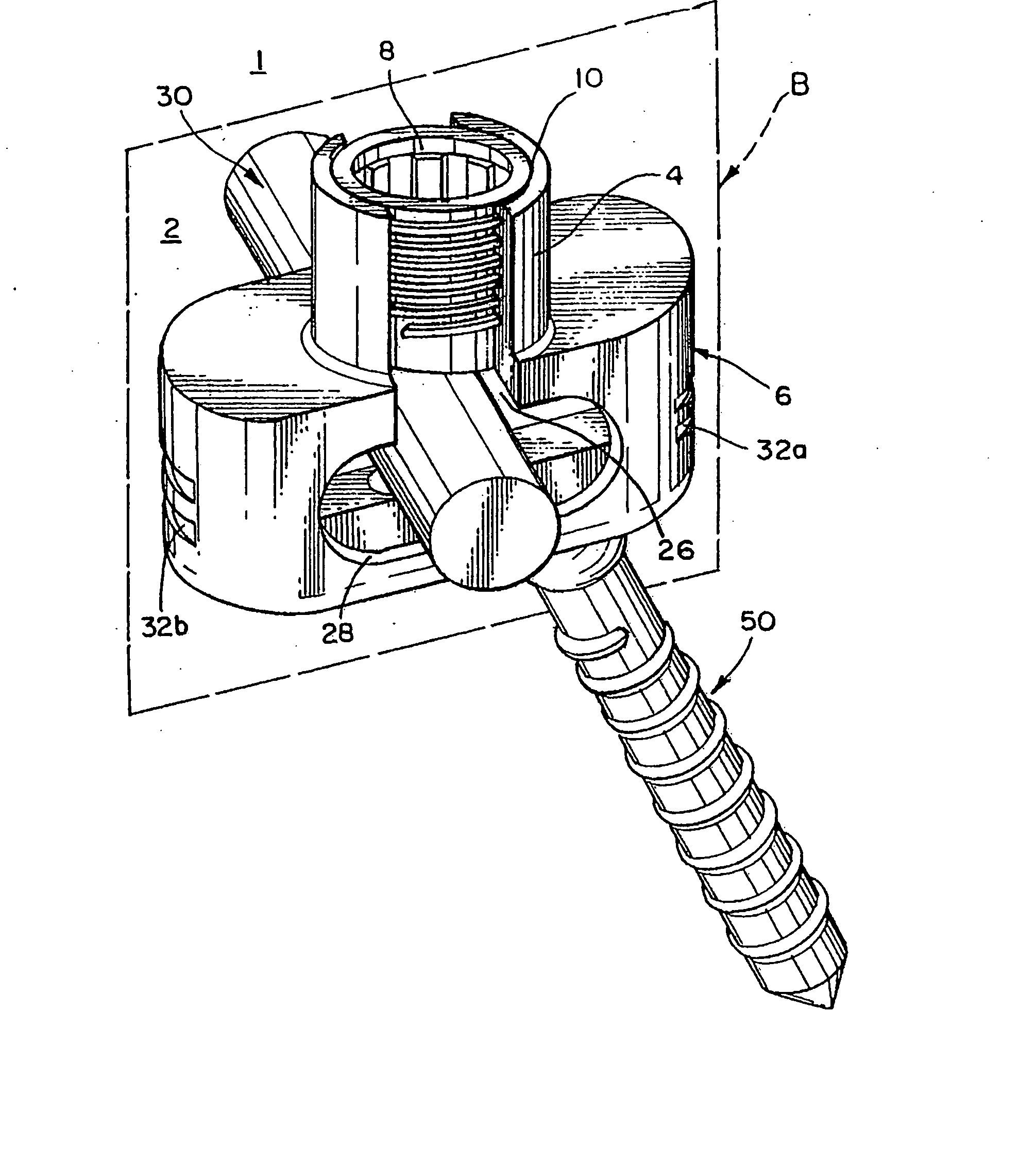
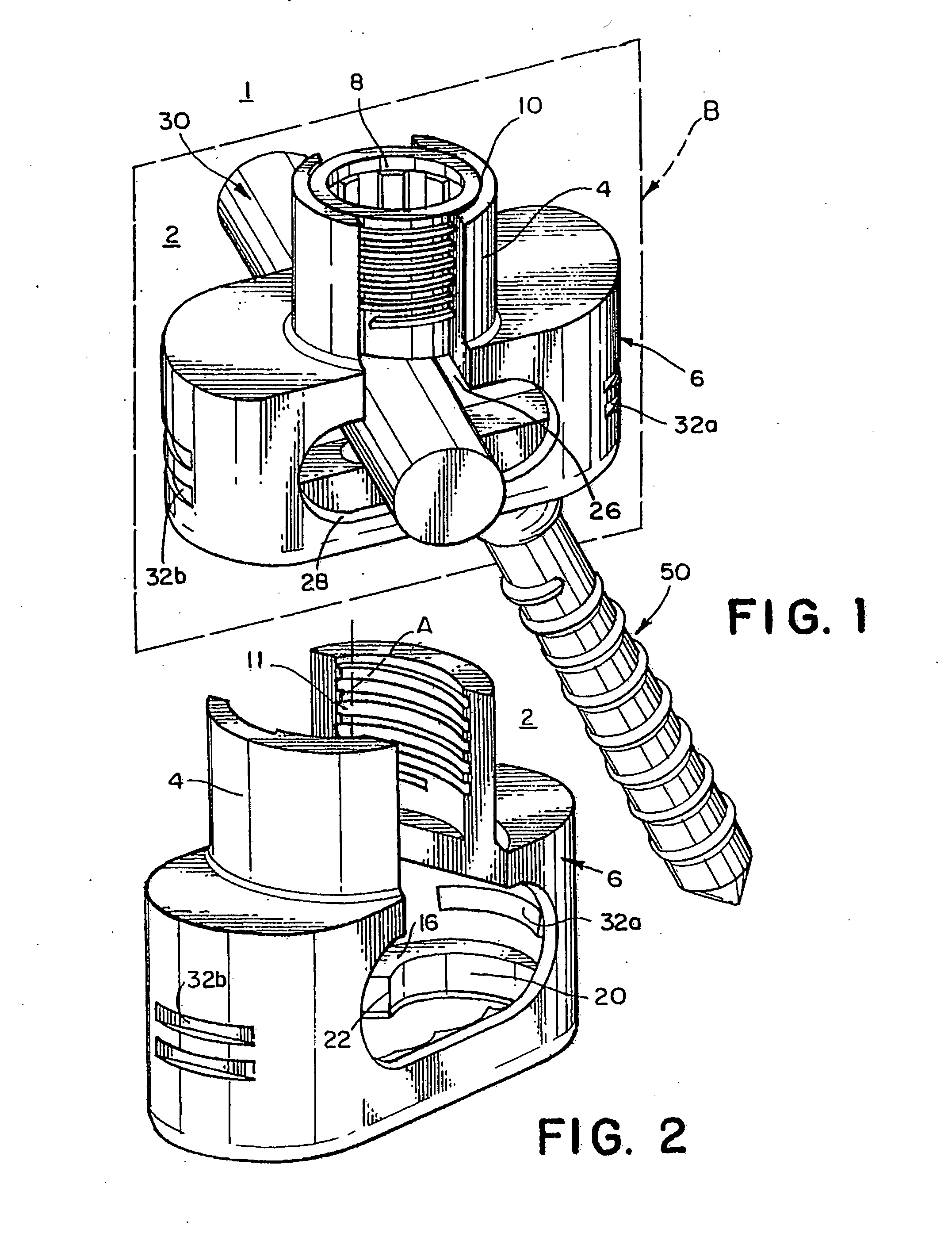
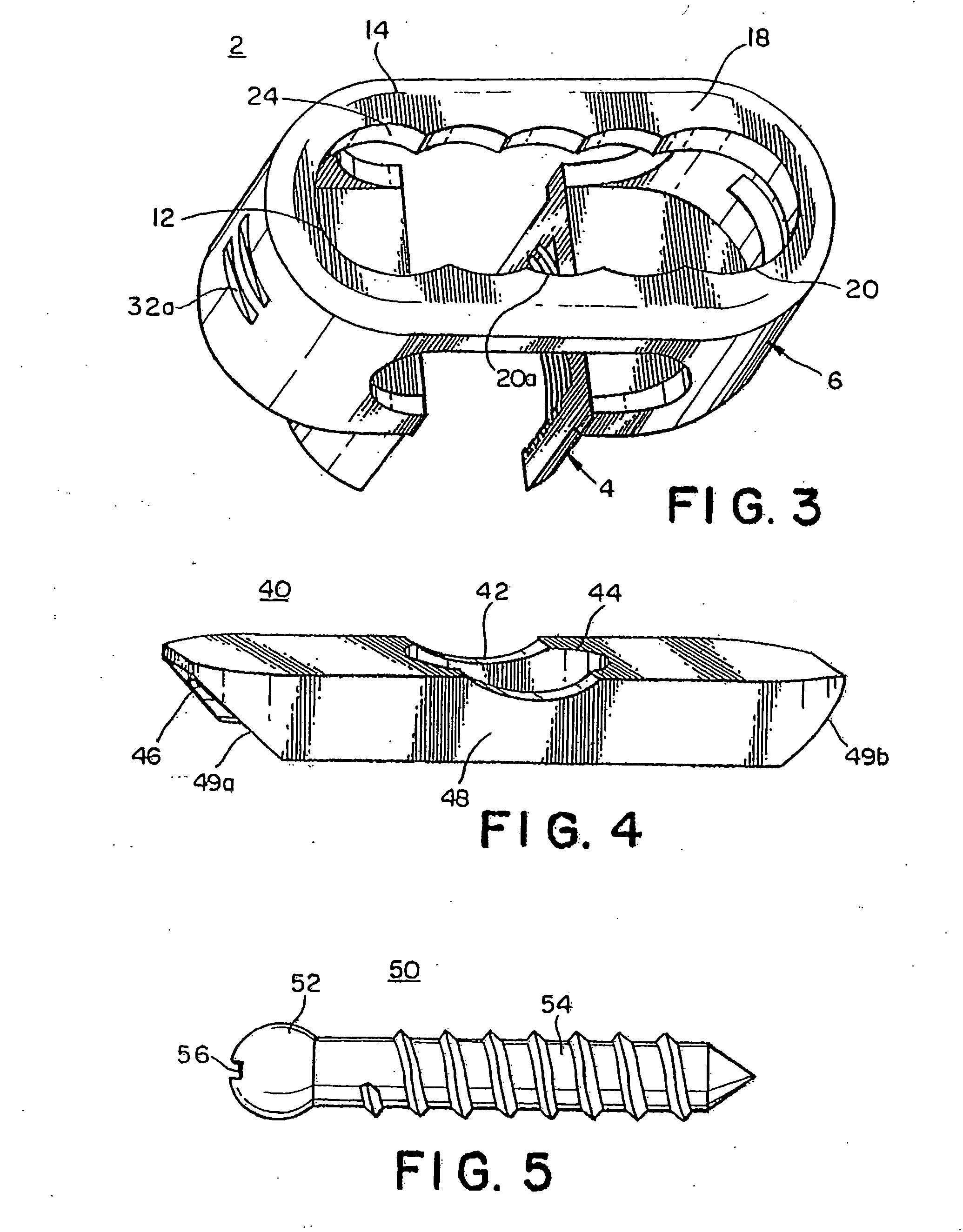
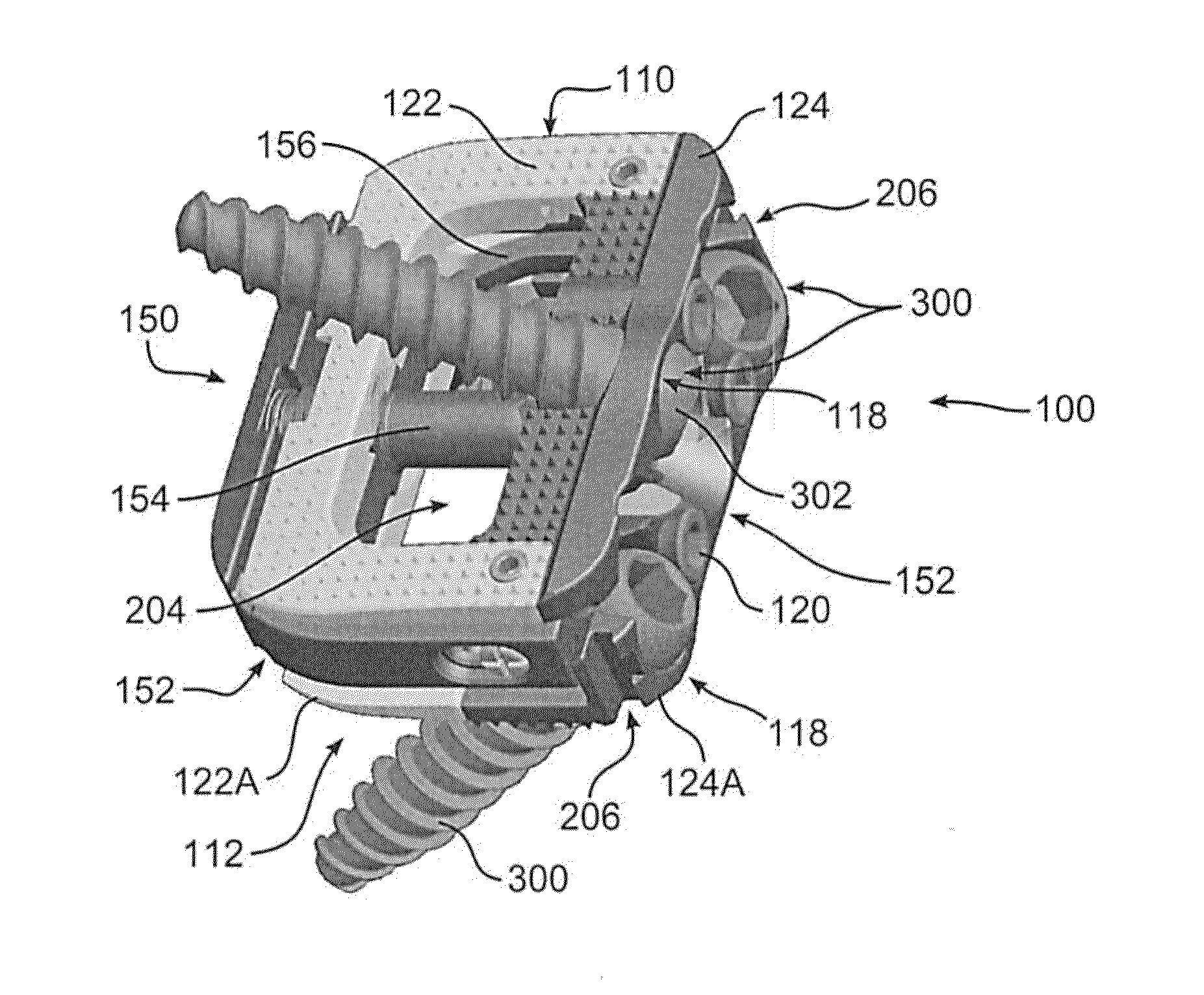
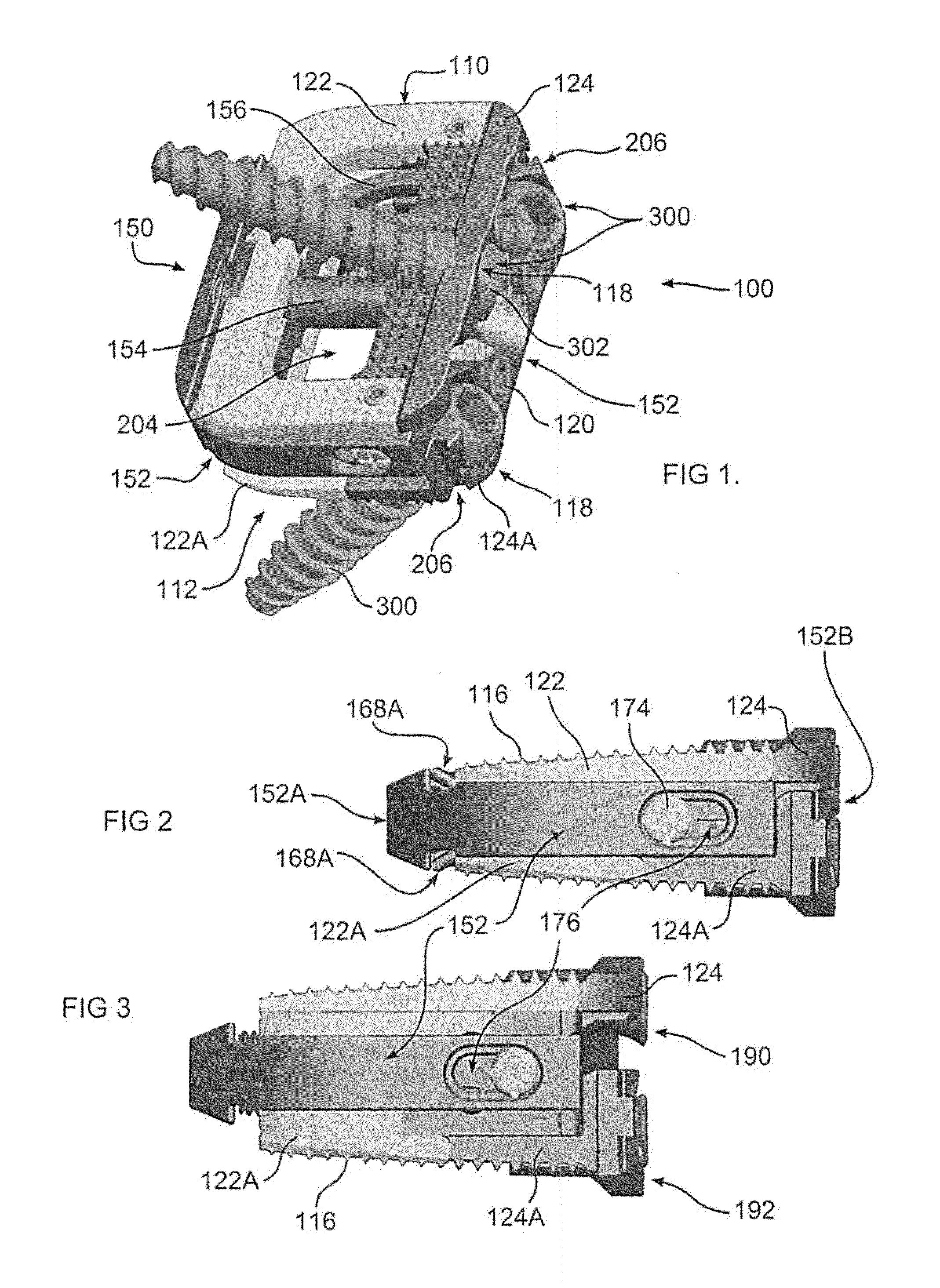
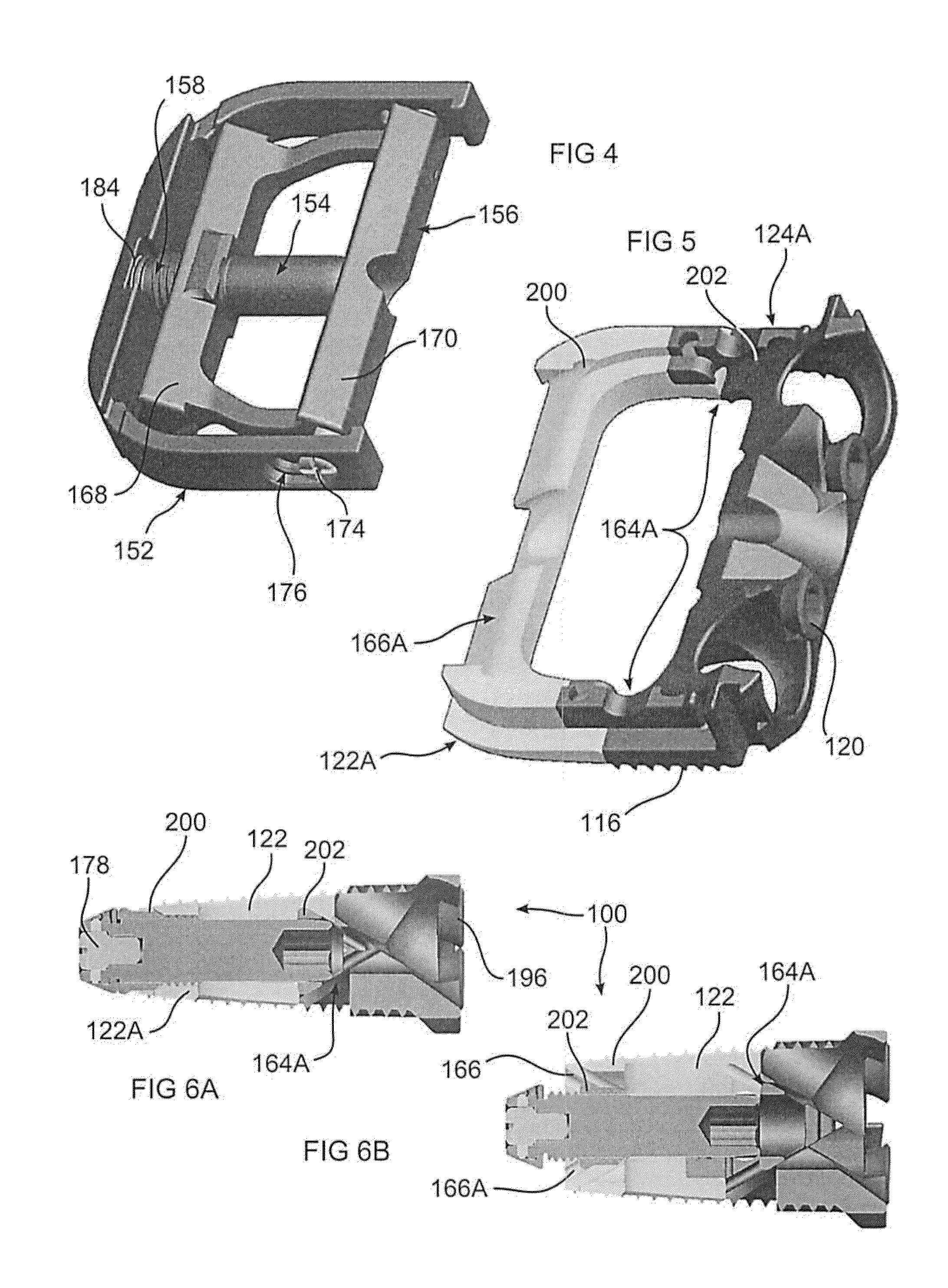
Apparatuses, systems and methods for bone fixation
Apparatuses, systems and methods for bone fixation are disclosed herein. A fixation apparatus is disclosed having a head portion having outer wall sections at least partially surrounding a central hollow area, and the head portion also having an inner bottom surface. A shank portion can extend from the head portion. An expander hub is provided for positioning at least partially within the central hollow area of the head portion and can be seated at least partially on the inner bottom surface of the head portion. The expander hub is rotatable to force the outer wall sections of the head portion outwardly for engaging and locking the fixation apparatus in place when the fixation apparatus is positioned within a hole of a plate. The fixation apparatus can advantageously be used with a plate whereby the fixation apparatus and plate can compress bone separately from locking the fixation apparatus in a desired position. Also, the angle, alignment or position of the fixation apparatus can be changed if desired even after locking of the fixation apparatus. Separate drivers can be used to drive the fixation apparatus, to rotate the expander hub to lock it in place, and to remove the fixation apparatus. The drivers can be cannulated as desired such that the drivers can be assembled in a nested and concentric configuration and can be used without removal from the nested configuration.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI
Stand alone intervertebral fusion device
InactiveUS20120078373A1Small incisionAvoid fixationBone implantSpinal implantsSpinal cageLamina terminalis
An angled fixation device, such as an angled screw. This angled fixation device may be used by the surgeon to secure a spacer to a spinal disc space. The proximal end portion of the angled fixation device is driven perpendicular to the anterior wall of the spacer, and so is parallel to the vertebral endplates and in-line with the inserter. The distal end portion of the angled fixation device is oriented at about a 45 degree angle (plus or minus 30 degrees) to the vertebral endplate it enters.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
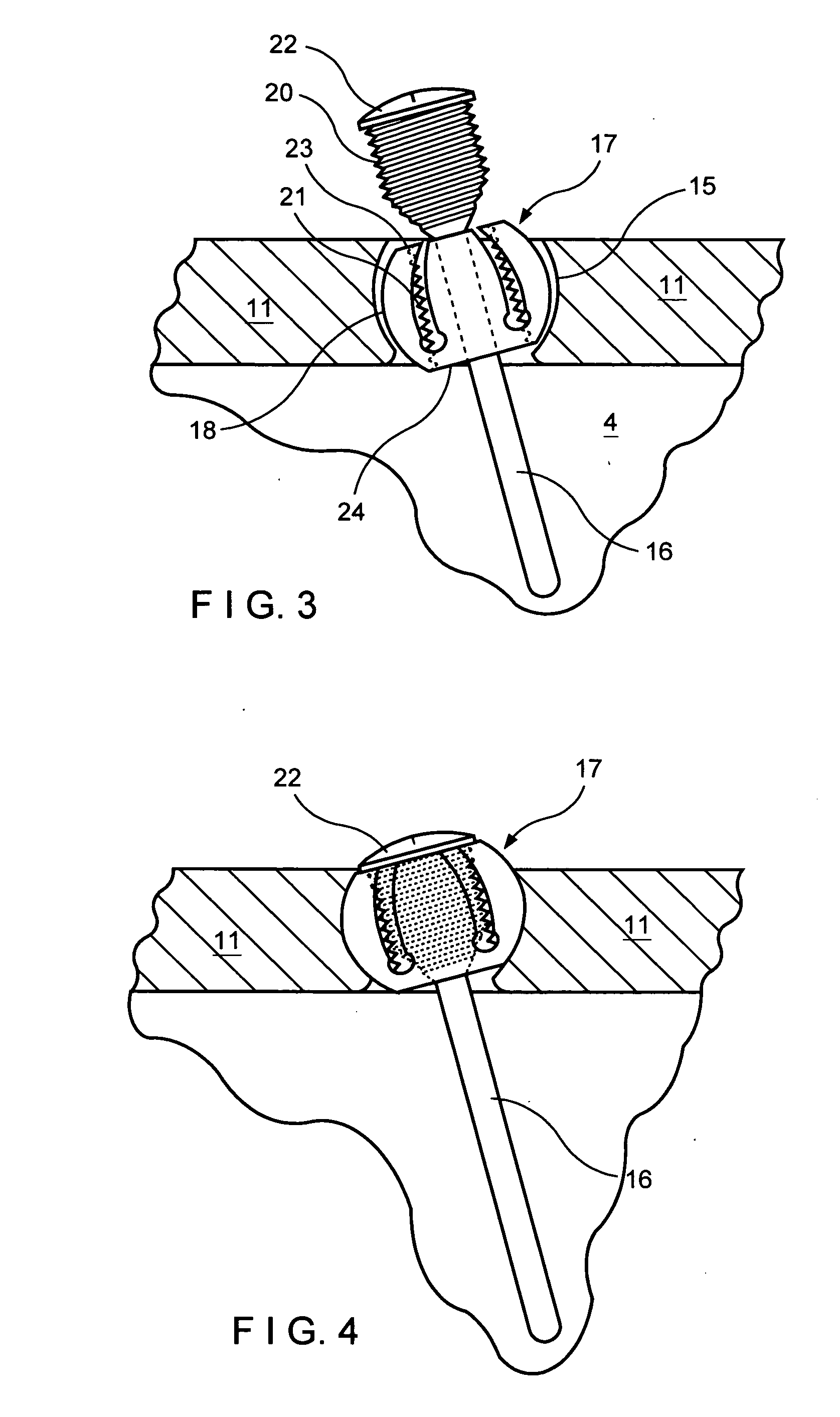
Bone anchor and deployment device therefor
A rivet-like bone anchor has a floating washer at its head that can adapt to an angled bone surface and, thereby, better secure a tissue thereto. The anchor includes a rivet, an expandable sleeve, and a washer. The rivet includes a head and an elongate body having proximal and distal ends, the head being mounted on the proximal end of the elongate body. The expandable sleeve has an inner bore adapted to receive the rivet body. The washer “floats” at a proximal end of the sleeve. As the rivet is inserted into sleeve, the sleeve expands into an interference fit with the bone. The head of the rivet, moreover, forces the floating washer into contact with the tissue at an angle that conforms to that of the underlying bone surface. A deployment tool permits the anchor to be deployed without application of unnecessary counterforce. The tool includes an outer tube, the distal end of which can hold the anchor housing, e.g., via a screw fit. A rod, which is slidably disposed within the bore of the tube, can be used to push the rivet into the expandable sleeve so that the sleeve expands into the bone, so that the floating washer is forced into position against the bone surface, and so that anchor is broken away from the housing. This can be effected, for example, by squeezing the distal ends of the outer tube and the rod together, e.g., in the manner that the end of a syringe is squeezed.
Owner:INNOVASIVE DEVICES
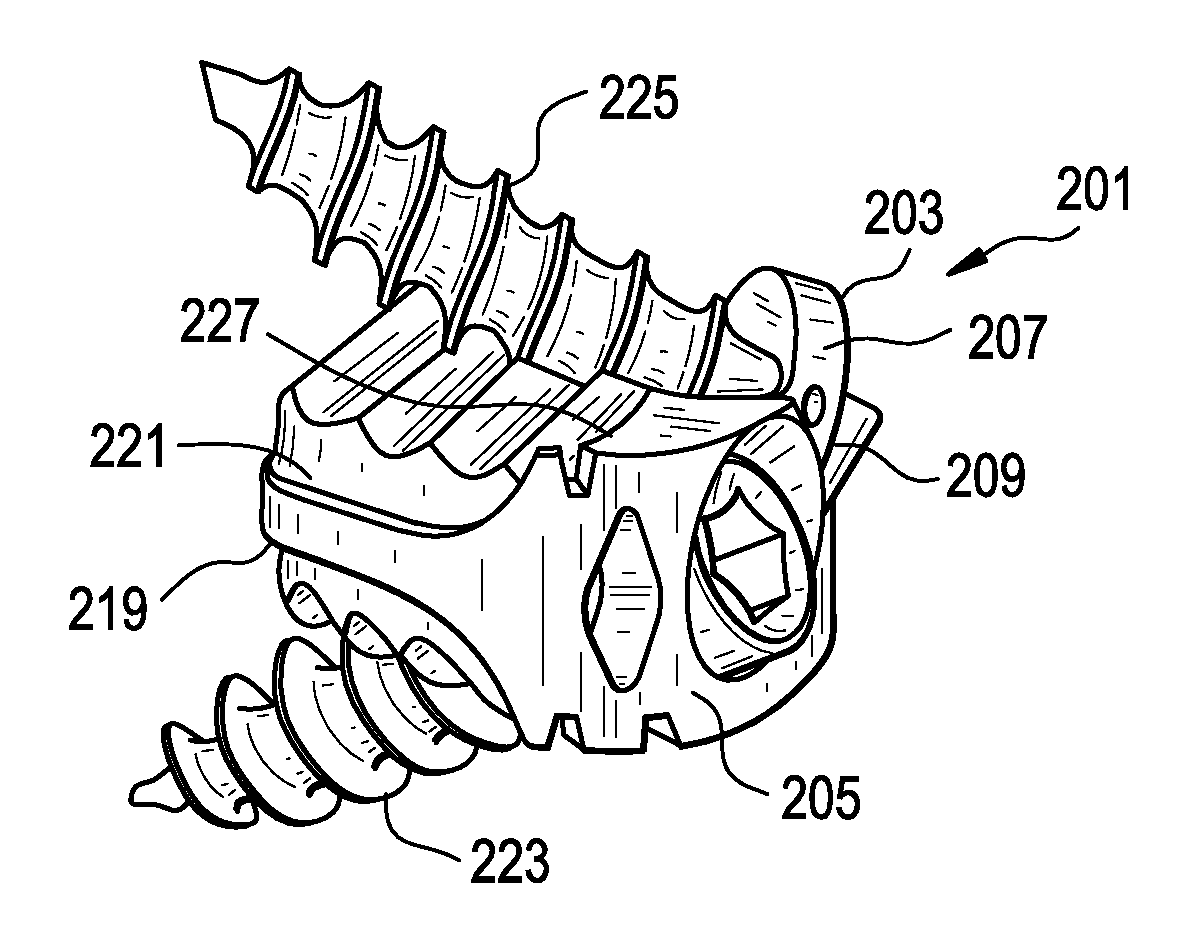
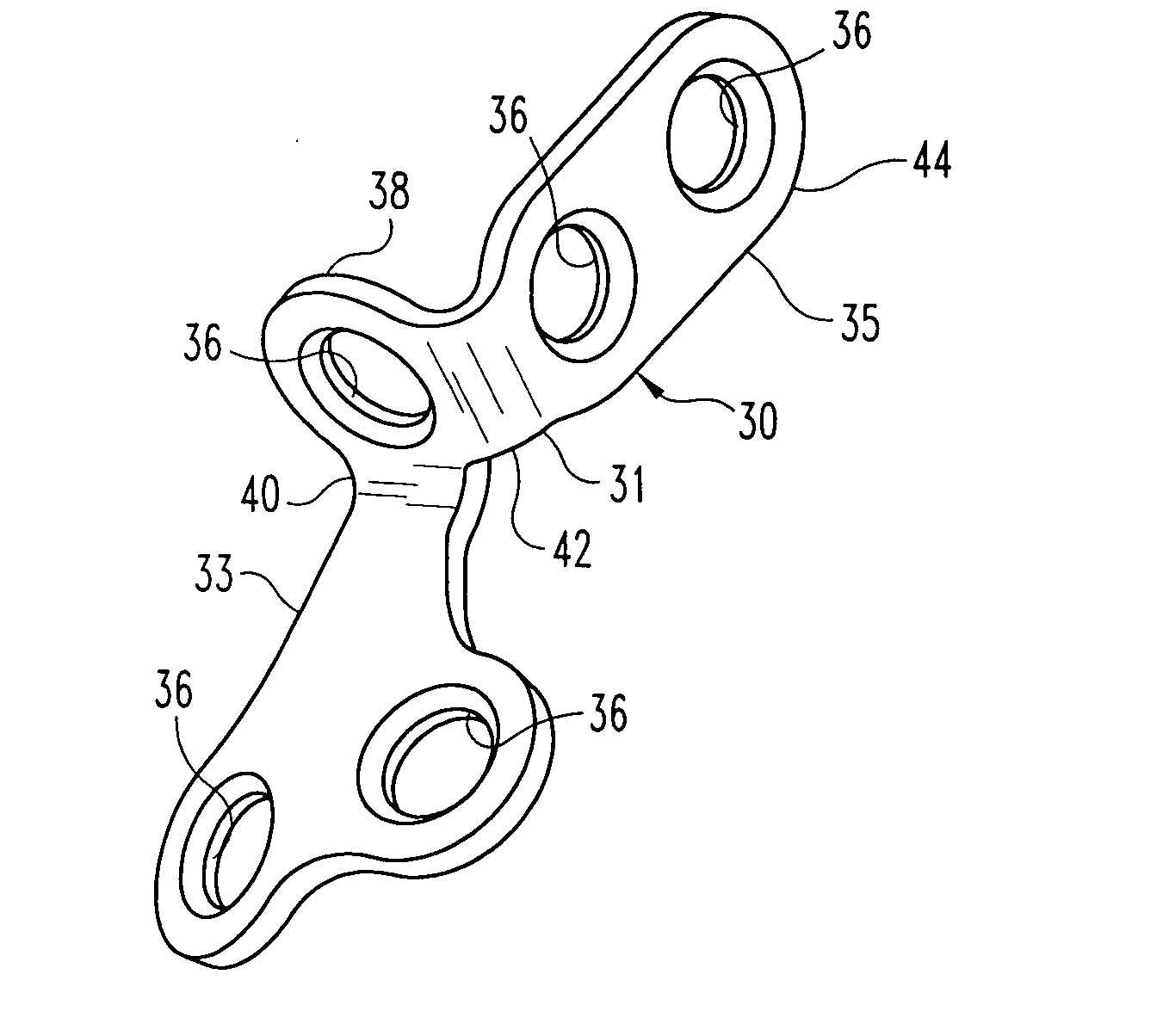
Bone fusion device
A bone fusion device for insertion between bones that are to be fused together, such as, for example, the vertebrae of a spinal column. The bone fusion device comprises at least one extendable tab and one or more tab extension assemblies. Each tab extension assembly is able to be adjusted in order to individually control the extension or contraction of a side of the tab thereby enabling adjustment of the height and / or angle of the tab with respect to the body of the bone fusion device. Each tab extension assembly is able to be individually adjusted such that the side controlled by each assembly is raised or lowered until the desired tab angle is achieved. The tab is advantageously positioned and angled to correspond to the vertebrae to help brace the device until the bone has fused.
Owner:NEUROPRO TECH
Method of Manufacturing Tissue Sealing Electrodes
ActiveUS20120046662A1Reduce widthReduce arcingSurgical instrument detailsSurgical forcepsEngineeringBiological activation
The present disclosure relates to an electrode assembly for use with an electrosurgical instrument. The electrode assembly includes a pair of opposing jaw members and an electrode positioned on each jaw member. One or both of the electrodes includes a tissue contacting surface that has an outer periphery and defines a side surface depending therefrom. The tissue contacting surface and the side surface include a conjoining edge formed at a first predetermined angle that defines a first linear transition zone dimensioned to reduce arcing between the opposing jaw members during activation of the electrosurgical instrument.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
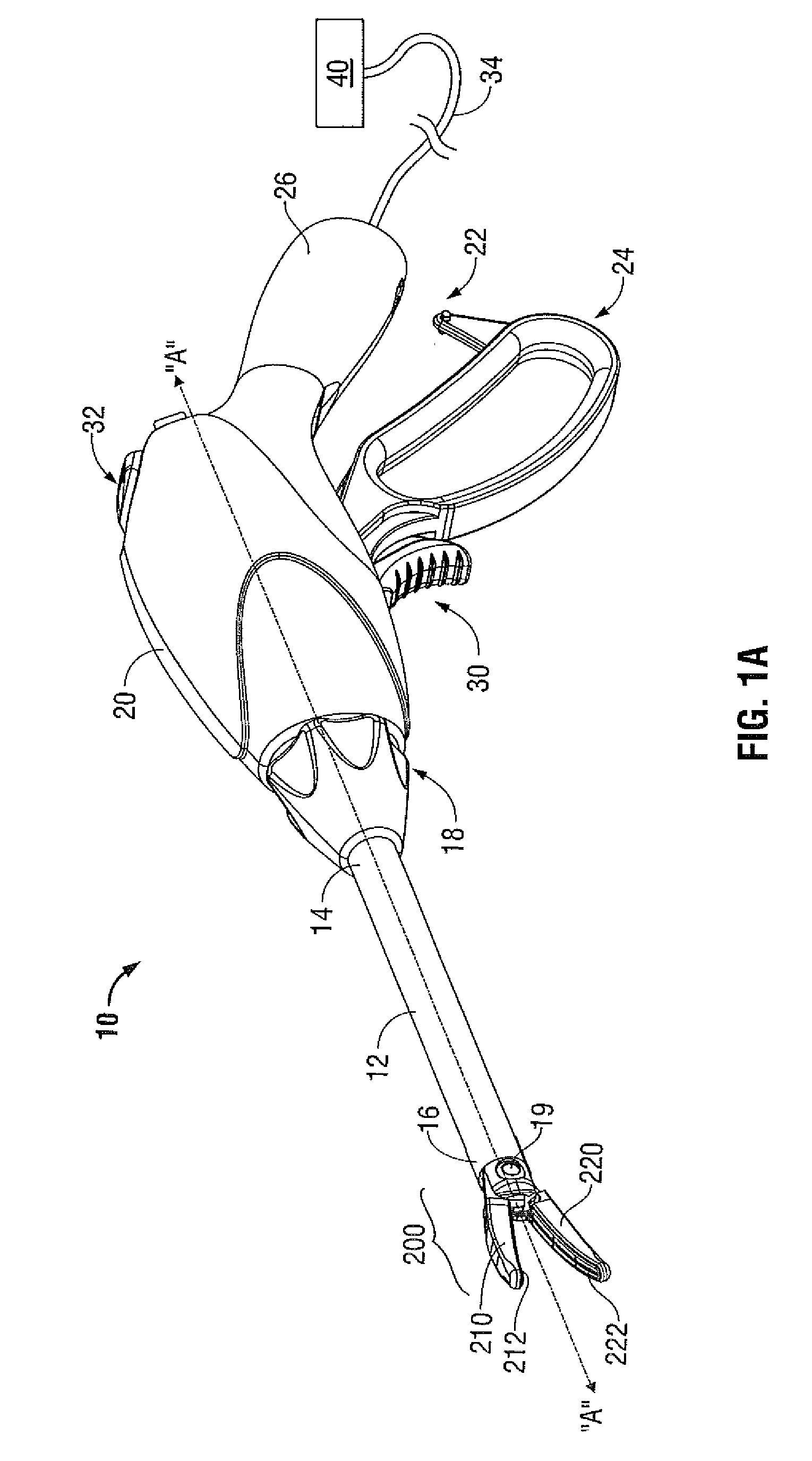
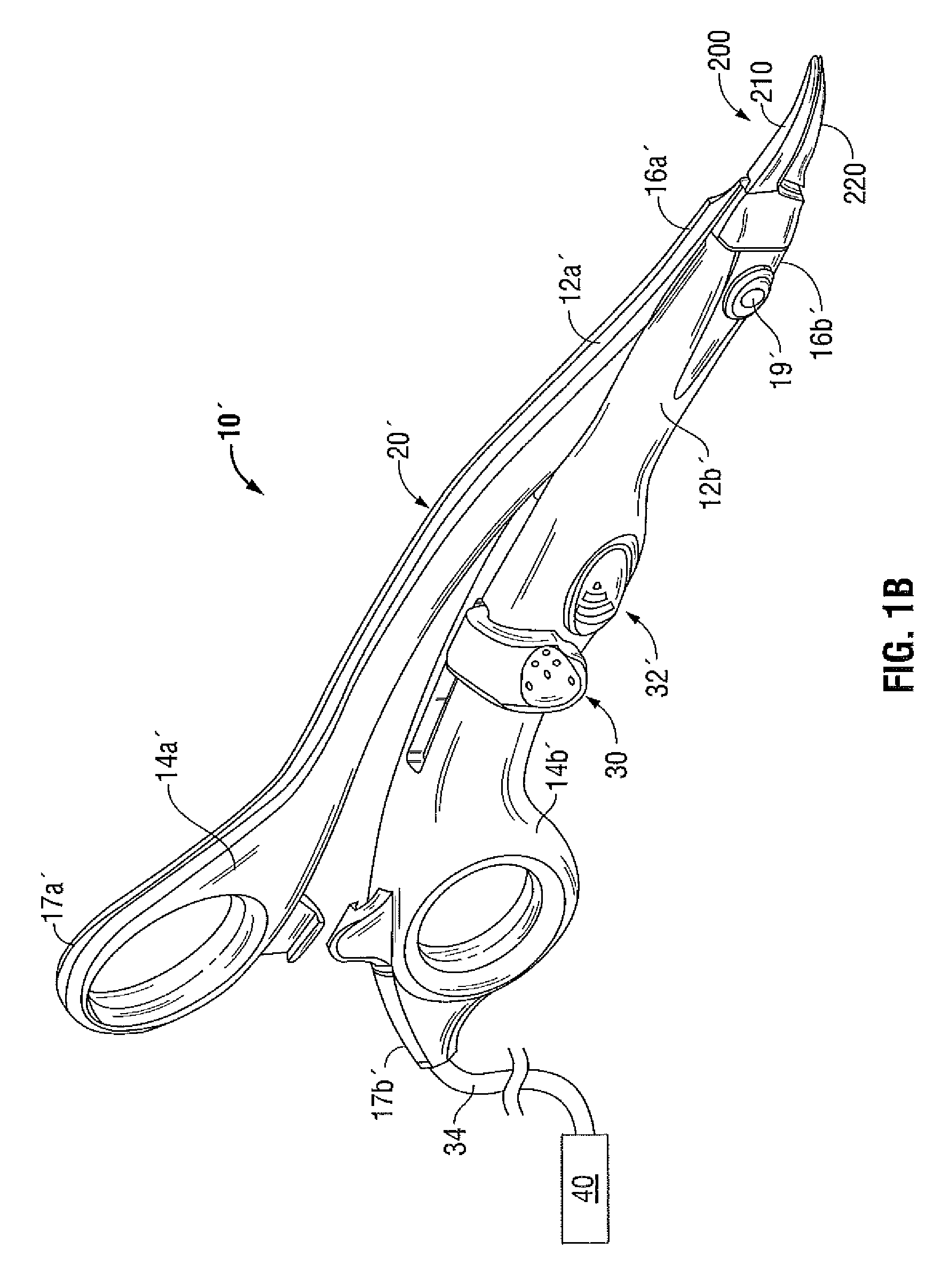
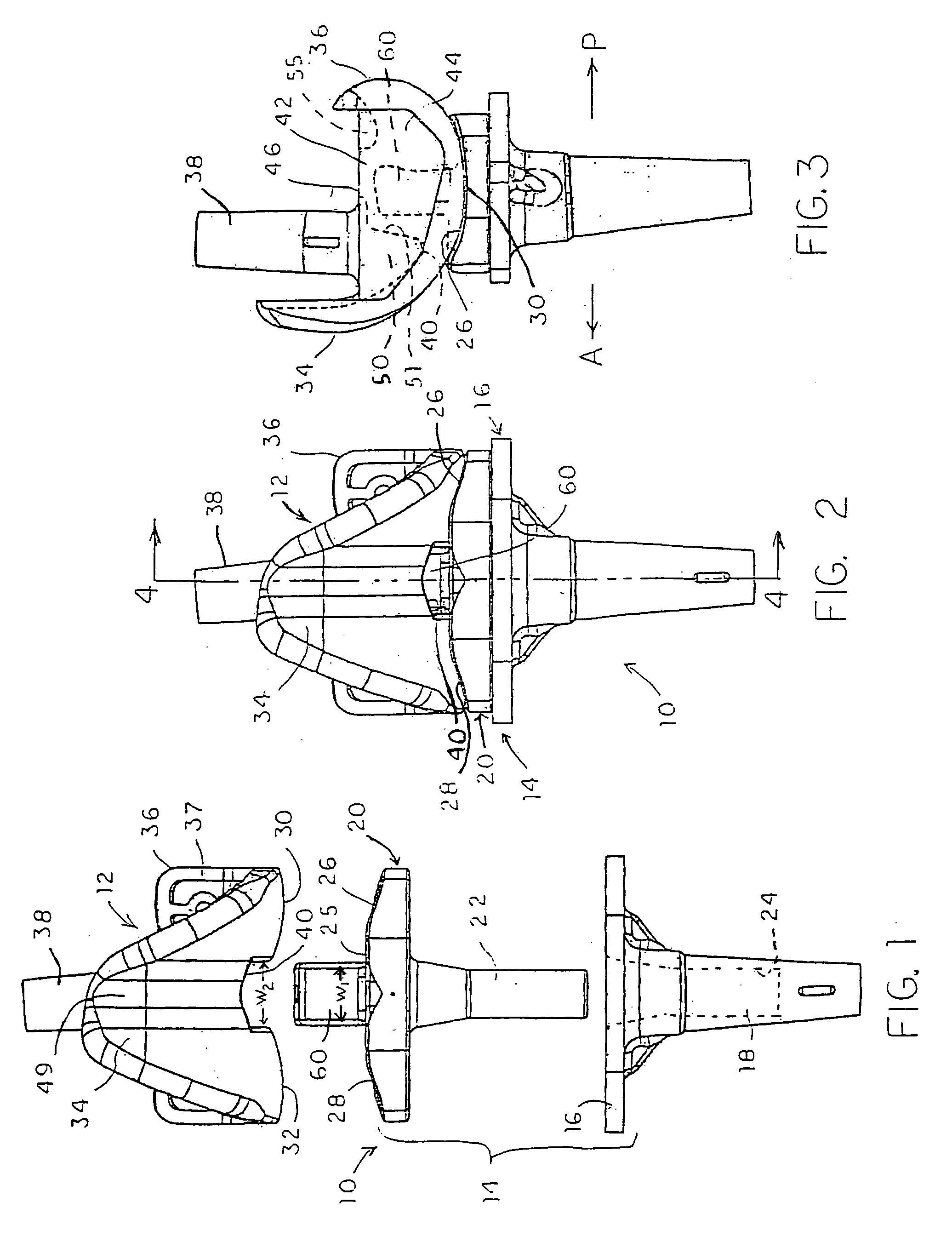
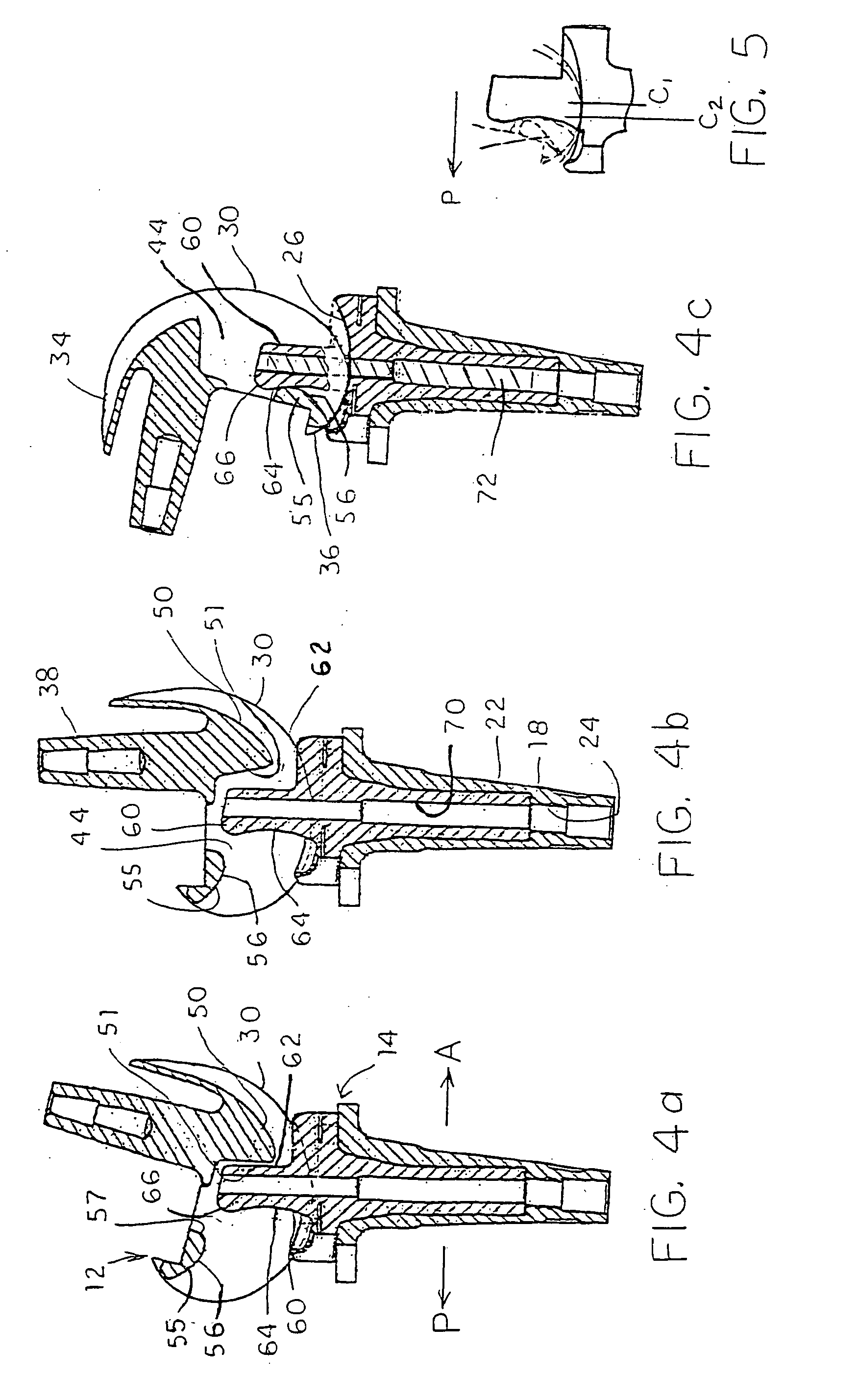
Articulating Steerable Clip Applier for Laparoscopic Procedures
A long articulating steerable clip applier affixed to a user-operated handle. A surgical jaw assembly is attached to the other end of the clip applier. The clip applier is composed of articulating phalanges that are connected end to end by pivoting links and capable of angulations relative to one another when subjected to a tensile force. Each phalange has opposing s-shaped exterior grooves that form two continuous spiral-shaped channels for holding tension wires once the phalanges are assembled. Multiple tension wires are attached to opposite ends of adjacent phalanges. When each wire is pulled, this tensile force causes the phalanges to pivot at equivalent angles with each other. As each individual phalange pivots by an equivalent angle, the sum of these angles causes the free end of the clip applier to pivot by a large angle or a cascading actuation effect.
Owner:CONMED CORP
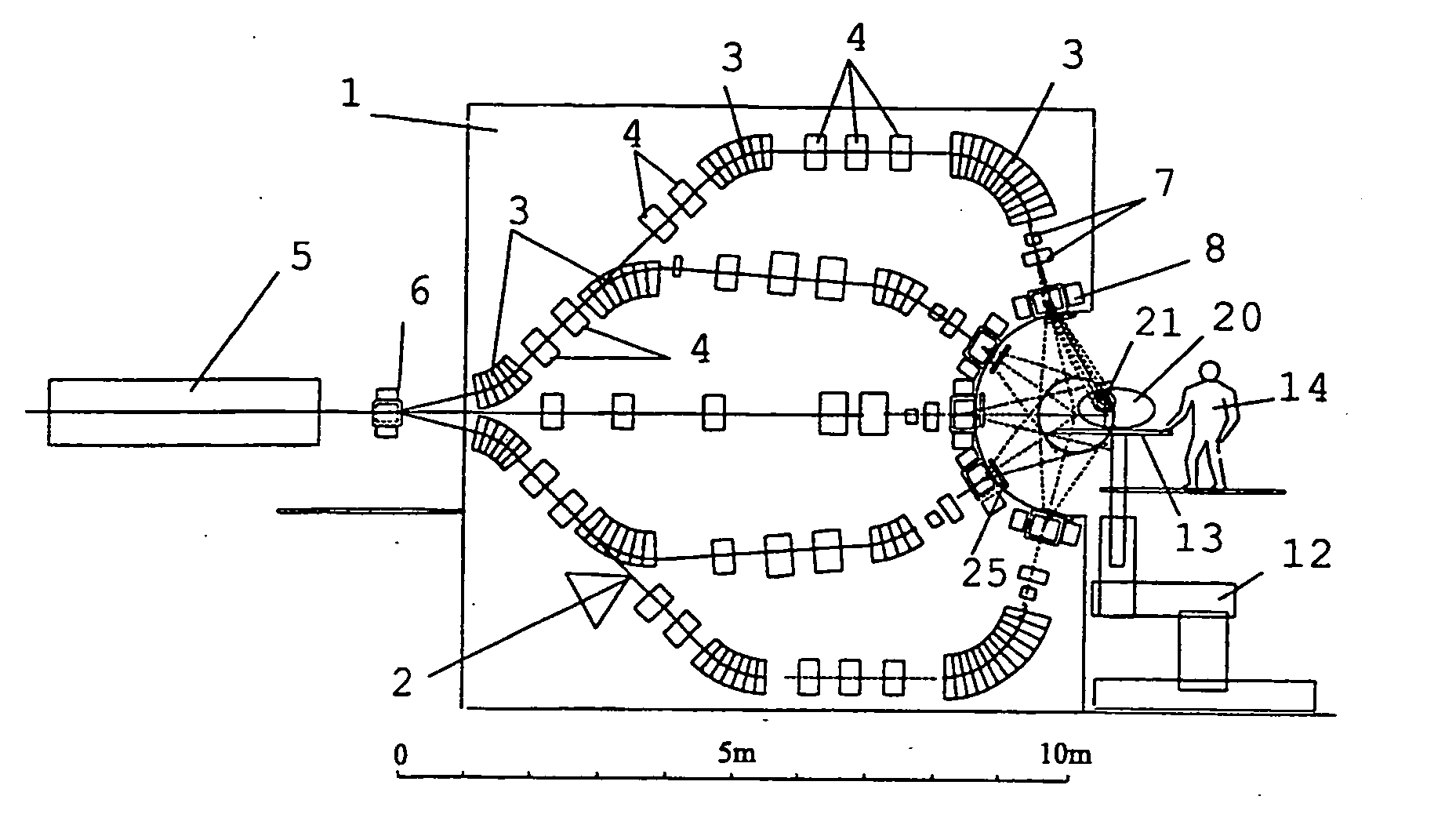
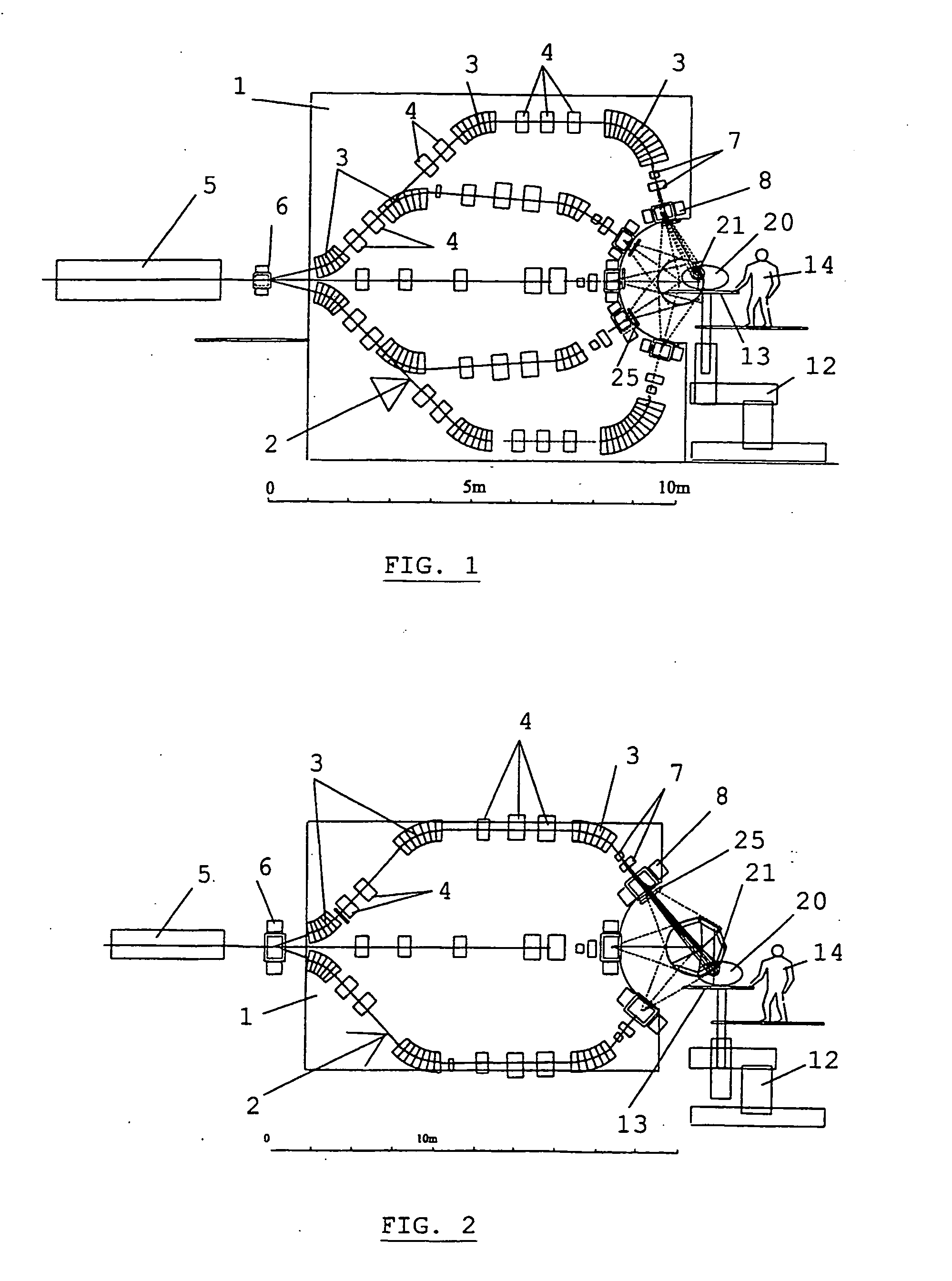
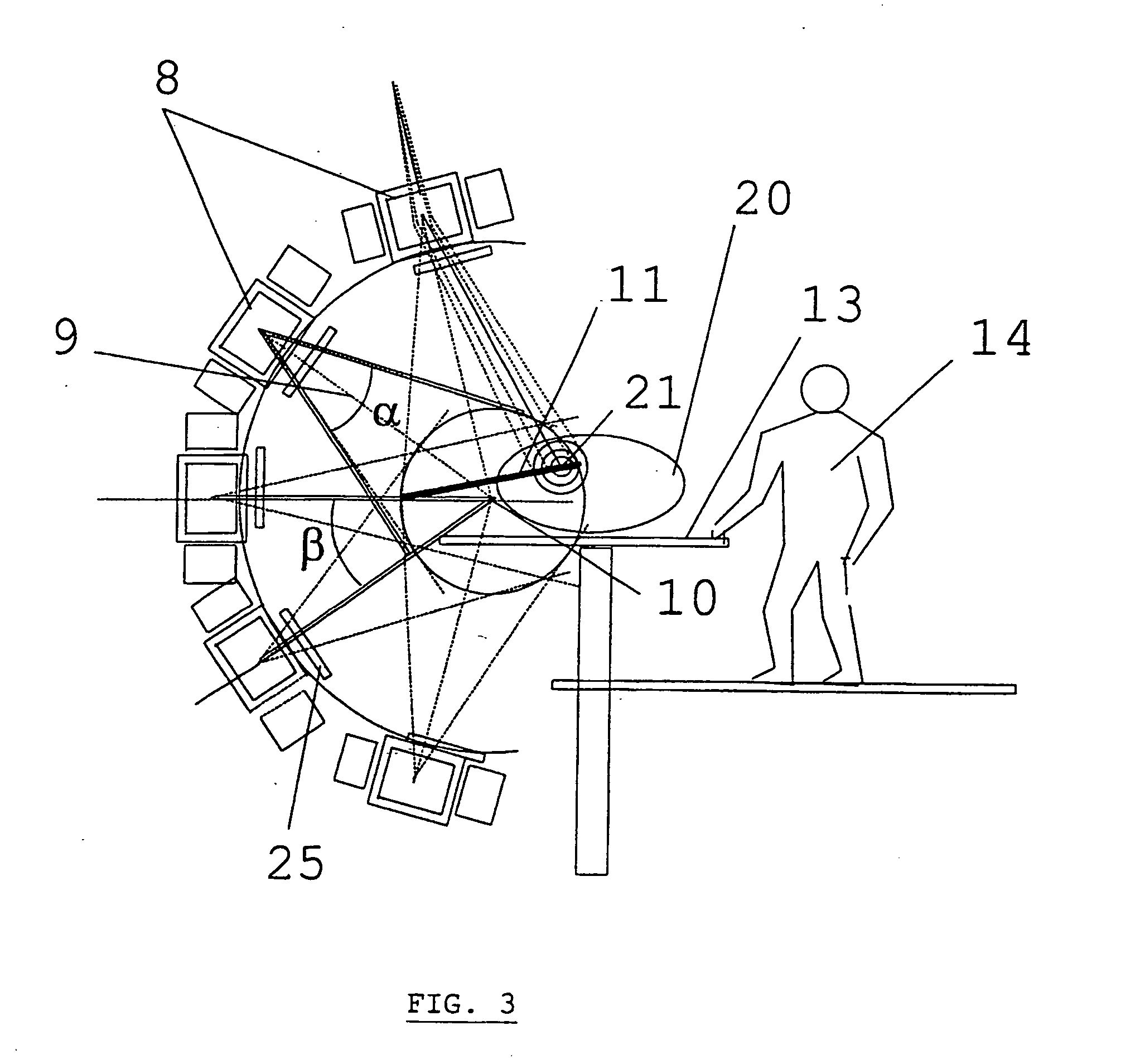
Device for irradiation therapy with charged particles
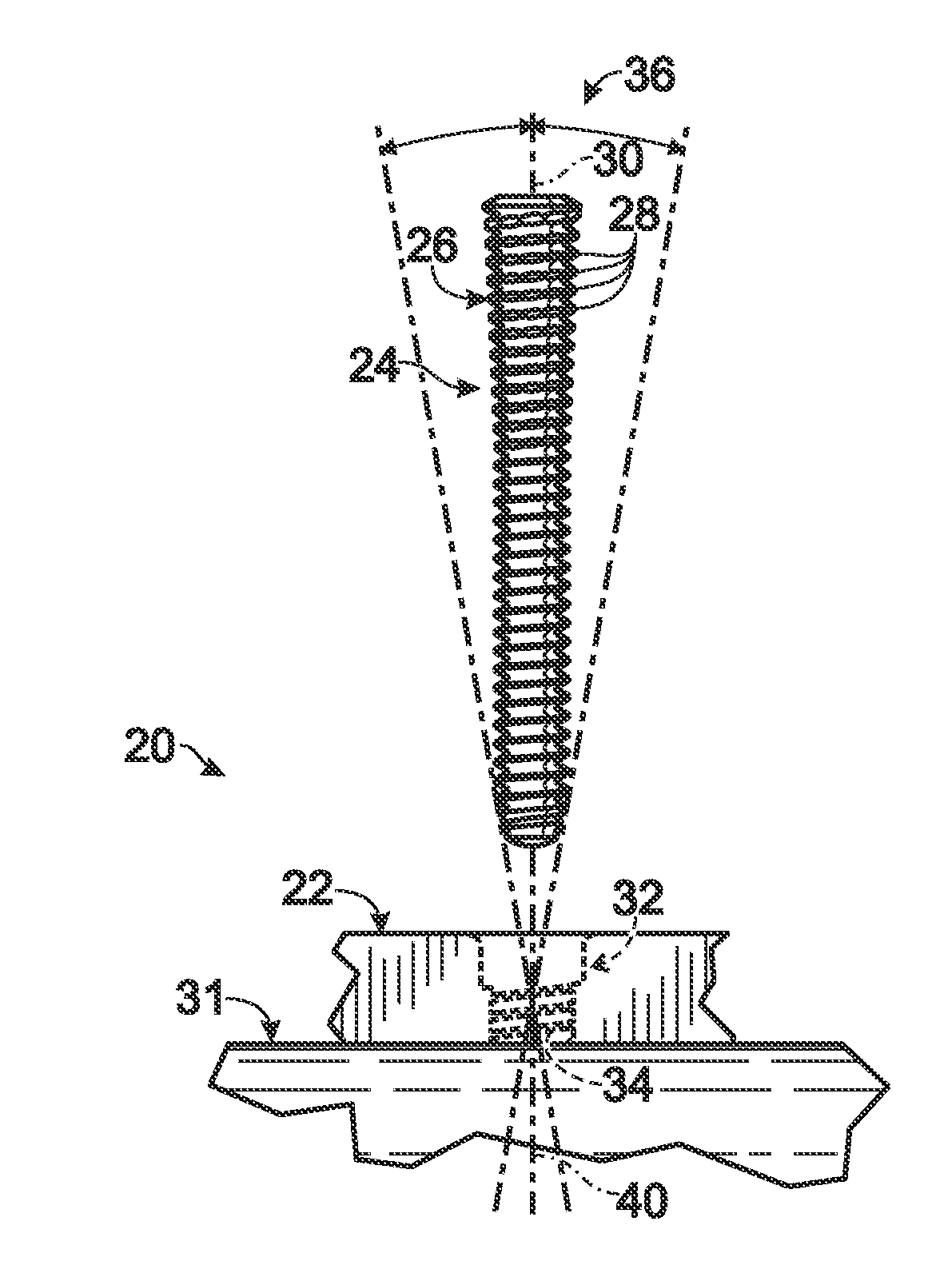
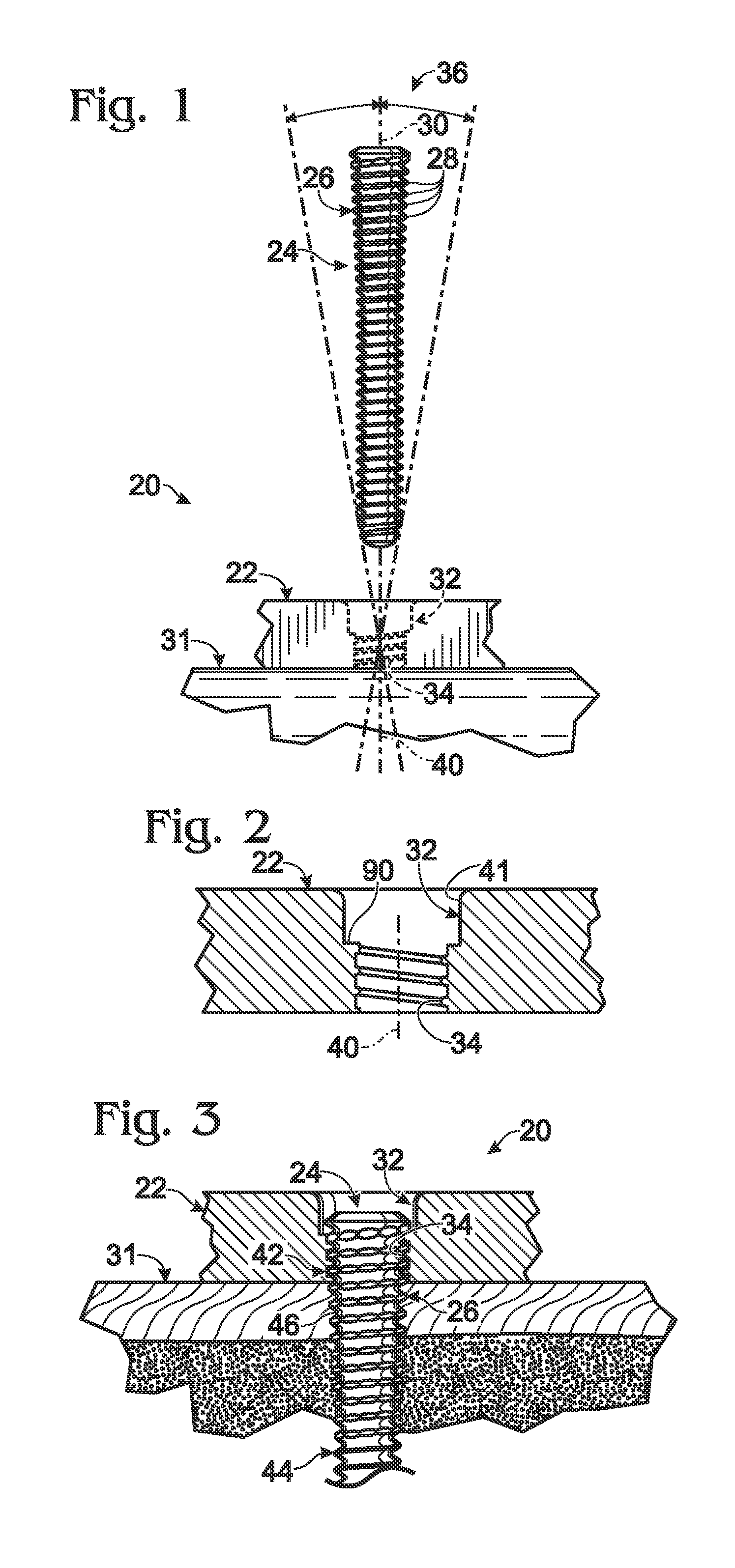
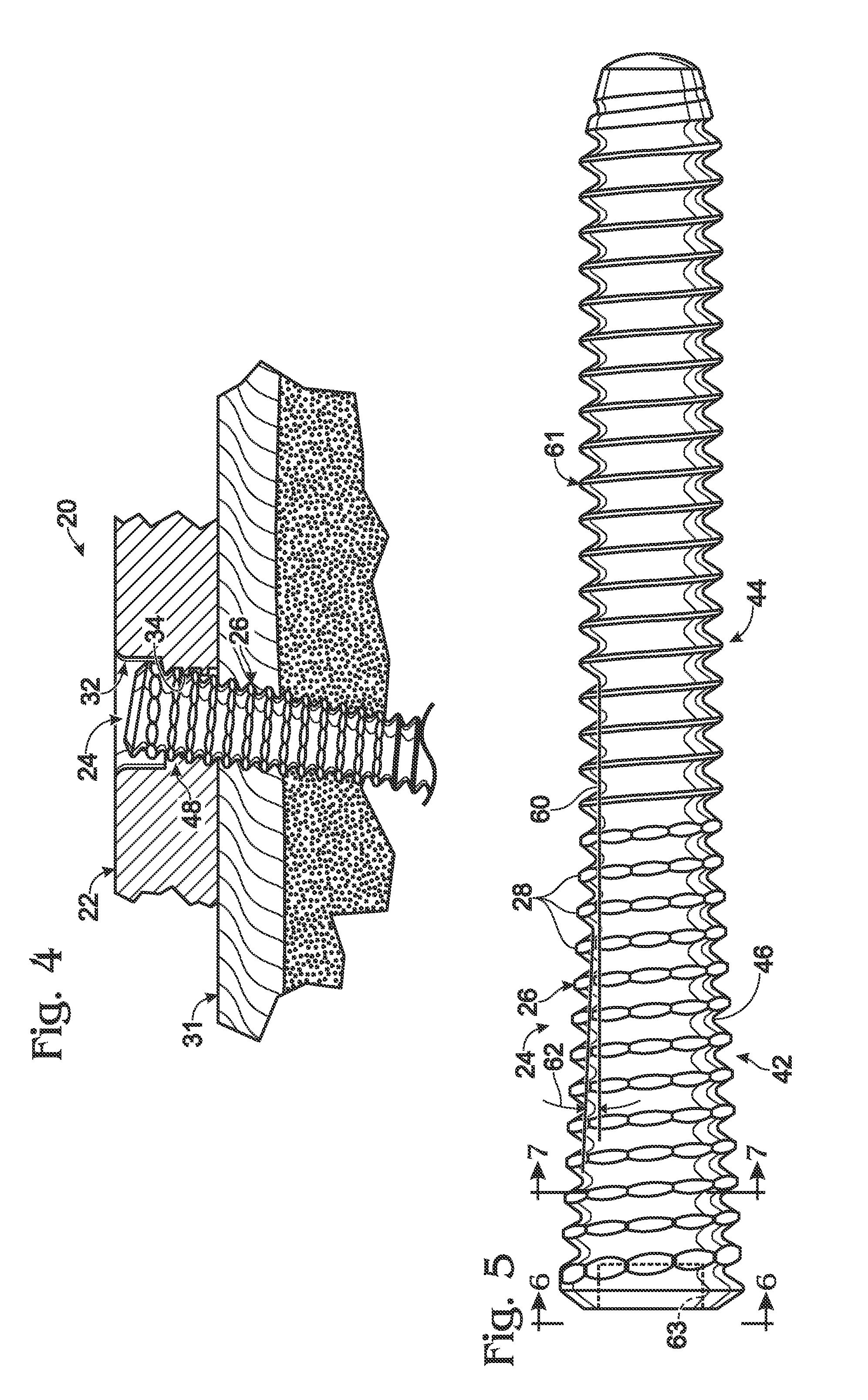
InactiveUS20060106301A1Radiation/particle handlingElectric discharge tubesVertical planeGonial angle
The present invention is related to a device for irradiating a patient with a charged particle beam, comprising a number of beam channels attached to a vertical wall, wherein a deflection magnet is present at the end of each channel. This deflection magnet is able to deflect the beam in the vertical plane over a given angle range. The couch whereon the patient is reclining is mobile in the vertical plane, so that the combined movement of the patient, and the variable deflection of the beam allow one point in the patient to be irradiated from several angles in the vertical plane.
Owner:ION BEAM APPL
Bone screw apparatus, system and method
A bone screw apparatus, system, and method for assisting in the placement and alignment of a bone screw and for aligning bone are described. The present invention allows a surgeon to position a bone screw in a desired position and adjust a coupling element in a variety of positions and angles with respect to the bone screw.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
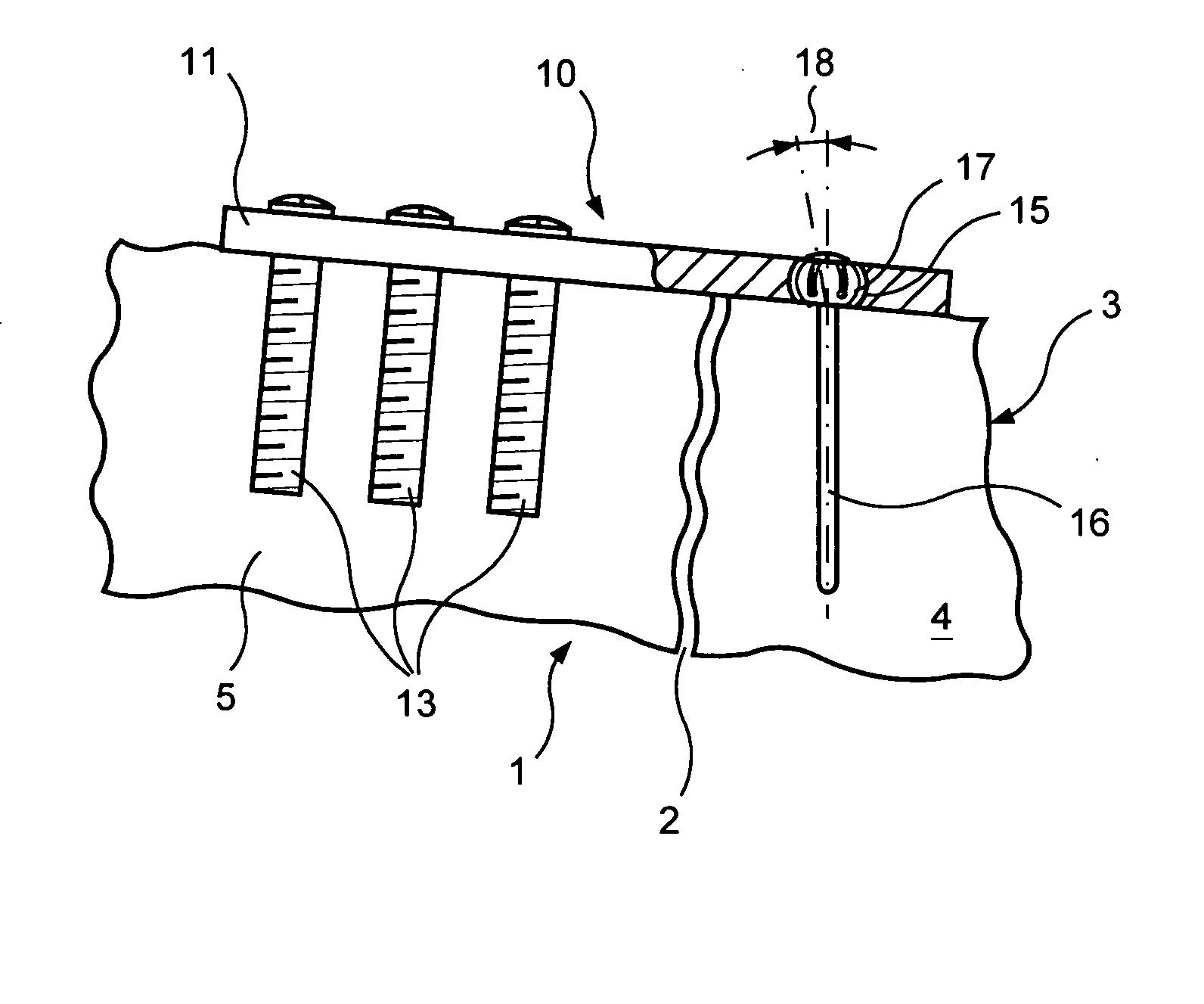
Fracture fixation system
ActiveUS20050154392A1Reliable simple securingImprove the immunitySuture equipmentsLigamentsMedicineGonial angle
A fracture fixation system in which a plate is secured to stable bone and posts are inserted at varying angles into an unstable bone fragment by engaging in rotatable bearings which are fixedly secured in the plate when the posts are fully engaged in the bone fragment. The bearings are formed as truncated spherical members having a number of longitudinal slots extending partway along the length of the bearing to form petals which are expanded outwardly when the posts are advanced in the bearing to produce non-uniform distribution of forces between the bearing and the plate which generate force couples to resist angulation of the posts and loss of fracture fixation. Various other ways of producing non-uniform force distribution are described.
Owner:MEDOFF ROBERT J +2
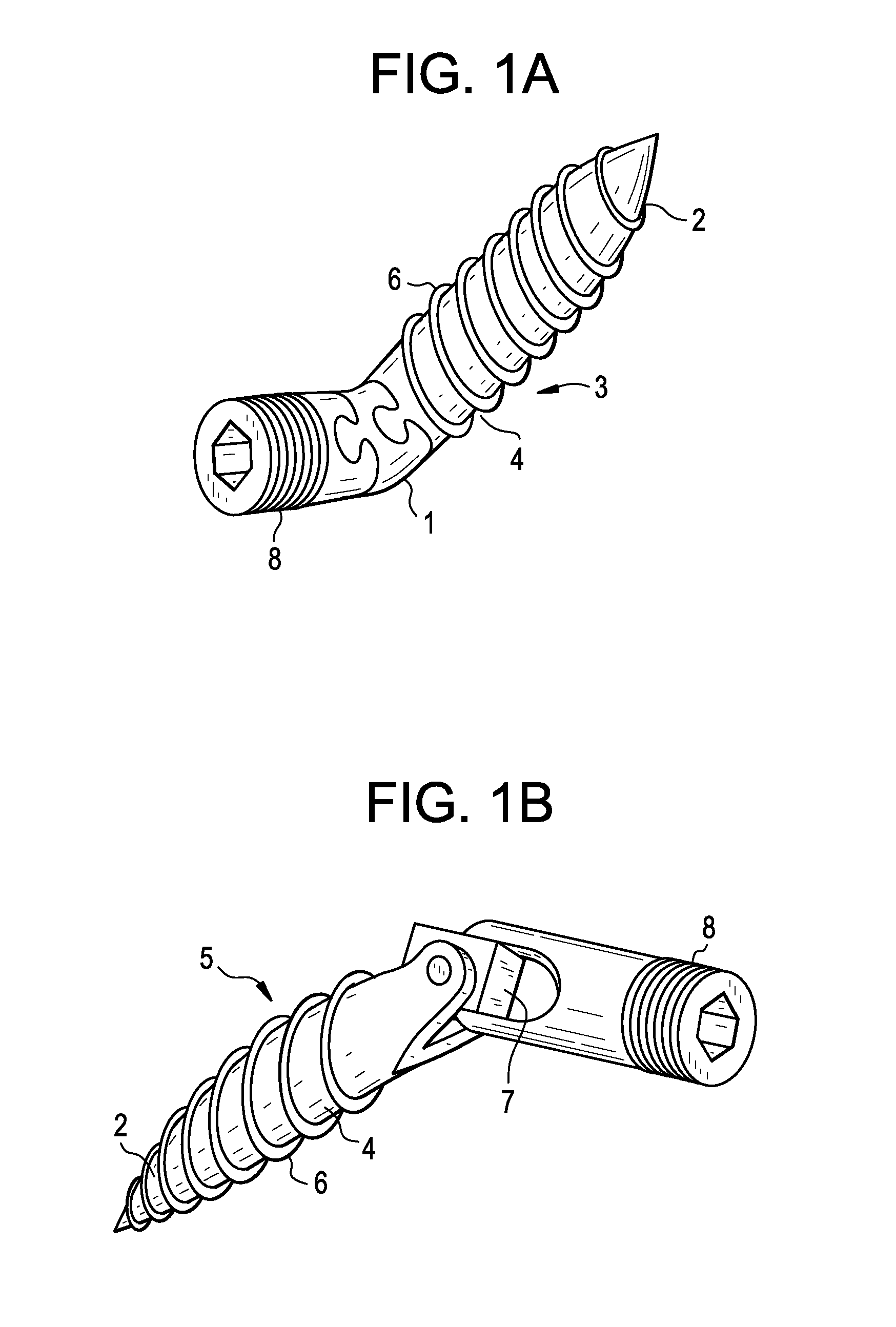
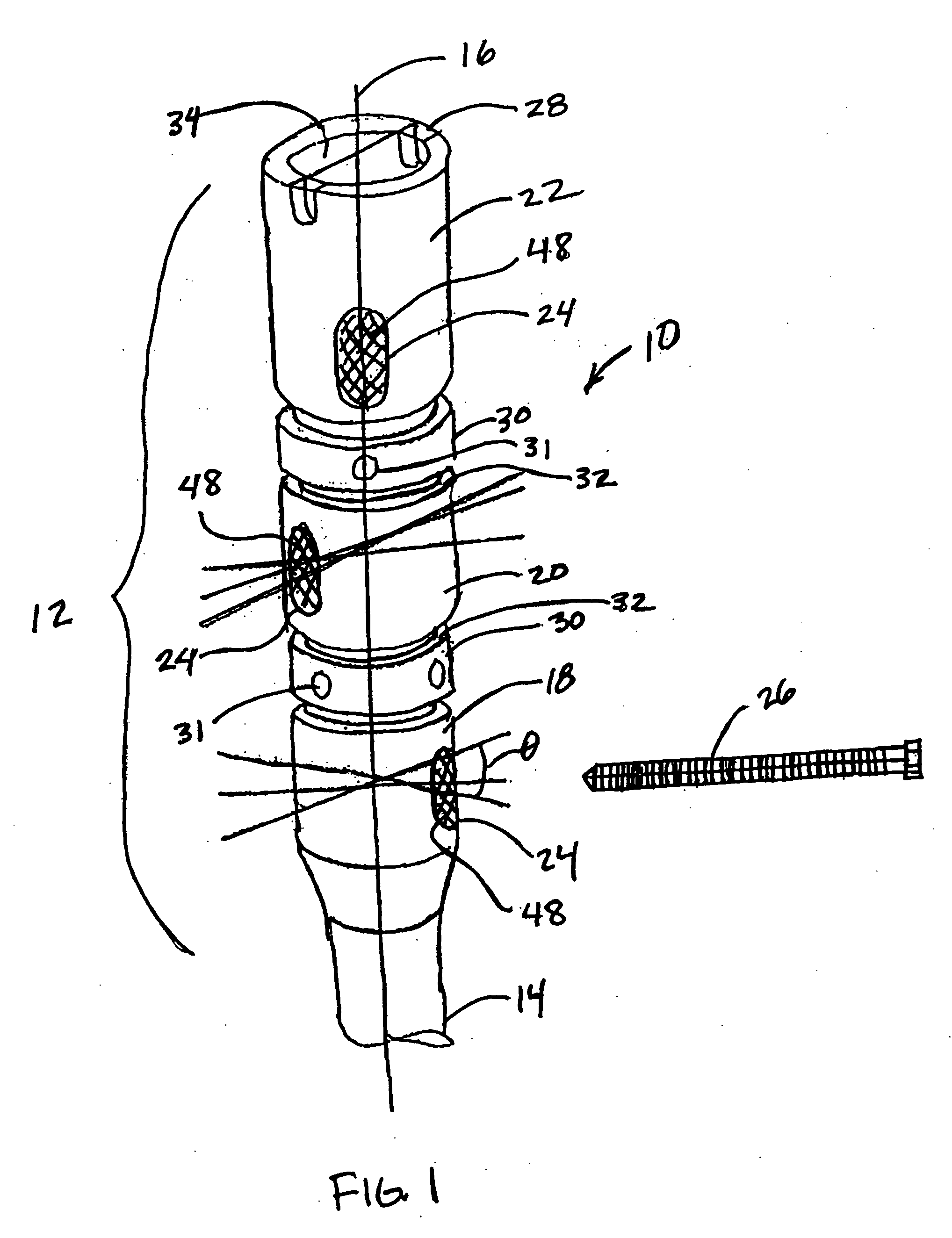
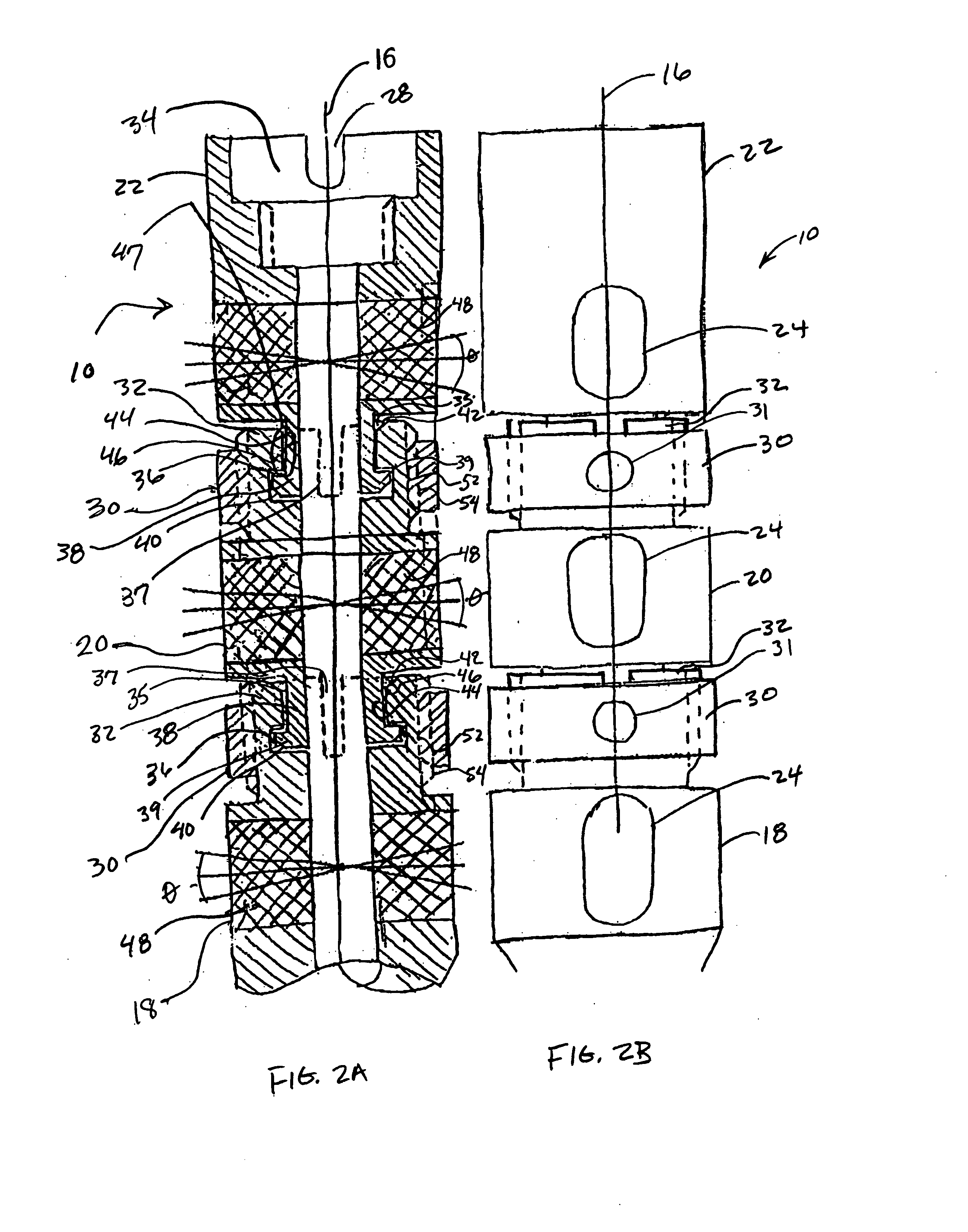
Intramedullary nail for long bone fractures
InactiveUS20050055023A1Simple designEasy to processInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsLocking mechanismLONG BONE FRACTURE
An intramedullary nail for treating long bone fractures. The nail includes a proximal portion that may have a plurality of segments. The segments may be rotatable 360 degrees about a longitudinal axis of the nail such that the position of bone screw openings in the segments can be adjusted to a desired orientation. Locking rings or other locking mechanisms may be provided between the segments to lock the segments in place and allow the segments to be unlocked for readjustment of the position of the segments. The bone screw openings may be configured to allow further angular adjustment of the bone screws with respect to the longitudinal axis of the nail. Inserts may be placed within the bone screw openings to support the bone screws in position.
Owner:ADVANCED ORTHOPAEDIC SOLUITONS
Multi-adjustable plate for osteotomy
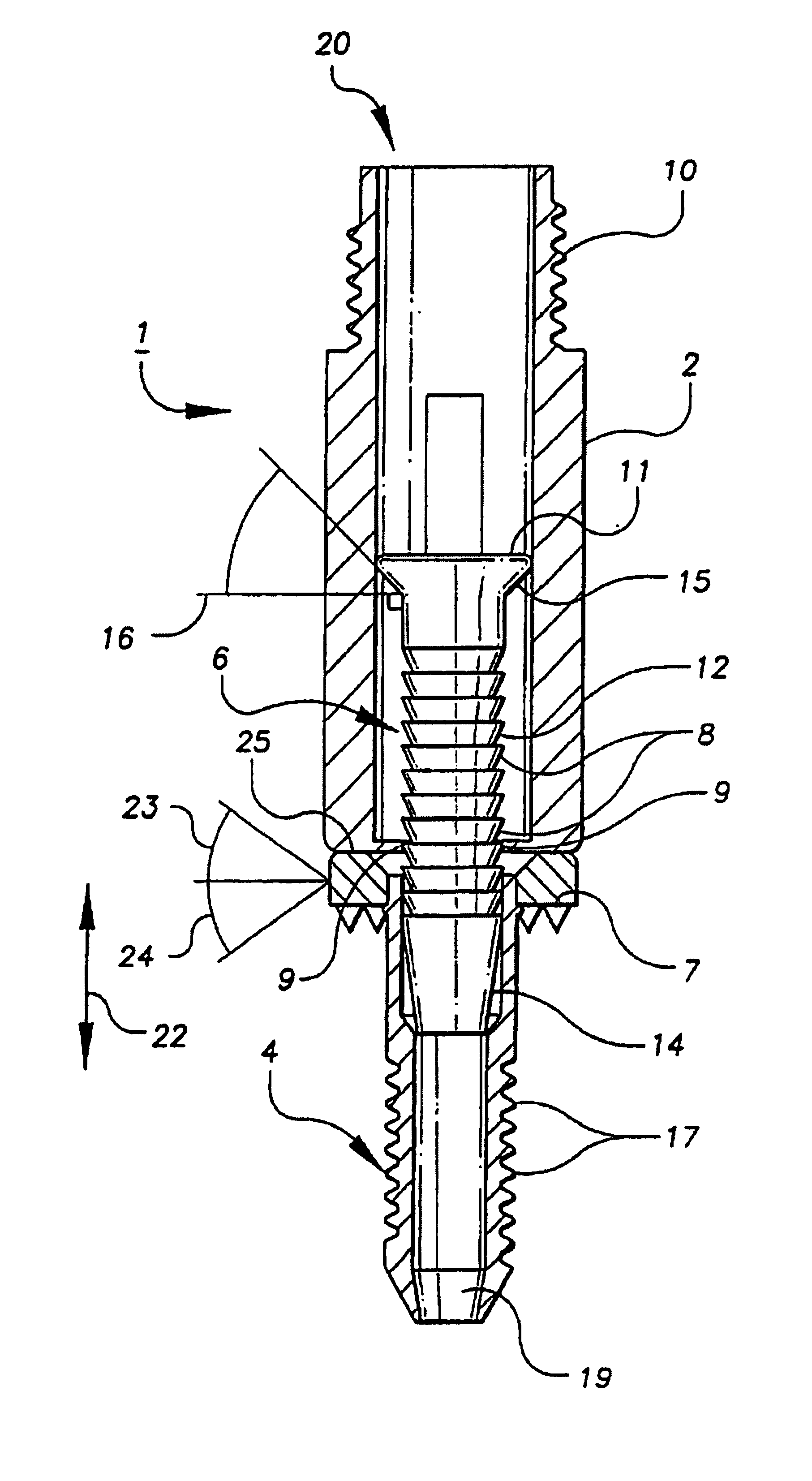
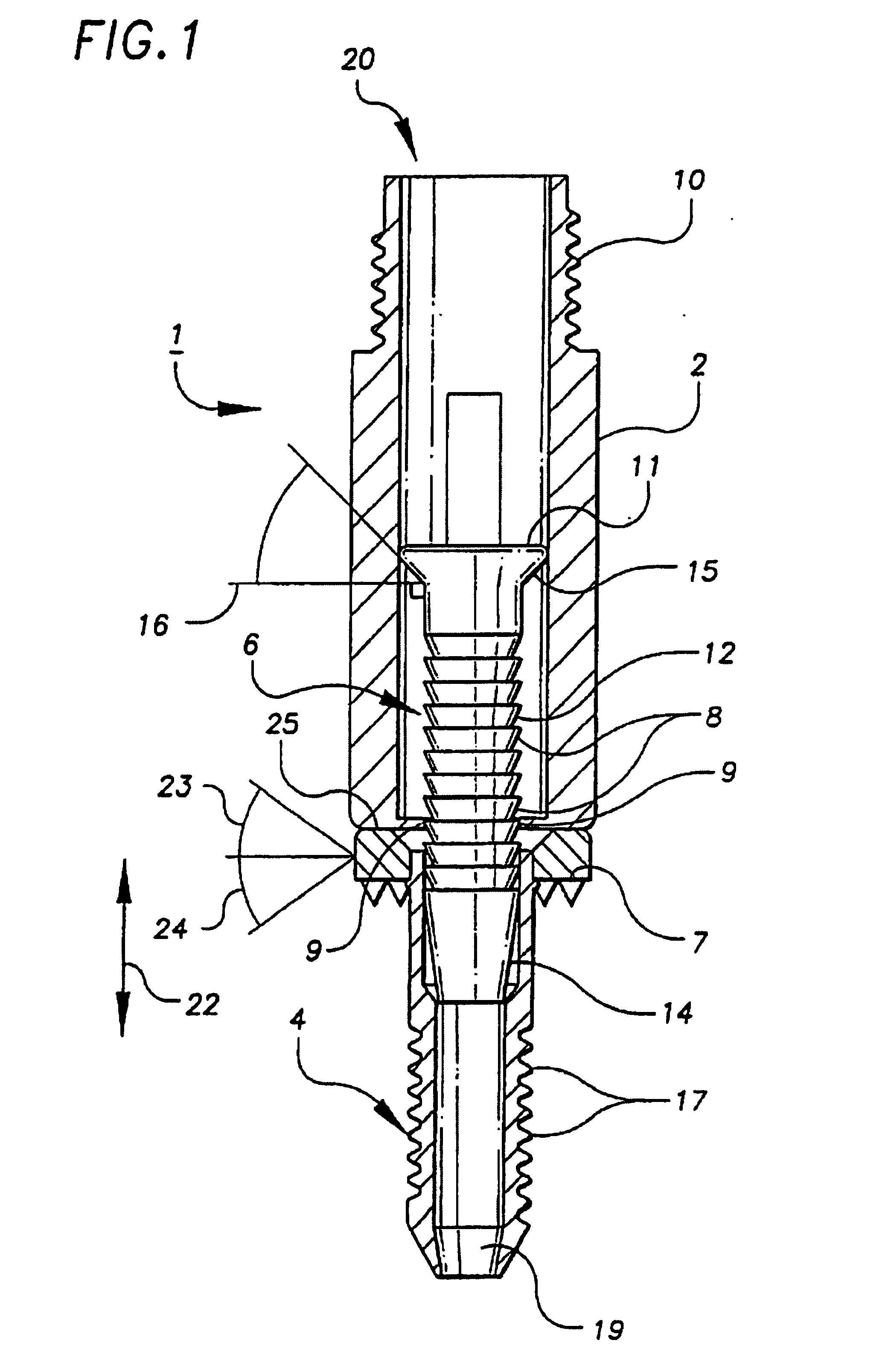
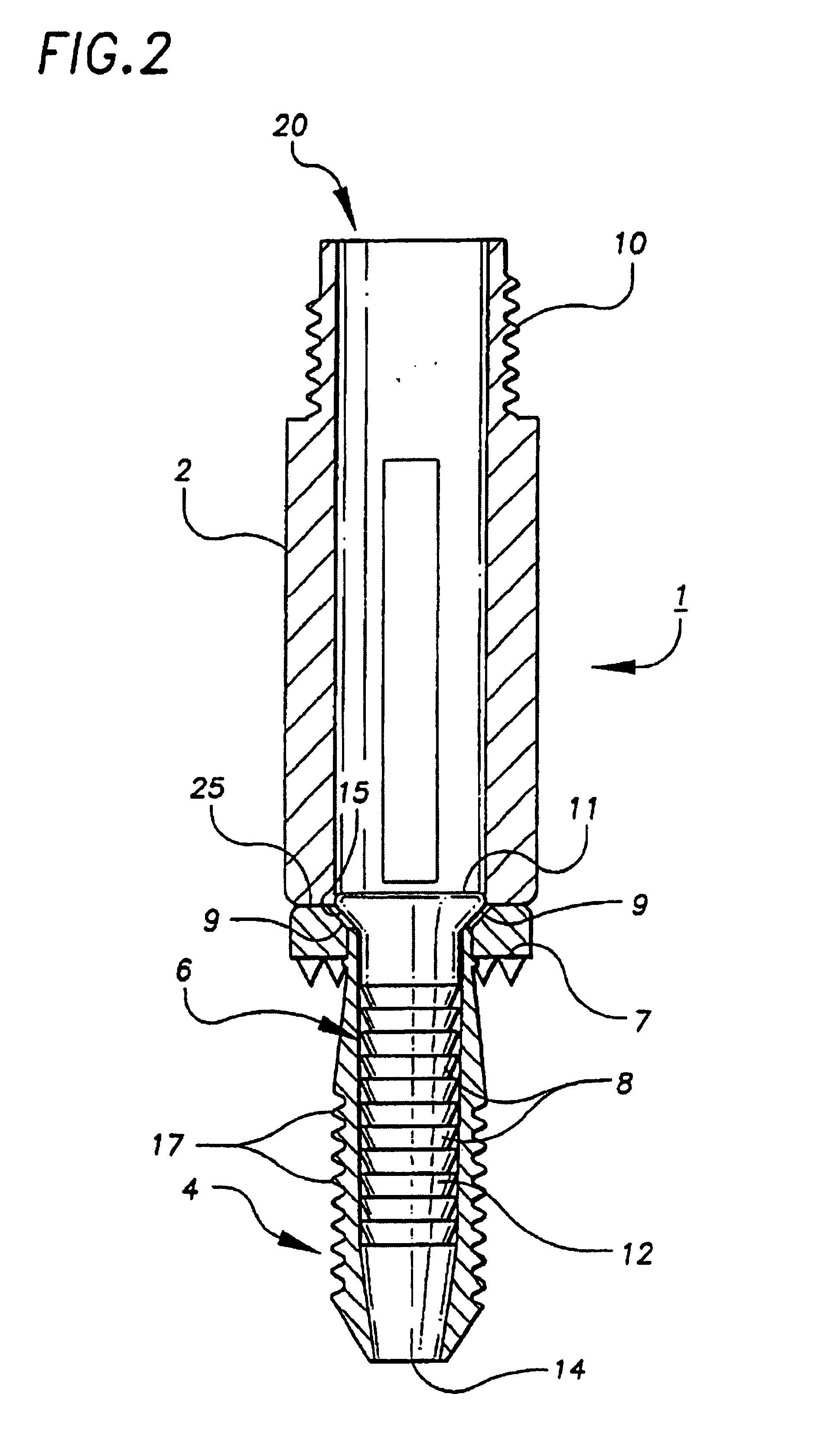
The invention relates to a mechanical device intended for correcting a malformation of the bones of the body. The device is continuously adjustable, making the surgeon's work easier and reducing surgery time, thus reducing the risk of infection and, above all, guaranteeing the desired precision for surgery. The device comprises a top plate (1) suitable for sliding over a bottom plate (2) by means of a guide (7). Said plates can be screwed on either side of an angled notch made in the bone. The plates comprise respectively top (5) and bottom (6) bearings of the notch of the bone. Said bearings form an acute-angle bevel which substantially matches the surfaces of the notch. One of the plates is provided with an adjustment screw (4) for continuous adjustment of the relative positions of the plates. The device also comprises a locking screw (3) suitable for maintaining the open position of the device and, consequently, the final angle of the notch of the bone in the desired position. The Top bearing of the notch of the bone having angular adjustment is suitable for correcting the angle of the bevelled surface of the bearing, in particular the tibial slope, by means of a tapered screw (8) adjustment an angular space in the bearing.
Owner:RIBEIRO CHRISTIANO HOSSRI +1
Spinal stabilization devices coupled by torsional member
Owner:APPLIED SPINE TECH
Intervertebral prosthesis
An expandable intervertebral prosthesis includes a bone graft implant member dimensioned for insertion within an intervertebral space defined between adjacent vertebrae, thereafter adapted to vertically elevate and expand a plurality of barbs into the surrounding bone. The expandable intervertebral prosthesis has a tubular outer body portion having an axial bore with an enlarged proximal end and an exterior surface dimensioned to fit snugly within the space, and a barbed expansion cylinder slidably or rotatably mounted within the axial bore. The tubular outer body portion of the expandable intervertebral prosthesis has a plurality of longitudinal slots or holes in the wall thereof to allow the expansion and retraction of the expansion cylinder's barbs into or out of the surrounding bone. The barbs on the expansion cylinder may be elastically deformed from a normal, retracted configuration to a locking, splayed configuration wherein the outer ends of the barbs extend outwardly through the slots and exterior surface of tubular outer body to penetrate the surrounding bone as the expansion cylinder is moved. The expansion cylinder and, in one embodiment, the exterior surface of the tubular outer body portion, have a plurality of barbs disposed in circumferentially spaced relation about the body and positioned in various angles and positions respect to the axial bore. In another embodiment, the intervertebral prosthesis includes an elevating cylinder rotatably mounted within a frangible tubular outer body portion. The elevating cylinder has one or more detent positions that expand and vertically elevate the frangible tubular outer body portion of the intervertebral prosthesis body upon rotation thereof.
Owner:RHAUSLER
Expandable Intervertebral Implant
An implant for therapeutically separating bones of a joint has two endplates each having an opening through the endplate, and at least one ramped surface on a side opposite a bone engaging side. A frame is slideably connected to the endplates to enable the endplates to move relative to each other at an angle with respect to the longitudinal axis of the implant, in sliding connection with the frame. An actuator screw is rotatably connected to the frame. A carriage forms an open area aligned with the openings in the endplates. The openings in the endplates pass through the carriage to form an unimpeded passage from bone to bone of the joint. The carriage has ramps which mate with the ramped surfaces of the endplates, wherein when the carriage is moved by rotation of the actuator screw, the endplates move closer or farther apart.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Accurate analogs for prostheses using computer generated anatomical models
ActiveUS20080124676A1Improve actionDental implantsAdditive manufacturing apparatusComputer generationEar prosthesis
Pre-surgical planning for cranial and facial reconstruction includes preparing a computer generated jaw or skull model for determining a locational position for a dental implant, a surgical bone implant to repair missing bone in the cranium, install ear prostheses, and / or install nose prostheses. The computer generated jaw or skull model is made from medical imagery and computer aided design. A surgical guide is prepared with oversize holes in registration with analogs for the dental or surgical bone implants to be inserted at the locational positions determined by a dentist or surgeon in the jaw or cranial skull model. The surgical guide is fitted atop each analog, and the surgical guide is bonded to the jaw or skull model at a predetermined angle of the analog in the jaw or skull. The surgical guide is removed from the model attached to the law or skull of a patient for accurate drilling during the dental or surgical procedure for insertion of the implants into the jaw or skull of the patient.
Owner:CLM ANALOGS LLC
Prosthetic glenoid component
A prosthetic glenoid component for attachment to a scapula to provide a bearing for a humeral head in a shoulder prosthesis has a one-piece bearing element having a concave lateral bearing surface for contact with the humeral head with which it is to be used. An opposing relatively hard medial surface of the bearing element is provided for attachment to a scapula. The lateral surface is a soft low modulus concave lateral bearing surface extends around the periphery of the bearing element and increases its thickness to provide a deformable rim to simulate the labrum in an anatomical glenoid. The bearing element preferably has two affixation pegs which project from the medial face thereof, one at a superior position which projects in a superior direction and the other which is located in an inferior position and which projects in an inferior direction which is angled in relation to the medial-lateral direction.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Surface guided knee replacement
InactiveUS20070135925A1Reduce consistencyAvoid large displacementJoint implantsKnee jointsGonial angleTibial surface
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the motion and stability characteristics of the anatomic knee. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, more so on the lateral side than on the medial side. This is accomplished by the interaction of a projecting tibial post inside a cupola in the center of the femoral component, and by the saggital radius on the medial side being smaller than that on the lateral side. The prevention of anterior sliding of the femur on the tibia in early flexion is accomplished by the interaction between a distal-anterior recess on the medial side of the femur and an apposing raised pad on the tibial surface. Rotational laxity at all angles is allowed by the presence of only one recess pad and by non-conforming femoral-tibial surfaces on the lateral side.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
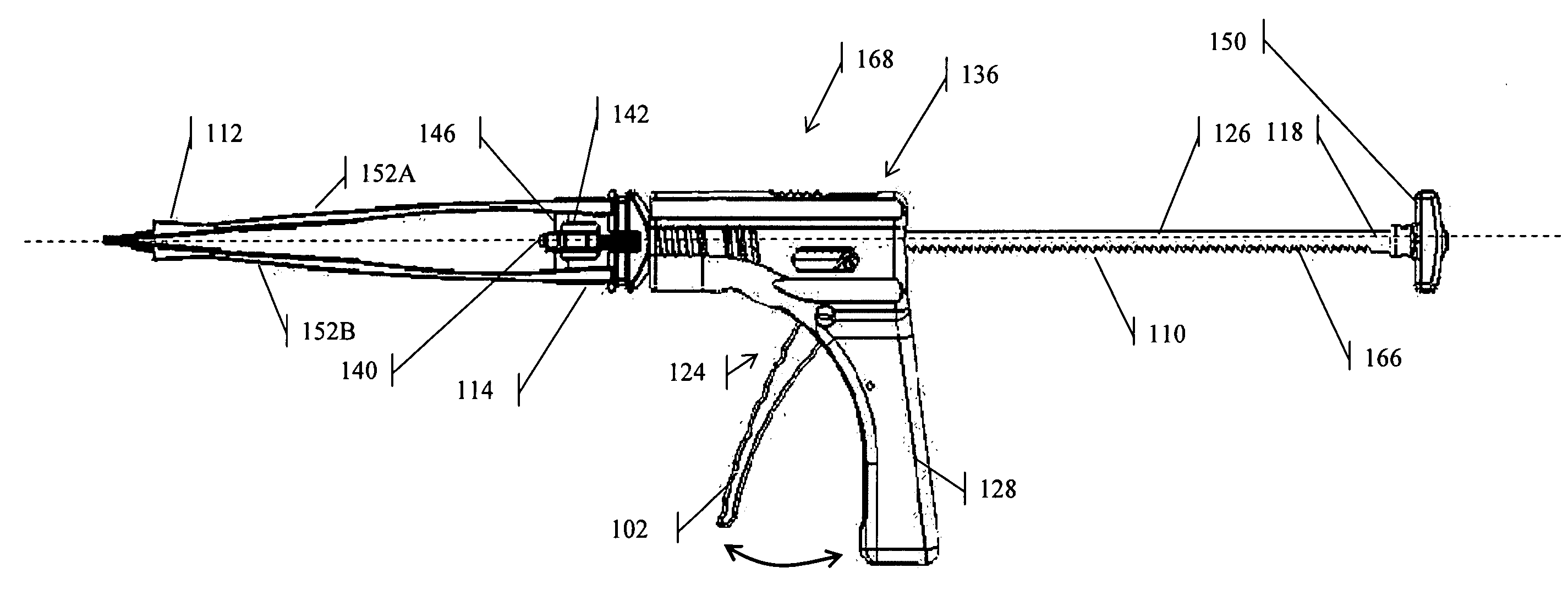
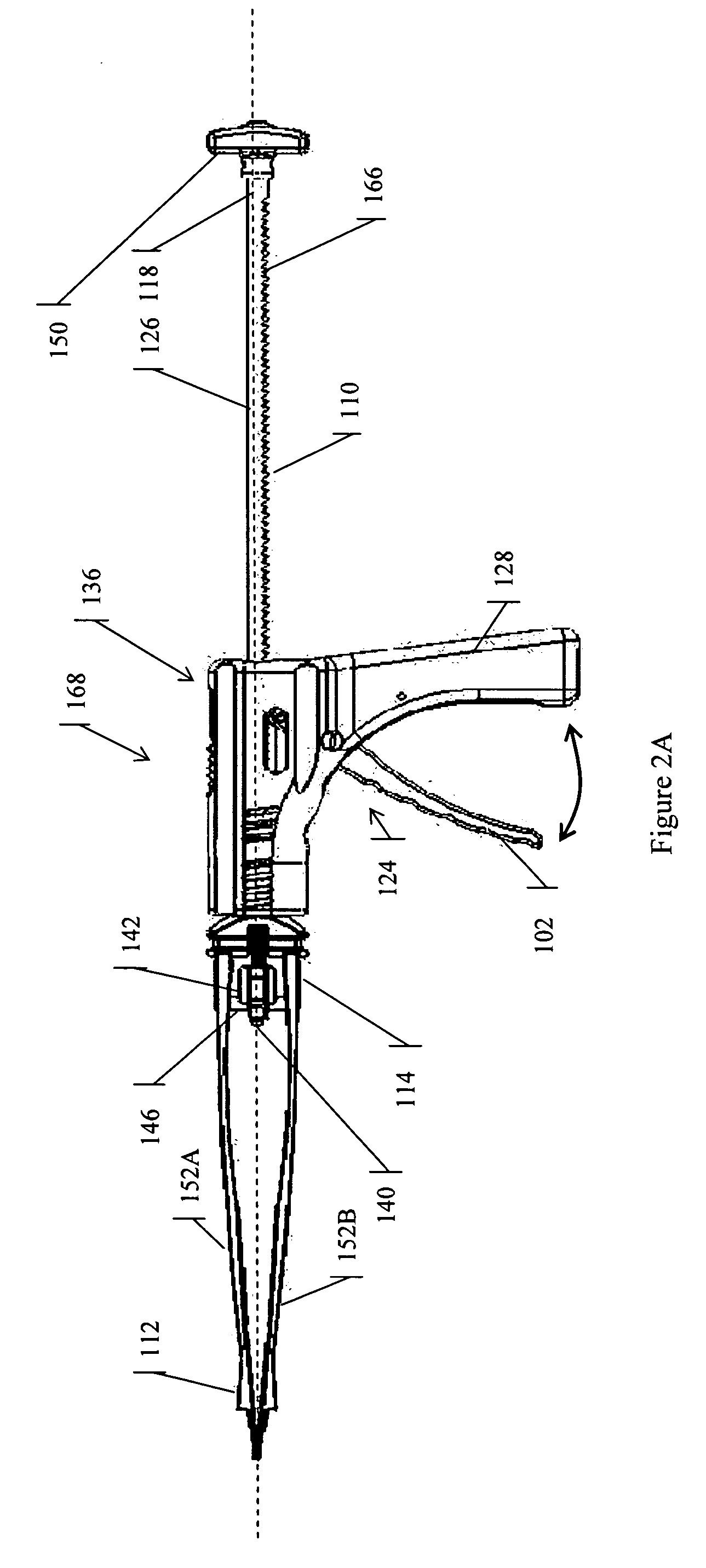
Spinal implant distractor/inserter
ActiveUS20090005784A1Distracting vertebraInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsIntervertebral spaceEngineering
A method for distracting a pair of adjacent vertebrae and inserting an implant within the intervertebral space between the adjacent vertebrae using a posterior angle is described. The method employs a vertebral distractor-inserter comprising a housing, a pair of opposing arms in mechanical communication with the housing, a driving rod extending through at least a portion of the housing and between the arms, wherein the driving rod comprises an axis and a surface with a plurality of angled ratchet teeth on at least a portion of the surface, and a ratchet drive mechanism in mechanical communication with the driving rod.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC
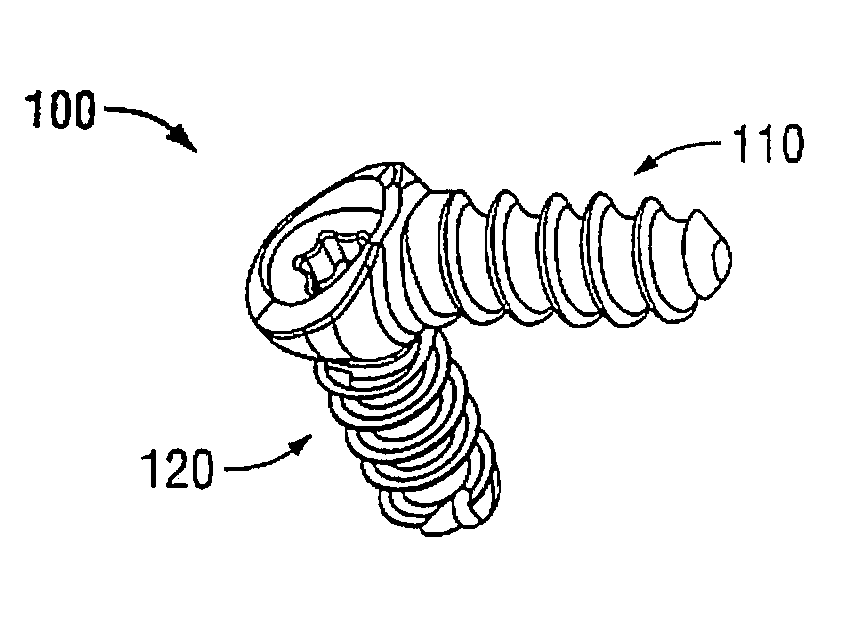
Fastener with serrated thread for attachment to a bone plate at a selectable angle
Bone plate system, including methods and apparatus, for attaching a fastener to a bone plate at a selectable angle. In an exemplary method, a bone plate and a fastener may be selected. The bone plate may define an aperture having an internal thread. The fastener may include a proximal region and a distal region. The proximal region may be tapered conically toward the distal region. The fastener may be disposed in the aperture and in bone, such that the serrated thread is cross-threaded with the internal thread to create an interference fit and locked engagement of the proximal region with the aperture.
Owner:ACUMED
Bone screw assembly
A bone screw assembly includes a first bone screw, second bone screw, and a coupler. The first bone screw defines a first axis and the second bone screw defines a second axis. The coupler is operably associated with the first bone screw and the second bone screw. The coupler is adapted to mount the first bone screw and the second bone screw to adjacent bone structures. The first axis of the first bone screw and the second axis of the second bone screw define an angle therebetween. The first bone screw and the second bone screw are securable to each other.
Owner:GOREK JOSEF
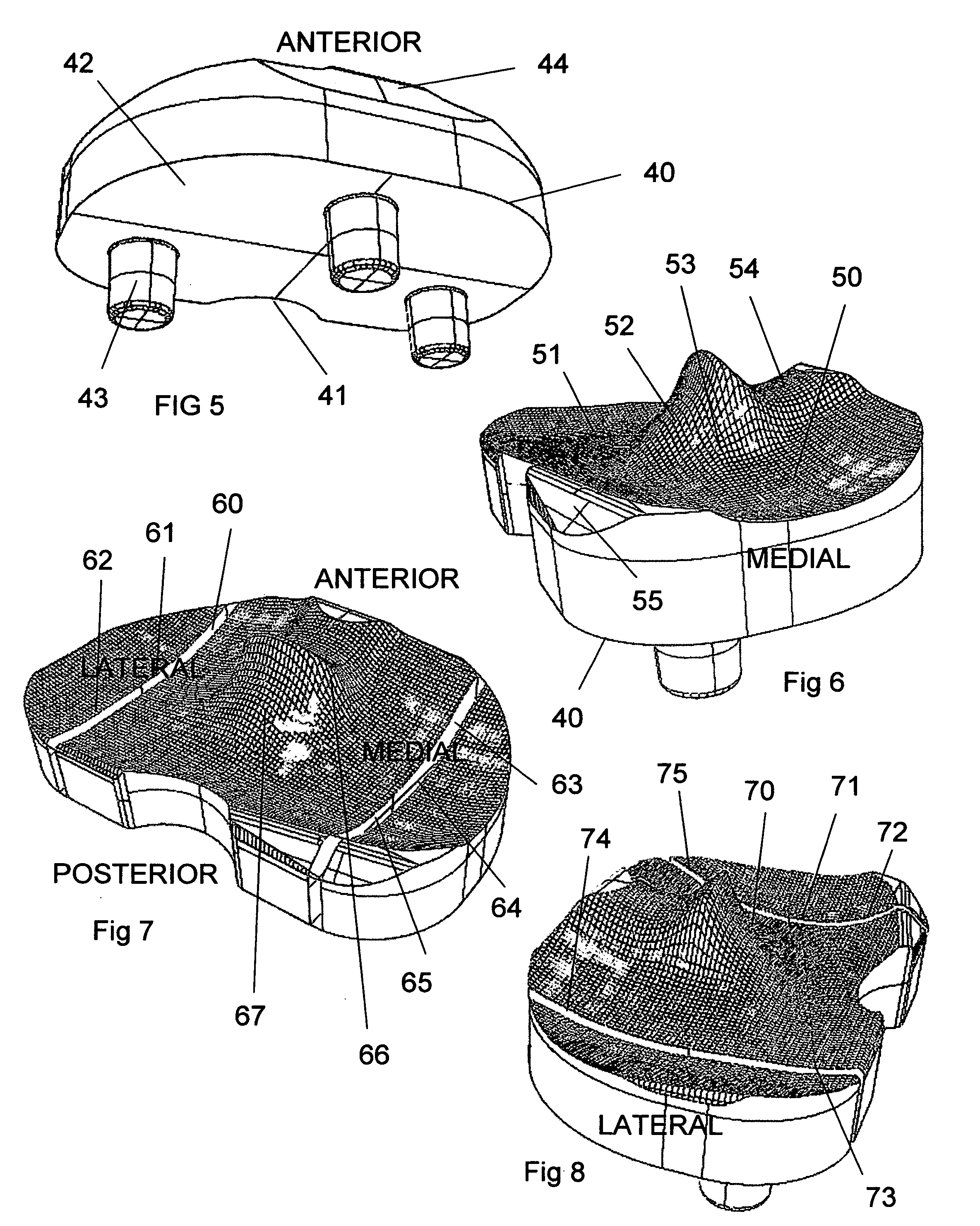
Knee prosthesis
A femoral component of a knee prosthesis comprises a femoral flange from an inner end of which extend lateral and medial condylar parts which are interconnected by a box-like bridging part at an intercondylar groove. The interior surface of the femoral component has six discrete flat sections, with the sixth flat section which extends to a free end of the femoral component being angled relative to a plane normal to the third flat section and to the length of the intercondylar groove. Also disclosed is a trial femoral component and a method of use thereof to prepare a femur for the fitting of the femoral component of the prosthesis.
Owner:MCMINN DEREK JAMES WALLACE
Variable angle spinal screw assembly
ActiveUS20080243189A1Relieving the pressure of the capExtended range of motionSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisEngineeringScrew thread
A spinal screw assembly providing an adjustable securement of a fixation rod across at least two vertebrae. The assembly includes a pedicle screw having a spherical head portion, a threaded shaft portion and a tool engagement surface in the head portion for use in driving the screw into a vertebrae. The head portion of the screw is positioned in a body member adjacent a curvilinear surface disposed about an aperture in the end of the body member such that the shaft portion of the screw extends therethrough and the curvilinear inner surface abuts and mates with the head portion of the screw so as to define a ball joint therewith. The body member additionally defines a pair of opposed parallel slots therein adapted to receive a portion of the fixation rod and a locking cap bears against the fixation rod to releasably secure the rod within the assembly.
Owner:ALPHATEC SPINE INC
Instruments and Methods for Non-Parallel Disc Space Preparation
ActiveUS20110319898A1Less endplate damageHigh preparation symmetryEar treatmentCannulasMedicineIntervertebral disk
Flexible shavers and curved access ports that reduce access and trajectory problems associated with conventional lateral approaches to the lower spine. These devices and methods allow for preparing a disc space in the lower spine at an angle that is parallel to the disc space. Consequently, these devices and methods allow for preparing with less endplate damage.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Posterior stabilized knee with varus-valgus constraint
ActiveUS20050192672A1Accurately and efficiently emulates kinematicsAccurately and efficiently and functionJoint implantsKnee jointsSpinal columnTibial bone
A femoral component of a knee prosthesis has spaced condyle surfaces defining a notch therebetween. The notch defines an elongated cam housing having an anterior cam and a posterior cam at opposite ends of the housing. The tibial component of the knee prosthesis includes a platform and a bearing supported on the platform, the bearing defining bearing surfaces configured to articulate with the condyle surfaces. The tibial component includes a spine projecting superiorly from the bearing that defines an anterior face and a posterior face. The posterior face and the posterior cam define complementary curved surfaces configured for cooperative engagement when the femoral component and the tibial component are at a predetermined flexion angle. The cam housing is configured to form a gap between the posterior cam and the spine when the knee is normally extended. In another feature, the spine includes a stiffening pin extending therethrough.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
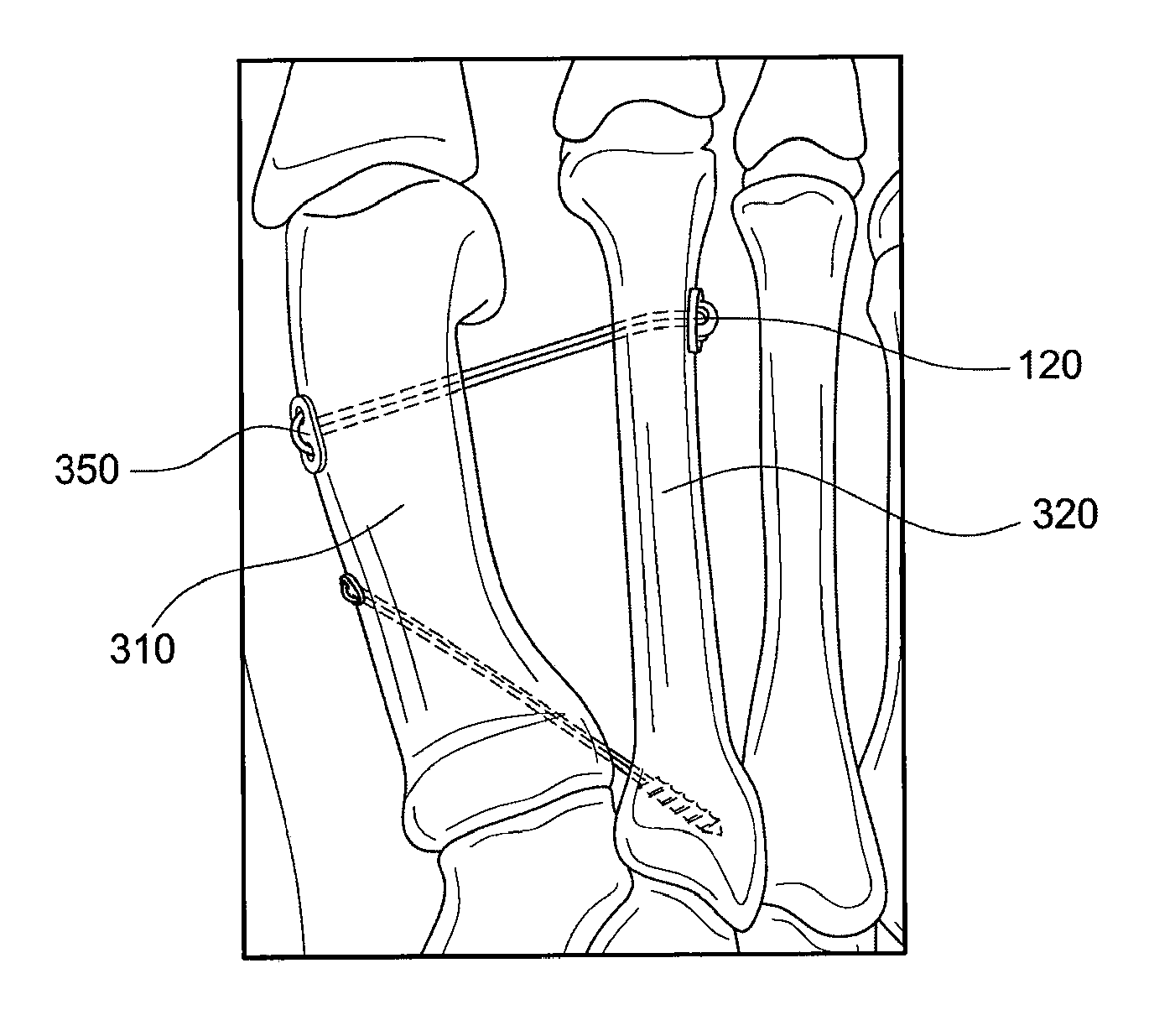
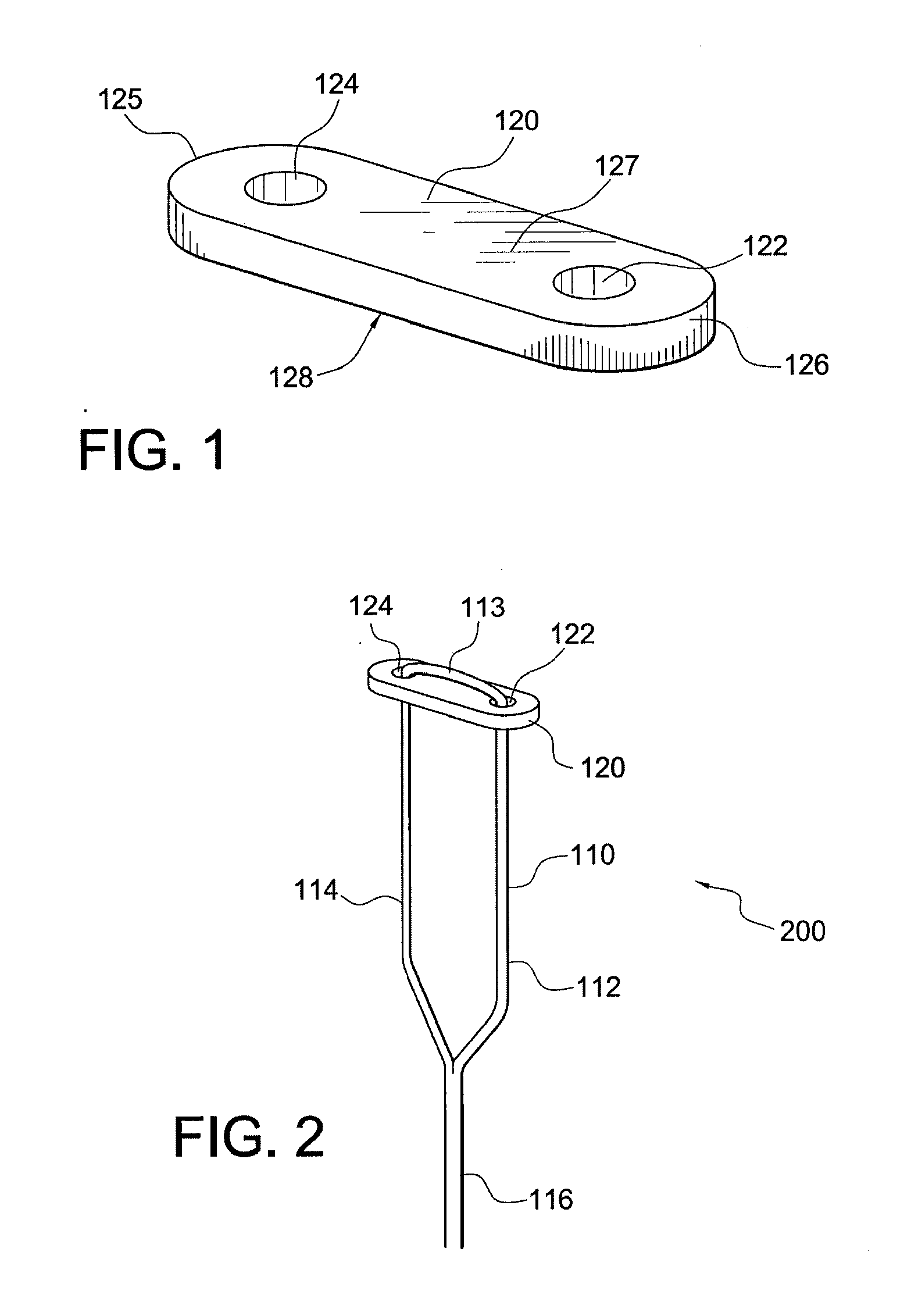
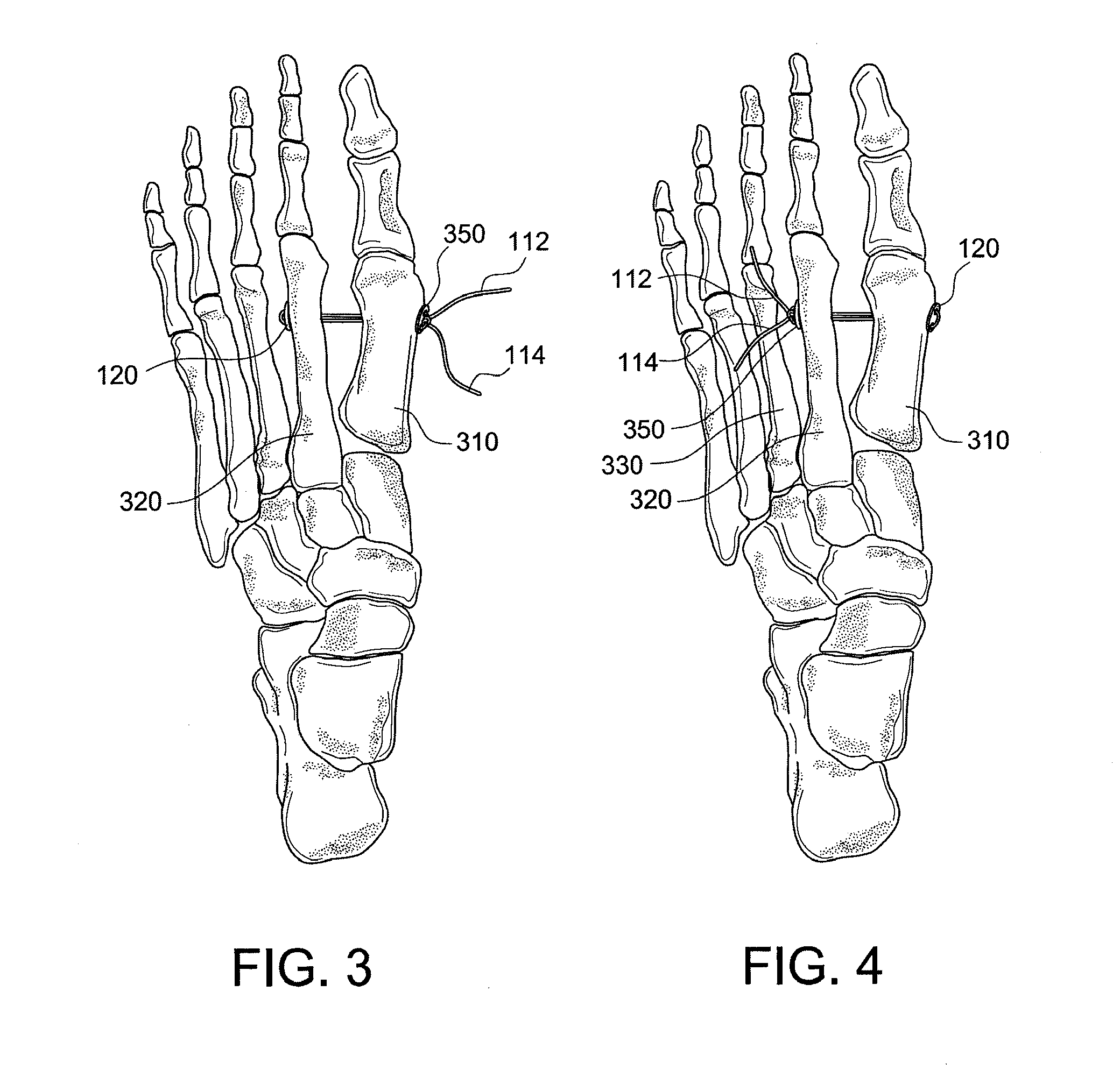
Hallux valgus repairs using suture-button construct
A technique and associated instrumentation for correcting large intermetatarsal angles that result from hallux valgus. The system includes a button and a suture loop attached to the button. A suture strand is threaded through holes in the button to attach the button to the suture. The suture ends are then brought together (by being swaged, spliced or cinched together, for example) to form the suture loop comprising a continuous, uninterrupted suture loop with a single strand of swaged-together ends. The swaged-together ends may be attached to a suture passing instrument such as a K-wire (Kirschner wire) that may be further used to drill a hole through the first and second metatarsals. The swaged-together ends of the suture are then passed through the drill holes in the first and second metatarsals; and the ends of the suture are pulled until the button abuts the second metatarsal. The swaged together portion of the suture loop is then cut, and the free suture ends are passed through holes in another (second) button. The suture ends are pulled to adjust the first metatarsal to a correct intermetatarsal angle, and the first metatarsal is secured in place by tying the ends of the suture together against the second button.
Owner:ARTHREX INC
In-situ formed intervertebral fusion device and method
InactiveUS20150173914A1MinimallyIncrease heightLuminescence/biological staining preparationBone implantOrthopedic devicesGonial angle
An orthopedic device for implanting between adjacent vertebrae comprising: an arcuate balloon and a hardenable material within said balloon.In some embodiments, the balloon has a footprint that substantially corresponds to a perimeter of a vertebral endplate. An inflatable device is inserted through a cannula into an intervertebral space and oriented so that, upon expansion, a natural angle between vertebrae will be at least partially restored. At least one component selected from the group consisting of a load-bearing component and an osteobiologic component is directed into the inflatable device through a fluid communication means.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Guide assembly for guiding cuts to a femur and tibia during a knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS20060189998A1Small and noninvasive approachQuick disassemblyInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTibiaDistraction
An assembly for guiding resection of a femur and tibia of a knee joint in preparation for installing a femoral and tibial knee components. For example, the assembly can include tibial and femoral IM rods to which are connected through a torque bolt that allows controlled adjustment of the distraction of the tibia and femur during cut positioning in a range of flexion angles. Also, the assembly is usable with relatively small, noninvasive approaches to the knee joint by way of relatively narrow, low profile components that attach to tibial and femoral IM rods. Further, the assembly includes several quick-release components to allow fast assembly and disassembly in a surgical setting. Each of these aspects, along with the ability of the assembly to accurately guide initial reference cuts to the tibia and femur, promotes an improved outcome for the patient.
Owner:RASMUSSEN INSTR LLC
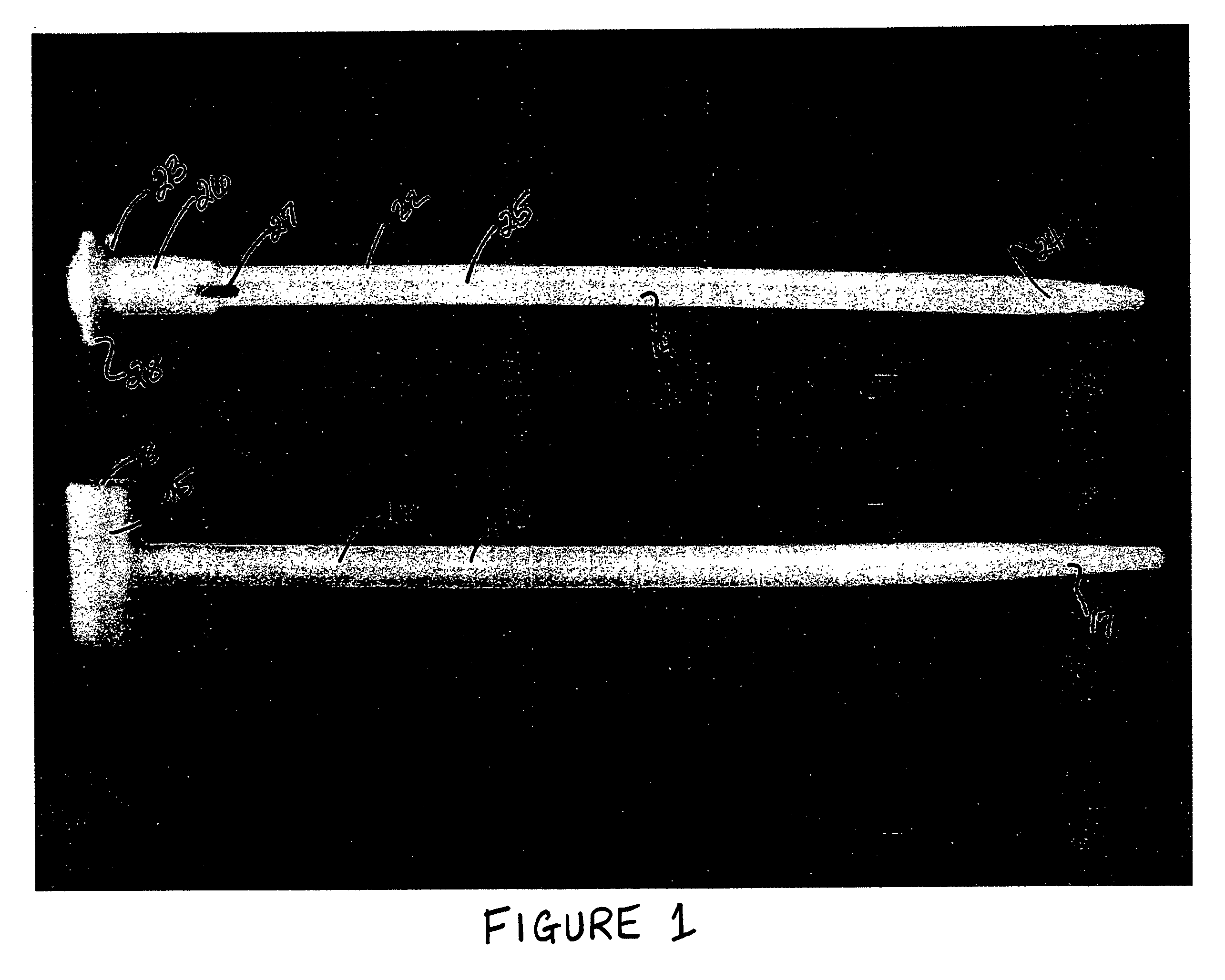
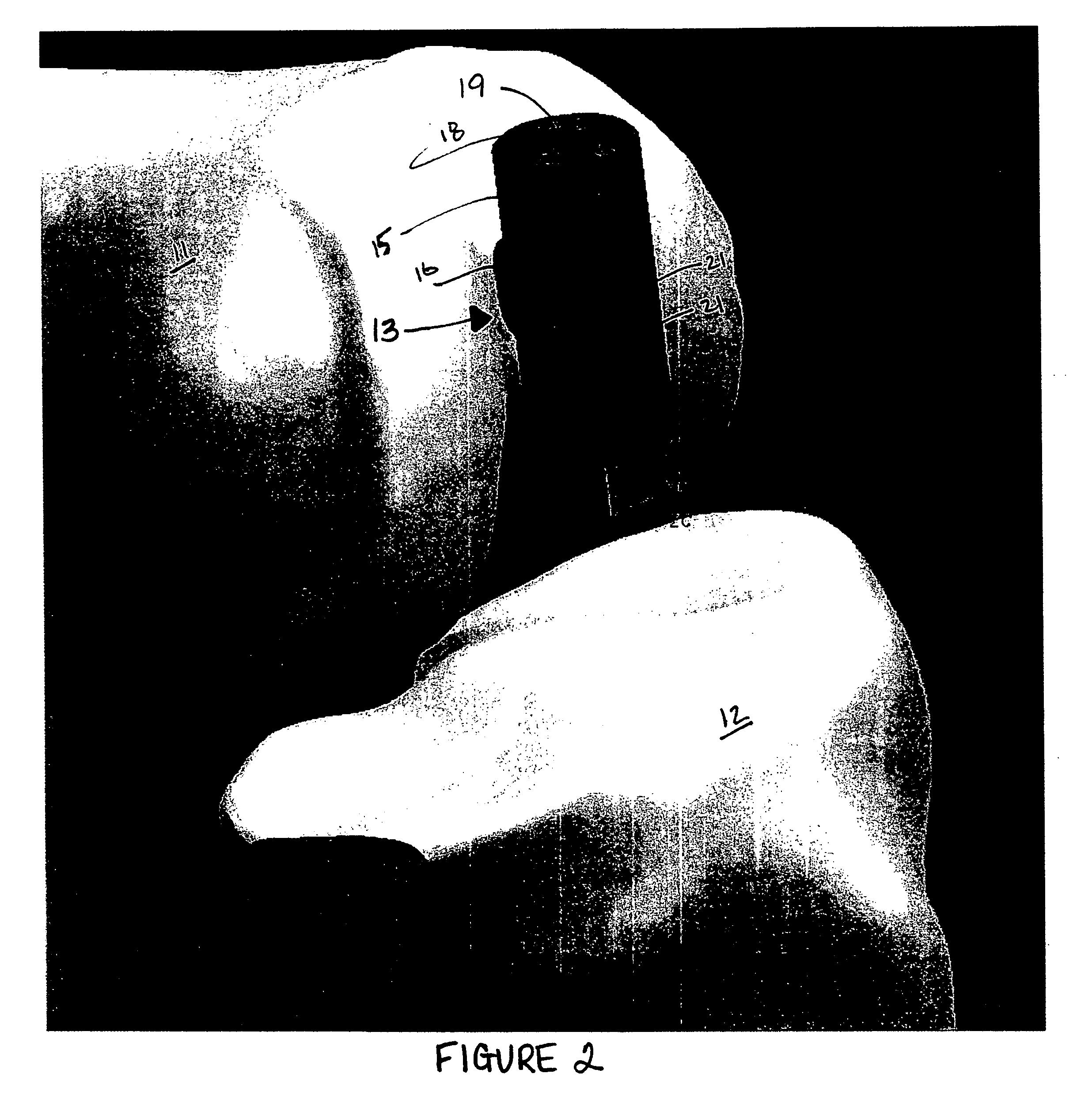
Fixation device for the talus
A fixation device for reduction and fixation of fractures of the talus bone of the foot includes a thin titanium alloy plate having a lower wing configured for attachment to the lateral aspect of the talus and an upper wing configured for attachment to the dorsal aspect of the talus. The plate includes a substantially perpendicular or right angle bend between the lower and upper wings. In one embodiment, each wing includes three screw holes arranged in a generally triangular pattern. Two holes on each plate are situated in tabs and the center of the plate has a reduced width so that the plate presents a minimal profile. One of the tabs on the upper wing is bent away from the lower wing at a pre-determined angle so that the wing conforms to the shape of the talus. In an alternative embodiment, the upper wing includes a step portion between the lower wing and the bent tab and carrying one screw hole. In this embodiment, the bent tab is generally elongated with one or two screw holes disposed along its length.
Owner:BIOMET CV
Insertion of medical devices through non-orthogonal and orthogonal trajectories within the cranium and methods of using
ActiveUS20120046531A1Increase riskLow impedanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryBiomedical engineeringNon orthogonal
The invention comprises an elongated device adapted for insertion, including self-insertion, through the body, especially the skull. The device has at least one effector or sensor and is configured to permit implantation of multiple functional components through a single entry site into the skull by directing the components at different angles. The device may be used to provide electrical, magnetic, and other stimulation therapy to a patient's brain. The lengths of the effectors, sensors, and other components may completely traverse skull thickness (at a diagonal angle) to barely protrude through to the brain's cortex. The components may directly contact the brain's cortex, but from there their signals can be directed to targets deeper within the brain. Effector lengths are directly proportional to their battery size and ability to store charge. Therefore, longer angled electrode effectors not limited by skull thickness permit longer-lasting batteries which expand treatment options.
Owner:HUA SHERWIN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com