Patents
Literature
665 results about "Femoral bone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
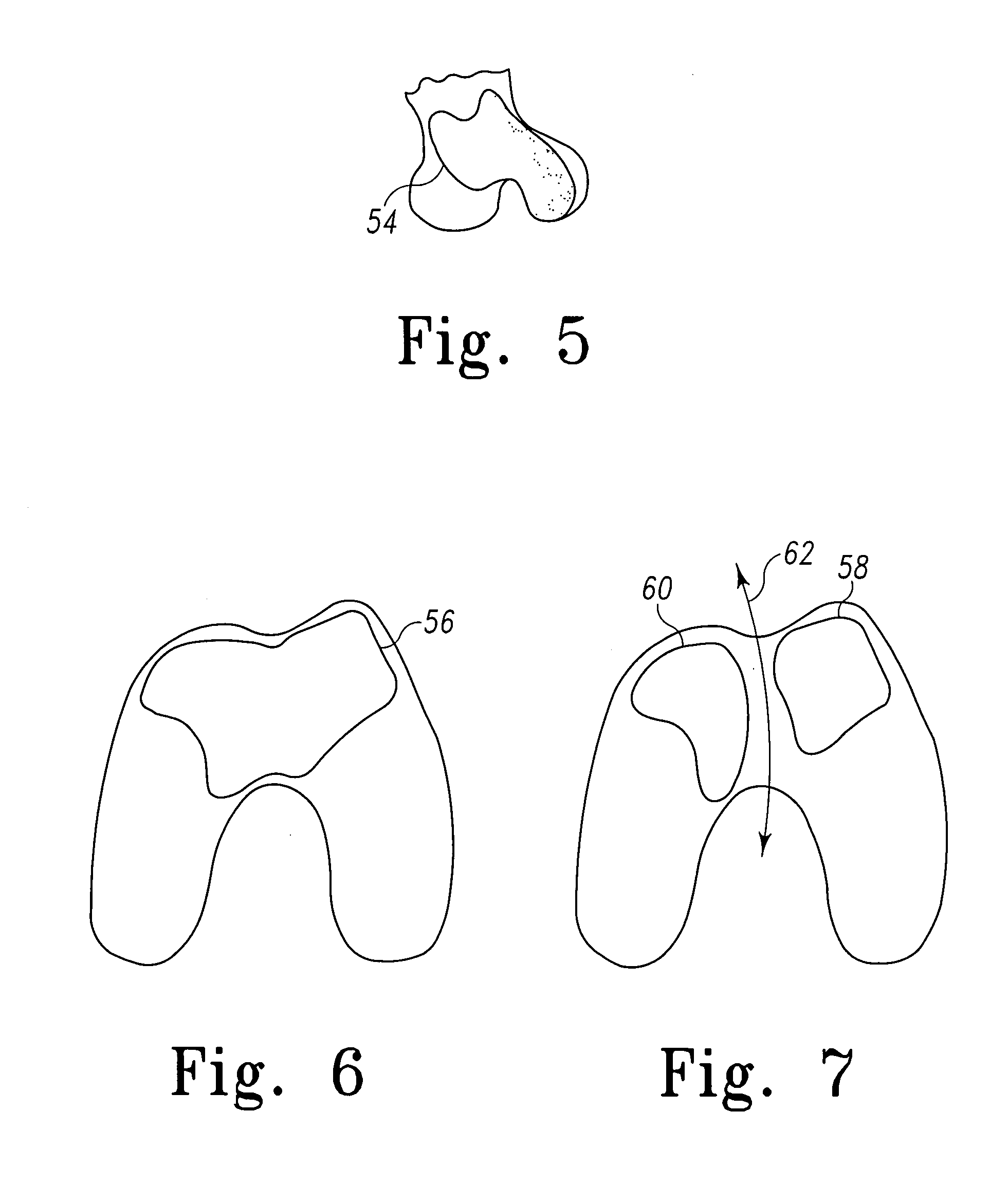
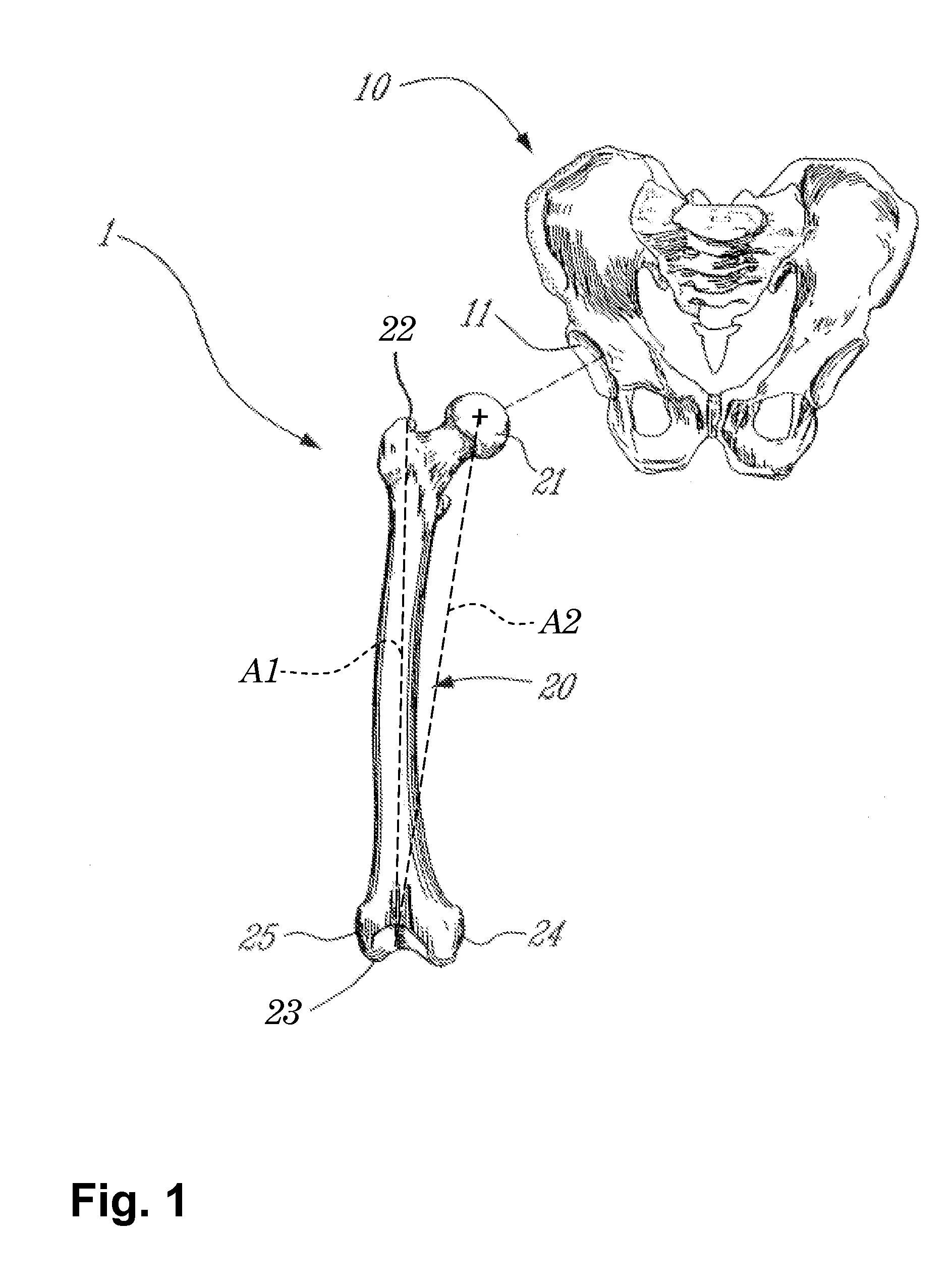
The femur is the leg bone (the thigh bone) connecting the knee joint to the pelvis. At the top of the femur is a thin piece or strip of bone that connects the long shaft of the thigh bone to the head of the femur. That thin strip of bone is femoral neck.
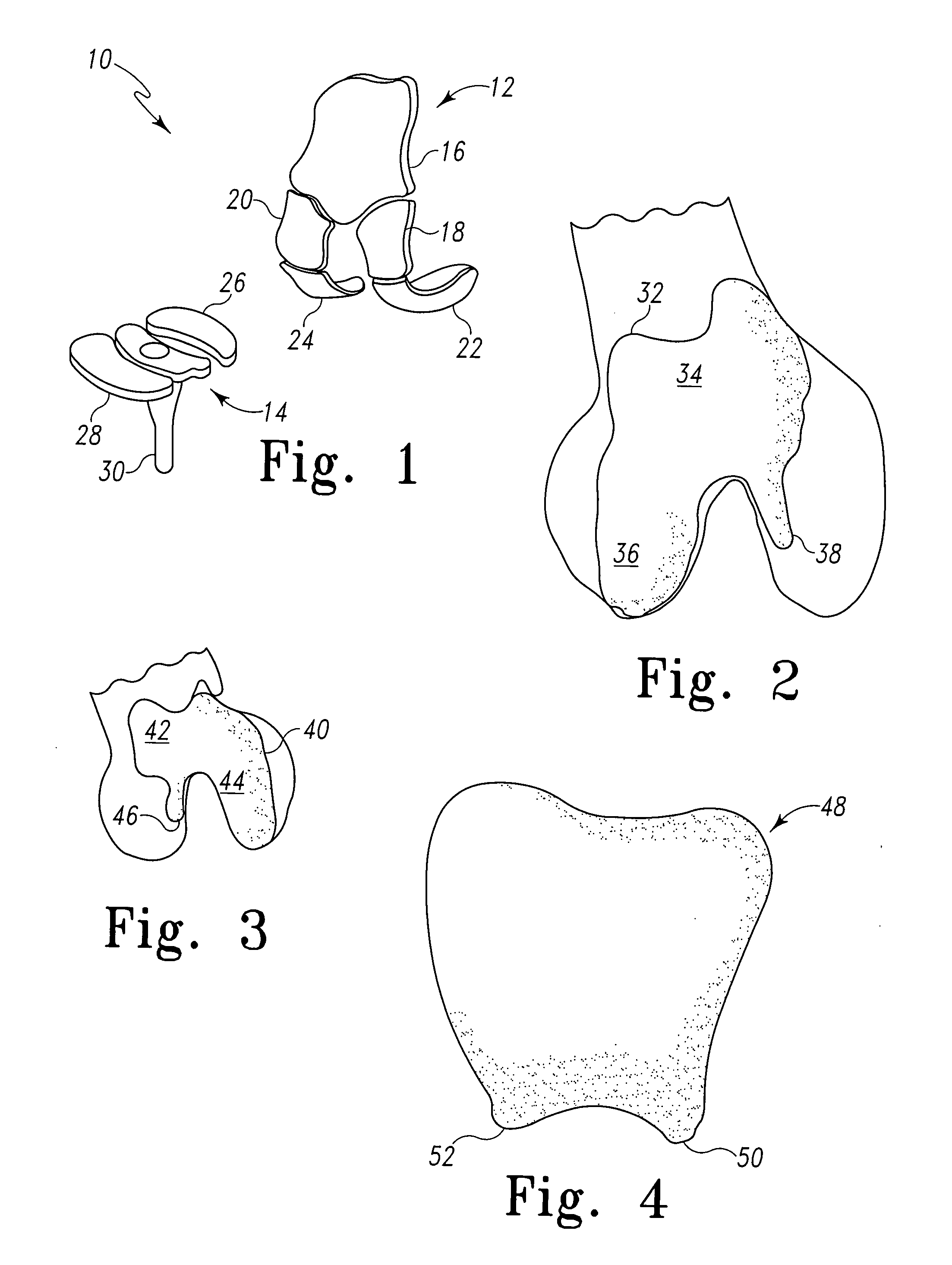
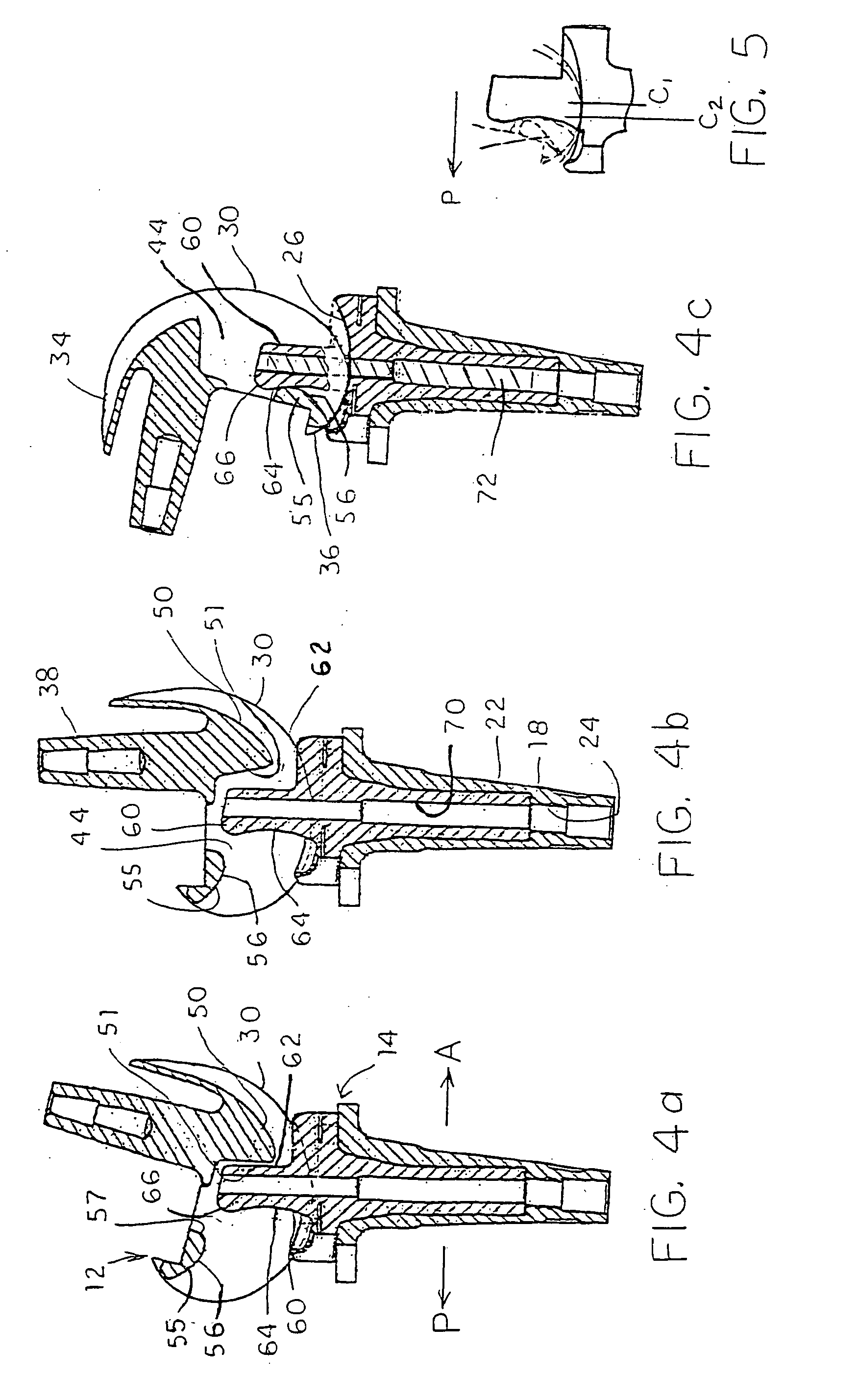
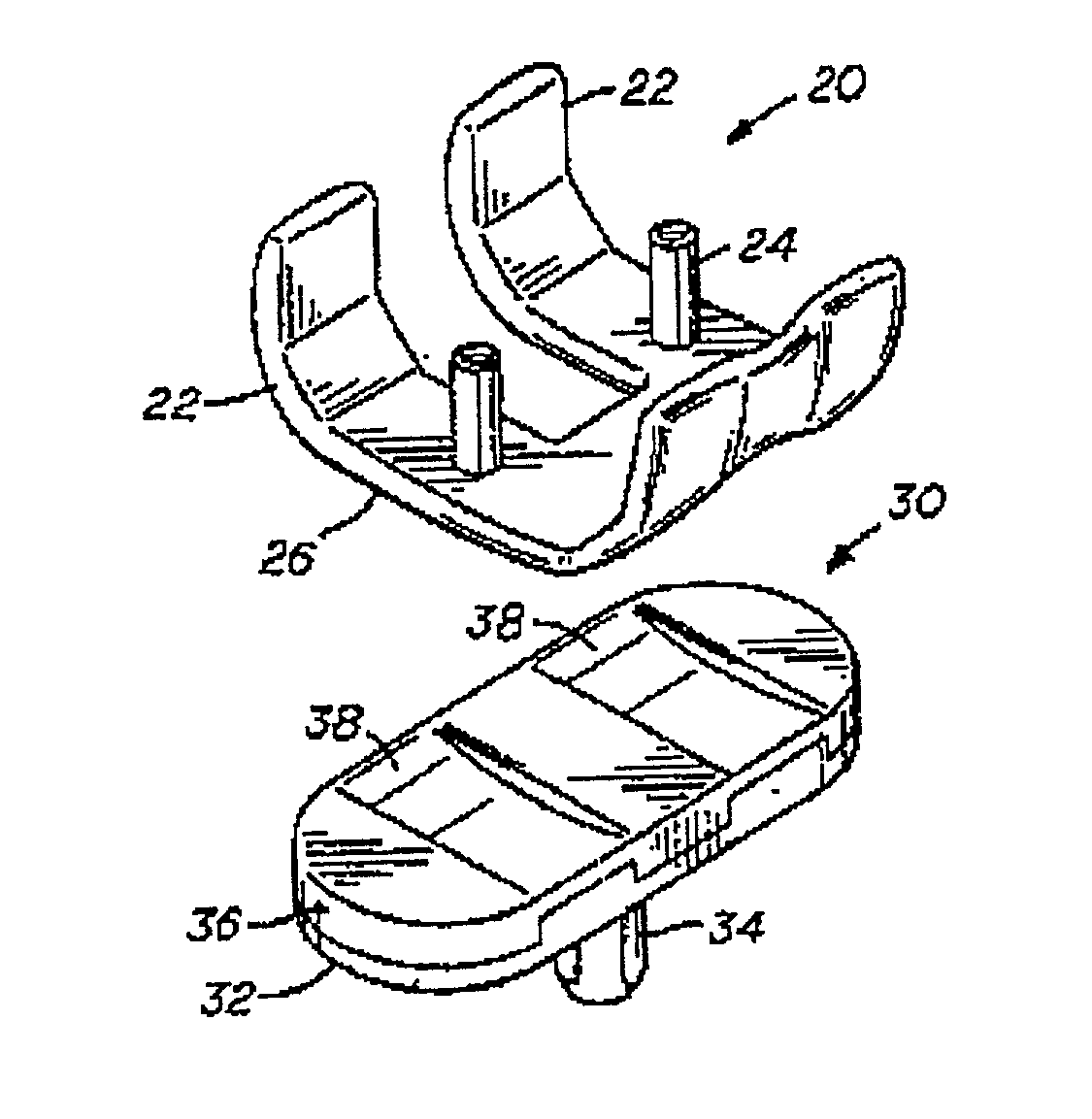
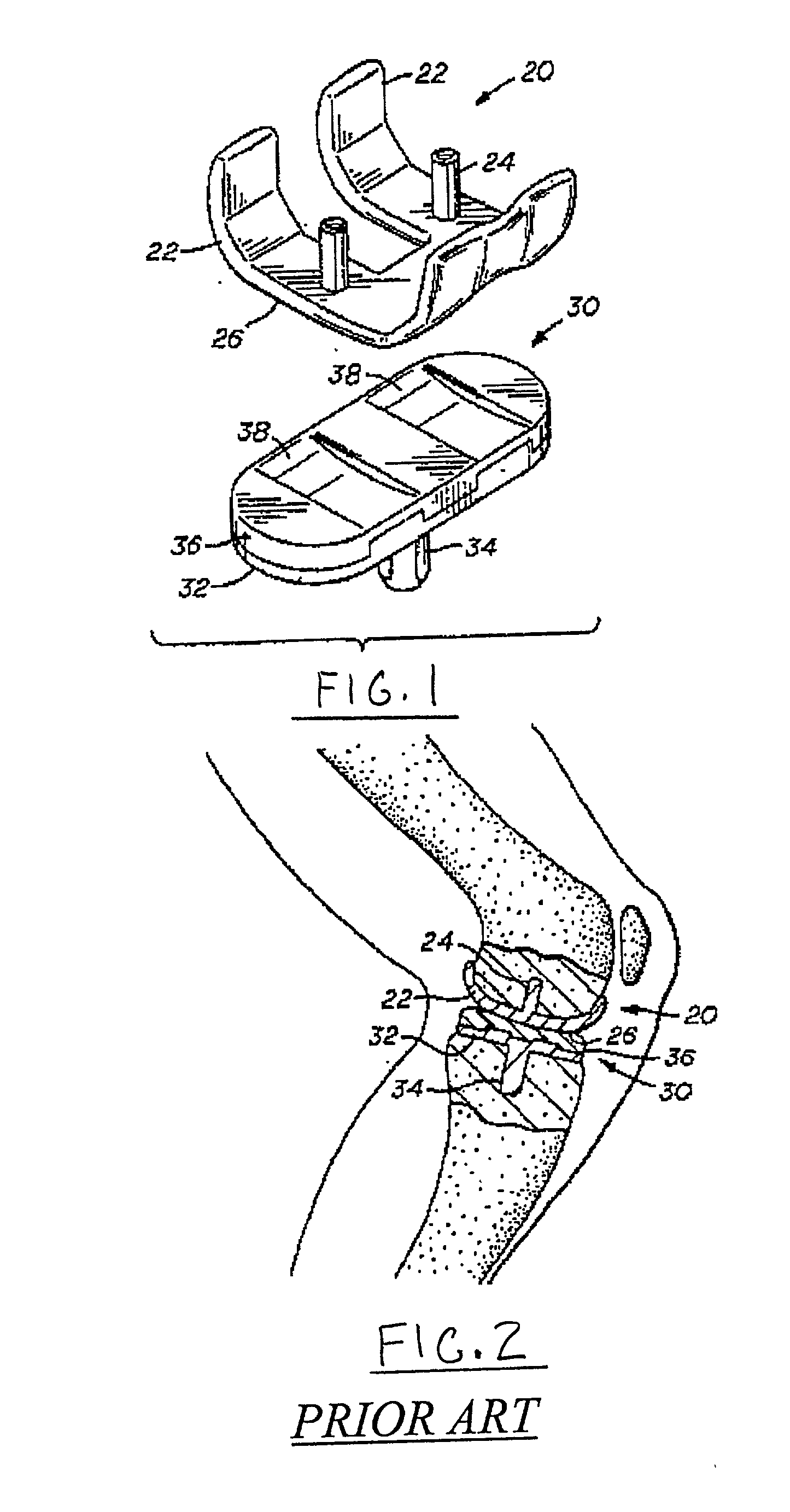
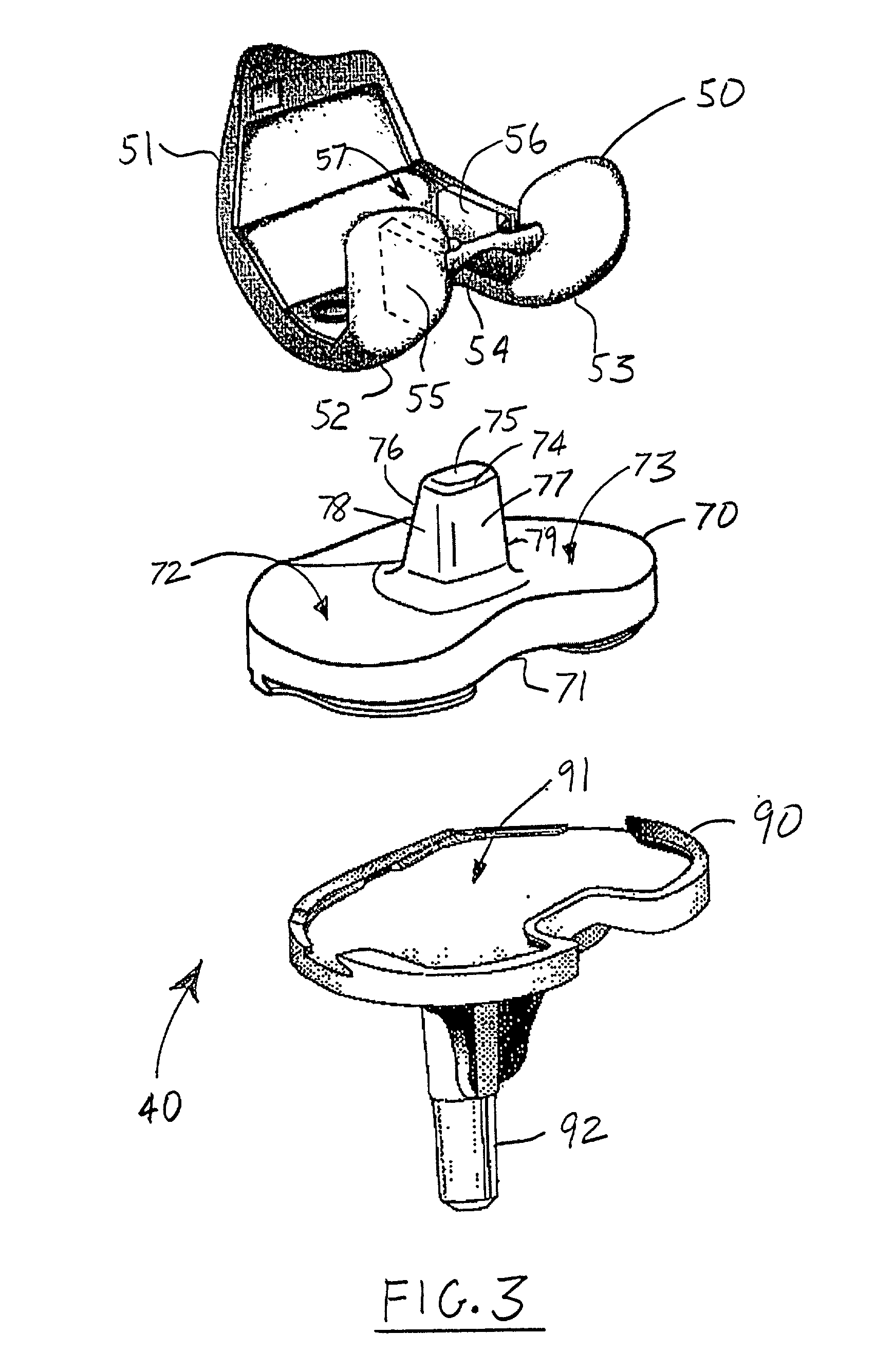
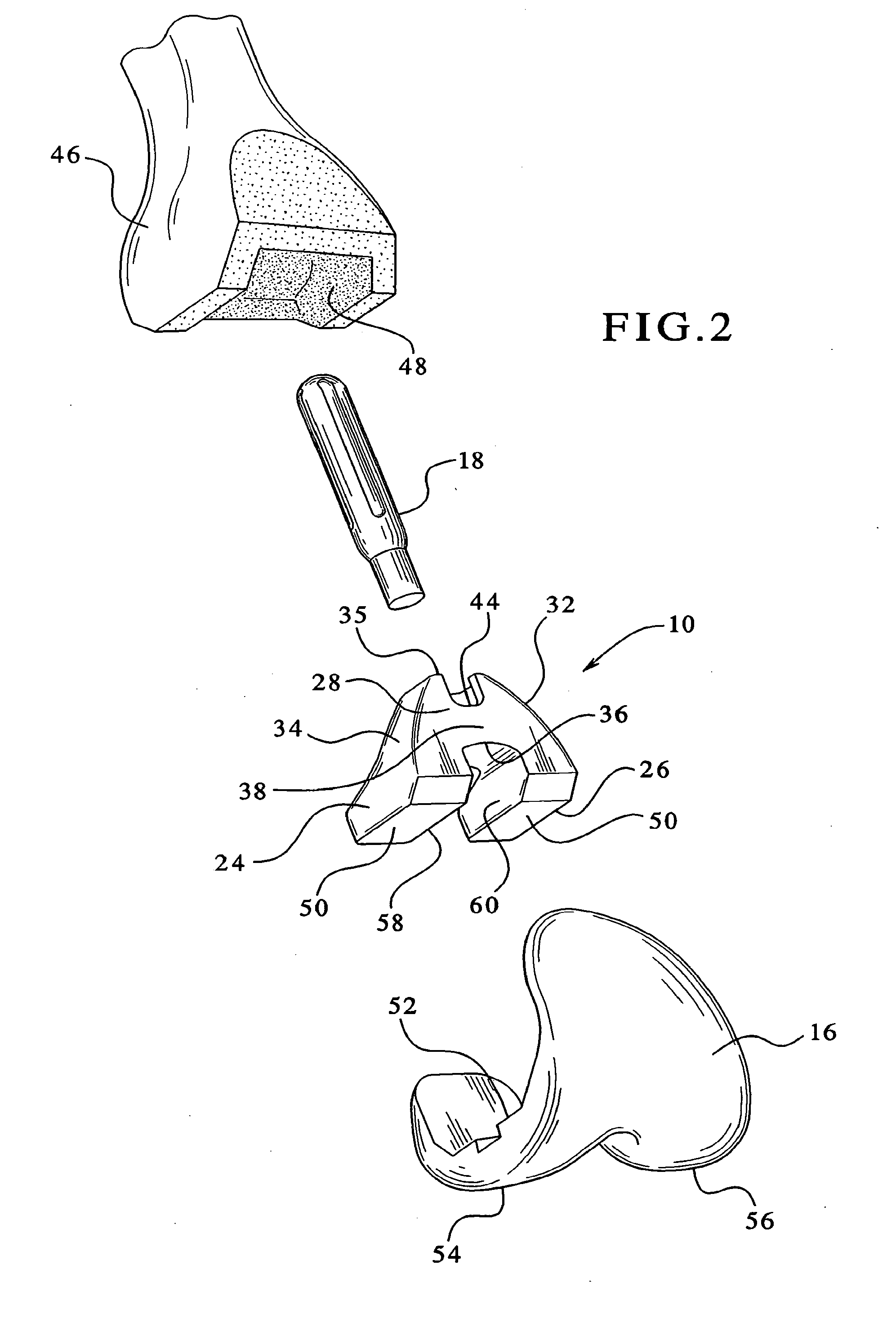
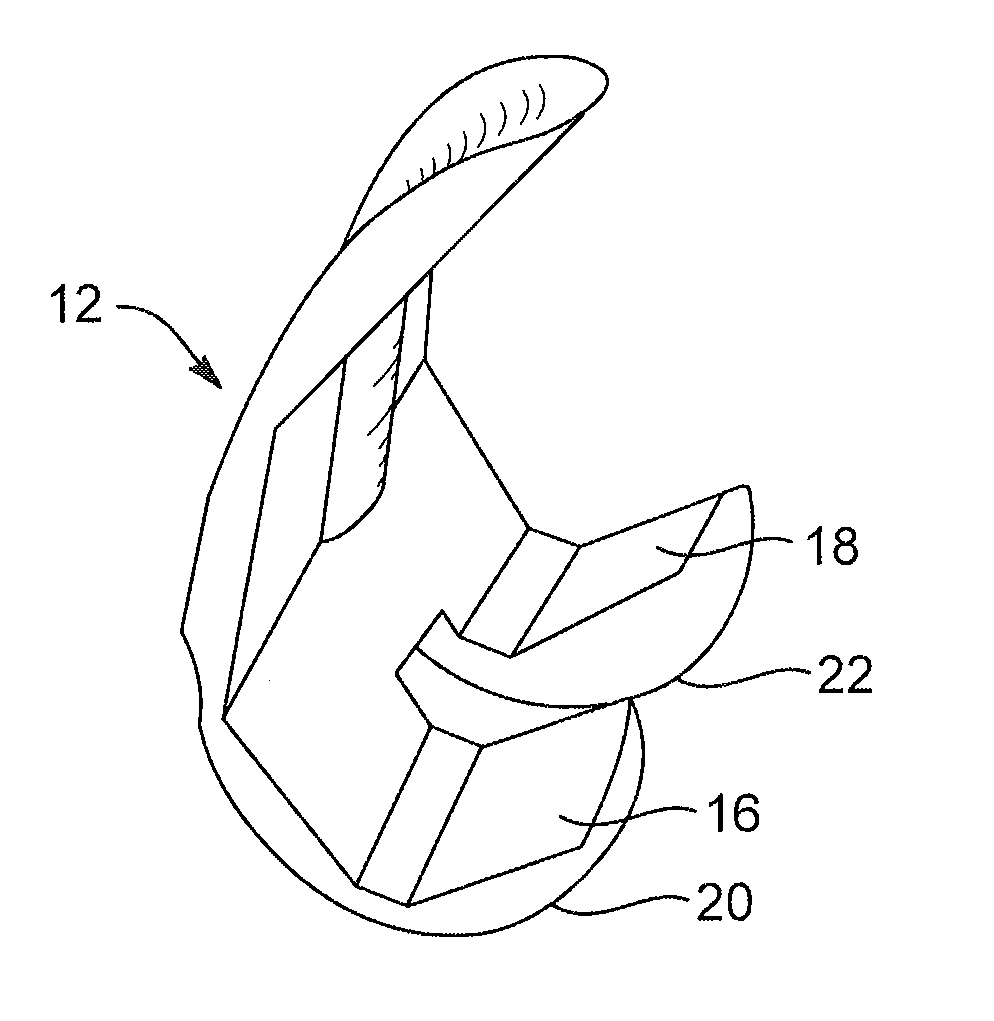
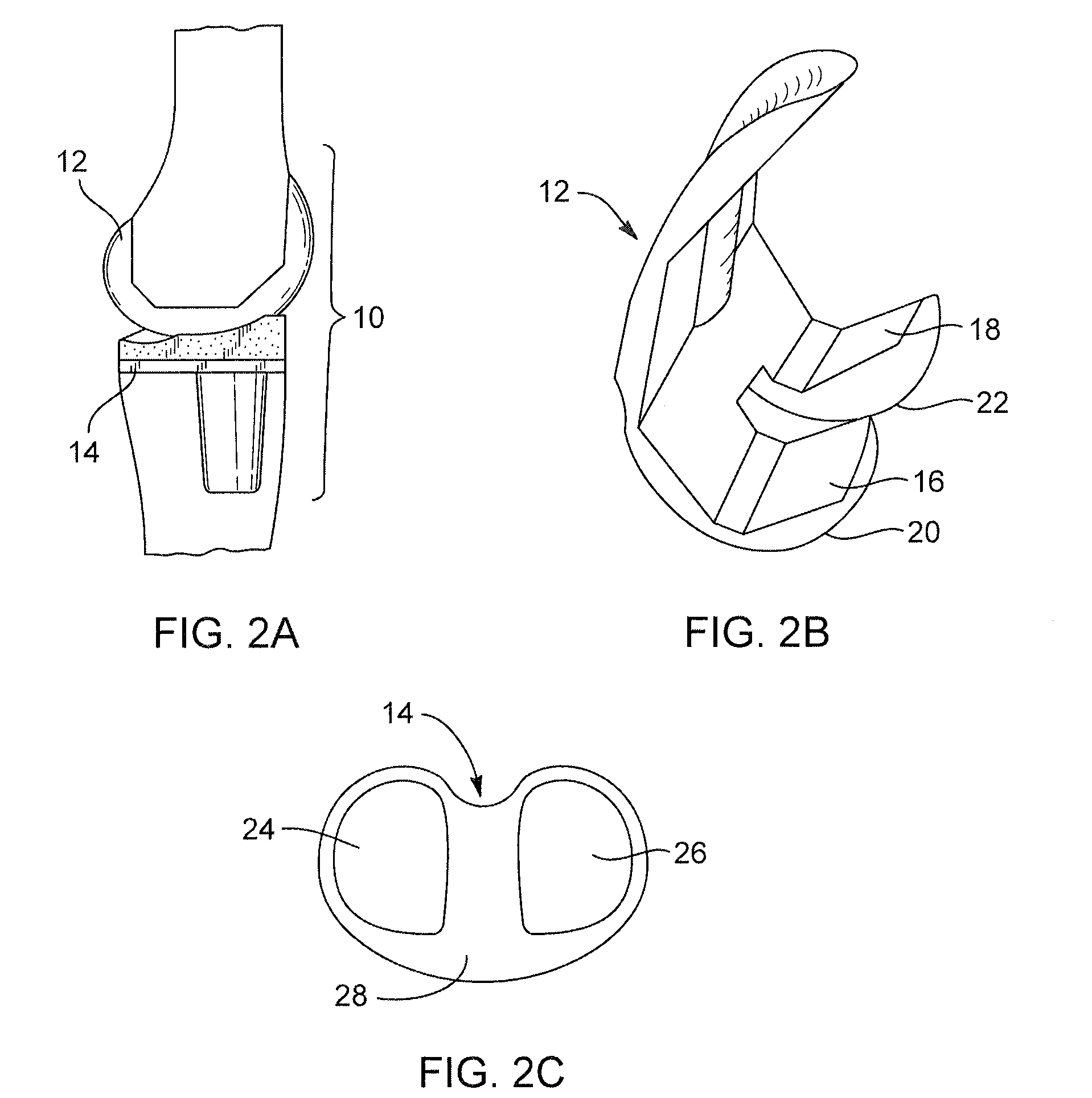
Modular knee prosthesis
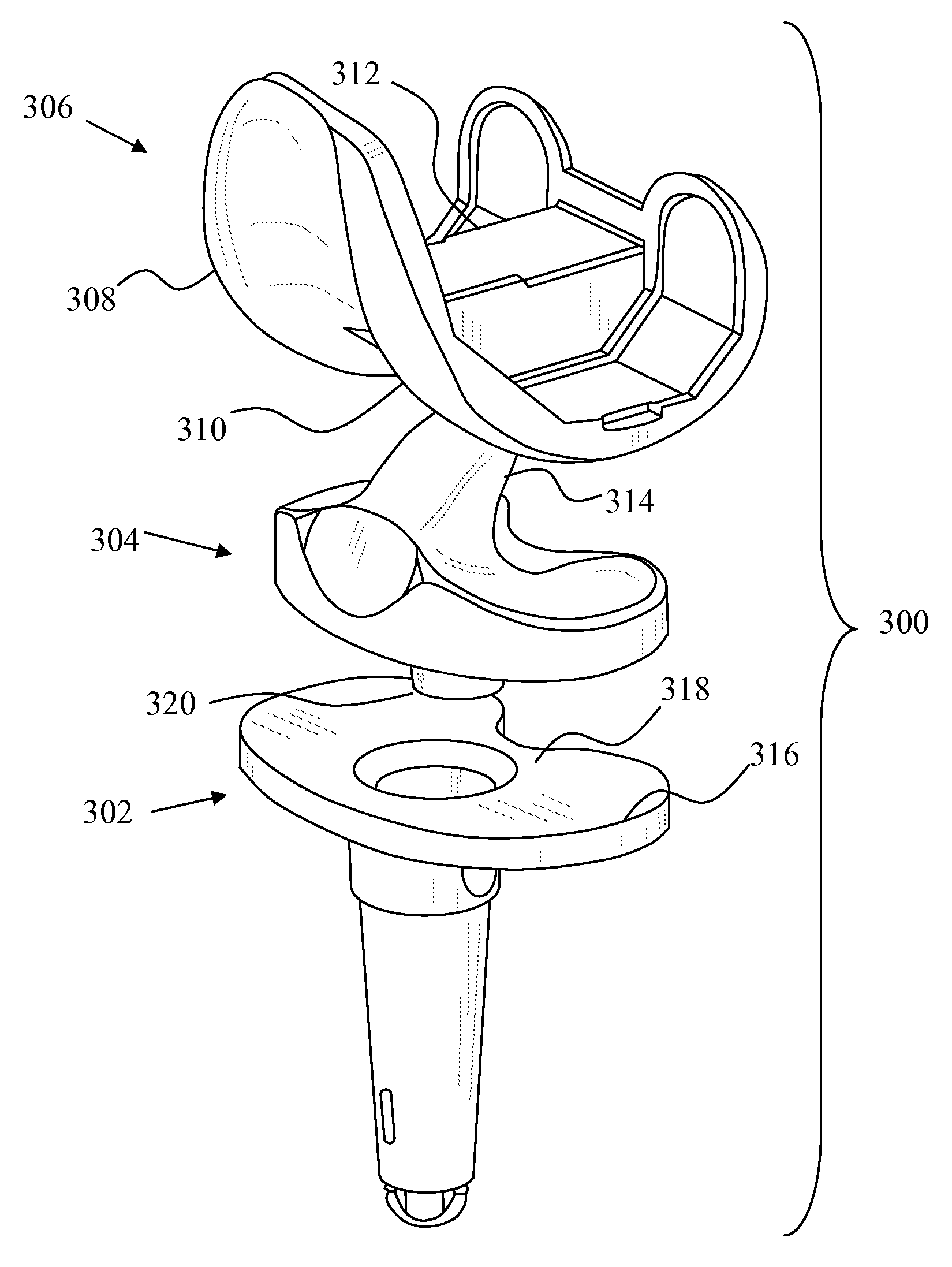
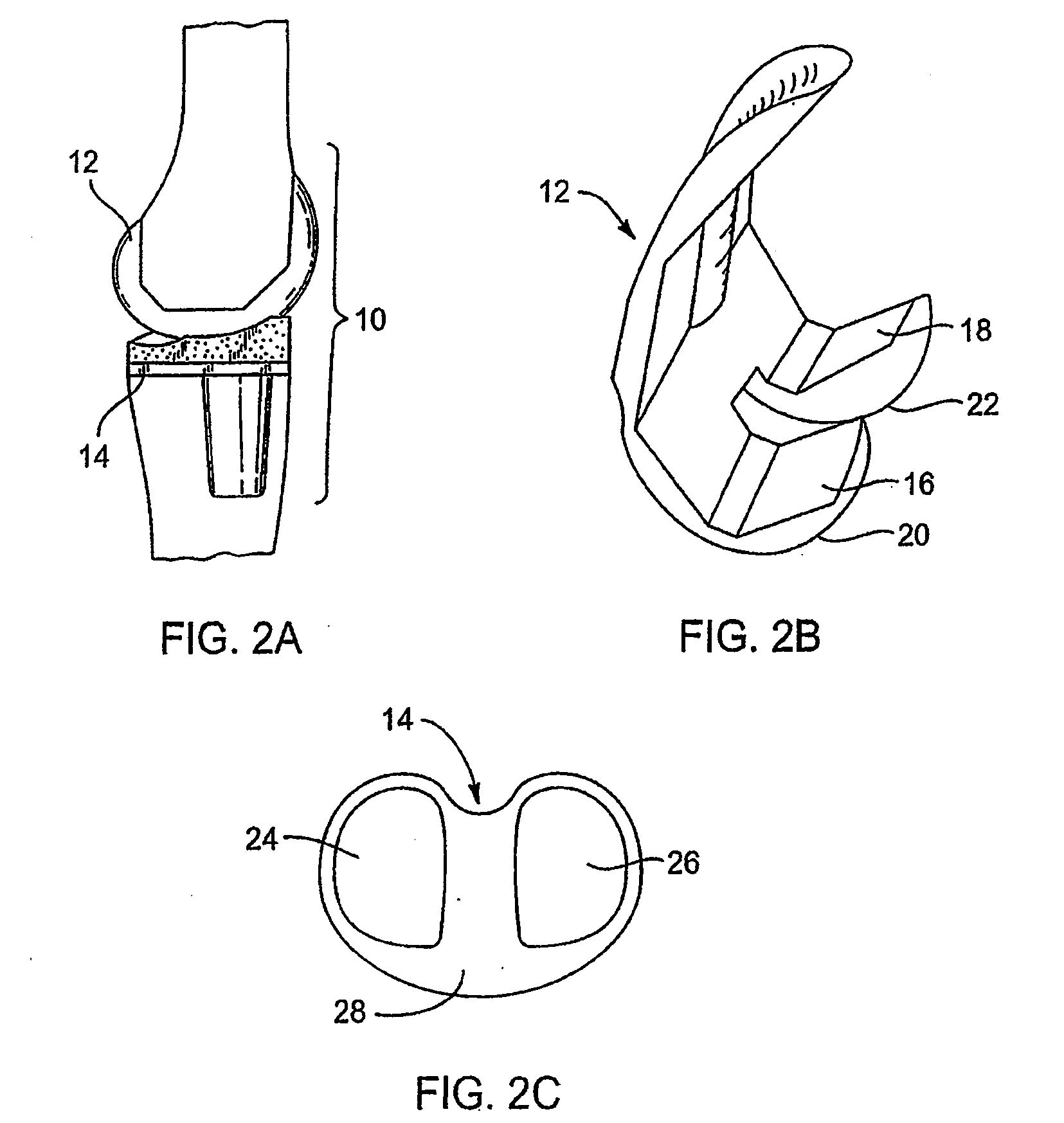
A modular prosthetic knee system used to replace the natural knee. The system includes a femoral knee prosthesis and a tibial knee prosthesis. Both prostheses are formed of modular components that are connectable in-vivo to form the prosthetic knee system. The femoral knee prosthesis includes two separate components, a lateral condyle and medial condyle; and the tibial knee prosthesis includes a multiple separate components, a medial baseplate, a lateral baseplate, a medial insert, and a lateral insert. The medial and lateral baseplate are connectable to form a complete baseplate with the medial and lateral inserts connectable to the complete baseplate.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
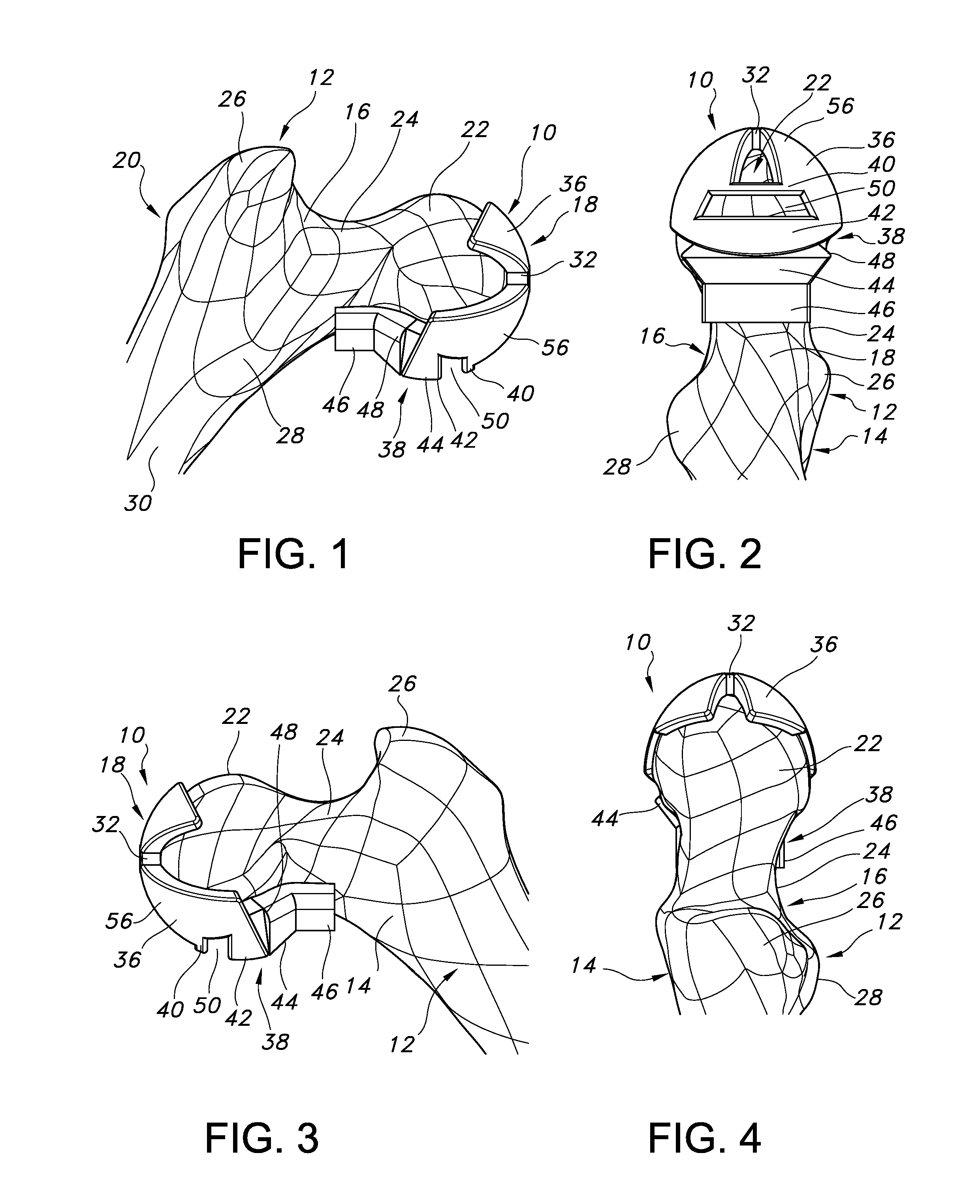
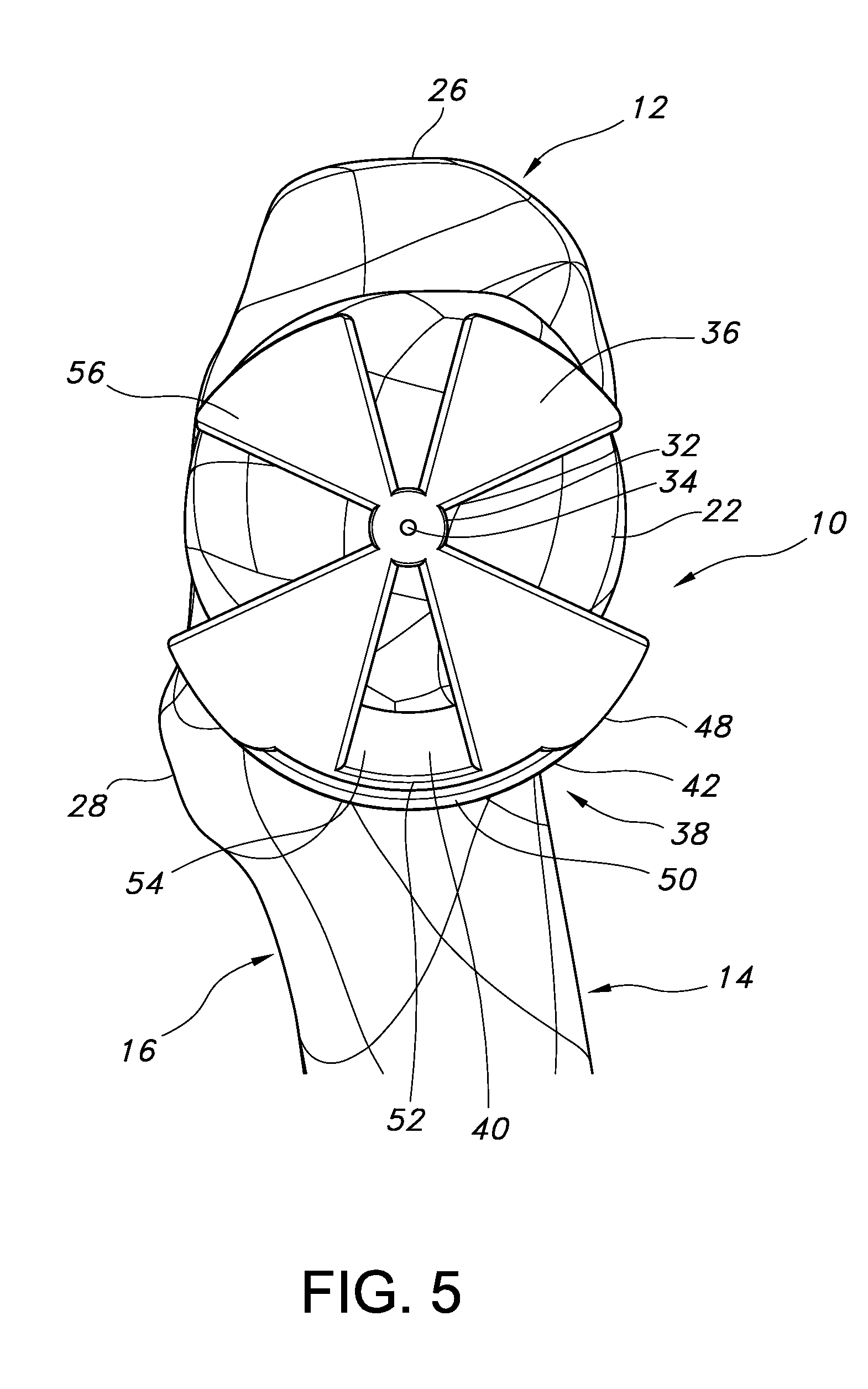
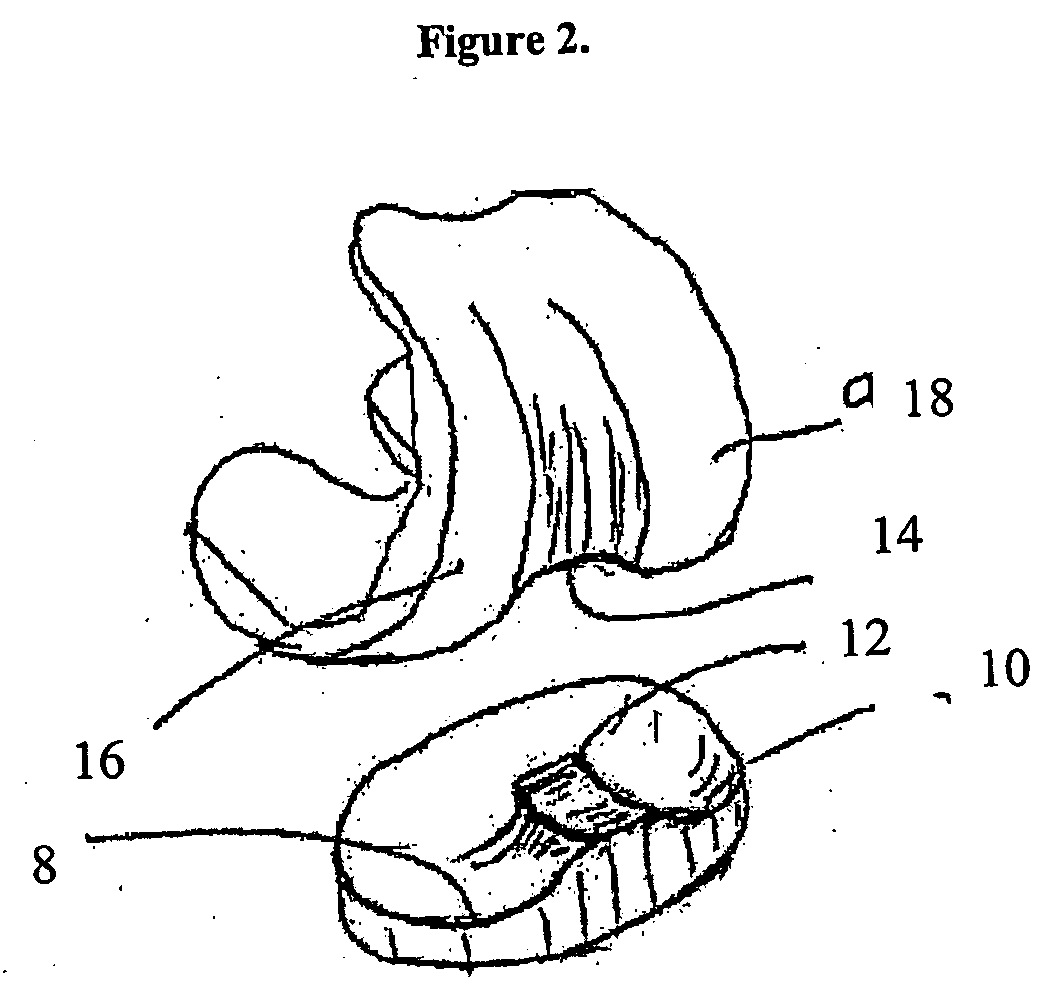
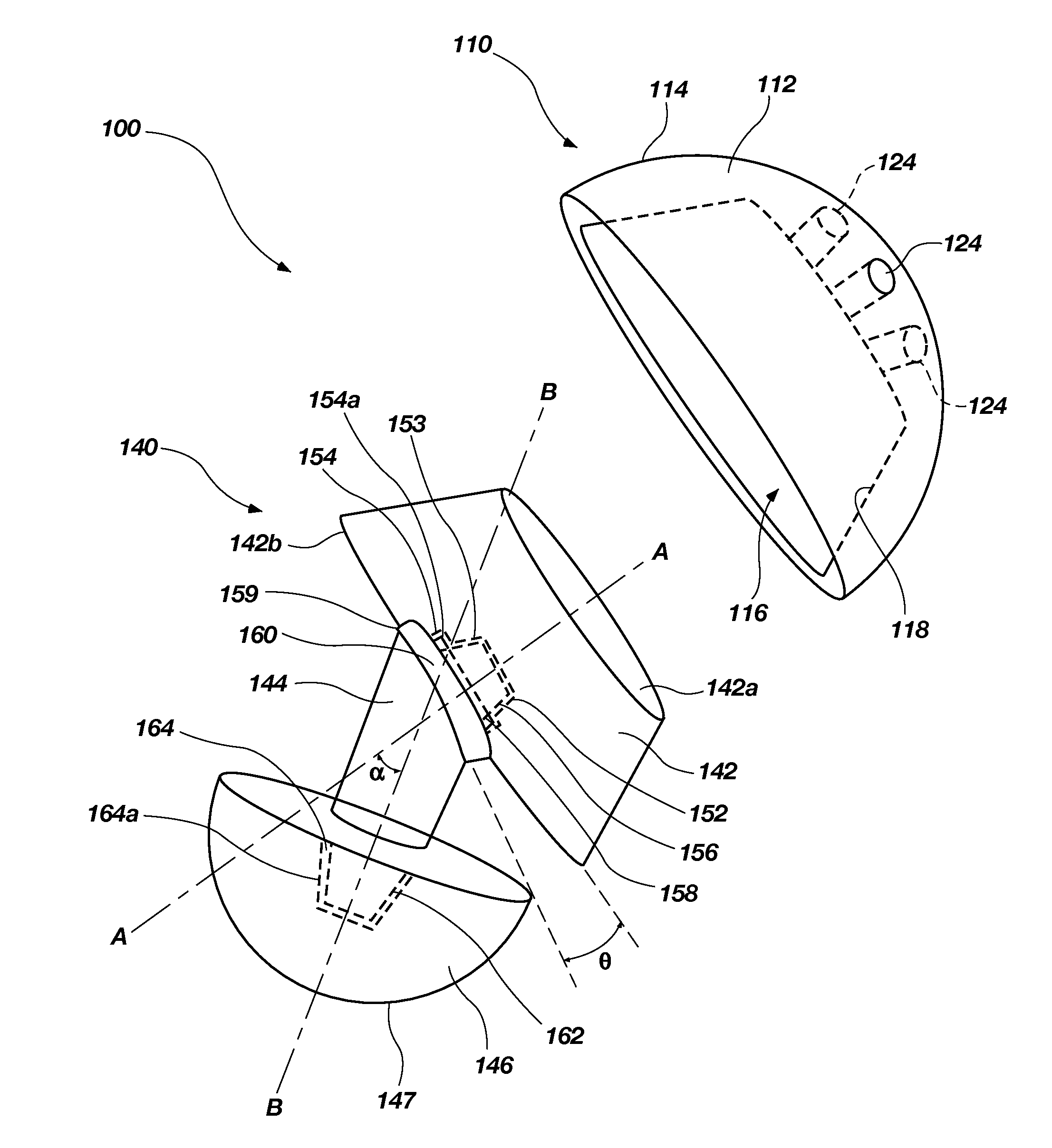
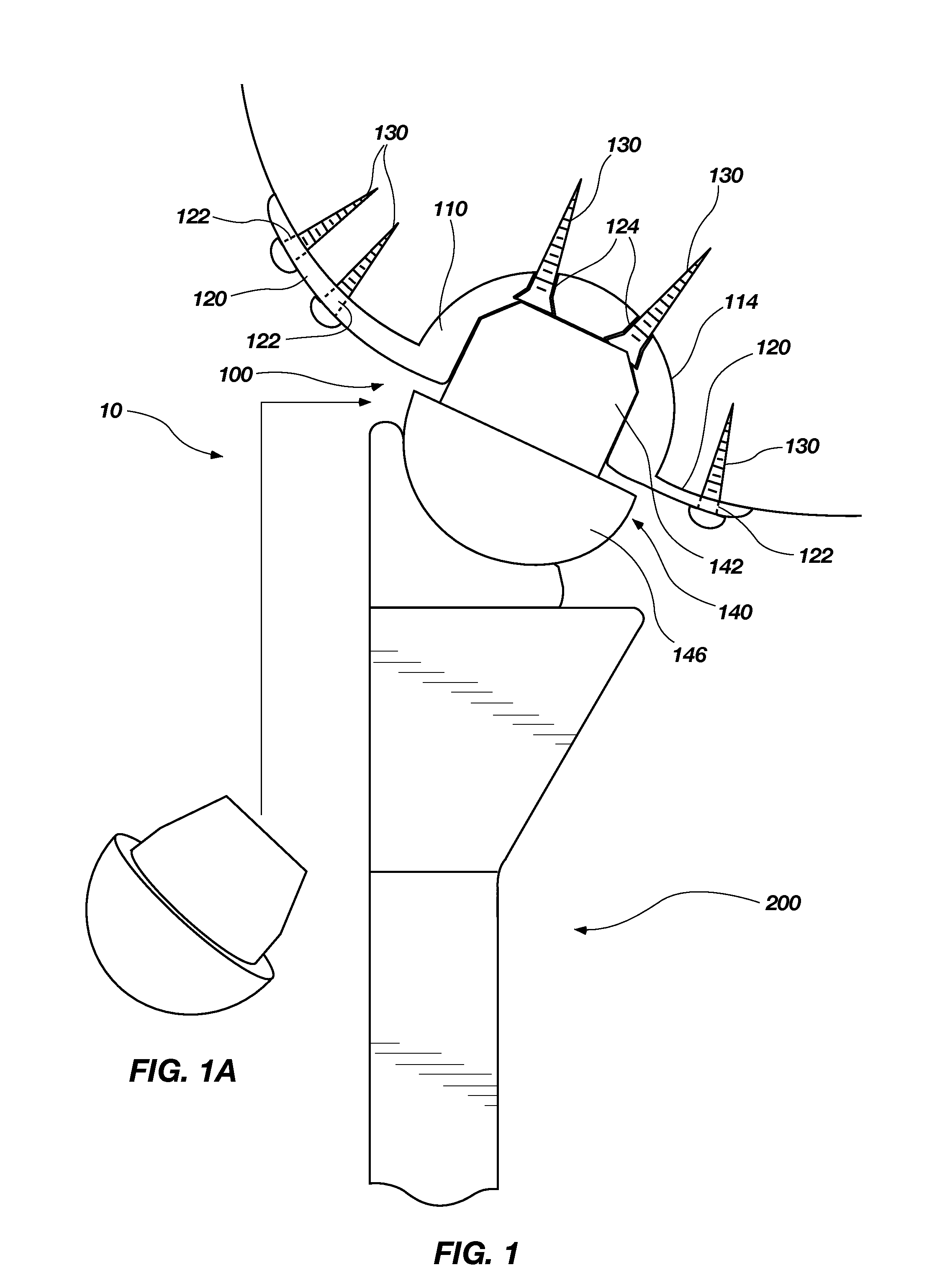
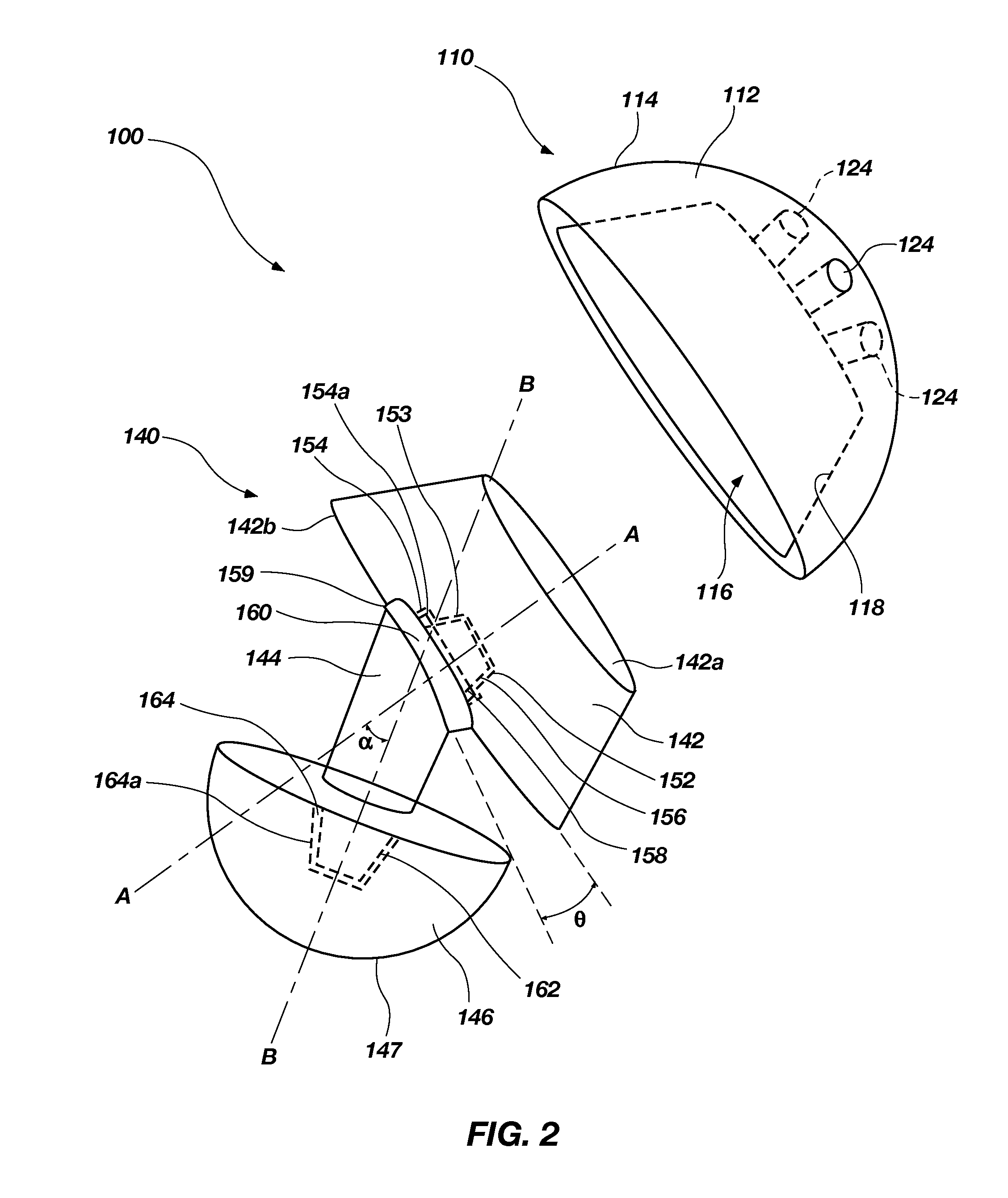
Patient specific alignment guide for a proximal femur
ActiveUS20100286700A1Easy to introducePrecise positioningDiagnosticsProsthesisRight femoral headGrip force
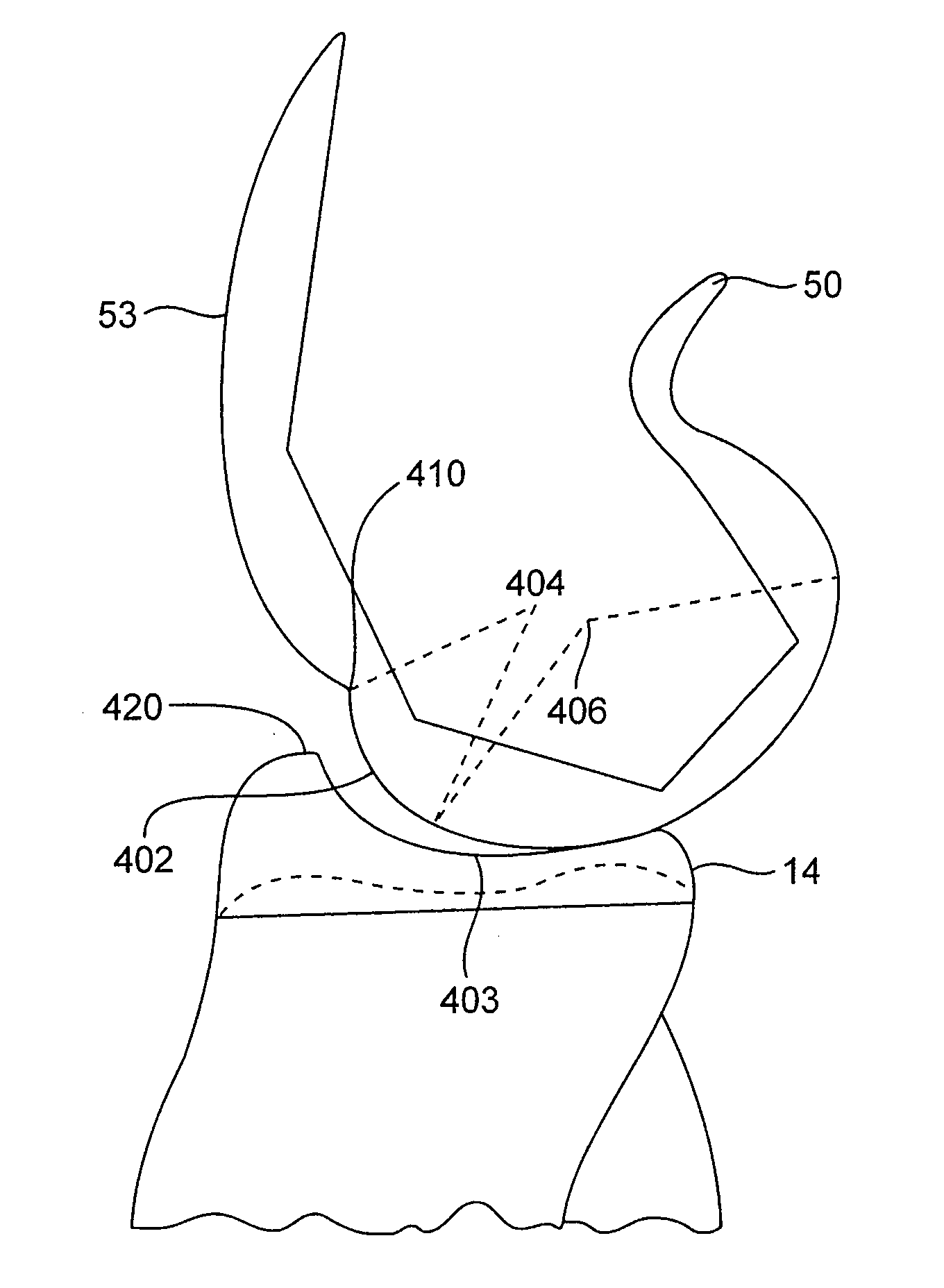
An alignment guide for aligning instrumentation along a proximal femur includes a neck portion configured to wrap around a portion of the neck of the femur, a head underside portion configured to abut a disto-lateral portion of the femoral head and a medial head portion configured to overlie a medial portion of the head. Portions of the guide can have an inner surface generally a negative of the femoral bone of a specific patient that the guide overlies; such surfaces can be formed using data obtained from the specific patient. The neck portion can be configured to rotationally stabilize the guide by abutting and generating a first gripping force on the neck. The femoral head portions can be configured to grip the head portion of the femur and can support a bore guide that is configured to guide an instrument to the femur in a specified location and along a given axis.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Systems and methods for compartmental replacement in a knee
A knee replacement system provides a knee implant that may be used to more accurately replicate the diameter of a natural knee. In one embodiment, a patellofemoral component is connected to the posterior portion of a condylar component by screws that pass through the femur allowing the patellofemoral component and the condylar component to be torqued against opposing sides of the femur. Two additional screws are used to connect the patellofemoral component to an anterior portion of the condylar component. A gap may be left between the patellofemoral component and the anterior portion of the condylar component if needed to provide precise replication of the diameter of the natural knee from the patellofemoral component to the condylar component.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Instrumentation and method for prosthetic knee
InactiveUS20050192588A1Shorten study timeImprove usabilityDiagnosticsSurgical sawsTibial boneFemoral bone
Instrumentation for guiding a surgeon in performing a unicompartmental knee replacement includes a tibial block having a guide, and a milling tool adapted to engage the guide, such that the surgeon can mill the desired tibial bone bed by directing the milling tool along the guide. Further including a femoral jig having a cutting slot, a guide, and a milling tool adapted to engage the guide, such that a surgeon can cut a portion of the femur through the slot, and mill the femoral bone bed by directing the milling tool about the guide. A femoral trial removal clamp facilitates in removing the femoral trial prosthesis, and a spreader compression clamp aids in compressing the final prostheses as the bone cement cures.
Owner:GARCIA DANIEL X
Surface guided knee replacement
ActiveUS20070135926A1Increase contact areaIncrease flexibilityJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaTibial surface
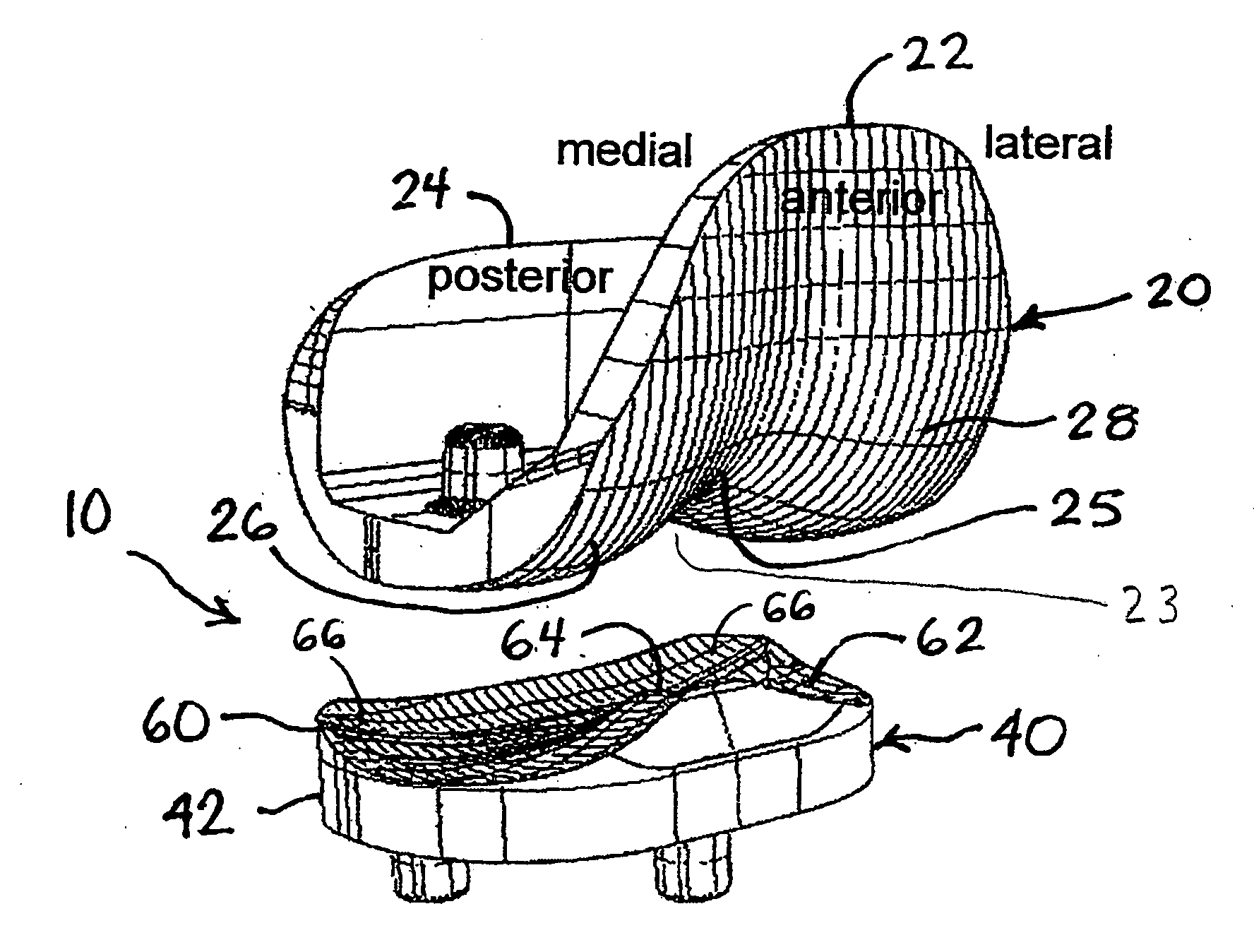
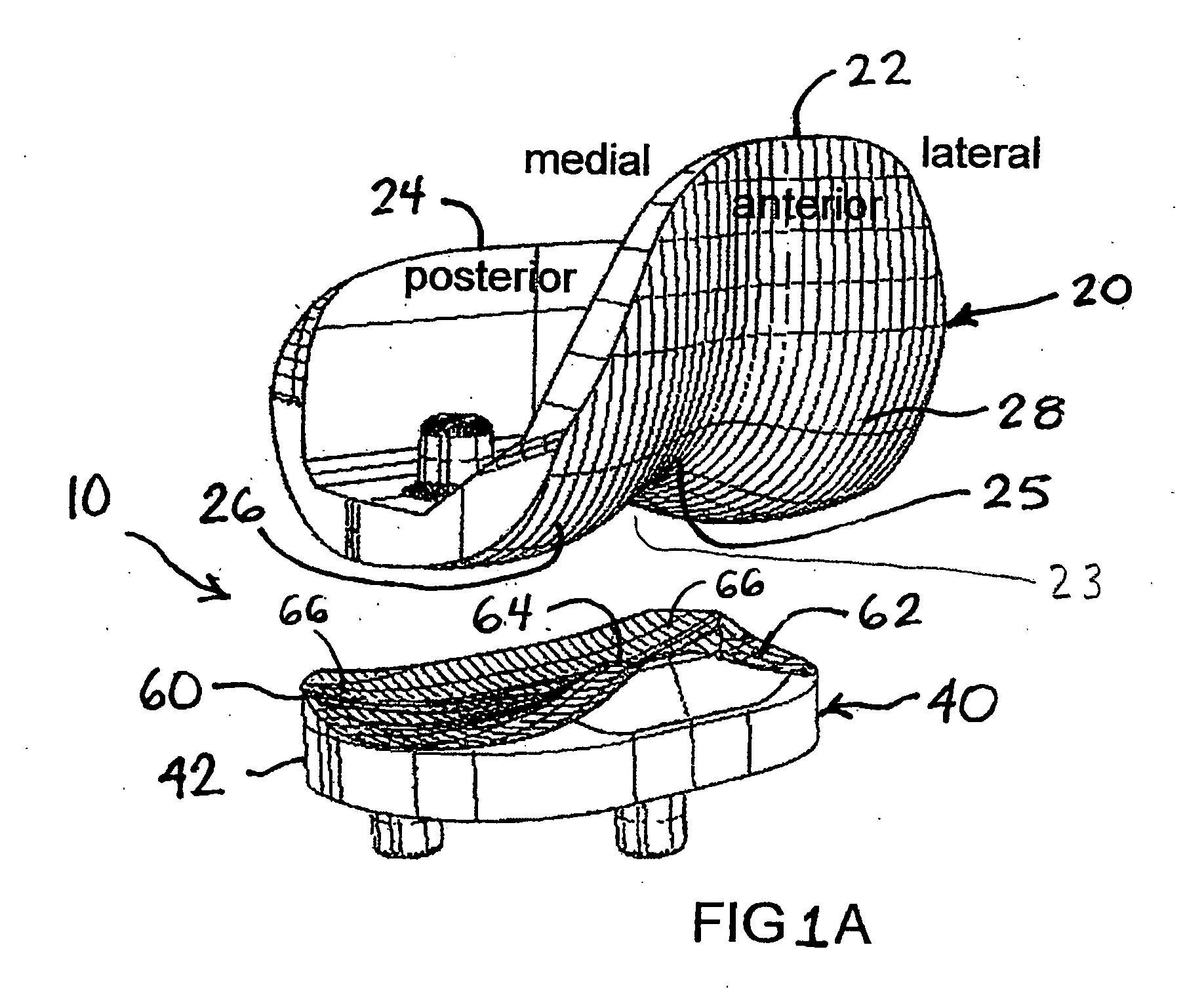
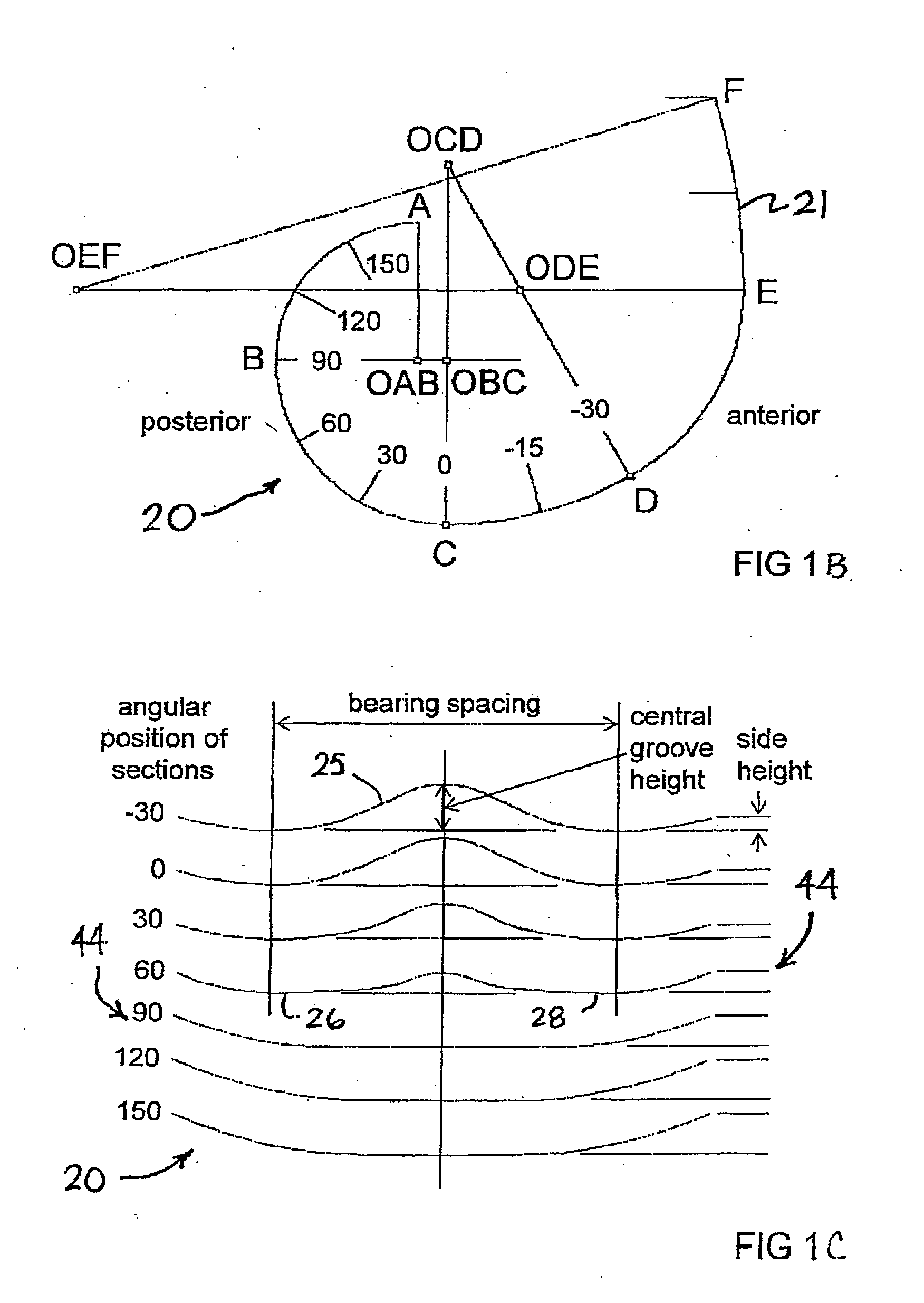
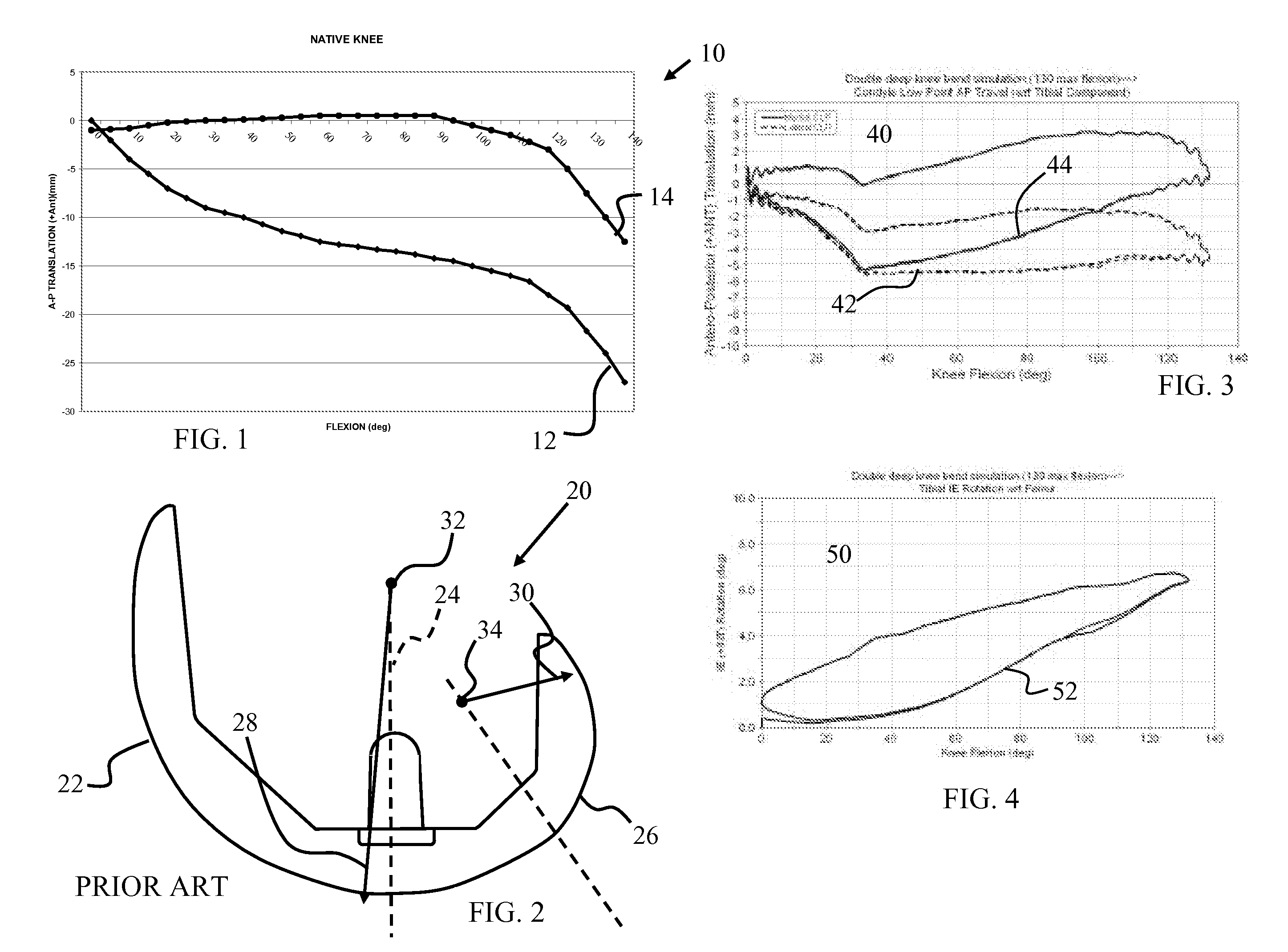
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the required motion and stability characteristics. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, by an amount similar to that in the anatomic knee. This is accomplished primarily by the depth and width of the femoral trochlea diminishing as the femoral component is flexed from zero to maximum, together with a ramp on the center of the tibial surface. The opposite motion, roll forward of the femur from a fully flexed to a more extended position, is accomplished by varying the outward radii of the lateral and medial femoral bearing surfaces, together with a ramp on the postero-lateral and postero-medial regions of the tibial surfaces. A variation of this is to generate a tibial surface which provides for a progressive internal rotation of the tibia as flexion proceeds.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Measuring apparatus for total knee replacement operation
ActiveUS20040122441A1Smooth movementEasy to disassembleJoint implantsDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurement devicePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
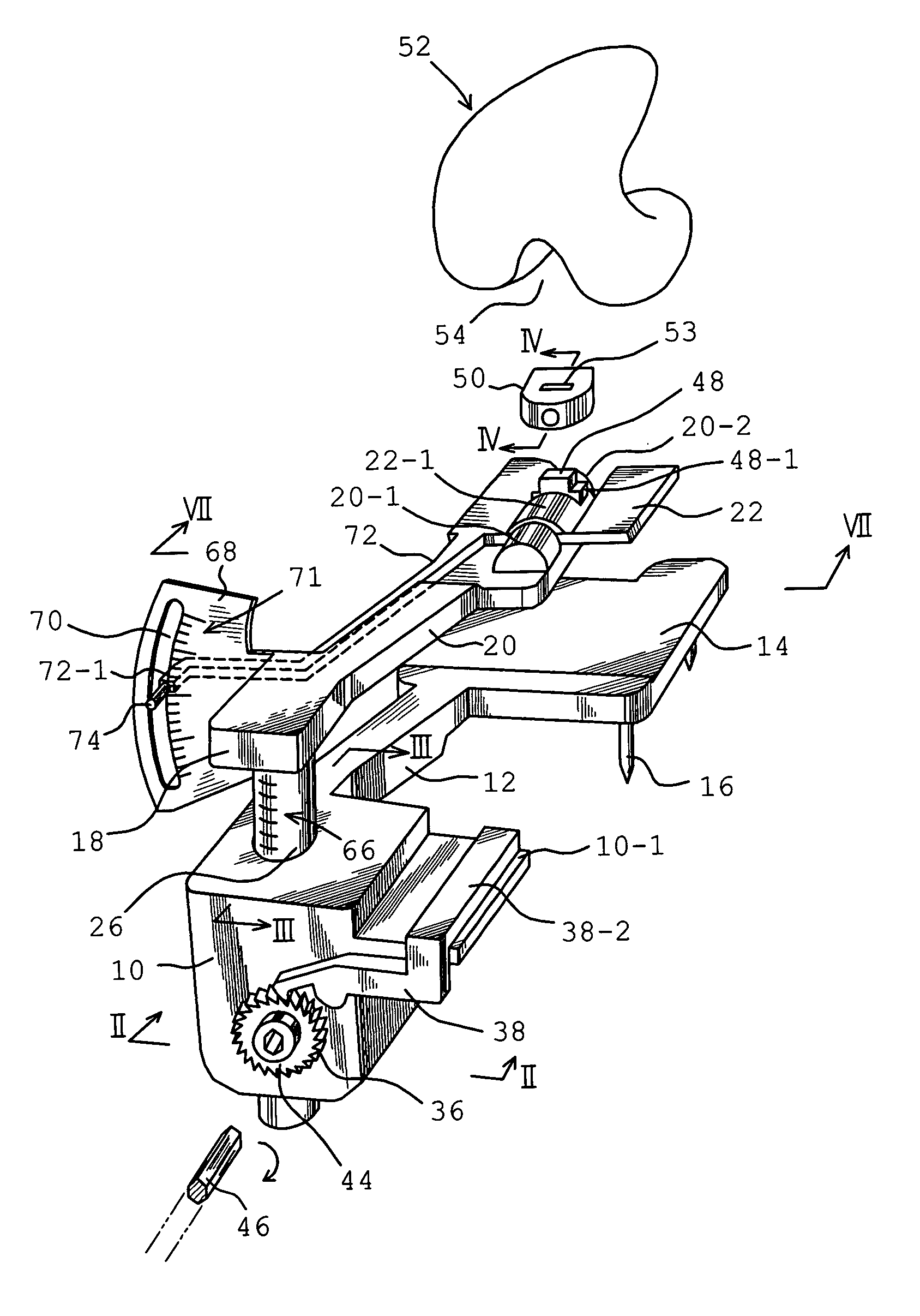
An apparatus in a total knee replacement and arthroplasty operation for measuring a joint gap and ligament balance between a osteotomized surface at a femoral distal end and a osteotomized surface at a tibial proximal end. The apparatus is provided with a base 10, from which an engaging plate 14 extends by way of an arm, so that the engaging plate 14 contacts with the osteotomized surface at the tibial proximal end. A moving body 18 is vertically movably connected to the base 10, from which moving body 18 an arm 20 extends, to which arm a supporting plate 22 is rotatably mounted about a central axis. The supporting plate 22 has, at its top surface, a projected portion 48. to which an auxiliary guiding piece 50 is connected under a snap like fitted manner. A femoral component 52 is mounted, at its groove portion 54, to the osteotomized surface at the femoral distal end. The engaging plate 14 as well as the supporting plate 22 are under an offset arrangement with respect to the base and moving body, respectively.
Owner:ZIMMER KK
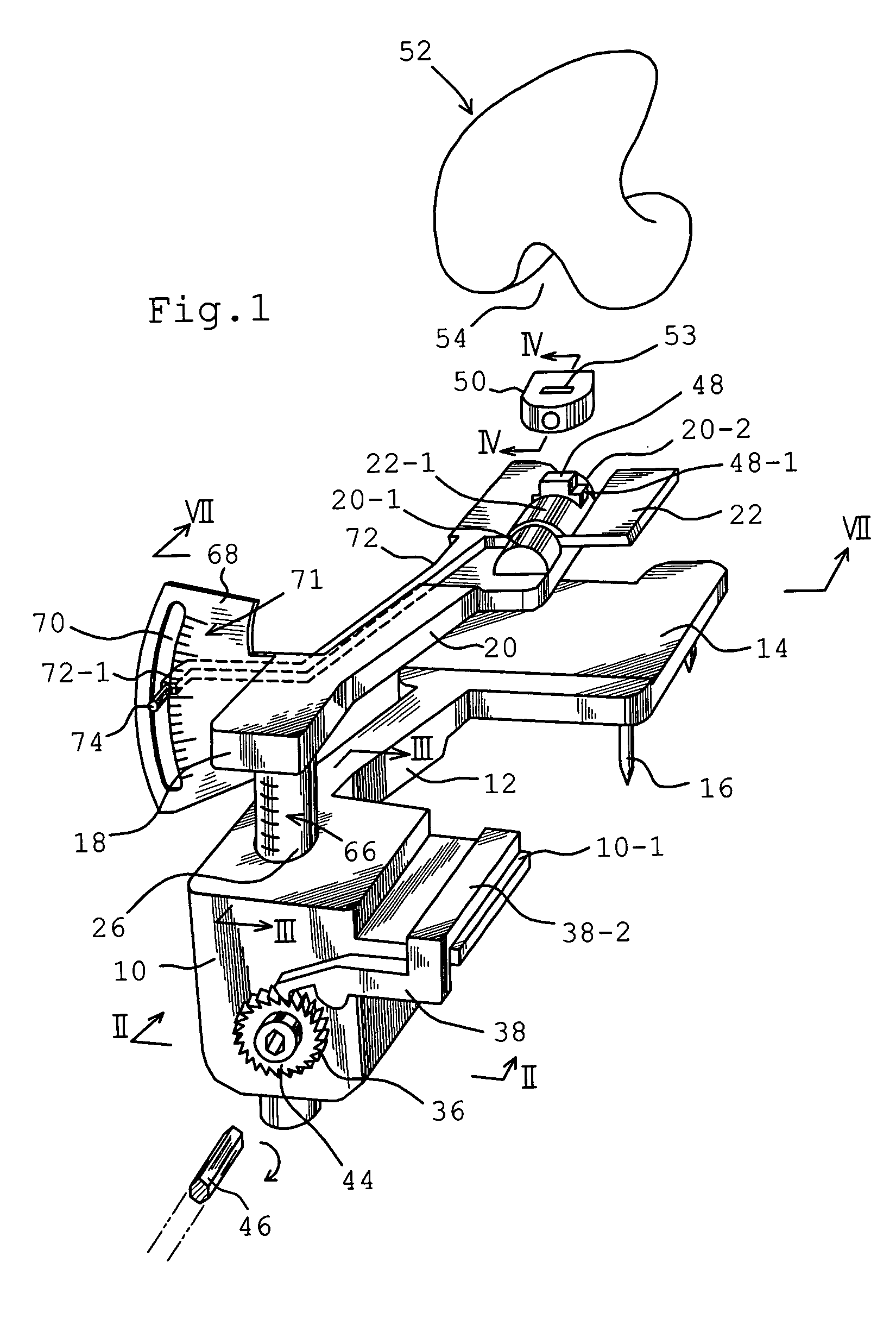
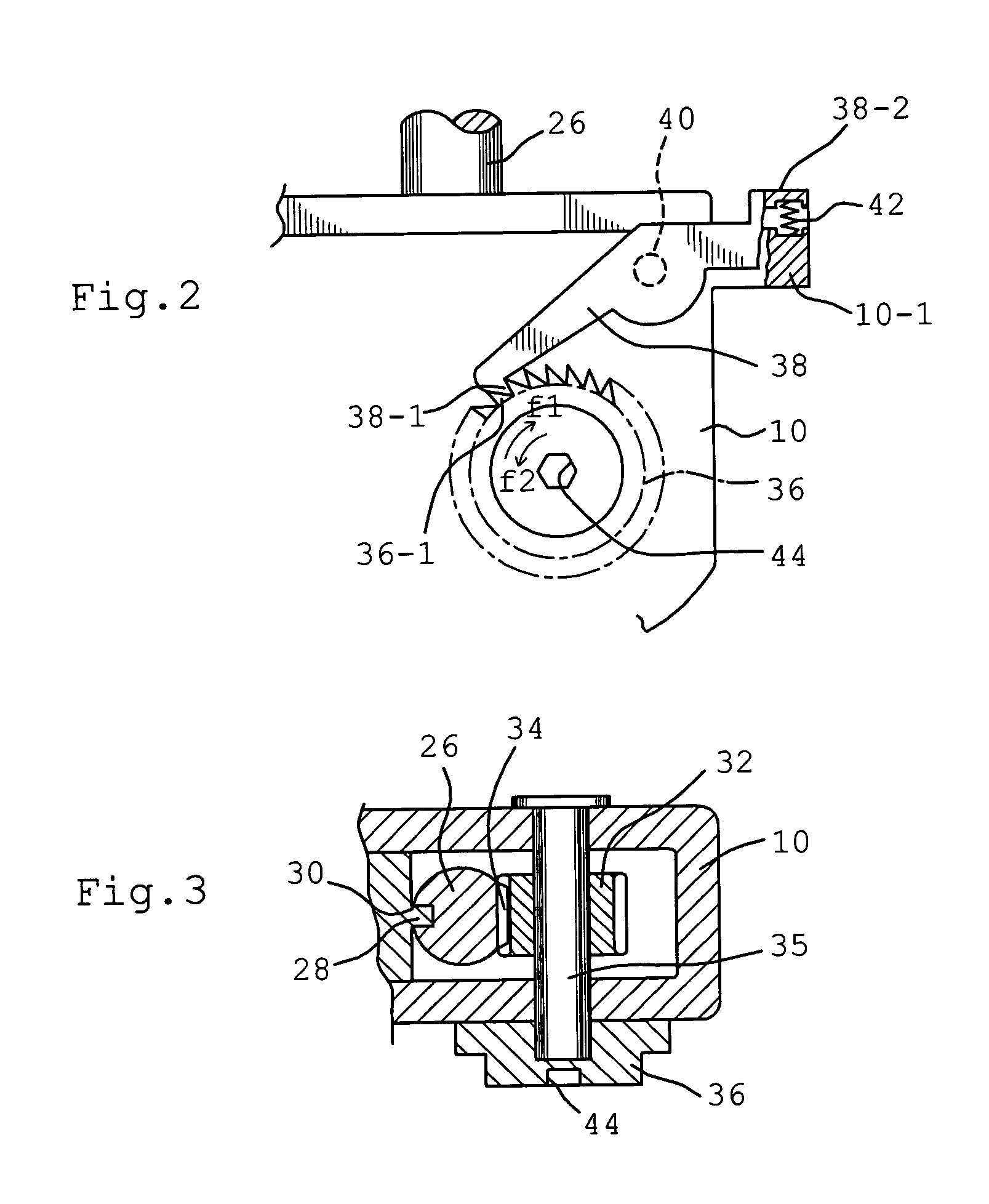
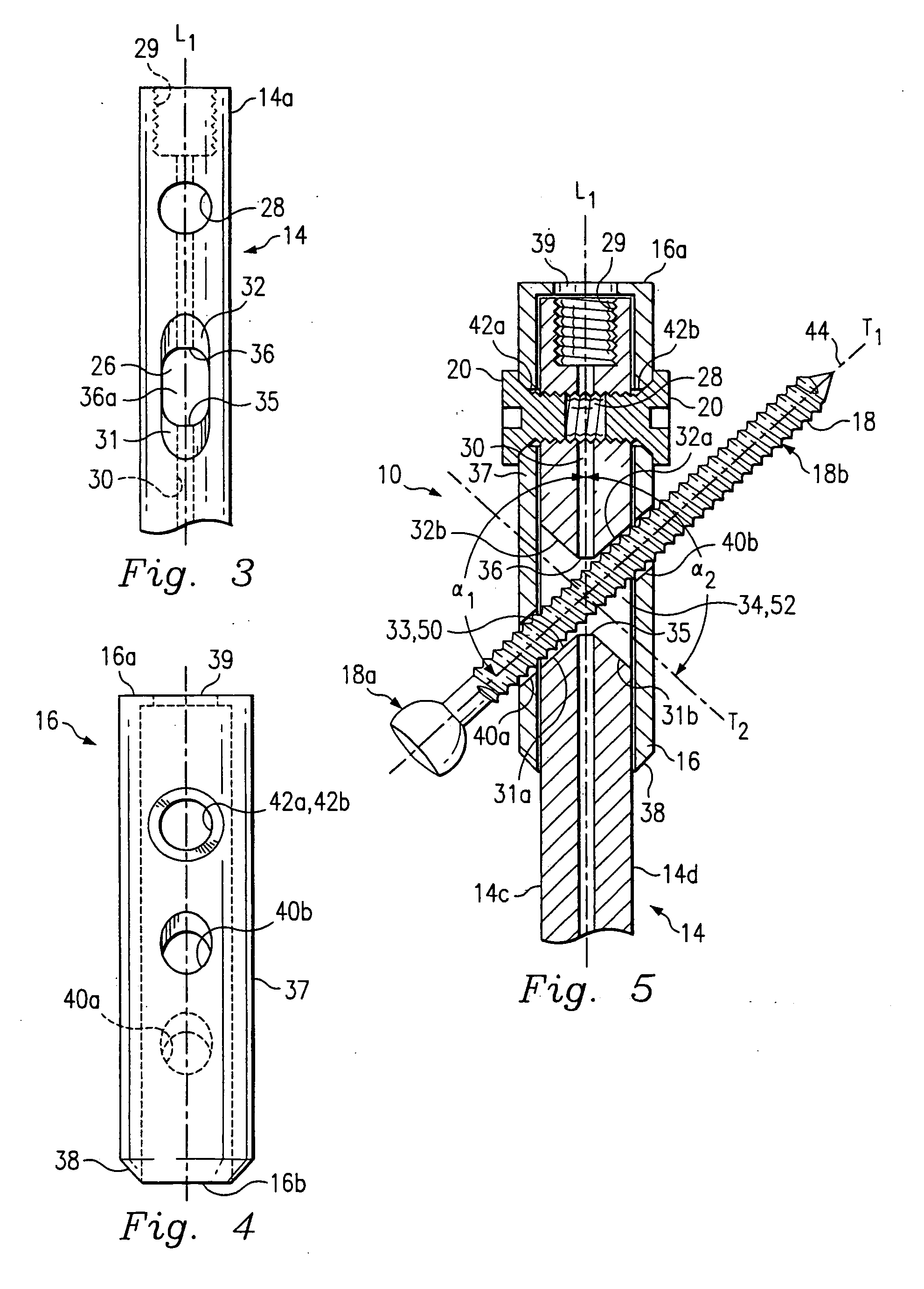
Femoral intramedullary rod system
InactiveUS20060122600A1Easy to compressFacilitate distractionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFemoral boneIntramedullary rod
Owner:ORTHODYNE
High flexion articular insert
A knee prosthesis is provided that allows for increased flexion. The knee prosthesis includes (a) a femoral component adapted to fit on a distal end of the femur which includes a lateral condylar structure and a medial condylar structure and (b) an intermediate structure configured to cooperate with a femoral component of a knee prosthesis. The intermediate structure includes at least one surface for contacting the femoral component and a transition of a sagittal curvature of the at least one contact surface from a concave surface into a convex surface at the contact interface of the femoral component and the intermediate structure when the knee is flexed at approximately 120° to 140°. The knee prosthesis minimizes impingement on the femoral posterior cortex in deep flexion, increases the dislocation safety factor and allows for easier reengagement of the articular surface should the femoral component externally rotate off of the tibial plateau.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Knee prostheses with enhanced kinematics
A knee replacement system includes a proximal tibial posterior camming portion defined by a first radius of curvature with a first origin in a first medio-lateral plane, a distal tibial posterior camming portion defined by a second radius of curvature with a second origin in a second medio-lateral plane, an anterior femoral camming portion of a posterior cam defined by a third radius of curvature with a third origin in the first medio-lateral plane, and a posterior femoral camming portion of the posterior cam and defined by a fourth radius of curvature with a fourth origin in the second medio-lateral plane, wherein the second origin is closer to the lateral tibial portion than the first origin, or the fourth origin is closer to the medial femoral portion than the third origin.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
High flexion articular insert
A knee prosthesis is provided that allows for increased flexion. The knee prosthesis includes (a) a femoral component adapted to fit on a distal end of the femur which includes a lateral condylar structure and a medial condylar structure and (b) an intermediate structure configured to cooperate with a femoral component of a knee prosthesis. The intermediate structure includes at least one surface for contacting the femoral component and a transition of a sagittal curvature of the at least one contact surface from a concave surface into a convex surface at the contact interface of the femoral component and the intermediate structure when the knee is flexed at approximately 120° to 140°. The knee prosthesis minimizes impingement on the femoral posterior cortex in deep flexion, increases the dislocation safety factor and allows for easier reengagement of the articular surface should the femoral component externally rotate off of the tibial plateau.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Implant device and method for manufacture
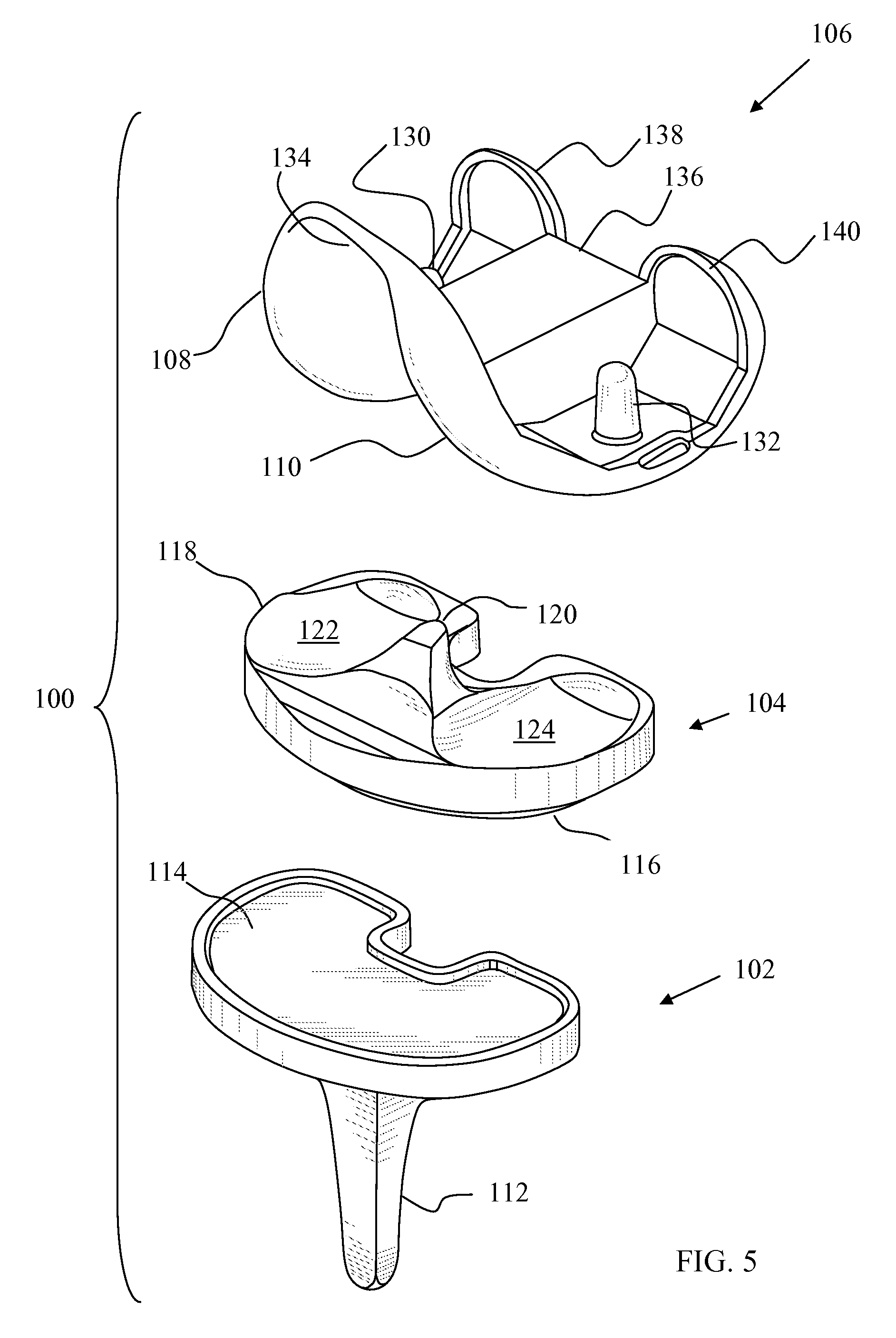
A knee implant includes a femoral component having first and second femoral component surfaces. The first femoral component surface is for securing to a surgically prepared compartment of a distal end of a femur. The second femoral component surface is configured to replicate the femoral condyle. The knee implant further includes a tibial component having first and second tibial component surfaces. The first tibial component surface is for contacting a proximal surface of the tibia that is substantially uncut subchondral bone. At least a portion of the first tibial component surface is a mirror image of the proximal tibial surface. The second tibial component surface articulates with the second femoral component surface.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Femoral intramedullary rod system
InactiveUS7041104B1Convenient treatmentReduce complexityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFemoral boneIntramedullary rod
A femoral intramedullary rod system capable of treating a variety of femoral bone fractures using a uniform intramedullary rod design. The system generally comprising an intramedullary rod defining an opening having an upper surface and a transverse member including a bone engaging portion and a connection portion defining a thru-hole with the nail sized to pass therethrough. A pin is selectively coupled to the transverse member to rigidly assemble the transverse member to the nail when the nail is passed through the thru-hole and the pin is received within the opening.
Owner:ORTHODYNE
Surface guided knee replacement
InactiveUS20070135925A1Reduce consistencyAvoid large displacementJoint implantsKnee jointsGonial angleTibial surface
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the motion and stability characteristics of the anatomic knee. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, more so on the lateral side than on the medial side. This is accomplished by the interaction of a projecting tibial post inside a cupola in the center of the femoral component, and by the saggital radius on the medial side being smaller than that on the lateral side. The prevention of anterior sliding of the femur on the tibia in early flexion is accomplished by the interaction between a distal-anterior recess on the medial side of the femur and an apposing raised pad on the tibial surface. Rotational laxity at all angles is allowed by the presence of only one recess pad and by non-conforming femoral-tibial surfaces on the lateral side.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
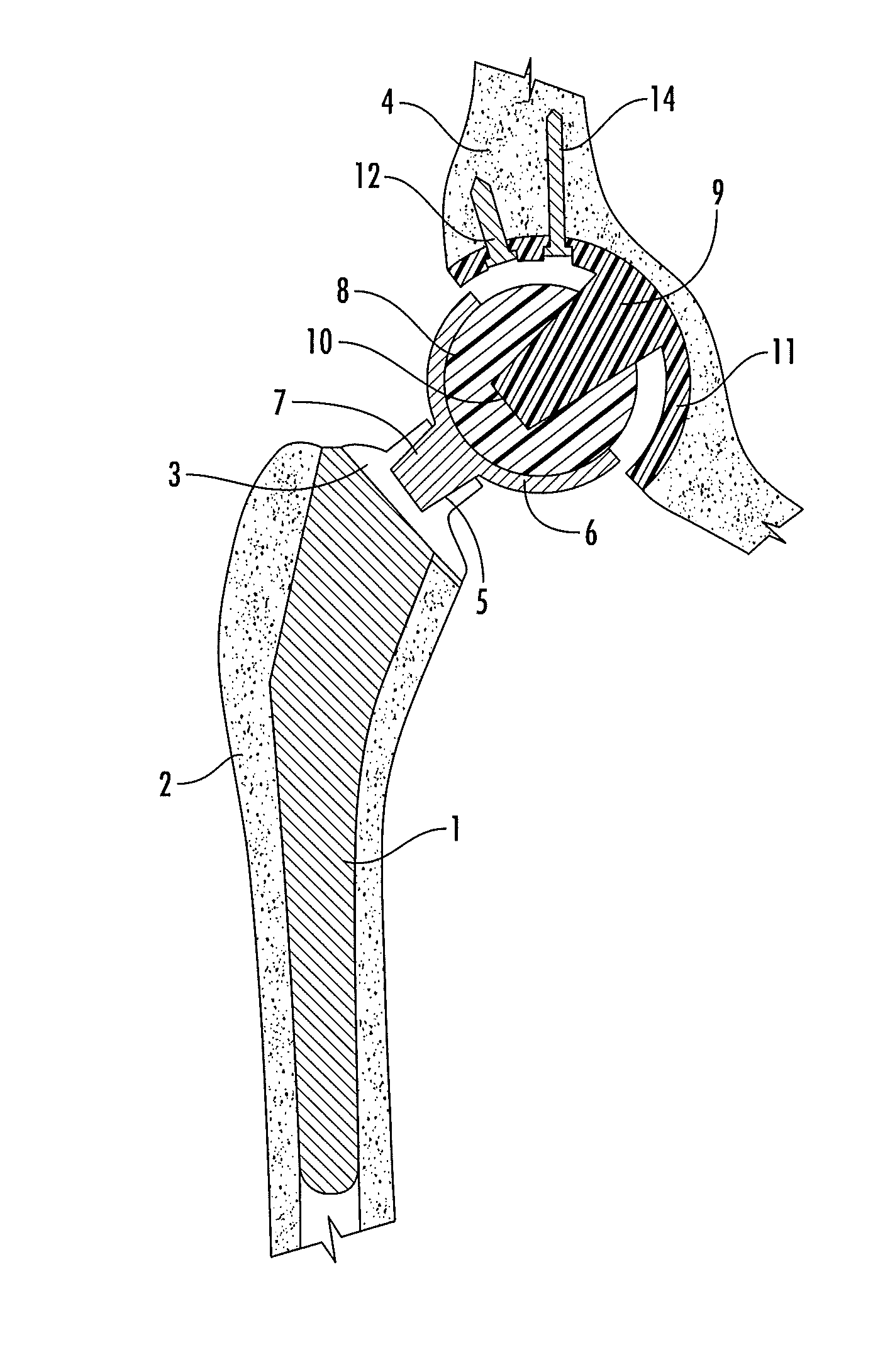
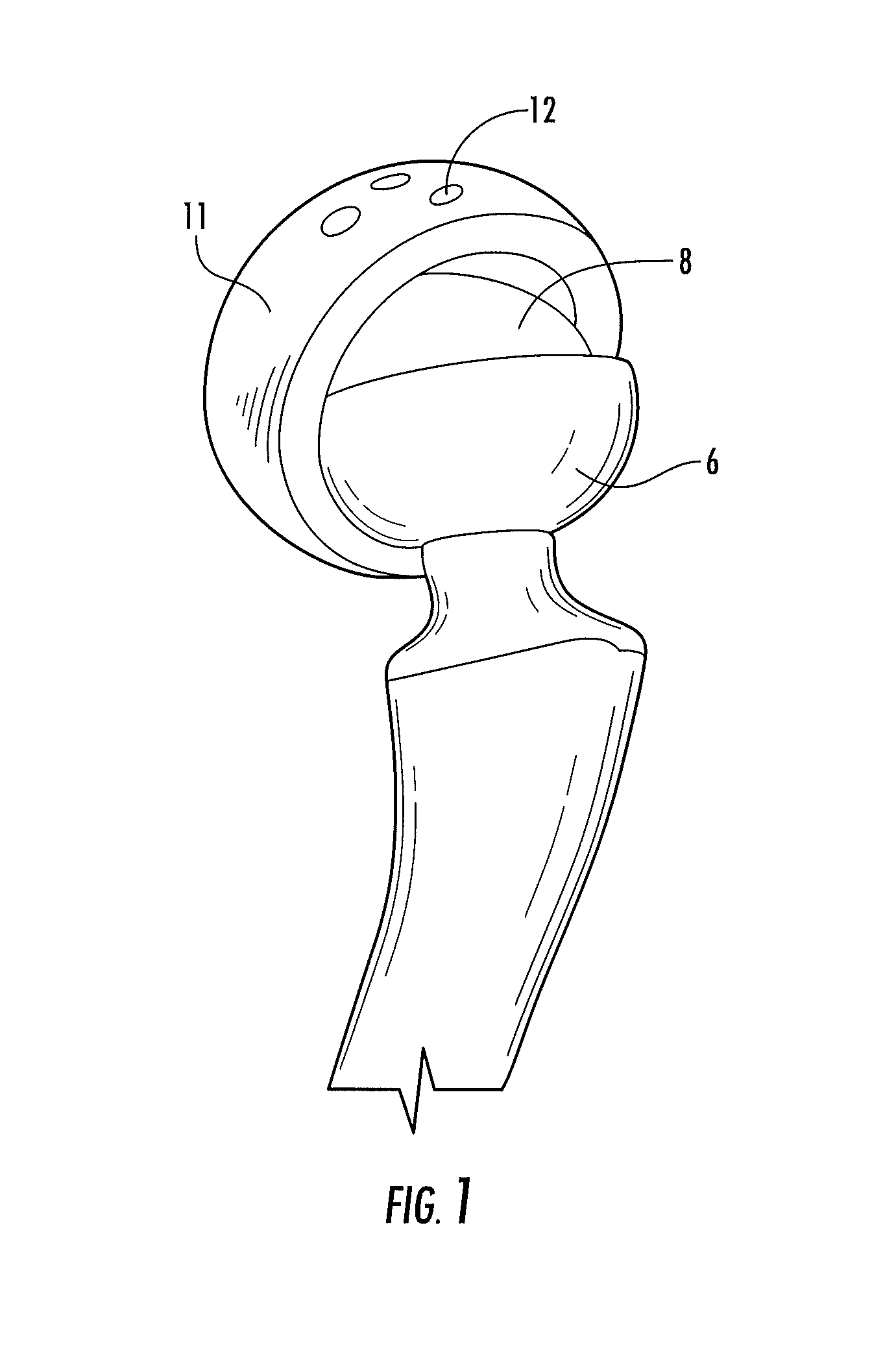
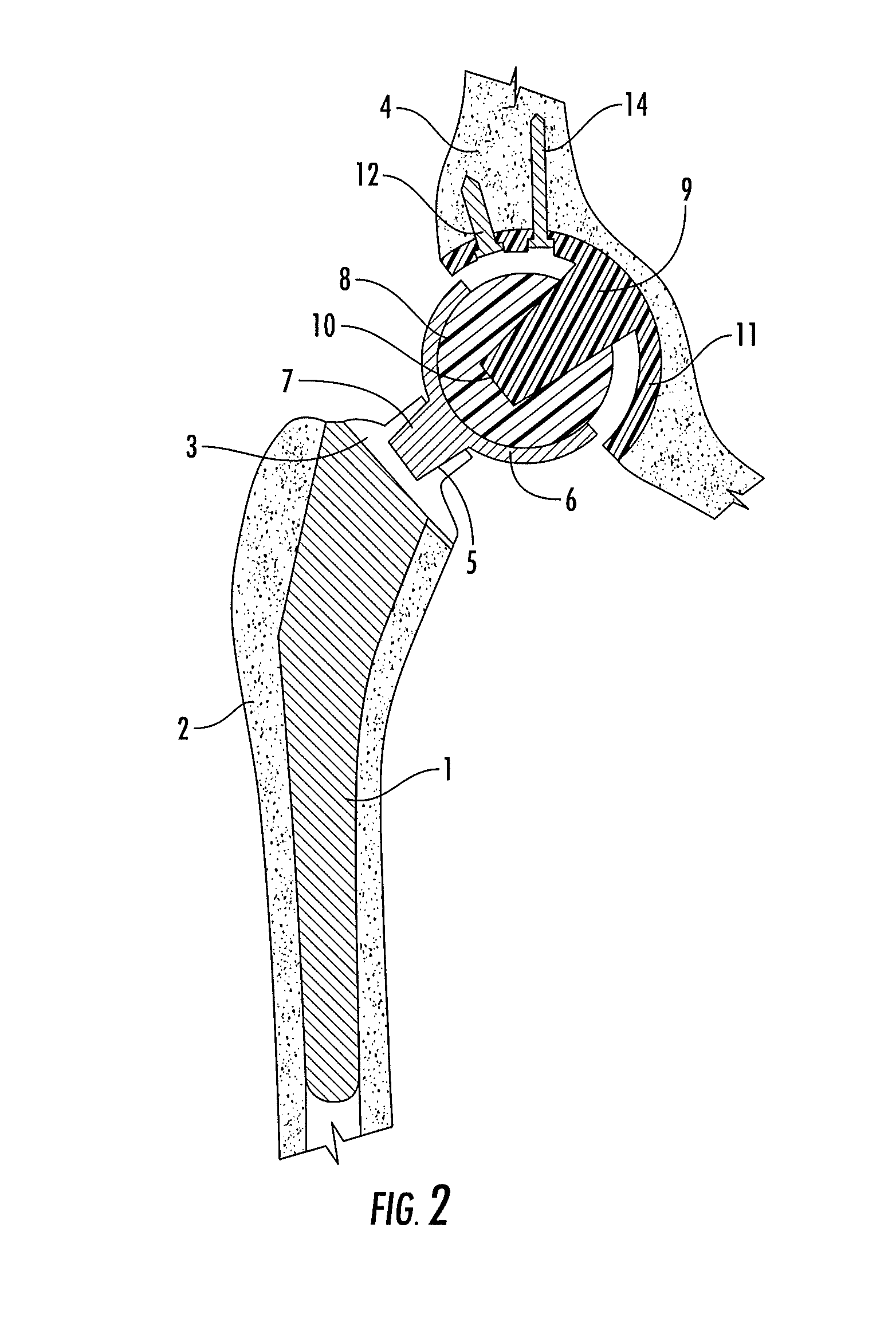
Interlocking reverse hip prosthesis and method
ActiveUS8313531B2Reduce wearReduce in quantityBone implantJoint implantsRange of motionFemoral component
An interlocking reversed hip prosthesis including an acetabular cup being implanted in the acetabular cavity having an acetabular articular ball, firmly attached to the central portion of the cup via Morse taper. The femoral component having a hemispherical cup attached to the neck of the implant via Morse taper in a modular fashion thereby allowing use of several length necks. After implantation of the acetabular cup and the femoral cup, the two members are assembled together for relative movement. The acetabular cup secured by several screws or resorbable fixation studs. During range of motion, the edge of the femoral cup becomes inserted into space located between the acetabular cup and the acetabular ball and becomes restrained thus reducing the likelihood of dislocation during extreme range of motion.
Owner:HIP INNOVATION TECHONOLOGY LLC
Anterior cruciate ligament substituting knee replacement prosthesis
There is disclosed a total knee replacement prosthesis, which can substitute the function of an anterior and / or a posterior cruciate ligament. A femoral component containing two intercondylar surfaces and an intercondylar region, a tibial component having a tibial platform and a bearing component, and a protrusion from the bearing component also are disclosed.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Reflex fixation geometry revision and reconstruction system reverse articulation
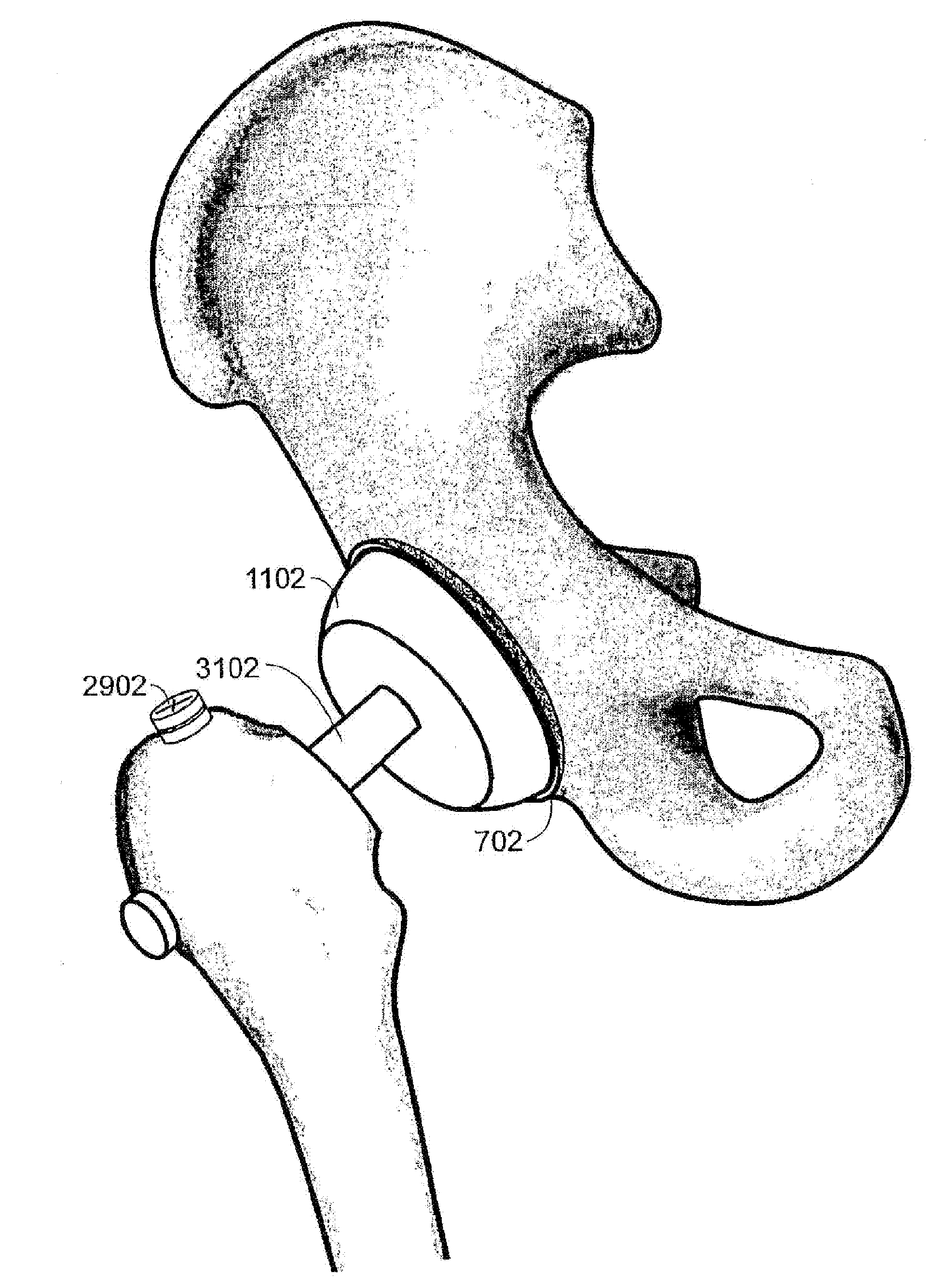
An orthopedic device is disclosed for restoring the normal or natural joint mechanics in, for example, a hip joint. The device includes a first component, such as an acetabular component in a hip implant, that includes a convex articulation surface and a second component, such as a femoral component in a hip implant, that includes a concave articulation surface. It will be appreciated that the convex articulation surface of the device disclosed herein articulates with the concave articulation surface in a mating engagement that may be reversed with respect to the traditional hip implant, in which the concave articulation surface is part of the acetabular component and the convex articulation surface is part of the femoral component.
Owner:GLOBAL ORTHOPAEDIC TECH
Prostheses
InactiveUS6986792B2Reduce wearIncreasing or at least not compromising ability of the shell/linerJoint implantsFemoral headsFemoral stemWear resistance
Bipolar prostheses which include various structures and other techniques for optimizing material wear and mechanical strength properties. Such prostheses feature, for example, improved resistance to polyethylene wear while also reducing potential for dislocation of the femoral stem from the prosthesis. Such techniques and structures include varying wear resistance and mechanical strength treatment in various components of the prostheses or portions of those components as desired to improve, accentuate or optimize wear performance and dislocation reduction, locking ring structural features, structures for retaining locking rings in the bipolar prosthesis shell, and structures for limiting or reducing movement or rotation of locking rings and liners in bipolar prosthesis shells.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Knee brace having lateral/medial width adjustment
Owner:OSSUR HF
Posterior stabilized knee with varus-valgus constraint
ActiveUS20050192672A1Accurately and efficiently emulates kinematicsAccurately and efficiently and functionJoint implantsKnee jointsSpinal columnTibial bone
A femoral component of a knee prosthesis has spaced condyle surfaces defining a notch therebetween. The notch defines an elongated cam housing having an anterior cam and a posterior cam at opposite ends of the housing. The tibial component of the knee prosthesis includes a platform and a bearing supported on the platform, the bearing defining bearing surfaces configured to articulate with the condyle surfaces. The tibial component includes a spine projecting superiorly from the bearing that defines an anterior face and a posterior face. The posterior face and the posterior cam define complementary curved surfaces configured for cooperative engagement when the femoral component and the tibial component are at a predetermined flexion angle. The cam housing is configured to form a gap between the posterior cam and the spine when the knee is normally extended. In another feature, the spine includes a stiffening pin extending therethrough.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Posterior stabilized knee system prosthetic devices employing diffusion-hardened surfaces
InactiveUS20030153979A1Restrict movementReduce frictionJoint implantsSolid state diffusion coatingOrthopedic departmentKnee Joint
An orthopedic implant with a diffusion-hardened surface on non-load bearing areas of the implant for interaction with non-load bearing surfaces of a polymeric bio-compatible material, such as UHMWPE. The orthopedic implant is a posterior stabilized knee prosthetic and system where a coating of oxidized zirconium is formed in the cam of the femoral prosthetic for interaction with the central post of a polymeric tibial insert. The diffusion-hardened surface of the orthopedic implant provides a strengthened cam and reduction in wear in the central post of the polymeric tibial insert.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Leg alignment and length measurement in hip replacement surgery
InactiveUS20090125117A1Surgical navigation systemsJoint implantsHip joint replacement operationPelvic fixation
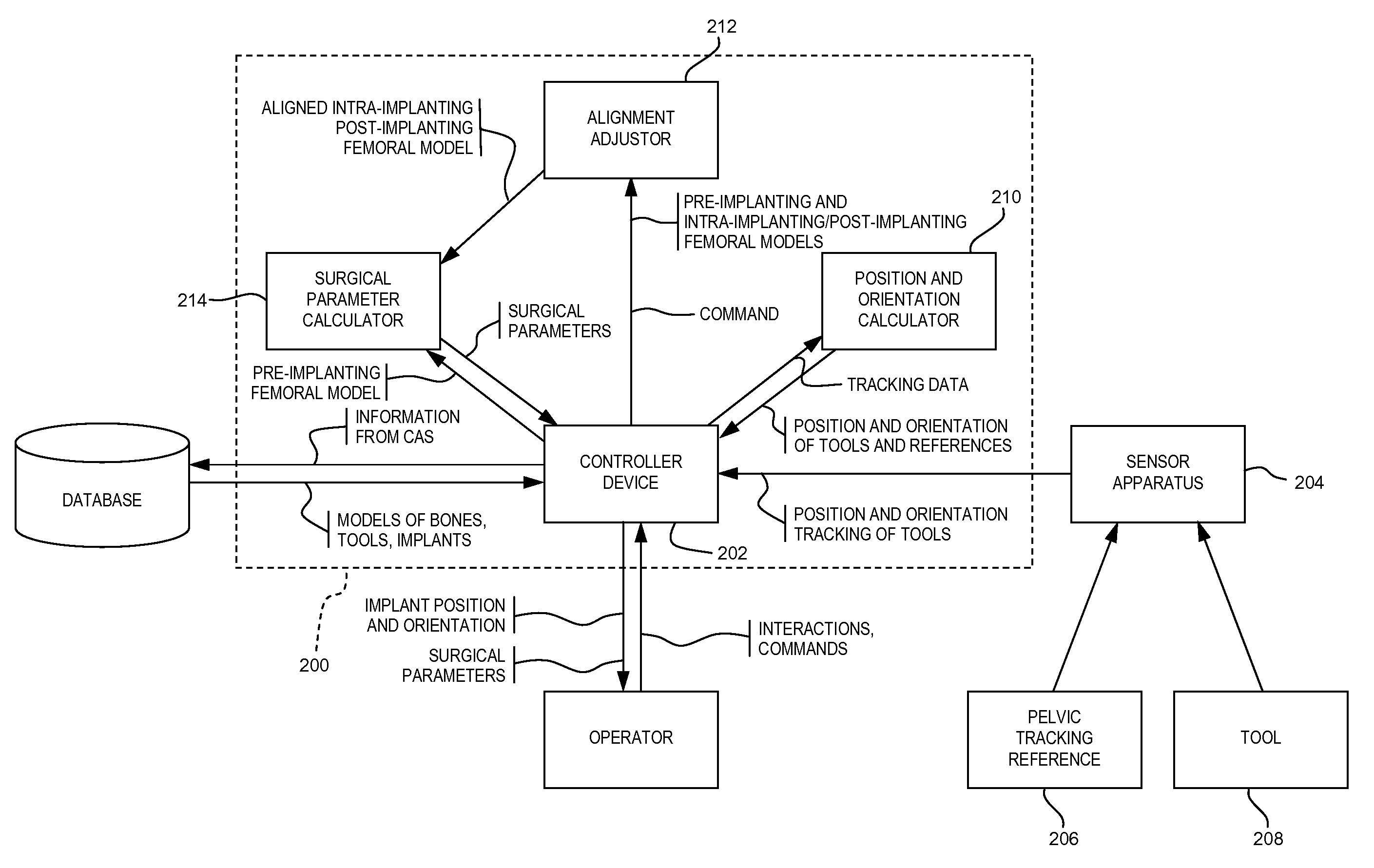
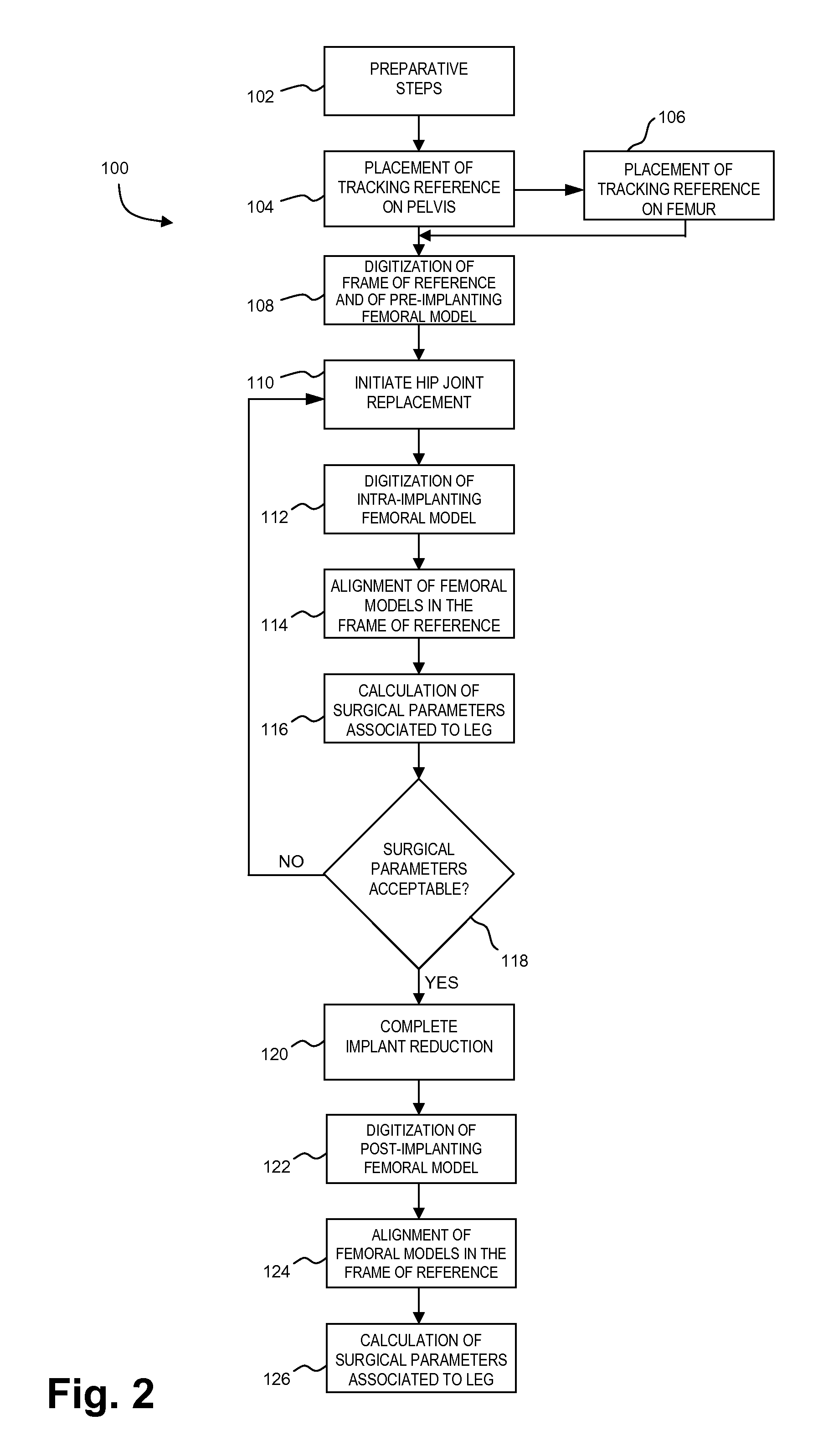
A CAS system for measuring surgical parameters during hip replacement surgery comprises a first tracking reference in fixed relation with the pelvis to form a frame of reference. A registration tool is trackable. A sensor apparatus tracks the first tracking reference and the registration tool. A controller unit receives tracking data for the first trackable reference and the registration tool. The controller unit has a position and orientation calculator for calculating from the tracking data a position and orientation of the pelvic tracking reference to track the frame of reference, and of the registration tool to produce femoral models at a first and a second sequential operative steps. An alignment adjustor aligns the femoral models with the frame of reference. A surgical parameter calculator calculates surgical parameters as a function of the femoral models as aligned by the alignment adjustor.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT
Method for separating meat and bone of fowl and device used by the method
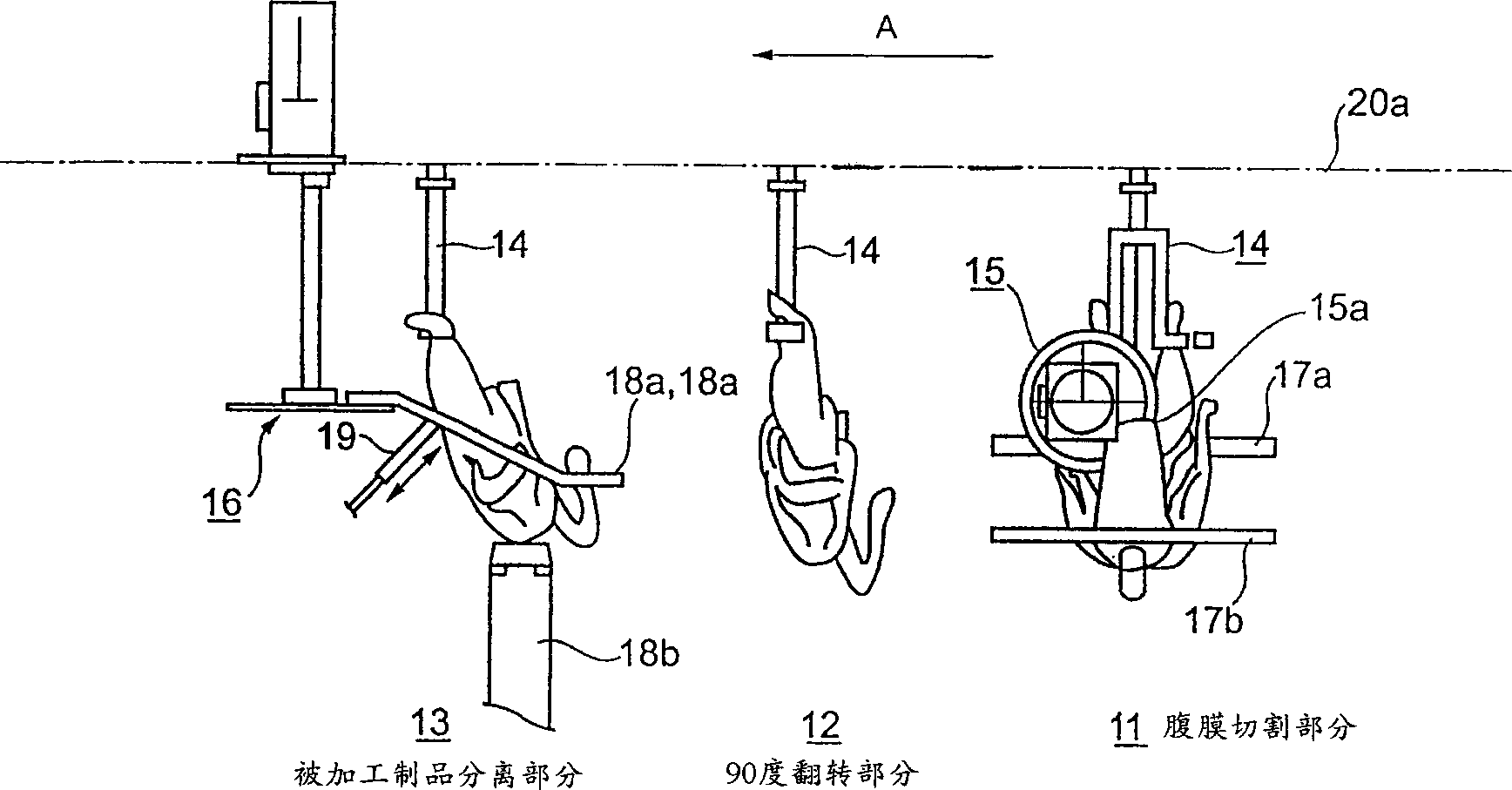
The present invention provides a first processing step and a second processing step in the case where the hollow carcass of the poultry is broken down into a lower carcass including the thighs and the back part, and an upper carcass including the remaining part of the rib-containing breast and back parts. , in the first processing step, when the hollow body is transported in a suspended state, the hollow body is cut from the thigh root through the tail end of the intestinal bone without cutting the spine; in the second processing step, the femoral part is cut The tendon and connective tissue are cut, that is, the thigh is peeled off. The present invention performs the above processing steps with high productivity. The first processing step includes a conveying line, a peritoneal cutting part, a 90-degree turning part and a processed product separation part. The second processing step consists of a conveyor with teeth, which conveys the lower body half hooked at the femur through an underside running belt; a parallel moving conveyor arranged under the conveyor with teeth for peeling off the thighs of the lower body half; A parallel guide plate is arranged under the lower running belt.
Owner:MAYEKAWA MFG CO LTD
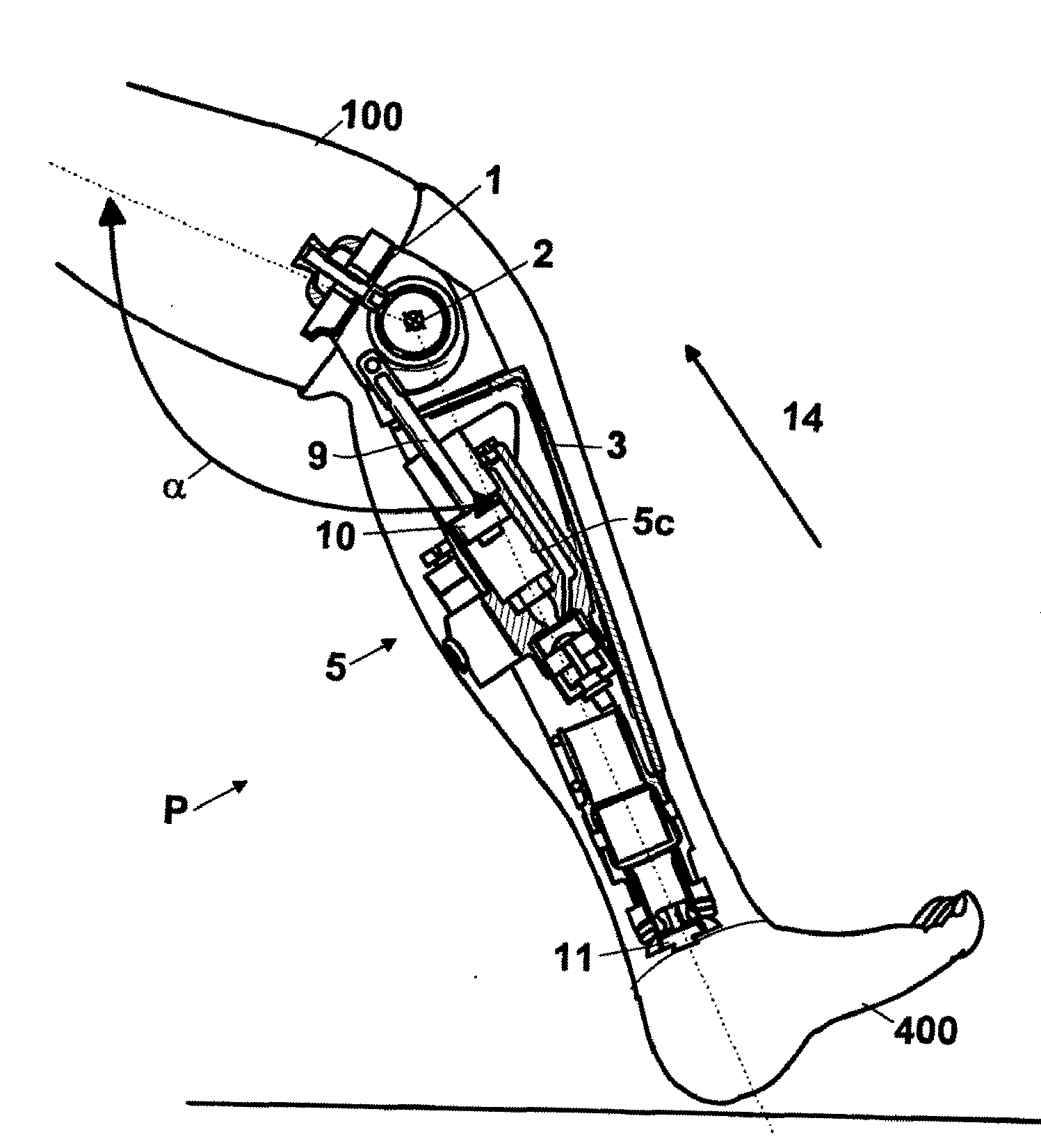
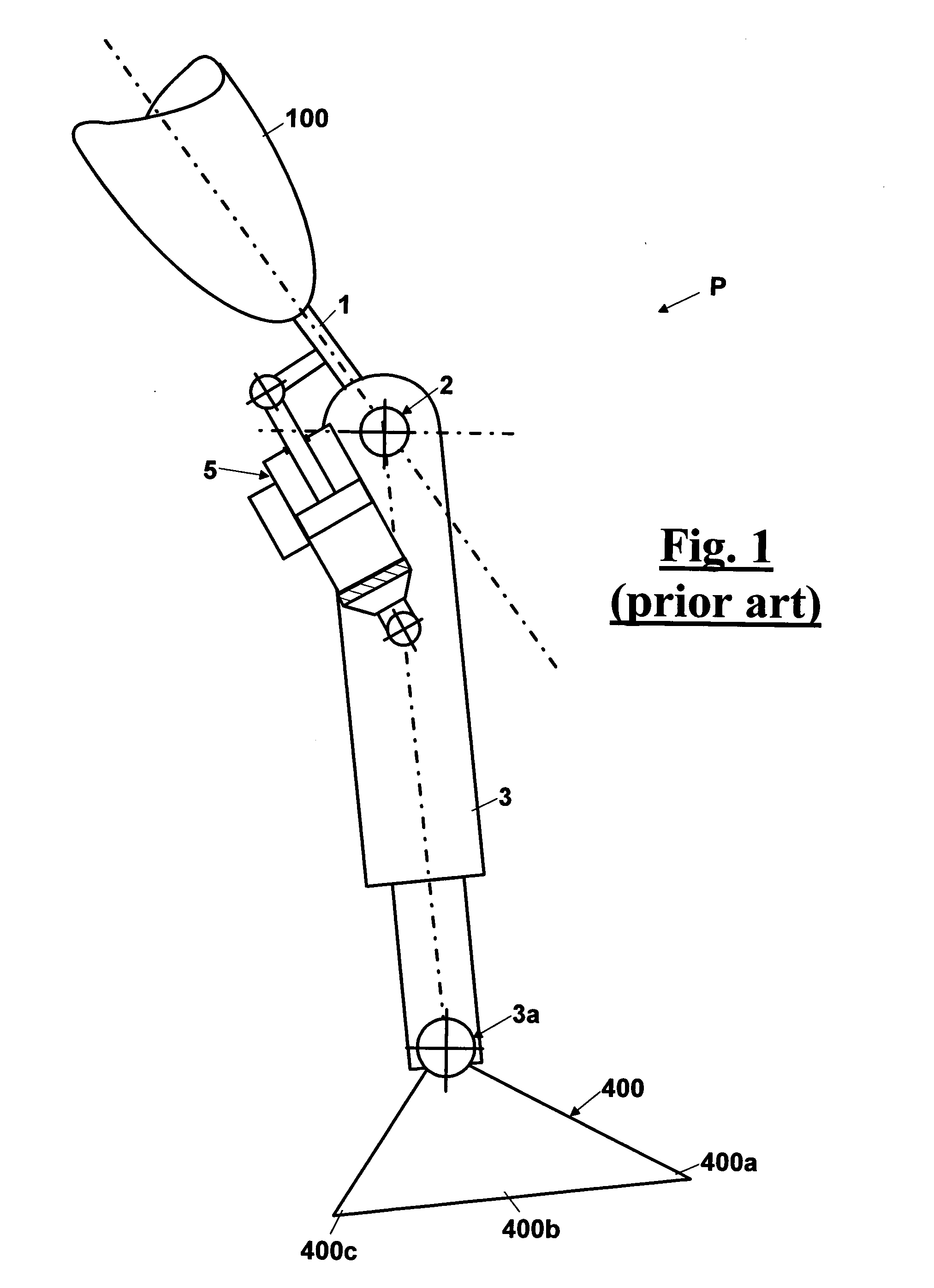
Automatic prosthesis for above-knee amputees
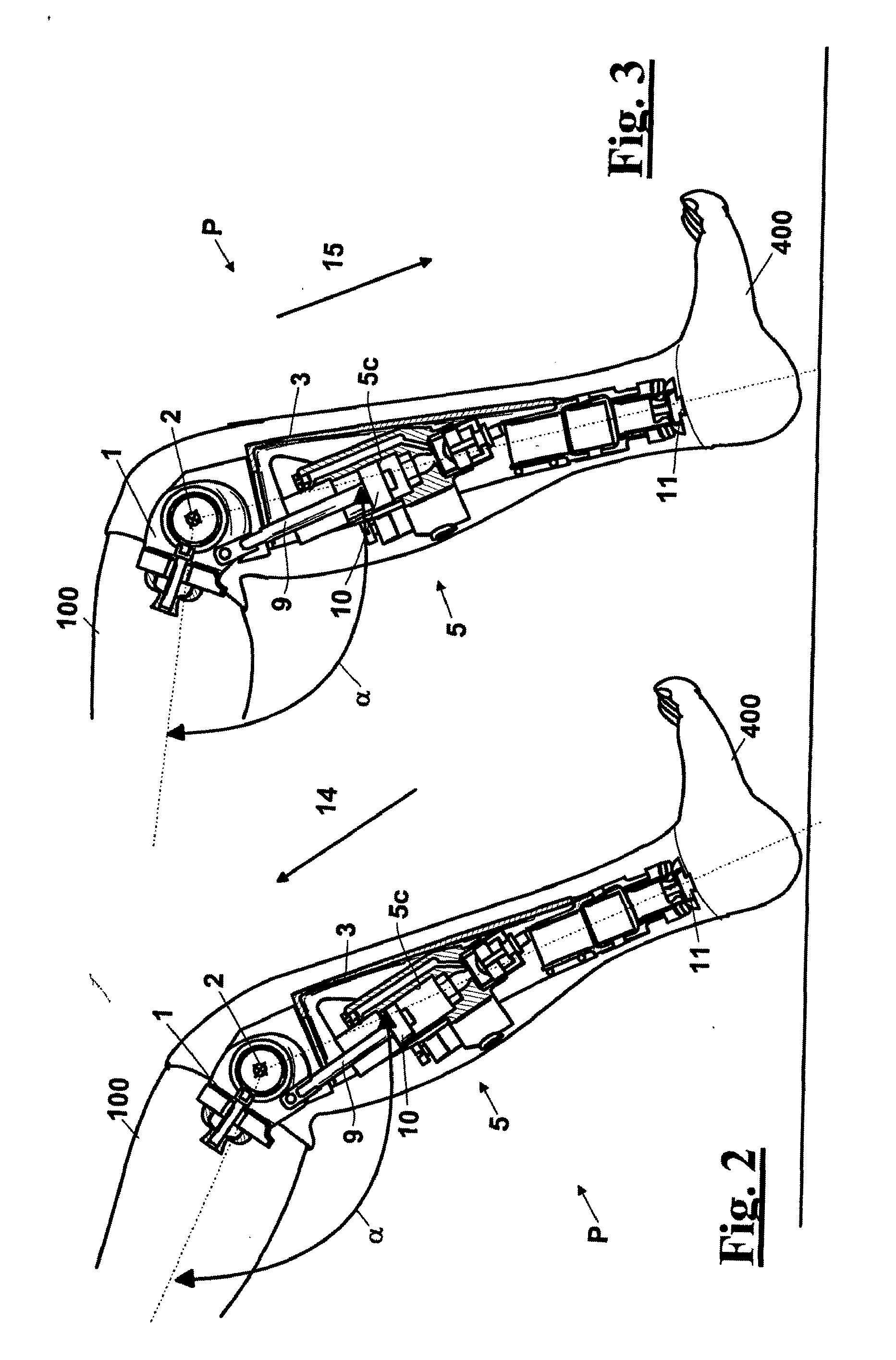
A above knee prosthesis (P) applied to femoral connection (100) of an amputee that comprises a upper hinge (1) connected to femoral connection of the patient, an articulation axis (2) with the function of reproducing the knee movements, a tibia-calf muscle unit (3) pivotally connected to the femoral•segment and a damper (5) that reproduces some functions of the calf muscle and ensures to the prosthesis to brake and to allow the sequential swing and stance phases typical of the gait. The damper comprises a cylinder (5c) wherein a piston (10) and a stem (9) act connected to each other and adapted to carry out a damping reaction of said damper responsive to the forces loaded on the prosthesis. In particular, a force transducer is provided in the damper arranged, in particular, in the stem with a microprocessor that receives a force signal from the transducer and operates means for adjusting the reaction of the damper responsive to the detected force signal.
Owner:OFFICINE ORTOPEDICHE RIZZOLI SRL
Method and apparatus for hip replacement
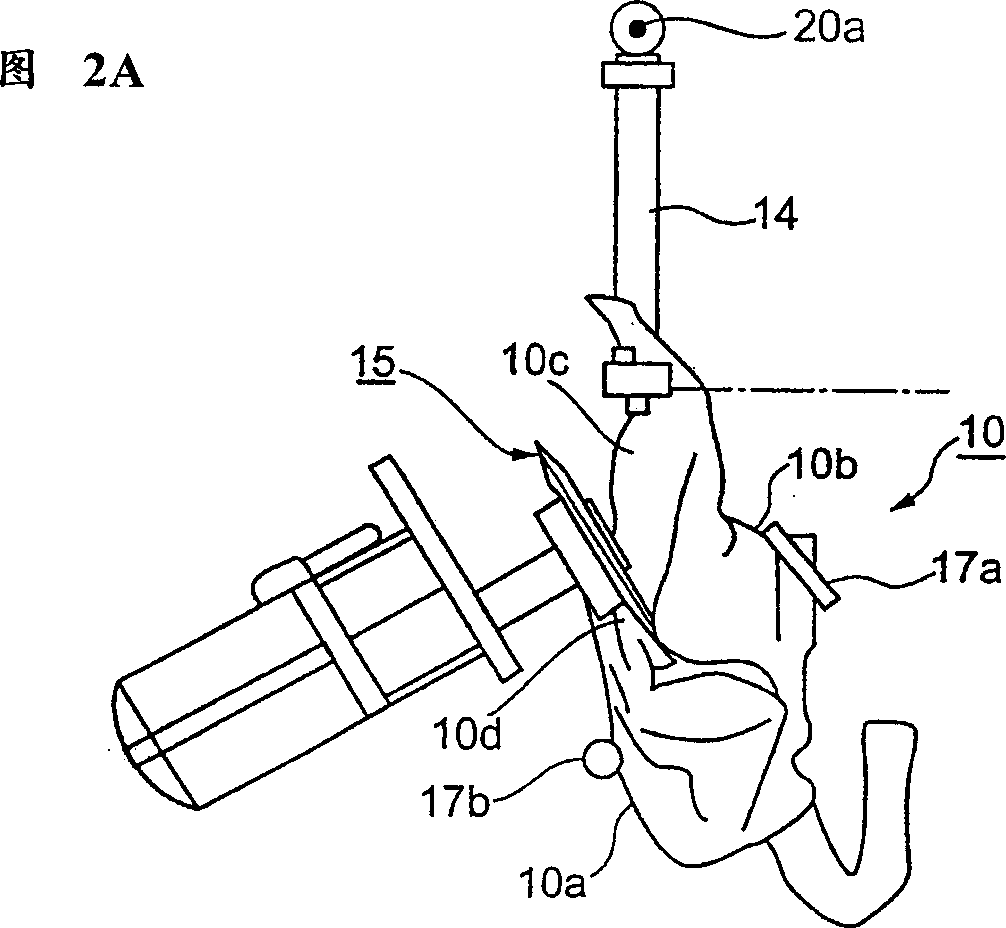
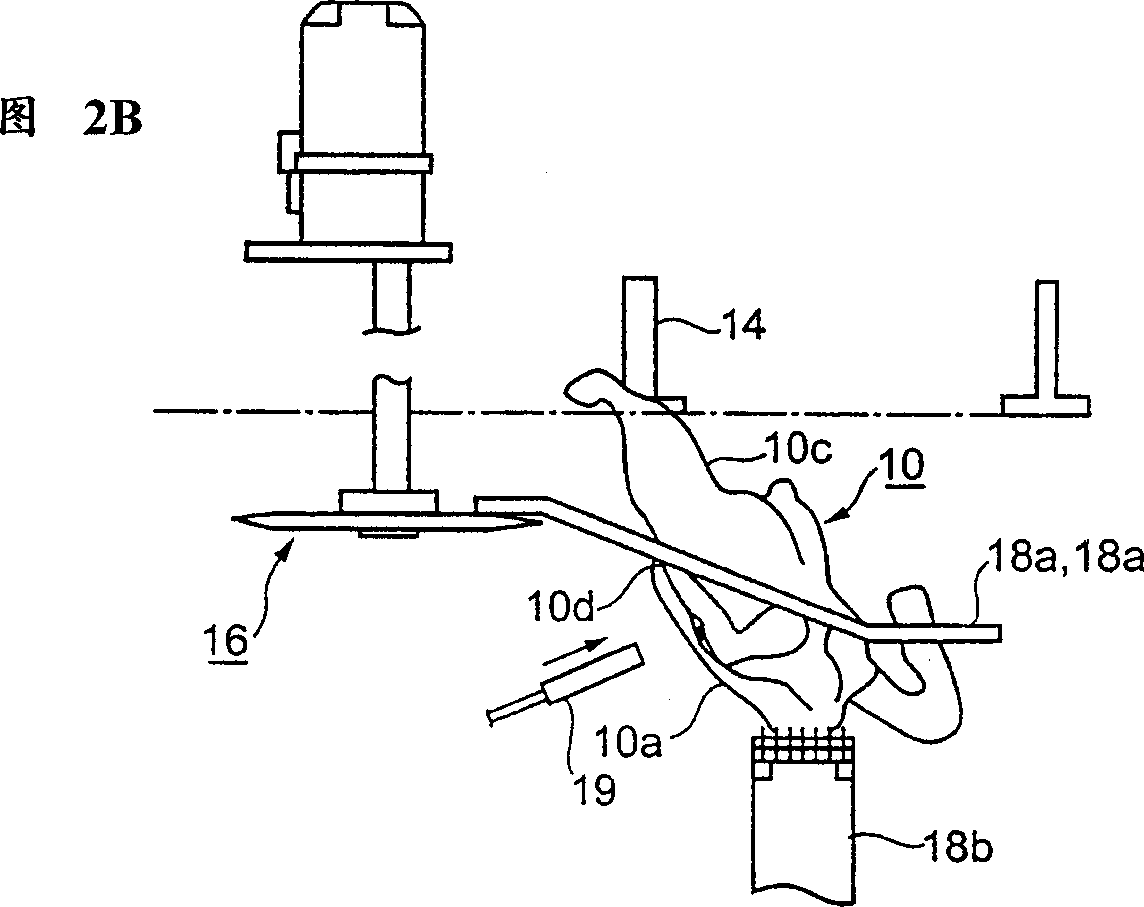
InactiveUS20120130502A1Quality improvementImprove reliabilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsInterference fitRight femoral head
Methods and apparatus for orthopedic replacement of the hip through three incisions with a modular prosthetic system assembled in vivo while substantially preserving muscles and soft tissues around the hip joint resulting in reduced healing time and decreased risk of dislocation. A prosthetic femoral stem is inserted into the femur. A prosthetic femoral neck is inserted from a point along the side of the patient's body and into the side of the femur and through a lateral bore in the prosthetic femoral stem to join the prosthetic femoral head. The methods and apparatus include structures and techniques for fixing or enhancing interconnection of implant components, such as by increasing the interconnection in an interference fit with one or more tapers, threads, and / or cooling of components prior to assembly.
Owner:IHIP SURGICAL LLC
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities for knee prosthesis patients
InactiveUS20100292804A1Deep knee flexion capabilityClosely replicate physiologic loadingJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaArticular surfaces
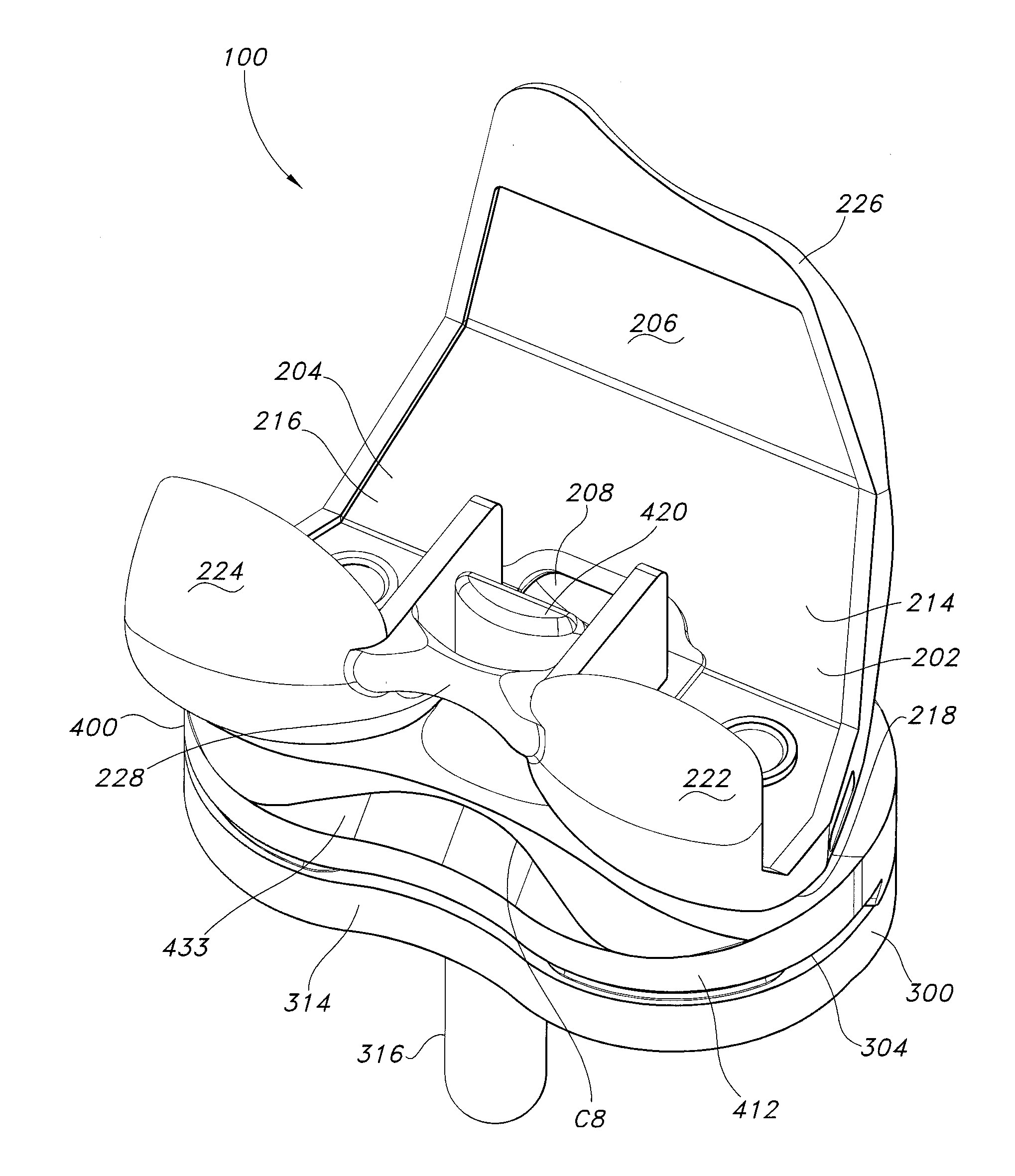
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities, more physiologic load bearing and improved patellar tracking for knee prosthesis patients. Such systems and methods include (i) adding more articular surface to the antero-proximal posterior condyles of a femoral component, including methods to achieve that result, (ii) modifications to the internal geometry of the femoral component and the associated femoral bone cuts with methods of implantation, (iii) asymmetrical tibial components that have an unique articular surface that allows for deeper knee flexion than has previously been available, (iv) asymmetrical femoral condyles that result in more physiologic loading of the joint and improved patellar tracking and (v) modifying an articulation surface of the tibial component to include an articulation feature whereby the articulation pathway of the femoral component is directed or guided by articulation feature.
Owner:SAMUELSON KENT M +1
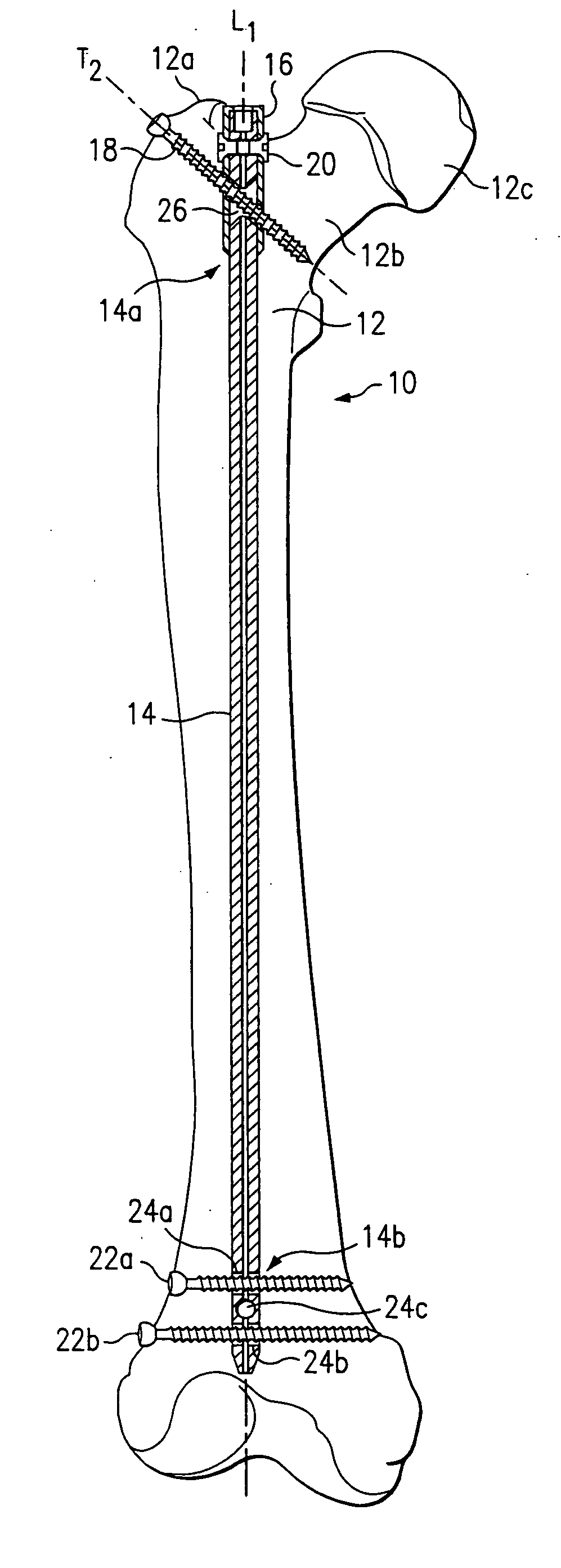
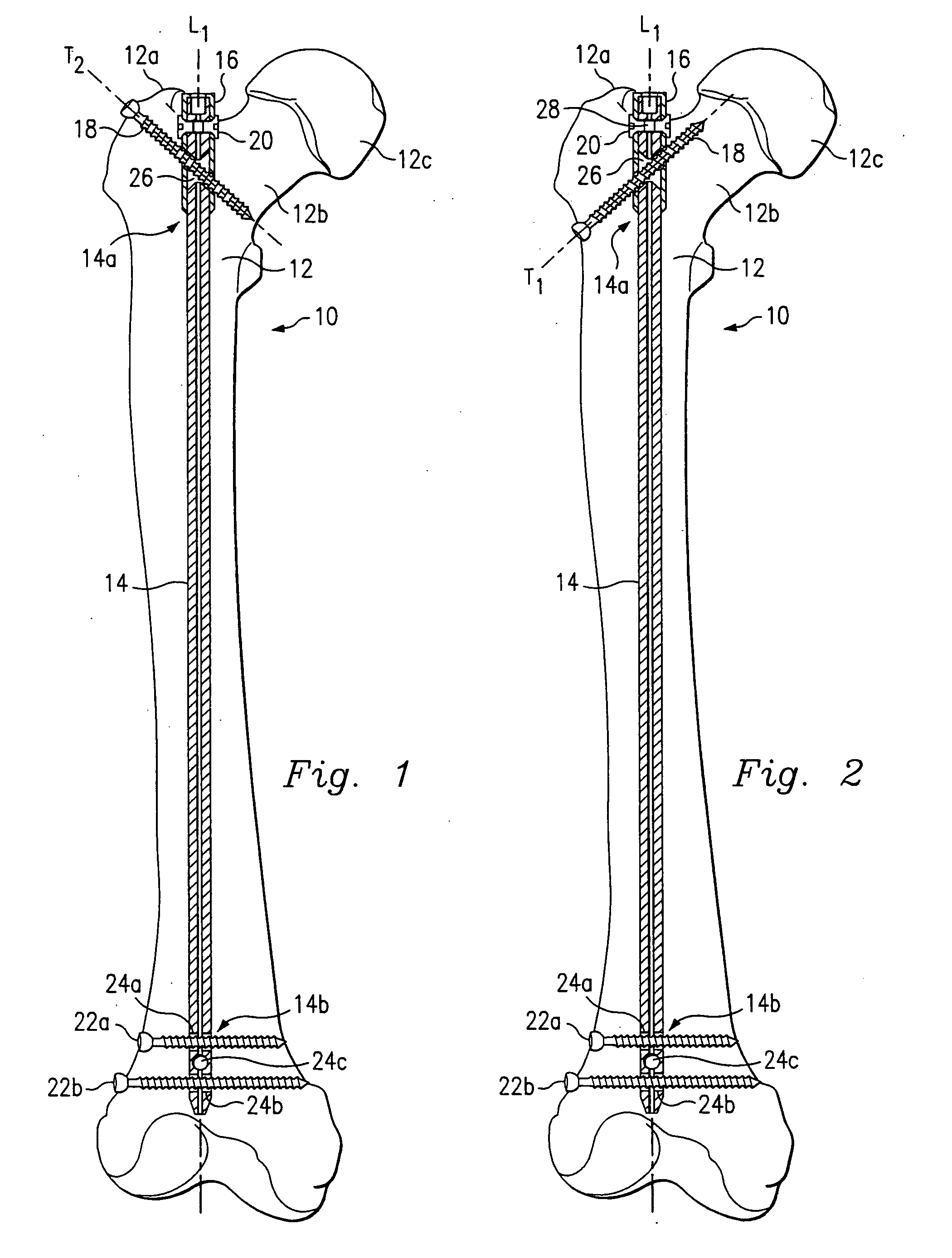
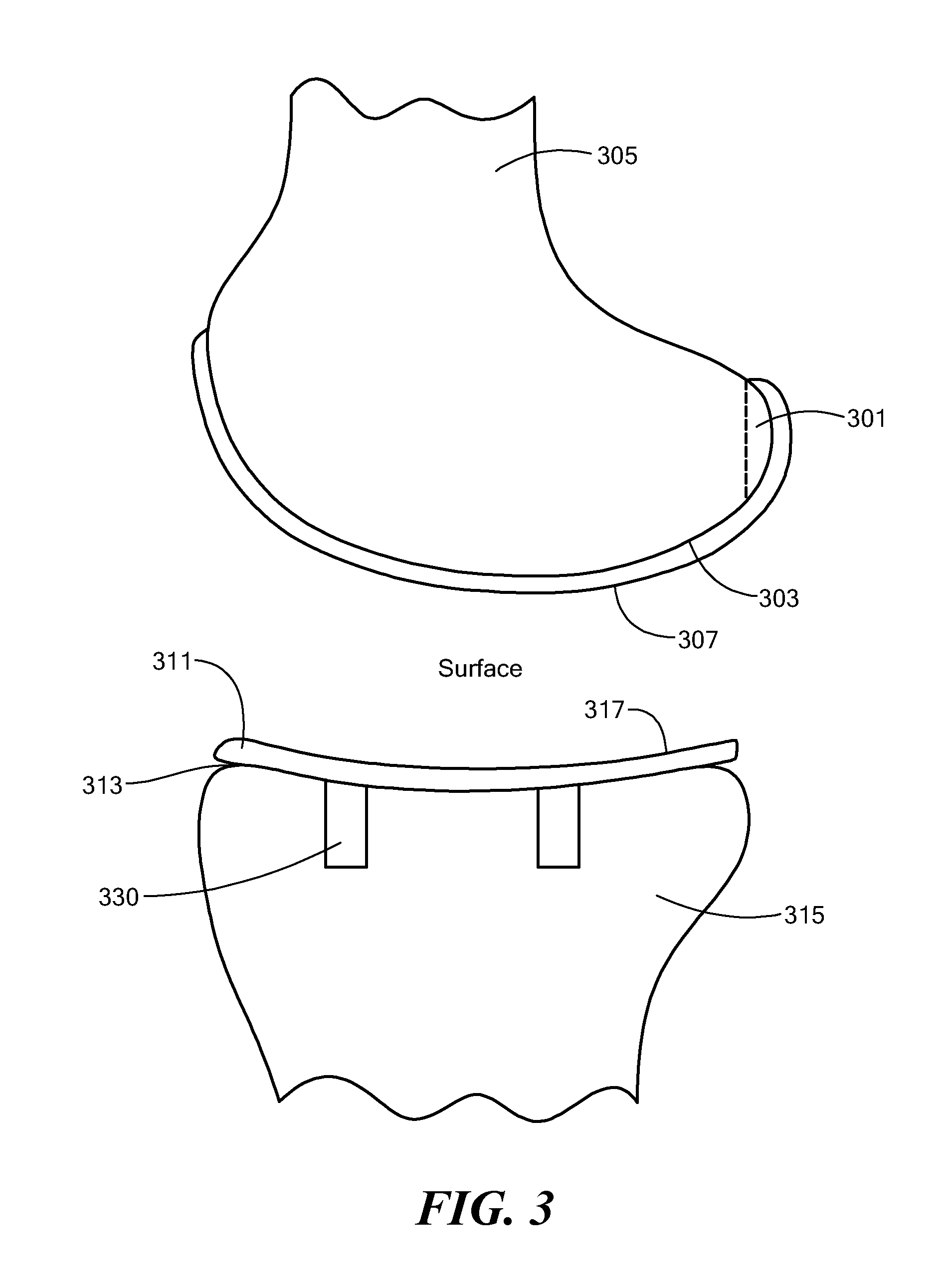
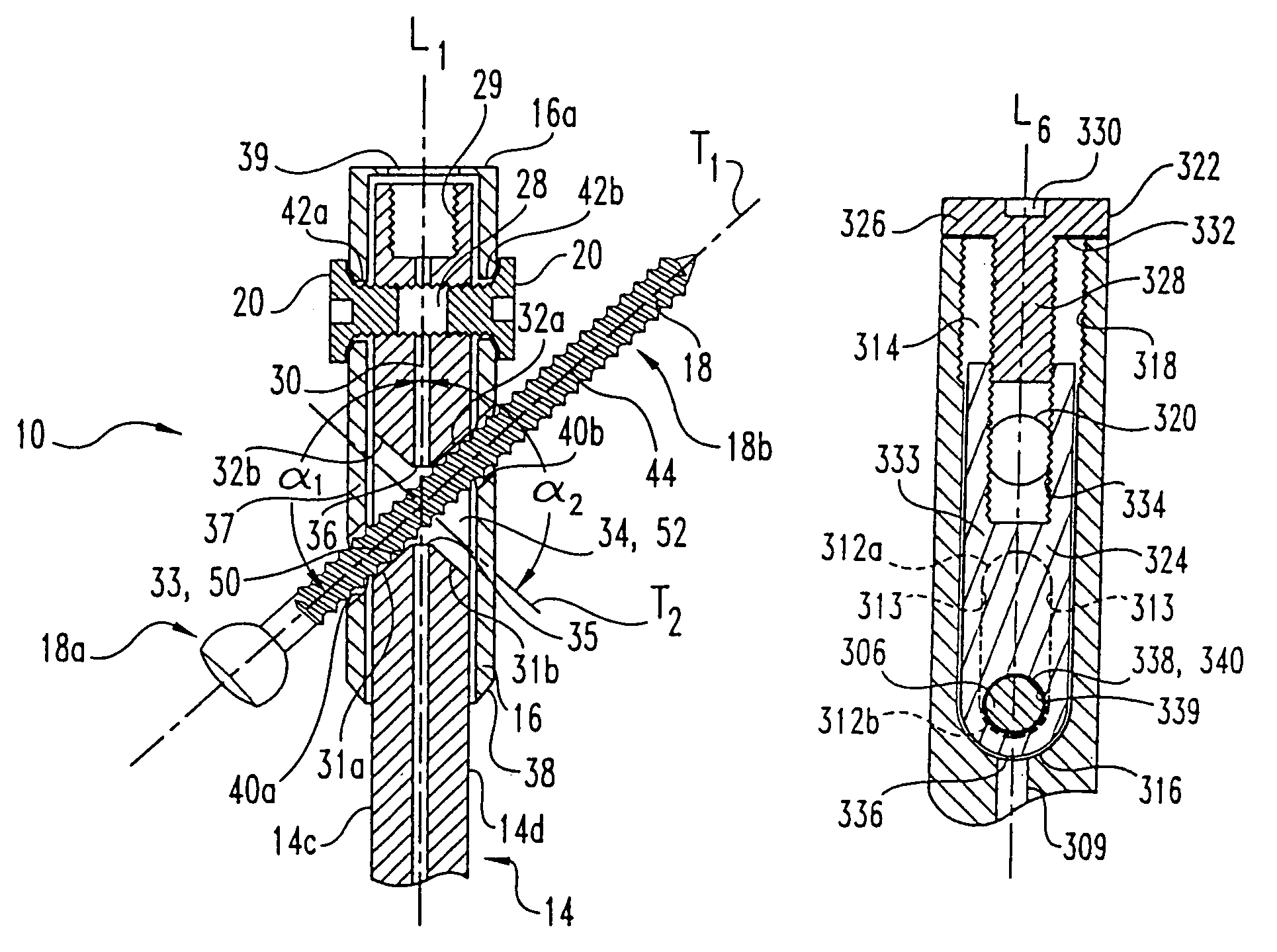
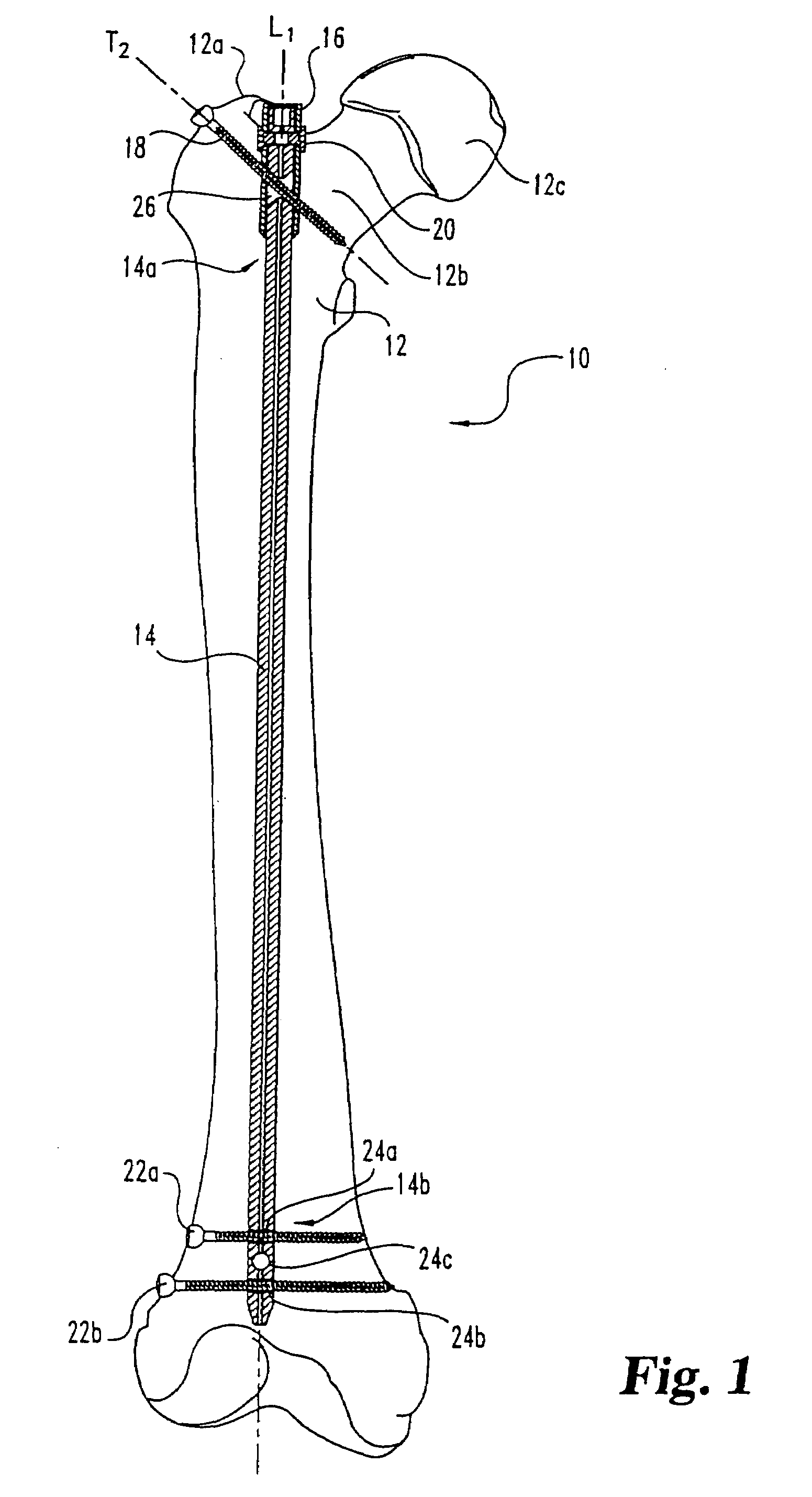
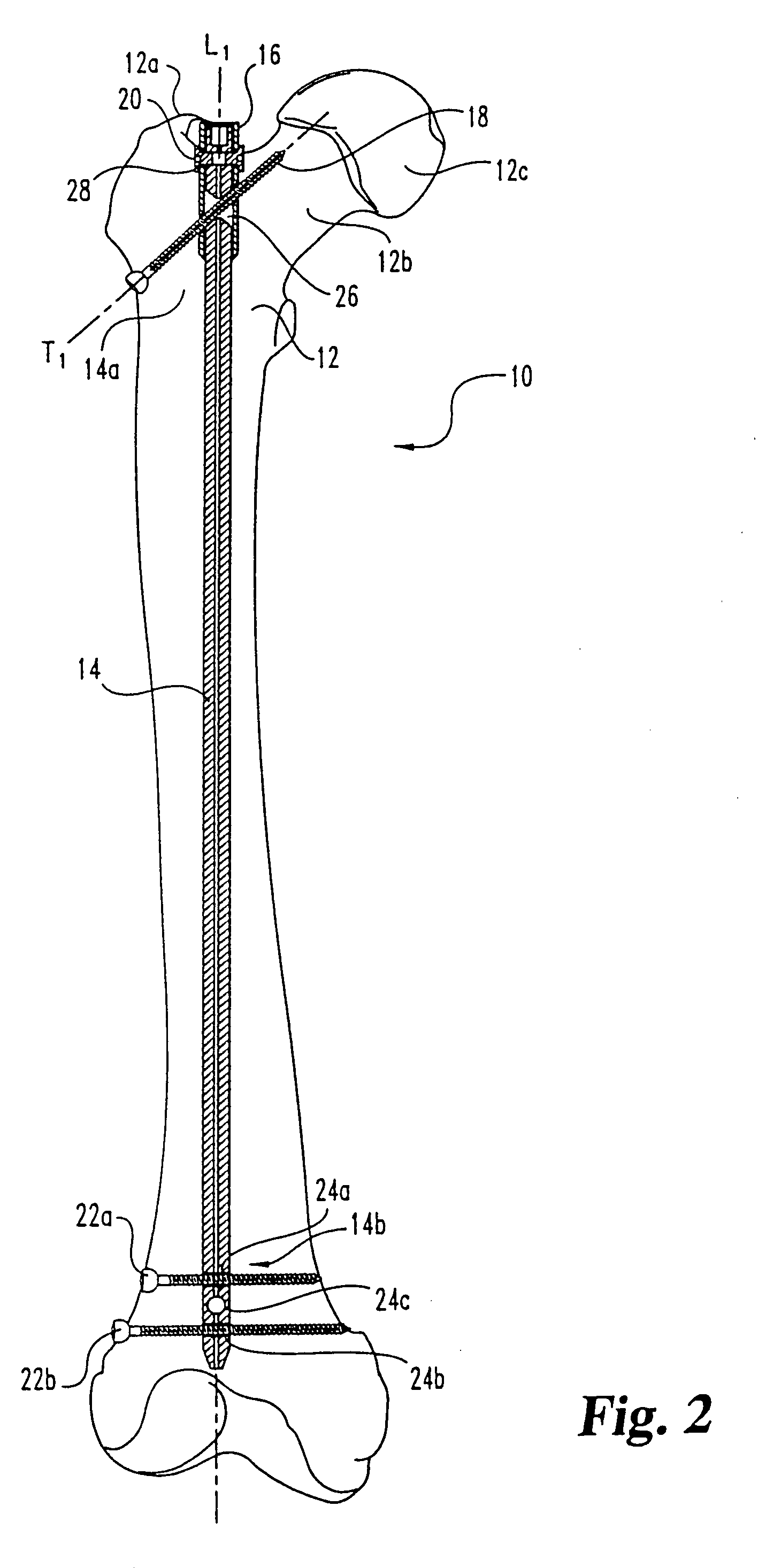
Device for the treatment of femoral fractures
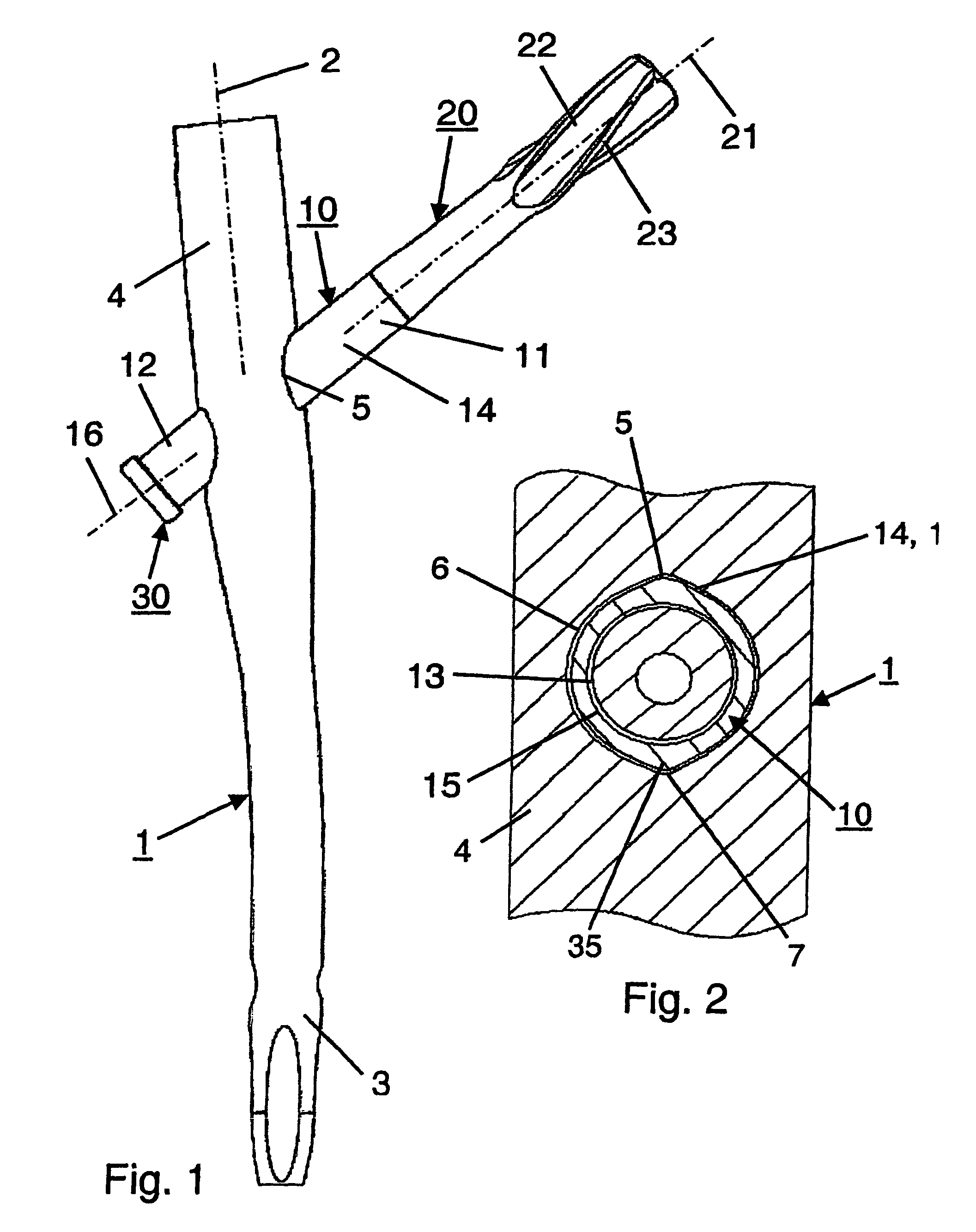
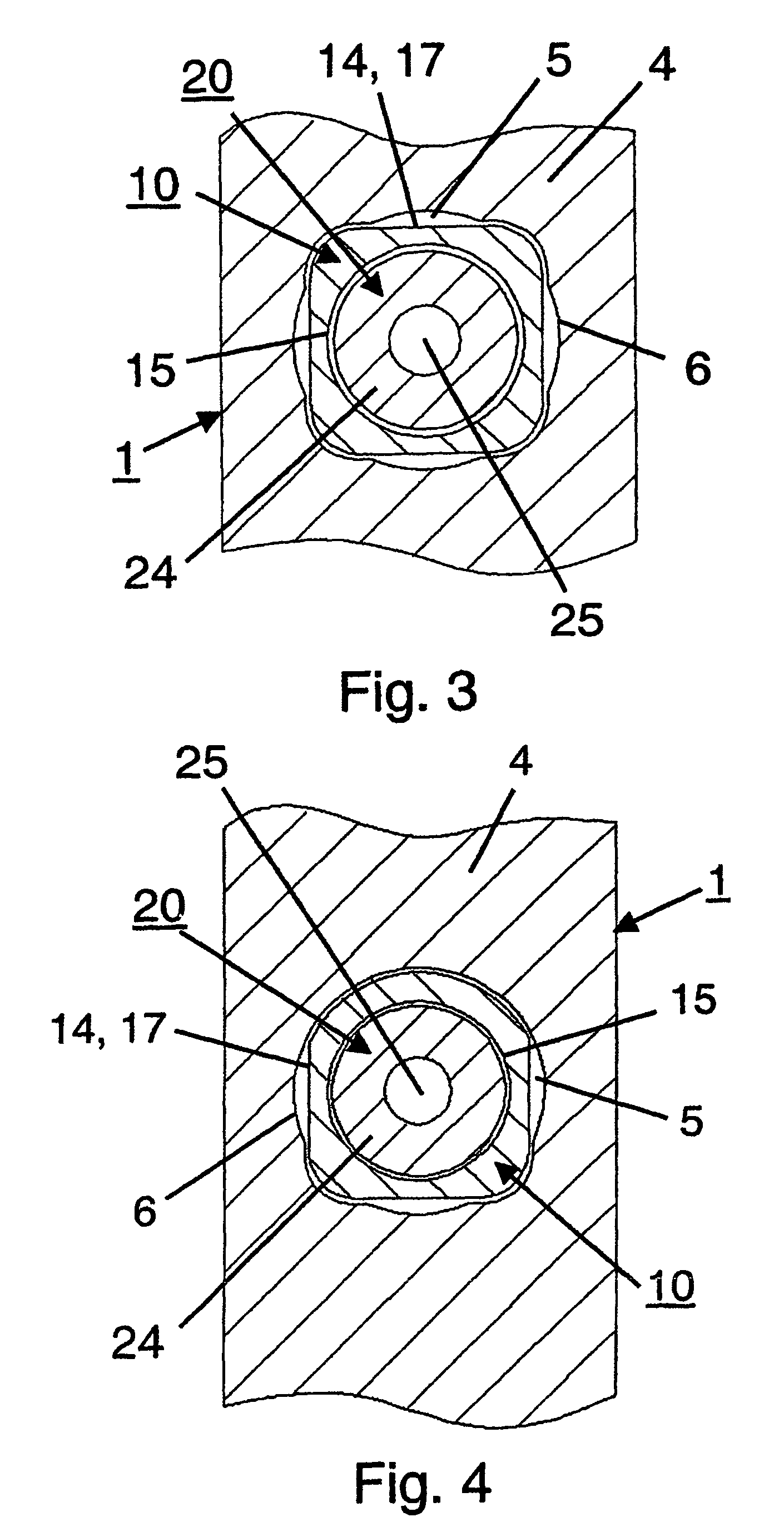
ActiveUS7850690B2Operation can be simplified and shortenedPrevents excessive medial movementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsFemoral boneRight femoral head
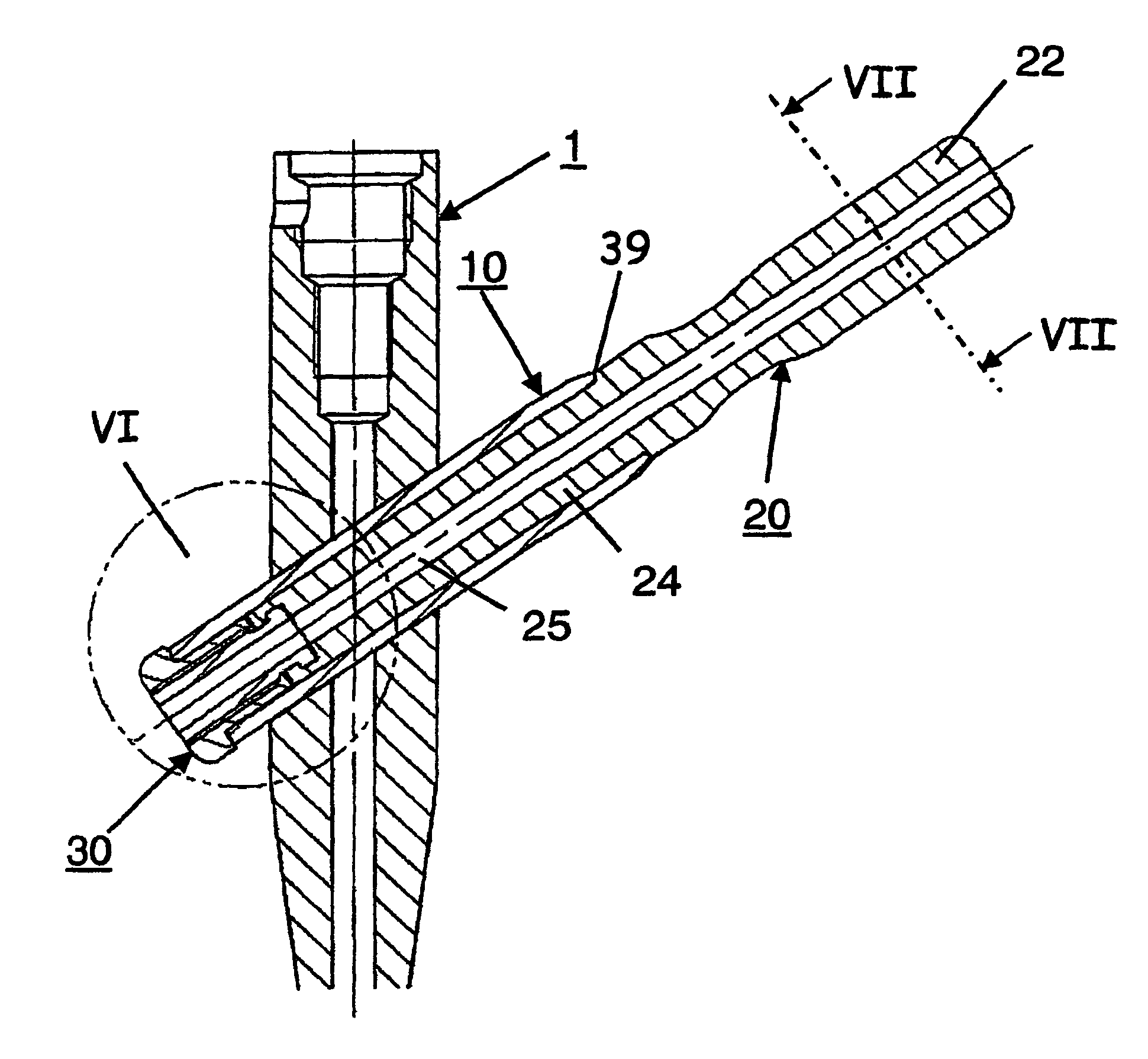
A femoral fracture treatment device including: an intramedullary pin (1) with a central longitudinal axis (2) and a passage (5) of non-circular cross-section (6) through a proximal portion (4) of the pin oblique to the longitudinal axis (2), a sliding sleeve (10) configured to pass through the non-circular passage (5), a longitudinal bone fixing element (20) having a head portion (22) with fixing means (23) for engaging the femoral head and a shaft (24) that may be coaxially introduced into the sliding sleeve (10). Both an external jacket surface (14) of the sliding sleeve (10) and an internal jacket surface (15) of the sliding sleeve (10) have non-circular cross-sections at least in a partial section. The shaft (24) is rotatably mounted in the longitudinal bore (13) of the sliding sleeve (10), and locking means are provided at the free end (27) of the shaft (24), such that rotation of the longitudinal bone fixing element (20) relative to the sliding sleeve (10) can be optionally locked or released.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
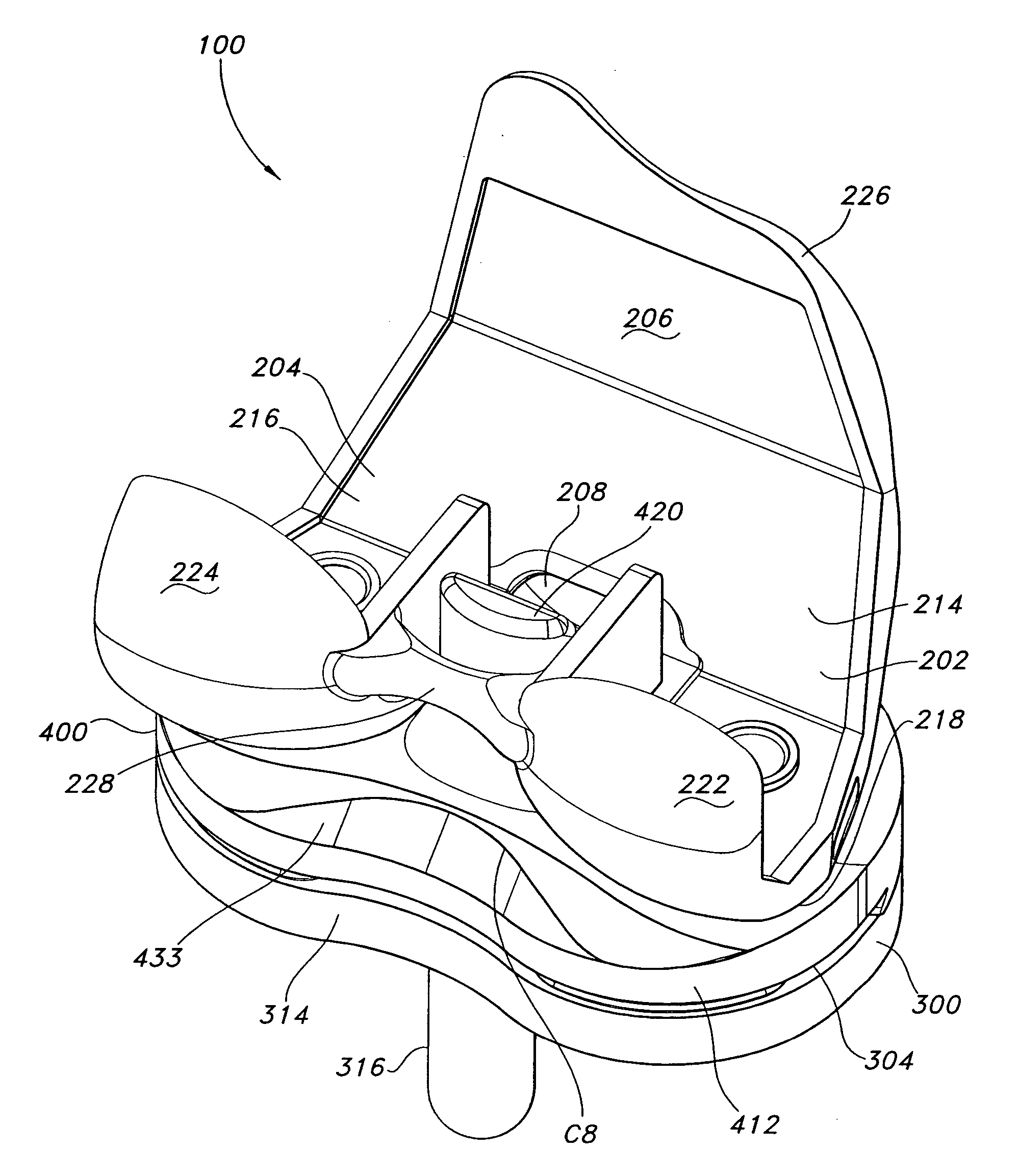
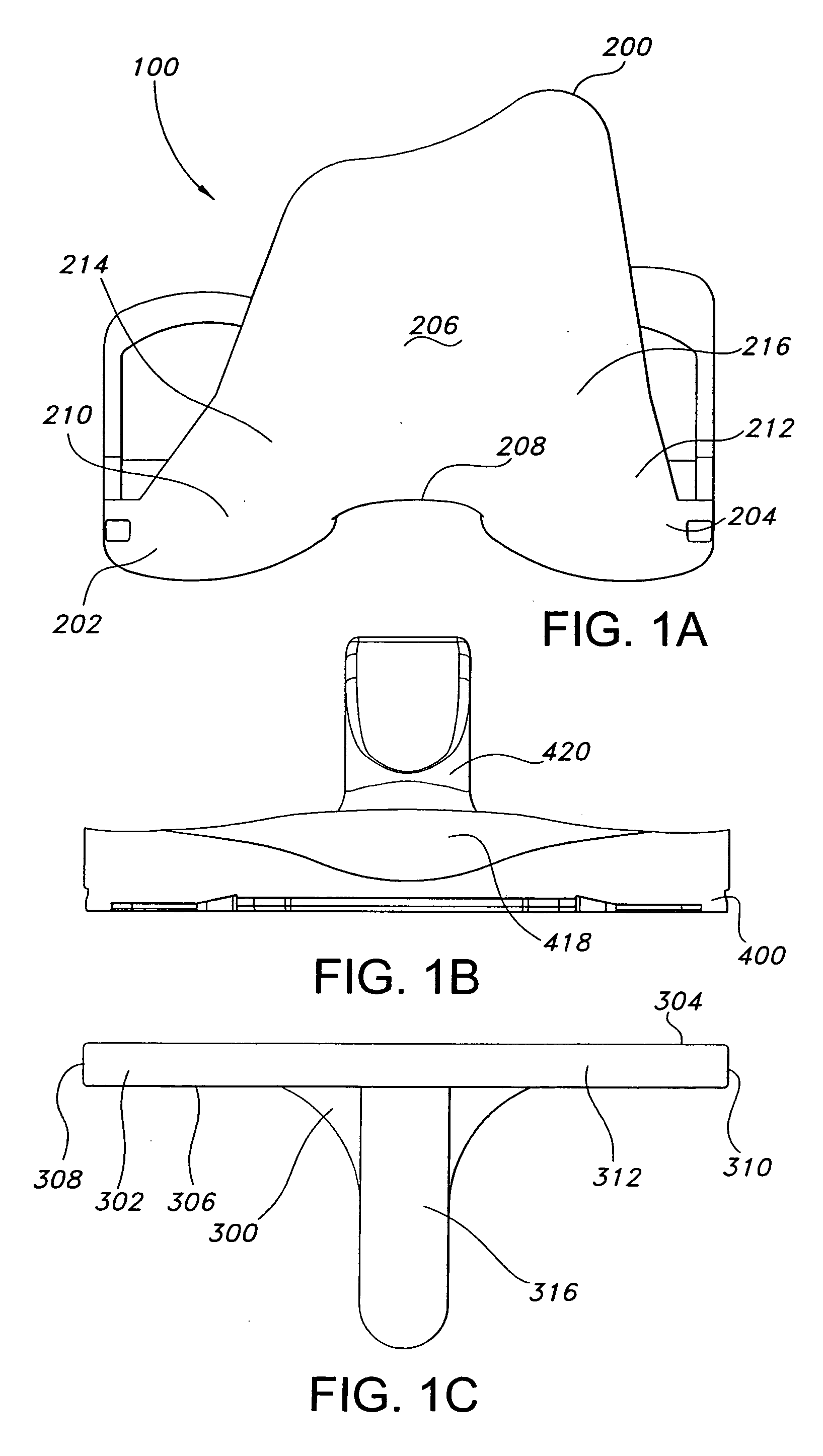
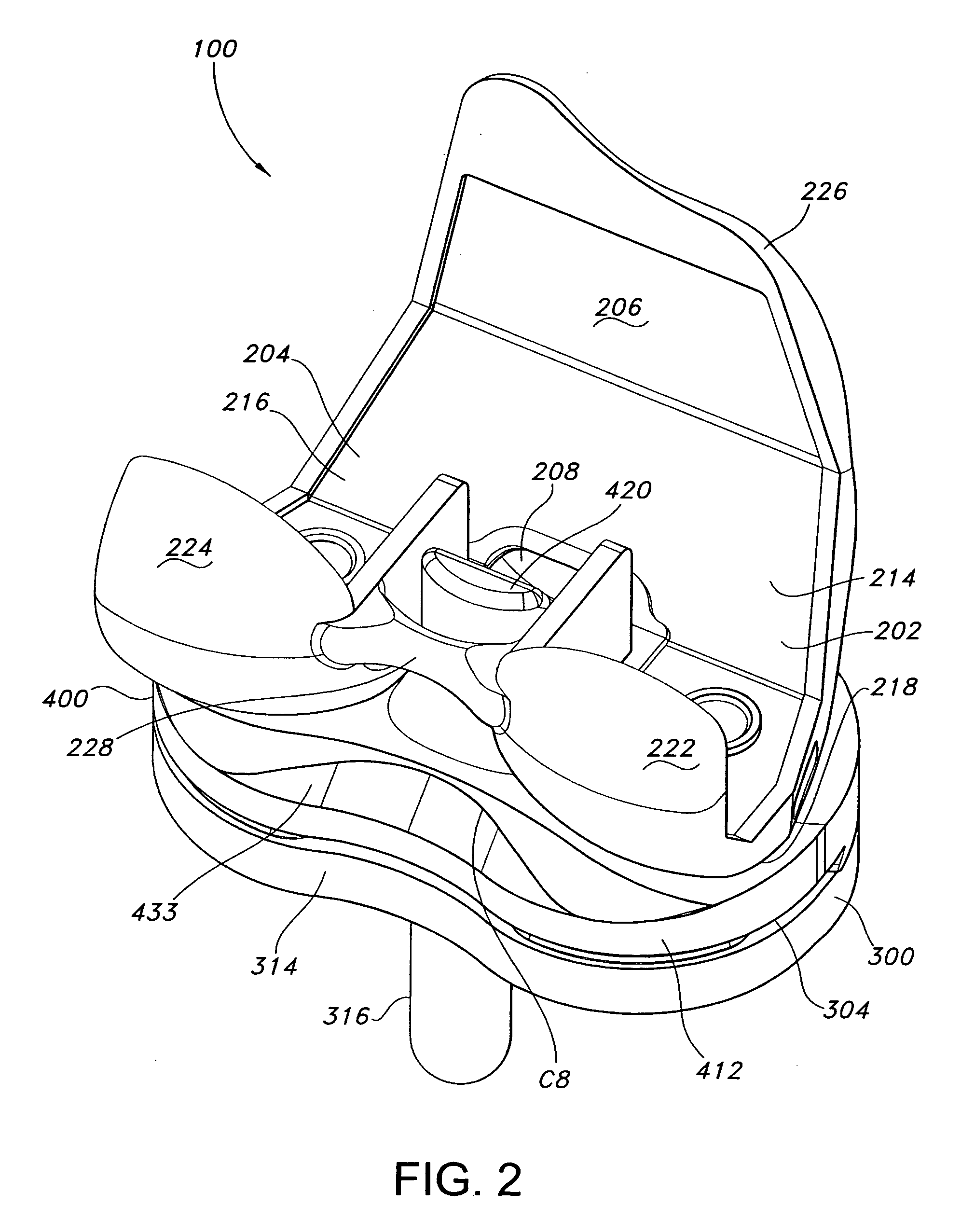
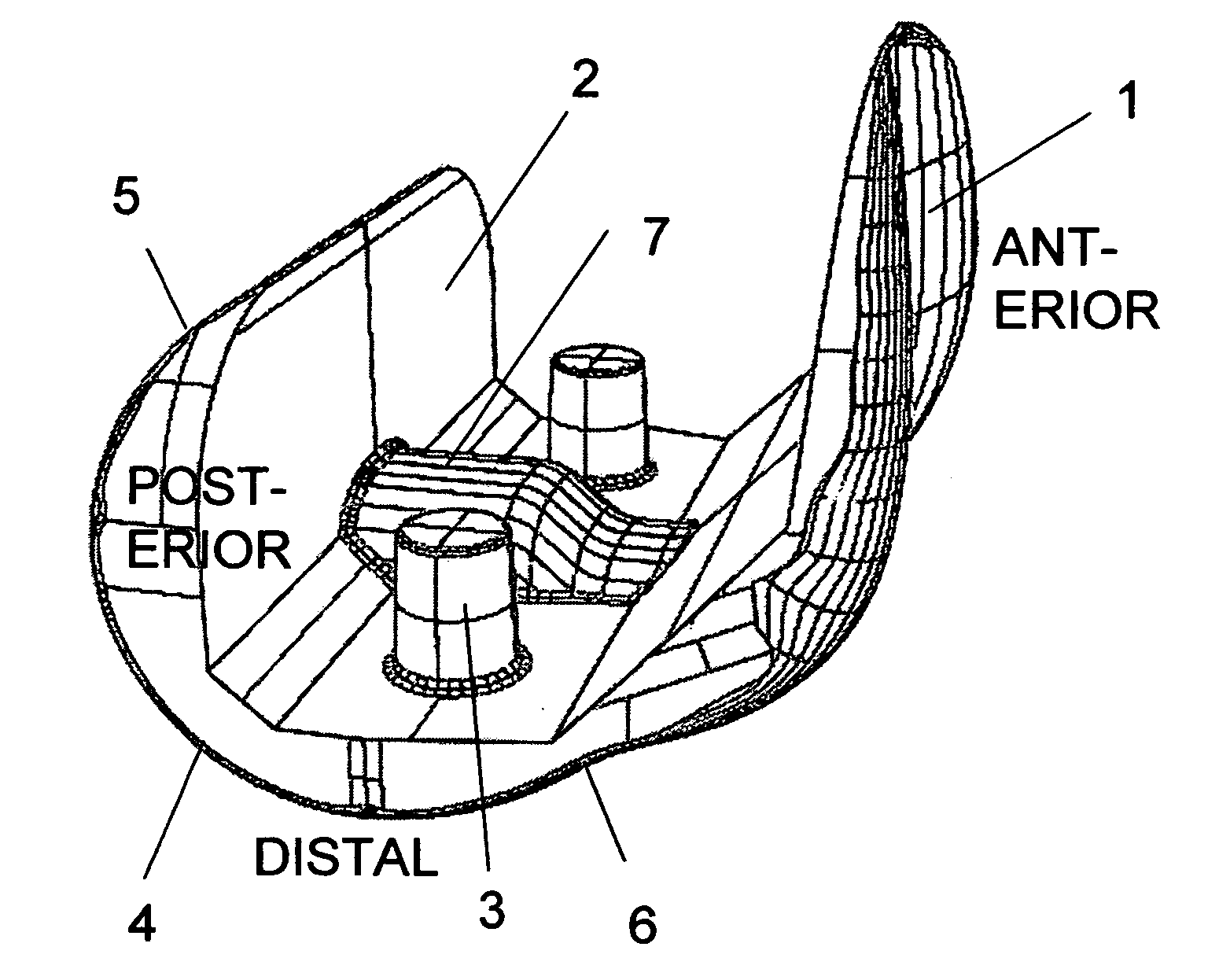
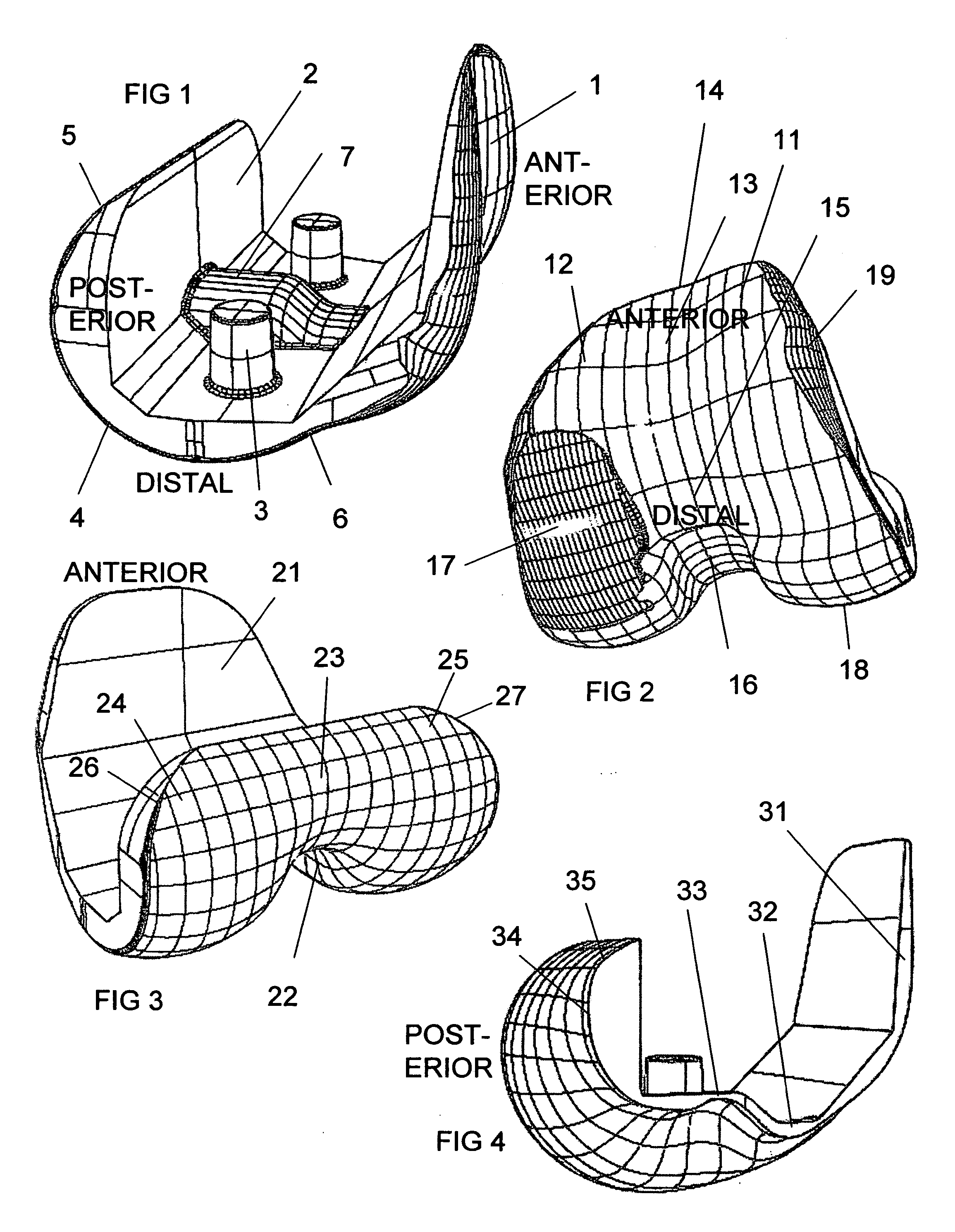
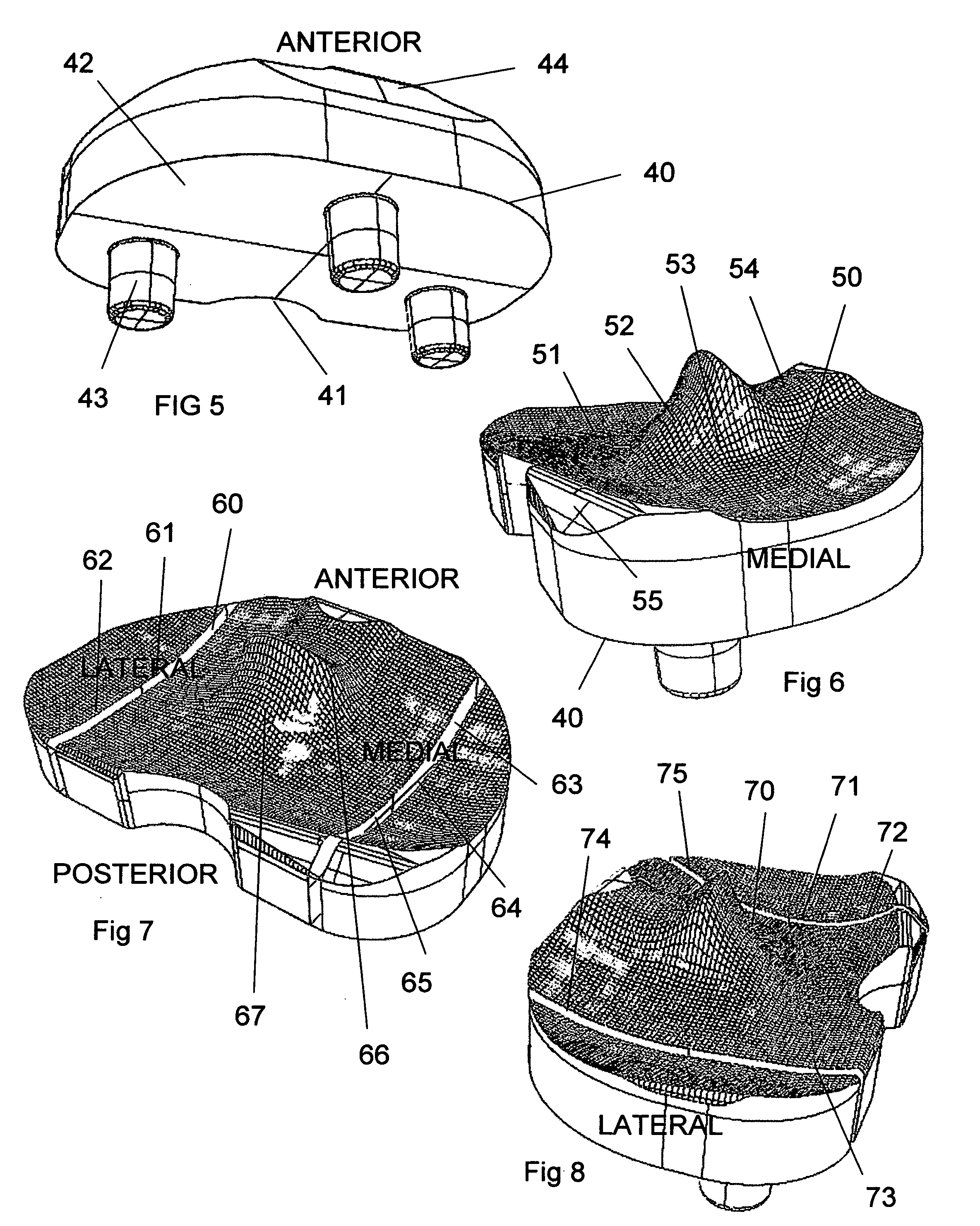
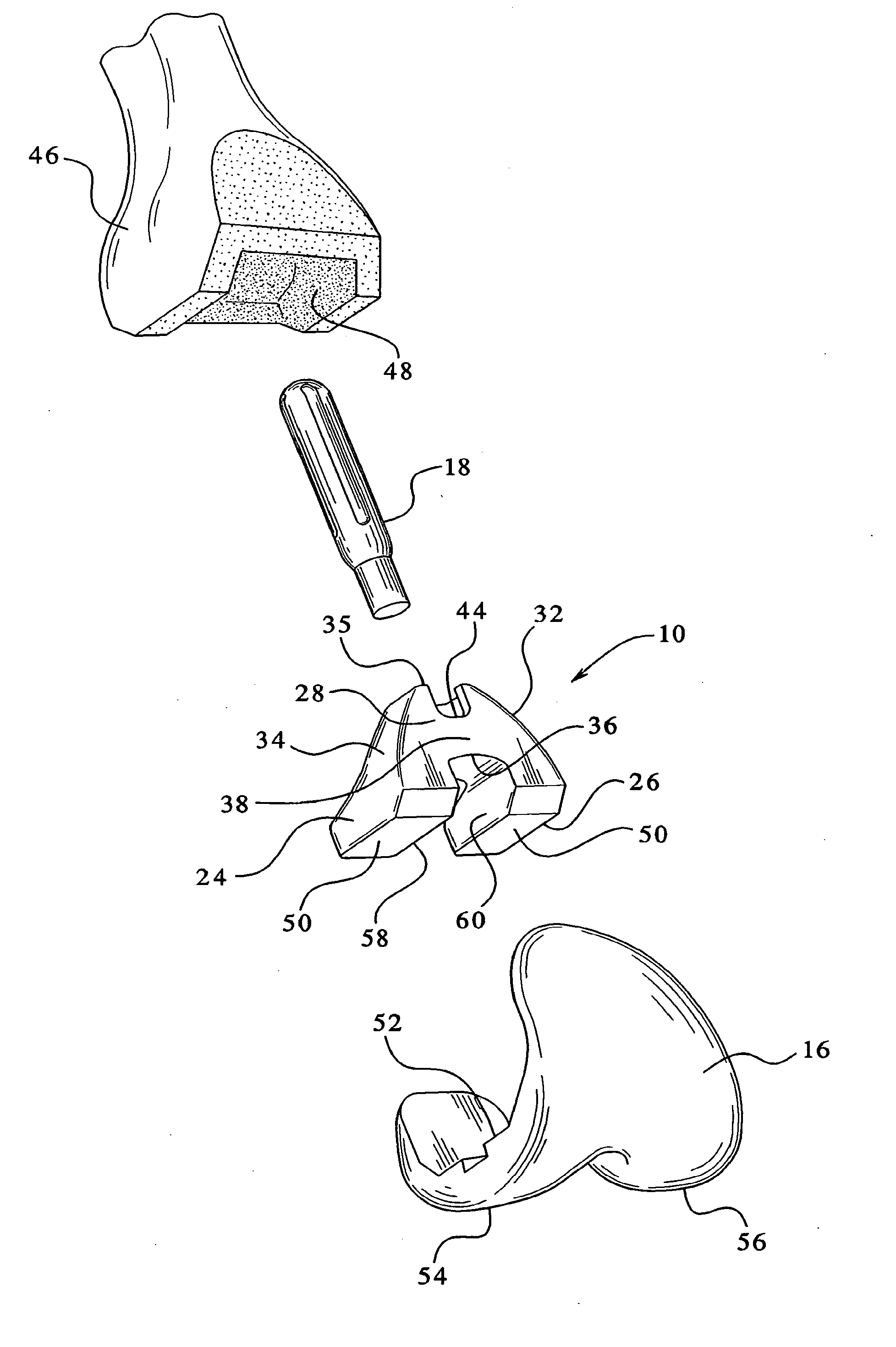
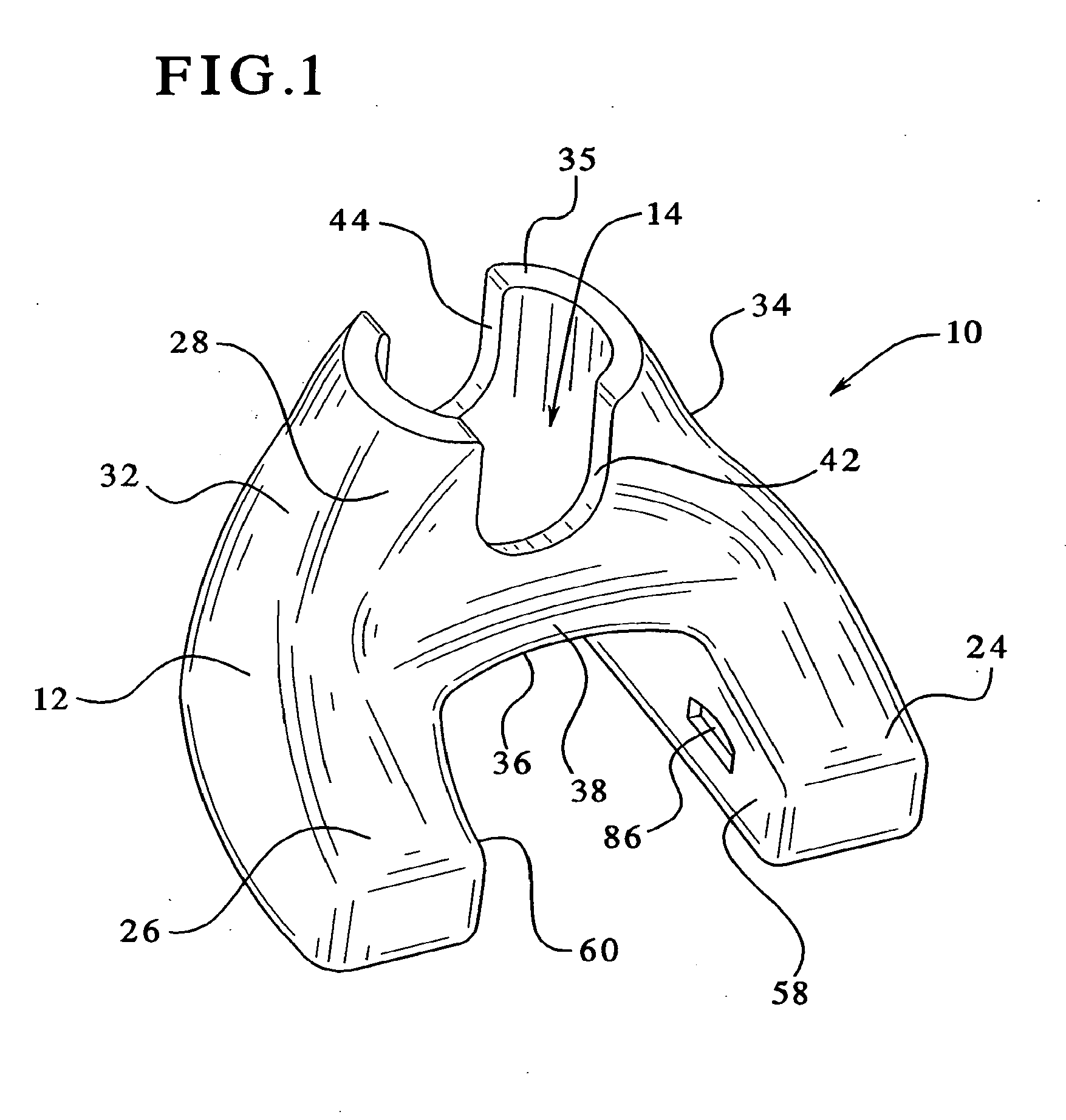
Femoral augments for use with knee joint prosthesis
A femoral augment, or set of augments, for use with a knee joint prosthesis, where the femoral augment includes a main body portion, an aperture formed within the main body portion and extending in a generally distal / proximal direction, and a pair of legs extending outwardly from said main body portion in a generally posterior direction. In the preferred embodiment, the aperture is configured to receive a stem extension implant, and to allow it to pass through. Additionally, the legs of the femoral augment are preferably configured to be seated proximal of a proximal side of a pair of condylar portions of a femoral component of a knee joint prosthesis. The present invention is intended for situations in which the distal portion of the femur is defective, and it provides a method and devices that allow for preservation of healthy peripheral bone, while still providing the necessary augmentation to the distal portion of the femur.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
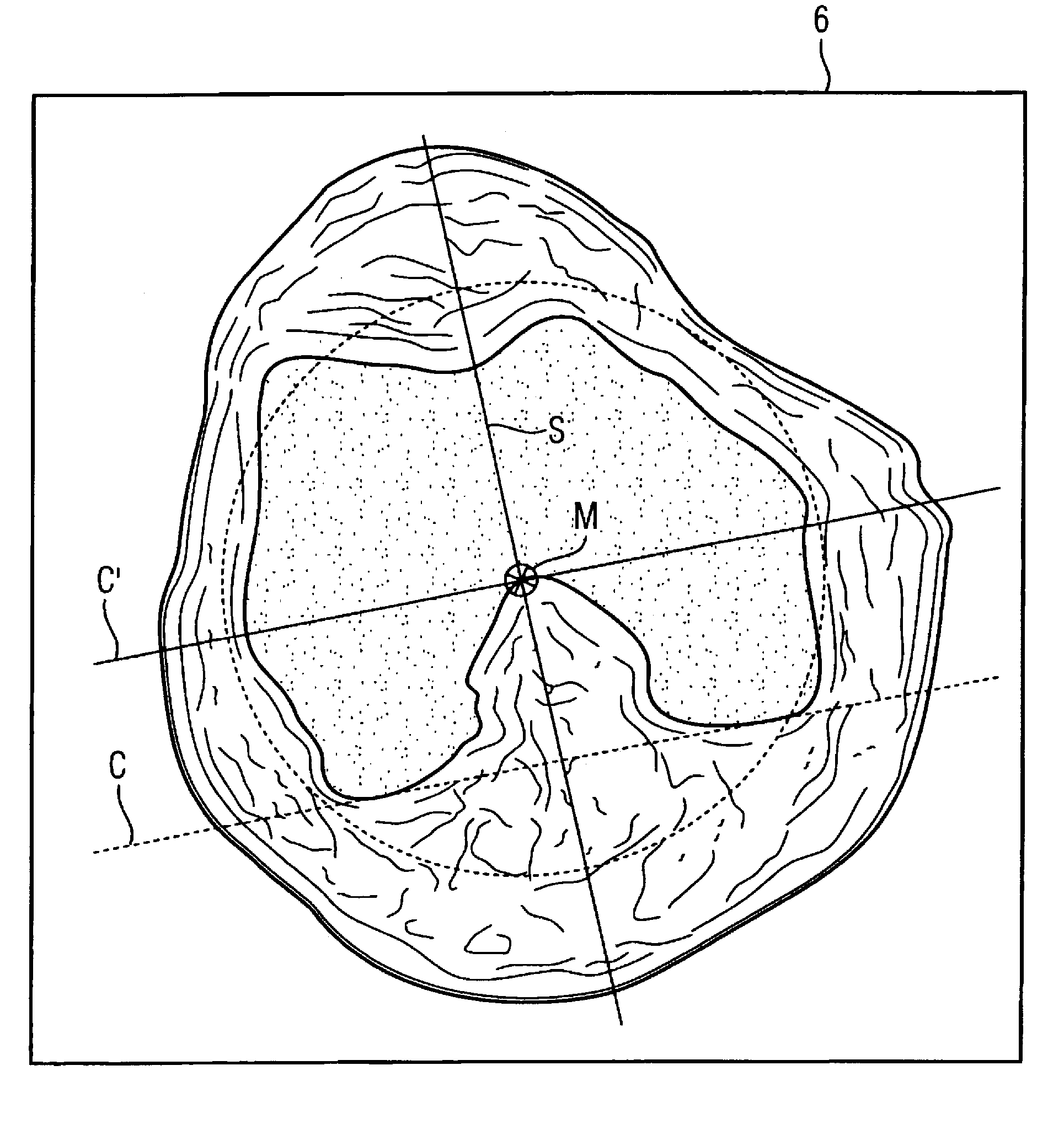
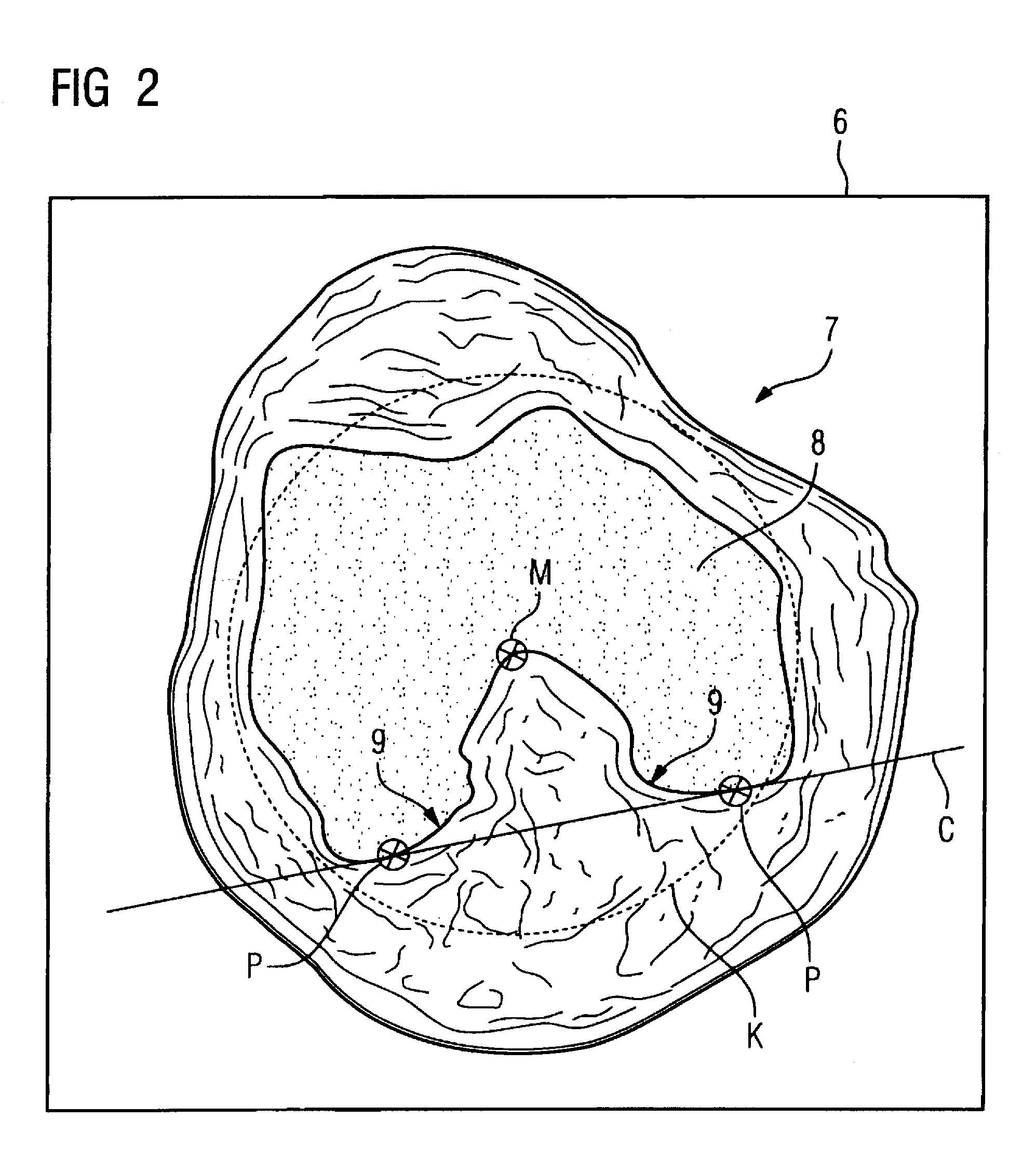
Mr method and apparatus for determining coronal and sagittal image planes from an image data set of a knee joint
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities for knee prosthesis patients
InactiveUS20090062925A1Closely replicate physiologic loadingEasy to trackJoint implantsFemoral headsArticular surfacesArticular surface
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities, more physiologic load bearing and improved patellar tracking for knee prosthesis patients. Such systems and methods include (i) adding more articular surface to the antero-proximal posterior condyles of a femoral component, including methods to achieve that result, (ii) modifications to the internal geometry of the femoral component and the associated femoral bone cuts with methods of implantation, (iii) asymmetrical tibial components that have an unique articular surface that allows for deeper knee flexion than has previously been available and (iv) asymmetrical femoral condyles that result in more physiologic loading of the joint and improved patellar tracking.
Owner:SAMUELSON KENT M
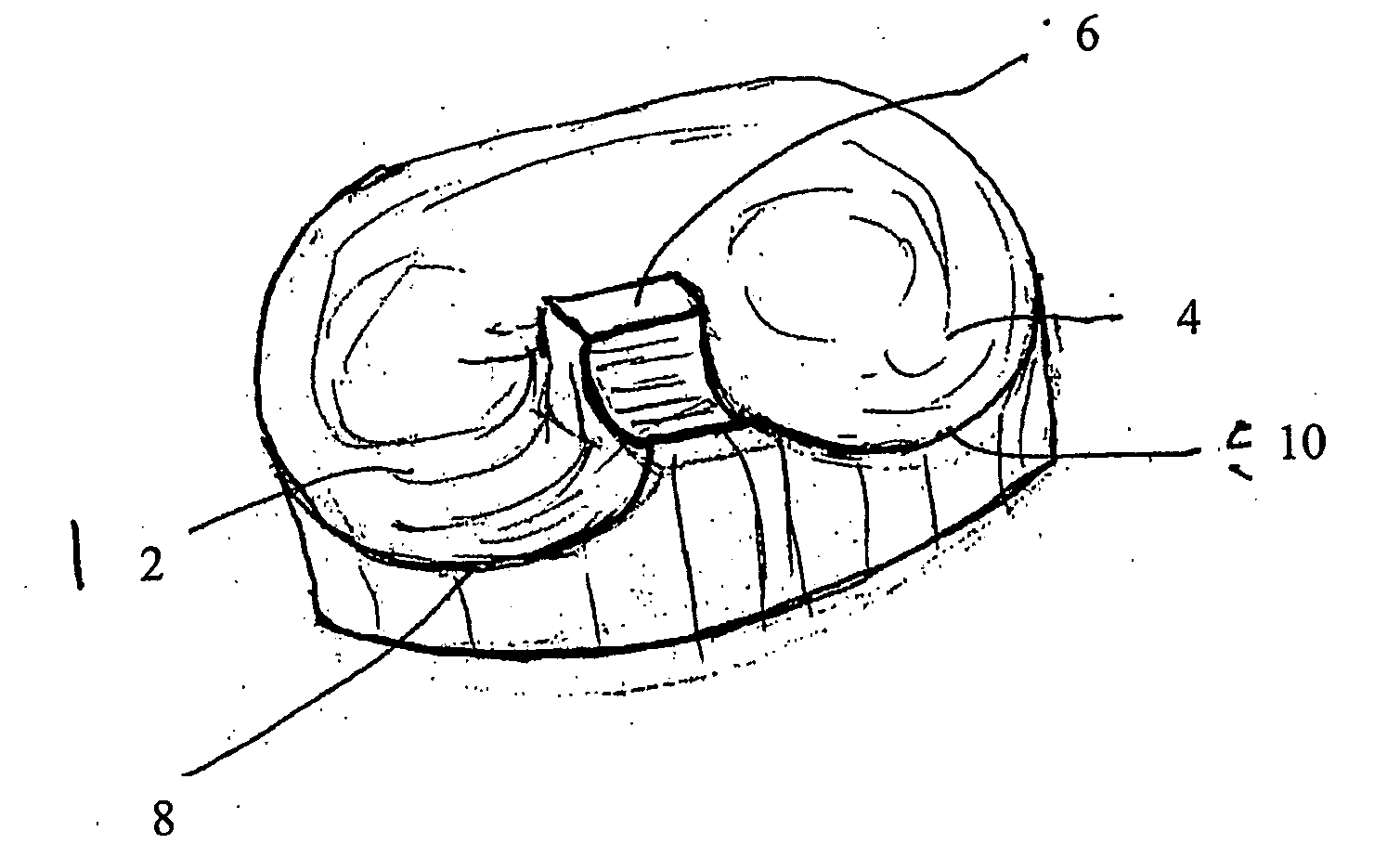
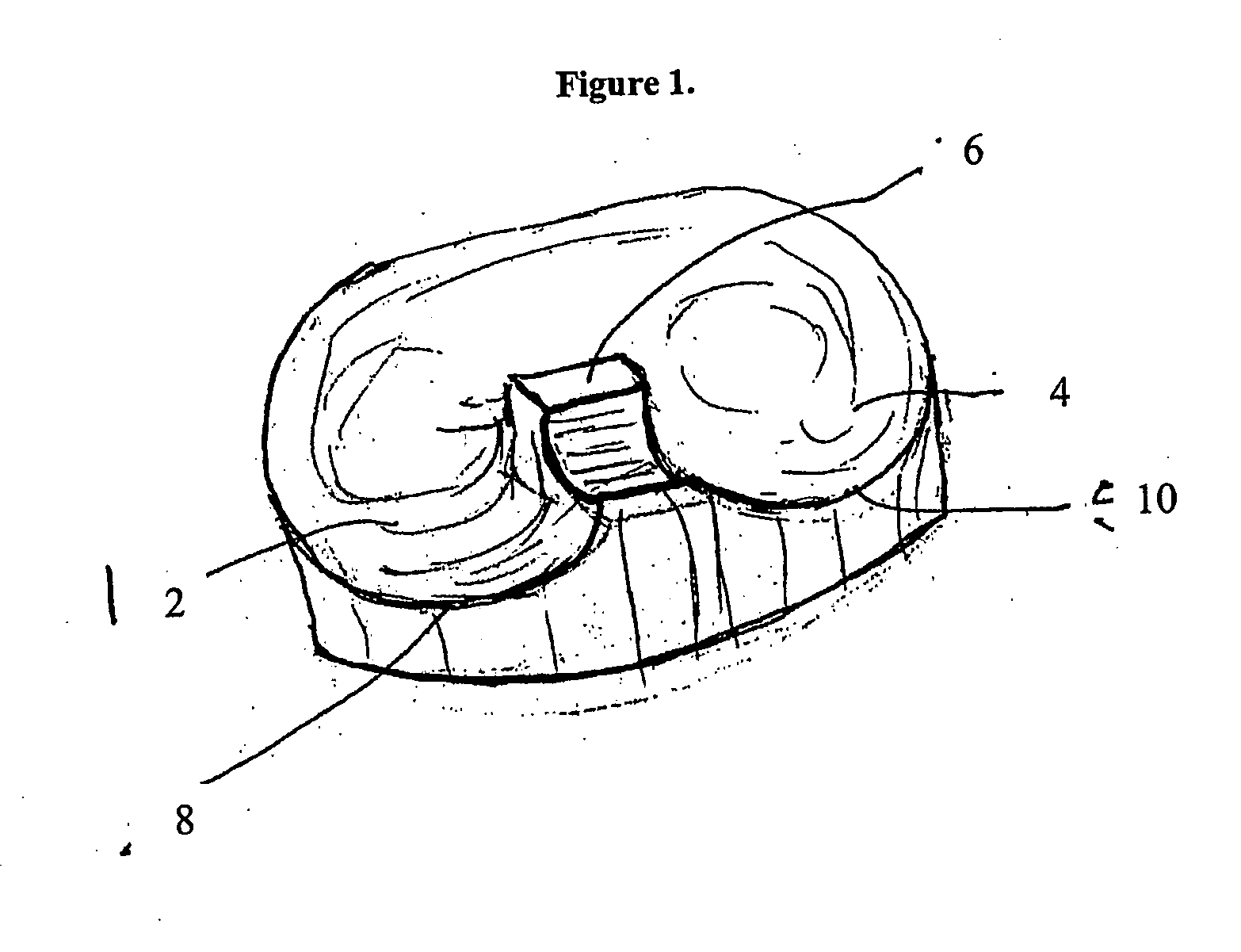
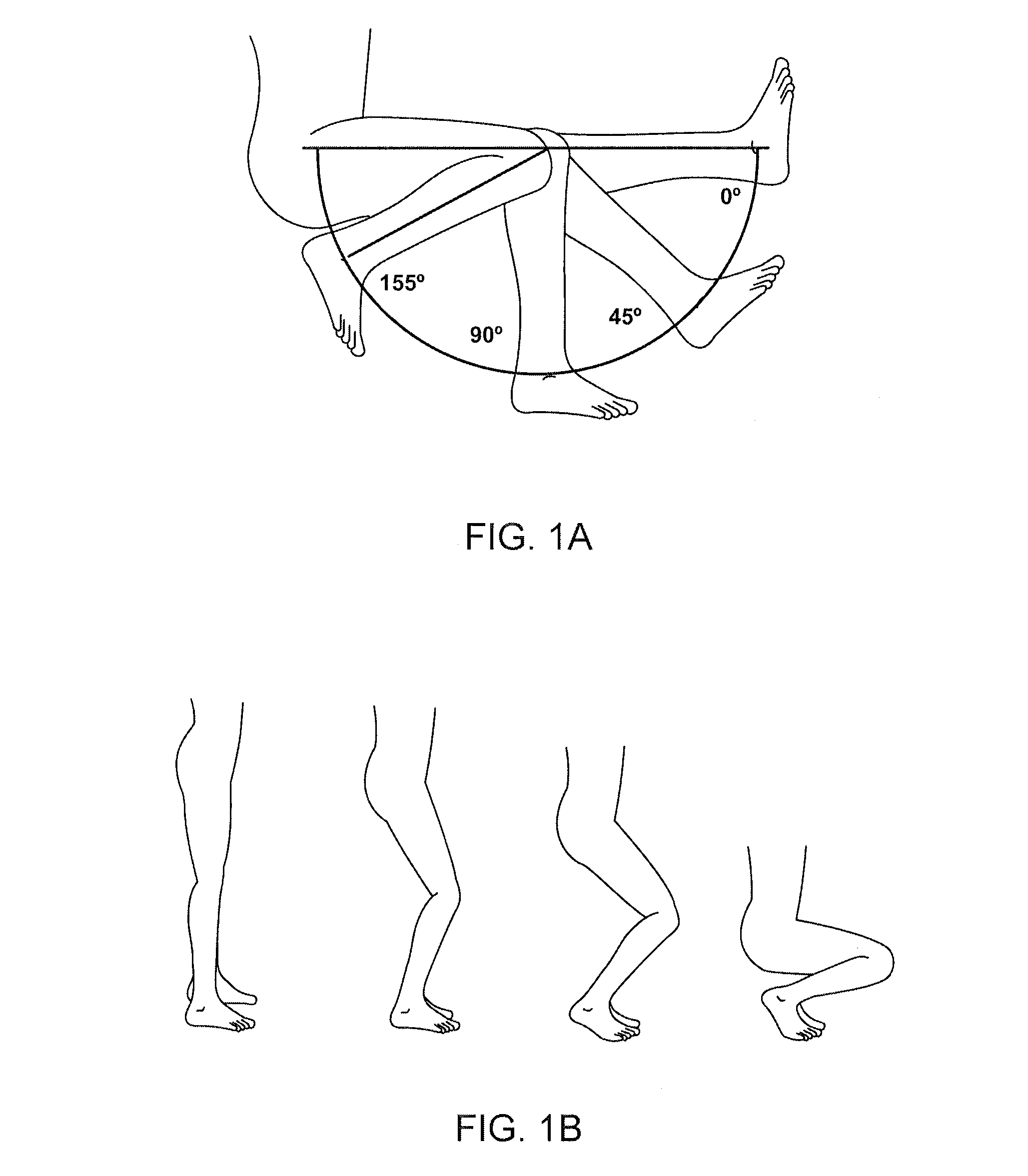
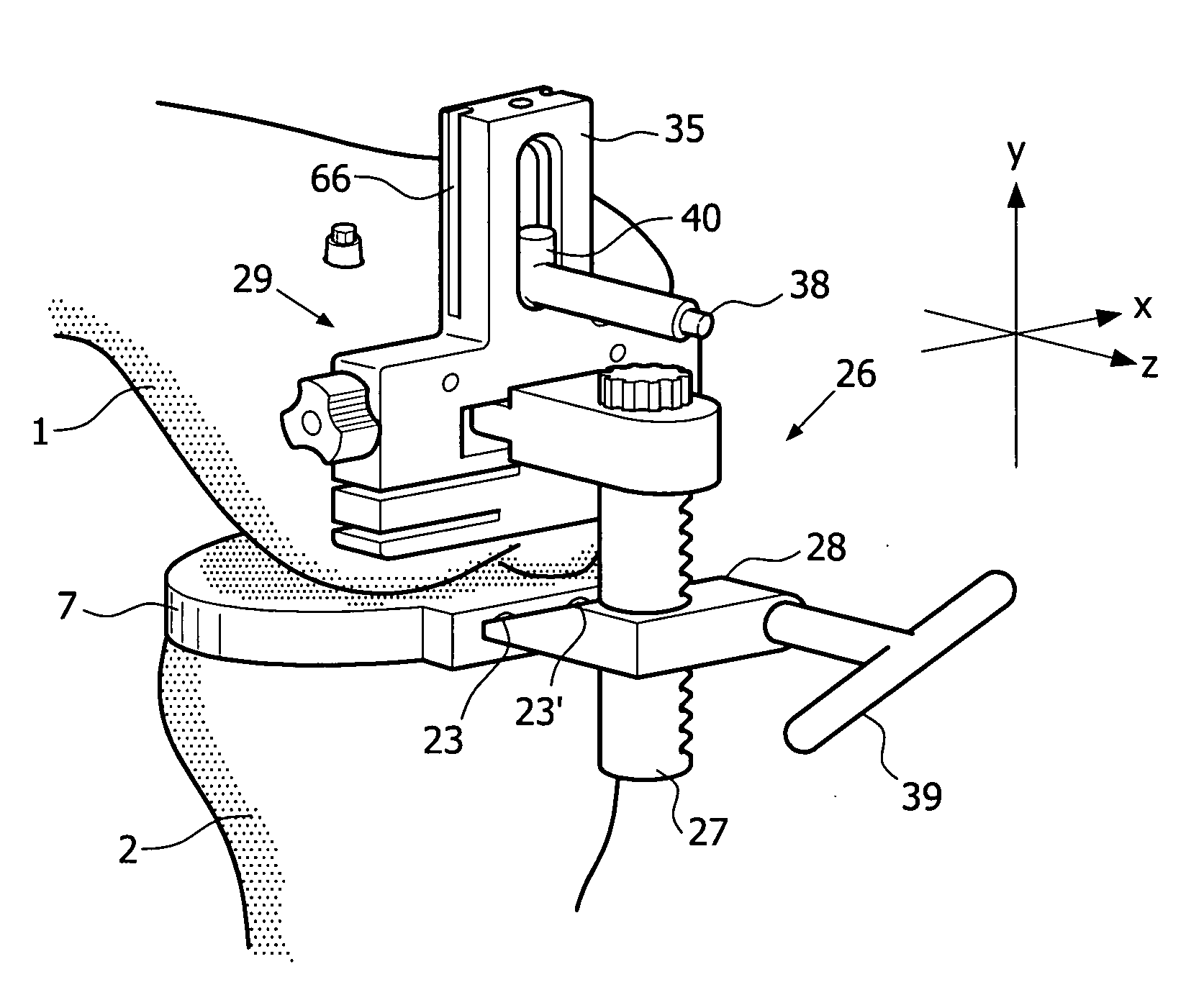
Device and method for installing femoral prosthetic knee joint
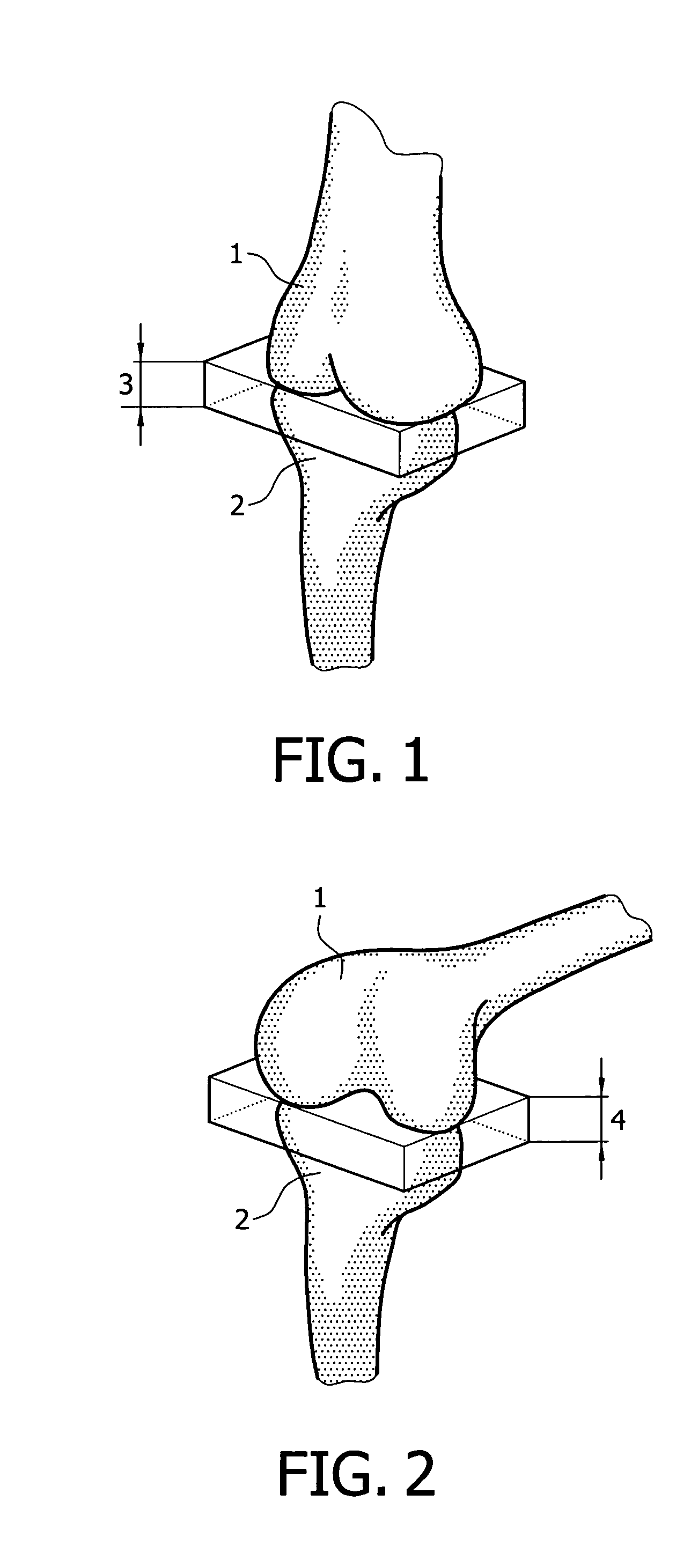
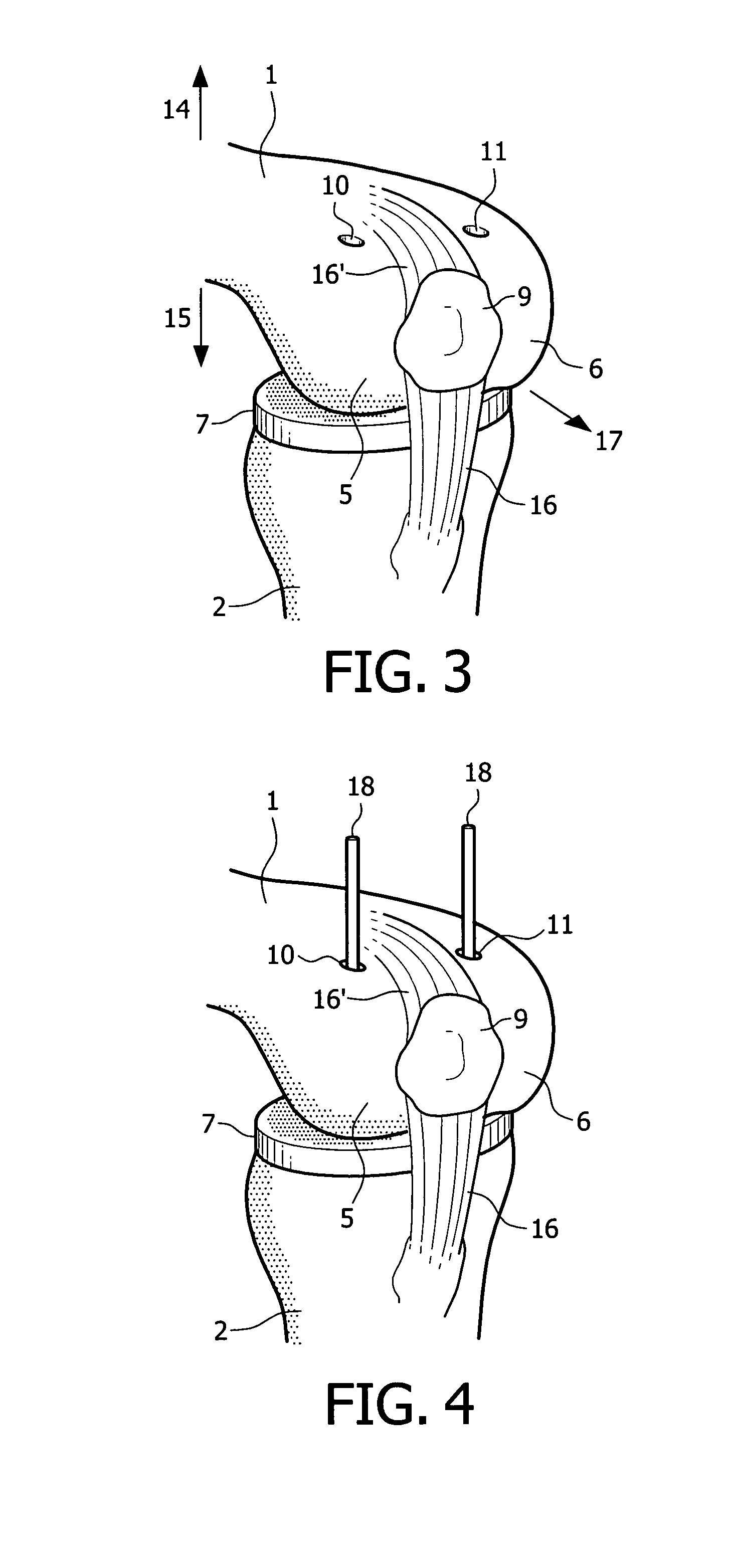
Devices and method for performing replacement prosthetic knee surgery are disclosed in which a spacing means is introduced between the femur (1) and tibia (2) while the patella (9) is in place. The spacing means separates the femur (1) from the tibia (2) by an amount essentially equal to or greater than the required flexion gap (4). An alignment device (26) is used for performing femoral bone cuts, which device attaches temporarily to a fitted tibial plate.
Owner:GHIJSELINGS IGNACE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com