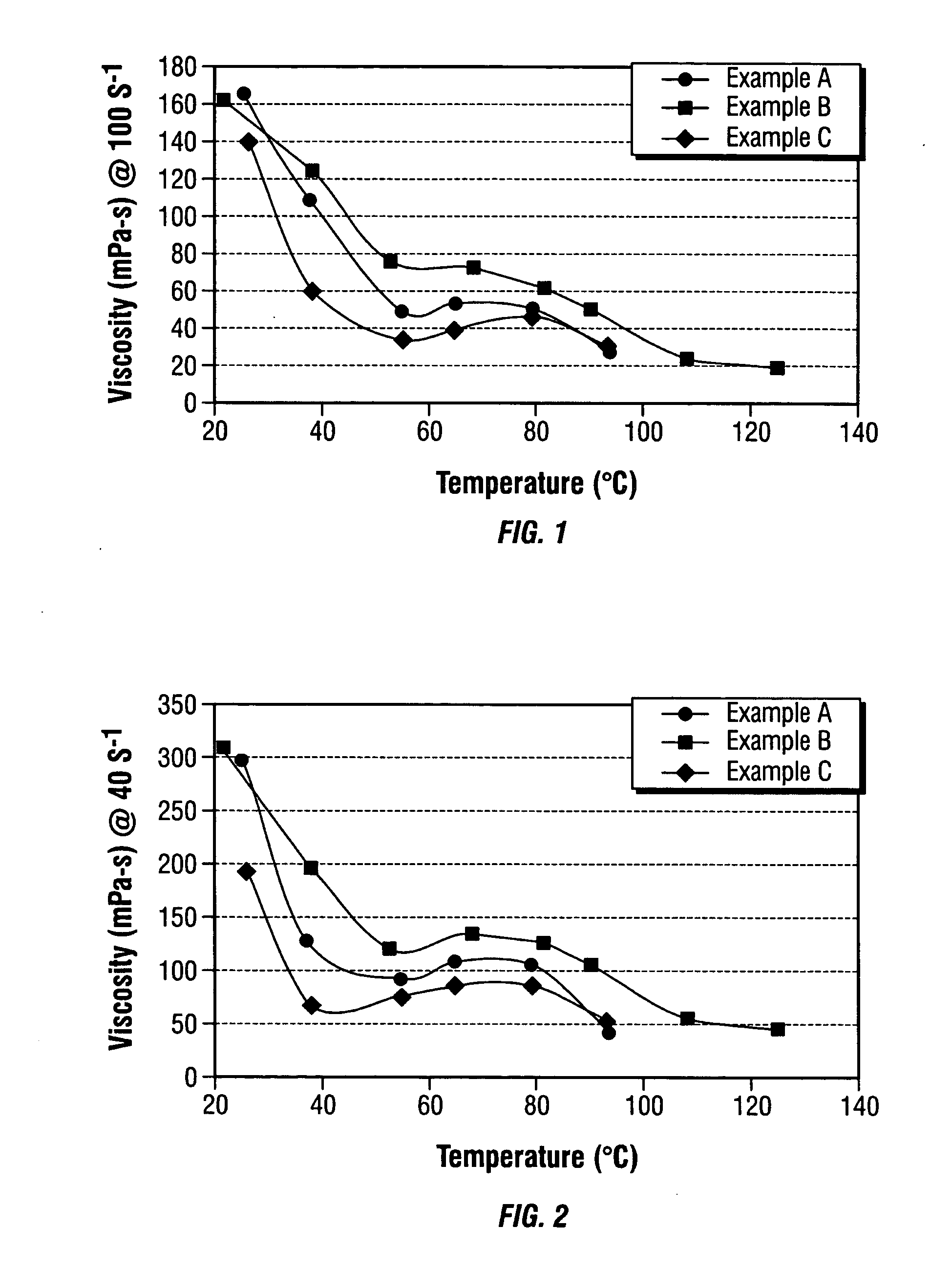
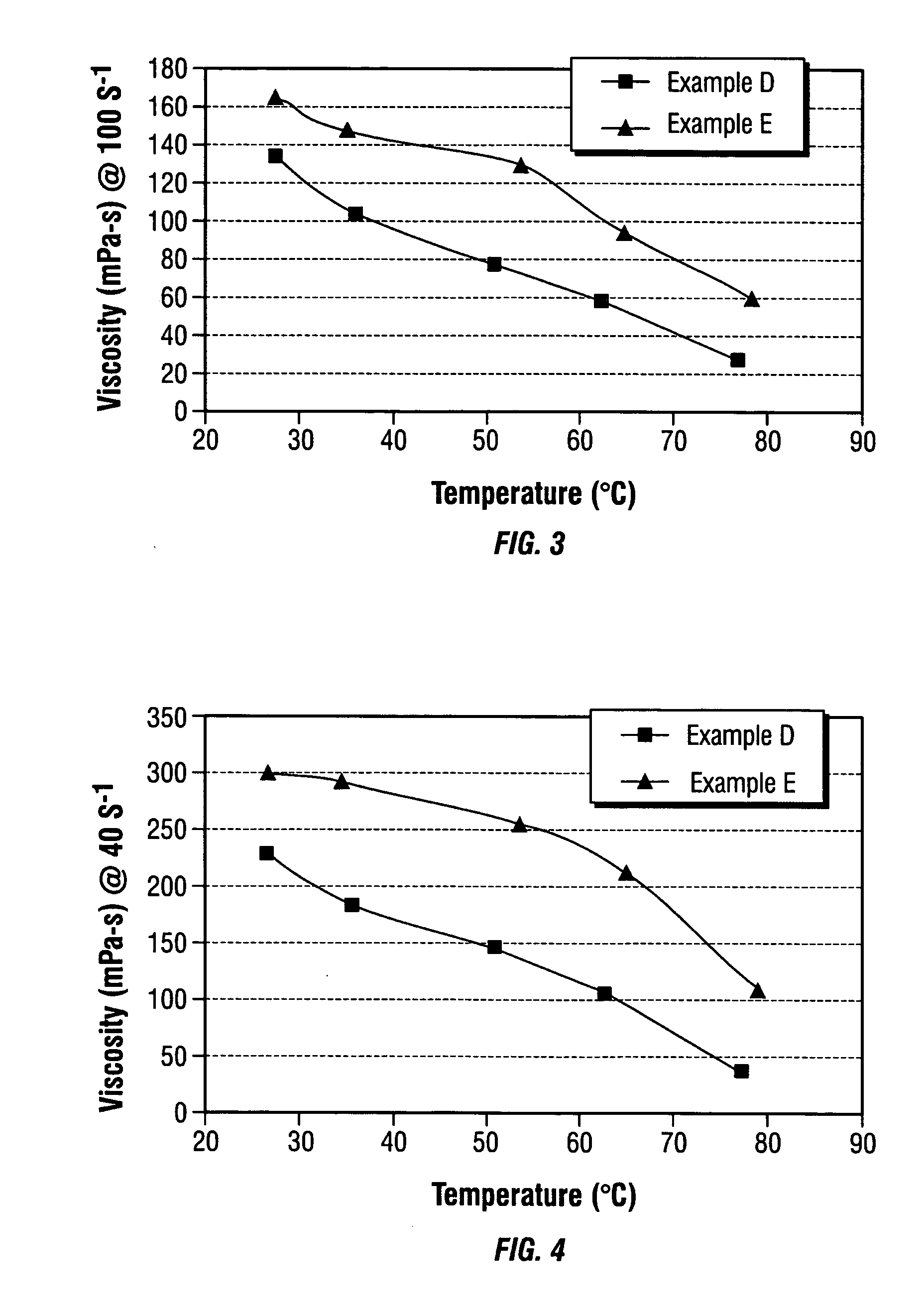
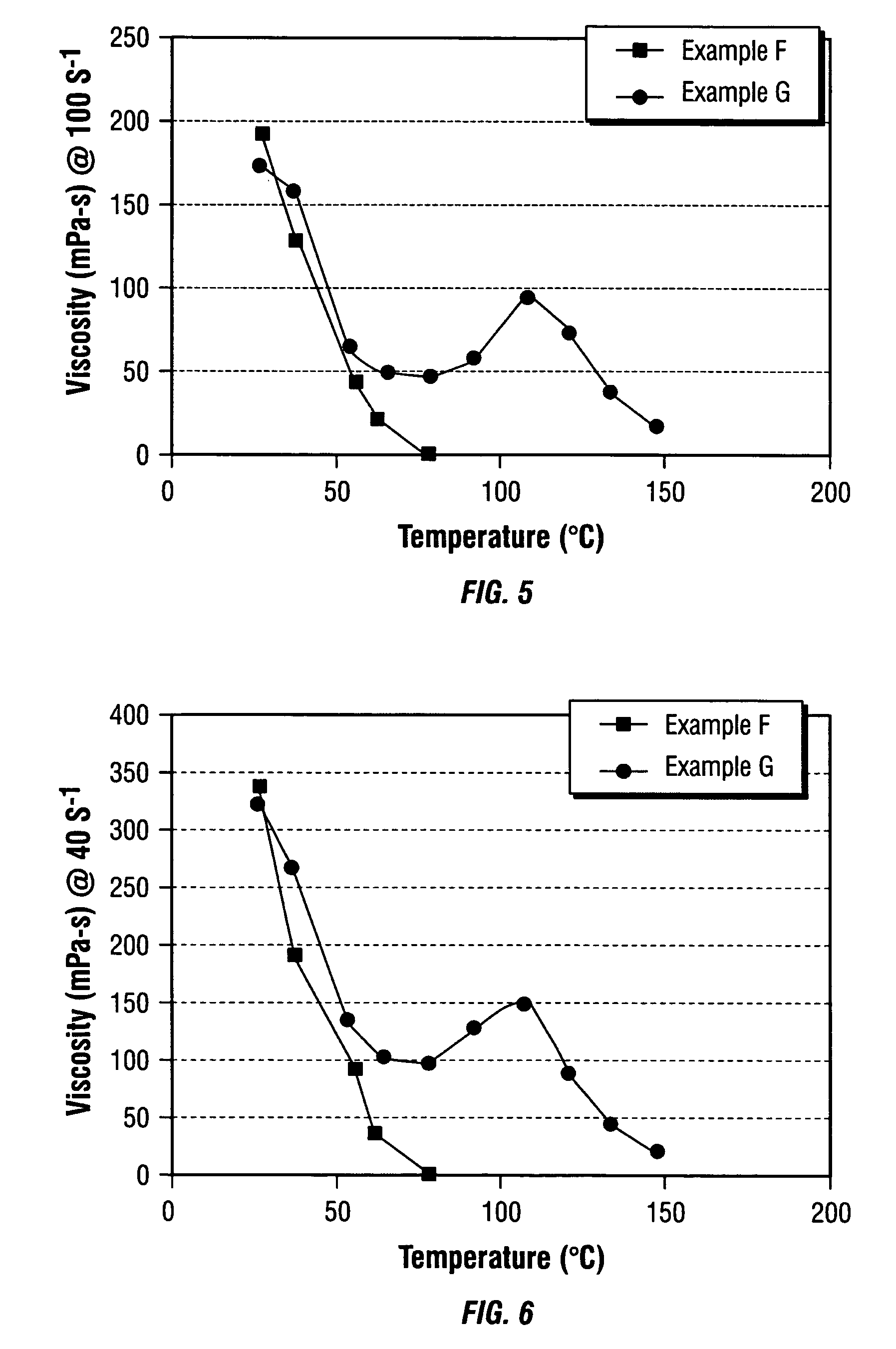
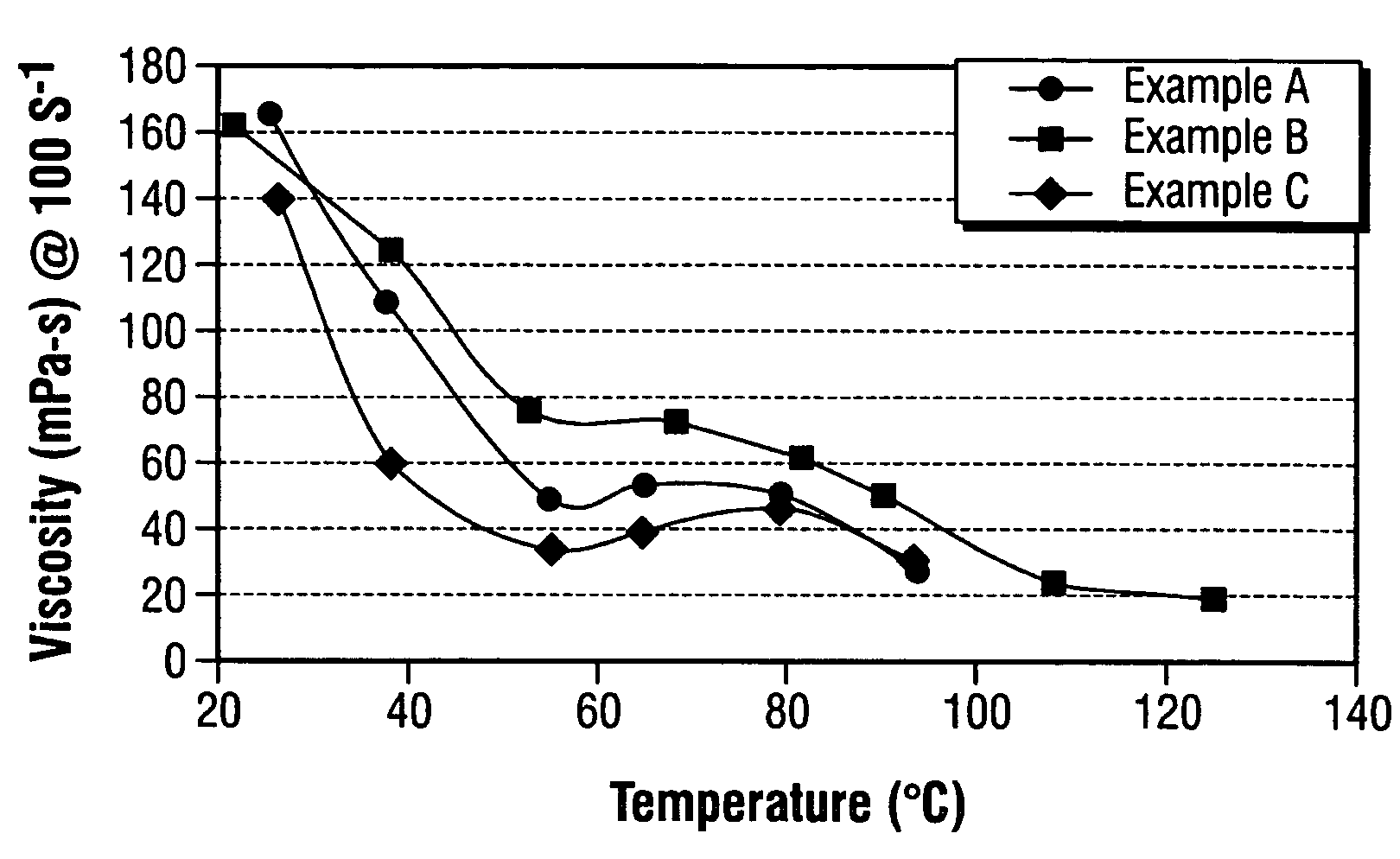
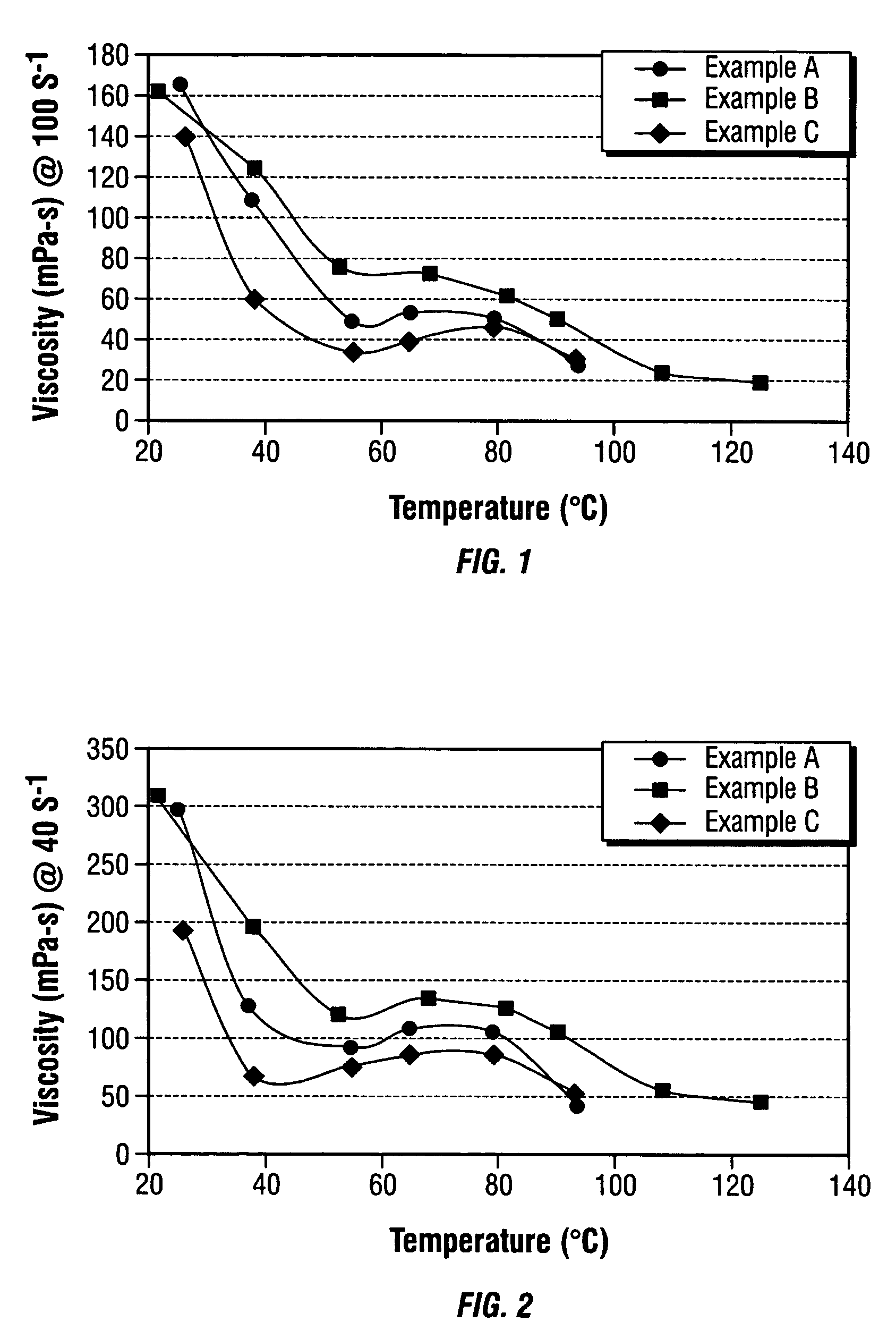
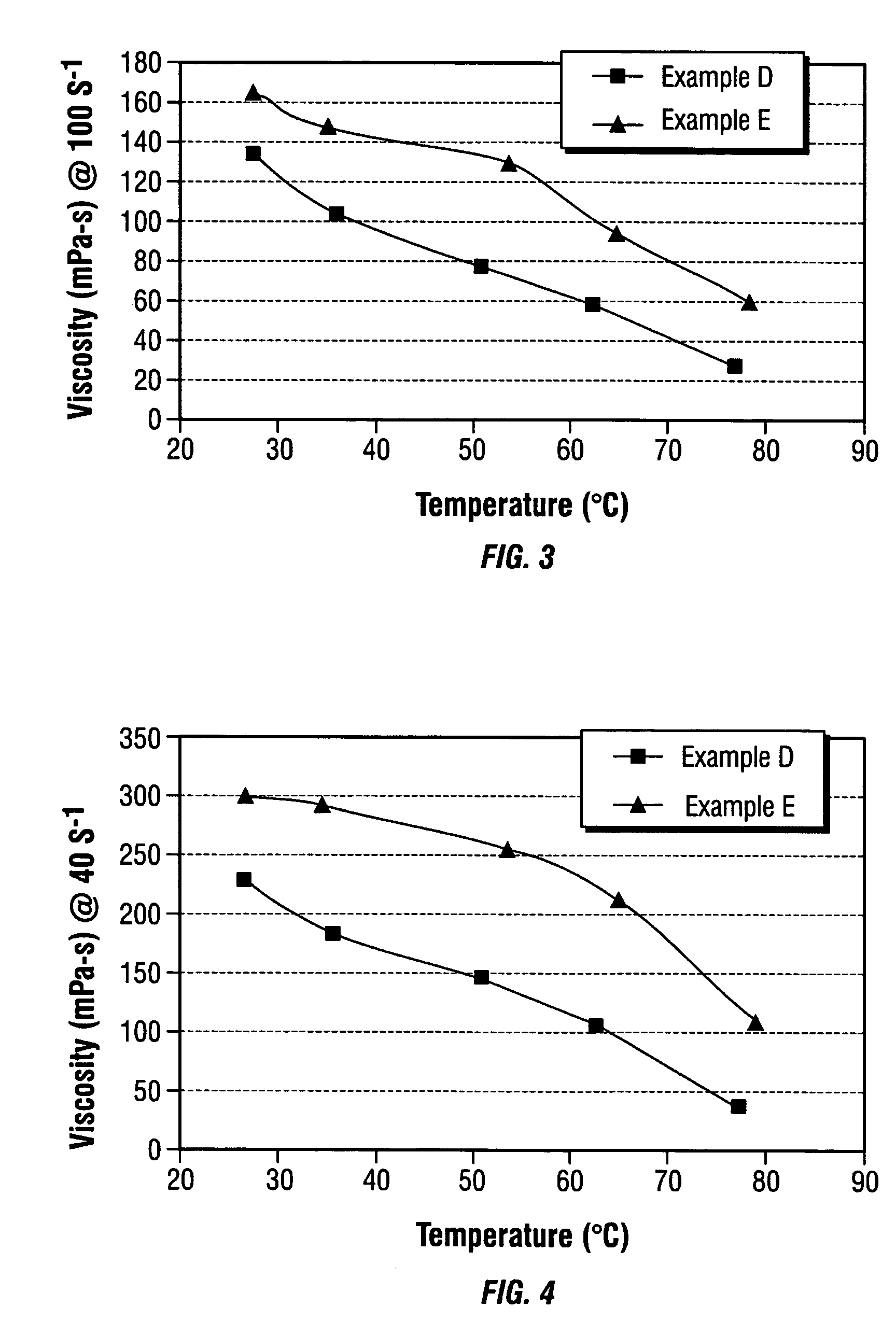
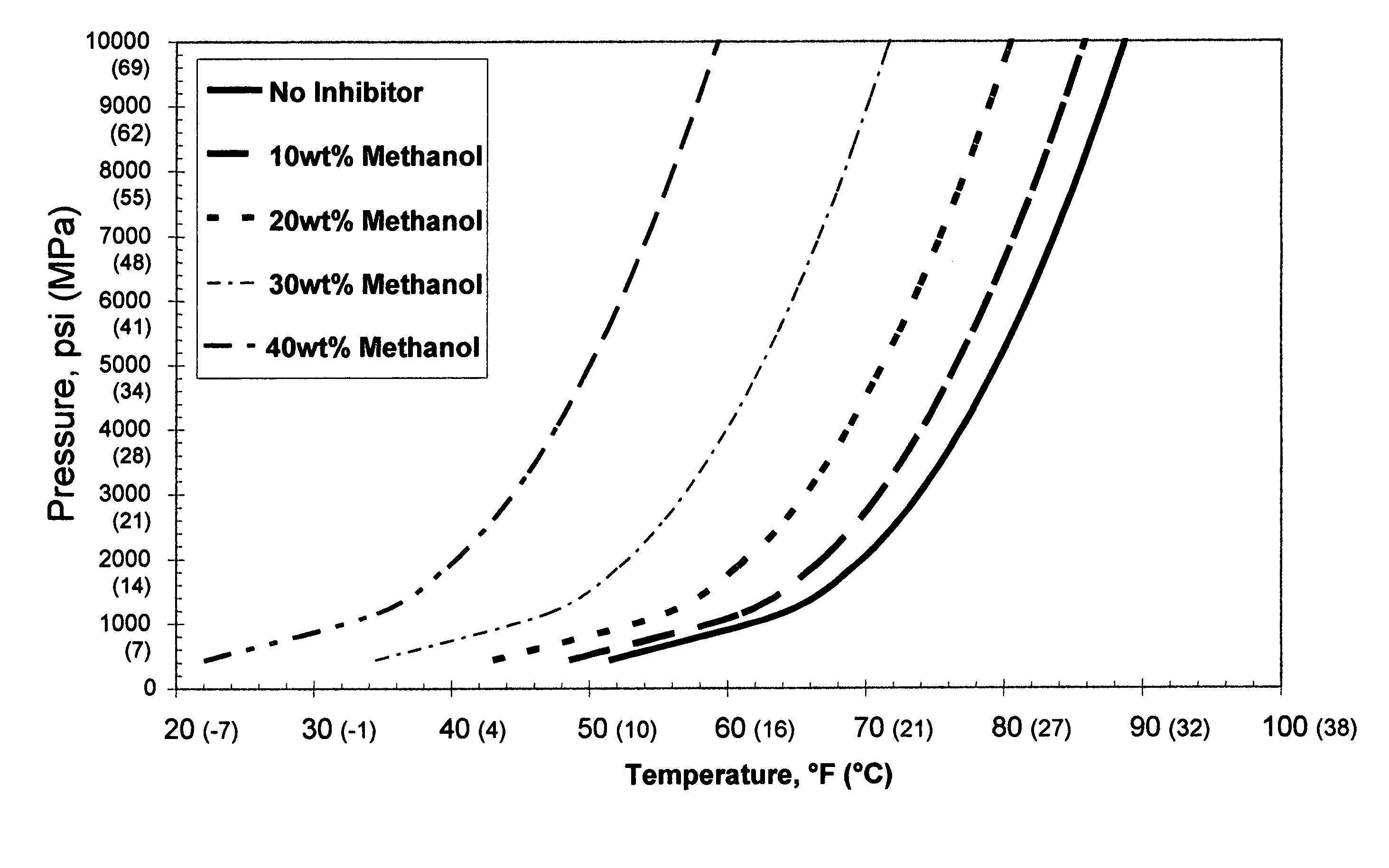
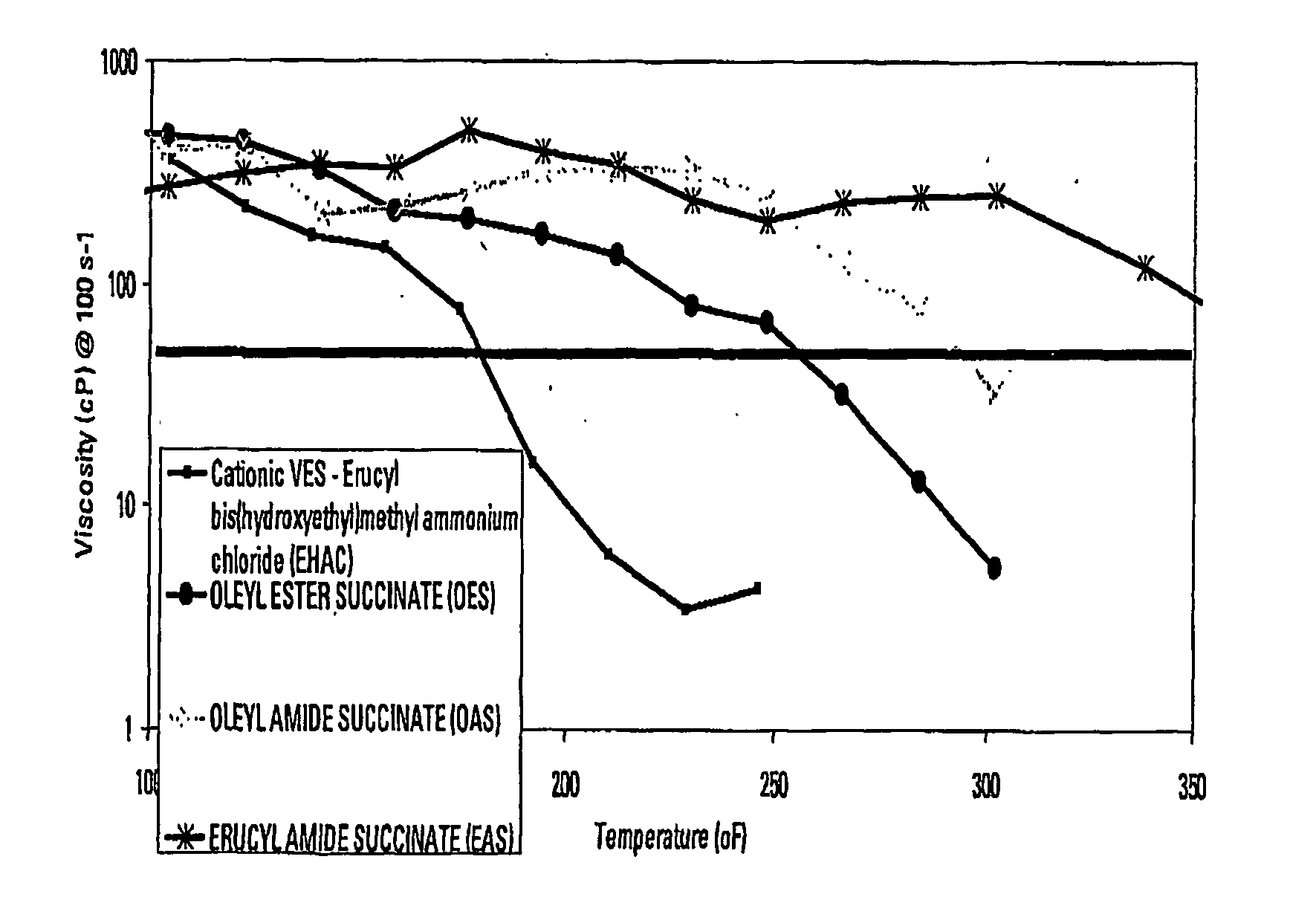
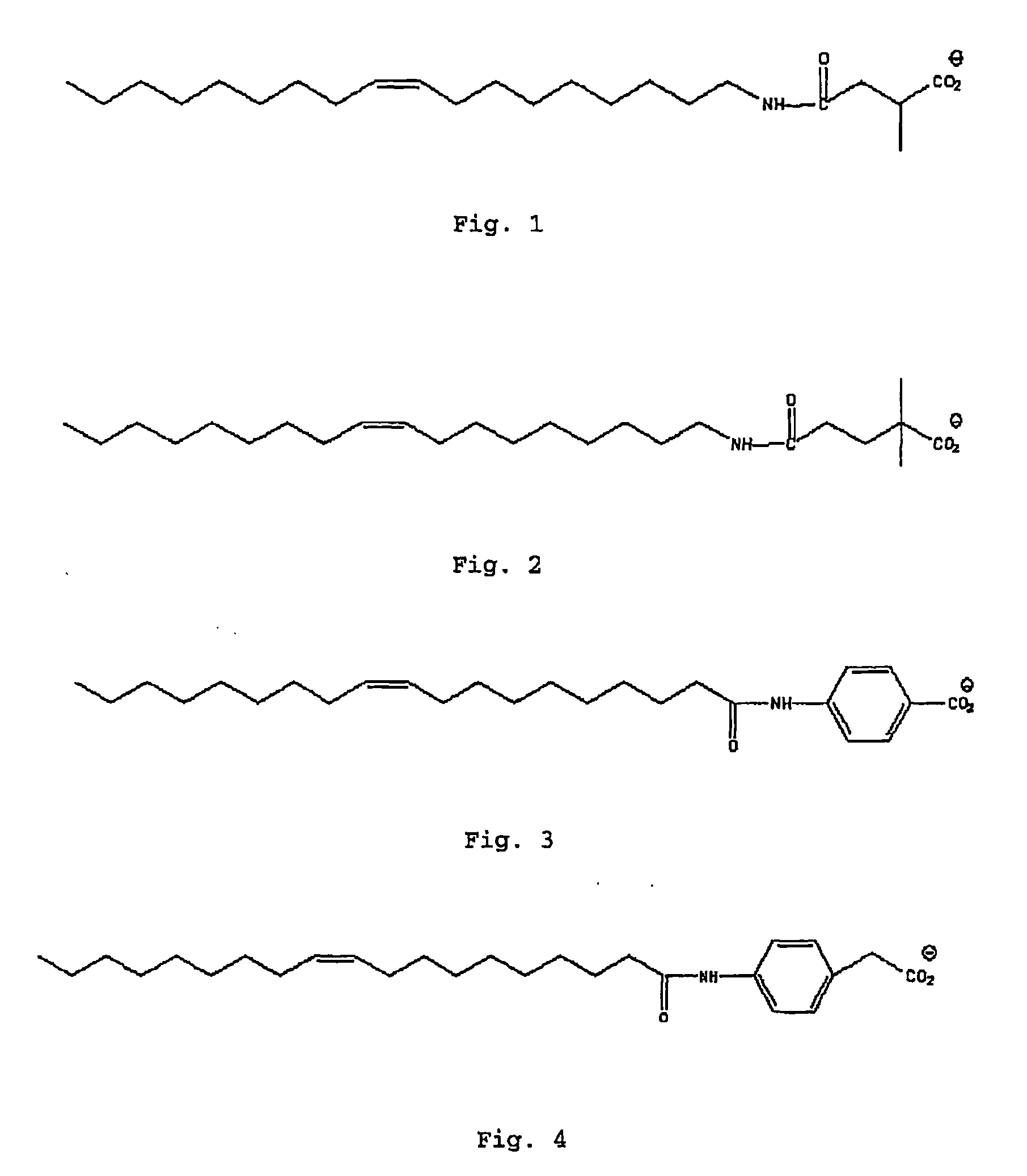
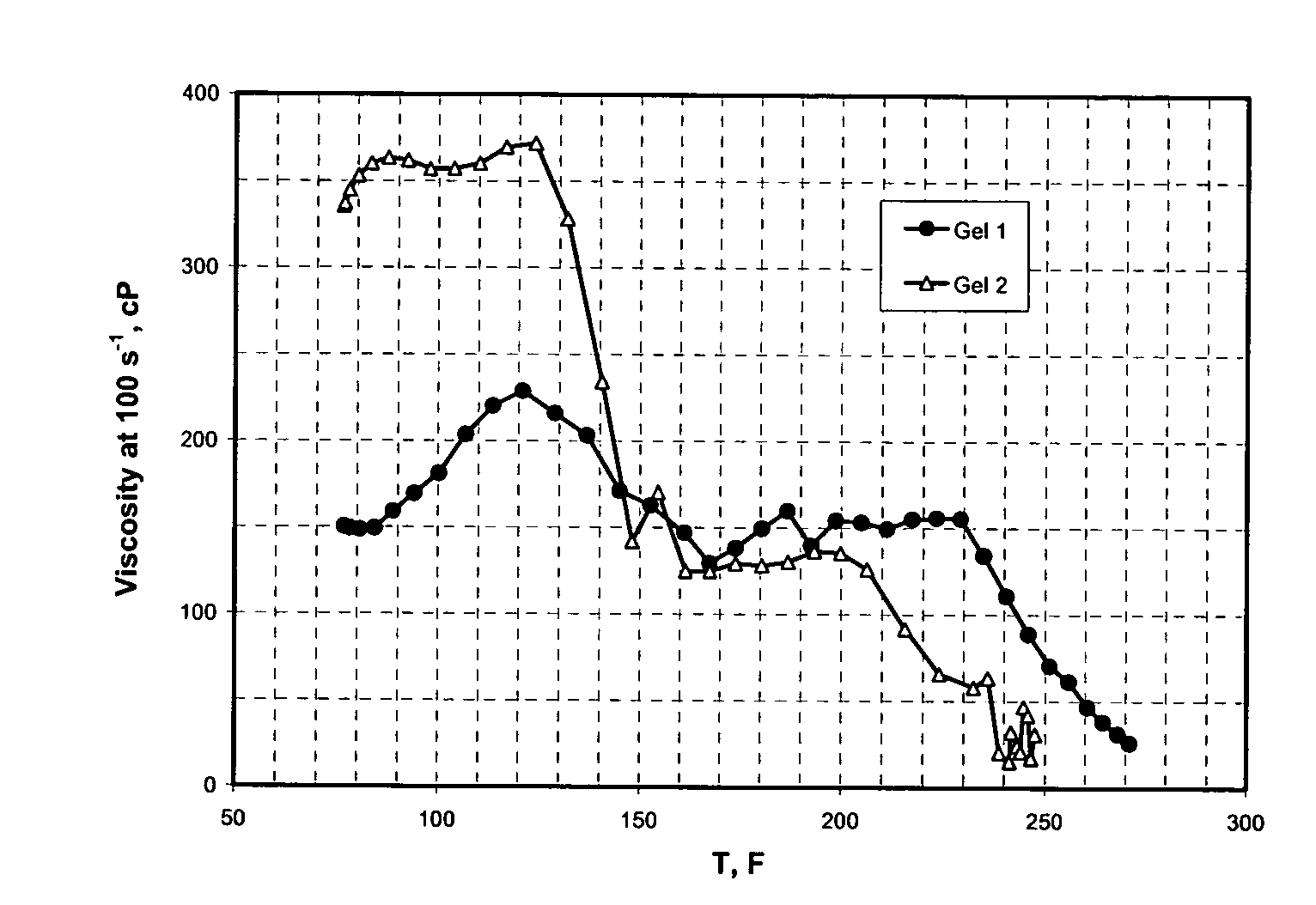
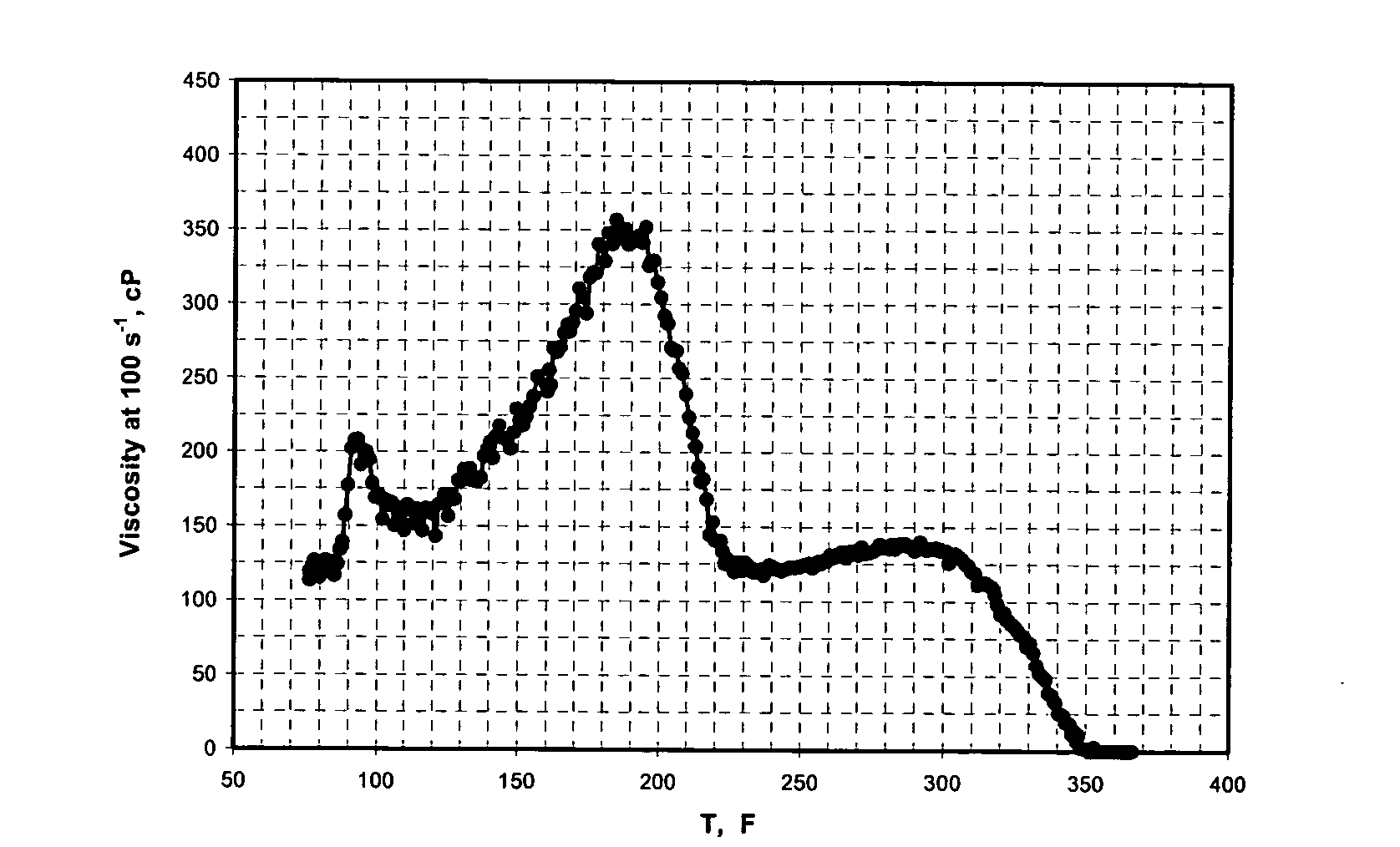
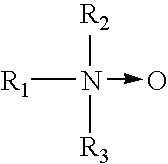
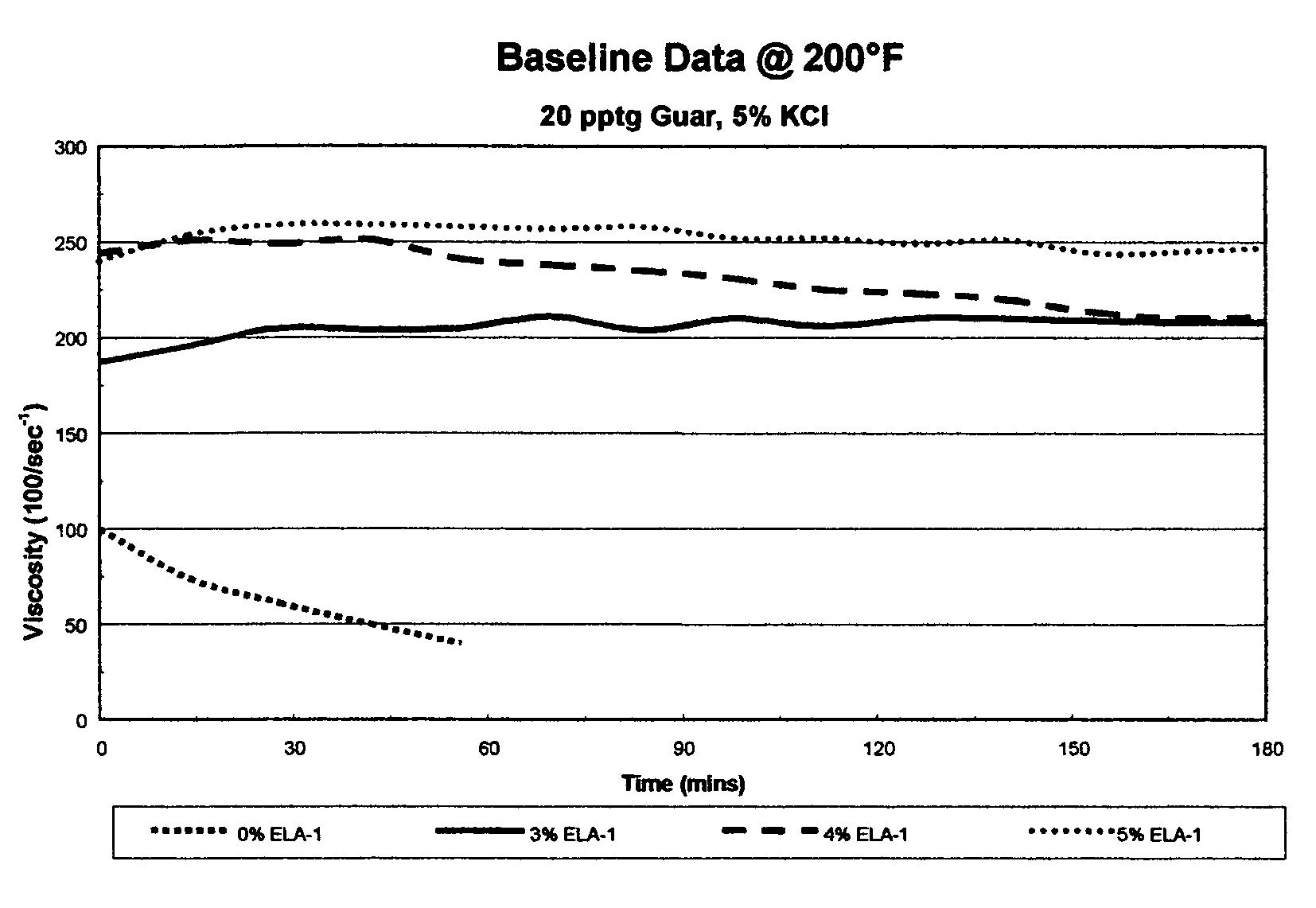
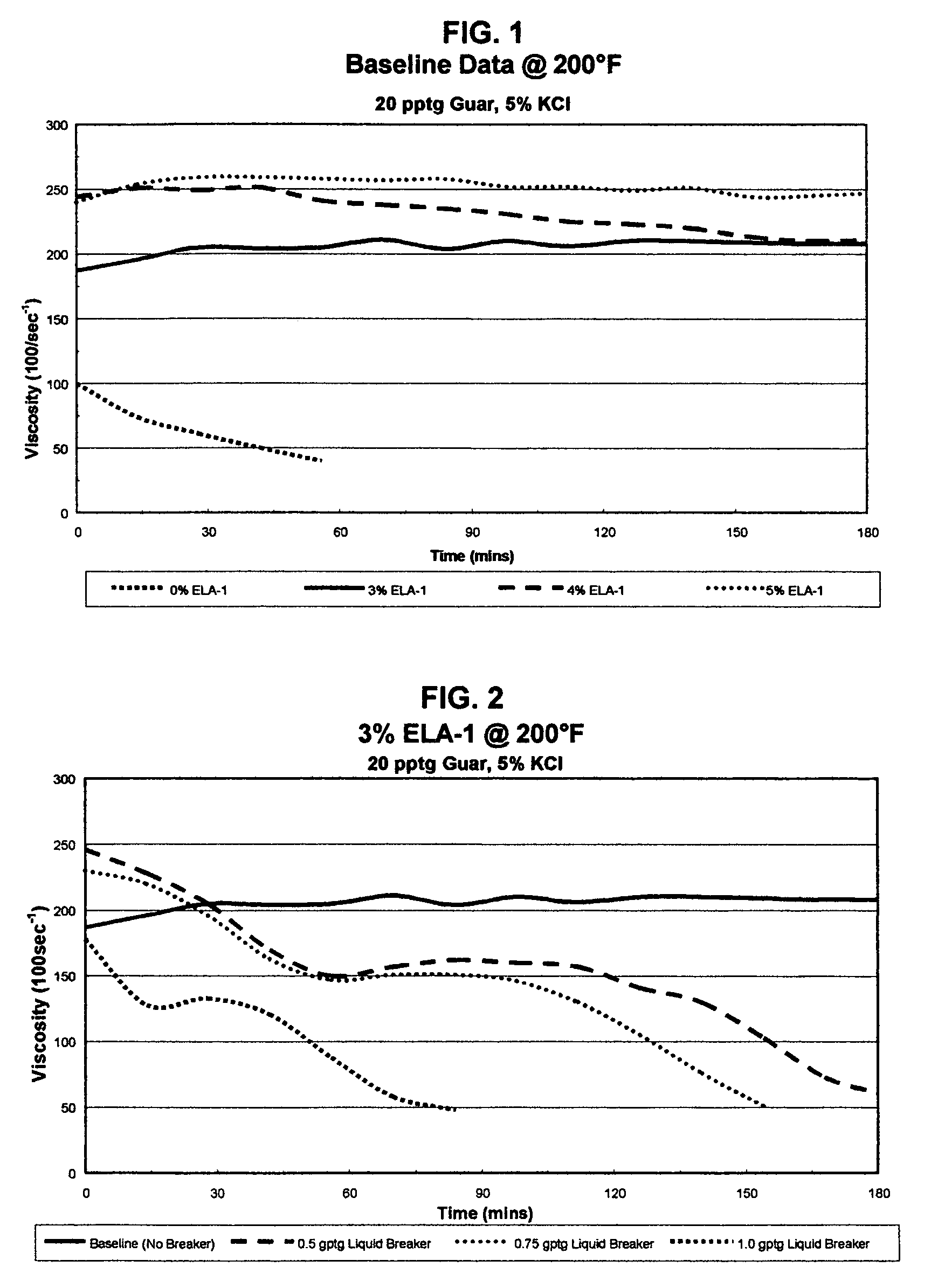
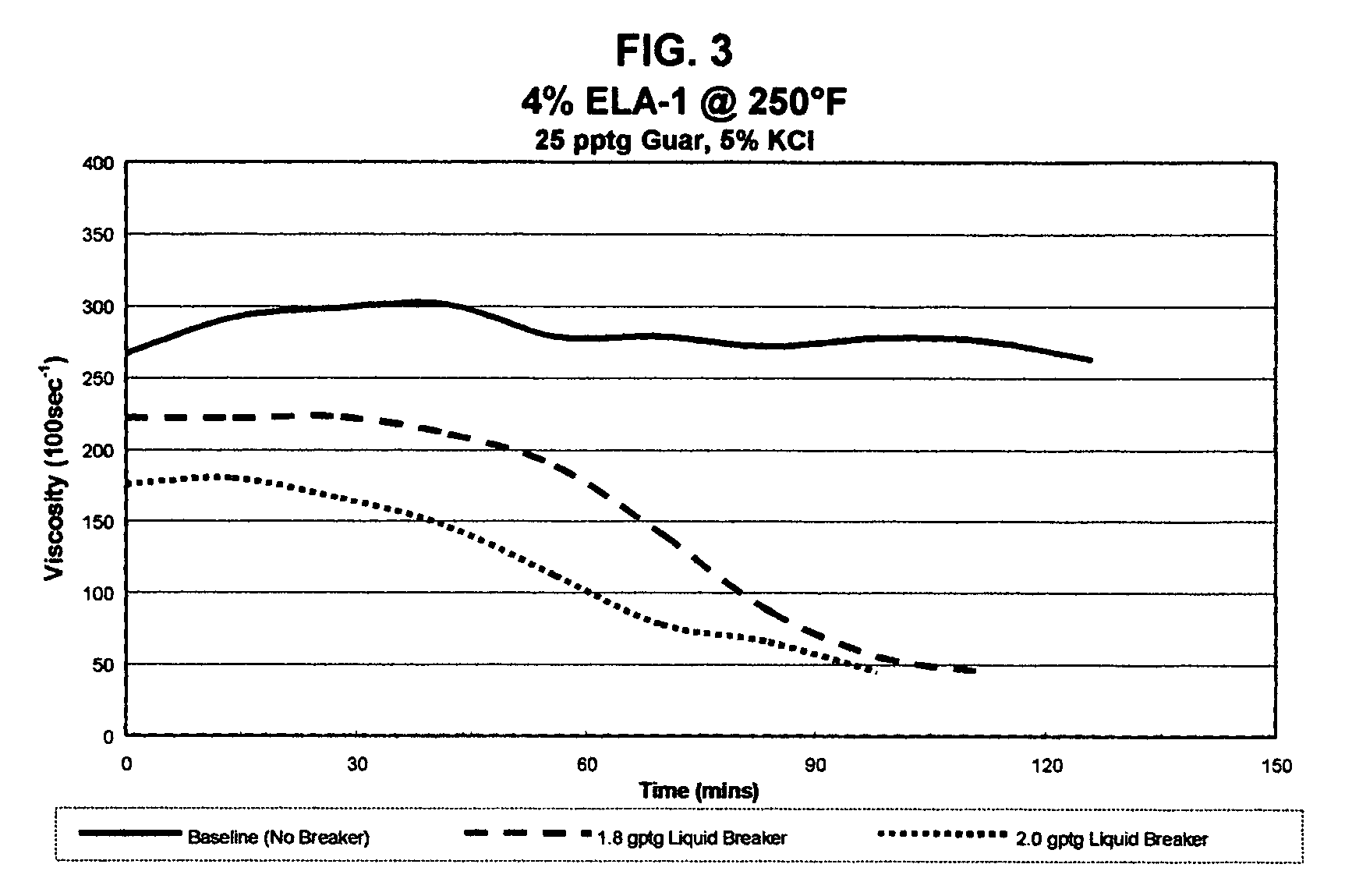
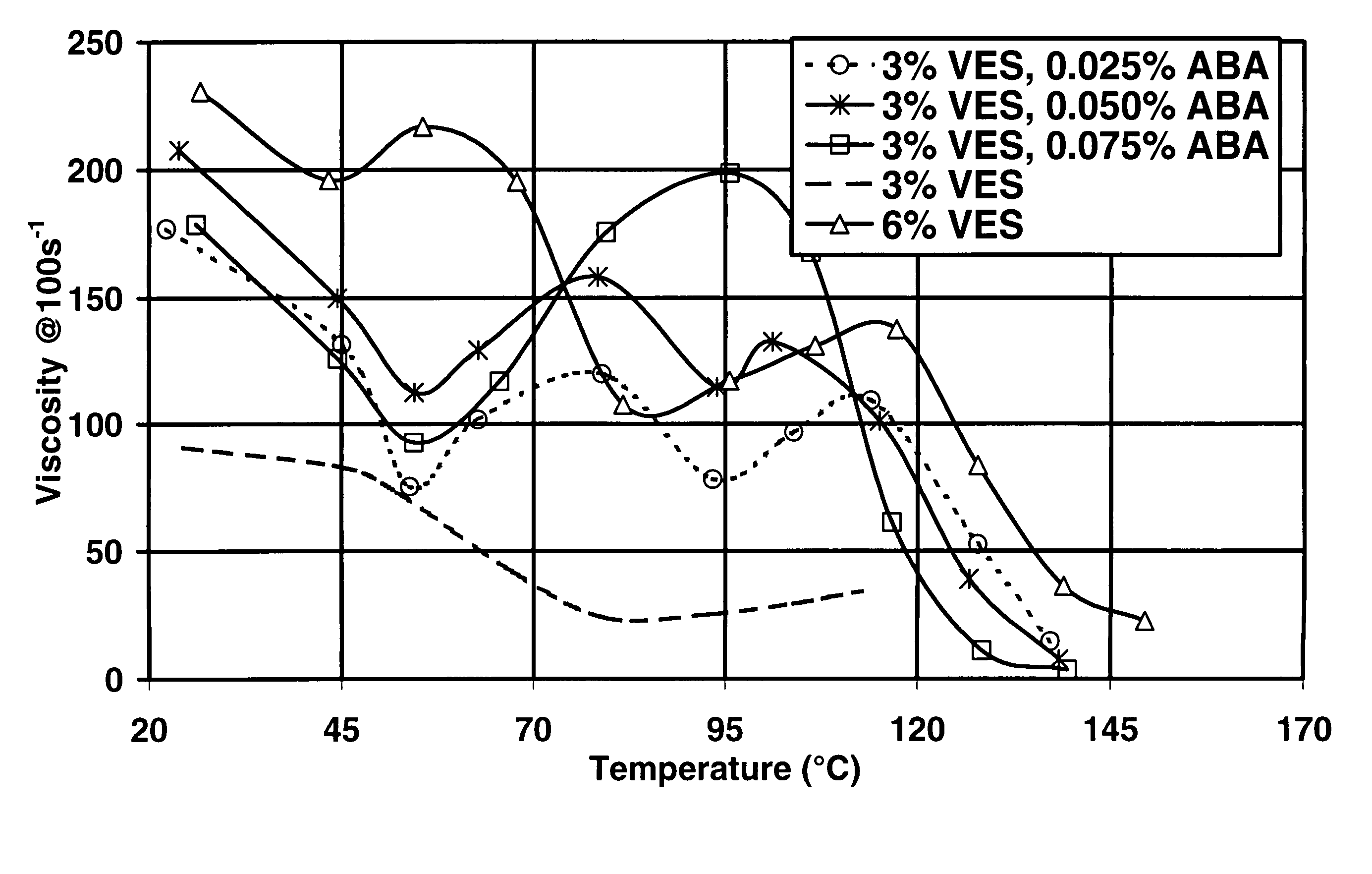
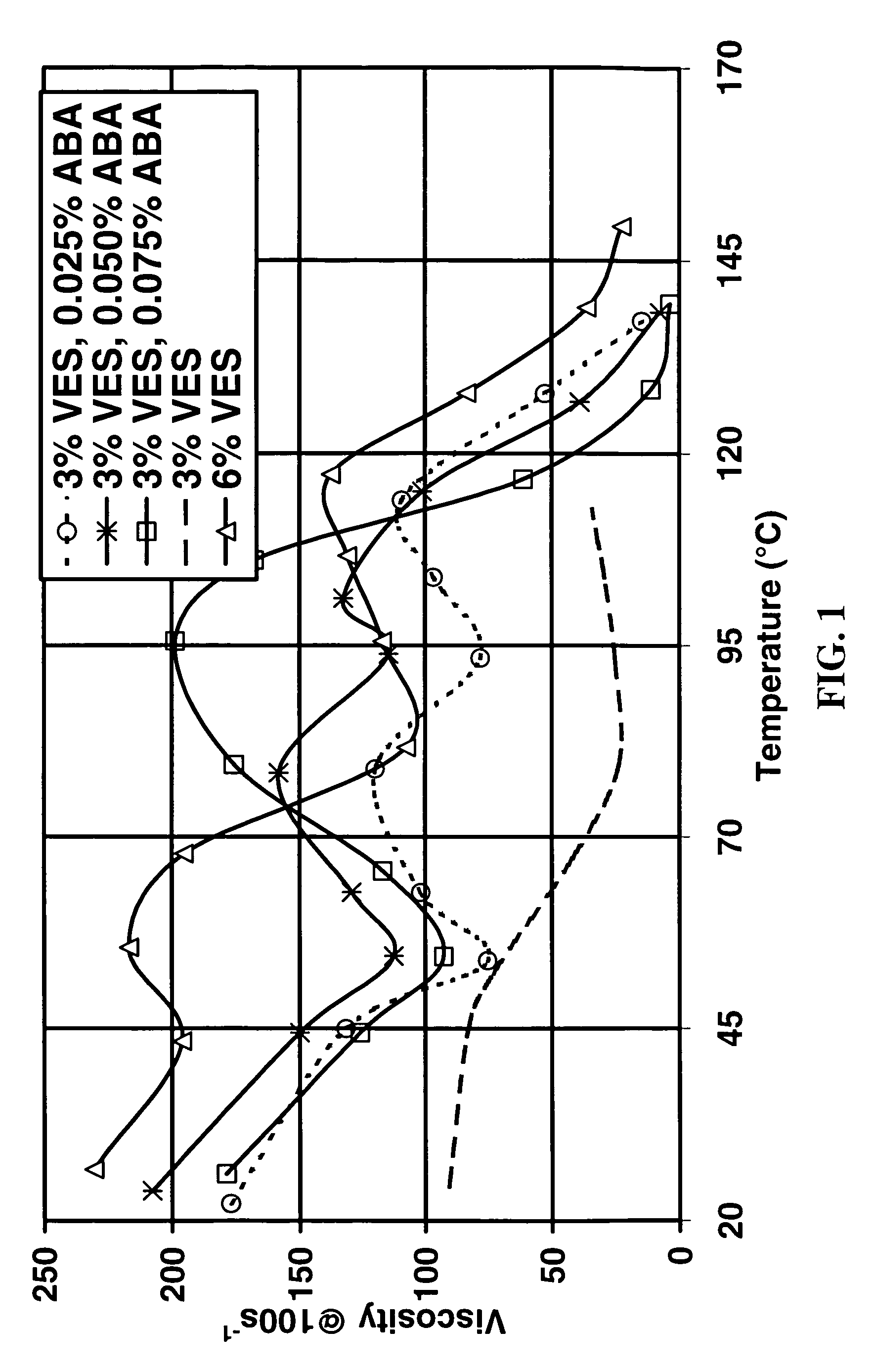
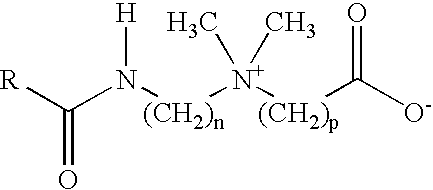
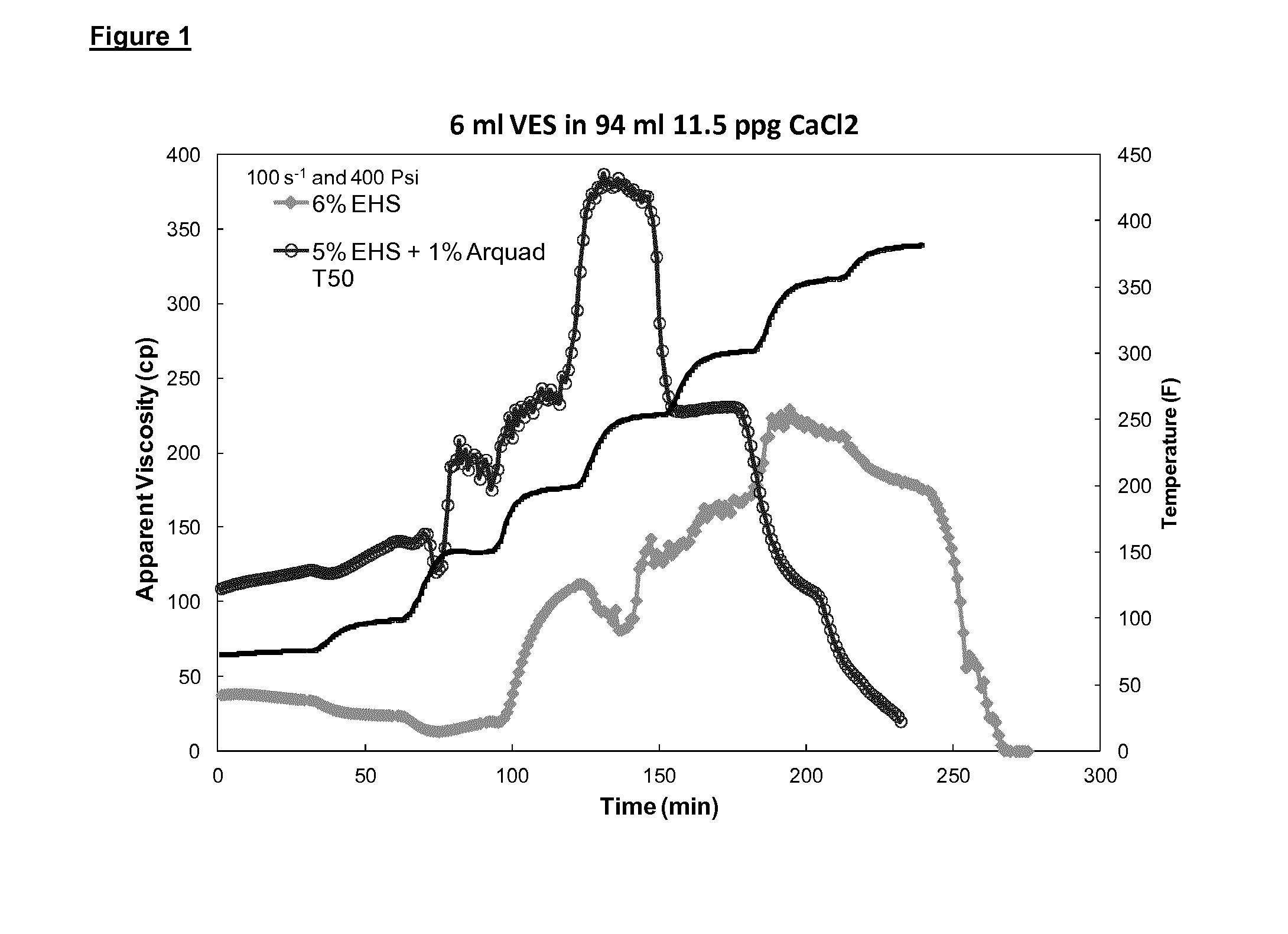
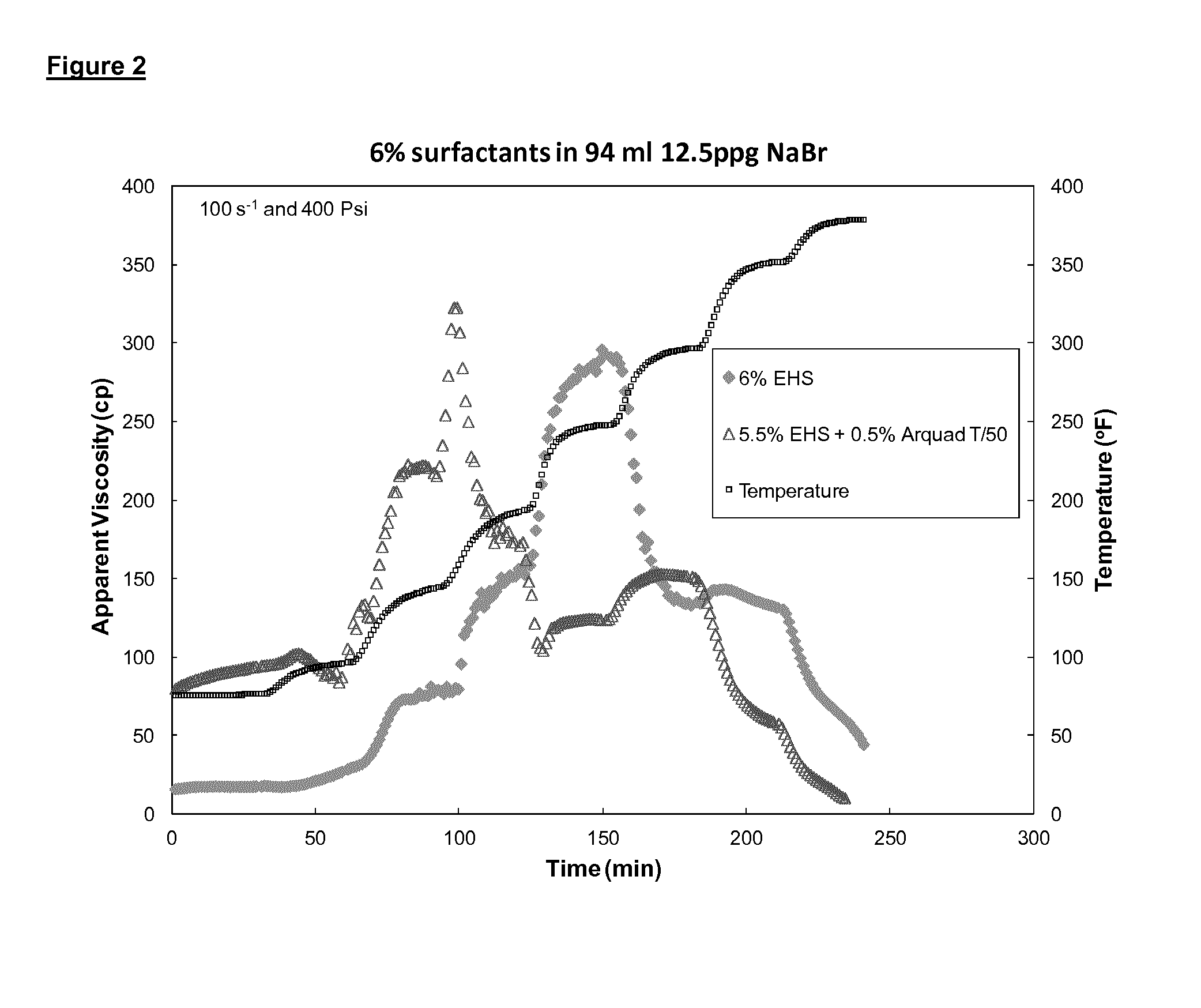
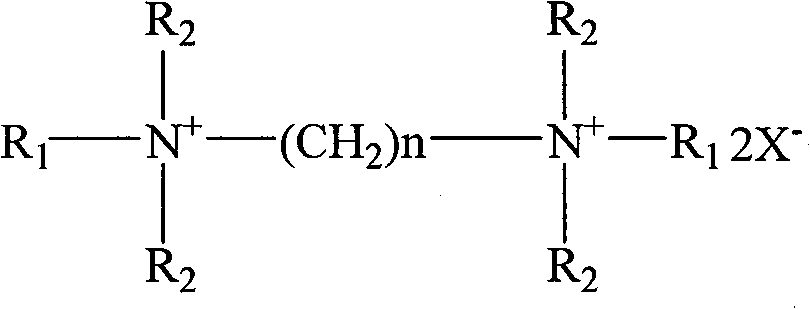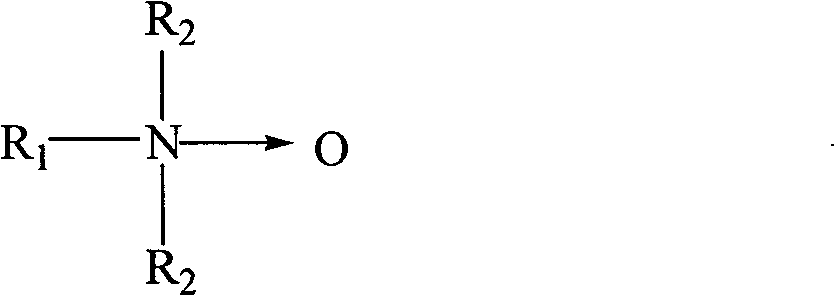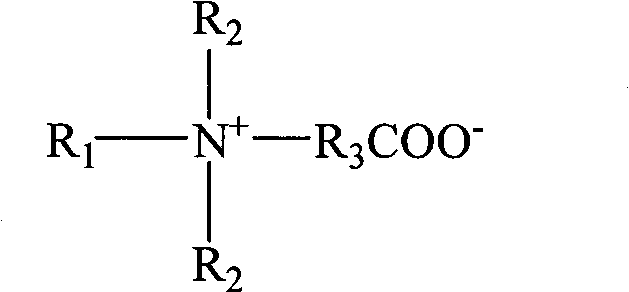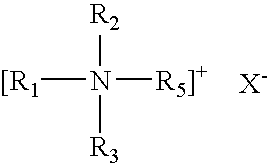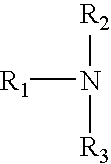Patents
Literature
164 results about "Viscoelastic fluid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Viscoelastic fluids are a common form of non-newtonian fluid. They can exhibit a response that resembles that of an elastic solid under some circumstances, or the response of a viscous liquid under other circumstances. Typically, fluids that exhibit this behavior are macromolecular in nature (that is,...
Low profile bioactive agent delivery device
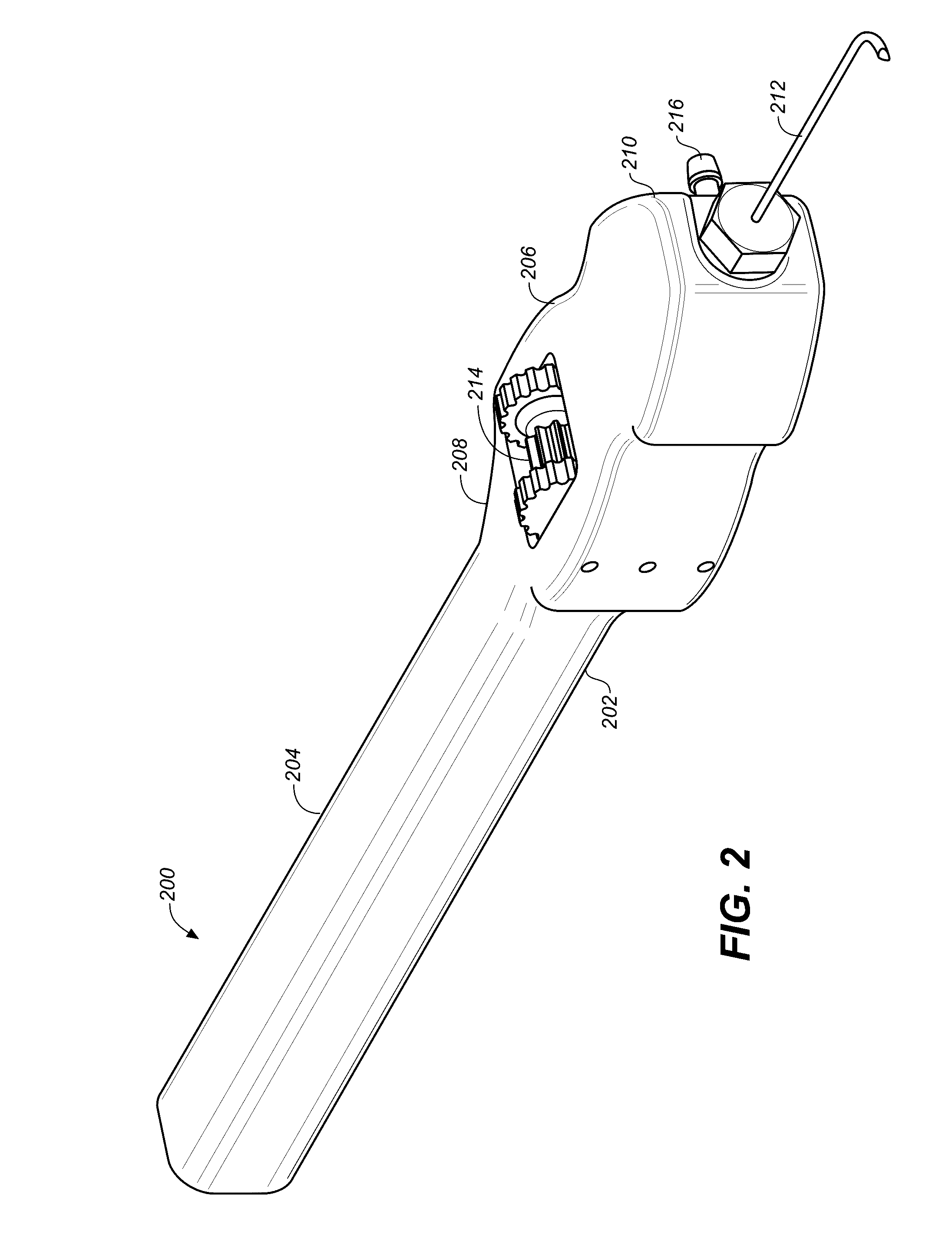
InactiveUS20080057106A1Low external profileMinimize damageEye implantsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDevice implantDistal portion
Disclosed are implantable devices that are configured for implantation through tissue or membrane and into an implantation site comprising viscoelastic fluid or non-osseous tissue. In embodiments of the invention, the implantable devices comprise: (a) a nonlinear body member having a direction of extension, a longitudinal axis along the direction of extension, and a proximal portion and a distal portion, wherein at least a portion of the body member deviates from the direction of extension, (b) a retention element at the proximal portion of the body member, the retention element configured to retain the implantable device at the implantation site, the retention element presenting an external profile of no greater than 0.5 mm when the device is implanted in a patient; and (c) a bioactive agent delivery system at the distal portion of the body member, the bioactive agent delivery system comprising one or more bioactive agents. Also disclosed are methods of delivering a bioactive agent to a patient using the devices.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
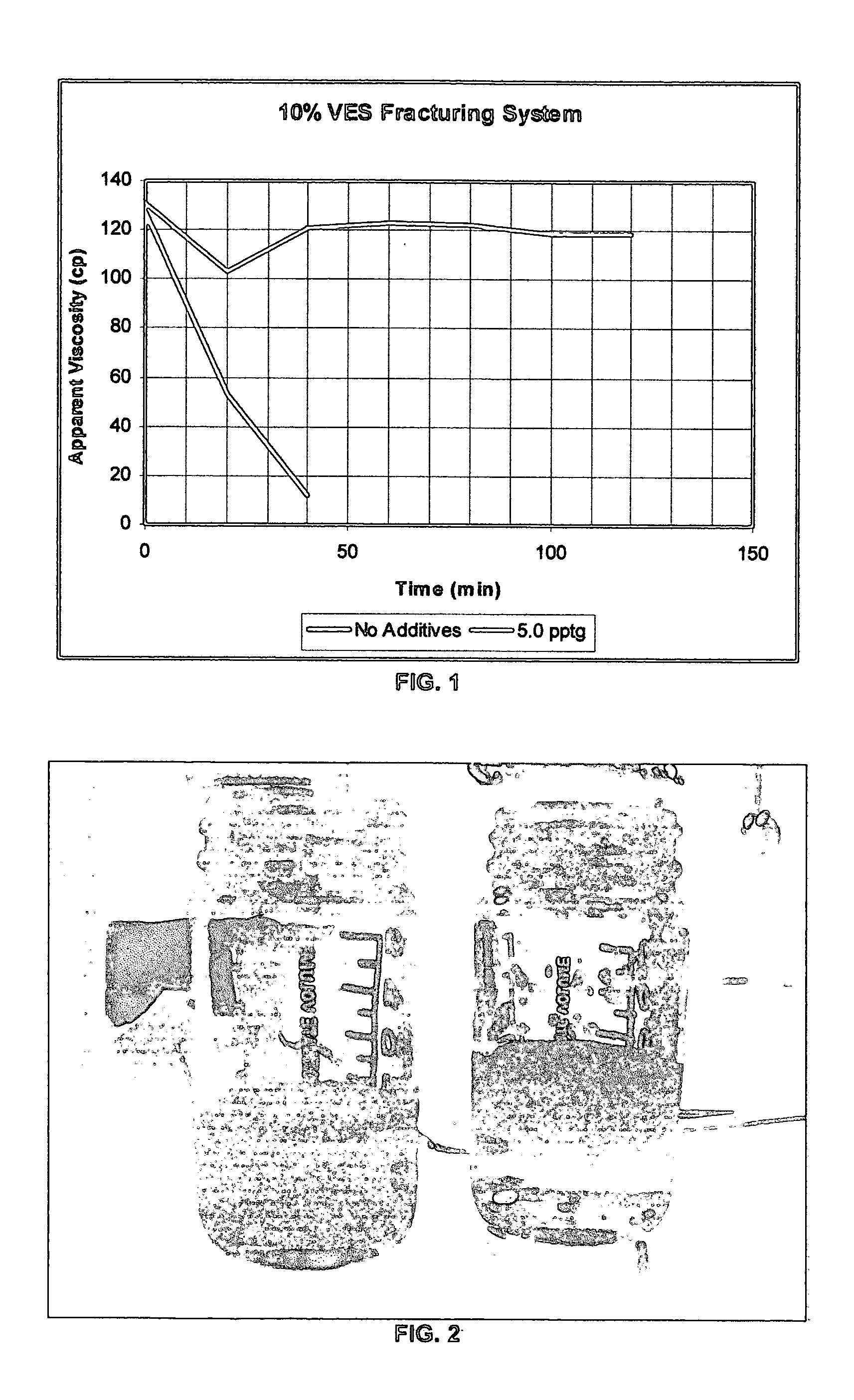
System stabilizers and performance enhancers for aqueous fluids gelled with viscoelastic surfactants
InactiveUS20050252658A1Improve stabilityReduce precipitationFluid removalDrilling compositionFluid gelHydraulic fracturing
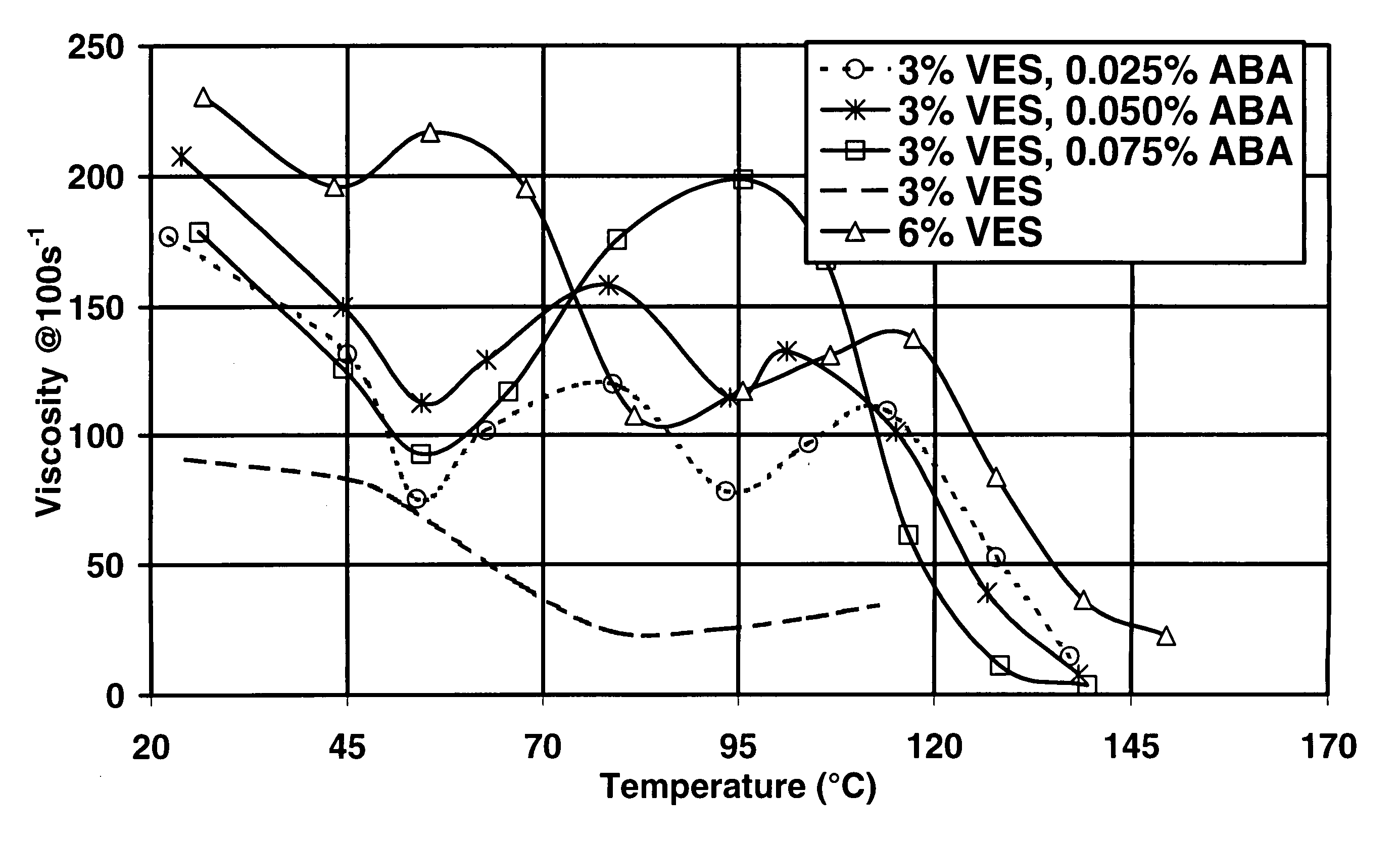
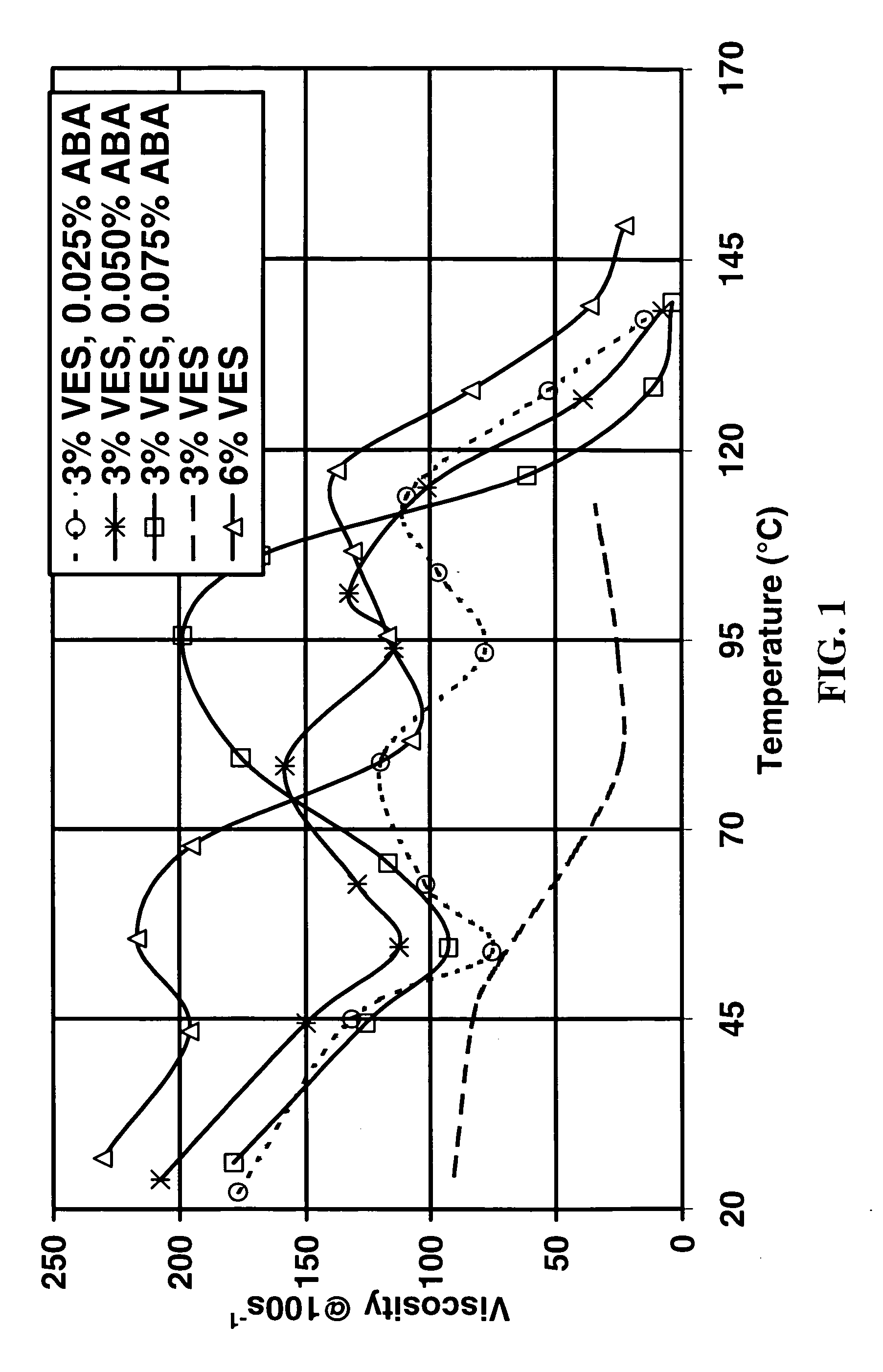
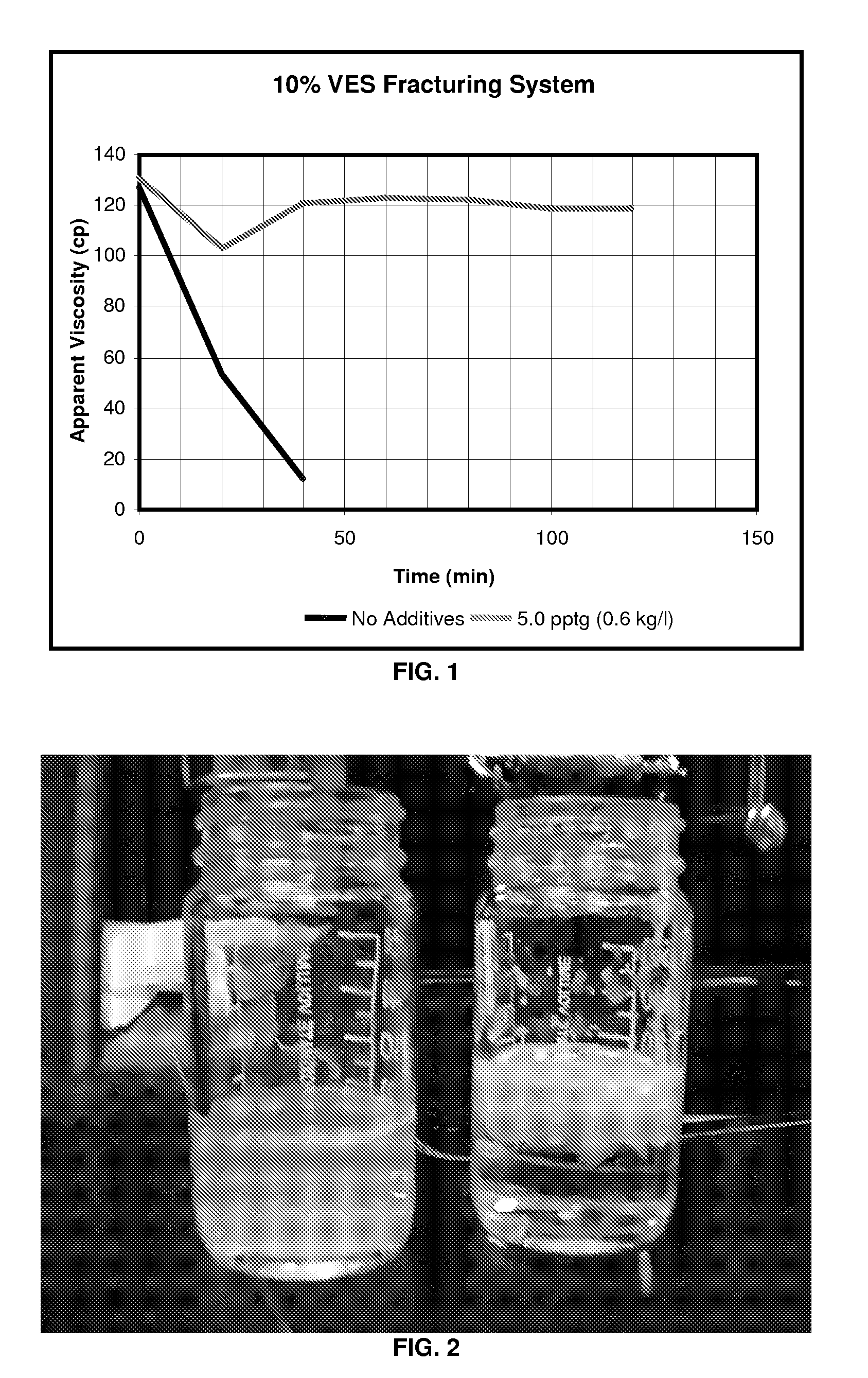
An aqueous, viscoelastic fluid gelled with a viscoelastic surfactant (VES) is stabilized and improved with an effective amount of an alkali earth metal oxide and / or alkali earth metal hydroxide. These fluids are more stable and have reduced or no tendency to precipitate, particularly at elevated temperatures. The additives may also increase viscosity to the point where less VES is required to maintain a given viscosity. These stabilized, enhanced, aqueous viscoelastic fluids may be used as treatment fluids for subterranean hydrocarbon formations, such as in hydraulic fracturing.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
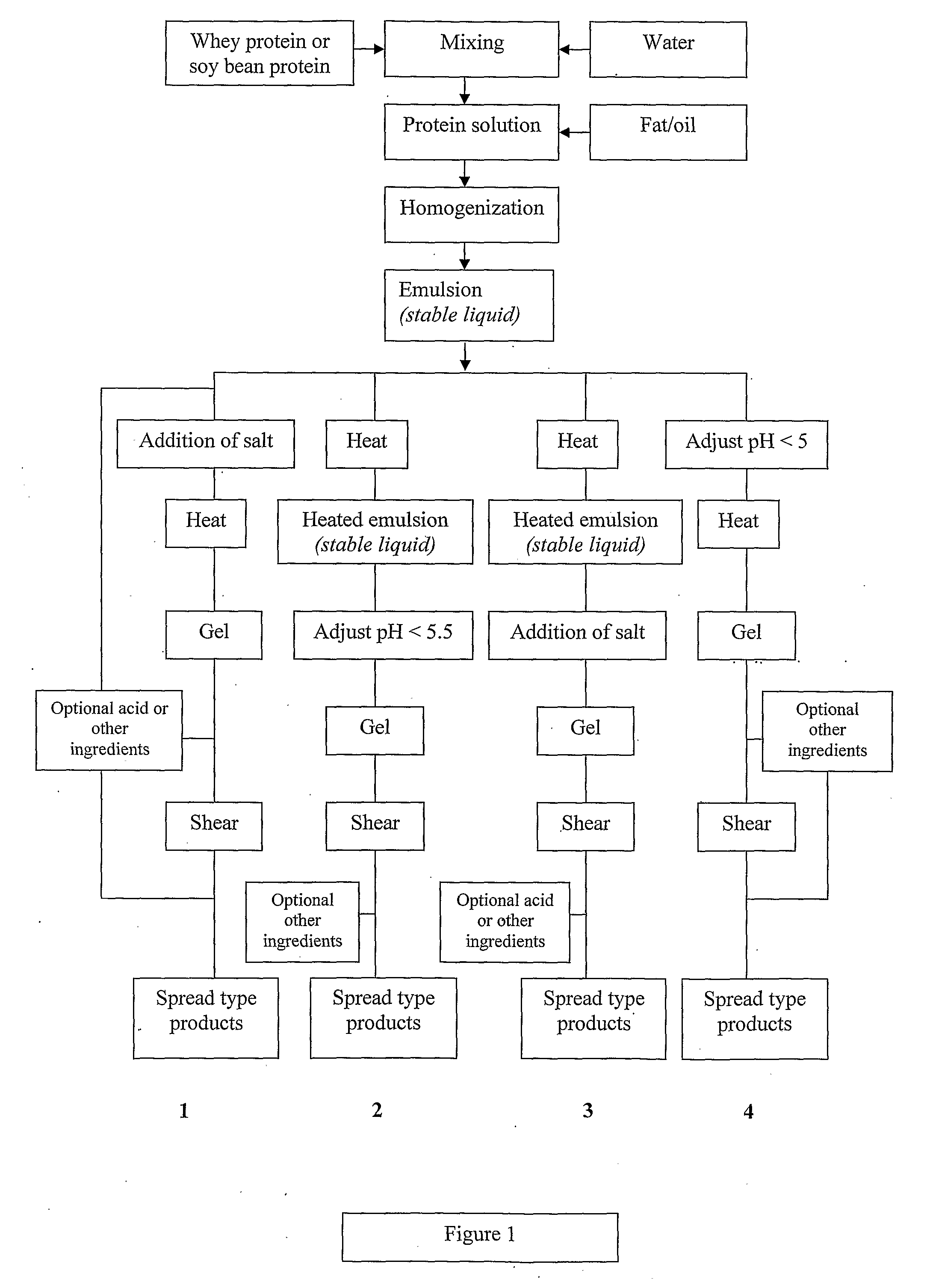
Dairy product and process
InactiveUS20100143567A1Lower pHLow viscosityMilk preparationEdible oils/fats ingredientsWhey proteinHeat treated
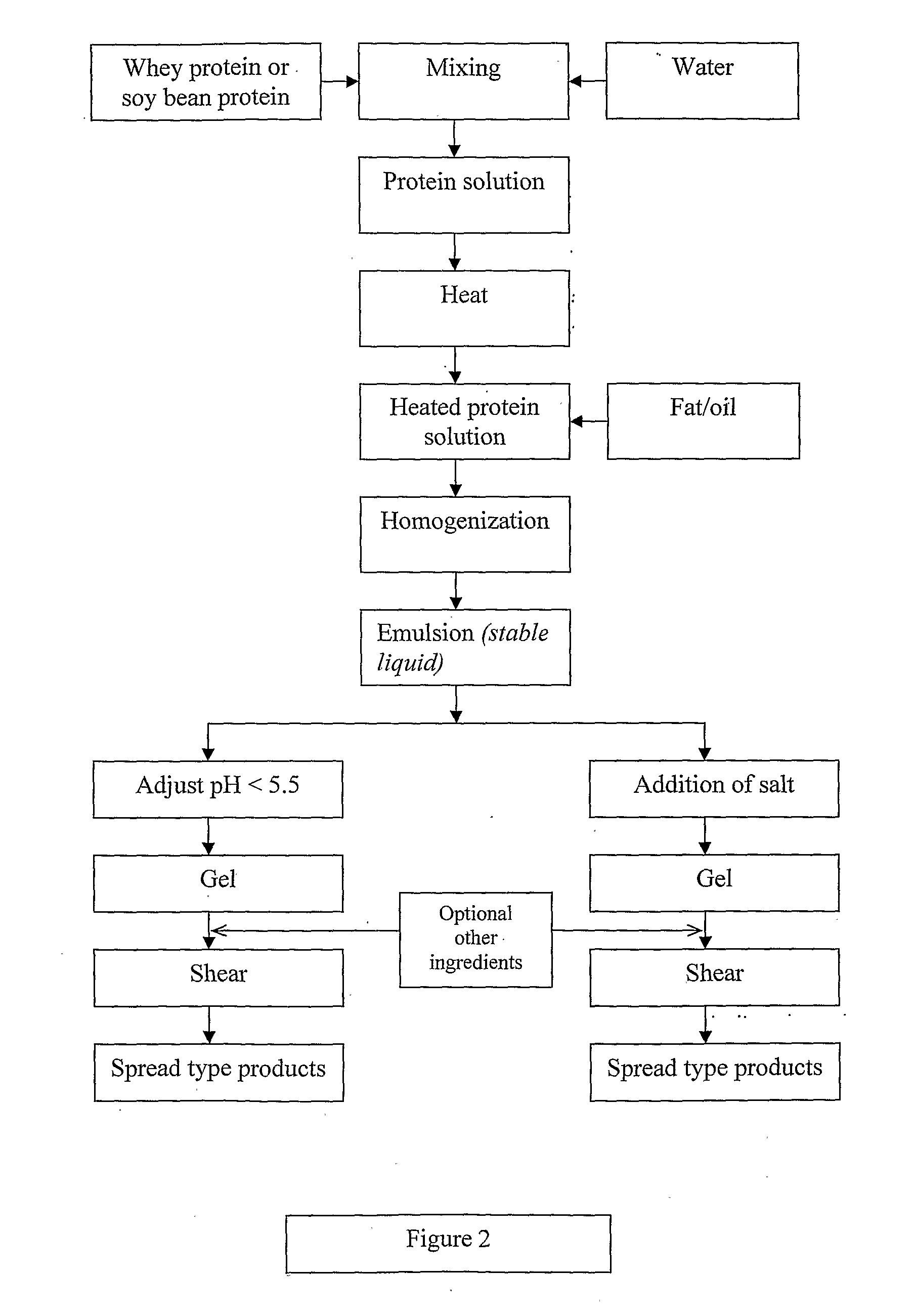
A viscoelastic fluid is prepared by shearing a gelled emulsion. The emulsion is an oil-in-water emulsion comprising 2% 12% (w / w) of a heat-treated protein that can form a heat-set gel and 5% 40% fat. The proteins used include whey protein and soy protein. The viscoelastic fluid may be used as a spread. It may also be used for the preparation of a plurality of different ultimate products formed from the original gel.
Owner:FONTERRA COOP GRP LTD
Bacteria-based and enzyme-based mechanisms and products for viscosity reduction breaking of viscoelastic fluids
ActiveUS7052901B2Low viscosityBreak viscosityDeodrantsFlushingIndirect actionPseudomonas fluorescens
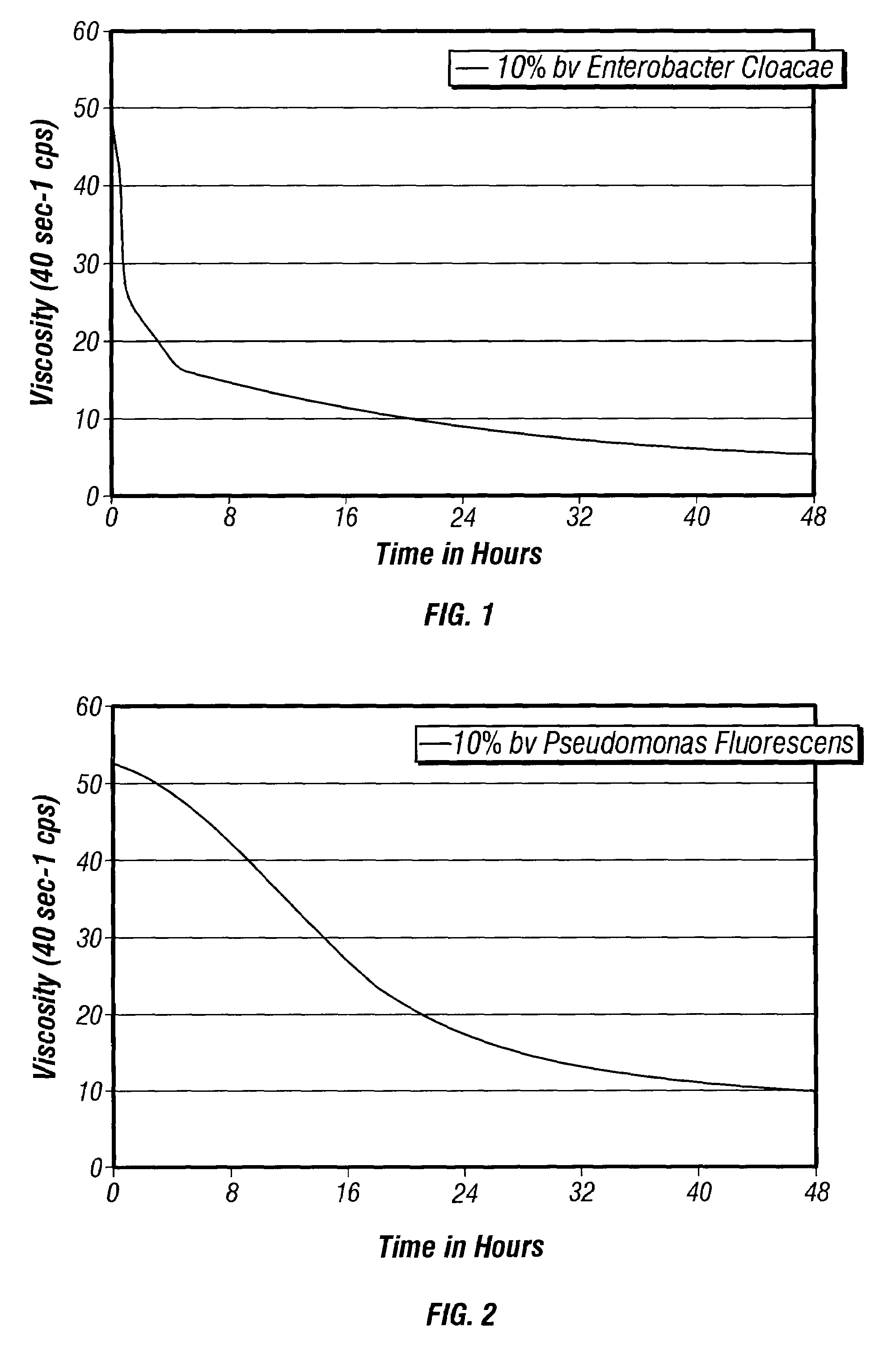
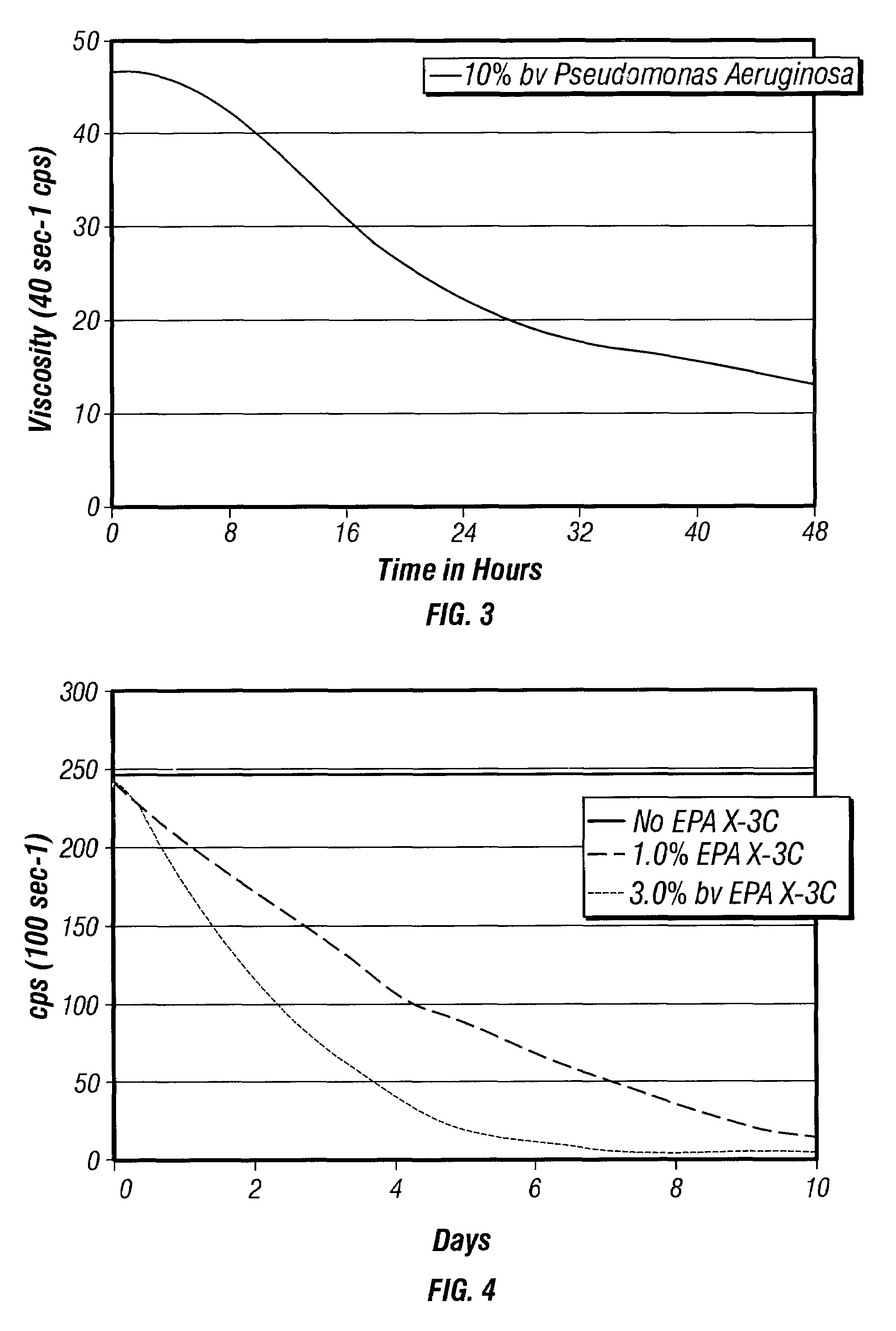
It has been discovered that fluids viscosified with viscoelastic surfactants (VESs) may have their viscosities reduced (gels broken) by the direct or indirect action of a biochemical agent, such as bacteria, fungi, and / or enzymes. The biochemical agent may directly attack the VES itself, or some other component in the fluid that produces a by-product that then causes viscosity reduction. The biochemical agent may disaggregate or otherwise attack the micellar structure of the VES-gelled fluid. The biochemical agent may produce an enzyme that reduces viscosity by one of these mechanisms. A single biochemical agent may operate simultaneously by two different mechanisms, such as by degrading the VES directly, as well as another component, such as a glycol, the latter mechanism in turn producing a by-product (e.g. an alcohol) that causes viscosity reduction. Alternatively, two or more different biochemical agents may be used simultaneously. In a specific, non-limiting instance, a brine fluid gelled with an amine oxide surfactant can have its viscosity broken with bacteria such as Enterobacter cloacae, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and the like.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Composition and wipe for reducing viscosity of viscoelastic bodily fluids
ActiveUS20060140924A1Degradation of fluid propertyInhibition of attachmentBiocideCosmetic preparationsMedicineLotion
The present invention provides a topical composition for application to the perianal and / or labial areas of the skin which helps prevent viscoelastic fluids, such as menses and feces, from attaching to the skin and aids in the reducing the viscoelastic properties of the fluid so that the fluid can flow into absorbent articles. The composition contains at least one viscoelastant material and at least one an anti-adherent material. the composition may be applied with a wipe, including mitts and gloves, a solid stick composition, an aerosol dispenser, a pump spray, a trigger spray, a squeeze bottle, as a foam, as a cream, as an ointment, as a salve, as a gel, as a wash or as a lotion. In addition, absorbent articles, such as pads or pants, diapers and the like may also be used as a means to transfer the composition to the skin.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Viscoelastic fluids containing nanotubes for oilfield uses
InactiveUS20060046937A1Low fluid viscosityMaterial nanotechnologyFluid removalAcid fracturingInorganic salts
The present invention relates to viscoelastic fluids that contain nanotube structures that may be used advantageously as oilfield stimulation fluids in many different applications, most particularly as a fracturing fluid. Viscoelastic fluid compositions of the present invention include an aqueous medium, a viscoelastic surfactant, an organic or inorganic acids, or salt thereof, organic acid salts, inorganic salts, and a nanotube component. The invention is also called to a methods of treating a subterranean well bores in which the viscoelastic fluid is injected into the wellbore to perform operations such as fracturing, drilling, acid fracturing, gravel placement, removing scale, matrix acidizing, and removing mud cake. Further, a method of preparing a nanotube viscoelastic fluid comprising the steps of effectively mixing a carbon nanotube component into a viscoelastic fluid, and sonicating the mixture in order to incorporate the carbon nanotube component is claimed.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Medium-temperature and high-temperature clean fracturing fluid and preparation method thereof
The invention provides medium-temperature and high-temperature clean fracturing fluid used under high formation temperature and a preparation method thereof. The clean fracturing fluid contains Gemini cation surfactant, amphoteric surfactant, electrolyte salt, counter-ion salt, cosolvent and water. The clean fracturing fluid of the invention is used for oil and gas field fracturing and mainly comprises 2-5 percent of surfactant, 1-4 percent of amphoteric surfactant, 1-4 percent of electrolyte, 0.05-0.15 percent of counter ion and 0.1-1.5 percent of cosolvent by weight percent. Viscoelastic fluid is formed under agitation. The invention has the advantages that the viscoelasticity of the system is high, the friction resistance is low and good sand suspending performance is kept within 90-130 DEG C.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Polymeric materials, their preparation and use
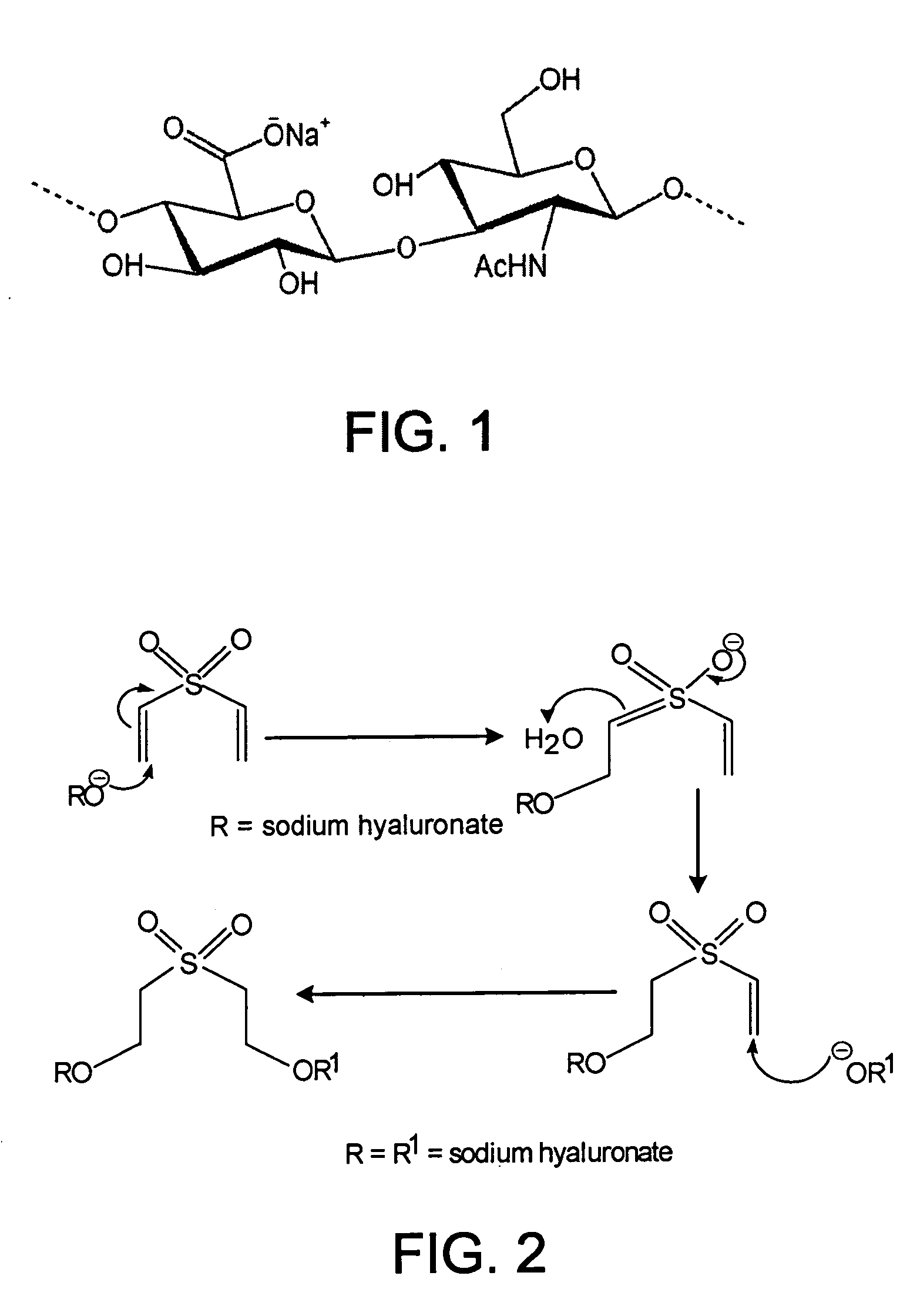
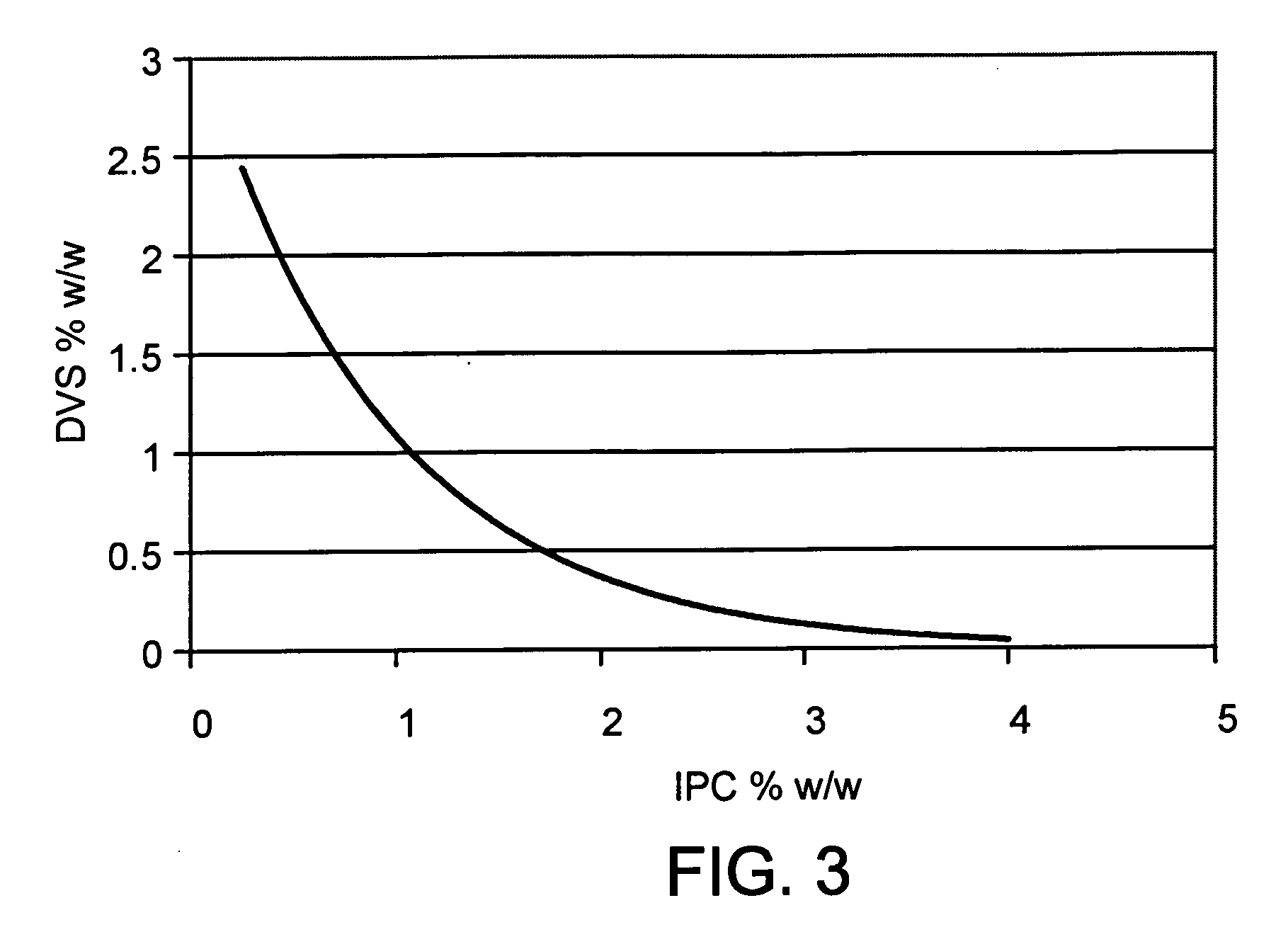
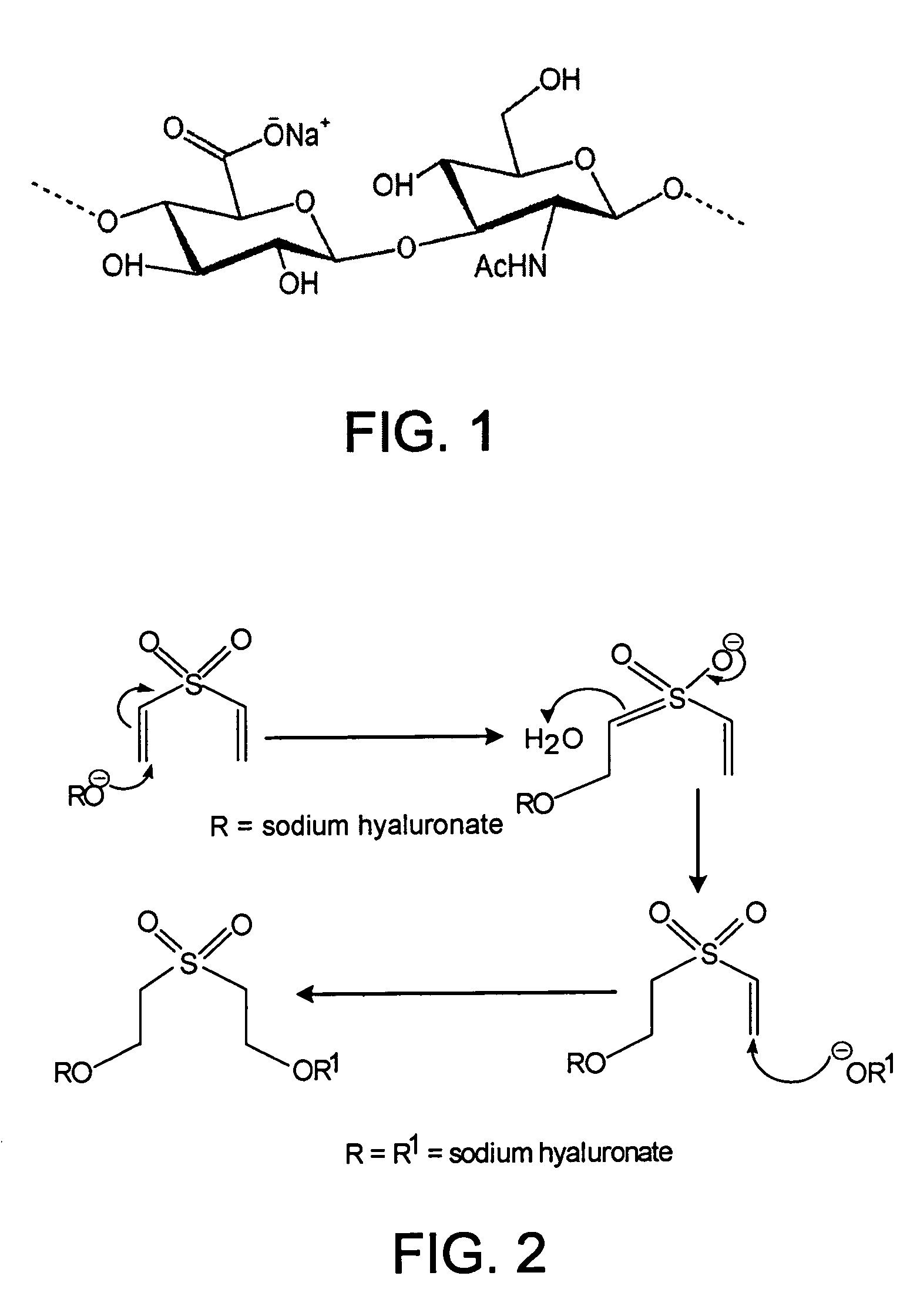
ActiveUS20070036745A1Improve mechanical propertiesImprove cohesionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCross-linkHardness
Disclosed are highly resilient and cohesive gels formed by the cross-linking of hyaluronan or hylan, their salts or derivatives thereof, using divinyl sulfone (DVS) as the cross-linking agent. Also disclosed are viscoelastic fluids containing alkylsulfone groups covalently attached to the backbone of the polymer, formed by the mono-functionalization of the cross-linking monomer DVS with hyaluronan and / or hylan. Mechanical properties such as values of hardness and cohesiveness are specified by the rheological properties of the gels. Also disclosed are methods for the preparation of such products. They have use in many applications as injectable and / or implantable devices and as drug delivery systems.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Integrated chip system for high-throughput sorting and counting detection of biological particles, and application
ActiveCN103191791AMeet the damageNo damageMaterial analysis by optical meansLaboratory glasswaresInertial effectLiquid Change
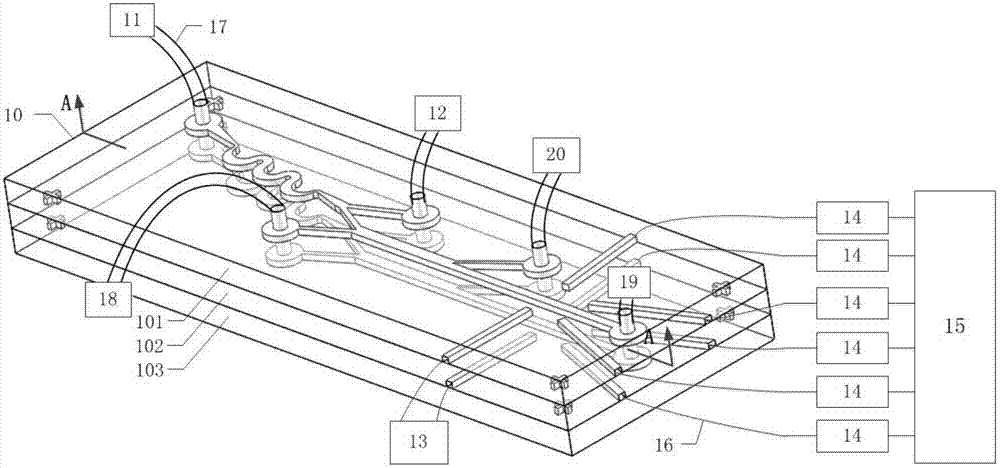
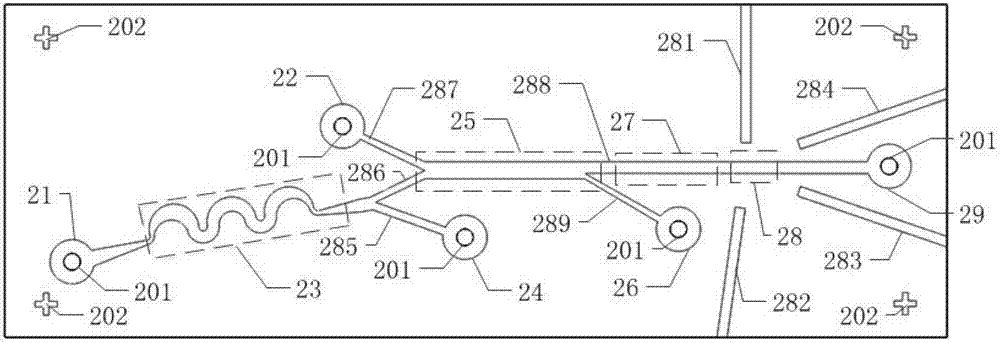
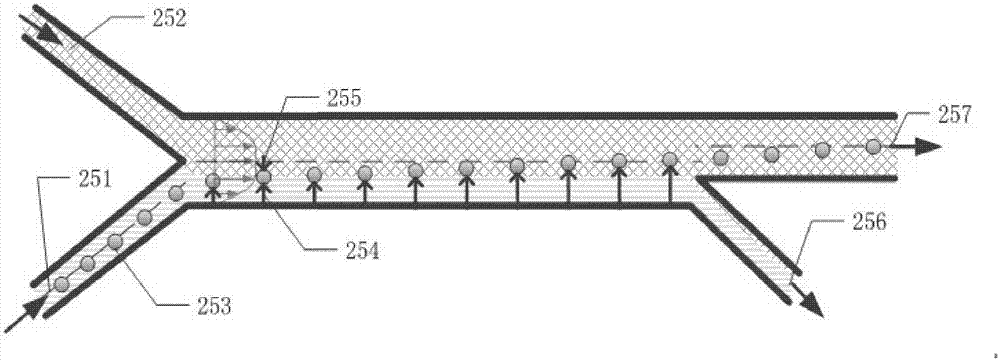
The invention discloses an integrated chip system for high-throughput sorting and counting detection of biological particles, and an application. The chip system comprises a main microfluidic chip, a micropipe, a sample liquid micropump, an exchange liquid micropump, a first waste liquid collecting device, a second waste liquid collecting device, a third waste liquid collecting device, laser emitters, photoelectric conversion devices, optical fibers and a computer, wherein the main microfluidic chip comprises an asymmetric curved flow path, a first branch channel, a second branch channel, a third branch channel, a main flow path, a branch flow path, aligning marks, etc. The system utilizes the asymmetric curved flow path to realize pre-focusing and sorting for the particles, utilizes a liquid changing flow channel to realize change of a carrier liquid of to-be-tested particles and particle cleaning, and utilizes a viscoelastic effect and an inertial effect of a viscoelastic fluid to realize focus of single equilibrium position of section centers of the particles. The system does not need a sheath liquid, complex pre-cleaning of the particles, and optical alignment, has advantages of high speed, high precision, integration, miniaturization, automation, low cost, simple production process, easy batch production, etc.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Menses specific absorbent systems
A personal care absorbent article such as a disposable diaper, sanitary pad or tampon, wound dressing or bandage which includes a nonwoven web material made from a plurality of polymeric fibers having at least one treatment chemistry suitable for modifying at least one characteristic of a high viscoelasticity fluid upon contact with the high viscoelasticity fluid. In accordance with one particularly preferred embodiment, the treatment chemistry is suitable for immobilizing the high viscoelasticity fluid within the nonwoven web material.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Additive for viscoelastic fluid
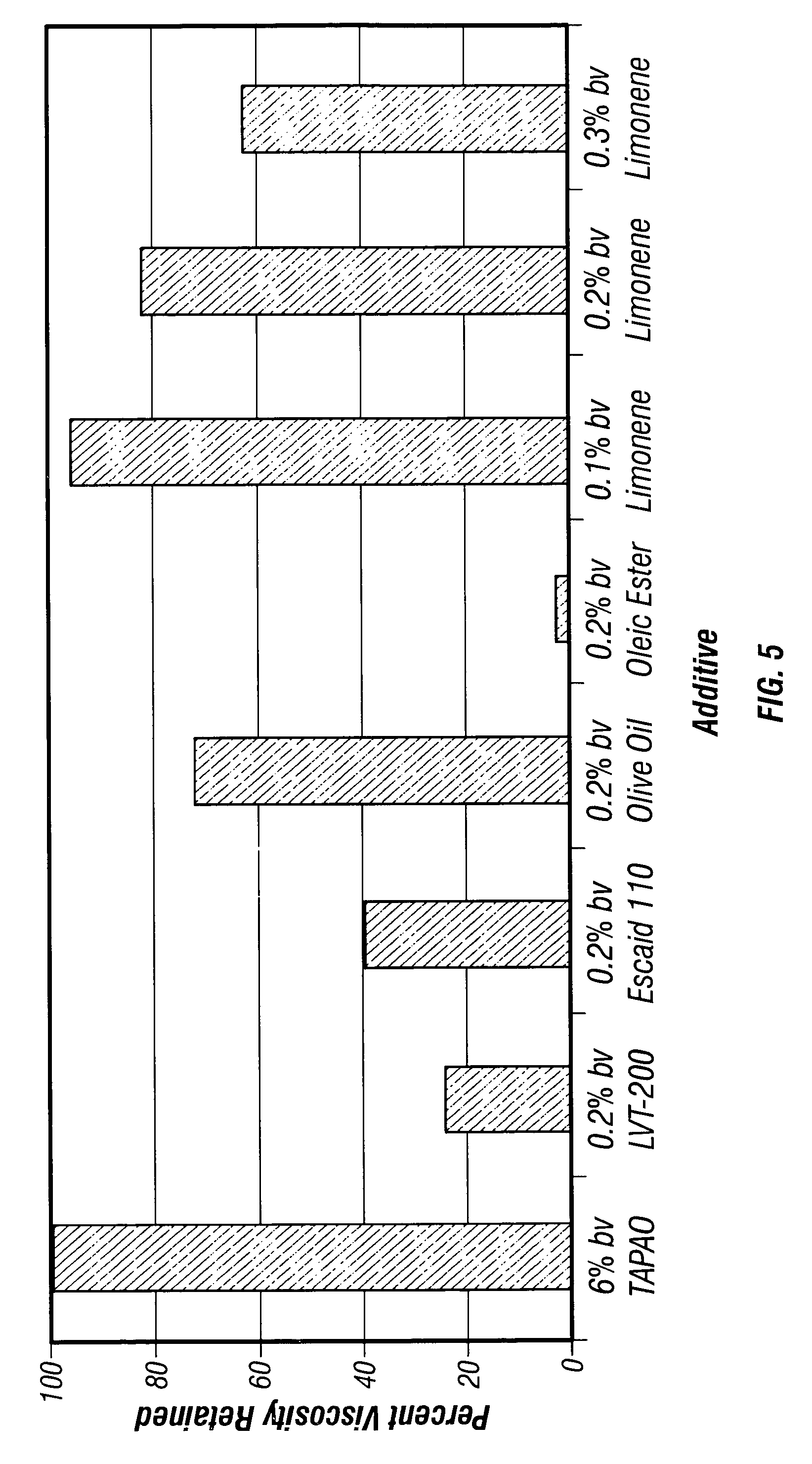
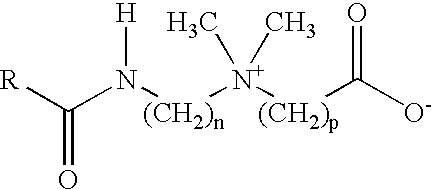
InactiveUS20050155762A1Shortening shear recovery timeShorten recovery timeReciprocating drilling machinesConstructionsBetaineFluid viscosity
Composition and method for shortening the shear recovery time of cationic, zwitterionic, and amphoteric viscoelastic surfactant fluid systems by adding an effective amount of a co-gelling agent selected from triblock oligomeric compounds having hydrophilic (for example polyether) and hydrophobic (for example alkyl) portions. The co-gelling agent also increases fluid viscosity and very low co-gelling agent concentration is needed. Preferred surfactants are betaines and quaternary amines. The fluids are useful in oilfield treatments, for example fracturing and gravel packing.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
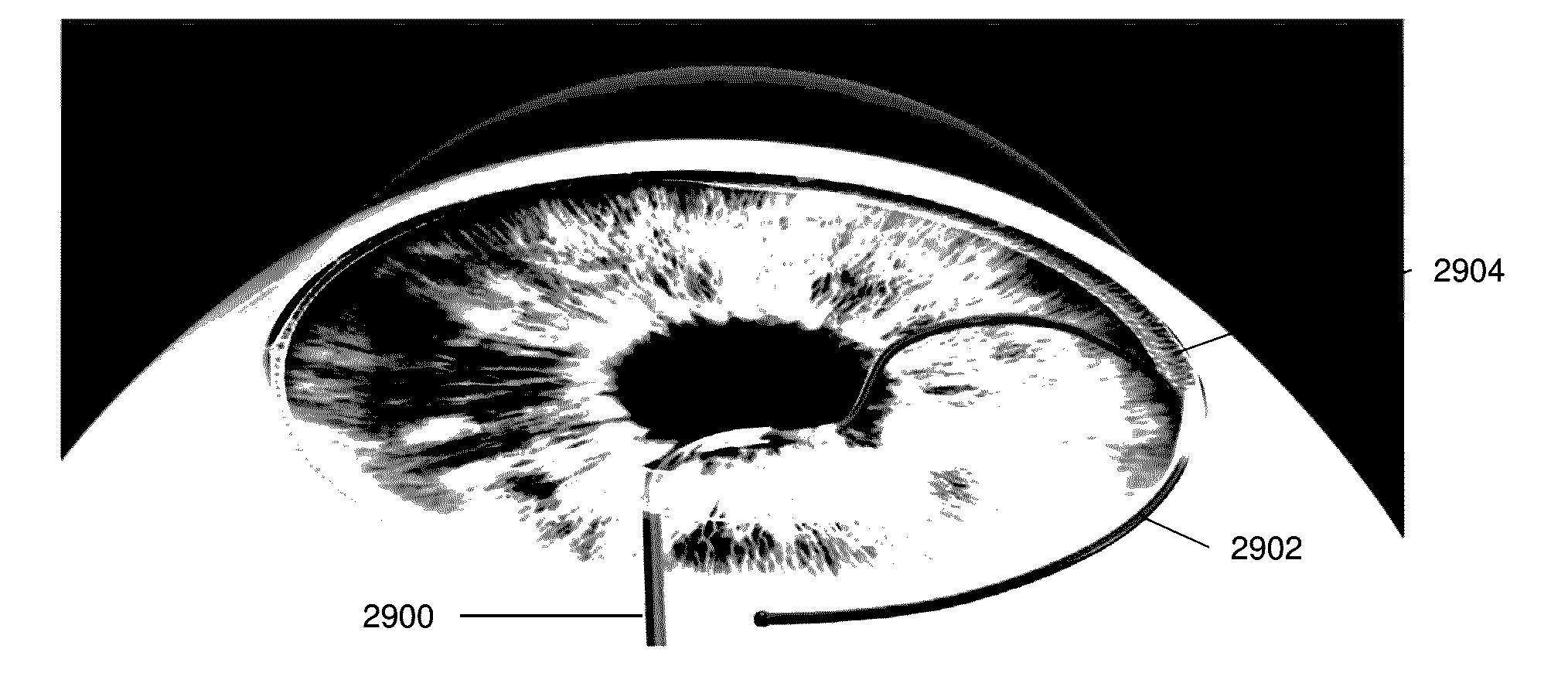
Ocular delivery systems and methods
ActiveUS20160287438A1Easily and reliably accessingMinimal and reduced traumaGuide needlesOrganic active ingredientsAqueous humorSchlemm's canal
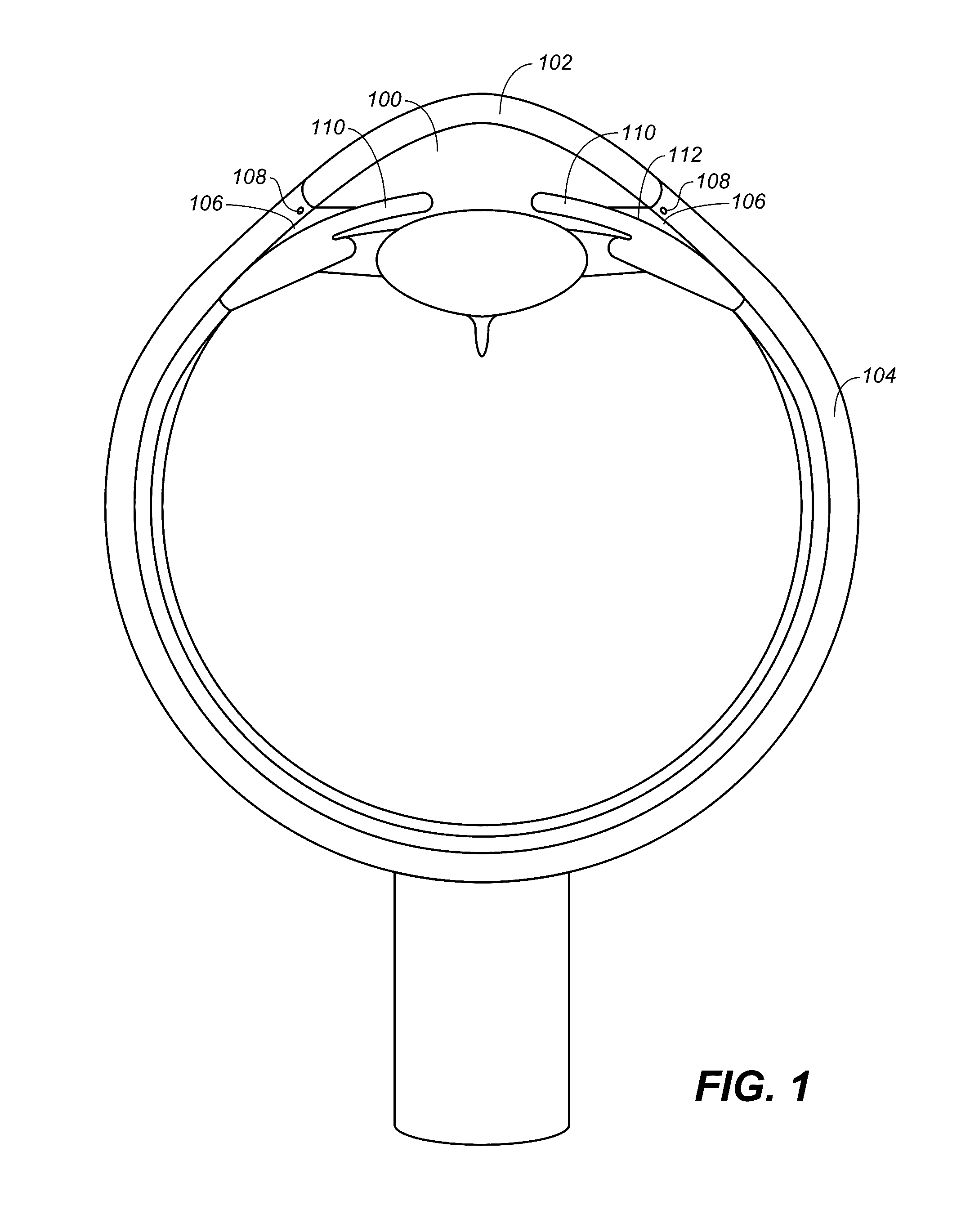
Described here are systems and methods for accessing Schlemm's canal and for delivering an ocular device, tool, or fluid composition therein. The ocular devices may maintain the patency of Schlemm's canal without substantially interfering with transmural fluid flow across the canal. The fluid composition may be a viscoelastic fluid that is delivered into the canal to facilitate drainage of aqueous humor by disrupting the canal and surrounding trabeculocanalicular tissues. Some systems described here may be configured to cut or tear the trabecular meshwork with the body of an elongate member located within Schlemm's canal. Other tools for disrupting these tissues and minimally invasive methods for treating medical conditions associated with elevated intraocular pressure, including glaucoma, are also described.
Owner:SIGHT SCI
Viscoelastic fluids containing nanotubes for oilfield uses
InactiveUS7244694B2Low fluid viscosityMaterial nanotechnologyFluid removalInorganic saltsOrganic acid
The present invention relates to viscoelastic fluids that contain nanotube structures that may be used advantageously as oilfield stimulation fluids in many different applications, most particularly as a fracturing fluid. Viscoelastic fluid compositions of the present invention include an aqueous medium, a viscoelastic surfactant, an organic or inorganic acids, or salt thereof, organic acid salts, inorganic salts, and a nanotube component. The invention is also called to a methods of treating a subterranean well bores in which the viscoelastic fluid is injected into the wellbore to perform operations such as fracturing, drilling, acid fracturing, gravel placement, removing scale, matrix acidizing, and removing mud cake. Further, a method of preparing a nanotube viscoelastic fluid comprising the steps of effectively mixing a carbon nanotube component into a viscoelastic fluid, and sonicating the mixture in order to incorporate the carbon nanotube component is claimed.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
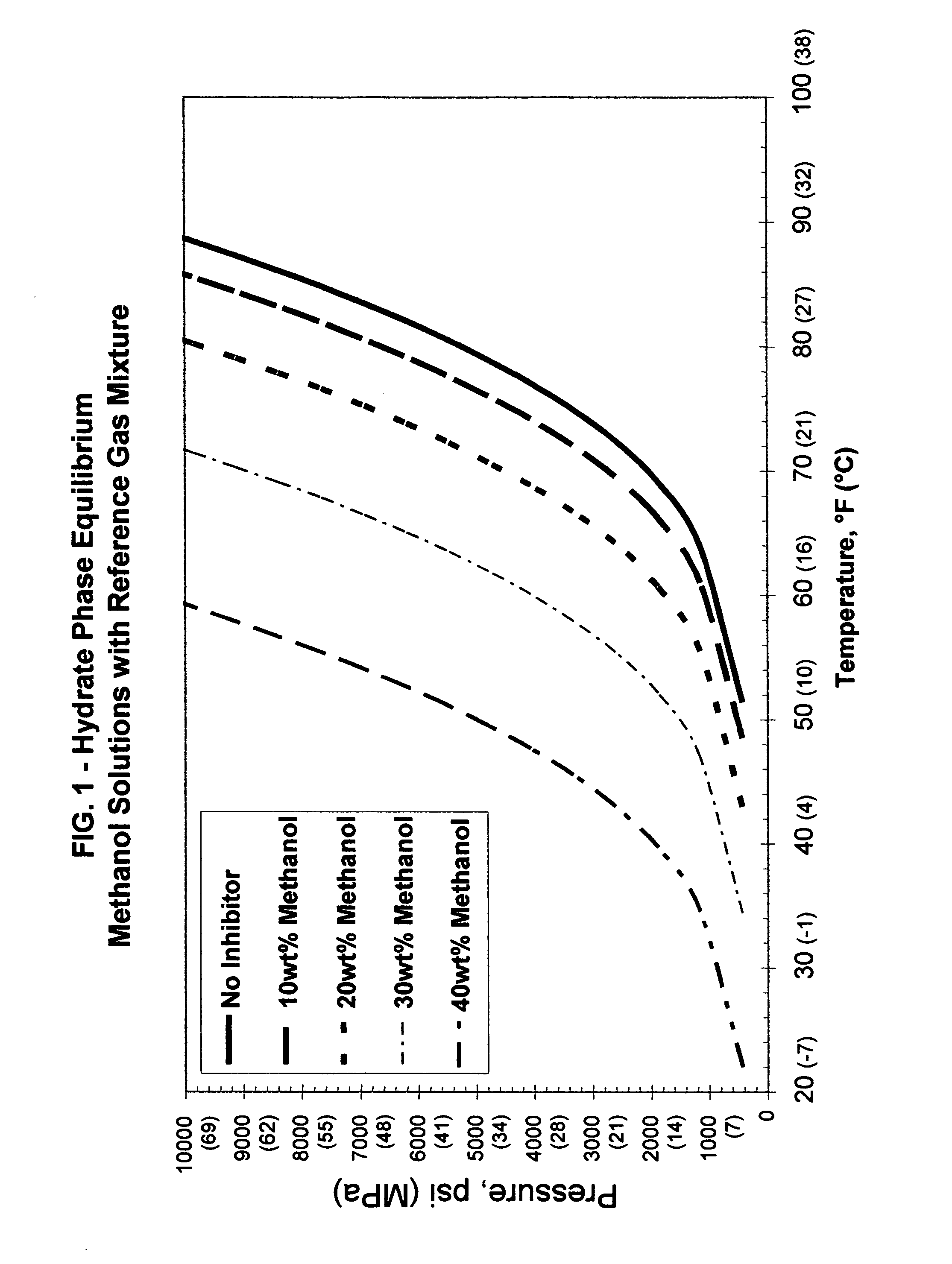
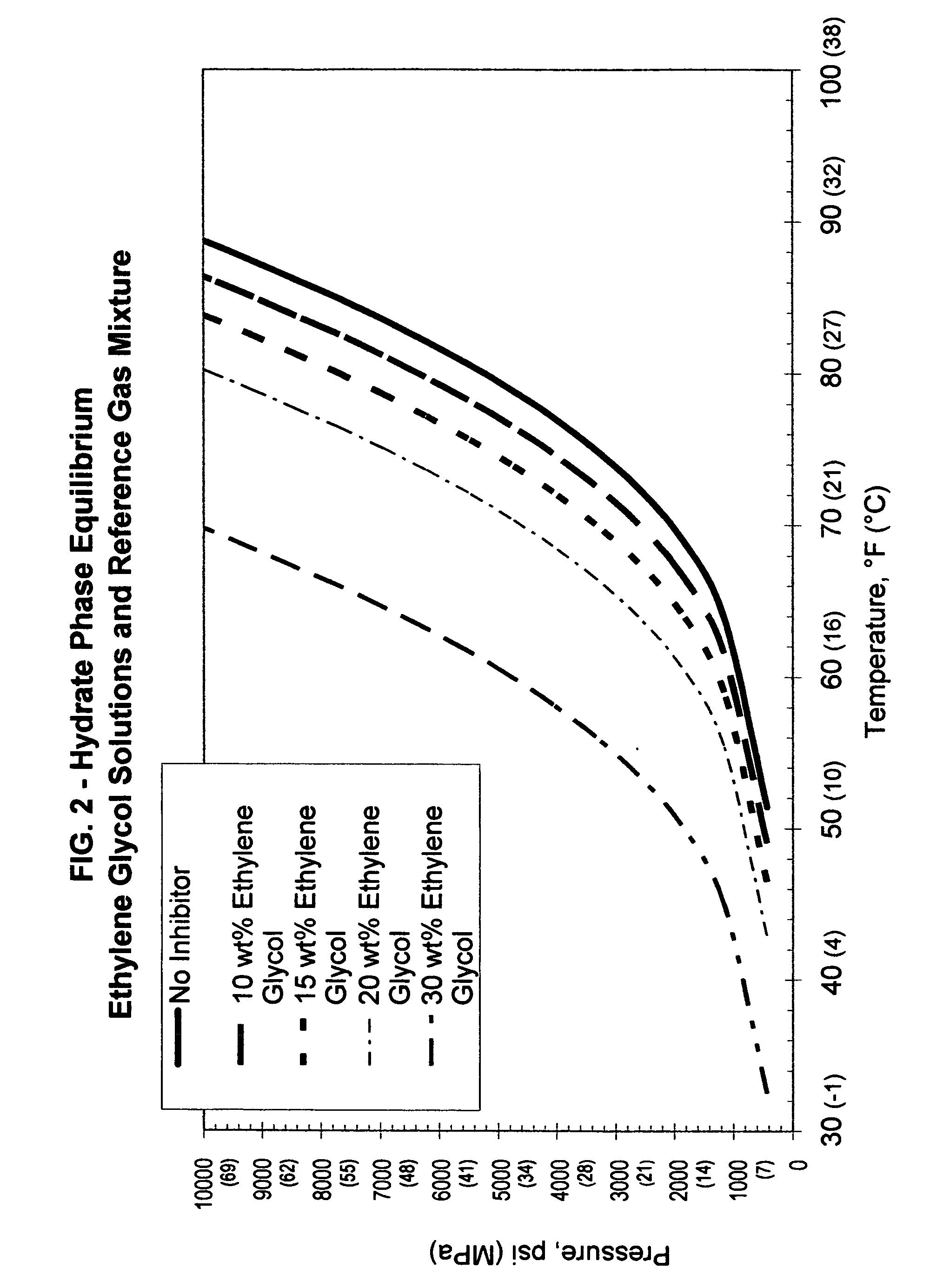
Additives for hydrate inhibition in fluids gelled with viscoelastic surfactants
An aqueous, viscoelastic fluid gelled with a viscoelastic surfactant (VES) is inhibited against hydrate formation with an effective amount of an additive that could be one or more halide salts of alkali metals and alkali earth metals, formate salts, alcohols, glycols, glycol amines, sugars, sugar alcohols, amidoamine oxides, polymers such as polyamines, polyvinylpyrrolidones and derivatives thereof, polyvinyl alcohols and derivatives thereof, polycaprolactams and derivatives thereof, hydroxyethylcellulose, and mixtures thereof. These fluids are inhibited against hydrate formation and may have increased viscosity as well. The additives may increase viscosity to the point where less VES is required to maintain a given viscosity. These inhibited, aqueous, viscoelastic fluids may be used as treatment fluids for subterranean hydrocarbon formations, such as in stimulation treatments, e.g. hydraulic fracturing fluids.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Polymeric materials, their preparation and use
ActiveUS8524213B2Enhancing mechanical property and cohesion and elasticityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCross-linkBackbone chain
Disclosed are highly resilient and cohesive gels formed by the cross-linking of hyaluronan or hylan, their salts or derivatives thereof, using divinyl sulfone (DVS) as the cross-linking agent. Also disclosed are viscoelastic fluids containing alkylsulfone groups covalently attached to the backbone of the polymer, formed by the mono-functionalization of the cross-linking monomer DVS with hyaluronan and / or hylan. Mechanical properties such as values of hardness and cohesiveness are specified by the rheological properties of the gels. Also disclosed are methods for the preparation of such products. They have use in many applications as injectable and / or implantable devices and as drug delivery systems.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method of using viscoelastic vesicular fluids to enhance productivity of formations
A process for enhancing the productivity of a formation consists of introducing into the formation a viscoelastic fluid which contains at least one surfactant, at least one quaternary amine polyelectrolyte, water, and a non-aqueous solvent. The surfactant forms aggregation structures or vesicles. The fluid, which significantly enhances fluid viscosity and thermal stability, is particularly effective as a diverting fluid to divert an acid treatment package from a high permeability or damaged portion of a formation to a low permeability or undamaged portion of a formation as well as a fracturing fluid. In addition, the fluid is useful for sand control completion.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
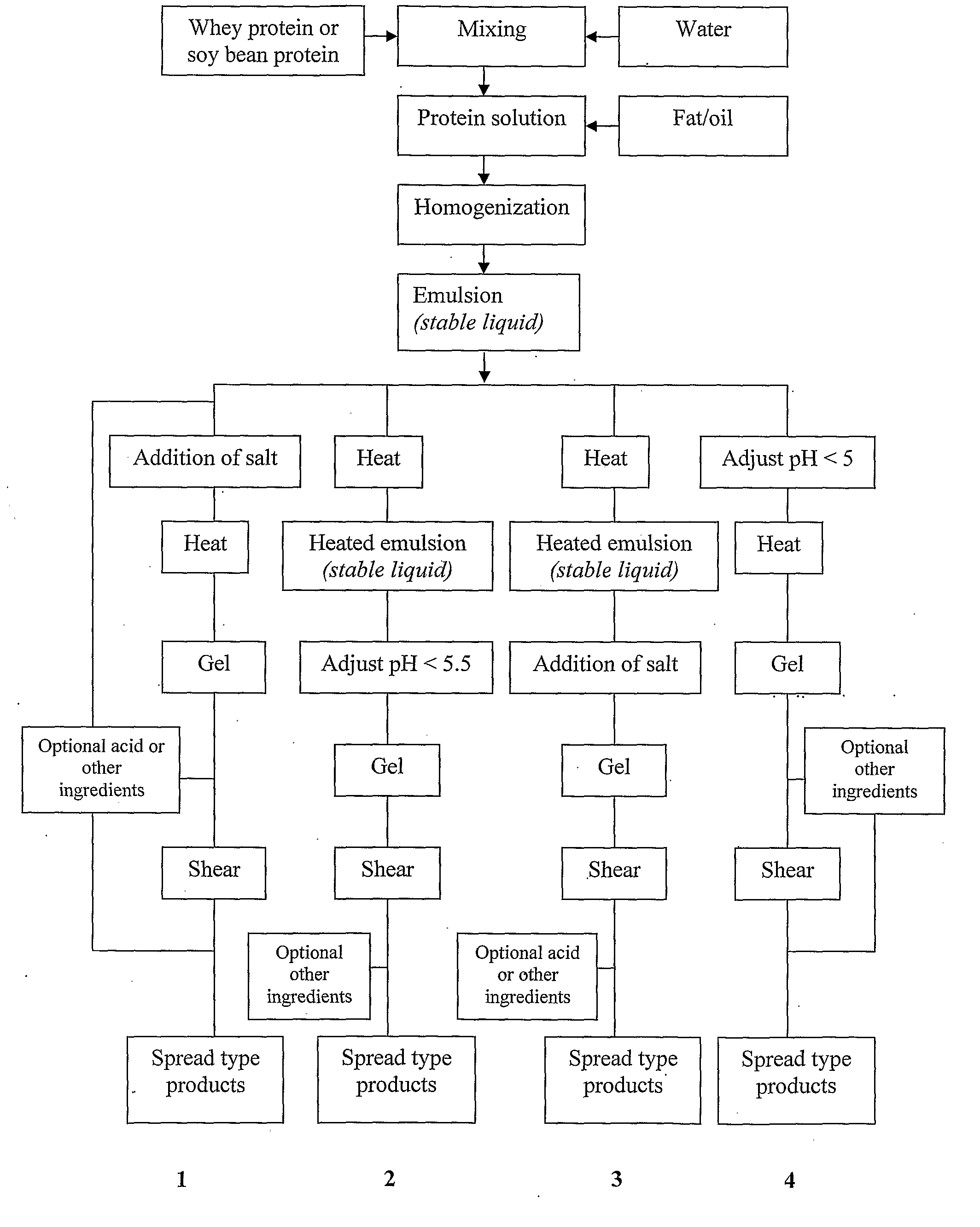
System stabilizers and performance enhancers for aqueous fluids gelled with viscoelastic surfactants
InactiveUS7343972B2Improve stabilityReduce precipitationFluid removalDrilling compositionFluid gelAlkaline earth oxides
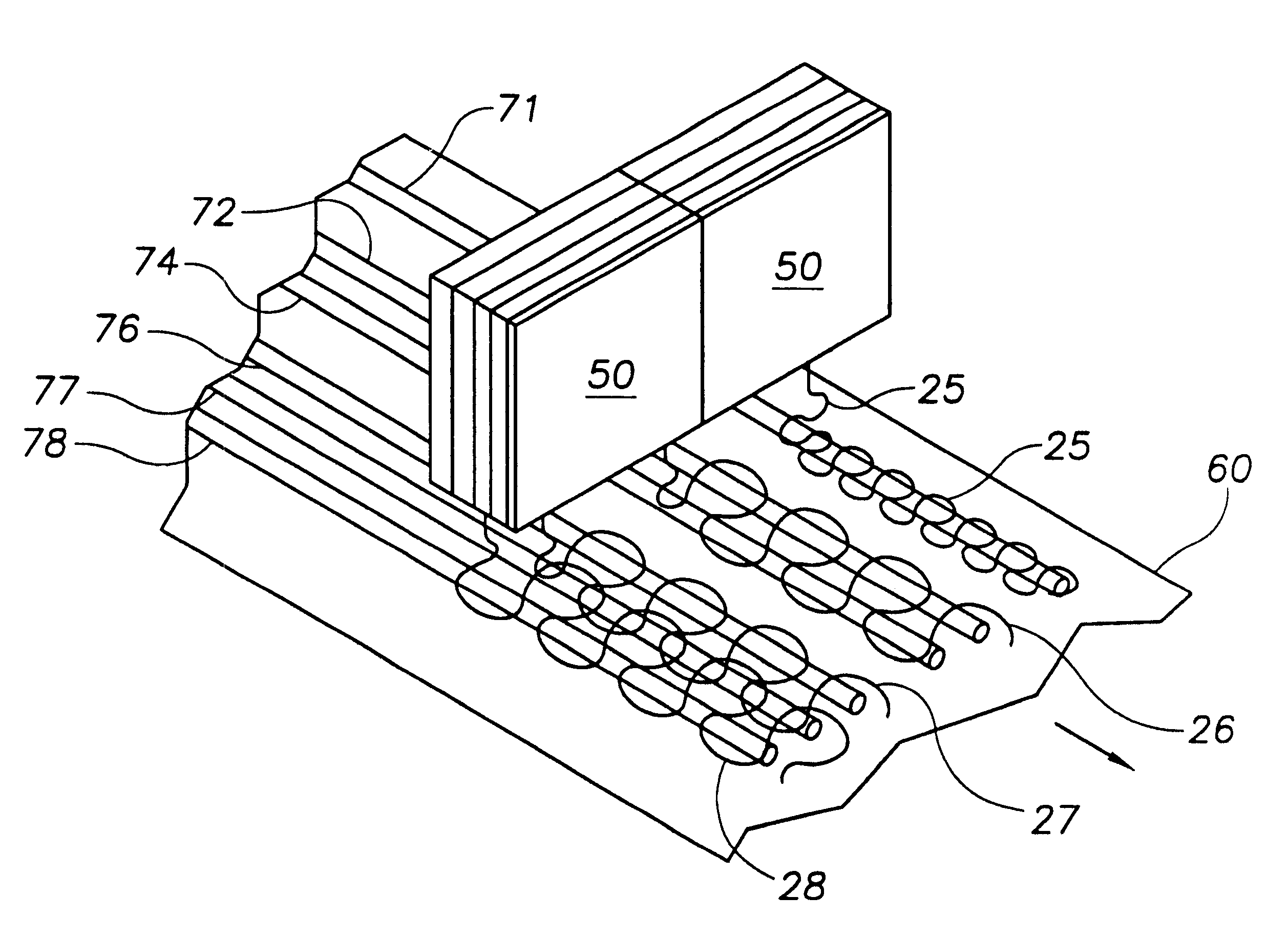
An aqueous, viscoelastic fluid gelled with a viscoelastic surfactant (VES) is stabilized and improved with an effective amount of an alkali earth metal oxide and / or alkali earth metal hydroxide. These fluids are more stable and have reduced or no tendency to precipitate, particularly at elevated temperatures. The additives may also increase viscosity to the point where less VES is required to maintain a given viscosity. These stabilized, enhanced, aqueous viscoelastic fluids may be used as treatment fluids for subterranean hydrocarbon formations, such as in hydraulic fracturing.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Omega spray pattern and method therefor
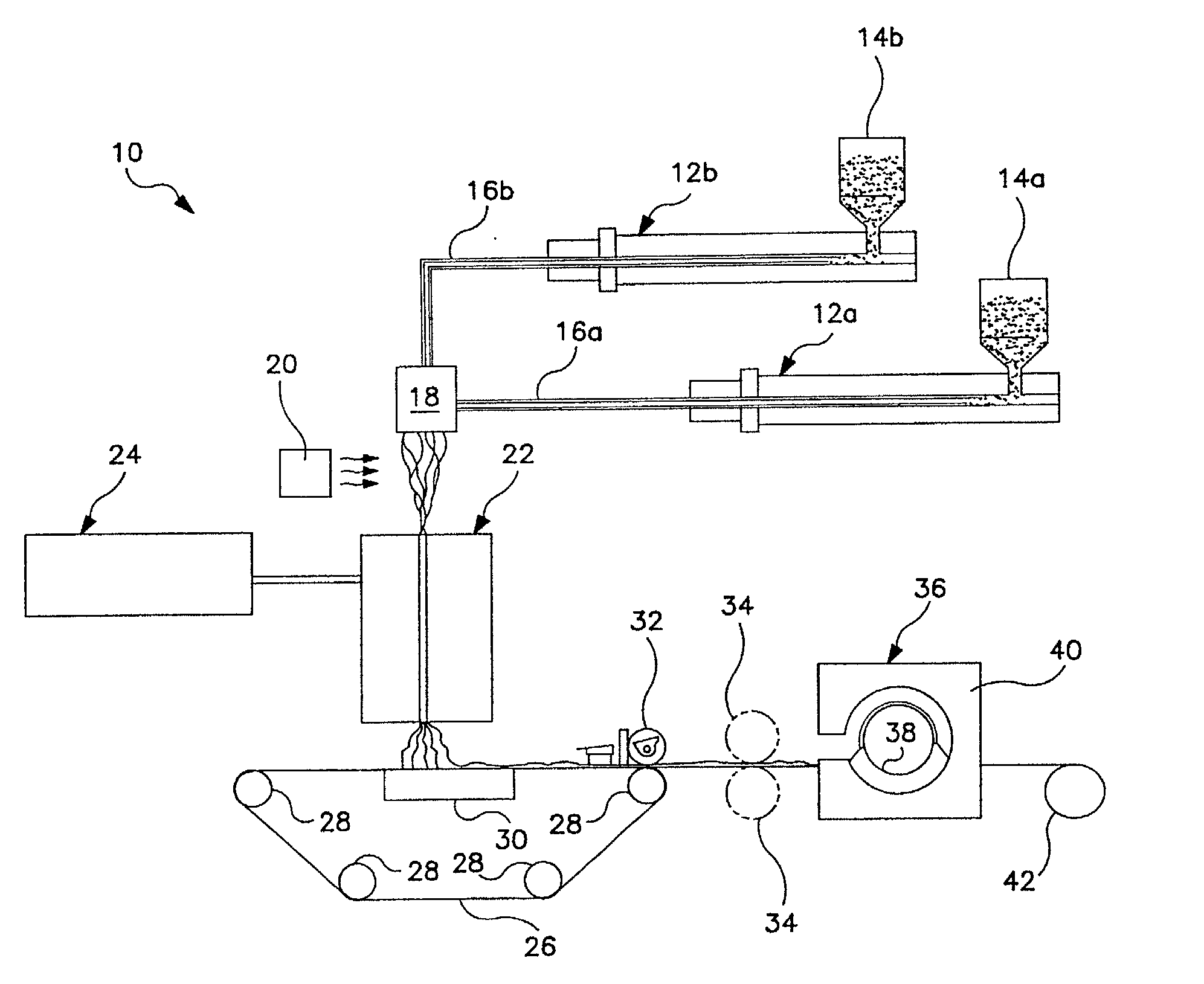
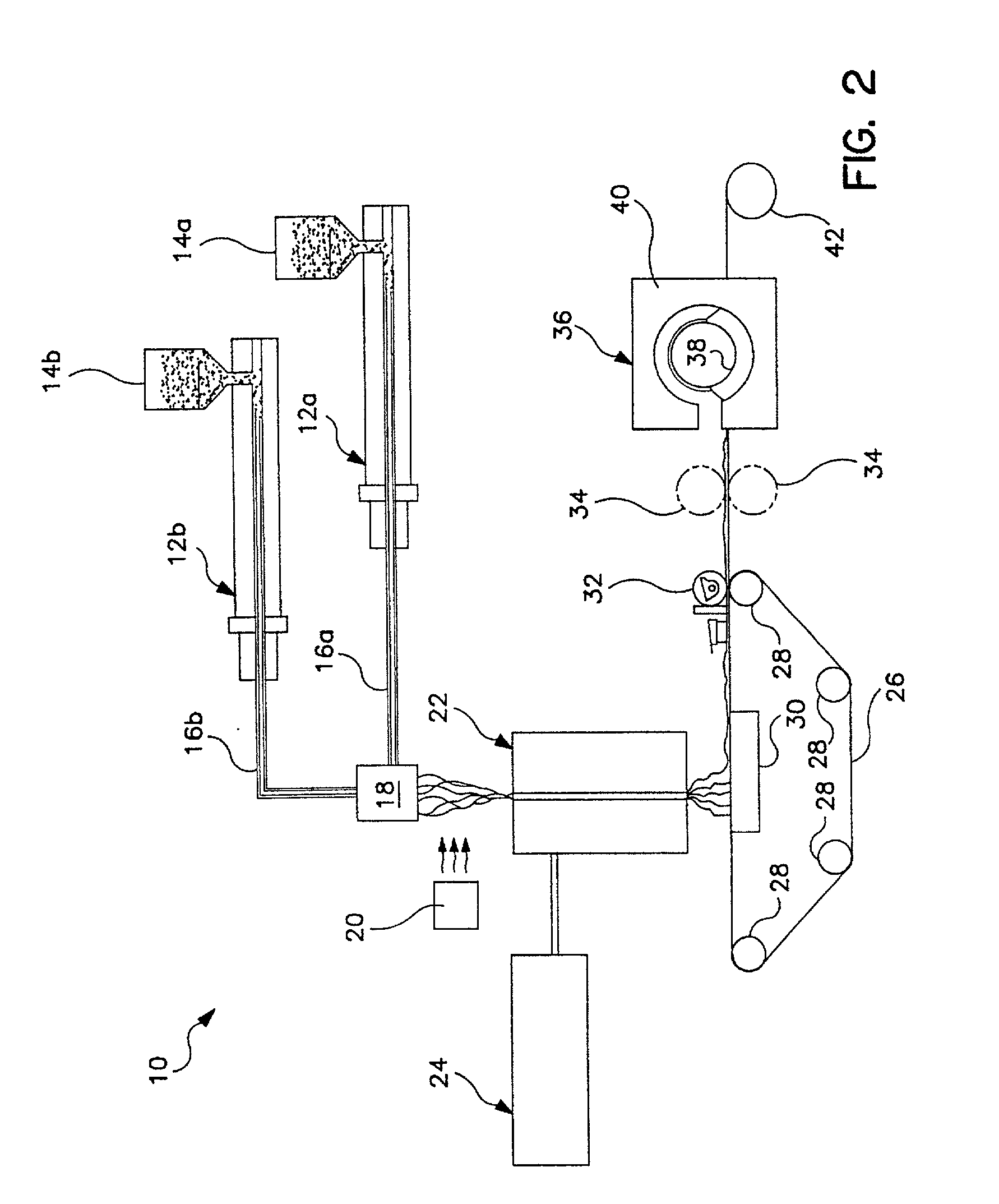
A method for producing visco-elastic fluidic material flows by drawing a visco-elastic fluidic material with corresponding separate second fluid flows associated therewith to form a visco-elastic fiber vacillating in a repeating, generally omega-shaped pattern having a bowed portion with first and second side portions that first converge toward each other and then diverge outwardly in generally opposing directions. In one operation, the visco-elastic fiber vacillating in the repeating, generally omega-shaped pattern is an adhesive material deposited onto woven and non-woven fabric substrates and stretched elongated elastic strands in the manufacture of a variety of bodily fluid absorbing hygienic articles.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Thickened viscoelastic fluids and uses thereof
The present invention generally relates to a viscoelastic fluids, thickened acid compositions and the like and to methods of using said gelled compositions. The thickened compositions of the present invention can usefully be employed in methods of stimulating and / or modifying the permeability of underground formations, in drilling fluids, completion fluids, workover fluids, acidizing fluids, fracturing, gravel packing and the like.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL CHEM INT BV
Aqueous viscoelastic fluid
The invention concerns an aqueous viscoelastic fluid for use in the recovery of hydrocarbons. According to the invention, the aqueous viscoelastic fluid comprises a monomer, a dimer or an oligomer of a viscoelastic surfactant able to form a viscoelastic gel under downhole conditions, said surfactant comprising a hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic head, and being of the following formulae: R-X-Y-Z where R is the hydrophobic tail of the surfactant, Z is the hydrophilic head of the surfactant, said hydrophilic head being charged, X is a stabilising group and Y chain is a linear, saturated or unsaturated, hydrocarbon chain of 1, 2 or 3 carbon atoms or a branched, saturated or unsaturated hydrocarbon chain wherein the main chain is of 1, 2 or 3 carbon atoms, possibly incorporating an aromatic ring.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
High temperature gellant in low and high density brines
In accordance with the present invention, the rheology of an aqueous fluid is modified by a method which comprises adding to said aqueous fluid an amount of a viscoelastic composition sufficient to form a viscoelastic fluid. The viscoelastic composition of the invention comprises a combination of i) at least one alkyl amido quaternary amine, and ii) at least one coadditive that comprises a C8-24 linear alkyl and / or alpha-olefin sulfate and / or sulphonate.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL NV
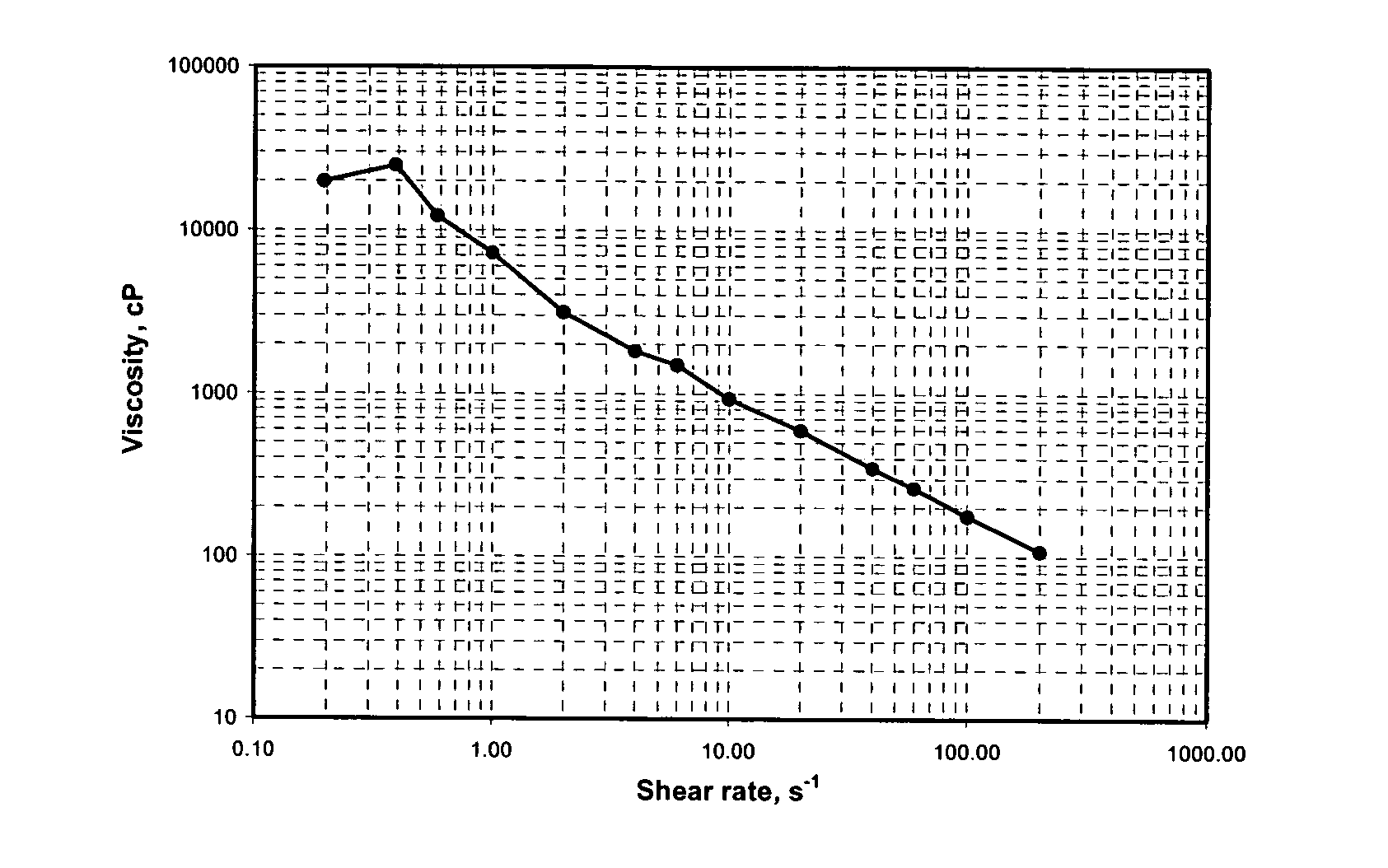
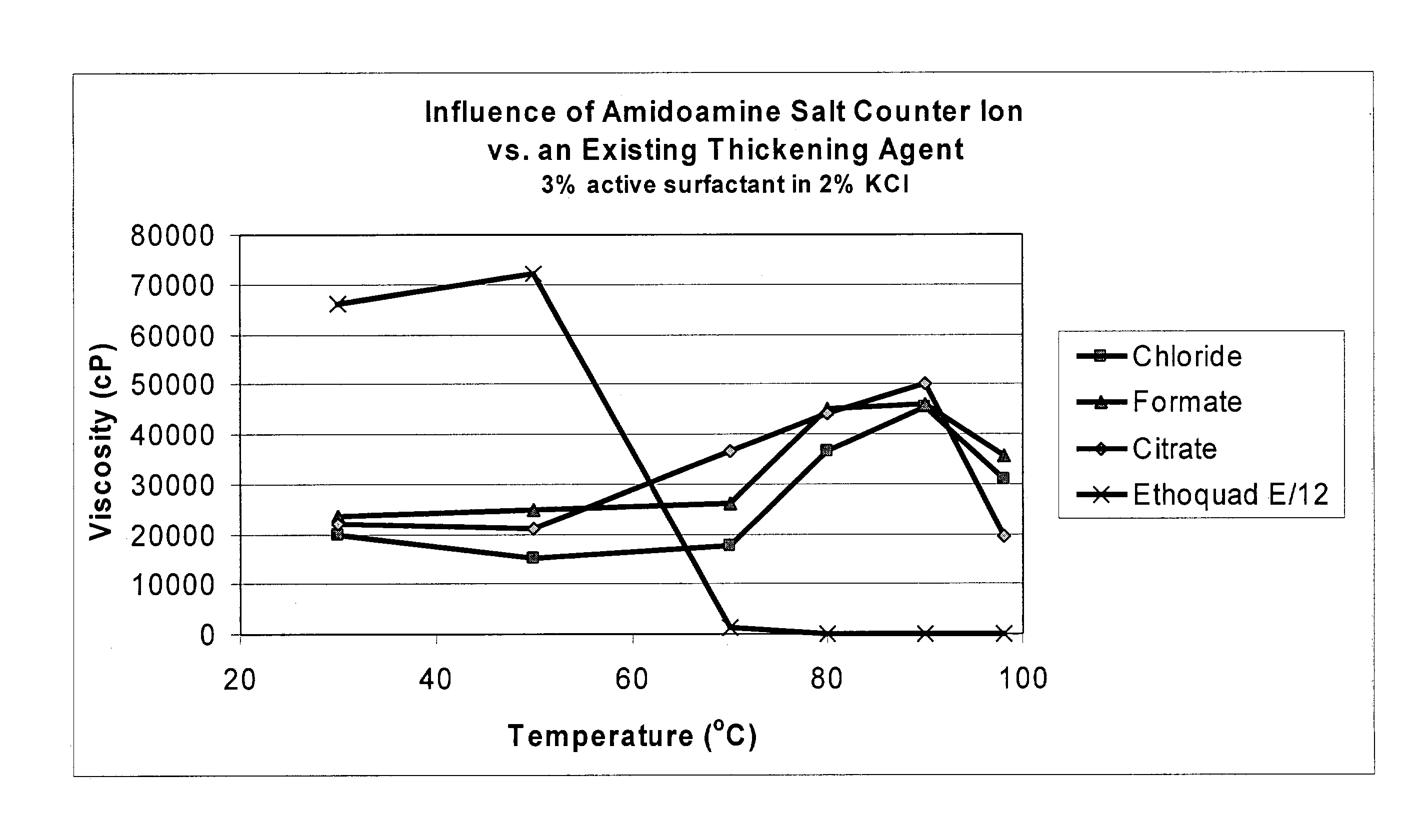
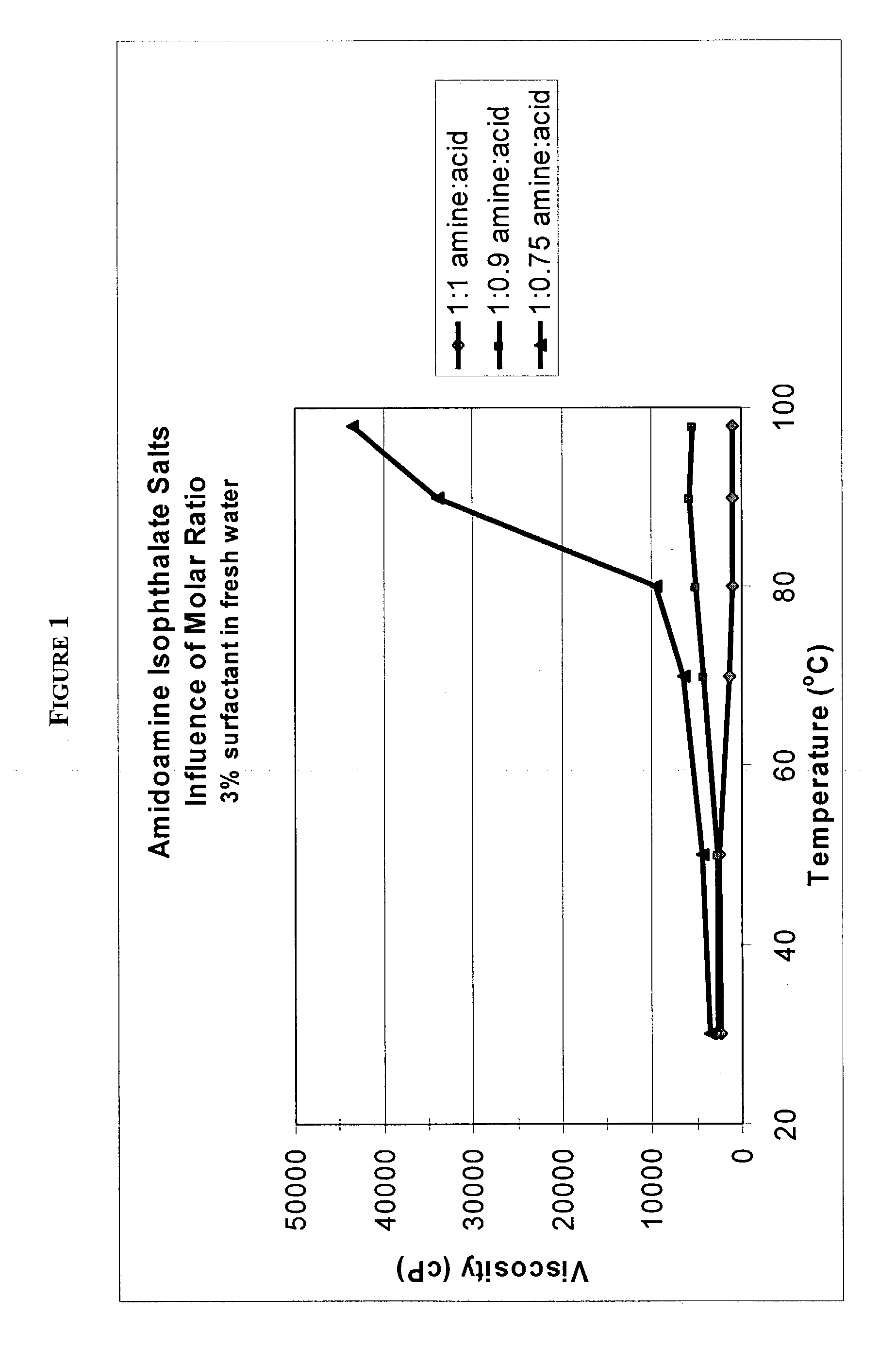
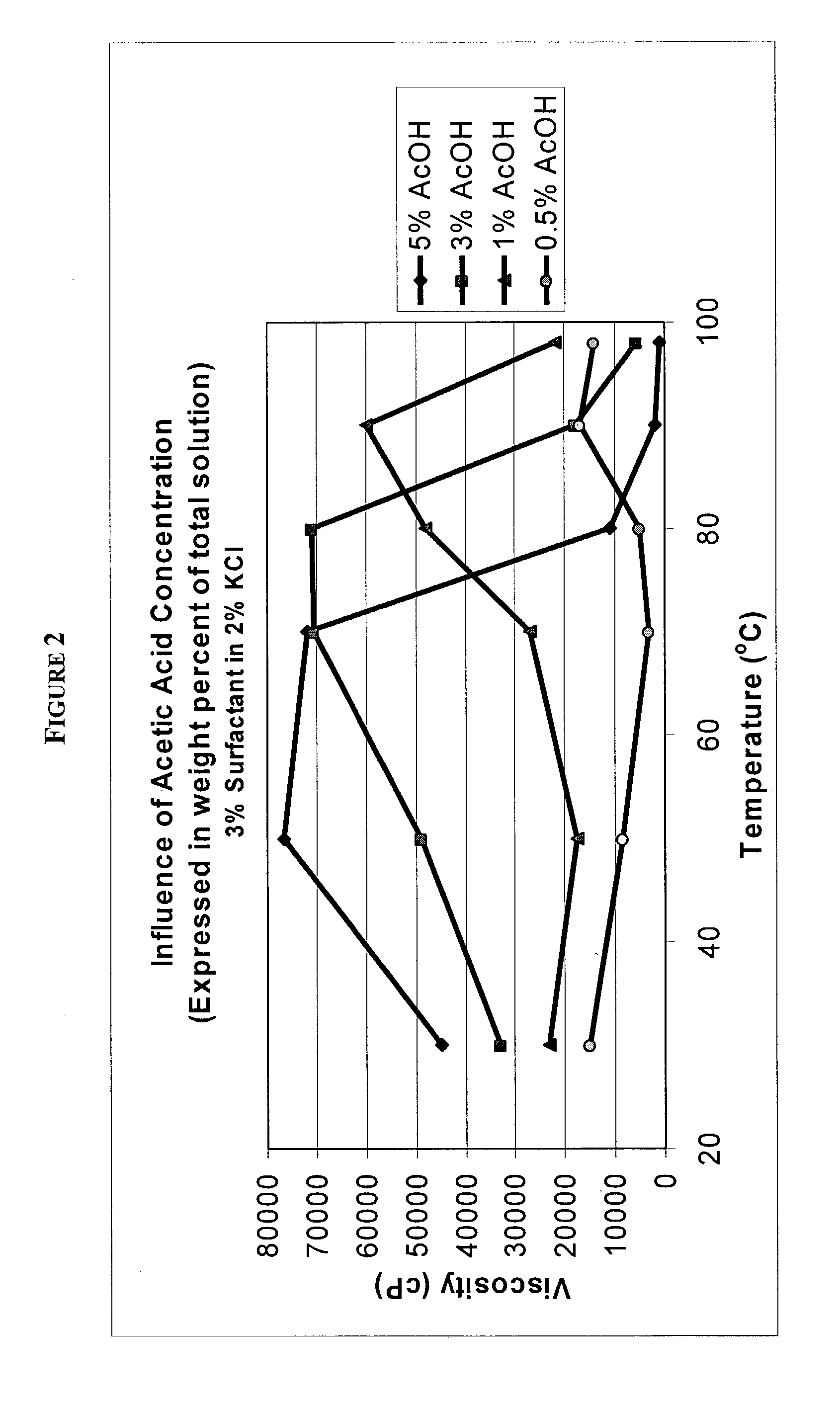
Amidoamine salt-based viscosifying agents and methods of use
Viscoelastic surfactants are described for use in aqueous systems to generate thickened fluids. The surfactants are alkyl amidoamine salts of inorganic acids and / or organic acids. The fluids may also contain inorganic salts, organic salts or mixtures thereof. Additionally, the fluids may contain a co-surfactant. These fluids are particularly useful in oilfield applications such as hydraulic fracturing, gravel packing, drilling, completion, etc. Viscoelastic fluids of the invention are also useful in industrial and consumer product fluid applications as rheology control agents.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL SURFACE CHEM LLC +1
Multicomponent viscoelastic surfactant fluid and method of using as a fracturing fluid
InactiveUS20060019836A1High viscosityGood shear recoveryFluid removalFlushingFracturing fluidAnionic polymers
There is a viscoelastic fluid. The fluid has one or more cationic surfactants selected from the group consisting of certain quaternary salts, certain amines, and combinations thereof; one or more anionic polymers / anionic surfactants; one or more of certain zwitterionic / amphoteric surfactants; and water. There is also a method of fracturing a subterranean formation. The viscoelastic fluid is pumped through a wellbore and into a subterranean formation at a pressure sufficient to fracture the formation.
Owner:RHONDIA INC
Menses specific absorbent systems
A personal care absorbent article such as a disposable diaper, sanitary pad or tampon, wound dressing or bandage which includes a nonwoven web material made from a plurality of polymeric fibers having at least one treatment chemistry suitable for modifying at least one characteristic of a high viscoelasticity fluid upon contact with the high viscoelasticity fluid. In accordance with one particularly preferred embodiment, the treatment chemistry is suitable for immobilizing the high viscoelasticity fluid within the nonwoven web material.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Stabilizing crosslinked polymer guars and modified guar derivatives
An aqueous, viscoelastic treating fluid gelled with a crosslinked guar or guar derivative is stabilized and improved with an effective amount of a glycol, such as ethylene glycol. These fluids are more stable in that viscosity is maintained, particularly at elevated temperatures. The additives may also increase viscosity to the point where less of a crosslinked guar or guar derivative gelling agent is required to maintain a given viscosity. These stabilized, enhanced, aqueous, viscoelastic fluids may be used as treatment fluids for subterranean hydrocarbon formations, such as in hydraulic fracturing.
Owner:SUPERIOR ENERGY SERVICES LLC
Aqueous viscoelastic fluid
InactiveUS20040221989A1Low viscosityOrganic chemistryTransportation and packagingViscositySURFACTANT BLEND
The invention concerns an aqueous viscoelastic fluid for use in the recovery of hydrocarbons. According to the invention this fluid comprises a first viscoelastic surfactant and a second surfactant able to decompose under downhole conditions to to reduce the viscosity of the aqueous viscoelastic fluid.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Stabilizing crosslinked polymer guars and modified guar derivatives
An aqueous, viscoelastic treating fluid gelled with a crosslinked guar or guar derivative is stabilized and improved with an effective amount of a glycol, such as ethylene glycol. These fluids are more stable in that viscosity is maintained, particularly at elevated temperatures. The additives may also increase viscosity to the point where less of a crosslinked guar or guar derivative gelling agent is required to maintain a given viscosity. These stabilized, enhanced, aqueous, viscoelastic fluids may be used as treatment fluids for subterranean hydrocarbon formations, such as in hydraulic fracturing.
Owner:SUPERIOR ENERGY SERVICES LLC
Additive for viscoelastic fluid
InactiveUS7320952B2Reduce recoveryShortening shear recovery timeTransportation and packagingFluid removalBetaineFluid viscosity
Composition and method for shortening the shear recovery time of cationic, zwitterionic, and amphoteric viscoelastic surfactant fluid systems by adding an effective amount of a co-gelling agent selected from triblock oligomeric compounds having hydrophilic (for example polyether) and hydrophobic (for example alkyl) portions. The co-gelling agent also increases fluid viscosity and very low co-gelling agent concentration is needed. Preferred surfactants are betaines and quaternary amines. The fluids are useful in oilfield treatments, for example fracturing and gravel packing.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Synergistic Effect of Cosurfactants on the Rheological Performance of Drilling, Completion and Fracturing Fluids
ActiveUS20160017210A1High gel strengthImprove salt toleranceFluid removalFlushingFracturing fluidUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to the viscoelastic surfactant based fluids and methods for utilizing same in oilfield applications including, but not limited to gravel packing, cleanup, drilling, acidizing, fracturing and the like in a subterranean formation. The viscoelastic fluid of the invention comprises at least one amphoteric surfactant and at least one synergistic cosurfactant that increases the gel strength and extends the brine tolerance of said viscoelastic-based fluid.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL CHEM INT BV
Magneto-rheological viscoelastic fluid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103031194AImprove wear resistanceHigh viscosity in zero magnetic fieldLubricant compositionCompressibilityCarrier fluid
The invention discloses a magneto-rheological viscoelastic fluid and a preparation method thereof. The fluid raw materials comprise the following components in percentage by weight: 15-70% of hydroxy iron powder, 25-80% of methylsiloxane, 3-4% of phenyl siloxane, 0.1-0.2% of basic catalyst, 0.1-0.3% of neutralizer, 0.1-0.3% of blocking agent, 0.1-0.3% of thixotropic agent and 0.2-0.5% of lubricant. The magneto-rheological viscoelastic fluid has compressibility, can improve the wear resistance of the magneto-rheological plaster, so as to prolong the service life; zero magnetic field viscosity of the carrier fluid is higher, no occurrence of sedimentation or agglomeration happens to the suspended phase for a long time, thereby having a favorable static stability; the carrier medium and the additive have a wide range of temperature adaptation, the magneto-rheological viscoelastic fluid material has a favorable stability in a temperature range of minus 90 to 250 DEG C; at a shear rate of 300 1 / second, the magnetic induction intensity of the magneto-rheological viscoelastic fluid is 0-0.6T, the variation range of shear stress is 75-105KPa, and the viscosity of the zero magnetic field is 4.5-6Pa.S.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com