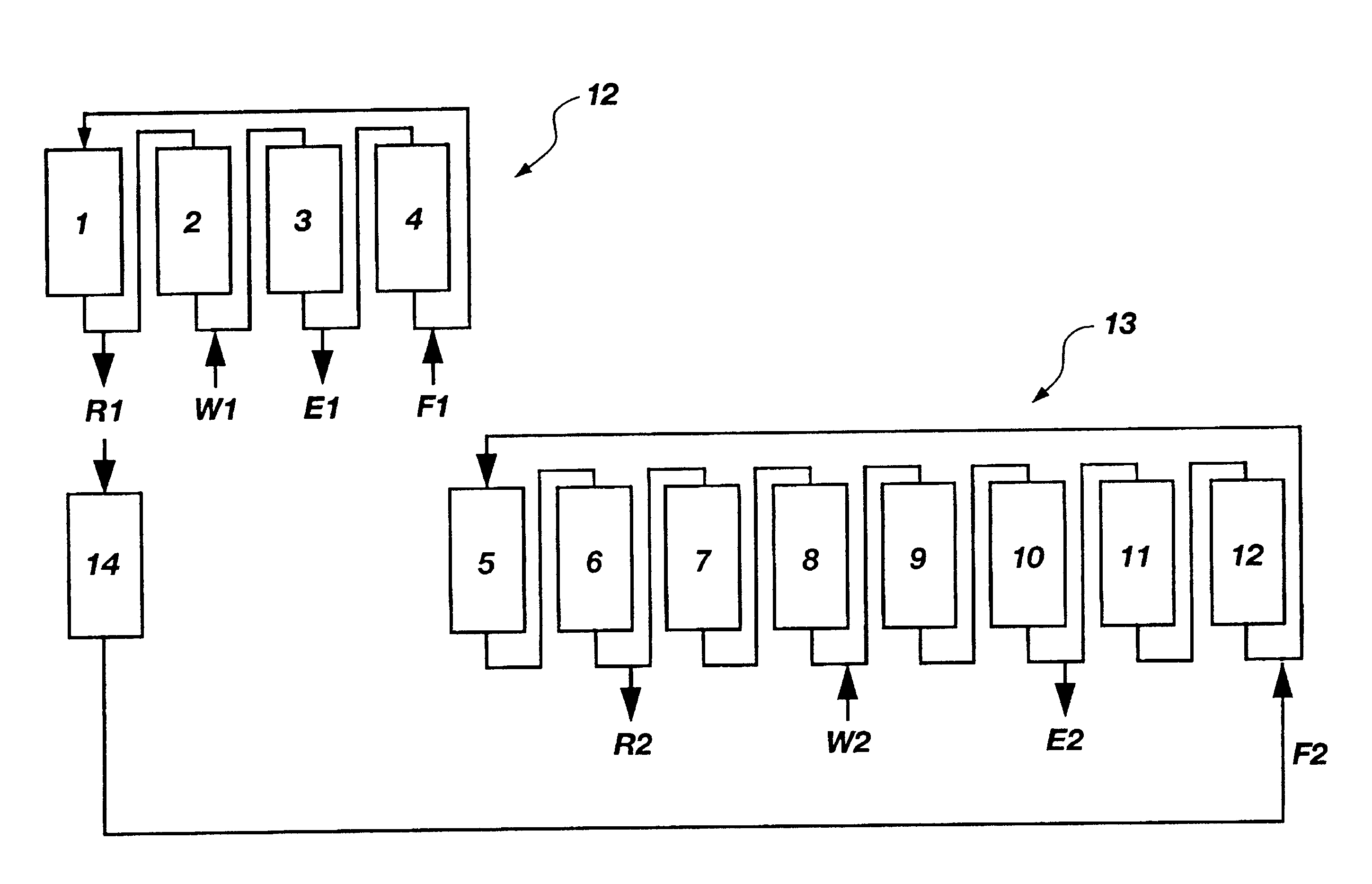
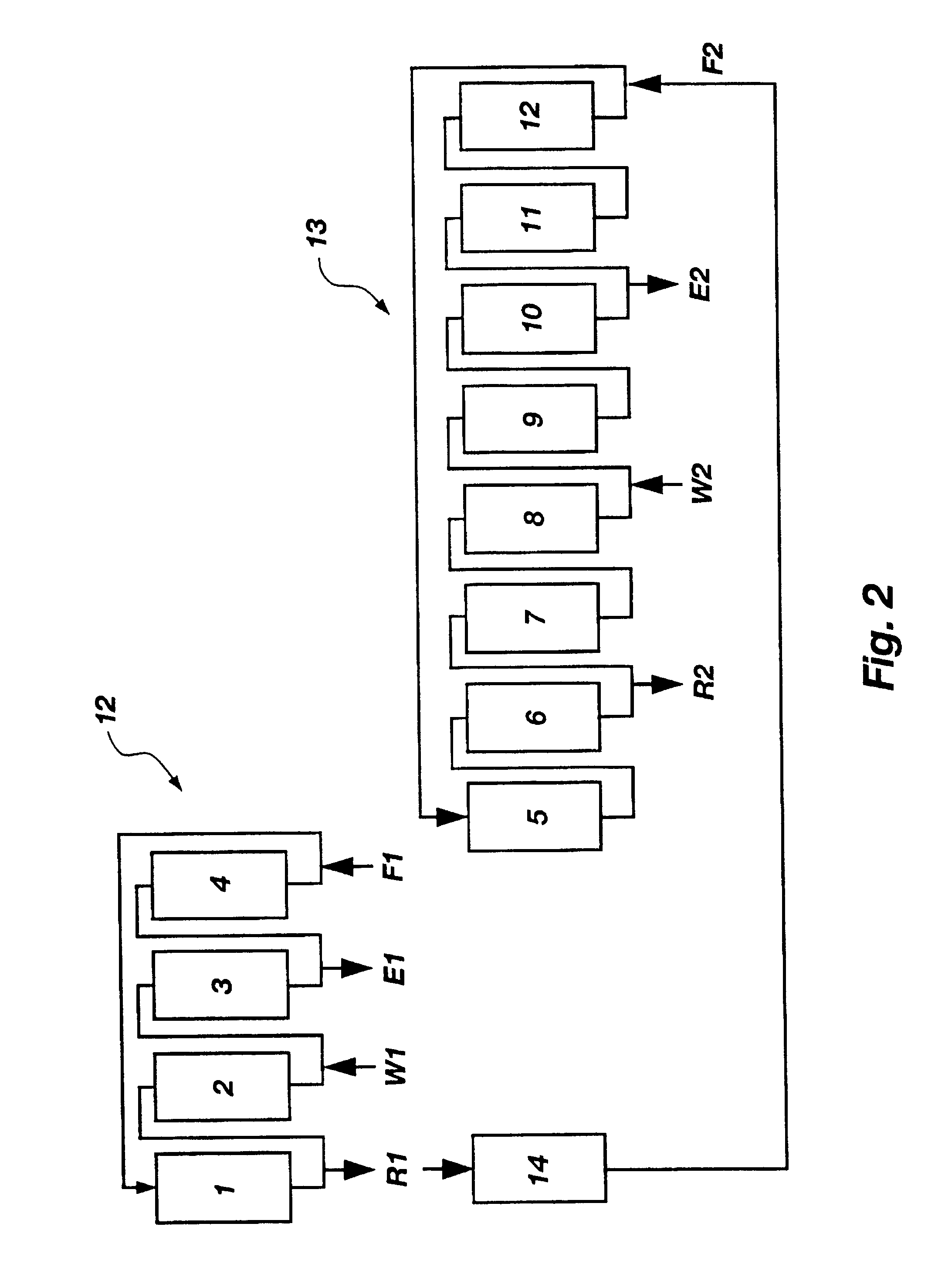
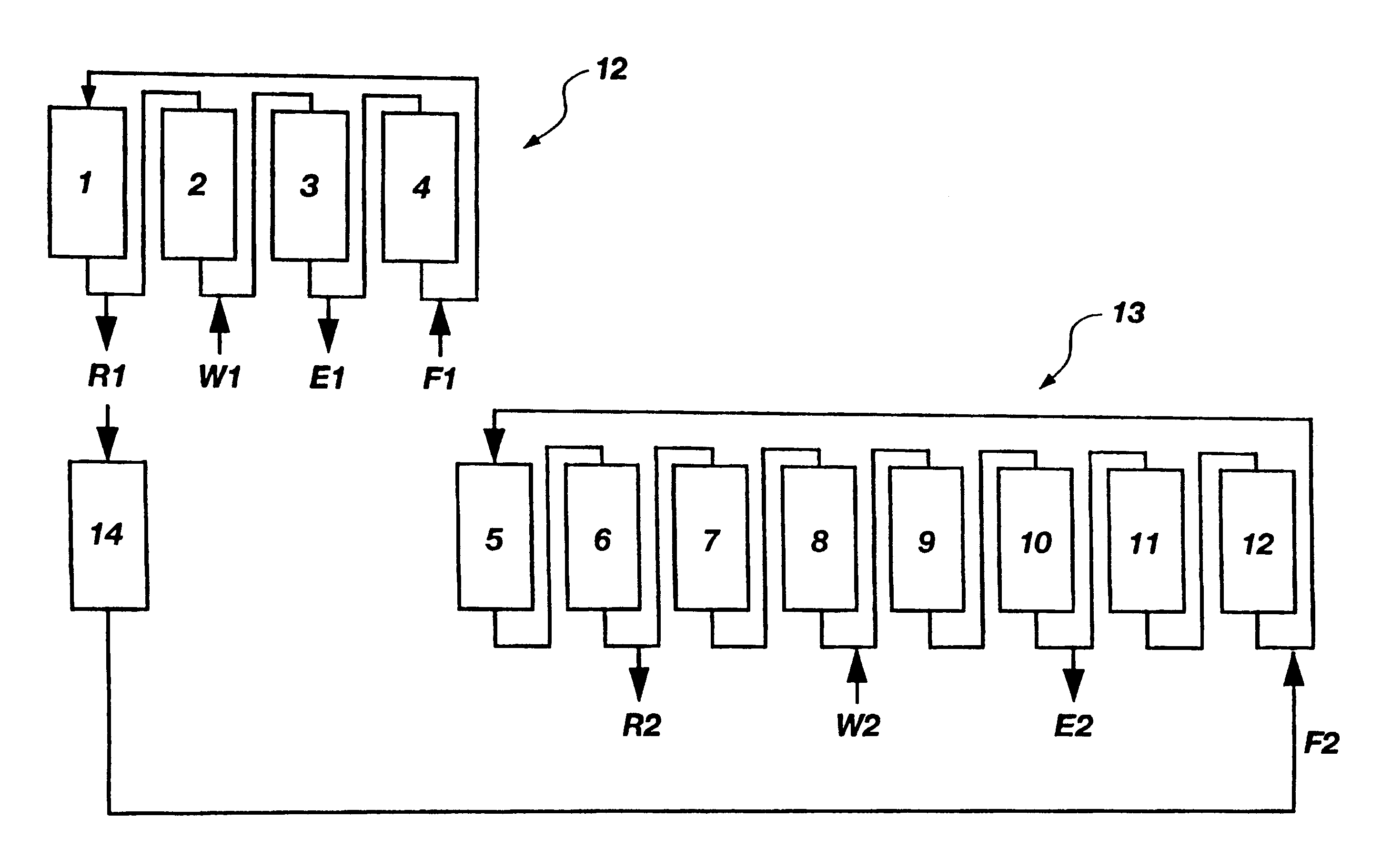
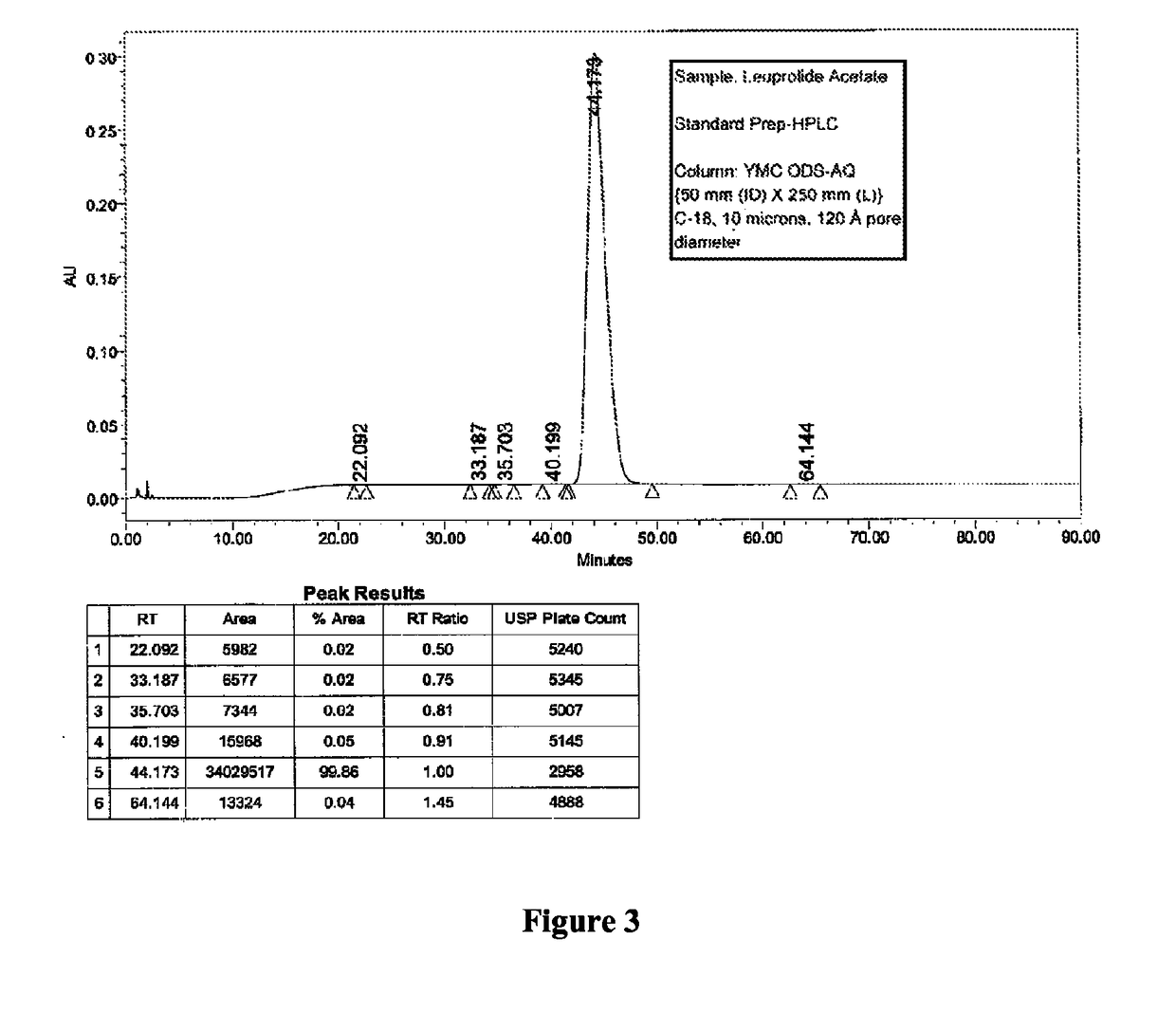
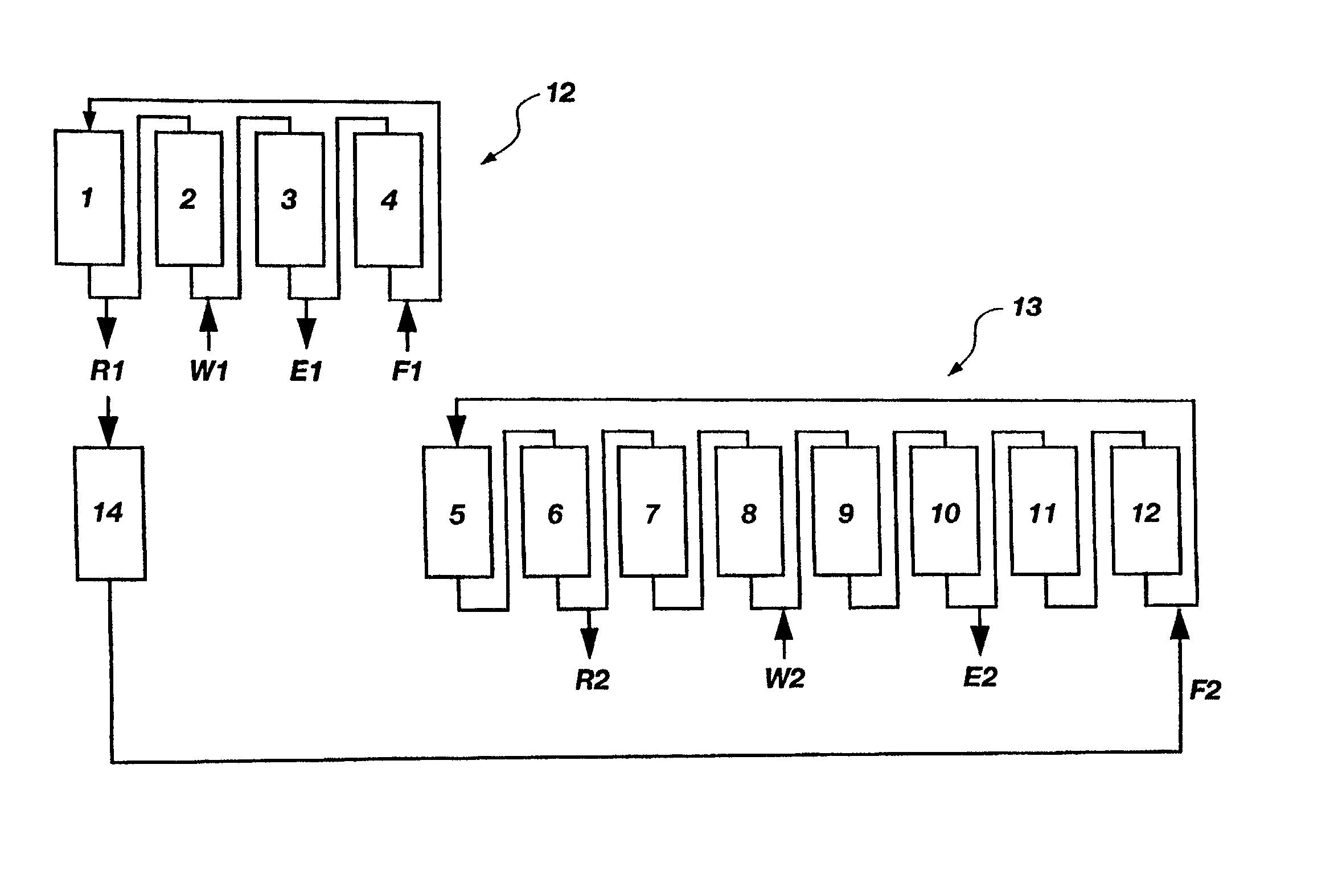
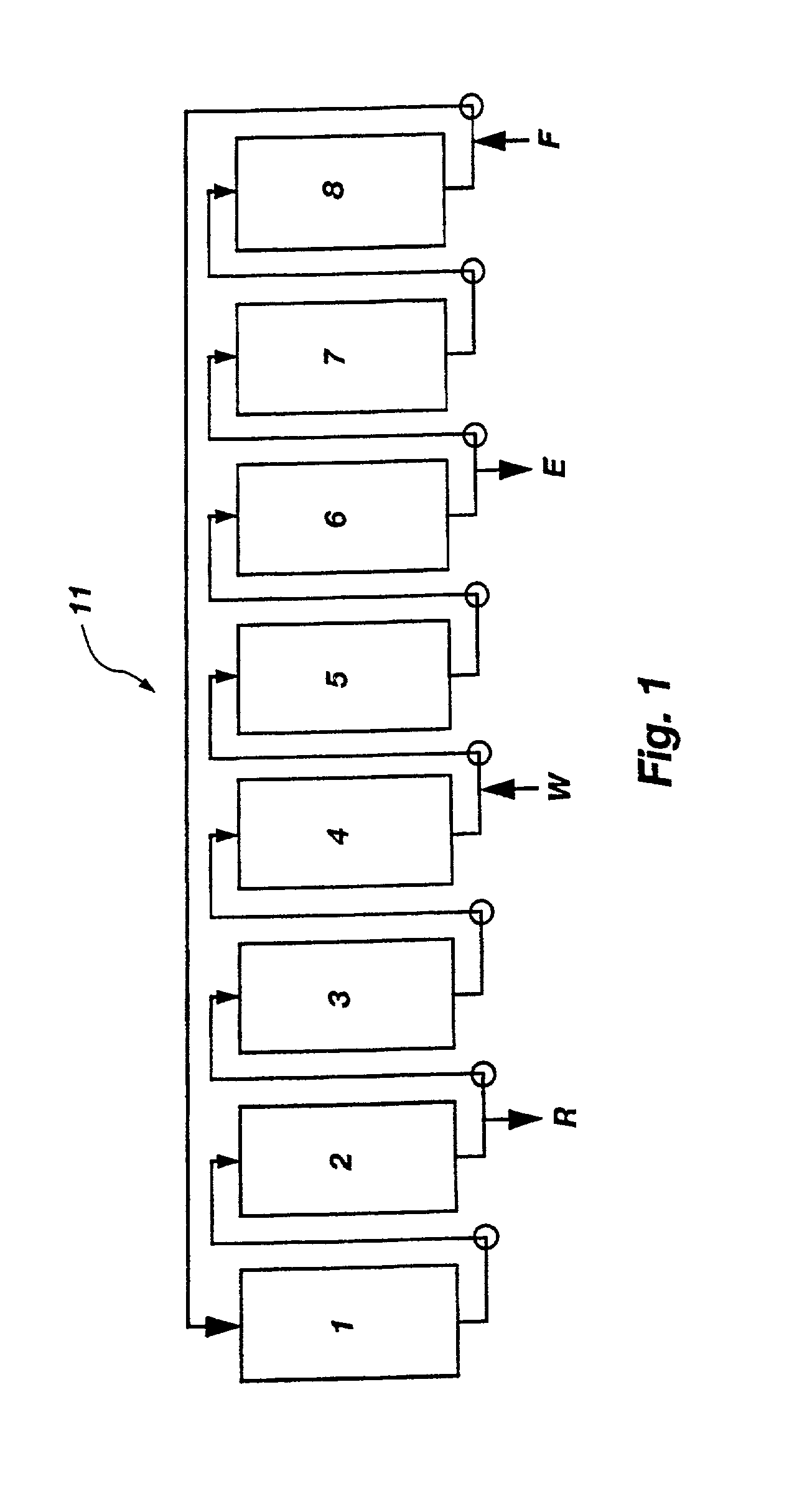
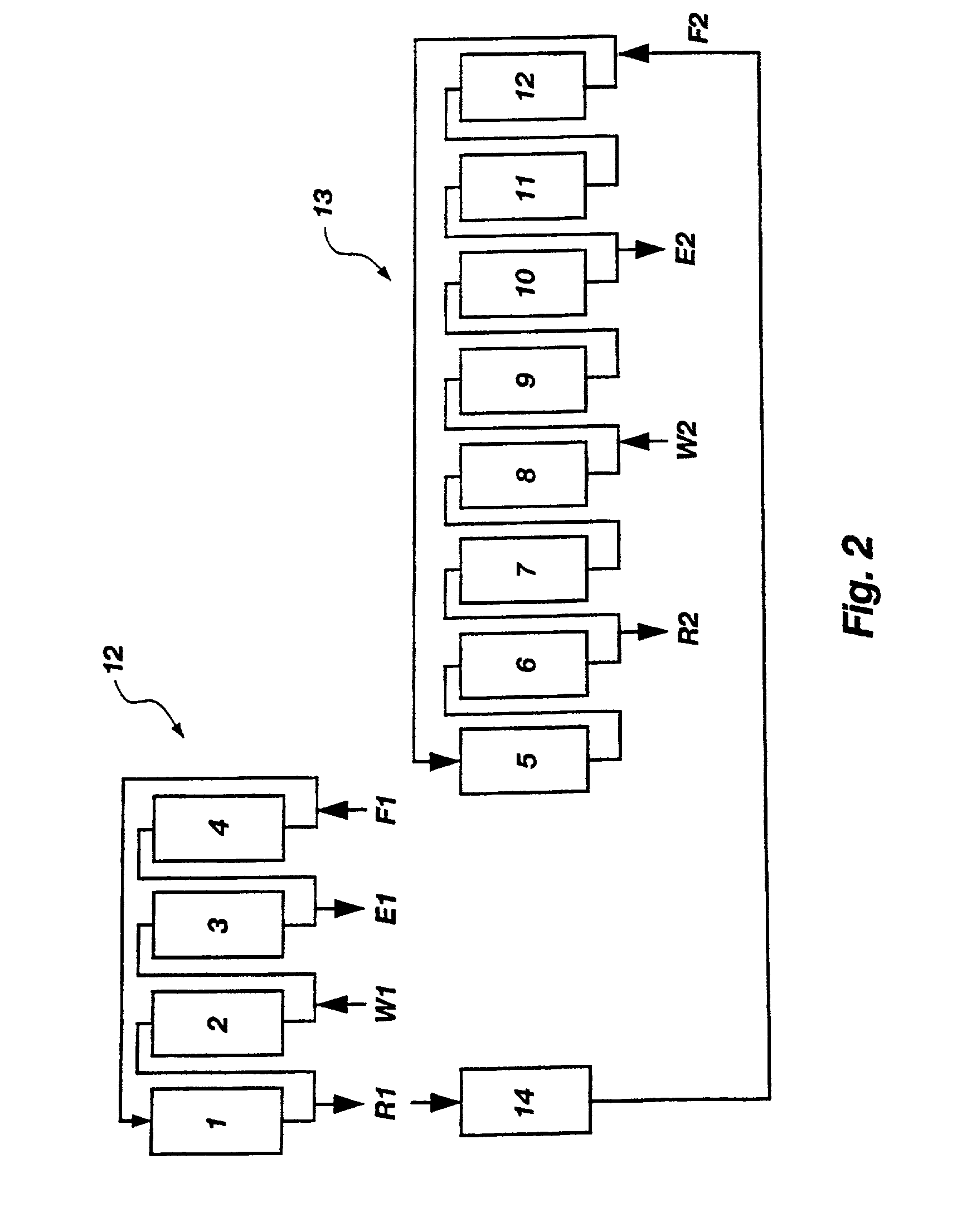
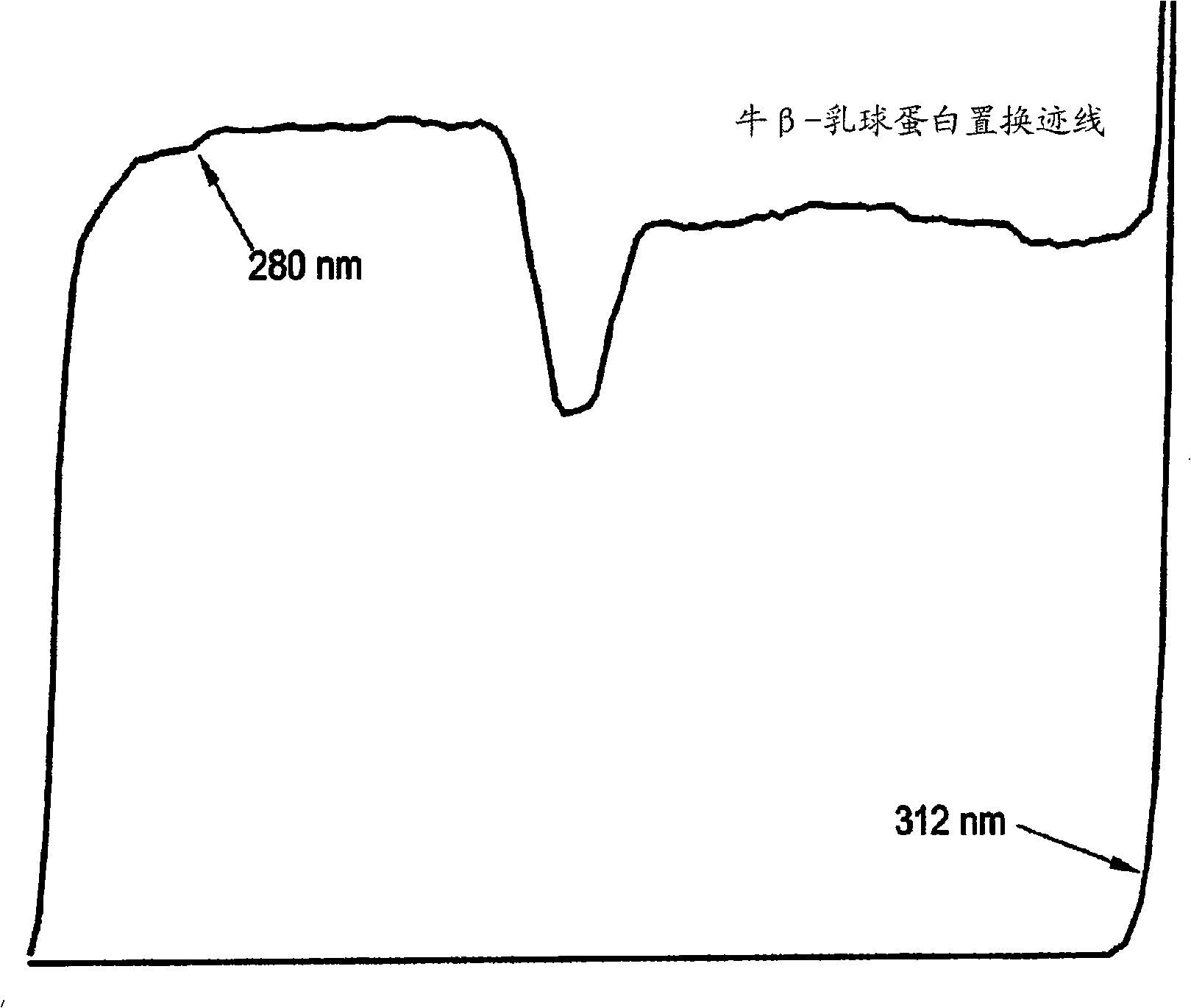
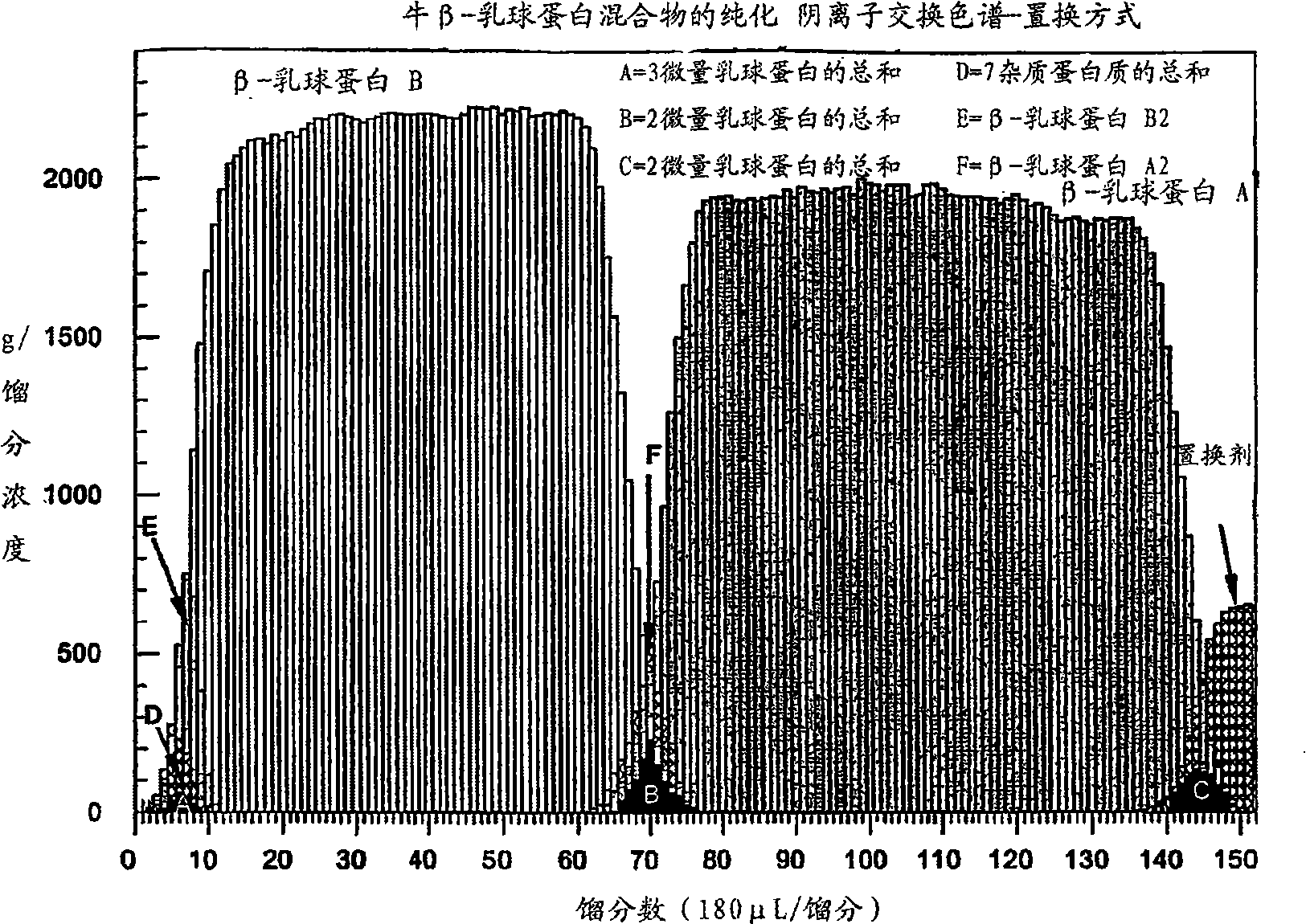
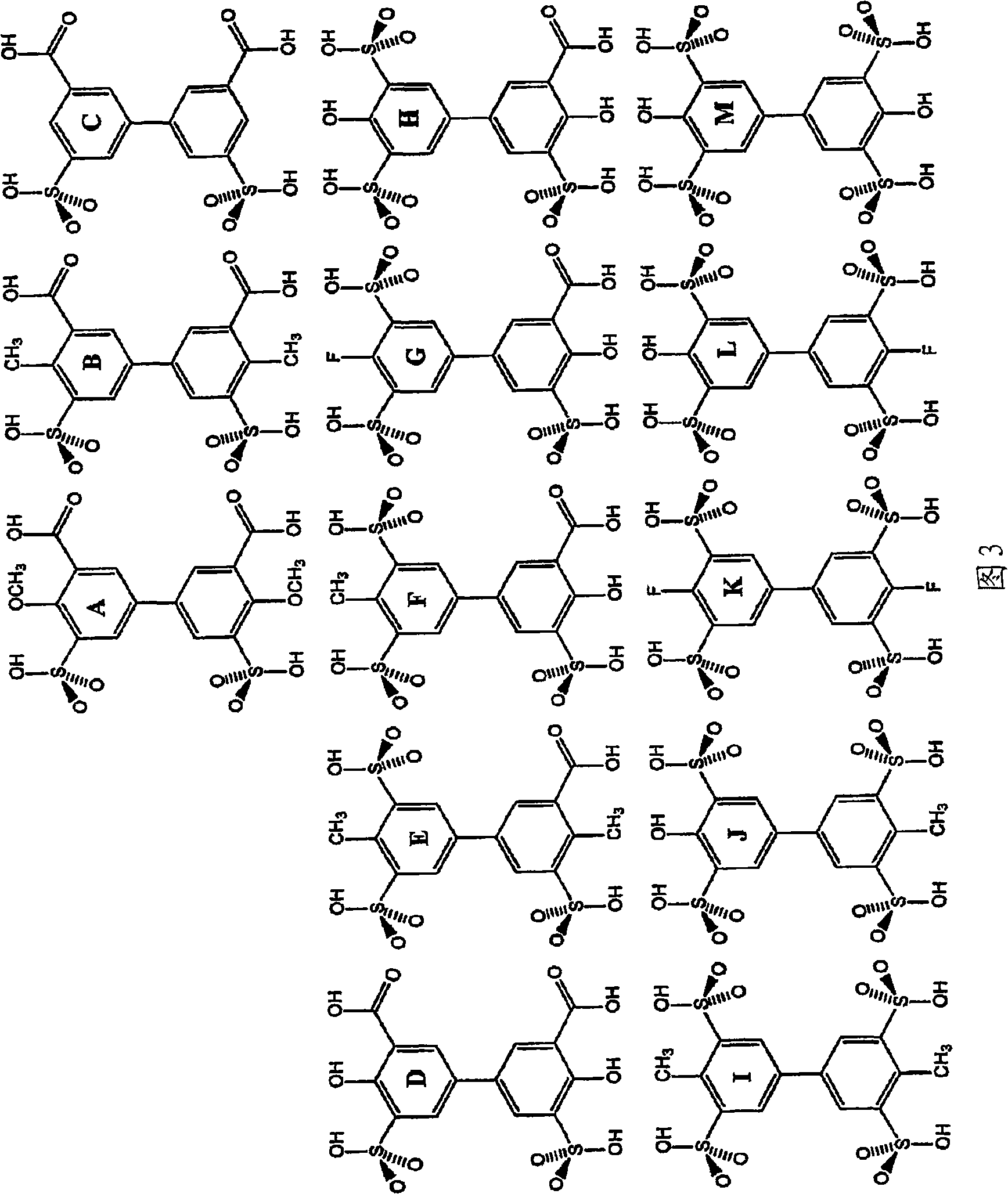
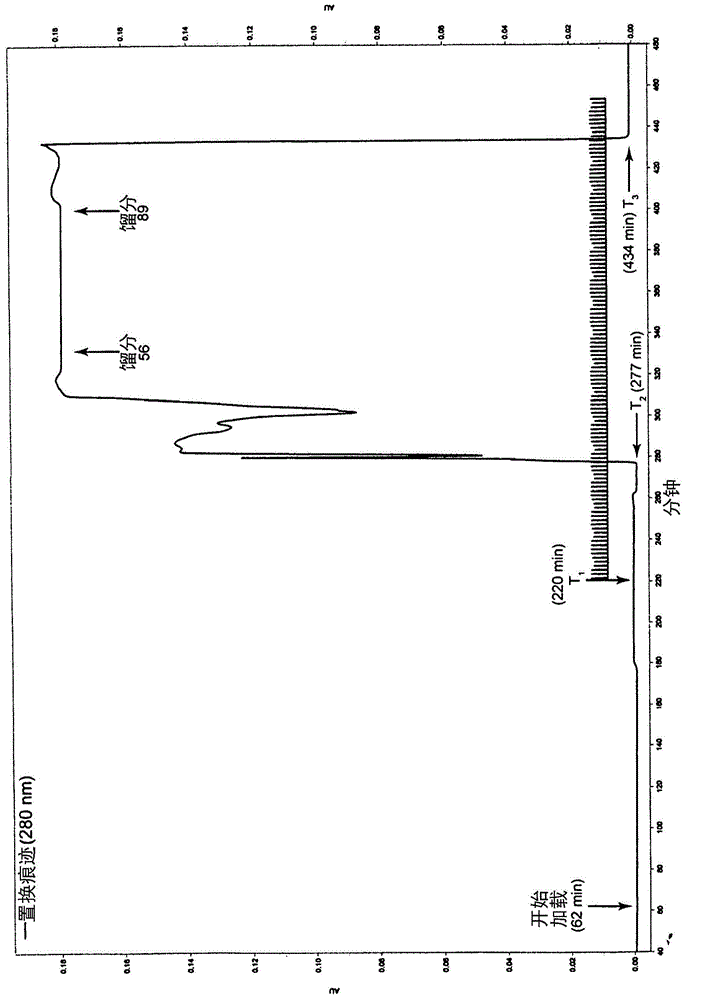
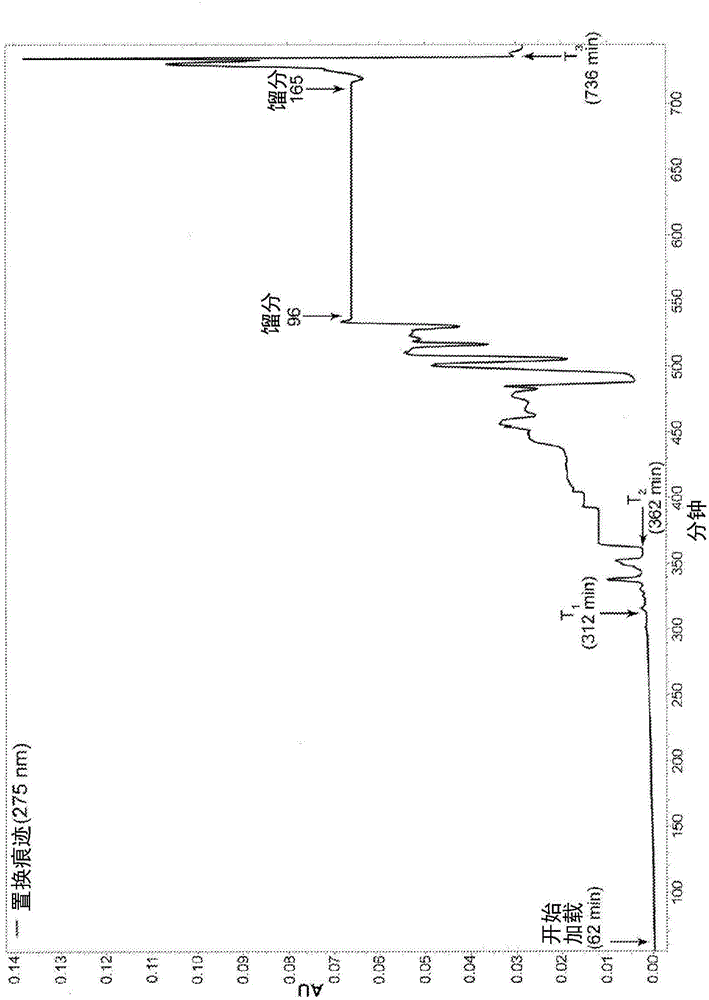
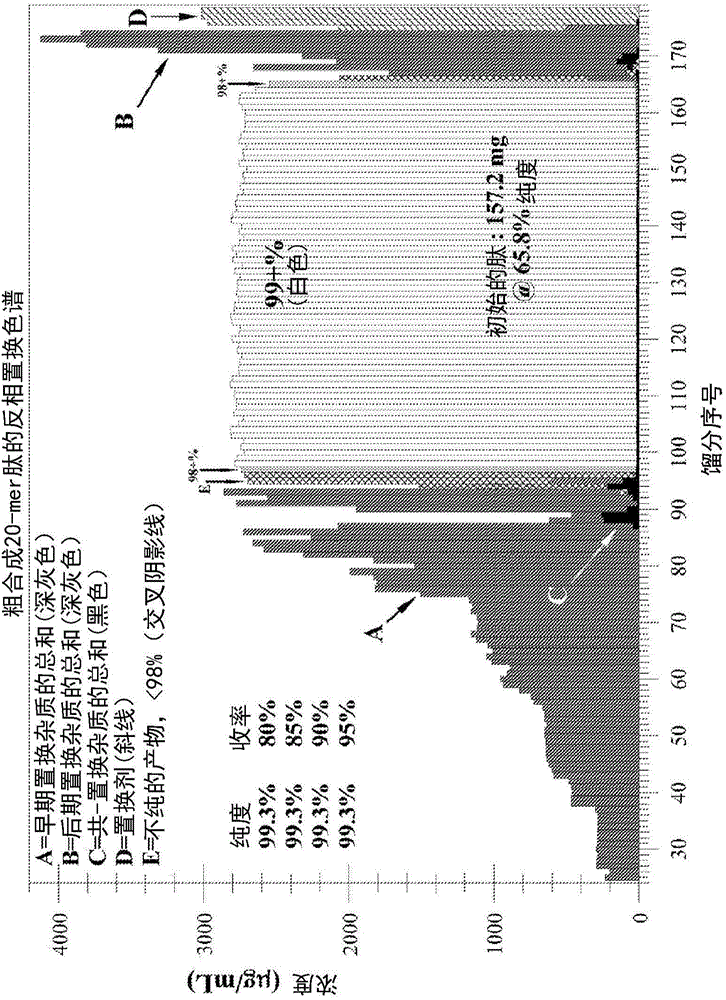
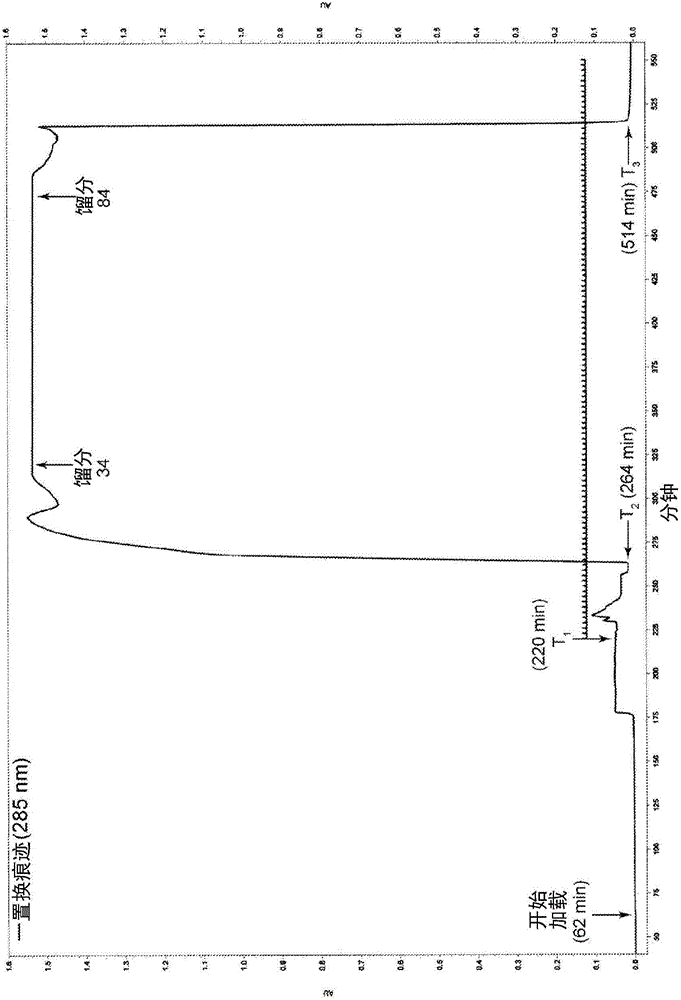
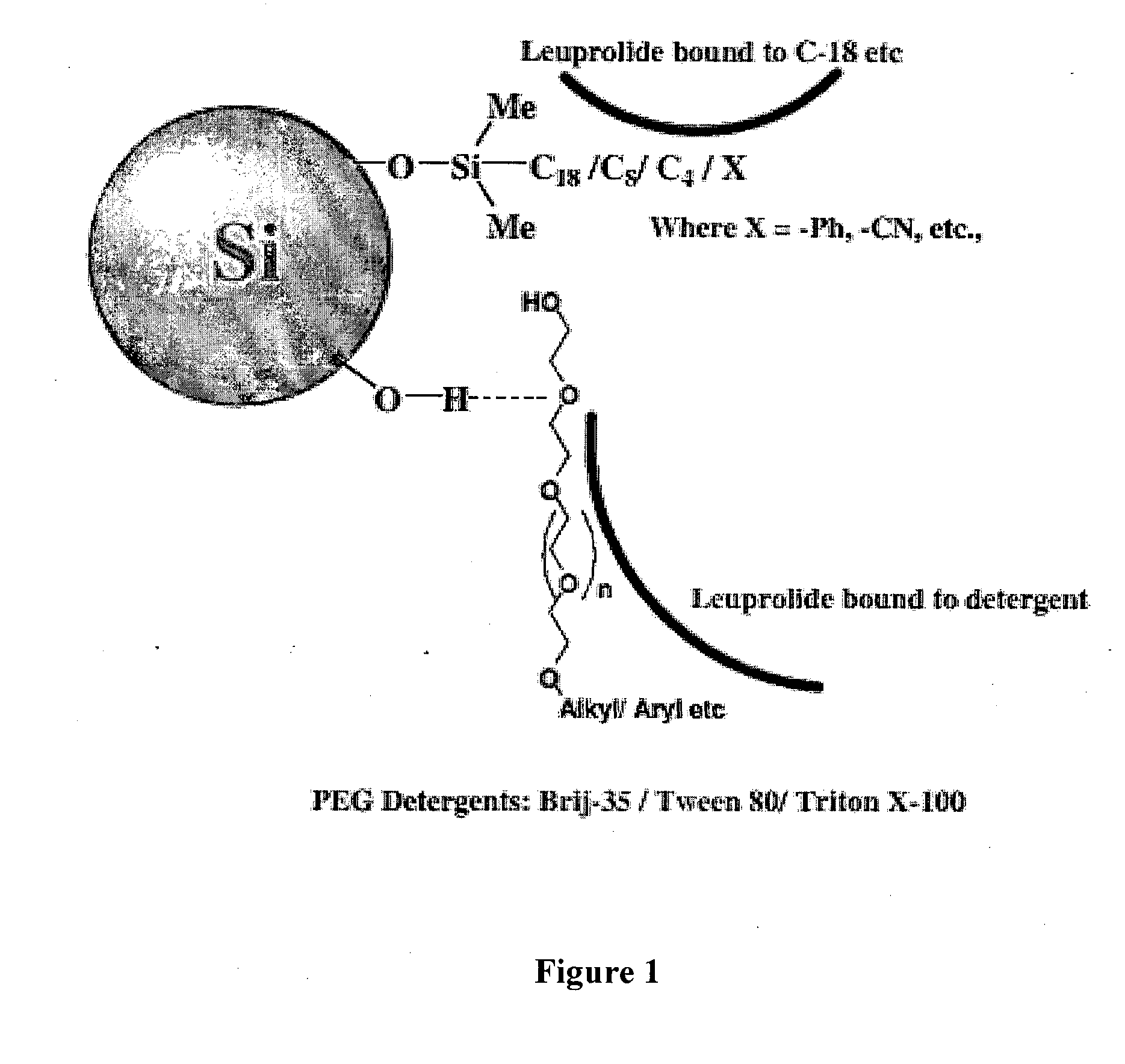
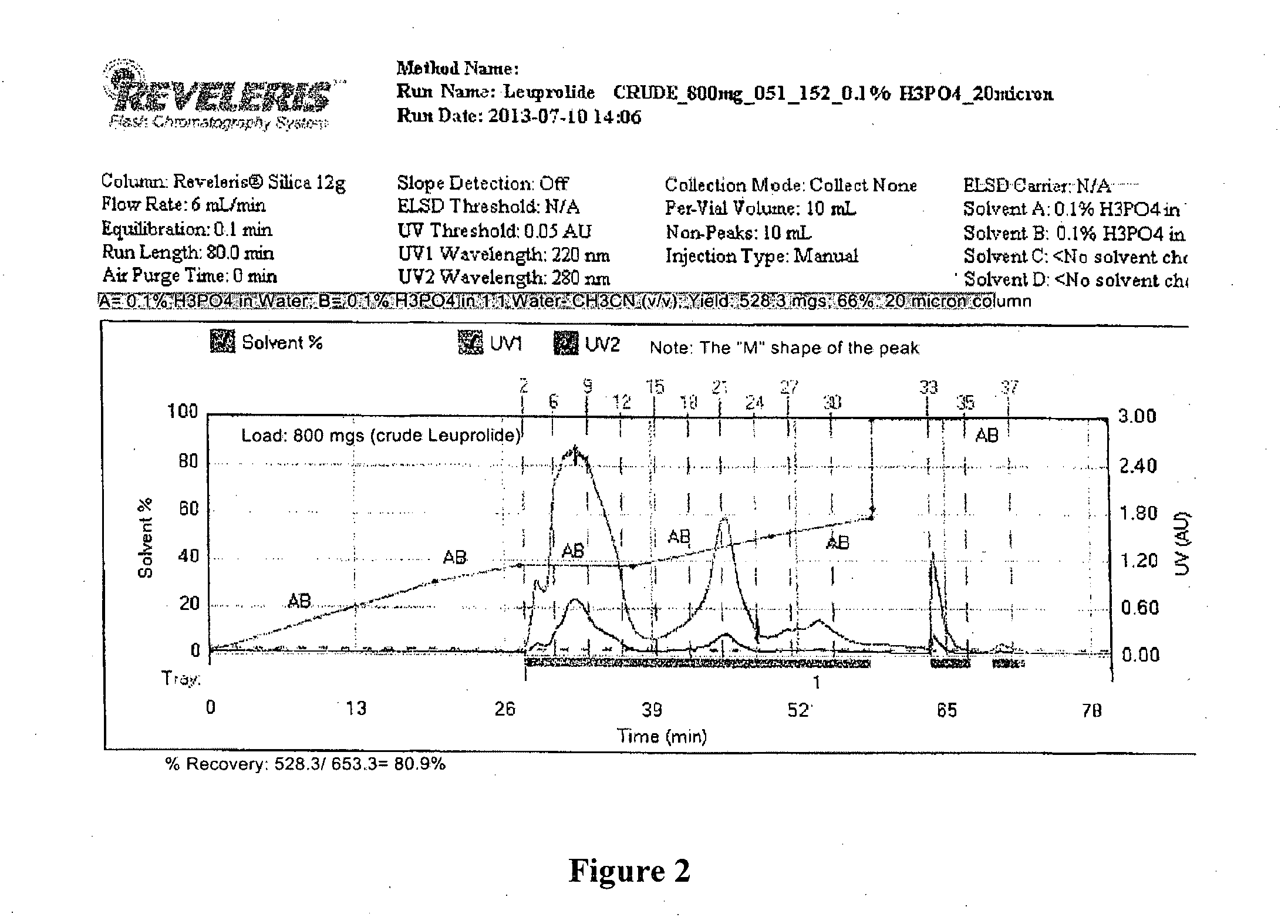
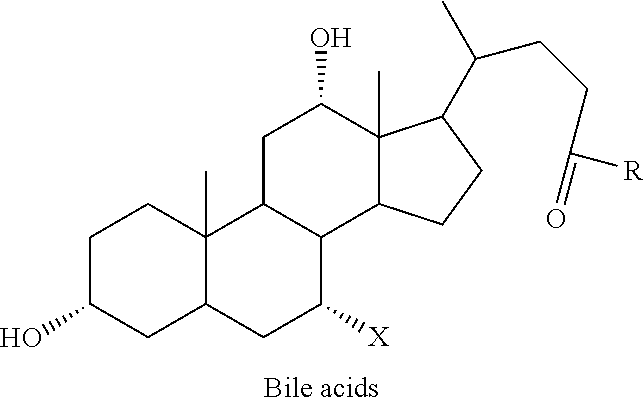
Patents
Literature
38 results about "Displacement chromatography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
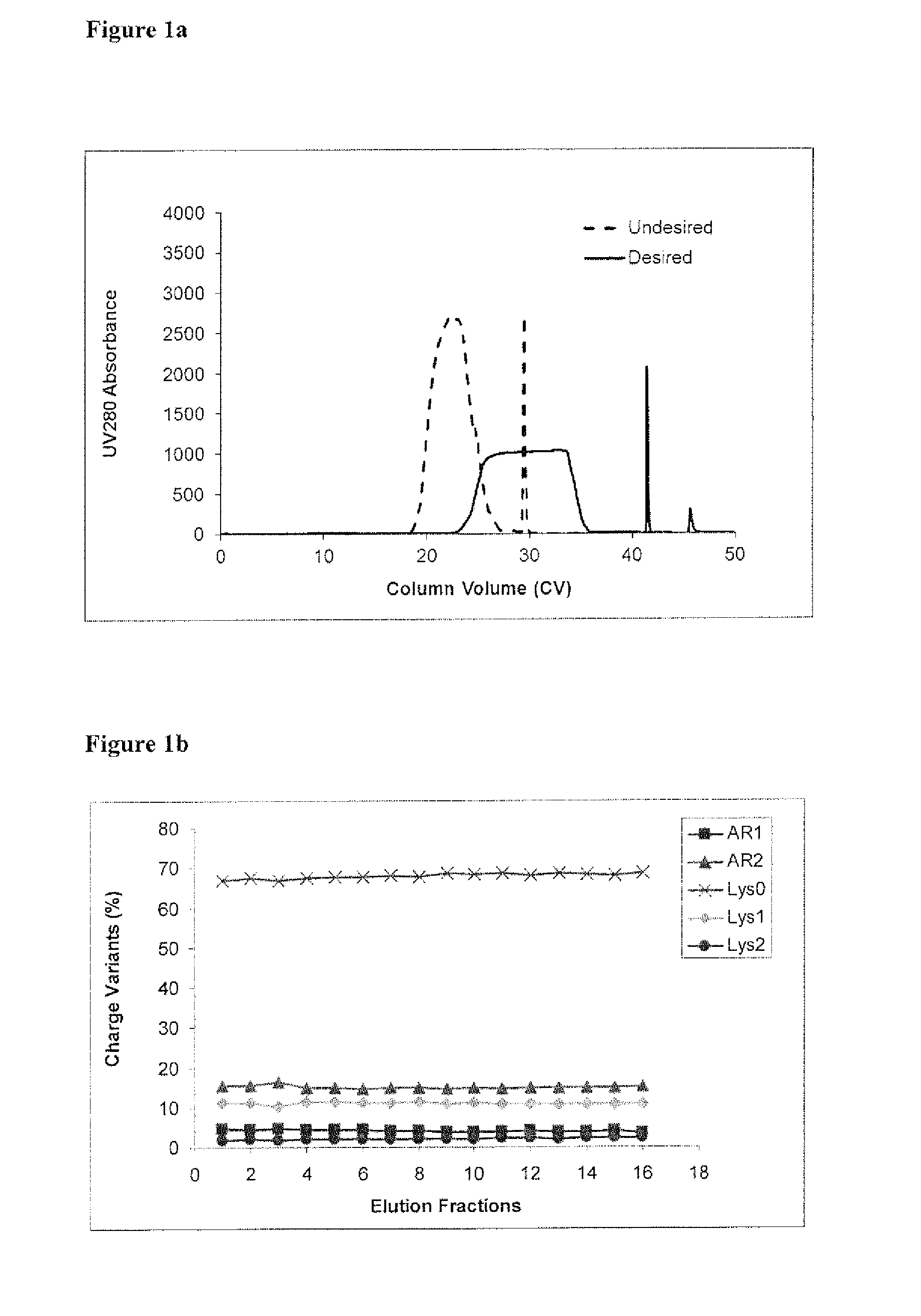
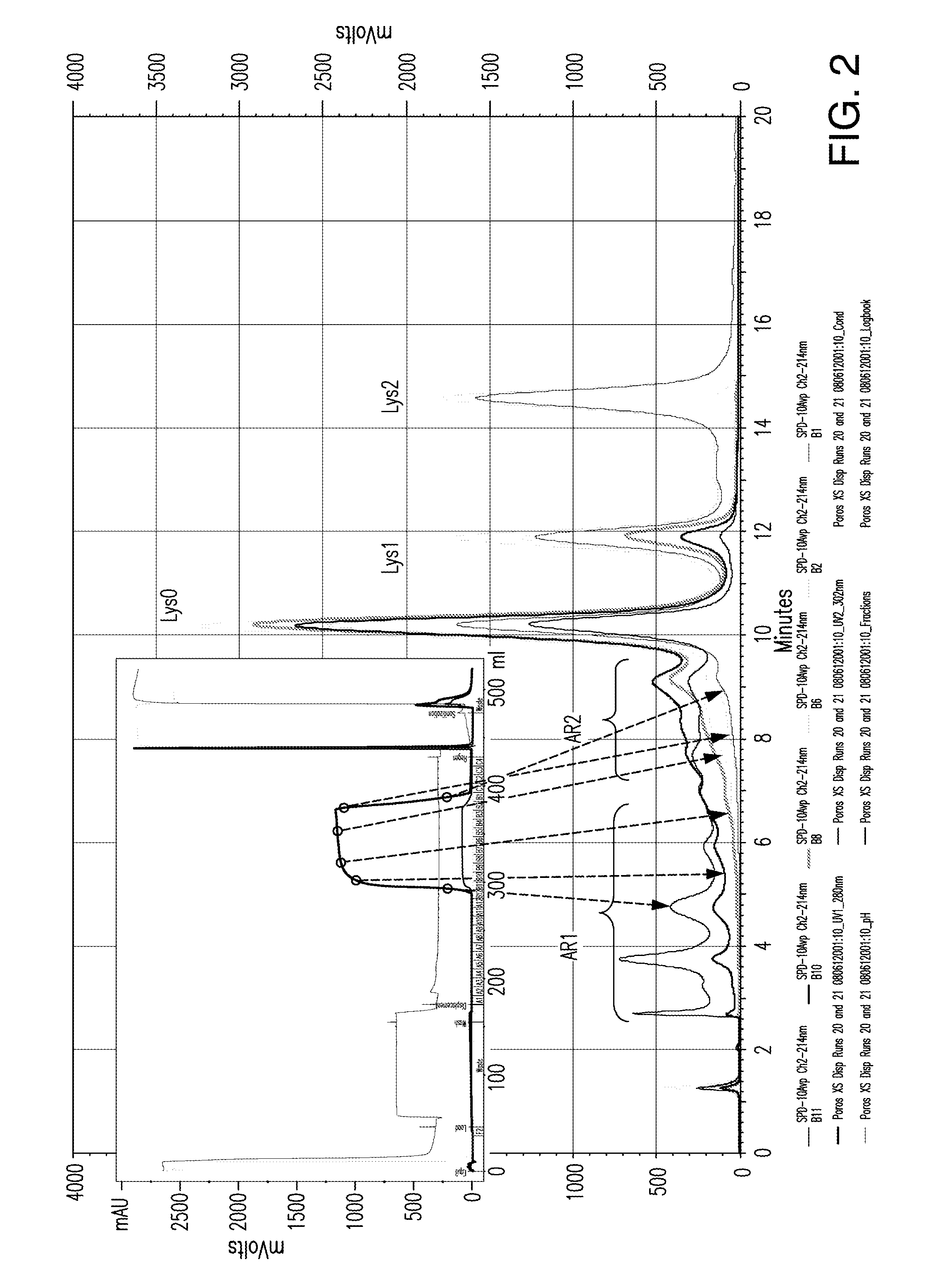
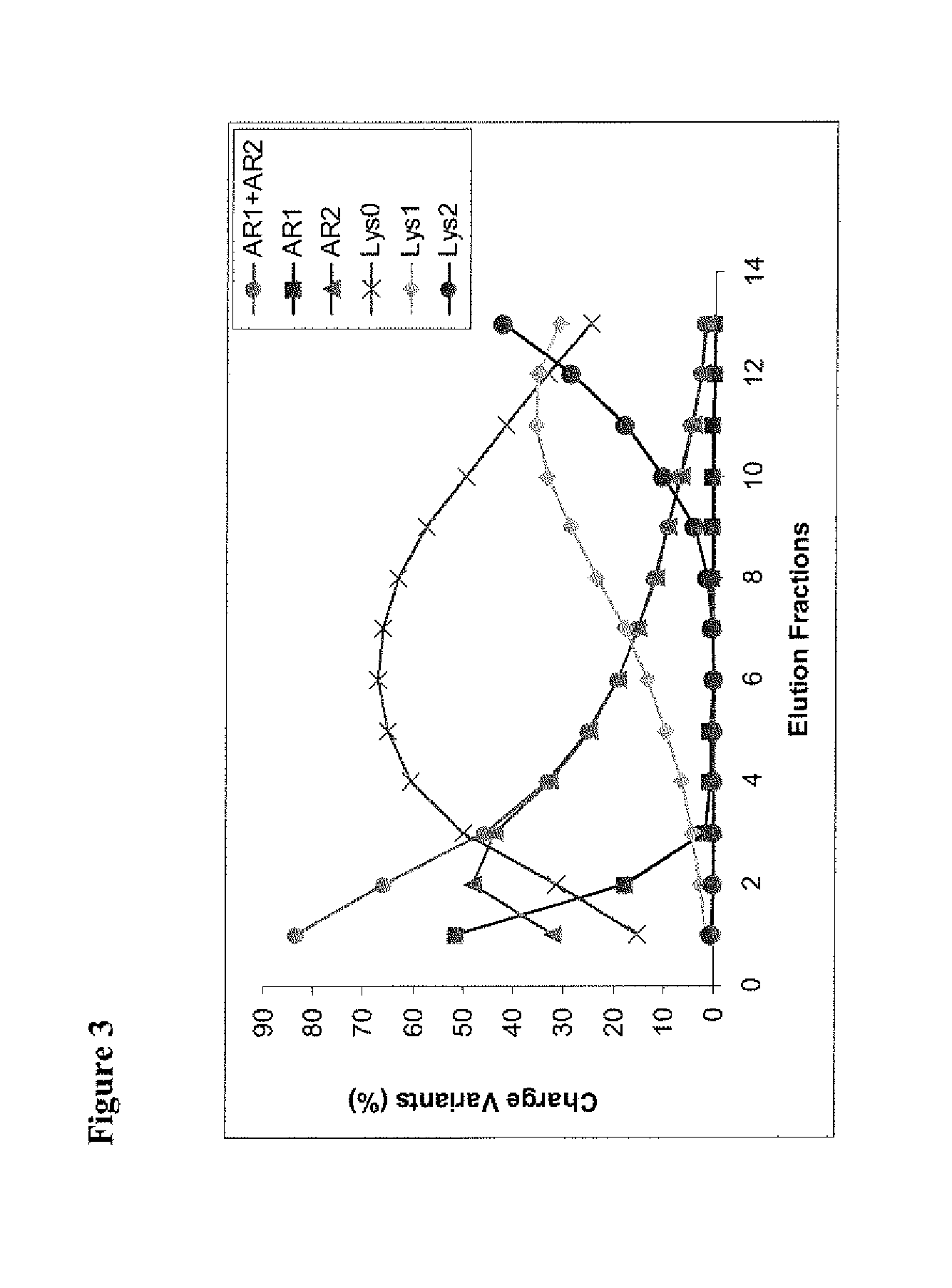
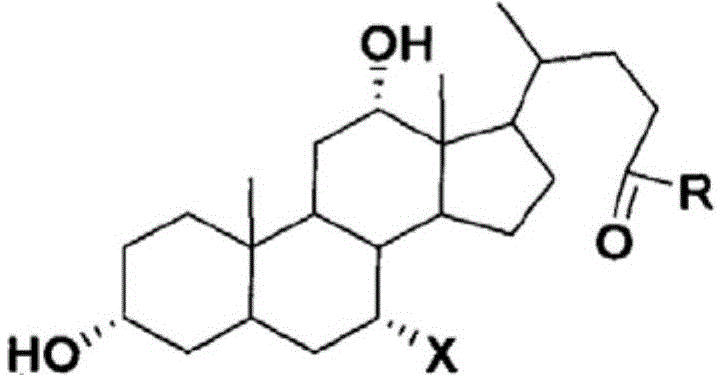
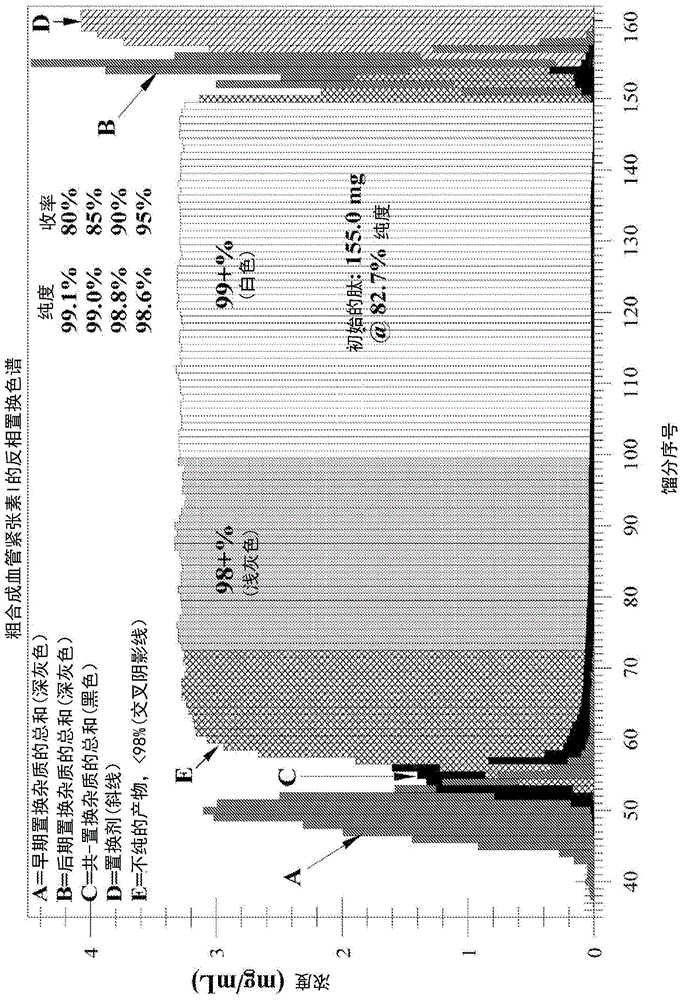
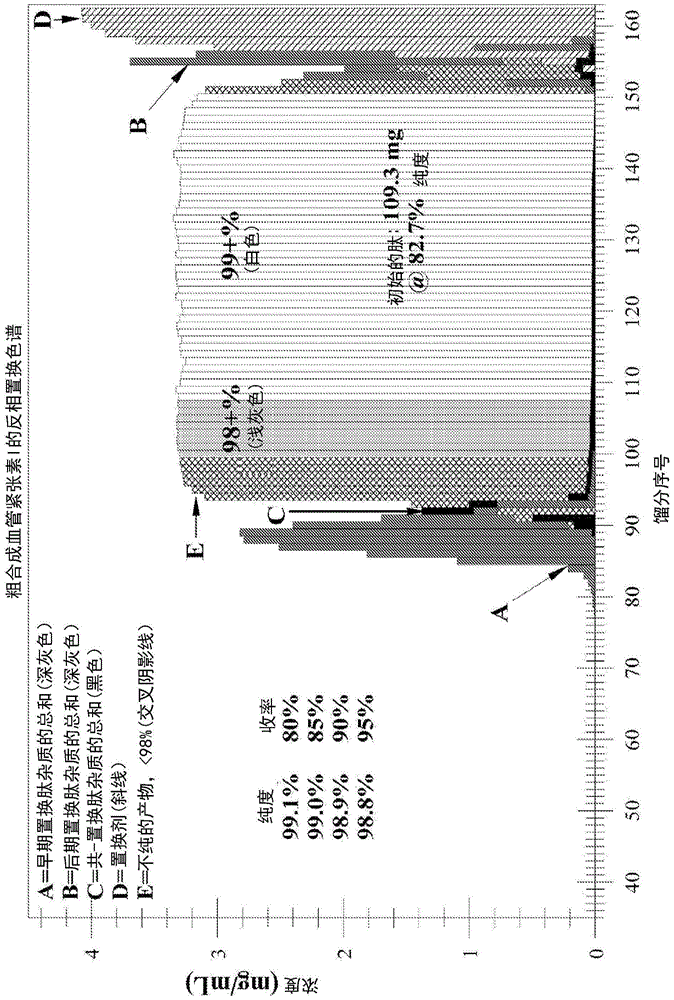
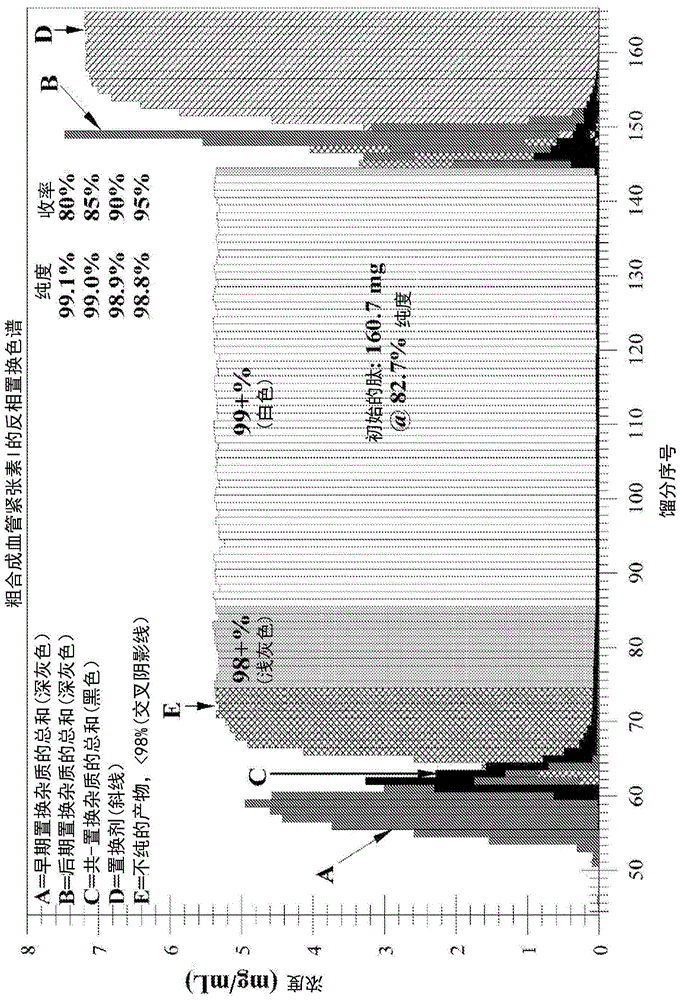
Displacement chromatography is a chromatography technique in which a sample is placed onto the head of the column and is then displaced by a solute that is more strongly sorbed than the components of the original mixture. The result is that the components are resolved into consecutive “rectangular” zones of highly concentrated pure substances rather than solvent-separated “peaks”. It is primarily a preparative technique; higher product concentration, higher purity, and increased throughput may be obtained compared to other modes of chromatography.
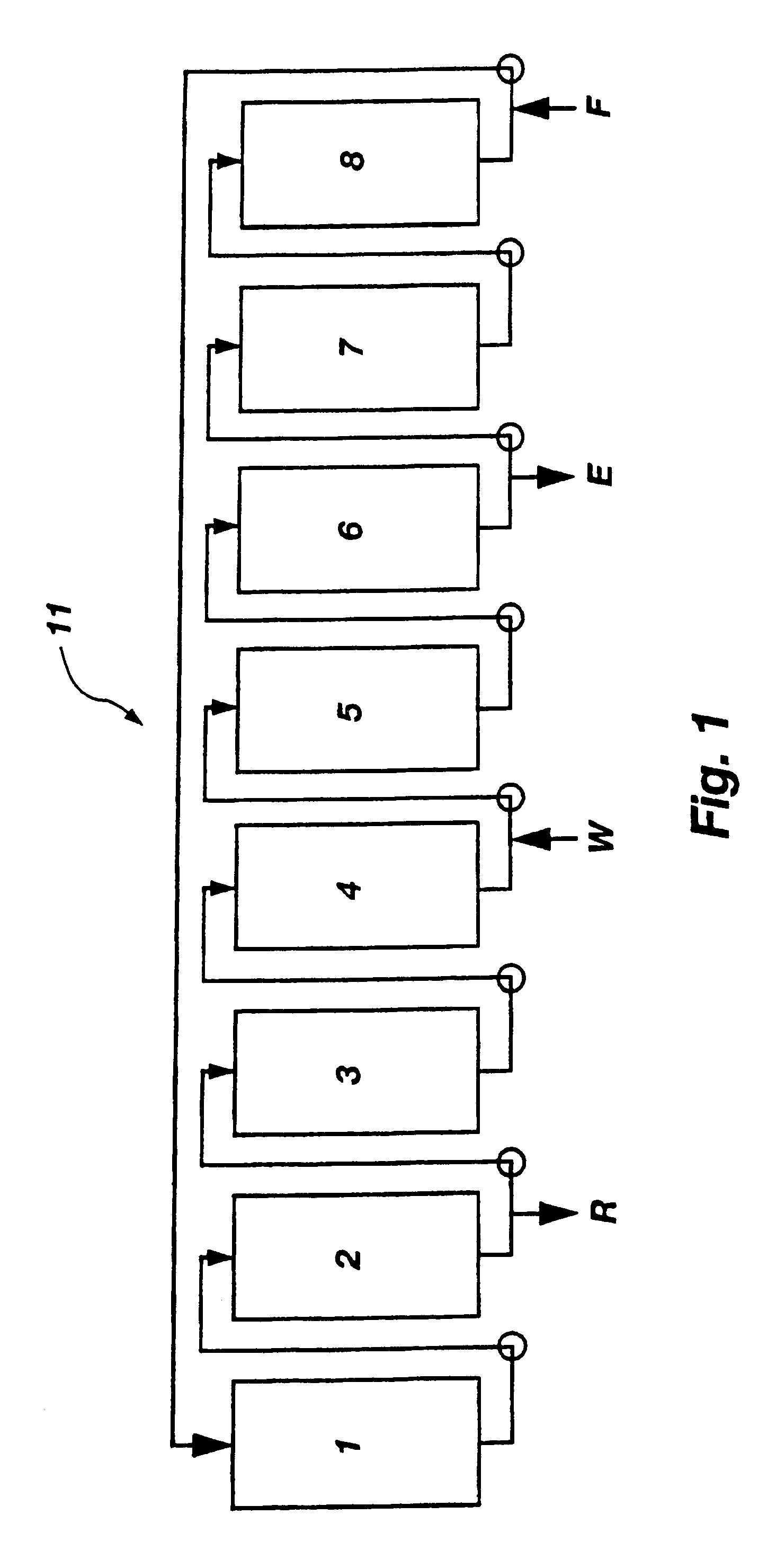
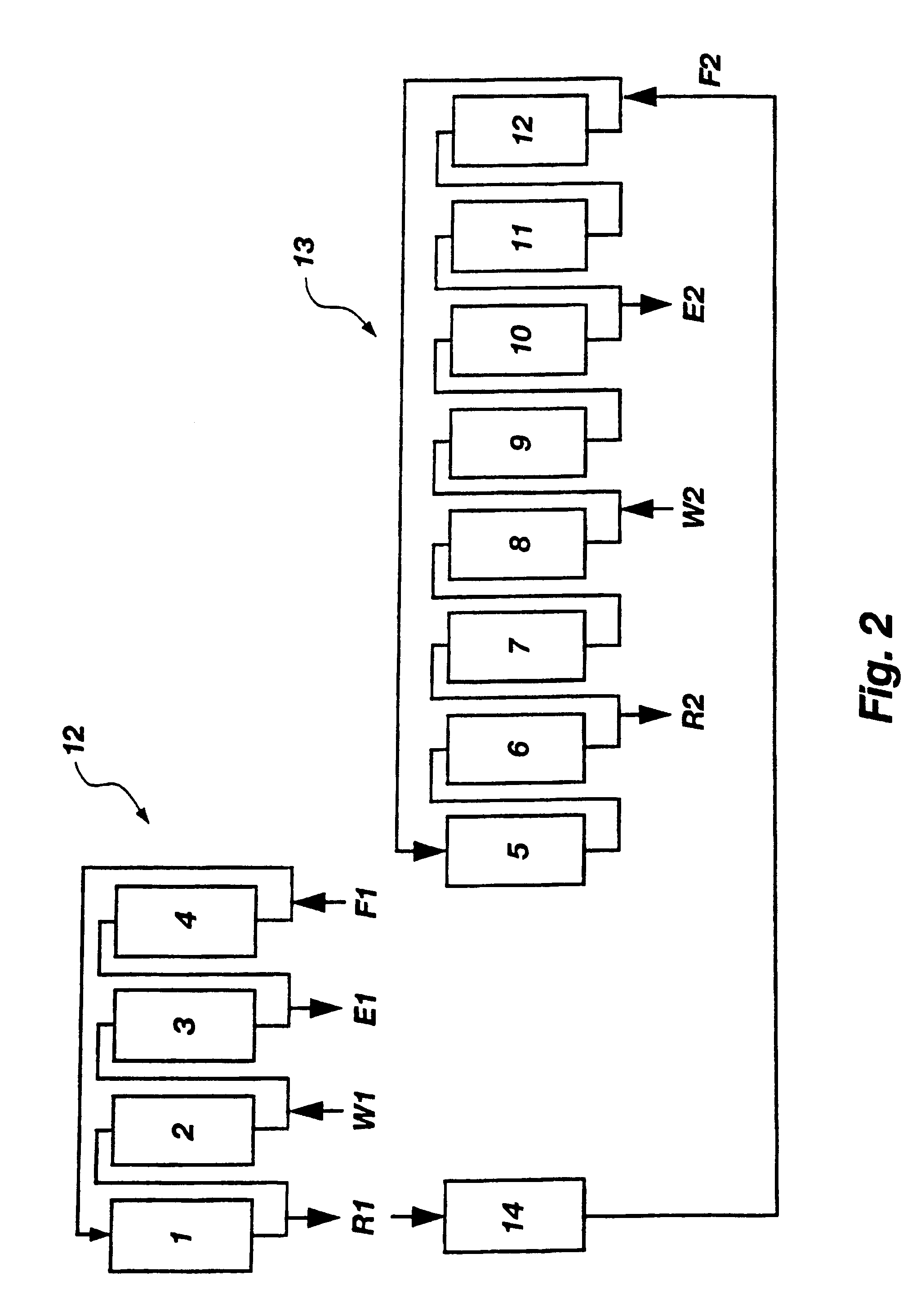
Method of displacement chromatography
InactiveUS6379554B1Efficient separationLower requirementIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatographic separationBetaine
A plurality of chromatographic separation operations, including a first simulated moving bed operation, are coupled into a process which functions, preferably through the application of continuous displacement chromatography, to recover a fraction rich in small organic molecules, notably betaine and / or invert from sucrose solutions, enabling the subsequent production of a high purity sucrose product.
Owner:AMALGAMATED RES
Method of displacement chromatography
InactiveUS6602420B2Efficient separationLower requirementIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatographic separationBetaine
A plurality of chromatographic separation operations, including a first simulated moving bed operation, are coupled into a process which functions, preferably through the application of continuous displacement chromatography, to recover a fraction rich in small organic molecules, notably betaine and / or invert from sucrose solutions, enabling the subsequent production of a high purity sucrose product.
Owner:AMALGAMATED RES
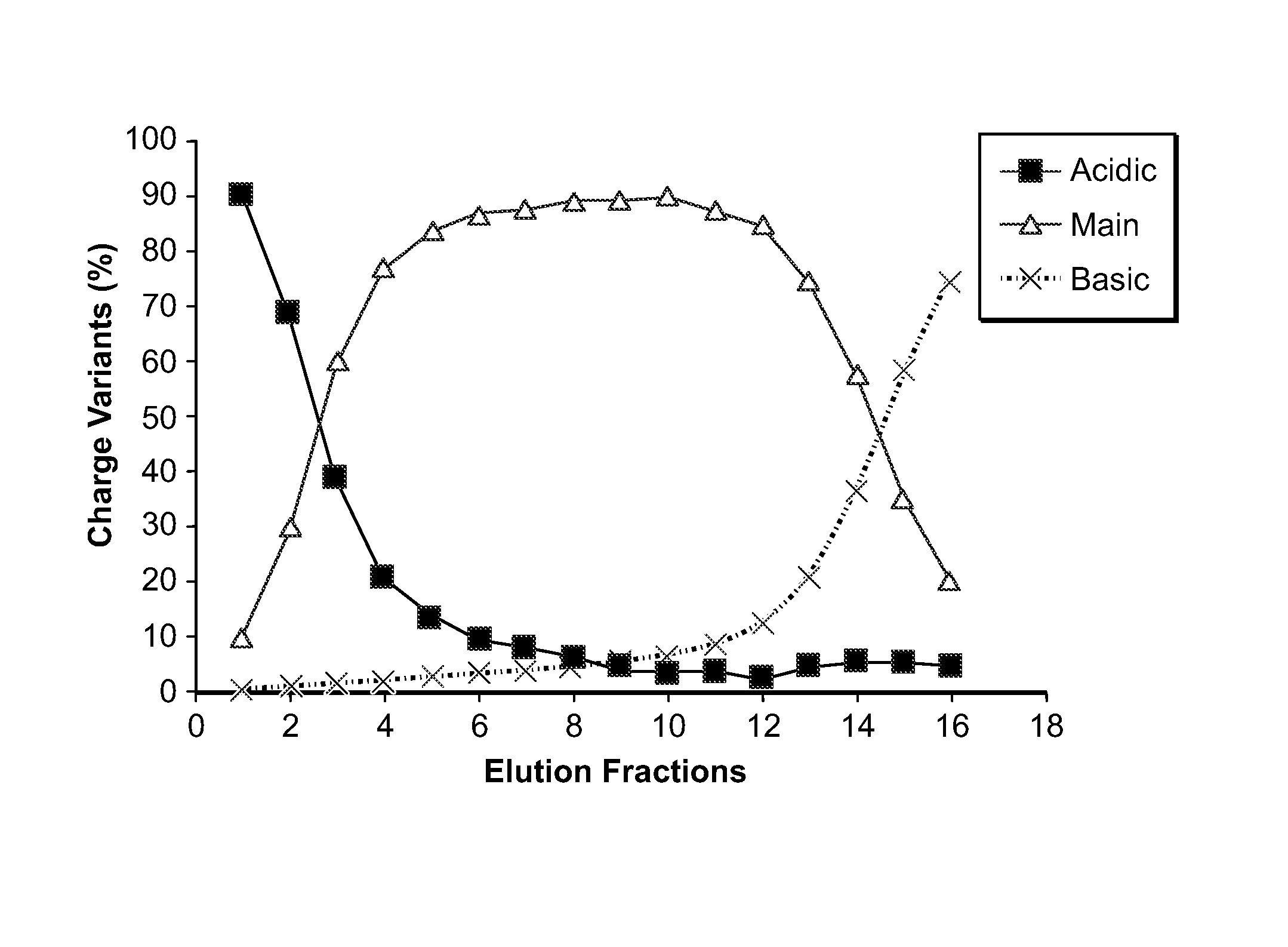
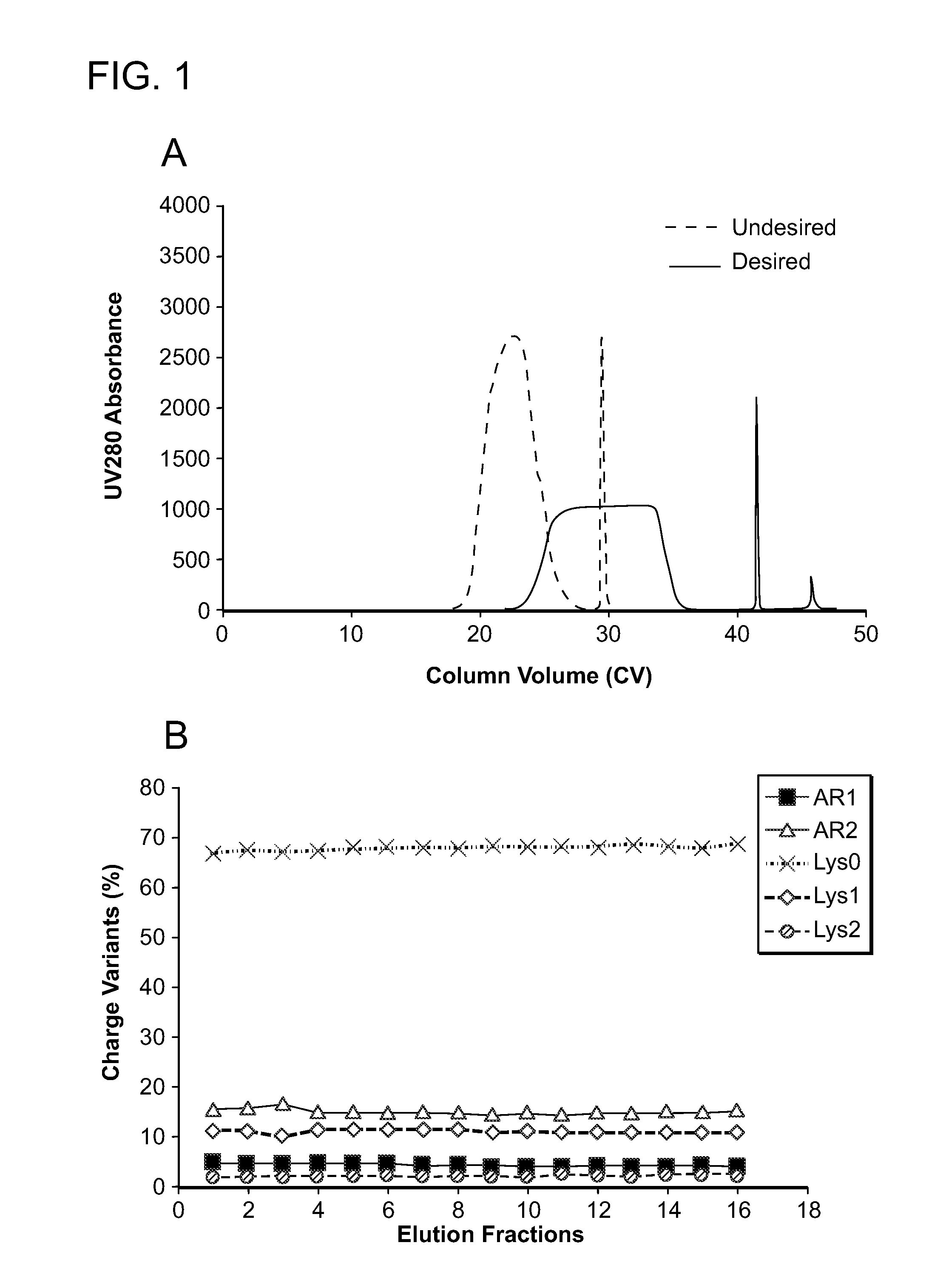
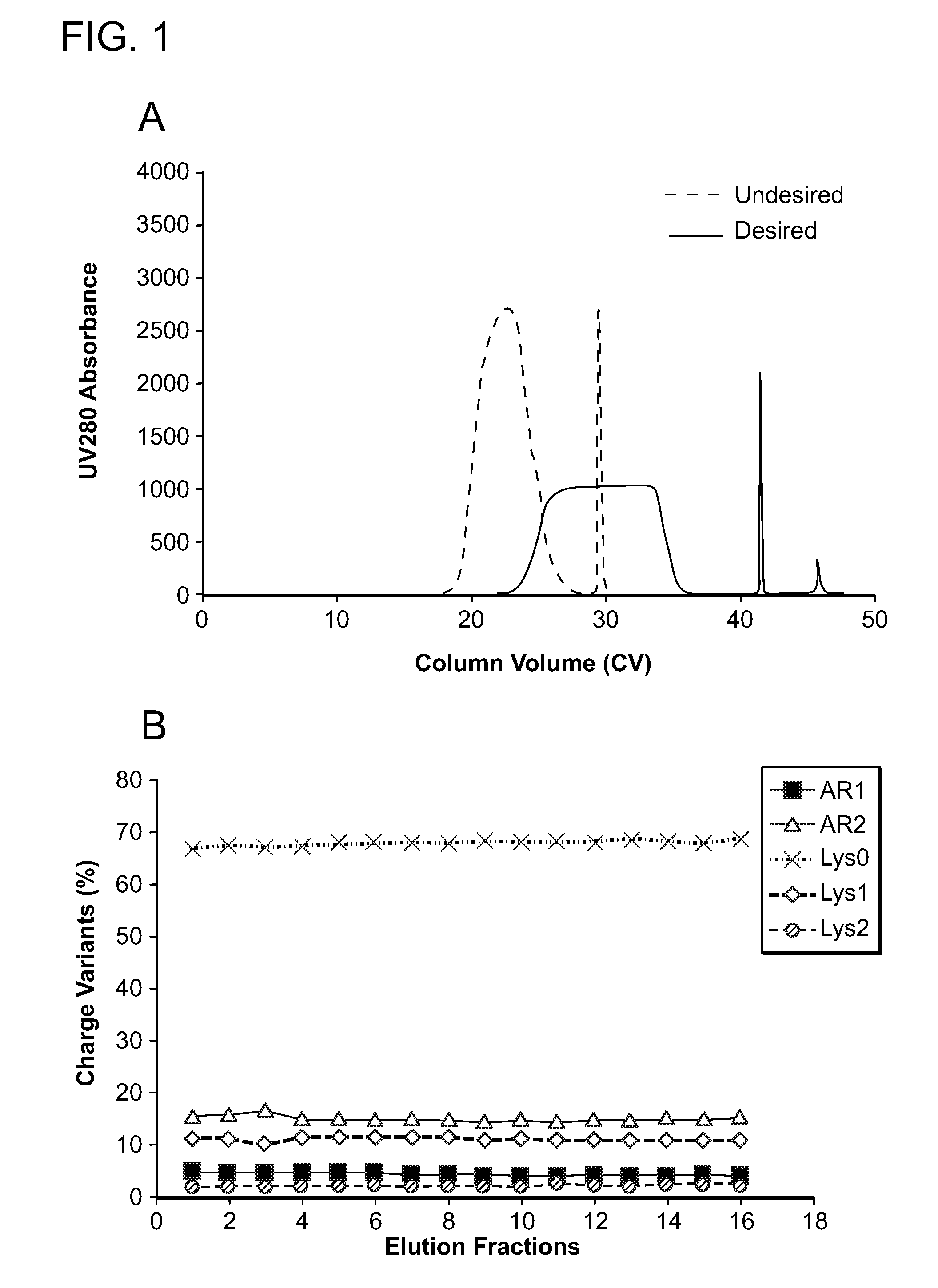
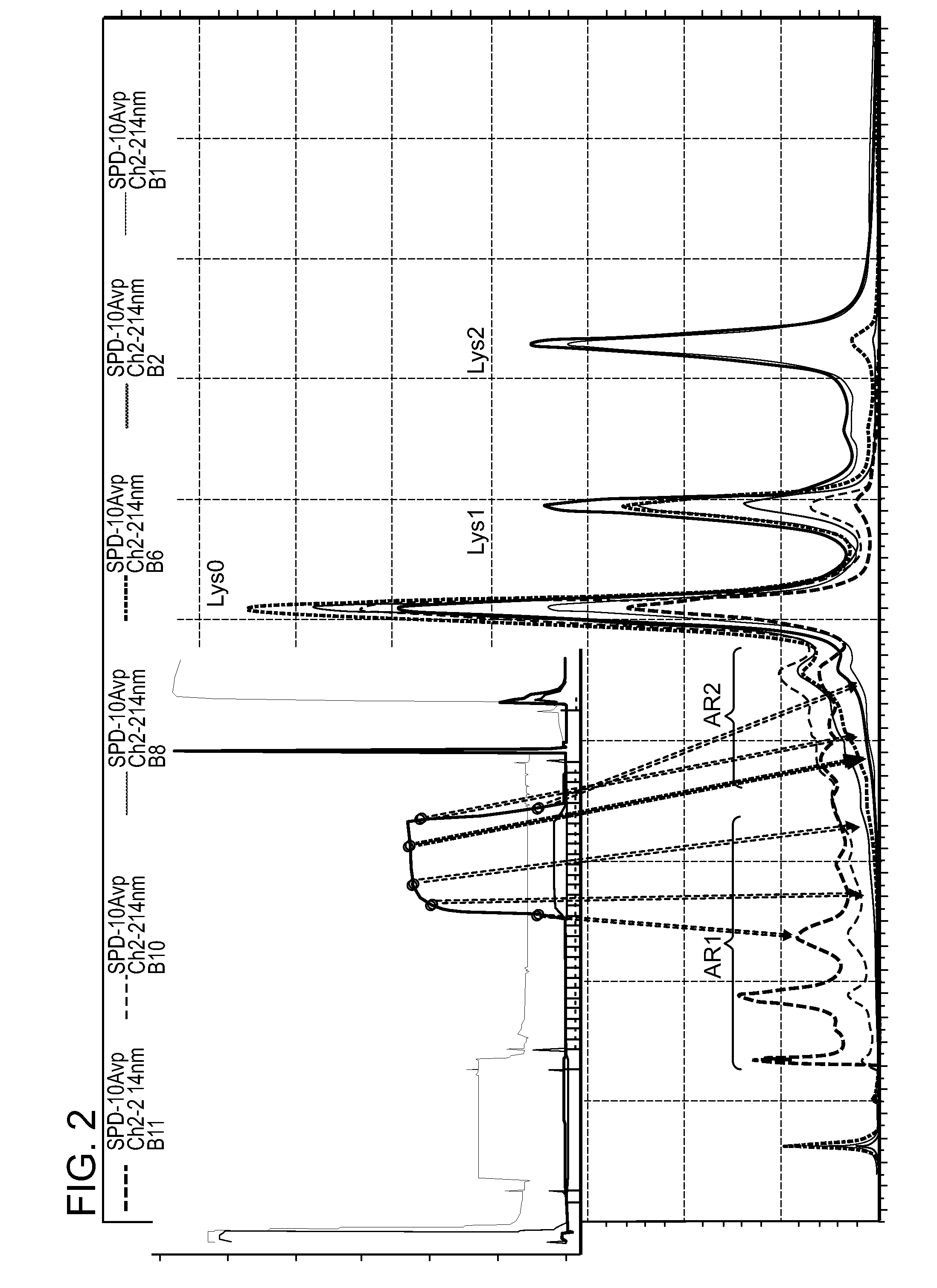
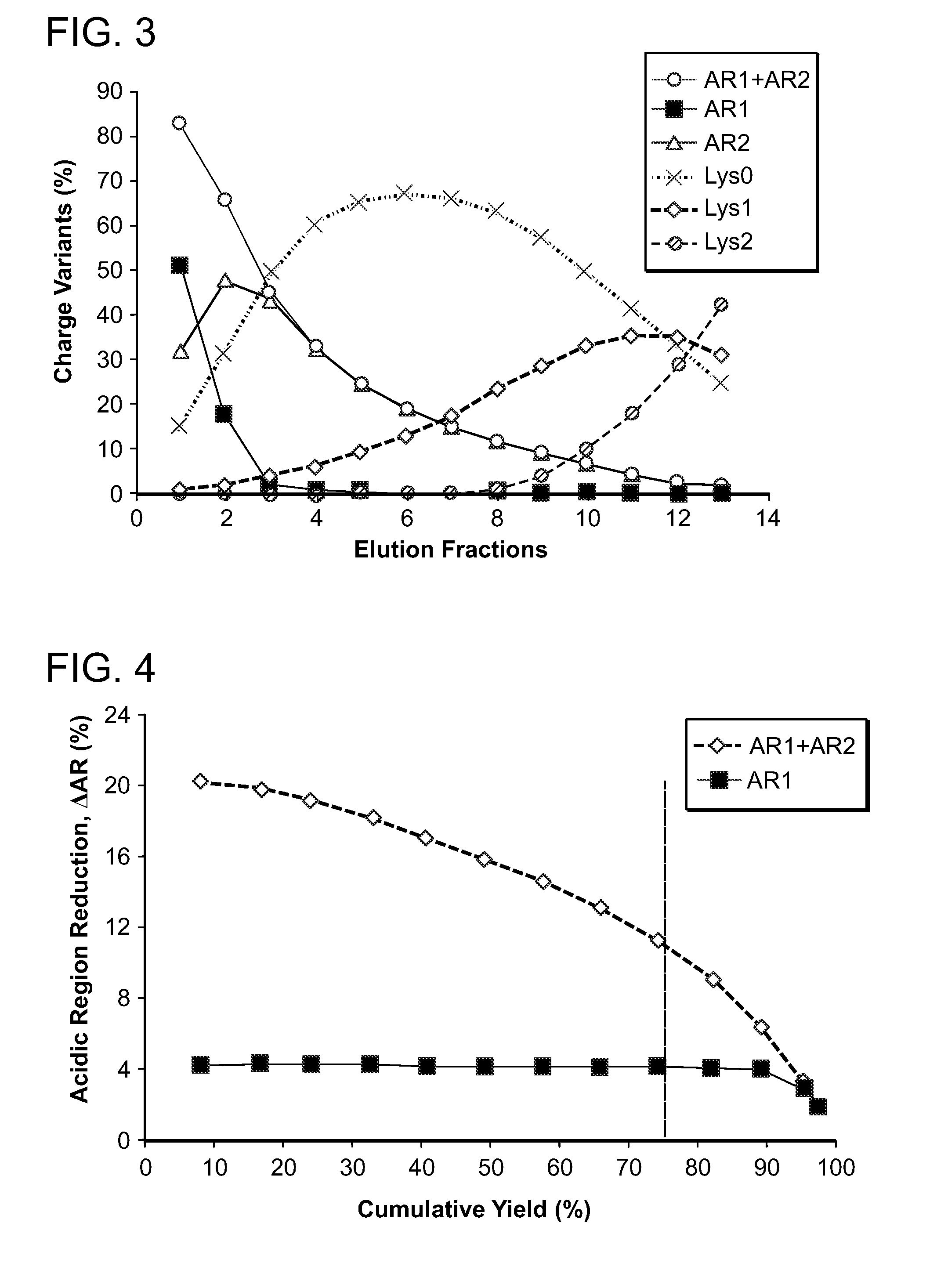
Low acidic species compositions and methods for producing and using the same using displacement chromatography
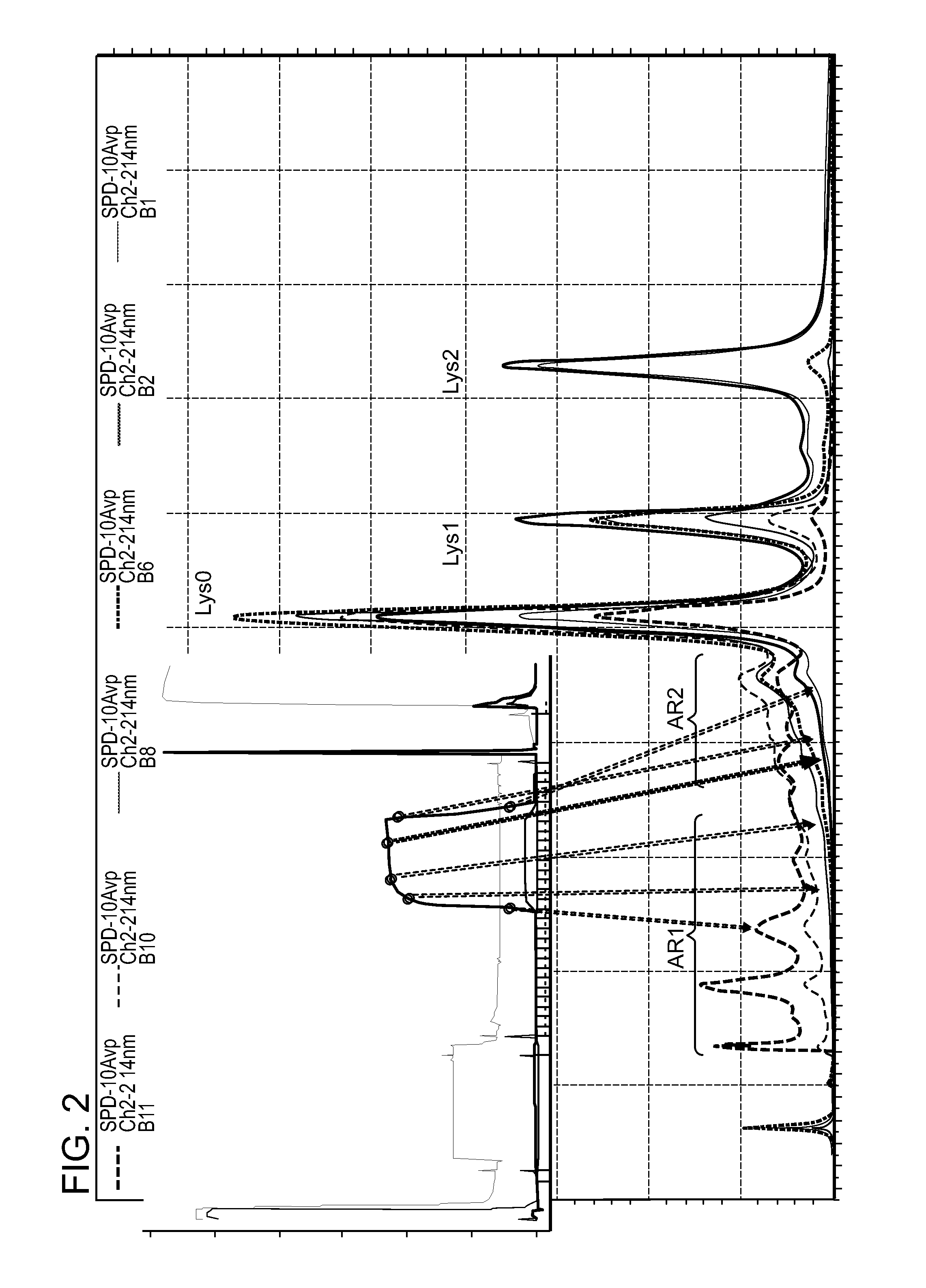
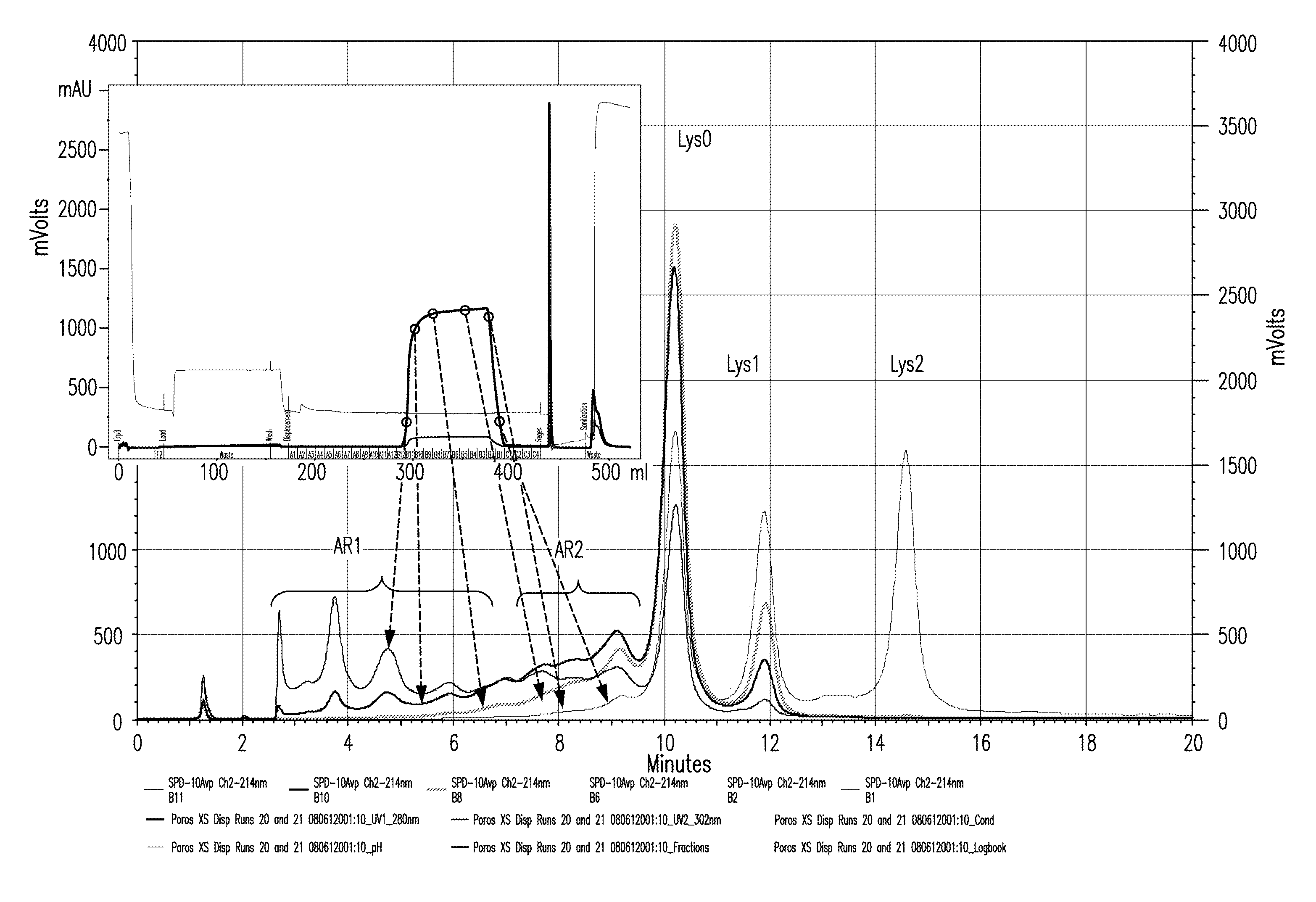
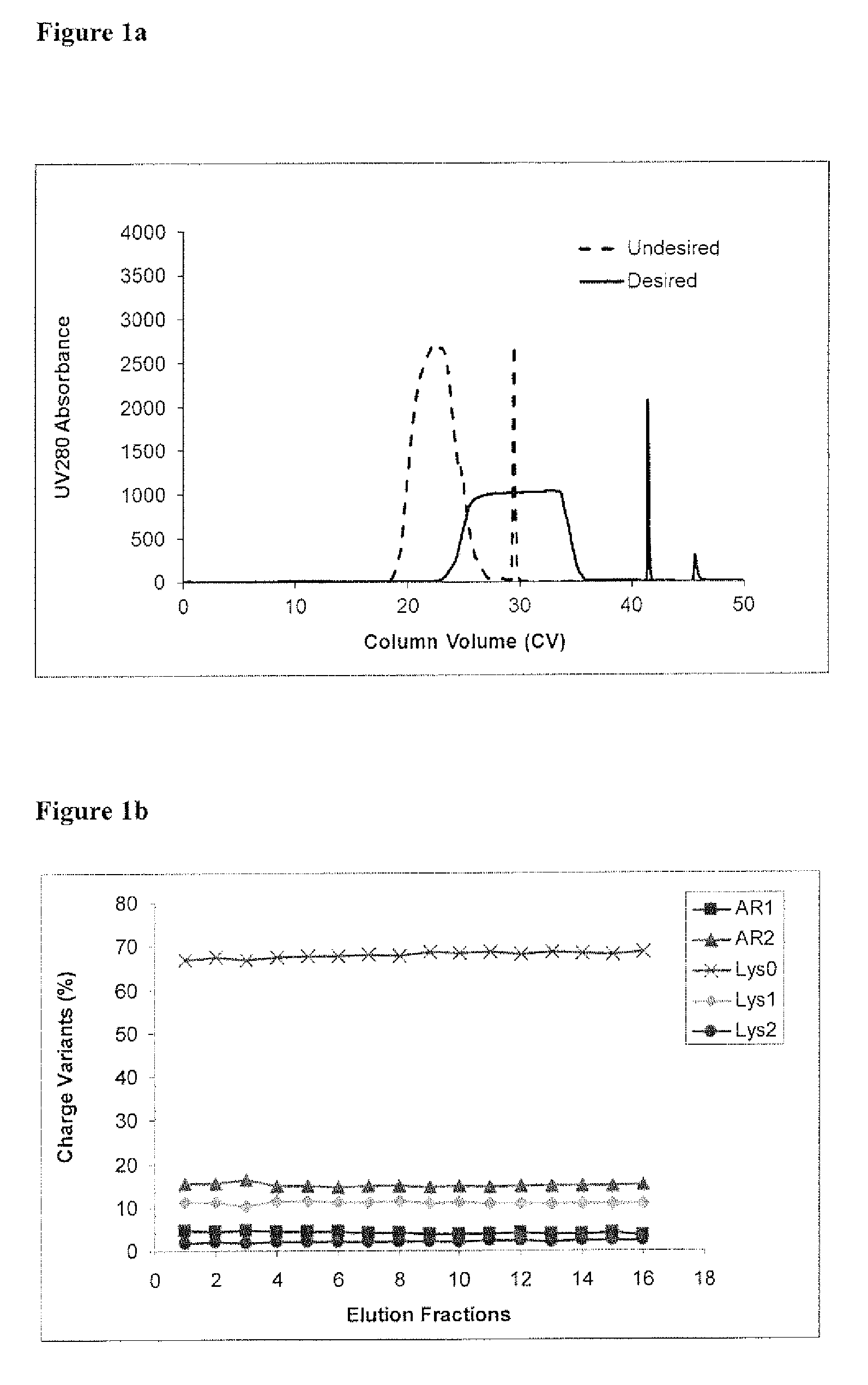
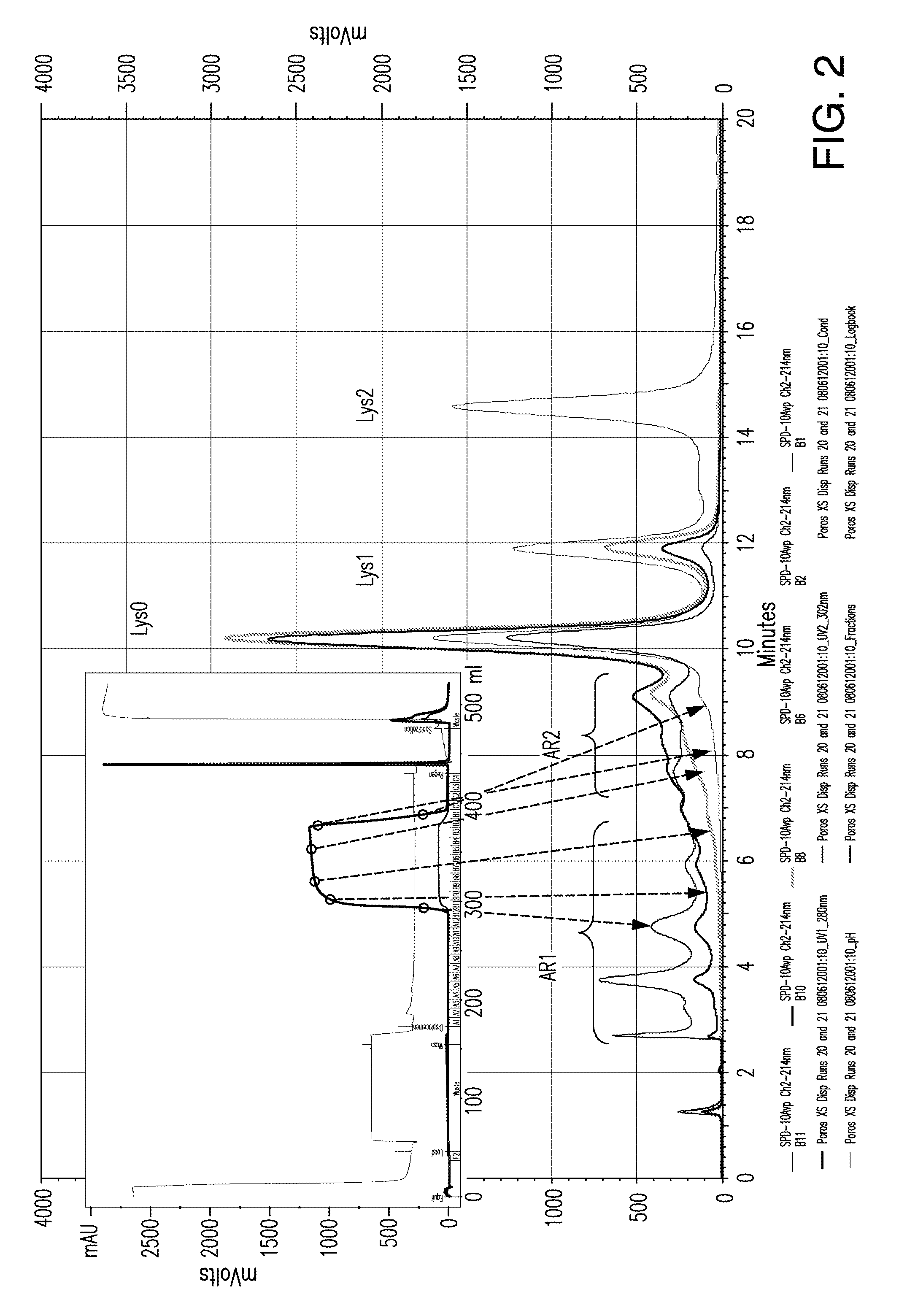
ActiveUS9017687B1Good curative effectGood biological propertiesTumor necrosis factorImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsAntigen bindingDisplacement chromatography
The present invention relates to low acidic species (AR) compositions comprising a protein, e.g., an antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, and methods for producing such low AR compositions using displacement chromatography. Methods for using such compositions to treat a disorder, e.g., a disorder in which TNFα is detrimental, are also provided.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Protein purification using displacement chromatography
ActiveUS9067990B2Easy to identifyImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsPeptide preparation methodsDisplacement chromatographyProtein purification
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Protein purification using displacement chromatography
ActiveUS20140275494A1Easy to identifyIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationDisplacement chromatographyProtein purification
Owner:ABBVIE INC
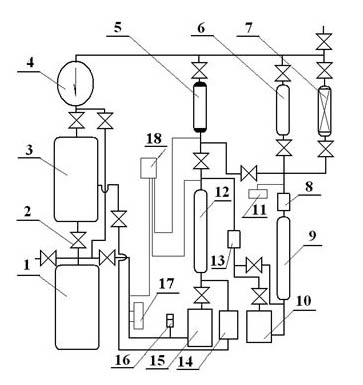
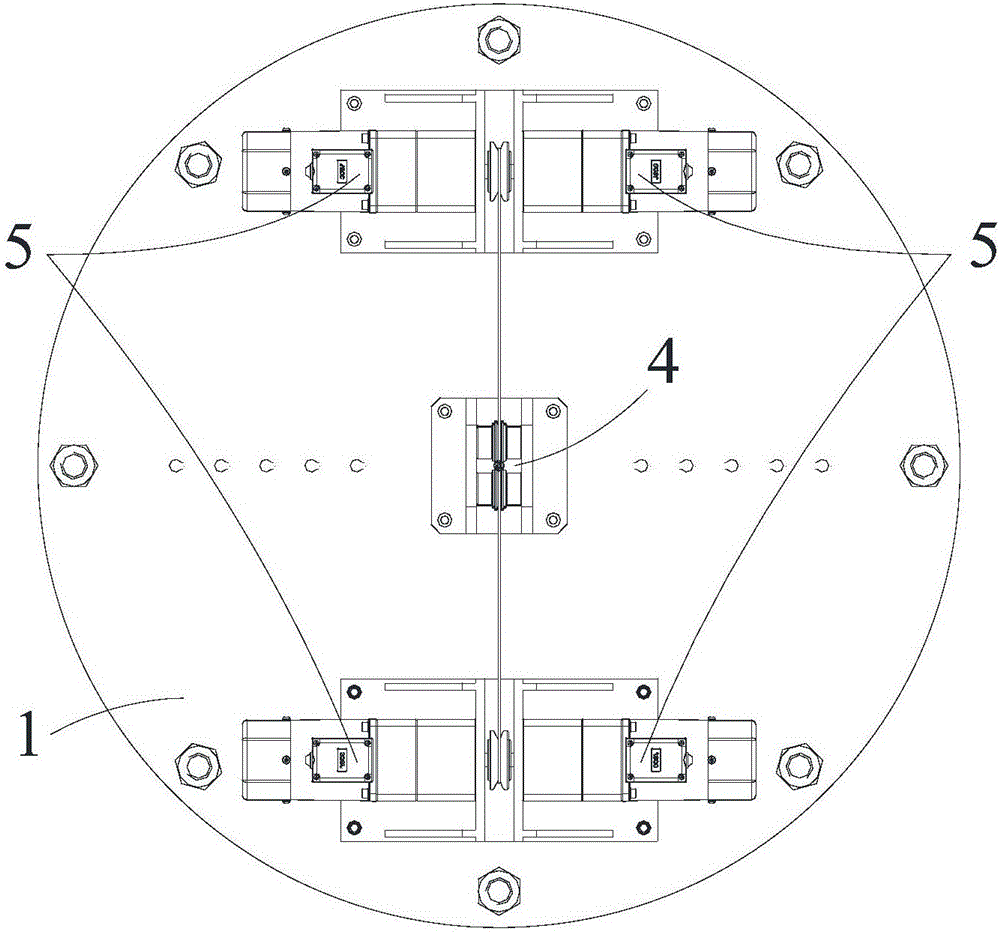
Low-temperature displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device and method
ActiveCN101850215AAchieving Self-Displacement ChromatographyOvercome the disadvantage of low separation coefficientCation exchanger materialsOrganic anion exchangersSeparation factorGas release
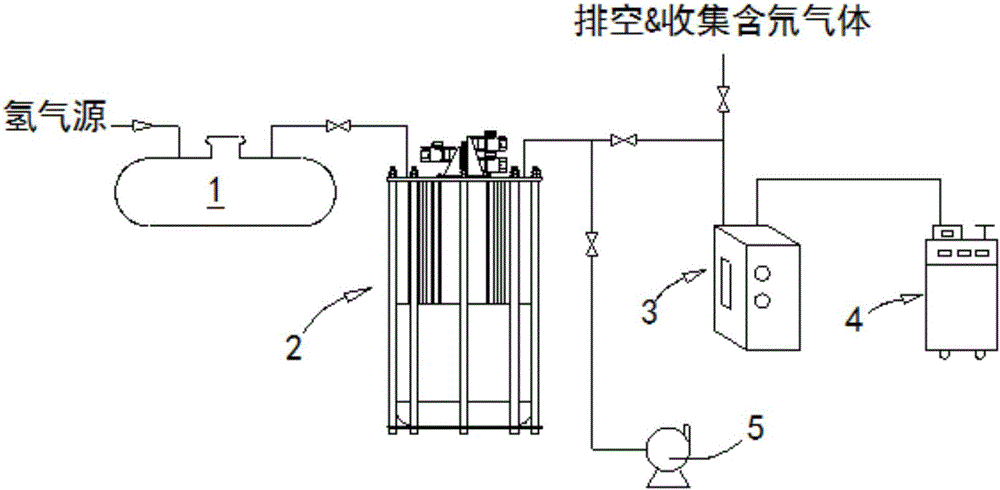
The invention provides a low-temperature displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device and a method. The invention makes the mixed gas of hydrogen isotope gas and helium after being cooled sequentially pass through a cooled main separation column and a cooled product gas collecting column which are filled with granulate palladium-loaded aluminum trioxide (Al2O3 / Pd) to obtain the product gas rich in heavy isotope components of deuterium and tritium; a hot helium flow passes through and heats the main separation column so as to make the released gas sequentially pass through the cooled secondary separation column and the product gas collecting column which are filled with granulate palladium-loaded aluminum trioxide (Al2O3 / Pd) to obtain the product gas rich in heavy isotopecomponents of deuterium and tritium; after the product gas is collected, middle rich gas flowing out from the secondary separation column is directly fed back into a raw material gas tank; and after the middle rich gas feedback process is accomplished, the main separation column and the secondary separation column are heated, and the gas released by heating is collected via a tail gas collecting column. The separation device has simple structure, reasonable separation process, and low cost for the construction and operation of the device. The invention has higher separation factor for hydrogen isotope separation.
Owner:SICHUAN INST OF MATERIALS & TECH
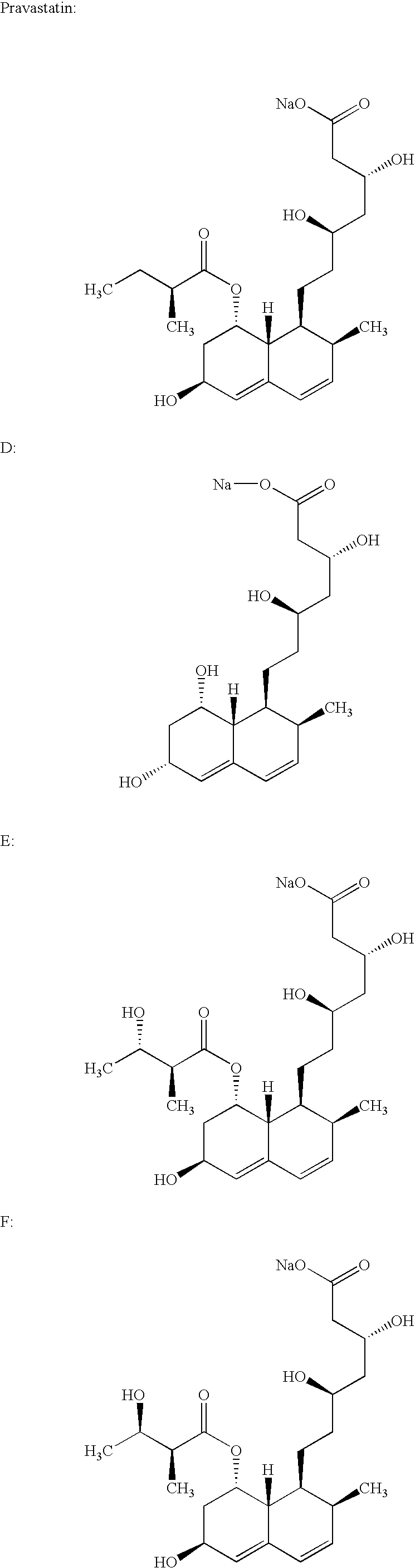
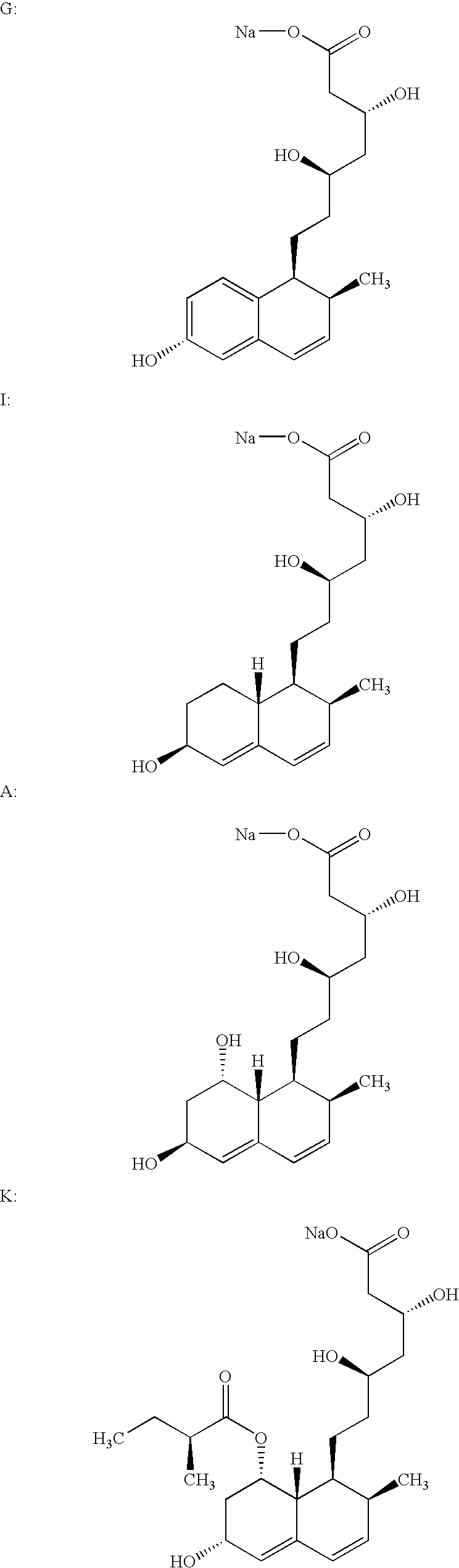
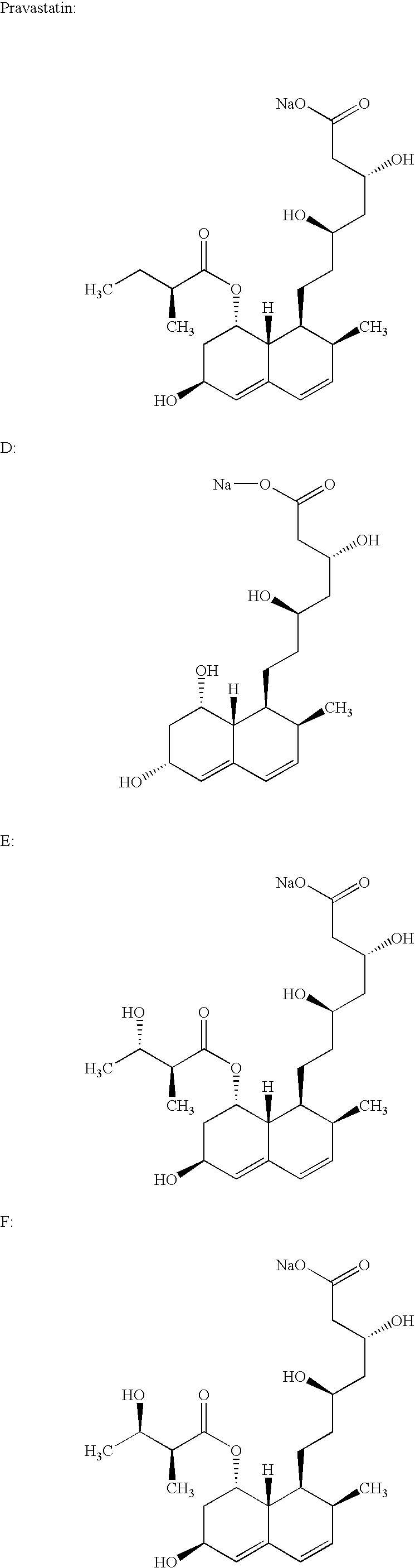
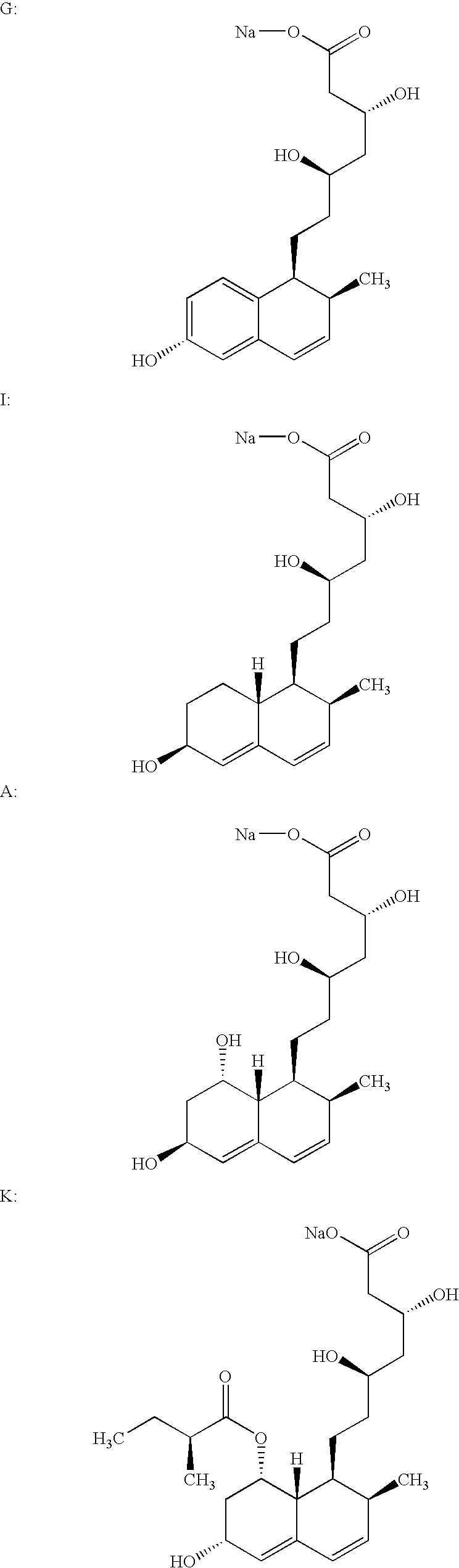
Process for obtaining HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors of high purity
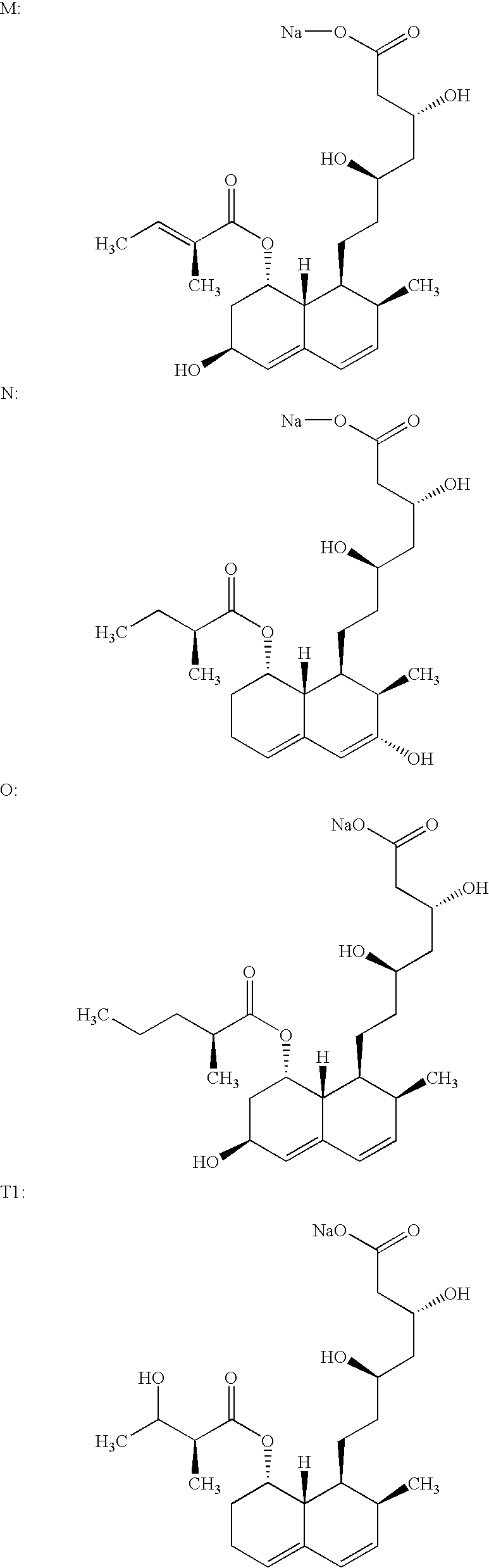
Lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin, mevastatin, atorvastatin, and derivatives and analogs thereof are known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and are used as antihypercholesterolemic agents. The majority of them are produced by fermentation using microorganisms of different species identified as species belonging to Aspergillus, Monascus, Nocardia, Amycolatopsis, Mucor or Penicillium genus, Streptomyces, Actinomadura, Micromonospora, some are obtained by treating the fermentation products using the method of chemical synthesis or they are the products of total chemical synthesis. The purity of the active ingredient is an important factor for manufacturing the safe and effective pharmaceutical, especially if the pharmaceutical product must be taken on a longer term basis in the treatment or prevention of high plasma cholesterol. The accumulation of the impurities from the pharmaceuticals of lower purity may cause many side effects during the medical treatment. The present invention relates to a new industrial process for the isolation of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors using so-called displacement chromatography. Use of the invention enables one to obtain HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors of high purity, with high yields, lower production costs and suitable ecological balance.
Owner:LEK PHARMA D D
Enrichment separation method of hydrogen isotopes through displacement chromatography
ActiveCN106693704AIncrease the lengthReduce volumeComponent separationIsotope separationLiquid waterDisplacement chromatography
The invention discloses an enrichment separation method of hydrogen isotopes through displacement chromatography. The enrichment separation method comprises the following steps: (1) reducing the temperature: making a molecular sieve column into a spiral coil, loading a container with liquid nitrogen, wholly immersing the molecular sieve column into the liquid nitrogen, and enabling the temperature of a molecular sieve to be maintained to be the temperature of the liquid nitrogen; (2) performing adsorption: enabling hydrogen to be introduced into the molecular sieve column, measuring the quantity of the hydrogen introduced into the molecular sieve, and after the gas pressure in the molecular sieve reaches to a definite pressure, stopping introducing the hydrogen; (3) performing warming for separation: upwards lifting the spiral molecular sieve column, so that the molecular sieve column is separated from the liquid surface of the liquid nitrogen, heating the molecular sieve column with air, and controlling the speed of the molecular sieve column being lifted out of the liquid surface of the liquid nitrogen to be 0.5-5 cm / min; and (4) performing detection and collection: oxidizing hydrogen into liquid water through an oxyhydrogen compositor at a rear end for the hydrogen discharged from the molecular sieve column, and then detecting the deuterium abundance in the liquid water through a magnetic mass spectrometer. According to the enrichment separation method of tritium through displacement chromatography disclosed by the invention, changes in the controlled process of reducing the temperature and raising the temperature have continuity, the hydrogen isotope separation efficiency is extremely high, and the separation effects are good.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
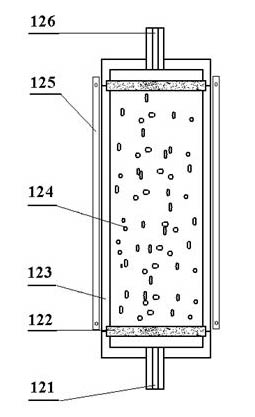
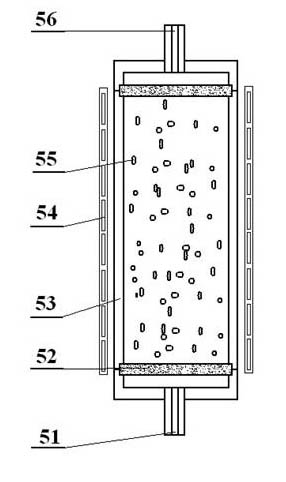
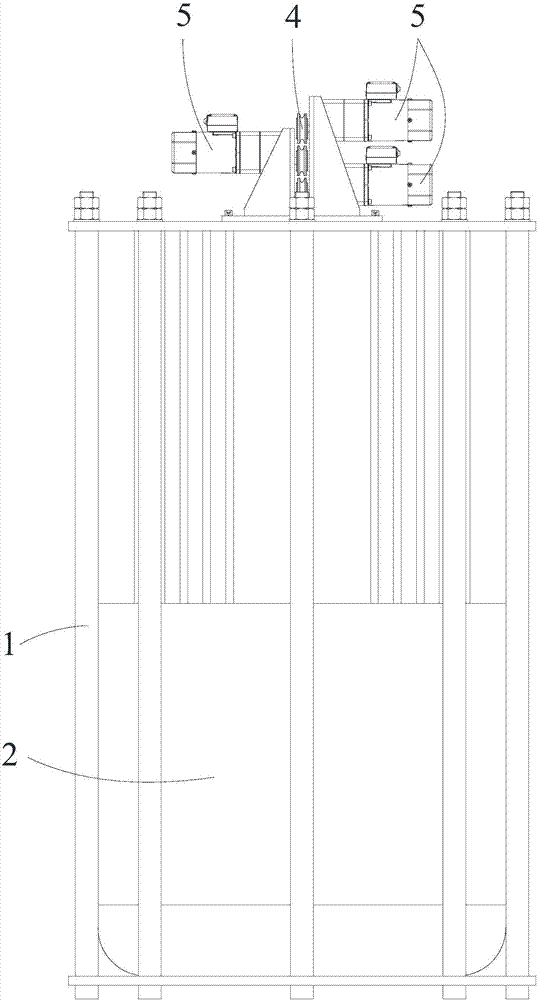
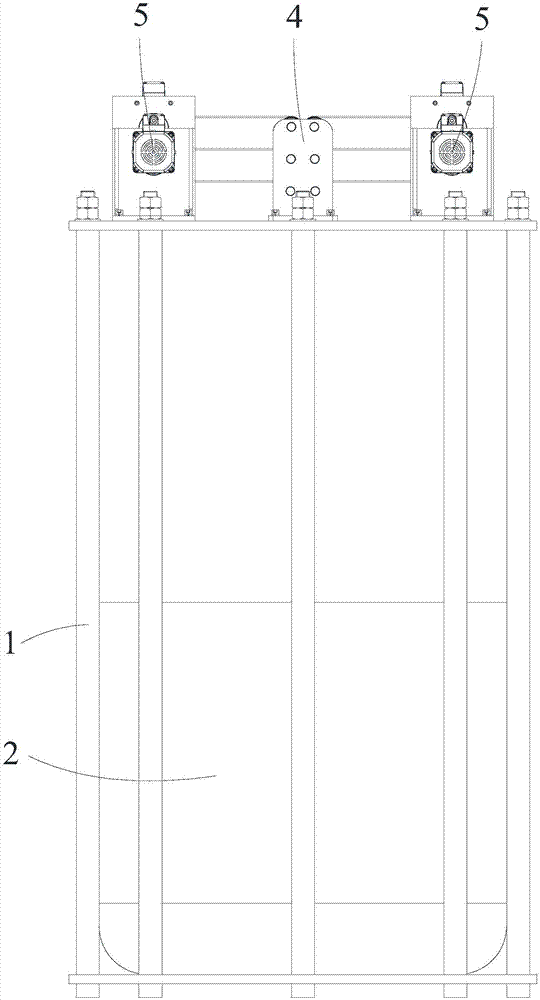
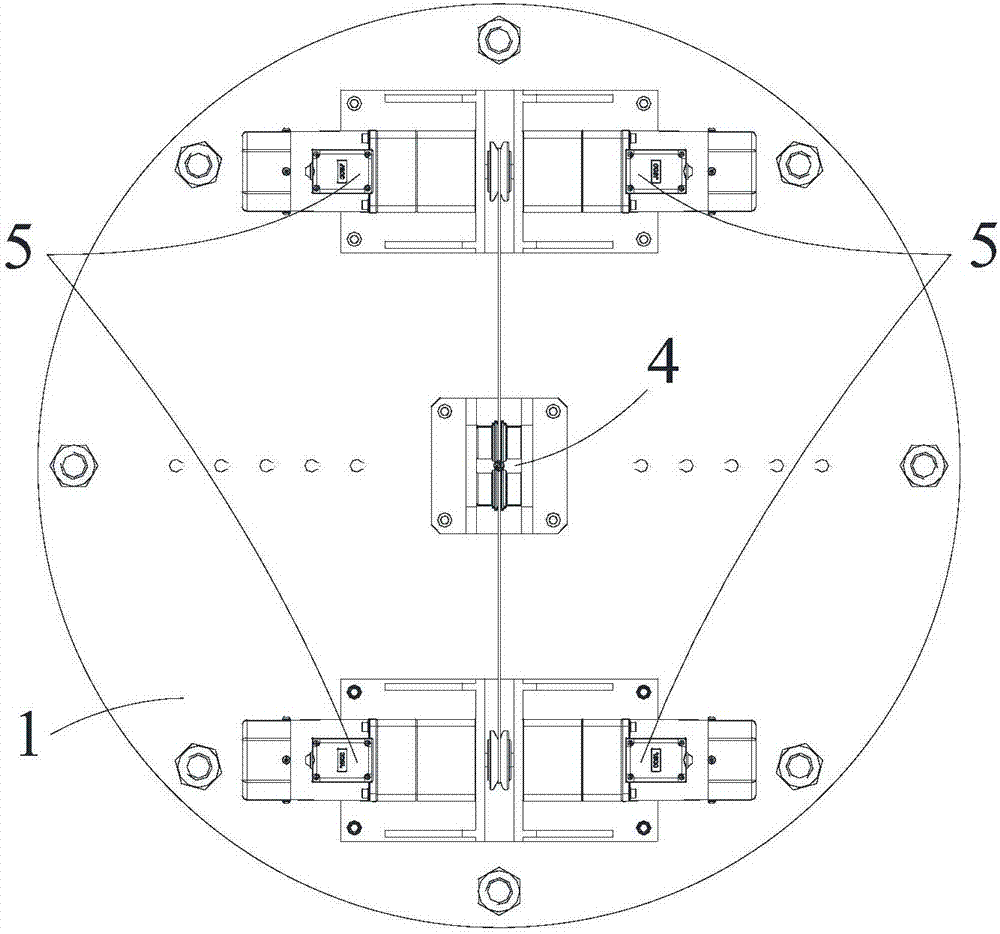
Displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device
ActiveCN106693703AExtend effective lifeExtended service lifeIsotope separationDesorptionDisplacement chromatography
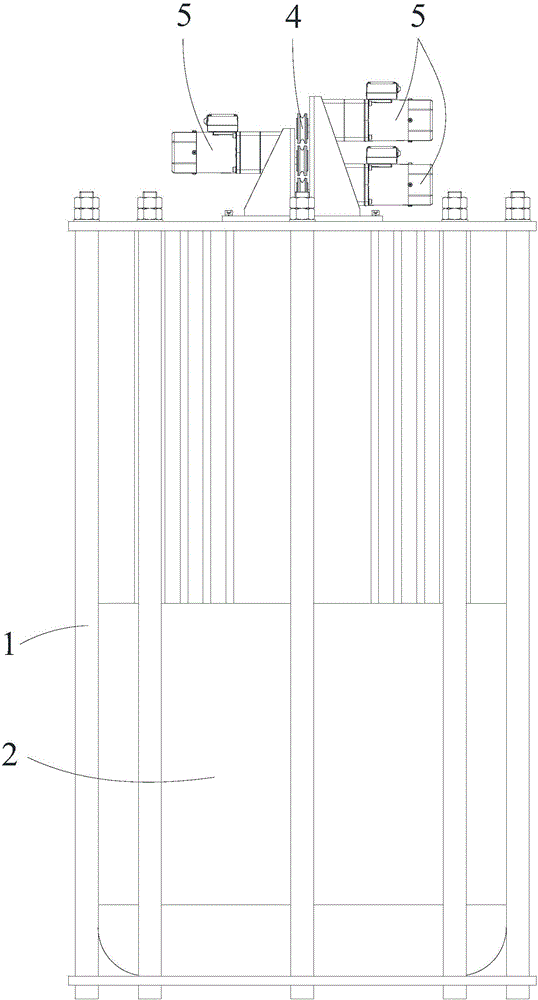
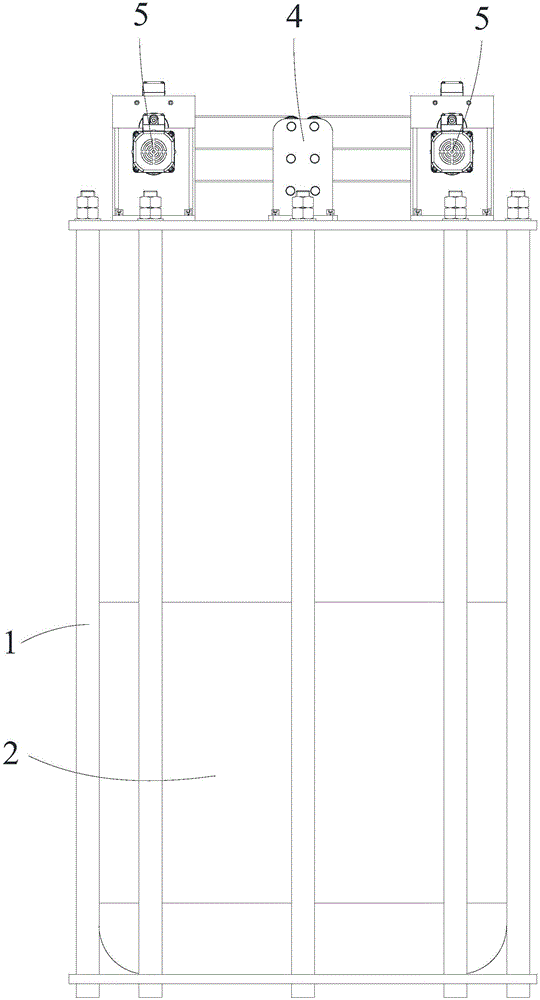
The invention discloses a displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device which comprises a rack as well as a cooling part, a separation column, an air supply part, an air collection part, a lifting part and a driving part. By adopting the displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device disclosed by the invention, different adsorption functions that hydrogen and hydrogen isotope are replaced and separated by using a separation material can be achieved, the lifting part is driven by the driving part to precisely control the lifting position of the separation column, and then the separation column can be descended or lifted off the cooling part, so that adsorption or desorption of hydrogen isotope by the separation material under different temperature conditions can be achieved, a high retention rate of deuterium-tritium isotope in the separation material can be ensured, and a deuterium-tritium isotope gas obtained through final separation and selection is relatively high in purity; compared with the prior art, the device needs no parts for introducing deuterium or separating deuterium, meanwhile deuterium and tritium do not need to be replaced by introducing hydrogen after the separation material is in saturation adsorption of hydrogen, and in addition, the device is simple in structure, low in energy consumption rate, simple in process and low in cost.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
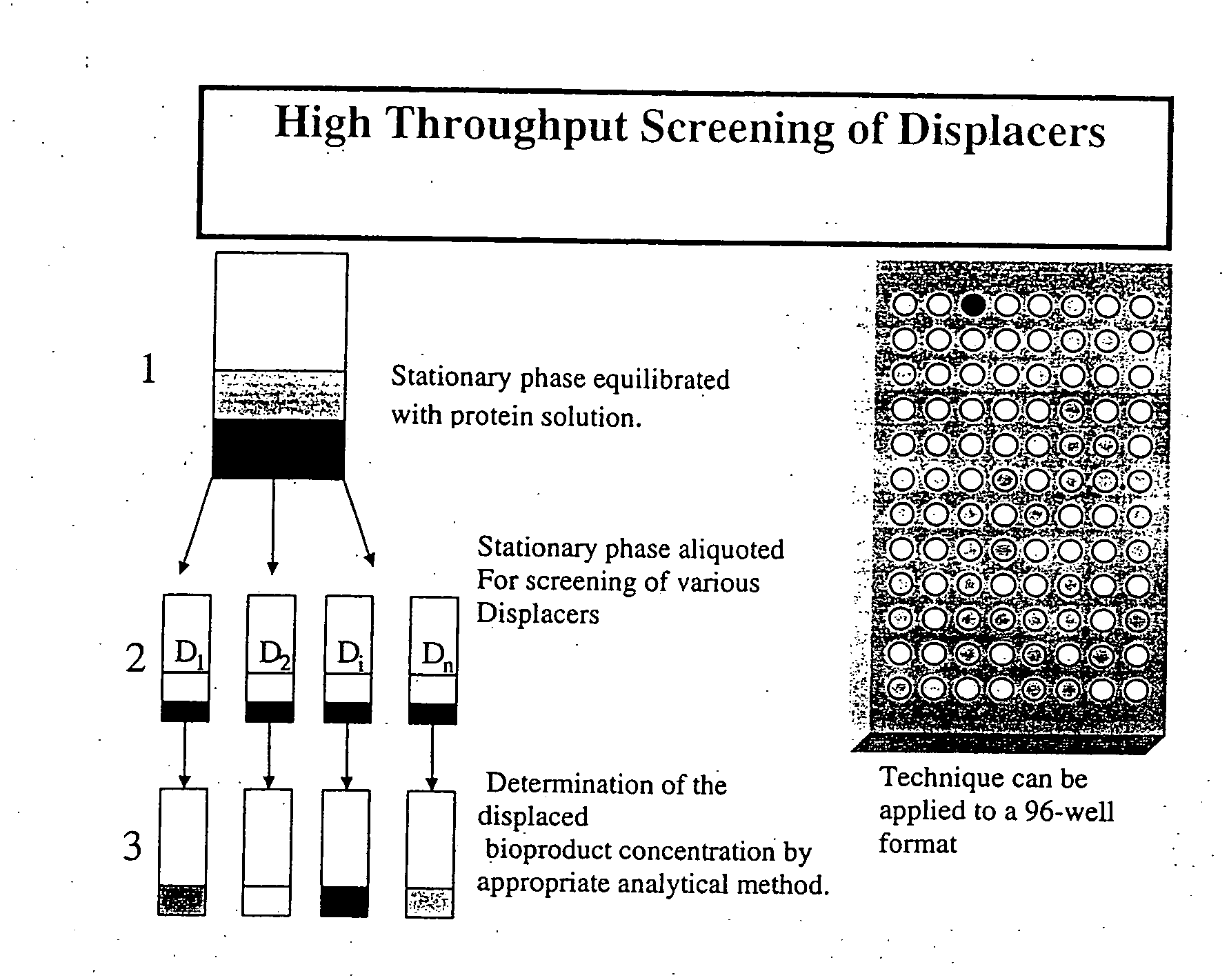
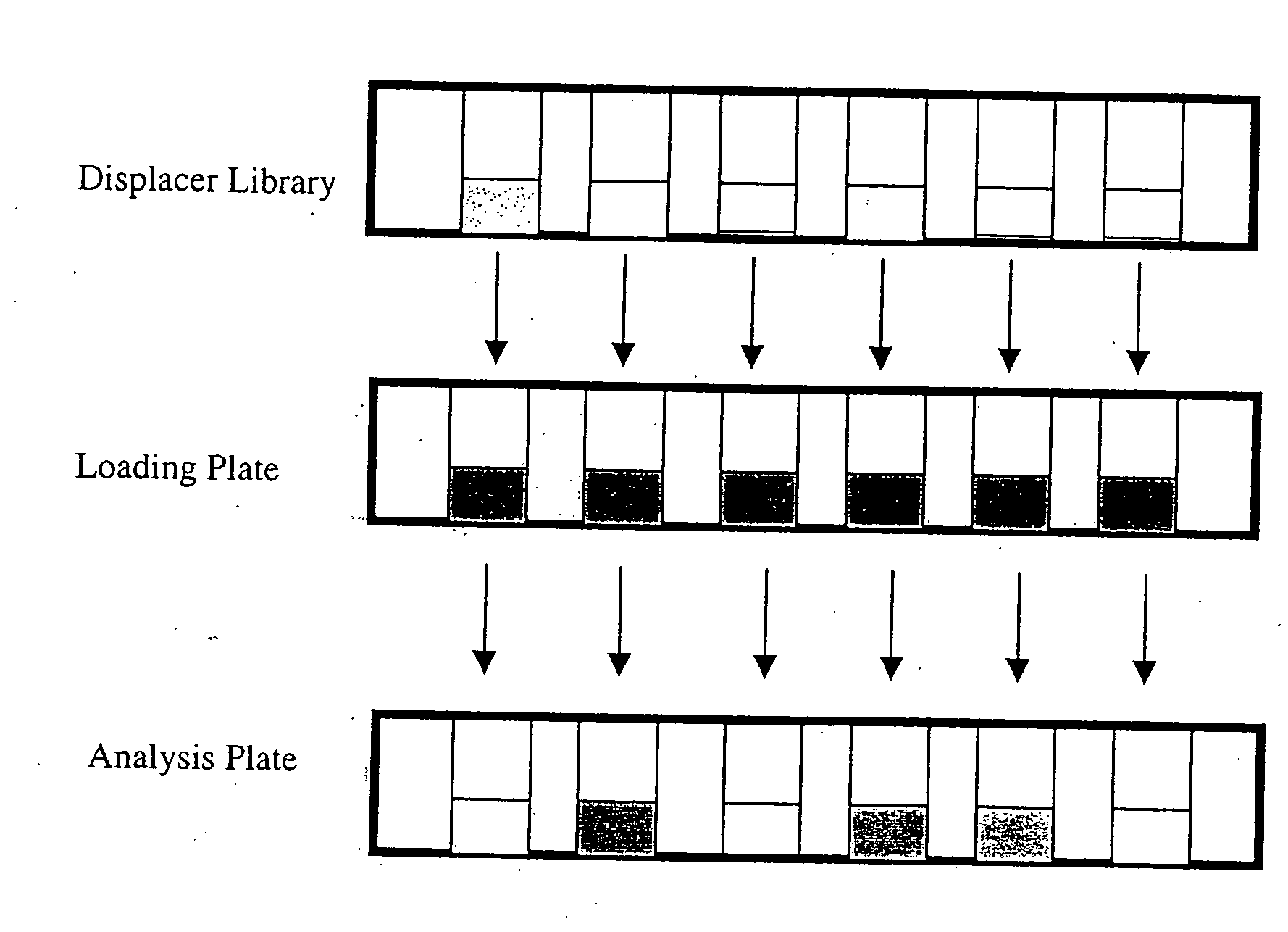
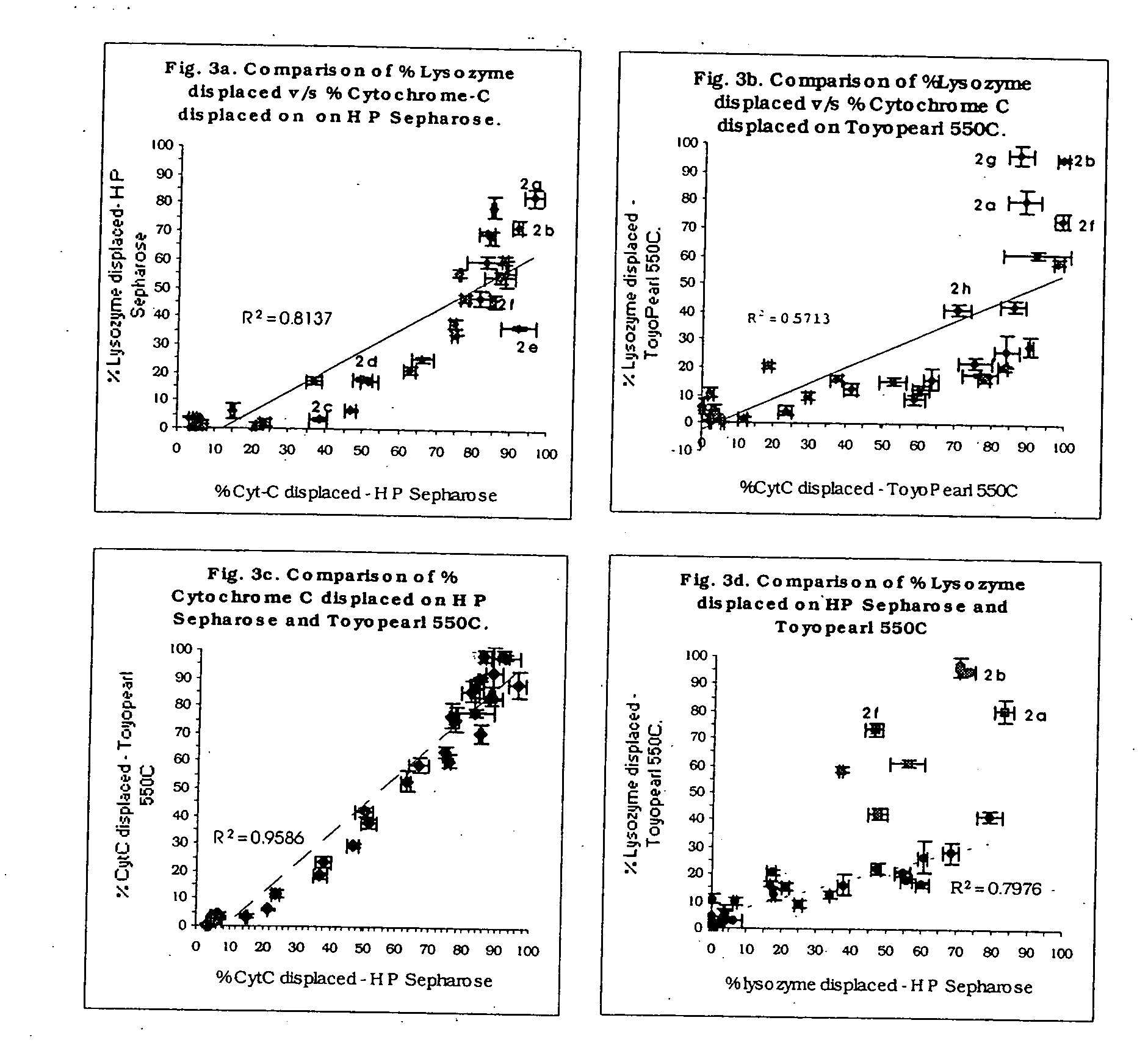
High throughput screening of potential displacer molecules
InactiveUS20050176937A1Rapid assessmentSugar derivativesSolid sorbent liquid separationBioproductsHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
A bioproduct may be selectively separated from one or more impurities by means of a displacement chromatography system that includes a solvent, a chromatographic resin and a chemically selective displacer. The method includes: dissolving the bioproduct and the one or more impurities in a solvent; loading the bioproduct and the one or more impurities, in the solvent, on a chromatographic resin; displacing the bioproduct from the chromatographic resin with chemically selective displacer; and retaining the one or more impurities on the chromatographic resin. For this method, the bioproduct and the impurities have similar binding affinity for the chromatographic resin in the absence of the displacer.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Preparation method of chiral ligand exchange chromatographic stationary phase
InactiveCN1538171AAchieving a direct splitEasy to operateIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationStationary phaseDisplacement chromatography
A process for using L-isoleucine as the chiral selective agent to prepare the stationary phase for chiral ligand displacement chromatography is disclosed. Its advantages are simple operation (directly splitting the chiral substance in simple experimental condition), high analysis speed, and wide application range.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of traceable enzyme calibration substance
InactiveCN101532047AReliable methodWide range of usesMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular sieveEnzyme Gene
A preparation method of traceable enzyme calibration substance includes the followings: firstly, human-derived seroenzyme gene clone and expression; secondly, purification of high-purity gene recombination seroenzyme; thirdly, preparation of stroma ground substance with fine interchangeability; fourthly, interchangeability verification of calibration substance candidate; fifthly, homogeneity determination after subpackage; sixthly, freeze drying: the human-derived seroenzyme gene clone and expression are as follows: enzyme gene expression carrier Pet21b-HMCK specific construction process and protein optimization expression; the purification of high-purity gene recombination seroenzyme finishes high-purity protein of enzyme mainly by three reaction steps such as the first stage separation, anion displacement chromatography and the third molecular sieve gel chromatography; and then hybrid enzyme is determined and eliminated; the preparation method has the characteristics of reliable method, wide use, fine interchangeability and traceable performance, and the like.
Owner:嘉兴博泰生物科技发展有限公司
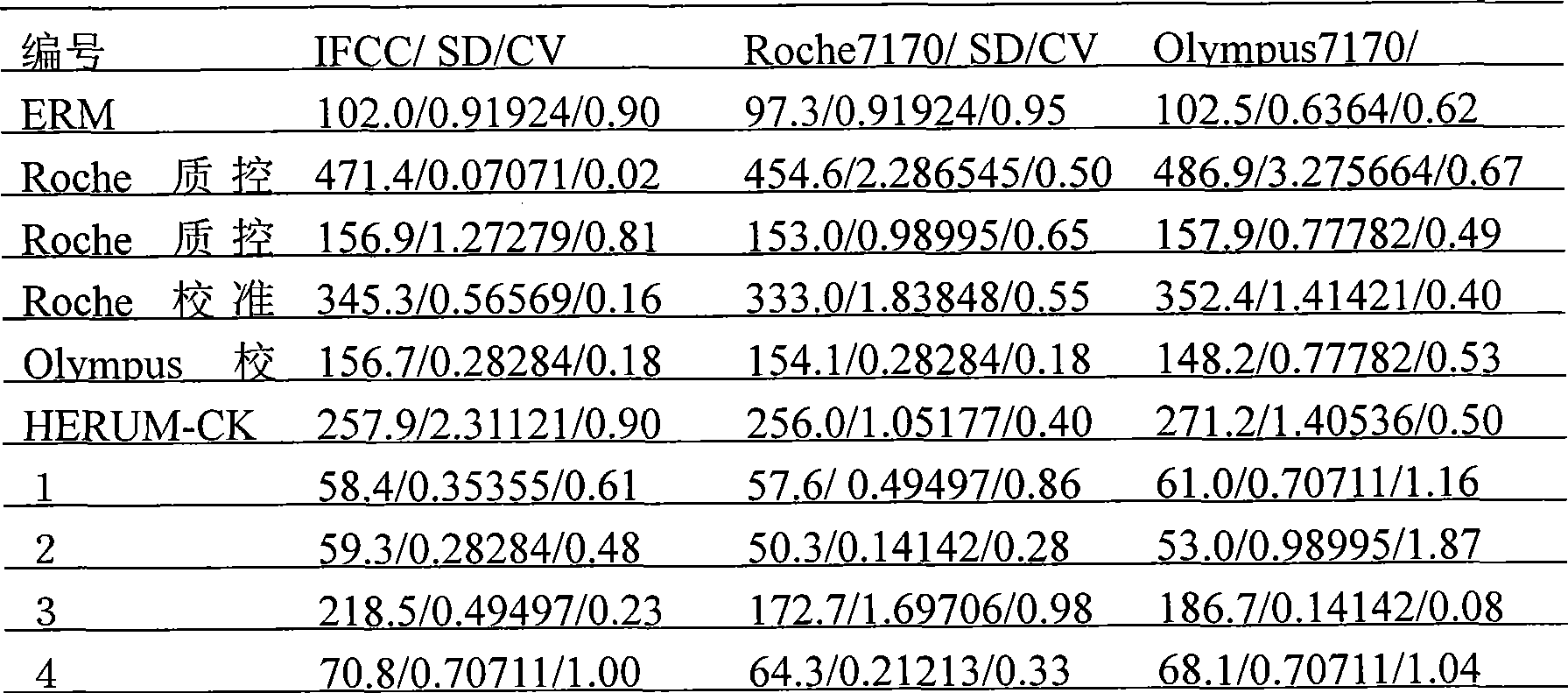
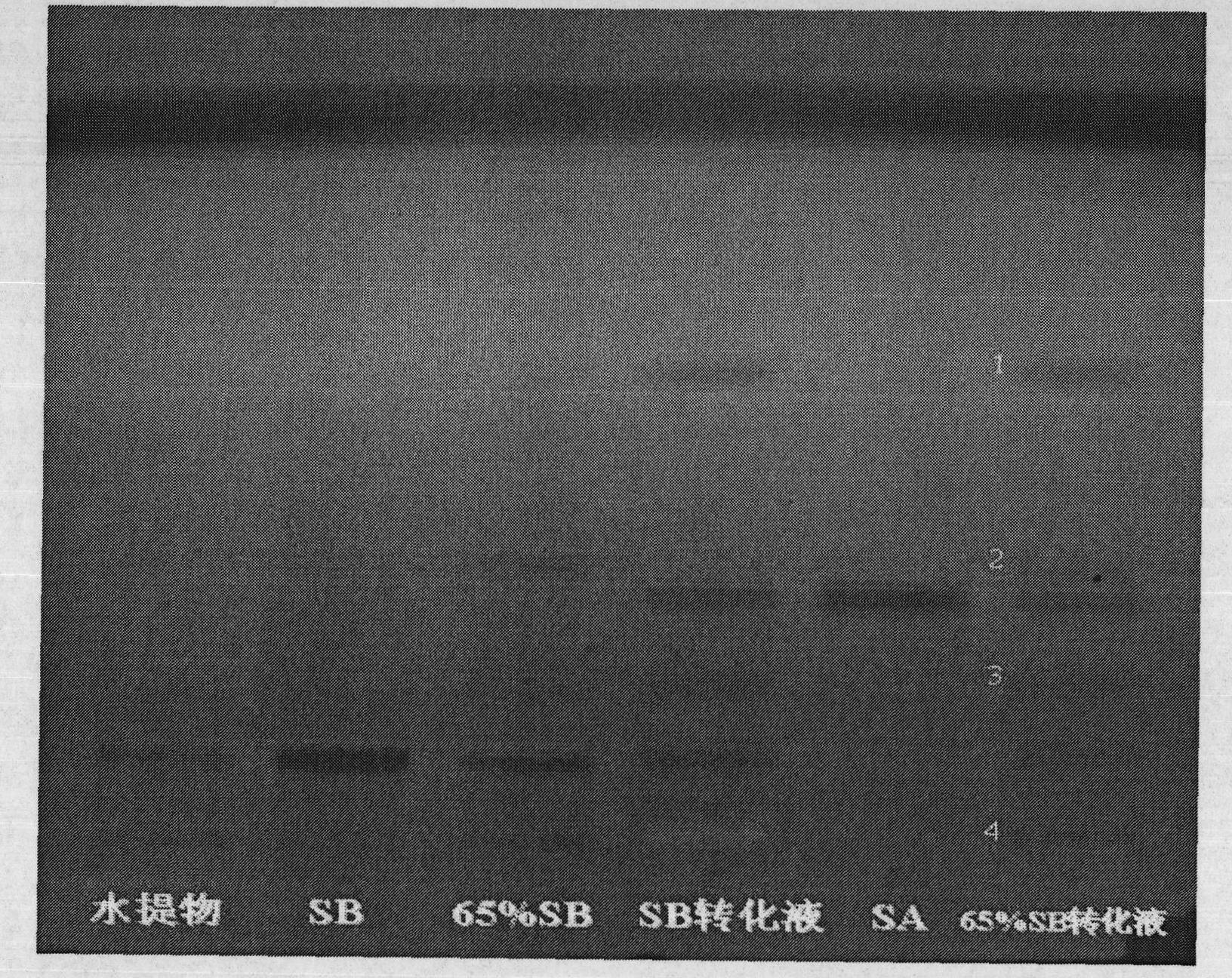
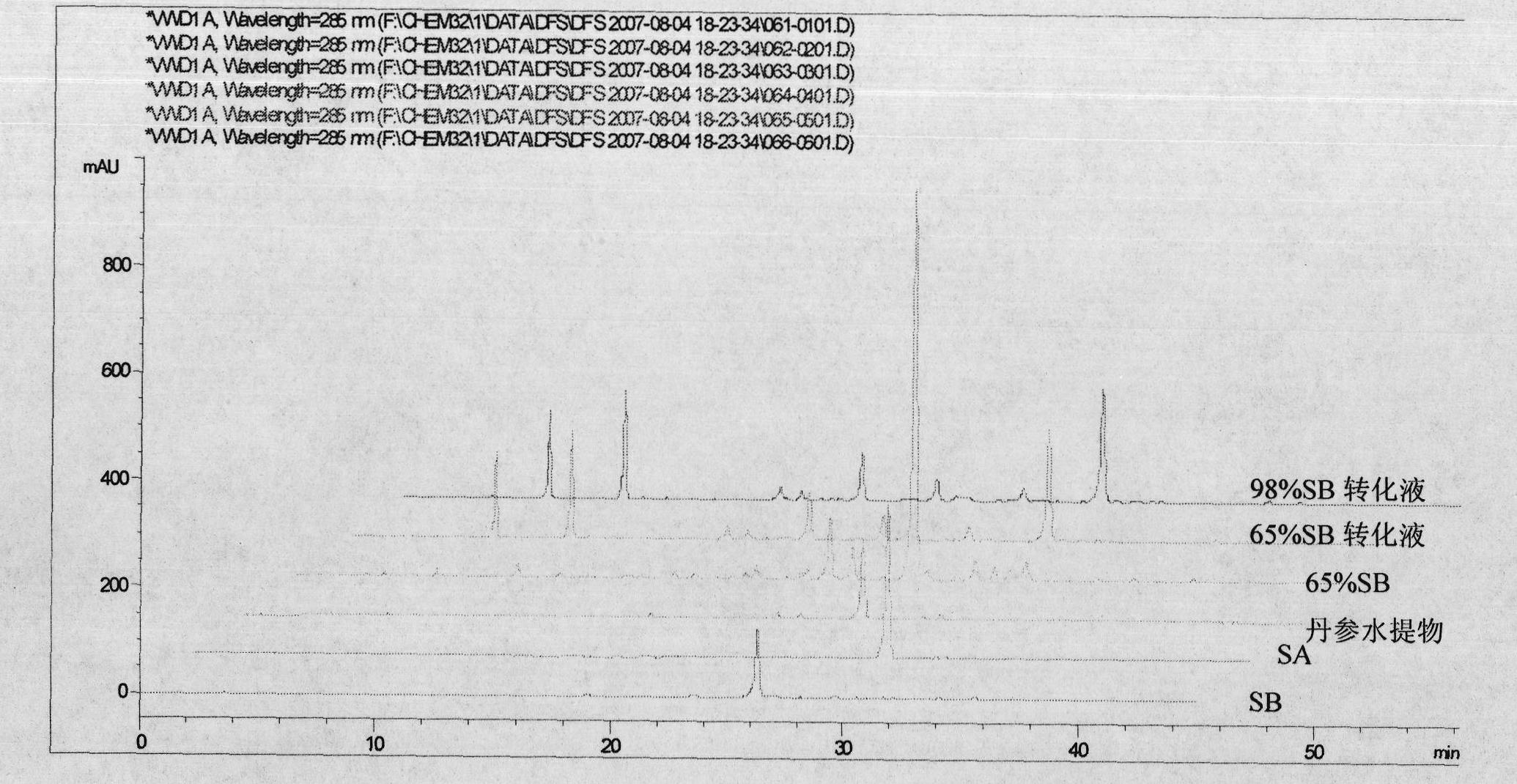
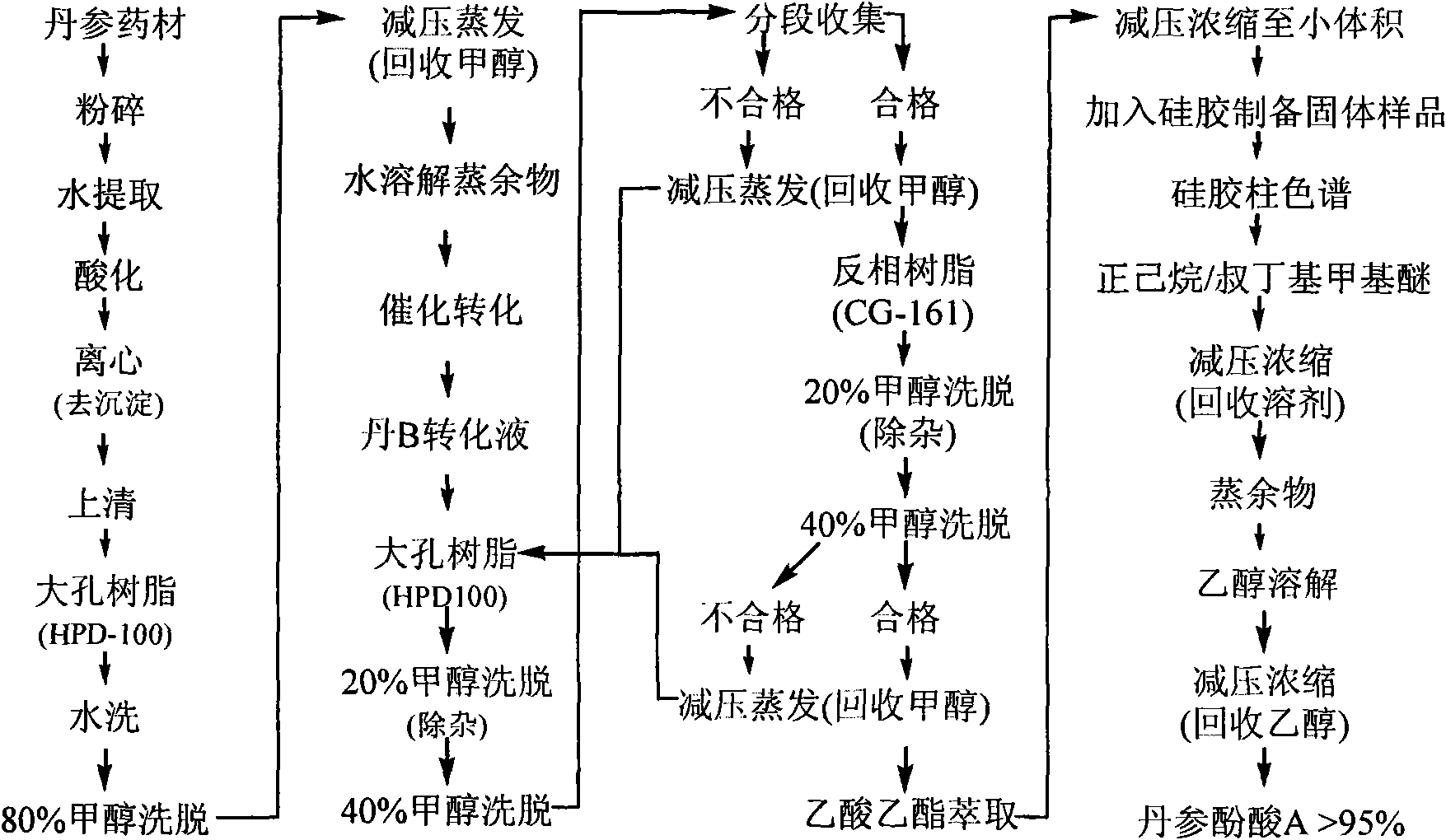
Batch preparation method of high-purity salvianolic acid A
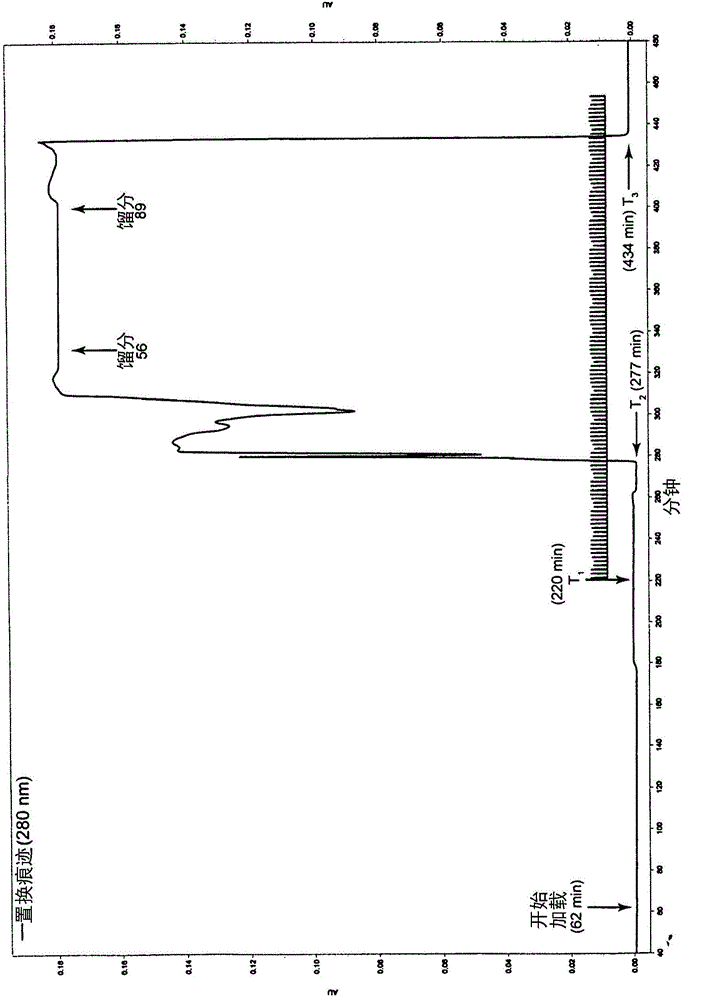
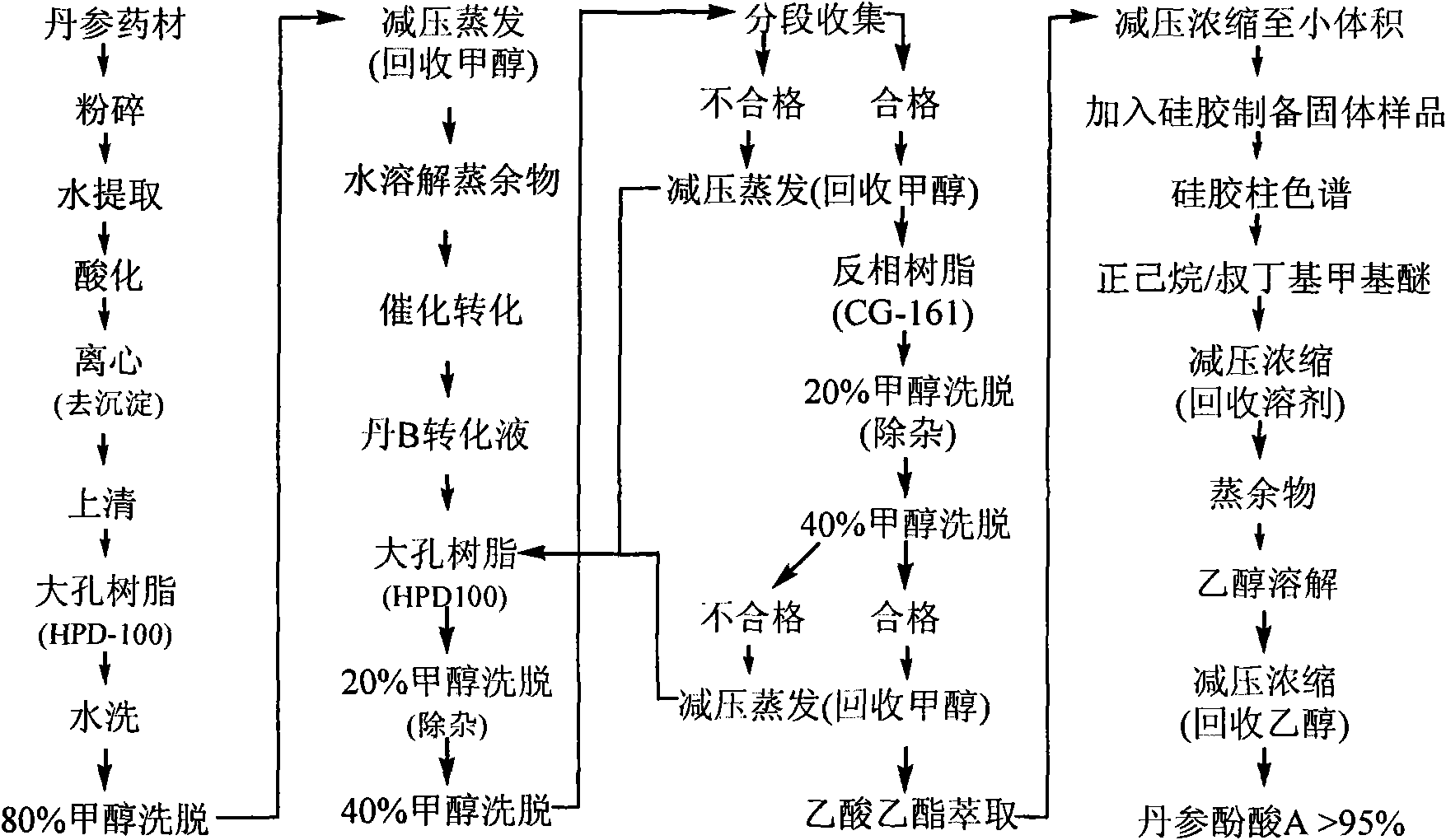
InactiveCN102212002AEfficient separationEfficient removalOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSalvianolic acid BChemical composition
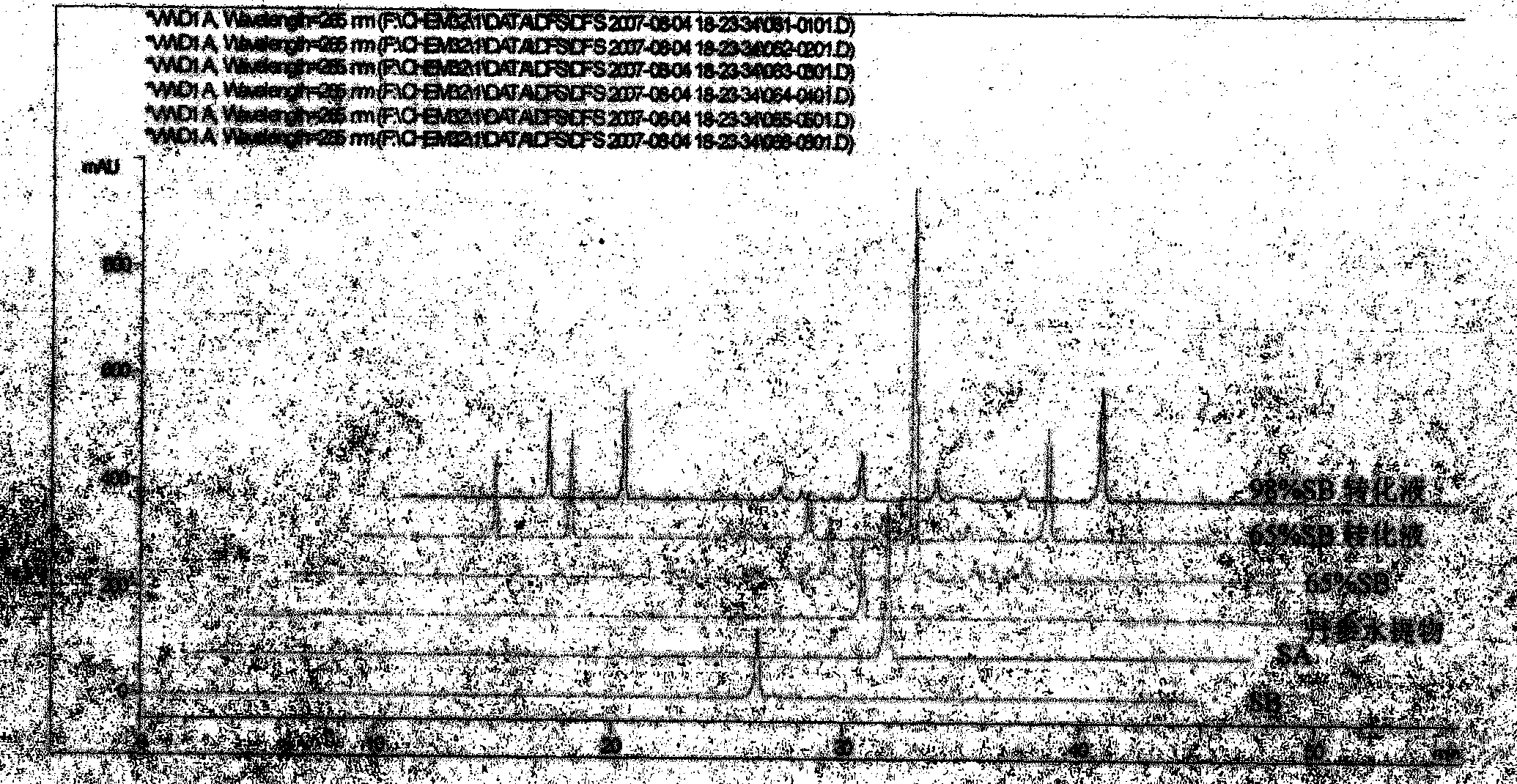
The invention relates provides a batch preparation method of high-purity salvianolic acid A based on physical and chemical properties and chromatograph behavior of a chemical component in salvia miltiorrhiza as well as adaptability of salvia miltiorrhiza to a cell separation technology. In the method, a salvianolic acid B transformation liquid containing salvianolic acid A is subjected to three-time chromatograph purification, namely hyphenated chromatography, reversed-phase chromatography and normal-phase silica gel chromatography, wherein the hyphenated chromatography refers to that macroporous resin frontal chromatography and macroporous resin displacement chromatography are jointly used. The product prepared by the method is controllable in quality, is acceptable in cost and can be used for injection medicaments. The content of salvianolic acid A prepared by the method is more than or equal to 98%, the total recovery of salvianolic acid A is more than or equal to 10% (based on salvianolic acid B), and the total yield of salvianolic acid A is more than or equal to 0.5% (based on salvianolic acid B).
Owner:YANTAI TARGET DRUG RES +1
Expression and purification method for bombyx mori odorant binding protein (BmOBP2)
InactiveCN103103209AHigh purityLow expressionPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesPurification methodsBombyx mori
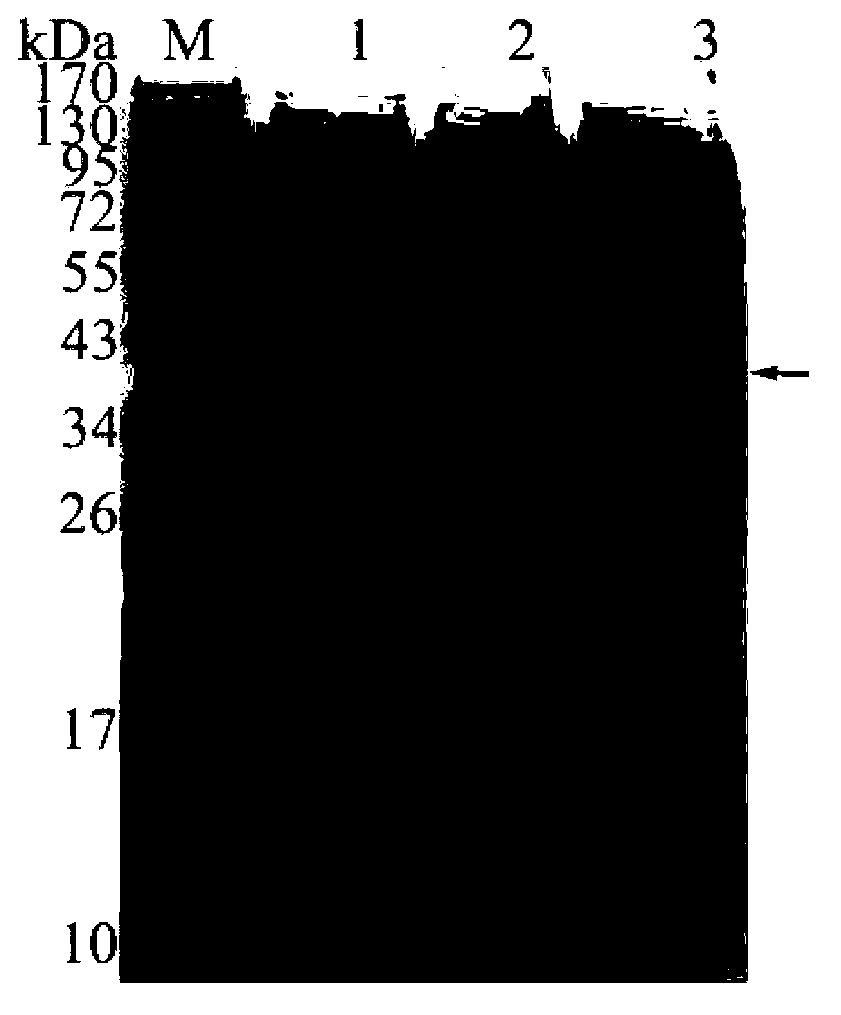
The invention relates to an expression and purification method for bombyx mori odorant binding protein (BmOBP2). By designing a primer, an expression vector Pet-32a-BmOBP2 is constructed and recombined, a great quantity of recombined interest protein is obtained through inducible expression, and high-purity recombined protein can be obtained by carrying out two simple purification technologies namely nickel ion affinity chromatography and anion displacement chromatography on the recombined protein, so that the method lays a very important foundation for research of the three dimensional structure and biological function of the recombined protein, and the problem that the natural membrane protein has low expression quantity and is difficult to purify is solved.
Owner:TIANJIN YAOYU BIOLOGICAL TECH
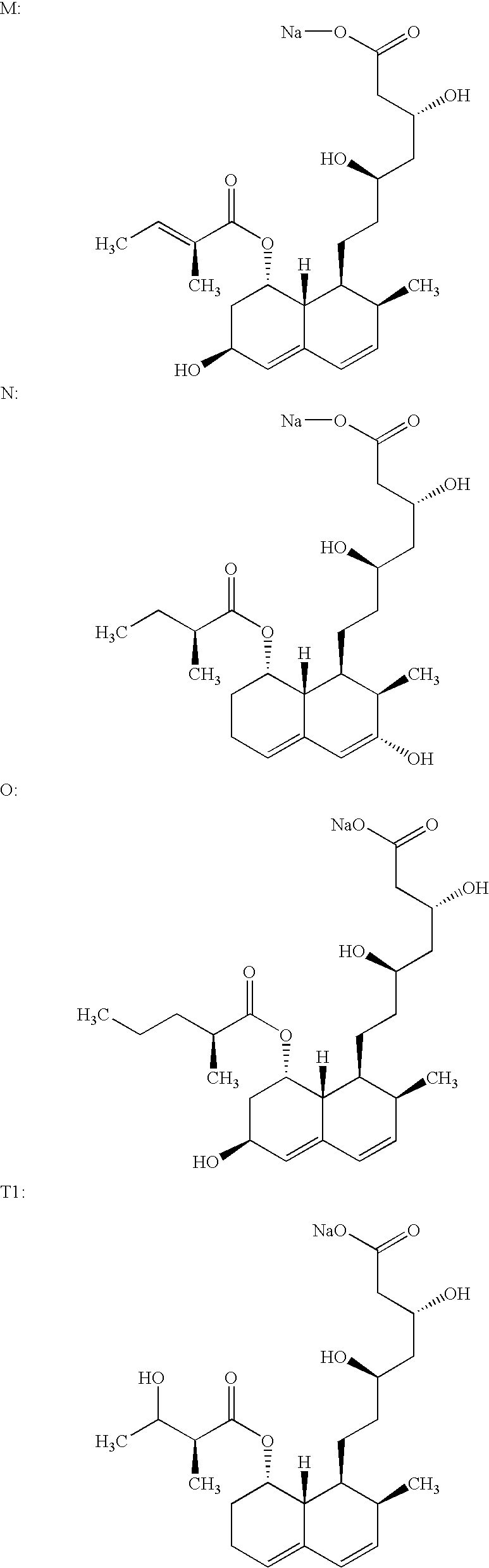
Purification of organic compounds using surrogate stationary phases on reversed phase columns
ActiveUS9724622B2Limited use of solventReduce waste disposalCation exchanger materialsComponent separationStationary phasePhosphonium salt
There are only two ways to increase the amount of sample that can be purified by preparative reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (Prep-RP-HPLC) in a single run: (1) The traditional approach is to use a bigger column (greater amount of stationary phase); and (2) Use displacement chromatography which uses the stationary phase more effectively. This invention describes a unique Prep-RP-HPLC technique that uses a C-18 / C-8 derivatized silica coated with a hydrophobic quaternary ammonium salt or quaternary phosphonium salt to result in 7 to 12 fold increase in sample loading (of the crude mixture of organic compounds including synthetic crude peptides) in contrast to the conventional Prep-RP-HPLC technique. This increase in sample loading capacity and output is due to the additional surrogate stationary phase characteristic of the C-18 / C8 bound quaternary salt. The quaternary surfactant is bound to the C-18 / C-8 chains and silanols of the stationary phase.
Owner:NEULAND HEALTH SCI
Method of displacement chromatography
InactiveUS20020027104A1Equilibration time can be reducedEfficient separationIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationChromatographic separationBetaine
A plurality of chromatographic separation operations, including a first simulated moving bed operation, are coupled into a process which functions, preferably through the application of continuous displacement chromatography, to recover a fraction rich in small organic molecules, notably betaine and / or invert from sucrose solutions, enabling the subsequent production of a high purity sucrose product.
Owner:AMALGAMATED RES
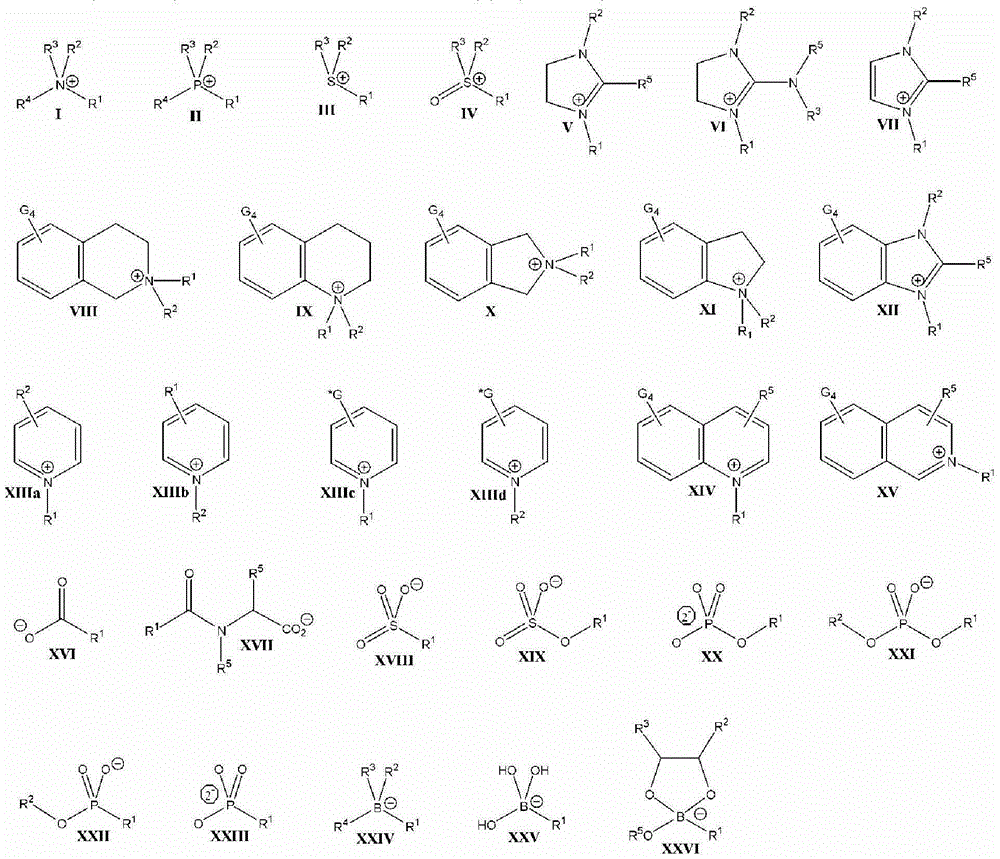
Anion-exchange displacement chromatography process and anionic organic compounds for use as displacer compounds in anion-exchange displacement chromatography
InactiveCN101336124AEasy to synthesizeEasy to purifySolid sorbent liquid separationSulfonic acid preparationStationary phaseHalogen
A displacement chromatography process, including: loading onto a stationary phase comprising an anion-exchange material a mixture comprising one or more component to be separated; displacing at least one of the one or more component from the stationary phase by applying to the stationary phase a mixture comprising an polyaromatic polyanionic displacer compound having a general formula Cen (Ar)w, in which Cen is a central bond or group, Ar is an aromatic nucleus, w = 2 to the maximum number of sites one Cen, and Ar is substituted with a plurality of An<->, in which each An<-> is independently defined as sulfonate, carboxylate, phosphonate, phosphate, sulfate; and Ar is further substituted with a plurality of G, in which G is defined as independently H, C1-C6 alkyl, halogen, nitro, hydroxy, C1-C6 alkoxy. In addition, a group of polyaromatic polyanionic displacer compounds useful in the process is disclosed.
Owner:SACHEM INC
Neutral zwitterionic displacer molecules for hydrophobic displacement chromatography
InactiveCN103958016ASolid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsStationary phaseOrganic solvent
A process for separating organic compounds from a mixture by reverse- phase displacement chromatography, including providing a hydrophobic stationary phase; applying to the hydrophobic stationary phase a mixture comprising organic compounds to be separated; displacing the organic compounds from the hydrophobic stationary phase by applying thereto an aqueous composition comprising a non-surface active hydrophobic neutral zwitterionic displacer molecule and optionally an organic solvent; and collecting a plurality of fractions eluted from the hydrophobic stationary phase containing the separated organic compounds, in which the non-surface active hydrophobic neutral zwitterionic displacer molecule comprises a hydrophobic zwitterion having the general formula, as defined in the disclosure: [CM-R*-CM'].
Owner:SACHEM INC
Low acidic species compositions and methods for producing and using the same using displacement chromatography
ActiveUS20150110803A1Good curative effectIncreased cartilage tissue penetrationTumor necrosis factorPeptide preparation methodsAntigen bindingDisplacement chromatography
The present invention relates to low acidic species (AR) compositions comprising a protein, e.g., an antibody, or antigen-binding portion thereof, and methods for producing such low AR compositions using displacement chromatography. Methods for using such compositions to treat a disorder, e.g., a disorder in which TNFα is detrimental, are also provided.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
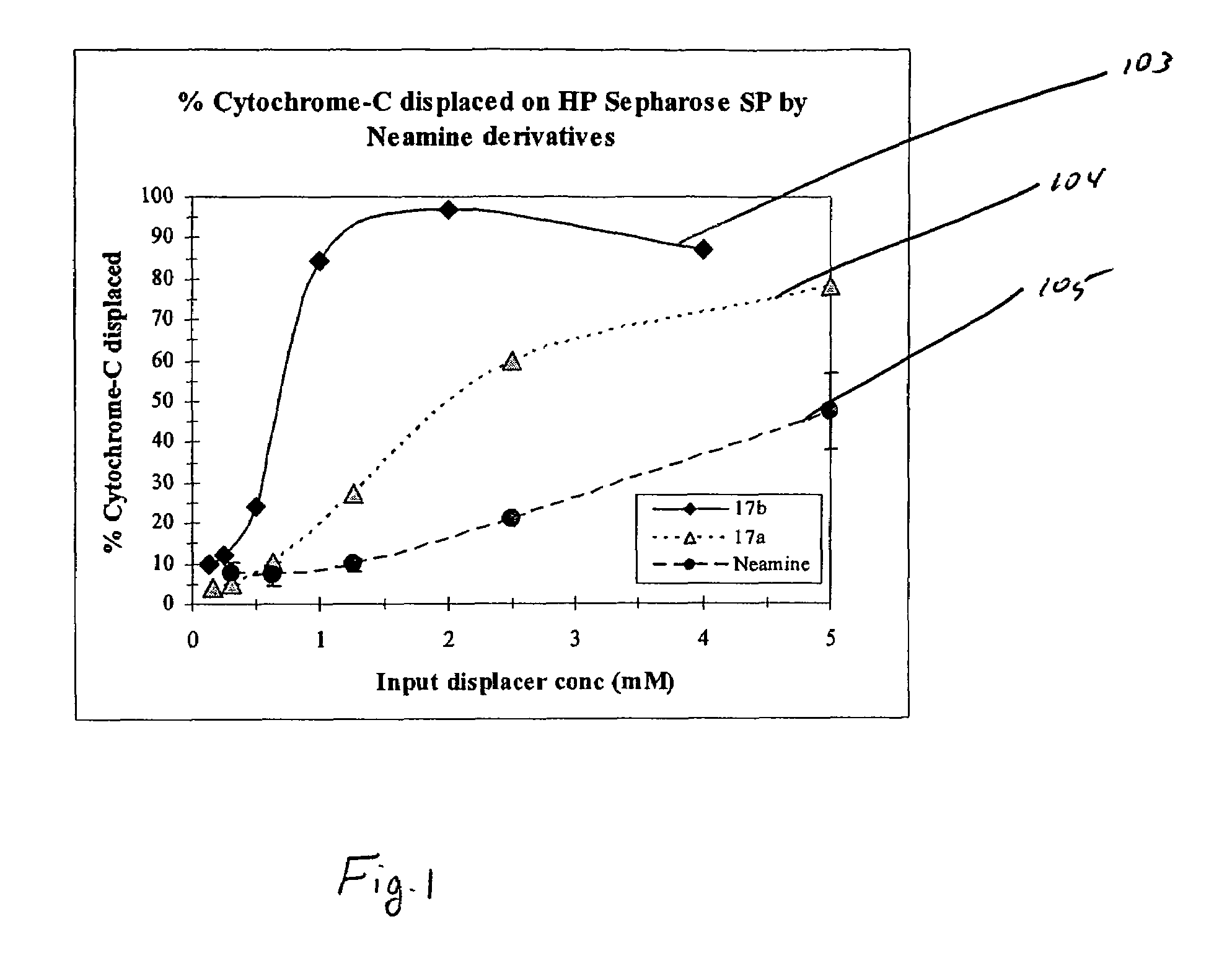
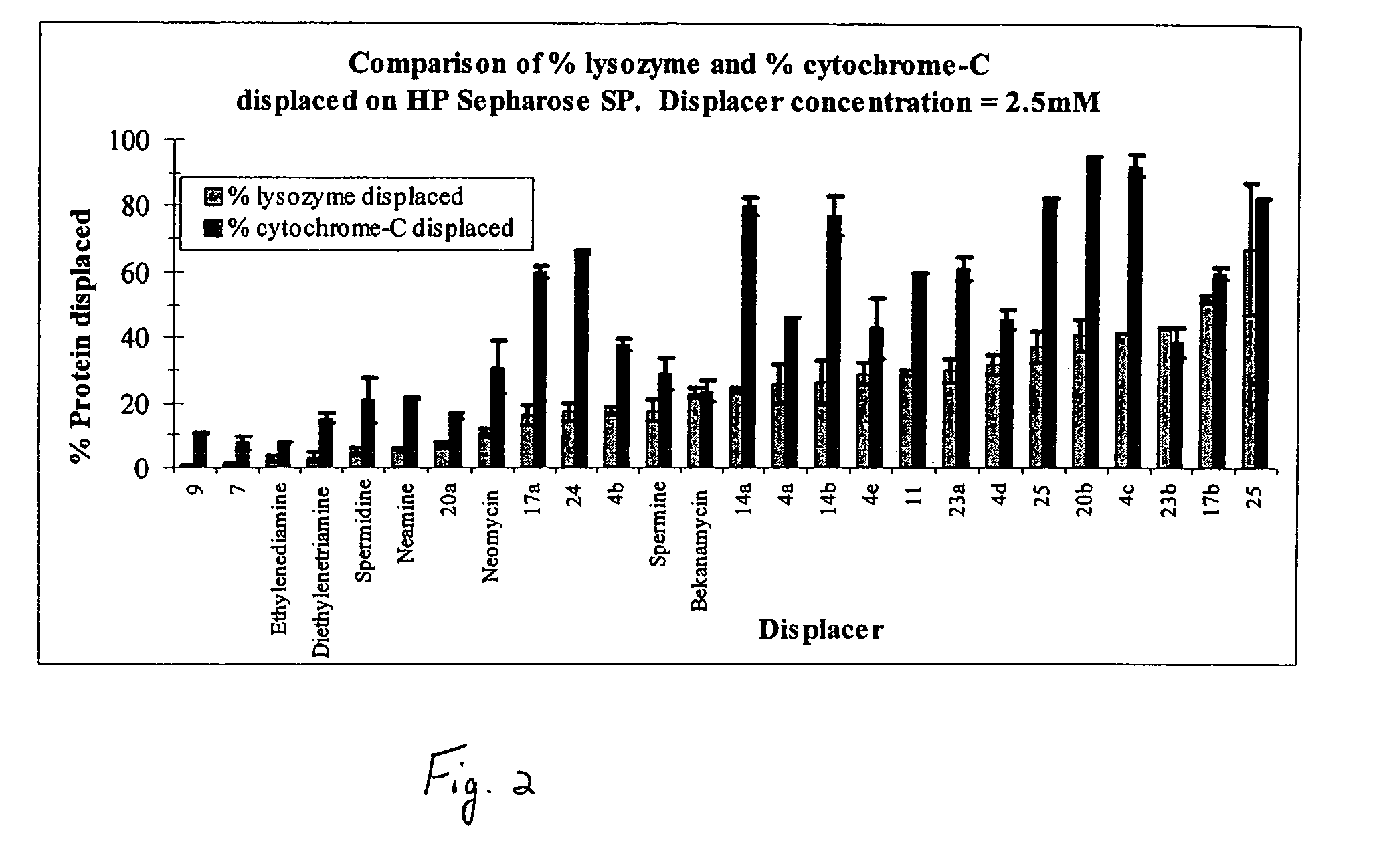
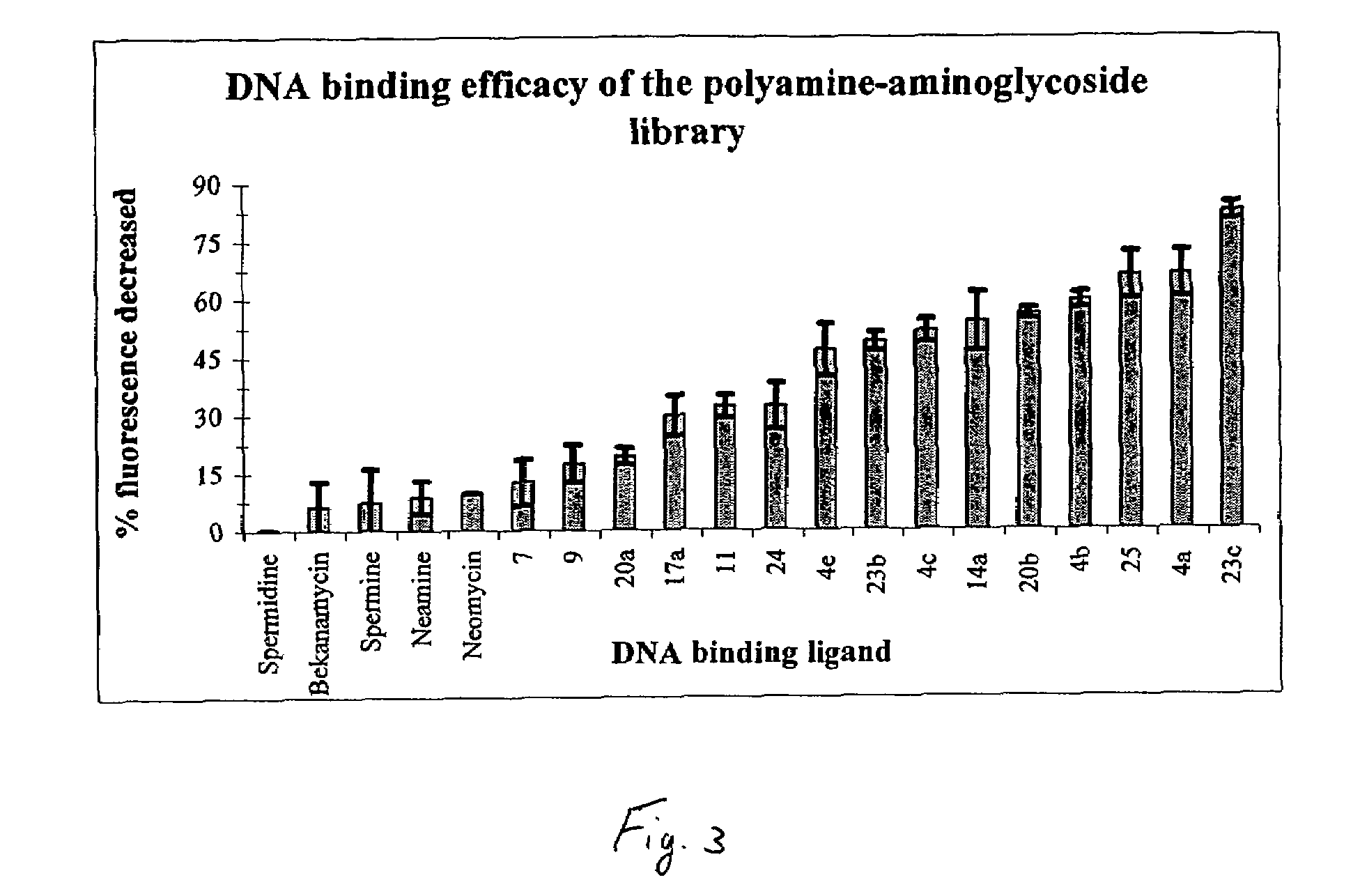
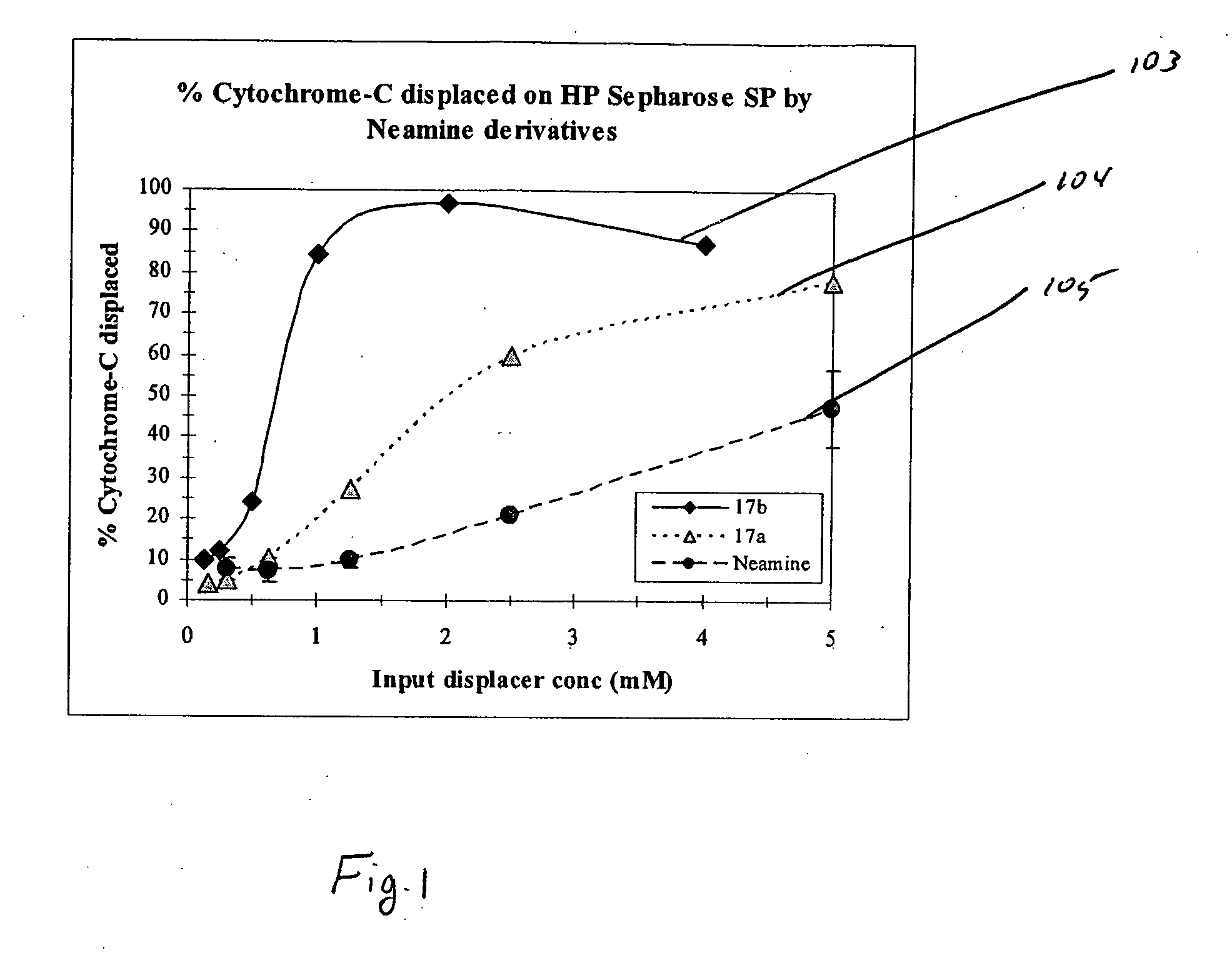
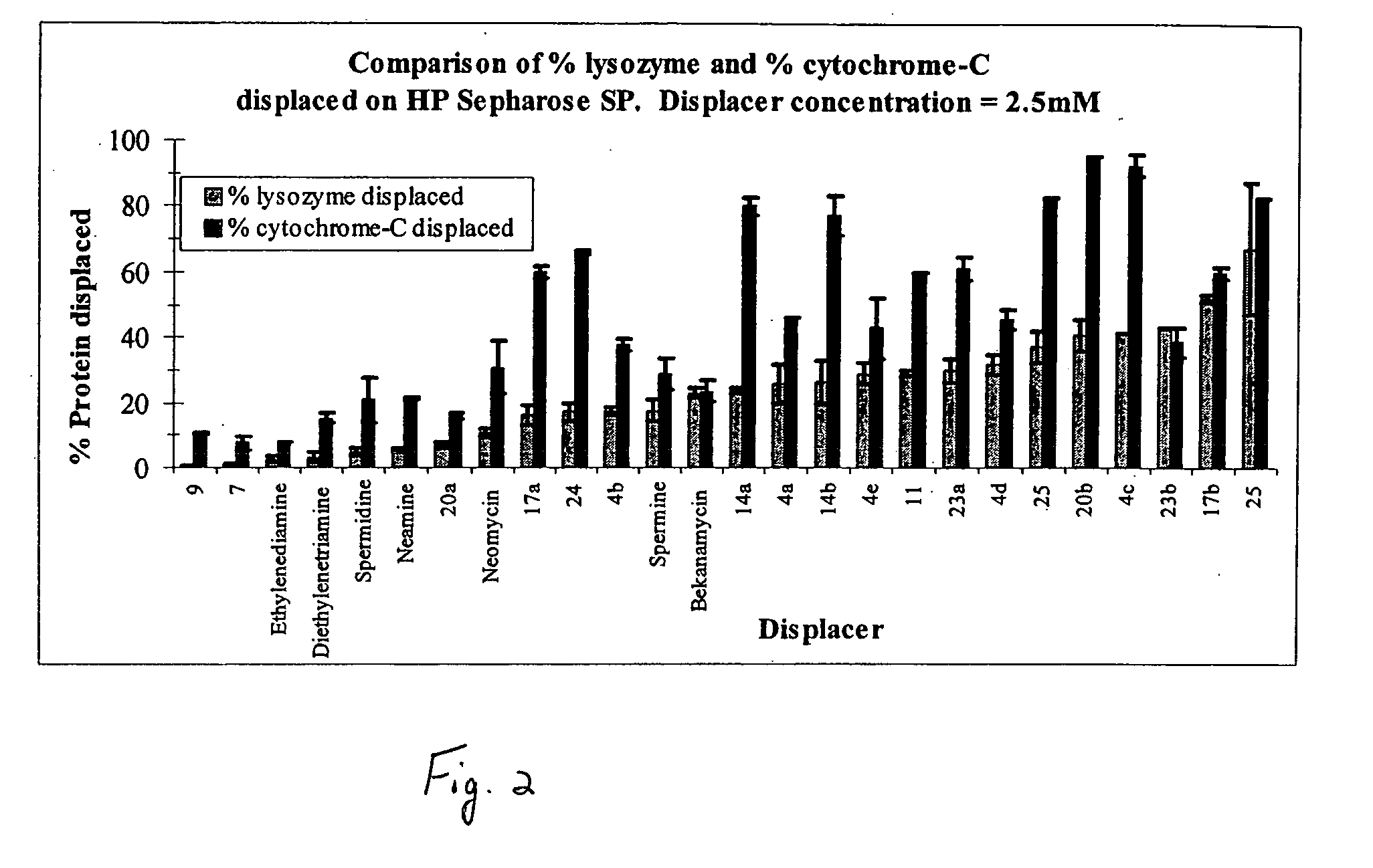
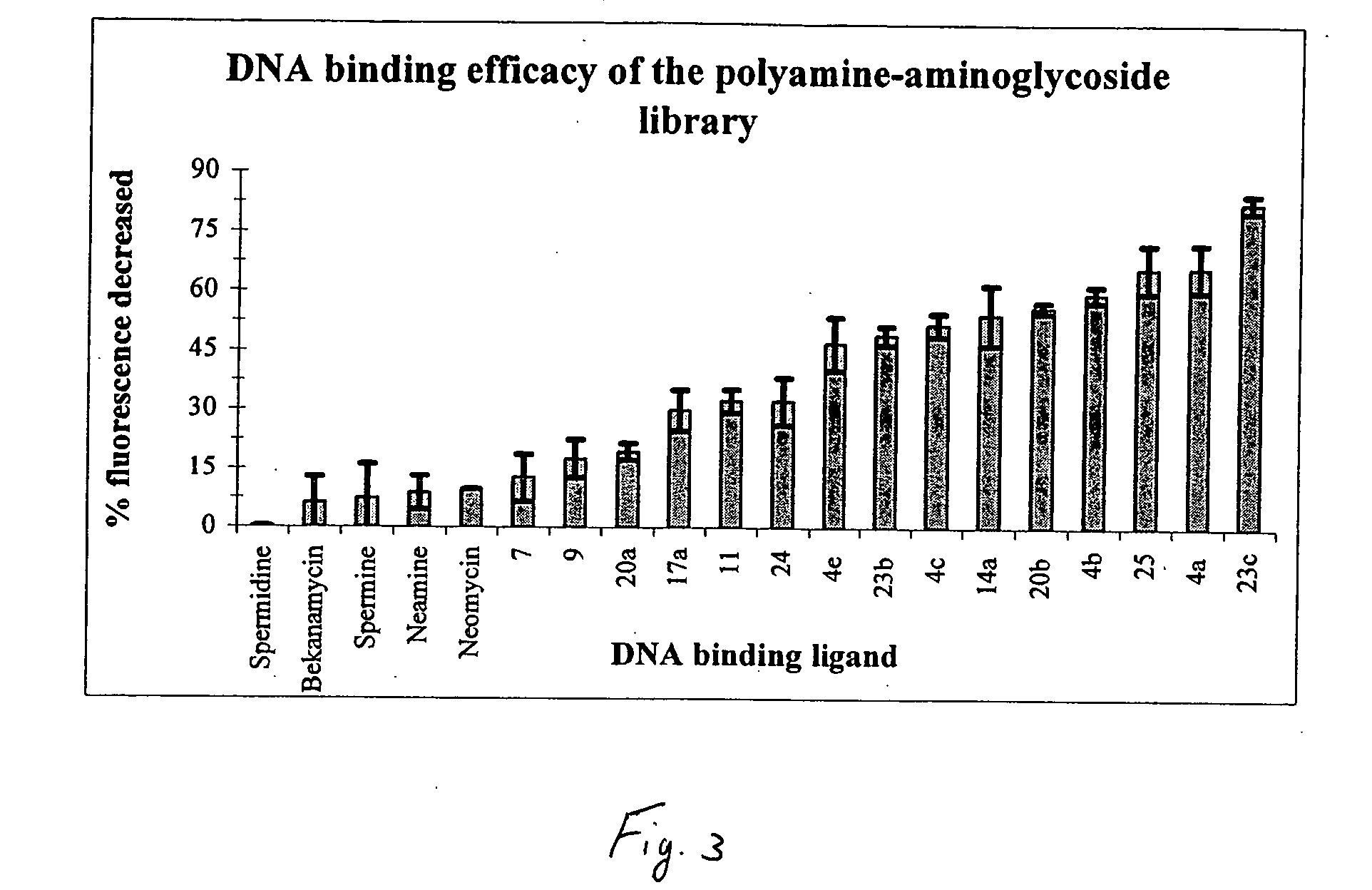
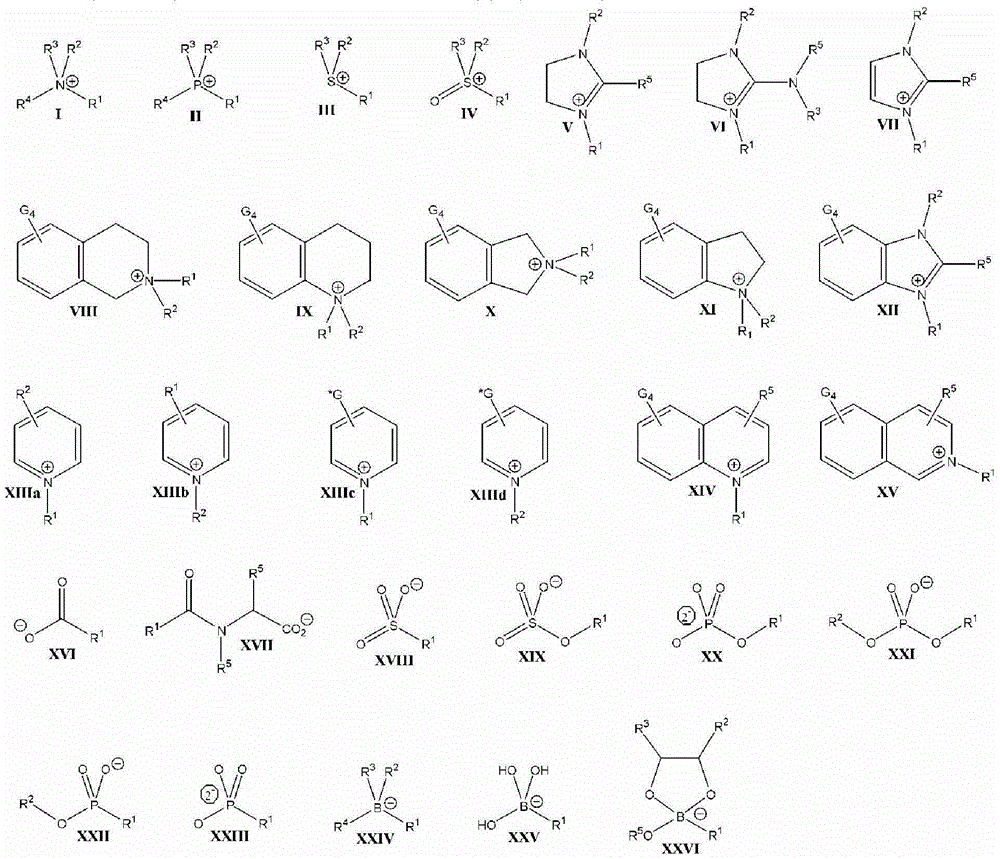
Aminoglycoside-polyamine displacers and methods of use in displacement chromatography
InactiveUS7439343B2Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesSugar amineDisplacement chromatography
Aminoglycoside-polyamines are disclosed along with methods of use thereof in displacement chromatography and as DNA-binding ligands. The aminoglycoside-polyamines are derivatives of carbohydrates, such as sugars, amino sugars, deoxysugars, glycosides, nucleosides and their substituted counterparts. The subject polyamines possess agroup in place of at least one hydrogen atom of at least one hydroxyl group of the carbohydrate compound. In these compounds R1 is an alkyl group or an azaalkyl group, and R2 is a primary or secondary amino group.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Aminoglycoside-polyamine displacers and methods of use in displacement chromatography
InactiveUS20070049741A1Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesSugar amineDisplacement chromatography
Aminoglycoside-polyamines are disclosed along with methods of use thereof in displacement chromatography and as DNA-binding ligands. The aminoglycoside-polyamines are derivatives of carbohydrates, such as sugars, amino sugars, deoxysugars, glycosides, nucleosides and their substituted counterparts. The subject polyamines possess a group in place of at least one hydrogen atom of at least one hydroxyl group of the carbohydrate compound. In these compounds R1 is an alkyl group or an azaalkyl group, and R2 is a primary or secondary amino group.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Process for obtaining HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors of high purity
Lovastatin, pravastatin, simvastatin, mevastatin, atorvastatin, and derivatives and analogs thereof are known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors and are used as antihypercholesterolemic agents. The majority of them are produced by fermentation using microorganisms of different species identified as species belonging to Aspergillus, Monascus, Nocardia, Amycolatopsis, Mucor or Penicillium genus, Streptomyces, Actinomadura, Micromonospora, some are obtained by treating the fermentation products using the method of chemical synthesis or they are the products of total chemical synthesis. The purity of the active ingredient is an important factor for manufacturing the safe and effective pharmaceutical, especially if the pharmaceutical product must be taken on a longer term basis in the treatment or prevention of high plasma cholesterol. The accumulation of the impurities from the pharmaceuticals of lower purity may cause many side effects during the medical treatment. The present invention relates to a new industrial process for the isolation of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors using so-called displacement chromatography. Use of the invention enables one to obtain HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors of high purity, with high yields, lower production costs and suitable ecological balance.
Owner:LEK PHARMA D D
Purification of organic compounds by surfactant mediated preparative HPLC
InactiveCN105555385ALimited useReduce processingIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationPreparative hplcStationary phase
There are only two ways to increase the amount of sample that can be purified by preparative reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (Prep-RP-HPLC) in a single run in spite of recent advances in the production of reversed phase derivatized silica stationary supports: (1) the traditional approach is to use a bigger column (greater amount of stationary phase); and (2) use displacement chromatography which (while labor intensive to develop) uses the stationary phase more effectively. This invention describes a unique Prep-RP-HPLC technique that uses a C-18 / C-8 derivatized silica coated with a surfactant such as Triton X-100 to result in 7 to 10 fold increase in sample loading (of the crude mixture of organic compounds including synthetic crude peptides) in contrast to the conventional Prep-RP-HPLC technique. This increase in sample loading capacity and output is due to the additional surrogate stationary phase characteristic of the C-18 / C8 adsorbed (bound) surfactant. The surfactant is bound to the C-18 / C-8 chains of the stationary phase via Van der Waals forces (hydrophobic interactions) and ionic interactions with the residual silanols of the stationary phase.
Owner:拉马莫罕·拉奥·达瓦鲁利
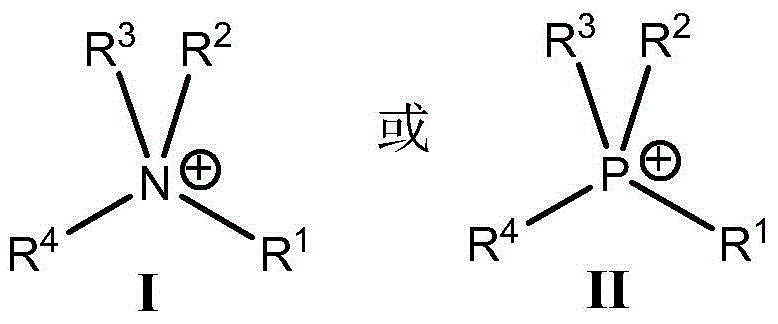
Cationic displacer molecules for hydrophobic displacement chromatography
A process for separating organic compounds from a mixture by reverse-phase displacement chromatography, including providing a hydrophobic stationary phase; applying to the hydrophobic stationary phase a mixture comprising organic compounds to be separated; displacing the organic compounds from the hydrophobic stationary phase by applying thereto an aqueous composition comprising a non-surface active hydrophobic cationic displacer molecule and about 10 wt% or less of an organic solvent; and collecting a plurality of fractions eluted from the hydrophobic stationary phase containing the separated organic compounds; in which the non-surface active hydrophobic cationic displacer molecule comprises a hydrophobic cation and a counterion, CI, having the general formula A or B, as defined in the disclosure.
Owner:SACHEM INC
Anionic displacer molecules for hydrophobic displacement chromatography
InactiveCN103958017ASolid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsStationary phaseOrganic solvent
A process for separating organic compounds from a mixture by reverse-phase displacement chromatography, including providing a hydrophobic stationary phase; applying to the hydrophobic stationary phase a mixture comprising organic compounds to be separated; displacing the organic compounds from the hydrophobic stationary phase by applying thereto an aqueous composition comprising a non-surface active hydrophobic anionic displacer molecule and about 10 wt% or less of an organic solvent; and collecting a plurality of fractions eluted from the hydrophobic stationary phase containing the separated organic compounds; in which the non-surface active hydrophobic anionic displacer molecule comprises a hydrophobic anion and a counterion, CI, having the general formula A or B, as defined in the disclosure: [CM][Cl]d[CM-R*-CM'][Cl]d A B.
Owner:SACHEM INC
Purification of organic compounds by surfactant mediated preparative HPLC
InactiveUS20160237112A1Simple and cost-effective and scalable separation processLimited use of solventSolid sorbent liquid separationLuteinising hormone-releasing hormonePreparative hplcStationary phase
A sample is provided that can be purified by preparative reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (Prep-RP-HPLC) in a single run in spite of recent advances in the production of reversed phase derivatized silica stationary supports: (1) The traditional approach is to use a bigger column (greater amount of stationary phase); and (2) Use displacement chromatography which (while labor intensive to develop) uses the stationary phase more effectively. This disclosure describes a unique Prep-RP-HPLC technique that uses a C-18 / C-8 derivatized silica coated with a surfactant such as Triton X-100 to result in 7 to 10 fold increase in sample loading (of the crude mixture of organic compounds including synthetic crude peptides) in contrast to the conventional Prep-RP-HPLC technique. This increase in sample loading capacity and output is due to the additional surrogate stationary phase characteristic of the C-18 / C8 adsorbed (bound) surfactant.
Owner:DAVULURI RAMAMOHAN RAO
Expression and purification method for bombyx mori odorant binding protein (BmOBP2)
InactiveCN103103209BHigh purityPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesPurification methodsBombyx mori
The invention relates to an expression and purification method for bombyx mori odorant binding protein (BmOBP2). By designing a primer, an expression vector Pet-32a-BmOBP2 is constructed and recombined, a great quantity of recombined interest protein is obtained through inducible expression, and high-purity recombined protein can be obtained by carrying out two simple purification technologies namely nickel ion affinity chromatography and anion displacement chromatography on the recombined protein, so that the method lays a very important foundation for research of the three dimensional structure and biological function of the recombined protein, and the problem that the natural membrane protein has low expression quantity and is difficult to purify is solved.
Owner:TIANJIN YAOYU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Neutral Zwitterionic Displacer Molecules for Hydrophobic Displacement Chromatography
InactiveCN103958016BSolid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsSimple Organic CompoundsStationary phase
Owner:SACHEM INC
Batch preparation method of high-purity salvianolic acid A
InactiveCN102212002BEfficient separationEfficient removalOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSalvianolic acid BChemical composition
The invention relates provides a batch preparation method of high-purity salvianolic acid A based on physical and chemical properties and chromatograph behavior of a chemical component in salvia miltiorrhiza as well as adaptability of salvia miltiorrhiza to a cell separation technology. In the method, a salvianolic acid B transformation liquid containing salvianolic acid A is subjected to three-time chromatograph purification, namely hyphenated chromatography, reversed-phase chromatography and normal-phase silica gel chromatography, wherein the hyphenated chromatography refers to that macroporous resin frontal chromatography and macroporous resin displacement chromatography are jointly used. The product prepared by the method is controllable in quality, is acceptable in cost and can be used for injection medicaments. The content of salvianolic acid A prepared by the method is more than or equal to 98%, the total recovery of salvianolic acid A is more than or equal to 10% (based on salvianolic acid B), and the total yield of salvianolic acid A is more than or equal to 0.5% (based on salvianolic acid B).
Owner:YANTAI TARGET DRUG RES +1
A replacement chromatographic hydrogen isotope separation device
ActiveCN106693703BExtended service lifeRaise the ratioIsotope separationChromatographic separationDesorption
The invention discloses a displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device which comprises a rack as well as a cooling part, a separation column, an air supply part, an air collection part, a lifting part and a driving part. By adopting the displacement chromatography hydrogen isotope separation device disclosed by the invention, different adsorption functions that hydrogen and hydrogen isotope are replaced and separated by using a separation material can be achieved, the lifting part is driven by the driving part to precisely control the lifting position of the separation column, and then the separation column can be descended or lifted off the cooling part, so that adsorption or desorption of hydrogen isotope by the separation material under different temperature conditions can be achieved, a high retention rate of deuterium-tritium isotope in the separation material can be ensured, and a deuterium-tritium isotope gas obtained through final separation and selection is relatively high in purity; compared with the prior art, the device needs no parts for introducing deuterium or separating deuterium, meanwhile deuterium and tritium do not need to be replaced by introducing hydrogen after the separation material is in saturation adsorption of hydrogen, and in addition, the device is simple in structure, low in energy consumption rate, simple in process and low in cost.
Owner:MATERIAL INST OF CHINA ACADEMY OF ENG PHYSICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com