Patents
Literature
62 results about "Flexion angle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
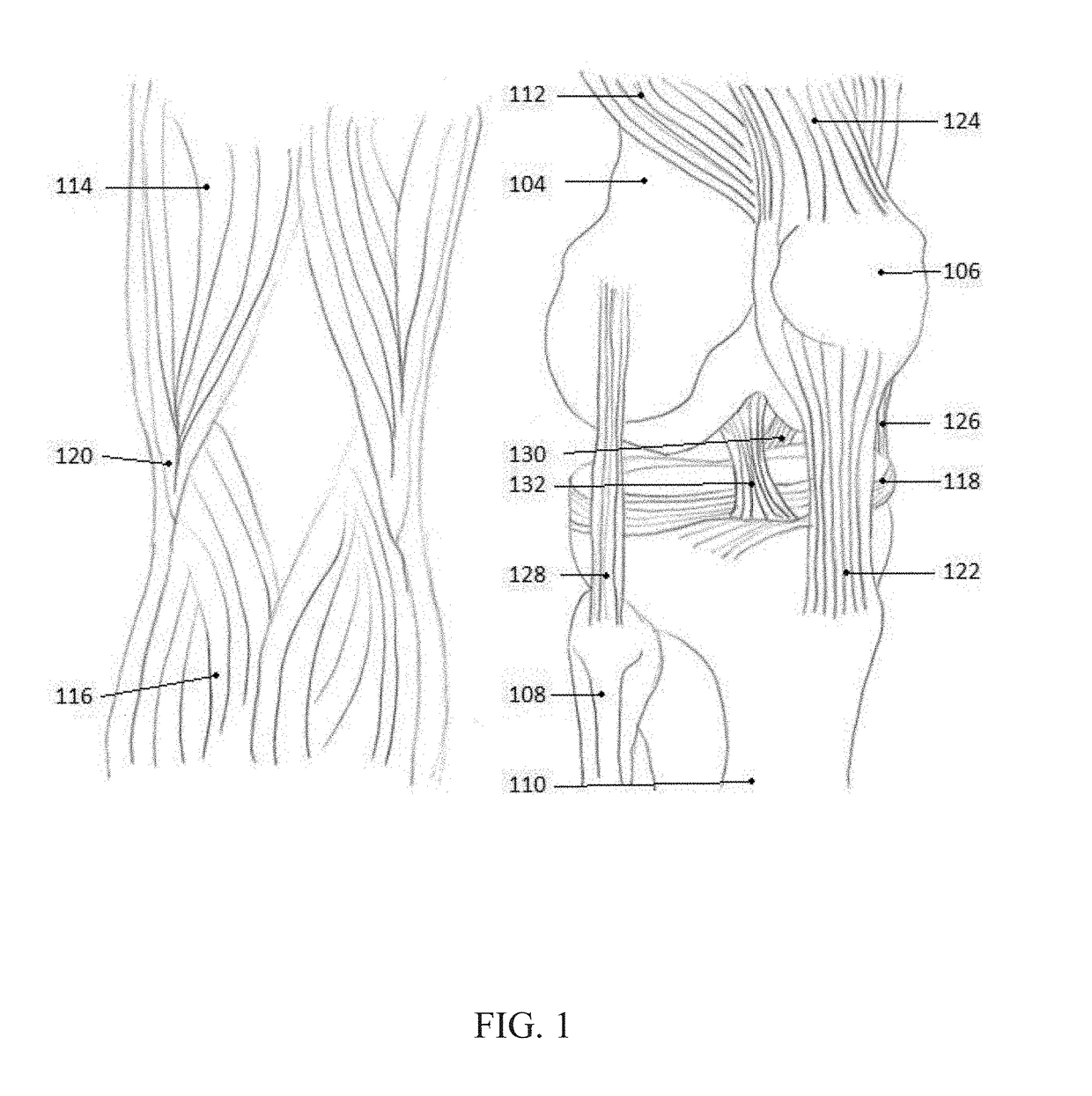
Flexion refers to a movement that decreases the angle between two body parts. Flexion at the elbow is decreasing the angle between the ulna and the humerus. When the knee flexes, the ankle moves closer to the buttock, and the angle between the femur and tibia gets smaller.
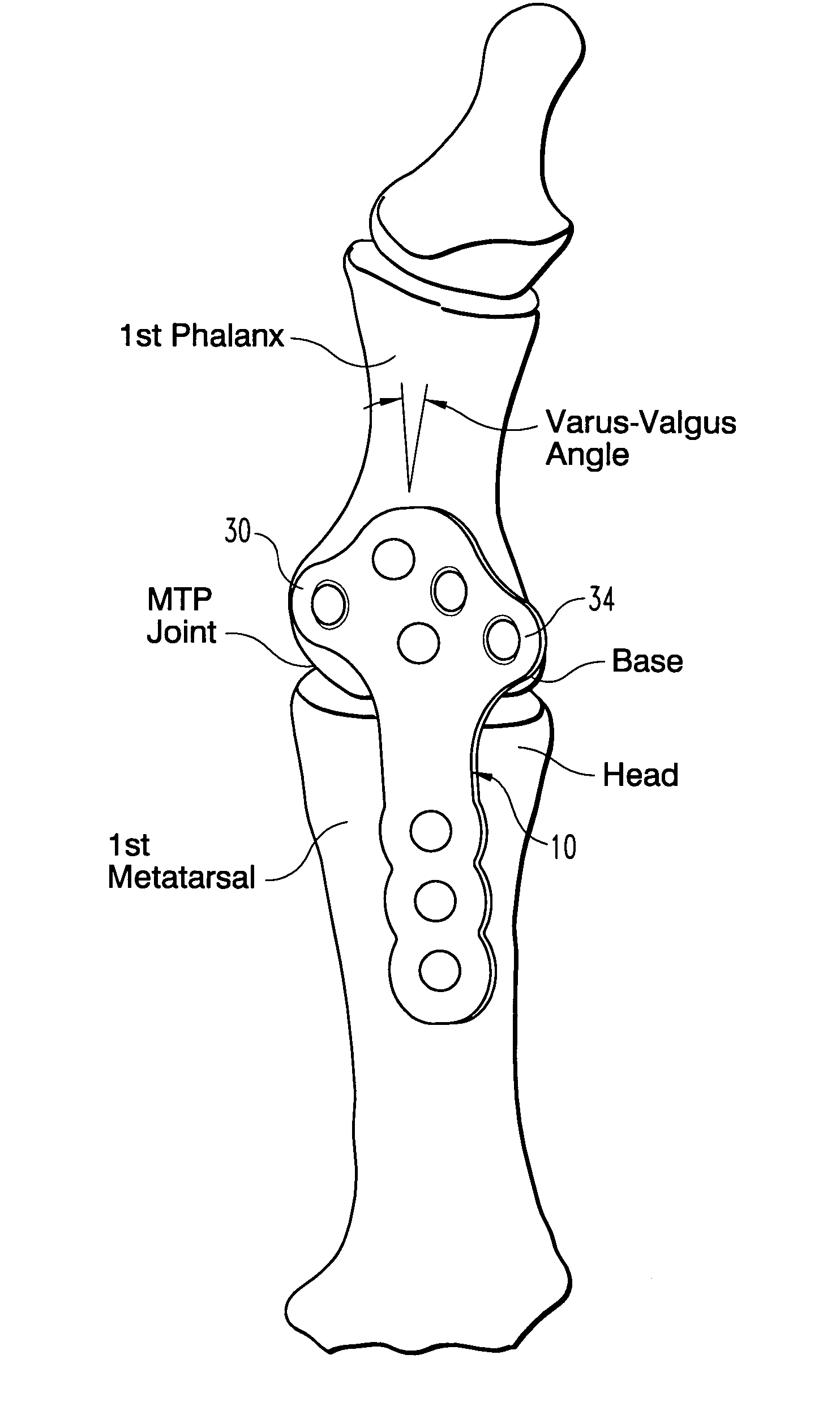
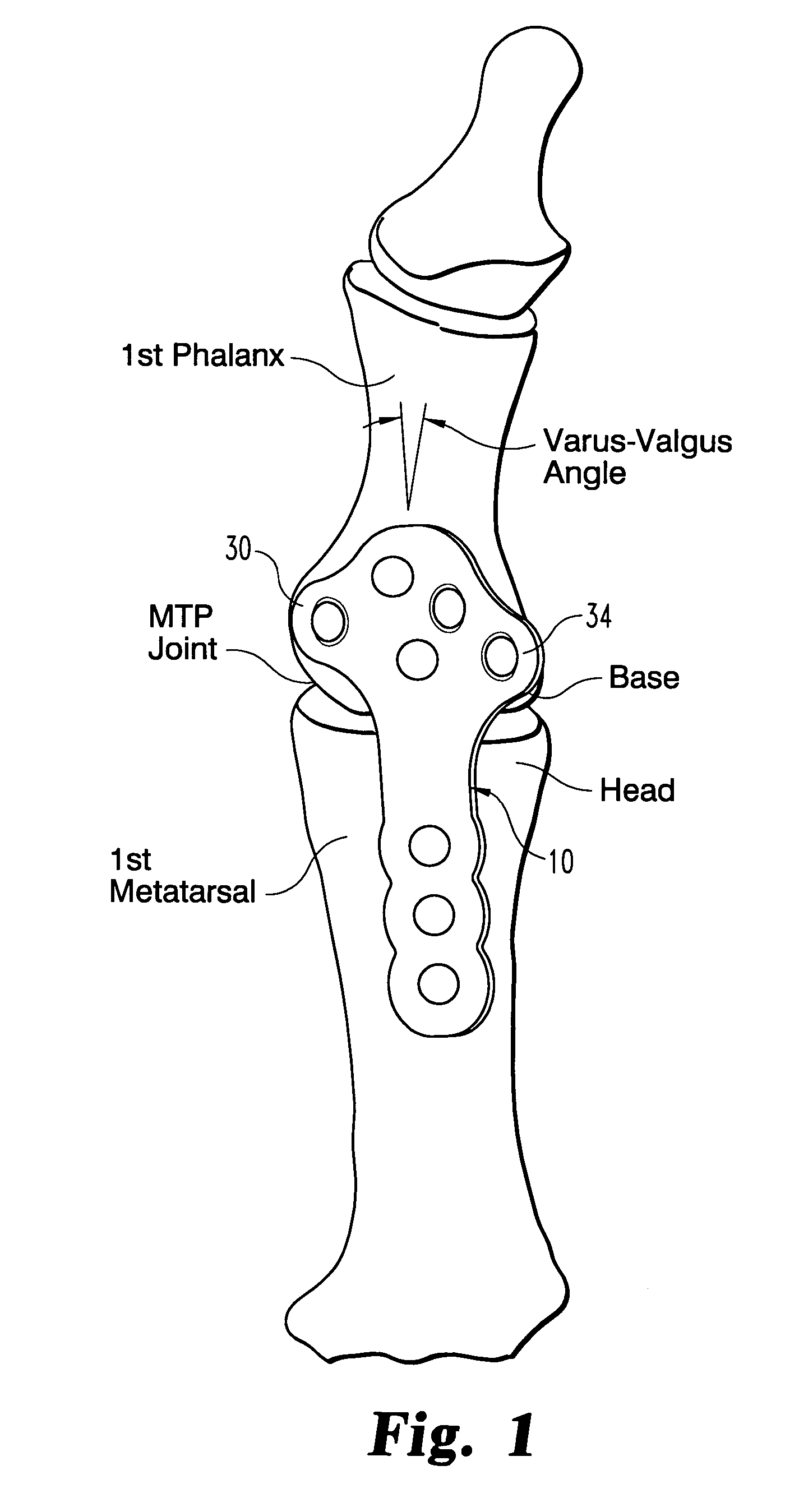
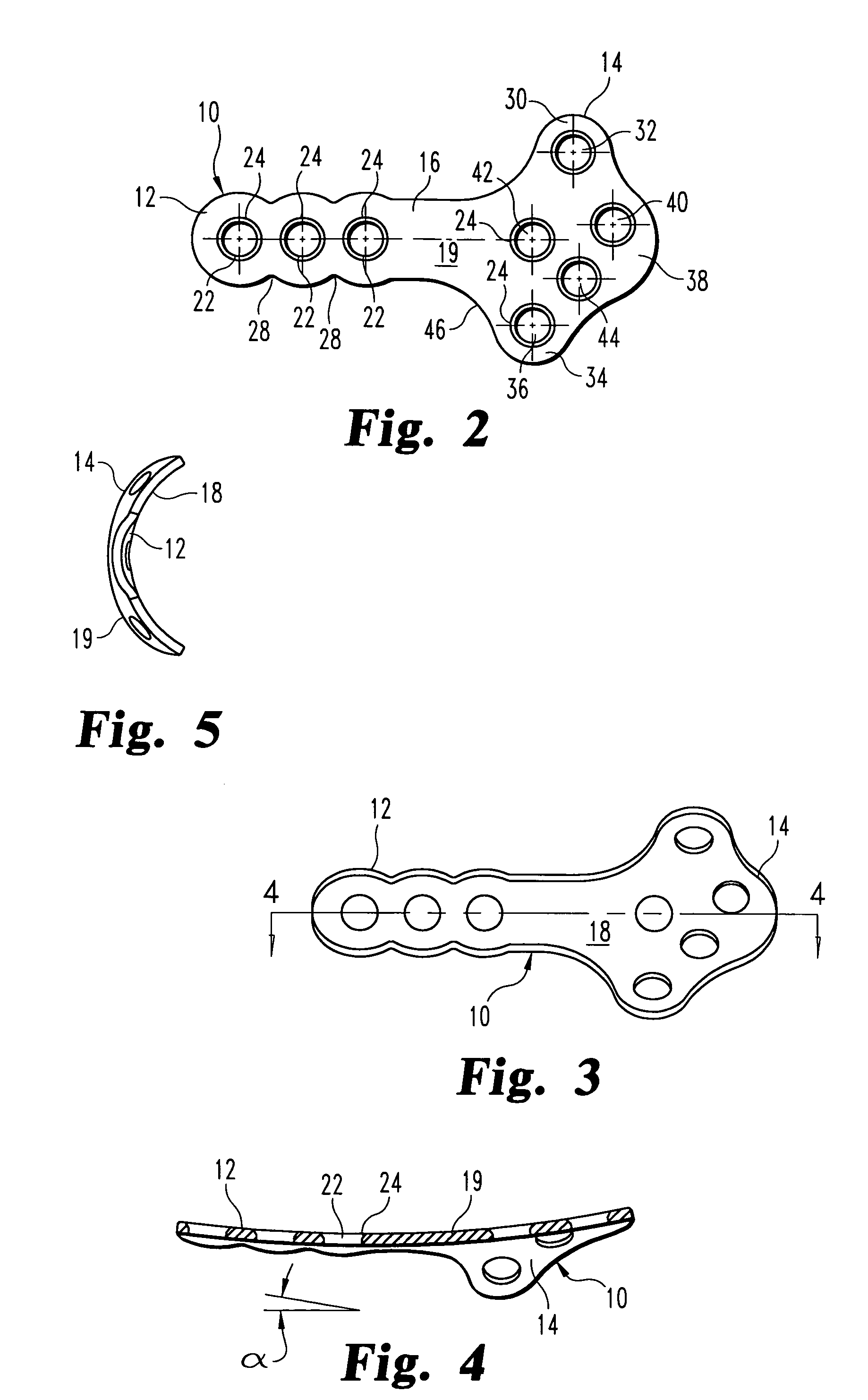
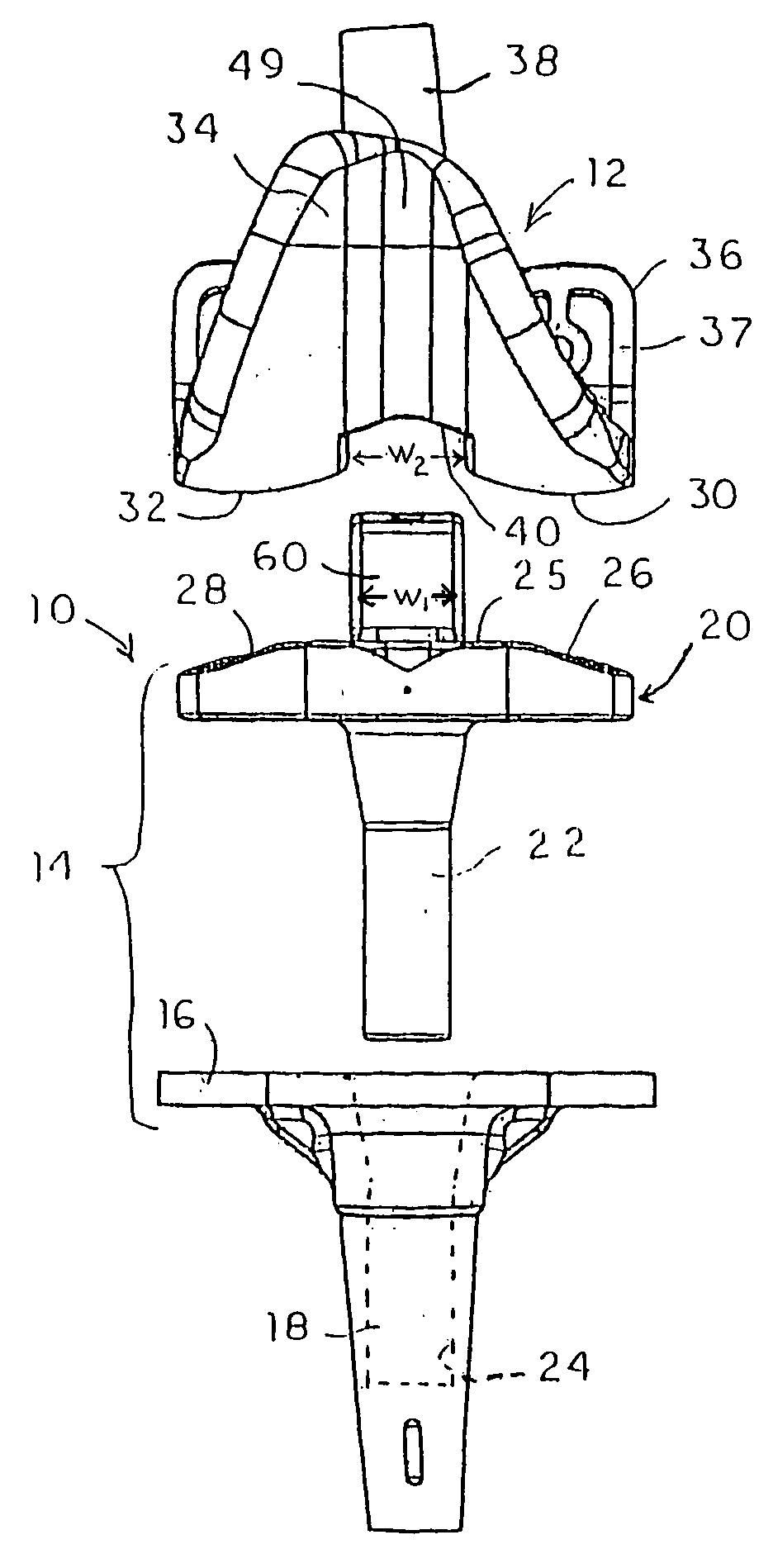
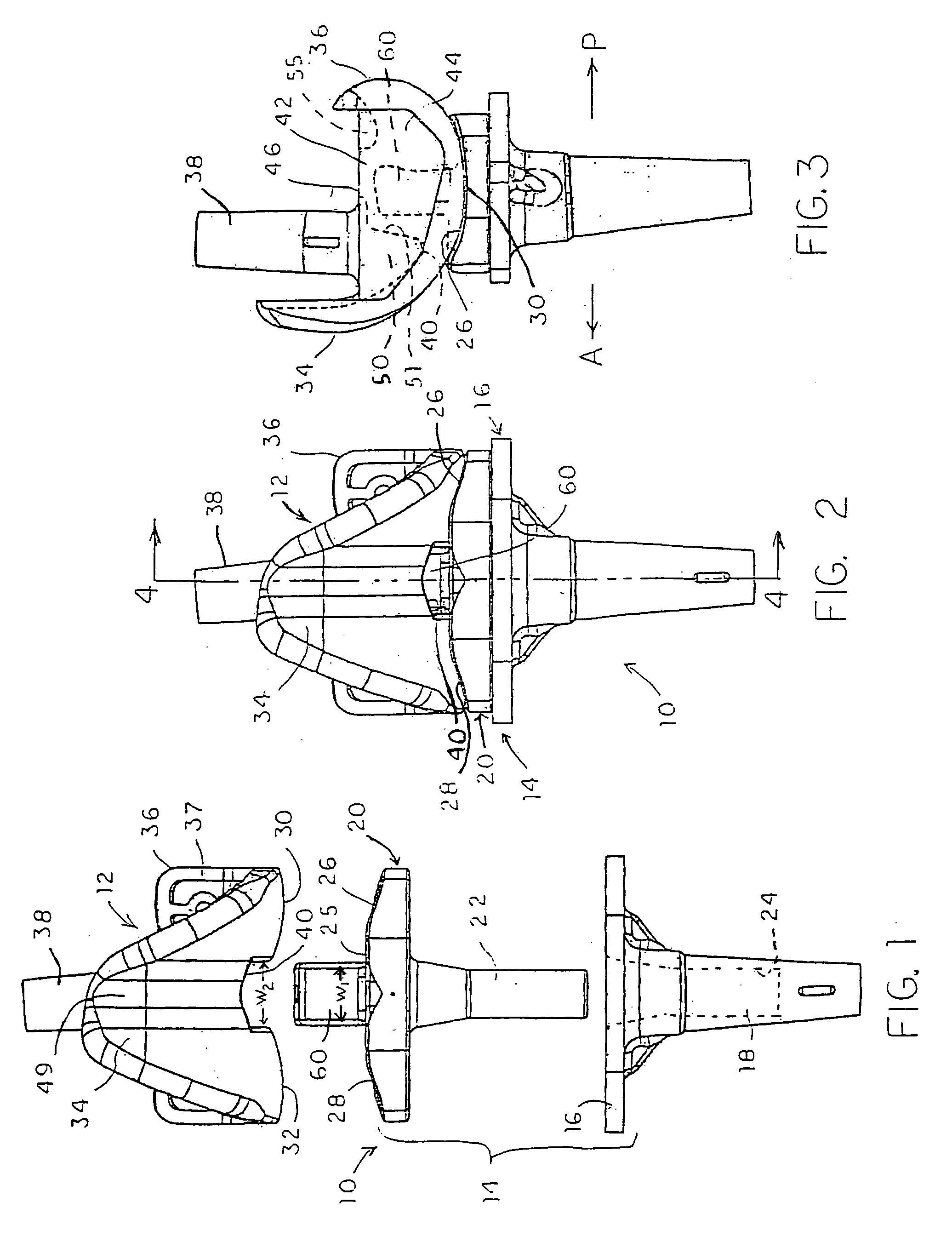
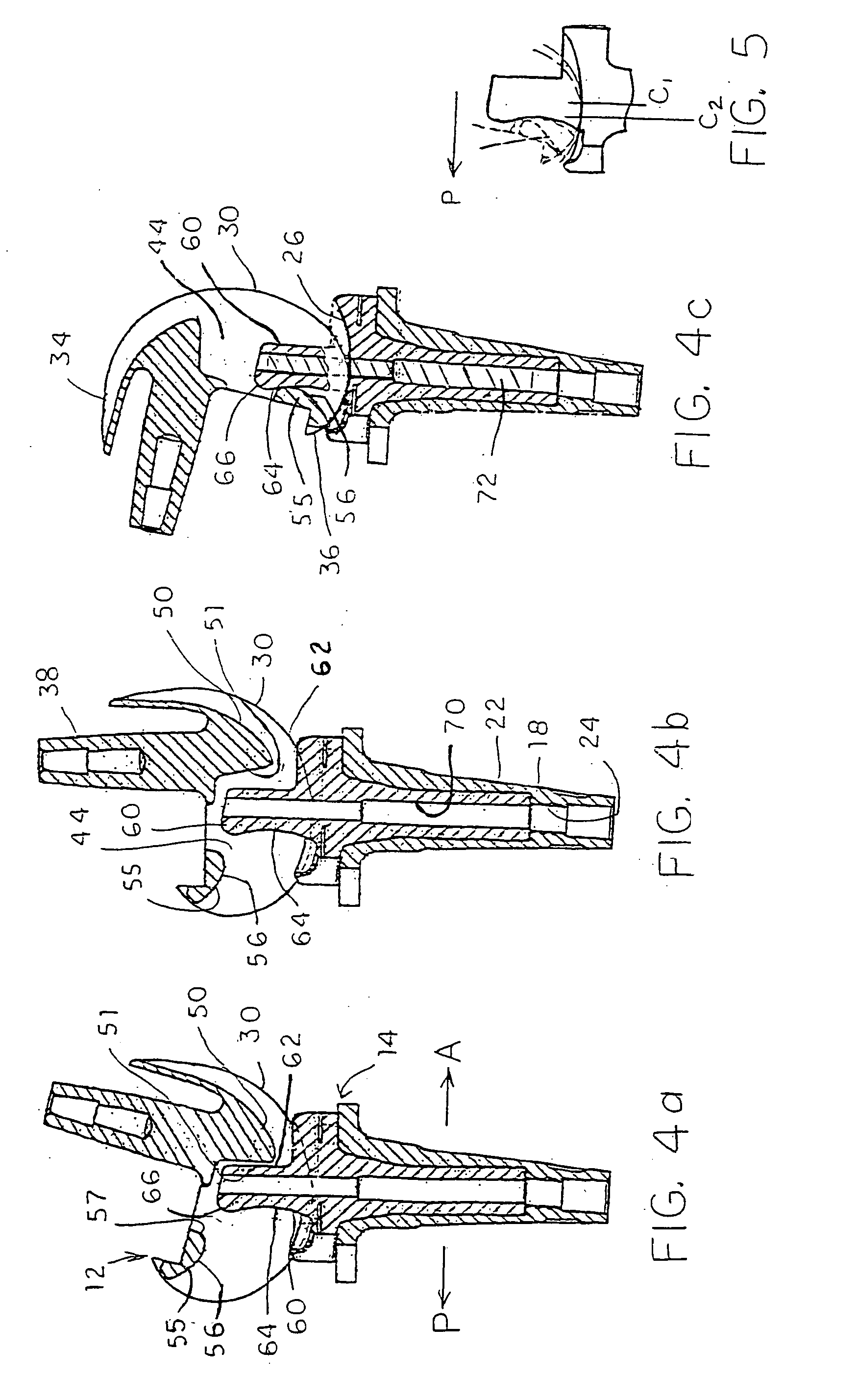
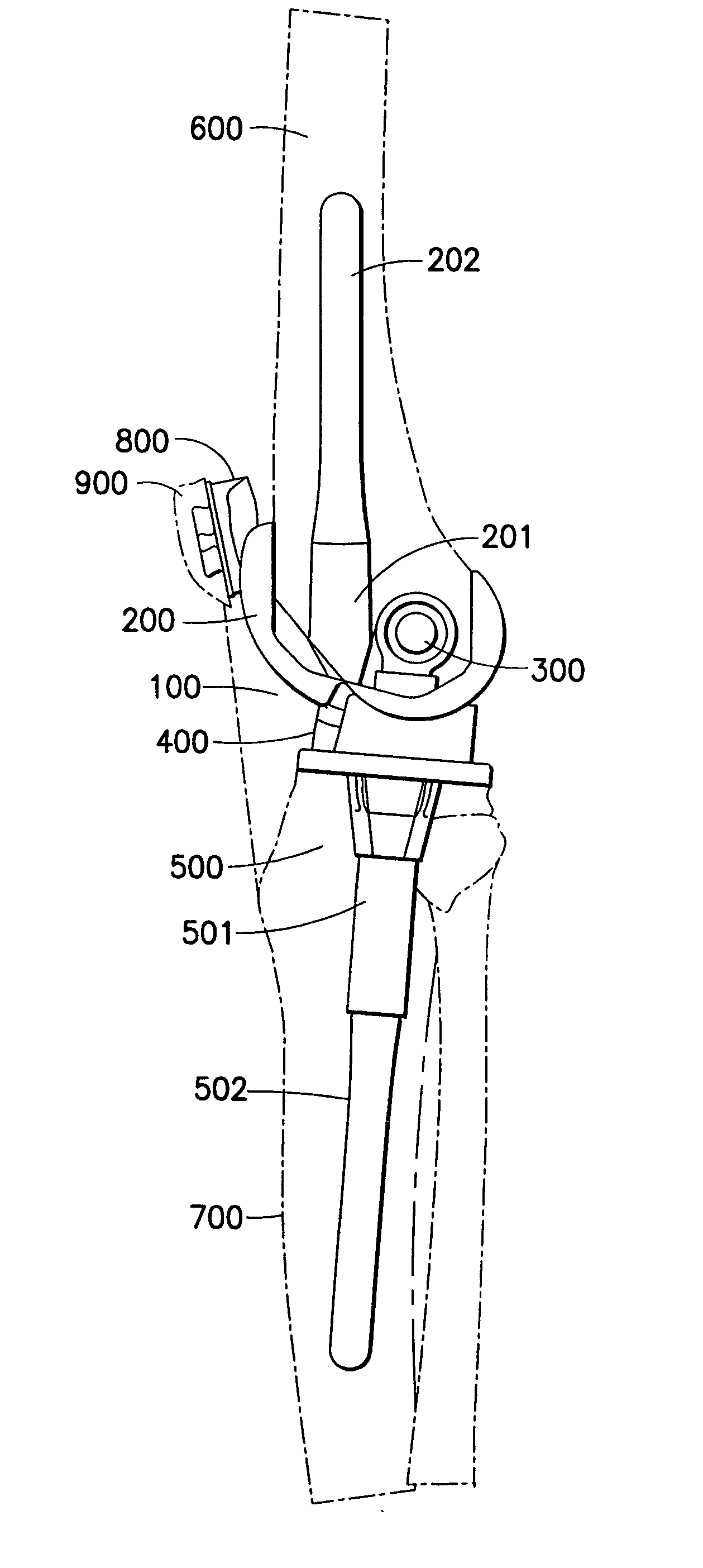
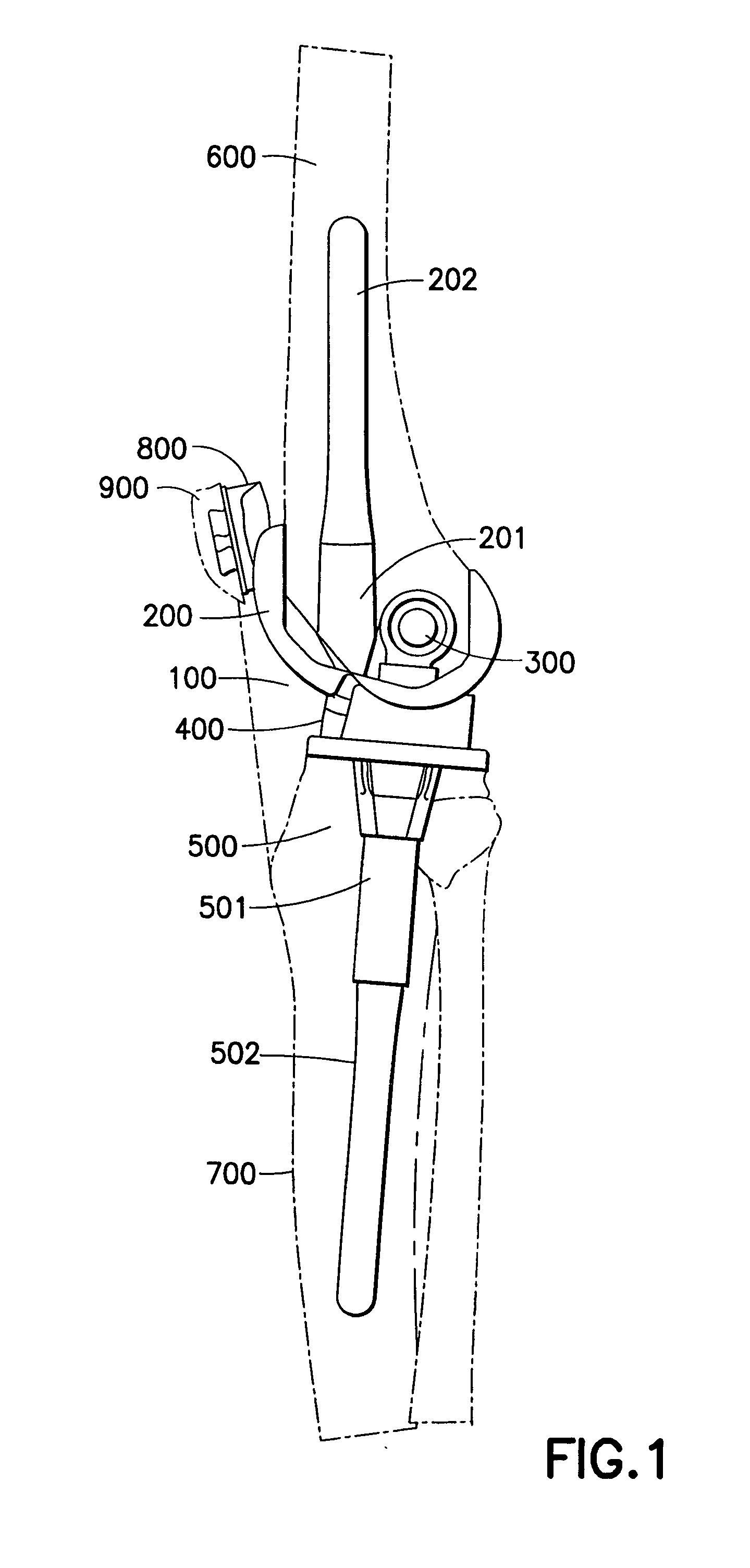
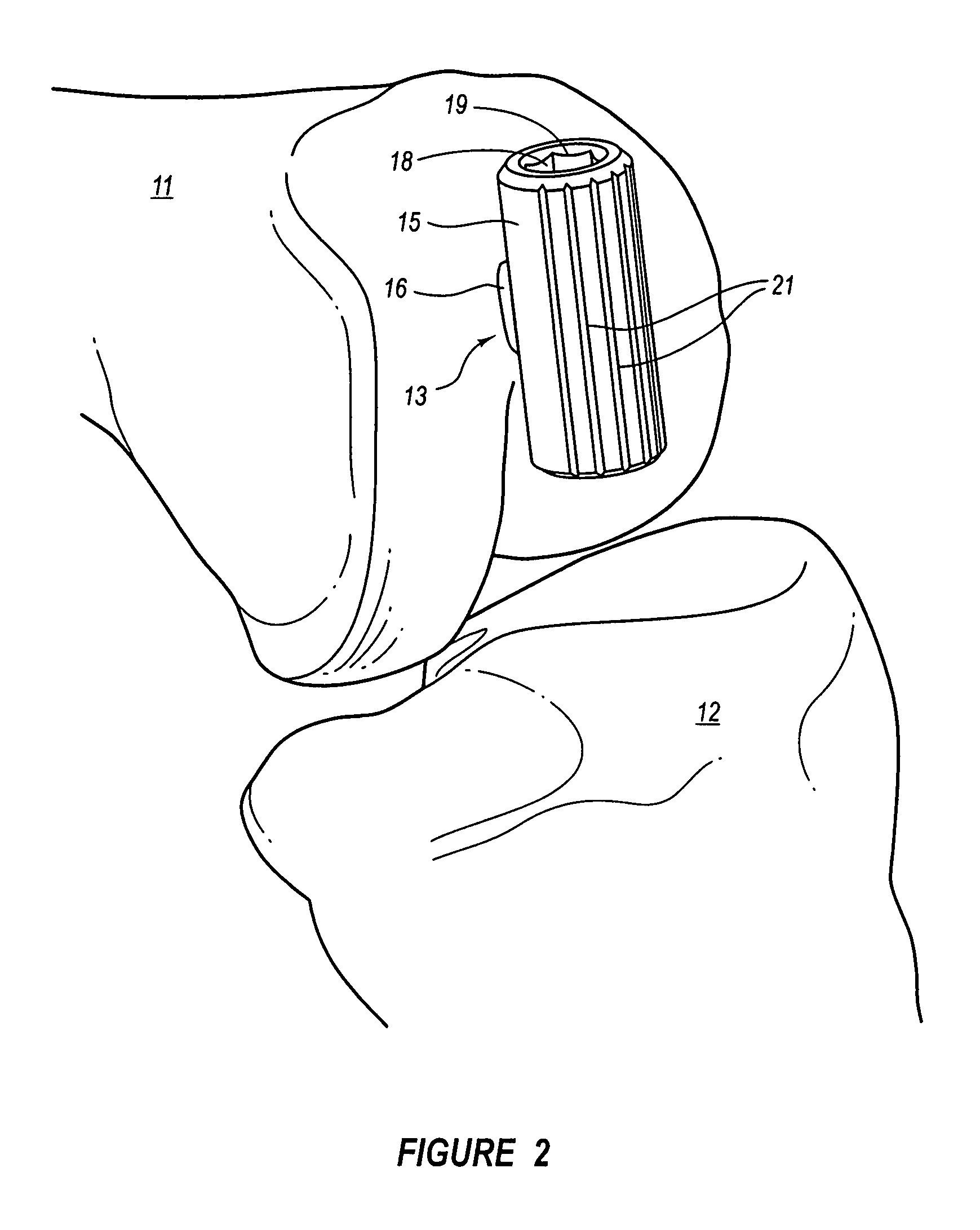
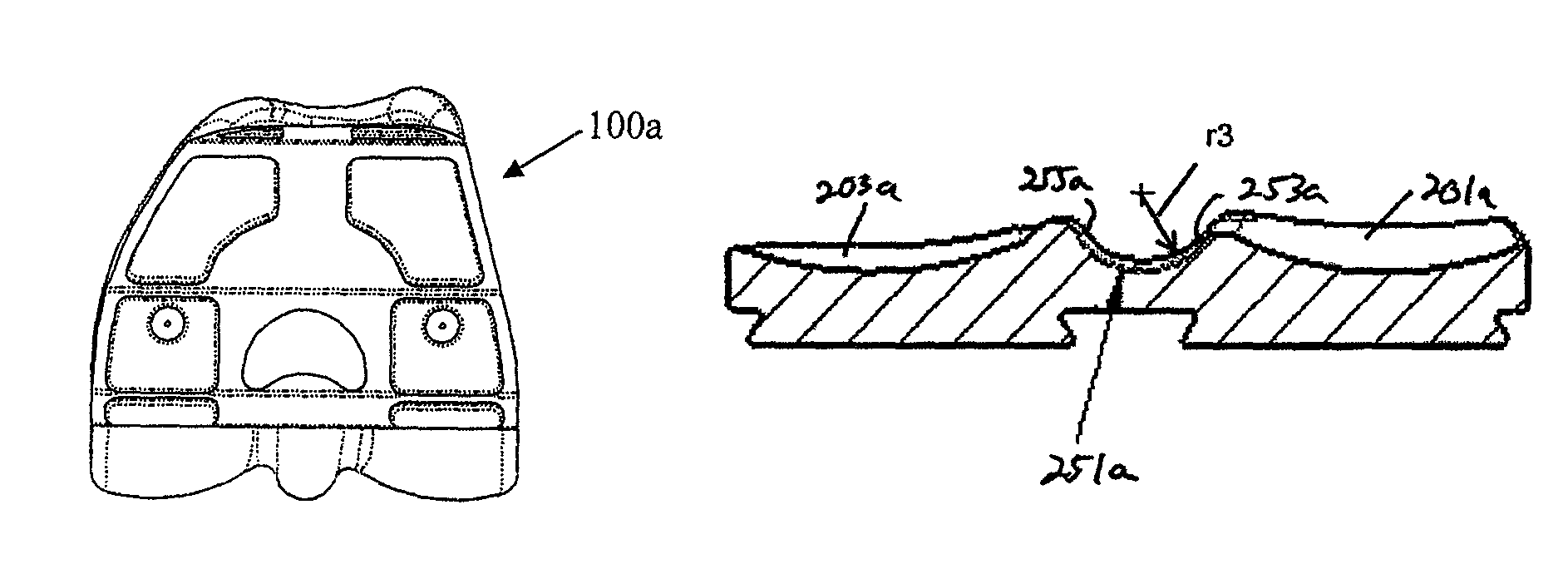
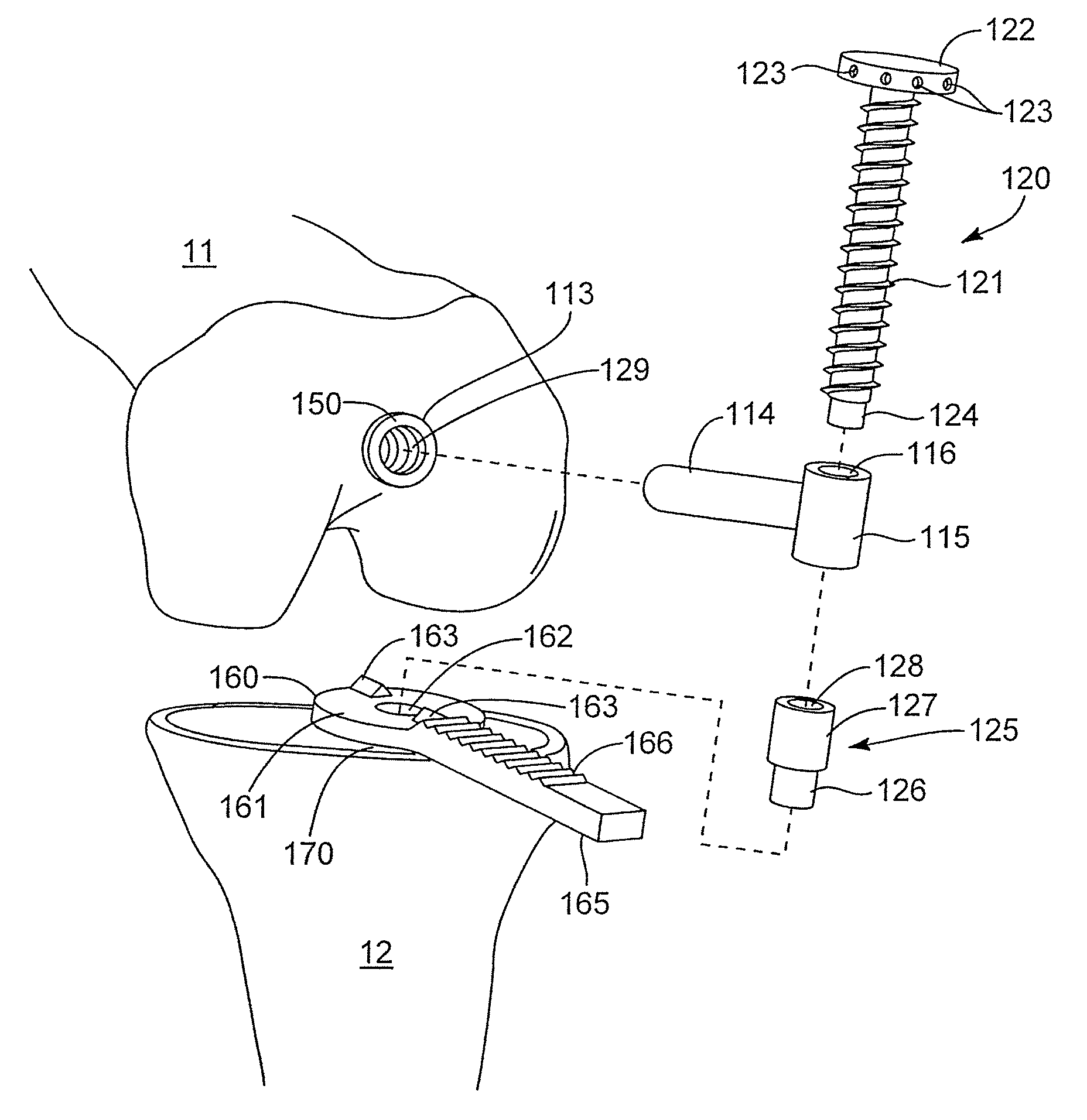
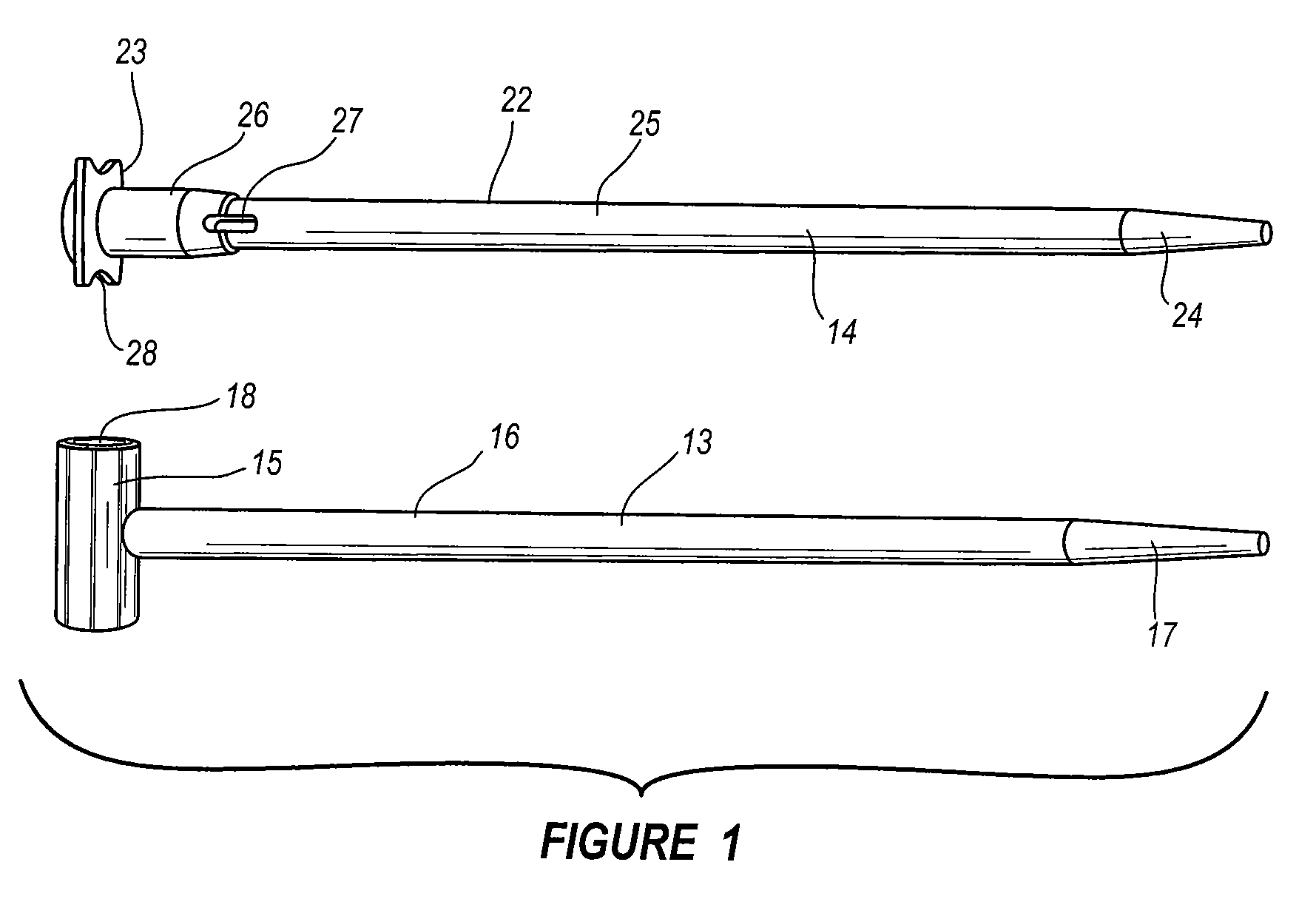
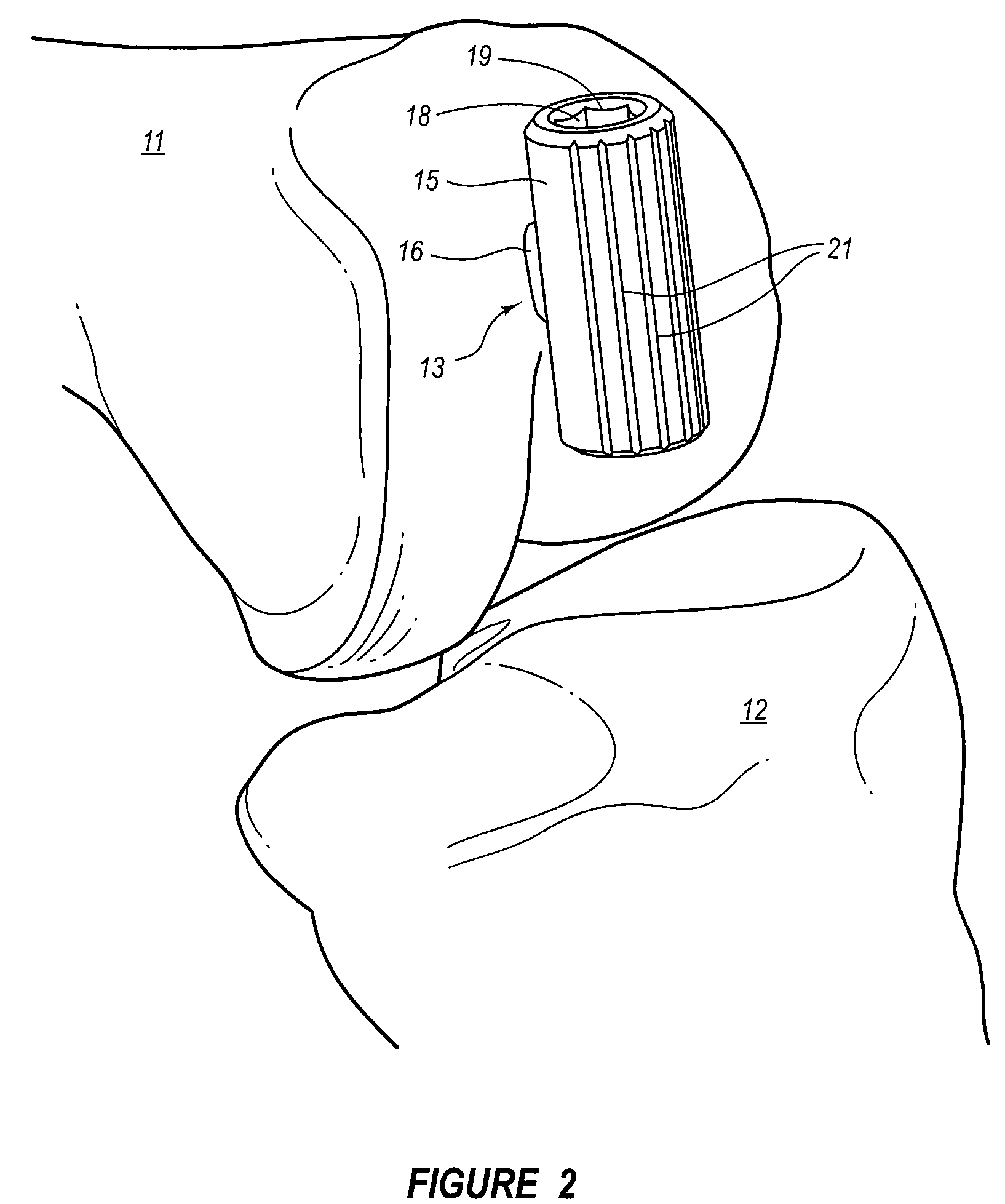
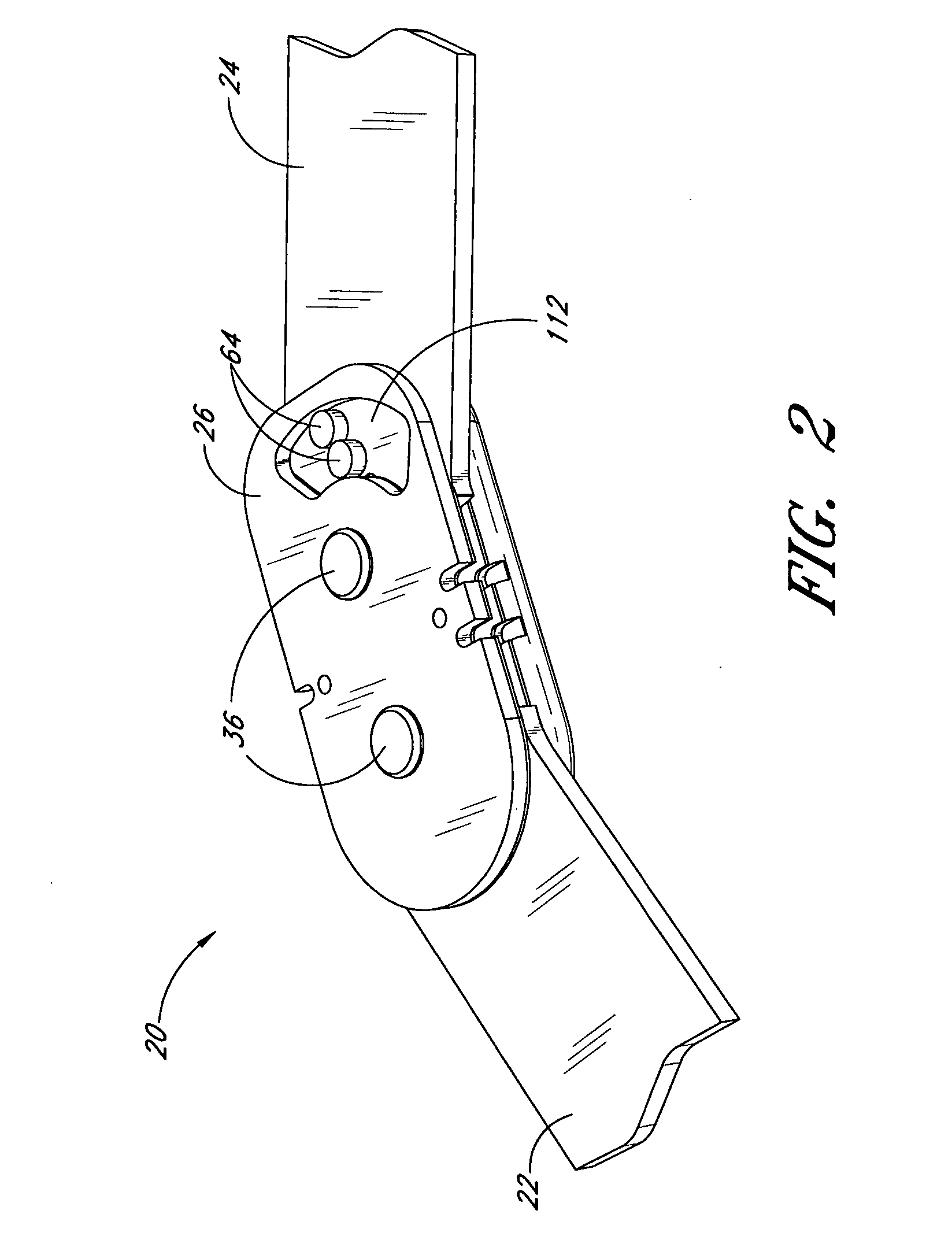
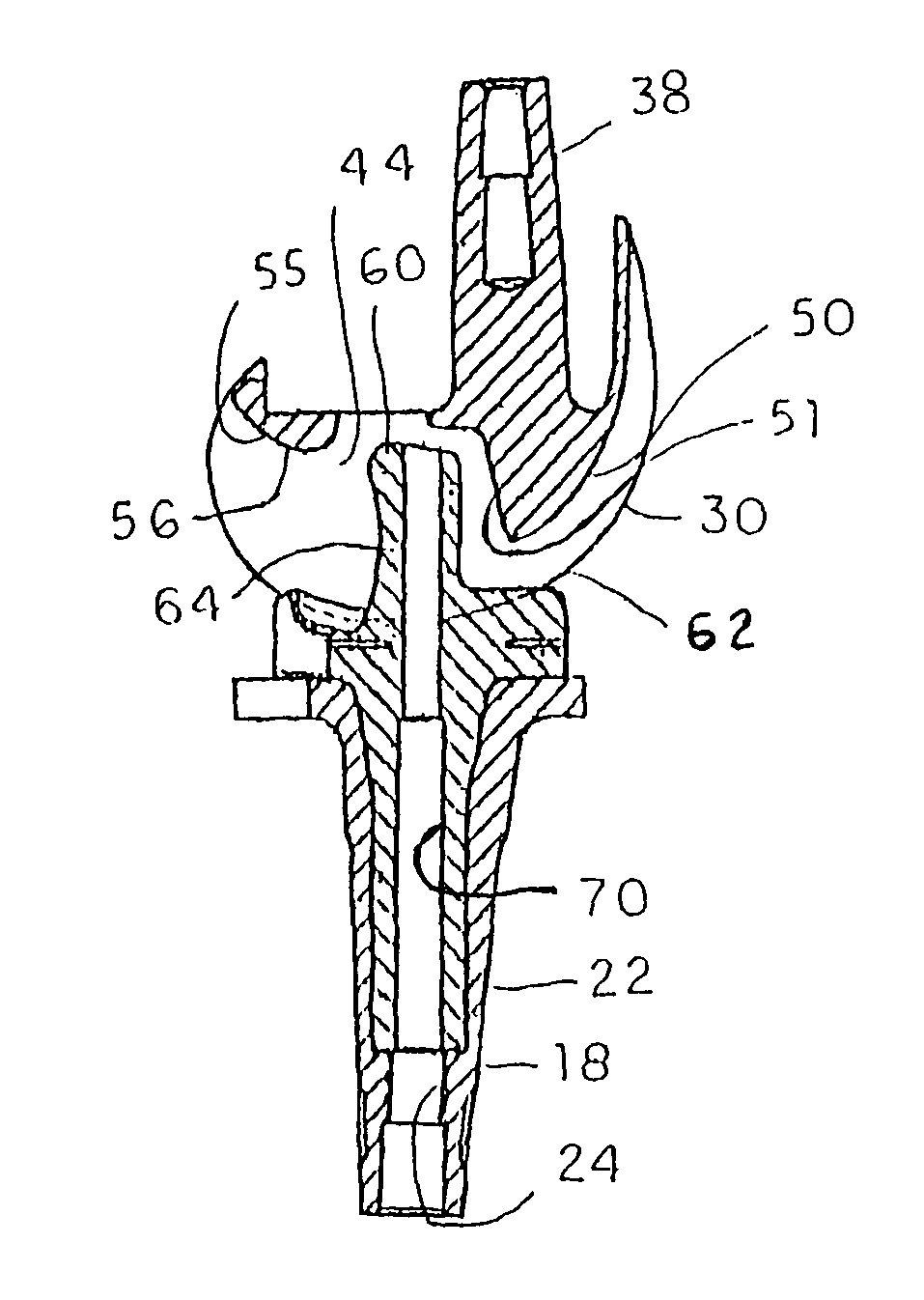
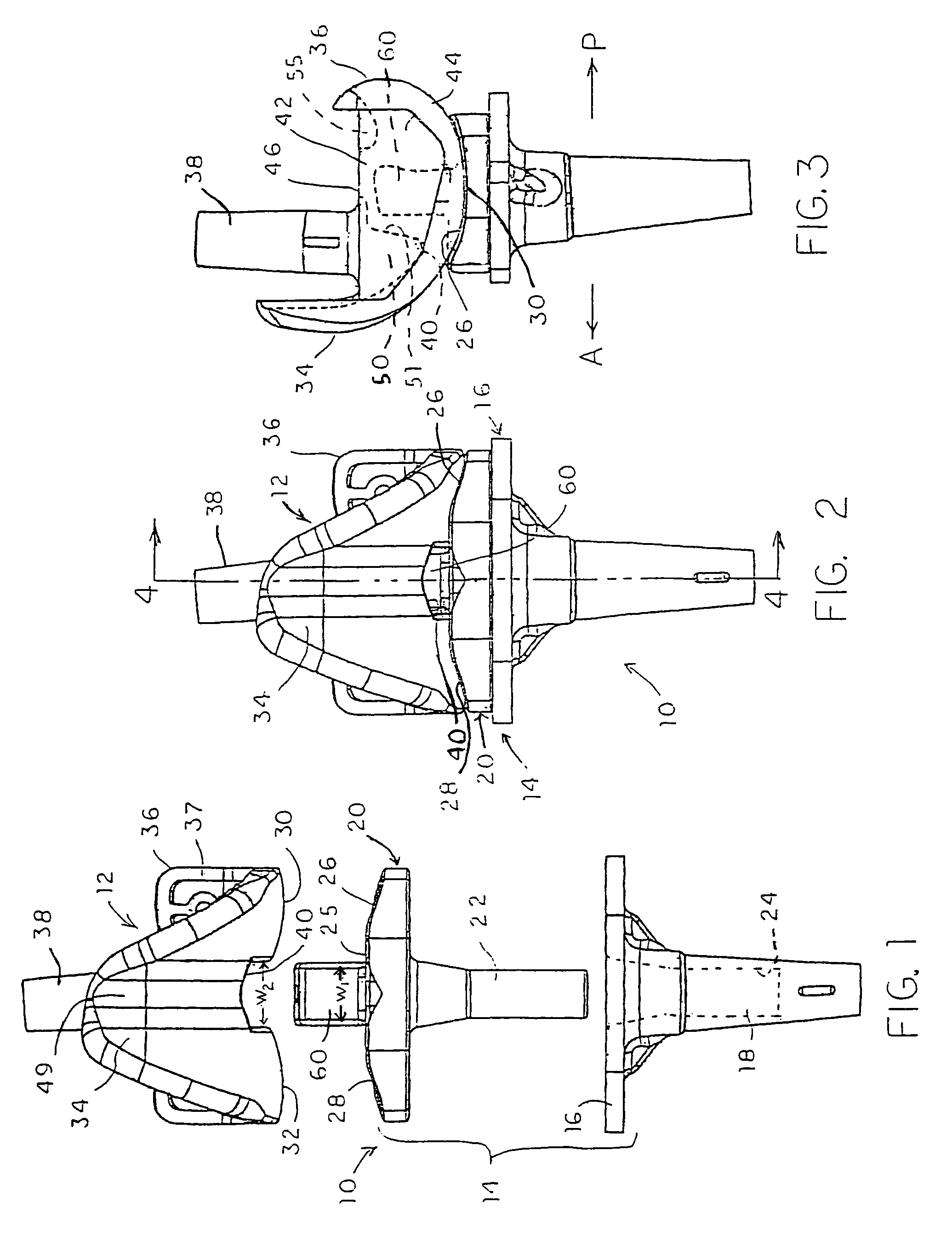
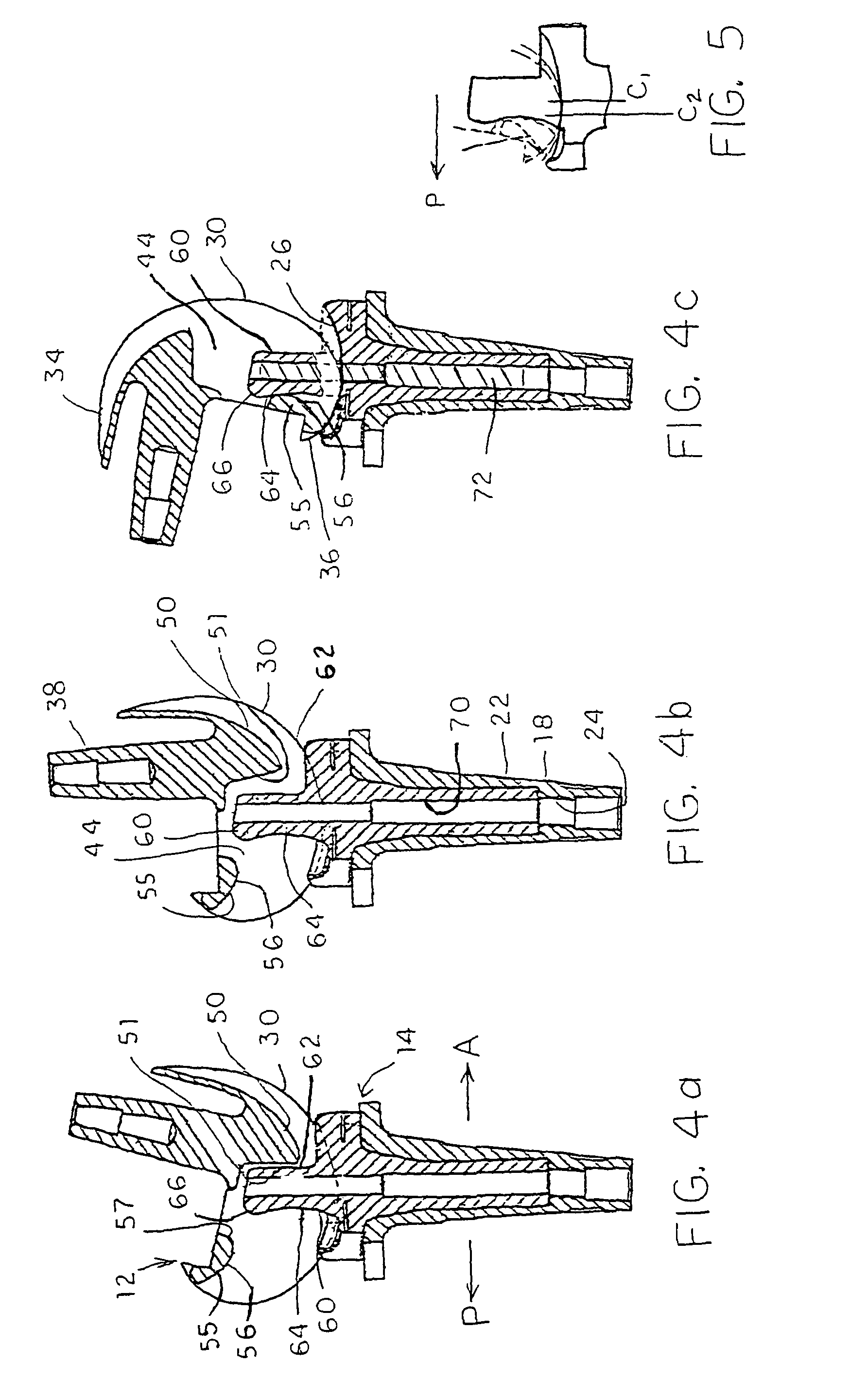
Plate for fusion of the metatarso-phalangeal joint
InactiveUS20060241608A1Minimized overall profileReduce the amount requiredJoint implantsBone platesDistal portionPhalanx bone
A fixation plate for use in fusion of the metatarsal-phalangeal joint includes a distal portion configured to engage the metatarsus bone and a proximal portion configured to engage the phalanx bone. The distal portion is elongated with several screw defined therethrough along a longitudinal axis passing through the portion. The proximal portion includes a plurality of screw holes that are all offset relative to each other along axes parallel and perpendicular to the longitudinal axis. No more than one of the screw holes in the proximal portion is aligned with the longitudinal axis. The fixation plate is contoured to cup the bones of the MTP joint. The plate may include an intermediate portion that is bent at a pre-determined dorsi-flexion angle.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
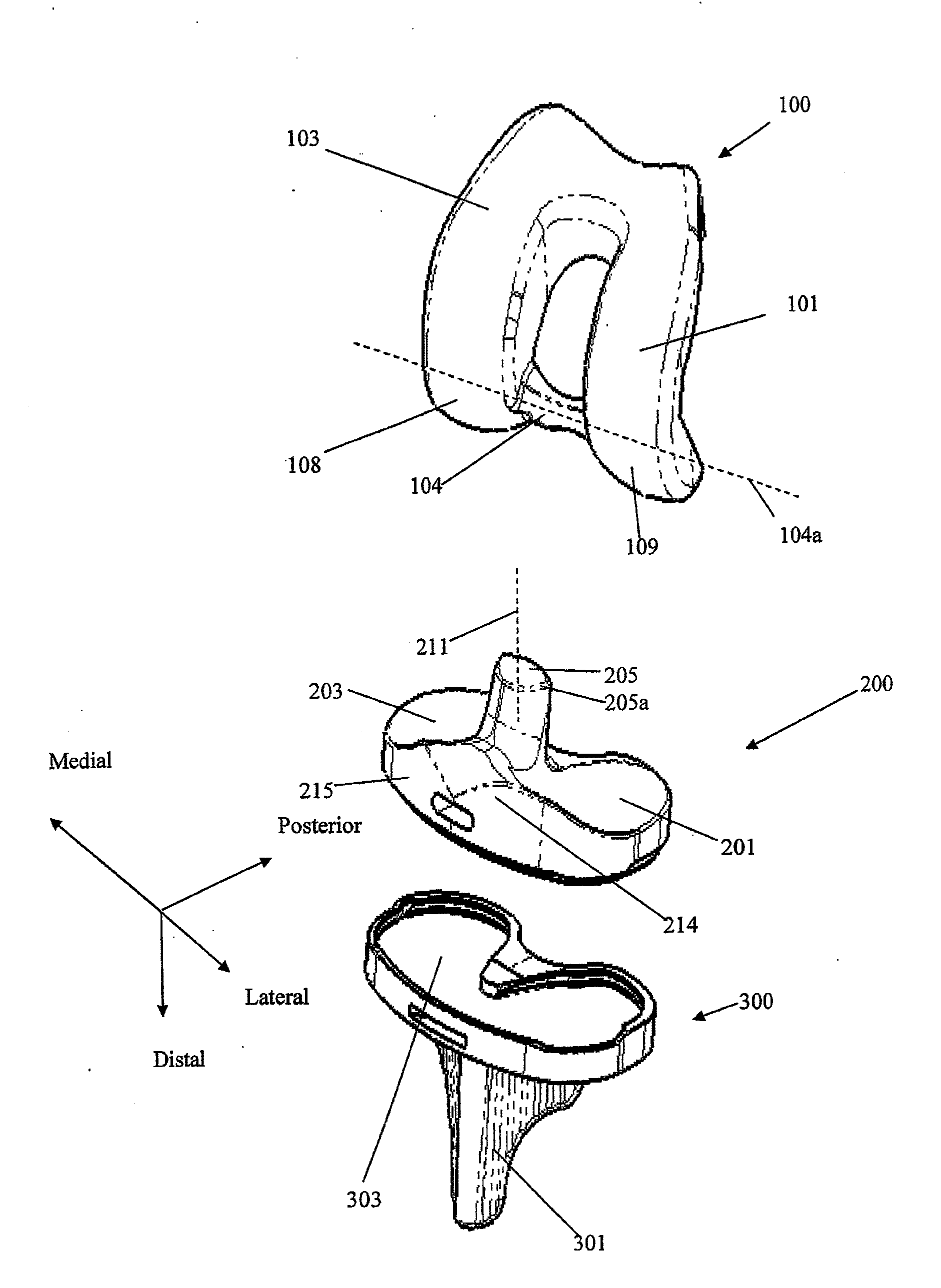
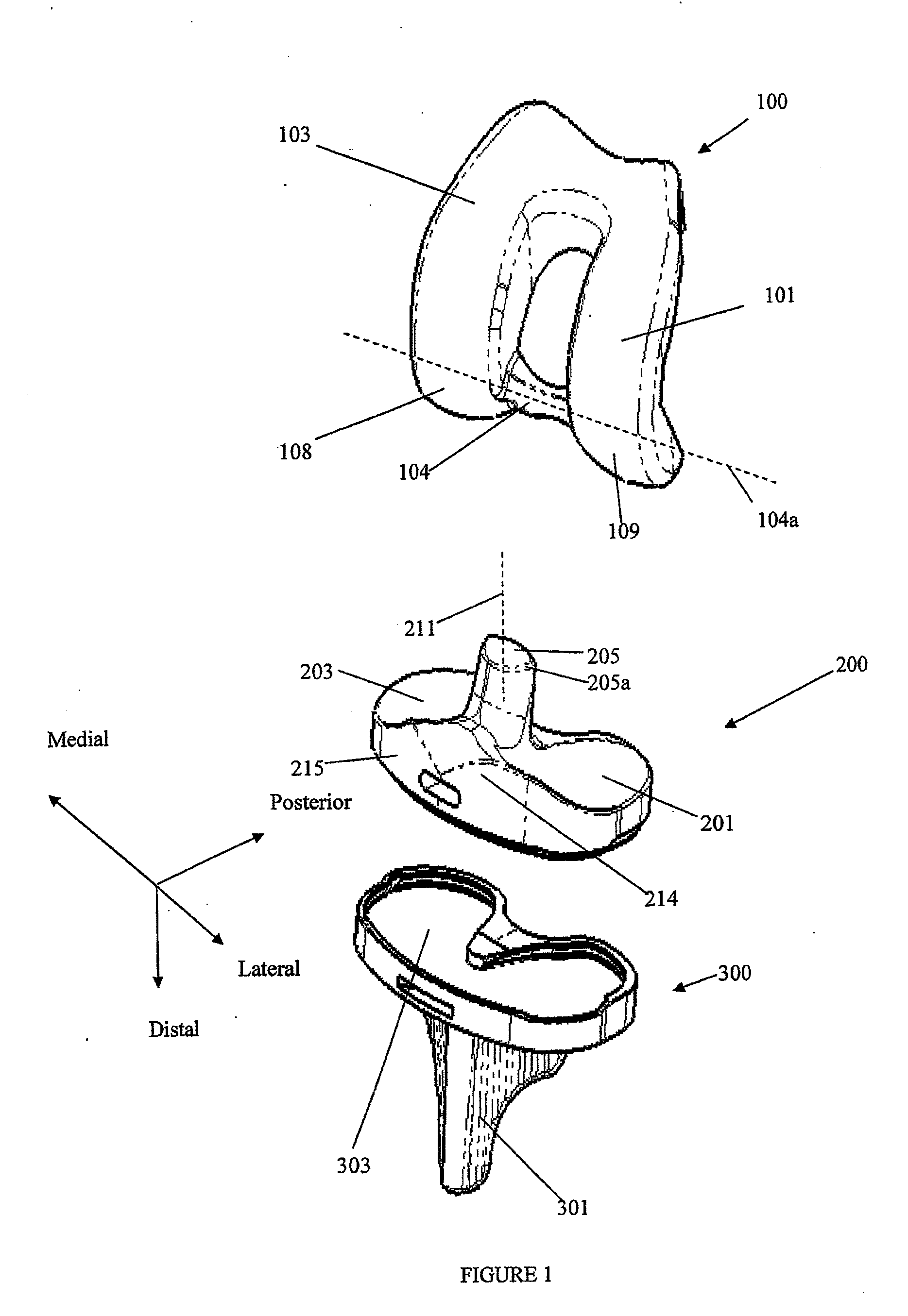
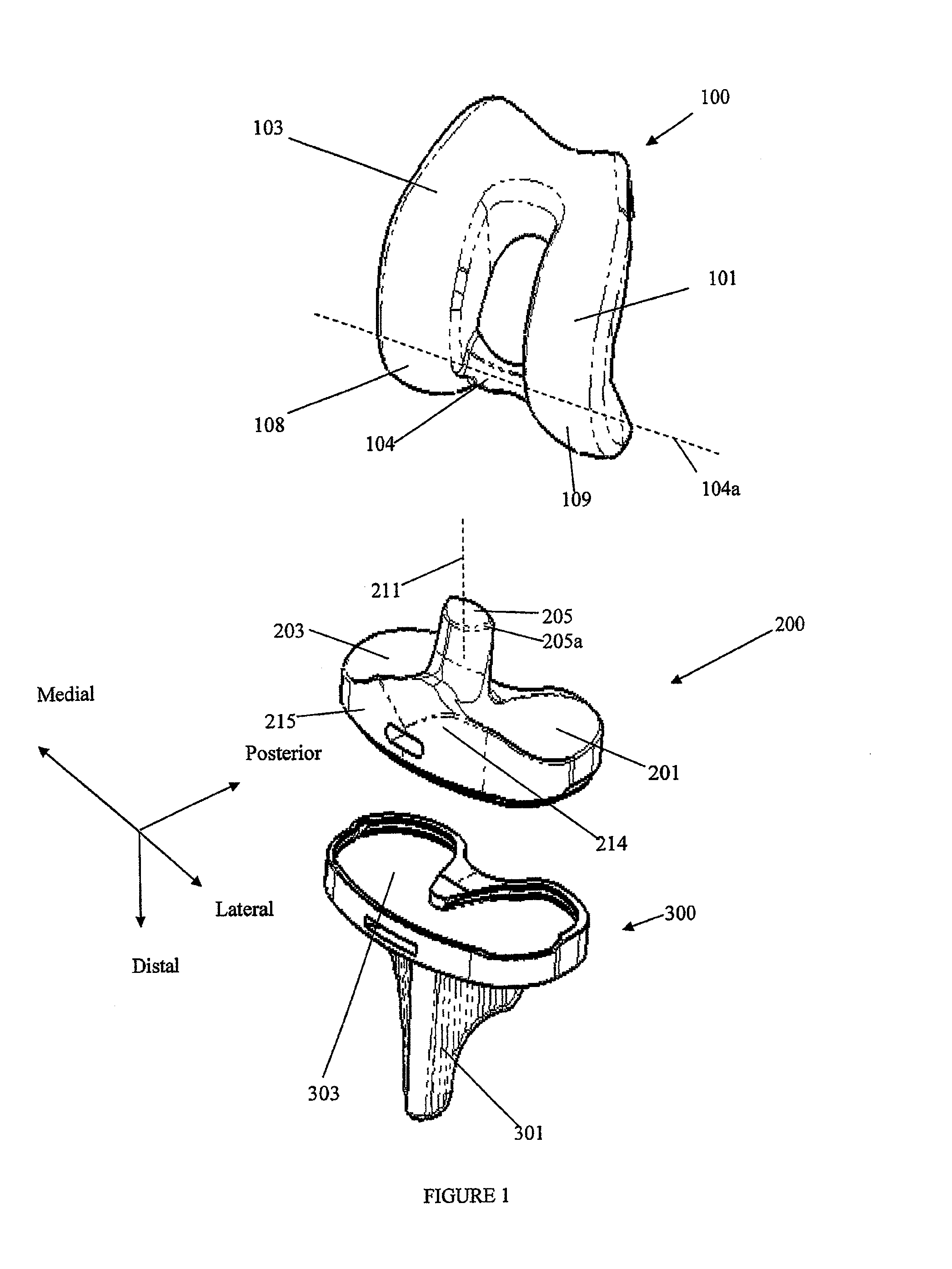
Posterior stabilized knee with varus-valgus constraint
ActiveUS20050192672A1Accurately and efficiently emulates kinematicsAccurately and efficiently and functionJoint implantsKnee jointsSpinal columnTibial bone
A femoral component of a knee prosthesis has spaced condyle surfaces defining a notch therebetween. The notch defines an elongated cam housing having an anterior cam and a posterior cam at opposite ends of the housing. The tibial component of the knee prosthesis includes a platform and a bearing supported on the platform, the bearing defining bearing surfaces configured to articulate with the condyle surfaces. The tibial component includes a spine projecting superiorly from the bearing that defines an anterior face and a posterior face. The posterior face and the posterior cam define complementary curved surfaces configured for cooperative engagement when the femoral component and the tibial component are at a predetermined flexion angle. The cam housing is configured to form a gap between the posterior cam and the spine when the knee is normally extended. In another feature, the spine includes a stiffening pin extending therethrough.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Guide assembly for guiding cuts to a femur and tibia during a knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS20060189998A1Small and noninvasive approachQuick disassemblyInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTibiaDistraction
An assembly for guiding resection of a femur and tibia of a knee joint in preparation for installing a femoral and tibial knee components. For example, the assembly can include tibial and femoral IM rods to which are connected through a torque bolt that allows controlled adjustment of the distraction of the tibia and femur during cut positioning in a range of flexion angles. Also, the assembly is usable with relatively small, noninvasive approaches to the knee joint by way of relatively narrow, low profile components that attach to tibial and femoral IM rods. Further, the assembly includes several quick-release components to allow fast assembly and disassembly in a surgical setting. Each of these aspects, along with the ability of the assembly to accurately guide initial reference cuts to the tibia and femur, promotes an improved outcome for the patient.
Owner:RASMUSSEN INSTR LLC
Prosthetic knee
A hinged knee prosthesis includes a femoral component with a tibiofemoral articular surface that is distinct from the patellofemoral articulating surface. Fully congruent tibiofemoral articulation is provided for virtually all flexion angles. Additionally, the bearing is capable of at least limited axial rotation relative to the tibial component but is restrained against dislocation. Accordingly, dislocation is much less likely even n those situations where collateral ligaments are insufficient.
Owner:BUECHEL PAPPAS TRUST
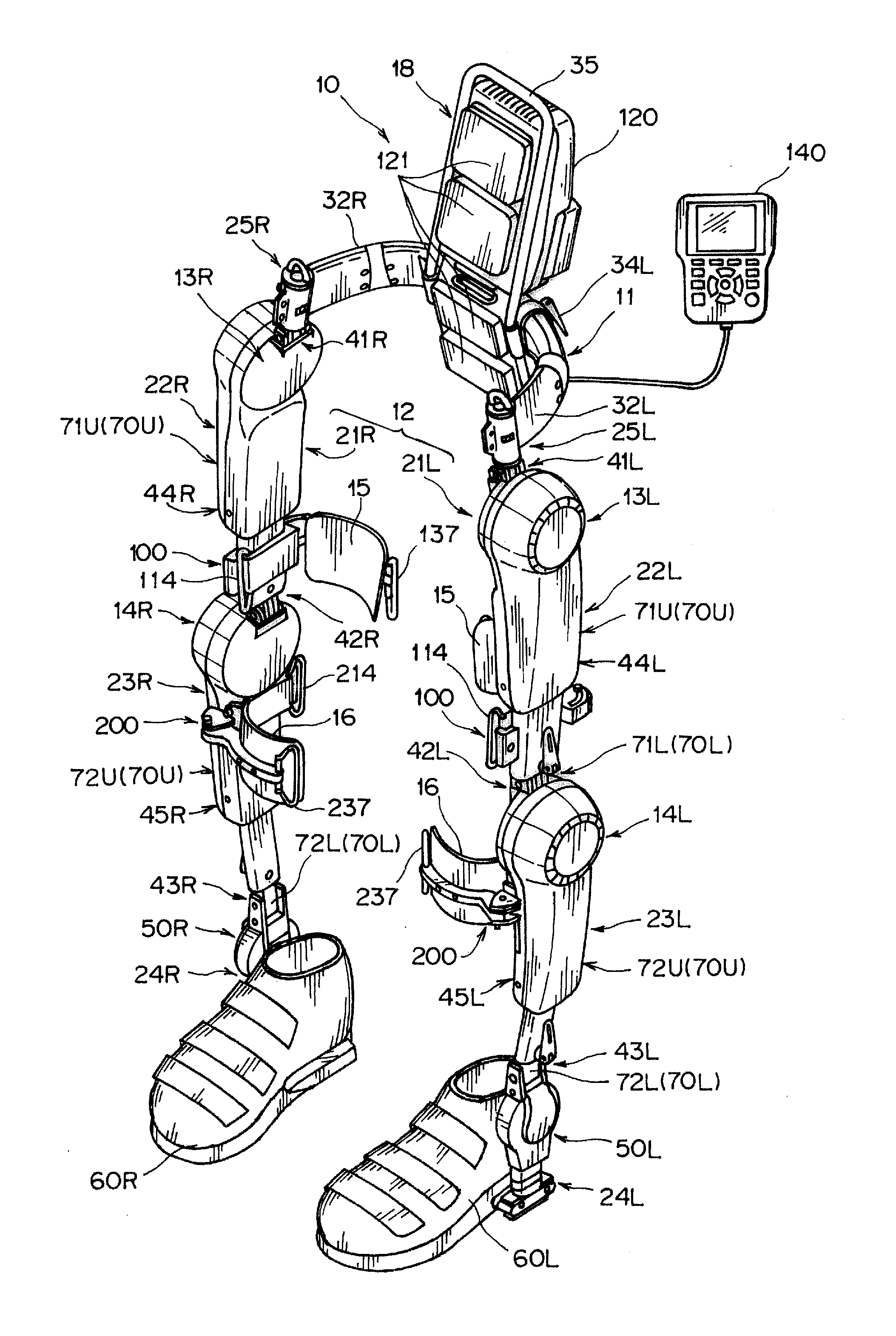
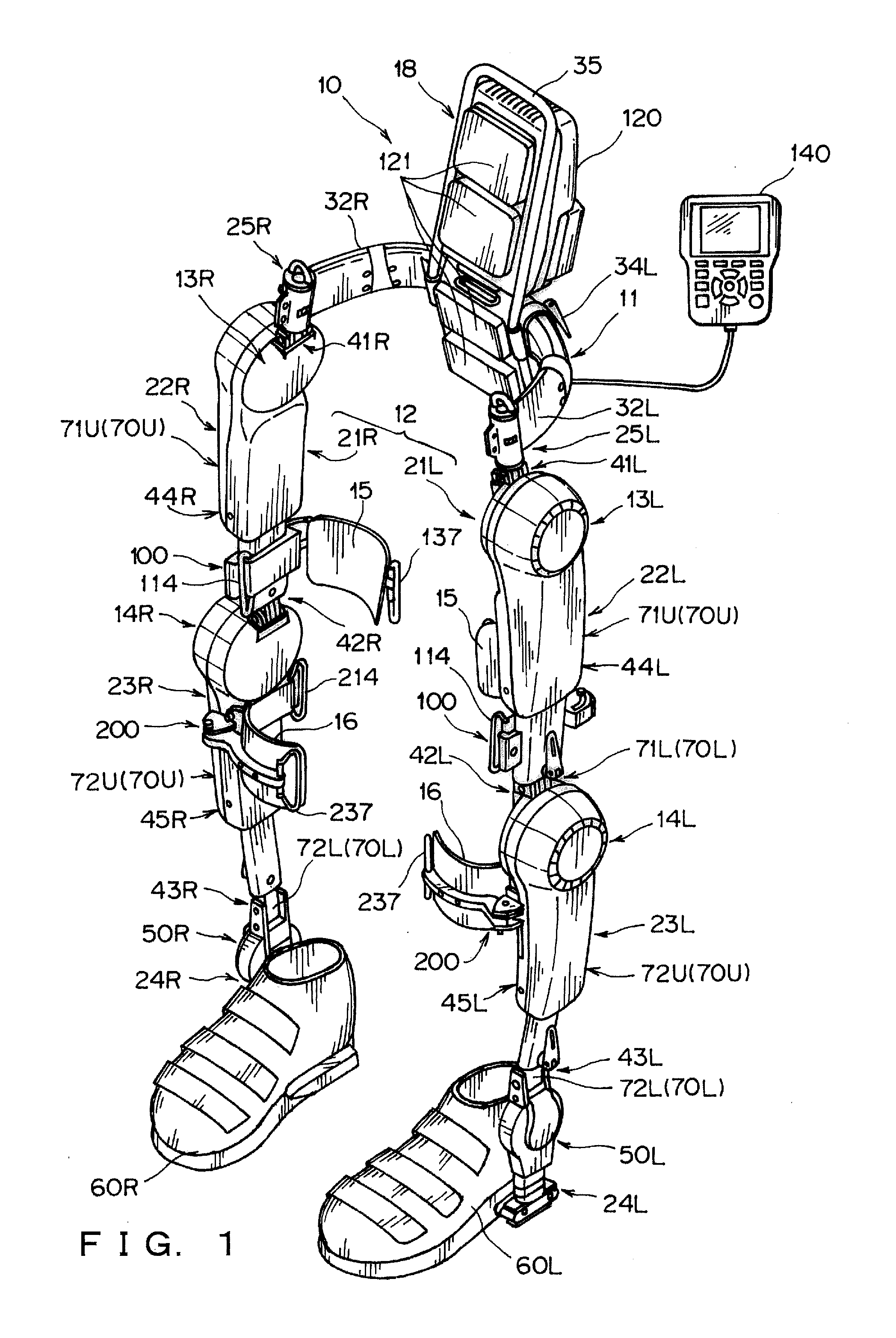
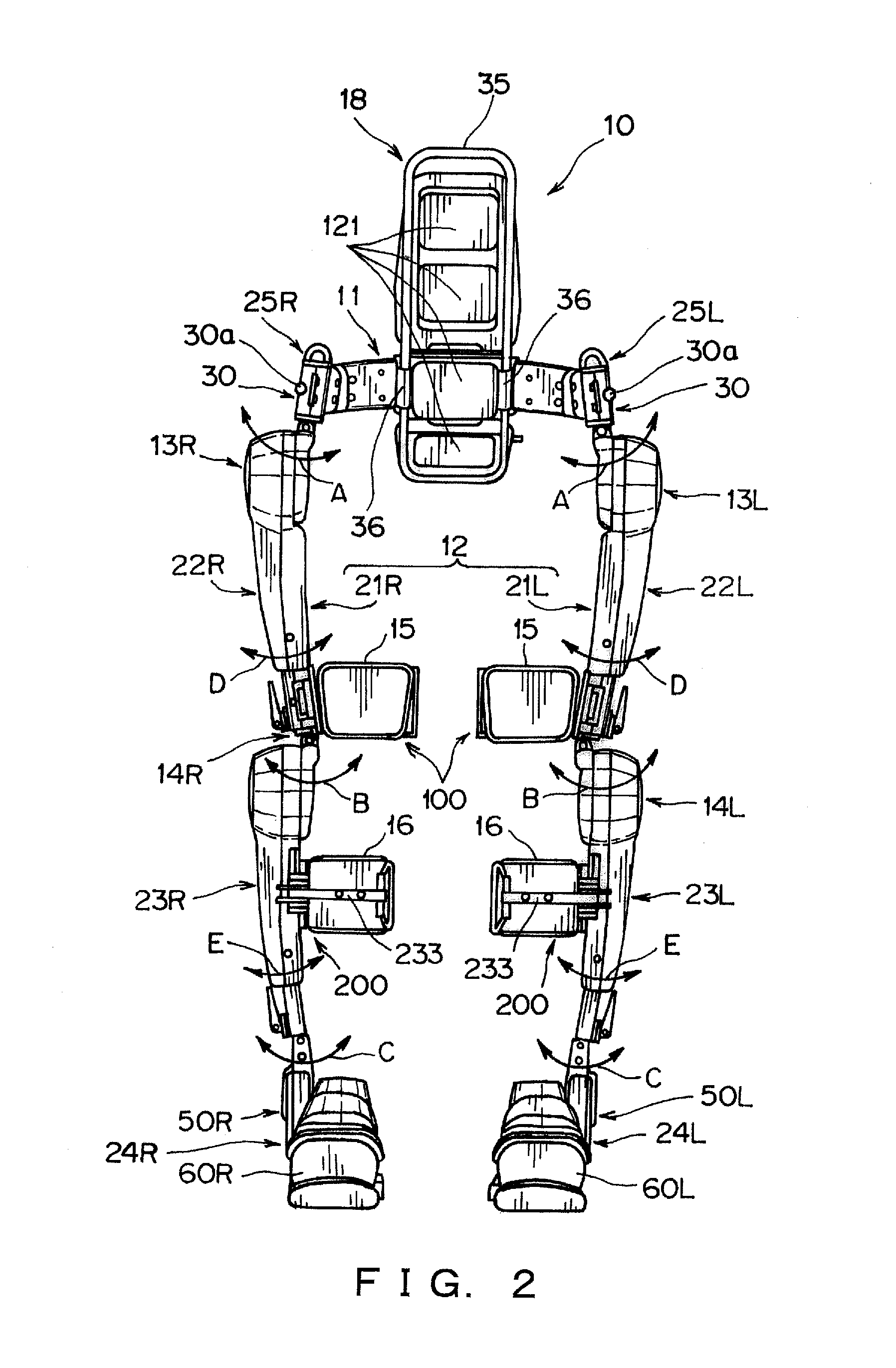
Wearable Action-Assistance Device
InactiveUS20160331624A1Easy to put inEasy to takeProgramme-controlled manipulatorDiagnosticsEngineeringSacroiliac joint
A wearable action-assistance device includes a hip frame that is capable of being worn on hips of a wearer, a lower limb frame that is capable of being worn on a lower limb of the wearer, a plurality of drive portions provided on the lower limb frame in correspondence with joints of the wearer, and a control portion that controls the drive portions based on a signal that is caused by an action of the wearer. The lower limb frame has a variable shape portion that can bend a portion other than the drive portions to left and right to adjust a flexion angle thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF TSUKUBA +1
Guide assembly for guiding cuts to a femur and tibia during a knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS7927336B2Small and noninvasive approachPromote resultsInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDistractionTibia
An assembly for guiding resection of a femur and tibia of a knee joint in preparation for installing a femoral and tibial knee components. For example, the assembly can include tibial and femoral IM rods to which are connected through a torque bolt that allows controlled adjustment of the distraction of the tibia and femur during cut positioning in a range of flexion angles. Also, the assembly is usable with relatively small, noninvasive approaches to the knee joint by way of relatively narrow, low profile components that attach to tibial and femoral IM rods. Further, the assembly includes several quick-release components to allow fast assembly and disassembly in a surgical setting. Each of these aspects, along with the ability of the assembly to accurately guide initial reference cuts to the tibia and femur, promotes an improved outcome for the patient.
Owner:RASMUSSEN INSTR LLC
Prosthetic joint
InactiveUS20130197653A1Preventing posterior subluxationIncrease maximum flexionJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesTibia
A joint prosthesis comprising, e.g., a femoral component and a tibial component. The medial and lateral condylar articular surfaces may have substantially uniform and equal radii from full extension to about 90° of flexion. From 90°, the lateral condylar articular surface has a smaller radius than the medial condylar articular surface such that the medial condyle gradually becomes increasingly more proud than the lateral condyle to facilitate internal rotation of the tibia at deep flexion. Also, the tibial articular component may include a post intermediate the medial and lateral compartments that engages a cam on the femoral articular component between the medial and the lateral condylar articular surfaces. The cam and post become congruent at flexion angles of approximately 70° flexion and mate symmetrically during the first 20°-30° of further flexion, and then mate asymmetrically at greater degrees of flexion to force internal rotation of the tibia.
Owner:EPIC ORTHO
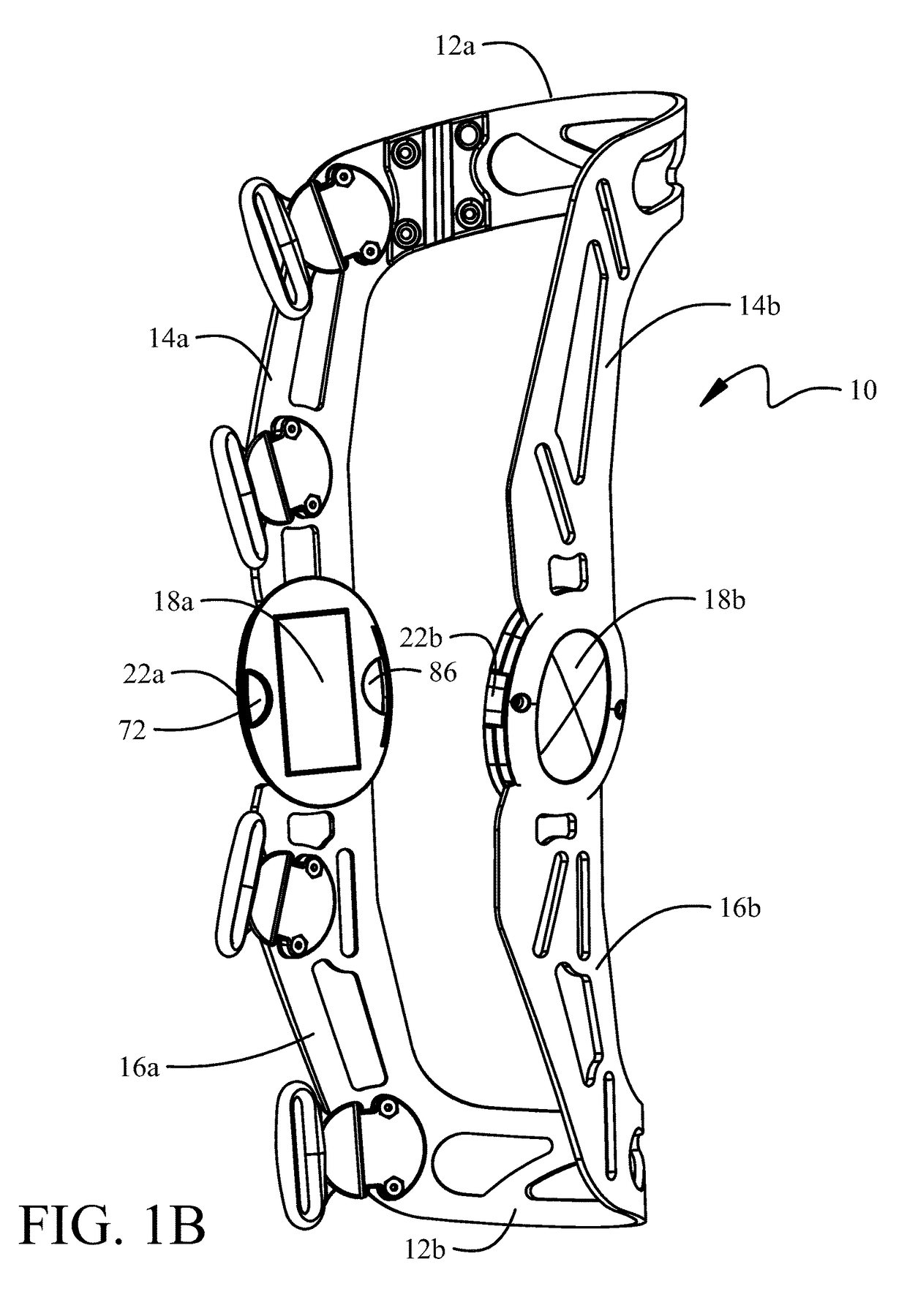
Motion controlling hinge for orthopedic brace
A motion controlling hinge for an orthopedic brace is provided. The hinge includes an actuator secured to one arm, and at least one spring member. As the arm with the actuator pivots in a first direction, at a predetermined flexion angle the actuator applies a force to the spring member, causing the spring member to flex. The spring member exerts a force on the actuator tending to bias the actuator away from the spring member, and tending to bias the arm in a second direction opposite the first direction. In a preferred embodiment, the spring member comprises a plurality of flat bar leaf springs. A movable fulcrum enables adjustment of a force exerted by the spring member on the actuator. A variety of differently sized adapters are securable to the actuator. The size of the adapter determines the flexion angle at which the spring member first exerts force on the actuator.
Owner:DJO
Motion controlling hinge for orthopedic brace
A motion controlling hinge for an orthopedic brace is provided. The hinge includes an actuator secured to one arm, and at least one spring member. As the arm with the actuator pivots in a first direction, at a predetermined flexion angle the actuator applies a force to the spring member, causing the spring member to flex. The spring member exerts a force on the actuator tending to bias the actuator away from the spring member, and tending to bias the arm in a second direction opposite the first direction. In one embodiment, the spring member comprises a plurality of flat bar leaf springs. A movable fulcrum enables adjustment of a force exerted by the spring member on the actuator. A variety of differently sized adapters are securable to the actuator. The size of the adapter determines the flexion angle at which the spring member first exerts force on the actuator. In some embodiments, the hinge includes an “ON” / “OFF” switch that enables a user to disengage biasing force provided by the spring member. When the switch occupies the “OFF” position, the hinge is freely pivotable to a maximum extension angle.
Owner:DJO
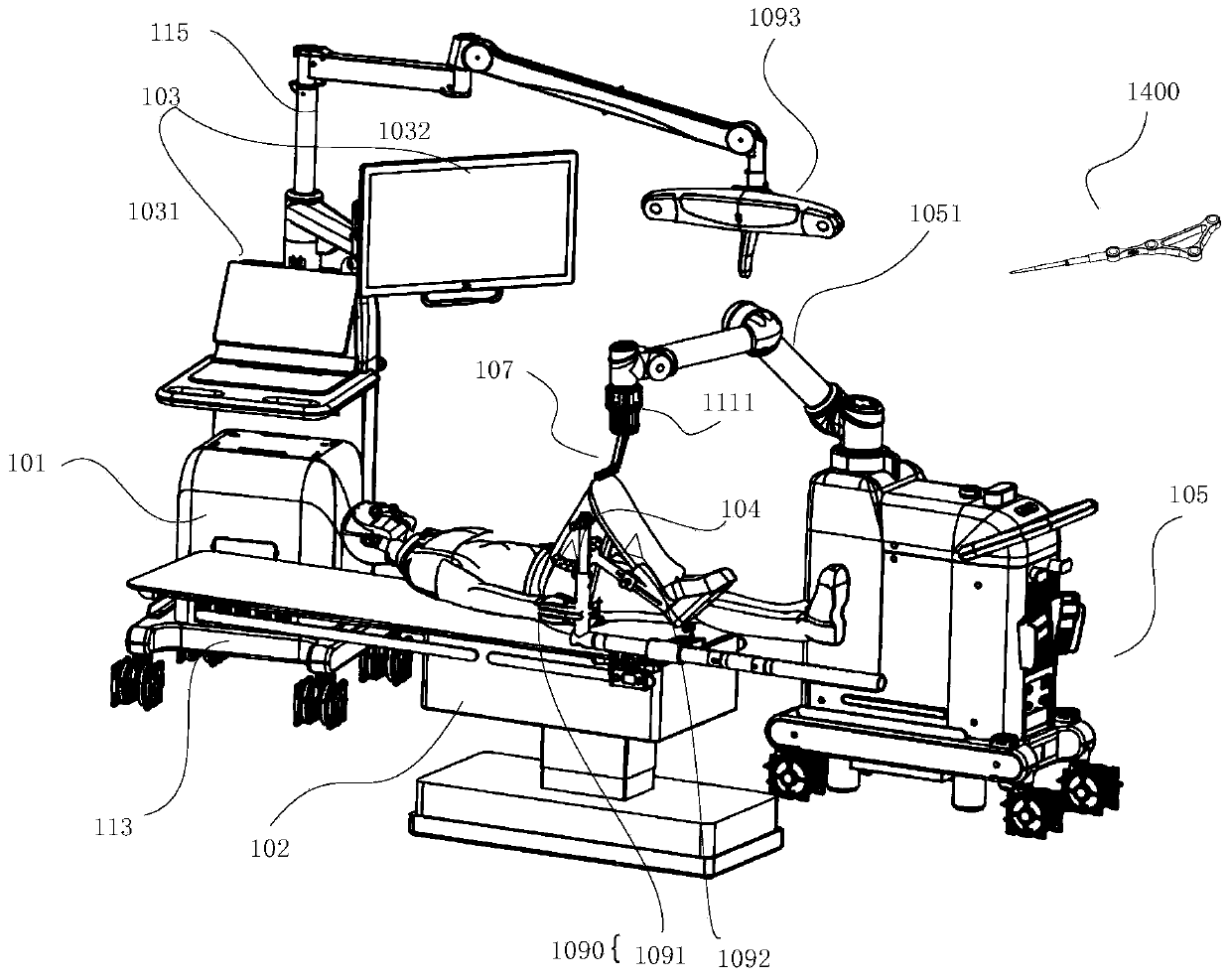
Total knee arthroplasty robot auxiliary system, control method and electronic equipment
ActiveCN111345895AHigh precisionPromote reconstructionSurgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceData graphTotal knee replacement
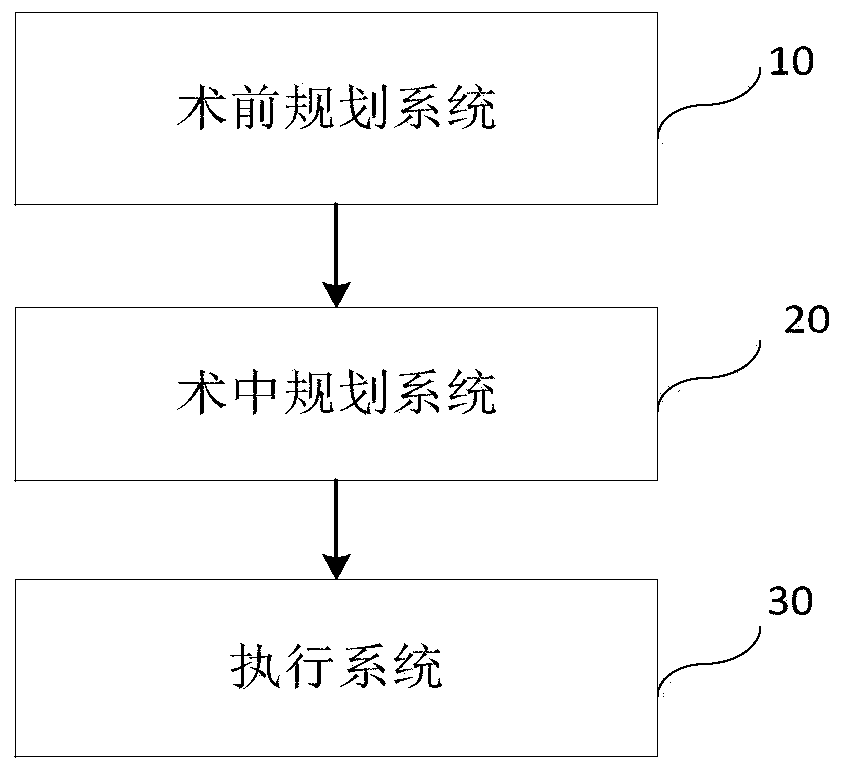
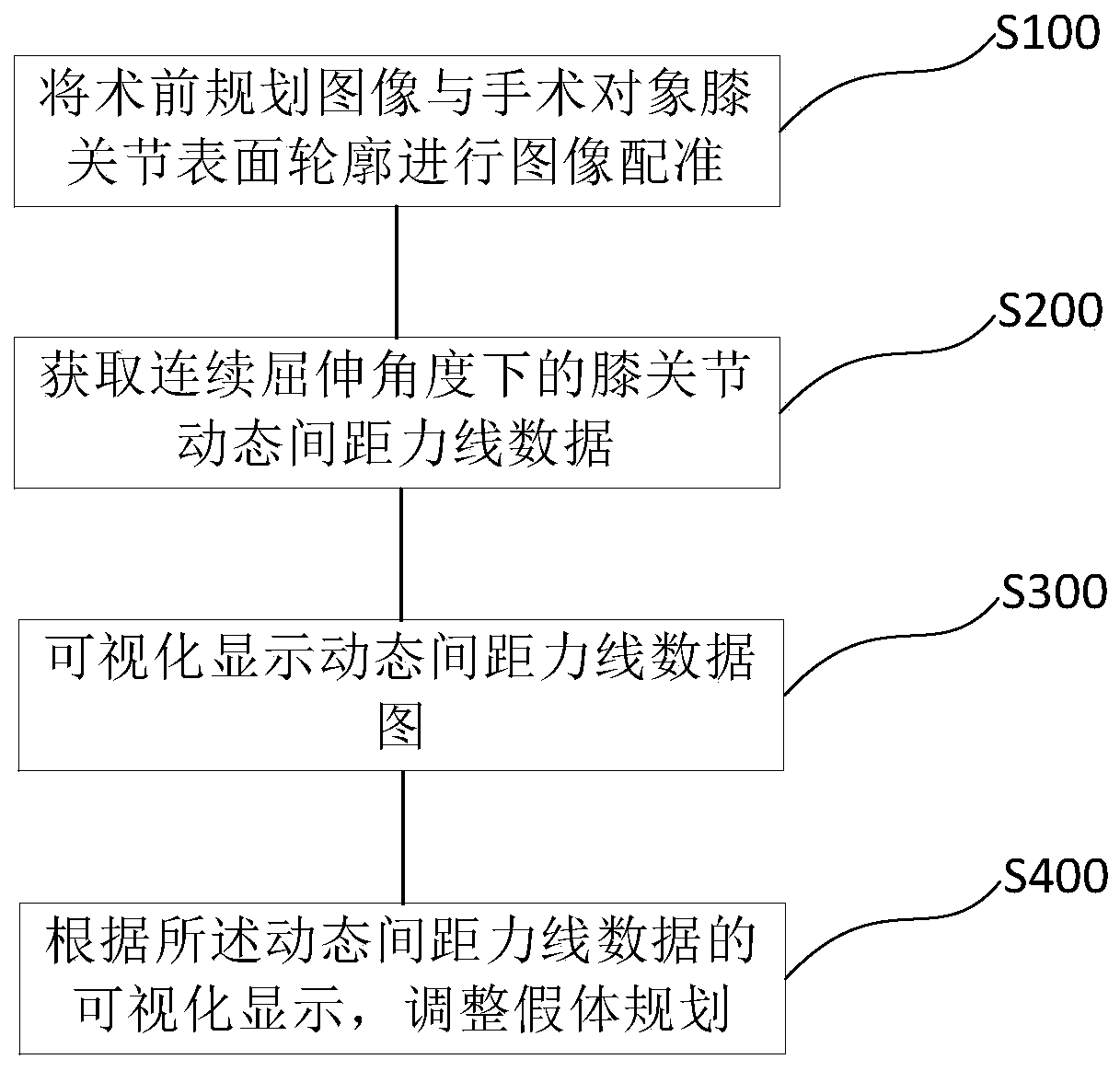
The invention provides a total knee arthroplasty robot auxiliary system, a control method, electronic equipment, and a computer-readable medium. The auxiliary system comprises a pre-operative planningsystem, an intraoperative planning system and an execution system, wherein the pre-operative planning system is used for formulating pre-operative planning, wherein the pre-operative planning data comprises a knee image; the intraoperative planning system is used for formulating intraoperative planning, wherein the knee image in the pre-operative plan and a knee surface profile determined in theoperation of a patient are subjected to image registration; knee dynamic spacing force line data at a continuous flexion angle is acquired; visual displaying of a dynamic spacing force line data graphis performed; prosthesis planning is adjusted according to the visual display of the dynamic spacing force line data graph to obtain intraoperative planning; and the execution system is used for guiding an osteotomy guide mounted at the operating end of a mechanical arm of the surgical robot to be located in a predetermined position in the planning, wherein the osteotomy guide is used for positioning an osteotomy saw.
Owner:BEIJING TINAVI MEDICAL TECH
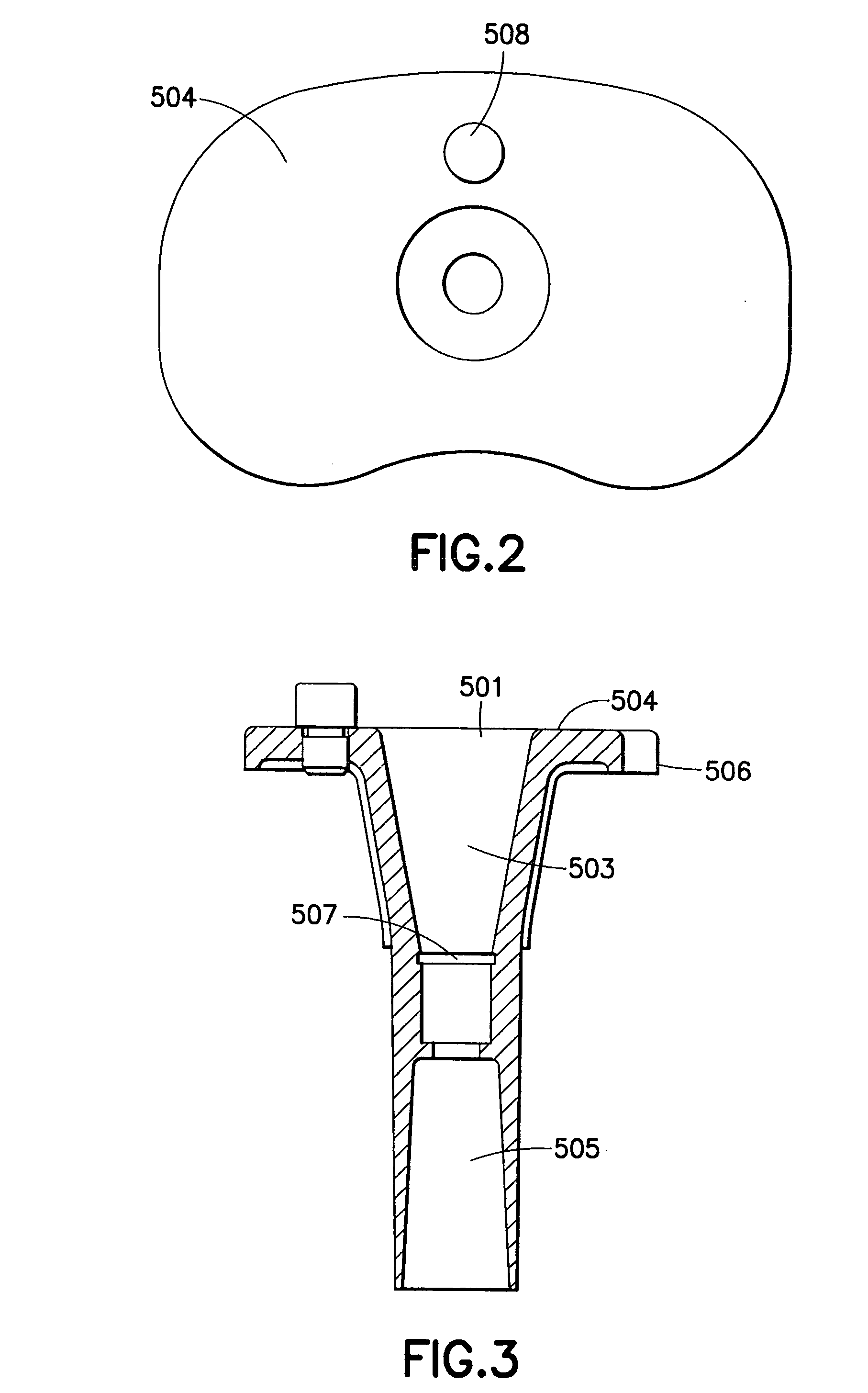
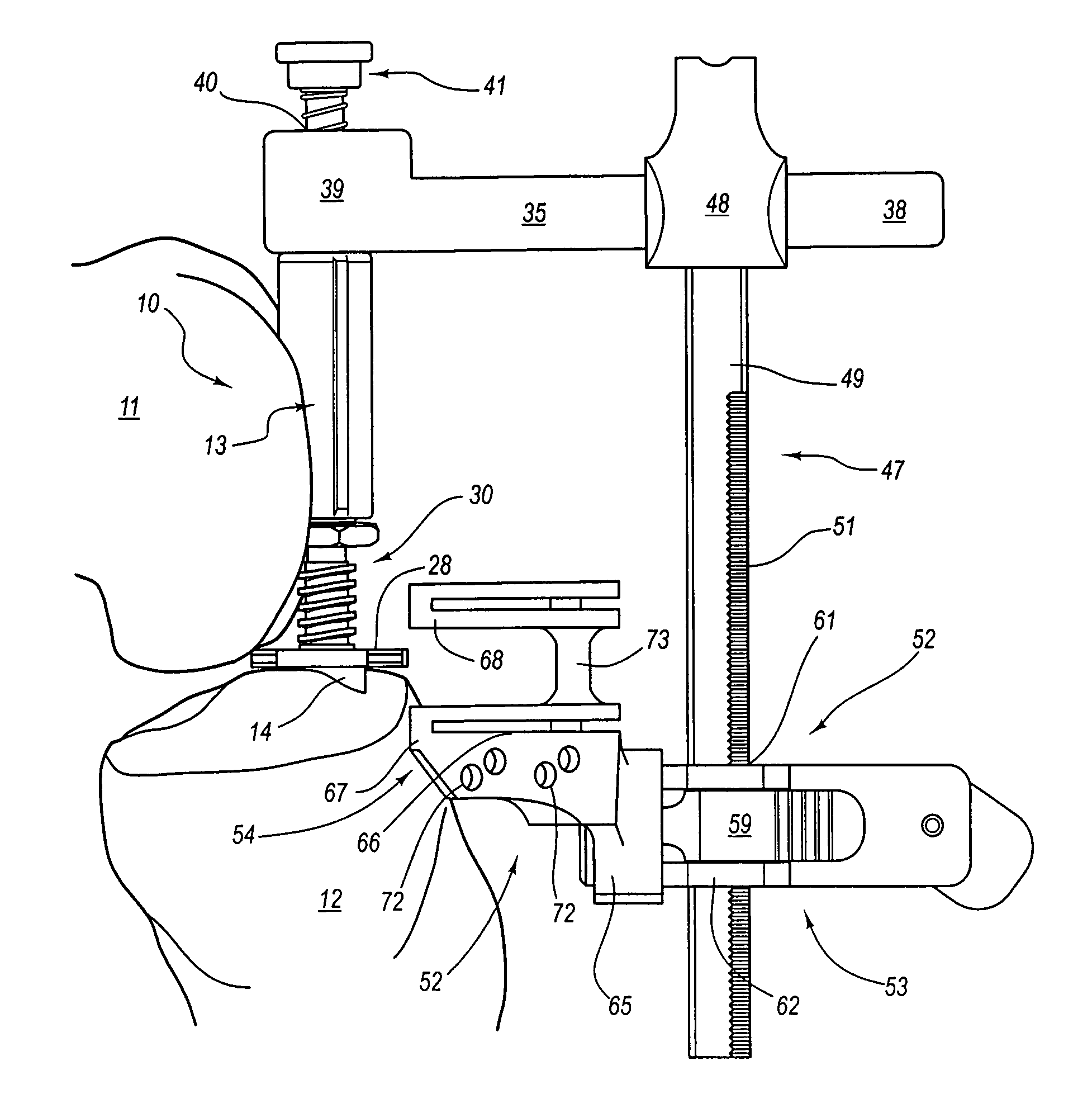
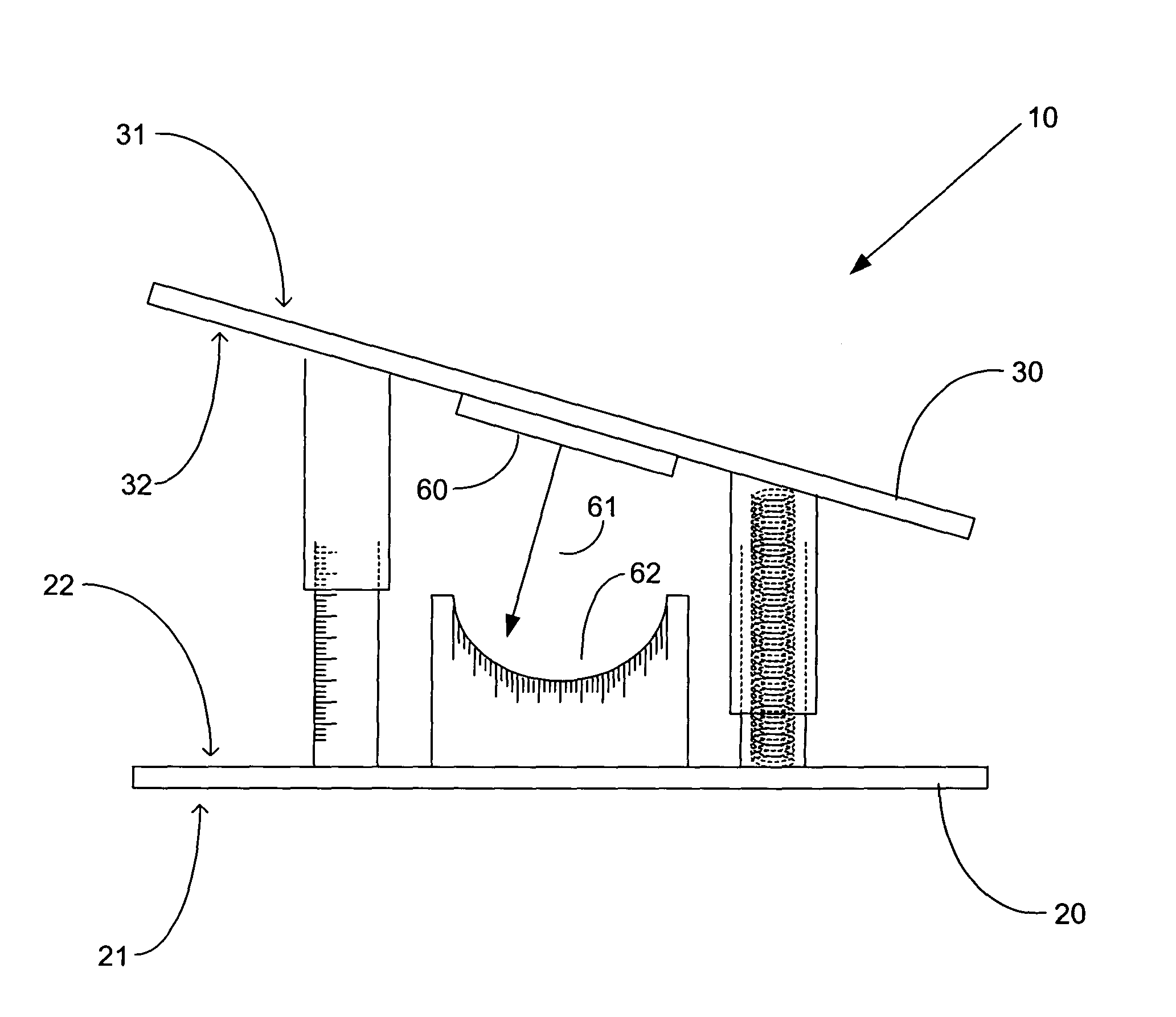
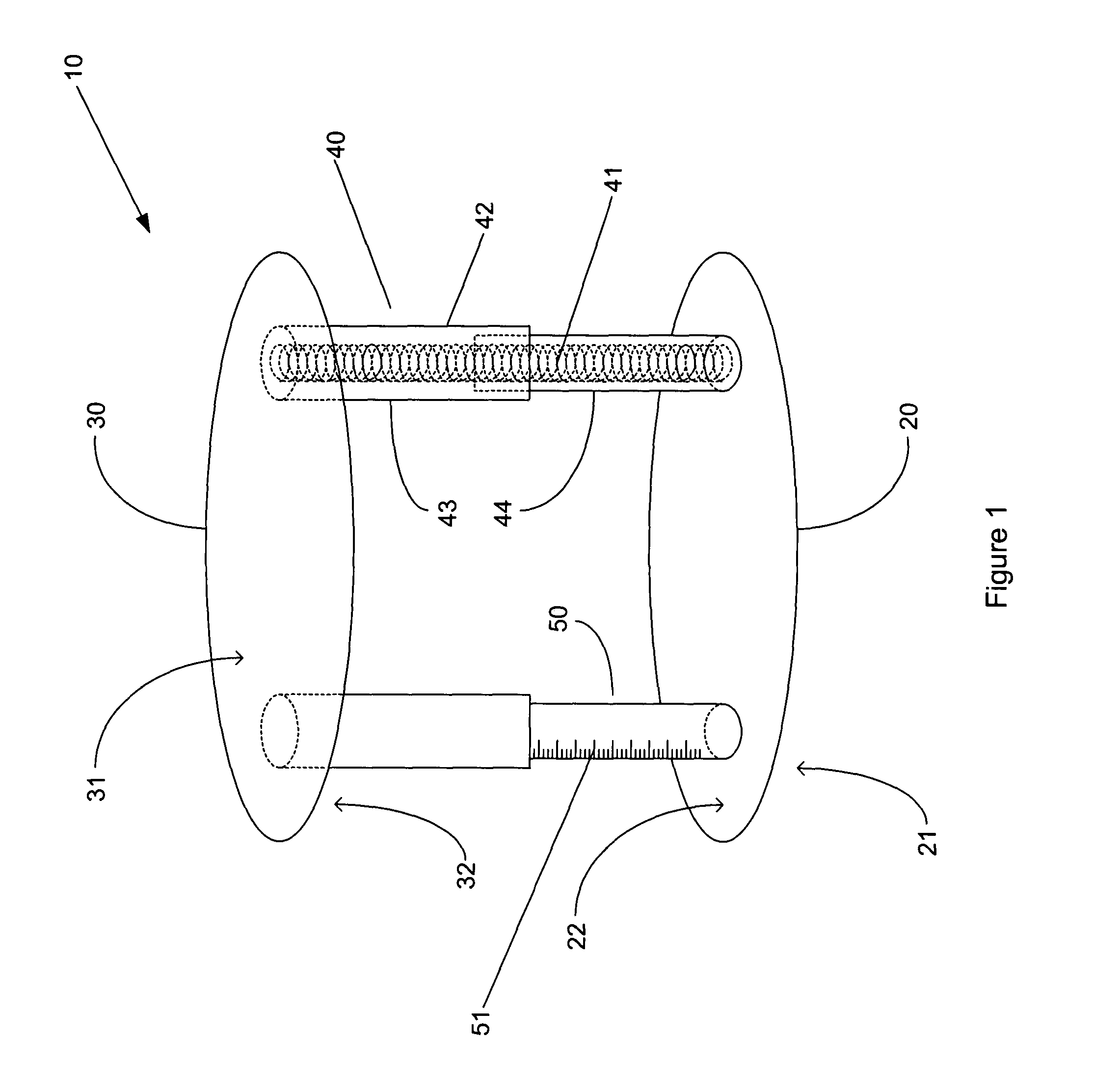
Dynamic spacer for total knee arthroplasty
InactiveUS7455647B2Easy to useEasy constructionSurgeryPerson identificationTotal hip arthroplastyPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A dynamic spacer is provided for measuring flexion-extension gap during total knee arthroplasty. The dynamic spacer includes a first planar member having a lower tissue engaging surface, and a second planar member having an upper tissue engaging surface. A tensioner is disposed between the first planar member and the second planar member for applying a tensile force acting upon the first and second planar members. The tensioner is attached to the first and second planar members, such that the first planar member is held substantially parallel to the second planar member in the absence of compressive load. The dynamic spacer allows for accurately measuring flexion-extension gaps and angular deviation in flexion indicating the appropriateness of femoral rotation.
Owner:TARABICHI SAMIH
Prosthetic joint
InactiveUS8808387B2Increase maximum flexionFacilitate longitudinal rotationJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaArticular surfaces
A joint prosthesis includes e.g., a femoral component and a tibial component. The medial and lateral condylar articular surfaces may have substantially uniform and equal radii from full extension to about 90° of flexion. From 90°, the lateral condylar articular surface has a smaller radius than the medial condylar articular surface such that the medial condyle gradually becomes increasingly more proud than the lateral condyle to facilitate internal rotation of the tibia at deep flexion. Also, the tibial articular component may include a post intermediate the medial and lateral compartments that engages a cam on the femoral articular component between the medial and the lateral condylar articular surfaces. The cam and post become congruent at flexion angles of approximately 70° flexion and mate symmetrically during the first 20°-30° of further flexion, and then mate asymmetrically at greater degrees of flexion to force internal rotation of the tibia.
Owner:EPIC ORTHO
Systems and methods for guiding cuts to a femur and tibia during a knee arthroplasty
ActiveUS8303597B2Small and noninvasive approachPromote resultsInternal osteosythesisNon-surgical orthopedic devicesDistractionTibia
An assembly for guiding resection of a femur and tibia of a knee joint in preparation for installing a femoral and tibial knee components. For example, the assembly can include tibial and femoral IM rods to which are connected through a tensioning bolt that allows controlled adjustment of the distraction of the tibia and femur during cut positioning in a range of flexion angles. Also, the assembly is usable with relatively small, noninvasive approaches to the knee joint by way of relatively narrow, low profile components that attach to tibial and femoral IM rods. Further, the assembly includes several quick-release components to allow fast assembly and disassembly in a surgical setting. Each of these aspects, along with the ability of the assembly to accurately guide initial reference cuts to the tibia and femur, promotes an improved outcome for the patient.
Owner:RASMUSSEN INSTR LLC
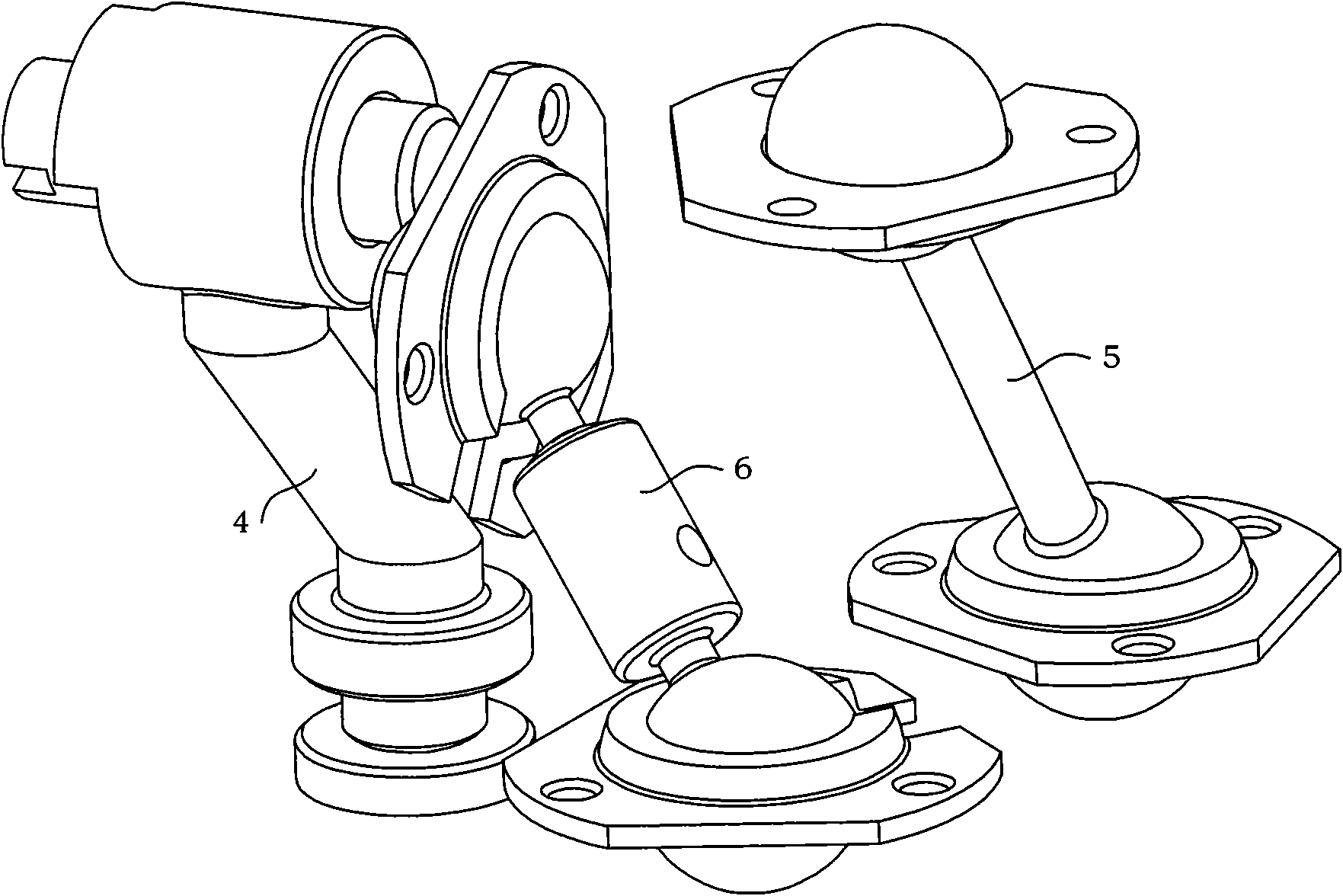
Force-closed knee replacement prosthesis
InactiveCN101653387AEliminate loose defectsAchieve flexionJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaPosterior cruciate ligament
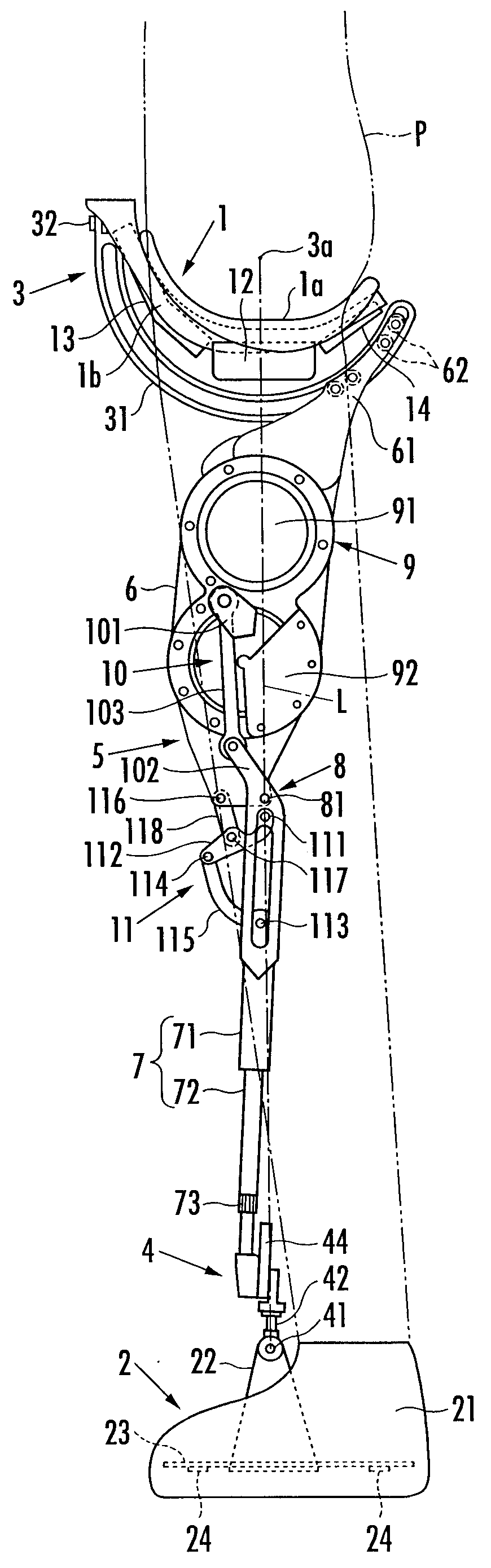
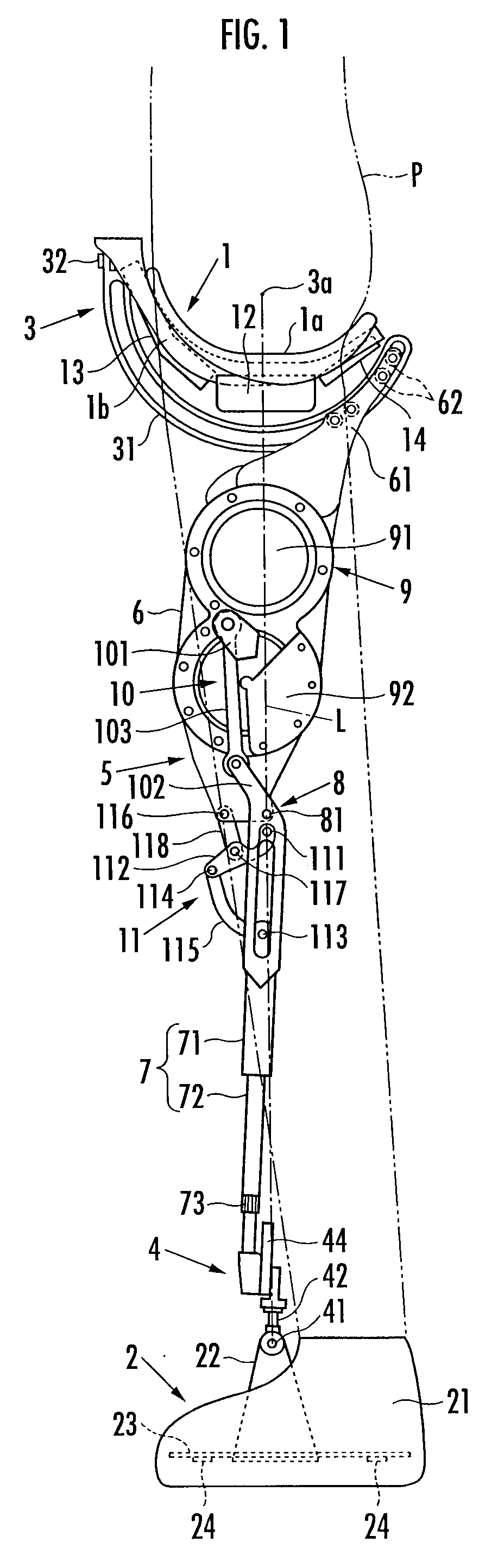
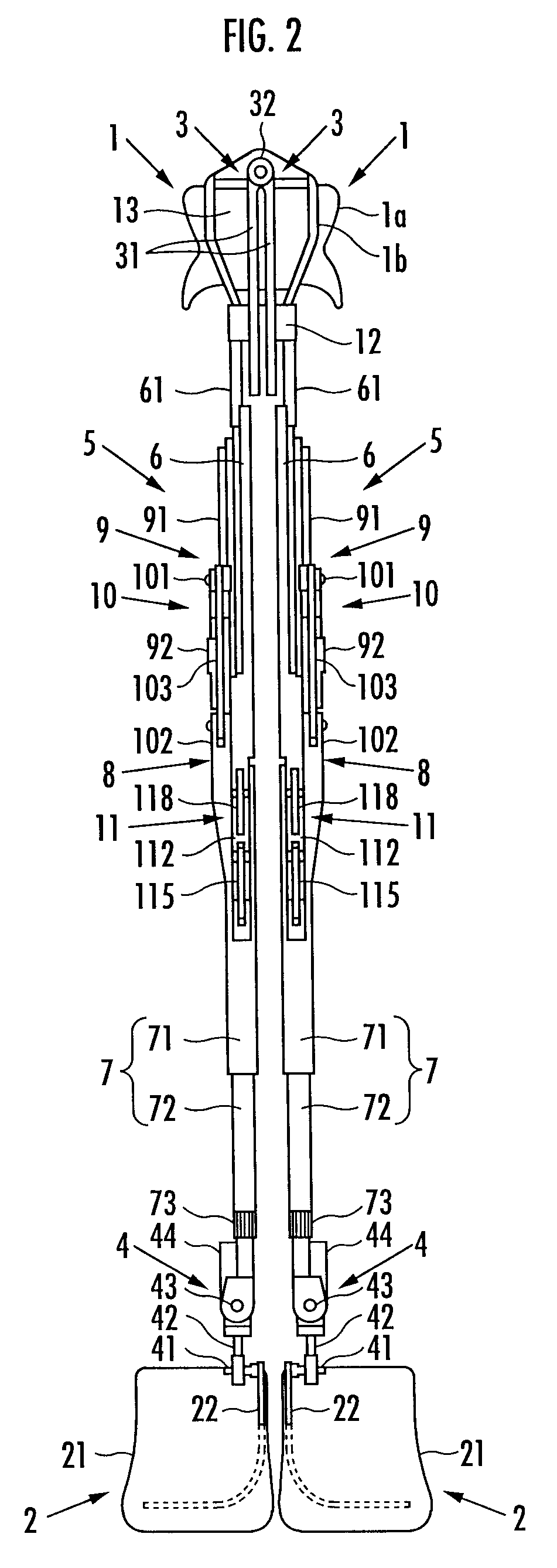
The invention discloses a force-closed knee replacement prosthesis which is composed of a thighbone prosthesis, a thighbone support, a shin bone support, a rotating link rod component, an anterior cruciate ligament branched chain and a posterior cruciate ligament branched chain; the thighbone prosthesis is arranged on the thighbone support, and the rotating link rod component, the anterior cruciate ligament branched chain and the posterior cruciate ligament branched chain are arranged between the thighbone support and the shin bone support. The patellar surface profile of the thighbone prosthesis is a 3D thighbone patellar surface profile which is re-built by thighbone CT / MRI scanning based on knee joints of a replaced person. In the force-closed knee replacement prosthesis, the anterior cruciate ligament branched chain adopts a fixed long rod piece structure, and the posterior cruciate ligament branched chain adopts a spherical hinge with a spring structure to be connected, so as to avoid the phenomenon of negative bending angle and overlarge bending angle in the bending / stretching process of the joints and be capable of realizing bending movement of the knee joint prosthesis within a range of from 0 degree to 135 degrees.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Neuromuscular electrical stimulation system with supplementary external skeleton
PendingCN106334267APrevent fallingSmooth motionElectrotherapyGymnastic exercisingElectricityPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses a neuromuscular electrical stimulation system with supplementary external skeleton. The system comprises an electric stimulator for stimulating the movement of the limb muscles, and an external skeleton for restricting the excessive movement of the limbs. The external skeleton comprises an upper body fixing frame, a lower limb external skeleton and a damping controller for limiting the flexion angle of the limb. The lower limb external skeleton is connected to the lower end of the upper body fixing frame, and the damping controller is arranged at the joint of the lower limb external skeleton. The electric stimulator and the external skeleton cooperate to restrict patients with hemiplegia from falling off due to their excessive movement in recovery trainings, therefore, making the recovery training more secure and reliable.
Owner:徐钧 +1
Walking assisting device
ActiveUS20080009778A1Shorten speedFlexible cuttingGymnastic exercisingWalking aidsEngineeringPush ups
A walking assisting device that transmits a force generated by a leg link to a user's trunk via a load transfer portion. The leg link includes a first link connected to the load transfer portion via a first joint portion, a second link connected to a foot attachment portion via a second joint portion, a third joint portion which connects the first link to the second link so as to be free to bend and stretch, and a driving source which drives the third joint portion. Even if a flexion angle of the third joint portion reaches zero degree, the controllability is maintained in the direction of pushing up the load transfer portion so that the leg link can be extended straight with the user's leg extended straight. An interlock system retracts and extends the second link and increases and decreases the flexion angle of the third joint portion.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
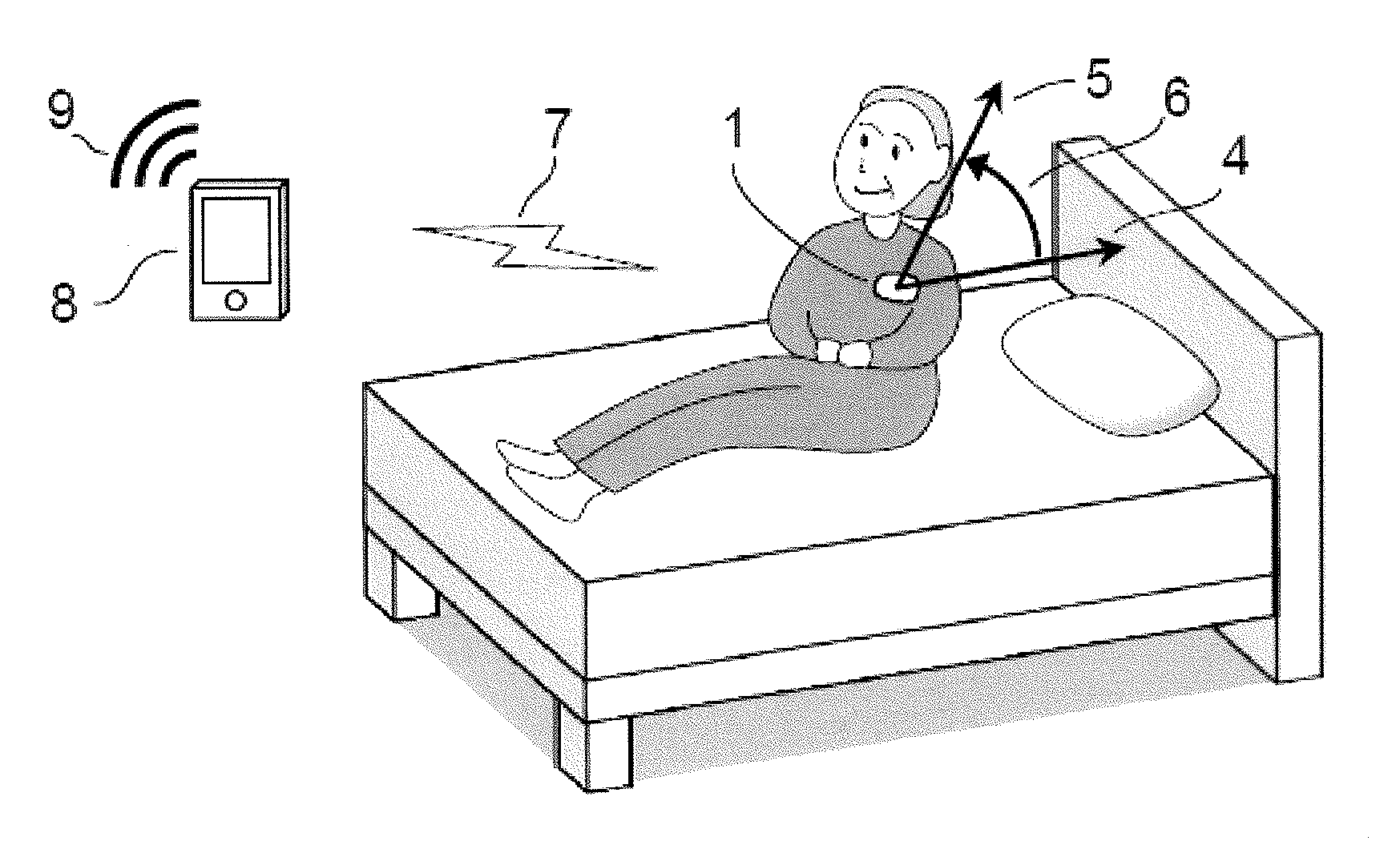
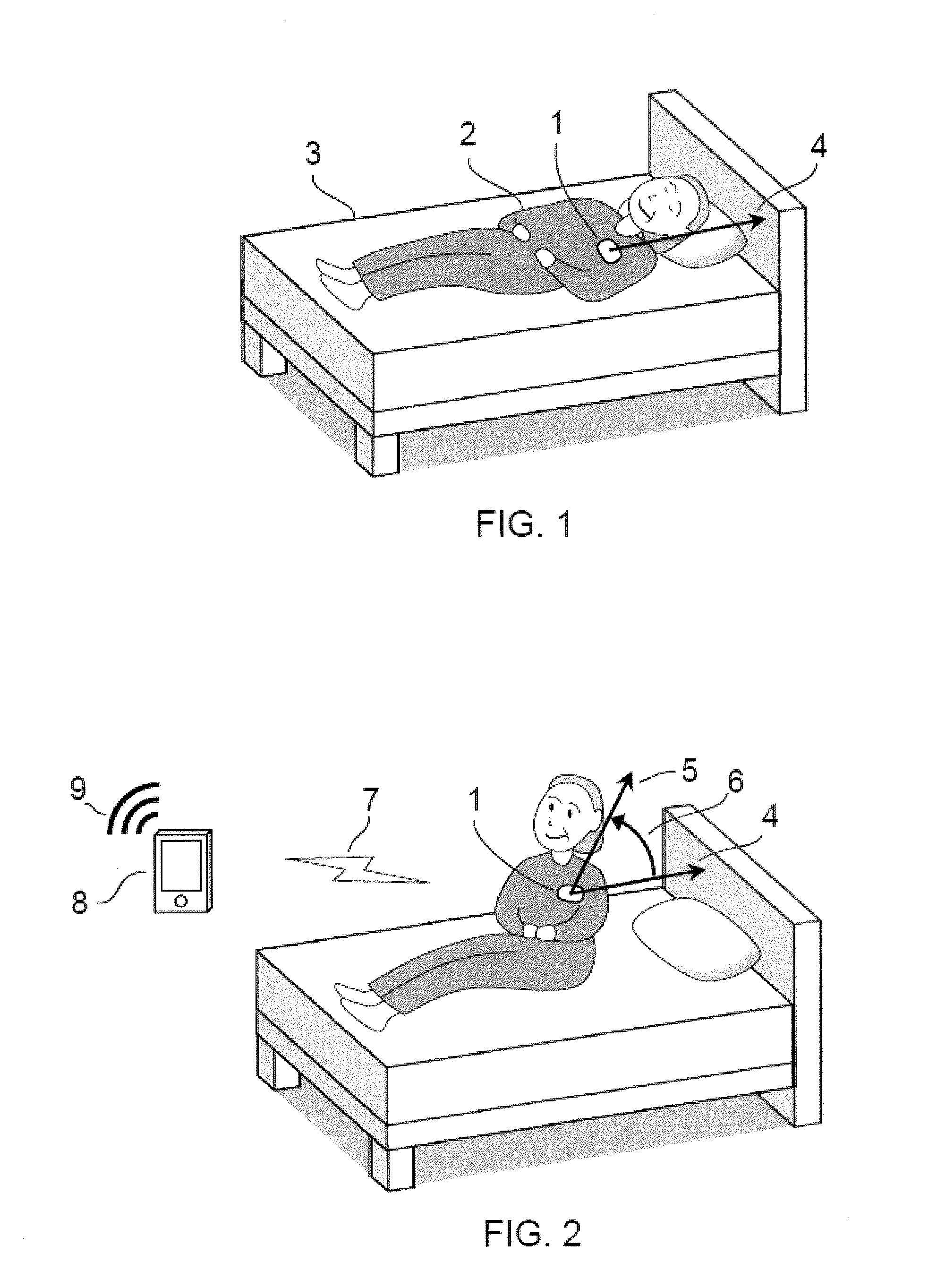
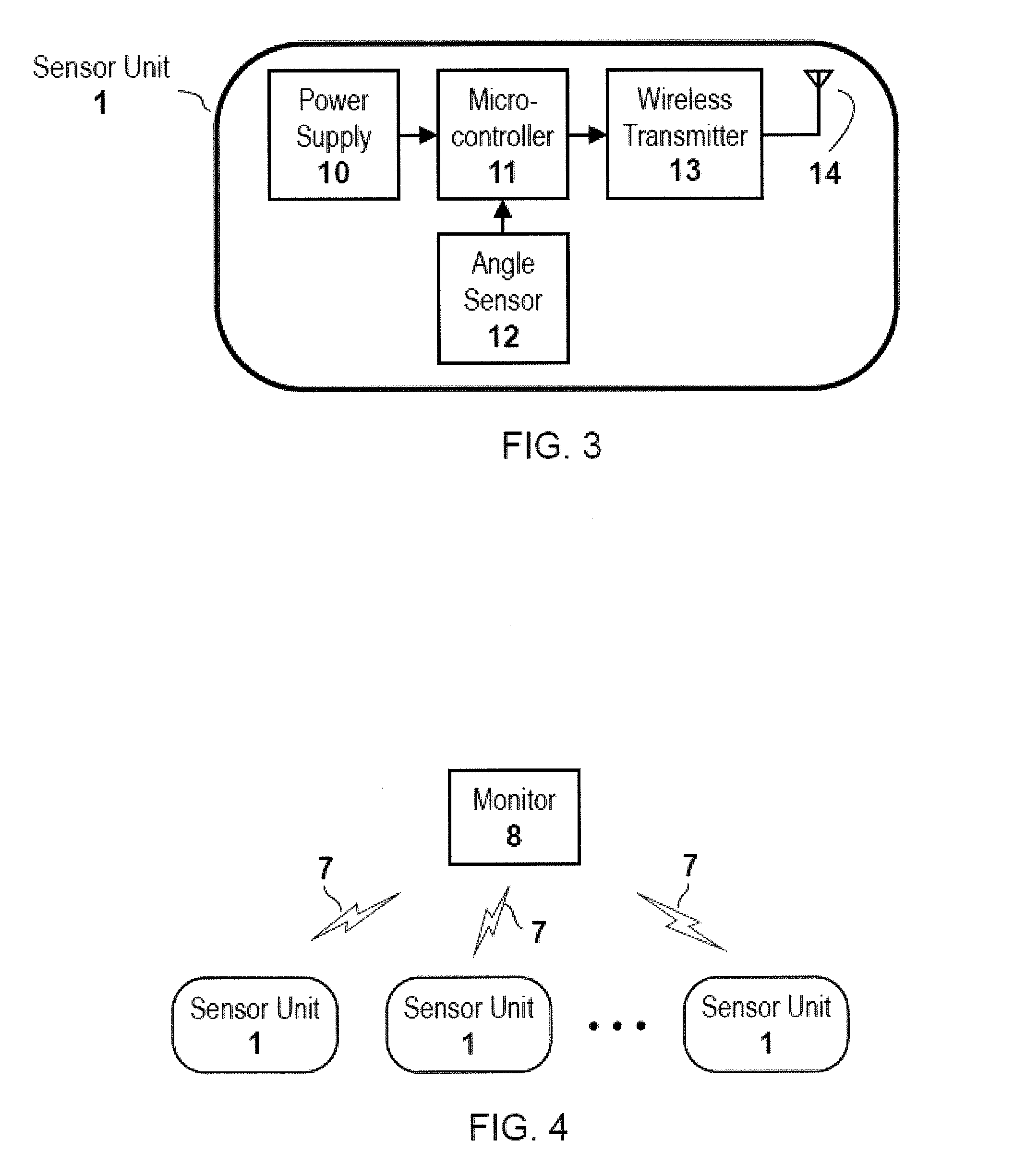
Detection of changes from a seated or lying body position by sensing body angle
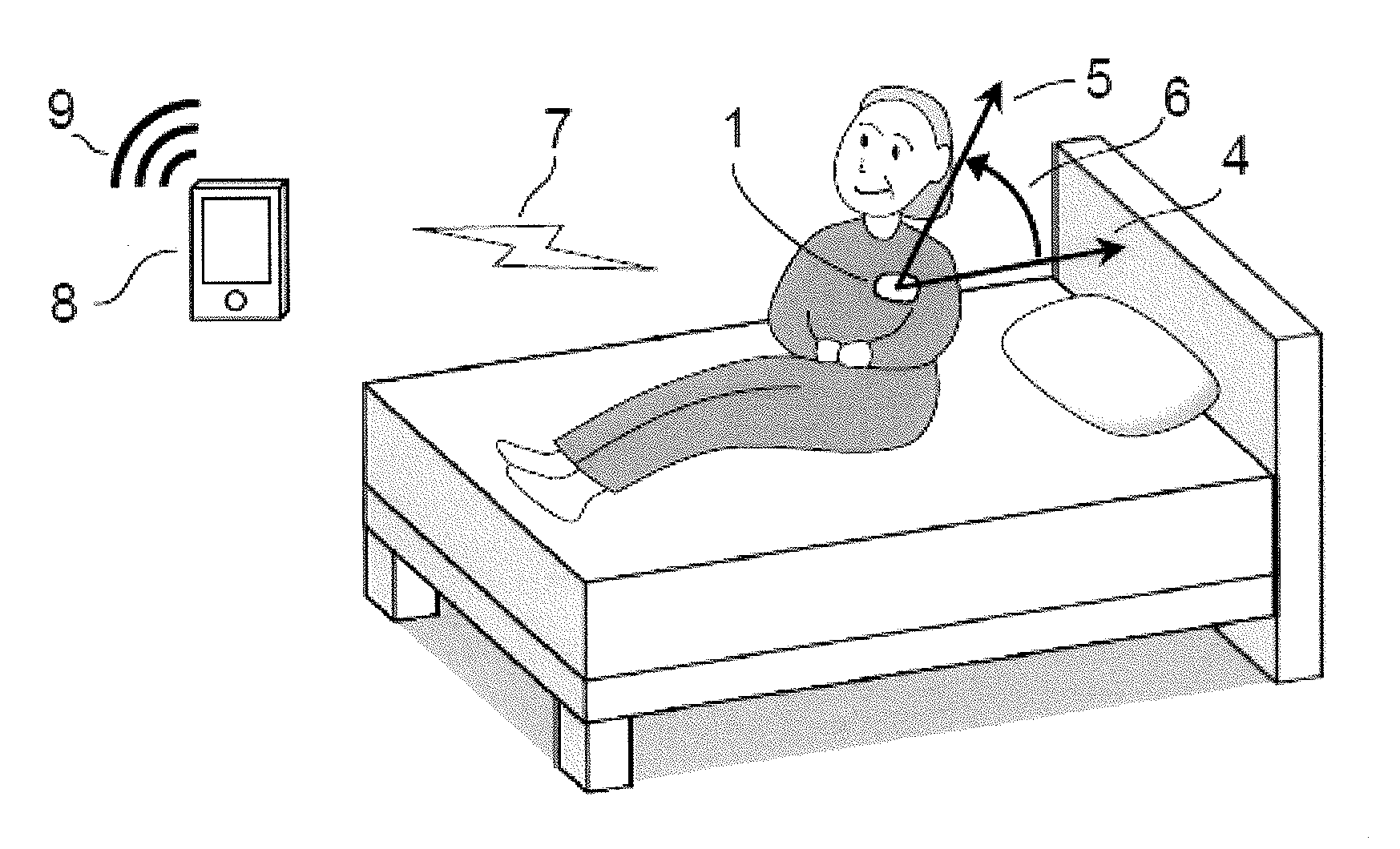
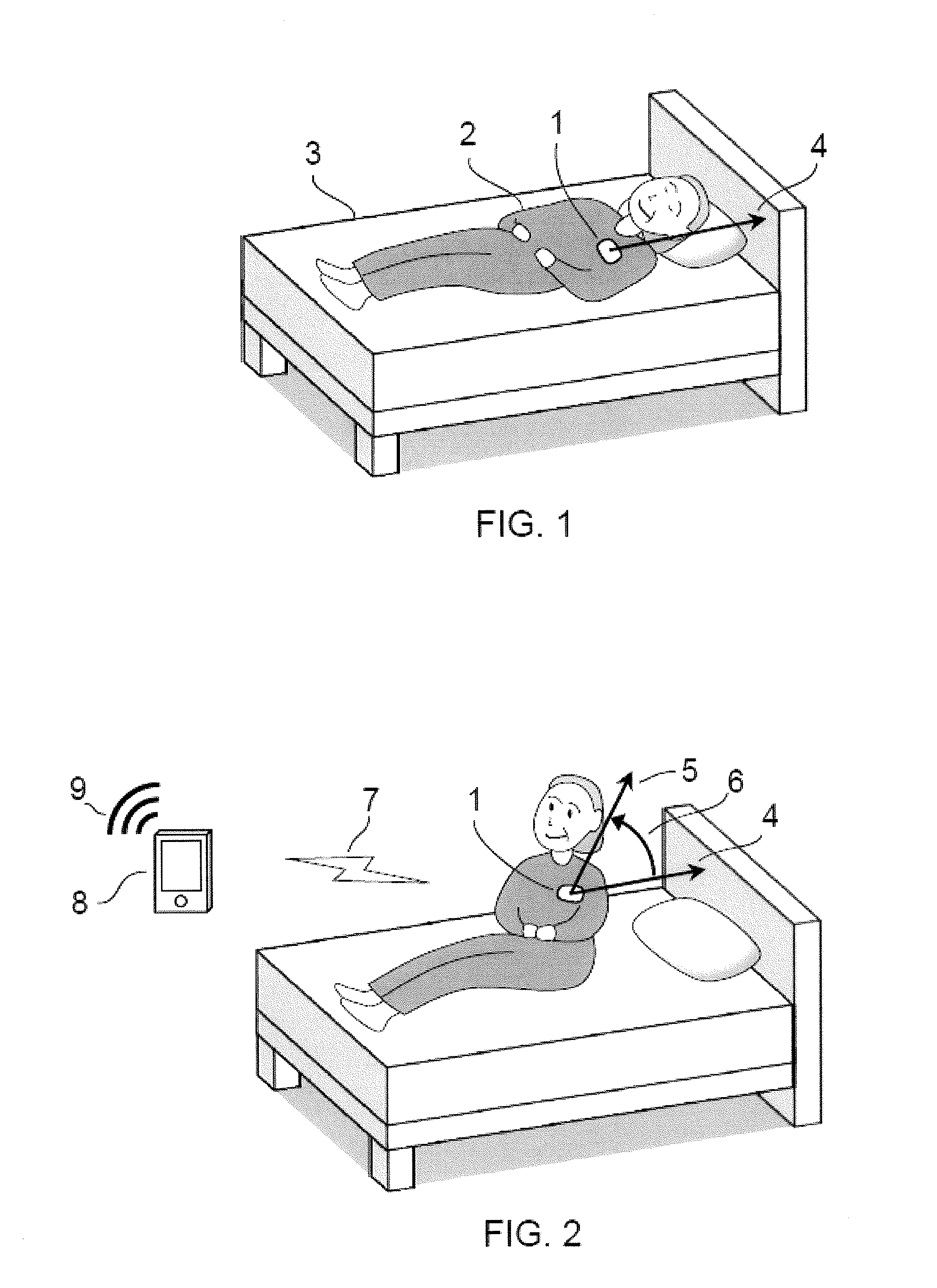
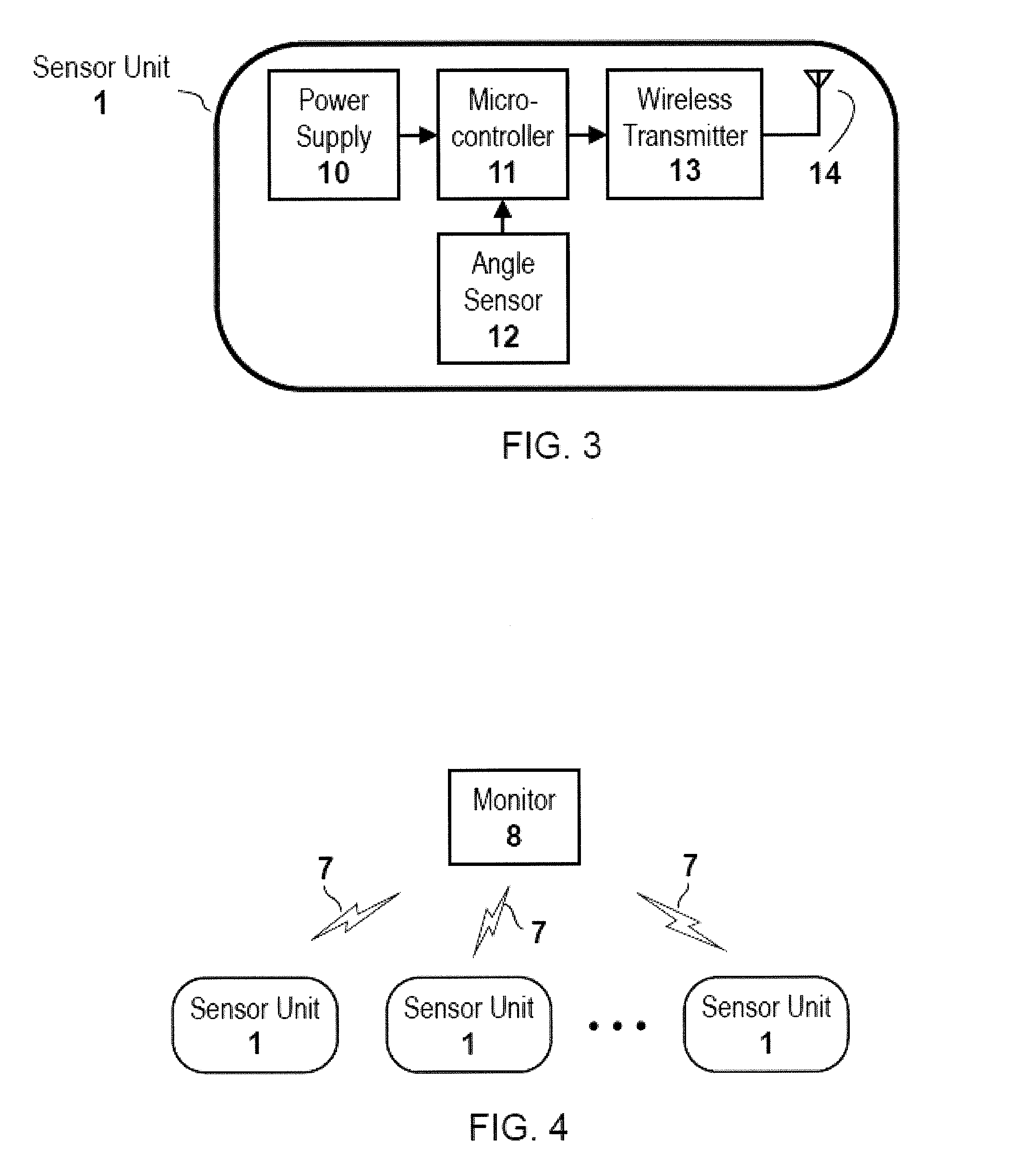
ActiveUS20160157754A1Simple andFall preventionGeneral fastenersDiagnostic recording/measuringBody anglePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Methods and apparatuses for detecting when a subject gets up out of bed or out of chair by detecting changes in body flexion angle with respect to a threshold. Also described herein are systems for monitoring one or more subjects each wearing an angle-sensing unit.
Owner:SENSARX
Motion controlling hinge for orthopedic brace
A motion controlling hinge for an orthopedic brace is provided. The hinge includes an actuator secured to one arm, and at least one spring member. As the arm with the actuator pivots in a first direction, at a predetermined flexion angle the actuator applies a force to the spring member, causing the spring member to flex. The spring member exerts a force on the actuator tending to bias the actuator away from the spring member, and tending to bias the arm in a second direction opposite the first direction. In one embodiment, the spring member comprises a plurality of flat bar leaf springs. A movable fulcrum enables adjustment of a force exerted by the spring member on the actuator. A variety of differently sized adapters are securable to the actuator. The size of the adapter determines the flexion angle at which the spring member first exerts force on the actuator. In some embodiments, the hinge includes an “ON” / “OFF” switch that enables a user to disengage biasing force provided by the spring member. When the switch occupies the “OFF” position, the hinge is freely pivotable to a maximum extension angle.
Owner:DJO
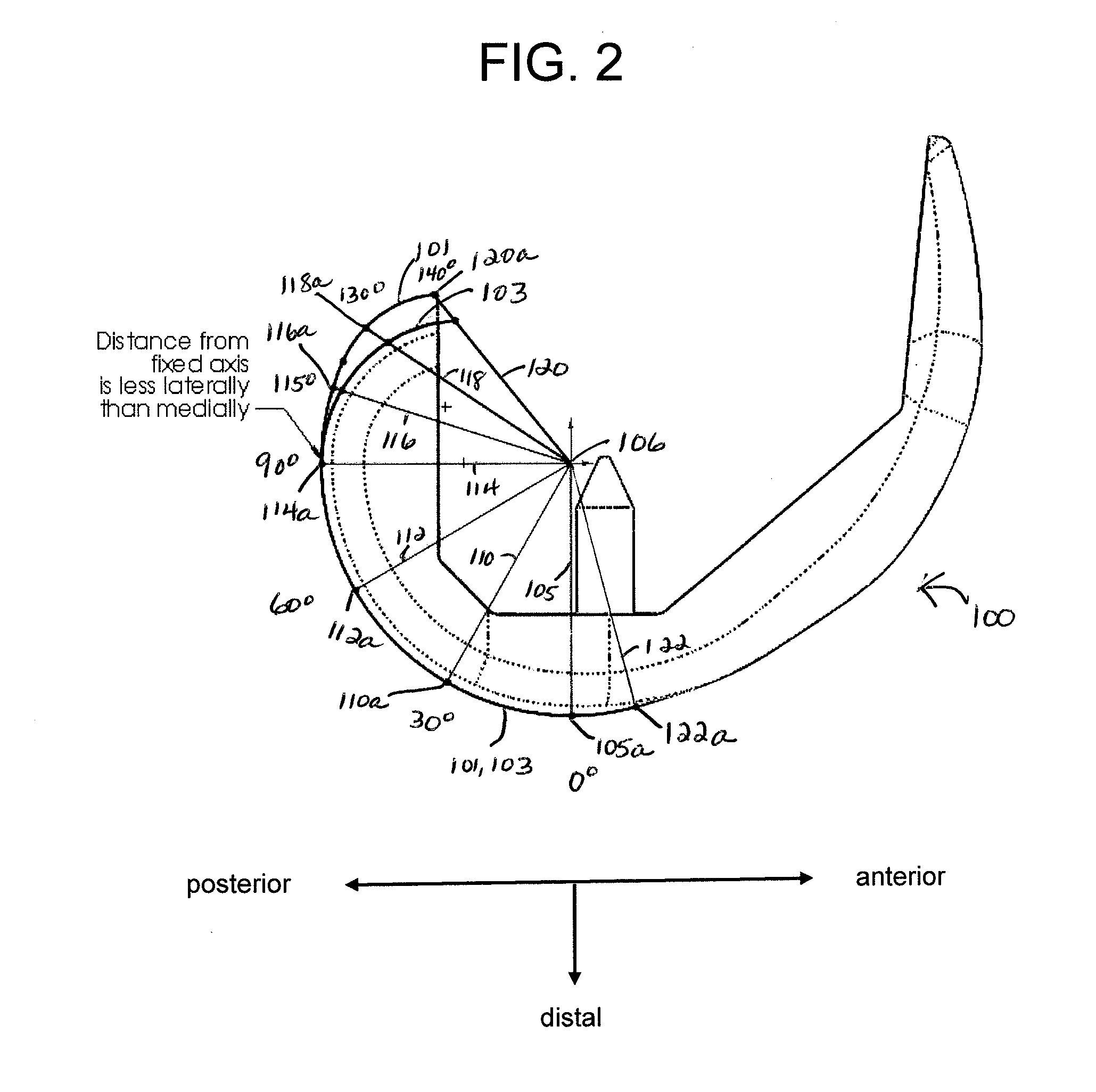
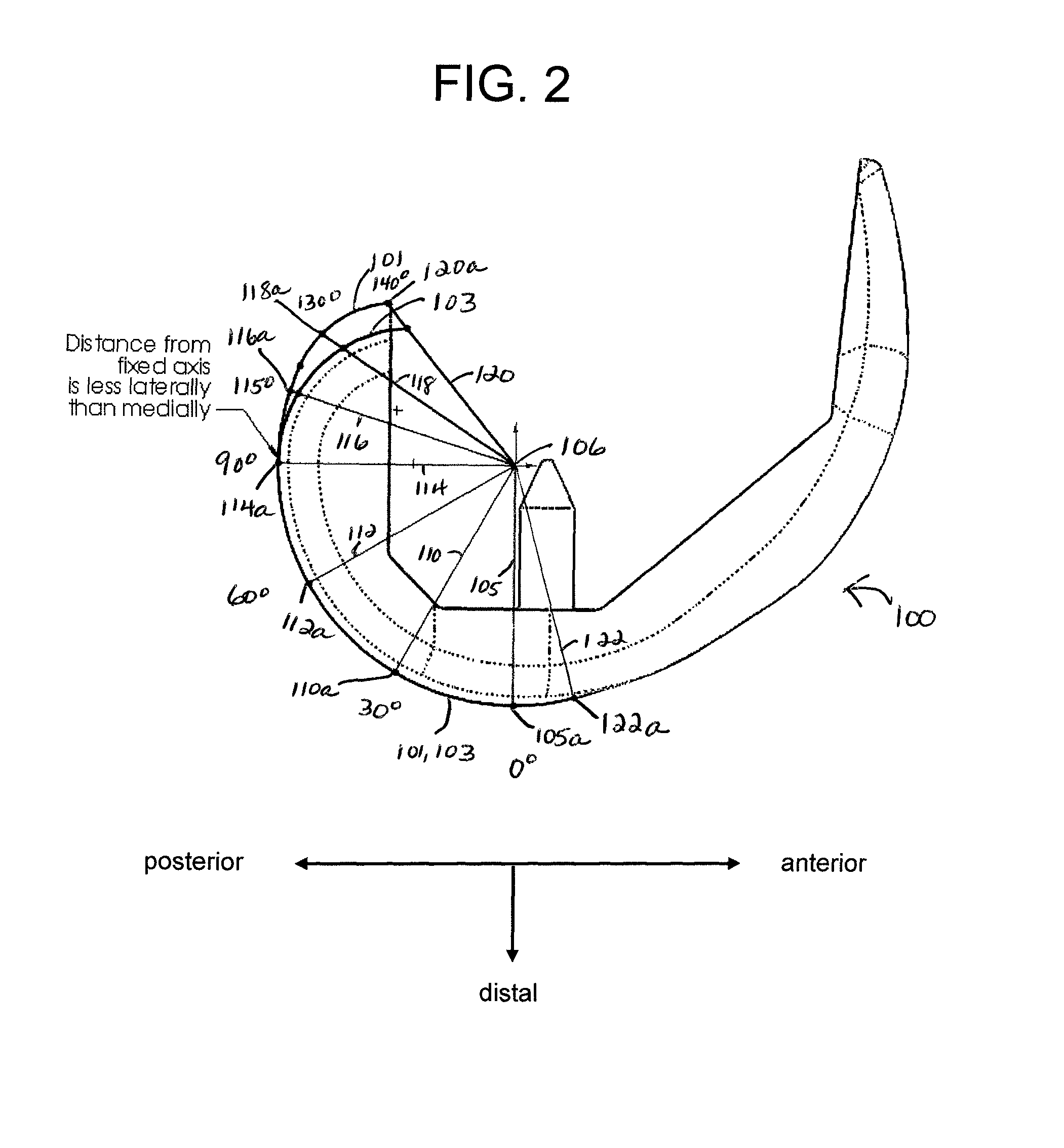
Knee prosthesis
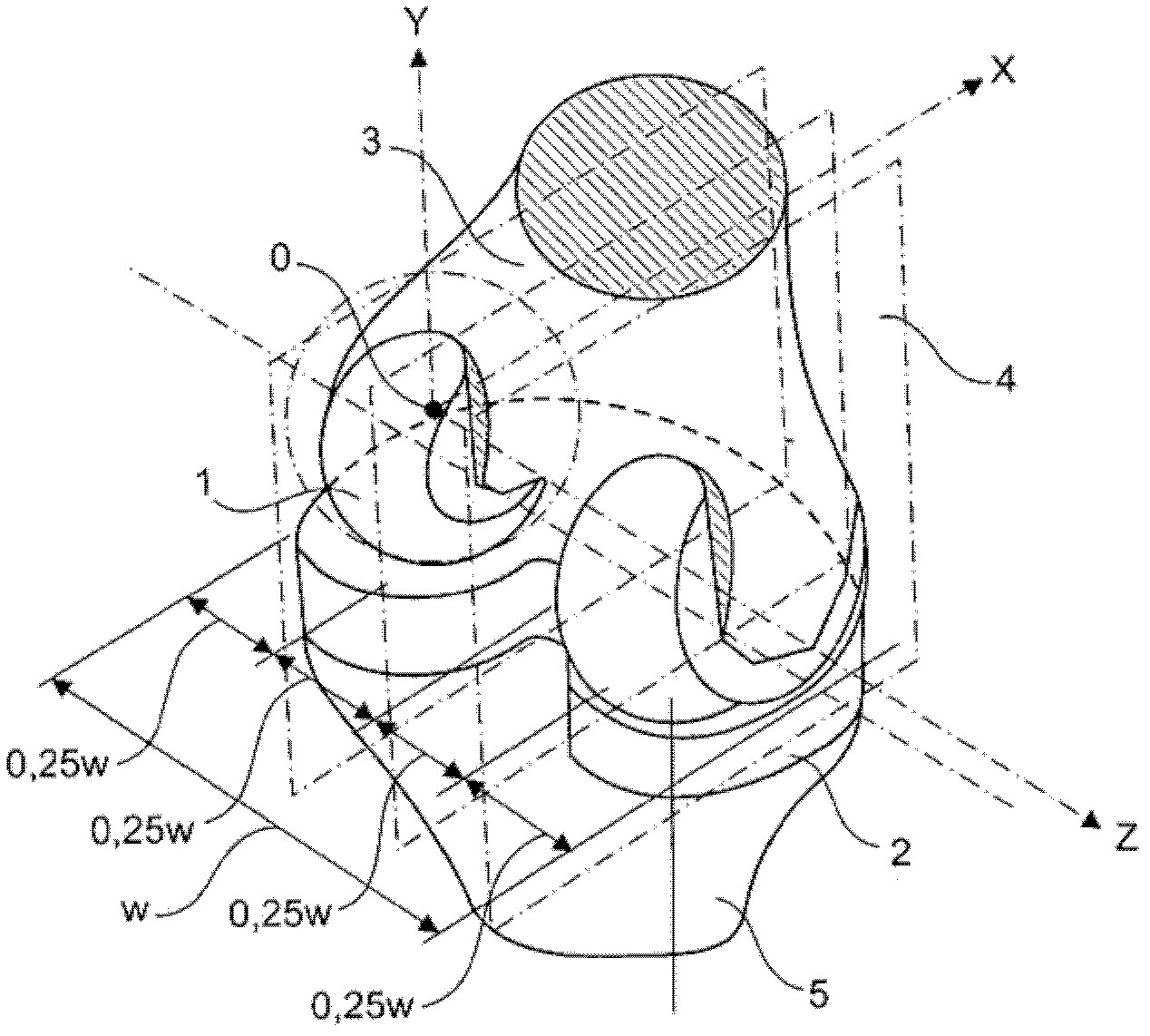
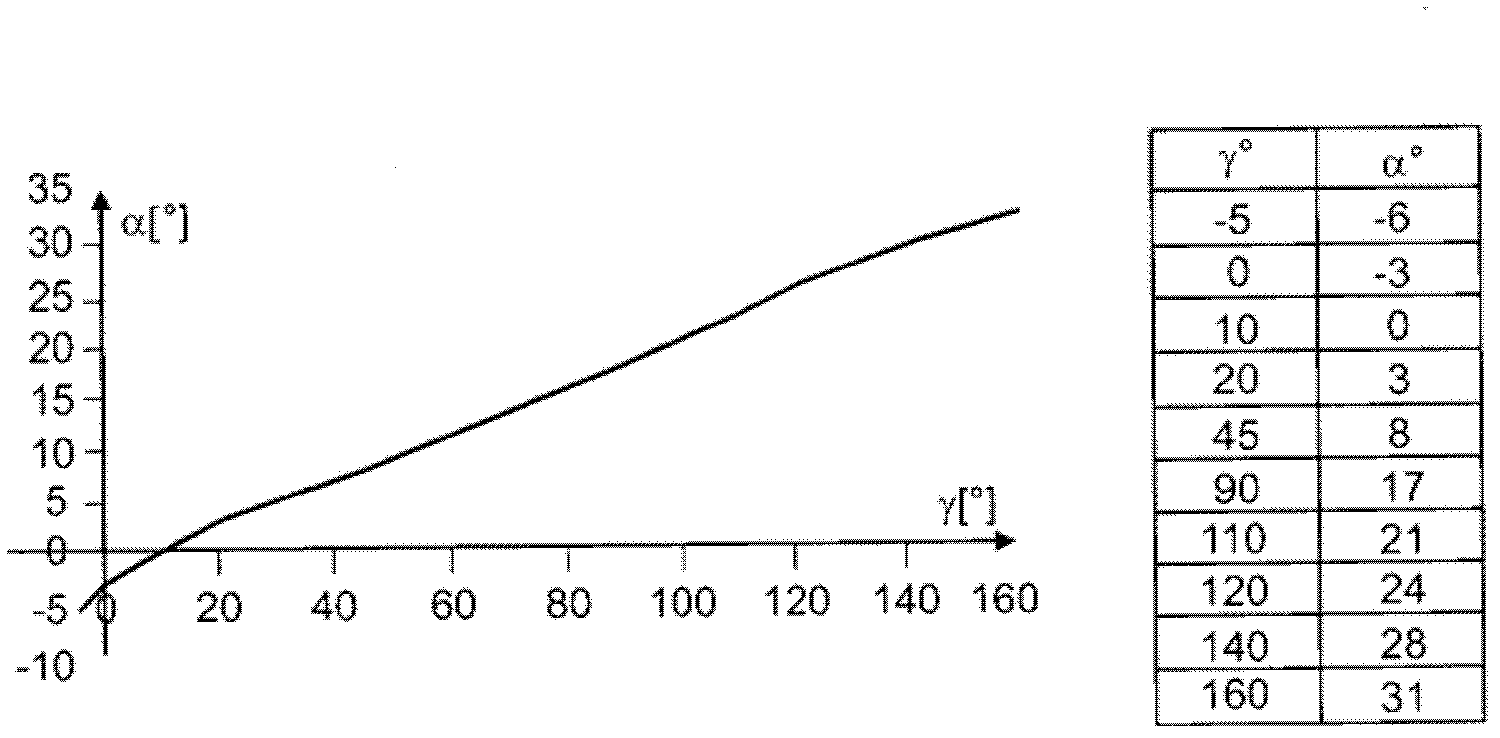
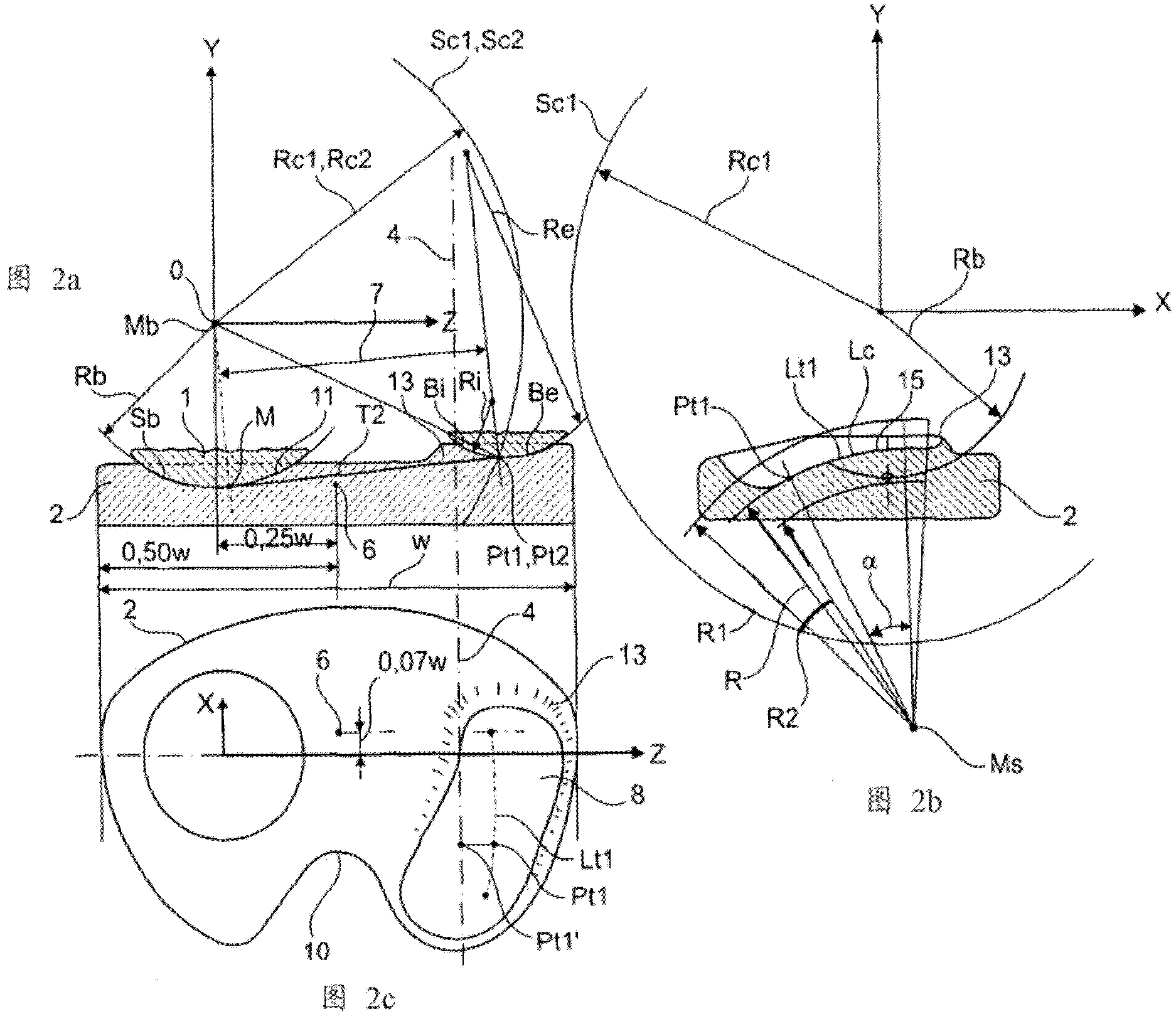
A knee prosthesis for a knee joint with a medial ball- like femoral condyle and with a width "w" is characterized on the lateral compartment by: - a trace-line "Lt1" of contact points "Pt1" for the tibia component (2) as a predetermined curve (15 ) on a spherical surface "Sc1", which has its centre at the centre Mb of the medial ball 1 and which has a radius in the range "Rc1" = 0.65 w + / - 0.25 w - a trace-line "Lt2" of common contact points "Pt2" at given flexion angles gamma for a similar spherical surface "Sc2" attached to the femoral component with radius "Rc2"= Rc1, whereby at a given flexion angle gamma there exists a plane "E1" through the centre Mb and the common contact point Pt1 / Pt2, which contains the same guiding curves "Bi", "Be" on the tibial and on the femoral components, "Bi" towards medial and "Be" towards lateral, both of which stay in a geometrically fixed relation to the common contact point Ptl / Pt2, and - guiding curves "Bi" and "Be", which generate an enforced gliding and rolling movement in both directions.
Owner:厄斯·威斯 +2
Posterior stabilized knee with varus-valgus constraint
A femoral component of a knee prosthesis has spaced condyle surfaces defining a notch therebetween. The notch defines an elongated cam housing having an anterior cam and a posterior cam at opposite ends of the housing. The tibial component of the knee prosthesis includes a platform and a bearing supported on the platform, the bearing defining bearing surfaces configured to articulate with the condyle surfaces. The tibial component includes a spine projecting superiorly from the bearing that defines an anterior face and a posterior face. The posterior face and the posterior cam define complementary curved surfaces configured for cooperative engagement when the femoral component and the tibial component are at a predetermined flexion angle. The cam housing is configured to form a gap between the posterior cam and the spine when the knee is normally extended. In another feature, the spine includes a stiffening pin extending therethrough.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
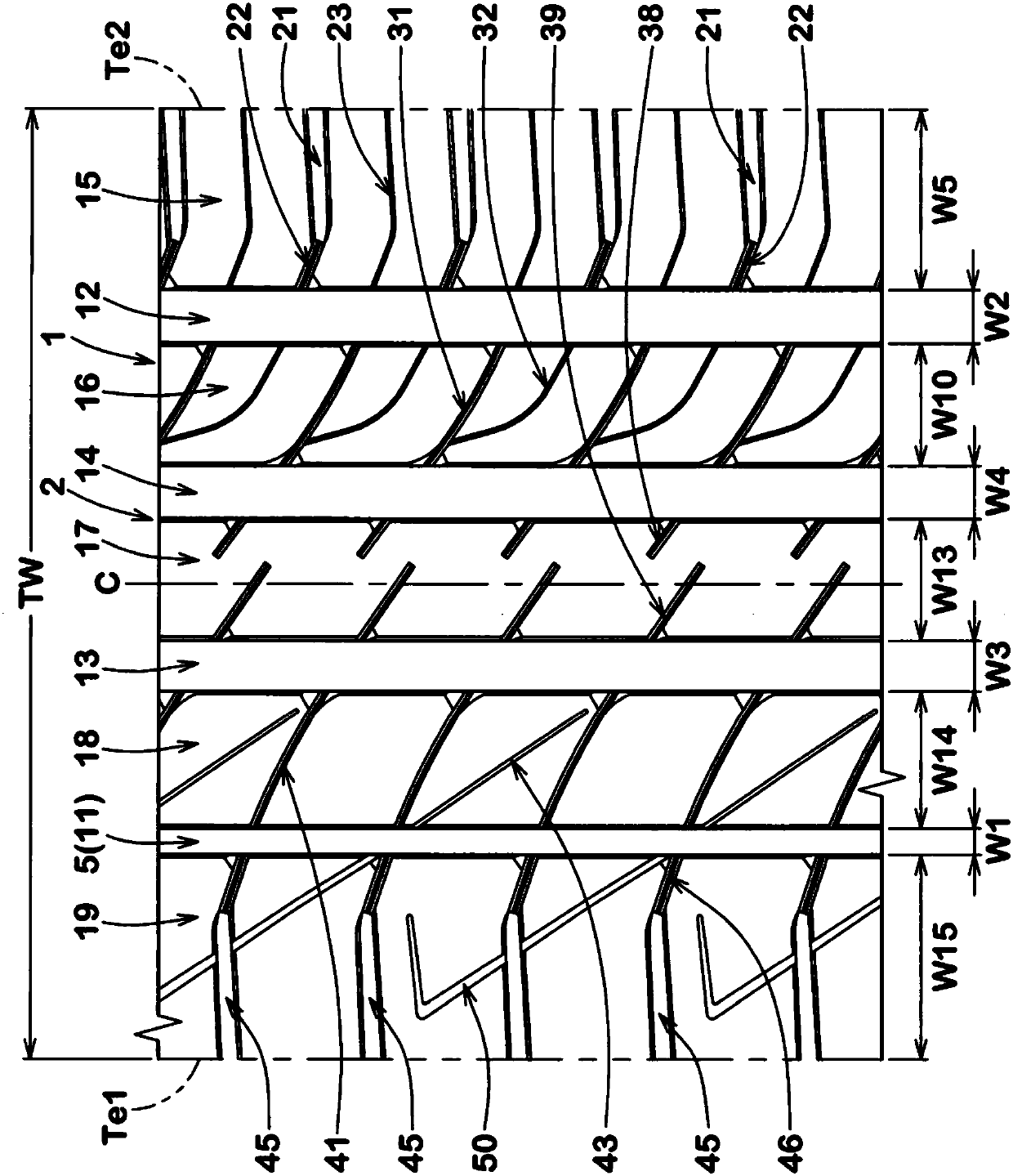
Pneumatic tire
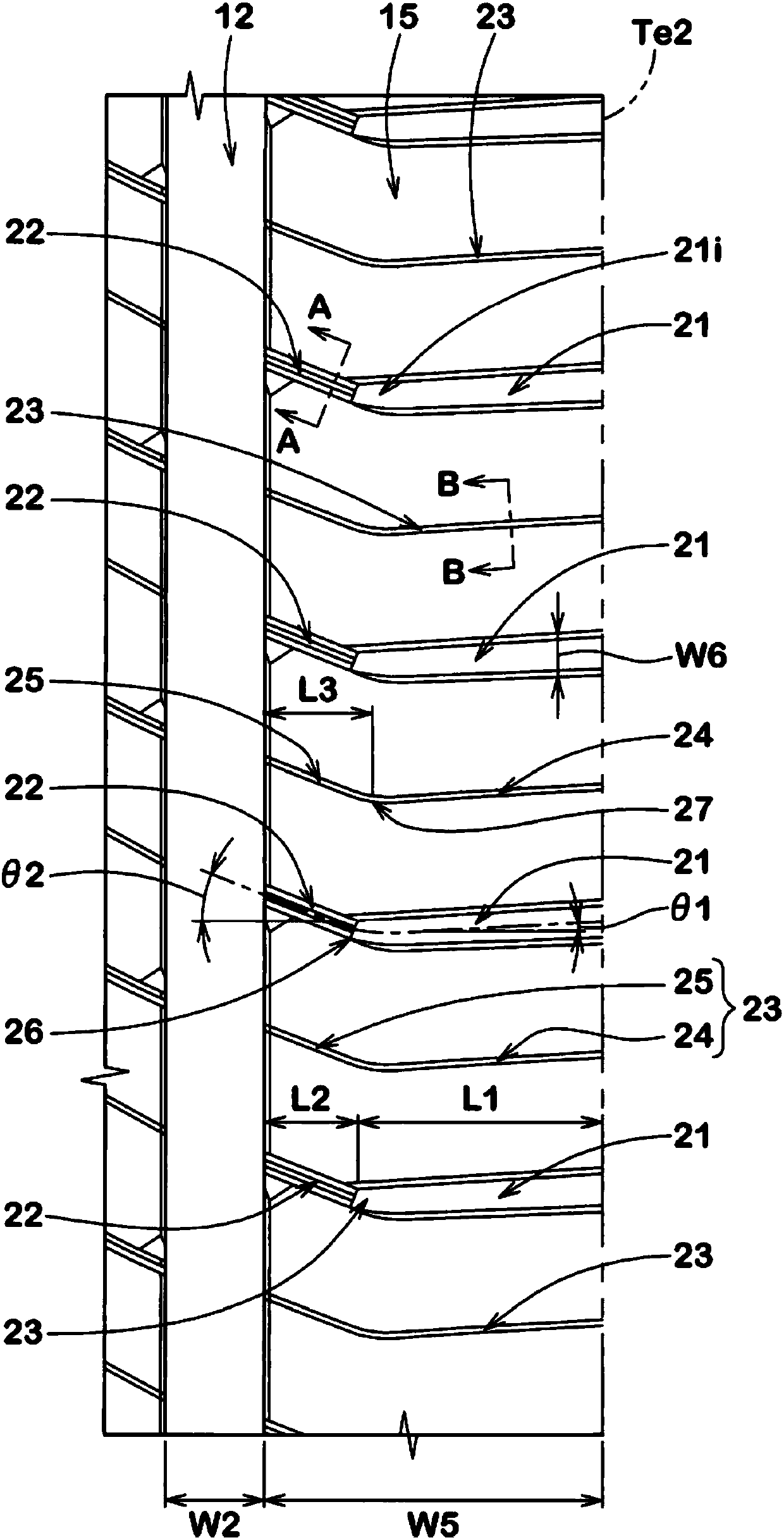
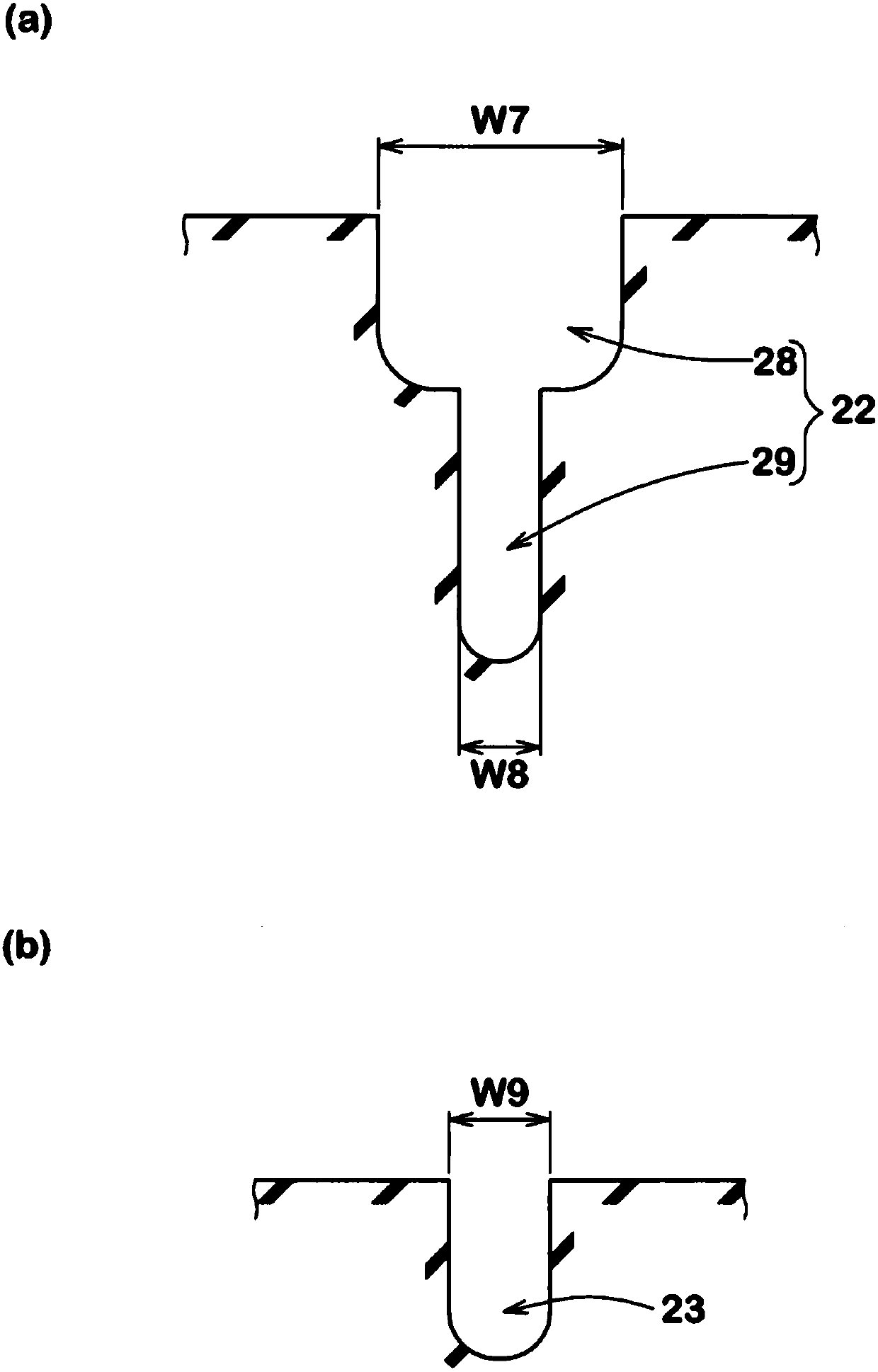
ActiveCN107813661AImprove rigidityImprove performanceTyre tread bands/patternsEngineeringFlexion angle
The invention aims to provide a pneumatic tire, which has excellent wetland properties and operation stability. A pneumatic tire 1 comprises a tread portion 2 having an outboard tread edge Te1 to be positioned away from the center of a vehicle body and an inboard tread edge Te2 to be positioned close to the center of the vehicle body. The tread portion 2 is provided with an inboard shoulder main groove 12, and an inboard shoulder land region 15 between the inboard shoulder main groove 12 and the inboard tread edge Te2. The inboard shoulder land region 15 is provided with inboard shoulder rug grooves 21, connecting sipes 22, and inboard shoulder sipes 23. The inboard shoulder sipe 23 is made up of a straight outer part 24 extending from the inboard tread edge Te2 toward the axially inside,and a straight inner part 25 extending to the inboard shoulder main groove 12 at a flexion angle with respect to the outer part 24. The axial length of the inner part 25 is more than the axial lengthof the connecting sipe 22.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Flexion and extension range limiting hinge for an orthopedic brace
An angle limitation system for an orthopedic brace employs a hinge assembly rotatably receiving an upper strut and a lower strut and having a hinge plate and a hinge assembly cap. An extension angle limit element is removably insertable in an anterior port between the hinge plate and hinge assembly cap. The extension angle limit element has a body with limiting surfaces adapted to engage mating faces indented in the anterior edges of the upper and lower strut. A flexion angle limit element is removably insertable in a posterior port between the hinge plate and hinge assembly cap. The flexion angle limit element has a body with limiting surfaces adapted to engage mating faces indented in the posterior edges of the upper and lower strut. Engagement mechanisms are adapted to releasably secure the flexion angle limit element in the posterior port and the engagement angle limit element in the anterior port.
Owner:UNITED SURGICAL ASSOC
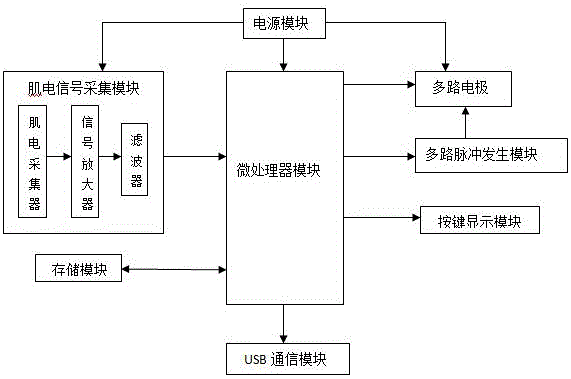
System and method for a wearable knee injury prevention
InactiveUS20180028109A1Strain gaugeDiagnostic recording/measuringMovement activityPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A method and system for actively monitoring anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) strain experienced at the knee joint during athletic activity or dynamic movement. Sensors are used in proximity of the knee joint to actively record parameters such as flexion angle and ground impact force at the knee joint. Sensor measurements are then inputted into a processing unit that will quantify a tibial shear force (TSF) value based on the sensor outputs and dynamically generate user feedback and / or warning signals when unsafe levels of TSF conducive to ACL injury are detected.
Owner:TESNOW ANDREW
Elbow joint flexion-extension trainer
InactiveCN105982809ASimple structureSimple and fast operationChiropractic devicesEngineeringFlexion angle
The invention provides an elbow joint flexion-extension trainer. The elbow joint flexion-extension trainer comprises a forearm protecting jacket, a flexion-extension switching guiding arm, a support sliding arm, a movement sliding arm, a handle, an extending frame and an upper arm protecting jacket, wherein the forearm protecting jacket is fixed at the first end of the flexion-extension switching guiding arm; the second end of the flexion-extension switching guiding arm is fixed on the support sliding arm; a rack is arranged at the first end of the movement guiding arm, and the support sliding arm is meshed with the rack by virtue of a gear, so that the support sliding arm is fixed on the movement guiding arm; the handle is connected to a central shaft of the gear; the upper arm protecting jacket is fixed on the extending frame; and the extending frame is fixed on a second end of the movement guiding arm. When the elbow joint flexion-extension trainer is used, an upper arm and a forearm are respectively placed in the forearm protecting jacket and the upper arm projecting jacket to be fixed, the gear is driven to rotate on the rack of the movement guiding arm by rotating the handle so as to adjust angles of the support sliding arm and the movement guiding arm, and further adjustment of an elbow joint flexion angle is realized; and the trainer is simple in structure and easy to operate, and a patient does not need professional guidance of a rehabilitation trainer and can purchase personally and train and use the elbow joint flexion-extension trainer at home.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIQUE PRODS DEV
Patient specificity knee articulation prosthesis
InactiveCN107753156AReduce wearAvoiding the problem of a femoral trochlear detachment from the femoral condyleJoint implantsKnee jointsPatella prosthesisCoronal plane
The invention provides a patient specificity knee articulation prosthesis. The patient specificity knee articulation prosthesis is used for a total knee articulation replacement operation to replace an impaired articulation surface and recover normal articulation motion. The patient specificity knee articulation prosthesis comprises a thighbone condyle arranged on the thighbone of a patient and atibia pad which is matched with the thighbone condyle, wherein the thighbone condyle is provided with a thighbone trochlea which is matched with a patella prosthesis, the thighbone trochlea is provided with a patella articulation surface, and the patella articulation surface on the coronal plane is constituted by multiple hook faces with different curvatures. The patella articulation surface has acurvature radius which has the tendency of firstly decreasing along with increasing of the articulation flexion angle and then maintaining unchanged on the coronal plane, an included angle which is constituted by hook face tangent lines and has the tendency of firstly decreasing along with increasing of the articulation flexion angle and then maintaining unchanged, and a depth which is increasedalong with increasing of the articulation flexion angle. The thighbone trochlea of the thighbone condyle can be in continuous and stable contact with the patella prosthesis, the situation that the patella prosthesis is separated from the thighbone condyle while conducting articulation high-flexion motion is avoided, and the stability of the patient specificity knee articulation prosthesis is improved.
Owner:刘方
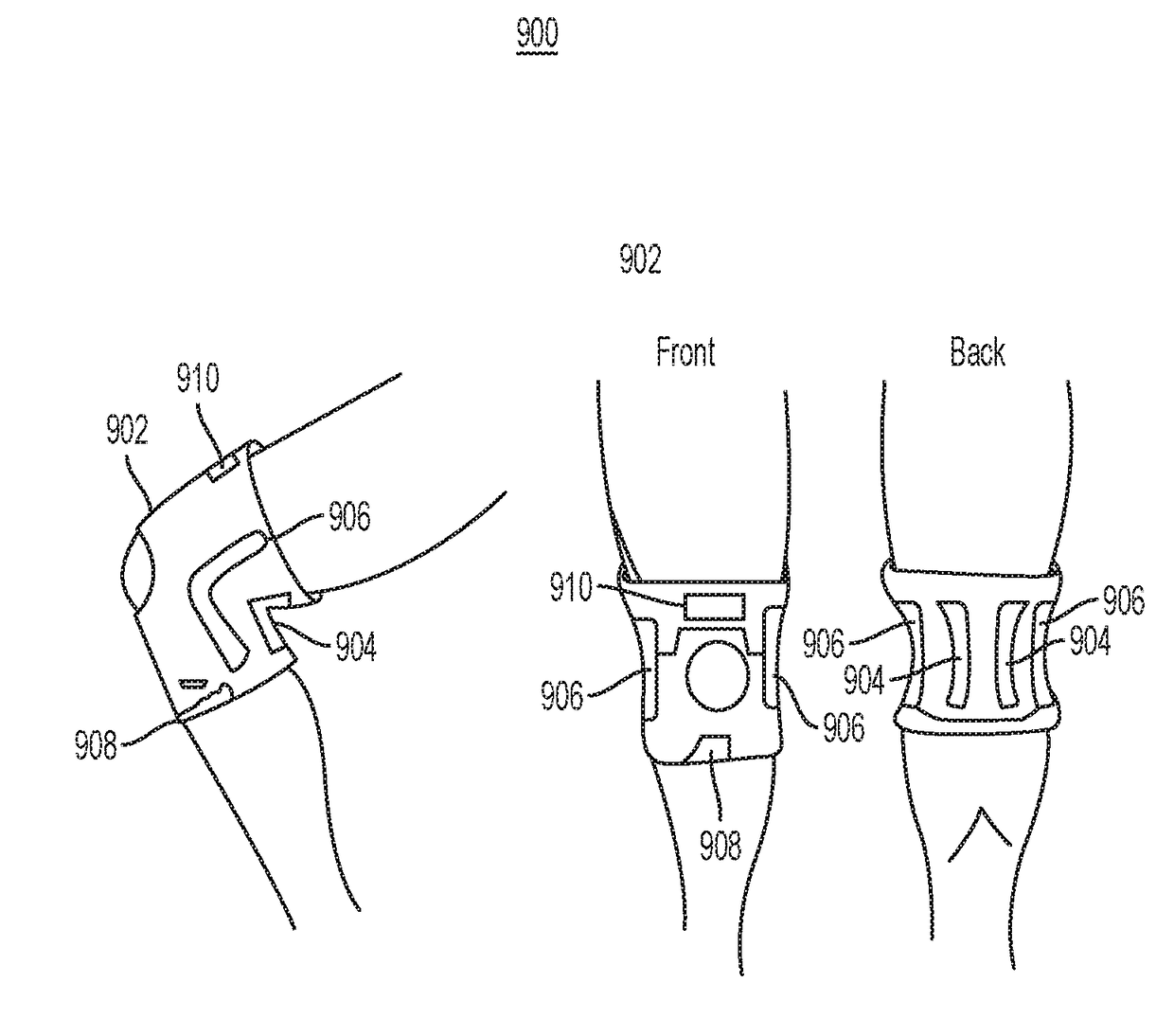
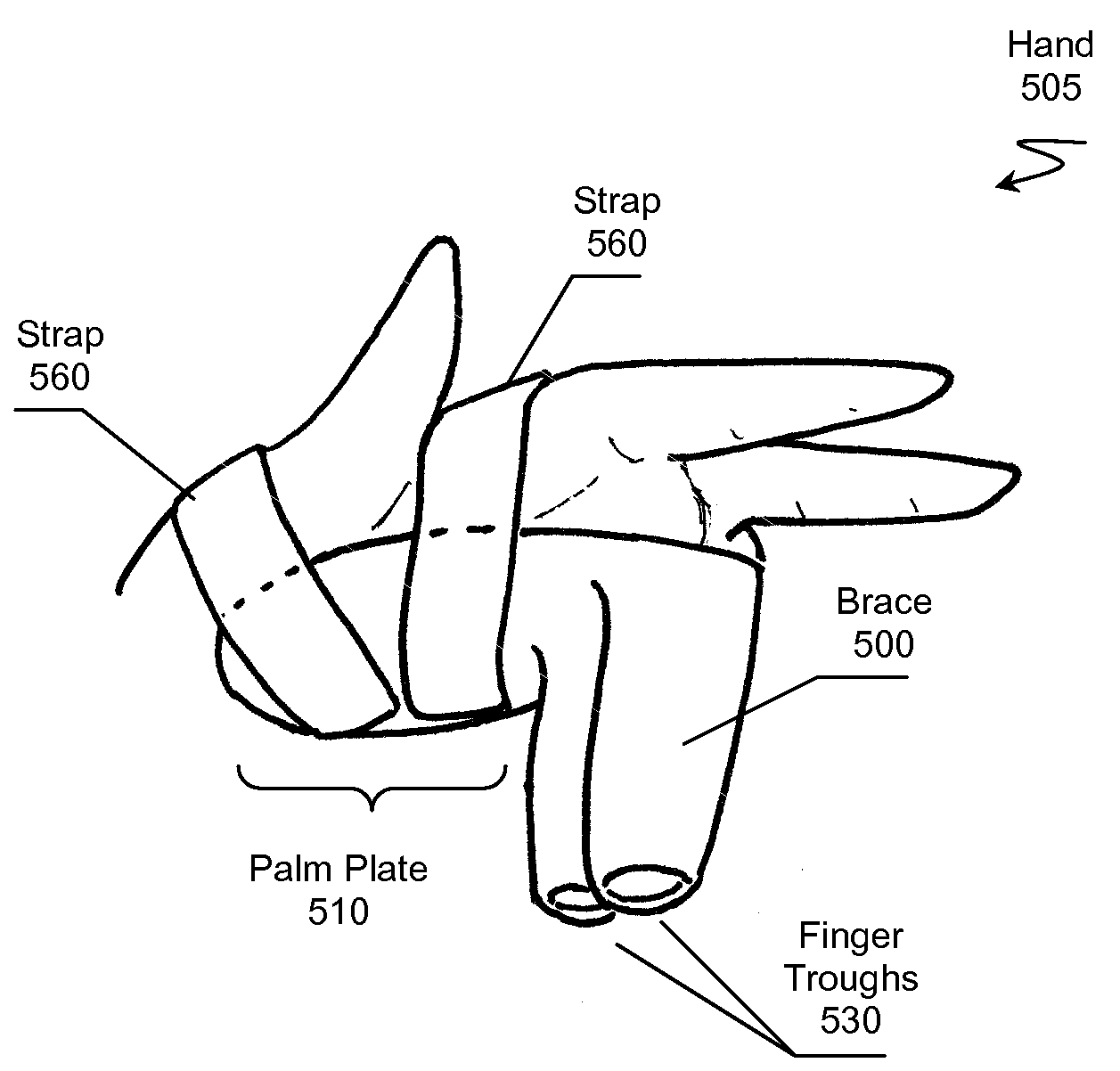
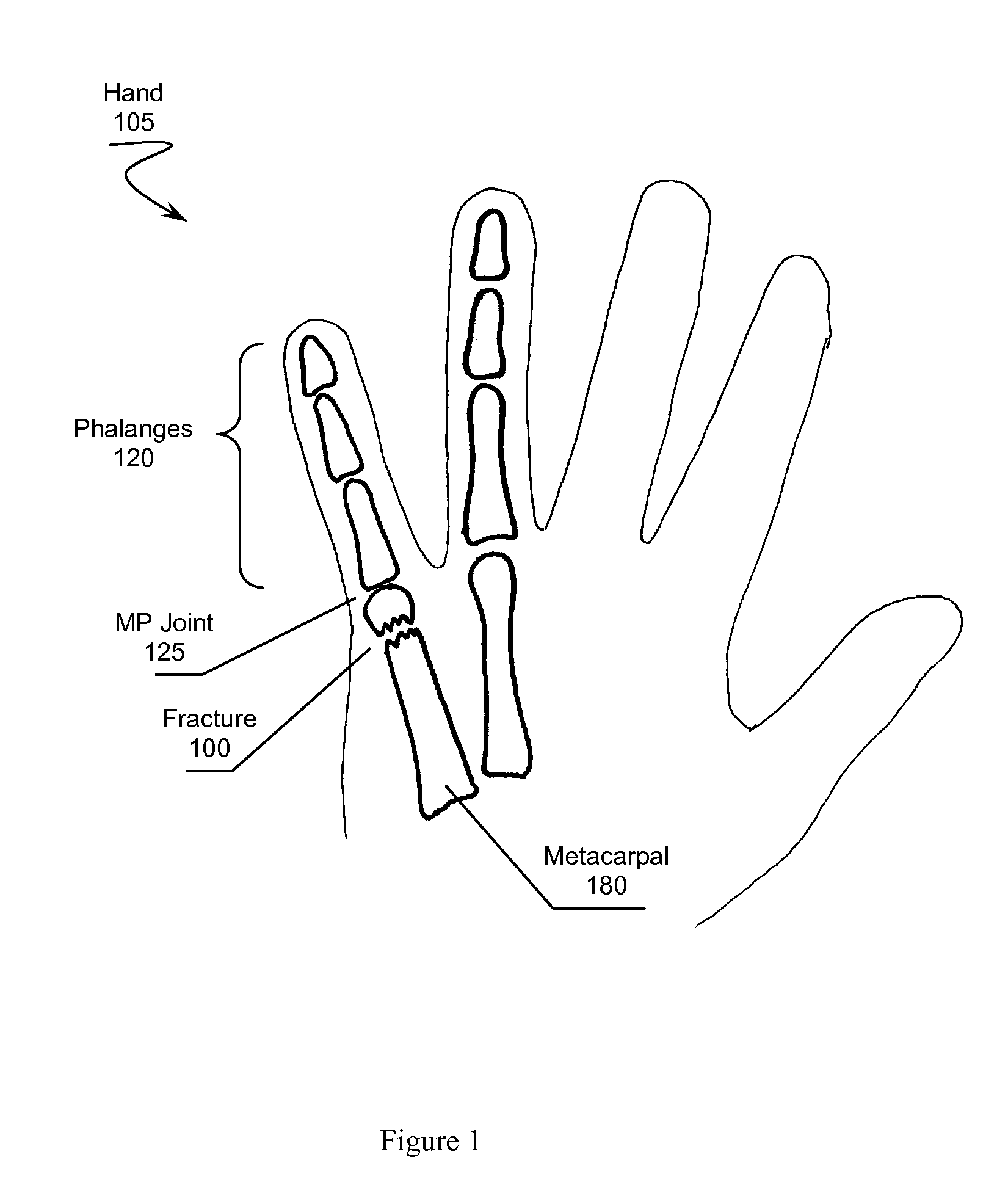
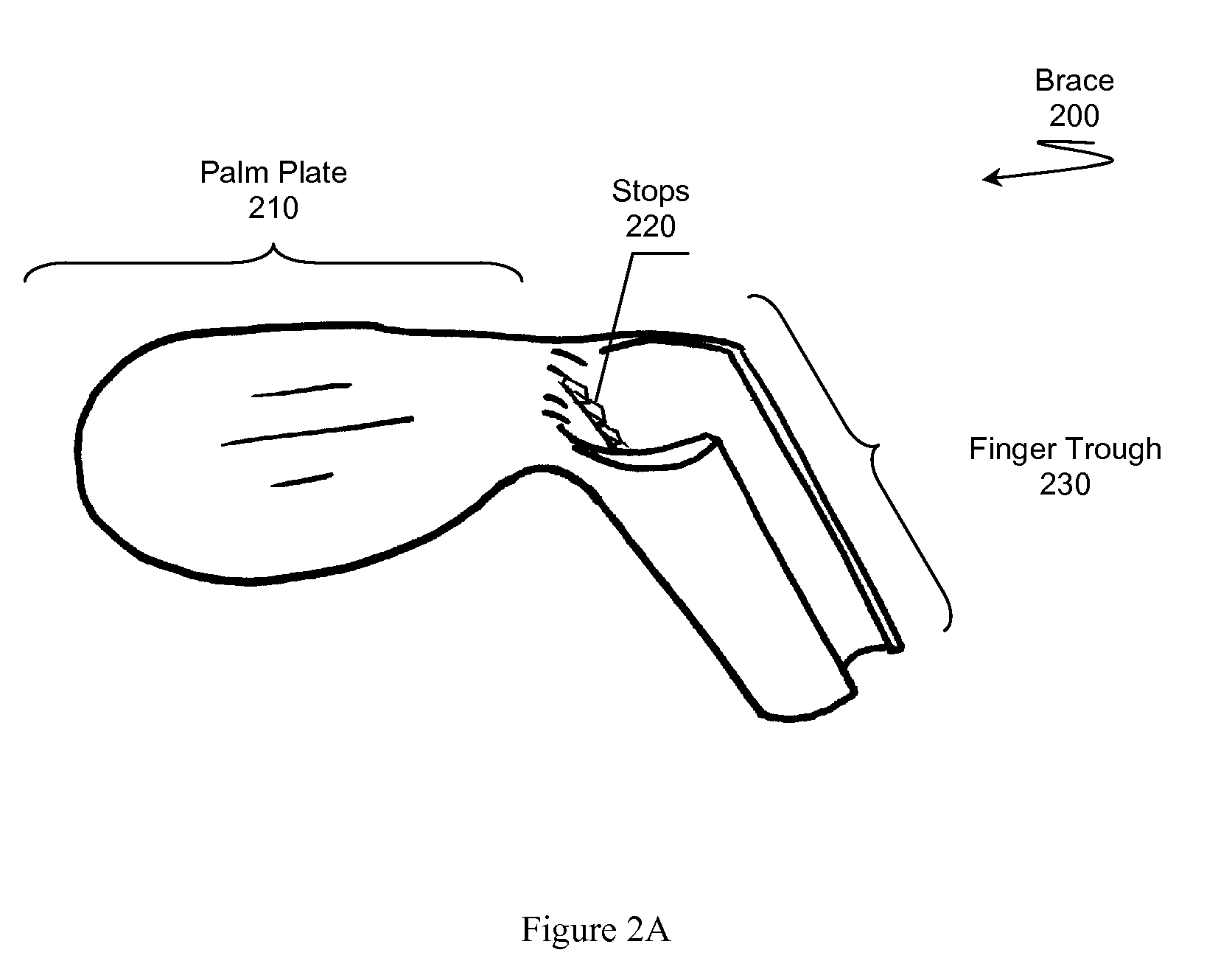
Brace for Reducing a Metacarpal Fracture
InactiveUS20090093744A1Reduce fracturesPrecise positioningFractureFracture reductionAxial compression
A brace for reducing a metacarpal fracture is presented. The brace comprises a palm plate and a finger trough for receiving a finger having a metacarpal fracture. The trough couples to the palm plate at a proper angle of flexion for reducing the fracture. An individual places the brace on the plamar side of their hand and places the finger having the fracture in the trough. A fastening system holds the brace in a stable position on the hand. The trough maintains the metacarpal-phalangeal joint at the proper angle of flexion while also maintaining necessary axial compression along the finger to reduce the fracture.
Owner:MACARTHUR ROBERT
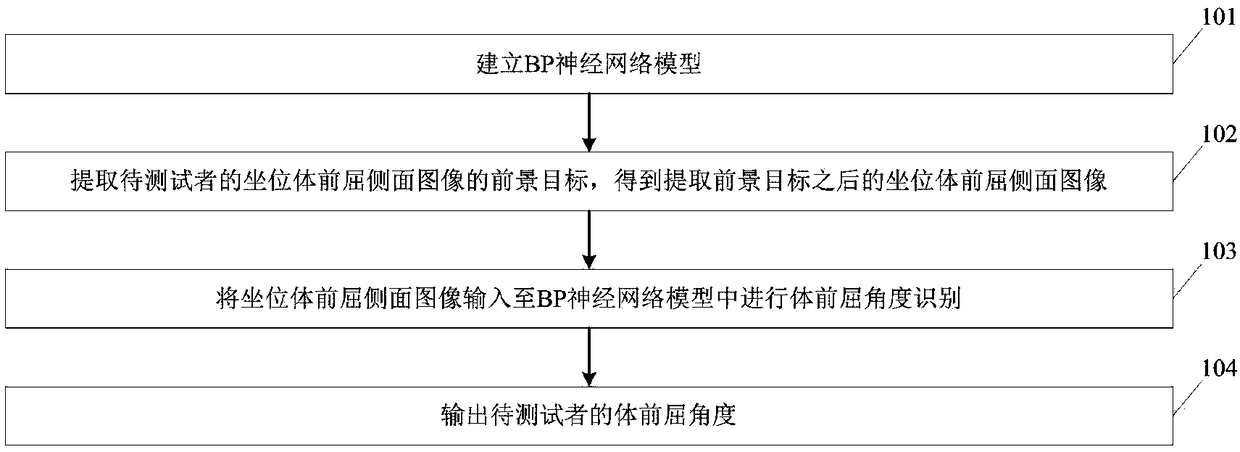
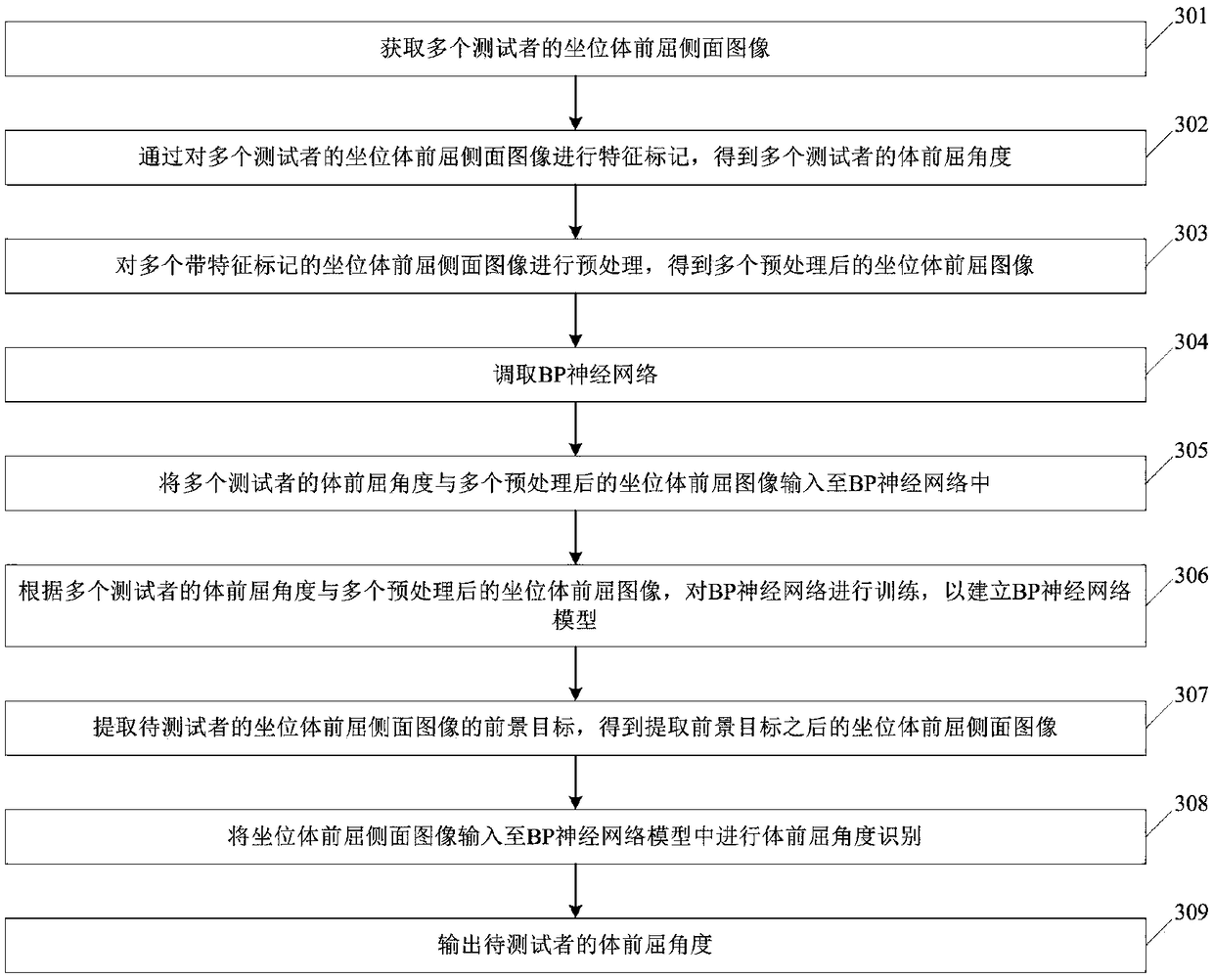
A method and a device for human body flexion angle recognition based on BP neural network
InactiveCN109214292AAccurate measurementImprove measurement efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesObservational errorHuman body
The invention discloses a human body flexion angle identification method and a device based on a BP neural network, wherein, the method comprises the following steps of: establishing a BP neural network model; the foreground object of the sitting body flexion side image is extracted, and the sitting body flexion side image after the foreground object is extracted is obtained. Inputting the sittingbody flexion side image into the BP neural network model for body flexion angle identification; outputting the body flexion angle of the subject. The invention can overcome the measurement error caused by different limb lengths, makes the measurement result more accurate, and further improves the detection efficiency.
Owner:GUANGDONG POLYTECHNIC NORMAL UNIV
Fixing orthosis after restoration of extensor tendon rupture
InactiveCN101773423AReduced flexion angleAvoid the disadvantages of fixation in strong flexionMedical sciencePhysical medicine and rehabilitationProximal phalanx
The invention relates to a fixing orthosis after the restoration of extensor tendon rupture, which is characterized in that: the fixing orthosis after the restoration of extensor tendon rupture is made of thermoplastic mounded plastic, and is divided into five parts: a front arm part, a hand back part, a proximal phalanx part, a middle phalanx part, and a distal phalanx part. Each part is provided with a fixing band and a woolen hasp, and an angle-adjusting hinge axis is arranged between two parts. During use, after the angles among the parts are adjusted by adjusting the hinge axes, the fixing orthosis can be fixed on the affected limb through the fixing band and the woolen hasp which are arranged on each part. The fixing orthosis has the following advantages that: the fixing orthosis can selectively fix corresponding joints, only fixes the joints of injured fingers and avoids the stiffness of normal finger joints; and after the operation, flexion angles of the fingers are gradually reduced by adjusting the hinge axes, and the defect that the fixing orthosis is always fixed at a strong flexion position after the operation is overcome.
Owner:乔永平
Walking assisting device
ActiveUS7534218B2Decrease flexion angleShorten speedGymnastic exercisingWalking aidsPush upsEngineering
A walking assisting device that transmits a force generated by a leg link to a user's trunk via a load transfer portion. The leg link includes a first link connected to the load transfer portion via a first joint portion, a second link connected to a foot attachment portion via a second joint portion, a third joint portion which connects the first link to the second link so as to be free to bend and stretch, and a driving source which drives the third joint portion. Even if a flexion angle of the third joint portion reaches zero degree, the controllability is maintained in the direction of pushing up the load transfer portion so that the leg link can be extended straight with the user's leg extended straight. An interlock system retracts and extends the second link and increases and decreases the flexion angle of the third joint portion.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Detection of changes from a seated or lying body position by sensing body angle
ActiveUS9468399B2Simple andFall preventionGeneral fastenersDiagnostic recording/measuringBody anglePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Methods and apparatuses for detecting when a subject gets up out of bed or out of chair by detecting changes in body flexion angle with respect to a threshold. Also described herein are systems for monitoring one or more subjects each wearing an angle-sensing unit.
Owner:SENSARX
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com