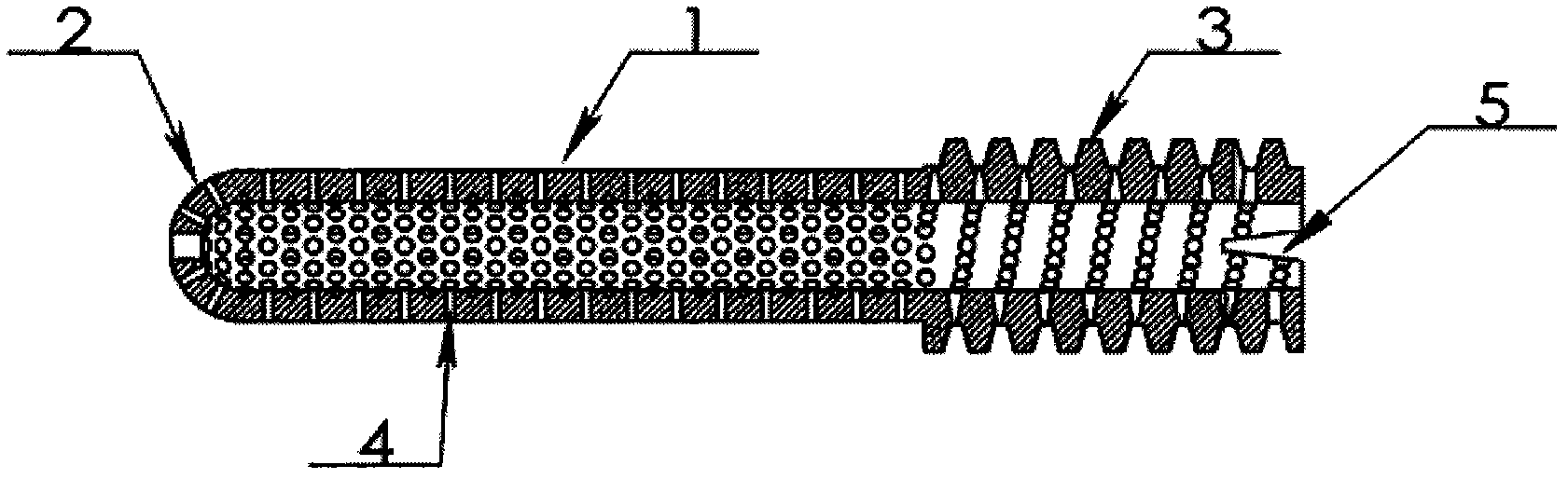
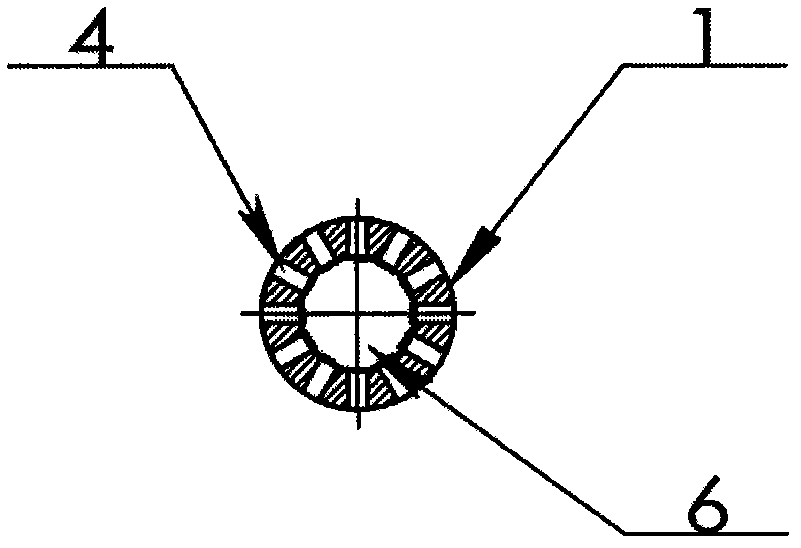
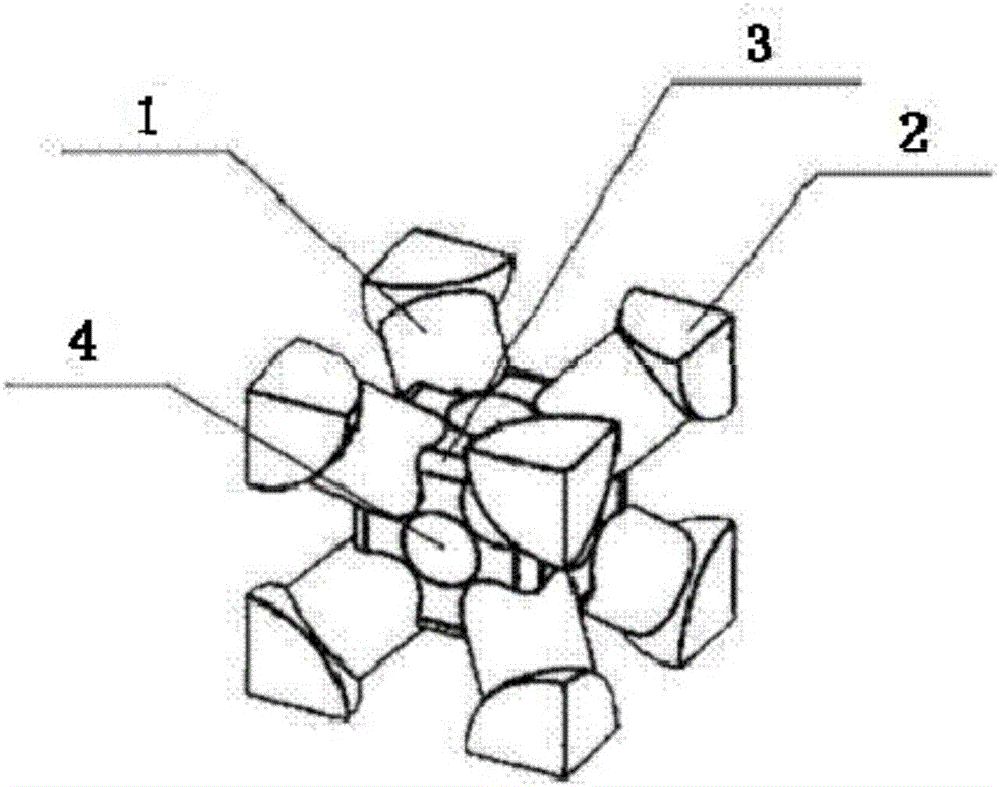
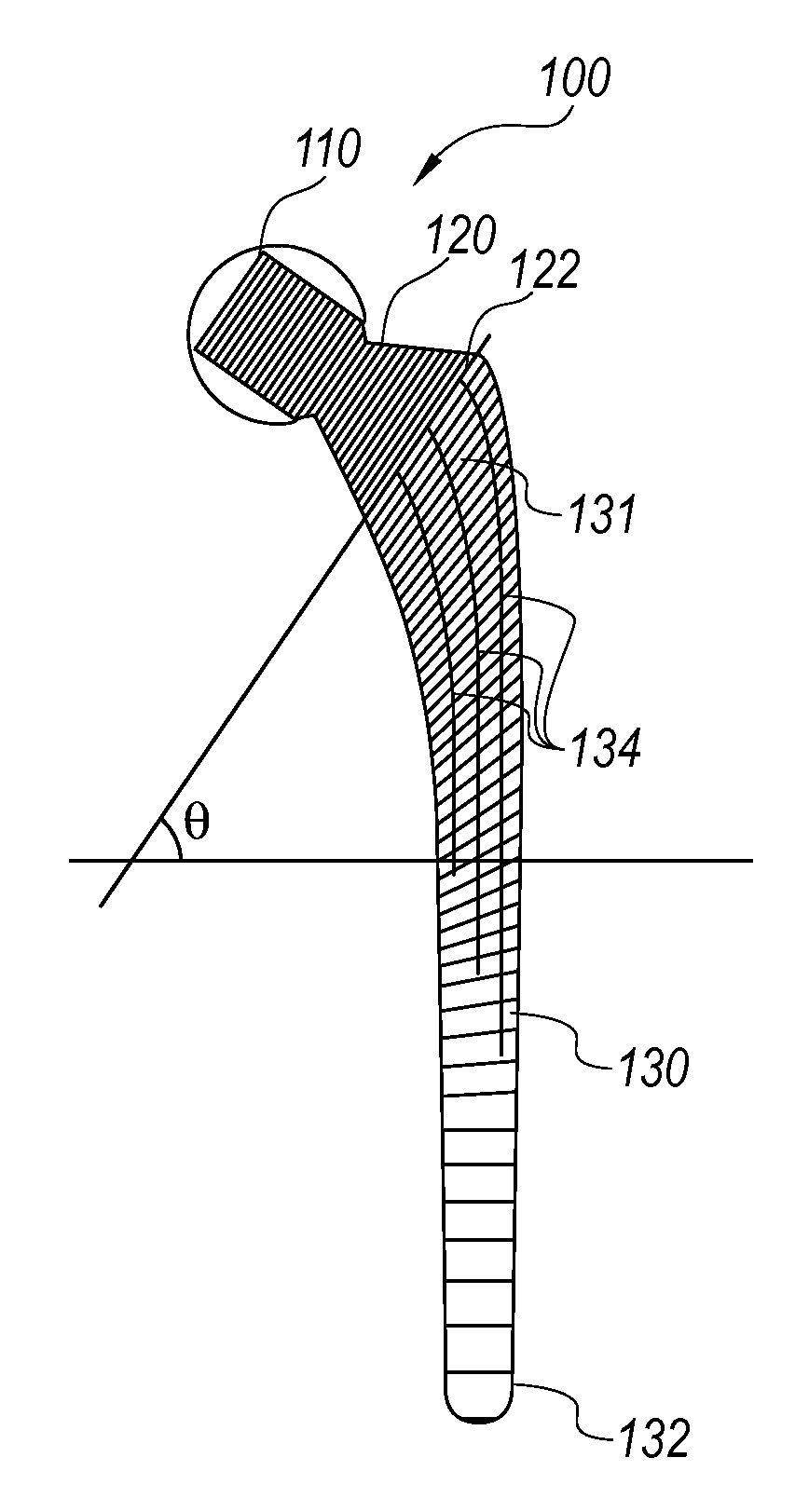
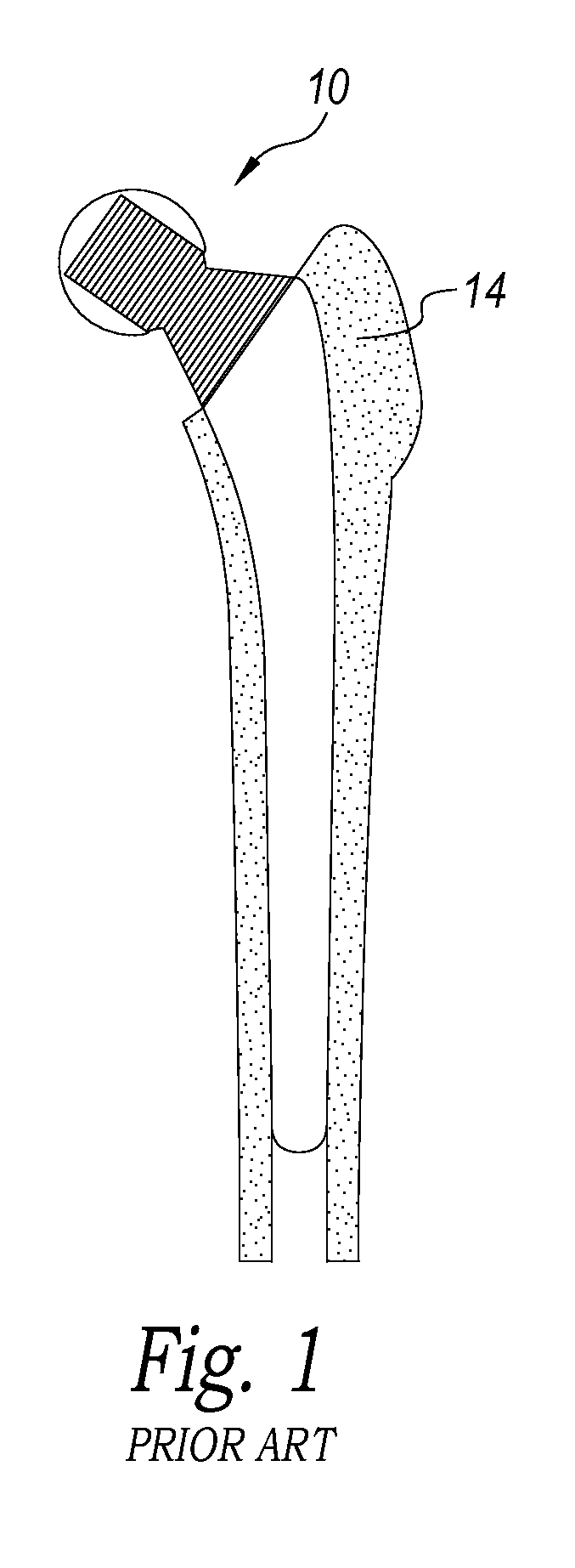
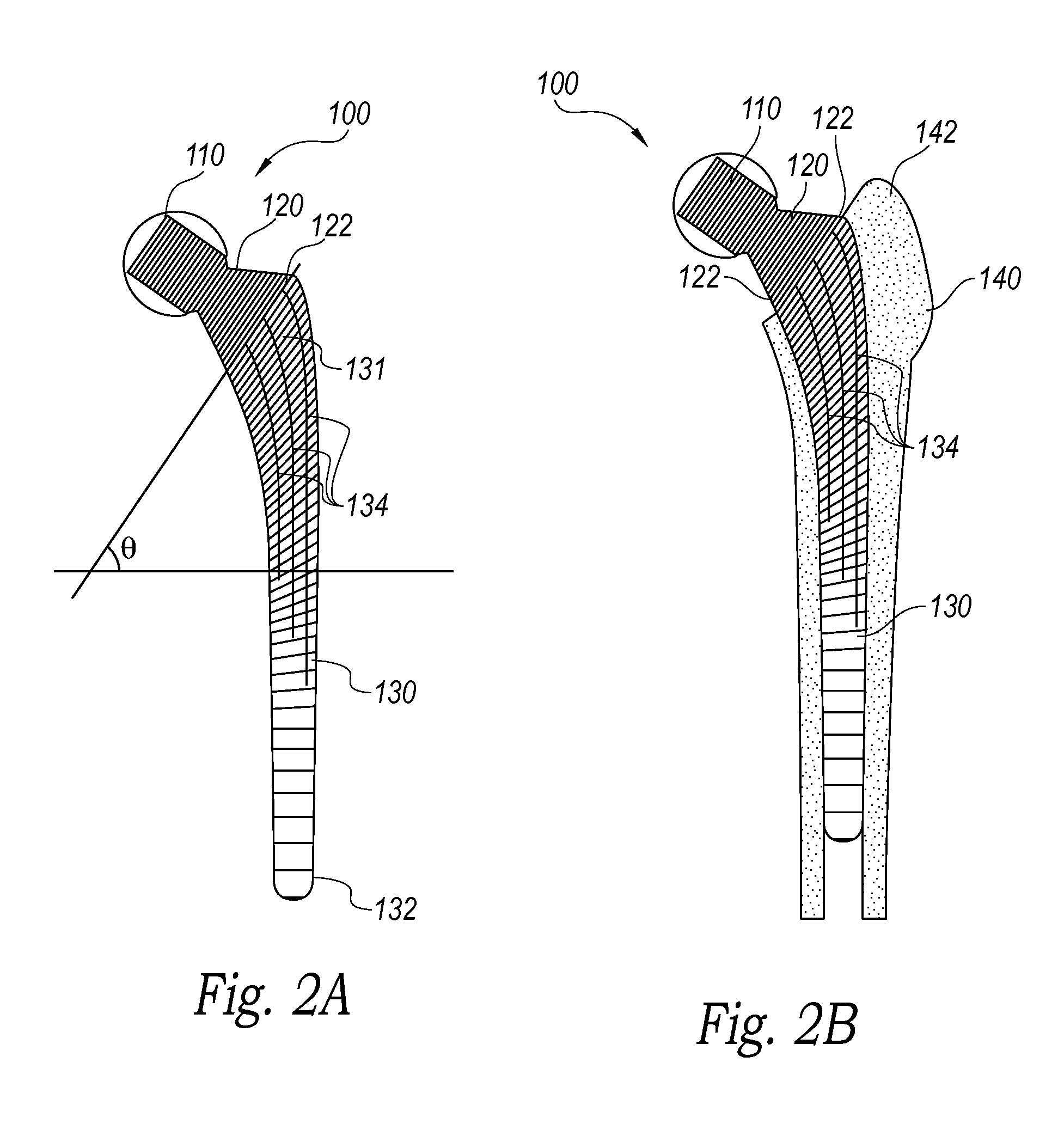
Patents
Literature
337 results about "Stress shielding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
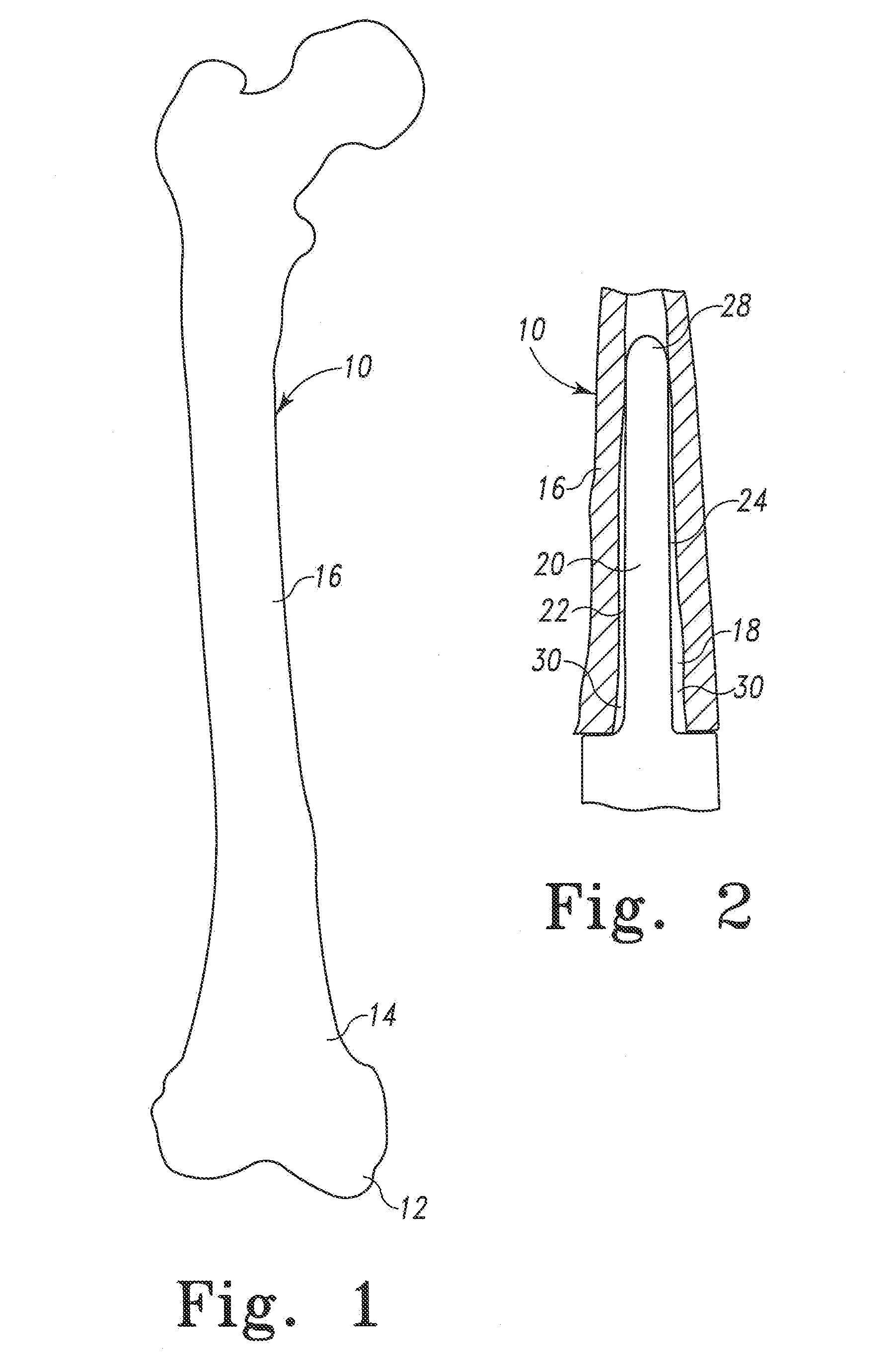
Stress shielding refers to the reduction in bone density (osteopenia) as a result of removal of typical stress from the bone by an implant (for instance, the femoral component of a hip prosthesis). This is because by Wolff's law, bone in a healthy person or animal will remodel in response to the loads it is placed under. Therefore, if the loading on a bone decreases, the bone will become less dense and weaker because there is no stimulus for continued remodeling that is required to maintain bone mass.
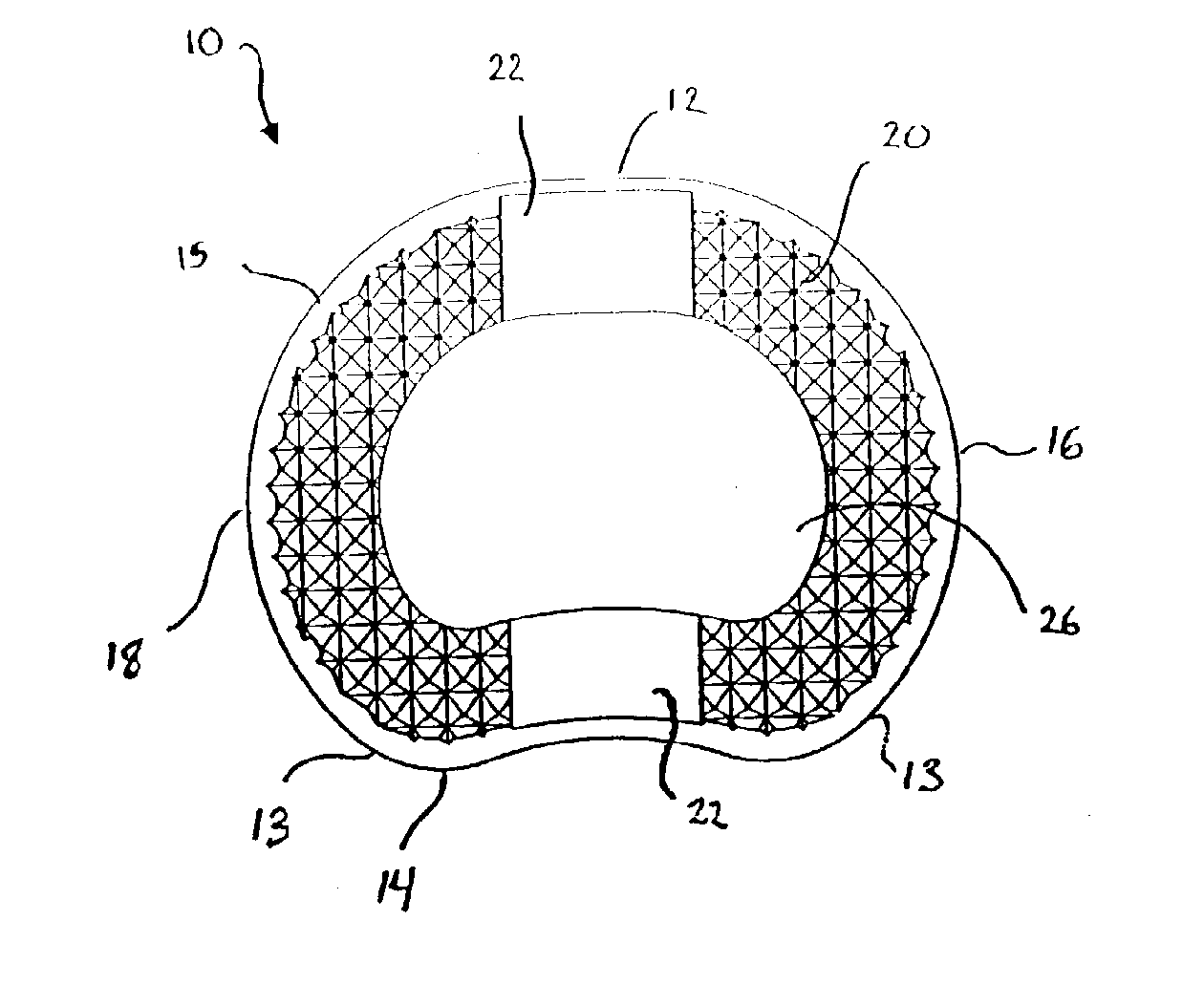
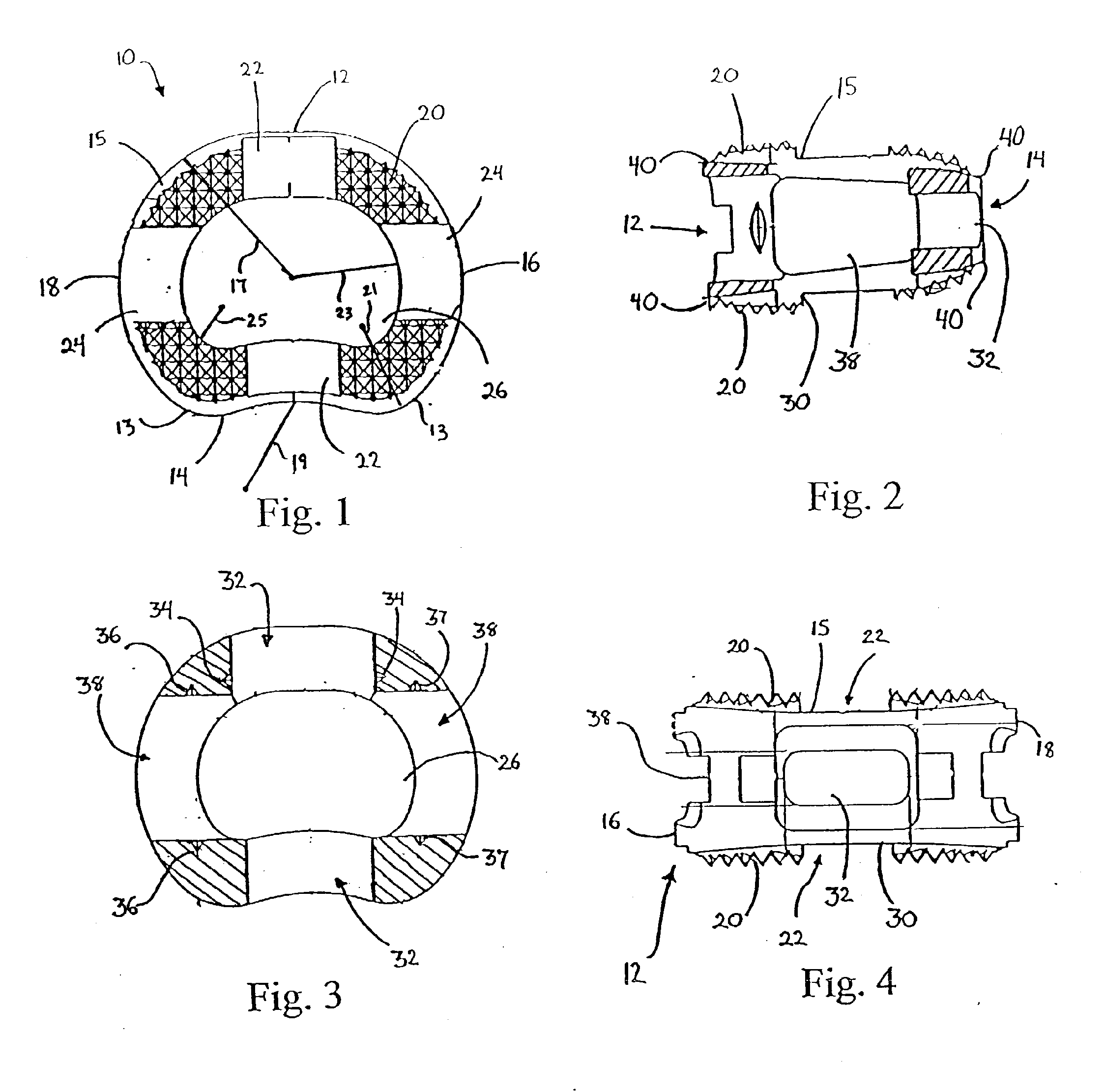
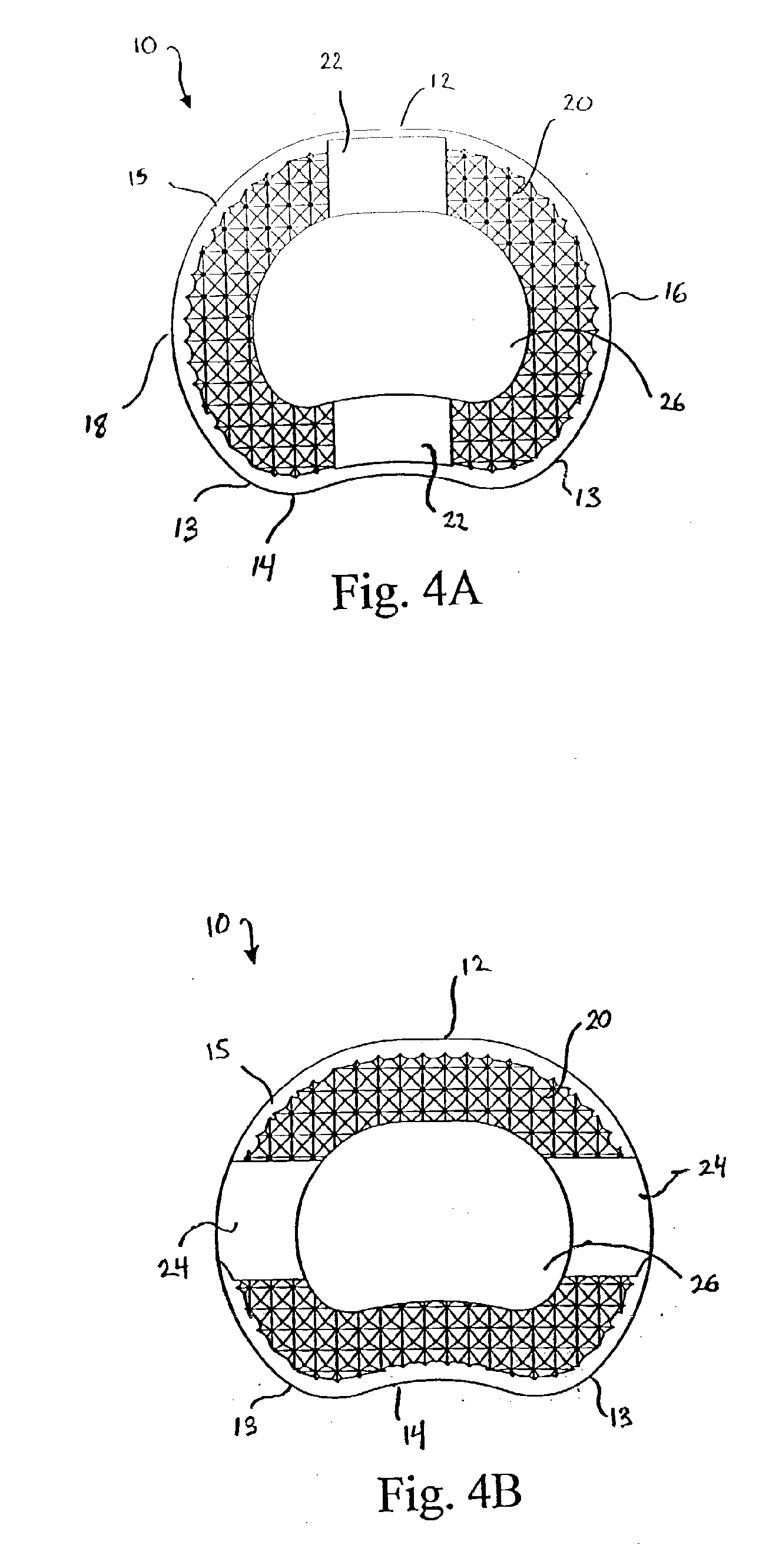
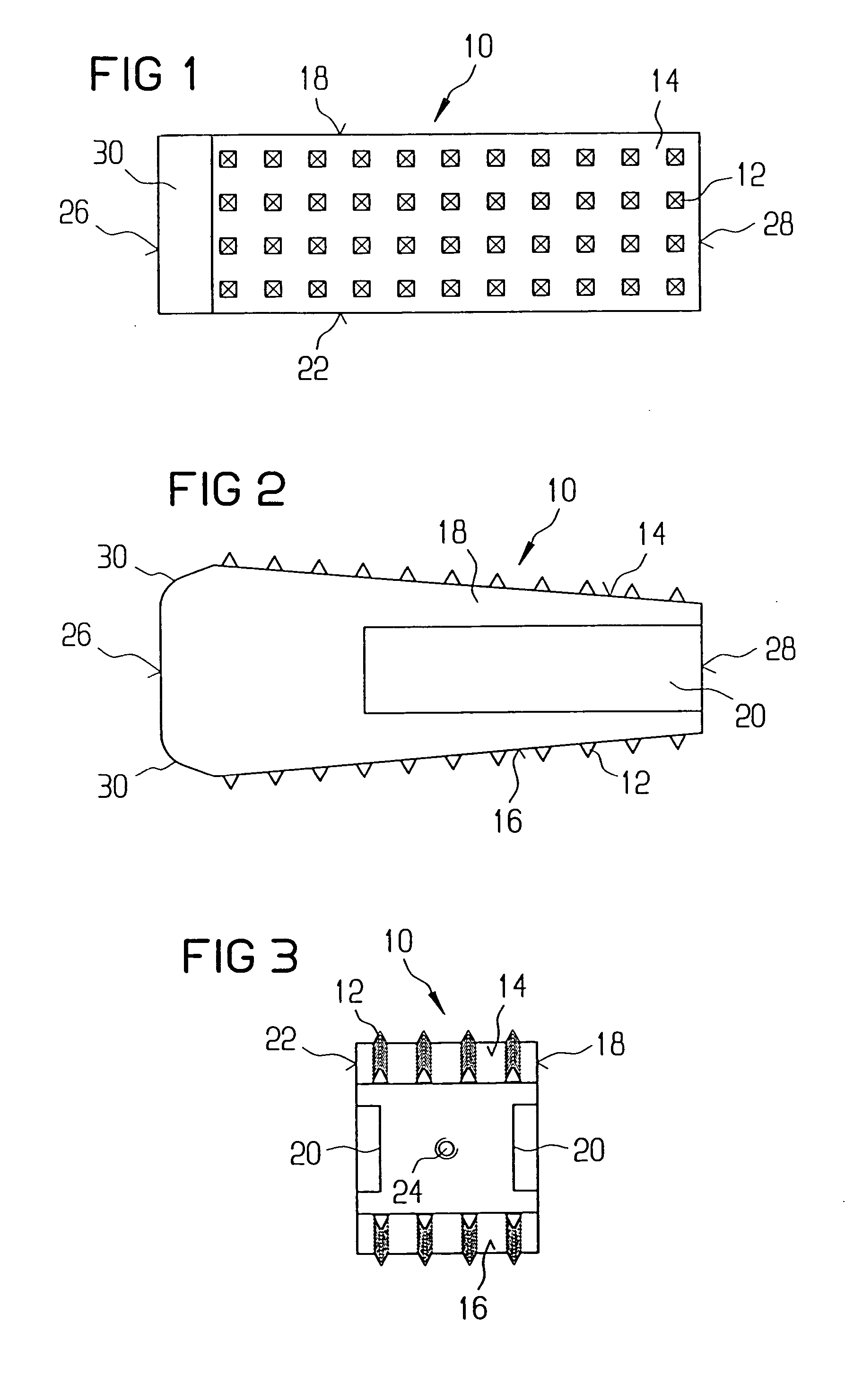
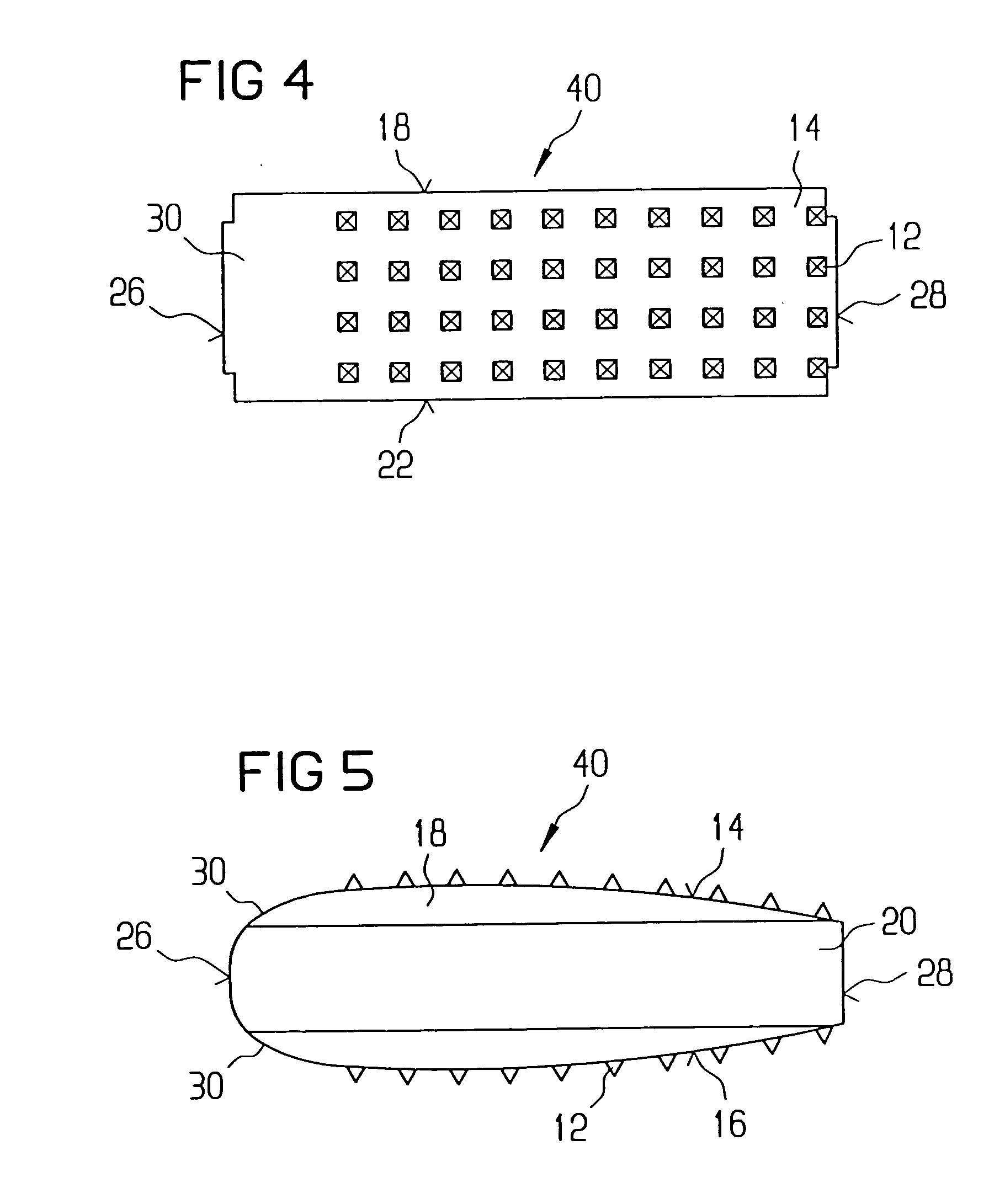
Intervertebral implant
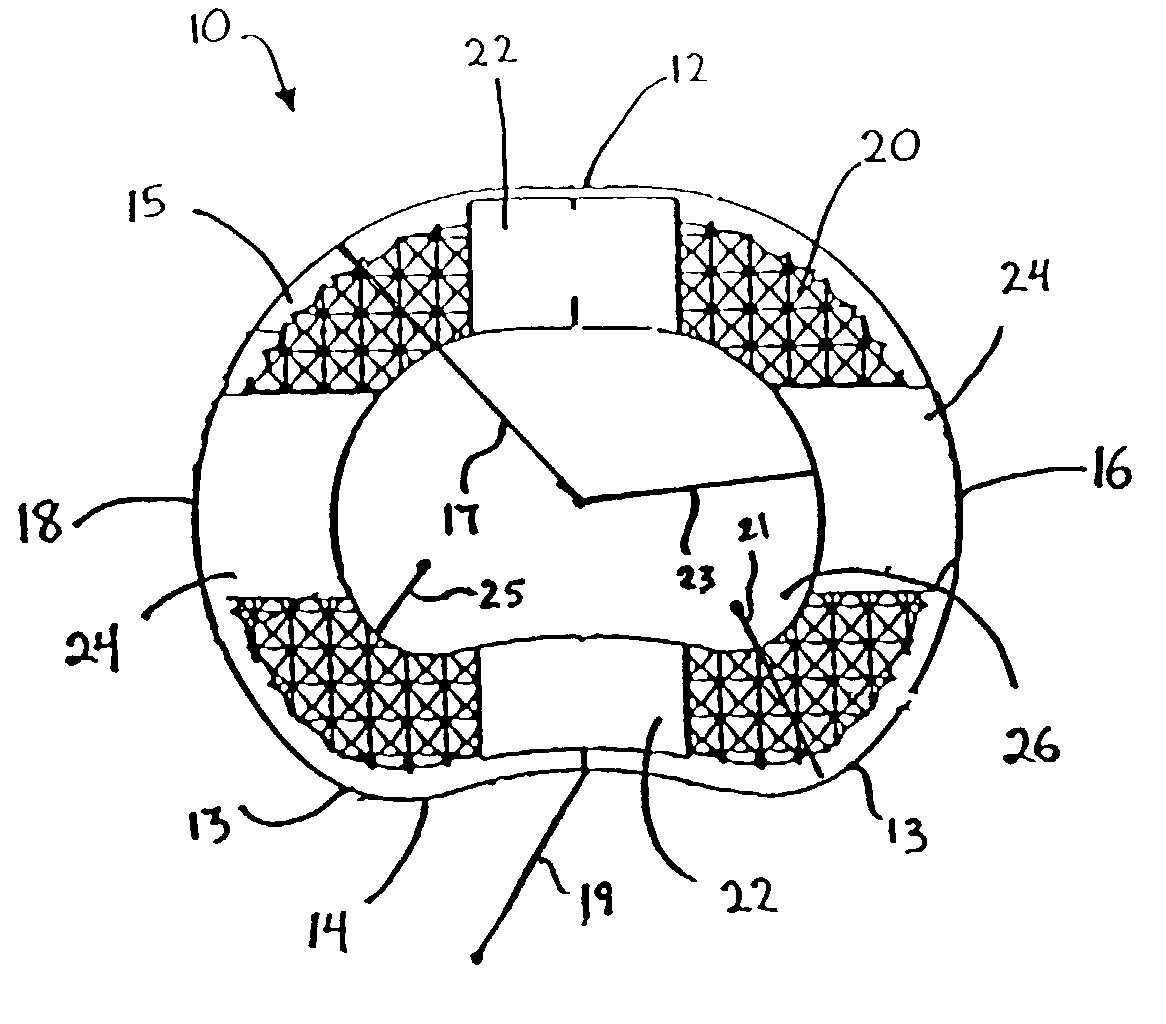
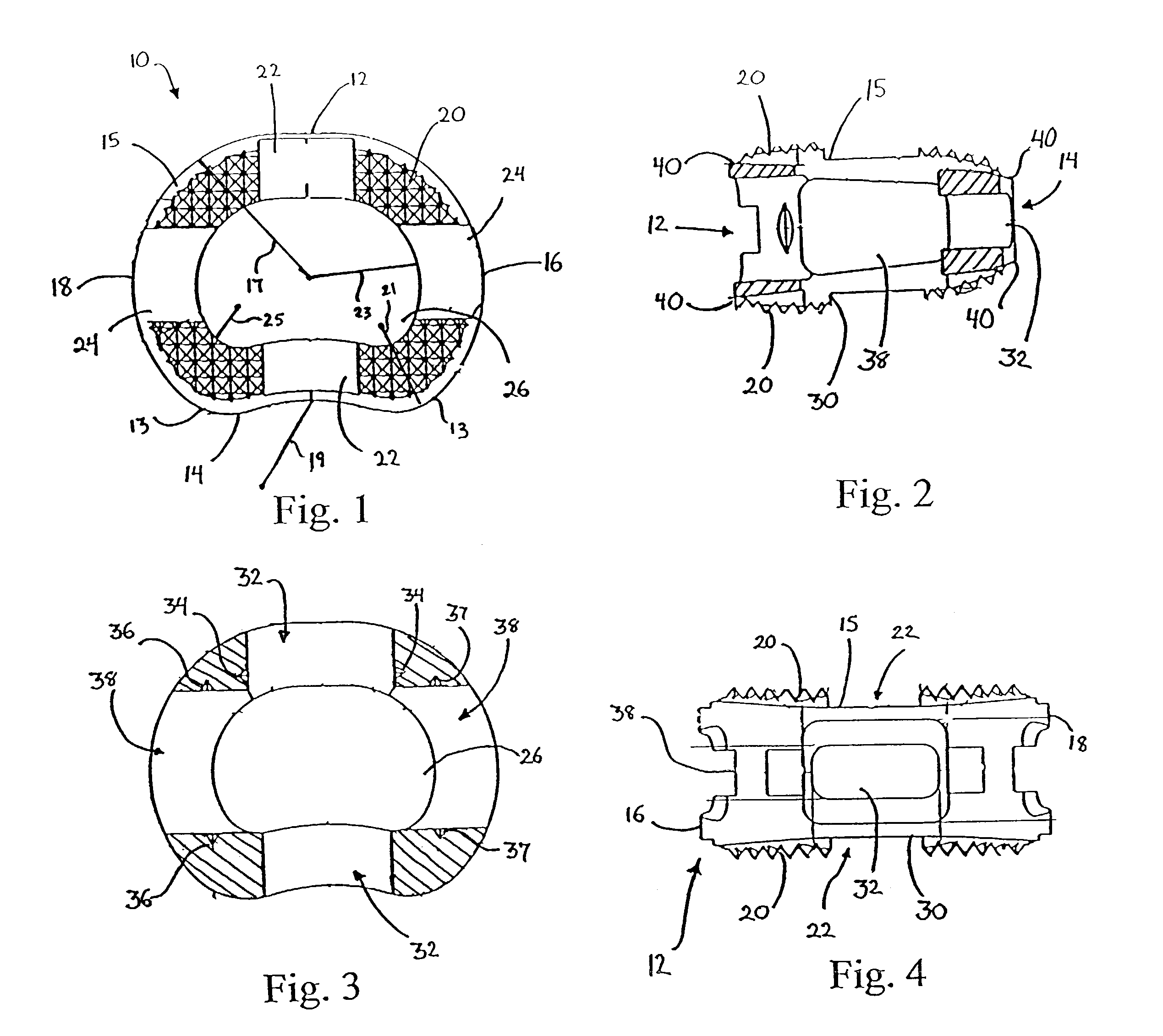
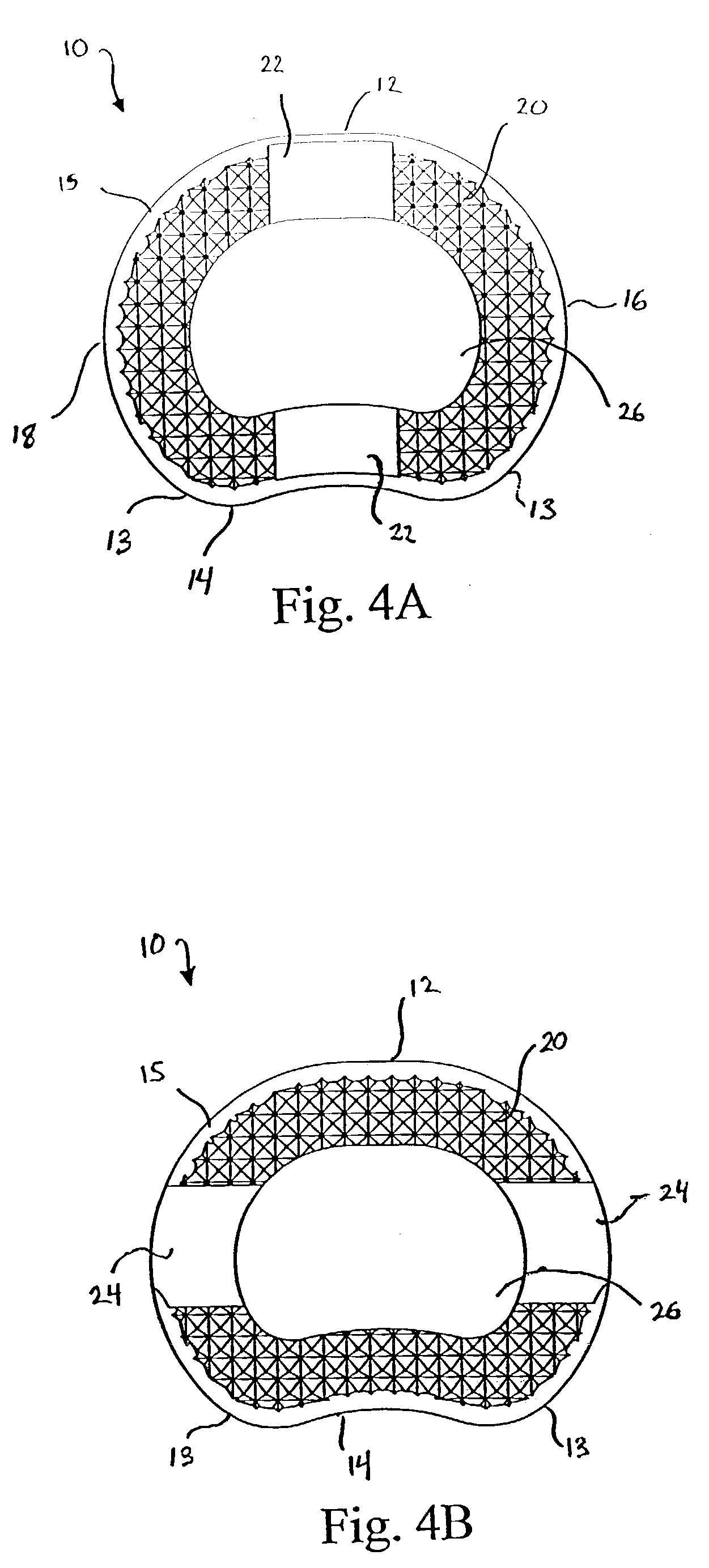
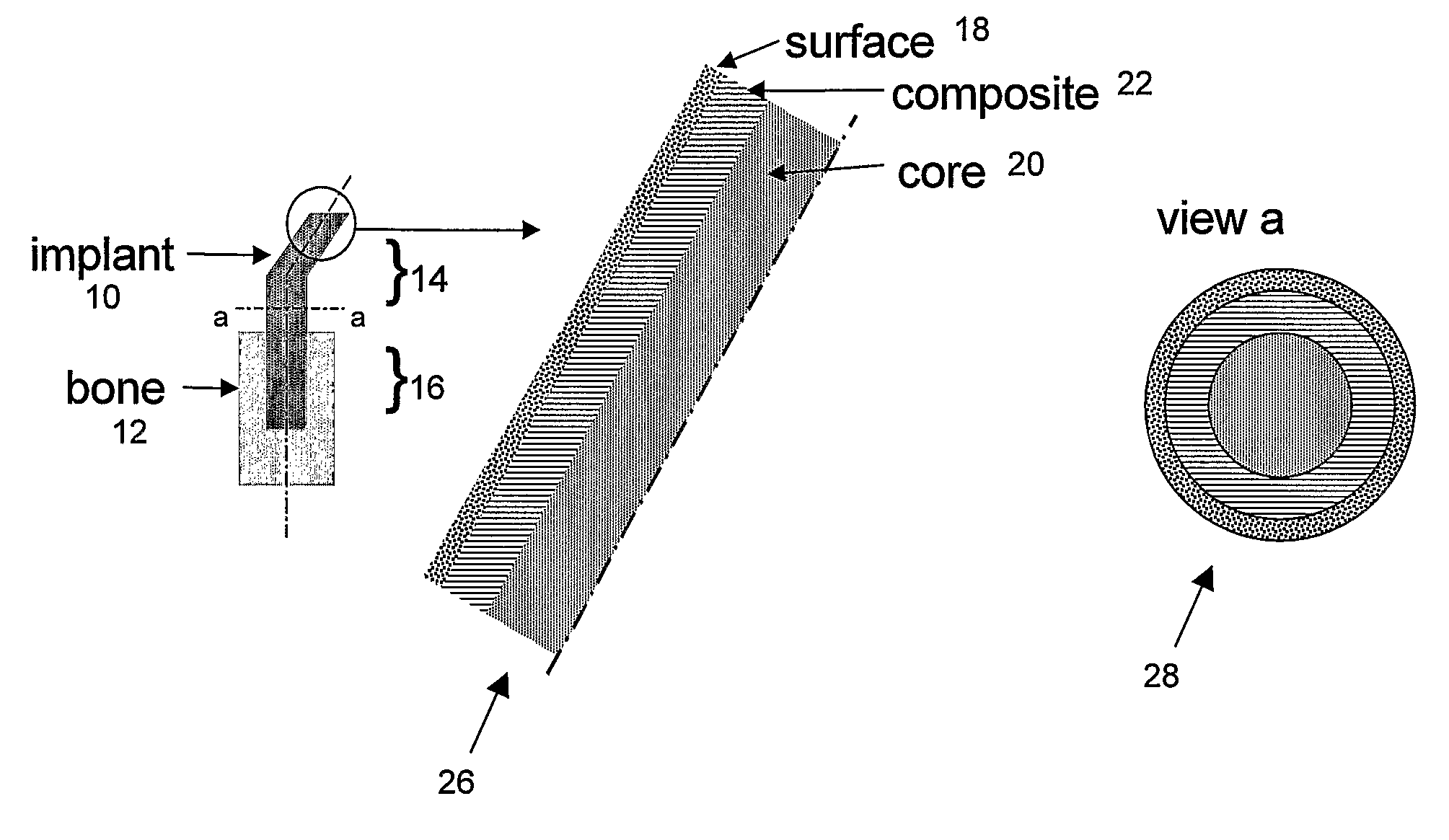
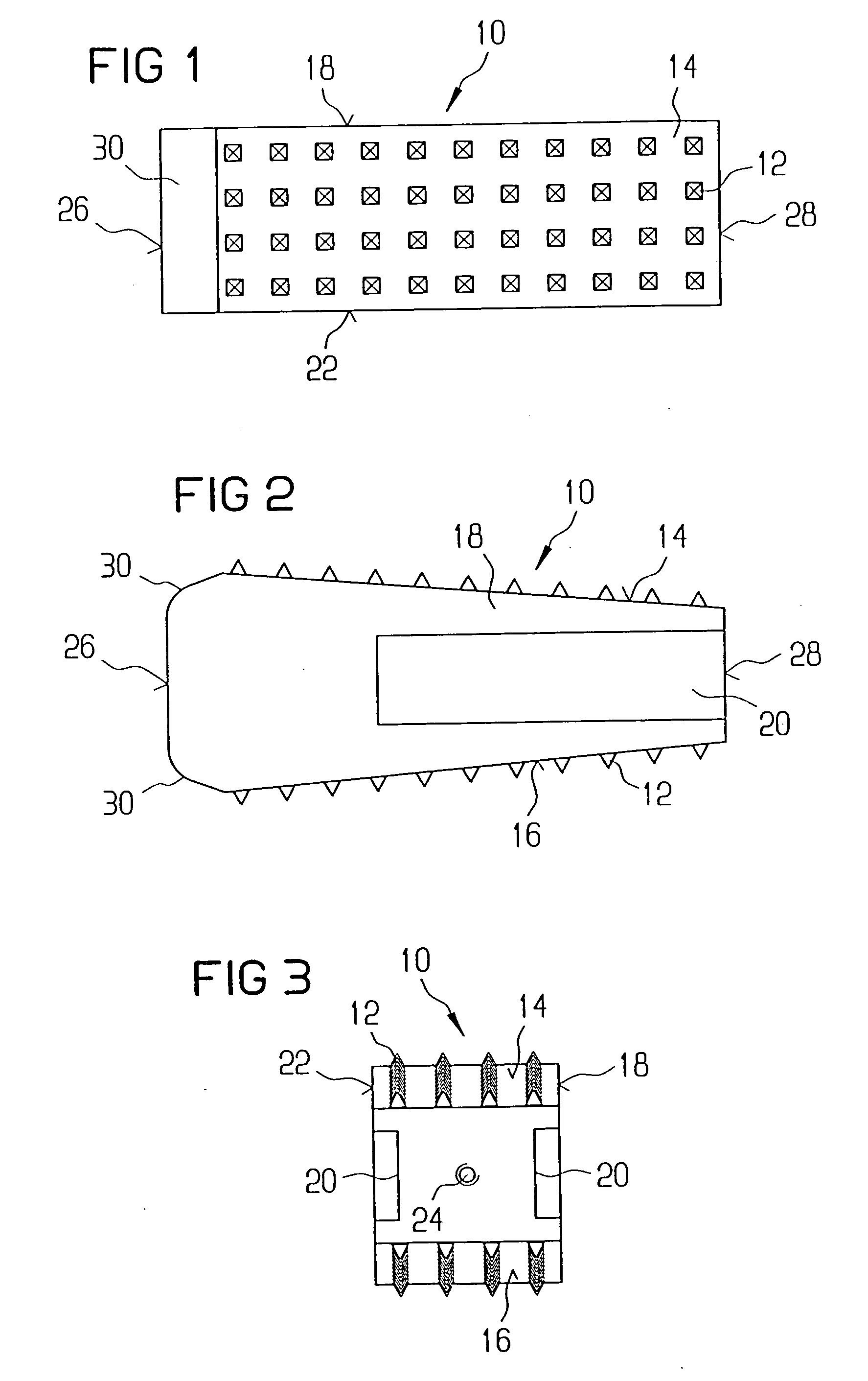
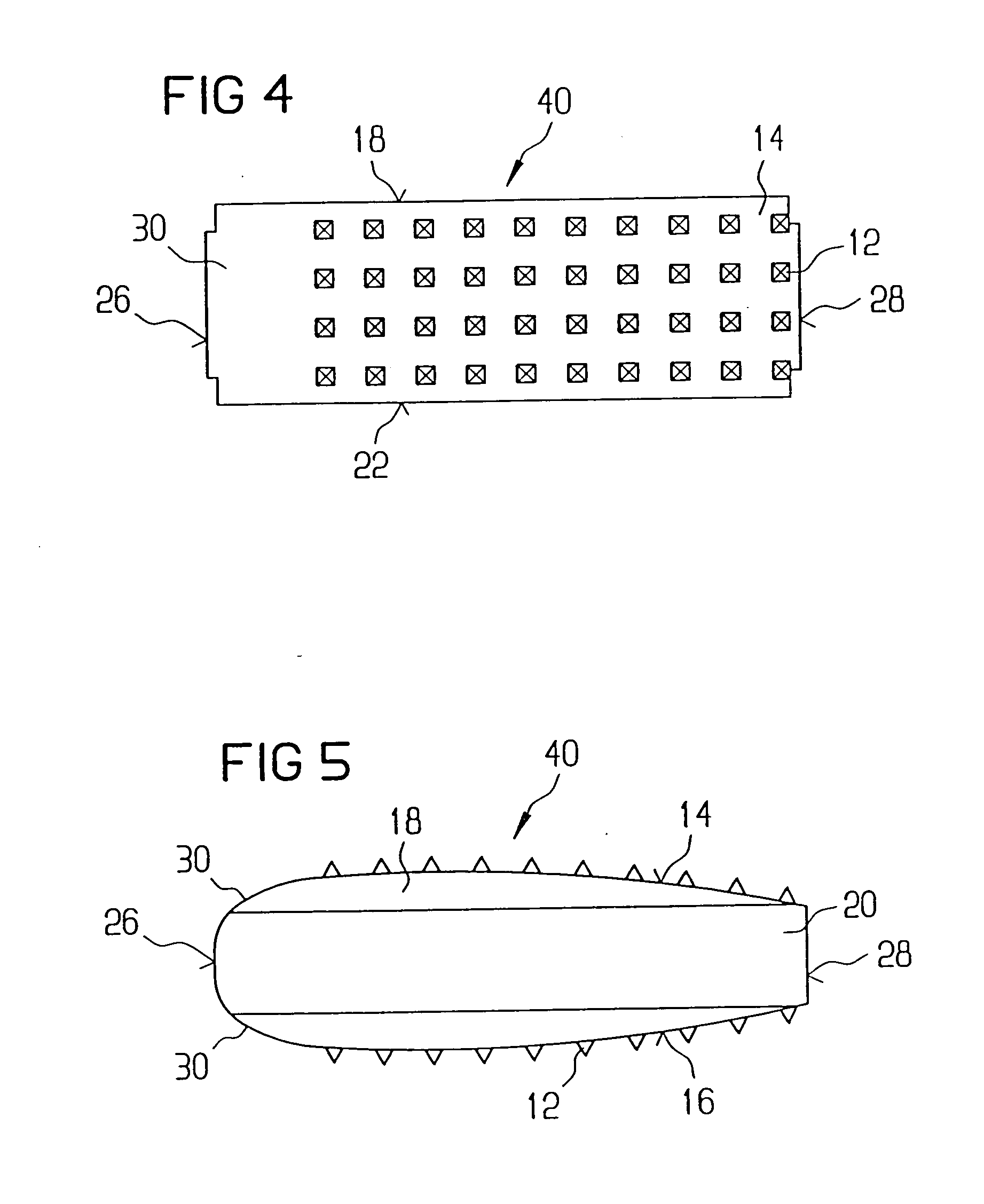
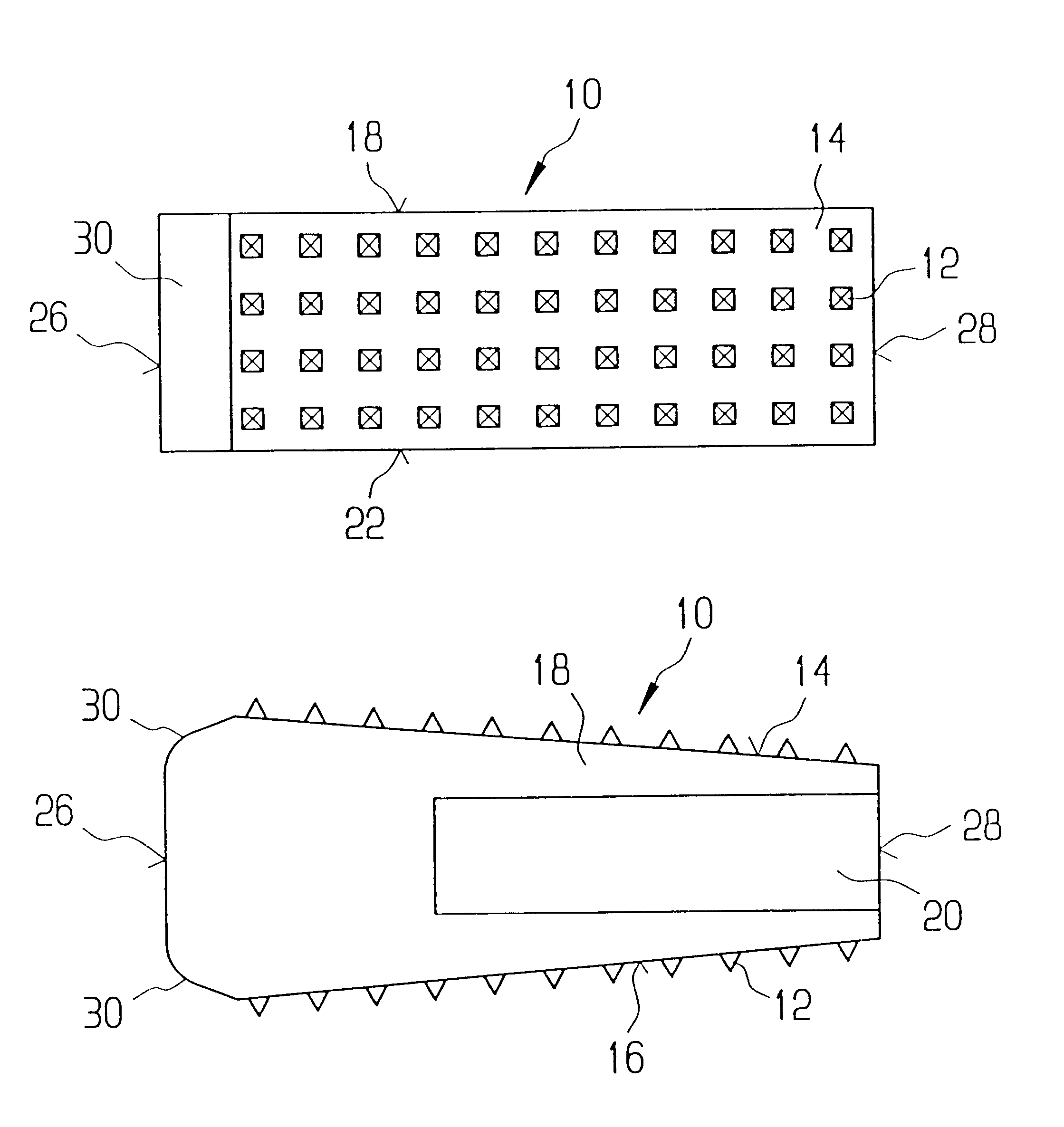
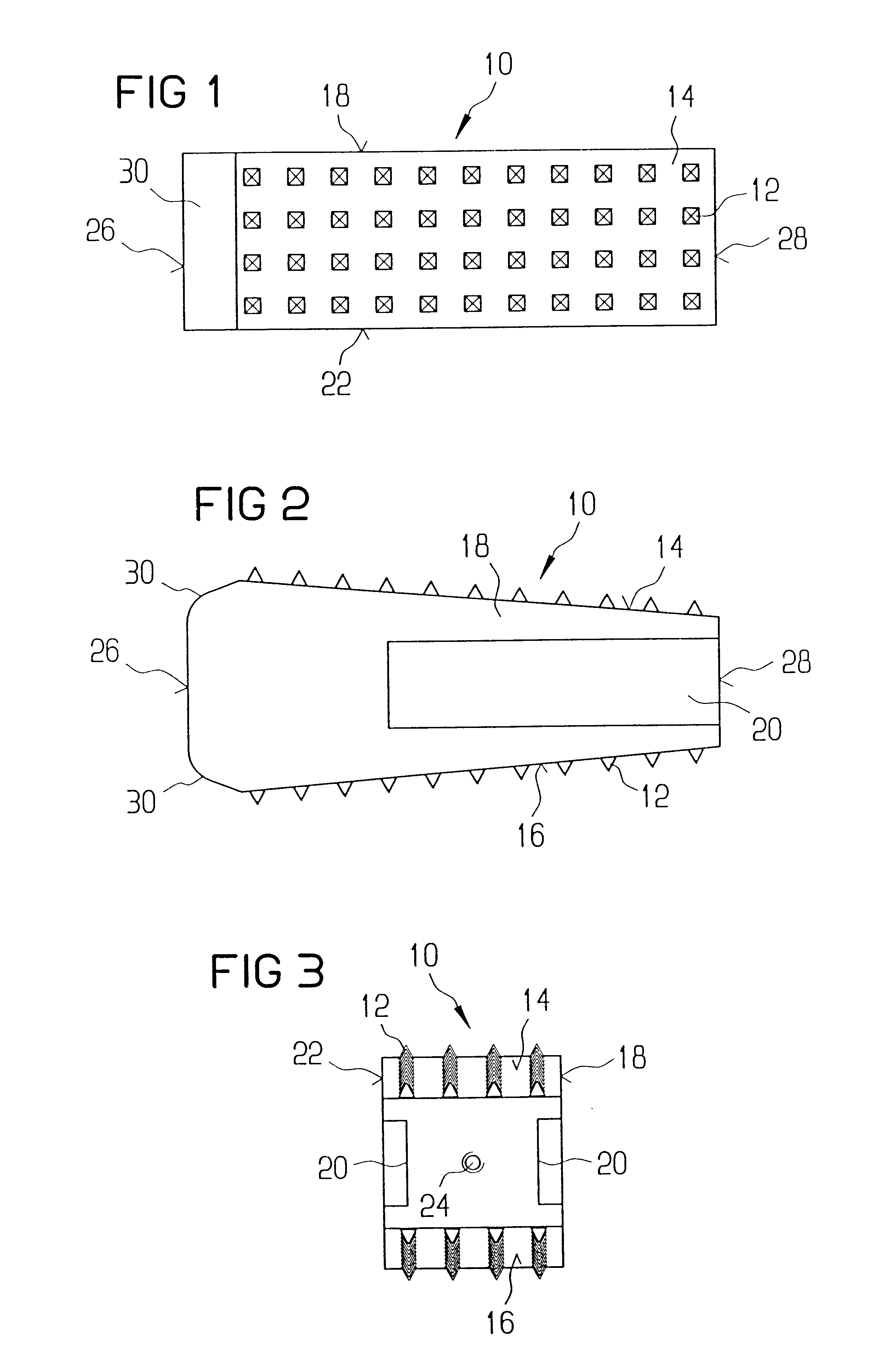
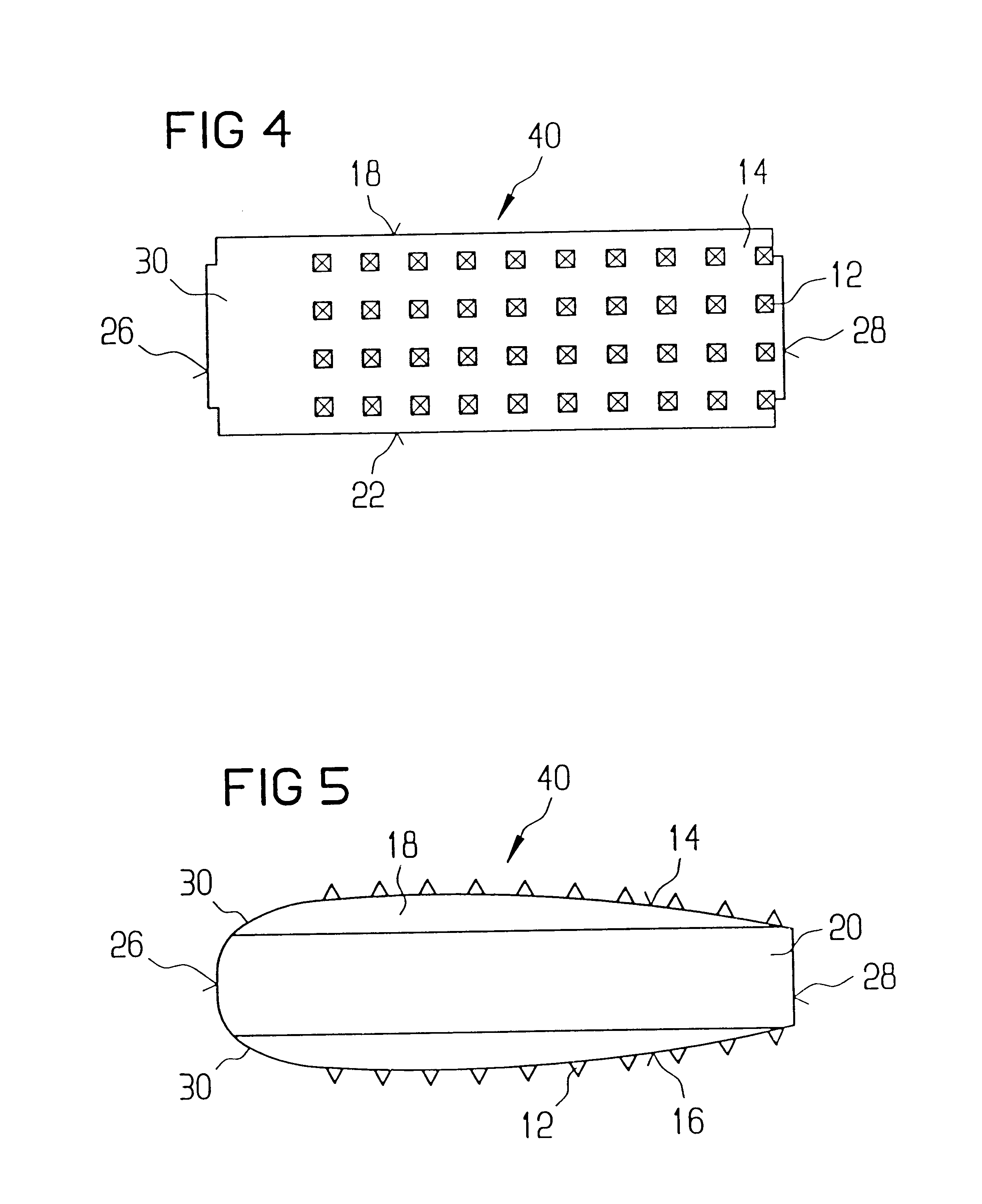
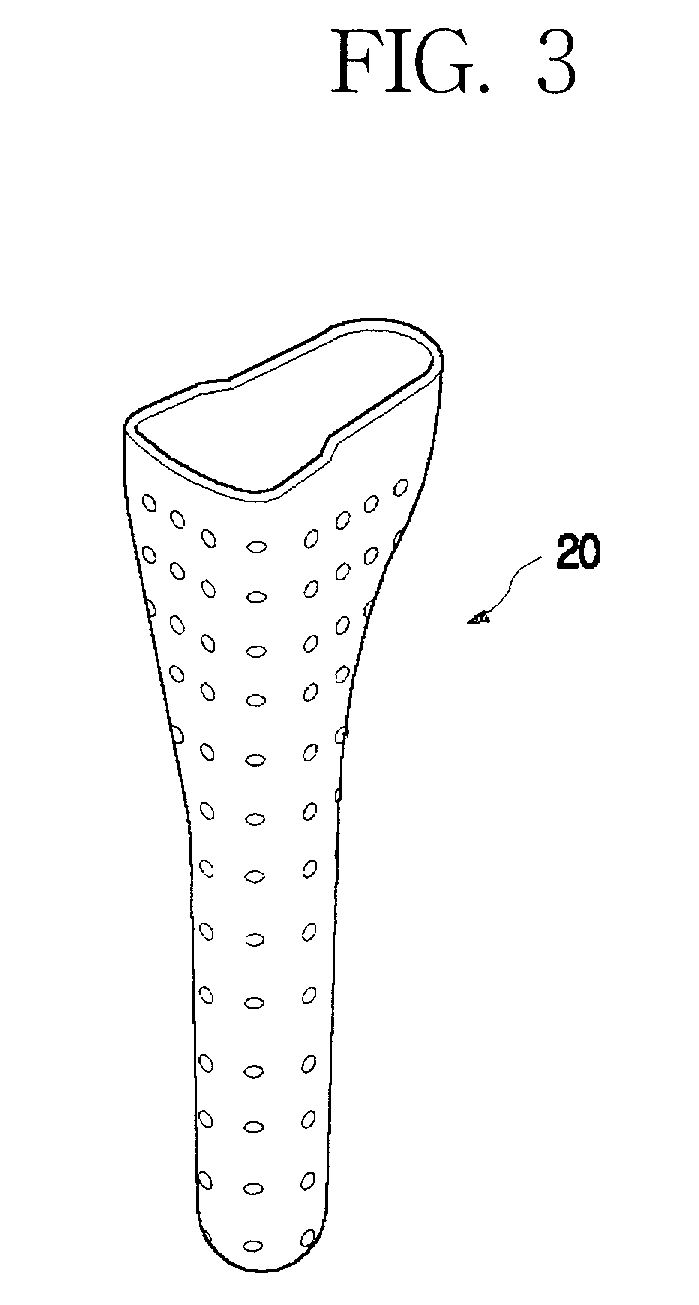
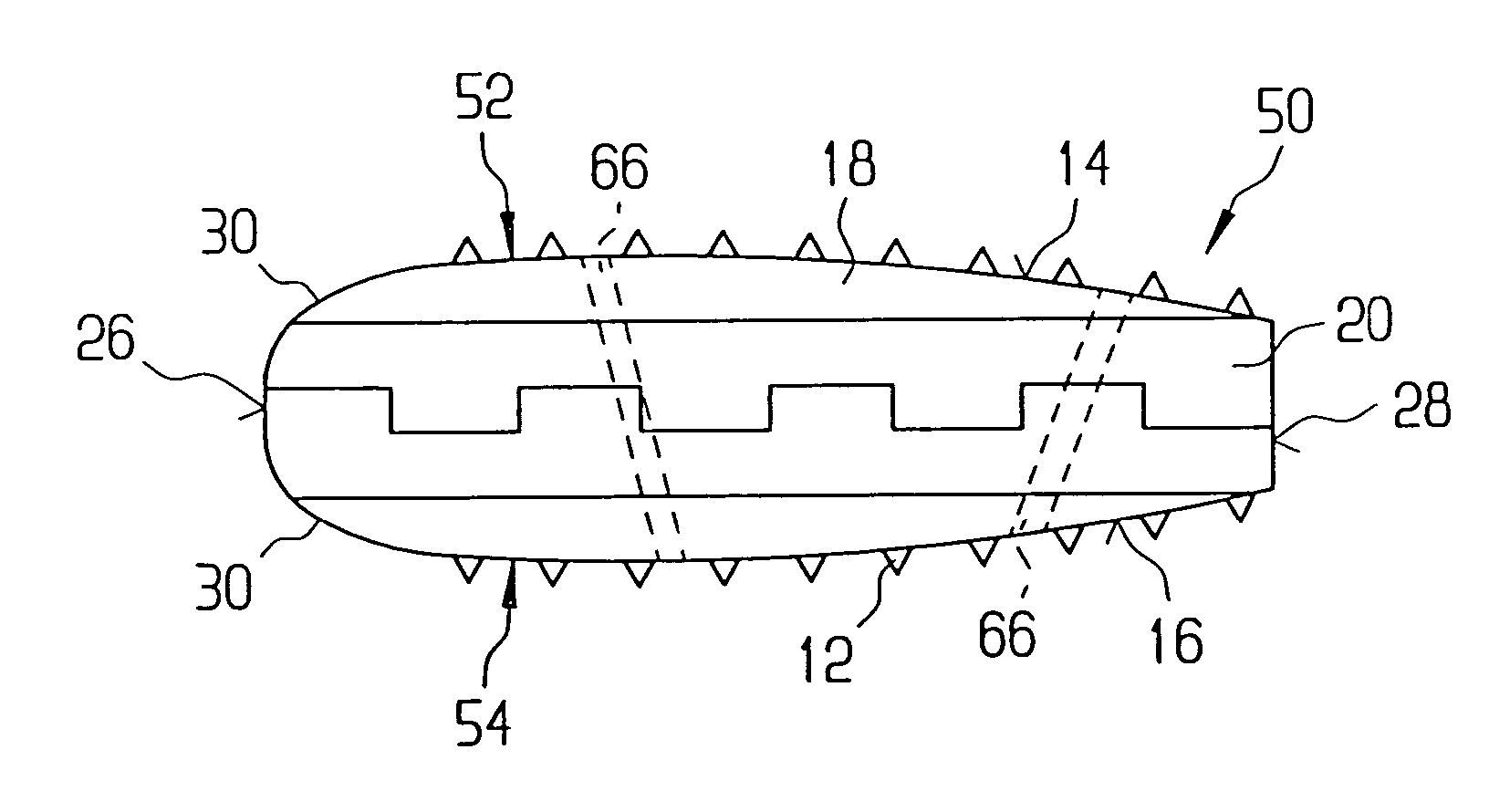
A vertebral implant for fusing adjacent vertebrae or for replacing vertebral bodies is disclosed. The implant is a biocompatible metal, resorbable, or radiolucent implant conforming substantially in size and shape with an end plate of a vertebra. The implant preferably has a wedge-shaped profile to restore disc height and the natural curvature of the spine. The top and bottom surfaces of the implant have areas with a plurality of teeth to resist expulsion and provide initial stability and areas devoid of any protrusions to receive implantation instrumentation. The implant also has a stackability feature. The implant provides initial stability needed for fusion without stress shielding.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Implantable biomimetic prosthetic bone
InactiveUS20090177282A1Reduce riskMolten spray coatingLamination ancillary operationsNormal boneFiber-reinforced composite
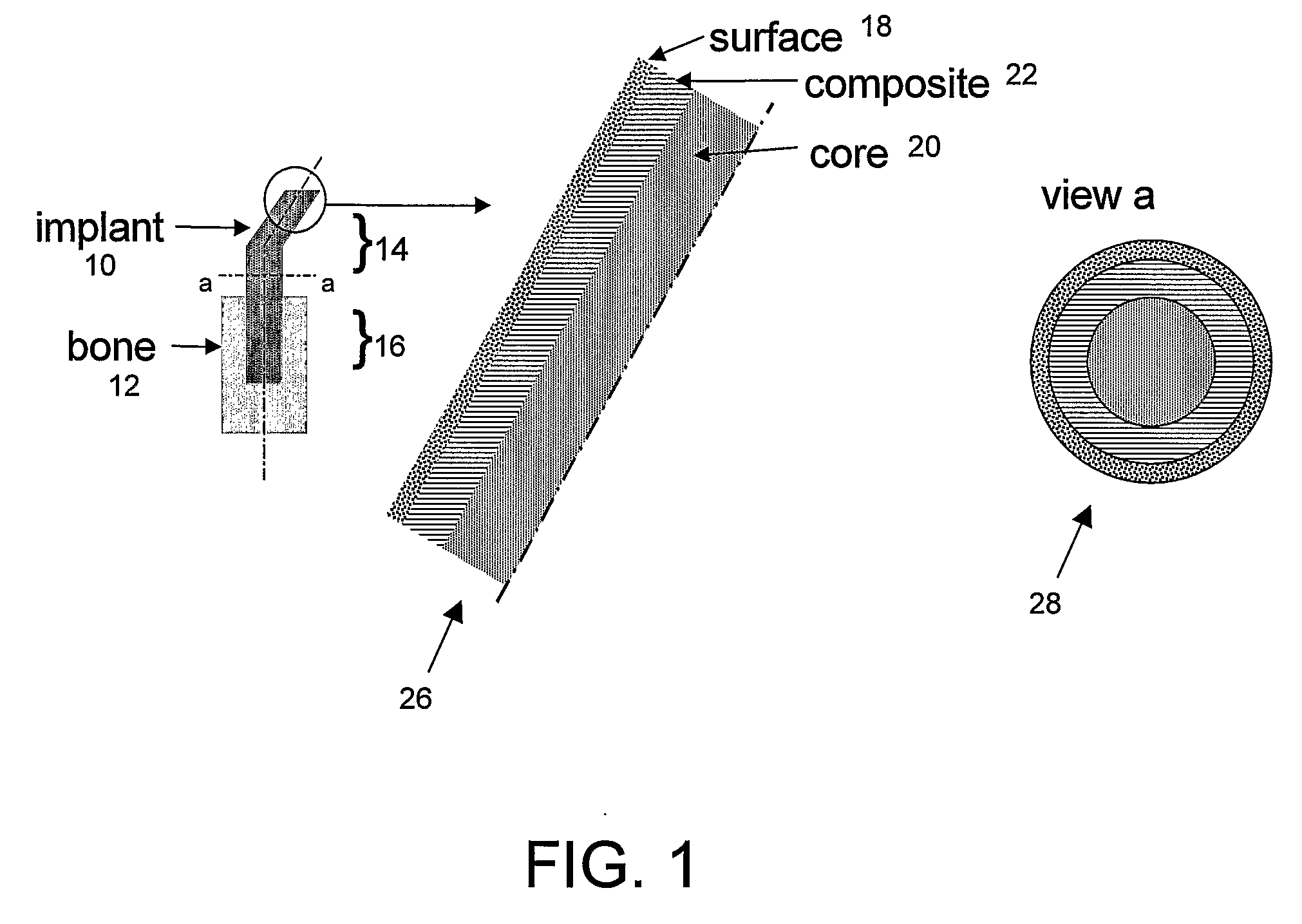
Bone tissue at the interface of a bone implant is shielded from stresses found in normal bone because of the higher stiffness or rigidity in the implant versus in bone. The resulting “stress shielding” of the bone by the implant eventually results in resorption of bone at the bone-implant interface and ultimately necessitates replacement of the bone implant. To overcome these problems, an implantable biomimetic prosthetic bone having a porous surface, a fiber-reinforced composite structure, and a polymer-based core is disclosed. The prosthetic bone is a good match for structure, stiffness, viscoelastic properties, specific weight and overall structure as real bone or host tissues adjacent to the prosthetic bone. The prosthetic bone may be formed as a total hip prosthesis.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Vertebral Stabilizer
ActiveUS20080234736A1Improve the immunitySmooth motionInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsEngineeringStress shielding
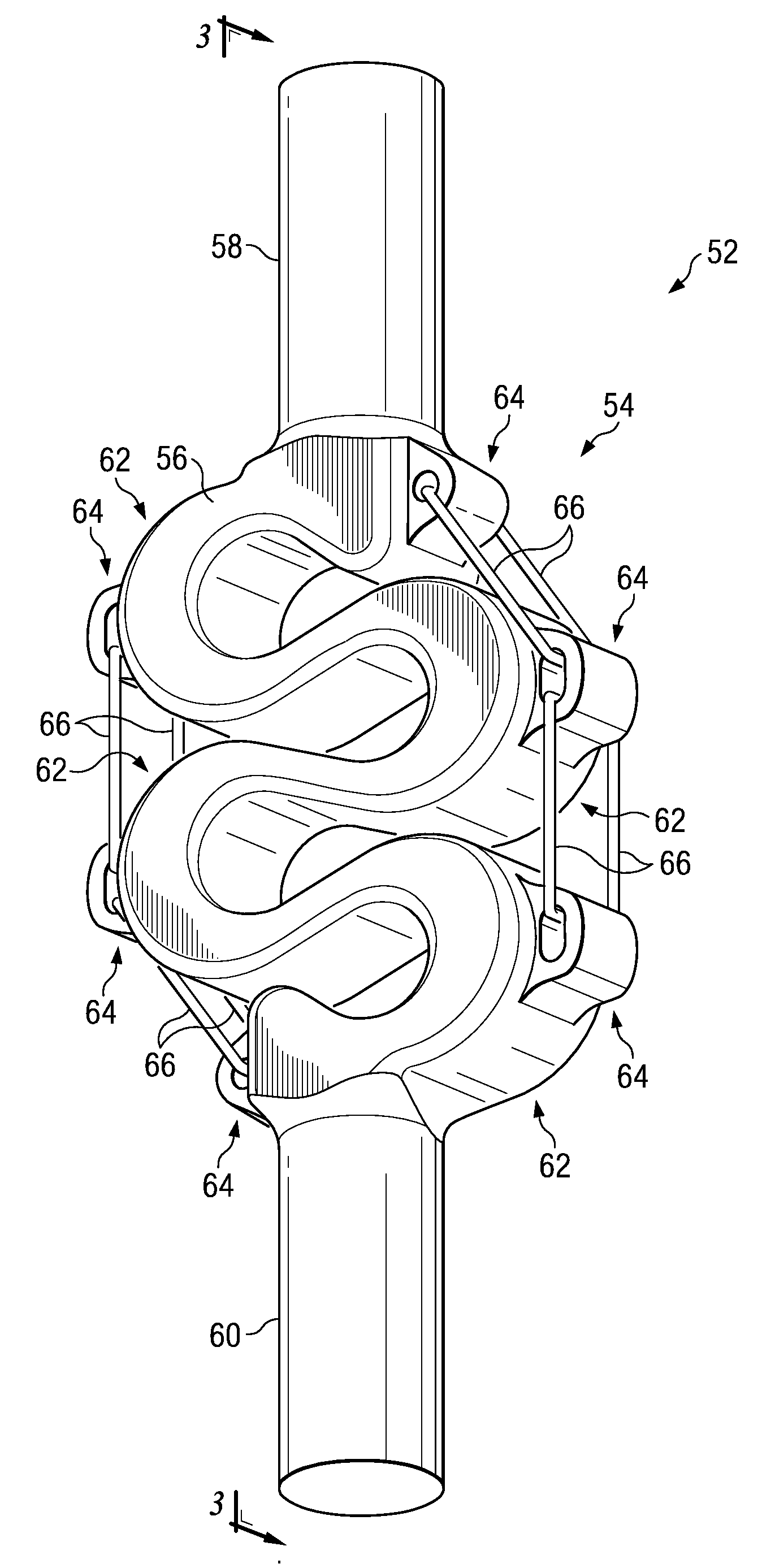
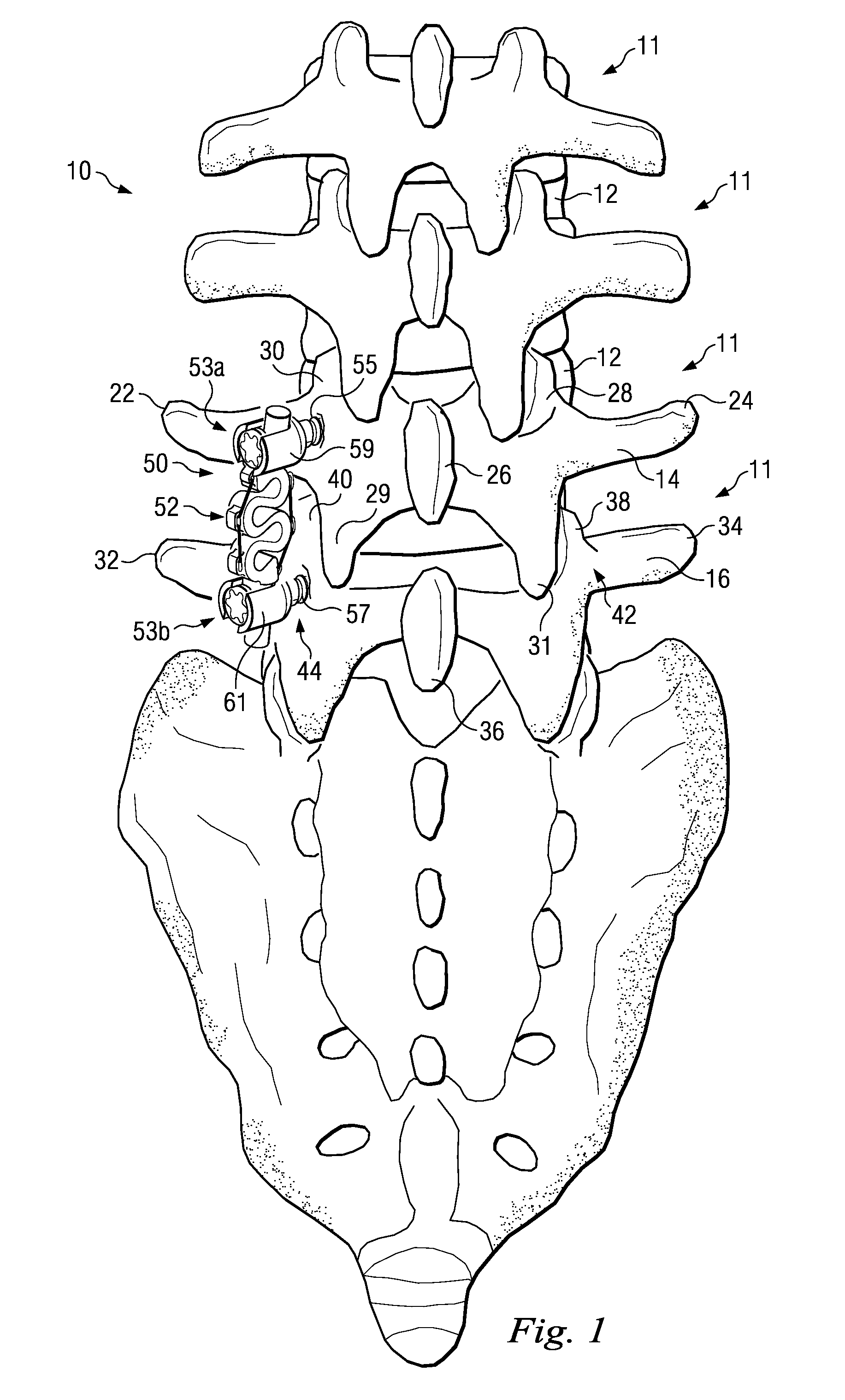
A bio-compatible stabilization system includes one or more inserters and a connector for traversing a space between one or more bony structures. The stabilization system is designed to reduce or eliminate stress shielding effects while functioning as a tension band. The connector includes an extendable member and an over-extension limiter that limits extension of the extendable member.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHODEPIC
Prosthesis for restoring motion in an appendage or spinal joint and an intervertebral spacer
A motion restoring prosthesis to be interposed between the ends of two bones adjoining a mammalian appendage or spinal joint is formed of two components with the components having inner cooperating articulating surfaces and outer bone engaging surfaces. At least one of the components has an inner section made of relatively hard, stiff material defining one or the articulating surfaces and an outer section made of a softer material defining the bone engaging surface. The softer material having a hardness / stiffness characteristic compatible with the bone to reduce stress shielding and more evenly distribute the forces from the articulating surfaces to the associate bone interface.
Owner:SEASPINE
Osteogenic fusion device
InactiveUS7179293B2Support of loadMinimize radiopacityBone implantJoint implantsDevice formBone growth
An interbody osteogenic fusion device is provided that includes opposite end pieces with an integral central element. The end pieces are sized to maintain the height of an intervertebral disc space. The central element has a much smaller diameter so that the osteogenic fusion device forms an annular pocke around the central element. An osteogenic material is disposed within the annular pocket between the opposite end pieces. In one embodiment,the osteogenic material constitutes a collagen sheet soaked in asolution containing a bone morphogenetic protein. The osteogenic fusion device is configured so that the osteogenic material is in direct contact with the adjacent vertebral bone. In addition to the enhanced area of contact between the vertebral bone and the fusion material, the inventive osteogenic fusion device reduces stress-shielding and minimizes the radiopacity of the implant so that growth of the fusion mass can be continuously assessed. In yet another embodiment, the osteogenic fusion device includes at least one end piece with a truncated surface. The osteogenic fusion devices of the present invention may be combined with other fusion devices to form an implant system. The implant system includes at least one load bearing member having a truncated surface configured to nest within another load bearing member, preferably the load bearing, osteogenic fusion device of the present invention. The invention also provides implant systems comprising adjacent load bearing members connected to one another to resist lateral separation. Methods of promoting fusion bone growth in the space between adjacent vertebrae utilizing devices and systems of the invention are also described.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Intervertebral allograft spacer
An allogenic intervertebral implant for fusing vertebrae is disclosed. The implant is a piece of allogenic bone conforming in size and shape with a portion of an end plate of a vertebra. The implant has a wedge-shaped profile to restore disc height and the natural curvature of the spine. The top and bottom surfaces of the implant have a plurality of teeth to resist expulsion and provide initial stability. The implant according to the present invention provides initial stability need for fusion without stress shielding.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Intervertebral allograft spacer
Owner:SYNTHES USA
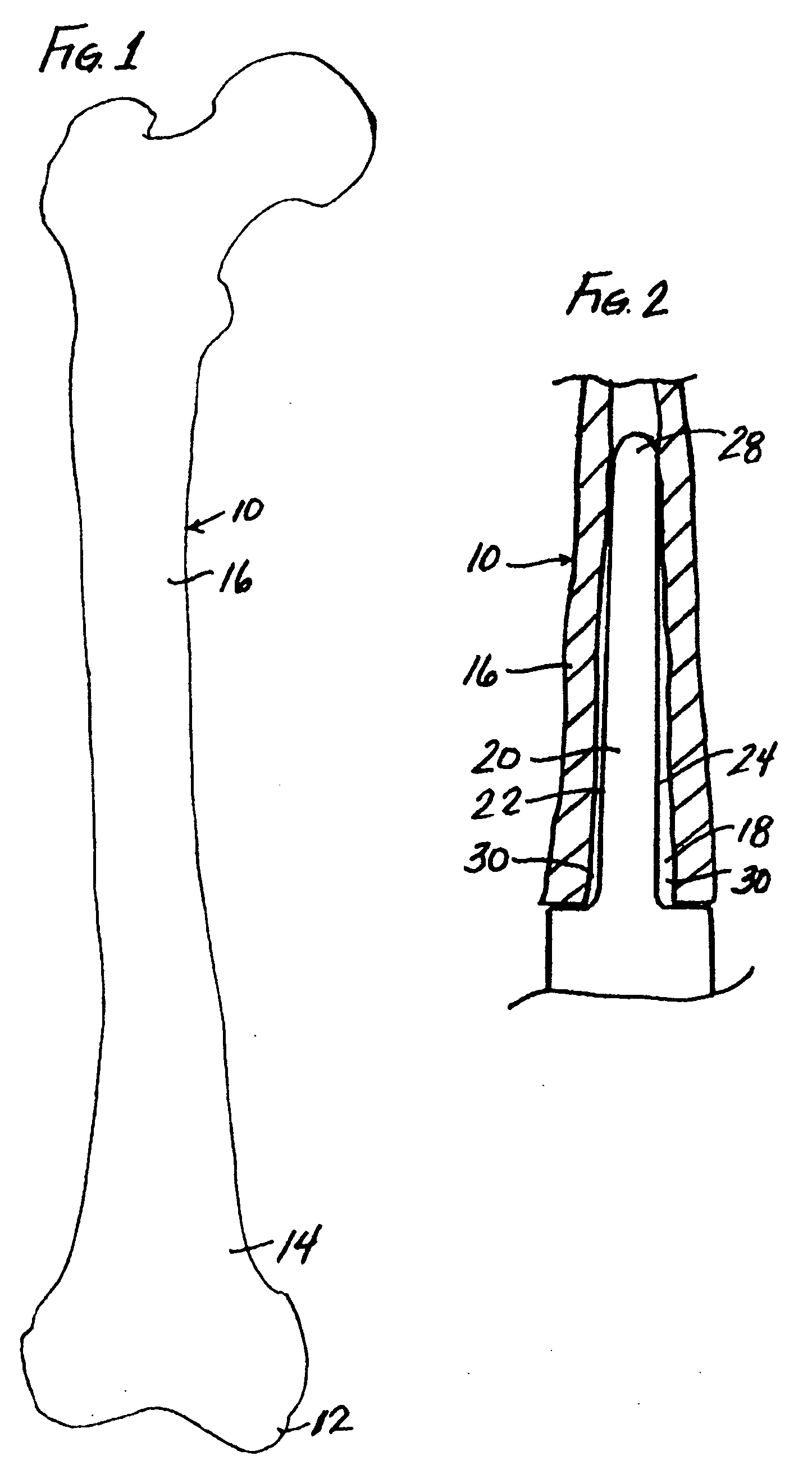
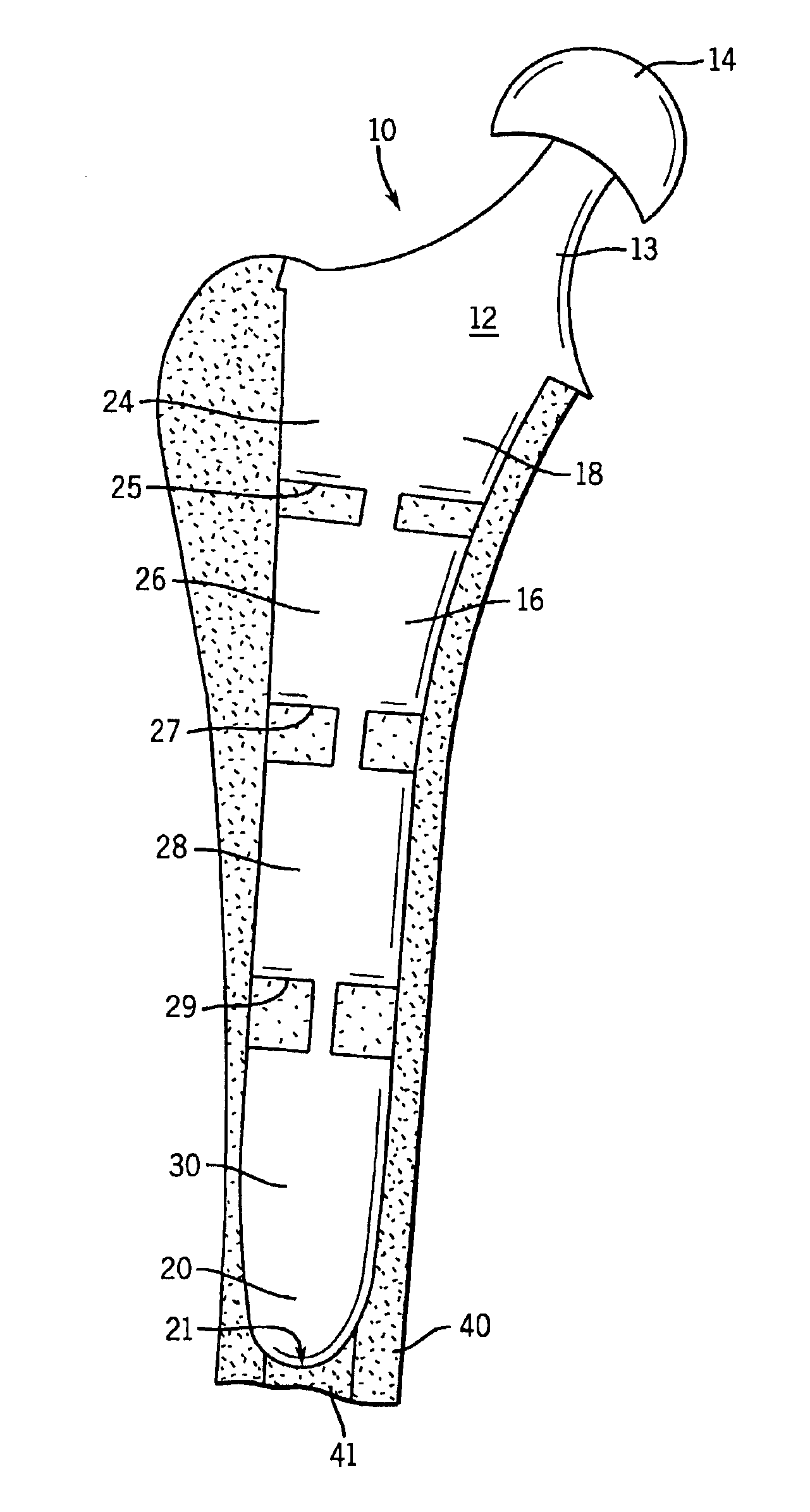
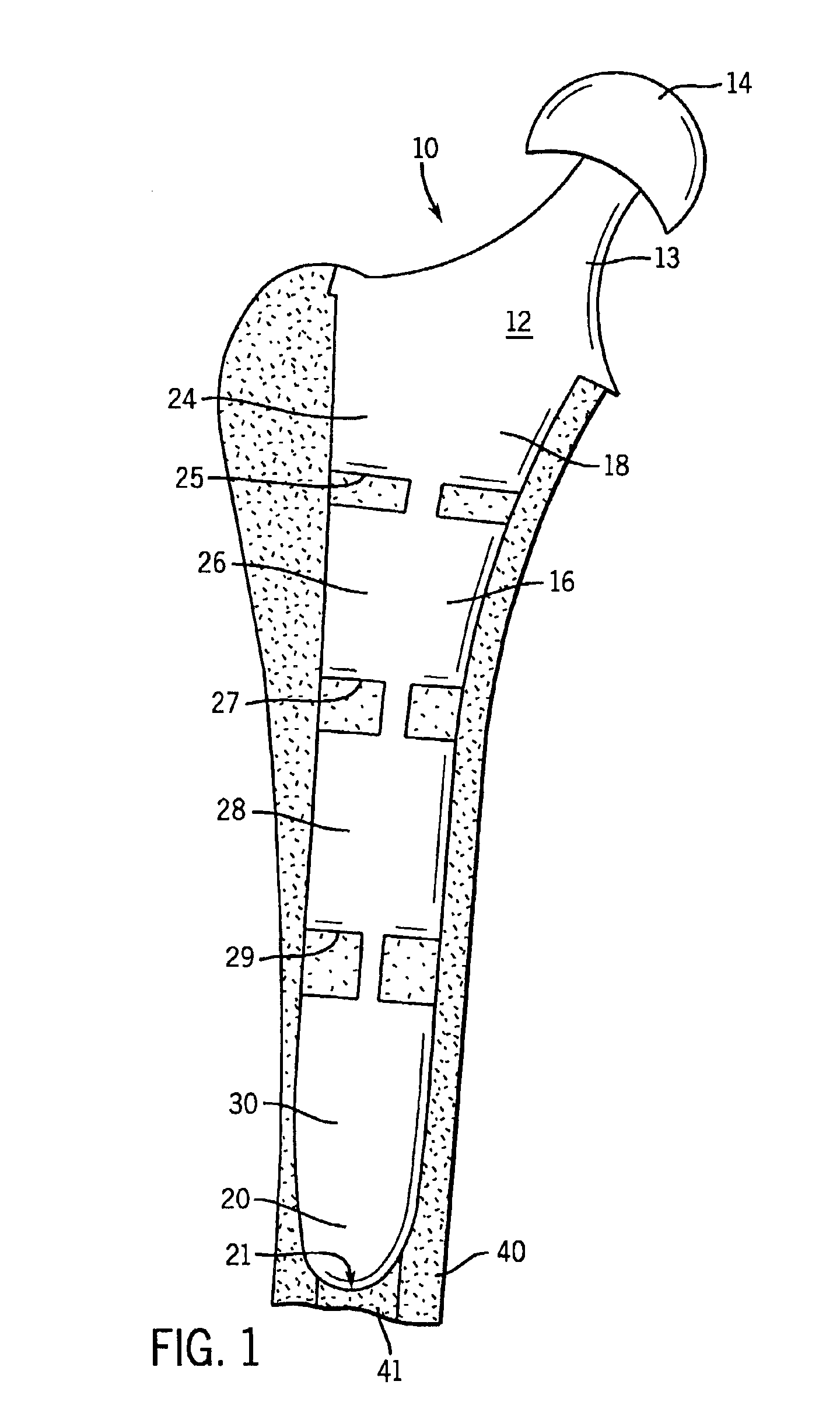
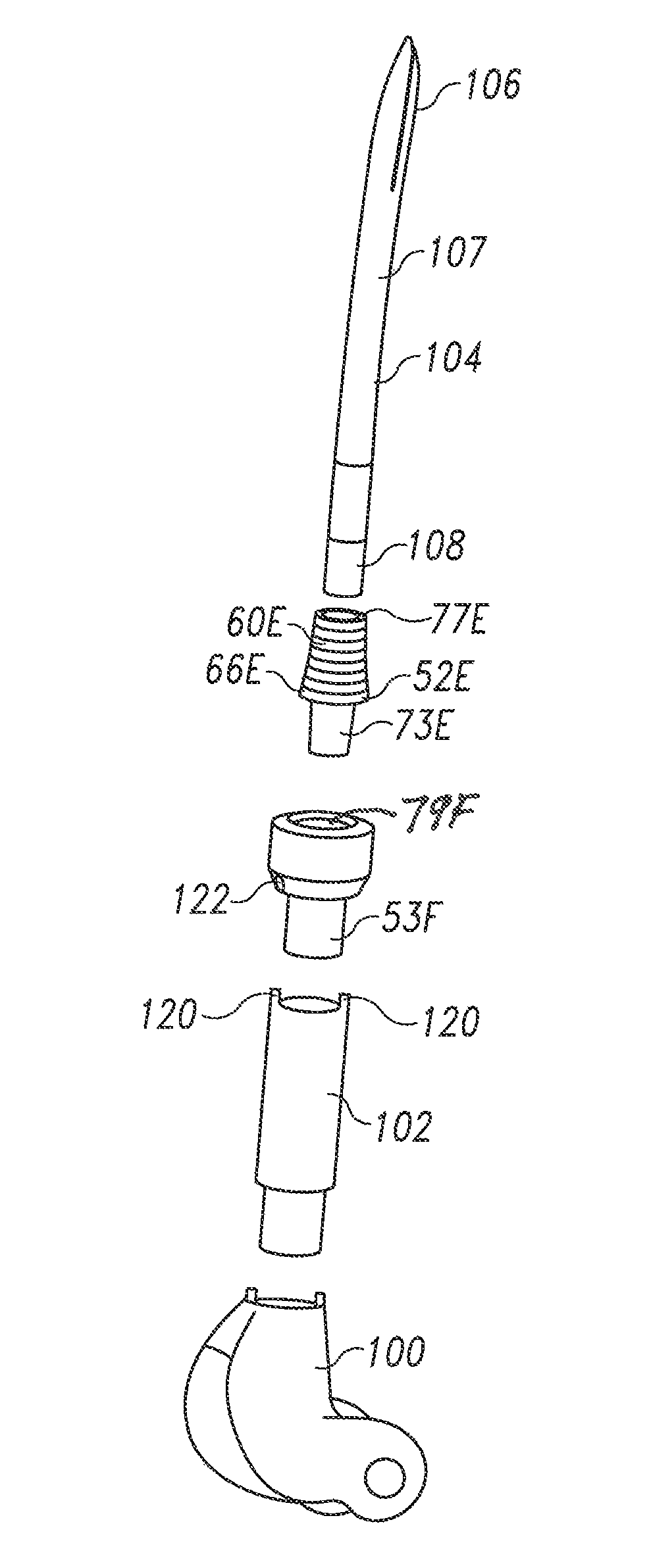
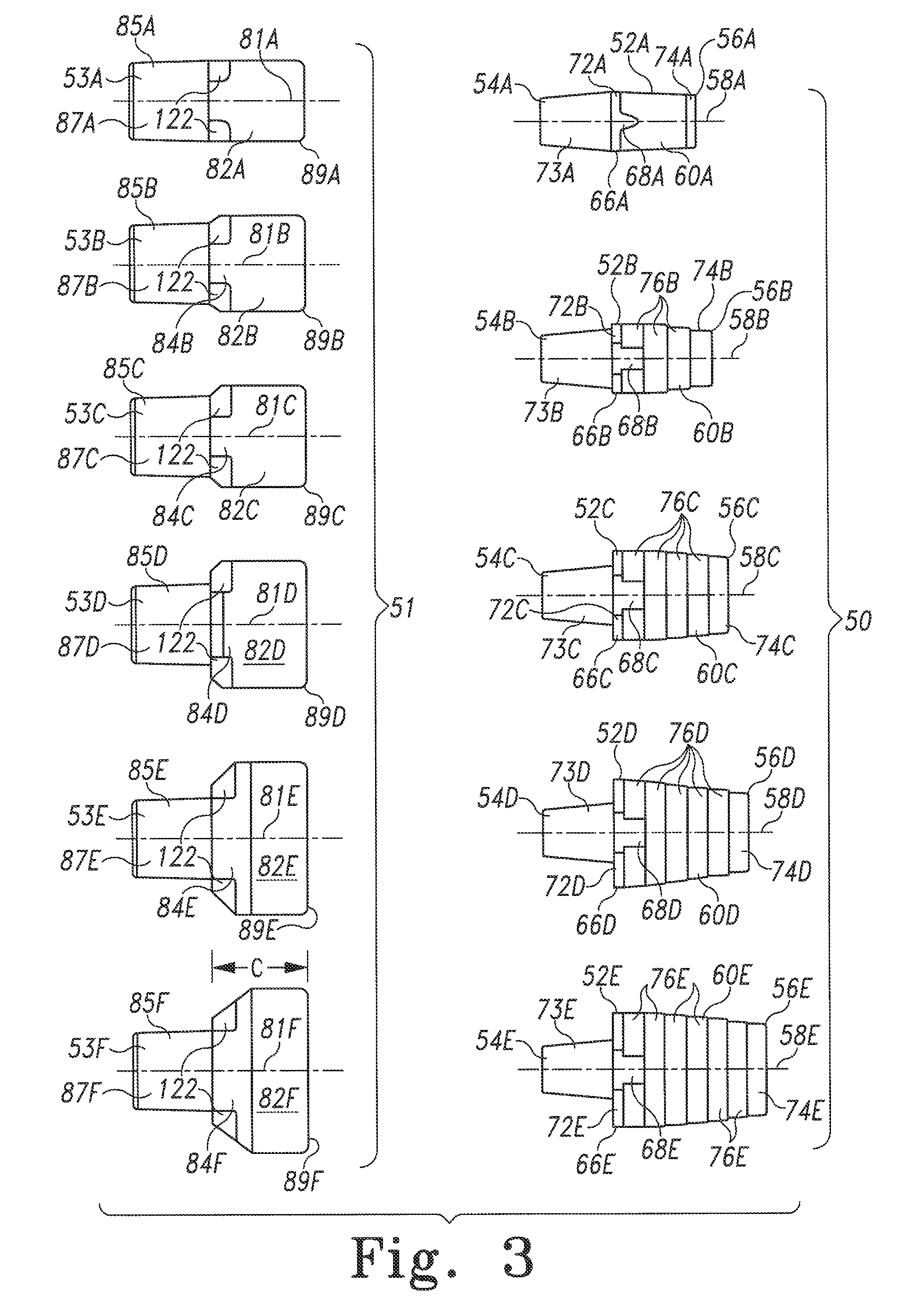
Modular implant system and method with diaphyseal implant and adapter
A modular implant system includes a set of anatomically-designed diaphyseal fitting and filling modular implant components and adapters for connection to another implant component such as a modular articular component, a segmental component or an intercalary component. The other end of each diaphyseal component is a tapered porous surface. The tapered porous surface is received with a tapered bore in the bone diaphysis that is prepared to match the size and shape of the tapered porous surface. The diaphyseal implant is easy to insert and remove, does not bind before fully seating, and is designed to prevent stress shielding. The diaphyseal sleeve eliminates the long lever arm created when fixation occurs only at the tip of the stem, and should therefore eliminate related stem loosening.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Metal jacket for a cementless artificial joint stem and artificial joint having the jacket
InactiveUS6497728B2Suppress formationMinimize osteolysisBone implantJoint implantsHuman bodyArtificial joints
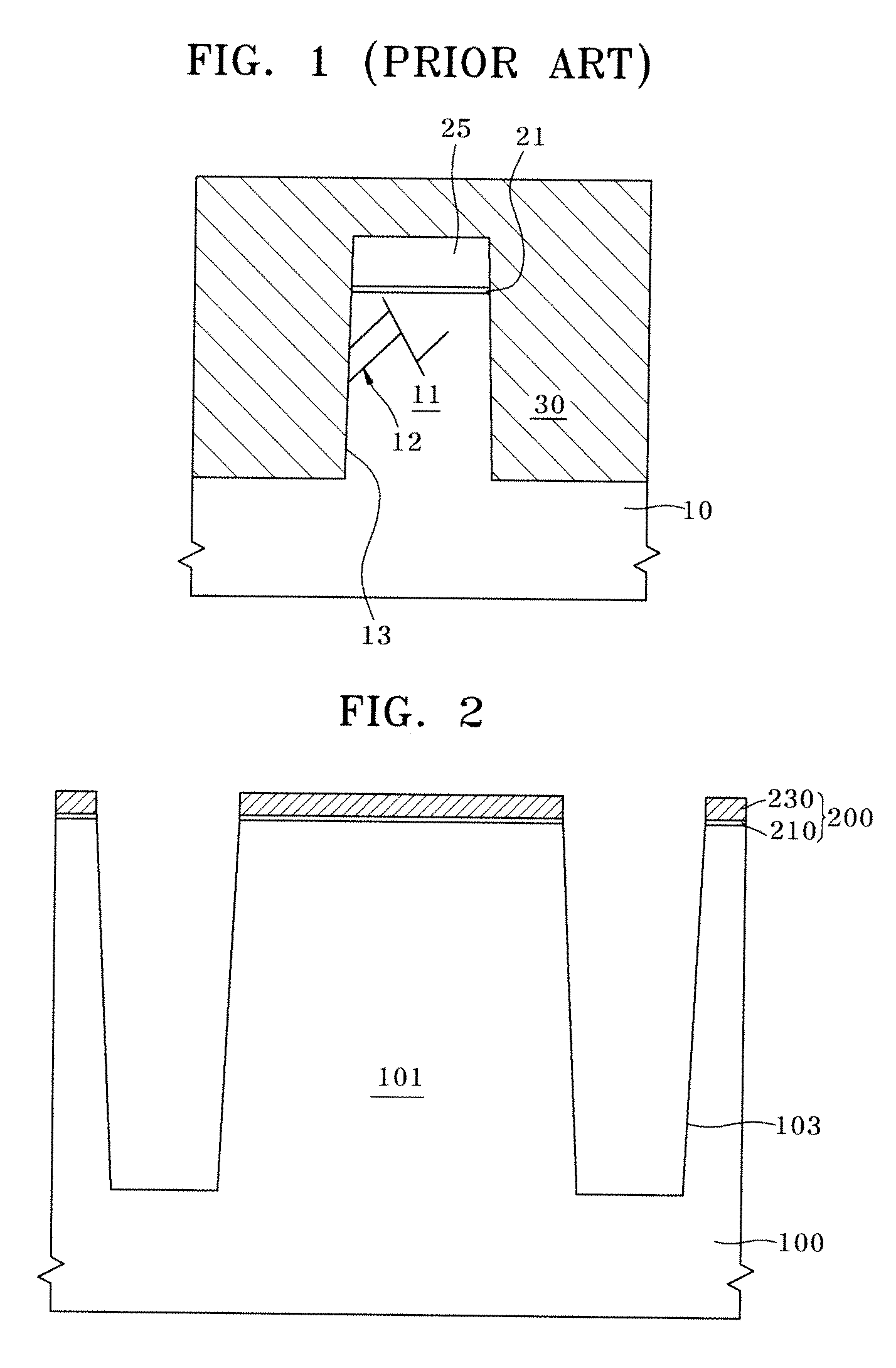
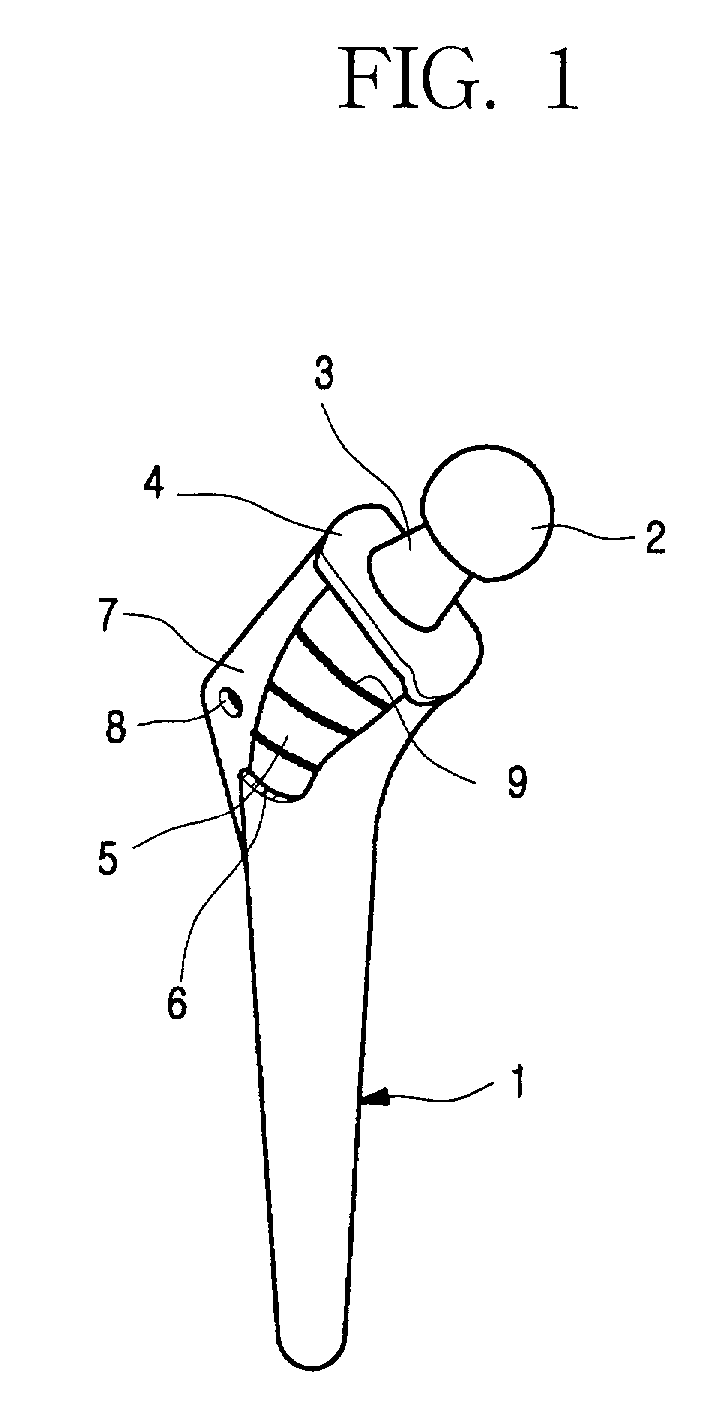
The present invention is intended to provide a metal jacket for a cementless artificial joint stem, wherein shear force detrimental to the service life of an artificial joint can be markedly reduced and stress shielding phenomena can also be markedly relieved, due to the construction of the metal jacket which can be fixed to the bone and can enclose the surface of the stem so as to allow for the stem of artificial joint to slide vertically relative to the bone, and wherein osteolysis of a bone due to the infiltration of wear particles can be minimized by curbing the gap formation between the bone and the stem.To that end, there is provided according to the invention, a metal jacket for a cementless artificial joint stem, which jacket is so formed as to enclose at least a part of the cementless artificial joint stem 21, said stem with jacket being inserted longitudinally in the opening formed in the bone canal of a human body, and on the surface of which jacket surface-processed metal layer or metal wires 12 is formed so that the bone can make interlocking with the metal jacket as the bone gets on-growth onto the metal jacket.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
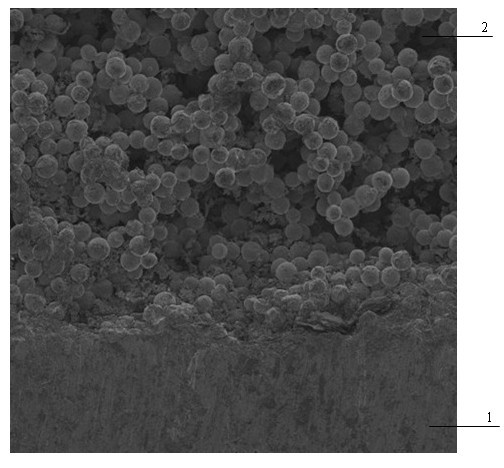
Medicinal porous titanium implant and method for preparing same
InactiveCN101518467AAchieve long-term stabilityIncrease initiativeDental implantsImpression capsStress concentrationMicrosphere
The invention discloses a medicinal porous titanium implant and a method for preparing the same. The porous titanium implant is prepared by a powder coinjection molding method; and a nano HA and TGF loaded sustained-release gelatin microsphere compound coating is deposited on the porous outer layer of the product. The outer layer of the implant has a communicated porous structure, the thickness of the porous layer is 0.4 to 1.1 millimeters, the porosity of the porous layer is 50 to 70 percent, and the aperture of the porous layer is 50 to 400 mum; the surface of the porous layer is deposited; and the binding strength of the outer layer and an inner core is 150 to 300MPa. Compared with the prior medicinal titanium implant material, the material of the medicinal porous titanium implant has higher mechanical strength, is in accordance with the mechanical performance of osseous tissue, avoids stress concentration and stress shielding, promotes stress transmission and growth of new bones, reduces time for osseointegration, and ensures the long-term stability of the implant. The method adopts once-for-all molding without post machining, thereby considerably reducing the cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Absorbable metal intramedullary nail and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101690676AAvoid or reduce stress shielding effectsPromotes fracture healingInternal osteosythesisCoatingsAlloyVolumetric Mass Density
The invention discloses an absorbable metal intramedullary nail and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of medical appliance. The intramedullary nail is a straight nail or a radian nail and is characterized in that the intramedullary nail comprises the follow components in percentage by mass: 0.01 to 10 percent of Zn, 0.01 to 5 percent of Ca, 0.001 to 5 percent of Fe, 0.01 to 5 percent of Mn and the balance of Mg; and the outer surface of the intramedullary nail is provided with a compound coating. The elastic modulus and the density of the intramedullary nail are close to those of a human body, which avoids or reduces stress shielding effect and promotes fracture union; and simultaneously, the intramedullary nail has higher intensity so as to make up the shortage of a degradable polymeric material. The intramedullary nail can be absorbed continuously in the human body and can generate a phosphate layer of Ca and Mg during the absorption and degradation, which contributes to bone conduction. The degradation rate can be regulated effectively by changing components and a structure of alloy, and components and a structure of a coated coating.
Owner:CHANGSHU MICROTUBE TECH
Inner supporting frame for femoral head
InactiveCN102028566ADissolution inhibitionImprove growing conditionsJoint implantsFemoral headsRight femoral headBone tissue
The invention relates to an inner supporting frame for a femoral head. A main body of the inner supporting frame is a hollow cylinder, a body part of the inner supporting frame is a round tube body, and a front end is connected with a hemispherical head; a tube wall of the tail part of the inner supporting frame is thickened compared with the body part and is provided with an external screw thread, and a back end face of the tail part is a plane and is provided with a straight line slot or a cruciform slot; lateral through holes are arranged on a spherical wall of the head of the inner supporting frame and the side walls of the body part and the tail part; and an artificial osteoinduction material is filled in a hollow cavity from the head to the tail part of the supporting frame. When the inner supporting frame for the femoral head is applied, the stress shielding and the dissolving of some metallic elements caused by big elastic modulus are avoided, therefore, the sufficient overall strength is not only provided, but also the bone tissue growth condition for transferring ossification and inducing ossification is reinforced.
Owner:北京畅想天行医疗技术有限公司
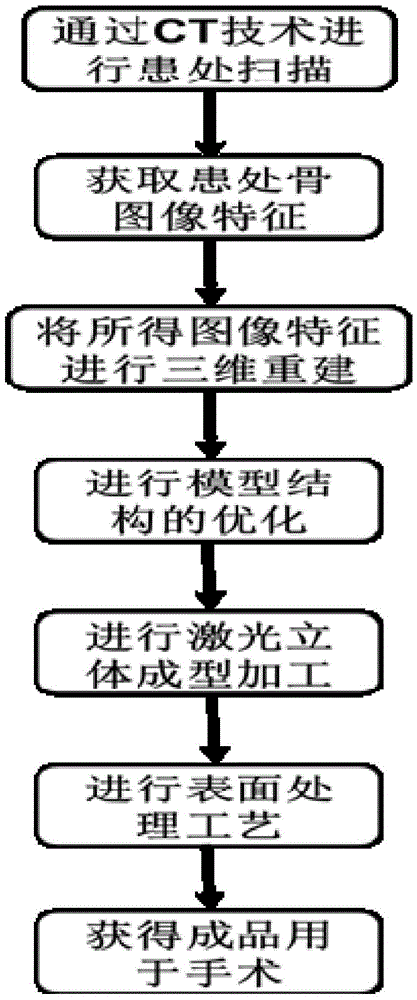
Low-elasticity-modulus titanium-based jawbone implant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104985183AMeet individual needsReduce concentrated stressBone implantStress concentrationPersonalization
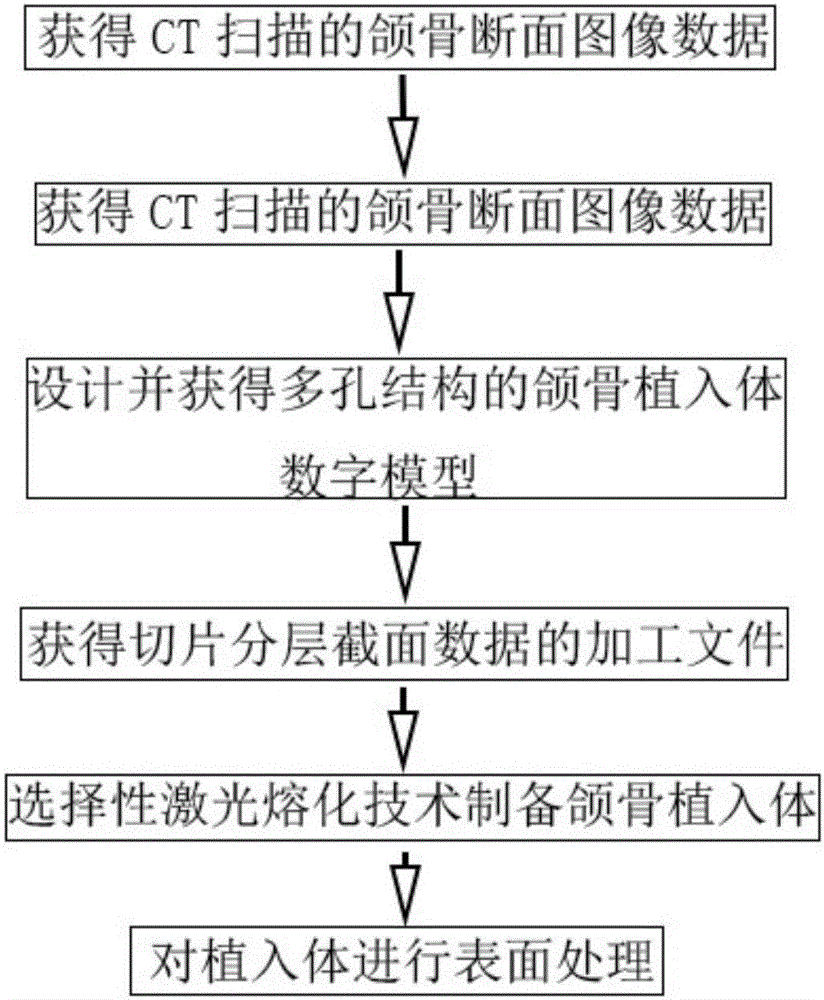
The invention discloses a low-elasticity-modulus titanium-based jawbone implant and a preparation method of the implant. The preparation method mainly comprises the six steps that CT-scanned jawbone section image data are obtained; a rebuilt jawbone three-dimensional digital model is obtained; a jawbone implant digital model of a multi-hole structure is designed and obtained; a machining file of slice layered cross section data is obtained; the selective laser melting technology is adopted for preparing the jawbone implant; and surface treatment is carried out on the implant. The implant is used for treating a patient with jawbone defects, and the CAD digital design technology is used in the design of the implant; and jawbone repairing individualized design and multi-hole support structure design are combined, and through the selective laser melting technology, the low-elasticity-modulus titanium-based jawbone implant is prepared. The implant can meet the individual needs of the patient, and meanwhile can reduce the elastic modulus; and the problems of stress concentration and stress shielding of a traditional jawbone implant are solved, the preparation time is shortened, and the machining difficulty and the production cost are reduced.
Owner:东莞市唯信三维科技有限公司
Modular implant system and method with diaphyseal implant
A modular implant system allows a surgeon to secure an implant assembly to thee diaphysis of a long bone. The system includes a set of anatomically-designed diaphyseal fitting modular implant components. One end of each diaphyseal implant component is a Morse taper post for connection to another implant component such as a modular articular component, a segmental component or an intercalary component. The other end of each diaphyseal component is a tapered porous surface. In some sizes, the tapered porous surface includes a plurality of steps. The tapered porous surface is received with a tapered bore in the bone diaphysis that is prepared to match the size and shape of the tapered porous surface. The diaphyseal implant is easy to insert and remove, does not bind before fully seating, is designed to prevent stress shielding and provides the surgeon with a host of stem options with its modularity.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
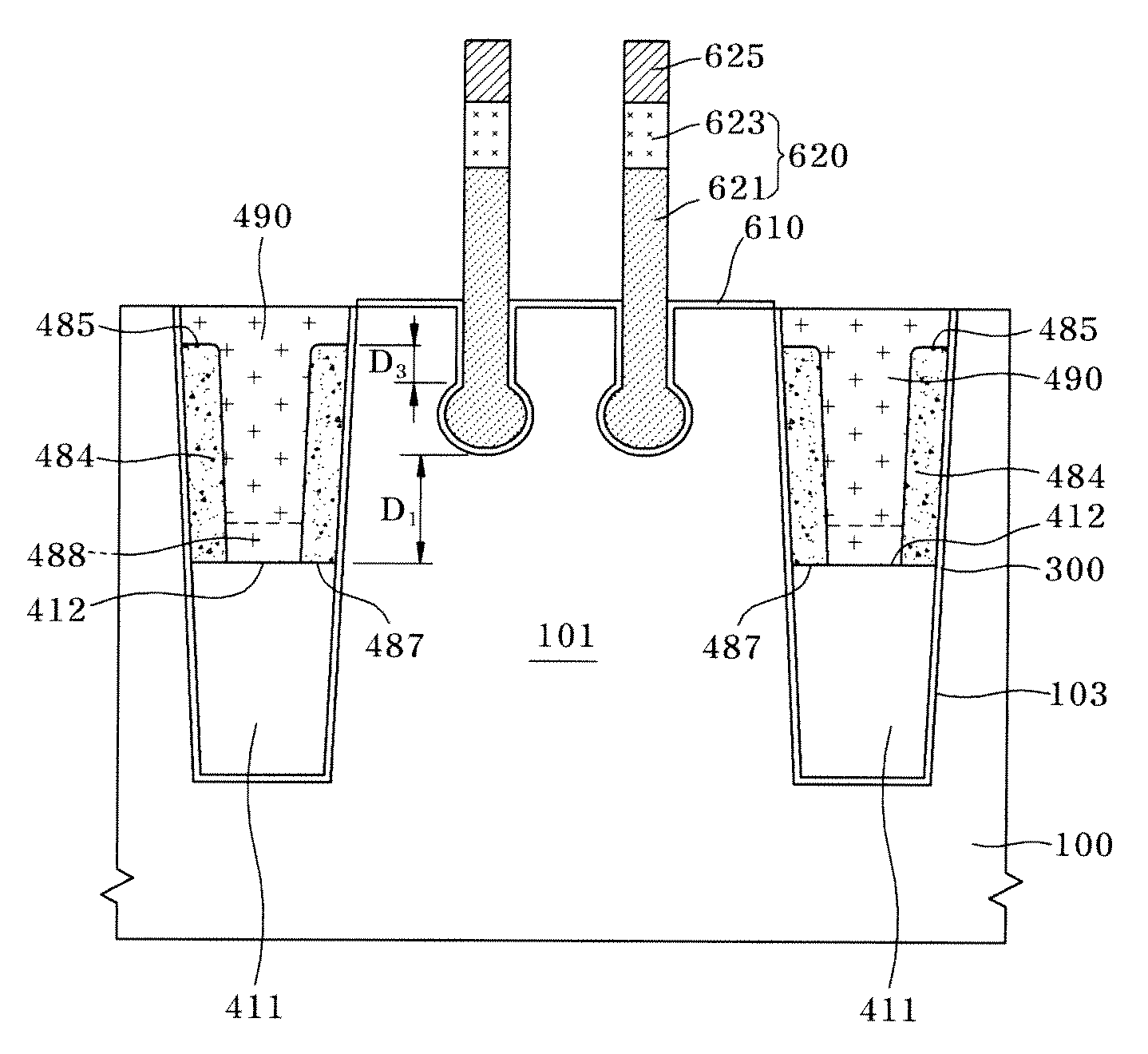
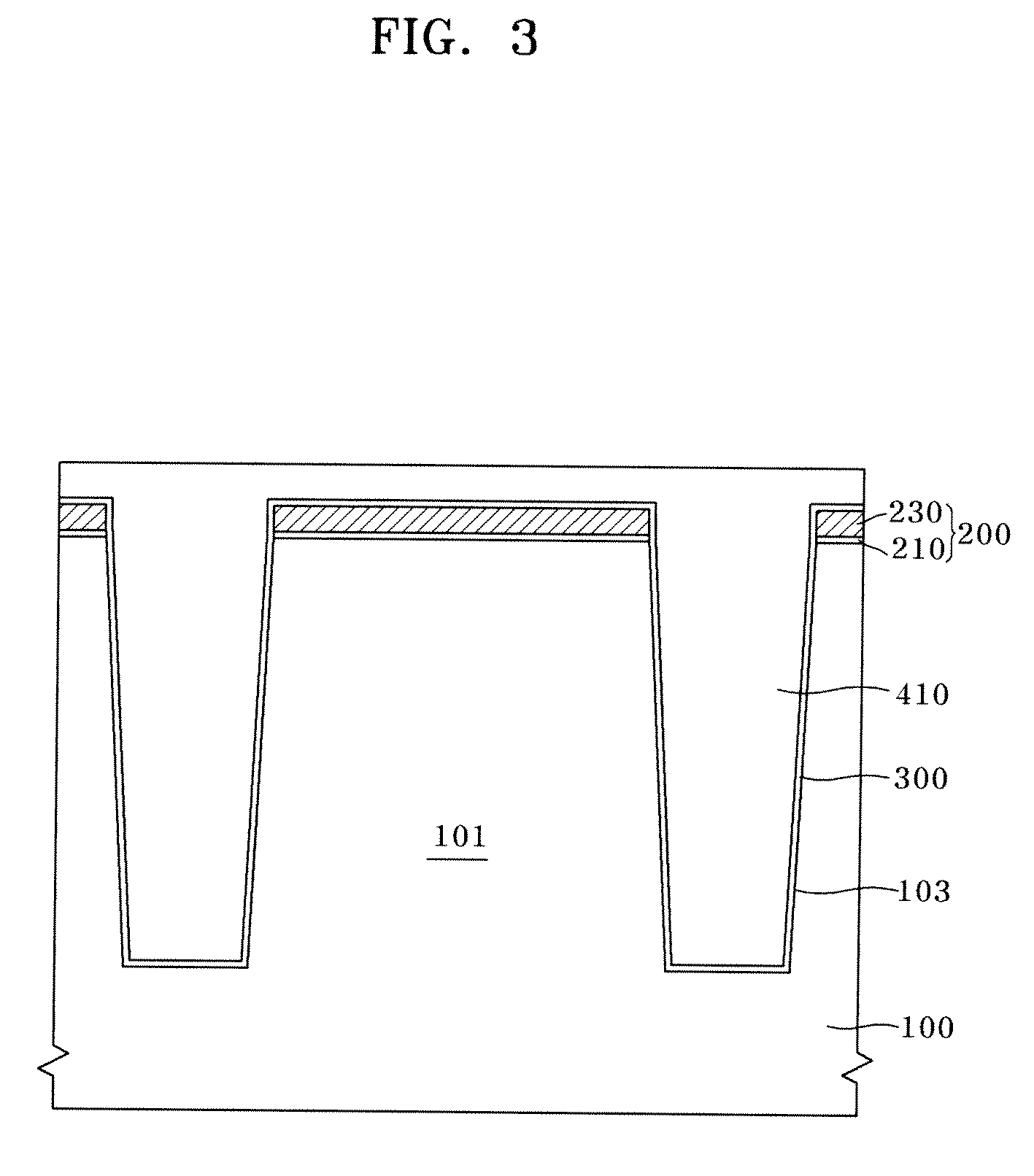
Semiconductor device having recess gate and isolation structure and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20100078757A1Restrict of operation propertySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringStress shielding
Disclosed herein is a semiconductor device including an isolation structure and a recess gate and a method for fabricating the same. The method for fabricating a semiconductor device includes: forming a trench by selectively etching an isolation region of a semiconductor substrate to define an active region; forming a first SOD partially filling the trench; forming a stress shielding layer, which is denser than the first SOD, over the first SOD; forming a second SOD that fills the trench over the first SOD including the stress shielding layer; forming a recess groove by selectively etching a portion of the active region, wherein an upper surface of the first SOD is spaced downwardly from a bottom of the recess groove, and an upper surface of the stress shielding layer is spaced upwardly from the bottom of the recessed groove; and forming a gate of a transistor that fills the recess groove.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Method for preparing bone repair implant on basis of selective laser melting technology
InactiveCN105455925ASimplify the surgical processShorten operation timeAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantSelective laser meltingOriginal data
The invention provides a method for preparing a bone repair implant on the basis of the selective laser melting technology. The method includes the steps that original data is scanned on the basis of standard medical images of bones of a patient, and a digital three-dimensional model of a primary skeleton of the patient is extracted through image segmentation, editing and three-dimensional computation; according to individual conditions of the patient, osteotomy is directly conducted on the digital three-dimensional model of the primary skeleton to obtain a three-dimensional model of the bone repair implant; a porous structure capable of preventing stress shielding is designed in the three-dimensional model of the bone repair implant; an embedded structure capable of enhancing fixed connection with the primary skeleton is designed on the surface of the three-dimensional model of the bone repair implant; on the basis of the modified and designed three-dimensional model of the bone repair implant, the model is imported into quick forming auxiliary software for processing such as placement positioning, support adding, parameter setting and slicing and layering, a multi-layer slicing two-dimensional data model of the bone repair implant is obtained, metal 3D printing is conducted through the selective laser melting technology, and the bone repair implant is obtained.
Owner:广东中科安齿生物科技有限公司
Intervertebral Implant
A vertebral implant for fusing adjacent vertebrae or for replacing vertebral bodies is disclosed. The implant is a biocompatble metal resorbabler or radiolucent implant conforming substantially in size and shape with an end plate of a vertebra. The implant preferably has a wedge-shaped profile to restore disc height and the natural curvature of the spine. The top and bottom surfaces of the implant have areas with a plurality of teeth to resist expulsion and provide initial stability and areas devoid of any protrusions to receive implantation instrumentation. The implant also has a stackability feature. The implant provides initial stability needed for fusion without stress shielding.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
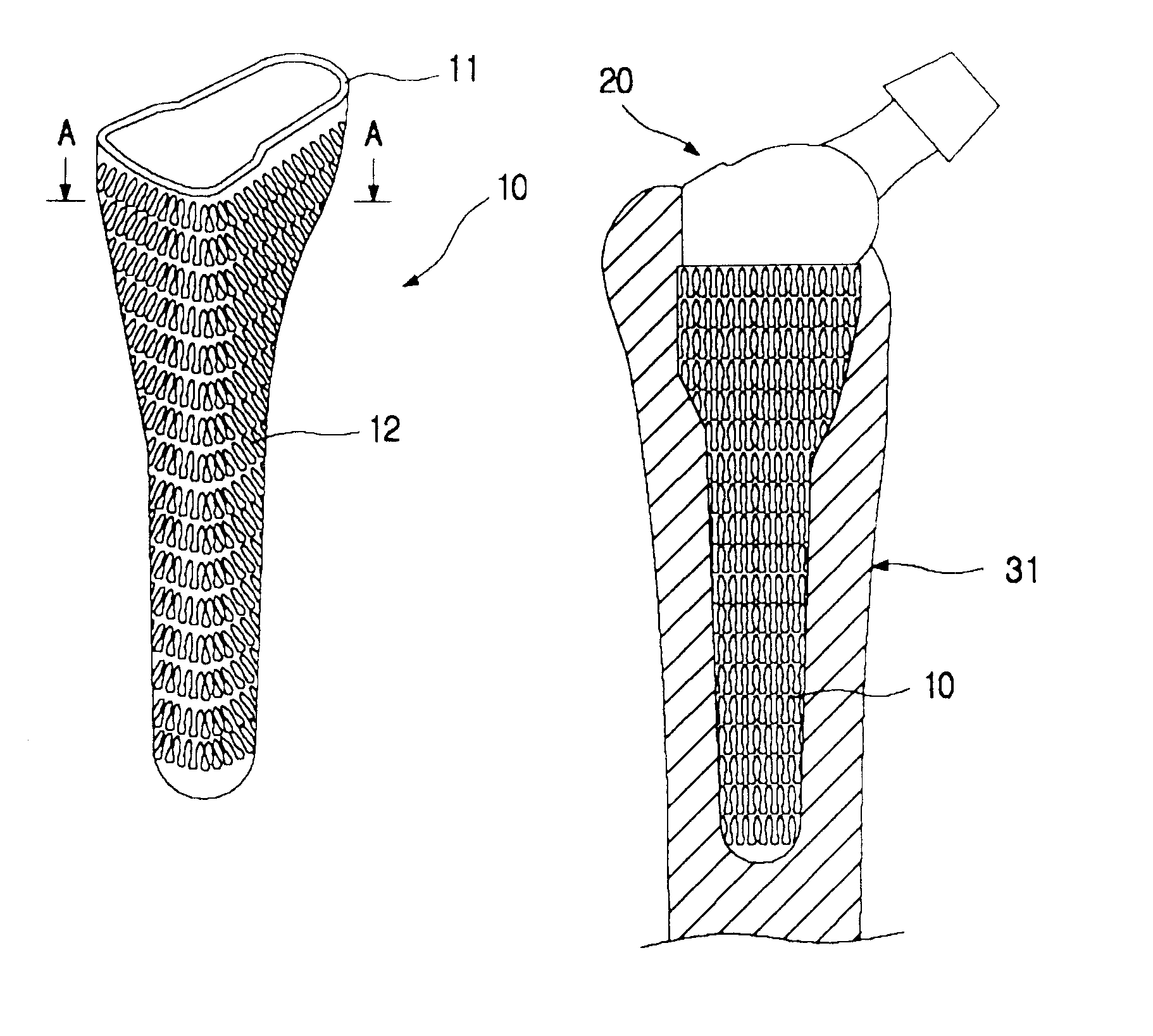
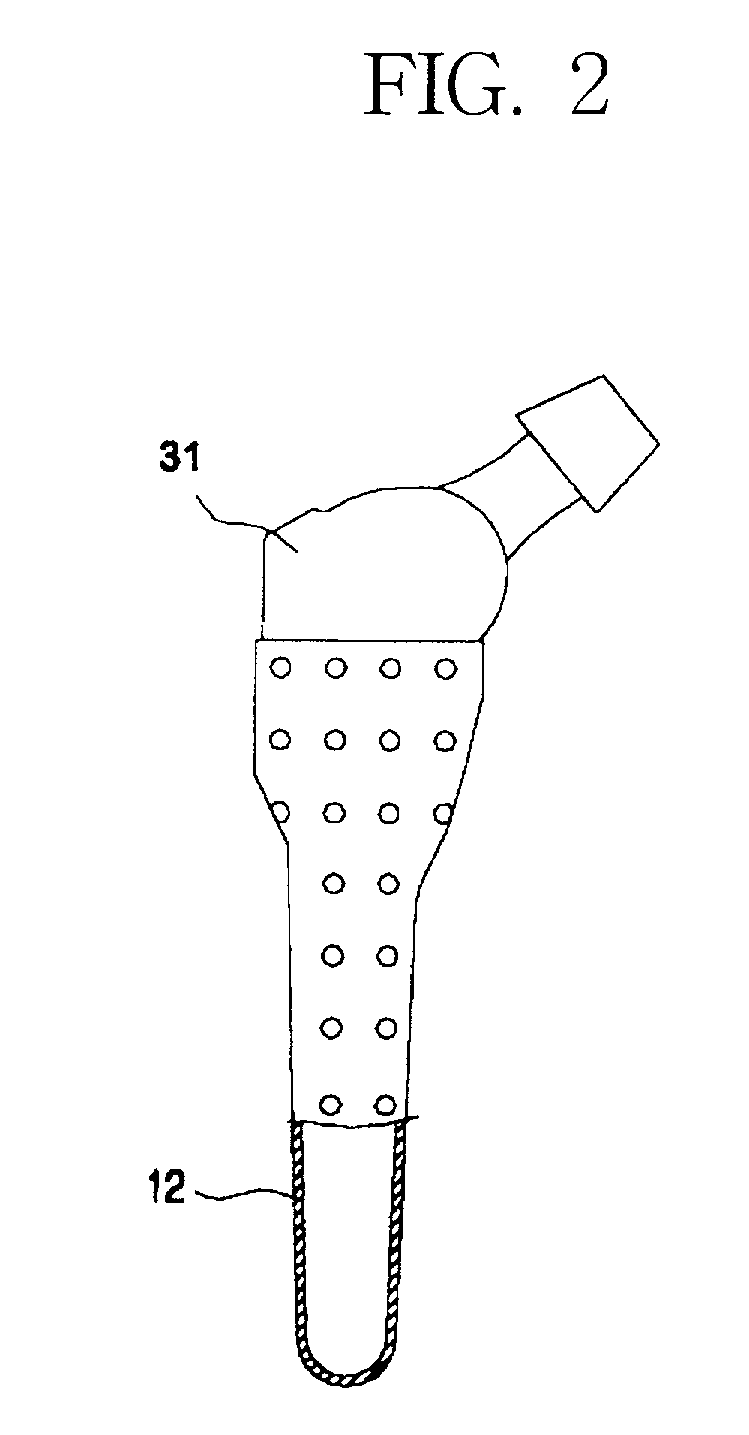
Plastic jacket for a cementless artificial joint stem and artificial joint having the jacket
The present invention is intended to provide a plastic jacket for a cementless artificial joint stem, wherein shear force detrimental to the service life of an artificial joint can be markedly reduced and stress shielding phenomena can also be markedly relieved, due to the construction of the plastic jacket which can be fixed to the bone canal and can enclose the surface of the stem so as to allow for the stem of artificial joint to slide vertically relative to the bone, and wherein osteolysis of a bone due to the infiltration of wear particles can be minimized by curbing the gap formation between the bone and the stem. To that end, there is provided according to the invention, a plastic jacket 20 for a cementless artificial joint stem 31, which is made of plastics and is so formed as to enclose at least a part of the stem 31 of a cementless artificial joint 30, said stem with jacket being inserted longitudinally in the opening formed in the bone canal of a human body, and which has a porous or roughened surface so that a femur can make interlocking with the plastic jacket as the bone gets in-growth onto the porous plastic jacket surface.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Intervertebral allograft spacer
An allogenic intervertebral implant for fusing vertebrae is disclosed. The implant is a piece of allogenic bone conforming in size and shape with a portion of an end plate of a vertebra. The implant has a wedge-shaped profile to restore disc height and the natural curvature of the spine. The top and bottom surfaces of the implant have a plurality of teeth to resist expulsion and provide initial stability. The implant according to the present invention provides initial stability need for fusion without stress shielding.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Prosthetic implant having segmented flexible stem
InactiveUS6887278B2Reduced and varying stiffnessHigh mechanical stiffnessJoint implantsFemoral headsHigh stiffnessTransverse groove
A prosthetic implant having a fixation stem with varying stiffness is disclosed. The stem comprises an elongated core and segments extending outward from the core. The segments are spaced apart so as to define transverse grooves surrounding the core between adjacent segments. The longitudinal length of the grooves, and the materials used for the core and the segments are selected such that the stiffness of the stem varies from the proximal end to the distal end. Typically, the stiffness of the stem will be lower at the distal end such that the distal end of the stem bears less force when loaded and thereby transfers more load to the proximal end of the stem, which has a higher stiffness. As a result, stress shielding, in which the load bypasses the proximal end of the stem, is minimized and bone resorption adjacent the proximal end of the stem is decreased.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Modular implant system and method with diaphyseal implant
A modular implant system allows a surgeon to secure an implant assembly to thee diaphysis of a long bone. The system includes a set of anatomically-designed diaphyseal fitting modular implant components. One end of each diaphyseal implant component is a Morse taper post for connection to another implant component such as a modular articular component, a segmental component or an intercalary component. The other end of each diaphyseal component is a tapered porous surface. In some sizes, the tapered porous surface includes a plurality of steps. The tapered porous surface is received with a tapered bore in the bone diaphysis that is prepared to match the size and shape of the tapered porous surface. The diaphyseal implant is easy to insert and remove, does not bind before fully seating, is designed to prevent stress shielding and provides the surgeon with a host of stem options with its modularity.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Medical degradable magnesium alloy bone-fixing screw
InactiveCN102813966ALow equilibrium electrode potentialAvoid stress shieldingCoatingsFastenersInfection rateBiocompatibility Testing
A medical degradable magnesium alloy bone-fixing screw relates to bone-fixing screws and solves the problem that the existing bone-fixing screws are non-degradable. The medical degradable magnesium alloy bone-fixing screw is made of degradable magnesium alloy. The medical degradable magnesium alloy bone-fixing screw is fine in biocompatibility, has few tissue reaction and fine metal mechanical performance, can be absorbed in vivo without one more operation for removing the screws, relieves wound, reduces infection rate, saves cost, and has no metal stimulation, and degrading of the medical degradable magnesium alloy bone-fixing screw avoids metal stress shielding and reduces risks of osteoporosis after operation. The medical degradable magnesium alloy bone-fixing screw can be completely biodegraded to become harmless micromolecule after in vivo planting and the micromolecule can be discharged in vitro or absorbed in vivo, and accordingly rejection reaction of human bodies to implant is reduced and better curative effect is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
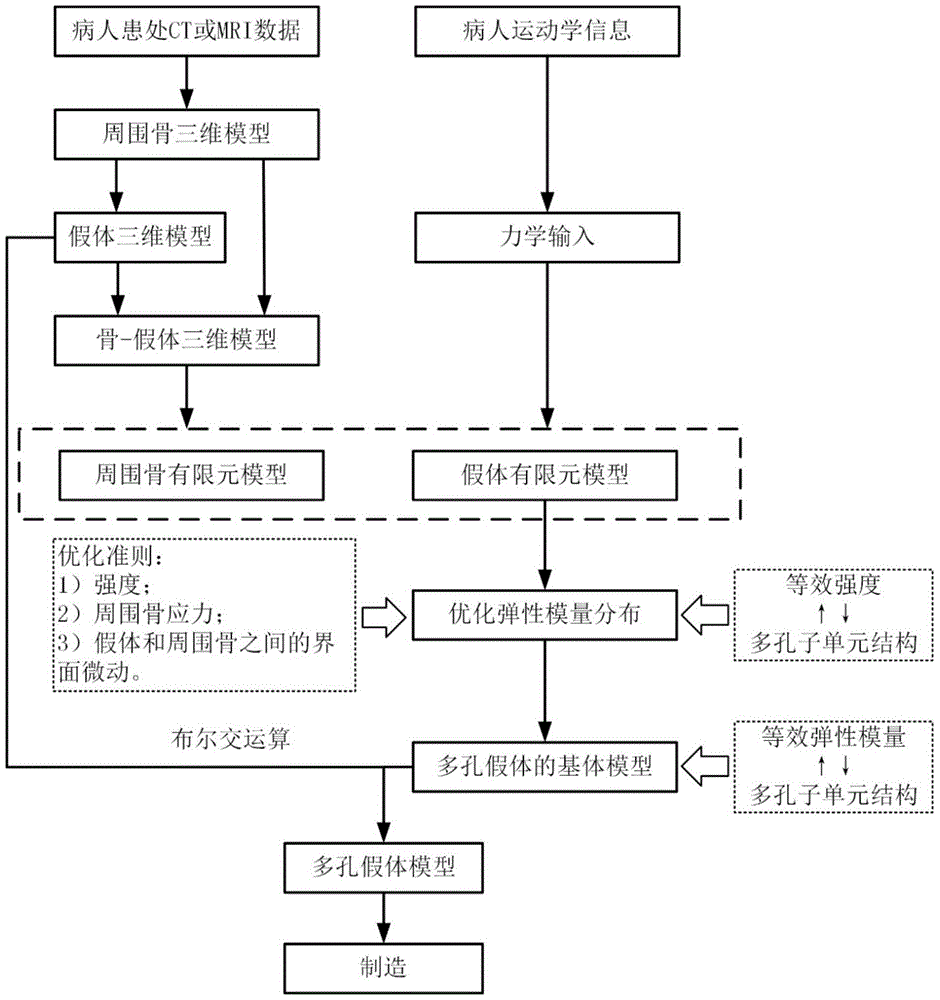
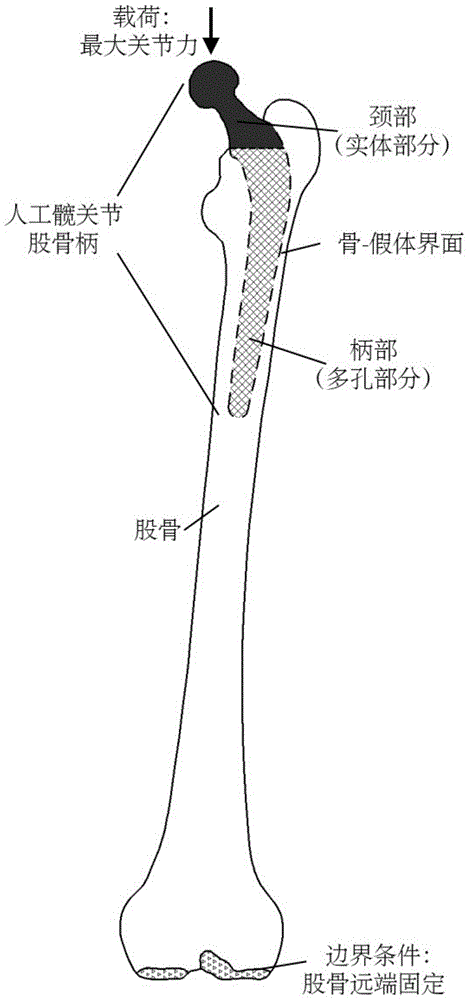
Host bone stress environment based custom prosthesis optimization design method
ActiveCN105740523AAdapt to boneAdapt to the situationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsPersonalizationBones stress
The invention, for reducing a stress shielding effect after prosthesis implantation, proposes a host bone stress environment based custom prosthesis optimization design method. Three criteria, namely, the strength, the surrounding bone stress and the interface micro-motion between a prosthesis and a bone, in prosthesis elastic modulus optimization calculation are proposed, and the mechanical property of the host bone and a personalized kinematic input are considered in optimization; the prosthesis elastic modulus distribution is optimized through finite element software to achieve the purpose of optimizing a porous structure in the prosthesis; and for the designed prosthesis, on the premise of meeting the strength requirement, the stress shielding effect after implantation is reduced and the service life of the prosthesis after implantation is prolonged.
Owner:深圳协同创新高科技发展有限公司
Load bearing implants with engineered gradient stiffness and associated systems and methods
Implants are made of materials having asymmetric modulus gradients. For example, an implant, such as a hip implant, is made of a material having a stiffness gradient between a proximal portion near a hip joint and a distal portion extending downward into the marrow of the femur. Among other benefits, the asymmetric modulus gradient mitigates problems associated with stress shielding and does not excessively wear or deteriorate the proximal portion of the implant.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Modular diaphyseal and collar implant
A modular implant system includes a set of anatomically-designed diaphyseal fitting and filling modular implant components and collars. The diaphyseal component connects with a selected intramedullary stem and with a selected collar component. The collar component connects to another implant component such as a modular articular component, a segmental component or an intercalary component. The diaphyseal component has a tapered porous surface that is received with a tapered bore in the bone diaphysis that is prepared to match the size and shape of the tapered porous surface. The collar component has a porous surface for tissue ingrowth, such as the periosteum, to seal the intramedullary canal. The diaphyseal implant is easy to insert and remove, does not bind before fully seating to prevent stress shielding, and eliminates the long lever arm created when fixation occurs only at the tip of the stem, and should eliminate related stem loosening.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
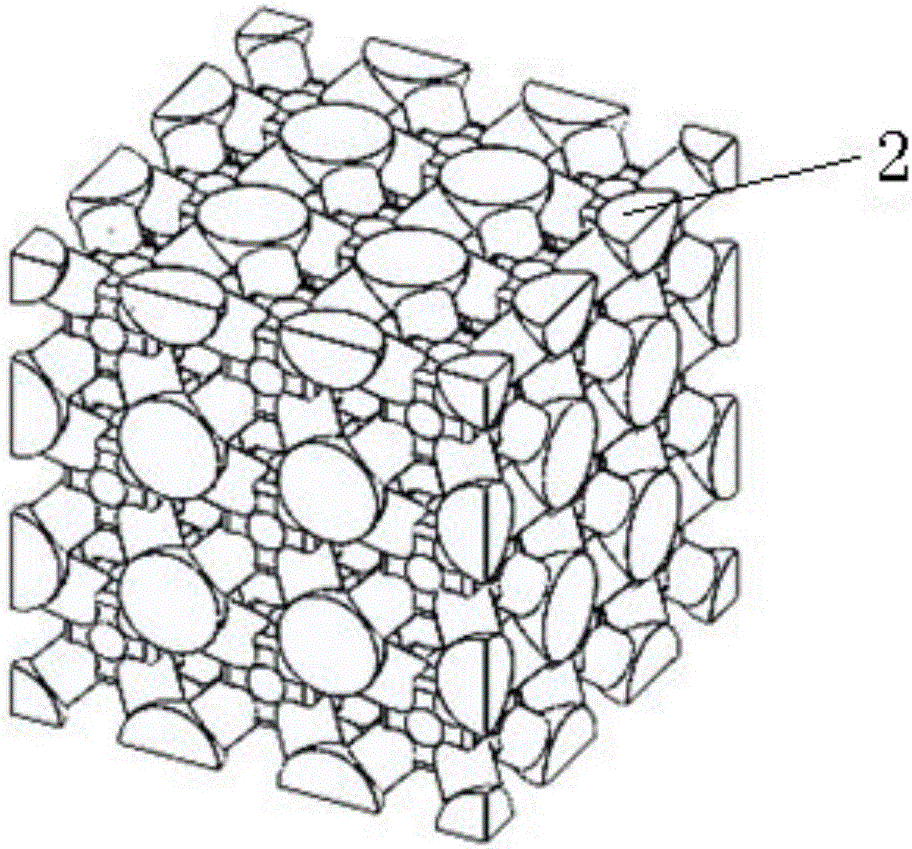
Bio-medicinal porous titanium material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101912635AReduce Insufficient StrengthReduced stress shieldingProsthesisNatural boneBiocompatibility
The invention discloses a bio-medicinal porous titanium material. The porous titanium material comprises at least two layers, the porosity of the material is enlarged layer by layer from inside to outside, the porosity of the innermost layer is 0 to 50 percent, the porosity of the outermost layer is 30 to 90 percent, and the size of aperture is 50 to 500 microns. The porous titanium material has excellent corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, has the mechanical property matched with natural bones, meanwhile can provide a good transmission passage for growth of bone cells, and can solve the stress shielding phenomenon and the problems of loosening, breakage and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Metal jacket for a cementless artificial joint stem and artificial joint having the jacket
InactiveUS20010016780A1Suppress formationMinimize osteolysisBone implantJoint implantsHuman bodyStress shielding
The present invention is intended to provide a metal jacket for a cementless artificial joint stem, wherein shear force detrimental to the service life of an artificial joint can be markedly reduced and stress shielding phenomena can also be markedly relieved, due to the construction of the metal jacket which can be fixed to the bone and can enclose the surface of the stem so as to allow for the stem of artificial joint to slide vertically relative to the bone, and wherein osteolysis of a bone due to the infiltration of wear particles can be minimized by curbing the gap formation between the bone and the stem. To that end, there is provided according to the invention, a metal jacket for a cementless artificial joint stem, which jacket is so formed as to enclose at least a part of the cementless artificial joint stem 21, said stem with jacket being inserted longitudinally in the opening formed in the bone canal of a human body, and on the surface of which jacket surface-processed metal layer or metal wires 12 is formed so that the bone can make interlocking with the metal jacket as the bone gets on-growth onto the metal jacket.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
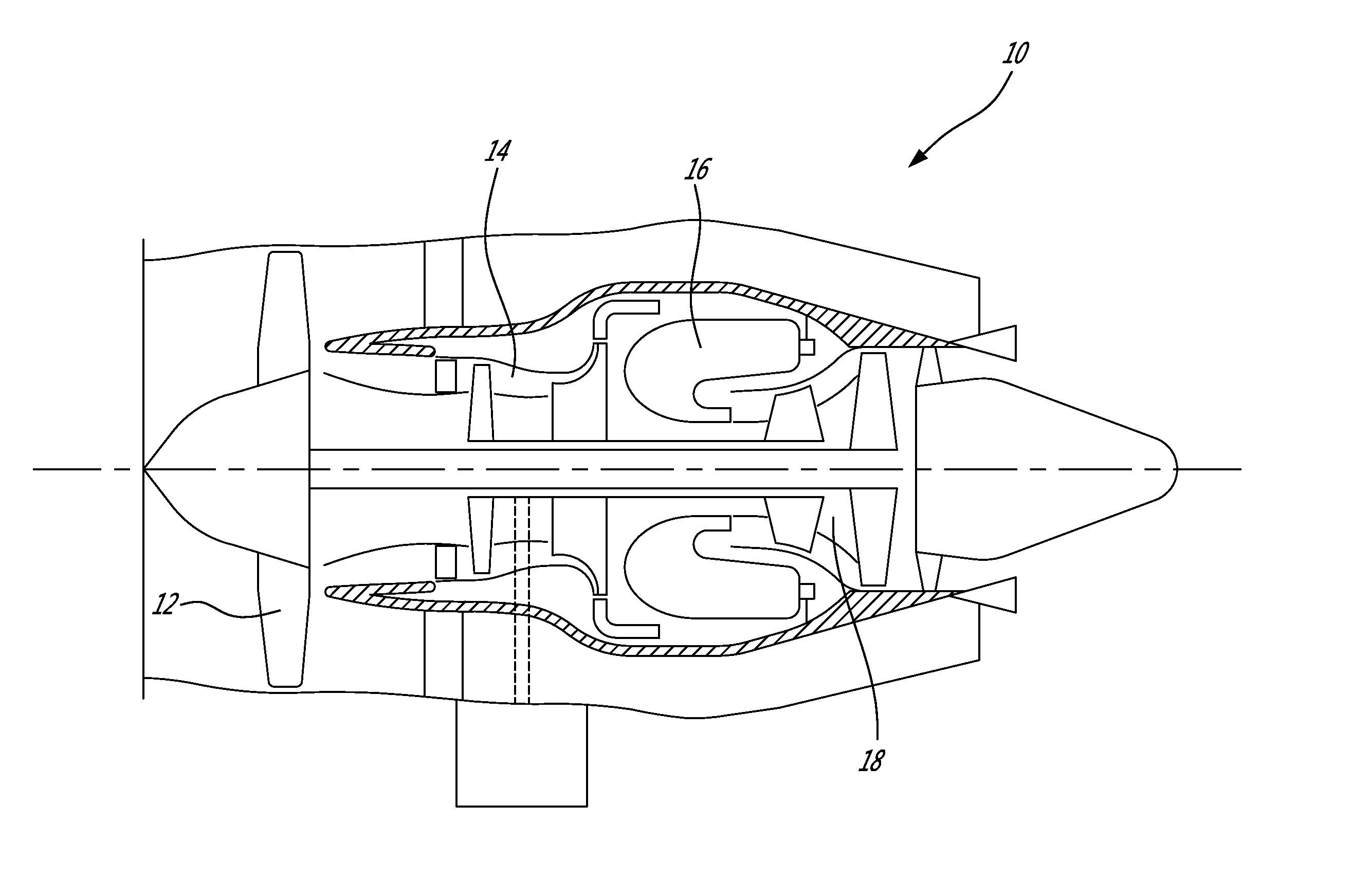
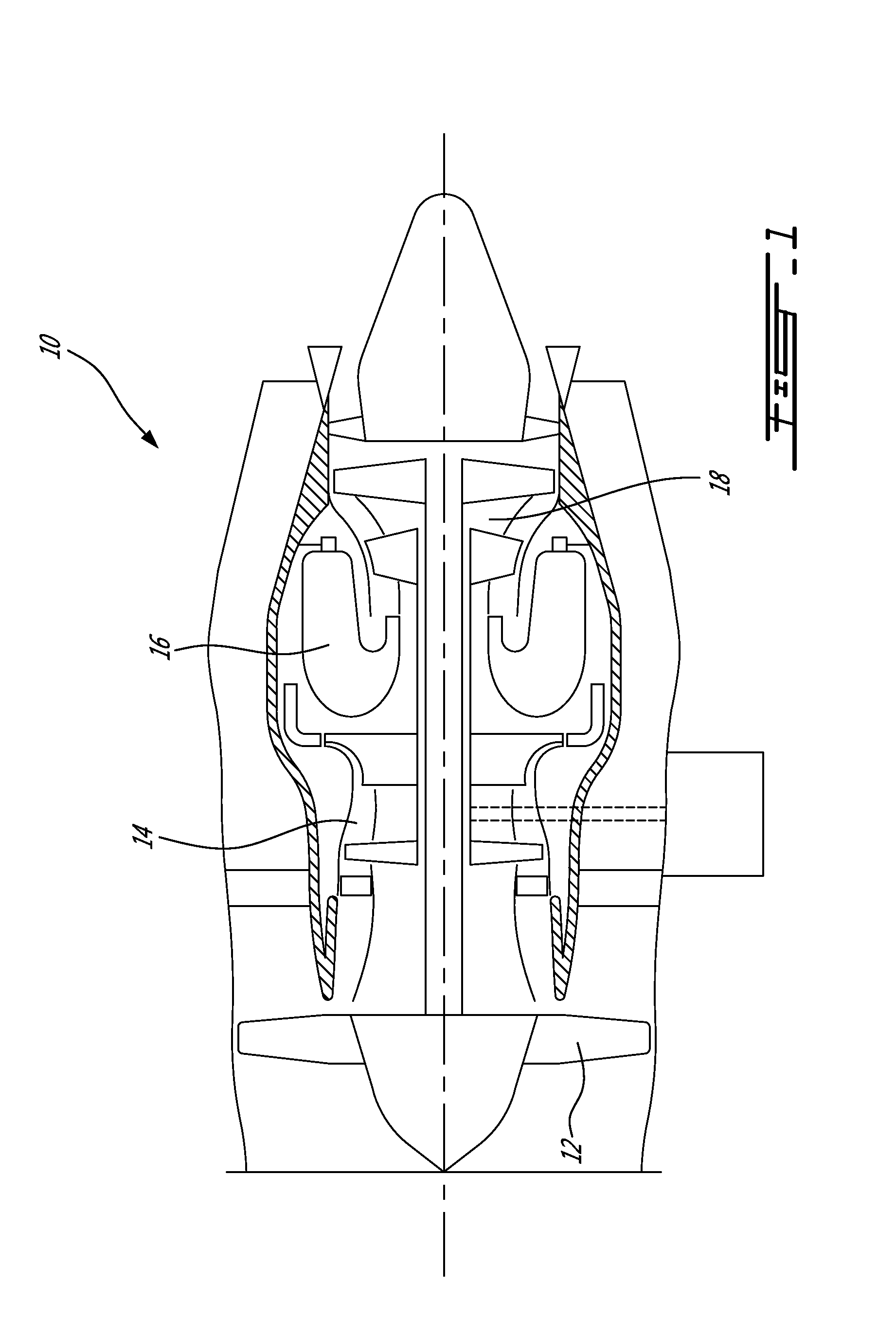
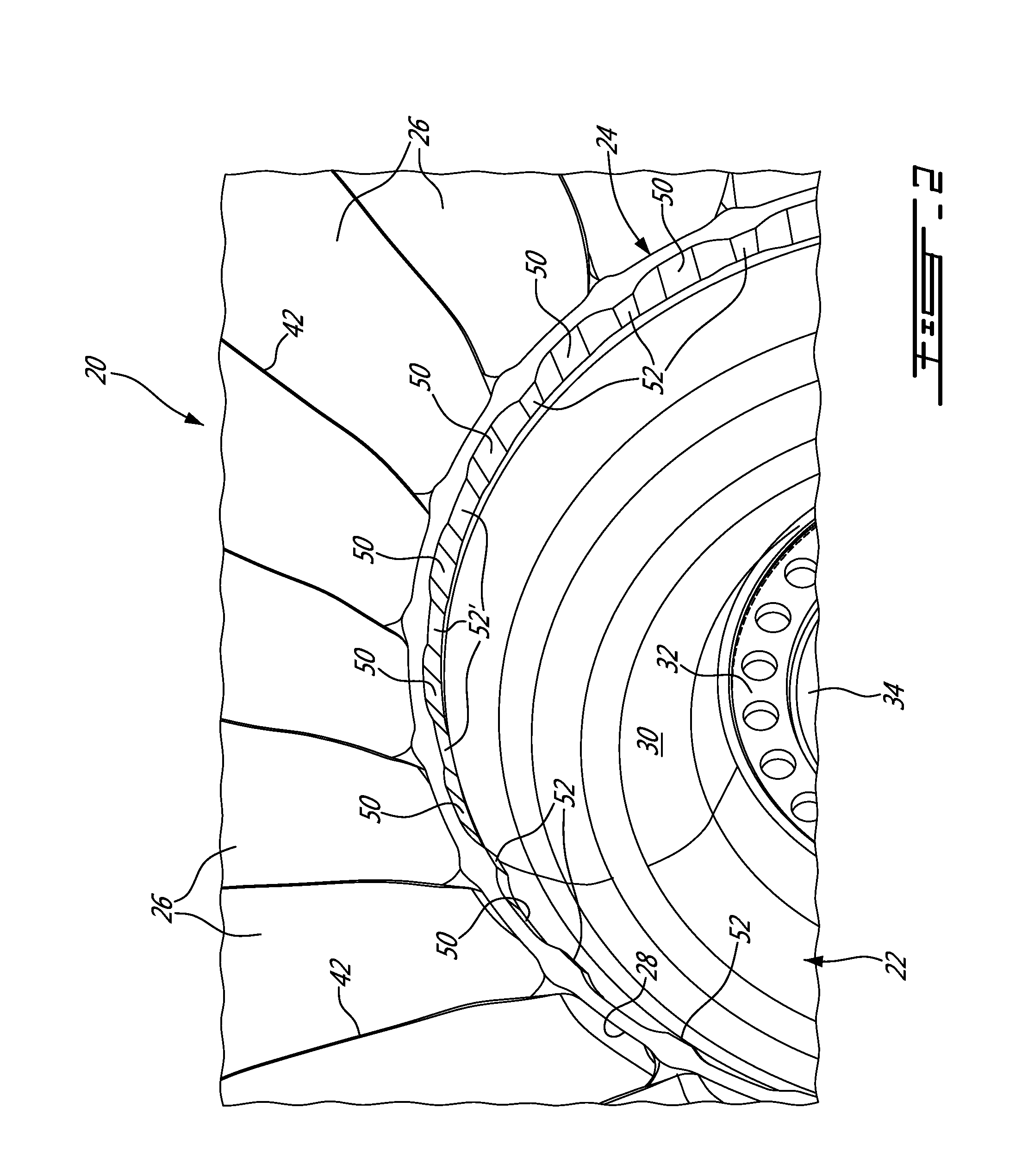
Gas turbine engine rotor balancing
A method of balancing a gas turbine engine rotor comprises the step of obtaining a rotor disc with a circumferential array of balance tabs projecting from a peripheral rim of the disc. Stress shielding scallops are defined in the rotor disc between the tabs. The balancing is achieved by removing material from at least one of the tabs.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Preparing method of zinc magnesium function gradient biological composite
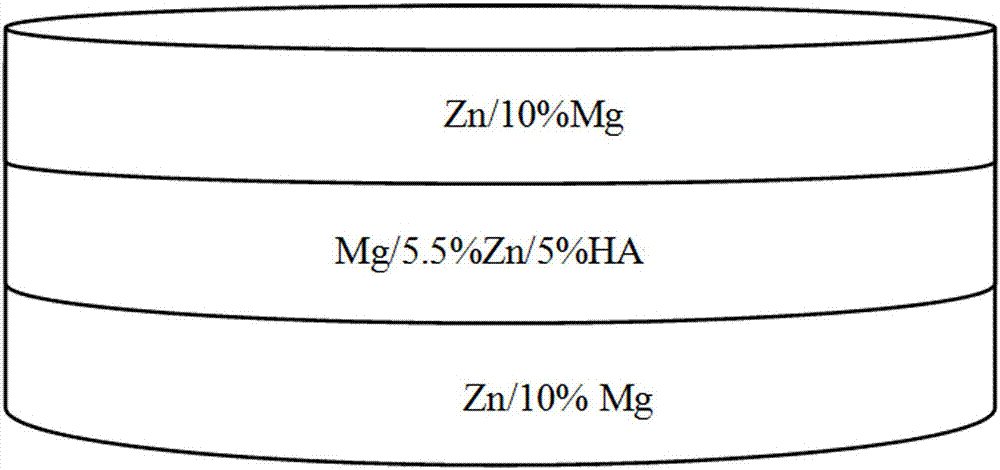
ActiveCN107385251AImprove the bonding strength of the interfaceNo debondingGradient materialStress shielding
The invention relates to a preparing method of a zinc magnesium function gradient biological composite. Magnesium powder, zinc powder and HA powder are adopted to serve as raw materials, ball milling powder mixing, die filling and vacuum discharge plasma sintering are carried out, and a zinc magnesium composite of two gradient structures is prepared. The preparing method is advanced in technology, data are full and accurate, a prepared zinc magnesium gradient material is high in combination strength on the interface, the debinding phenomenon is avoided, wear resistance and mechanical properties(the crush resistance strength is 293.66MPa, the elasticity modulus is 8.0 GPa, and breaking tenacity is 9.327 MPa.mm<1 / 2>) of all gradient layers are matched with the natural bone, the stress shielding effect is effectively avoided, and the preparing method is an ideal preparing method for a degradable biomedical metal gradient material.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
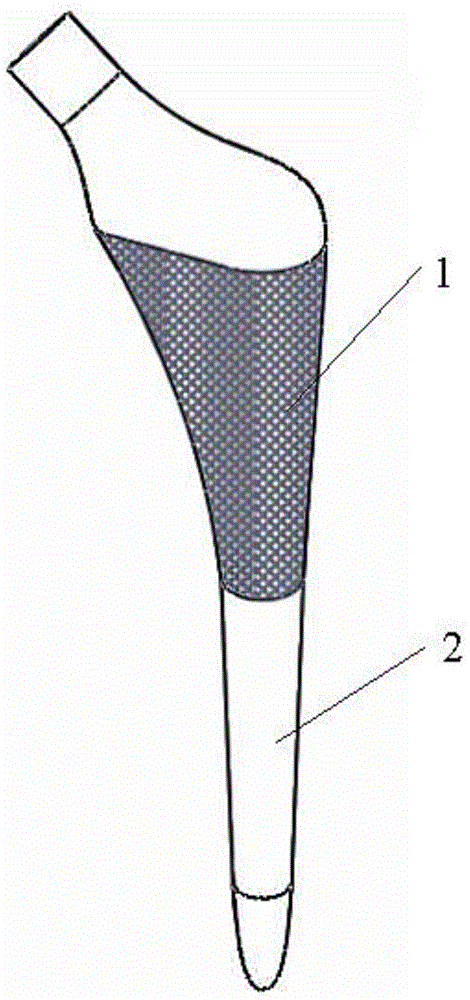
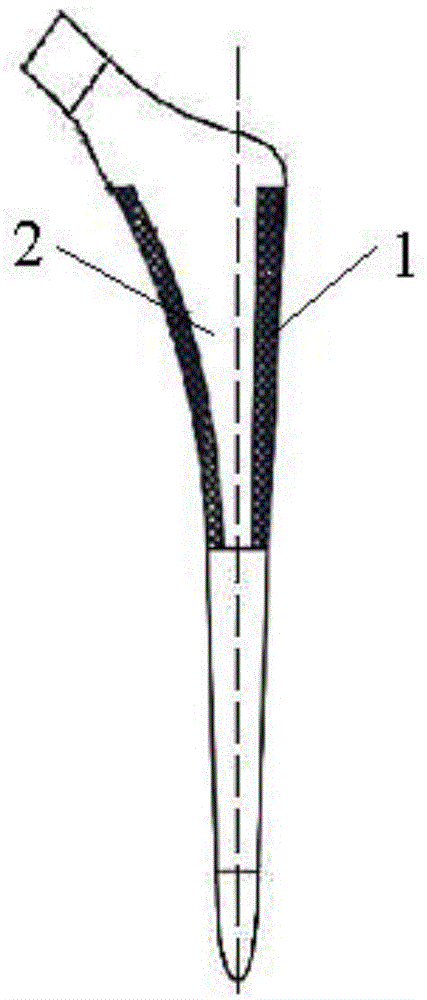
Low-elastic-modulus integrated titanium-based femoral handle and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104784760AReduce concentrated stressAlleviate shieldingProsthesisStress concentrationSelective laser melting
The invention discloses a low-elastic-modulus integrated titanium-based femoral handle and a preparation method thereof. According to the preparation method, a femoral handle model is designed by adopting CAD software; the model is divided into two parts; the first part adopts a porous scaffold structure, and the second part is a femoral handle body, wherein the porous scaffold structure coats the neck of the femoral handle body; the porous scaffold structure adopts cancellous bone-like porous scaffold design; pores are distributed uniformly; the pores are the same in size from the inside to the outside; the aperture range is 100 [mu]m to 1 mm; the depth range of a porous structure part is 40 to 60 percent of the depth of the cross section of a femur from the outside to the inside; the designed femoral handle model is converted into a CLI file with cross section processing information; according to the CLI file, the integrated titanium-based femoral handle is processed and manufactured layer by layer by adopting a selective laser fusing technology. According to the low-elastic-modulus integrated titanium-based femoral handle and the preparation method thereof, the problems of stress concentration and stress shielding of a combination interface of an implant and a bone tissue can be effectively reduced; moreover, the preparation method for the low-elastic-modulus integrated titanium-based femoral handle has good application in the field of biomedicine.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA INST OF COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com