Patents
Literature
95 results about "Arthroplasty knee" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
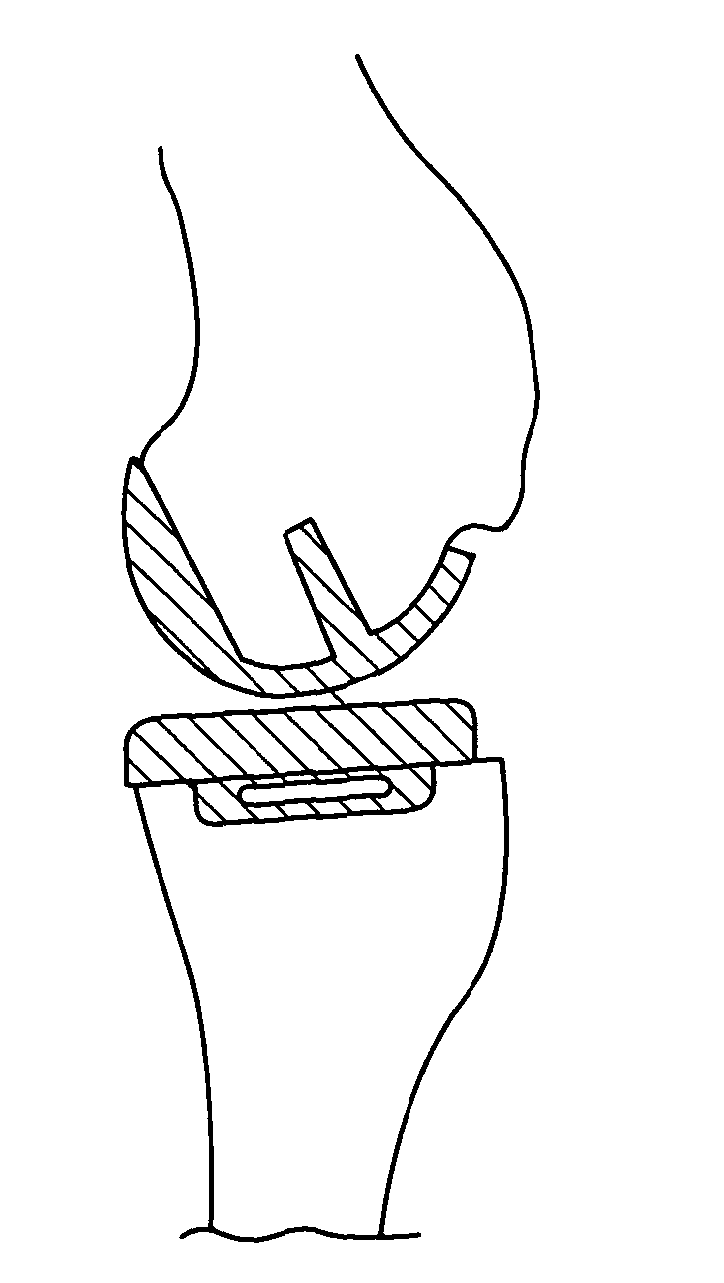
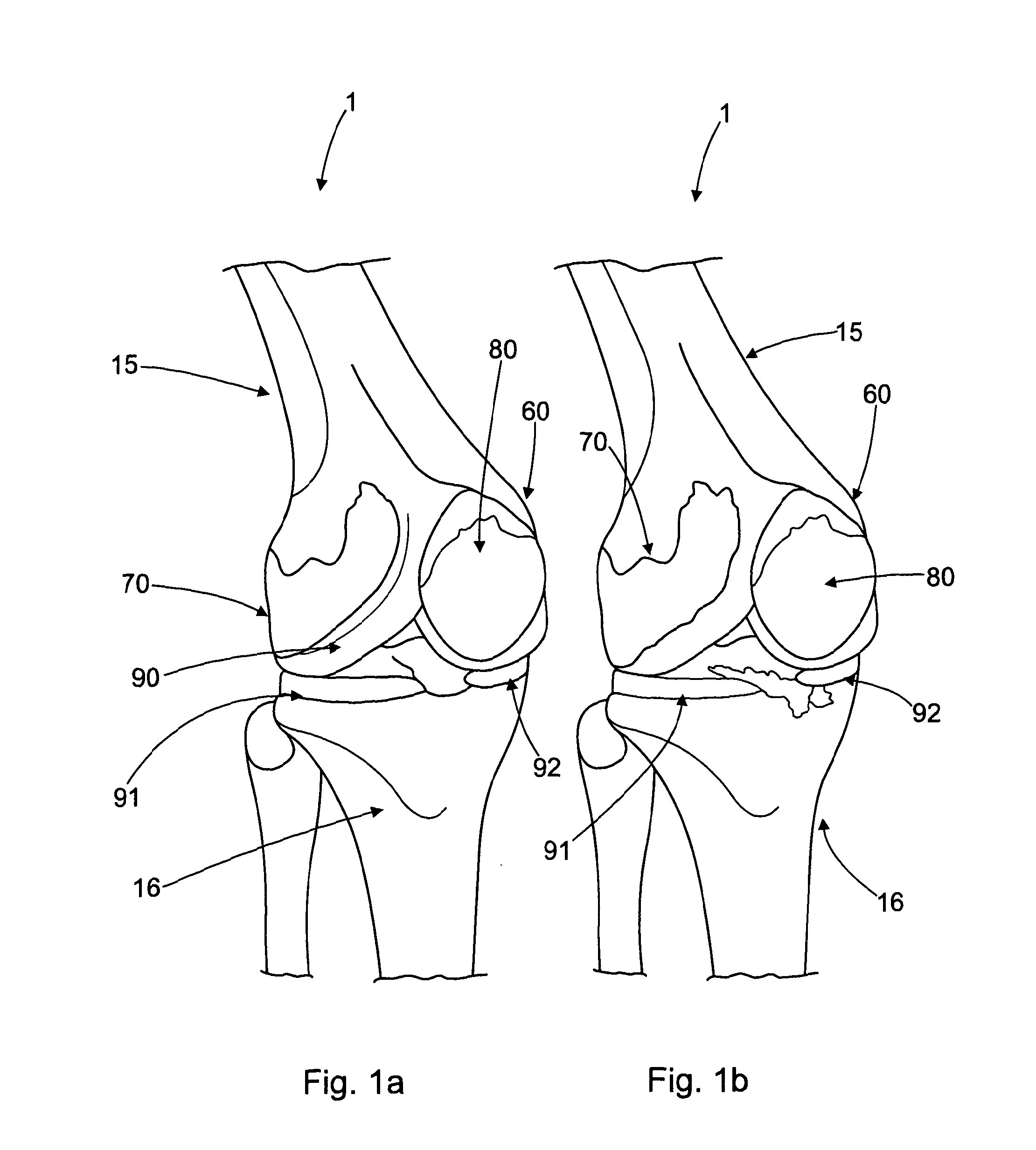
[edit on Wikidata] Knee replacement, also known as knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure to replace the weight-bearing surfaces of the knee joint to relieve pain and disability. It is most commonly performed for osteoarthritis, and also for other knee diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis.
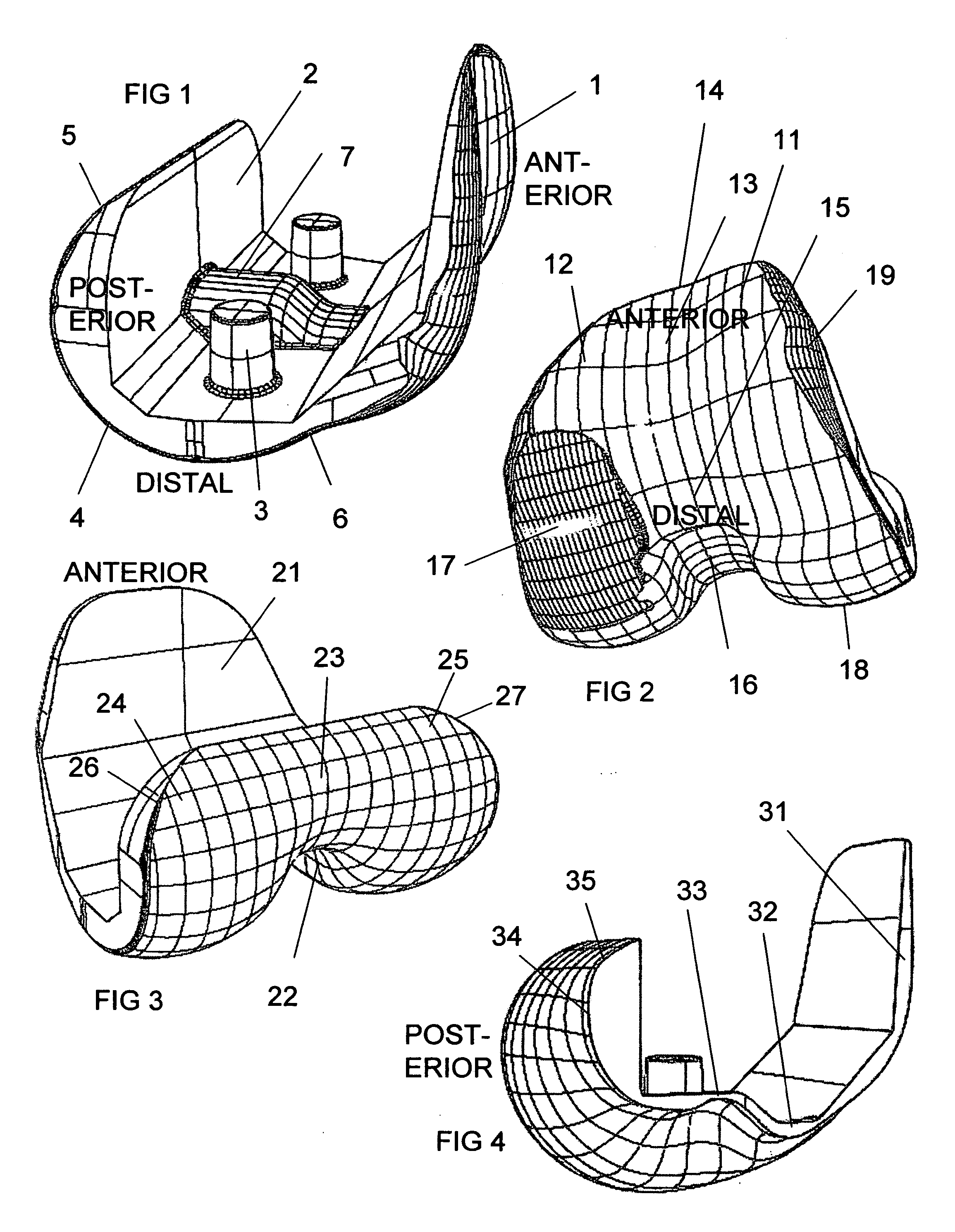
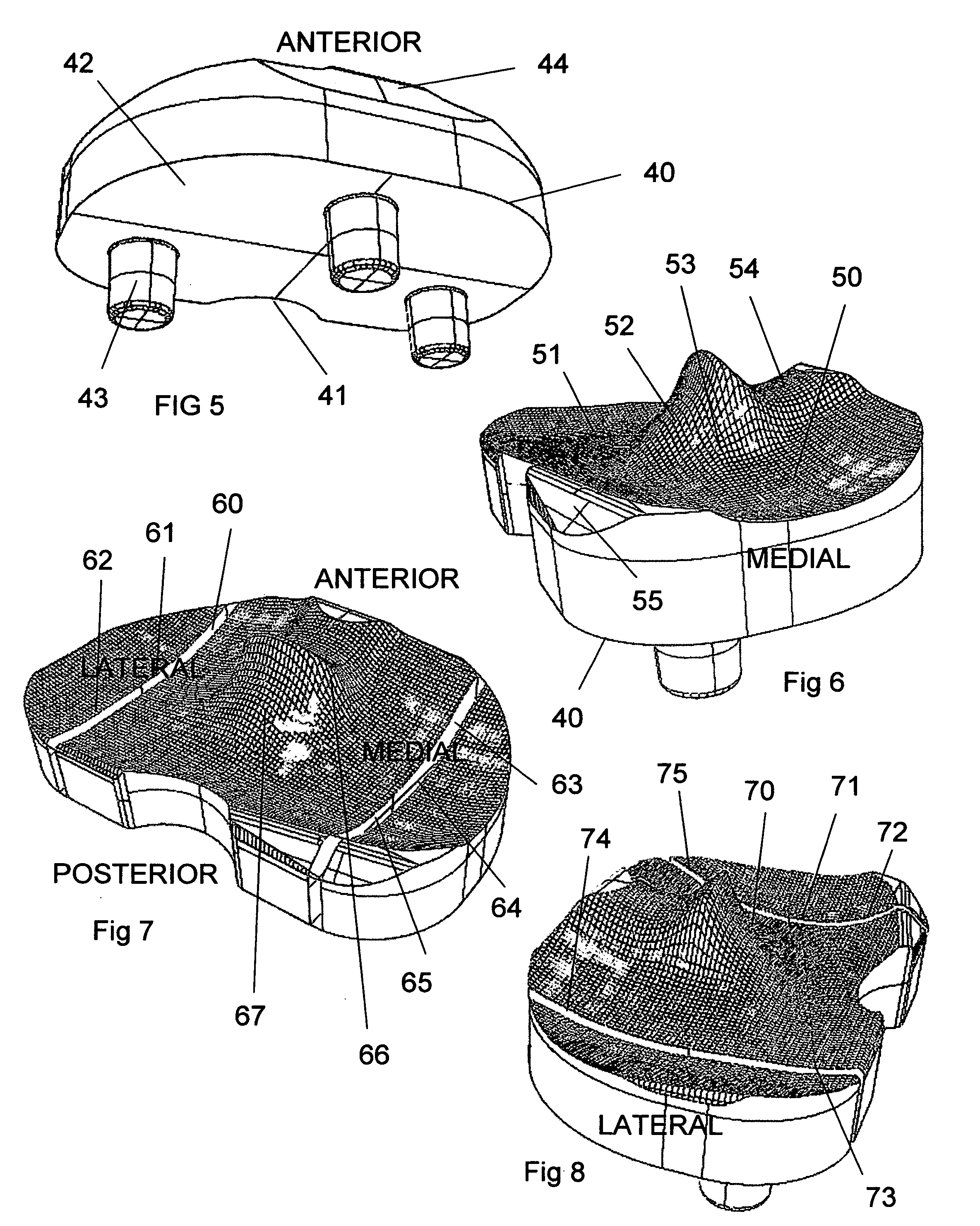
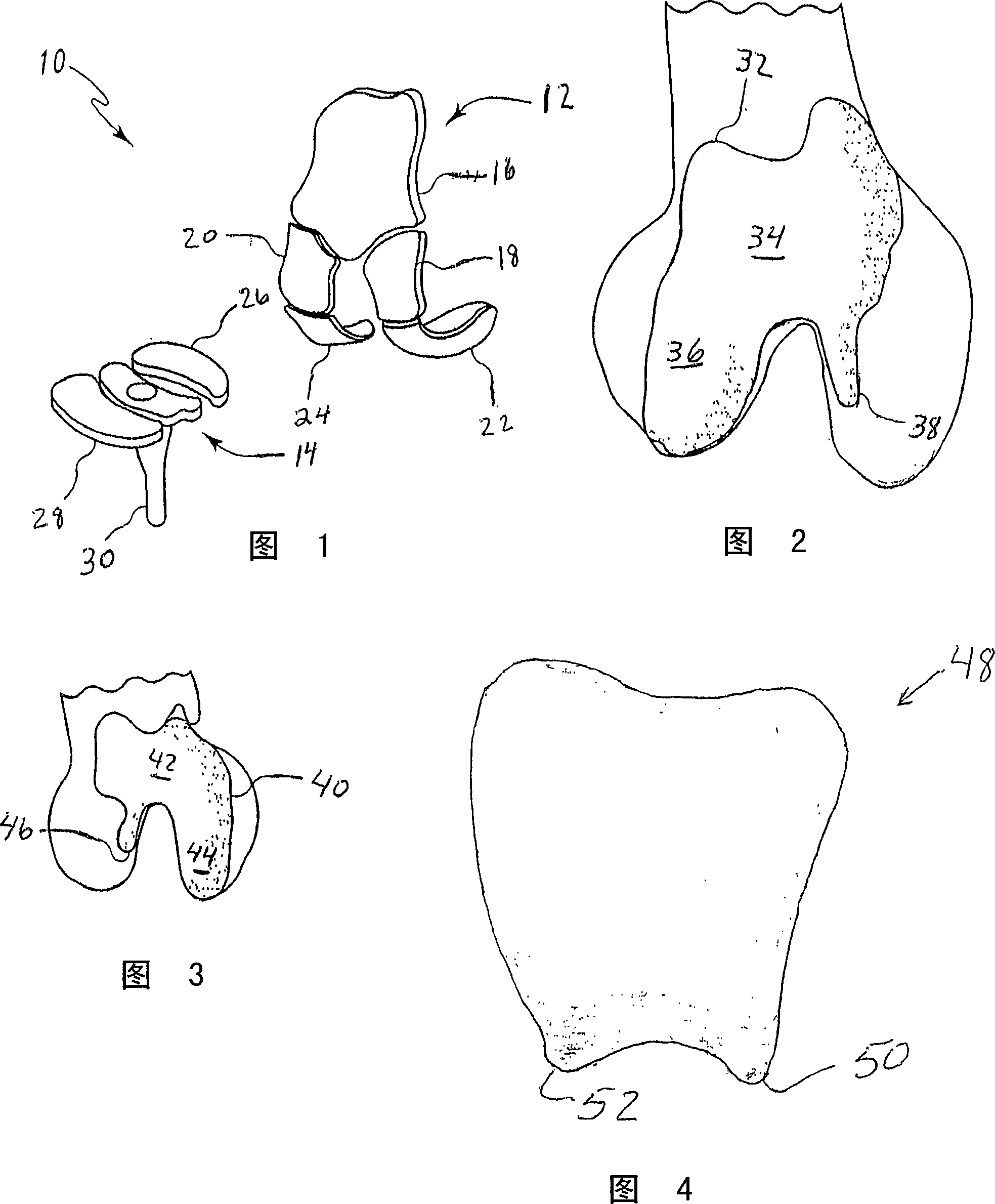
Knee implant
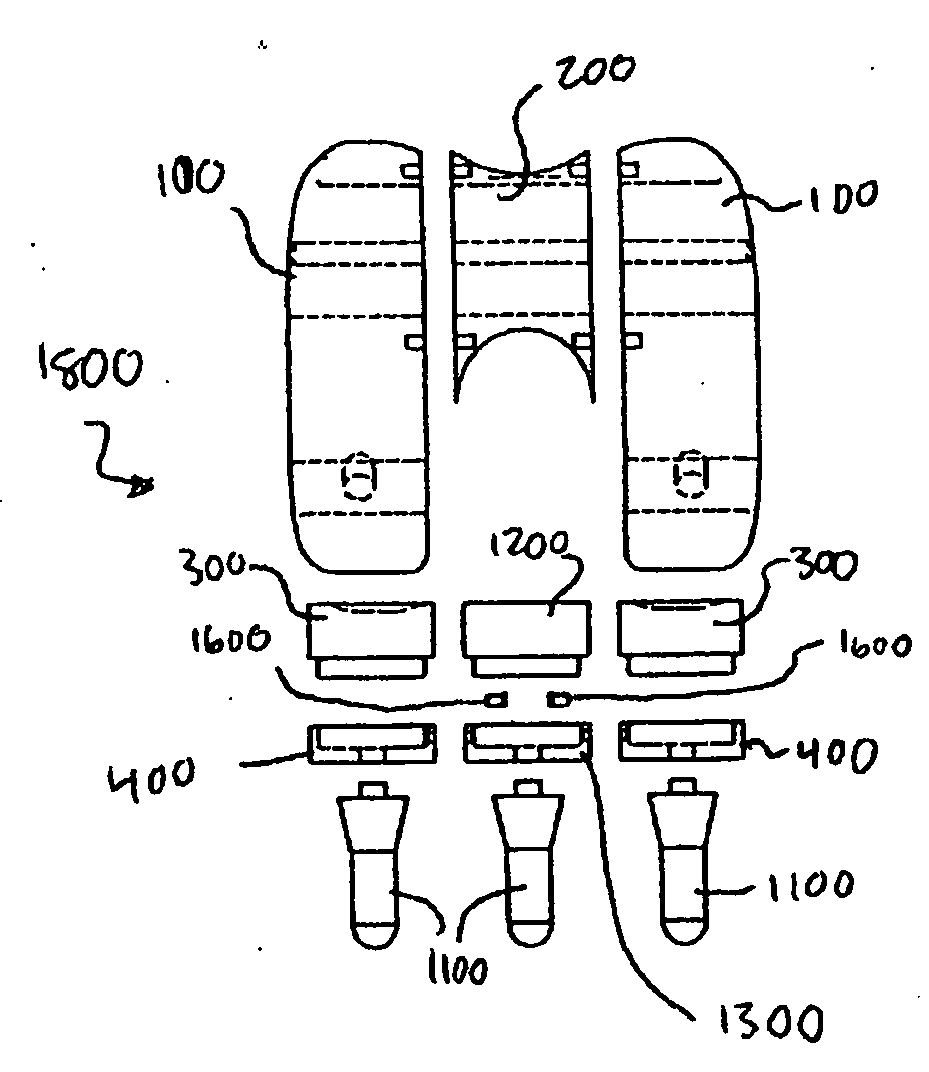
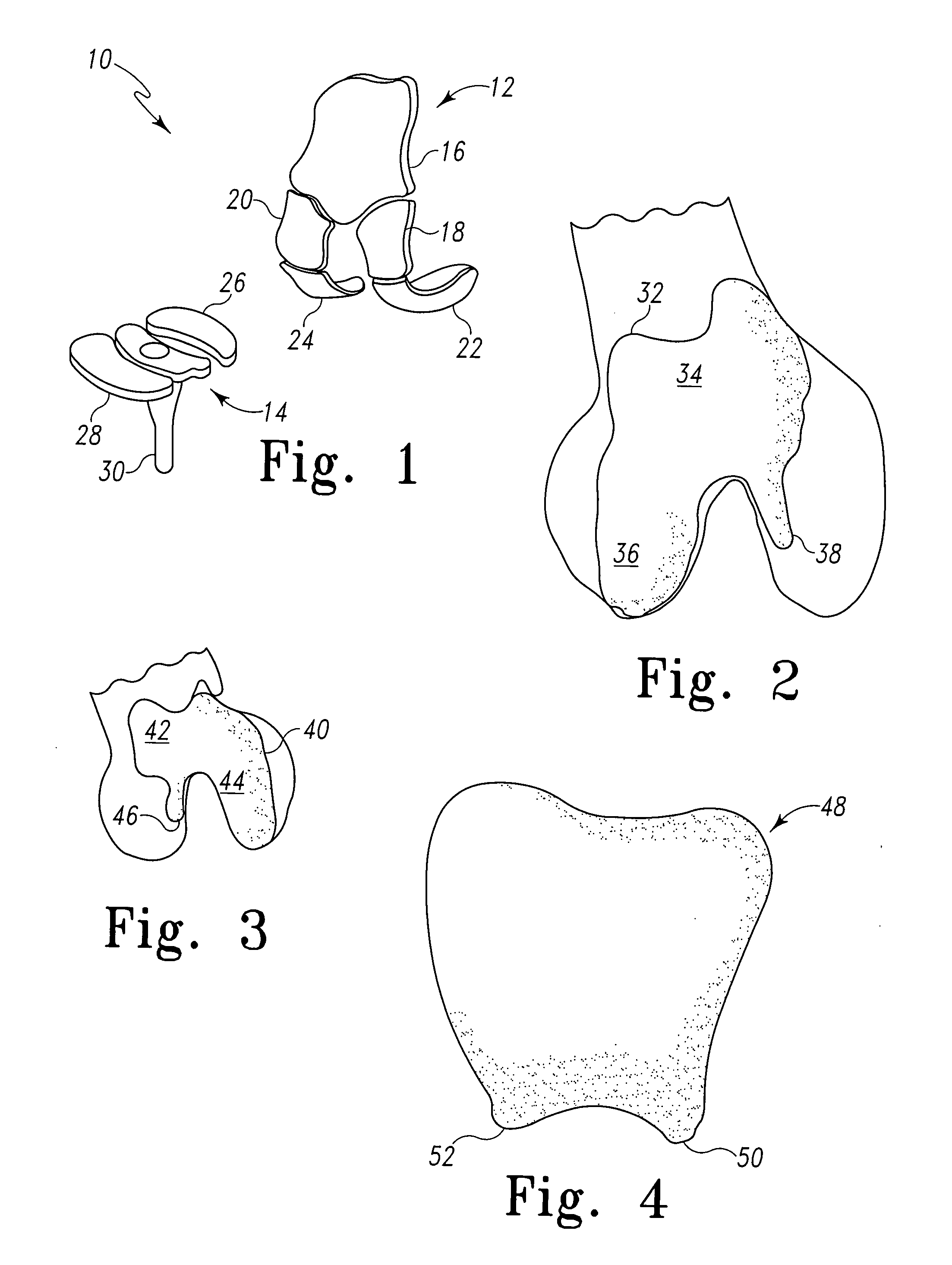
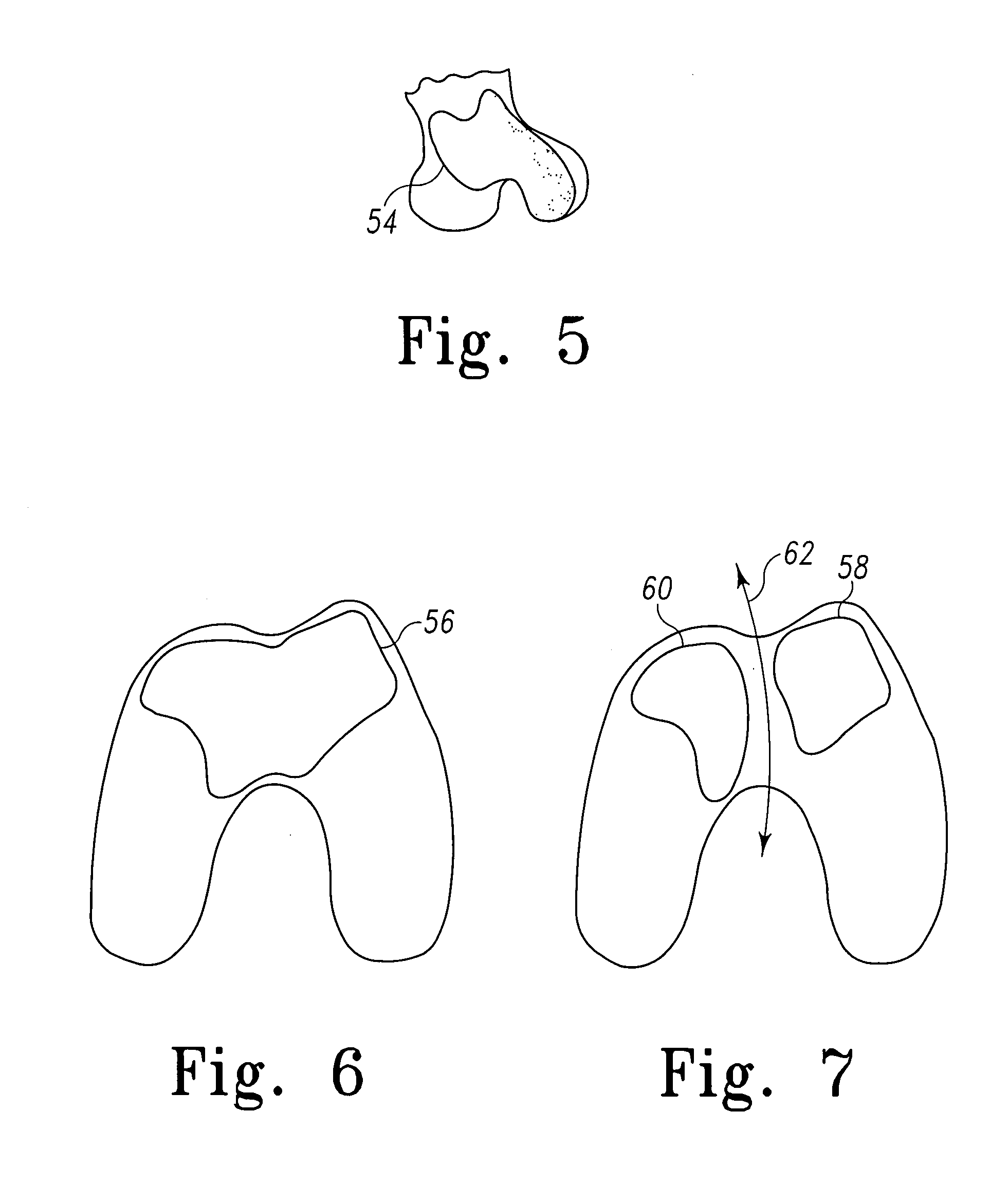
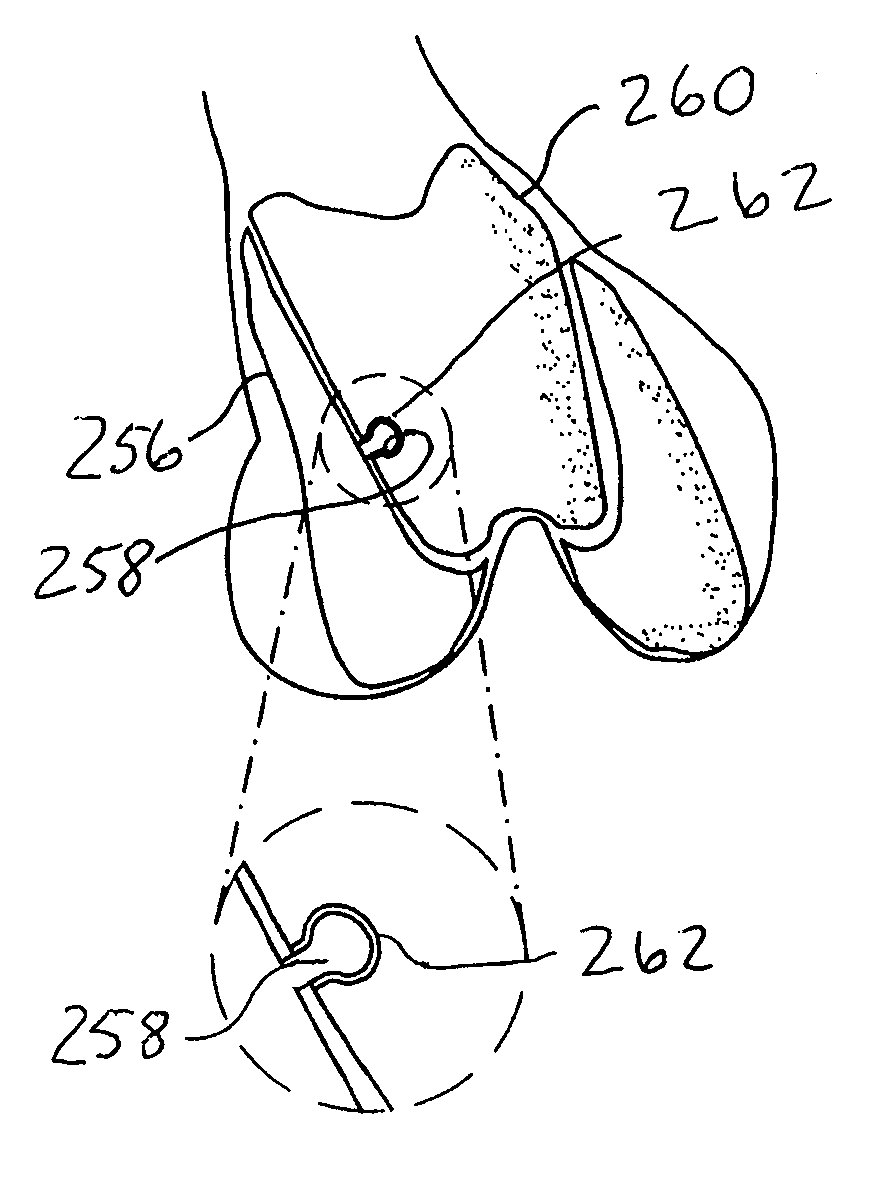
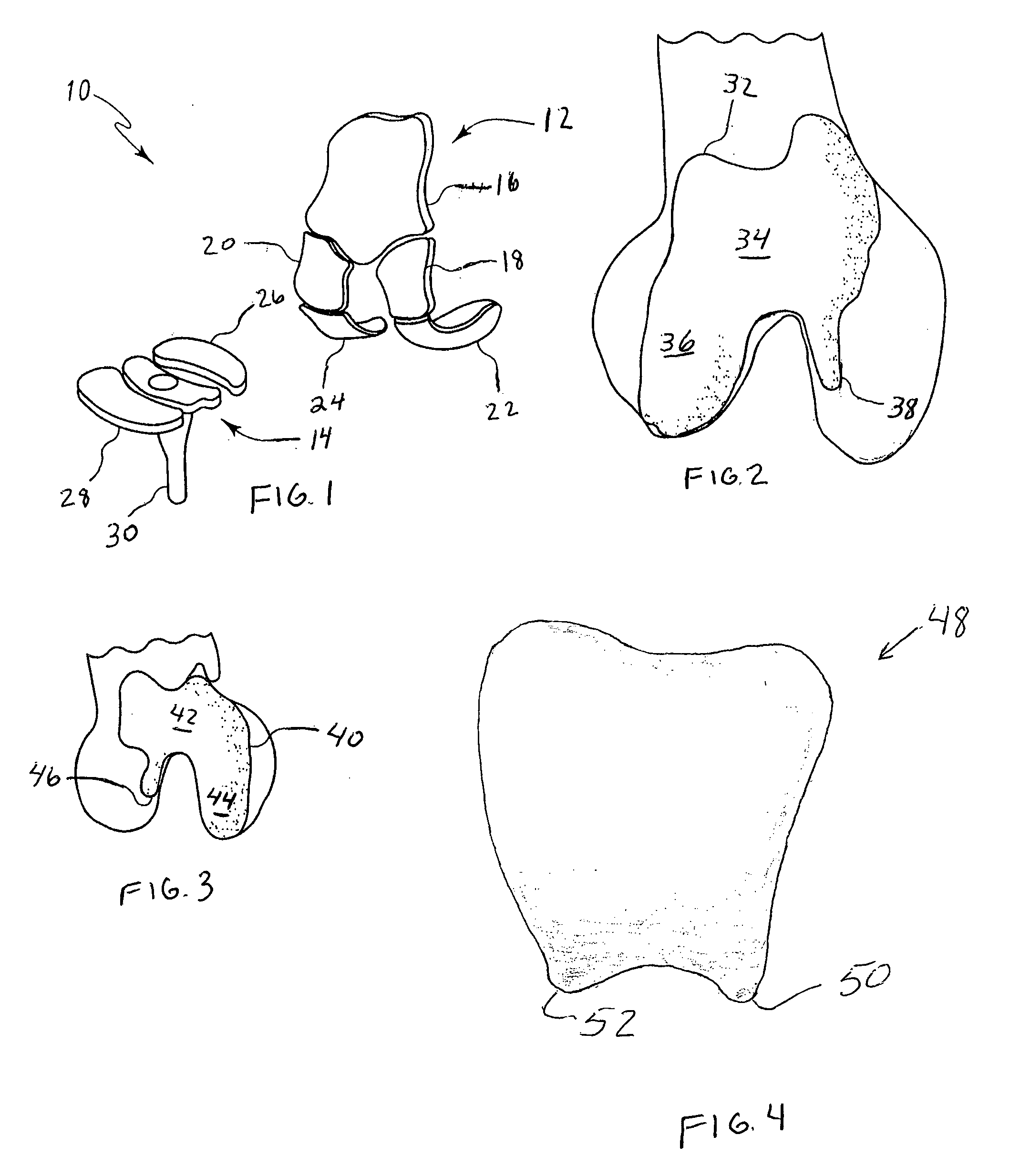
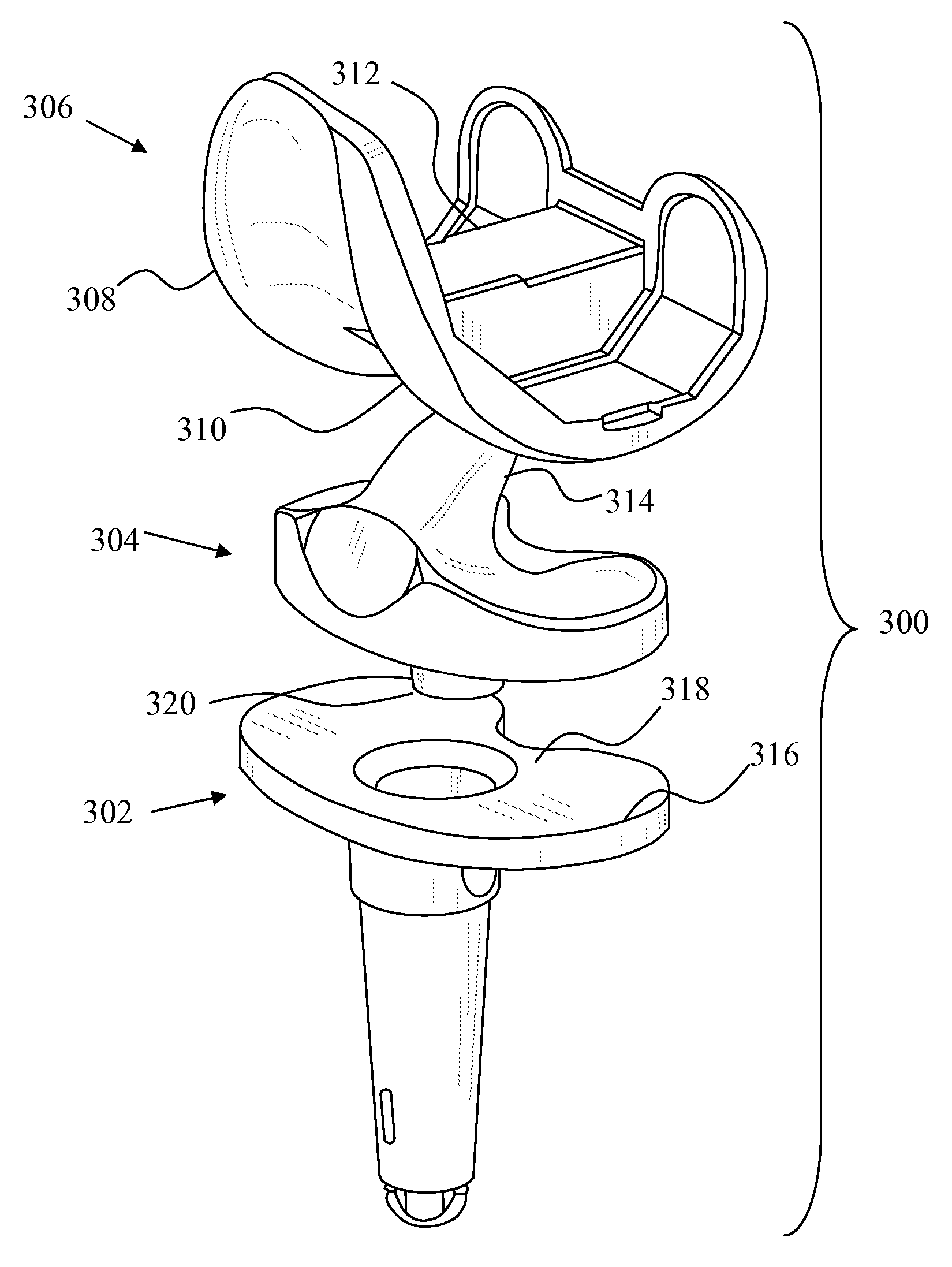
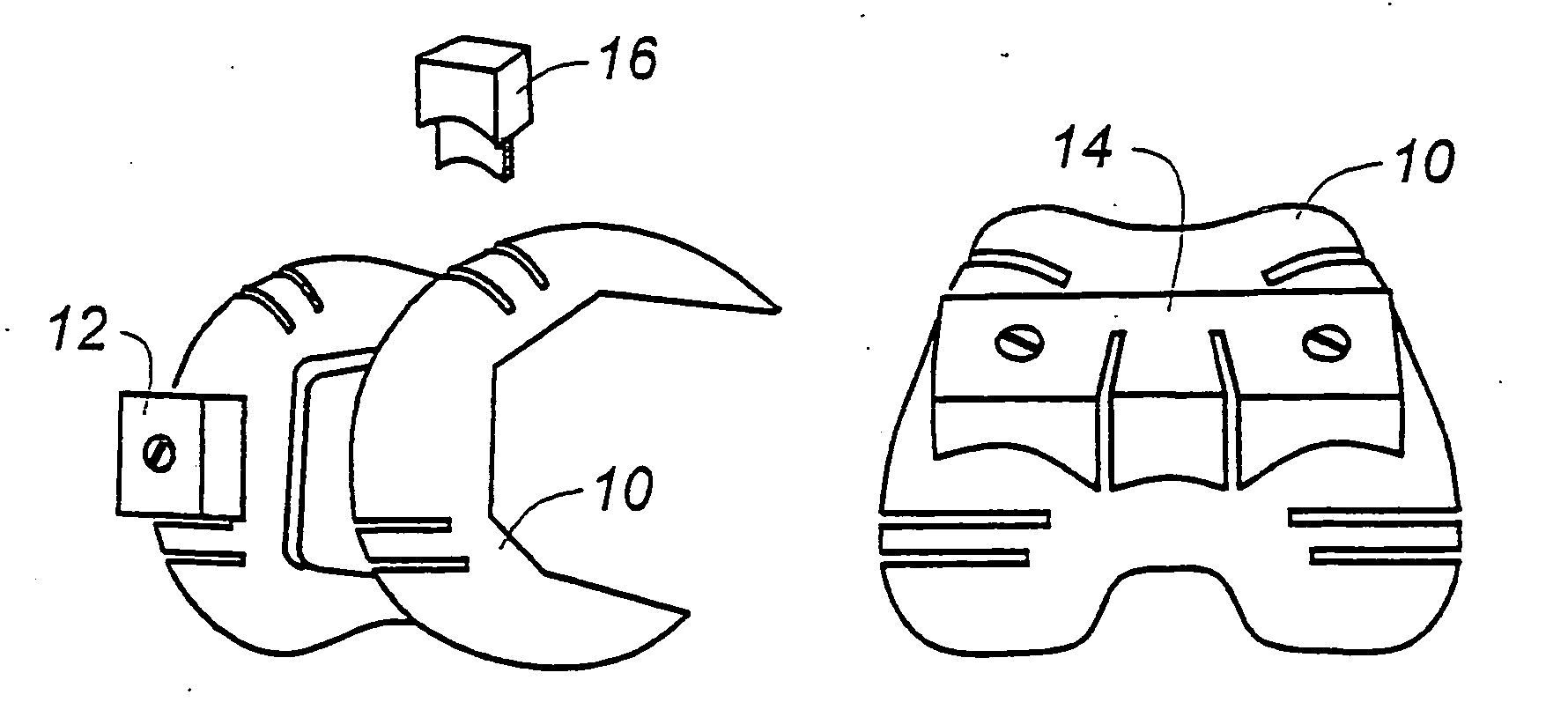
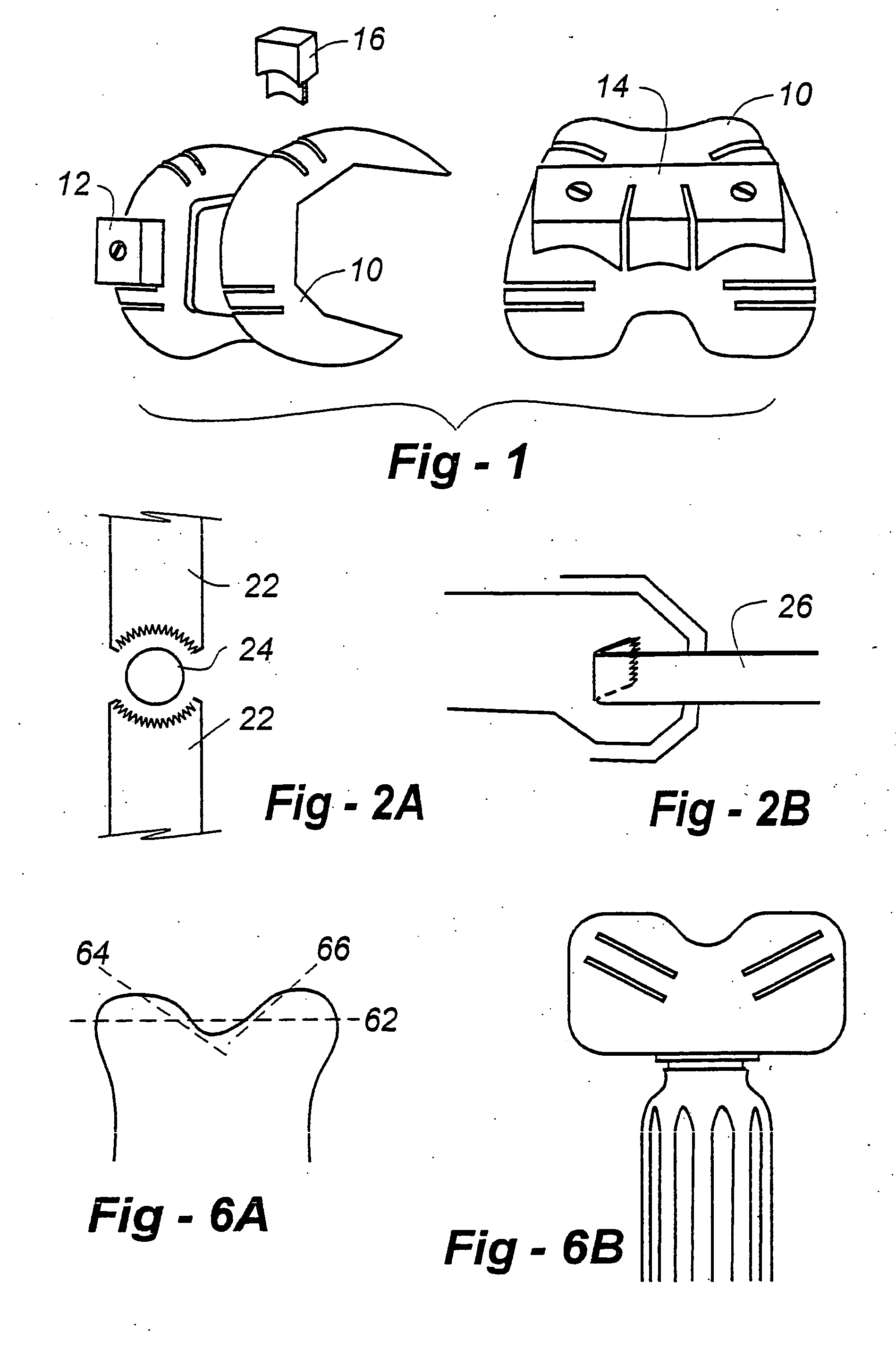
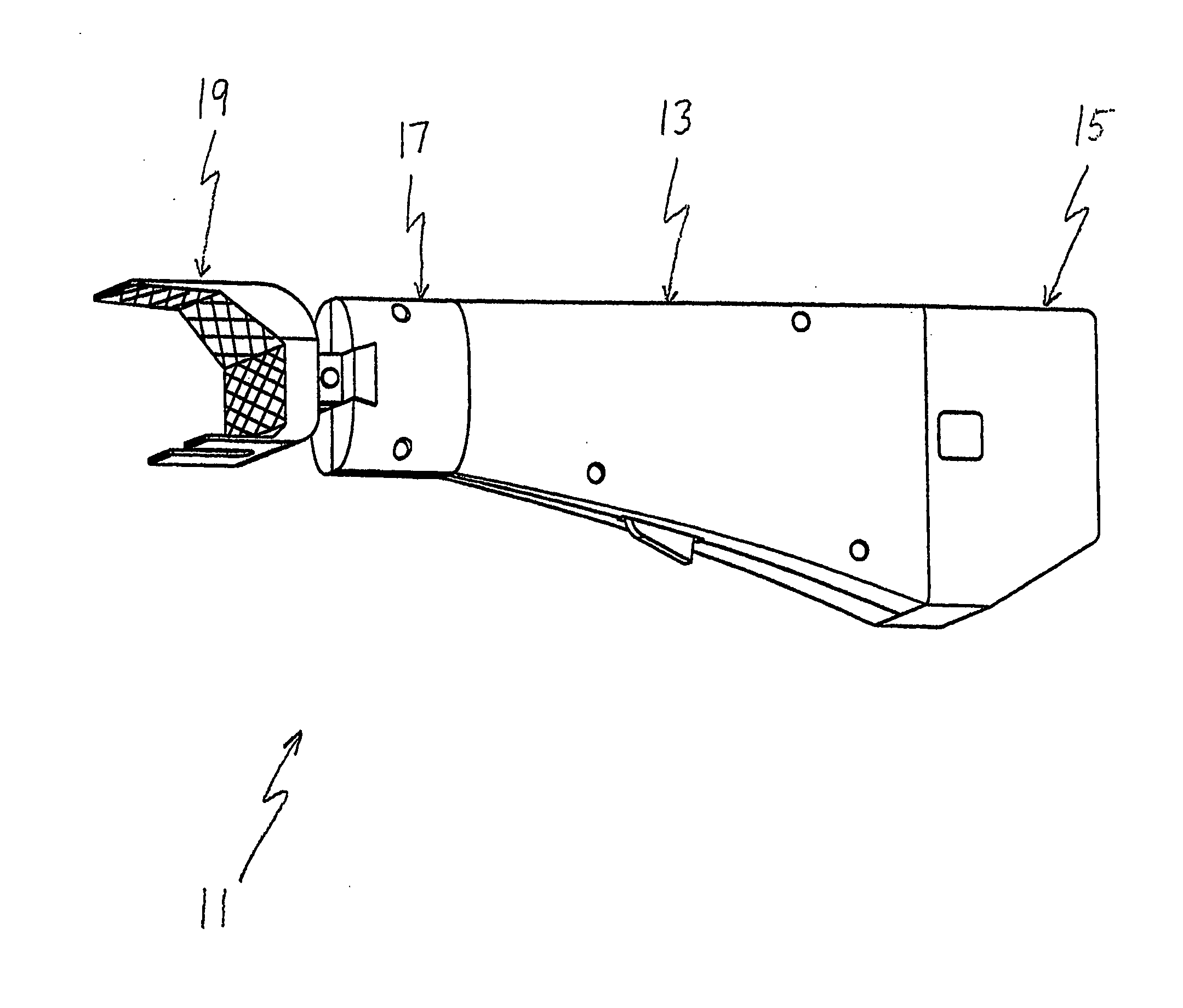
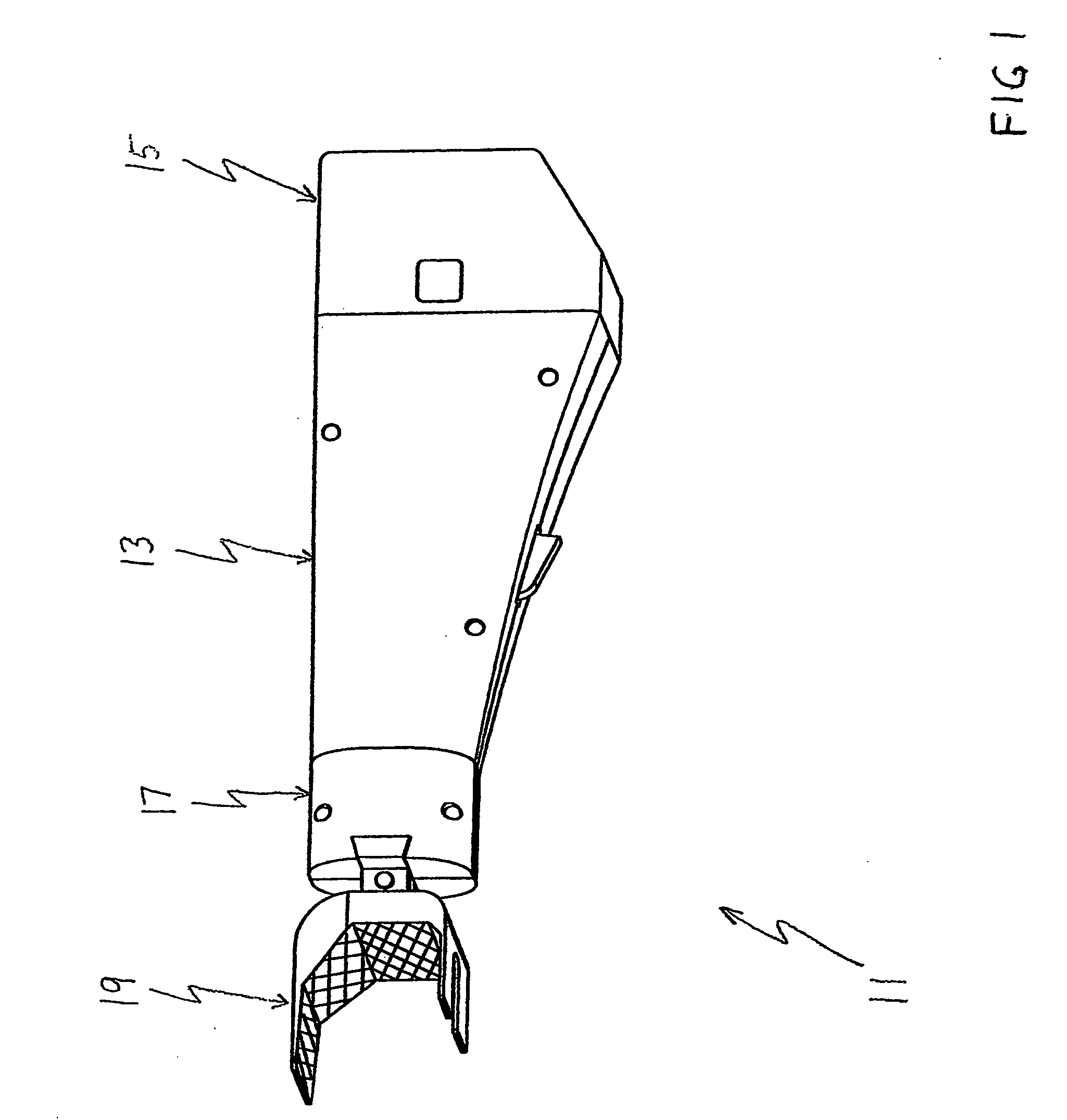
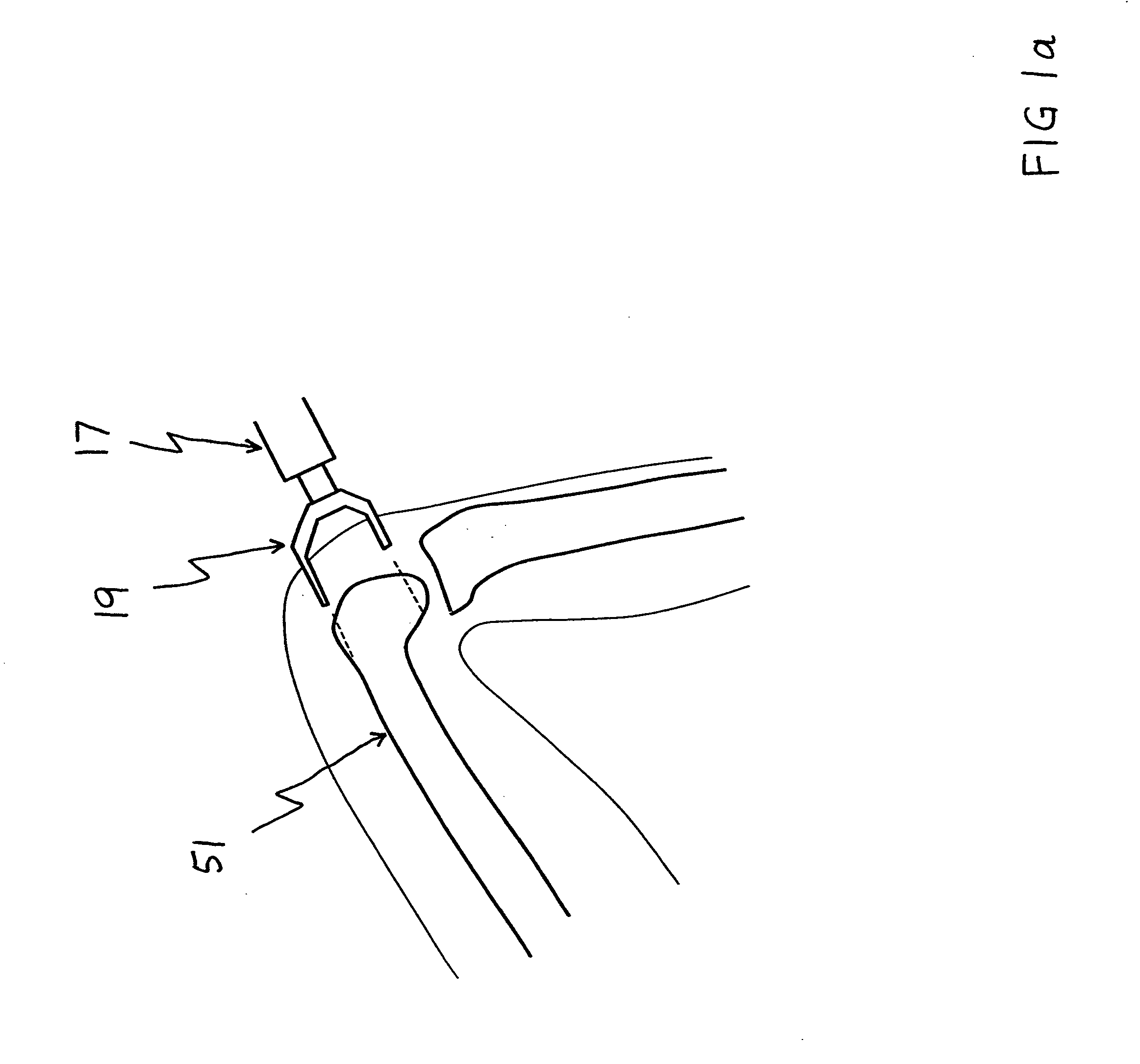
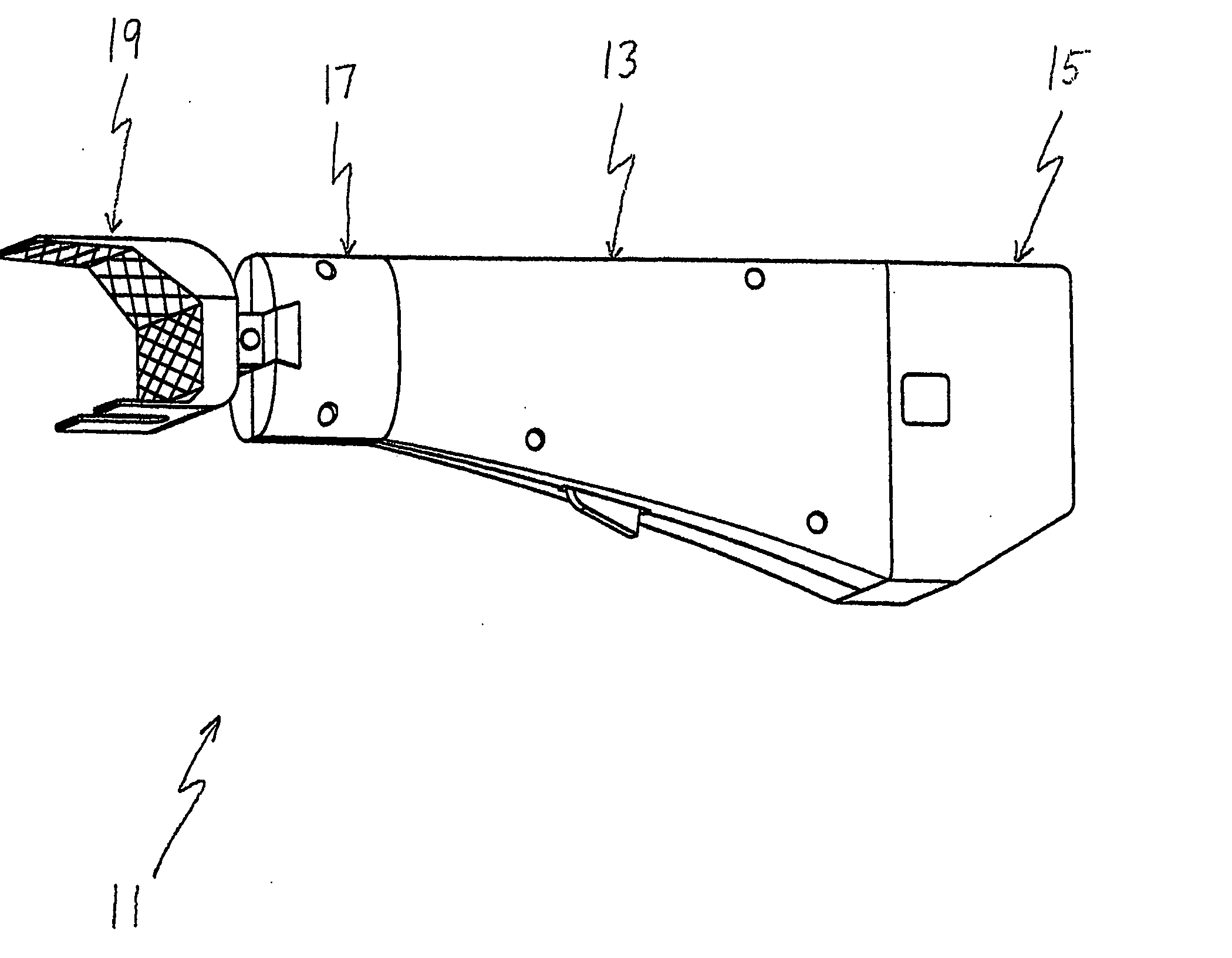
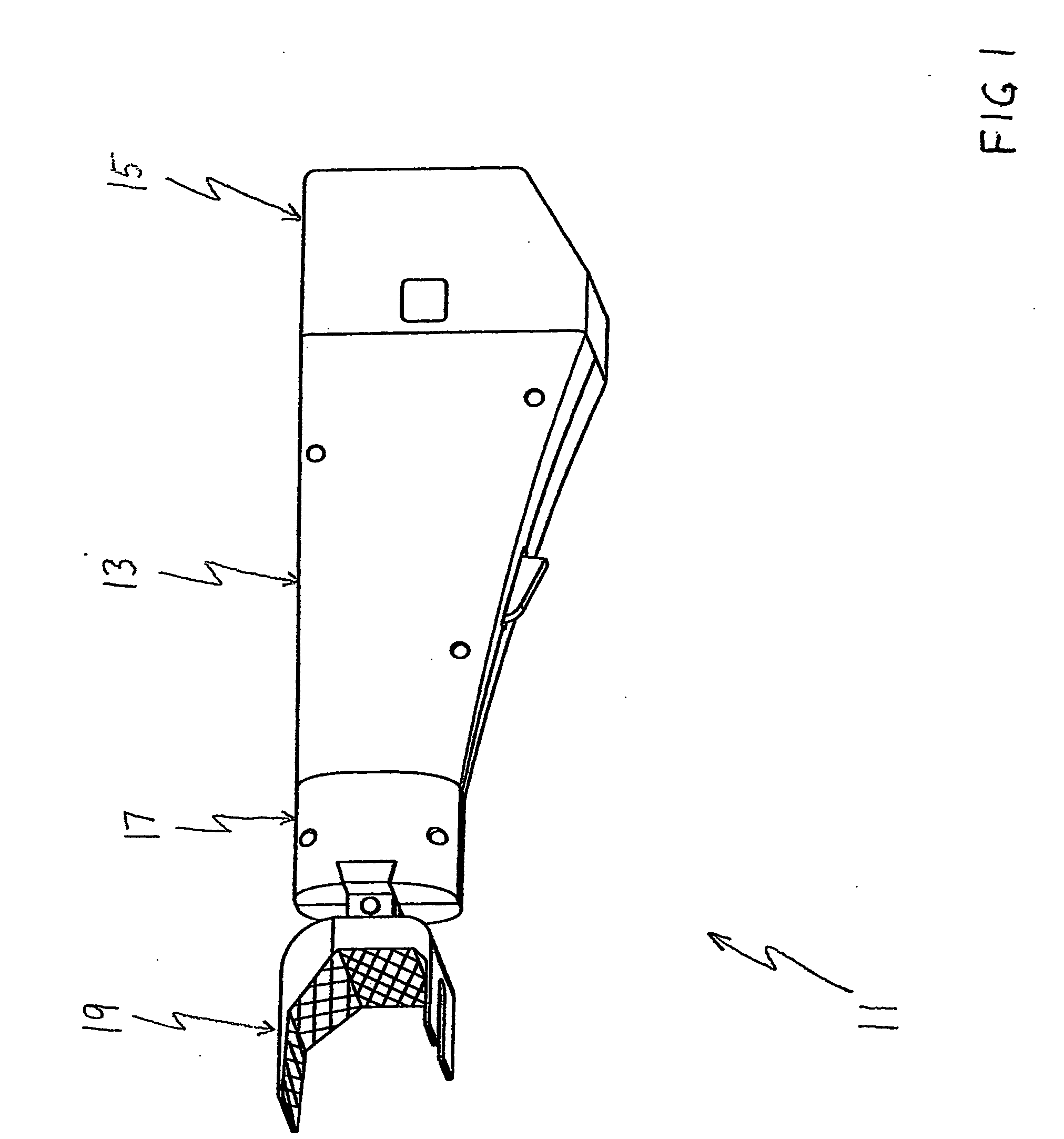
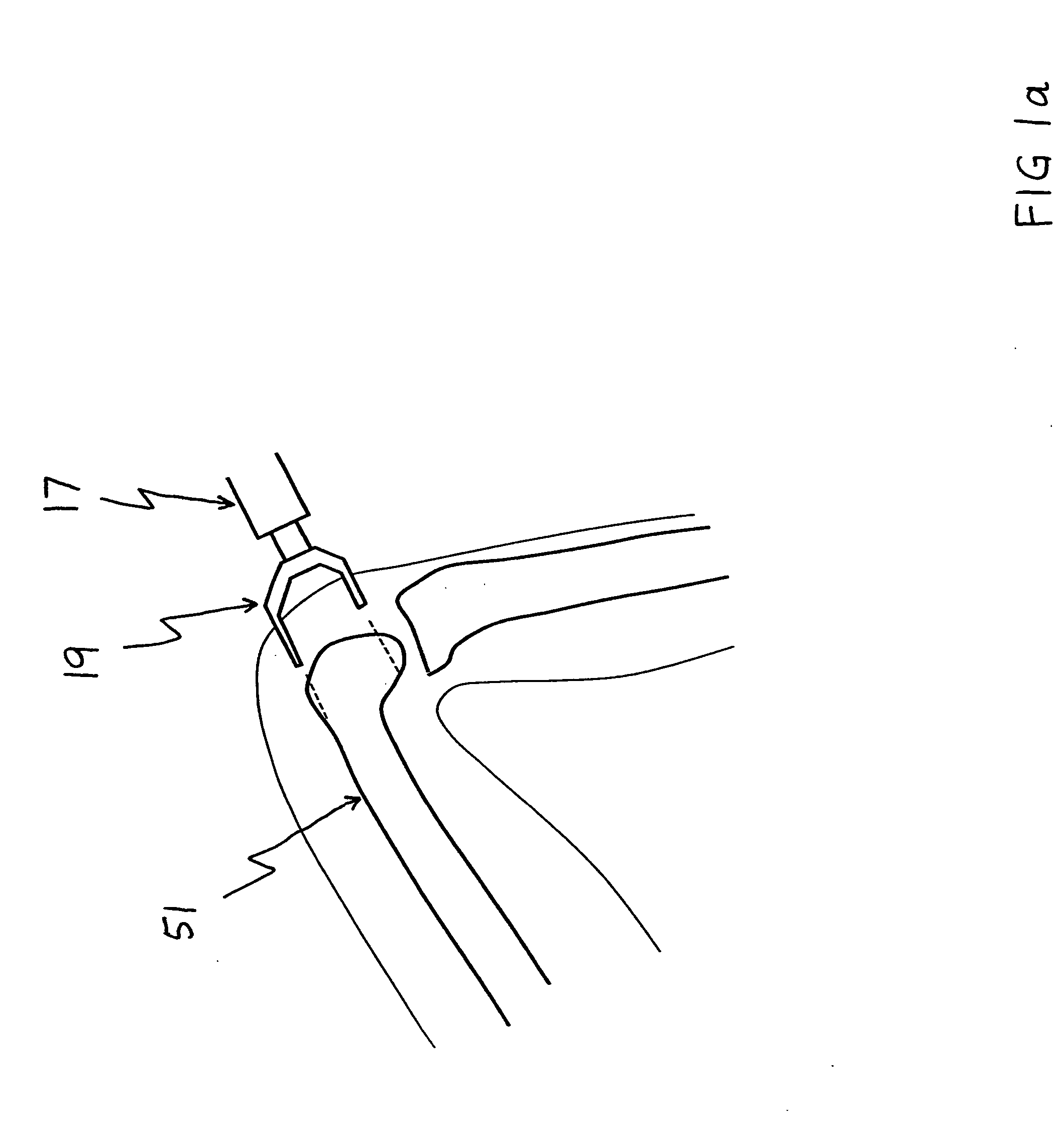
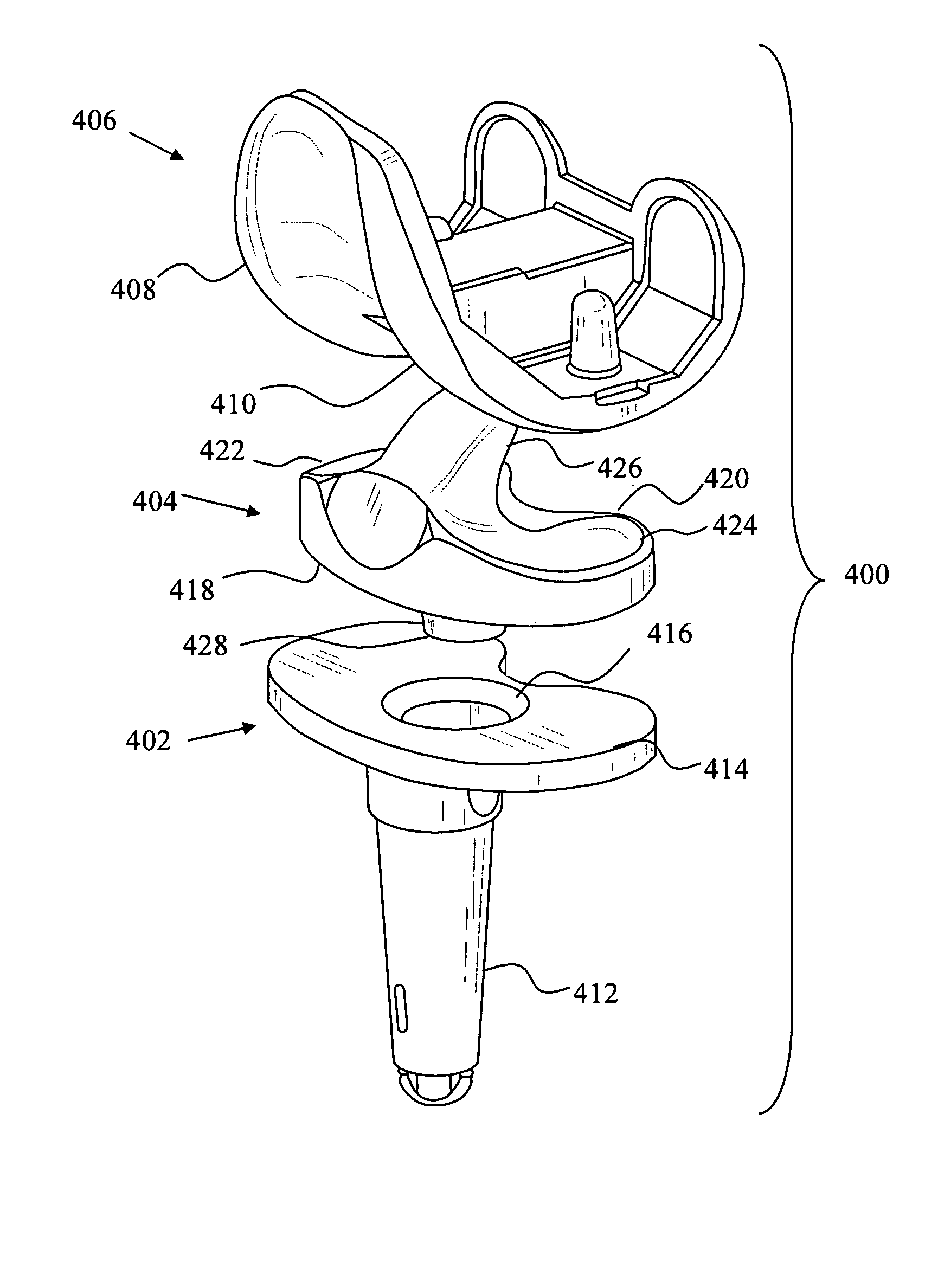
A modular prosthetic device is provided for replacement of the knee. The device is assembled from a plurality of components, each of which can be inserted through a small incision. After inserting the components through the incision, the device can be assembled within the knee cavity. The modularity of the device enables a surgeon to replace only those regions of the knee that are diseased or damaged, thereby avoiding a complete knee replacement. If, at a later time, additional regions of the knee become diseased or damaged, those additional regions of the knee can be replaced by additional device components and those additional components can be connected to the previously implanted components. By replacing only those regions of the knee that are diseased or damaged and by implanting each of the components through the small incision, the surgery is minimally invasive and, therefore, requires reduced time for healing and rehabilitation.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Systems and methods for compartmental replacement in a knee
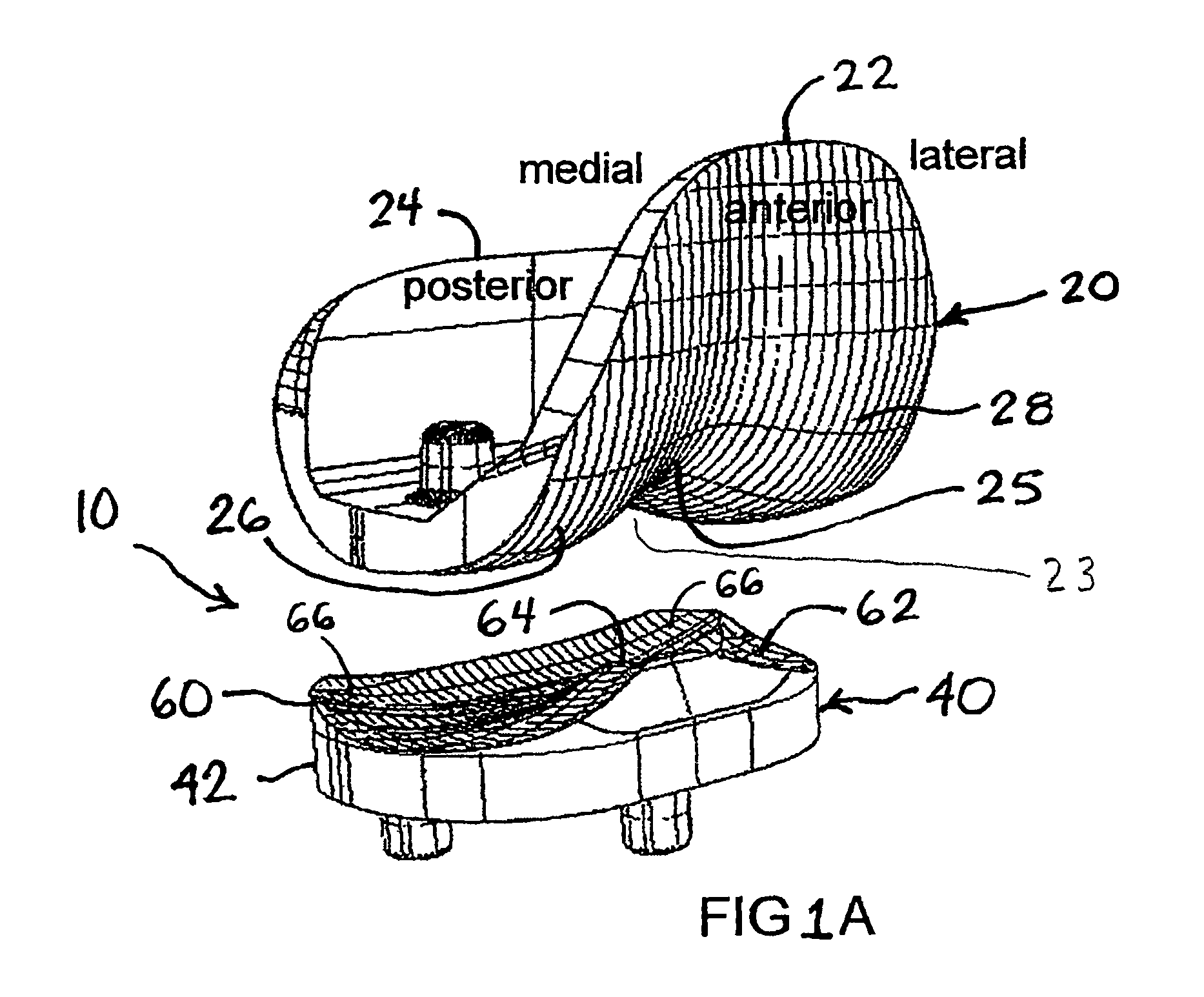
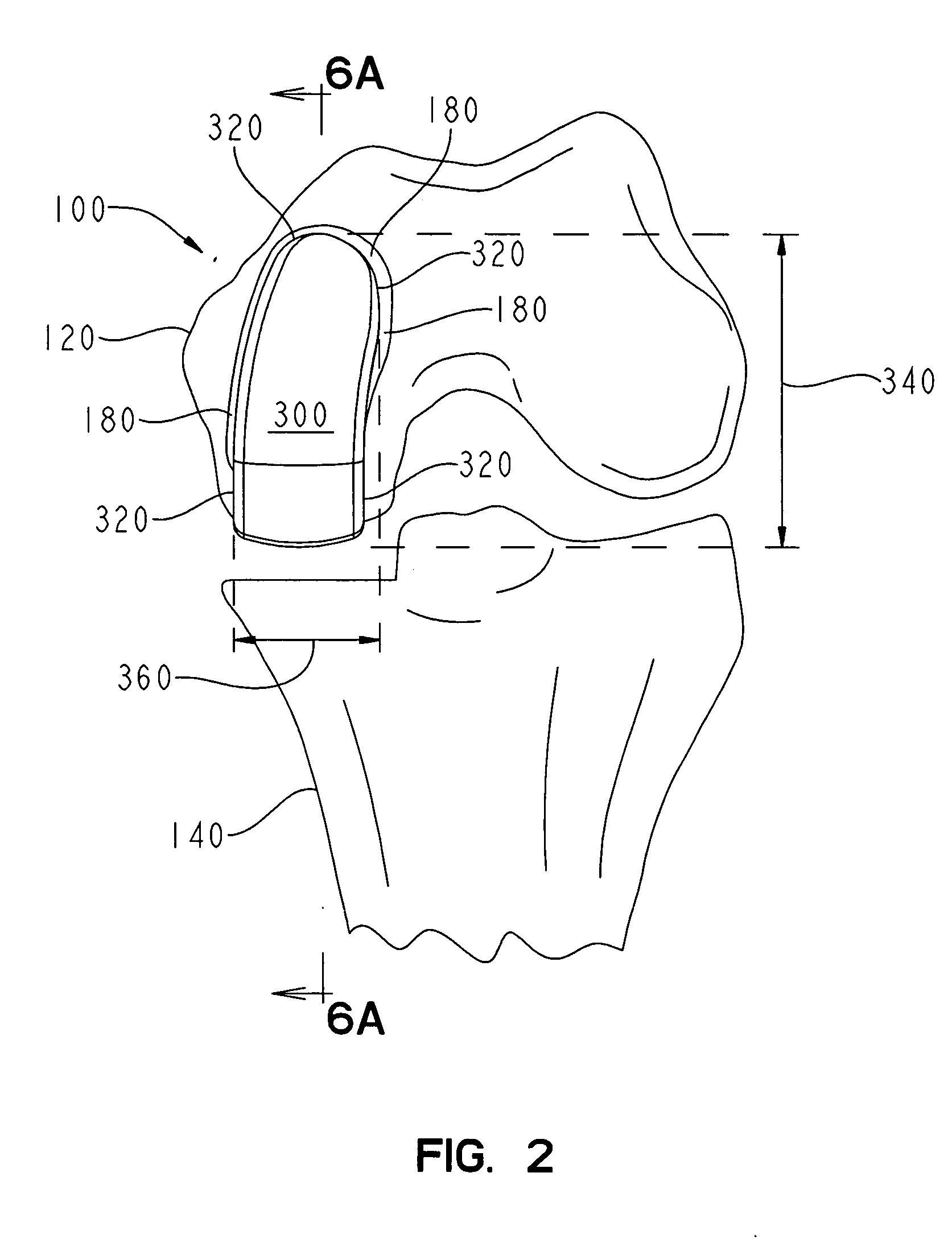
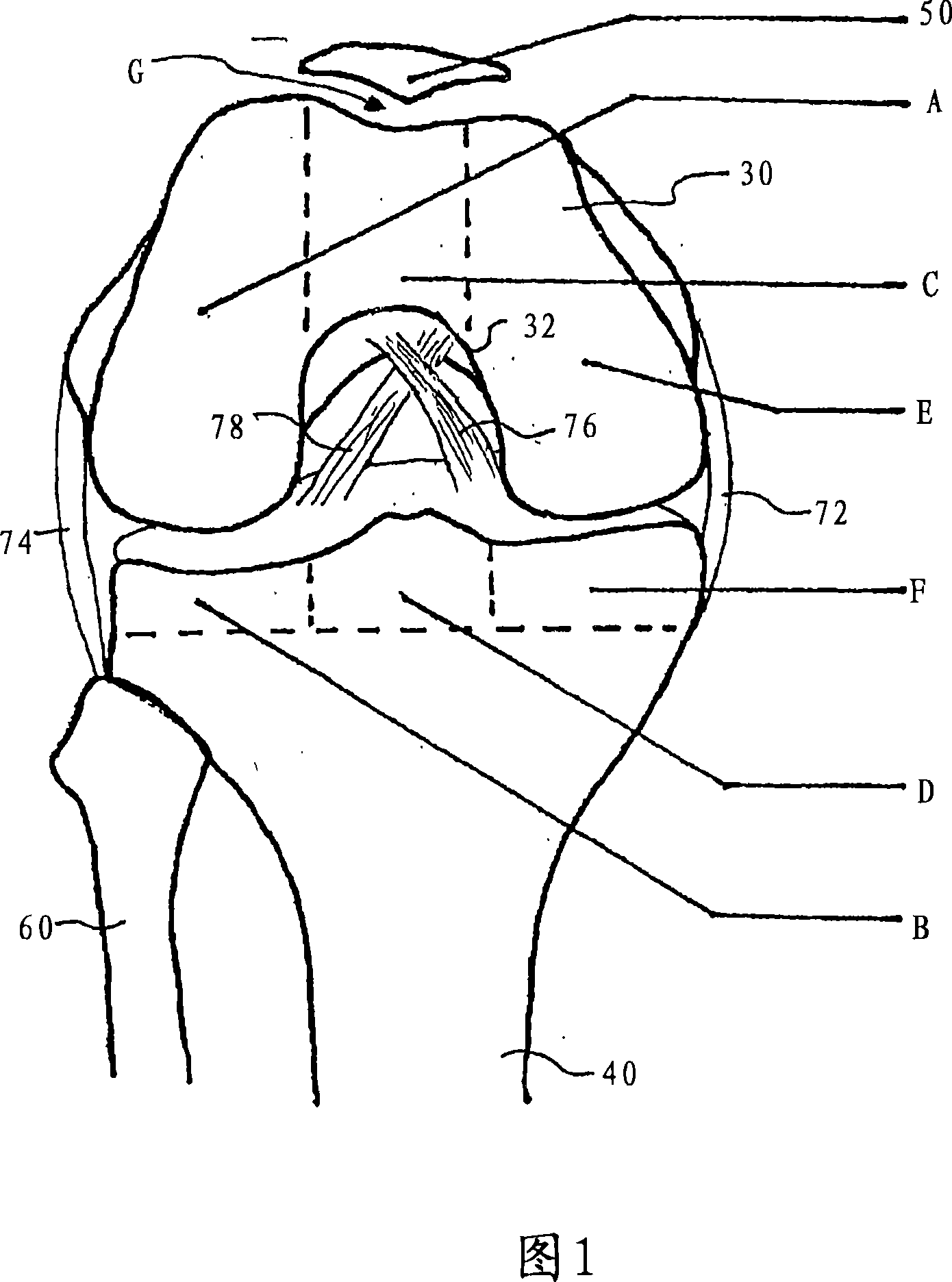
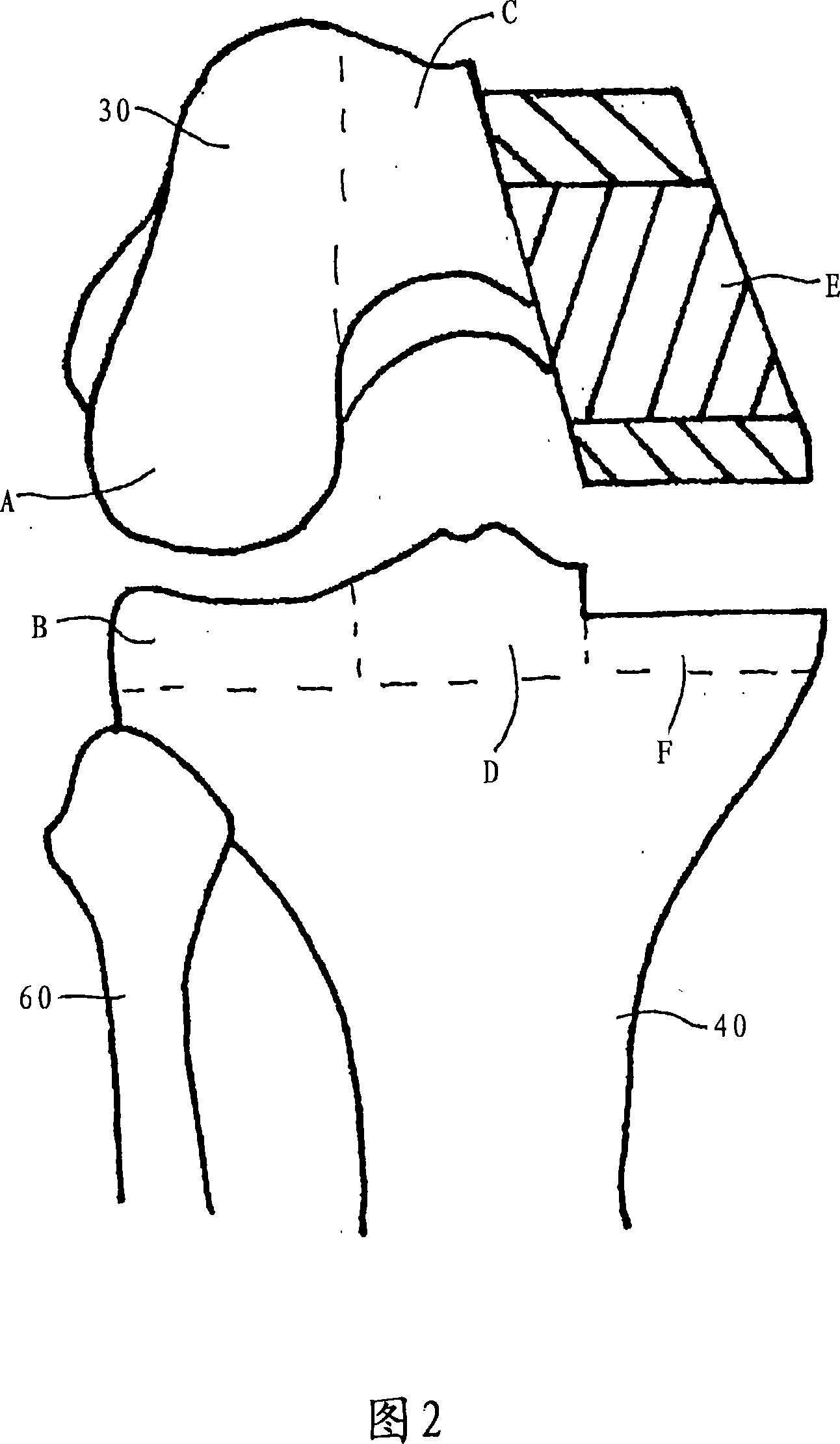
A knee replacement system provides a knee implant that may be used to more accurately replicate the diameter of a natural knee. In one embodiment, a patellofemoral component is connected to the posterior portion of a condylar component by screws that pass through the femur allowing the patellofemoral component and the condylar component to be torqued against opposing sides of the femur. Two additional screws are used to connect the patellofemoral component to an anterior portion of the condylar component. A gap may be left between the patellofemoral component and the anterior portion of the condylar component if needed to provide precise replication of the diameter of the natural knee from the patellofemoral component to the condylar component.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Systems and methods for compartmental replacement in a knee
A knee replacement system provides a knee implant that may be used to more accurately replicate the diameter of a natural knee. In one embodiment, a patellofemoral component is connected to the posterior portion of a condylar component by screws that pass through the femur allowing the patellofemoral component and the condylar component to be torqued against opposing sides of the femur. Two additional screws are used to connect the patellofemoral component to an anterior portion of the condylar component. A gap may be left between the patellofemoral component and the anterior portion of the condylar component if needed to provide precise replication of the diameter of the natural knee from the patellofemoral component to the condylar component.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
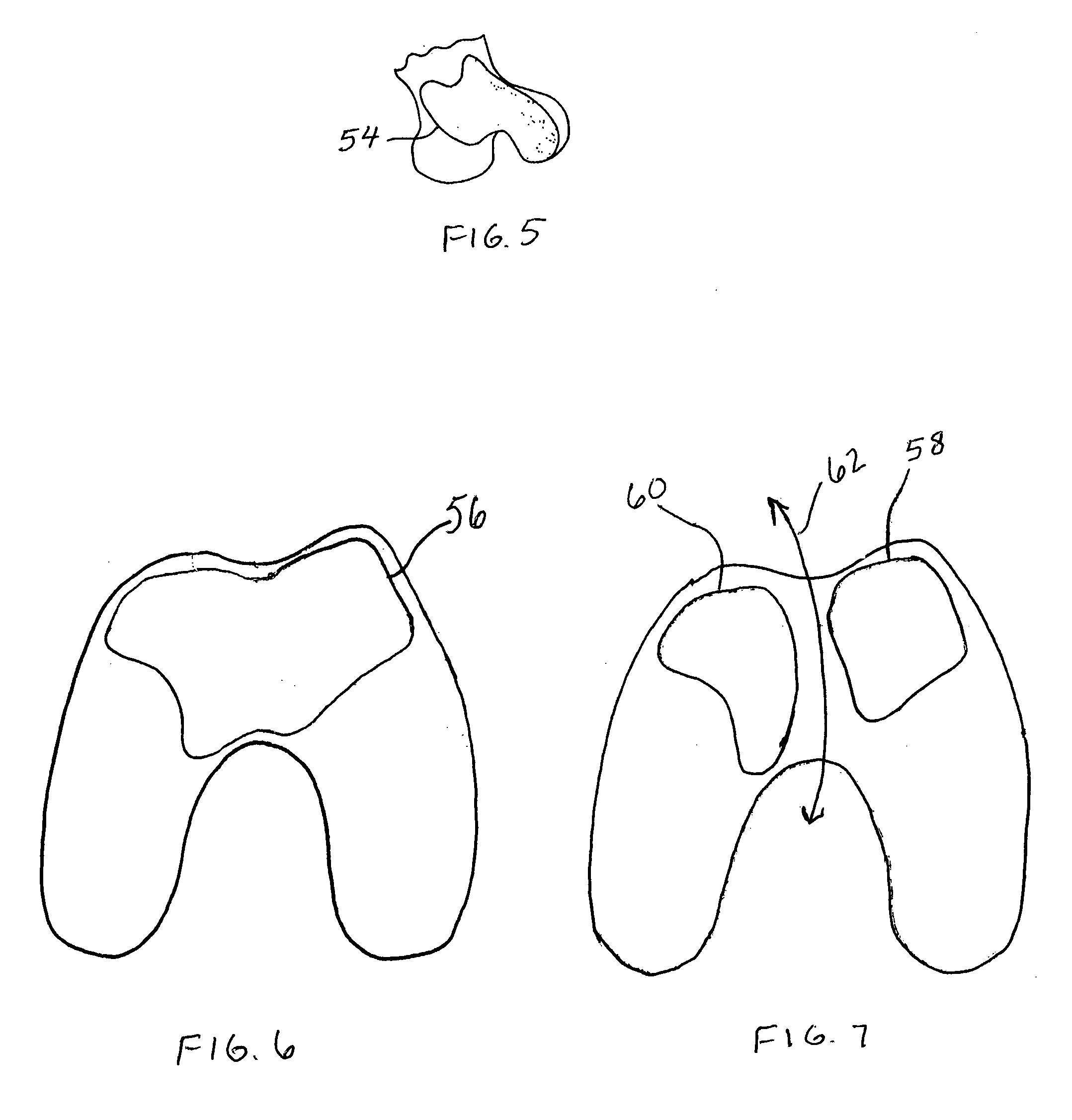
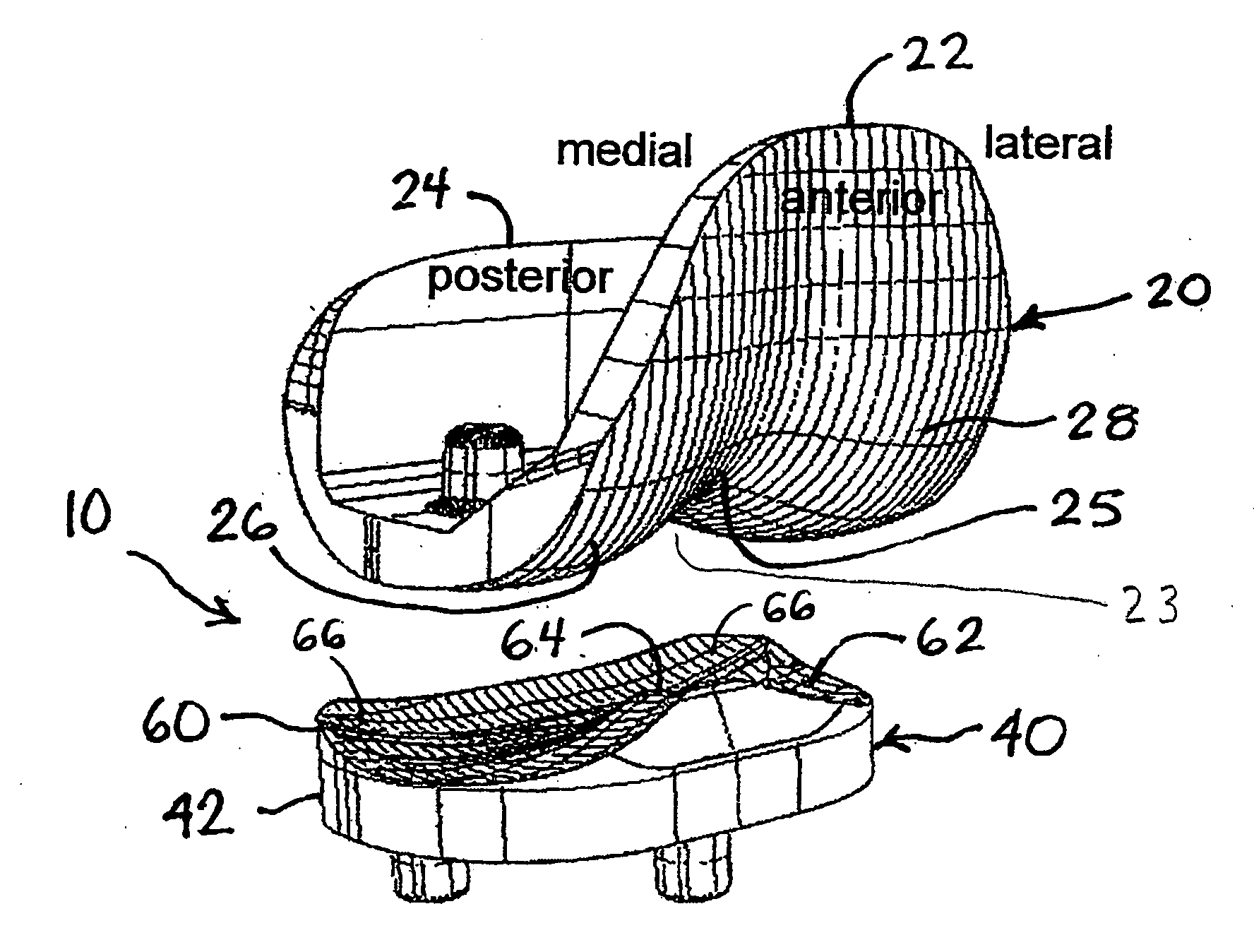
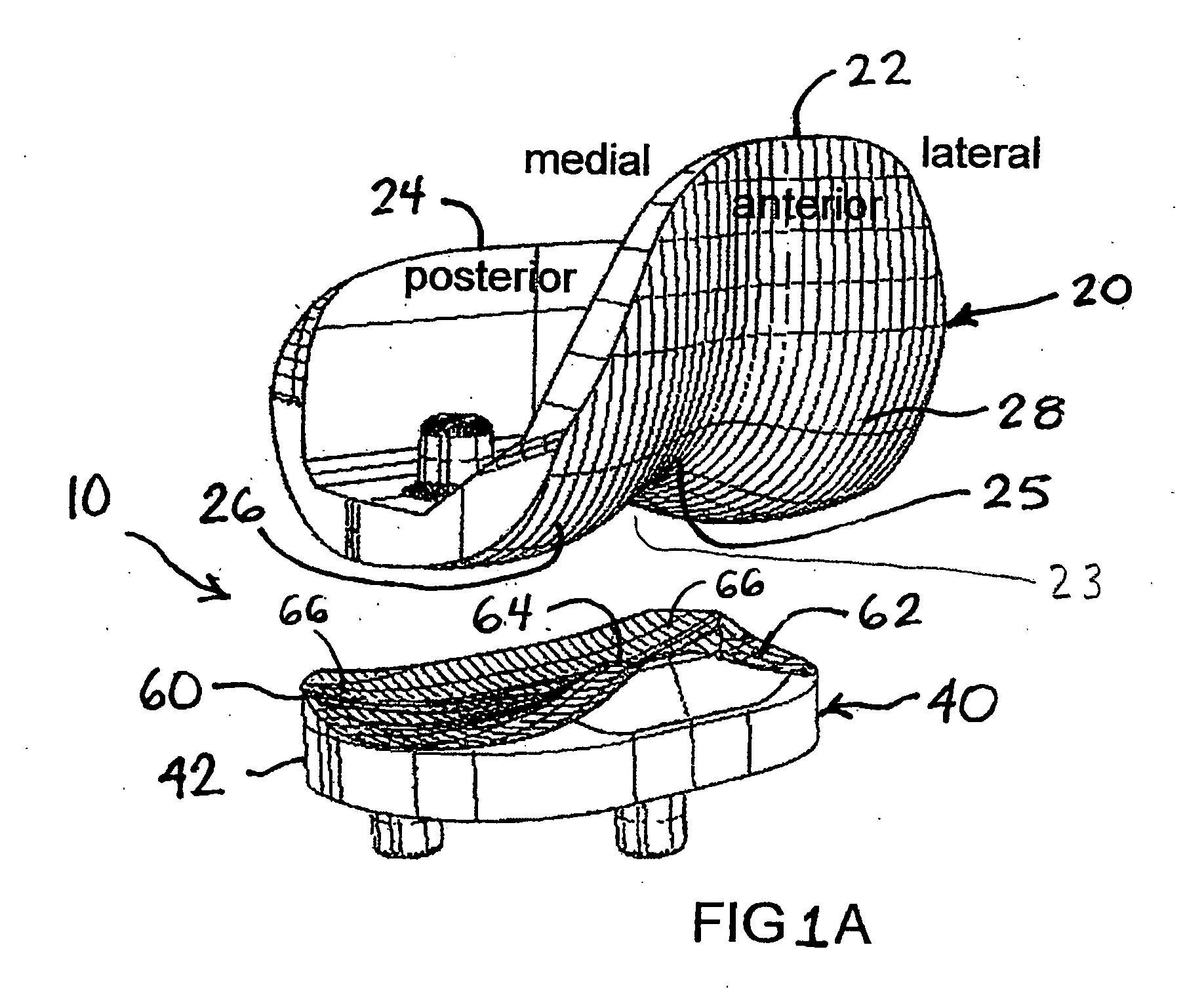
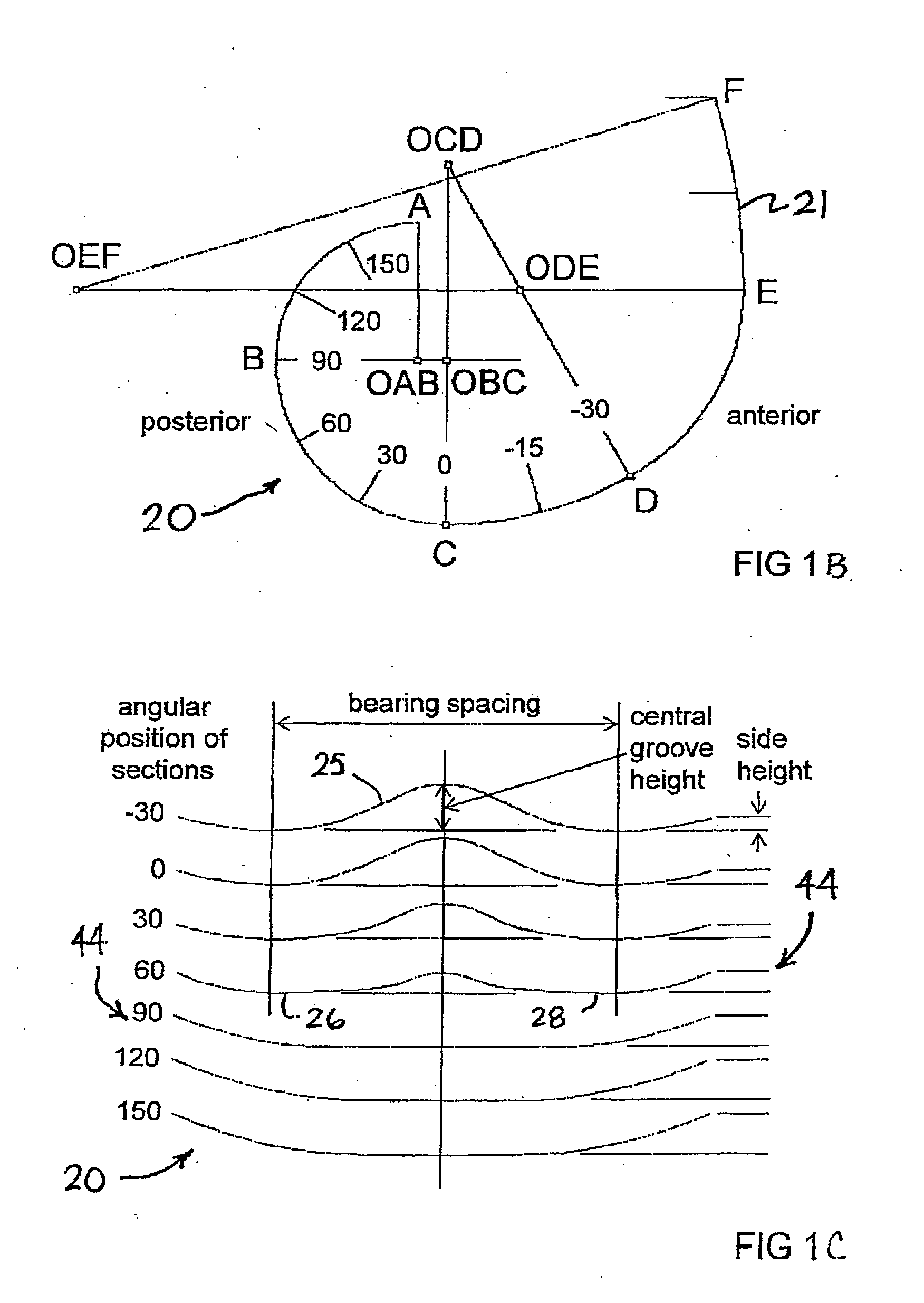
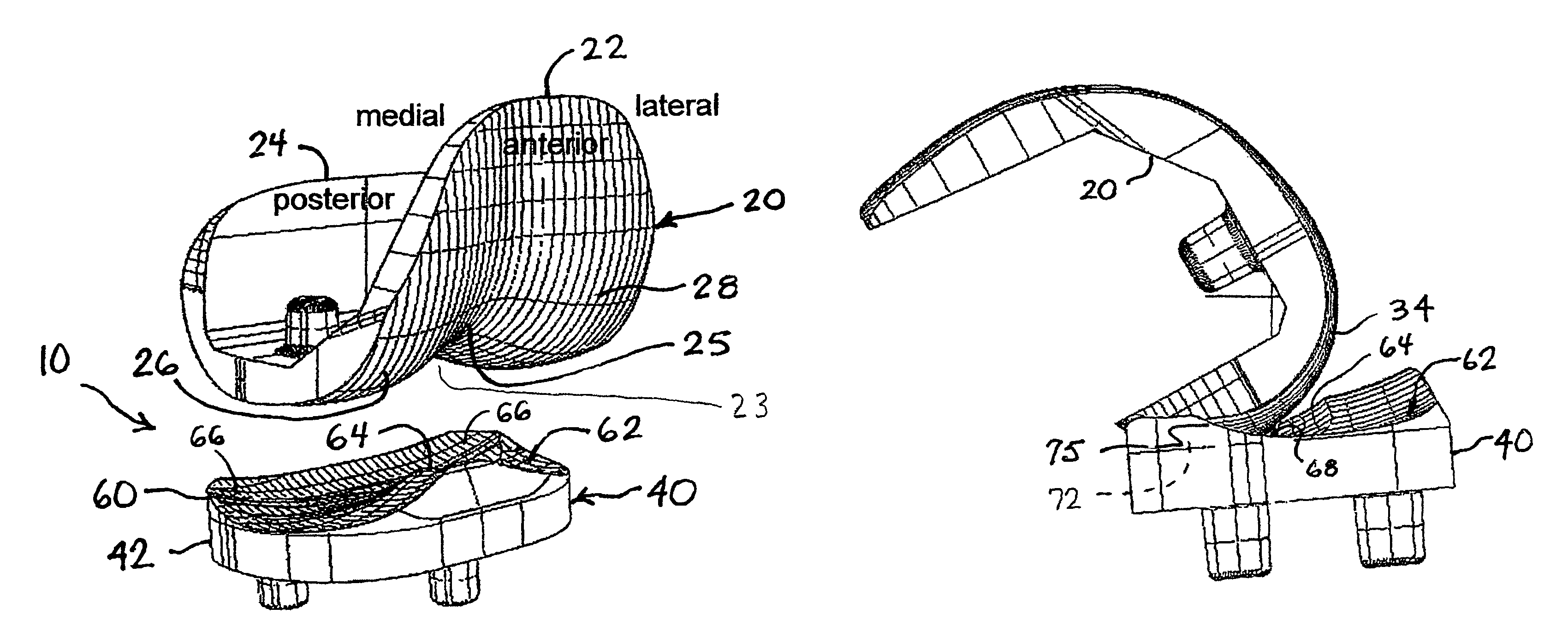
Surface guided knee replacement
ActiveUS20070135926A1Increase contact areaIncrease flexibilityJoint implantsKnee jointsTibiaTibial surface
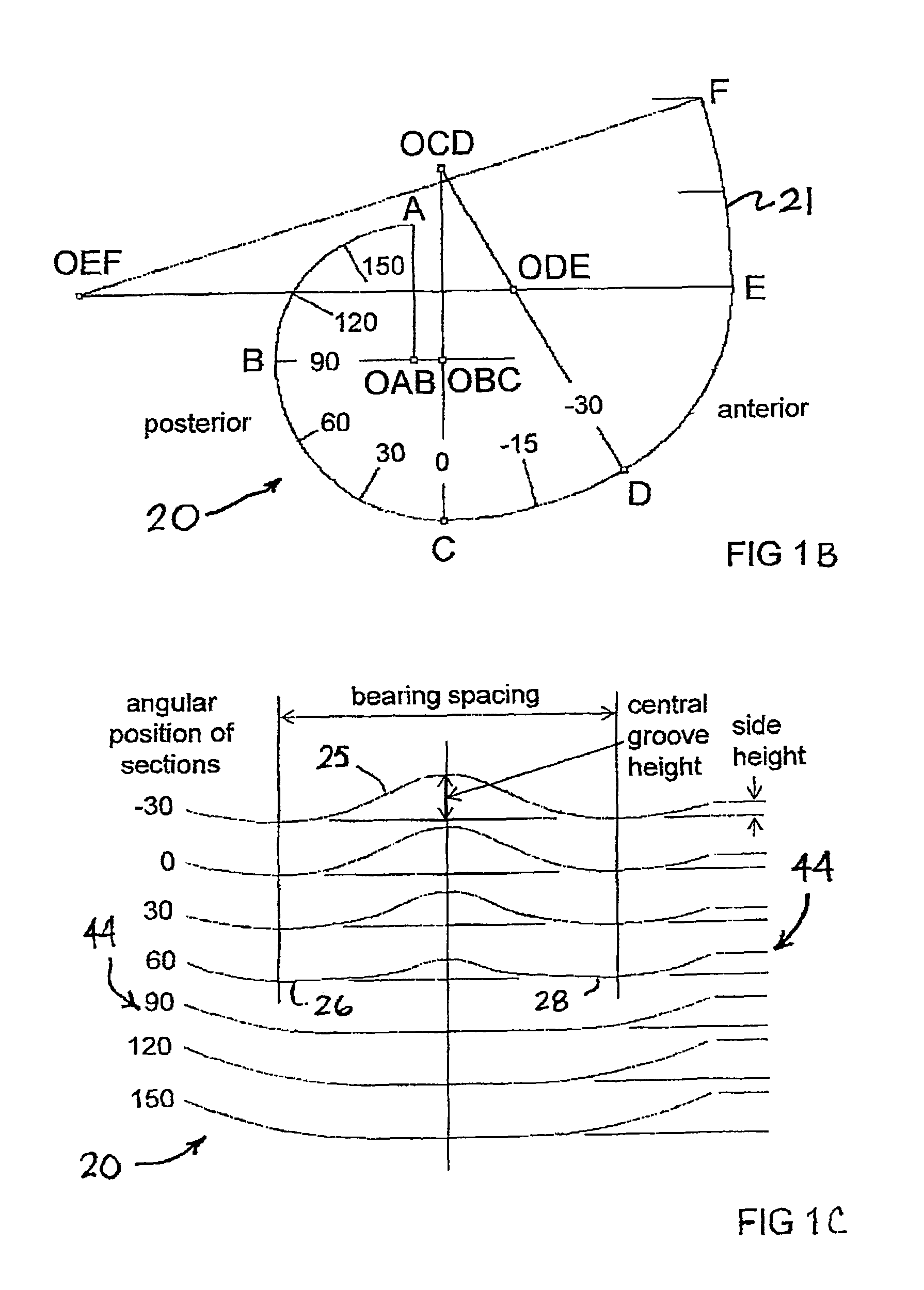
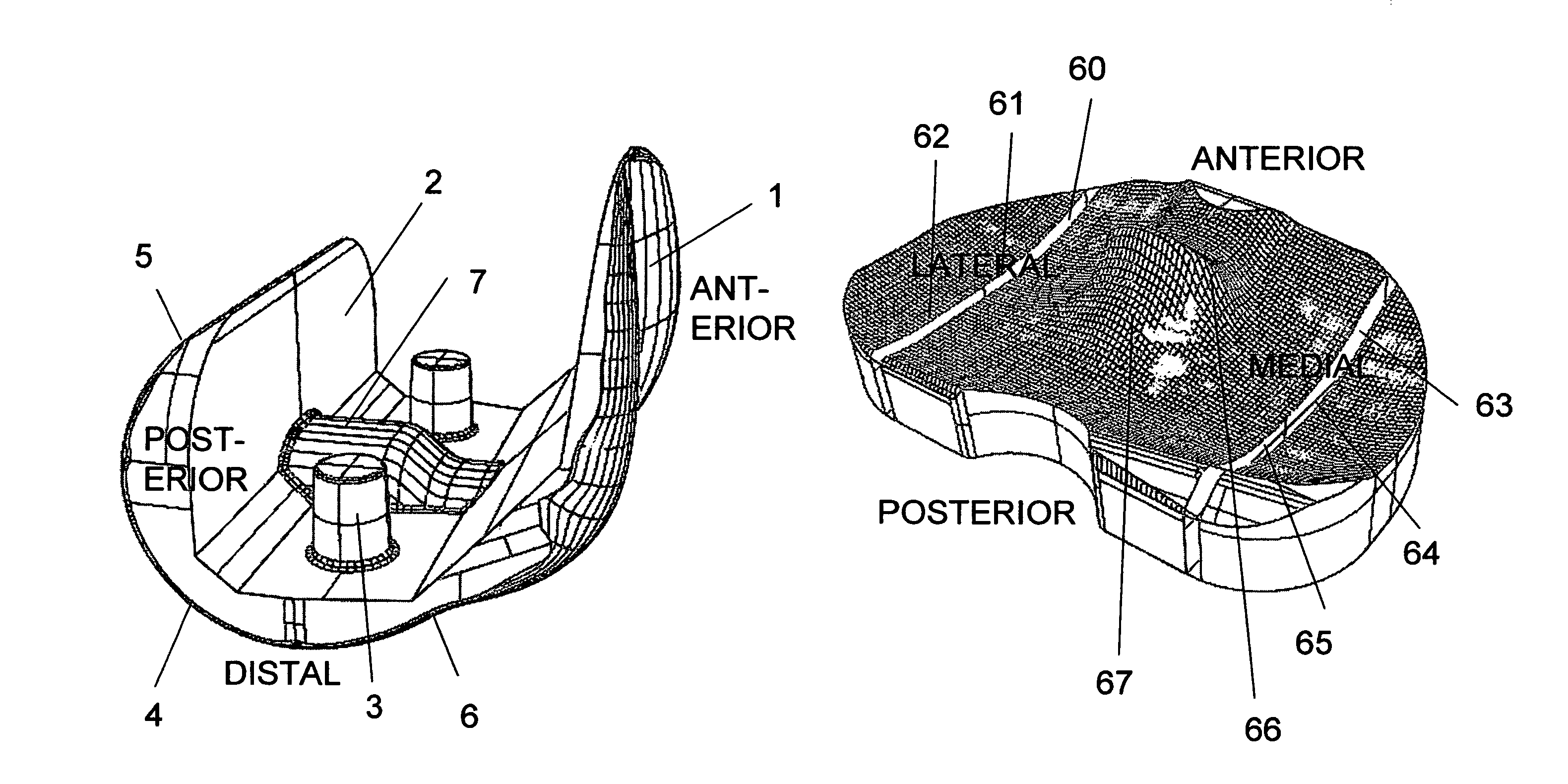
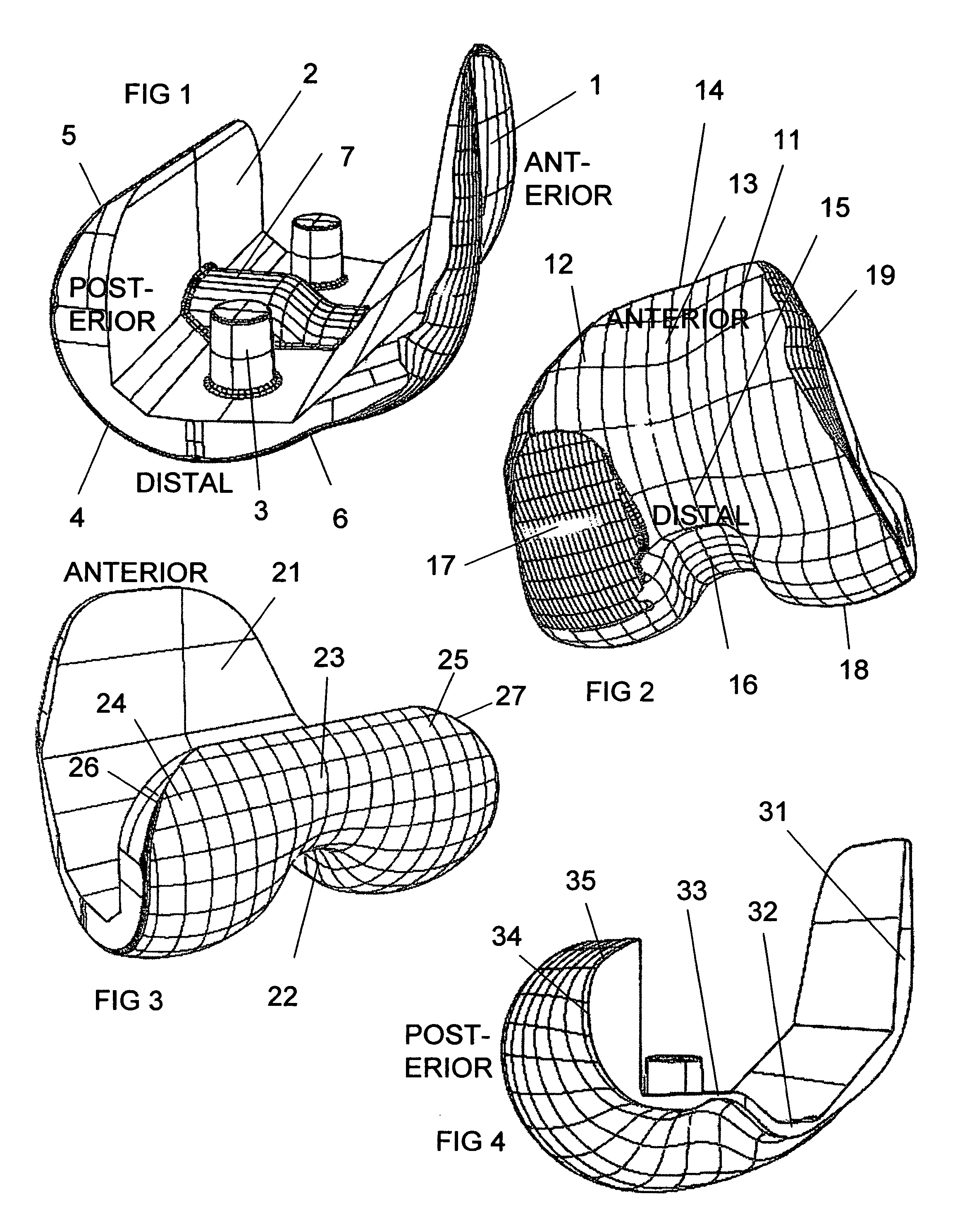
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the required motion and stability characteristics. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, by an amount similar to that in the anatomic knee. This is accomplished primarily by the depth and width of the femoral trochlea diminishing as the femoral component is flexed from zero to maximum, together with a ramp on the center of the tibial surface. The opposite motion, roll forward of the femur from a fully flexed to a more extended position, is accomplished by varying the outward radii of the lateral and medial femoral bearing surfaces, together with a ramp on the postero-lateral and postero-medial regions of the tibial surfaces. A variation of this is to generate a tibial surface which provides for a progressive internal rotation of the tibia as flexion proceeds.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
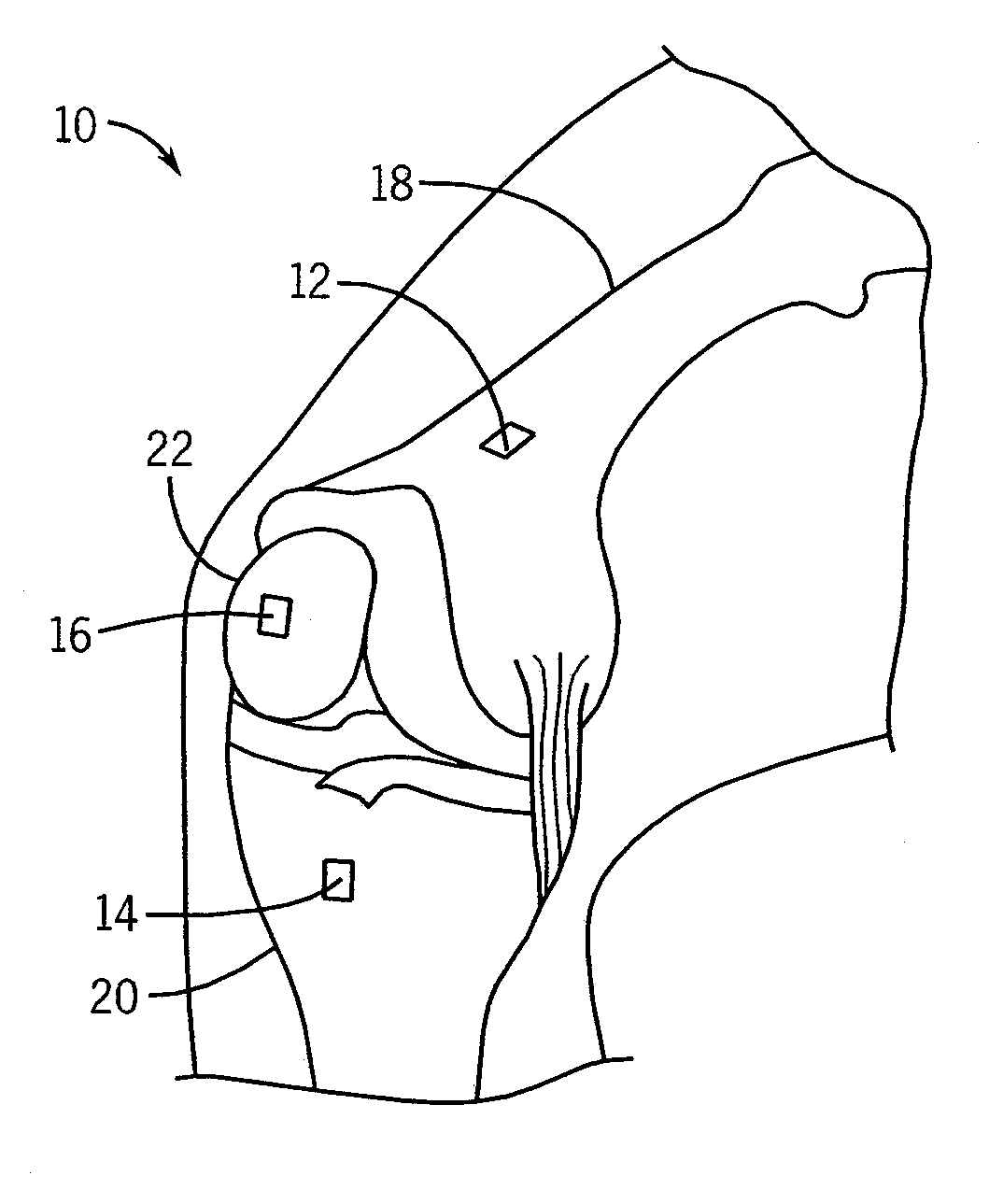
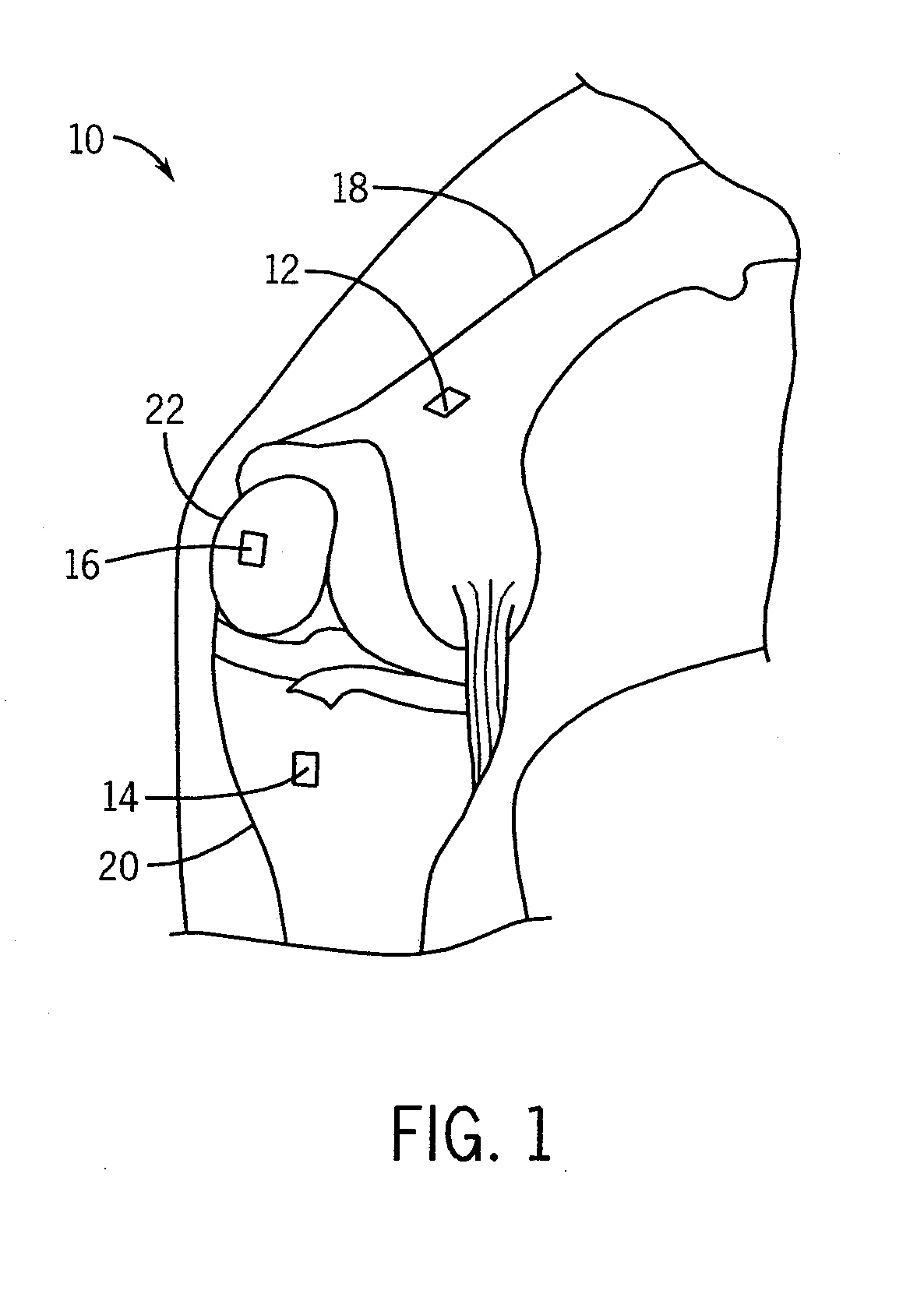
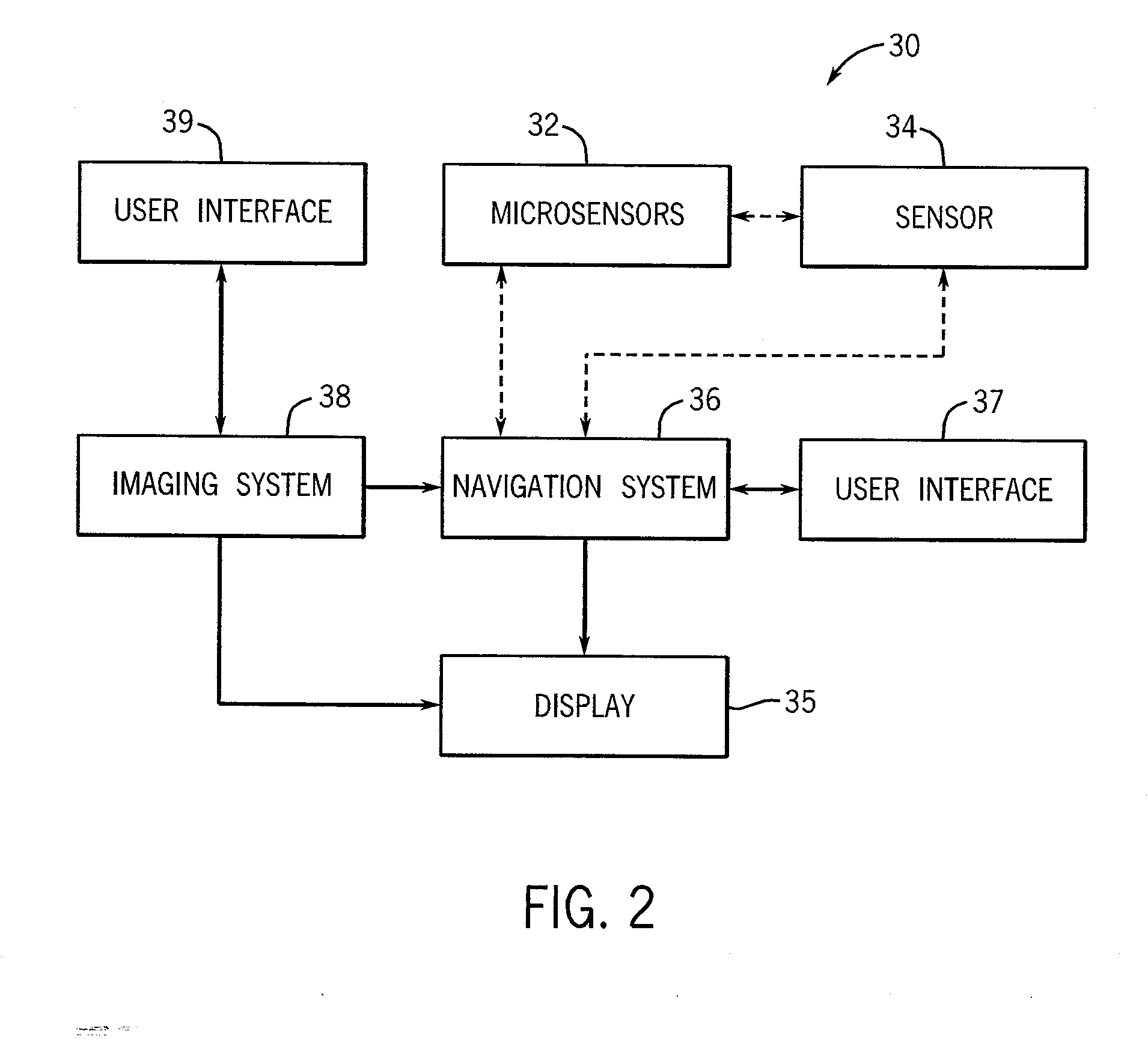
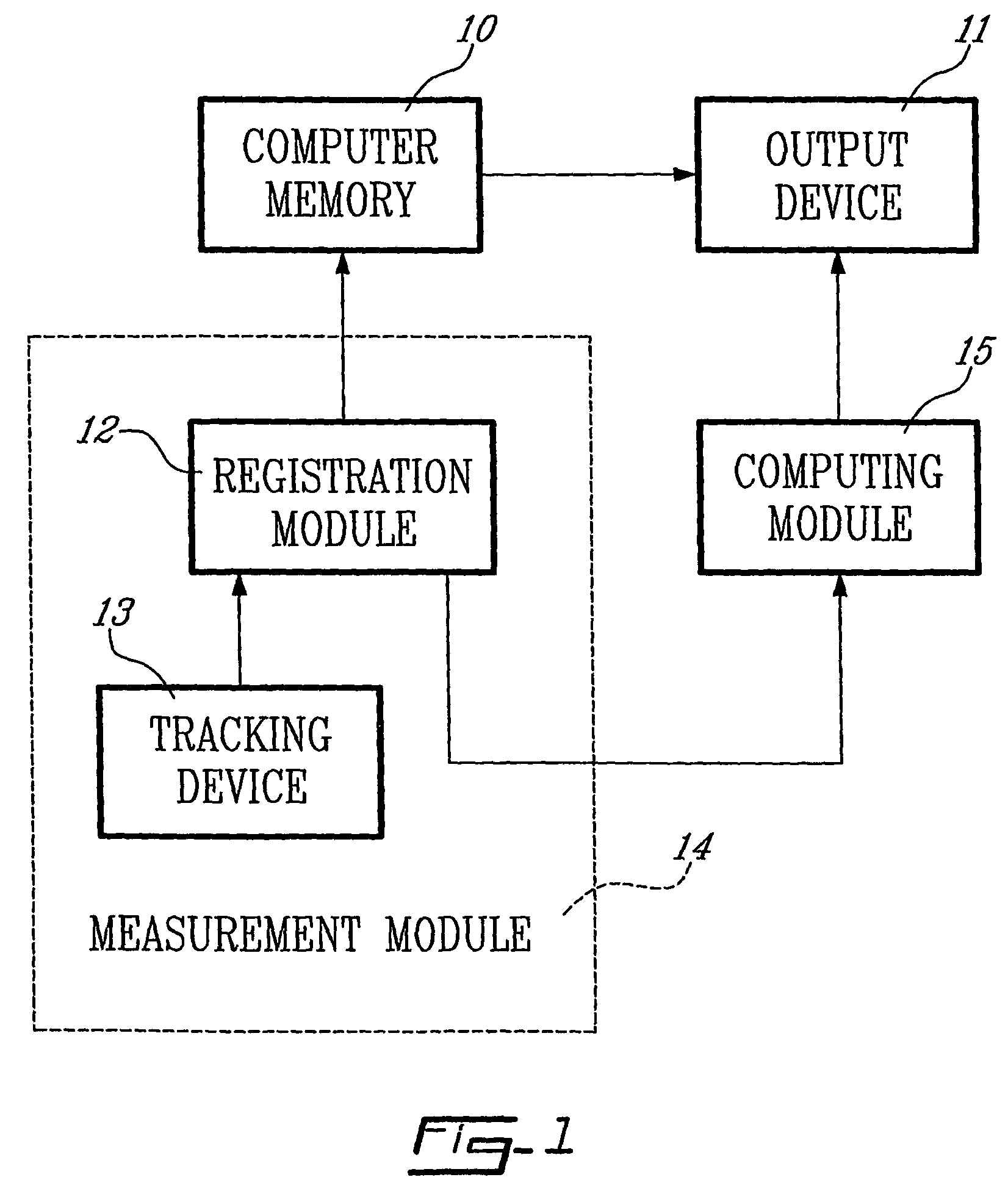
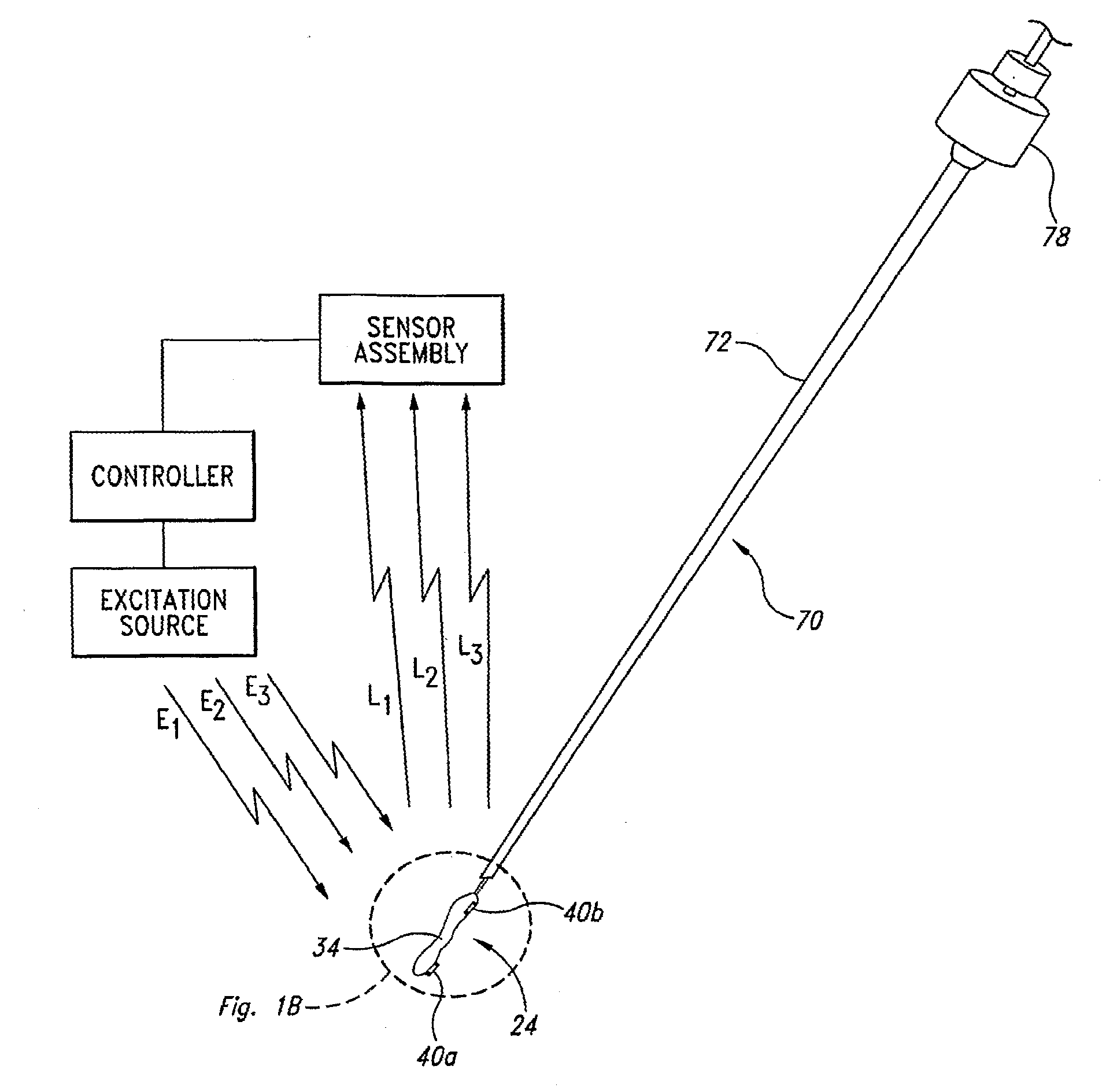
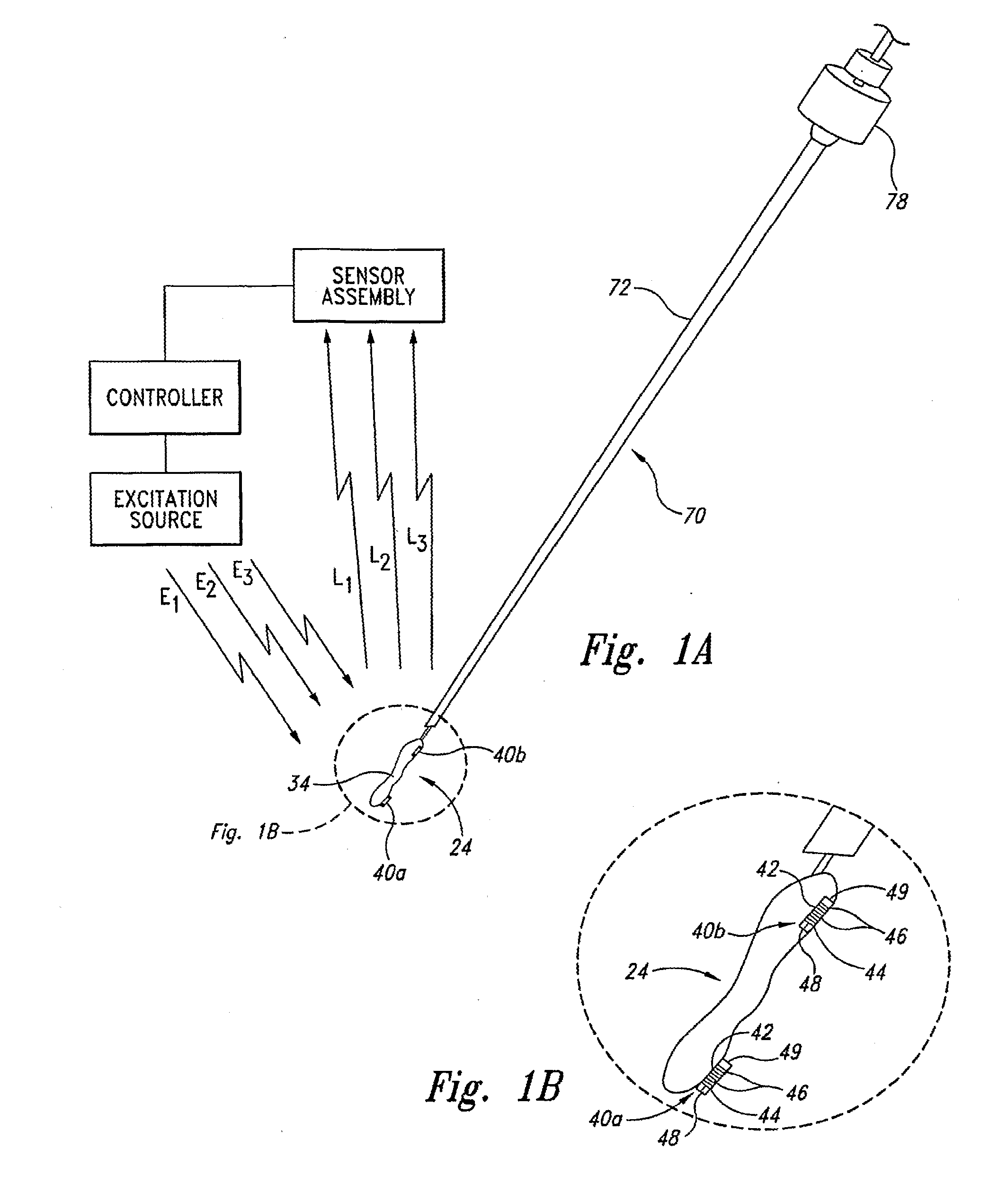
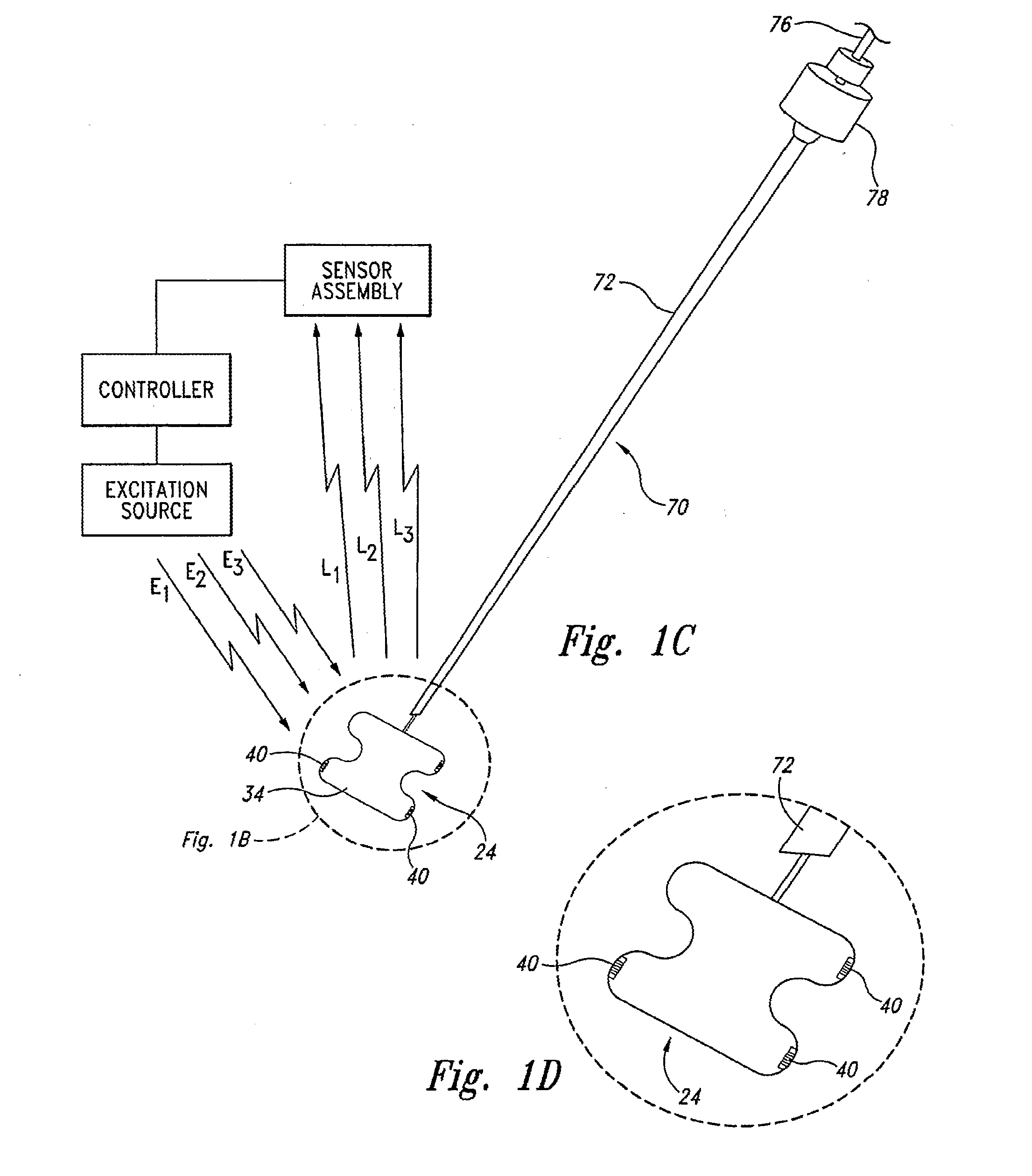
System and method for measurement of clinical parameters of the knee for use during knee replacement surgery
A system and method for measuring biomechanical parameters of a knee prior to total knee replacement (TKR) surgery includes a plurality of microsensors removably attached to the femur, tibia and patella; at least one sensor communicating with the plurality of microsensors; a navigation system coupled to the at least one sensor; an imaging system coupled to the navigation system for performing imaging of the joint; and at least one display for displaying imaging and tracking data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Knee prostheses with enhanced kinematics
A knee replacement system includes a proximal tibial posterior camming portion defined by a first radius of curvature with a first origin in a first medio-lateral plane, a distal tibial posterior camming portion defined by a second radius of curvature with a second origin in a second medio-lateral plane, an anterior femoral camming portion of a posterior cam defined by a third radius of curvature with a third origin in the first medio-lateral plane, and a posterior femoral camming portion of the posterior cam and defined by a fourth radius of curvature with a fourth origin in the second medio-lateral plane, wherein the second origin is closer to the lateral tibial portion than the first origin, or the fourth origin is closer to the medial femoral portion than the third origin.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
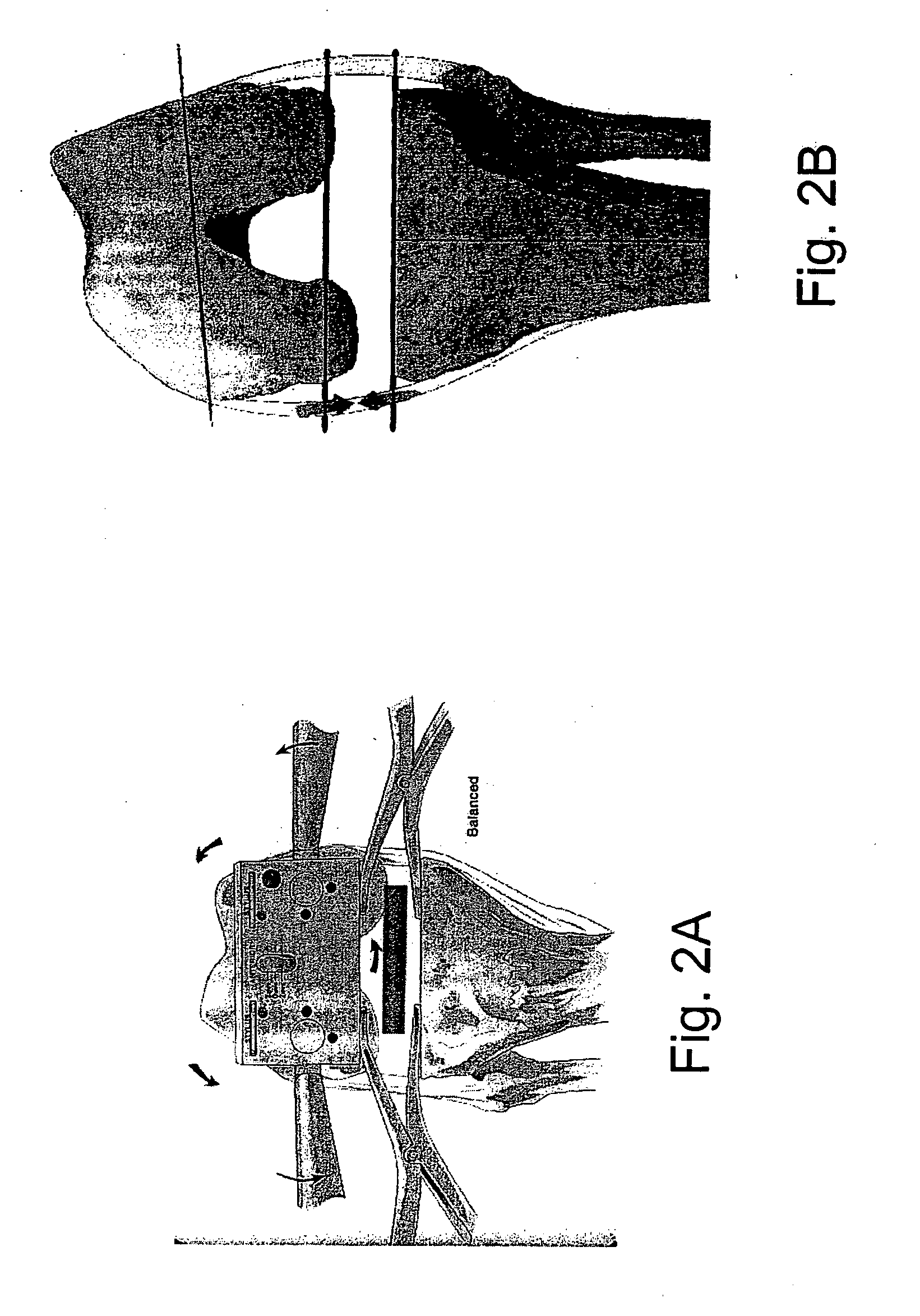
Sensing force during partial and total knee replacement surgery
ActiveUS8211041B2Accurate and quantifiable measurementPrecise tensionAnkle jointsPerson identificationTibiaTotal knee replacement surgery
Systems, devices, and methods are provided for measuring forces in the space of a knee during surgery. Such forces can be caused by tension in the ligaments of the knee. A femoral member is engaged with a distal femur. While the knee is flexed, partially extended, or fully extended, a force sensor and a gauge shim can be placed in the gap between the femoral member and the tibial plateau to measure the forces therebetween. The force sensor provides an accurate and quantifiable measurement of force, making knee replacement surgery and ligament tension balancing more accurate, standardized and repeatable. The force sensor comprises an elongate housing which comprises a thin force sensing distal portion and a proximal handle portion.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
Total Knee Replacement Prosthesis With High Order NURBS Surfaces
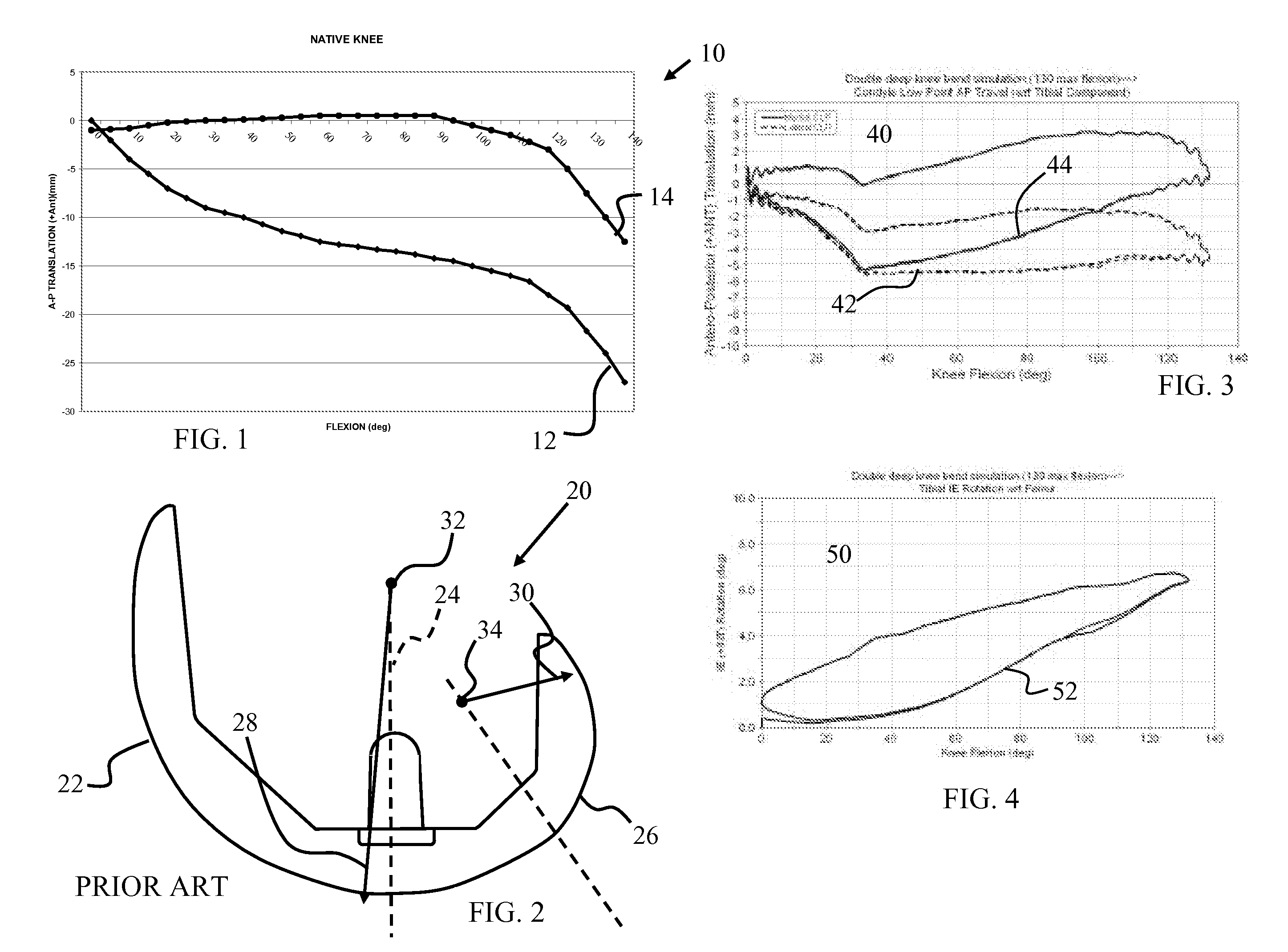
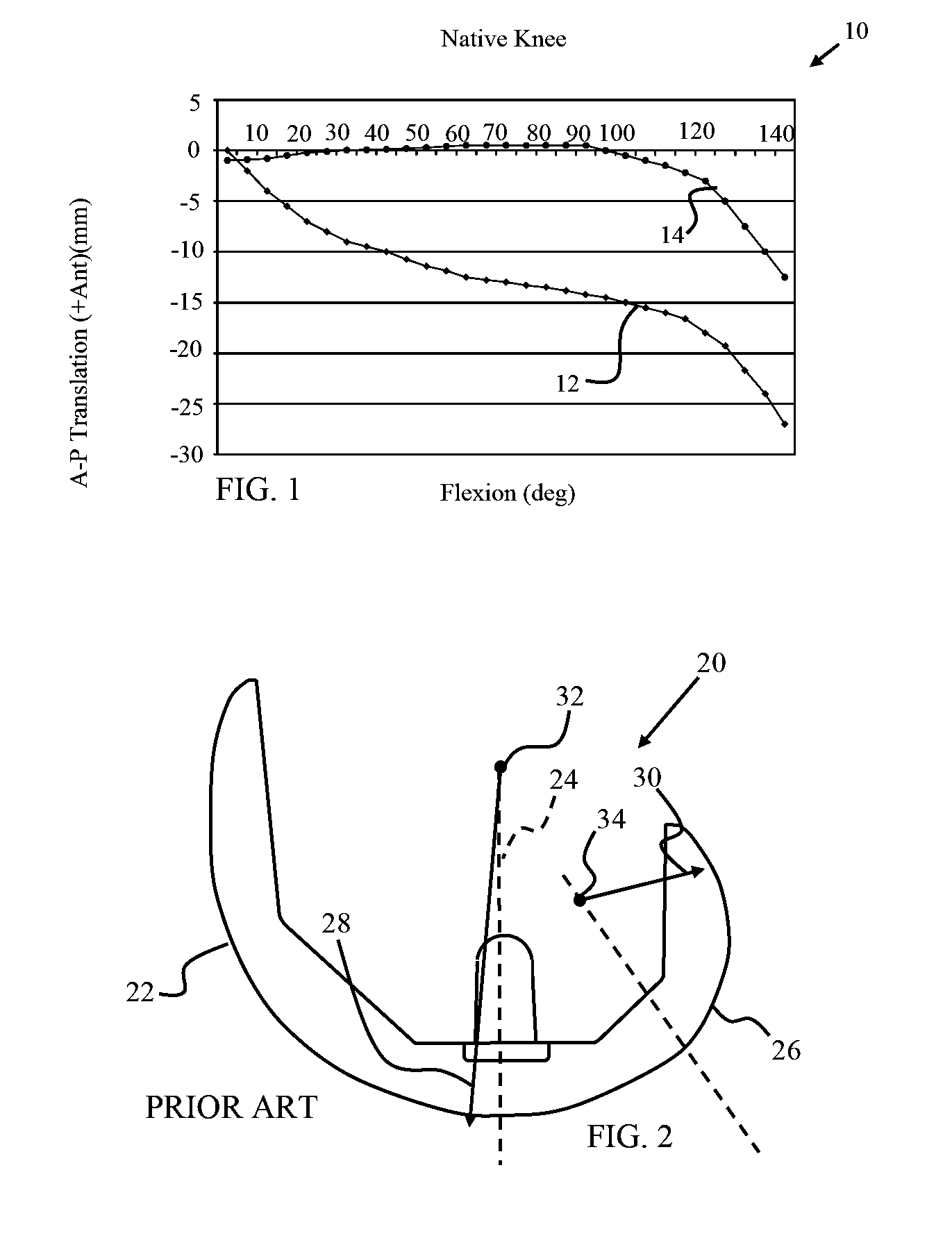
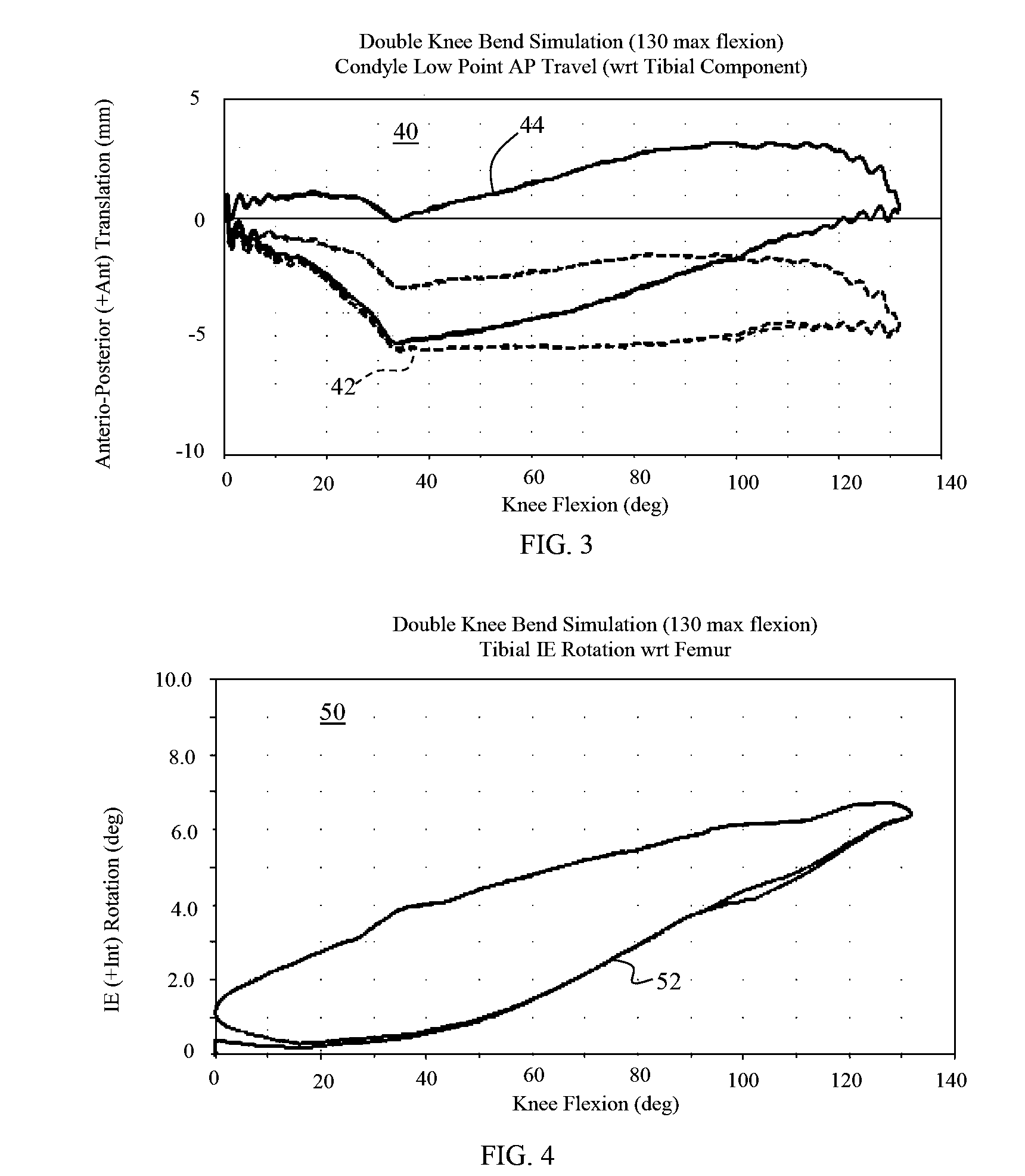
A knee replacement prosthesis comprising a femoral component and a tibial component that enable anterior-posterior translation of the femur relative to the tibia and enable the tibia to rotate about its longitudinal axis during flexion of the knee. The femoral component connects to the distal end of a resected femur and includes medial and lateral condyles having distal, articulating surfaces, and a patellar flange having a patellar articulating surface. The tibial component connects to the proximal end of a resected tibia and includes a proximal bearing surface with medial and lateral concavities that articulate with the medial and lateral condyles. The condylar articulating surfaces and the said concavities are substantially defined by non-uniform, rational B-spline surfaces (NURBS).
Owner:MAXX ORTHOPEDICS INC
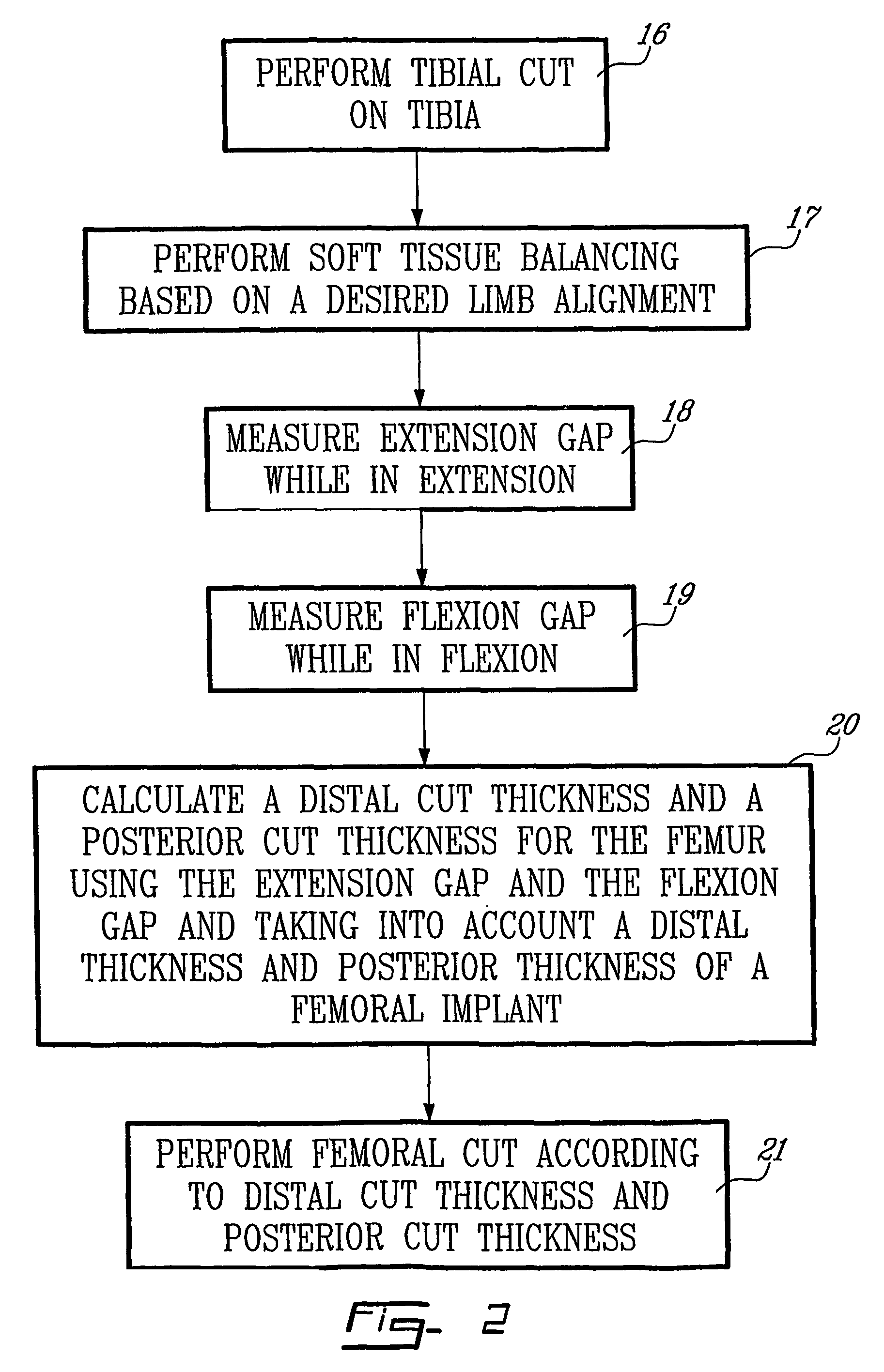
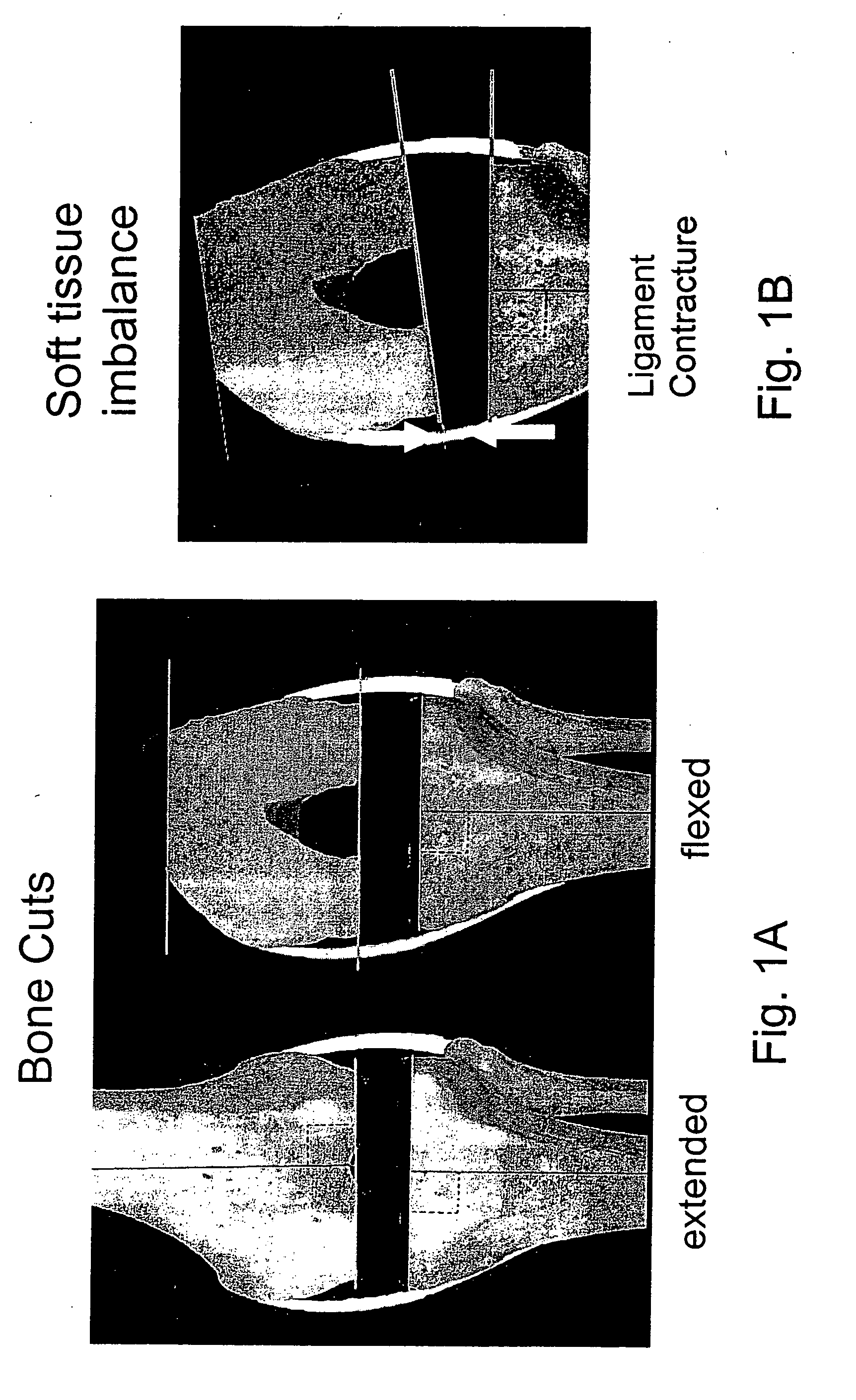
Determining femoral cuts in knee surgery
ActiveUS8257360B2Extended service lifeEasy to placeDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTibiaKnee surgery
There is provided a method and system for determining a distal cut thickness and posterior cut thickness for a femur in a knee replacement operation, the method comprising: performing a tibial cut on a tibia; performing soft tissue balancing based on a desired limb alignment; measuring an extension gap between the femur and said tibial cut while in extension; measuring a flexion gap between the femur and the tibial cut while in flexion; calculating a distal cut thickness and a posterior cut thickness for the femur using the extension gap and the flexion gap and taking into account a distal thickness and posterior thickness of a femoral implant; and performing said femoral cut according to the distal cut thickness and posterior cut thickness.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
Surface guided knee replacement
InactiveUS20070135925A1Reduce consistencyAvoid large displacementJoint implantsKnee jointsGonial angleTibial surface
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the motion and stability characteristics of the anatomic knee. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, more so on the lateral side than on the medial side. This is accomplished by the interaction of a projecting tibial post inside a cupola in the center of the femoral component, and by the saggital radius on the medial side being smaller than that on the lateral side. The prevention of anterior sliding of the femur on the tibia in early flexion is accomplished by the interaction between a distal-anterior recess on the medial side of the femur and an apposing raised pad on the tibial surface. Rotational laxity at all angles is allowed by the presence of only one recess pad and by non-conforming femoral-tibial surfaces on the lateral side.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Anterior cruciate ligament substituting knee replacement prosthesis
There is disclosed a total knee replacement prosthesis, which can substitute the function of an anterior and / or a posterior cruciate ligament. A femoral component containing two intercondylar surfaces and an intercondylar region, a tibial component having a tibial platform and a bearing component, and a protrusion from the bearing component also are disclosed.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
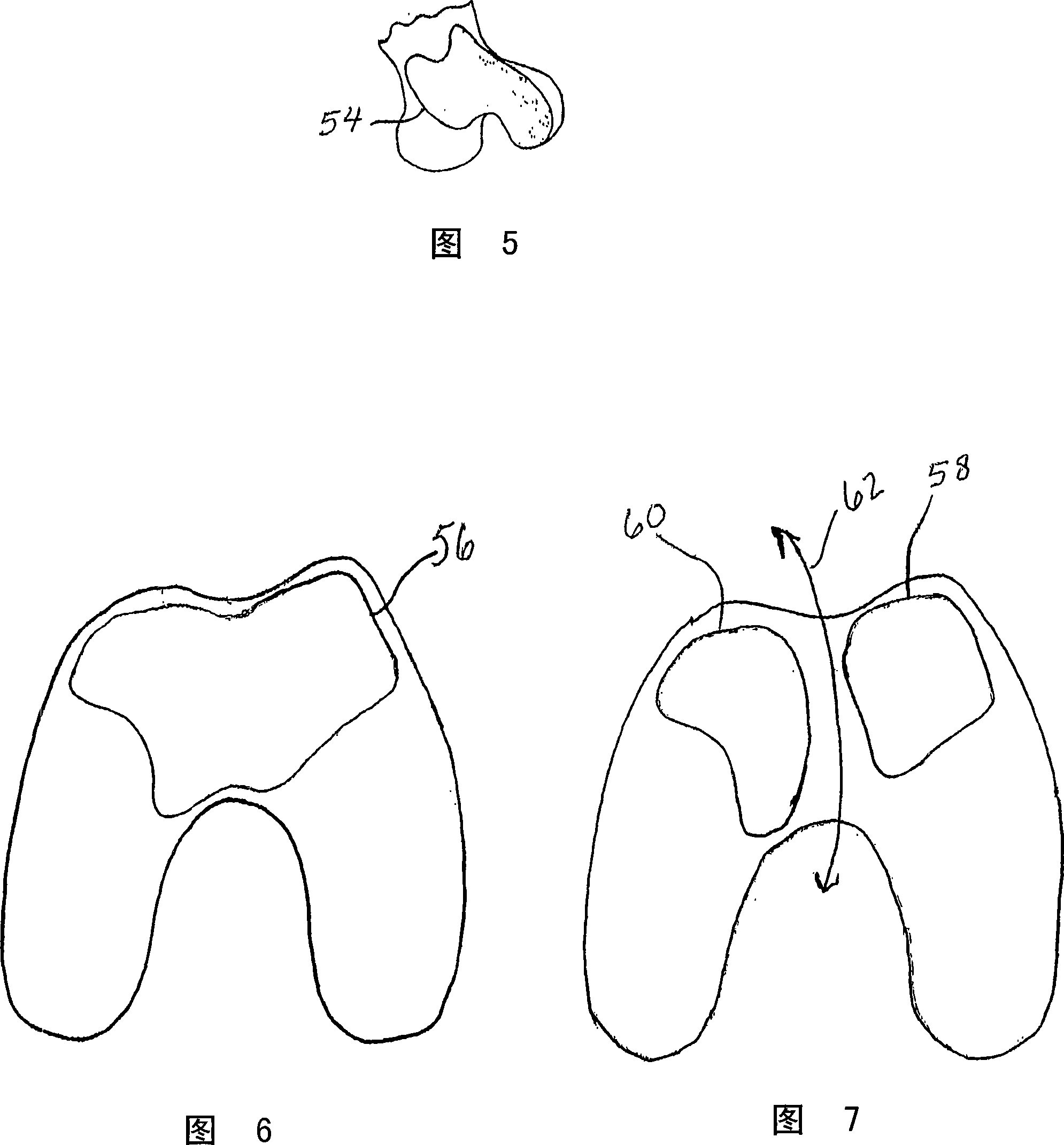
Apparatus, operating means and process
InactiveUS20050038442A1Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesJoint implantsSurgical operationEngineering
The invention relates to surgical instruments, a computer program element which provides control or information relating to the surgical instruments, a computer program providing the same, a computer readable medium comprising the computer program, a method for implementing a computer-aided means of guiding a surgeon through a desired surgical procedure and to a computer aided surgical procedure. In a preferred embodiment, the invention relates to instruments, a computer program element, computer programs, a computer readable medium and methods for use in knee replacement operations.
Owner:FINSBURY DEV
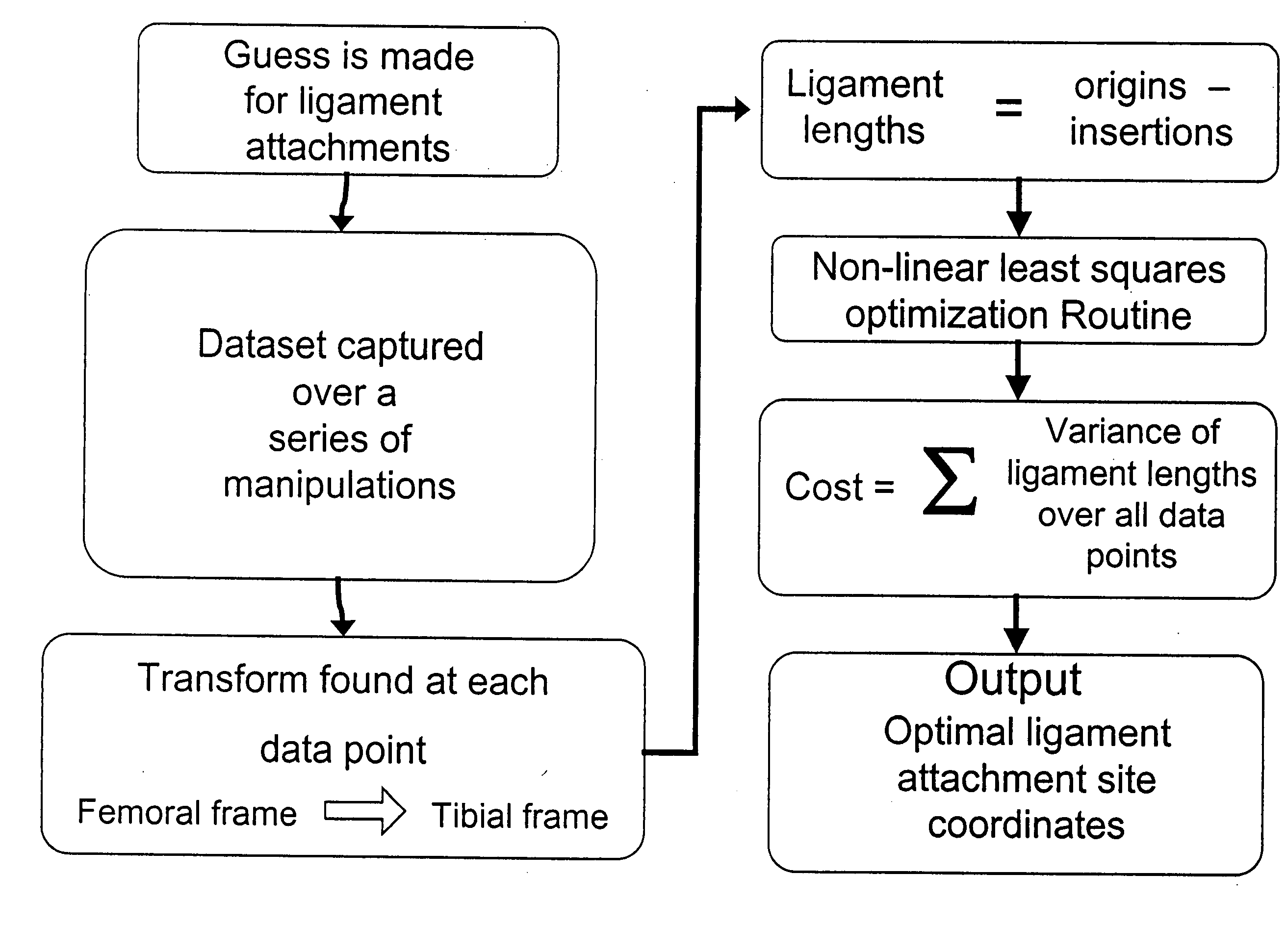
Methods and systems for intraoperative measurement of soft tissue constraints in computer aided total joint replacement surgery
InactiveUS20050119661A1Maintaining soft tissue balance of the replacement kneeDraw tensionDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTibiaMathematical model
Methods and systems are described to quantitatively determine the degree of soft tissue constraints on knee ligaments and for properly determining placement parameters for prosthetic components in knee replacement surgery that will minimize strain on the ligaments. In one aspect, a passive kinetic manipulation technique is used in conjunction with a computer aided surgery (CAS) system to accurately and precisely determine the length and attachment sites of ligaments. These manipulations are performed after an initial tibial cut and prior to any other cuts or to placement of any prosthetic component. In a second aspect, a mathematical model of knee kinematics is used with the CAS system to determine optimal placement parameters for the femoral and tibial components of the prosthetic device that minimizes strain on the ligaments.
Owner:HODGSON ANTONY J +1
Surface guided knee replacement
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
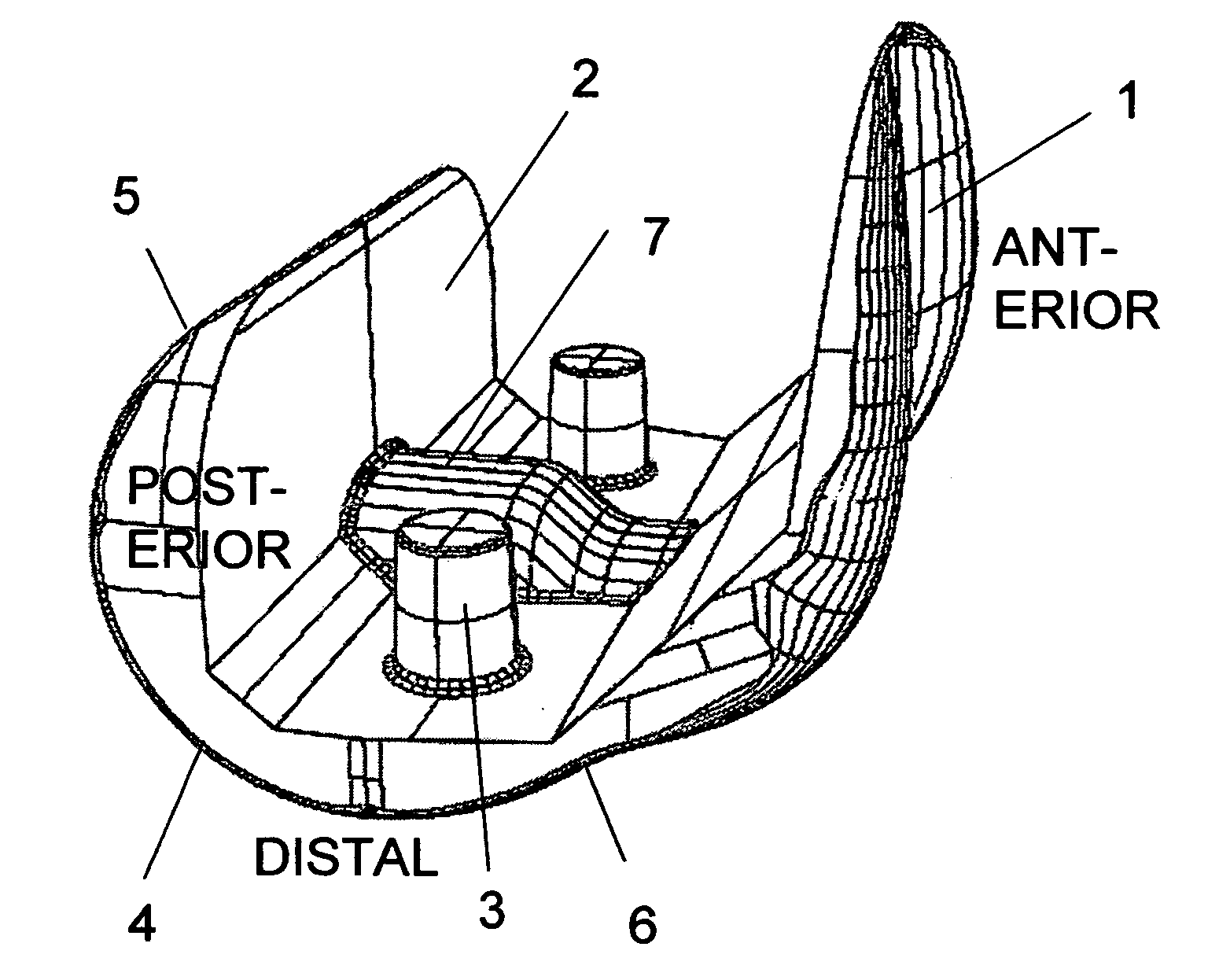
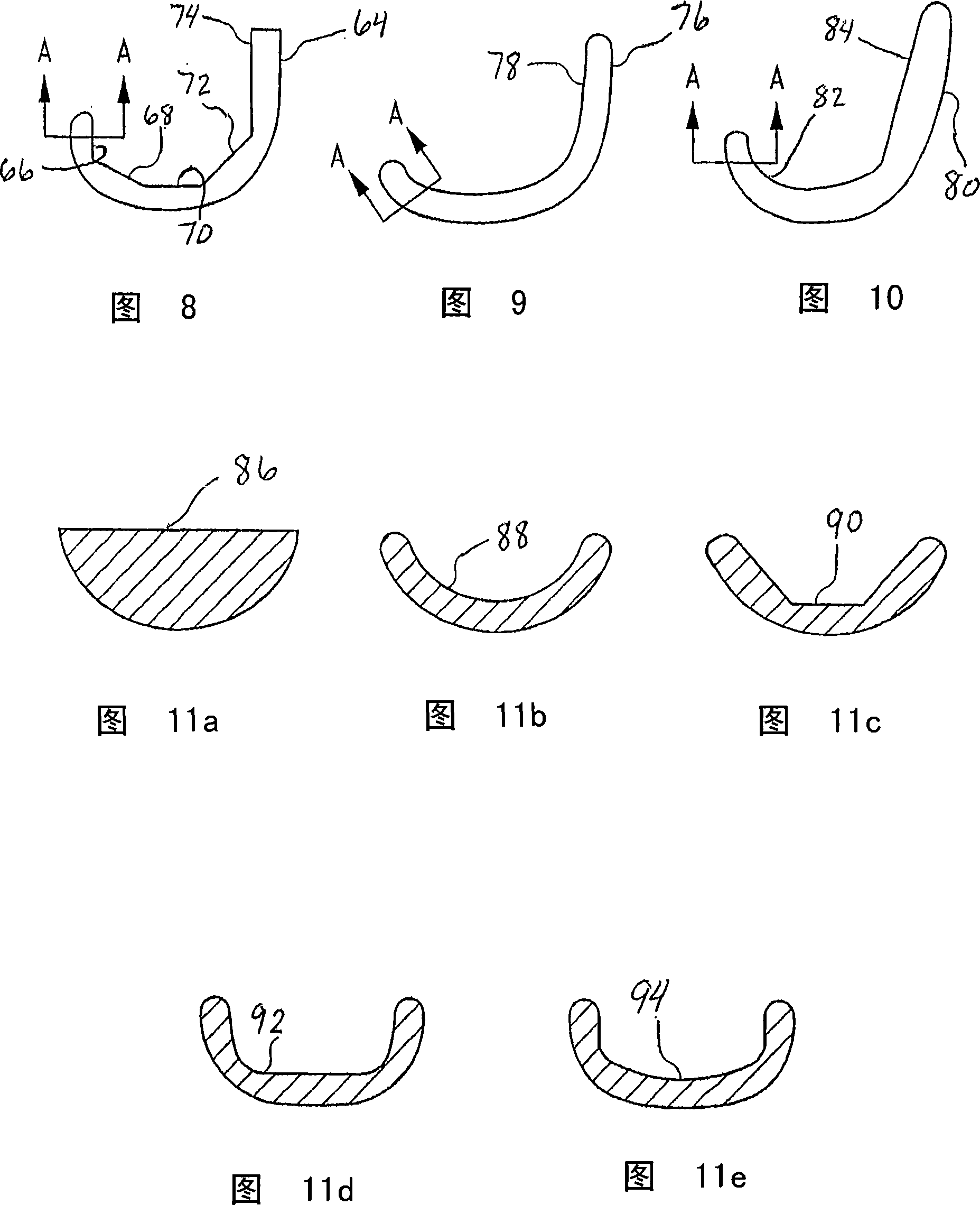
Femoral resection guide apparatus and method
An apparatus for resecting a distal femoral condyle includes a resection guide defining a first bone fixation aperture extending about an axis. The resection guide further defines a first bone saw slot and a second bone saw slot. The resection guide is configured to position the first bone fixation aperture relative to the condyle. The resection guide is further configured to concurrently arcuately translate the first bone saw slot and the second bone saw slot relative to the axis. A knee replacement kit includes a femoral implant defining a first plan contour. The kit further includes a resection guide defining a second plan contour modeling the first plan contour.
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
Joint replacement methods and apparatus
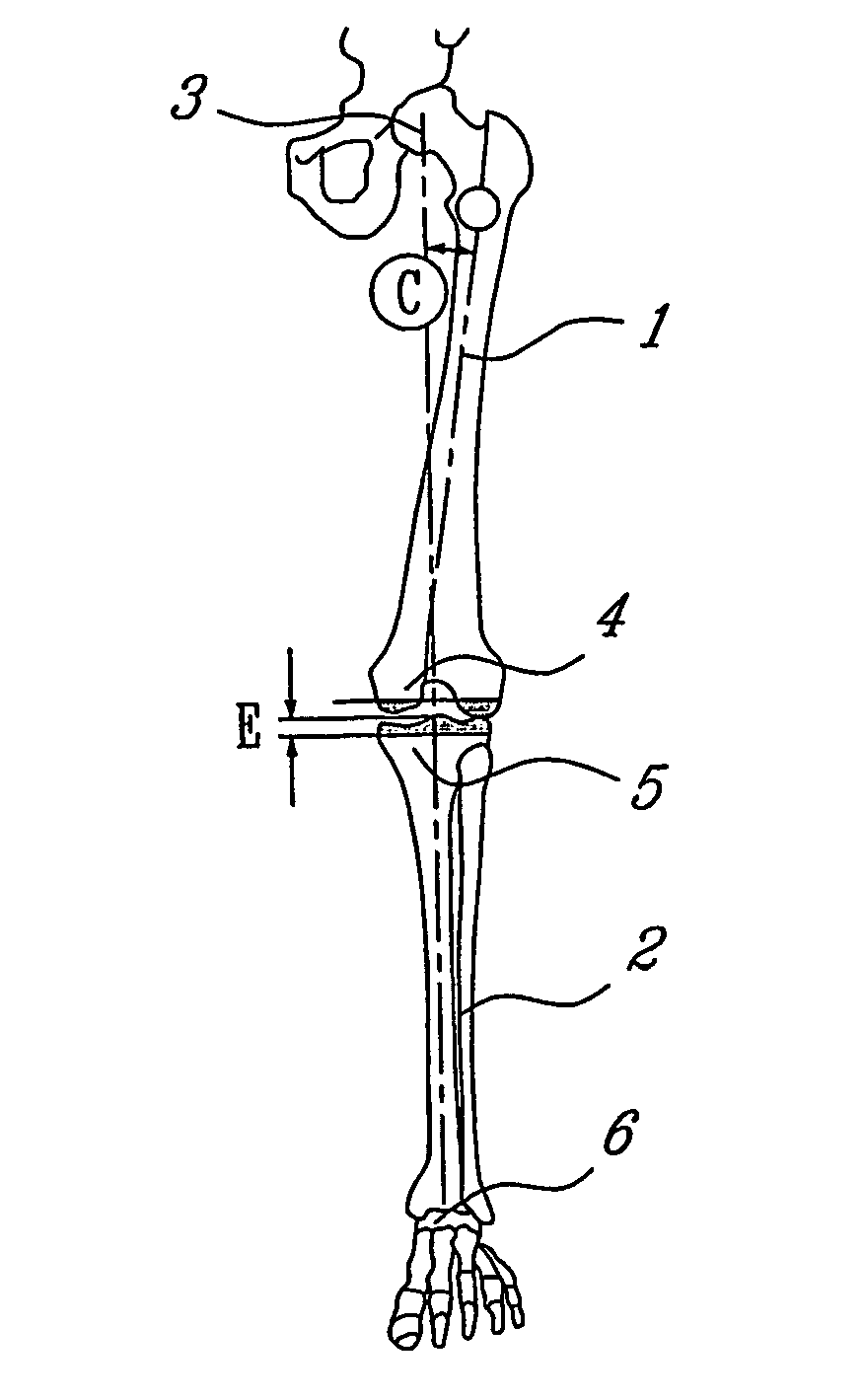
Apparatus and surgical techniques provide alternative cutting fixtures and other features to improve bone resection accuracy and joint stability. According to one embodiment, stabilizers are removably attached to a cutting guide to temporarily lengthen the surface against which a saw or other cutting device rests. Another embodiment provides differently shaped saw blades, having curved distal ends and right-angle bends applicable to box cuts of the type associated with cruciate sacrifice knee-replacement surgery. Methods are also disclosed whereby the box cuts, distal and posterior augment cuts may be approached from a distal perspective, both laterally and medially. A different embodiment provides a trial / cutting guide having flat surfaces as opposed to curved surfaces adapted for articulation within a joint. Yet a further alternative embodiment teaches a device for determining the joint line relative to a tibia using the fibula as reference.
Owner:MASINI MICHAEL A
Sensing force during partial and total knee replacement surgery
ActiveUS20100217156A1Accurate and quantifiable measurementPrecise tensionAnkle jointsPerson identificationTibiaTotal knee replacement surgery
Systems, devices, and methods are provided for measuring forces in the space of a knee during surgery. Such forces can be caused by tension in the ligaments of the knee. A femoral member is engaged with a distal femur. While the knee is flexed, partially extended, or fully extended, a force sensor and a gauge shim can be placed in the gap between the femoral member and the tibial plateau to measure the forces therebetween. The force sensor provides an accurate and quantifiable measurement of force, making knee replacement surgery and ligament tension balancing more accurate, standardized and repeatable. The force sensor comprises an elongate housing which comprises a thin force sensing distal portion and a proximal handle portion.
Owner:SYNVASIVE TECH
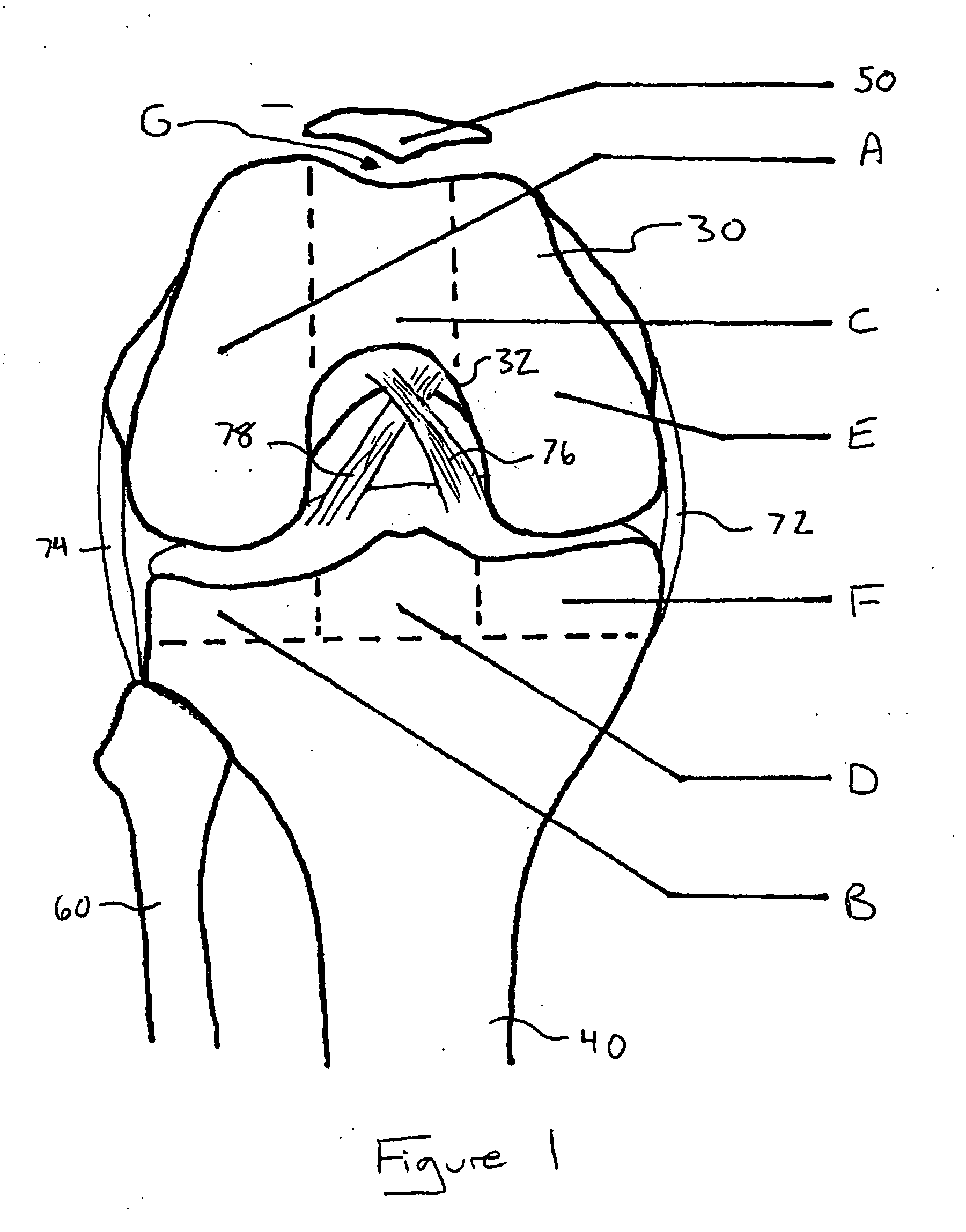
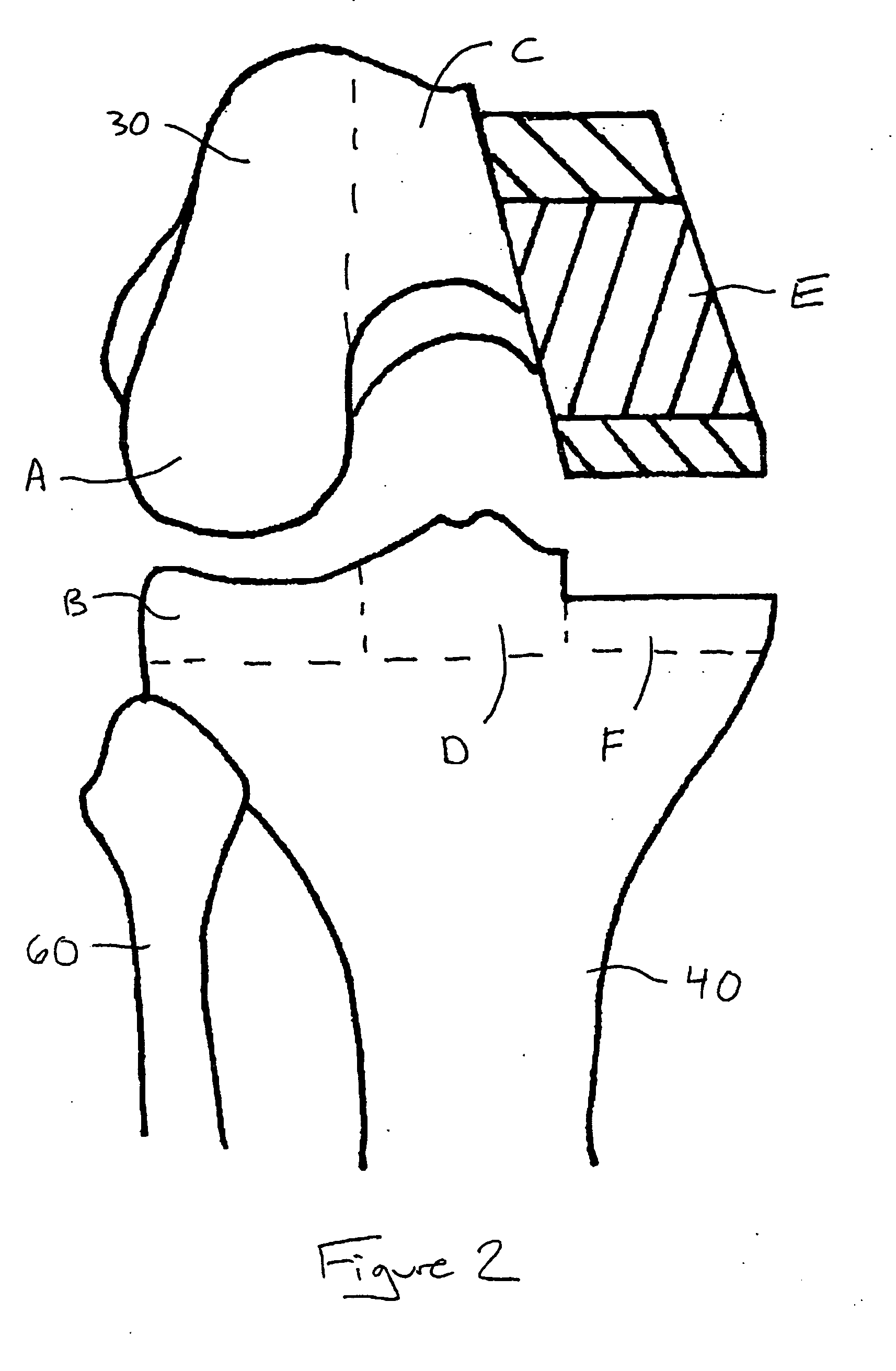
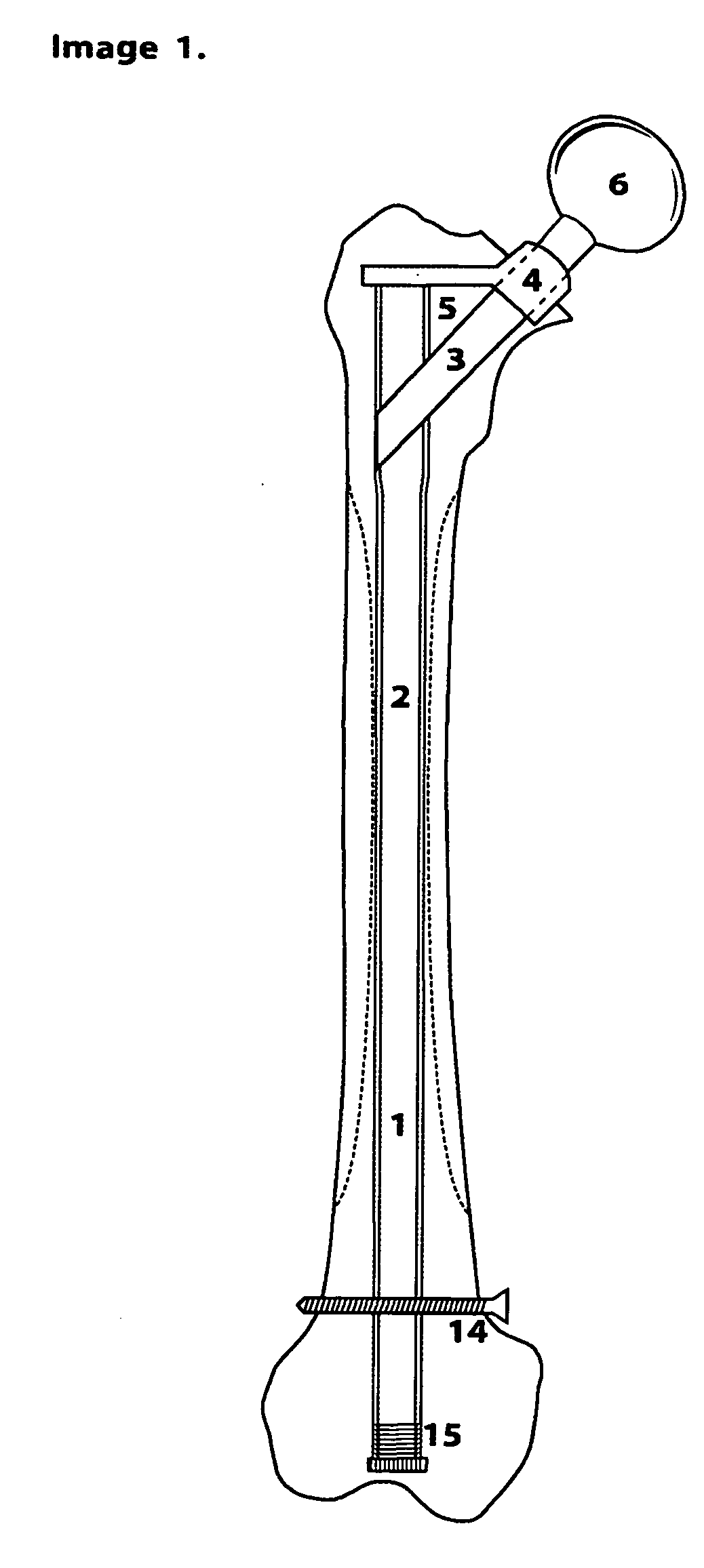
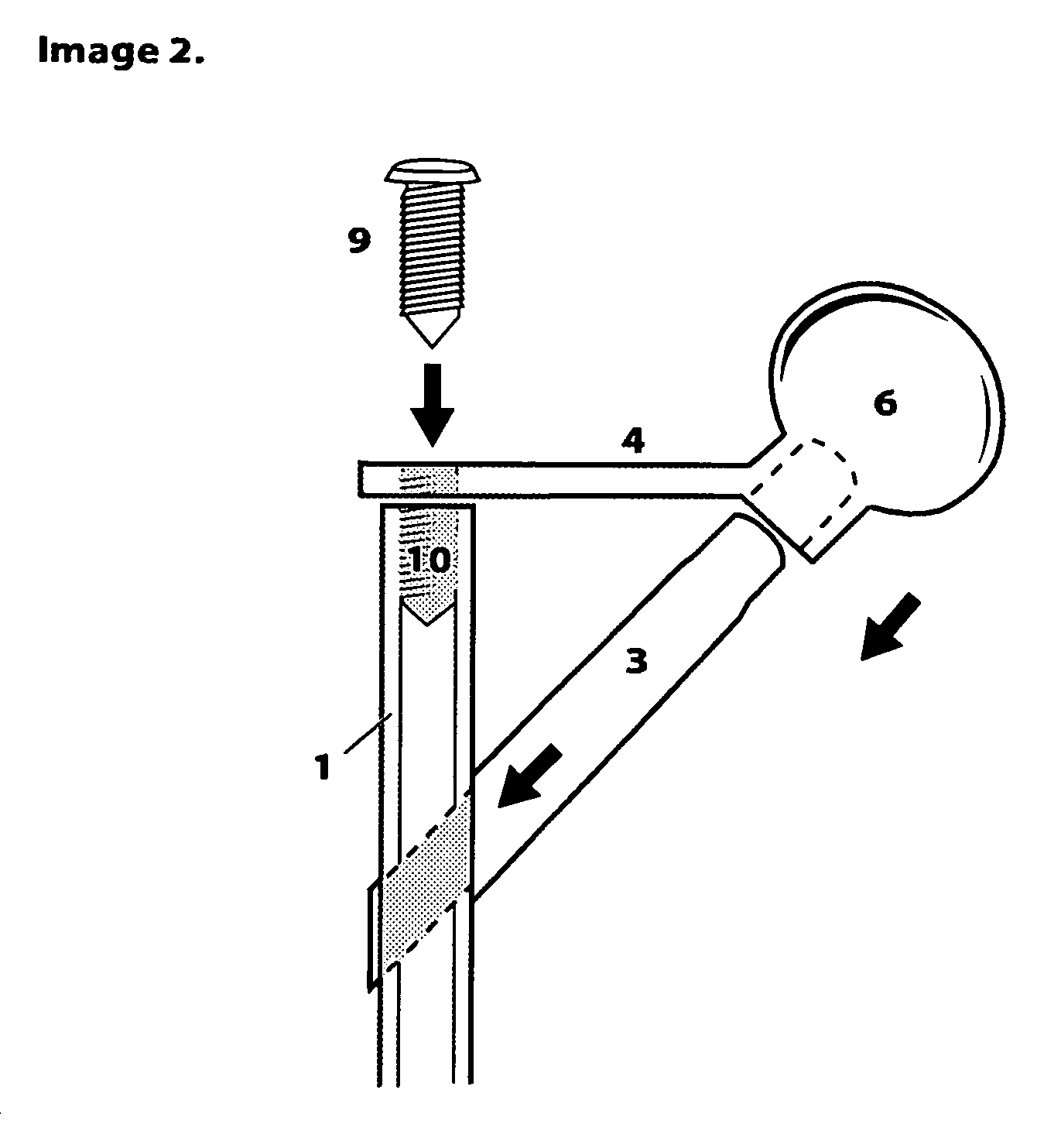
O'Gara femur prosthesis
This patent describes a device to replace the proximal femoral head and neck. The uniqueness of the device is in its proximal design which incorporates a transverse tension bar which prevents failure of the femoral neck portion of the device in tension. This design characteristic permits the use of thinner materials which more closely resemble the elastic nature of bone itself while at the same time endowing the prosthesis with strength and resistance to failure. The device is designed to have a long intramedullary portion which would load the femur throughout its length as well as a modular attachment on its distal end for the insertion of a future knee replacement.
Owner:OGARA TADHG JAMES
Devices, systems and methods for monitoring knee replacements
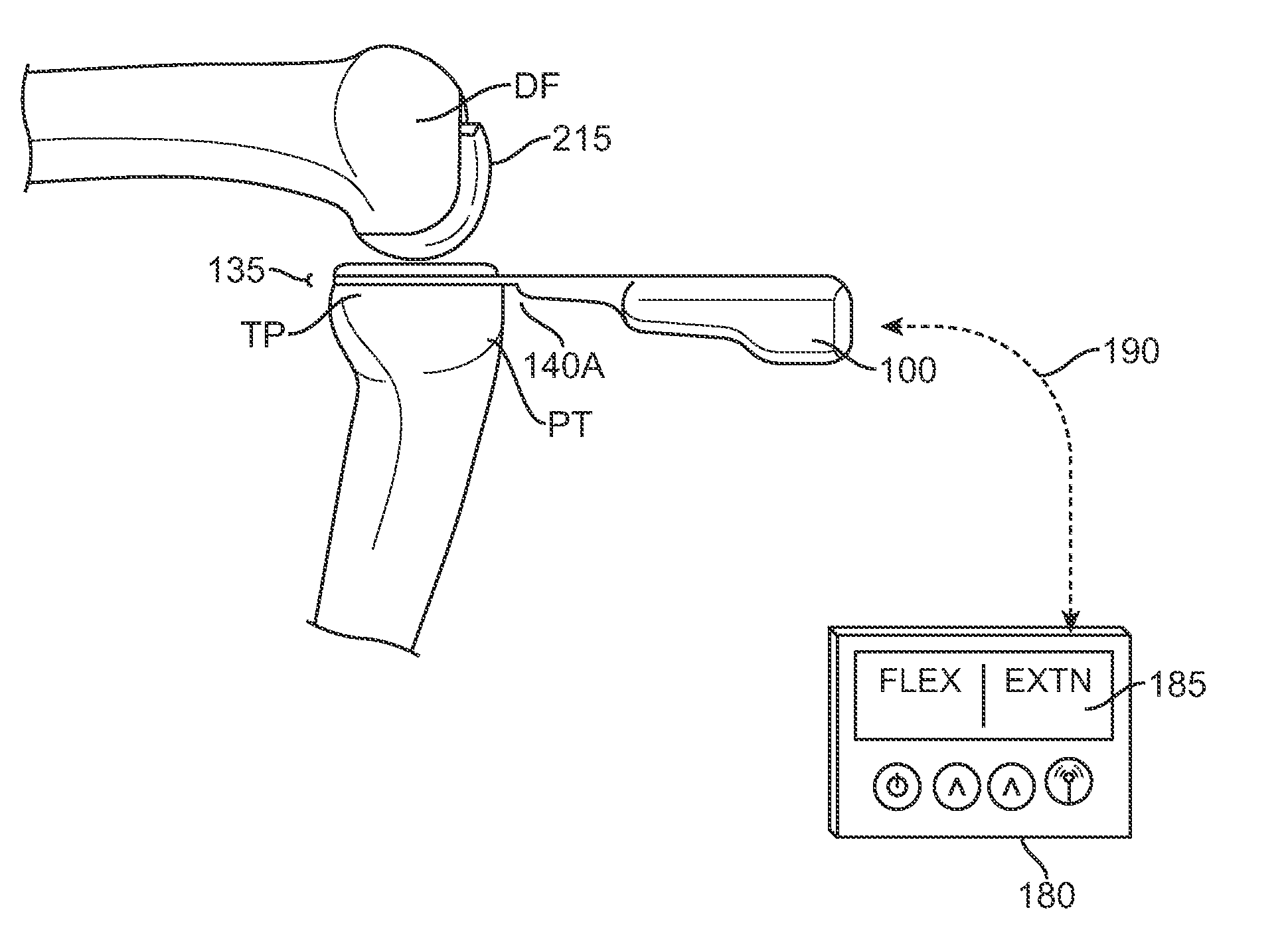
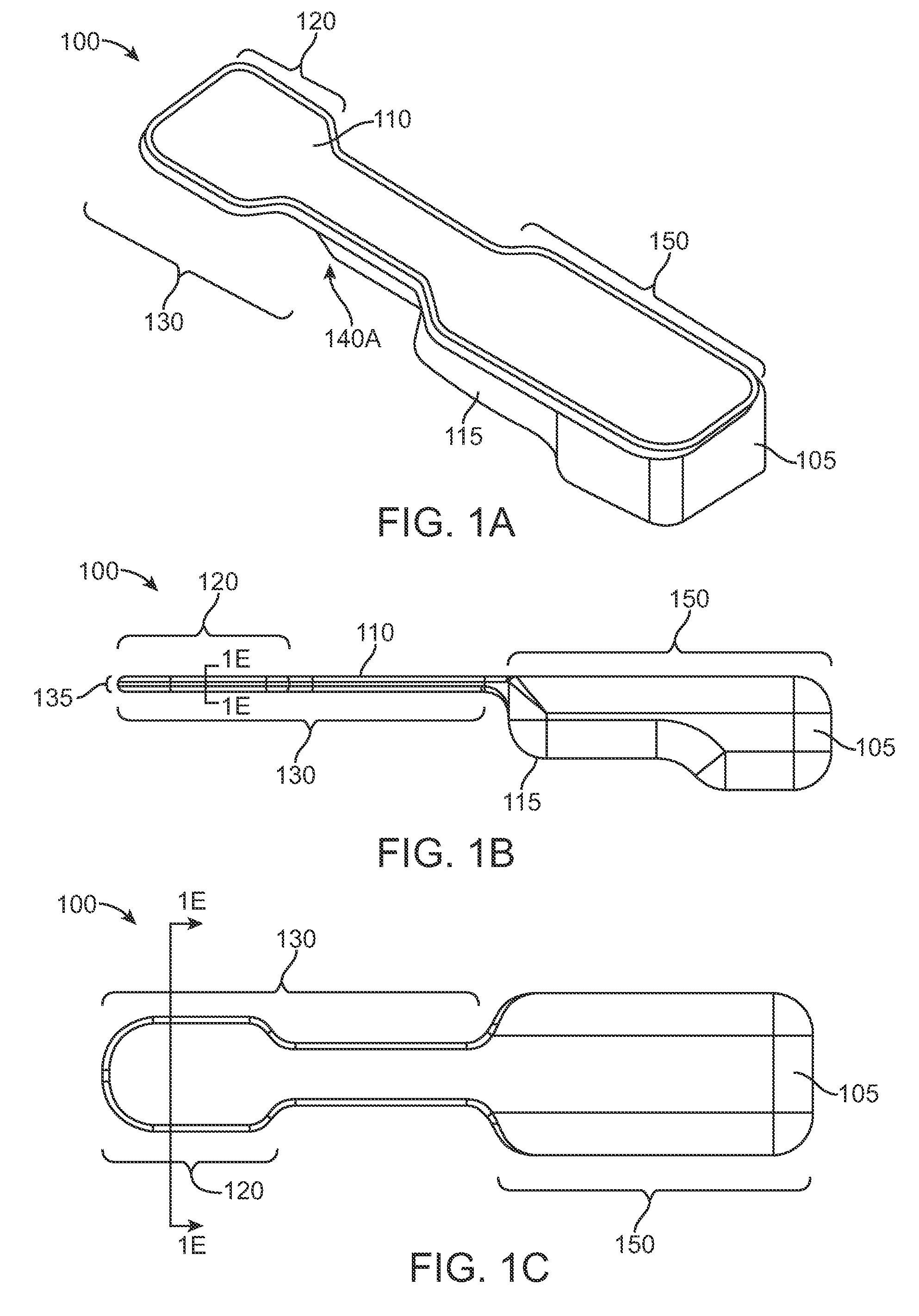
InactiveUS20160192878A1Accurately determineAccurate measurementInertial sensorsJoint implantsKnee JointFemoral component
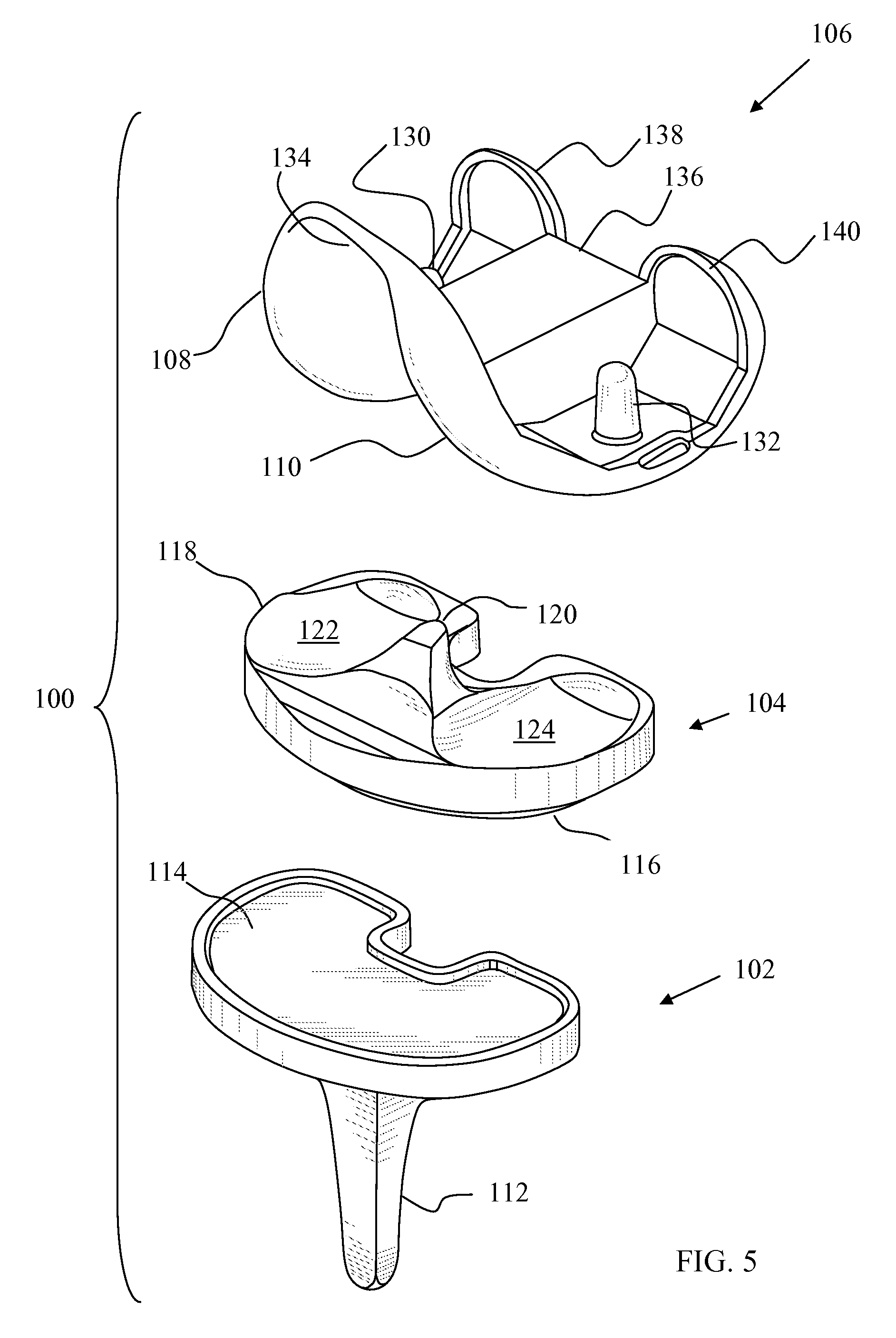
Knee replacement prosthesis are provided, comprising a plurality of sensors and at least one of a femoral component, a patellar prosthesis and a tibial component.
Owner:CANARAY MEDICAL INC
Knee prosthesis
The invention relates to an orthopedic prosthetic device and a method of implanting such device. More particularly, the invention relates to a knee replacement prosthesis having femoral, patellar, and tibial components having surfaces for receiving bone cement and surfaces which promotes bone ingrowth.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT
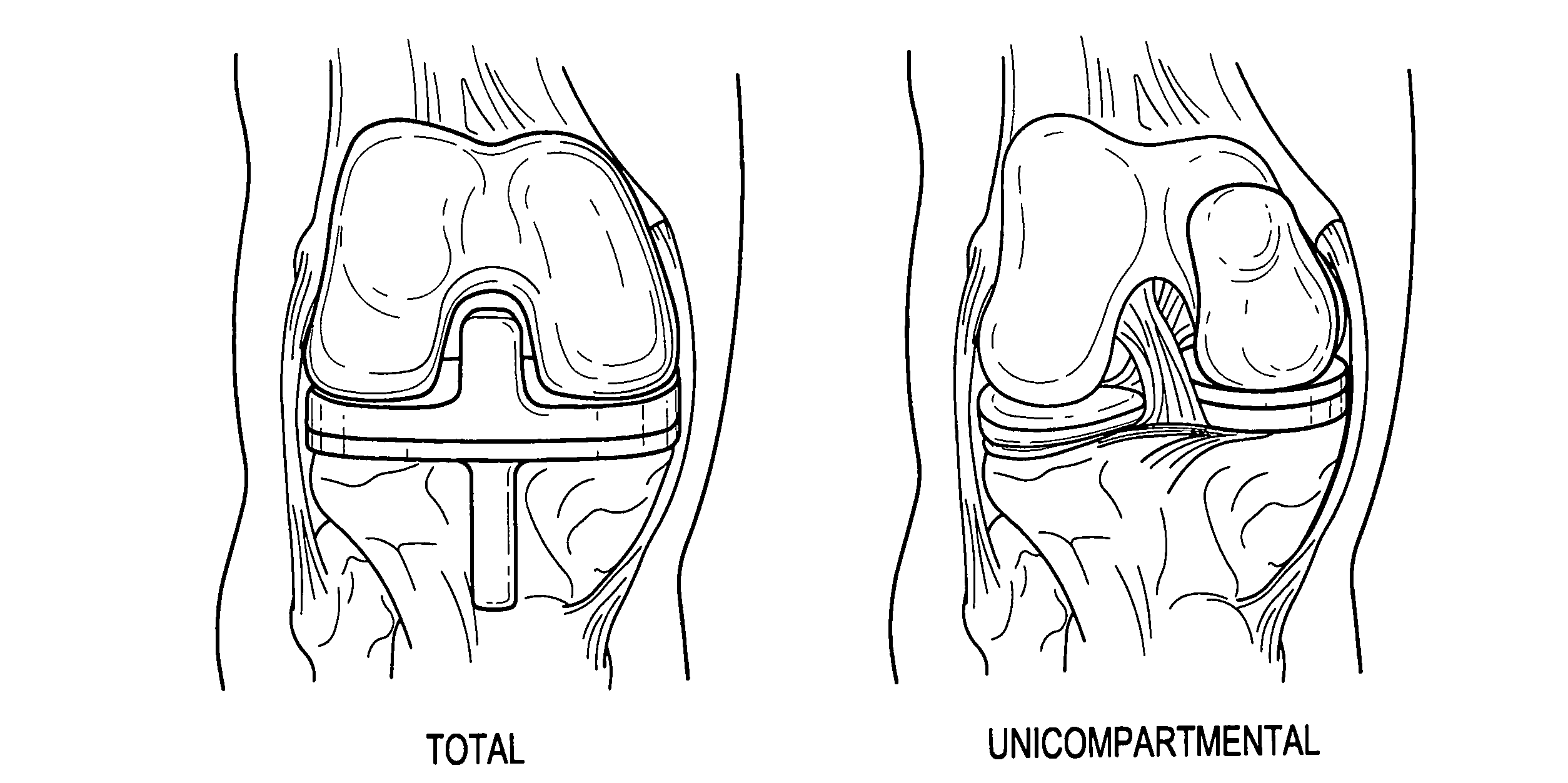
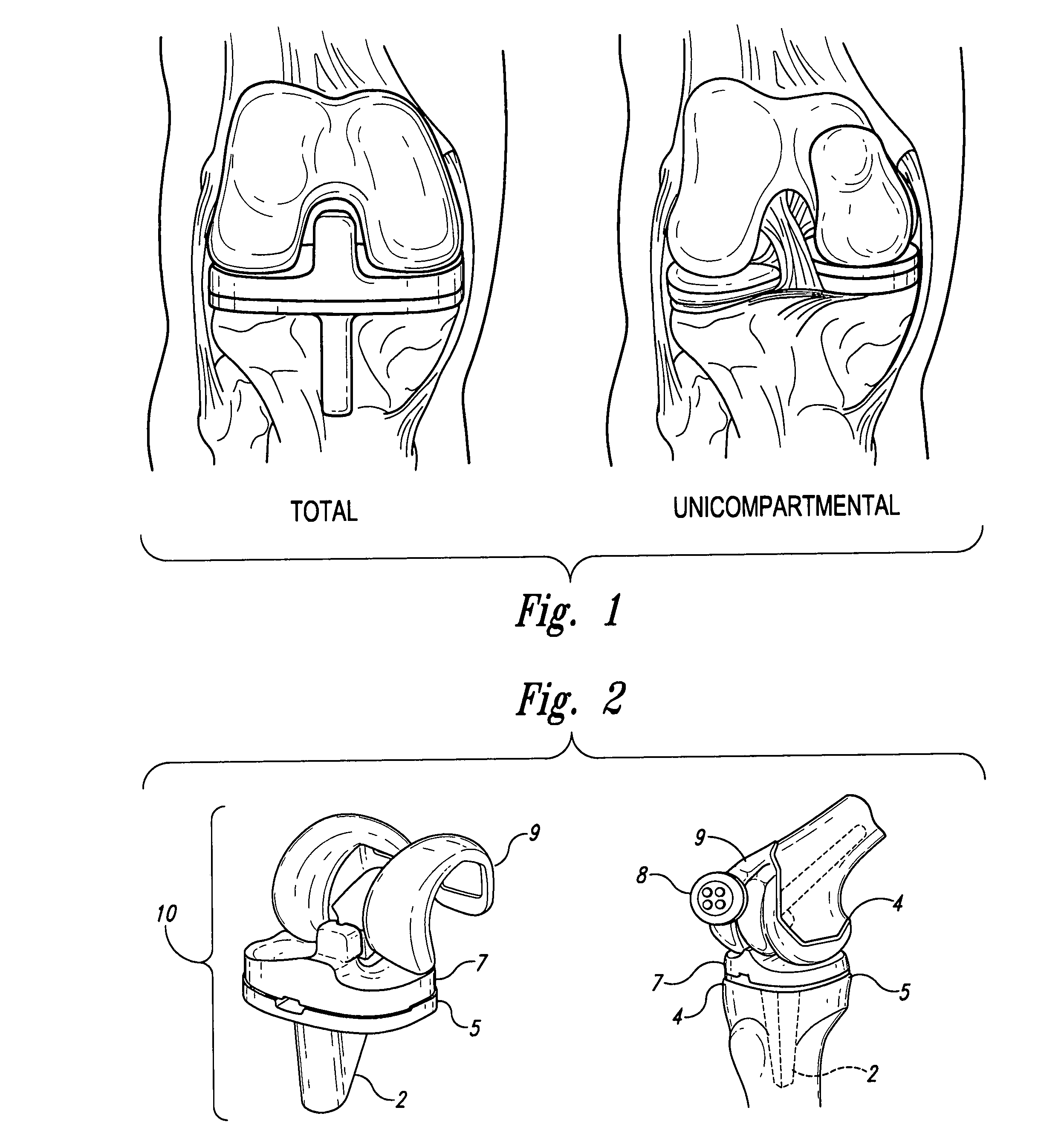
Bone shaping device for knee replacement
InactiveUS20050192583A1Improve accuracyImprove consistencyDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTotal knee replacement surgeryArthroplasty knee
A bone surgery device with a reciprocating cutting head. The device comprises several sets of shaping surfaces sometimes including cutting blades, which are located and oriented so as to shape the distal end of the femur and the proximal end of the tibia for total knee replacements and unicompartmental knee replacements. The device, which may be hand directed or aided by spatial and directional guiding mechanisms or an optical navigation system, may also include both coolant supply for controlling heat during bone, cutting and shaping, and a suction method for carrying away fluid and debris. The device is substantially configured to the artificial joint component to be attached thereto.
Owner:WALKER PETER STANLEY +1
Bone shaping device for knee replacement
InactiveUS20050192584A1Reduction in time taken to cutReduction in to shape bone surfaceDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTibiaKnee Joint
A bone surgery device with a reciprocating cutting head. The device comprises several sets of shaping surfaces sometimes including cutting blades, which are located and oriented so as to shape the distal end of the femur and the proximal end of the tibia for total knee replacements and unicompartmental knee replacements. The device, which may be hand directed or aided by spatial and directional guiding mechanisms or an optical navigation system, may also include both coolant supply for controlling heat during bone cutting and shaping, and a suction method for carrying away fluid and debris. The device is substantially configured to the artificial joint component to be attached thereto.
Owner:WALKER PETER STANLEY +1
Surface guided knee replacement
An artificial knee joint that includes a femoral component with a specially shaped bearing surface and a tibial component, whose surface interacts with the femoral surfaces. The interaction provides for the motion and stability characteristics of the anatomic knee. The interaction between the femoral and tibial surfaces is such that as the knee is flexed to maximum, the femoral component moves posteriorly on the tibial surface, more so on the lateral side than on the medial side. This is accomplished by the interaction of a projecting tibial post inside a cupola in the center of the femoral component, and by the saggital radius on the medial side being smaller than that on the lateral side. The prevention of anterior sliding of the femur on the tibia in early flexion is accomplished by the interaction between a distal-anterior recess on the medial side of the femur and an apposing raised pad on the tibial surface. Rotational laxity at all angles is allowed by the presence of only one recess pad and by non-conforming femoral-tibial surfaces on the lateral side.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
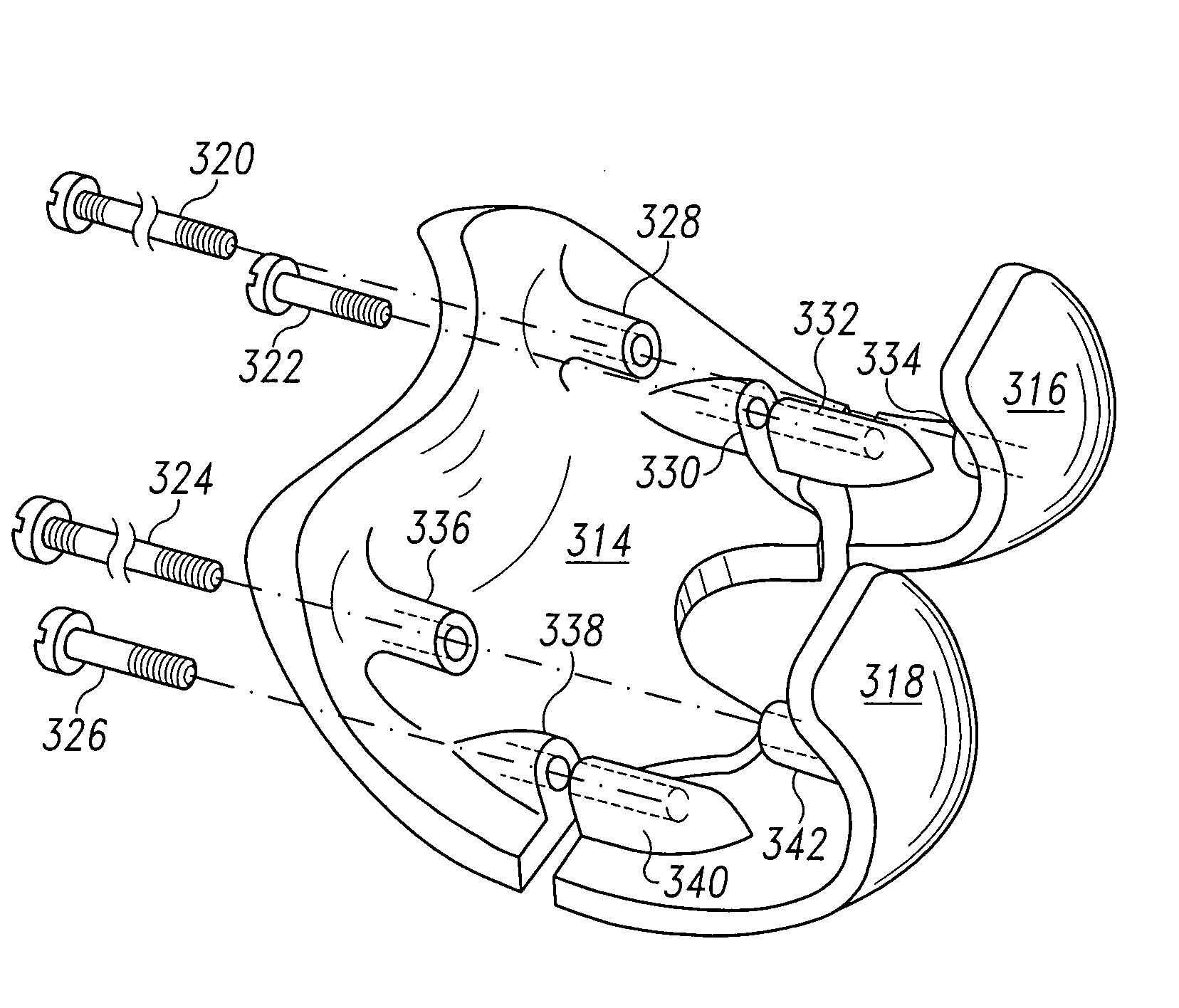
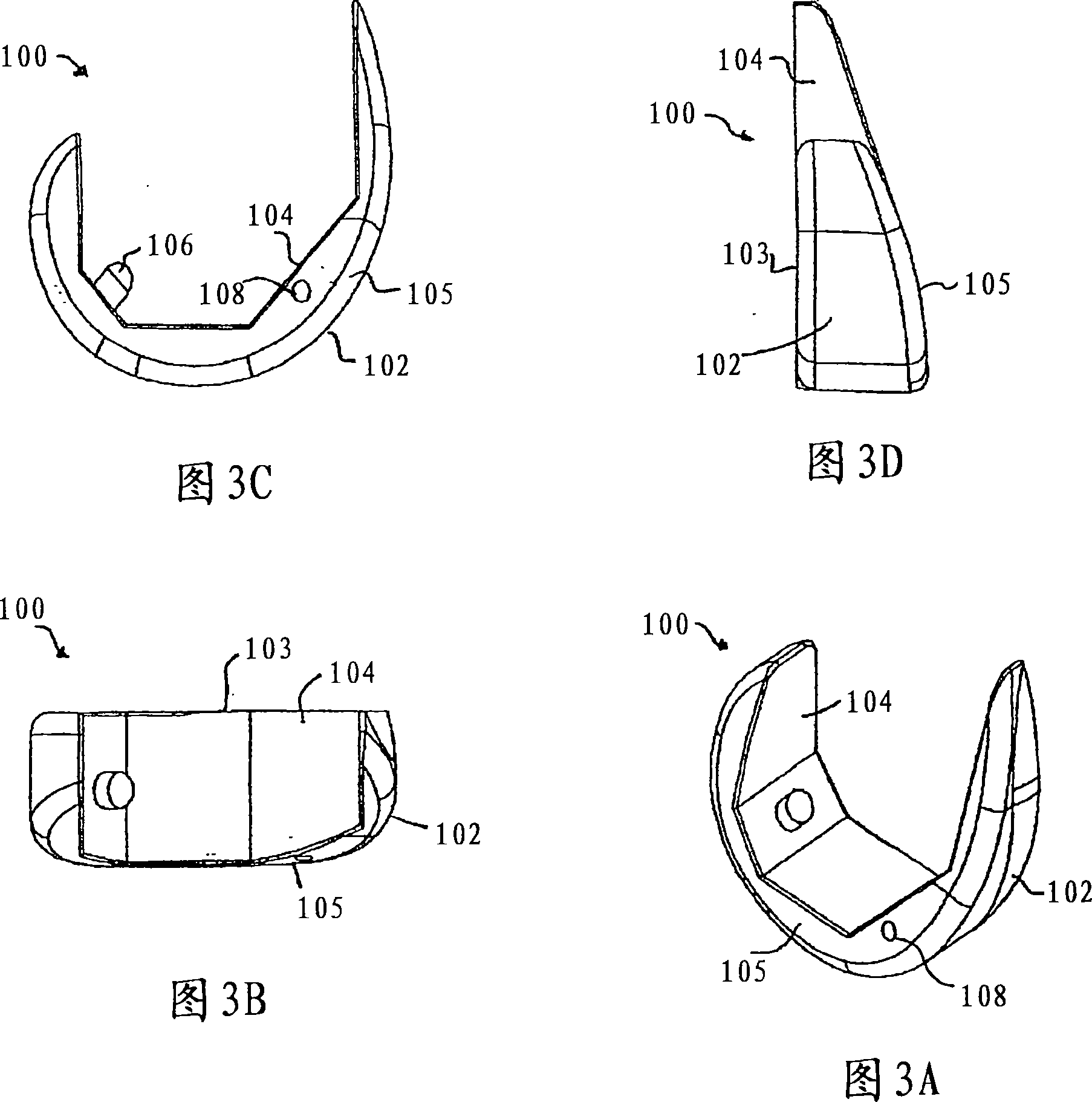
Tibial prosthetic component for a partial or unicondylar bearing knee replacement, method of selecting such a tibial prosthetic component, method of implanting such a tibial prosthetic component and a kit for a surgeon
ActiveUS20130166037A1Great capacity to handle stressReduce the amount requiredBone implantJoint implantsKnee JointBone tibia
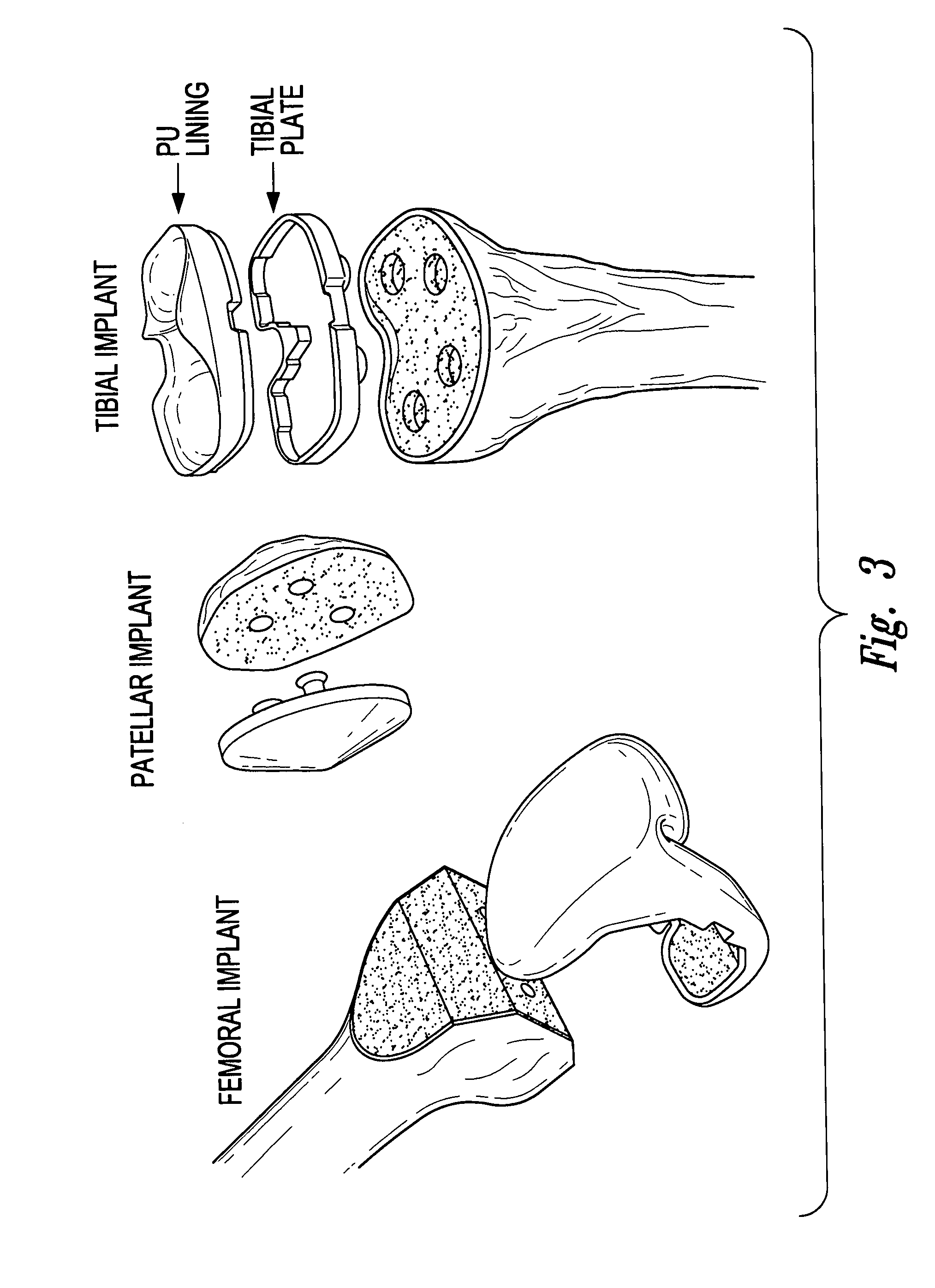
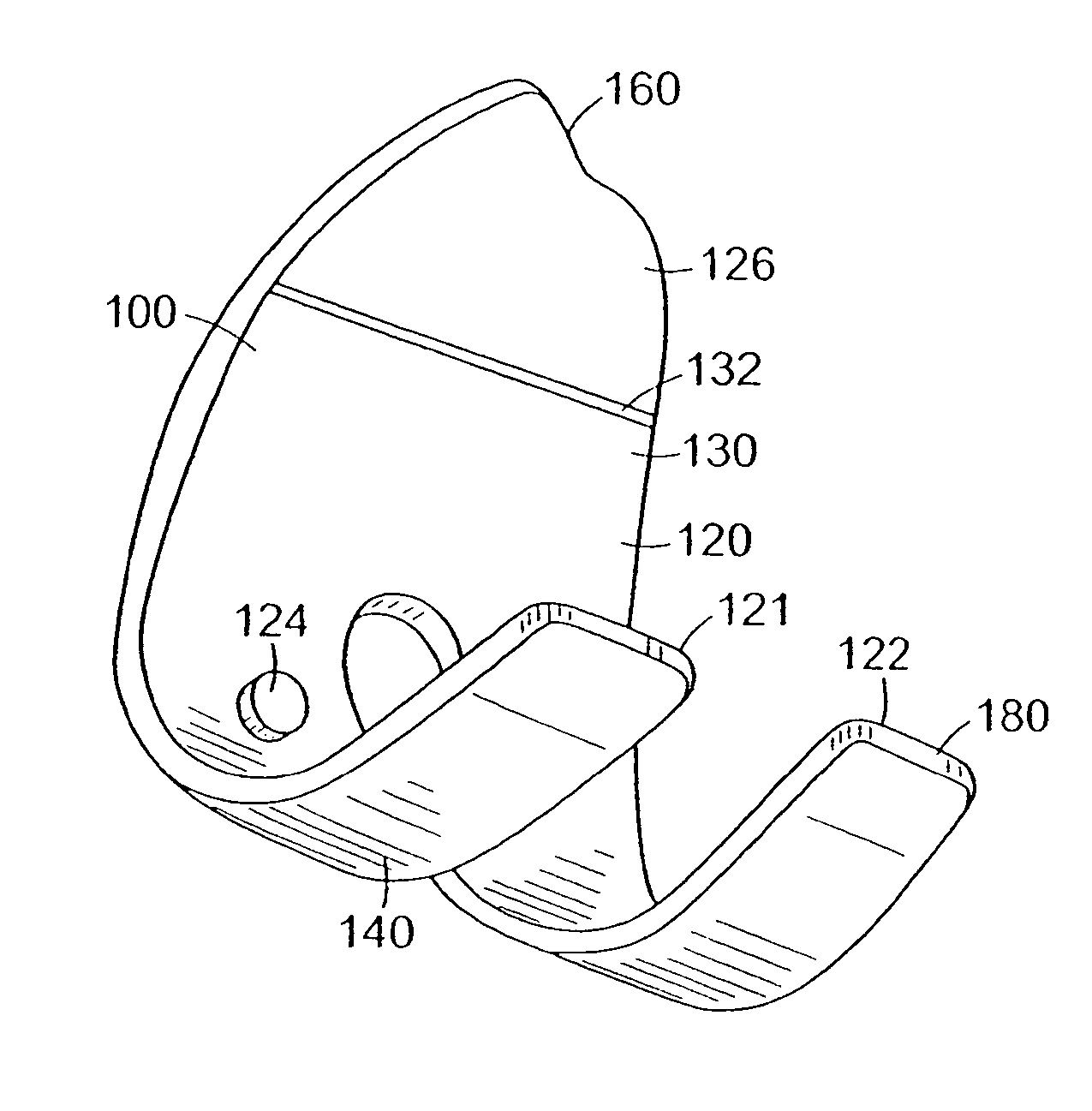
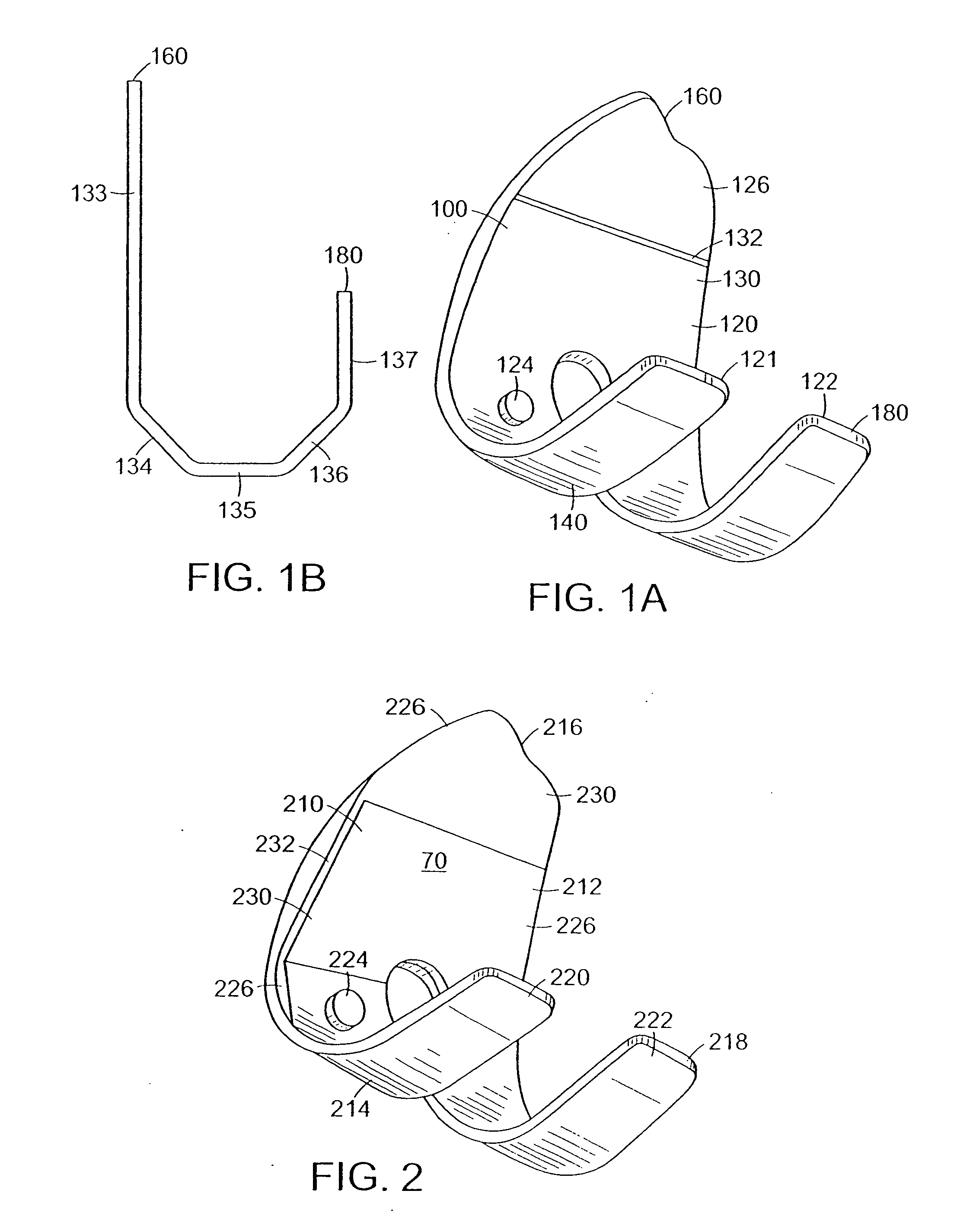
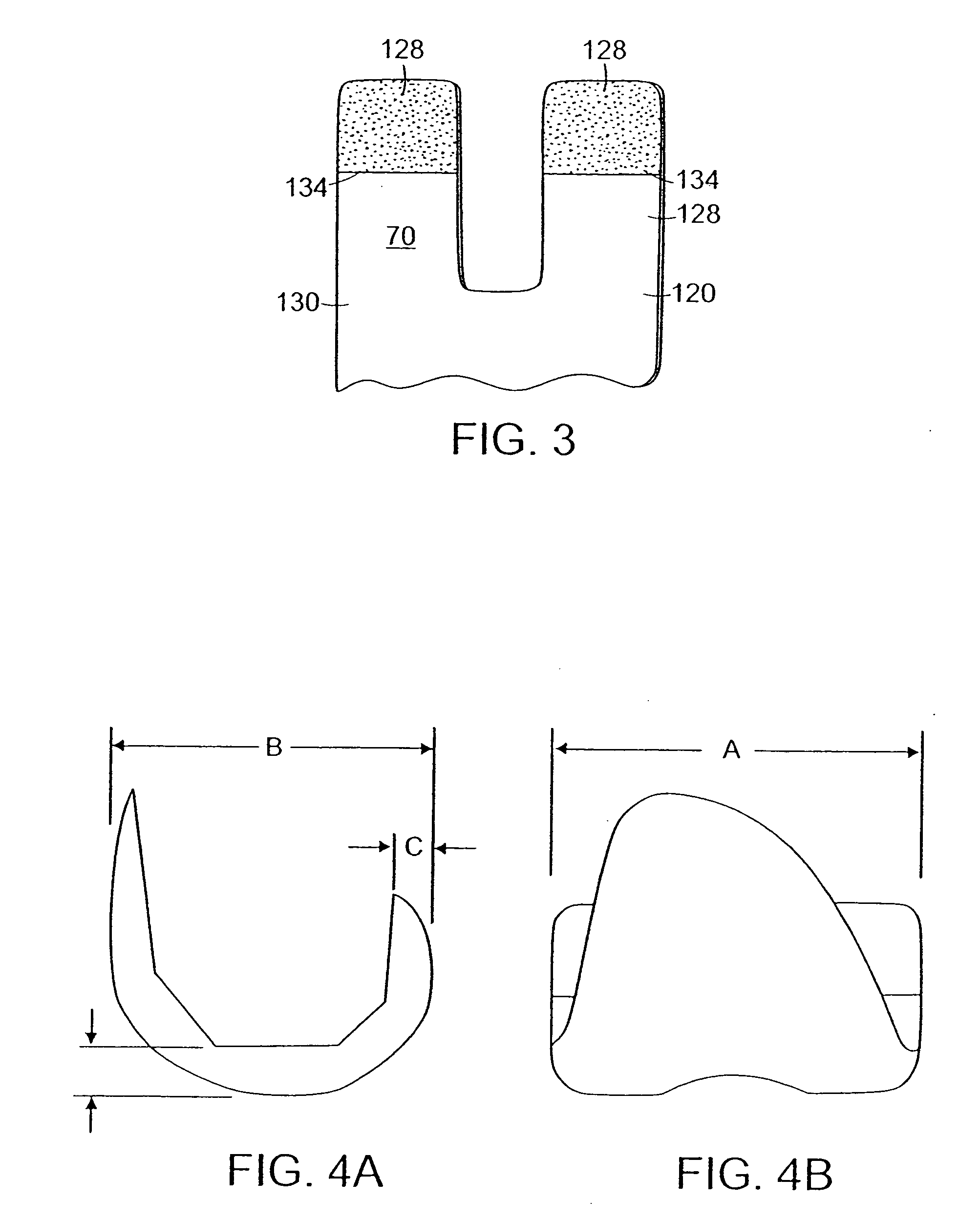
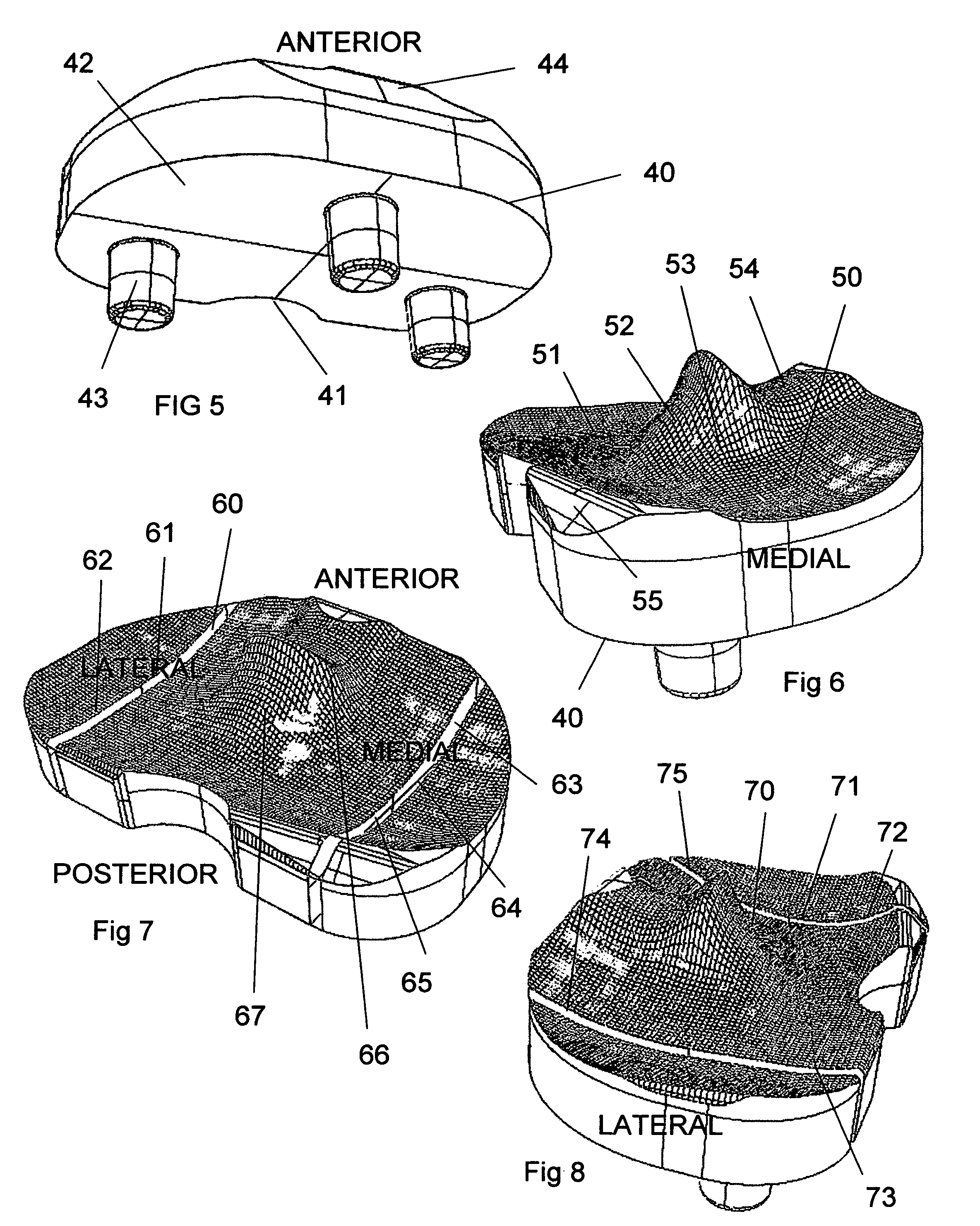
The invention concerns a tibial prosthetic component comprising a plate (100) for forming a tibial plateau of a tibia (16), wherein a peripheral region of the plate (100) has a thickness of less than 3 mm. The invention also concerns a tibial prosthetic component having a keel of depth less than 9 mm. The invention also concerns a method of selecting a tibial prosthetic component comprising receiving measurements of at least one physical attribute of an individual into whom the tibial prosthetic component is to be implanted, selecting a thickness of a plate (100) and depth of keel of the tibial prosthetic component based on the measurements and providing a tibial prosthetic component comprising a plate (100) having the selected thickness and a keel having the selected depth. The invention may also comprise implanting a tibial prosthetic component selected in accordance with this method into an individual and a kit comprising a plurality of prosthetic components comprising plates having different thicknesses with keels of different depths.
Owner:OCONNOR JOHN +3
Knee implant
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Antero-posterior placement of axis of rotation for a rotating platform
A knee replacement system includes a femoral component including a lateral condylar articulating portion and a medial condylar articulating portion, a tibial tray including an upper articulating surface, and a tibial insert including (i) a first articulating portion for articulating with the lateral condylar articulating portion with a first condylar dwell point, (ii) a second articulating portion for articulating with the medial condylar articulating portion with a second condylar dwell point, (iii) a lower articulating surface for articulating with the upper articulating surface, and (iv) a coupling member for coupling with the tibial tray and defining an axis of rotation about which the tibial insert rotates with respect to the tibial tray, the axis of rotation intersecting the upper articulating surface at a location posterior to a dwell axis including the condylar dwell points when the dwell axis is projected onto the upper articulating surface.
Owner:DEPUY (IRELAND) LTD
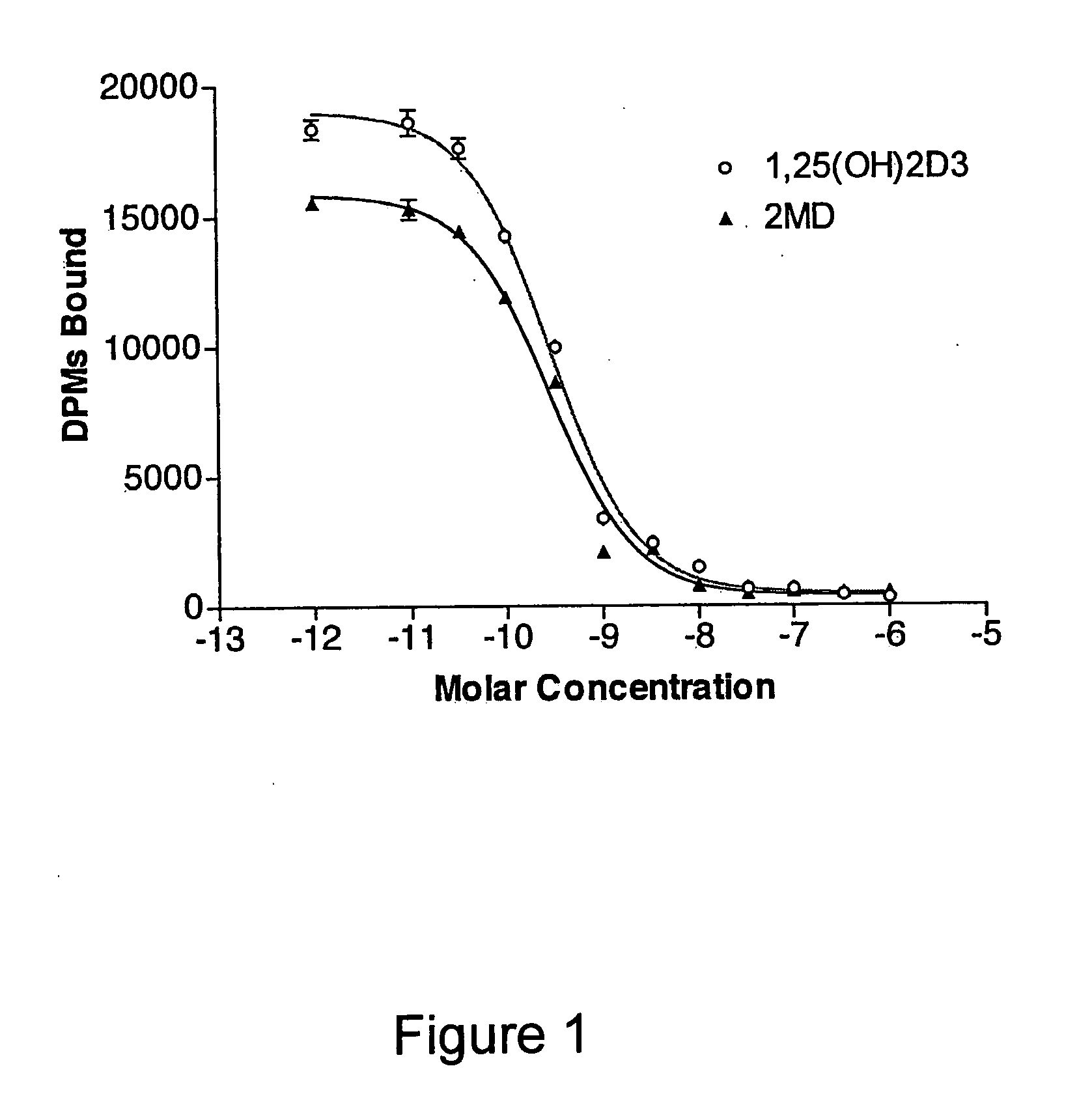
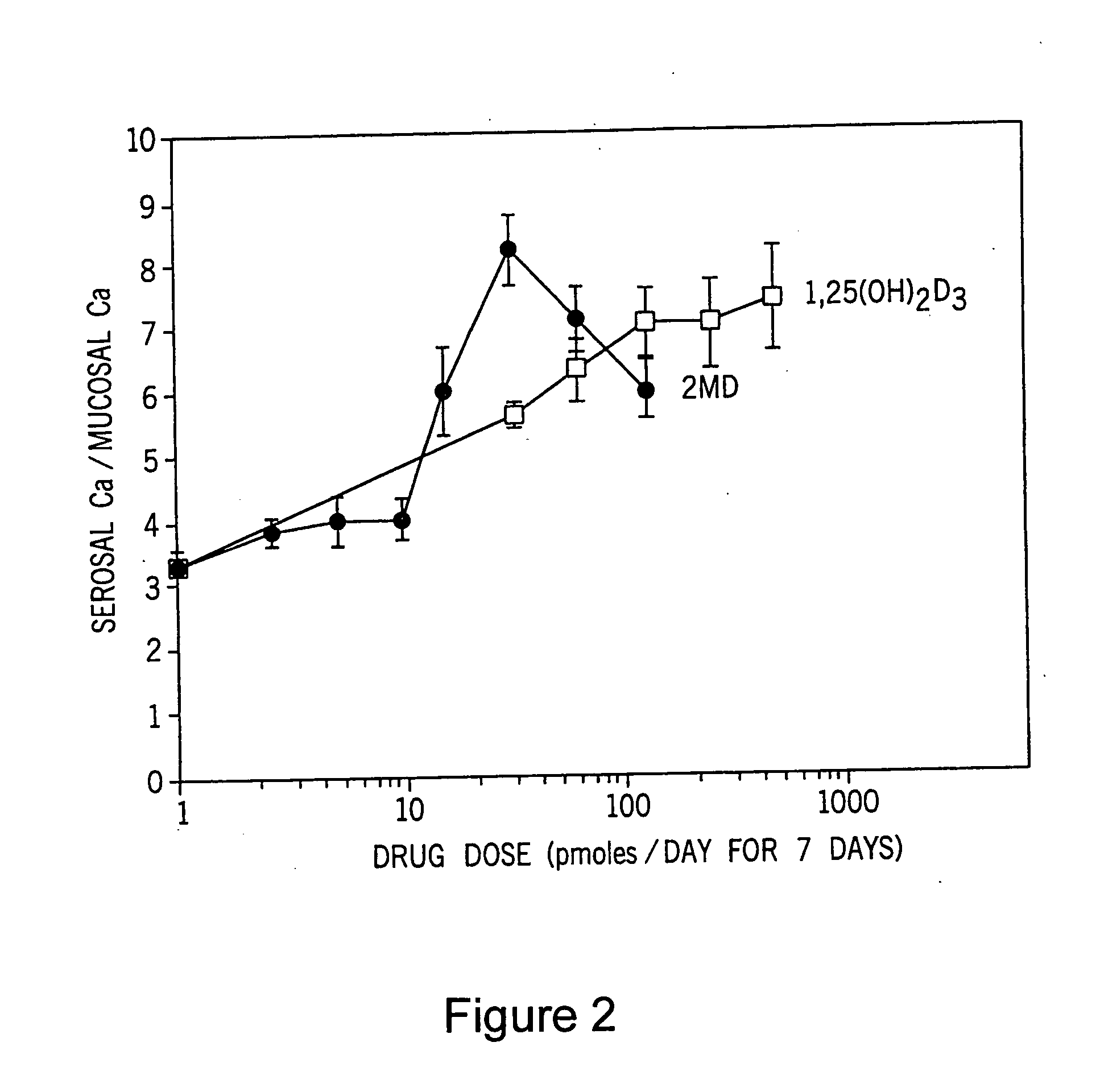
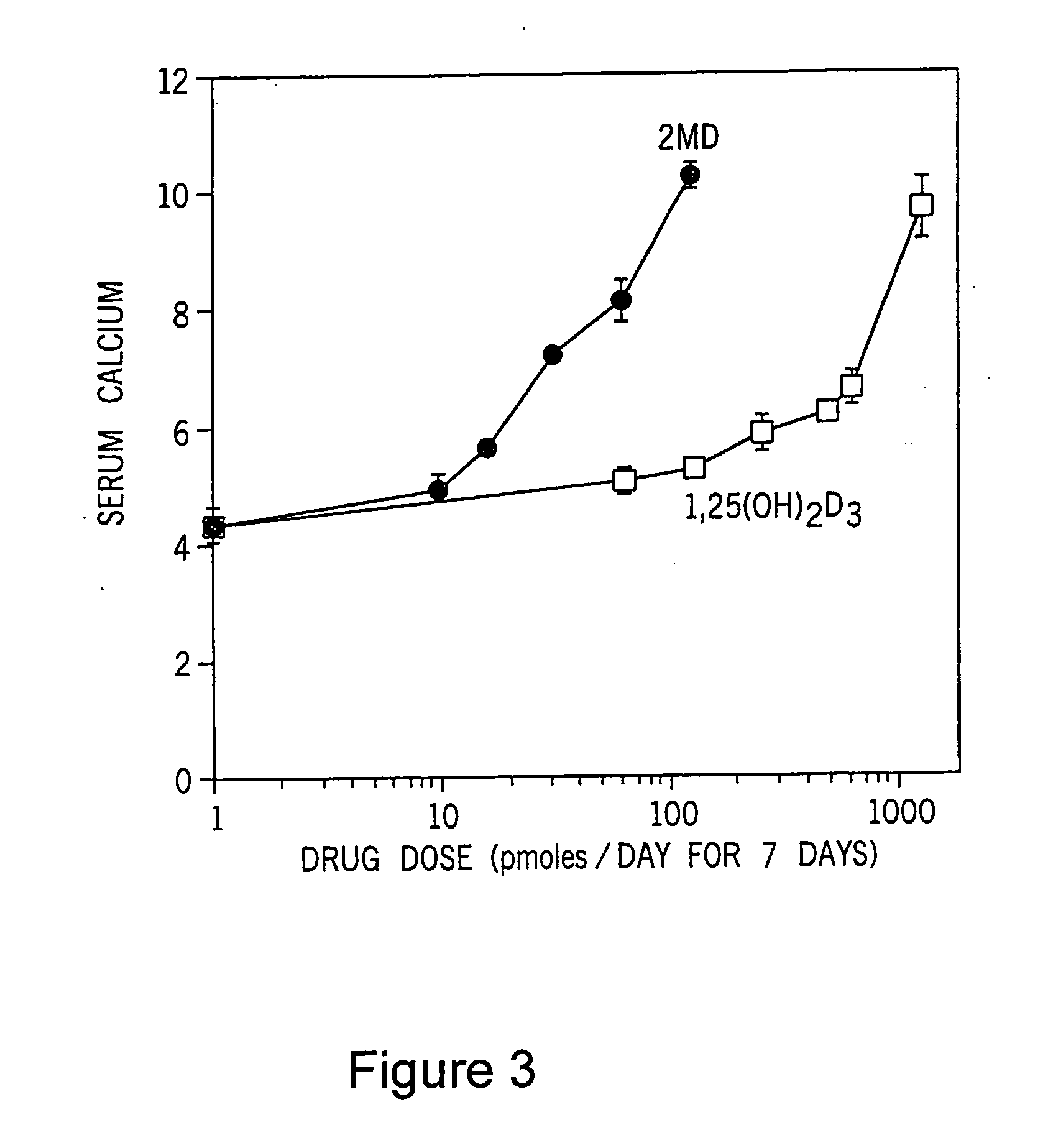
Use of 2-methylene-19-nor-20(S)-1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 for the prophylaxis of bone diseases
ActiveUS20050187201A1High breaking strengthImprove bone strengthBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBone formationArthroplasty knee
This invention provides pharmaceutical uses for 2-methylene-19-nor-20(S)-1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. This compound is characterized by high bone calcium mobilization activity demonstrating preferential activity on bone. This results in a novel therapeutic agent for the treatment and prophylaxis of diseases where bone formation is desired, particularly osteoporosis. This compound also increases both breaking strength and crushing strength of bones evidencing use in conjunction with bone replacement surgery such as hip and knee replacements, as well as use by normal subjects when high bone mass is desired.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
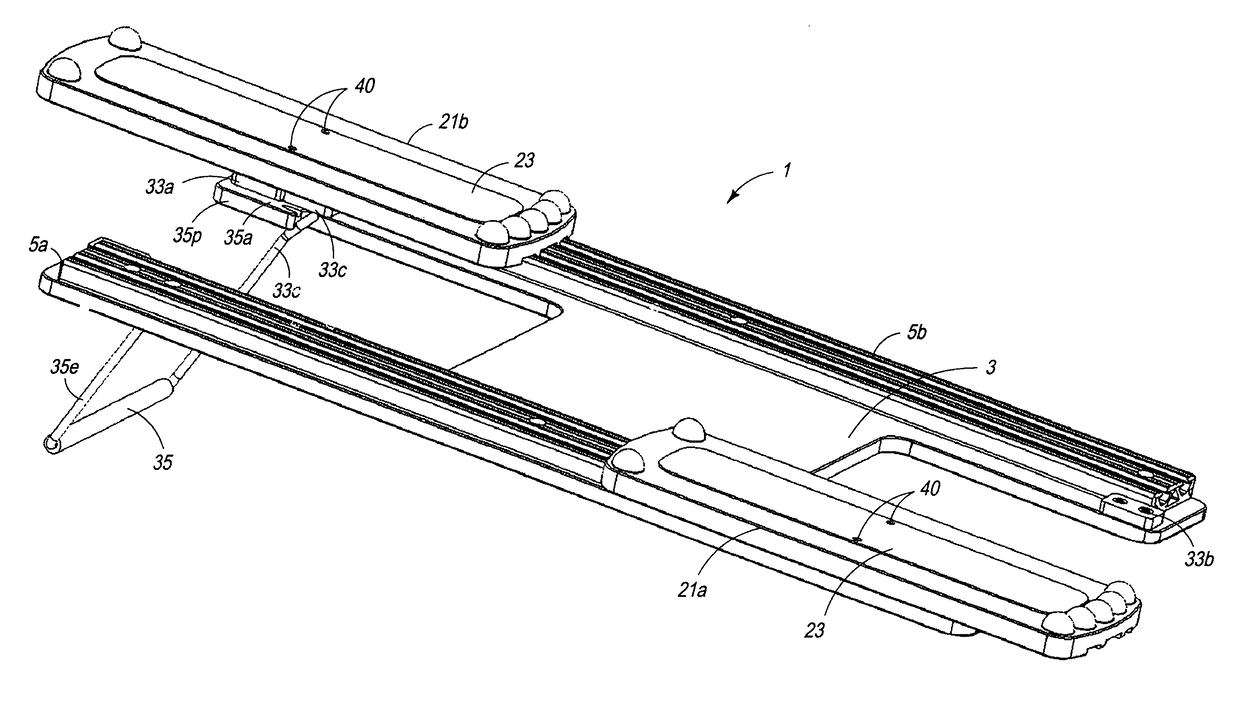
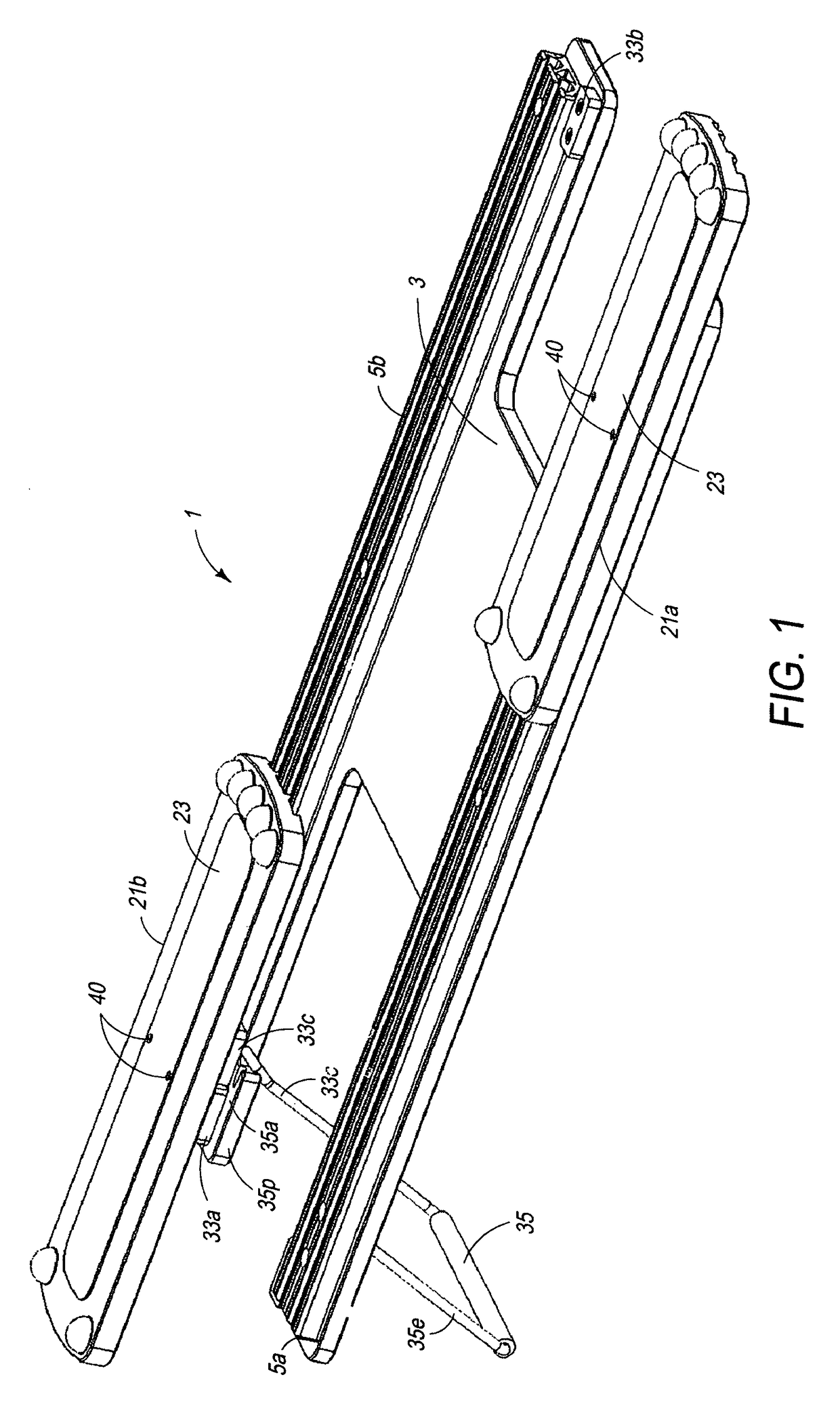
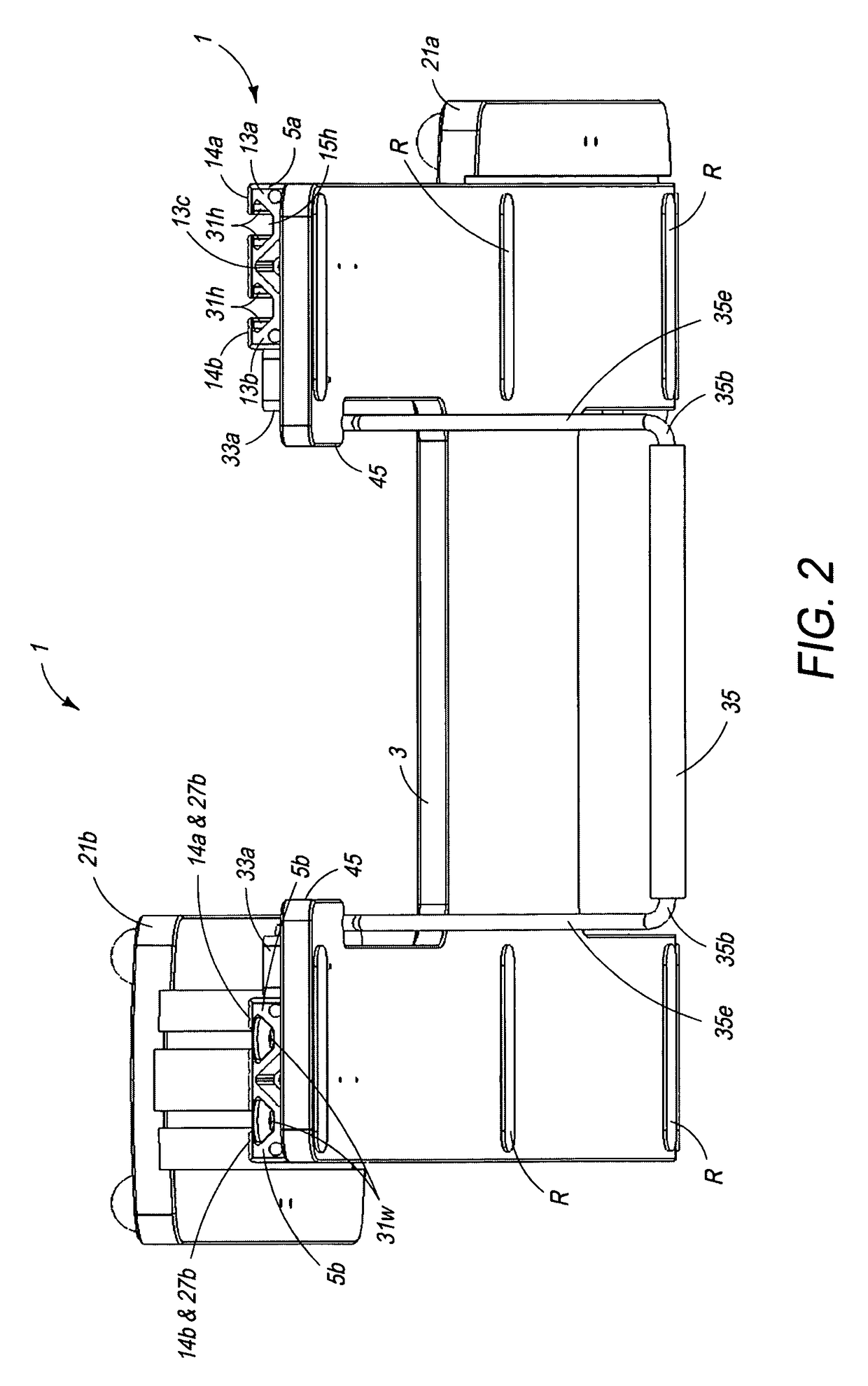
Therapeutic device
ActiveUS9616283B1Lower levelPromote recoveryChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesTherapeutic DevicesKnee Joint
A low stress therapeutic device is provided by utilizing foot plates and guide rails having operationally tracking surfaces of a low coefficient of friction supported by a platform. The device includes a rail stabilizer equipped with extending longitudinally recess or slot and a slideably mounted foot plate having upon its underside a longitudinal projection slideably retained within the rail recess. The therapeutic device may be designed to operate under relatively effortless strain at a low coefficient of friction. The therapeutic device is useful for knee replacement, stroke victims, ACL repair, and other therapeutic treatments requiring a nominal initiating effort of movement for rehabilitation. The device may be provided as a one or two footed device of a light weight particularly useful in a patient sitting or lying position. The foot plates may be appropriately equipped with longitudinally underside tracking guides reciprocating sliding within longitudinal slots provided by a tracking rail.
Owner:FAMOUS PT LLC
Apparatus and methods for using an electromagnetic transponder in orthopedic procedures
Electromagnetic transponders as markers are used to localize and guide orthopedic procedures including: knee replacement, hip replacement, shoulder replacement, damaged bone reconstruction, and spine surgery, and more particularly, to guide orthopedic surgical navigation and alignment techniques and instruments. For example, the marker could further be used in any number of guides or templates that attach to the bony anatomy; such as a surgical guide, cutting guide, cutting jig, resection block and / or resurfacing guide. Further, the marker could be incorporated into an existing intramedullary guide rod for a femur and an extramedullary guide rod for a tibia in a knee replacement surgery; or into an external surgical guide system, or the marker could eliminate the need for an external template altogether. According to yet another anticipated use of the tracking system, the marker could be used in conjunction with or replace an optical alignment system.
Owner:VARIAN MEDICAL SYSTEMS
Systems and methods for compartmental replacement in a knee
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com