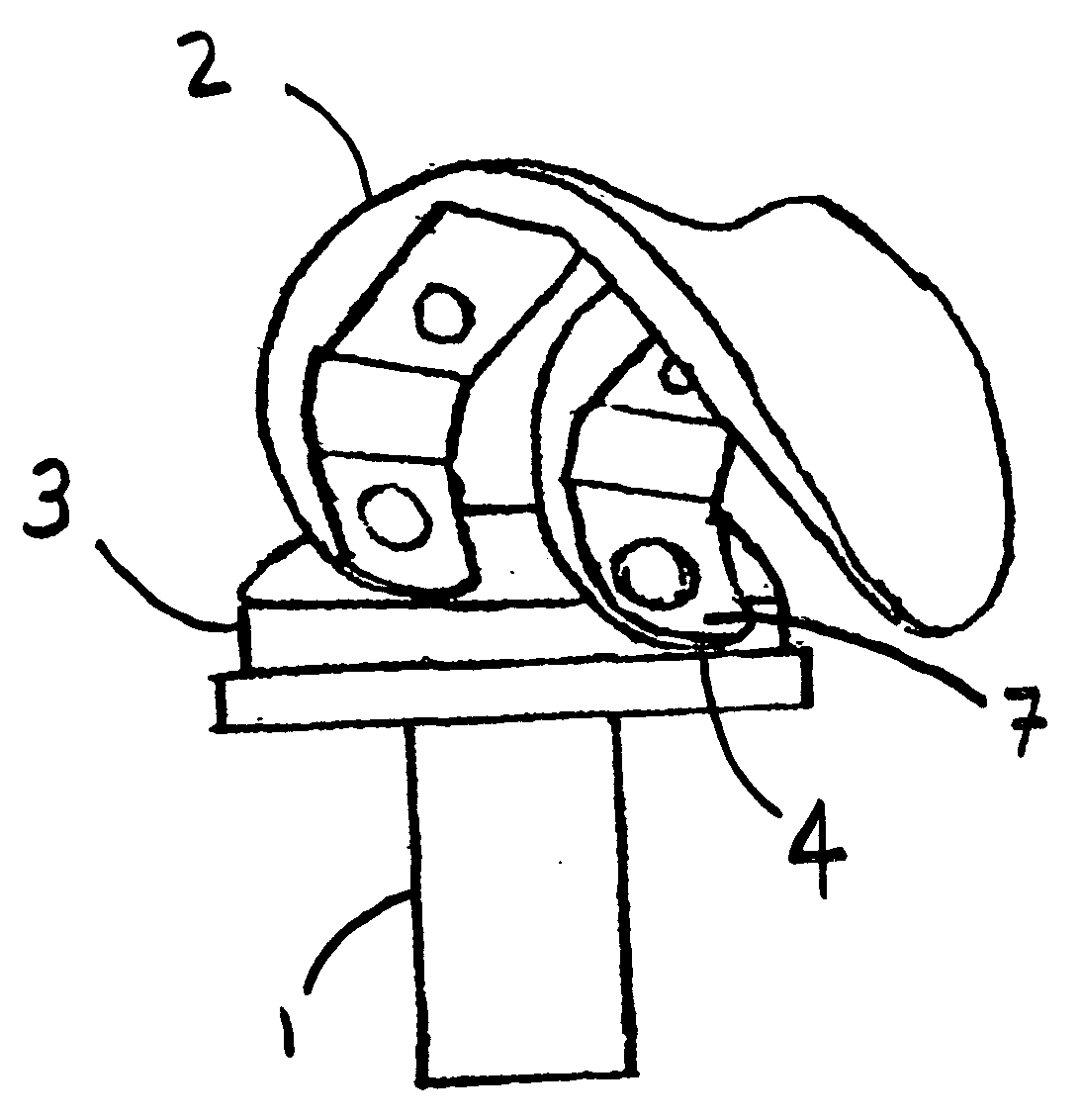
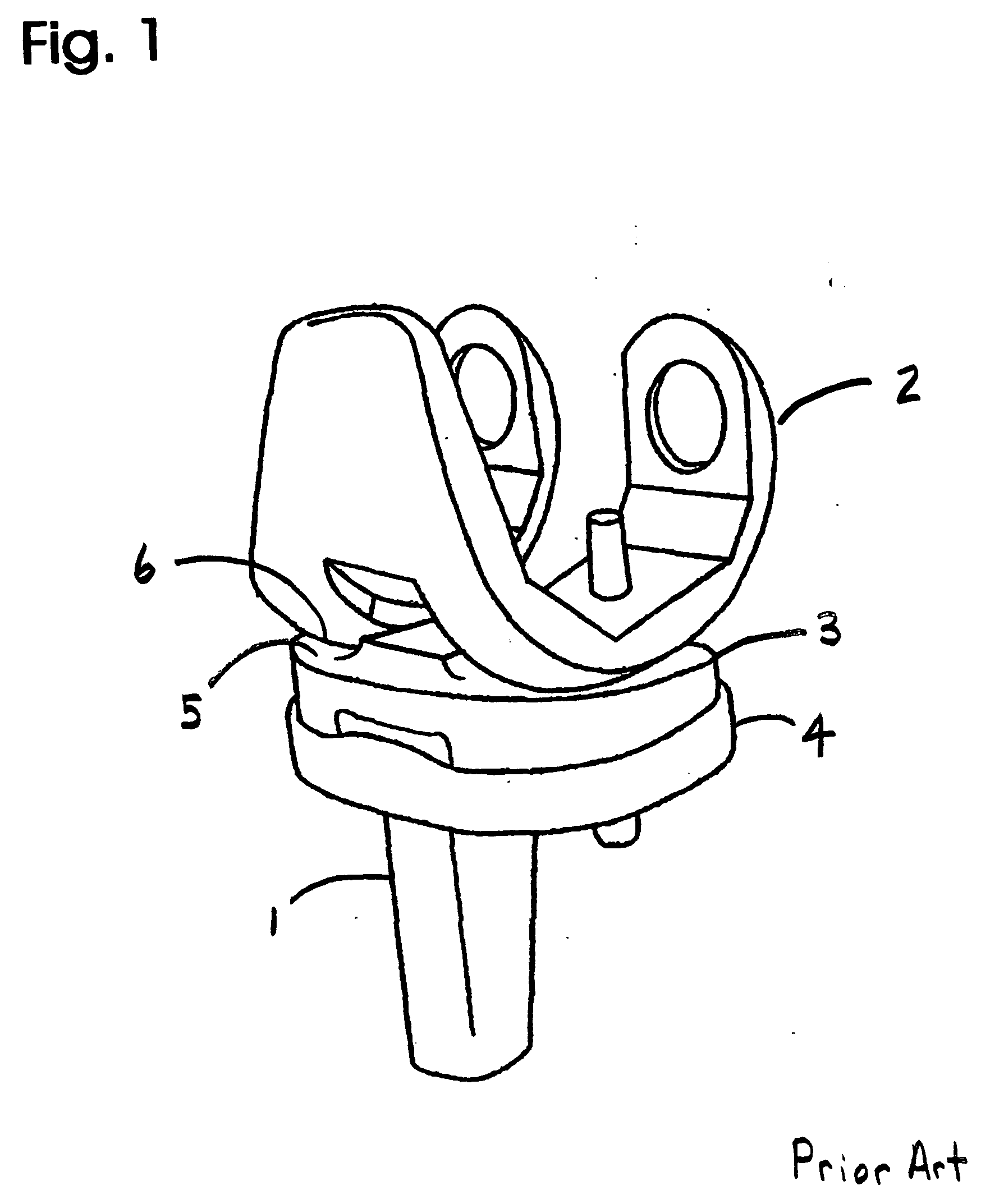
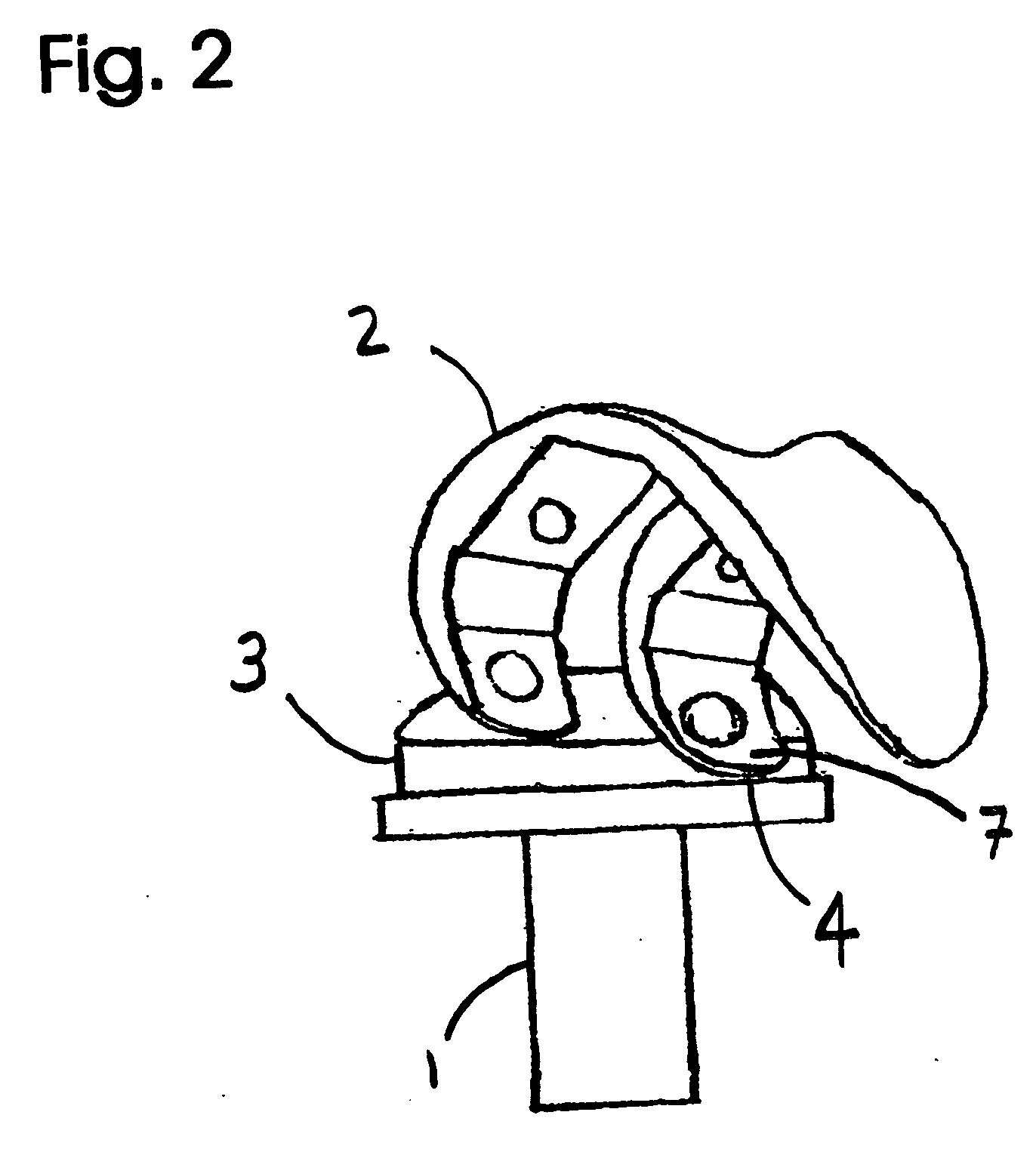
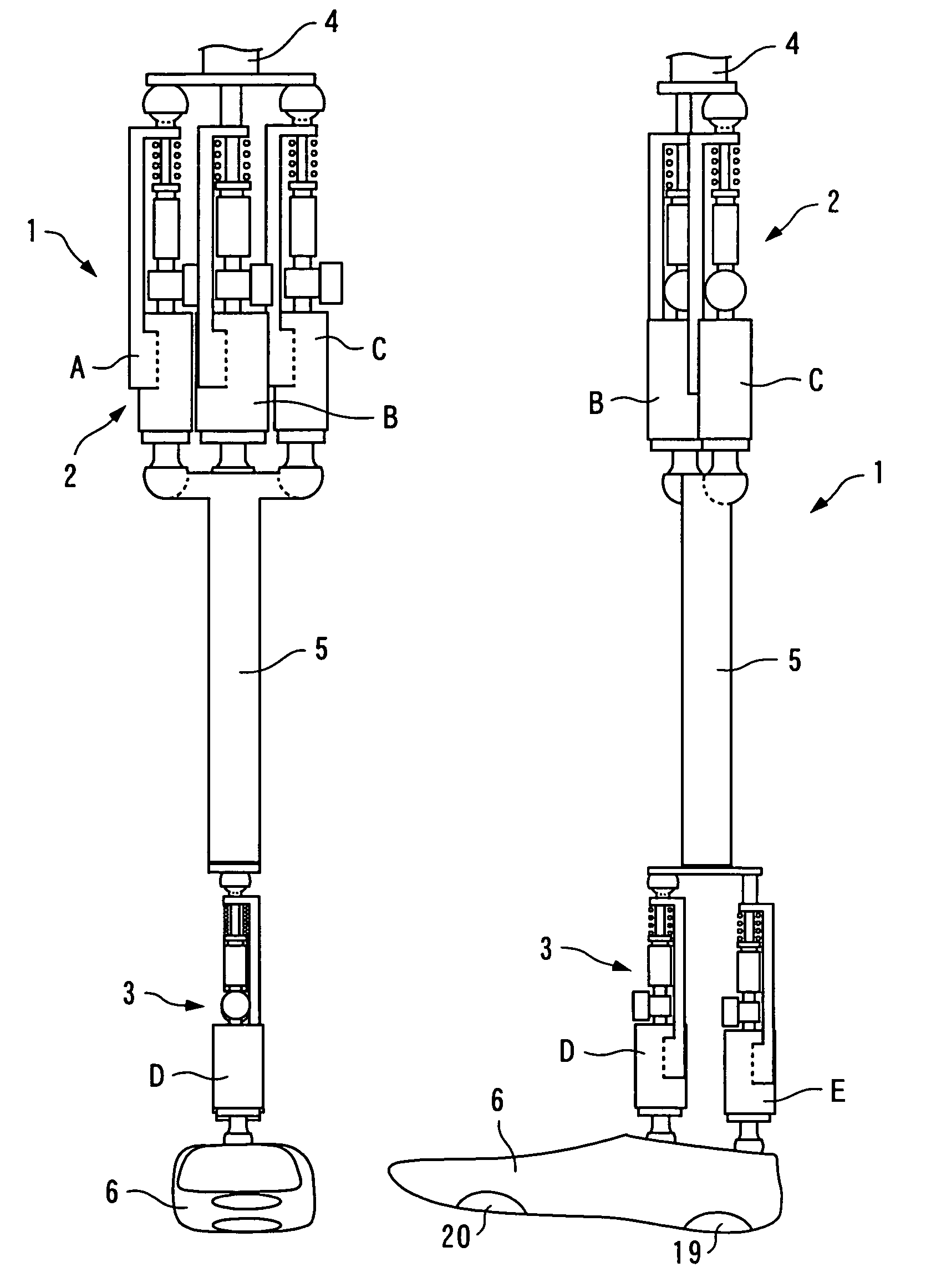
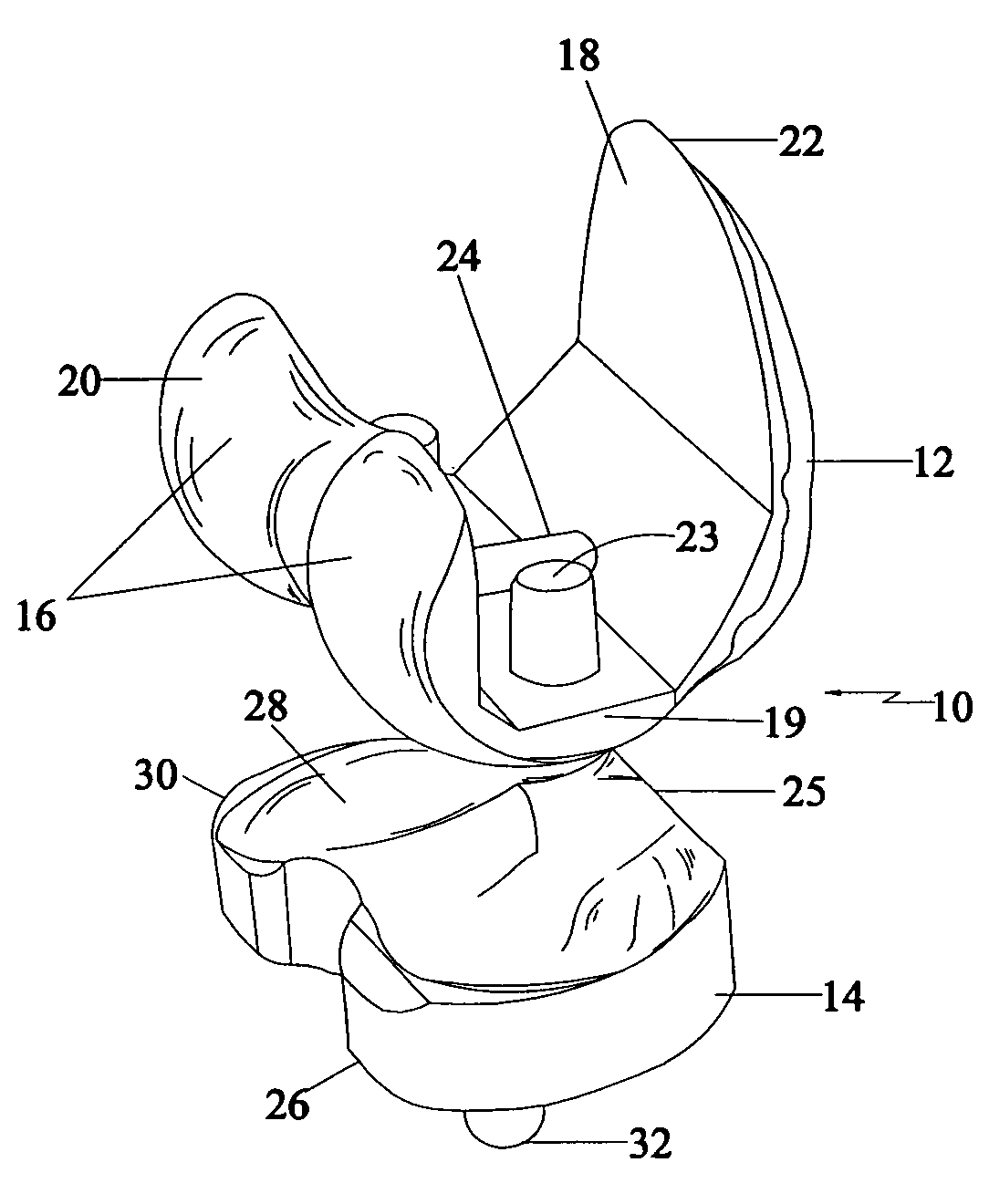
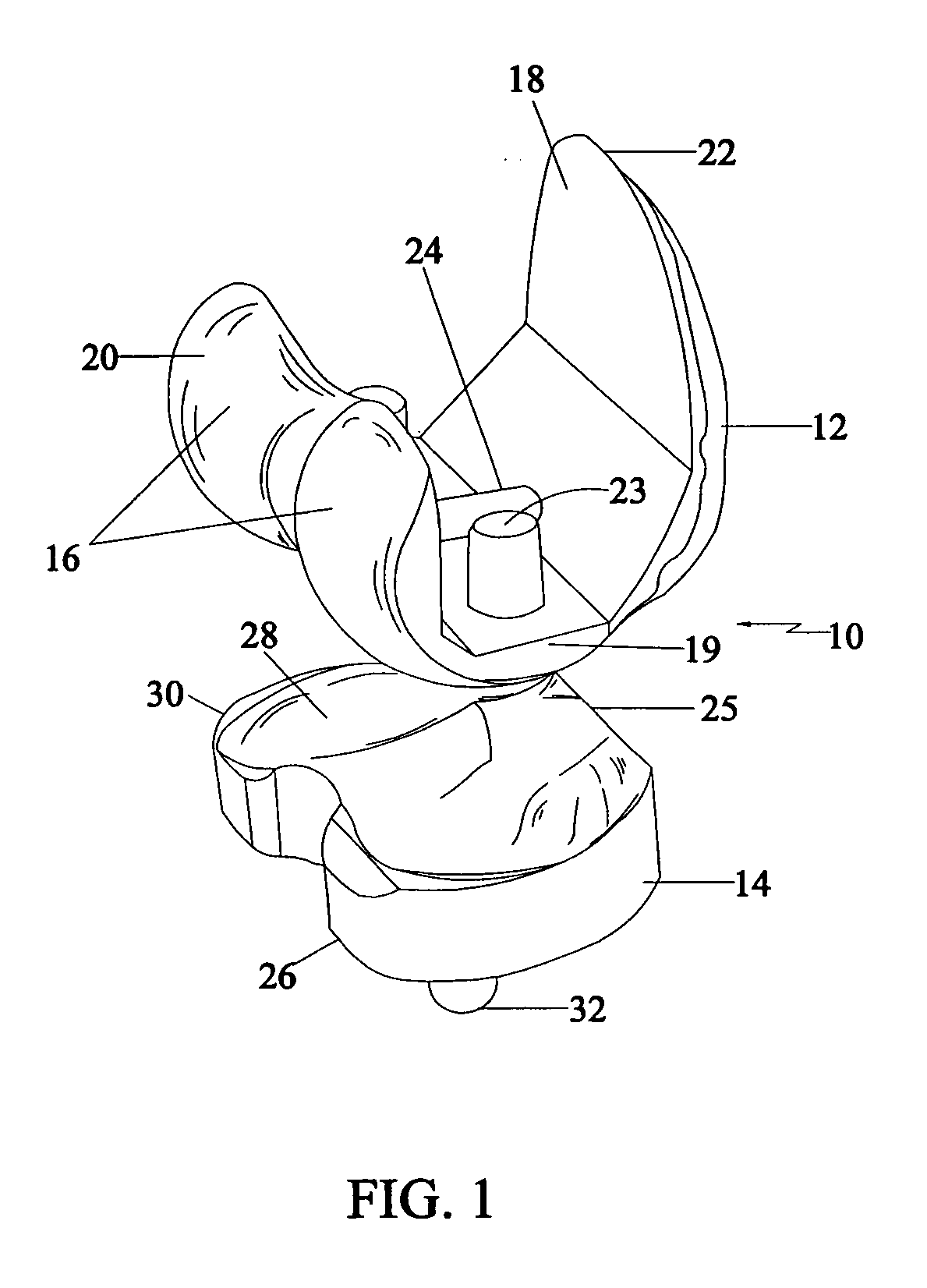
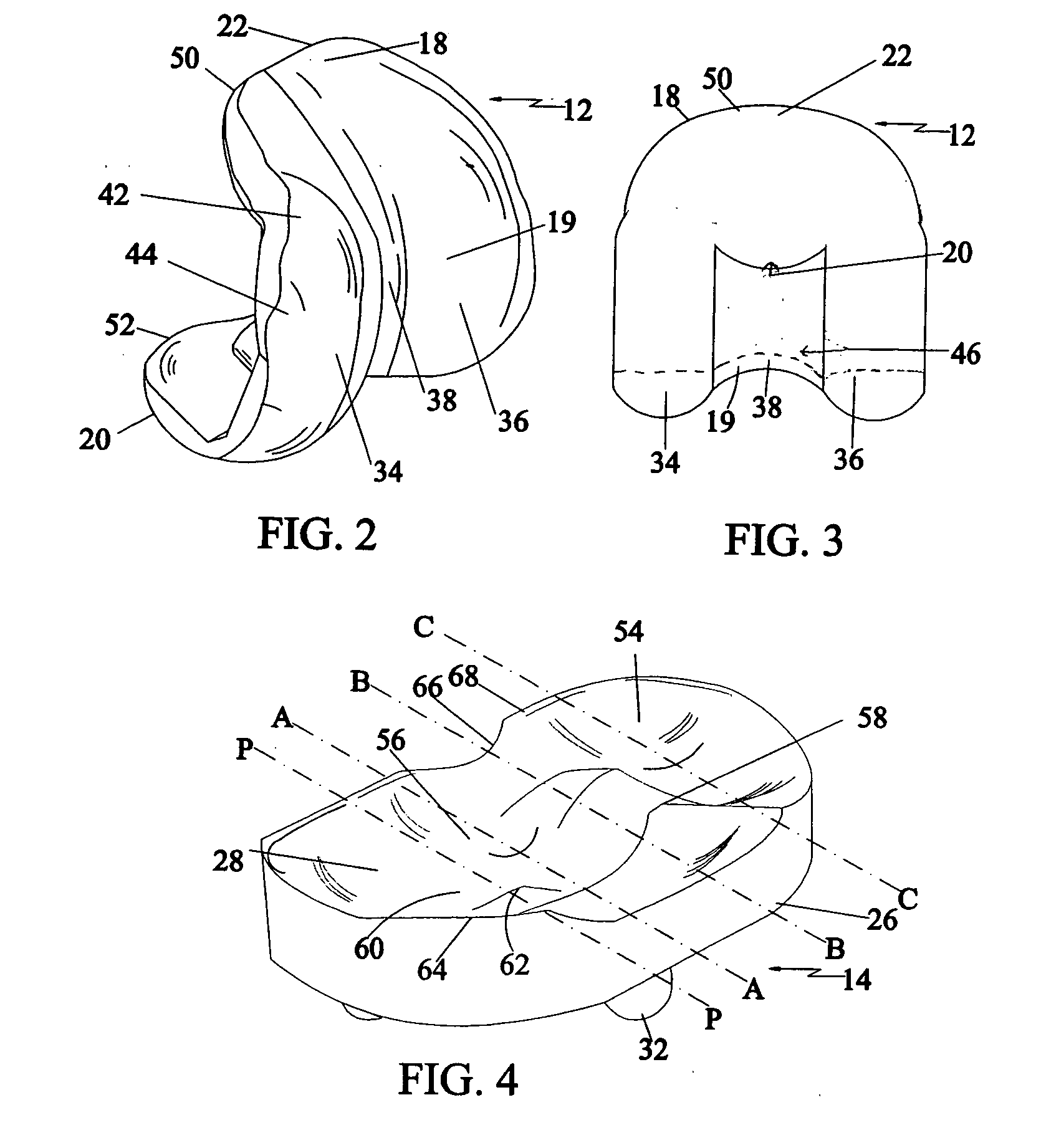
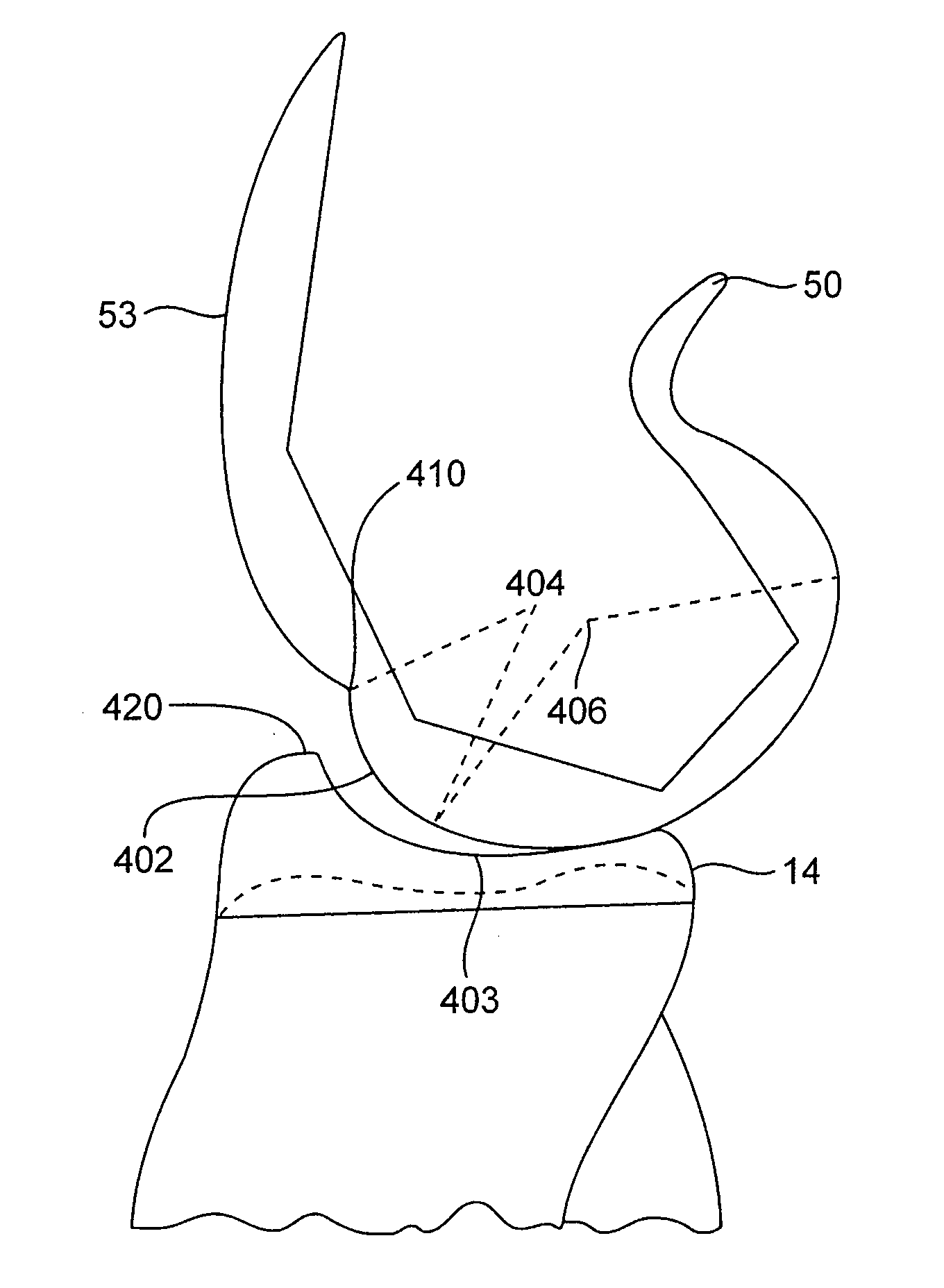
Patents
Literature
137 results about "Knee flexion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
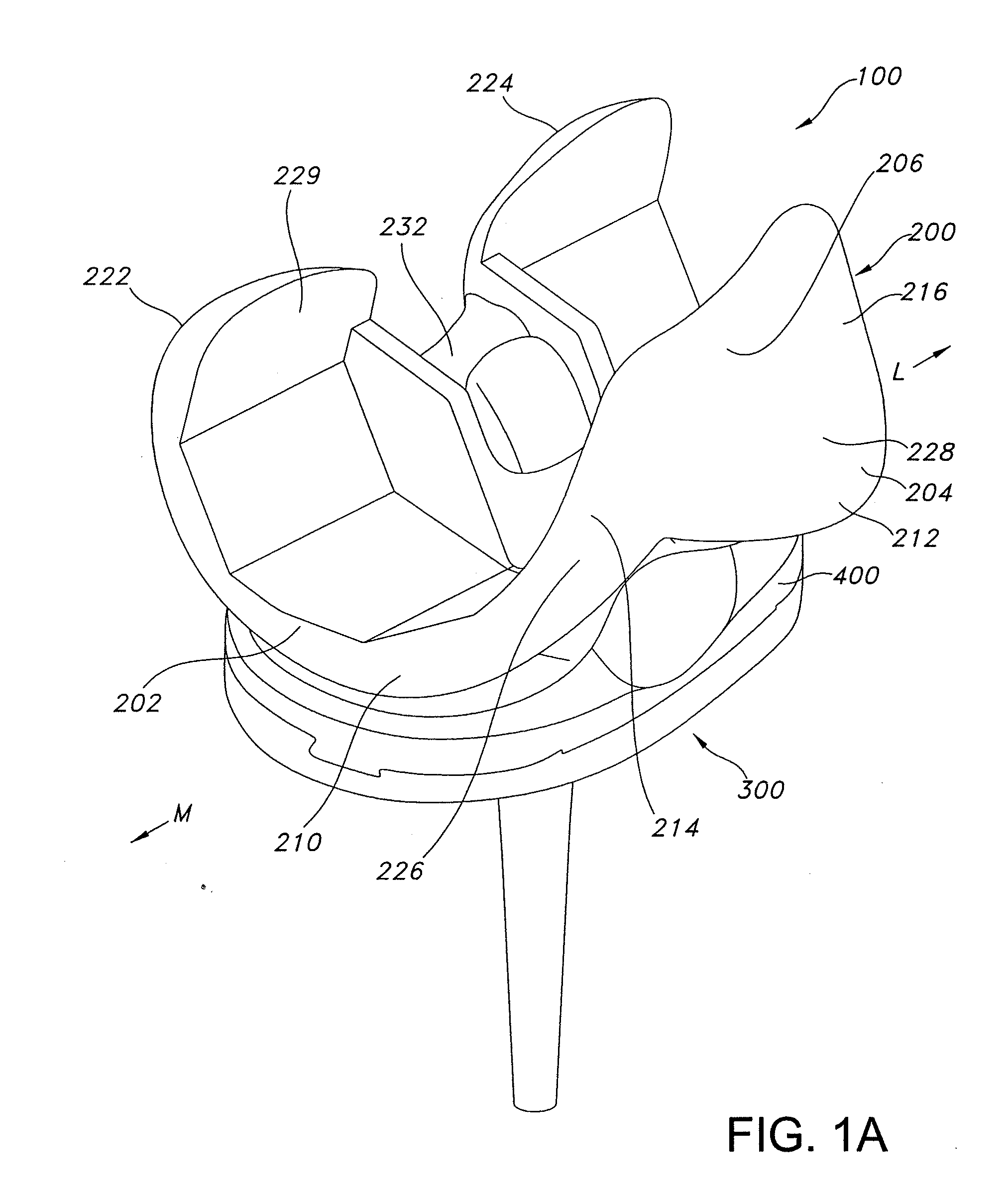
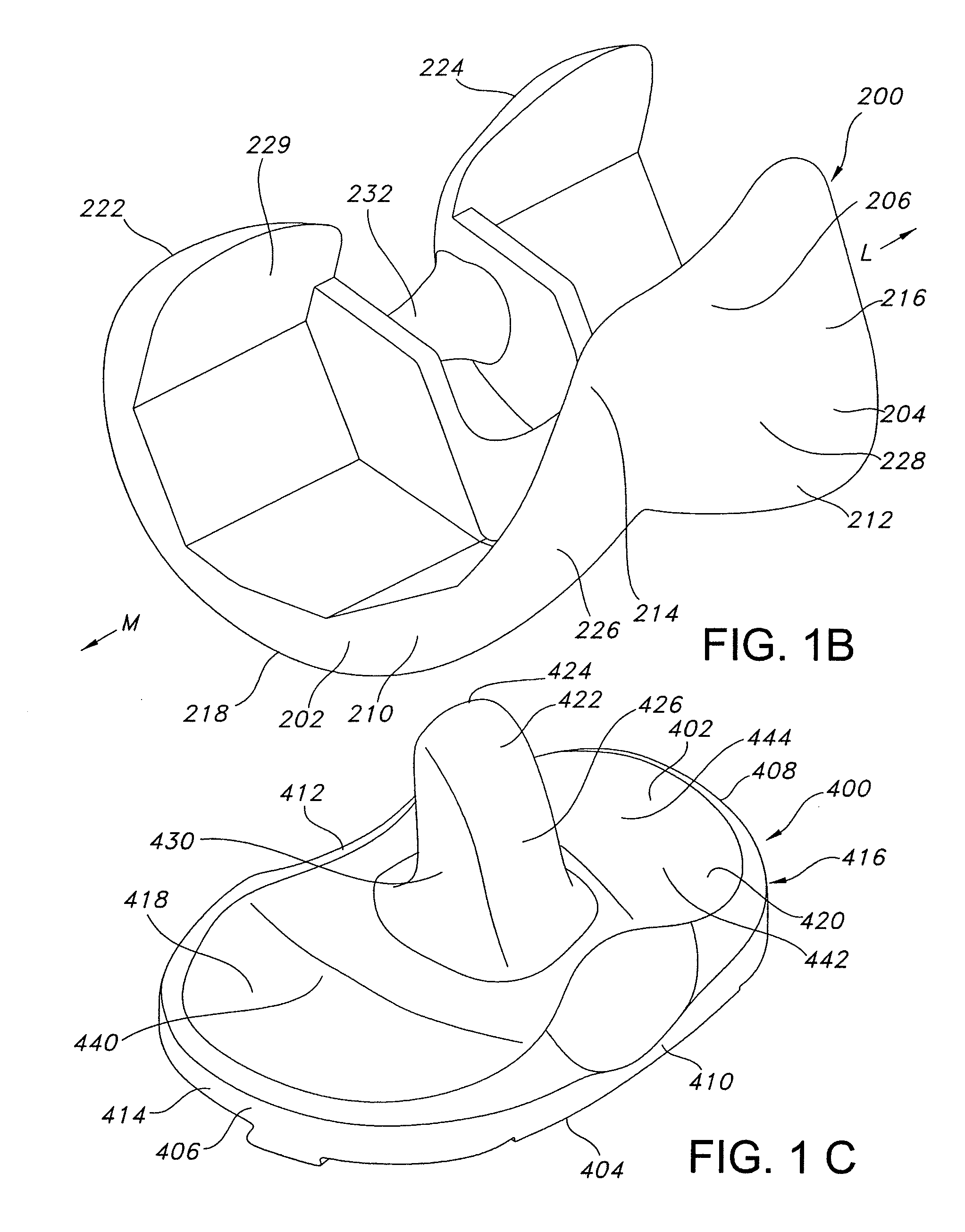
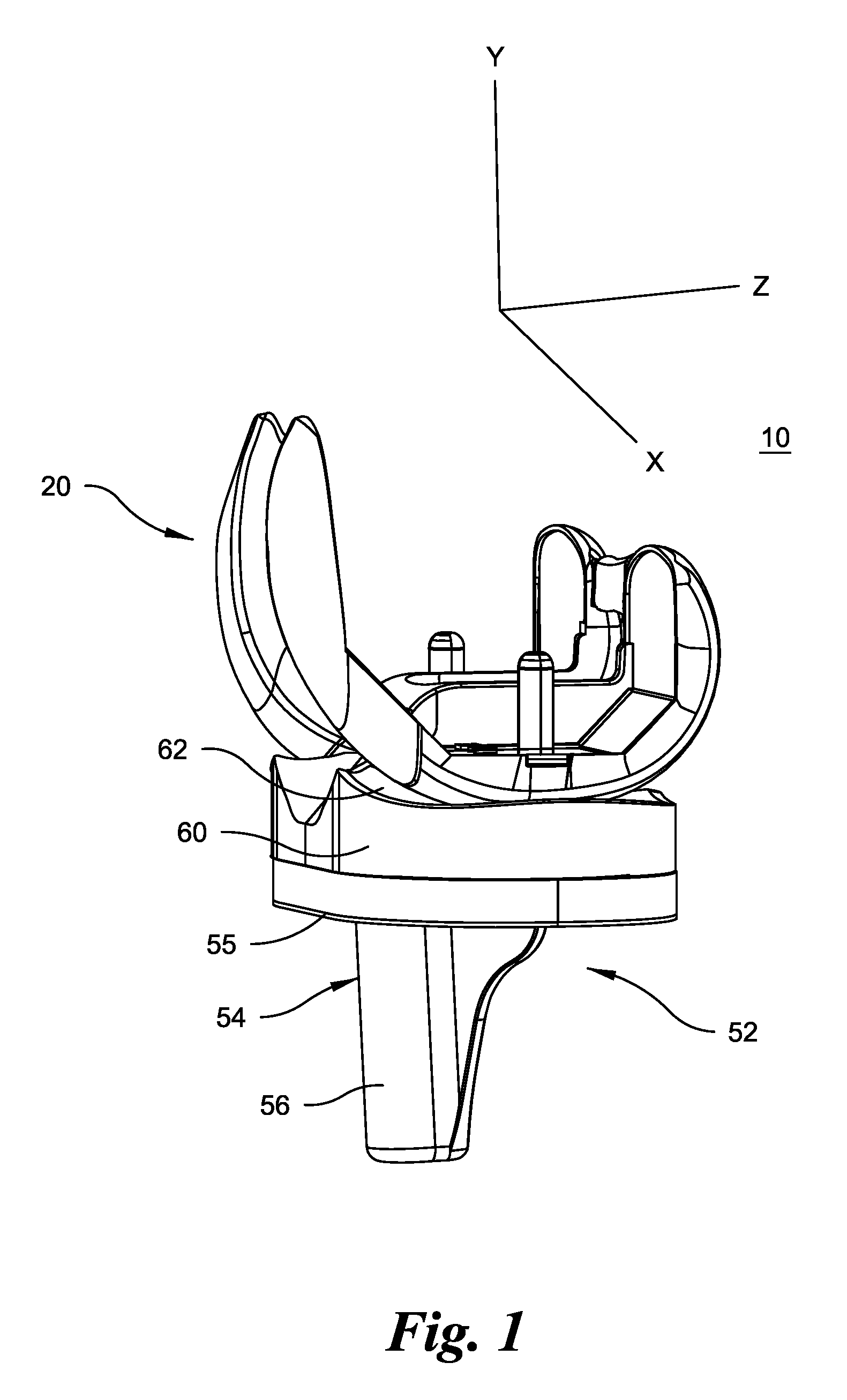
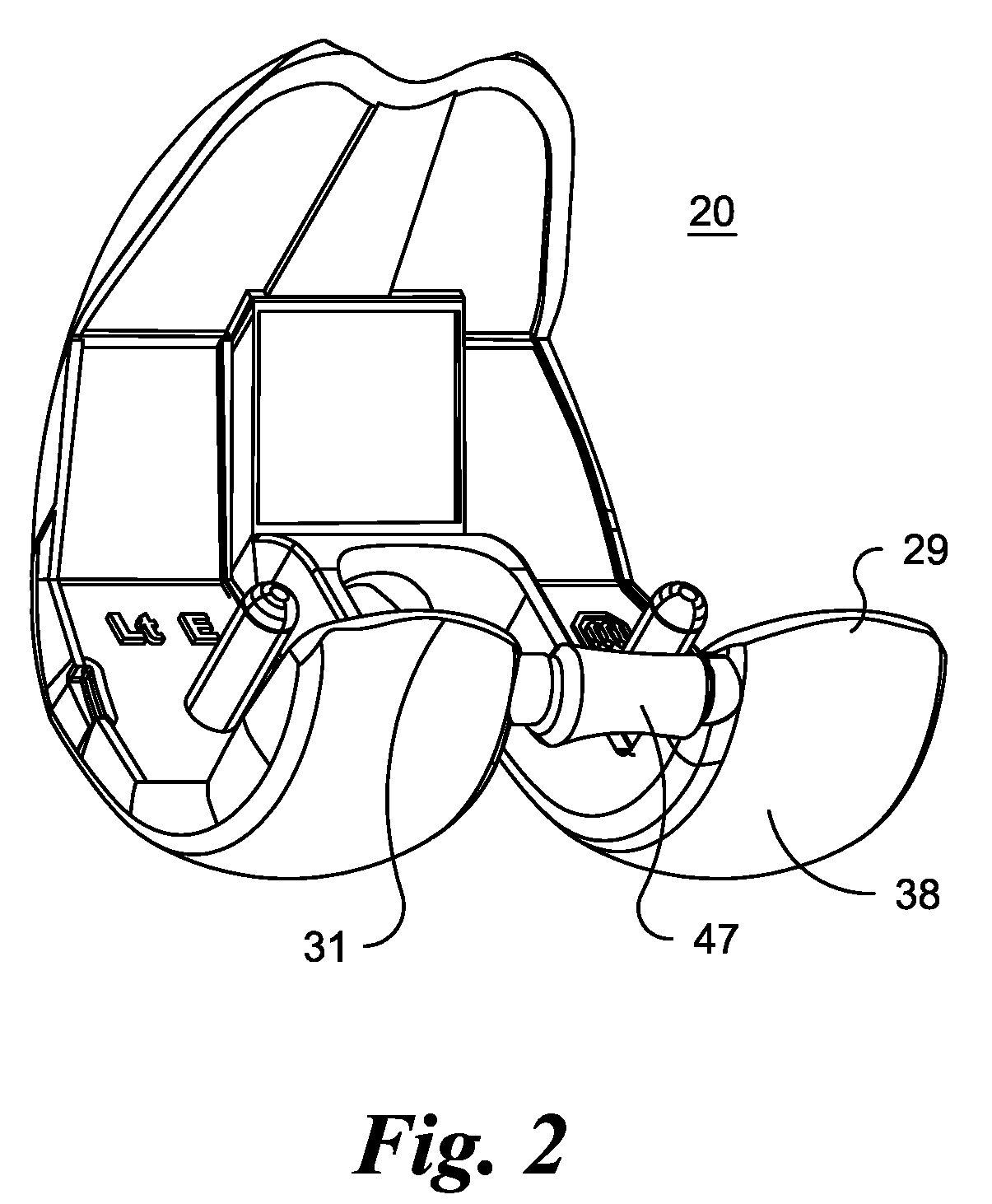
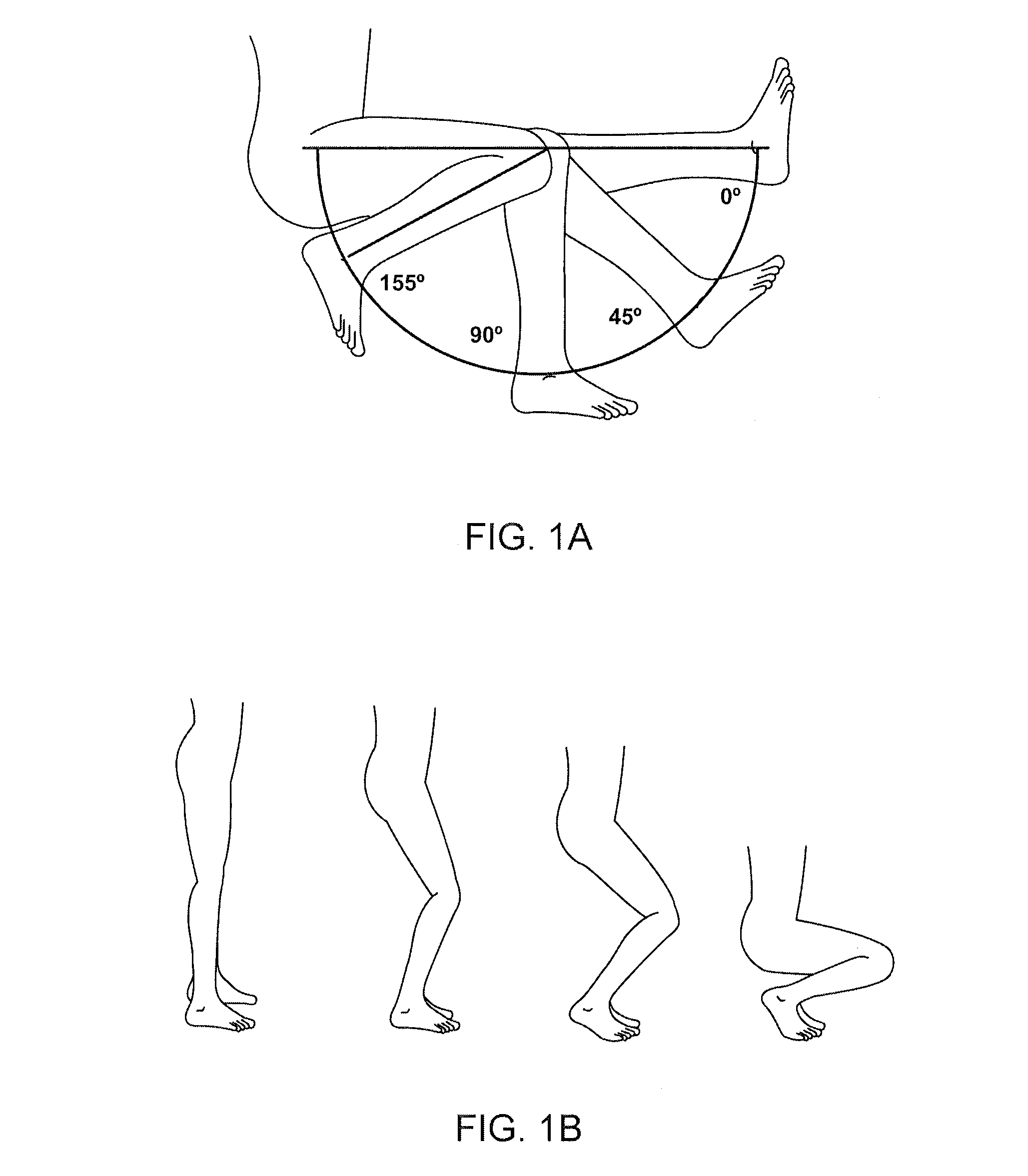
High performance knee prostheses
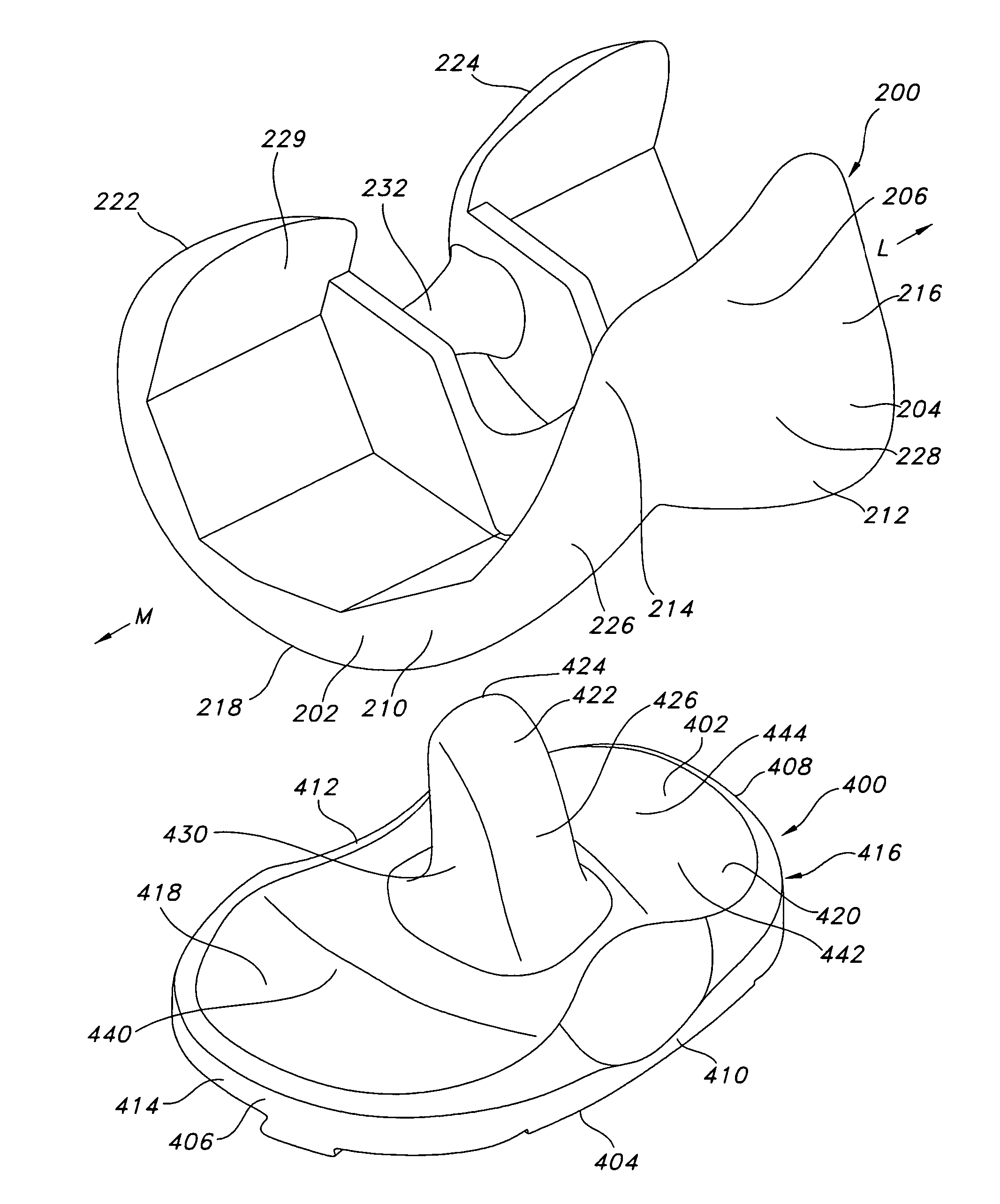
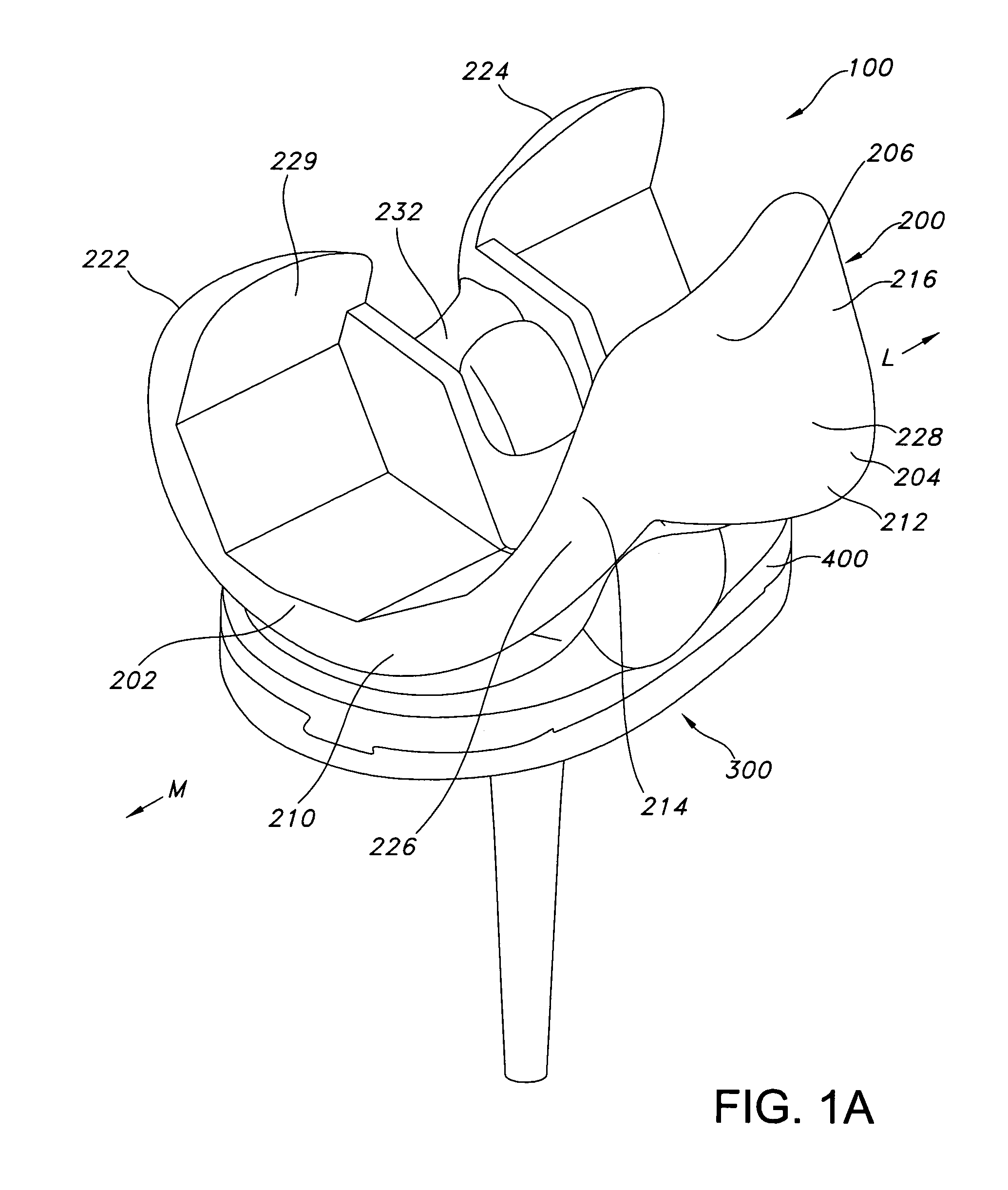
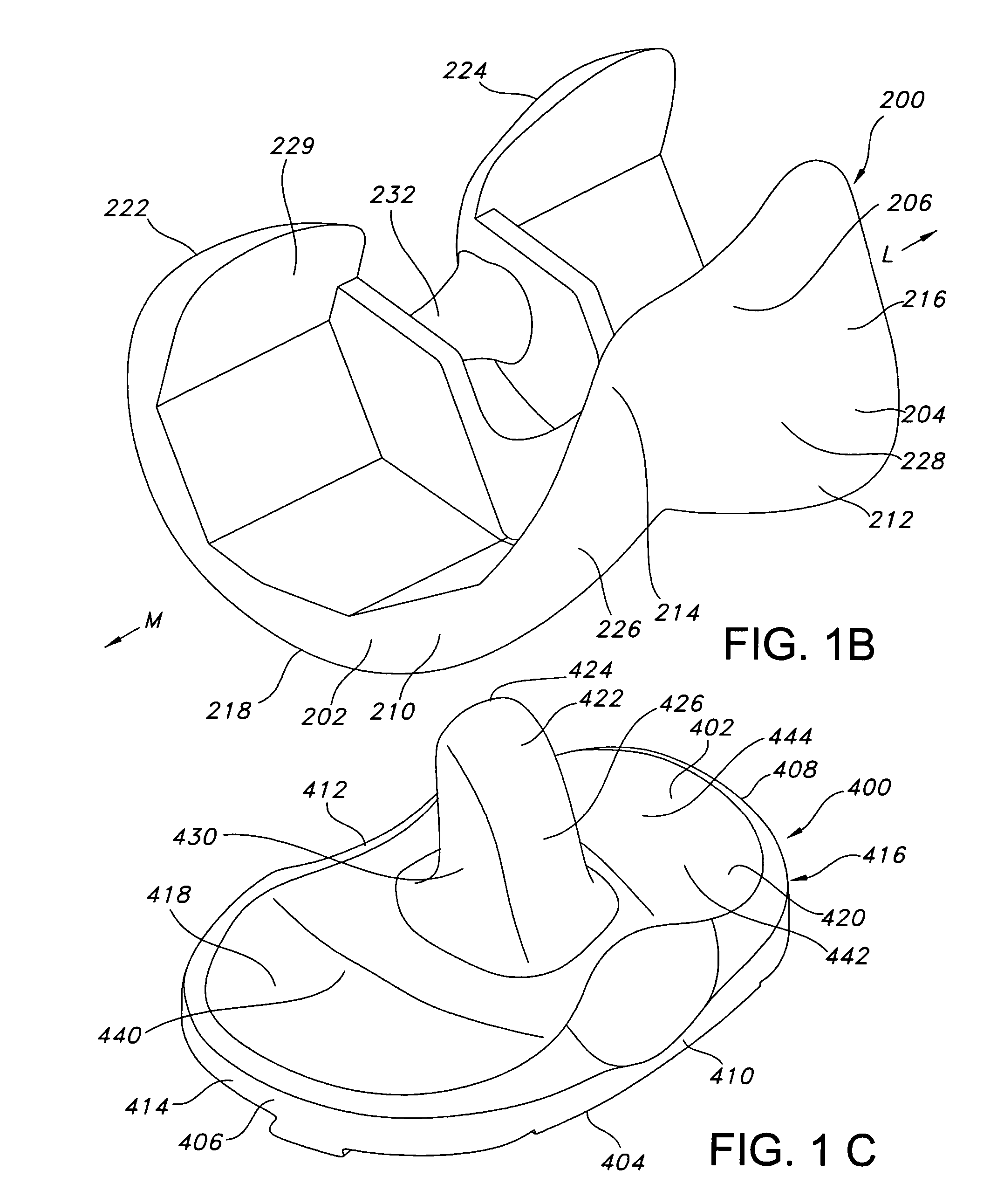
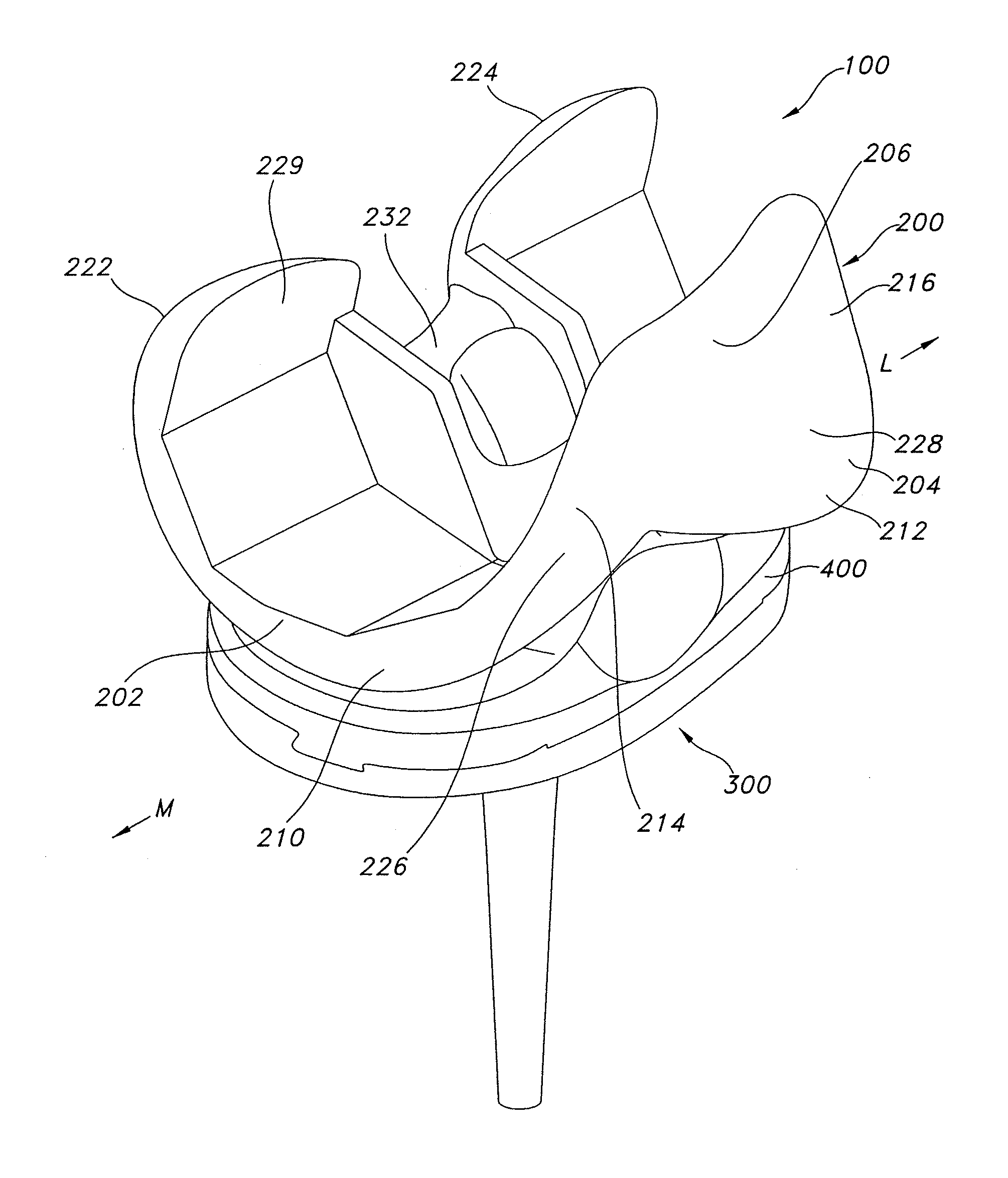
ActiveUS7326252B2Faithful replicationLittle strengthJoint implantsKnee jointsStructure and functionFemoral component
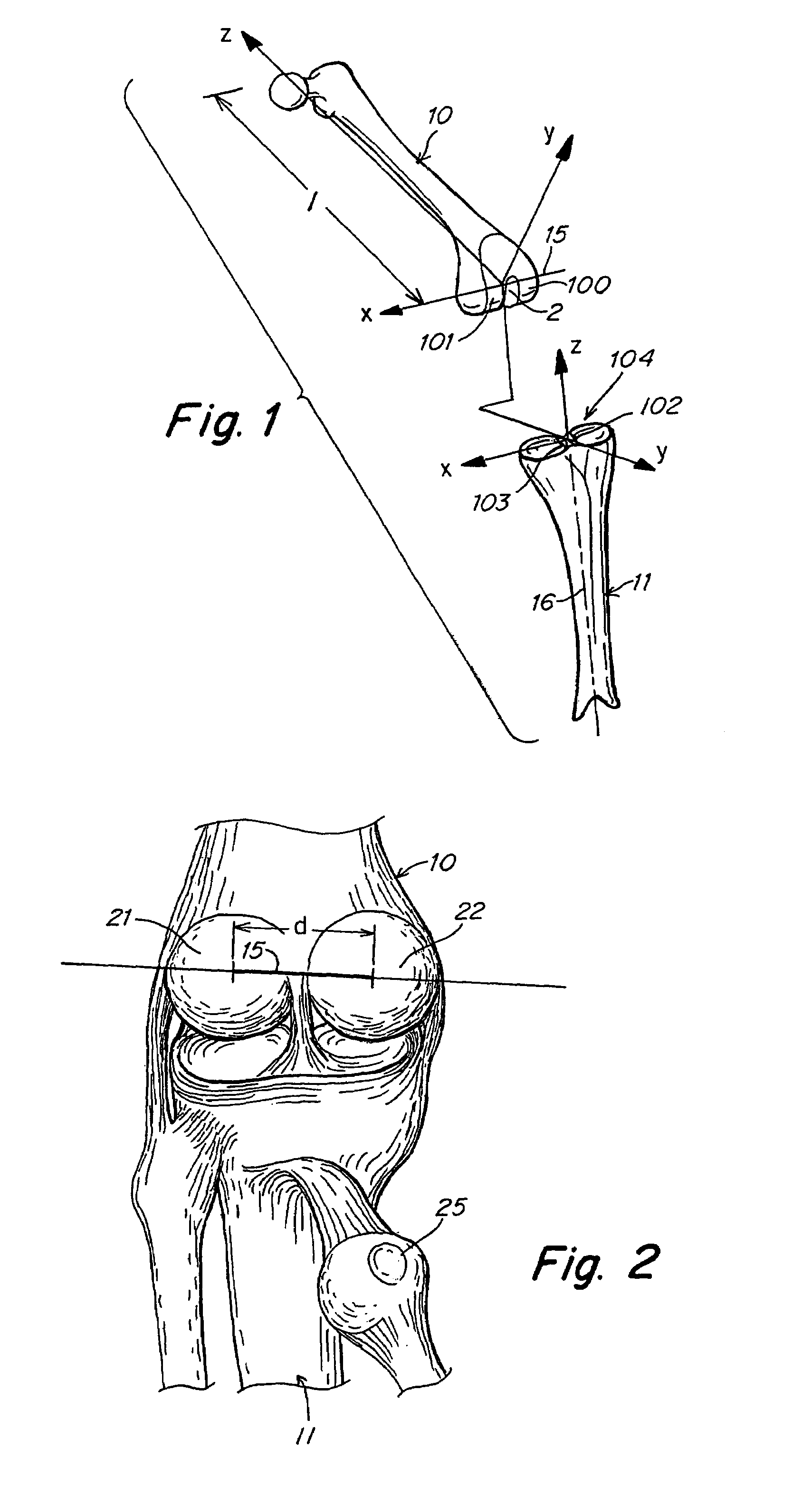
Knee prostheses featuring components that more faithfully replicate the structure and function of the human knee joint in order to provide, among other benefits: greater flexion of the knee in a more natural way by promoting or at least accommodating internal tibial rotation in a controlled way, replication of the natural screw home mechanism, and controlled articulation of the tibia and femur respective to each other in a more natural way. In a preferred embodiment, such prostheses include an insert component disposed between a femoral component and a tibial component, the insert component preferably featuring among other things a reversely contoured postereolateral bearing surface that helps impart internal rotation to the tibia as the knee flexes. Other surfaces can also be specially shaped to achieve similar results, preferably using iterative automated techniques that allow testing and iterative design taking into account a manageable set of major forces acting on the knee during normal functioning, together with information that is known about natural knee joint kinetics and kinematics.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
High performance knee prostheses
ActiveUS20080119940A1Faithful replicationLittle strengthJoint implantsKnee jointsStructure and functionFemoral component
Knee prostheses featuring components that more faithfully replicate the structure and function of the human knee joint in order to provide, among other benefits: greater flexion of the knee in a more natural way by promoting or at least accommodating internal tibial rotation in a controlled way, replication of the natural screw home mechanism, and controlled articulation of the tibia and femur respective to each other in a more natural way. In a preferred embodiment, such prostheses include an insert component disposed between a femoral component and a tibial component, the insert component preferably featuring among other things a reversely contoured posterolateral bearing surface that helps impart internal rotation to the tibia as the knee flexes. Other surfaces can also be specially shaped to achieve similar results, preferably using iterative automated techniques that allow testing and iterative design taking into account a manageable set of major forces acting on the knee during normal functioning, together with information that is known about natural knee joint kinetics and kinematics.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
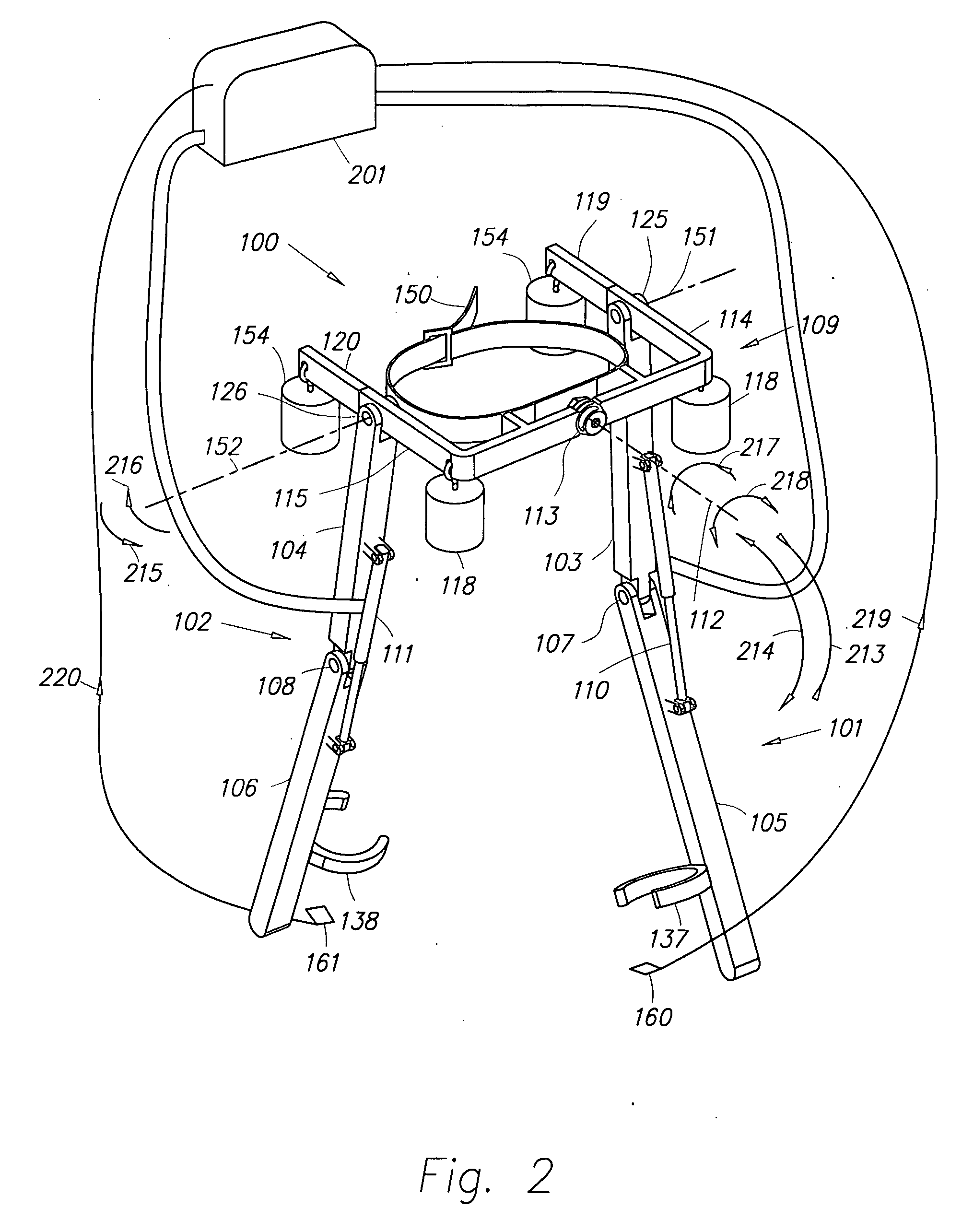
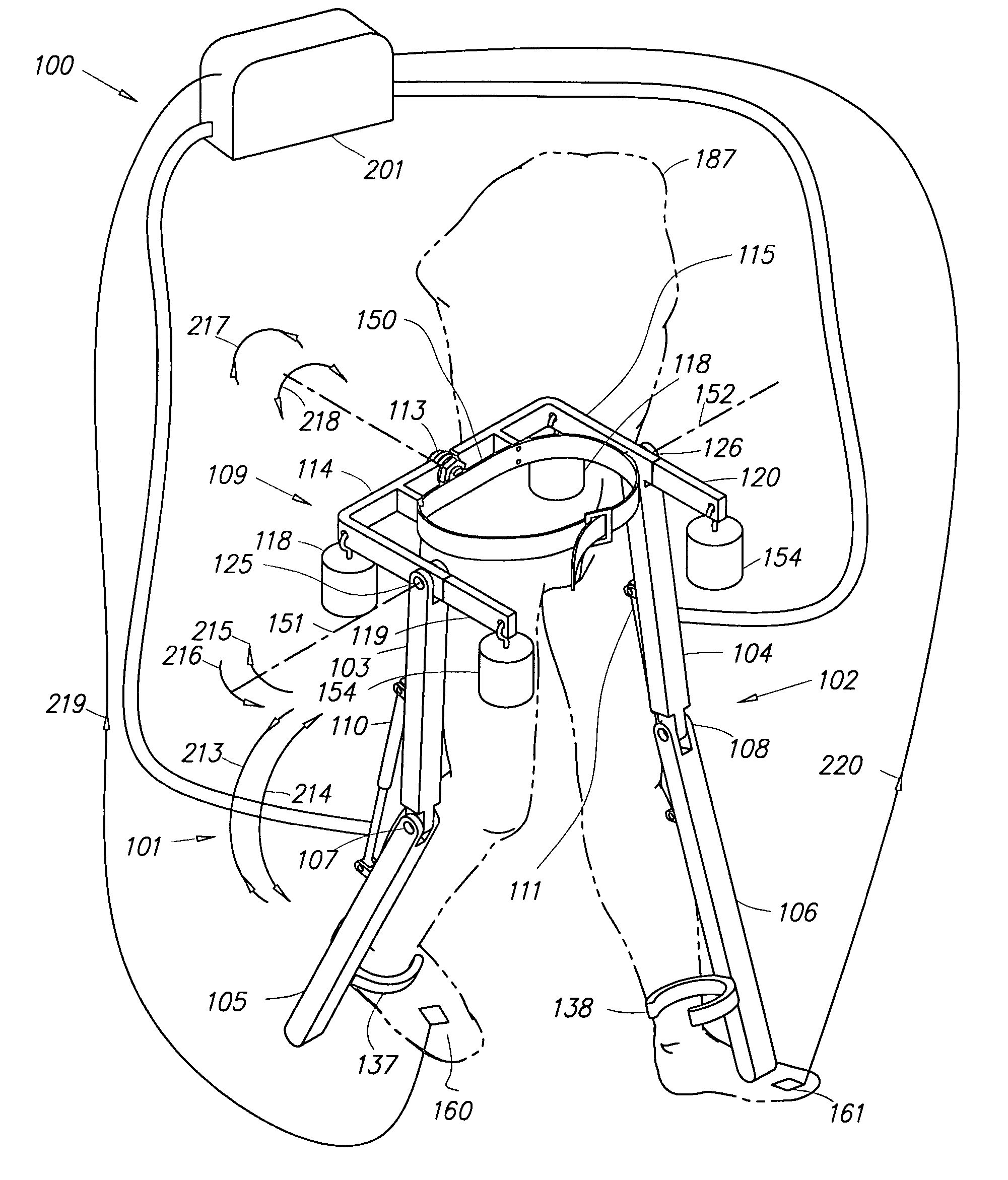
Semi-powered lower extremity exoskeleton
ActiveUS20070056592A1Drag minimizationProgramme-controlled manipulatorOperating chairsKnee JointEngineering
The lower extremity exoskeleton comprises two leg supports connectable to person's lower limbs and configured to rest on the ground during their stance phase. Each leg support comprises a thigh link and a shank link; a knee joint configured to allow flexion and extension between the shank link and the thigh link. The lower extremity exoskeleton further comprises an exoskeleton trunk connectable to the person'supper body. The exoskeleton trunk is connectable to the thigh links of the leg supports allowing for the flexion and extension between the leg supports and the exoskeleton trunk. Two torque generators are coupled to each of the knee joints. A power unit, capable of providing power, is coupled to the torque generators. In operation when a leg support is in a stance phase and climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit injects power into the respective torque generator thereby extending the respective knee angle. When a leg support is in stance phase and not climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to resist flexion of the respective knee joint. When a leg support is in a swing phase, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to minimize its resistance to knee flexion and extension.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
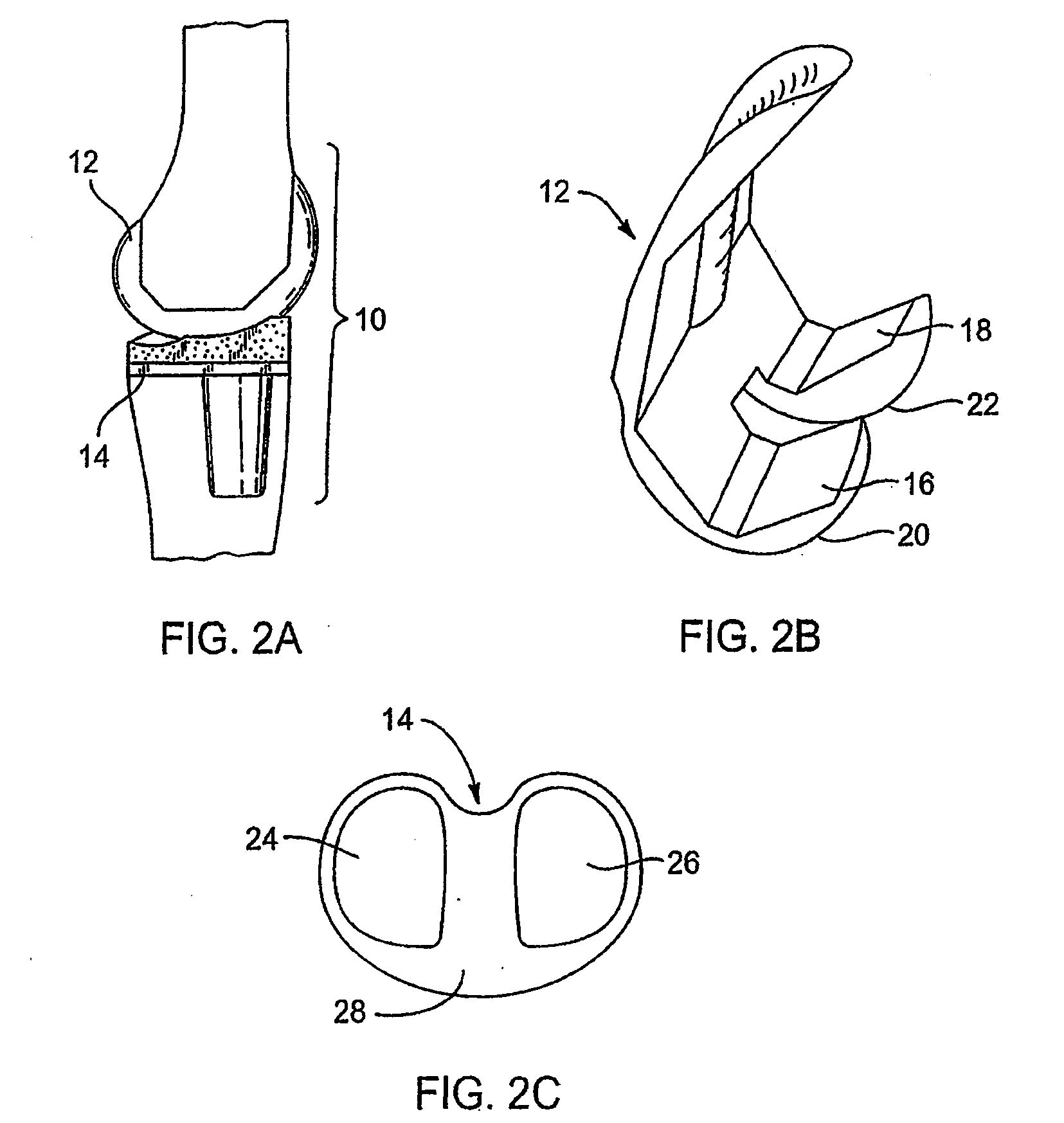
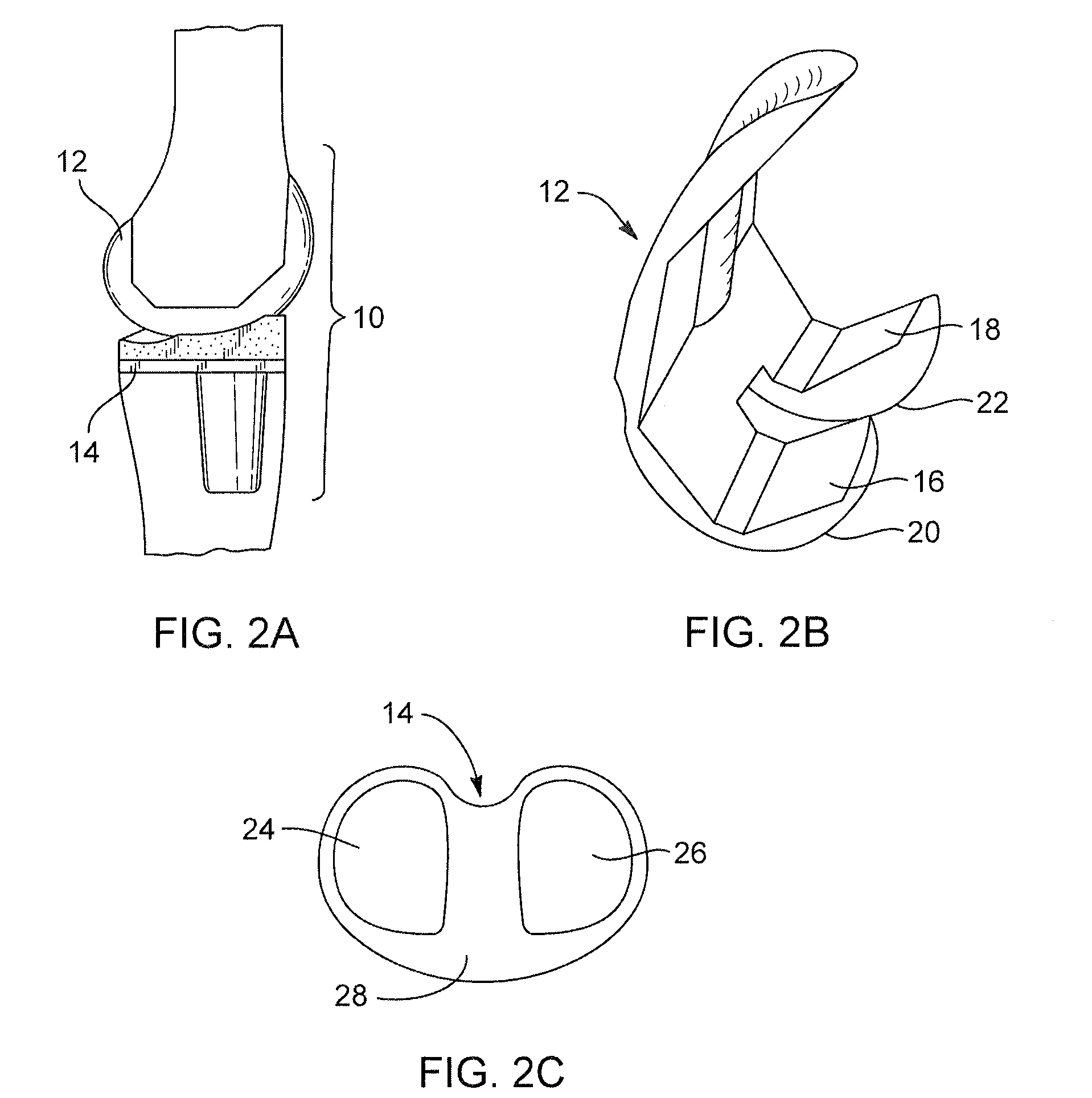
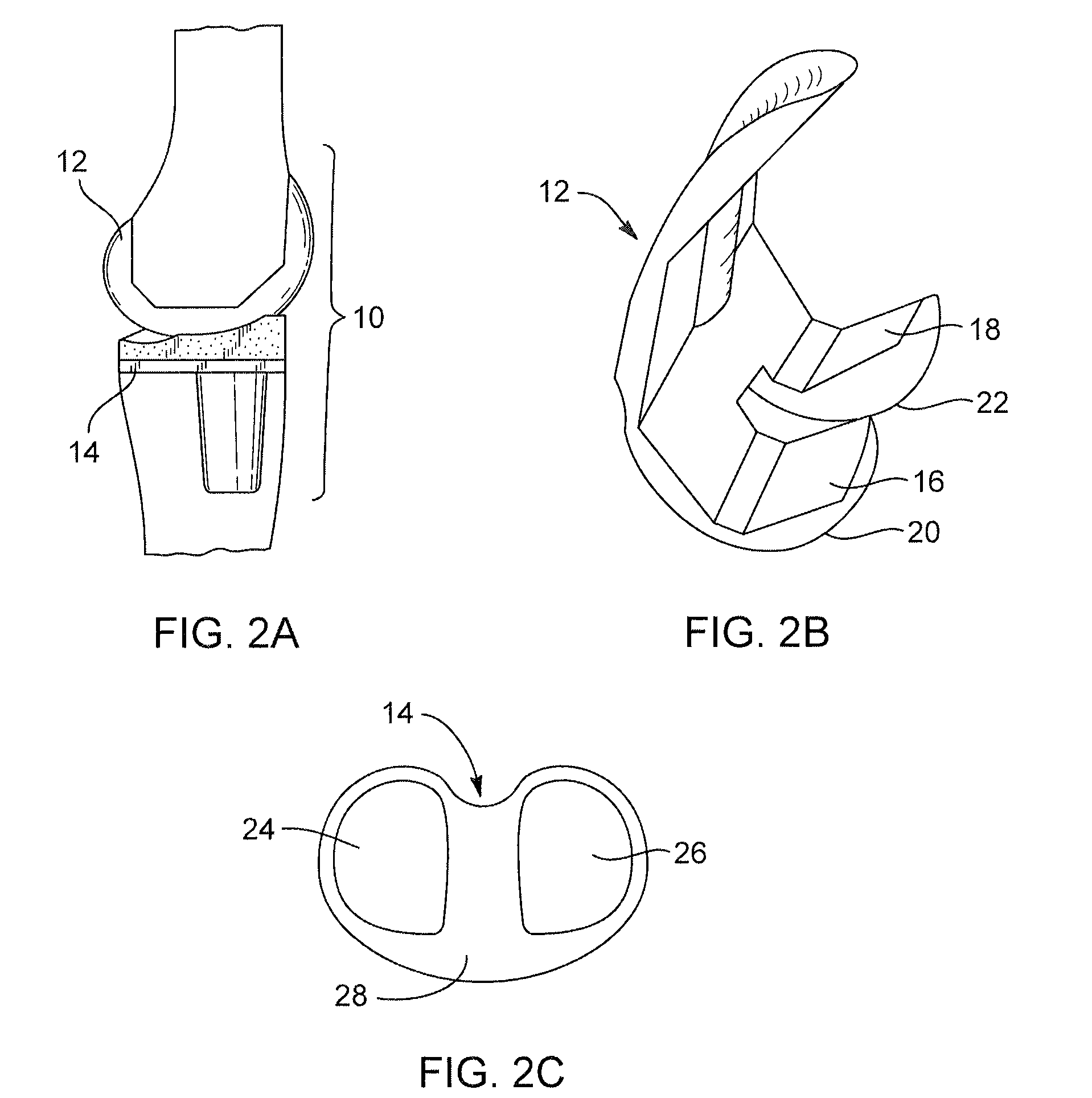
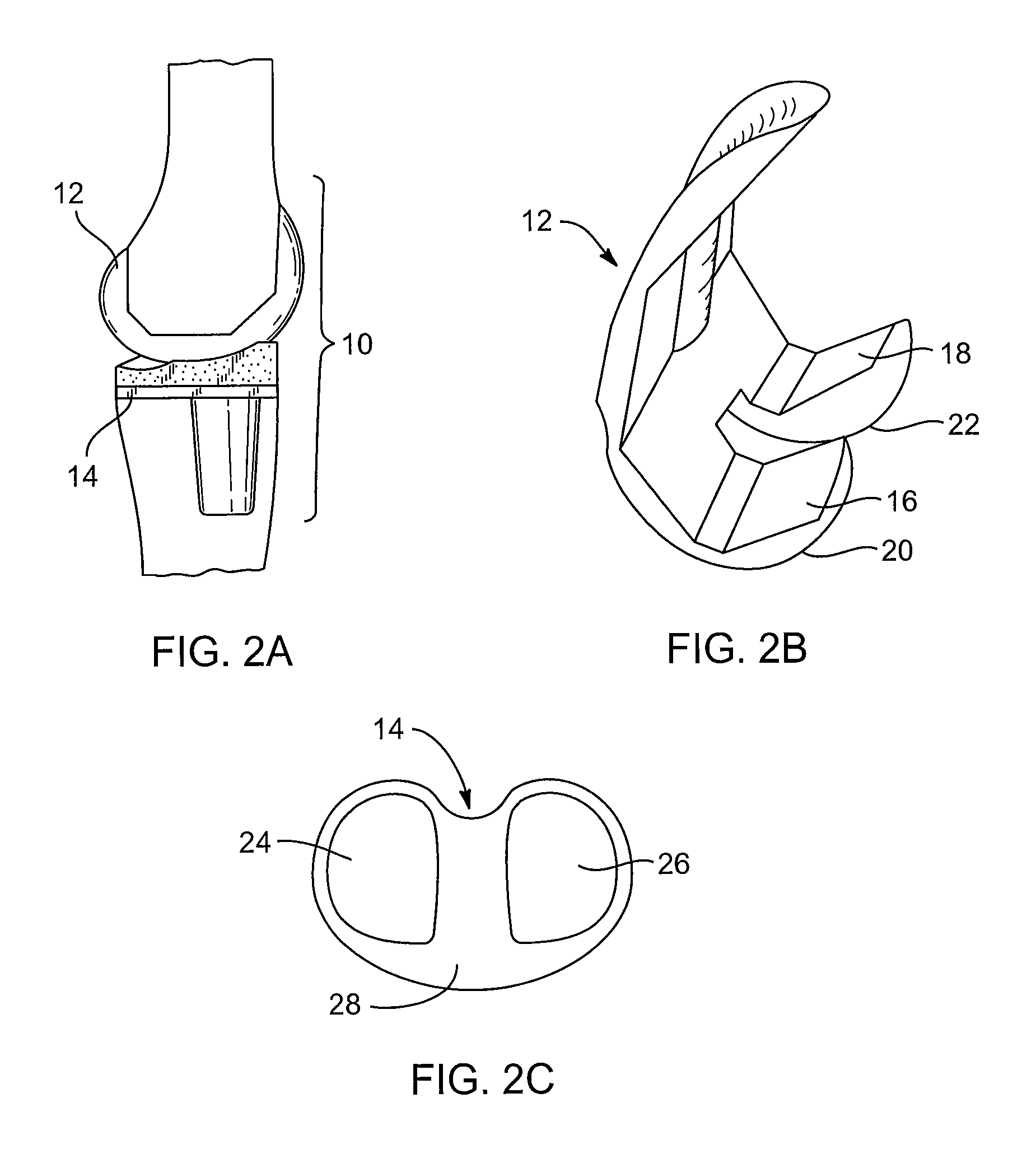
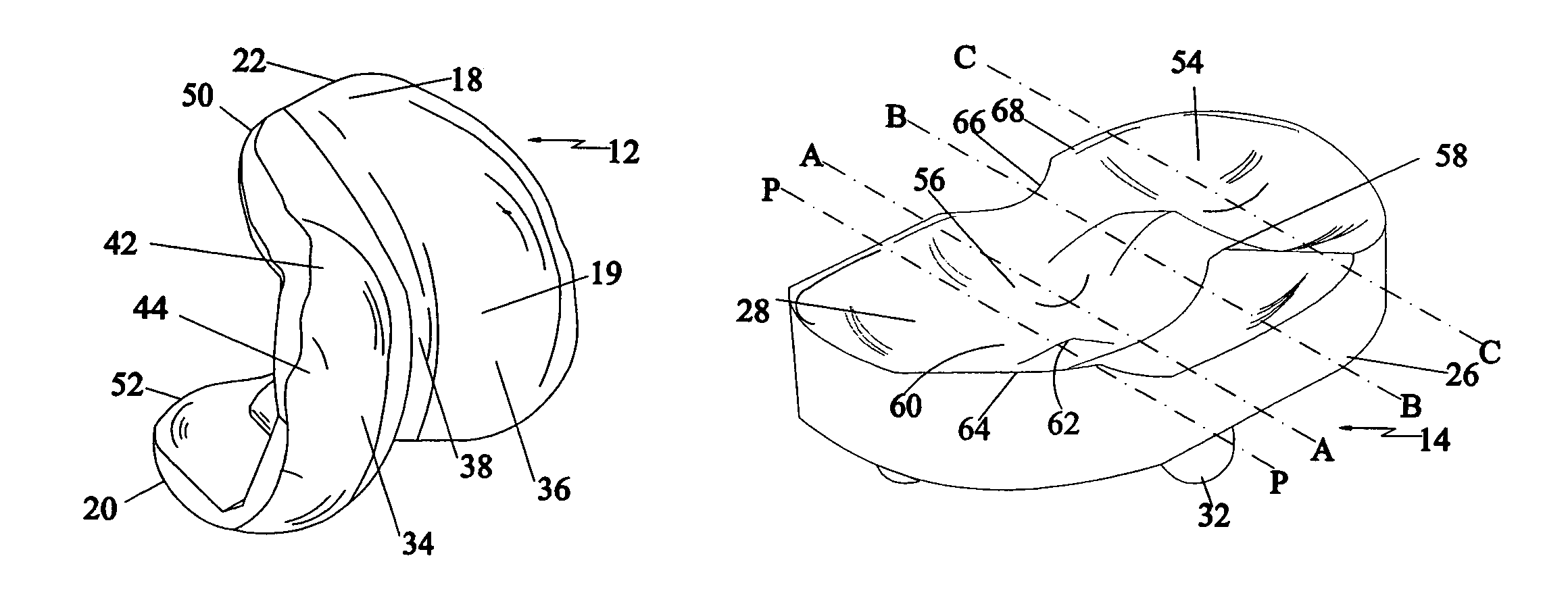
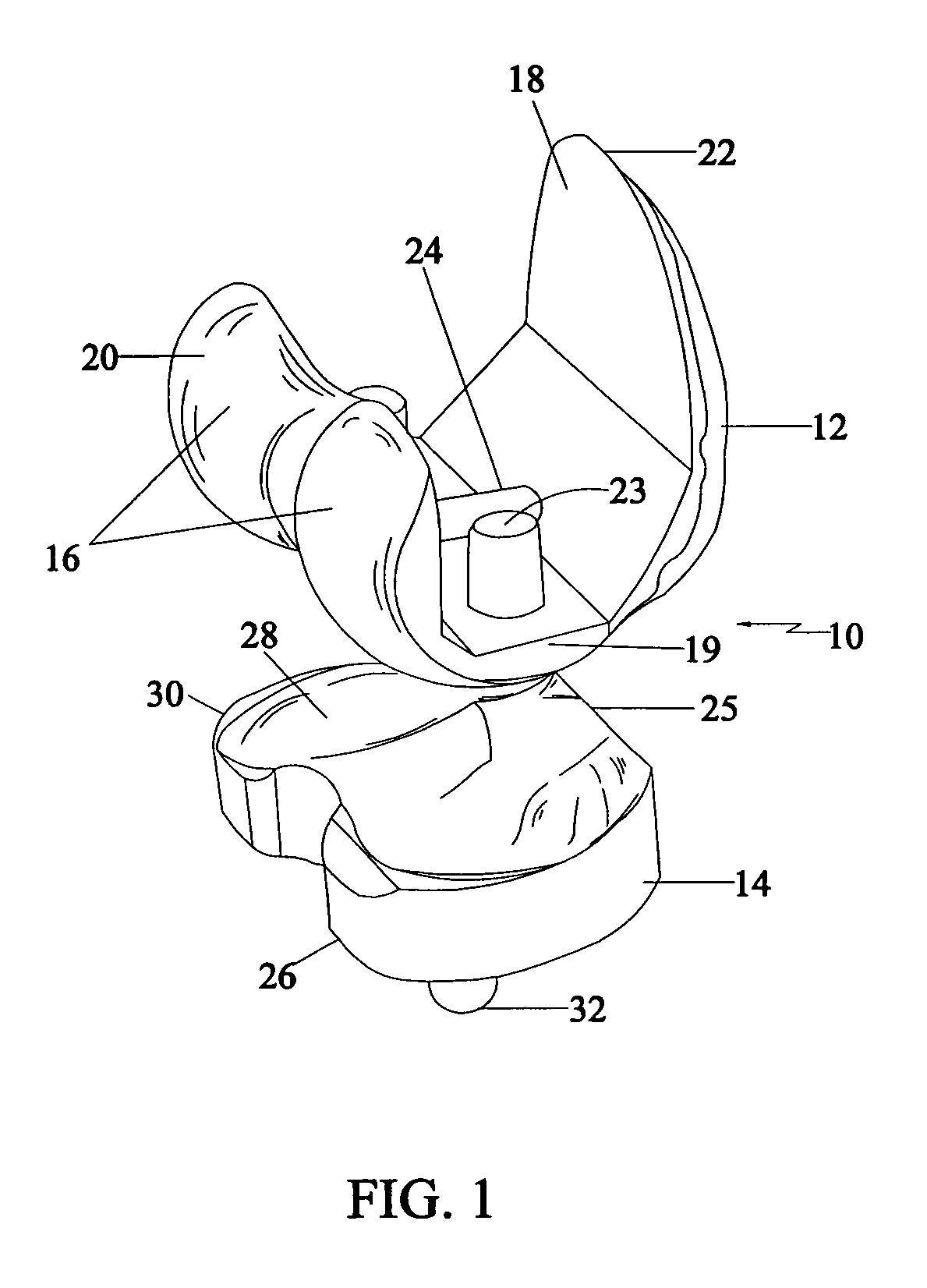
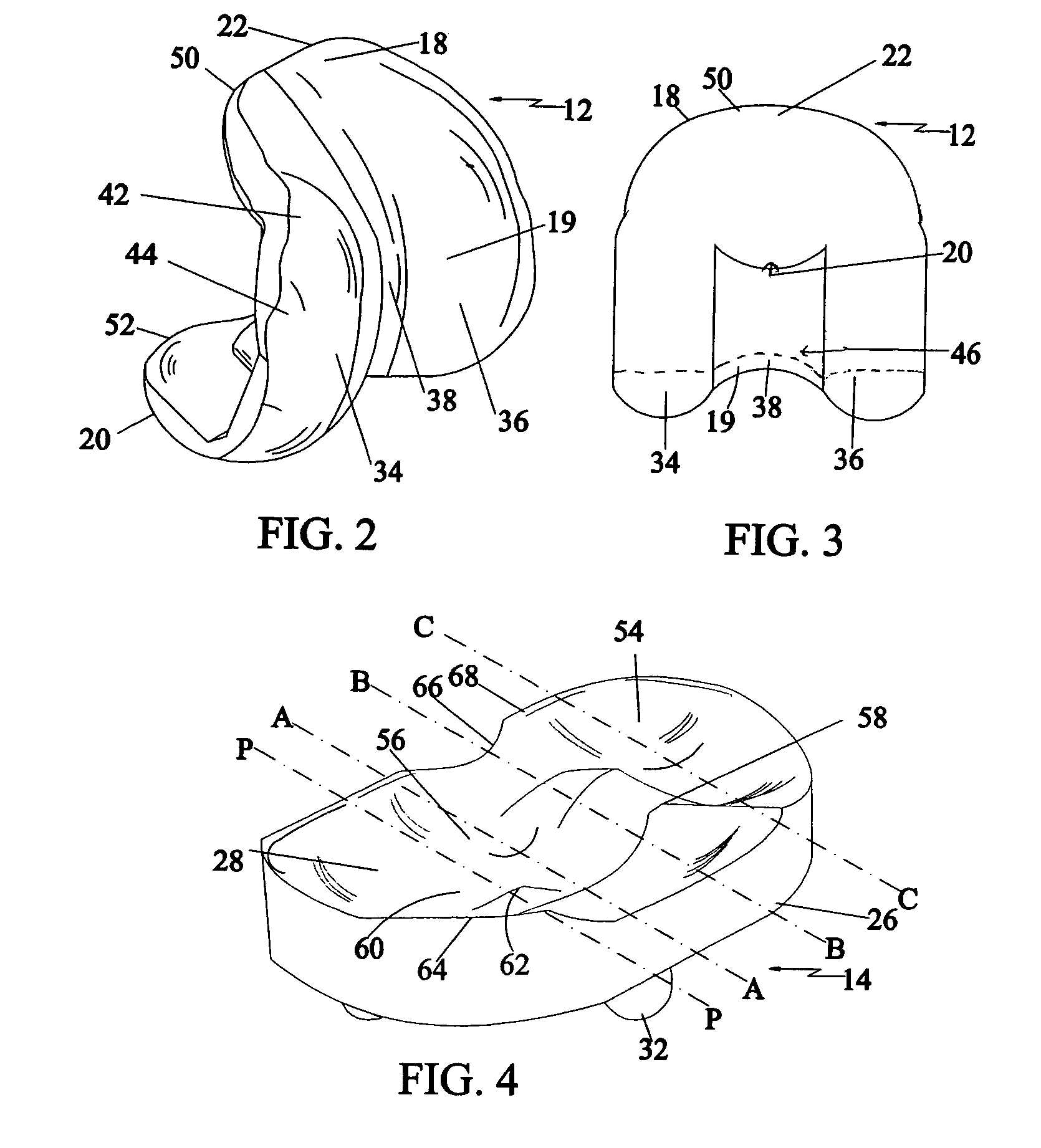
Tibial knee prosthesis
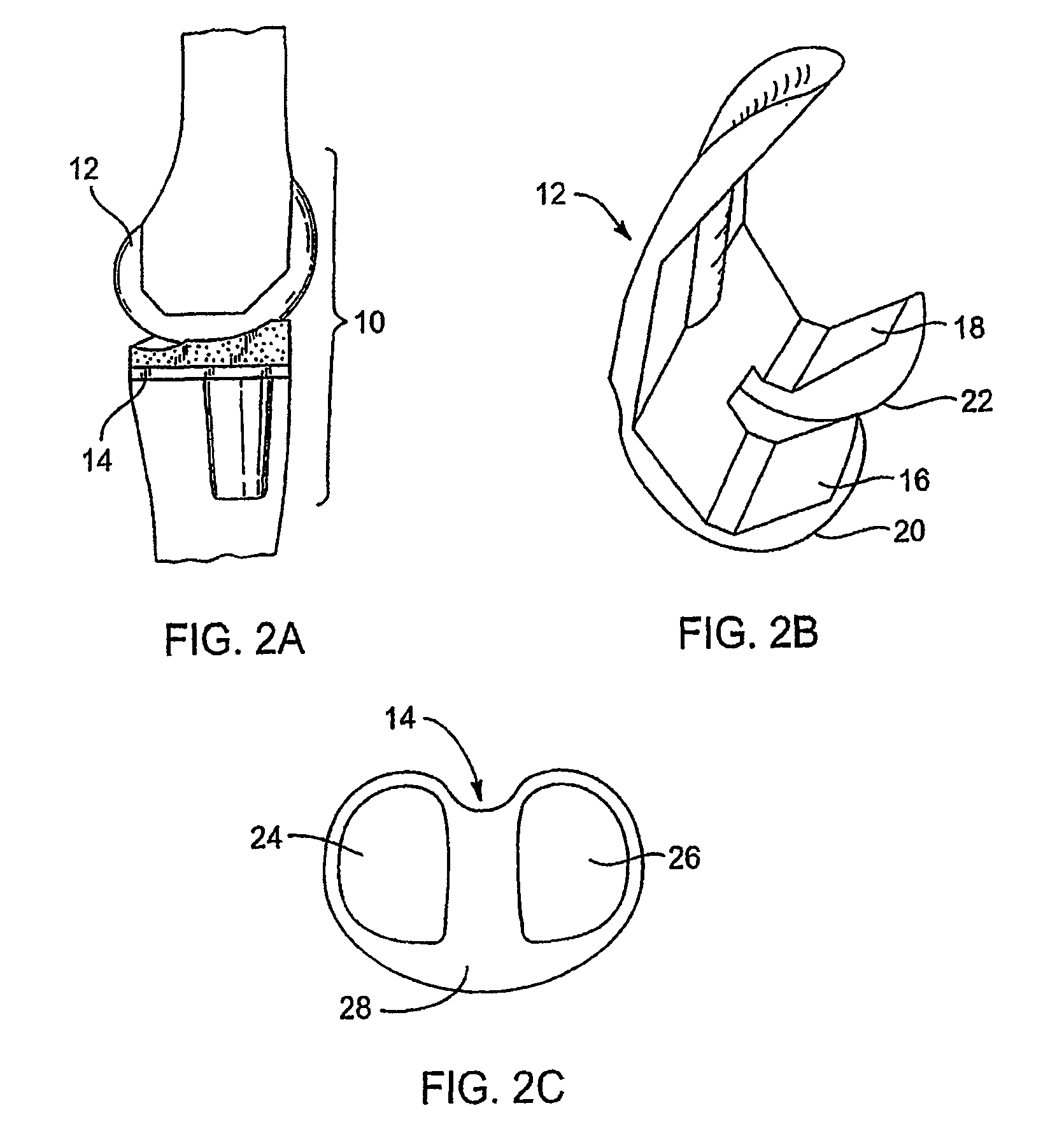
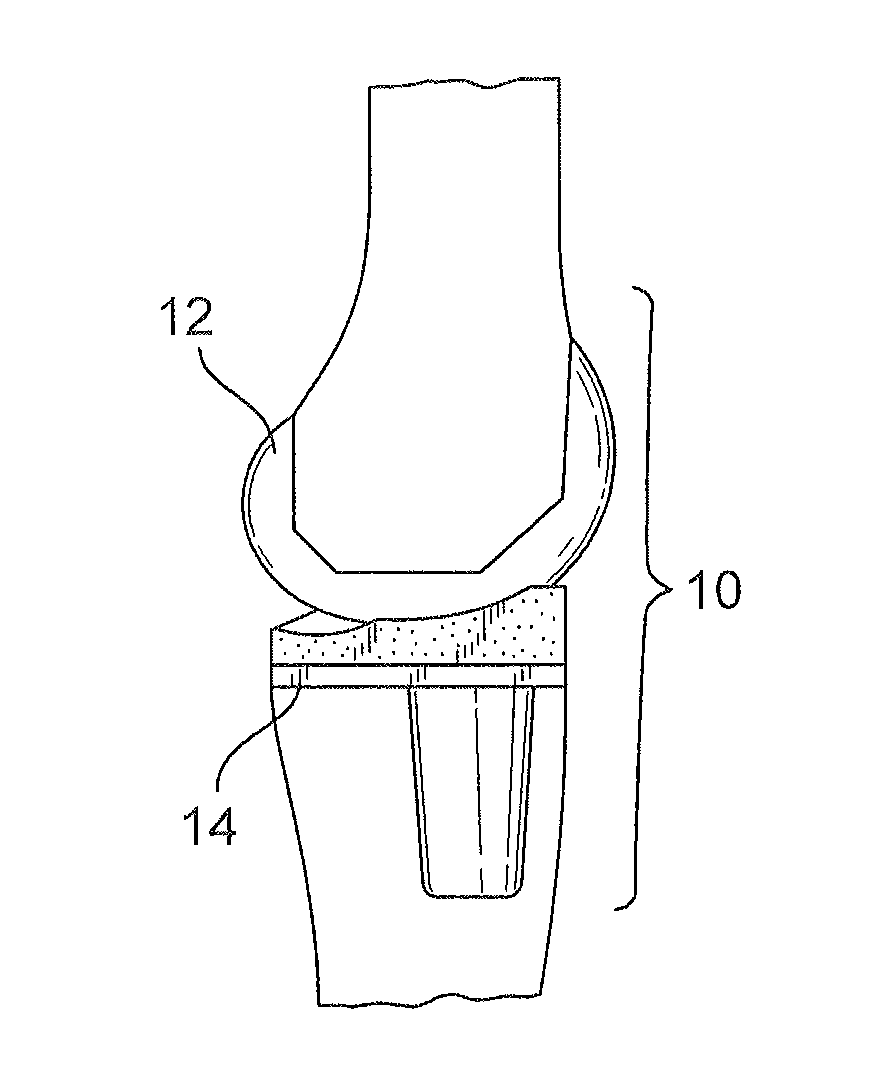
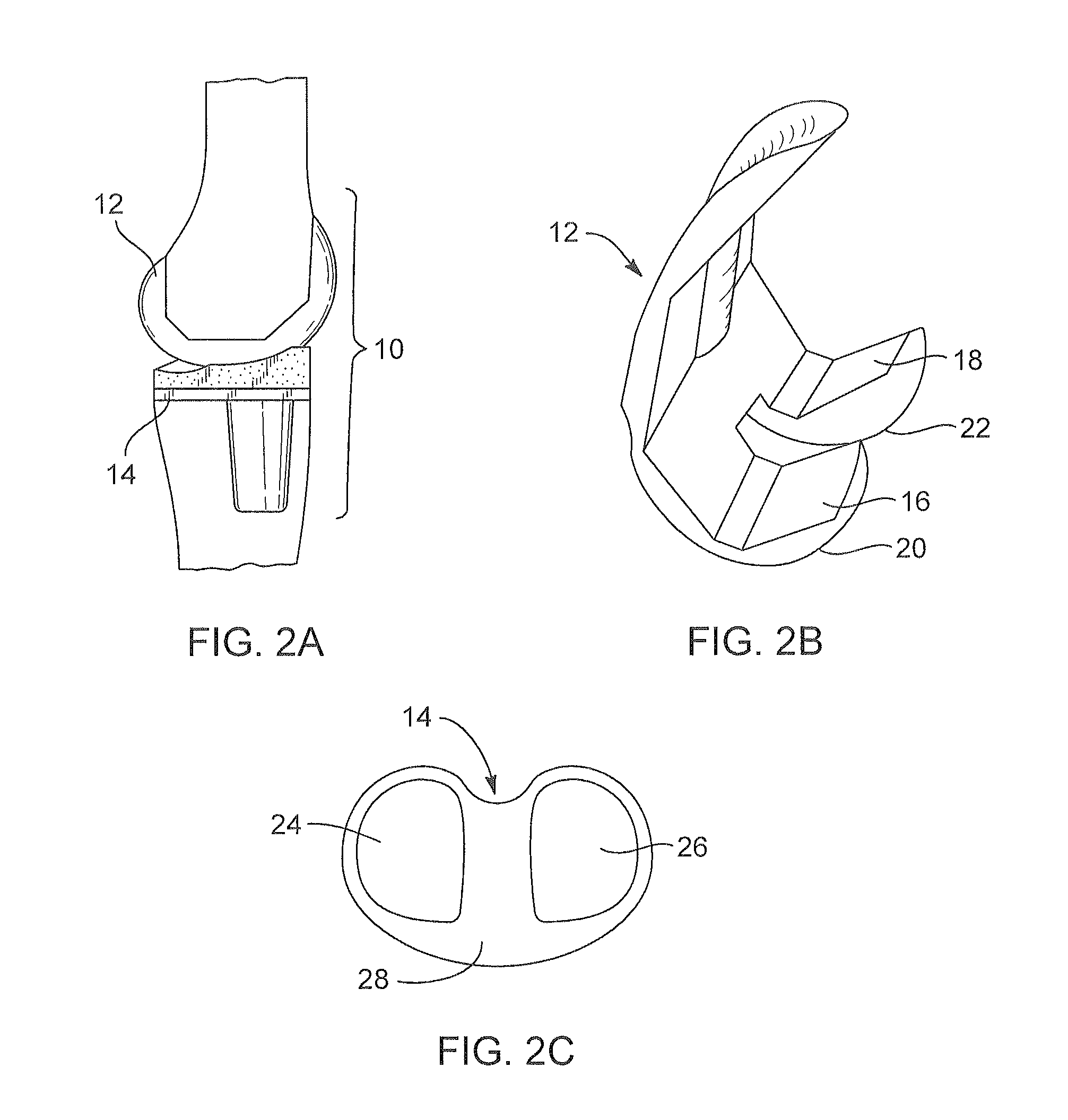
A knee prosthetic including a tibial component defining medial and lateral concavities shaped to receive medial and lateral femoral condyles of the femur. The concavities have first portions for contact with the condyles during normal knee flexion and second portions for contact with the condyles during deep, or high, knee flexion. The medial concavity can include a conforming boundary that encompasses at least the first and second portions, wherein an area inside the conforming boundary has a generally flat surface. The flat surface allows the medial femoral condyle to slide and rotate posteriorly during high knee flexion. The conforming boundary can have a generally triangular shape with an apex extending anteriorly and a relatively wider base extending posteriorly, wherein the apex includes the first portion and the base includes the second portion. The relatively wider base portion advantageously allows additional area for posteriorly directed articulating contact during high knee flexion.
Owner:MICROPORT ORTHOPEDICS HLDG INC
Total Knee Replacement Prosthesis
A knee replacement prosthesis comprising a femoral component and a tibial component that enable anterior-posterior translation of the femur relative to the tibia and enable the tibia to rotate about its longitudinal axis during flexion of the knee. The femoral component connects to the distal end of a resected femur and includes medial and lateral condyles having distal, articulating surfaces, and a patellar flange having a patellar articulating surface. The tibial component connects to the proximal end of a resected tibia and includes a proximal bearing surface with medial and lateral concavities that articulate with the medial and lateral condyles. The articulating surfaces of the condyles and concavities are defined by sections of toroids.
Owner:MAXX ORTHOPEDICS INC
Semi-powered lower extremity exoskeleton
The lower extremity exoskeleton comprises two leg supports connectable to person's lower limbs and configured to rest on the ground during their stance phase. Each leg support comprises a thigh link and a shank link; a knee joint configured to allow flexion and extension between the shank link and the thigh link. The lower extremity exoskeleton further comprises an exoskeleton trunk connectable to the person'supper body. The exoskeleton trunk is connectable to the thigh links of the leg supports allowing for the flexion and extension between the leg supports and the exoskeleton trunk. Two torque generators are coupled to each of the knee joints. A power unit, capable of providing power, is coupled to the torque generators. In operation when a leg support is in a stance phase and climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit injects power into the respective torque generator thereby extending the respective knee angle. When a leg support is in stance phase and not climbing a slope or stairs, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to resist flexion of the respective knee joint. When a leg support is in a swing phase, the power unit does not inject any power to the respective torque generator, but without dissipating any stored power in said power unit, it forces the torque generator to minimize its resistance to knee flexion and extension.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Sensing force during partial and total knee replacement surgery
ActiveUS8211041B2Accurate and quantifiable measurementPrecise tensionAnkle jointsPerson identificationTibiaTotal knee replacement surgery
Systems, devices, and methods are provided for measuring forces in the space of a knee during surgery. Such forces can be caused by tension in the ligaments of the knee. A femoral member is engaged with a distal femur. While the knee is flexed, partially extended, or fully extended, a force sensor and a gauge shim can be placed in the gap between the femoral member and the tibial plateau to measure the forces therebetween. The force sensor provides an accurate and quantifiable measurement of force, making knee replacement surgery and ligament tension balancing more accurate, standardized and repeatable. The force sensor comprises an elongate housing which comprises a thin force sensing distal portion and a proximal handle portion.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Total Knee Replacement Prosthesis With High Order NURBS Surfaces
A knee replacement prosthesis comprising a femoral component and a tibial component that enable anterior-posterior translation of the femur relative to the tibia and enable the tibia to rotate about its longitudinal axis during flexion of the knee. The femoral component connects to the distal end of a resected femur and includes medial and lateral condyles having distal, articulating surfaces, and a patellar flange having a patellar articulating surface. The tibial component connects to the proximal end of a resected tibia and includes a proximal bearing surface with medial and lateral concavities that articulate with the medial and lateral condyles. The condylar articulating surfaces and the said concavities are substantially defined by non-uniform, rational B-spline surfaces (NURBS).
Owner:MAXX ORTHOPEDICS INC
Physiological total knee implant
The present invention generally comprises a fixed bearing prosthesis and a mobile bearing prosthesis. The fixed bearing prosthesis comprises a tibial component, a femoral component and a meniscal component and addressees the loss of congruency during deep knee flexion and the possible direct, repetitive contact of the tibial and femoral components. The tibial component of the fixed bearing prosthesis includes a tibial platform having an anterior and posterior edge. The meniscal component of the fixed bearing prosthesis includes a posterior ridge overlapping the posterior edge of the tibial platform that prevents metal-to-metal contact during deep knee flexion. The mobile bearing prosthesis comprises generally a tibial component, a femoral component and a meniscal component addresses the lack of conformity to natural biomechanical movement. The tibial component comprises a tibial platform having a curved rail system designed to mimic the asymmetrical rotation of femoral rollback while simultaneously providing sufficient anterior-posterior translation.
Owner:TARABICHI SAMIH
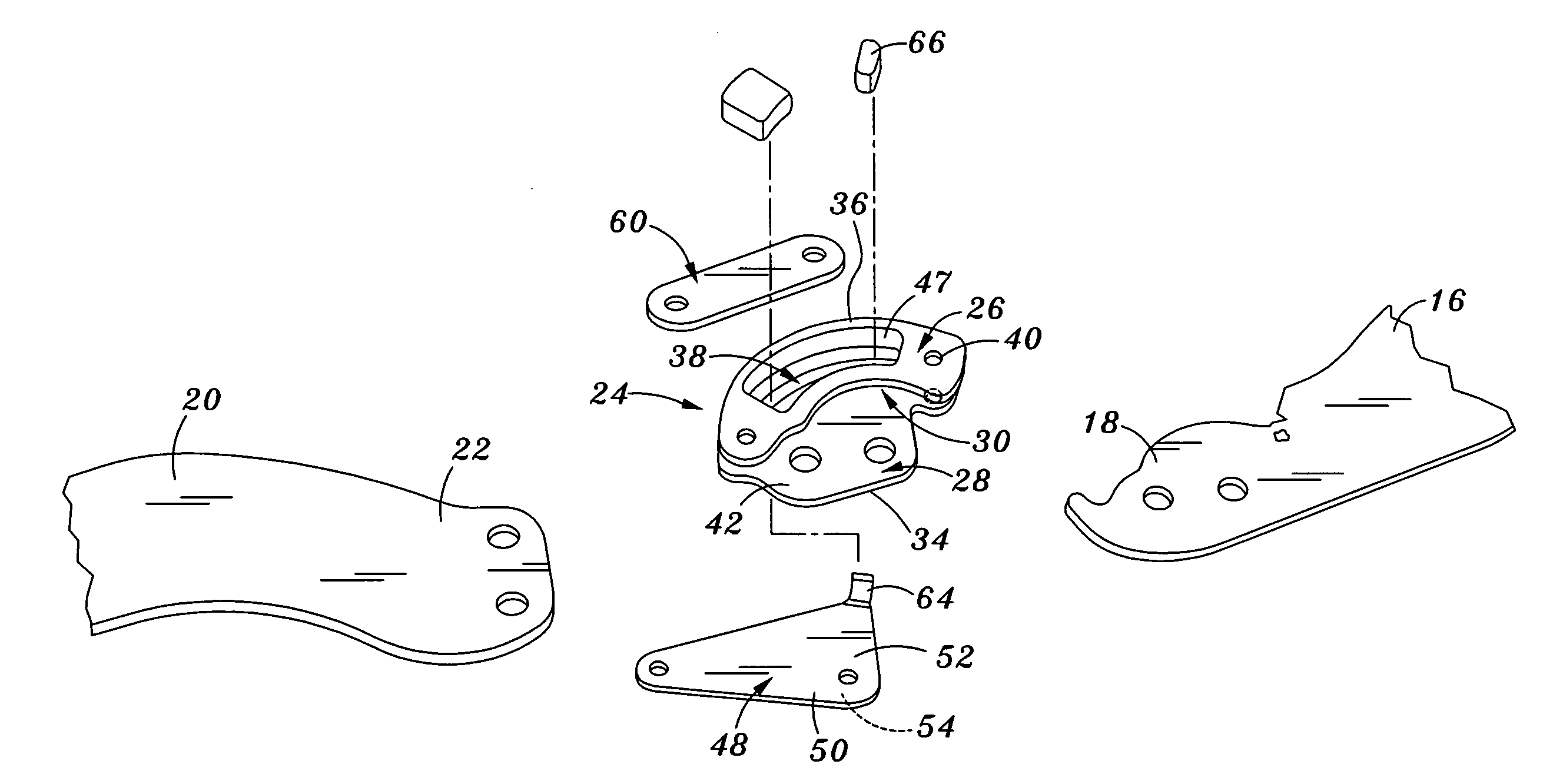
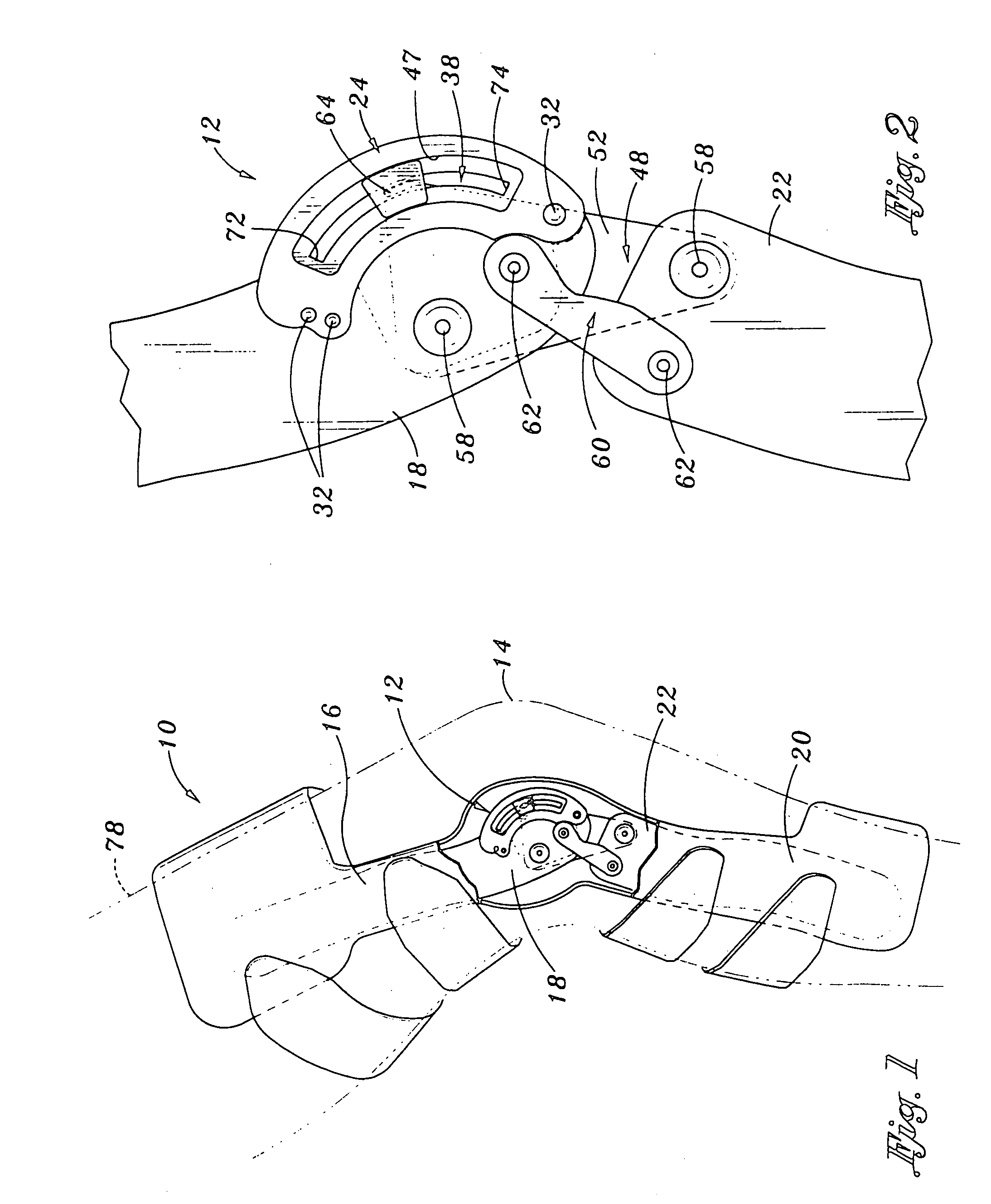
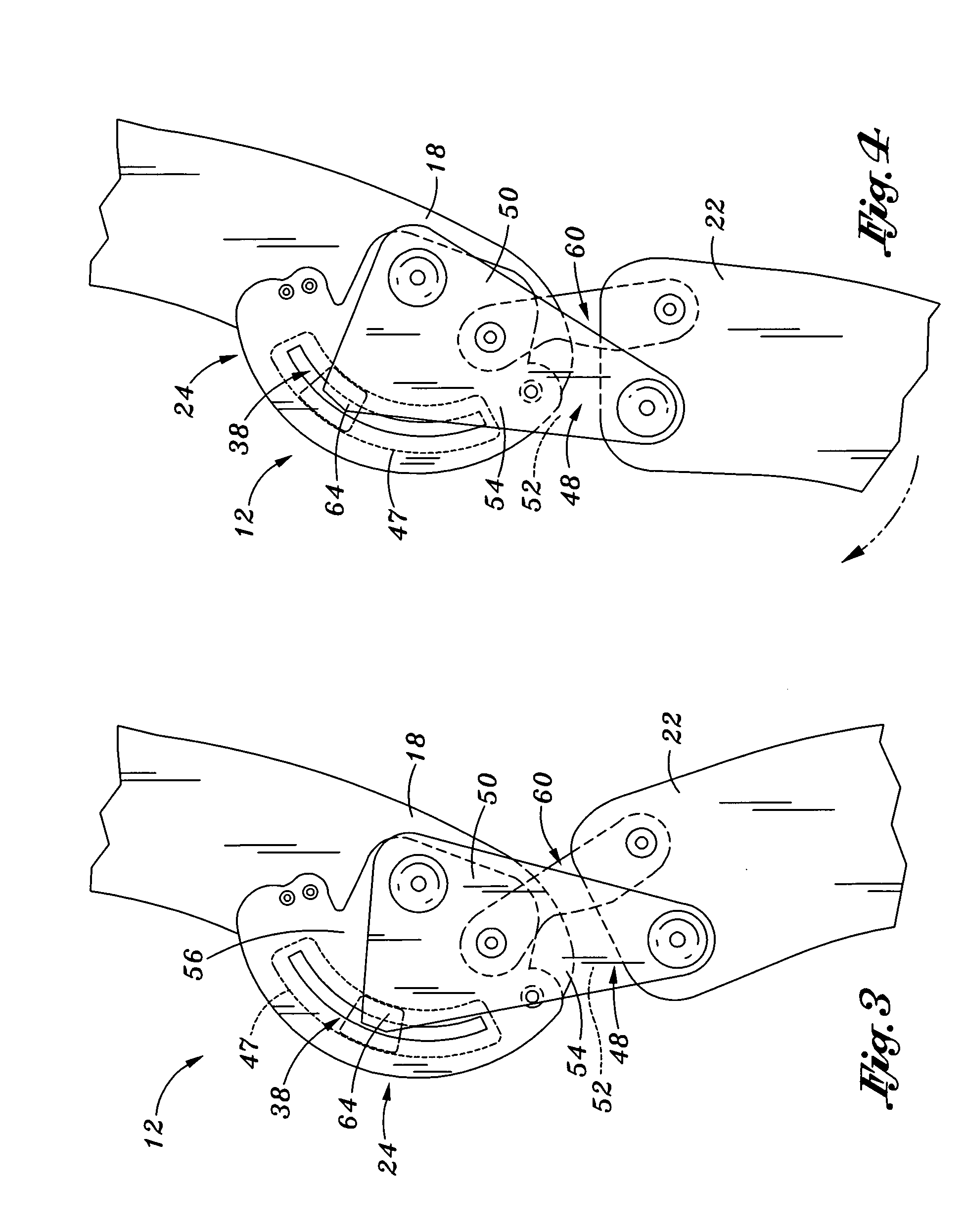
Joint device for artificial leg, method of controlling the joint device, and control unit
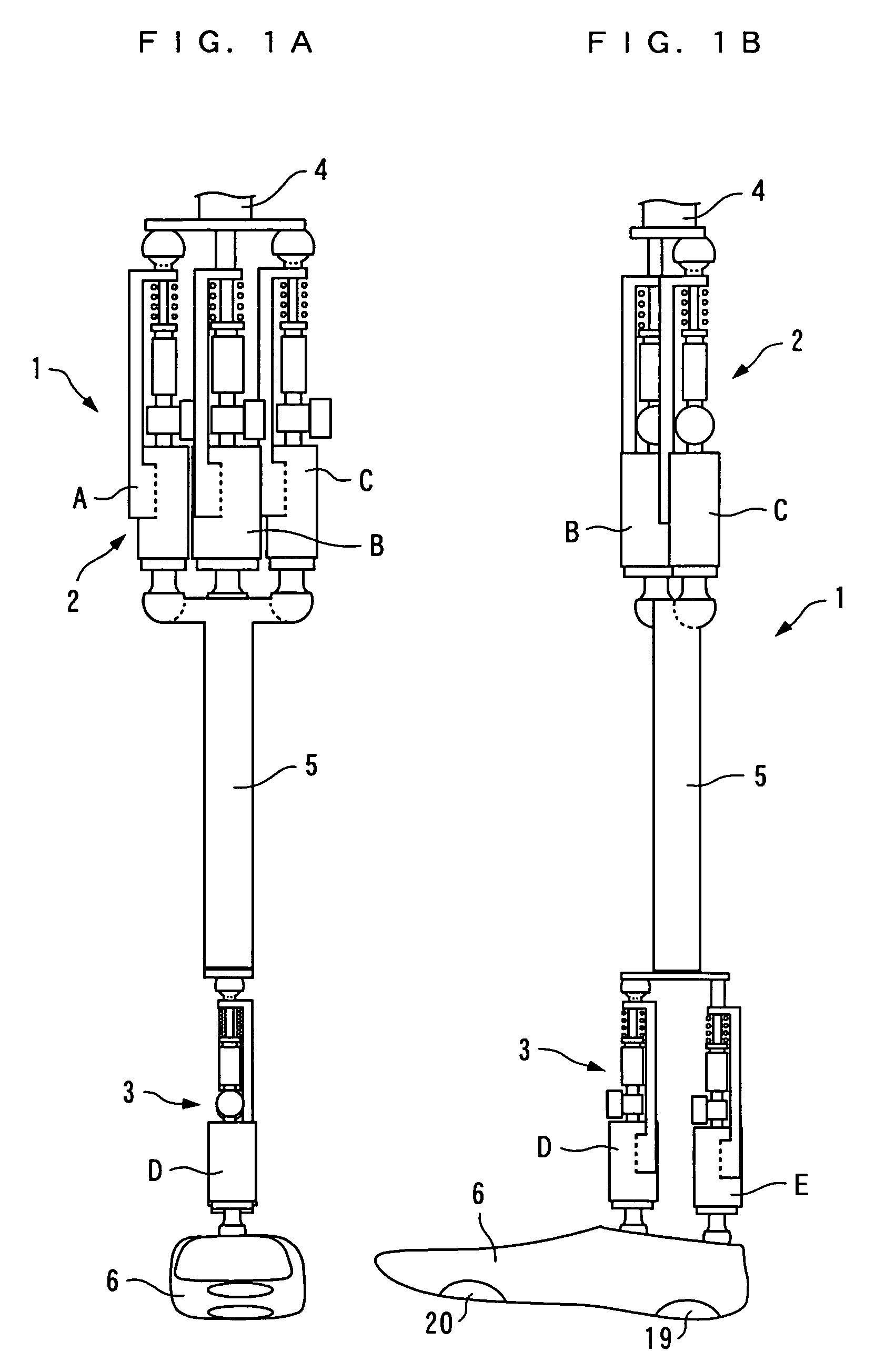
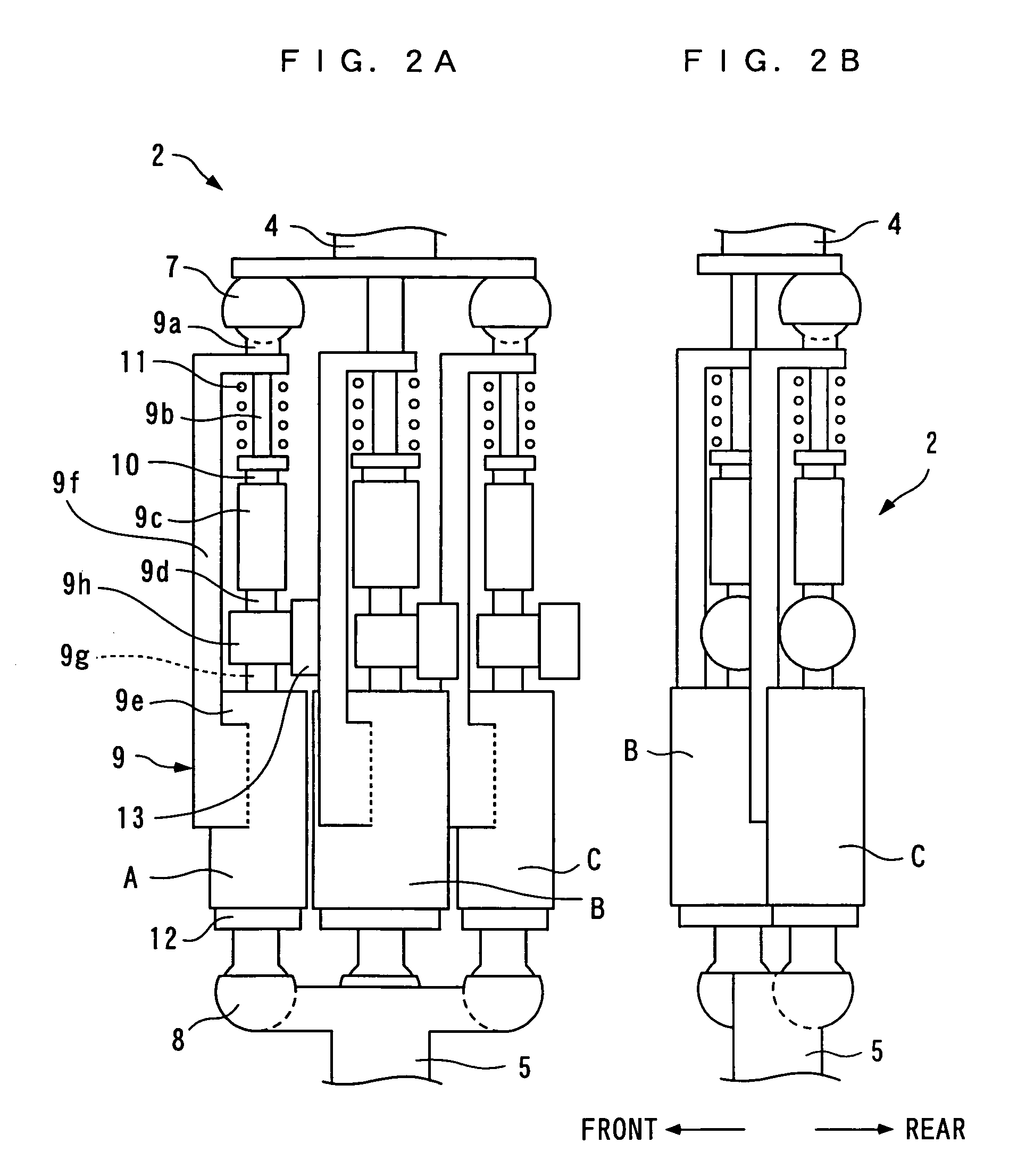
There is provided a joint device for an artificial leg, which makes it possible to dramatically achieve reduction of the weight of a power source and an increase in duration of the same, as well as facilitates knee bending / stretching motion, toe-up motion, and kicking motion. The joint device has an above-knee member and an under-knee member spaced from each other. Three expansible links are connected between the above-knee member and the under-knee member, for accumulating energy generated by the weight of a user's body acting on the artificial leg, and operating by releasing the accumulated energy to actuate the under-knee member into joint motion.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Tibial knee prosthesis
A knee prosthetic including a tibial component defining medial and lateral concavities shaped to receive medial and lateral femoral condyles of the femur. The concavities have first portions for contact with the condyles during normal knee flexion and second portions for contact with the condyles during deep, or high, knee flexion. The medial concavity can include a conforming boundary that encompasses at least the first and second portions, wherein an area inside the conforming boundary has a generally flat surface. The flat surface allows the medial femoral condyle to slide and rotate posteriorly during high knee flexion. The conforming boundary can have a generally triangular shape with an apex extending anteriorly and a relatively wider base extending posteriorly, wherein the apex includes the first portion and the base includes the second portion. The relatively wider base portion advantageously allows additional area for posteriorly directed articulating contact during high knee flexion.
Owner:MICROPORT ORTHOPEDICS HLDG INC
Surface guided knee replacement
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
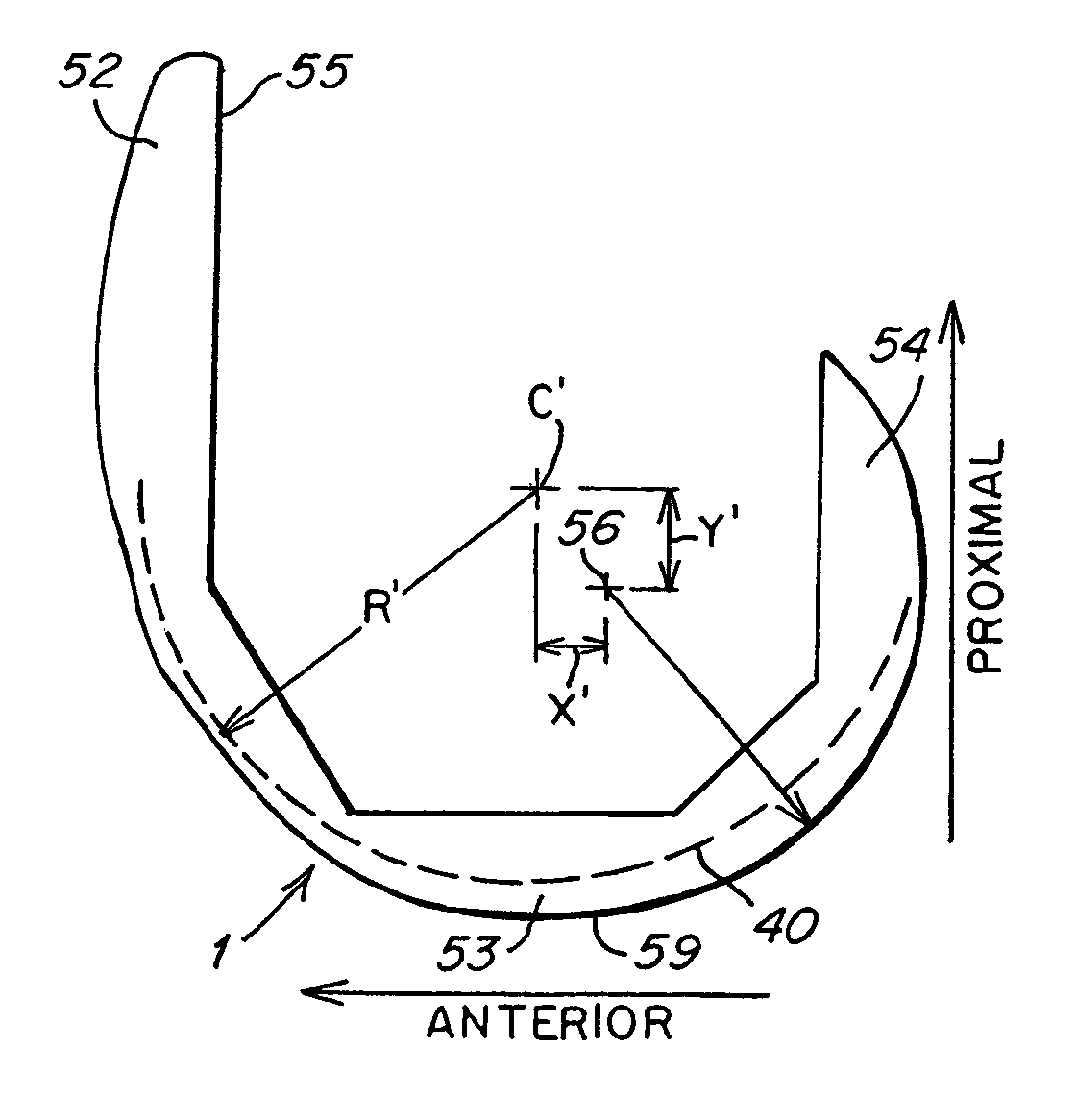
Knee joint with a ramp
InactiveUS20090204221A1Minimize wear and deformationIncrease the areaJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaTibial surface
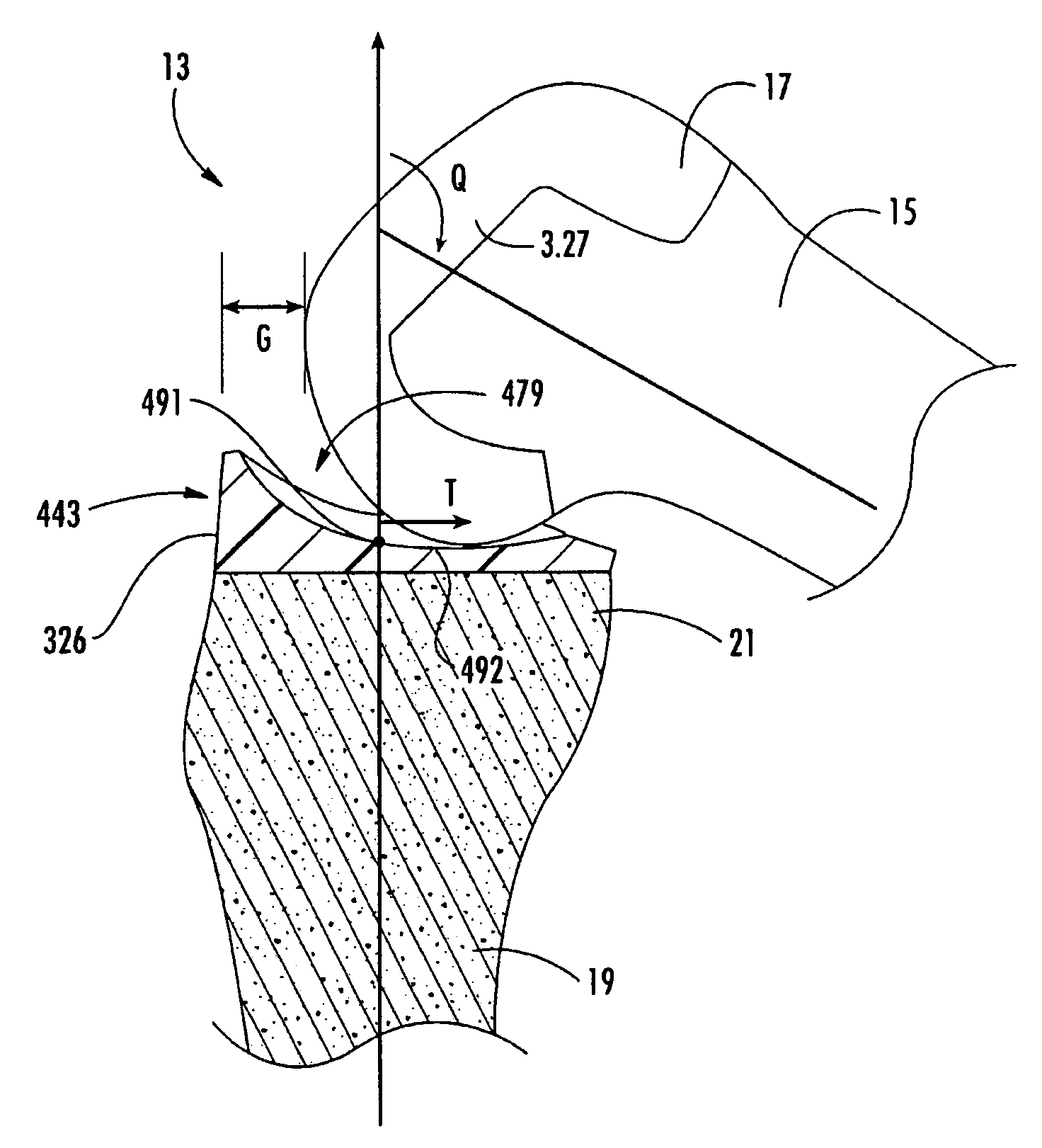
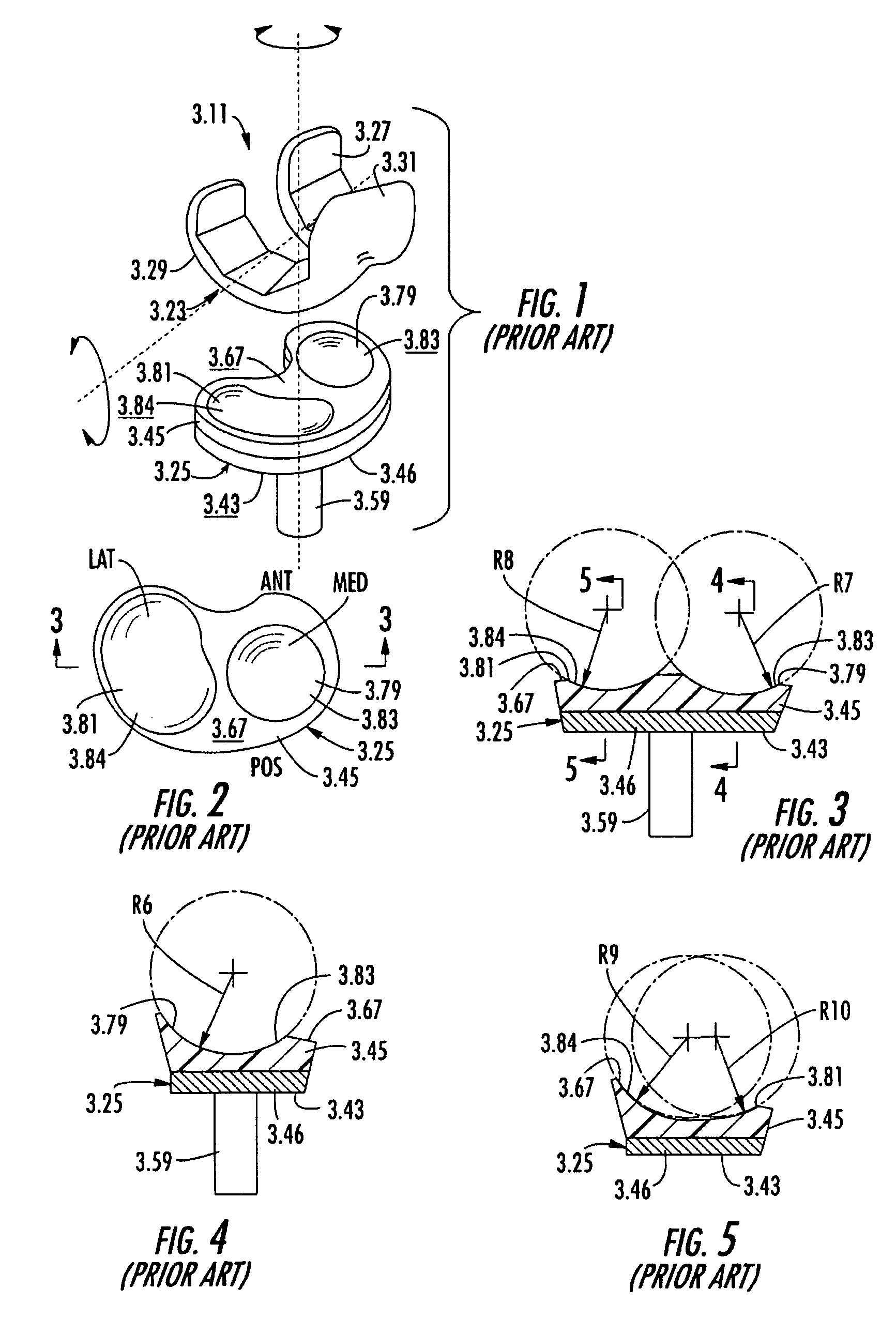
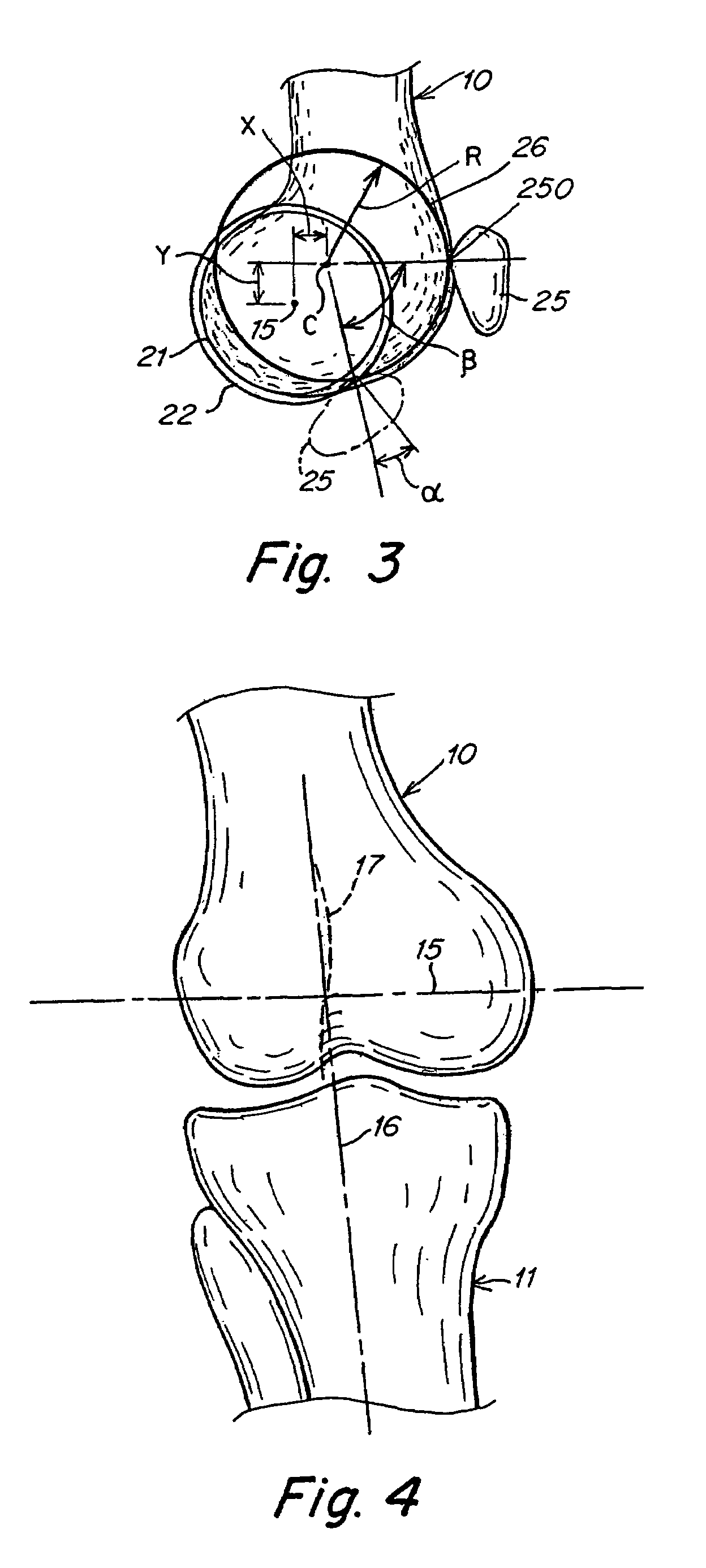
An artificial knee joint is described that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the required motion and stability characteristics. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, by an amount similar to that in the anatomic knee. The opposite motion, roll forward of the femur from a fully flexed to a more extended position, is accomplished by varying the outward radii of the lateral and medial femoral bearing surfaces, together with a ramp on the postero-lateral and postero-medial regions of the tibial surfaces.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
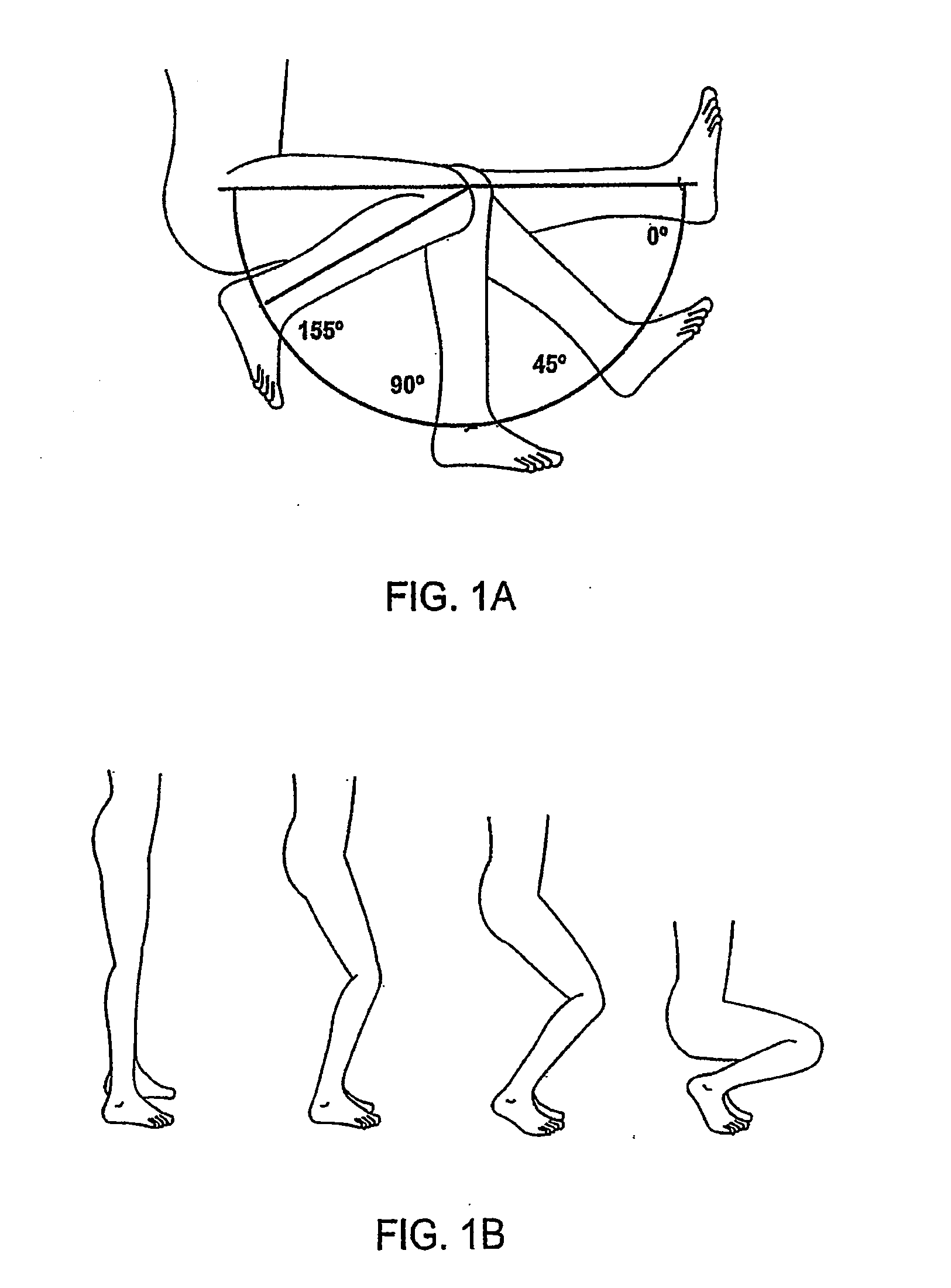
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities for knee prosthesis patients
InactiveUS20100292804A1Deep knee flexion capabilityClosely replicate physiologic loadingJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaArticular surfaces
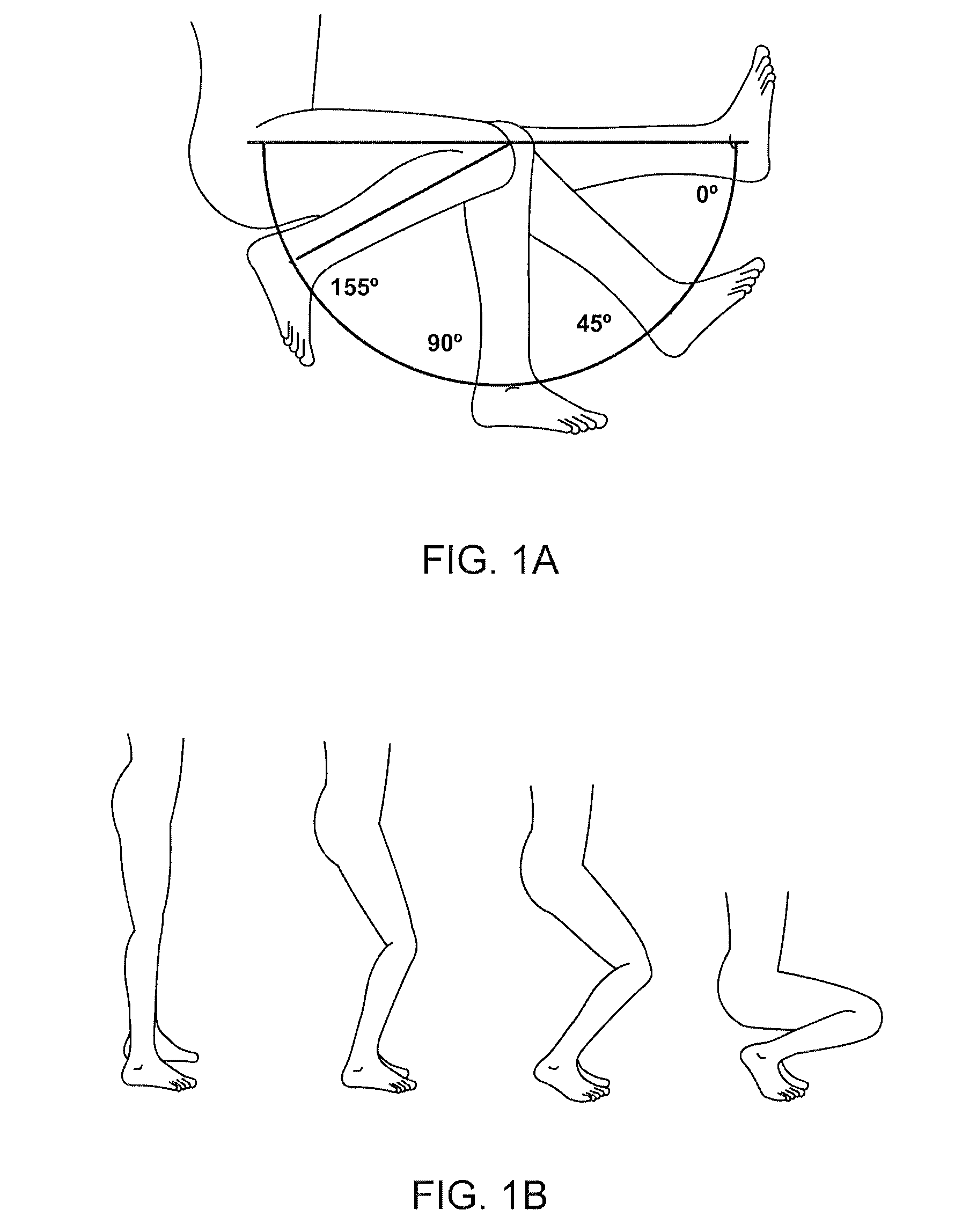
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities, more physiologic load bearing and improved patellar tracking for knee prosthesis patients. Such systems and methods include (i) adding more articular surface to the antero-proximal posterior condyles of a femoral component, including methods to achieve that result, (ii) modifications to the internal geometry of the femoral component and the associated femoral bone cuts with methods of implantation, (iii) asymmetrical tibial components that have an unique articular surface that allows for deeper knee flexion than has previously been available, (iv) asymmetrical femoral condyles that result in more physiologic loading of the joint and improved patellar tracking and (v) modifying an articulation surface of the tibial component to include an articulation feature whereby the articulation pathway of the femoral component is directed or guided by articulation feature.
Owner:SAMUELSON KENT M +1
Sensing force during partial and total knee replacement surgery
ActiveUS20100217156A1Accurate and quantifiable measurementPrecise tensionAnkle jointsPerson identificationTibiaTotal knee replacement surgery
Systems, devices, and methods are provided for measuring forces in the space of a knee during surgery. Such forces can be caused by tension in the ligaments of the knee. A femoral member is engaged with a distal femur. While the knee is flexed, partially extended, or fully extended, a force sensor and a gauge shim can be placed in the gap between the femoral member and the tibial plateau to measure the forces therebetween. The force sensor provides an accurate and quantifiable measurement of force, making knee replacement surgery and ligament tension balancing more accurate, standardized and repeatable. The force sensor comprises an elongate housing which comprises a thin force sensing distal portion and a proximal handle portion.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
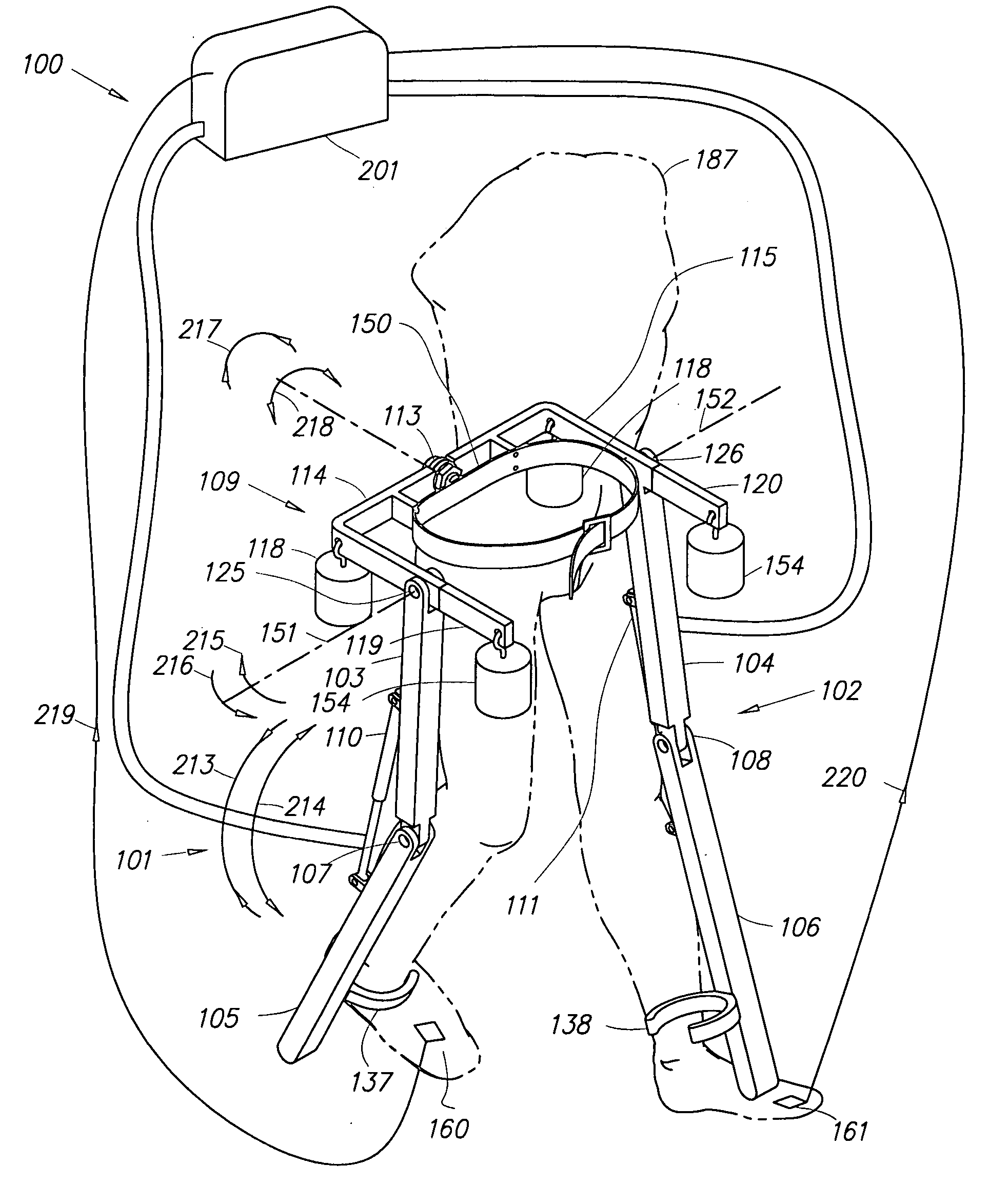
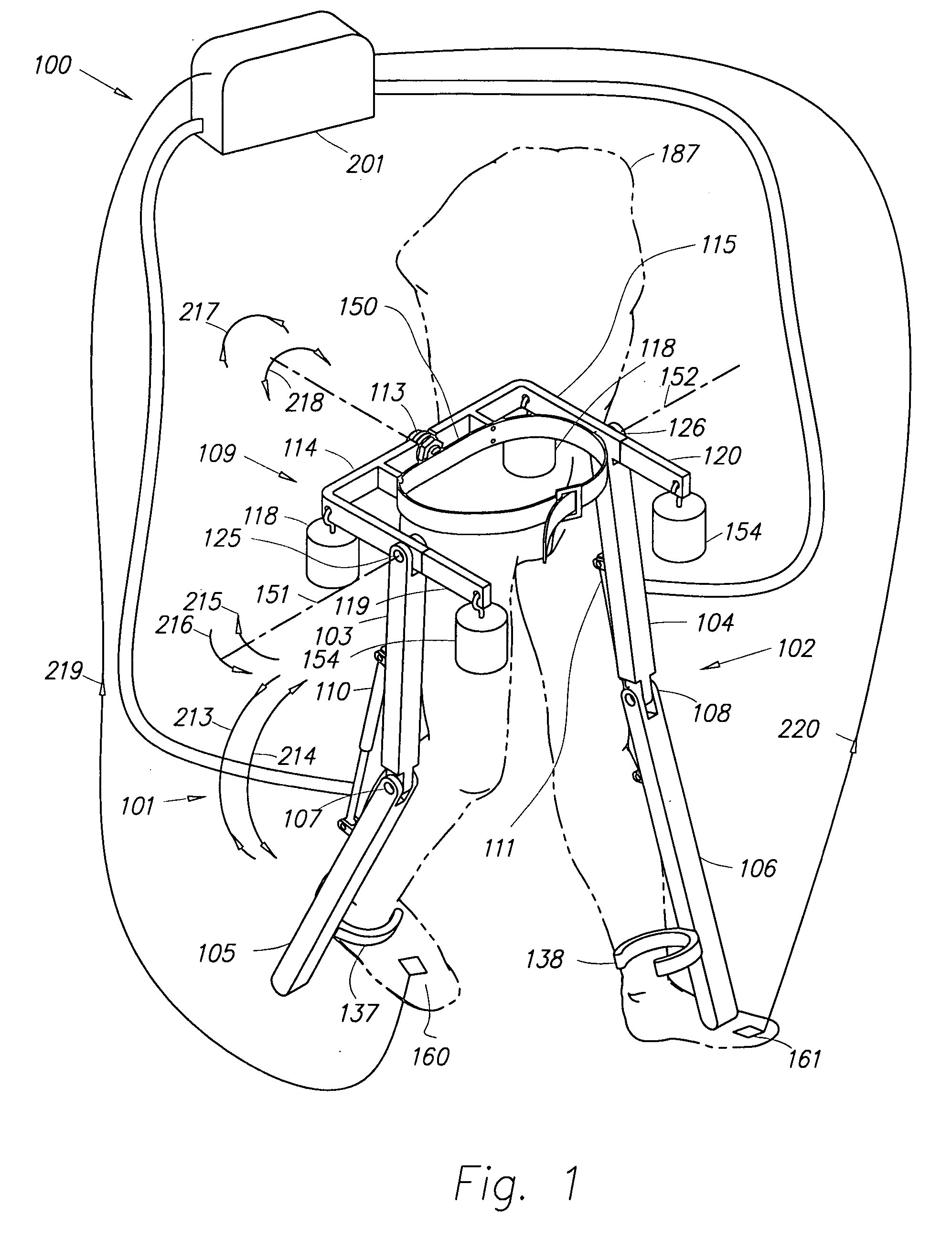
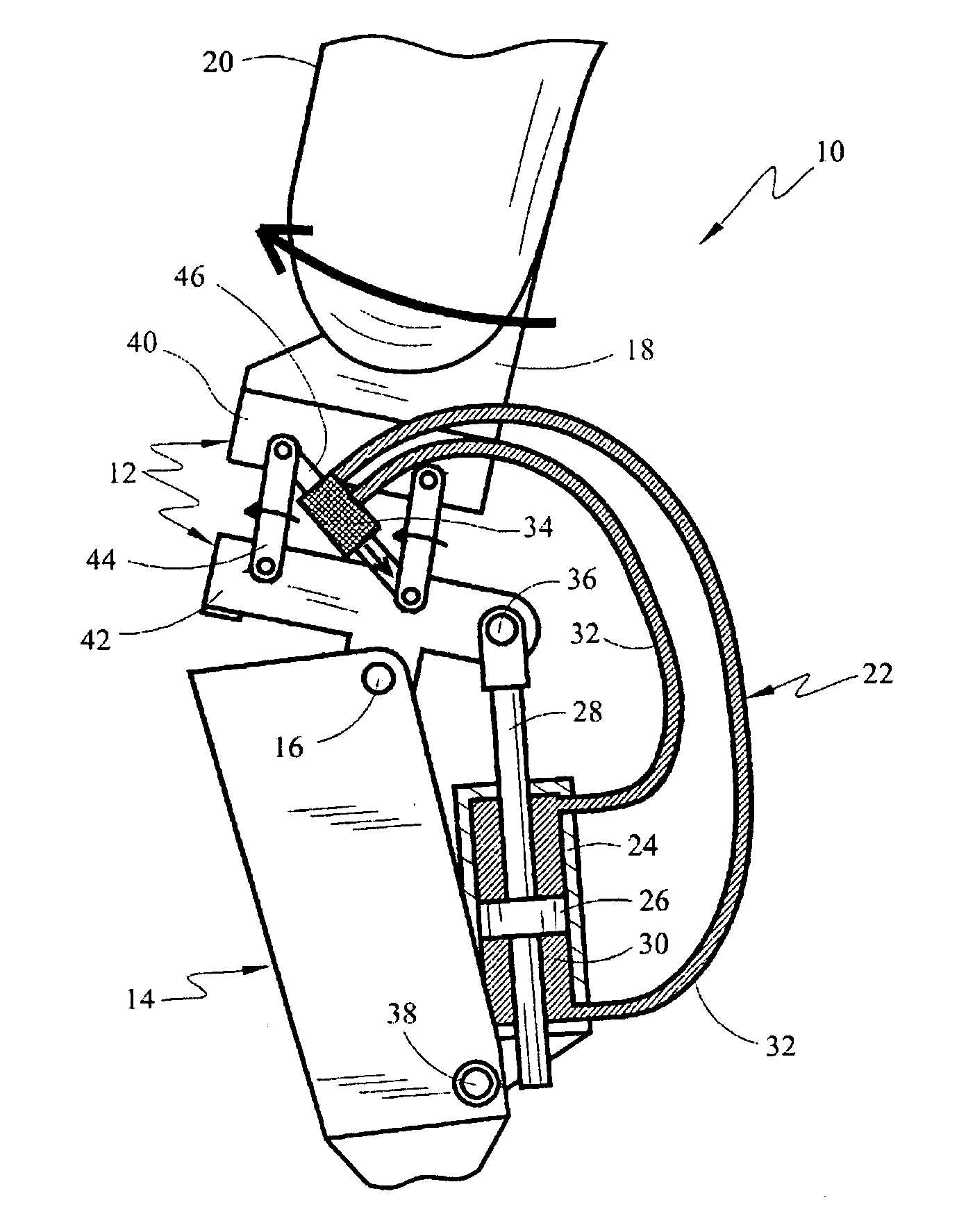
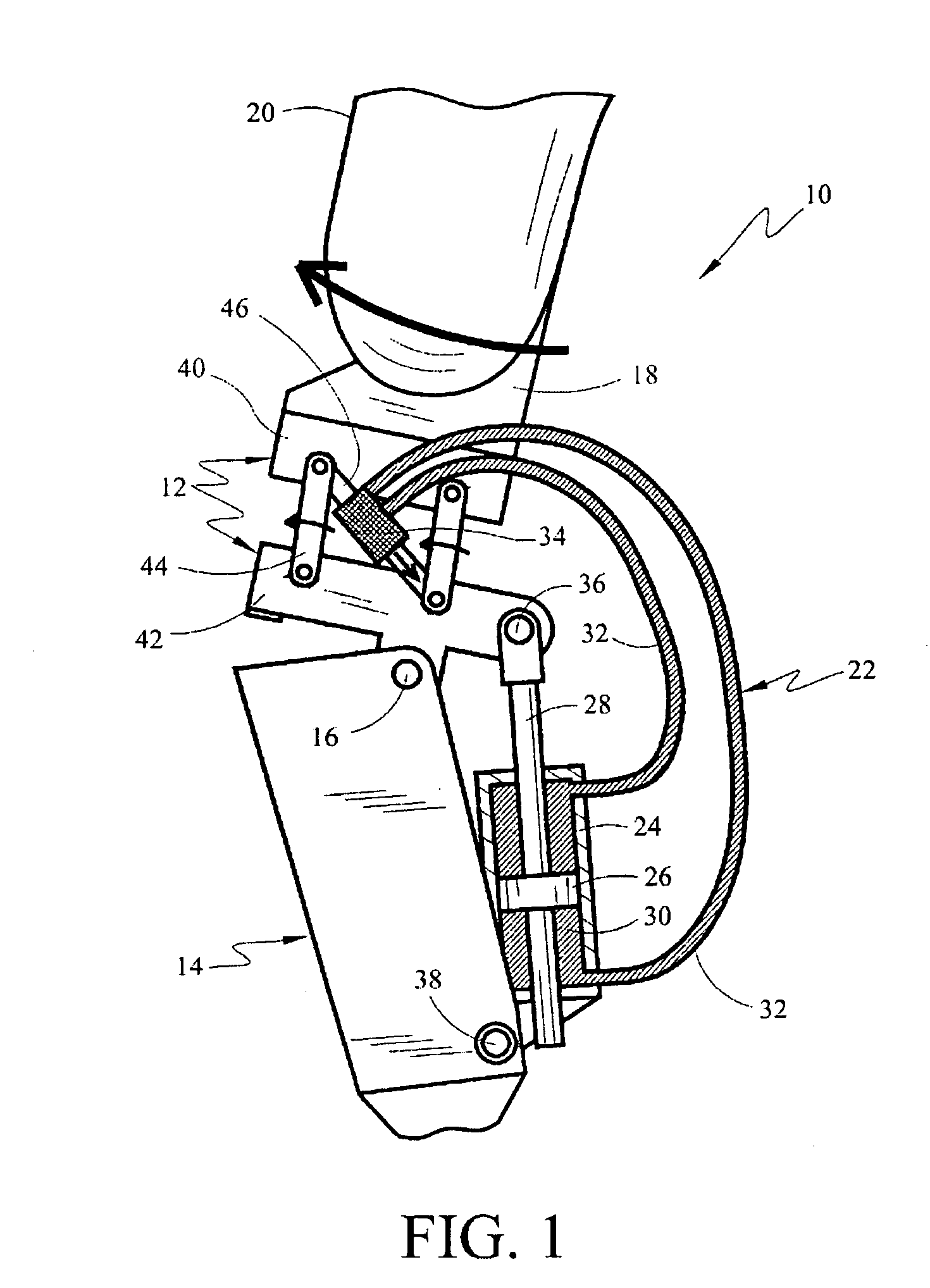
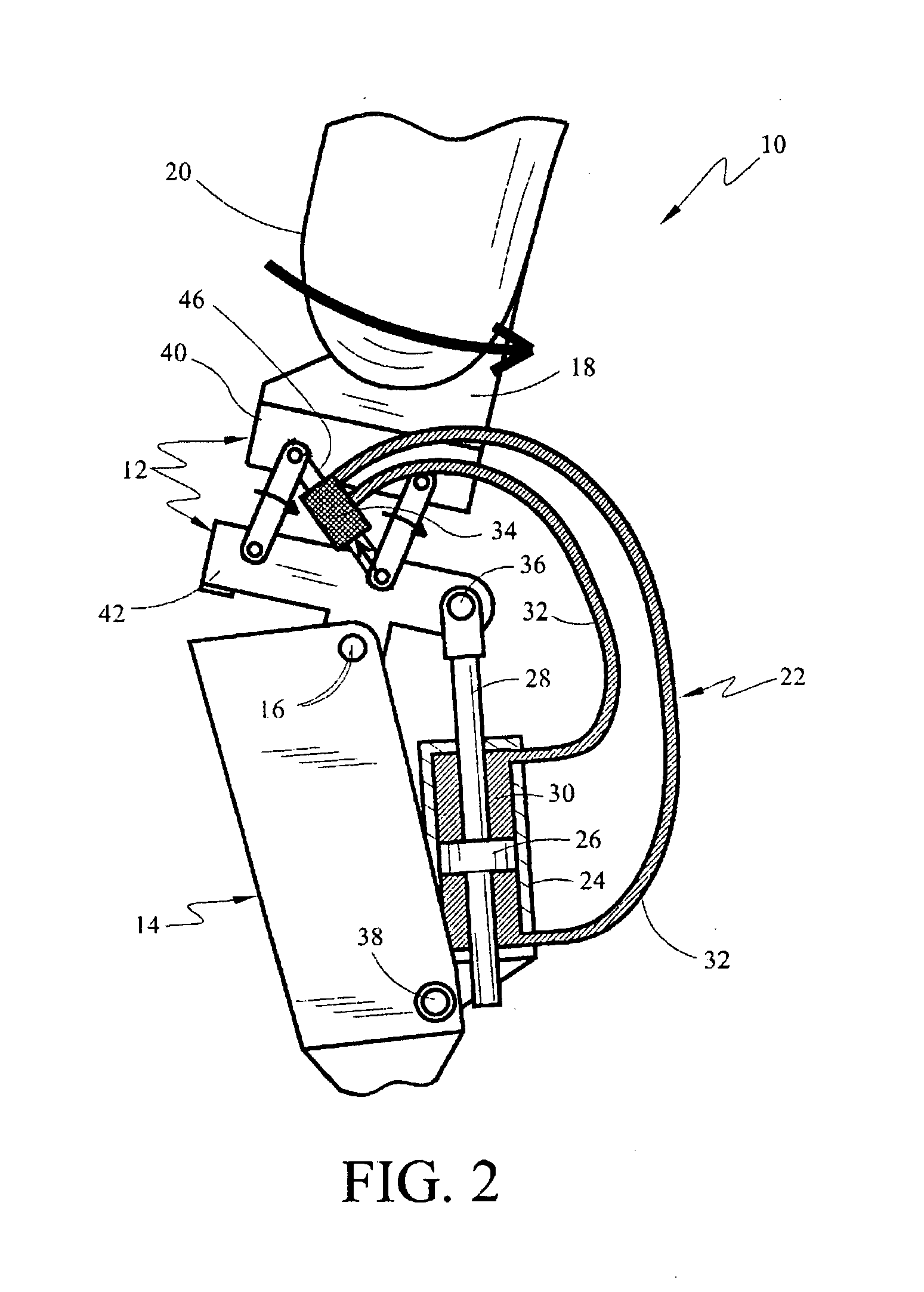
Above-knee prosthesis with variable resistance knee joint
InactiveUS20050015156A1Decrease resistance of flexion and extensionImprove the immunityArtificial legsFree rotationVALVE PORT
An above-knee prosthesis that allows the user to control the resistance of knee flexion or extension, and to voluntary lock and release the knee joint, at any and all bending angles, comprising a thigh frame assembly that receives a thigh stump; a leg frame assembly with foot attached; a hinge interconnecting the thigh frame and leg frame assemblies to form an artificial knee joint; a closed hydraulic system further interconnecting the thigh frame and leg frame assemblies to provide resistance to the bending of said artificial knee joint, a means to vary the resistance provided by said closed hydraulic system, and a means to translate the AP movement of said thigh stump into the degree of resistance provided by said closed hydraulic system. In its preferred embodiments, the AP movement of the thigh stump is communicated by means of a linkage, sliding or screw assembly, to a flow rate control valve. The flow rate control valve varies the amount of the resistance provided by the closed hydraulic system controlling, thereby, the amount of resistance within the artificial knee. Pressing the thigh stump backwards within the thigh frame assembly increases the resistance within the hydraulic system and slows knee bending until the knee locks. Pressing the thigh stump forward decreases the hydraulic resistive force and allows the artificial knee joint to yield to outside forces, such as gravity and / or stump thrust, until the prosthesis rotates freely about the knee hinge. The above-knee prosthetic prevents the knee joint from giving way, promotes a balanced stance, and facilitates a near normal reciprocating gate while ascending and descending stairs and slopes.
Owner:HIKICHI YUICHI
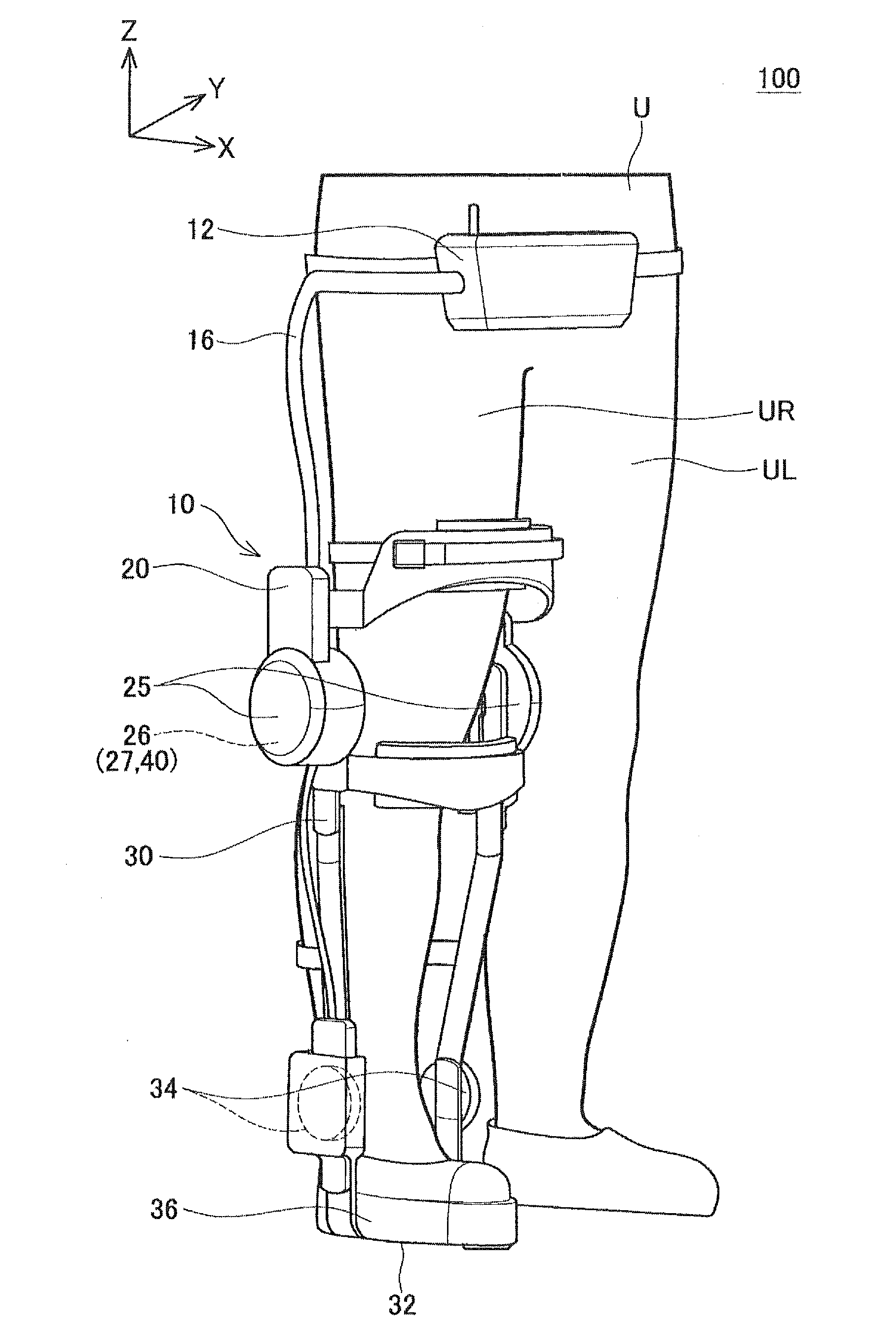
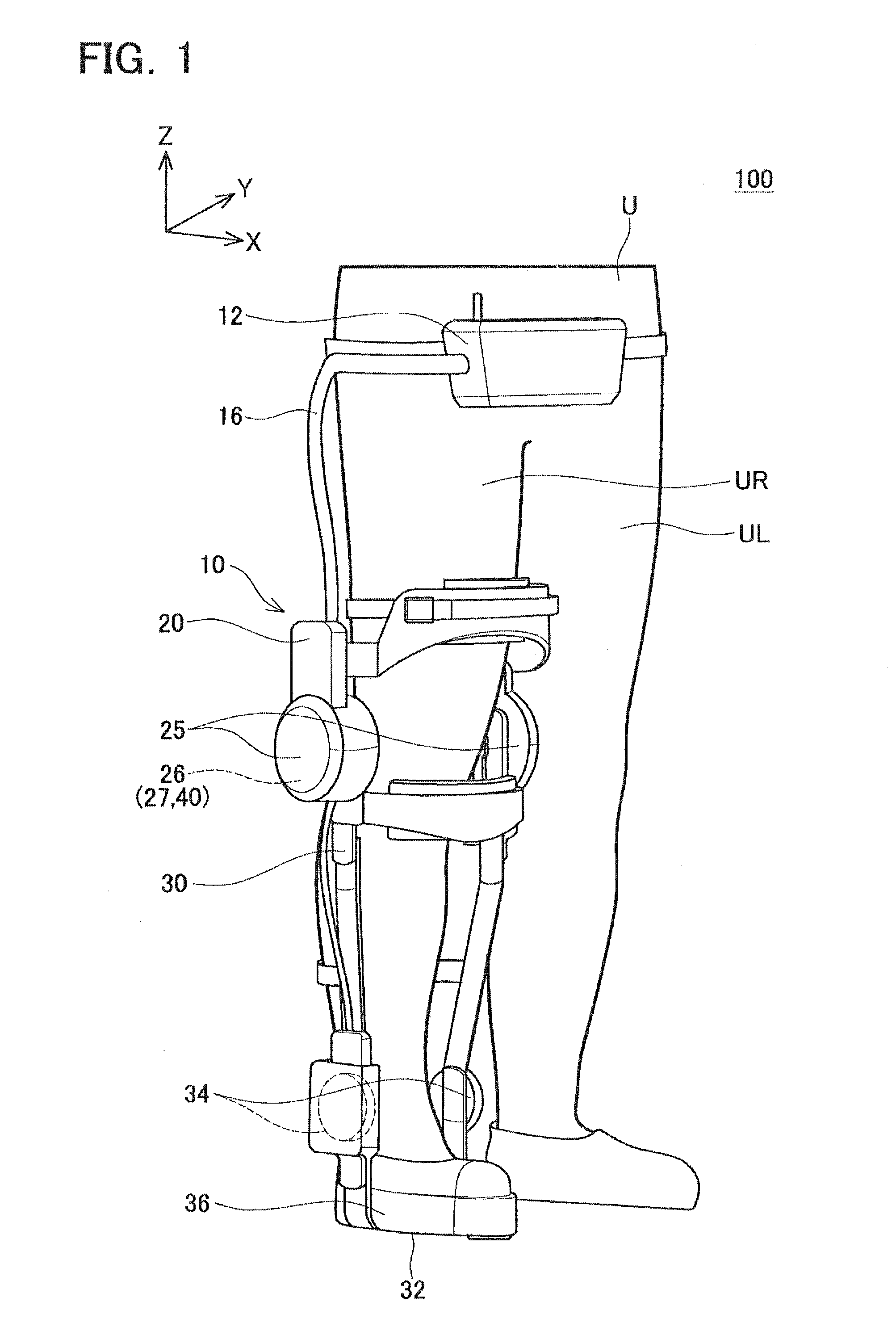
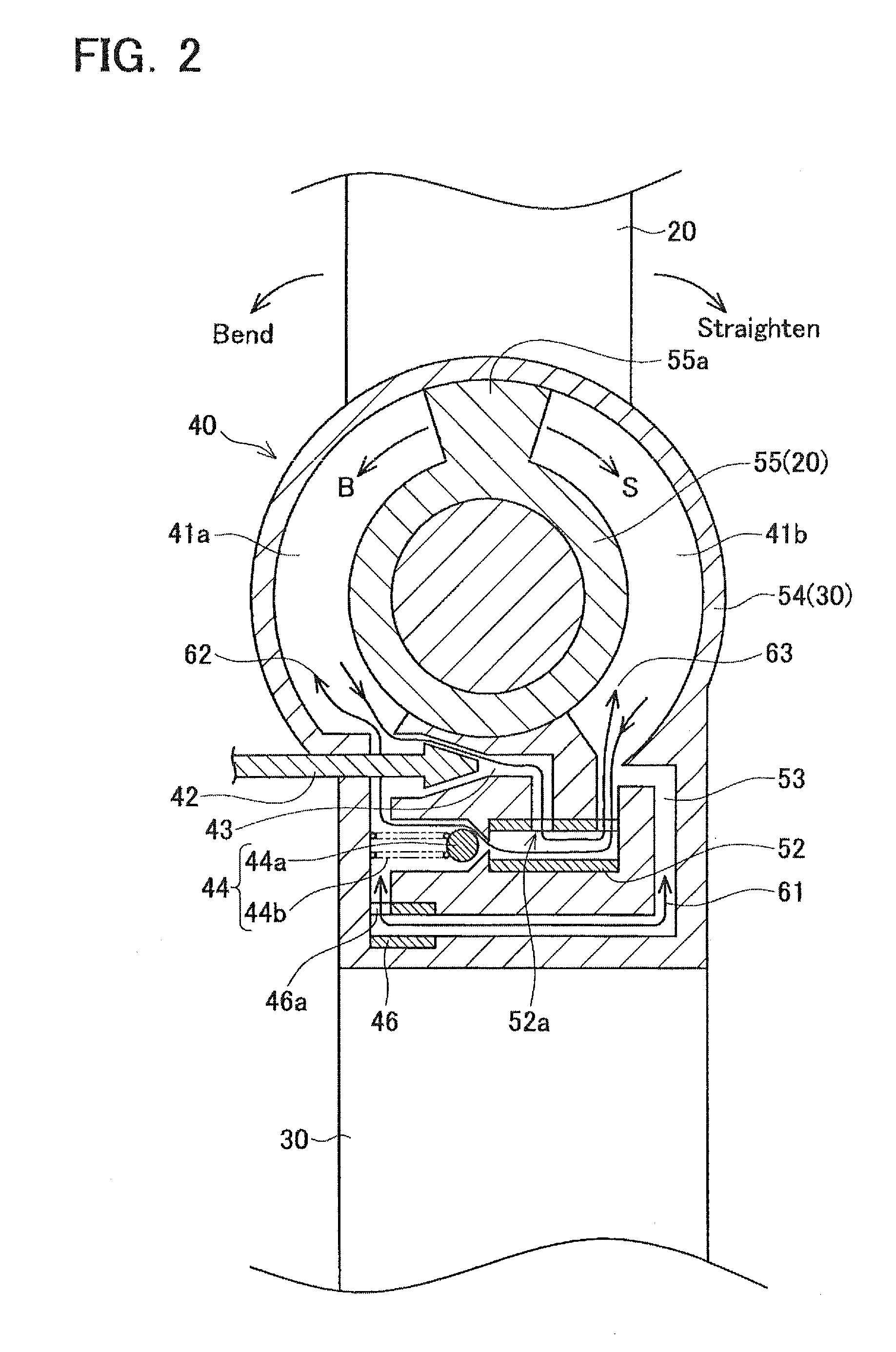
Walking assist device
A walking assist device having a safety mechanism that mitigates an impact upon falling is provided. A walking assist device has an upper and lower leg links, a motor, and a controller. The controller controls the motor to apply torque to the lower leg link. The walking assist device also has a one-way damper which generates a resisting force against rotation of the lower leg link in the knee bending direction, and does not generate a resisting force against rotation of the lower leg link in the knee straightening direction. The controller engages the one-way damper while controlling the motor to apply torque to the lower leg link in the knee straightening direction, and disengages the one-way damper while controlling the motor to apply torque to the lower leg link in the knee bending direction.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities for knee prosthesis patients
InactiveUS20090062925A1Closely replicate physiologic loadingEasy to trackJoint implantsFemoral headsArticular surfacesArticular surface
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities, more physiologic load bearing and improved patellar tracking for knee prosthesis patients. Such systems and methods include (i) adding more articular surface to the antero-proximal posterior condyles of a femoral component, including methods to achieve that result, (ii) modifications to the internal geometry of the femoral component and the associated femoral bone cuts with methods of implantation, (iii) asymmetrical tibial components that have an unique articular surface that allows for deeper knee flexion than has previously been available and (iv) asymmetrical femoral condyles that result in more physiologic loading of the joint and improved patellar tracking.
Owner:SAMUELSON KENT M
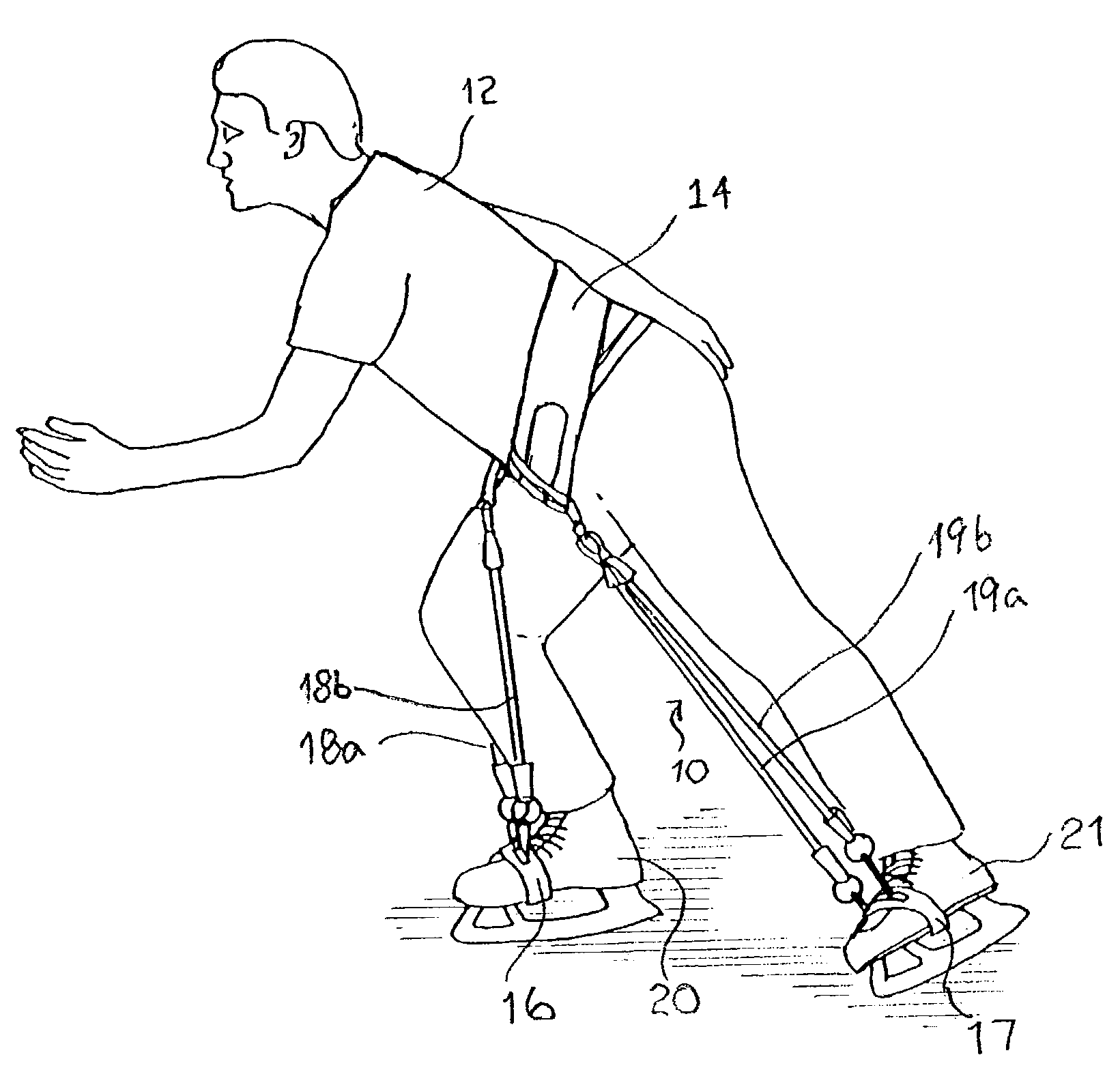
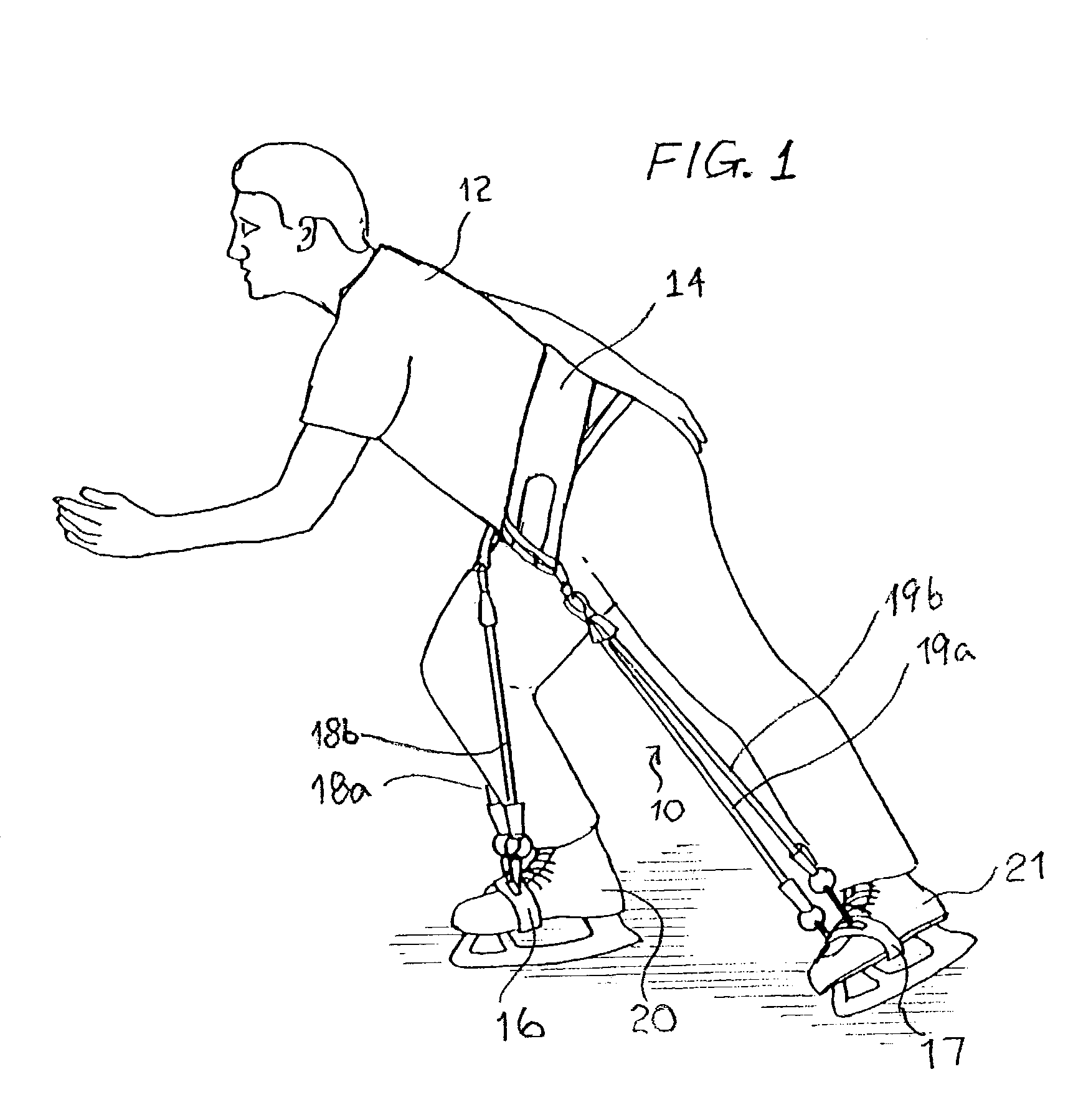
Training device for and method for training gliding sport athlete
A training device for a gliding sport athlete trains the athlete to have the proper knee bend for gliding sports such as ice skating, inline skating, skiing, etc. The device includes a belt and a pair of foot attachments adapted to be fastened to a front portion of the respective feet or footwear of the athlete. One end of each pair of cords is connected to the belt at a position between the front portion and a respective side portion, and another end connected to one of the foot attachments. Each of the cords has an unstretched length less than a length between the athlete's waist and feet, to apply a force to urge the athlete's knee into a bent position.
Owner:MARCO WENDY G
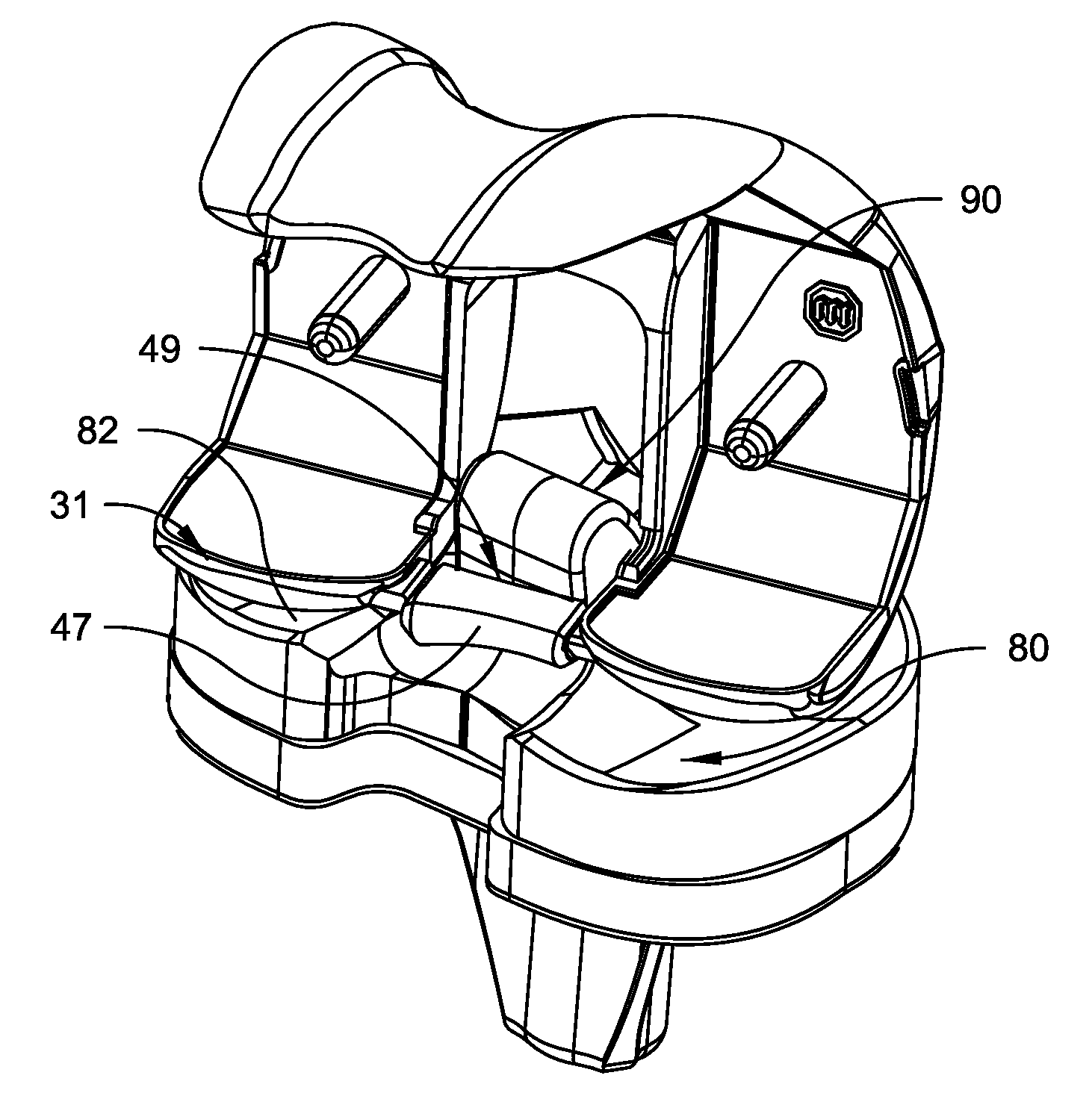
Artificial knee joint
InactiveUS20110082558A1Maximum flexionEasy to bendJoint implantsKnee jointsFemoral componentSurface geometry
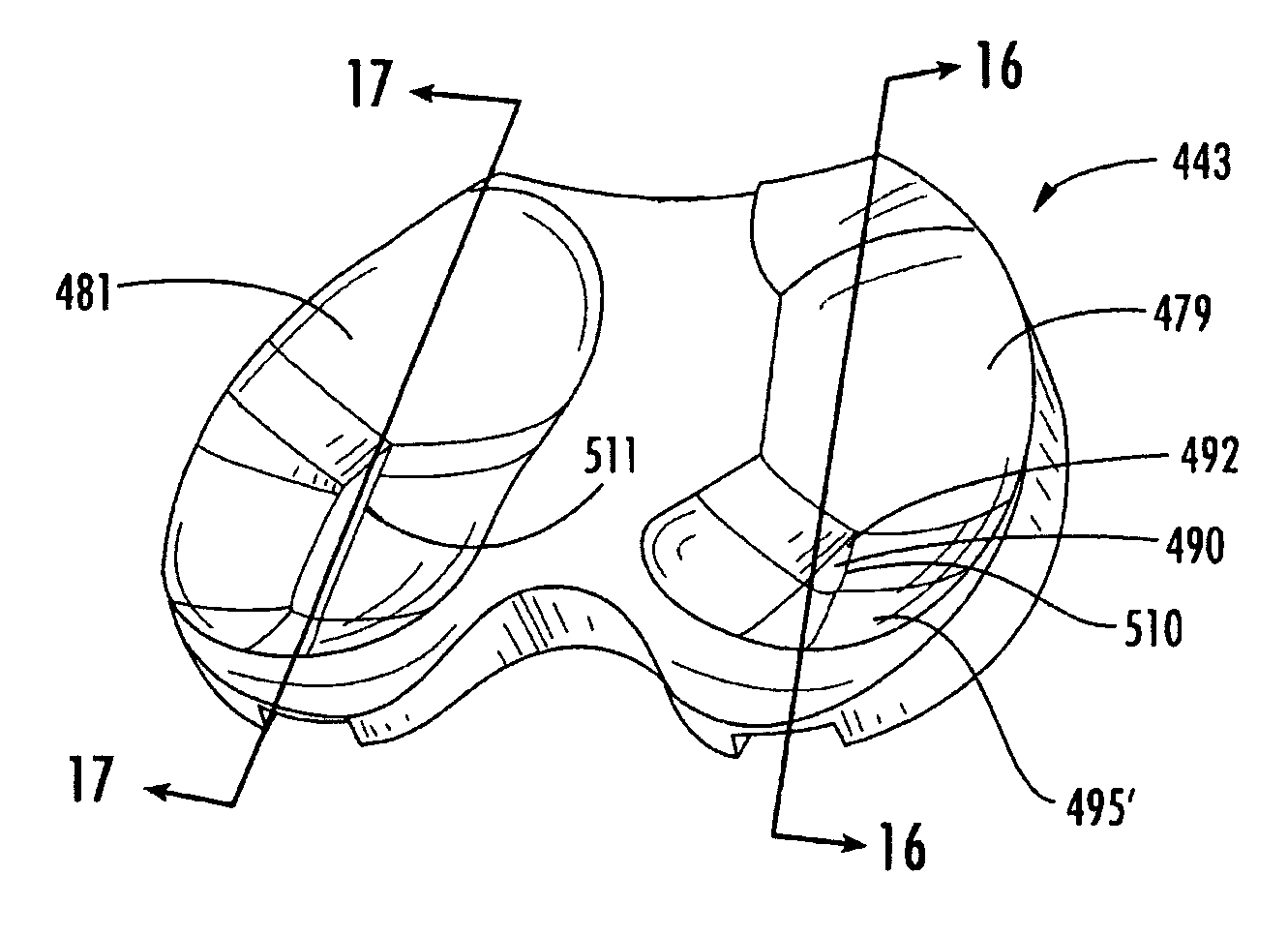
An artificial knee joint comprise a femoral component and tibial component. The posterior side of the femoral component comprises medial and lateral condyles, wherein the width and offset of the posteromedial condyle is greater than the width and offset of the posterolateral condyle. At the posterior the tibial bearing component comprises medial and lateral articulating surface geometries, wherein the posterior slope of the lateral articulating geometry is greater than the posterior slope of the medial articulating geometry. The medial articulating surface geometry of the tibial bearing component supports the medial condyle of the femoral component and the lateral articulating surface geometry of the tibial bearing component supports the lateral condyle of the femoral component. The greater slope of the lateral articulating geometry allows the femoral component condyle to roll down to the posterior during knee flexion. This invention of an artificial knee joint for a prosthetic knee implant system facilitates deep knee flexes beyond 130 degrees.
Owner:OTISBIOTECH
Automatic patient turner
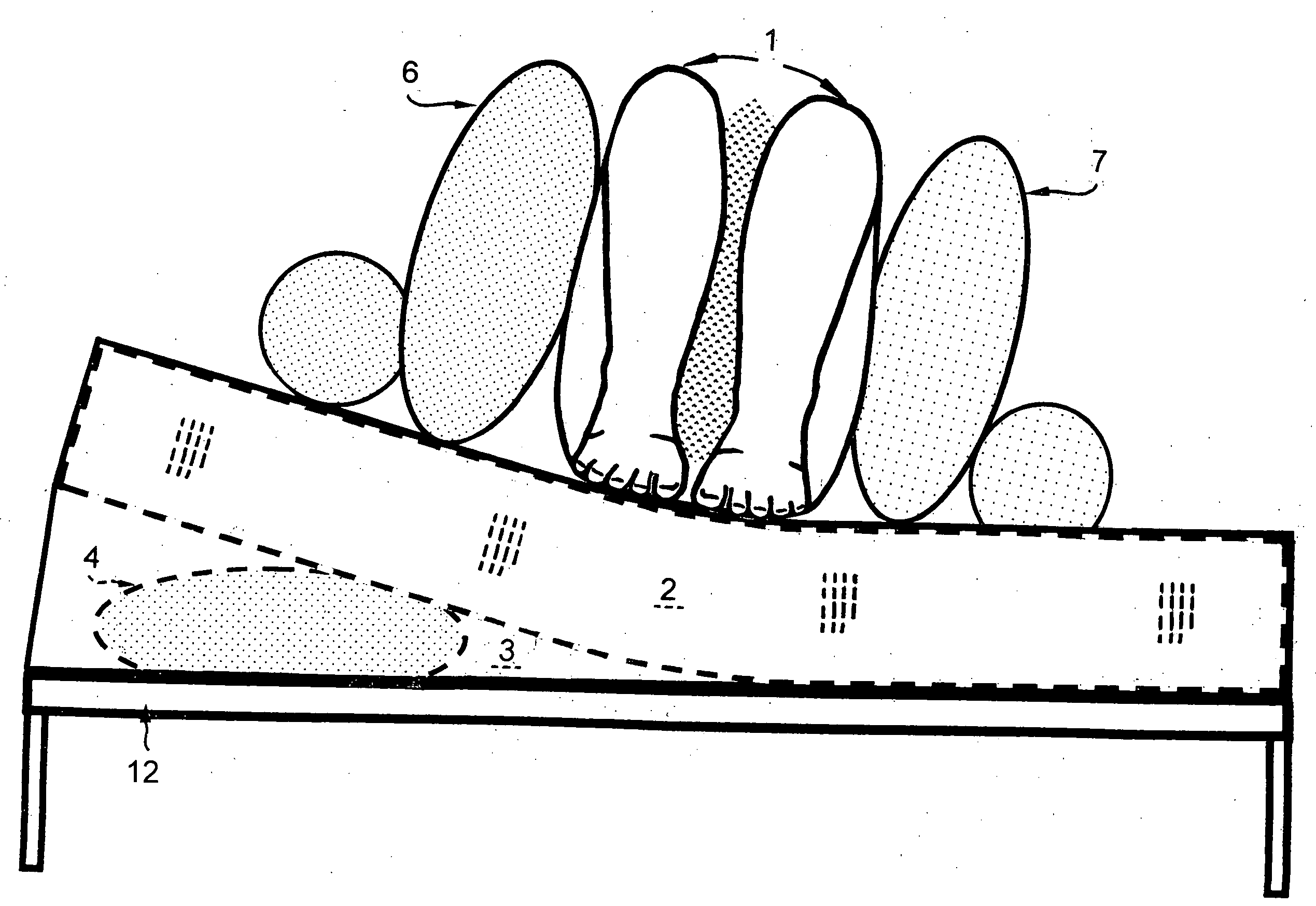
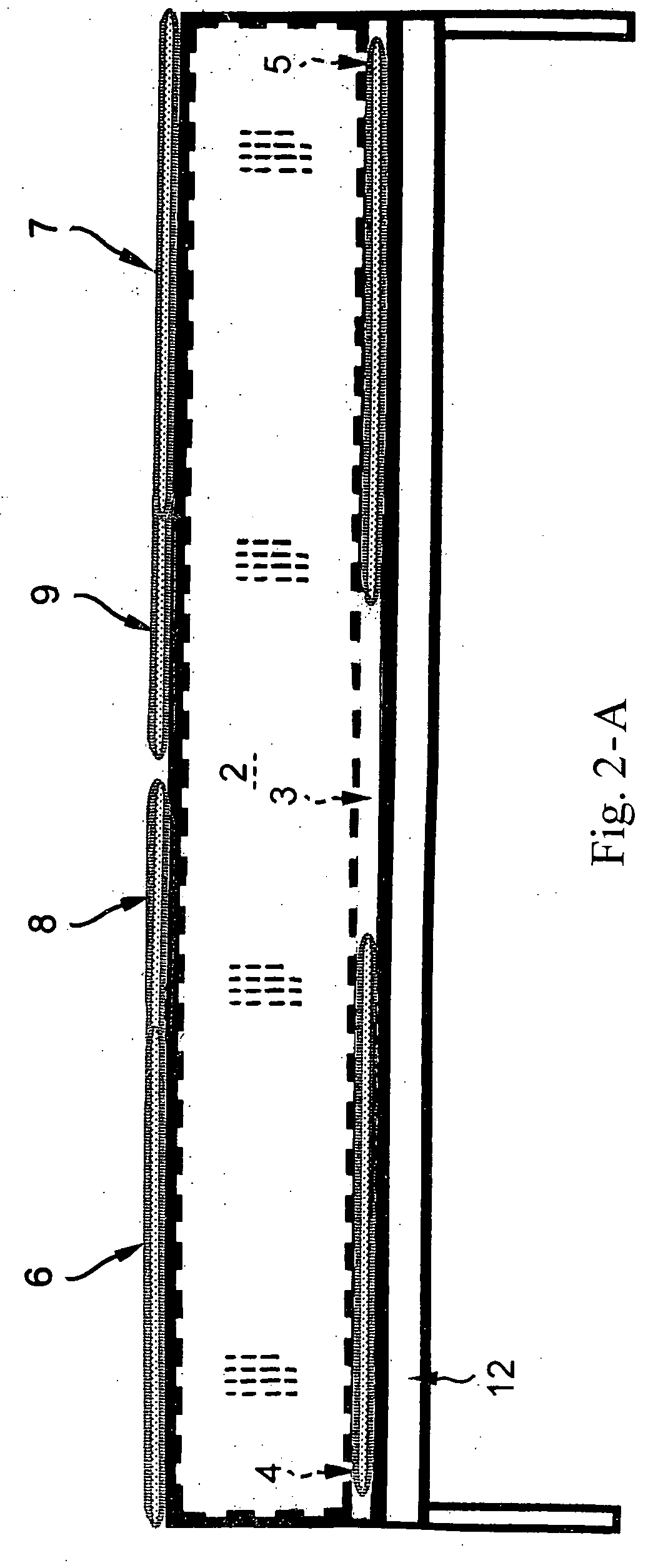
The Automatic Patient Turner is the ultimate in pressure sore prevention by automatically, periodically, and alternately tilting, and then laterally turning an immobile patient from one complete side to the other in a manner similar to, yet gentler and less intrusive than, manual turning. This is accomplished by the patterned, sequential inflation and deflation of six strategically-placed inflatables. When the bent knees (1) are perpendicular and sandwiched between a pair of inflated knee inflatables (6 and 7), they can serve as a lever arm in the turning process. When pressure is exerted against the bent knees (1), it causes them to move well beyond their perpendicular position. They then descend in the direction of the turn as the knee inflatables (6 and 7) deflate. The descending knees laterally pull the entire body of the patient completely to the side of the turn as a back-support pillow (8 or 9) inflates.
Owner:BEN LEVI FAMILY TRUST
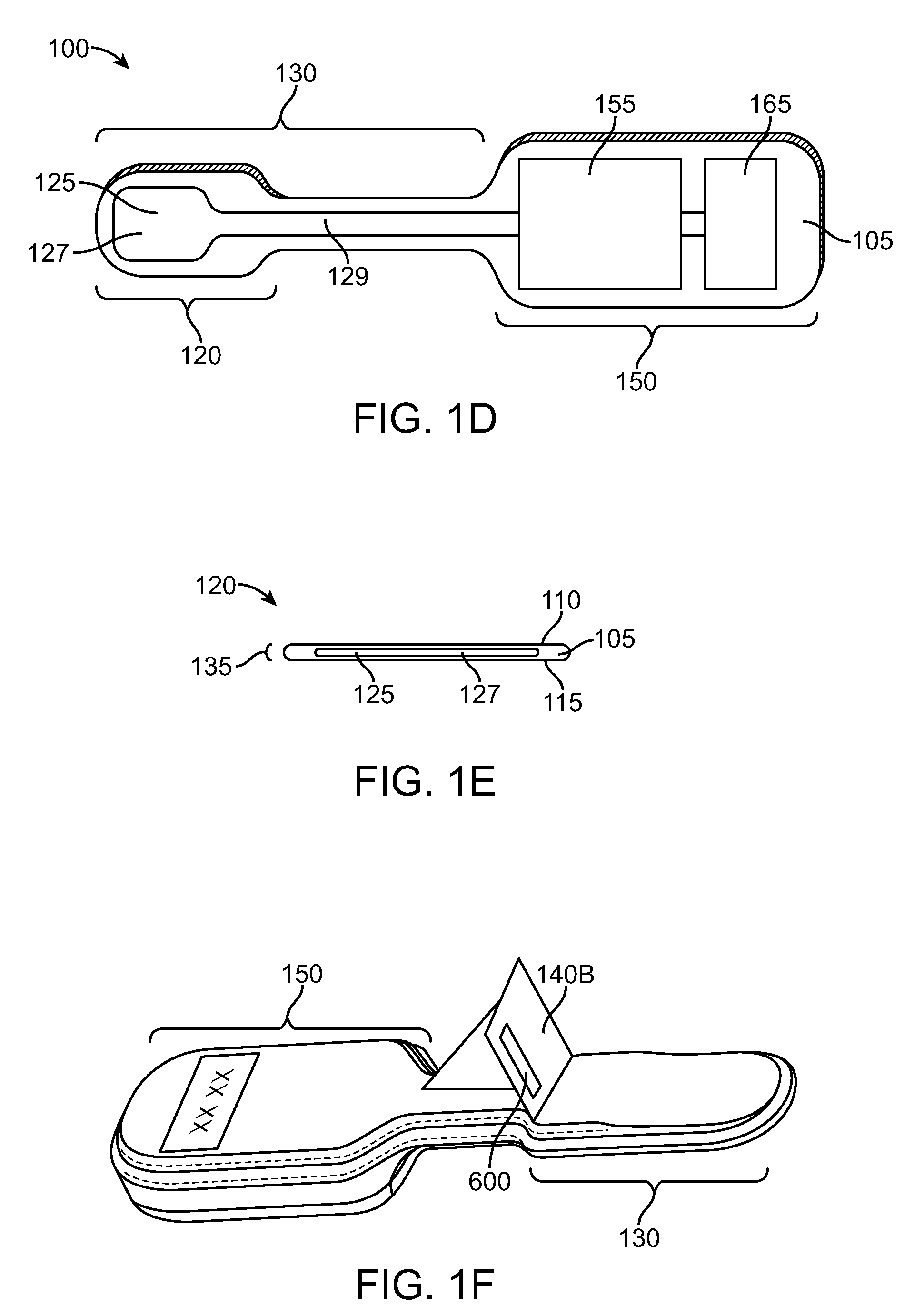
Polymeric Prosthetic Liner With Controlled Stretch Characteristics
A controlled-stretch prosthetic liner comprising a polymeric material covered with at least a stretch-controlling fabric. Certain liner types, such as below knee (BK) liners, may also include a panel of more stretchable fabric so as to prevent any interference with knee flexion. The polymeric material of the liner may also be used to control liner stretch, such as by adding Kevlar pulp or other materials that increase the strength and reduce the elasticity of the polymeric material and / or by reducing the amount of plasticizer(s) present therein. The stretch-controlling fabric, possibly in conjunction with the polymeric material, acts to limit the longitudinal stretch of the liner while not adversely affecting the radial stretch thereof.
Owner:WILLOWWOOD GLOBAL LLC
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities for knee prosthesis patients
InactiveUS8366783B2Closely replicate physiologic loadingEasy to trackJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaArticular surfaces
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities, more physiologic load bearing and improved patellar tracking for knee prosthesis patients. Such systems and methods include (i) adding more articular surface to the antero-proximal posterior condyles of a femoral component, including methods to achieve that result, (ii) modifications to the internal geometry of the femoral component and the associated femoral bone cuts with methods of implantation, (iii) asymmetrical tibial components that have an unique articular surface that allows for deeper knee flexion than has previously been available, (iv) asymmetrical femoral condyles that result in more physiologic loading of the joint and improved patellar tracking and (v) modifying an articulation surface of the tibial component to include an articulation feature whereby the articulation pathway of the femoral component is directed or guided by articulation feature.
Owner:SAMUELSON KENT M +1
Systems and methods for providing a femoral component
InactiveUS20130197654A1Deep knee flexion capabilityOptimized areaJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfaceMedicine
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities. In some instances, such systems and methods include a femoral knee replacement component that includes an articular surface, a first interior surface, and a second interior surface, wherein the first and second interior surfaces run substantially parallel to each other. In some cases, the articular surface includes an anterior condylar extension that is configured to replace an anterior articular cartilage of a femur such that the anterior extension is configured to terminate adjacent to a proximal limit of the anterior articular cartilage of the femur. Other implementations are also discussed.
Owner:SAMUELSON KENT M +1
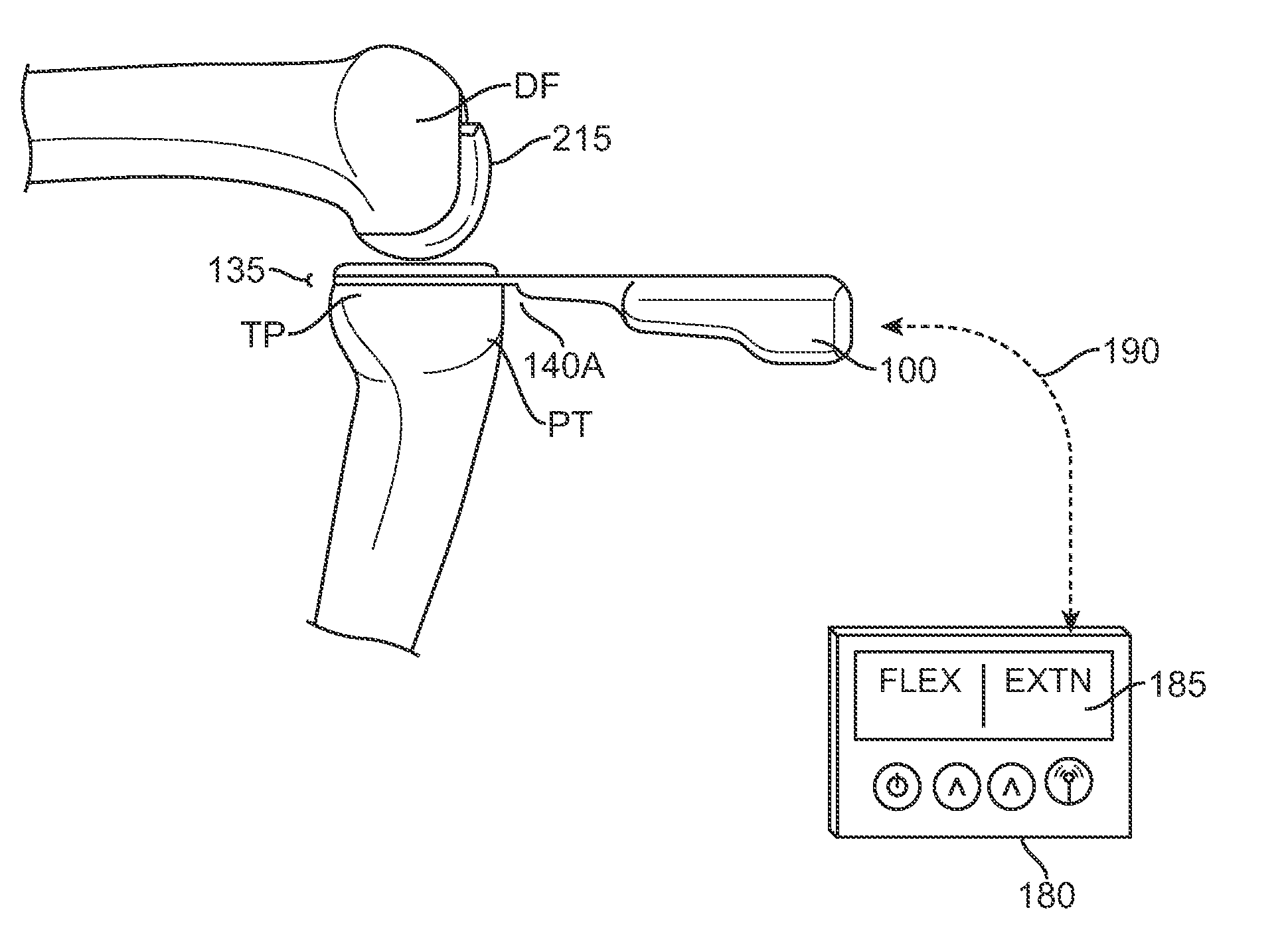
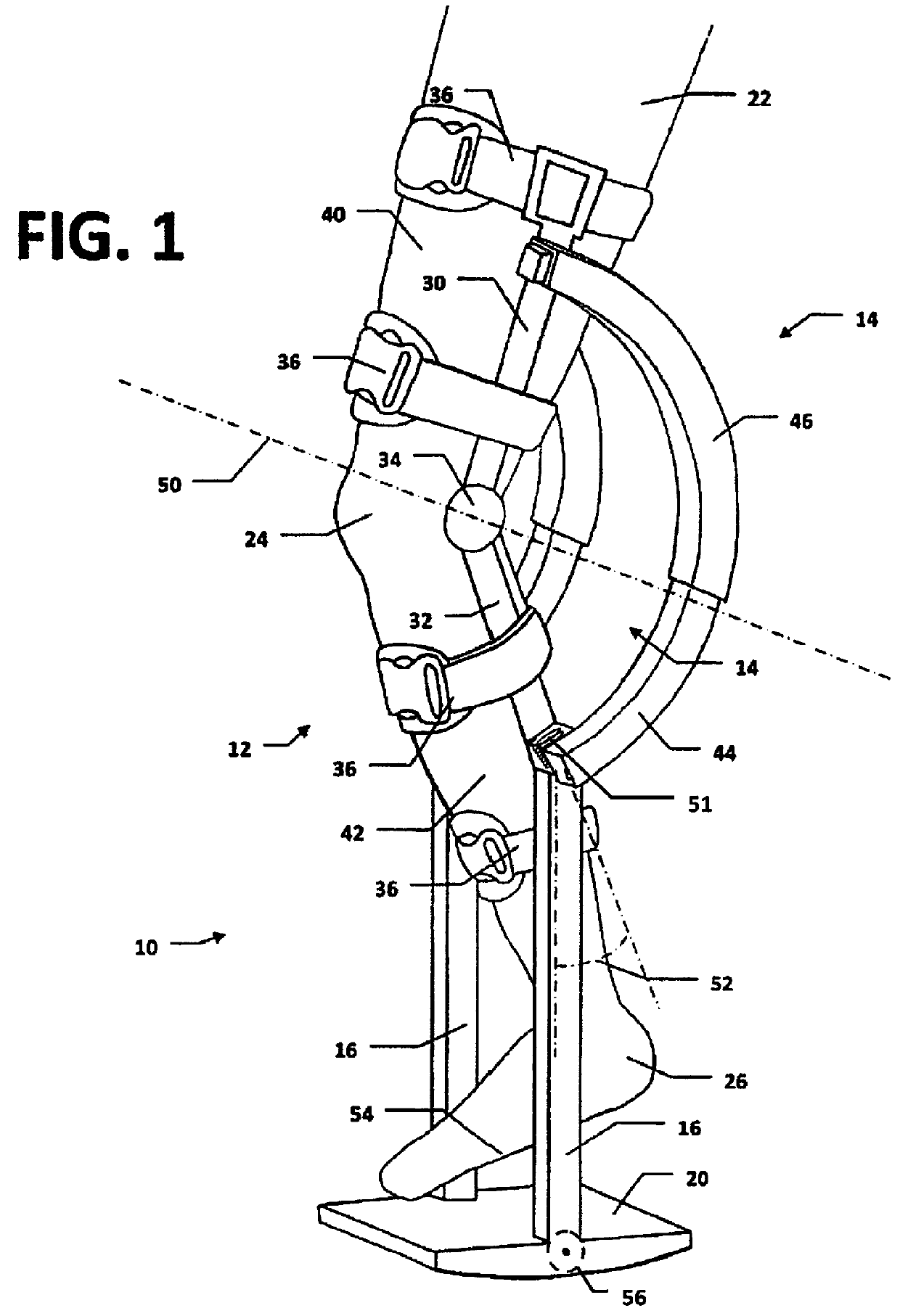
Hinge system for regulating knee joint flexion and extension
ActiveUS7044925B2Avoid re-injuryAlleviates the above-referenced deficienciesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesRange of motionKnee Joint
A hinge system for a knee brace features a flexion-extension regulating device which is adapted to engage an end portion of the knee brace's upper strut. An elongated main slot is formed through the regulating device to provide a fixed boundary for limiting range of motion. A motion limiting member is connected to the regulating device and is further adapted for connection to an end portion of the knee brace's lower strut. The motion limiting member includes a motion limiter that is disposed within the main slot. The motion limiter is caused to move therealong when the upper and lower struts pivot about a user's knee joint. By confining the motion limiter within the fixed boundary formed by the main slot, the hinge system ensures that the user's knee joint flexes and extends within the prescribed range of motion.
Owner:OSSUR HF
Knee joint prosthesis with a femoral component which links the tibiofemoral axis of rotation with the patellofemoral axis of rotation
A femoral component is provided for use in a knee joint prosthesis. The femoral component may be configured to provide one or more desirable kinematic relationships with a tibial component and / or patella so as to mimic the flexion and extension motion of a natural knee joint. The femoral component may be configured so that the patella follows a substantially circular pathway during knee flexion and extension. The femoral component may be configured so that the patella follows a curved patellar path during flexion and extension, and the curved patellar path has an origin located anterior and proximal to the geometrical center axis of the knee. The femoral component may be configured so that the patella follows a curved patellar path that lies in a plane which is parallel to and offset from a plane that extends through the center of the femoral head of a femur and is perpendicular to the geometric center axis of the knee. The femoral component may be configured so that at least a portion of the patella substantially follows a patellar path in a plane perpendicular to the geometrical center axis of a knee throughout knee flexion.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities for knee prosthesis patients
InactiveUS8273133B2Closely replicate physiologic loadingEasy to trackJoint implantsFemoral headsArticular surfacesArticular surface
Owner:SAMUELSON KENT M
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities for knee prosthesis patients
InactiveUS8382846B2Closely replicate physiologic loadingEasy to trackJoint implantsKnee jointsArticular surfacesTibial bone
Systems and methods for providing deeper knee flexion capabilities, more physiologic load bearing and improved patellar tracking for knee prosthesis patients. Such systems and methods include (i) adding more articular surface to the antero-proximal posterior condyles of a femoral component, including methods to achieve that result, (ii) modifications to the internal geometry of the femoral component and the associated femoral bone cuts with methods of implantation, (iii) asymmetrical tibial components that have an unique articular surface that allows for deeper knee flexion than has previously been available, (iv) asymmetrical femoral condyles that result in more physiologic loading of the joint and improved patellar tracking and (v) modifying an articulation surface of the tibial component to include an articulation feature whereby the articulation pathway of the femoral component is directed or guided by articulation feature.
Owner:SAMUELSON KENT M +1
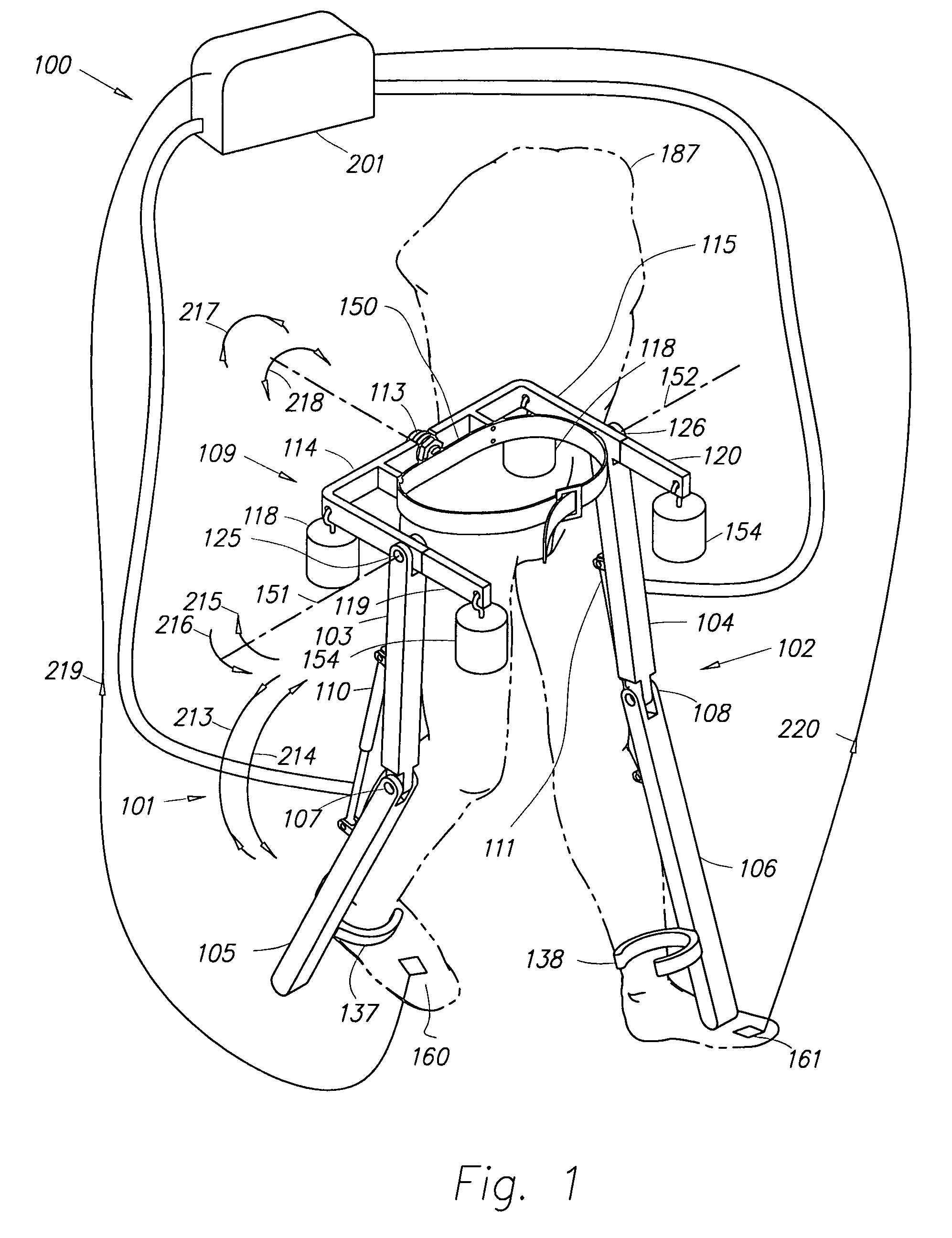
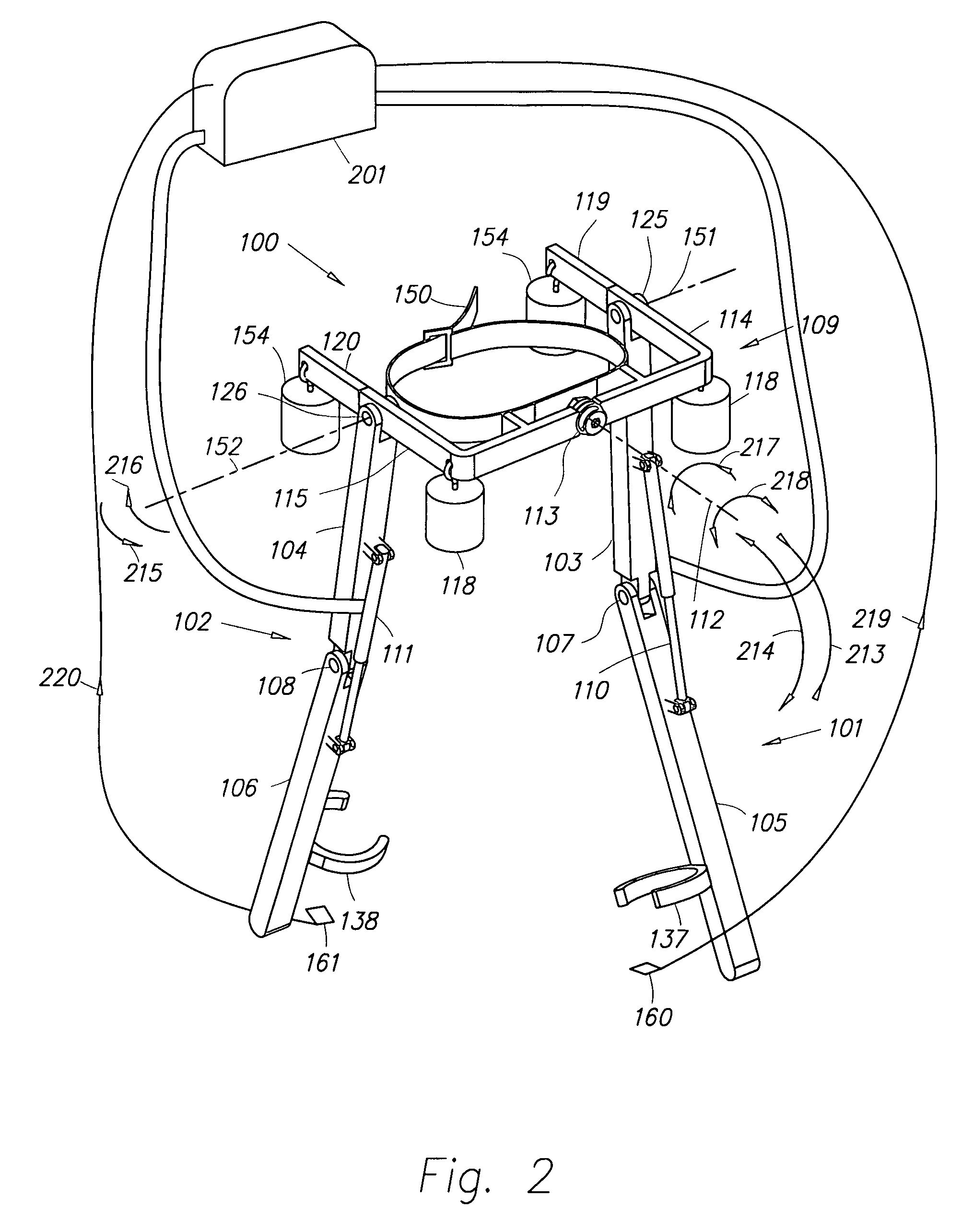
Hands-free crutch assembly
A hands-free crutch assembly allows a user's foot to float suspended over an artificial foot, while transferring at least a portion of the walking load to the upper leg and permitting more natural knee flexion and extension while walking.
Owner:EDWARDS AMANDA MARIE
Knee joint with a ramp
InactiveUS8292965B2Minimize wear and deformationIncrease the areaJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaTibial surface
An artificial knee joint is described that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the required motion and stability characteristics. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, by an amount similar to that in the anatomic knee. The opposite motion, roll forward of the femur from a fully flexed to a more extended position, is accomplished by varying the outward radii of the lateral and medial femoral bearing surfaces, together with a ramp on the postero-lateral and postero-medial regions of the tibial surfaces.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com