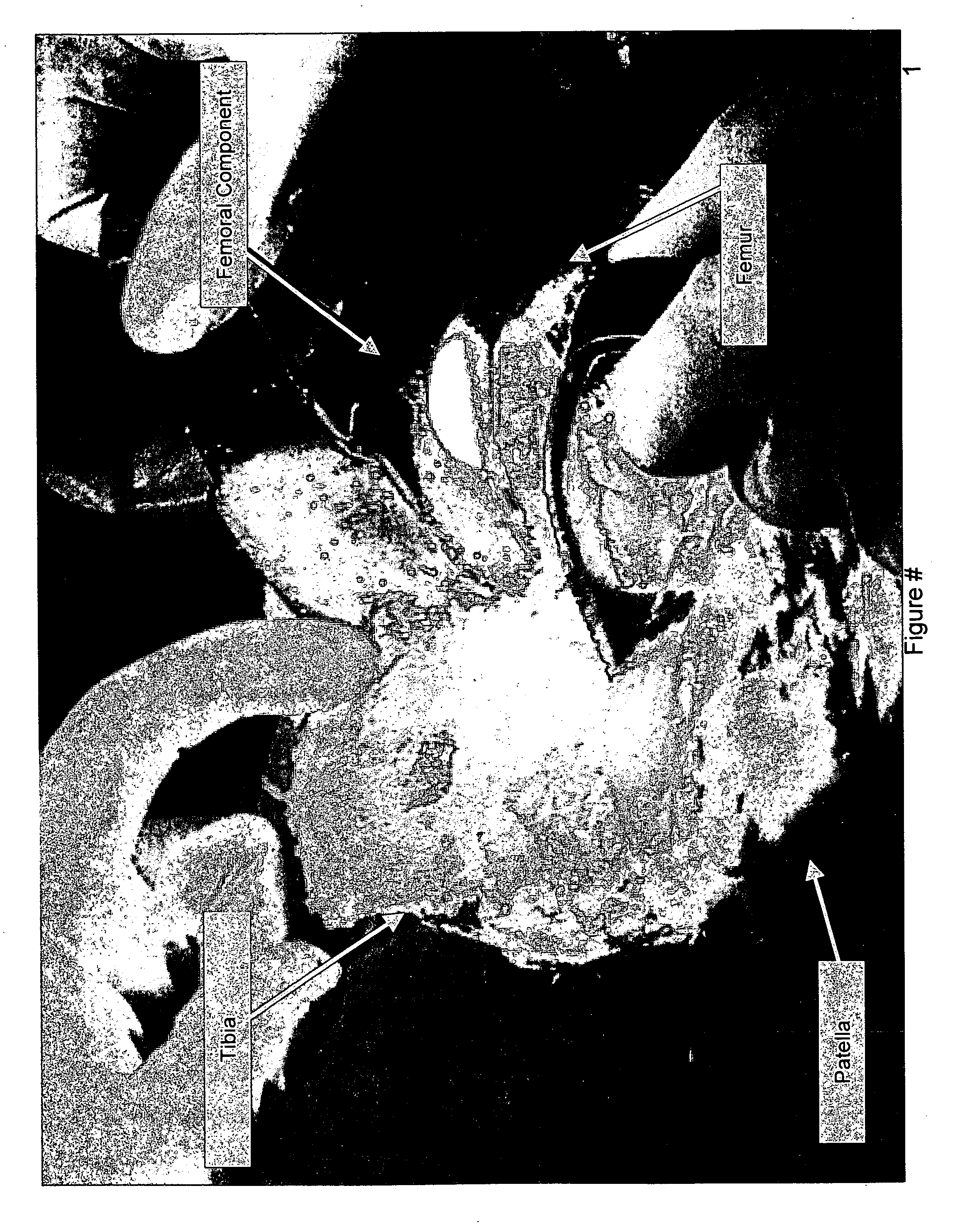
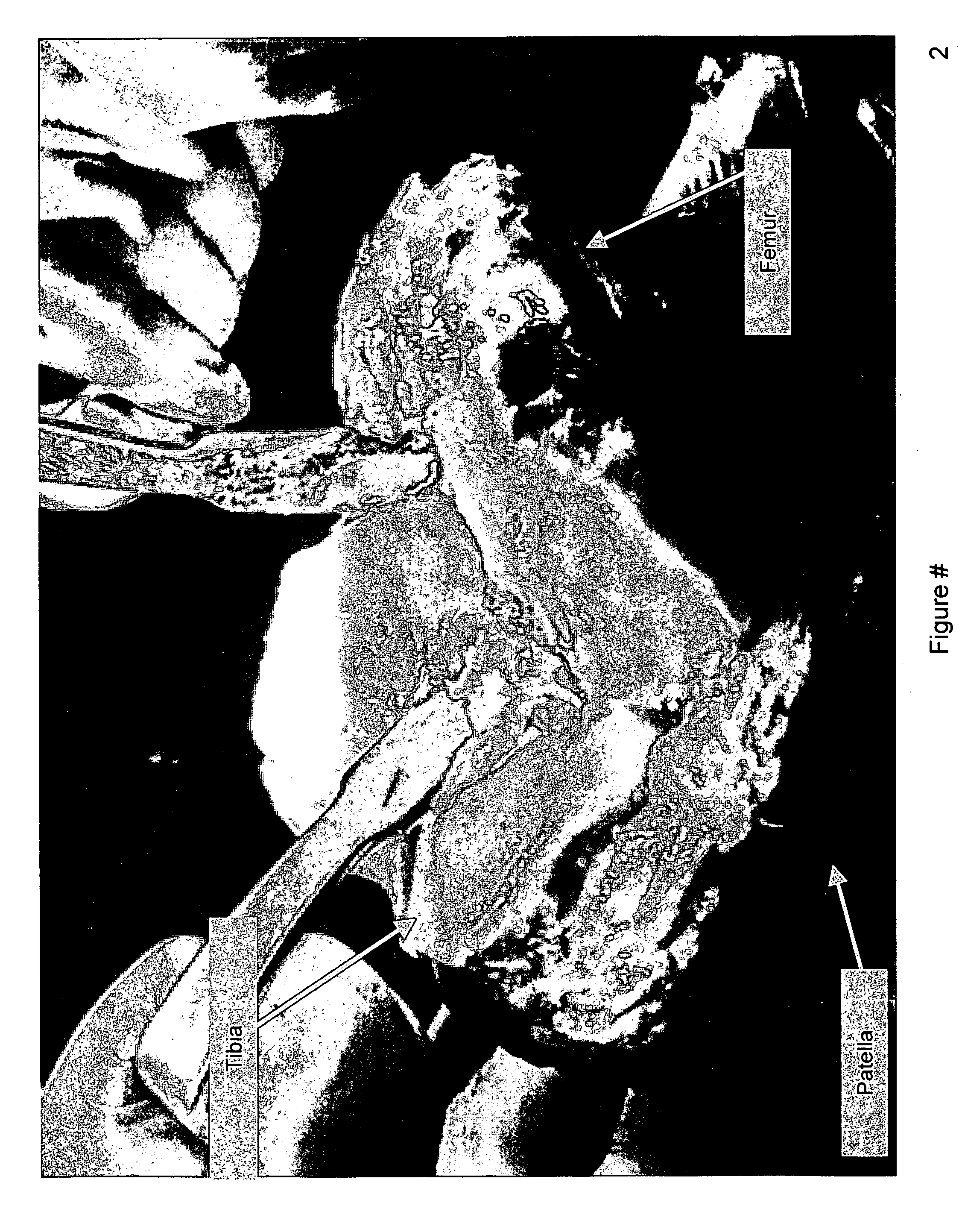
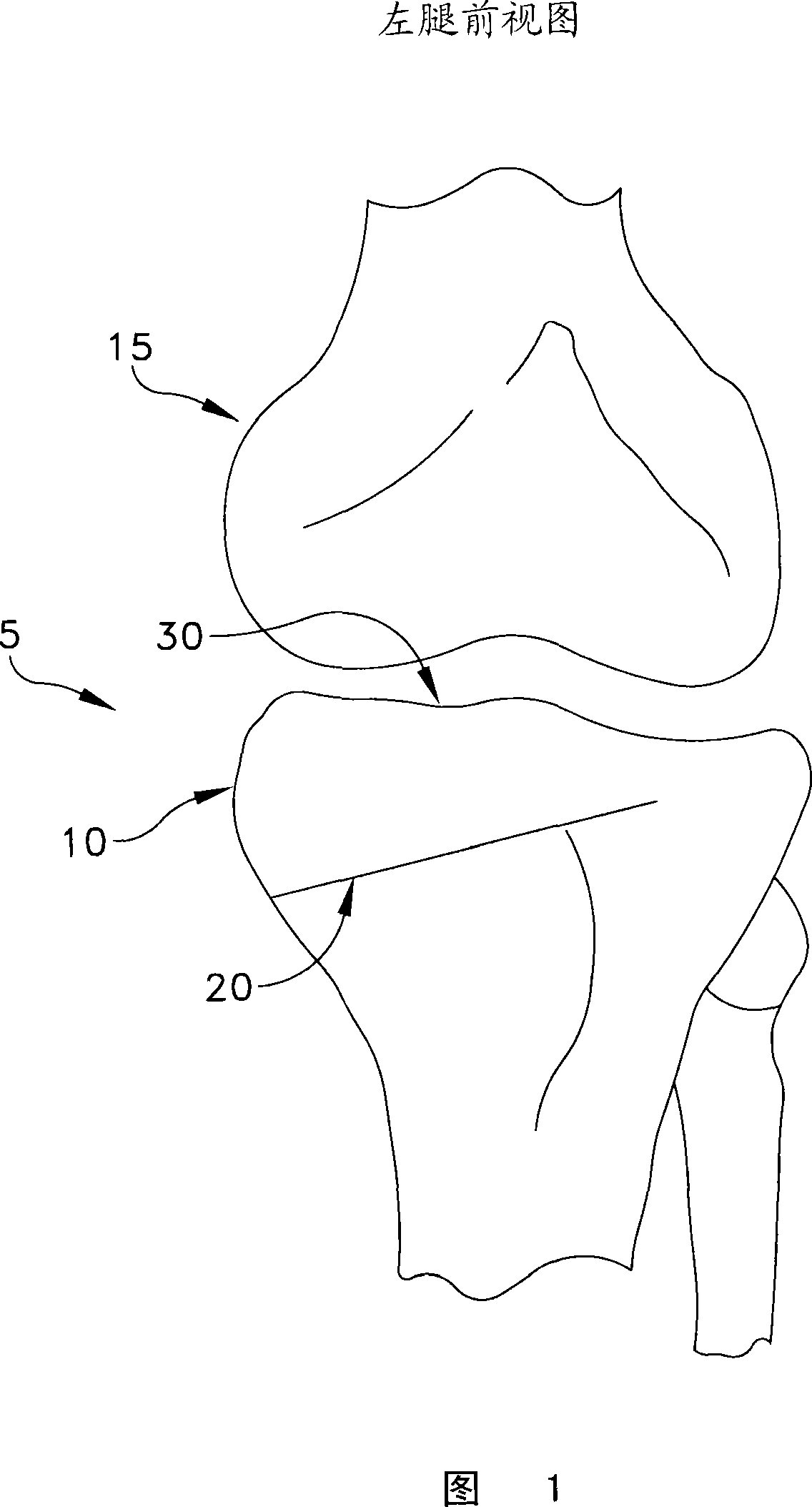
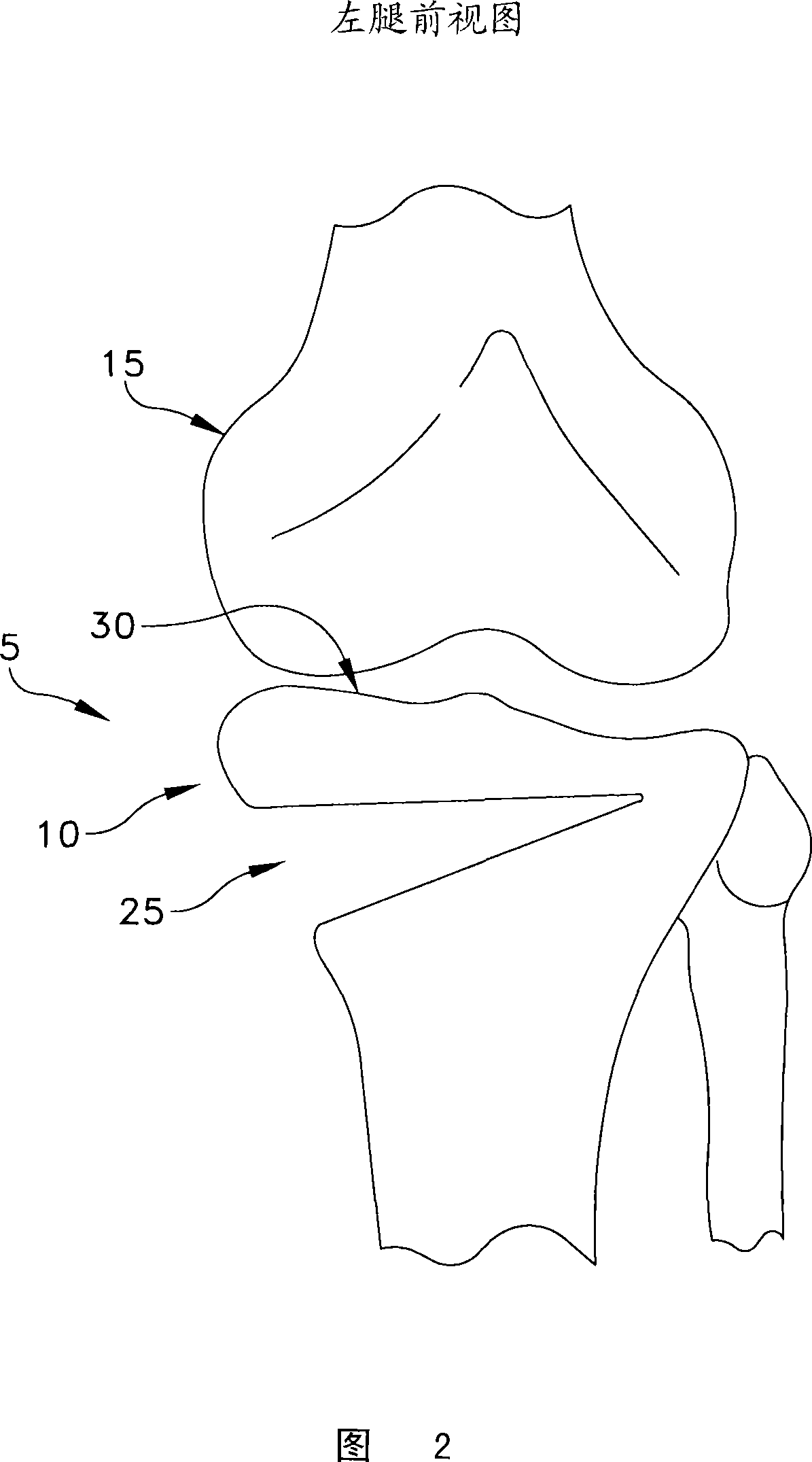
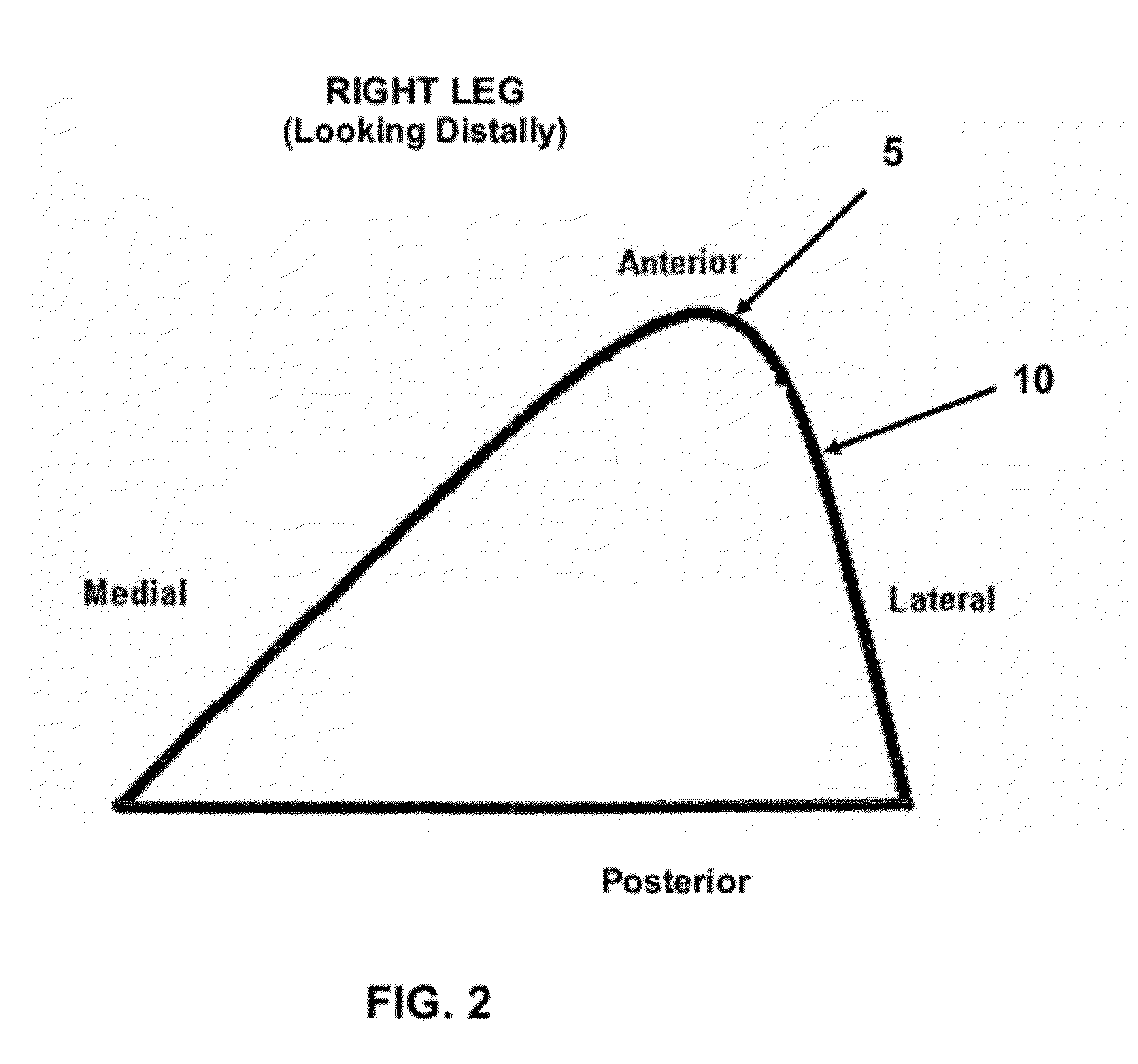
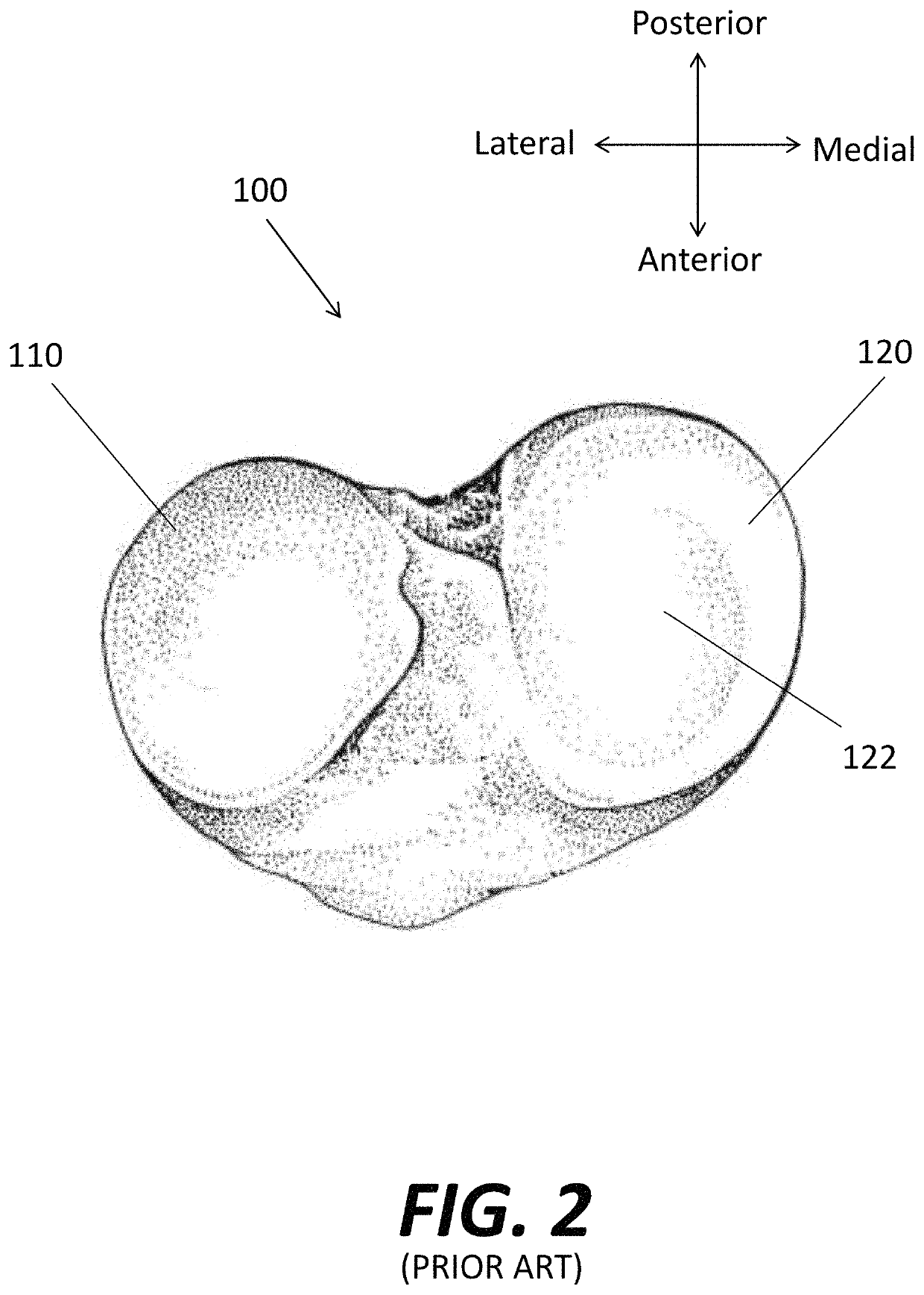
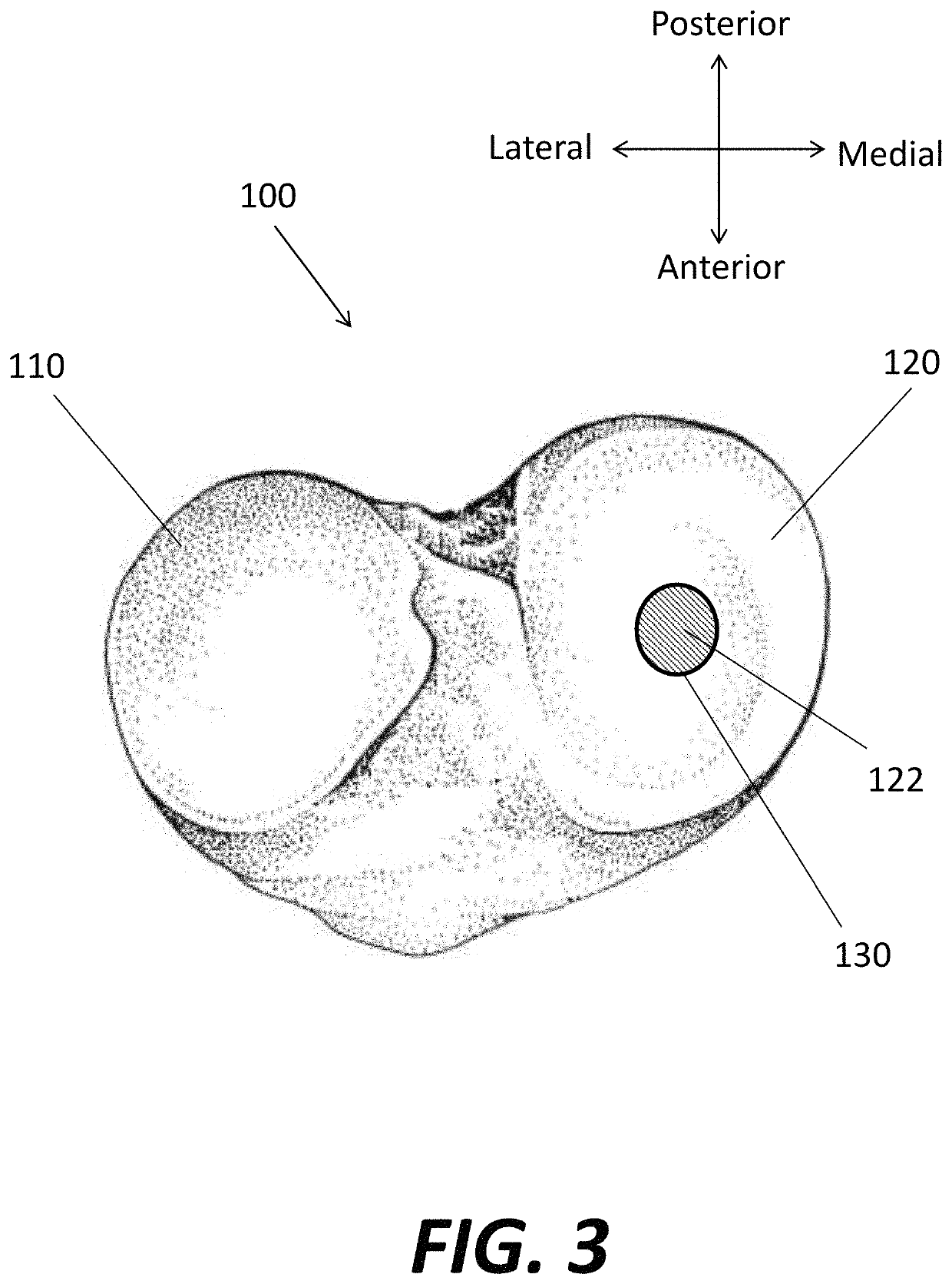
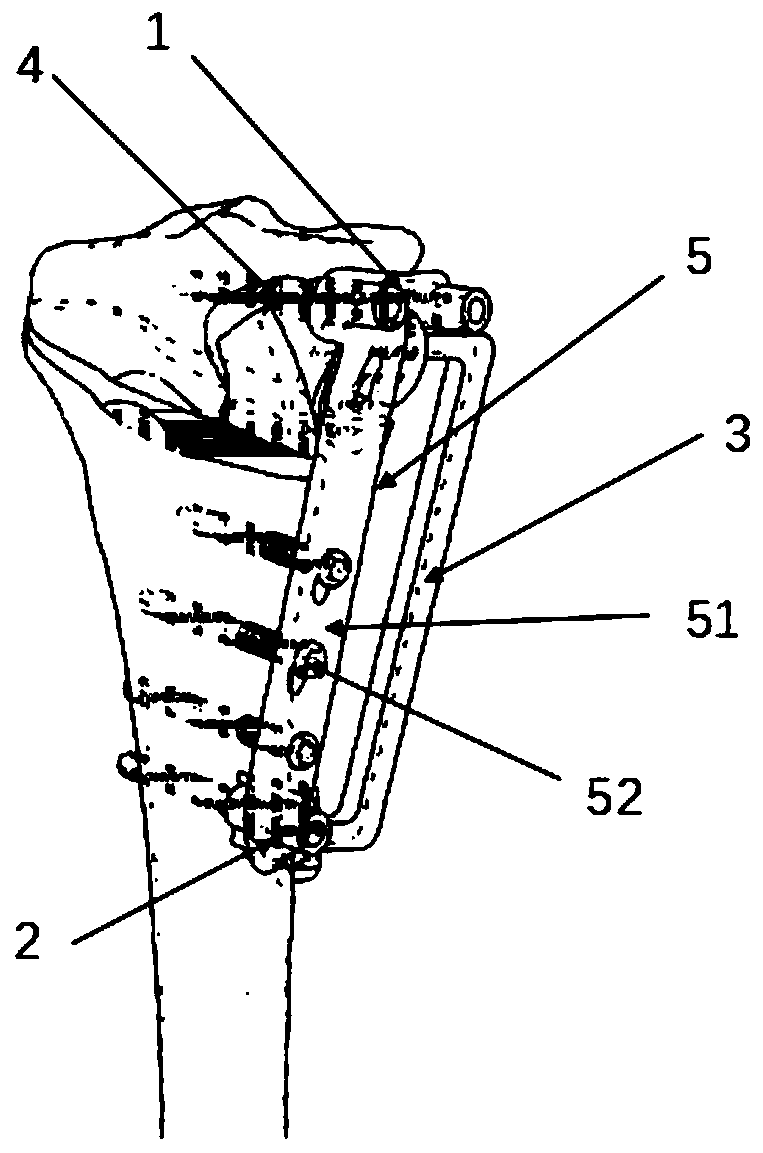
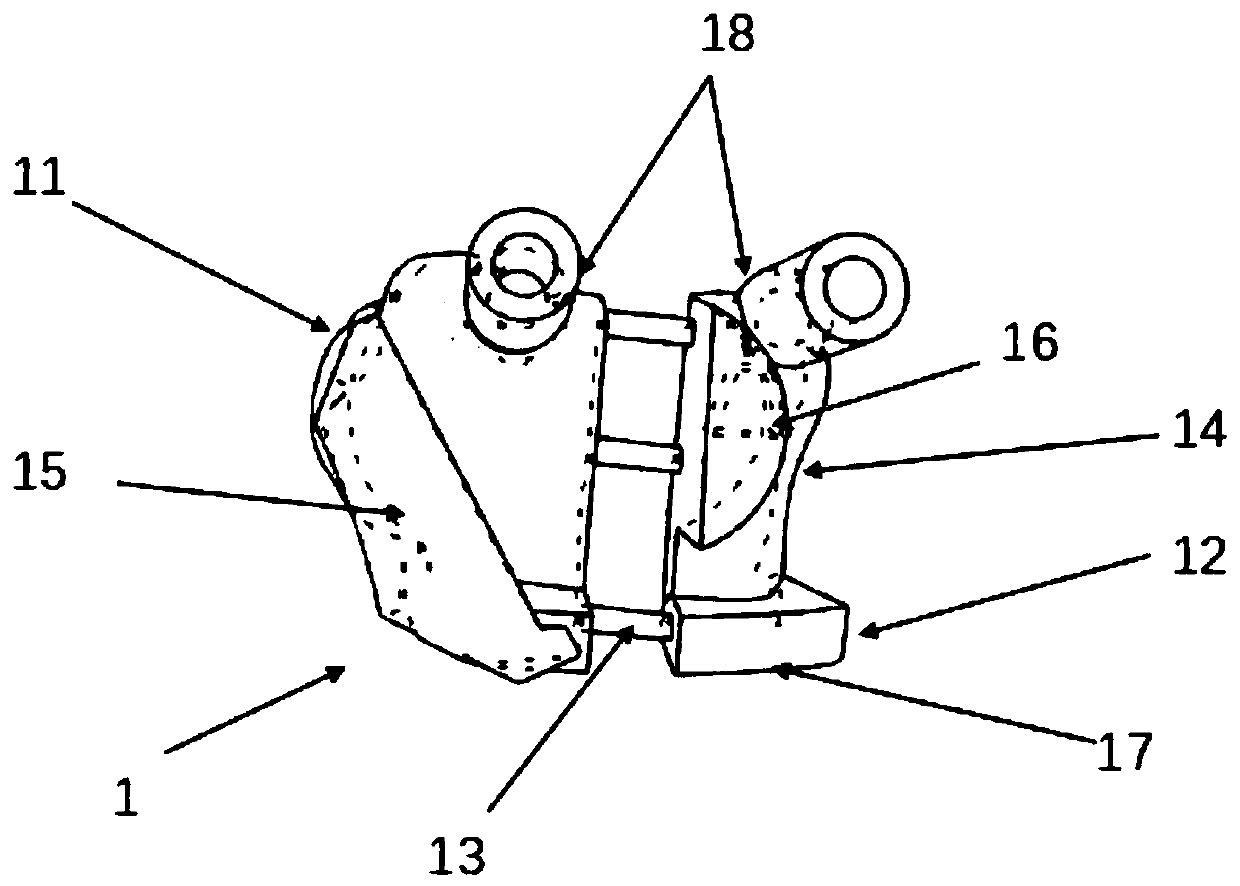
Patents
Literature
195 results about "Bone tibia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
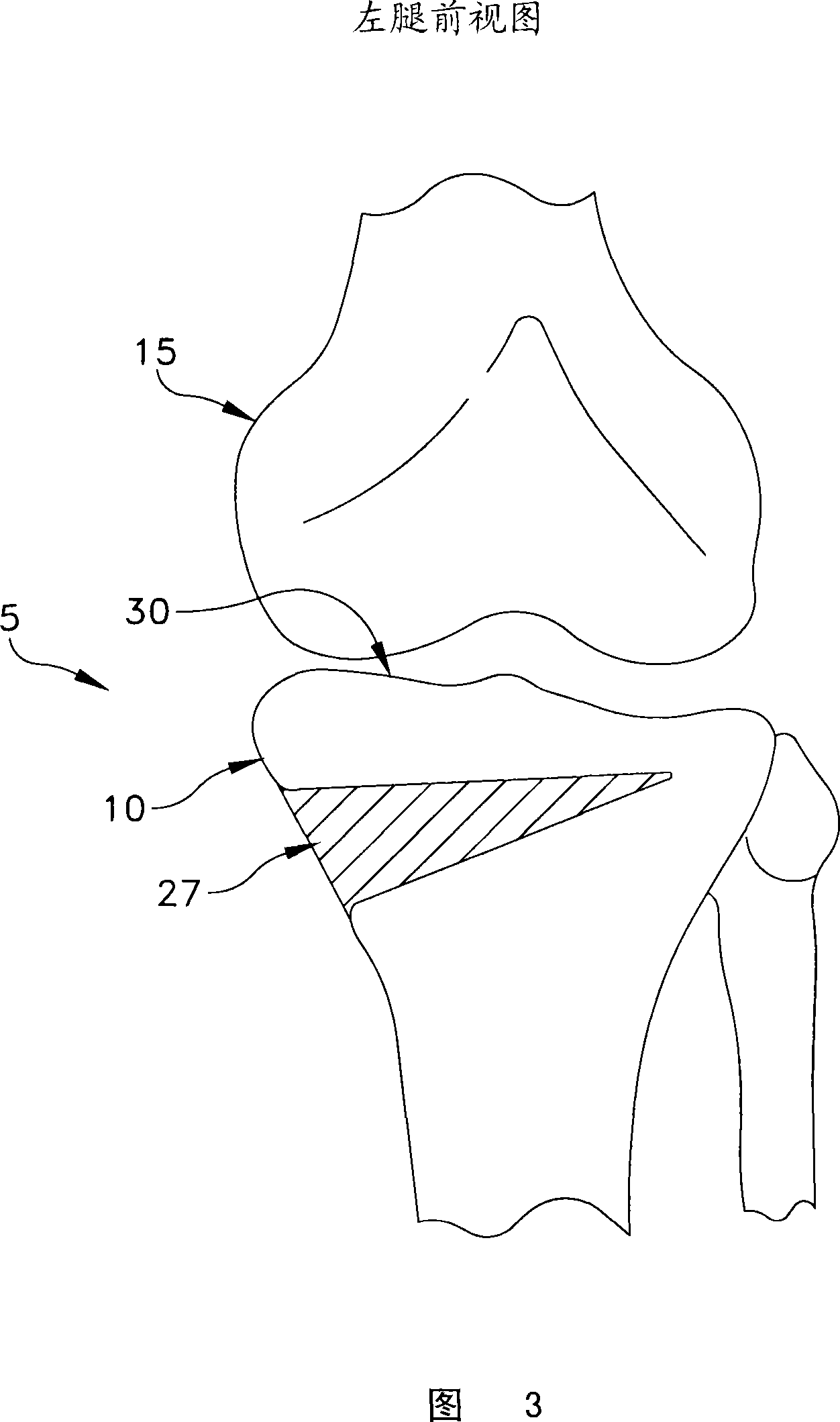
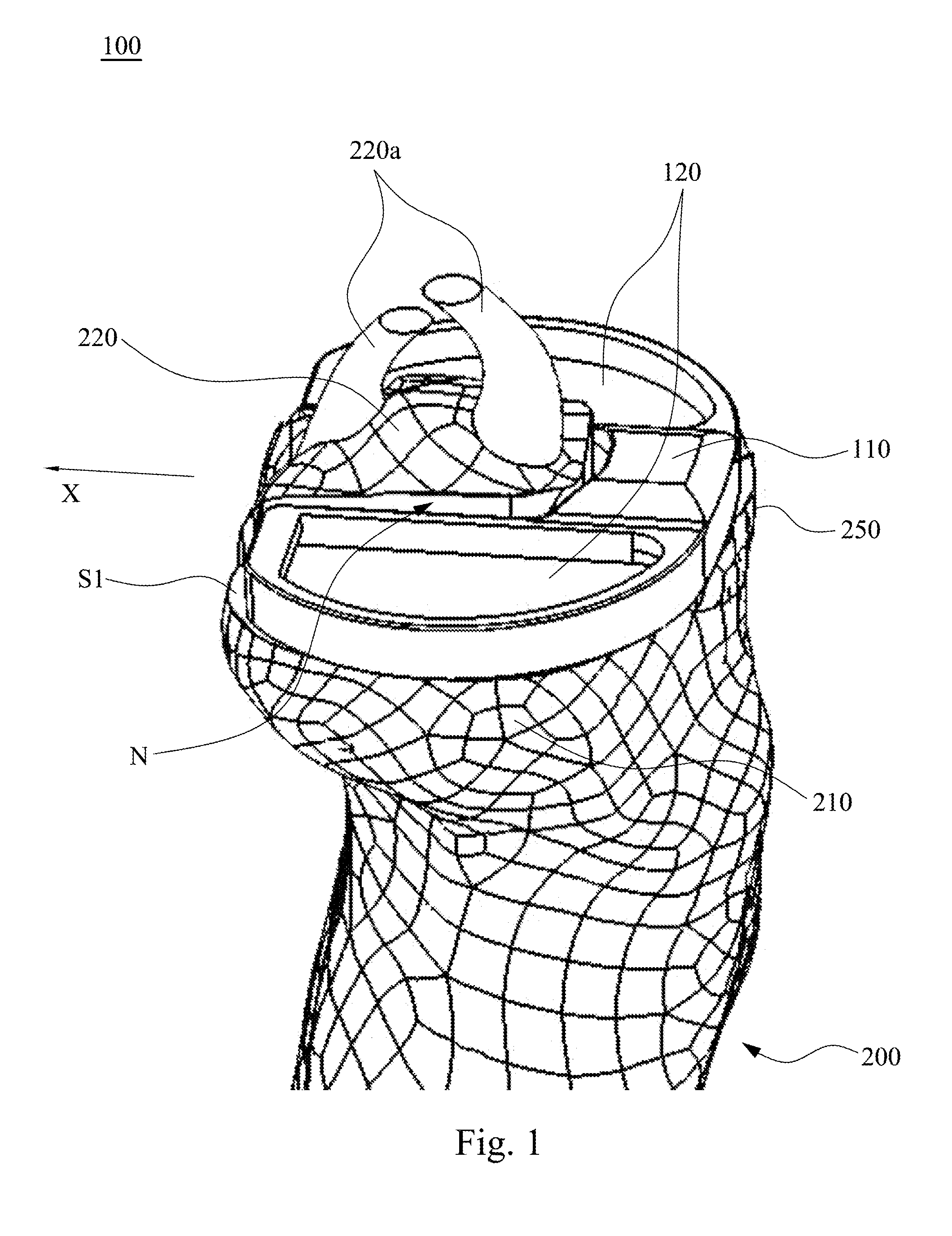
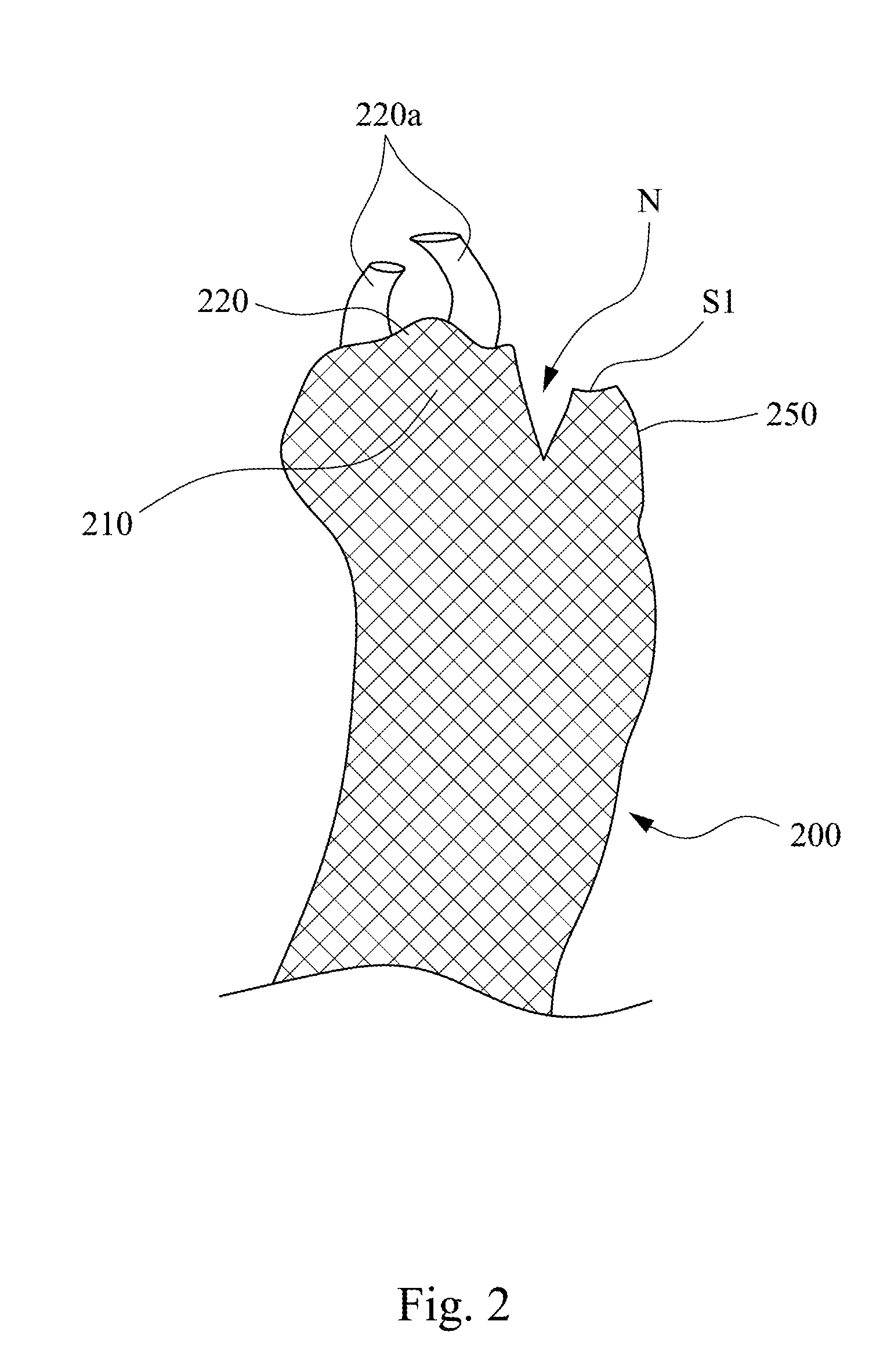
Open wedge osteotomy system and surgical method
ActiveUS20050273114A1Reduce overall surgeon learning curveInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsImplantSurgical methods
Owner:ARTHREX
Methods and apparatus for improved cutting tools for resection
ActiveUS20060015109A1Facilitating intraoperativeFacilitating postoperative efficacyJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaSacroiliac joint
A cutting tool is provided with an arcuate cutting blade that preferably engages a guide tool to create a curved resected surface during an arthorplasty procedure. In one embodiment, a depth of the cutting blade is sufficient to permit the simultaneous creation of resected surfaces on two bones that articulate, such as both the femor and the tibia for a given condyle, without the need to reposition the guide or the leg. In another embodiment, a cutting member has a generally rectangular cross-section along a longitudinal axis with a first and second surface having cutting teeth defined thereon and a third and fourth surface adapted to interface with a cutting guide positioned proximate the bone. In this embodiment, the cutting tool can resect the bone in two different directions without reorienting the cutting member.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Method and apparatus for performing an open wedge, high tibial osteotomy
An apparatus for performing an open wedge high tibiotomy comprising: a cutting apparatus for forming an osteotomy incision in the tibia, the cutting apparatus comprising: identifying a cutting plane through the tibia and terminating Targeting device of the borderline of the cut along the cutting plane, wherein the borderline is positioned inside the tibia, parallel to the anterior-posterior slope of the tibia and parallel to the sagittal plane of the patient. A method for performing an open wedge high tibiotomy, the method comprising: positioning a targeting device for identifying a cutting plane through the tibia and a borderline for terminating cuts made along the cutting plane, wherein the borderline is positioned at Inside the tibia, parallel to the anterior-posterior slope of the tibia and parallel to the patient's sagittal plane; cut the bone along the cutting plane, with the cut terminating at the borderline; move the bone on each side of the cut apart to create a wedge-shaped opening in the bone; and stable bone.
Owner:ARTHREX
Adaptable therapeutic, diagnostic or surgical guide
ActiveUS20120179147A1Precise targeting and controlAccurate fitAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical sawsTibiaEngineering
The present invention relates to an adaptable therapeutic, diagnostic or surgical guide for an intra-operative adjustment of a guidance element to a pre-planned position. An advantage and innovation of the present invention is that it provides a template or guide that adapts in a controlled way to a changed intra-operative anatomical situation compared to the default planned situation. This adaption maybe purely positional but it may also include force feedback. Feedback, either visual feedback or force feedback that results in an adjustment of a guidance element is also an aspect of the present invention. For example, the feedback can contain information either about the fit of the guide or template onto a bone (in case the guide or template fits onto one bone) or about the relative position of two bones of bone fragments (e.g. ligament tension between the femur and tibia).
Owner:MATERIALISE NV
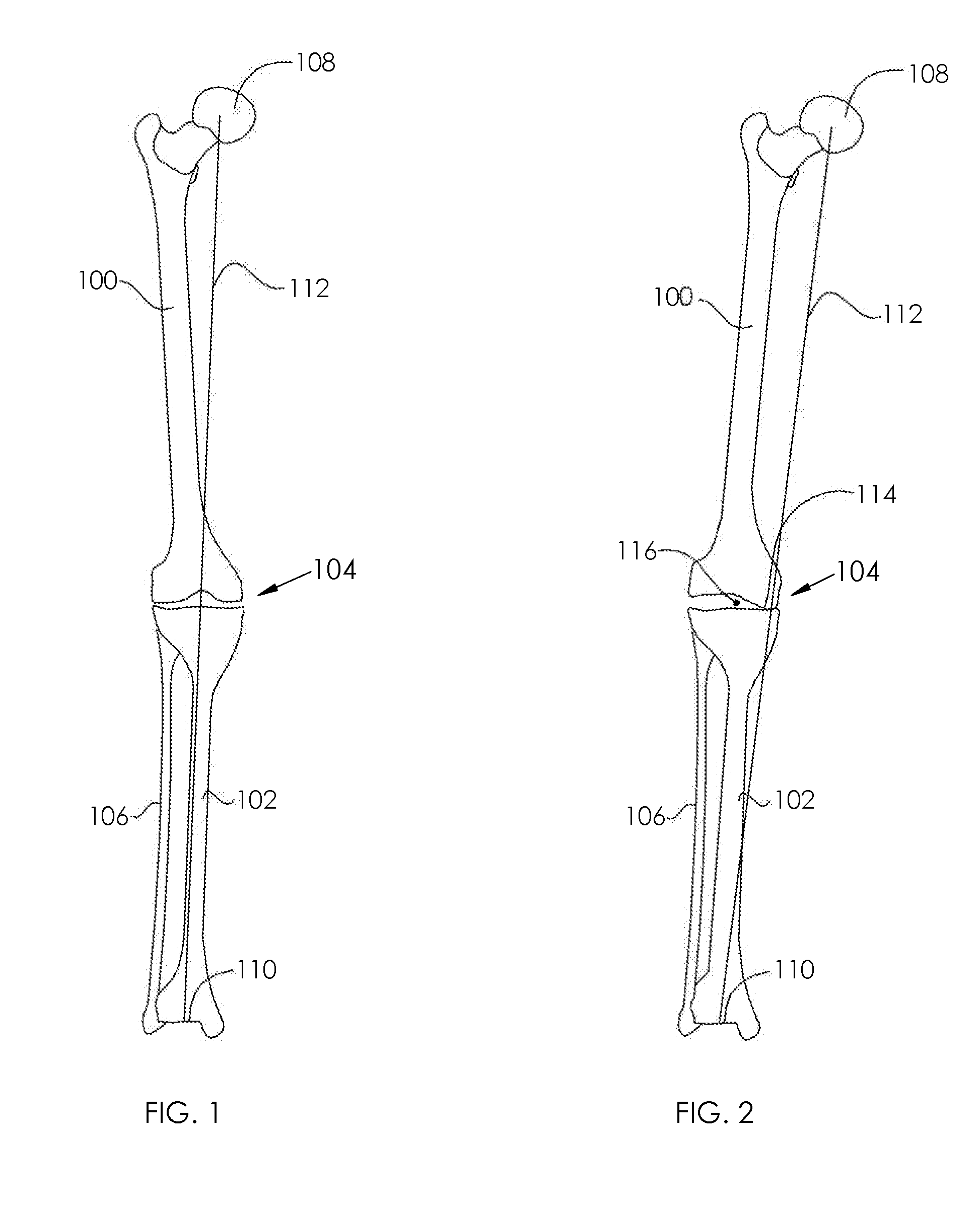
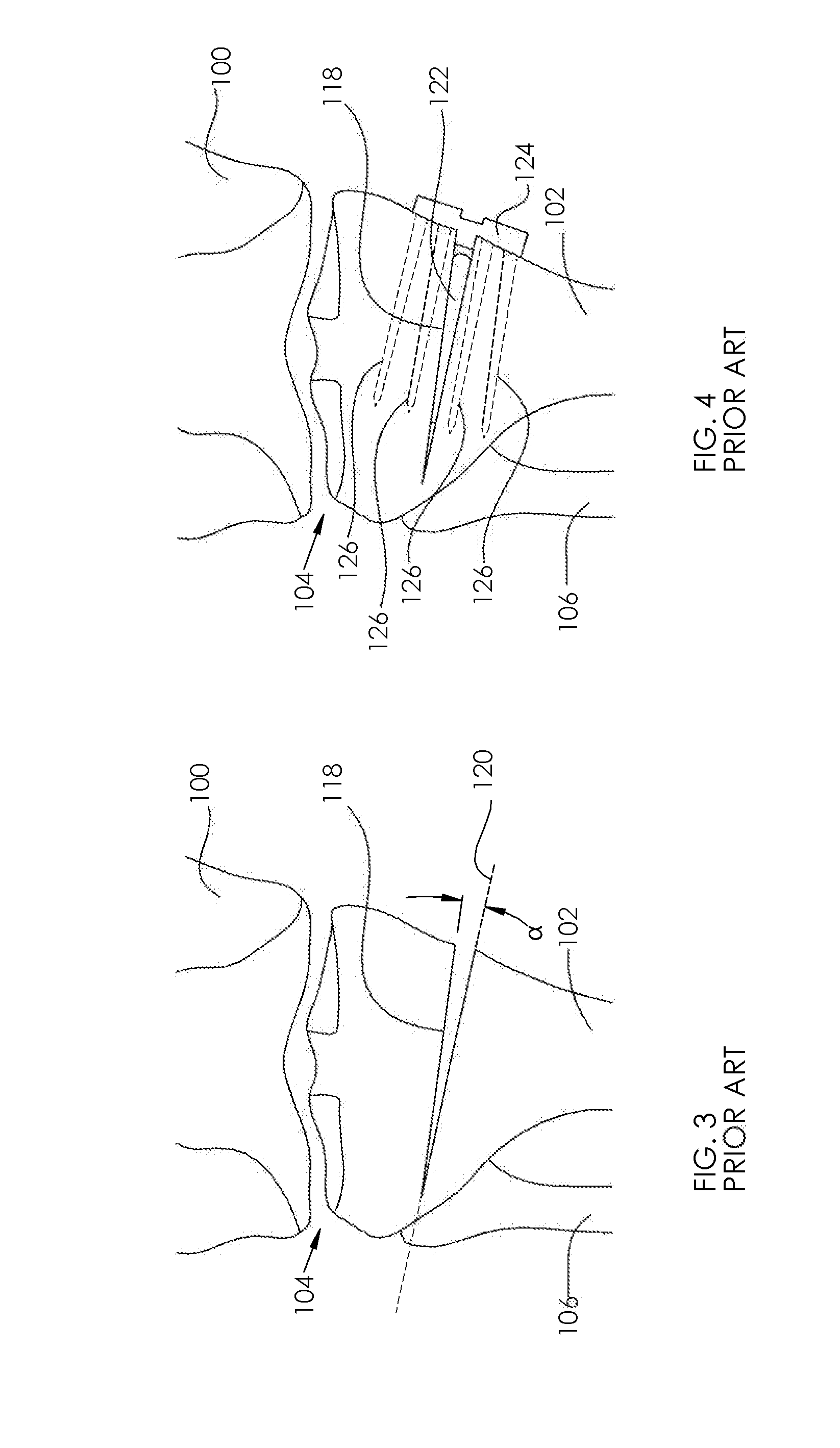
Instrument for Fracture Fragment Alignment and Stabilization
ActiveUS20080264109A1Avoid placingPrecise alignmentInternal osteosythesisStraight-bar knitting machinesEngineeringDrill
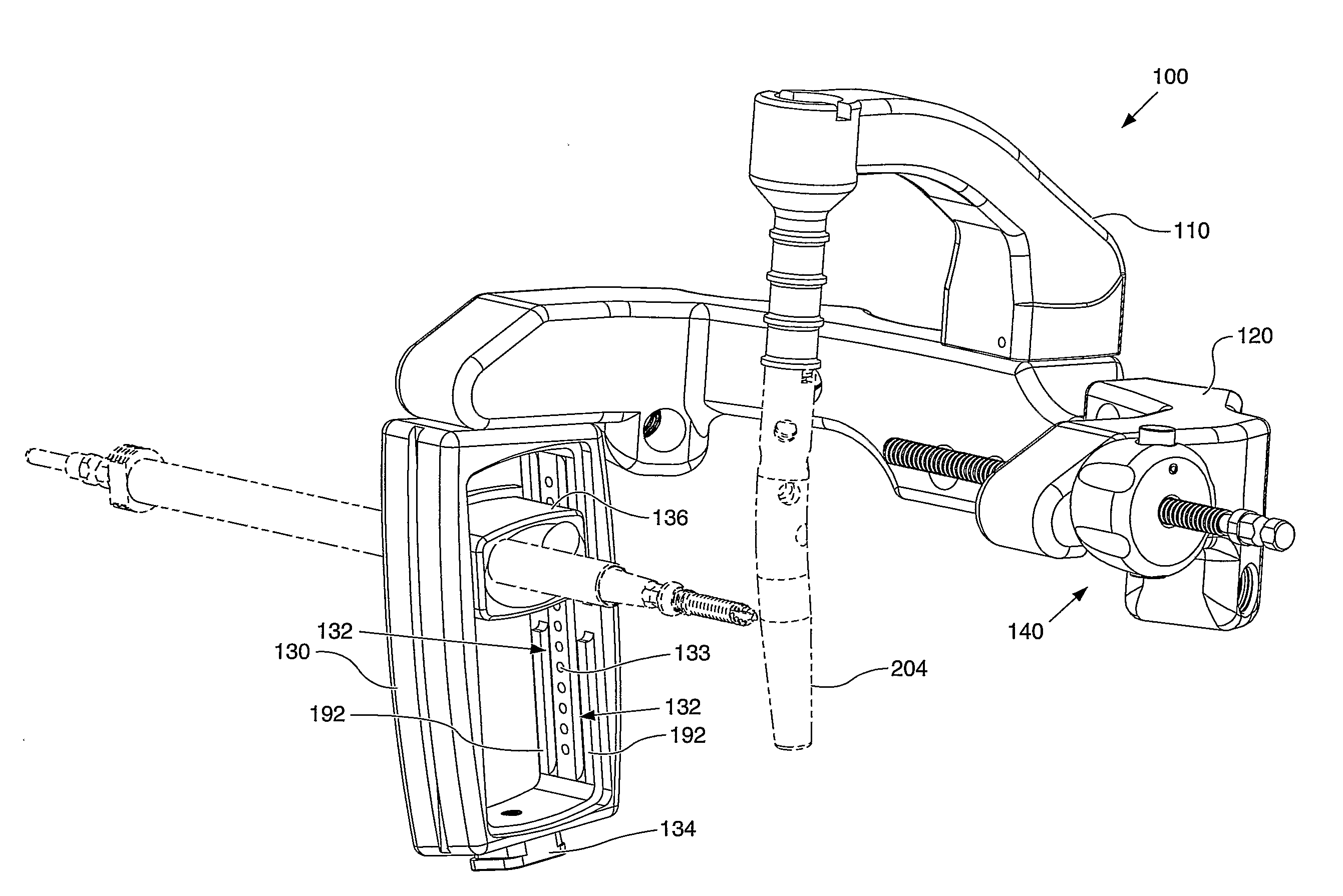
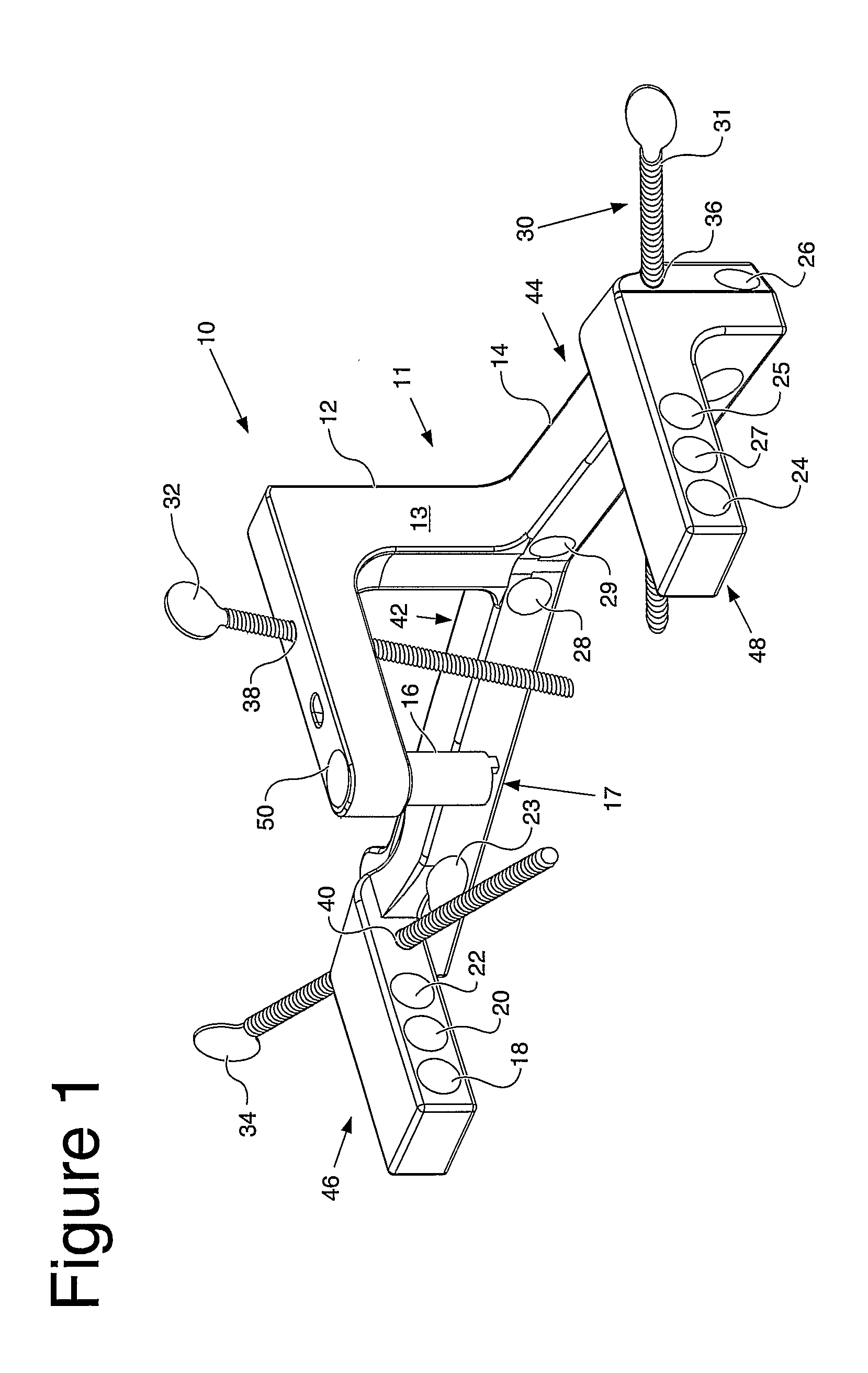
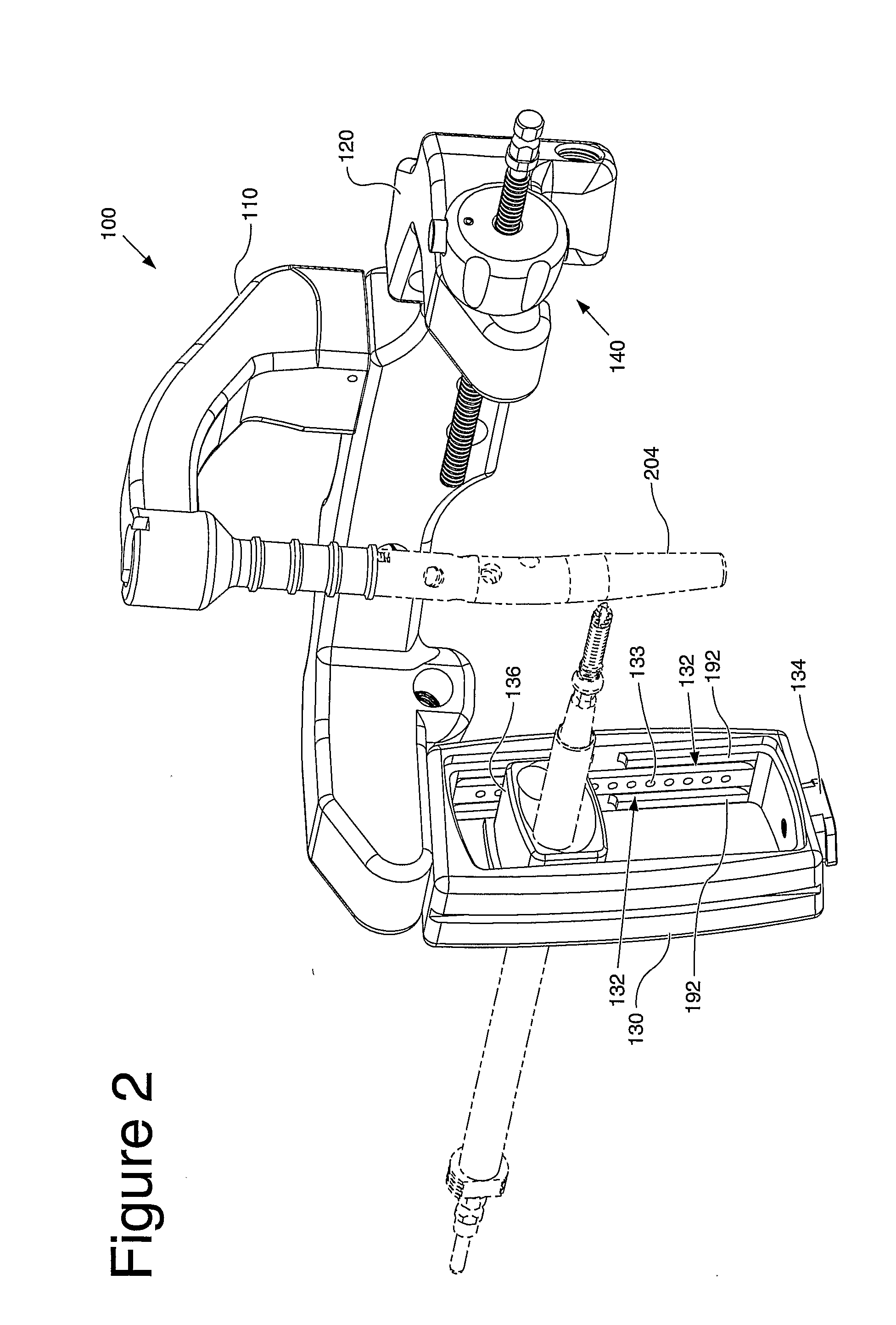
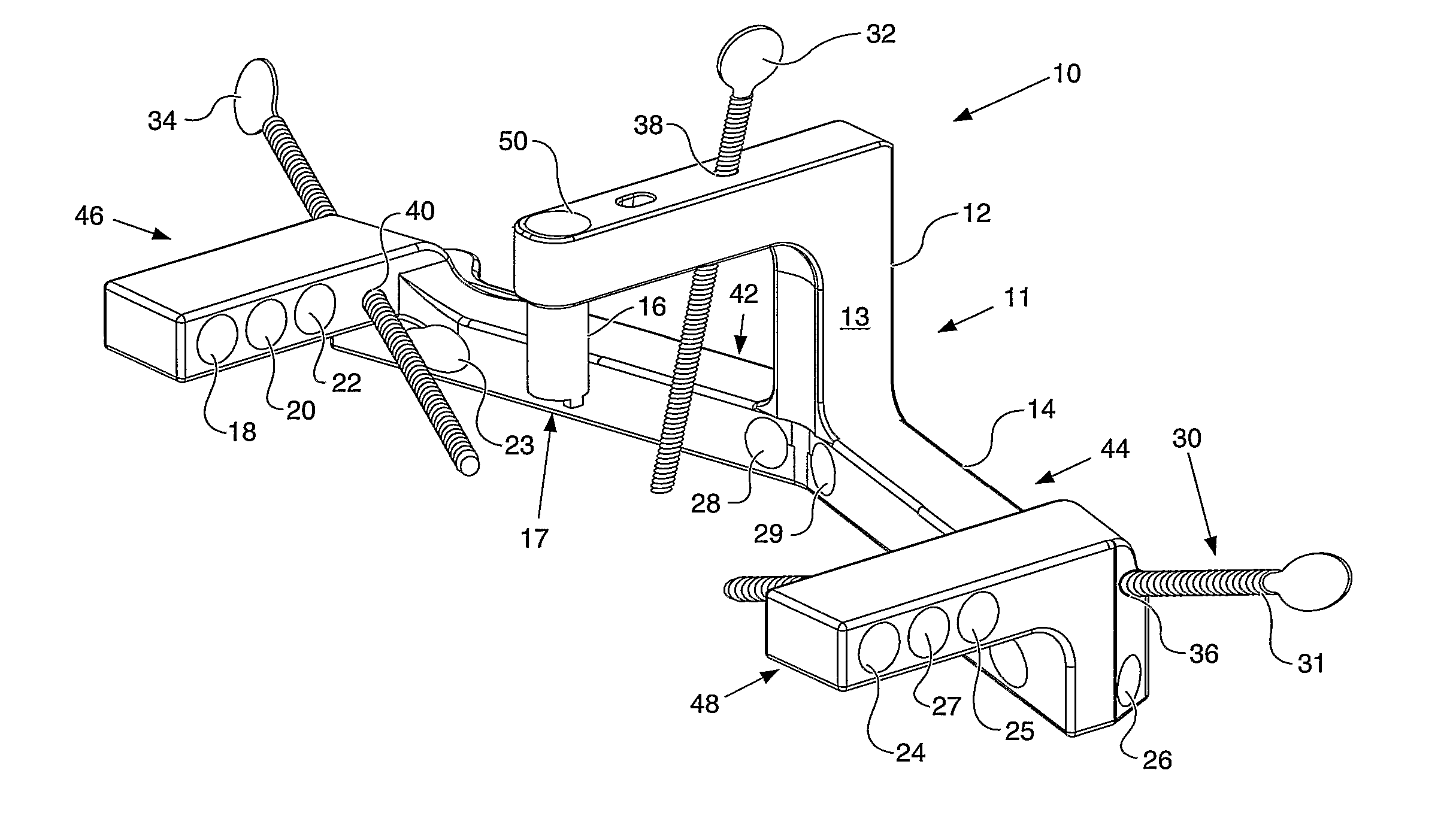
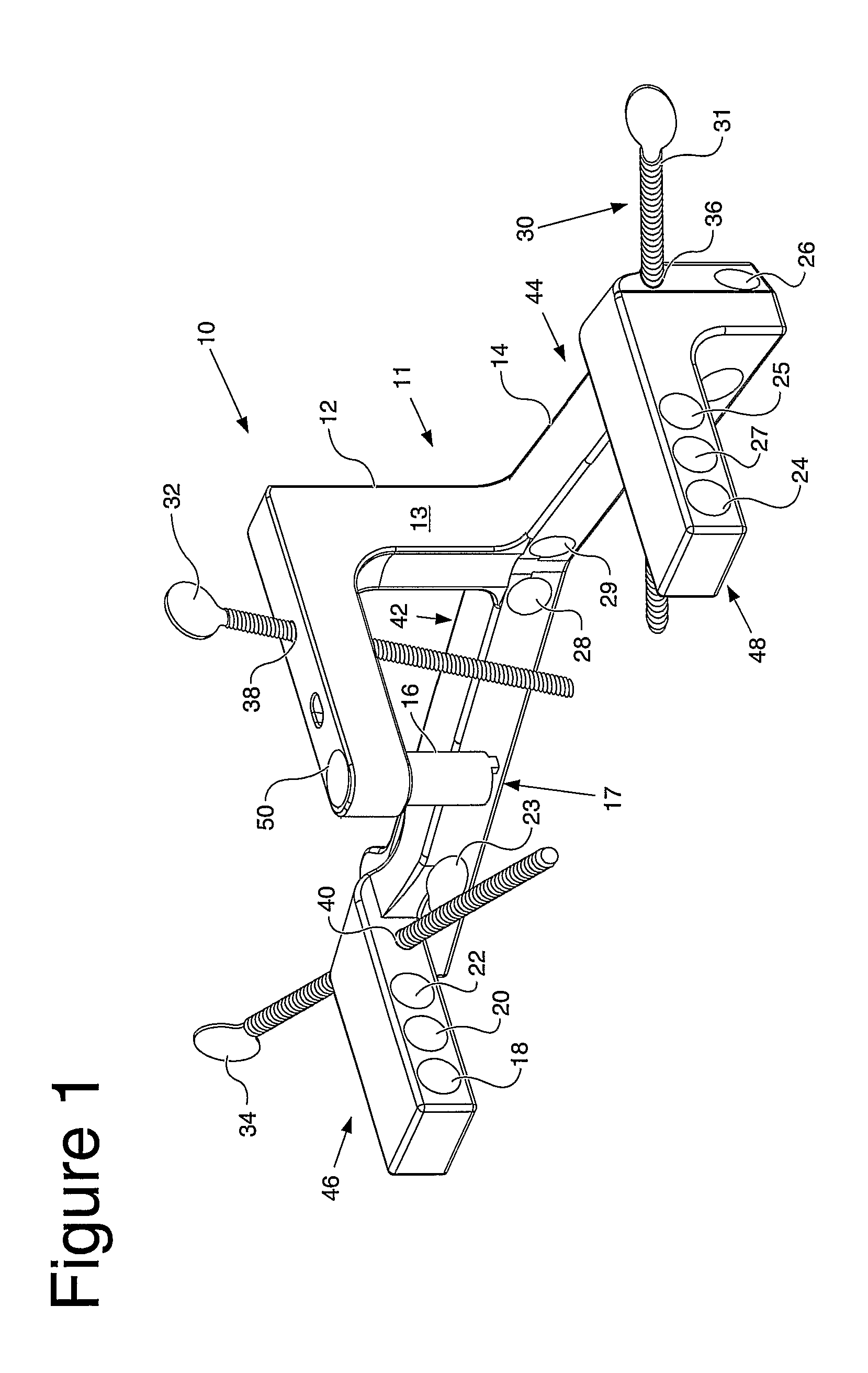
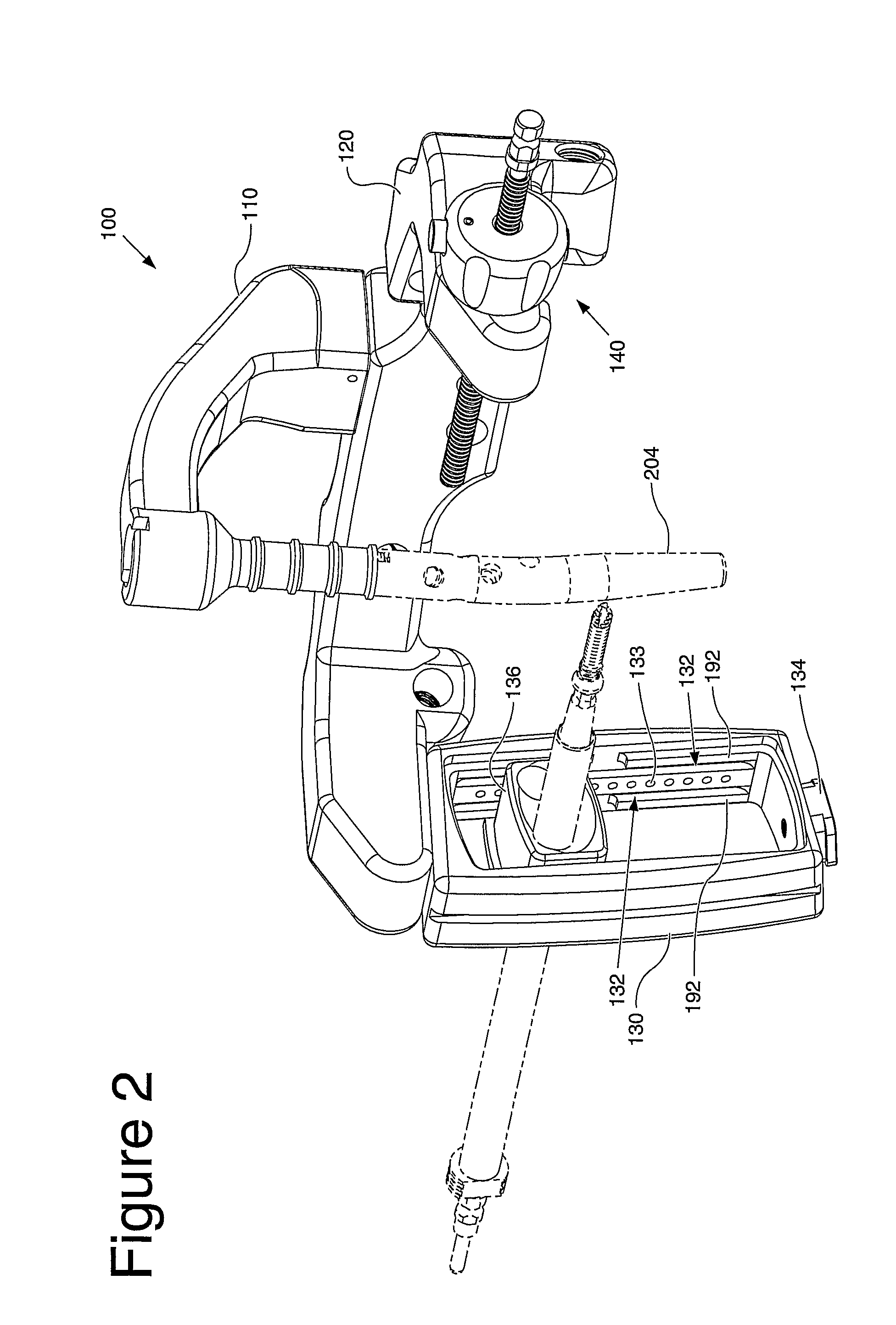
An instrument (10, 100) for locating an axis of a blocking screw is disclosed. The instrument (10, 100) is applicable for a retrograde installation of a femoral intramedullary device or an antegrade installation of a tibial intramedullary device. The instrument (10, 100) includes a drill jig (11, 105) with a radiolucent frame portion (14, 120) and a mounting portion (12, 110). The mounting portion (12, 110) is adapted to connect to an intramedullary device (204), and the frame portion (14, 120) has at least one aperture (18, 22, 24, 25, 28, 29, 126, 137, 337) for locating the axis of the blocking screw (210). The drill jig (11, 105) is adjustable to locate the aperture (18, 22, 24, 25, 28, 29, 126, 137, 337) in a longitudinal or rotational direction relative to the intramedullary device (204).
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Adjustable devices for treating arthritis of the knee
A method of changing a bone angle includes creating an osteotomy between a first portion and a second portion of a tibia of a patient; creating a cavity in the tibia by removing bone material along an axis extending in a substantially longitudinal direction from a first point at the tibial plateau to a second point; placing a non-invasively adjustable implant into the cavity, the non-invasively adjustable implant comprising an adjustable actuator having an outer housing and an inner shaft, telescopically disposed in the outer housing, and a driving element configured to be remotely operable to telescopically displace the inner shaft in relation to the outer housing; coupling one of the outer housing or the inner shaft to the first portion of the tibia; coupling the other of the outer housing or the inner shaft to the second portion of the tibia; and remotely operating the driving element to telescopically displace the inner shaft in relation to the outer housing, thus changing an angle between the first portion and second portion of the tibia.
Owner:NUVASIVE SPECIALIZED ORTHOPEDICS INC
Systems, methods and devices for tibial resection
Systems, methods and device for tibial resection comprise a first cutting guide and a second cutting guide. The first cutting guide (12) is configured to overlay a portion of the tibia and to direct a cutting instrument in a plane. The first cutting guide has a length extending from a generally medial portion of the tibia to a generally lateral portion of the tibia. The first cutting guide has a depth extending in a posterior direction generally perpendicular to the length and a groove extending along the length and depth of the first cutting guide such that the groove extends along a generally transverse plane. The second cutting guide (34) is oriented at an angle to the first cutting guide and configured to extend generally in a posterior direction from the first cutting guide (12). The second cutting guide limits the cutting instrument in the transverse plane from cutting bone.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
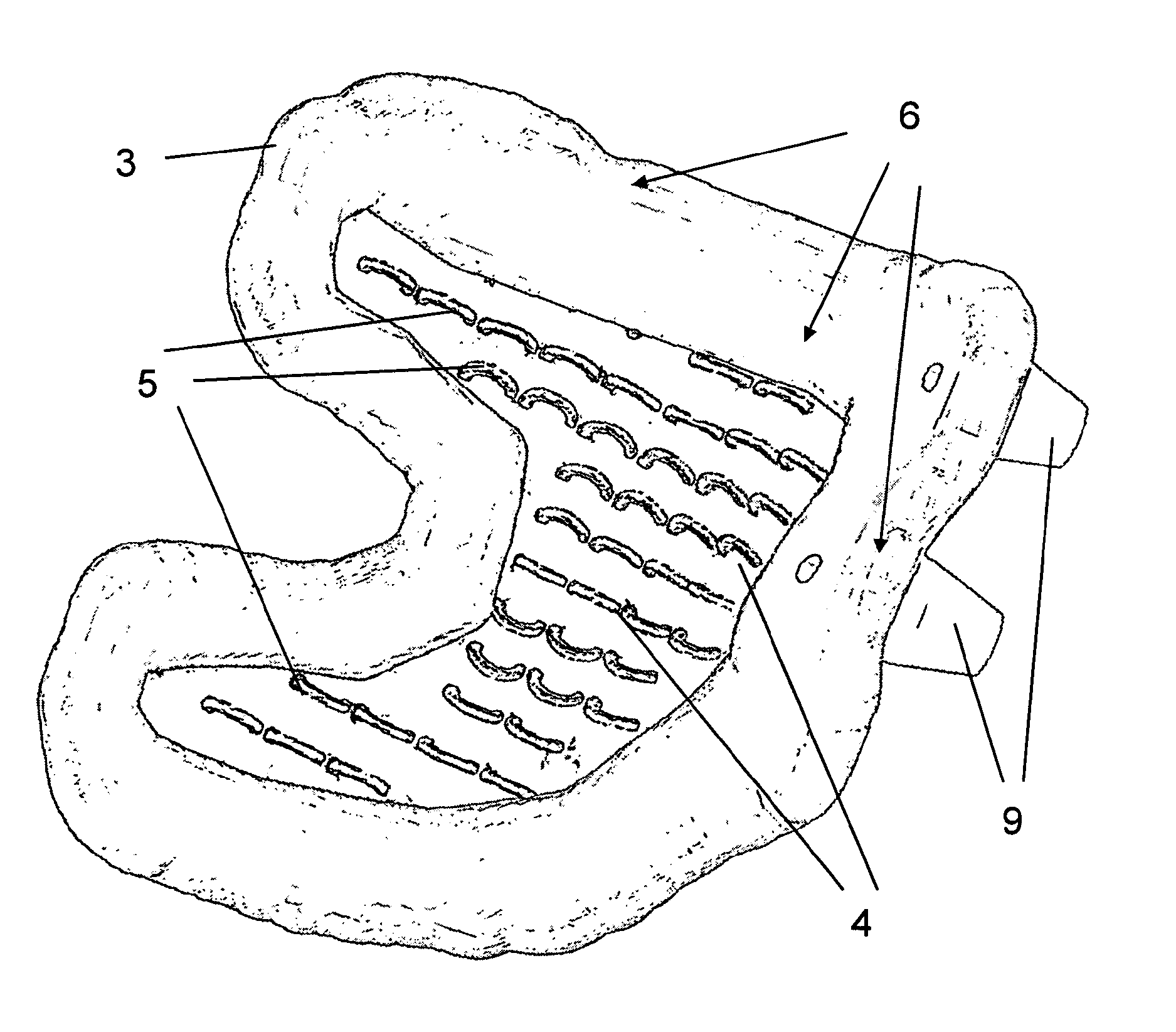
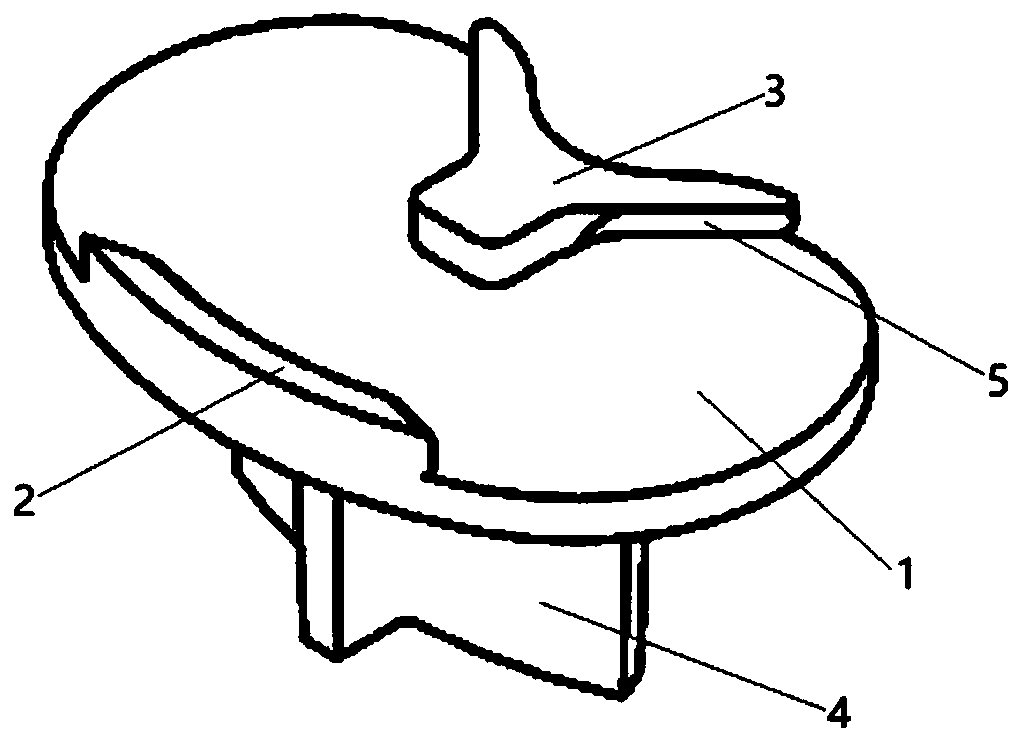
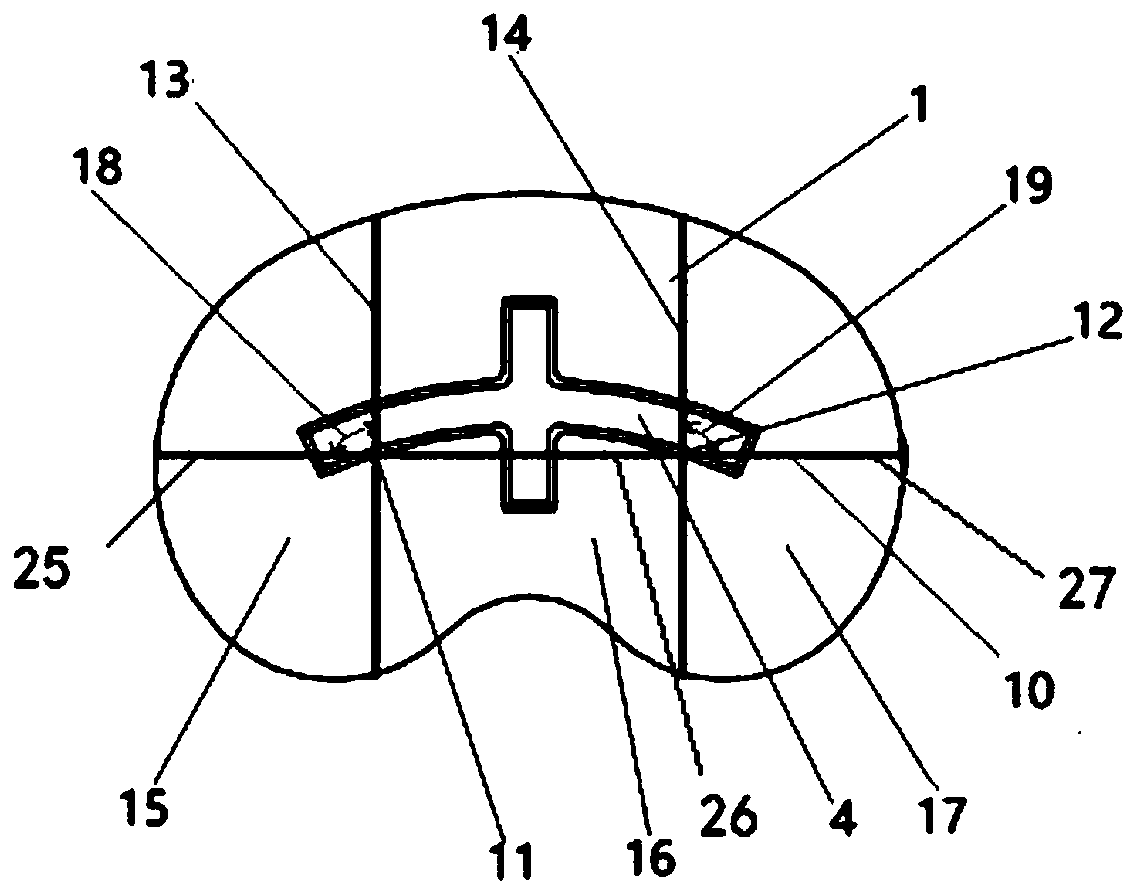
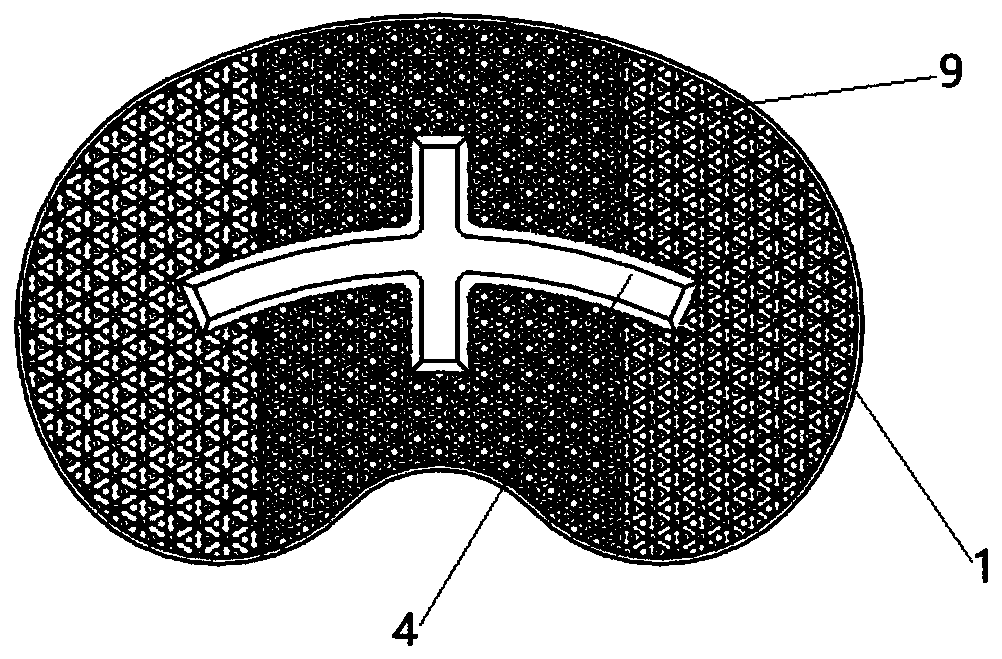
Biological-type knee joint partition bone trabecula tibial plateau
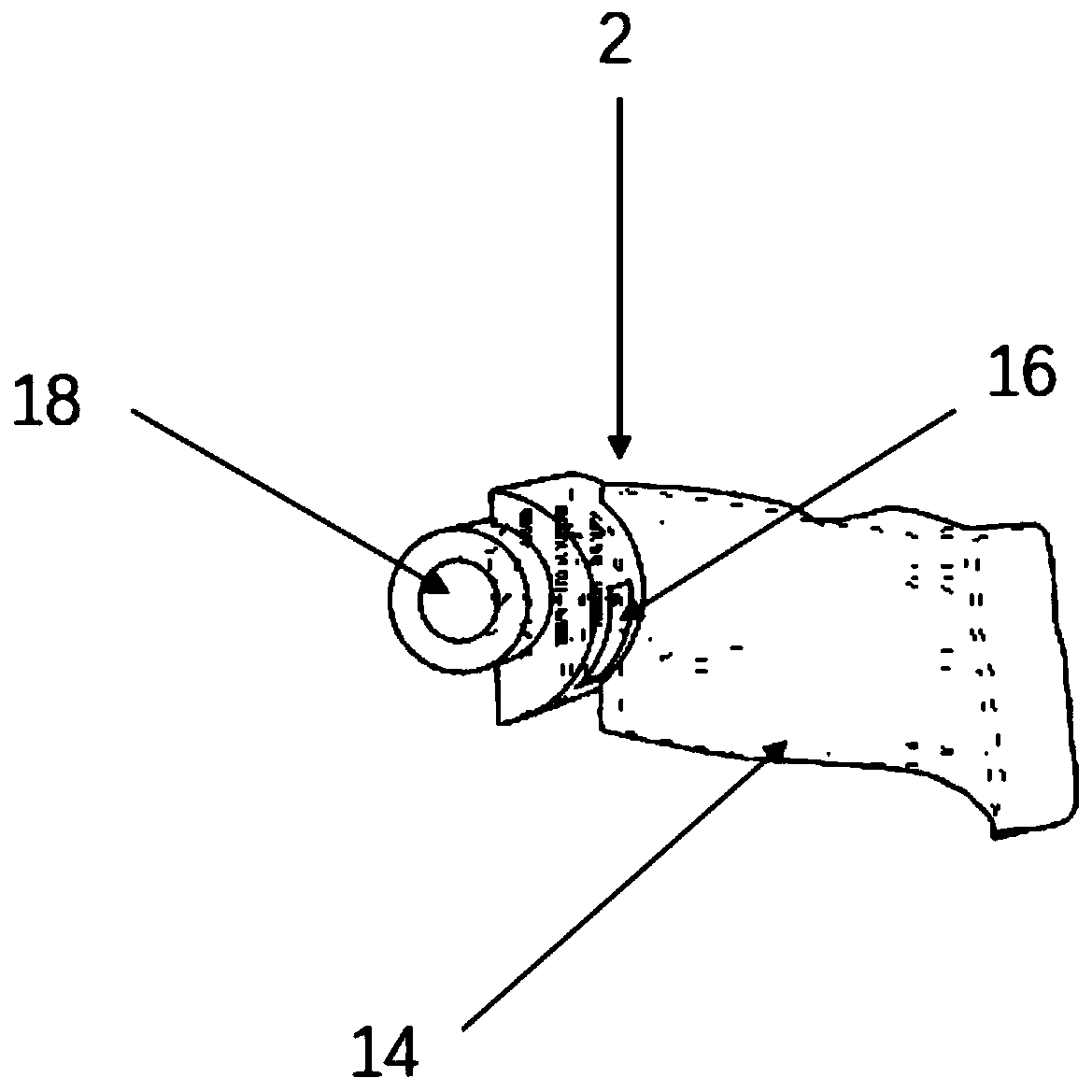
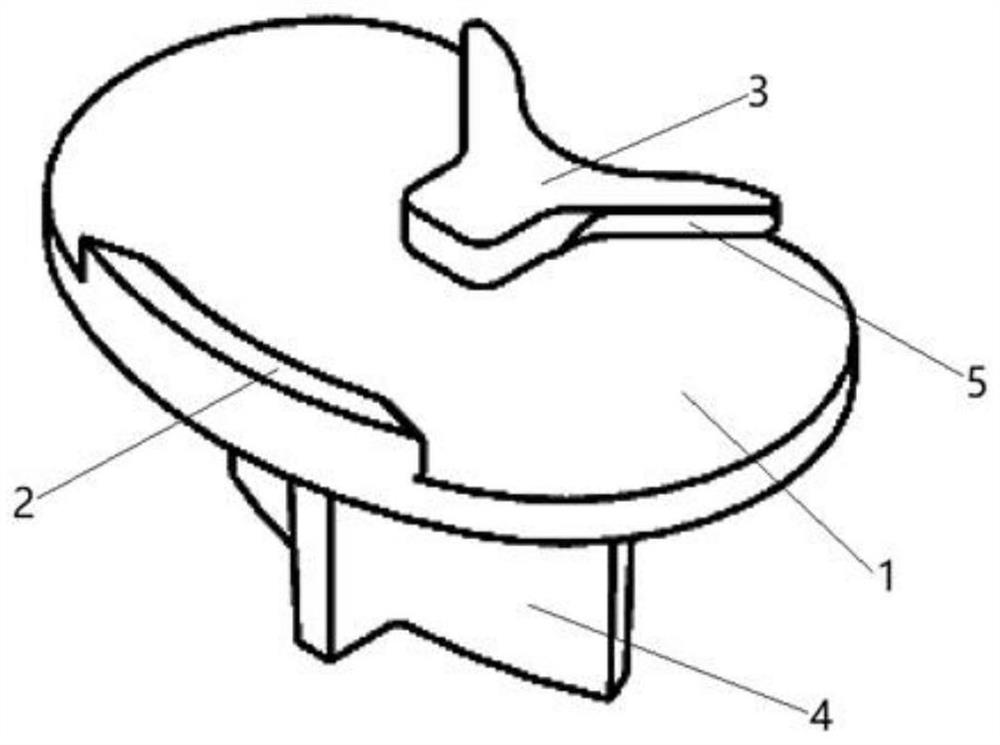
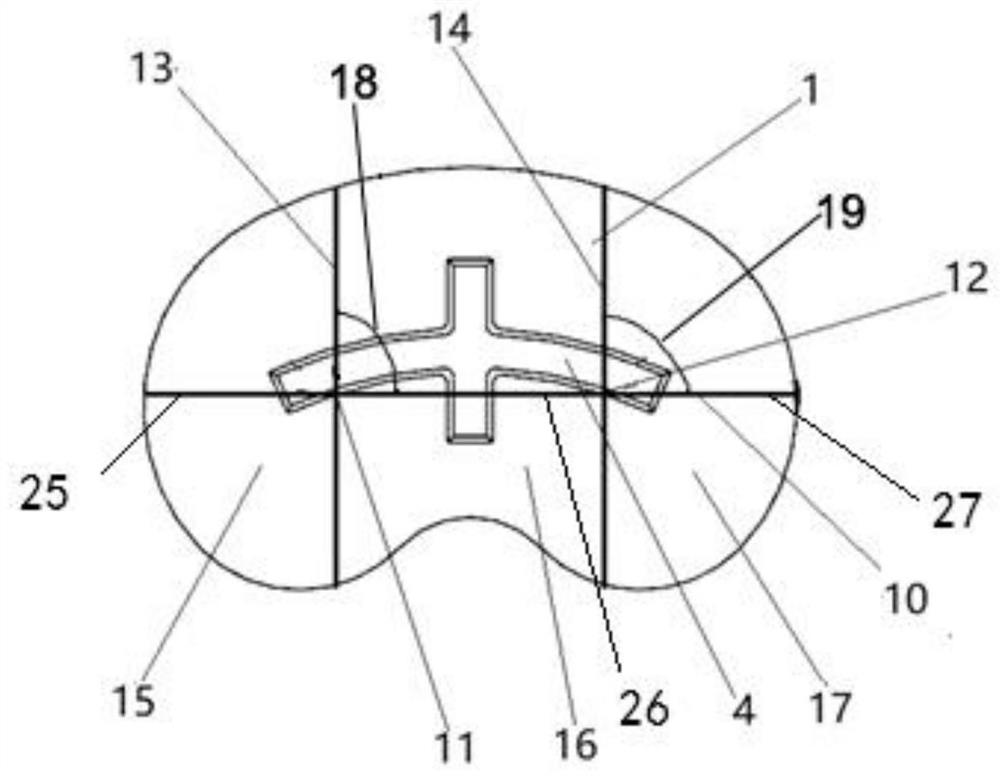
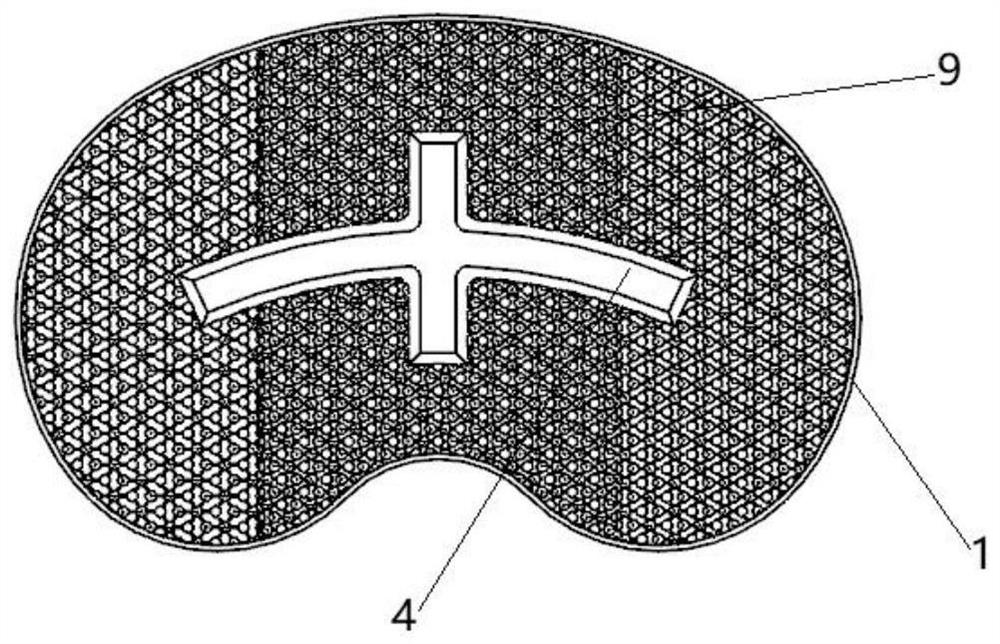
PendingCN109938888AUniform bone ingrowthImprove long-term stabilityJoint implantsKnee jointsPorosityBone Trabeculae
The invention discloses a biological-type knee joint partition bone trabecula tibial plateau. The biological-type knee joint partition bone trabecula tibial plateau comprises a reniform plateau bearing part, a handle is arranged in the middle of the lower surface of the reniform plateau bearing part, parts, except the connecting handle, of the lower surface of the reniform plateau bearing part areprovided with bone trabeculae, and the reniform plateau bearing part is divided into an inner side area, a middle area and an outer side area; the hole diameter and porosity of the bone trabeculae inthe inner side area are larger than those of the bone trabeculae in the outer side area and the middle area in sequence. The partition bone trabecula tibial plateau is integrally formed through 3D printing of titanium alloy, and the hole diameters and porosities of the bone trabeculae arranged in different areas of the lower surface of the tibial plateau are different. An experiment proves that through partition arrangement of the bone trabecula of the biological-type knee joint tibial plateau, under the actual circumstance of uneven stress of the tibia, uniform bone ingrowth is achieved, andthe long-time stability of the biological-type tibial plateau is improved. through 3D printing, the surface of the whole component is rough, friction between the plateau and the tibia is increased, and the initial stability of the plateau is improved.
Owner:JIASITE HUAJIAN MEDICAL EQUIP (TIANJIN) CO LTD
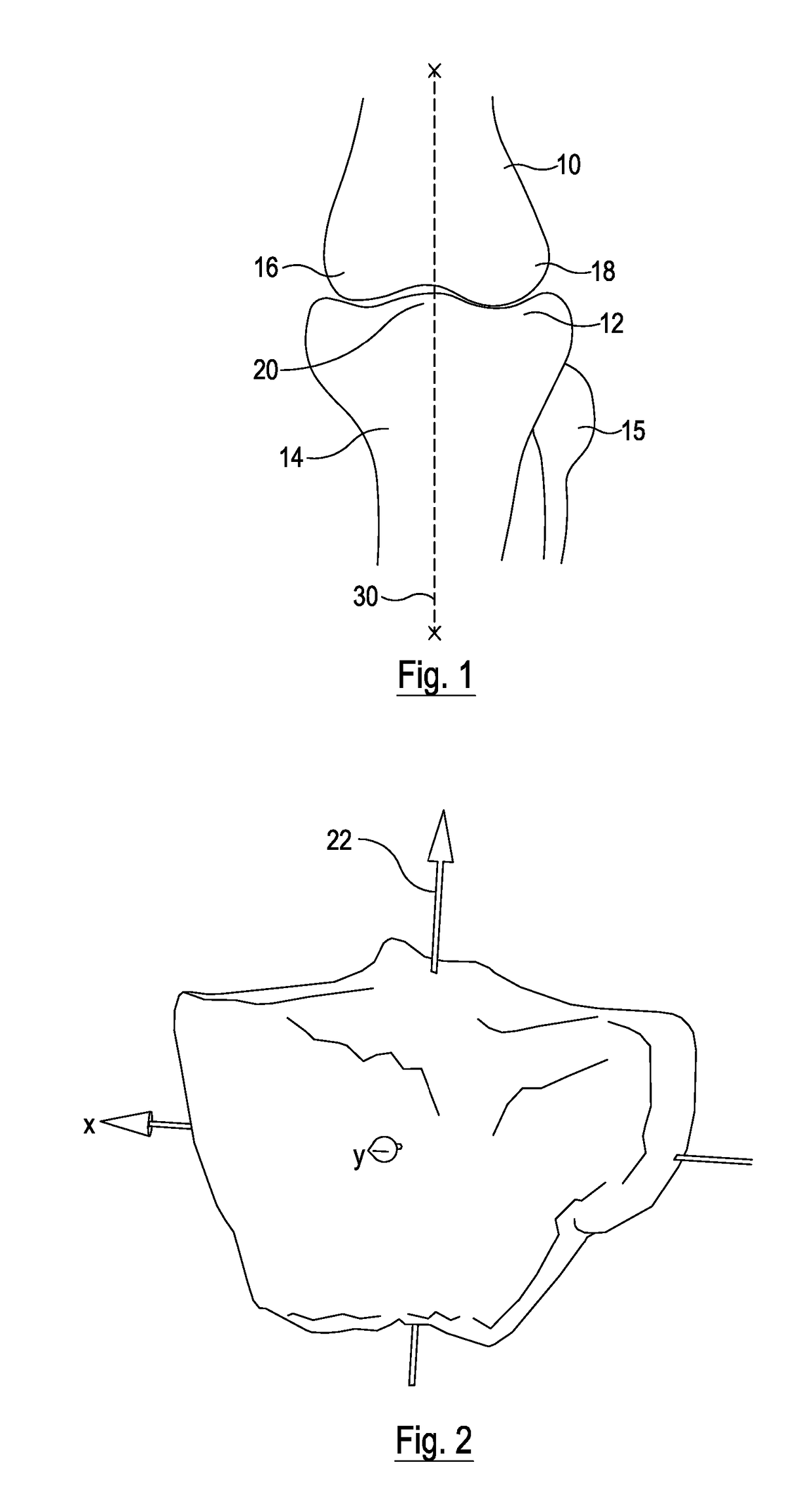
Tibial prosthetic component for a partial or unicondylar bearing knee replacement, method of selecting such a tibial prosthetic component, method of implanting such a tibial prosthetic component and a kit for a surgeon
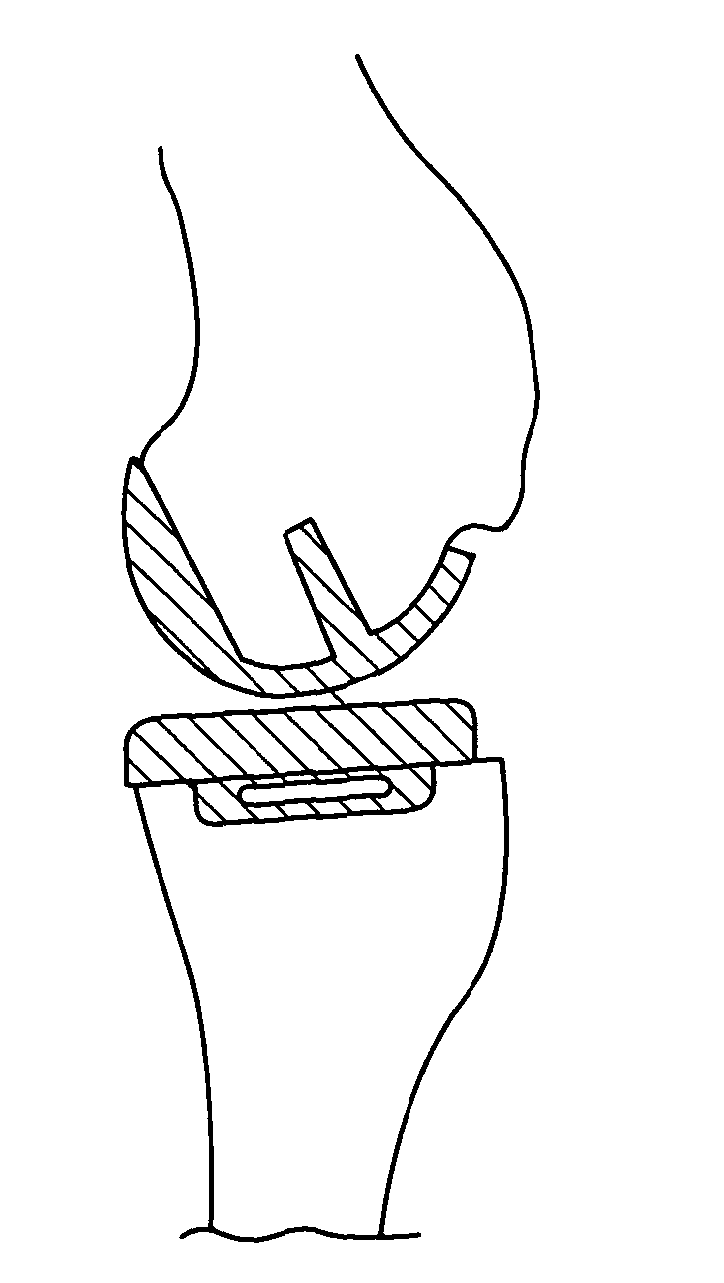
ActiveUS20130166037A1Great capacity to handle stressReduce the amount requiredBone implantJoint implantsKnee JointBone tibia
The invention concerns a tibial prosthetic component comprising a plate (100) for forming a tibial plateau of a tibia (16), wherein a peripheral region of the plate (100) has a thickness of less than 3 mm. The invention also concerns a tibial prosthetic component having a keel of depth less than 9 mm. The invention also concerns a method of selecting a tibial prosthetic component comprising receiving measurements of at least one physical attribute of an individual into whom the tibial prosthetic component is to be implanted, selecting a thickness of a plate (100) and depth of keel of the tibial prosthetic component based on the measurements and providing a tibial prosthetic component comprising a plate (100) having the selected thickness and a keel having the selected depth. The invention may also comprise implanting a tibial prosthetic component selected in accordance with this method into an individual and a kit comprising a plurality of prosthetic components comprising plates having different thicknesses with keels of different depths.
Owner:OCONNOR JOHN +3
Tibial base plate and method for attaching a tibial base plate on a tibia
A tibial base plate for attaching to a resected surface at a proximal end of a tibia is provided. The tibial base plate includes a bridge, a pair of compartments and a stem. The bridge has a first contact surface sitting on the resected surface. The compartments are disposed at opposite sides of the bridge and extend in an anterior-posterior direction to form a notch to accommodate a tibial eminence. Each of the compartments has a second contact surface sitting on the resected surface. The stem is connected to the bridge and the compartments and inset into the proximal end of the tibia. The stem has an outer surface. The outer surface is canted towards the notch as insetting into the proximal end of the tibia. The stem is engaged with a cutting slot on the resected surface into the proximal end of the tibia.
Owner:AOD HLDG
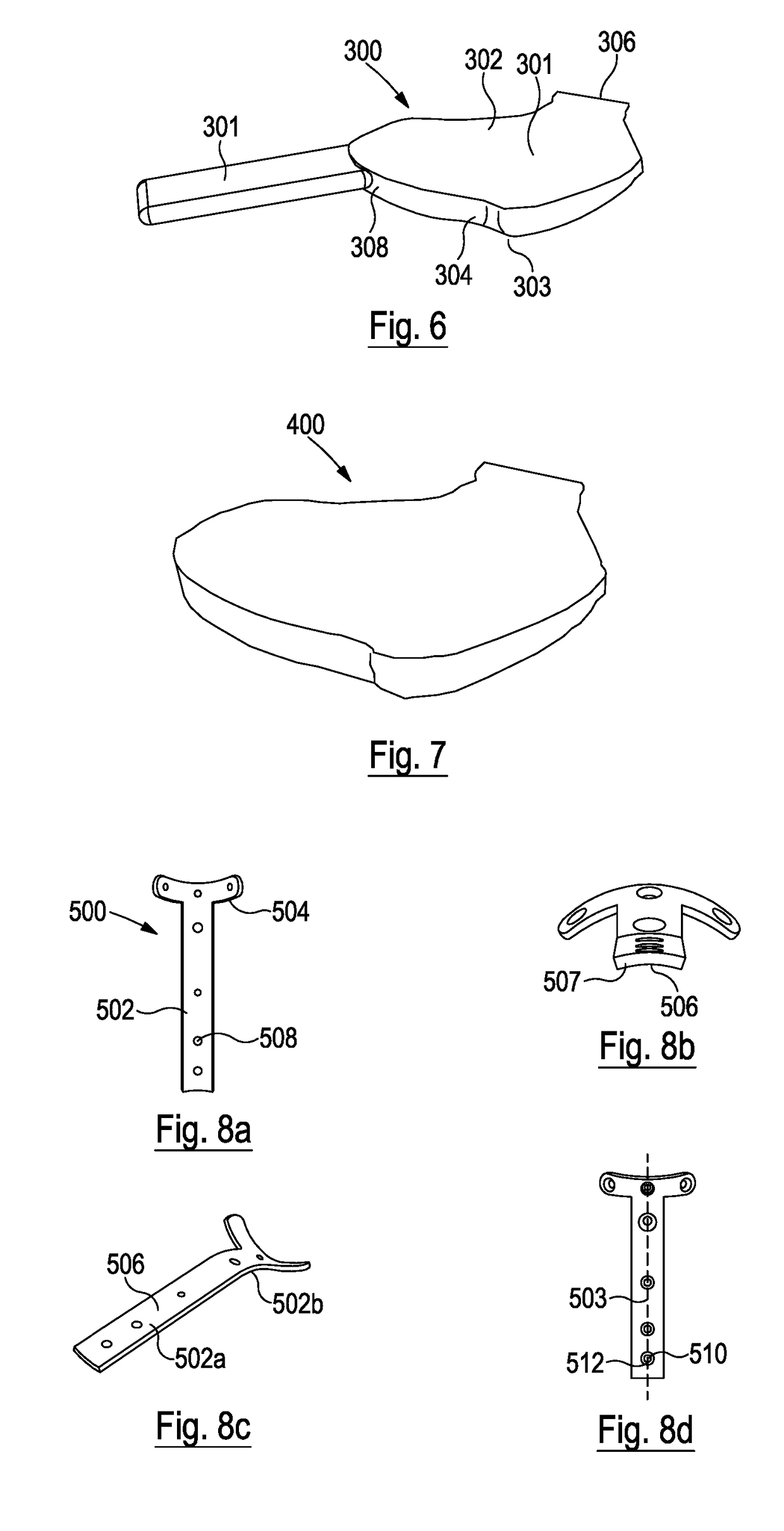
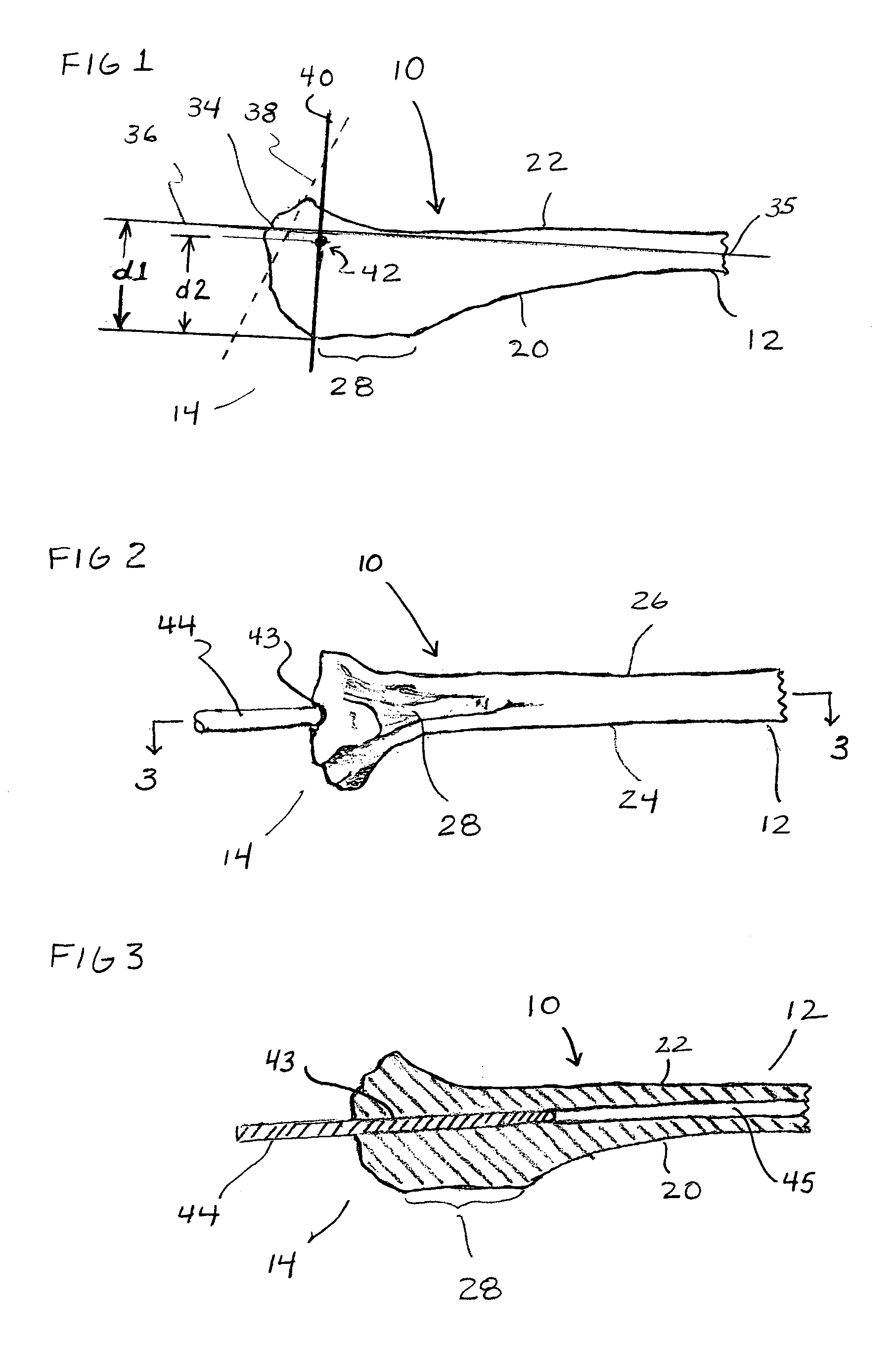
Proximal Tibial Osteotomy System
A support plate, for supporting the two parts of a tibia after a tibial osteotomy, is generally in the shape of a T with a stem having top and bottom ends and a cross piece extending across the top end of the stem. The support plate has a rear surface arranged to contact the tibia. The rear surface of the stem is convex in its central longitudinal plane over a first region of the plate, and the rear surface of the cross piece is concave in its transverse plane.
Owner:OXFORD UNIV INNOVATION LTD
Tibia unicompartmental osteotomy device
PendingCN107007319AImprove accuracyPrecise positioningSurgical sawsBone drill guidesBone tibiaOsteotomy
The invention discloses a tibia unicompartmental osteotomy device. The tibia unicompartmental osteotomy device comprises an osteotomy plate, a guiding plate and a connecting structure, and osteotomy grooves are formed in the osteotomy plate. The guiding plate comprises a first surface, and the first surface is matched with a tibia platform and used for positioning the tibia unicompartmental osteotomy device; the connecting structure comprises a first connecting piece and a second connecting piece, the first connecting piece is arranged on the second connecting piece in a sliding mode, the first connecting piece is fixed on the guiding plate, and the second connecting piece is fixedly arranged on the osteotomy plate. The first connecting piece is arranged on the second connecting piece in a sliding mode, the osteotomy plate can move relative to the guiding plate to achieve position adjustment of the osteotomy plate, and therefore accurate positioning of the osteotomy plate is achieved.
Owner:聂宇 +1
Adjustable devices for treating arthritis of the knee
A method of changing a bone angle includes creating an osteotomy between a first portion and a second portion of a tibia of a patient; creating a cavity in the tibia by removing bone material along an axis extending in a substantially longitudinal direction from a first point at the tibial plateau to a second point; placing a non-invasively adjustable implant into the cavity, the non-invasively adjustable implant comprising an adjustable actuator having an outer housing and an inner shaft, telescopically disposed in the outer housing, and a driving element configured to be remotely operable to telescopically displace the inner shaft in relation to the outer housing; coupling one of the outer housing or the inner shaft to the first portion of the tibia; coupling the other of the outer housing or the inner shaft to the second portion of the tibia; and remotely operating the driving element to telescopically displace the inner shaft in relation to the outer housing, thus changing an angle between the first portion and second portion of the tibia.
Owner:NUVASIVE SPECIALIZED ORTHOPEDICS INC
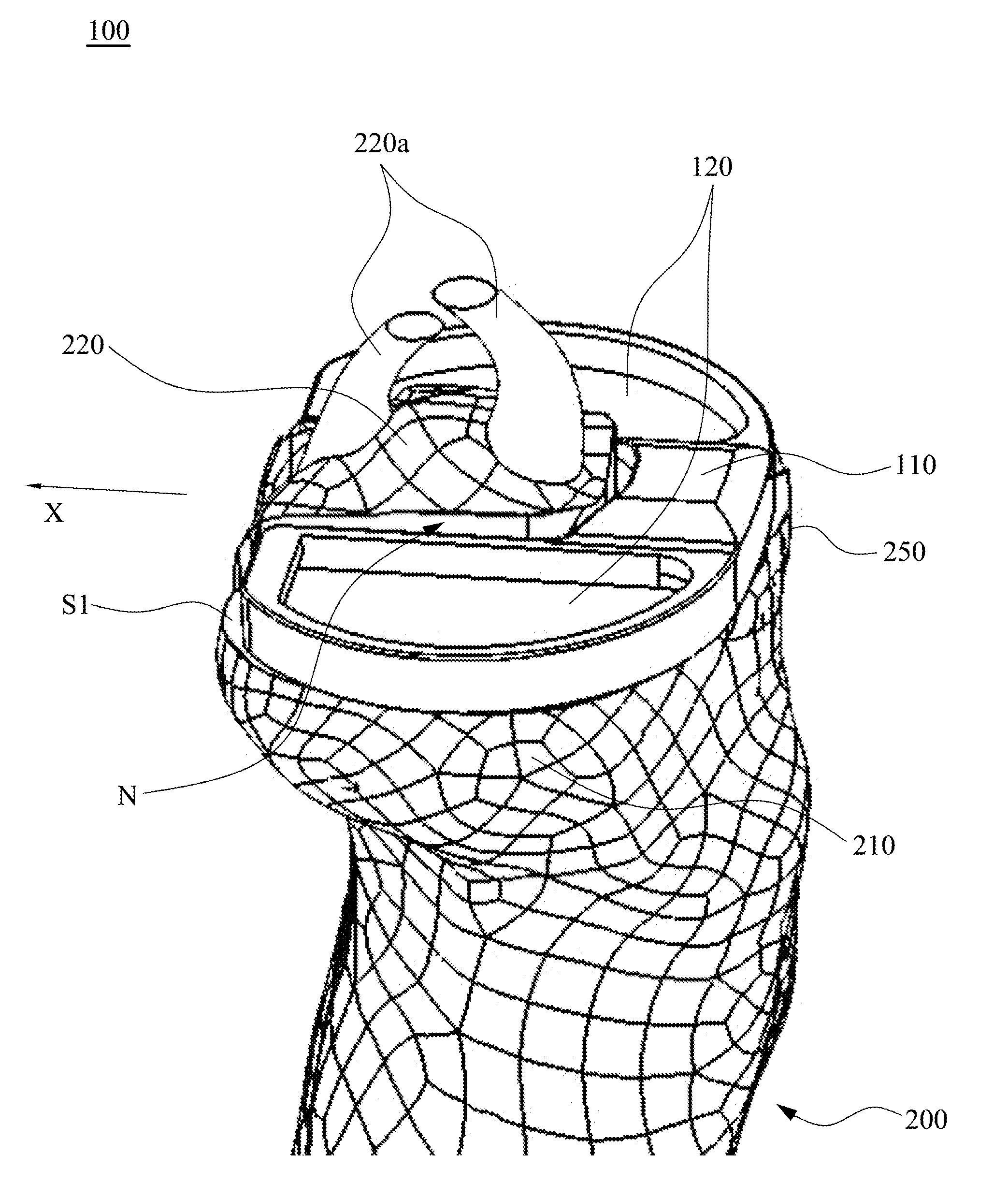
Flipping-type graft fixation device and method
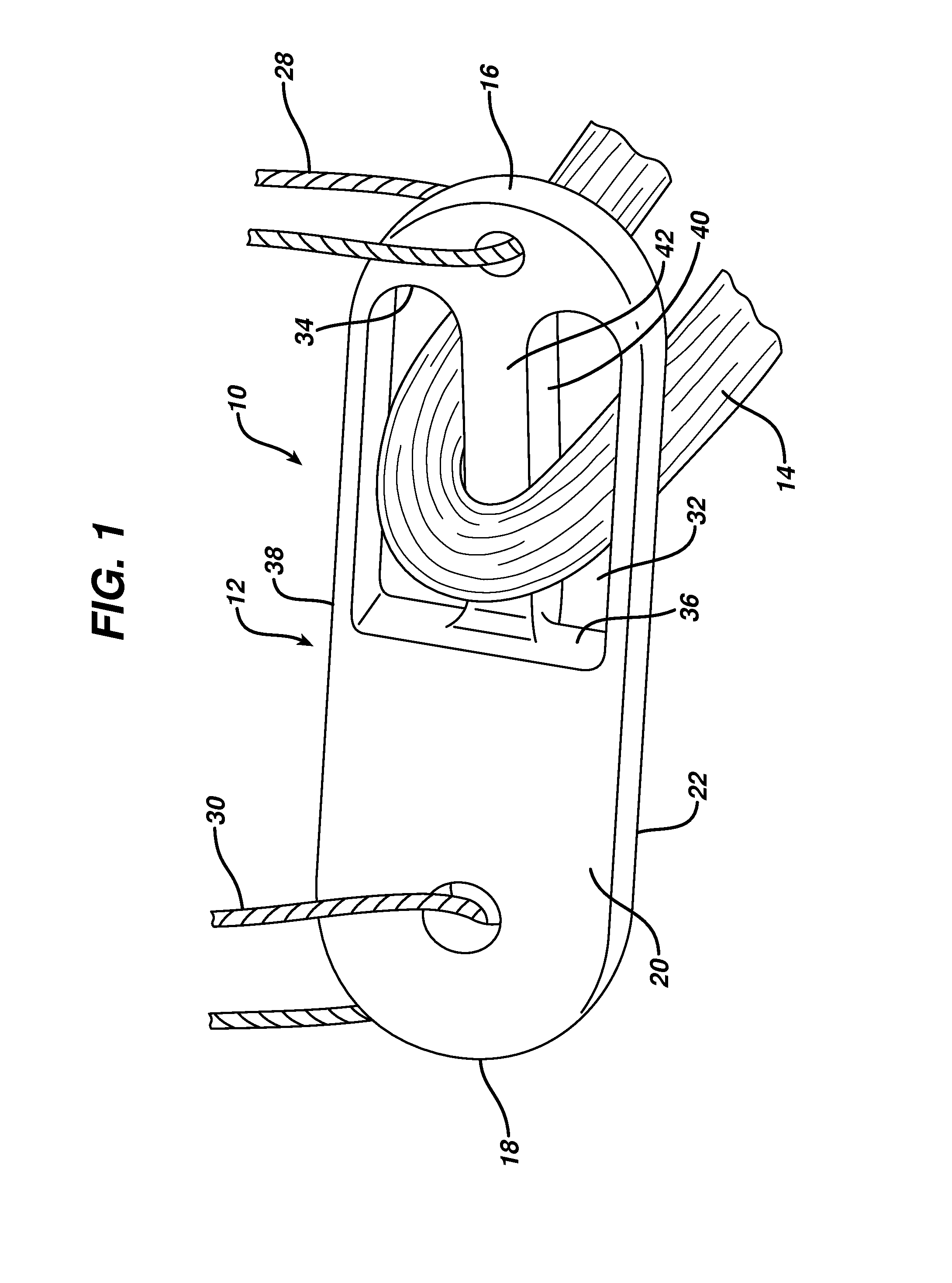
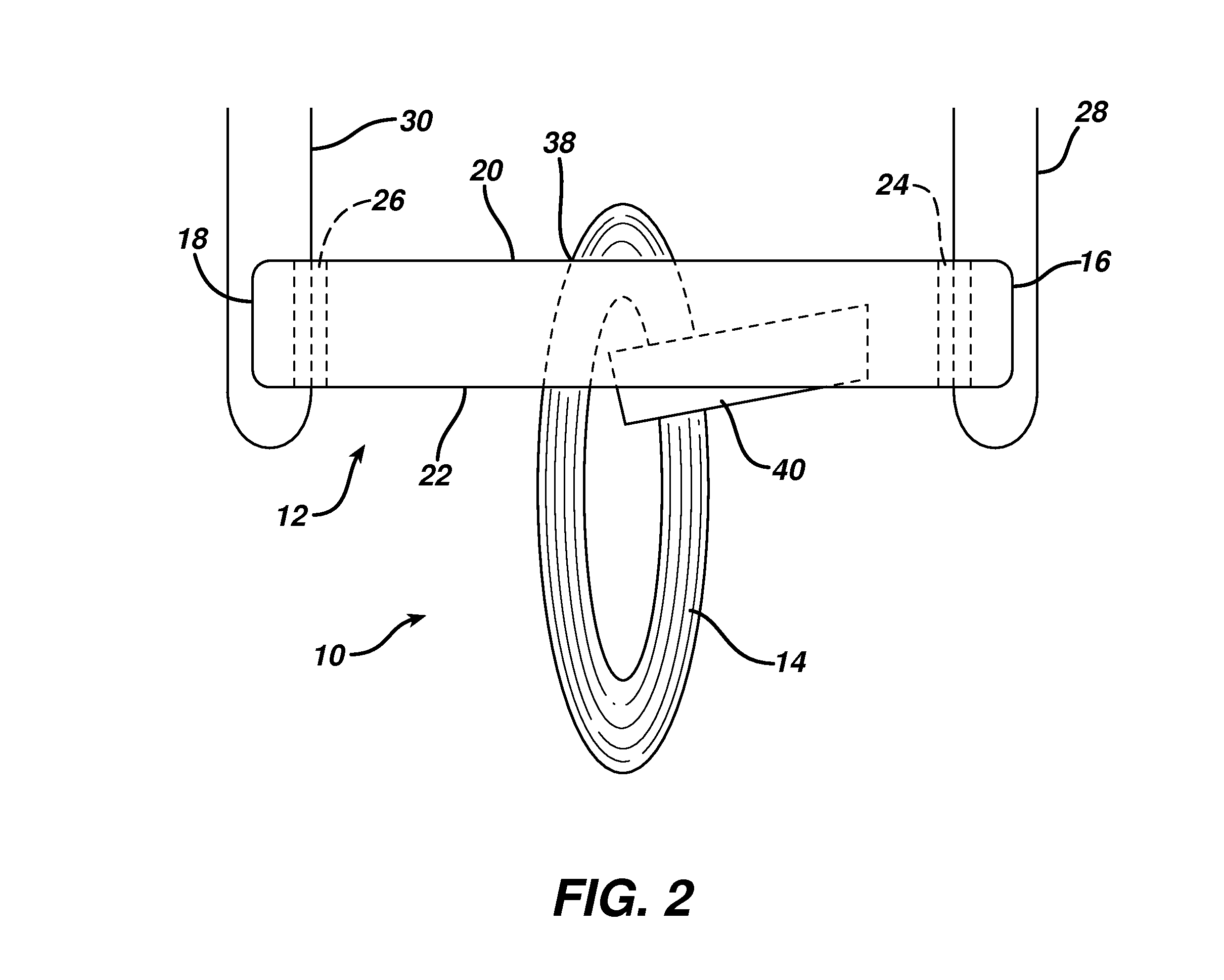
A buckle useful for cortical fixation has a graft retention loop slidably affixed thereto for movement from a first position adjacent a first end of the buckle to a second position at about the midpoint of the buckle. The buckle, with a graft over the loop, is drawn up lengthwise through a bone tunnel through a tibia and then flipped sideways to rest against the surface of the bone with the loop and graft depending back into the tunnel. The sliding attachment of the loop permits flipping of the buckle minimizes the flipping distance, which is the excess amount of the loop which must be pulled free of the tunnel to allow the buckle to be flipped sideways.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
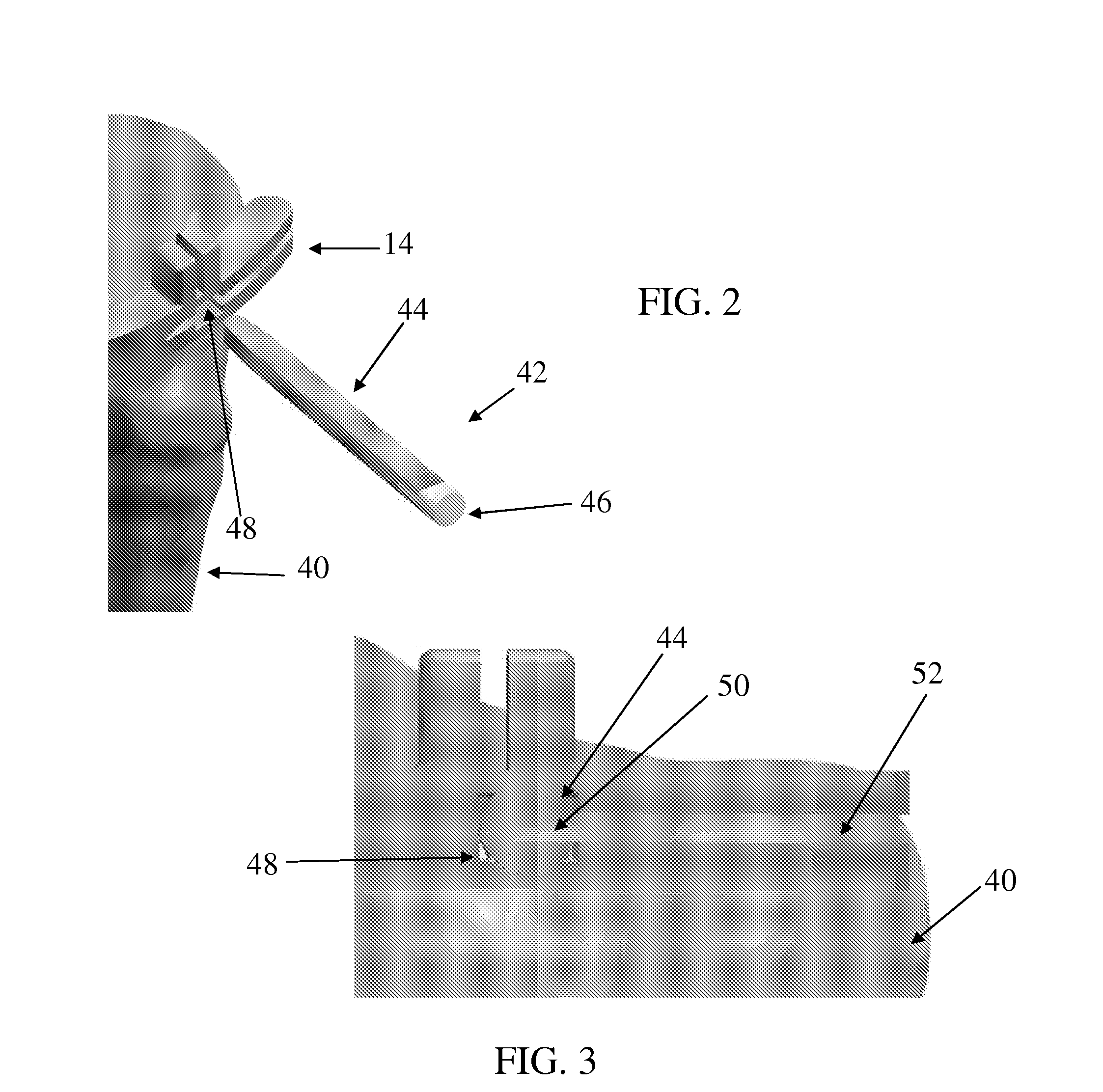
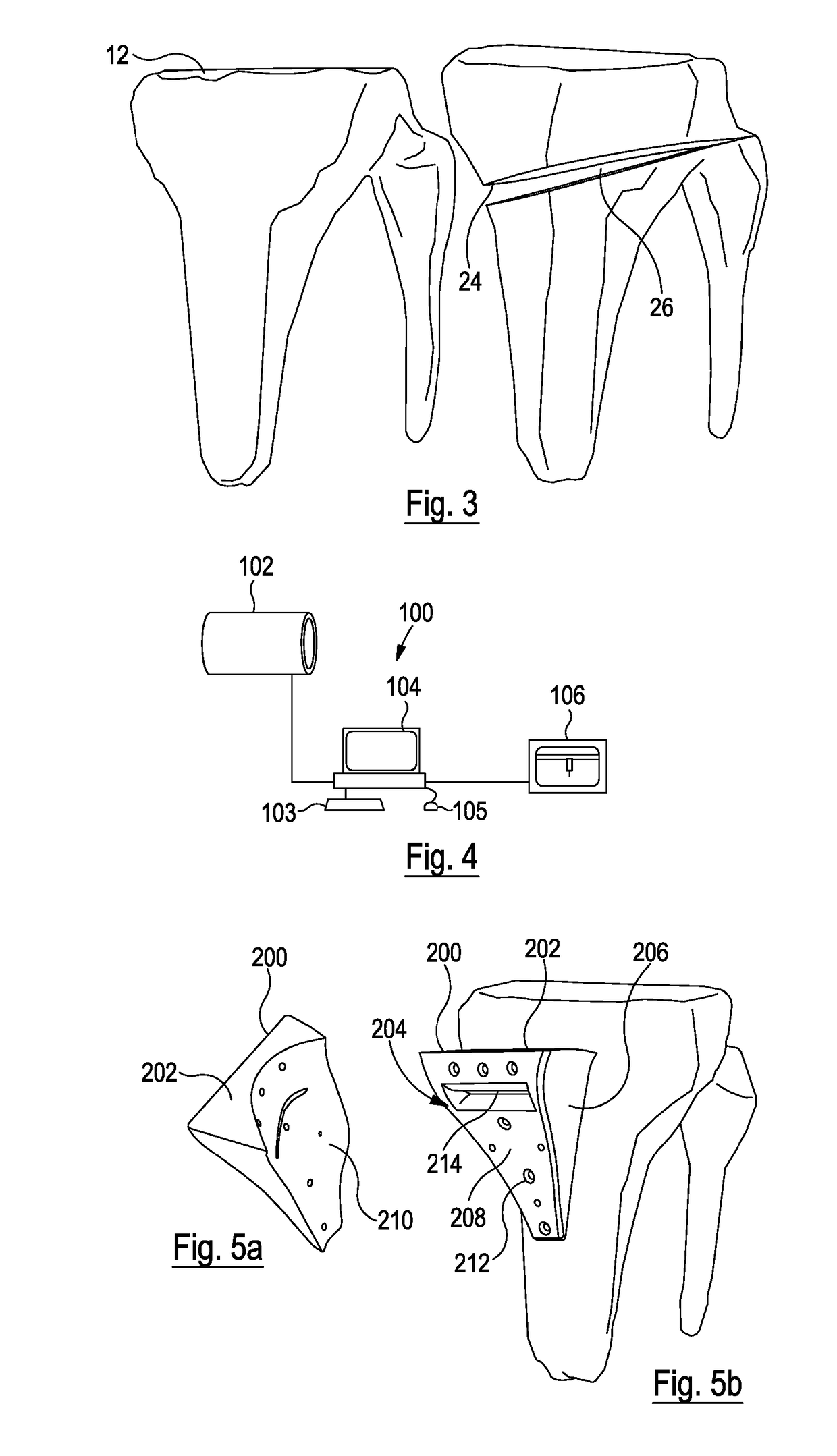
Instrument for fracture fragment alignment and stabilization
ActiveUS8257361B2Avoid placingInternal osteosythesisStraight-bar knitting machinesBone tibiaIliac screw
An instrument (10, 100) for locating an axis of a blocking screw is disclosed. The instrument (10, 100) is applicable for a retrograde installation of a femoral intramedullary device or an antegrade installation of a tibial intramedullary device. The instrument (10, 100) includes a drill jig (11, 105) with a radiolucent frame portion (14, 120) and a mounting portion (12, 110). The mounting portion (12, 110) is adapted to connect to an intramedullary device (204), and the frame portion (14, 120) has at least one aperture (18, 22, 24, 25, 28, 29, 126, 137, 337) for locating the axis of the blocking screw (210). The drill jig (11, 105) is adjustable to locate the aperture (18, 22, 24, 25, 28, 29, 126, 137, 337) in a longitudinal or rotational direction relative to the intramedullary device (204).
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Route planning method for robot assisted fracture reduction
PendingCN111134842AHigh precisionImprove securityComputer-aided planning/modellingSurgical robotsFracture reductionFemoral bone
The invention relates to a route planning method for robot assisted fracture reduction. A reduction route planning method of remote fracture end posture adjustment and double-plane collision prevention based on an A* algorithm is employed. In software mimics and Geomagic studio, fracture deviation parameters are confirmed based on an uninjured side image matching method, and fracture reduction route planning based on the A* algorithm is implemented in two different coordinate planes respectively. By adopting the fracture reduction route planning method provided by the invention, large-amplitude traction of a remote end and collision of the remote fracture end with surrounding tissue in reduction can be effectively avoided, and fracture reduction operation which is short in time, high in precision and safe in collision prevention can be achieved. The method has the advantages of being simple, safe, effective and the like, is applicable to robot assisted fracture reduction operations oflong bone such as thighbone and tibiae, and is capable of improving precision and security of fracture reduction operation, improving reduction efficiency and alleviating the working intensity of doctors.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Apparatus and method for anterior cruciate repair
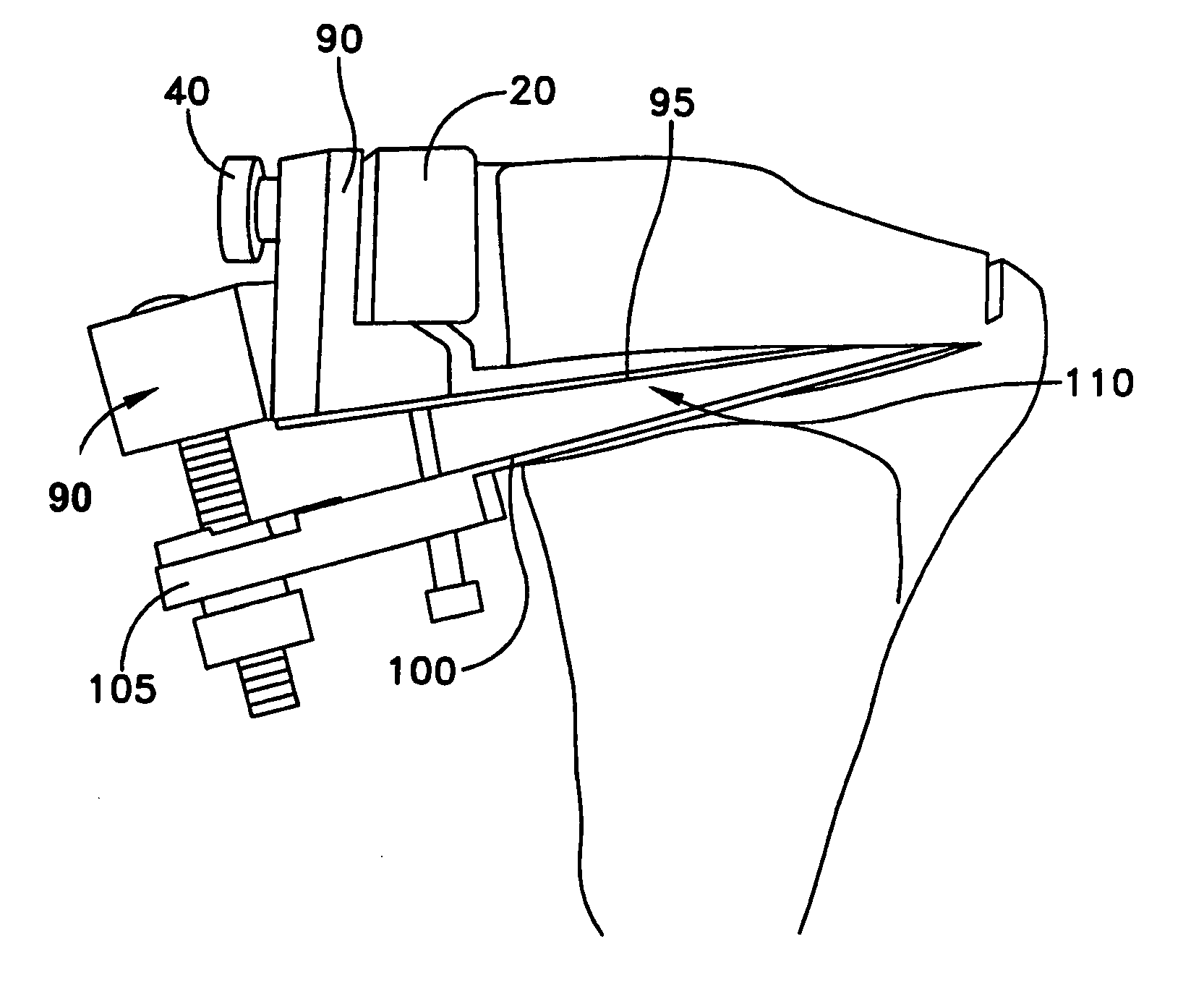
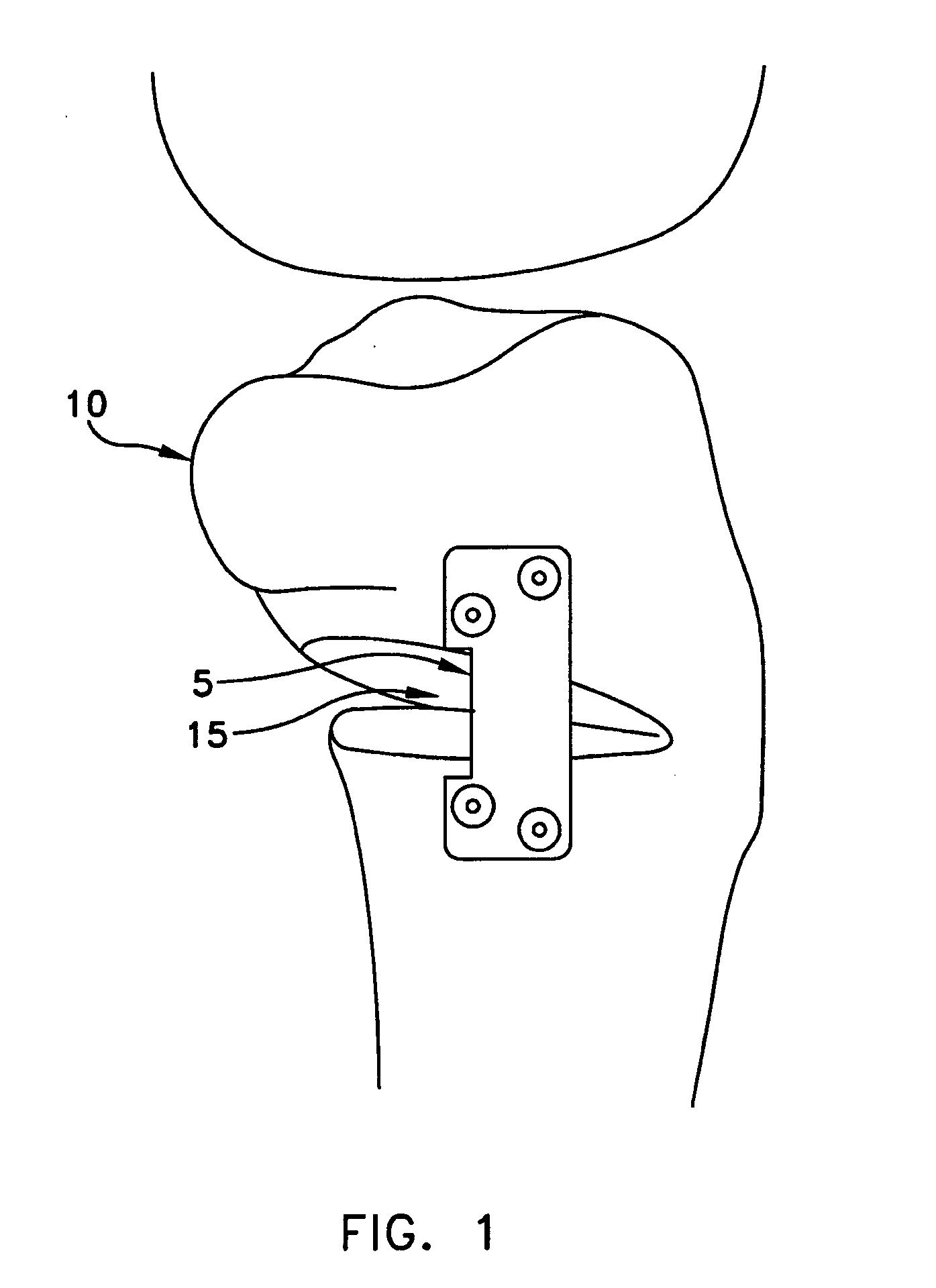
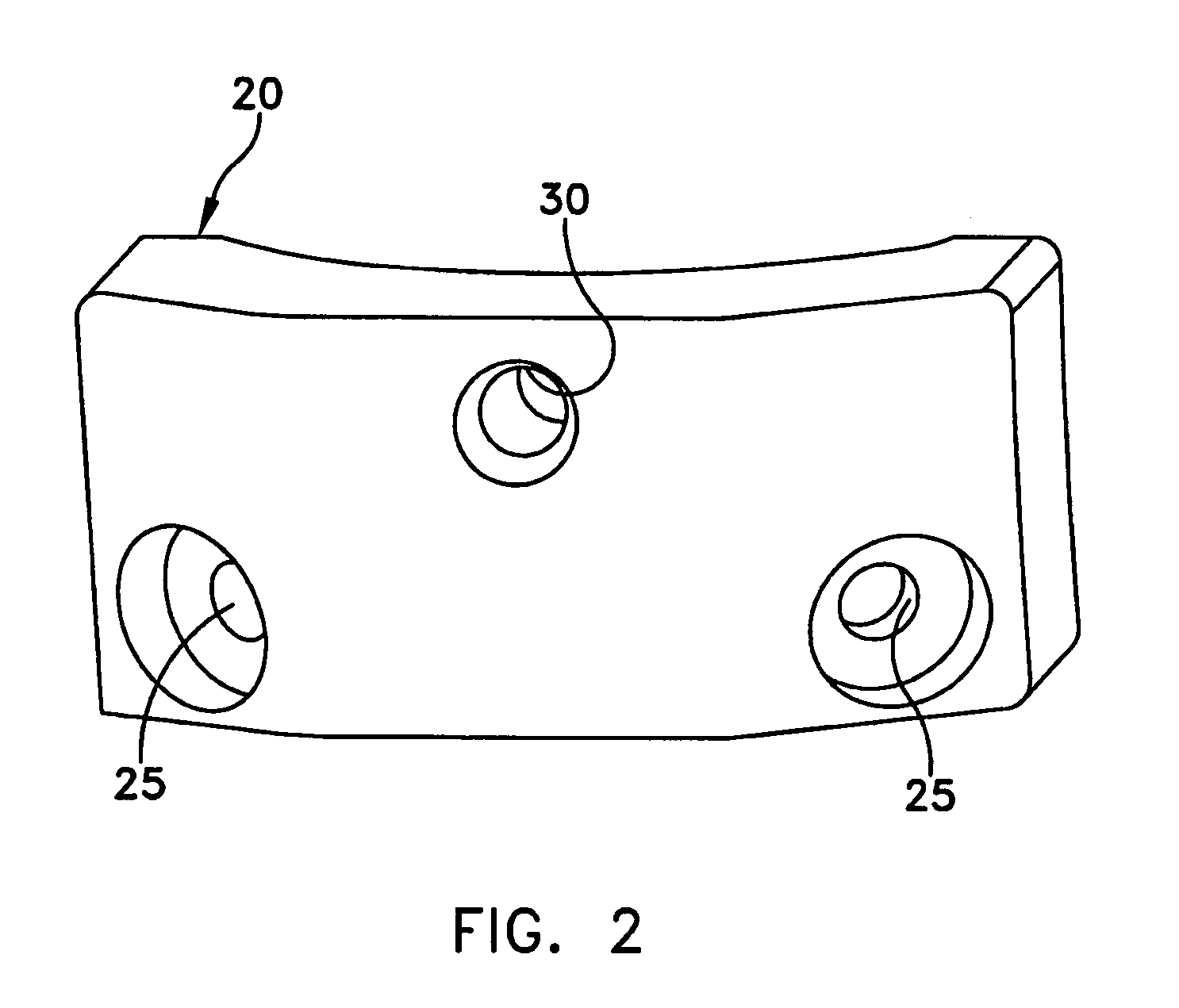
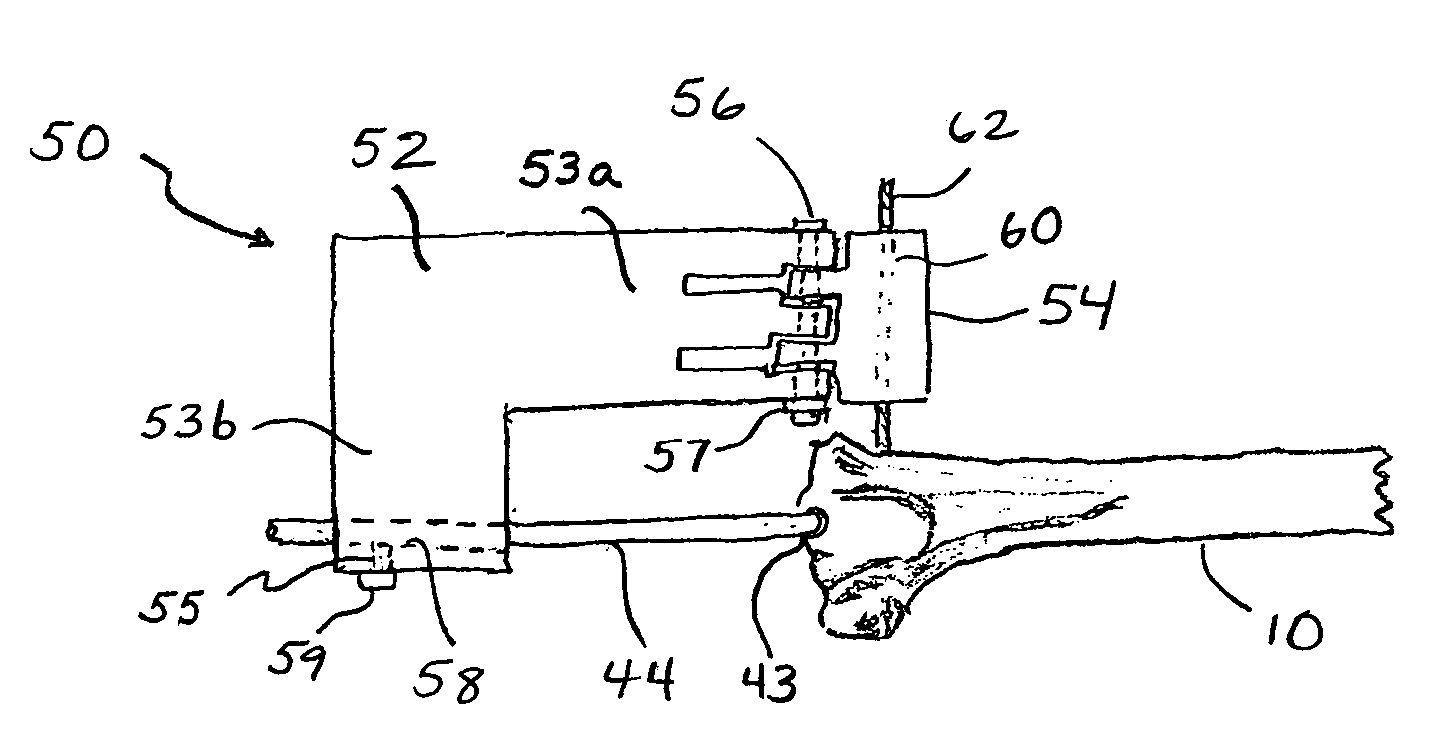
A system and method for repairing anterior cruciate injuries in animals is disclosed. The system includes a fixture used to locate a pilot hole in a tibia, a drill guide used to locate and drill additional holes in the tibia, an angle gauge used to position the drill guide so that it is able to locate and drill additional holes in the tibia, a saw assembly that separates the proximal end of the tibia from the shaft of the tibia. The repositioned proximal end may be secured to the tibia by an optional fixation plate or by a suitable adhesive.
Owner:THORSGARD ERIC O
Method and apparatus for performing multidirectional tibial tubercle transfers
Apparatus for performing a multidirectional tibial tubercle transfer, comprising a jig for positioning against the anterior portion of the tibia, the jig comprising first and second guide surfaces which simultaneously converge towards one another as they extend distally down, and posteriorly towards, the tibia; a medial extender for attaching to the jig, wherein the medial extender comprises a third guide surface which is directed towards a point distal to the point of convergence of the first and second guide surfaces as the third guide surface extends distally down, and posteriorly towards, the tibia; and a lateral extender for attaching to the jig, wherein the lateral extender comprises a fourth guide surface which is directed towards a point distal to the point of convergence of the first and second guide surfaces as the fourth guide surface extends distally down, and posteriorly towards, the tibia.
Owner:KINAMED
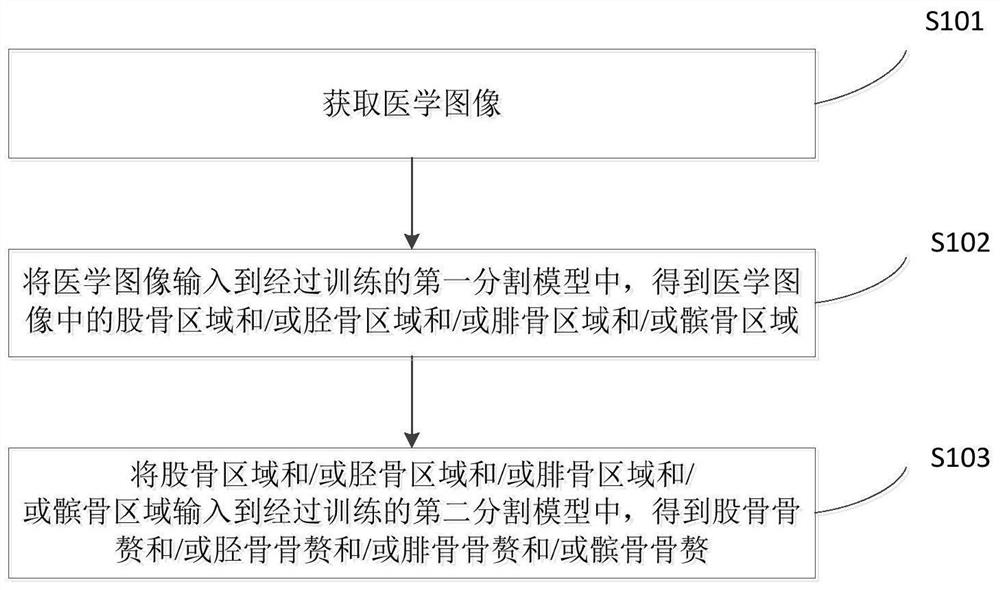
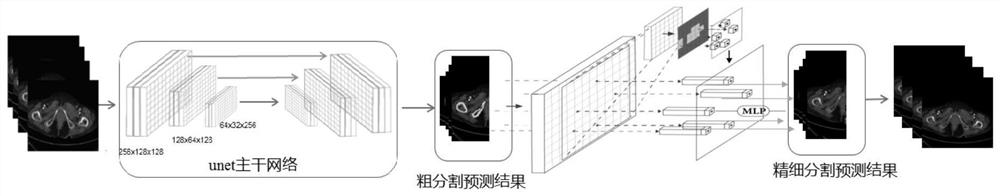
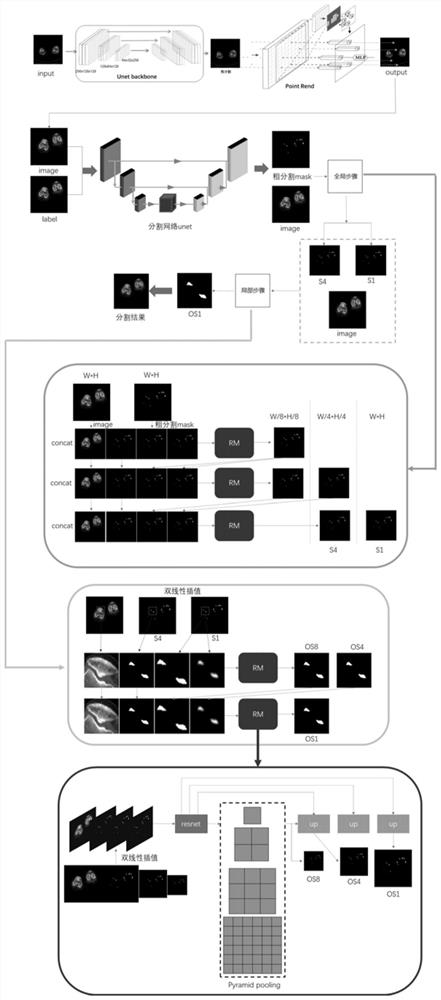
Osteophyte recognition method and device, electronic equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN113076987ACharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesFibular tarsal bonePatellar region
The invention discloses an osteophyte recognition method and device, electronic equipment and a storage medium. The osteophyte recognition method comprises the following steps: acquiring a medical image; inputting the medical image into a trained first segmentation model to obtain a femur region and / or a tibia region and / or a fibula region and / or a patella region in the medical image; and inputting the femur region and / or the tibia region and / or the fibula region and / or the patella region into a trained second segmentation model to obtain a femur osteophyte and / or a tibia osteophyte and / or a fibula osteophyte and / or a patella osteophyte. Accordingly, the osteophyte can be quickly, accurately and intelligently identified by utilizing the first segmentation model and the second segmentation model. Doctors can be assisted in surgical planning, operation is easy, accuracy is high, and individual differences of patients can be met, and meanwhile, the accuracy of follow-up surgeries can be improved and a large amount of time can be saved for orthopedists by perfecting basis data of preoperative planning and guiding surgical planning and prosthesis selection.
Owner:LONGWOOD VALLEY MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +2
Method for constructing three-dimension finite element model which treats tibial plateau posterior-lateral fracture with different inner fixing manners
ActiveCN103871104AQuick buildAccurately establishedComputerised tomographsTomographyElement modelBiomechanics
The invention relates to a method for constructing a three-dimension finite element model which treats a tibial plateau posterior-lateral fracture with different inner fixing manners. The method specially includes the following steps that CT tomography is used for obtaining cross-sectional image data of a normal tibia attached outer steel plate and a normal tibia attached rear steel plate; application open source software ITK-SNAP is used for carrying out medical image processing and cutting; a solid geometric model is generated in professional three-dimension finite-element mesh generating software HyperMesh; solid geometric models in different assemblies are selected according to needs in the HyperMEsh and assembled, a needed model containing the whole tibia, a tibial fracture model and a model for treating the tibial fracture with different inner fixing manners are generated, each model is composed of multiple assemblies, each assembly is divided into grids respectively and multiple tetrahedron finite element models which treat the tibial fracture with different inner fixing manners and of the tibia are finally generated. According to the method for constructing the three-dimension finite element model which treats the tibial plateau posterior-lateral fracture with different inner fixing manners, the ITK-SNAP and the HyperMesh software are used for rapidly and accurately setting up the three-dimension finite element model which treats the tibial plateau posterior-lateral fracture with different inner fixing manners, the modeling speed and the modeling quality are greatly improved and a base is laid for further biomechanical analysis.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
Medicinal liquor for strengthening bone
ActiveCN102552538AImprove use valueGood curative effectAntipyreticAnalgesicsDISEASE RELAPSEZaocys dhumnades dhumnades
The invention discloses medicinal liquor for strengthening bone and a preparation method thereof. The medicinal liquor for strengthening bone contains sheep tibia, sheep kidney, cinnamon, medlar, zaocys dhumnades and white spirit. The preparation method for the medicinal liquor for strengthening bone comprises the following steps of: adding cinnamon, medlar, and zaocys dhumnades into sheep tibia lyophilized powder and sheep kidney lyophilized powder, putting a mixture into a cloth bag, putting the cloth bag into a container, adding wine into the container, covering, and heating the container over fire for more than 10 minutes, keeping the container away from the fire, cooling, sealing for immersing for more than 3 days, and shaking everyday and filtering dregs out to obtain the medicinal liquor for strengthening bone. The medicinal liquor is convenient to prepare, stable in medicinal property, and safe and effective; the effect of the medicinal liquor is achieved through the mutual effect of the white spirit and medicines; the curative effect is improved; the medicinal liquor is used for treating wind-toxin and waist and knee weakness which are caused by liver-kidney deficiency, and exogenous and endogenous pathogenic factors, patients who suffer from pain, swelling, and stiffness of shoulders, backs and limbs and have symptoms of rheumatic arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and senile degenerative osteoarthritis or patients who suffer from arthralgia, swelling and stiffness after trauma and bone fracture; and the medicinal liquor for strengthening bone can address both the symptoms and root causes, and does not have toxic or side effects; and after the medicinal liquor for strengthening bone is taken by patients, disease relapse is prevented.
Owner:东乌珠穆沁旗悦艺生物科技有限责任公司 +1
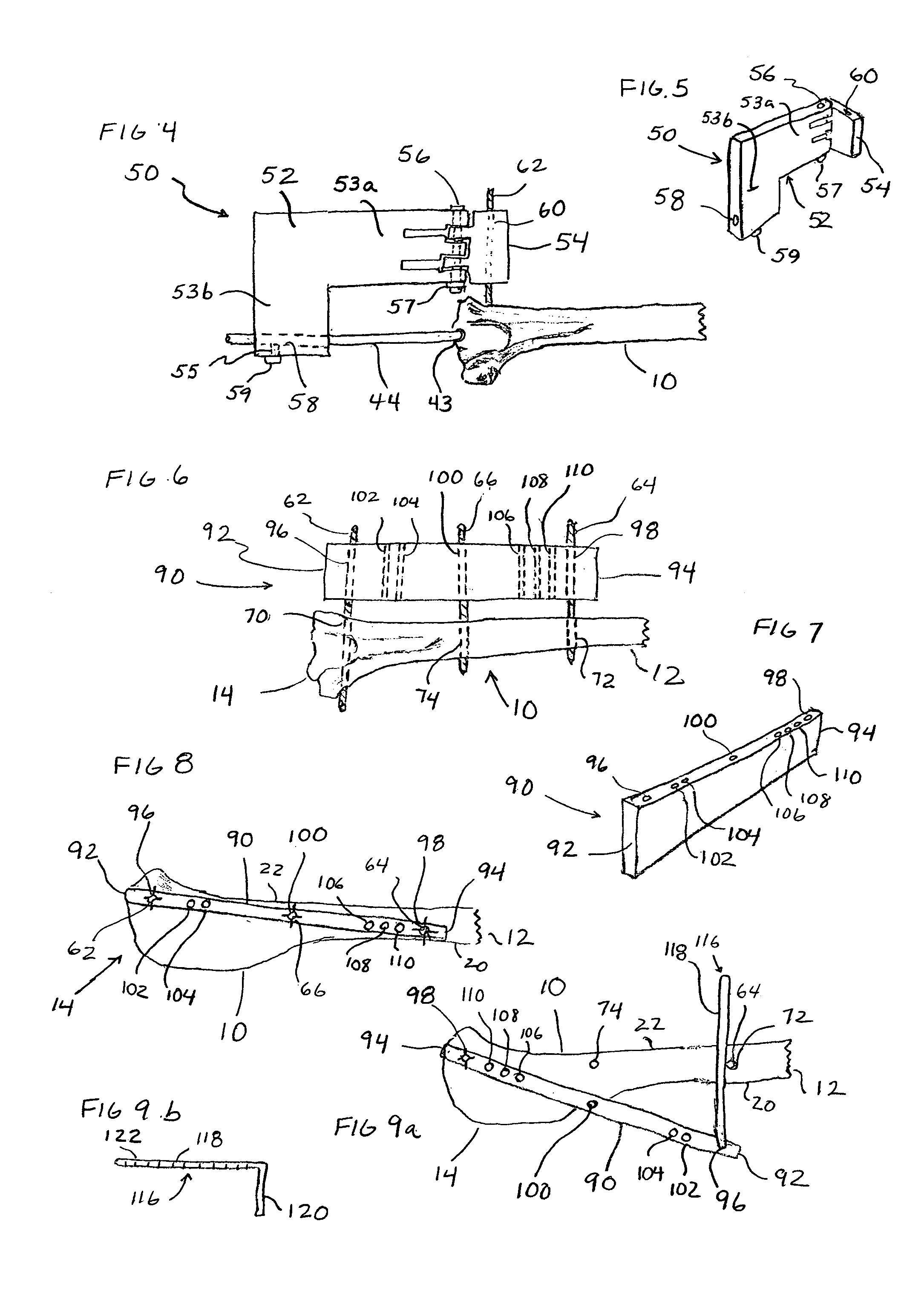
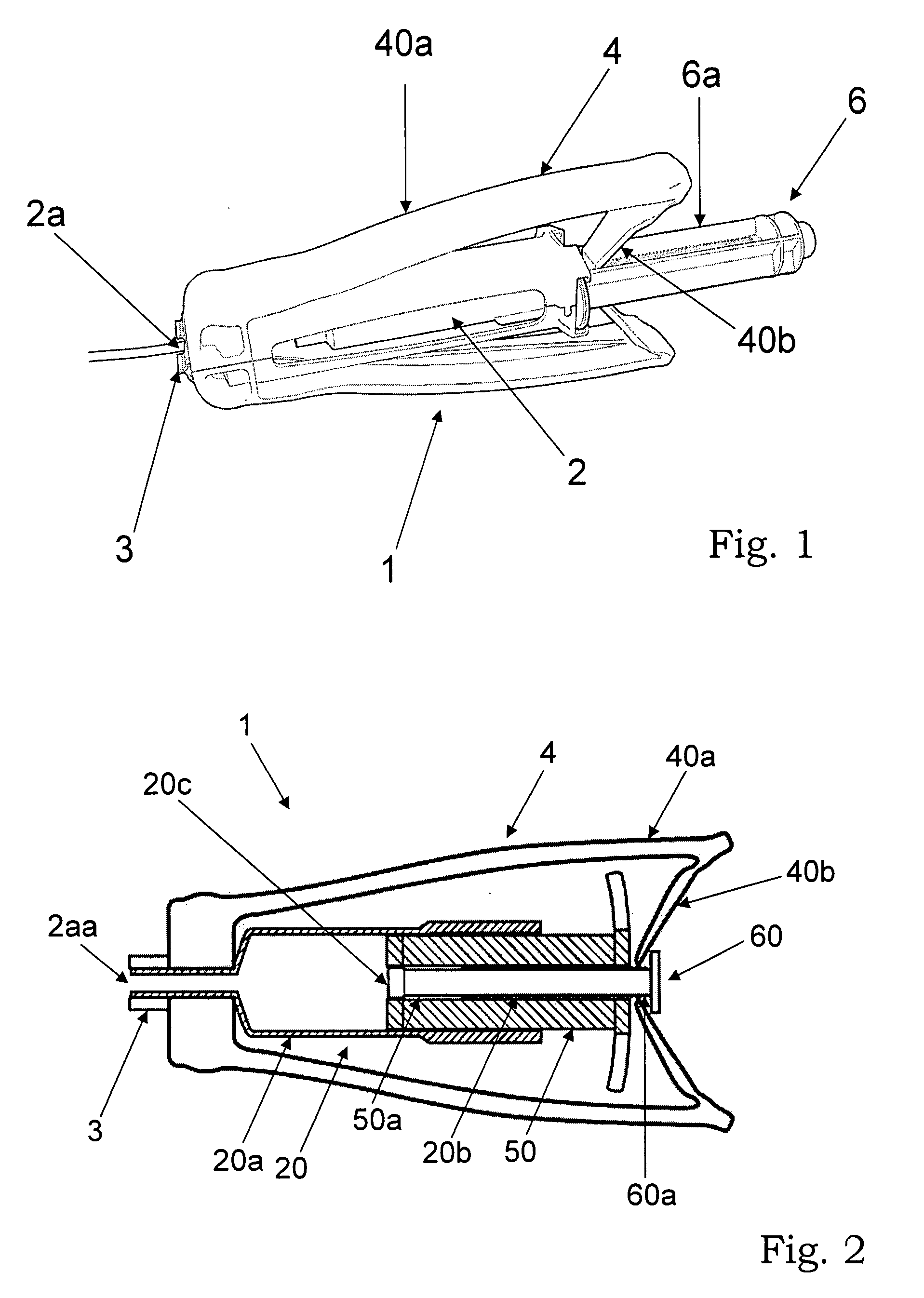
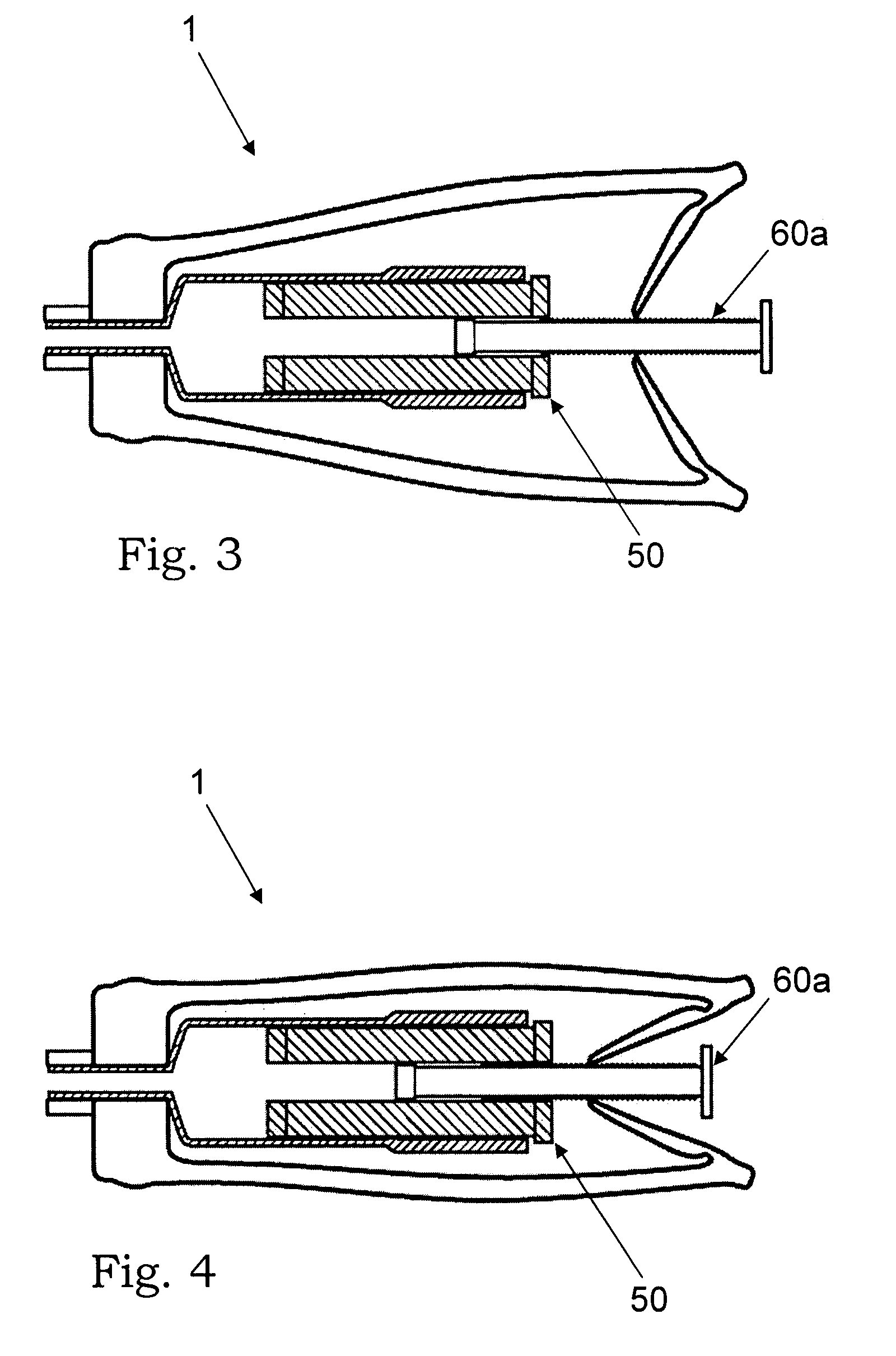
Fixing tool for open-wedge high tibial osteotomy
InactiveUS10245089B2Integrality is enhancedEnsure convenienceInternal osteosythesisFastenersBone tibiaTibial osteotomy
The present invention relates to a fixing tool for an open-wedge high tibial osteotomy, and a fixing tool for an open-wedge high tibial osteotomy, which is installed on a tibia cut open due to a tibial osteotomy, includes: a fixing plate which includes a head portion that has a plurality of nut holes, and an elongated plate that has a plurality of nut holes and a long hole and is formed to protrude from one side of the head portion; screws which are coupled to the nut holes; and a block which is detachably installed in the long hole by using a fixing screw. Therefore, the fixing tool is closely fixed to a tibia, which has been cut open due to a procedure of a high tibial osteotomy, thereby enabling solid union of the tibia.
Owner:PAIK HAE SUN
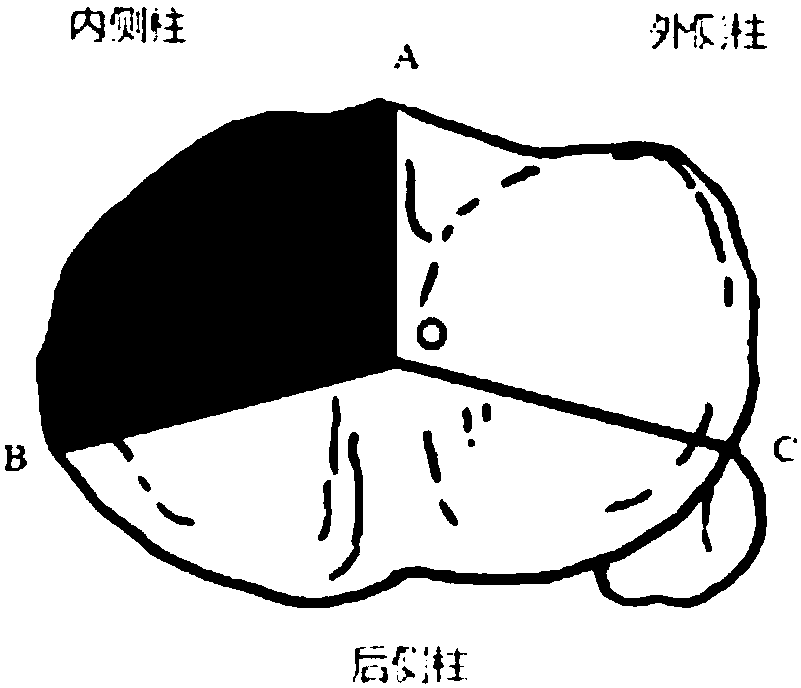
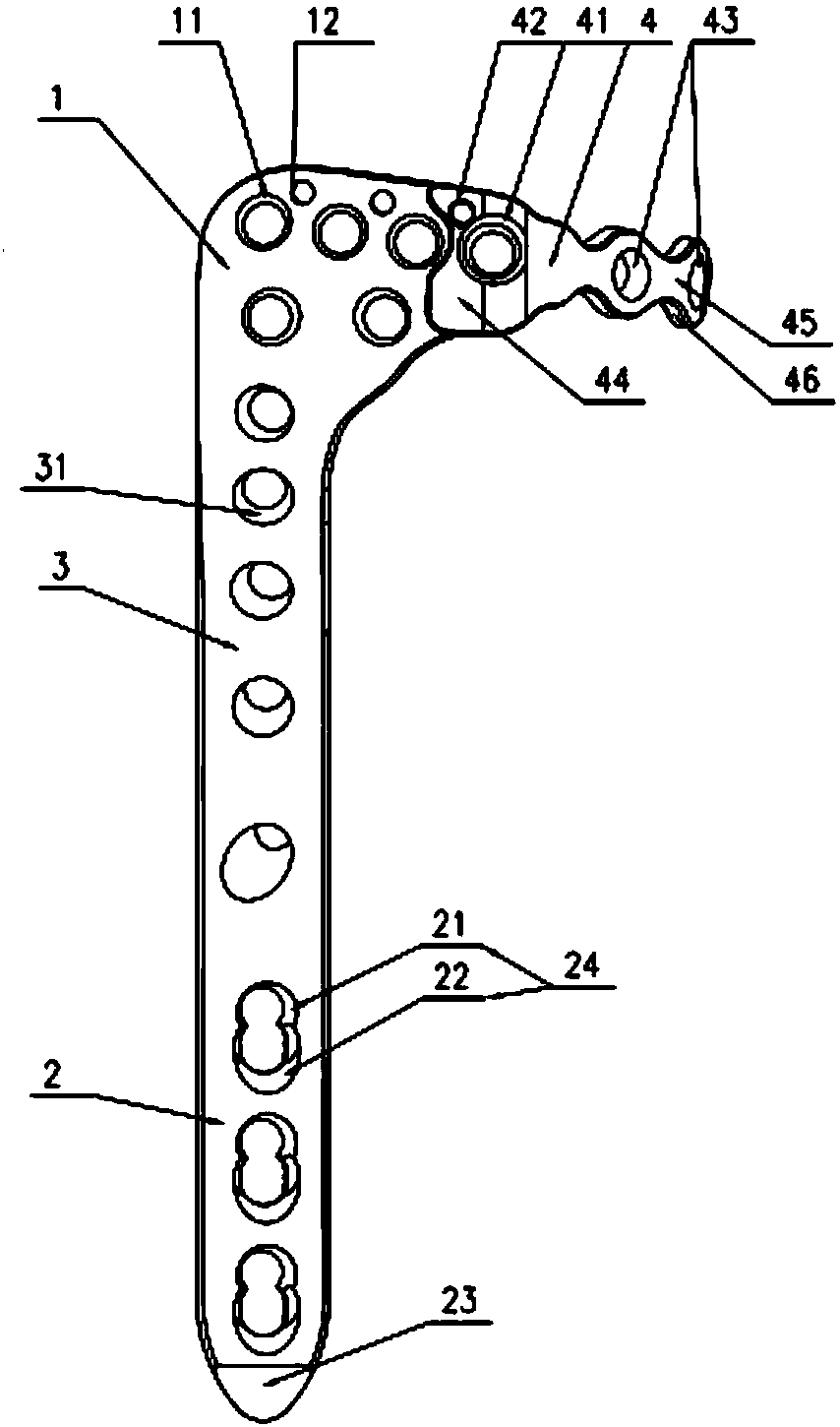
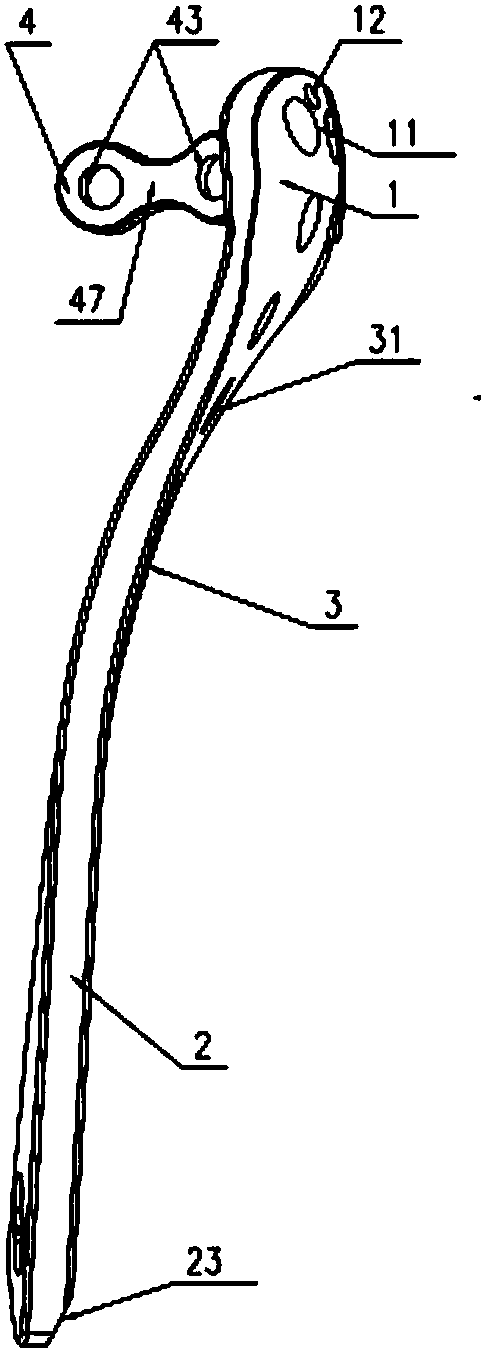
Proximal tibia outer side locking plate
The invention provides a proximal tibia outer side locking plate. The proximal tibia outer side locking plate comprises a main body component and a connecting plate component, wherein the main body component is used for fixing a proximal tibia outer side; the main body component comprises a head part, a rod part and a connecting part for connecting the head part with the rod part; the head part wraps and fixes an outer side column of a proximal tibia platform; the rod part is attached to the outer side surface of a tibial shaft and is fixed; the connecting part is adhered to a tibia surface and is bent; the connecting plate component is connected with the head part and is used for fixing a connecting plate component of a rear side column of the proximal tibia platform. By the main body component, the outer side of a tibia is fixed; by the design of the connecting plate component, fixation to the rear side column of the proximal tibia platform is enhanced, so that the proximal tibia outer side locking plate can be used in surgeries such as proximal tibia fracture, metaphysis fracture, intra-articular fracture and periprosthetic fracture. In addition, the head part of the main body component warps the outer side column of the proximal tibia platform. Compared with an existing curved-surface bone fracture plate, the proximal tibia outer side locking plate is fixed firmly and reliably.
Owner:SHANGHAI KINETIC MEDICAL
System and method for predicting tissue integrity
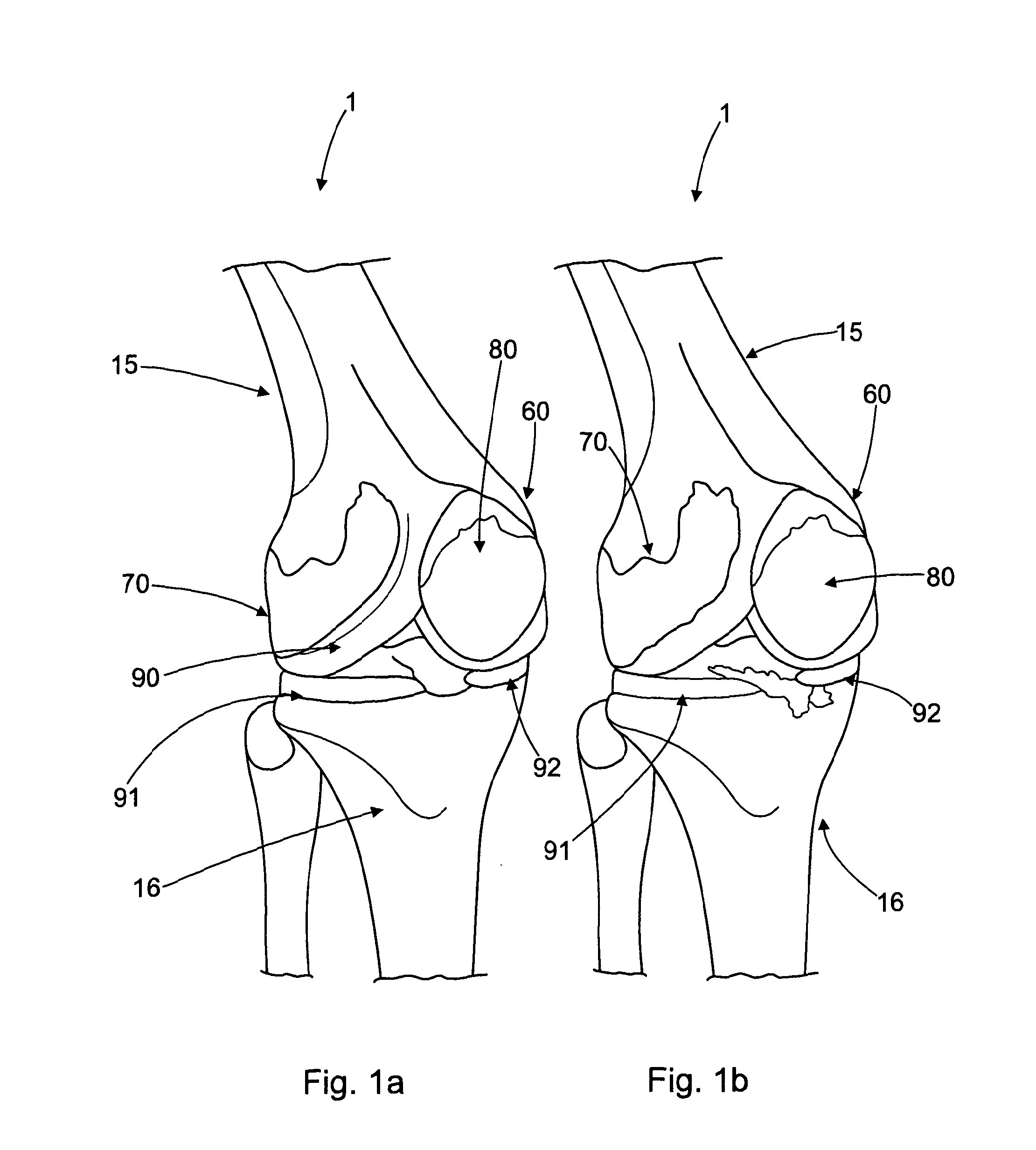
A system and method of diagnosing tissue integrity related to a joint of a patient may include imaging a first bone of the joint of the patient, determining a bone density profile of the first bone based on results of the imaging step, comparing the bone density profile of the first bone to at least one reference bone density profile of a reference first bone, and predicting an integrity of a tissue with respect to the first bone based on the comparison. The first bone may be a tibia and the bone density profile of the tibia may include a bone density profile of a sulcus of a medial tibial condyle of the tibia. The tissue may be an anterior cruciate ligament (“ACL”) and the predicting step may include predicting the integrity of both an anteromedial bundle and a posterolateral bundle of the ACL.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Device for high tibial osteotomy
PendingCN111329583AProtect surrounding tissueInstallation does not hinderComputer-aided planning/modellingBone drill guidesArthritisProximal tibia
The invention relates to the field of medical instruments, in particular to a device for high tibial osteotomy. The device comprises a near-end component, a far-end component, a connecting bridge component, Kirschner wires, a fixing component and a calibration force line component, wherein the near-end component and the far-end component are located at the two ends of the connecting bridge component respectively and fixed to a tibia through Kirschner wires; the calibration force line component is connected with the near-end component through a bolt; and the fixing component is attached to thesurface of the tibia having undergone force line correction and connected with the near end and the far end of the tibia through Kirschner wire hole sites. According to the invention, the design of bony wainscots for the near end and the far end of the tibia is adopted, so the area of a tibia incision near an osteotomy line can be reduced, an operative wound is narrowed, and tissue around the osteotomy line is better protected; the device integrates three functions of osteotomy, force line correction and temporary immobilization and steel plate installation in a high tibial osteotomy operation; operation steps are simplified, operation time is shortened, operation risks are reduced, and the effect of treating knee osteoarthritis through the high tibial osteotomy operation can be better promoted.
Owner:XIANGYA HOSPITAL CENT SOUTH UNIV
Zirconium-niobium alloy tibial plateau prosthesis containing oxide layer and provided with bone trabecula as well as preparation method
PendingCN112315627AImprove mechanical adaptabilityHigh bonding strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOsseointegrationElement model
The invention discloses a zirconium-niobium alloy tibial plateau prosthesis containing an oxide layer and provided with bone trabecula as well as a preparation method. According to the method, zirconium-niobium alloy powder is used as a raw material, an intermediate product is obtained through 3D printing integral forming, and then the tibial plateau prosthesis comprising a near-plateau support bone trabecula layer and a far-plateau support bone trabecula layer is prepared through hot isostatic pressing, cryogenic treatment and surface oxidation, the pore diameter and porosity of the near-plateau support bone trabecula layer are uniformly arranged, and the pore diameter and porosity of the far-plateau support bone trabecula layer are arranged in different areas; the bone trabecula topological structure of the tibial plateau prosthesis is in three-dimensional gradient distribution, the micro-strain of 64%-72% of a finite element model is between the lowest effective strain threshold value and the hyper-physiological strain threshold value, the mechanical adaptability of the prosthesis is improved, and the prosthesis has excellent bone ingrowth performance; and the oxide layer of thetibial plateau prosthesis can integrally realize excellent biocompatibility of an osseointegration interface and superhigh wear resistance and low wear rate of a friction interface.
Owner:JIASITE HUAJIAN MEDICAL EQUIP (TIANJIN) CO LTD
Adjustable tibia probe
The invention discloses an adjustable tibia probe. The adjustable tibia probe comprises a vertical rod, a rotating rod is arranged at the upper end of the vertical rod, a sleeve is arranged outside the rotating rod, a probe is arranged in the middle of the vertical rod, a guide rod is arranged at the lower end of the vertical rod, a height adjusting mechanism is arranged in the middle of the rotating rod, a prompting mechanism is arranged at the lower end of the rotating rod, and a connecting mechanism is arranged on one side of the guide rod; the height adjusting mechanism can accurately adjust the height of the probe, the prompting mechanism makes a sound every time when the probe is adjusted by 1 mm, a doctor can conveniently and accurately judge the adjusting height of the probe, the measuring precision is improved, the connecting mechanism can be very conveniently connected with a tibia osteotomy module, and the operation time is shortened.
Owner:天衍医疗器材有限公司
Mixing and injection system for injectable biomaterials or artificial materials in orthopaedic applications
InactiveUS20070249994A1Risk minimizationMinimize exposureShaking/oscillating/vibrating mixersInfusion syringesSpinal columnInjectable biomaterial
The present invention specifically relates to a mixing and injection device for mixing, handling and injecting of biomaterials, such as ceramic biomaterials, PMMA and other materials intended for stabilising and healing fractures and lesions, and for filling voids in orthopaedic, spinal, cranio-maxillofacial, distal radius, tibia plateau or other applications where natural or artificial substances are to be delivered to such fractures, lesions or voids in the skeleton.
Owner:DOXA AB
Tibia bone fracture plate of medical equipment for orthopedic surgery
InactiveCN104840242AGood biocompatibilityHigh strengthPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCoatingsSurgical operationMedical equipment
The invention discloses a tibia bone fracture plate of medical equipment for an orthopedic surgery. The tibia bone fracture plate comprises a bone plate body which is in the shape of Y, wherein the bone plate body comprises an attachment surface contacting with the surface of the tibia bone, and a bone plate body installation surface opposite to the attachment surface; installing through holes are formed in the bone fracture plate, the attachment surface is a titanium nitride ceramic material layer, and the installation surface is a titanium oxide ceramic material layer, and the surface treatment process of pickling and passivation is performed on the titanium alloy of the ingredient, and thus dark spots on any surface are avoided from occurrence and the prepared surface is clean and tidy; chemical agents composed of a specific pickling solution and a passivation solution are used, so that the period of surface treatment can be greatly saved and the surface treatment effect is very good.
Owner:刘乐
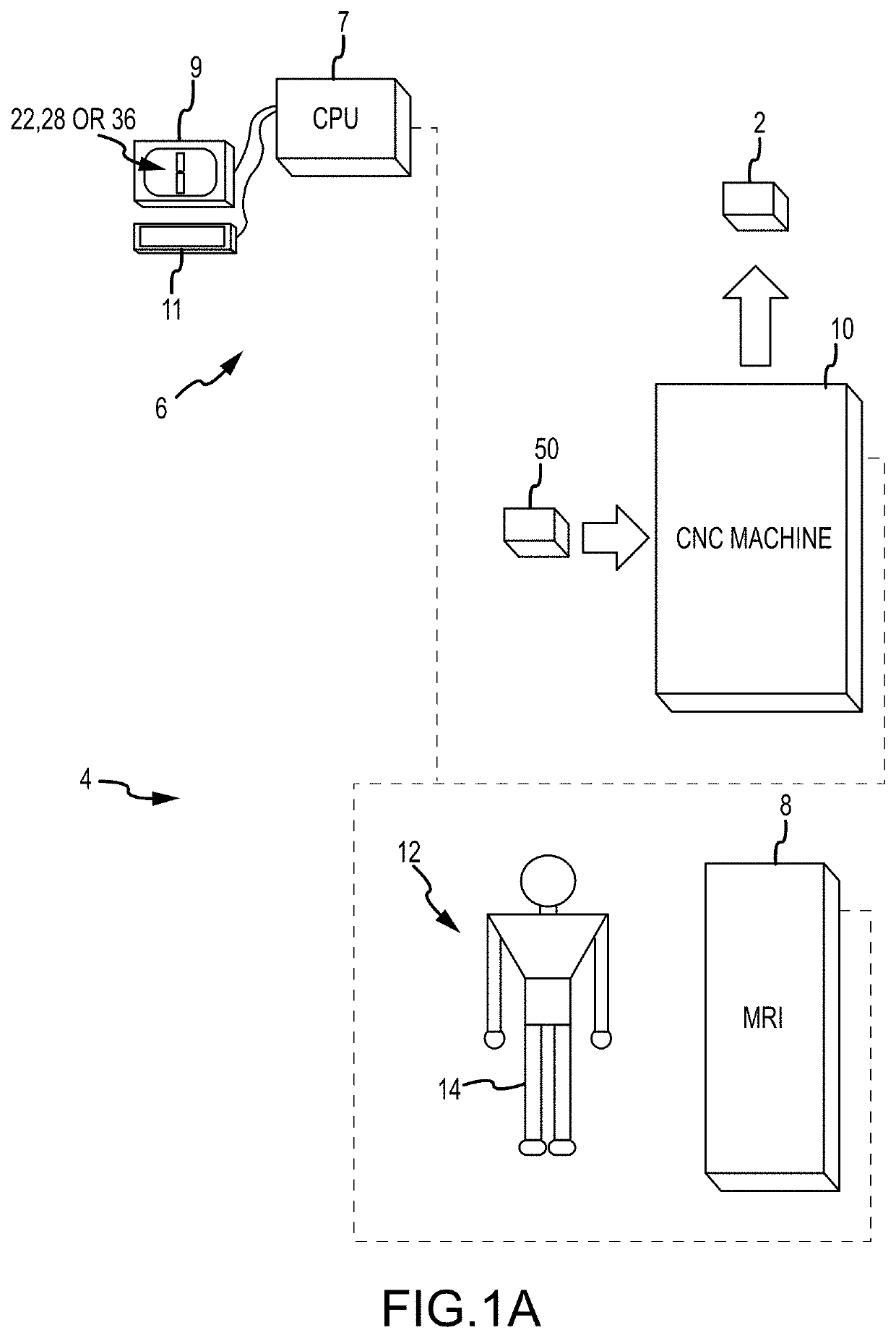
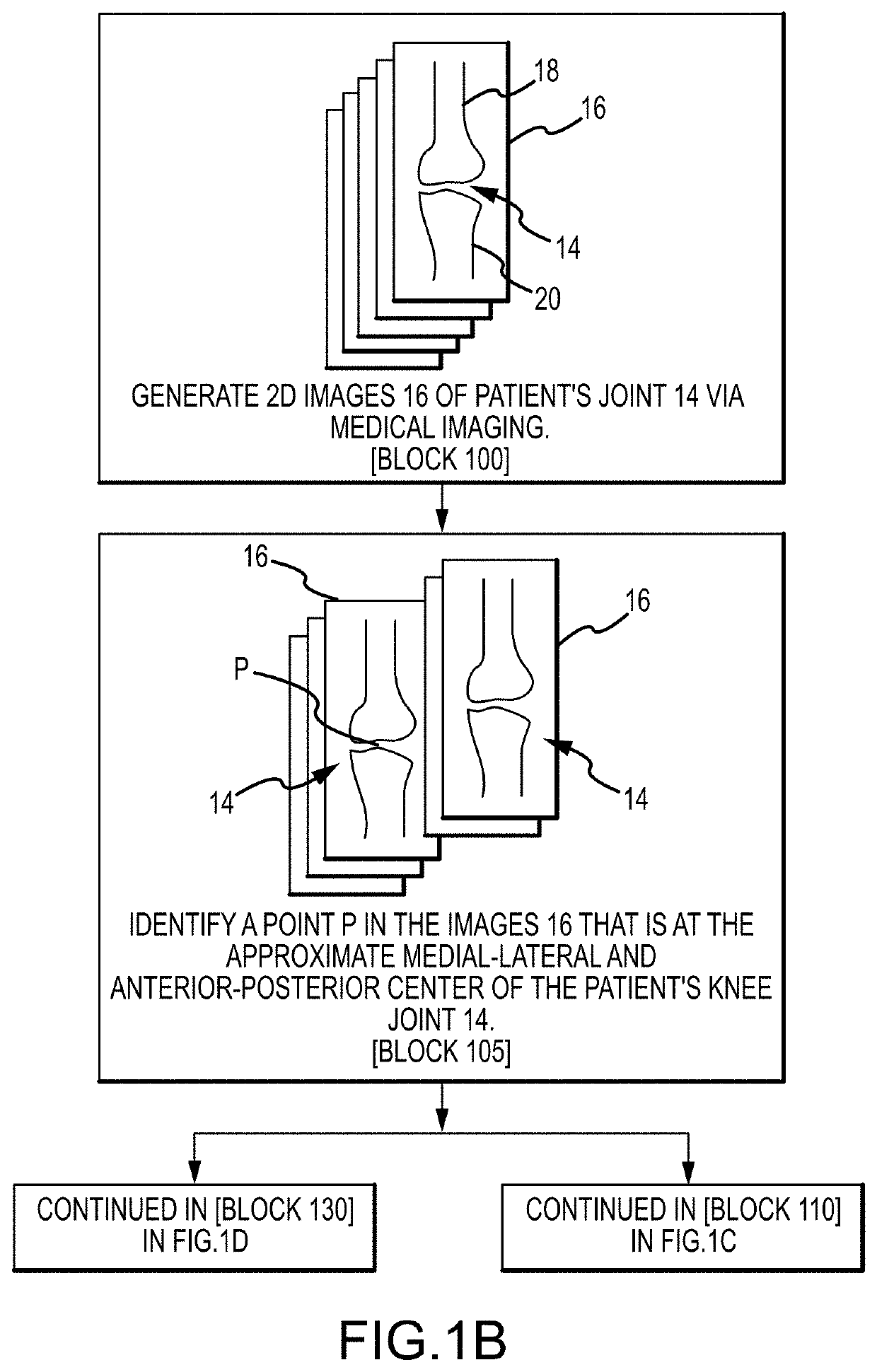
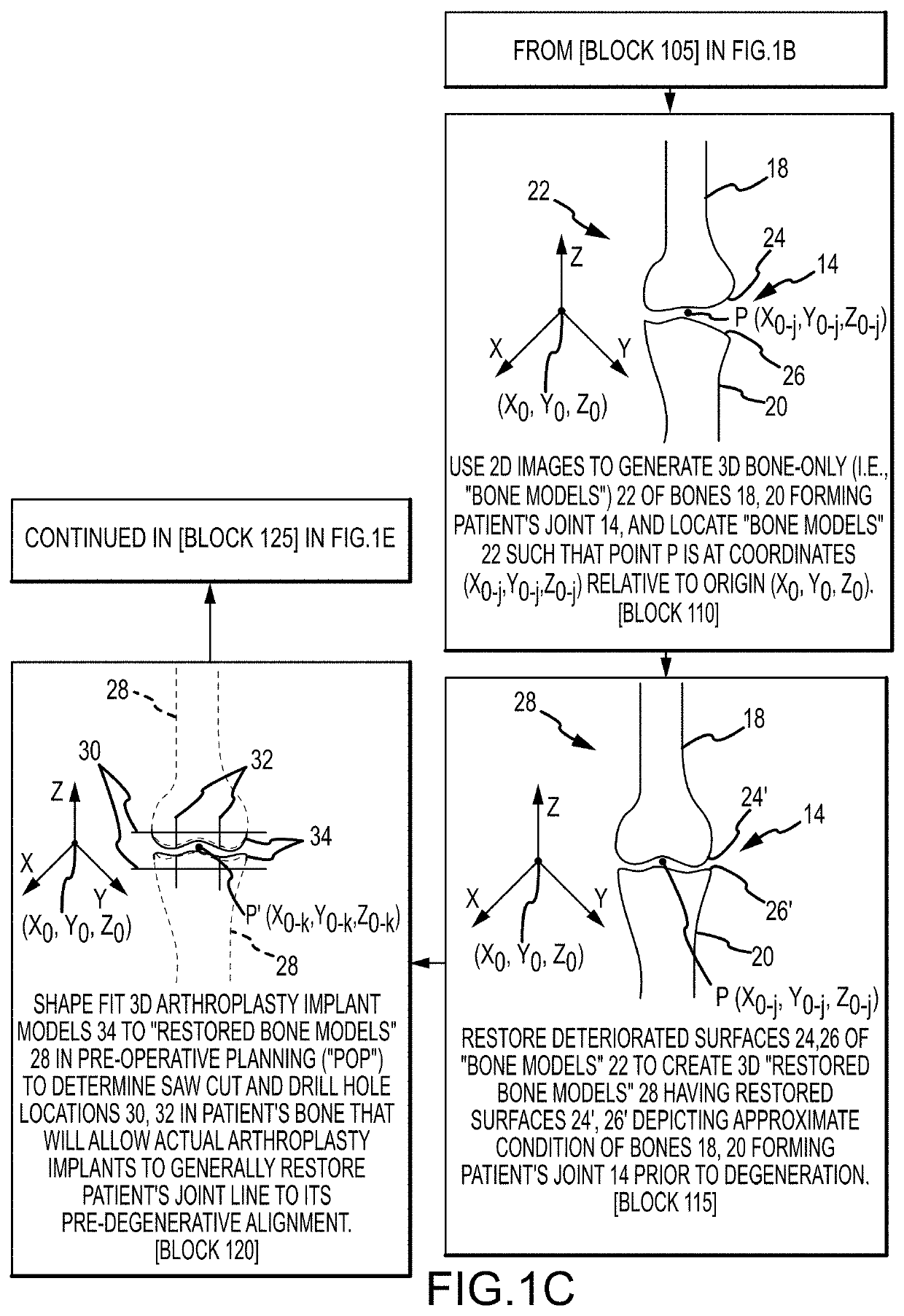
System and method for image segmentation, bone model generation and modification, and surgical planning
ActiveUS10687856B2Image enhancementMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesSurgical operationFemoral bone
A computer-implemented method of preoperatively planning a surgical procedure on a knee of a patient including determining femoral condyle vectors and tibial plateau vectors based on image data of the knee, the femoral condyle vectors and the tibial plateau vectors corresponding to motion vectors of the femoral condyles and the tibial plateau as they move relative to each other. The method may also include modifying a bone model representative of at least one of the femur and the tibia into a modified bone model based on the femoral condyle vectors and the tibial plateau vectors. And the method may further include determining coordinate locations for a resection of the modified bone model.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com