Patents
Literature
3364 results about "Bone tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
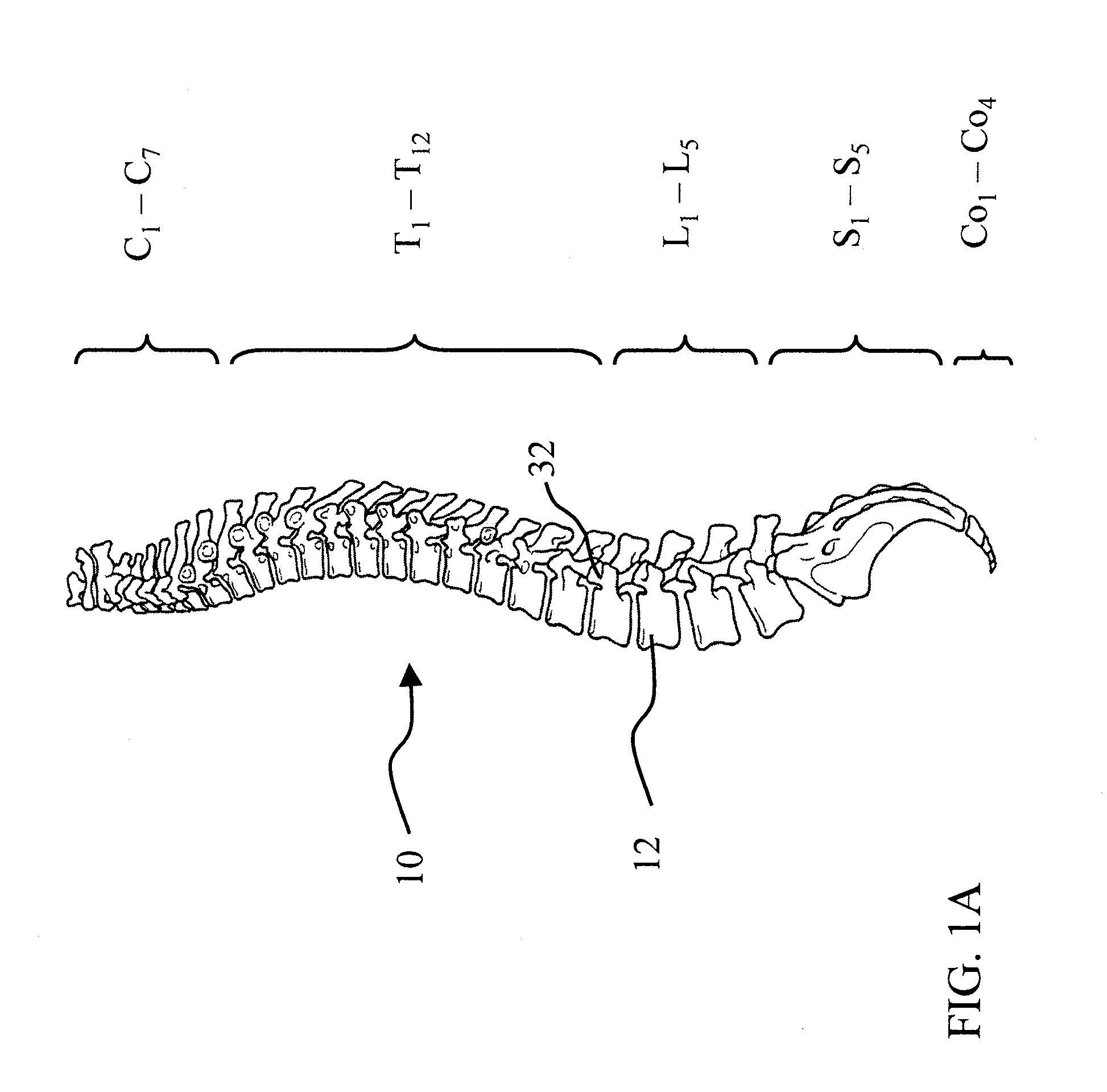
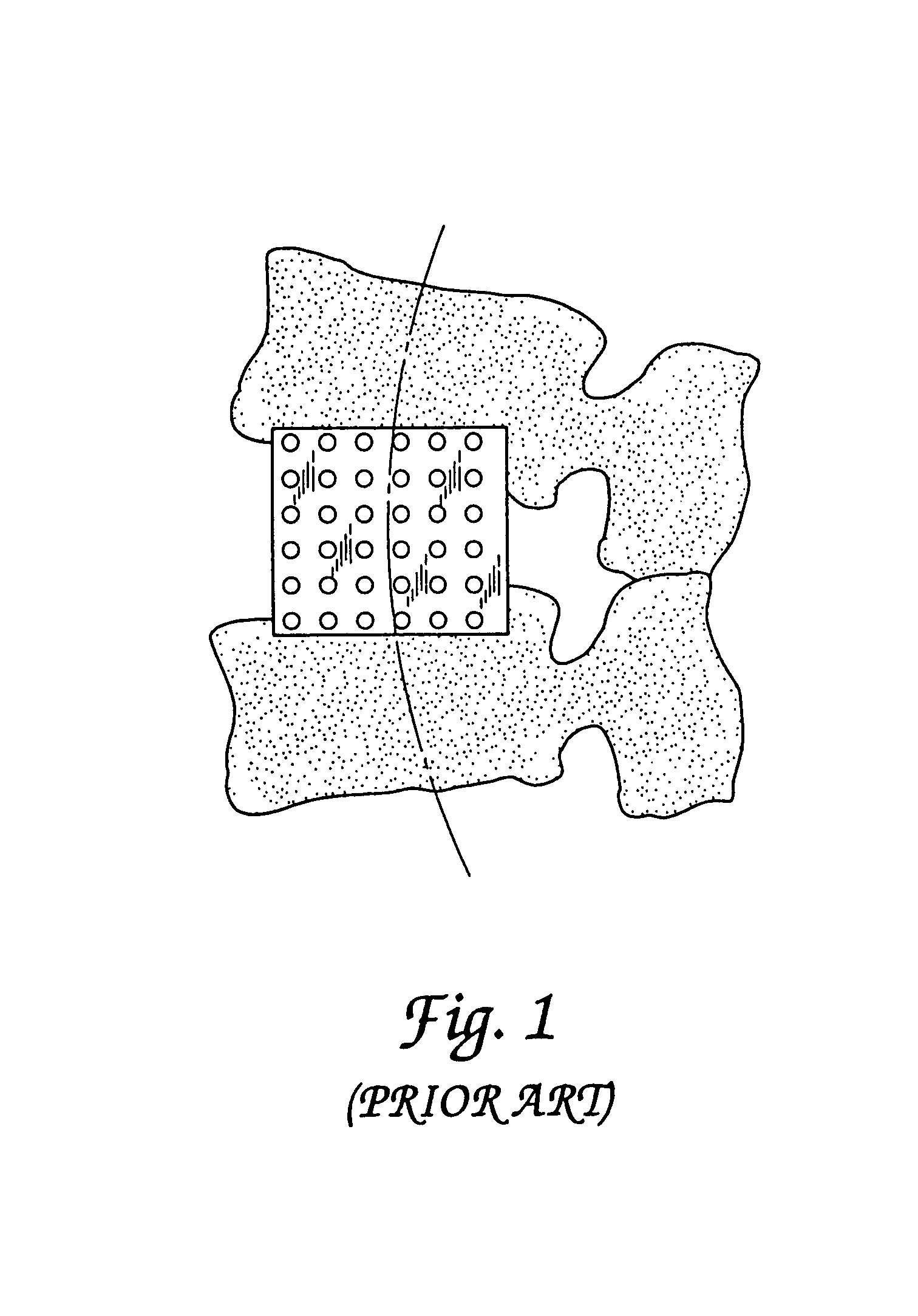
Osseous tissue, or bone tissue, is the major structural and supportive connective tissue of the body. Osseous tissue forms the rigid part of the bones that make up the skeletal system. Bone tissue is different from bones themselves — bones are organs made up of bone tissue as well as marrow, blood vessels, epithelium and nerves, while bone tissue refers specifically to the mineral matrix that form the rigid sections of the organ.
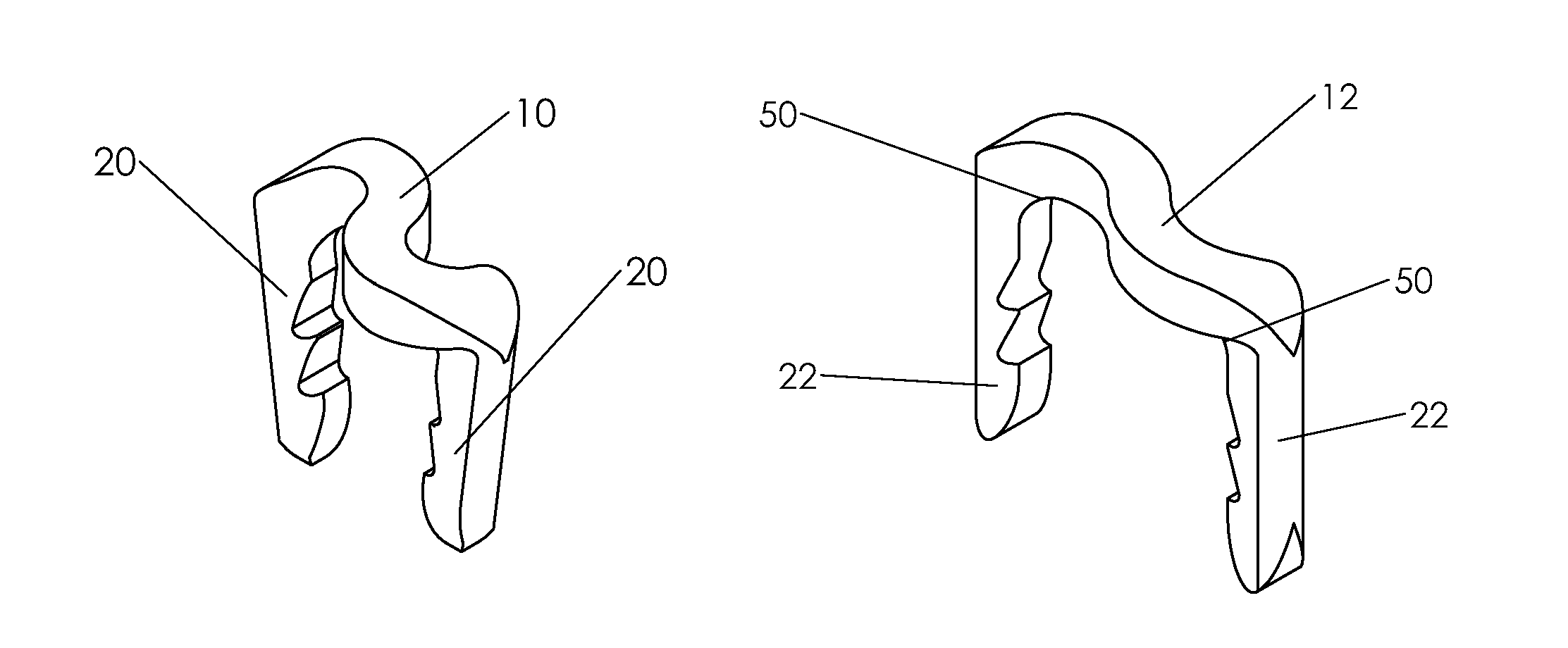
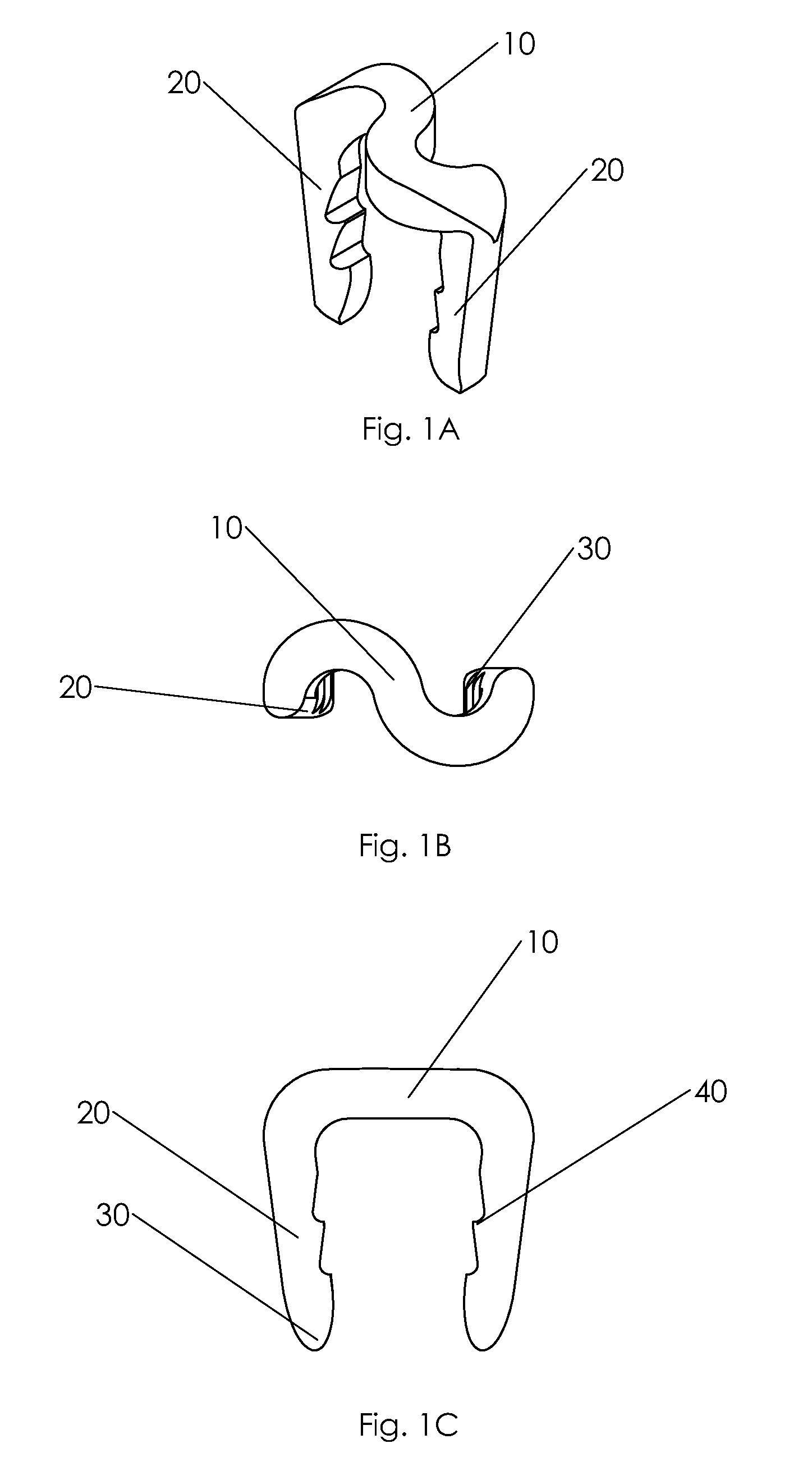
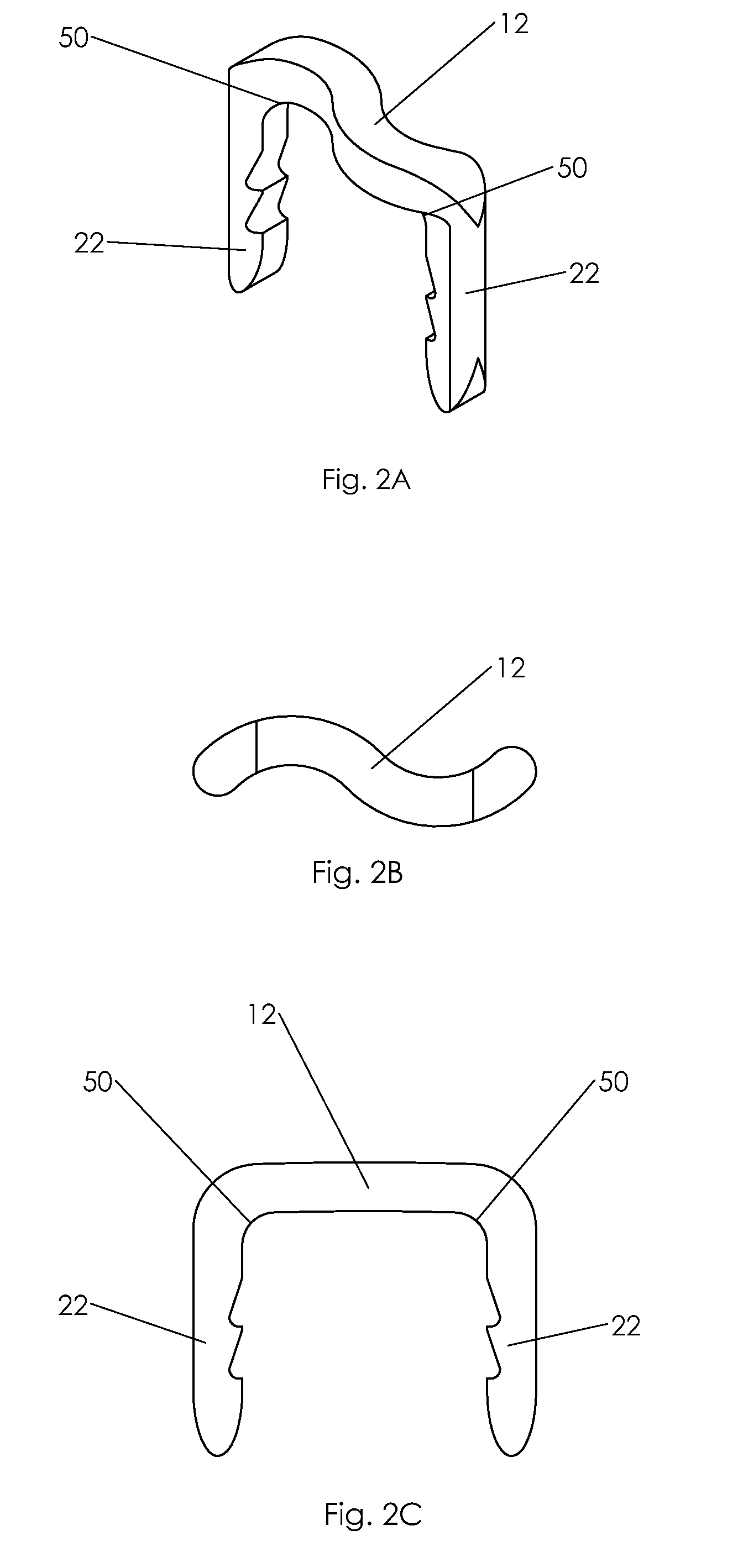
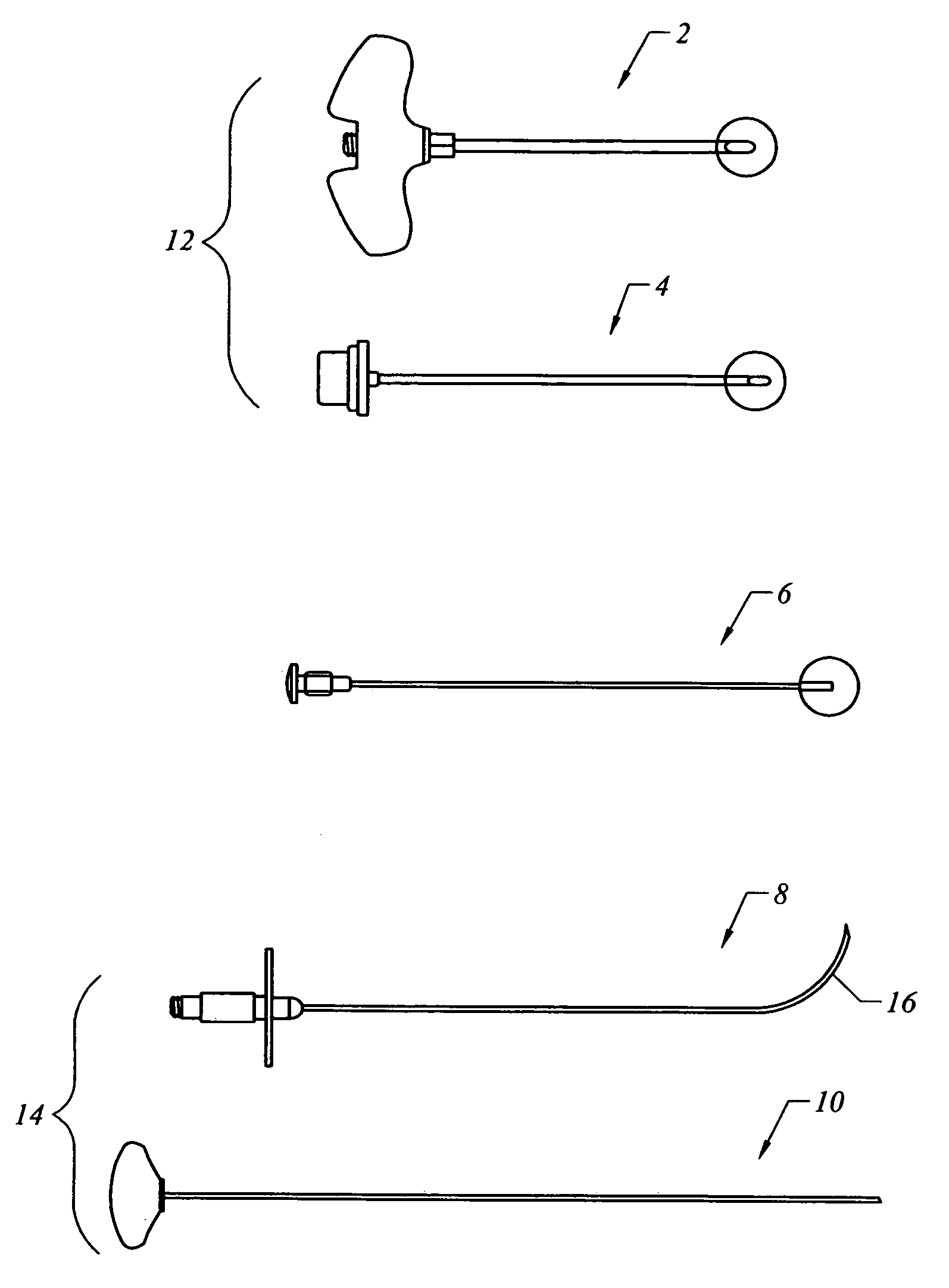
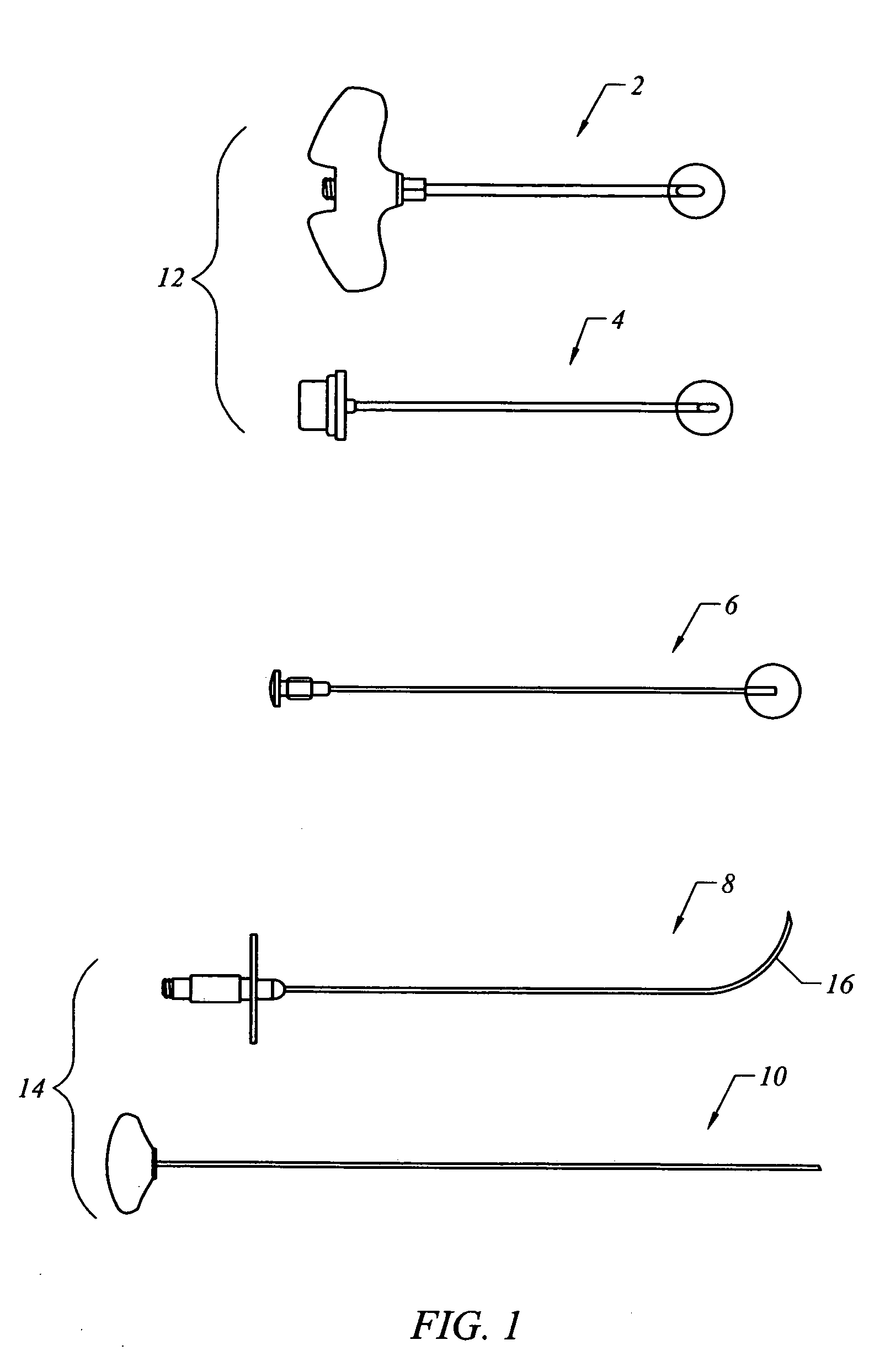
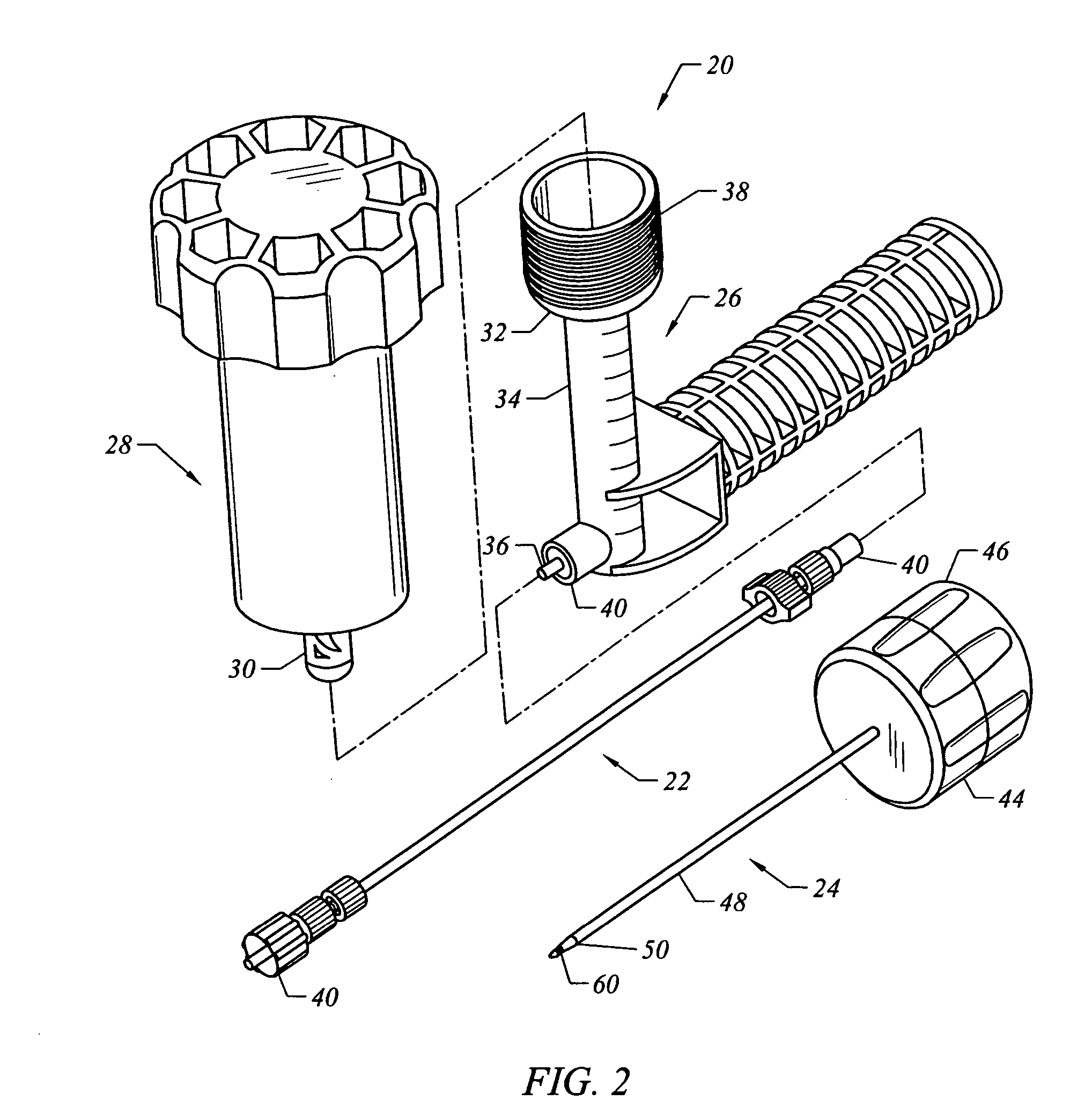
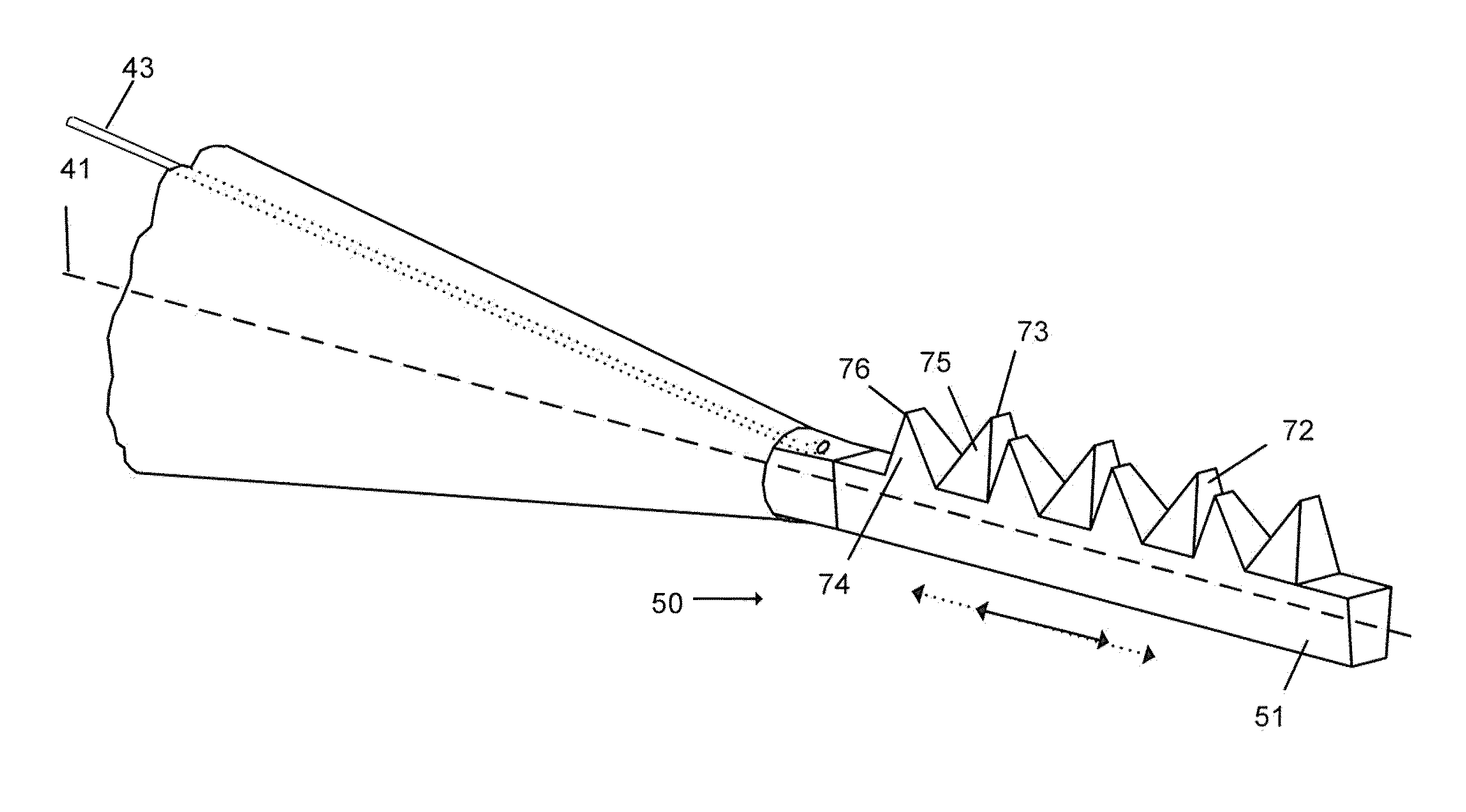
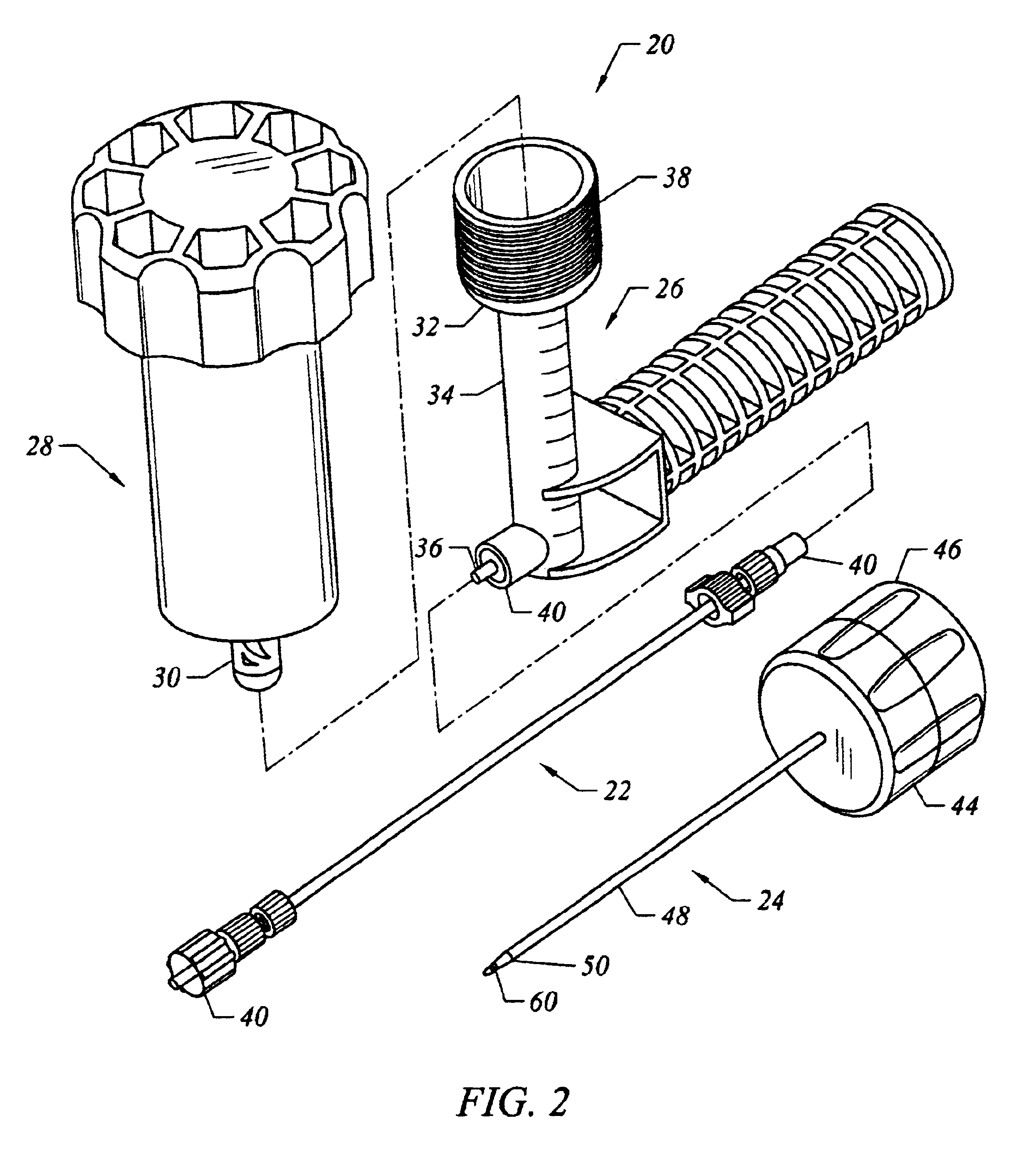
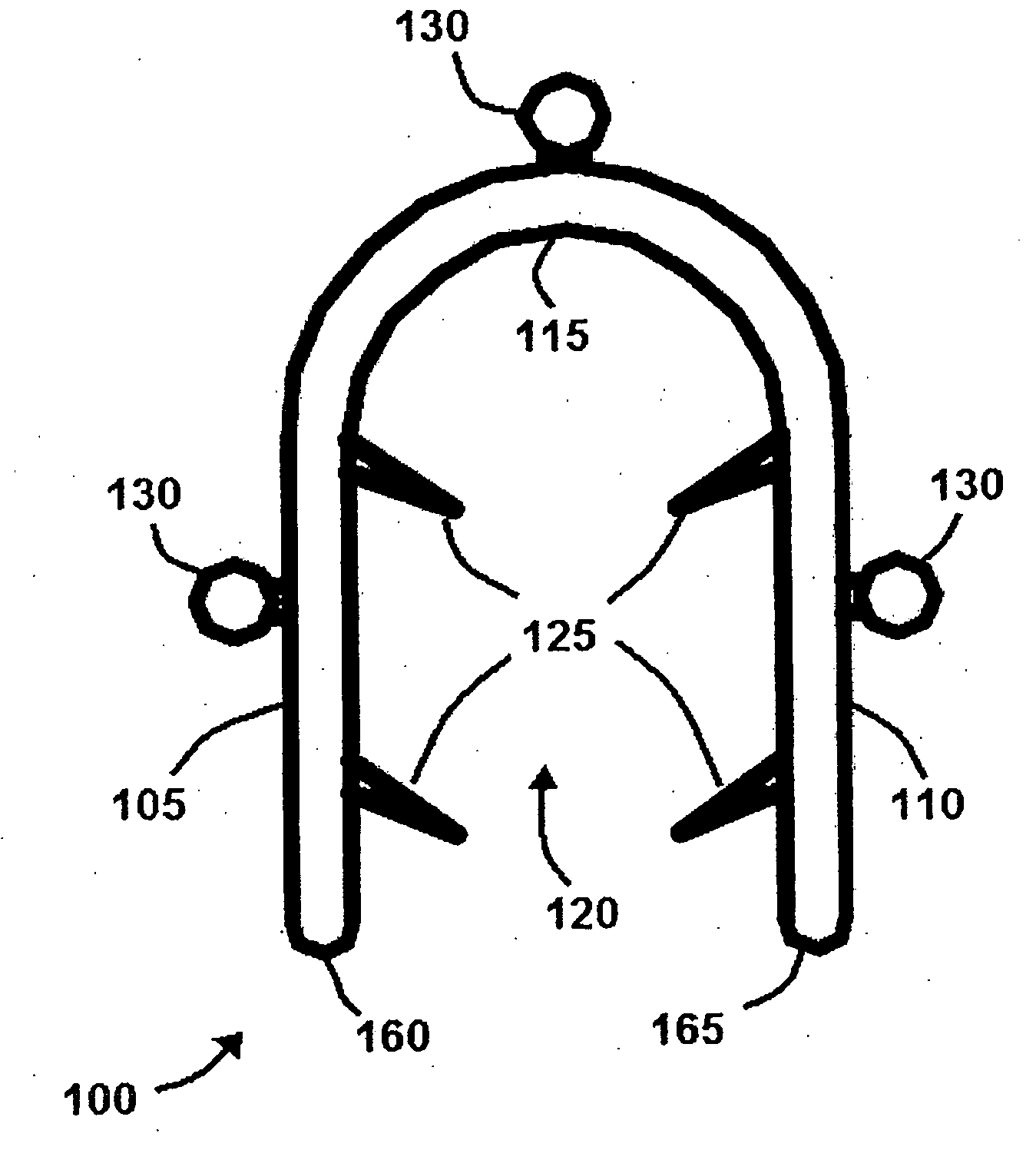
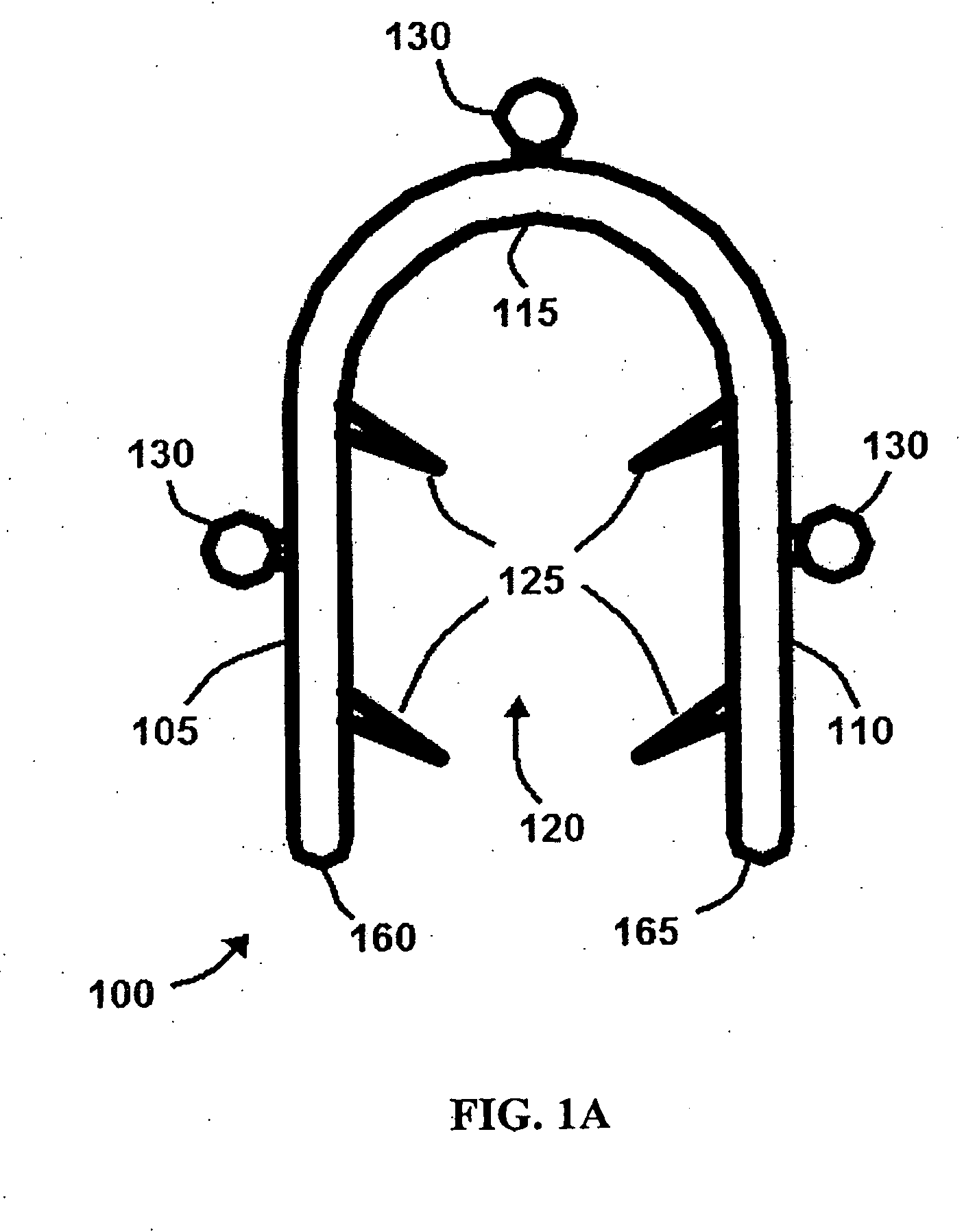
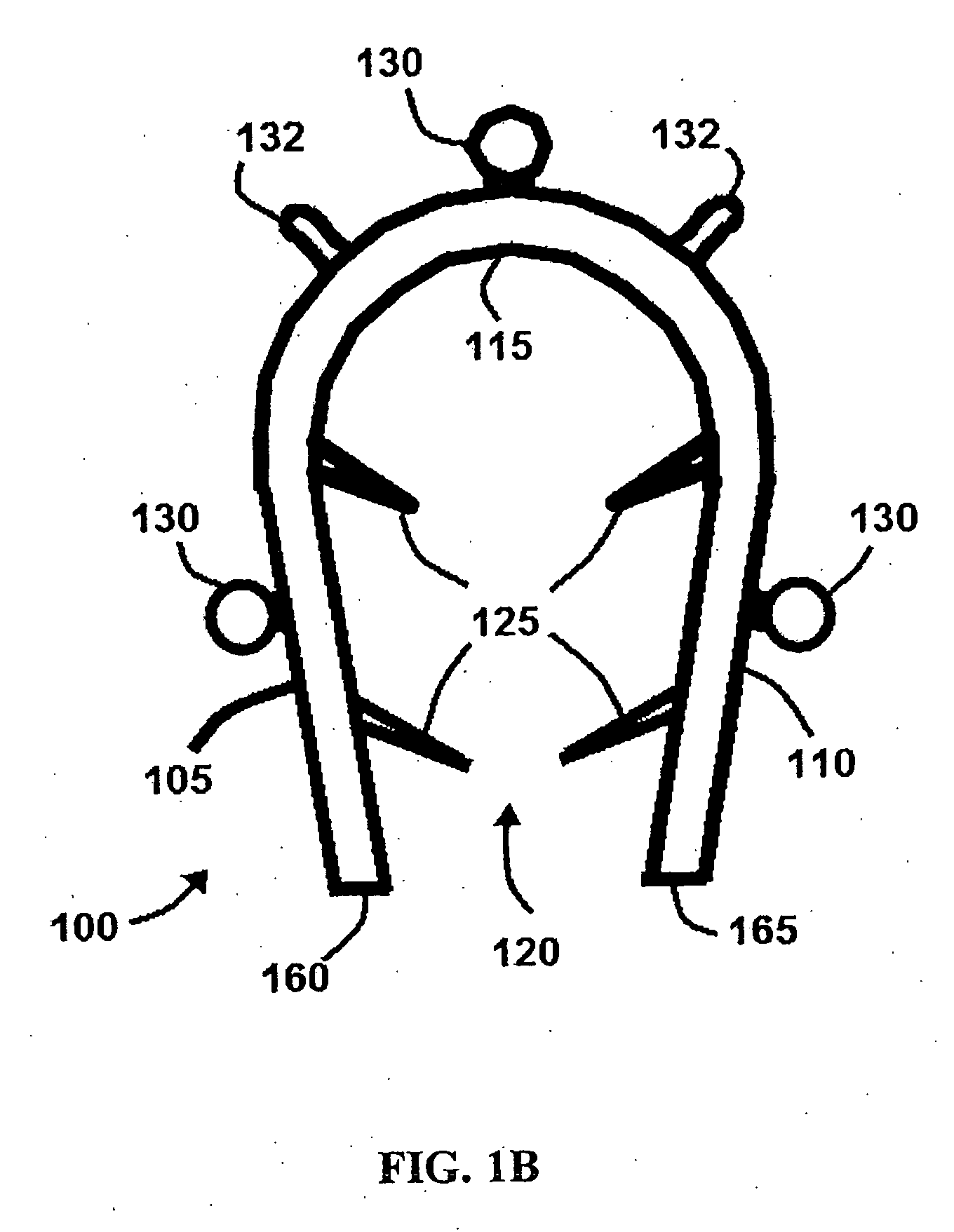
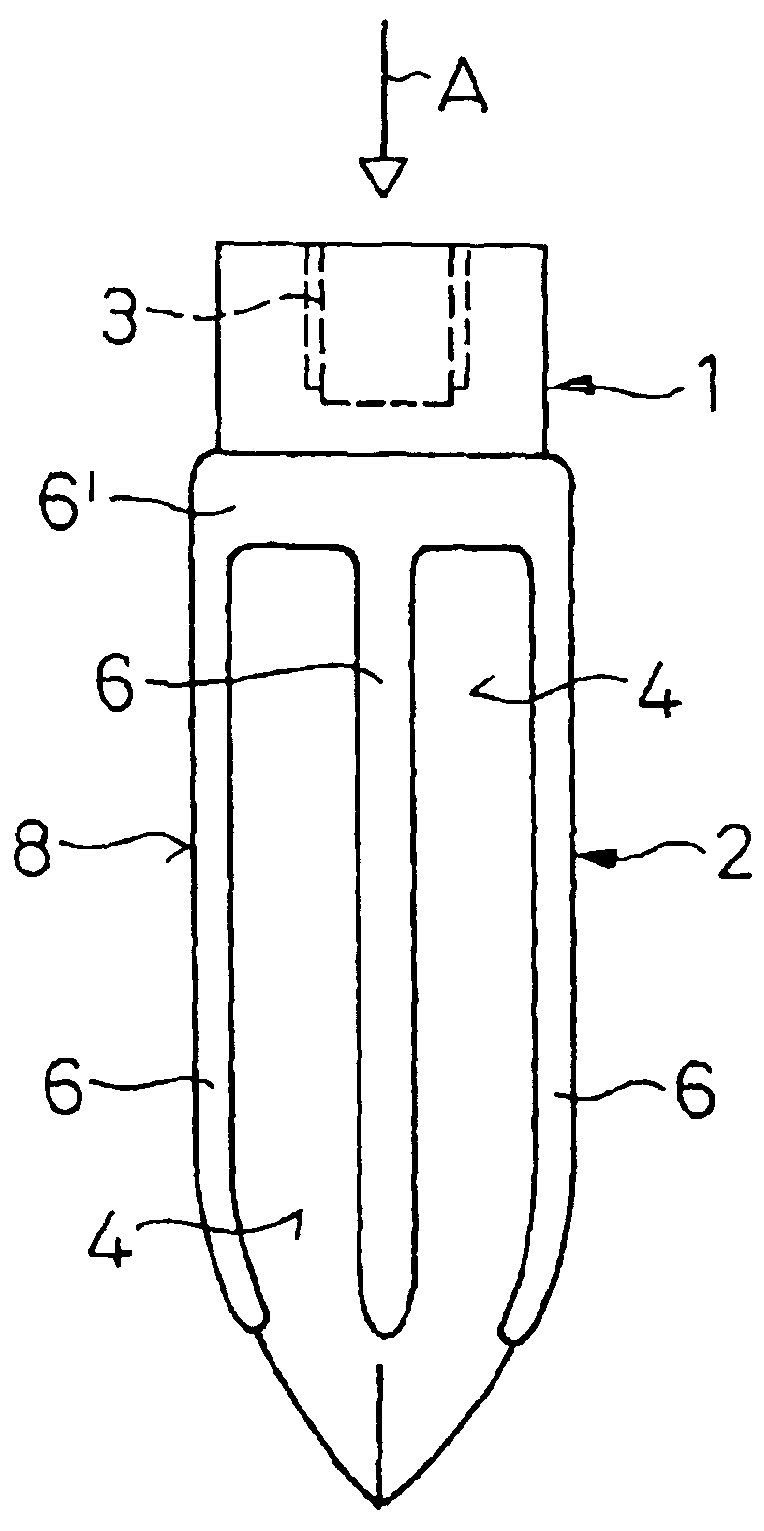
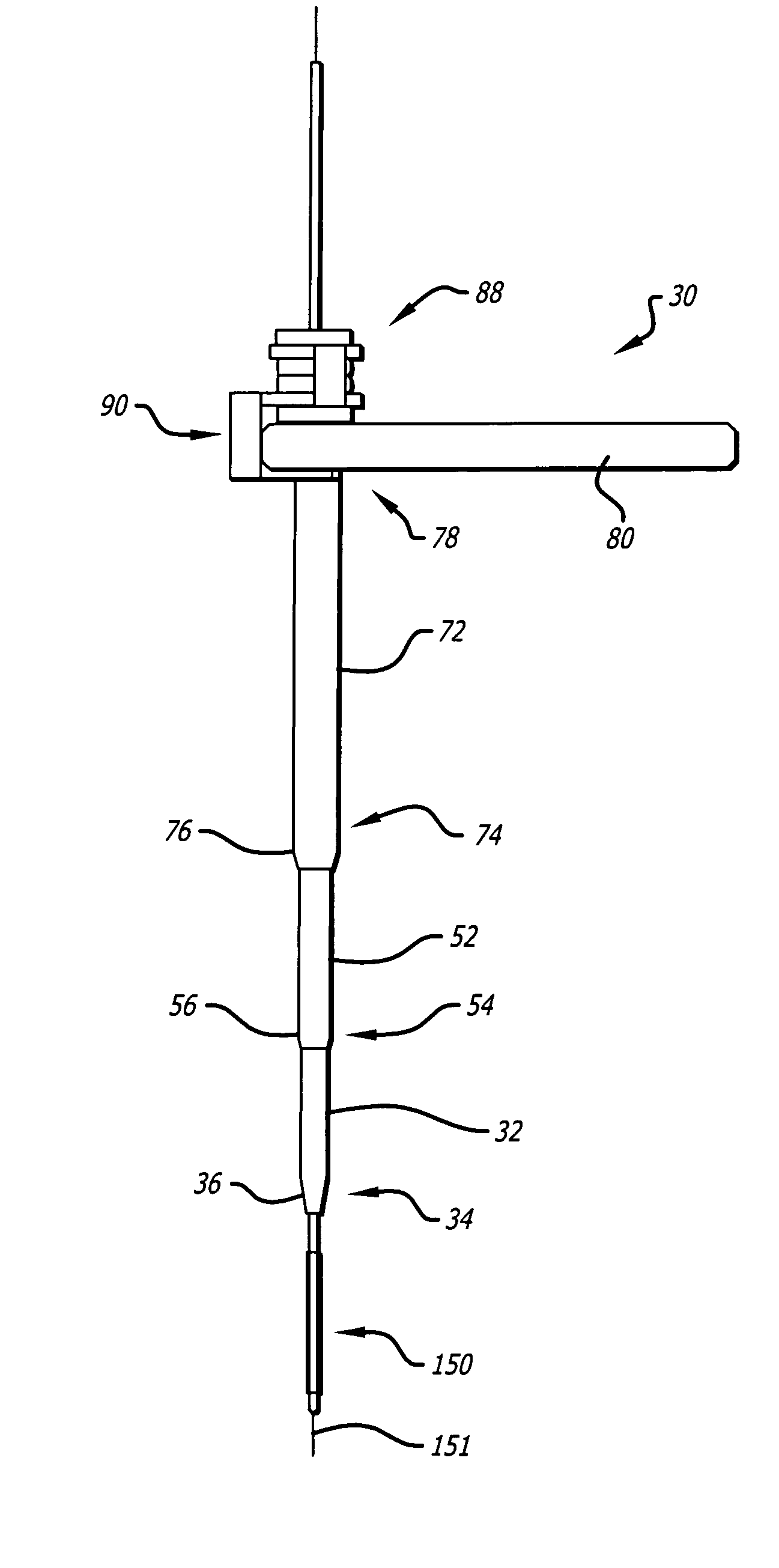
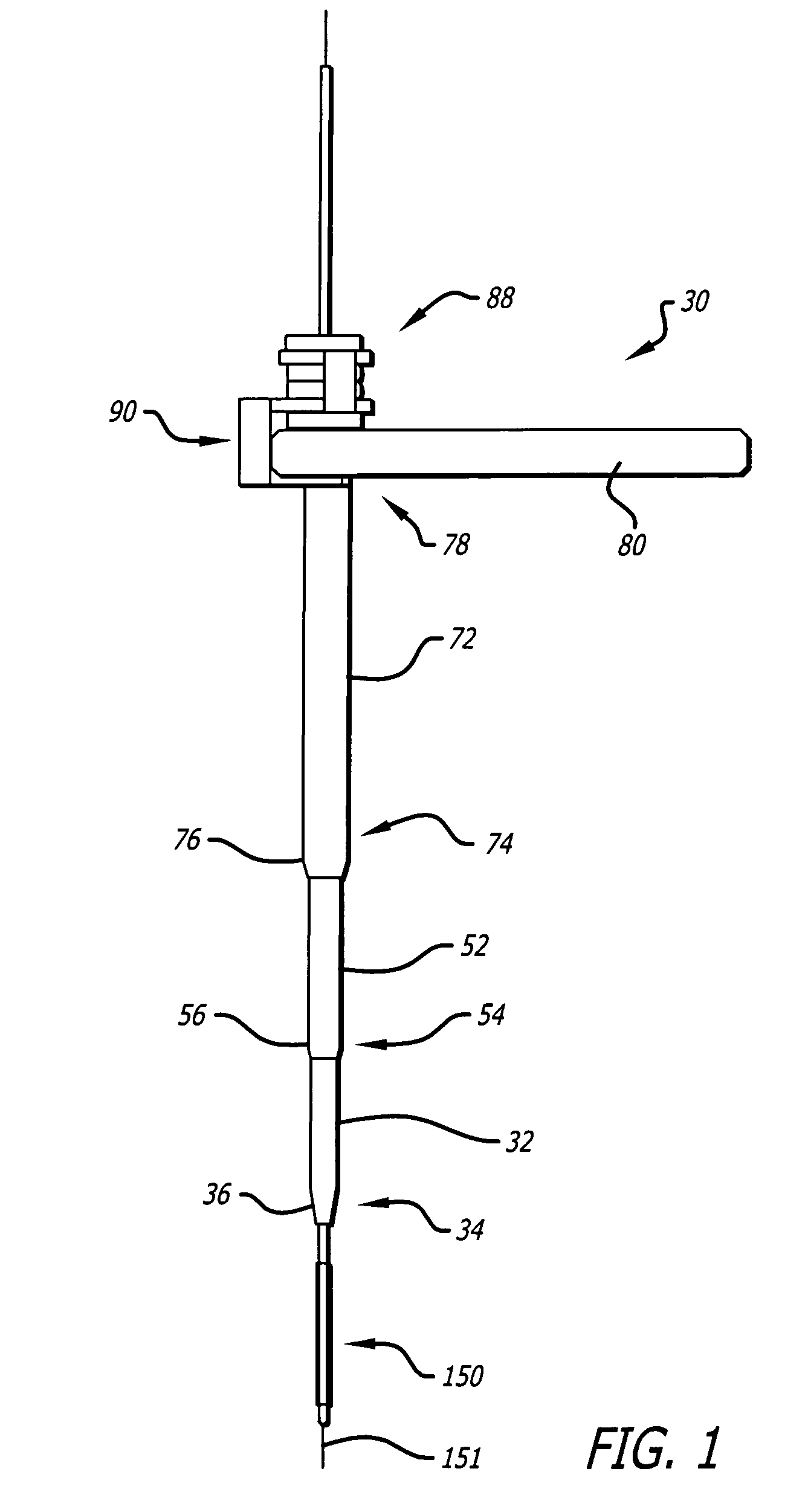
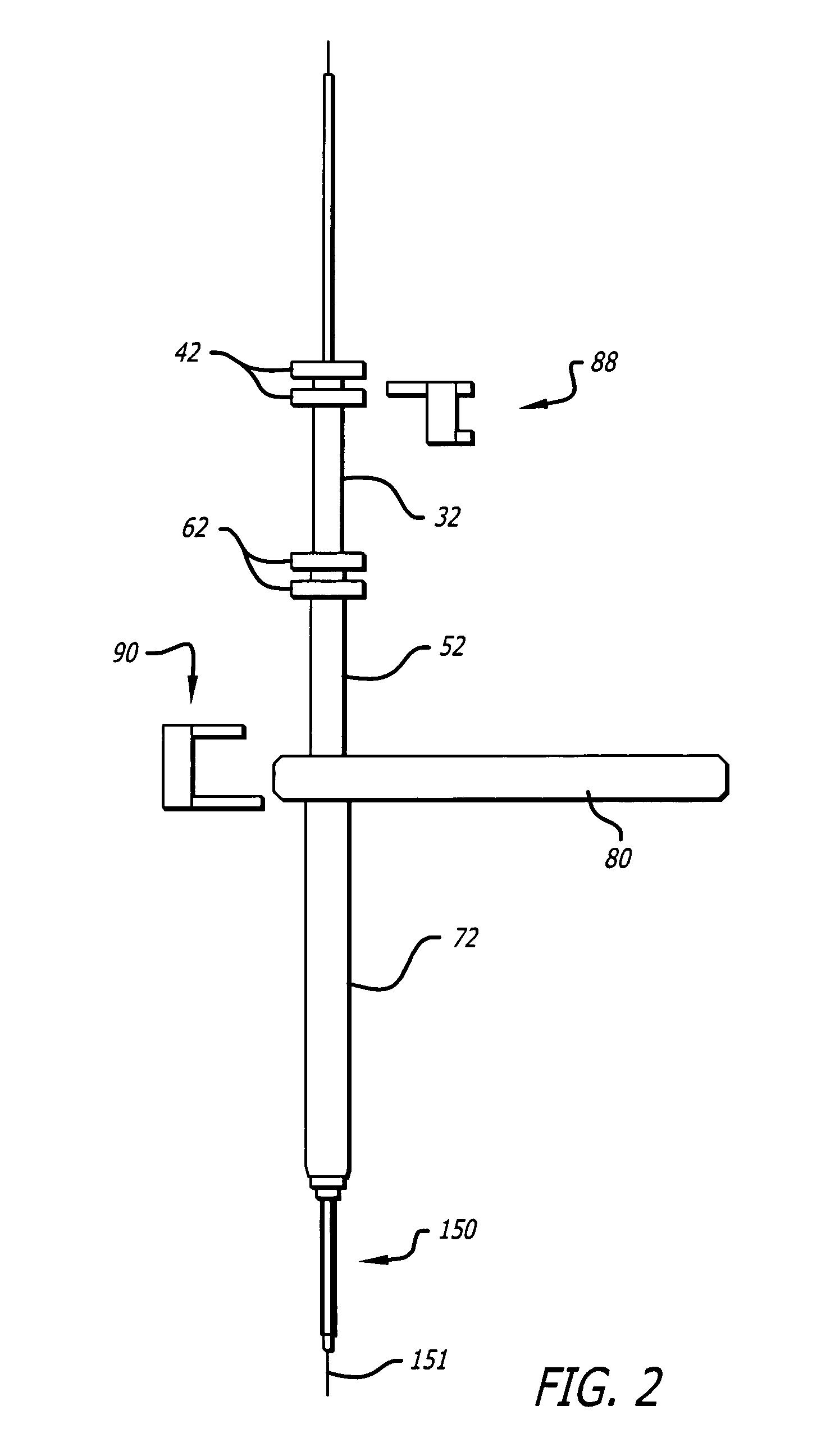
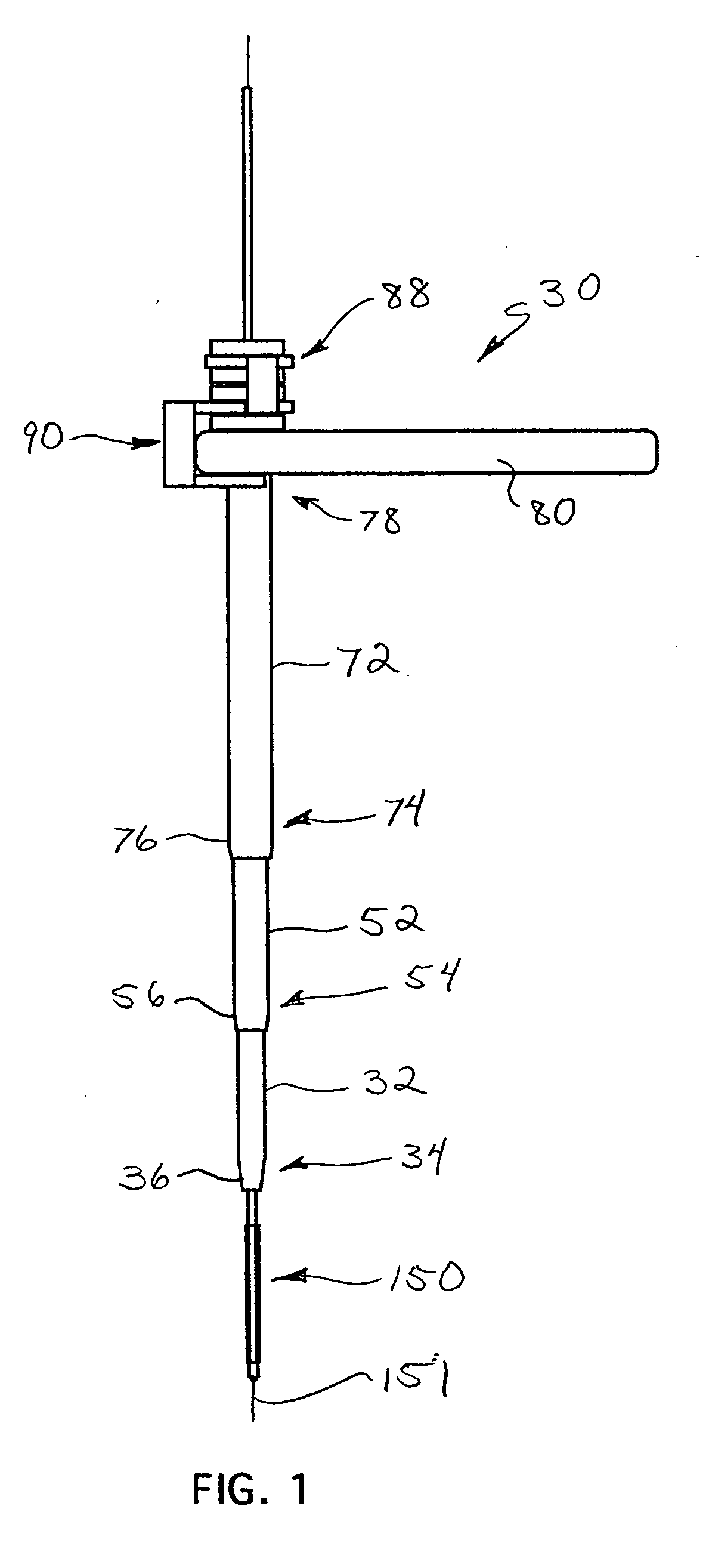
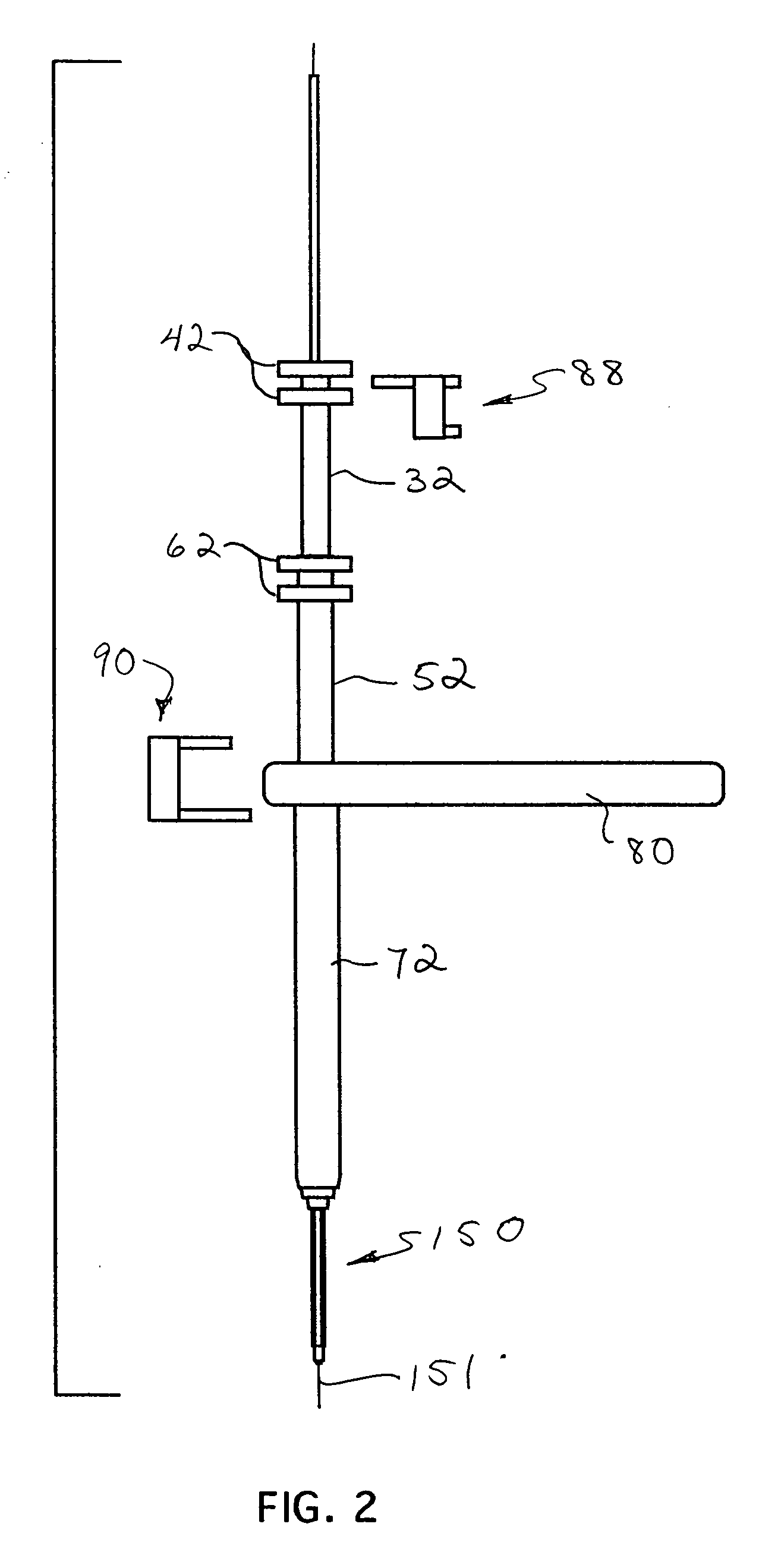
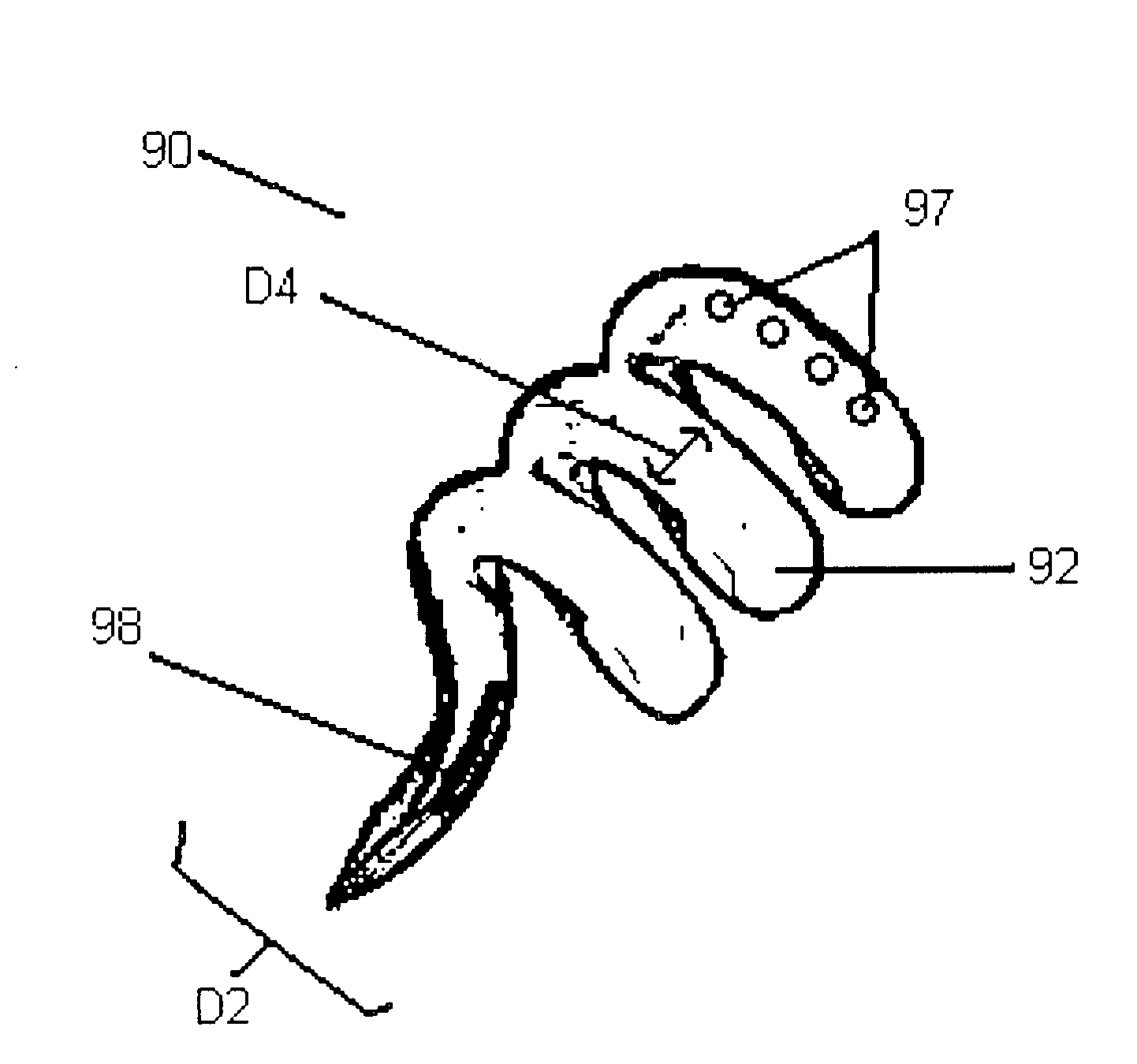
Bone staple, instrument and method of use and manufacturing
ActiveUS9017331B2Stores recoverable mechanical energyEasy to implantPinsInternal osteosythesisShape changeMechanical energy
Owner:FOX WILLIAM CASEY
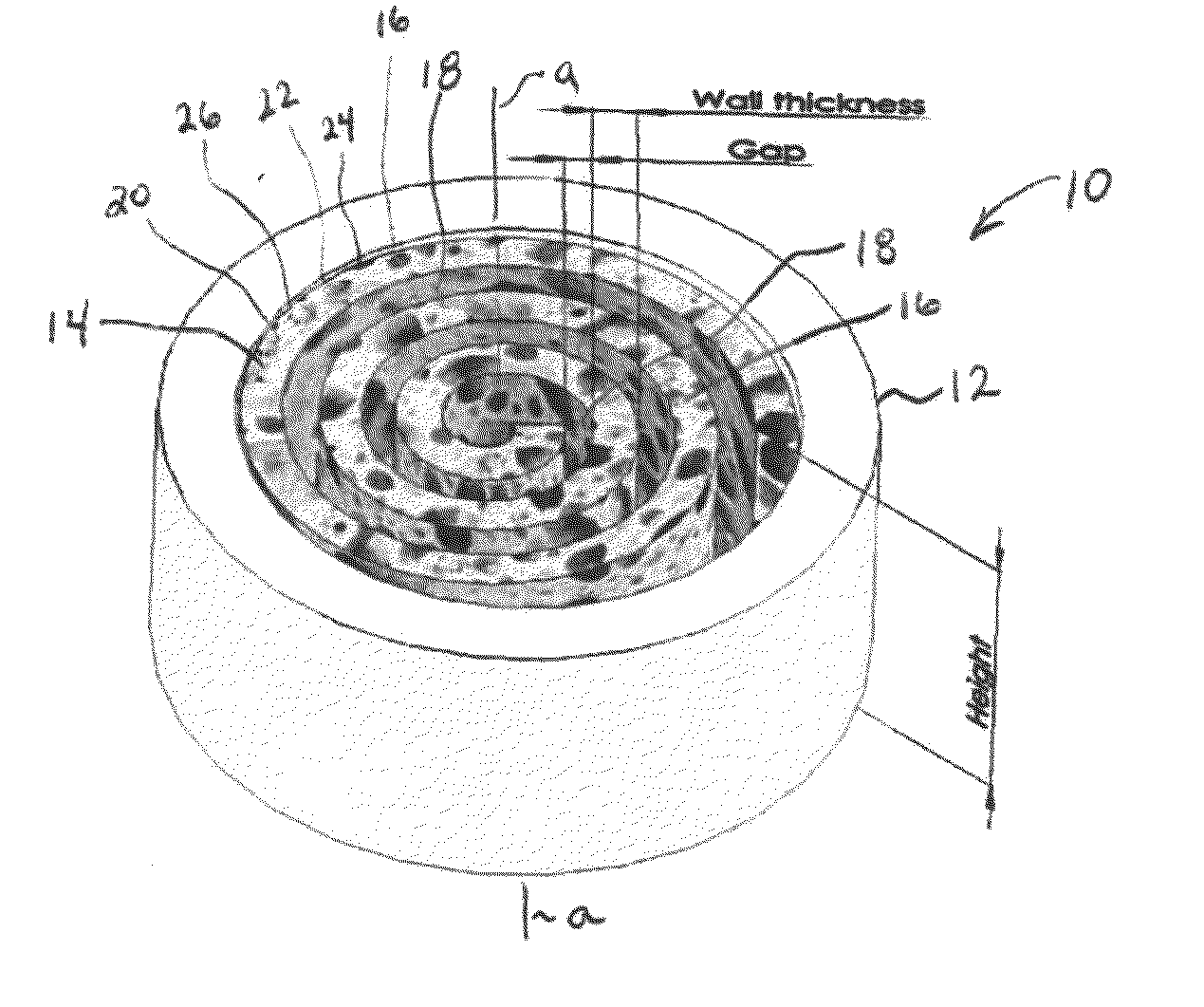
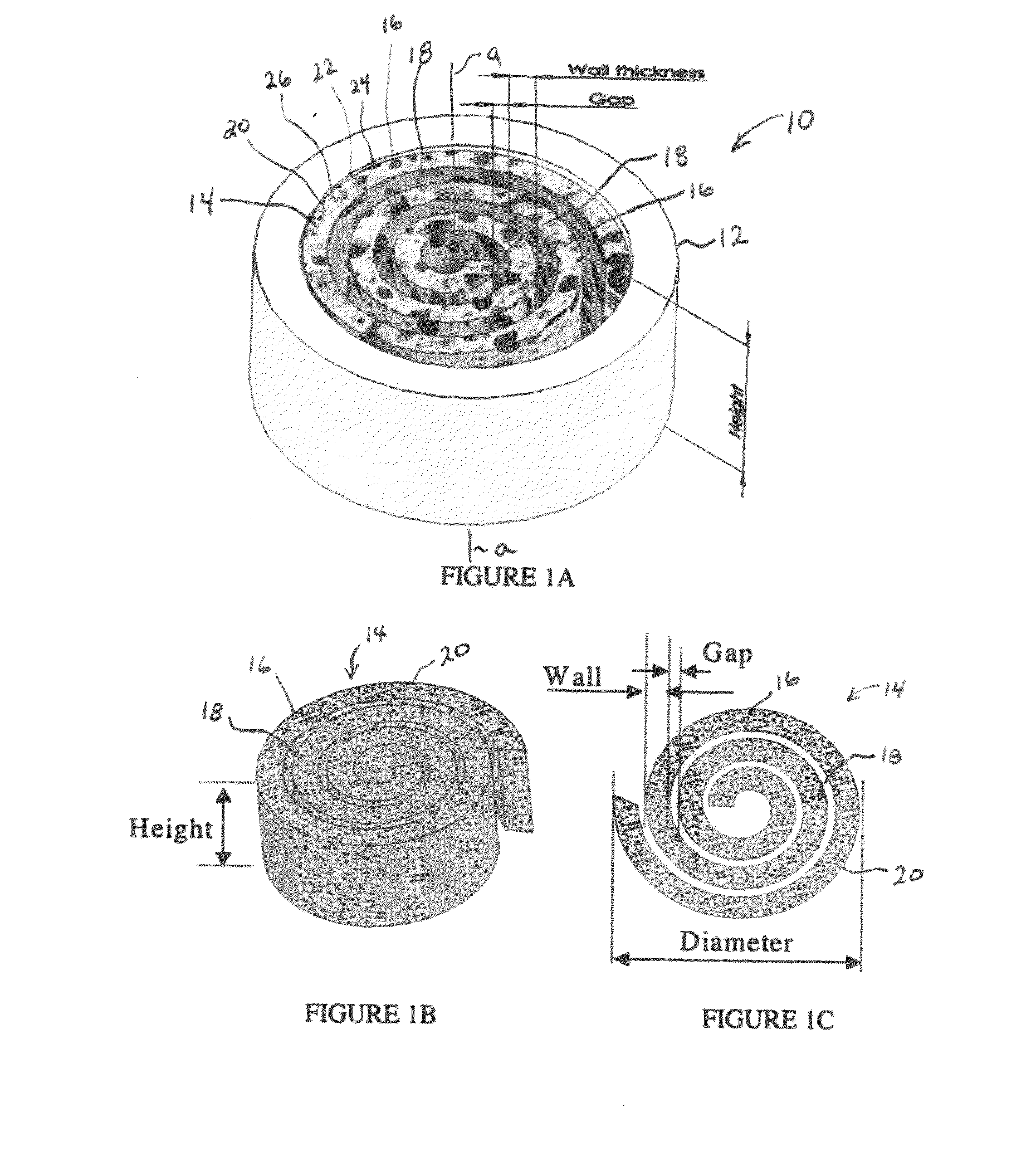
Synergetic functionalized spiral-in-tubular bone scaffolds
InactiveUS20100310623A1Increase the number ofIncrease alkaline phosphatase activityPeptide/protein ingredientsBone implantPorous sheetCell seeding
An integrated scaffold for bone tissue engineering has a tubular outer shell and a spiral scaffold made of a porous sheet. The spiral scaffold is formed such that the porous sheet defines a series of spiral coils with gaps of controlled width between the coils to provide an open geometry for enhanced cell growth. The spiral scaffold resides within the bore of the shell and is integrated with the shell to fix the geometry of the spiral scaffold. Nanofibers may be deposited on the porous sheet to enhance cell penetration into the spiral scaffold. The spiral scaffold may have alternating layers of polymer and ceramic on the porous sheet that have been built up using a layer-by-layer method. The spiral scaffold may be seeded with cells by growing a cell sheet and placing the cell sheet on the porous sheet before it is rolled.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Surgical instrument
ActiveUS9579158B2Reduce usageReduce frictionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMechanical resistanceBone tissue
Owner:AO TECH AG
Bone access system
InactiveUS20060064101A1Reduce riskLow stiffnessSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingBone tissueCatheter
Instruments and methodology for nonlinear access to bone tissue sites are described. Embodiments disclosed include a conduit for delivering material or a medical device to a site and a core member that is able to steer the conduit and allow the combination to be advanced thorough cancellous bone. A cannula and stylet may be provided to first advance through hard bone. The core member includes a curved tip that may be straightened by the cannula or an actuator sheath to vary sweep of the curve. An obturator may be included in the system. This instrument may include a flexible portion as well. Each of the obturator and conduit may be provided with any of a variety of active tips. The systems may be used to perform hard tissue site implantation, for example, in connection with a high pressure injection system.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
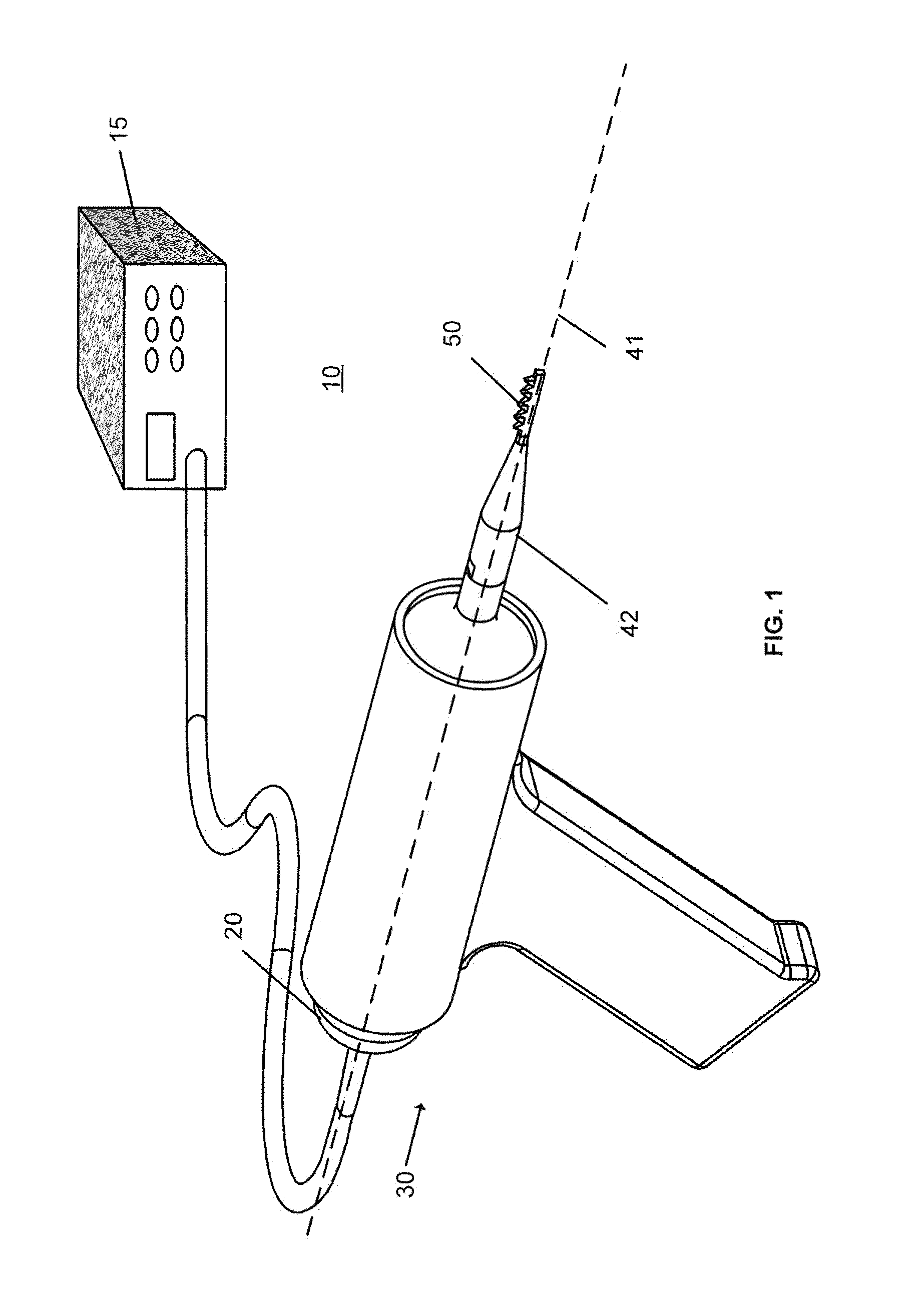
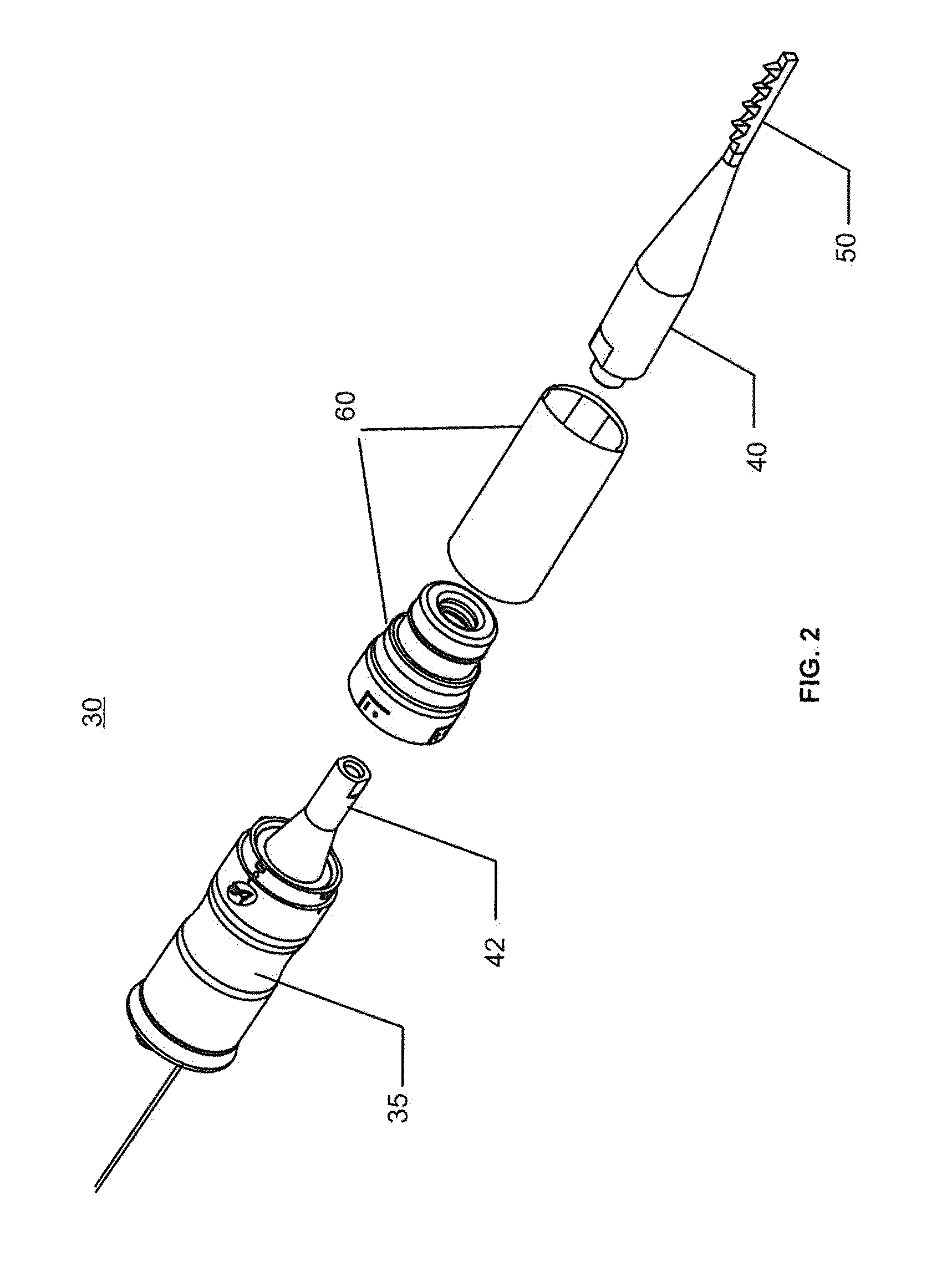
Ultrasound surgical saw
This invention discloses methods and devices using ultrasound energy for resecting bone tissue during surgical procedures. The disclosure describes the use of ultrasound surgical saw consisting of an ultrasound generator, ultrasound transducer and ultrasound horn including a cutting blade to resect bone tissue without excessive temperature rise during typical surgical procedures. The cutting blade provides a self-clearing design that includes at least two teeth disposed to prevent accumulation of bone chips within the proximity of the teeth. The design of the cutting blade allows the mechanical motion of the blade and the emission of the ultrasound energy to remove accumulated bone chips and prevent excessive temperature rise.
Owner:BABAEV ELIAZ
Bone access system
InactiveUS6875219B2Reduce riskLow stiffnessSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBone tissueCatheter
Instruments and methodology for nonlinear access to bone tissue sites are described. Embodiments disclosed include a conduit for delivering material or a medical device to a site and a core member that is able to steer the conduit and allow the combination to be advanced thorough cancellous bone. A cannula and stylet may be provided to first advance through hard bone. The core member includes a curved tip that may be straightened by the cannula or an actuator sheath to vary sweep of the curve. An obturator may be included in the system. This instrument may include a flexible portion as well. Each of the obturator and conduit may be provided with any of a variety of active tips. The systems may be used to perform hard tissue site implantation, for example, in connection with a high pressure injection system.
Owner:NEUROTHERM
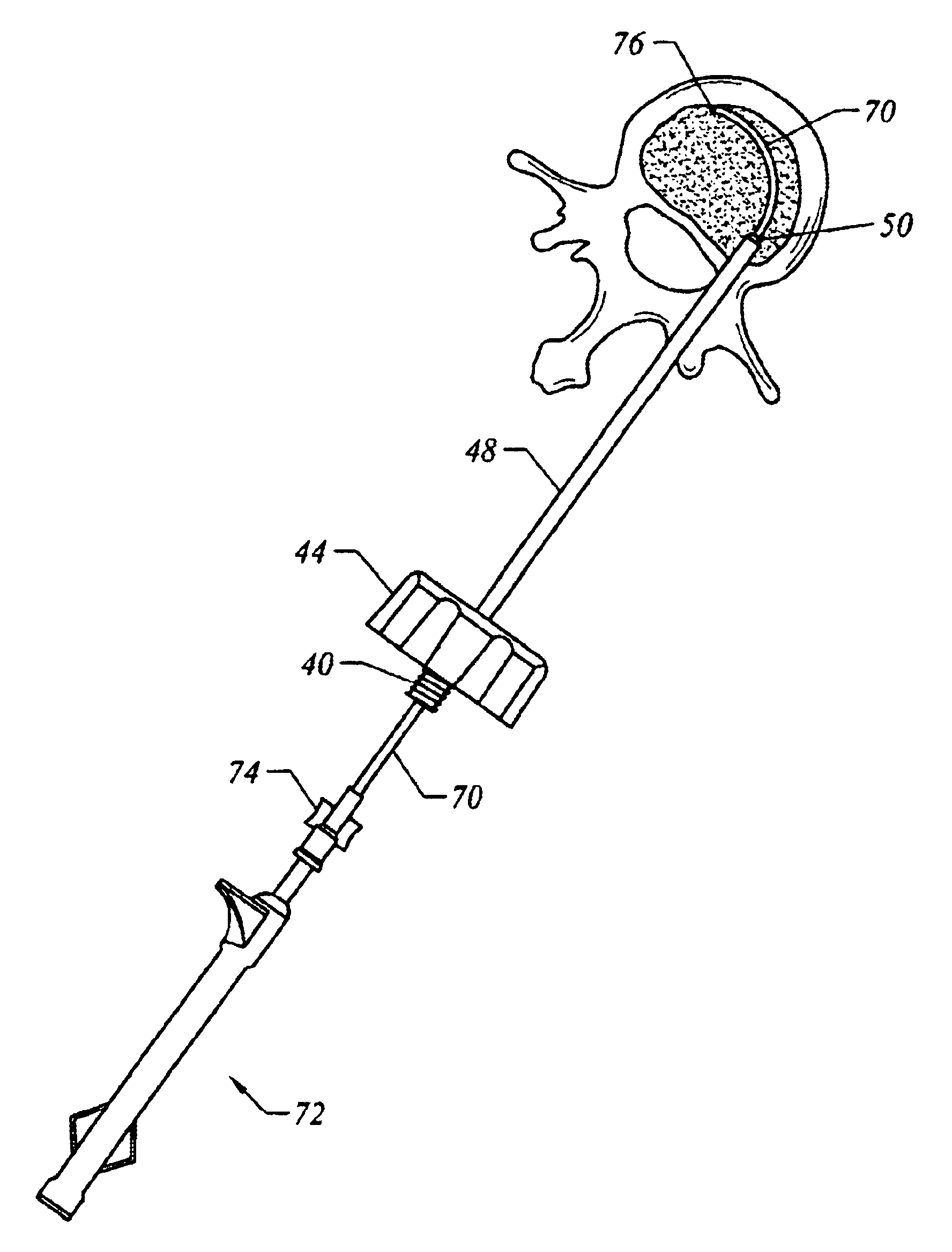
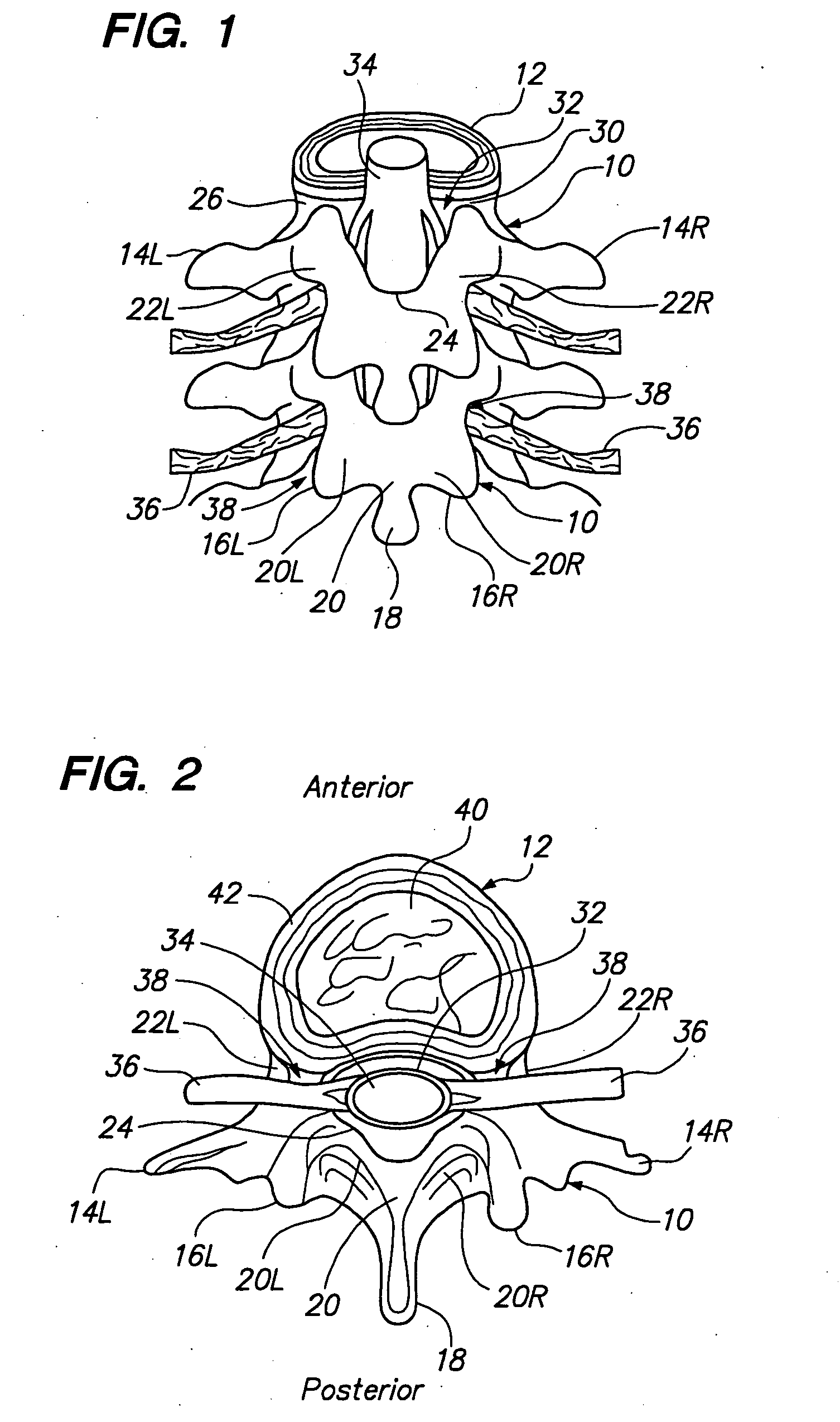
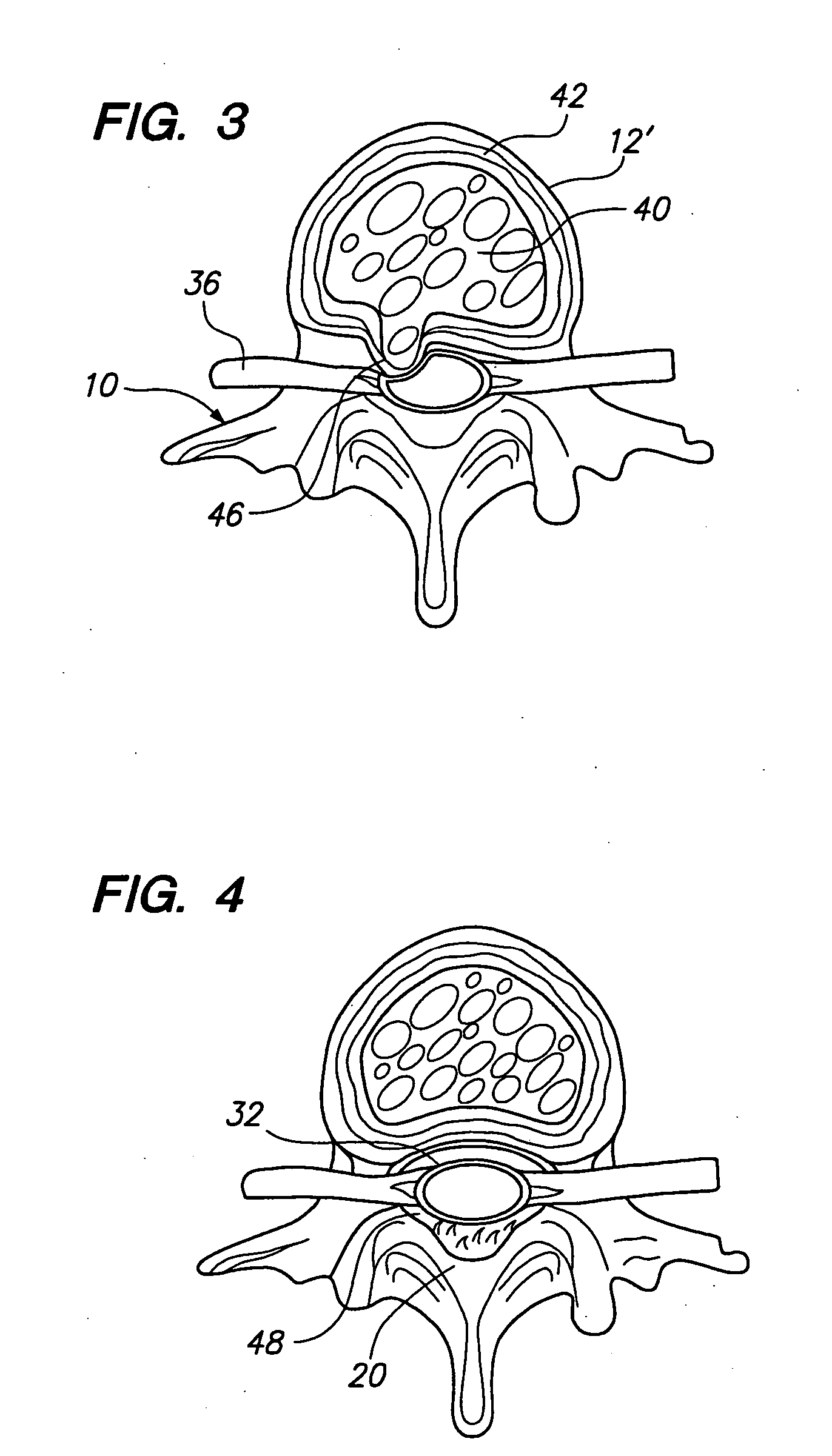
Implantable devices and methods for treating micro-architecture deterioration of bone tissue
InactiveUS20070067034A1Prevent slippagePrevent movementInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsBone tissueImplanted device
An expandable stabilization device is disclosed that is suitable for deployment within cancellous bone, including, for example, within a vertebral body of a spine. The device comprises: an elongate expandable shaft adapted to be positioned within a vertebral body having a first profile and a second profile; wherein the shaft is adapted to cut through cancellous bone within the vertebral body during expansion from the first profile to the second profile; and further wherein the shaft is adapted to abut a surface of cortical bone within the vertebral body without passing therethrough. The invention also includes a method for treating cancellous bone, such as cancellous bone of a vertebral body. The method comprises: delivering an expandable device within the cancellous bone of in an interior of a vertebral body; expanding the delivered device within the cancellous bone of the vertebra body; applying force from a surface of the device to an inner surface of a cancellous bone of the vertebral body sufficient to cut through the cancellous bone; and applying force from a surface of the device to an inner surface of a cortical bone of the vertebral body sufficient to support the vertebral body
Owner:SPINEALIGN MEDICAL
Medical and dental implant devices for controlled drug delivery
Implantable devices and methods for use in the treatment of osteonecrosisare provided. The device includes at least one implant device body adapted for insertion into one or more channels or voids in bone tissue; a plurality of discrete reservoirs, which may preferably be microreservoirs, located in the surface of the at least one implant device body; and at least one release system disposed in one or more of the plurality of reservoirs, wherein the release system includes at least one drug selected from the group consisting of bone growth promoters, angiogenesis promoters, analgesics, anesthetics, antibiotics, and combinations thereof. The device body may be formed of a bone graft material, a polymer, a metal, a ceramic, or a combination thereof. The device body may be a monolithic structure, such as one having a cylindrical shape, or it may be in the form of multiple units, such as a plurality of beads.
Owner:MICROCHIPS INC
Porous β-tricalcium phosphate granules for regeneration of bone tissue
InactiveUS6949251B2Improve regenerative abilitySurgical adhesivesSkeletal disorderActive agentBone tissue
A porous β-tricalcium phosphate material for bone implantation is provided. The multiple pores in the porous TCP body are separate discrete voids and are not interconnected. The pore size diameter is in the range of 20-500 μm, preferably 50-125 μm. The porous β-TCP material provides a carrier matrix for bioactive agents and can form a moldable putty composition upon the addition of a binder. Preferably, the bioactive agent is encapsulated in a biodegradable agent. The invention provides a kit and an implant device comprising the porous β-TCP, and a bioactive agent and a binder. The invention also provides an implantable prosthetic device comprising a prosthetic implant having a surface region, a porous β-TCP material disposed on the surface region and optionally comprising at least a bioactive agent or a binder. Methods of producing the porous β-TCP material and inducing bone formation are also provided.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Integral flexible spine stabilization device and method
InactiveUS20050096652A1Promote additional cellular ingrowthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBone tissueDonor bone
Provided are a device and a method for stabilizing two or more vertebrae by joining the vertebrae with a flexible device. The flexible device is of unitary construction and includes anchor posts constructed and arranged for insertion into holes drilled into the vertebrae, preferably after removing all or a portion of the pedicles from the target vertebrae. Removal of the pedicles provides an acceptable fastening site, prevents interference with the device by the pedicles, and provides native donor bone tissue, thereby obviating the need for a second surgery to harvest bone tissue from a different site, such as the hip.
Owner:BURTON CHARLES V
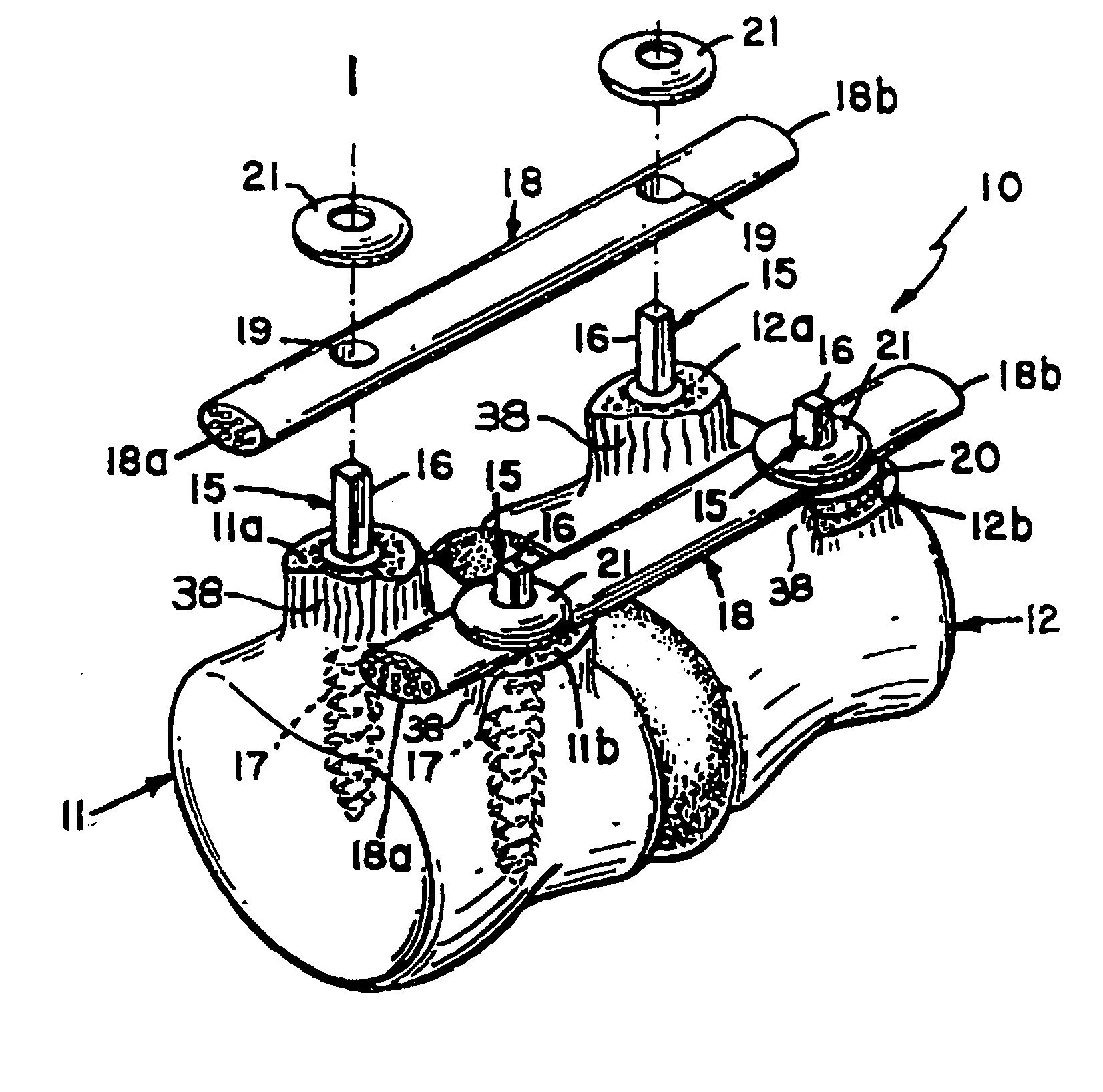
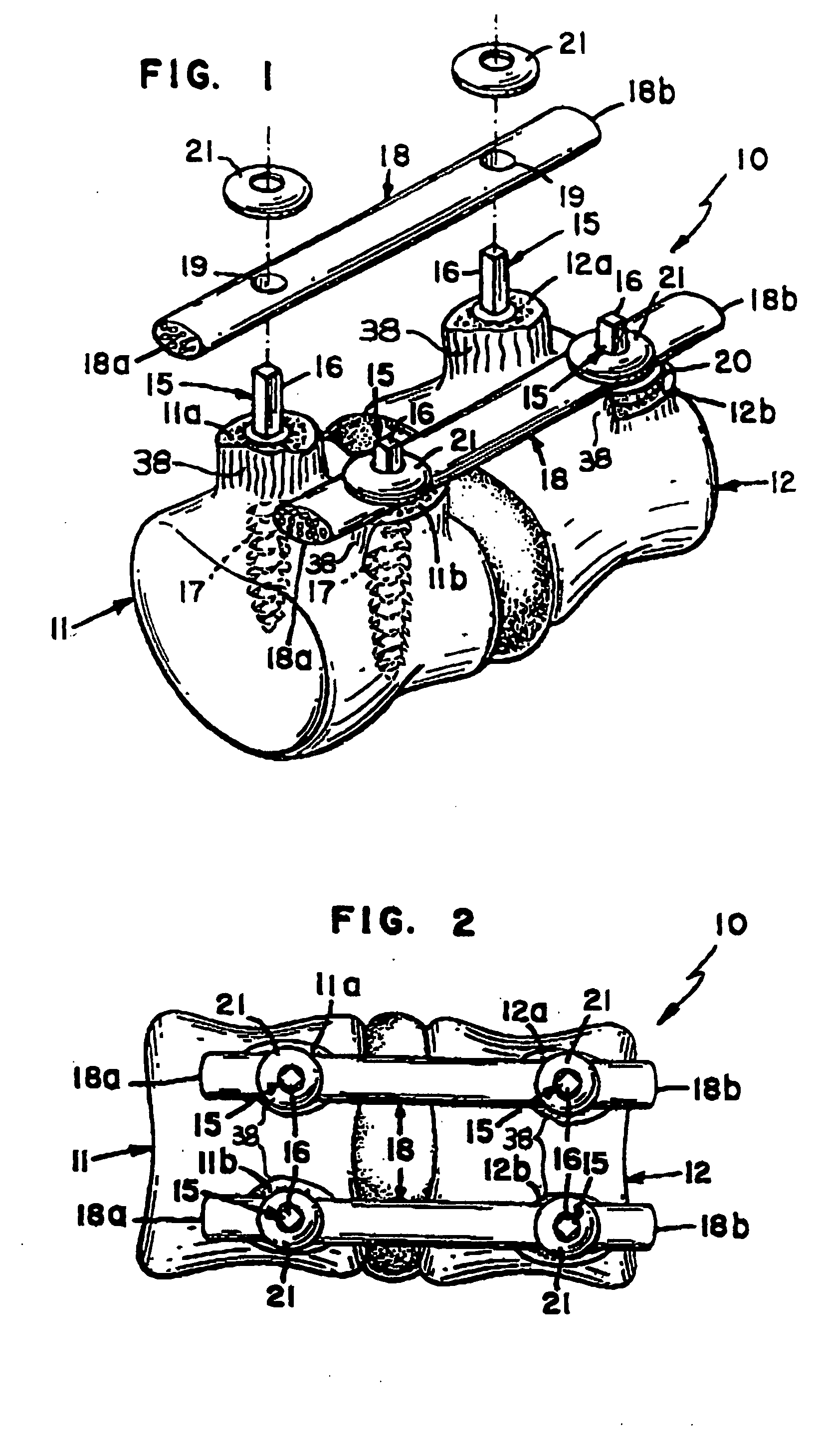
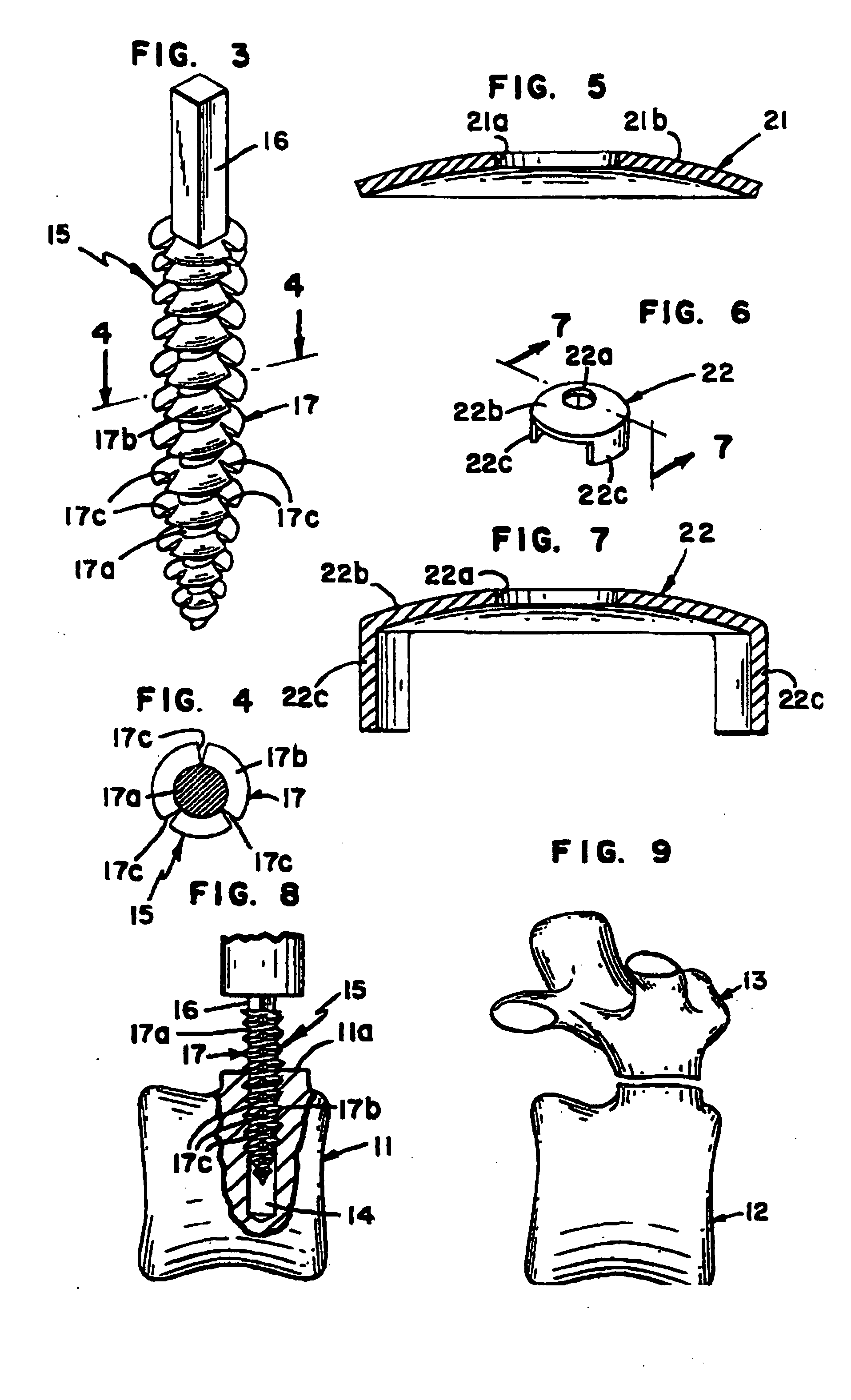
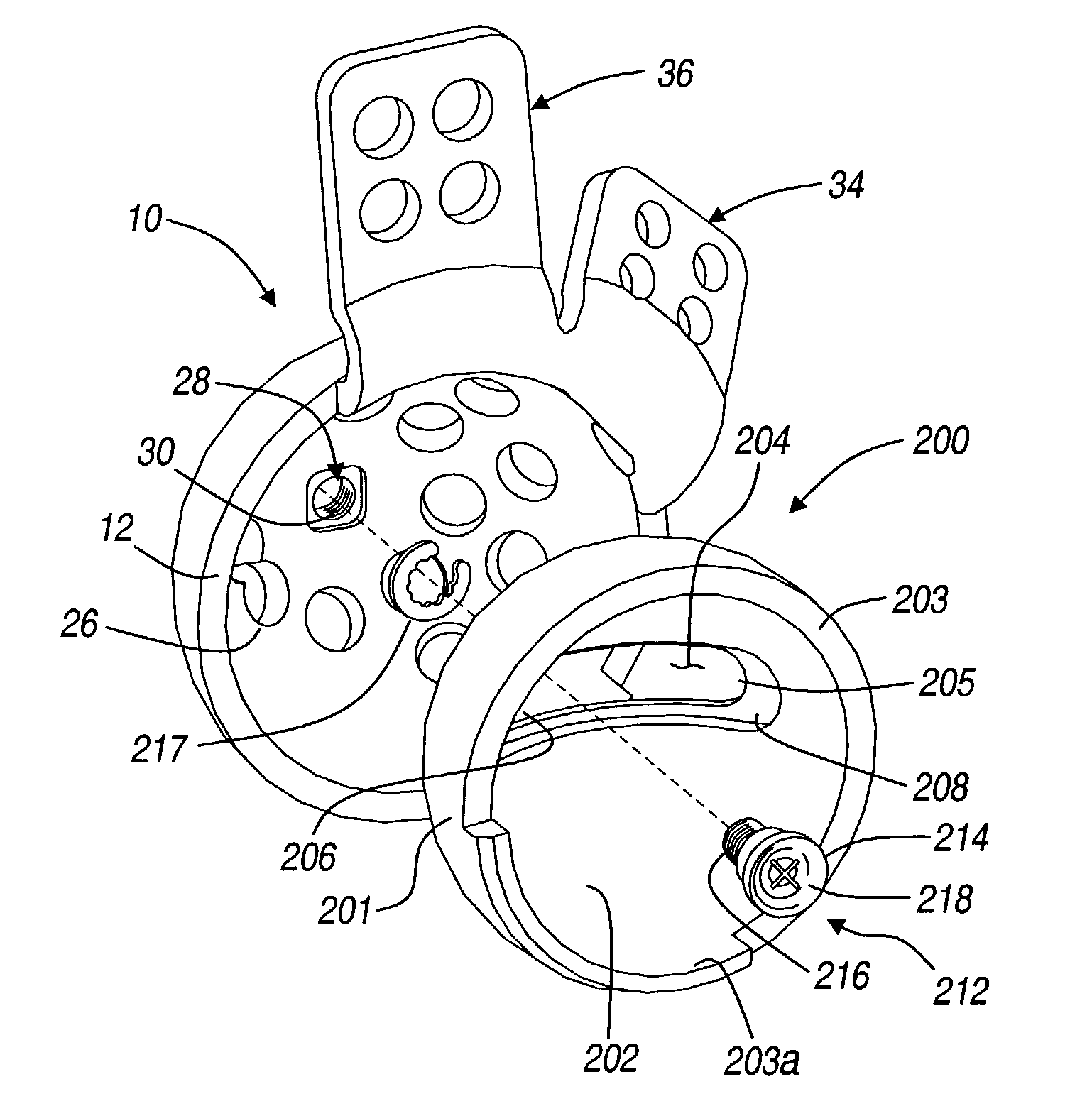
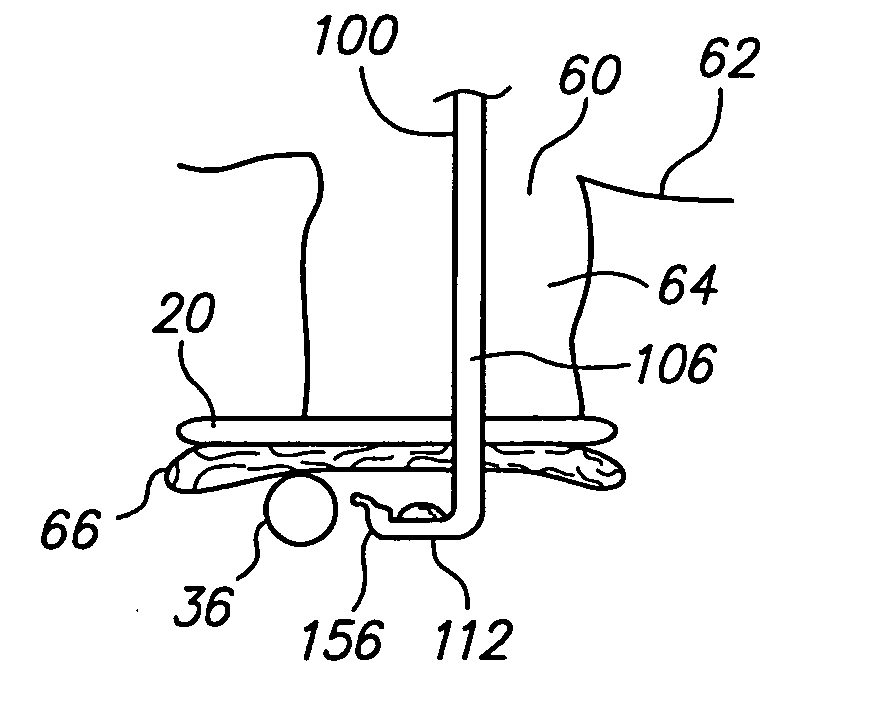
Bone tissue fixation device and method
ActiveUS20090198277A1Increase flexibilityEasy and safe to accessSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisBone tissueSpinous process
Systems, methods, and kits incorporating a clamp for securing to bone tissue. The clamp includes gripping members to secure the clamp to the bone tissue without the use of screws. The clamp may be used to treat spinal conditions, and may be secured to the spinous process of vertebrae. Systems, methods and kits can incorporate a fusion member configured to fuse between adjacent spinous processes.
Owner:WENZEL SPINE +1
Implant to be implanted in bone tissue or in bone tissue supplemented with bone substitute material
InactiveUS6921264B2High softening temperatureLow softening temperatureDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBone tissueGrowth promoting
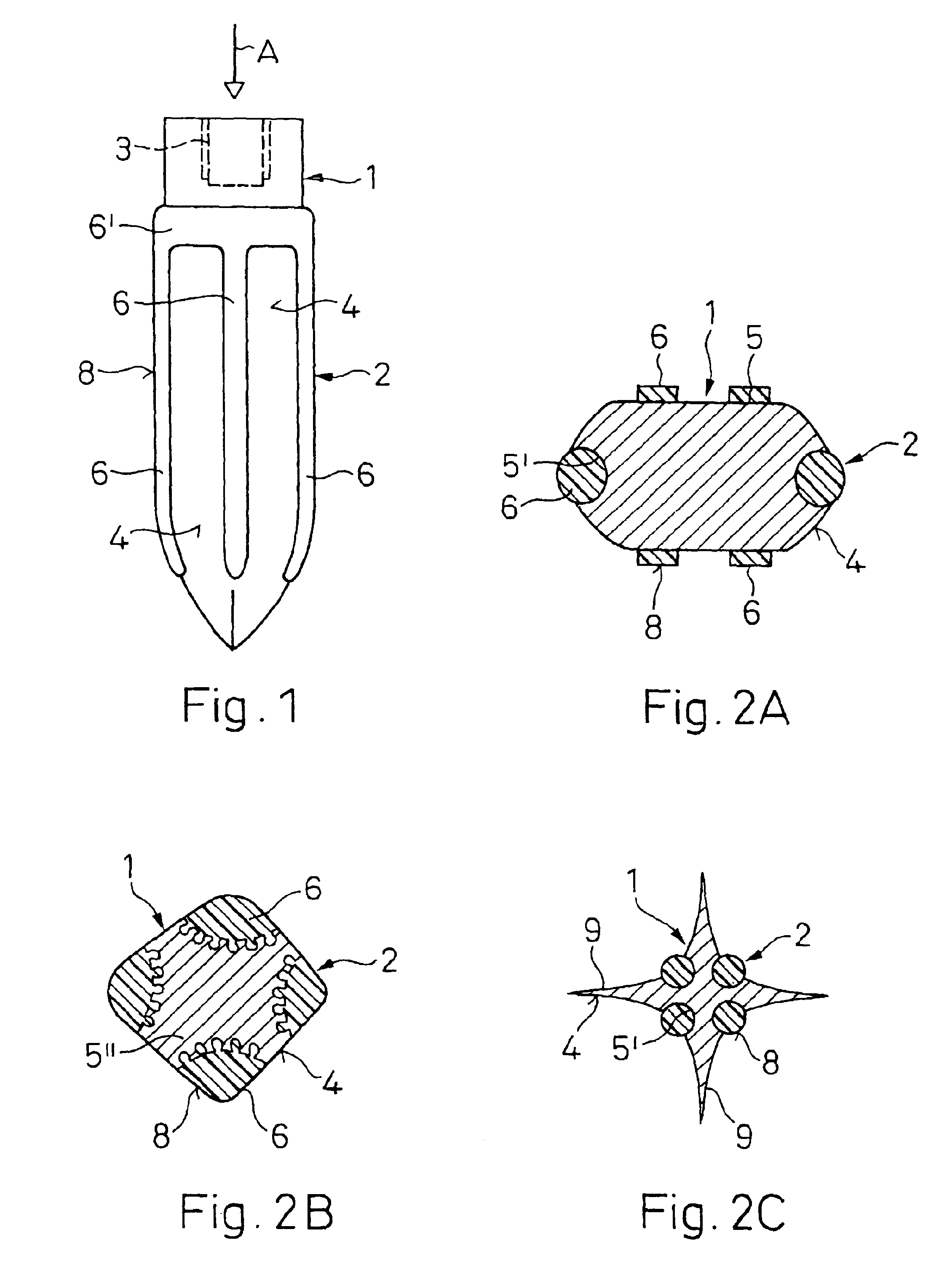
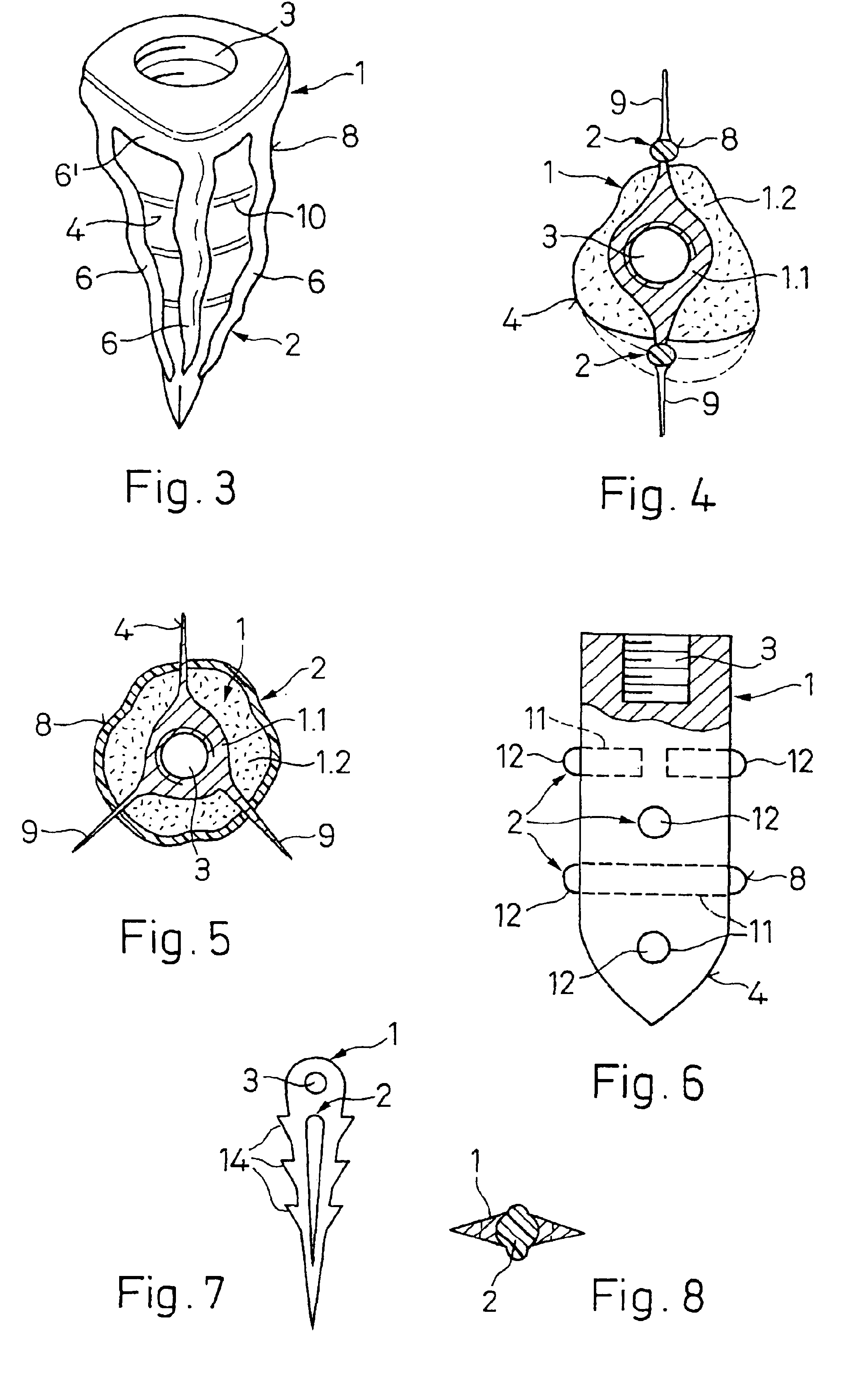
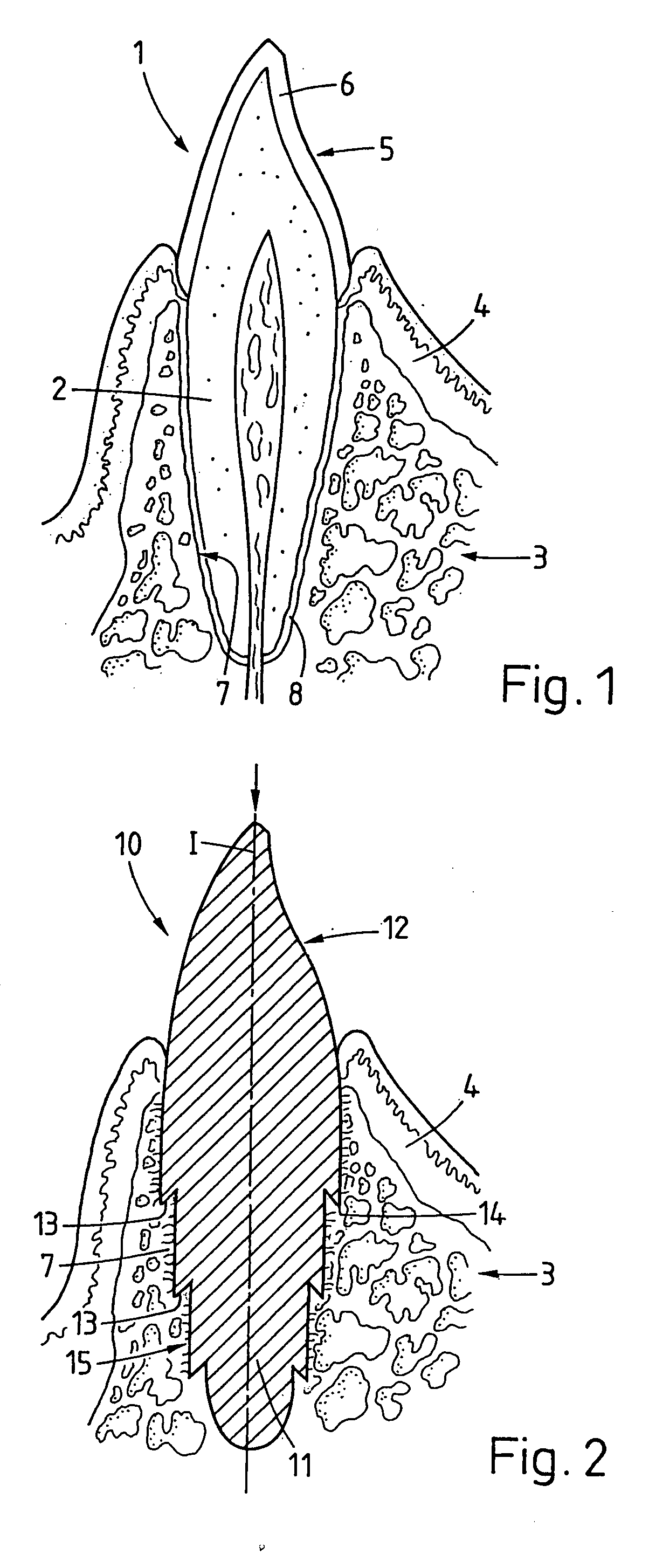
An implant (1) to be implanted in bone tissue, e.g. a dental implant or an implant for an orthopedic application, comprises surface regions (4) of a first type which have e.g. osseo-integrative, inflammation-inhibiting, infection-combating and / or growth-promoting properties, and surface regions (8) of a second type which consist of a material being liquefiable by mechanical oscillation. The implant is positioned in an opening of e.g. a jawbone and then mechanical oscillations, e.g. ultrasound is applied to it while it is pressed against the bone. The liquefiable material is such liquefied at least partly and is pressed into unevennesses and pores of the surrounding bone tissue where after resolidification it forms a positive-fit connection between the implant and the bone tissue. The surface regions of the two types are arranged and dimensioned such that, during implantation, the liquefied material does not flow or flows only to a clinically irrelevant degree over the surface regions of the first type such enabling the biologically integrative properties of these surface regions to start acting directly after implantation. The implant achieves with the help of the named positive fit a very good (primary) stability, i.e. it can be loaded immediately after implantation. By this, negative effects of non-loading are prevented and relative movements between implant and bone tissue are reduced to physiological measures and therefore have an osseo-integration promoting effect.
Owner:WOODWELDING
Implant that can be implanted in osseous tissue and method for producing said implant corresponding implant
ActiveUS20060105295A1Strong long-term anchoringProcess stabilityDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBone implantCavity wall
A bone implant (10) is implanted in a cavity parallel to an implant axis (I) and without substantial rotation. The implant includes, on an implant portion to be implanted, cutting edges (14), which do not extend in a common plane with the implant axis and are facing toward the distal end of the implant. The implant also includes surface ranges (16) of a material that is liquefiable by mechanical oscillations. The cutting edges (14) are dimensioned such that they are lodged in the cavity wall after implantation. For implantation, the implant is impinged with mechanical oscillations, resulting in the thermoplastic material being at least partially liquefied and pressed into unevennesses and pores of the cavity wall to form a form-fit and / or material-fit connection between implant (10) and cavity wall, when re-solidified. The cutting edges (14) anchor the implant in the cavity wall.
Owner:WOODWELDING
Method and apparatus for acetabular reconstruction
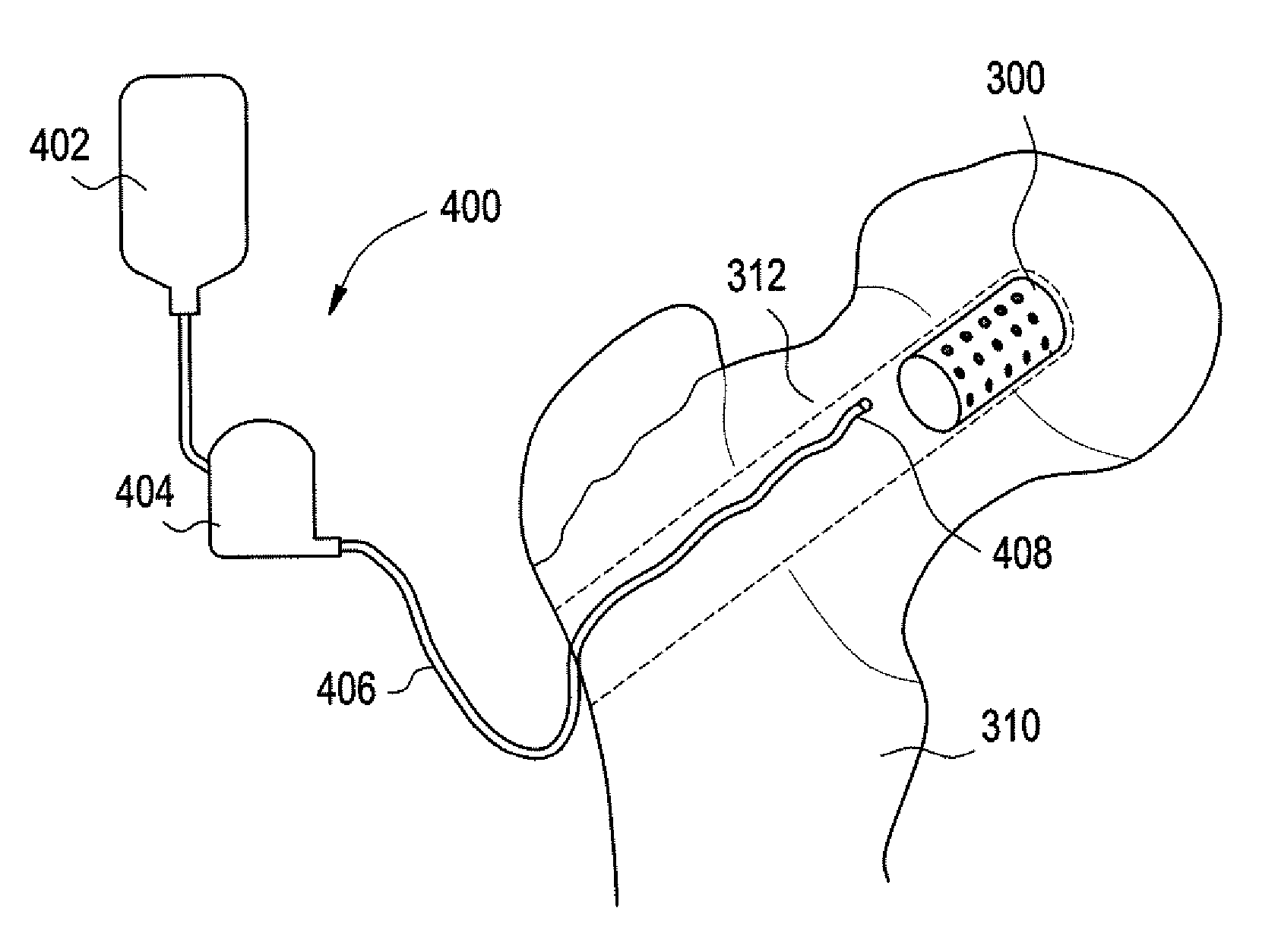
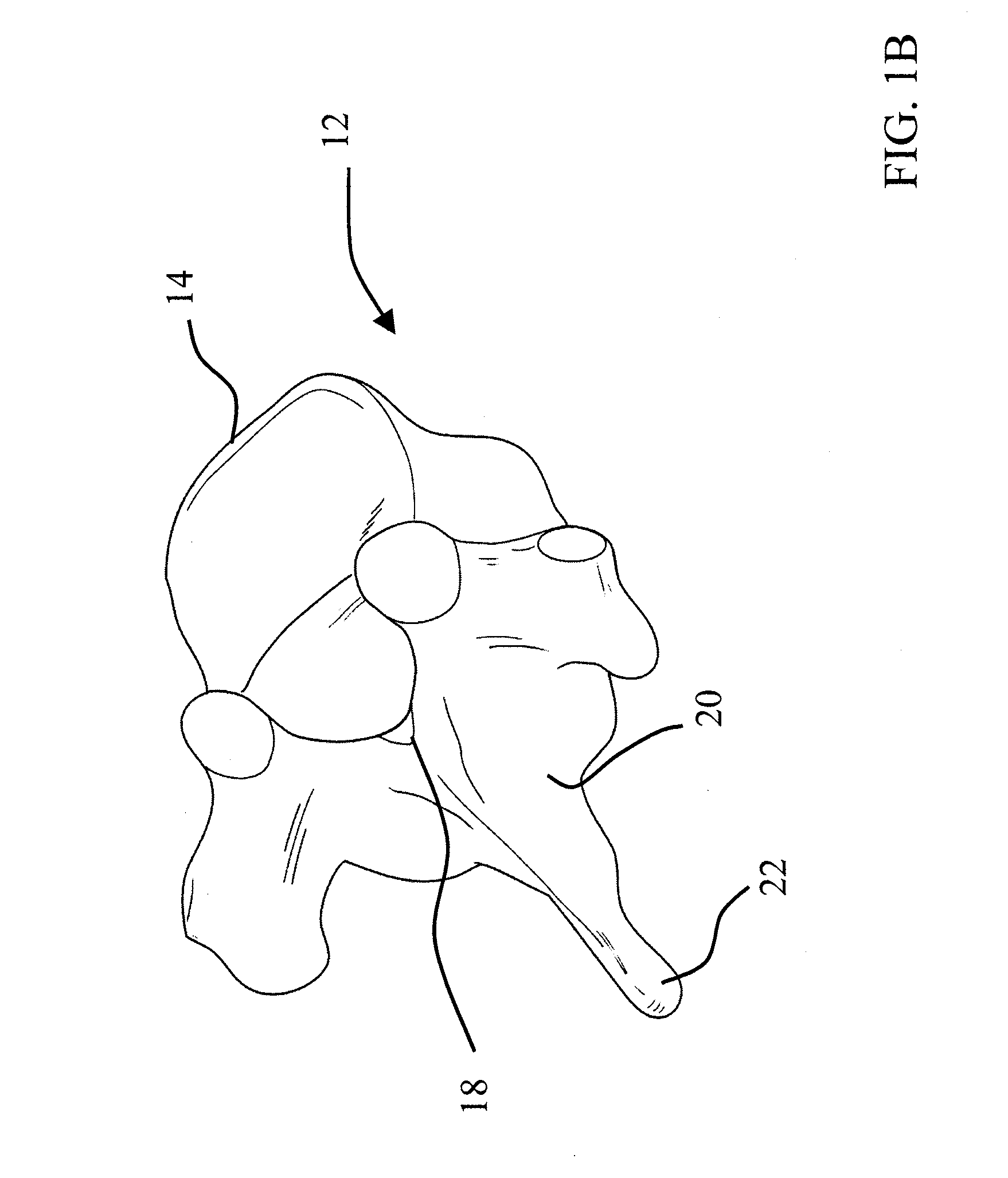
A trial system for an acetabular prosthesis is described. The acetabular prosthesis is generally for implantation in an acetabulum and surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. The described acetabular prosthesis is especially useful in revision hip implant procedures where significant bone tissue loss has occurred either in or around the acetabulum and / or the pelvis. A collection of trial shells are provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a prosthetic shell into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Dilation introducer for orthopedic surgery
InactiveUS20050256525A1Lowering chance damageInvasive surgical procedureOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDilatorBone tissue
The dilation introducer has a locked assembled configuration for placement of the dilation introducer against a patient's tissue to be treated, and an unlocked, collapsed configuration for dilating the patient's soft tissue down to tissue to be treated. Dilator tubes are successively released and advanced to progressively expand the patient's soft tissue down to the bone tissue to be treated. The dilator tubes and a guide insert may include spikes for engaging bone tissue. The dilation introducer may include a light emitter disposed in a dilator tube. A telescoping expander sleeve is also provided.
Owner:INTERVENTIONAL SPINE
Method and apparatus for acetabular reconstruction
A trial system for an acetabular prosthesis is described. The acetabular prosthesis is generally for implantation in an acetabulum and surrounding pelvis. The acetabular prosthesis includes an acetabular cup having a substantially concave inner surface and a substantially convex outer surface. The described acetabular prosthesis is especially useful in revision hip implant procedures where significant bone tissue loss has occurred either in or around the acetabulum and / or the pelvis. A trial shell is provided to trial a range of motion of the hip joint before implanting a prosthetic shell into the acetabular prosthesis.
Owner:BIOMET MFG CORP
Methods and apparatus for wireplasty bone resection
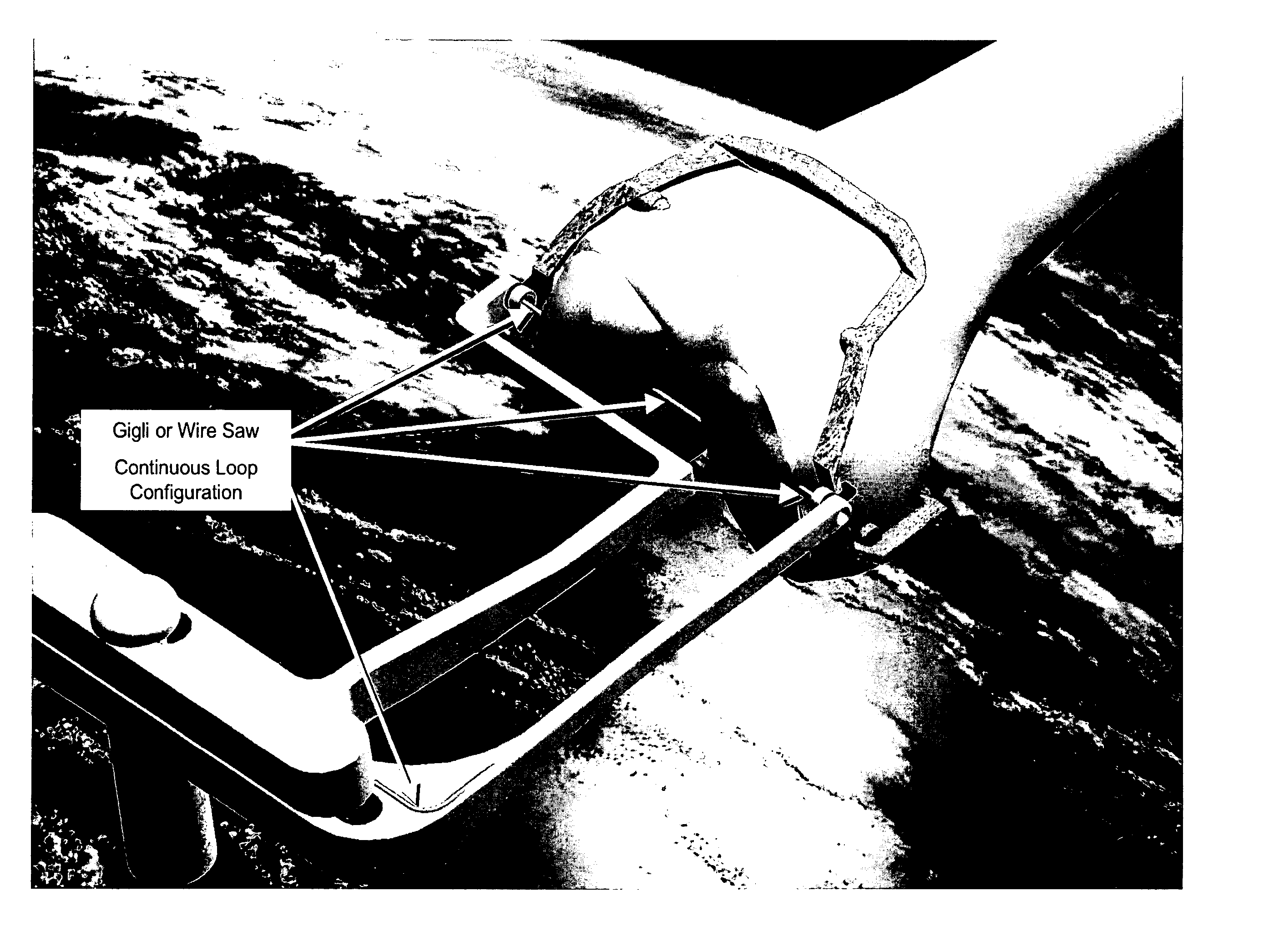
InactiveUS20060030854A1Thin cutting profileMinimize size of incisionSurgical sawsProsthesisBone tissueWire cutting
A cutting tool to be utilized in the resection or removal of bone tissue from patients includes a handle that tensions a wire or cable-like cutting member with a small diameter between at least two features on the handle to present a thin cutting profile. The design of the cutting tool includes features that protect against soft tissue damage and minimize the incision size necessary to utilize the tool. Some embodiments feature details of the cutting tool that interface with a surgical cutting guide system. Other embodiments describe a cutting tool with a selectively changeable length of the cutting profile of the wire cutting member. In one embodiment, the wire cutting member of the cutting tool is energized by mechanical energy in the form of a unidirectional rotation of the cutting member, a mechanical vibration of the cutting member, or an oscillating movement of the wire cutting member.
Owner:PUGET BIOVENTURES
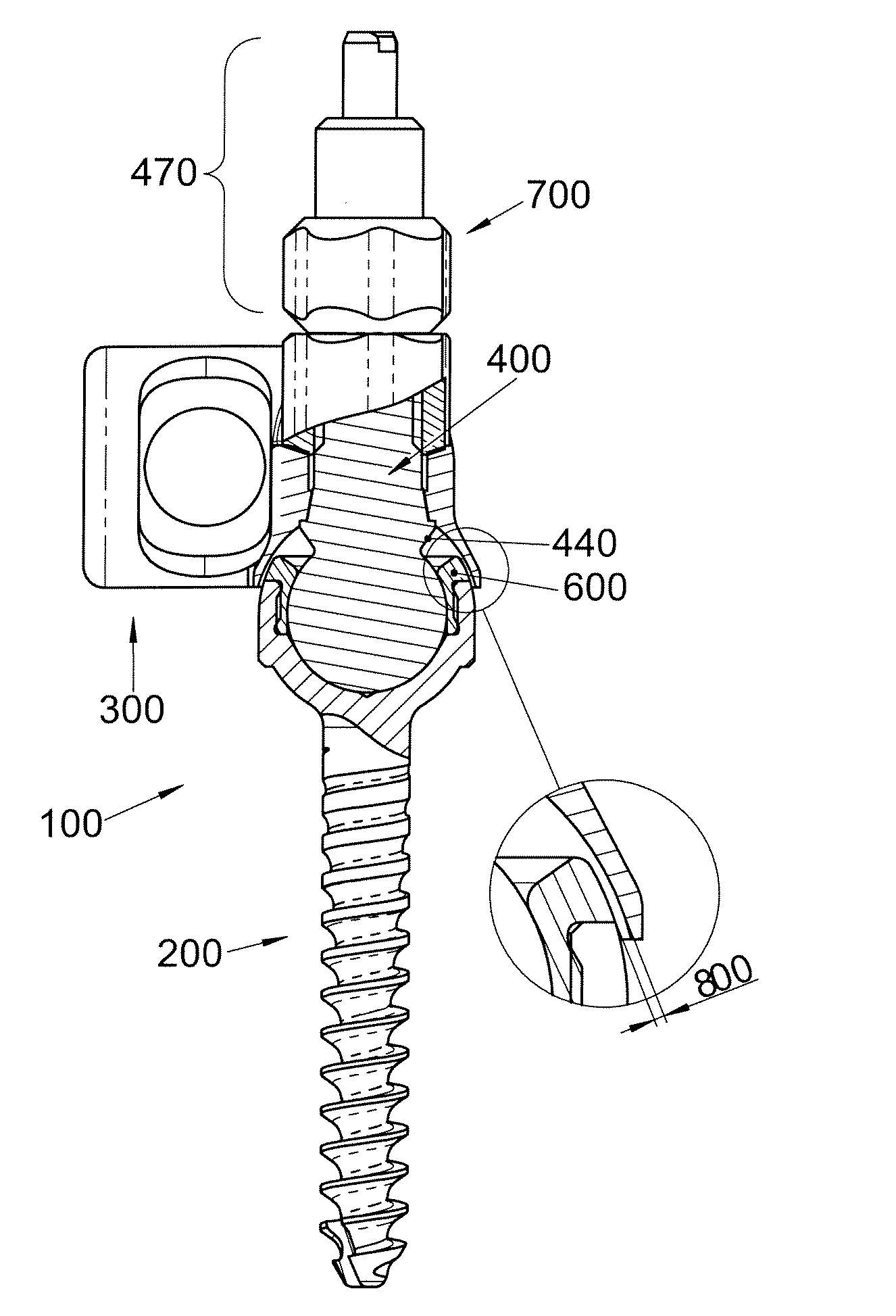
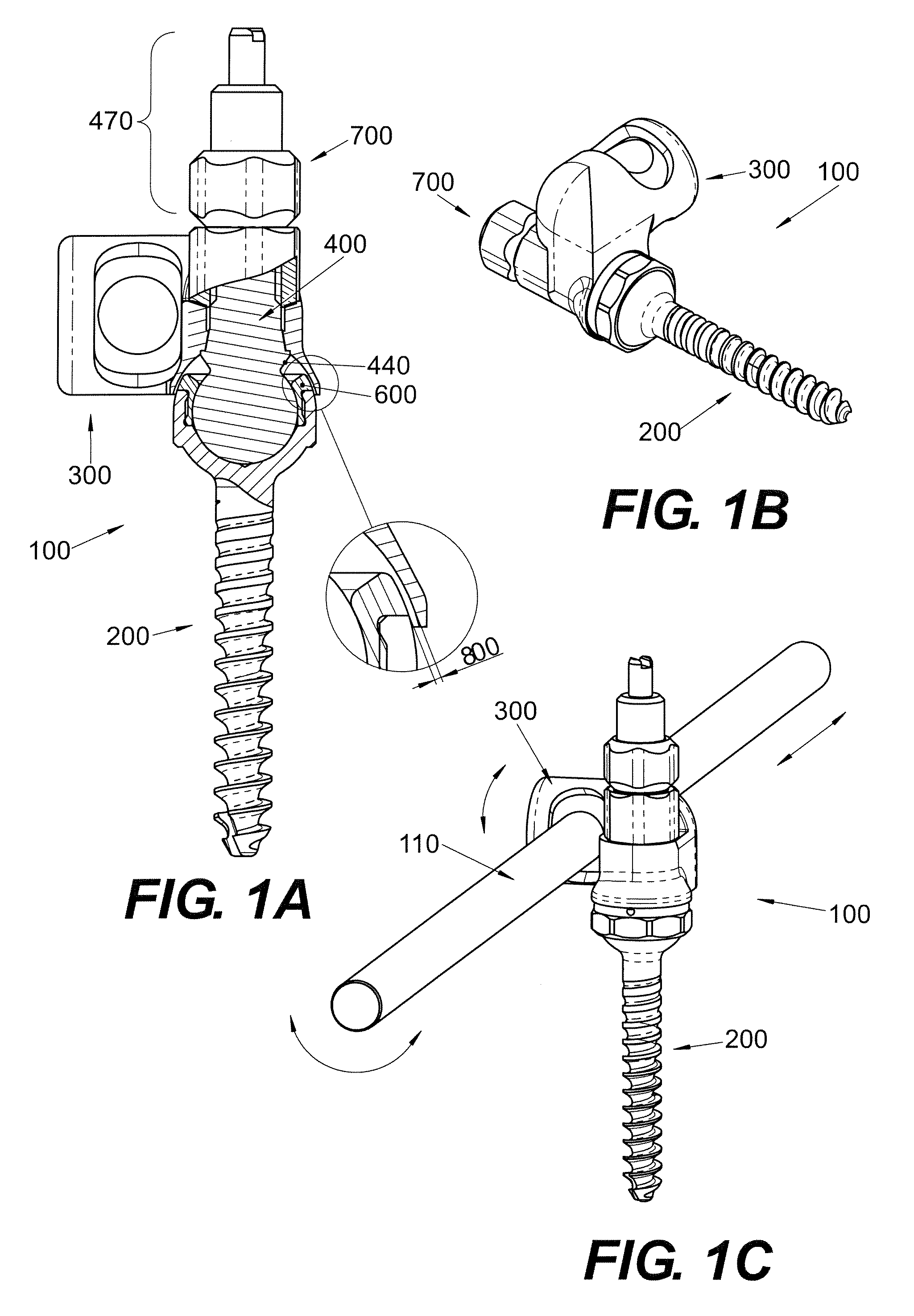
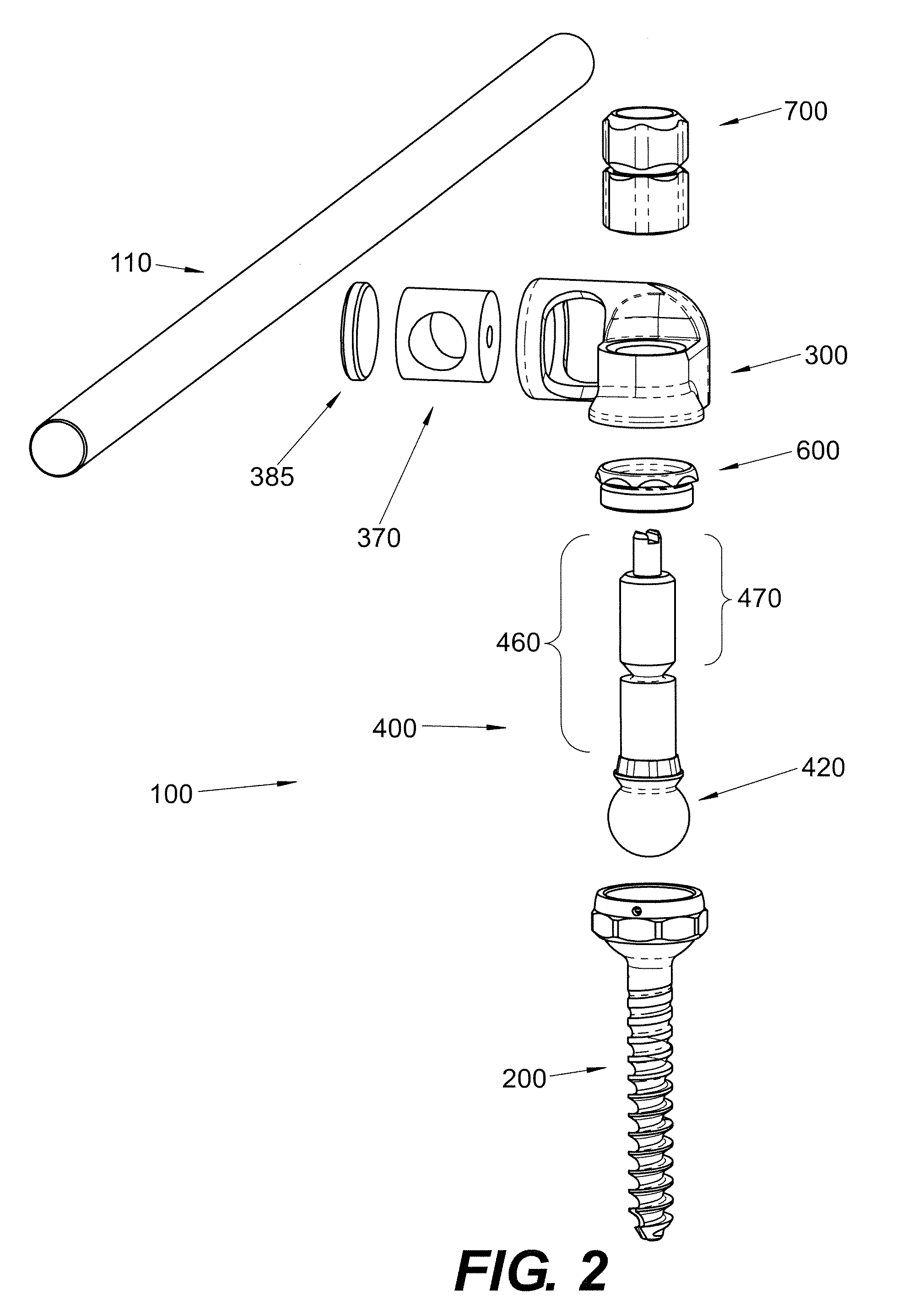
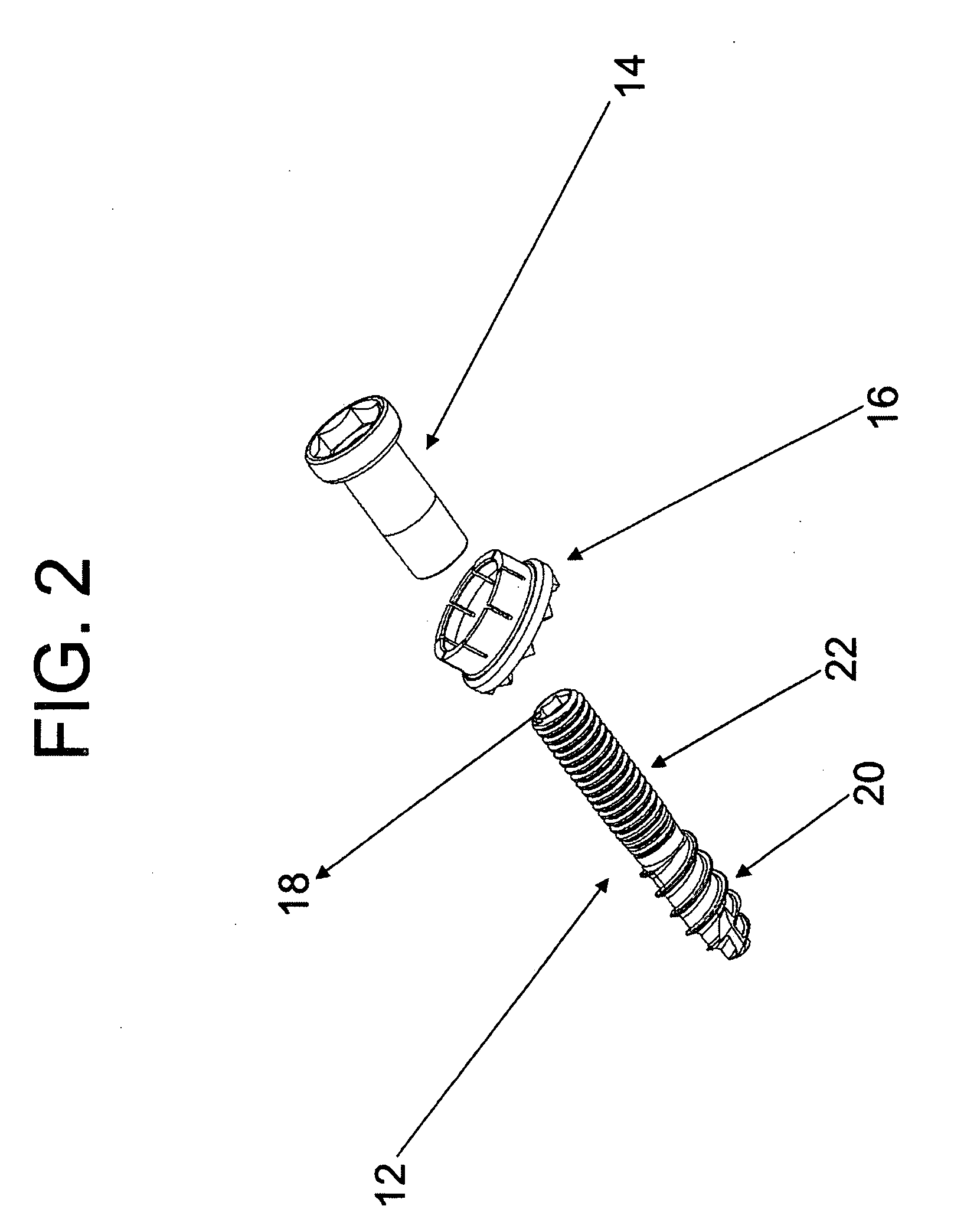
Polyaxial Screw
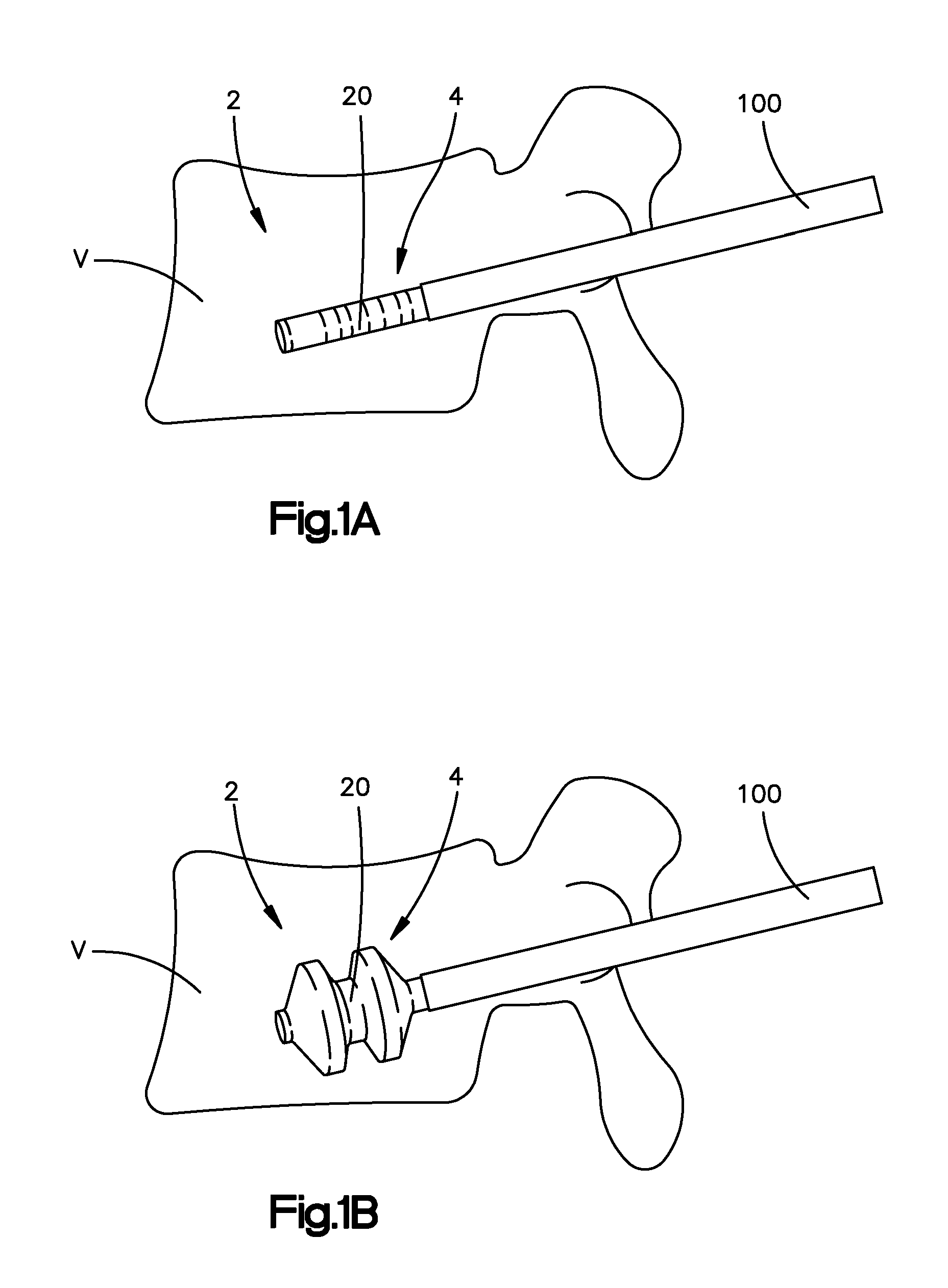
A bone-anchoring device is provided. The bone-anchoring device may comprise a screw including a threaded shaft portion configured to engage bone tissue, and a head portion having a cup-shaped cavity. The device may further include a rod connector and a linking member, wherein the linking member includes a spherical head portion configured to engage the cup-shaped cavity of the head of the screw, a widened flange s configured to engage the linking member, and an elongate body extending from the widened flange portion and configured to extend through an opening in the rod connector.
Owner:PARADIGM SPINE LLC
Facet Fixation Prosthesis
A facet screw system for surgical implantation into bone tissue having a shaft, a compression member and a washer. The shaft includes a shaft having a bone engaging portion and a compression member engaging portion. The compression member includes a spherical head portion having a recess for engaging with a driving instrument, and an elongated coupling portion having internal threads for coupling with the compression member engaging portion of the shaft and a washer coupled to the spherical head portion of the compression member and having a plurality of bone engaging protrusions. The washer is adapted to be polyaxially rotatable with respect to the compression member.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Tissue removal probe with sliding burr in cutting window
InactiveUS20050197661A1Endoscopic cutting instrumentsAbrasive surgical cuttersDrive shaftBone tissue
A probe and method for removing tissue is provided. The probe comprises an elongated member, a window laterally formed on the distal end of the member, a drive shaft rotatably disposed within the lumen of the member, and a rotatable and longitudinally slidable tissue removal element disposed on the drive shaft. The probe can be used to remove tissue along the window of the probe. In one method, target tissue along the window, e.g., bone tissue, can be removed without removing non-target tissue, e.g., nerve tissue, by rotating and longitudinally sliding the tissue removal element relative to the window.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Implantable biomimetic prosthetic bone
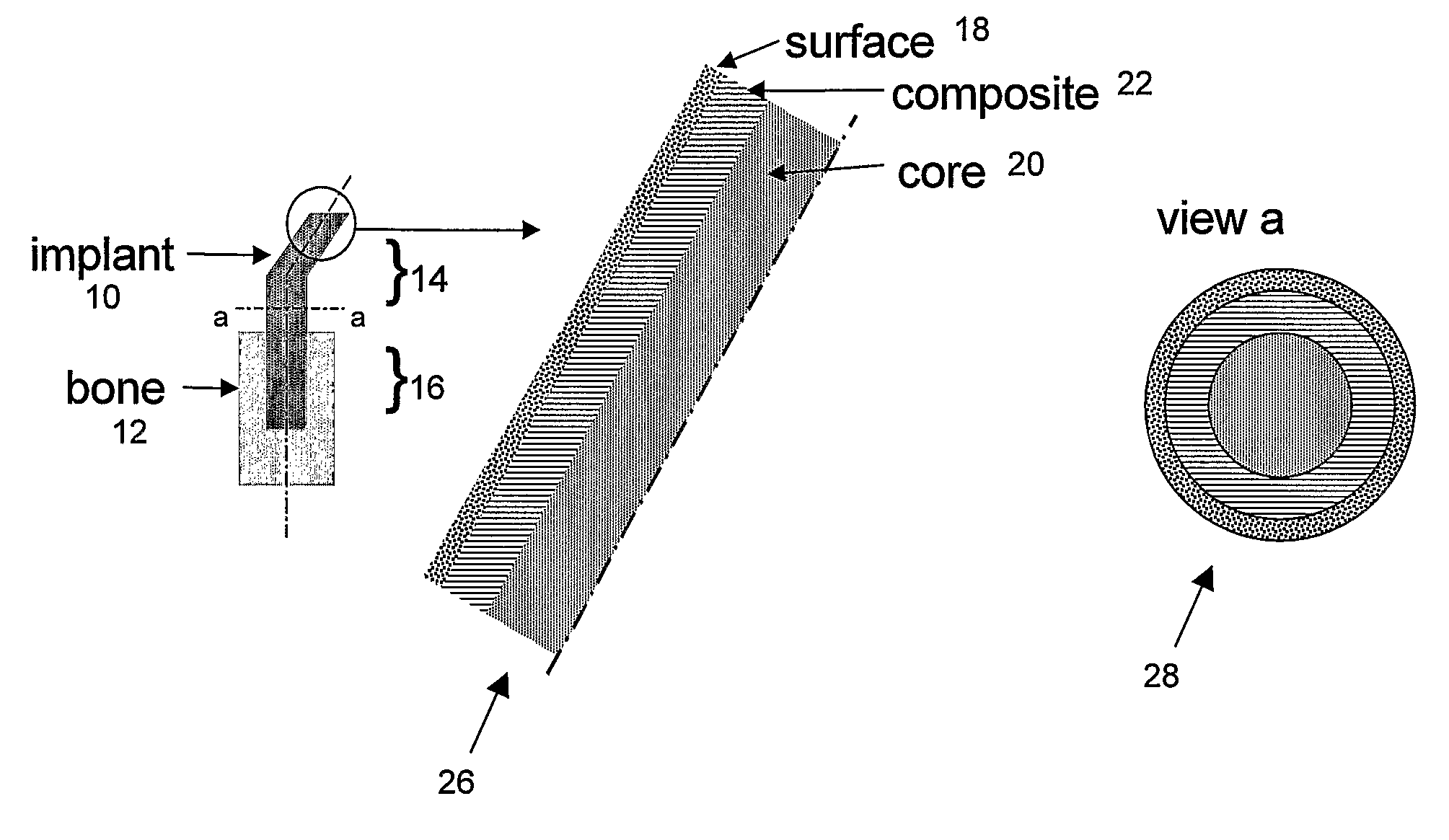
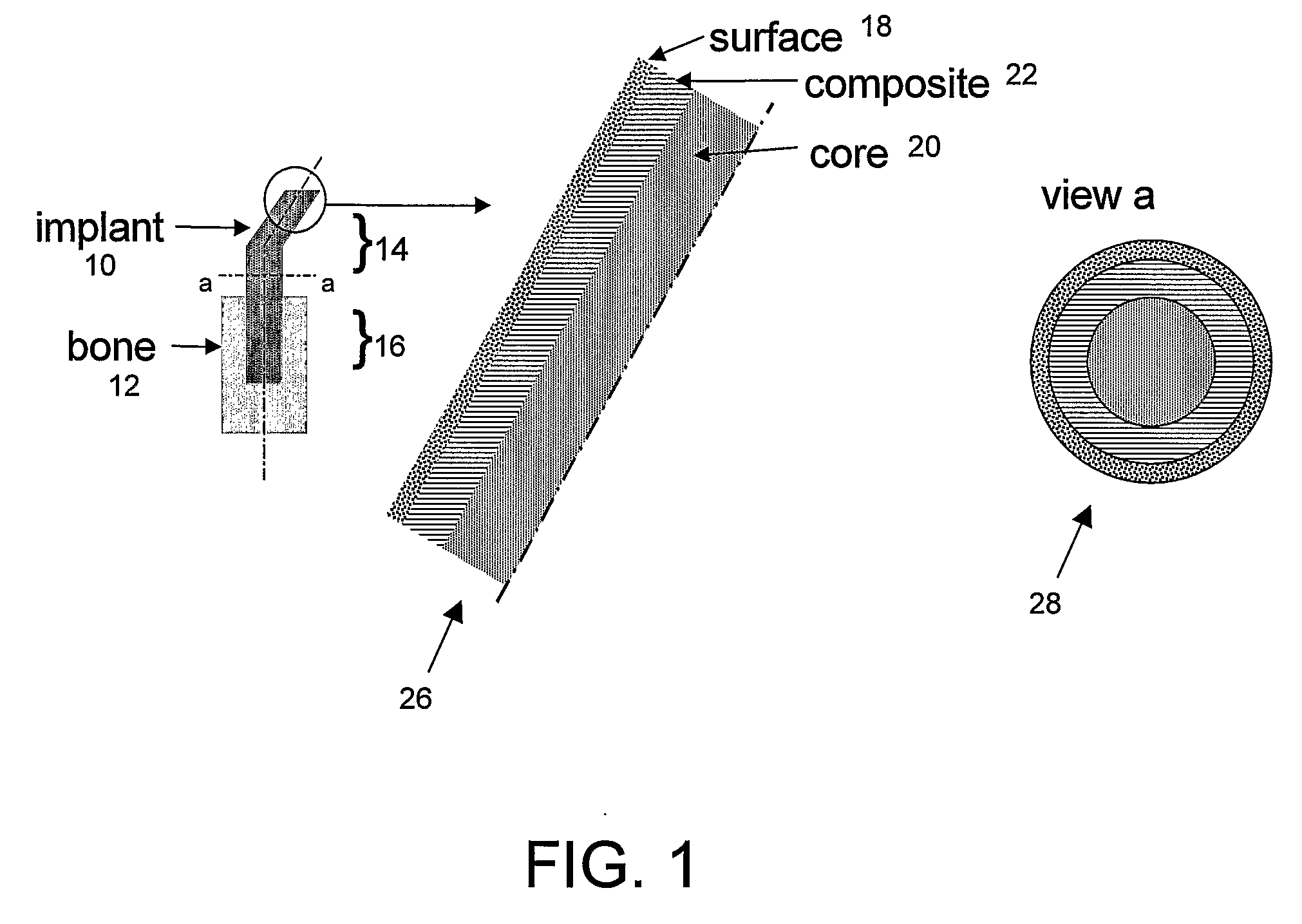
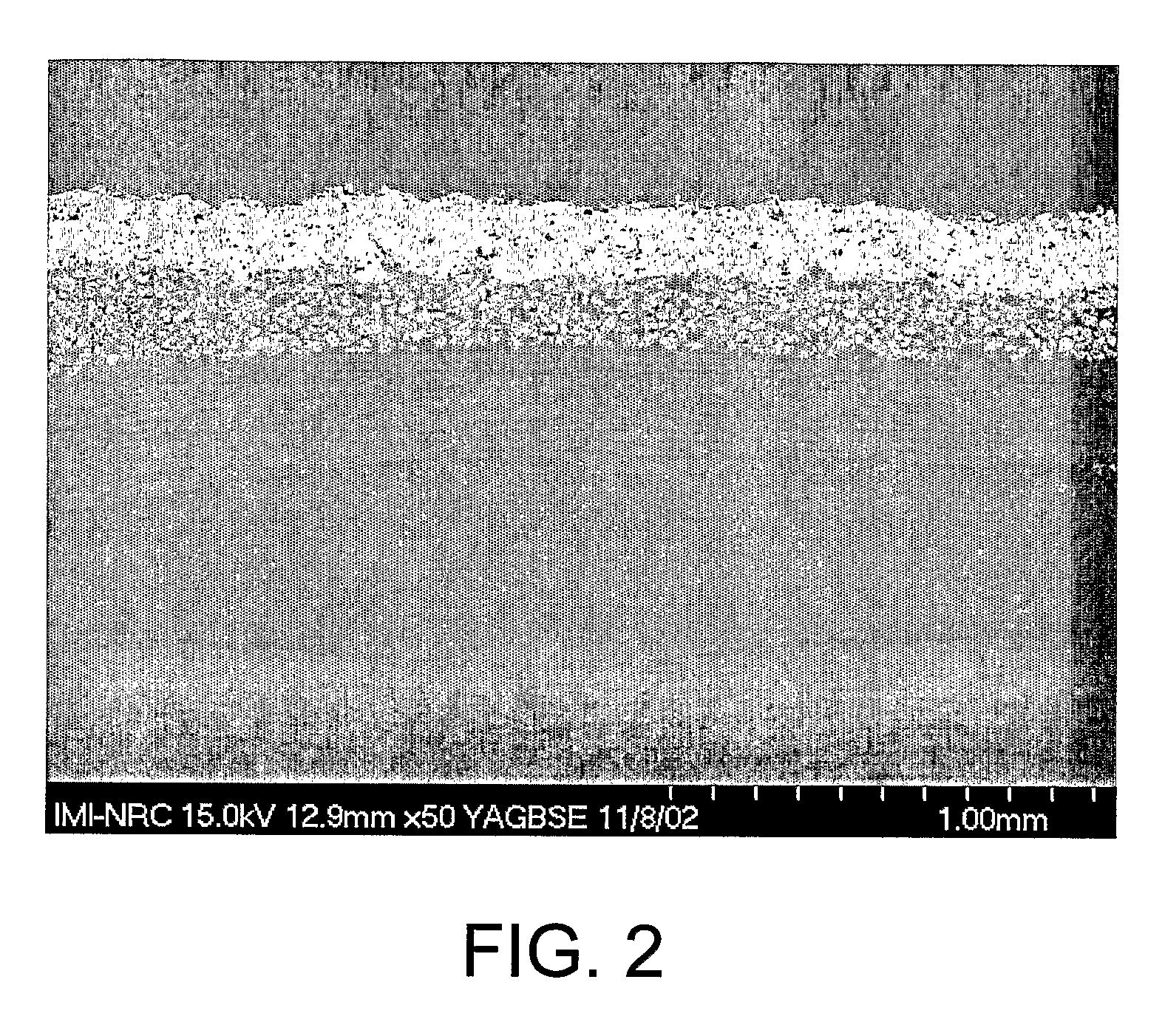
InactiveUS20090177282A1Reduce riskMolten spray coatingLamination ancillary operationsNormal boneFiber-reinforced composite
Bone tissue at the interface of a bone implant is shielded from stresses found in normal bone because of the higher stiffness or rigidity in the implant versus in bone. The resulting “stress shielding” of the bone by the implant eventually results in resorption of bone at the bone-implant interface and ultimately necessitates replacement of the bone implant. To overcome these problems, an implantable biomimetic prosthetic bone having a porous surface, a fiber-reinforced composite structure, and a polymer-based core is disclosed. The prosthetic bone is a good match for structure, stiffness, viscoelastic properties, specific weight and overall structure as real bone or host tissues adjacent to the prosthetic bone. The prosthetic bone may be formed as a total hip prosthesis.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Implantable devices and methods for treating micro-architecture deterioration of bone tissue
InactiveUS20090234398A1Prevent movementInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBone tissueImplanted device
Owner:SPINEALIGN MEDICAL
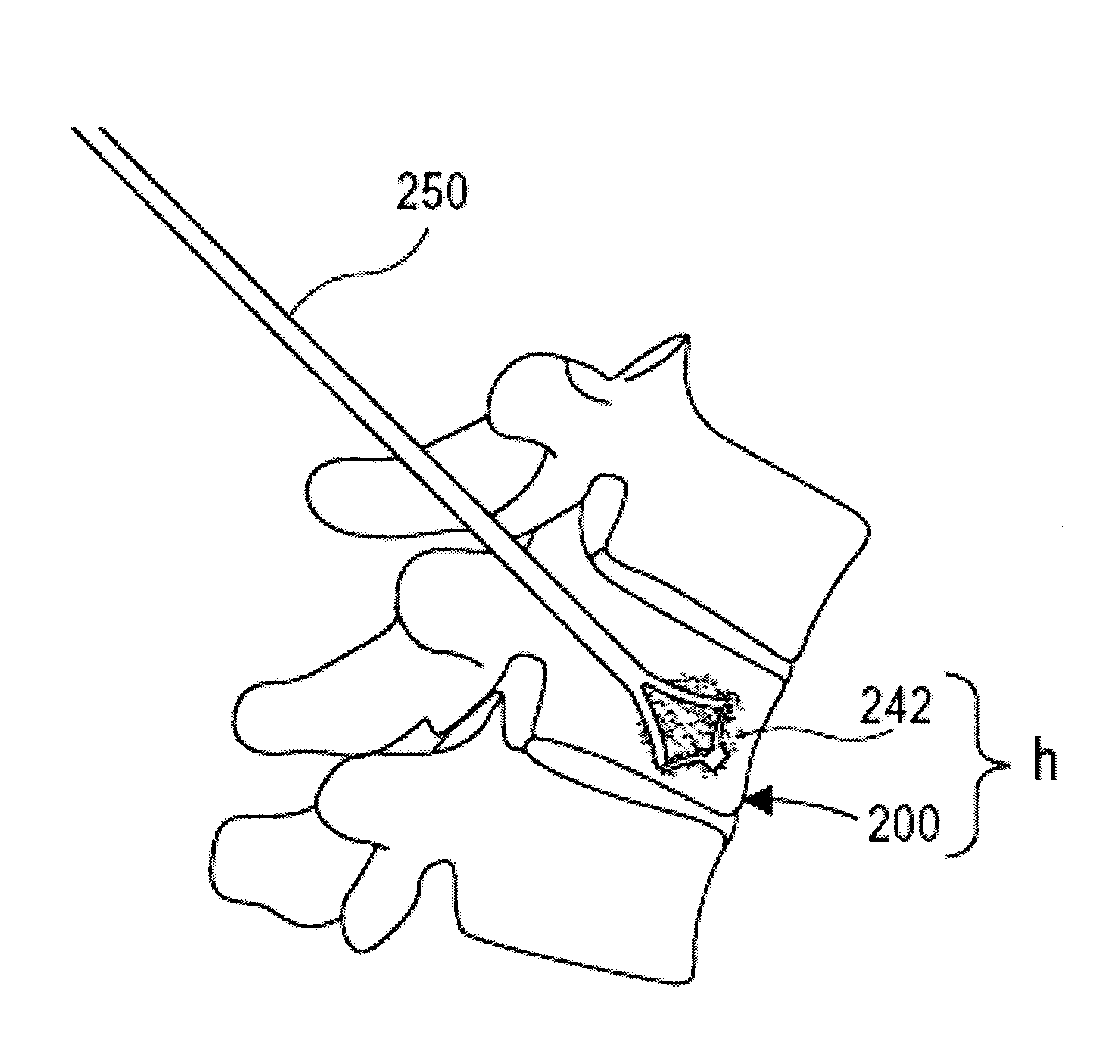
Porous containment device and associated method for stabilization of vertebral compression fractures
ActiveUS20100262240A1Restoring anatomyEasy to optimizeInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsFilling materialsMedicine
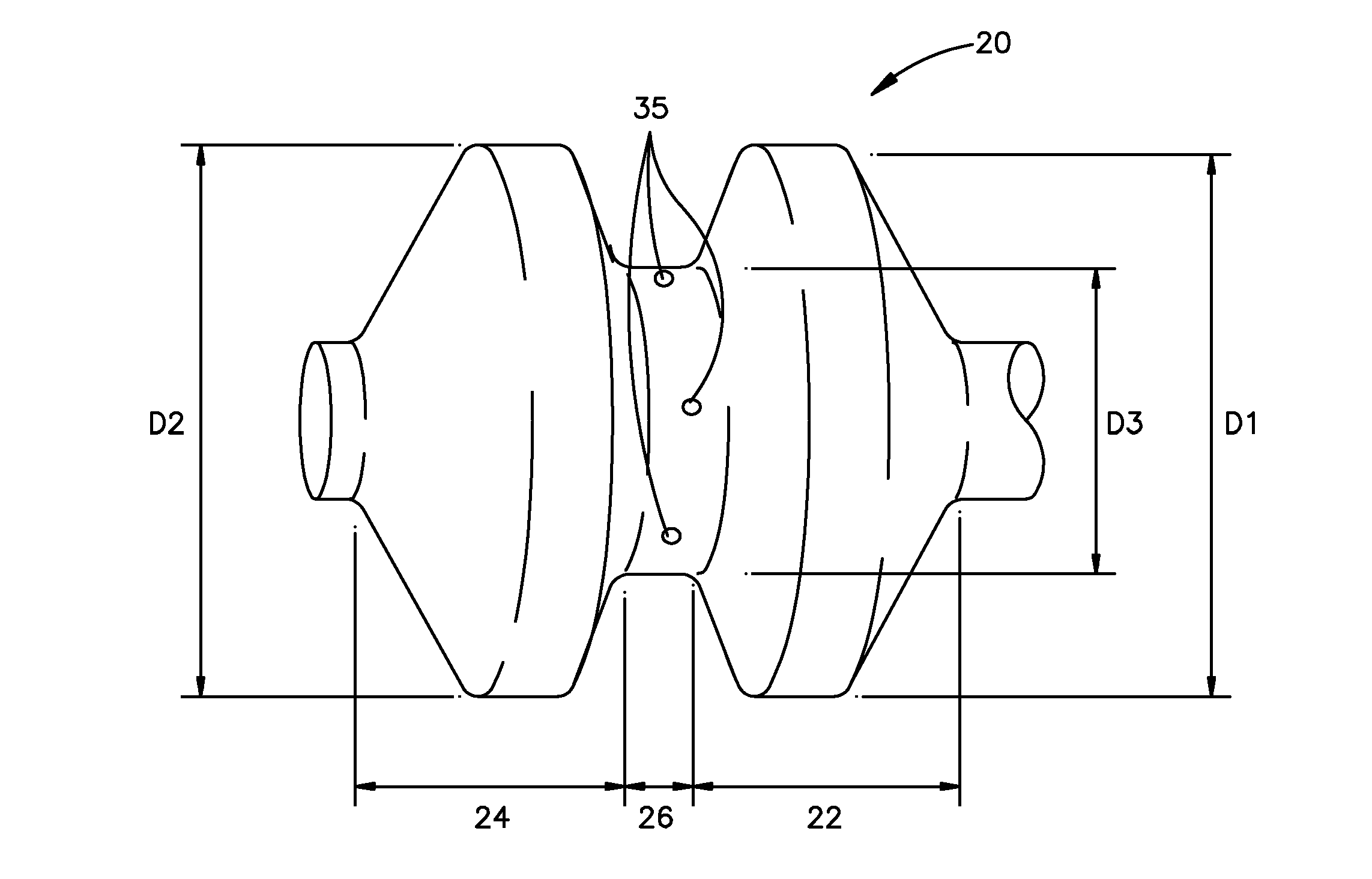
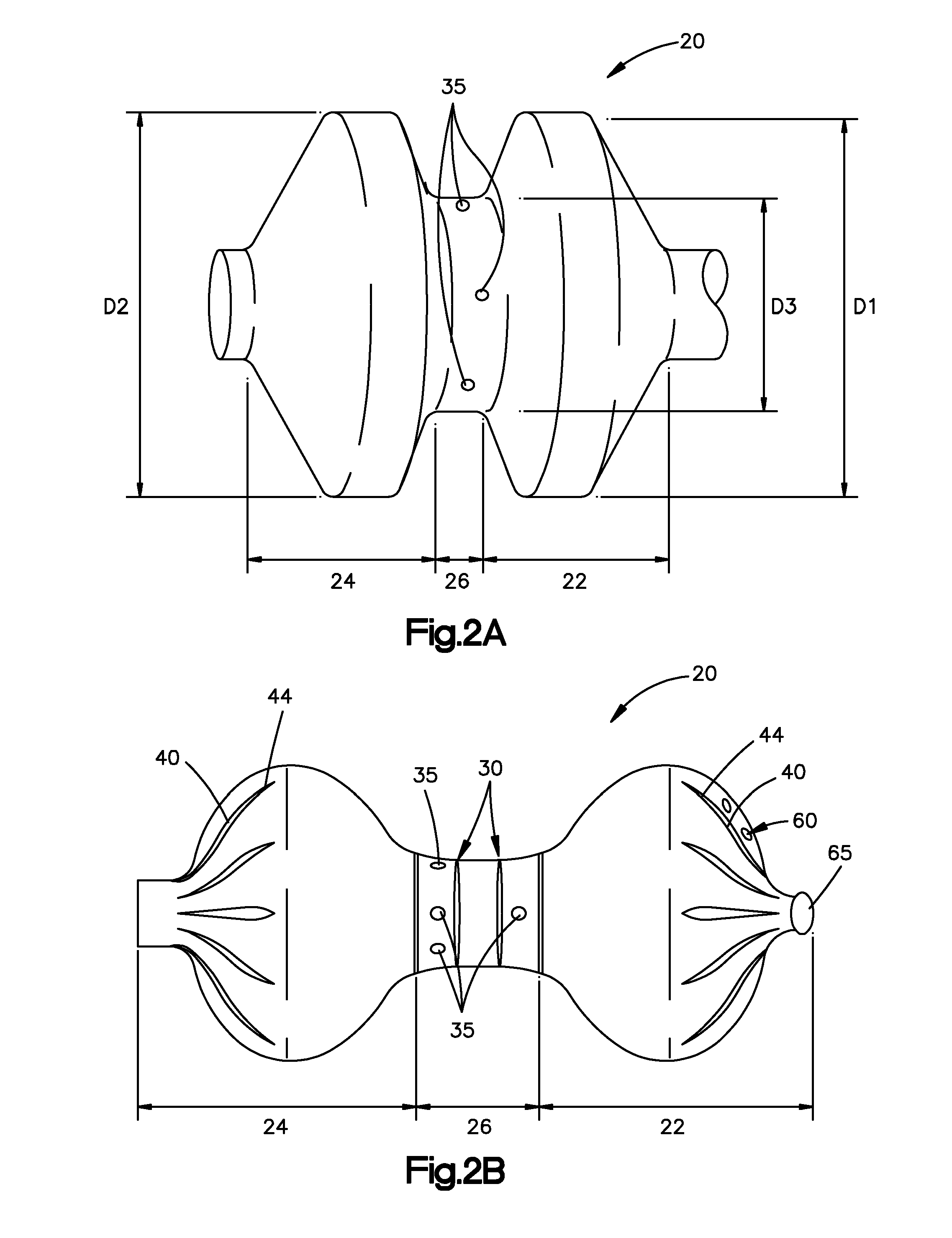
The present invention is directed to a porous or permeable containment device for implanting into the interior volume of a targeted vertebral body for use in restoring the anatomy of the targeted vertebral body. The containment device is expandable from an insertion configuration to an expanded configuration via, for example, a bone filler material. The containment device preferably permits the bone filler material to flow out of the containment device via, for example, one or more pores, one or more flow-directing tentacles, etc. so that the bone filler material may interdigitates with the surrounding bone tissue. The containment device is preferably configured to have a pre-determined, ‘dog-bone’ shape, when in the expanded configuration. The containment device preferably also includes one or more knobs or ribs to facilitate anchoring of the containment device to the surrounding bone tissue, one or more air or fluid evacuation pores to permit air or fluid from escaping from the interior volume of the containment device and / or one or more radiopacity rings or markers to enable a surgeon to locate and / or position the containment device under X-ray imaging.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Bone replacement materials
ActiveUS20070203584A1Easy adhesionFacilitate cell growthAdditive manufacturing apparatusBone implantBone tissueBone tissue engineering
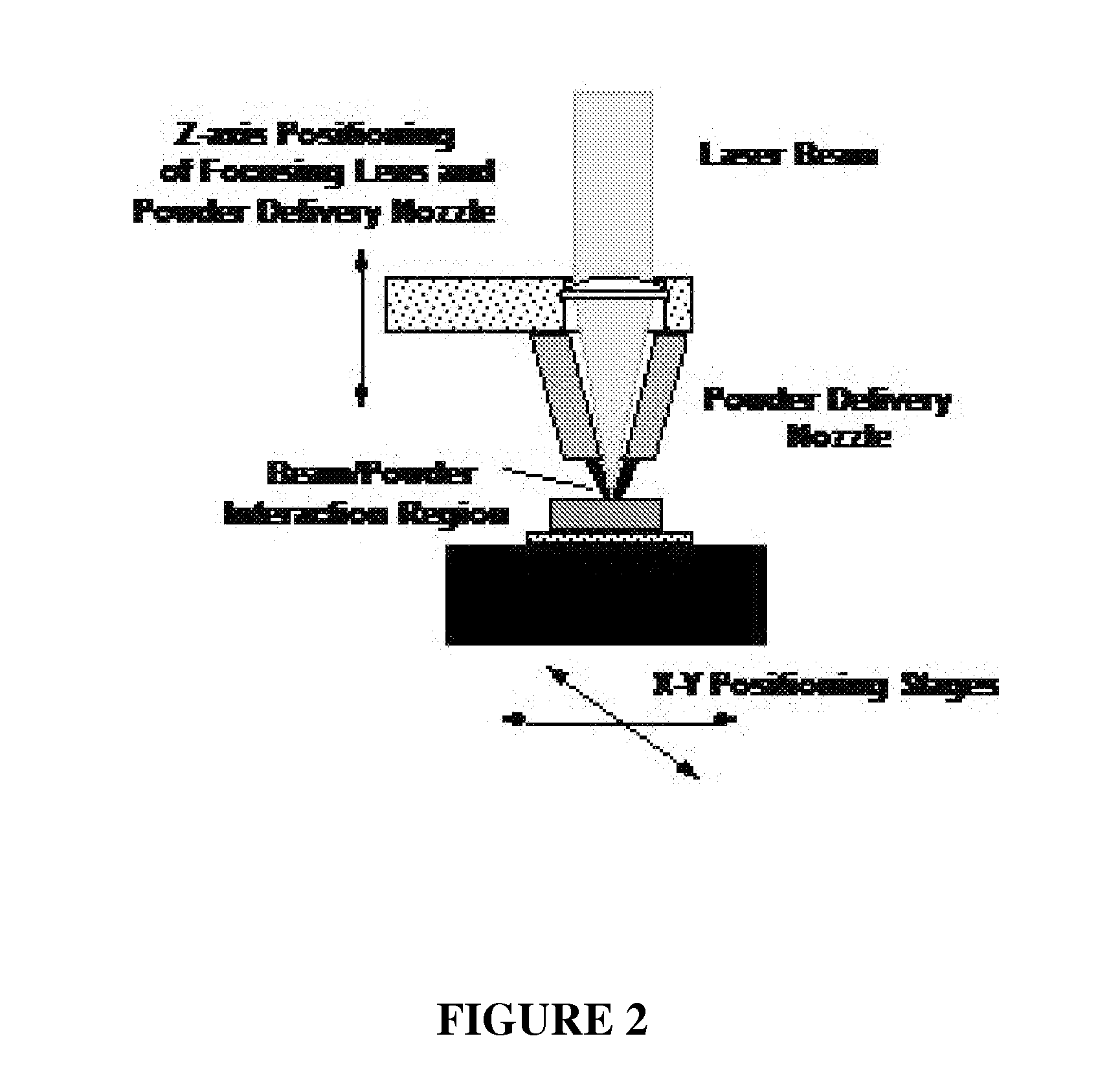
Particular aspects provide novel devices for bone tissue engineering, comprising a metal or metal-based composite member / material comprising an interior macroporous structure in which porosity may vary from 0-90% (v), the member comprising a surface region having a surface pore size, porosity, and composition designed to encourage cell growth and adhesion thereon, to provide a device suitable for bone tissue engineering in a recipient subject. In certain aspects, the device further comprises a gradient of pore size, porosity, and material composition extending from the surface region throughout the interior of the device, wherein the gradient transition is continuous, discontinuous or seamless and the growth of cells extending from the surface region inward is promoted. Additional aspects provide a device for bone tissue engineering, comprising a metal or metal-based composite member / material comprising an interior porous structure, wherein the pore size, porosity and material composition is selected to provide a device having an optimal density and / or elastic modulus and / or compression strength for a specific recipient. Novel methods for fabricating the devices are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON STATE UNIVERSITY
Interbody fusion device and method for restoration of normal spinal anatomy
InactiveUS7238186B2Maintain patency and stabilityRapid and stable arthrodesisInternal osteosythesisBone implantSpinal columnPorous tantalum
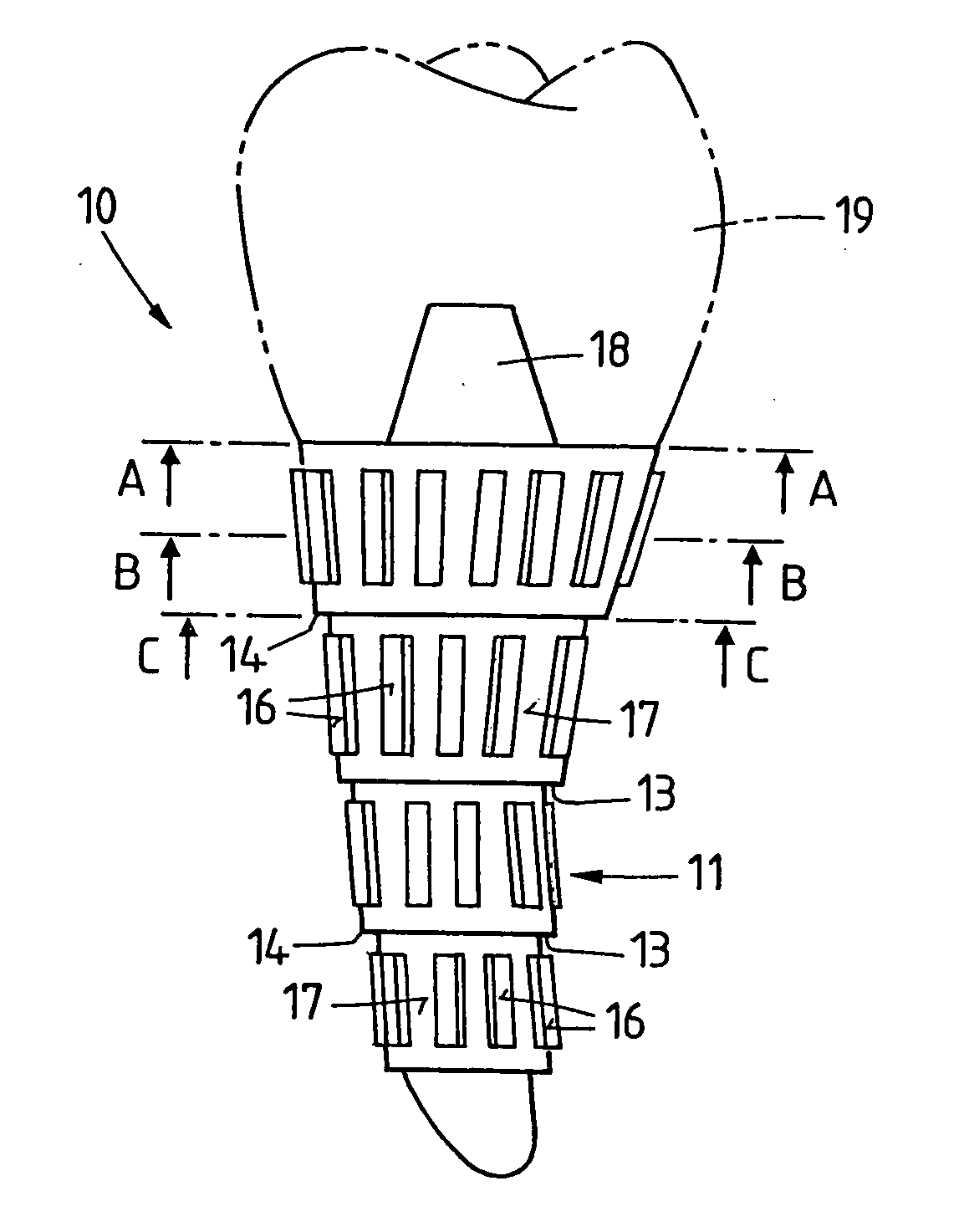
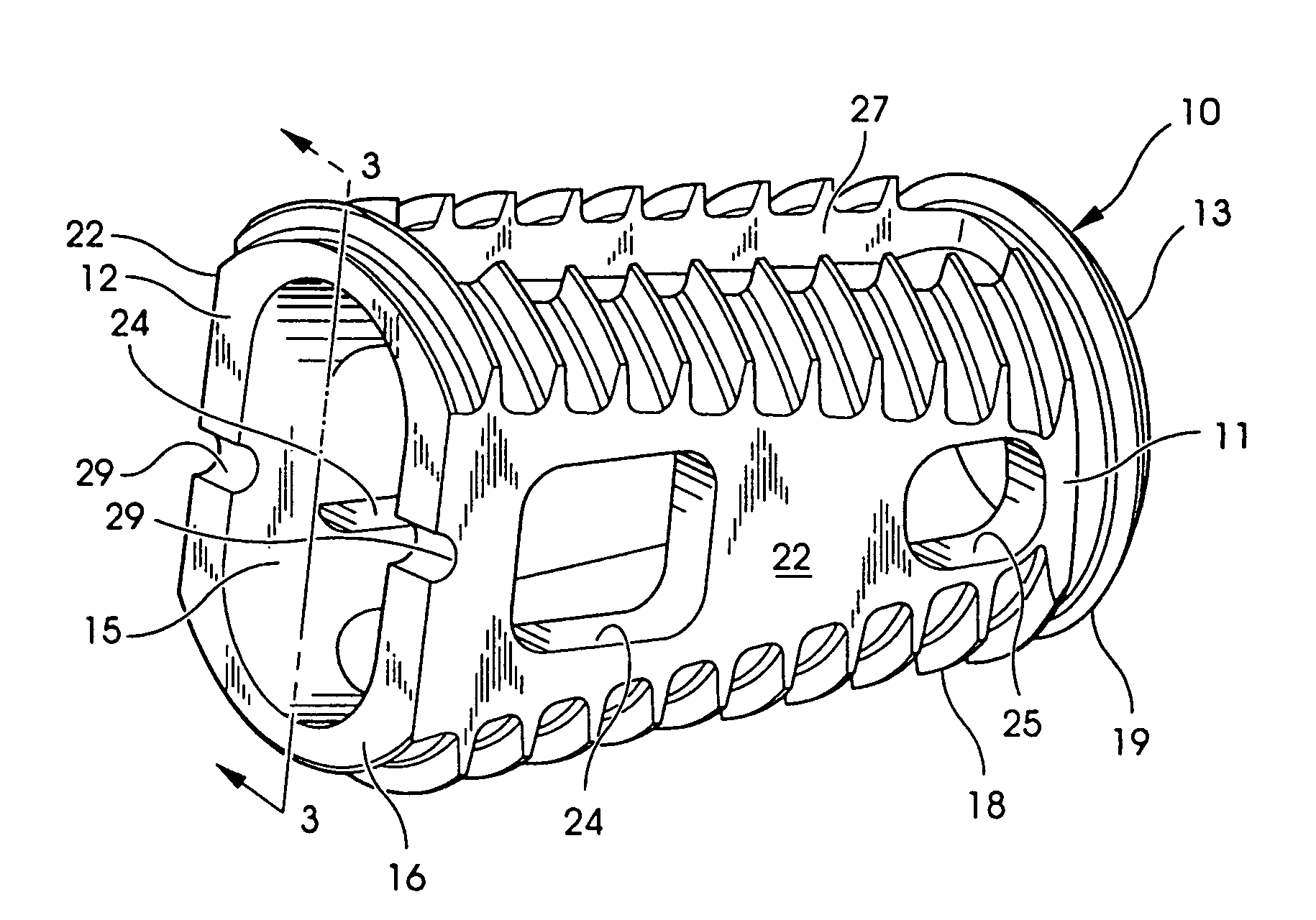
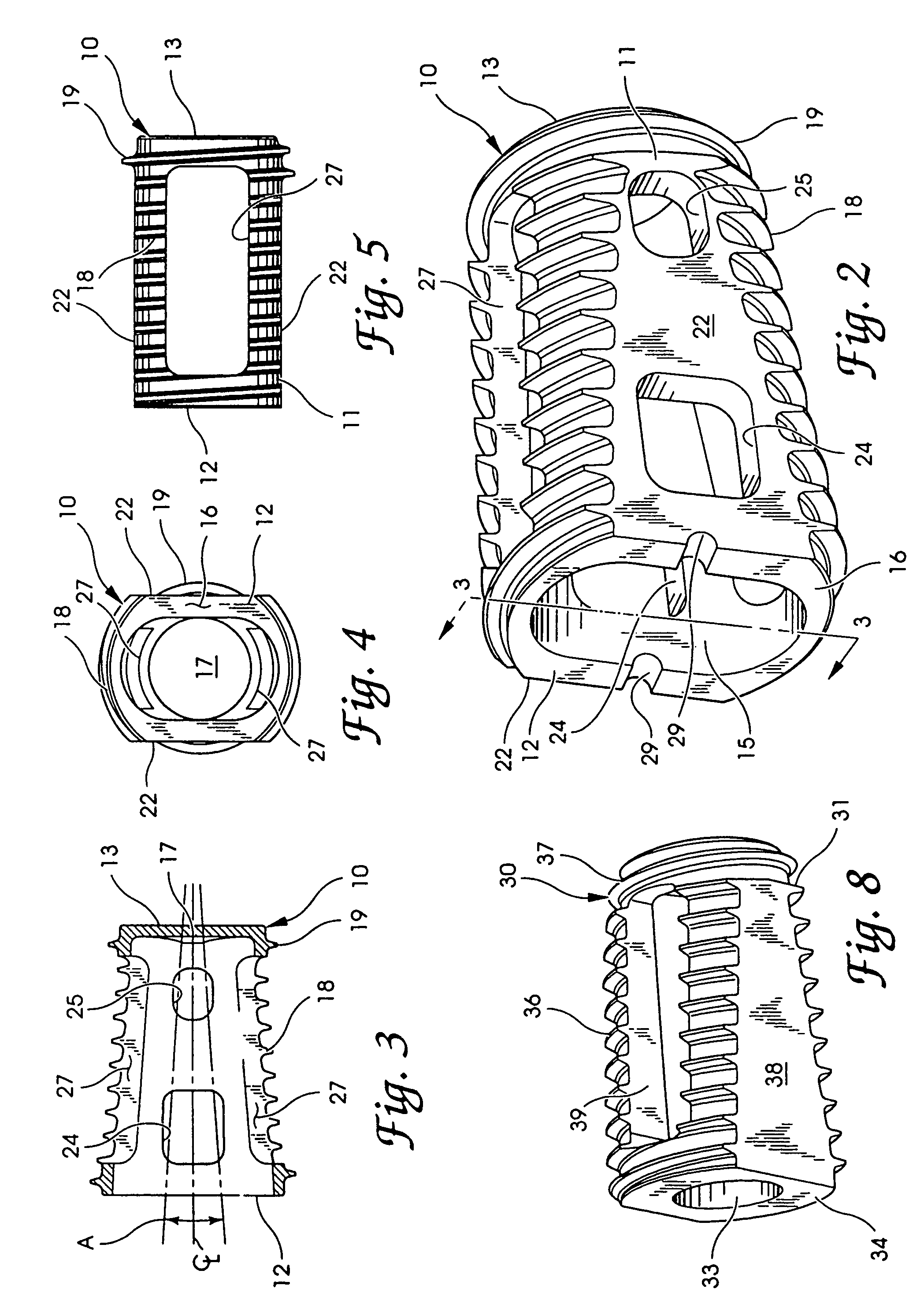
An interbody fusion device in one embodiment includes a tapered body defining a hollow interior for receiving bone graft or bone substitute material. The body defines exterior threads which are interrupted over portions of the outer surface of the device. The fusion device defines truncated side walls so that on end view the body takes on a cylindrical form. The side walls are provided with vascularization openings, and the body wall device includes opposite bone ingrowth slots extending through the interrupted thread portion of the body. In another embodiment, the tapered body is solid and formed of a porous biocompatible material having sufficient structural integrity to maintain the intradiscal space and normal curvature. The material is preferably a porous tantalum having fully interconnected pores to facilitate complete bone tissue ingrowth into the implant. An implant driver is provided which engages the truncated side walls to complete the cylindrical form of the implant at the root diameter of the interrupted threads, to thereby facilitate threaded insertion of the implant to the intra-discal space between adjacent vertebrae. Methods for posterior and anterior insertion of the fusion device are also disclosed.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Dilation introducer for orthopedic surgery
InactiveUS20060030872A1Easy to observeLowering chance damageCannulasSurgical needlesMini invasive surgeryDilator
The dilation introducer has a locked assembled configuration for placement of the dilation introducer against a patient's bone tissue to be treated, and an unlocked, collapsed configuration for dilating the patient's soft tissue down to the bone tissue to be treated to a desired degree of dilation to permit minimally invasive surgical procedures on the patient's bone tissue to be treated. Dilator tubes are successively released and advanced to progressively expand the patient's soft tissue down to the bone tissue to be treated. A method for a minimally invasive procedure utilizing the telescoping dilation introducer to insert a bone fixation device into a patient's spine for posterior spine fusion is also provided.
Owner:INTERVENTIONAL SPINE
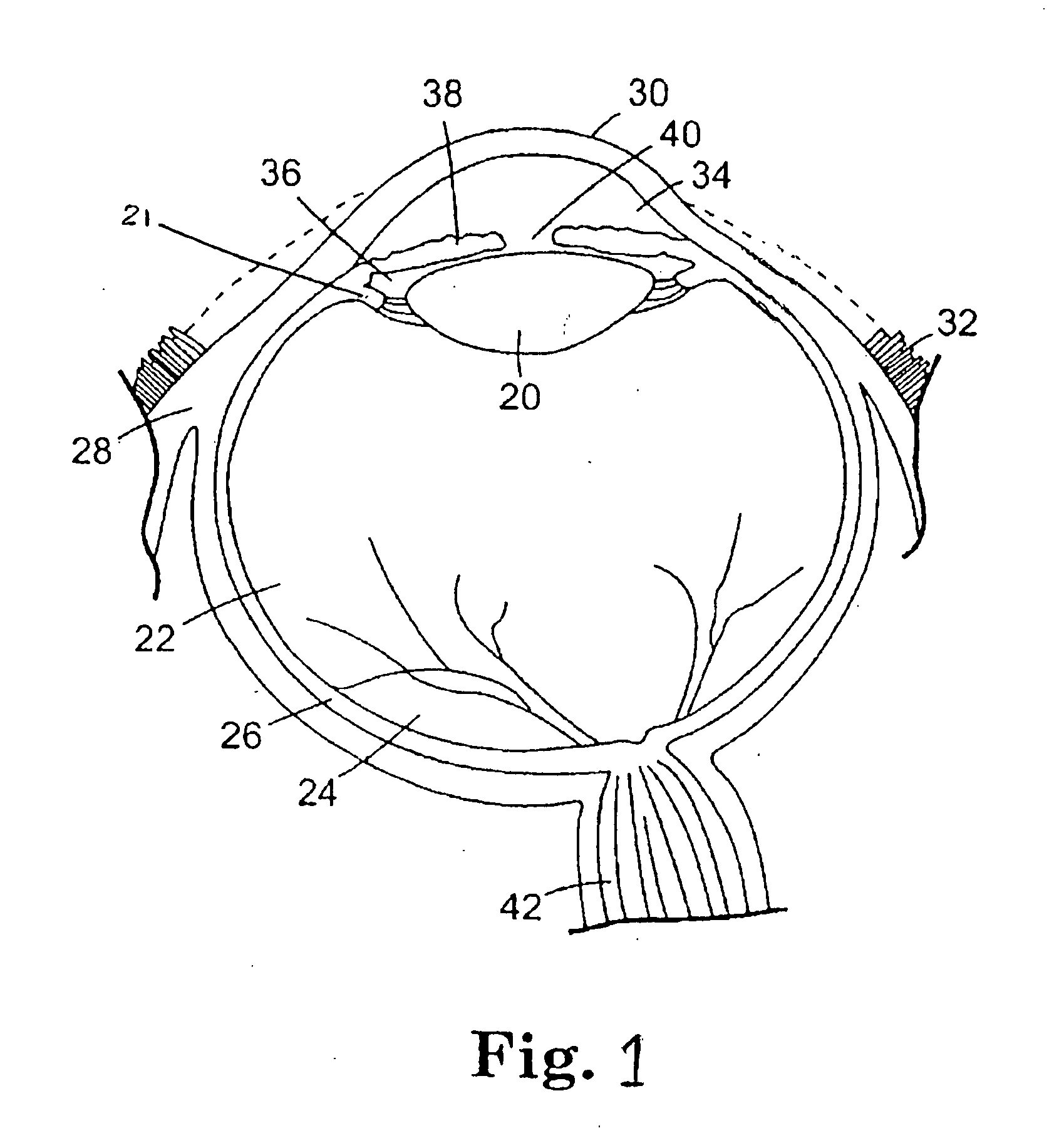
Low profile bioactive agent delivery device
InactiveUS20080057106A1Low external profileMinimize damageEye implantsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDevice implantDistal portion
Disclosed are implantable devices that are configured for implantation through tissue or membrane and into an implantation site comprising viscoelastic fluid or non-osseous tissue. In embodiments of the invention, the implantable devices comprise: (a) a nonlinear body member having a direction of extension, a longitudinal axis along the direction of extension, and a proximal portion and a distal portion, wherein at least a portion of the body member deviates from the direction of extension, (b) a retention element at the proximal portion of the body member, the retention element configured to retain the implantable device at the implantation site, the retention element presenting an external profile of no greater than 0.5 mm when the device is implanted in a patient; and (c) a bioactive agent delivery system at the distal portion of the body member, the bioactive agent delivery system comprising one or more bioactive agents. Also disclosed are methods of delivering a bioactive agent to a patient using the devices.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Bone implants with central chambers
InactiveUS7087082B2Easy to implantRestore disc height and natural curvature of spineJoint implantsSpinal implantsBone tissueBone splinters
A bone fusion implant for repair or replacement of bone includes a hollow body formed from at least two bone fragments which are configured and dimensioned for mutual engagement and which are coupled together. The hollow body may be formed of autograft, allograft, or xenograft bone tissue, and may include a core formed of at least one of bone material and bone inducing substances, with the core being disposed in the hollow body.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
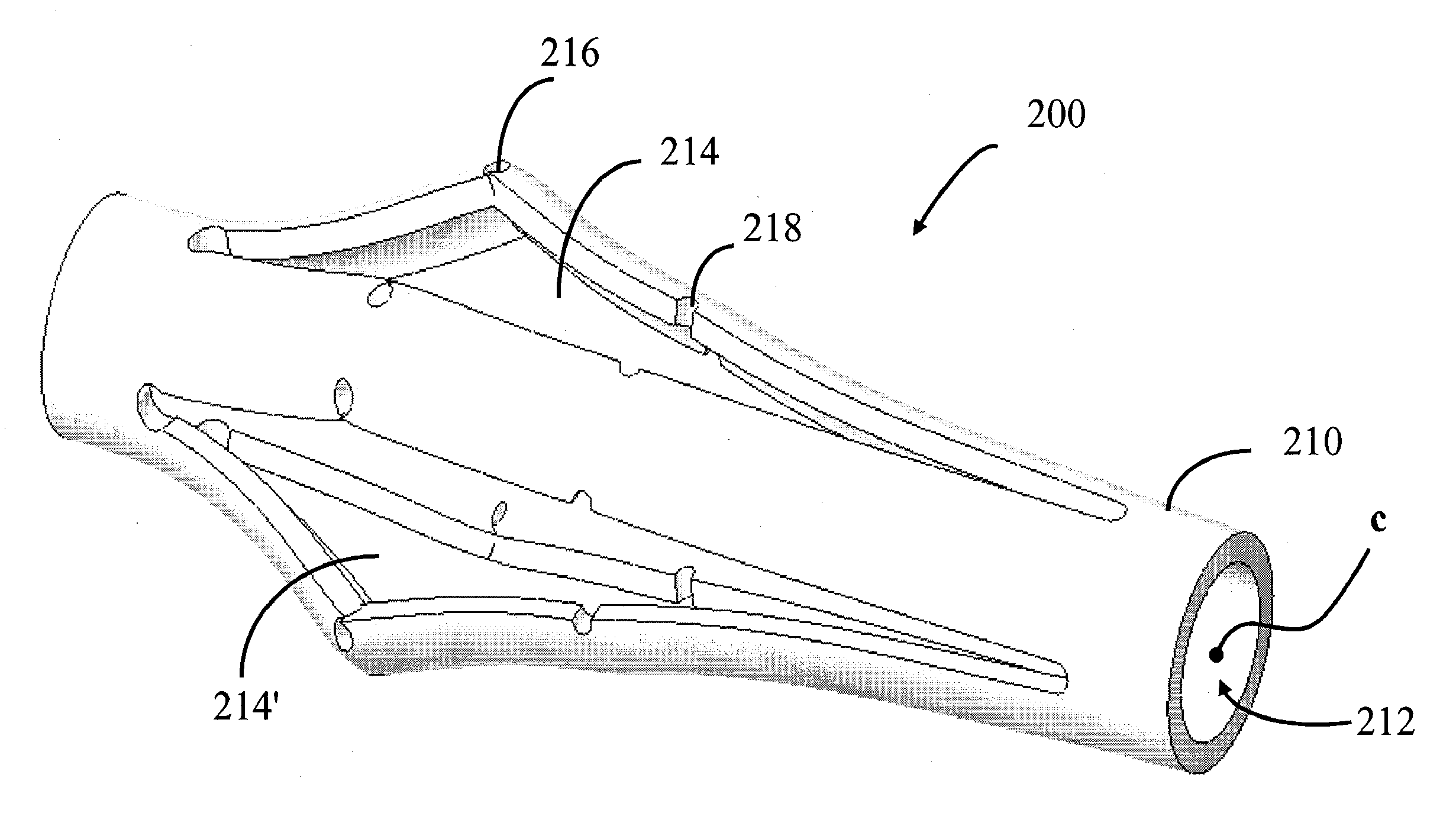
Impacted orthopedic bone support implant
InactiveUS7537616B1Promote bone growthProvide supportBone implantJoint implantsDiseaseBone structure
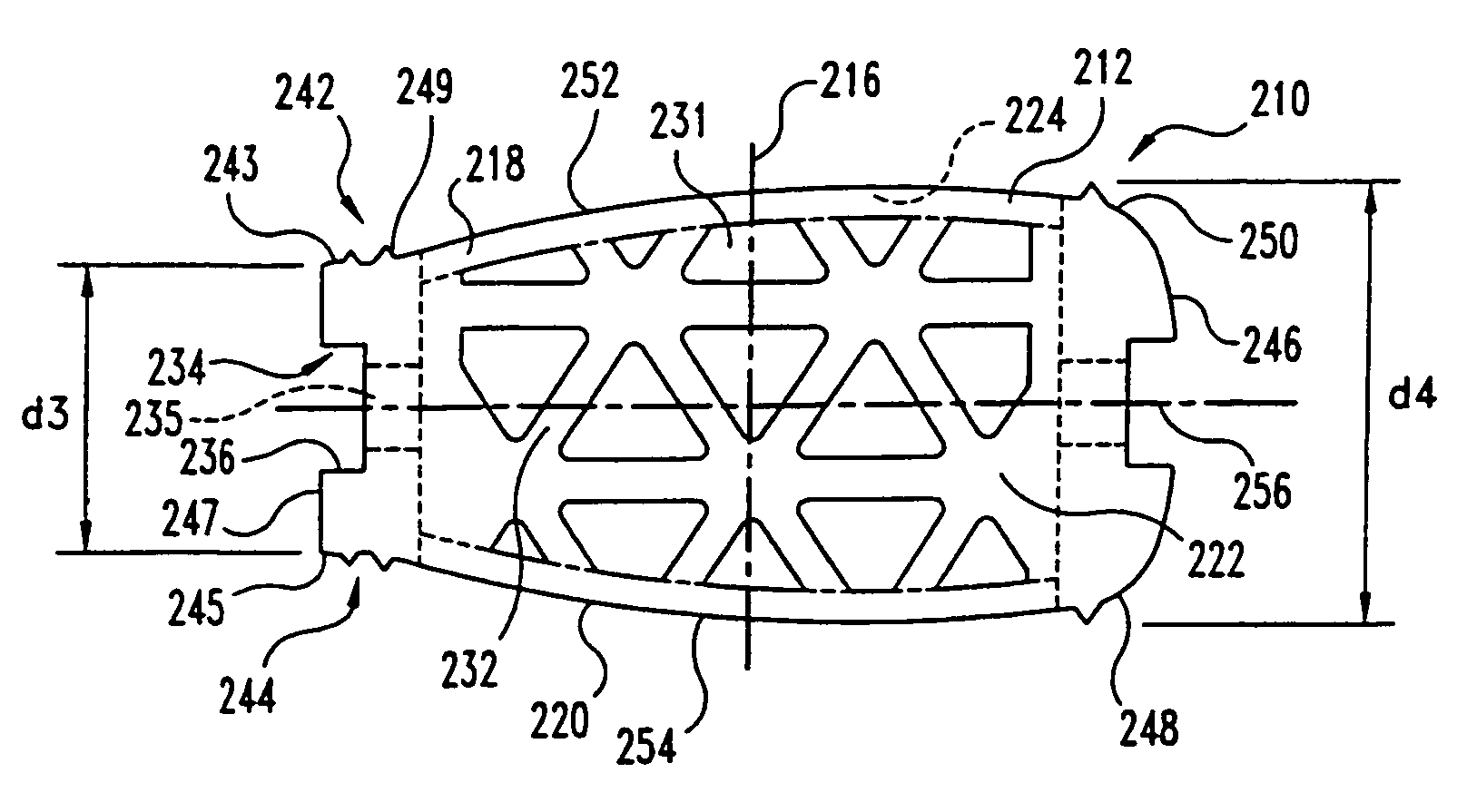
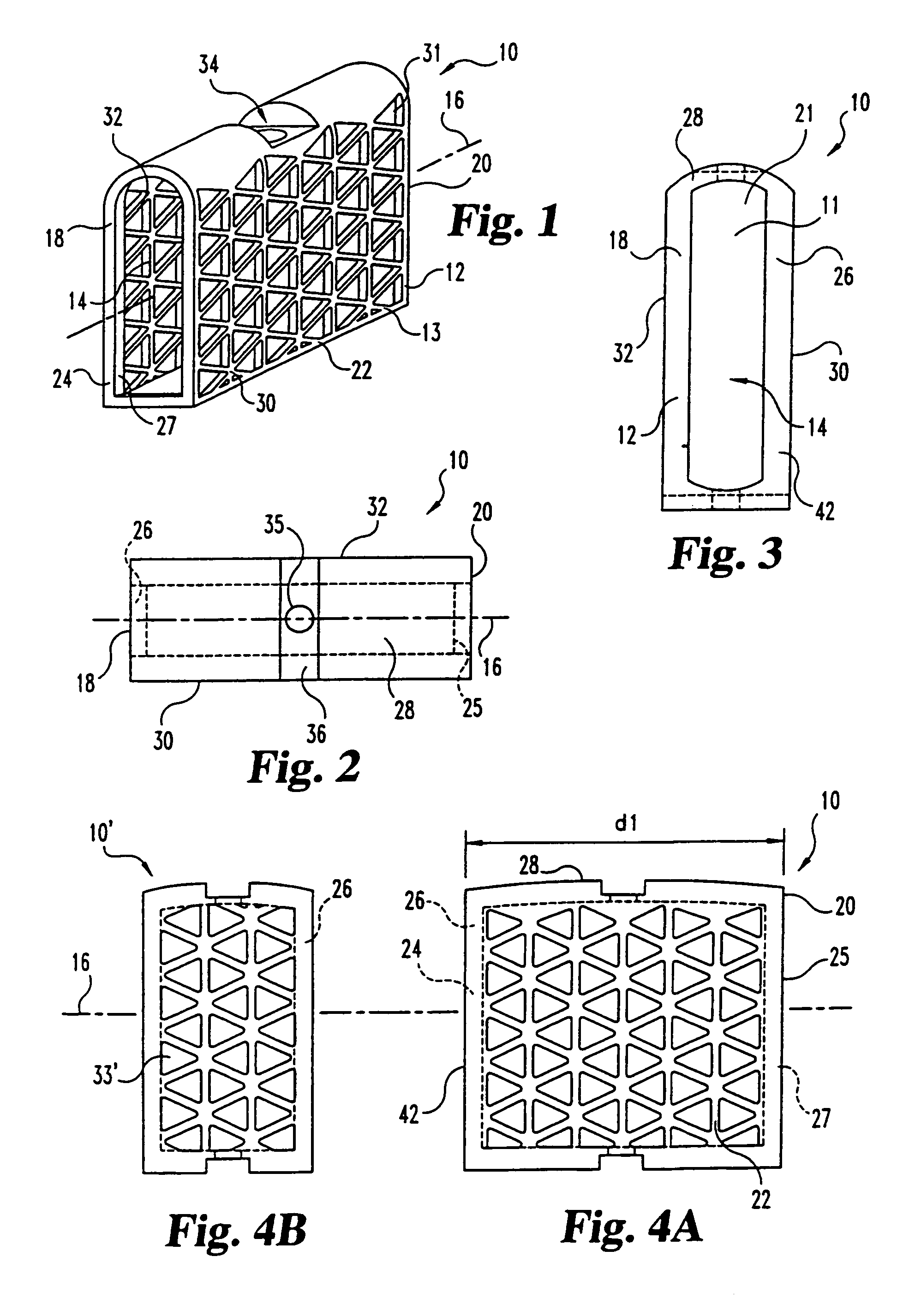
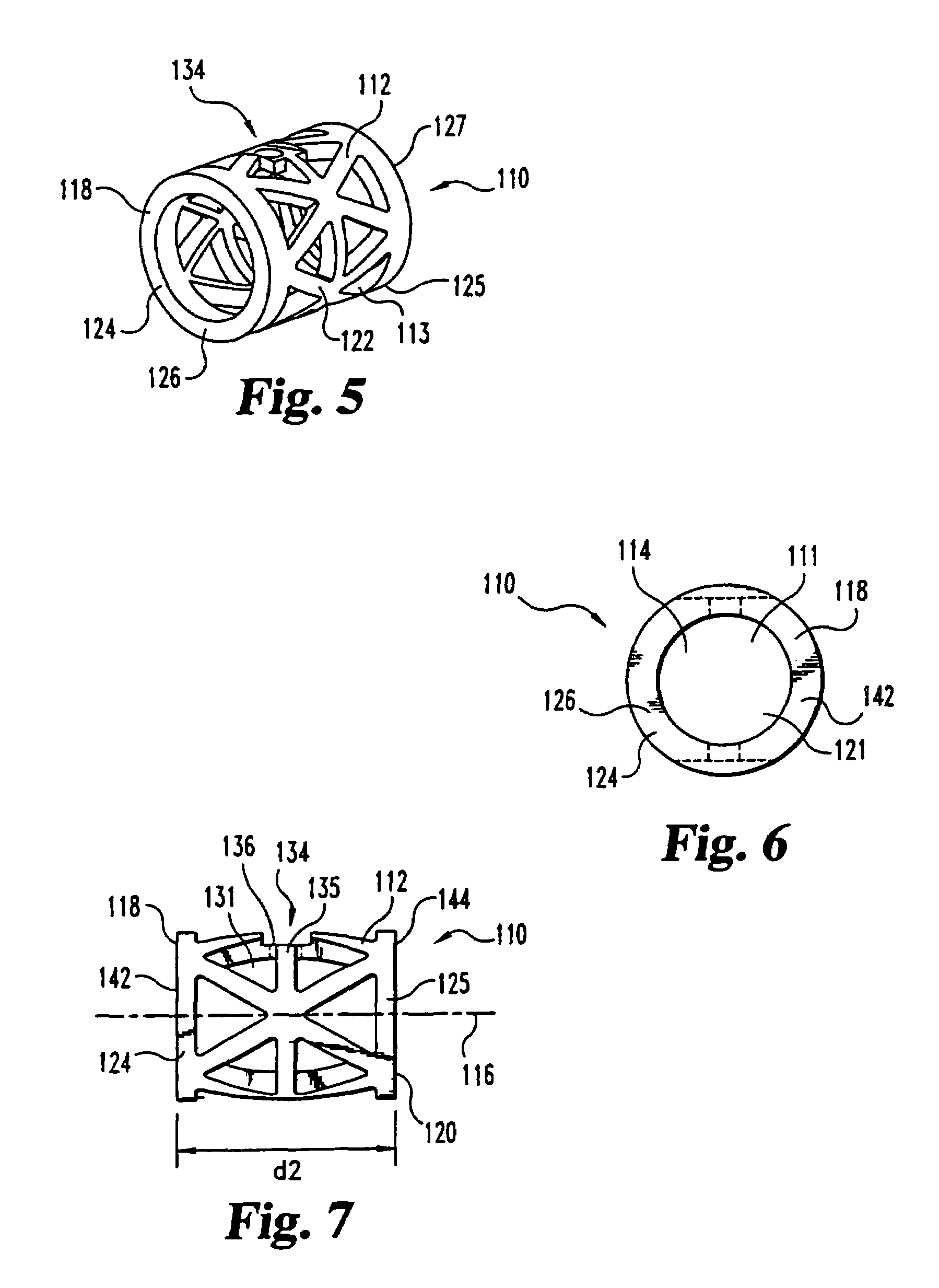
This invention relates to a porous bone implant (10, 110, and 210), a method of manufacturing the implant and a method of orthopedic treatment. The mesh implant can be manufactured using extrusion techniques and a variety of cutting and machining processes to provide the implant with the desired structural features and in the required dimensions to be matingly received within the bone defect or cavity. The implant can be used to strengthen bone structures and support bone tissue adjacent to a defect of cavity. Thus, the implant can be used to provide improved treatment of patients having bone defects or diseases with decreased postoperative pain and a shorter recovery time.
Owner:SDGI HLDG
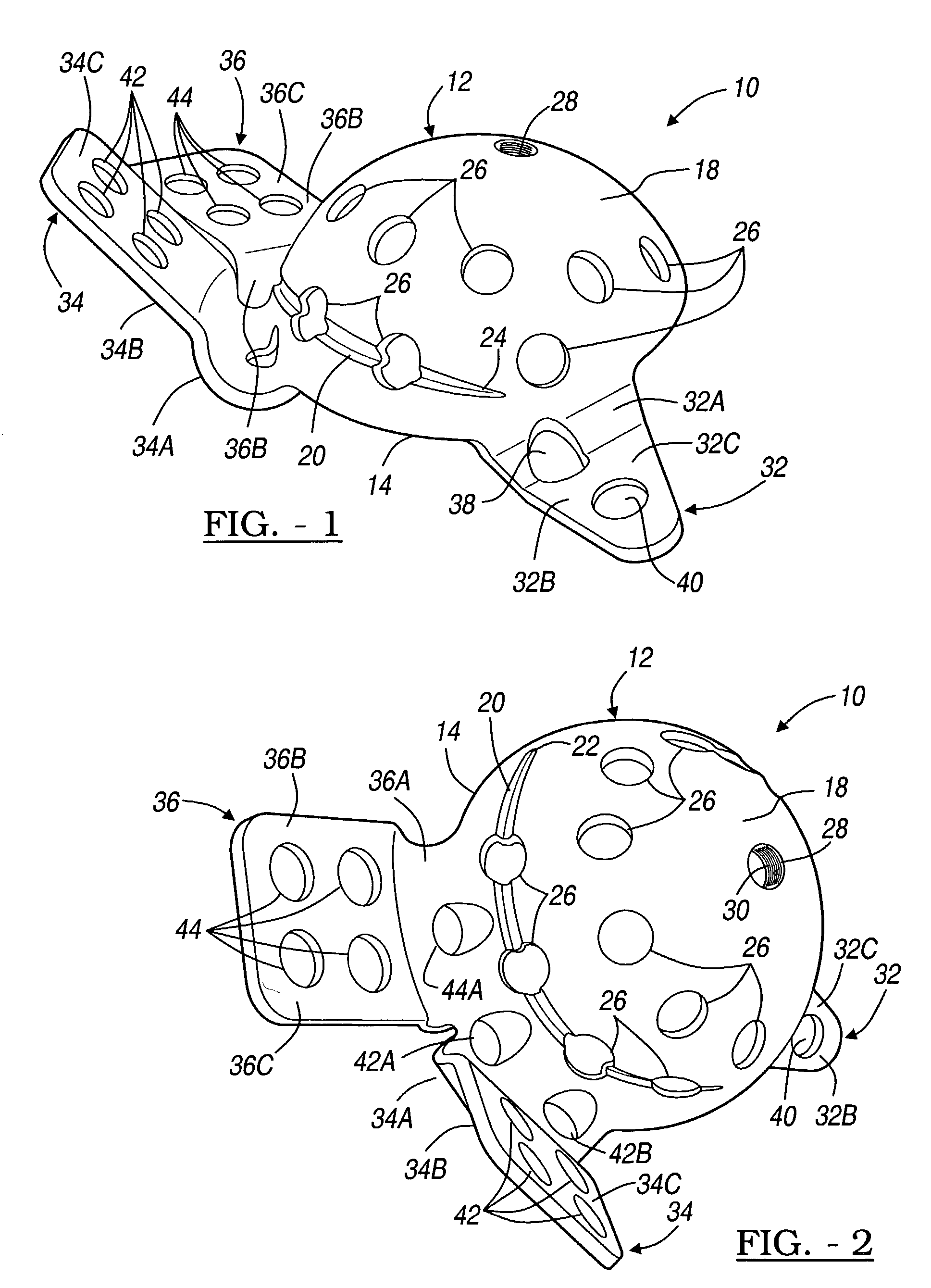
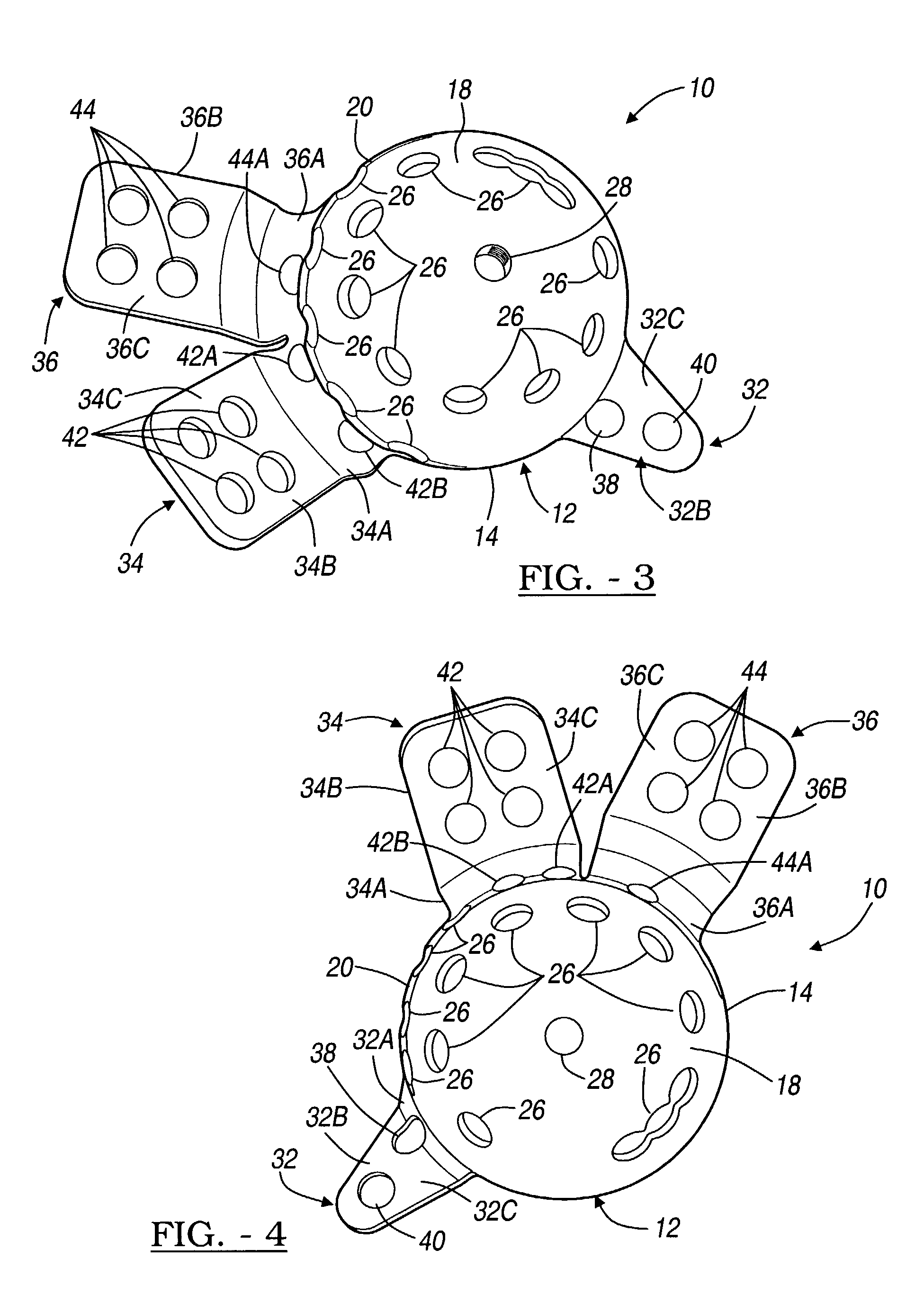
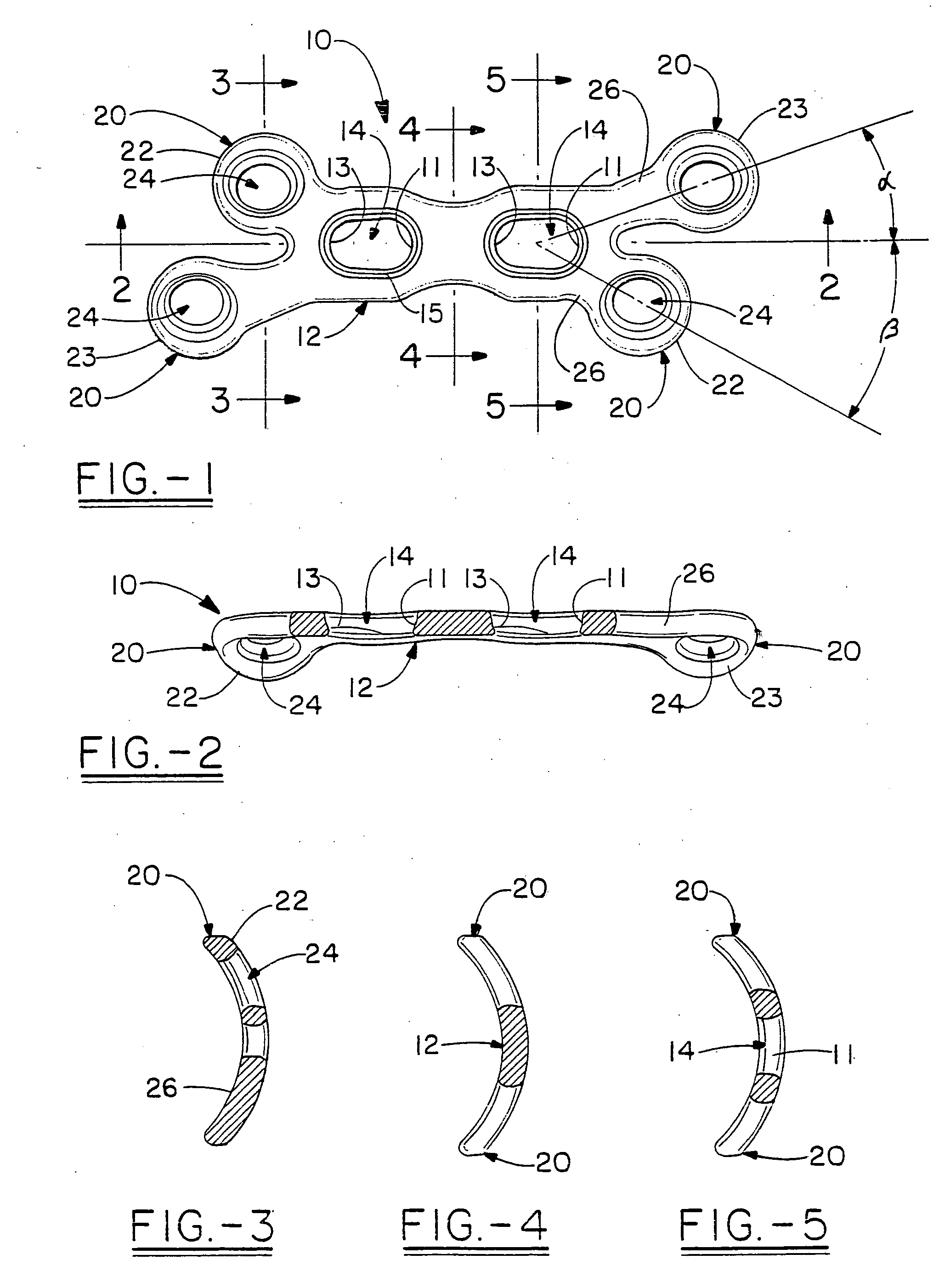
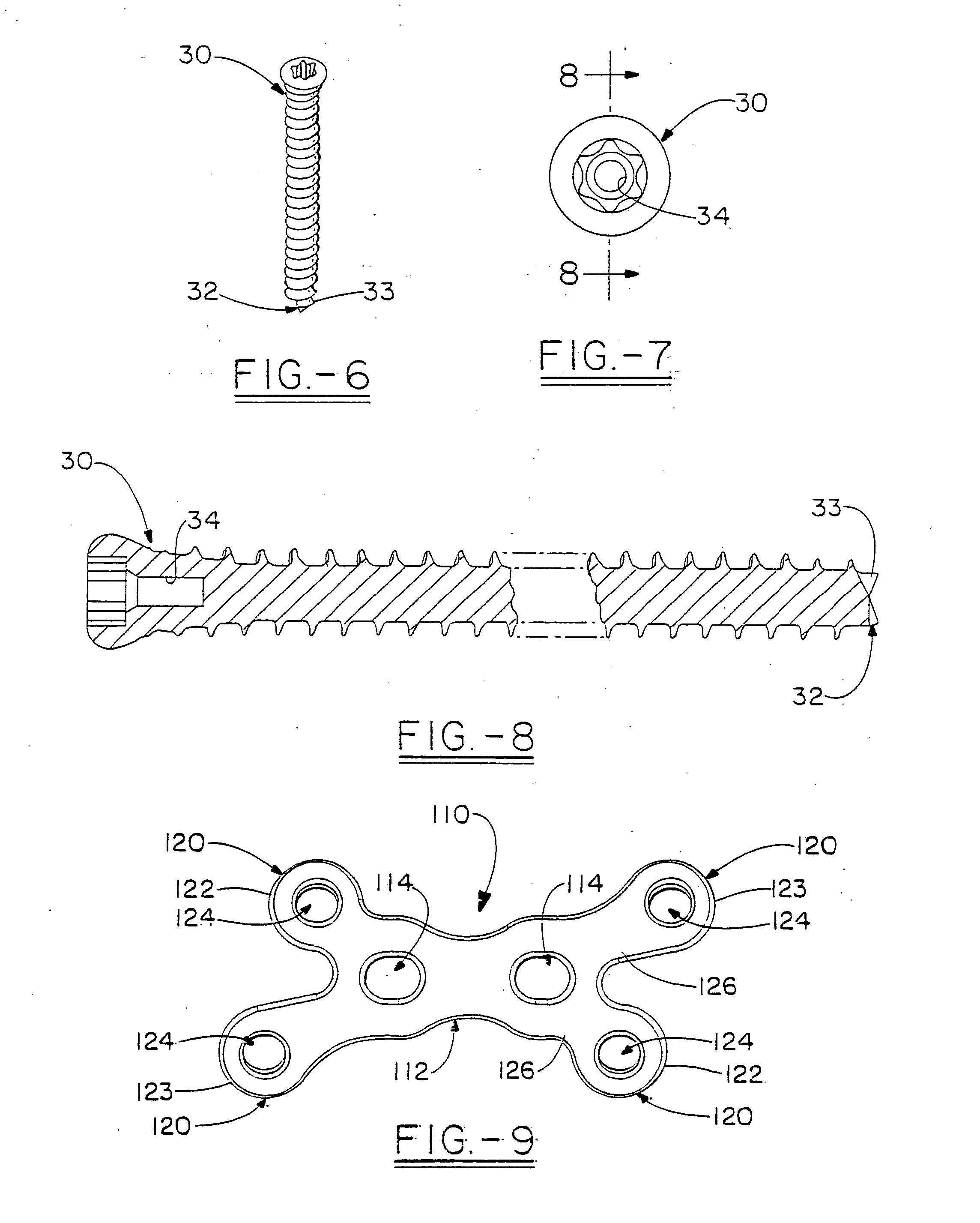
Orthopedic plate for use in small bone repair
The present invention relates to an orthopedic plate and screw system and instruments for surgical fixation of a small bone or bones. The plate facilitates three dimensional contouring to provide for a variety of applications and to accommodate individual variation in bone shape. The plate has a modified x shape including a central trunk portion including one or more screw holes along a longitudinal axis and a set of divergent upper and an oppositely extending set of divergent lower arms, each arm including screw holes which are placed at a radially equal distance but which diverging asymmetrically from the longitudinal axis relative to its paired upper or lower mate. The screws of the system are self-starting, self-tapping screws including the option of partial or full cannulation.
Owner:WRIGHT MEDICAL TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com