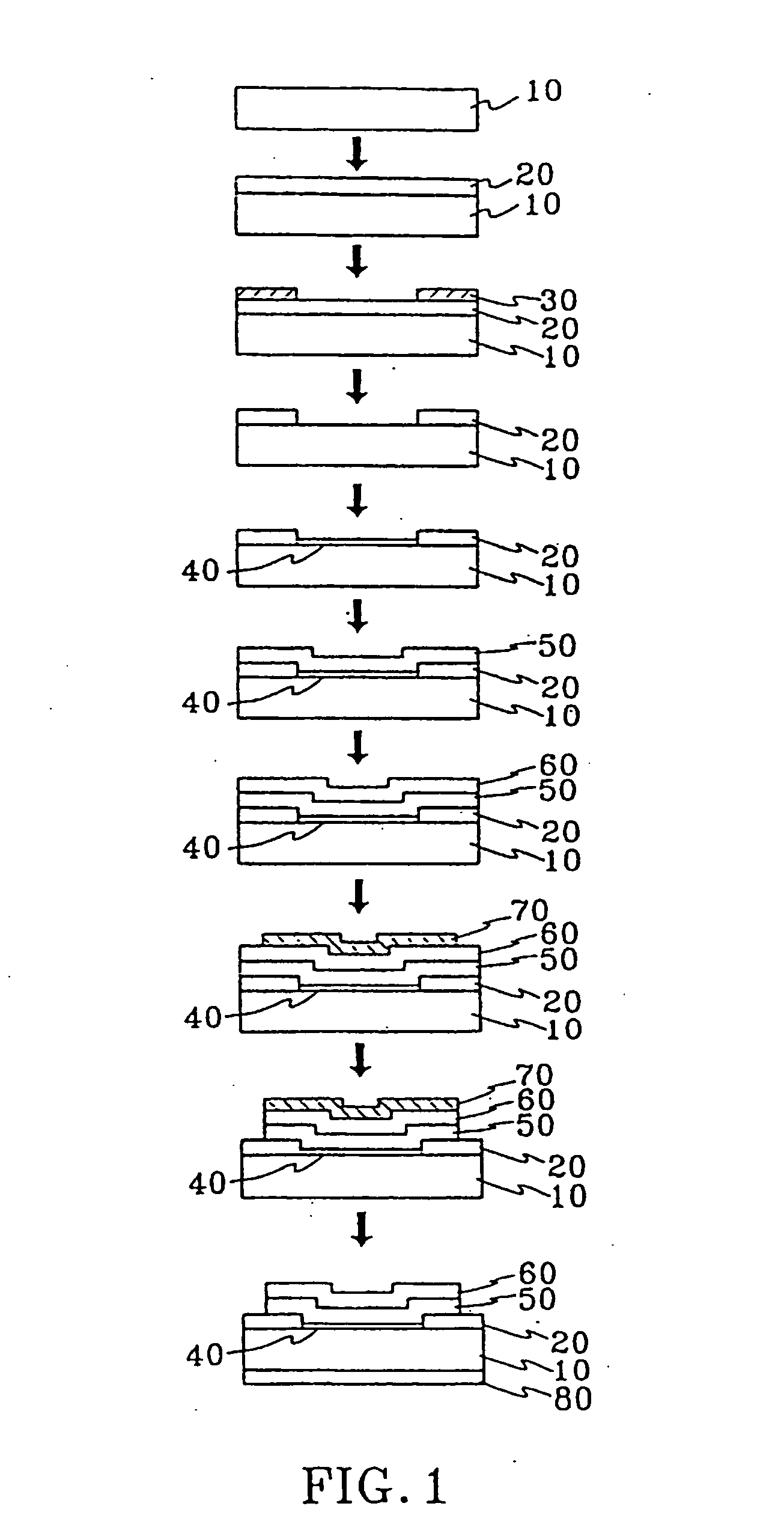
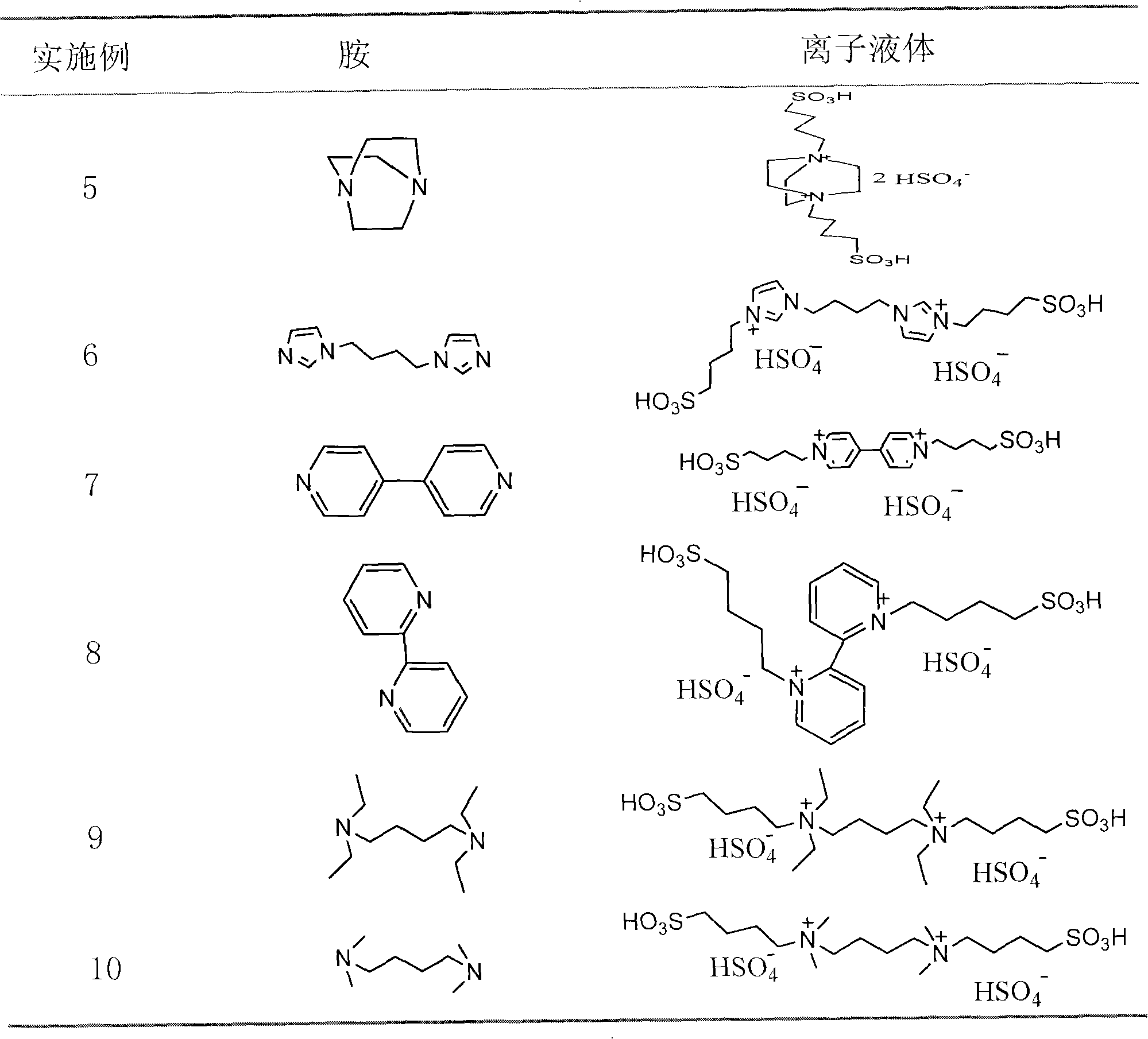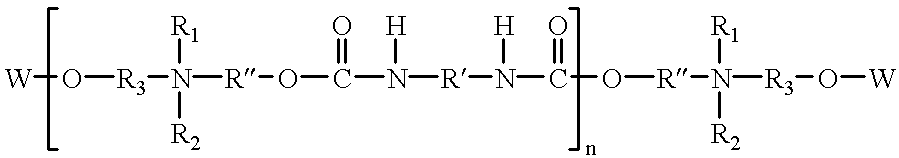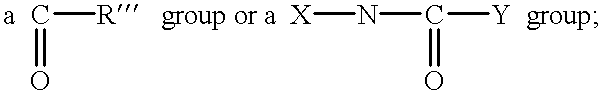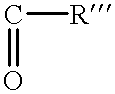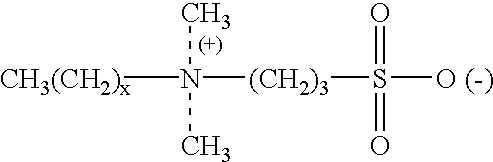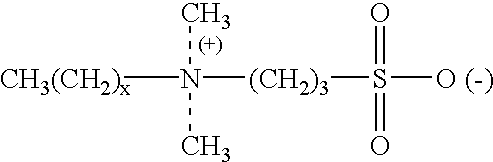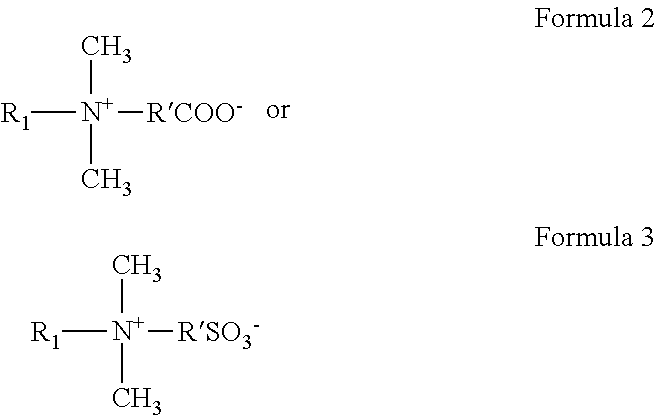Patents
Literature
5050 results about "Betaine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
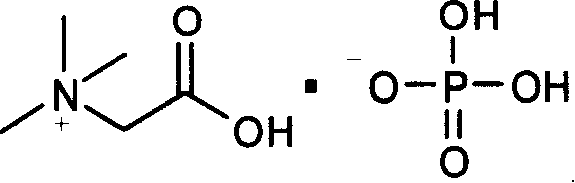
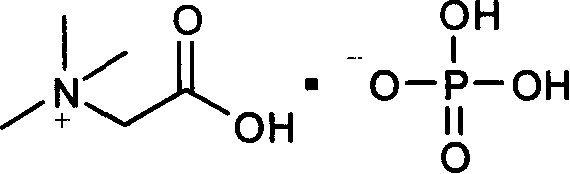
A betaine (/ˈbiːtə.iːn, bɪˈteɪ-, -ɪn/) in chemistry is any neutral chemical compound with a positively charged cationic functional group such as a quaternary ammonium or phosphonium cation (generally: onium ions) that bears no hydrogen atom and with a negatively charged functional group such as a carboxylate group that may not be adjacent to the cationic site. A betaine thus may be a specific type of zwitterion. Historically, the term was reserved for TMG (trimethylglycine) only. Biologically, TMG is involved in methylation reactions and detoxification of homocysteine.
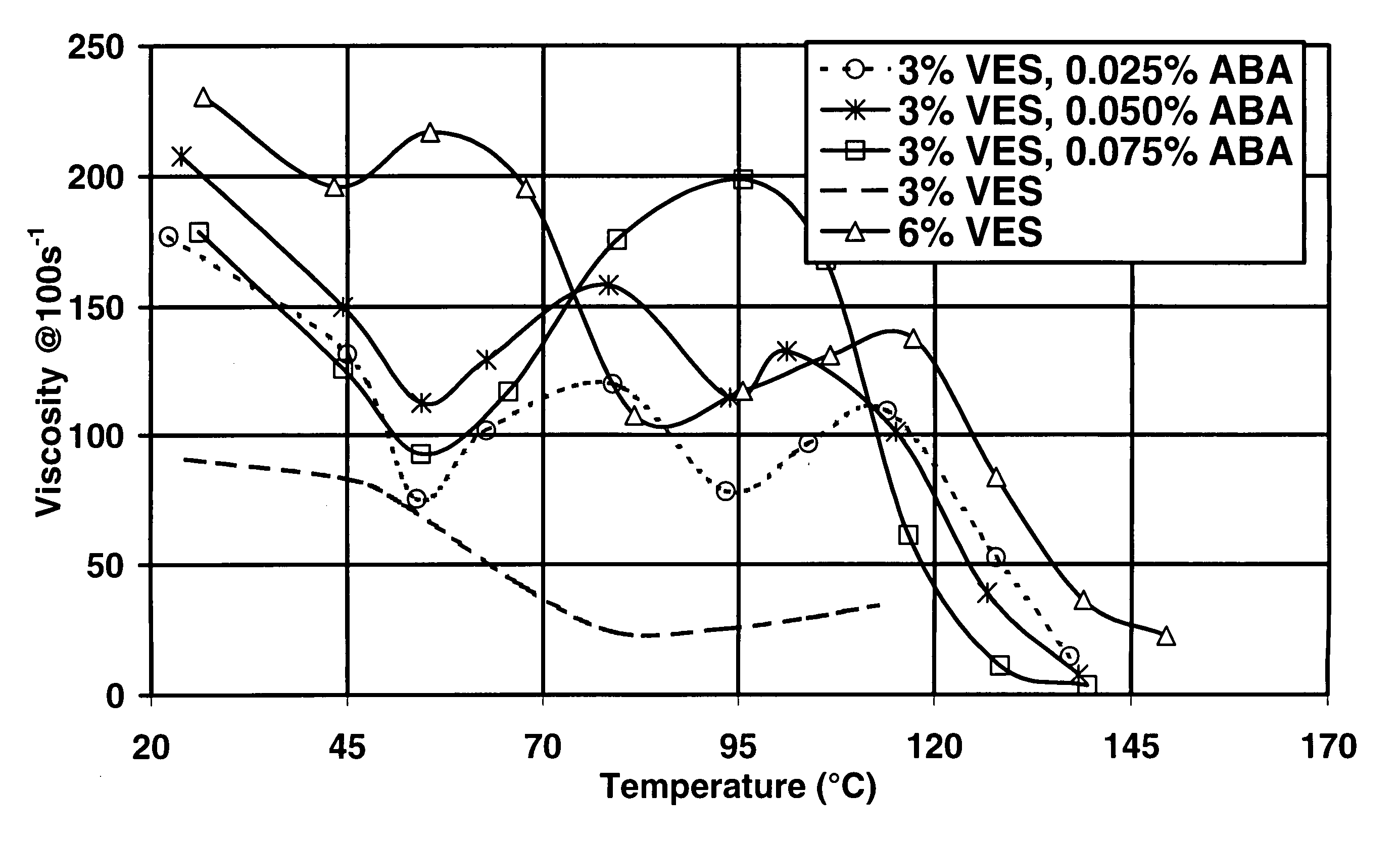
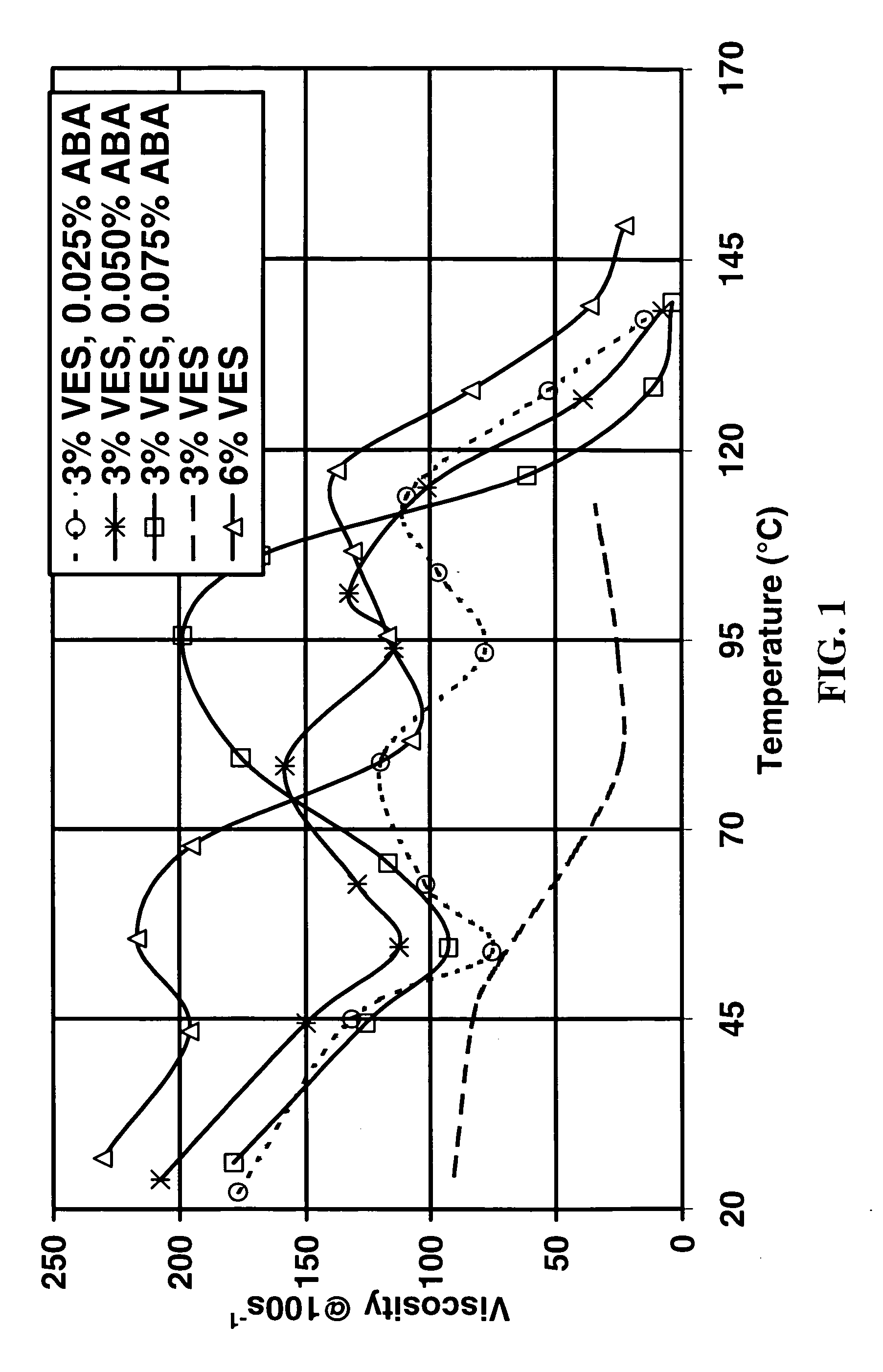
Prevention of Water and Condensate Blocks in Wells
InactiveUS20070029085A1Better placementReduce capillary pressureCleaning apparatusFluid removalBetaineCarbamate
Compositions and methods are given to prevent, alleviate and remedy water blocks and gas blocks (condensate block or condensate banking). Wettability modifiers are contacted with the formation to change the surfaces from water wet or oil wet to intermediate wet or gas wet. Preferred wettability modifiers include partially or completely fluorinated surfactants or polymers, for example fluorosilanes such as perfluorosilanes, urethane oligomers containing perfluoro alkyl moieties, fluoroacrylates, and fluoroalkyl containing terpolymers or their mixtures. Other examples include surfactants, for example viscoelastic surfactants such as cationic surfactants such as quaternary amines, and zwitterionic surfactants, such as betaines, optionally mixed with co-surfactants.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Thermochromic responsive elastic polymer substrate
InactiveUS20090143516A1Male contraceptivesTemperature measurement in household appliancesBetaineThermochromism
A material composition including a flexible, polymeric matrix and a reverse-thermochromic colorant is described. When subjected to a heat source, the polymeric material can change color from a pale or neutral color to a darker or more vibrant color of a Delta E (ΔE) change of >3. The reverse-thermochromic colorant exhibits a color change when exposed to a heat source within a period of about 30 seconds, and is observable by an unaided human eye under either natural daylight or ambient artificial normal lighting conditions. One or more different reverse-thermochromic colorants in combination may be incorporated. The polymeric matrix surrounds or encapsulates a solvatochromic dye molecule with a phenolate betaine structure. The polymeric matrix includes a dipole orientating agent that induces said solvatochromic dye to express locally when subjected to a temperature change. Various uses for the composition and articles that incorporate the composition are also described, in addition to a method of indicating the temperature of an object or environmental condition.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Appetite satiation and hydration beverage
InactiveUS20050276839A1Sufficient nutritional valueAvoid malnutritionBiocideTetrapeptide ingredientsBetaineAdditive ingredient
Appetite satiation and hydrating beverages and methods of delivering appetite satiation ingredients and nutrients are disclosed. According to one embodiment of the invention, the appetite satiationhydrating beverage comprises at least one complex carbohydrate, at least one chelated electrolyte, hoodia gordonii cactus, gymnema sylvestre, betaine and piperine.
Owner:RIFKIN CALMAN H
Nutritional system for nervous system disorders
A novel composition for treating nervous system disorders. The composition is formed by preparing a mixture comprising an effective amount of vitamin B-6, folic acid, vitamin C, magnesium, vitamin B-3, copper, probiotics, fructo-oligosaccharide (FOS), betaine, pancreatin, papain, pepsin, vitamin B-1, vitamin B-2, vitamin B-12, biotin, pantothenic acid, chromium polynicotinate and a digestive support ingredient selected from the group consisting of dandelion root, juniper, aloe vera, burdock, ginger root, artichoke, and kelp. Other ingredients may include: beta carotene, vitamin E, selenium, zinc, sea vegetation, alfalfa, trace minerals and molybdenum.
Owner:C&D FOREMAN
Anti-emulsification water-soluble metal washing agent
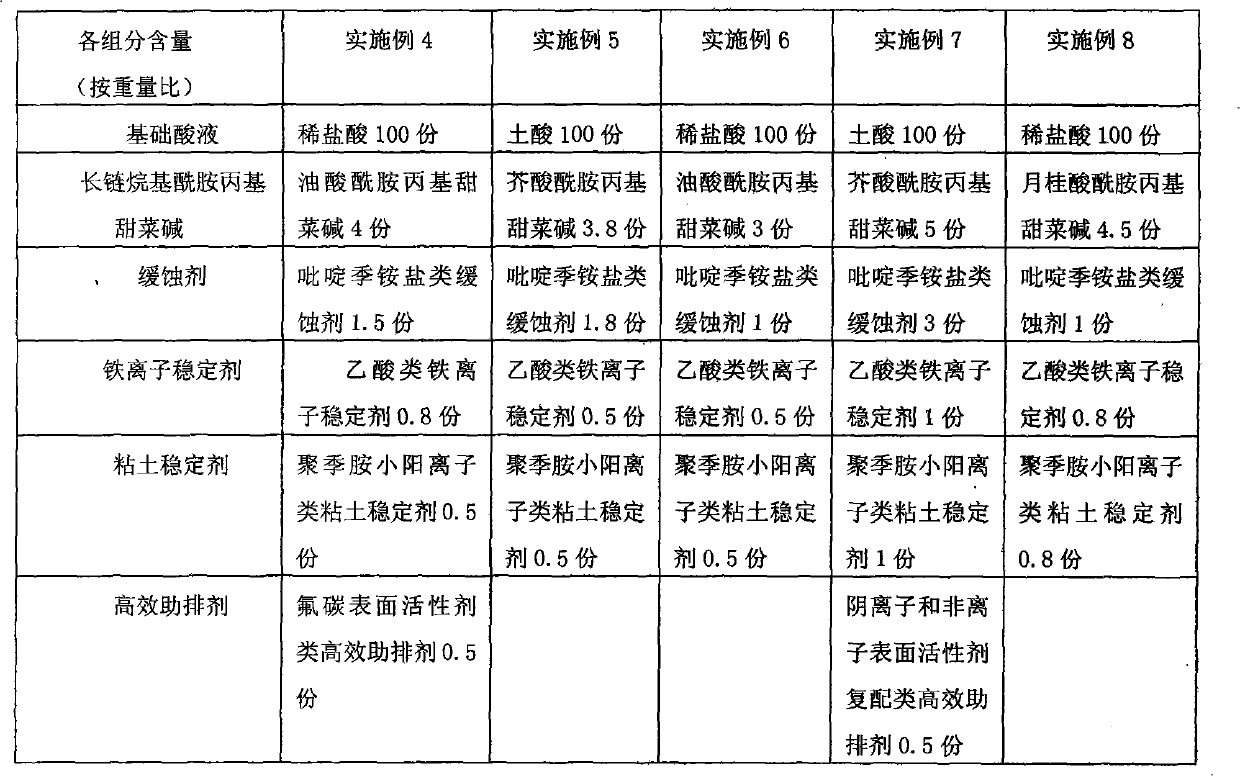
The invention relates to an anti-emulsification water-soluble metal washing agent. Every 100 parts of the anti-emulsification water-soluble metal washing agent include the following components according to parts by weight: 3-7 non-ionic surfactant, 3-7 bi-ion active agent, 1-5 chelator, 1-5 rust preventive, 5-10 inorganic builder and the balance water, wherein the non-ionic surfactant is any one of fatty amine polyoxypropylene ether, alkylphenol ether and fatty amine polyoxyethylene alkyl ether ammonium sulfate, the bi-ion active agent is any one of alkyl dimethylin acetic acid betaine, lauramidopropyl betaine and cocamidopropyl betaine, the chelator is any one of sodium citrate, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid tetrasodium salt and nitrilotriacetic acid sodium salt, the rust preventive is any one of sodium borate, sodium nitrite, sodium benzoate and long carbon chain carboxylic acid amine, and the inorganic builder is any one of trisodium phosphate, sodium metasillcate, sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate and sodium hydroxide. The anti-emulsification water-soluble metal washing agent has the advantage of higher cleaning capacity and reutilization capacity.
Owner:NANJING KERUN LUBRICANTS
Method and synergistic composition for treating attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder
InactiveUS6541043B2Minimize side effectsBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsBeta-CaroteneBetaine
A composition and method for treating Attention Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is provided which can be used both with and without ethical drugs now used to treat ADHD. The composition contains dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE), omega 3-fatty acids, betaine, oligomeric proanthocyanidins (OPC), folic acid, vitamins C, E, B12, B6, B5 and beta-carotene and minerals (calcium, magnesium, zinc and selenium). Ethical drugs such as amphetamines, methylphenidate HCl and pemoline are known to control ADHD, but each has significant side effects when used in their therapeutic dose. When combining the composition with such ethical drugs, the amount of the ethical drug can be lowered below a level which causes undesirable side effects which is an important feature. Preferred compositions contain one or more of lecithin, choline, 5-hydroxytryptophan, tyrosine, Reishi Extract, Kava Extract, Gingko, Ginseng and St. John's Wort.
Owner:PHILIP C LANG
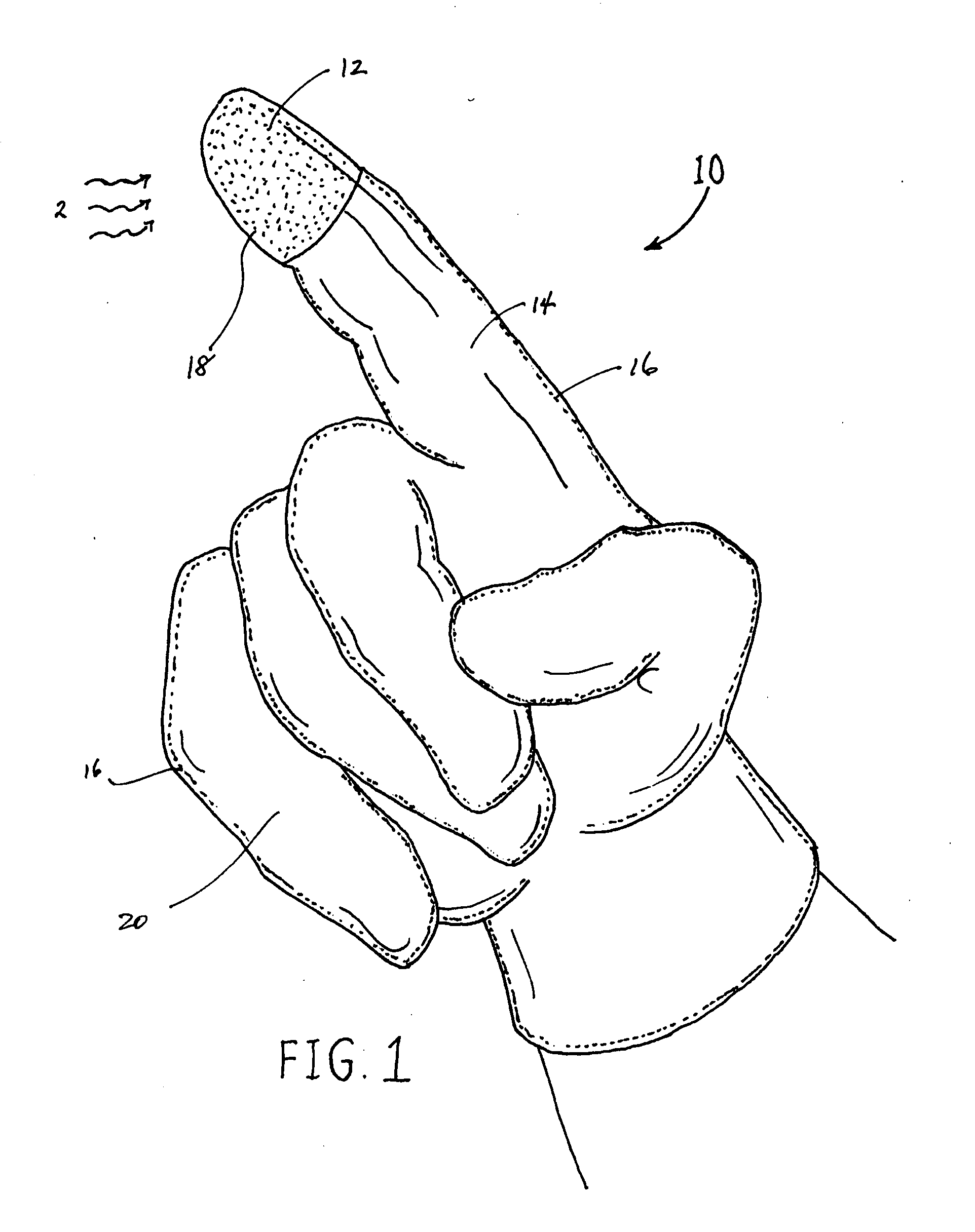
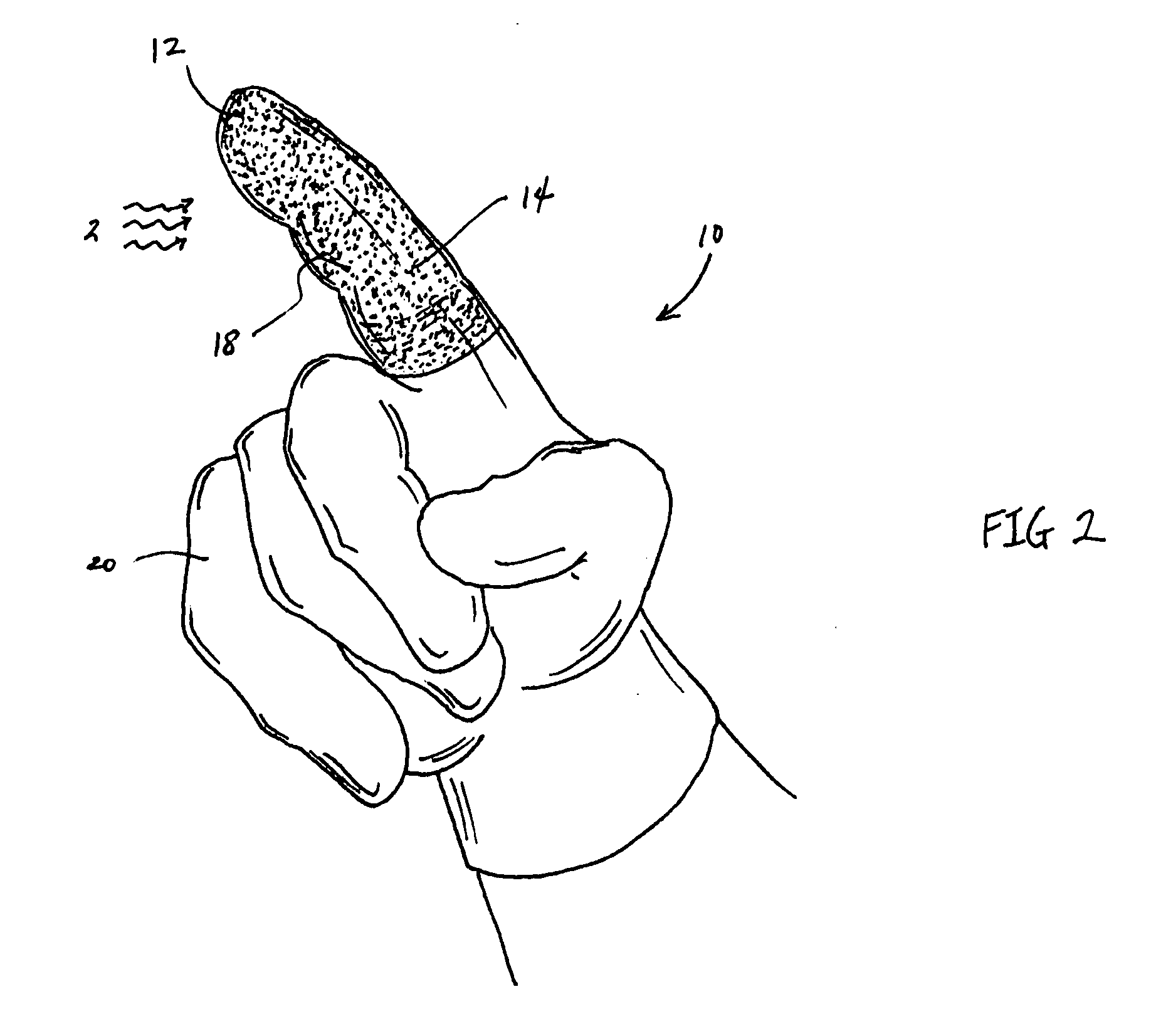
Betaine with Calcium and/or Strontium Antiperspirants
InactiveUS20070020211A1Good curative effectImprove skinCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAntiperspirantsBetaine
Aluminum and aluminum-zirconium antiperspirant compositions comprising basic aluminum chlorides that have a particular molecular size distribution defined by having an SEC-HPLC Band III / II ratio of at least 0.5, having SEC-HPLC Band III plus Band II area of at least 70% of the total area and having SEC-HPLC Band I content no more than 5% and containing betaine (trimethylglycine), calcium and / or strontium are disclosed. Also disclosed are the methods of making these compositions and the use thereof in consumer acceptable antiperspirant vehicles such as aerosols, gels, roll-on, sticks and soft solids.
Owner:SUMMIT RES LAB
Method of displacement chromatography
InactiveUS6379554B1Efficient separationLower requirementIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatographic separationBetaine
A plurality of chromatographic separation operations, including a first simulated moving bed operation, are coupled into a process which functions, preferably through the application of continuous displacement chromatography, to recover a fraction rich in small organic molecules, notably betaine and / or invert from sucrose solutions, enabling the subsequent production of a high purity sucrose product.
Owner:AMALGAMATED RES
Hydrogen peroxide-based skin disinfectant
InactiveUS20050255172A1Increase attractivenessImproved rheological propertiesCosmetic preparationsBiocideBetaineDisinfectant
A skin disinfectant in ready-to-use concentrated liquid or dry powdered form. Ready-to-use liquid forms have a pH of from about 2 to about 6 and include: (a) hydrogen peroxide in a concentration of from about 0.01 to about 4% w / w of the solution; (b) at least one surfactant chosen from imidazoline derivatives, alkyl betaines, alkyl amidopropyl betaine amides, alkyl amidopropyl betaines, alkylsulfo betaines, amine oxides and derivatives thereof in a concentration of from about 0.01 to about 15% w / w of the solution; (c) at least one hydrogen peroxide stabilizer in a concentration of from about 0.01 to about 4% w / w of the solution; (d) at least one member chosen from cyclic carboxylic acids and salts thereof in a concentration of from about 0.01 to about 4% w / w of the solution; and (e) at least one skin conditioning agent in a concentration of from about 0.01 to about 10% w / w of the solution.
Owner:JOHNSONDIVERSEY INC
Fermentation method for preparing L-amino acid
ActiveCN101235401AIncrease acid production rateEase of industrial productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBetainePhosphate
The invention relates to a method for preparing L-amino acid through fermenting. The method of the invention uses fermentation additive betaine phosphate. With the method of the invention, the acid yield of the L-amino acid can be prominently increased, the cost of manufacture is lowered, and the method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:山东祥维斯医药科技有限公司
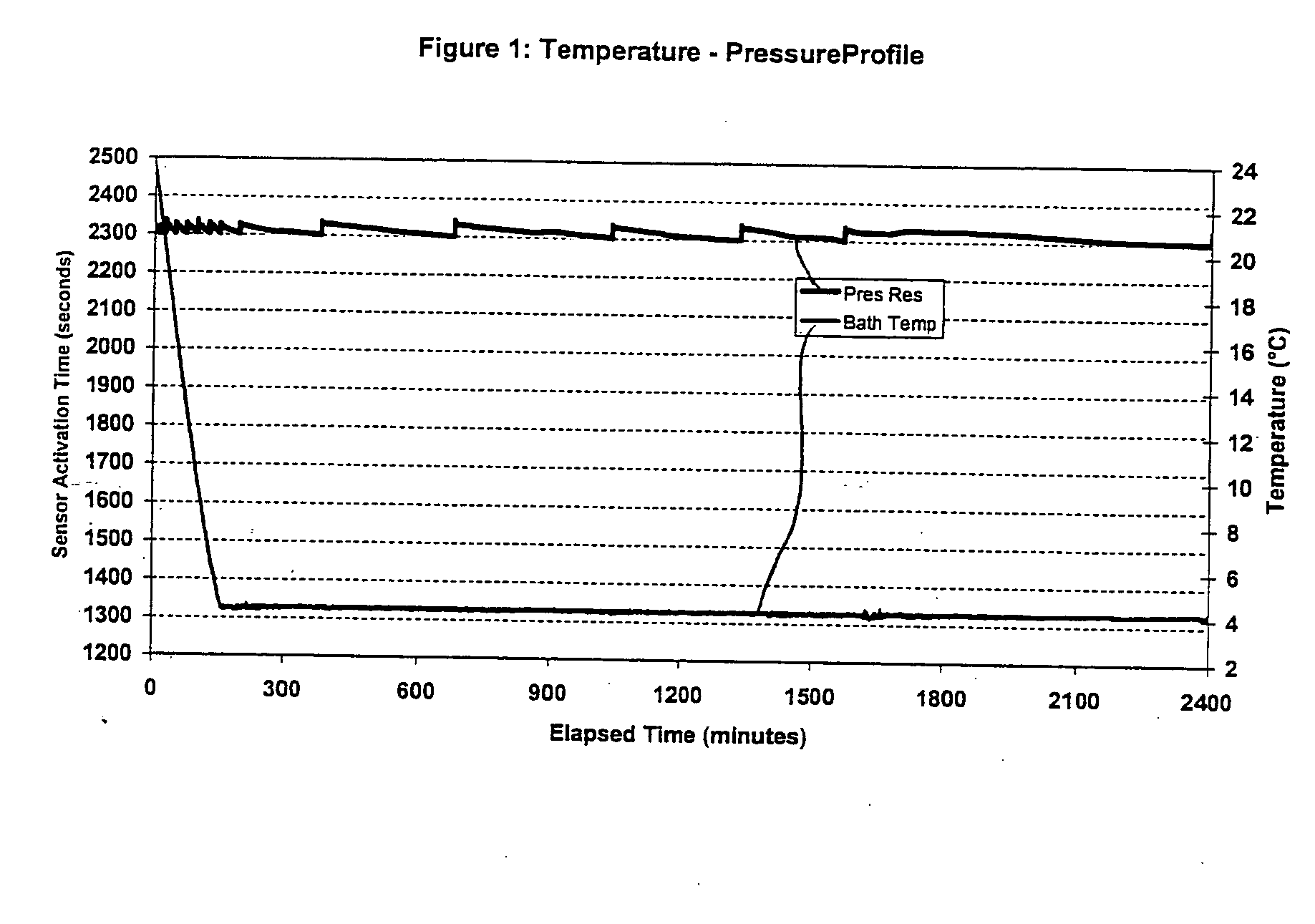
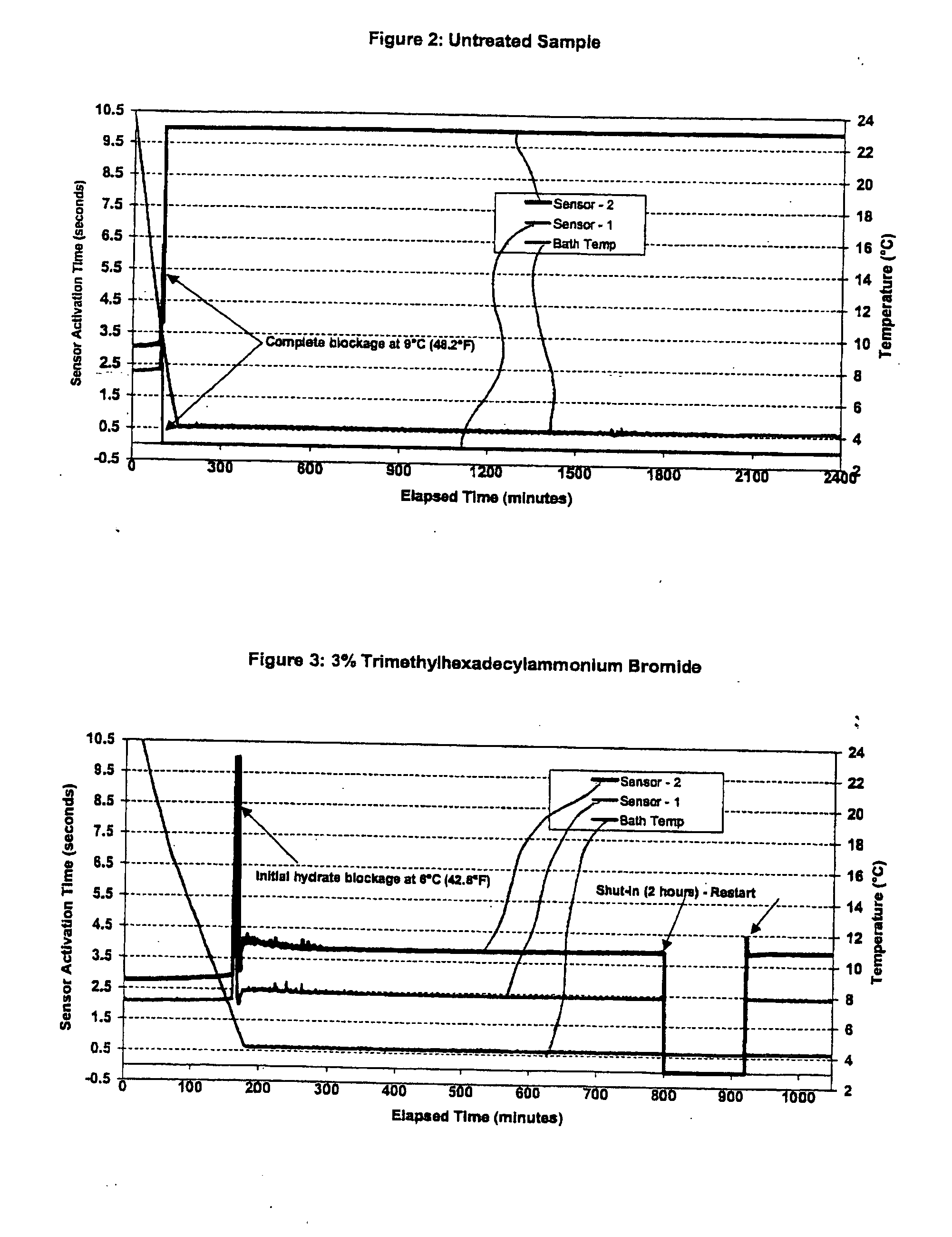
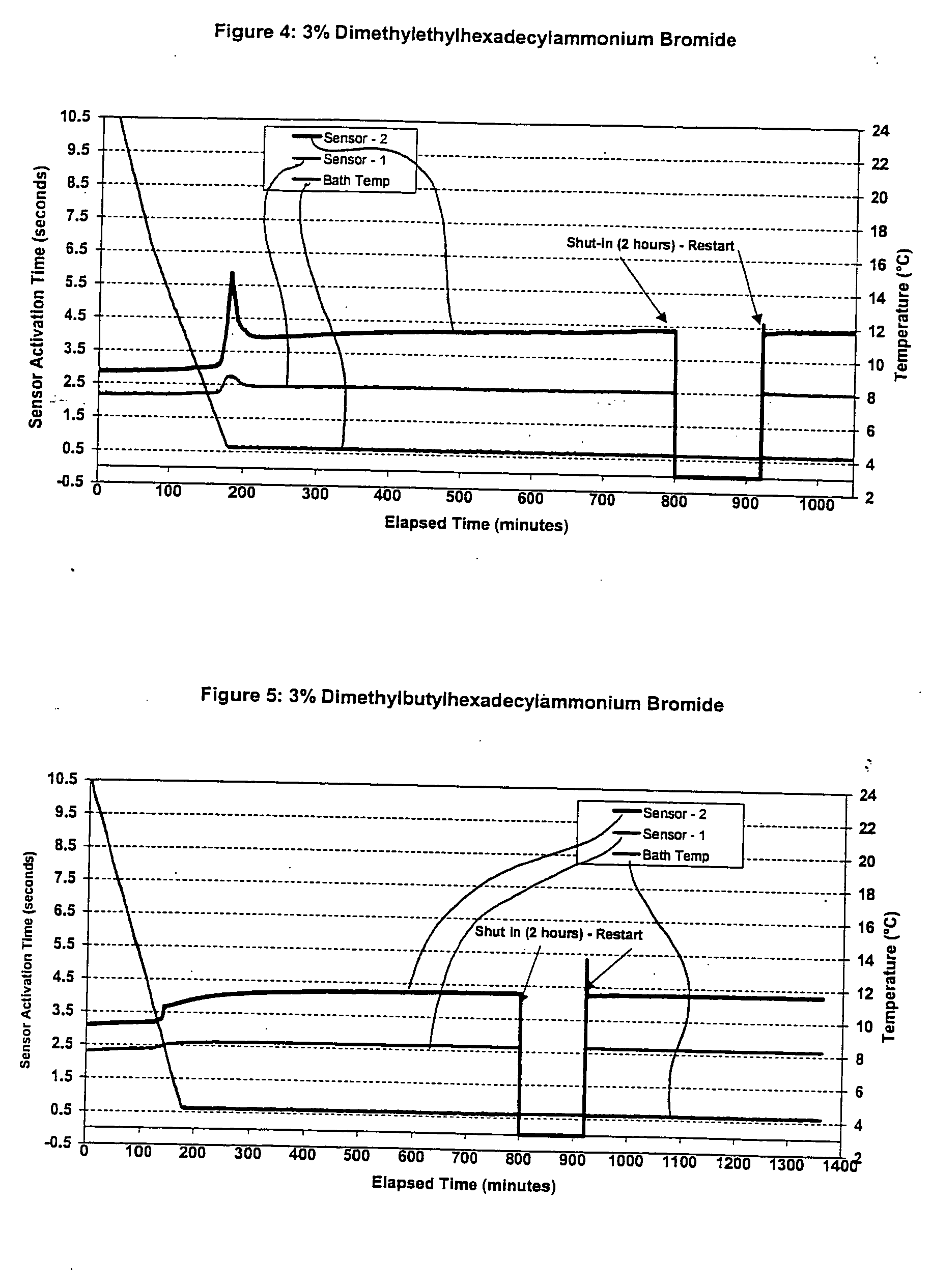
Methods for inhibiting hydrate blockage in oil and gas pipelines using amide compounds
A method and an amide composition used therein for inhibiting, retarding, mitigating, reducing, controlling and / or delaying formation of hydrocarbon hydrates or agglomerates of hydrates. The method may be applied to prevent or reduce or mitigate plugging of conduits, pipes, transfer lines, valves, and other places or equipment where hydrocarbon hydrate solids may form under the conditions. At least one amide compound is added into the process stream, where the compound may be mixed with another compound selected from amino alcohols, esters, quaternary ammonium, phosphonium or sulphonium salts, betaines, amine oxides, other amides, simple amine salts, and combinations thereof.
Owner:CLARIANT INT LTD
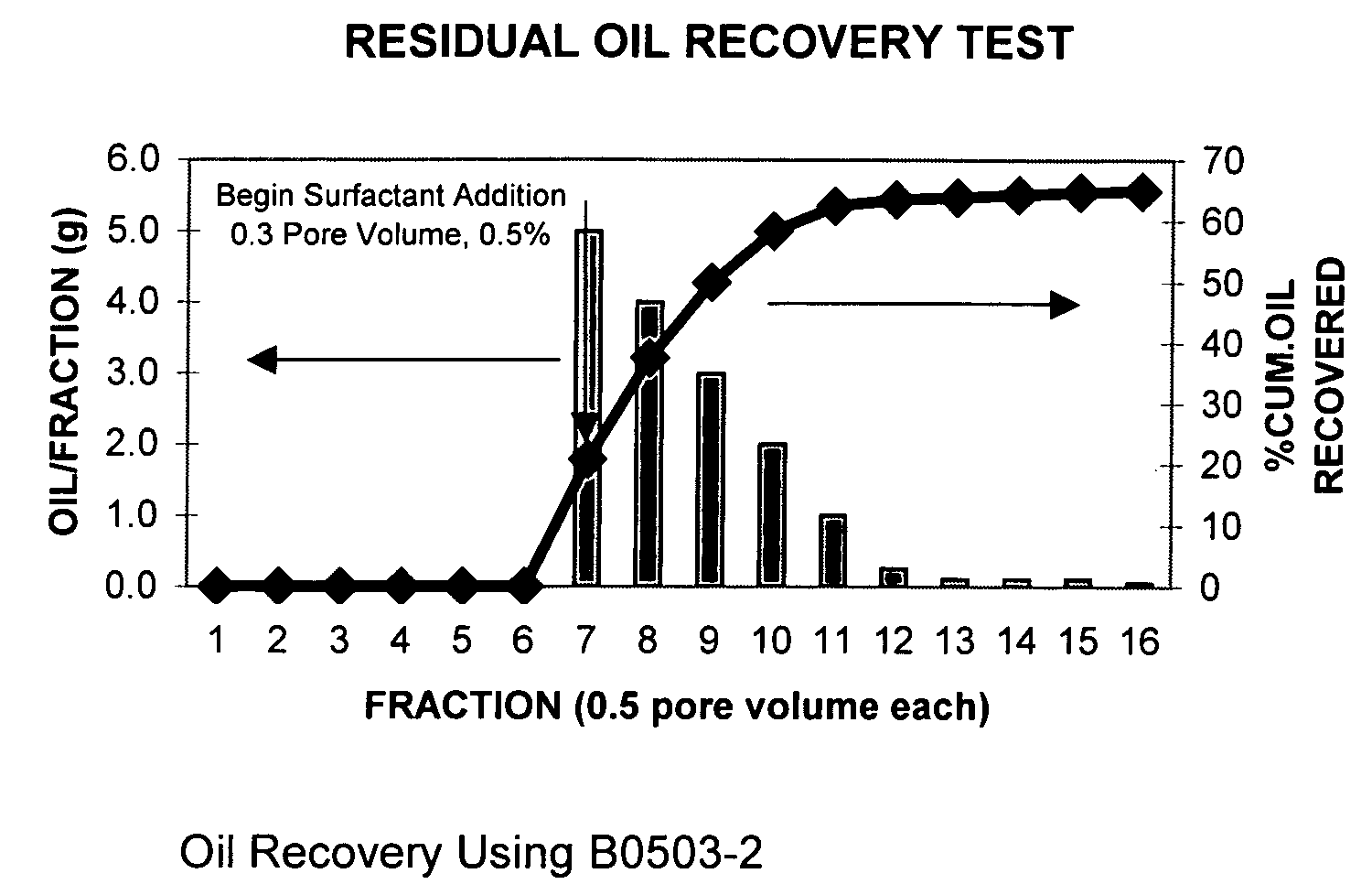
Process for oil recovery employing surfactant gels
Owner:OIL CHEM TECH
Compositions and methods for the regulation of homocysteine levels within the body
InactiveUS20050171034A1Reduce harmful metabolic waste productLower Level RequirementsBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsMethylcobalaminBetaine
Described herein is a method for reducing levels of the harmful metabolic waste product of S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe), homocysteine, and provide vitamin and other nutritional co-factors that reduce the production of homocysteine and either re-methylate homocysteine back to S-adenosylmethionine, or facilitate its conversion downstream to cystathione. The method of the invention may be achieved by administering 5-methyl tetrahydrofolate, methylcobalamin, and one or more compounds selected from the group consisting of betaine, pyridoxal-5-phosphate, N-acetyl-cysteine, and other cofactors.
Owner:FAST BALANCE
Feed additive for improving stress resistance, meat color and meat quality of grown fattening pig and application thereof
ActiveCN102172265AImprove stress resistanceThe comprehensive effect is outstandingAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsBiotechnologySide effect
The invention discloses a feed additive for improving the stress resistance, meat color and meat quality of a grown fattening pig and application thereof. The feed additive comprises the following components in parts by weight: 0.3-0.5 part of L-carnitine, 10-20 parts of betaine, 10-15 parts of electrolyte, 1-3 parts of selenium preparation, 2-5 parts of iron preparation, 3-5 parts of magnesium preparation, 0.5-1 part of chromium preparation, 1-2 parts of decavitamin, 5-10 parts of compound amino acid, 1-5 parts of tea polyphenol, 5-10 parts of isatis root and 20-61.2 parts of carrier. The feed additive provided by the invention has the following advantages: (1) the feed additive is composed of nutrient substances, Chinese herbal medicines and plant extracts, has non-toxic side effect, and is beneficial for the health of animals and human beings; (2) the raw material used by the invention is stable in resource, low in price, simple in production process, easy for industrial production; and (3) the feed additive provided by the invention can be used for rapidly supplementing various nutritive stress resisting substances, reliefing the stress of animals, improving the meat color and meat quality, and reducing the drip loss.
Owner:湖南鑫广安农牧股份有限公司
Method for growing blueberry
InactiveCN101904286AIncrease contentIncrease productionOther chemical processesCultivating equipmentsBetainePropanoic acid
The invention relates to a method for growing blueberry, which comprises soil modification, seedling cultivation, seedling planting and fertilization. In the invention, a soil modifier is applied to soil and the organic materials in the soil modifier increase the content of fatty acids such as acetic acid and propionic acid of the soil, so the rate of mycorrhizal infection, which is capable of promoting the growth of the blueberry, improving blueberry yield, contributing to productivity improvement and soil modification and improving quality and sugar content of fruits, of the blueberry is improved; meanwhile, pine soil and grass carbon are used to regulate the pH value of the soil. In the invention, a rooting medium which contains IAA growth hormone and glycine betaine is used to cultivate the seedlings, so the rooting rate of cuttings and transplanting survival rate are improved, the seedling cultivation time is reduced greatly, and the propagation efficiency is improved obviously. In the invention, a microbial fertilizer, a potassium sulfate type compound fertilizer, ammonium sulfate and diammonium phosphate are used for fertilizing the blueberry, wherein the ammonium sulfate can lower the pH value of the soil, namely the ammonium sulfate provides nutrients for the blueberry for growth and improves the growing environment of the blueberry; and thus, the blueberry yield is more improved effectively.
Owner:董文卓
Phosphor surface treatment method
A red phosphor in the form of a Mn-activated complex fluoride having the formula: A2MF6:Mn wherein M is one or more tetravalent elements selected from Si, Ti, Zr, Hf, Ge, and Sn, and A is one or more alkali metals selected from Li, Na, K, Rb, and Cs, and contains at least Na and / or K, is surface treated with a treating solution containing a surface treating agent selected from an organic amine, quaternary ammonium salt, alkyl betaine or fluorochemical surfactant, alkoxysilane, and fluorinated polymer.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
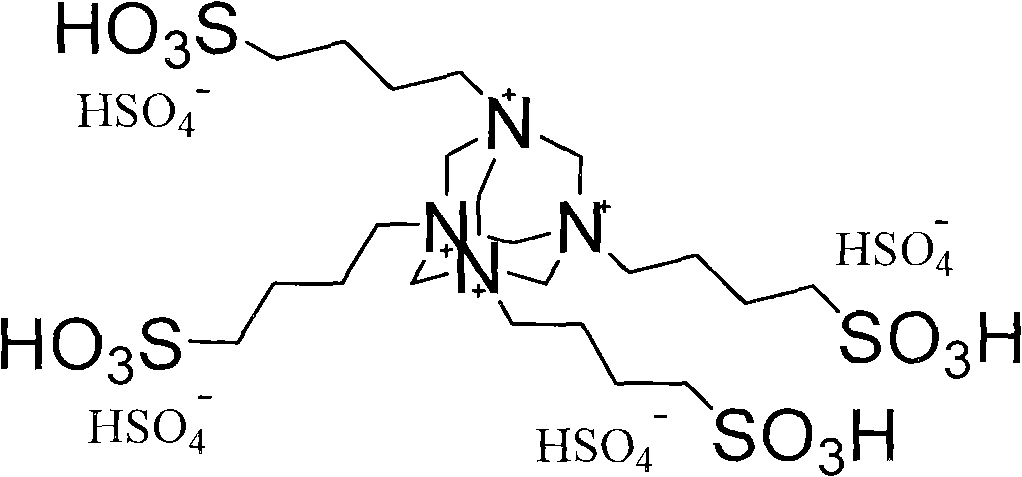
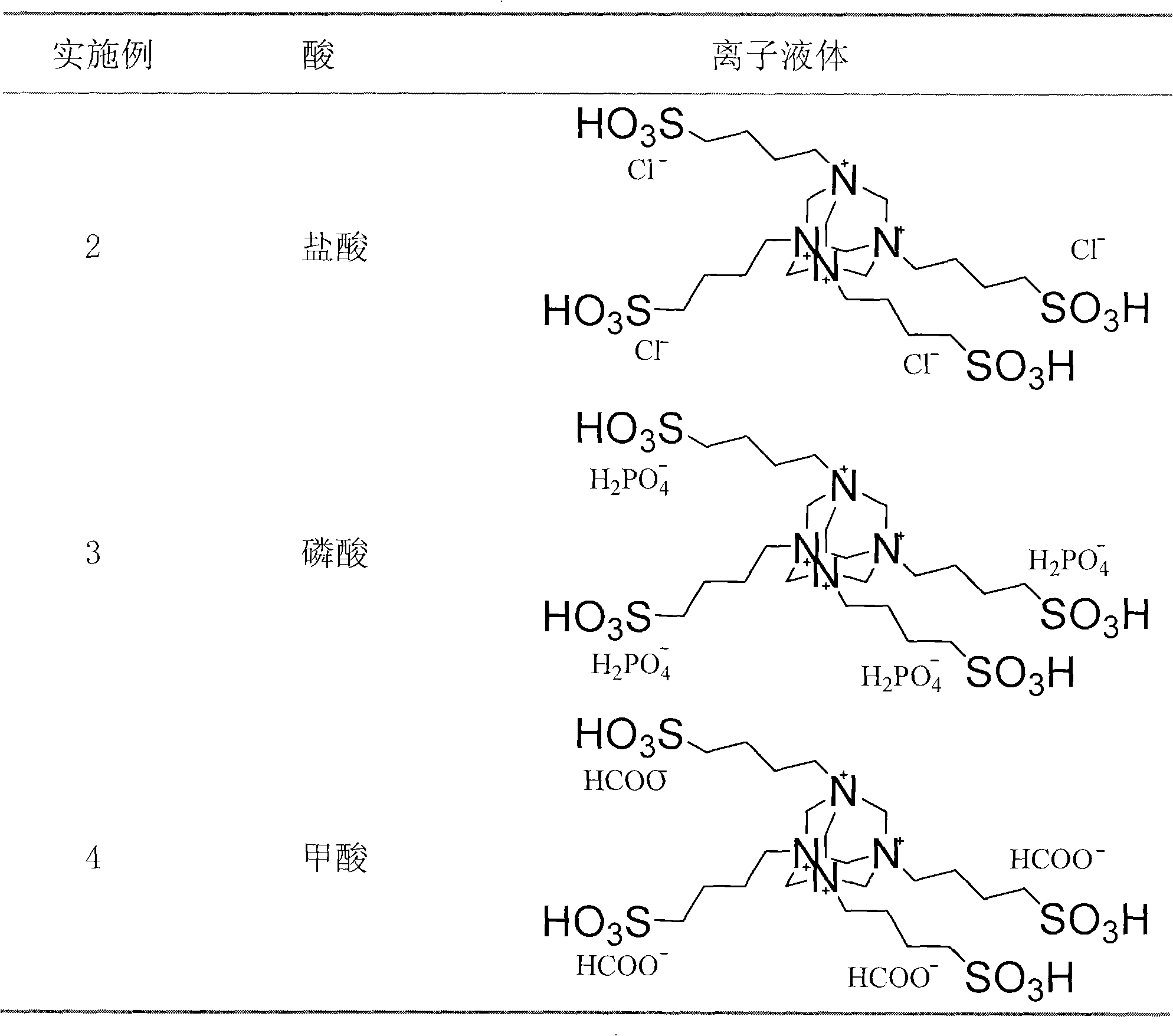
Preparation of multi-sulfonic functional ion liquid
InactiveCN101348487AHigh acid valueLow costOrganic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsBetaineAcid value
The invention discloses a method for preparing a multi-sulfonic acid group functionalized ionic liquid. In the method, a poly-nitrogen tertiary amine reacts with a sultone to an obtain multi-sulfonic acid radical betaine, and the obtained betaine is subjected to acidification by an acid to obtain the multi-sulfonic acid group functionalized ionic liquid. The ionic liquid prepared by the invention has the characteristics of high thermal stability, high acid value, low synthesis cost and good catalytic effect, etc.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
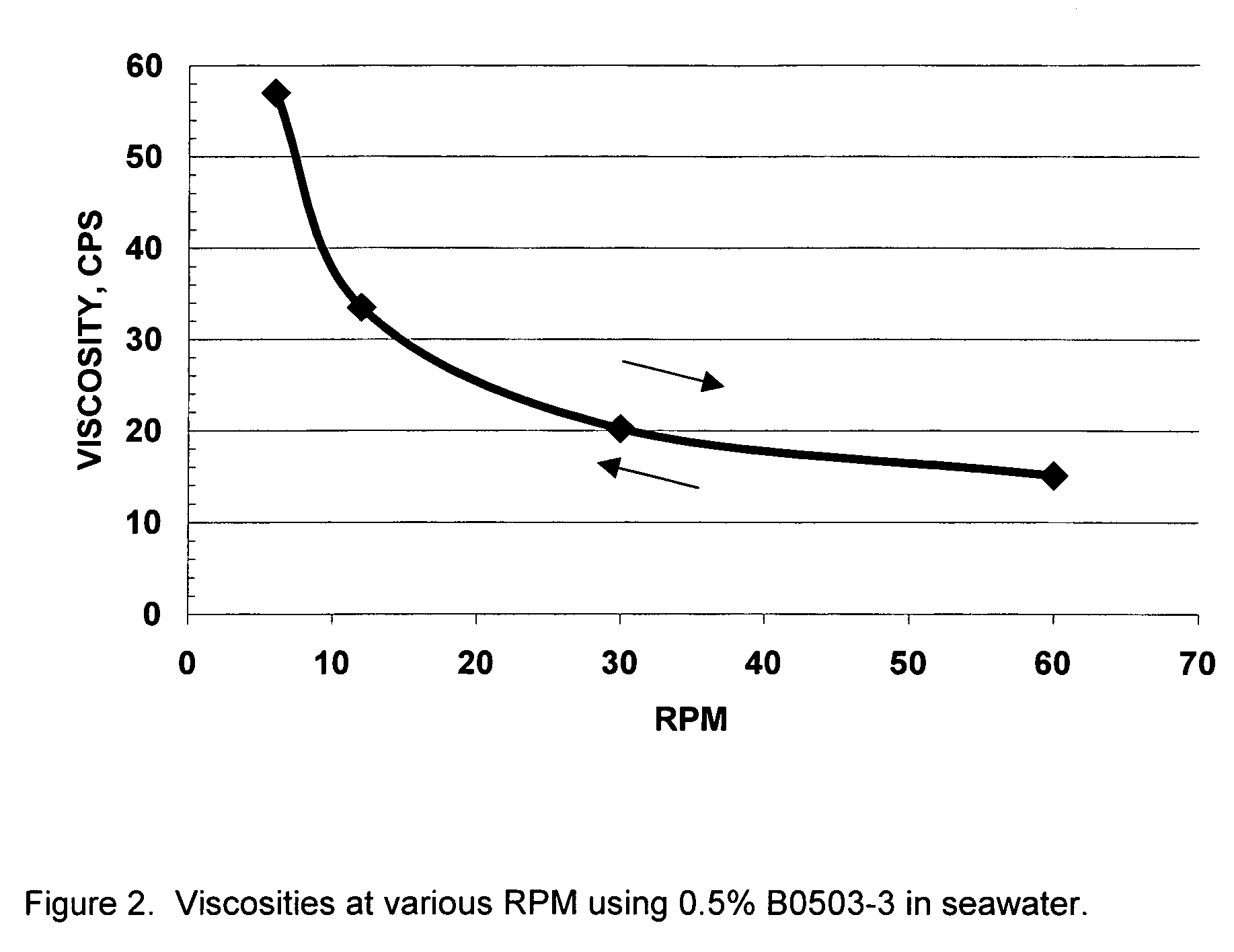
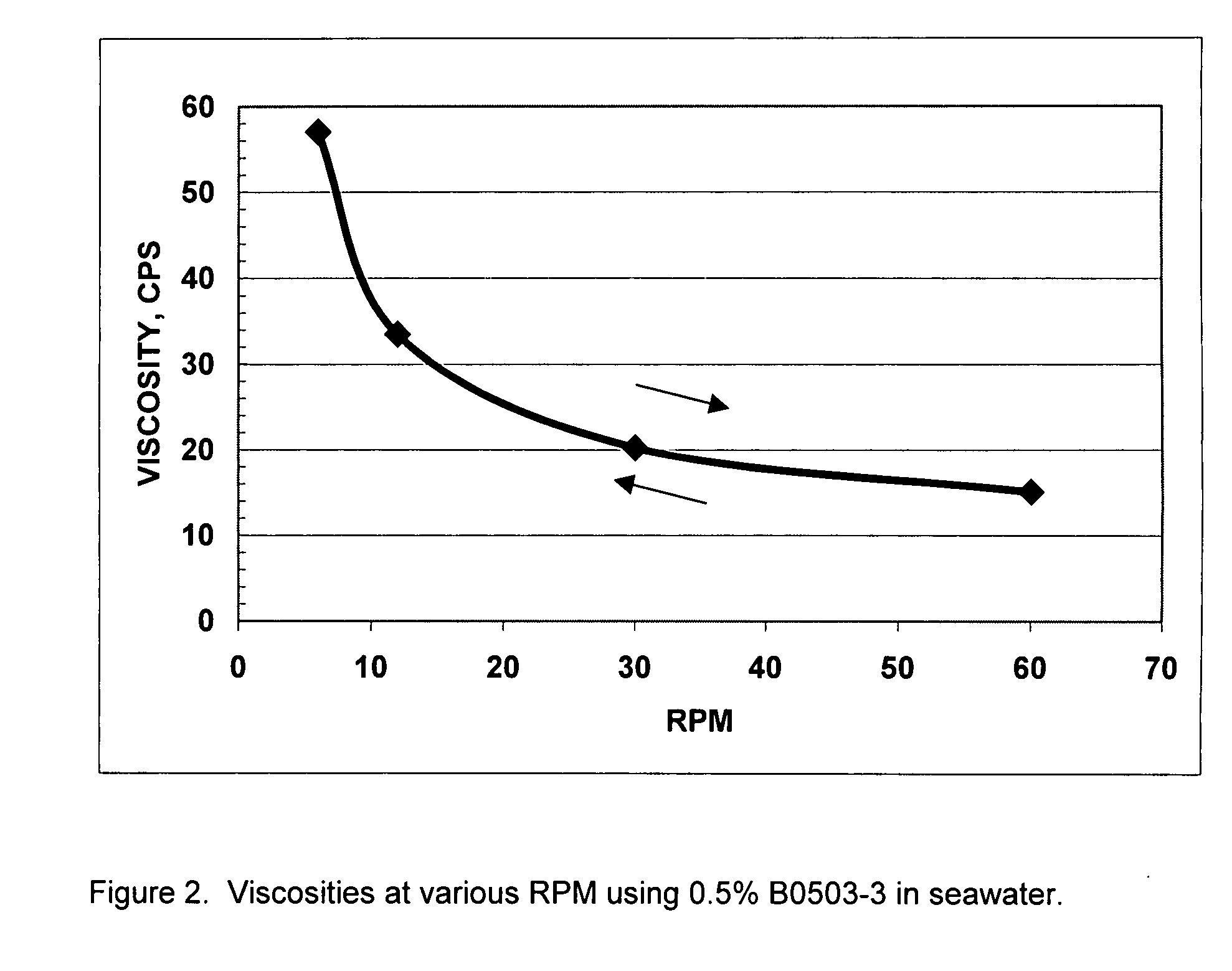
Viscoelastic surfactant rheology modification
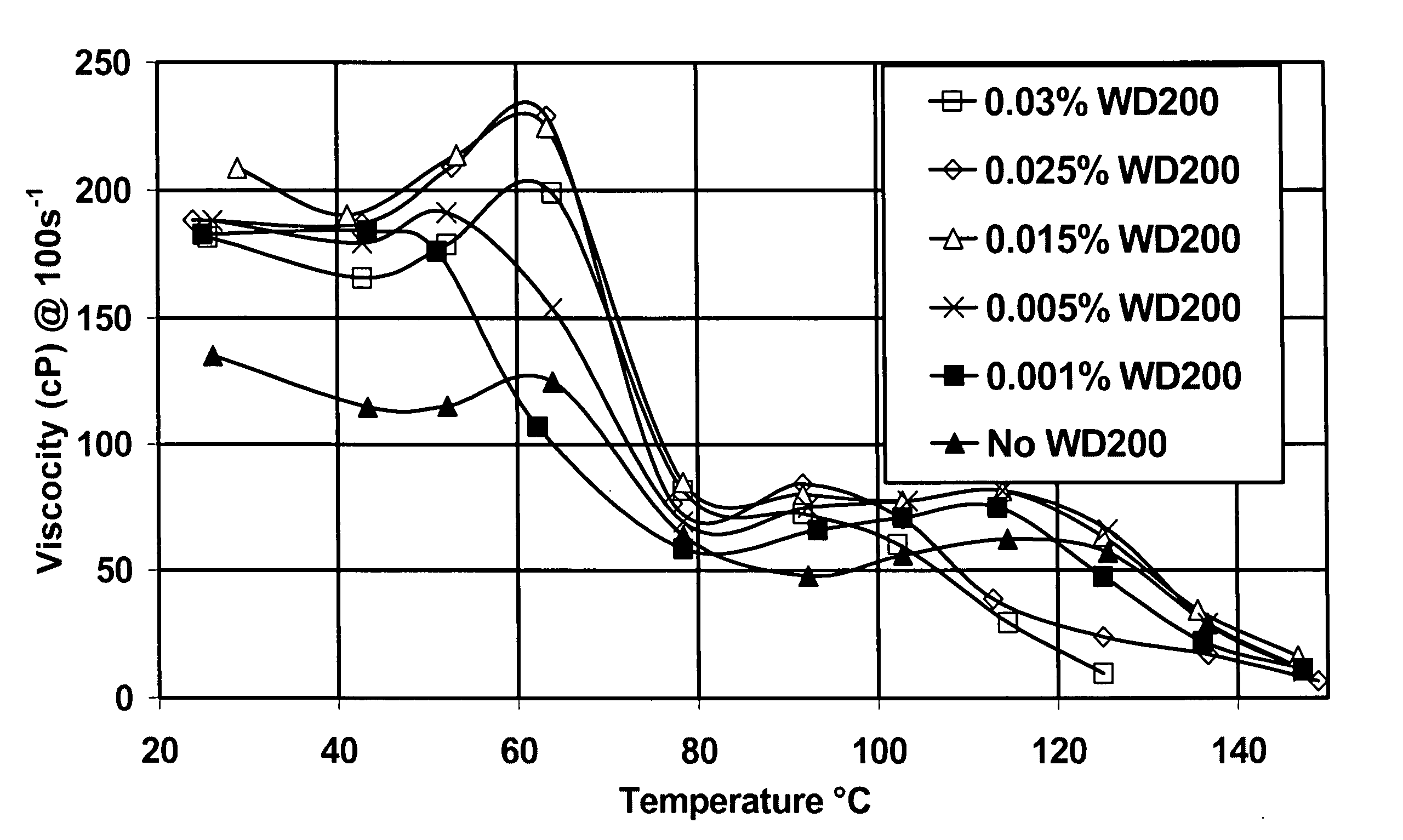
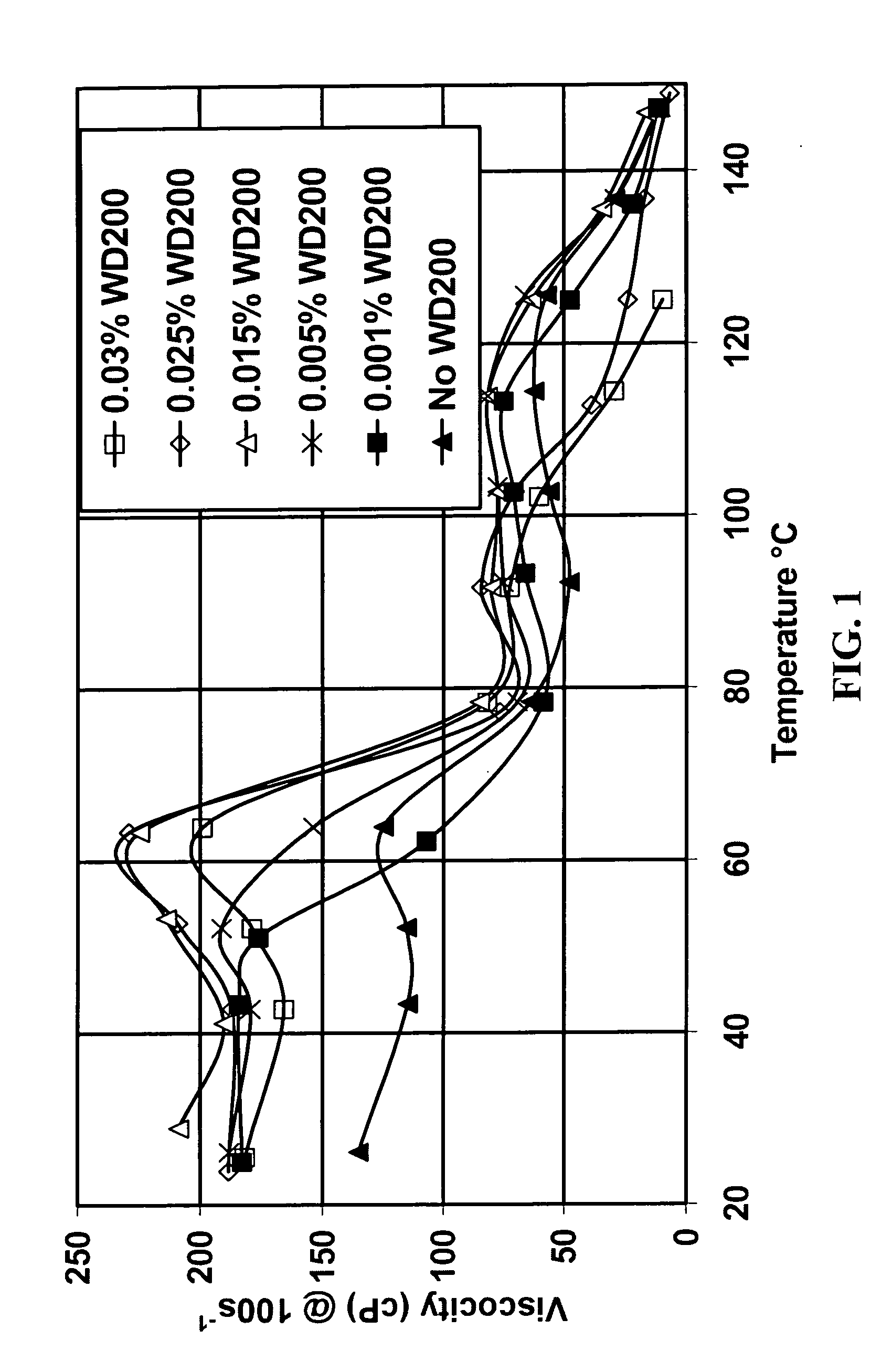
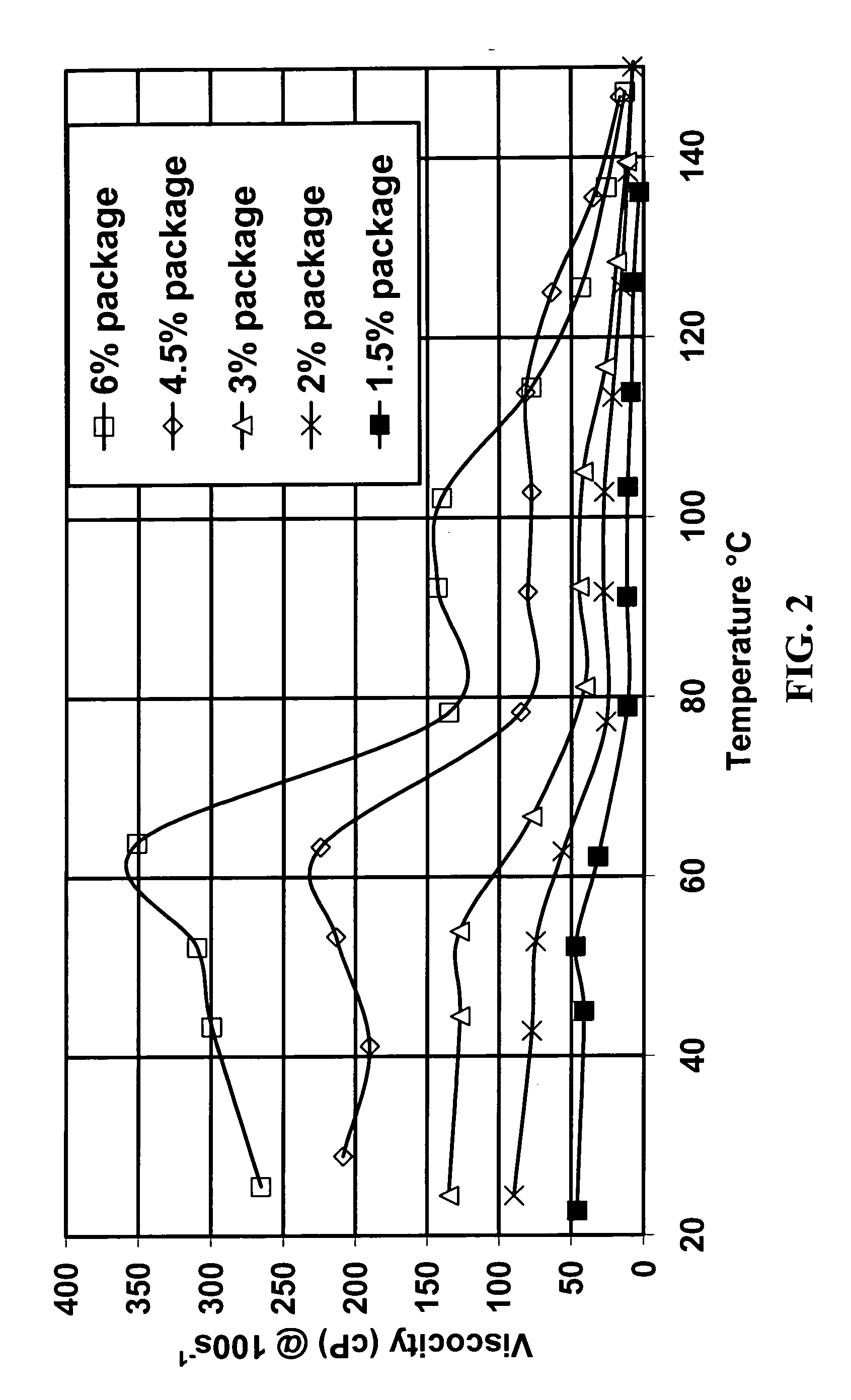
ActiveUS20060128597A1Shortening shear recovery timeShorten recovery timeSurface-active detergent compositionsFluid removalBetaineFluid viscosity
A method for shortening the shear recovery time of cationic, zwitterionic, and amphoteric viscoelastic surfactant fluid systems by adding an effective amount of a rheology enhancer selected from partially hydrolyzed polyvinyl ester and partially hydrolyzed polyacrylates. The rheology enhancer also increases fluid viscosity and very low rheology enhancer concentration is needed. Preferred surfactants are betaines and quaternary amines. The fluids are useful in oilfield treatments, for example fracturing and gravel packing.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Additive for viscoelastic fluid
InactiveUS20050155762A1Shortening shear recovery timeShorten recovery timeReciprocating drilling machinesConstructionsBetaineFluid viscosity
Composition and method for shortening the shear recovery time of cationic, zwitterionic, and amphoteric viscoelastic surfactant fluid systems by adding an effective amount of a co-gelling agent selected from triblock oligomeric compounds having hydrophilic (for example polyether) and hydrophobic (for example alkyl) portions. The co-gelling agent also increases fluid viscosity and very low co-gelling agent concentration is needed. Preferred surfactants are betaines and quaternary amines. The fluids are useful in oilfield treatments, for example fracturing and gravel packing.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Solutions for cleaning silicon semiconductors or silicon oxides
InactiveUS20060073997A1Provide efficiencyQuantity minimizationOrganic detergent compounding agentsDetergent mixture composition preparationBetaineStrong acids
A solution for cleaning silicon semiconductors or silicon oxides, and methods for cleaning silicon semiconductors or silicon oxides using the solution, is disclosed. The solution includes hydrogen peroxide, ammonium hydroxide, an alkanolamine, and at least one of a tetraalkylammonium hydroxide, an alkanolamide, an amido-betaine, an α,α-dihydroxyphenol, a carboxylic acid, a phosphonic acid, a chelating agent or a surfactant. The weight ratio of ammonium hydroxide to peroxide to water is between about 1:1:5 and 1:1-4:50, the weight ratio of ammonium hydroxide to water is between 1:5 and 1:50, and the molar ratio of component A to ammonium hydroxide is between 1:10 and 1:5000 is disclosed. The solution can achieve the efficiency equivalent to that of the conventional RCA two-step cleaning solution within a shorter time by one step preserving the silicon and silicon oxide substrate integrity and effectively remove contaminants such as organics, particles and metals from the surfaces of silicon semiconductors and silicon oxides without using strong acids such as HCl and sulfuric acid.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Urethane surfactants and their use in personal care formulations
InactiveUS6315991B1Maximization of colorMinimizationBiocideCosmetic preparationsPersonal careNatural source
The present invention is directed to monomeric and polymeric compositions based upon polymeric urethane surfactants which are derived from linear, branched, or aromatic compounds of synthetic or natural origin, preferably from tertiary amines and diisocyanate compounds. The urethane polymers of the present invention may be in the form of betaines, quaternium salts, tertiary amine salts or N-oxides. The compounds of the present invention may be incorporated into personal care formulations such as cosmetics, dental care products and toiletries to improve at least one and preferably two or more characteristics of such formulations.
Owner:FLEET BANK NAT ASSOC
Viscosity-variable diverting acid for improving stratigraphic acidified section
InactiveCN102020983AViscosity auto-increasingConing reductionDrilling compositionBetaineActive agent
The invention discloses viscosity-variable diverting acid for improving a stratigraphic acidified section. An oil layer is uniformly acidified, and the coning of acid liquor in a high permeable stratum is reduced to ensure that part of acid liquor enters middle and low permeable target stratums so as to improve and expand an acidified sweep section. In the viscosity-variable diverting acid, each component is controlled by a pH value, and the viscosity-variable diverting acid mainly comprises the following components in part by weight: 100 parts of basic acid liquor, 3 to 5 parts of long chain alkylamide propyl betaine, 1 to 3 parts of corrosion inhibitors, 0.5 to 1 part of ferrous stabilizer and 0.5 to 1 part of clay stabilizer. The viscosity-variable diverting acid consisting of the components is injected into a target oil layer. In the acidification process, the initial viscosity of the acid liquor is lower, and the initial viscosity at the temperature of 20 DEG C is 10 to 15mPa.s, the acid liquor is easy to enter the high permeable stratum, and subsequent unreacted low-viscosity acid liquor automatically diverts to enter the middle and low permeable stratums. The long chain alkylamide propyl betaine serving as a diverter is an ampholytic surfactant, does not have any macromolecular residues after a gel is broken and does not have any secondary damage to a reservoir.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Gelled oil with surfactant
A viscoelastic gelled oil, for example gelled diesel or paraffin oil, is made with a gelling agent, for example a phosphate ester, a metal carboxylate, for example an aluminum carboxylate, and a gel-enhancing surfactant, for example a zwitterionic surfactant, for example erucylamidopropyl betaine. The gel-enhancing surfactant makes the gel viscoelastic, increases the stability and decreases the sensitivity to the concentrations of the gelling agent and the metal carboxylate. The enhanced viscoelastic gelled oils are used, as examples, in hydraulic fracturing, frac packing, gravel packing, diversion, fluid loss control, lost circulation control, sand control, wellbore cleanout, wellbore or pipeline sweeping, organic scale dissolution, organic scale removal, and drilling.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Polynucleotides encoding choline monooxygenase and plants transformed therewith
A full length choline monooxygenase (CMO) cDNA was cloned from spinach and used to transform plants which do not naturally express CMO. A method is presented to improve stress tolerance of crops following engineering of CMO and BADH in plants that lack glycine betaine accumulation. Also provided are fragments useful as probes to isolate other CMO-type genes, and antisense sequences which inhibit the production of CMO. Reduction of glycine betaine as a consequence of antisense expression of CMO in species naturally accumulating glycine betaine, improves the transgenic plant's tolerance toward pathogens and pests and / or enhances its nutritional quality.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method of displacement chromatography
InactiveUS6602420B2Efficient separationLower requirementIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatographic separationBetaine
A plurality of chromatographic separation operations, including a first simulated moving bed operation, are coupled into a process which functions, preferably through the application of continuous displacement chromatography, to recover a fraction rich in small organic molecules, notably betaine and / or invert from sucrose solutions, enabling the subsequent production of a high purity sucrose product.
Owner:AMALGAMATED RES
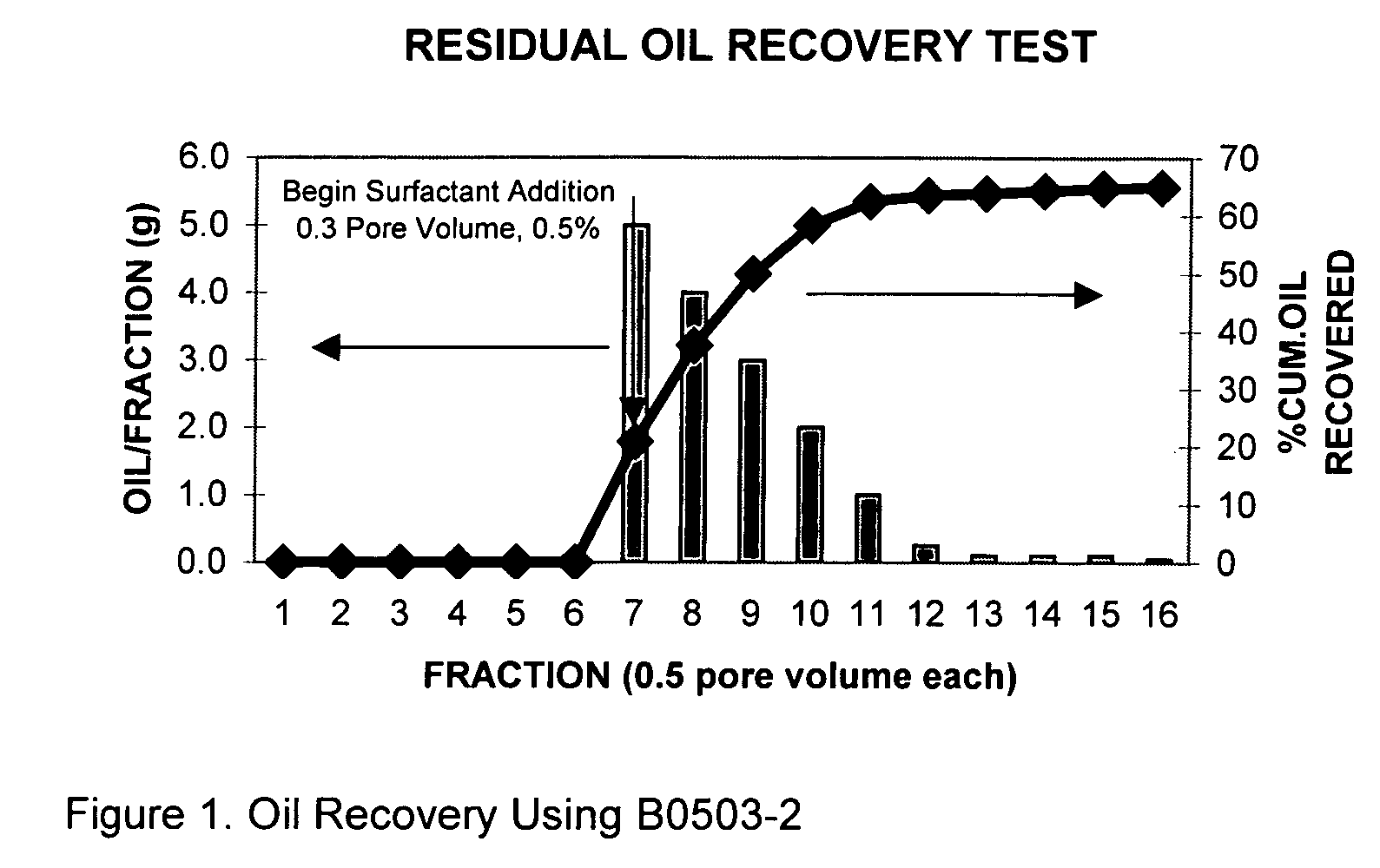
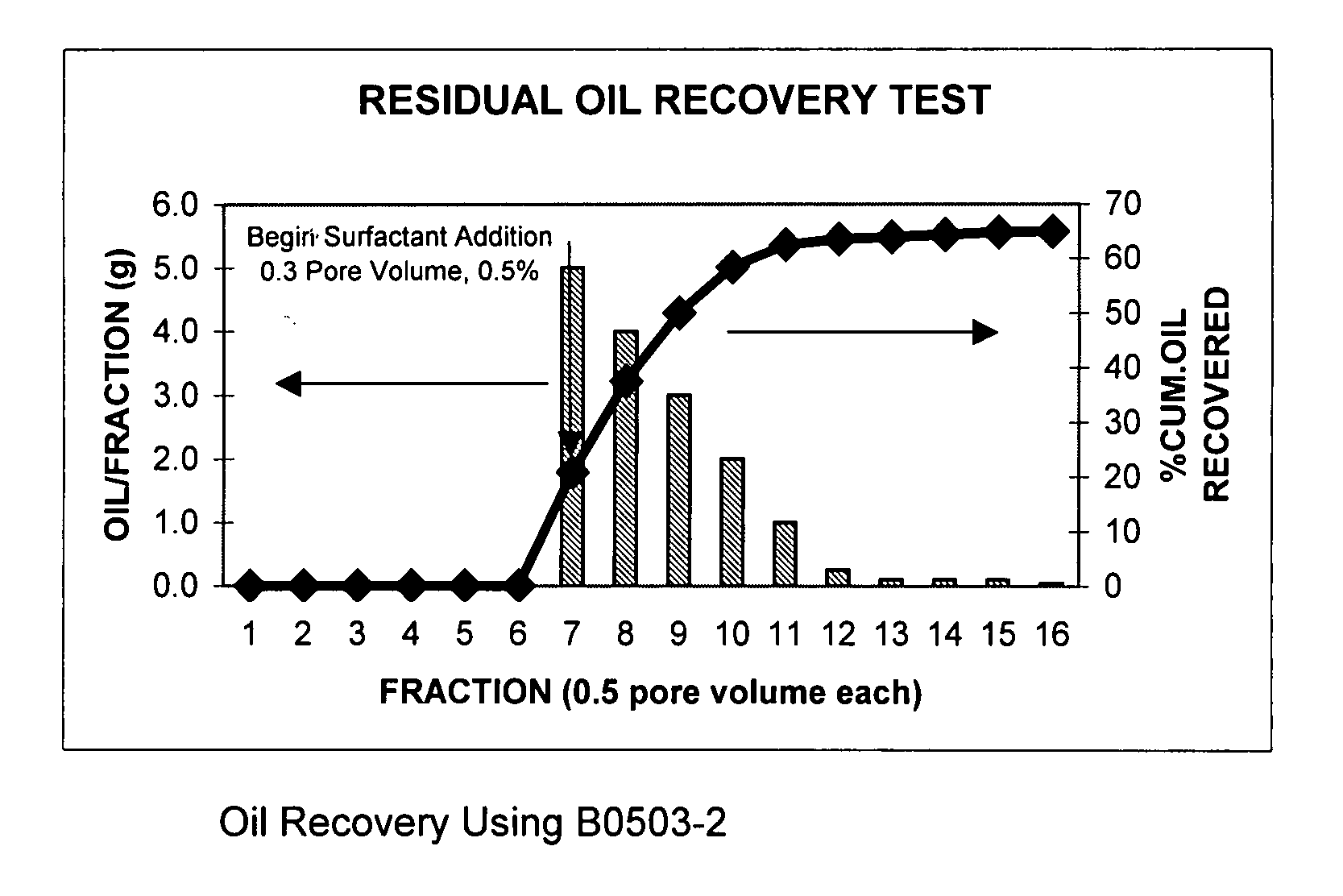
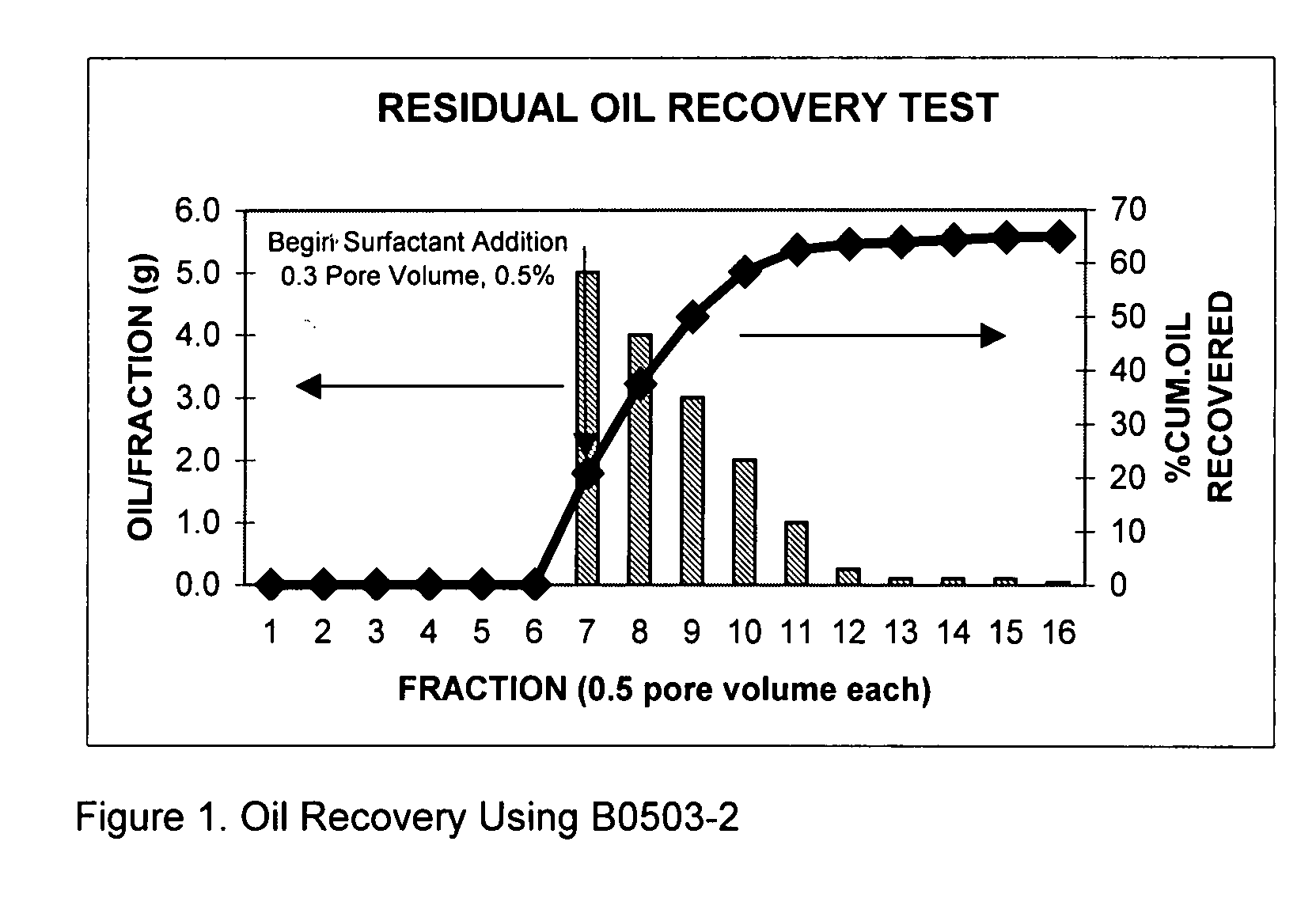
Process for oil recovery using surfactant gels
InactiveUS20070142235A1Potential damageHigh viscosityFlushingDrilling compositionHigh concentrationPorosity
A composition and process for recovering oil by injecting an aqueous solution into a subterranean oil-bearing formation through one or more injection wells, displacing the solution into the formation, and recovering the oil from one or more production wells. This aqueous solution contains one or more amphoteric alkyl amido betaine surfactants that form a viscoelastic surfactant gels that can reduce the interfacial tension (IFT) and increase the viscosity of the injection fluid simultaneously in certain oils and brines. These viscoelastic gels are tolerant to electrolytes and multivalent cations. They are shear reversible and adsorbed little on the reservoir rock. The viscosity of the gels is reduced when they encountered certain hydrocarbons but remains high when contacting water or brine. This allows the fluid to preferentially penetrate the oil-bearing portions of the formation and resulting additional oil recovery. These amphoteric viscoelastic surfactant gels are particular suitable for use with reservoirs and brines characterized by medium to high temperatures, higher salinity, higher concentrations of divalent cations, and low formation porosities.
Owner:BELGER PAUL DANIEL
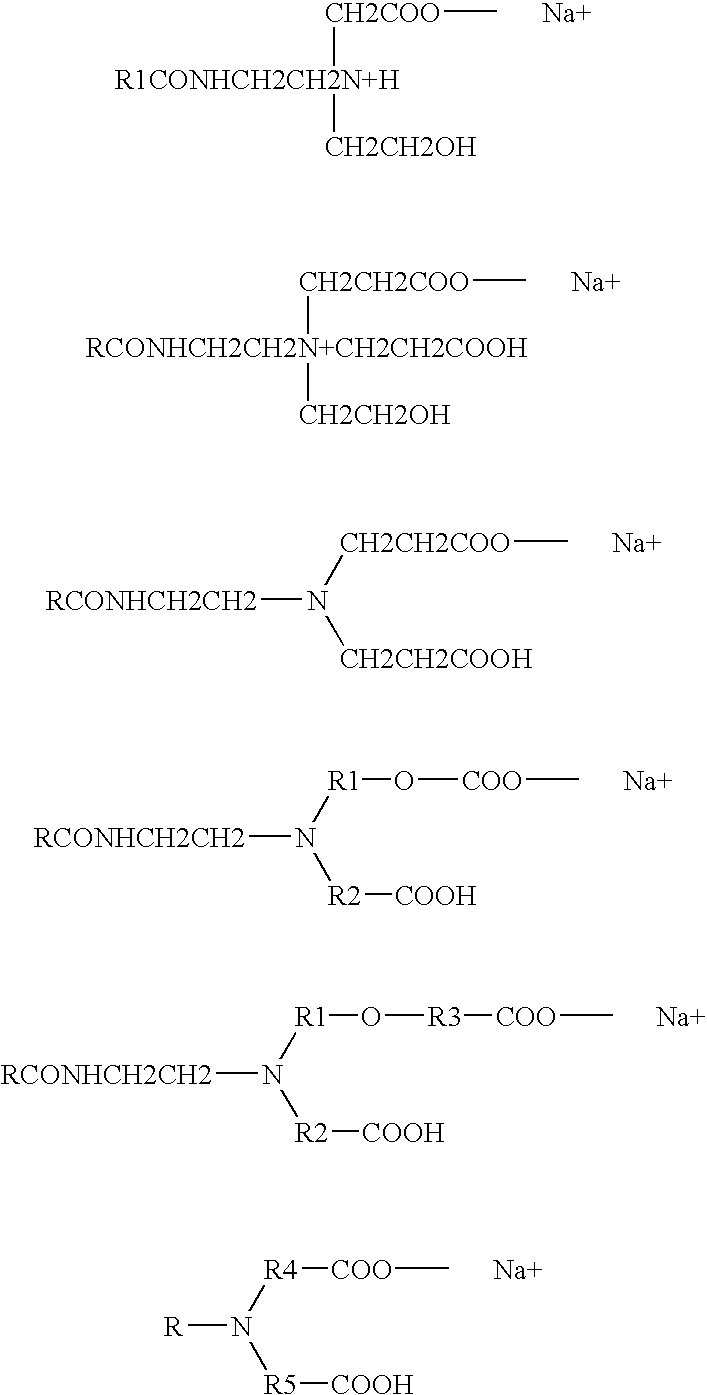
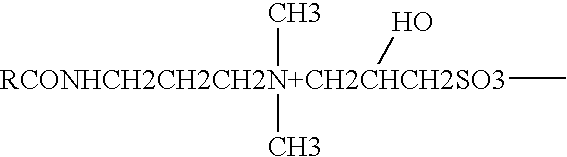
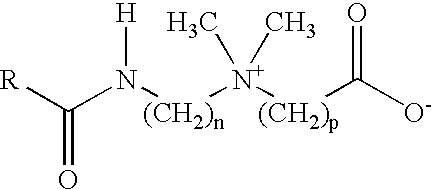
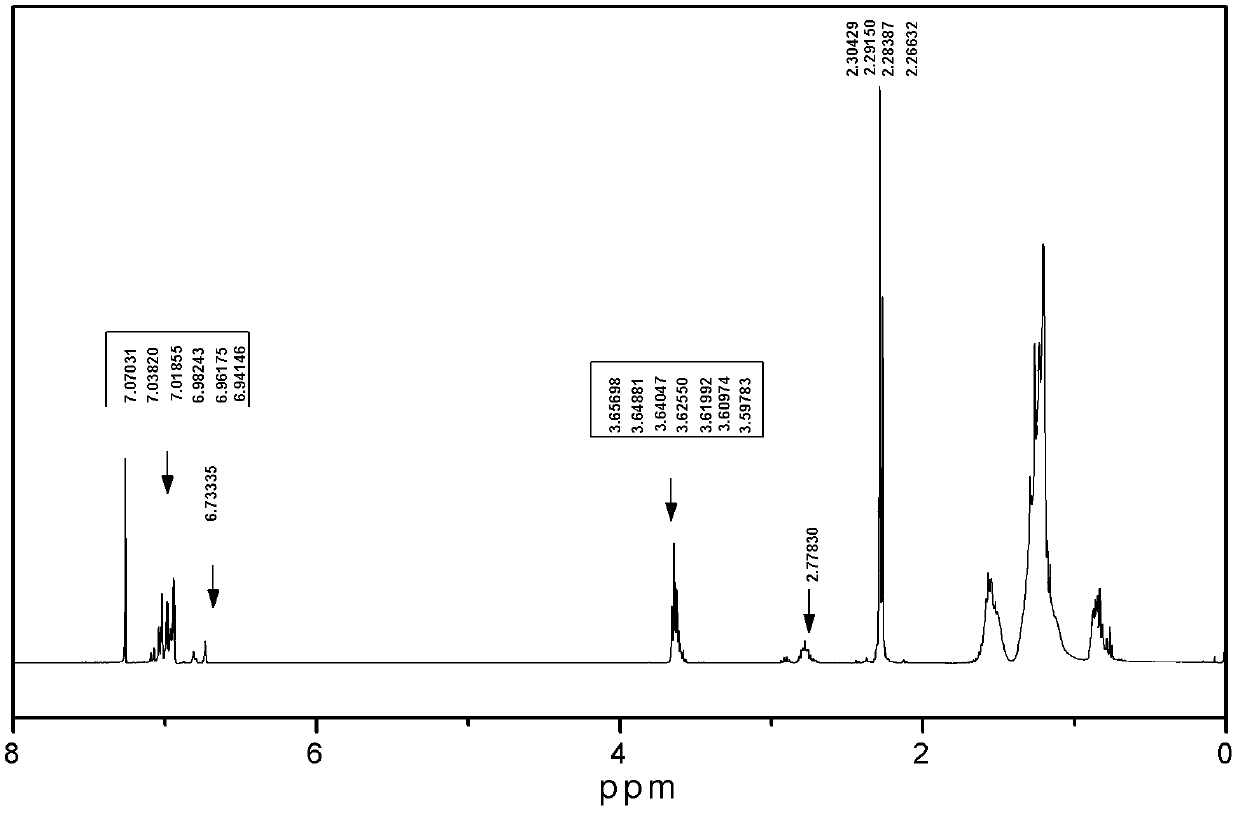
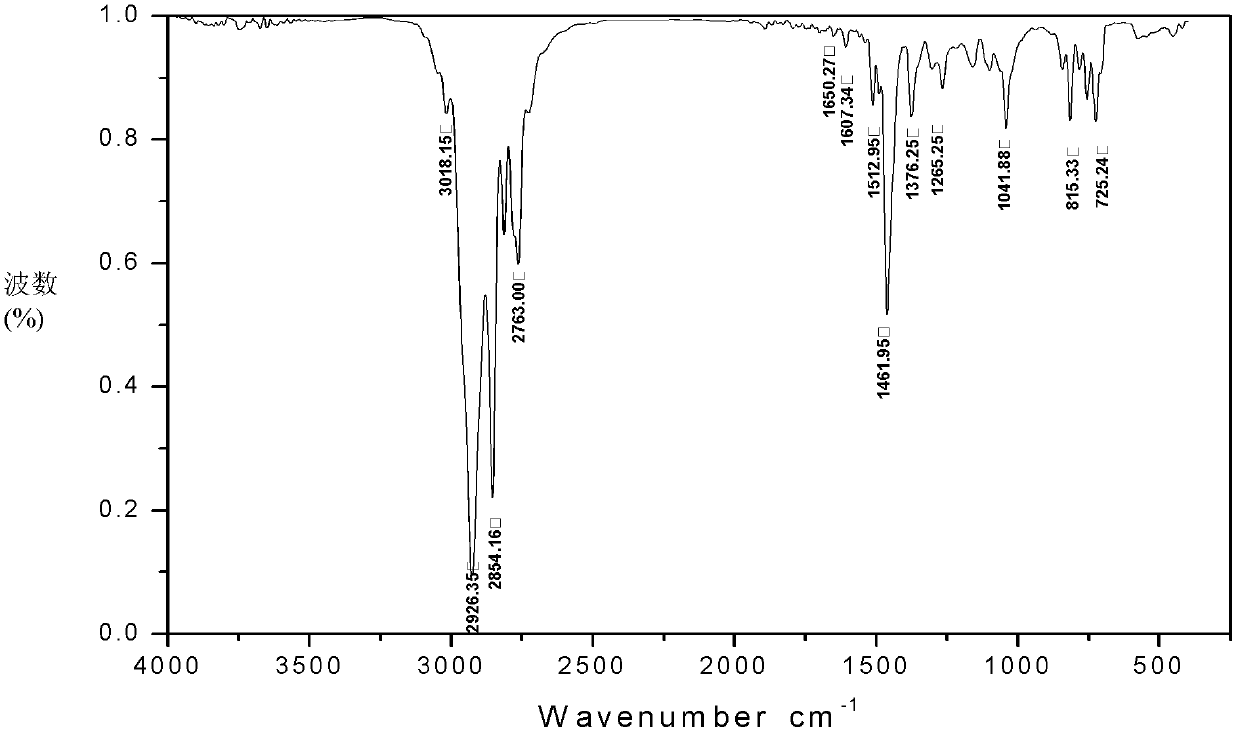
Betaine surfactant and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102618244ALow priceHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acids salts preparationBetaineHydrogen
The invention relates to a betaine surfactant and a preparation method and application thereof. The betaine surfactant is shown as a formula I, wherein the m is 0 or a positive integer, the n is 0 or a positive integer, the m and the n cannot be 0 simultaneously, the R1 is hydrogen (H) or alkyl, the R2 is H or alkyl, the R3 is alkyl and the R4 is alkyl. The invention further provides a preparation method of the betaine surfactant and application of the betaine surfactant in tertiary oil recovery as a surfactant of a binary compound oil-displacing agent. The betaine surfactant has strong temperature resistance, mineralization resistance and dilution resistance and wide application prospect in the field of the tertiary oil recovery.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Hair analysis method
InactiveUS6949344B1Reliable solubilizationAccurate methodPre-tanning chemical treatmentMicrobiological testing/measurementBetaineDigestion
A method the direct analysis of an analyte in keratinized structures, e.g., hair and fingernails, which comprises preparing a mixture containing a low redox potential activator compound such as dithiothreitol or dithioerythritol, an enzyme suitable for the digestion of the keratin structure, a sample of the keratin structure and a biological detergent that aids the digestion of the keratinized structure at a relatively low pH, e.g., between about 6.2 and 8; permitting the enzyme to at least substantially digest the sample of keratin structure, and subjecting the digest solution to analysis, preferably by radioimmunoassay, to determine the identity and amount of analyte in the keratin structure sample. To accelerate the method, cupric sulfate may be added to the mixture after degradation of the keratin sample. The enzyme may be a peptidase, endopeptidase or proteinase, with papain, chymopapain, and proteinase K being preferred for use in the invention. The preferred biological detergents include betaine, sulfo-betaine, alkylglucosides and bile acids.
Owner:PSYCHEMEDICS CORPORATION
Viscous Liquid Cleansing Compositions Comprising Sulfonated Fatty Acids, Esters, or Salts Thereof and Betaines or Sultaines
InactiveUS20120208898A1High viscosityImprove skinInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsBiocideViscous liquidPersonal care
Formulations of personal care compositions and personal care concentrate compositions containing salts of sulfonated fatty acid esters and / or salts of sulfonated fatty acids, and an alkyl betaine or sultaine are described. Personal care compositions of the present technology include liquid hand soaps, bath and shower washes, shampoos, 2-in-1 or 3-in-1 shampoos, antidandruff shampoo, facial cleaners, among others.
Owner:STEPAN COMPANY
Viscoelastic surfactant fluids and related methods of use
InactiveUS7238648B2Increase droplet sizeIncrease in sizeInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsSuspended particlesBetaine
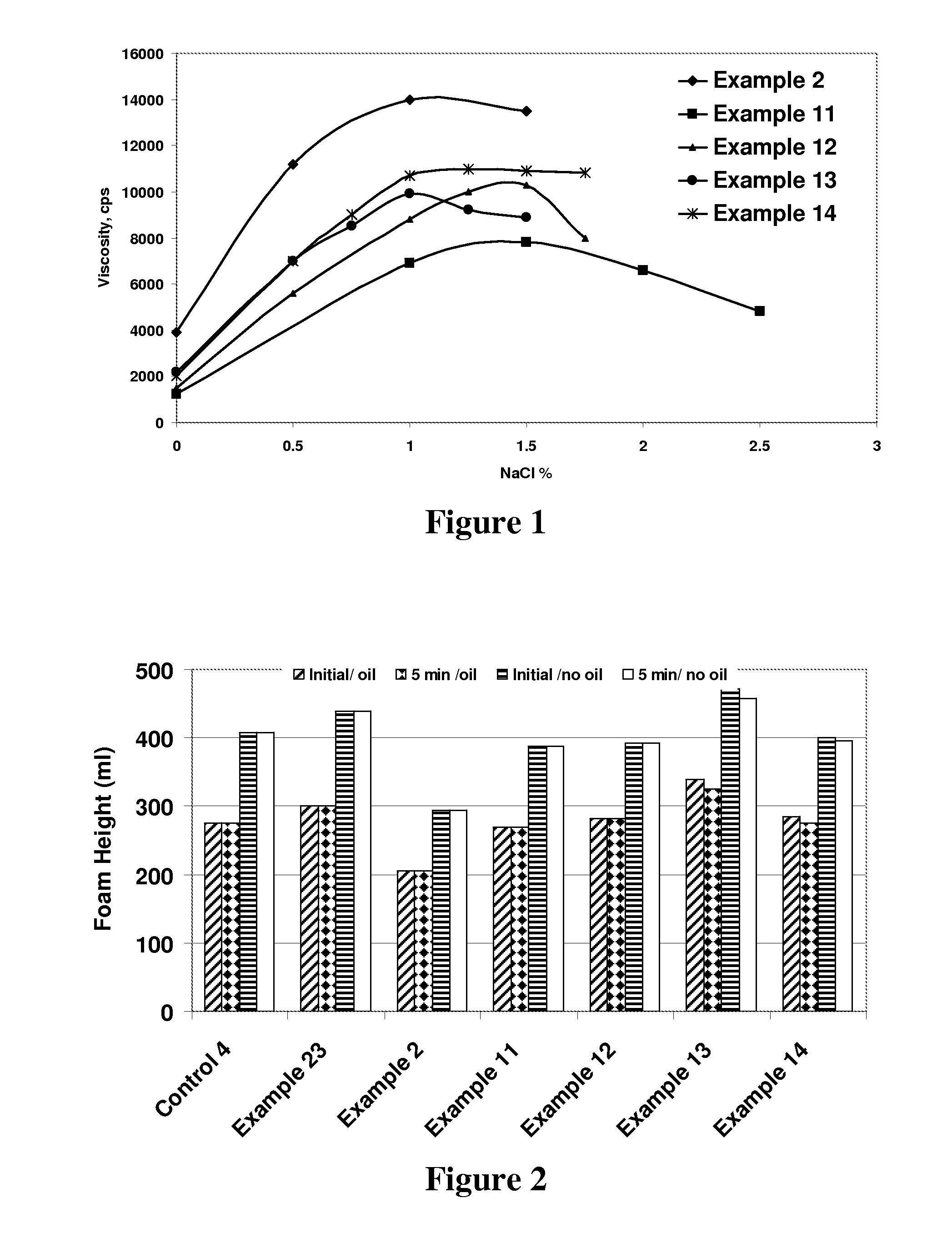
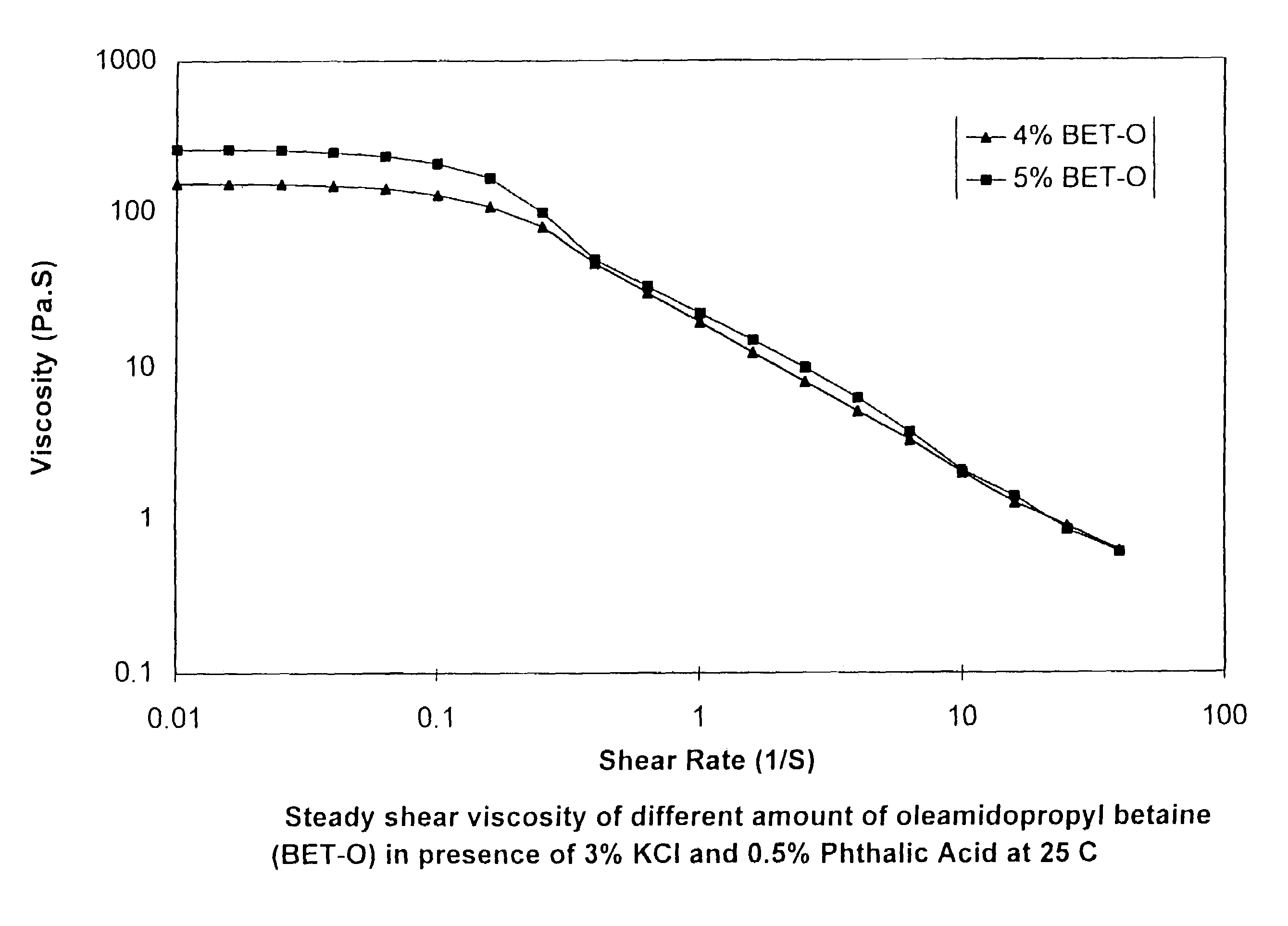
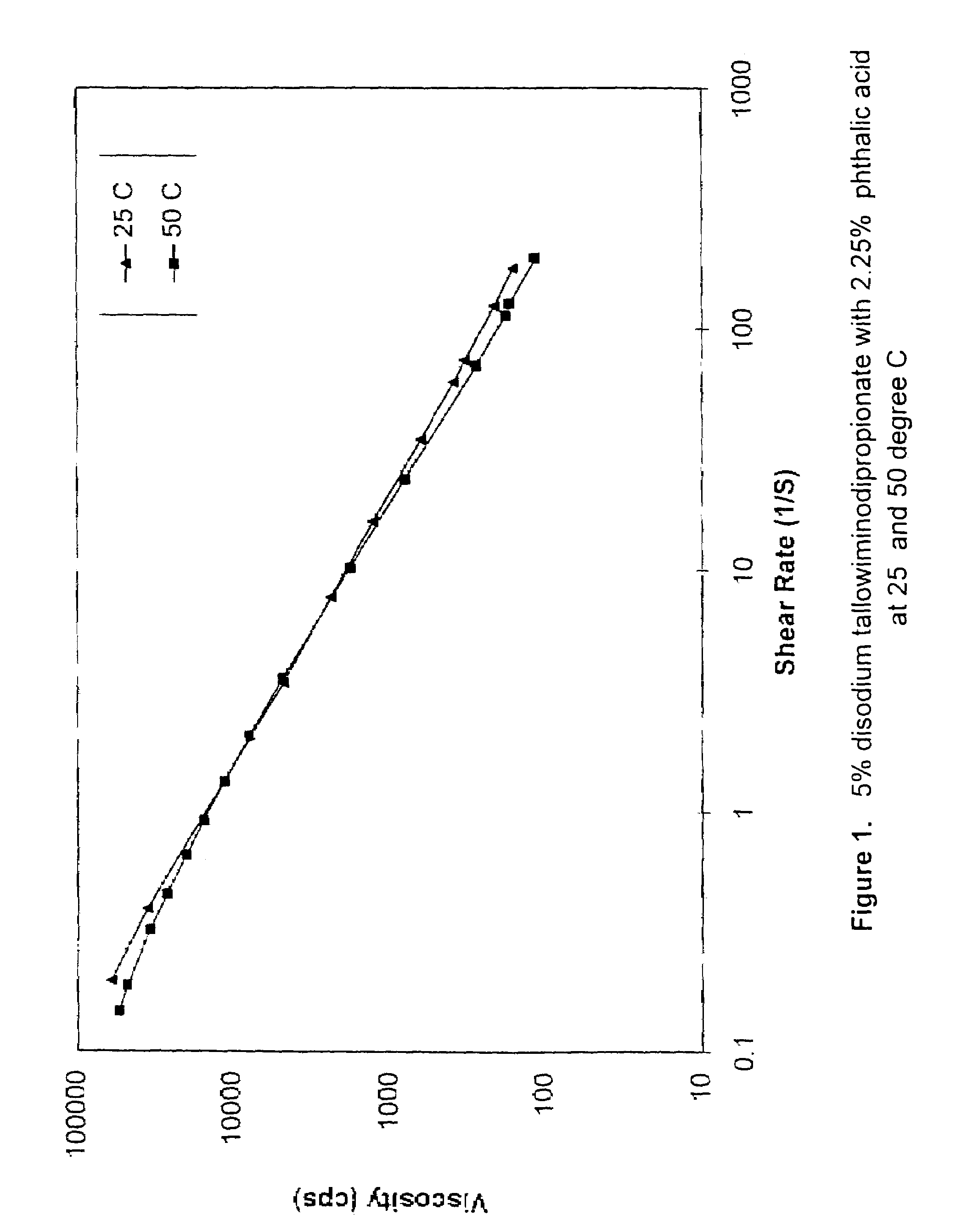
Viscoelastic surfactant based aqueous fluid systems useful as thickening agents in various applications, e.g. to suspend particles produced during the excavation of geologic formations. The surfactants are zwitterionic / amphoteric surfactants such as dihydroxyl alkyl glycinate, alkyl ampho acetate or propionate, alkyl betaine, alkyl amidopropyl betaine and alkylimino mono- or di-propionates derived from certain waxes, fats and oils. The thickening agent is used in conjunction with an inorganic water-soluble salt or organic additive such as phthalic acid, salicylic acid or their salts.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com