Patents
Literature
116 results about "Host tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
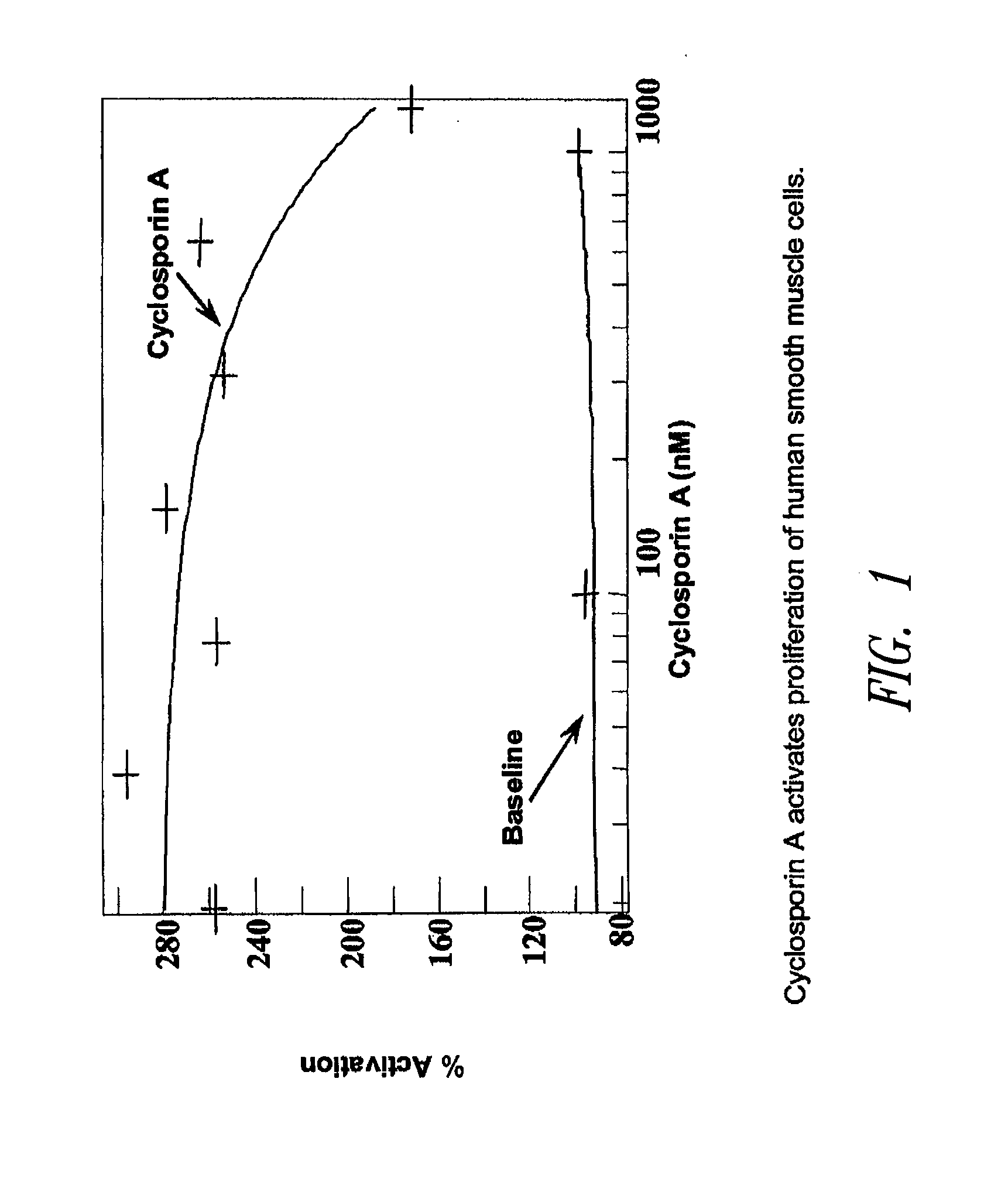
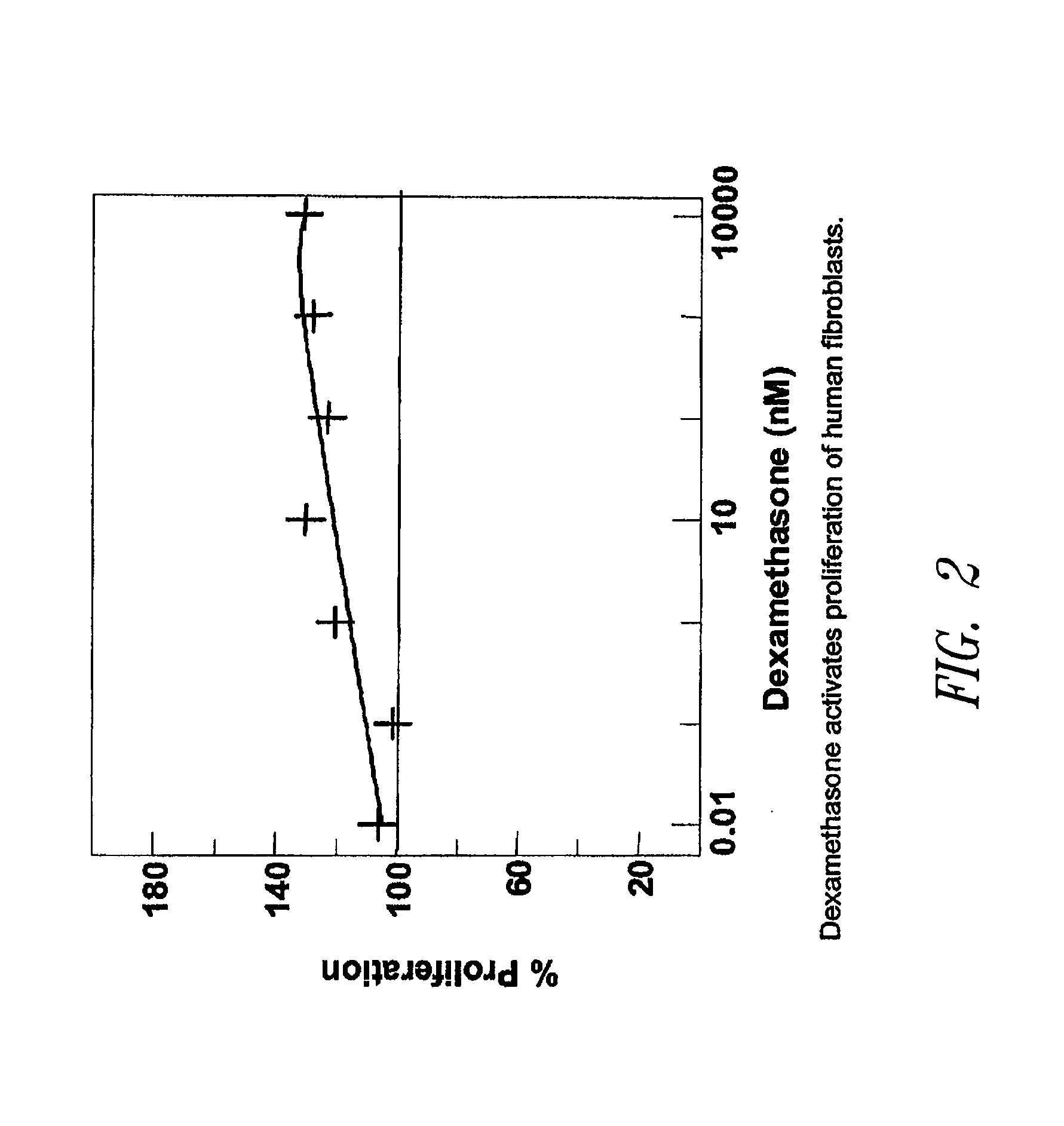
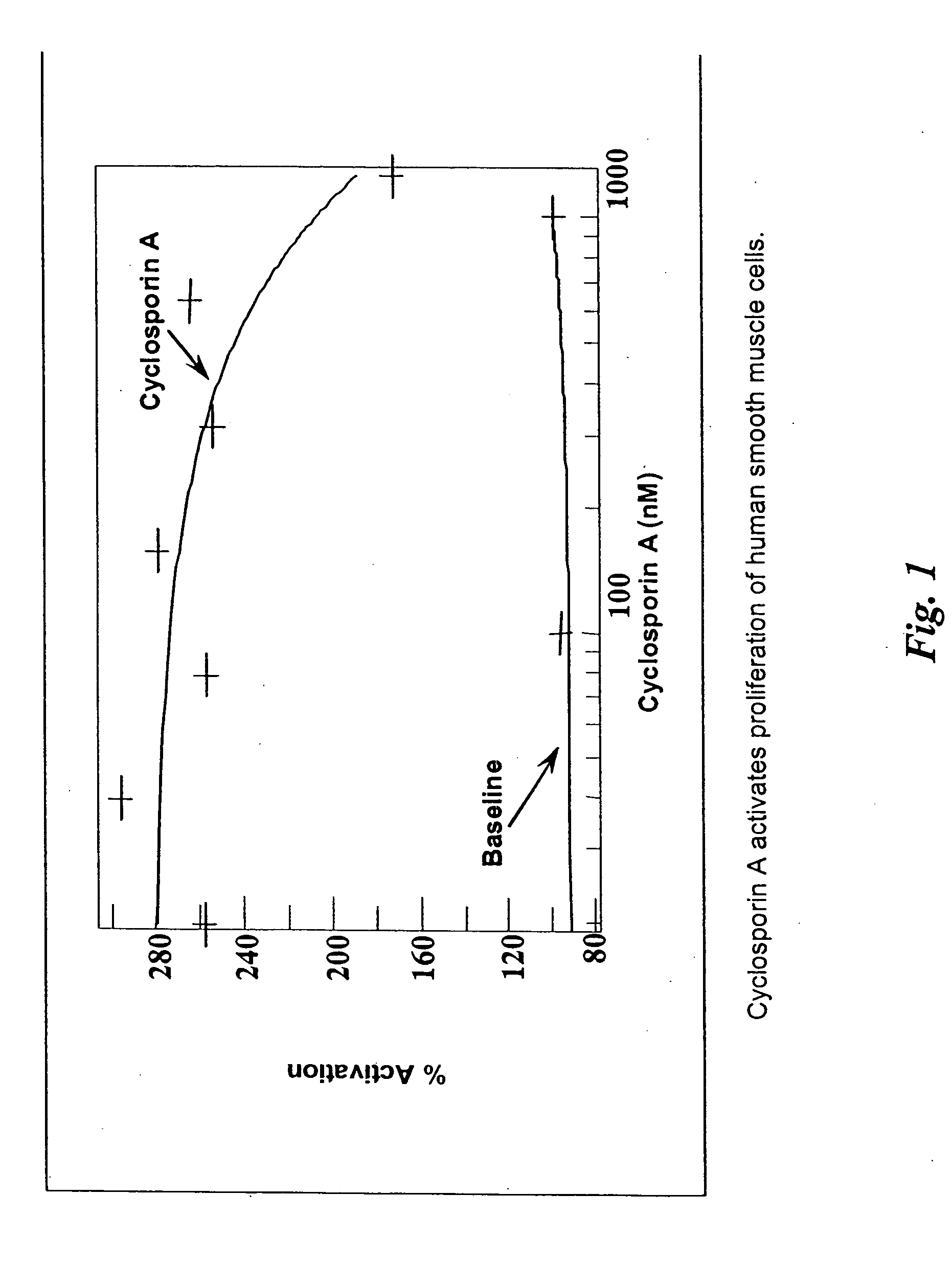
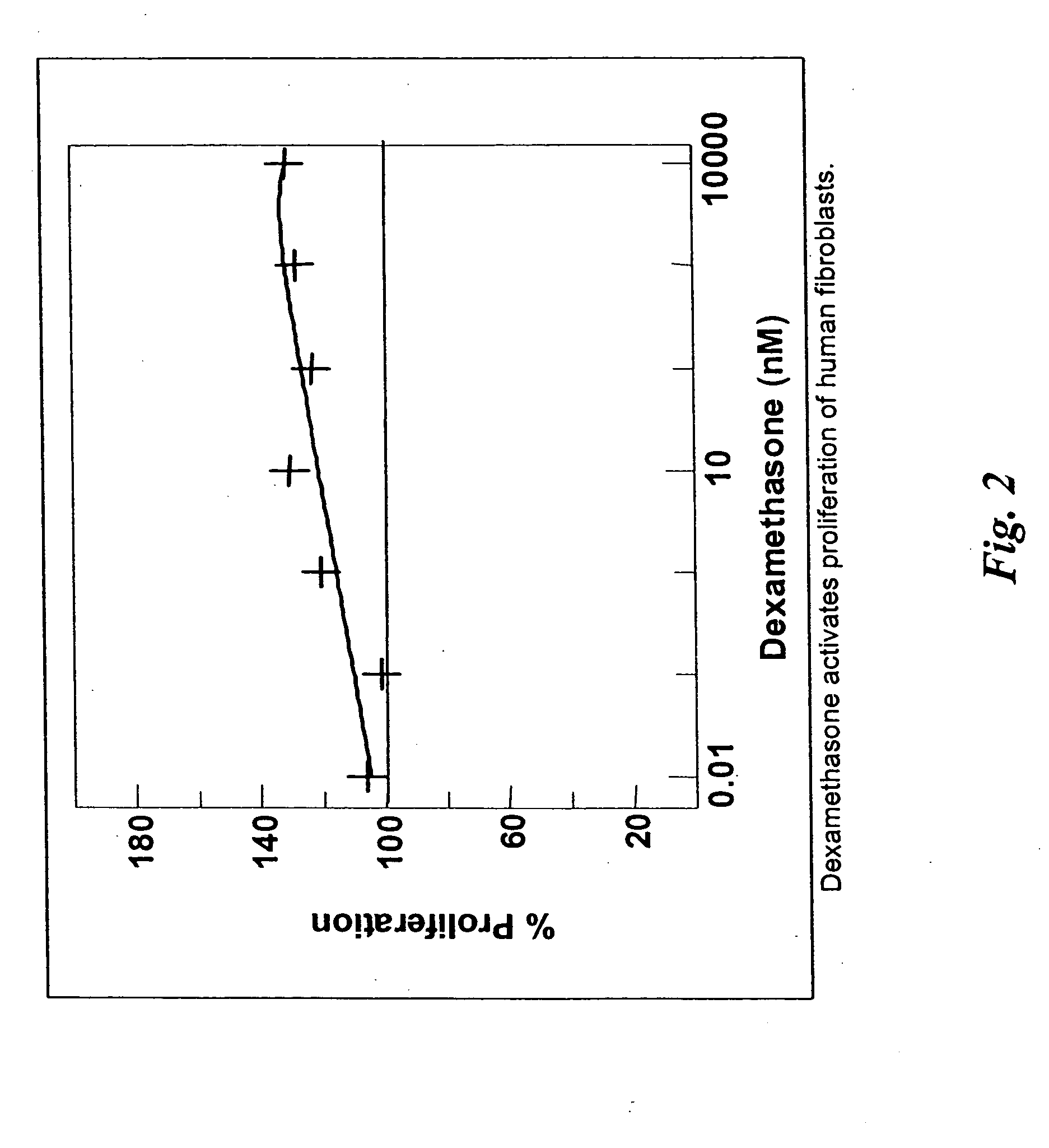
Host tissue defence concerns the biological response of tissues to environmental or infective agents that are encountered throughout life.
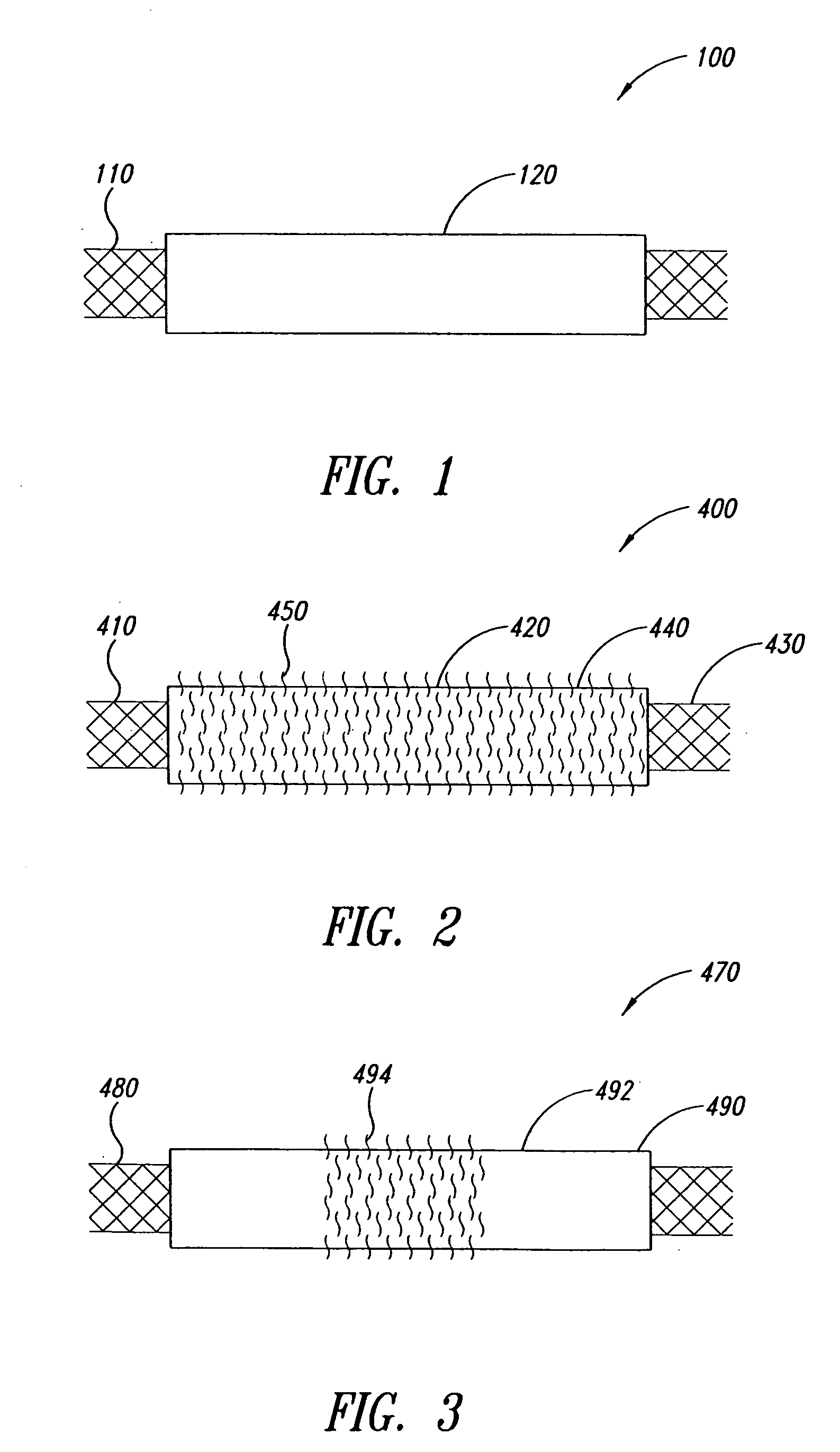
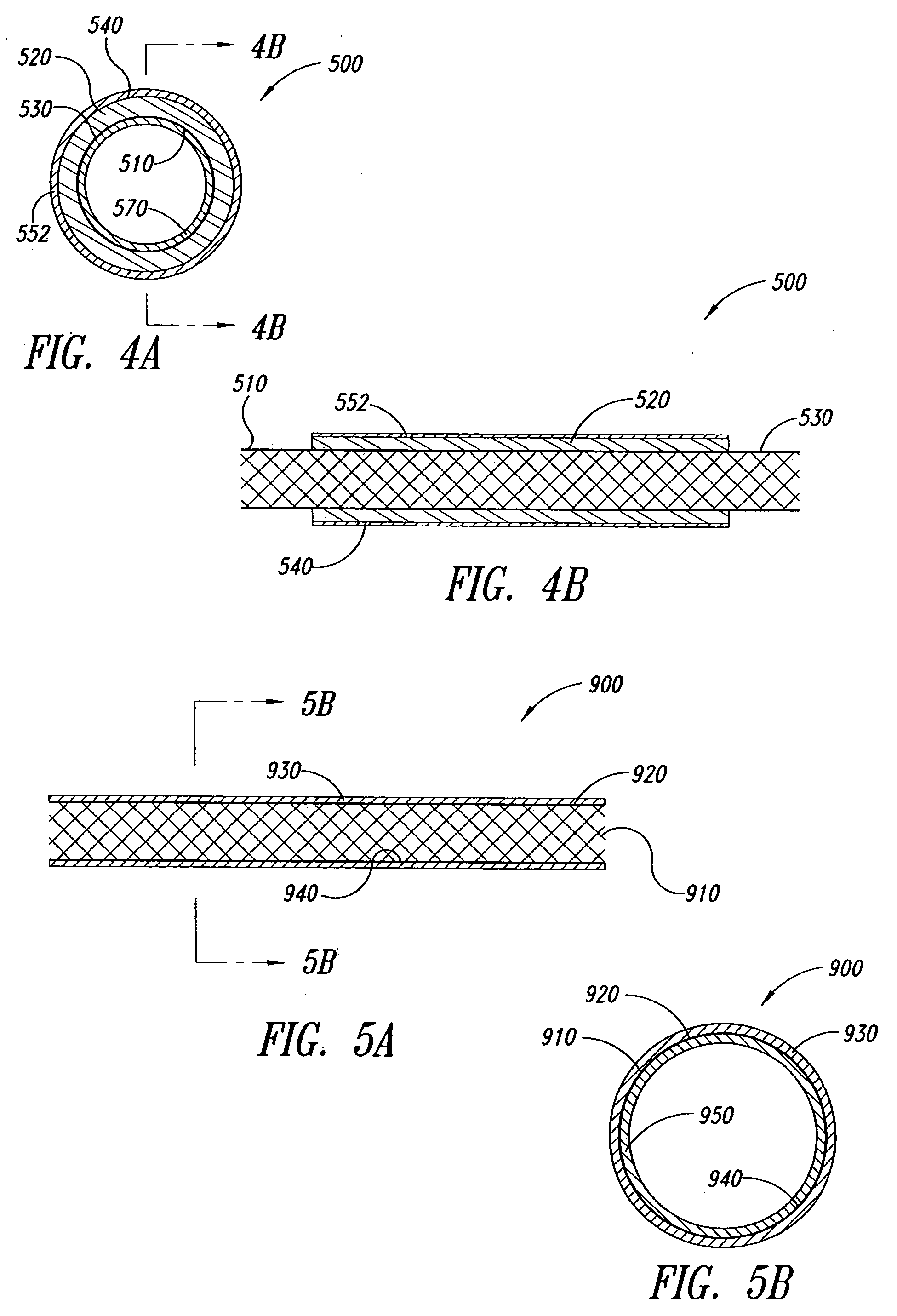
Devices and methods for treating defects in the tissue of a living being
InactiveUS7166133B2Restore mechanical and architectural and structural competenceSuture equipmentsPeptide/protein ingredientsHost tissueBiomedical engineering
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Transcutaneous analyte sensor
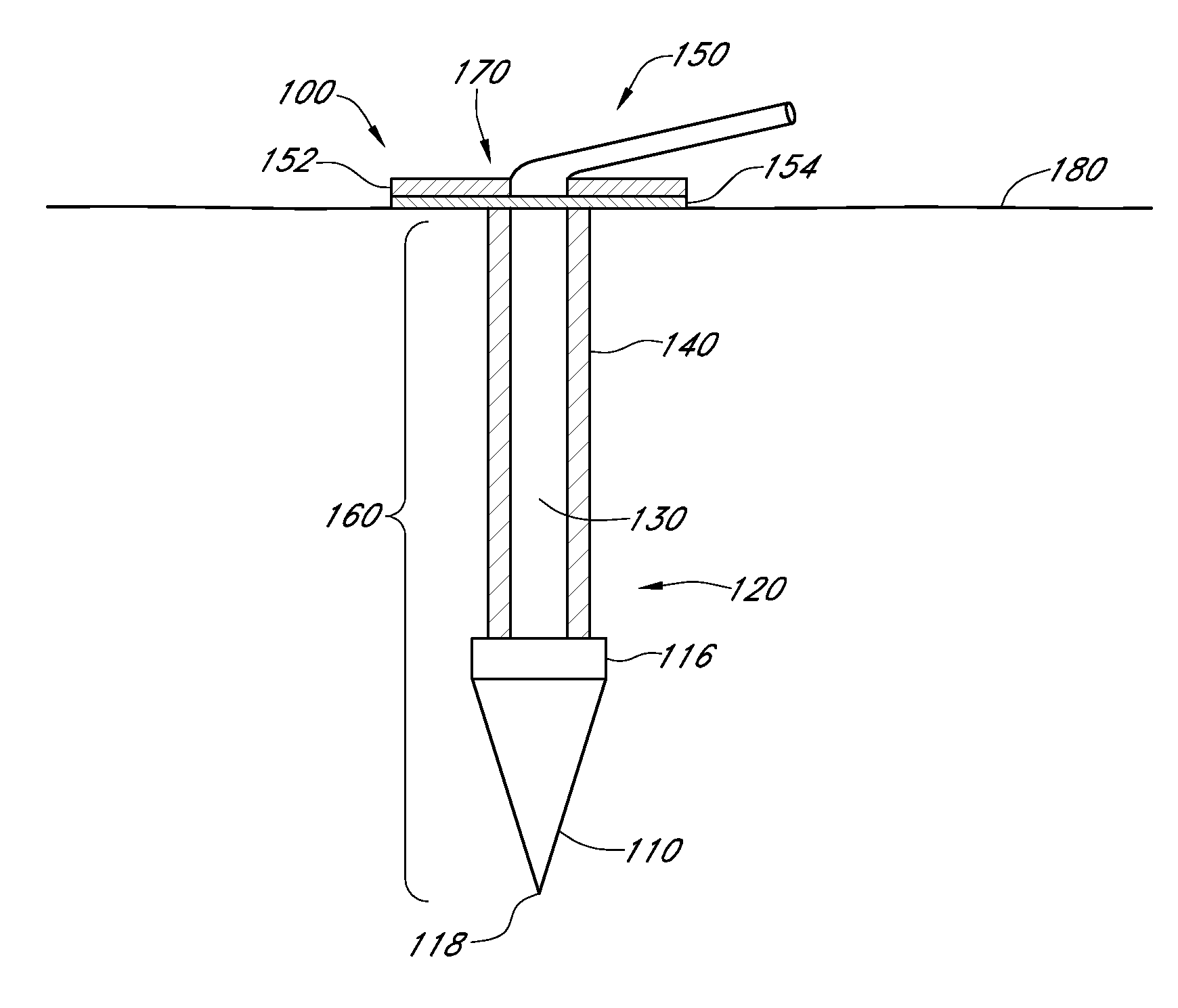
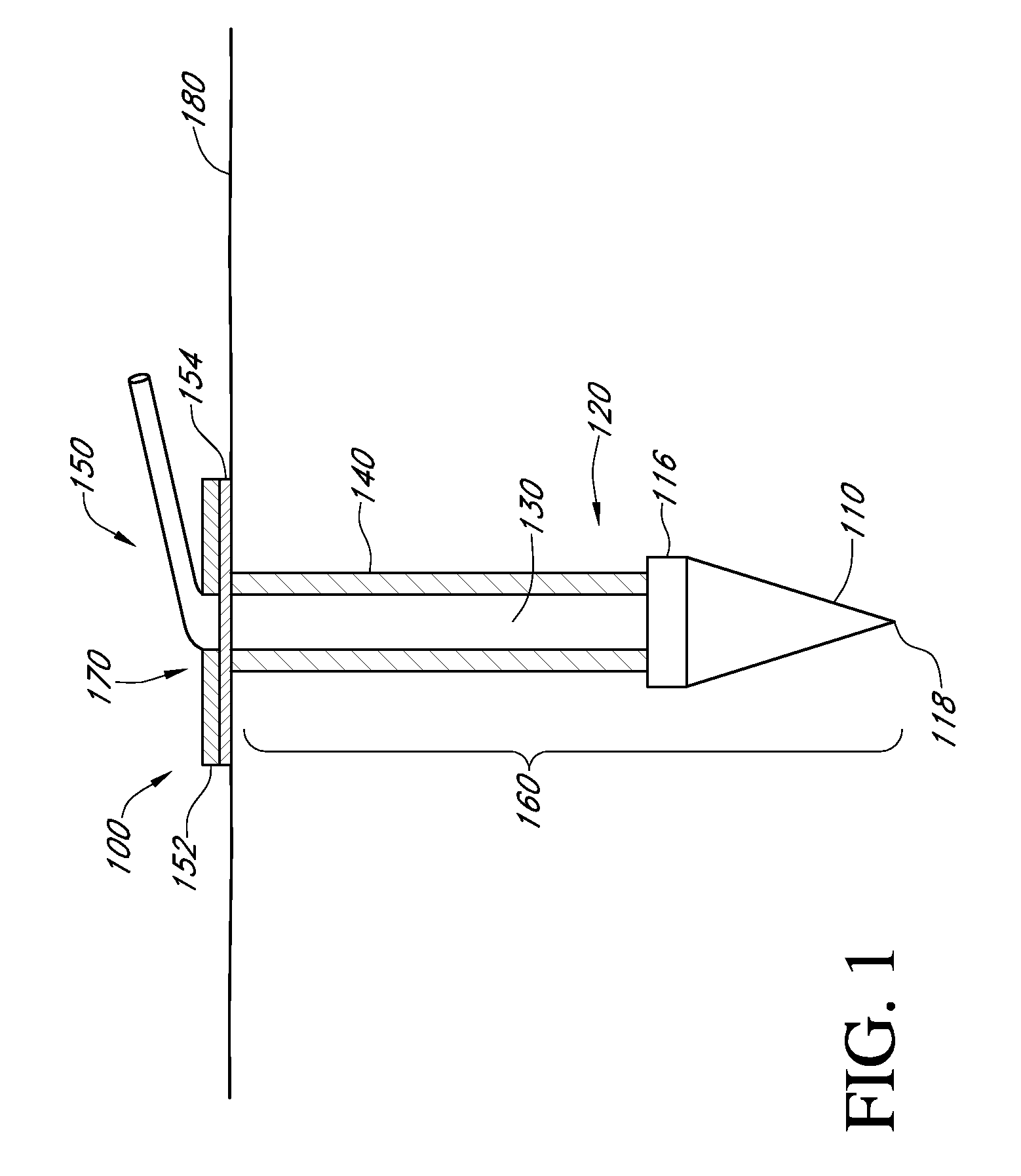
A transcutaneous sensor device configured for continuously measuring analyte concentrations in a host is provided. In some embodiments, the transcutaneous sensor device 100 comprises an in vivo portion 160 configured for insertion under the skin 180 of the host and an ex vivo portion 170 configured to remain above the surface of the skin 180 of the host after sensor insertion of the in vivo portion. The in vivo portion may comprise a tissue piercing element 110 configured for piercing the skin 180 of the host and a sensor body 120 comprising a material or support member 130 that provides sufficient column strength to allow the sensor body to be pushable in a host tissue without substantial buckling. The ex vivo portion 170 may be configured to comprise (or operably connect to) a sensor electronics unit and may comprise a mounting unit 150. Also described here are various configurations of the sensor body and the tissue piercing element that may be used to protect the membrane of the sensor body.
Owner:DEXCOM
Devices and methods for treating defects in the tissue of a living being
InactiveUS7156880B2Provide structural integrityRestore mechanical and architectural and structural competenceSuture equipmentsPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineHost tissue
An implantable material for deployment in select locations or select tissue for tissue regeneration is disclosed. The implant comprises collagen, ceramics, and or other bio-resorbable materials or additives, where the implant may also be used for therapy delivery. Additionally, the implant may be “matched” to provide the implant with similar physical and / or chemical properties as the host tissue.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Implantable prosthesis
InactiveUS6610006B1Reduce the possibilityReduce postoperative painDiagnosticsLigamentsRepair siteIntraabdominal pressure
An implantable prosthesis for repairing an anatomical defect, such as a soft tissue and muscle wall defect. The prosthesis is configured to reduce the likelihood that an applied force at the repair site, such as due to intraabdominal pressure or tissue shrinkage, can lead to detrimental effects associated with tension at the anchoring locations between the prosthesis and host tissue and / or contraction of the prosthesis. In this regard, the prosthesis may be configured to limit the amount of tension at the anchoring locations caused by the application of a force or pressure to the prosthesis and / or contraction of the prosthesis. Alternatively, the prosthesis may be configured to compensate for contraction of the prosthesis due to tissue shrinkage at the repair site. The prosthesis may be configured to both limit tension at the anchoring locations and compensate for tissue shrinkage. The prosthesis may facilitate a reduction in postoperative discomfort, a recurrence of the defect, or the creation of a new defect associated with tension and / or prosthetic contraction.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050149173A1Reducing perigraft leakageFacilitate “anchoring”StentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050149175A1Reducing perigraft leakageFacilitate “anchoring”StentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
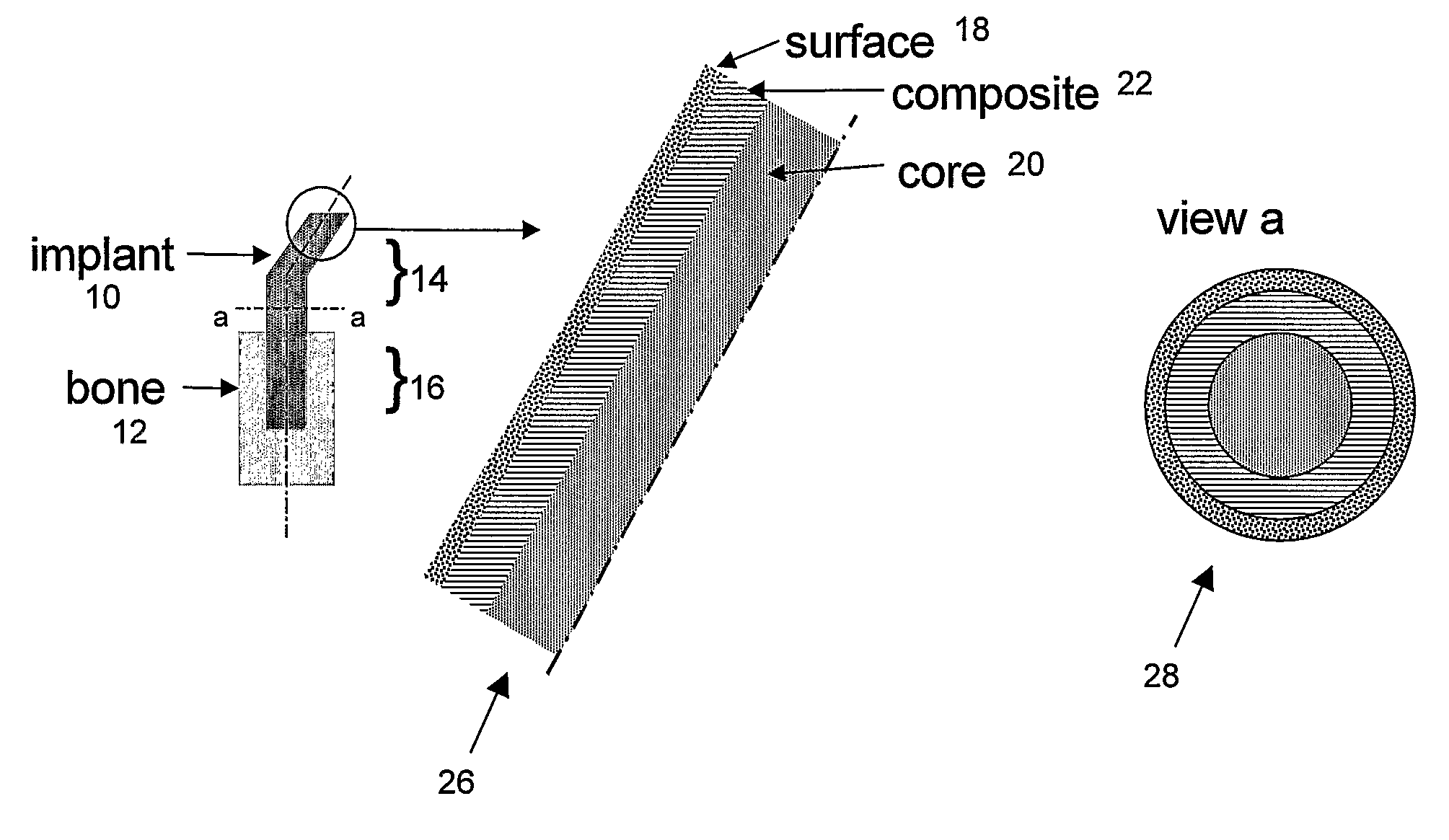
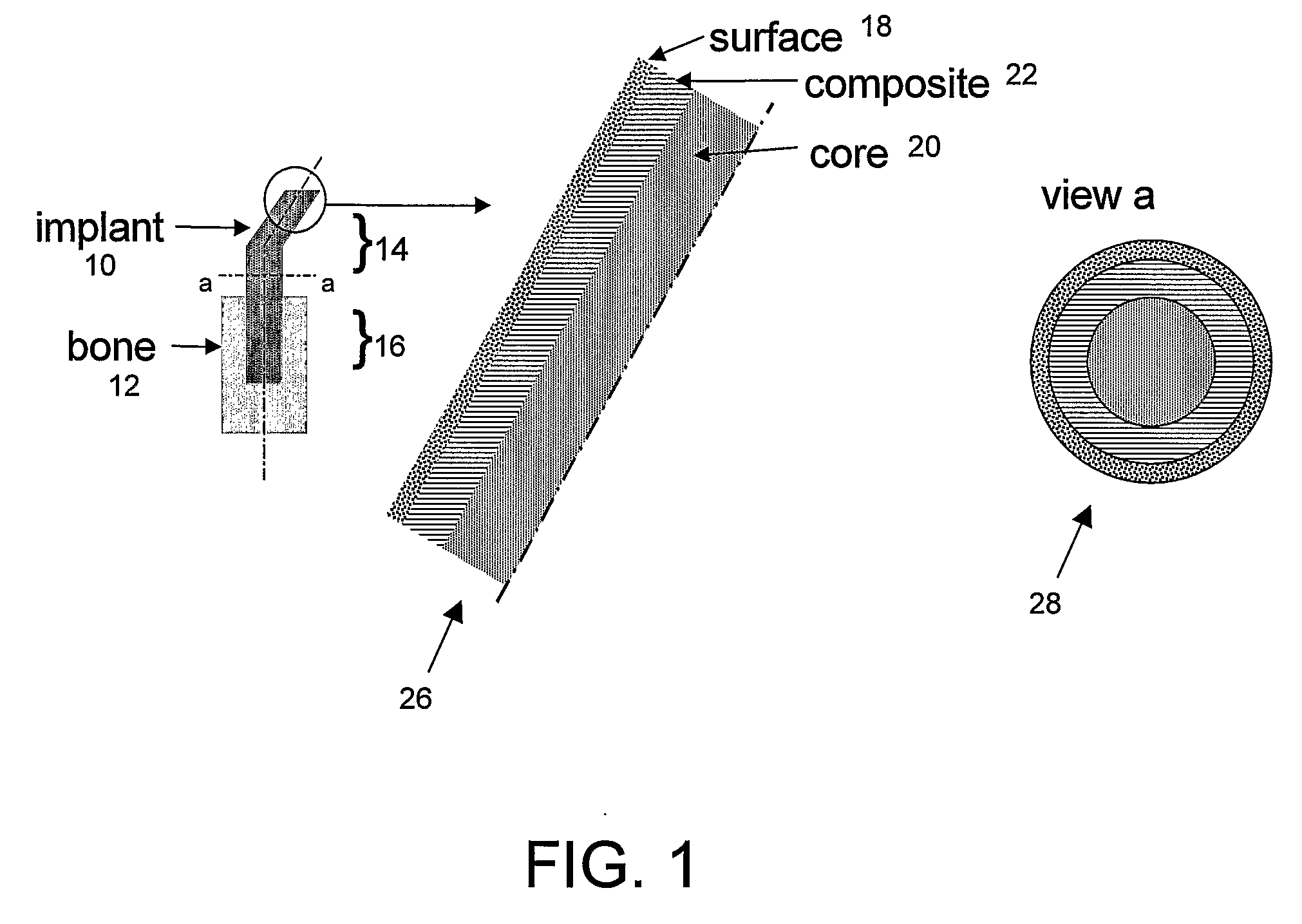
Implantable biomimetic prosthetic bone
InactiveUS20090177282A1Reduce riskMolten spray coatingLamination ancillary operationsNormal boneFiber-reinforced composite
Bone tissue at the interface of a bone implant is shielded from stresses found in normal bone because of the higher stiffness or rigidity in the implant versus in bone. The resulting “stress shielding” of the bone by the implant eventually results in resorption of bone at the bone-implant interface and ultimately necessitates replacement of the bone implant. To overcome these problems, an implantable biomimetic prosthetic bone having a porous surface, a fiber-reinforced composite structure, and a polymer-based core is disclosed. The prosthetic bone is a good match for structure, stiffness, viscoelastic properties, specific weight and overall structure as real bone or host tissues adjacent to the prosthetic bone. The prosthetic bone may be formed as a total hip prosthesis.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Soft tissue implants with improved interfaces
InactiveUS20060293760A1Facilitates dual functionInduce new tissue formationAnkle jointsBone implantHost tissueDual function
Specialization of the end(s) or host tissue contact points of biocompatible scaffolds brings a functionality to the scaffold that facilitates the dual function of inducing new tissue formation and facilitating attachment and site-specific tissue formation at the scaffolds' functionalized points of fixation.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US) +1
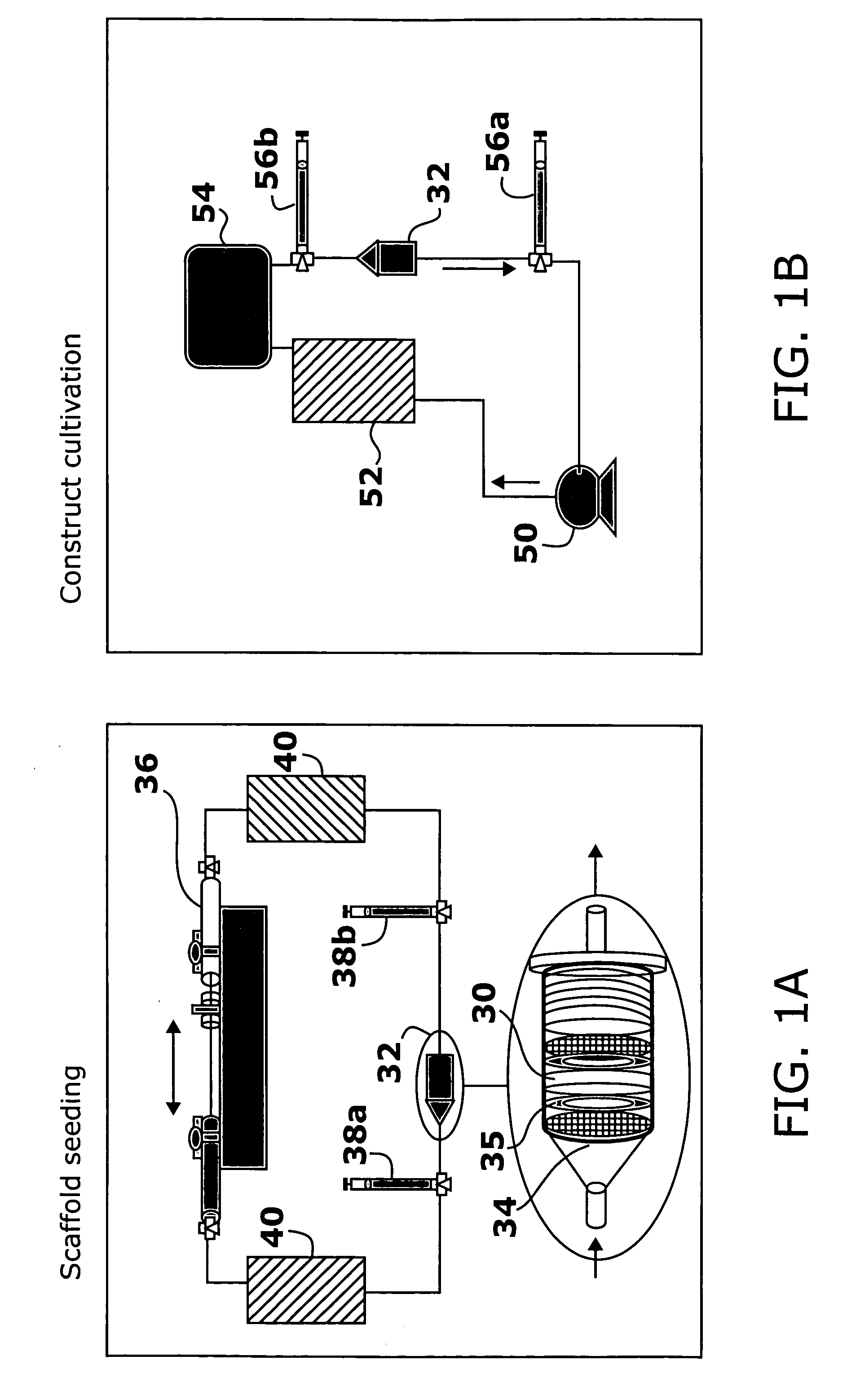
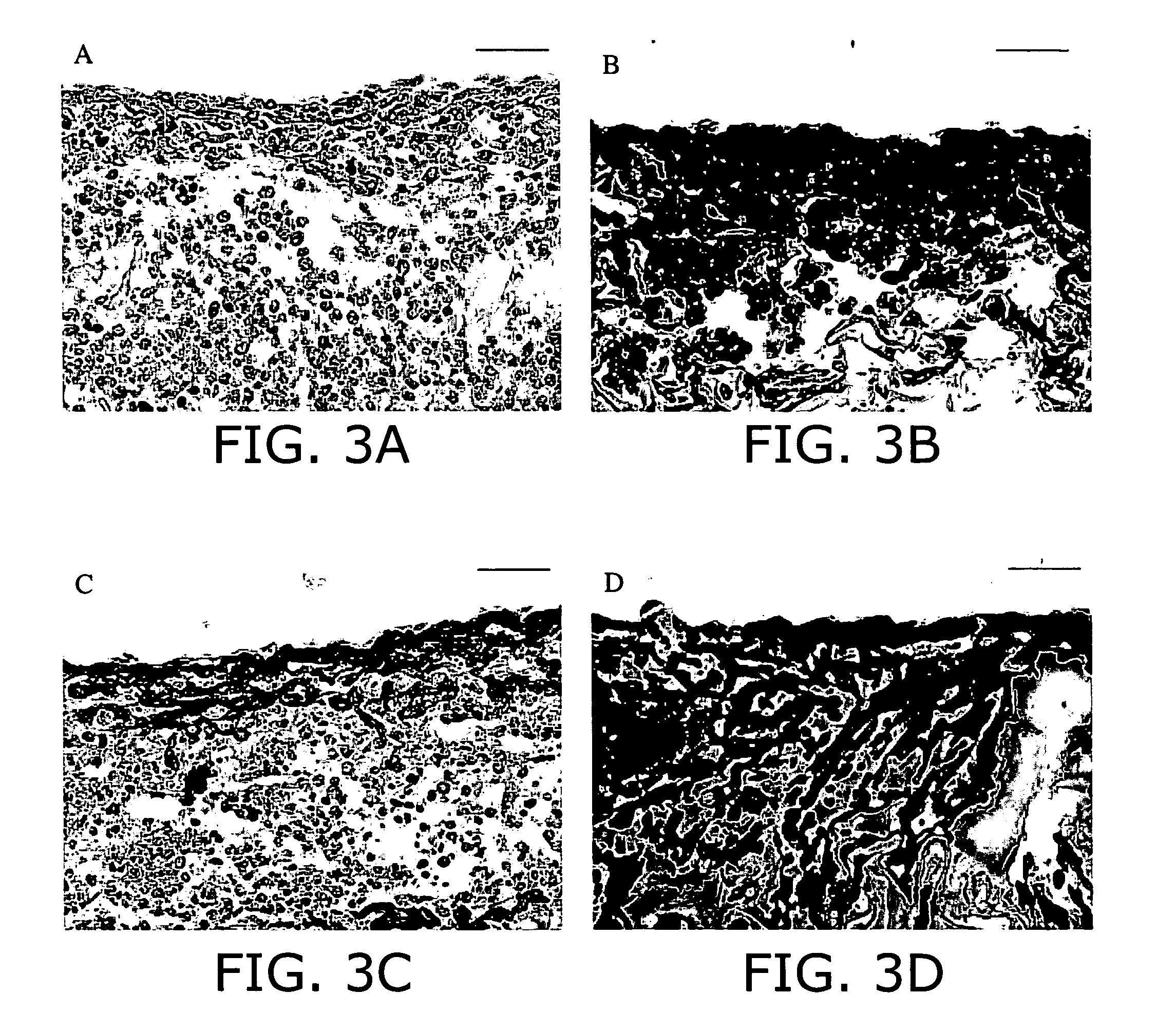
Application of electrical stimulation for functional tissue engineering in vitro and in vivo
InactiveUS20050112759A1Highly integratedImprove functionalityMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processIt integrationCell survival
The present invention provides new methods for the in vitro preparation of bioartificial tissue equivalents and their enhanced integration after implantation in vivo. These methods include submitting a tissue construct to a biomimetic electrical stimulation during cultivation in vitro to improve its structural and functional properties, and / or in vivo, after implantation of the construct, to enhance its integration with host tissue and increase cell survival and functionality. The inventive methods are particularly useful for the production of bioartificial equivalents and / or the repair and replacement of native tissues that contain electrically excitable cells and are subject to electrical stimulation in vivo, such as, for example, cardiac muscle tissue, striated skeletal muscle tissue, smooth muscle tissue, bone, vasculature, and nerve tissue.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050154454A1Facilitate “anchoring”Good curative effectStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050154445A1Facilitate “anchoring”Good curative effectStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Intravascular devices and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050154453A1Facilitate “anchoring”Good curative effectStentsPeptide/protein ingredientsFibrosisCoil embolization
Intravascular devices (e.g., stents, stent grafts, covered stents, aneurysm coils, embolic agents and drug delivery catheters and balloons) are used in combination with fibrosing agents in order to induce fibrosis that may otherwise not occur when the implant is placed within an animal or to promote fibrosis betweent the devices and the host tissues. Compositions and methods are described for use in the treatment of aneurysms and unstable arterial (vulnerable) plaque.
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Sutures and Anti-scarring agents
InactiveUS20090226500A1Reducing excessive scarringReducing surgical adhesionSuture equipmentsBiocideHost tissueFibrosis
Sutures are used in combination with anti-scarring agents to inhibit fibrosis between the sutures and the host tissues into which the sutures are inserted. Compositions and methods are described for use in reducing excessive scarring, surgical adhesion, and other disorders.
Owner:ANGIOTECH PHARMA INC
Sutures and fibrosing agents
InactiveUS20080009902A1Stable internal structureSuture equipmentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicineHost tissue
Sutures are used in combination with fibrosing agents to induce or stimulate fibrosis that between the sutures and the host tissues into which the sutures are inserted. Compositions and methods are described for use in lifting tissue, closing wound, and other applications.
Owner:ANGIOTECH PHARMA INC
Medical implants and fibrosis-inducing agents
InactiveUS20050169959A1Good curative effectInduce adhesion or fibrosis in the surrounding tissueHeavy metal active ingredientsInternal osteosythesisHost tissueIncreased fibrosis
Owner:ANGIOTECH INT AG (CH)
Bioerodible matrix for tissue involvement
InactiveUS20100249924A1Improve efficiencyPromote wound healingBiocideMammary implantsPorosityBreast implant
Disclosed herein are polyurethane polymer matrices with a porosity of from about 20 microns to about 90 microns that are useful in promoting closure and protection of incision sites; supporting the lower pole position of breast implants; and providing a partial or complete covering of breast implants to provide a beneficial interface with host tissue and to reduce the potential for malpositioning or capsular contracture. The disclosed matrices can be seeded with mammalian cells.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Absorbable implants for plastic surgery
ActiveUS20150223928A1Solve the lack of mechanical propertiesMinimization requirementsMammary implantsDiagnosticsPullout strengthThree dimensional shape
Absorbable implants for breast surgery that conform to the breast parenchyma and surrounding chest wall have been developed. These implants support newly lifted breast parenchyma, and / or a breast implant. The implants have mechanical properties sufficient to support a reconstructed breast, and allow the in-growth of tissue into the implant as it degrades. The implants have a strength retention profile allowing the support of the breast to be transitioned from the implant to regenerated host tissue, without significant loss of support. Three-dimensional implants for use in minimally invasive mastopexy / breast reconstruction procedures are also described, that confer shape to a patient's breast. These implants are self-reinforced, can be temporarily deformed, implanted in a suitably dissected tissue plane, and resume their preformed three-dimensional shape. The implants are preferably made from poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB) and copolymers thereof. The implants have suture pullout strengths that can resist the mechanical loads exerted on the reconstructed breast.
Owner:TEPHA INC
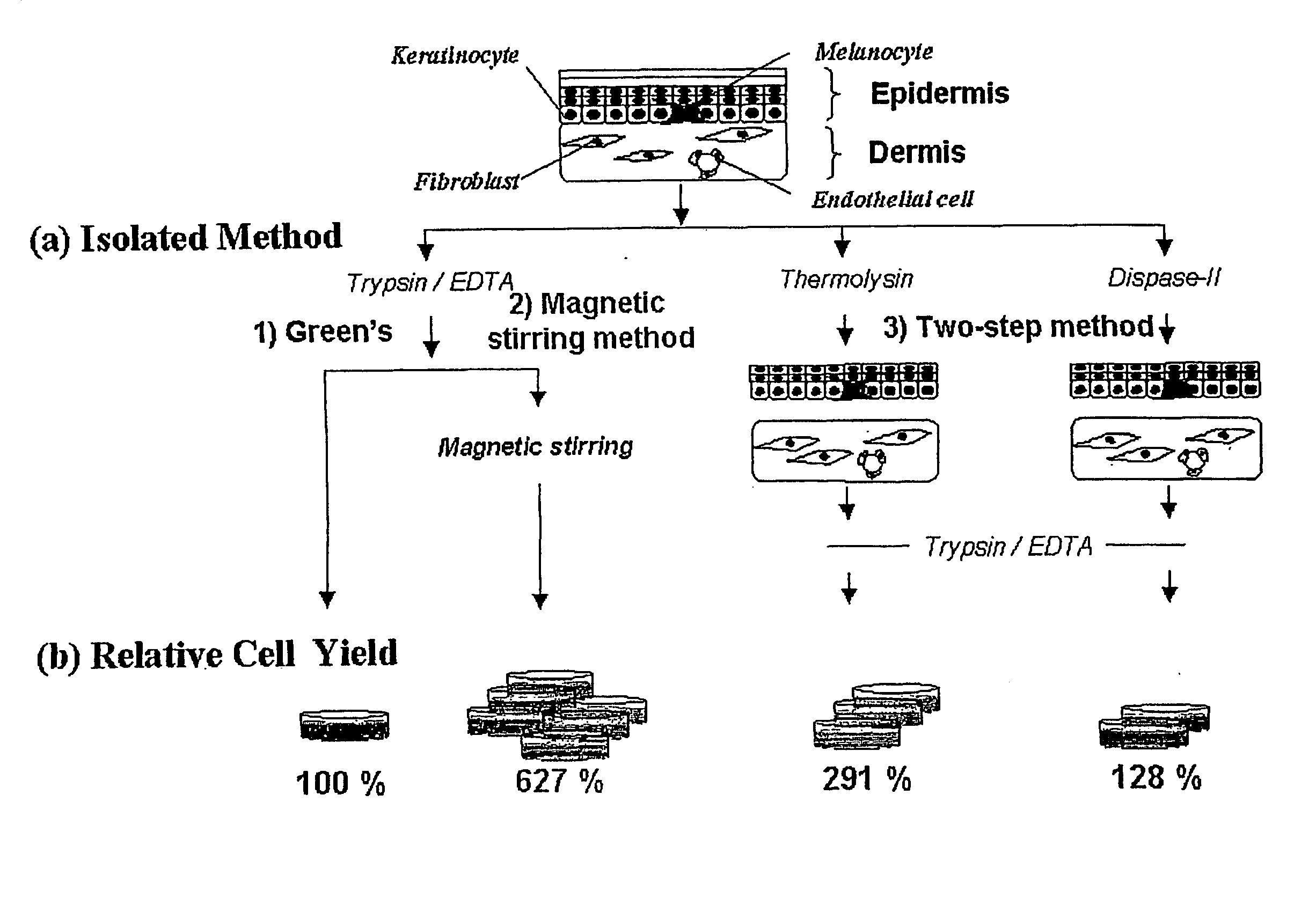
Method of isolating epithelial cells, method of preconditioning cells, and methods of preparing bioartificial skin and dermis with the epithelial cells or the preconditioned cells
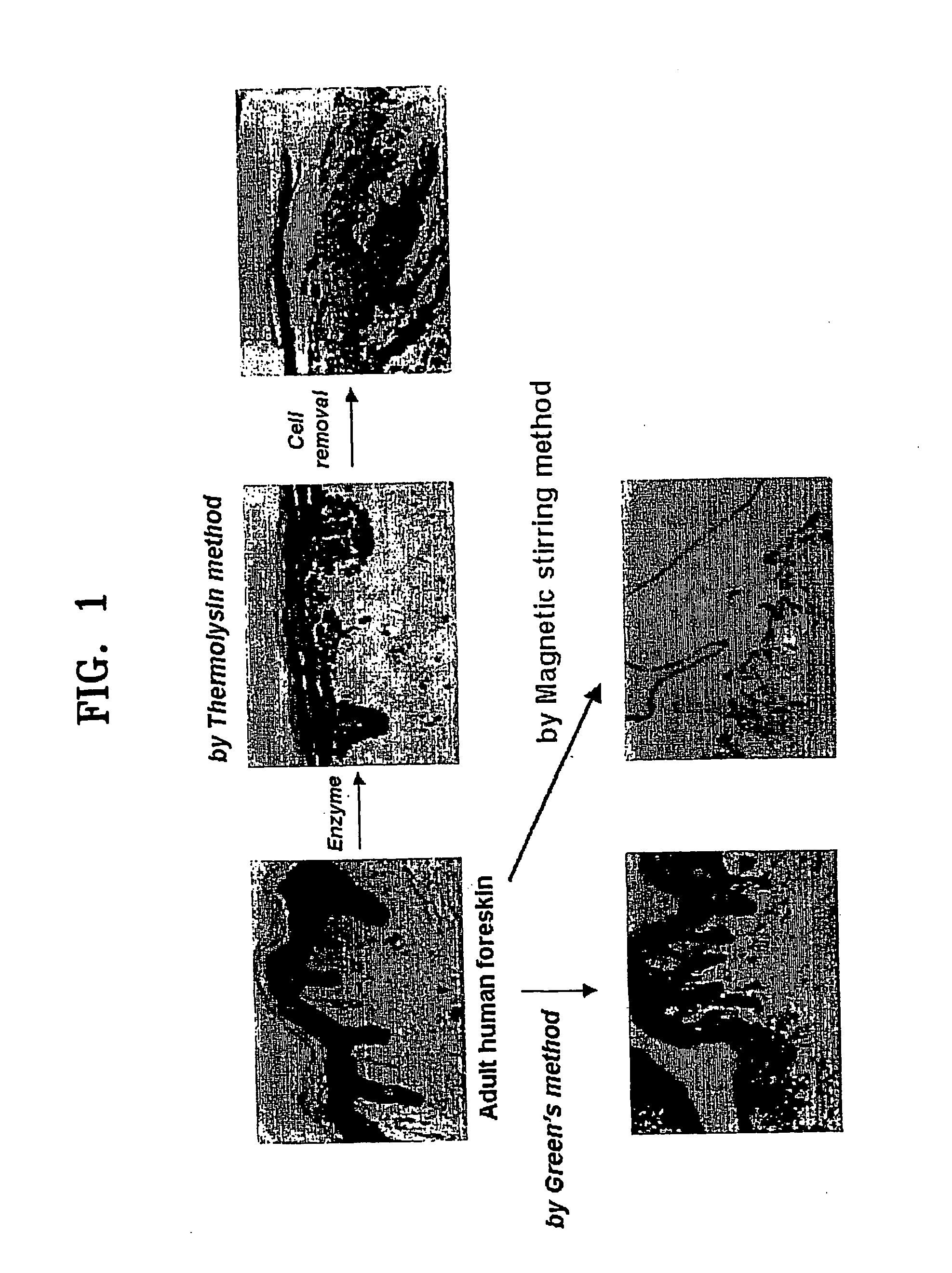
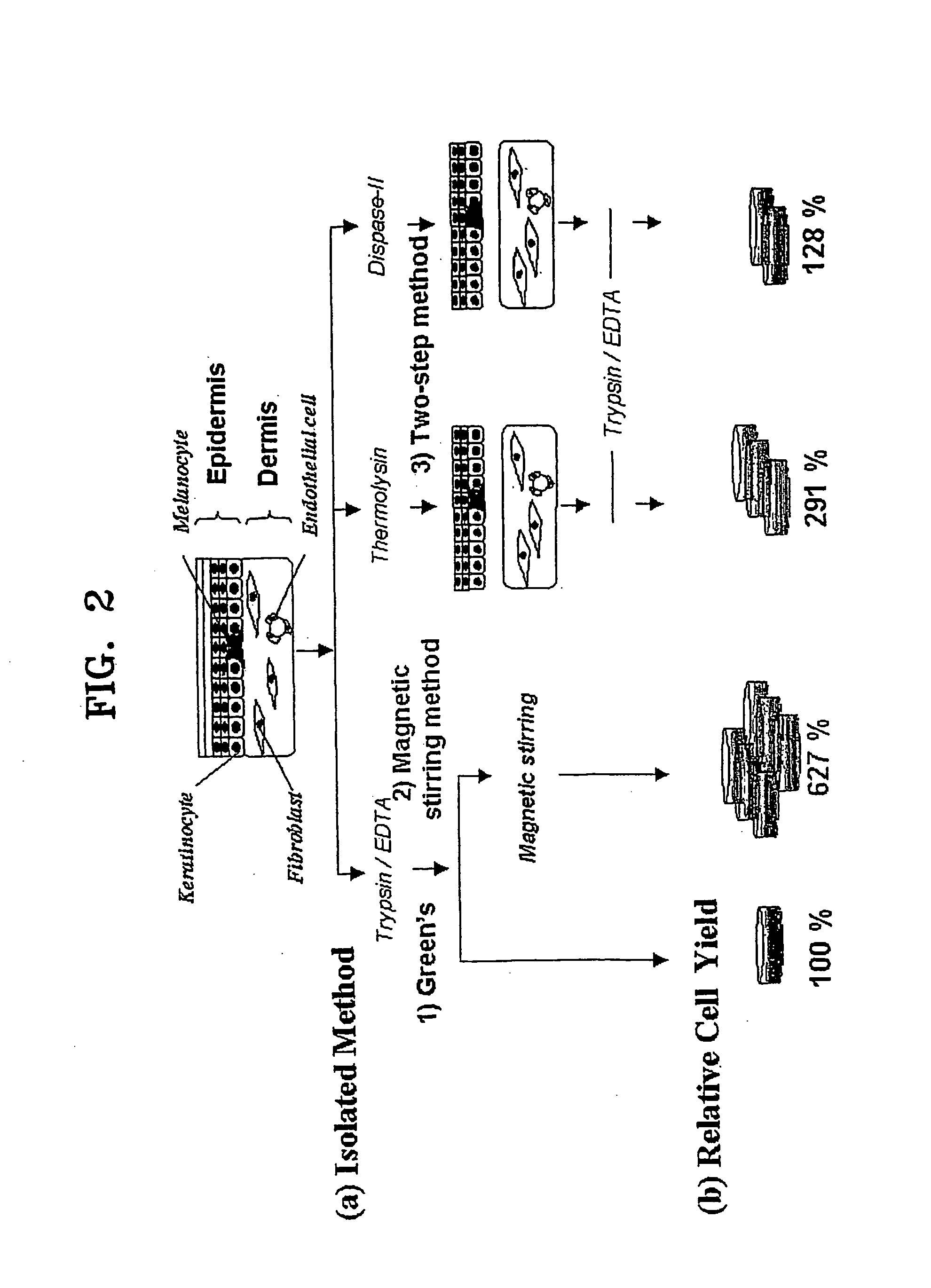
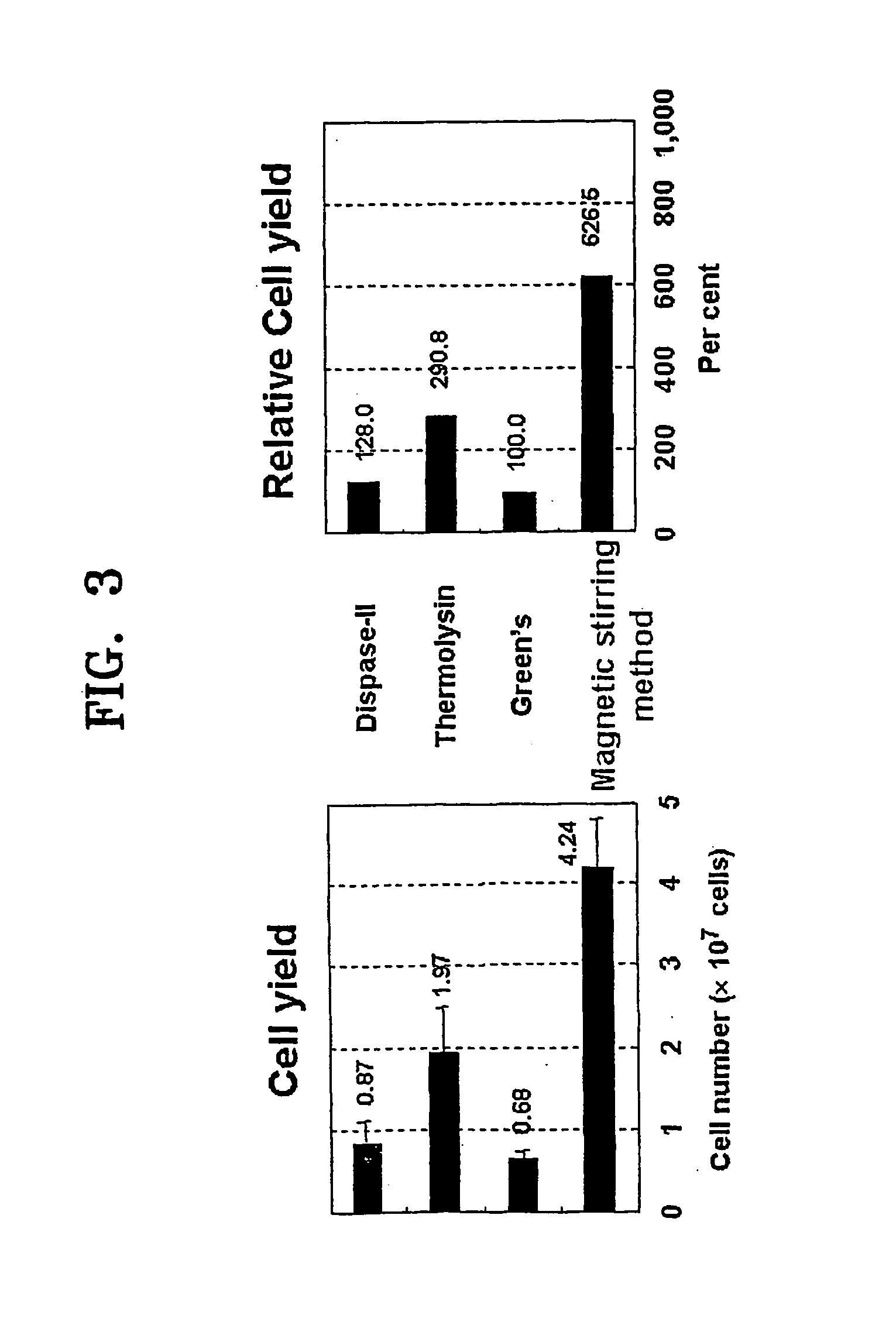
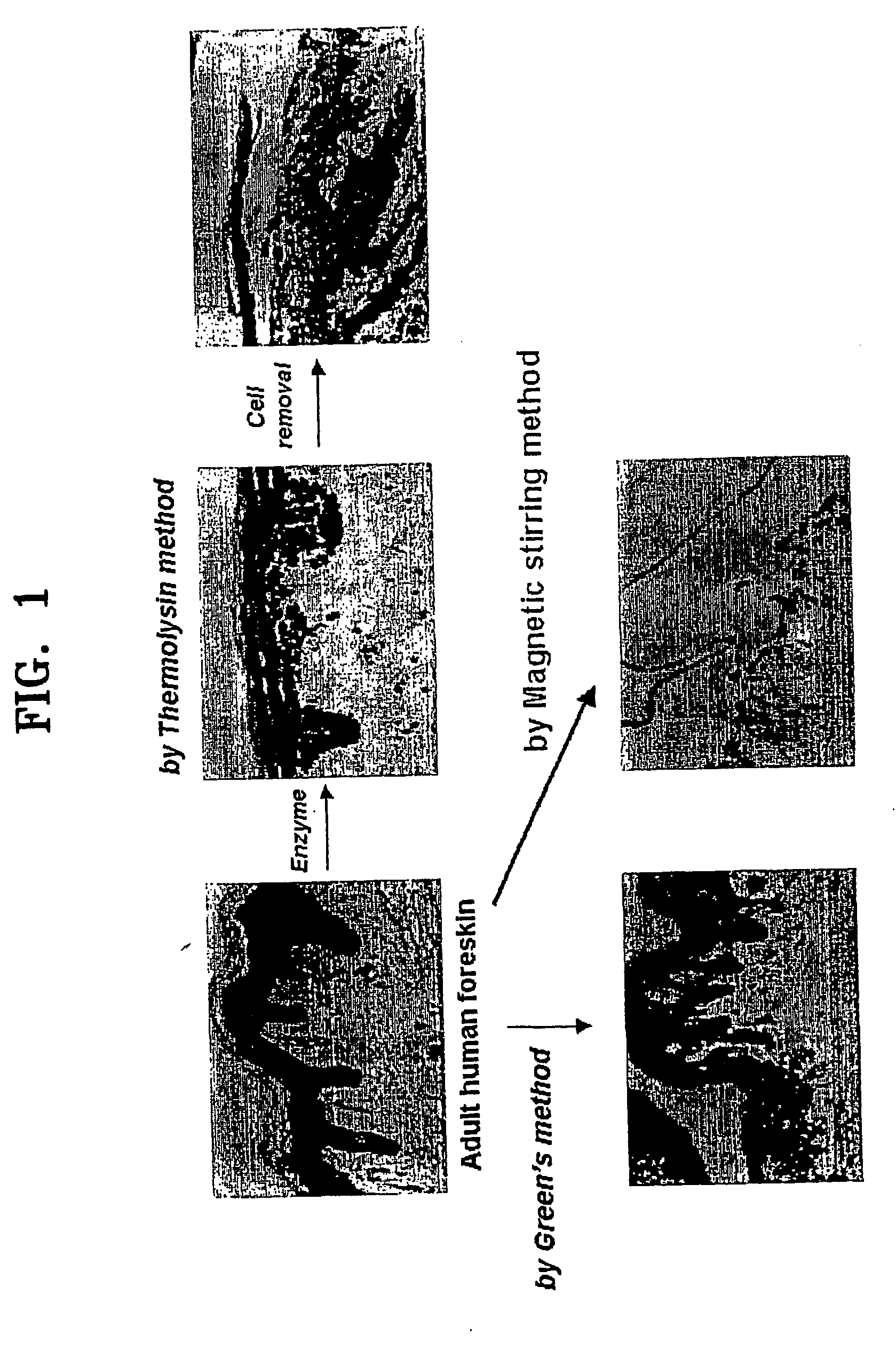
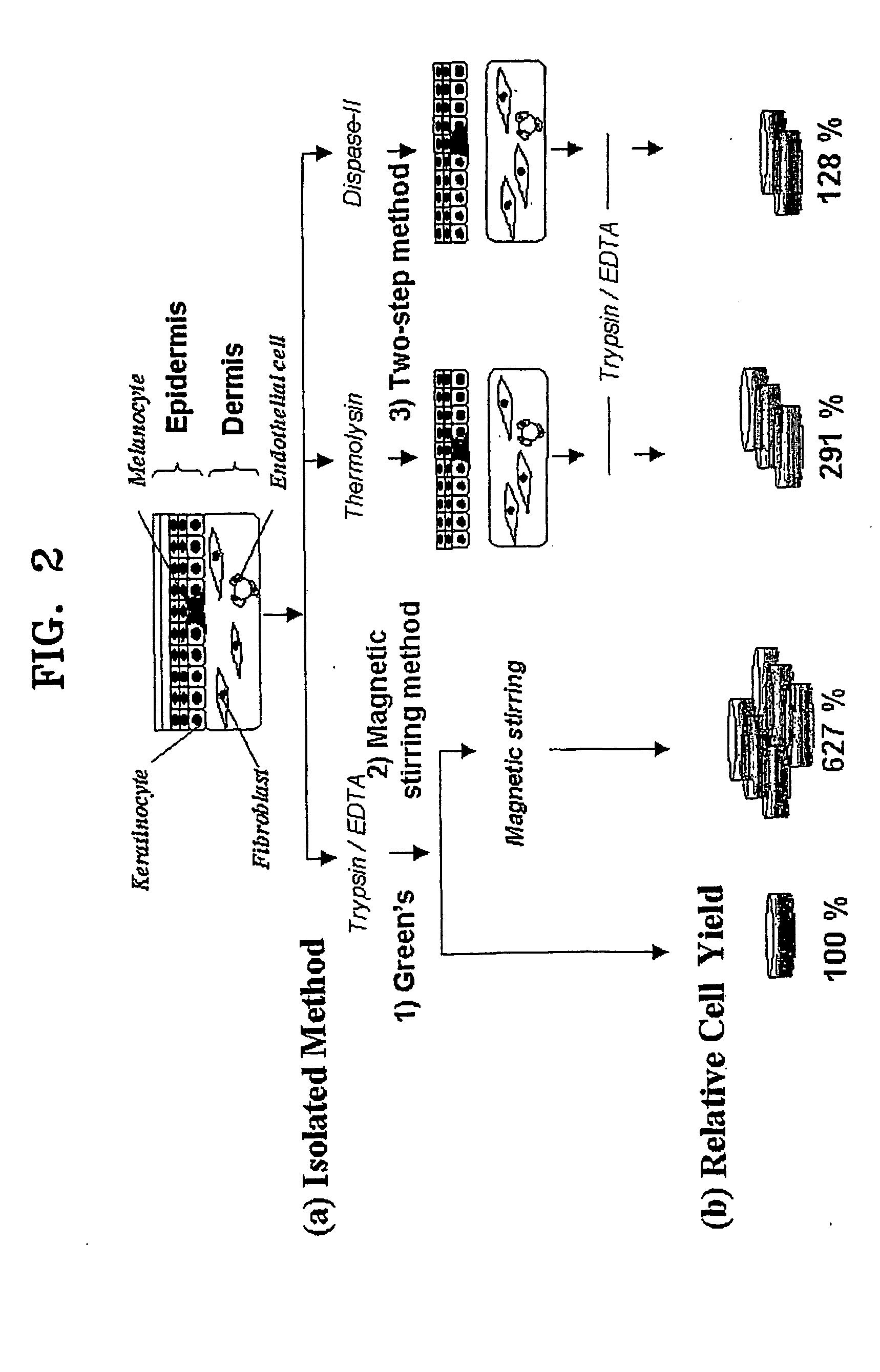
InactiveUS20060105454A1Increased cell yieldEasy to implantCell dissociation methodsEpidermal cells/skin cellsDamages tissueTrypsin
A method of isolating epithelial cells from a human skin tissue or internal organ tissue using trypsin and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) simultaneously with the application of magnetic stirring, a method of preconditioning isolated biological cells by the application of physical stimulus, i.e., strain, are provided. Epithelial cells can be isolated by the method with increased yield, colony forming efficiency (CFE), and colony size. Also, the increased percentage of stem cells in isolated cells is advantageous in therapeutic tissue implantation by autologous or allogeneic transplantation. In skin cells preconditioned by the application of strain, cell division is facilitated, and the secretion of extracellular matrix components and growth factors and the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are improved. When preconditioned cells are implanted by autologous or allogeneic transplantation to heal a damaged tissue, the improved cell adhesion, mobility, and viability provides a biological adjustment effect against a variety of stresses or physical stimuli which the cells would undergo after implantation, with improved capability of integration into host tissue, thereby markedly improving the probability of success in skin grafting.
Owner:KOREA INST OF RADIOLOGICAL & MEDICAL SCI
Bioerodible matrix for tissue involvement
InactiveUS20120209381A1Lower potentialImprove efficiencyBiocideMammary implantsPorosityBreast implant
Disclosed herein are polyurethane polymer matrices with a porosity of from about 20 microns to about 90 microns that are useful in promoting closure and protection of incision sites; supporting the lower pole position of breast implants; and providing a partial or complete covering of breast implants to provide a beneficial interface with host tissue and to reduce the potential for malpositioning or capsular contracture. The disclosed matrices can be seeded with mammalian cells.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Implantable prosthesis
InactiveUS20030187516A1Reduce the possibilityReduce postoperative painDiagnosticsSurgeryRepair siteIntraabdominal pressure
Owner:AMID PARVIZ K +1
Treatments for reduction of cytotoxicity and viral contamination of implantable medical devices
InactiveUS20060110370A1Reduce pathologic calcificationReduce pollutionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementCytotoxicityCalcification
A method for treating biomaterial is provided in which a biological tissue, typically after being cross-linked, is contacted with an anticalcification treatment solution under condition effective to render the biomaterial resistant to in vivo calcification upon implantation in a host animal. The anticalcification treatment solutions comprise higher alcohol solutions, a polyol solutions and / or a polar aprotic organic solvent solutions. Methods of reducing cytotoxicity to host tissue of bioprostheses that comprise fixed animal tissues, and treatments to reduce viral contamination of implantable medical devices are disclosed herein.
Owner:CARBOMEDICS
Absorbable Implants for Plastic Surgery
ActiveUS20160022416A1Sufficient mechanical propertyMinimization requirementsMammary implantsSurgeryPullout strengthThree dimensional shape
Absorbable implants for breast surgery that conform to the breast parenchyma and surrounding chest wall have been developed. These implants support newly lifted breast parenchyma, and / or a breast implant. The implants have mechanical properties sufficient to support a reconstructed breast, and allow the ingrowth of tissue into the implant as it degrades. The implants have a strength retention profile allowing the support of the breast to be transitioned from the implant to regenerated host tissue, without significant loss of support. Three-dimensional implants for use in minimally invasive mastopexy / breast reconstruction procedures are also described, that confer shape to a patient's breast. These implants are self-reinforced, can be temporarily deformed, implanted in a suitably dissected tissue plane, and resume their preformed three-dimensional shape. The implants are preferably made from poly-4-hydroxybutyrate (P4HB) and copolymers thereof. The implants have suture pullout strengths that can resist the mechanical loads exerted on the reconstructed breast
Owner:TEPHA INC
Bioerodible matrix for tissue involvement
InactiveUS20120207837A1Lower potentialImprove efficiencyPowder deliveryBiocidePorosityBreast implant
Disclosed herein are polyurethane polymer matrices with a porosity of from about 20 microns to about 90 microns that are useful in promoting closure and protection of incision sites; supporting the lower pole position of breast implants; and providing a partial or complete covering of breast implants to provide a beneficial interface with host tissue and to reduce the potential for malpositioning or capsular contracture. The disclosed matrices can be seeded with mammalian cells.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Uses of immunologically modified scaffold for tissue prevascularization cell transplantation
This invention provides method of making and using of a porous 3 dimensional cyclic RGD peptide-modified alginate scaffold that can be loaded with different cell types and / or growth factors for implantation at sites of tissue damage to promote tissue regeneration. The cyclic RGD peptide promotes vascular formation of the host tissue, cell binding and survival of seeded cells. Scaffolds with growth factors but without cells can also be implanted to create a vascular bed in which cells are transplanted at a later time point.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Formula and method for immobilizing tick sample for scanning electron microscopy
InactiveCN105486554ADry and completeShort timePreparing sample for investigationFreeze-dryingHigh energy
The invention relates to a formula and method for immobilizing a tick sample for scanning electron microscopy, which belongs to the technical field of methods for immobilizing samples for scanning electron microscopy. The immobilization formula comprises a PBS buffer solution, polysorbate and glutaraldehyde, and a glutaraldehyde immobilization liquid is prepared from the above-mentioned components. The method comprises the following steps: (1) observing whether host tissue is left in basis capituli of the tick sample and if so, removing the host tissue; (2) cleaning the surface of the tick sample; (3) immobilizing the tick sample at room temperature by using the glutaraldehyde immobilization liquid; (4) carrying out gradient dehydration with ethanol on the immobilized tick sample; (5) putting the tick sample into mixed liquor of absolute ethyl alcohol and acetone for displacement, and then putting the tick sample into acetone for displacement; and (6) drying the tick sample in a vacuum freeze drying instrument for drying and spraying gold on the tick sample. During scanning electron microscopic observation, the phenomenon of fuzzy and foggy images or incapable imaging due to ionization discharging of the sample as water vapor produced after electron beam bombardment of the sample encounters high-energy electron streams is prevented.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Full contour breast implant
Full contour absorbable implants for breast surgery redistribute breast volume between the breast's upper and lower poles in exact and desirable ratios. The implants preferably redistribute breast volume so that the upper pole breast volume is 20-40% of the total volume, and the lower pole breast volume is 60-80% of the total volume. The implants are also designed to provide specific curvatures to the poles of the breast, and to angulate the nipple areolar complex slightly skyward so that the patient's nipple is positioned at an angle above the nipple meridian reference line. The implants are designed to be transitory, with sufficient strength retention to allow transition from support of the breast by the implant to support by regenerated host tissue growing in and around the implants, without any significant loss of support during or subsequent to remodeling. The implants may optionally be used with permanent breast implants.
Owner:TEPHA INC
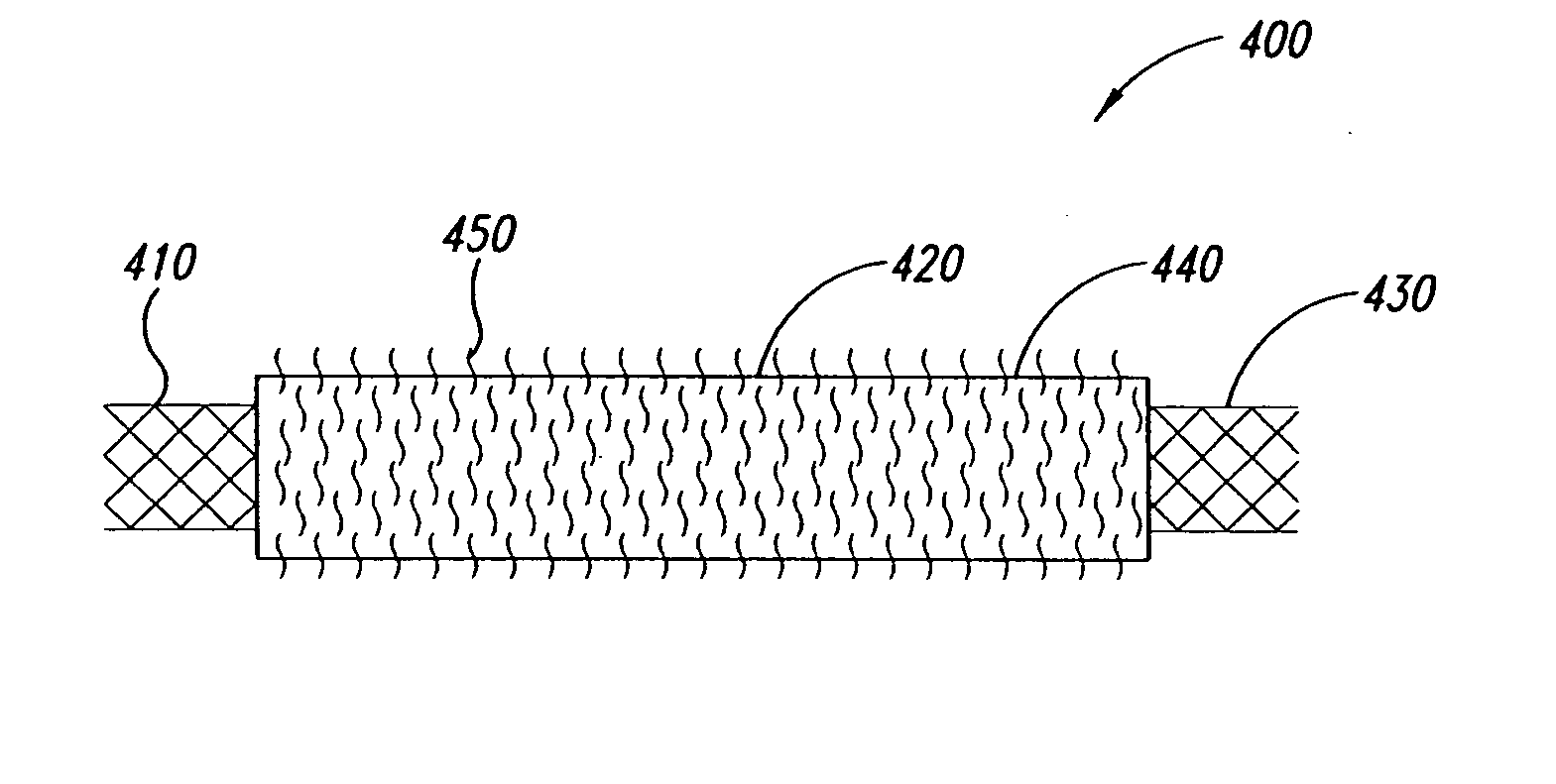
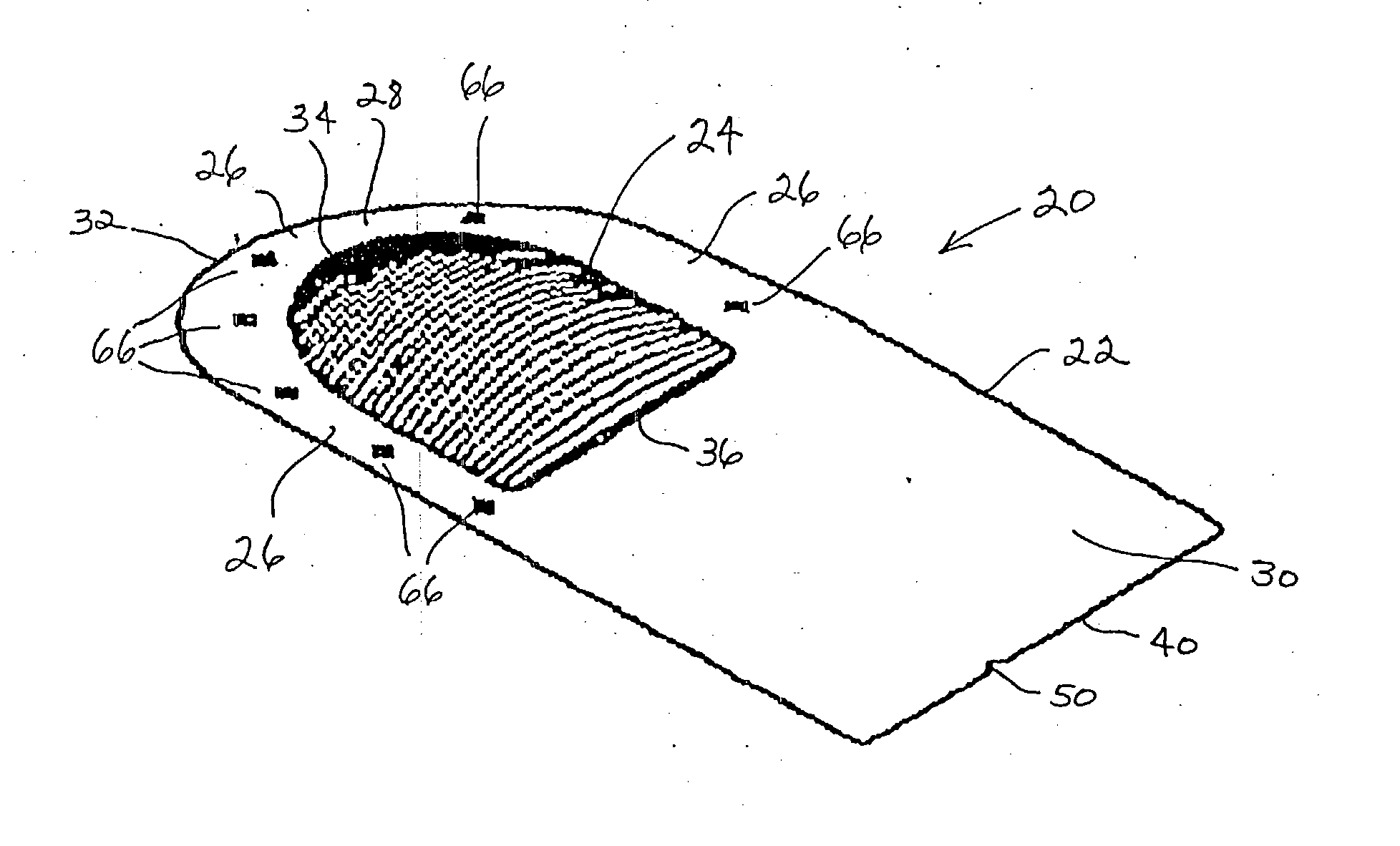
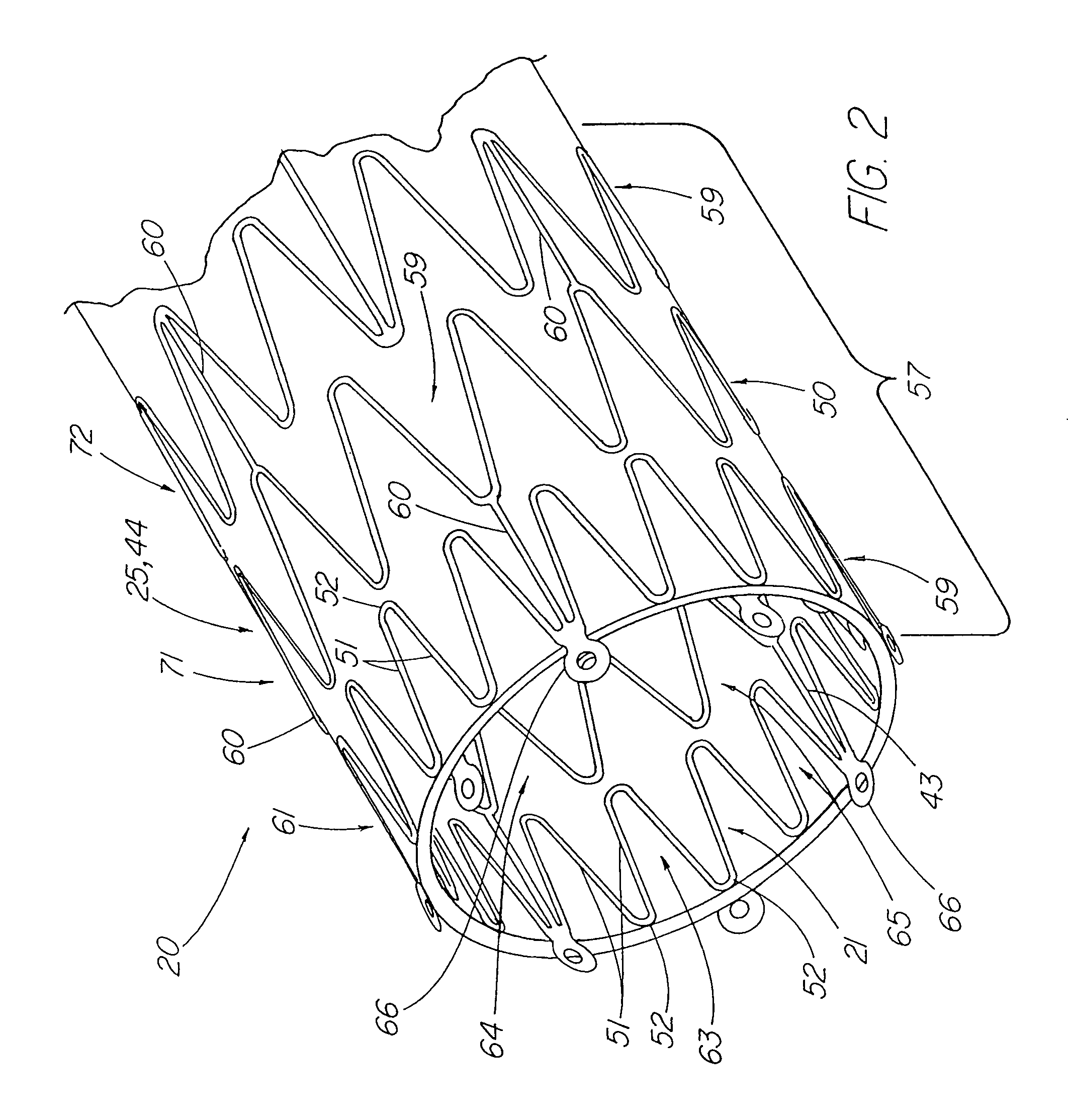
Stent tissue graft prosthesis
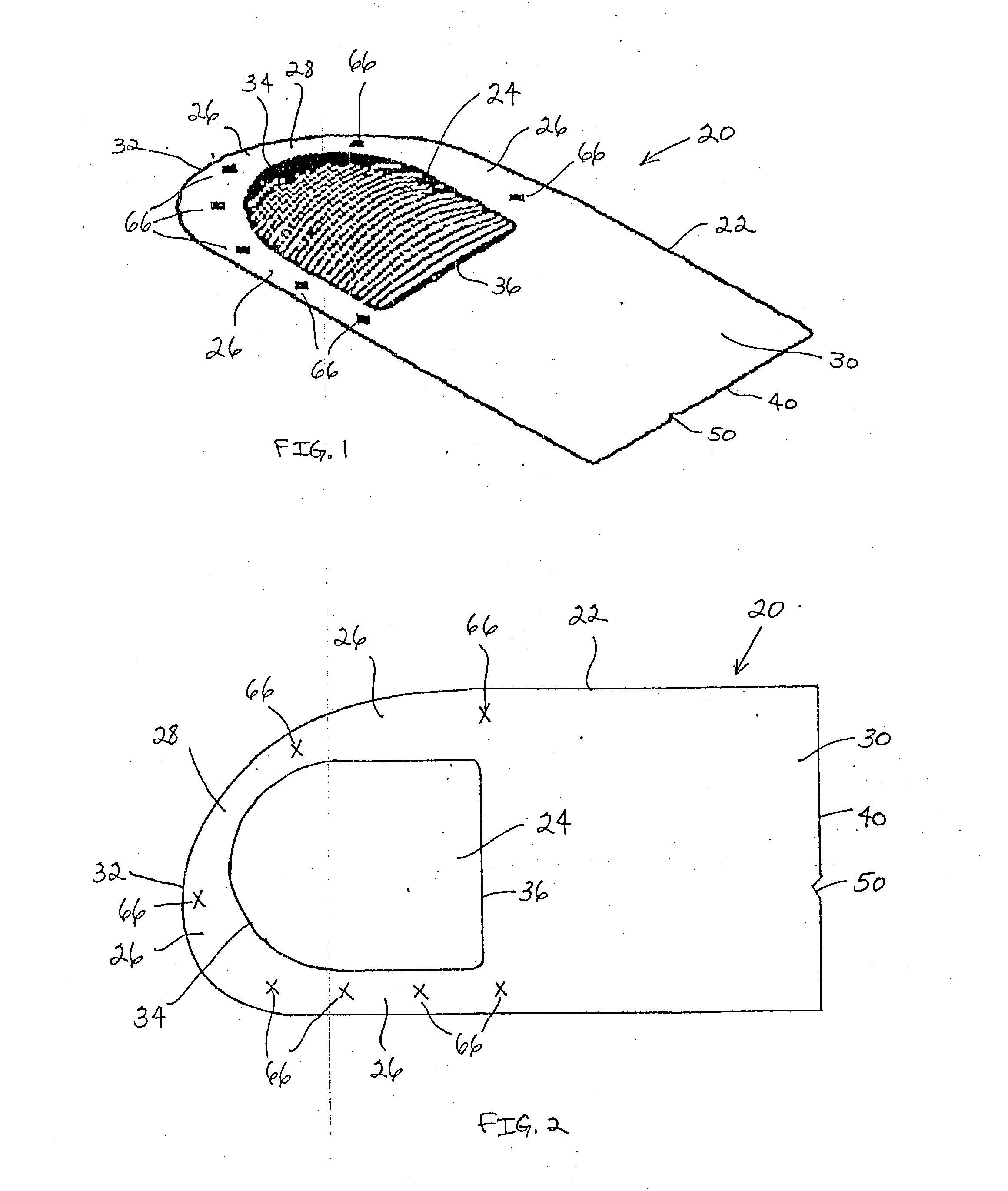
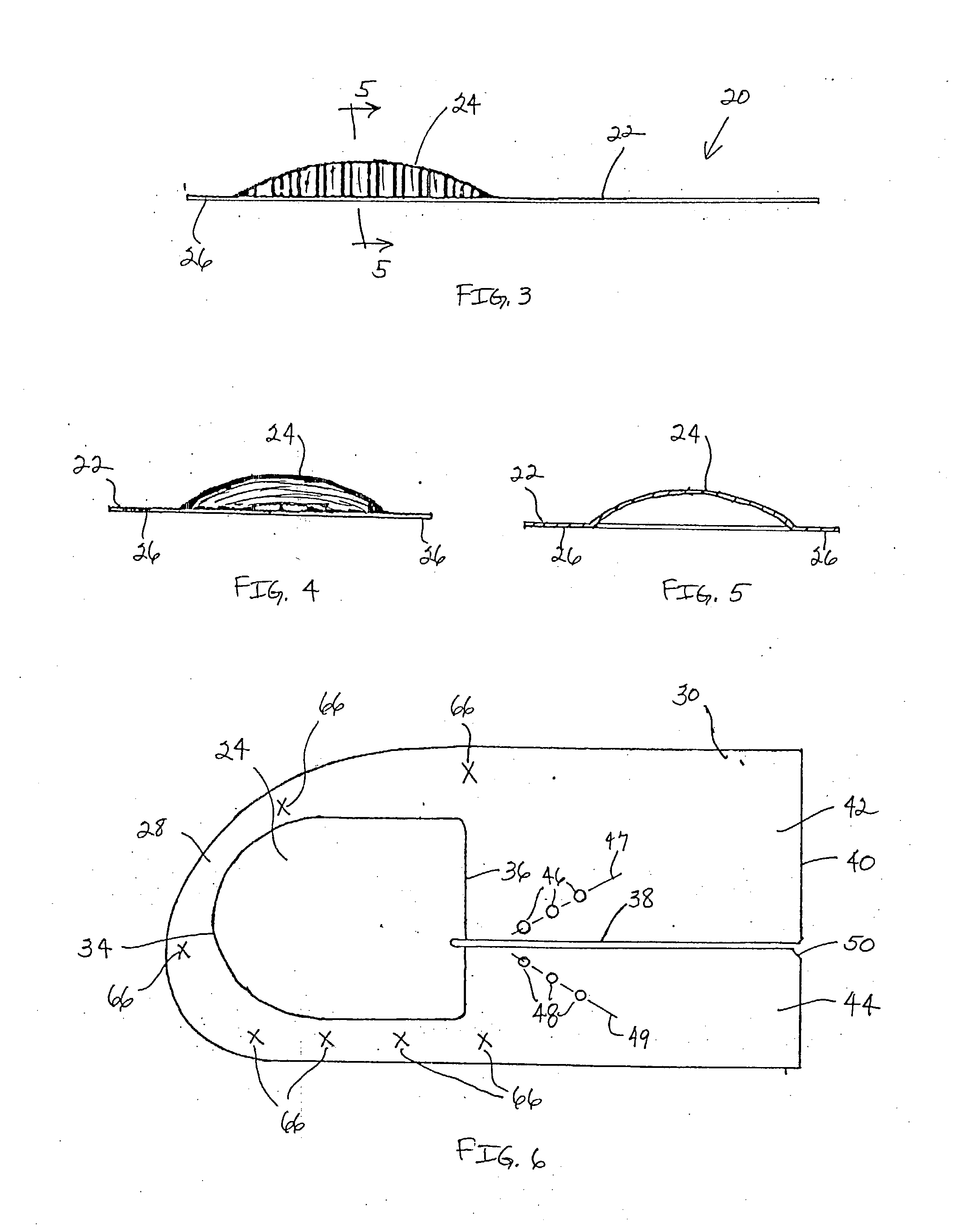
ActiveUS7914567B2Prevent eversionMinimize traumaStentsBlood vesselsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
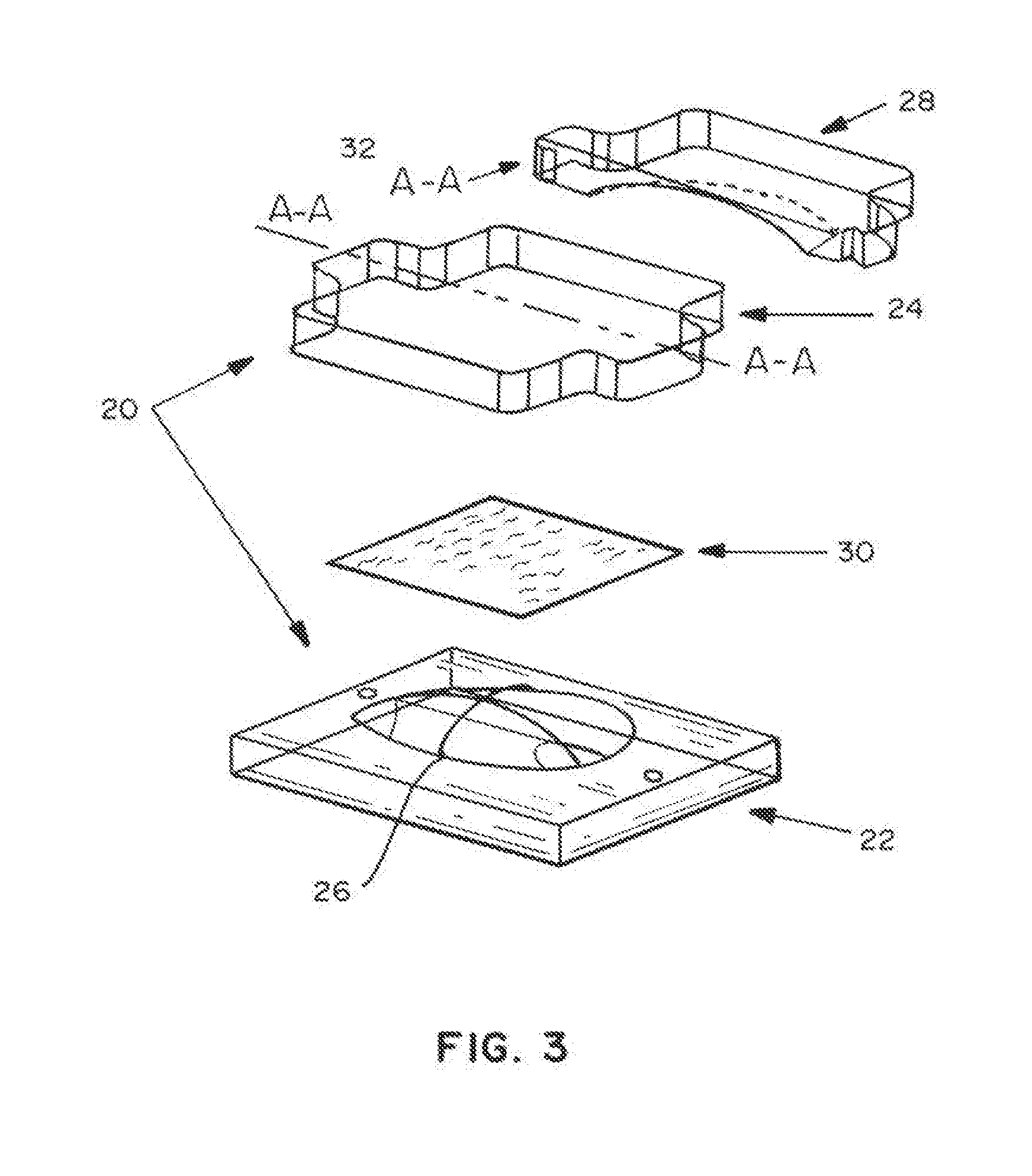
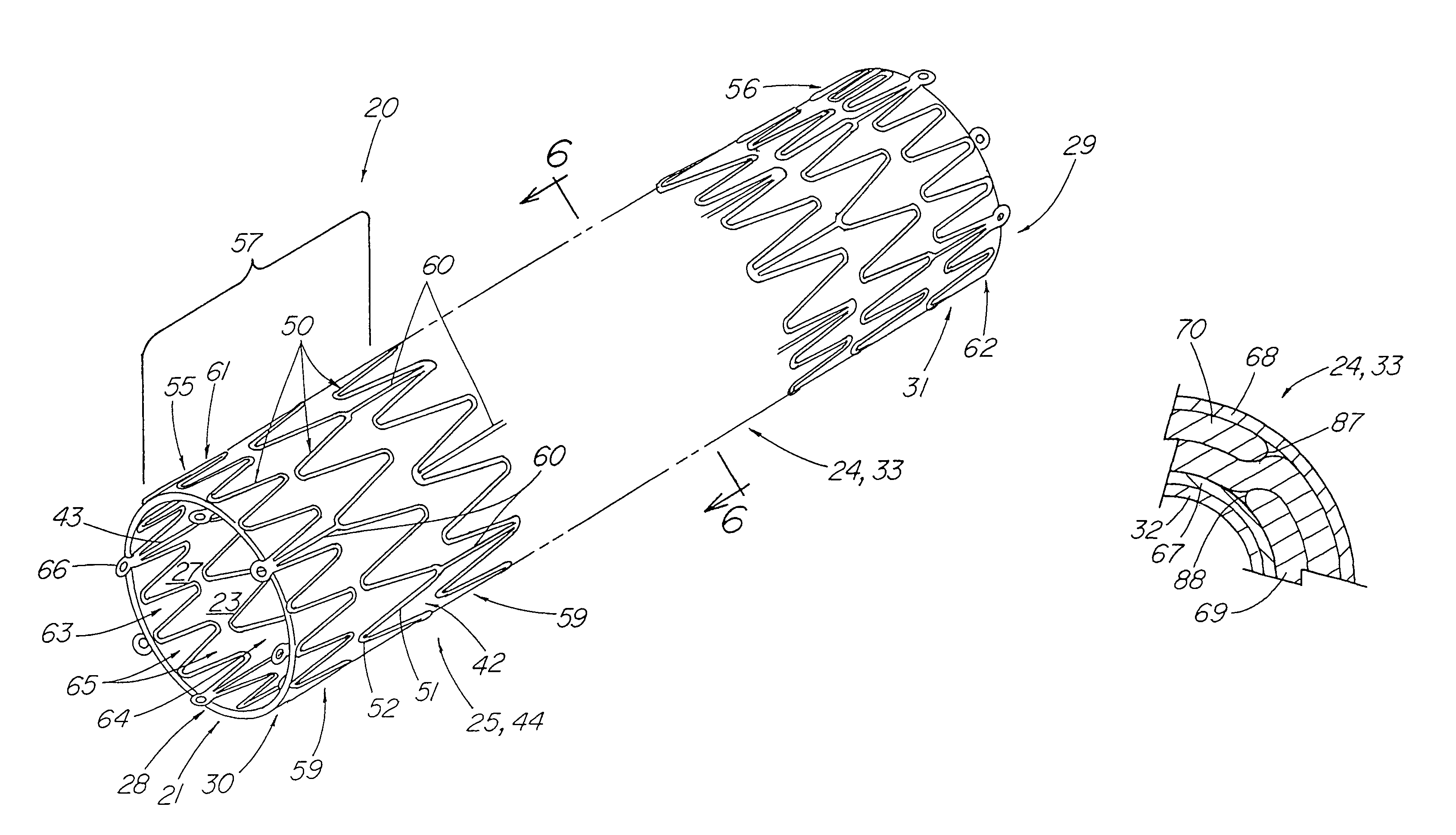
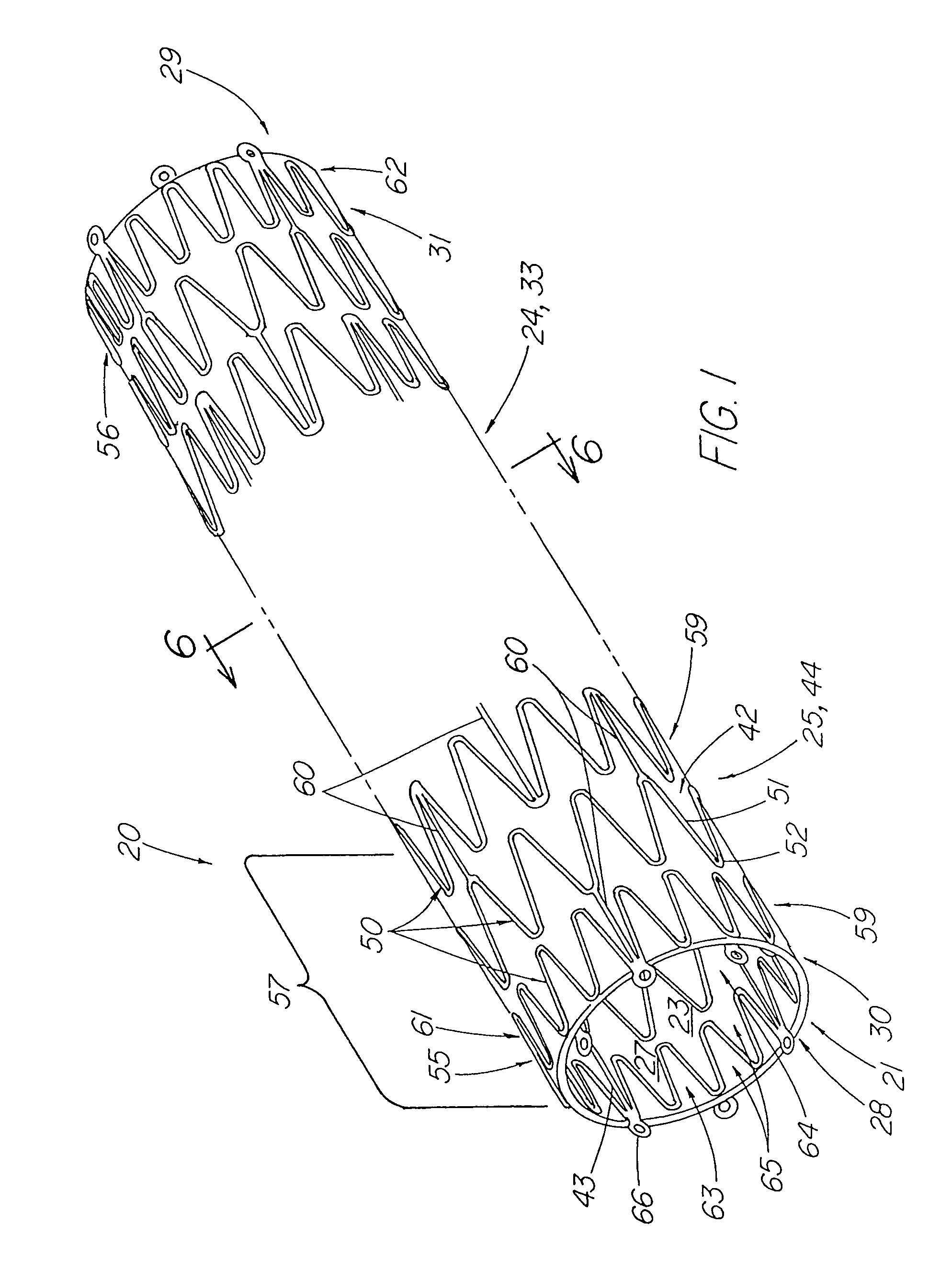
A stent tissue graft prosthesis (20) for repairing, excluding and / or reinforcing a vessel, duct and the like in a patient. The prosthesis includes an inner expandable stent (21) of which a tissue graft (24) and preferably a multilayered tissue construct (33) is disposed thereon for application to the host tissue of a vessel, duct and the like. The tissue construct includes an extracellular matrix material (36) such as small intestine submucosa (37) for remodeling the host tissue into the prosthesis. The prosthesis further includes an outer tubular member (25) such as an outer expandable stent (44) for retaining the tissue graft on the inner stent. The ends of the inner and outer stents are coincident with or extend beyond the ends of the tissue graft to prevent eversion or fold back of the tissue graft during withdrawal of a delivery catheter in a placement procedure.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV +2
Sutures and fibrosing agents
InactiveUS20110264139A1Stable internal structureSuture equipmentsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismClosing woundHost tissue
Sutures are used in combination with fibrosing agents to induce or stimulate fibrosis that between the sutures and the host tissues into which the sutures are inserted. Compositions and methods are described for use in lifting tissue, closing wound, and other applications.
Owner:ETHICON INC +1
Method of isolating epithelial cells, method of preconditioning cells, and methods of preparing bioartificial skin and dermis with the epithelial cells and preconditioned cells
InactiveUS20050164388A1Increased cell yieldEasy to implantCell dissociation methodsSkin implantsDamages tissueTrypsin
A method of isolating epithelial cells from a human skin tissue or internal organ tissue using trypsin and ethylene-diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) simultaneously with the application of magnetic stirring, a method of preconditioning isolated biological cells by the application of physical stimulus, i.e., strain, are provided. Epithelial cells can be isolated by the method with increased yield, colony forming efficiency (CFE), and colony size. Also, the increased percentage of stem cells in isolated cells is advantageous in therapeutic tissue implantation by autologous or allogeneic transplantation. In skin cells preconditioned by the application of strain, cell division is facilitated, and the secretion of extracellular matrix components and growth factors and the activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are improved. When preconditioned cells are implanted by autologous or allogeneic transplantation to heal a damaged tissue, the improved cell adhesion, mobility, and viability provides a biological adjustment effect against a variety of stresses or physical stimuli which the cells would undergo after implantation, with improved capability of integration into host tissue, thereby markedly improving the probability of success in skin grafting.
Owner:KOREA ATOMIC ENERGY RES INST
Methods for isolating molecular mimetics of unique Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B epitopes
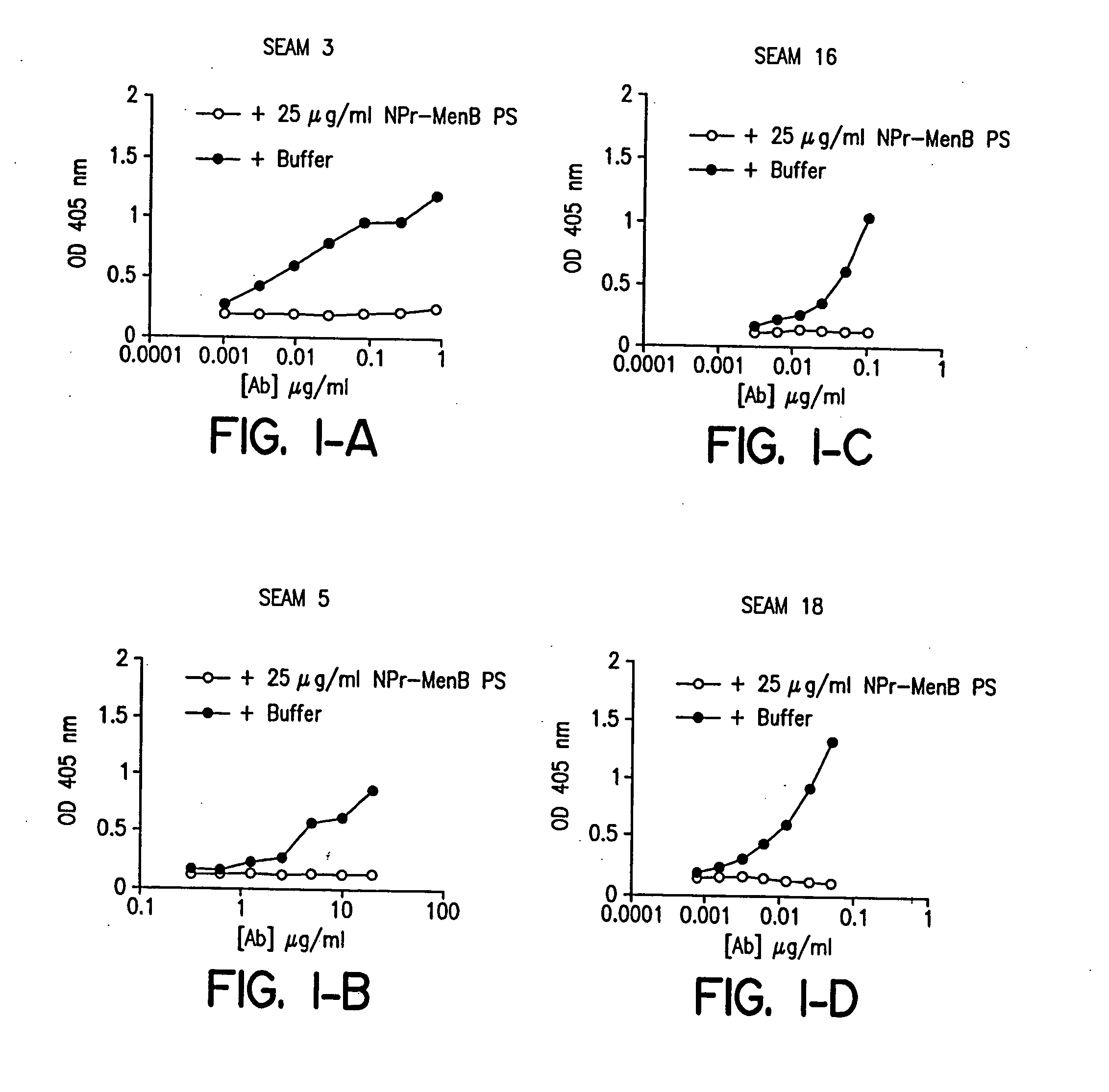
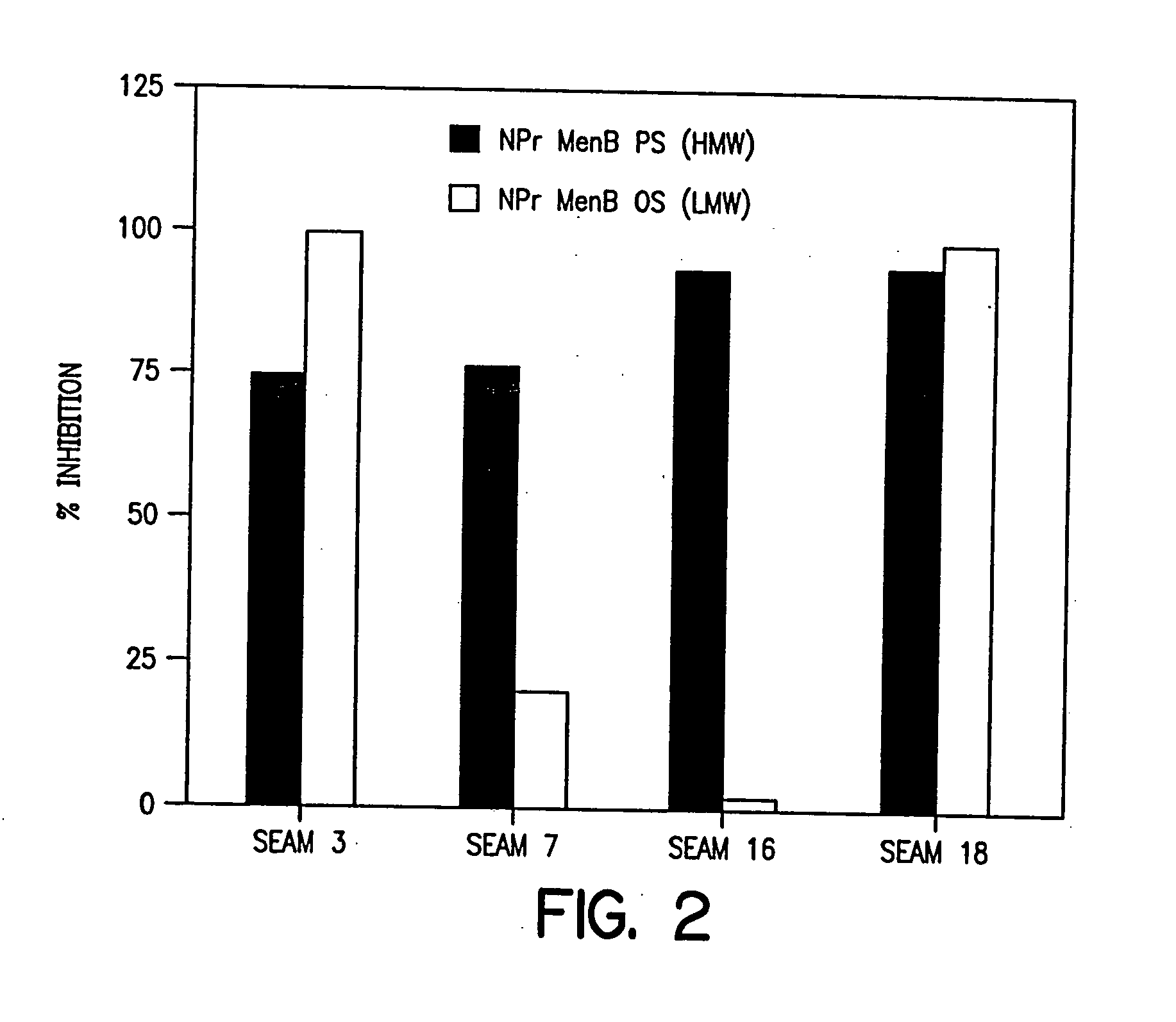
InactiveUS20060035284A1Determine autoreactivityLeast riskAntibacterial agentsAnimal cellsEscherichia coliSalmonella serotype typhi
Novel bactericidal antibodies against Neisseria meningitidis serogroup B (“MenB”) are disclosed. The antibodies either do not cross-react or minimally cross-react with host tissue polysialic acid and hence pose minimal risk of autoimmune activity. The antibodies are used to identify molecular mimetics of unique epitopes found on MenB or E. coli K1. Examples of such peptide mimetics are described that elicit serum antibody capable of activating complement-mediated bacteriolysis of MenB. Vaccine compositions containing such mimetics can be used to prevent MenB or E. coli K1 disease without the risk of evoking autoantibody.
Owner:CHILDREN S HOSPITAL &RES CENT AT OAKLAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com