Patents
Literature
43 results about "Total knee replacement surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
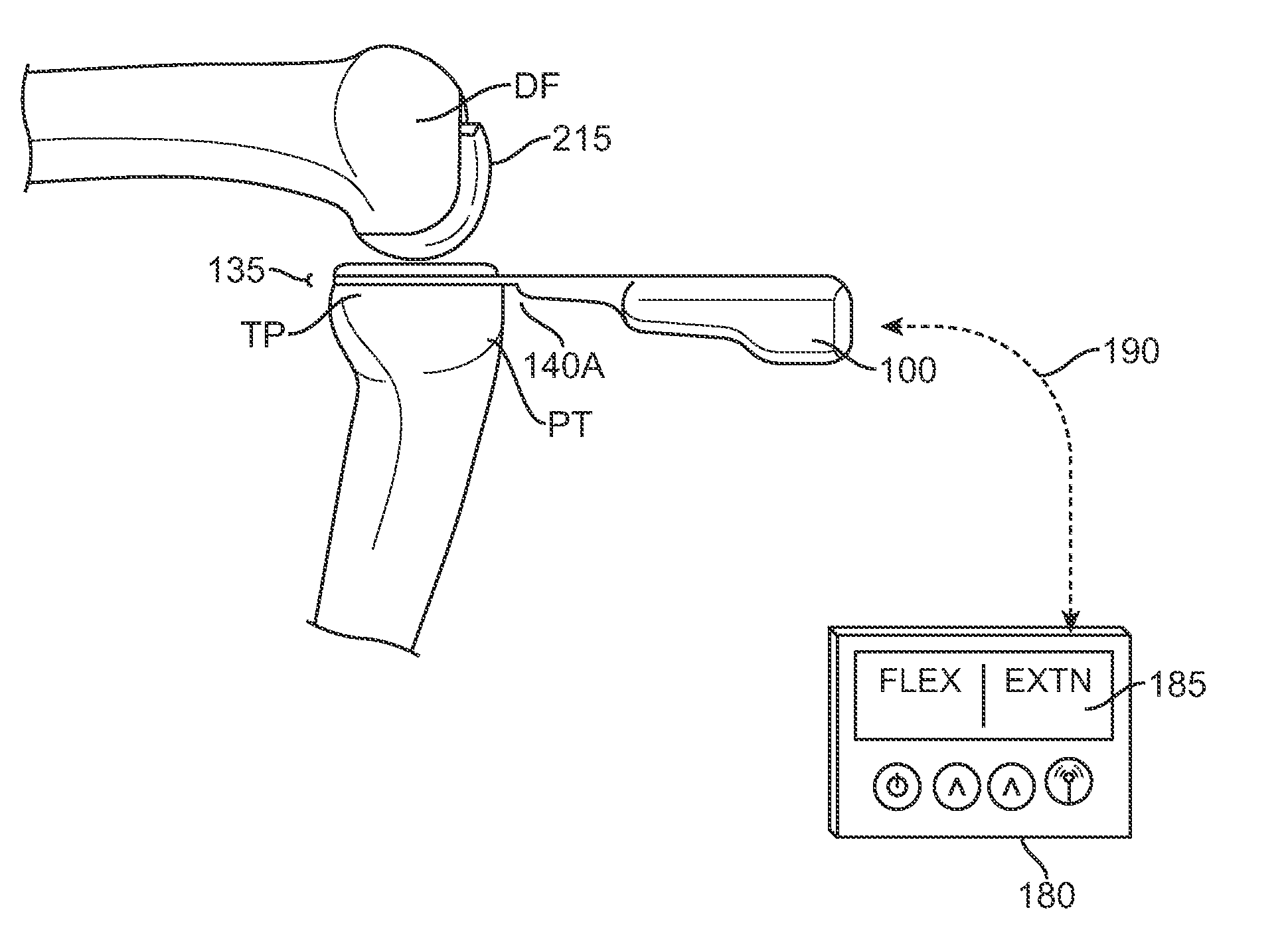
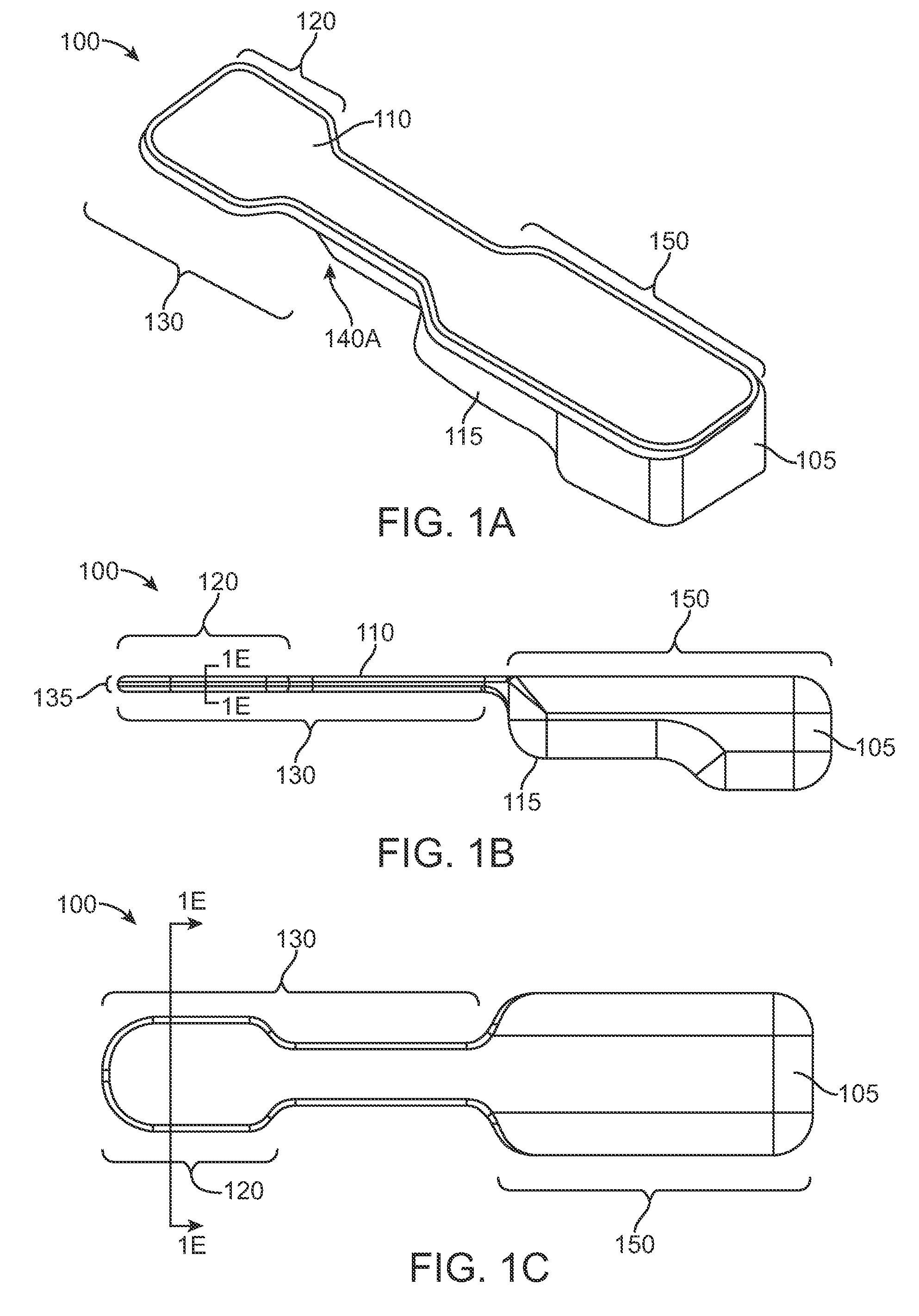
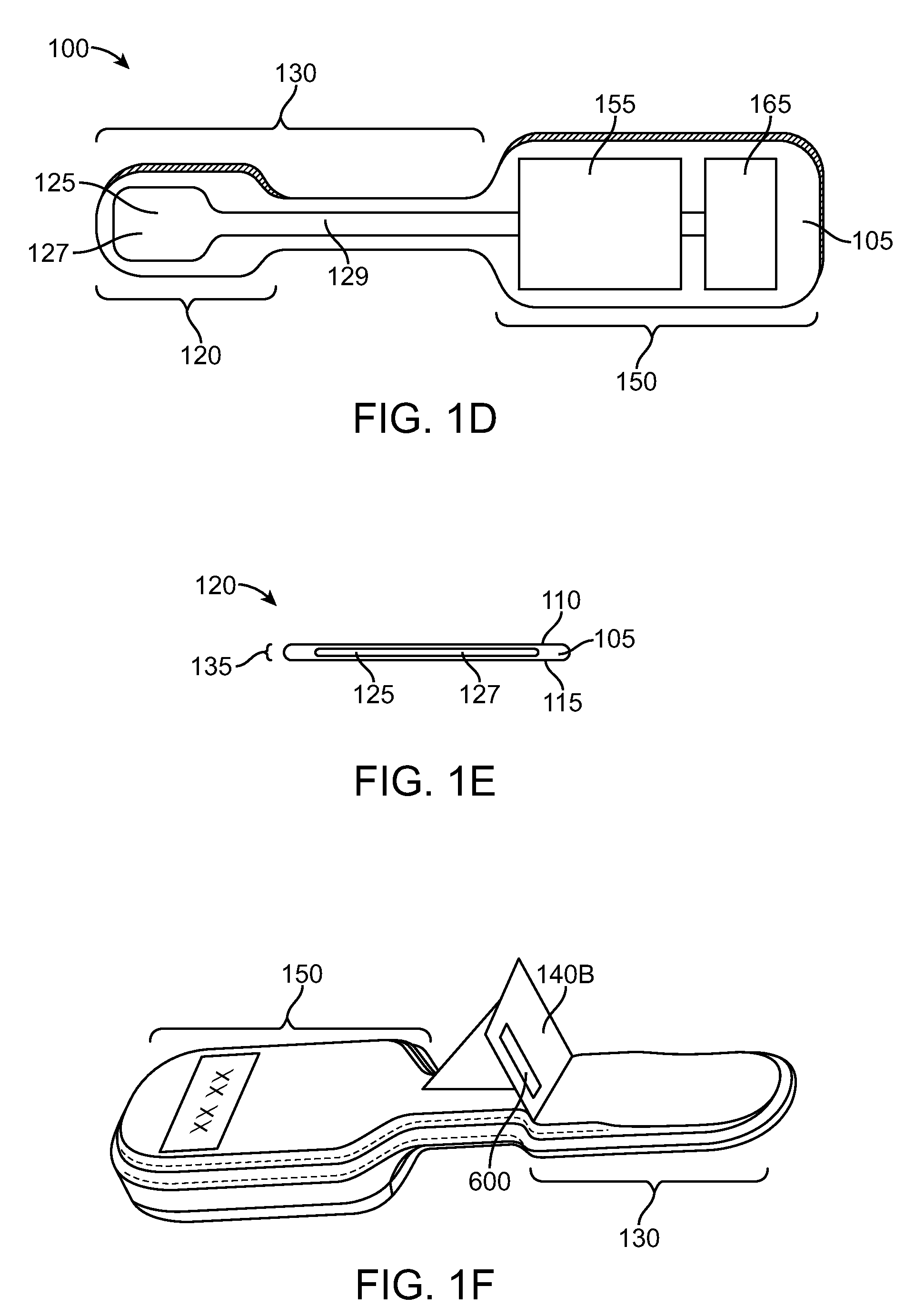
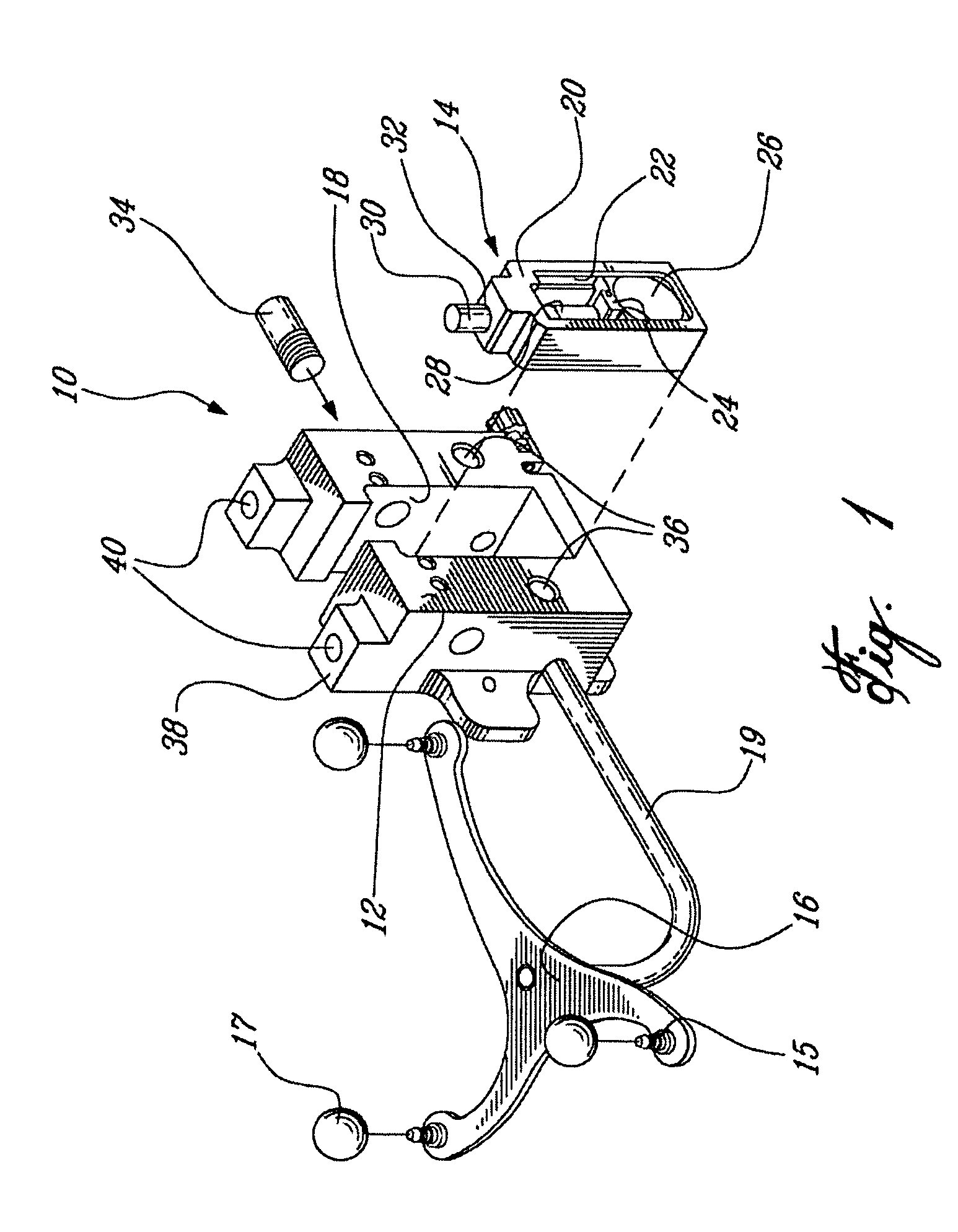
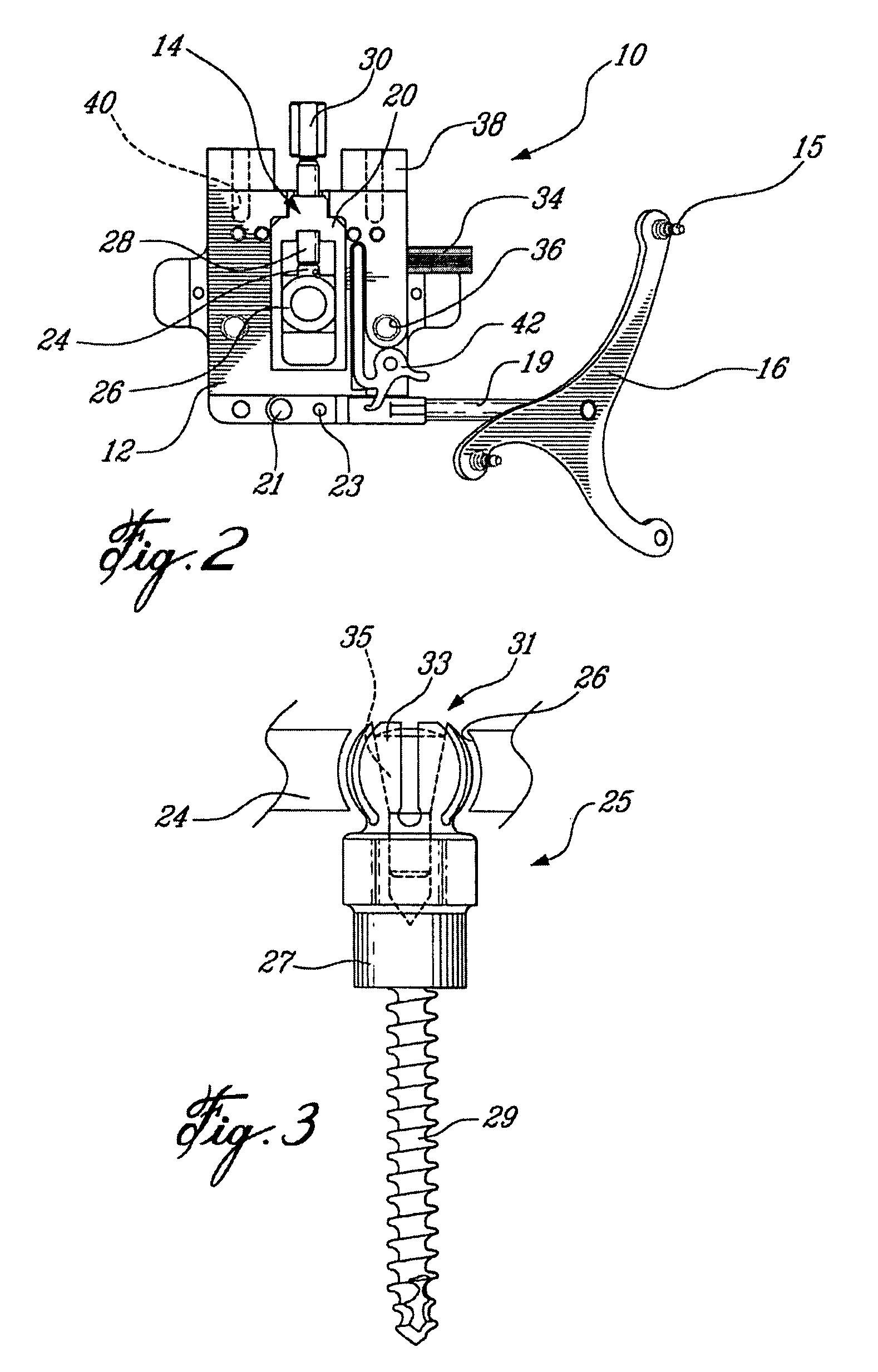
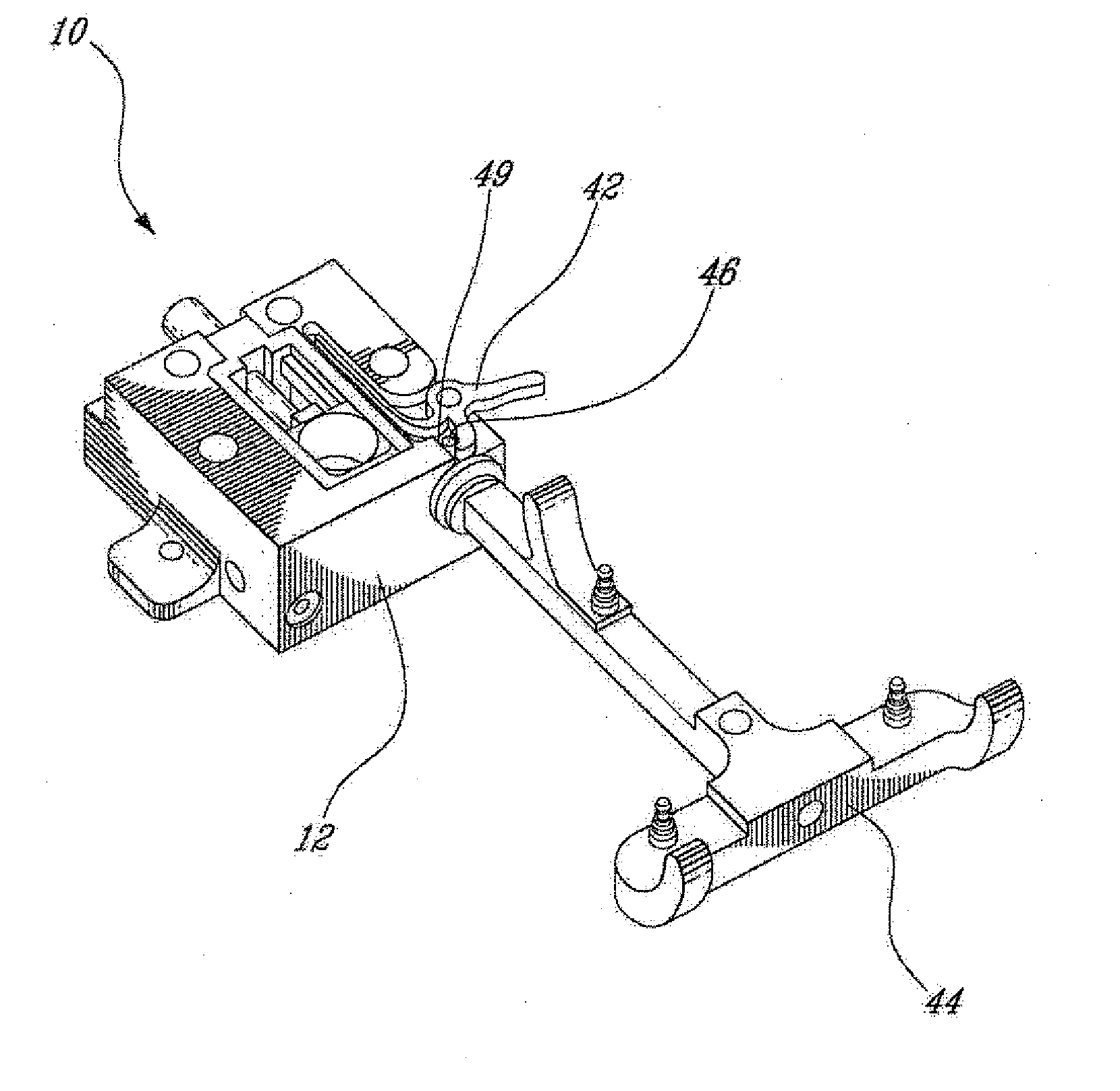
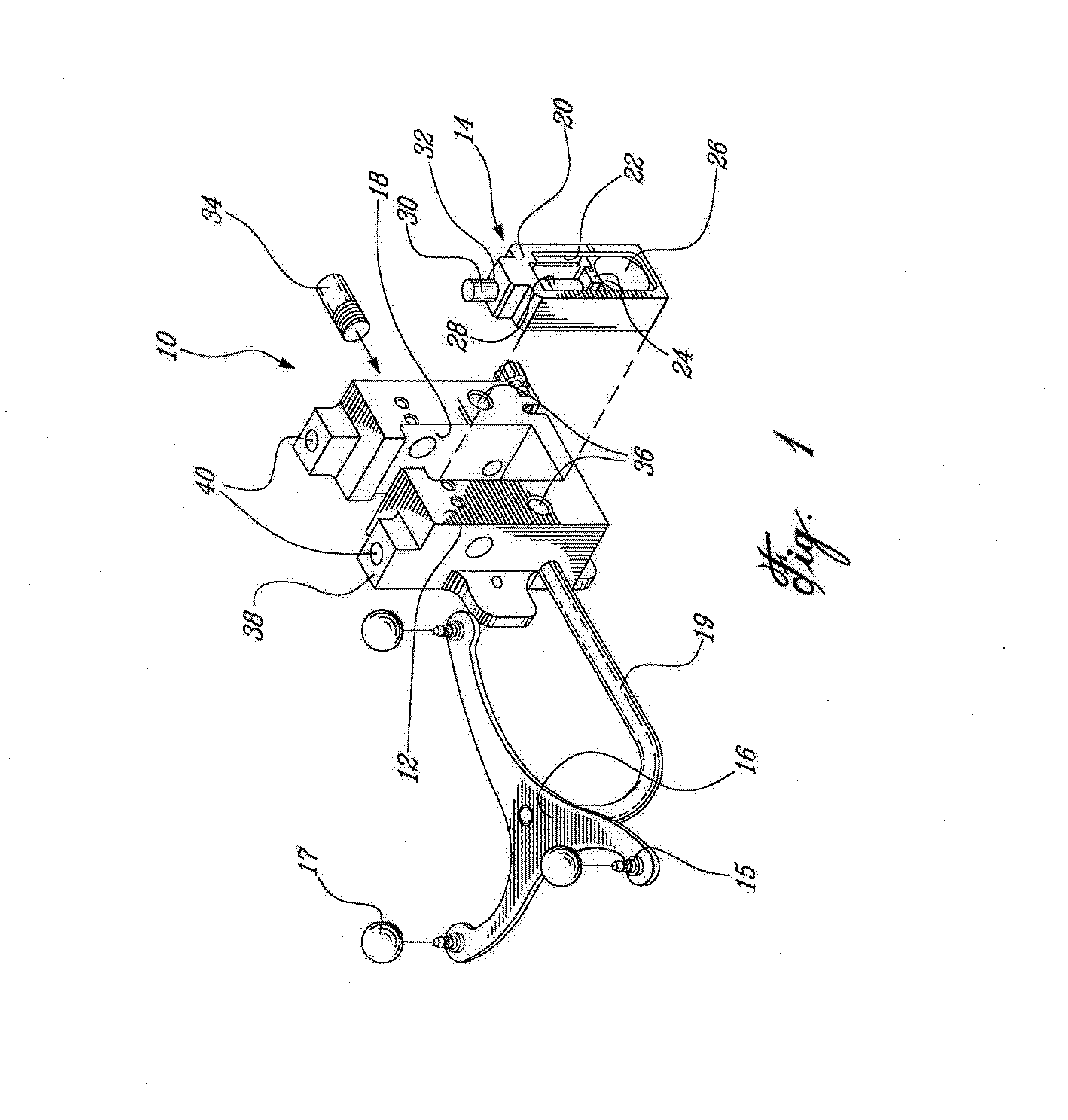
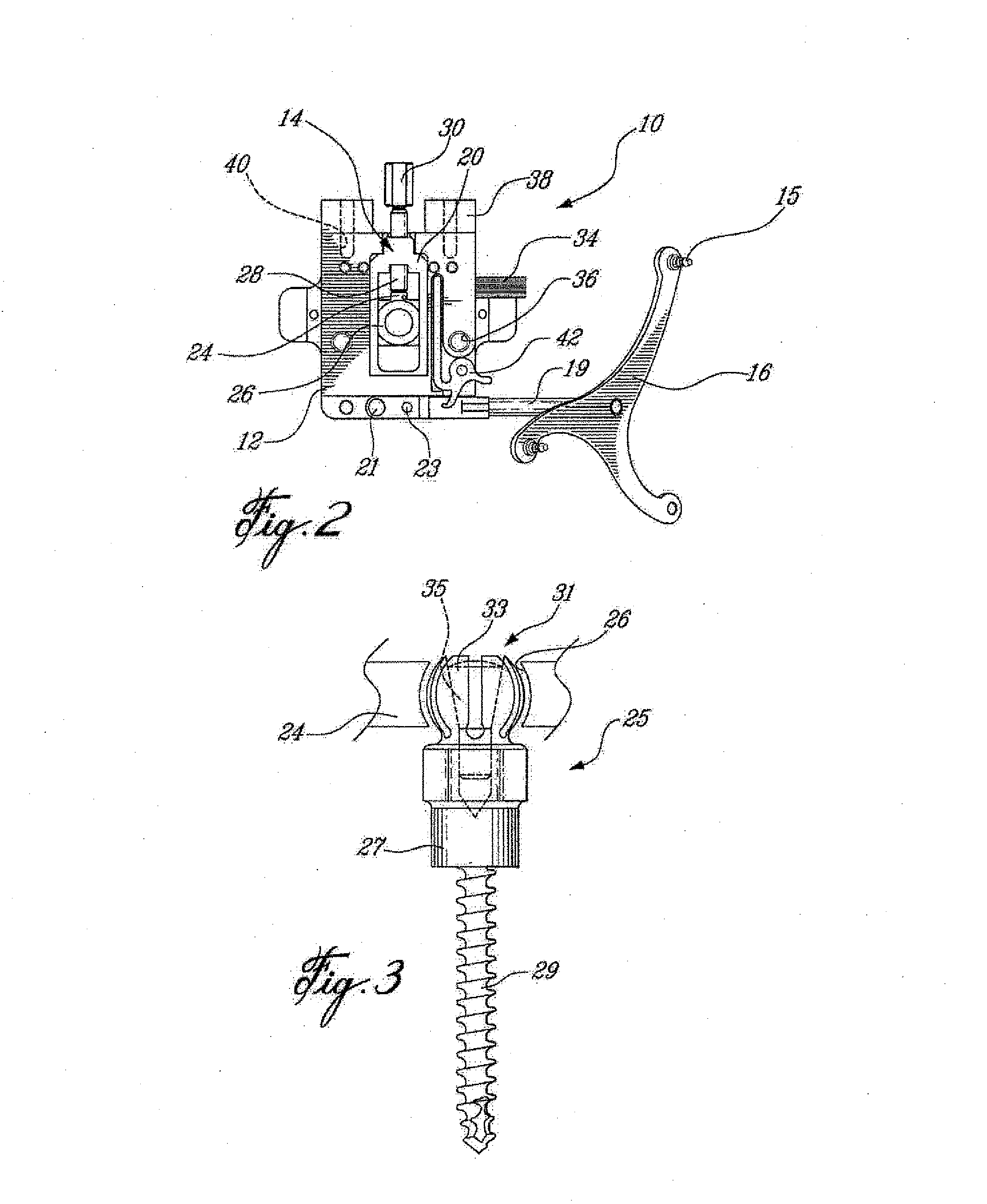
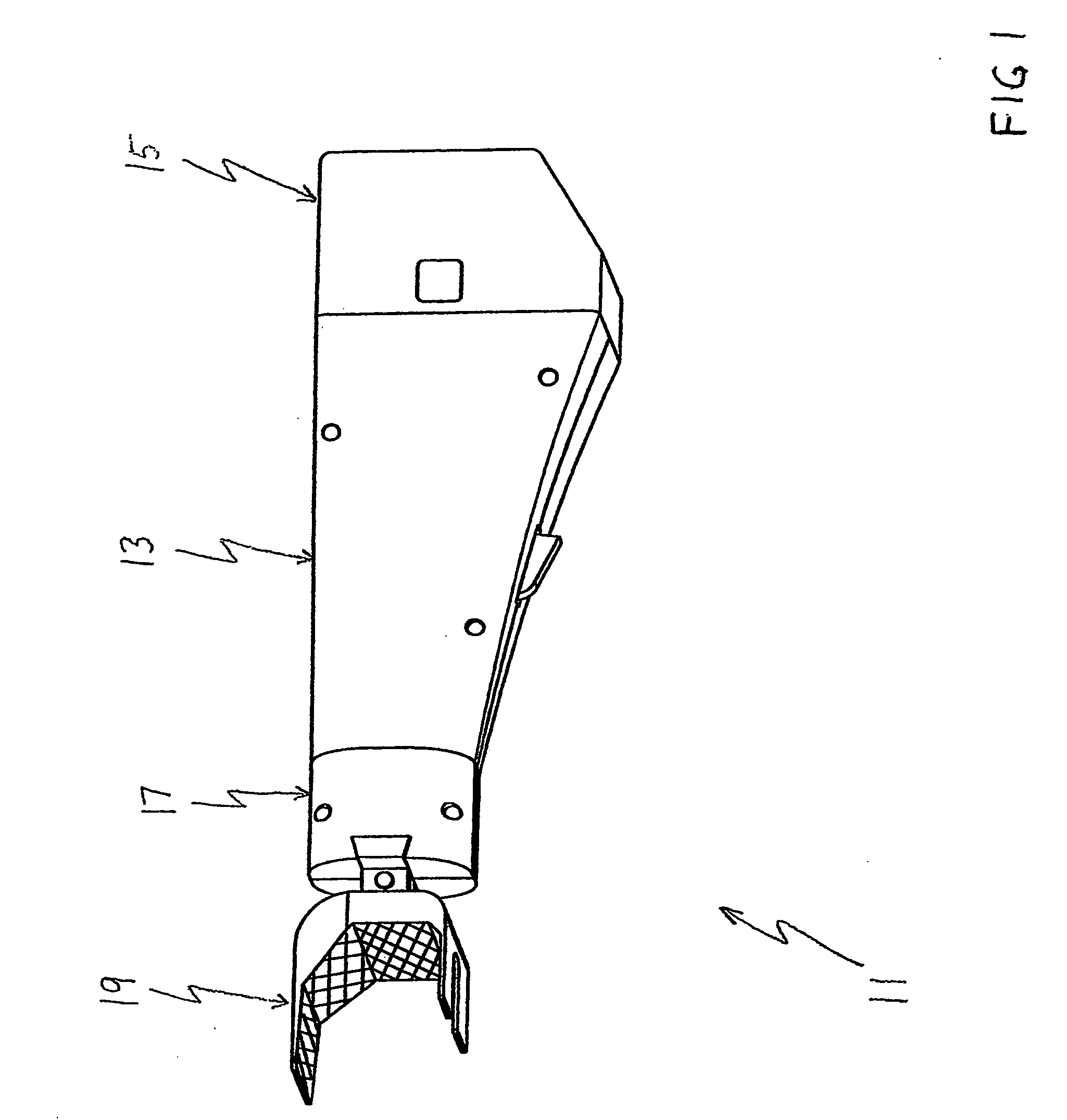
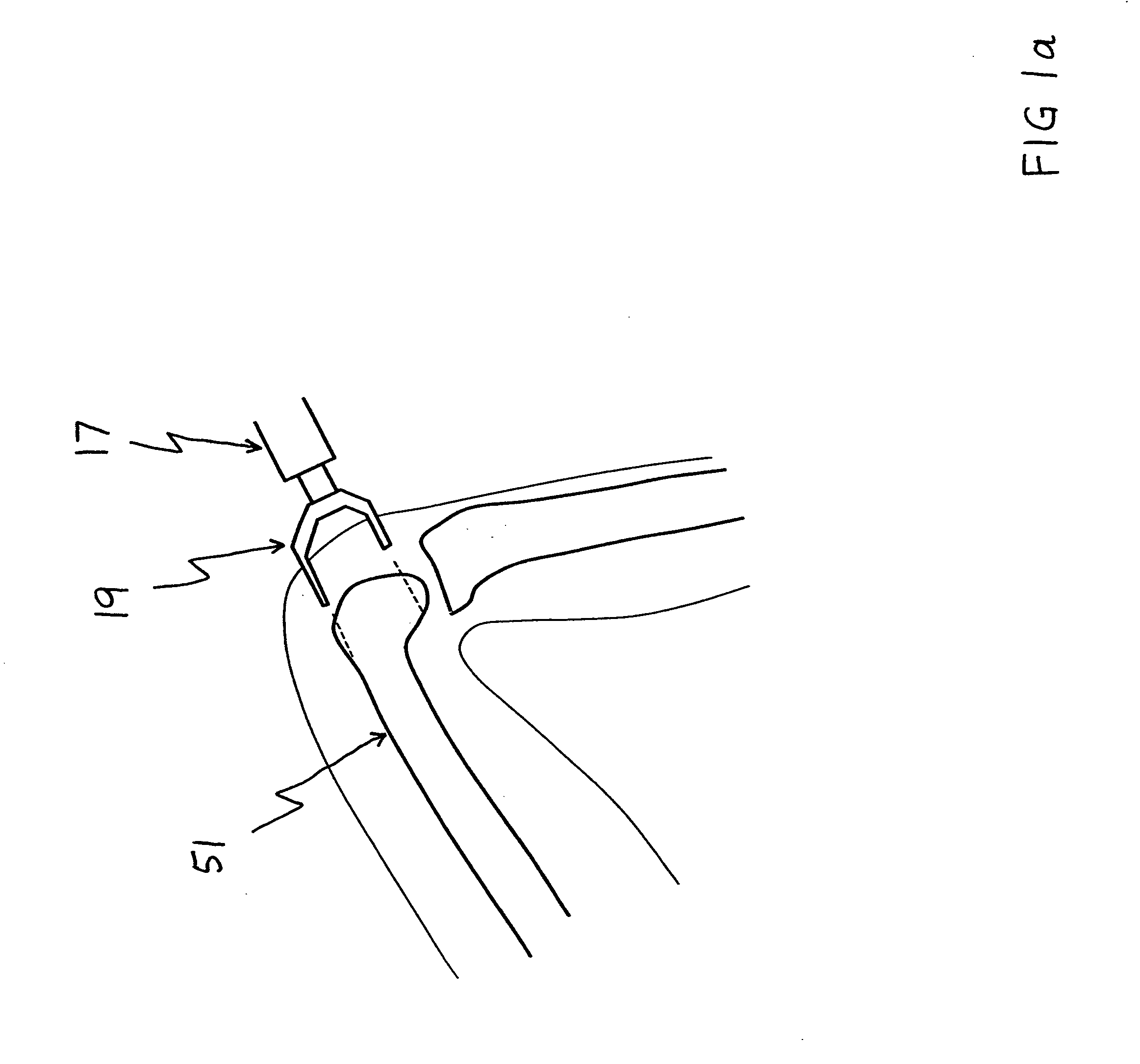
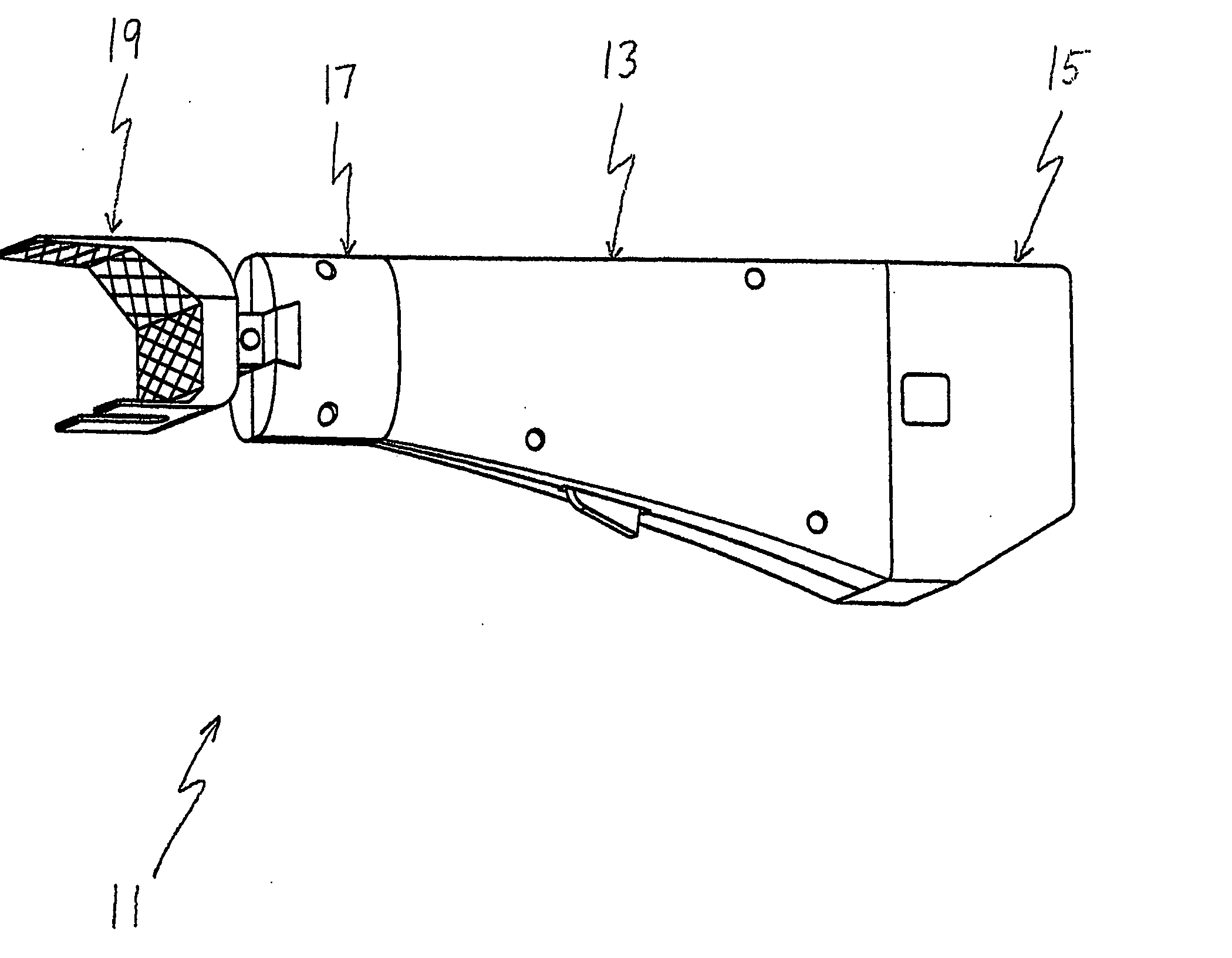
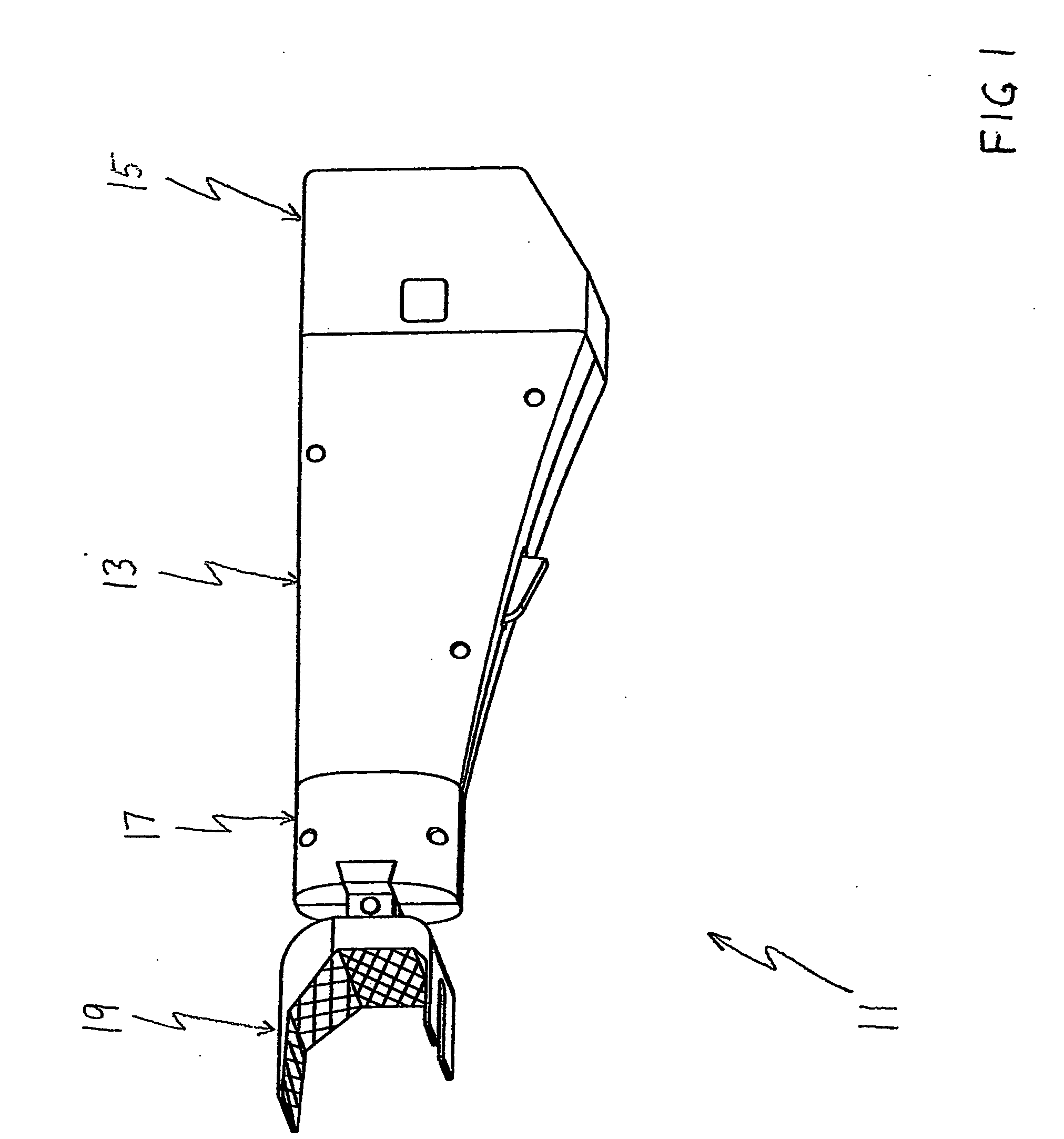
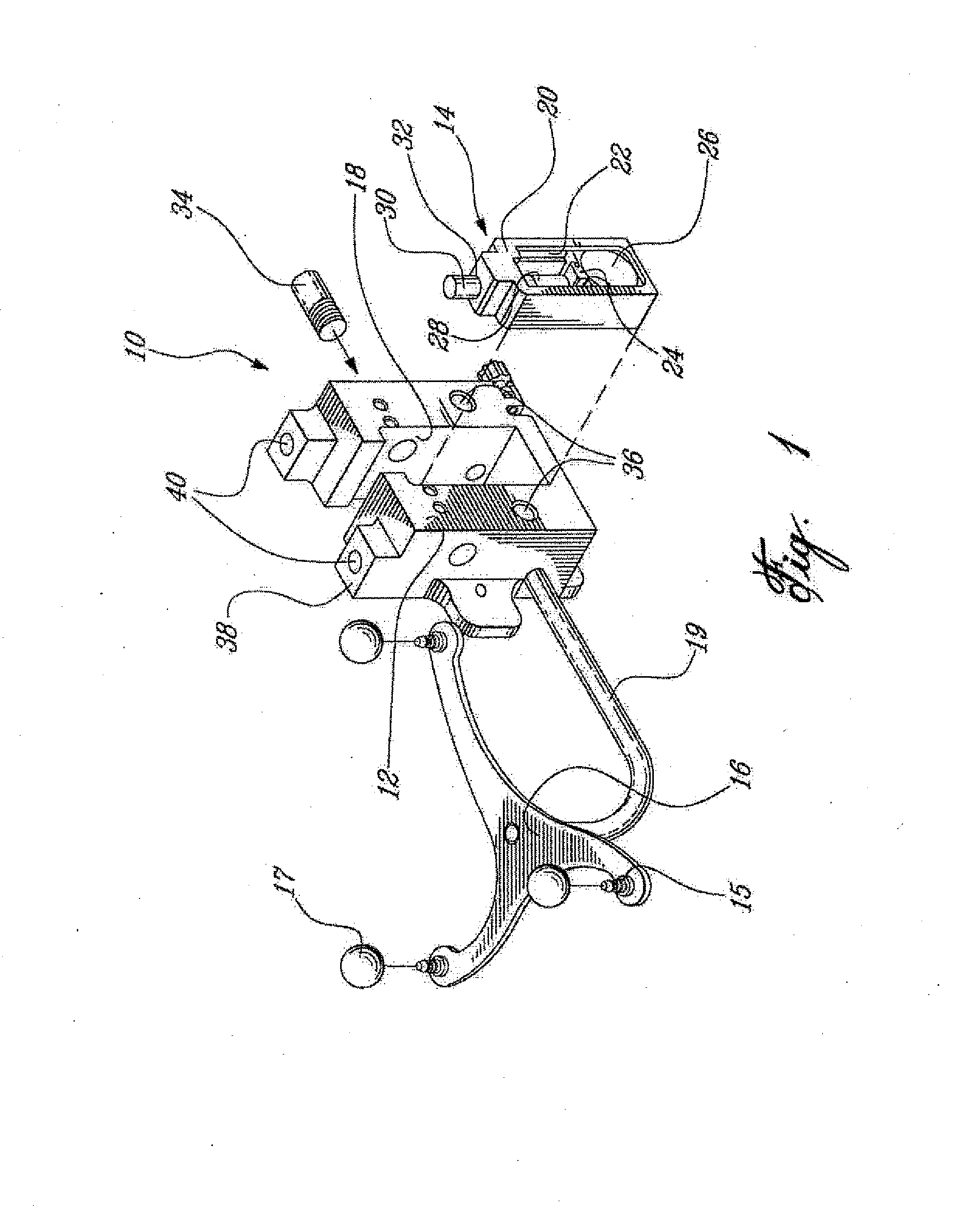
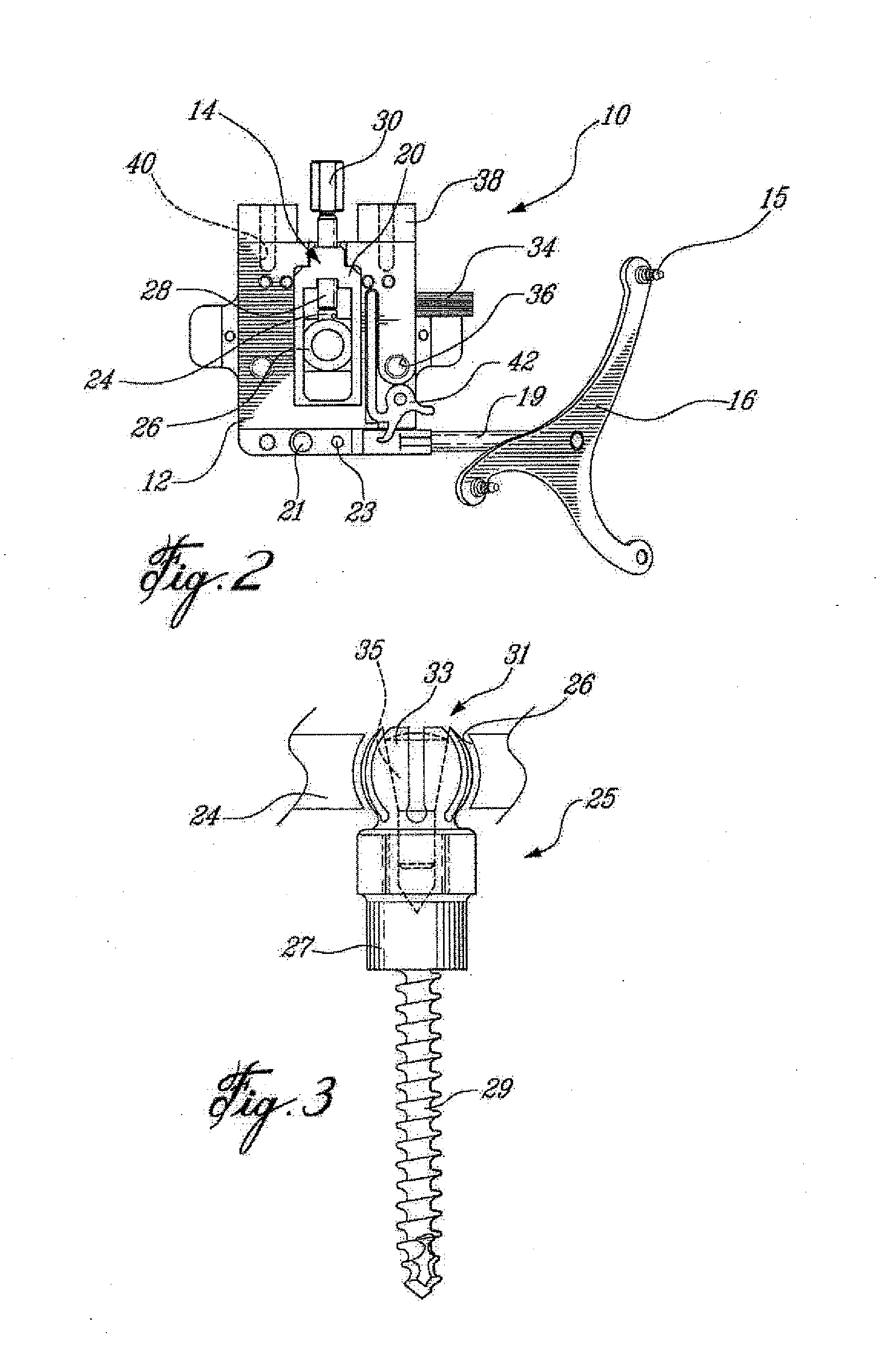
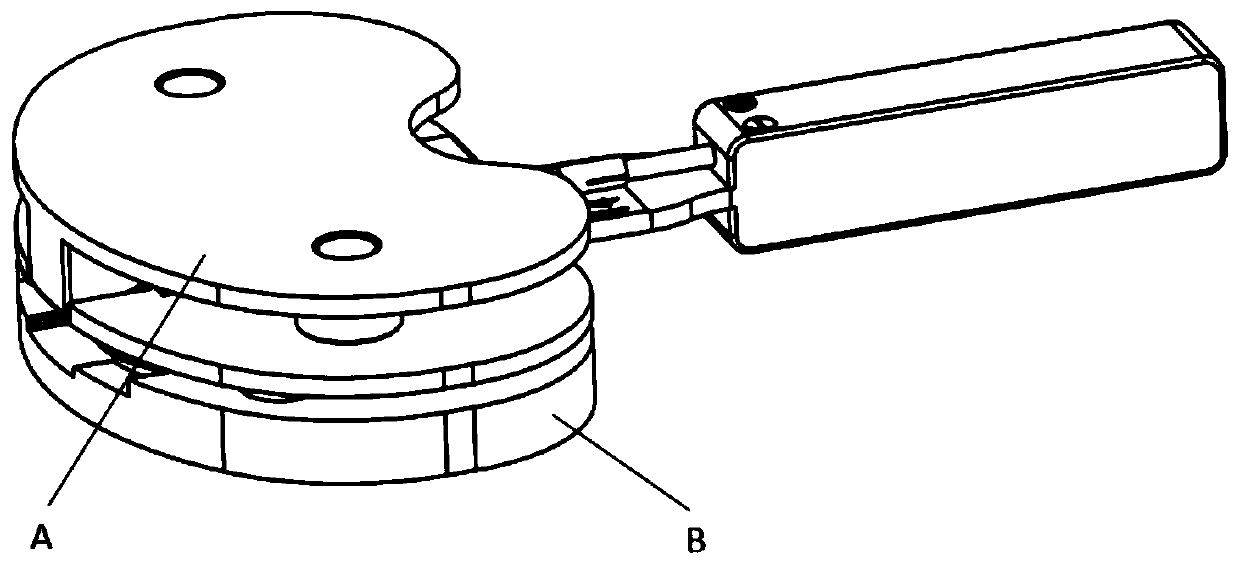
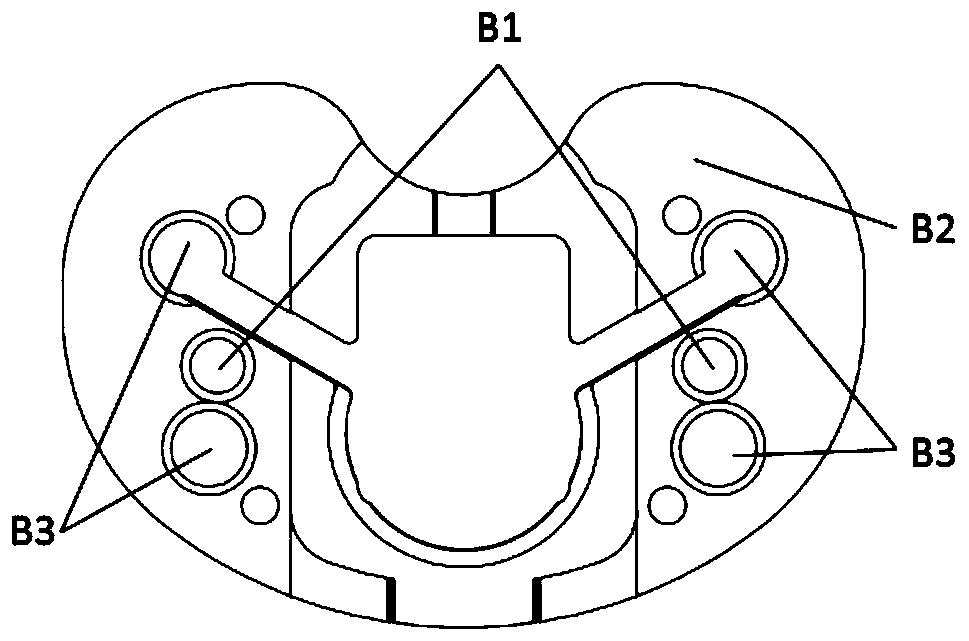
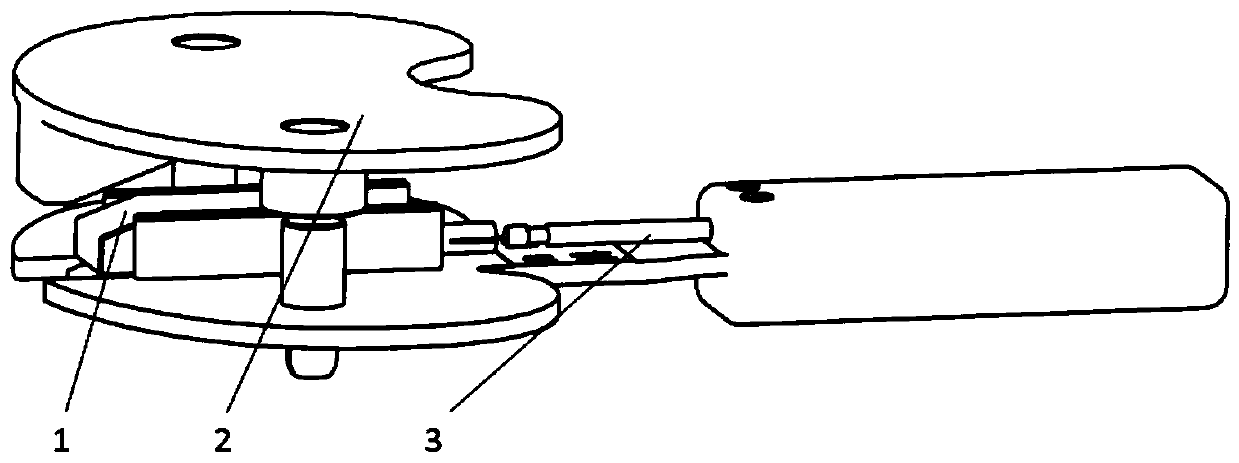
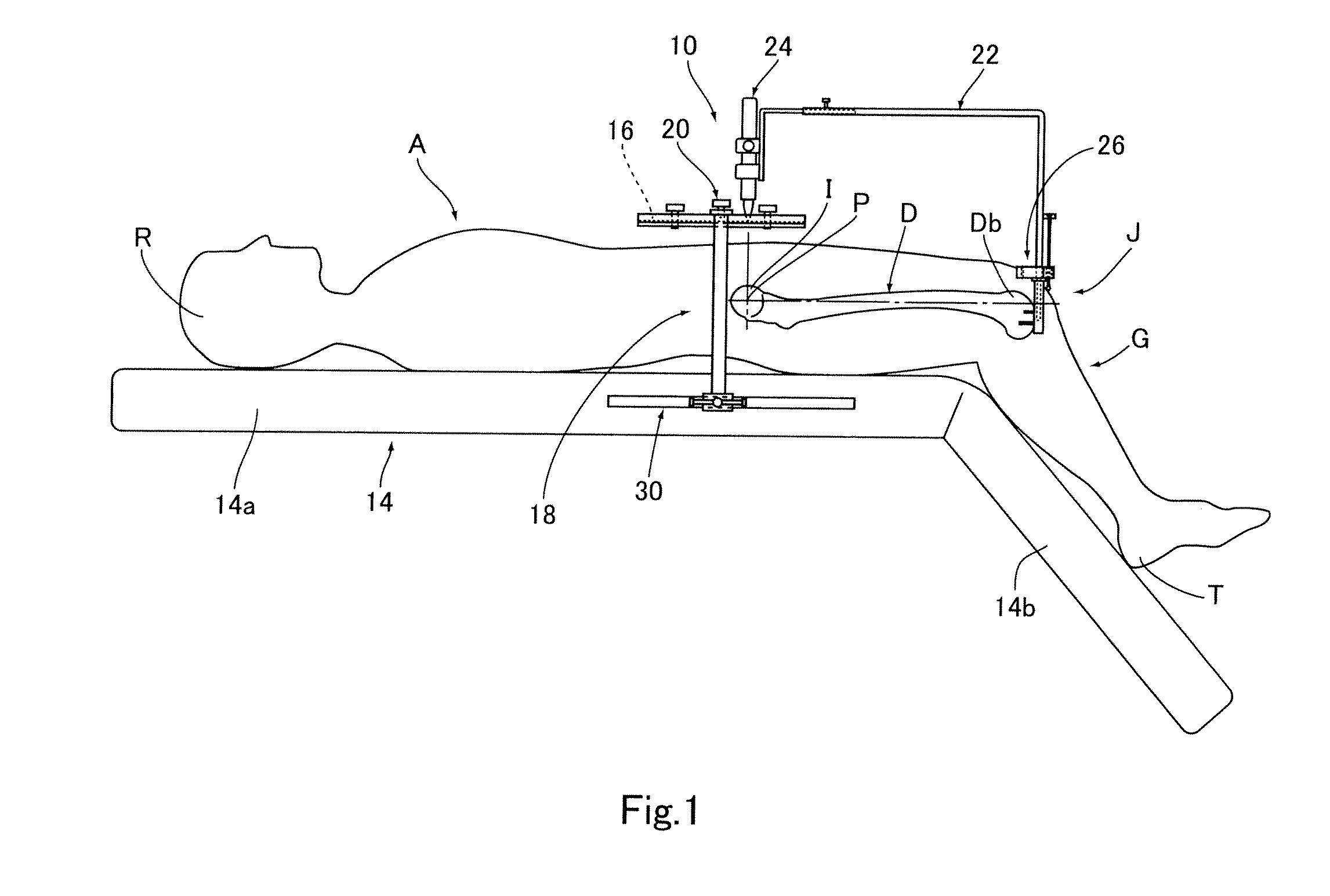
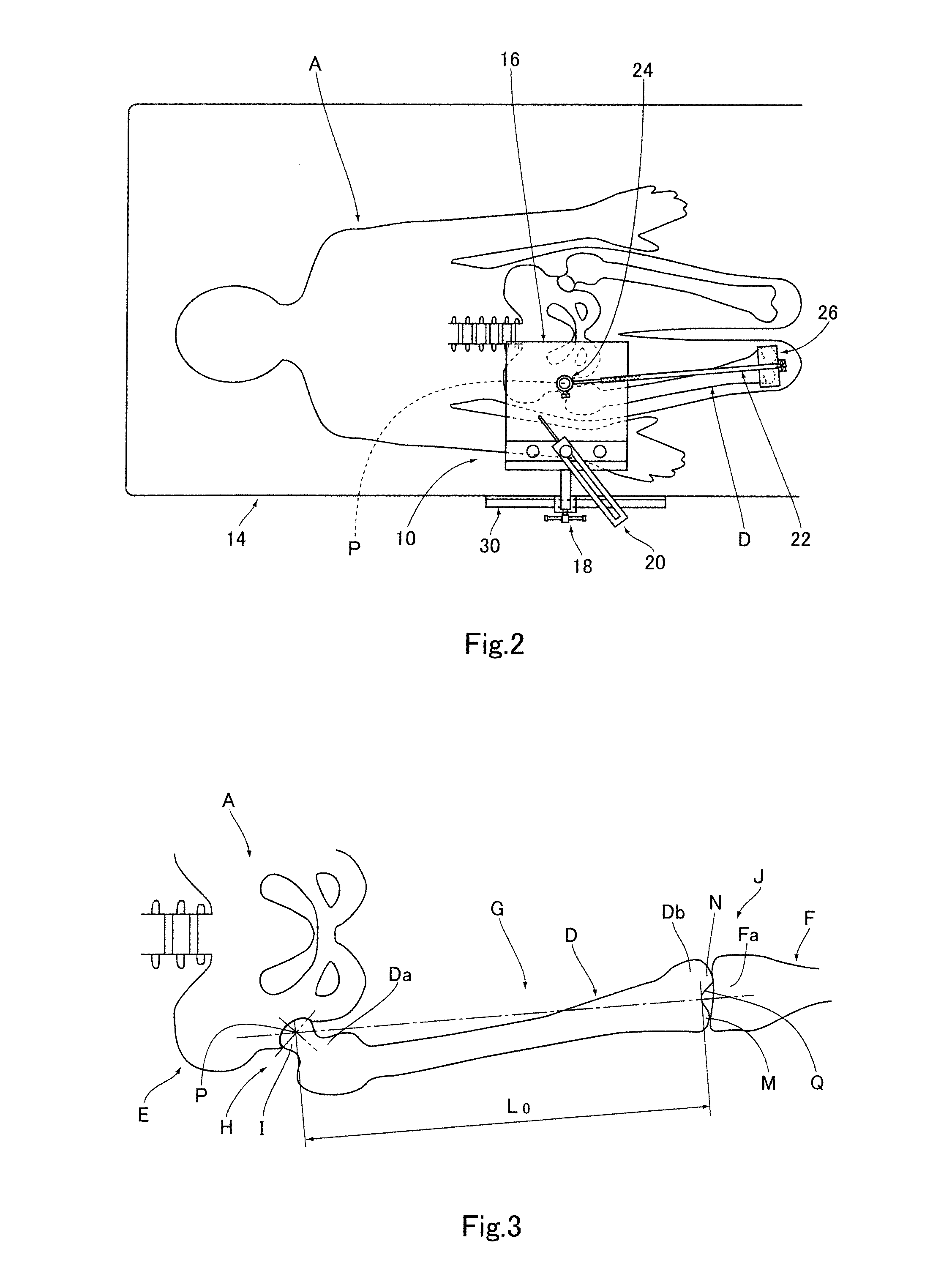
Sensing force during partial and total knee replacement surgery
ActiveUS8211041B2Accurate and quantifiable measurementPrecise tensionAnkle jointsPerson identificationTibiaTotal knee replacement surgery
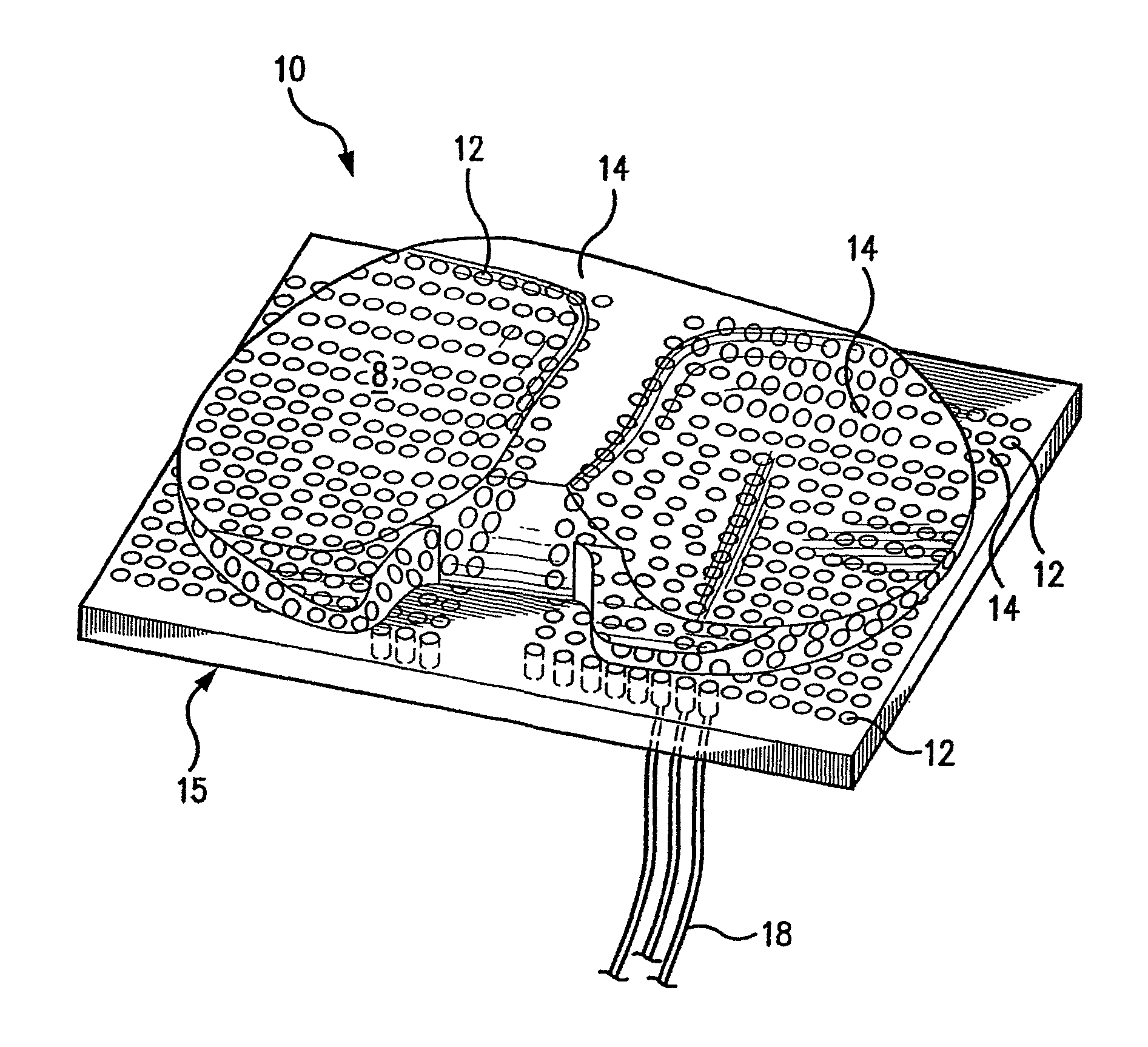
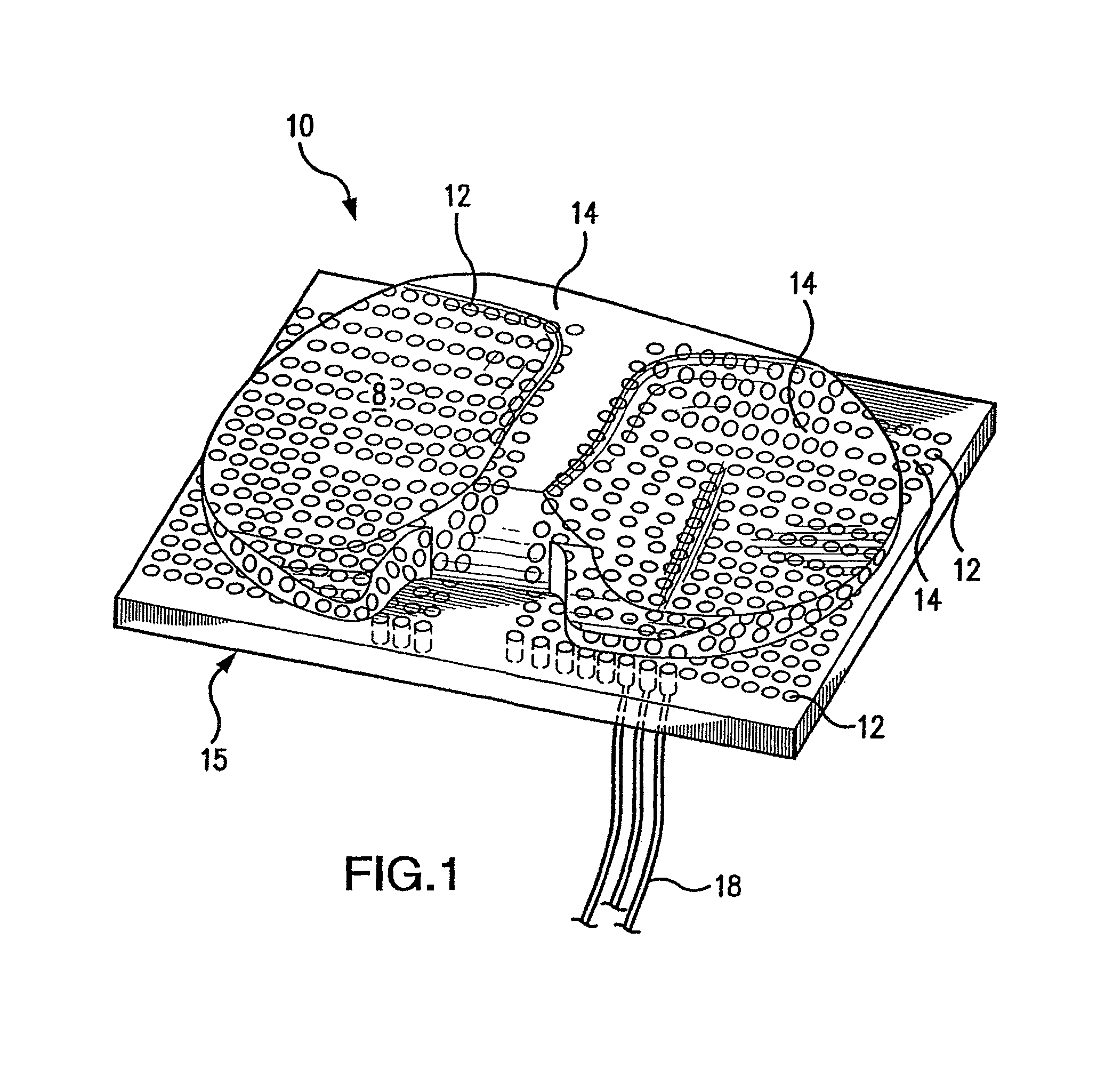
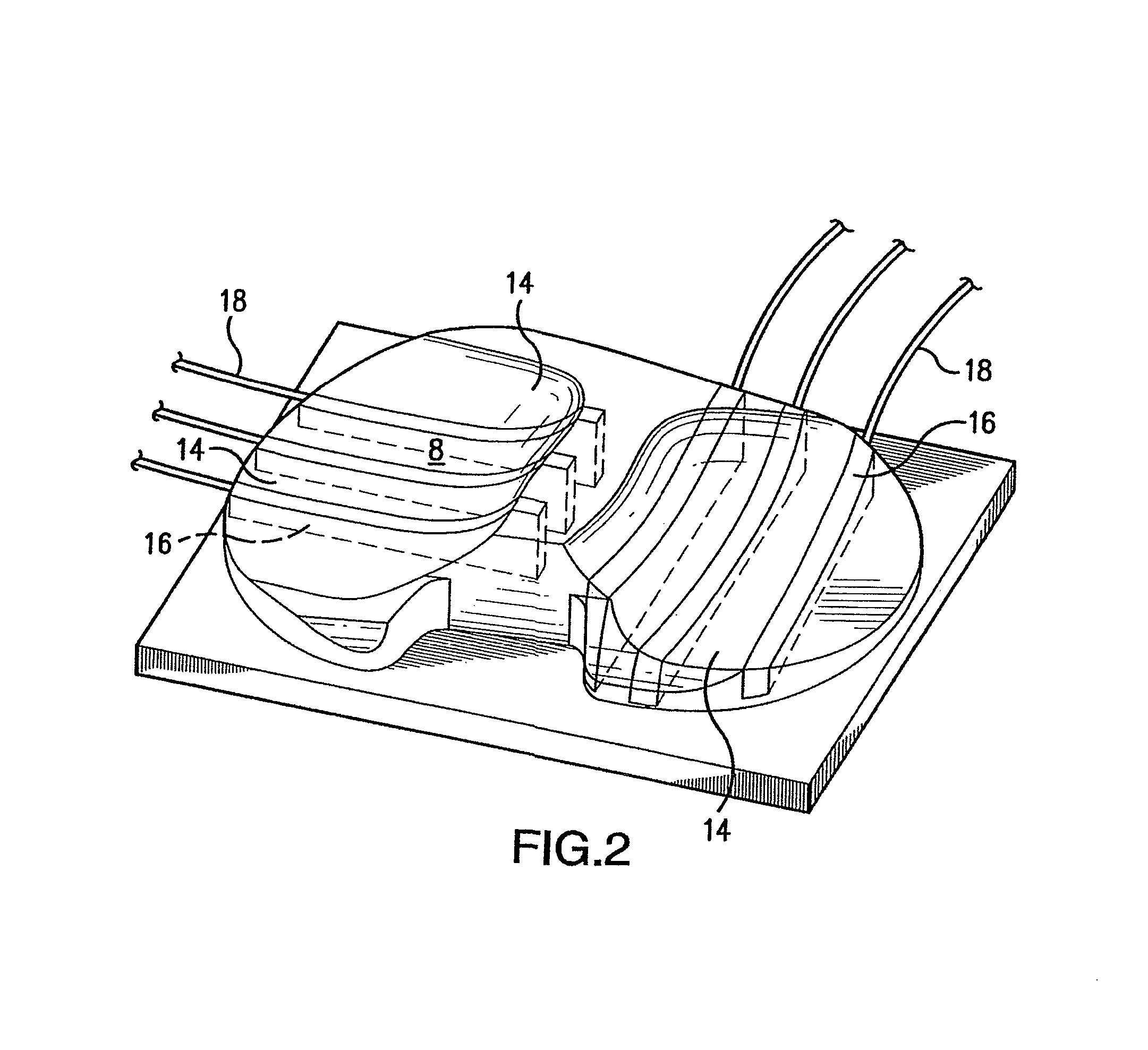
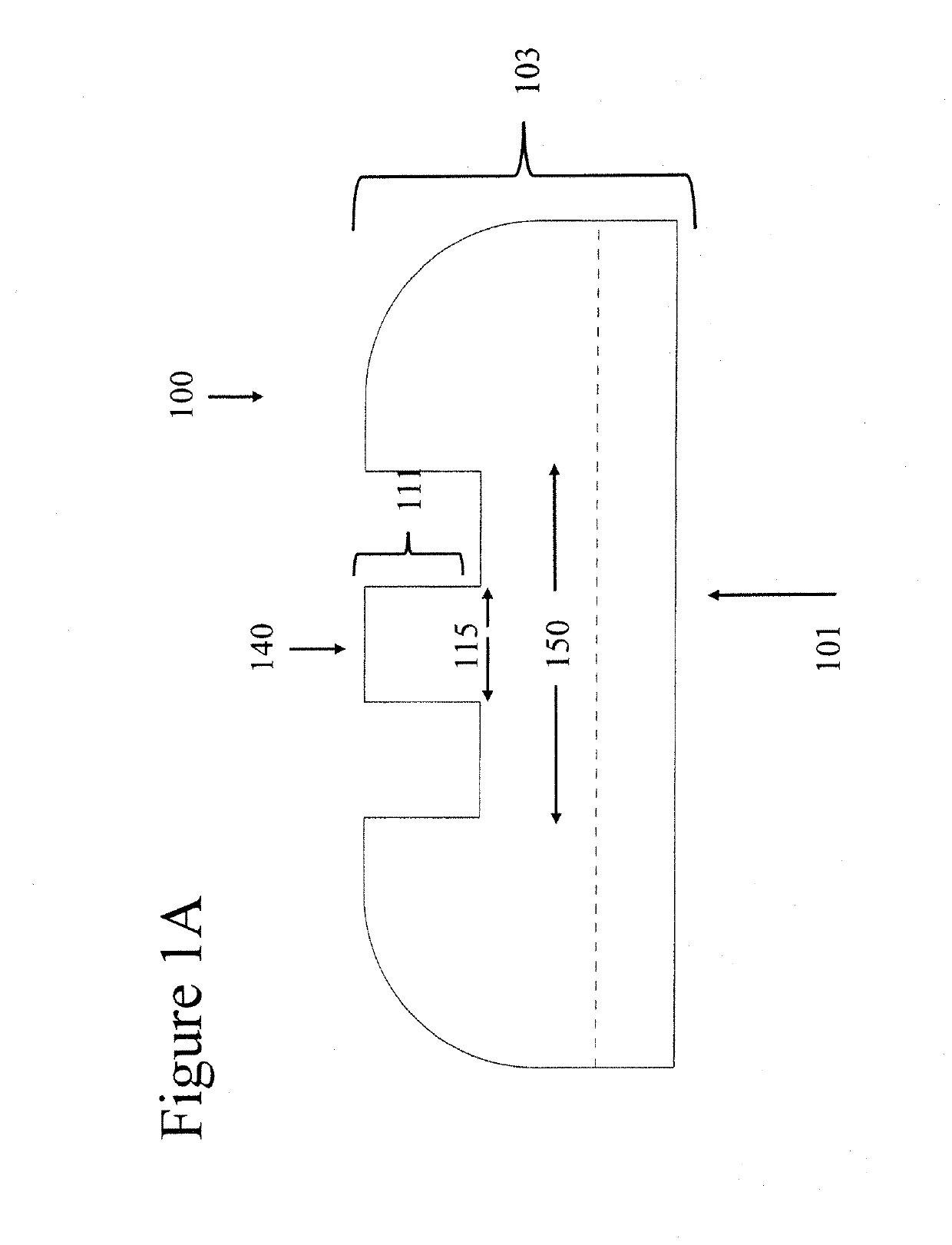
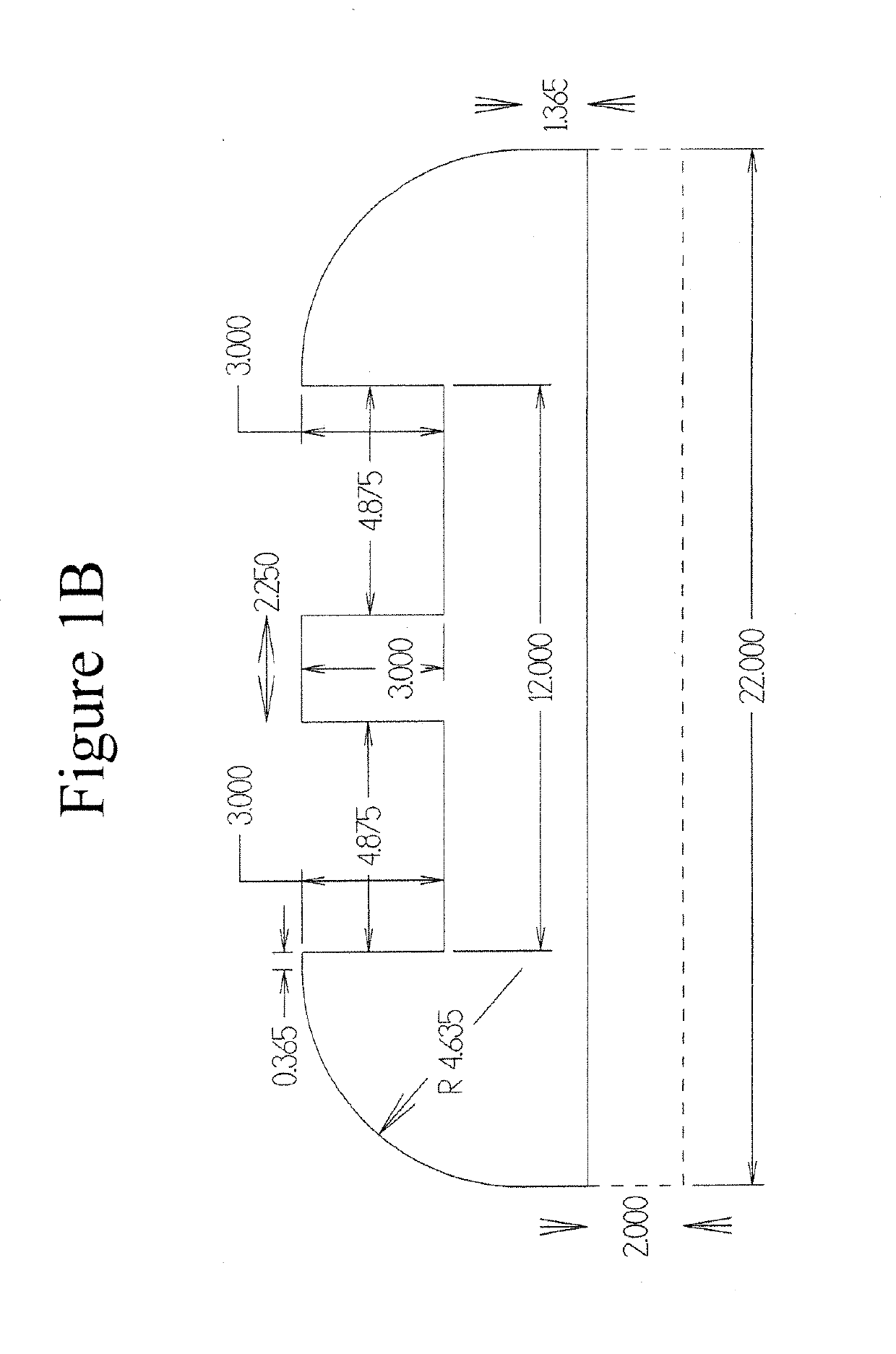
Systems, devices, and methods are provided for measuring forces in the space of a knee during surgery. Such forces can be caused by tension in the ligaments of the knee. A femoral member is engaged with a distal femur. While the knee is flexed, partially extended, or fully extended, a force sensor and a gauge shim can be placed in the gap between the femoral member and the tibial plateau to measure the forces therebetween. The force sensor provides an accurate and quantifiable measurement of force, making knee replacement surgery and ligament tension balancing more accurate, standardized and repeatable. The force sensor comprises an elongate housing which comprises a thin force sensing distal portion and a proximal handle portion.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
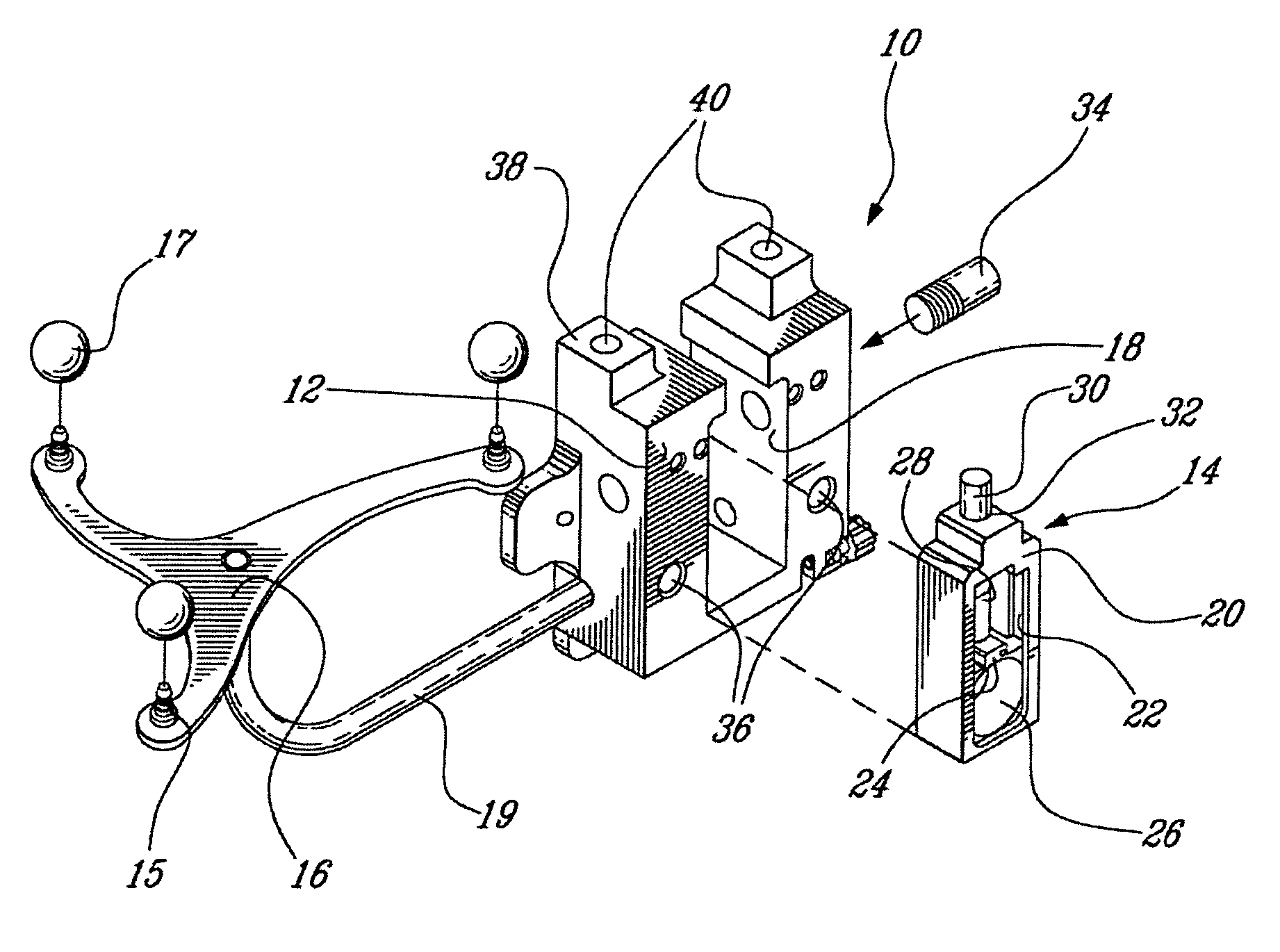
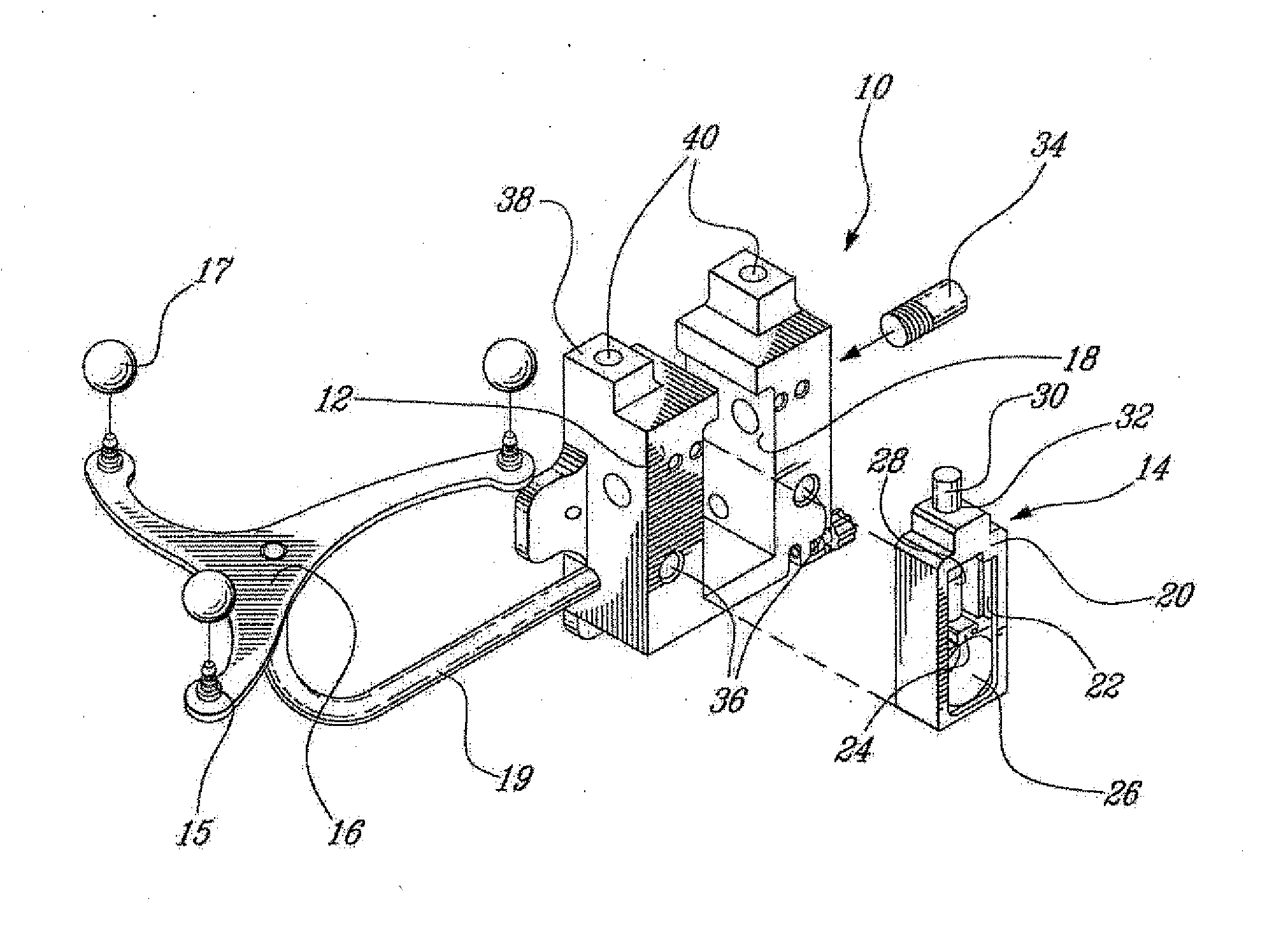
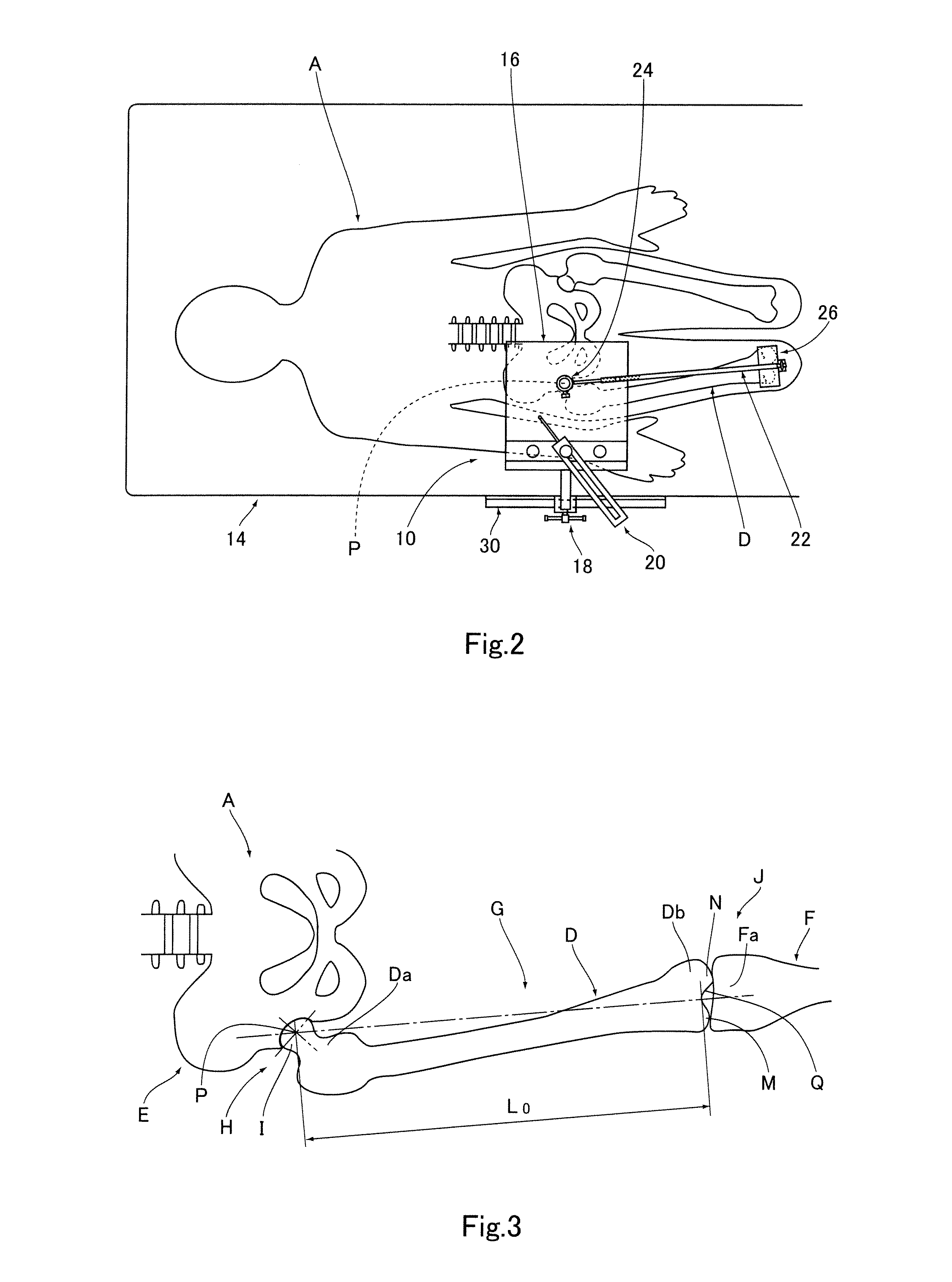
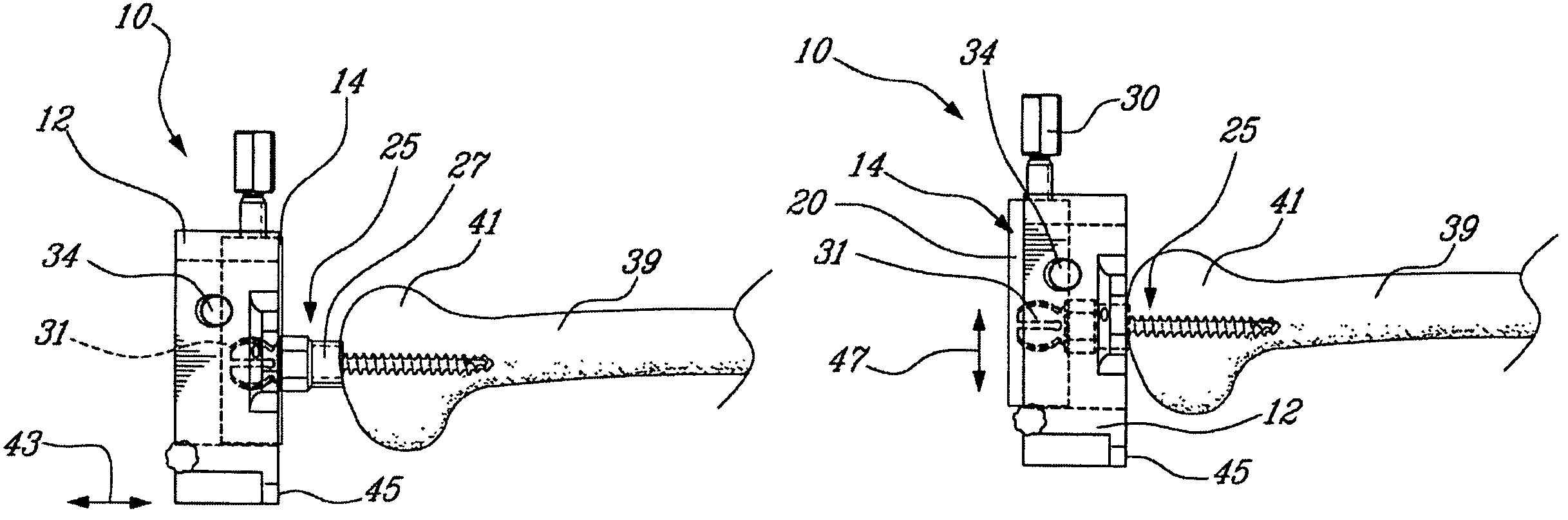
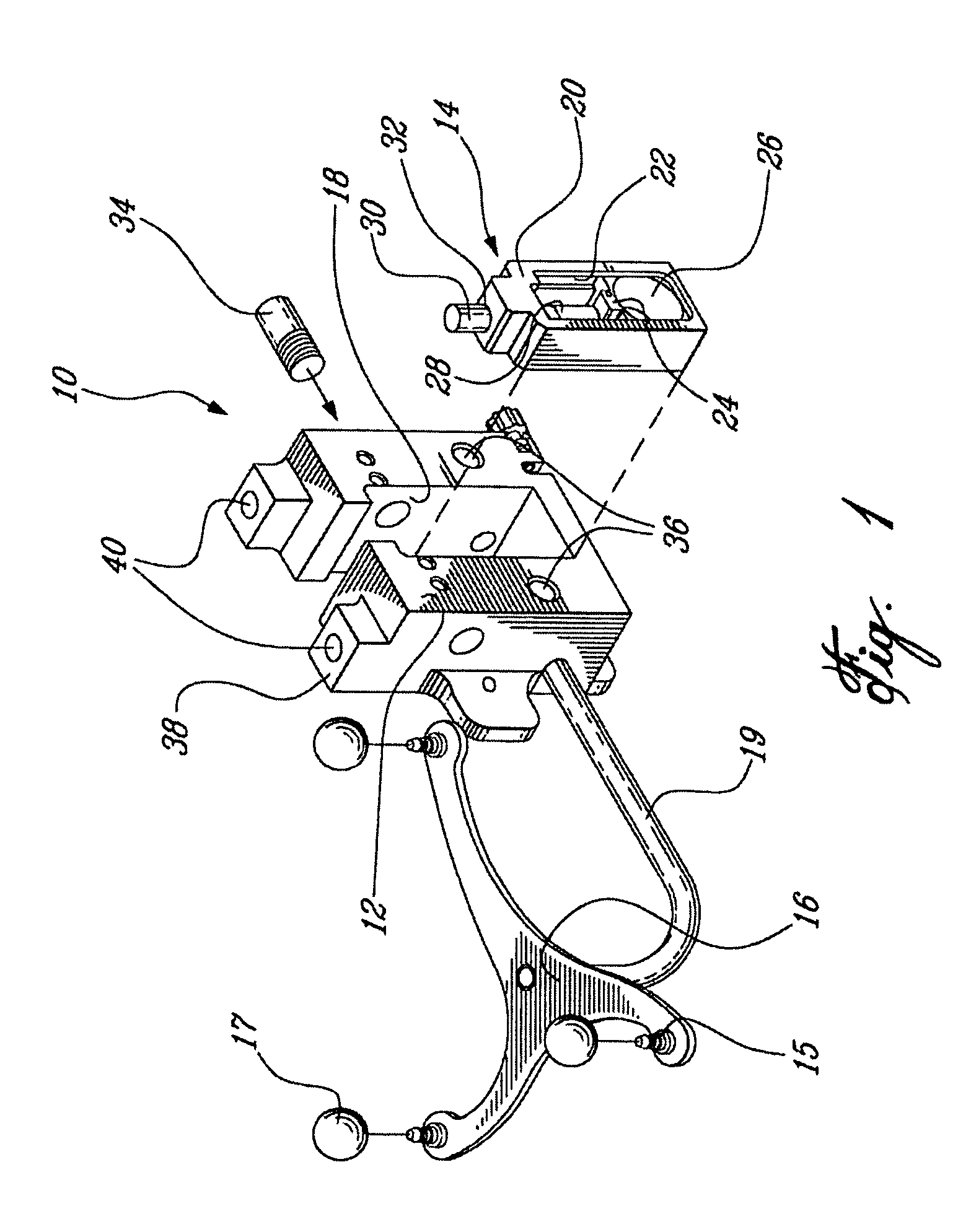
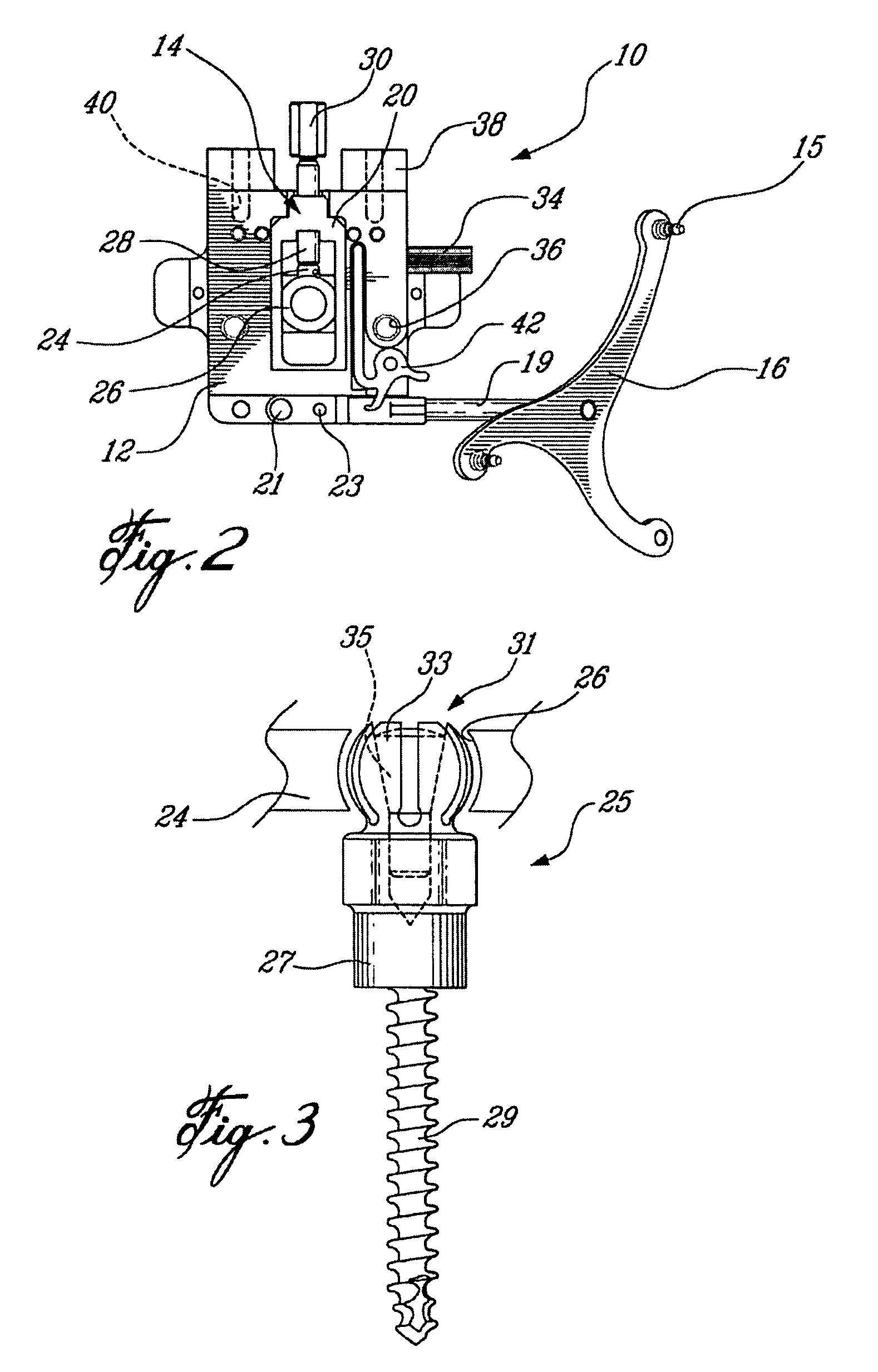
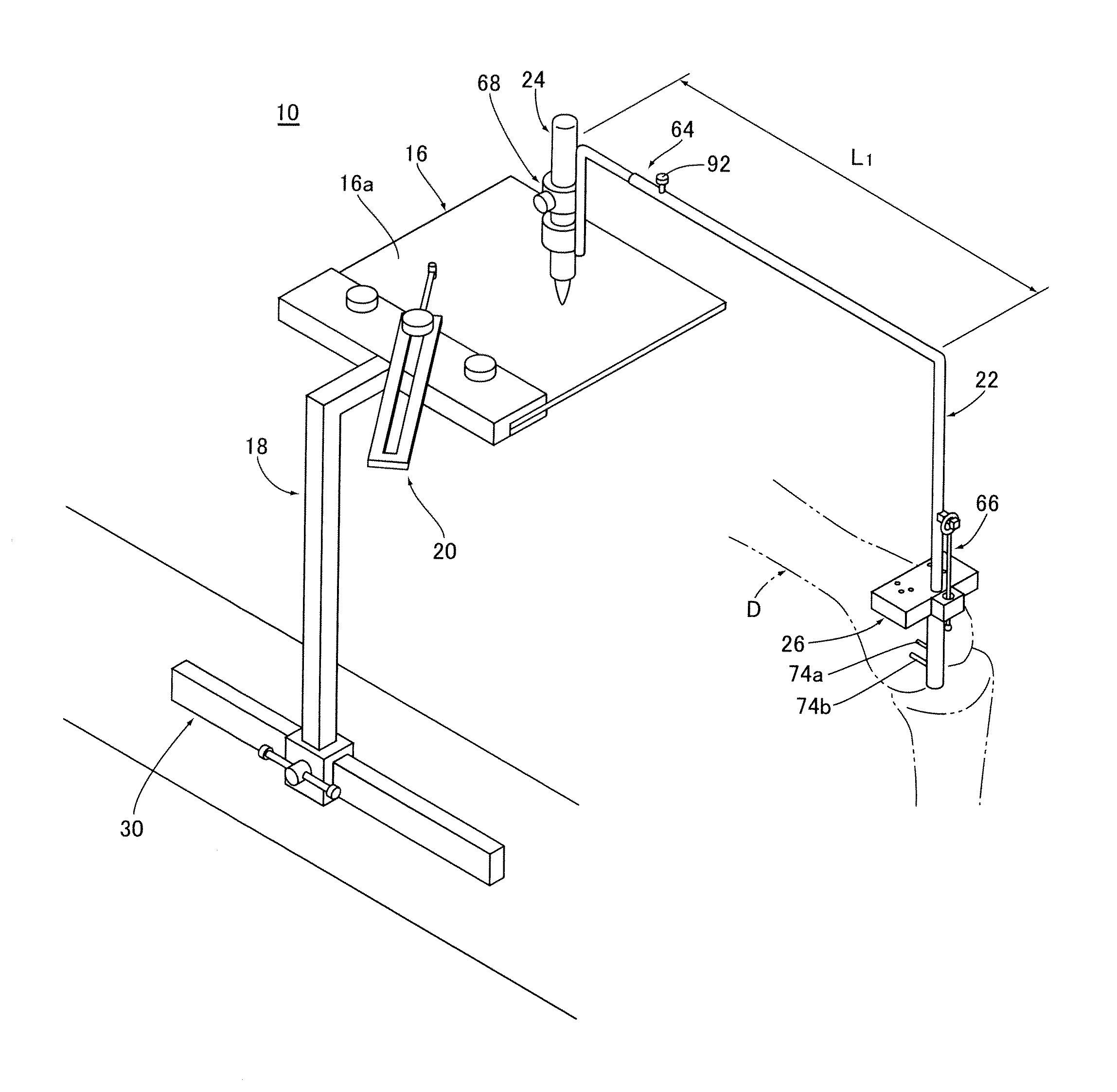
Surgical universal positioning block and tool guide
ActiveUS20050203528A1Easy to cleanImprove mobilityDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTotal knee replacement surgeryEngineering
A positioning block (10) for use in total knee replacement surgery, permitting five degrees-of-freedom movement relative to a bone element (39) to which it is fixed. The positioning block (10) comprises a rotational mounting element (14) that is removably engaged to the bone element such that the mounting element (14) is selectively rotatable relative to the bone element, about three substantially perpendicular axes of rotation. A guide body portion (12) is engaged with the mounting element (14) such that it is translatable relative thereto along a proximal-distal axis (43) and an anterior-posterior axis (47), while being rotationally fixed relative to the mounting element (14) such that the guide body portion (12) and the mounting element (14) rotate together relative to the bone element (39).
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
Sensing force during partial and total knee replacement surgery
ActiveUS20100217156A1Accurate and quantifiable measurementPrecise tensionAnkle jointsPerson identificationTibiaTotal knee replacement surgery
Systems, devices, and methods are provided for measuring forces in the space of a knee during surgery. Such forces can be caused by tension in the ligaments of the knee. A femoral member is engaged with a distal femur. While the knee is flexed, partially extended, or fully extended, a force sensor and a gauge shim can be placed in the gap between the femoral member and the tibial plateau to measure the forces therebetween. The force sensor provides an accurate and quantifiable measurement of force, making knee replacement surgery and ligament tension balancing more accurate, standardized and repeatable. The force sensor comprises an elongate housing which comprises a thin force sensing distal portion and a proximal handle portion.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Contact sensors and methods for making same
InactiveUS20120123716A1Reduced probability of early failureAccurately carry-outResistance/reactance/impedenceForce measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceTotal knee replacement surgery
Disclosed herein are novel contact sensors. The contact sensors disclosed herein include a conductive composite material formed of a polymer and a conductive filler. In one particular aspect, the composite materials can include less than about 10 wt % conductive filler. Thus, the composite material of the contact sensors can have physical characteristics essentially identical to the polymer, while being electrically conductive with the electrical resistance proportional to the load on the sensor. The sensors can provide real time dynamic contact information for joint members under conditions expected during use. In one particular aspect, the sensor can be used to properly balance the knee ligaments in a total knee replacement surgery.
Owner:SENCORABLES
Surgical universal positioning block and tool guide
ActiveUS20080065084A1Improve mobilityOptimize locationDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTotal knee replacement surgeryEngineering
A positioning block (10) for use in total knee replacement surgery, permitting five degrees-of-freedom movement relative to a bone element (39) to which it is fixed. The positioning block (10) comprises a rotational mounting element (14) that is removably engaged to the bone element such that the mounting element (14) is selectively rotatable relative to the bone element, about three substantially perpendicular axes of rotation. A guide body portion (12) is engaged with the mounting element (14) such that it is translatable relative thereto along a proximal-distal axis (43) and an anterior-posterior axis (47), while being rotationally fixed relative to the mounting element (14) such that the guide body portion (12) and the mounting element (14) rotate together relative to the bone element (39).
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
Bone shaping device for knee replacement
InactiveUS20050192583A1Improve accuracyImprove consistencyDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTotal knee replacement surgeryArthroplasty knee
A bone surgery device with a reciprocating cutting head. The device comprises several sets of shaping surfaces sometimes including cutting blades, which are located and oriented so as to shape the distal end of the femur and the proximal end of the tibia for total knee replacements and unicompartmental knee replacements. The device, which may be hand directed or aided by spatial and directional guiding mechanisms or an optical navigation system, may also include both coolant supply for controlling heat during bone, cutting and shaping, and a suction method for carrying away fluid and debris. The device is substantially configured to the artificial joint component to be attached thereto.
Owner:WALKER PETER STANLEY +1
Bone shaping device for knee replacement
InactiveUS20050192584A1Reduction in time taken to cutReduction in to shape bone surfaceDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTibiaKnee Joint
A bone surgery device with a reciprocating cutting head. The device comprises several sets of shaping surfaces sometimes including cutting blades, which are located and oriented so as to shape the distal end of the femur and the proximal end of the tibia for total knee replacements and unicompartmental knee replacements. The device, which may be hand directed or aided by spatial and directional guiding mechanisms or an optical navigation system, may also include both coolant supply for controlling heat during bone cutting and shaping, and a suction method for carrying away fluid and debris. The device is substantially configured to the artificial joint component to be attached thereto.
Owner:WALKER PETER STANLEY +1
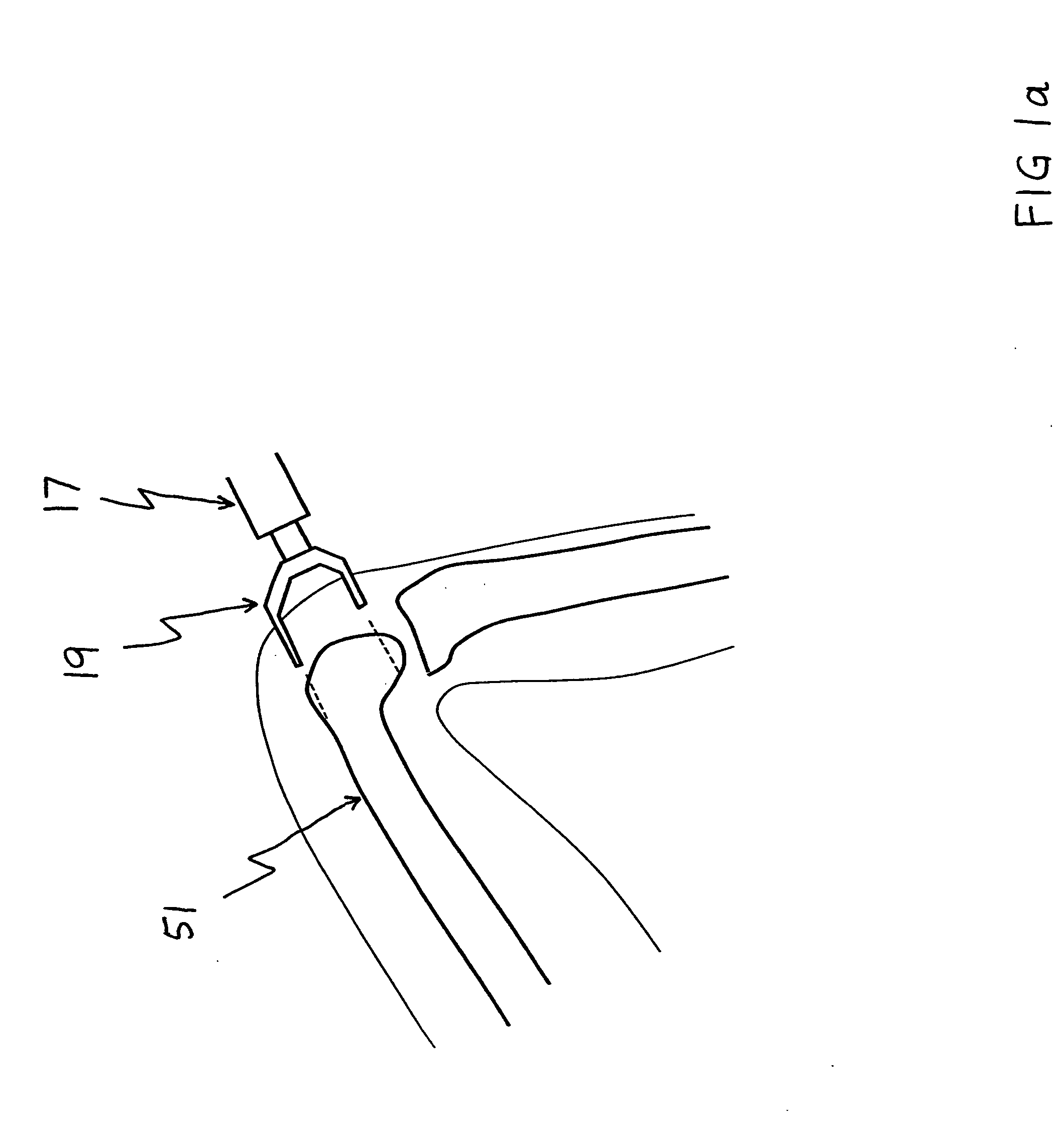
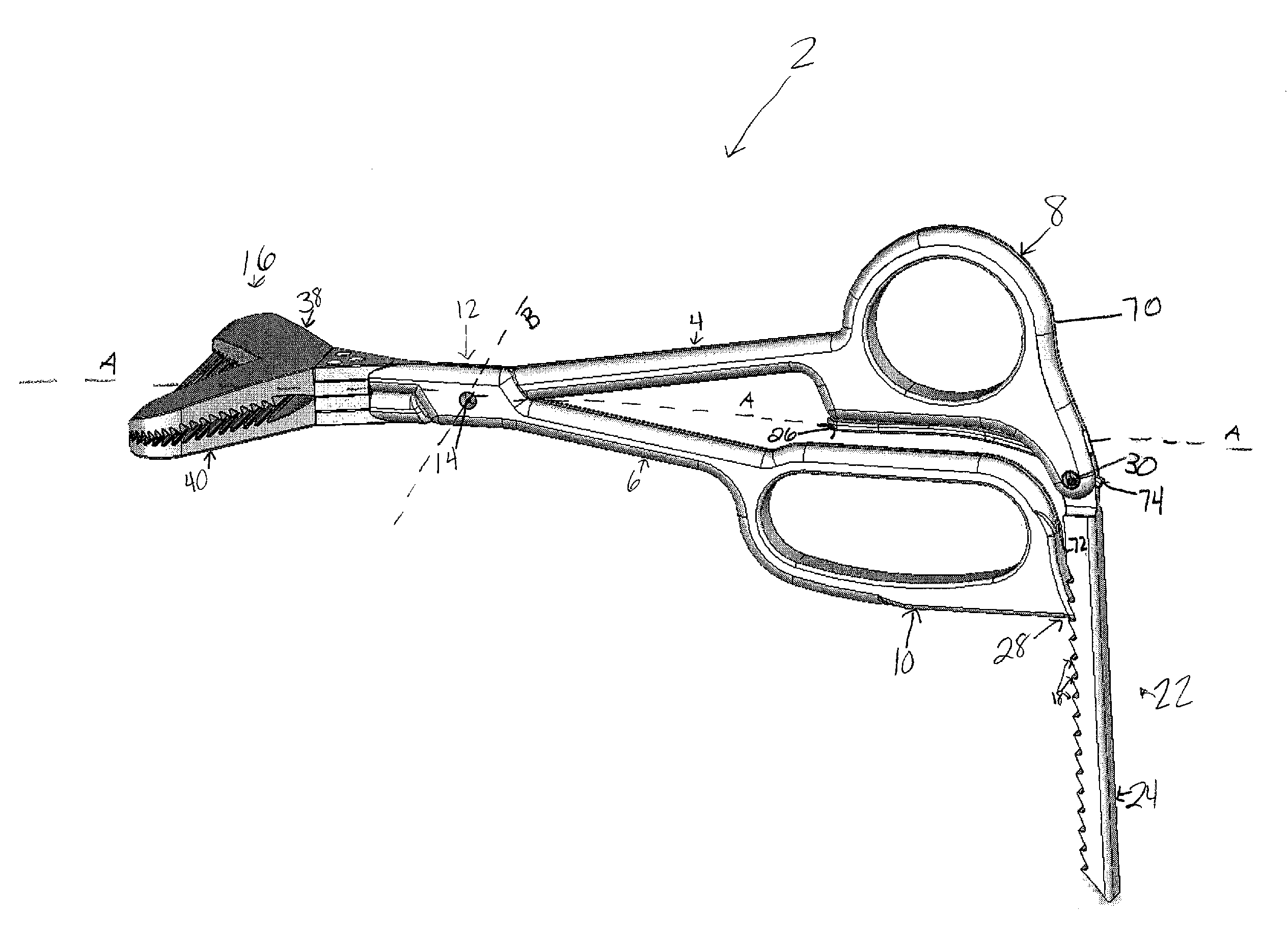
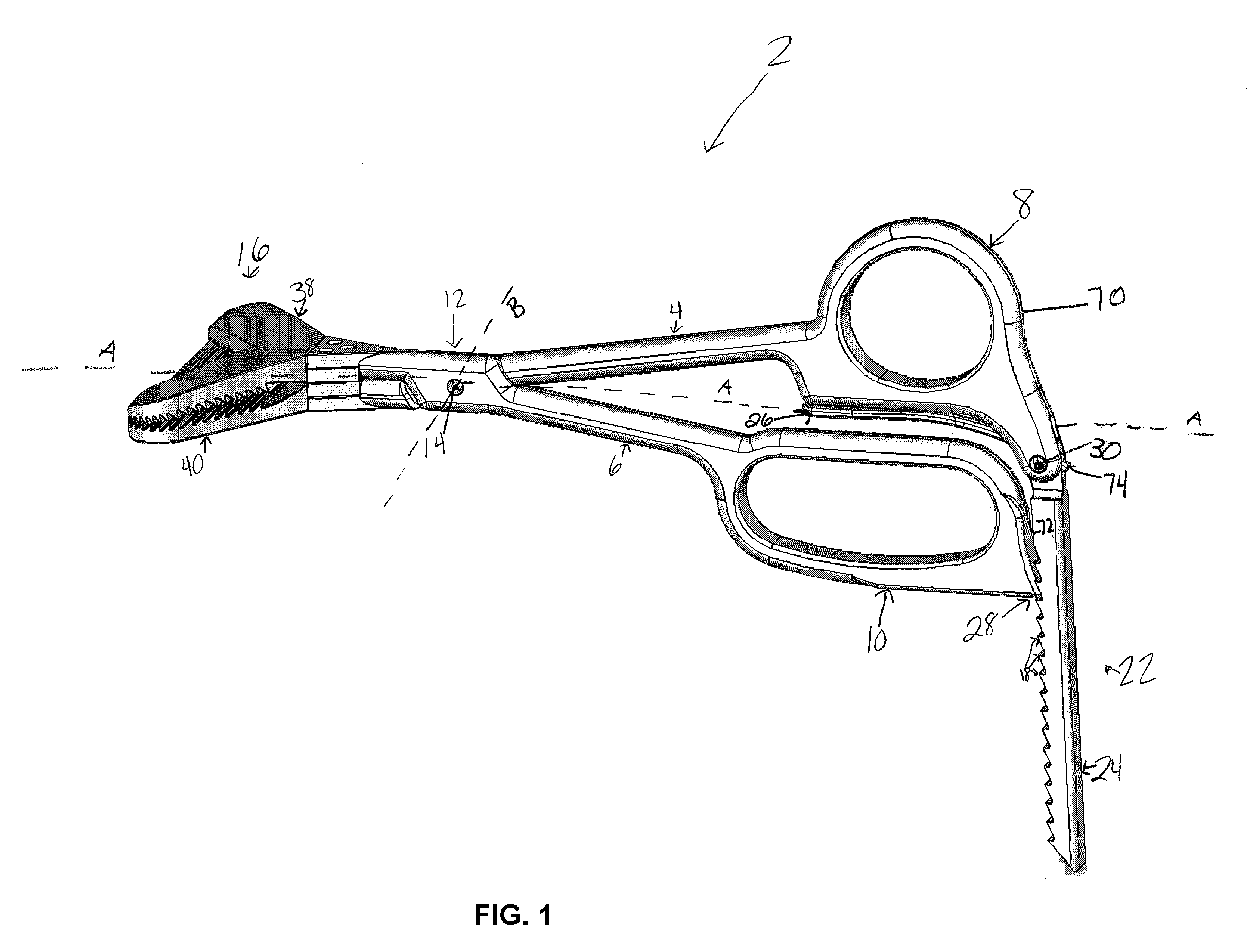
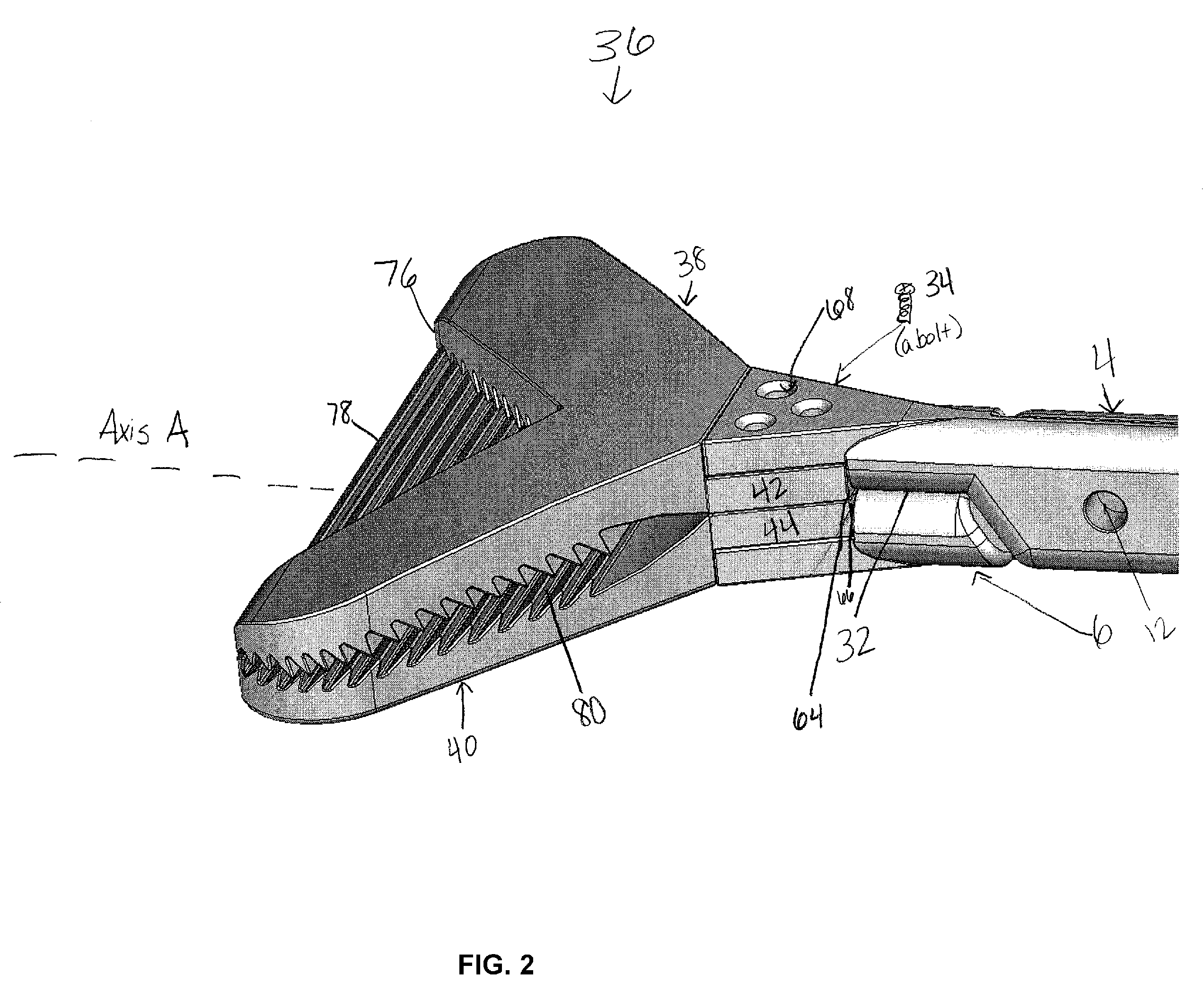
Surgical bone clamp
InactiveUS20100114154A1Easy to operateEasy constructionSuture equipmentsLigamentsGrip forceTotal knee replacement surgery
The surgical bone clamp securely grasps and removes bone and other tissue during surgery, such as total knee replacement surgery. In one embodiment, the device includes a handle portion, a clamp portion, and a ratchet portion. The handle portion includes two handle arms that are pivotally connected, and the ratcheting portion permits the handle arms to be spaced at any one of a plurality of step settings. One of the handle arms provides a finger loop to engage the thumb, while the other handle arm provides a finger loop to engage at least one opposing finger. The clamp portion includes two serrated clamping jaws designed to engage the bone or other tissue surface and to provide adequate gripping force to allow for removal of the bone piece or tissue from the body cavity. The device provides significant mechanical advantage to the user, may be operated with one hand, and may include removable clamping jaws.
Owner:SNELL CHRISTOPHER
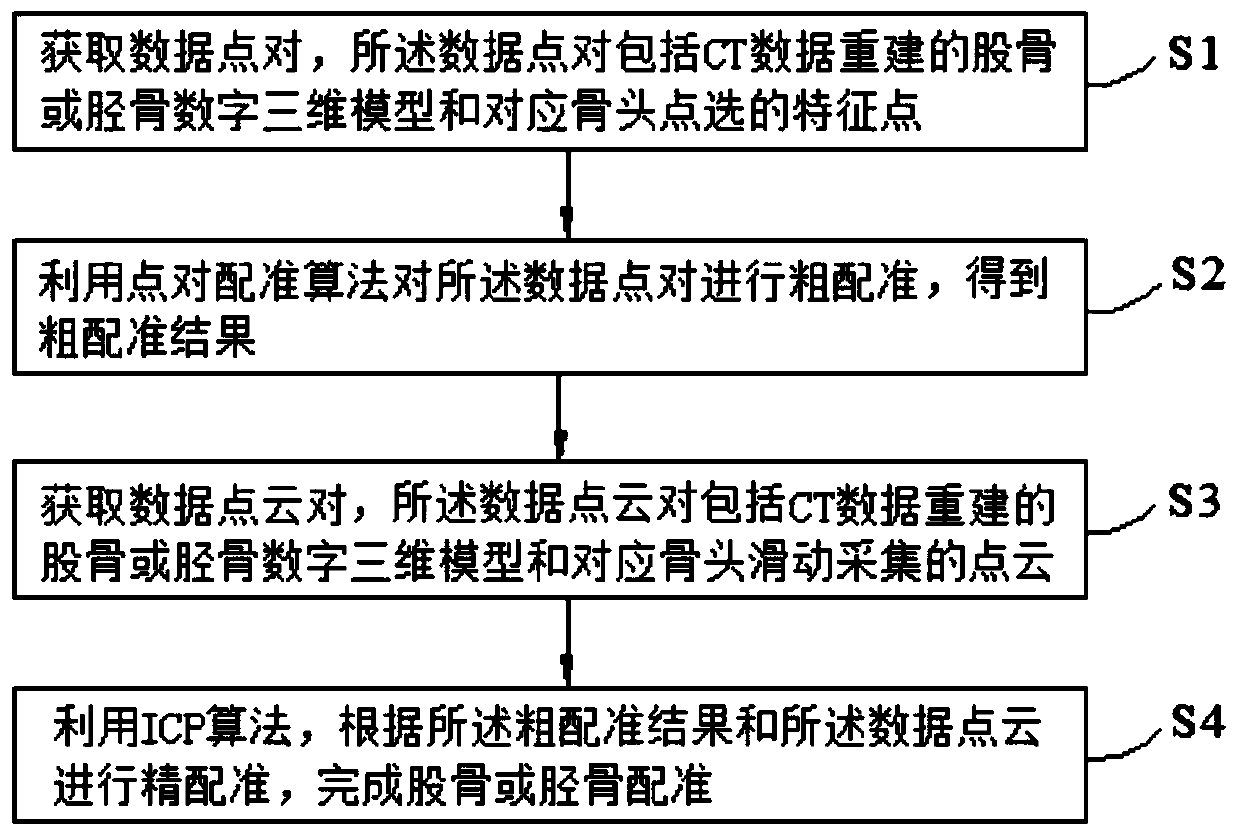
Femoral or tibial registration method and device based on total knee replacement surgery
ActiveCN110215281AImprove accuracyThe registration result is satisfactoryComputer-aided planning/modellingTibiaPoint cloud
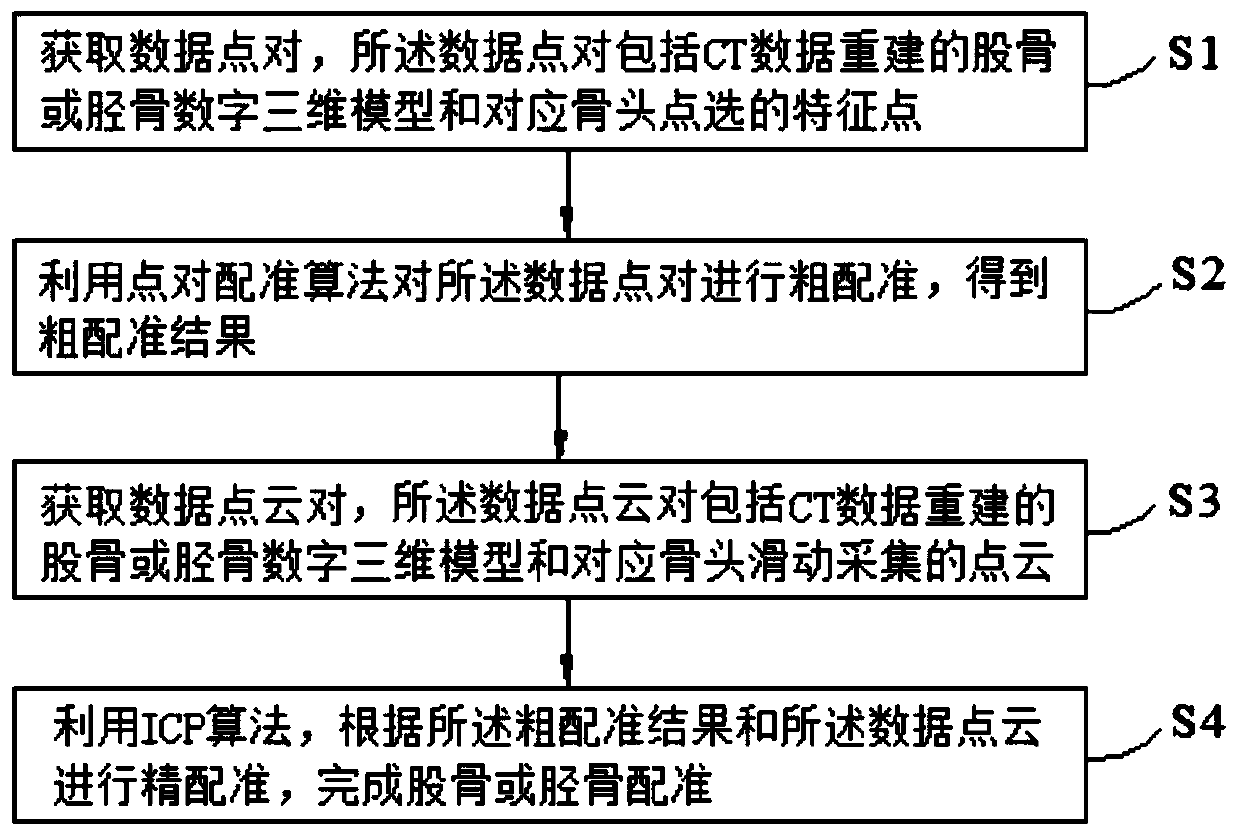
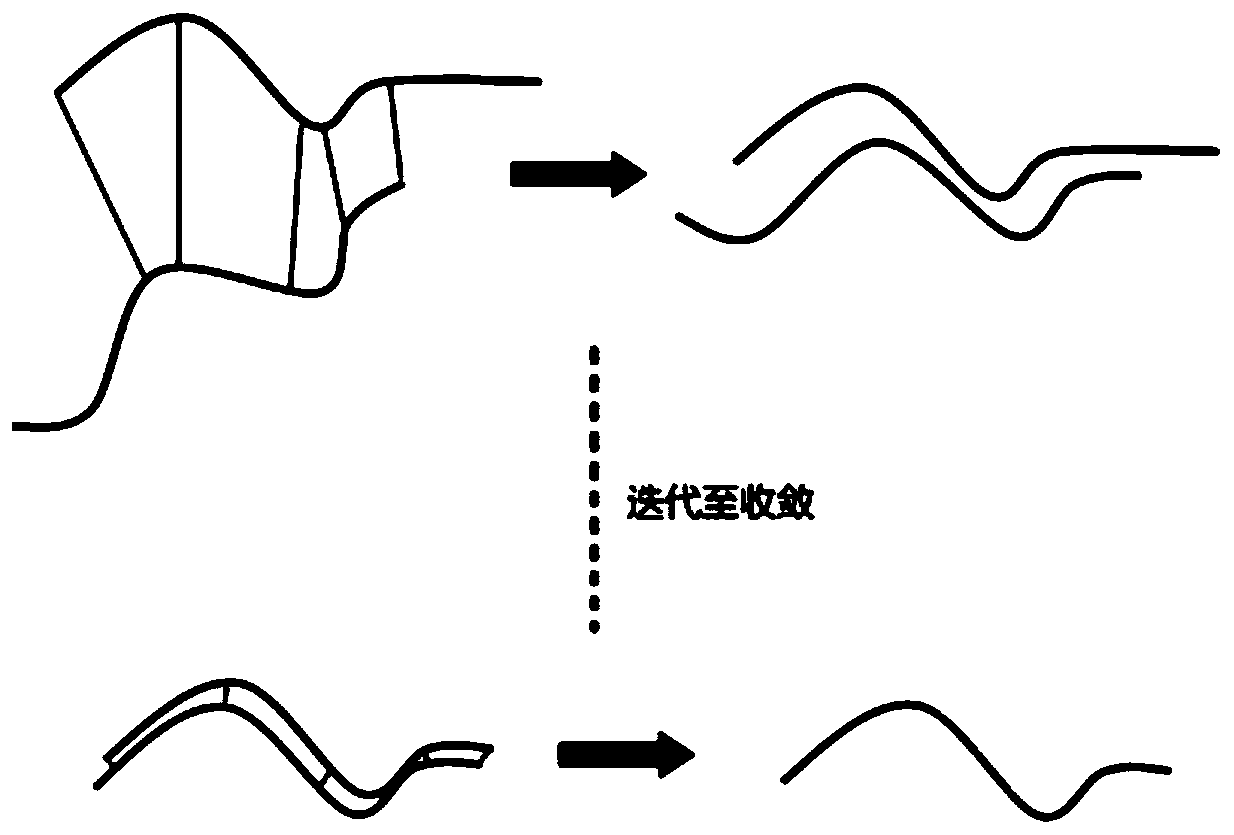
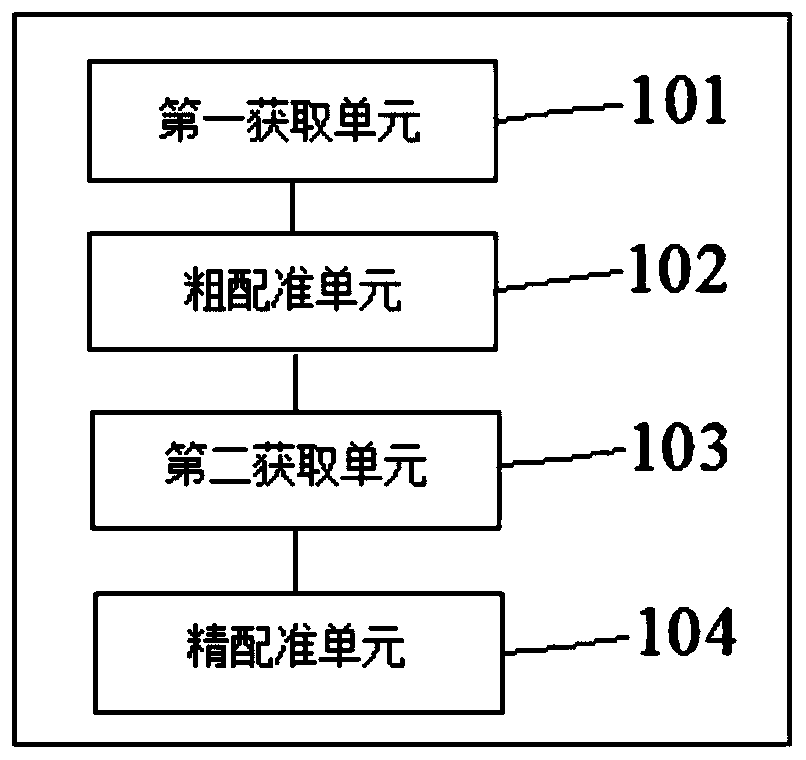
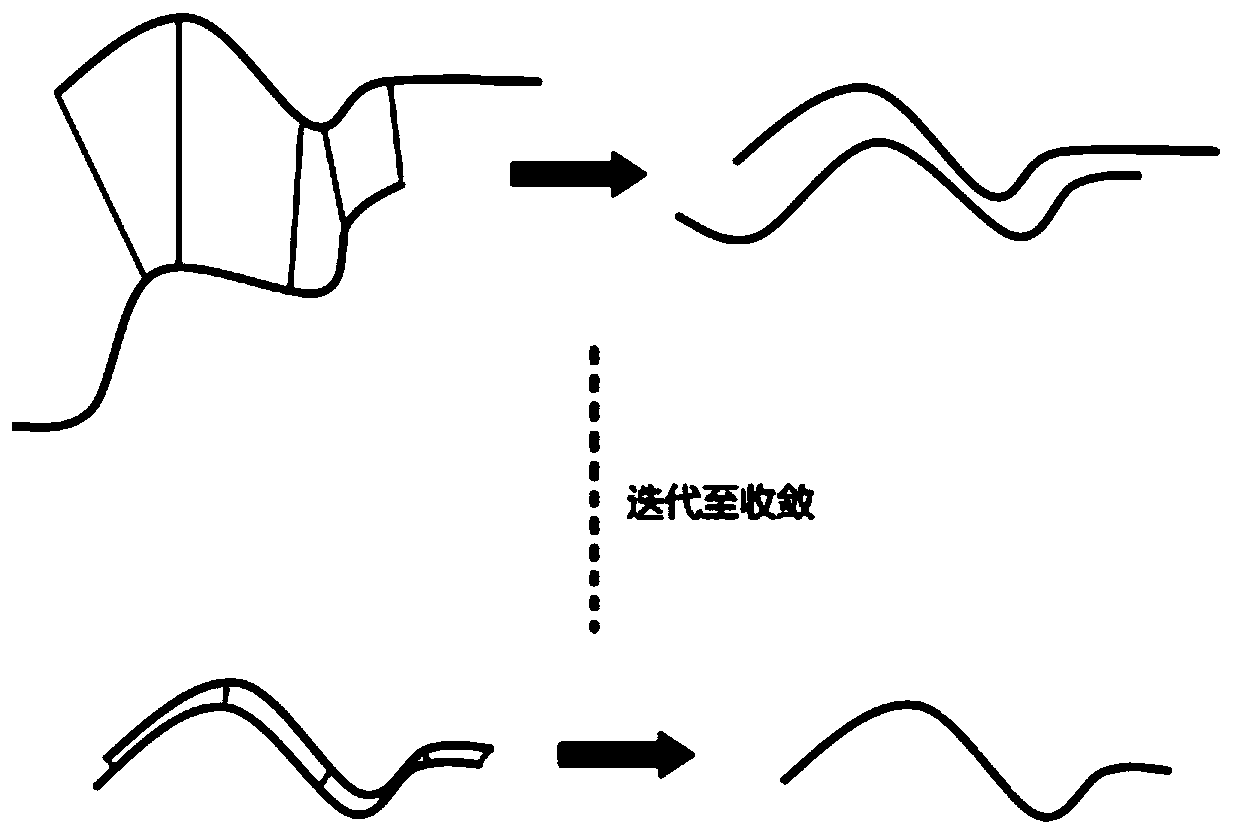
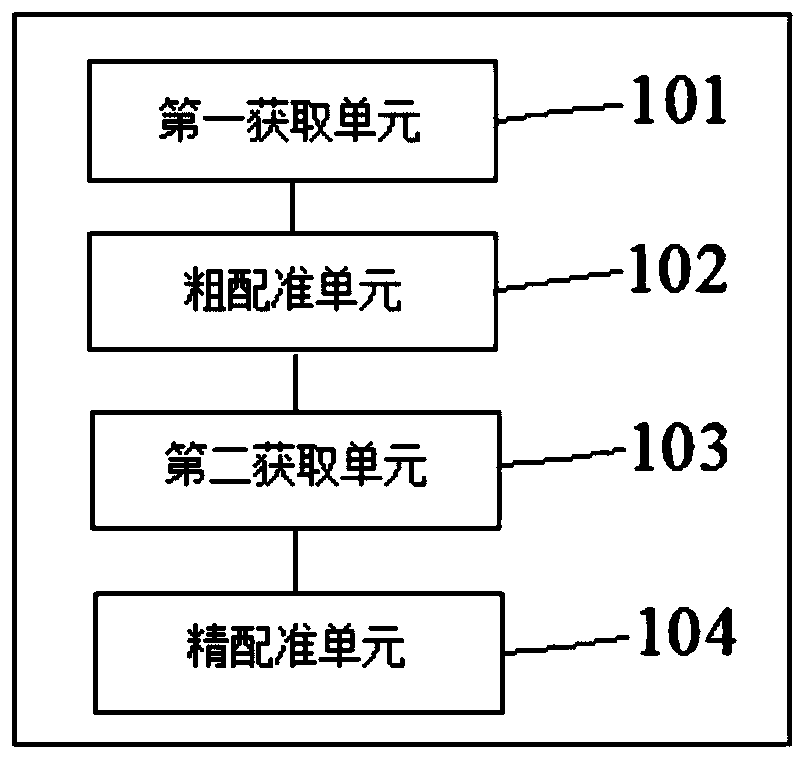
The invention discloses a femoral or tibial registration method and device based on total knee replacement surgery. The method comprises the steps of acquiring data point pairs, wherein the data pointpairs include a CT data reconstructed femoral or tibial digital three-dimensional model and selected feature points corresponding to bone points; adopting a point pair registration algorithm for performing rough registration on the data point pairs to obtain rough registration results; acquiring data point cloud pairs, wherein the data point cloud pairs include the CT data reconstructed femoral or tibial digital three-dimensional model and slidably collected point clouds corresponding to bones; performing precise registration according to the rough registration results and the data point clouds. According to the method and the device, anatomical feature points which are clear for a doctor are adopted for carrying out a rough registration algorithm, and dense three-dimensional point cloudstereoscopic data is further utilized to perform a fine registration algorithm, so that the registration accuracy rate is greatly increased. The first registration result based on SVD-ICP is used as the initial position of the next ICP registration, and the point cloud data is collected again to achieve a better registration effect from a more satisfactory initial position.
Owner:BEIJING HURWA ROBOT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Surgical universal positioning block and tool guide
InactiveUS20080065085A1Improve mobilityDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTotal knee replacement surgeryEngineering
A positioning block (10) for use in total knee replacement surgery, permitting five degrees-of-freedom movement relative to a bone element (39) to which it is fixed. The positioning block (10) comprises a rotational mounting element (14) that is removably engaged to the bone element such that the mounting element (14) is selectively rotatable relative to the bone element, about three substantially perpendicular axes of rotation. A guide body portion (12) is engaged with the mounting element (14) such that it is translatable relative thereto along a proximal-distal axis (43) and an anterior-posterior axis (47), while being rotationally fixed relative to the mounting element (14) such that the guide body portion (12) and the mounting element (14) rotate together relative to the bone element (39).
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
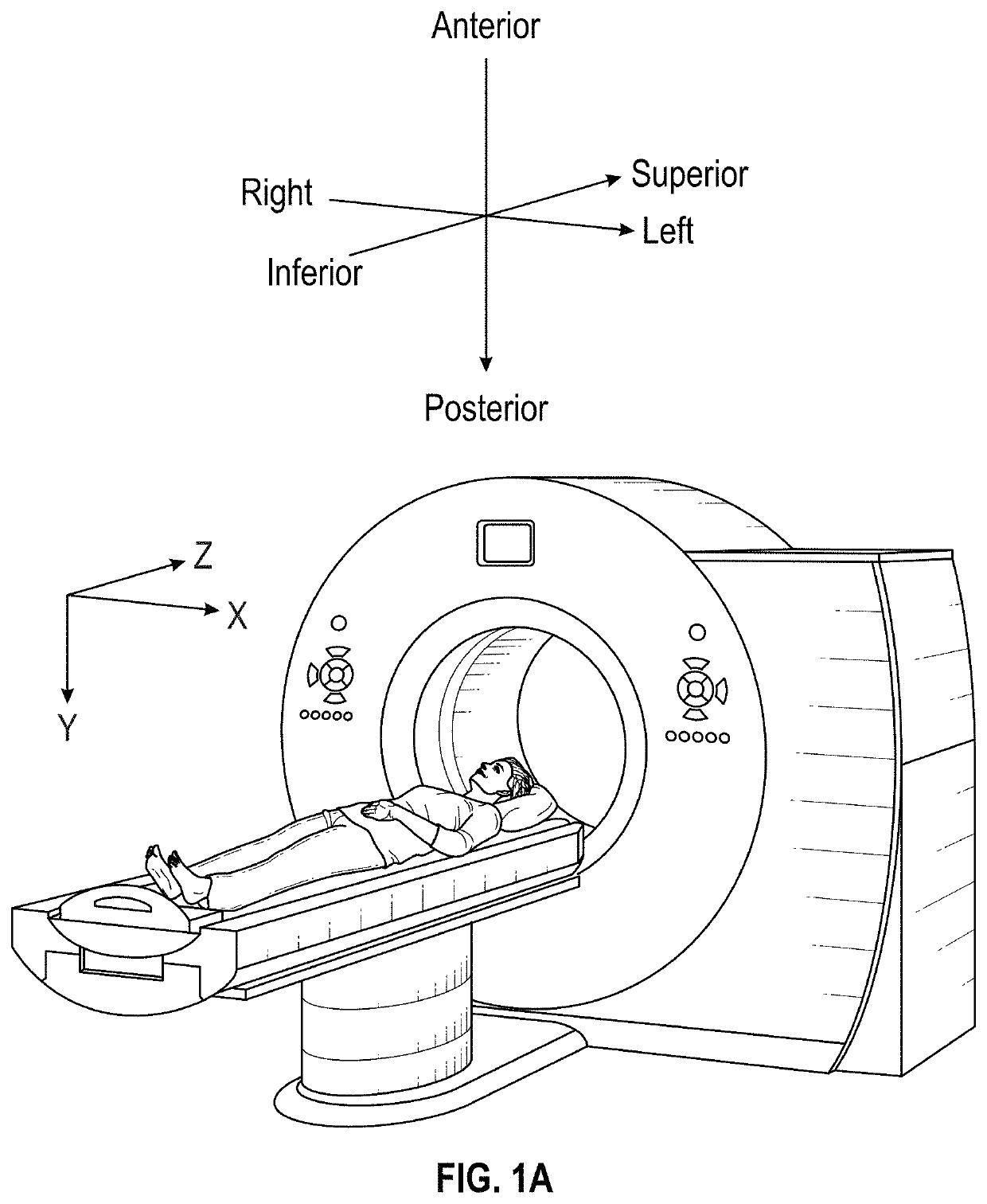
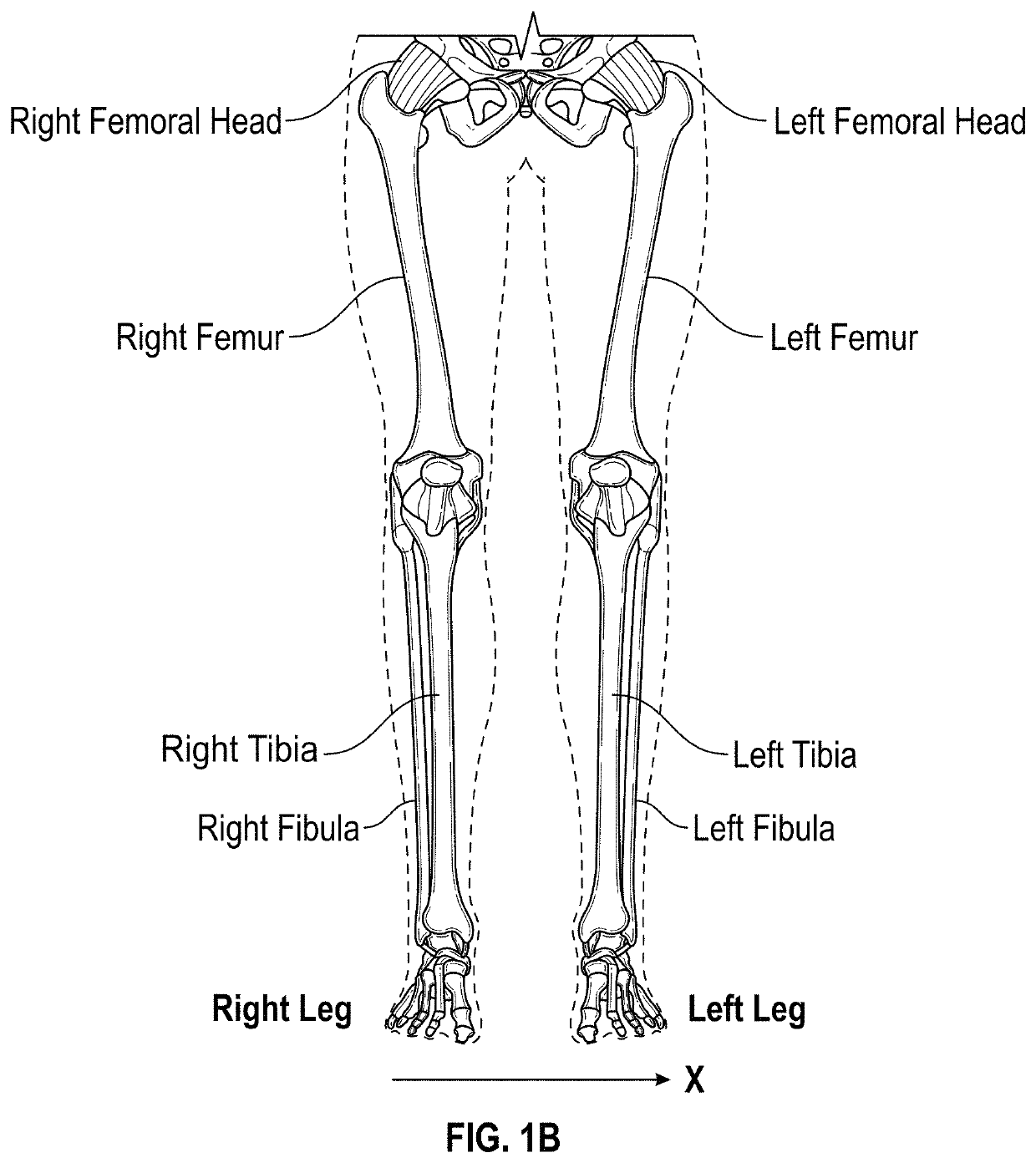
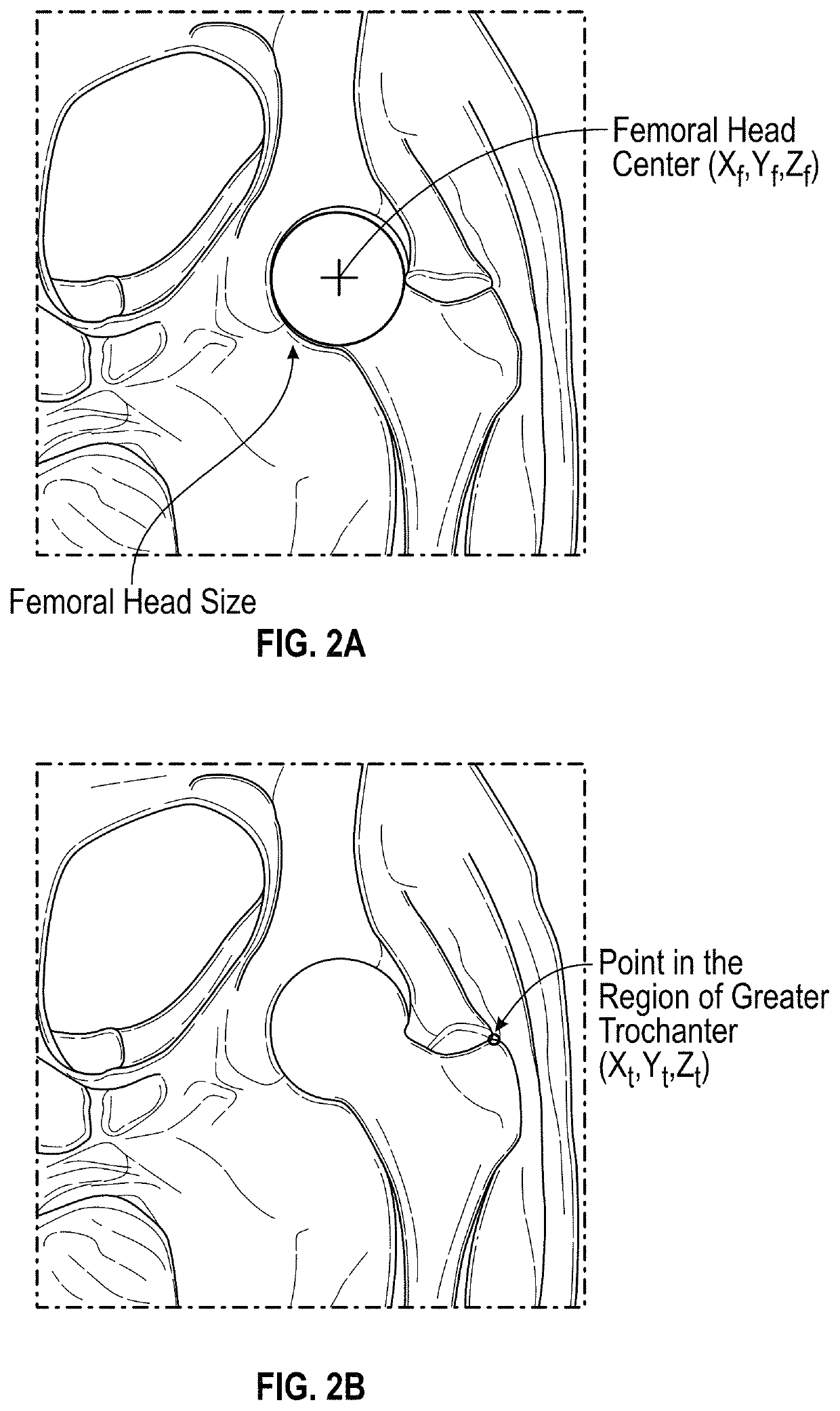
Apparatus for Identifying Femoral Head Center
InactiveUS20120029581A1Accurate identificationInexpensive configurationDiagnosticsJoint implantsRight femoral headTotal knee replacement surgery
An apparatus for identifying, during total knee replacement surgery, a position of a center of a femoral head of a patient within a plane parallel to a frontal plane, comprises a marking plate placed to cover, in a direction perpendicular to the frontal plane, a site where the femoral head center of the patient's body is located; a pivotal arm having a pivotal shaft arranged to extend in a direction perpendicular to the frontal plane; and a marker attached to the pivotal arm, for depicting a circular arc on the marking plate according to rotation of the pivotal arm; the pivotal shaft being placed at a distal end of a femur of the patient, a distance from the pivotal shaft to the marker in a direction parallel to the frontal plane being equal to a preliminarily measured distance from the distal end of the femur to the femoral head center.
Owner:KANEKASU KOICHI
Surgical universal positioning block and tool guide
ActiveUS7736368B2Improve mobilityDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTotal knee replacement surgeryDegrees of freedom
A positioning block (10) for use in total knee replacement surgery, permitting five degrees-of-freedom movement relative to a bone element (39) to which it is fixed. The positioning block (10) comprises a rotational mounting element (14) that is removably engaged to the bone element such that the mounting element (14) is selectively rotatable relative to the bone element, about three substantially perpendicular axes of rotation. A guide body portion (12) is engaged with the mounting element (14) such that it is translatable relative thereto along a proximal-distal axis (43) and an anterior-posterior axis (47), while being rotationally fixed relative to the mounting element (14) such that the guide body portion (12) and the mounting element (14) rotate together relative to the bone element (39).
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
Contact sensors and methods for making same
InactiveUS9095275B2Reduced probability of early failureAccurately carry-outResistance/reactance/impedenceForce measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceTotal knee replacement surgery
Owner:SENCORABLES
Bony balancing apparatus and method for total knee replacement
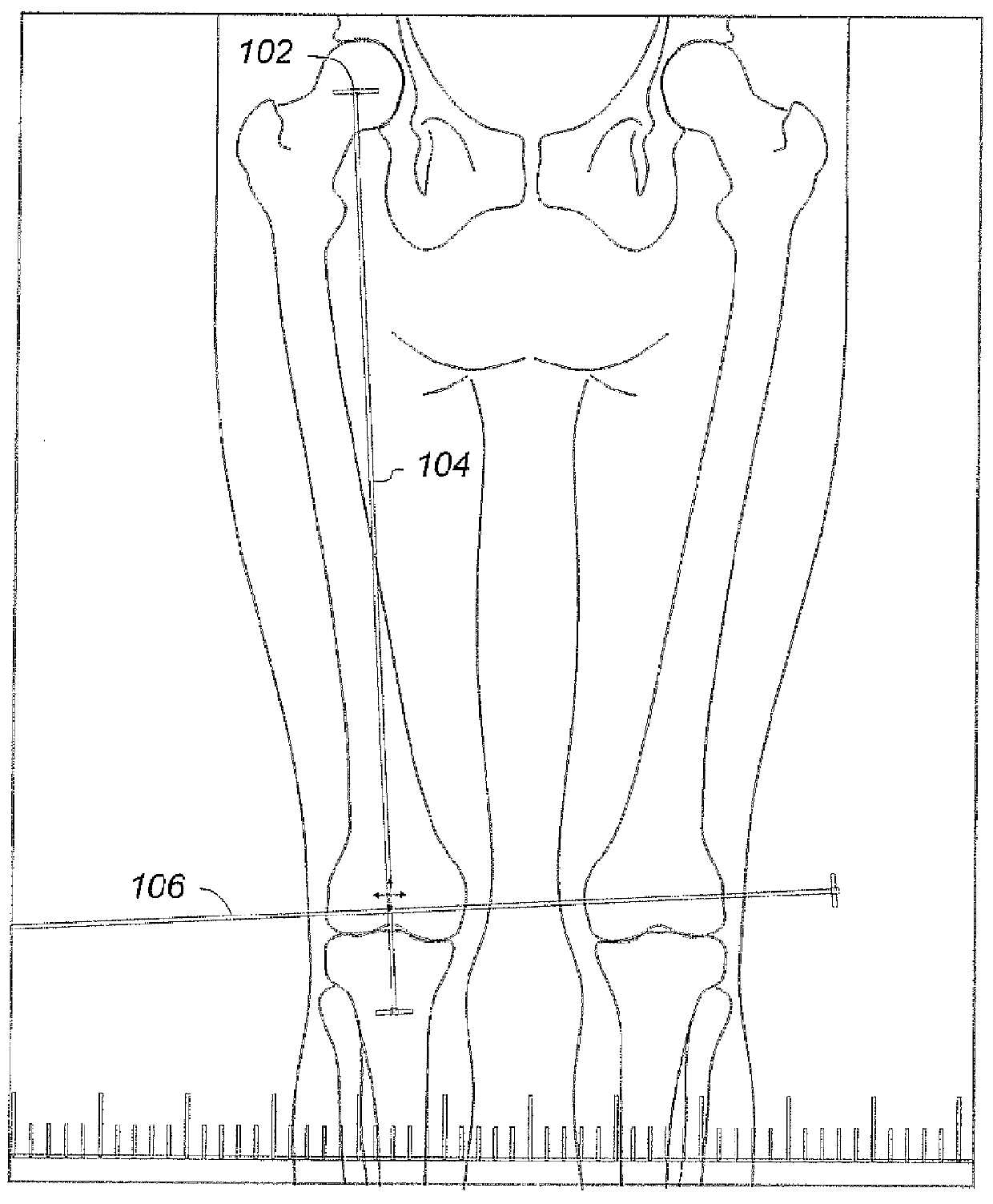
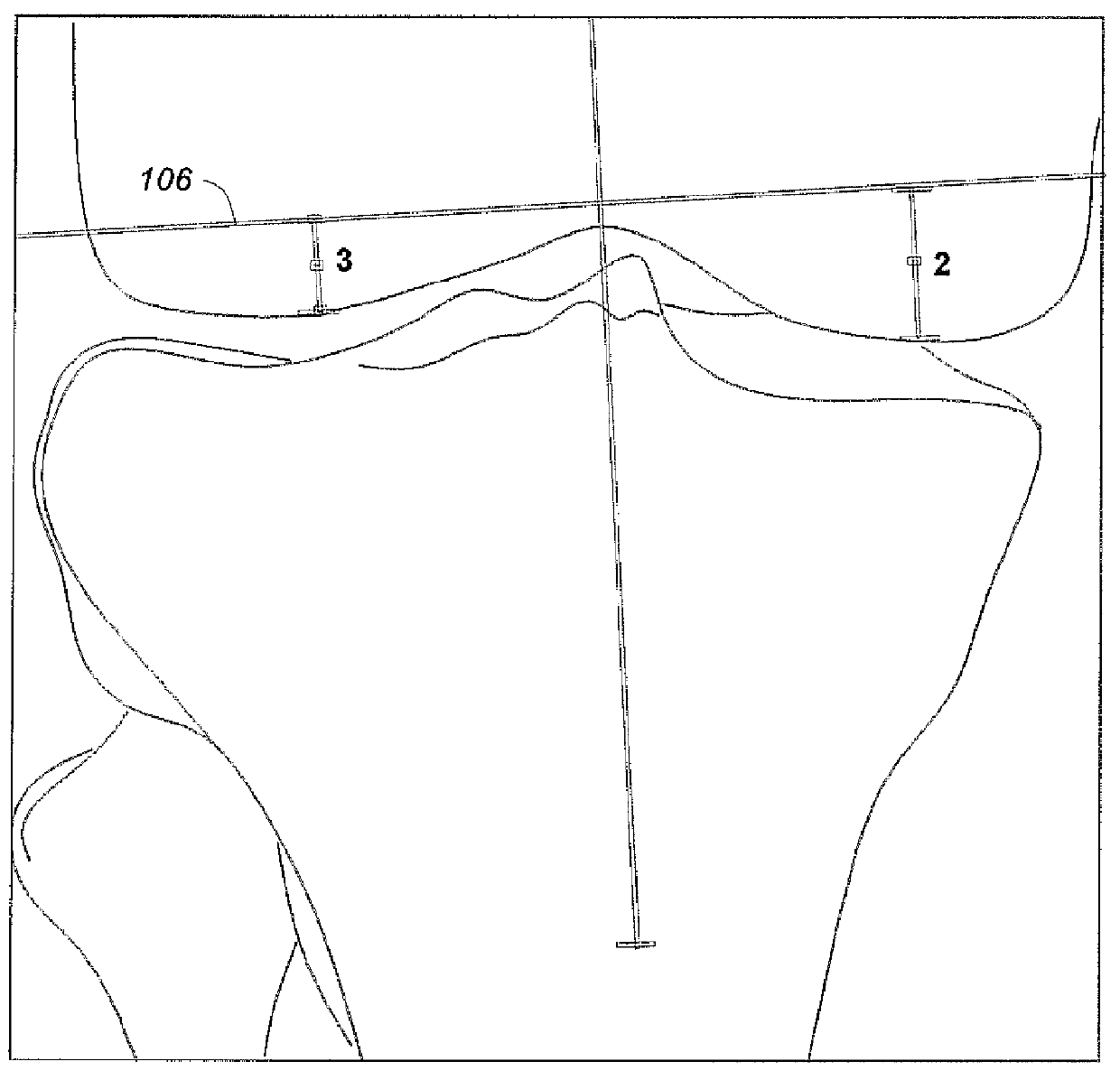
Total knee replacement surgery is improved through custom cuts on the distal femur without resorting to expensive computer navigation. The method involves measurement, on plain radiographs prior to surgery, the amount of bone that would be resected on each knee, medially and laterally on the distal femur. In the preferred embodiments, the predetermined distance is in the range of 8-10 mm, more preferably 10 mm, and the resulting distance from the second line to the apex of the lateral condyle is in the range of 6 to 7 mm. A cutting fixture is provided and used to resect the medial condyle at the predetermined distance and the lateral condyle at the measured resulting distance.
Owner:SURGENCO
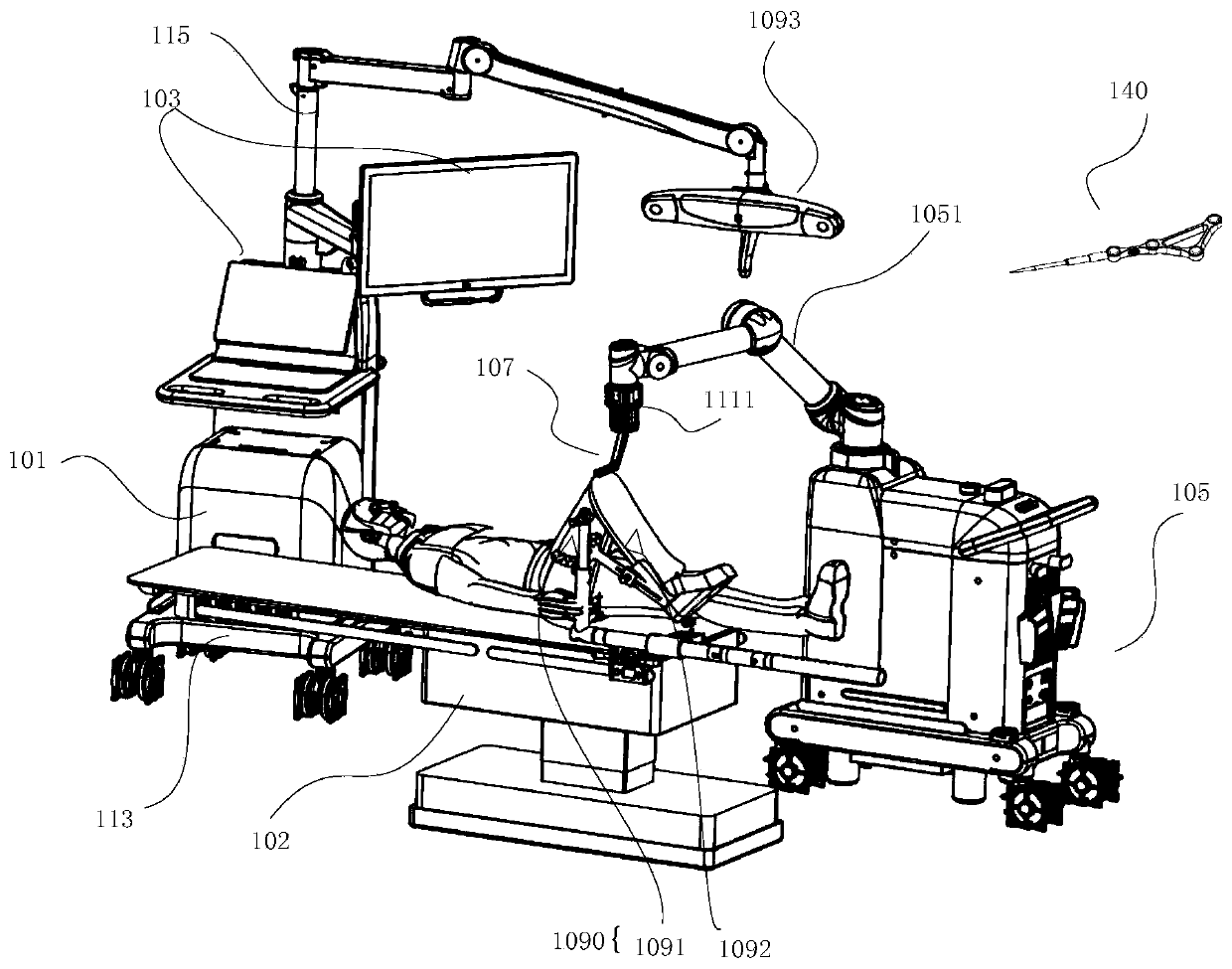
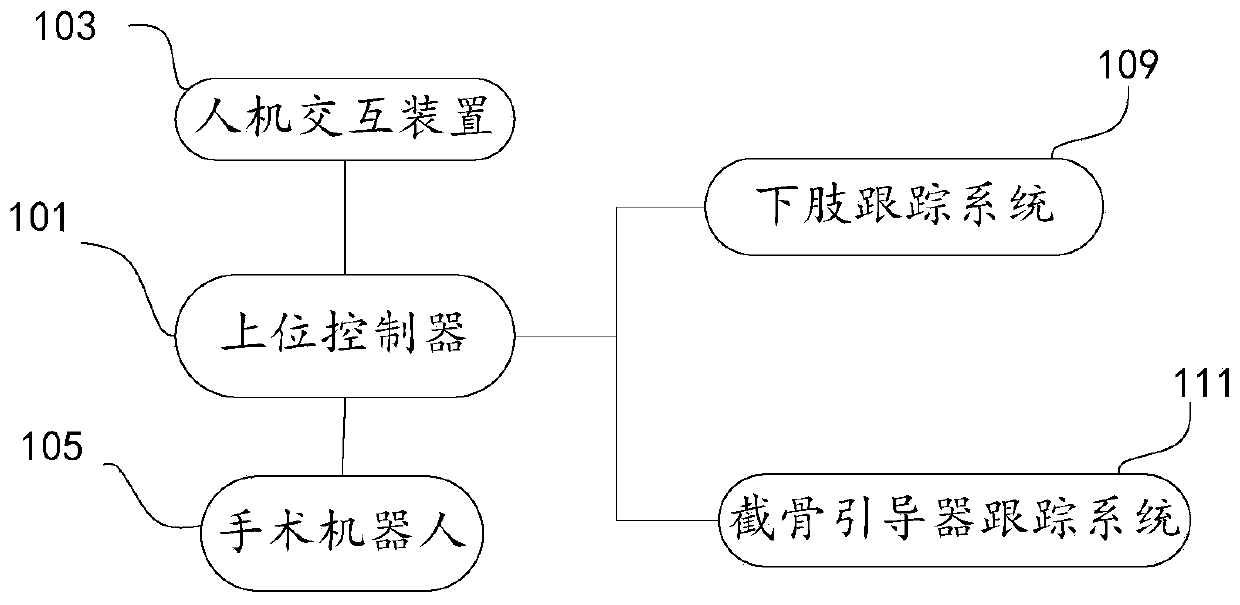
Osteotomy execution system, positioning, control and simulation execution methods and electronic equipment
ActiveCN111345896ASurgical navigation systemsComputer-aided planning/modellingTotal knee replacement surgeryKnee Joint
The invention provides an osteotomy execution system, a positioning method, a control method and a simulation execution method for primary total knee replacement surgery operation. The osteotomy execution system for the primary total knee replacement surgery operation comprises: a man-machine interaction device; a surgical robot which comprises a mechanical arm; an osteotomy guider which is fixedto the operation end of the mechanical arm and used for positioning and guiding an osteotomy tool during osteotomy operation of total knee replacement, wherein the osteotomy guider is provided with athrough groove for containing the osteotomy tool; a lower limb tracking system which is used for acquiring position data of thighbone and tibia; an osteotomy guider tracking system which is used for acquiring position data of the osteotomy guider; and an upper controller which is in communication connection with the man-machine interaction device, the surgical robot, the lower limb tracking systemand the osteotomy guider tracking system. The system provided by the invention can improve the execution effect and efficiency of the joint replacement surgery operation.
Owner:BEIJING TINAVI MEDICAL TECH
Oral pharmaceutical compositions of dabigatran etexilate
Compositions comprising a mixture of at least two types of particles wherein a) the first type of particles comprise dabigatran etexilate in the form of the free base or in the form of pharmaceutically acceptable salts, polymorphs, solvates or hydrates thereof; and b) the second type of particles comprise at least one pharmaceutically acceptable organic acid, use of said compositions in the reduction of the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and / or in the prevention of venous thromboembolic events in adult patients who have undergone elective total hip replacement surgery or total knee replacement surgery and processes for the preparation of said compositions.
Owner:BRECKENRIDGE PHARM INC
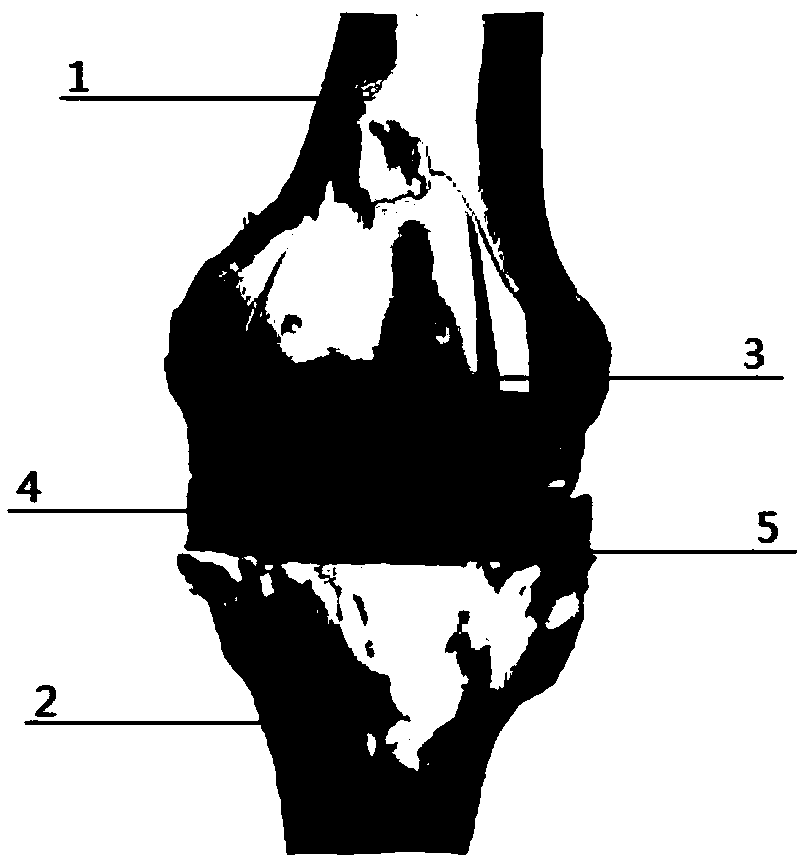
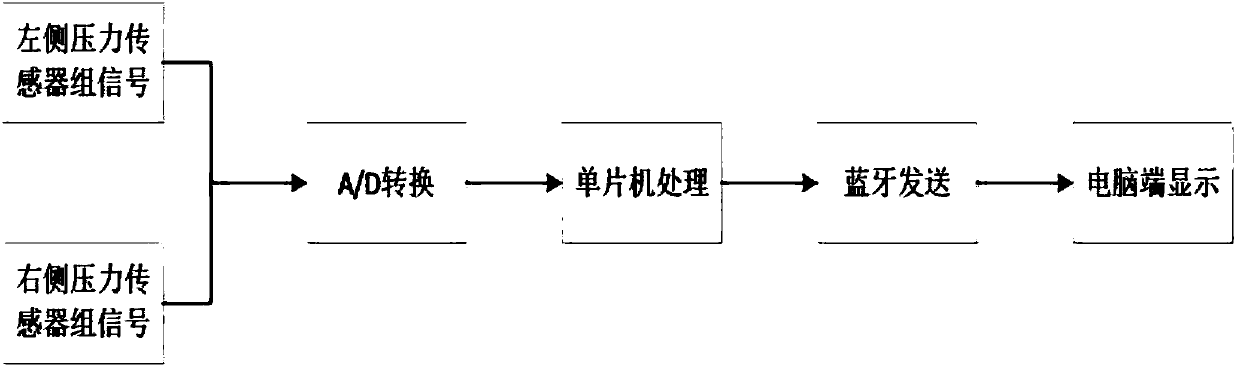
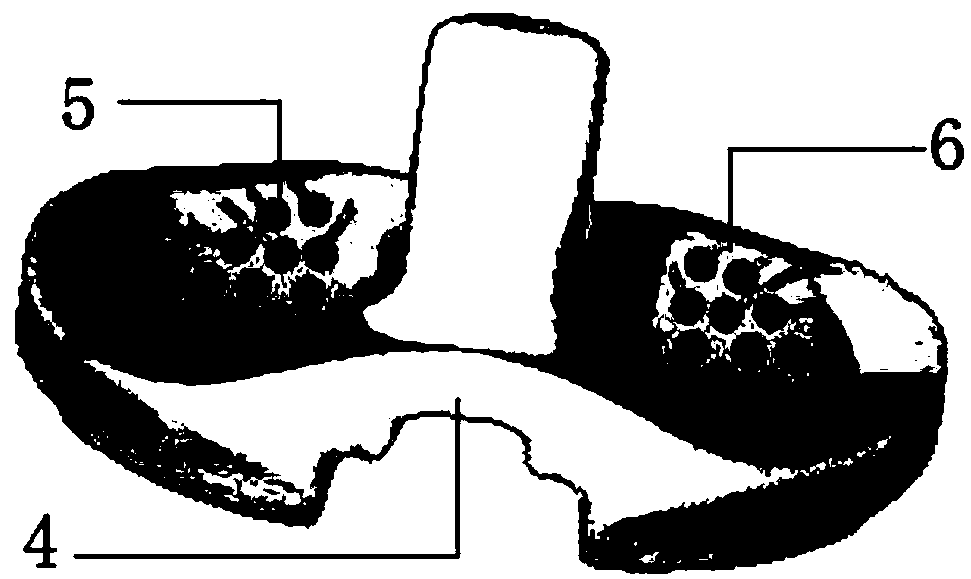
Knee joint balance detection system in total knee replacement and balance discrimination method thereof
PendingCN107802382AImprove accuracyImprove quality of life after surgeryJoint implantsKnee jointsTotal knee replacement surgeryTibial tray
The invention discloses a knee joint balance detection system in total knee replacement and a balance discrimination method thereof. The system is characterized in that a left pressure sensor set anda right pressure sensor set are attached to the left and right regions of a gasket, in the operation process, the gasket is placed in a gap between the thigh bone prosthesis and the tibia bracket, data of the left and right sensor sets can be obtained during 0-degree knee bending, 90-degree knee bending, internal rotation and ectropion, due to data analysis, whether the knee joints are located inthe balanced state or not is judged, and if the knee joints are in the non-balanced state, by properly repairing bones or adjusting the position of a prosthesis, the knee joints are in the balanced state finally. By keeping the position unchanged, surgical suturing is performed. By improving the accuracy of surgical knee joint balance, the important role in prolonging the service life of the postoperation prosthesis of a patient, reducing postoperative complications, and improving the postoperation living quality of the patient is achieved.
Owner:吴小玲 +1
Gap-adjustable knee joint pressure measuring device for total knee joint replacement
PendingCN110638476AReduce uncertaintyEliminates the hassle of repeatedly removing and reinserting tibial spacers of different thicknesses for trial useDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTotal knee replacement surgery
The present invention discloses a gap-adjustable knee joint pressure measuring device for total knee joint replacement. The gap-adjustable knee joint pressure measuring device comprises a tibia keel processing tool and a pressure measuring device, the pressure measuring device comprises a push block, a femur test pad and a tibia test pad, shape of the tibia keel processing tool is adapted to a tibial resected surface, and a front part of an upper surface of the push block is inclinedly arranged downward to form a support inclined surface; and the tibia test pad comprises a tibia pad body, a longitudinal rod, a handle, a push rod, a digital display screen, two push block guide grooves, two guide columns and two elastic positioning columns, the tibia pad body, the longitudinal rod and the handle are sequentially connected from front to back, and the push block is arranged in the push block guide groove in a back-and-forth moving mode. The gap-adjustable knee joint pressure measuring device for the total knee joint replacement is simple in structure and easy for use and cleaning, and thickness of the pressure measuring device can be controlled by adjusting positions of the push blockin the pressure measuring device, thereby detecting pressures of medial and lateral condyles of femur under the corresponding thickness.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROPORT ORTHOBOT CO LTD
Femoral guide plate for total knee replacement surgery and using method thereof
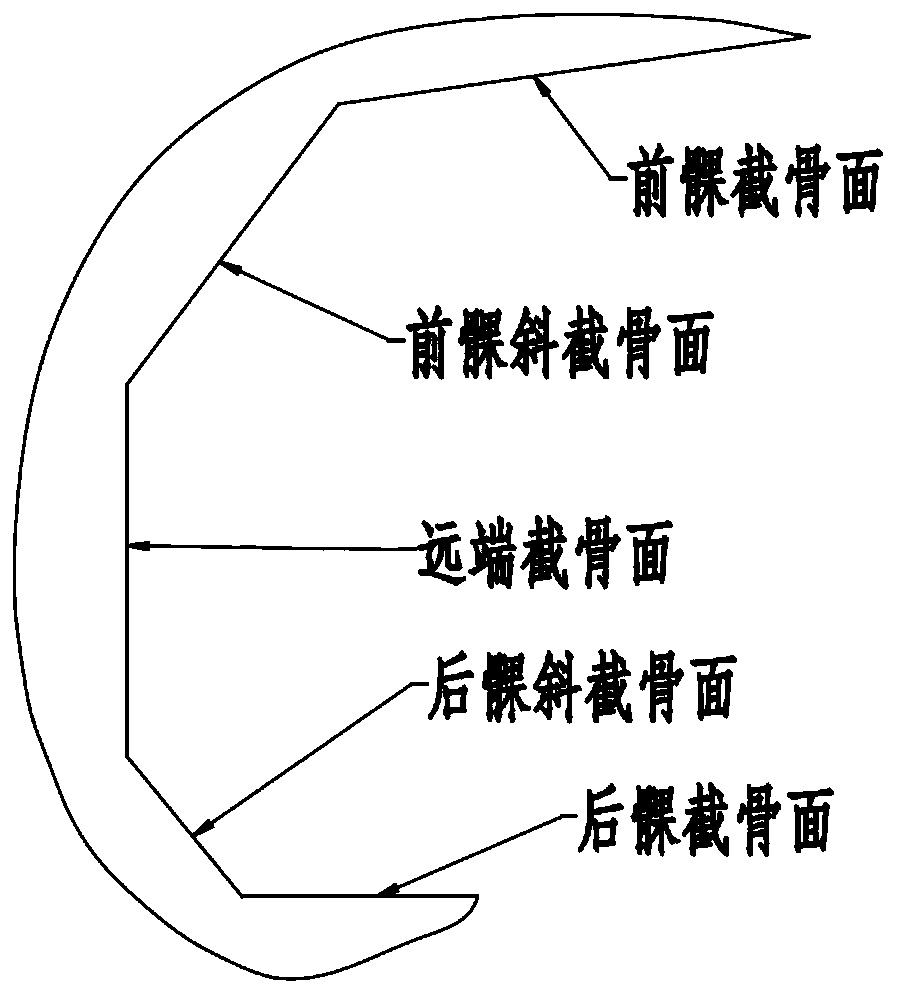
ActiveCN112617960AImprove securityIncrease success rateBone drill guidesDistal osteotomyTotal knee replacement surgery
The invention provides a femoral guide plate for total knee replacement surgery and a using method thereof. The femoral guide plate comprises a femoral guide plate body, a first side of the femoral guide plate body is provided with a distal femur osteotomy groove aligned with a distal femur osteotomy surface and a preartis osteotomy groove aligned with a femur preartis osteotomy surface, a first sickle blade capable of verifying the distal femur osteotomy amount is inserted into the distal osteotomy groove, a second sickle blade capable of verifying the preartis osteotomy amount is inserted into the preartis osteotomy groove, a femur preartis fitting area is arranged at a first end of a second side, opposite to a first side, of the femur guide plate body, a second end of the second side, opposite to the first side, of the femoral guide plate body is provided with a femur medial condyle fitting area and a femur lateral condyle fitting area. The femoral guide plate is accurately positioned and installed, the distal femur osteotomy amount and the preartis osteotomy amount are accurately verified, accurate positioning of osteotomy in an operation is guaranteed, and the safety and the success rate of the operation are improved.
Owner:LONGWOOD VALLEY MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +2
3D-printing femoral-condyle five-in-one integration osteotomy device and forming method thereof
PendingCN108784782AIt has the characteristics of not easy to deform under forceFit tightlySurgery3d printFemoral osteotomy
The invention provides a 3D-printing femoral-condyle five-in-one integration osteotomy device and a forming method thereof, and relates to the technical field of medical apparatuses and instruments. For solving the technical problem that errors are easy to generate in existing total knee replacement femoral-condyle osteotomy, the 3D-printing femoral-condyle five-in-one integration osteotomy devicecomprises a femoral osteotomy device model matched with the affected-side femoral condyle of a patient, the femoral osteotomy device model is provided with a femoral-condyle front fitting face, a femoral-medial-condyle fitting face and a femoral-lateral-condyle fitting face, and the femoral-condyle front fitting face is used for fixed with the femoral condyle; the femoral osteotomy device model is subjected to stress and is not front to deformation, and is formed in a 3D-printing mode. Two osteotomy processes can be merged into one process, femoral-condyle osteotomy is completed one time, theusing quantity of osteotomy guiding plates is decreased, and deviations are reduced.
Owner:THE SECOND AFFILIATED HOSPITAL ARMY MEDICAL UNIV +1
Methods And Devices For Supporting A Patient's Leg To Increase Comfort And Assist In Recovery
ActiveUS20190247214A1Operating tablesJoint implantsSupporting systemPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present disclosure relates to a support system for patients recovering from medical procedures, including from total knee replacement surgery. The disclosed system may include a foot support unit which supports a patient's feet, where the foot support may have leg grooves separated by a divider and a tapered height. The foot support may be placed in a patient's bed. Additionally hip support wedges may be placed beneath a patient's hip, where the hip supports provide the benefit of counteracting a leg's natural tendency to rotate outwards. The disclosed foot support and hip wedges promote proper alignment and in that way provide comfort and assist in recovery.
Owner:DLA MEDICAL LLC
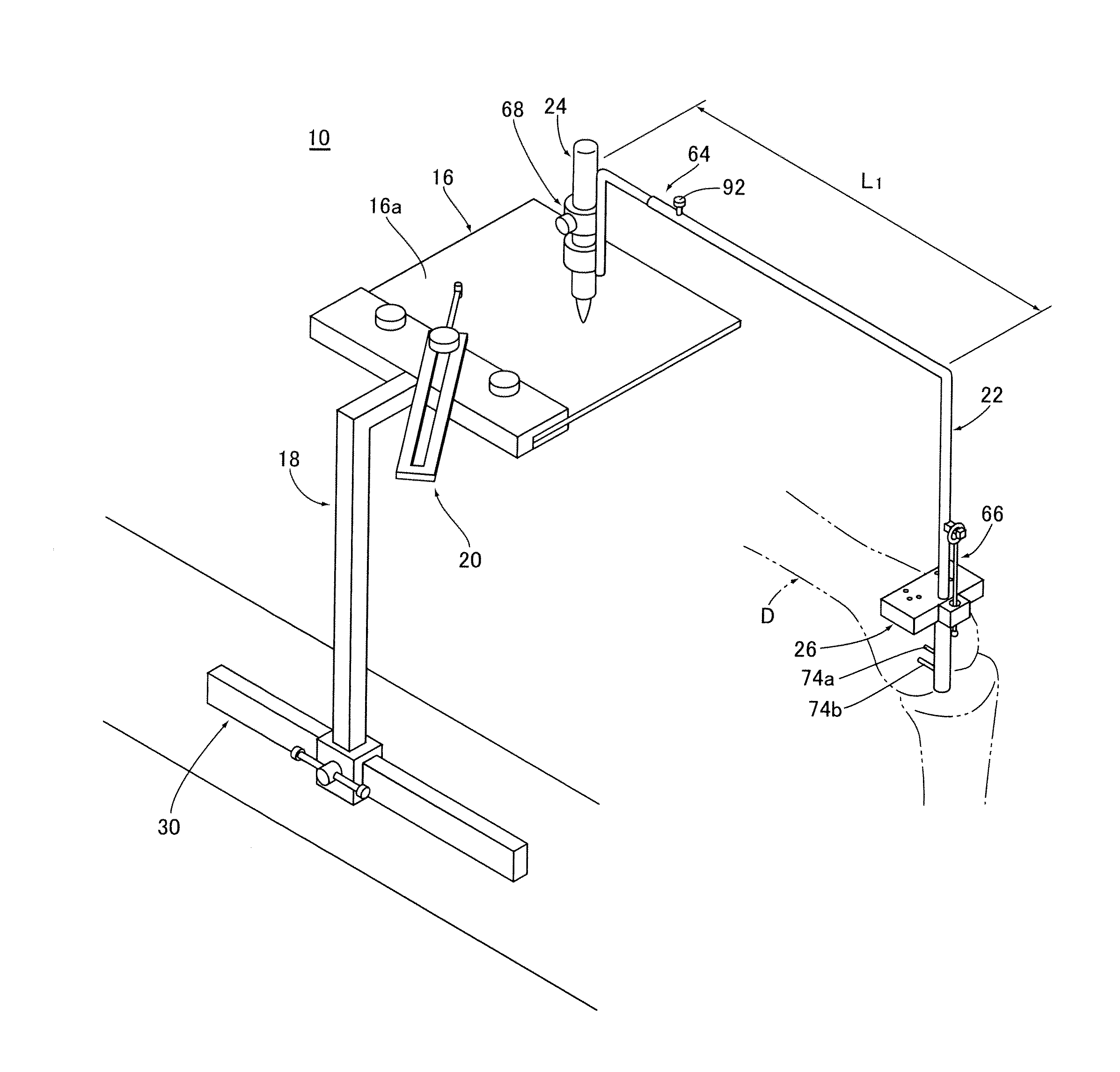
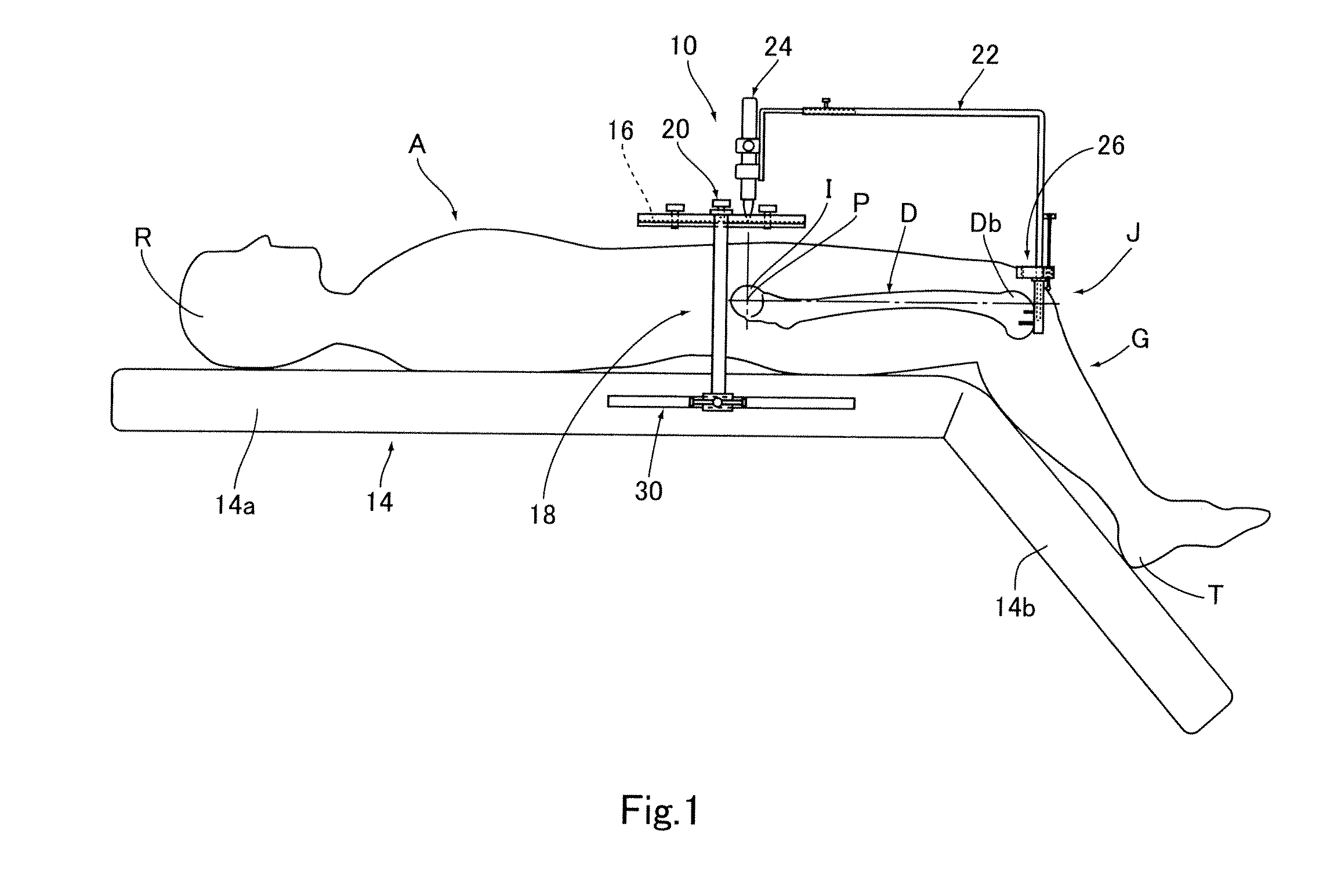
Knee replacement surgical cut planes estimation for restoring pre-arthritic alignment
ActiveUS11439467B1Improve stabilityMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesComputer-aided planning/modellingCoronary arteriesPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A computer-aided pre-operative planning tool with interactive surgeon interface for total knee replacement implements a method that allows implant size selection, implant positioning, and surgical cut planes estimation (with construction of corresponding surgical jig), based upon a series of coronal, axial and sagittal image slices of a patient's leg. Limb alignment and corresponding surgical cut planes are defined based upon joint anatomical-matching analysis to minimize joint wear and restore a pre-arthritic alignment (rather than an always fully neutral alignment). Using the interface, a surgeon has the option to adjust the varus / valgus alignment within recommended bounds between the pre-arthritic and fully neutral alignments. Implant size may be selected based on a best fit to the patient's leg obtained from analysis of the images.
Owner:LENTO MEDICAL INC
Apparatus for identifying femoral head center
InactiveUS8672862B2Accurate identificationInexpensive configurationPerson identificationJoint implantsRight femoral headTotal knee replacement surgery
An apparatus for identifying, during total knee replacement surgery, a position of a center of a femoral head of a patient within a plane parallel to a frontal plane, comprises a marking plate placed to cover, in a direction perpendicular to the frontal plane, a site where the femoral head center of the patient's body is located; a pivotal arm having a pivotal shaft arranged to extend in a direction perpendicular to the frontal plane; and a marker attached to the pivotal arm, for depicting a circular arc on the marking plate according to rotation of the pivotal arm; the pivotal shaft being placed at a distal end of a femur of the patient, a distance from the pivotal shaft to the marker in a direction parallel to the frontal plane being equal to a preliminarily measured distance from the distal end of the femur to the femoral head center.
Owner:KANEKASU KOICHI
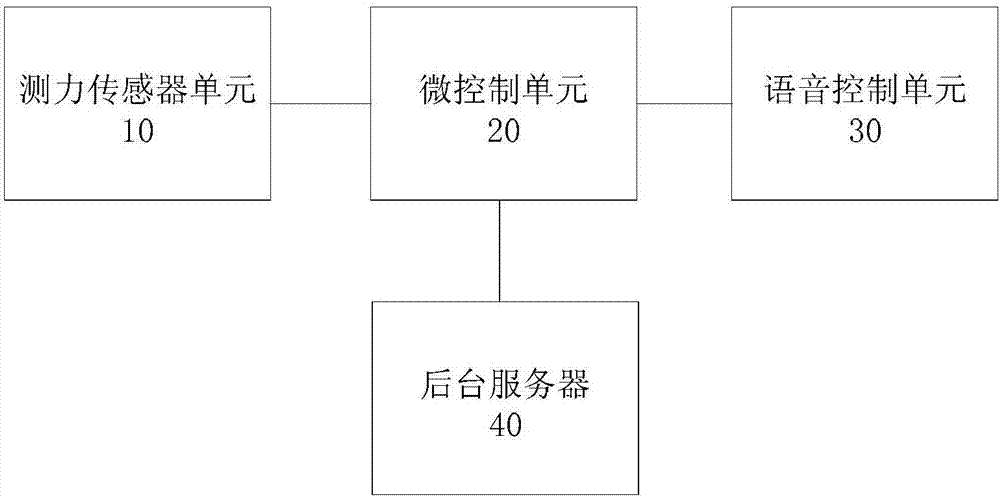
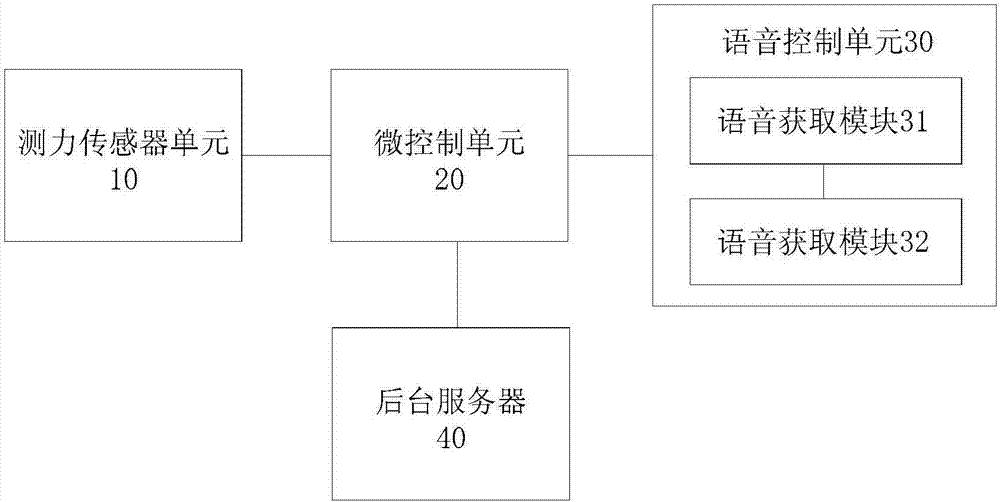
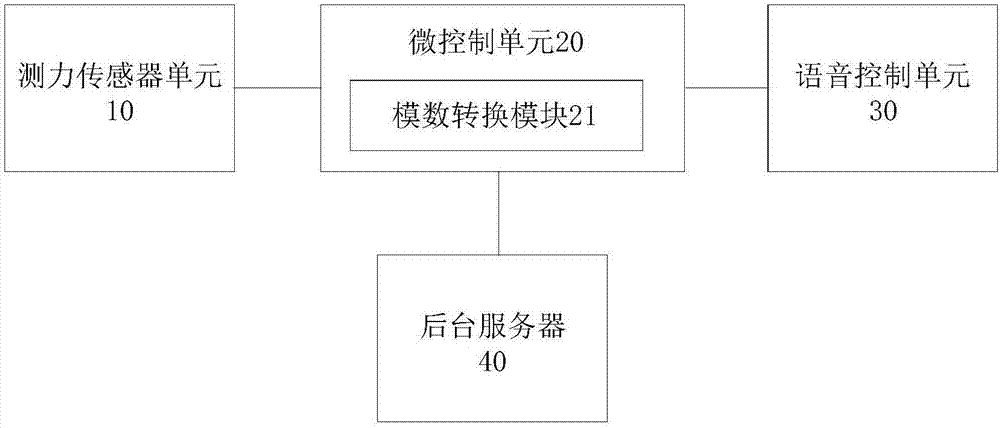
Balancing and force-measuring device for soft tissue
PendingCN107157589AAvoid secondary pollutionSolve the problem of easy secondary pollutionMusculoskeletal system evaluationSurgeryPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTotal knee replacement surgery
The invention provides a balancing and force-measuring device for soft tissue. The device comprises a force-measuring sensor, a micro-control unit and a voice control unit. The force-measuring sensor is used for detecting a pressure signal endured by to-be-tested soft issue. The micro-control unit is used for controlling the working state of the force-measuring sensor and acquiring the pressure signal detected by the force-measuring sensor as well as processing the pressure signal, storing the processed pressure signal and / or sending the signal to a back-end server. The voice control unit is used for receiving external voice information, converting external voice information into a control instruction and sending the instruction to the micro-control unit as well as controlling the working states of the micro-control unit and the force-measuring sensor. The balancing and force-measuring device for soft tissue has the following beneficial effects: during a displacement surgery for full knee joints, a surgeon instructs and controls the balancing and force-measuring device for soft tissue through voice; and the likelihood of secondary pollution is reducedduring operation through a button, a knob, a touch screen and other modes.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
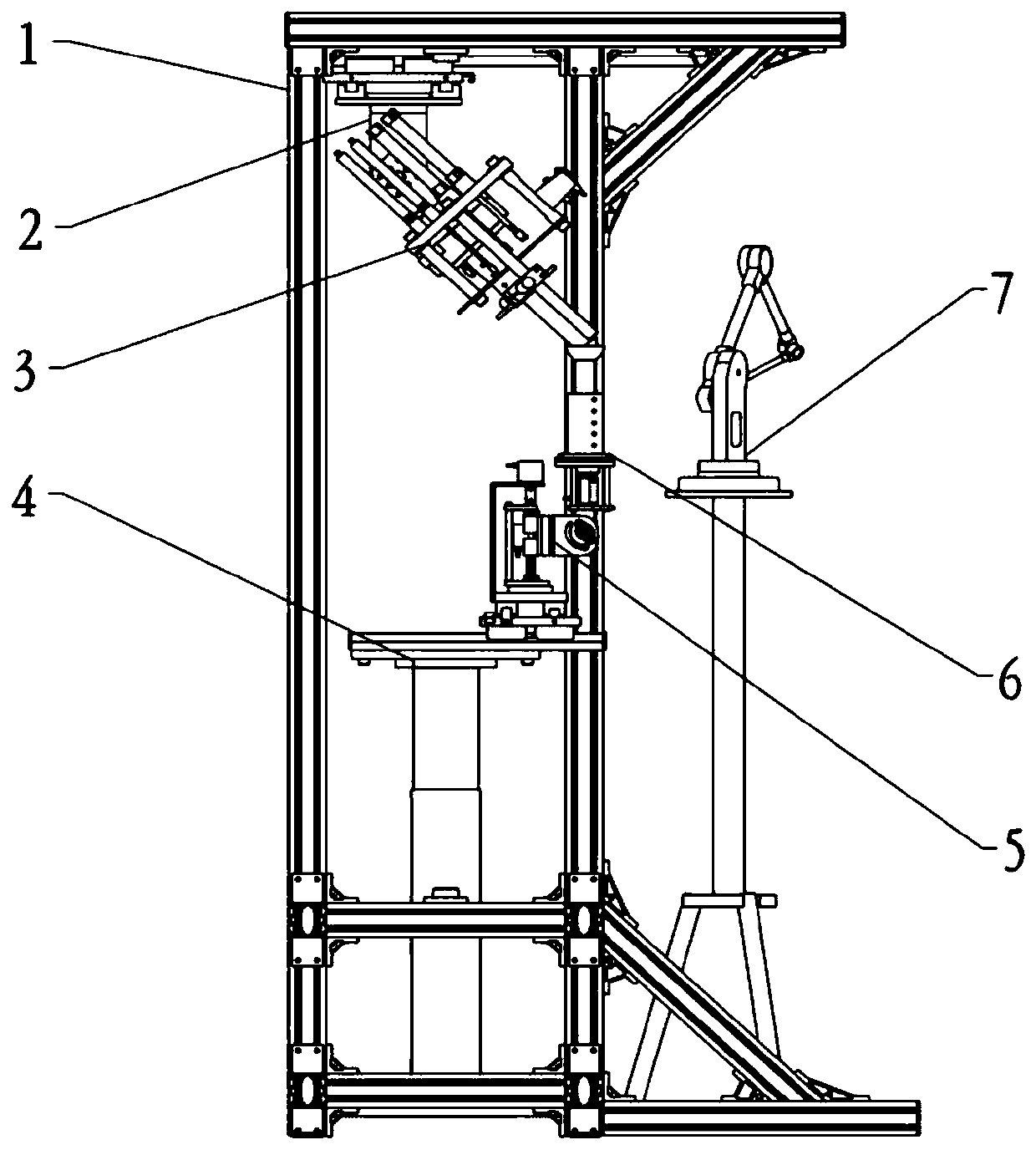
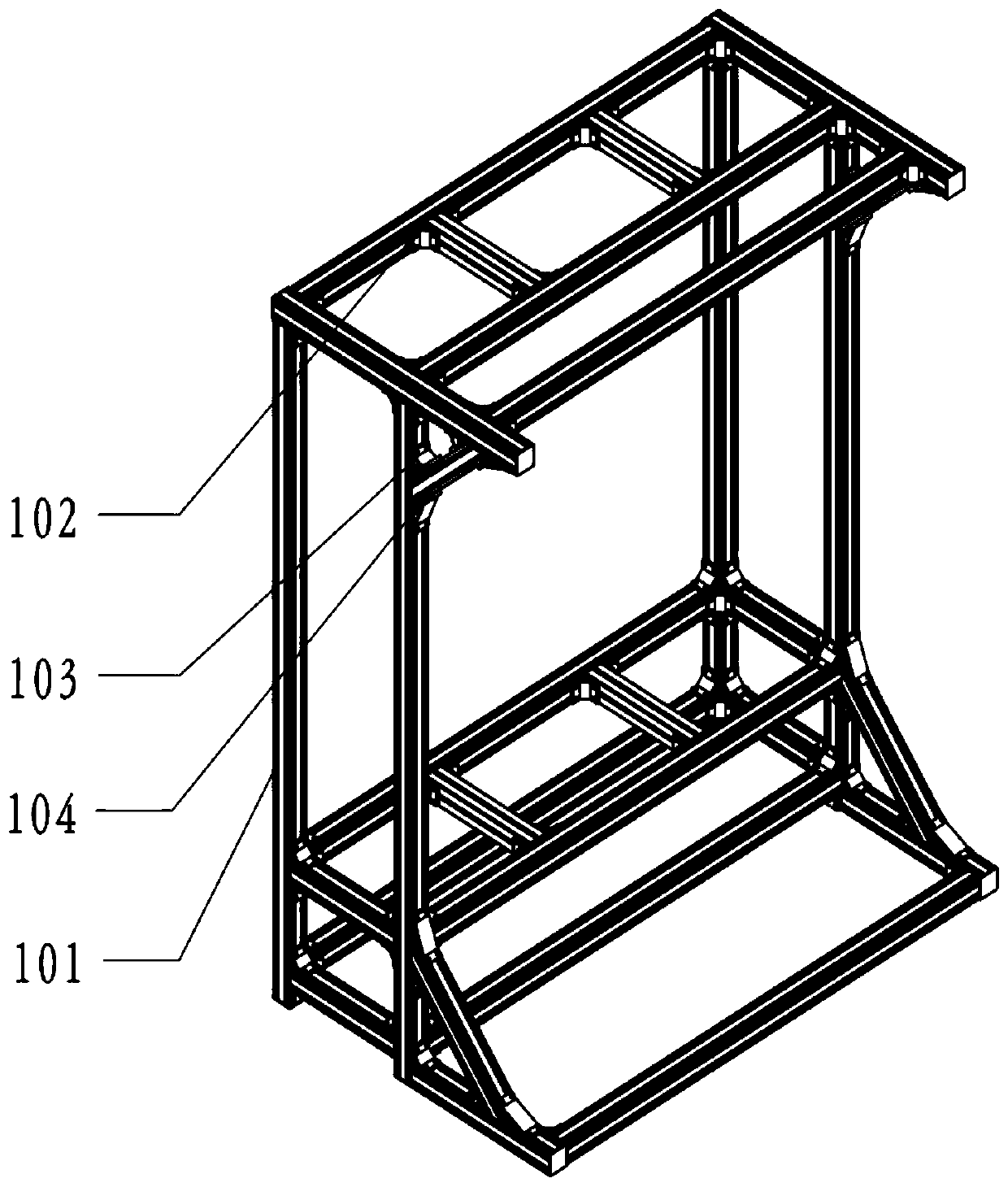
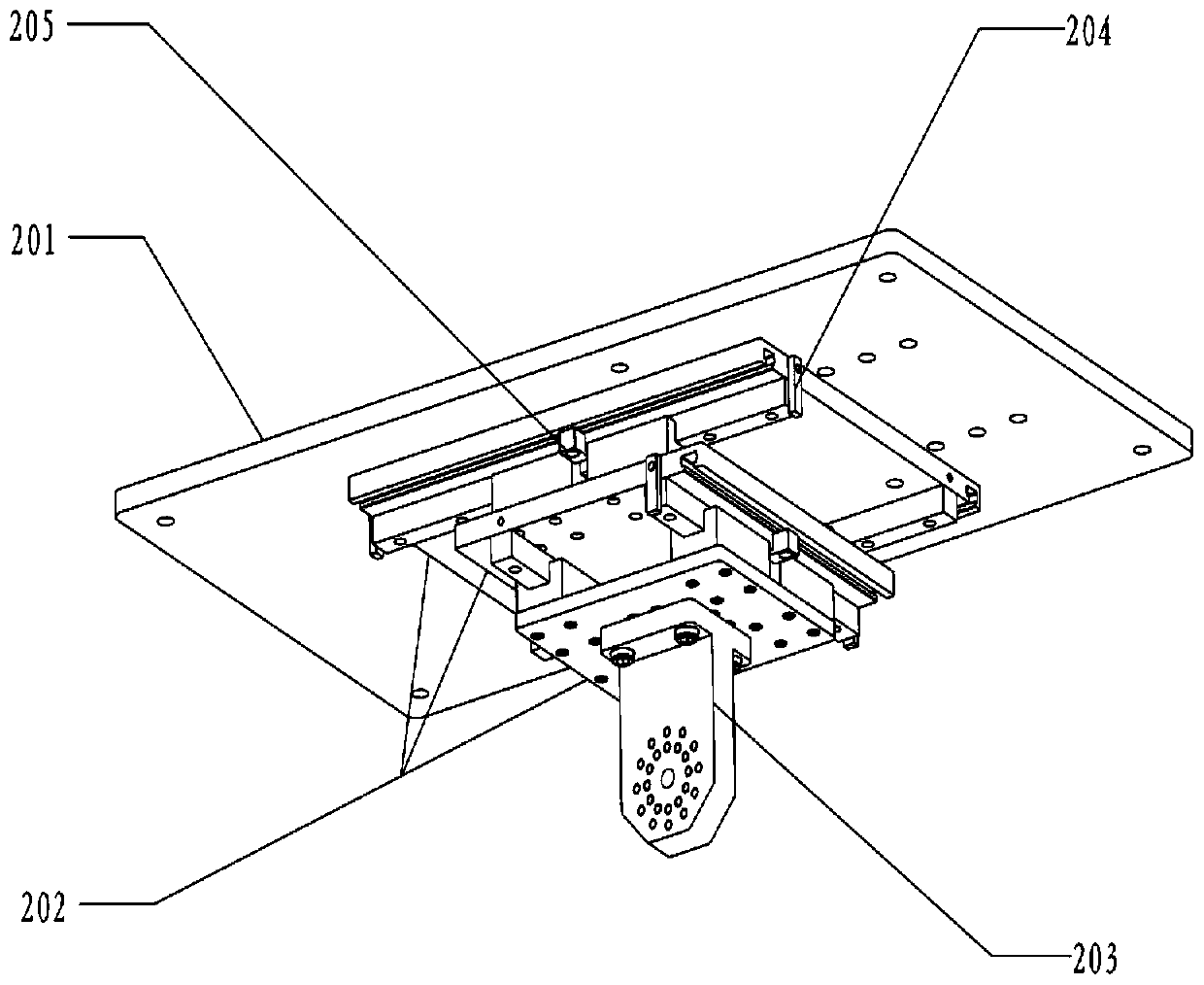
Knee joint force loading and biomechanical characteristics detection experimental platform
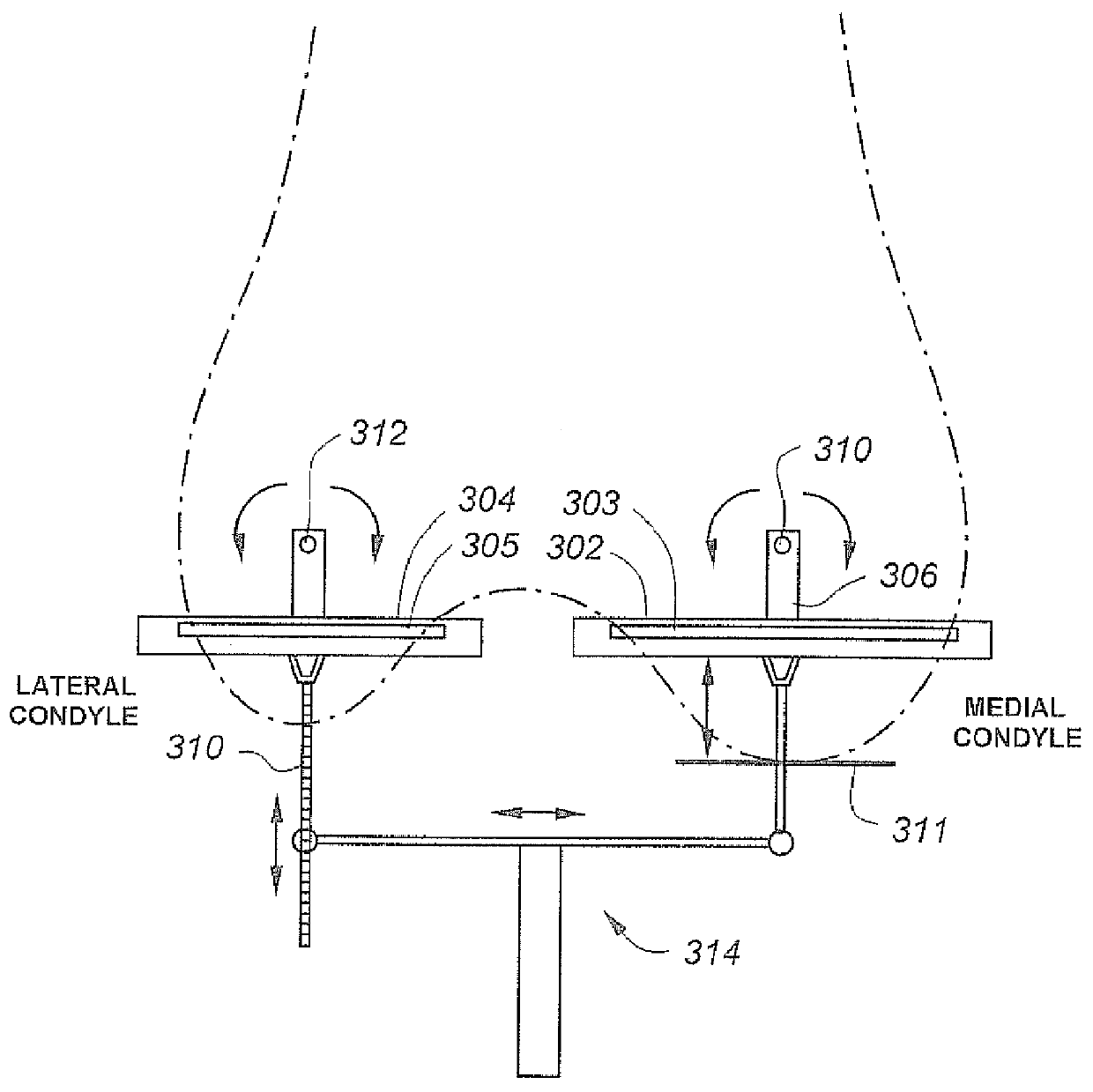
ActiveCN108766169BImplement servo controlQuick and easy muscle loading methodEducational modelsTotal knee replacement surgeryArticularis genus
The invention provides an experimental platform for knee joint force loading and biomechanical detection. The experimental platform is mainly composed of seven parts including a frame unit, a femoralpose adjustment unit, a femoral reactivity and ligament strain measurement and force loading unit, a knee joint flexion driving unit, a tibia pose driven unit, a tibia internal and external rotationmeasurement unit, and a patella pose detection unit. The device compares the biomechanical characteristics of the in-vitro knee joint under different surgical techniques by detecting the biomechanicalcharacteristics of the knee joint after surgeries such as total knee replacement, anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, and posterior cruciate ligament reconstruction.
Owner:SHANGHAI INNOMOTION
Postoperative rehabilitation device for total knee replacement
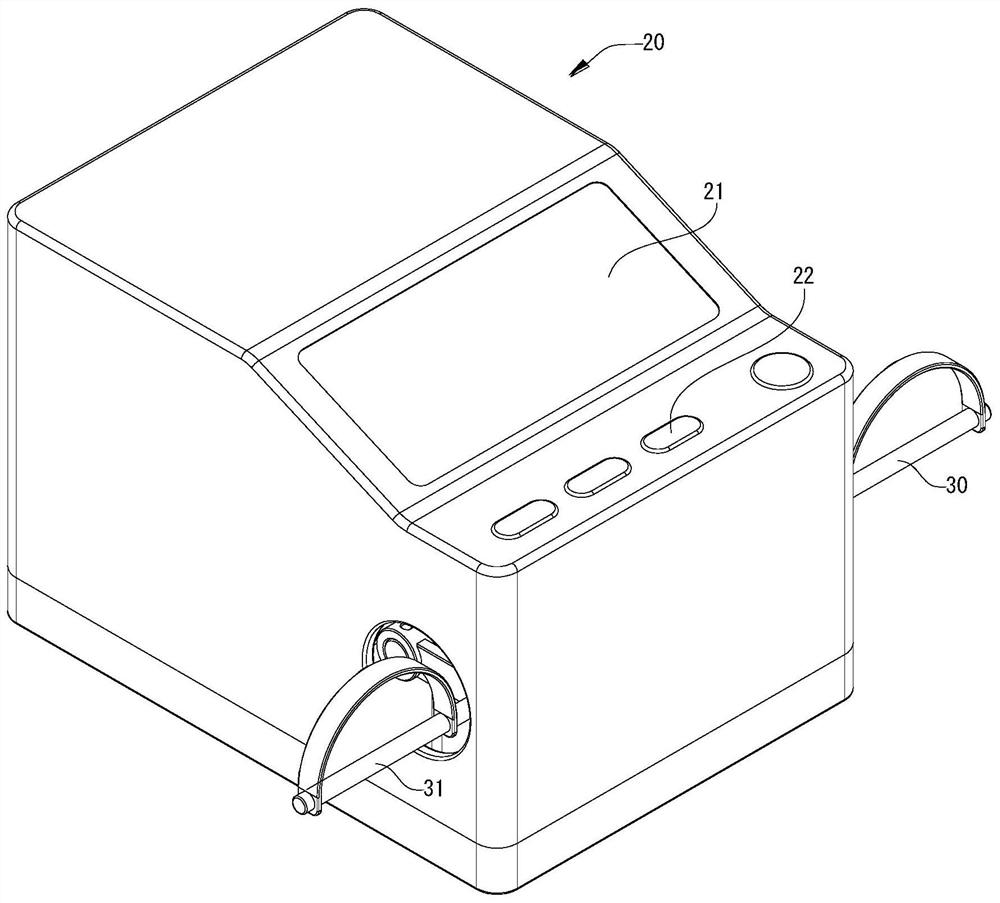
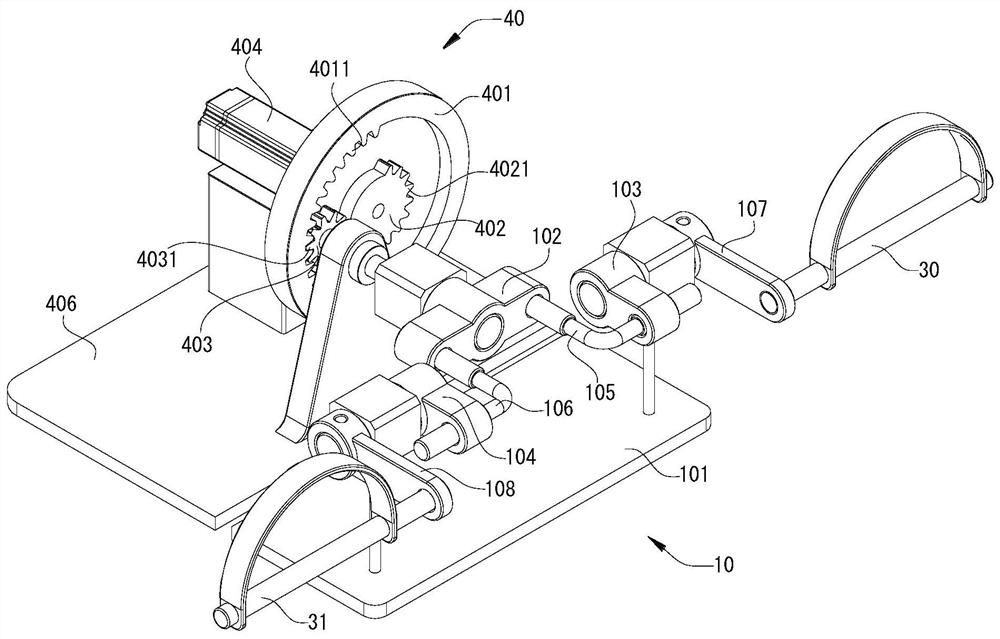
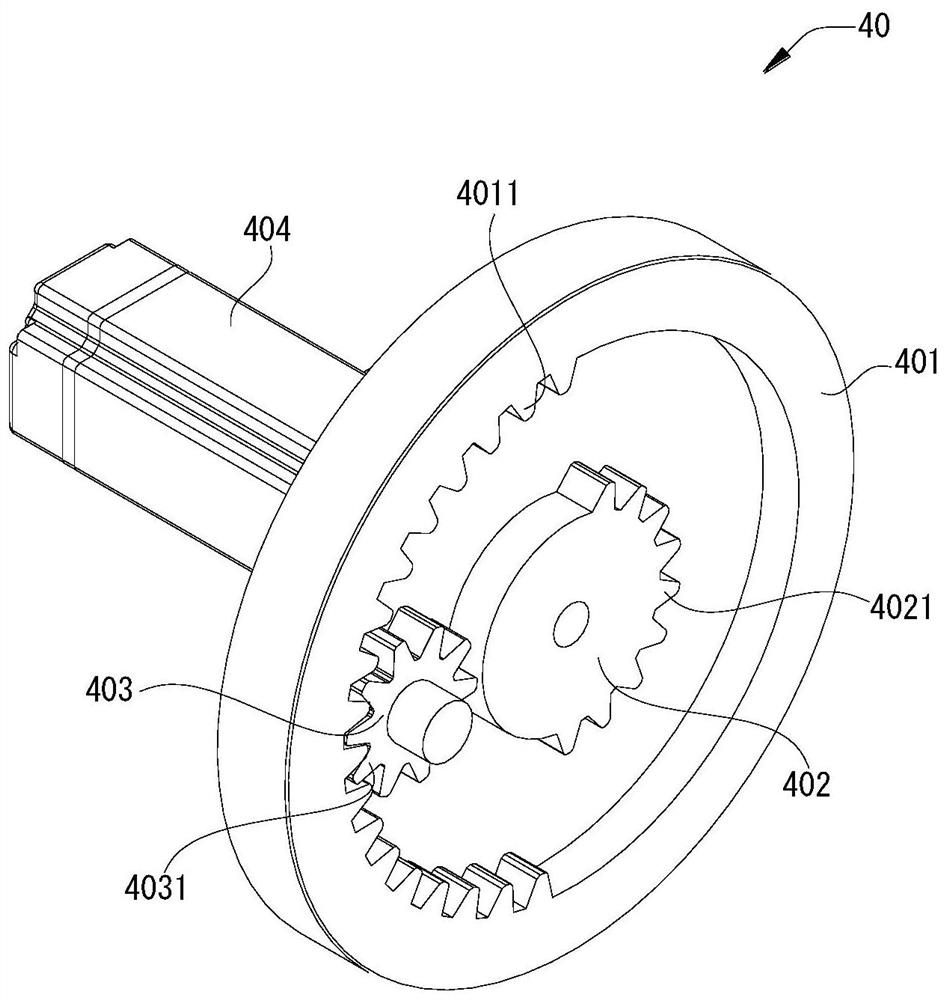
PendingCN113786312AChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTotal knee replacement surgery
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN HOSPITAL
A femur or tibia registration method and device based on total knee replacement surgery
ActiveCN110215281BImprove accuracyThe registration result is satisfactoryComputer-aided planning/modellingTotal knee replacement surgeryRadiology
Owner:BEIJING HURWA ROBOT MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
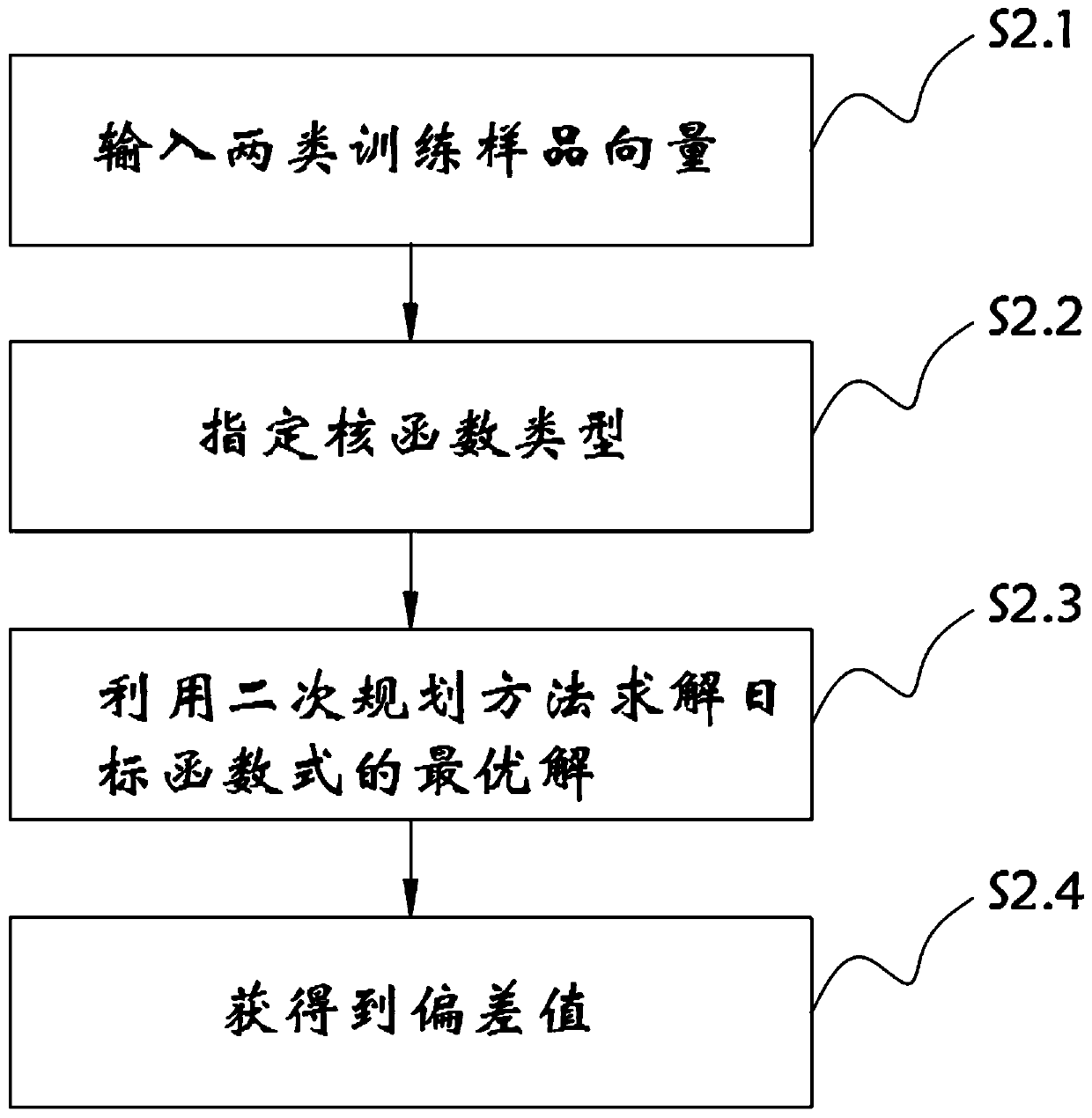
Judgment method for dynamic soft tissue balance during total knee replacement based on support vector machine
PendingCN111214233AAccurate recoveryImprove accuracyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationTotal knee replacement surgery
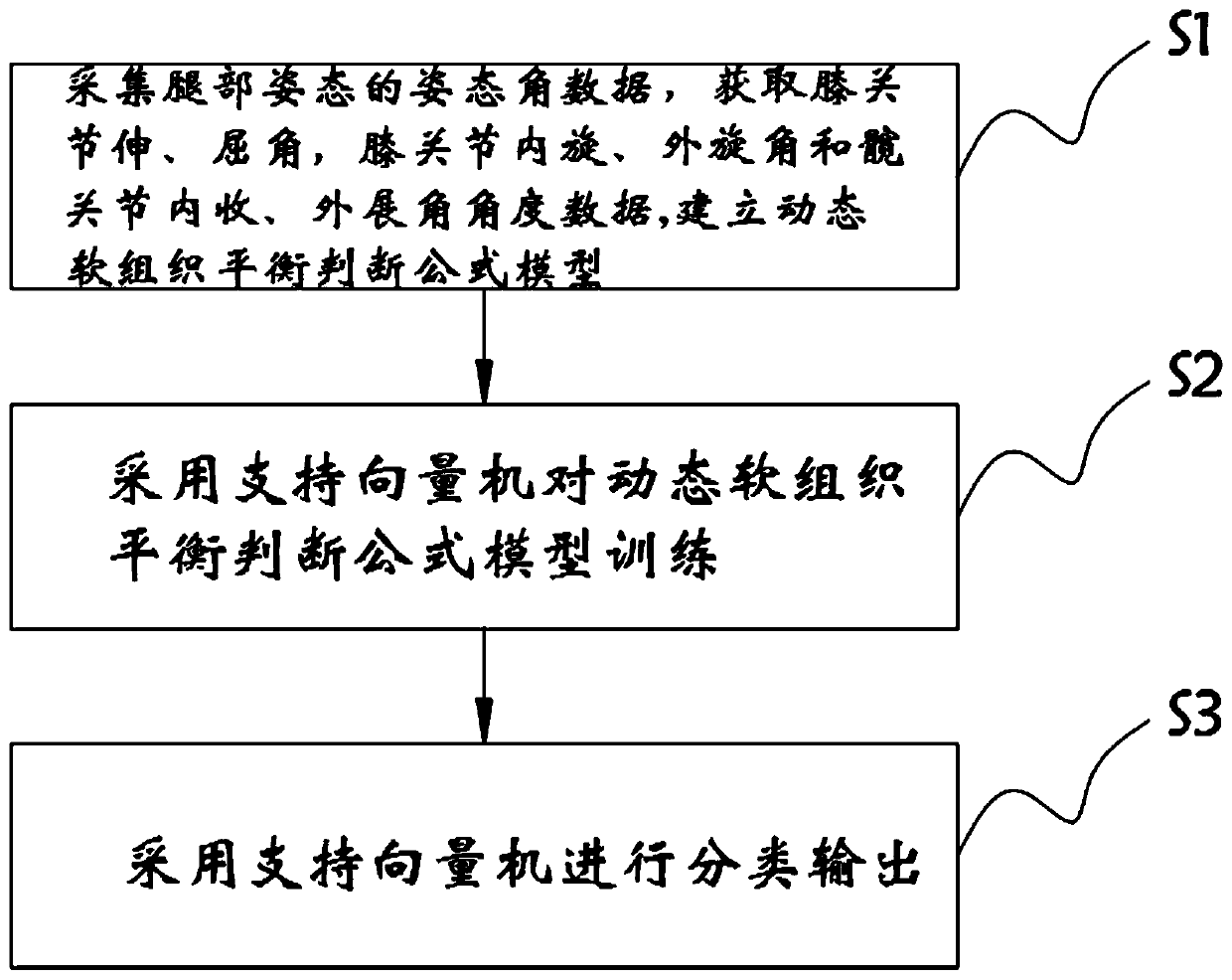
The invention relates to the technical field of total knee replacement, and in particular relates to a judgment method for dynamic soft tissue balance during total knee replacement surgery based on asupport vector machine. The method comprises the following steps: collecting posture angle data of leg postures, and establishing a dynamic soft tissue balance judgment formula model; training the dynamic soft tissue balance judgment formula model by using the support vector machine; and performing classification output by using the support vector machine. In the judgment method of the dynamic soft tissue balance during the total knee replacement surgery based on support vector machine, the dynamic soft tissue balance judgment formula is established, and soft tissue balance judgment is performed to guide doctors to make timely correction through a clinical technical means during operation, so that realize accurate recovery of a lower limb force line is realized; and a supervised machine learning classification algorithm is used for soft tissue balance judgment, so that errors caused by formula judgment are reduced, and the accuracy of balance judgment results is improved.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
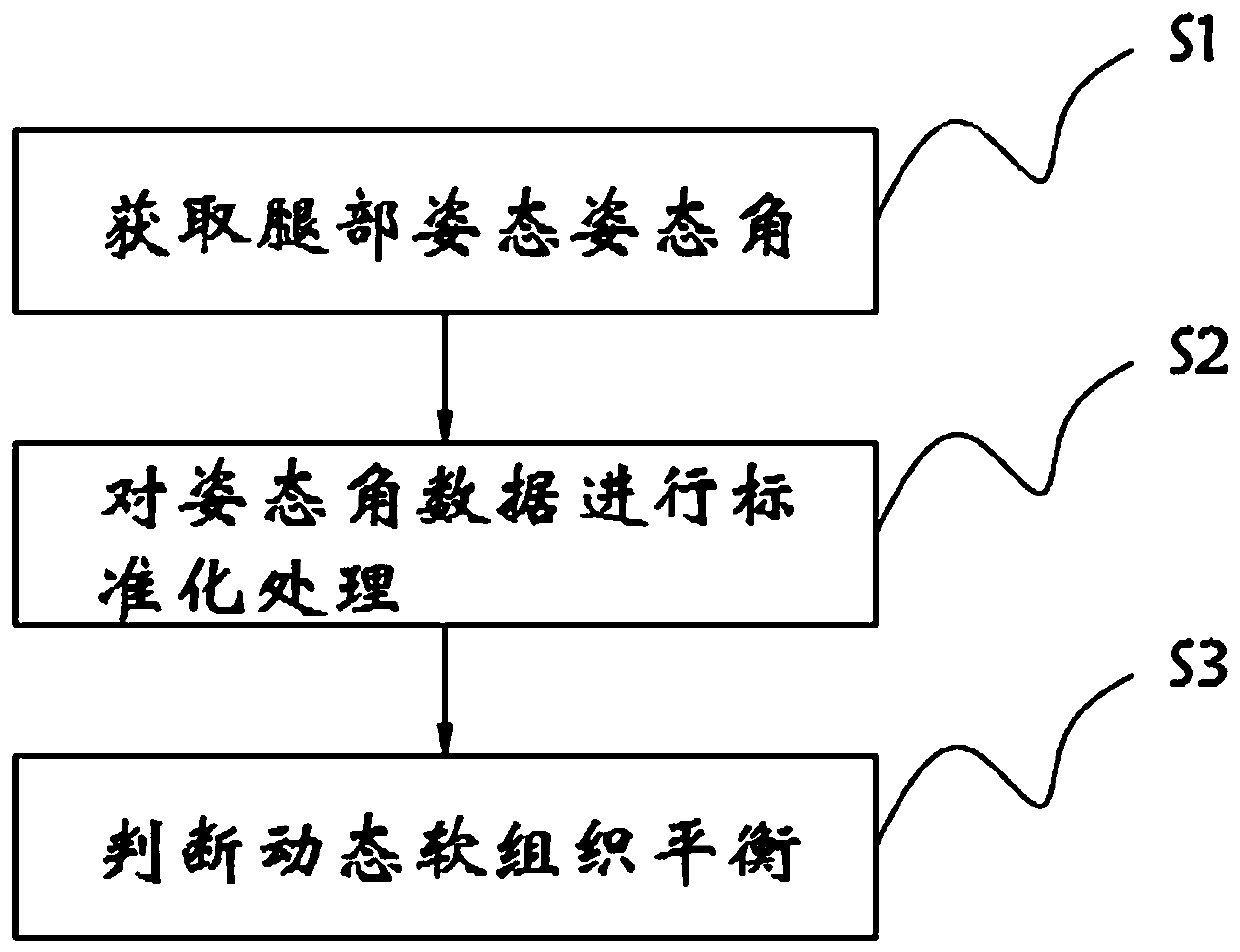
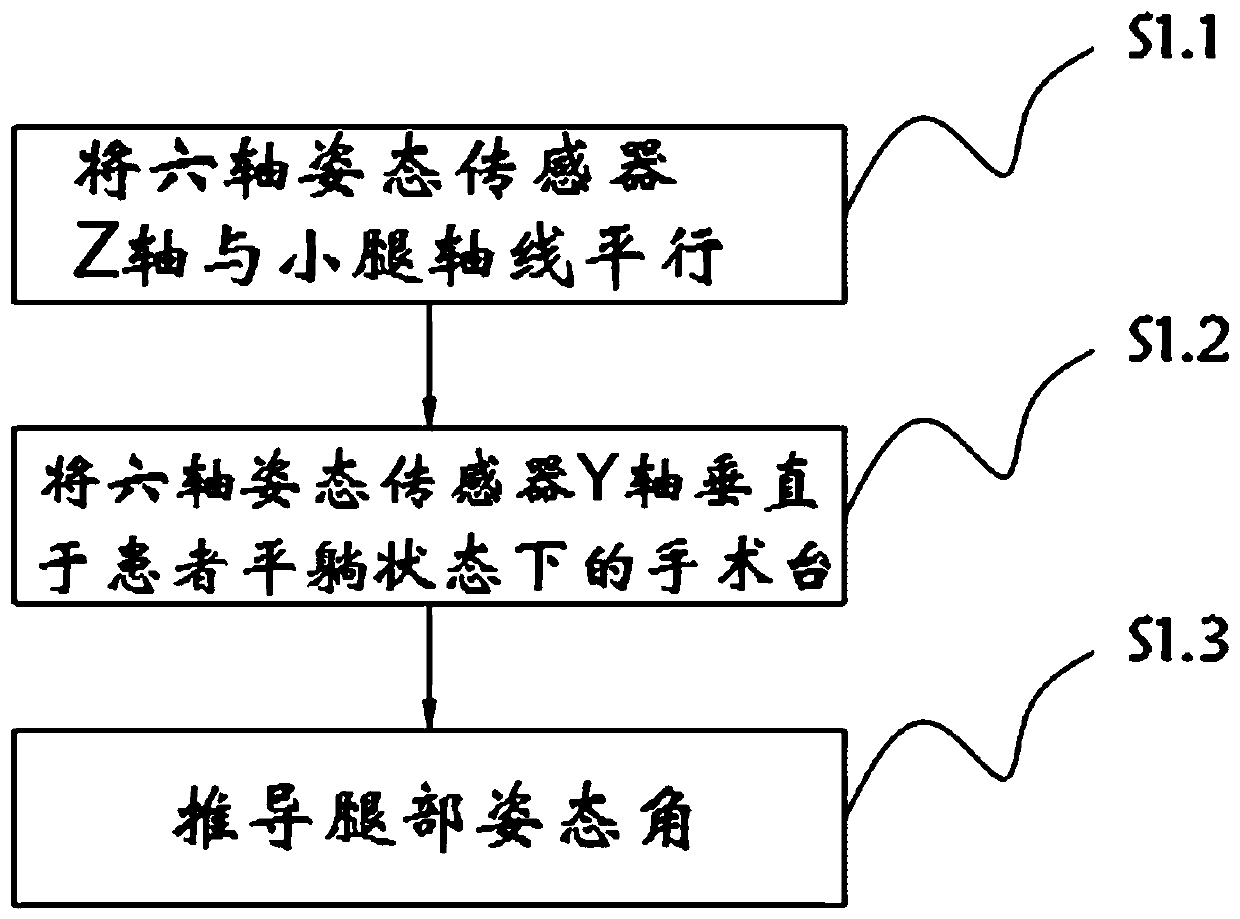
Method for realizing dynamic soft tissue balance judgment in total knee joint replacement
PendingCN111214234AAccurate recoverySimple and fast operationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMedial rotationTotal knee replacement surgery
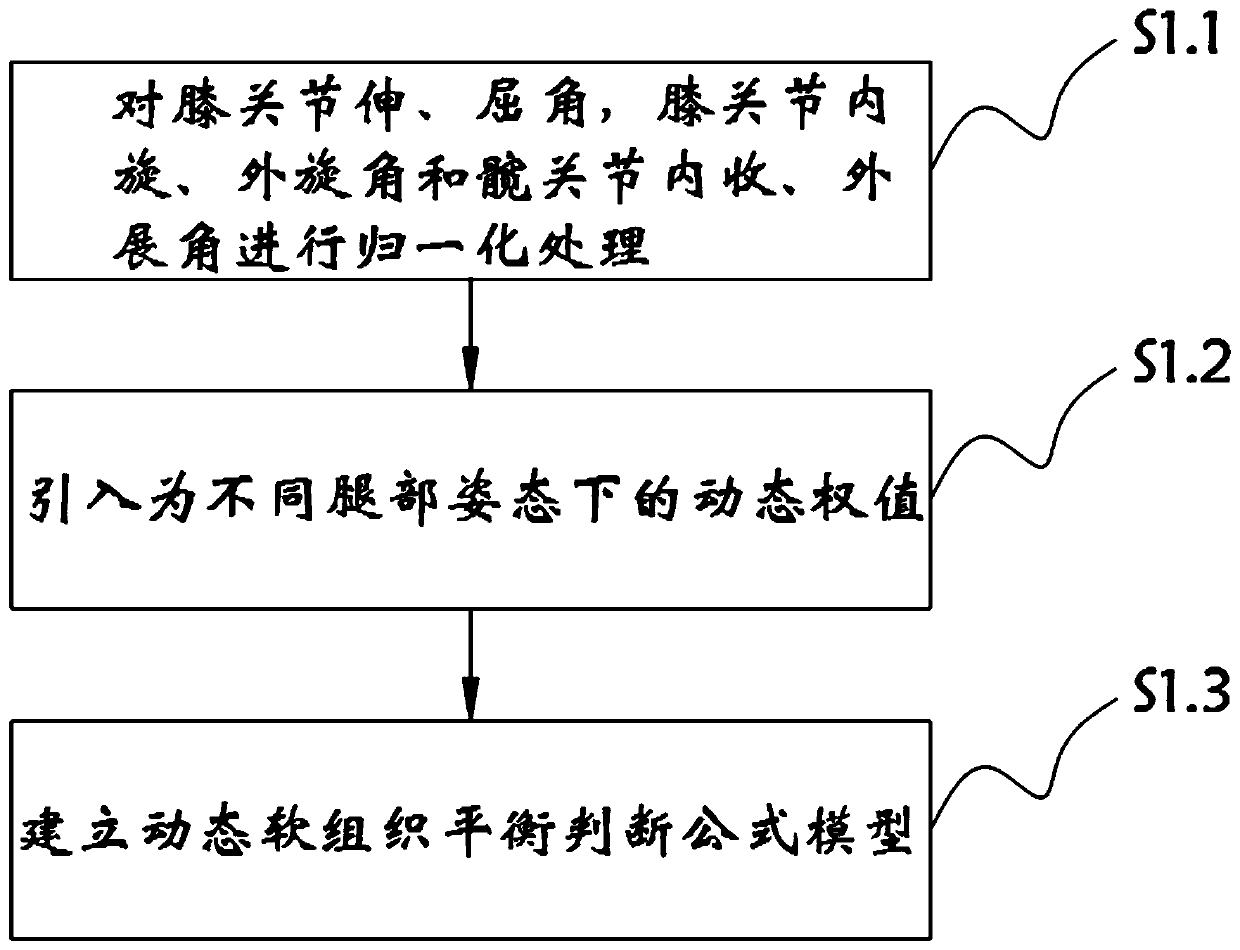
The invention relates to the technical field of total knee joint replacement, and in particular relates to a method for realizing dynamic soft tissue balance judgment in total knee joint replacement.The method includes the following steps: obtaining a posture angle of a leg posture, and obtaining the following three postures: a knee joint extension and flexion angle alpha, a knee joint internal rotation and external rotation angle beta and a hip joint adduction and abduction angle gamma; performing standardization treatment on the alpha, beta and gamma data, and performing data normalization;and performing dynamic soft tissue balance judgment. In the method for realizing the dynamic soft tissue balance judgment in the total knee replacement surgery, a six-axis posture sensor is used to collect the intraoperative leg posture data, and a dynamic soft tissue balance judgment formula is constructed to perform soft tissue balance judgment to guide a doctor to make timely correction through a clinical technical means during operation, so that accurate recovery of a lower limb force line is realized; and the dynamic soft tissue balance judgment provided by the invention does not requiremuch time to learn, is easy to operate, and is inexpensive for mass production in the future.
Owner:NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Proximal tibia bone cement pressurizing device
PendingCN112294417AEasy to pressFixedOsteosynthesis devicesKnee arthrodesis prosthesisTotal knee replacement surgery
The invention discloses a proximal tibia bone cement pressurizing device. The proximal tibia bone cement pressurizing device comprises a barrel, a pressurizing plate, a driving mechanism and a baffle,wherein the pressurizing plate is located in the barrel, is in sealed connection with the barrel and moves in the length direction of the barrel, the driving mechanism is fixedly connected with the top of the pressurizing plate and drives the pressurizing plate to move in the vertical direction, and the baffle is located below the barrel and used for blocking the bottom of the barrel. Bone cementis located in the barrel and located on the lower surface of the pressurizing plate, and the bone cement is pressed into proximal tibia cancellous bone by applying pressure to the pressurizing plate.By arrangement of the pressurizing plate and the driving mechanism, the bone cement can be conveniently pressed into the proximal tibia cancellous bone, the amount of the bone cement entering the proximal tibia cancellous bone is large, the bone cement entering the proximal tibia cancellous bone is deep, a proximal tibia and a tibia prosthesis are well fixed, larger shearing force can be borne, the probability of sterile loosening of the prosthesis caused by bone cement technical defects after total knee replacement is not likely to occur, and therefore, the service life of the knee joint prosthesis is prolonged.
Owner:潘建康
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com