Patents
Literature
72results about How to "Reduce postoperative pain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
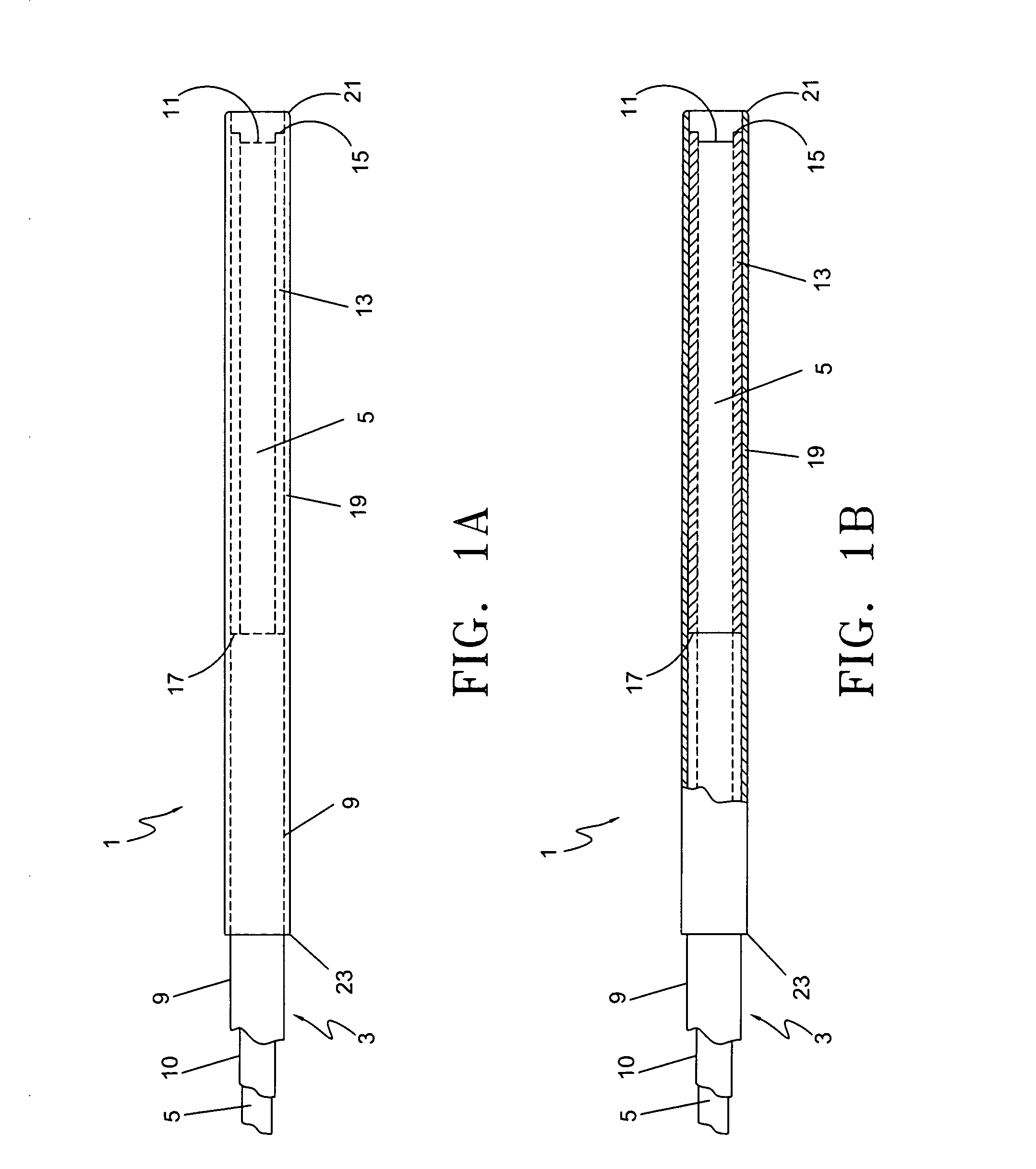
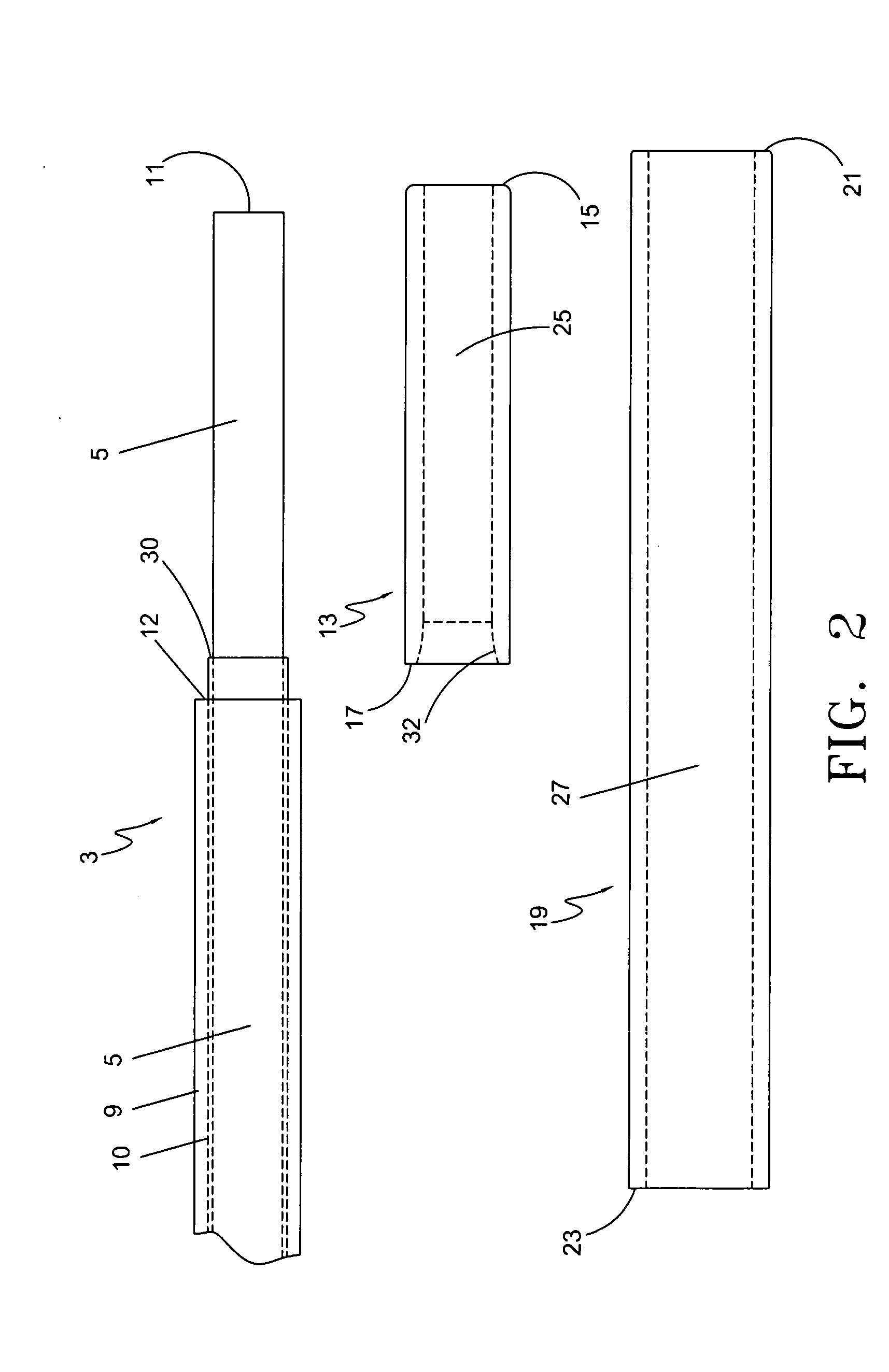
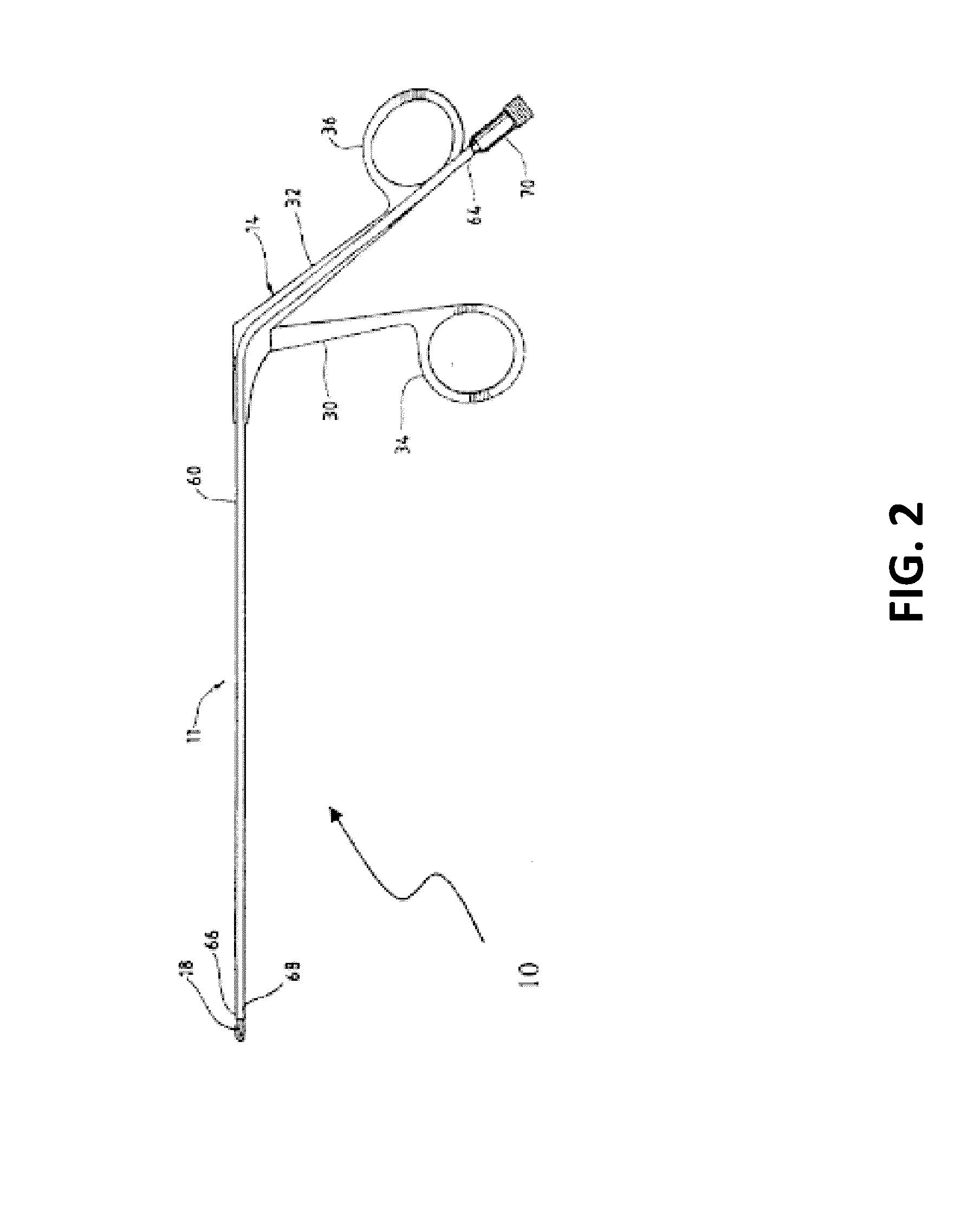
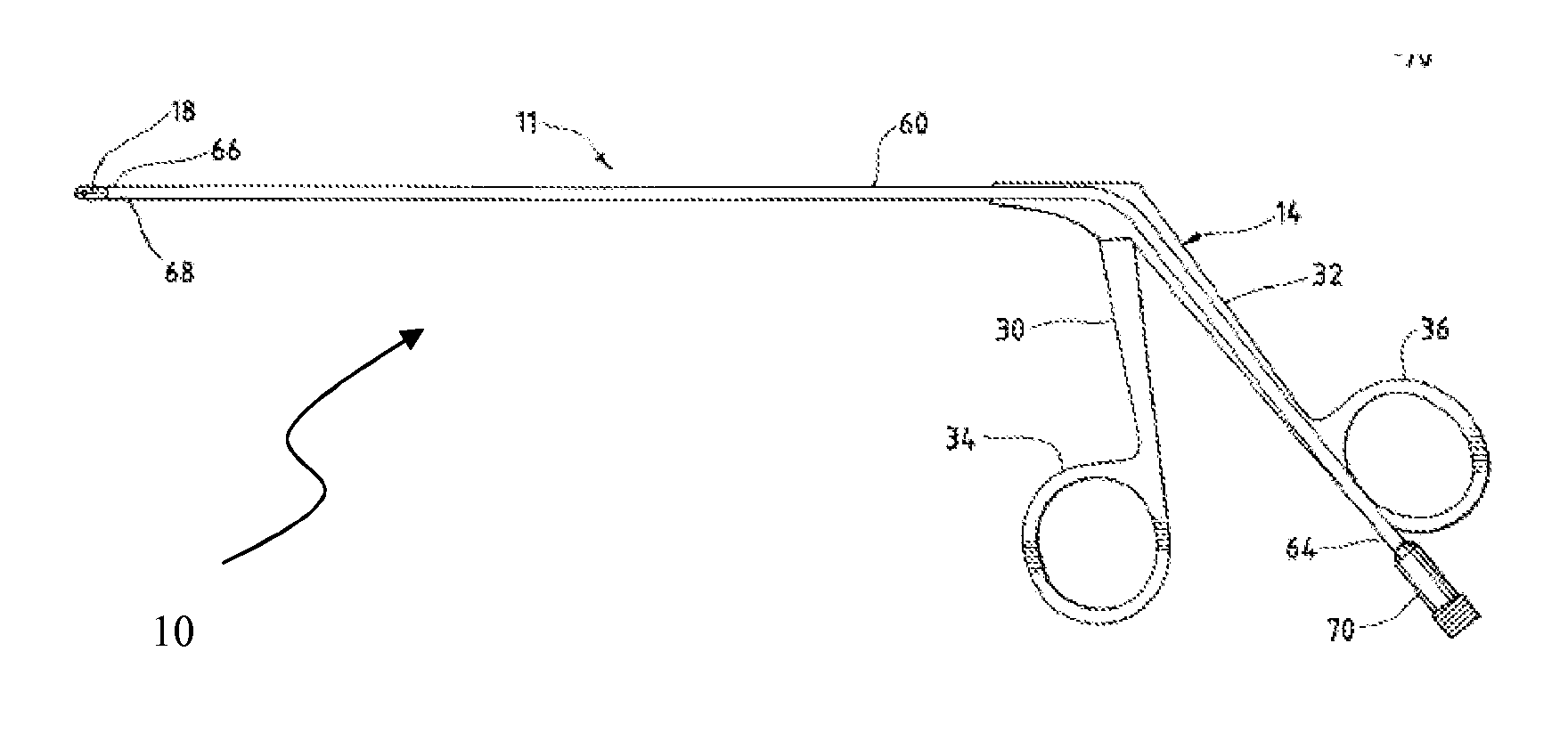
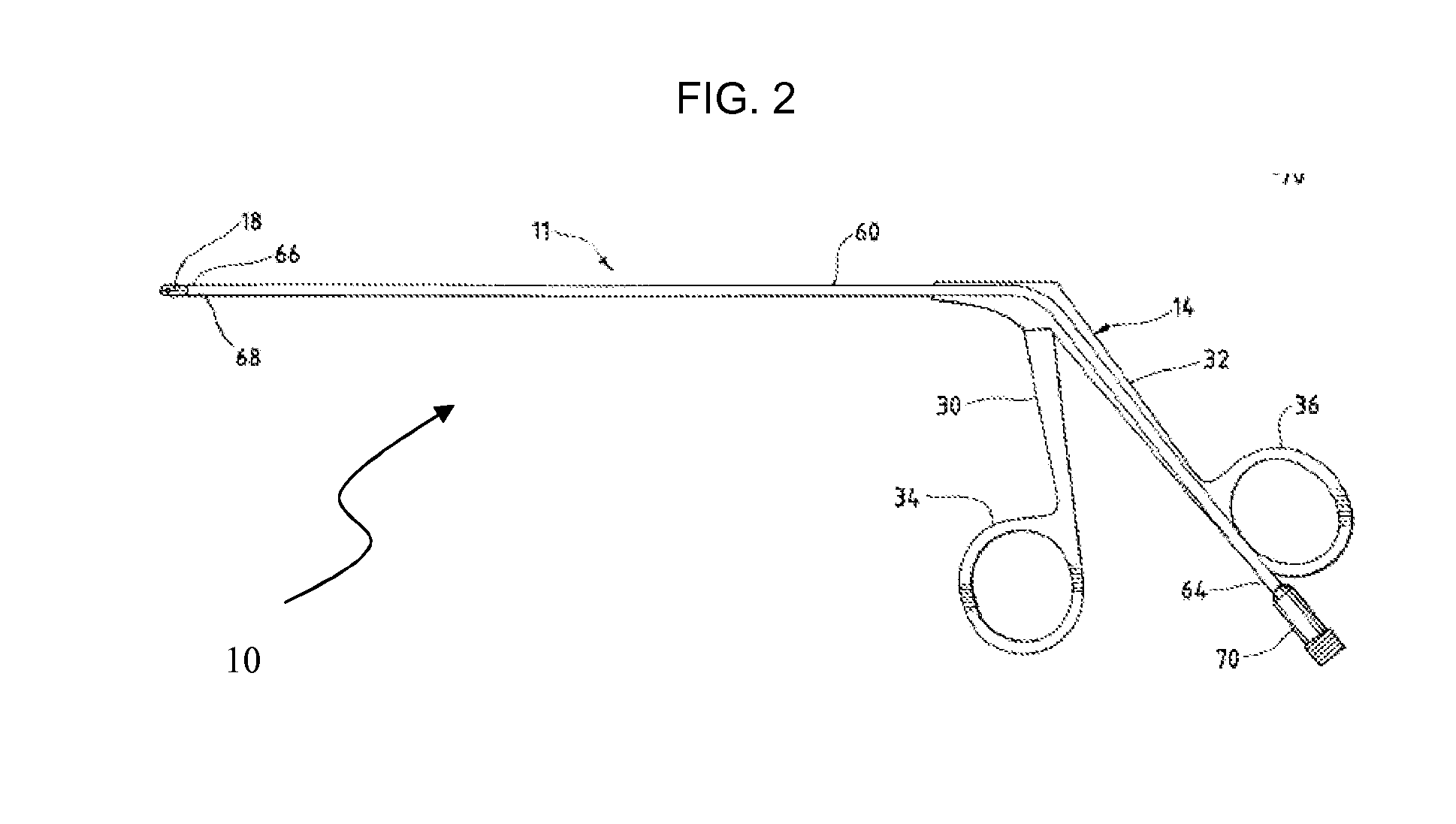
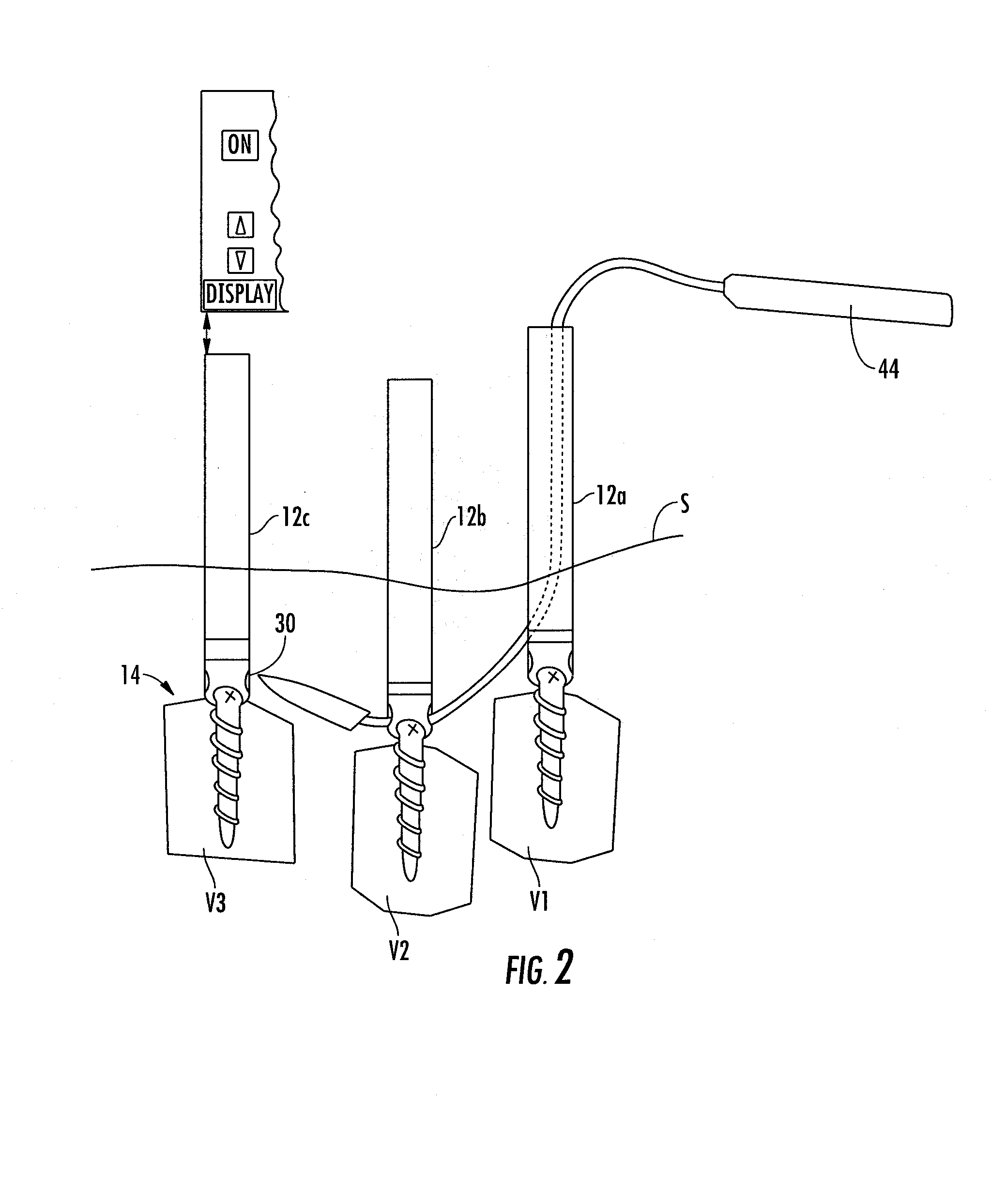
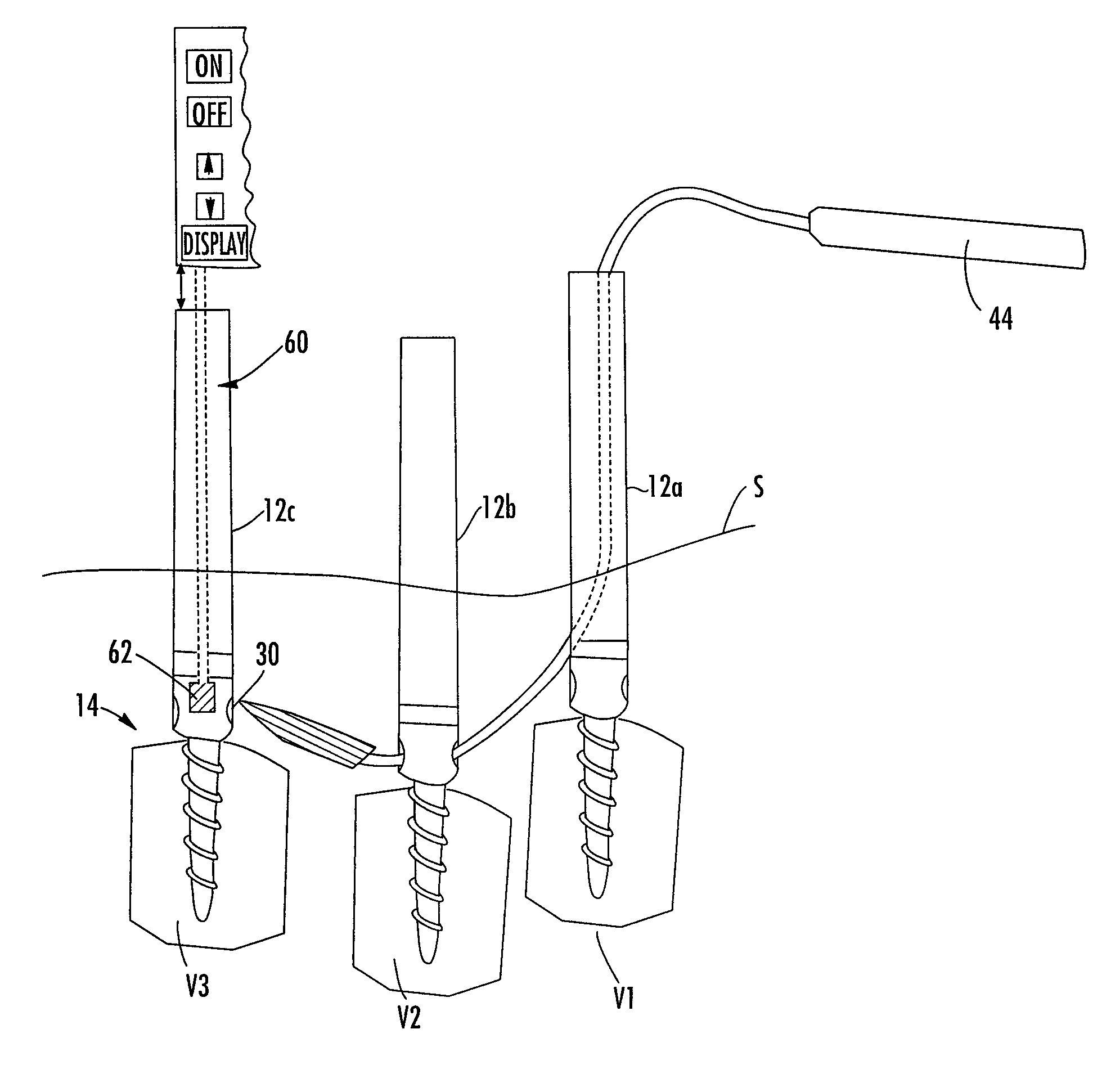
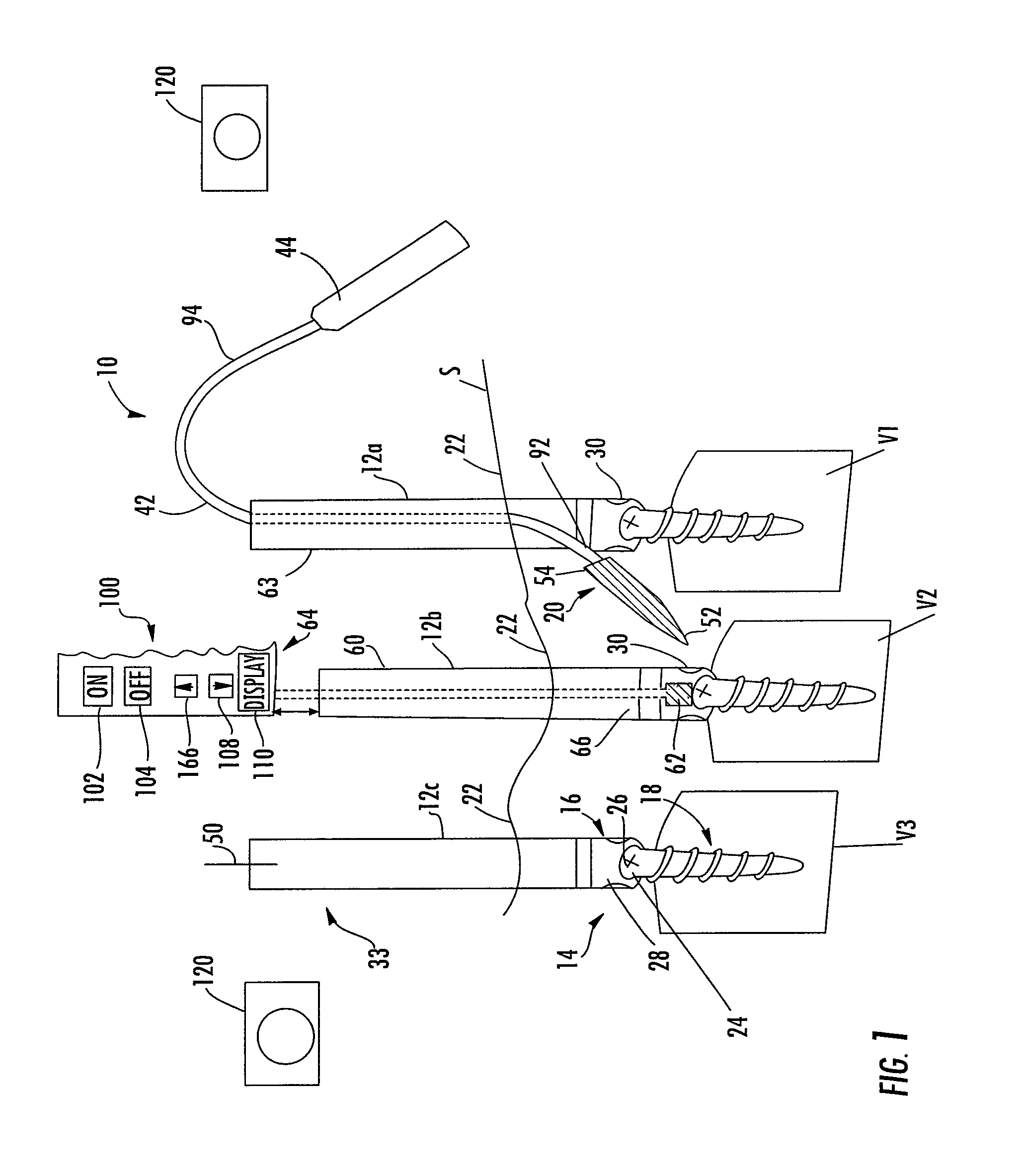
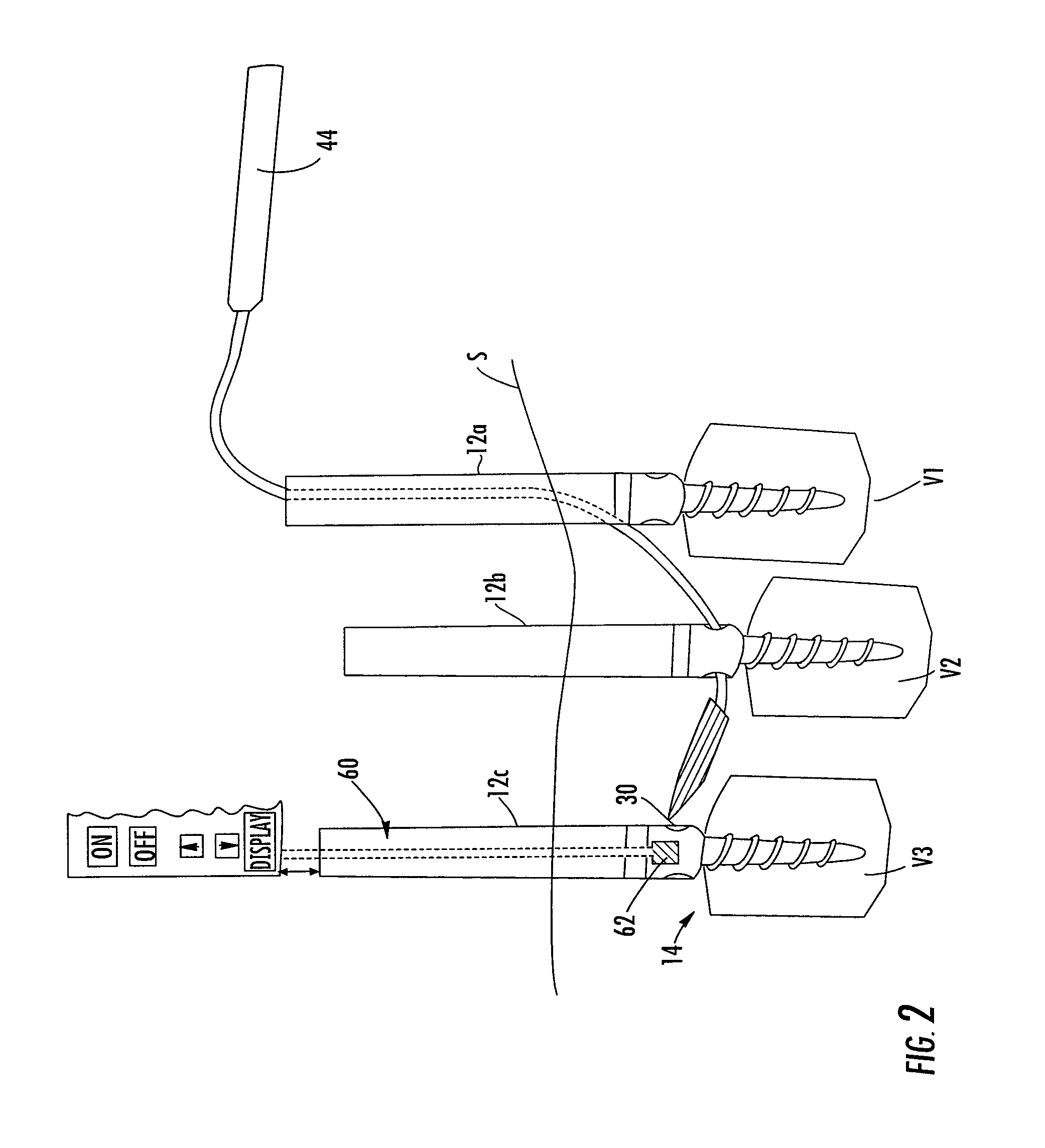
Methods and devices for improving percutaneous access in minimally invasive surgeries
ActiveUS20050065517A1Reduce the difficulty of operationReduce riskInternal osteosythesisCannulasLess invasive surgeryPost operative
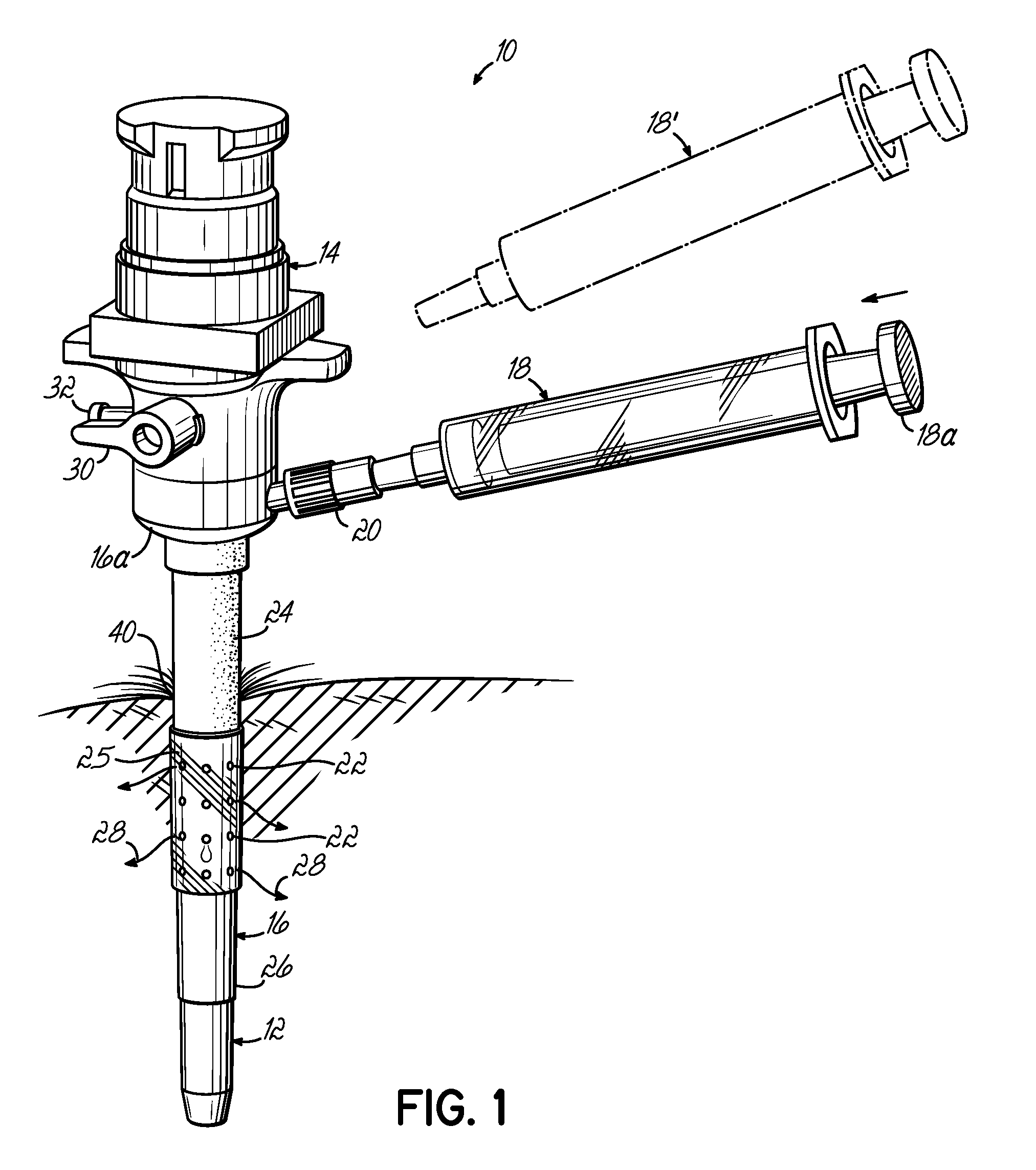
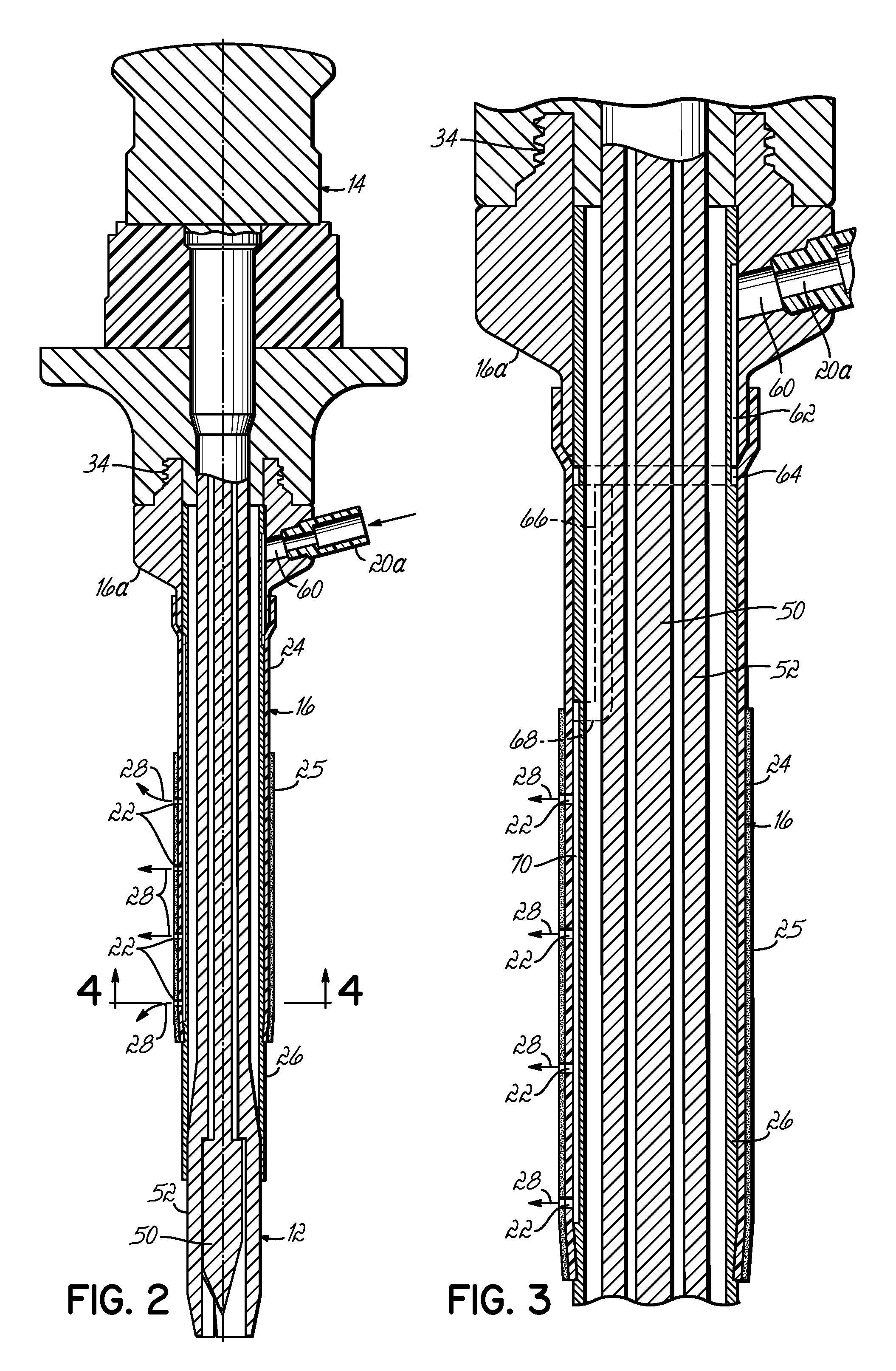
A device for use as a portal in percutaneous minimally invasive surgery performed within a patient's body cavity includes a first elongated hollow tube having a length adjusted with a self-contained mechanism. The first elongated tube includes an inner hollow tube and an outer hollow tube and the inner tube is adapted to slide within the outer tube thereby providing the self-contained length adjusting mechanism. This length-adjustment feature is advantageous for percutaneous access surgery in any body cavity. Two or more elongated tubes with adjustable lengths can be placed into two or more adjacent body cavities, respectively. Paths are opened within the tissue areas between the two or more body cavities, and are used to transfer devices and tools between the adjacent body cavities. This system of two or more elongated tubes with adjustable lengths is particularly advantageous in percutaneous minimally invasive spinal surgeries, and provides the benefits of minimizing long incisions, recovery time and post-operative complications.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Systems and methods for electrosurgical treatment of obstructive sleep disorders
InactiveUS7131969B1Increase surface areaImprove sealingCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsThroatSleeping disorders
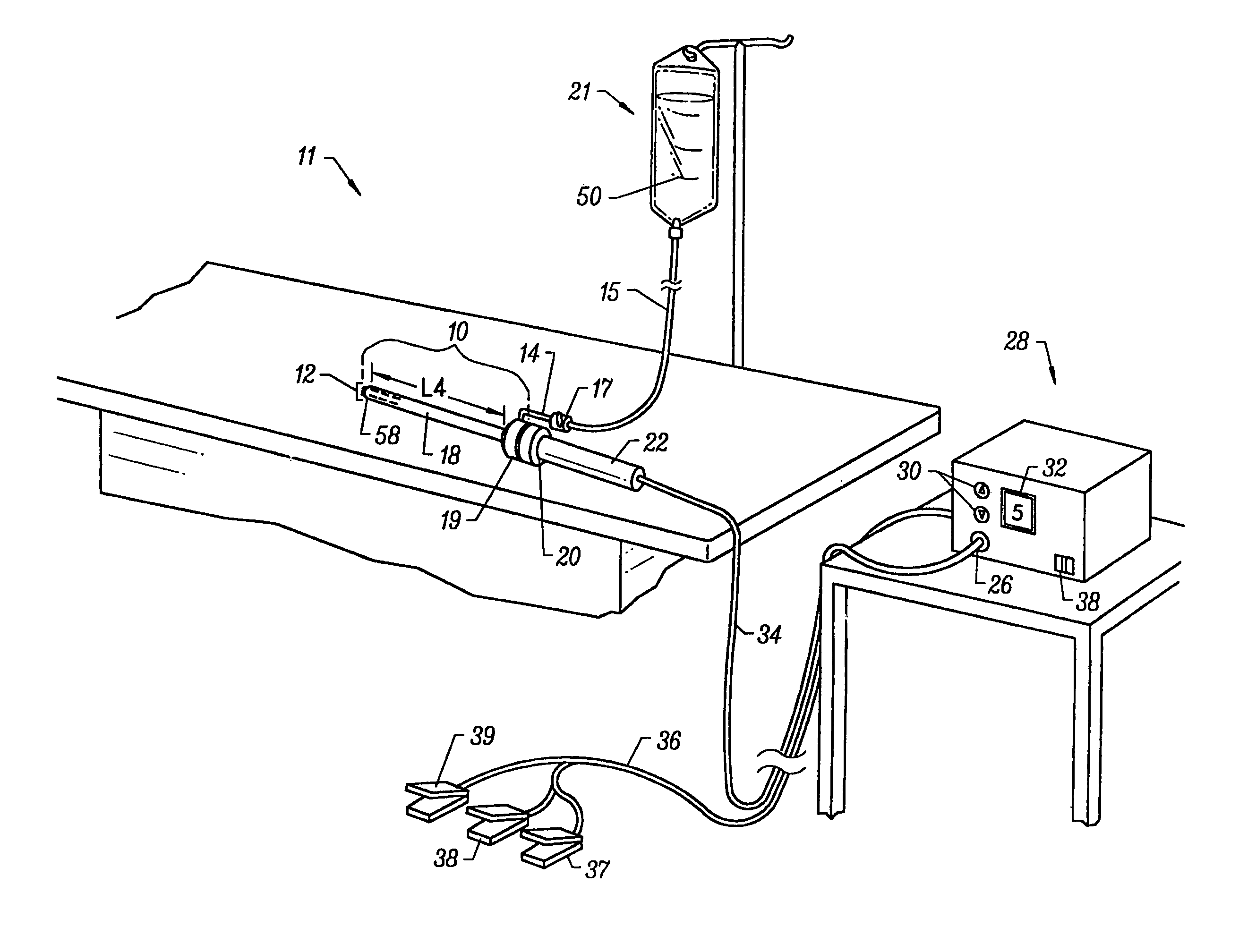
The present invention provides systems and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within the head and neck of a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the ear, nose and throat. The present invention applies high frequency (RF) electrical energy to one or more electrode terminals in the presence of electrically conductive fluid to remove and / or modify the structure of tissue structures. The present invention is particularly useful for treating sleep obstructive disorders, such as sleep apnea and snoring.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
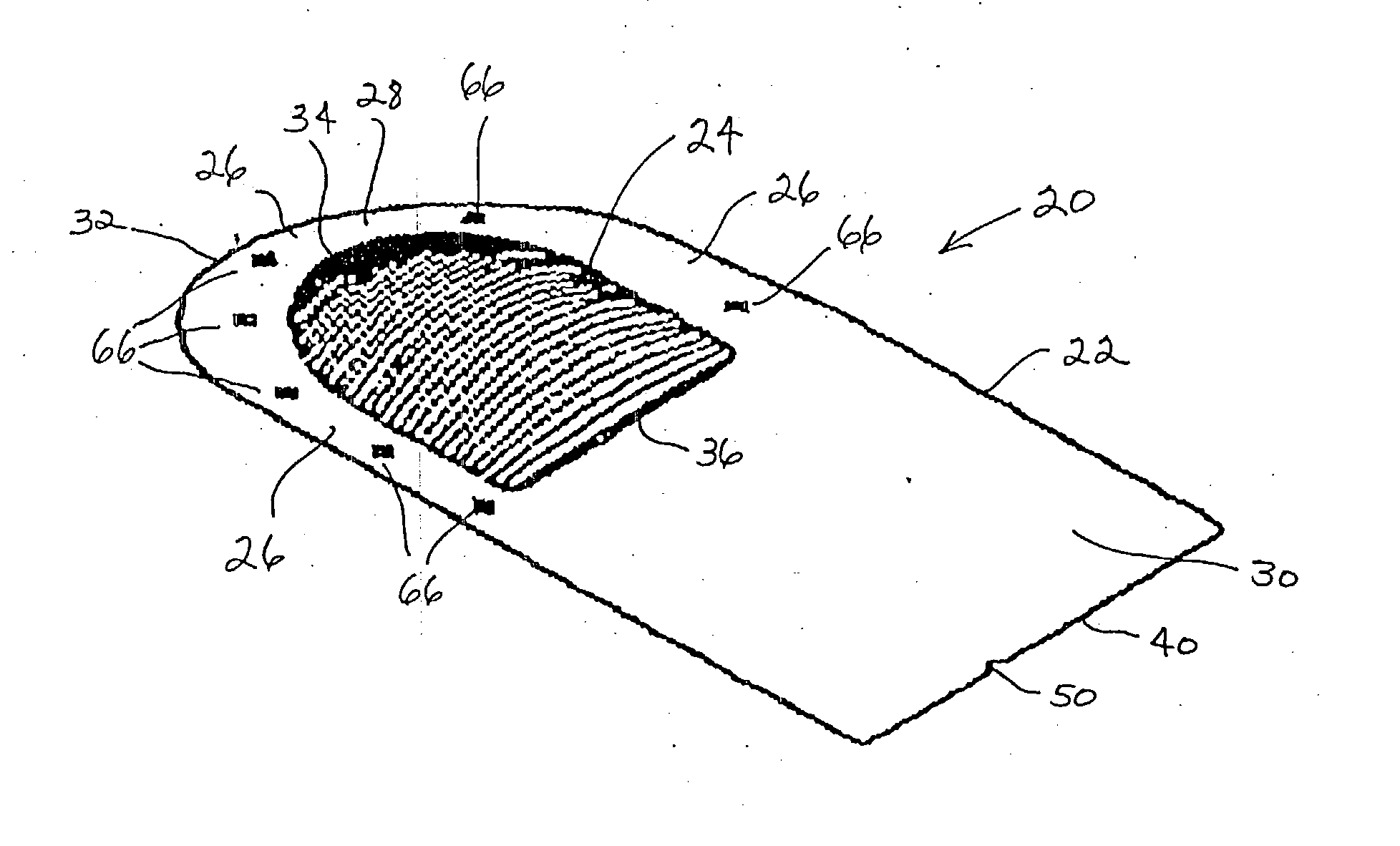
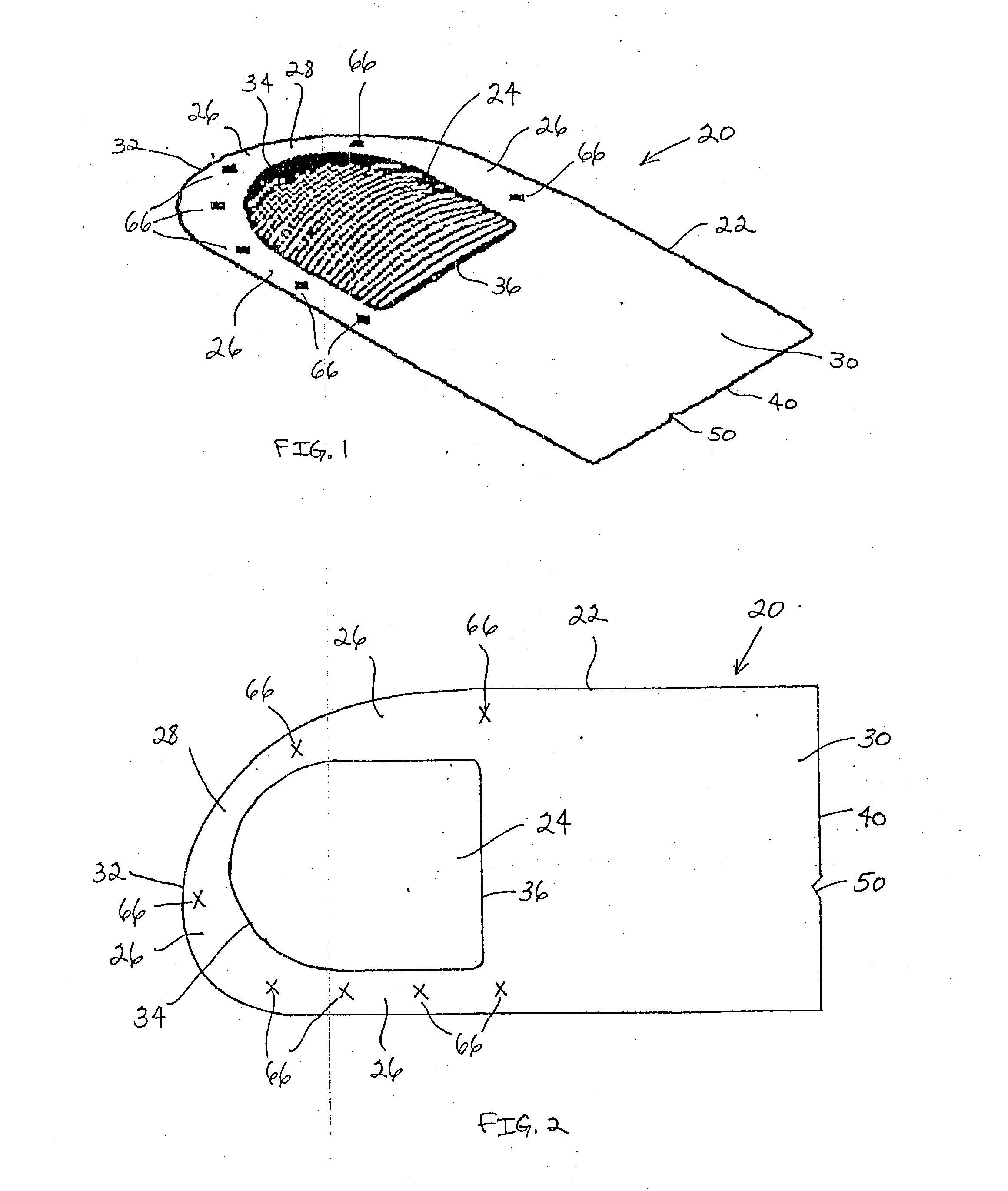
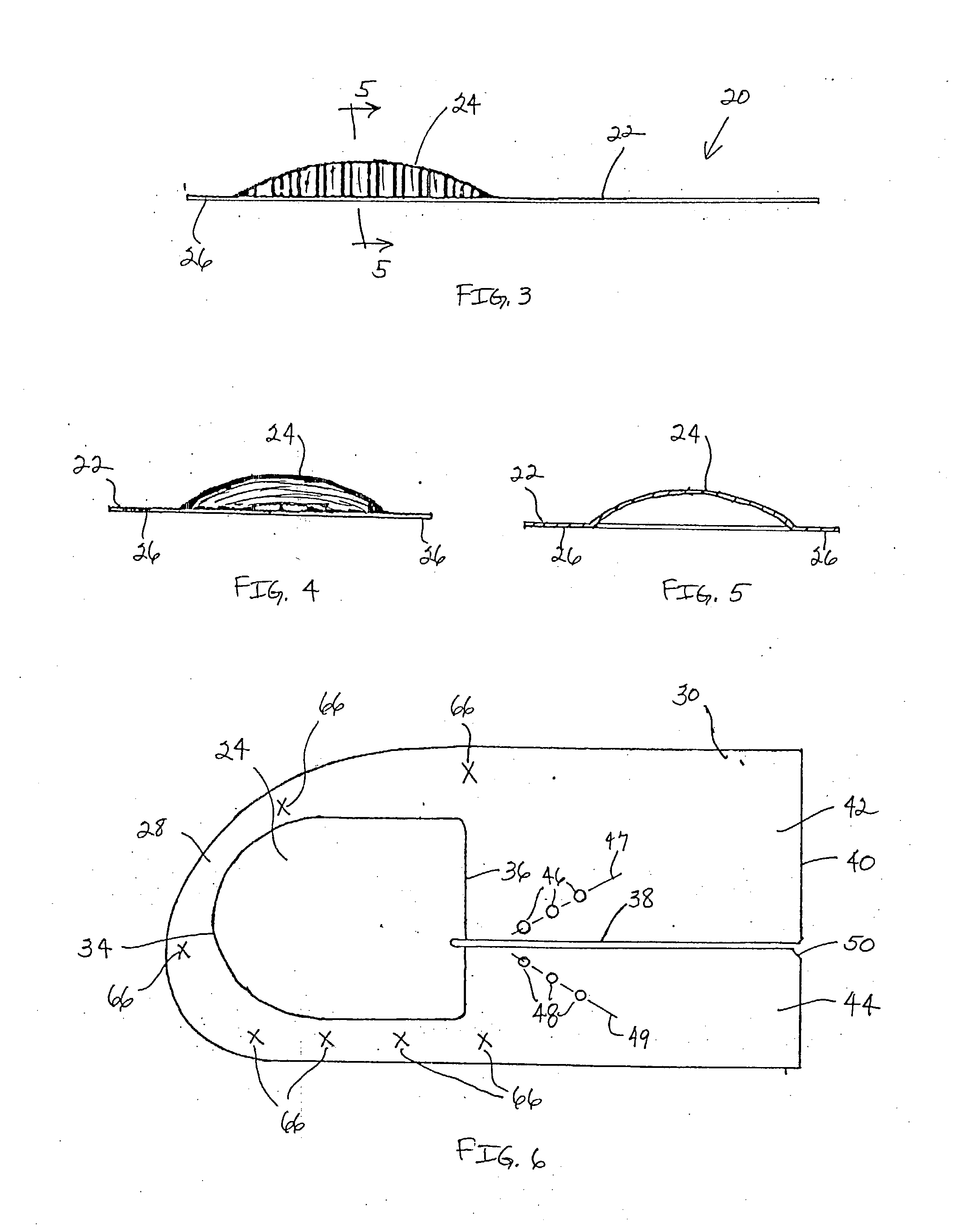
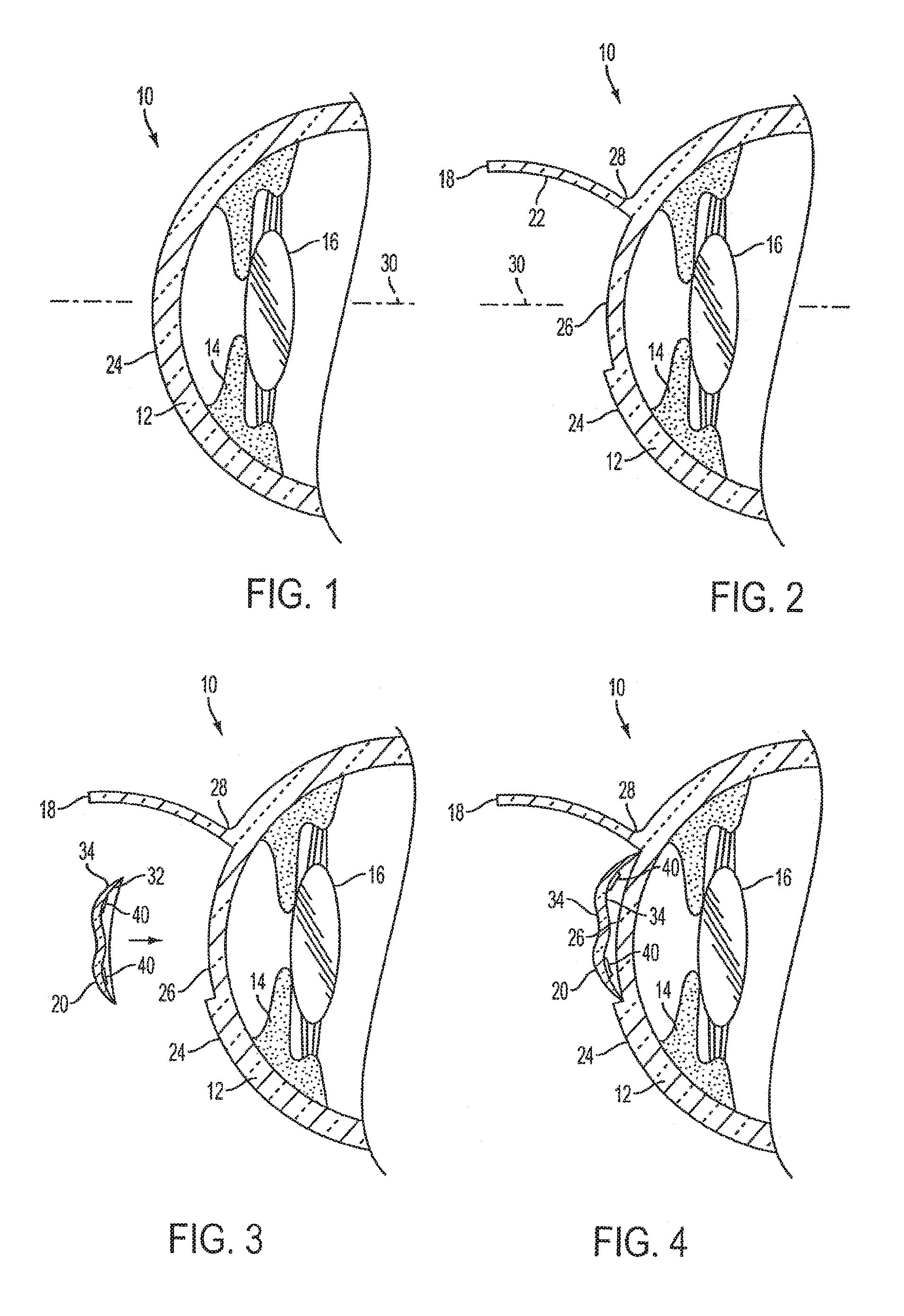
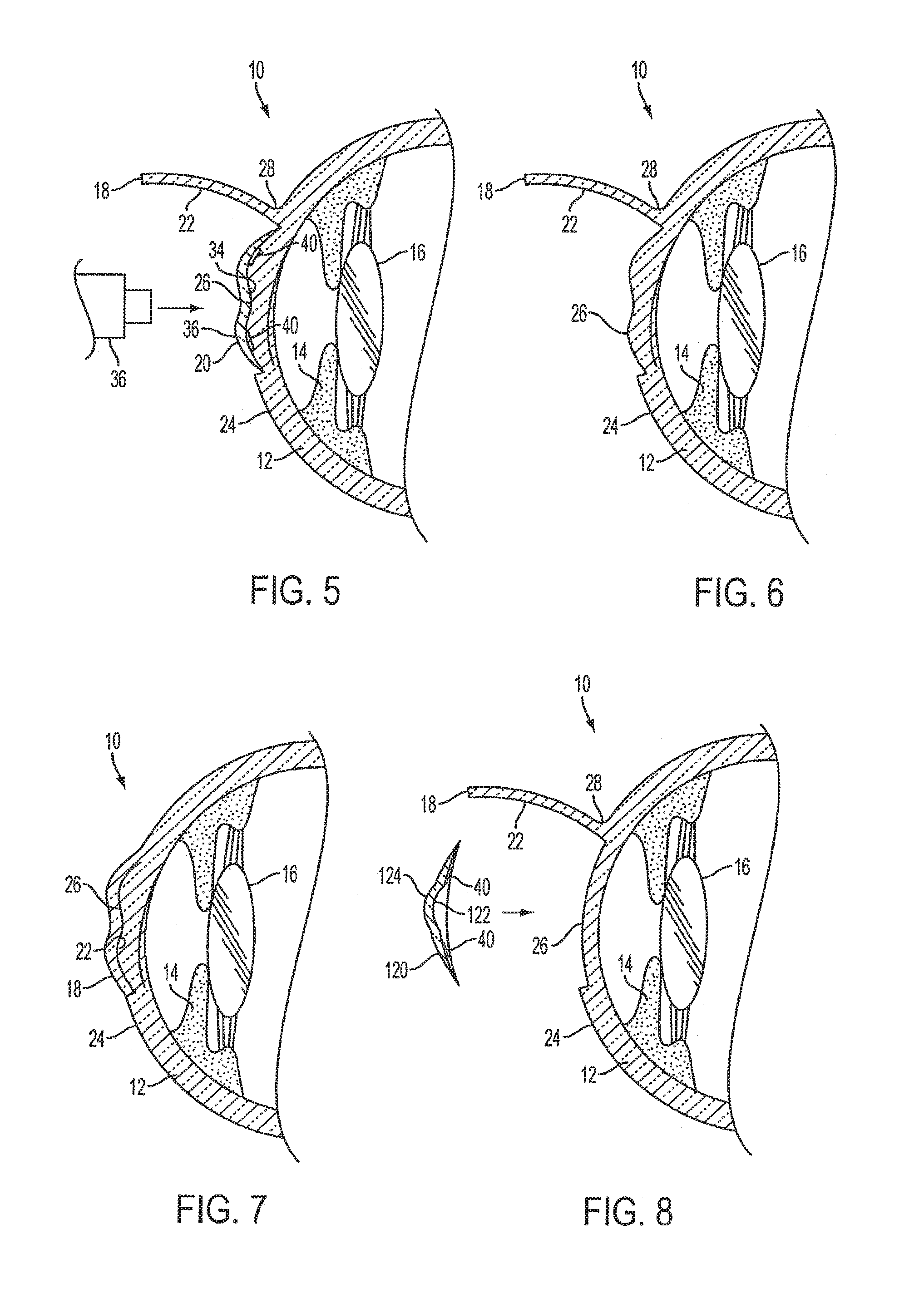
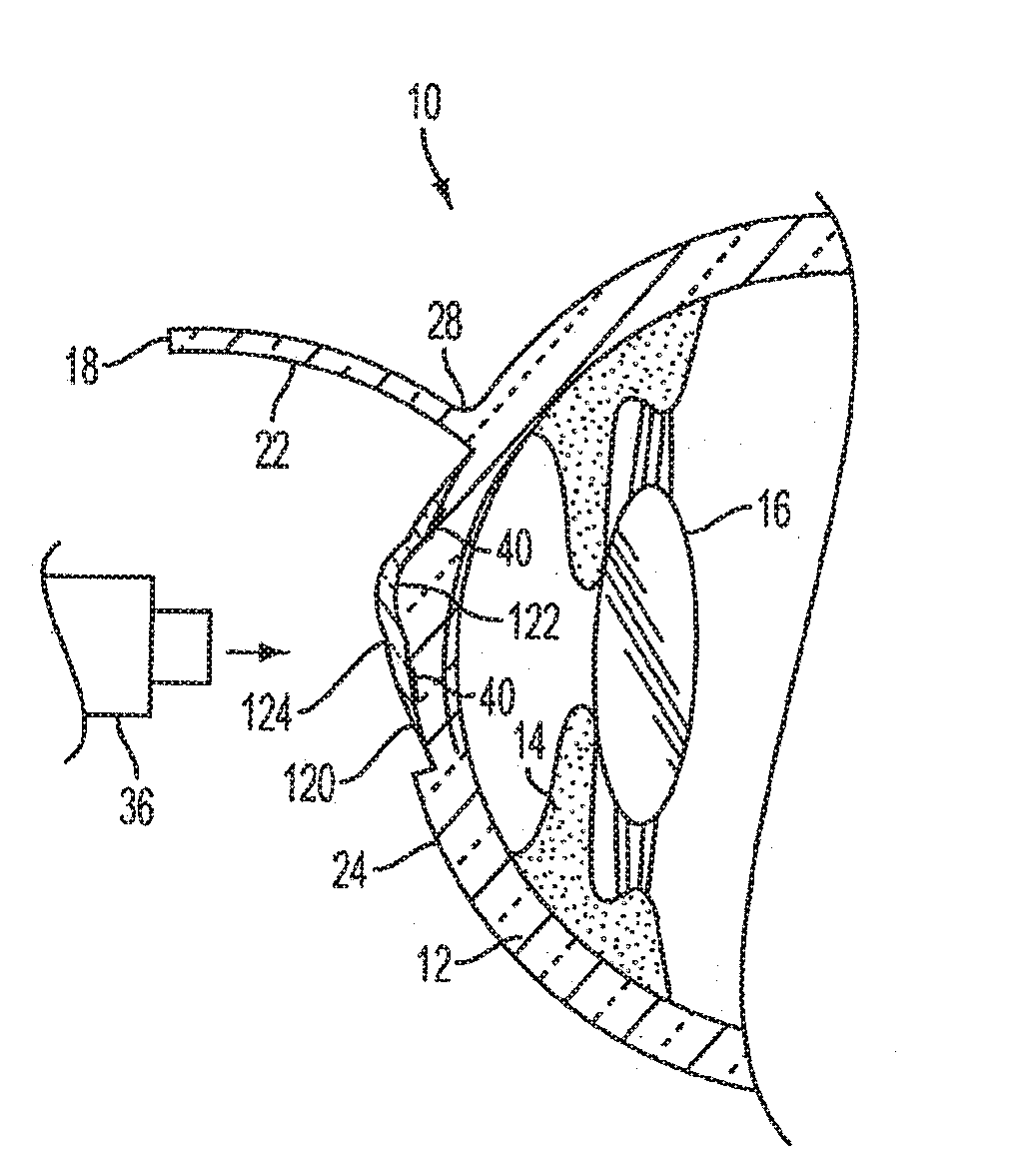
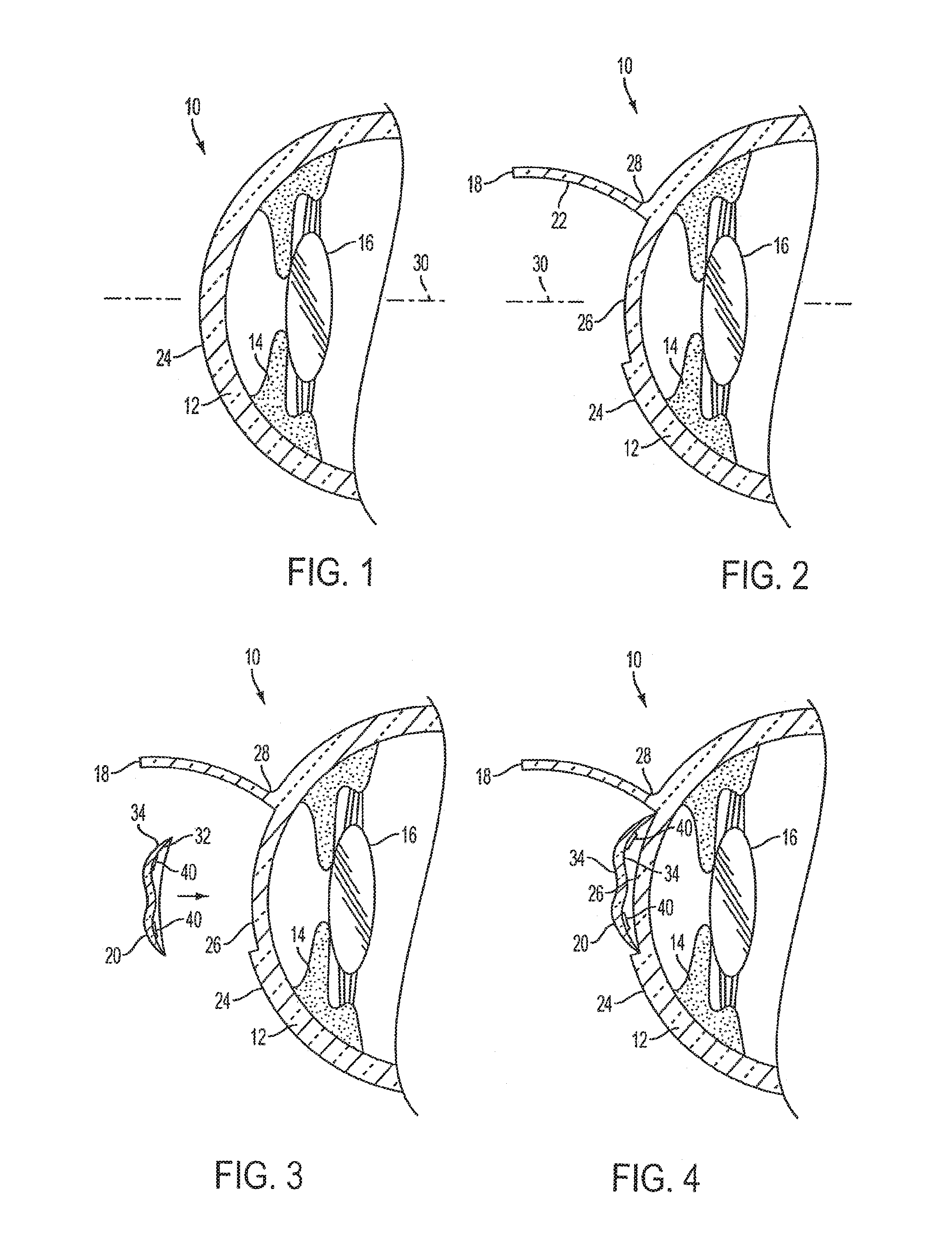
Implantable prosthesis
InactiveUS6610006B1Reduce the possibilityReduce postoperative painDiagnosticsLigamentsRepair siteIntraabdominal pressure
An implantable prosthesis for repairing an anatomical defect, such as a soft tissue and muscle wall defect. The prosthesis is configured to reduce the likelihood that an applied force at the repair site, such as due to intraabdominal pressure or tissue shrinkage, can lead to detrimental effects associated with tension at the anchoring locations between the prosthesis and host tissue and / or contraction of the prosthesis. In this regard, the prosthesis may be configured to limit the amount of tension at the anchoring locations caused by the application of a force or pressure to the prosthesis and / or contraction of the prosthesis. Alternatively, the prosthesis may be configured to compensate for contraction of the prosthesis due to tissue shrinkage at the repair site. The prosthesis may be configured to both limit tension at the anchoring locations and compensate for tissue shrinkage. The prosthesis may facilitate a reduction in postoperative discomfort, a recurrence of the defect, or the creation of a new defect associated with tension and / or prosthetic contraction.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Systems and methods for electrosurgical treatment of obstructive sleep disorders
InactiveUS20060253117A1Less tissue damageReduce postoperative painCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsThroatSleeping disorders
Owner:ARTHROCARE
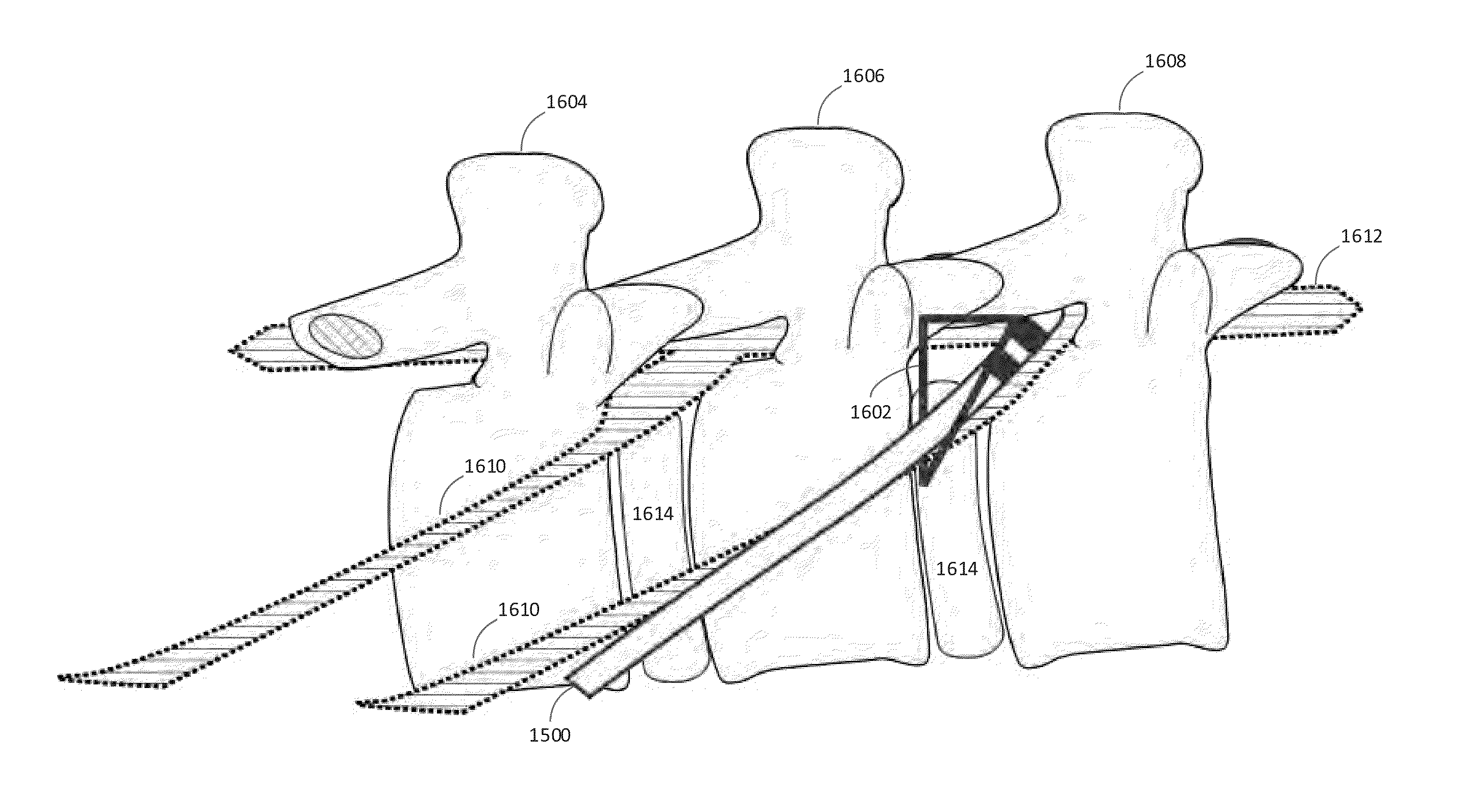
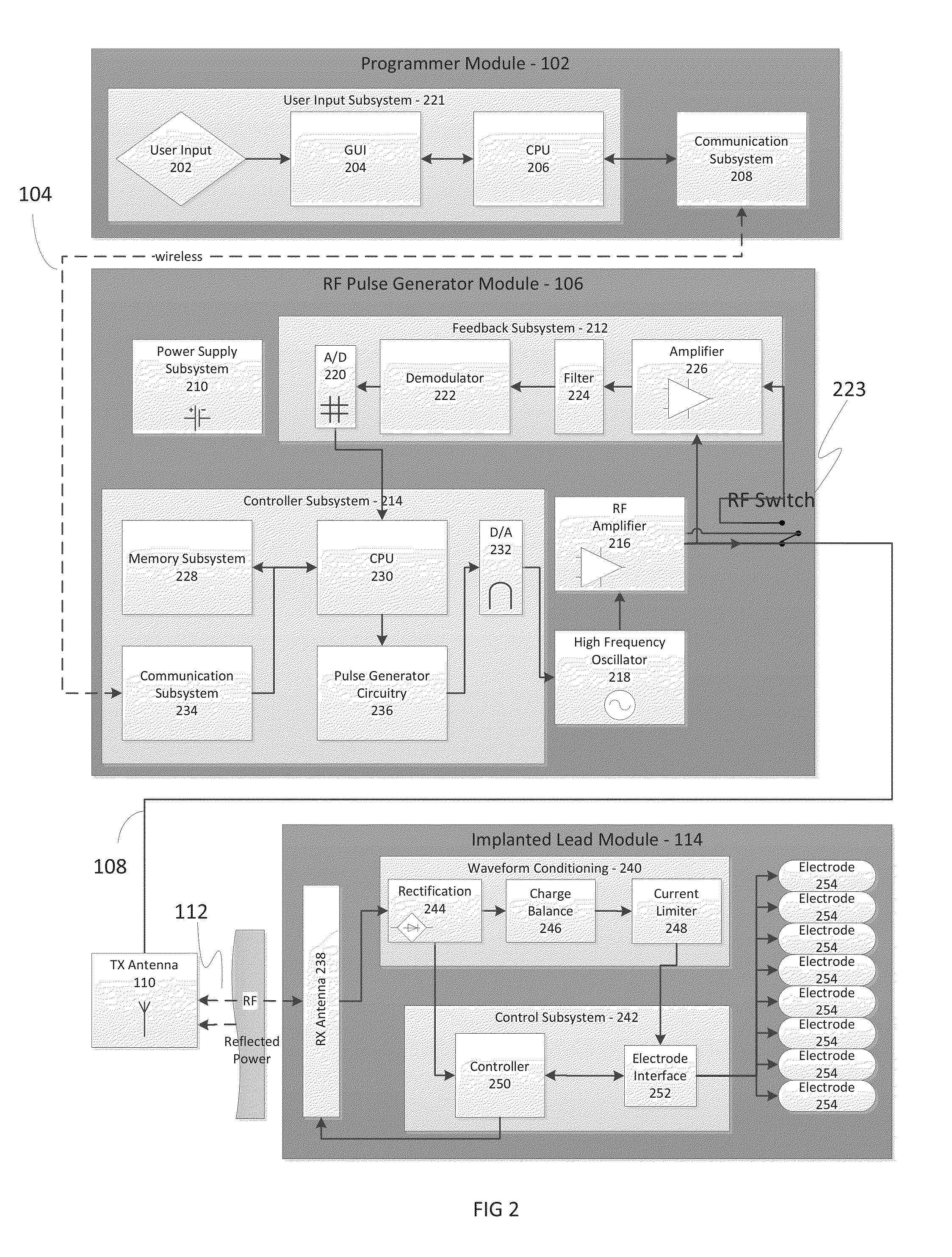
Methods and devices for modulating excitable tissue of the exiting spinal nerves
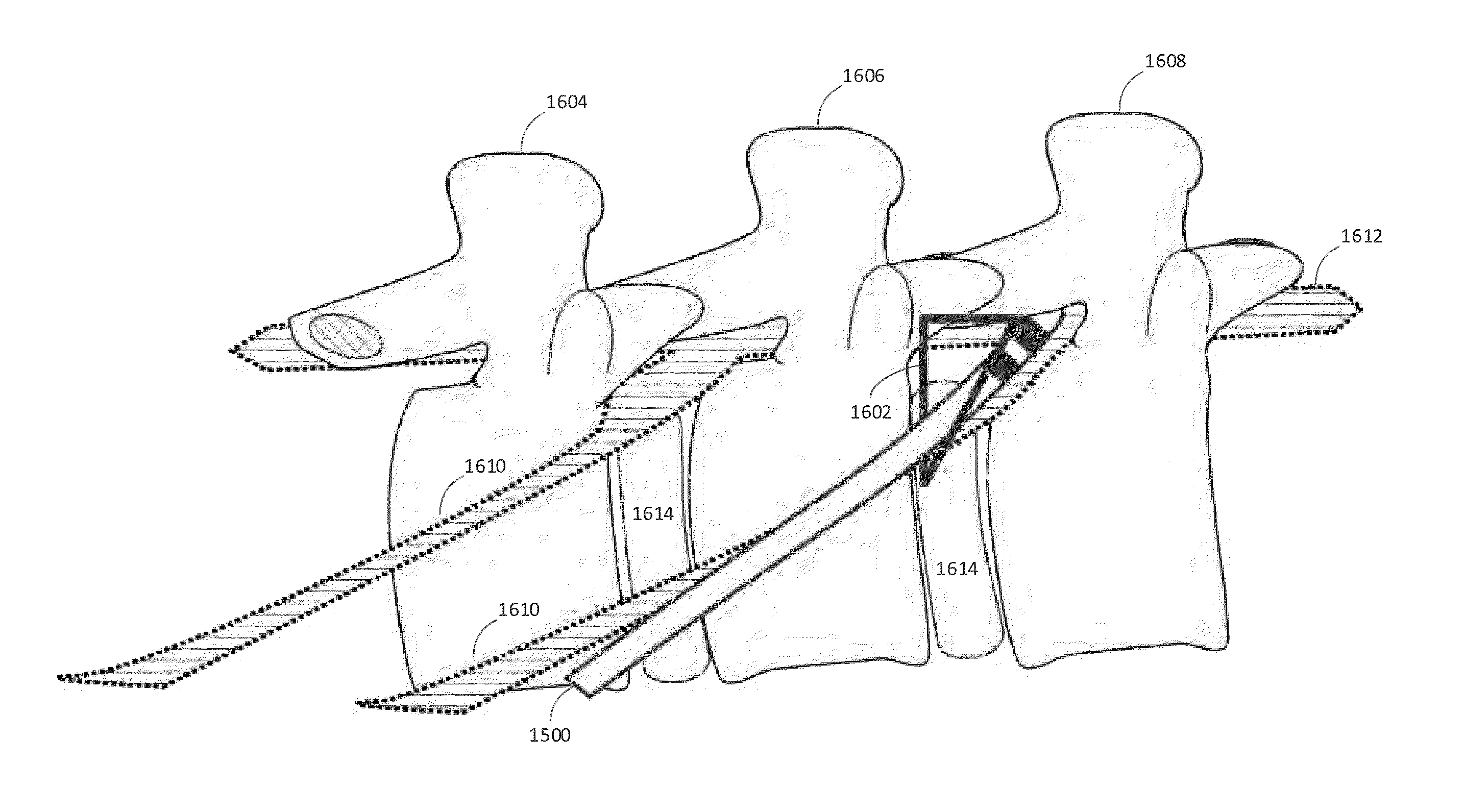
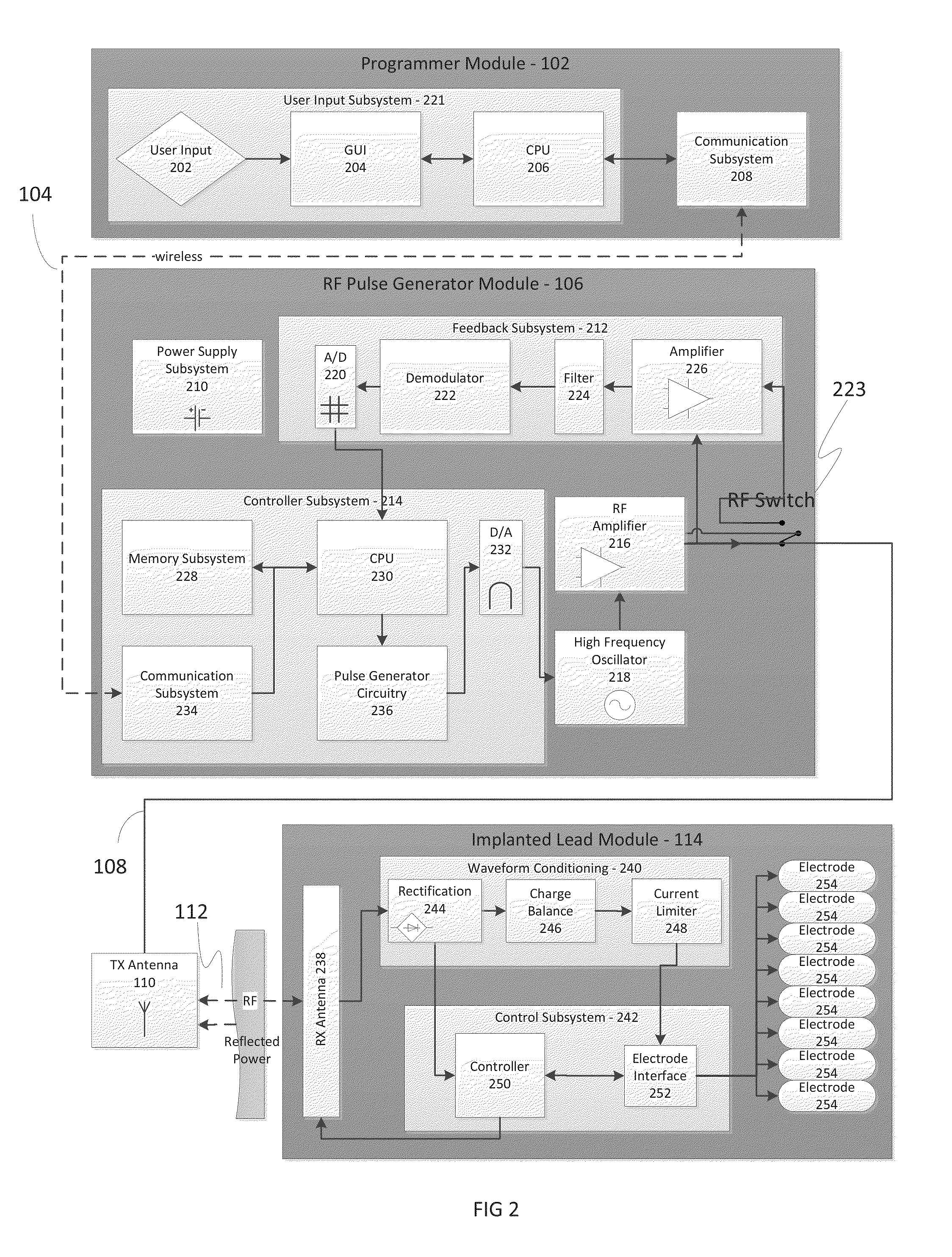
ActiveUS20130310901A1TestingReduce postoperative painSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesCouplingMedicine
A method for modulating nerve tissue in a body of a patient includes implanting a wireless stimulation device in proximity to a dorsal root ganglion or an exiting nerve root such that an electrode, circuitry and a receiving antenna are positioned completely within the body of the patient. An input signal containing electrical energy and waveform parameters is transmitted to the receiving antenna(s) from a control device located outside of the patient's body via radiative coupling. The circuitry within the stimulation device generates one or more electrical impulses and applies the electrical impulses to the dorsal root ganglion or the exiting nerve roots through the electrode.
Owner:MICRON MEDICAL LLC +1
Percutaneously deliverable orthopedic joint device
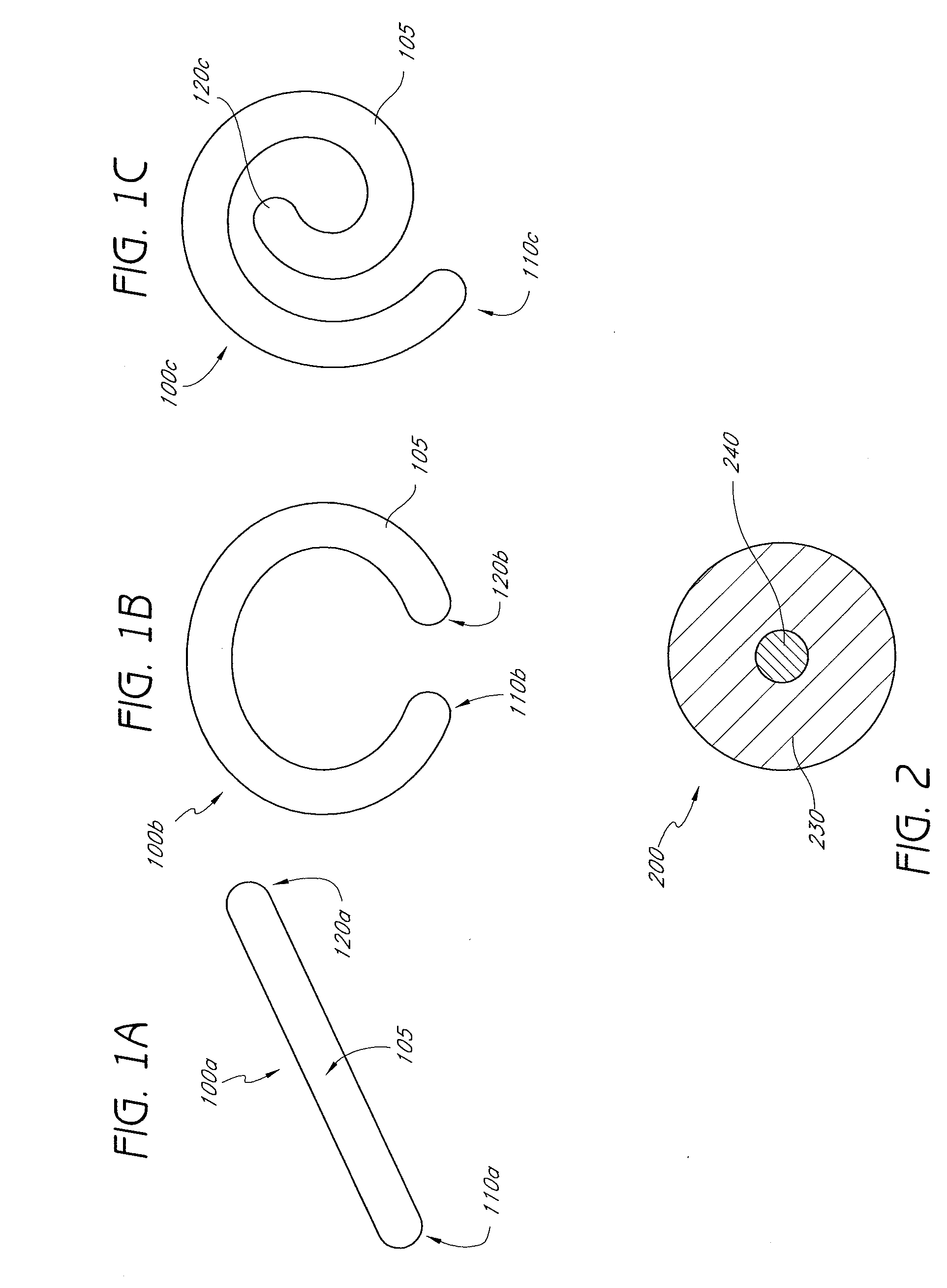
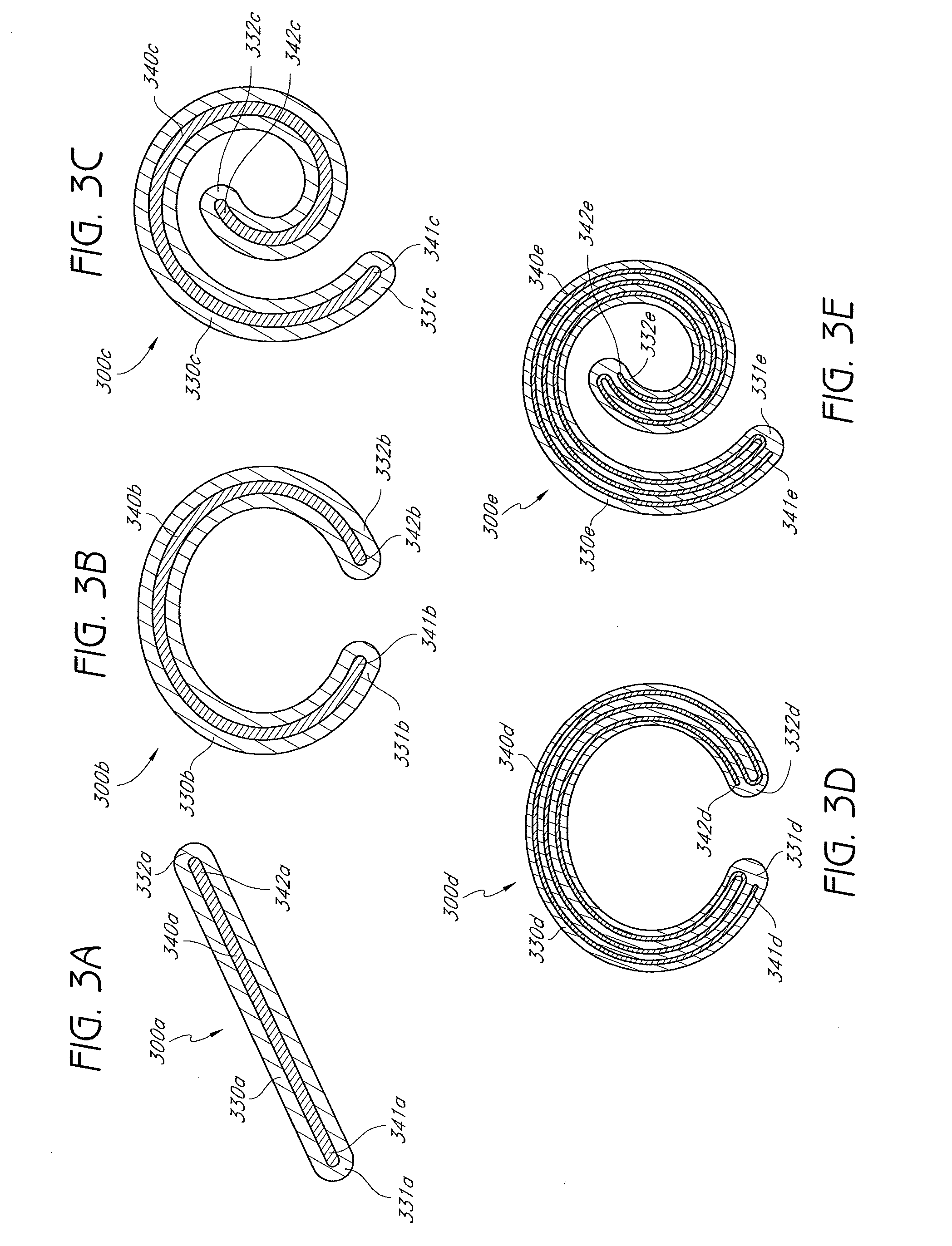
InactiveUS20080255664A1Slow deteriorationRelieve painInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsHypodermoclysisHypodermic needle
A percutaneously implantable orthopedic device is a shape-changing joint prosthesis with a generally arcuate or generally rectilinear configuration which is delivered through a delivery device in a substantially straightened or slightly curved configuration into a joint in a patient. The generally arcuate configuration may include an open ring or spiral shape. The generally rectilinear configuration may include a polygon or zig-zag shape. The delivery and retrieval device can be a syringe, hypodermic needle or cannula. The orthopedic device is moveable into its generally arcuate or generally rectilinear configuration in the joint by manipulation or a shape memory set. The orthopedic device acts as a soft compliant bearing surface or cushion that minimizes the bone-on-bone wear from articulation and loading.
Owner:ARTICULINX
Magnetic targeting system for facilitating navigation
ActiveUS20090082666A1Shorter surgeryReduce X-ray exposureInternal osteosythesisDiagnostic recording/measuringSet screwIn vivo
The present invention describes a magnetic targeting system suitable for guiding a biocompatible device to a target area within the body (in vivo) and method of using the same. The system includes a targeting member having a steering material and is attached to the biocompatible device. The system also includes at least one anchoring member constructed and arranged for the inclusion of a magnetic material effective for influencing the traversal of the steering material, in vivo. The magnetic material is configured and sized so as to positionable external of the anchoring member, in vivo. The magnetically influenced anchoring member interacts with the targeting member such that the biocompatible device is positionable relative to the target area. An extender and connector have threads indexed to a securing set screw to facilitate positioning and affixation of the biocompatible material
Owner:NUVASIVE
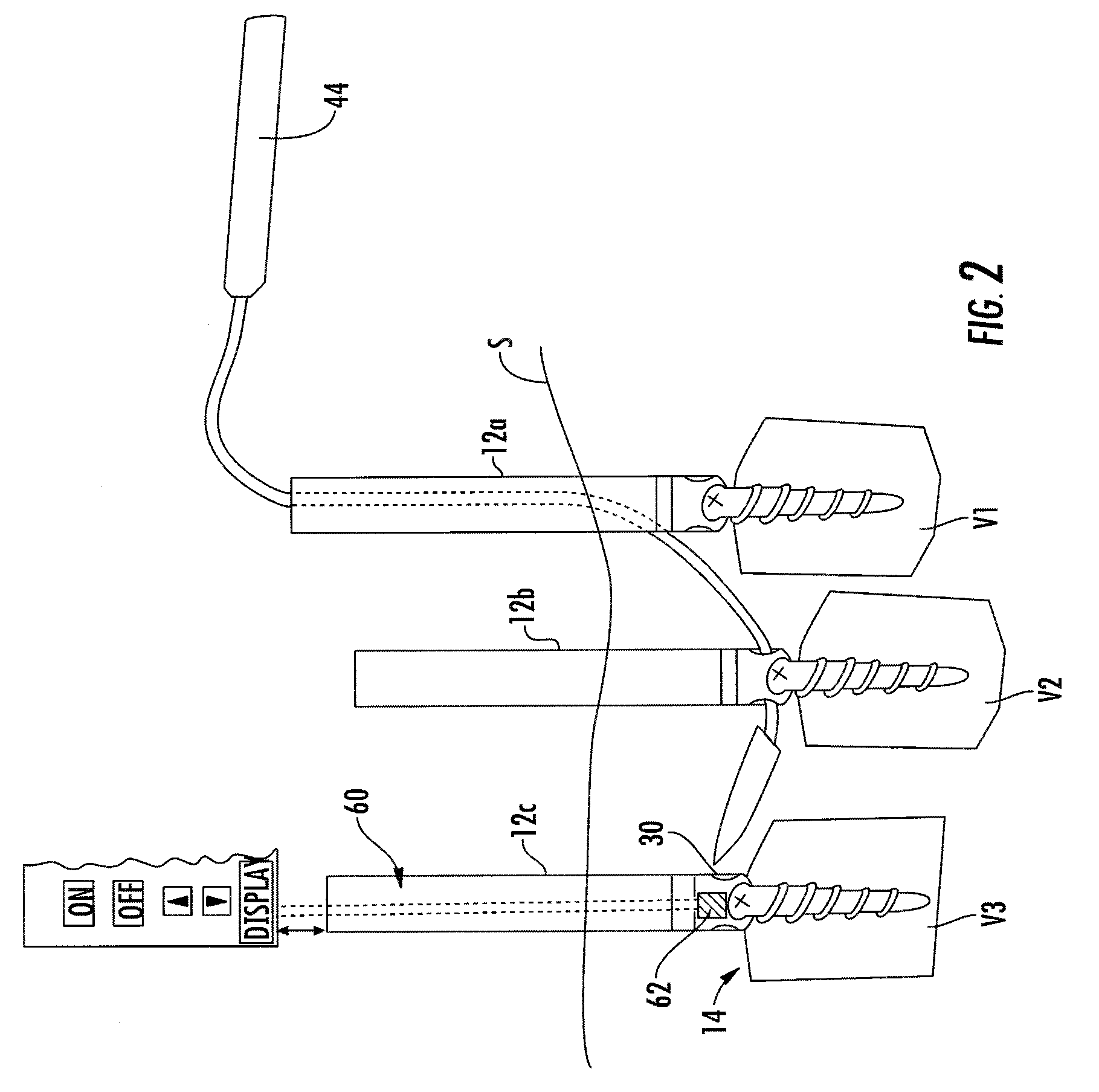
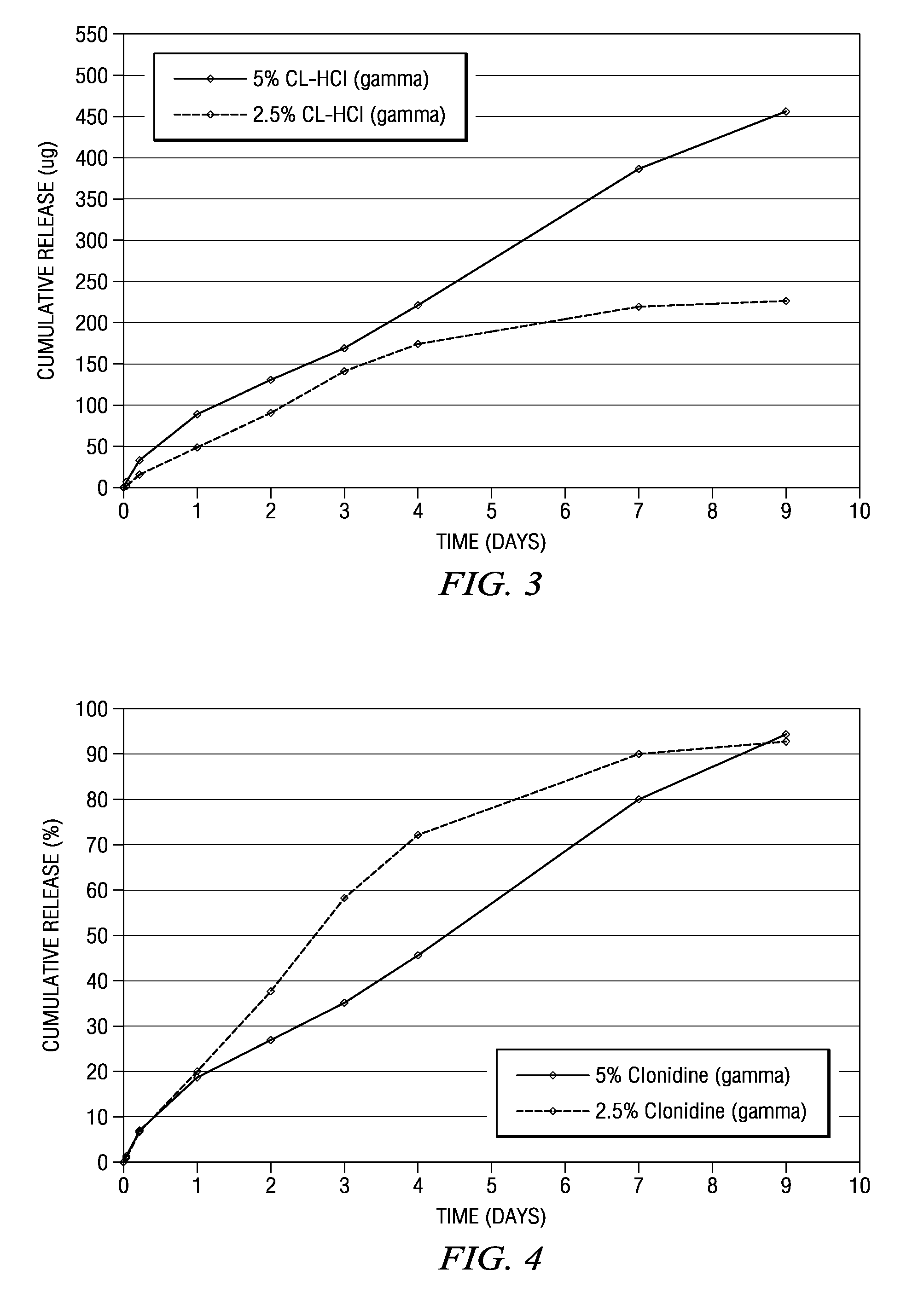
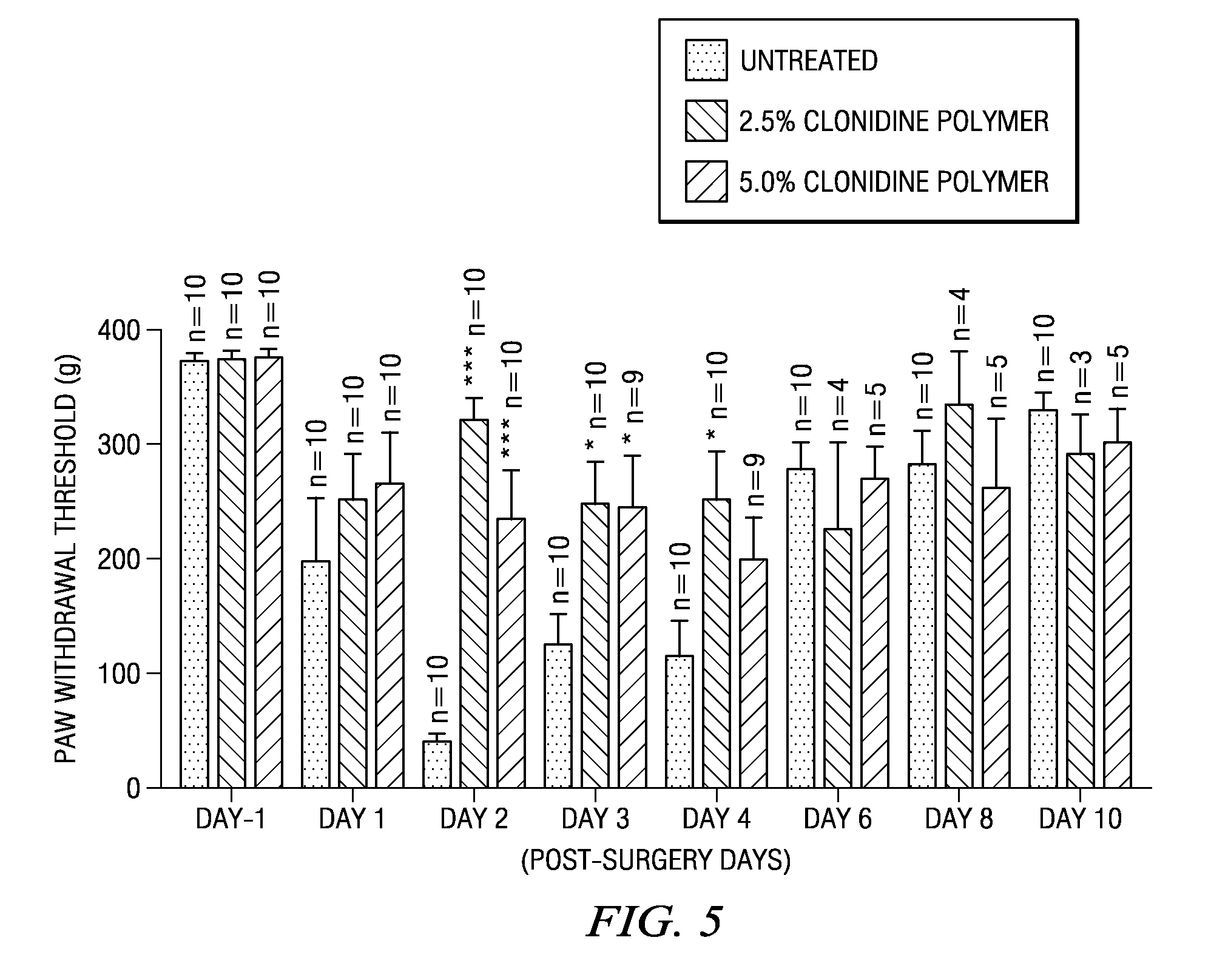
Methods and compositions for treating post-operative pain comprising clonidine
ActiveUS20090264491A1Ease the pain of treatmentReduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePolymerPostoperative pain
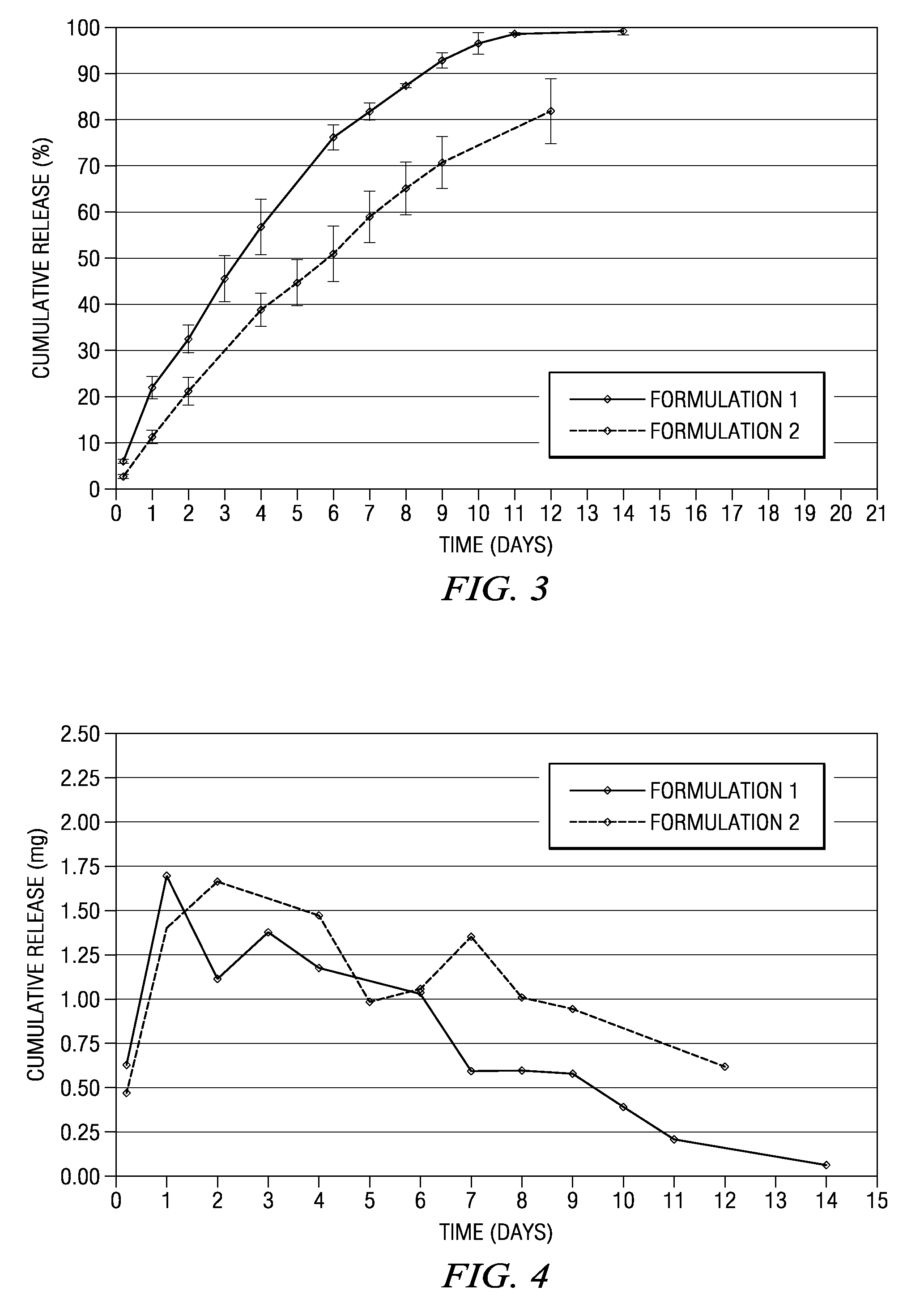
The present invention is directed to an implantable drug depot useful for reducing, preventing or treating post-operative pain in a patient in need of such treatment, the implantable drug depot comprising a therapeutically effective amount of clonidine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and a polymer; wherein the depot is implantable at a site beneath the skin to reduce, prevent or treat post-operative pain, and the depot is capable of releasing (i) about 5% to about 45% of the clonidine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof relative to a total amount of the clonidine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof loaded in the drug depot over a first period of up to 48 hours and (ii) about 55% to about 95% of the clonidine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof relative to a total amount of the clonidine or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof loaded in the drug depot over a subsequent period of at least 3 days.
Owner:COMPANION SPINE LLC +1
Methods and devices for modulating excitable tissue of the exiting spinal nerves
ActiveUS8903502B2TestingReduce postoperative painSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesMedicineCoupling
A method for modulating nerve tissue in a body of a patient includes implanting a wireless stimulation device in proximity to a dorsal root ganglion or an exiting nerve root such that an electrode, circuitry and a receiving antenna are positioned completely within the body of the patient. An input signal containing electrical energy and waveform parameters is transmitted to the receiving antenna(s) from a control device located outside of the patient's body via radiative coupling. The circuitry within the stimulation device generates one or more electrical impulses and applies the electrical impulses to the dorsal root ganglion or the exiting nerve roots through the electrode.
Owner:MICRON MEDICAL LLC +1
Device and method for endovascular treatment for causing closure of a blood vessel
ActiveUS20080188843A1Reduce power densityReduce temperature peaksCatheterSurgical instrument detailsEndovascular treatmentLaser light
An endovascular laser treatment device for causing closure of a blood vessel uses an optical fiber adapted to be inserted into a blood vessel. An inner sleeve is arranged around a distal portion of the optical fiber core such that both distal ends of the inner sleeve and the optical fiber core form an enlarged light emitting face. The enlarged emitting face provides substantially lower power density while providing the same amount of total energy during a treatment session. An outer sleeve arranged around the inner sleeve acts as a spacer to position the light emitting face away from an inner wall of the blood vessel. The enlarged light emitting face and the outer sleeve acting as a spacer reduces the possibility of thermal run-away and device damage, and reduce the possibility of vessel perforations, leading to less bruising, post-operative pain and other clinical complications. In yet another aspect of the present invention, a spacer comprises an inner sleeve and an outer sleeve both arranged around a distal portion of the core to prevent the laser light from traveling laterally and to position the light emitting face away from an inner wall of the vessel. The inner sleeve can be a heat resistive material such as ceramic and the outer sleeve can be, for example, a metallic sleeve to provide structural integrity and strength to the distal section of the treatment device.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Tissue visualization and modification devices and methods
InactiveUS20180271581A1Reduce capacitySusceptible to disc fissureLaproscopesSurgical instruments for heatingPlasma generatorHand held
Aspects of the invention include minimally invasive tissue modification systems. Embodiments of the systems include a minimally invasive access device having a proximal end, a distal end and an internal passageway. Positioned among the distal ends of the devices are a visualization element and an illumination element. Also provided are methods of using the systems in tissue modification applications, as well as kits for practicing the methods of the invention. Internal tissue visualization devices having RF-shielded visualization sensor modules are also provided. Minimally invasive RF tissue modulation devices are provided. In some aspects, the devices include a hand-held control unit and an elongated member. In some aspects, RF tissue modulation devices are provided and include an adapter that operably couples to a hand-held medical device. The adapter generates RF energy for delivery to a plasma generator on an elongated member.
Owner:TRICE MEDICAL
Implantable prosthesis
InactiveUS20030187516A1Reduce the possibilityReduce postoperative painDiagnosticsSurgeryRepair siteIntraabdominal pressure
Owner:AMID PARVIZ K +1
Minimally Invasive Tissue Modification Systems With Integrated Visualization
InactiveUS20100121155A1Reduce capacitySusceptible to disc fissureEndoscopesLaproscopesBiomedical engineering
Aspects of the invention include minimally invasive tissue modification systems. Embodiments of the systems include a minimally invasive access device having a proximal end, a distal end and an internal passageway. Also part of the system is an elongated tissue modification device having a proximal end and a distal end. The tissue modification device is dimensioned to be slidably moved through the internal passageway of the access device. The tissue modification device includes a tissue modifier. Positioned among the distal ends of the devices are a visualization element and an illumination element. Also provided are methods of using the systems in tissue modification applications, as well as kits for practicing the methods of the invention.
Owner:AXIS SURGICAL TECH
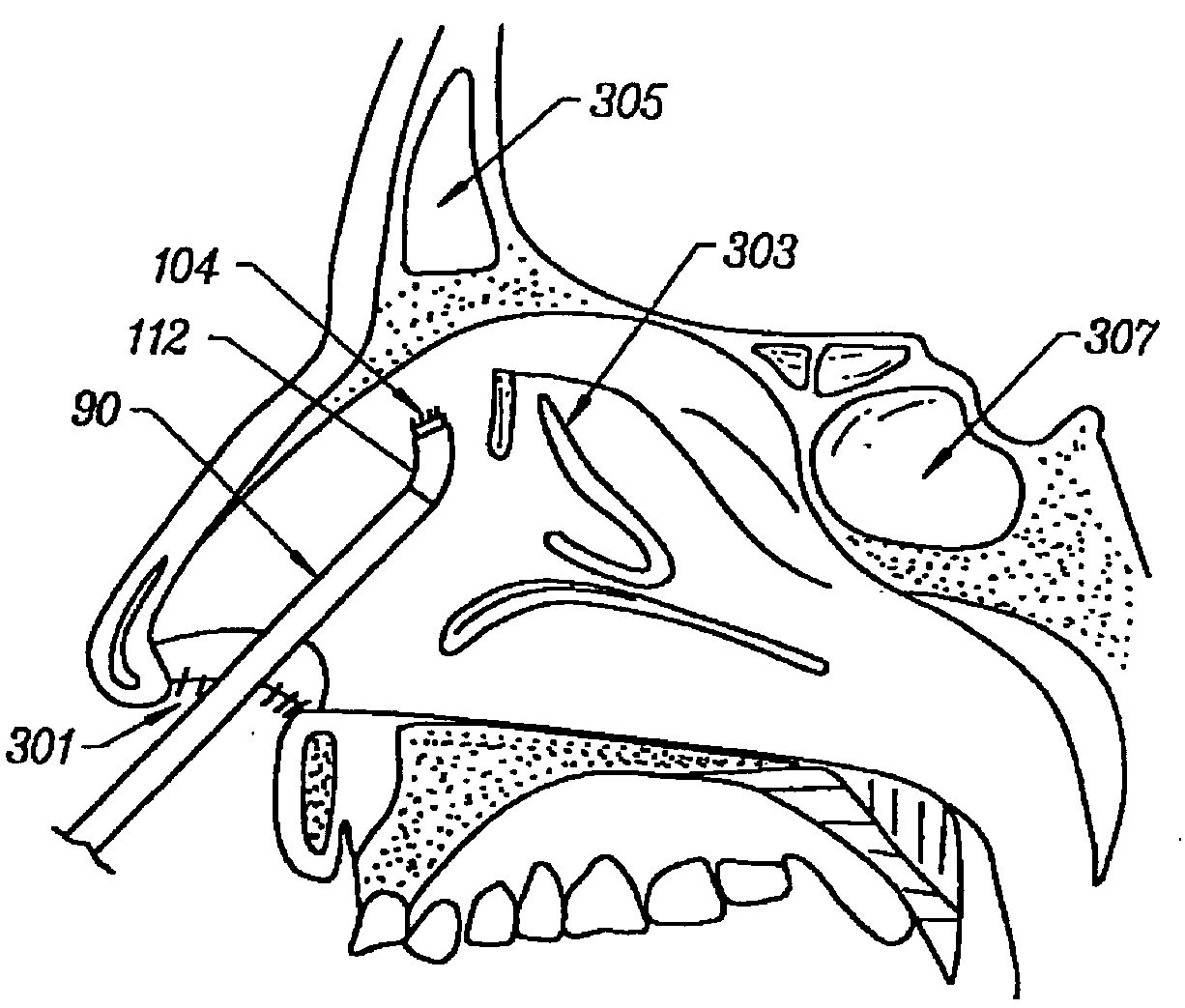
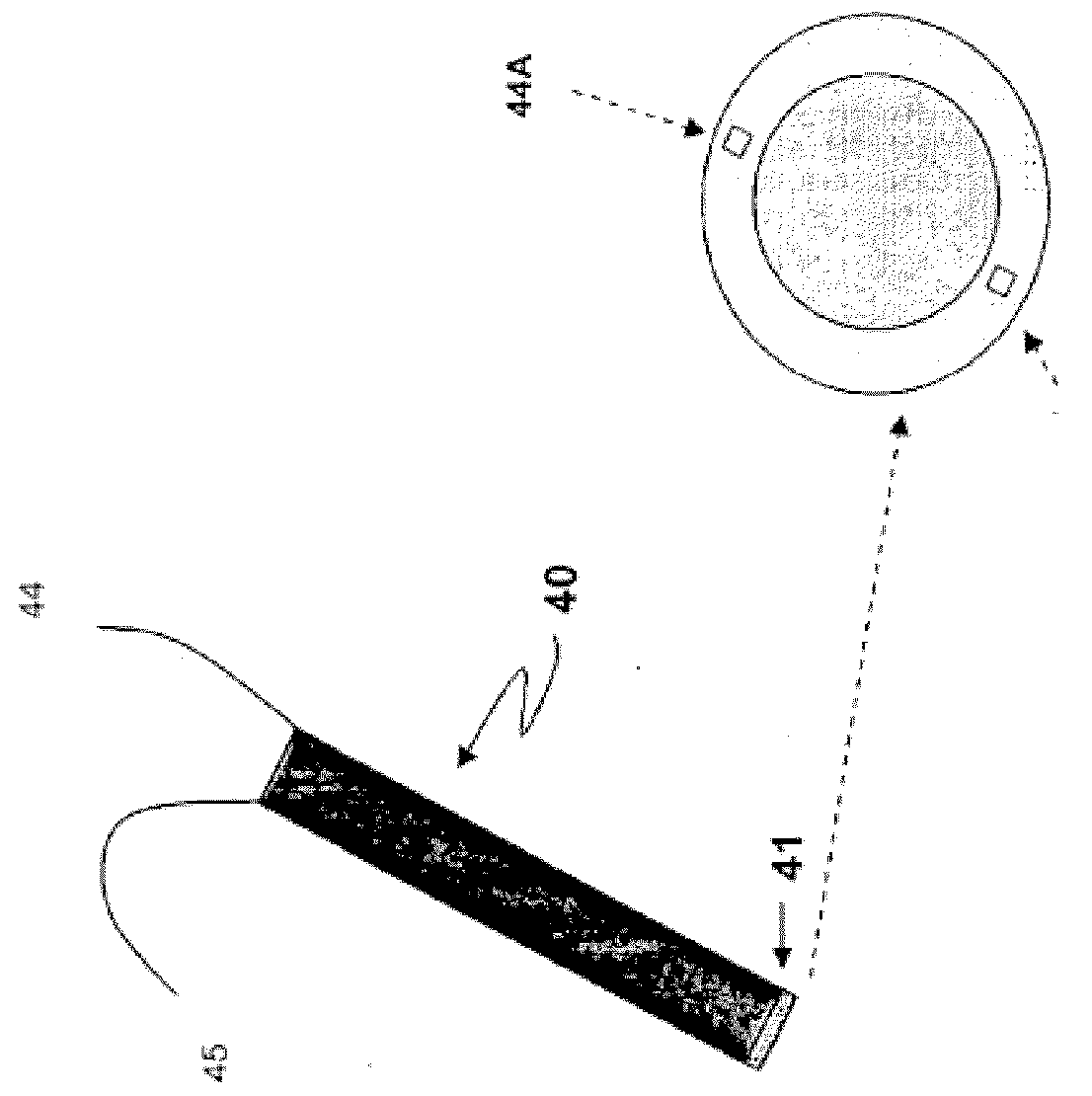
Trocar-cannula complex, cannula and method for delivering biologically active agents during minimally invasive surgery
InactiveUS20070073248A1Reduce eliminateReduce postoperative painCannulasSurgical needlesLess invasive surgeryActive agent
A trocar-cannula complex for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures performed through a port site of a patient and in the delivery of biologically active agents to the patient includes a trocar and a cannula. The cannula includes a tubular structure with a central lumen receiving the trocar and an outer surface adapted to interface with tissue at the port site. A first delivery mechanism is associated with the cannula for delivering a first biologically active agent to a patient and a second delivery mechanism is associated with the cannula for delivery of a second biologically active agent to the patient. Various other manners of delivering the agents are also disclosed.
Owner:RXTROCAR +1
Tissue visualization and modification devices and methods
InactiveUS20150157387A1Reduce capacitySusceptible to disc fissureLaproscopesSurgical instruments for heatingPlasma generatorHand held
Aspects of the invention include minimally invasive tissue modification systems. Embodiments of the systems include a minimally invasive access device having a proximal end, a distal end and an internal passageway. Positioned among the distal ends of the devices are a visualization element and an illumination element. Also provided are methods of using the systems in tissue modification applications, as well as kits for practicing the methods of the invention. Internal tissue visualization devices having RF-shielded visualization sensor modules are also provided. Minimally invasive RF tissue modulation devices are provided. In some aspects, the devices include a hand-held control unit and an elongated member. In some aspects, RF tissue modulation devices are provided and include an adapter that operably couples to a hand-held medical device. The adapter generates RF energy for delivery to a plasma generator on an elongated member.
Owner:TRICE MEDICAL
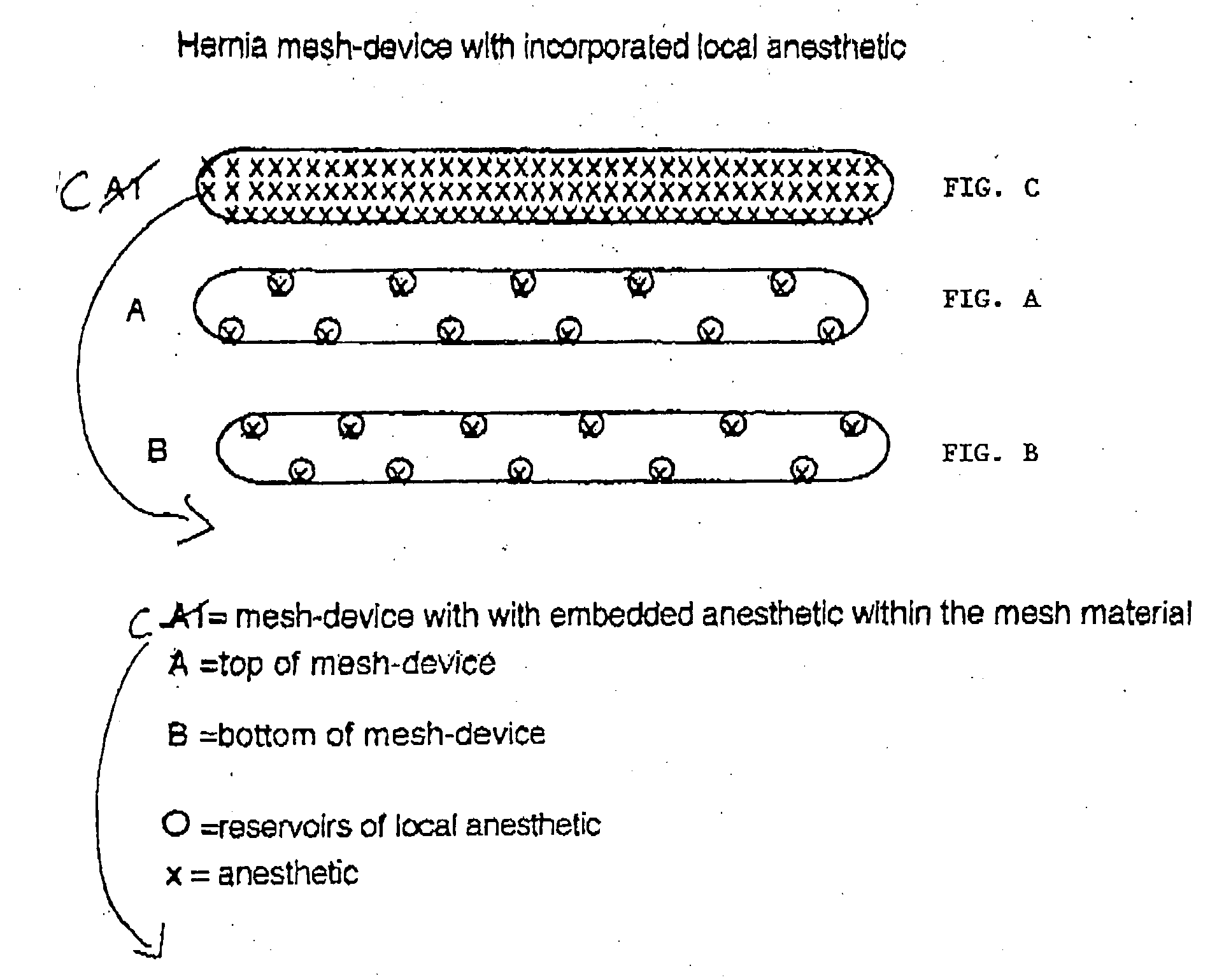
Hernia mesh-device with incorporated local anesthetic
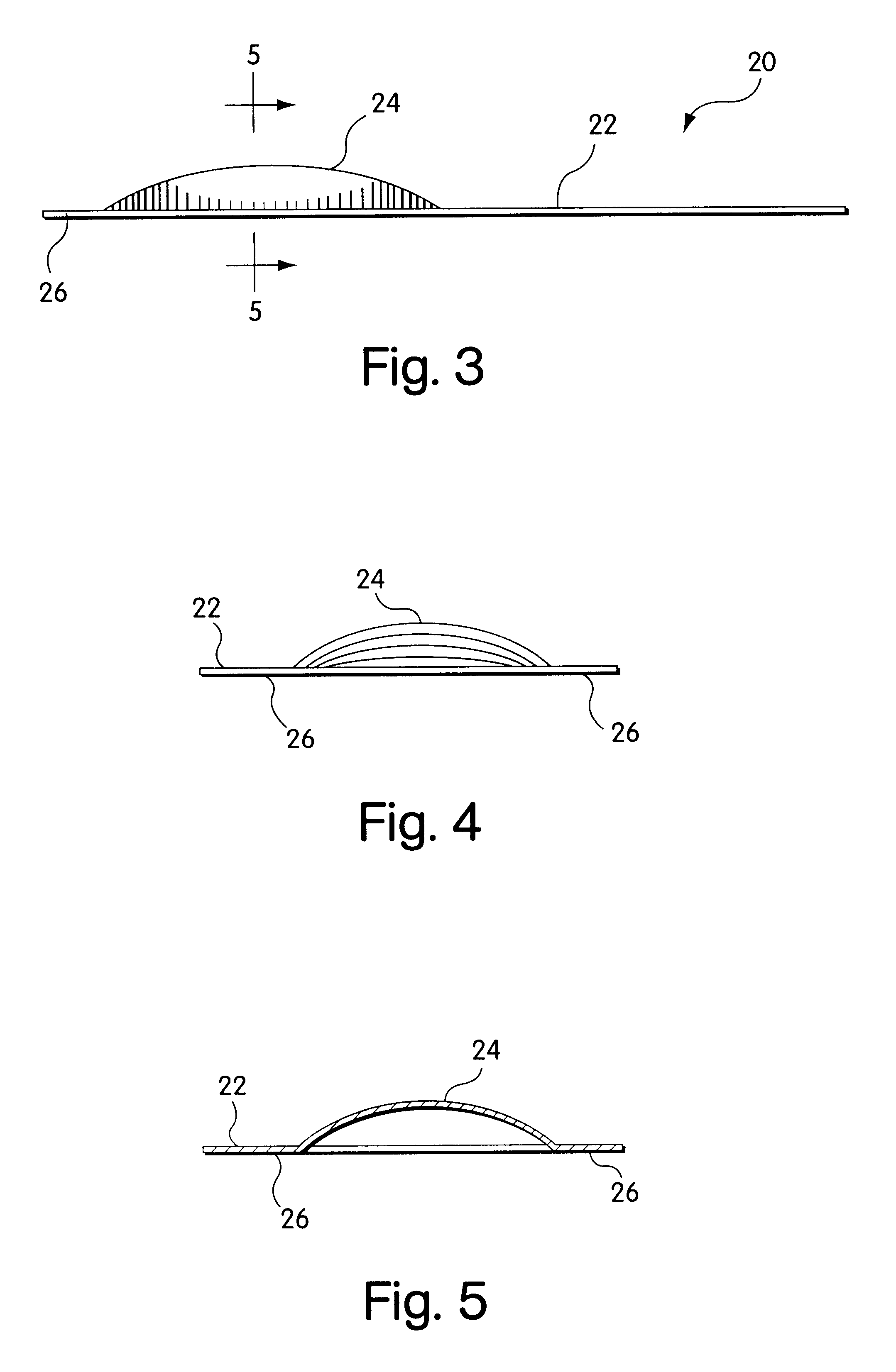
InactiveUS20050015102A1Reduce postoperative painEqually distributedProsthesisWound clampsHerniaSurgical repair
A mesh-device for surgical repair of a hernia which includes a local anesthetic. The local anesthetic may be either embedded within the mesh, or provided in reservoirs, but is generally evenly distributed across the mesh-device. The local anesthetic is released over a predetermined duration at a predetermined rate.
Owner:CHEFITZ ALLEN B
Method of altering the refractive properties of an eye
InactiveUS20170007395A1Altering refractive propertyReduce postoperative painLaser surgeryEye implantsPhotosensCross linker
The present invention relates to a method of altering the refractive properties of the eye, the method including forming a pocket in a cornea of an eye of a patient so as to gain access to tissue bounding the pocket; after the pocket in the cornea has been formed, applying a photosensitizer inside the pocket so that the photo sensitizer permeates at least a portion of the tissue bounding the pocket, the photosensitizer facilitating cross-linking of the tissue bounding the pocket; inserting a lens implant into the pocket so as to change the refractive properties of the eye; and irradiating the cornea so as to activate cross-linkers in the portion of the tissue bounding the pocket and thereby stiffen the cornea and prevent corneal ectasia of the cornea.
Owner:PEYMAN GHOLAM A
Method of altering the refractive properties of an eye
InactiveUS20160081852A1Reduce postoperative painStiffenLaser surgeryElectrotherapyRefractive errorRefractive surgery
The present invention relates to a method of altering the refractive properties of the eye, the method including applying a substance to a cornea of an eye, the substance configured to facilitate cross linking of the cornea, irradiating the cornea so as to activate cross linkers in the cornea, and altering the cornea so as to change the refractive properties of the eye.
Owner:PEYMAN GHOLAM A
Device for separating the epithelium layer from the surface of the cornea of an eye
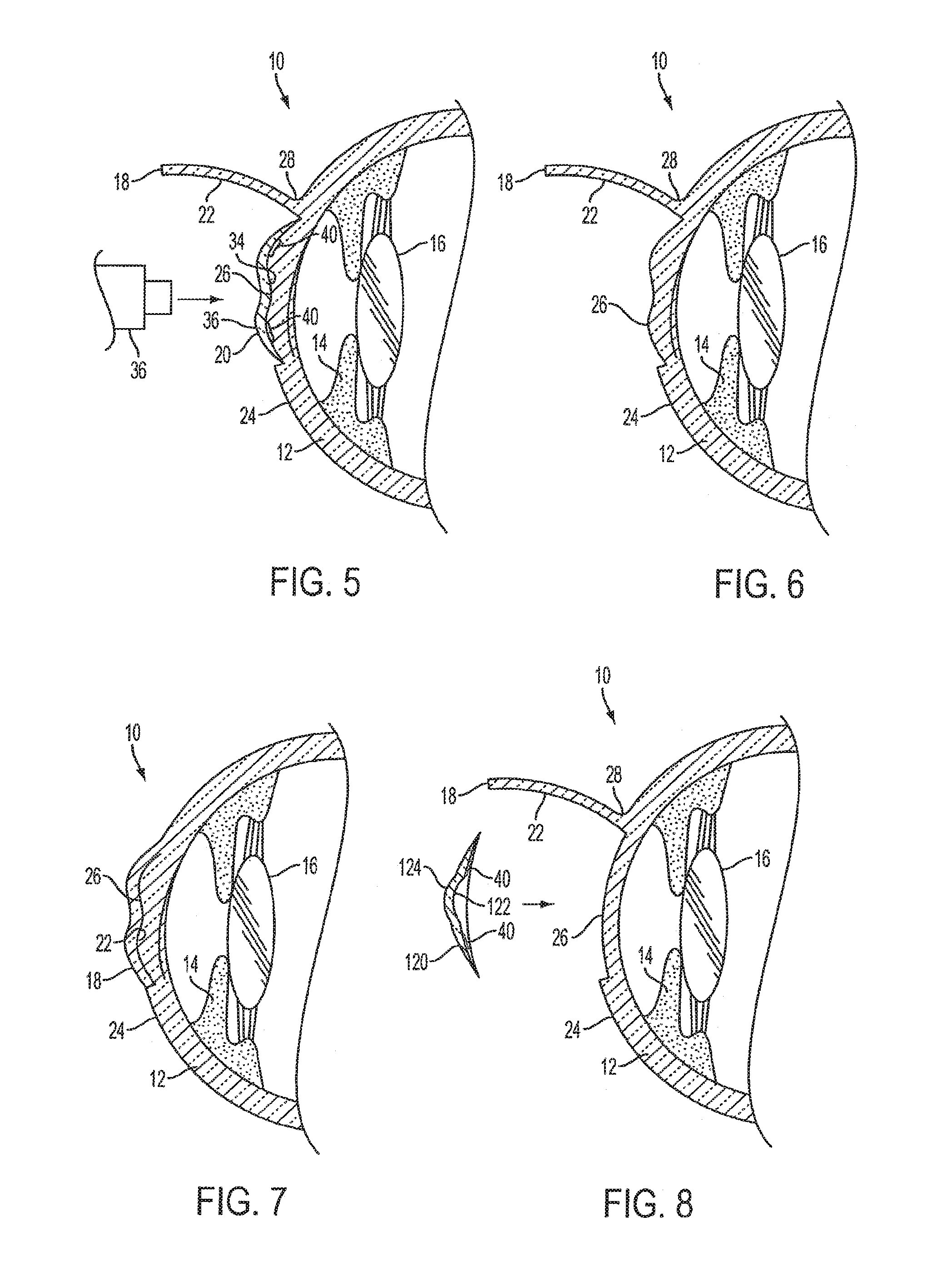
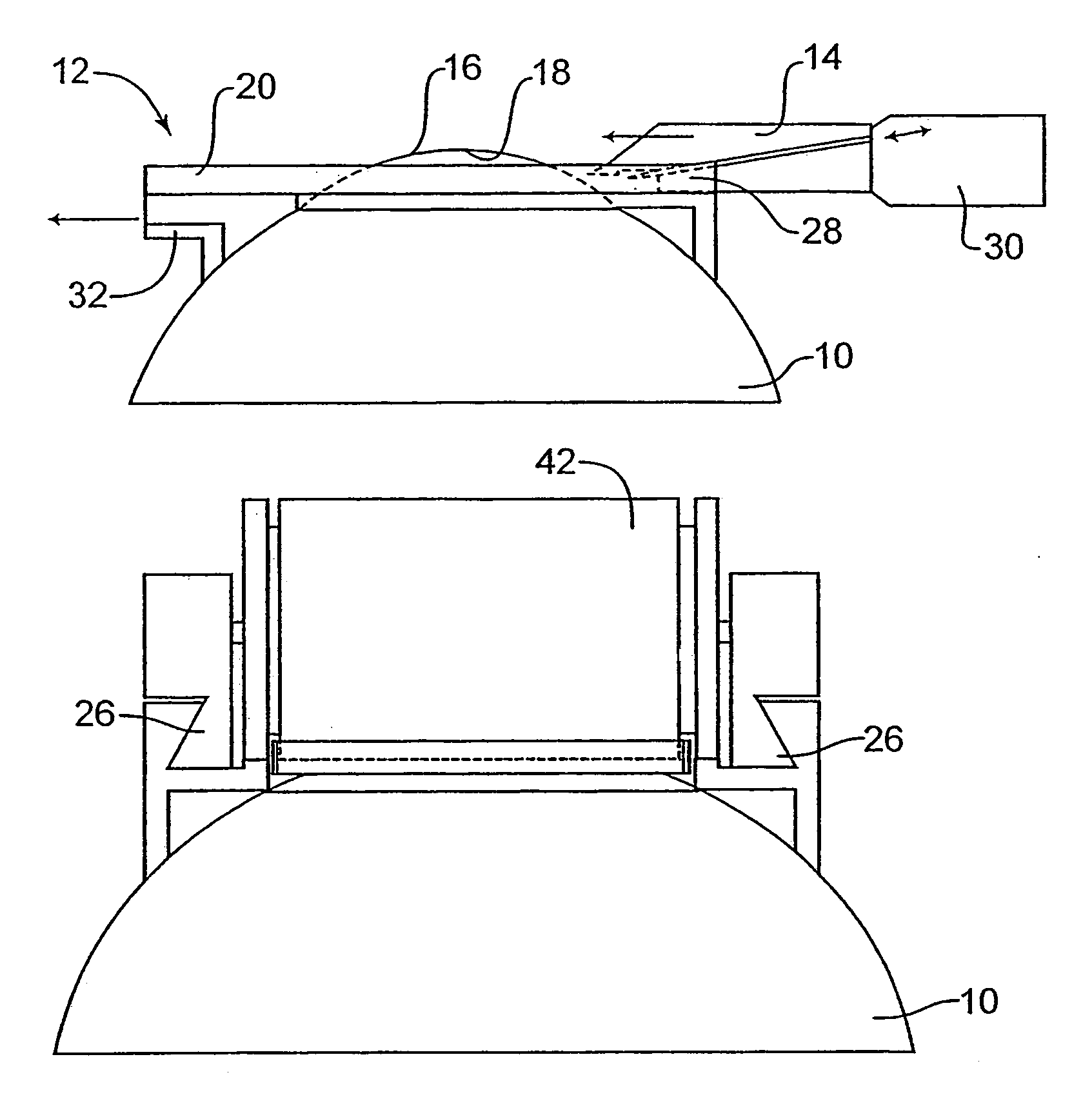
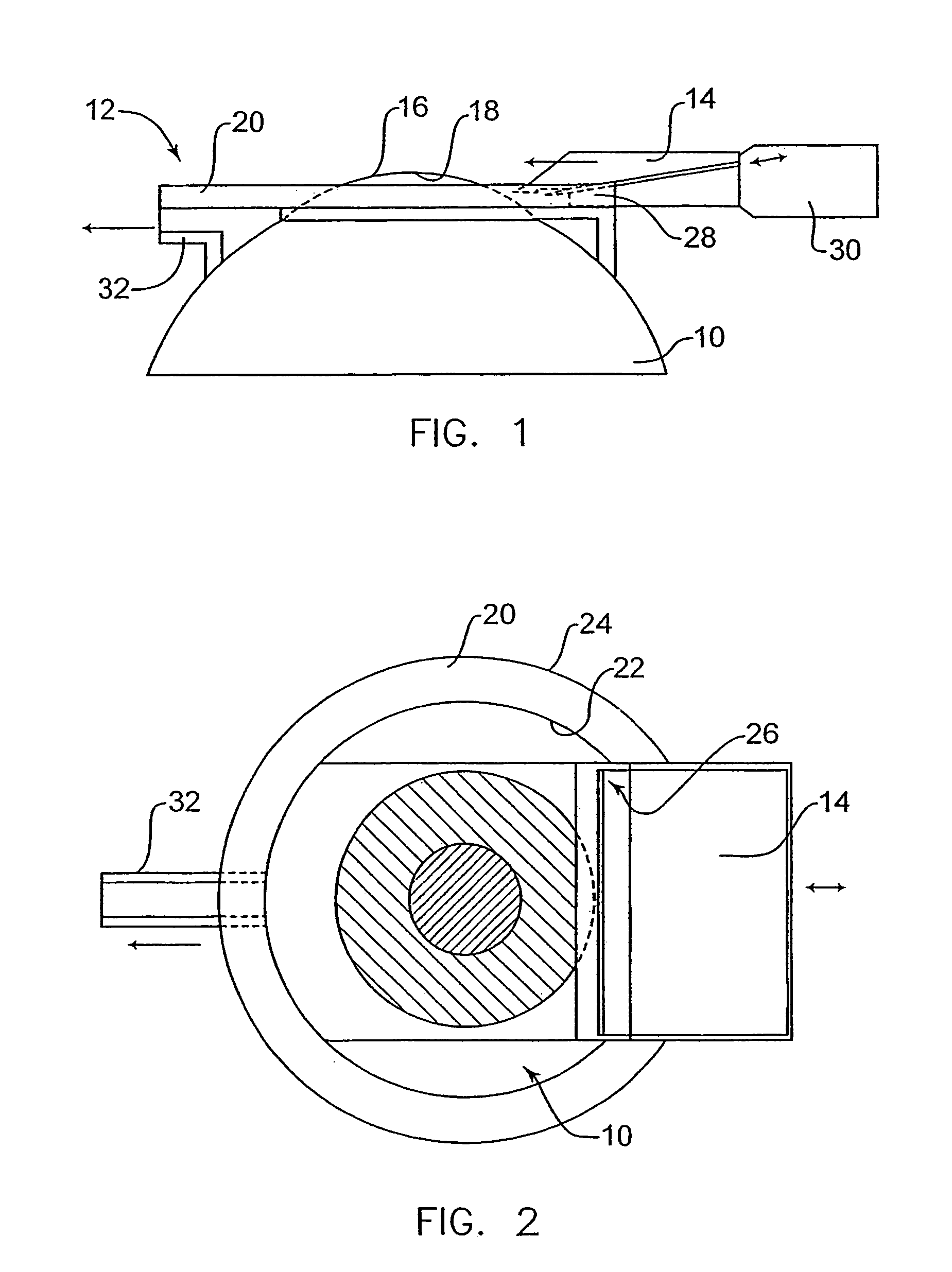
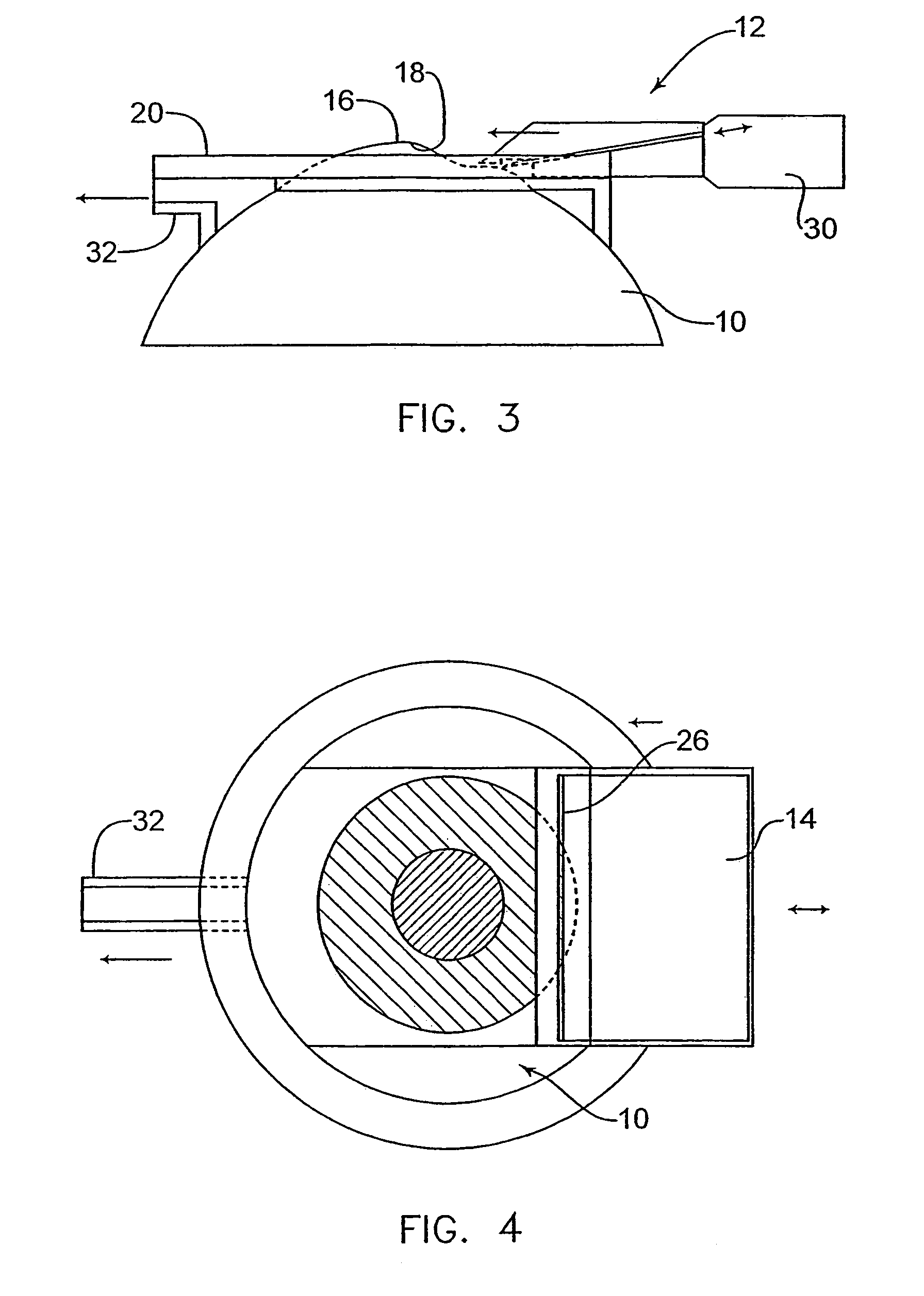
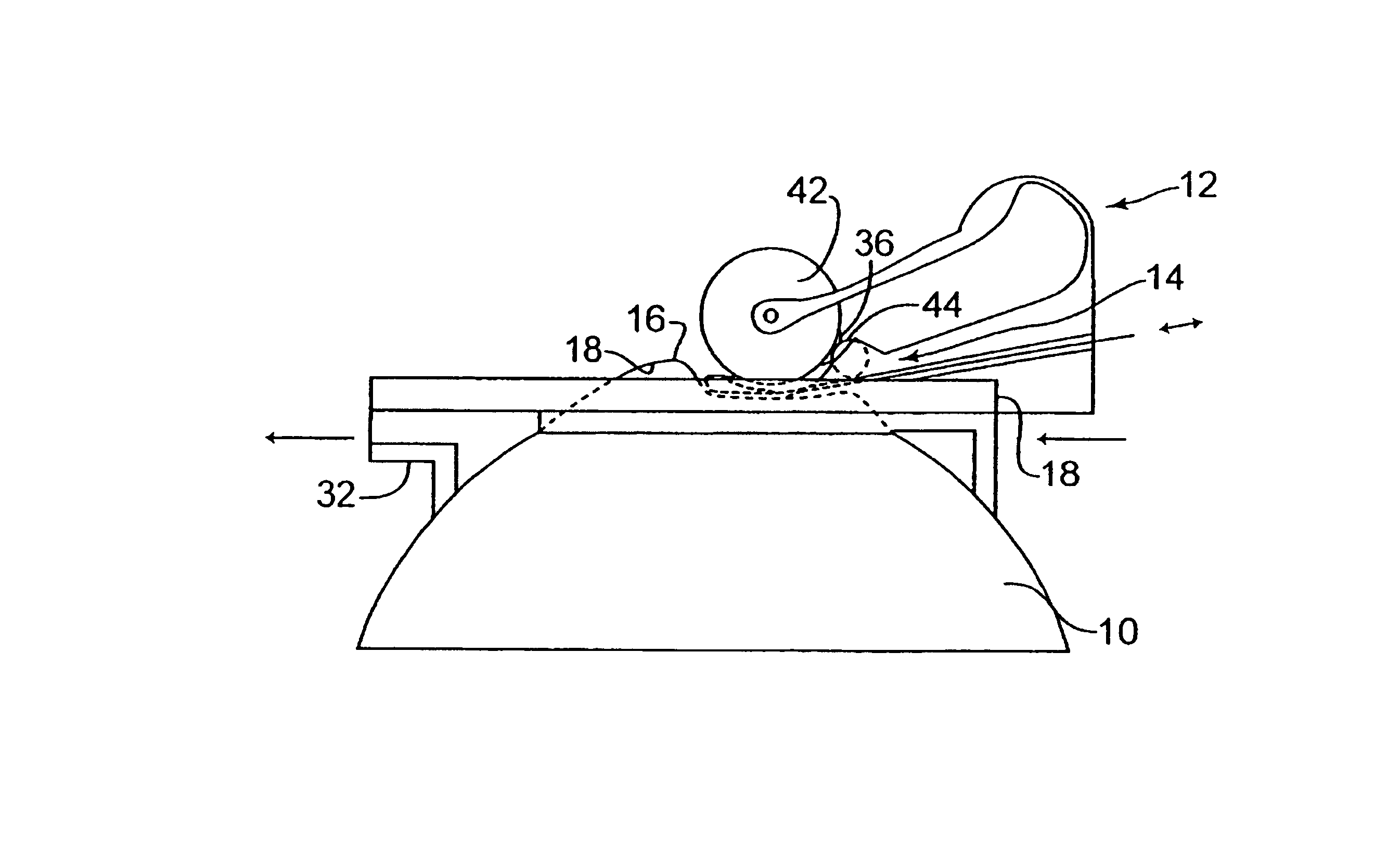
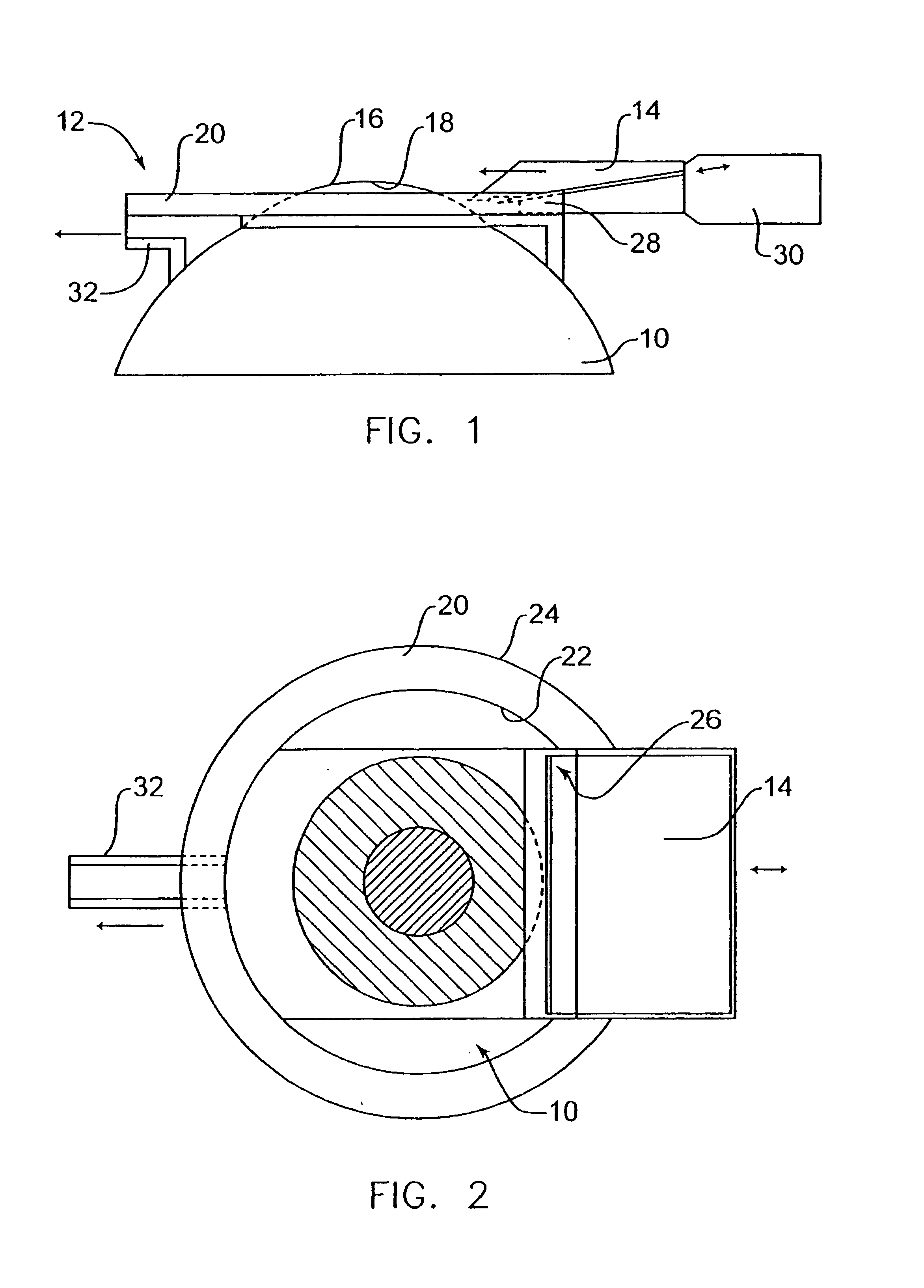
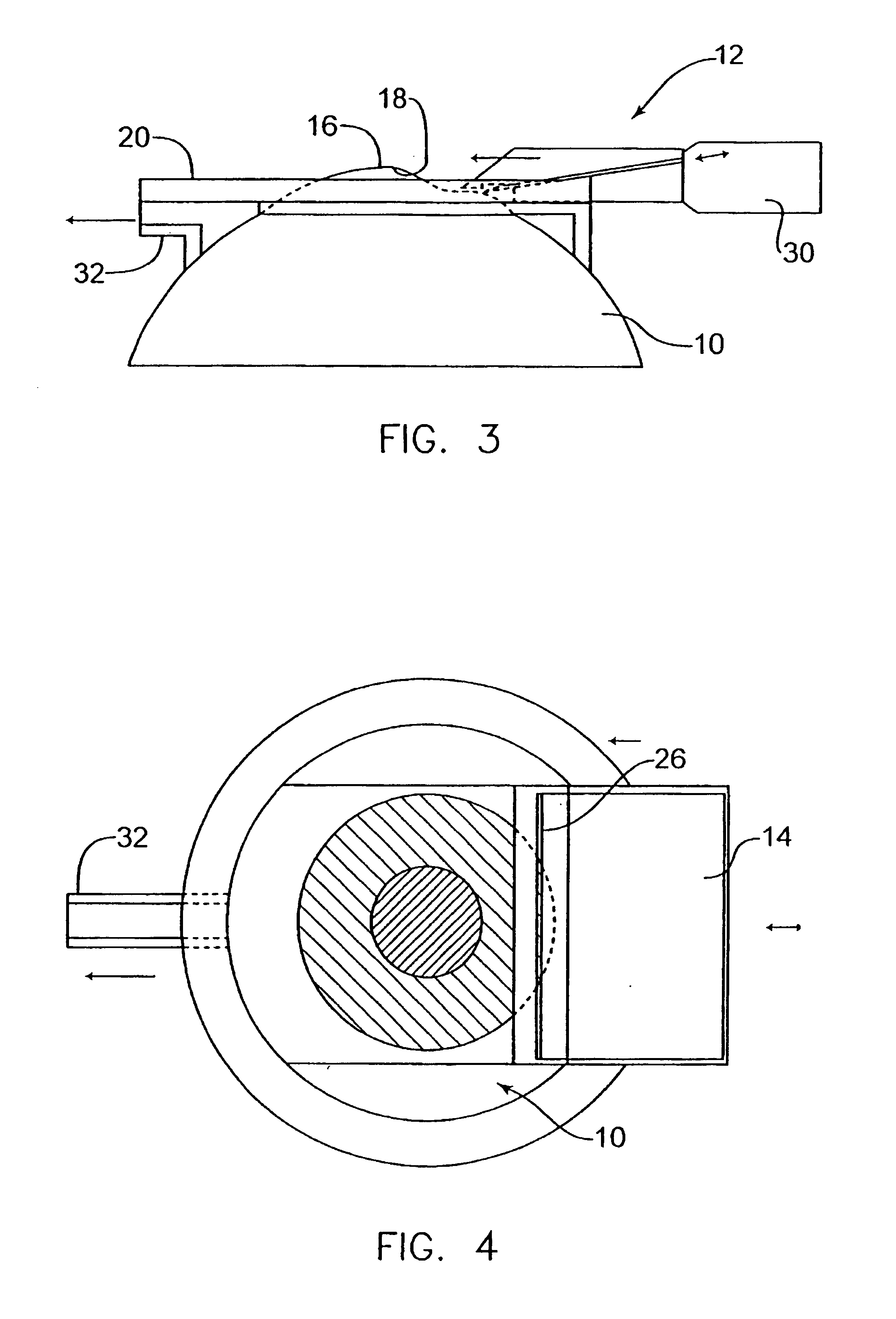
InactiveUS7004953B2Shorten the overall cycleReduce postoperative painEye surgeryMedical applicatorsEpitheliumEngineering
A device is disclosed for separating the epithelial layer of a cornea from the eye. The device includes a separator having an edge to remove the epithelial layer as the separator moves across the eye. The edge includes a thickness thicker than the thickness of at least one epithelial cell and less thick than the thickness of the epithelial layer. Separation can be performed mechanically, without the use of chemicals, so that the shape and integrity of the separated epithelial layer is preserved. The device can also be used with a polymer film that adheres to the epithelial layer to help preserve an integrity of the epithelial layer.
Owner:FOS HLDG SA
Minimally Invasive Tissue Modification Systems With Integrated Visualization
InactiveUS20120265009A1Reduce capacitySusceptible to disc fissureSurgeryLaproscopesBiomedical engineering
Aspects of the invention include minimally invasive tissue modification systems. Embodiments of the systems include a minimally invasive access device having a proximal end, a distal end and an internal passageway. Also part of the system is an elongated tissue modification device having a proximal end and a distal end. The tissue modification device is dimensioned to be slidably moved through the internal passageway of the access device. The tissue modification device includes a tissue modifier. Positioned among the distal ends of the devices are a visualization element and an illumination element. Also provided are methods of using the systems in tissue modification applications, as well as kits for practicing the methods of the invention.
Owner:TRICE MEDICAL
Magnetic Targeting System And Method Of Using The Same
ActiveUS20090099572A1Minimize damageReduce postoperative painInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsIn vivoBiomedical engineering
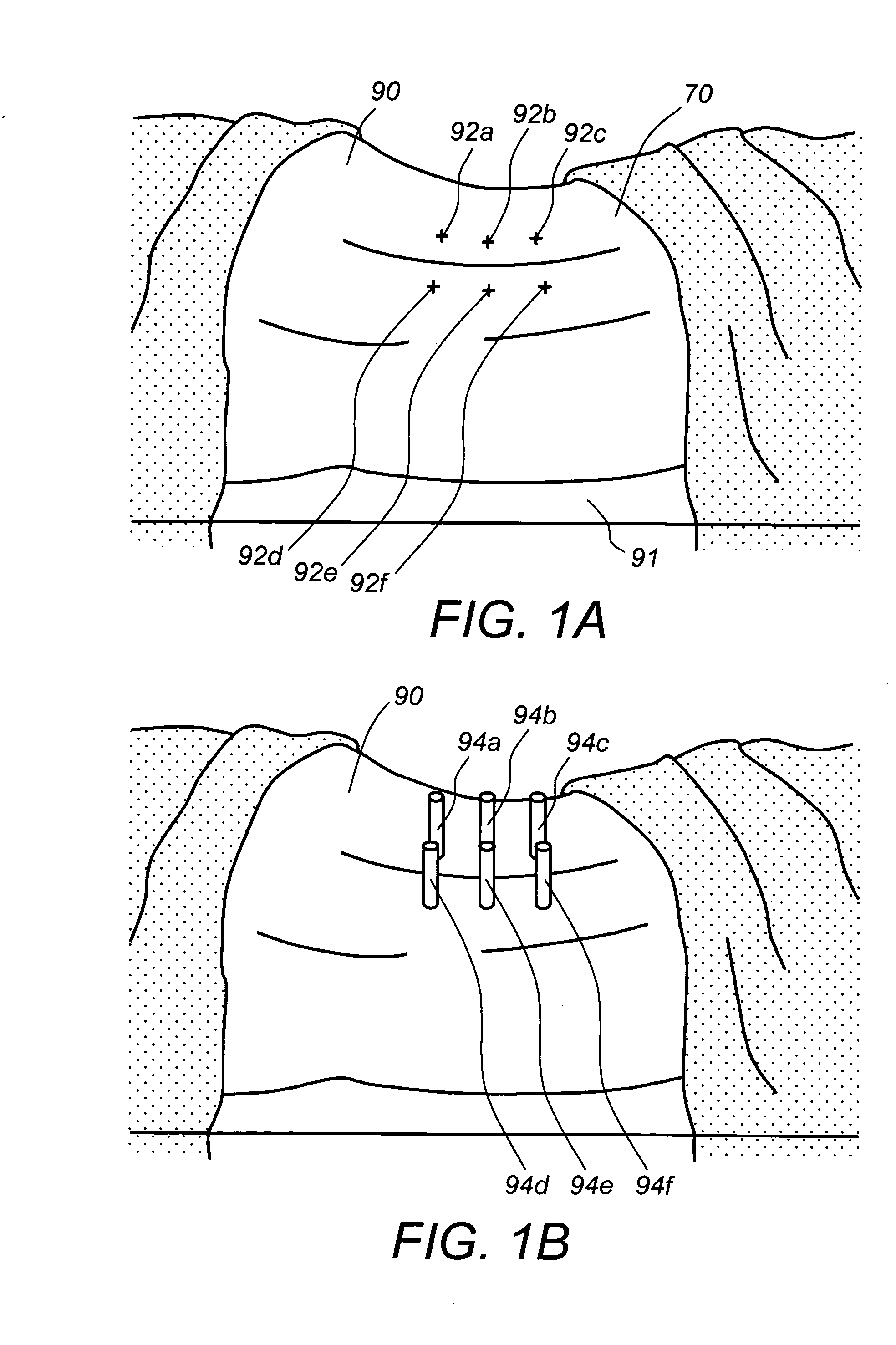
The present invention describes a magnetic targeting system suitable for guiding a biocompatible device to a target area within the body (in vivo) and method of using the same. The system includes a targeting member having a steering material and is attached to the biocompatible device. The system also includes at least one anchoring member constructed and arranged for the inclusion of a magnetic material effective for influencing the traversal of the steering material, in vivo. The magnetically influenced anchoring member interacts with the targeting member such that the biocompatible device is positionable relative to the target area.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Methods and compositions for treating post-operative pain comprising a local anesthetic
ActiveUS20090264472A1Ease the pain of treatmentReduce deliveryPowder deliveryBiocidePharmacyPharmaceutical drug
The present invention is directed to an implantable drug depot useful for reducing, preventing or treating post-operative pain in a patient in need of such treatment, the implantable drug depot comprising a polymer and a therapeutically effective amount of a local anesthetic or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein the drug depot is implantable at a site beneath the skin to reduce, prevent or treat post-operative pain, and the drug depot is capable of releasing (i) a bolus dose of the local anesthetic or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof at a site beneath the skin and (ii) a sustained release dose of an effective amount of the local anesthetic or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof over a period of at least 4 days.
Owner:COMPANION SPINE LLC +1
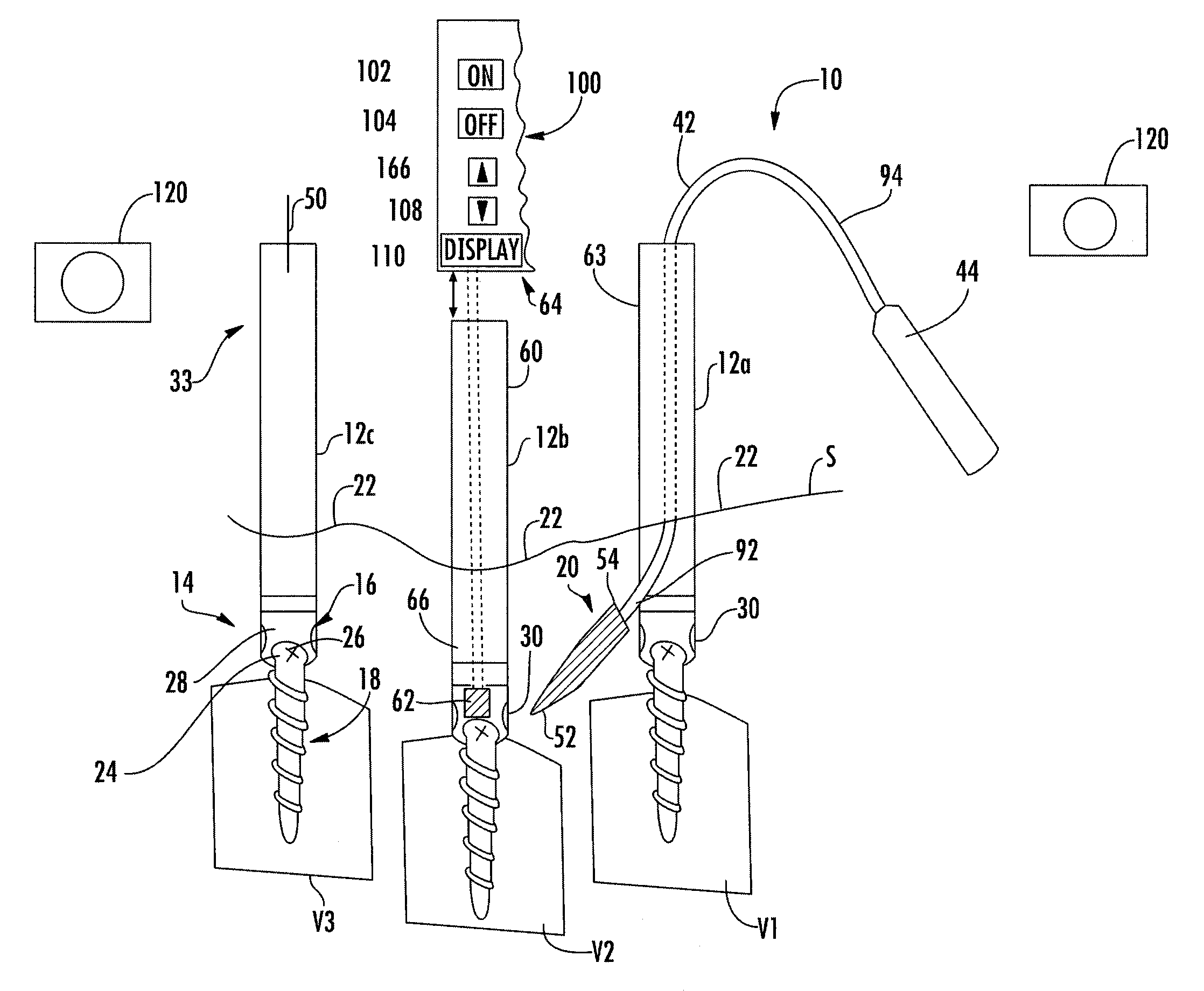
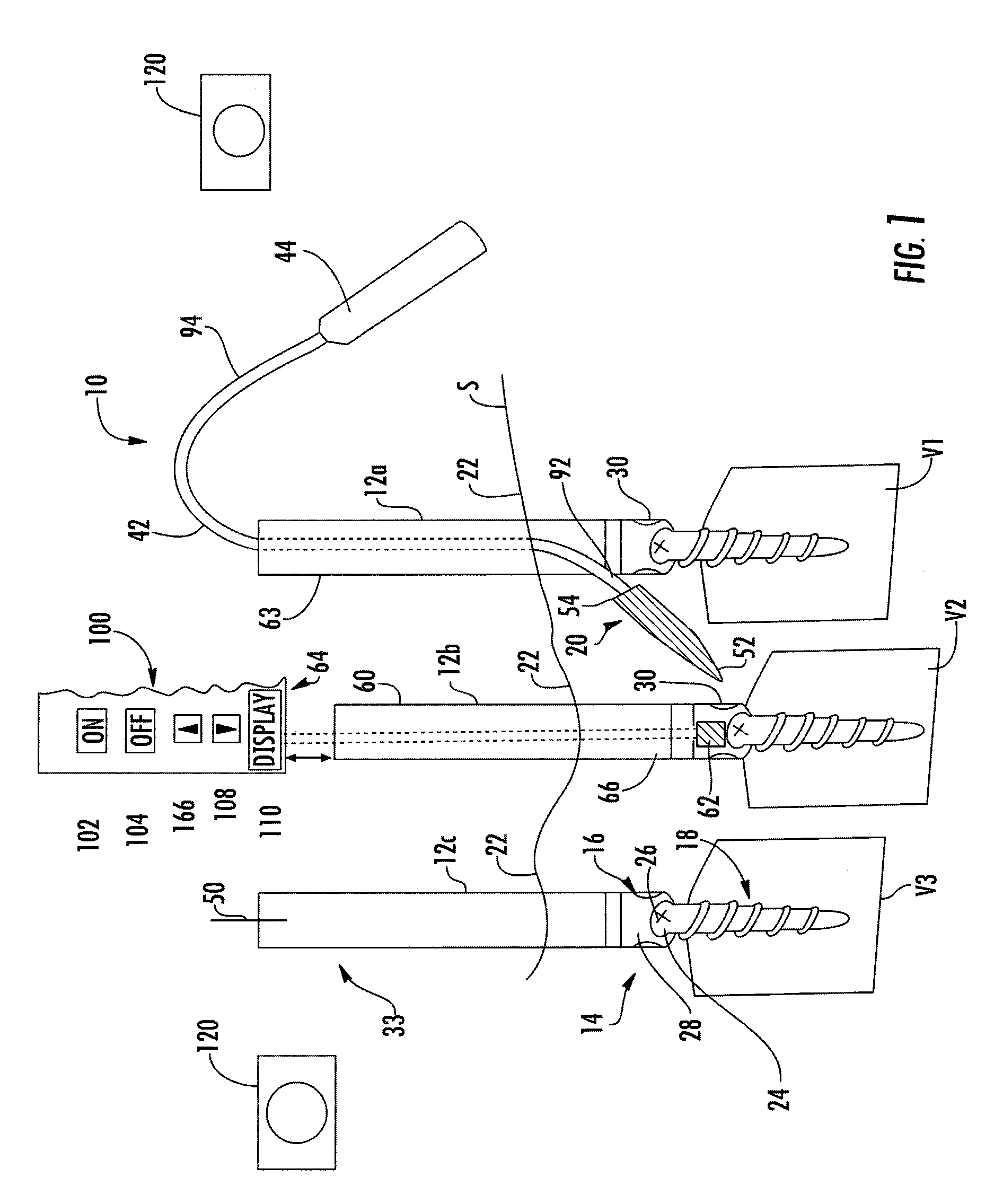
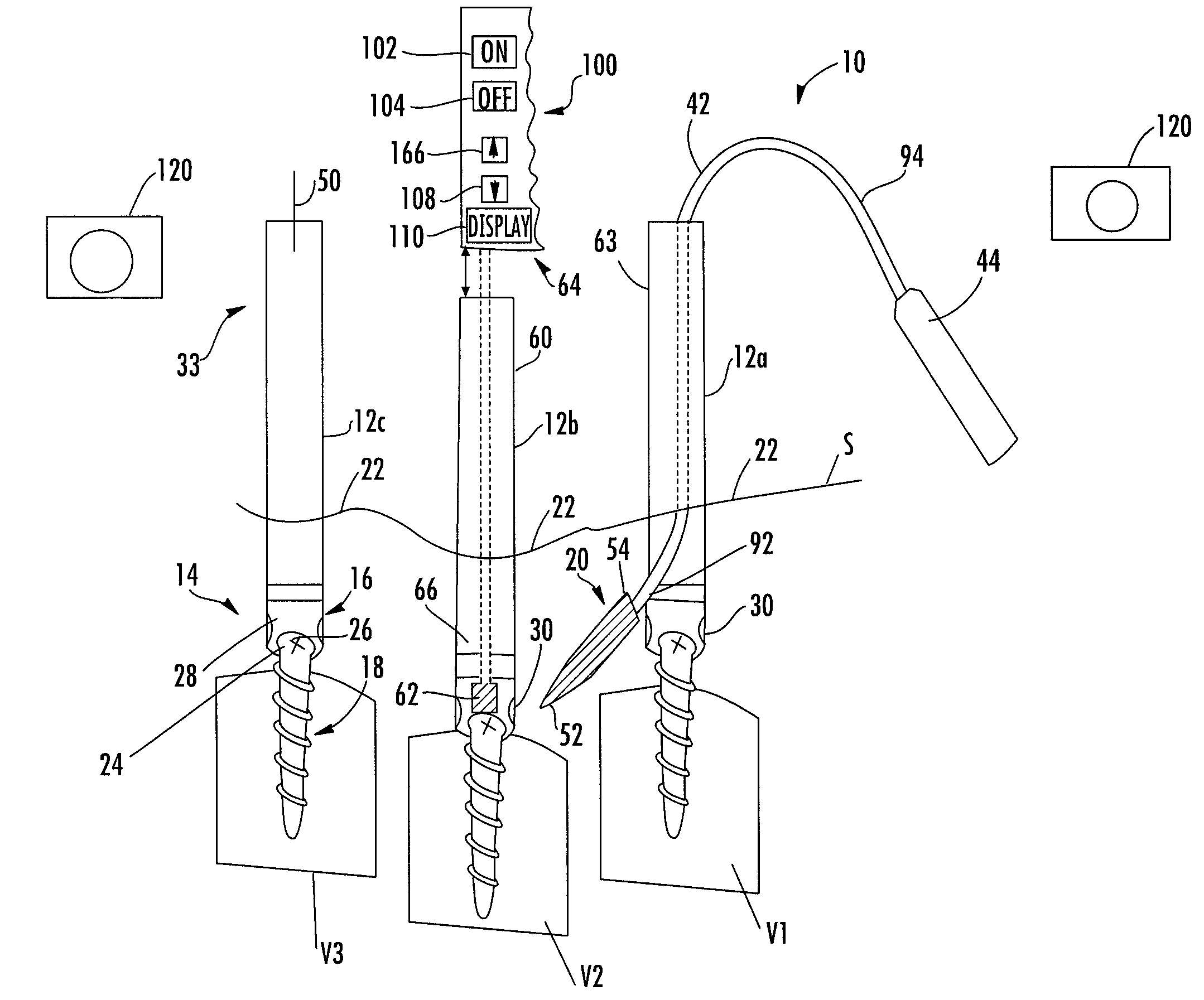
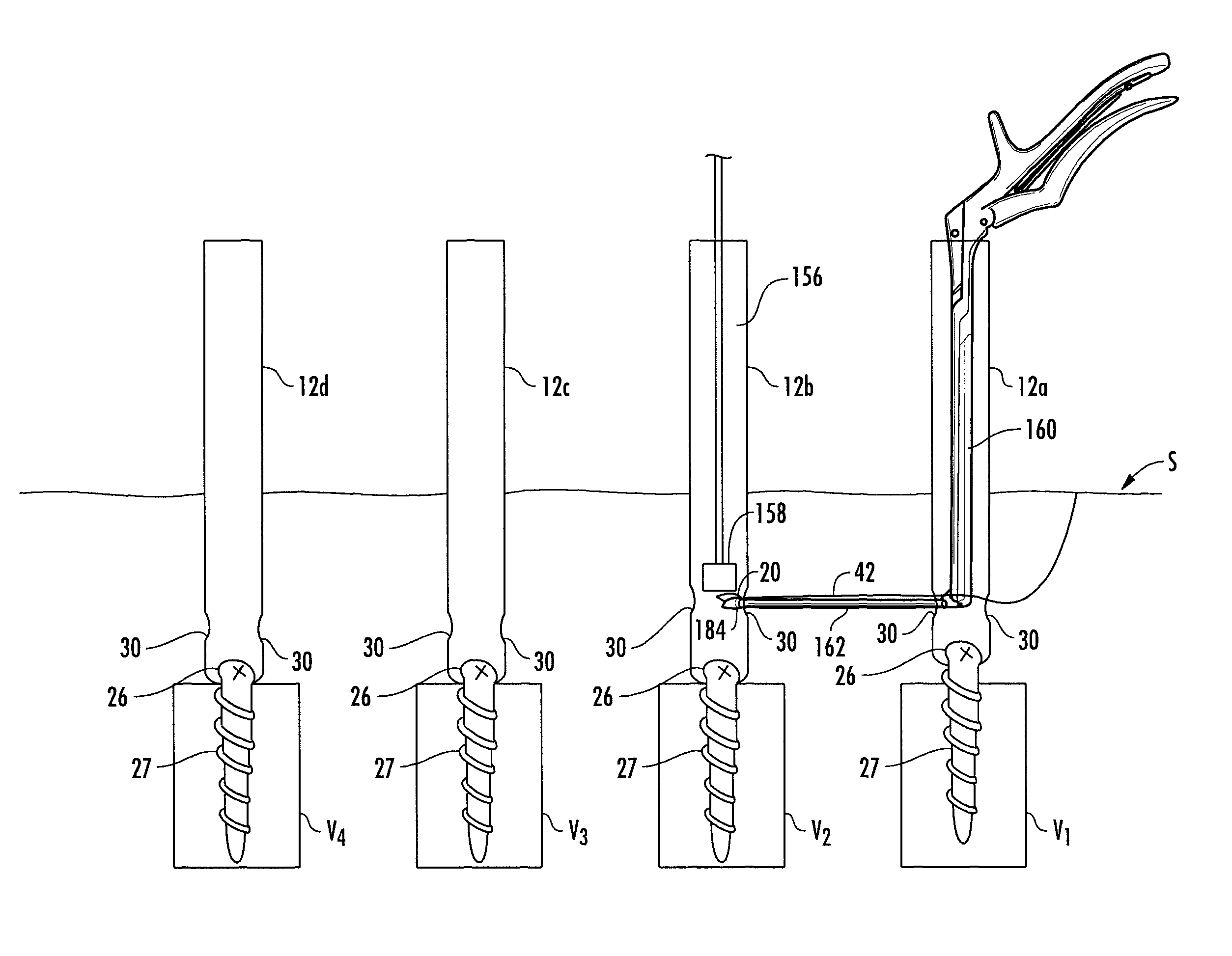
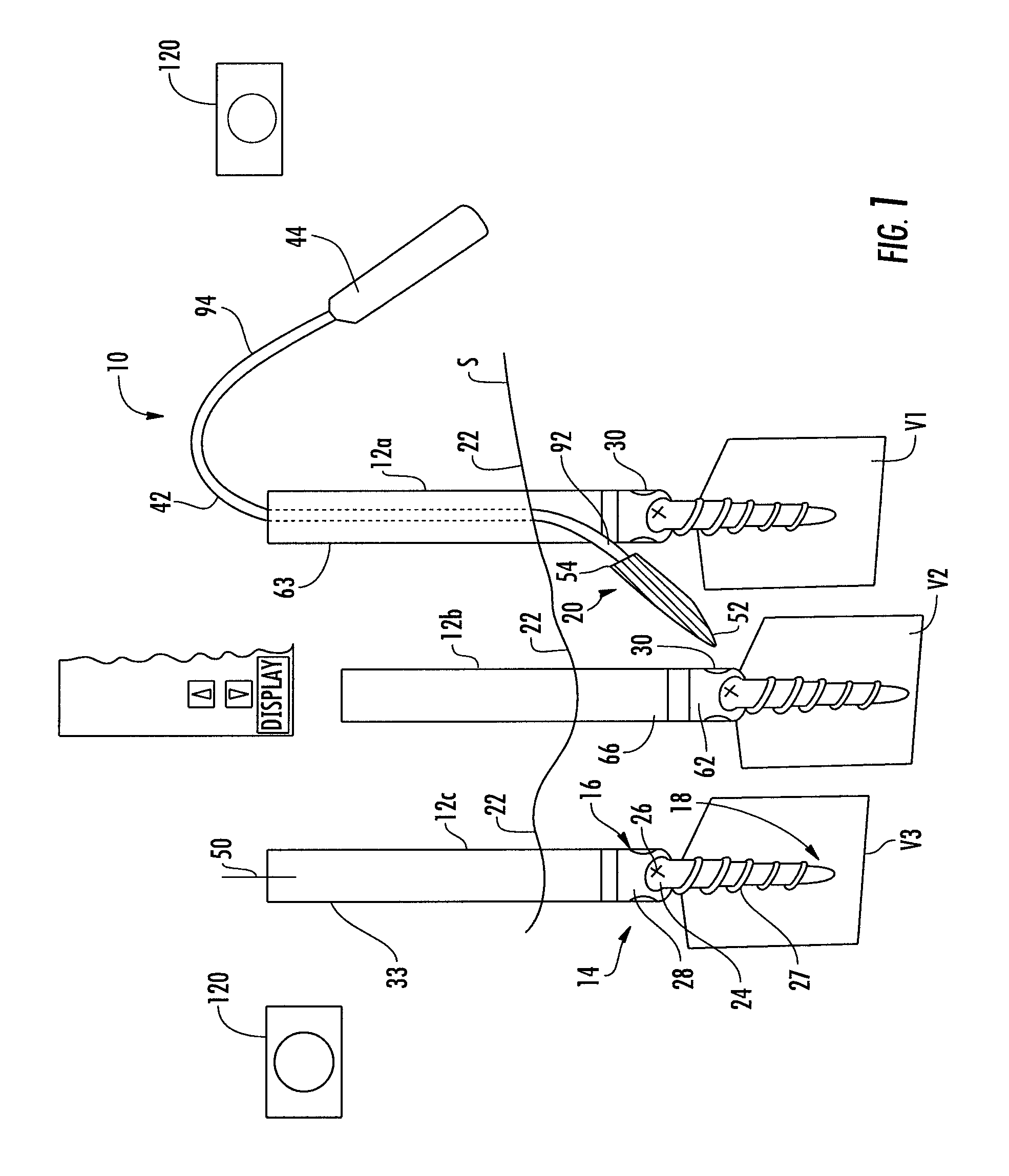
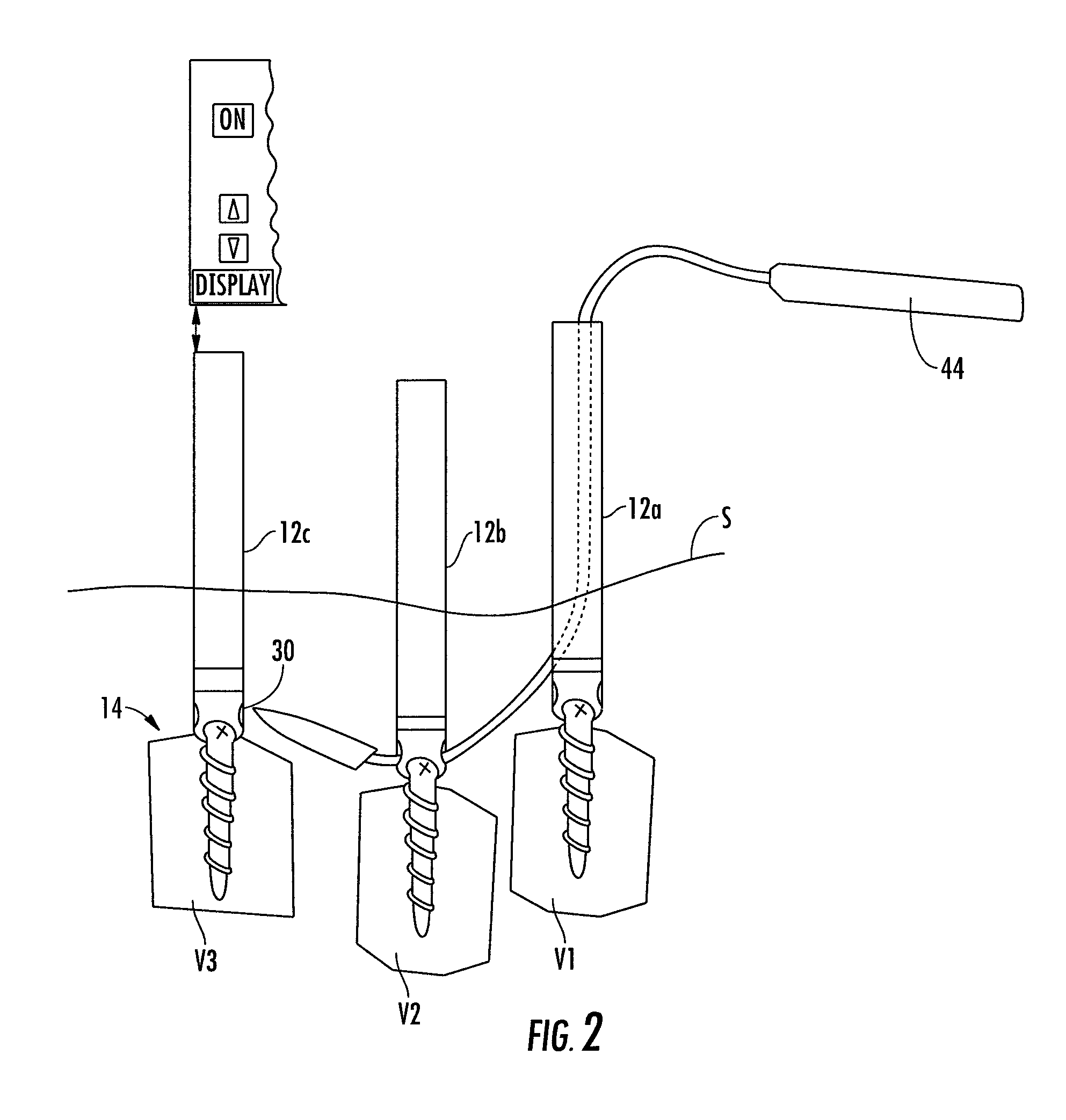
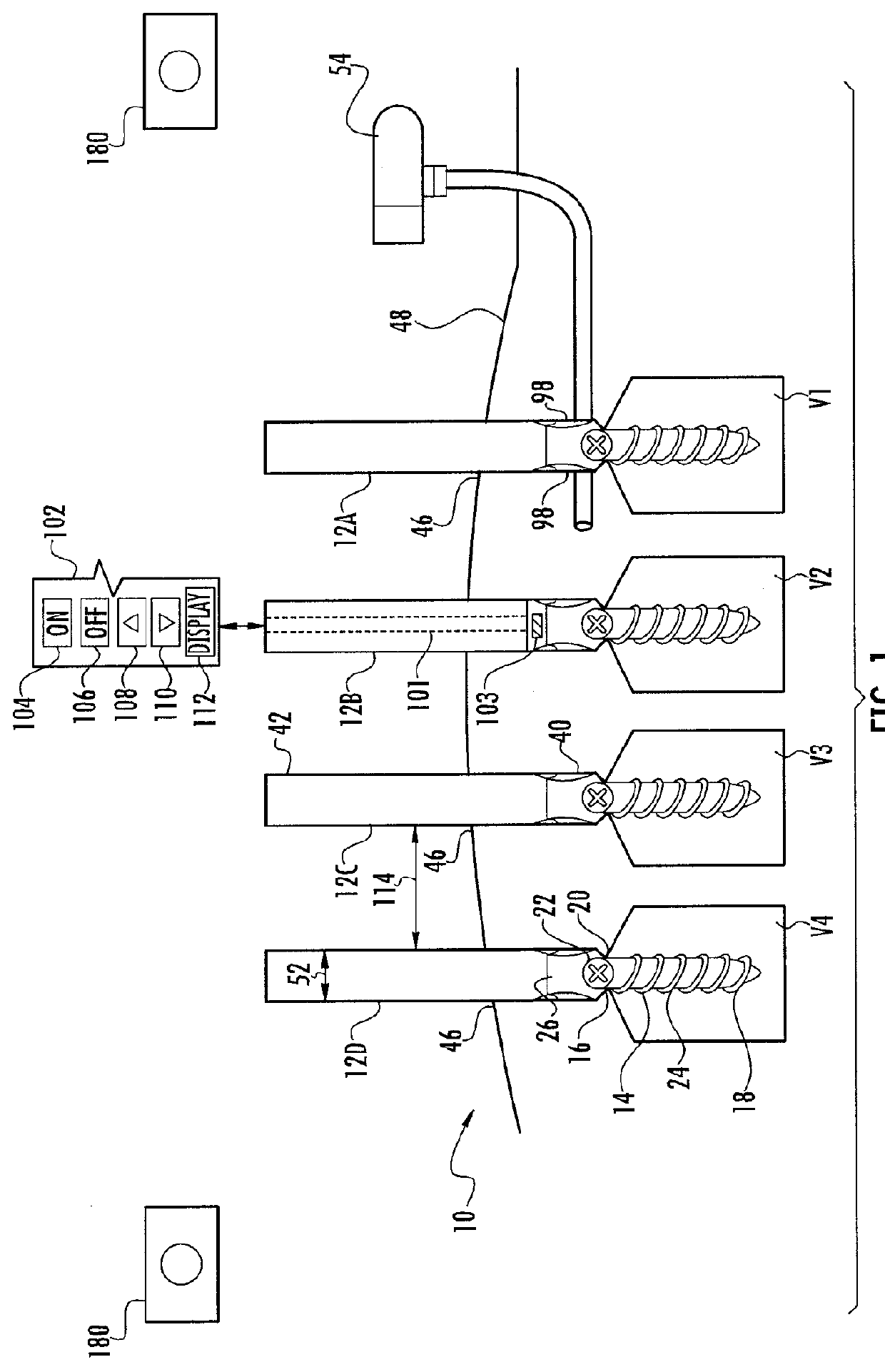
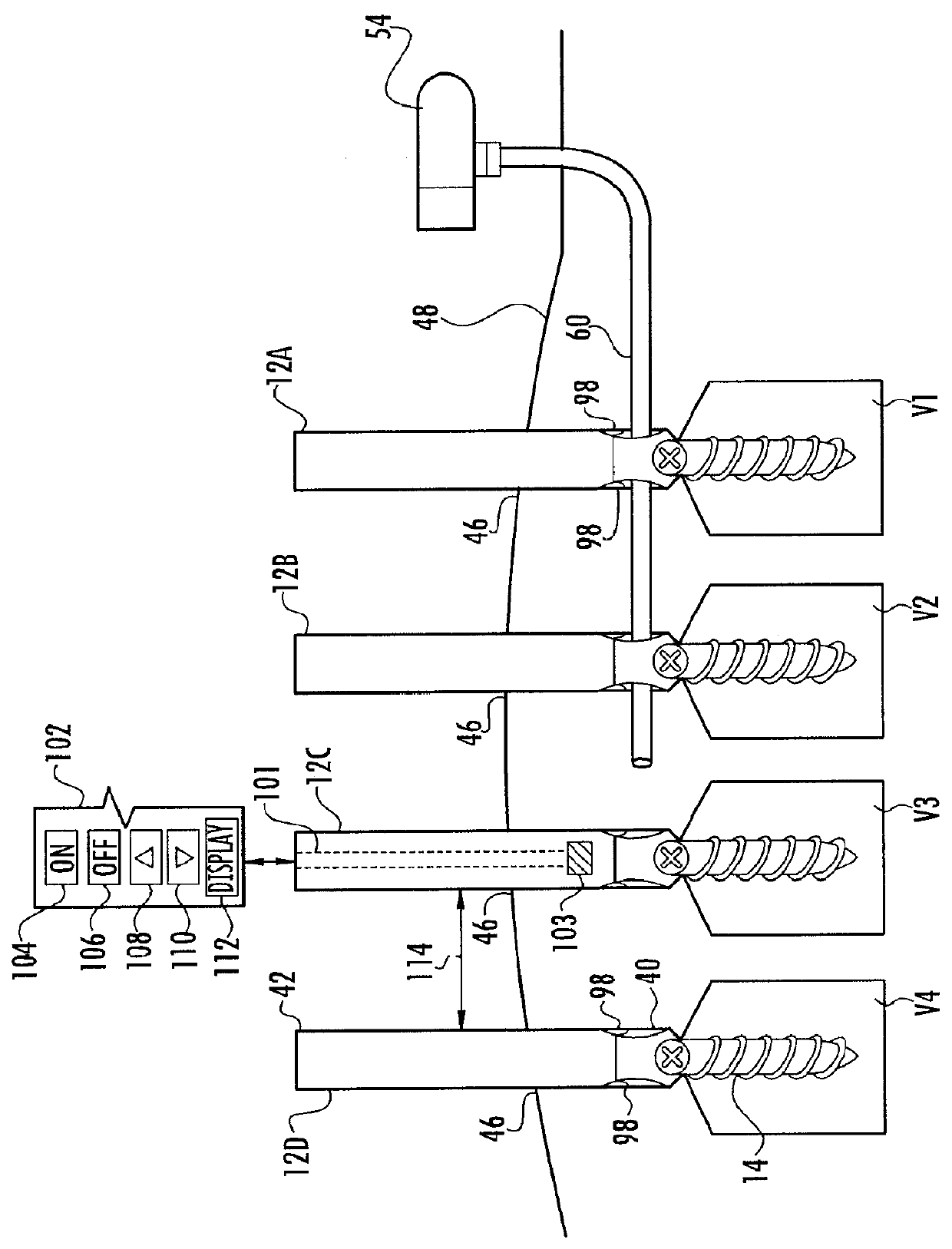
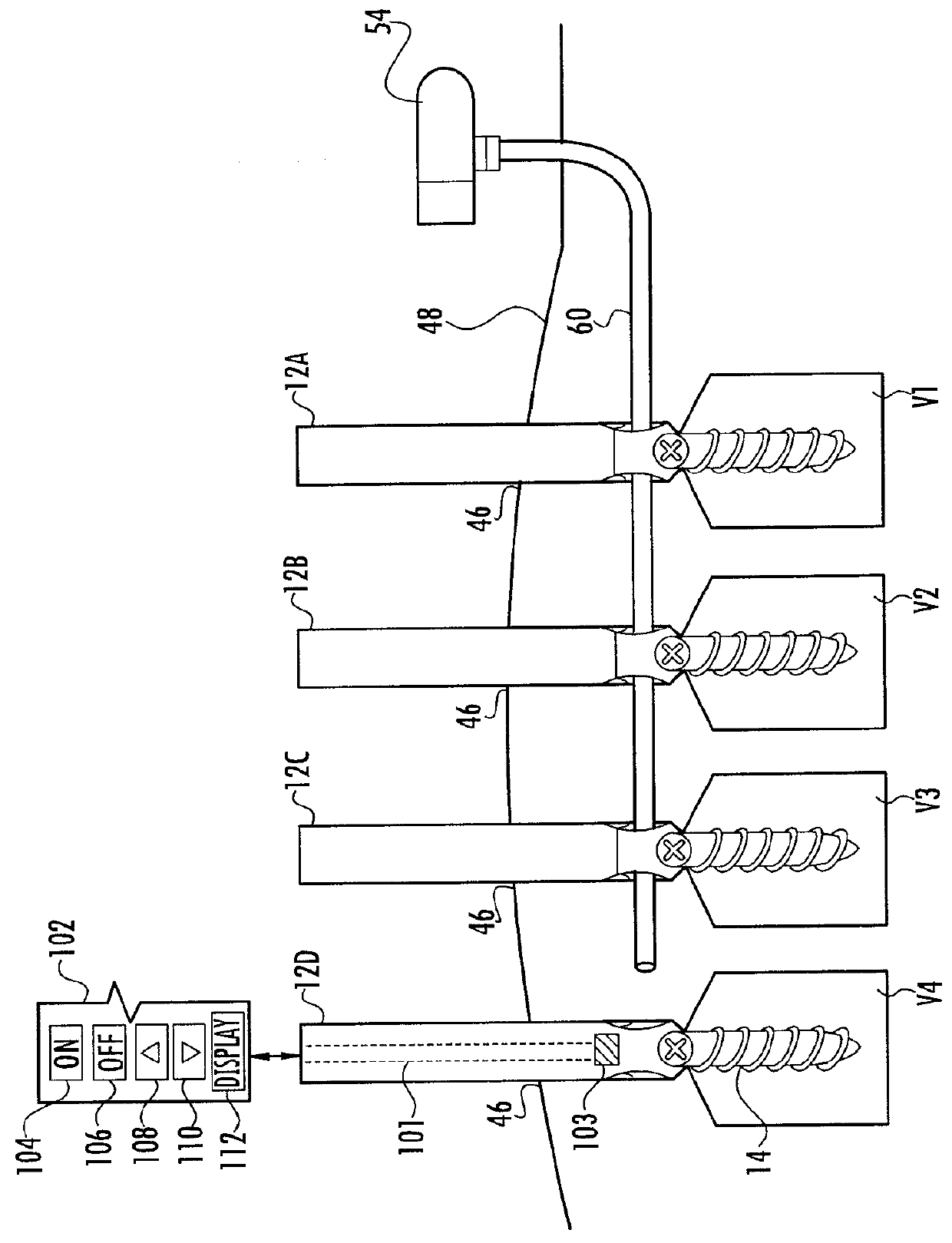
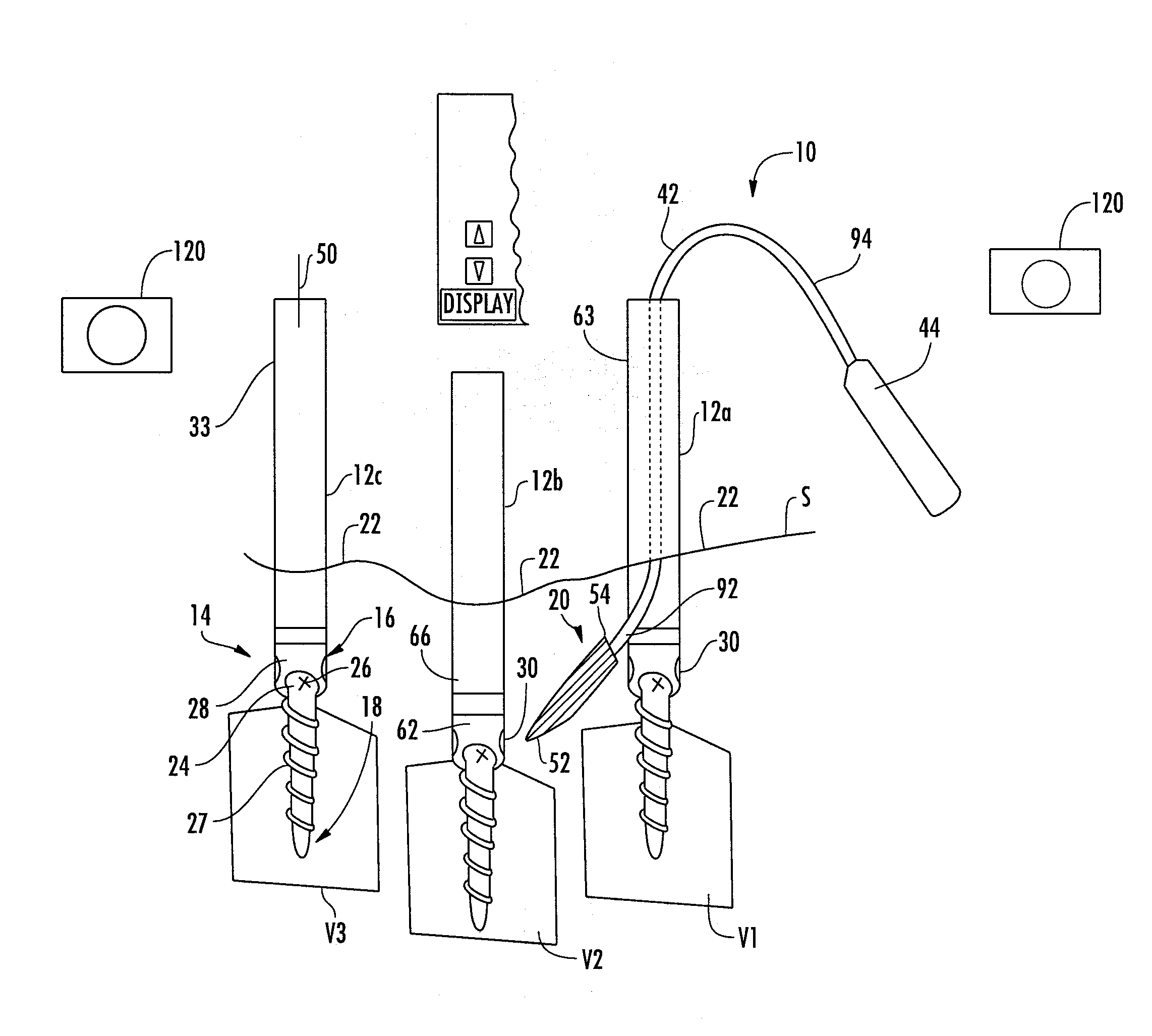
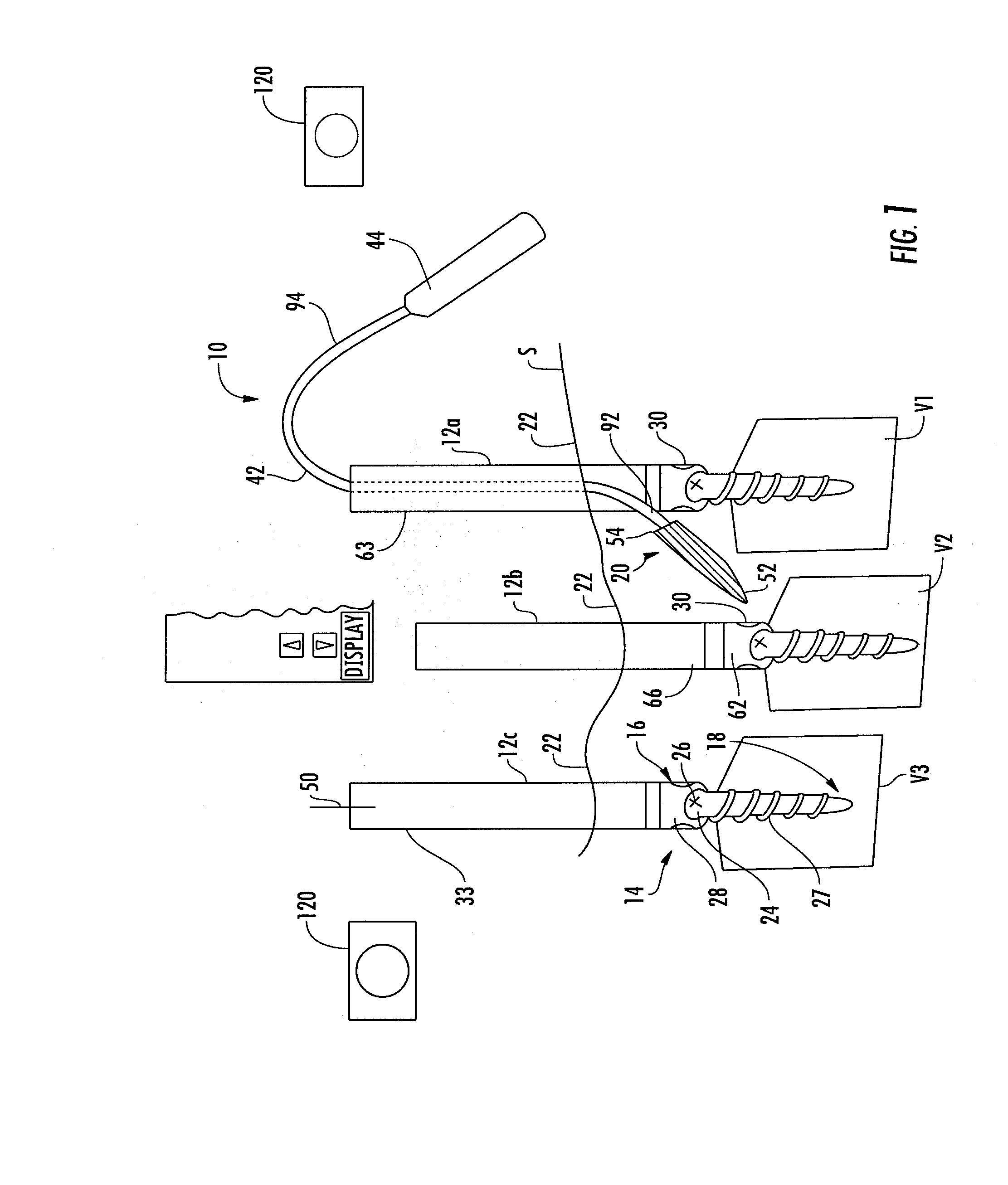
System and method for implanting spinal stabilization devices
InactiveUS7875031B2Reduce the difficulty of operationImprove visualizationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsIliac screwPedicle screw
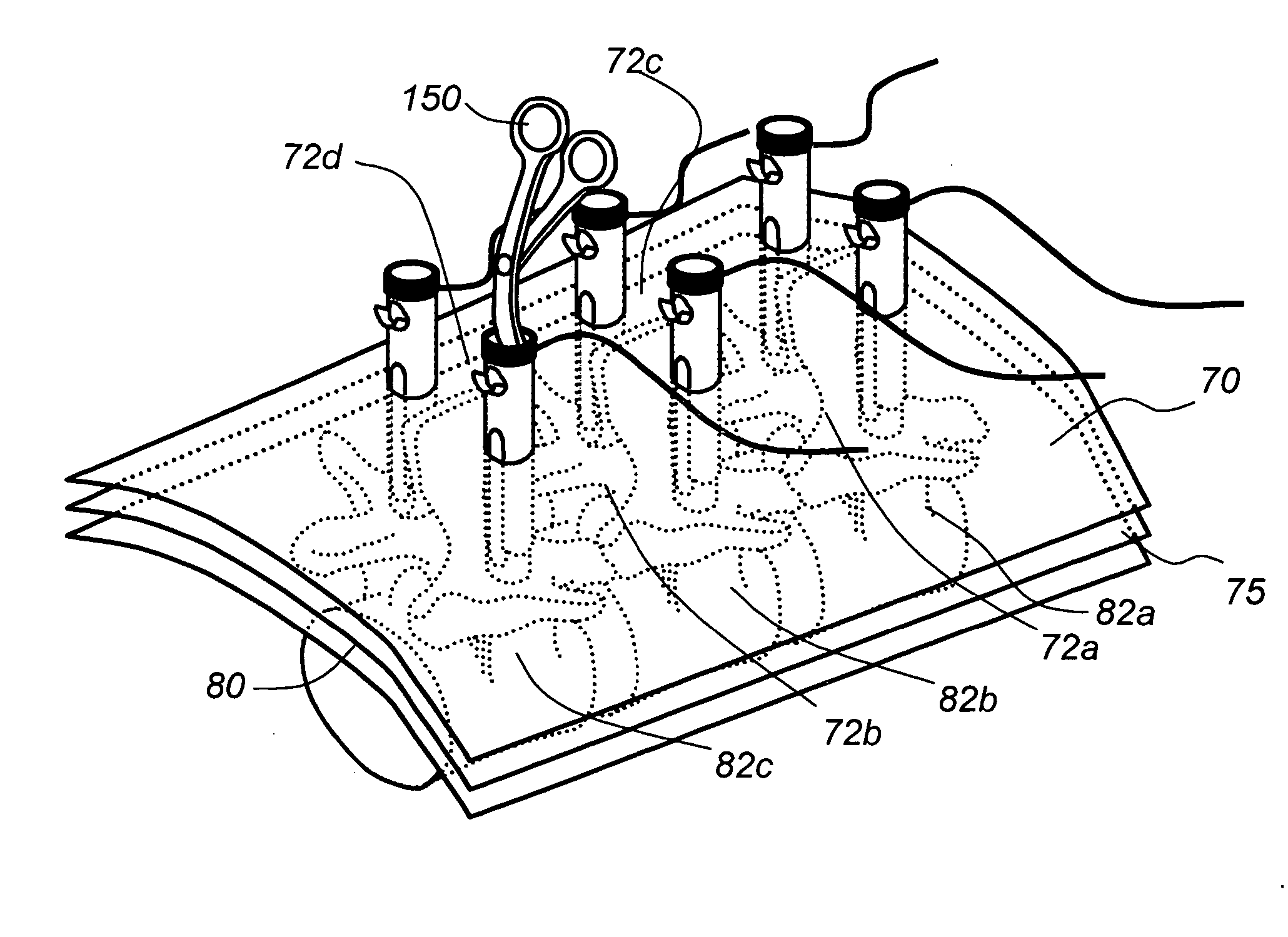
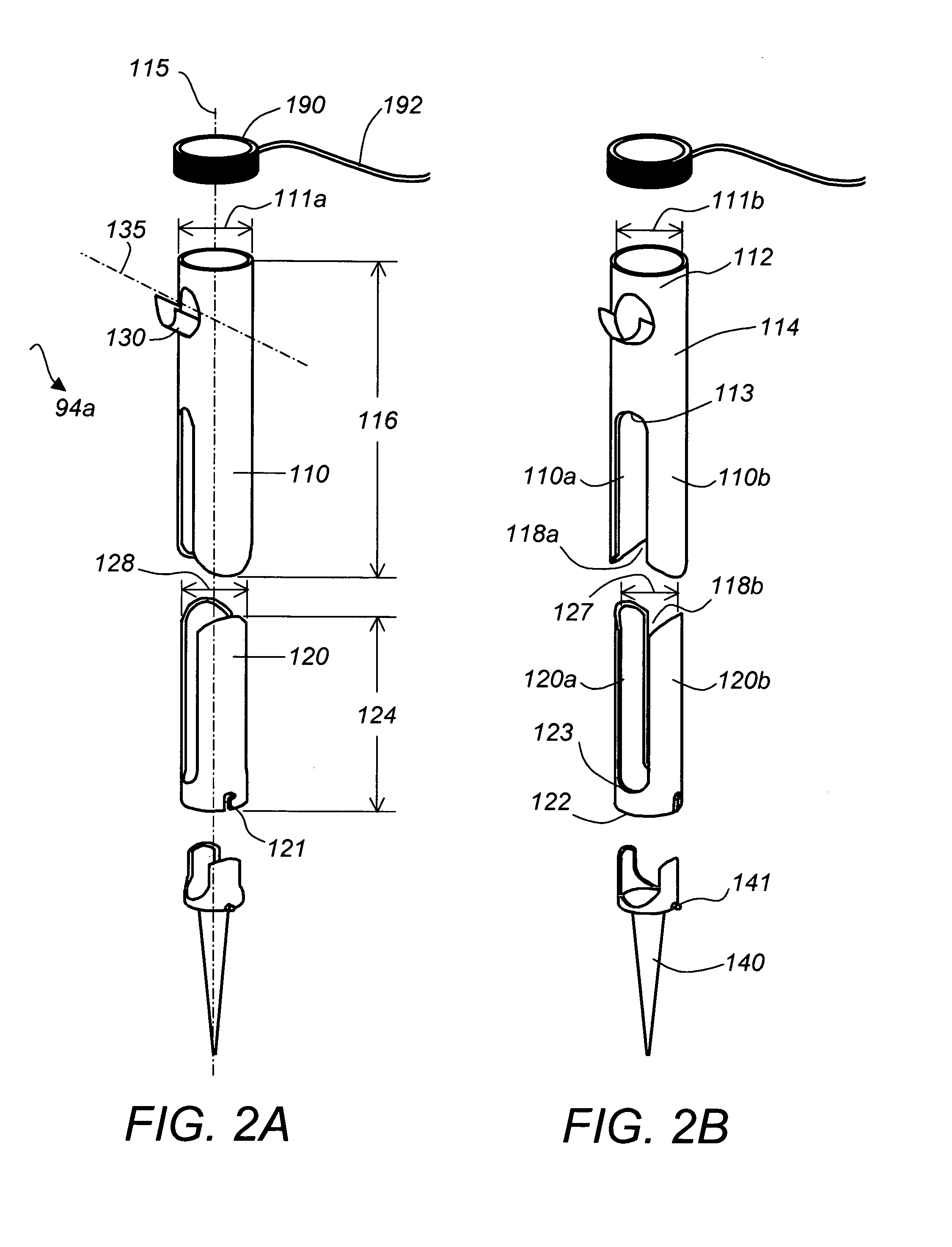
A system and a method for providing minimally invasive access to the spine of a patient and implanting spinal stabilization devices. The system utilizes one or more post-type access devices. The post-type access device includes a cage with an aperture and two or more posts extending from the cage and being removably attached to the cage. The posts are supported at the top of the access device by a support ring structure. A pedicle screw is inserted into the access device and through the cage aperture and the screw-access device assembly is inserted into an opening of the patient's body. The base aperture is dimensioned to securely support the head of the screw. Side openings between the posts allow the insertion and placement of stabilization devices, such as rods, wires, or plates from almost any direction.
Owner:KIC VENTURES LLC
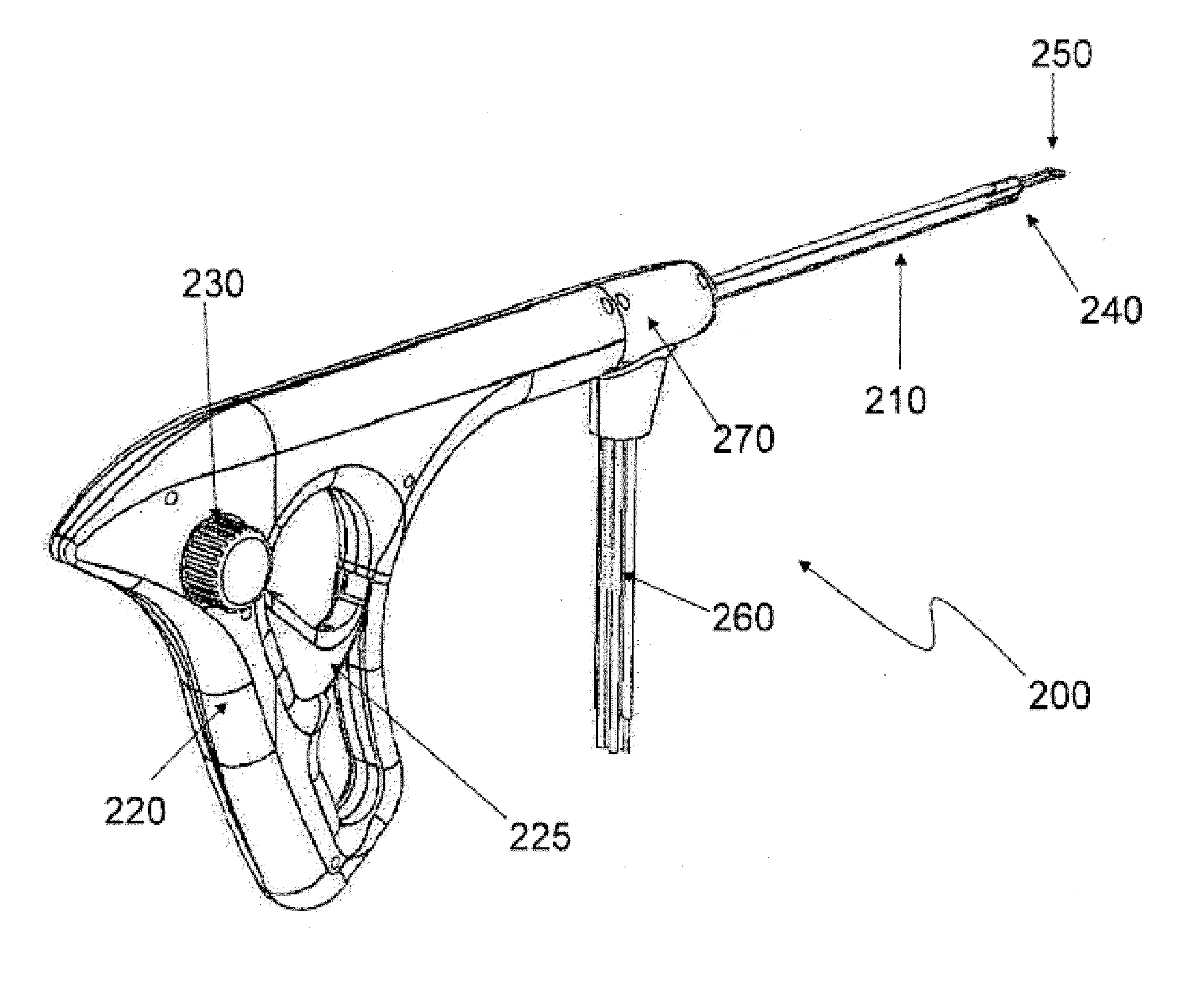
Method and apparatus for facilitating navigation of an implant
ActiveUS8092461B2Minimize damageReduce postoperative painInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsIn vivoBiomedical engineering
The present invention describes a targeting system suitable for guiding a biocompatible device to a target area within the body (in vivo) and method of using the same. The system includes a targeting member that is attached to the biocompatible device and may optionally include a steering material. The system includes a passer element located at the distal end of a wand. The wand includes a trigger like member adjacent a hand grip. Actuation of the trigger like member will result in a pivotal movement of the passer element that positions the targeting member such that the connected biocompatible device is positionable relative to the target area.
Owner:NUVASIVE
System for Pushing and Pulling Surgical Implants into Position in Vivo Via a Tether
ActiveUS20120179214A1Minimize damageReduce postoperative painInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsPush and pullIn vivo
The present invention describes a system suitable for guiding a biocompatible device to a target area within the body (in vivo) and method of using the same. The system includes a targeting member being constructed of, or having a steering material, which can be coupled to a biocompatible device. The system further includes one or more devices which are used to maneuver the targeting member into position prior to attachment of the biocompatible device. The biocompatible device is traversed into position through the passageway created by the targeting member and secured to one or more anchoring members.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Method And Apparatus For Facilitating Navigation Of An Implant
ActiveUS20100234725A1Shorter surgeryReduce X-ray exposureInternal osteosythesisDiagnostic recording/measuringIn vivoMarine navigation
The present invention describes a targeting system suitable for guiding a biocompatible device to a target area within the body (in vivo) and method of using the same. The system includes a targeting member that is attached to the biocompatible device and may optionally include a steering material. The system includes a passer element located at the distal end of a wand. The wand includes a trigger like member adjacent a hand grip. Actuation of the trigger like member will result in a pivotal movement of the passer element that positions the targeting member such that the connected biocompatible device is positionable relative to the target area.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Magnetic targeting system and method of using the same
ActiveUS8092458B2Minimize damageReduce postoperative painInternal osteosythesisDiagnostic recording/measuringIn vivoBiomedical engineering
The present invention describes a magnetic targeting system suitable for guiding a biocompatible device to a target area within the body (in vivo) and method of using the same. The system includes a targeting member having a steering material and is attached to the biocompatible device. The system also includes at least one anchoring member constructed and arranged for the inclusion of a magnetic material effective for influencing the traversal of the steering material, in vivo. The magnetically influenced anchoring member interacts with the targeting member such that the biocompatible device is positionable relative to the target area.
Owner:NUVASIVE
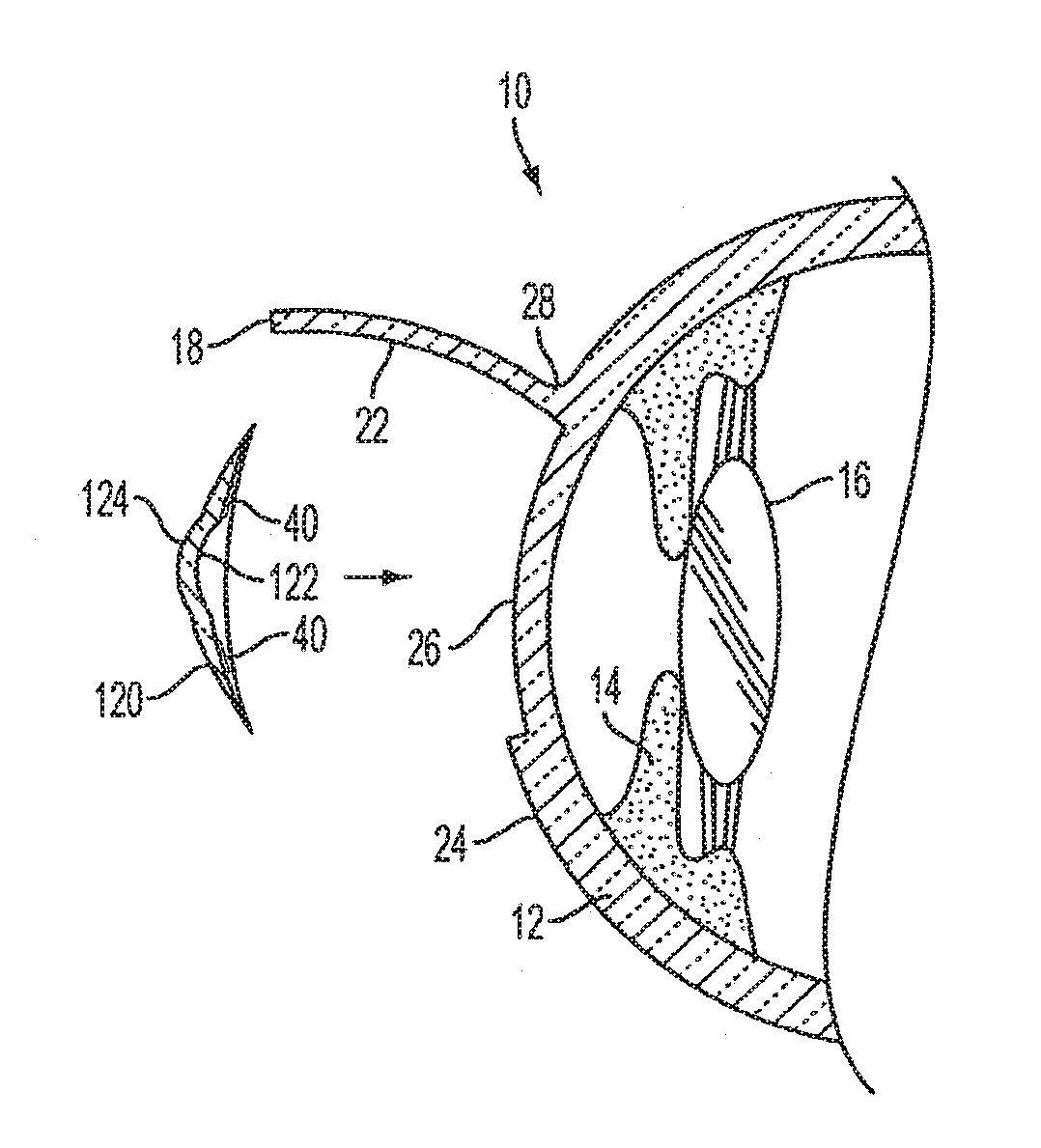
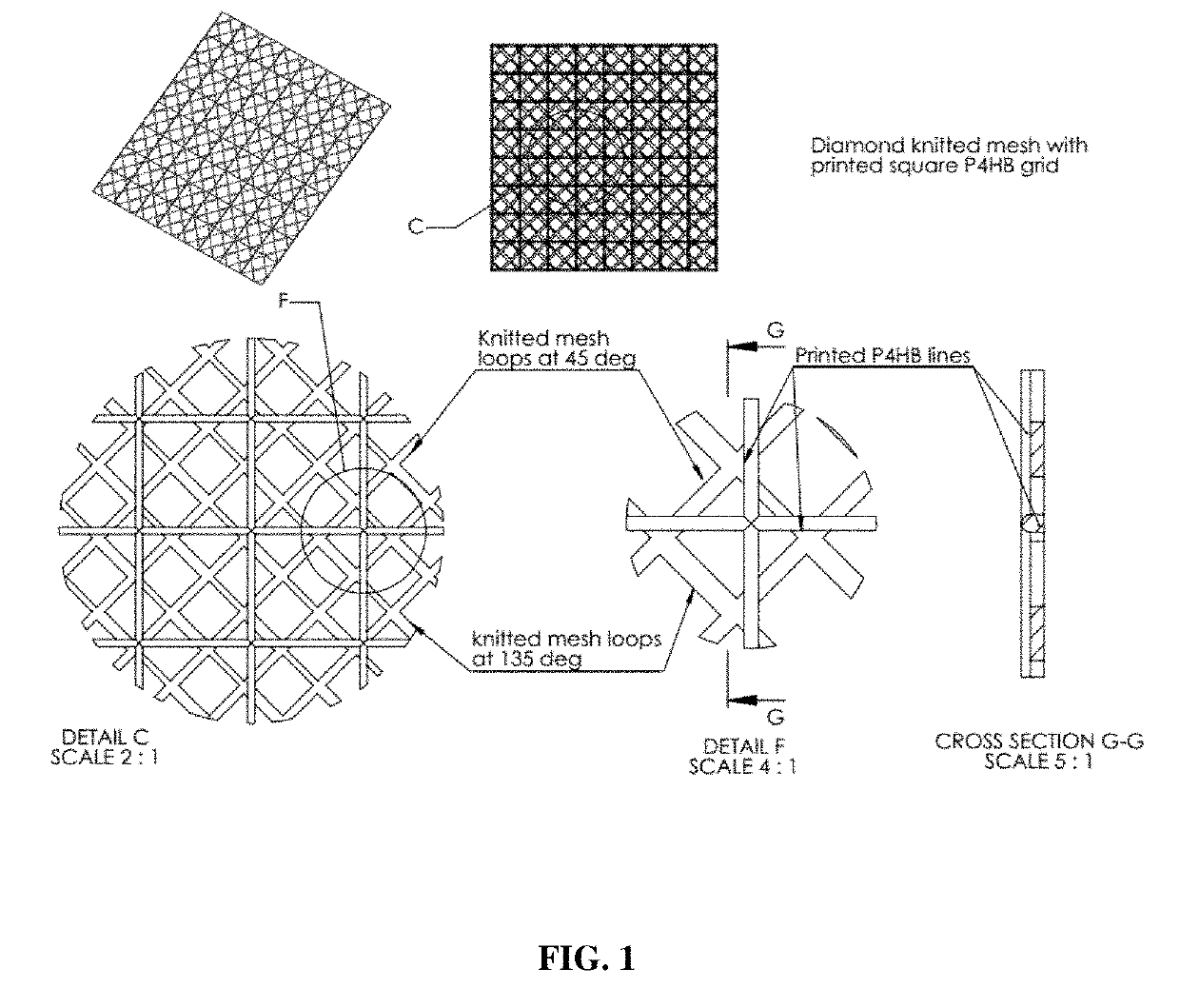
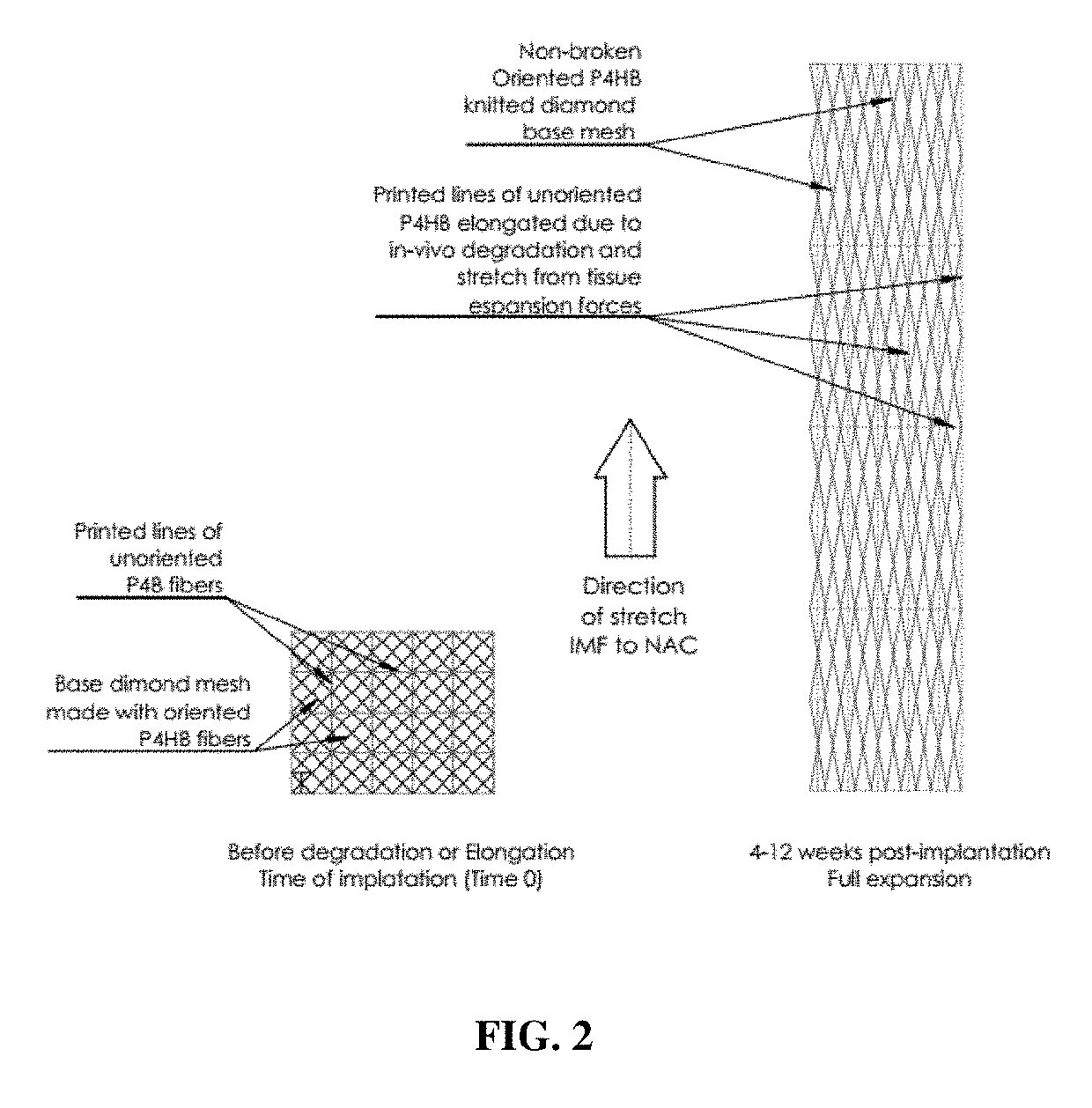
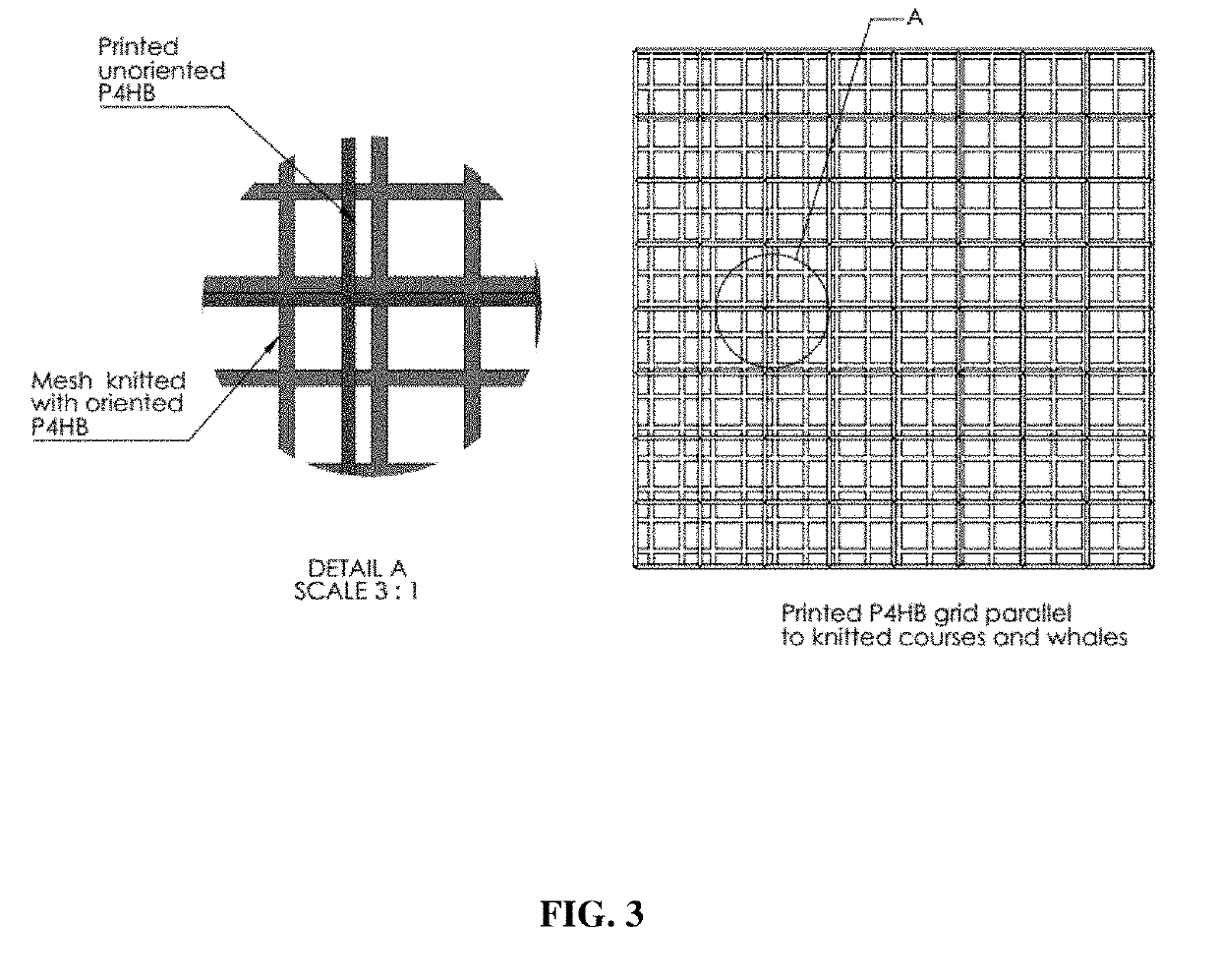
Expandable absorbable implants for breast reconstruction and augmentation
ActiveUS20190254807A1Relieve pressureDecreases short-termMammary implantsDiagnosticsBreast implantAbsorbable Implants
Expandable absorbable implants have been developed that are suitable for breast reconstruction following mastectomy. The implants can be implanted in the vicinity of a tissue expander, for example, by suturing to the detached edge of the pectoralis major muscle to function as a pectoralis extender, and used to form a sling for a tissue expander. The implants, which permit tissue-ingrowth and slowly degrade, can be expanded in the breast using a tissue expander in order to form a pocket for a permanent breast implant. After expansion, the tissue expander can be removed and replaced with a permanent breast implant. The expandable implants help reduce patient discomfort resulting from tissue expansion, and avoid the need to use allografts or xenografts to create the pocket for the tissue expander. The expandable absorbable implant preferably comprises poly-4-hydroxybutyrate or copolymer thereof.
Owner:TEPHA INC
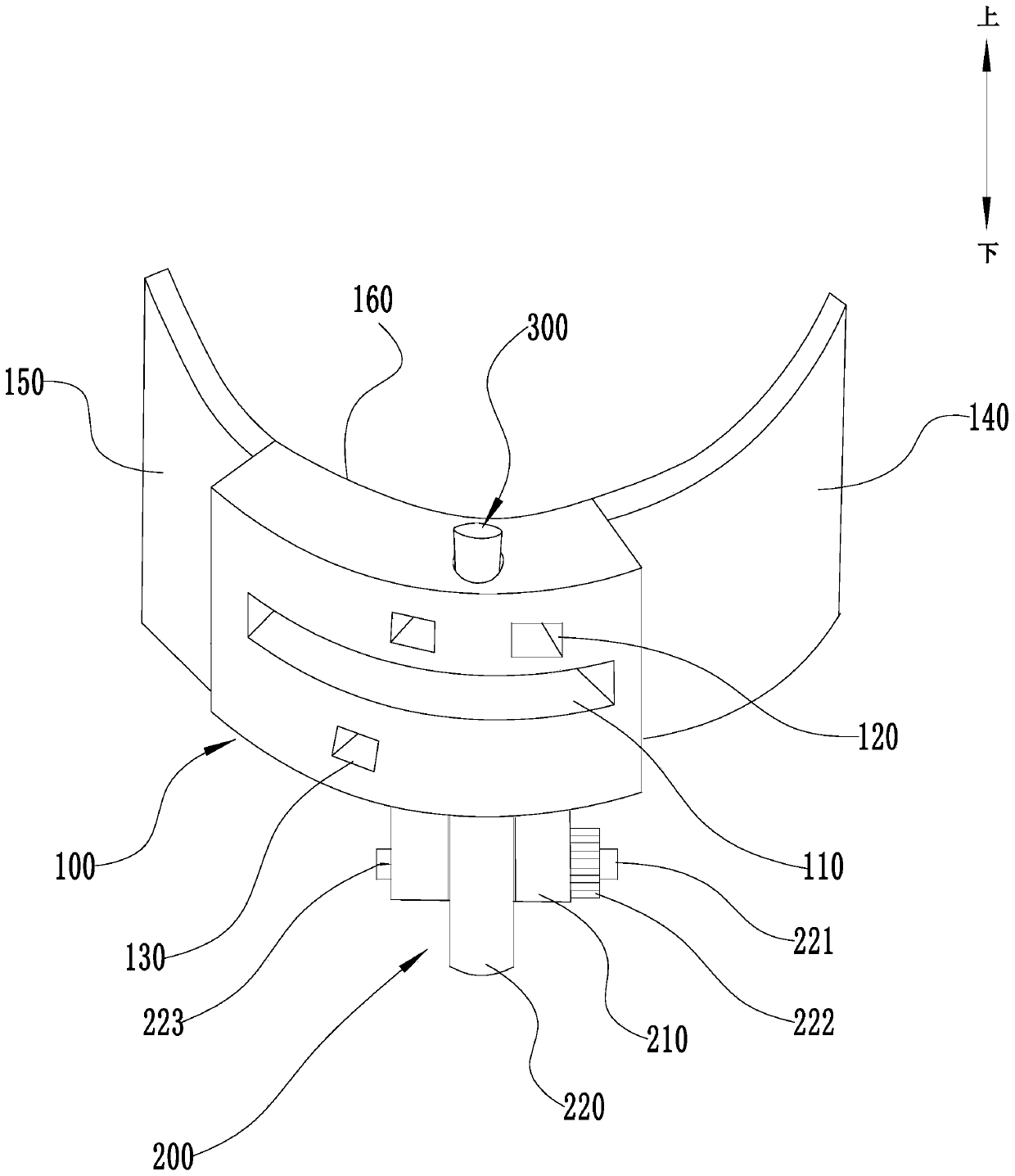
Tibia osteotomy positioning device for knee joint replacement surgery
The invention discloses a tibia osteotomy positioning device for a knee joint replacement surgery. The tibia osteotomy positioning device comprises an osteotomy unit, a backward inclination angle adjuster and a first toe and second toe aligner, wherein an arc-shaped contact surface is arranged at the inner side of the osteotomy unit; an osteotomy groove penetrating through the osteotomy unit is arranged at the outer side of the osteotomy unit; a plurality of first positioning holes and a plurality of second positioning holes are respectively arranged at the upper end and the lower end of the osteotomy groove; the number of the first positioning holes is larger than the number of the second positioning holes; and fixators used for fixing the osteotomy unit to the outer surface of the tibiaare detachably arranged in the first positioning holes and the second positioning holes. When the fixators penetrates through the first positioning holes and the second positioning holes to fix the osteotomy unit on the tibia, a majority of the fixators are nailed into the bone of the spinous process of the tibia located above the osteotomy groove, while the bone of the spinous process of the tibia located above the osteotomy groove is cut off in a surgery, so the injury of the fixators to the tibia can be greatly reduced; postoperative pain is reduced; and the postoperative recovery effect ofa patient is improved.
Owner:邬黎平
Device for separating the epithelium layer from the surface of the cornea of an eye
InactiveUS7156859B2Shorten the overall cycleReduce postoperative painEar treatmentEye surgeryEpitheliumEngineering
An automated mechanical device separates the epithelial layer of a cornea from the cornea. The device includes a separator such as a plate, wire or dull blade. The device can preserve a separated epithelial layer as a disk without rupturing the disk and without substantial epithelial cell loss. The epithelial layer is separated from the cornea without cutting the cornea.
Owner:FOS HLDG SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com