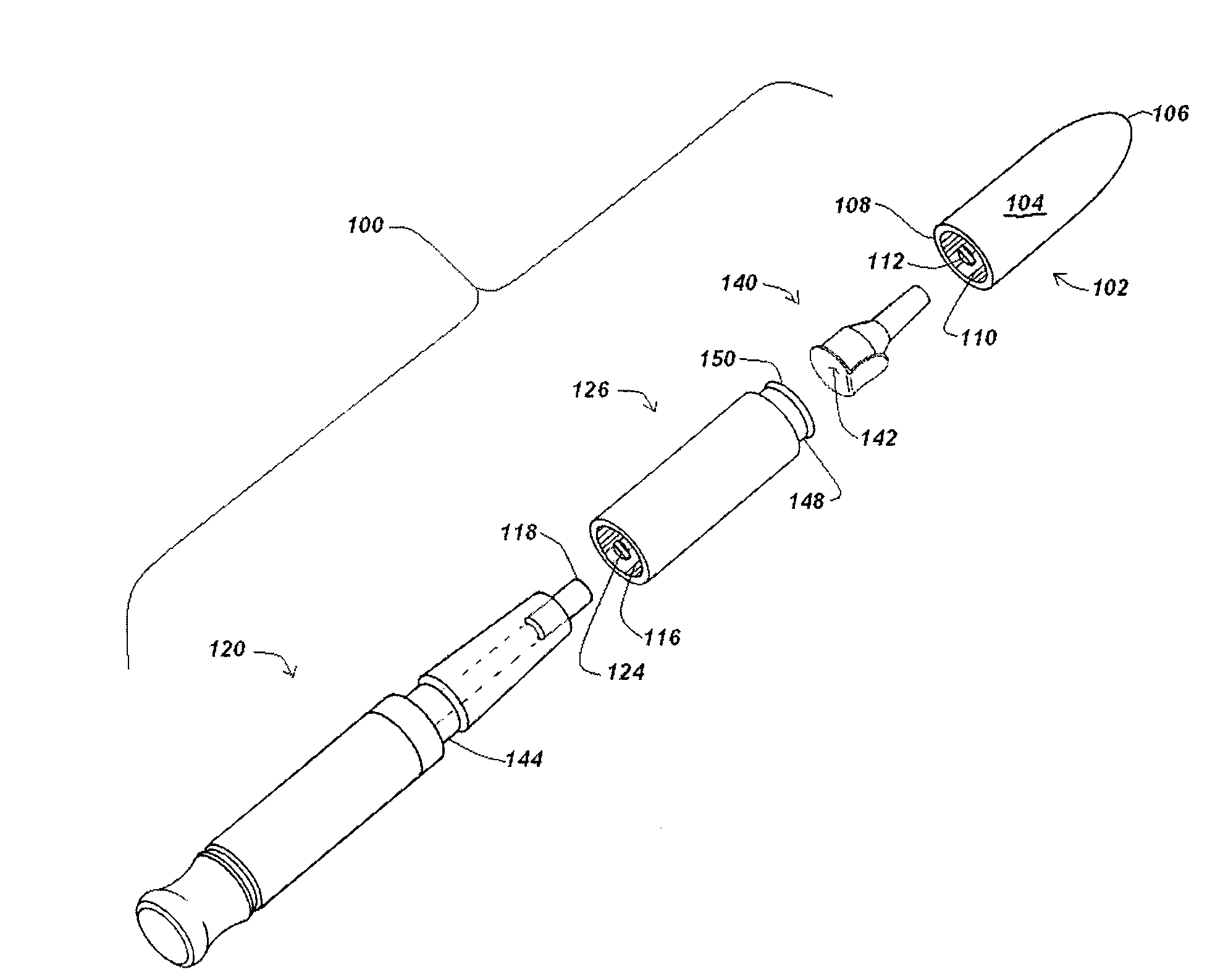
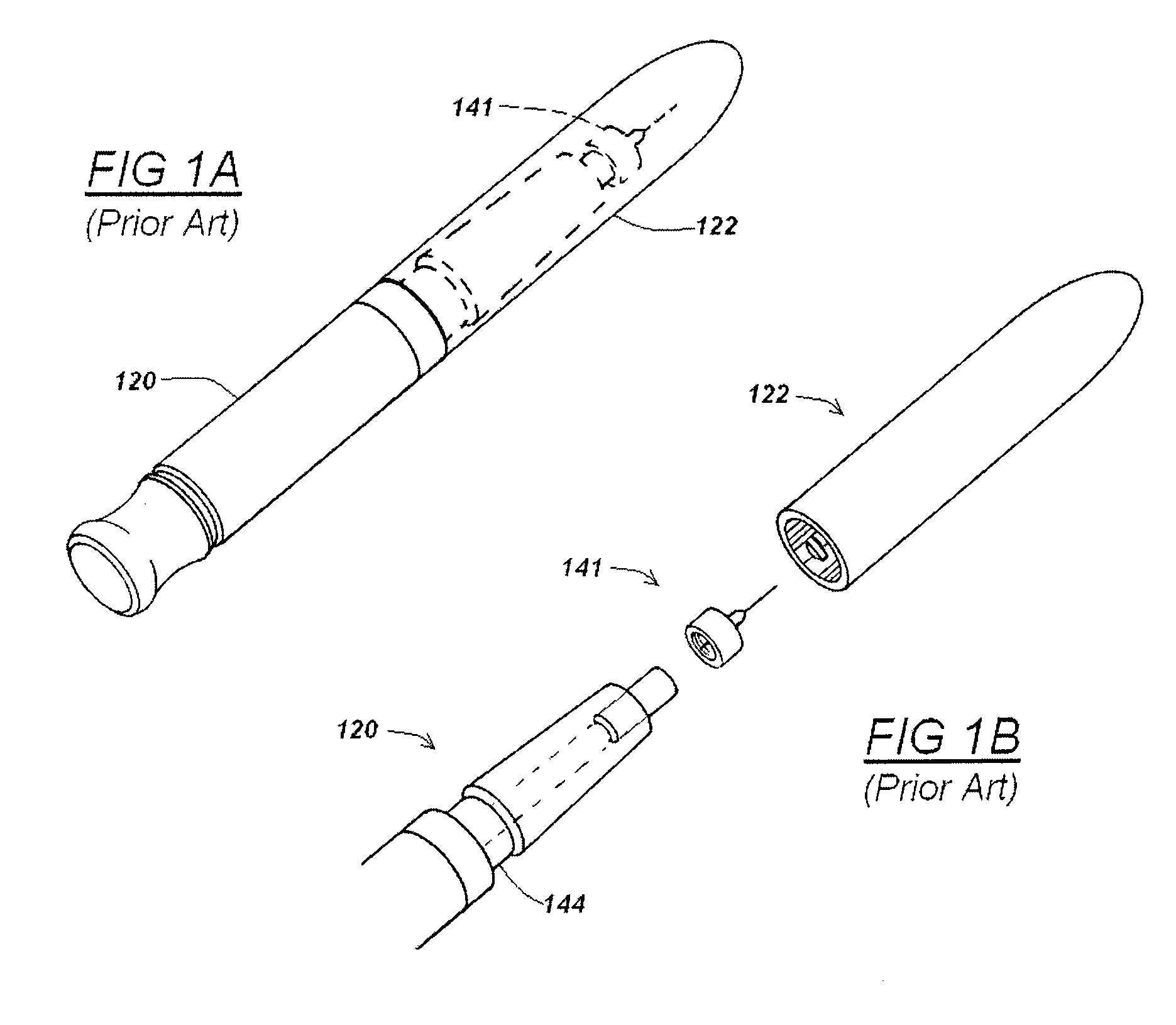
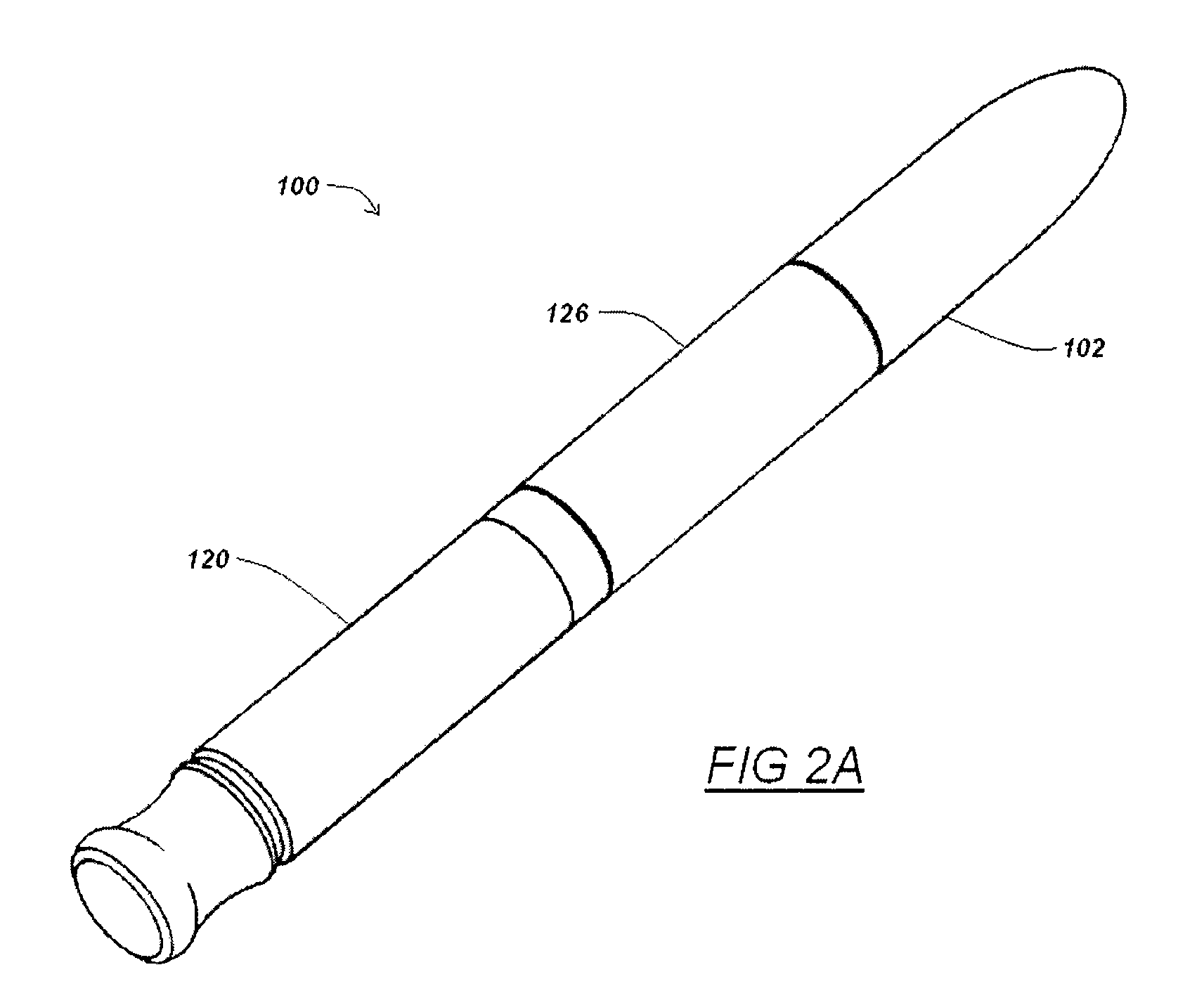
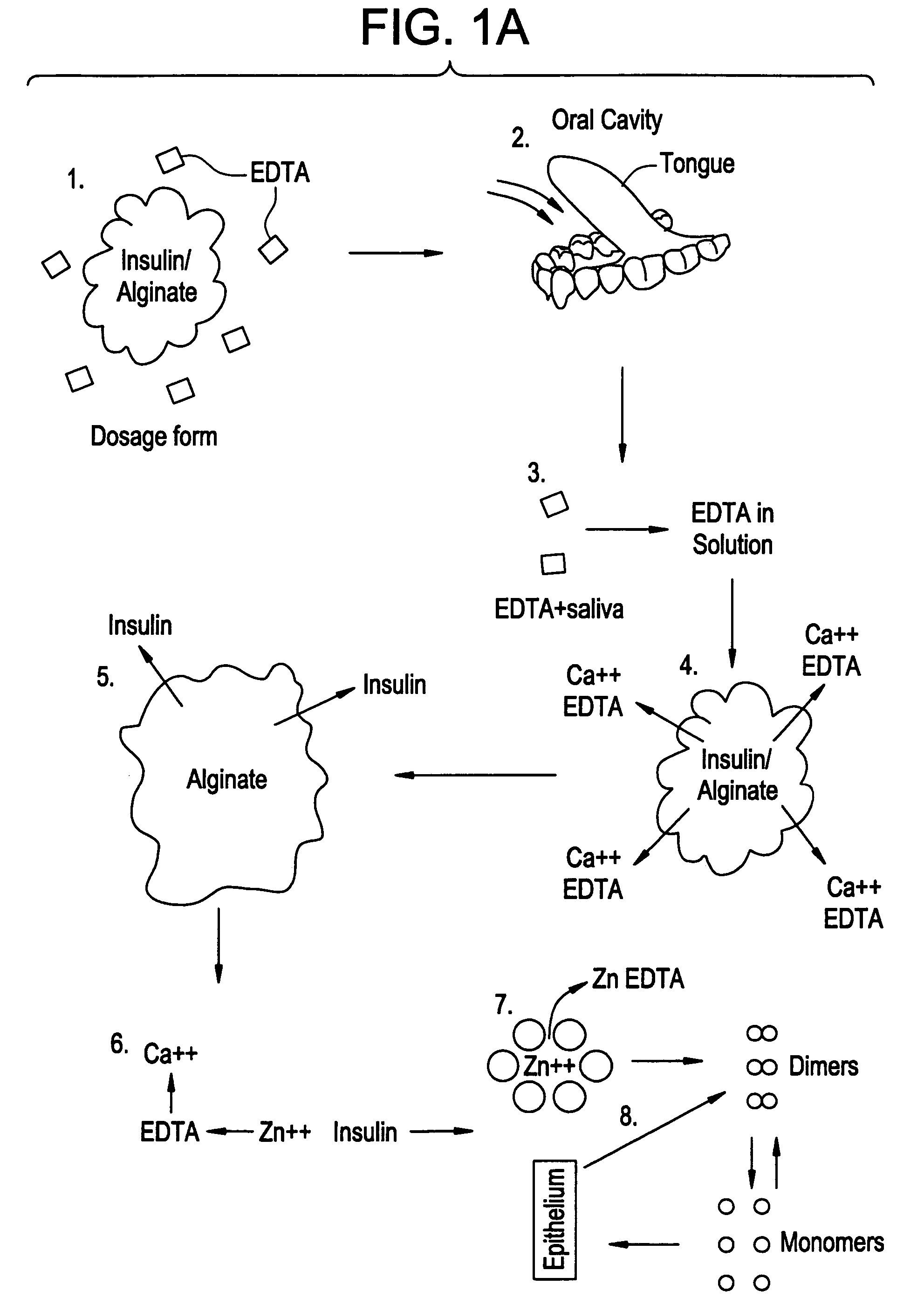
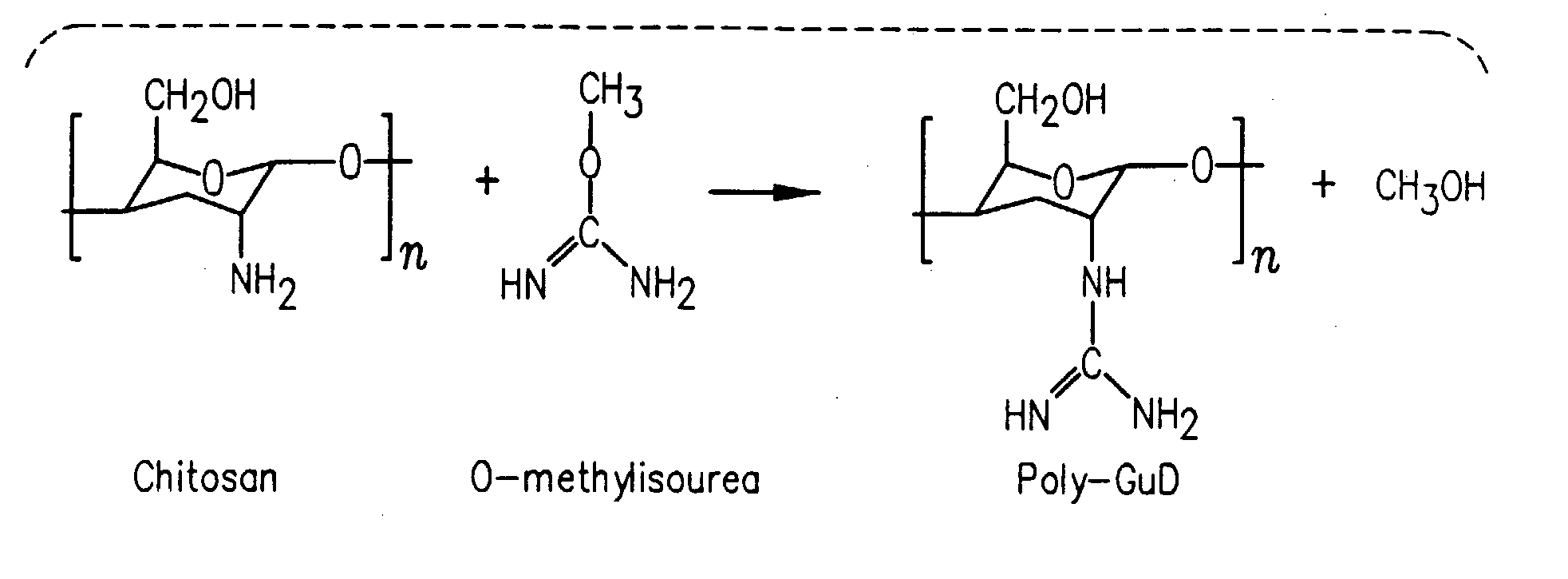
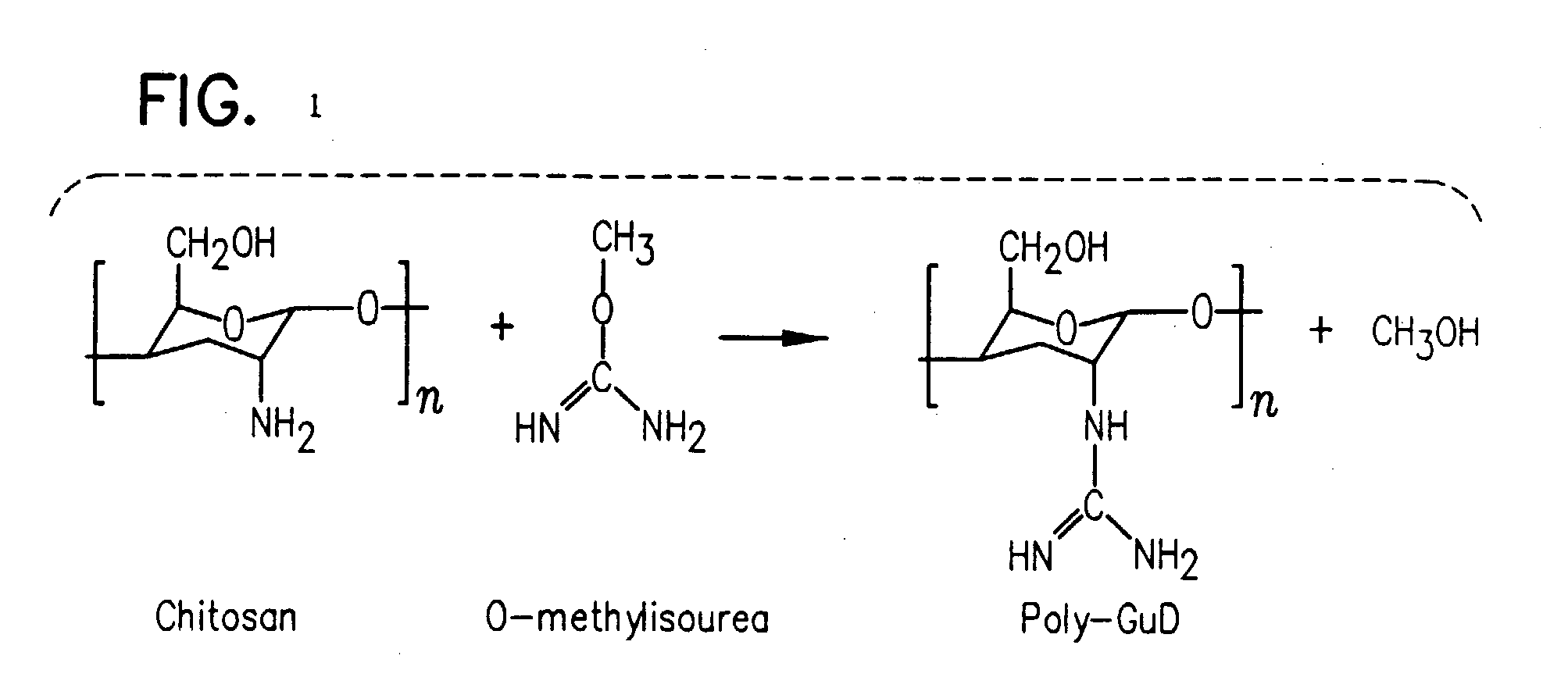
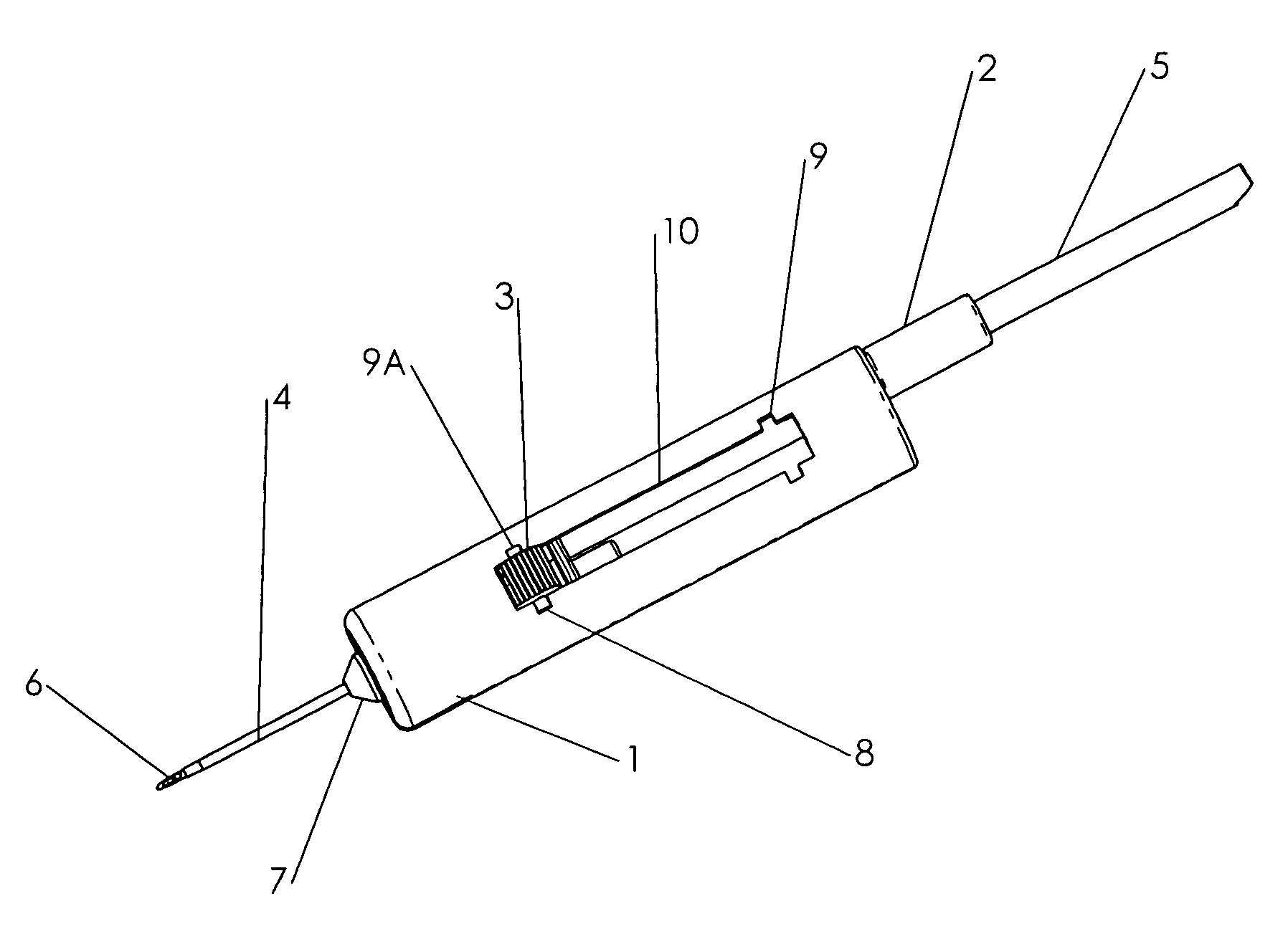
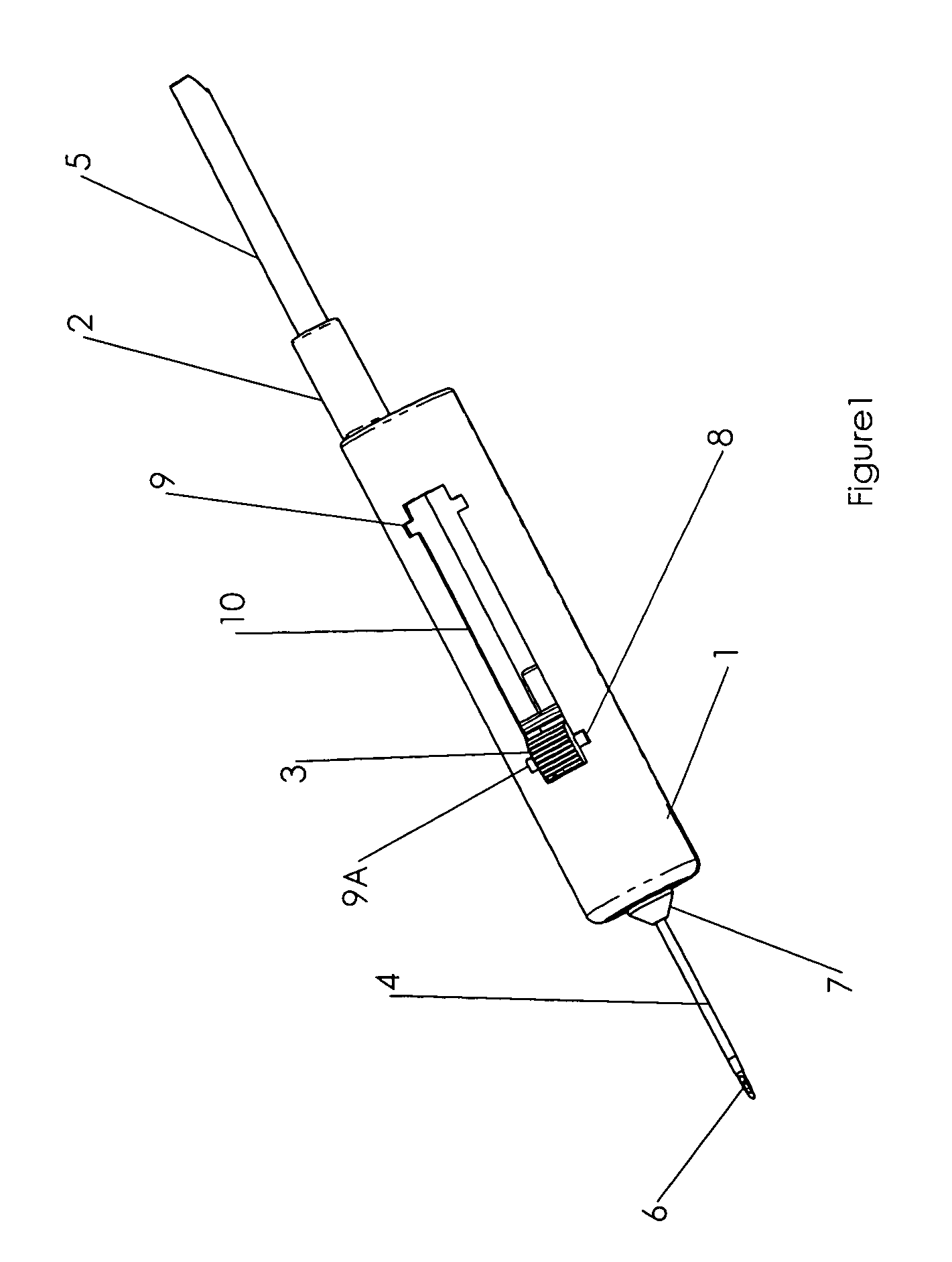
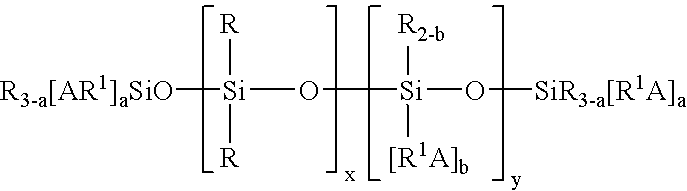Patents
Literature
471 results about "Hypodermoclysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hypodermoclysis, which can also be called interstitial infusion or subcutaneous infusion, is the subcutaneous administration of fluids to the body, often saline or glucose solutions. Hypodermoclysis can be used where a slow rate of fluid uptake is required compared to intravenous infusion. Typically, it is limited to 1 ml per minute, although it is possible to increase this by using two sites simultaneously. The chief advantages of hypodermoclysis over intravenous infusion is that it is cheap and can be administered by non-medical personnel with minimal supervision. It is therefore particularly suitable for home care. The enzyme hyaluronidase can be added to the fluid to improve absorption during hypodermoclysis.
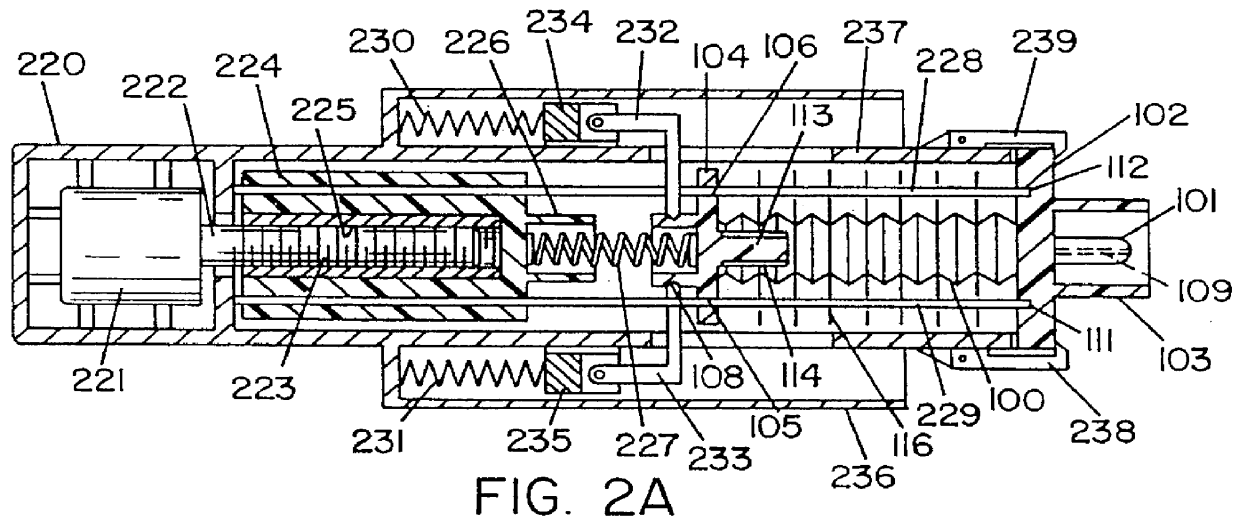
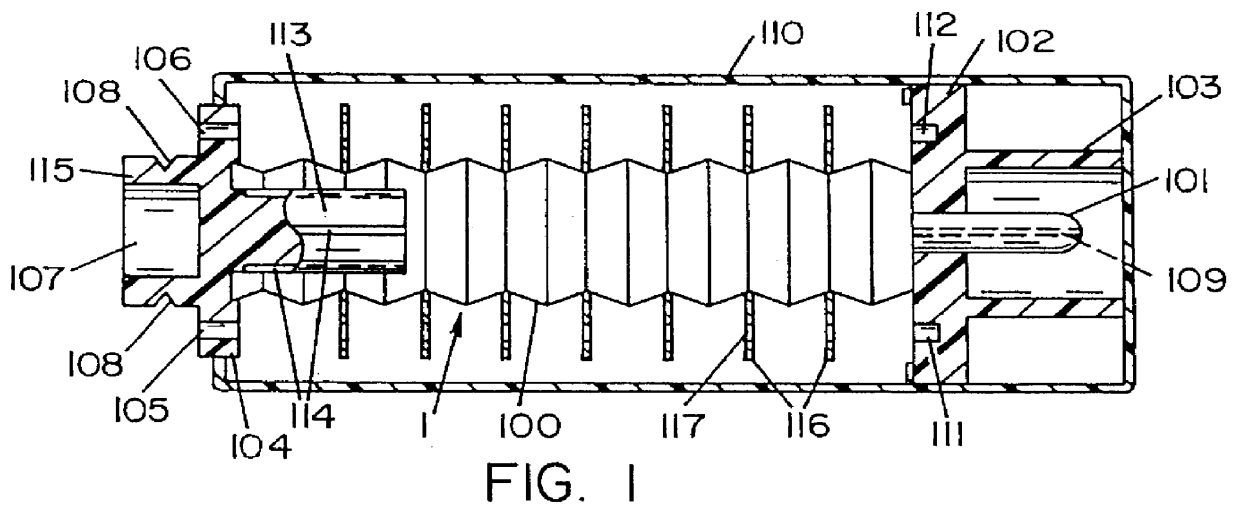
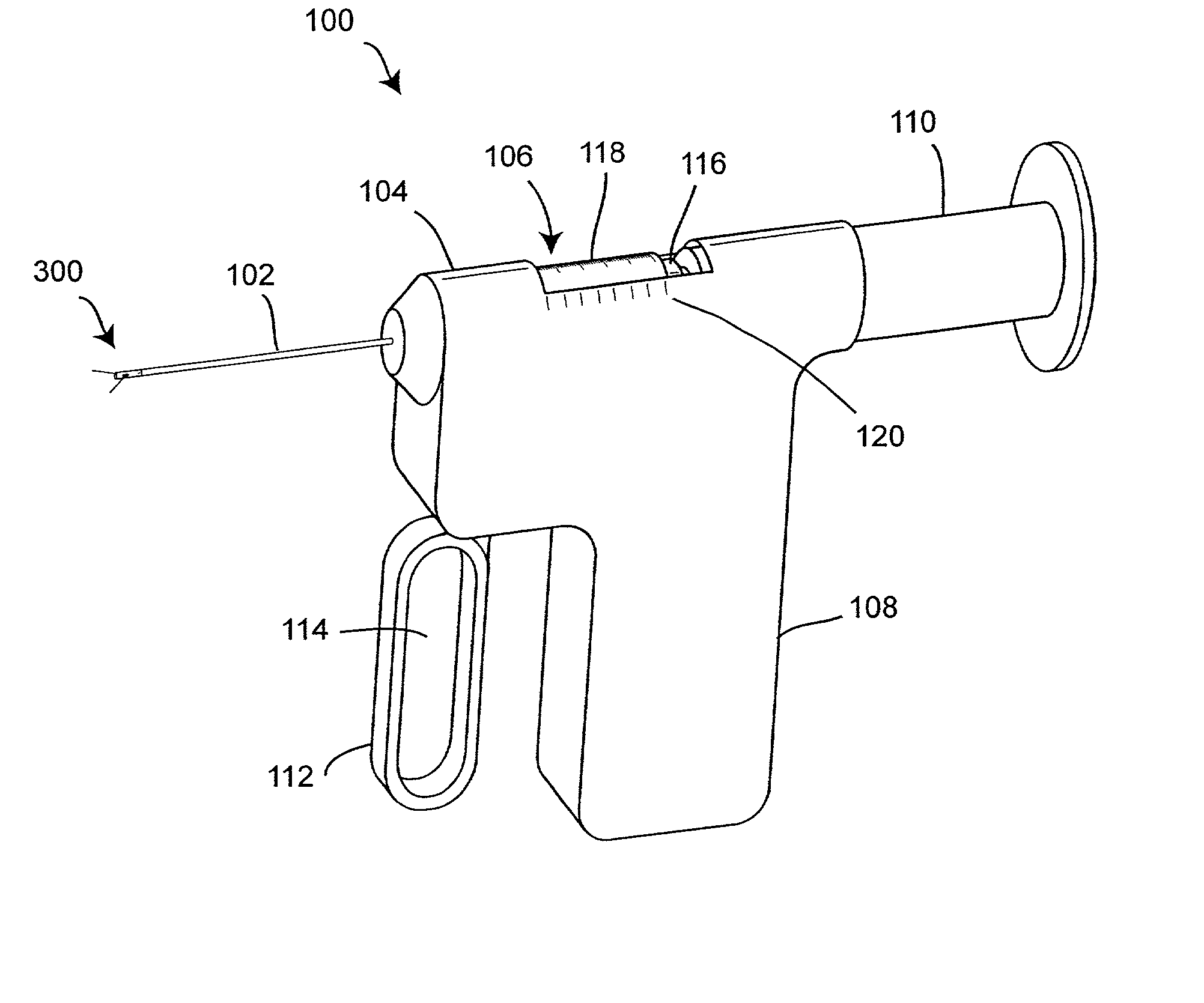
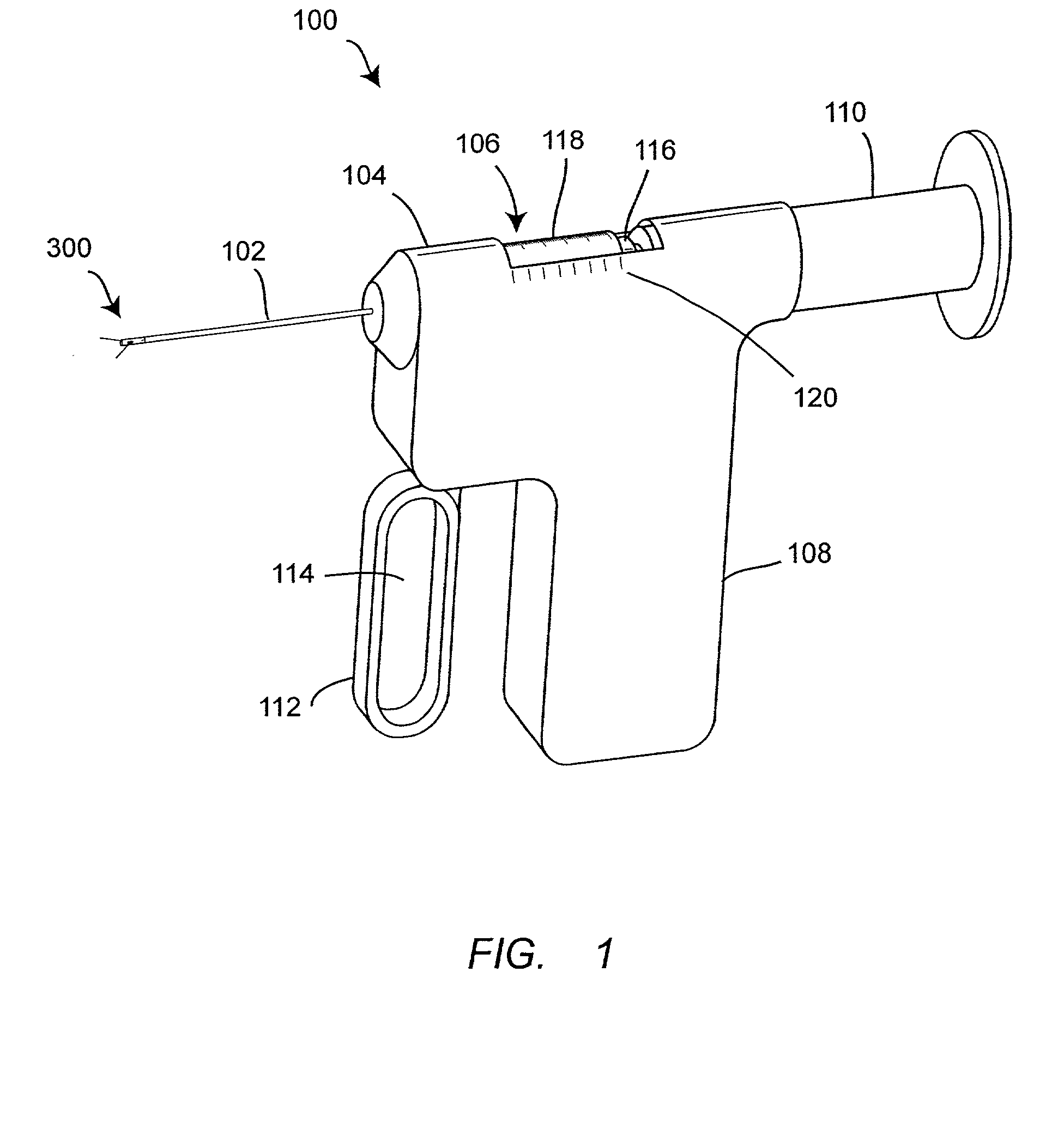
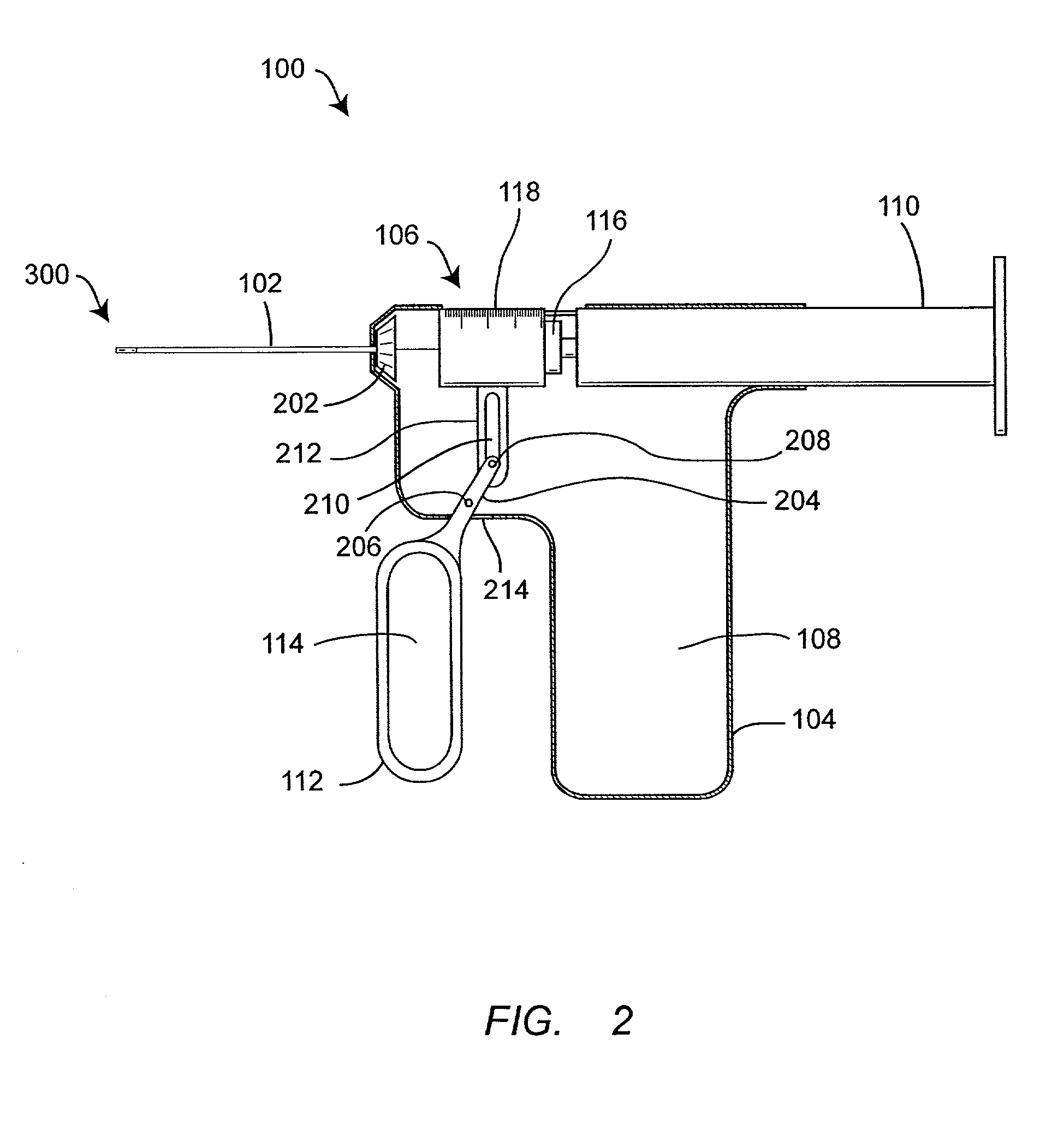
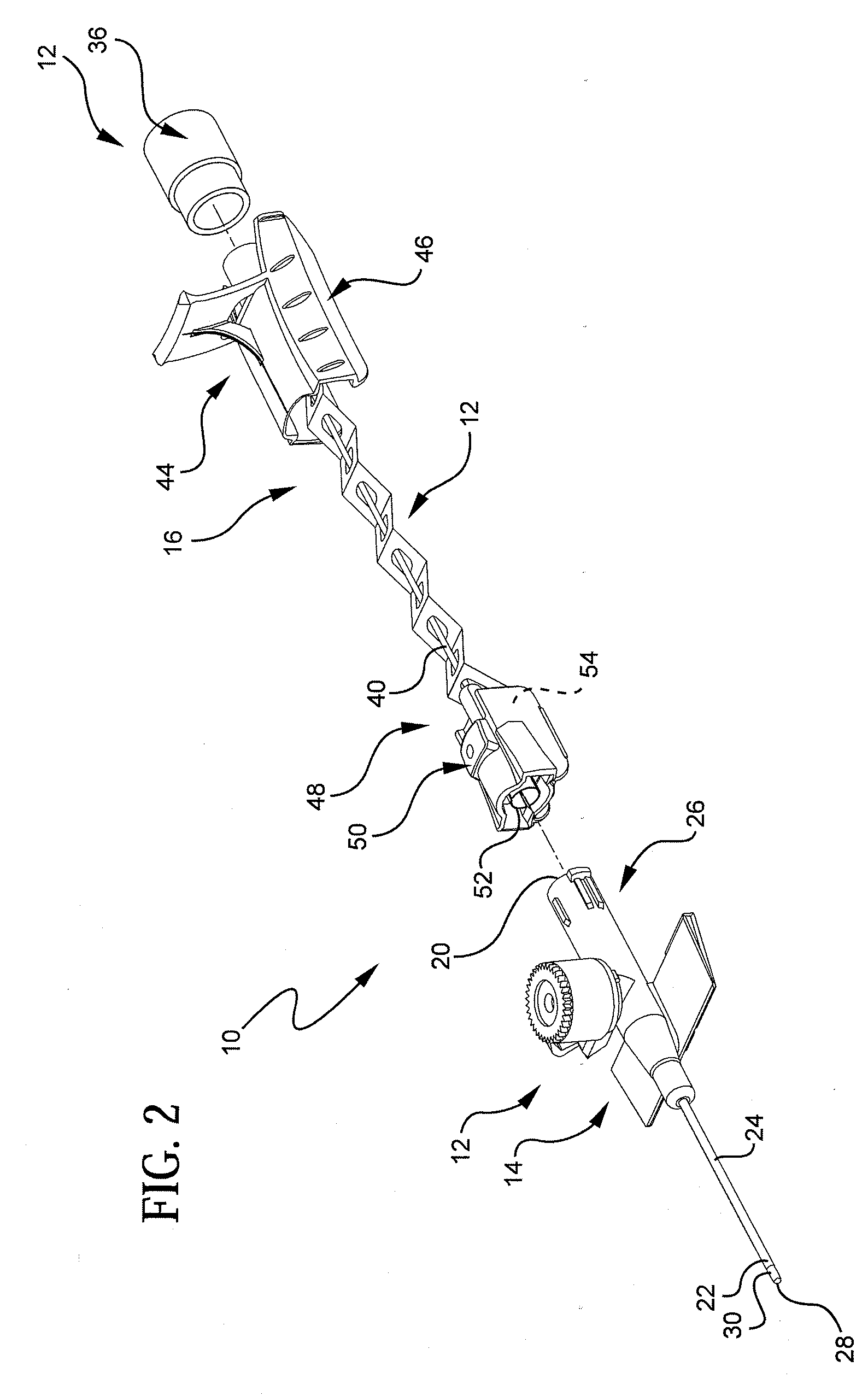
Automatic injection device
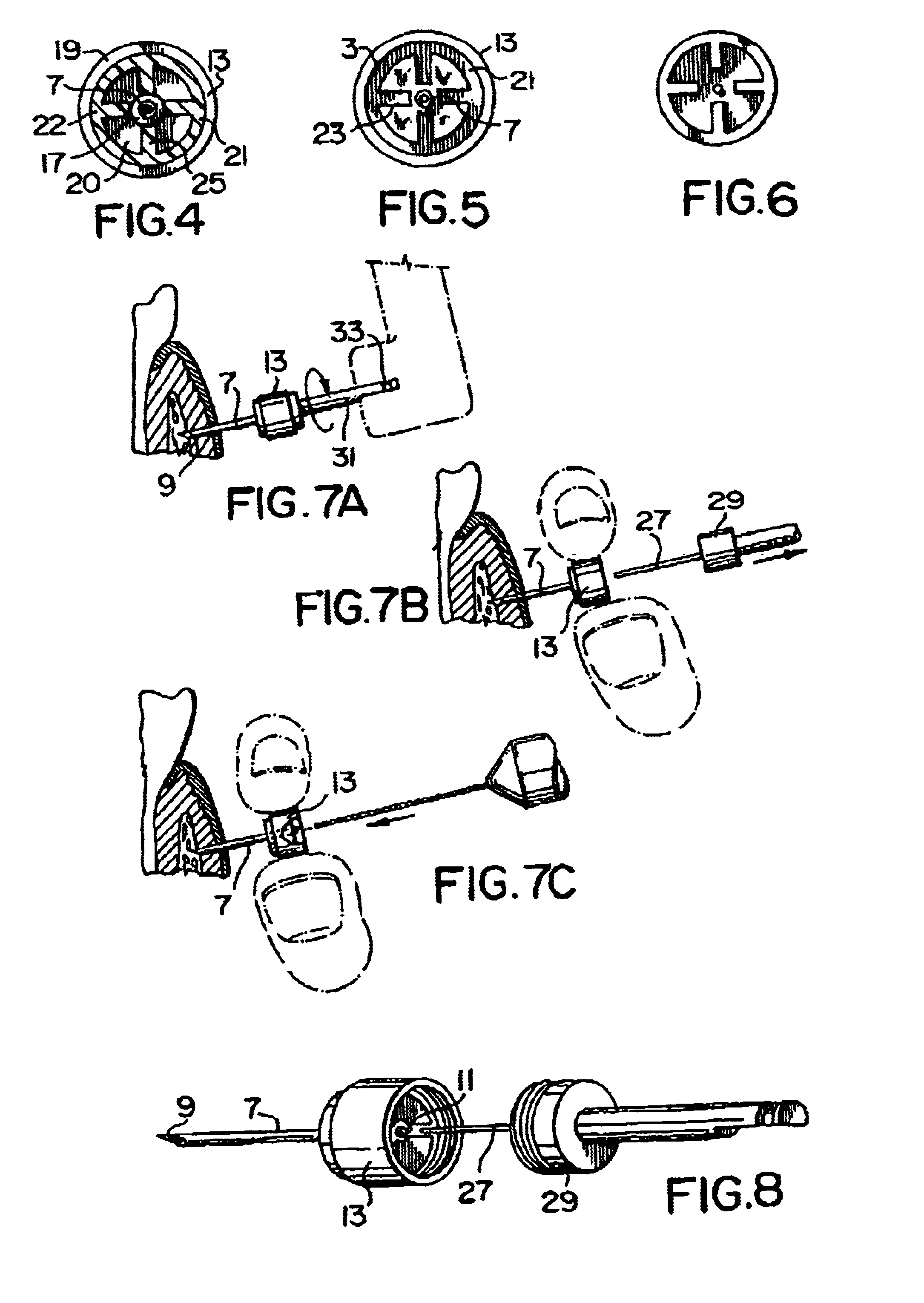
ActiveUS20100160894A1Easy to useReduce anxietyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticHypodermoclysisSubcutaneous injection
The invention provides an automatic injection device for providing a subcutaneous injection of a substance into a user, comprising: a housing having an open first end and a second end; a syringe movably disposed in the housing, the syringe including a barrel portion for holding the substance, a hollow needle in fluid communication with the barrel portion for ejecting the substance from the syringe, and a bung for sealing the barrel portion and selectively applying pressure to the substance to force the substance through the hollow needle; a plunger for first moving the syringe towards the first end such that the needle projects from the first end and subsequently applying pressure to the bung, the plunger including a rod connected at a first end to the bung, a compressible expanded central portion and a flange between a second end of the rod and the compressible expanded central portion; and a biasing mechanism for biasing the plunger towards the first open end of the housing, the biasing mechanism disposed about the second end of the rod between the flange and the second end of the housing. The present invention also provides methods and kits for using an automatic injection device, and methods and kits for promoting an automatic injection device comprising a medication based on advantageous properties of the device as compared to a pre-filled syringe. The invention also provides methods and kits for training a recipient on use of the automatic injection device.
Owner:ABBVIE BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD
Hypodermic fluid dispenser
InactiveUS6056716AEfficient injectionEliminate the problemAmpoule syringesJet injection syringesHypodermoclysisJet flow
A jet injector system for injecting fluid into a body. The jet injection system includes capsules for holding the material to be injected, apparatus for applying force to the capsule(s) to eject the injection material(s) and a perforator for directing the jet stream for the respective materials into the body. A flyweight system is described for developing jet injection pressures, and latching devices control the flyweight system. An injector system for injecting more than one fluid is described.
Owner:DANTONIO CONSULTANTS INT INC
Microneedle-based pen device for drug delivery and method for using same
ActiveUS7556615B2Accurate accessAccurate transmissionAmpoule syringesAutomatic syringesHypodermoclysisCompressible material
A system and method is provided for an injectable substance delivery pen comprising a microneedle hub assembly removably engaged with a pen device body which includes a cartridge, a plunger, and a drive mechanism. The hub assembly includes at least one microneedle for intradermal or shallow subcutaneous injection of the contents of the cartridge. The cartridge, plunger and drive mechanism components of the pen body are fabricated of non-compliant and non-compressible materials to allow effective communication of the cartridge contents via the microneedle patient interface.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
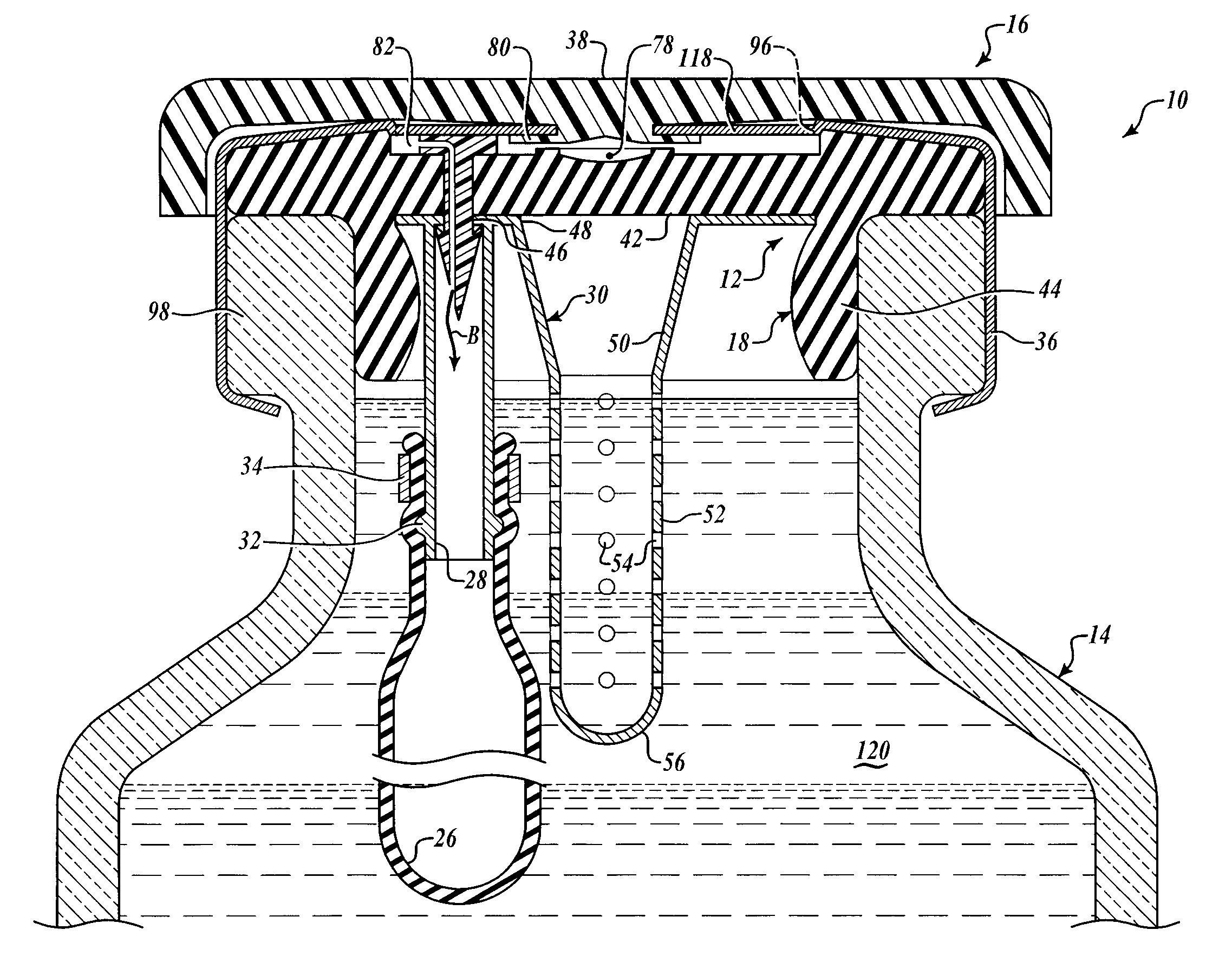
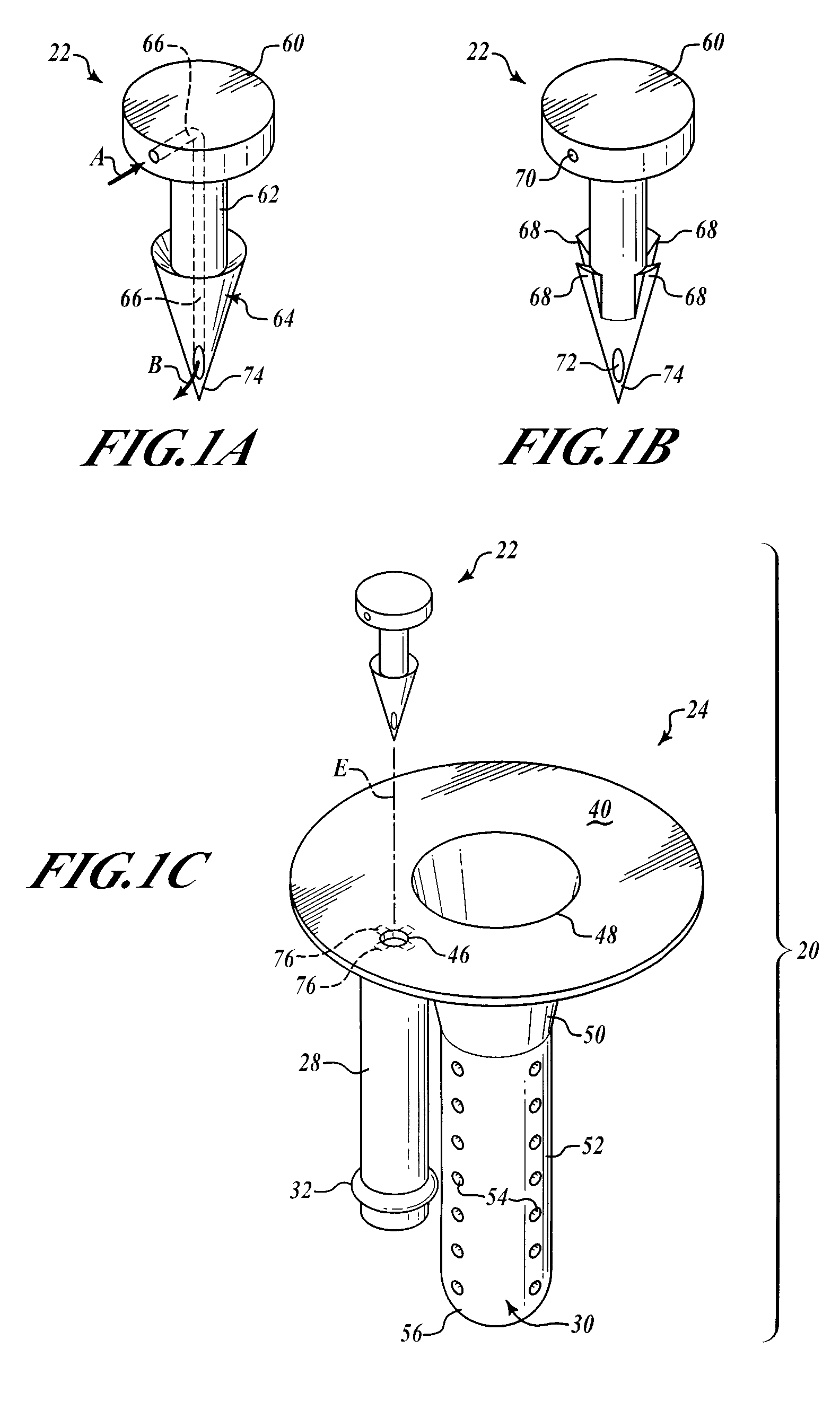
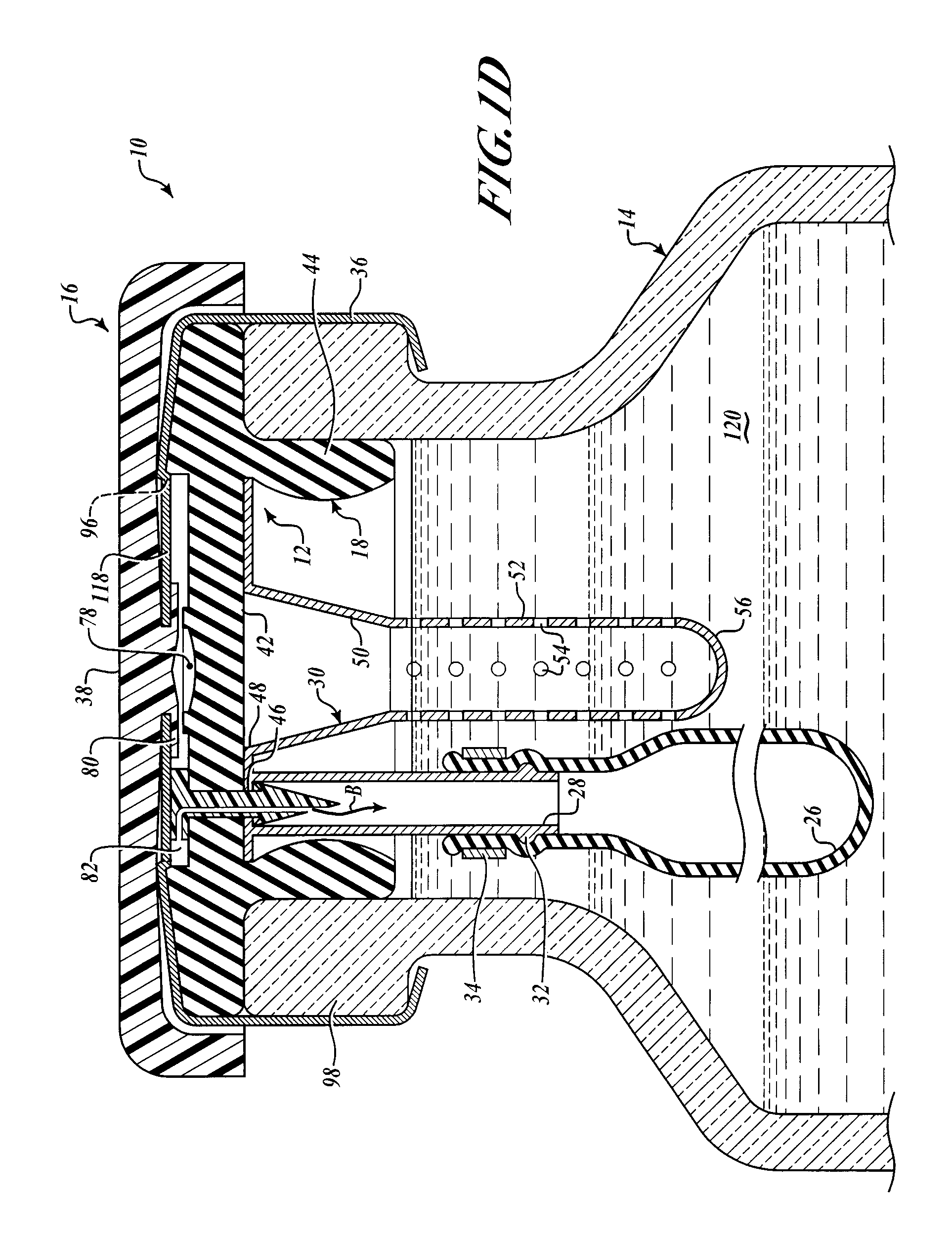
Hypodermic drug delivery reservoir and apparatus
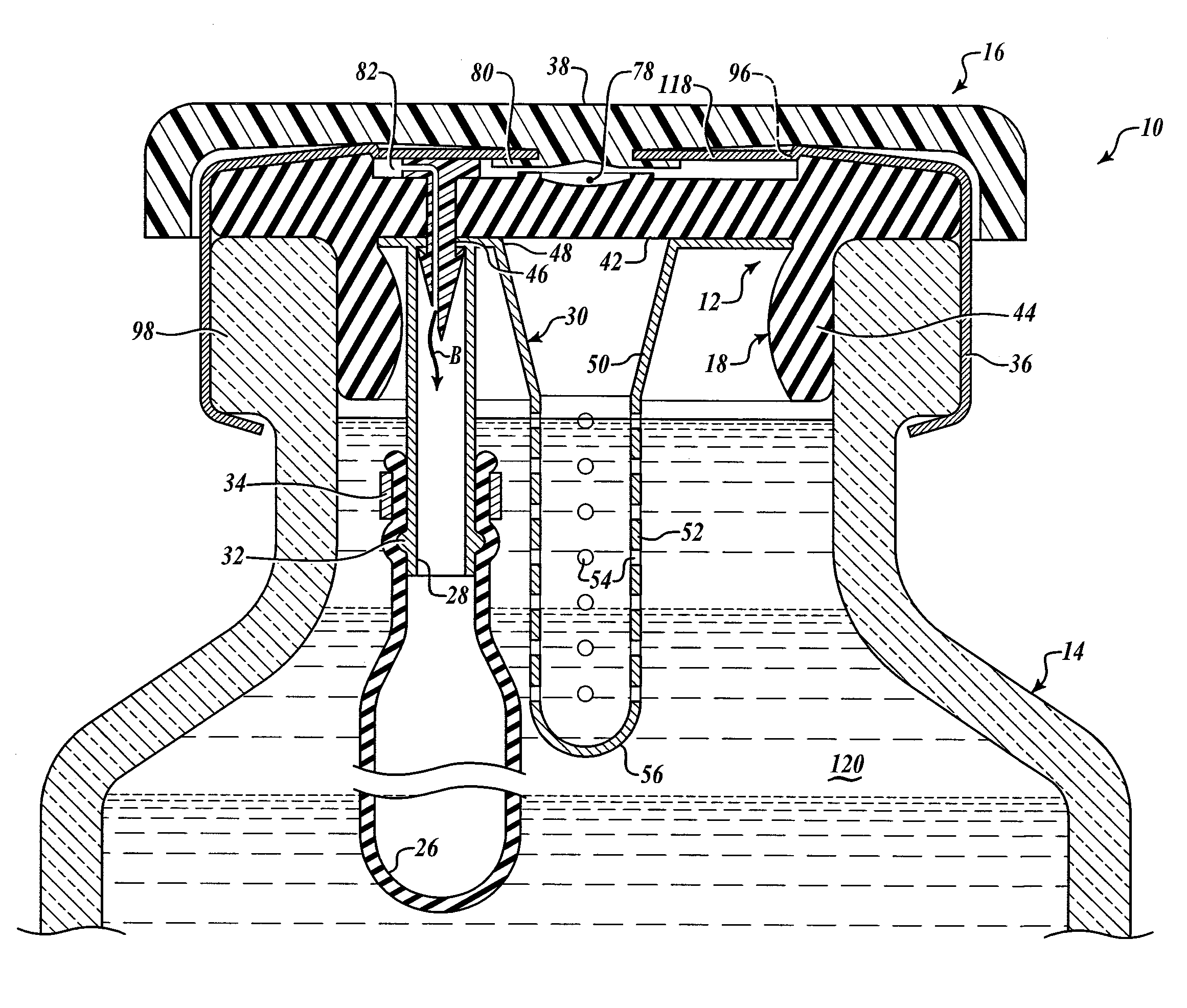
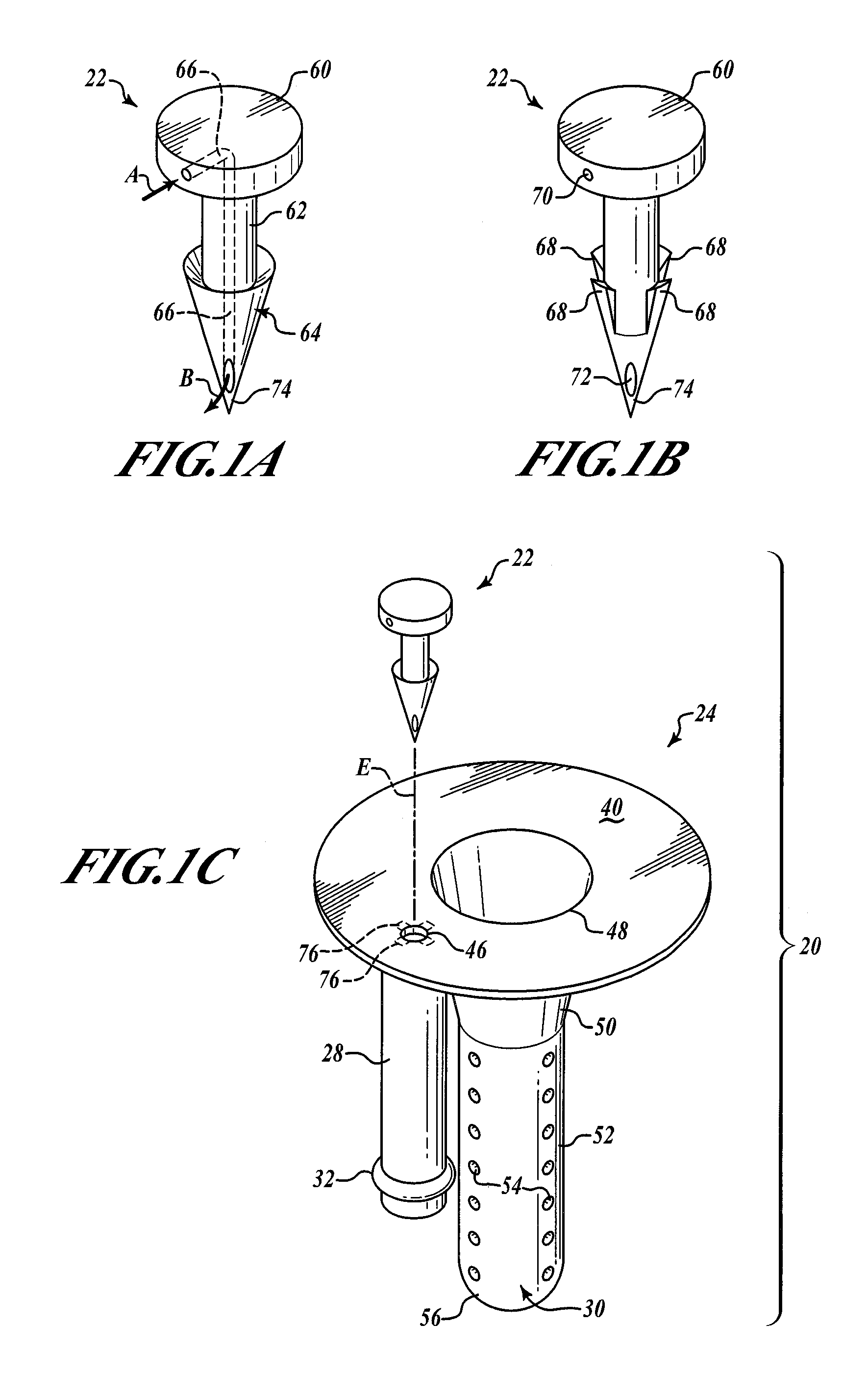
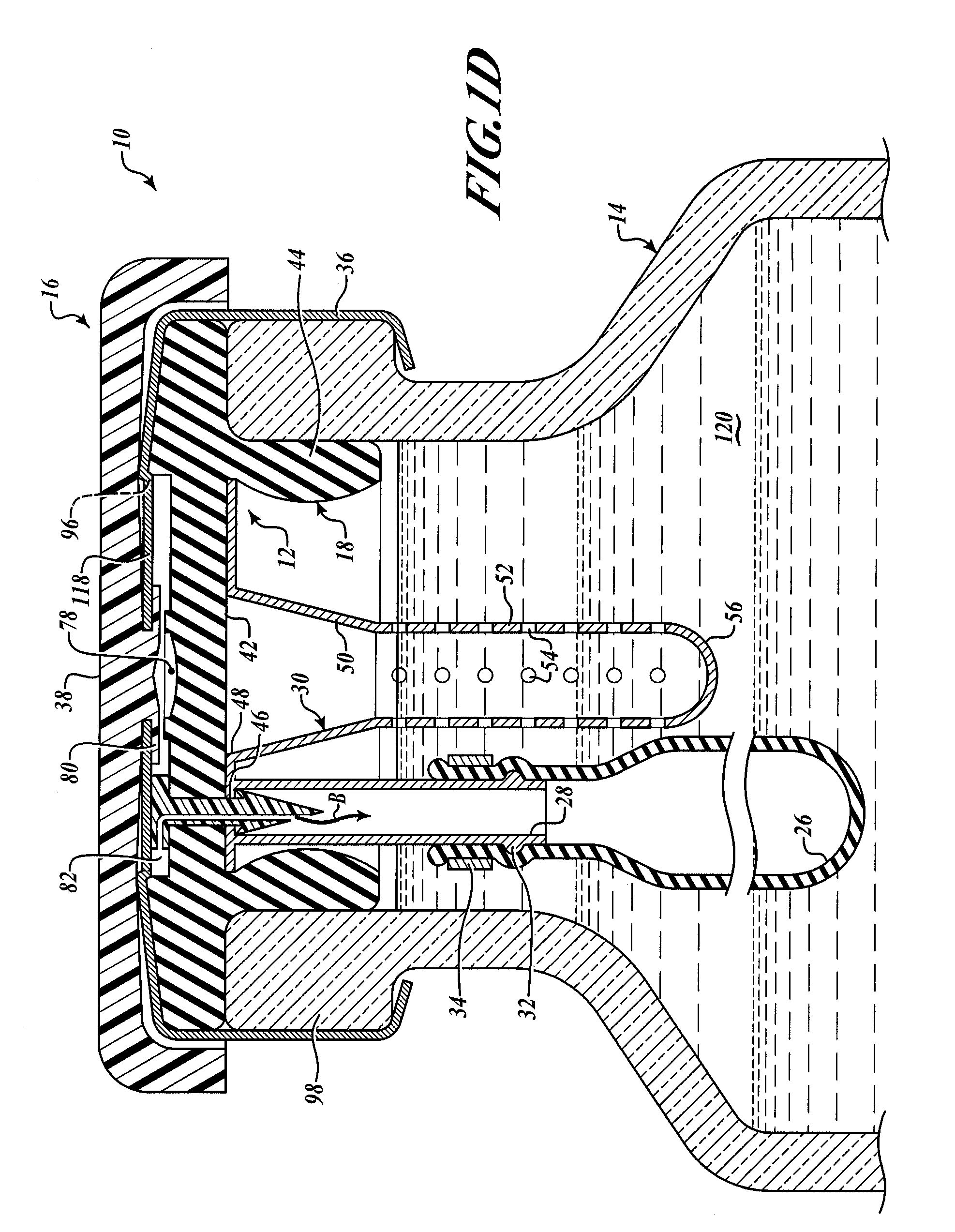
ActiveUS20100179473A1Preventing fluid connectionSeals be limitedJet injection syringesMicroneedlesHypodermoclysisDrug delivery reservoir
A hypodermic drug delivery apparatus (10) for delivering a pressurized medication fluid (23) comprising a reservoir (14) containing at least one deliverable fluid (23) and a rupturing member (25) the reservoir (14) having at least one portion of at least one wall (22) rupturable by the rupturing member (25).
Owner:AKTIVAX INC
Medical device container
InactiveUS20080108951A1Easy constructionReduce manufacturing costInfusion needlesRigid containersHypodermic needleHypodermoclysis
A storage system for a needleless pen delivery device syringe and a hypodermic needle adapted for attachment to and use with the pen delivery device syringe. A tubular sleeve has a first hollow chamber for receiving therein the needleless pen delivery device syringe, and a hollow cap has a second hollow chamber for receiving therein the hypodermic needle. The cap is adapted to affix to the sleeve to form a continuous tubular housing, and the sleeve is adapted to receive the pen delivery device syringe only when the needle is not attached to the syringe. Alternative exemplary embodiments provide means for storing other related accessories or additional spare needles.
Owner:JERDE STEVEN
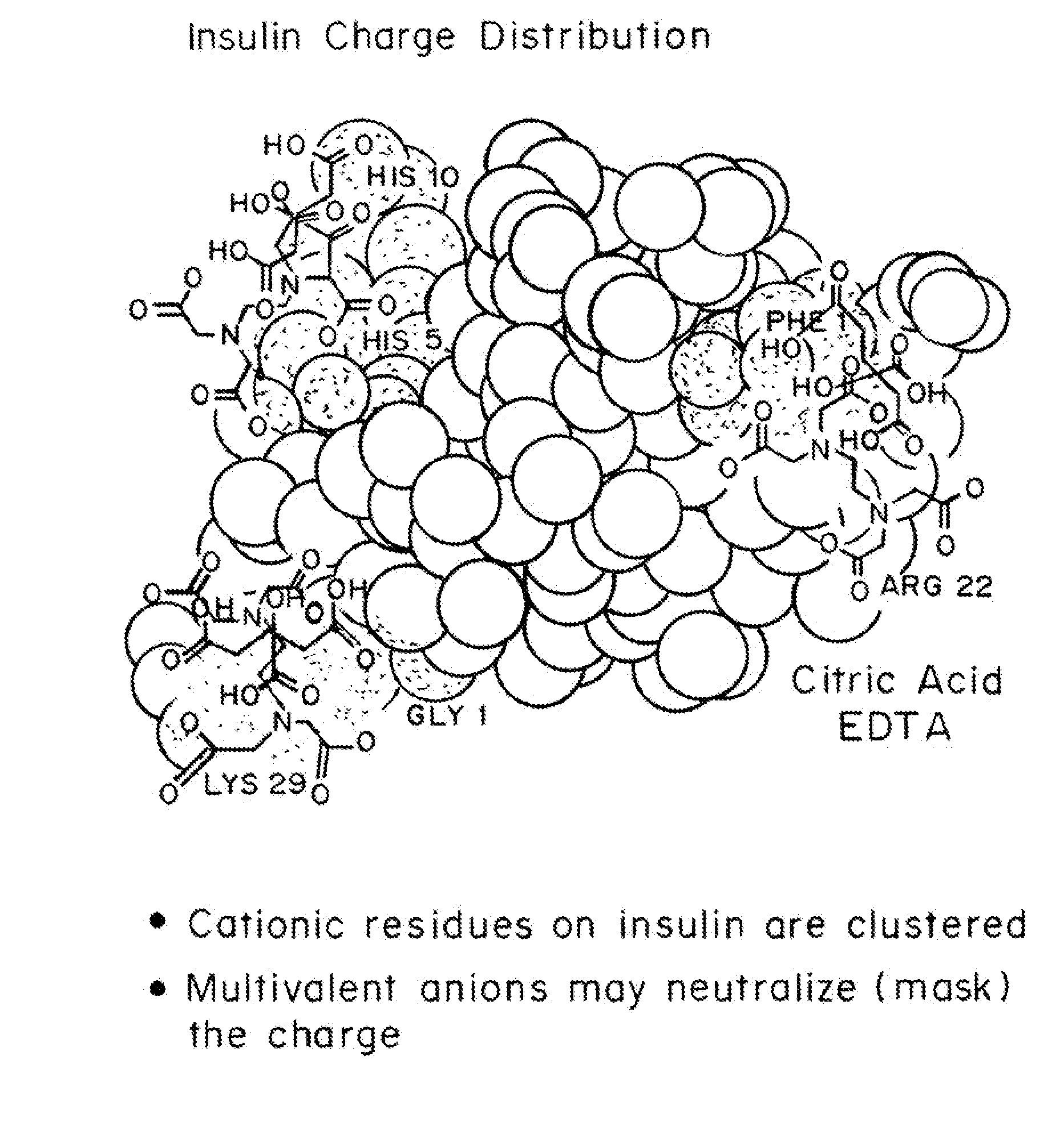
Rapid acting drug delivery compositions
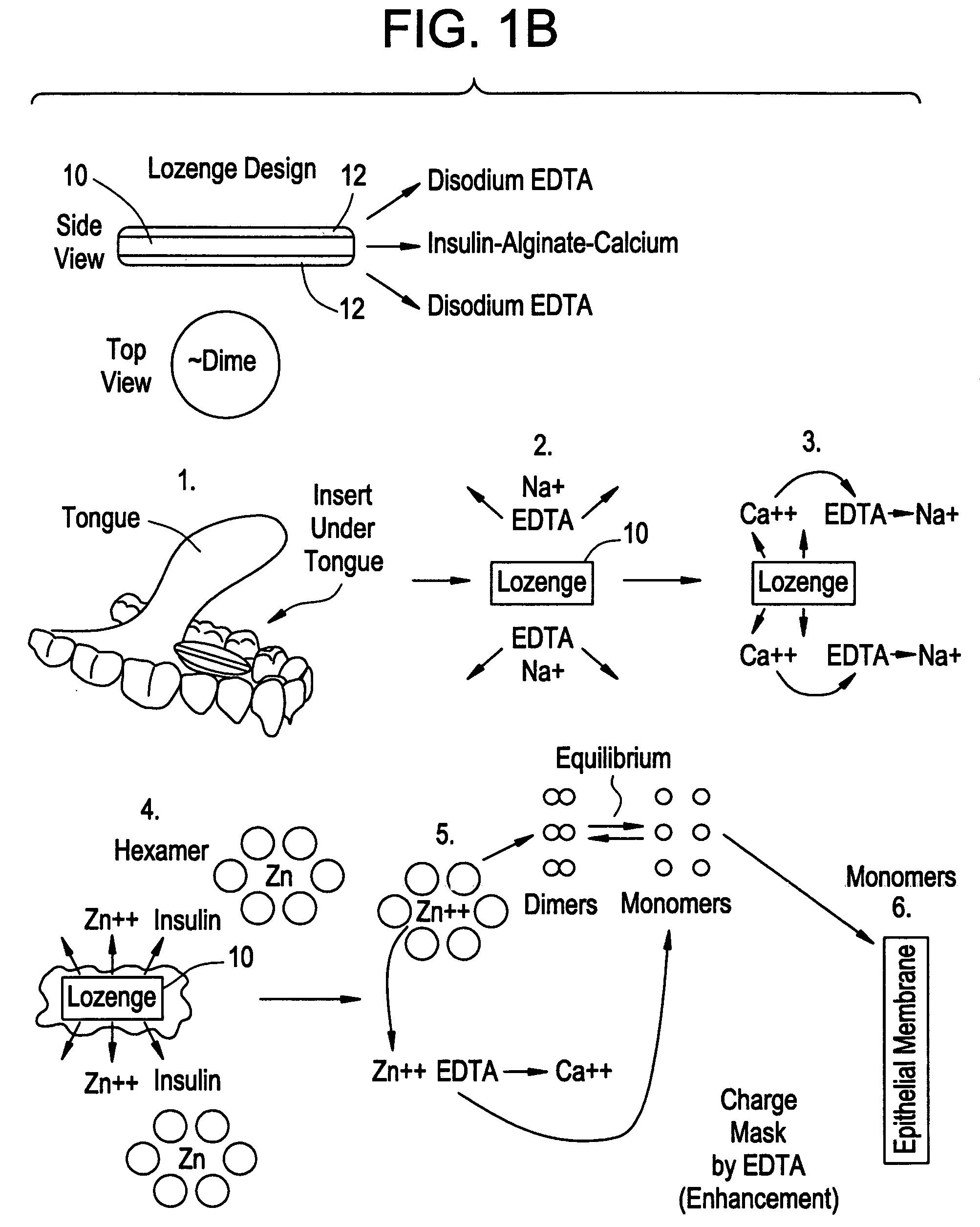
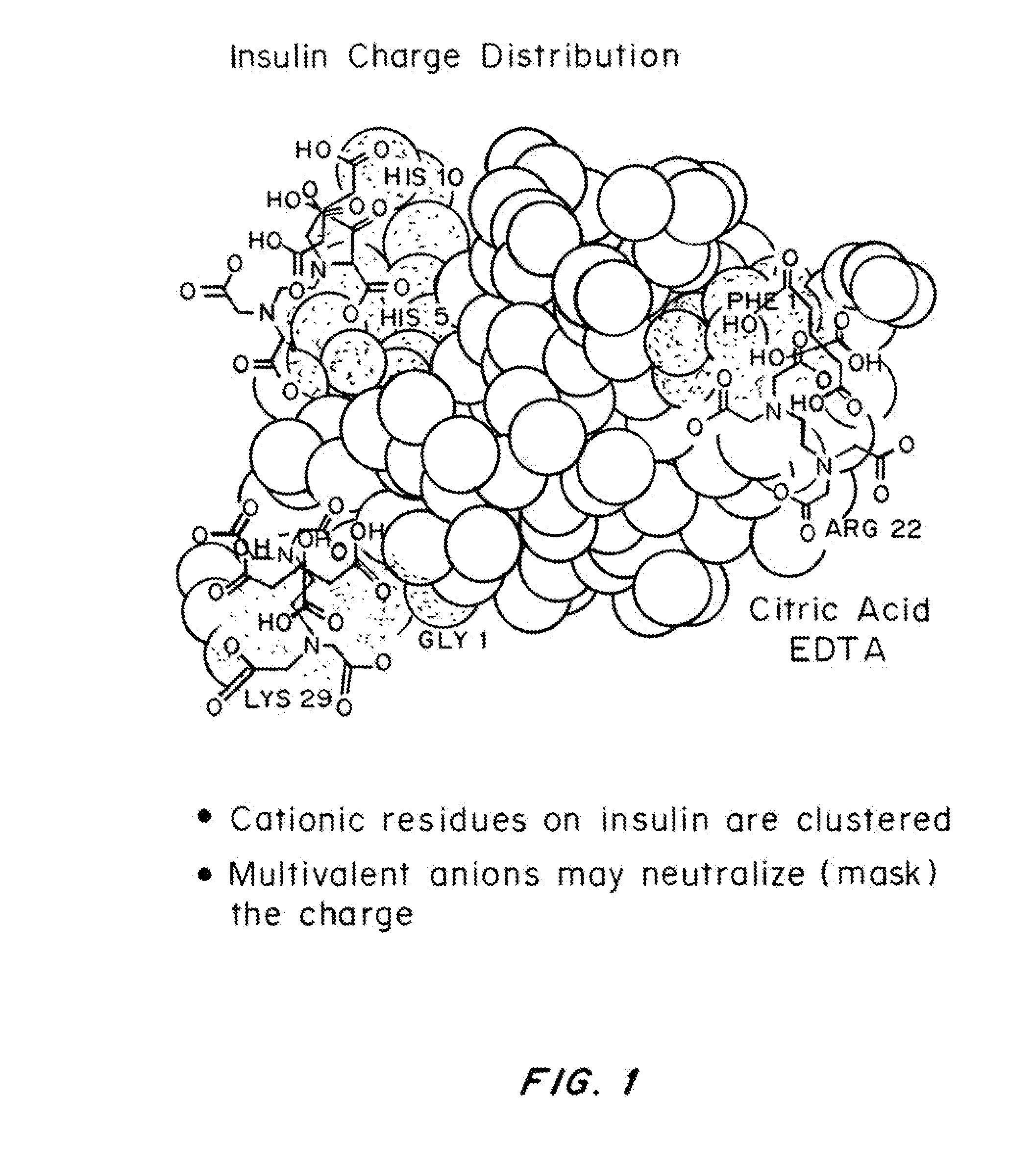
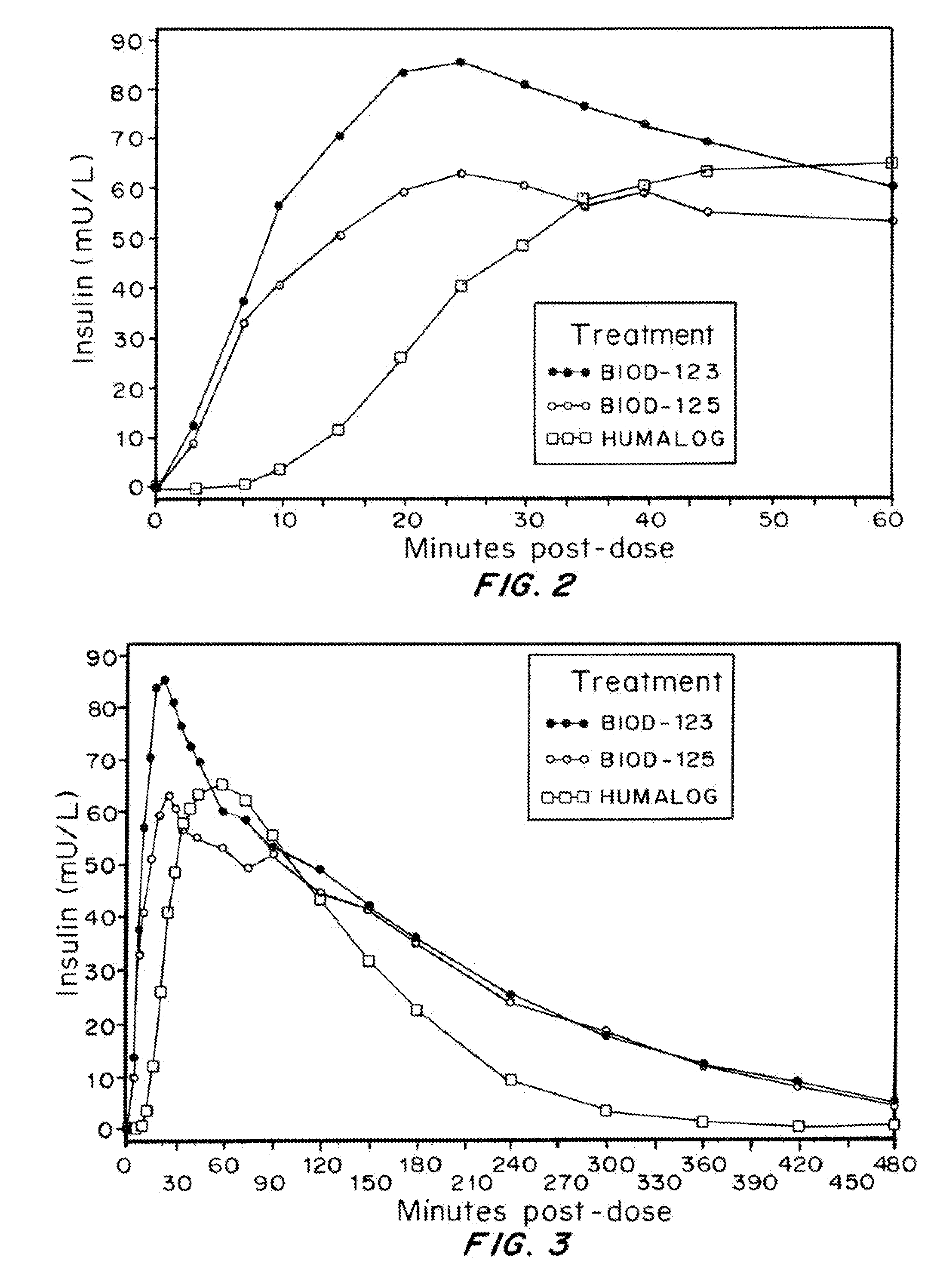
Drug formulations for systemic drug delivery with improved stability and rapid onset of action are described herein. The formulations may be administered via buccal administration, sublingual administration, pulmonary delivery, nasal administration, subcutaneous administration, rectal administration, vaginal administration, or ocular administration. In the preferred embodiments, the formulations are administered sublingually or via subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain an active agent and one or more excipients, selected to increase the rate of dissolution. In the preferred embodiment, the drug is insulin, and the excipients include a metal chelator such as EDTA and an acid such as citric acid. Following administration, these formulations are rapidly absorbed by the oral mucosa when administered sublingually and are rapidly absorbed into the blood stream when administered by subcutaneous injection. In one embodiment, the composition is in the form of a dry powder. In another embodiment, the composition is in the form of a film, wafer, lozenge, capsule, or tablet. In a third embodiment, a dry powdered insulin is mixed with a diluent containing a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, such as water or saline, a metal chelator such as EDTA and an acid such as citric acid. Devices for storing and mixing these formulations are also described.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
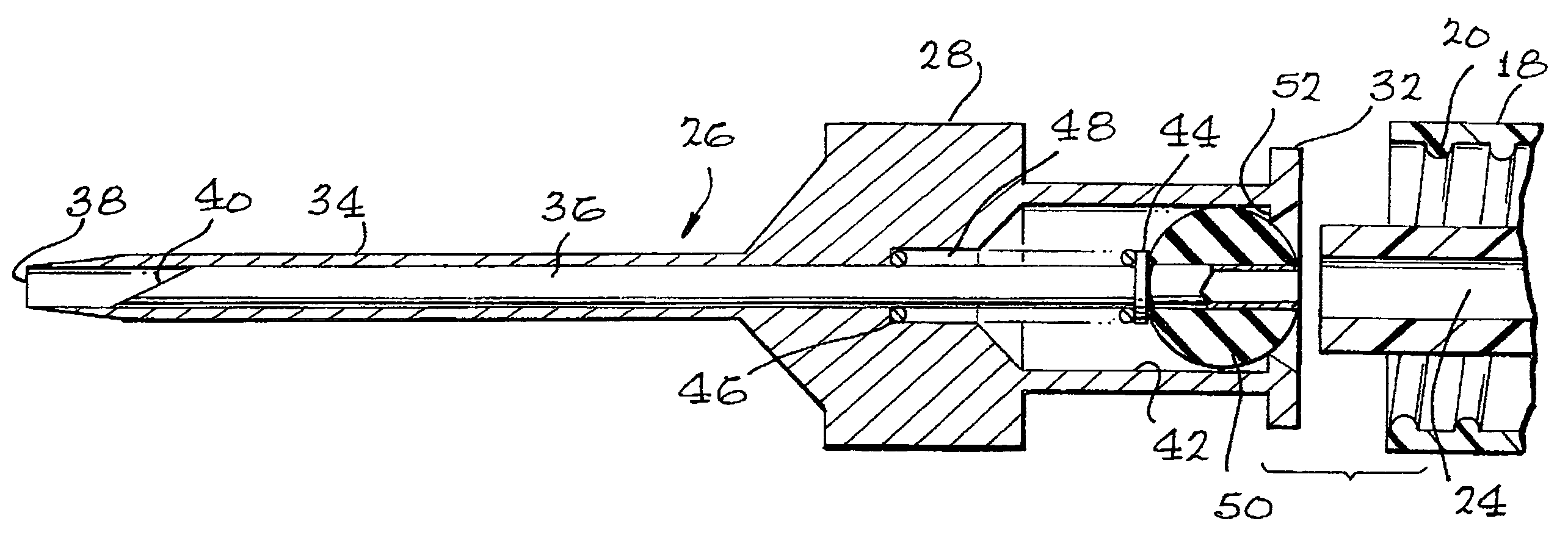
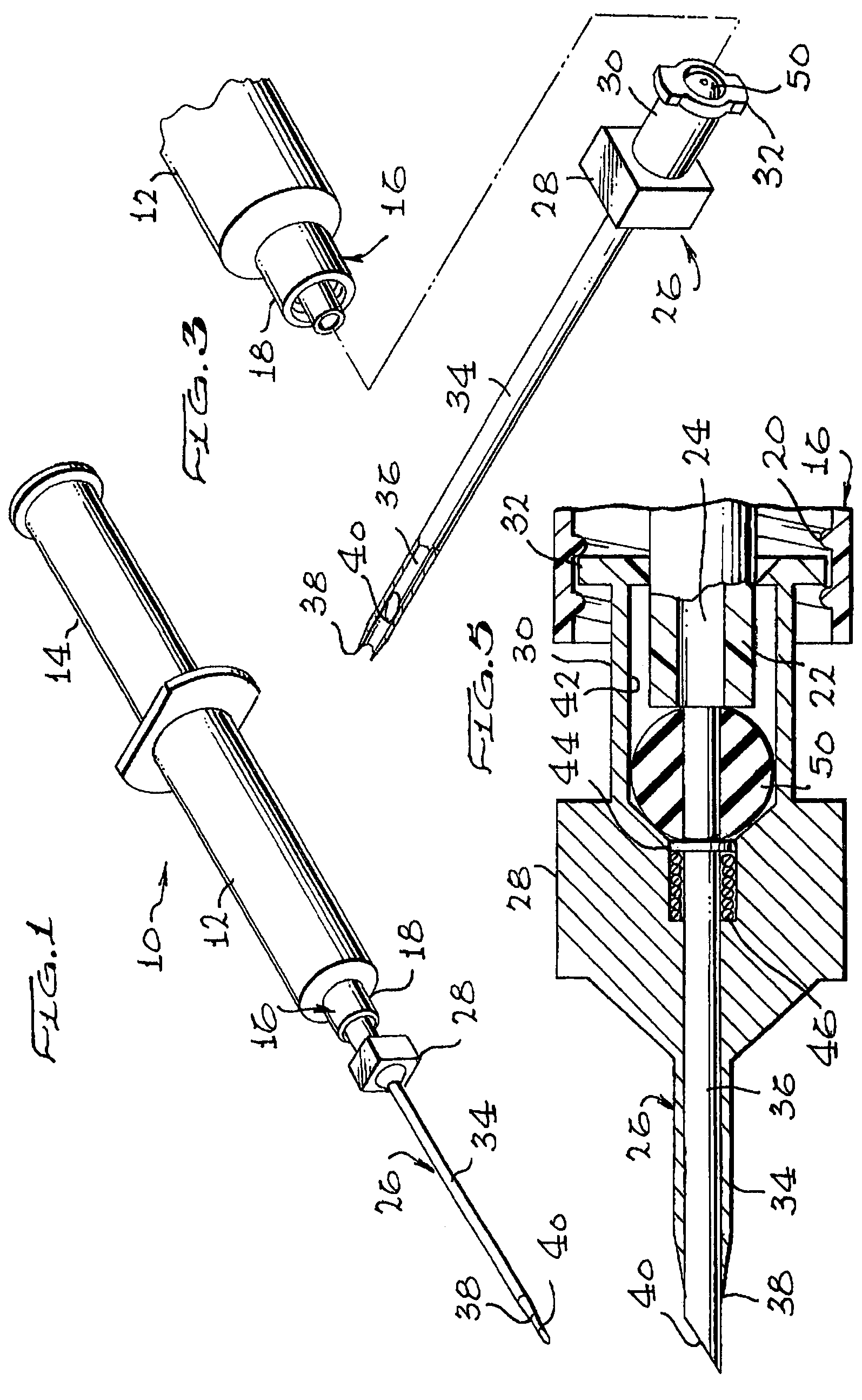
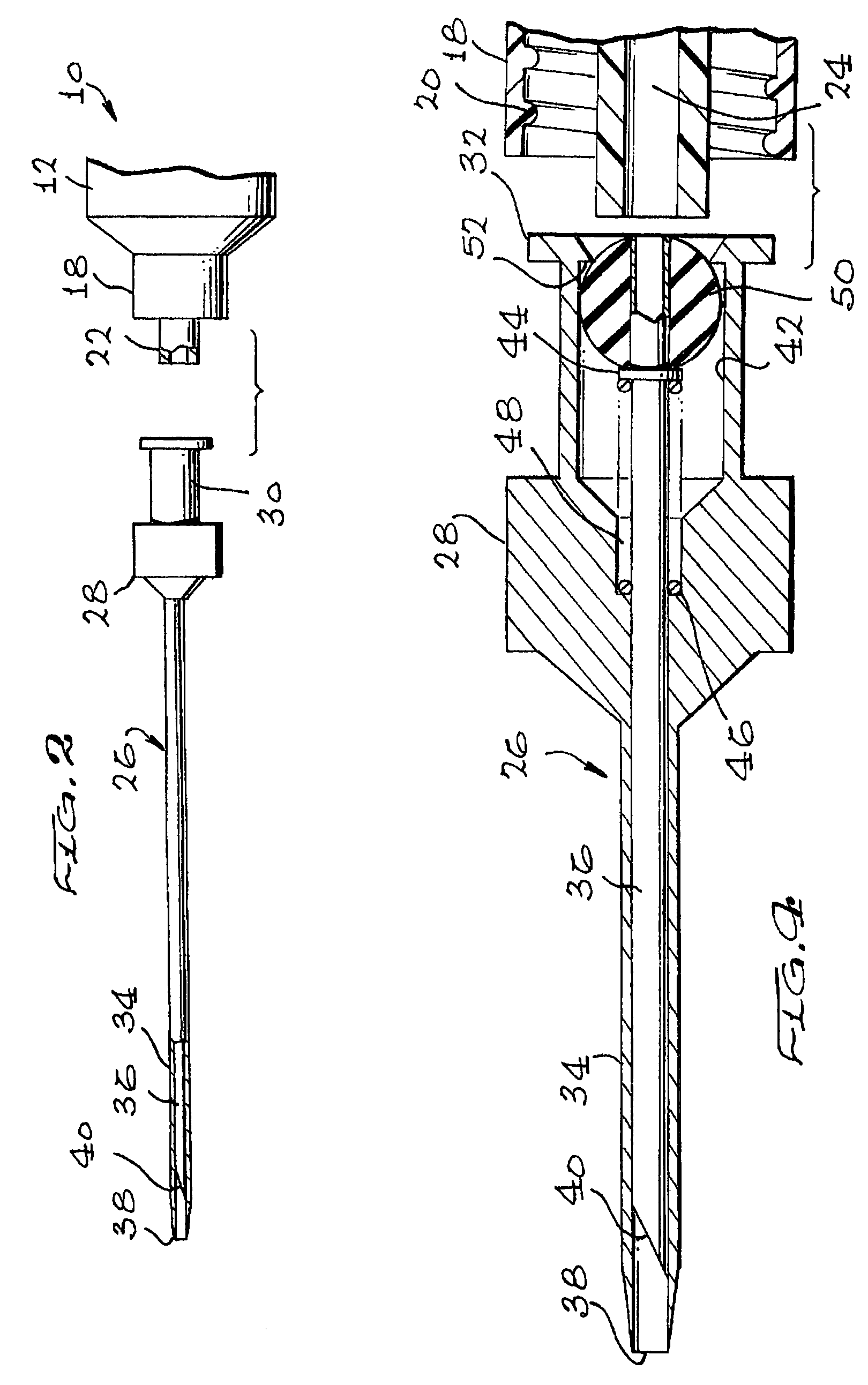
Apparatus for subcutaneous administration of an injectable product
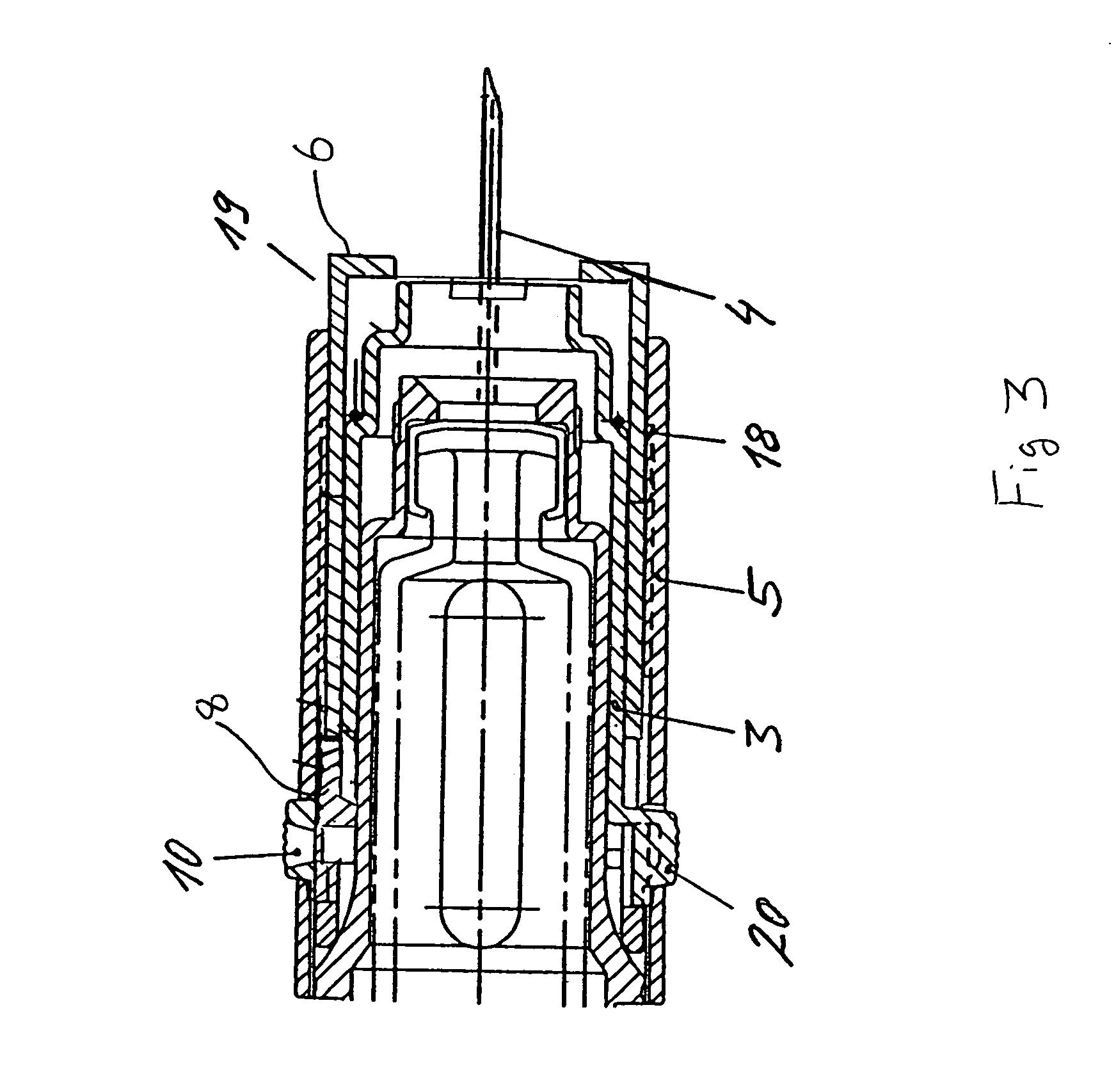
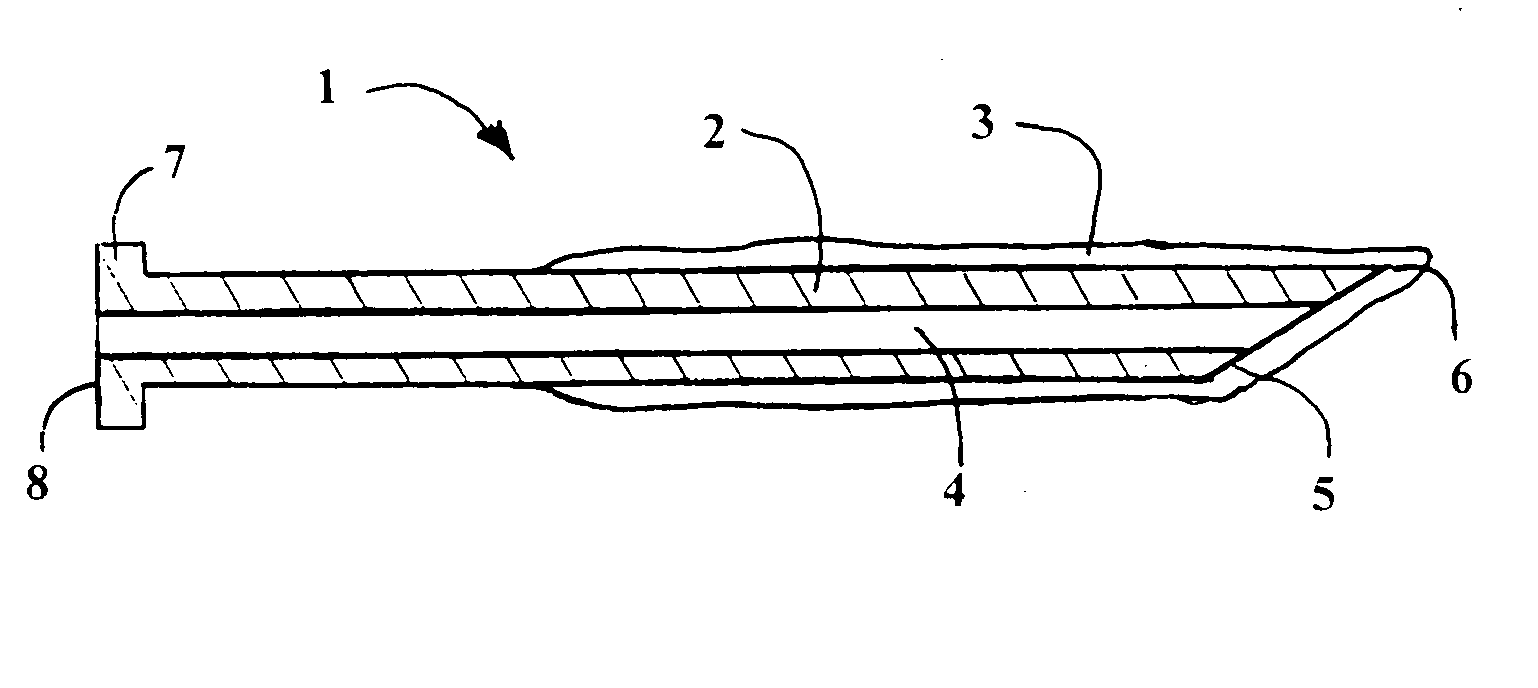
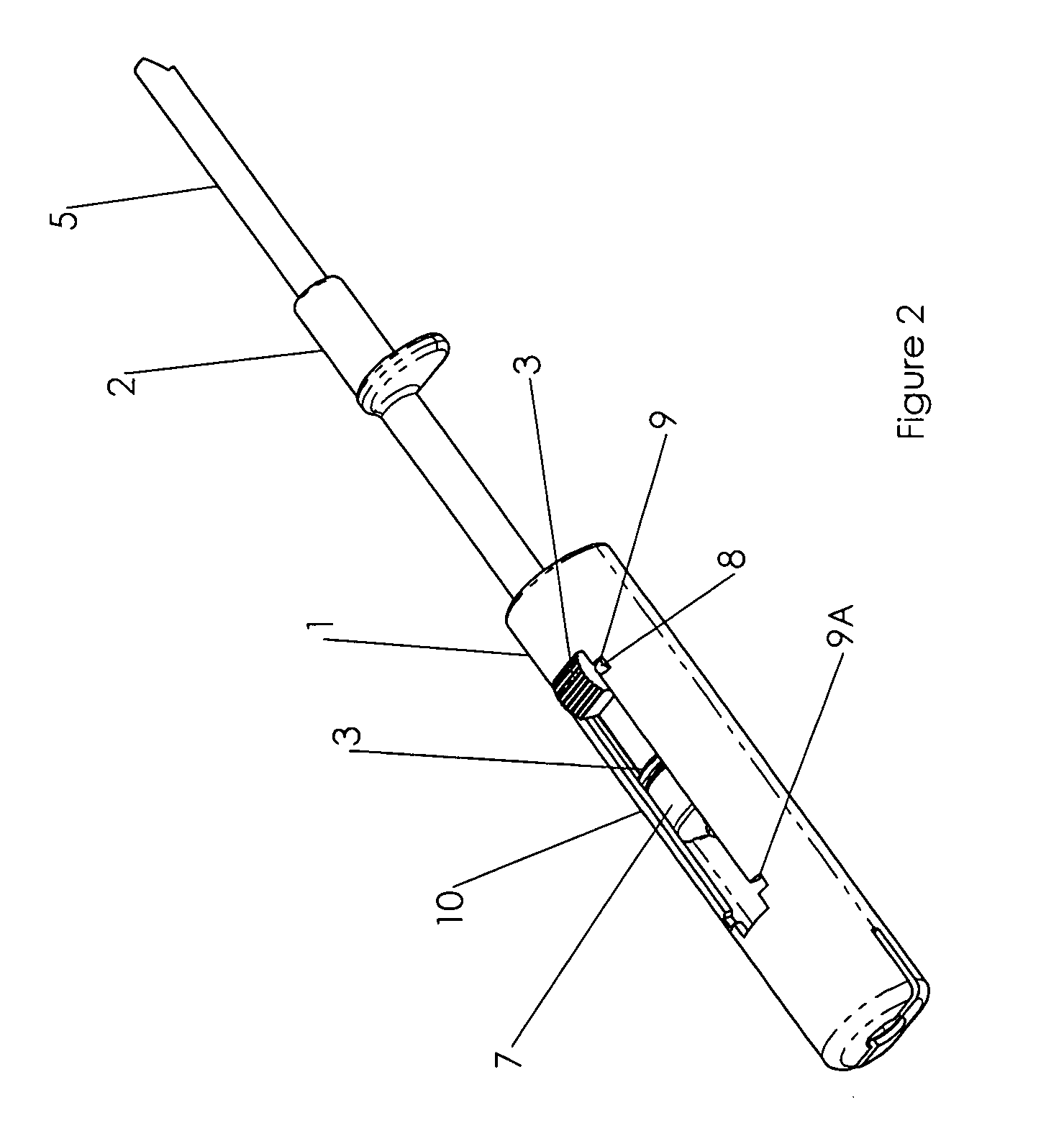
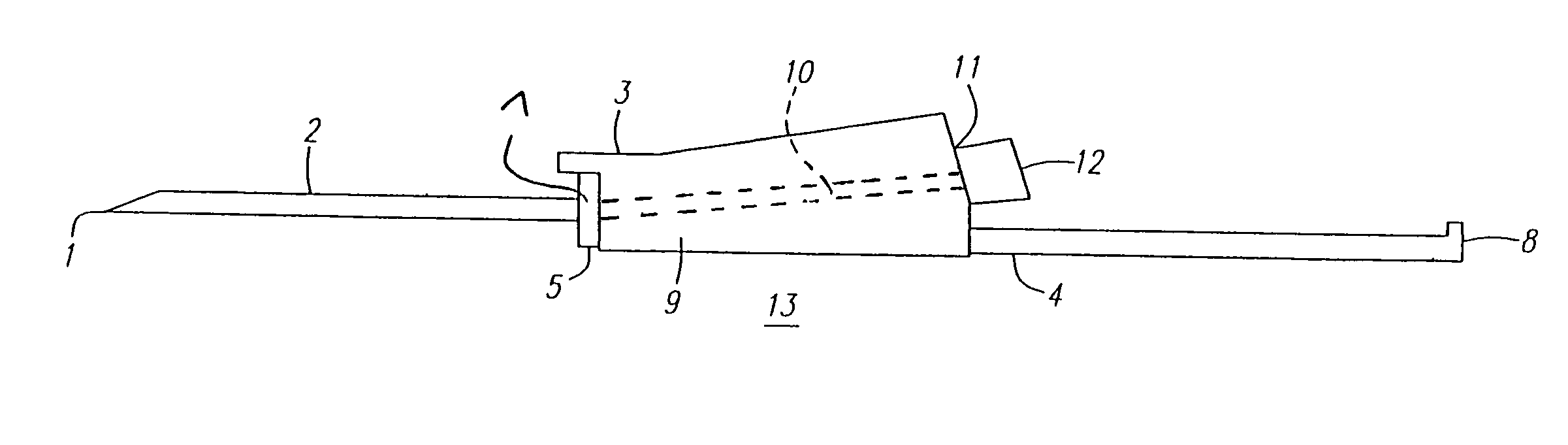
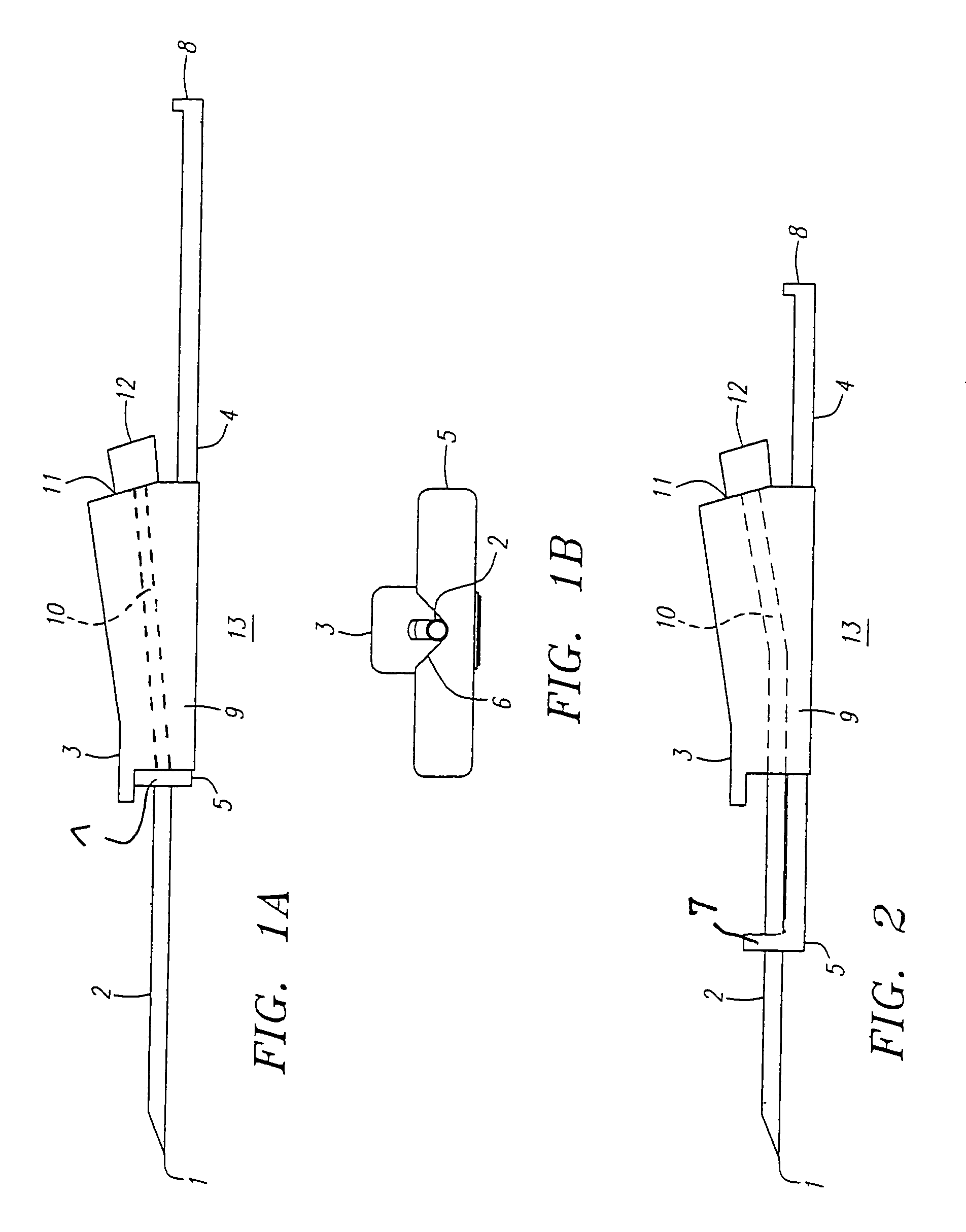
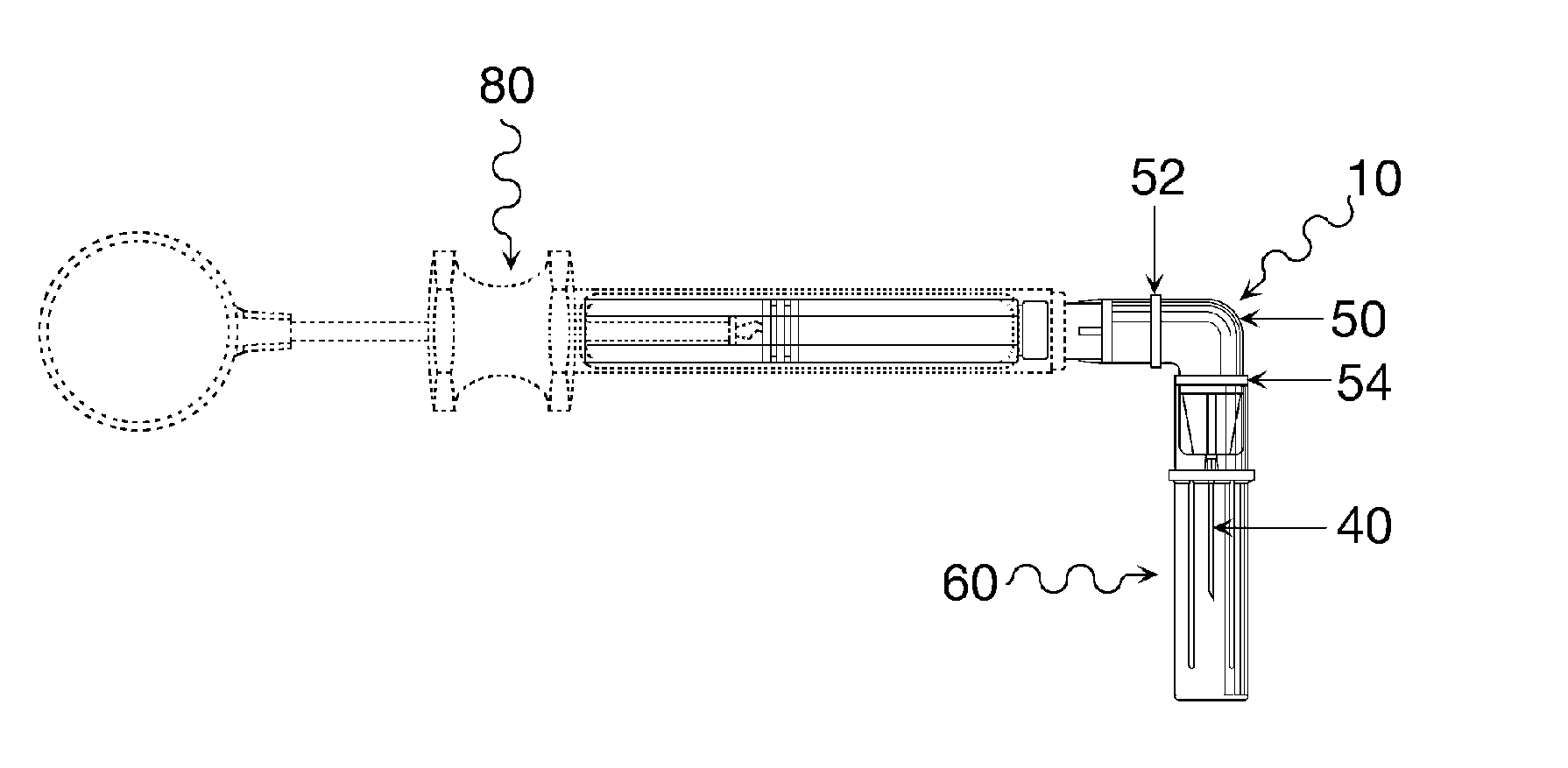
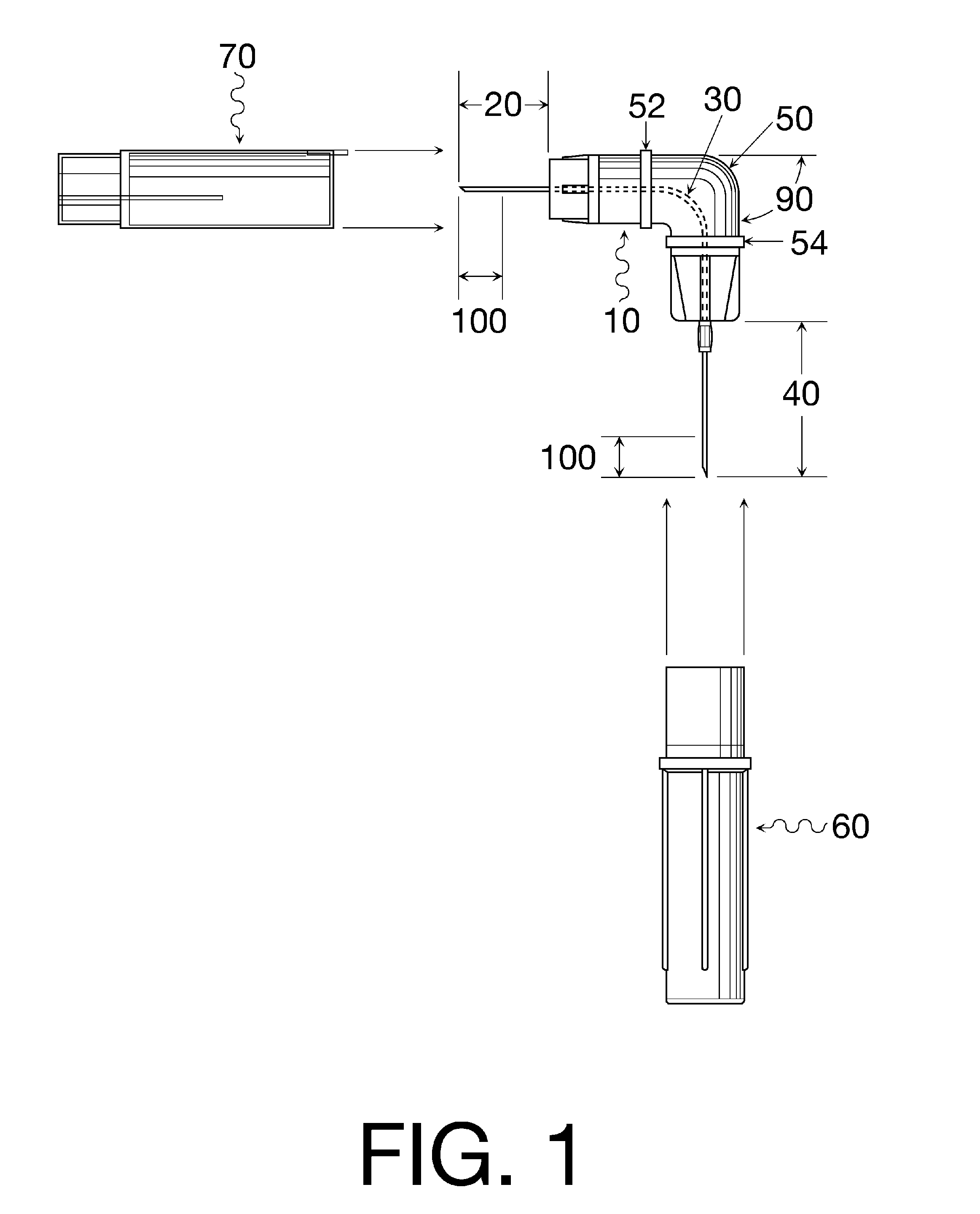
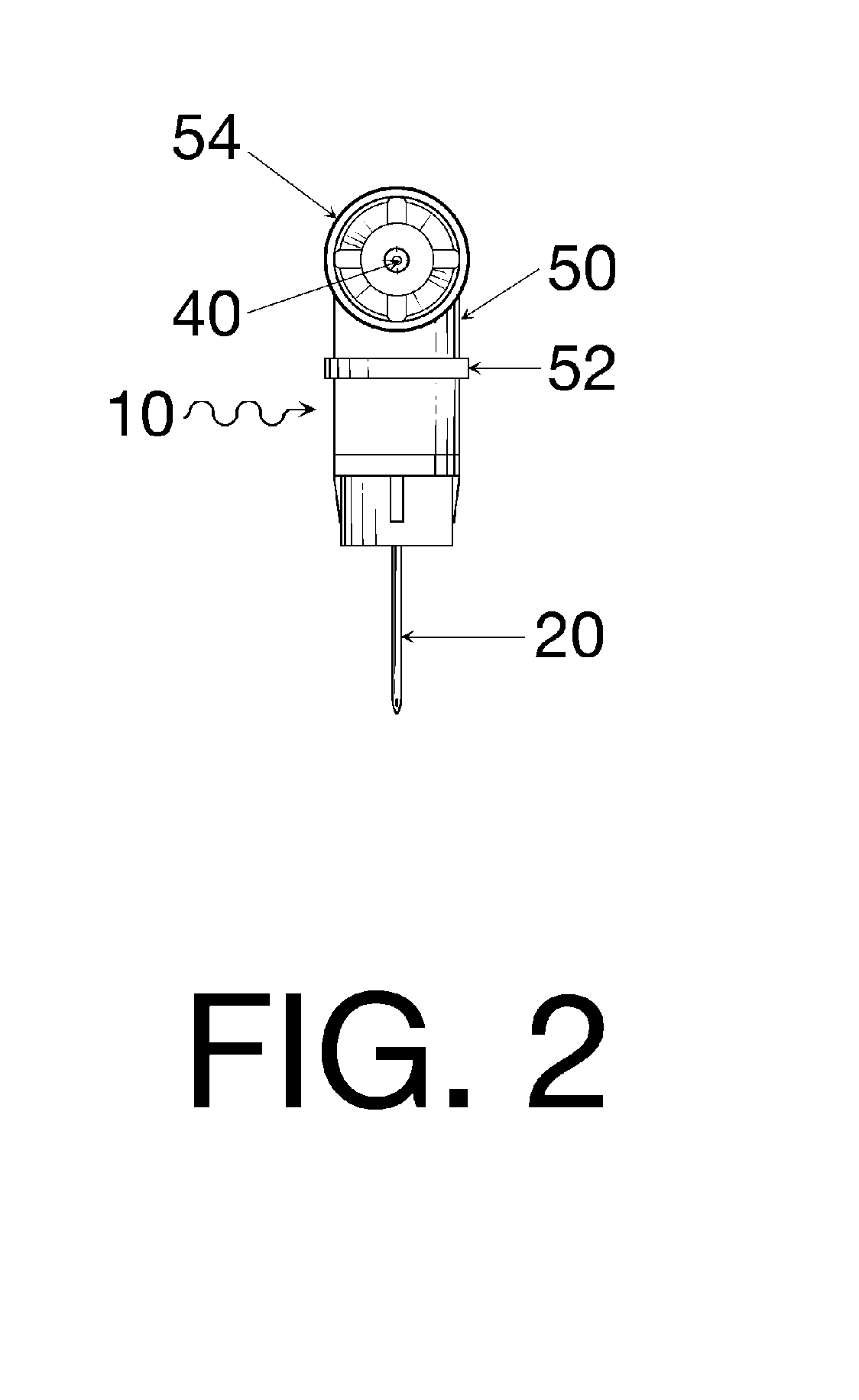
InactiveUS7074211B1Improve securityImprove user convenienceMedical devicesInfusion needlesHypodermoclysisInjectable Product
An apparatus for subcutaneous administration of an injectable product, including a housing, a container for the product to be injected, an injection needle and a needle protection sleeve surrounding the injection needle, wherein the apparatus also includes an indicator to tell a user when the needle protection sleeve has attained its maximum distal position.
Owner:TECPHARMA LICENSING AG
Ice coated hypodermic needle
An ice coating is placed on the hypodermic needle to cool the flesh during insertion. The ice coated front end is sharp, for penetration. The ice coating can be formed by cooling the needle and dipping it in water or molding ice onto the needle. A refrigeration chamber or cryogenic chamber can be used to cool the needle. The mold for forming an ice coating can be cooled by a cryogenic fluid or refrigerant being conducted into coils of the mold surrounding heat conducting mold walls that are used to form the ice coating on the needle. The water can be sterilized with disinfectant included.
Owner:SUN WILLIAM Y
Percutaneously deliverable orthopedic joint device
InactiveUS20080255664A1Slow deteriorationRelieve painInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsHypodermoclysisHypodermic needle
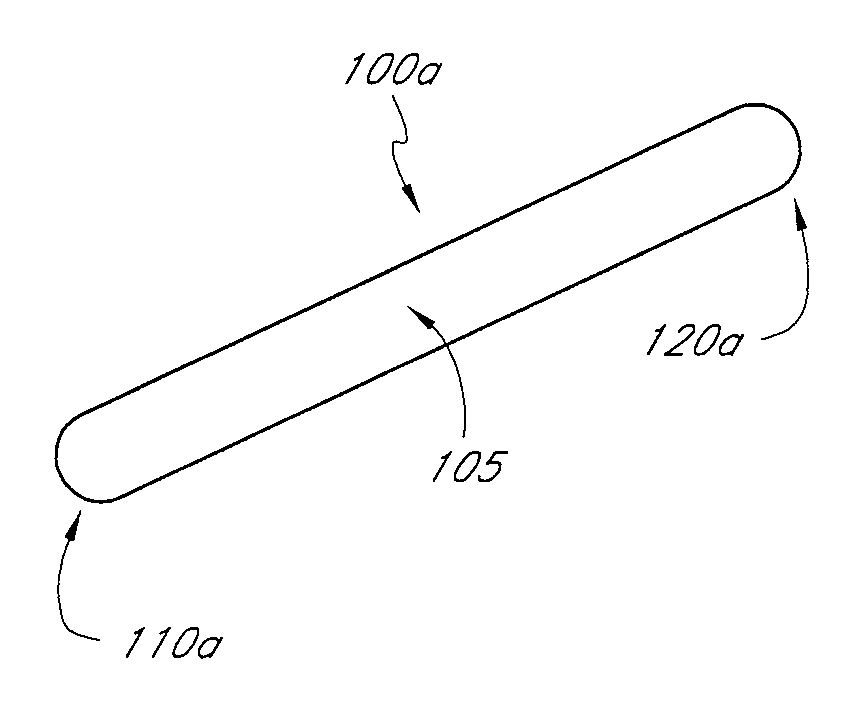
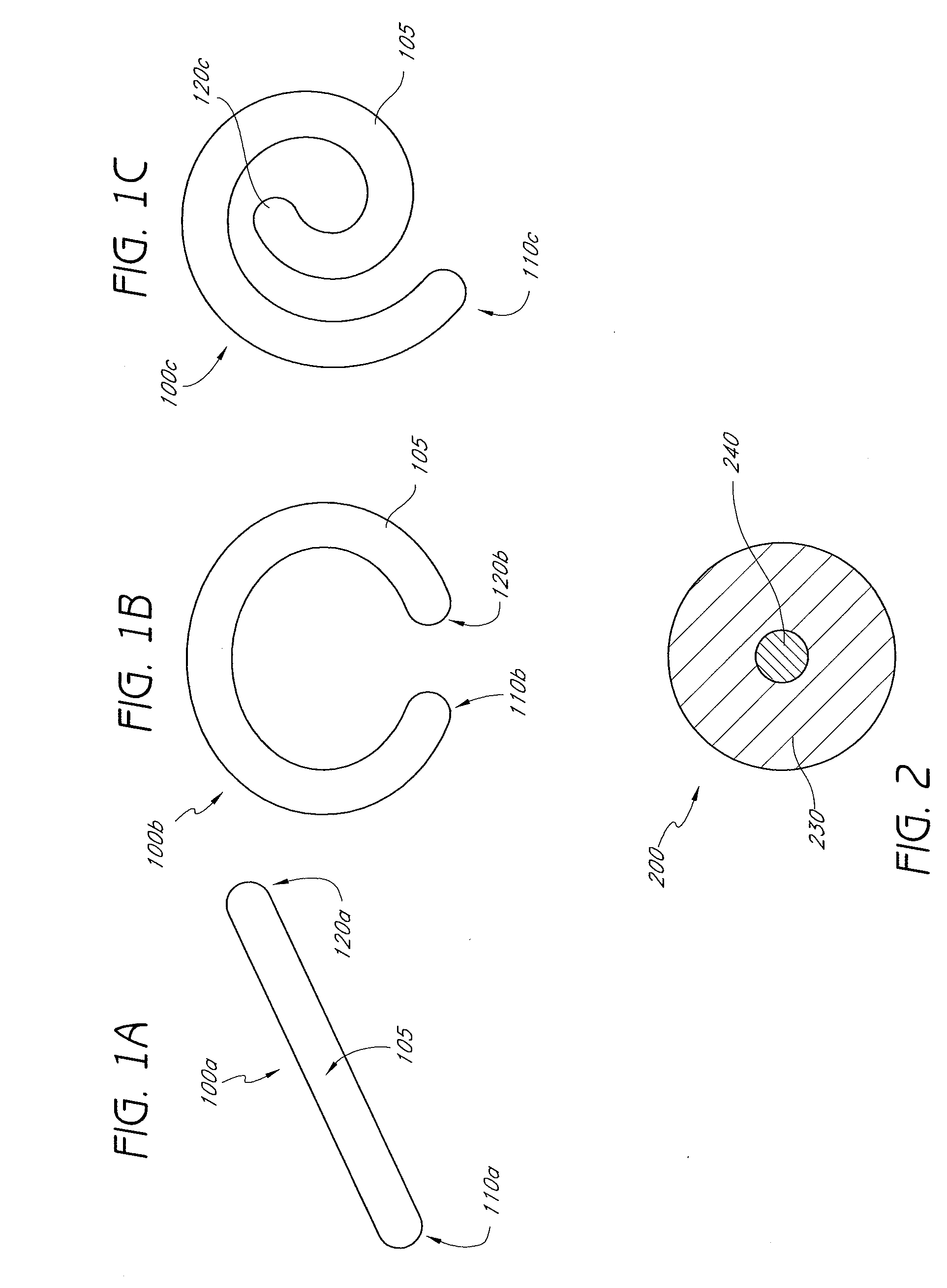
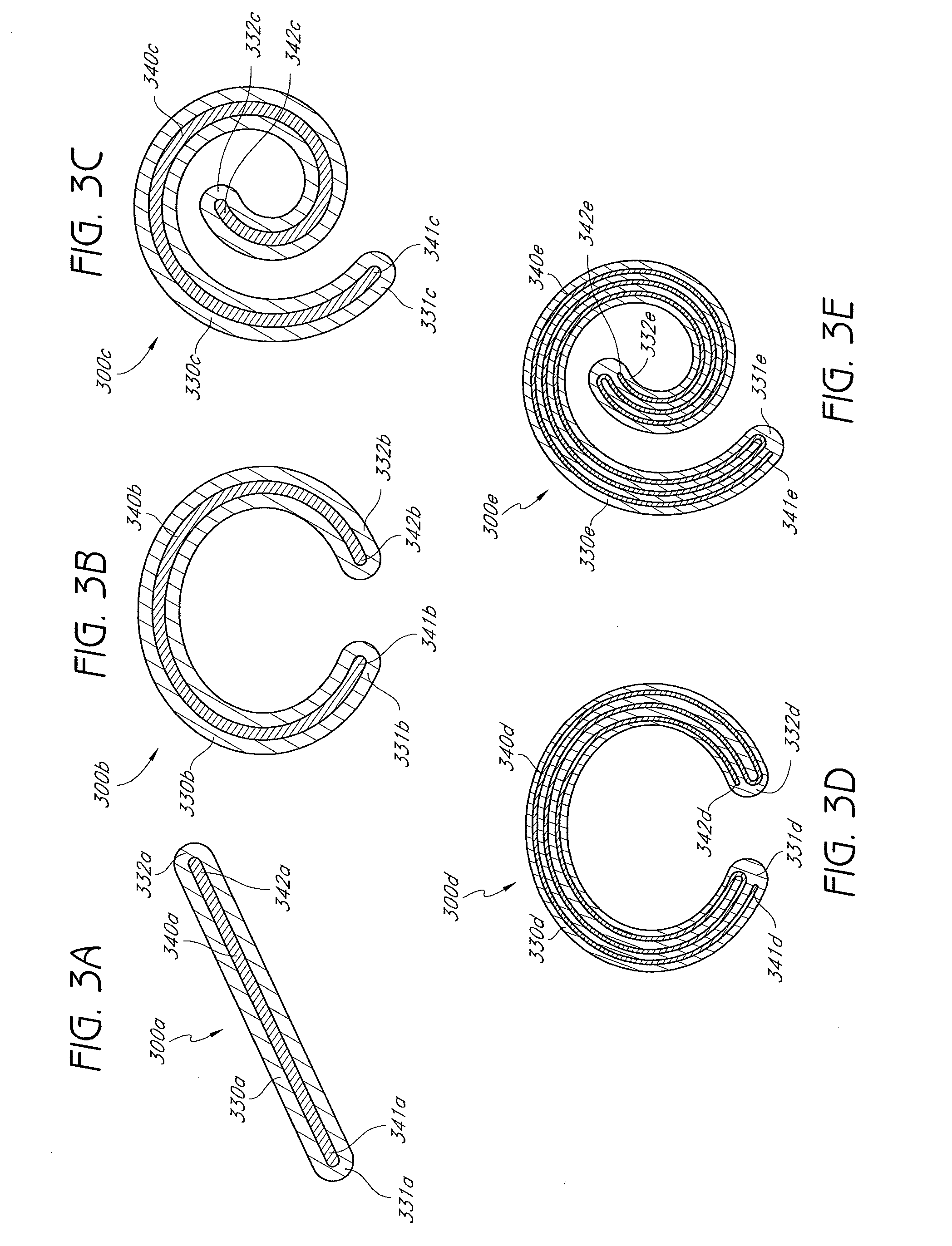
A percutaneously implantable orthopedic device is a shape-changing joint prosthesis with a generally arcuate or generally rectilinear configuration which is delivered through a delivery device in a substantially straightened or slightly curved configuration into a joint in a patient. The generally arcuate configuration may include an open ring or spiral shape. The generally rectilinear configuration may include a polygon or zig-zag shape. The delivery and retrieval device can be a syringe, hypodermic needle or cannula. The orthopedic device is moveable into its generally arcuate or generally rectilinear configuration in the joint by manipulation or a shape memory set. The orthopedic device acts as a soft compliant bearing surface or cushion that minimizes the bone-on-bone wear from articulation and loading.
Owner:ARTICULINX
Ice tip hypodermic needle
An ice tip is placed on the front end of a hypodermic needle to cool the flesh during insertion. The ice tip front end is sharp, for penetration, and the rear is provided with a recess, for reception of a hypodermic needle front end. The mold for forming the ice tip can be cooled by a cryogenic fluid being conducted into a main mold surrounding a tip forming heat conducting mold that is used to form the ice tip pointed front end and the recessed rear end.
Owner:RIGGS & SUN CO
Device for targeted, catheterized delivery of medications
InactiveUS6905486B2Reduce disadvantagesReduce problemsSurgical needlesMedical devicesHypodermoclysisHypodermic needle
Apparatus and method for catheterized delivery or infusion of medication and anaesthesia are disclosed. The perforating catheter is first used to perforate the periodontal ligament and / or the cortical plate of bone tissue, and is then left in place and used as a catheter for insertion of a hypodermic needle of smaller gauge to deliver medication or anaesthesia to a target area. The perforator is a bevelled needle for drilling into the ligament or bone tissue. For drilling, the device comprises an adaptor which transmits the rotational movement from a dental hand piece or the like to the bevelled needle. A cap is also included for protecting the bevelled needle during storage of the device. The adaptor may have a rod which extends axially into the bevelled needle when the device is assembled for drilling. The rod is used to prevent the debris resulting from drilling from blocking the passage in the bevelled needle. As well, the rod reinforces the needle and maintains the alignment between the perforator and the adaptor for improved drilling efficiency. An adapter is disclosed which couples with the catheter once in place easing access to supply medication to difficult to reach areas.
Owner:INTROSAN DENTAL PROD
Retractable hypodermic needle
InactiveUS7465294B1Inexpensive to buildEasy to useCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringHypodermoclysisHypodermic needle
A needle assembly includes a sheath into which a hypodermic needle is withdrawn in a protected position. Installation of the needle assembly onto a Luer lock causes the needle to be thrust forward out of the sheath. A spring urges the needle to the withdrawn position. An elastomeric ball in the needle assembly provides sealing.
Owner:VLADIMIRSKY ROMAN
Compositions and methods for enhanced mucosal delivery of peptide YY and methods for treating and preventing obesity
InactiveUS7166575B2Improved pharmacokineticImproved pharmacodynamic resultPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseHypodermoclysis
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods are described comprising at least one peptide YY compound and one or more intranasal delivery-enhancing agents for enhanced nasal mucosal delivery of the peptide YY, for treating a variety of diseases and conditions in mammalian subjects, including obesity. In one aspect, the intranasal delivery formulations and methods provide enhanced delivery of peptide YY to the blood plasma or central nervous system (CNS) tissue or fluid, for example, by yielding a peak concentration (Cmax) of the peptide YY in the blood plasma or CNS tissue or fluid of the subject that is 20% or greater compared to a peak concentration of the peptide YY in the blood plasma or CNS tissue or fluid of the subject following administration to the subject of a same concentration or dose of the peptide YY to the subject by subcutaneous injection.
Owner:MDRNA
Intravenous catheter device
A catheter device is disclosed which the hypodermic needle used for insertion is retracted into a protective sheath and left in place during use. An IV fluid flow path is provided that is blocked by the hypodermic needle prior to retraction but is opened by the retraction of the needle from the catheter. The insertion hypodermic needle is not discarded separately but only after the use of the whole catheter device to inject fluids.
Owner:SMITH P ROWAN
Vial assembly and method for reducing nosocomial infections
Vacuum break vial assembly and method for reducing the incidence of nosocomial infections, comprising a vial stopper having a 2-part withdrawn-fluid volume compensation assembly having a barbed vent element that secures an apertured needle sheath, a bladder-retainer tube and an expandable / unfoldable bladder. The vial has an aluminum cap holding a plastic flip-off top that removes a central portion of the cap to permit access by hypodermic needle through the stopper into the needle sheath. No pre-pressurization of the vial by ambient contaminated air via the hypodermic can occur. Rather, the needle is inserted in the vial through the stopper and the medicinal fluid withdrawn. Air is inlet into the separate bladder which expands to permit withdrawal of fluid into the hypodermic without vacuum lock. No air having pathogen vectors is introduced into the vial medicinal fluid as the bladder isolates volume-compensating air from the medicinal fluid. Plural embodiments are shown.
Owner:YANDELL MARION E
Hypodermic injection system
InactiveUS7235063B2Sufficient forceEliminate the problemAmpoule syringesJet injection syringesMultiple injectionHypodermoclysis
A hypodermic injection system particularly for use in mass immunizations having a handpiece with a grasping mechanism for holding ampules filled with injectate, a plunger for driving into the ampule to discharge the injectate in an injection process, an injection spring mechanism for driving the plunger, a motor and / or manual mechanism for cocking the injection spring mechanism, and an ampule ejection mechanism for ejecting ampules after use under control of a release mechanism. Ampules can be loaded, used and ejected without contact by the user of the system or the patient being injected. Also disclosed are a filling station for filling ampules through their injection orifices, and an arming device for setting the injection spring. Ampules are disclosed having a piston which is drivable towards an orifice to discharge injectate through the orifice. Ampules are also disclosed having enlarged proximal portions for easy grasping by the grasping mechanism of the injector. Ampules are further disclosed with separators for mixing lyophilized medication and a diluent. Further disclosed are magazines for holding ampules for sequential use by the hypodermic injector. The disclosed system finds particular use as a mass immunization kit for making numerous injections in the field.
Owner:DANTONIO CONSULTANTS INT INC
Medicament administration apparatus
InactiveUS20080287914A1Cost-effectiveSimple designPharmaceutical containersMedical devicesMedication injectionHypodermoclysis
An apparatus for removal of premixed drugs or reconstitution of lyophilized drugs and for the injection of the reconstituted drug into the patient. The apparatus includes a syringe assembly and an adapter assembly that can be removably connected to a medicament container containing a premixed drug or lyophilized medicament. The syringe assembly of the apparatus includes a body portion to form a liquid chamber between the forward end of the body portion and the piston and a syringe cannula assembly. The syringe cannula assembly, which can be removably interconnected with the body portion, comprises a cannula support and a hypodermic needle sealably connected to the cannula support. The adapter assembly comprises an adapter preferably molded from a moldable plastic that includes a top wall, an adapter cannula connected to and extending from the top wall and a variety of connectors connected to the top wall for removably interconnecting the adapter with the medicament container. The adapter assembly further includes syringe connector member connected to the top wall for removably interconnecting the syringe with the adapter in a manner to uniquely position the syringe cannula within the lumen of the adapter cannula wherein it is completely shielded from external contamination to prevent print damage and injury to the user.
Owner:MEDICAL ASSOCS NETWORK
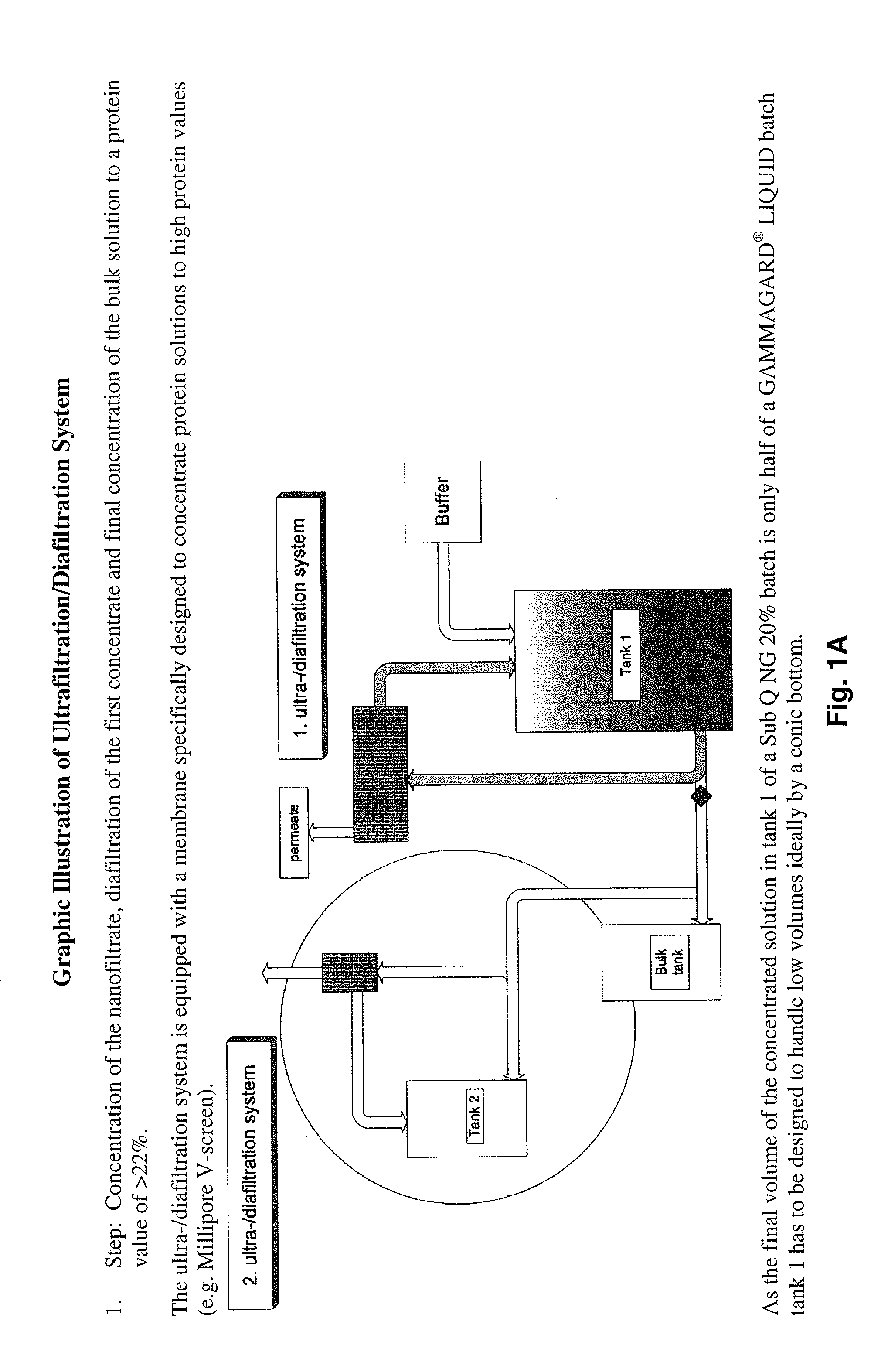
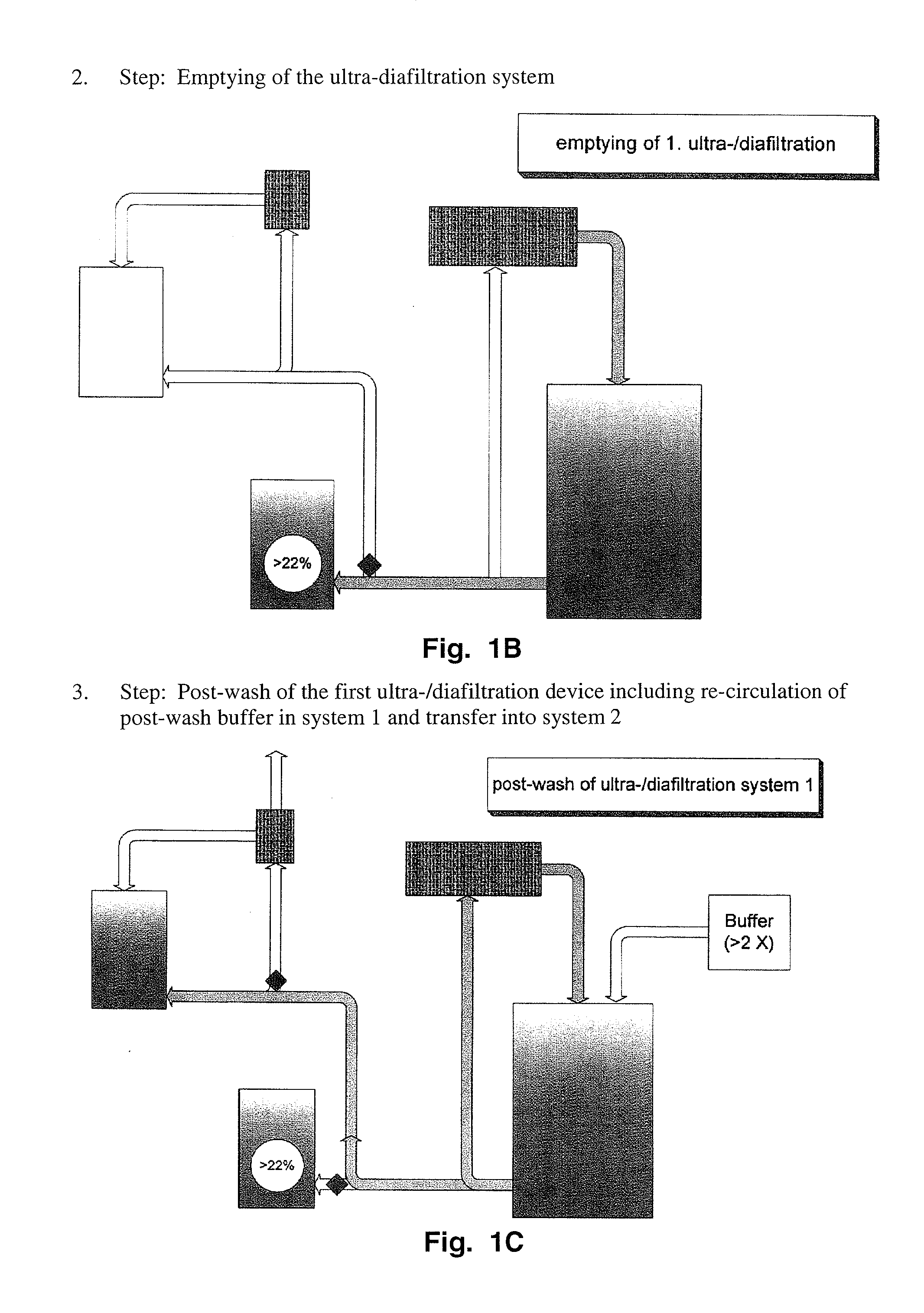
Method to produce a highly concentrated immunoglobulin preparation for subcutaneous use
The present invention relates to a new and improved method for preparing a highly concentrated immunoglobulin composition from pooled plasma for subcutaneous injection. A composition comprising 20% or more immunoglobulin suitable for subcutaneous use is also described.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Vial assembly and method for reducing nosocomial infections
InactiveUS7789871B1Eliminate pollutionAvoid piercingClosuresDiagnosticsHypodermic needleHypodermoclysis
Vacuum break vial assembly and method for reducing the incidence of nosocomial infections, comprising a vial stopper having a 2-part withdrawn-fluid volume compensation assembly having a barbed vent element that secures an apertured needle sheath, a bladder-retainer tube and an expandable / unfoldable bladder. The vial has an aluminum cap holding a plastic flip-off top that removes a central portion of the cap to permit access by hypodermic needle through the stopper into the needle sheath. No pre-pressurization of the vial by ambient contaminated air via the hypodermic can occur. Rather, the needle is inserted in the vial through the stopper and the medicinal fluid withdrawn. Air is inlet into the separate bladder which expands to permit withdrawal of fluid into the hypodermic without vacuum lock. No air having pathogen vectors is introduced into the vial medicinal fluid as the bladder isolates volume-compensating air from the medicinal fluid. Plural embodiments are shown.
Owner:YANDELL MARION E
Non-volatile lubricant system for medical devices
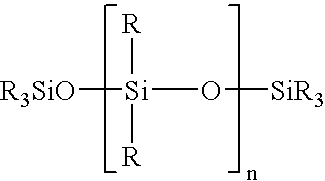
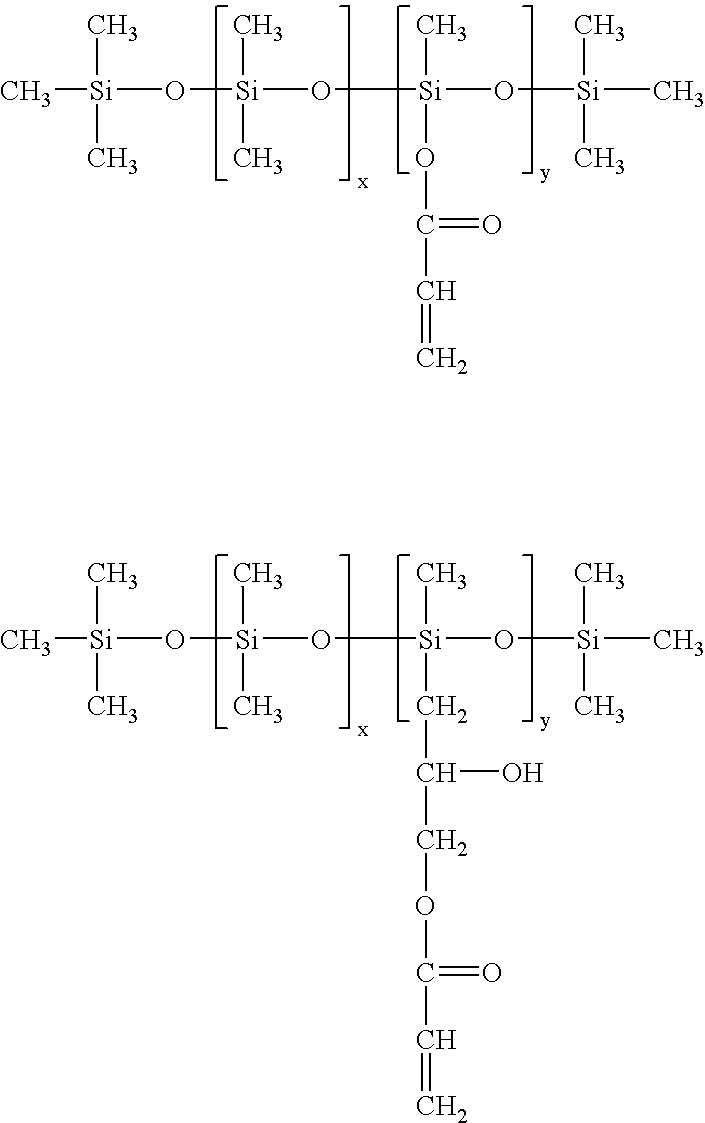
ActiveUS7332227B2Low viscosityEfficient deliverySilicon organic compoundsLayered productsPolymer chemistryMedical treatment
A non-volatile lubricious coating composition is provided for use with medical devices, such as hypodermic needles, catheters, and the like. The coating composition includes a first siloxane polymer having a very low viscosity less than about 50 centistokes, a second siloxane polymer having a high viscosity greater than about 1,000 centistokes, a reactive silicone polymer which is capable of crosslinking upon exposure to radiation, such as a UV curable silicone acrylate, and a photoinitiator to accelerate cross-linking of the reactive silicone polymer. The coating composition may further include an aminofunctional siloxane polymer to promote adhesion to metal surfaces when used with needles. The coating composition provides flowability without the need for any volatile organic solvent, and is capable of curing to provide adhesion and lubricity.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Magnesium Compositions for Modulating the Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Insulin and Insulin Analogs, and Injection Site Pain
ActiveUS20140113856A1Improved injection site tolerabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderEthylenediamineMagnesium salt
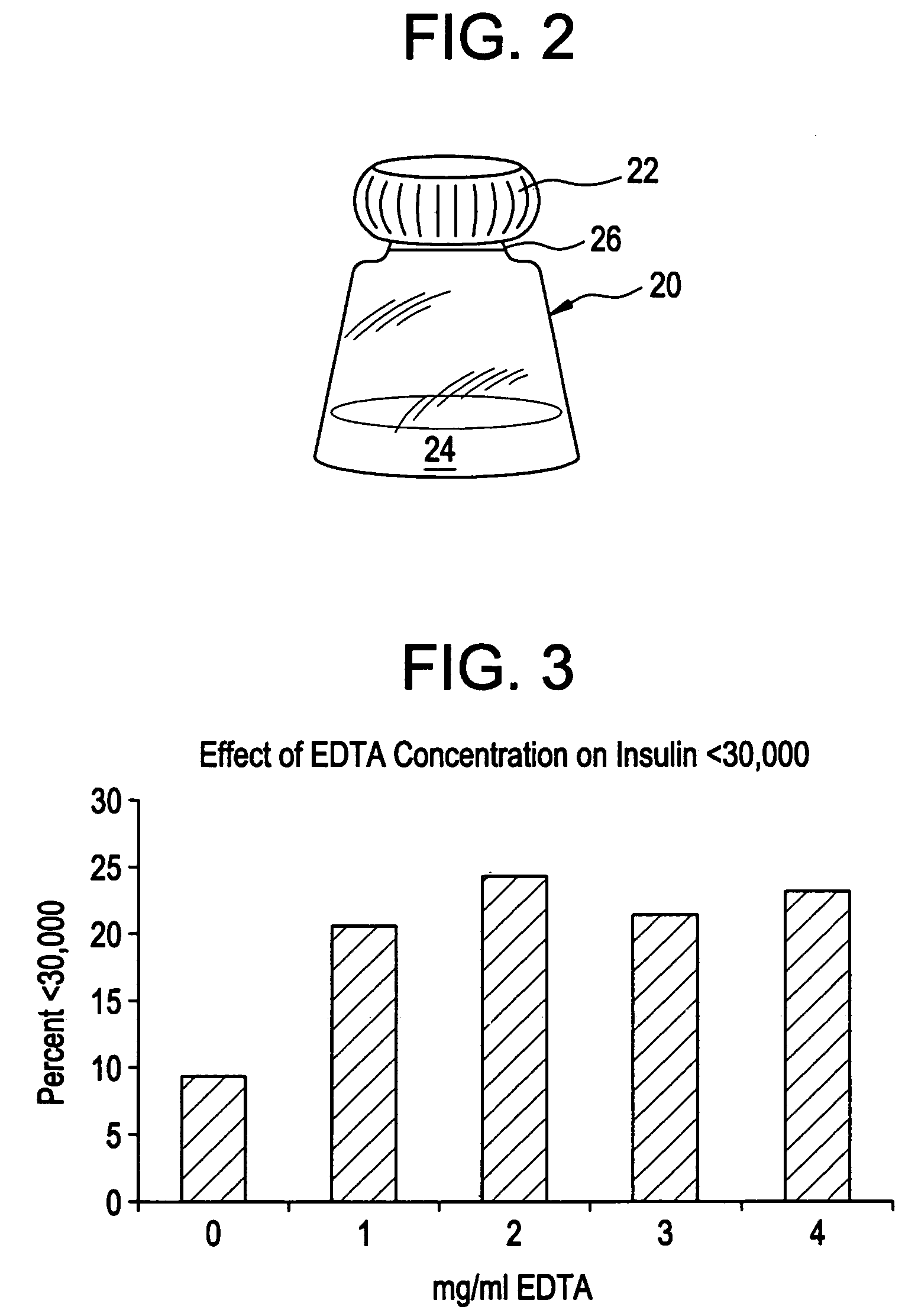
Compositions and methods for modulating injection site pain associated with rapid acting injectable insulin formulations have been developed for subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin in combination with a zinc chelator such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (“EDTA”), a dissolution / stabilization agent such as citric acid, a magnesium salt, and, optionally, additional excipients. New presentations include rapid acting concentrated insulin formulations and a way to enhance the absorption of commercially available rapid acting analog formulations by mixing them with a vial containing dry powder excipients that accelerate their absorption. Devices for mixing excipient and insulin together at the time of administration, while minimizing residence time of the mixture, are also described.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Safety needle introducer and universal needle protector for vascular access devices
InactiveUS7914488B2Avoid relative motionConveniently madeGuide needlesInfusion needlesHypodermoclysisIntravenous needles
A needle point protective device for hypodermic and intravenous needles, catheter introducers, and similar devices protects users from injury and infection. The needle point protective device includes a needle point guard that is slidably mounted within the needle handle. In use, the needle point guard is integral with a cannula guide that is engaged with the needle cannula with enough force to cause the needle cannula to be subject to spring tension when the needle point is retracted proximal to the needle point guard, the needle point springs downward and behind the needle point guard. In one embodiment, the needle point guard is held in position manually as the needle is retracted. In another embodiment, the needle point guard is held in place automatically as the needle is retracted.
Owner:C DICKERSON
Hypodermic drug delivery reservoir and apparatus
ActiveUS8684968B2Seals be limitedAvoid connectionJet injection syringesMicroneedlesHypodermoclysisMedicine
Owner:AKTIVAX INC
Fluid delivery and extraction device and method
A fluid delivery and extraction device enables the remote transfer of fluid to or from biological tissue. The device comprises an elongated member, a syringe movable relative to the elongated member and a pair of hypodermic needles movable relative to the elongated member. The elongated member has a distal portion which is adapted to be inserted into a biological structure. A steer wire or guide wire can be used to navigate the distal portion within cavernous biological structures, particularly body lumens. The distal portion has at least one retractable hypodermic needle that is configured to pierce the interior surface of a tubular biological structure and transfer fluid to or from the walls of the tubular biological structure. A physician can use a handle or other control mechanism provided at a proximal portion of the device to remotely move the hypodermic needles. A plunger can be used to transfer fluid through the hypodermic needles to or from the syringe. In operation, the hypodermic needles are deployed simultaneously or individually from the distal portion of the device. As the hypodermic needles move, they pierce the interior surface of the tubular biological structure. The hypodermic needles can also be configured to pass beyond the exterior surface of the tubular biological structure. The plunger is then used to transfer fluid either from the syringe to the patient or from the patient to the syringe. The hypodermic needles are then moved back to their retracted positions within the distal portion, and the device is withdrawn from the patient's body.
Owner:SUTURA
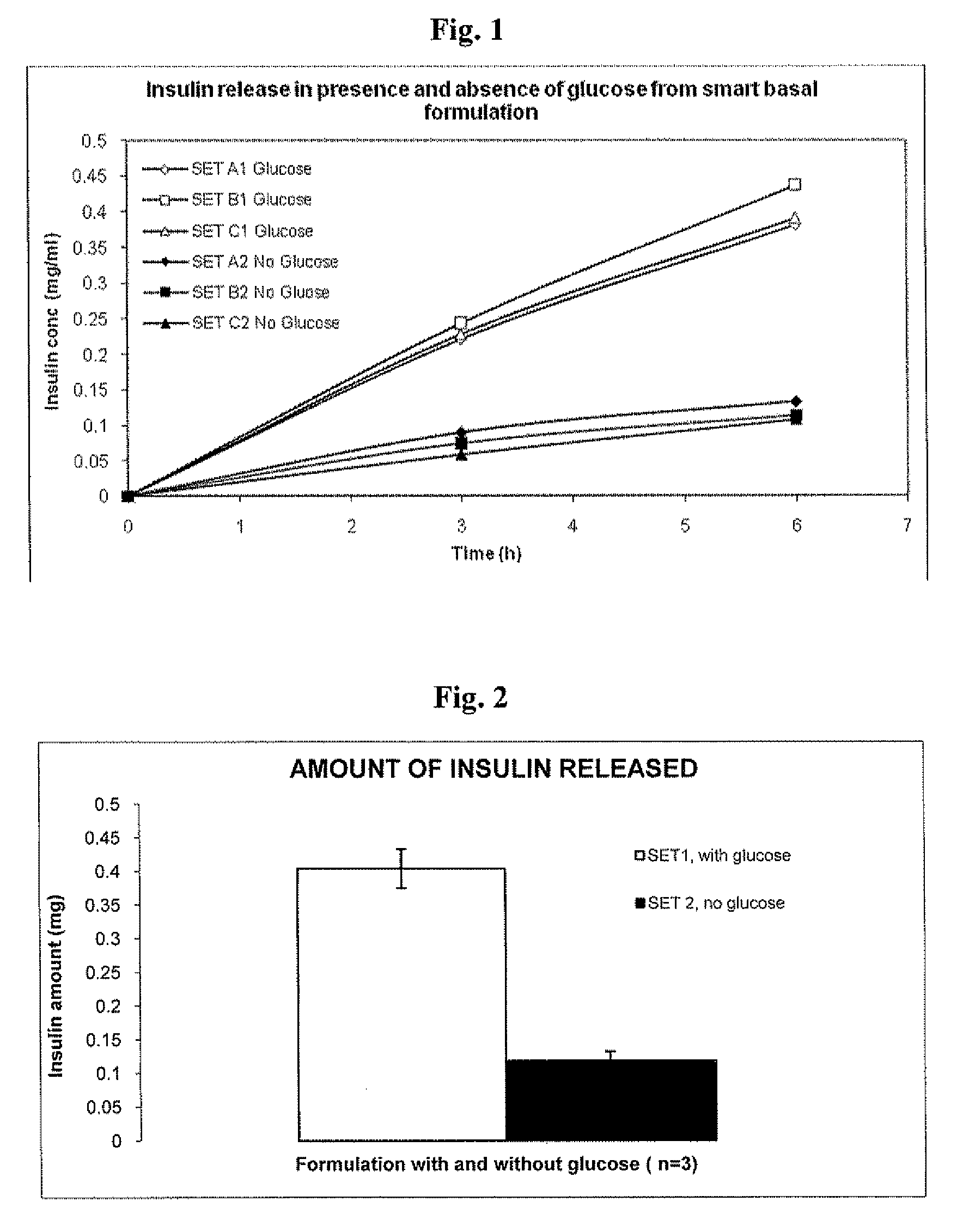
Insulin formulations for insulin release as a function of tissue glucose levels
InactiveUS20090175840A1Reduce productionRaise the pHPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInjections insulinReducing agent
Injectable insulin formulations that are capable of modifying the amount of insulin released based on the patient's tissue glucose levels, methods for making and using these formulations are described herein. The formulation may be administered via subcutaneous, intradermal or intramuscular administration. In one preferred embodiment, the formulations are administered via subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain insulin, an oxidizing agent or enzyme and a reducing agent or enzyme, a diluent and optionally one or more thickening agents. If a thickening agent is present in the formulation, the thickening agent increases the viscosity of the formulation following administration. Preferably the formulation contains an insulin, a diluent, glucose oxidase and peroxidase. Following administration to a patient, the insulin is released from the formulations as a function of the patient's tissue glucose level, which in turn maintains the patient's blood glucose level within an optimum range. The formulation is often referred to as a “smart” formulation since it modifies its release rate of insulin according to the patient's needs at a particular time. In a preferred embodiment, the formulation is designed to release insulin into the systemic circulation over time with a basal release profile following injection in a patient. In another embodiment, the formulation is designed to release insulin into the systemic circulation over time with a non-basal release profile following injection in a patient, such as a regular human insulin release profile or a prandial release profile.
Owner:BIODEL
Blood exposure prevention in vascular access devices
ActiveUS20080243086A1Reduce blood exposureReduce exposureCatheterInfusion needlesHypodermoclysisHypodermic needle
An apparatus for preventing blood exposure or contamination upon withdrawal of a hypodermic needle is provided. The apparatus may include a needle having a tip and a shield configured to at least partially entrap the needle tip upon withdrawal of the needle. The apparatus may further include a blood stabilizing material disposed such that upon withdrawal of the needle the blood stabilizing material is disposed in operative association with the needle tip such that blood carried by the needle is prevented from escaping the apparatus. In some exemplary implementations, the blood stabilizing material may be disposed on one or more surfaces of the shield. The shield of the hypodermic needle may include protective device and / or a housing for shielding the needle tip upon withdrawal. The housing may be adapted to at least partially cover the needle tip upon withdrawal of the needle. In some implementations, the housing may be adapted to allow the protective device to shield the needle before the needle is completely withdrawn.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
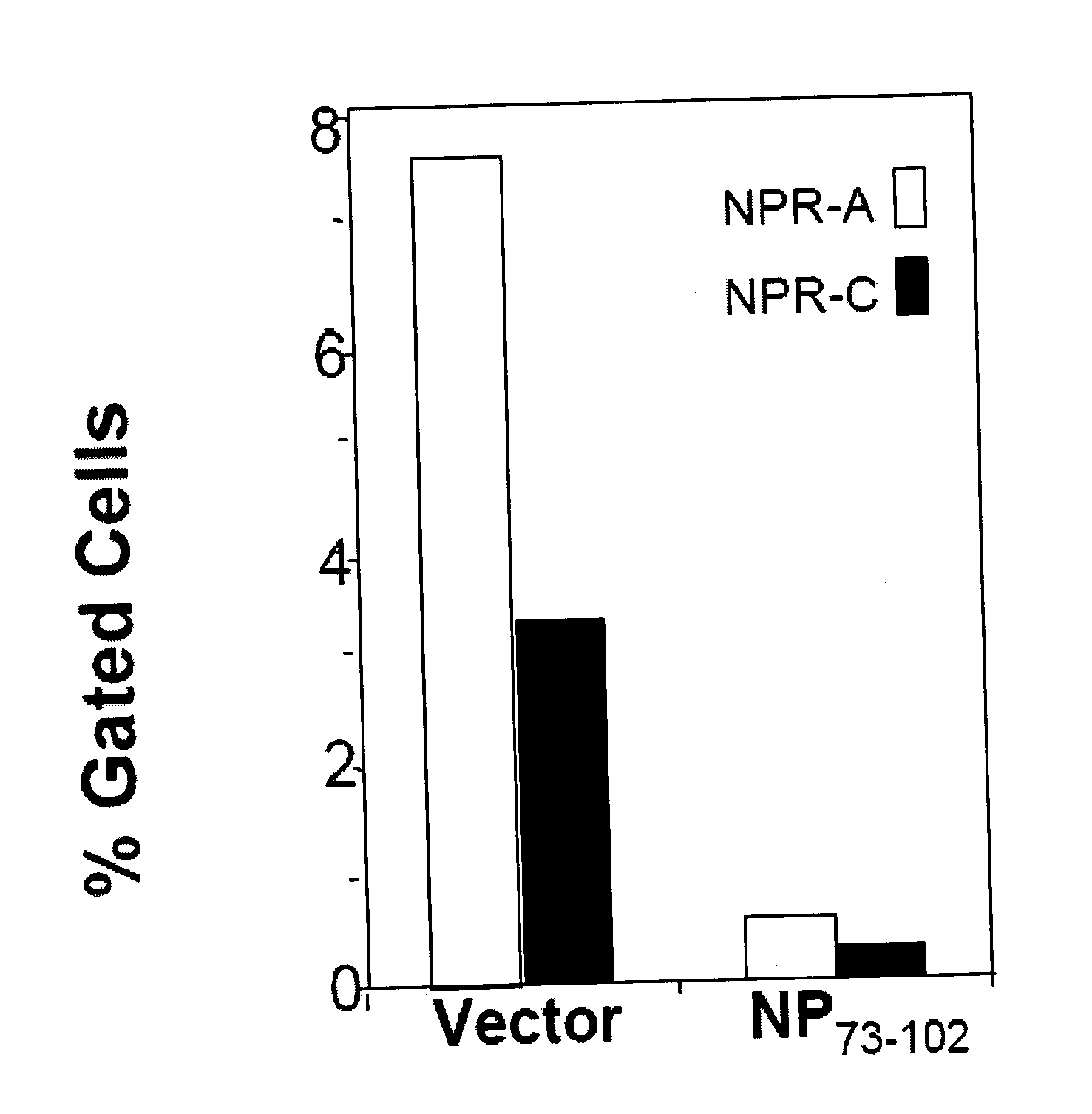
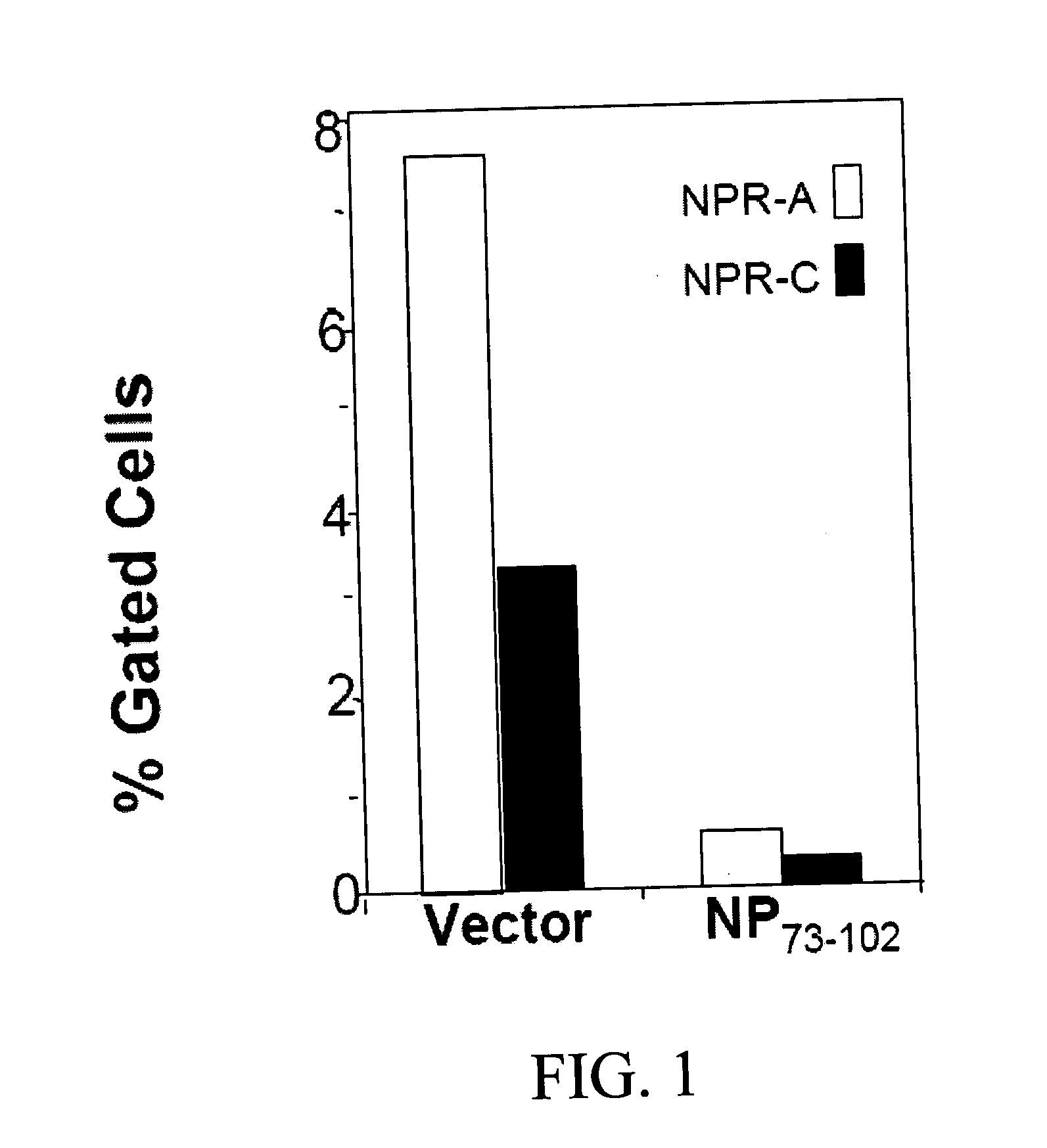
Methods and compositions for reducing activity of the atrial natriuretic peptide receptor and for treatment of diseases
InactiveUS20080214437A1Reduction in formation of tumorIncreased apoptosisCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationDisease
Methods, compositions and devices are provided by the present invention for reducing activity of a natriuretic peptide receptor and other signals. Therapeutic treatments are provided by use of polynucleotides encoding a natriuretic peptide or by regulating the expression of natriuretic peptide receptor, such as NPRA and NPRC, or combinations of these therapies. Routes used for delivering polynucleotides encoding a natriuretic peptide, or, for example, siRNA that down regulates natriuretic peptide receptor include subcutaneous injection, oral gavage, transdermal and intranasal delivery routes. Compositions can include chitosan, chitosan derivatives, and chitosan derivative and a lipid. Transdermal delivery can use a transdermal cream. Intranasal delivery can use a dropper or an aspirator for delivery of a mist. Oral gavage delivers equivalent to oral delivery. Delivery permits cell and tissue specific targeting of gene therapies resulting in expression of a natriuretic peptide or down regulation of natriuretic peptide receptor. A variety of cancers, asthma and viral diseases can be treated therapeutically using the methods and compositions of the present invention.
Owner:MOHAPATRA SHYAM S +4
Intravenous catheter device
A catheter appliance having a catheter in fluid communication with a luer connector is releasably secured to a catheter applicator having a track for slidably mounting a needle carrier module. The needle carrier module includes a hypodermic which extends through the catheter for insertion and which is in fluid communication with a flashback indicator on the module. The catheter applicator includes a needle cavity for containing the hypodermic needle after use.
Owner:SMITH JR P ROWAN
Nanocomposite temperature-sensitive gel and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102525882AEasy to prepareSuitable for mass productionGenetic material ingredientsEmulsion deliveryHypodermic injectionLung cancer
The invention relates to a nanocomposite temperature-sensitive gel and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: coating antitumor active substances with a high molecular polymer serving as a carrier material to obtain nanoparticles; and adding a temperature-sensitive high molecular material to obtain the nanocomposite temperature-sensitive gel. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient, is suitable for large-scale production, and is particularly suitable for preparing medicaments or diagnostic reagents having the characteristics of long cycle, biodegradability, slow release, passive targeting, active targeting, active substance conveying function and tumor resistance. An antitumor medicament prepared with the method disclosed by the invention is suitable for ways such as intravenous injection, intramuscular injection, hypodermic injection, intradermal injection, intratumor injection, tumor-side injection, oral administration or transdermal medicament delivery and the like, is applied to treatment and diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, lung cancer, gastric cancer, colorectal cancer, esophageal cancer, prostatic cancer, uterine cancer and ovarian cancer, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Oral cavity liquid delivery system including pre-angled needle assembly and method for using the same
A delivery system for dispensing sterile liquids into the oral cavity using a novel pre-angled needle hub assembly attached to a standard anesthetic syringe loaded with a novel cartridge ampule containing a certain liquid solution. This system substantially improves the efficiency of delivering small amounts of sterile fluid into the oral cavity by hypodermic means or by irrigation means using pre-angled needles or cannulas to reach otherwise impossible-to-reach locations within the oral cavity while also providing the ability to dispose of used needles without re-bending and thus complying with federal OSHA, state OSHA, and state regulatory disposal regulations.
Owner:SPECTOR DAVID M
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com