Patents
Literature
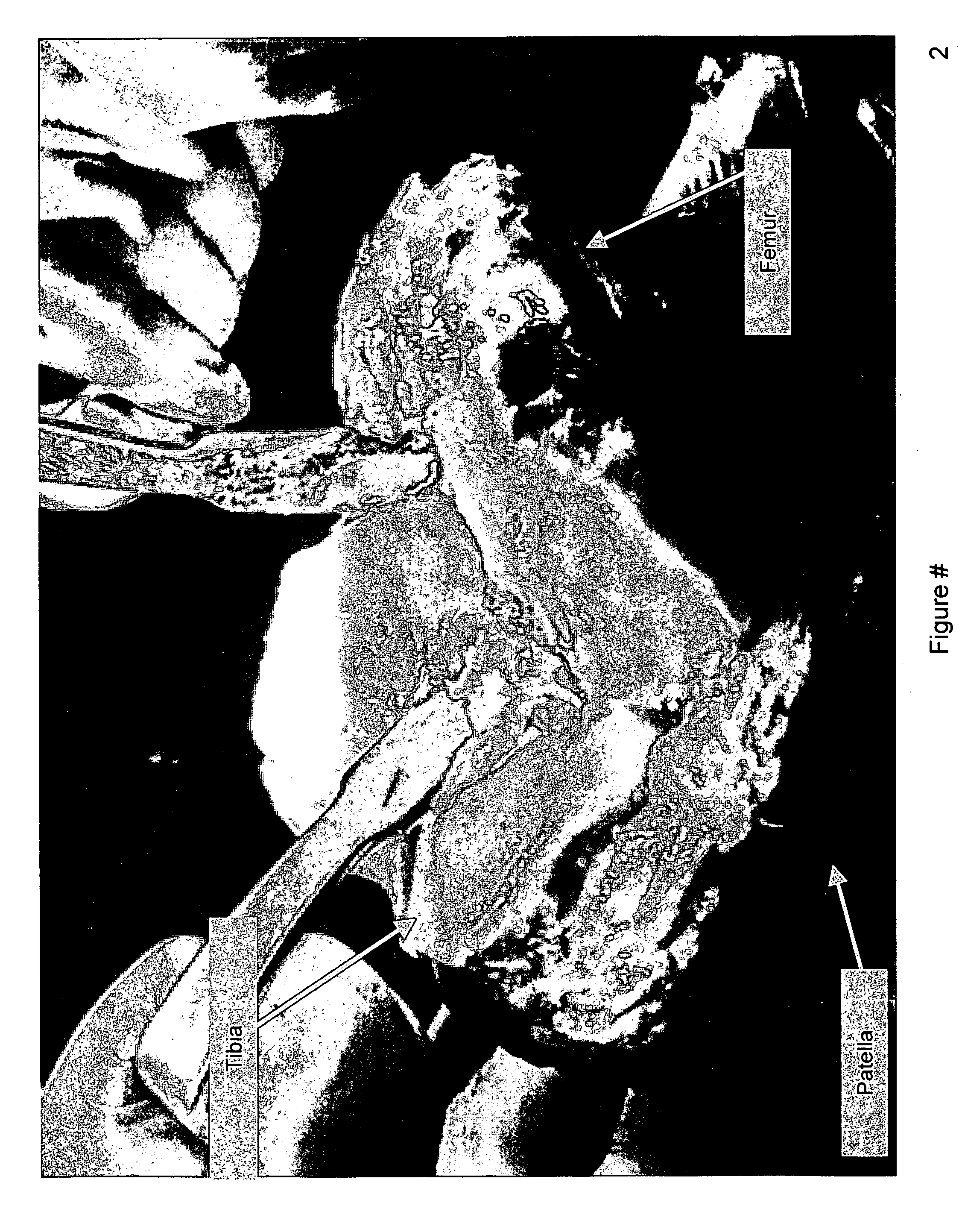
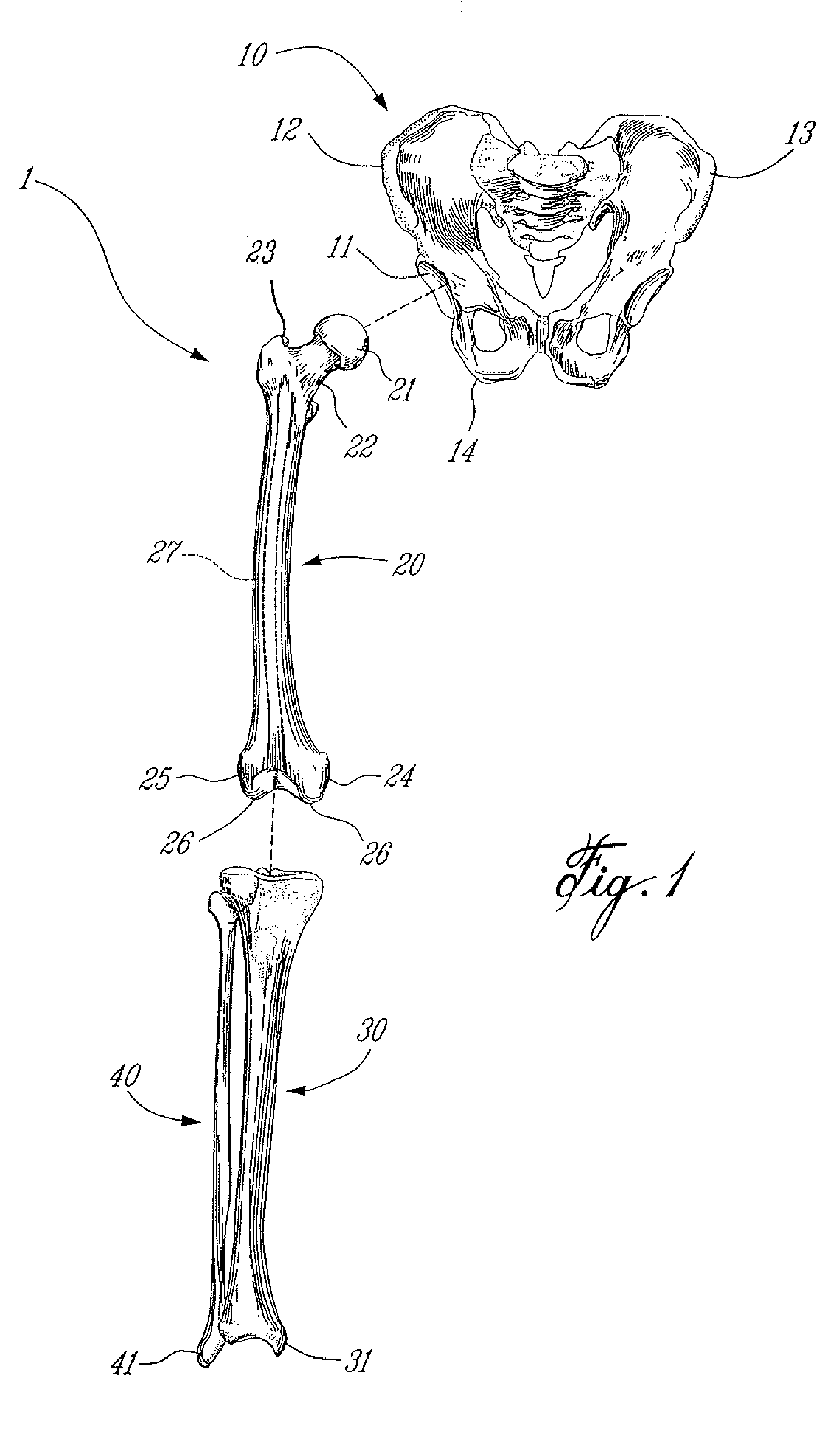
502 results about "Femur bone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
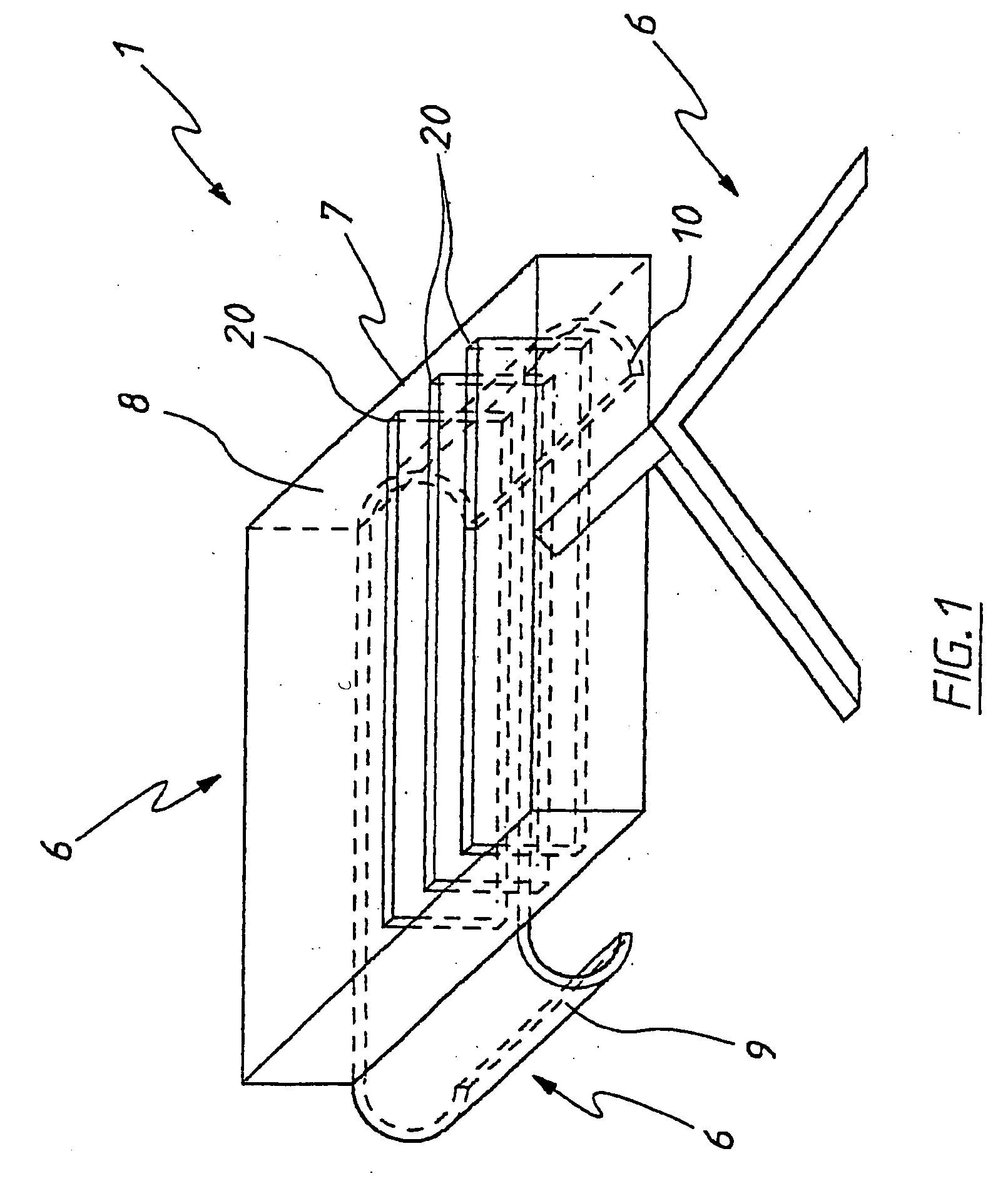
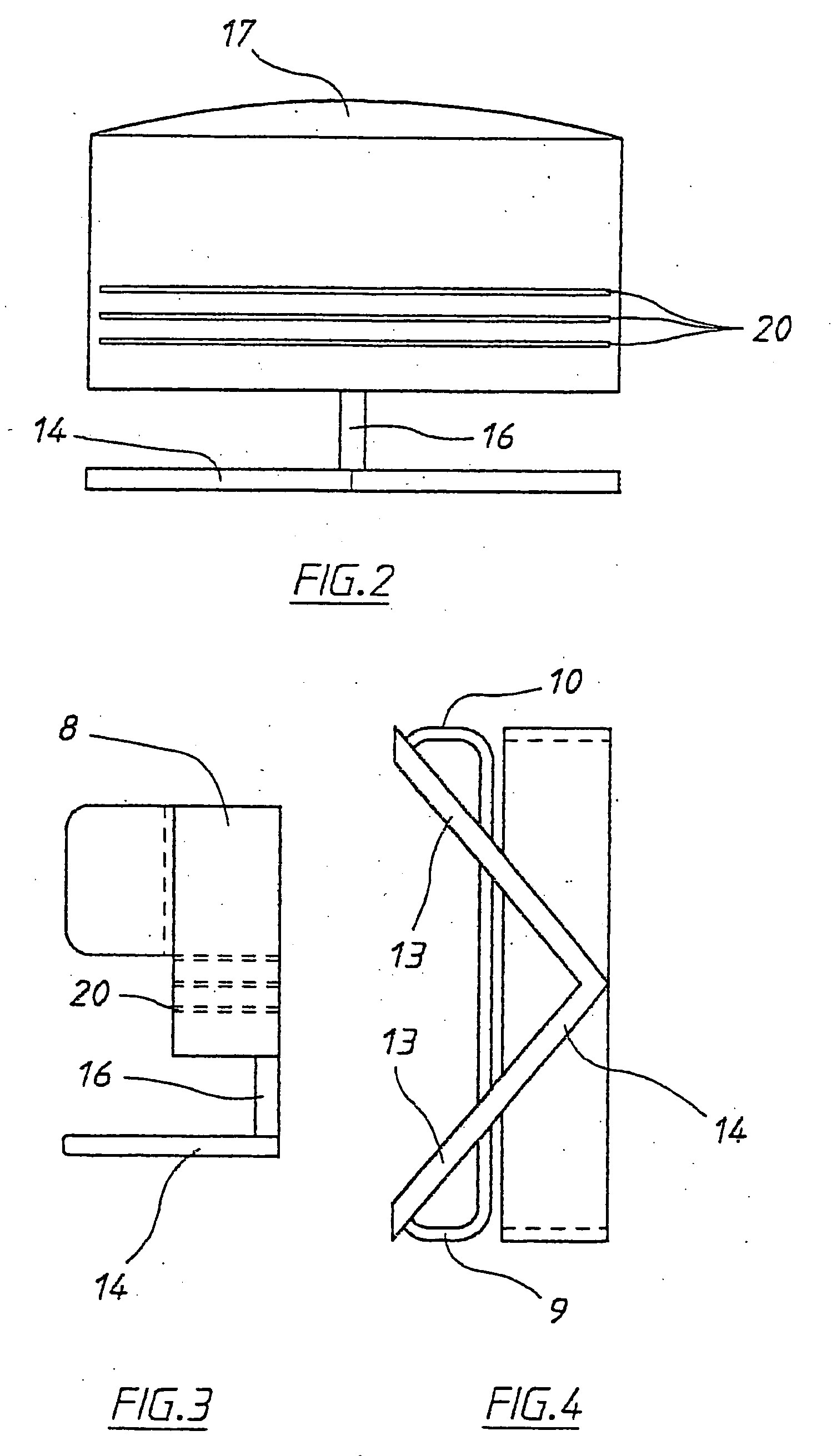
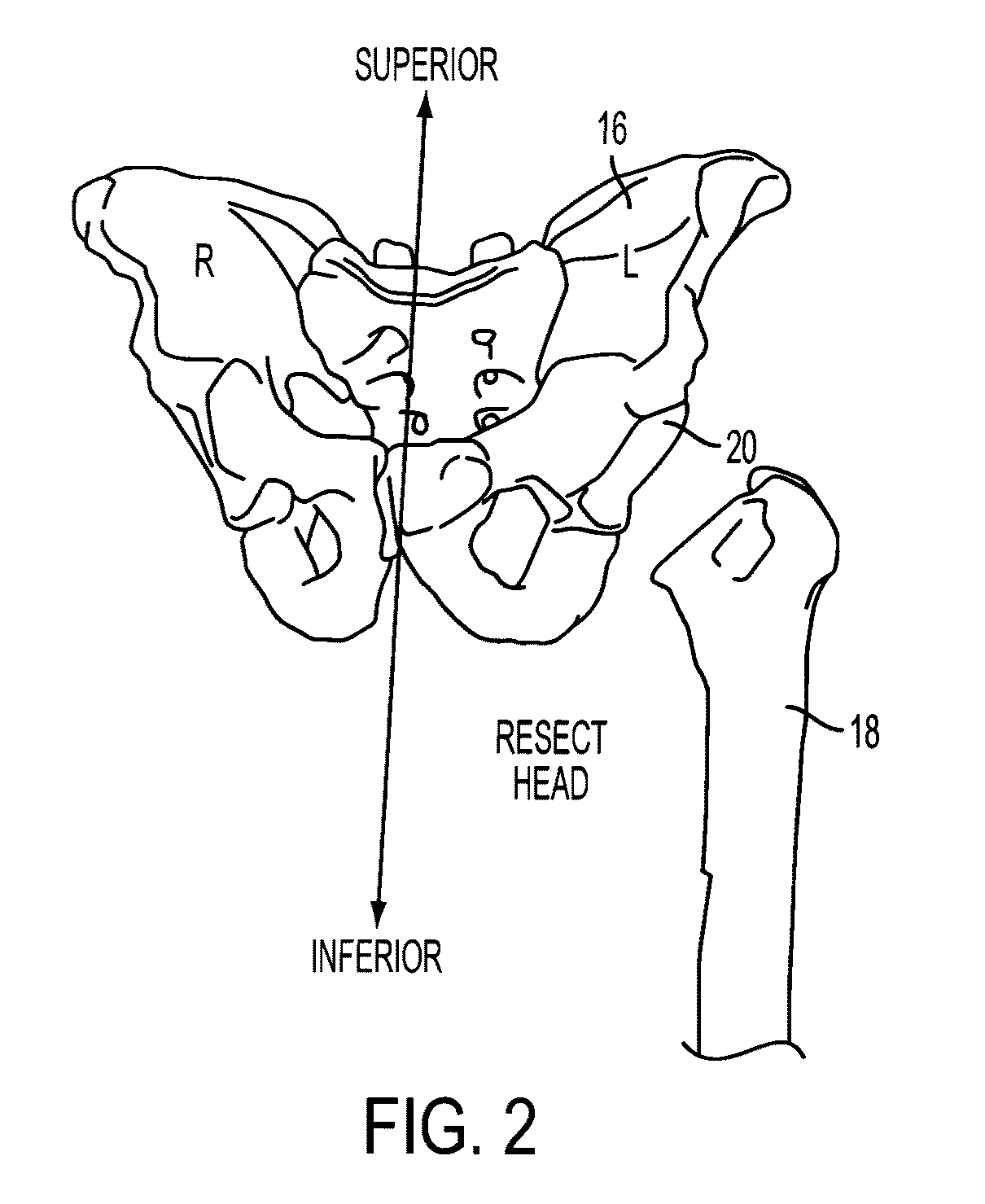
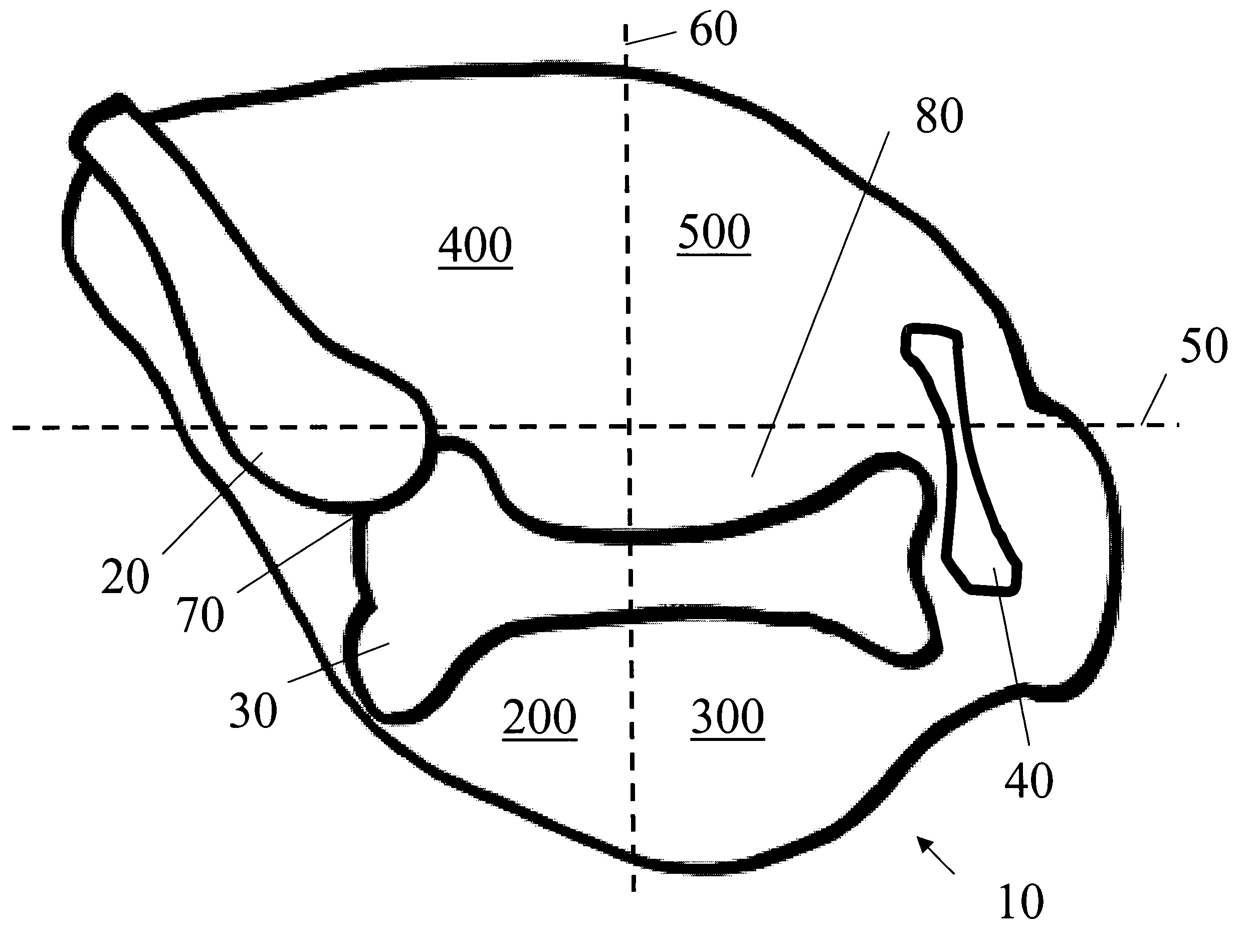
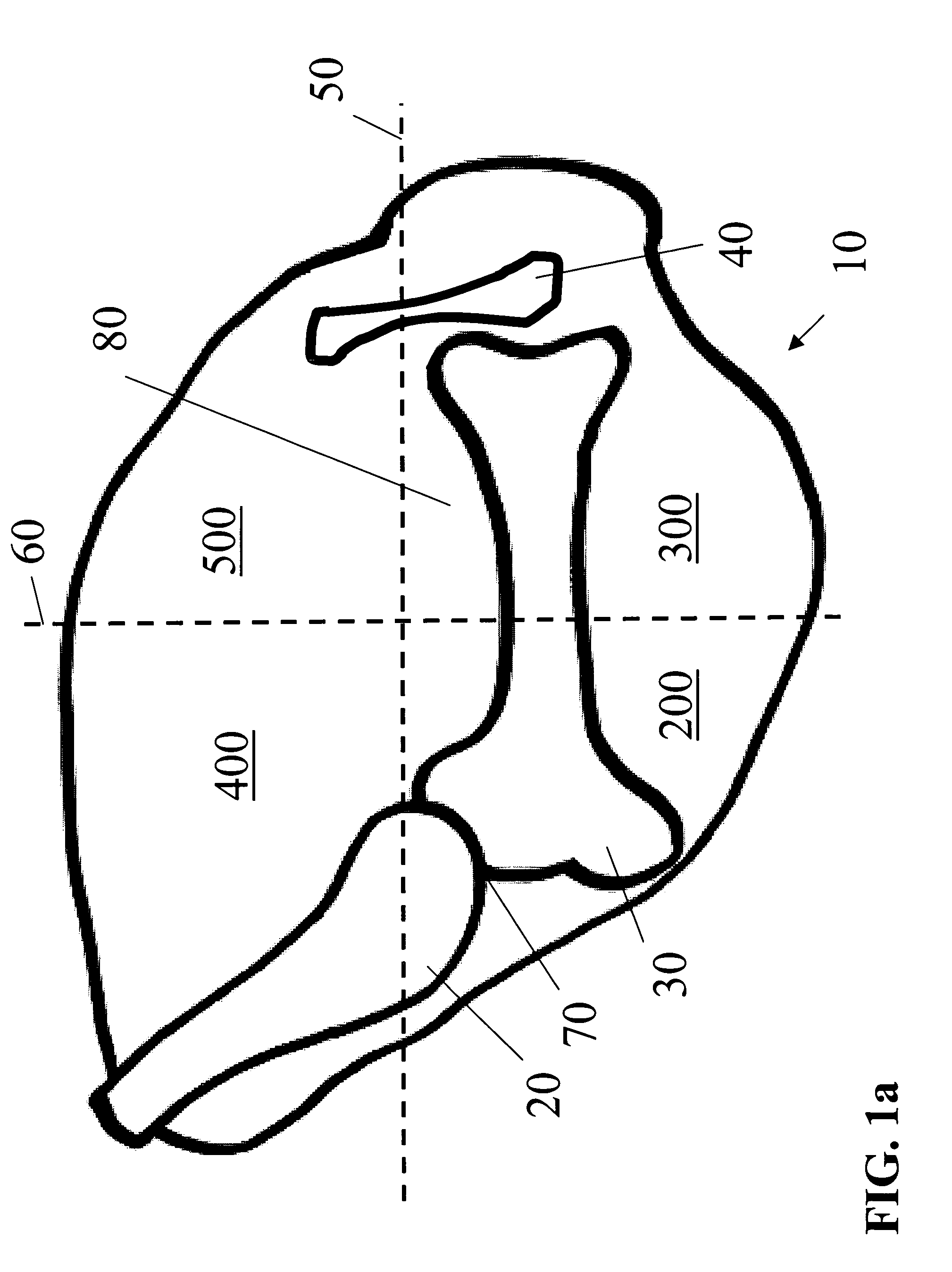
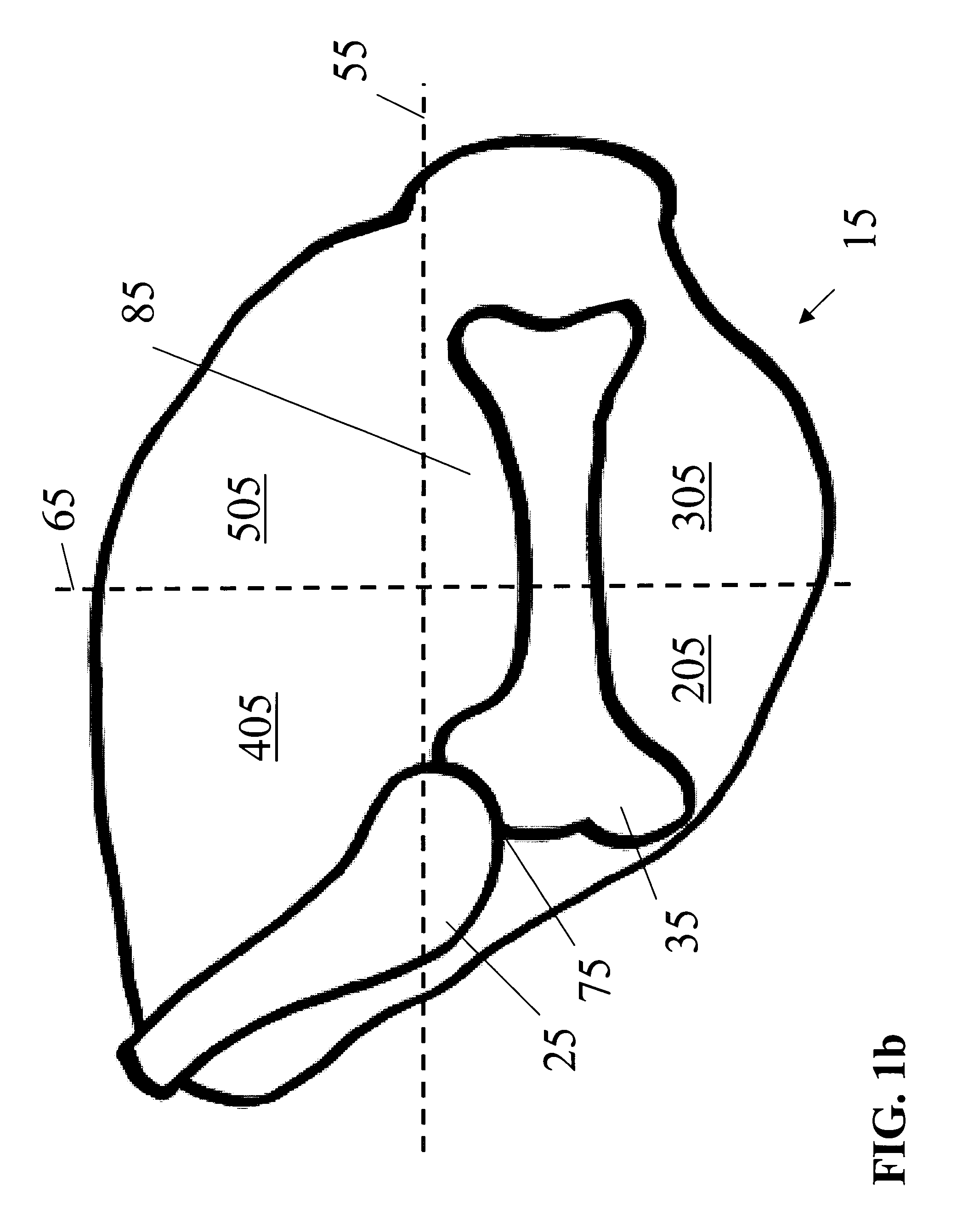
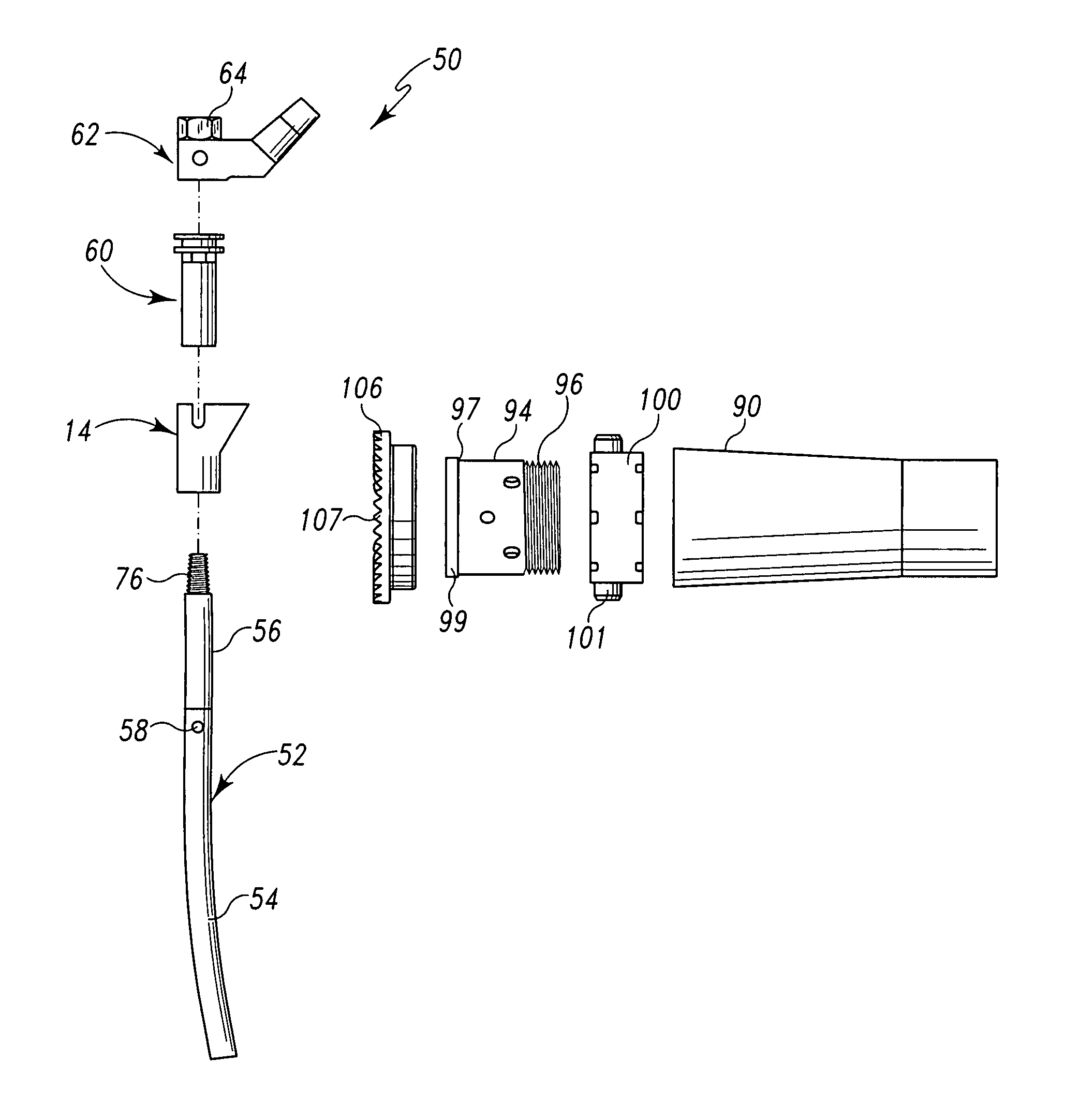
Tibial plateau and/or femoral condyle resection system for prosthesis implantation
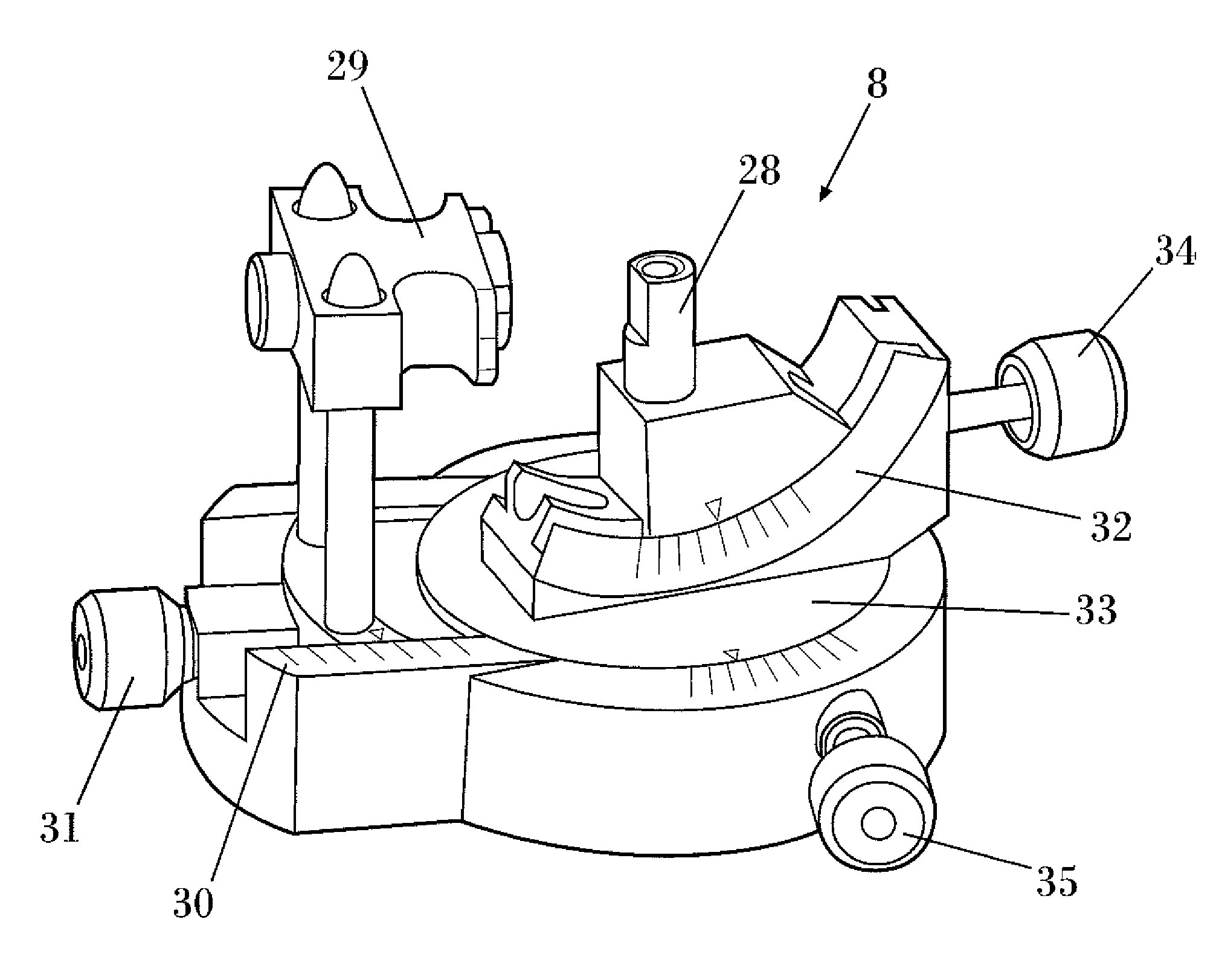
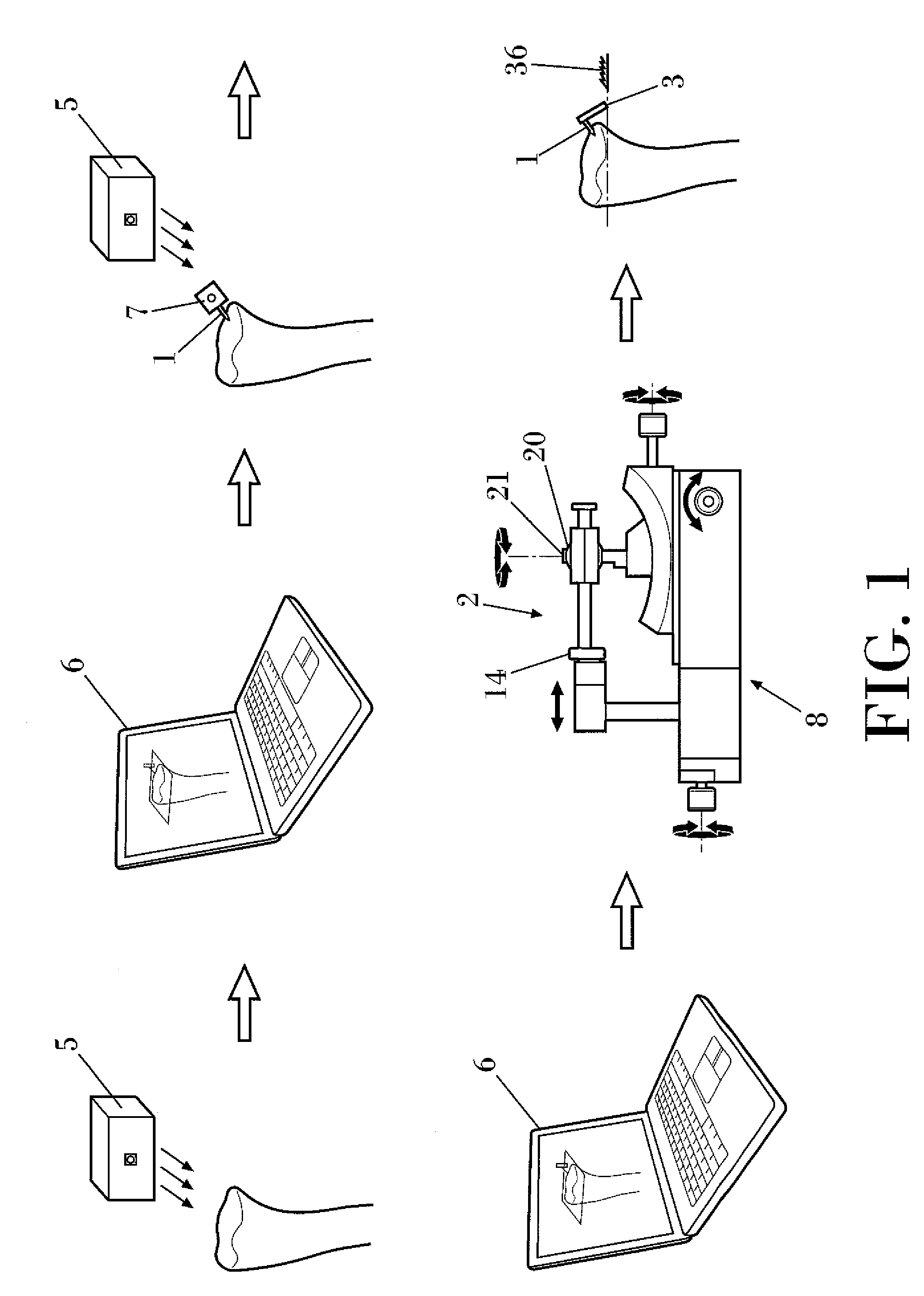
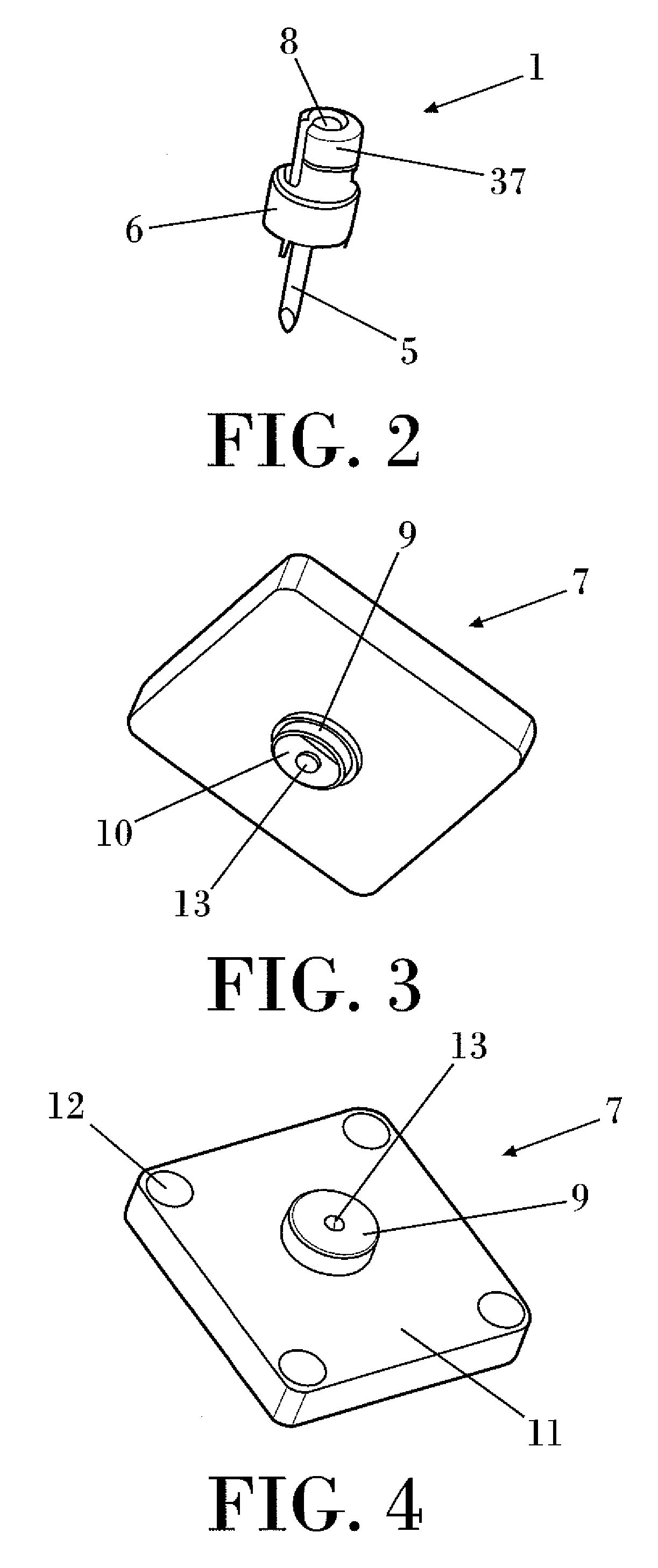
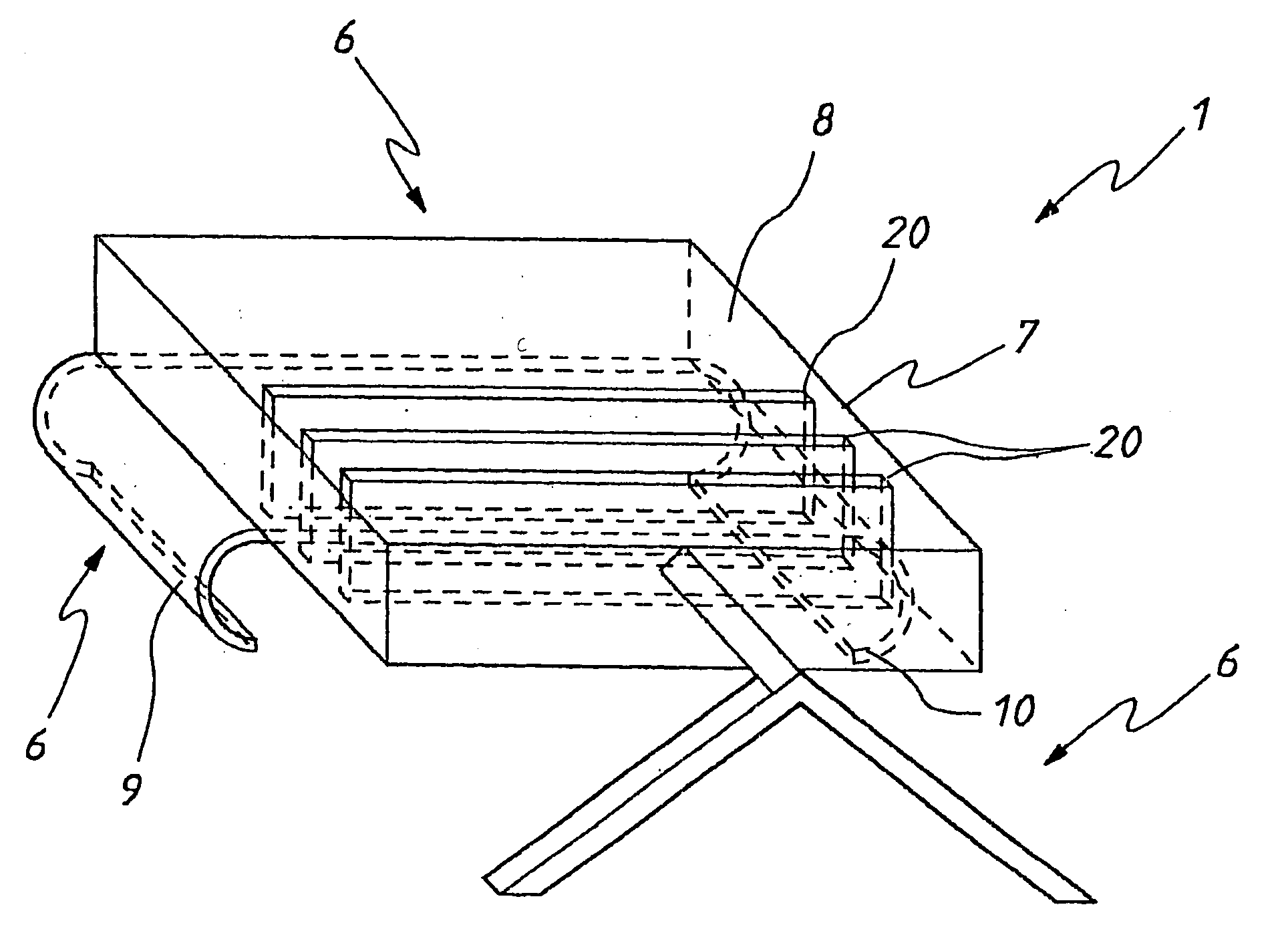
According to the invention, the system enables a preoperative study to be carried out wherein the tibia and / or femur is modelled on a computer (6) in 3D, the ideal cutting plane is defined and the position of the resection instruments (1, 2, 3) used to cut the bone is modelled. Additionally, according to the invention, the system enables redefinition of the ideal cutting plane and the positioning and orientation of the resection instruments (1, 2, 3) on the tibia and / or femur, in such a manner that the plane of the slot (4) of the cutting guide (3) through which the cutting tool is introduced coincides with the ideal cutting plane.
Owner:TRAIBER
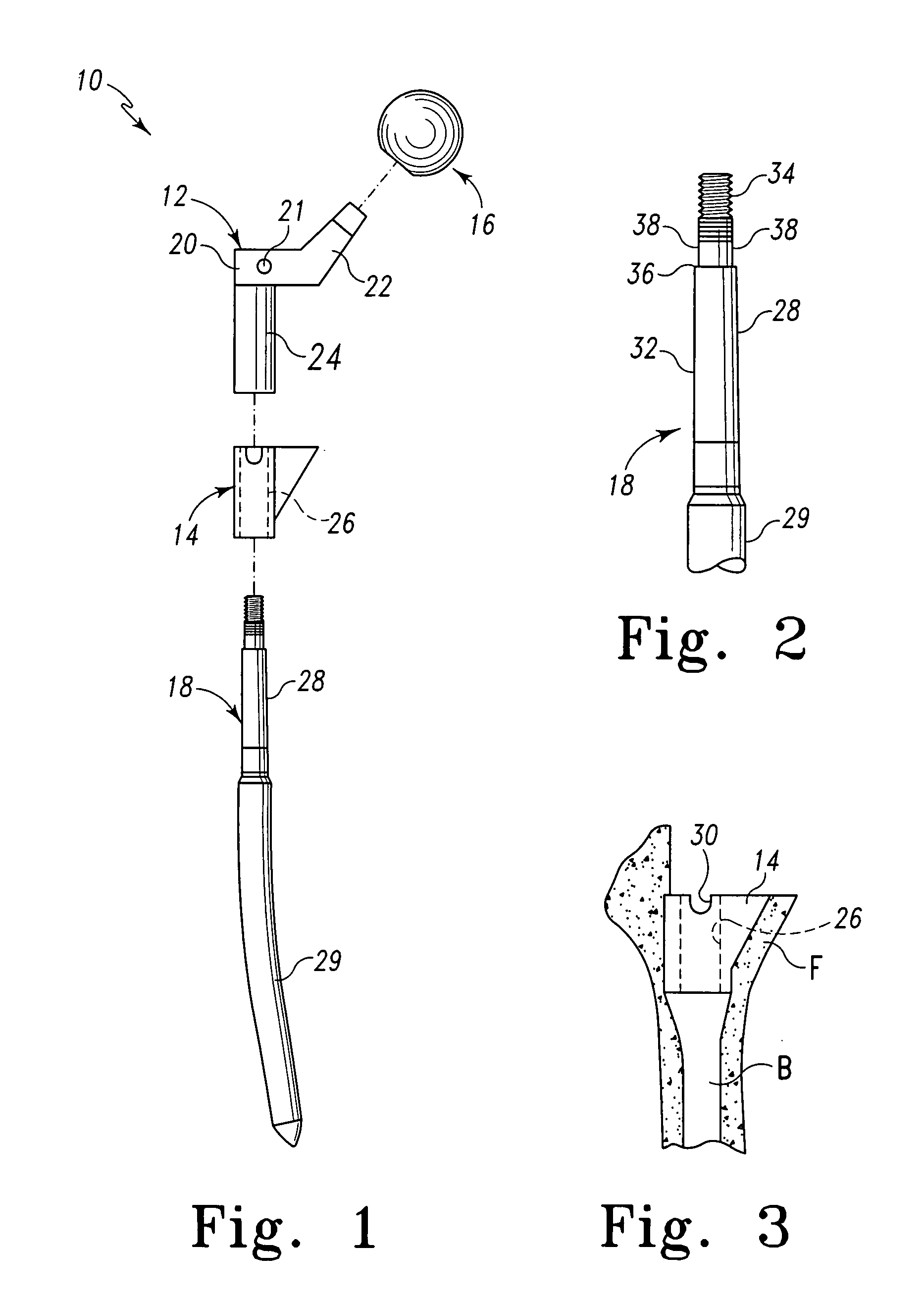
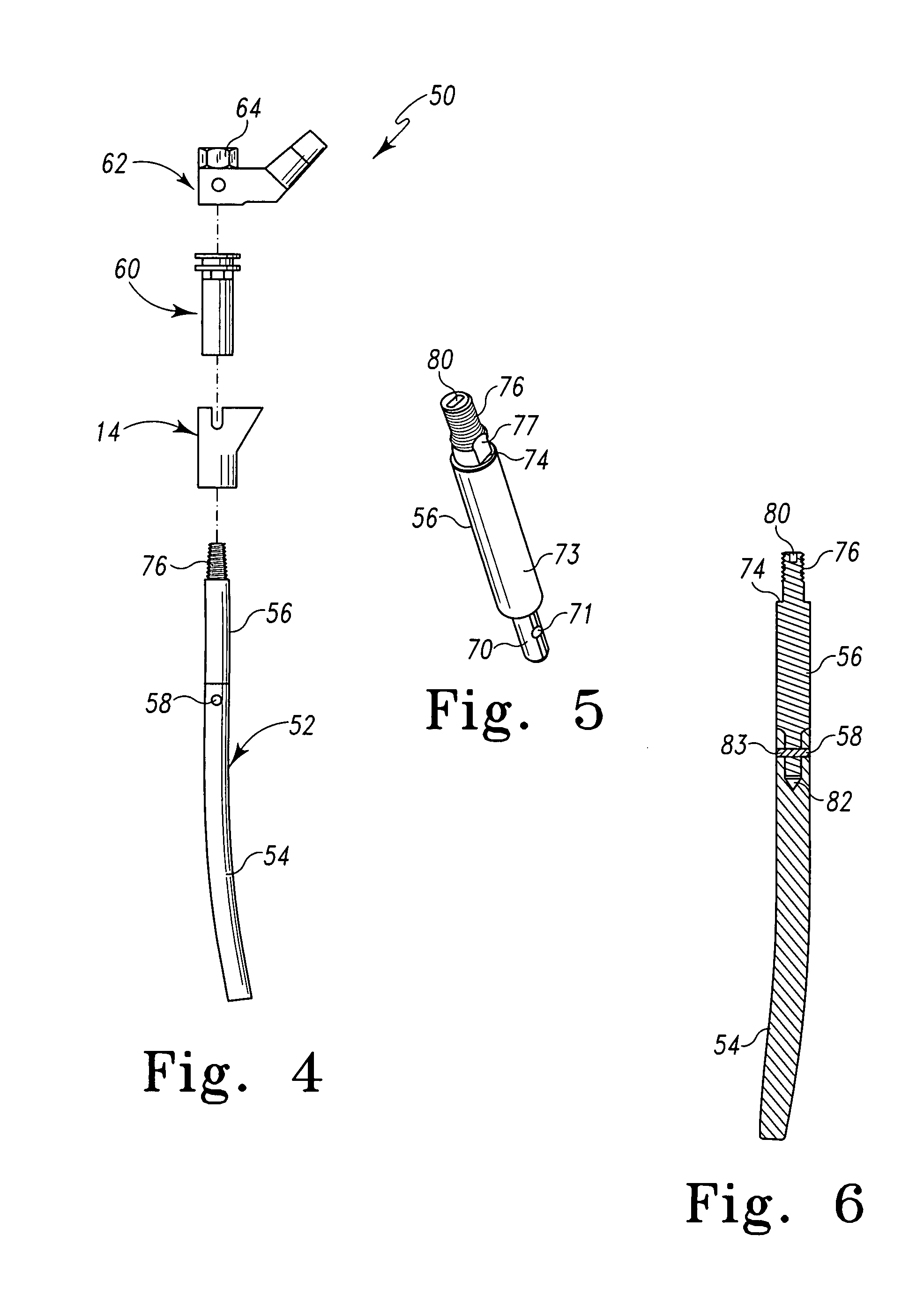
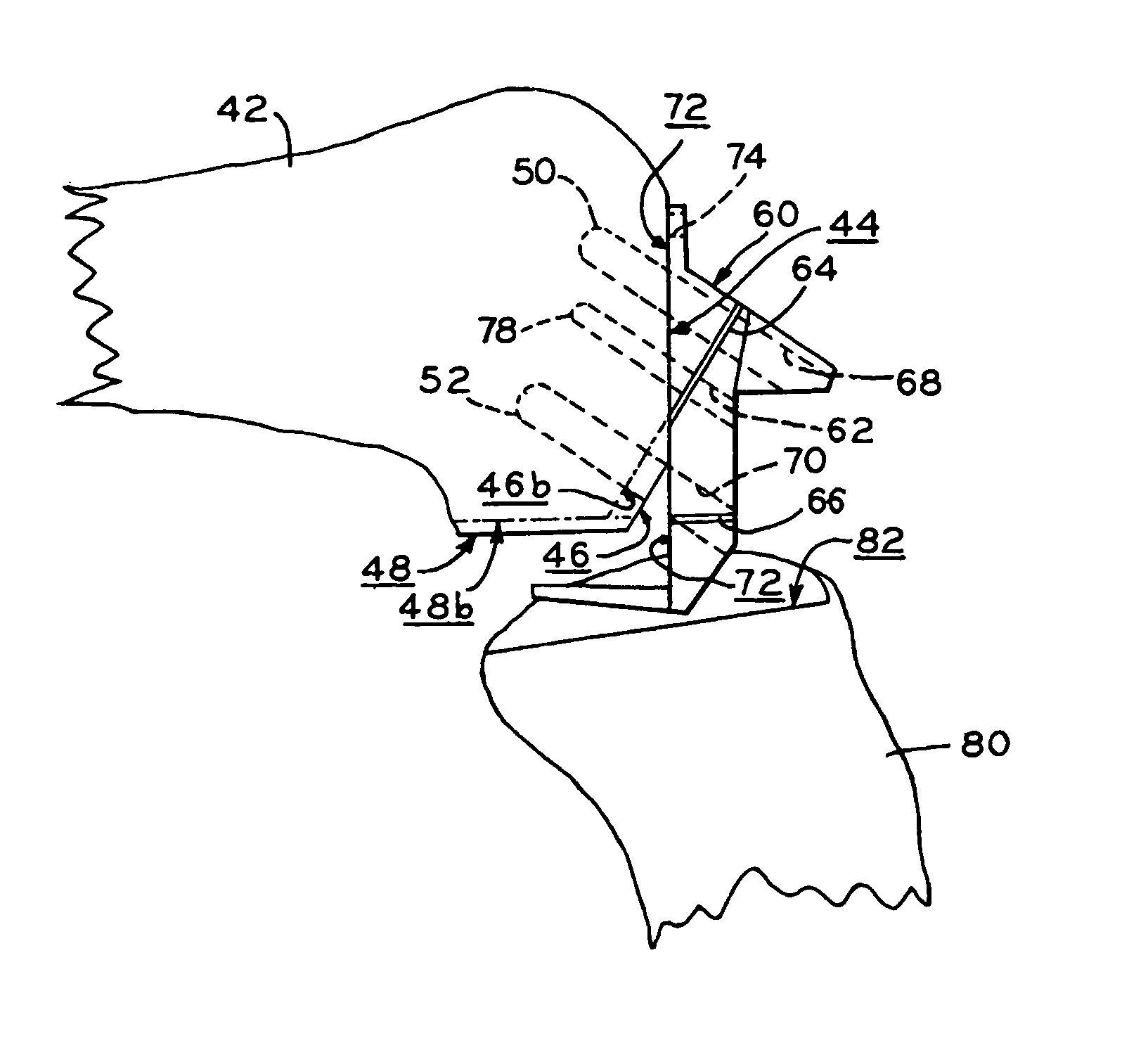
Apparatus and methods for bone surgery
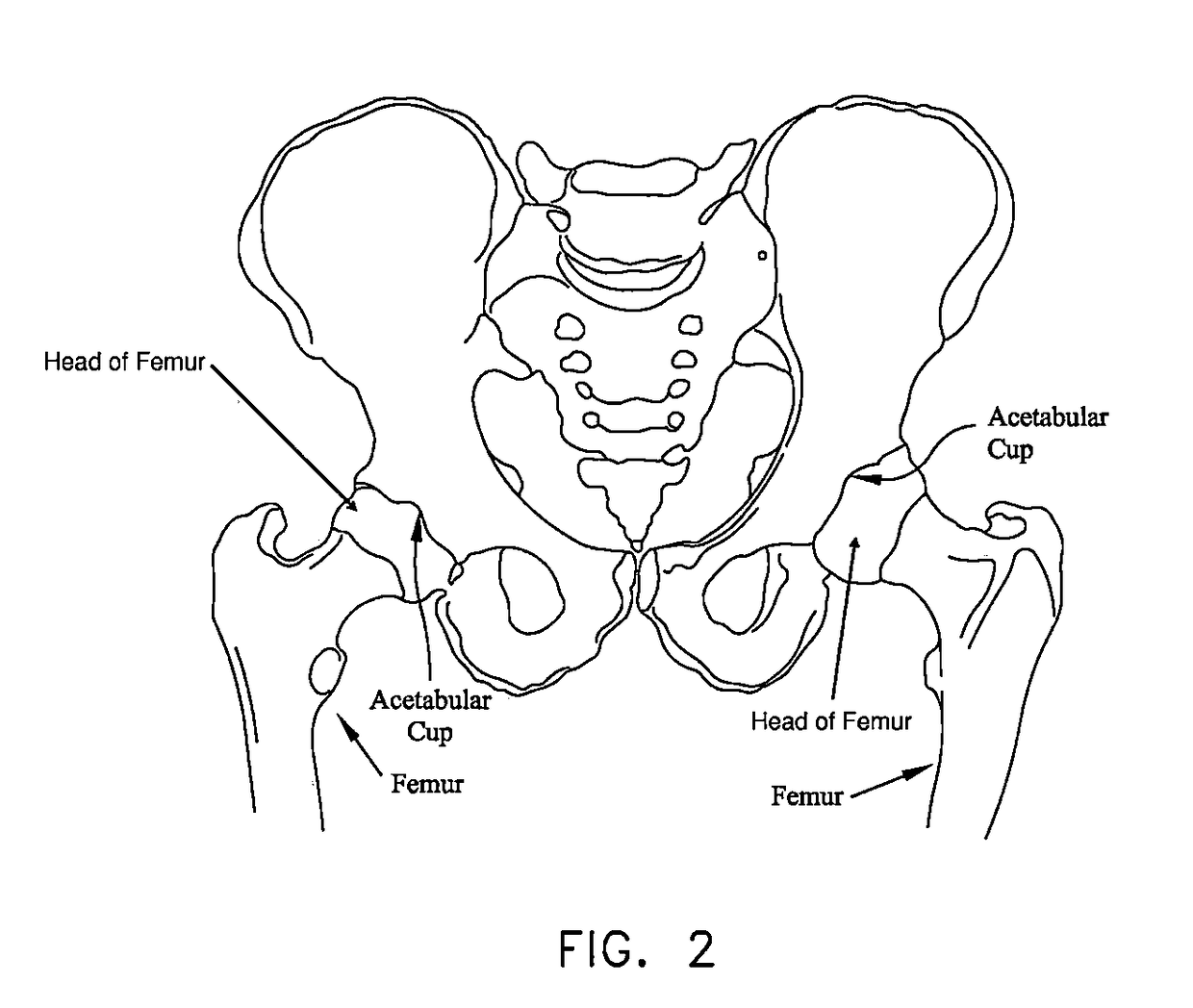
InactiveUS20050059978A1Joint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesRight femoral headLeft femoral head
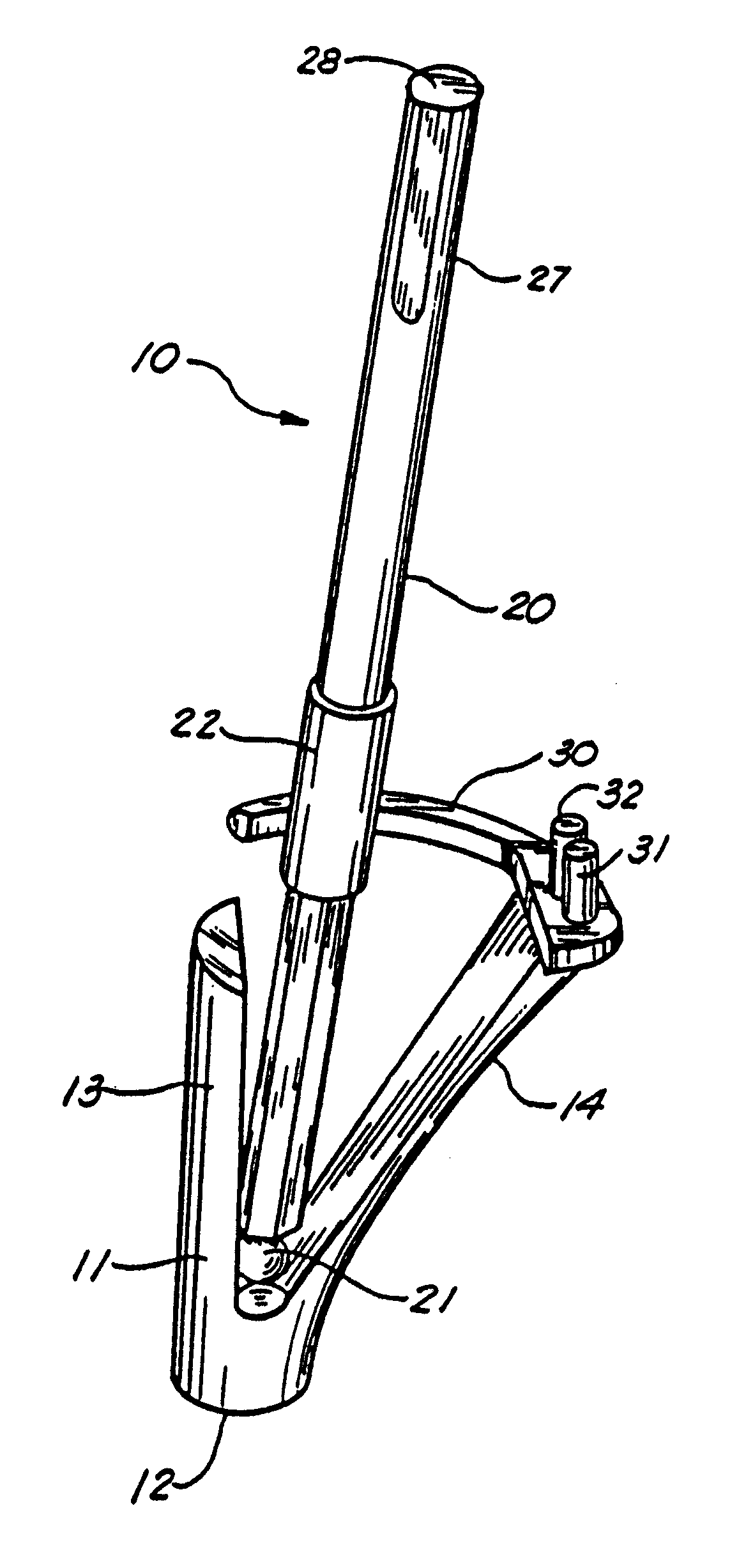
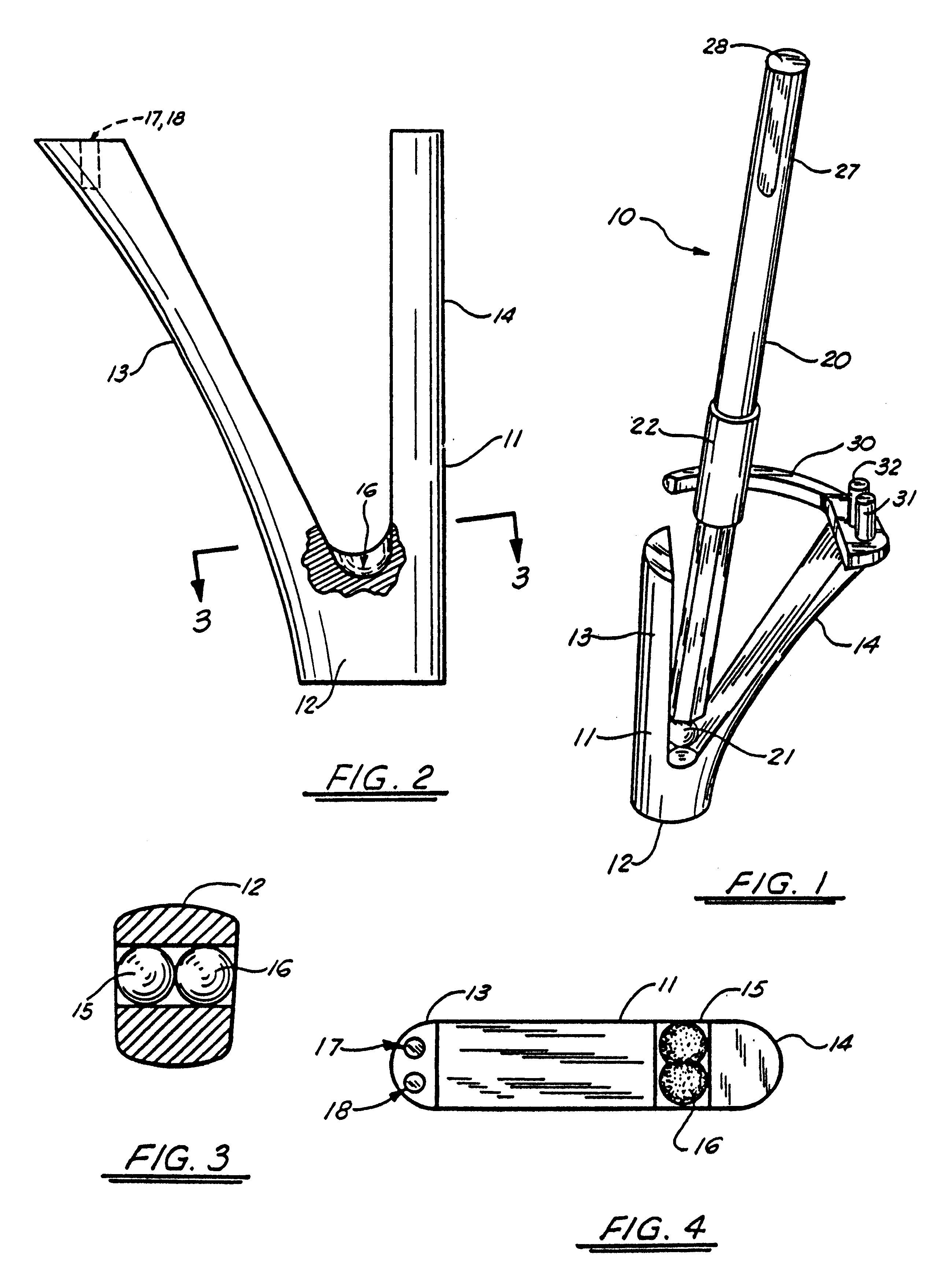
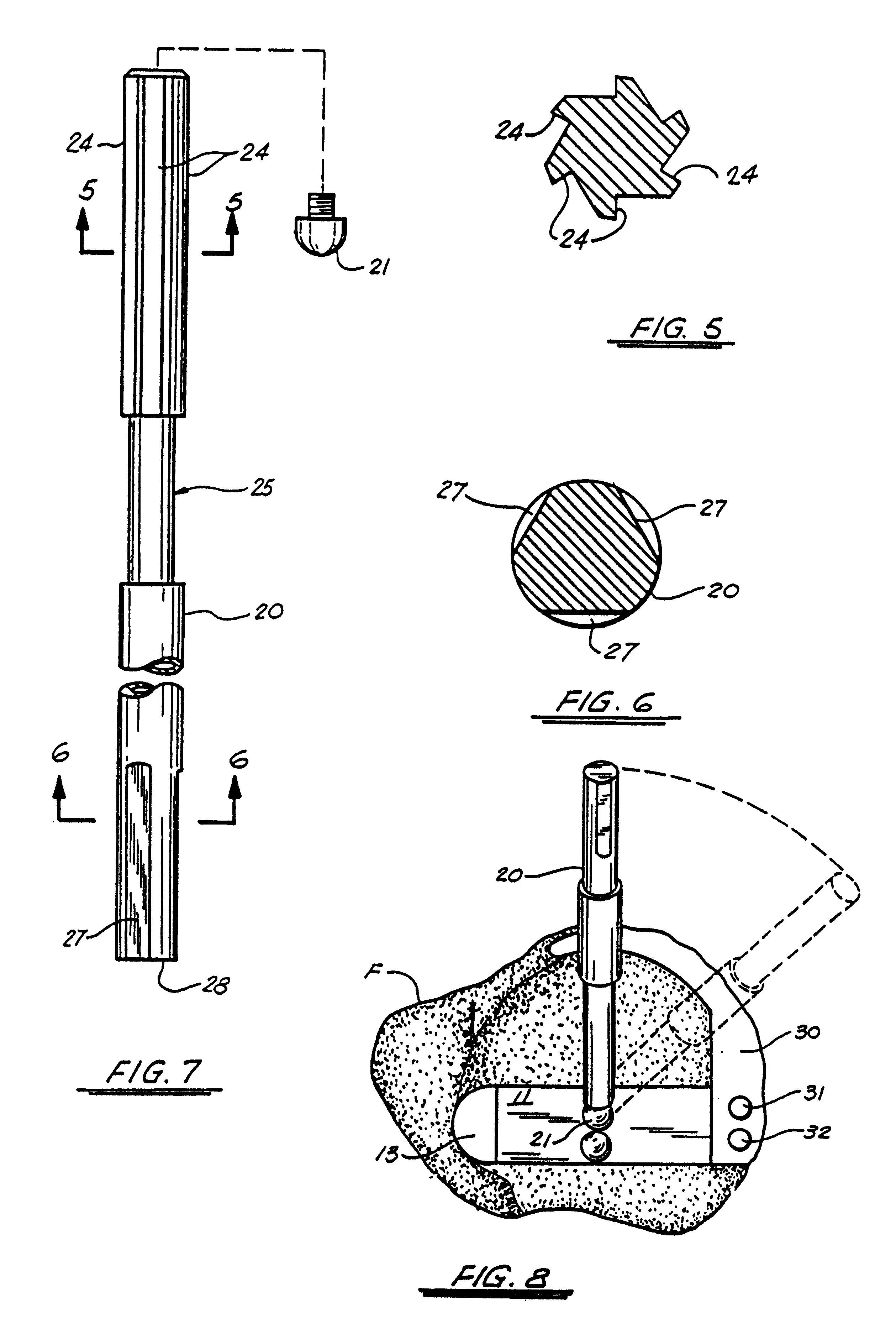
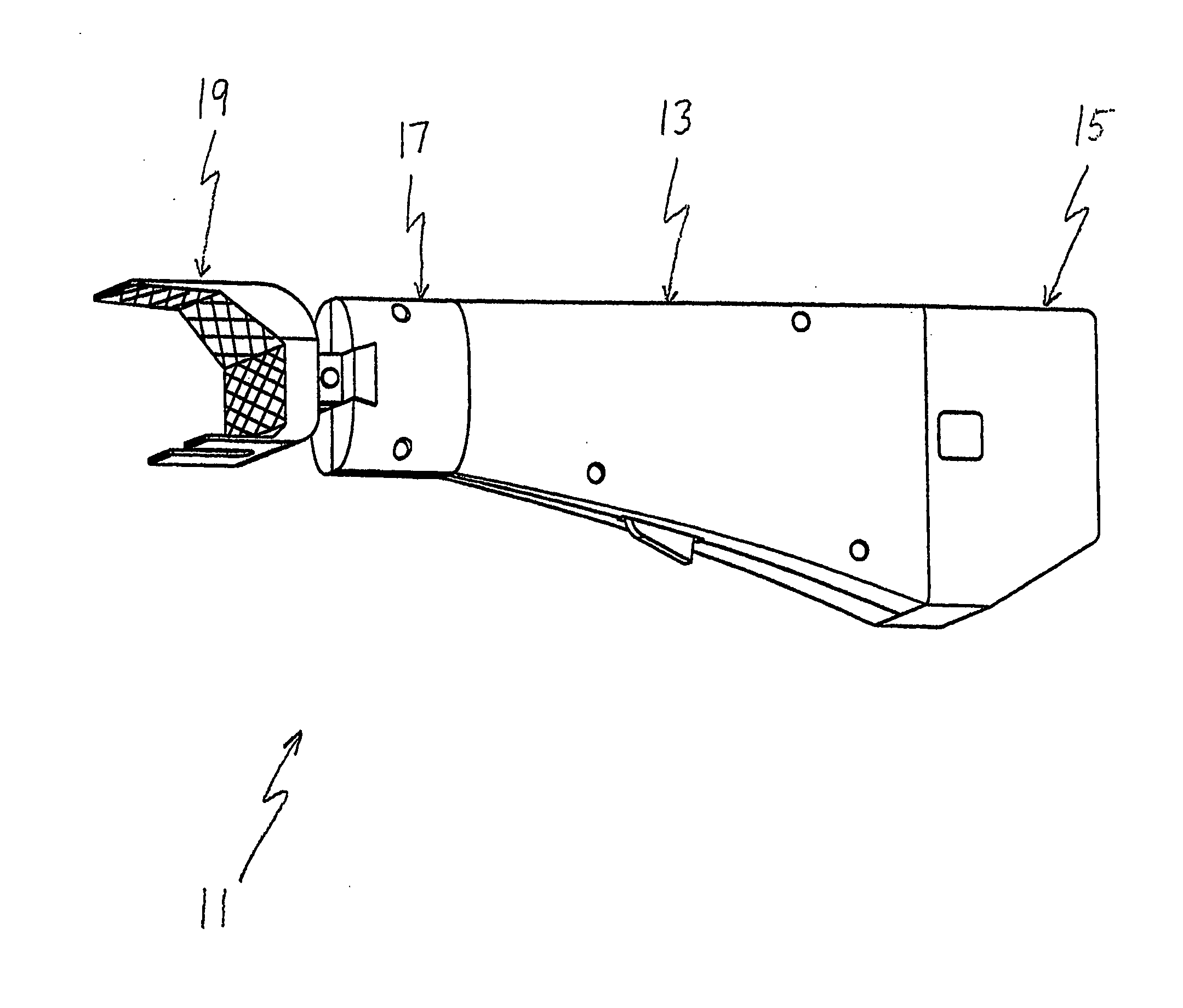
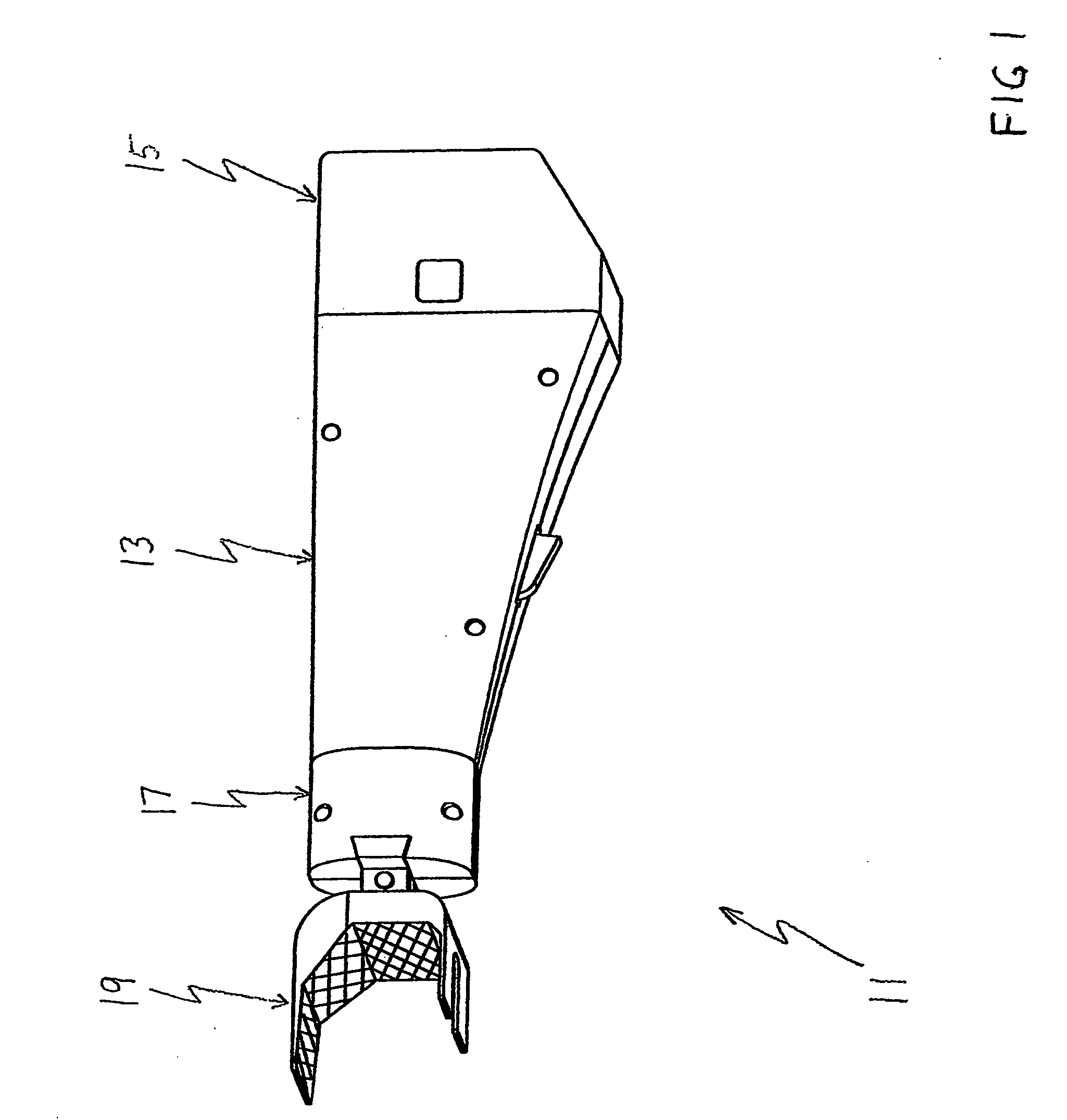
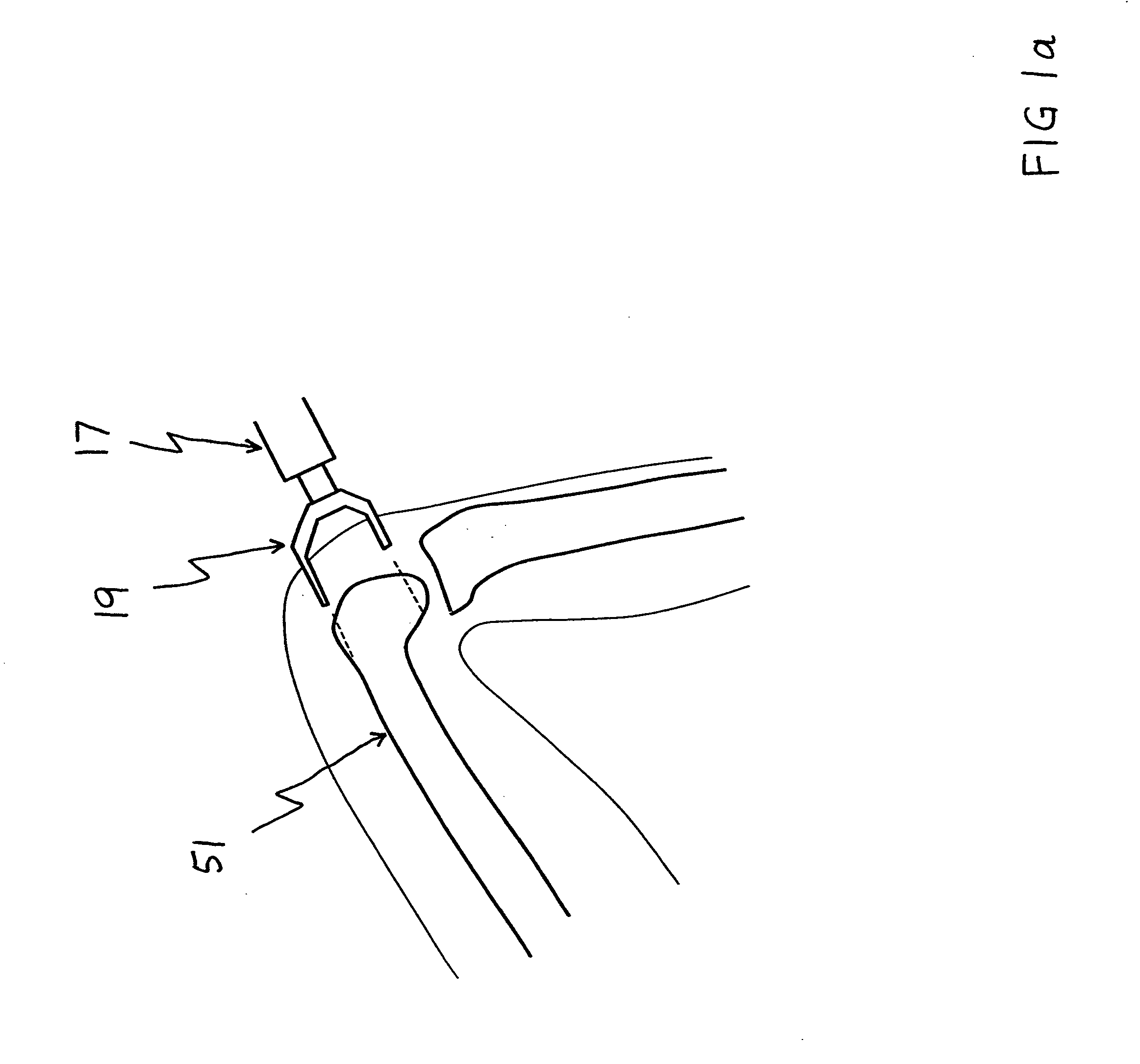
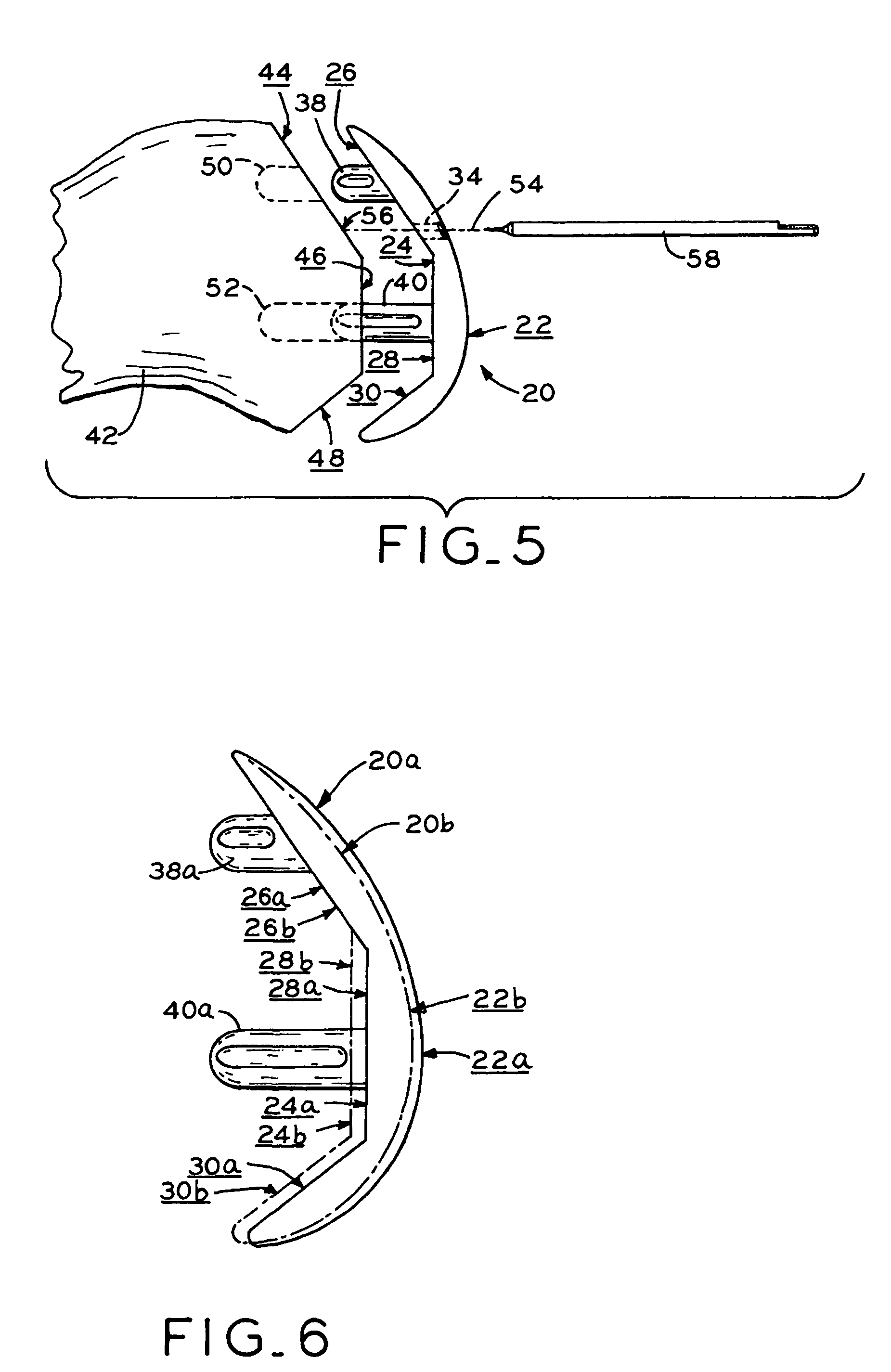
The surgeon grasps the jig by its handle and manipulates the head of the jig through the patient wound and onto the femoral neck. The head of the jig includes jig location means in the form of an elongate rod which acts as a spacer. The spacer has an end which abuts the trochanteric fossa so as to position the slot of the jig at the required position, which is between 5 mm and 25 mm, and most preferably 15 mm, from the trochantic fossa. Additional jig location means are provided by a surface adapted to receive a bone formation. This surface is provided by contours on the base of the head which are adapted to mate with contours of the femur. The slot is oriented generally perpendicularly to the elongate dimension of the rod. The slot functions as a surgical tool guide means which is positioned by the jig at the correct position for osteotomisation of the neck. Advantageously, osteotomisation takes place while the femoral head is still disposed within the acetabulum.
Owner:INT PATENT OWNERS CAYMAN
Methods and apparatus for improved cutting tools for resection
ActiveUS20060015109A1Facilitating intraoperativeFacilitating postoperative efficacyJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTibiaSacroiliac joint
A cutting tool is provided with an arcuate cutting blade that preferably engages a guide tool to create a curved resected surface during an arthorplasty procedure. In one embodiment, a depth of the cutting blade is sufficient to permit the simultaneous creation of resected surfaces on two bones that articulate, such as both the femor and the tibia for a given condyle, without the need to reposition the guide or the leg. In another embodiment, a cutting member has a generally rectangular cross-section along a longitudinal axis with a first and second surface having cutting teeth defined thereon and a third and fourth surface adapted to interface with a cutting guide positioned proximate the bone. In this embodiment, the cutting tool can resect the bone in two different directions without reorienting the cutting member.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Leg alignment for surgical parameter measurement in hip replacement surgery
ActiveUS20060293614A1Surgical navigation systemsPerson identificationHip joint replacement operationPelvic fixation
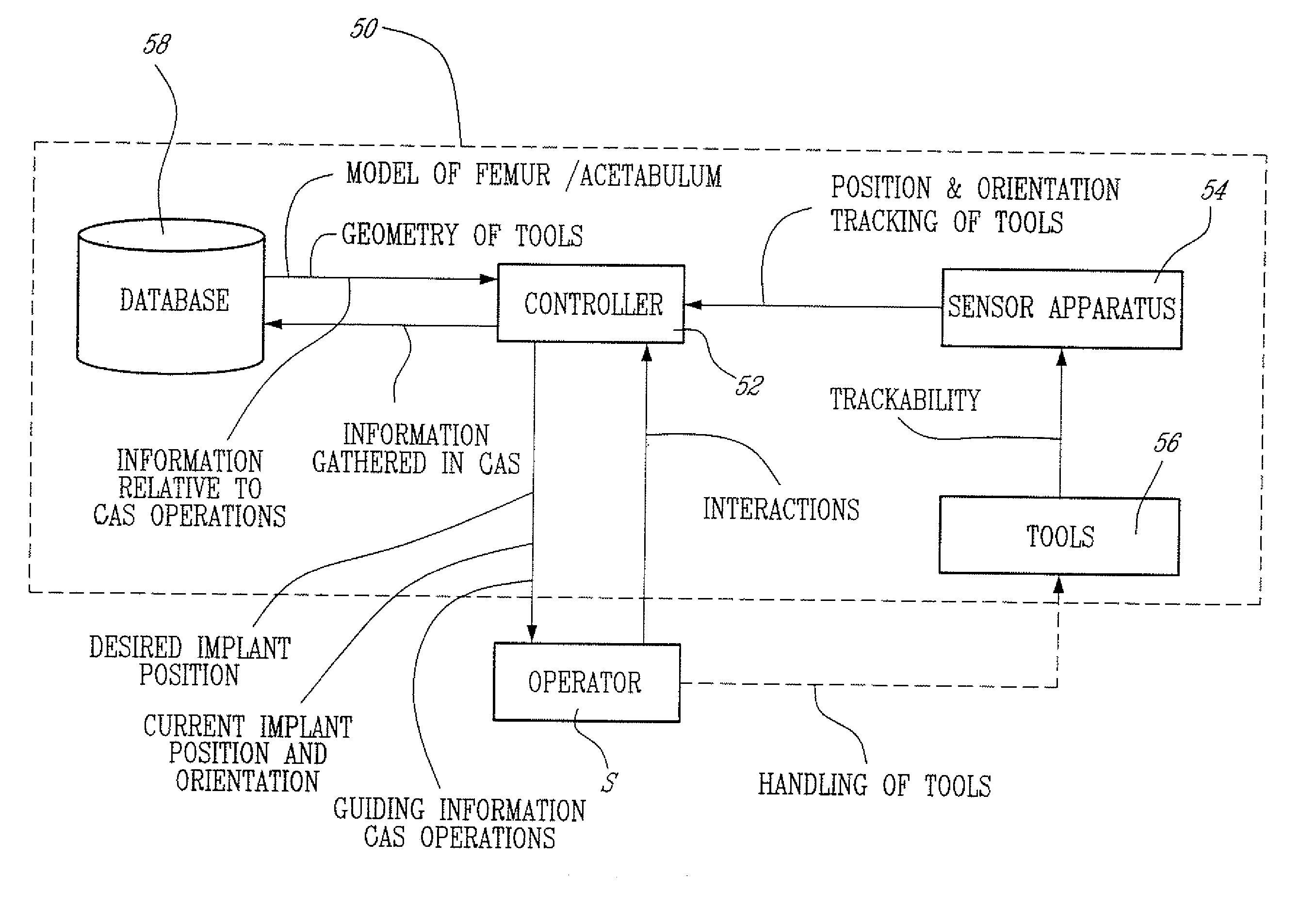
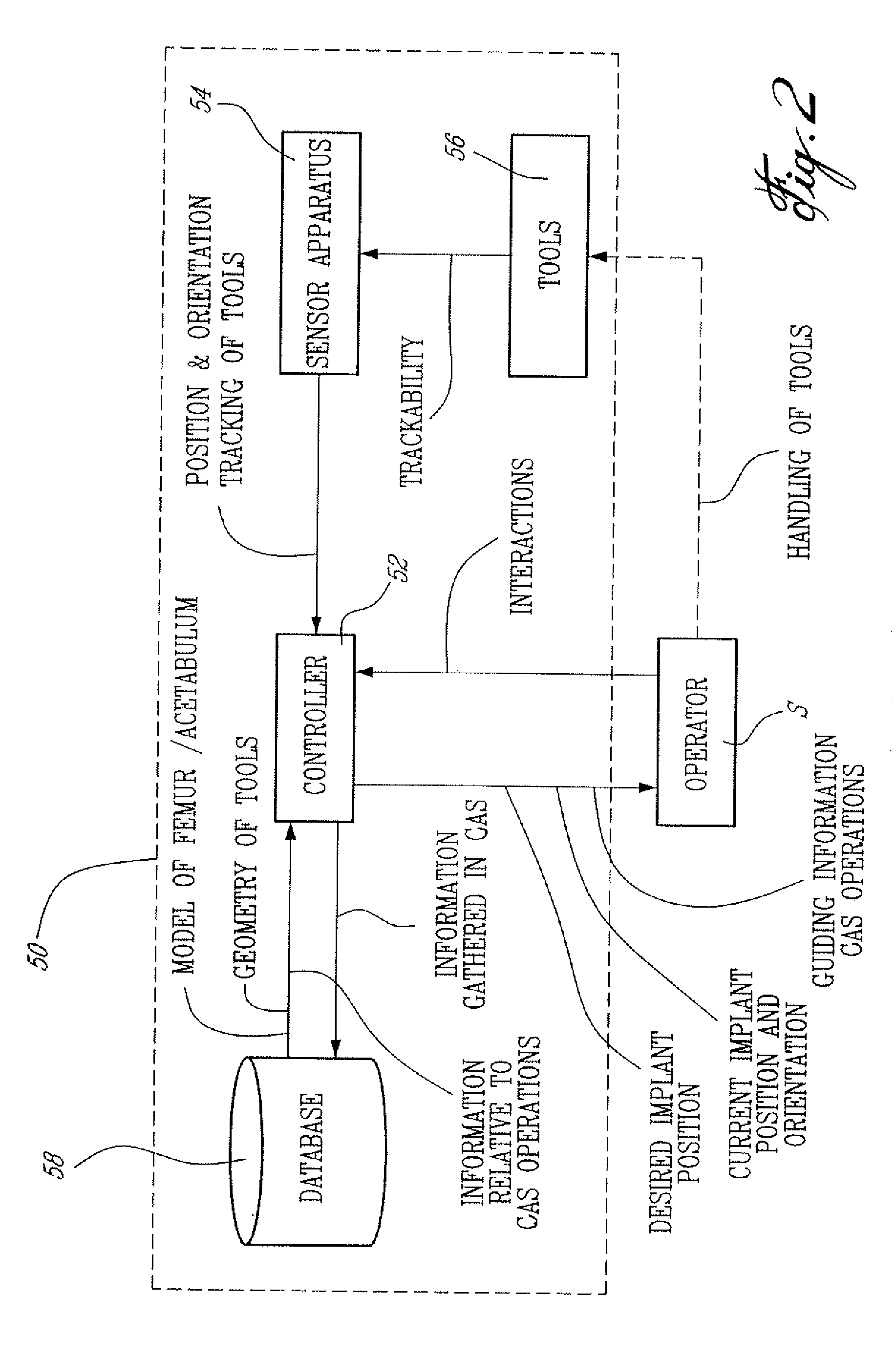
A CAS system and method for measuring surgical parameters during hip replacement surgery to guide an operator in inserting a hip joint implant in a femur, comprising a first trackable reference in fixed relation with the pelvis and a registration tool. A sensor apparatus tracks the first trackable reference and the registration tool. A controller unit is connected to the sensor apparatus so as to receive tracking data for the first trackable reference and the registration tool. The controller unit has a position and orientation calculator to calculate from the tracking data a position and orientation of the pelvic trackable reference to track the pelvic frame of reference, and of the registration tool to produce a femoral frame of reference at two sequential operative steps. A reference orientation adjustor receives tracking data for the pelvic frame of reference, and the femoral frame of reference associated with the first trackable reference, to orient the femoral frame of reference in a reference orientation with respect to the pelvic frame of reference, and to produce a reference adjustment value as a function of the reference orientation. A surgical parameter calculator receives tracking data from the registration tool to calculate surgical parameters as a function of the reference adjustment value, the surgical parameters at the two sequential operative steps being related by the reference orientation.
Owner:ORTHOSOFT ULC
Tibial prosthetic implant with offset stem
A tibial prosthetic implant includes a base or base plate with an offset tibial stem. The base includes an inferior surface adapted to abut a resected surface of a patient's tibia and forms a base for articulating surfaces adapted to articulate with the patient's femoral condyles. The longitudinal center axis of the tibial stem extends from the inferior surface of the base and is offset from a center of the base. The offset places the stem in position to extend into the central canal of the tibia so that it does not substantially interfere with the cortical bone when the inferior surface of the base substantially abuts and aligns with the resected surface of the tibia.
Owner:WRIGHT MEDICAL TECH
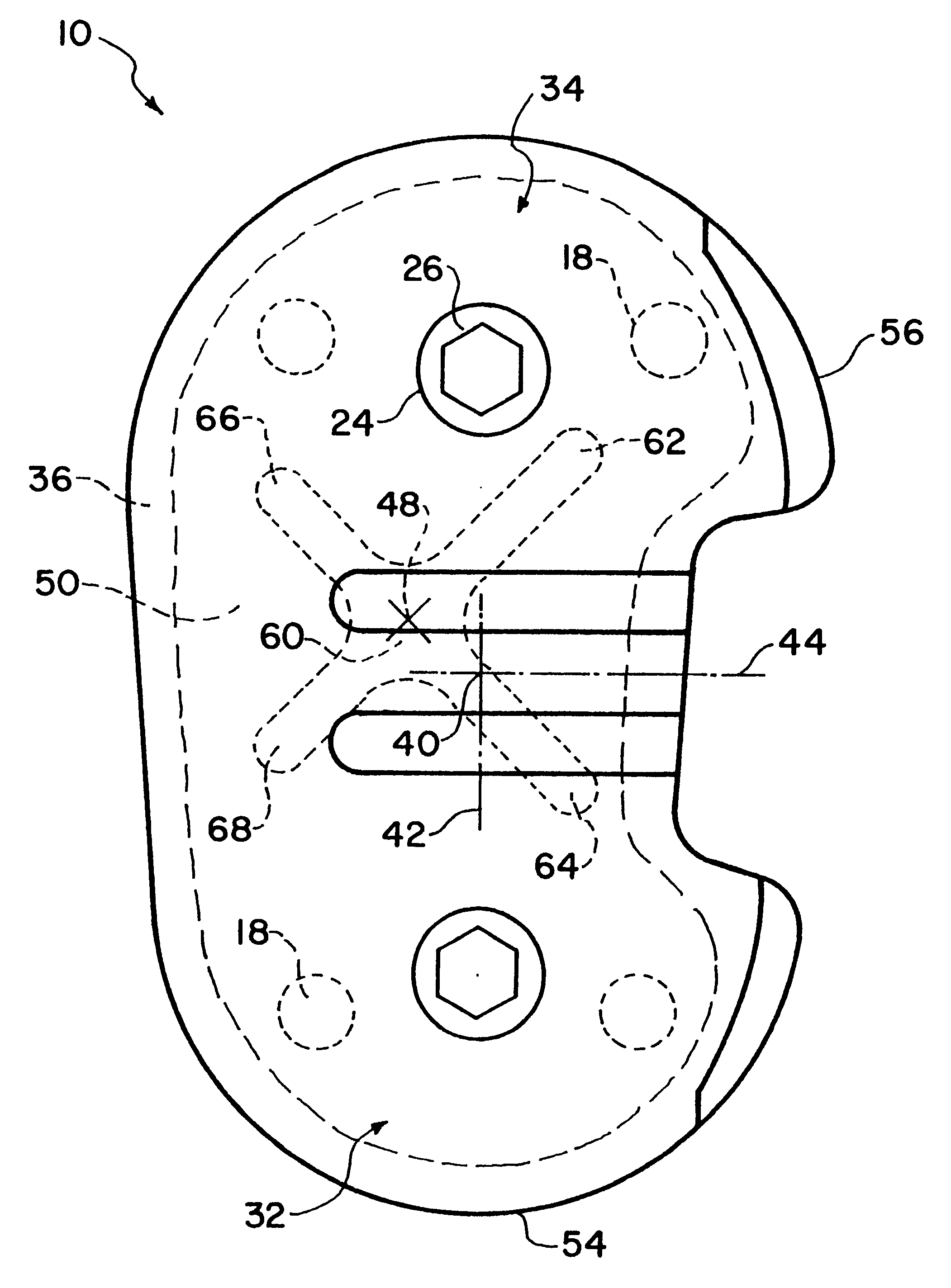
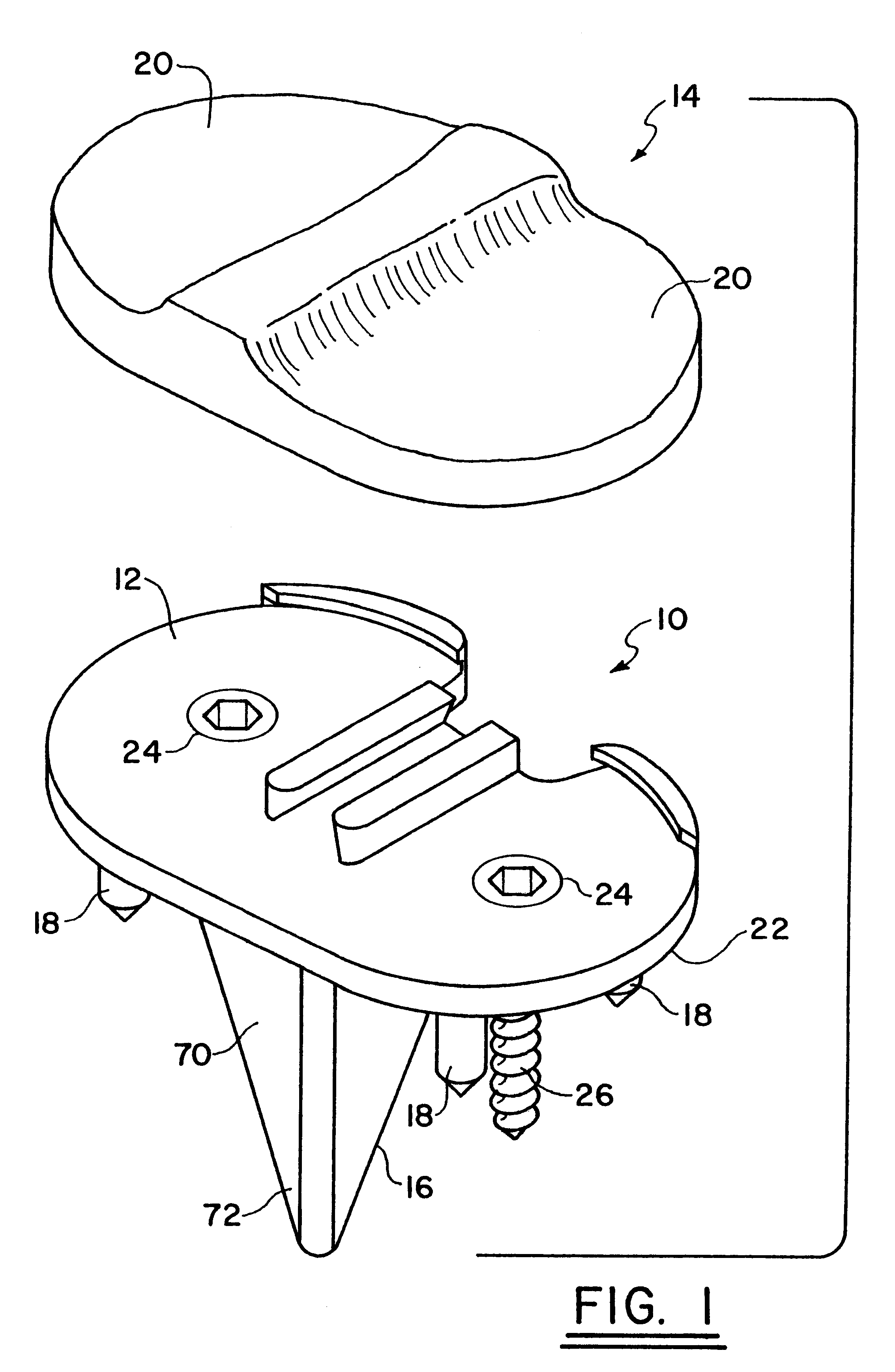
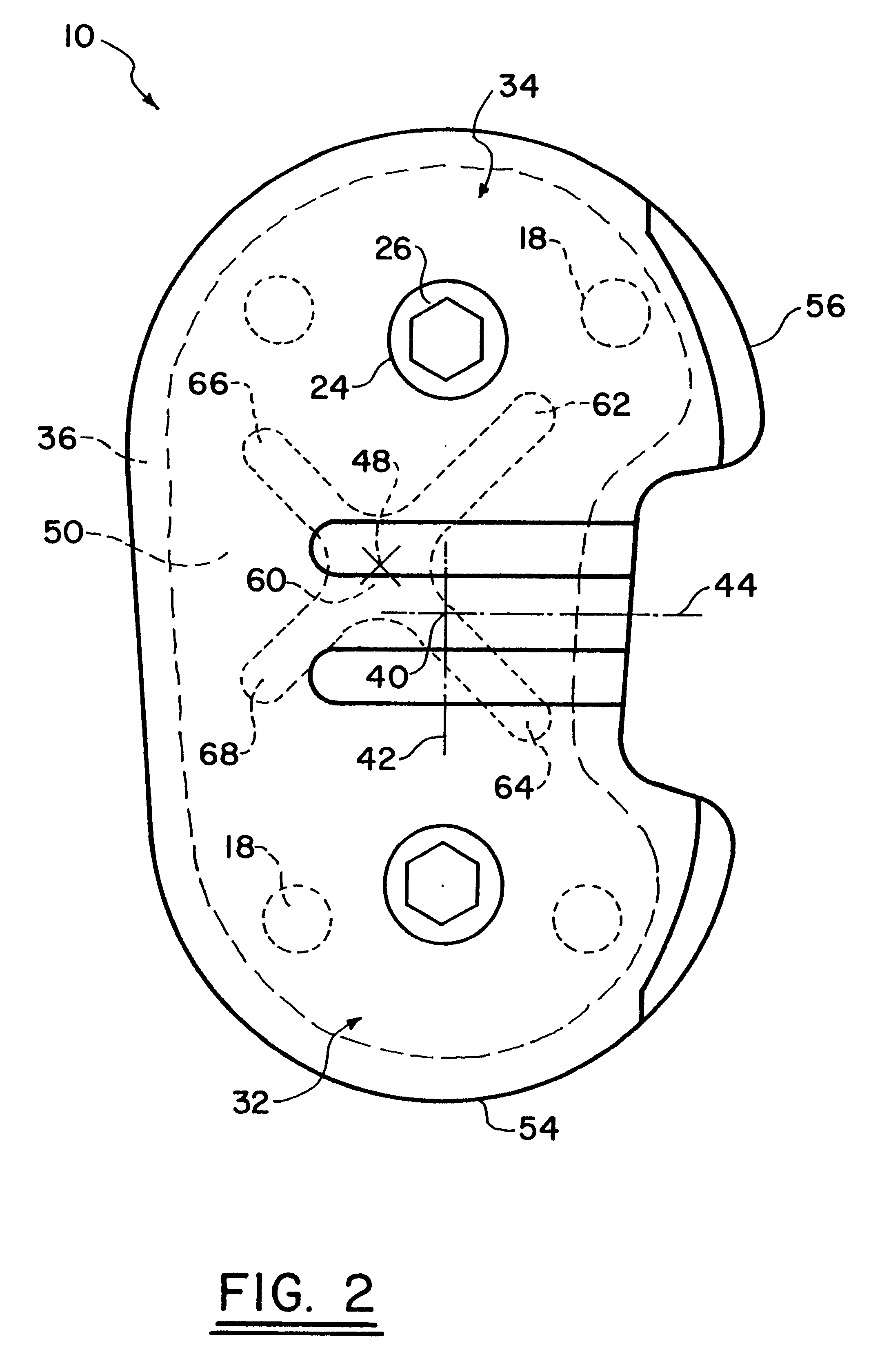
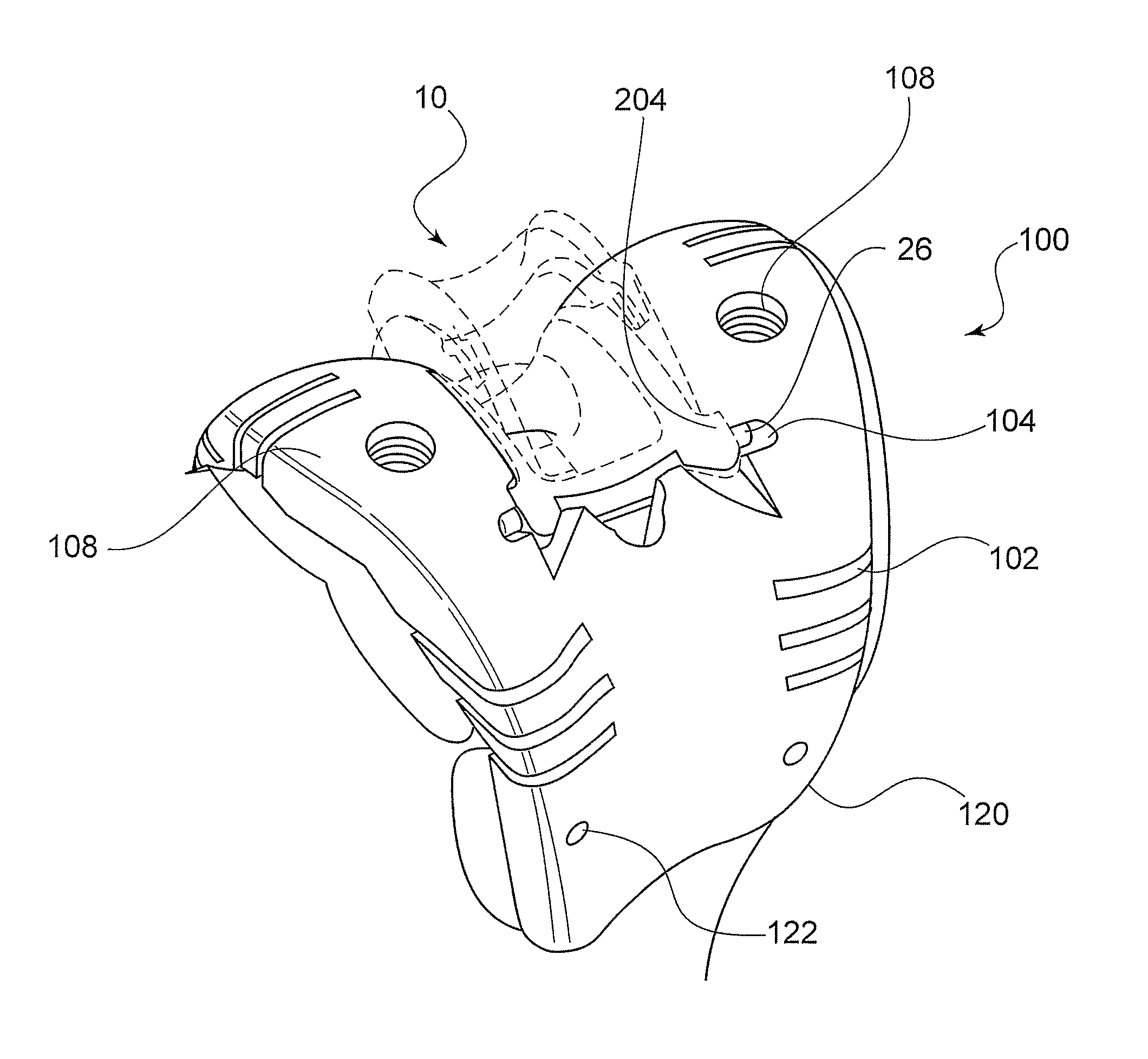
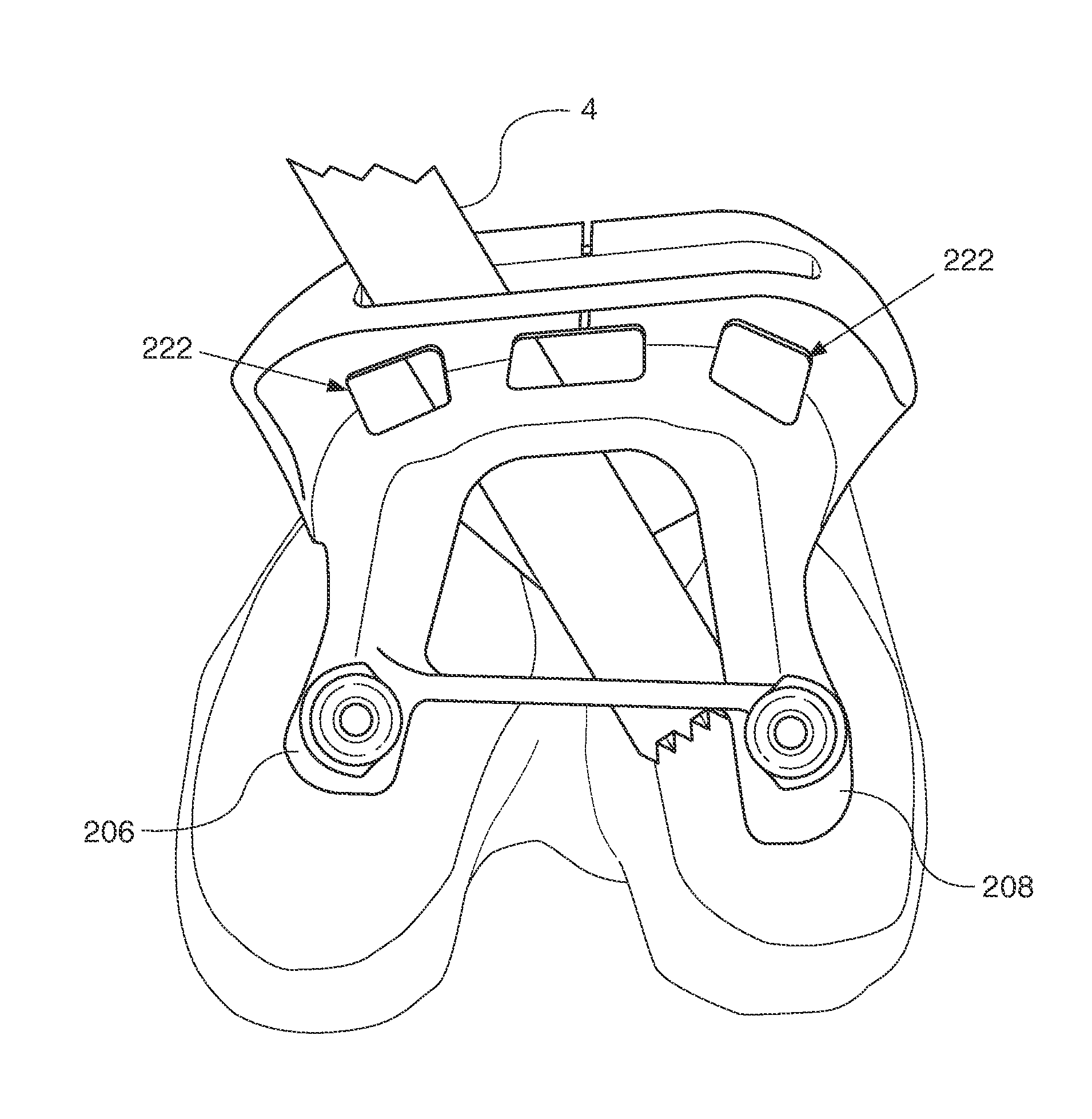
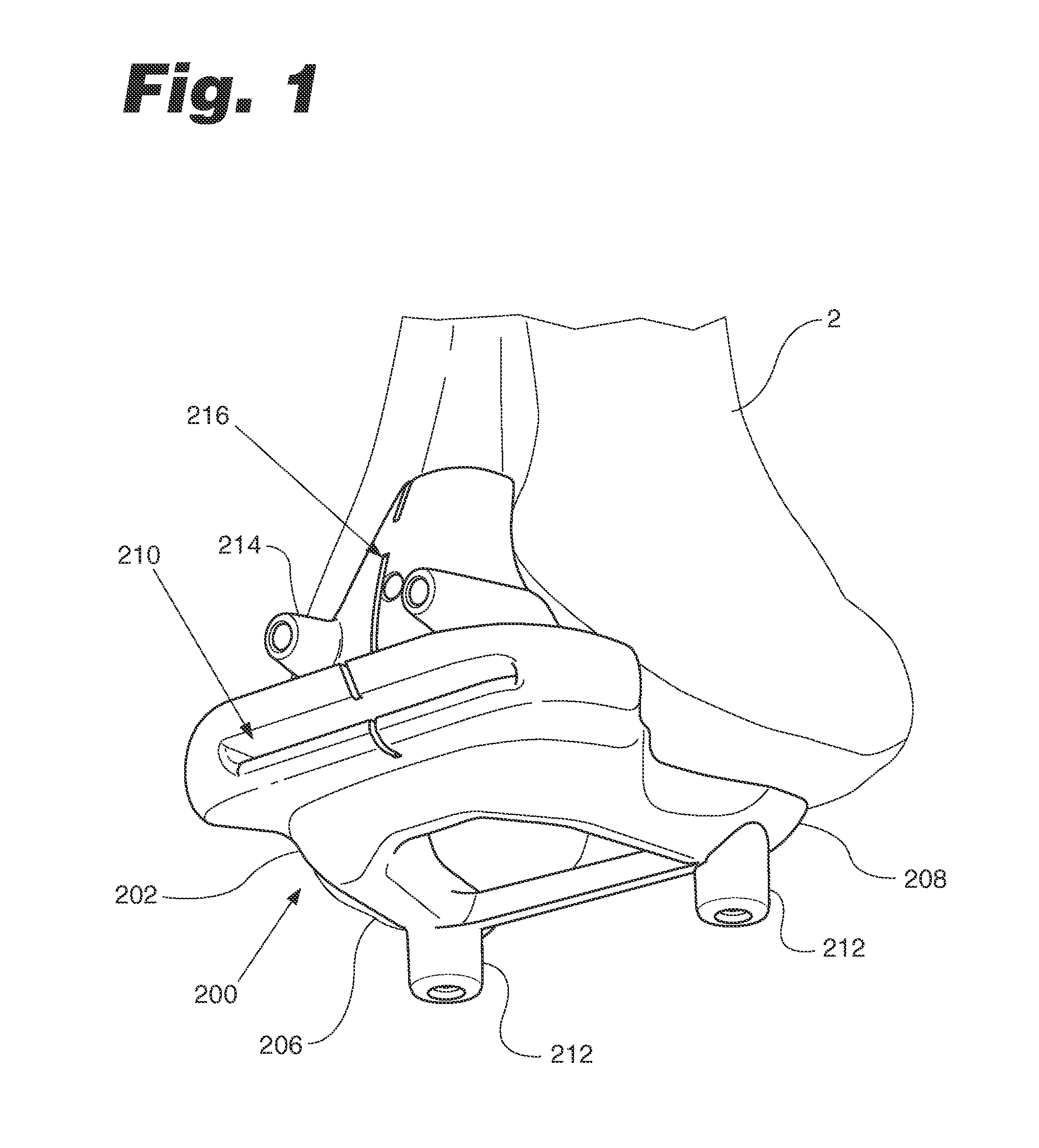
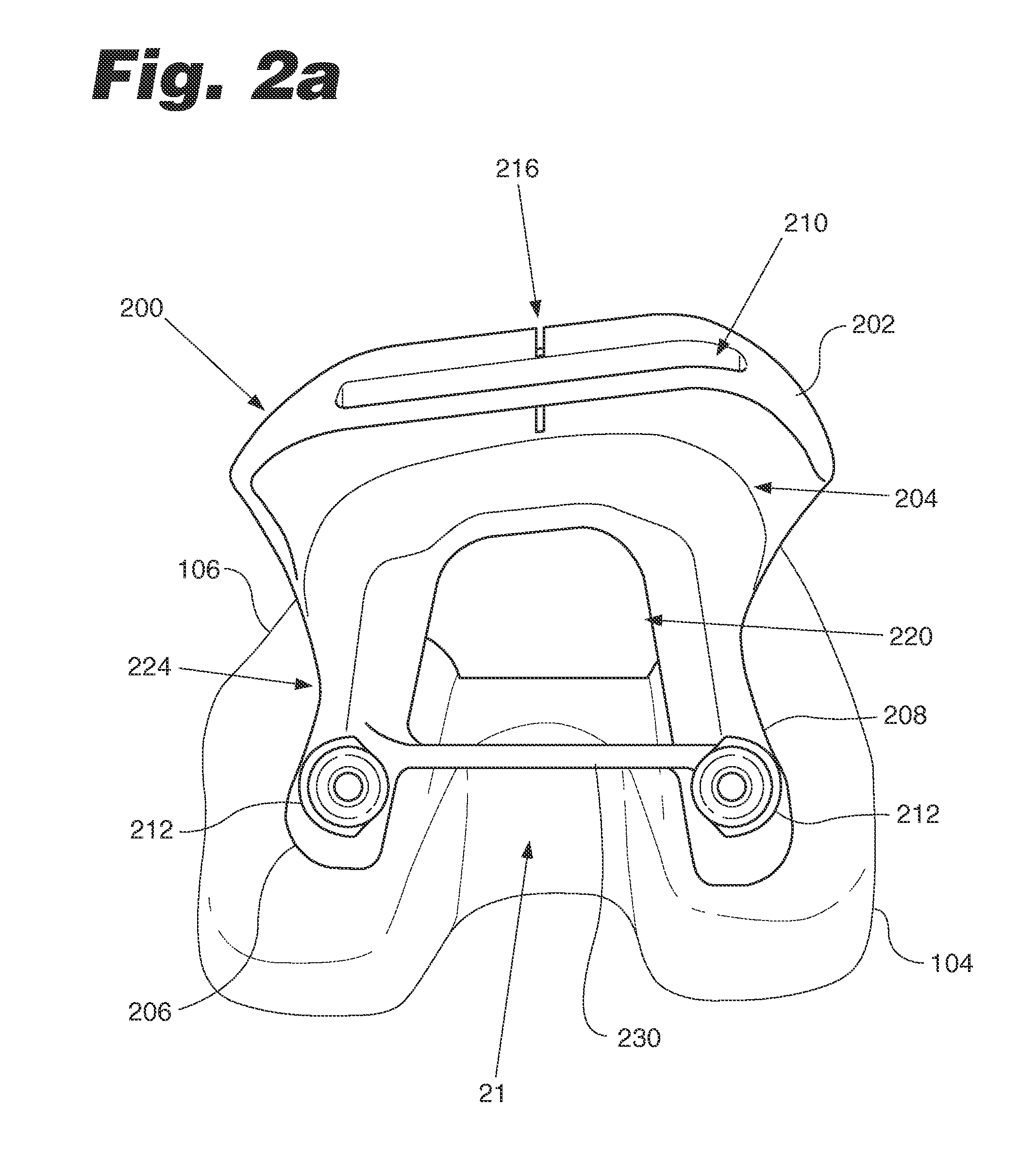
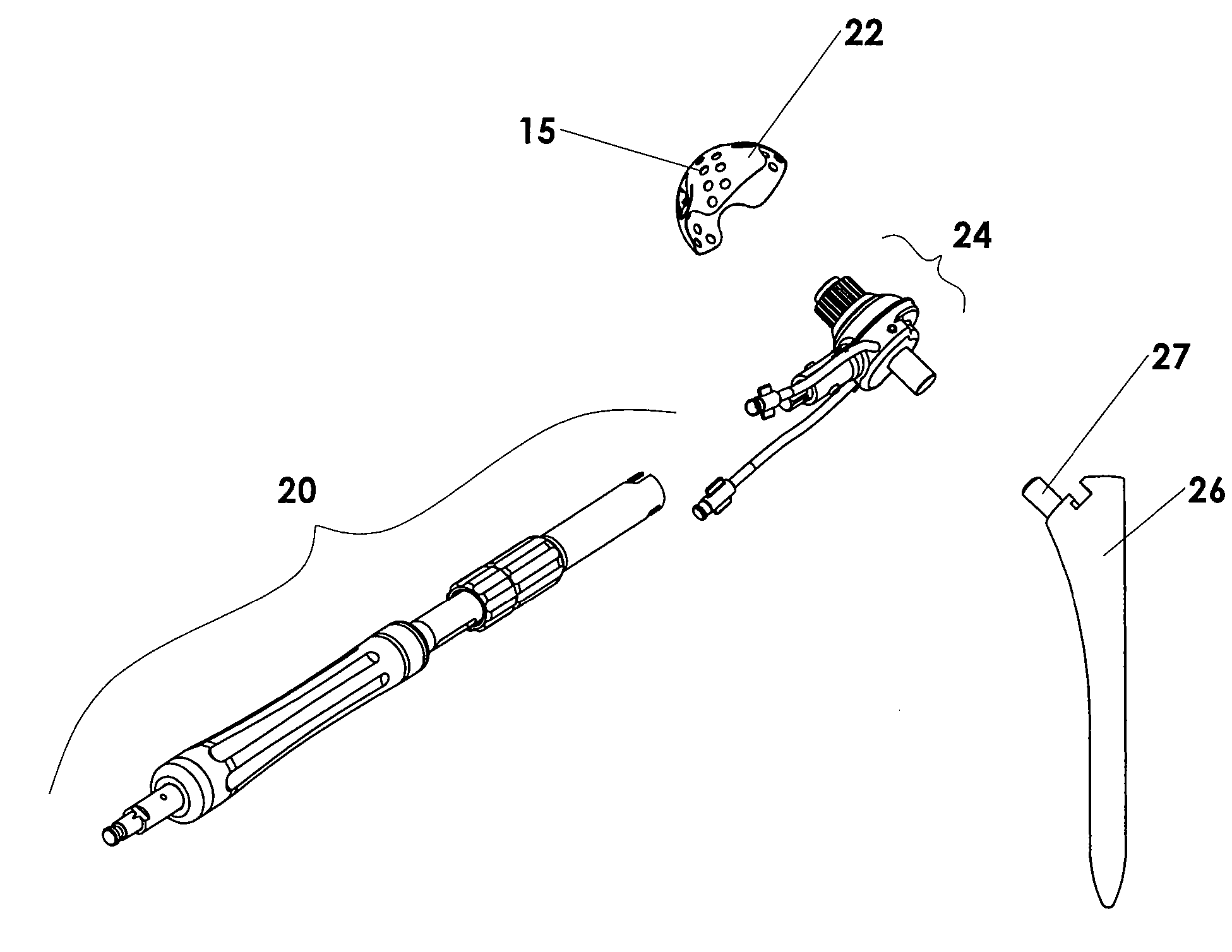
Trial femoral prosthesis and its use
Embodiments of the present application relate generally to provisional orthopedic components, and specifically, to a trial system including a cam module (10) and a trial femoral component (100) that can be used during joint replacement surgery. The systems and methods described help a surgeon prepare a patient's bone to receive a permanent implant by providing a system that can be used to guide preparatory box cuts, and that can then be completed with a cam module (10)—without removal from the patient's bone—so that the same component can be used for the trialing process.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Universal double offset surgical instrument
Instruments for use in anterior approach total hip arthroplasty. Instruments according to certain embodiments of the invention connect to a shaping member such as a broach, reamer or osteotome that is used to prepare the intramedullary canal of a desired femur or other bone for total hip arthroplasty. Such an instrument according to such embodiments can be configurable to allow operation on either the left or right leg, and in doing so to provide lateral offset and anterior offset of the instrument handle relative to the shaping member so that the patient's gut, musculature or other bodily portions may be avoided while still providing desired leverage and control over the shaping member to prepare the intramedullary canal.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
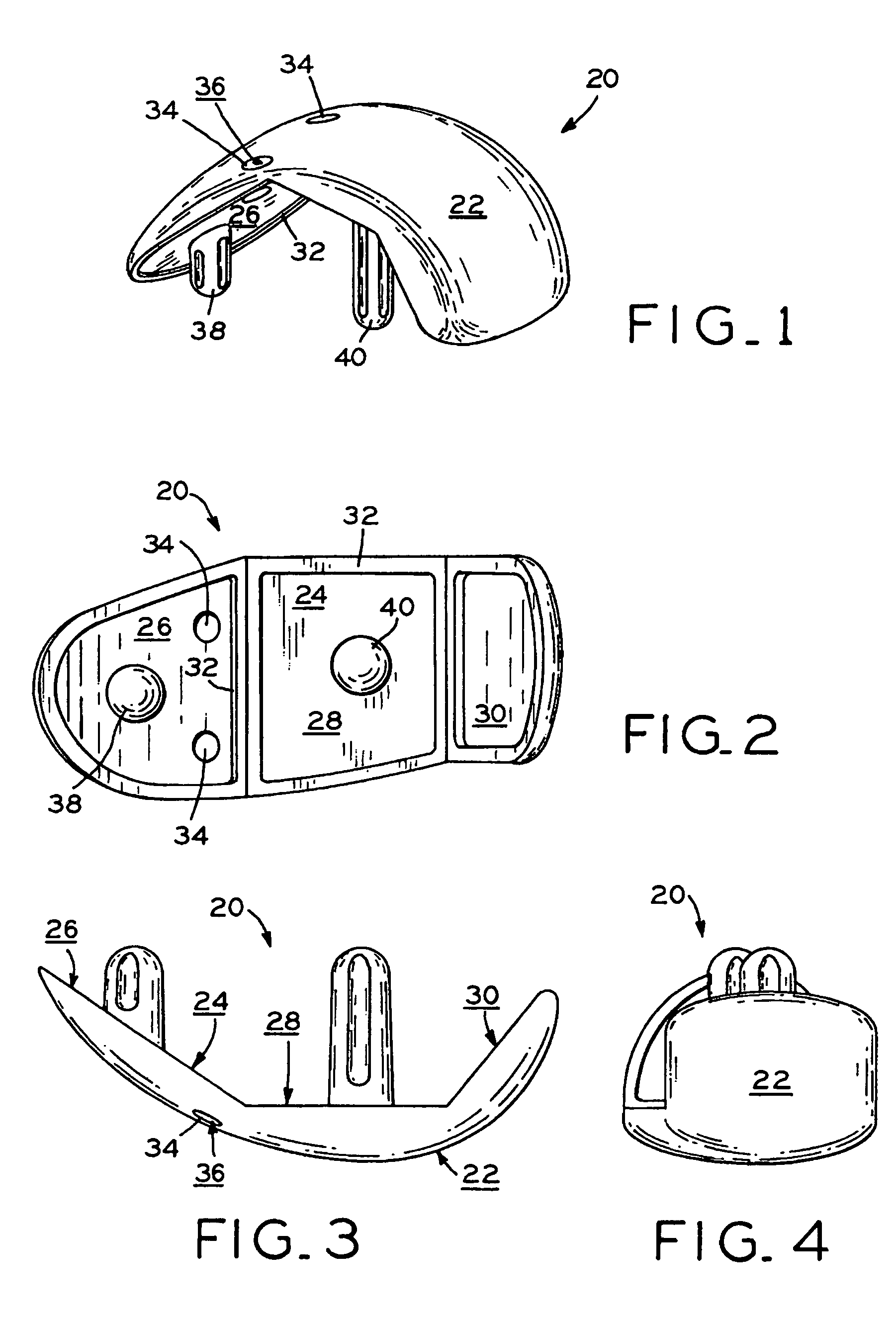
Patient match instrument
InactiveUS20140018813A1Good repeatabilityGood reproducibilitySurgical sawsProsthesisTangential contactTrochlear groove
A patient matched instrument for a patient's femur is disclosed. The instrument includes a body having a cutting slot and a patient matched surface that mates with the patient's trochlear groove, a first leg portion extending from the body, a second leg portion extending from the body; and each leg portion has a contacting pad for tangential contact with the patient's femoral medial and lateral condyles.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Mill and guide apparatus for preparation of a hip prosthesis
A guide apparatus for preparing the femur of a patient with a rotary mill to receive a femoral hip prosthesis includes a V-shaped guide body having a lower end base portion adapted to extend into the intermedullary canal of the femur and an upper end portion comprised of at least two spaced apart struts so that the overall guide body had a configuration substantially the same as the prosthesis body sought to be implanted in the patient. The lower end of the guide body base provides one or more hemispherical receptacles for holding the hemispherical end portion of a spinning mill bit. A preferably removable transverse guide rail has connection pins at one end portion thereof for forming a connection with the upper end of the guide body at one of the struts, the arm having a curved surface that is adapted to guide the mill bit during preparation of the intermedullary canal of the patient's femur for receiving a hip prosthesis thereafter.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Adaptable therapeutic, diagnostic or surgical guide
ActiveUS20120179147A1Precise targeting and controlAccurate fitAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical sawsTibiaEngineering
The present invention relates to an adaptable therapeutic, diagnostic or surgical guide for an intra-operative adjustment of a guidance element to a pre-planned position. An advantage and innovation of the present invention is that it provides a template or guide that adapts in a controlled way to a changed intra-operative anatomical situation compared to the default planned situation. This adaption maybe purely positional but it may also include force feedback. Feedback, either visual feedback or force feedback that results in an adjustment of a guidance element is also an aspect of the present invention. For example, the feedback can contain information either about the fit of the guide or template onto a bone (in case the guide or template fits onto one bone) or about the relative position of two bones of bone fragments (e.g. ligament tension between the femur and tibia).
Owner:MATERIALISE NV
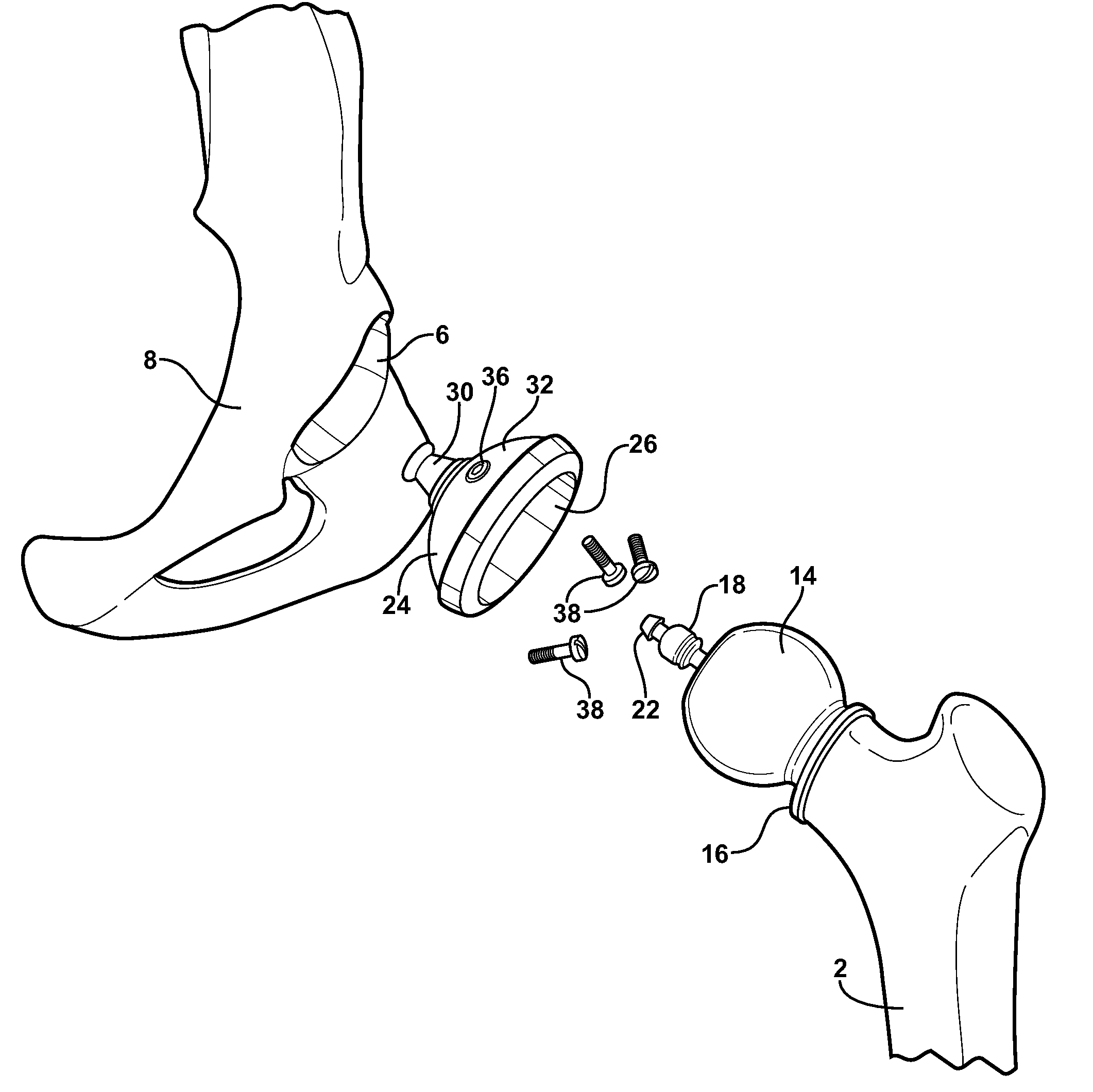
Hip prosthesis
InactiveUS7211113B2Improve stabilityAbility of the inventive structure to withstand numerous loadsBone implantJoint implantsCoxal jointBiomechanics
An endoprosthesis utilizes a biomechanical structure based on the lever model of first degree. Contrary to the widespread practice, the inventive structure has a stem placed inside the femur bone, which is not rigidly attached to this bone. Accordingly, the bone, following its known tendency to slightly pivot away from the medial plane of the body in response to the loads, does not directly contact the stem. The neck portion experiences even greater loads then the stem. The supporting anchor has a region extending laterally from the stem and pressing against a supporting surface of the housing, which also extends laterally from the body of the housing. Since the stem, supporting anchor and neck are typically constitute a one-piece component, the lateral surfaces of the supporting anchor and housing are in continuous frictional contact during displacement of the stem and housing relative to one another.
Owner:ZELENER LEV +3
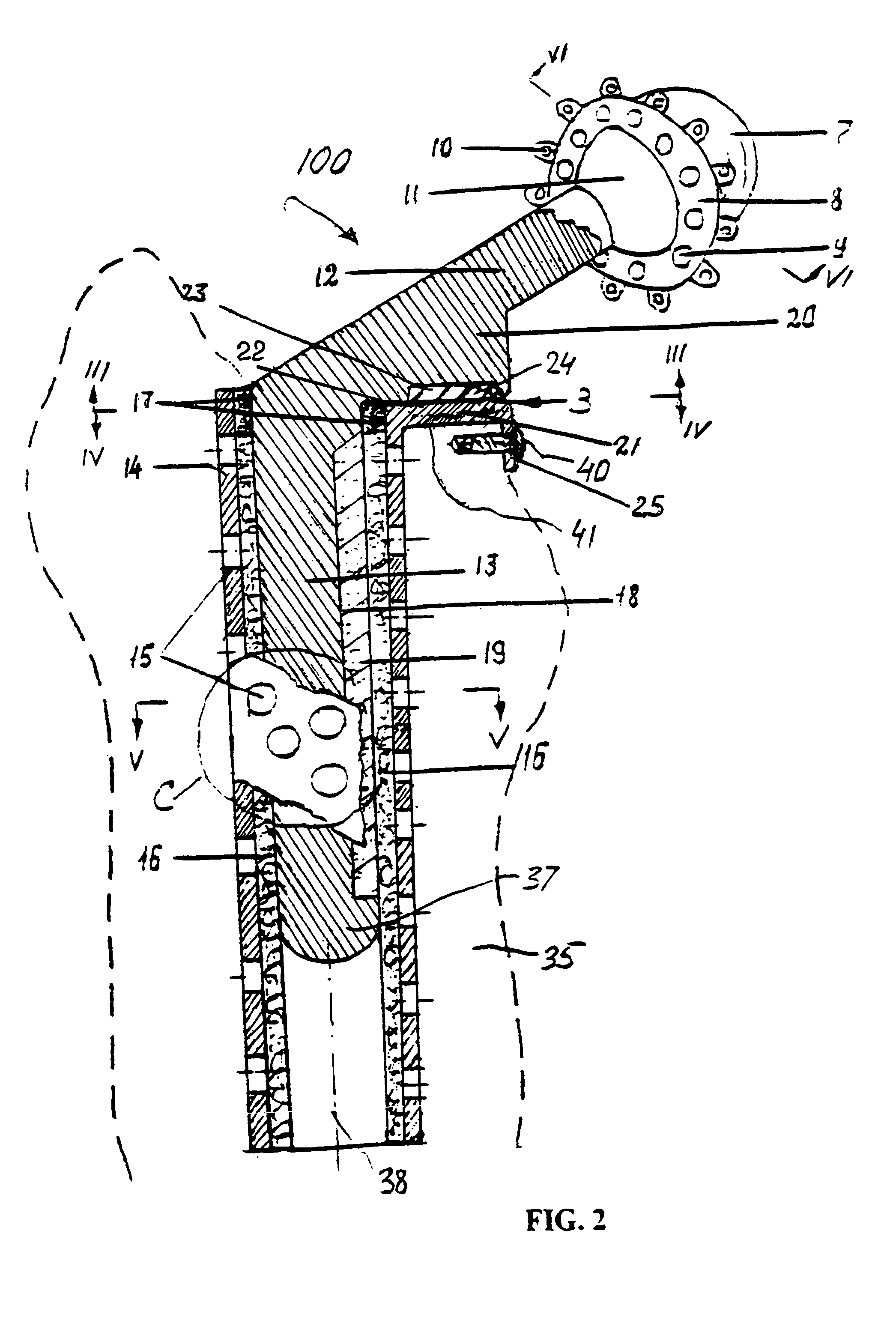
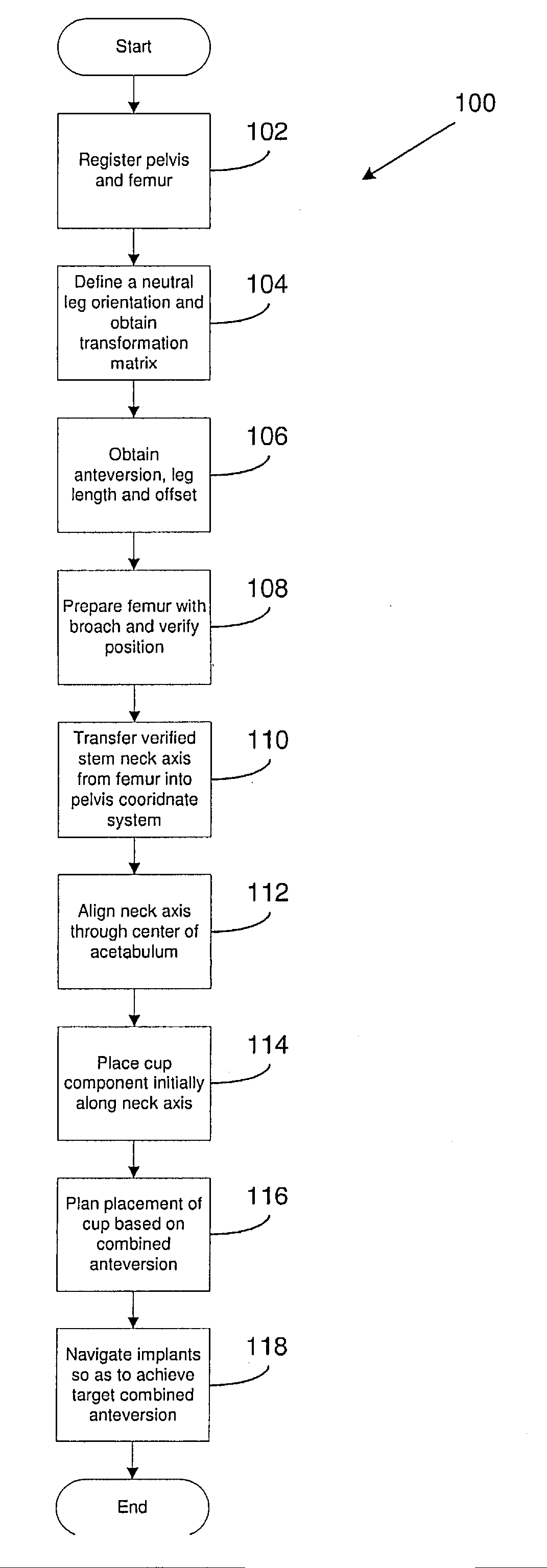
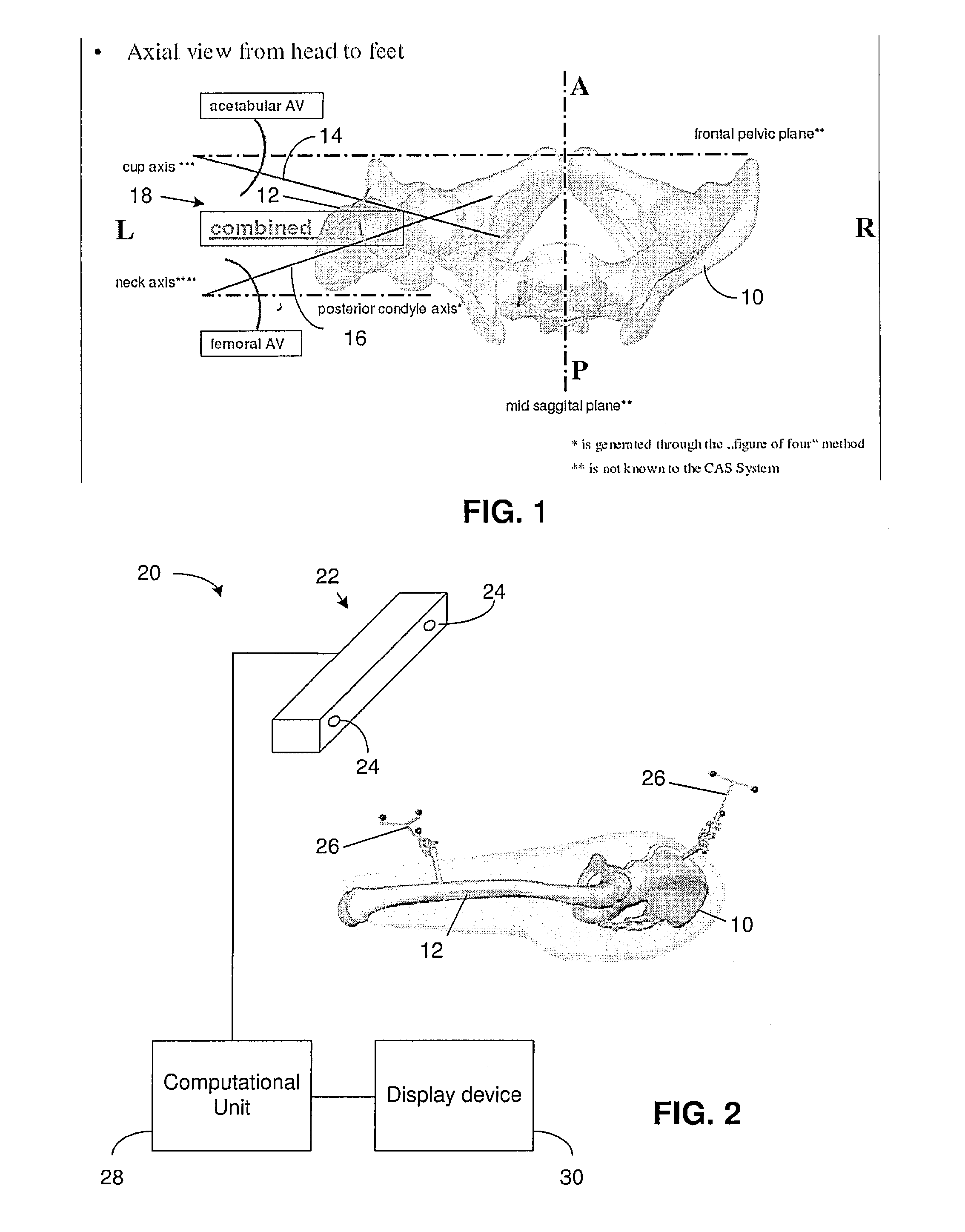
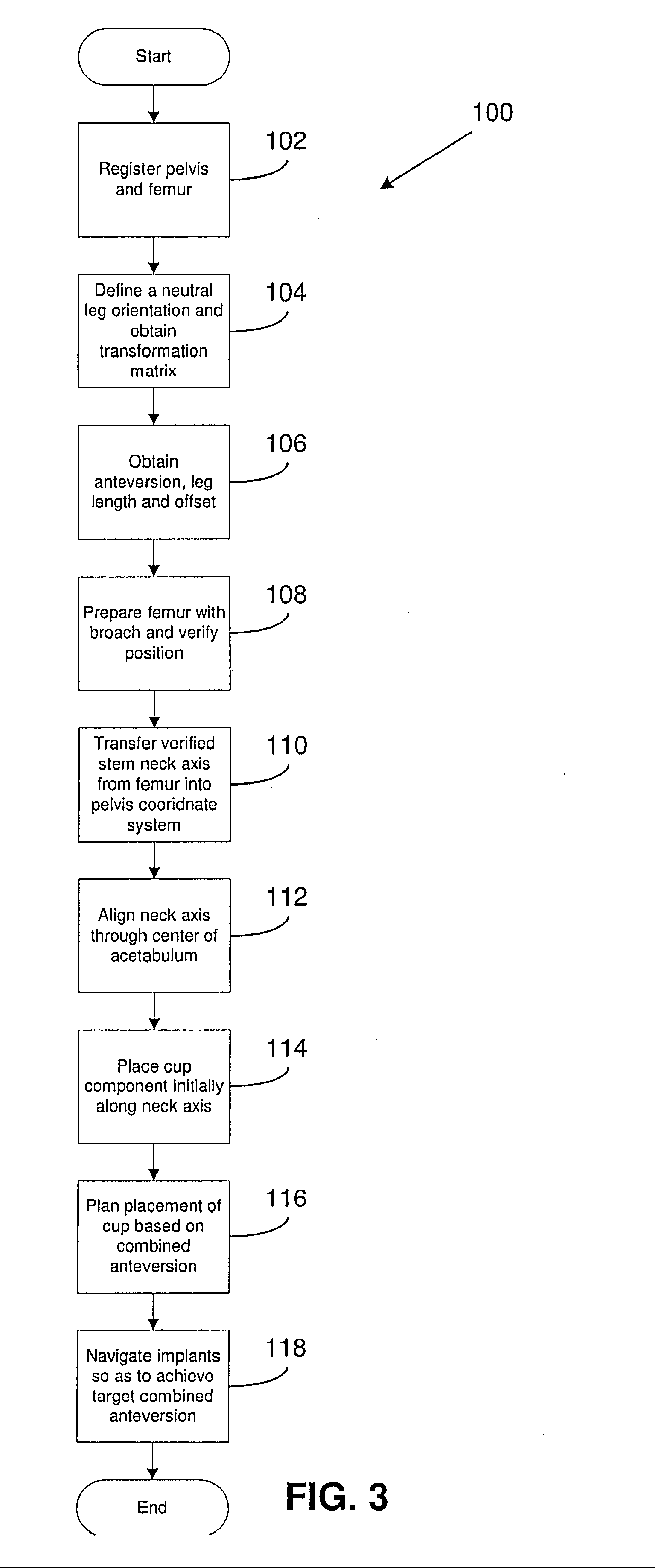
Navigated placement of pelvic implant based on combined anteversion by applying ranawat's sign or via arithmetic formula
ActiveUS20080294265A1Minimize occurrenceMinimize the possibilityAnkle jointsSurgical navigation systemsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationFemoral stem
A method for placing a pelvic implant including a cup and a femoral stem includes planning at least one of a location of the cup within a pelvis and a location of the stem within a femur such that a combined anteversion between a predetermined cup component and a predetermined femoral stem component satisfies a predetermined combined anteversion.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC +2
Bone shaping device for knee replacement
InactiveUS20050192583A1Improve accuracyImprove consistencyDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTotal knee replacement surgeryArthroplasty knee
A bone surgery device with a reciprocating cutting head. The device comprises several sets of shaping surfaces sometimes including cutting blades, which are located and oriented so as to shape the distal end of the femur and the proximal end of the tibia for total knee replacements and unicompartmental knee replacements. The device, which may be hand directed or aided by spatial and directional guiding mechanisms or an optical navigation system, may also include both coolant supply for controlling heat during bone, cutting and shaping, and a suction method for carrying away fluid and debris. The device is substantially configured to the artificial joint component to be attached thereto.
Owner:WALKER PETER STANLEY +1
Hip socket with assembleable male ball shape having integrally formed ligament and female receiver and installation kit
A hip implant assembly including a spherical shaped ball and an elongated stem. An annular defining rim separates the ball from the stem and abuts, in a maximum inserting condition, over an exterior reconditioned surface of the femur and upon inserting the stem within an interior passageway formed within the femur. A cup shaped support seats the ball in a universally articulating permitting fashion via a flexible and resilient ligament which extends from the ball and is received within a recess passageway of the cup. The cup also includes a mounting surface with a central projecting portion which is in turn resistively fitted within an undercut defined recess formed in the ilium bone in communication with a base surface of the reconditioned acetabulum socket. A corresponding installation kit assists the preparation of the femur and ilium bones defining the hip joint, as well as the installation of the implant body into the upper conditioned femur end and the cup shaped and outer socket support to a reconditioned acetabulum defined in the ilium bone.
Owner:LINARES MEDICAL DEVICES
Bone shaping device for knee replacement
InactiveUS20050192584A1Reduction in time taken to cutReduction in to shape bone surfaceDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsTibiaKnee Joint
A bone surgery device with a reciprocating cutting head. The device comprises several sets of shaping surfaces sometimes including cutting blades, which are located and oriented so as to shape the distal end of the femur and the proximal end of the tibia for total knee replacements and unicompartmental knee replacements. The device, which may be hand directed or aided by spatial and directional guiding mechanisms or an optical navigation system, may also include both coolant supply for controlling heat during bone cutting and shaping, and a suction method for carrying away fluid and debris. The device is substantially configured to the artificial joint component to be attached thereto.
Owner:WALKER PETER STANLEY +1
Load bearing implants with engineered gradient stiffness and associated systems and methods
Implants are made of materials having asymmetric modulus gradients. For example, an implant, such as a hip implant, is made of a material having a stiffness gradient between a proximal portion near a hip joint and a distal portion extending downward into the marrow of the femur. Among other benefits, the asymmetric modulus gradient mitigates problems associated with stress shielding and does not excessively wear or deteriorate the proximal portion of the implant.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
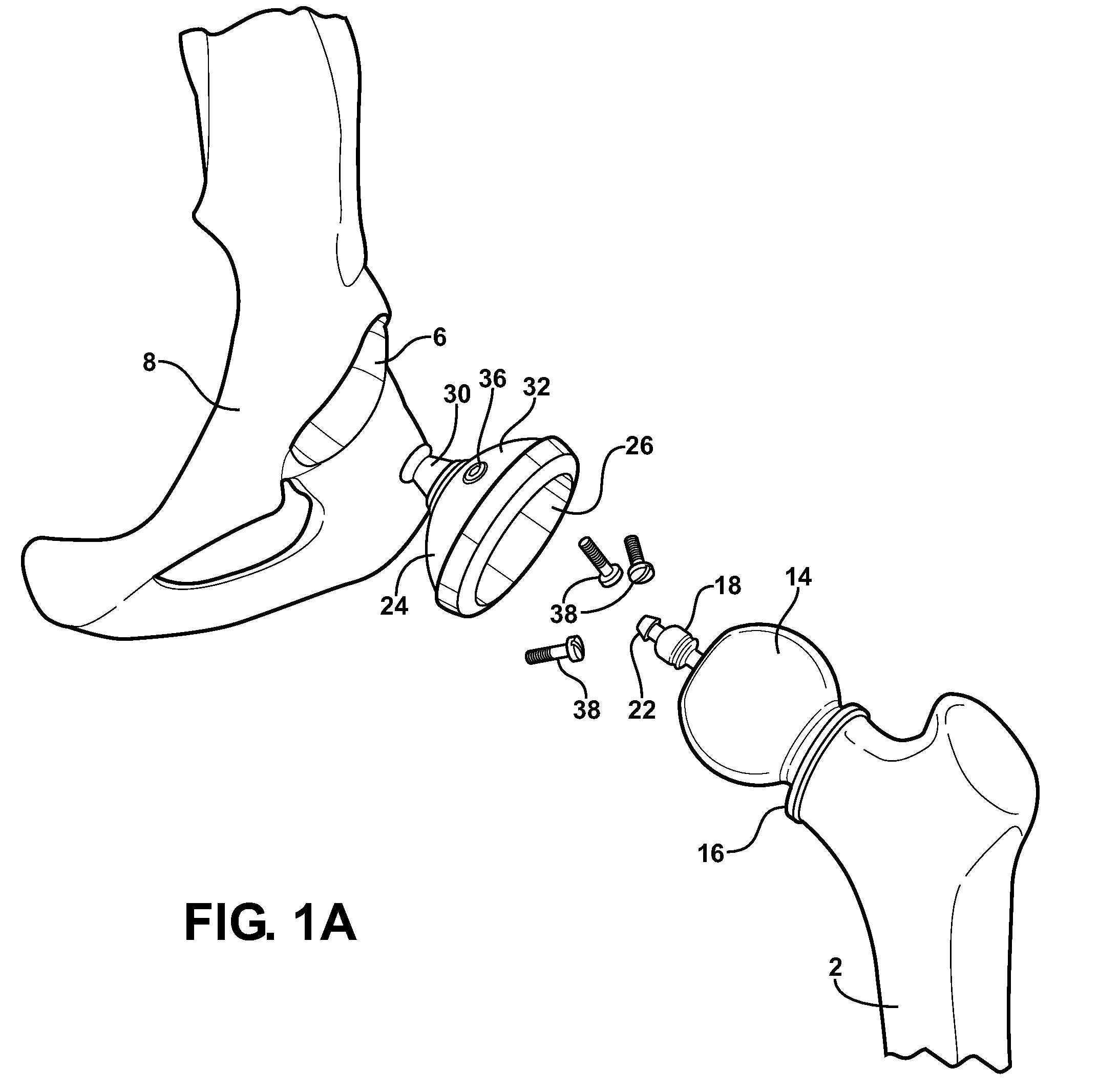
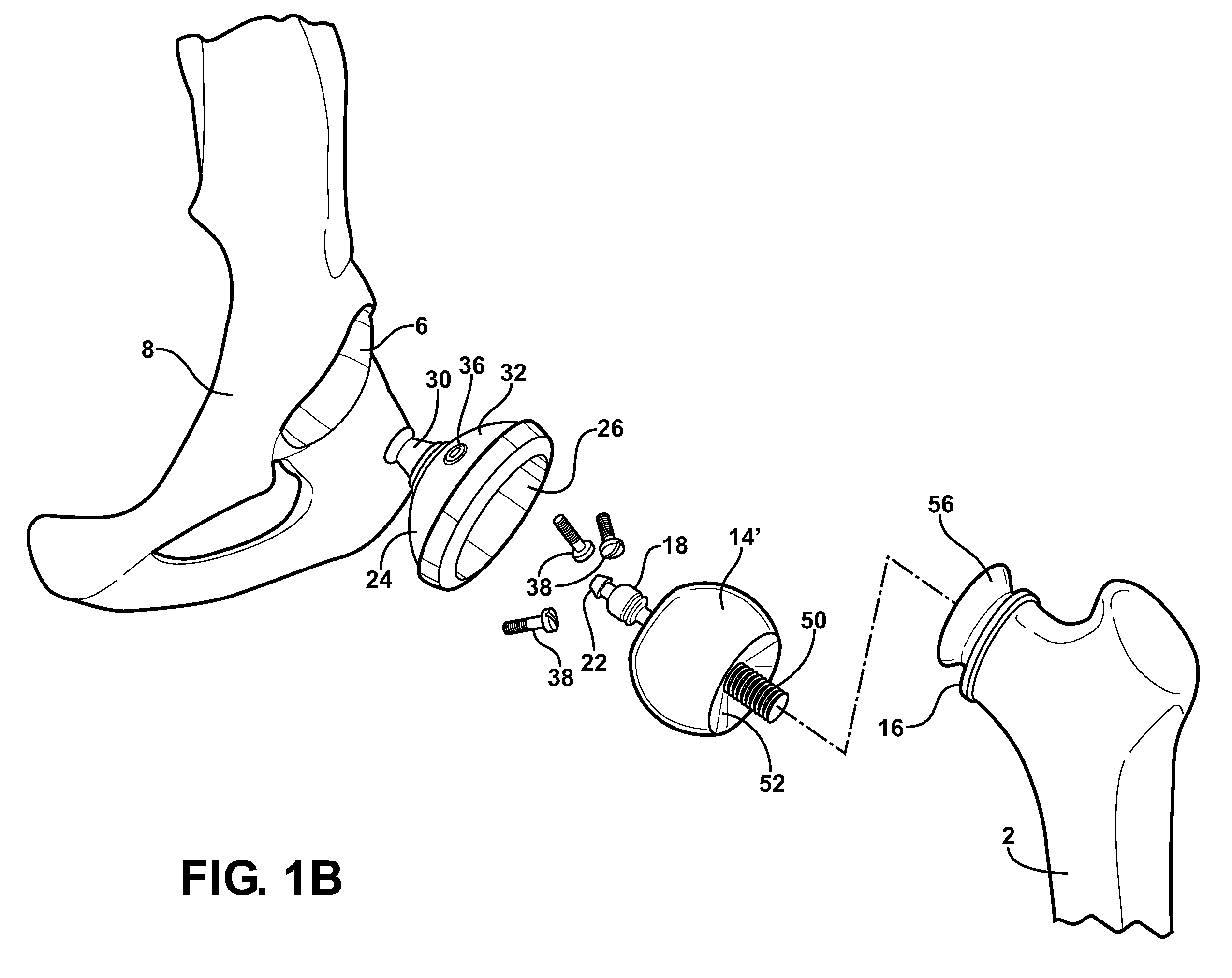
Cannulated femoral hip implant apparatus
The femoral hip implant is defined by a femoral ball and a femoral stem. The femoral stem has a proximal end, a distal end and a length. The femoral stem extends from the femoral ball and terminates at the distal end. The femoral stem is arranged and configured to be received by a femur bone. A method of use is also provided.
Owner:CHAPPUIS JAMES L
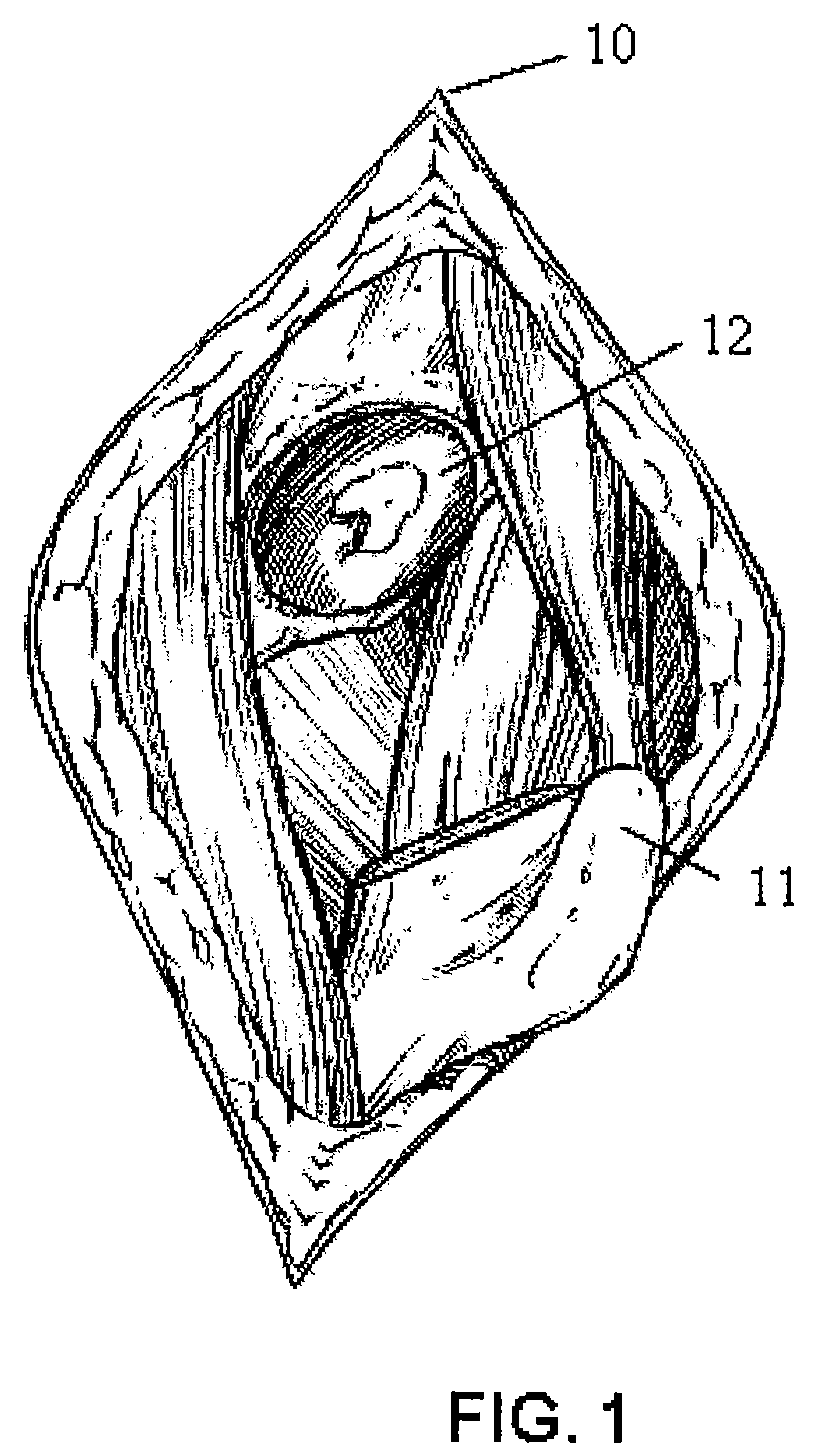
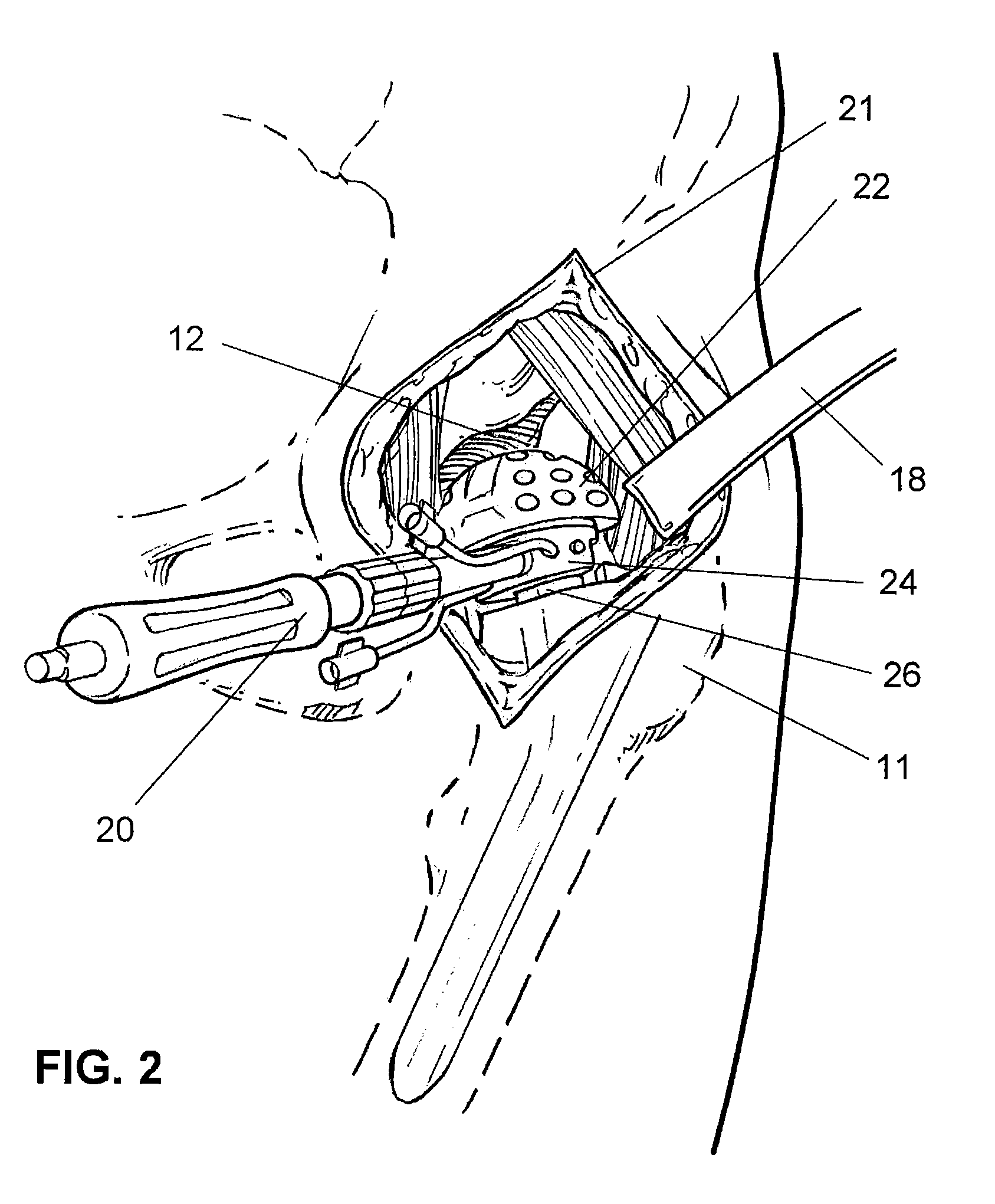
Method and apparatus for treating a joint, including the treatment of cam-type femoroacetabular impingement in a hip joint and pincer-type femoroacetabular impingement in a hip joint
A computer visual guidance system for guiding a surgeon through an arthroscopic debridement of a bony pathology, wherein the computer visual guidance system is configured to: (i) receive a 2D image of the bony pathology from a source; (ii) automatically analyze the 2D image so as to determine at least one measurement with respect to the bony pathology; (iii) automatically annotate the 2D image with at least one annotation relating to the at least one measurement determined with respect to the bony pathology so as to create an annotated 2D image; and (iv) display the annotated 2D image to the surgeon so as to guide the surgeon through the arthroscopic debridement of the bony pathology.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
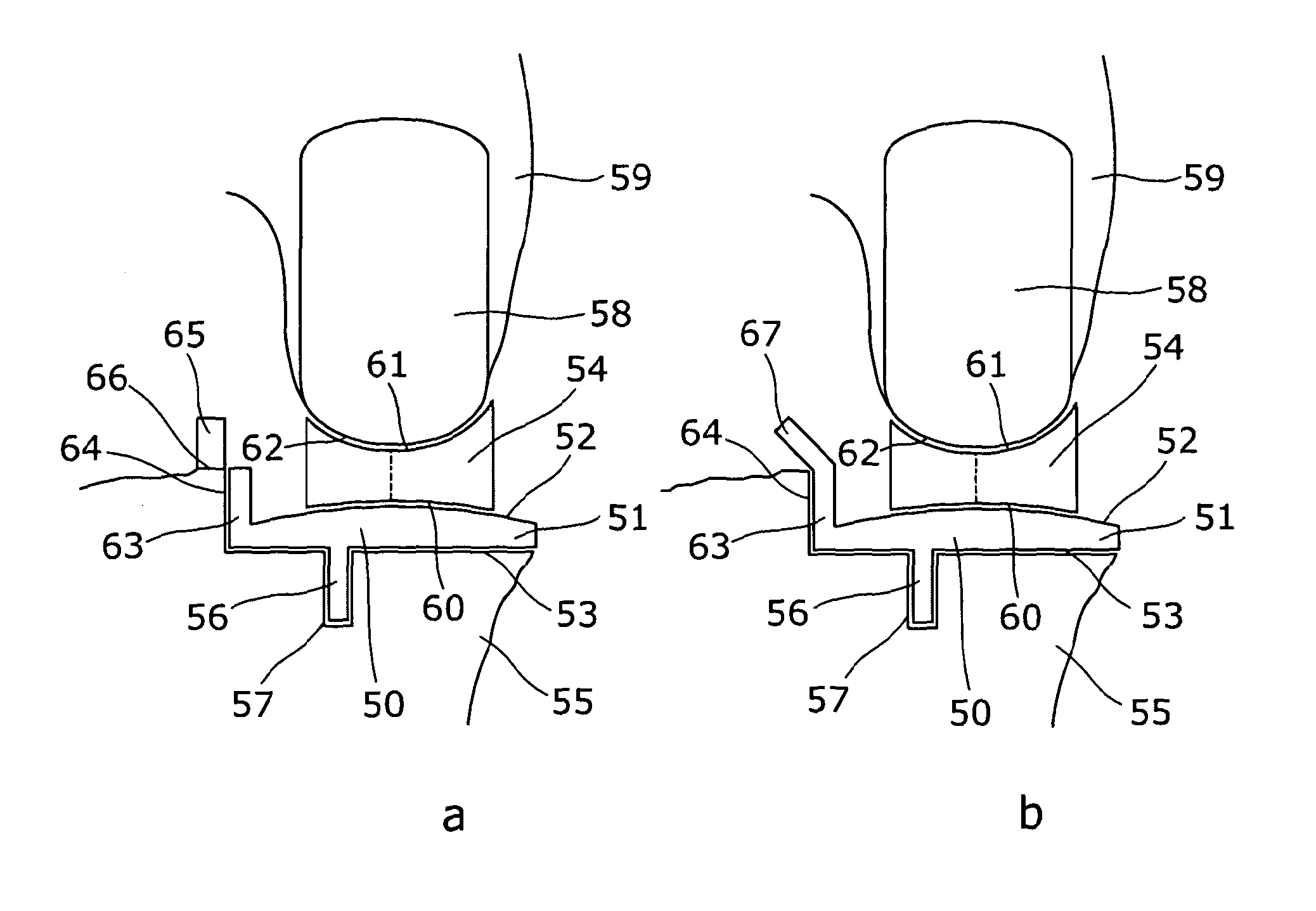
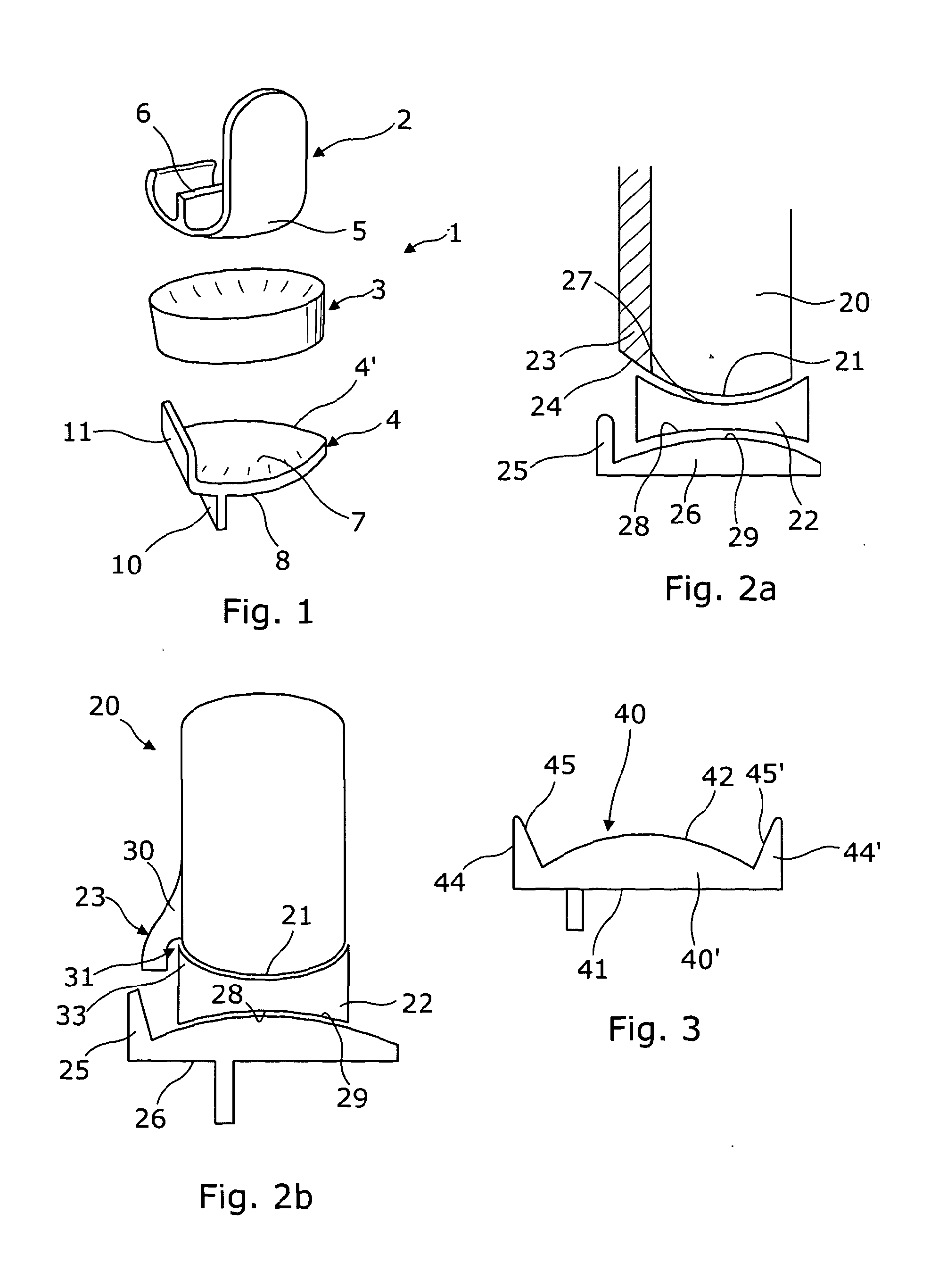
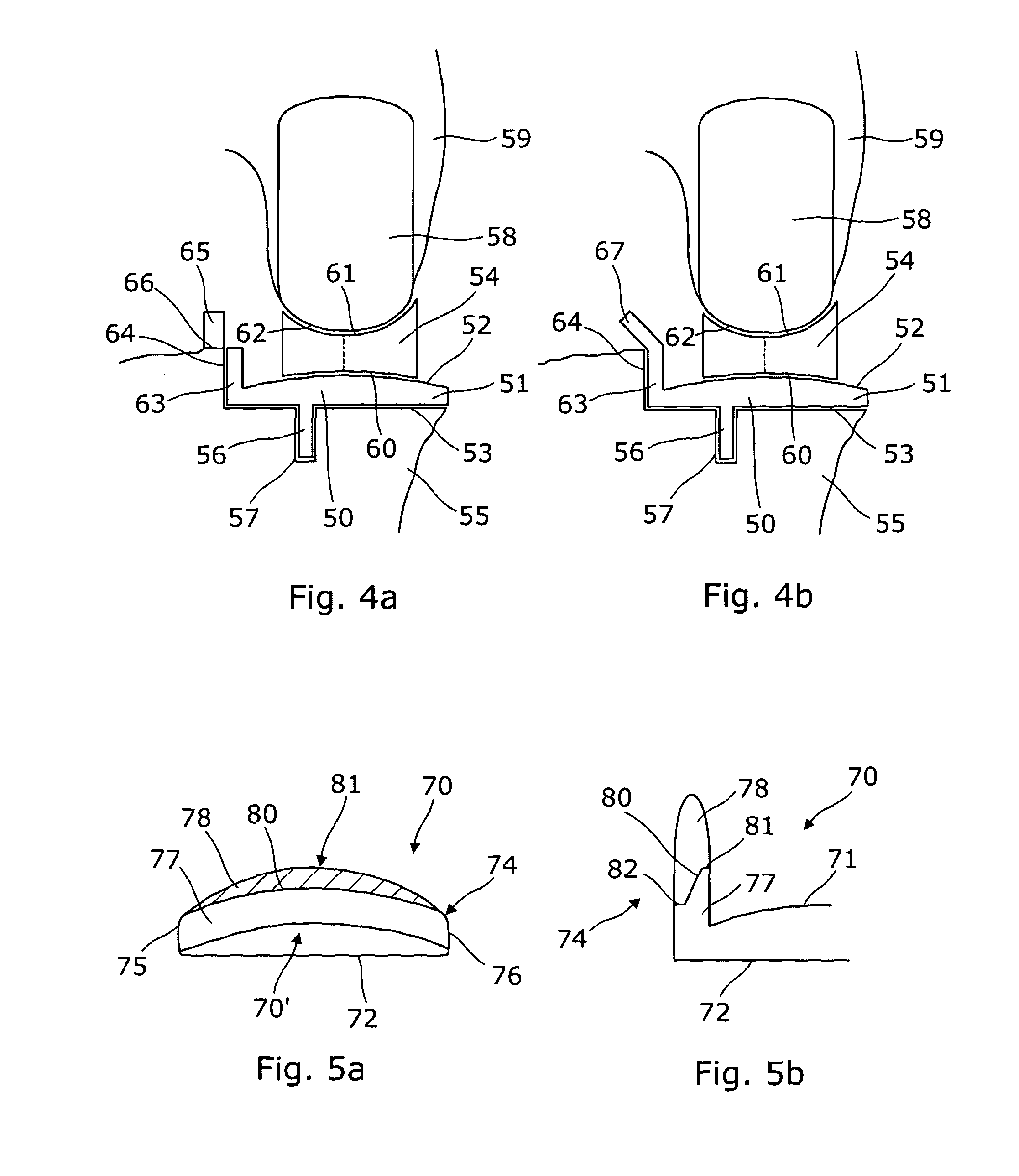
Proection pad for the trochantheric region and device comprising the pad
InactiveUS20050234380A1Improve protectionAccelerated dissipationFeet bandagesProtective garmentEngineeringGreat Trochanter
When people fall they tend to fall on their side. This can lead to them breaking their femur particularly at the head around the trochantheric region. The head of the femur includes a portion called the greater trochanter which projects outwards and which is covered by very little flesh. A pad for use in protecting trochantheric region of the body comprises at least two separate layers, a substantially rigid layer, and a layer of dense, closed-cell resilient foam material. The substantially rigid layer includes a protecting boss which, in use, is located in the region of the greater trochanter to increase the spacing between the outside of the rigid layer and the greater trochanter. Preferably, the layer of closed-cell foam material extends over a greater area than the substantially rigid layer so that the periphery of the rigid layer lies entirely within the periphery of the foam layer.
Owner:REMPLOY
Ham product and method for production thereof
ActiveUS7214403B1Low costImprove efficiencyMeat/fish preservationFood shapingFemur boneBiomedical engineering
A ham product and method for production thereof described herein separate bone-in hams into smaller pieces. Accordingly, pieces of bone-in ham, even those spirally-sliced, will be available to consumers in smaller portions. Unlike conventional methods, however, the ham product and method for production does not cut the femur bone longitudinally. As a result, one piece of the bone-in ham has substantially no bones. A method for separating a bone-in ham comprises the steps of providing a first separation through the ham to provide a first portion and a second portion, and providing a second separation through the first portion, wherein only one of the first separation or second separation is through a femur bone.
Owner:THE HONEY BAKED HAM CO LLC
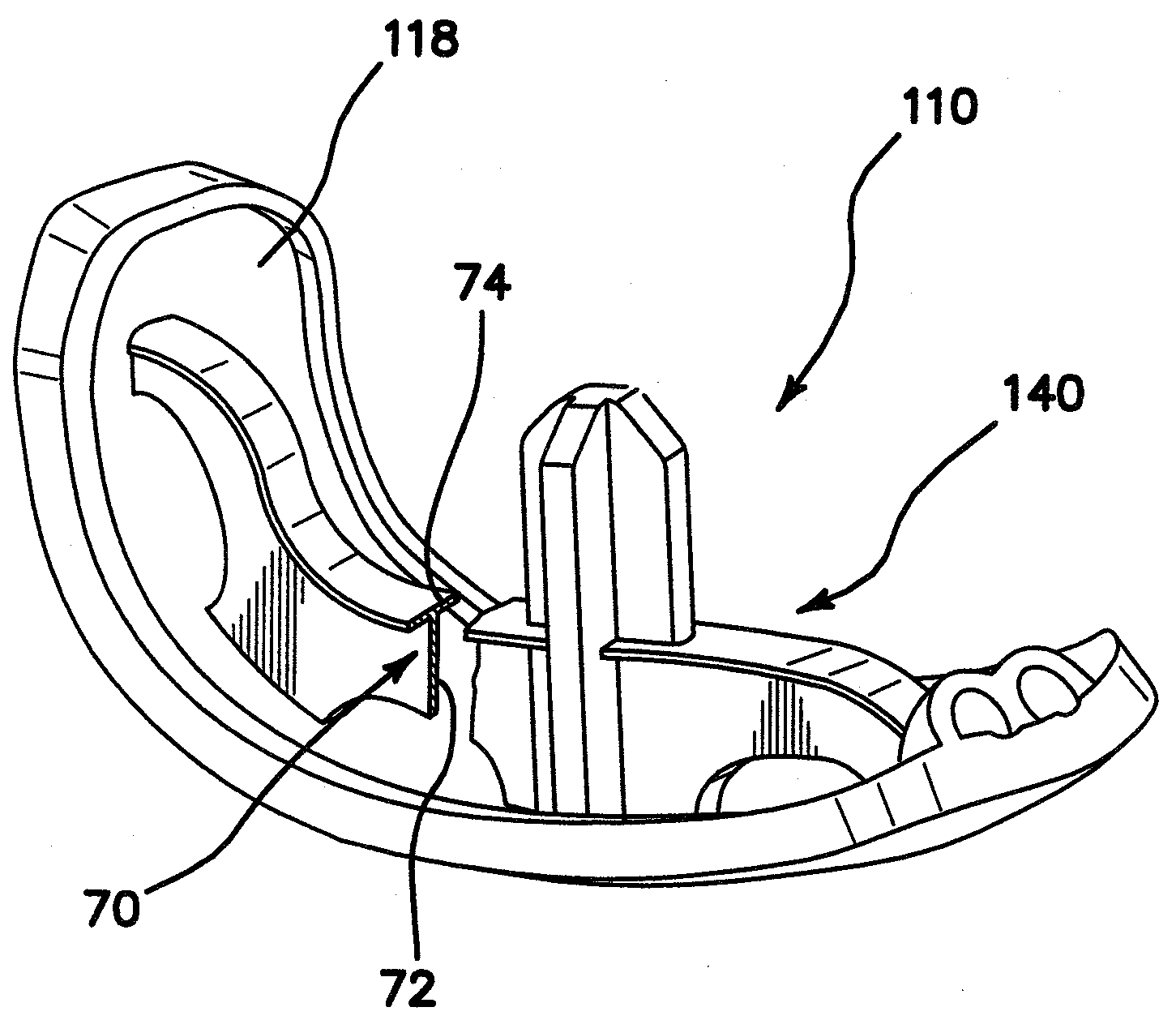
Trialing system and method for modular hip joint replacement system
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
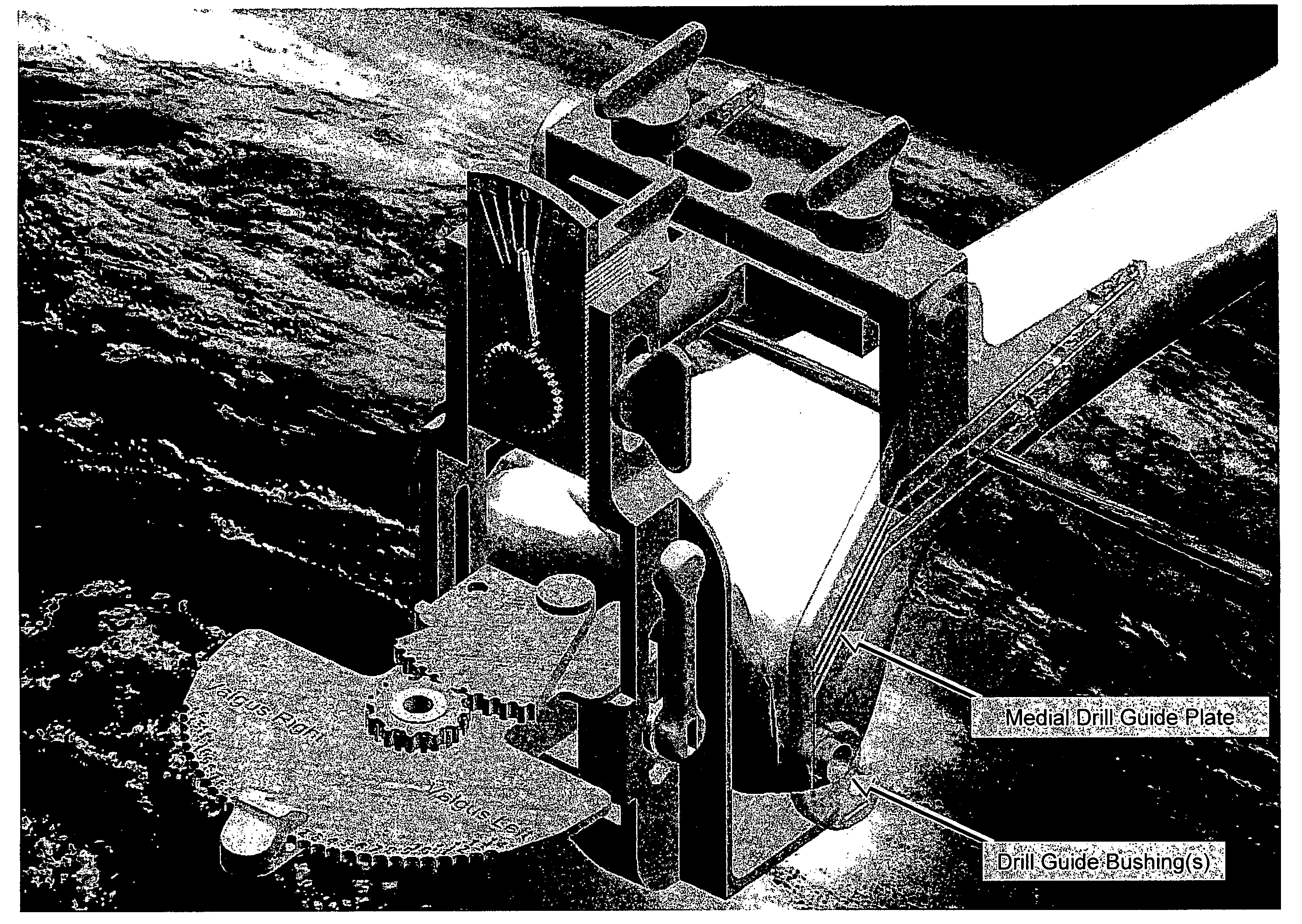
Provisional orthopedic implant and recutting instrument guide
InactiveUS7963969B2Easy alignmentPrecise alignmentJoint implantsKnee jointsOrthopedic departmentFemoral component
Owner:ZIMMER TECH INC
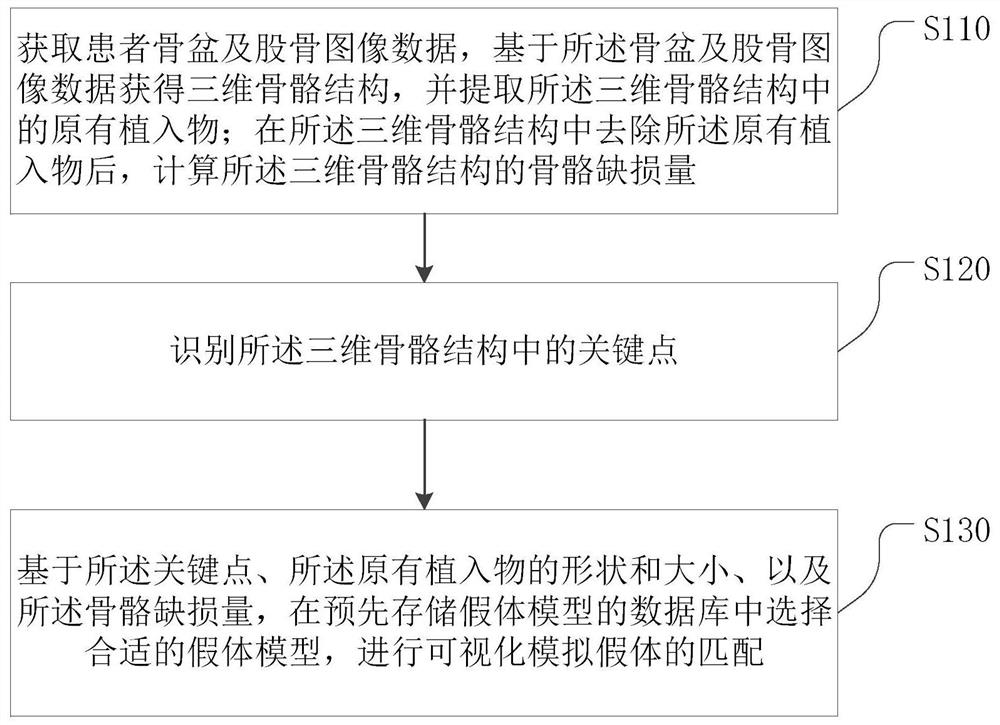
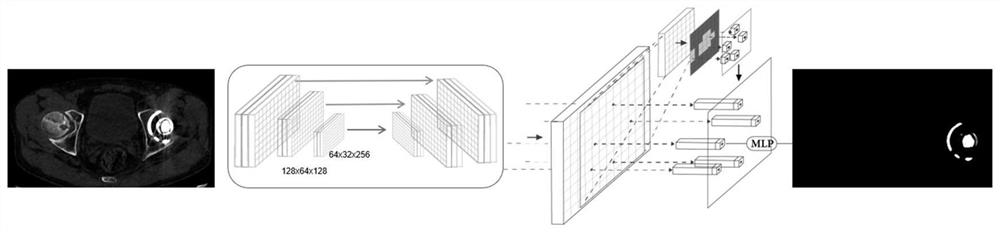
Total hip replacement revision preoperative planning method and equipment based on deep learning
The invention provides a total hip replacement revision preoperative planning method and equipment based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring pelvis and femur image data of a patient, acquiring a three-dimensional skeleton structure based on the pelvis and femur image data, and extracting an original implant in the three-dimensional skeleton structure; identifying key points in the three-dimensional skeleton structure; and based on the key points and the shape and size of the original implant, selecting a proper prosthesis model from a database in which prosthesis models are pre-stored, and carrying out visual simulation prosthesis matching. Technical support is provided for doctors to carry out total hip replacement revision, so that the surgical operation is more accurate and safer, and the development of the surgical operation towards the intelligent, precise and minimally invasive direction is promoted.
Owner:BEI JING LONGWOOD VALLEY MEDICAL TECH CO LTD +2
Femoral Prosthesis
The present invention relates to a femoral prosthesis that includes a cement introduction port which may be used to facilitate delivery or introduction of bone cement into the prosthesis / bone interface after the prosthesis component has been placed on a resurfaced femur bone. The femoral prosthesis may have a keel with undercuts which are configured to assist in controlling the flow of bone cement during implantation and to improve stability of the prosthesis following implantation. The femoral prosthesis is suitable for implantation using arthroscopic, as well as open, surgical procedures. The present prostheses may be used as unicondylar implants in either compartment of the knee or in both compartments of the knee.
Owner:MAXX ORTHOPEDICS INC
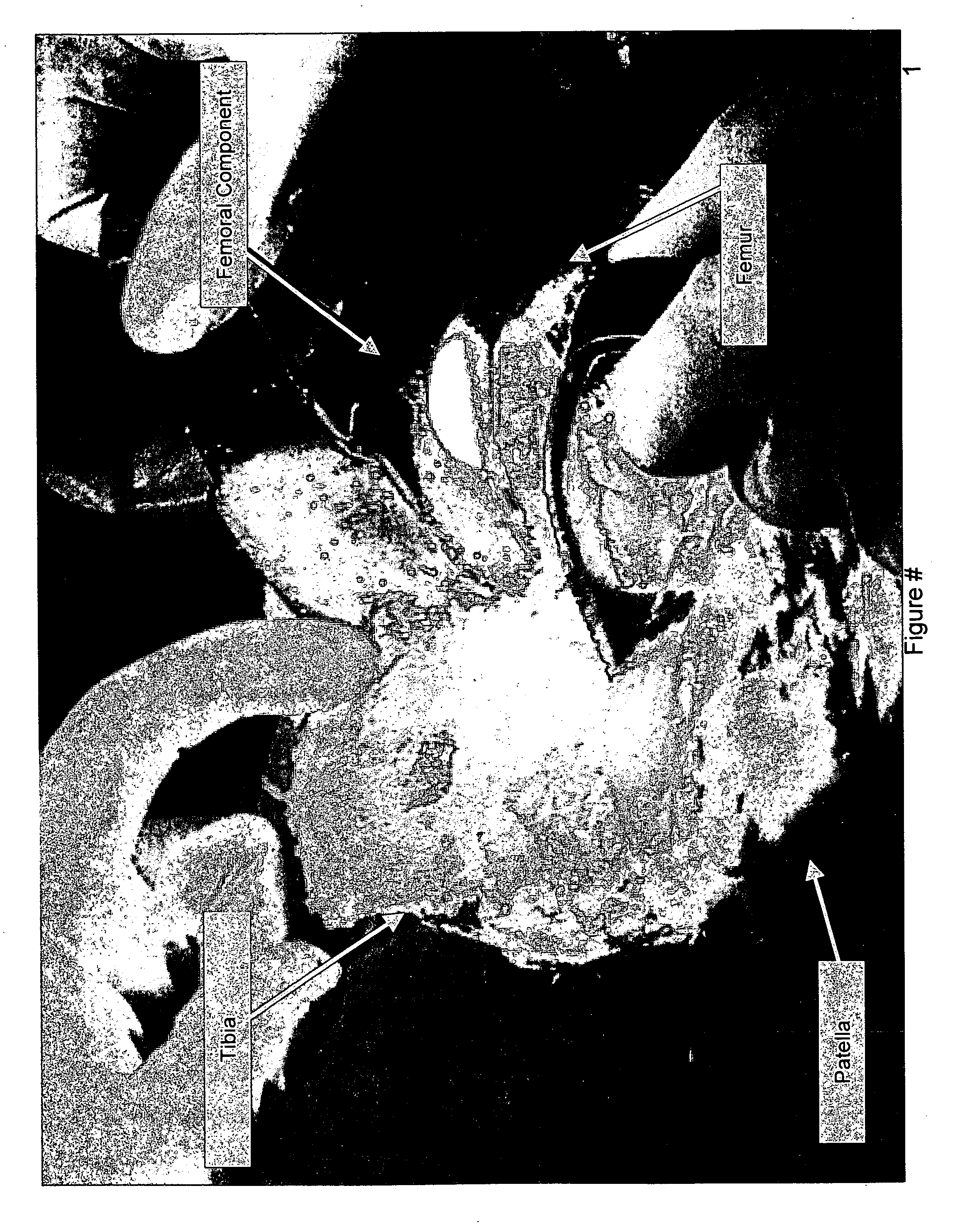
Knee flexion and extension gap tensioning and measuring method
A method for imparting tension across a human knee joint which includes a femur bone, a tibia bone, a patella bone, a patellar tendon, and ligaments, wherein the ligaments and patellar tendon are under anatomical tension to connect the femur and tibia together, creating a load-bearing articulating joint. The method includes: providing a tensioning device, including: a baseplate; a top plate; and a linkage interconnecting the baseplate and the top plate and operable to move the tensioning device between retracted and extended positions, wherein the top plate is pivotally connected to the linkage so as to be able to freely pivot about a pivot axis; positioning the tensioning device between the femur and the tibia; applying an actuating force to the linkage to move the tensioning device towards the extended position, so as to impart a controlled separating force driving the femur and tibia apart to extend the ligaments.
Owner:LITTLE ENGINE LLC
Ergometric chair apparatus
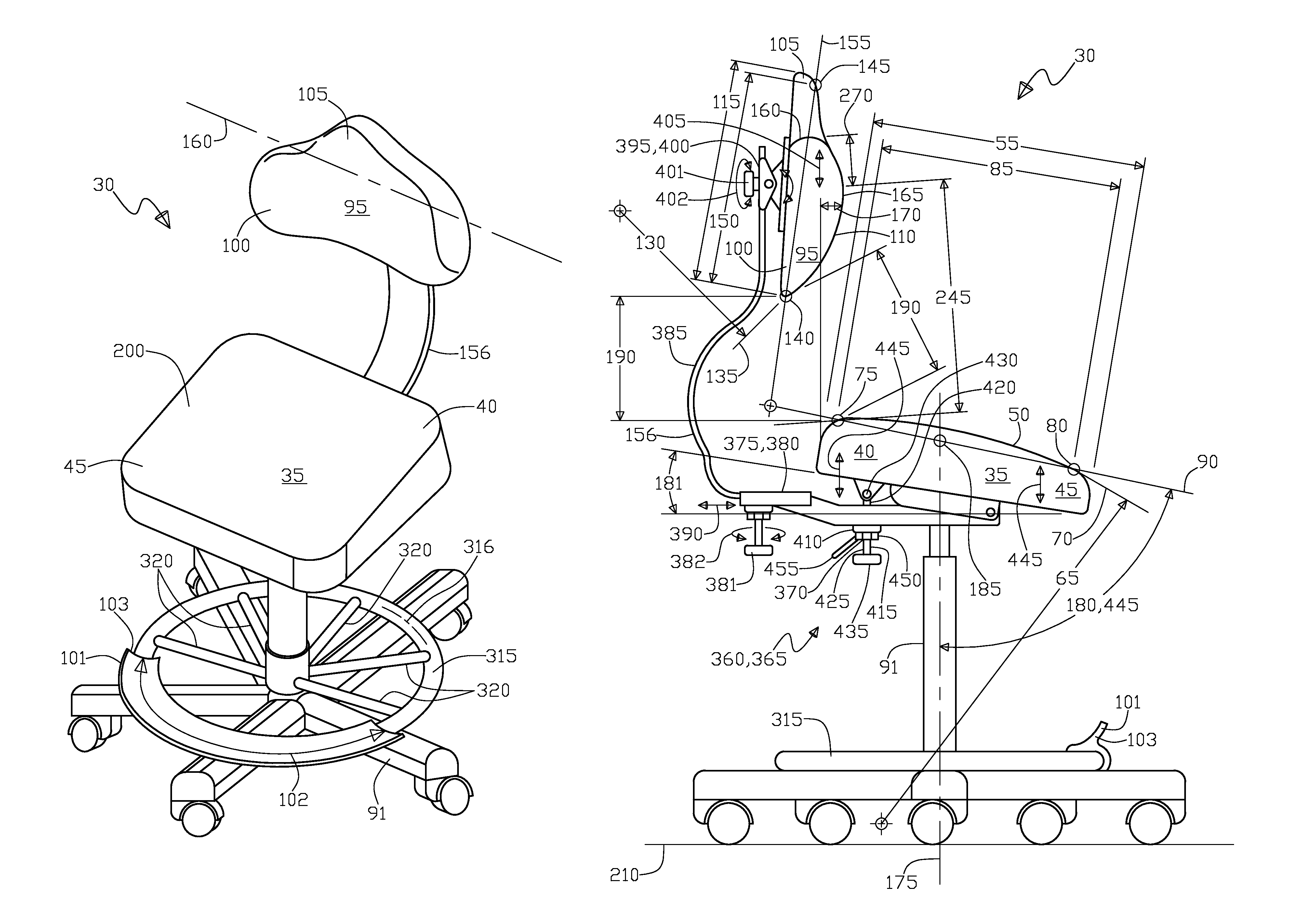
A chair and method of use is for a chair disposed upon a surface that is designed for a female anatomy; the chair includes a seat having proximate and distal end portions forming a first convex surface with a chord plane intersecting, the having a length shorter than its width. The chair includes a back having first and second end portions that form a second convex surface, wherein, a second lateral measure on the second end is less than a first lateral measure on the first end. The seat plane and an extension axis that is perpendicular to the surface are relatively positioned to one another to form an acute angle to one another, such that a user's femur bone lengthwise angles downward from hip to knee toward the surface while the user's shoulders arch rearward thus aligning the user's hip joint and shoulder joint vertically for better posture.
Owner:AUGUSTAT BETTY A
Femoral extension prosthetic component and tibial shelf prosthetic component for unicondylar meniscal bearing knee prosthesis and prosthesis including such a component
A femoral extension prosthetic component for use in a unicondylar meniscal bearing unicompartmental knee replacement is described. The femoral component comprises a securing element and a bearing surface, the securing element adapted to abut and be connected to a distal end of a femur bone, and the bearing surface adapted to abut a meniscal bearing. The femoral component includes an entrapment portion adapted to extend beyond the meniscal bearing. Tibial components and meniscal bearings are also described, as well as methods of using such components.
Owner:BIOMET UK +4
Support body in expansion fixing whirlbone
ActiveCN102824207APromote ingrowthThe function of preventing loosening and degenerative movementSurgeryStructural engineeringBone Cortex
The invention relates to a support body in an expansion fixing whirlbone, which comprises a support main body and an internal expansion bolt, wherein the support main body is sleeved outside the internal expansion bolt; the top part of the support main body is arc-shaped; the support main body is provided with a radial expansion wing; the expansion wing is composed of a plurality of wing fins; an expansion gap is formed between each wing fin; the internal expansion bolt is provided with an expansion section; after the internal expansion bolt is arranged in the support main body, the expansion wing can be opened by the expansion section; and the support main body is in threaded connection with the internal expansion bolt. According to the invention, the support body is fixed below the whirlbone or is fixed in bone tissues around a femoral neck through the expansion of a partial structure after the support body is planted on a predetermined position below the collapsing position of the whirlbone; the support body disclosed by the invention does not need to make cortical bone on the lower part of a whirlbone greater trochanter as support mechanics basis; therefore, the support body can be relatively short so that a osteotomy space between the greater trochanter and a lesser trochanter is kept in a future total hip replacement without taking out the support body deliberately.
Owner:BEIJING AKEC MEDICAL
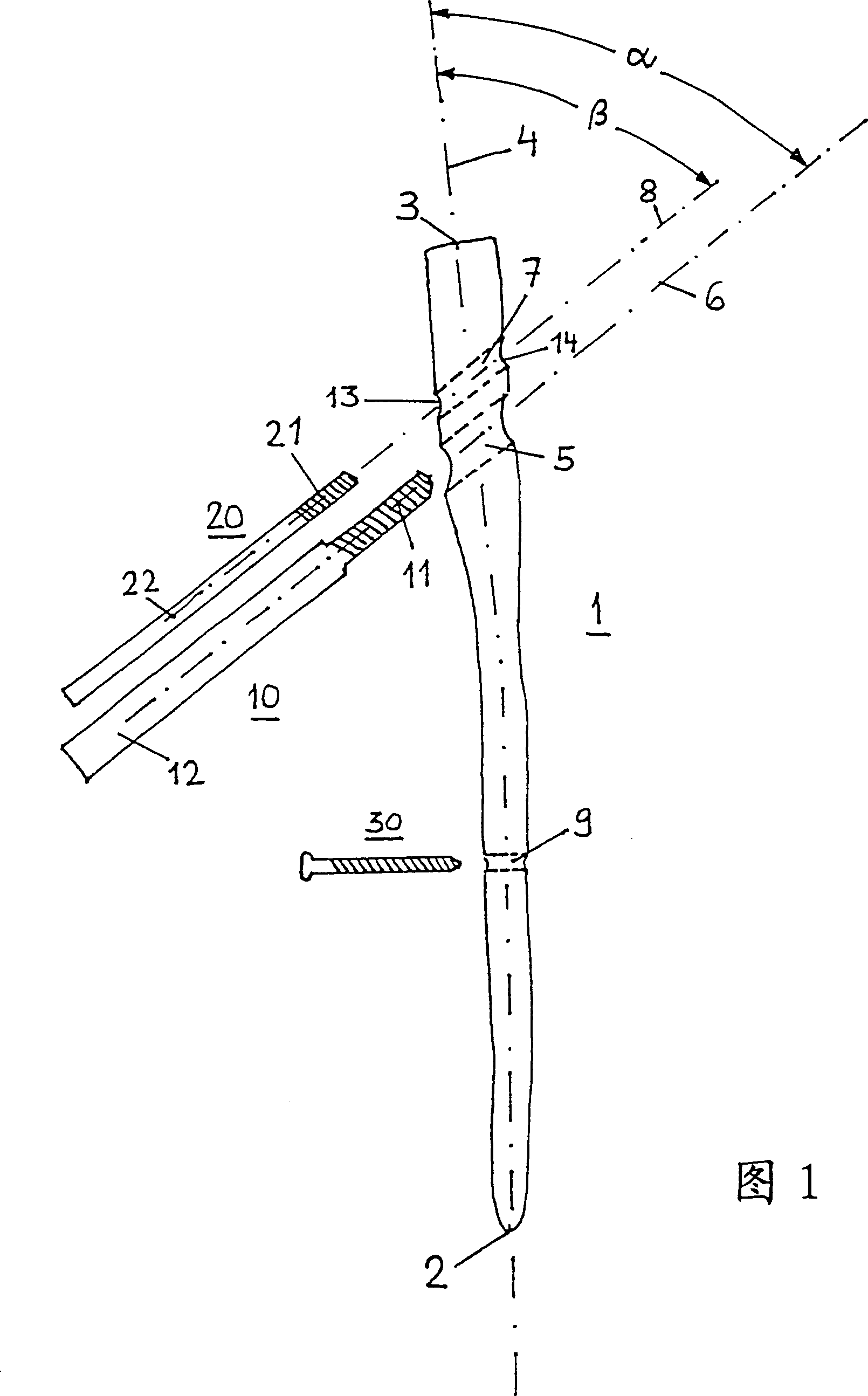
Intramedullary nail
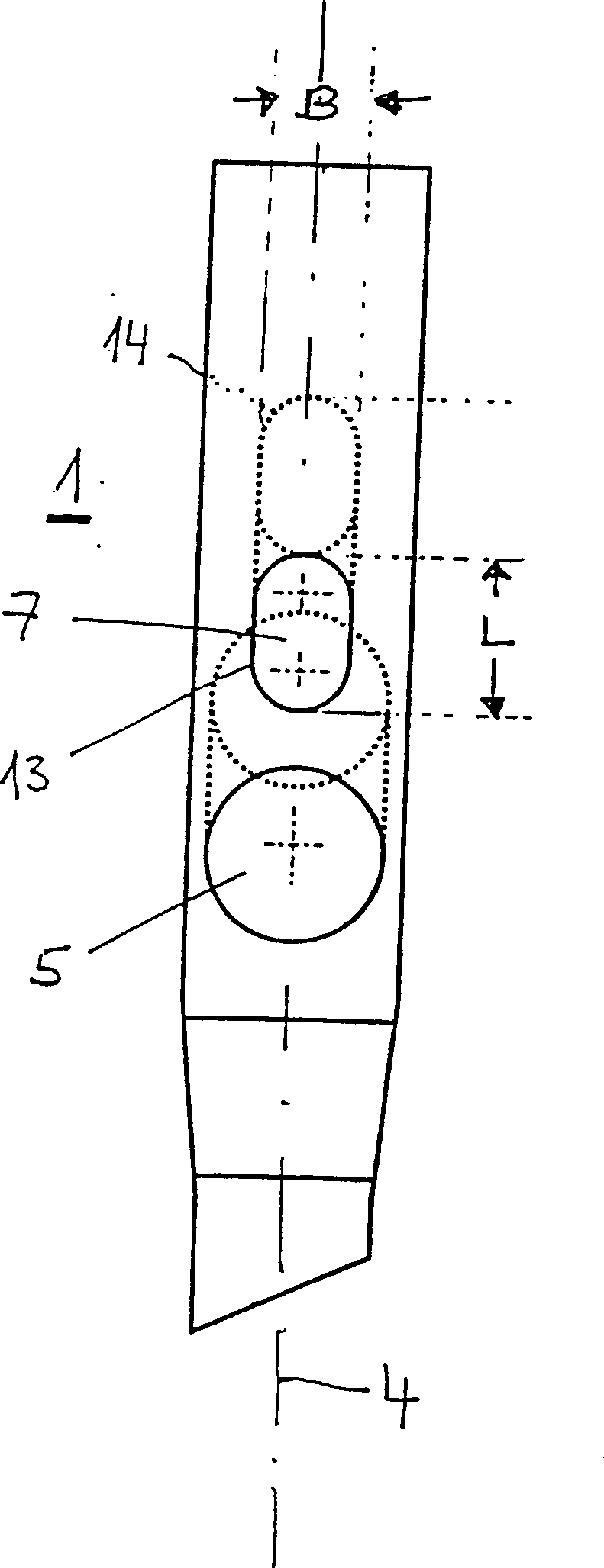
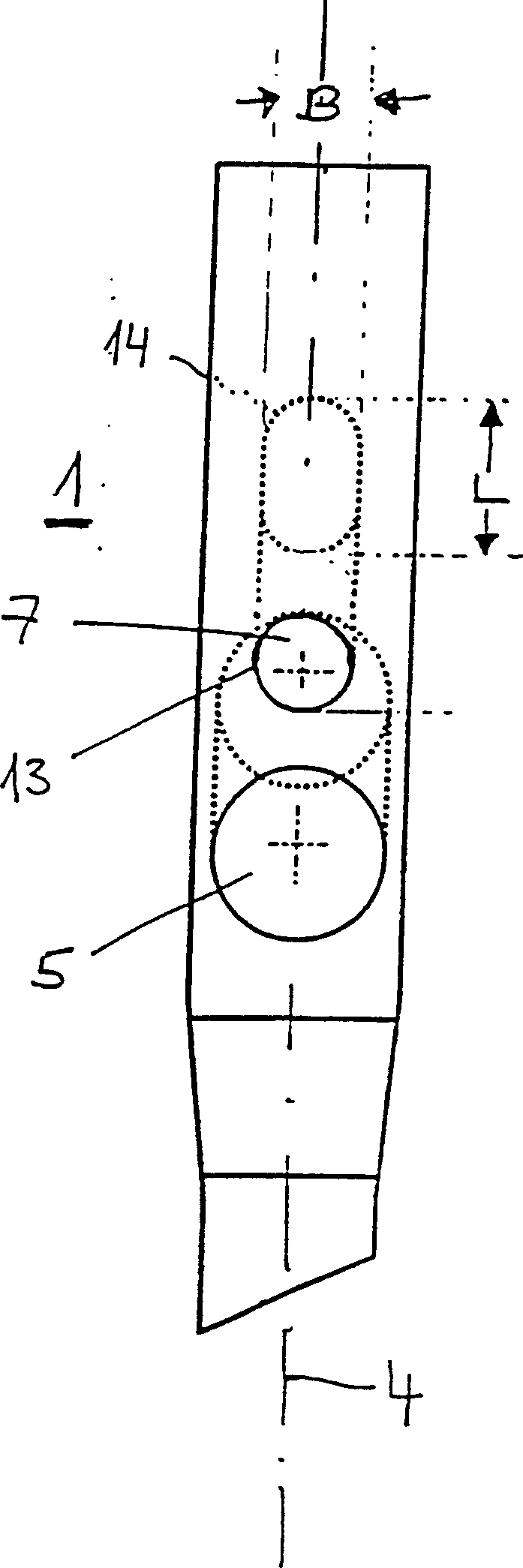
Intramedullary nails (1) are used to treat femur fractures. It has a distal end (2) determined for insertion into the medullary canal, a proximal end (3) and a longitudinal axis (4). A first hole (5) near the proximal end (3) and transversely intersecting the longitudinal axis (4) is used to accommodate a femoral head screw (10), wherein the center line (6) of the first hole (5) is in line with the The longitudinal axes intersect at an angle of 110° to 150°. A second hole (7) located between the first hole (5) and the proximal end (3) and transverse to the longitudinal axis (4) receives a hip pin (20). The second hole (7) is at least partially formed as a long hole, which has a width B and a length L>B, wherein the length of the long hole is distributed along the direction of the longitudinal axis (4).
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
Apparatus and method for minimally invasive total joint replacement
InactiveUS7559928B2Precise preparationExposure was also limitedDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsArticular surfacesArticular surface
A method and apparatus for minimally invasive total joint replacement is disclosed. The method involves sculpting the articular surface of a second bone that normally articulates with a first bone by attaching or supporting a bone sculpting tool directly or indirectly to the first bone with the tool in sculpting engagement with the articular surface of the second bone, and then sculpting the articular surface of the second bone with the joint reduced. The reamer system includes a reamer drive, a grater, a handle and a femoral broach.
Owner:CAYENNE MEDICAL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com