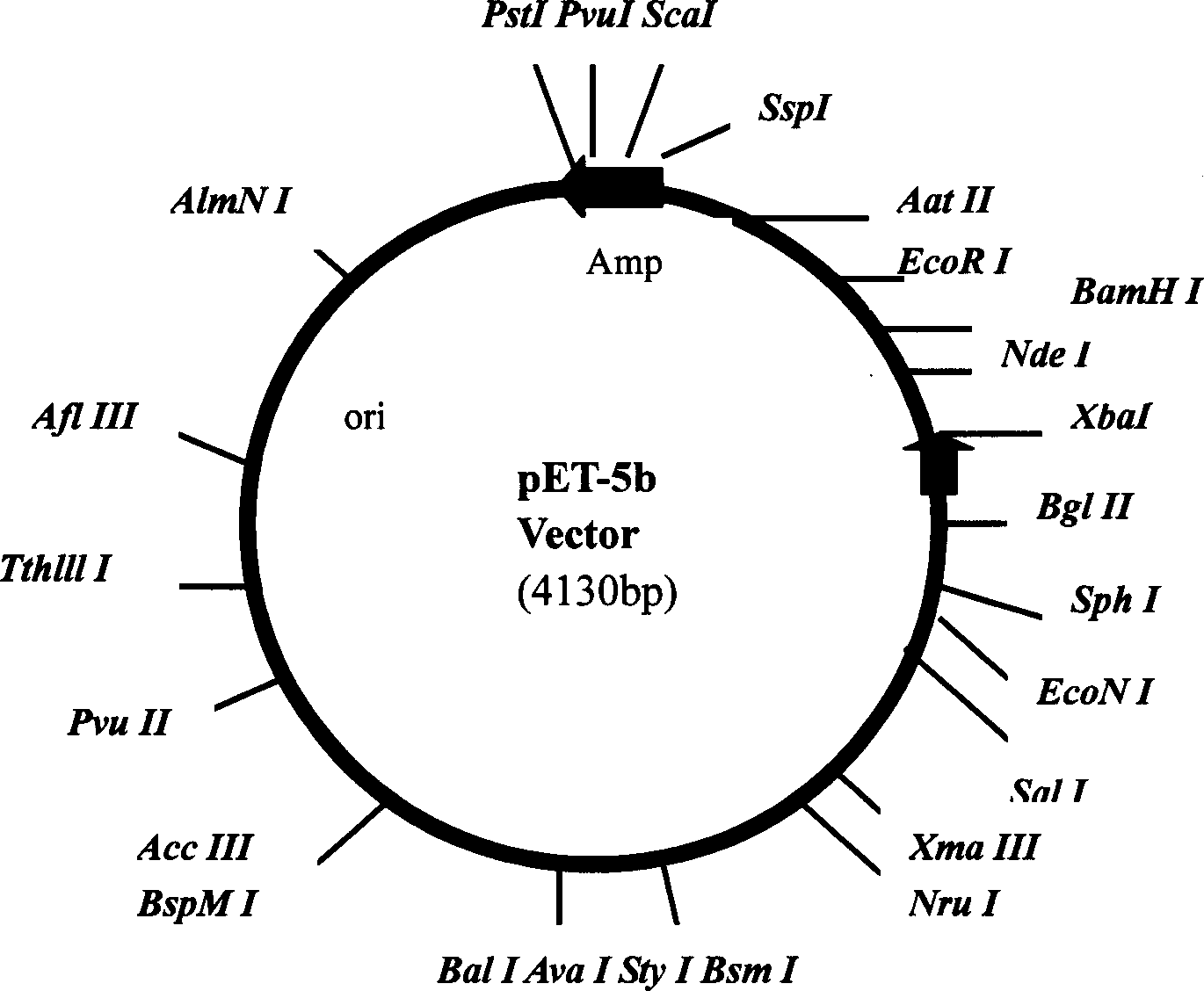
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Odorant-binding protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) are small (10 to 30 kDa) soluble proteins secreted by auxiliary cells surrounding olfactory receptor neurons, including the nasal mucus of many vertebrate species and in the sensillar lymph of chemosensory sensilla of insects. OBPs are characterized by a specific protein domain that comprises six α-helices joined by three disulfide bonds. Although the function of the OBPs as a whole is not well established, it is believed that they act as odorant transporters, delivering the odorant molecules to olfactory receptors in the cell membrane of sensory neurons.
OBPs originated from Adelphocoris lineolatus and its coding gene
InactiveCN102399277AHelps elucidate the mechanism of recognitionLow costBiocidePest attractantsCDNA libraryOdorant binding
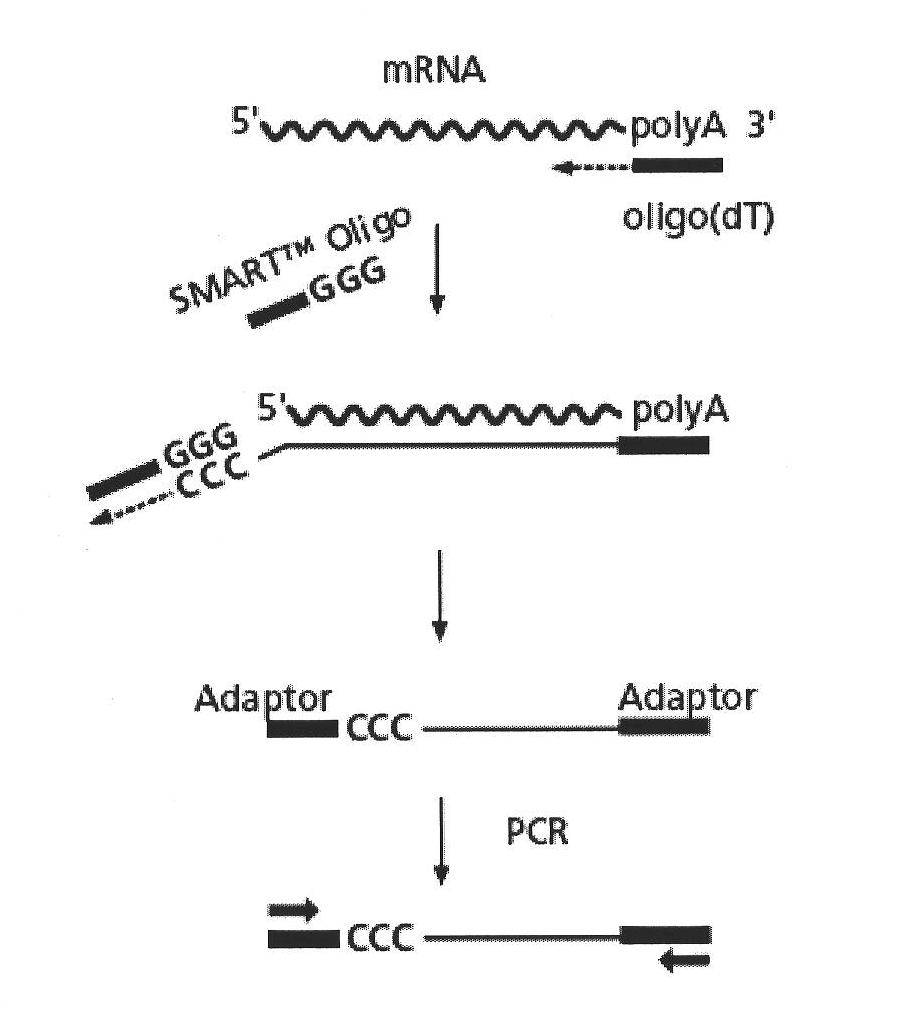
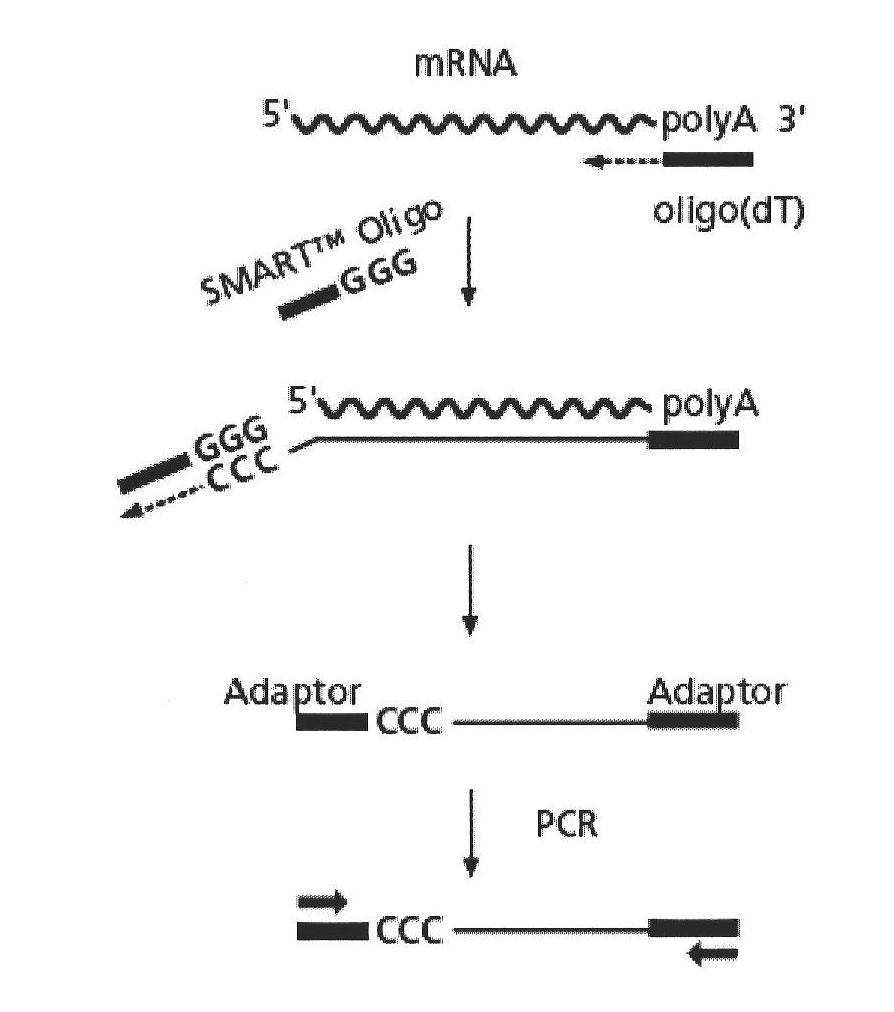
The invention discloses odorant binding proteins (OBPs) originated from Adelphocoris lineolatus and its coding genes. According to the invention, an antenna cDNA library is constructed by utilizing the technology of SMART, and OBPs are effectively separated and identified from antenna of Adelphocoris lineolatus by using an information biological method. Since OBPs have a critical effect on olfactory recognition of insects, and the genes related in the invention can play an important role in biological control of insects.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein-based attractant screening method
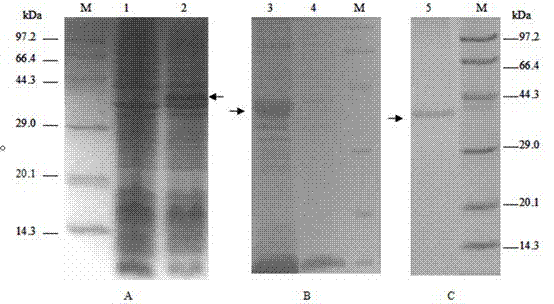
The invention discloses a citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein-based attractant screening method belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. The citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein-based attractant screening method comprises the following steps of: collecting the total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of antennae of a citrus fruit fly; obtaining the overall length of a citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein through RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction); constructing a prokaryotic expression vector of the citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein; inducing the expression of a citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein through IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside), and purifying the citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein through a nickel sepharose gel affinity column; obtaining a conjugation reaction spectrum of the citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein and a host fruit odor volatile matter through a competitive fluorescence combing method, wherein a dissociation constant (KD) is lower than below 10 mu mol / L host fruit smell; and the IC 50 value of fluorescence competition is less than 30 mu mol / L, determining a host fruit smell attractant suitable for the citrus fruit fly. The invention provides a new strategy for screening and designing a citrus fruit fly odorant host fruit smell odor information attractant formula.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Preparing method and application of odorant binding protein sensor based on impedance analysis
ActiveCN103472102AEasy to fixFixing is simple and convenientMaterial electrochemical variablesLower limitAnalysis method
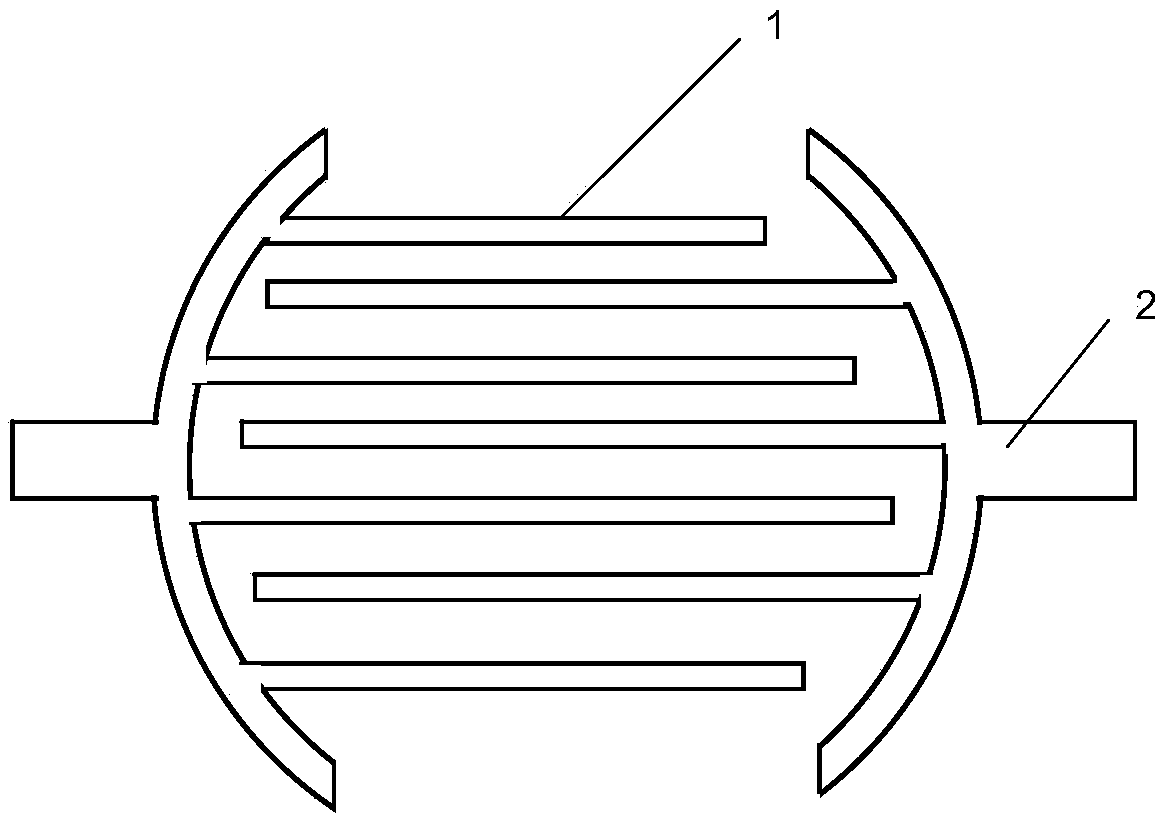
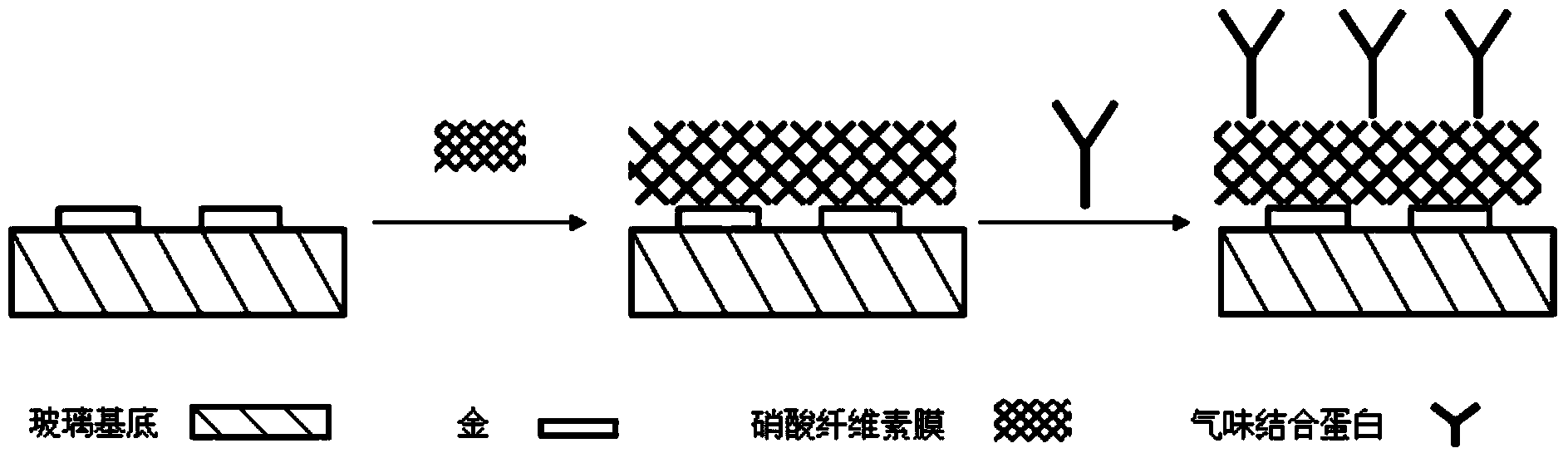
The invention discloses a preparing method and application of an odorant binding protein sensor based on impedance analysis. A plane interdigital gold electrode array is formed by machining in a standard MEMS technology, a nitrocellulose membrane is used for processing the surface of an interdigital gold electrode, odorant binding protein is directly fixed, and the impedance sensor is obtained. An analyzing method with impedance and molecular docking combined is used, and the Chinese bee odorant binding protein Acer-ASP2 is fixed on the interdigital gold electrode and is used for detecting flower fragrance matter and bee pheromone. The established electrochemical sensor can fix the odorant binding protein on the surface of the interdigital gold electrode stably and easily, sensor detecting sensitivity is high, detecting lower limit is low, and specificity is strong.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
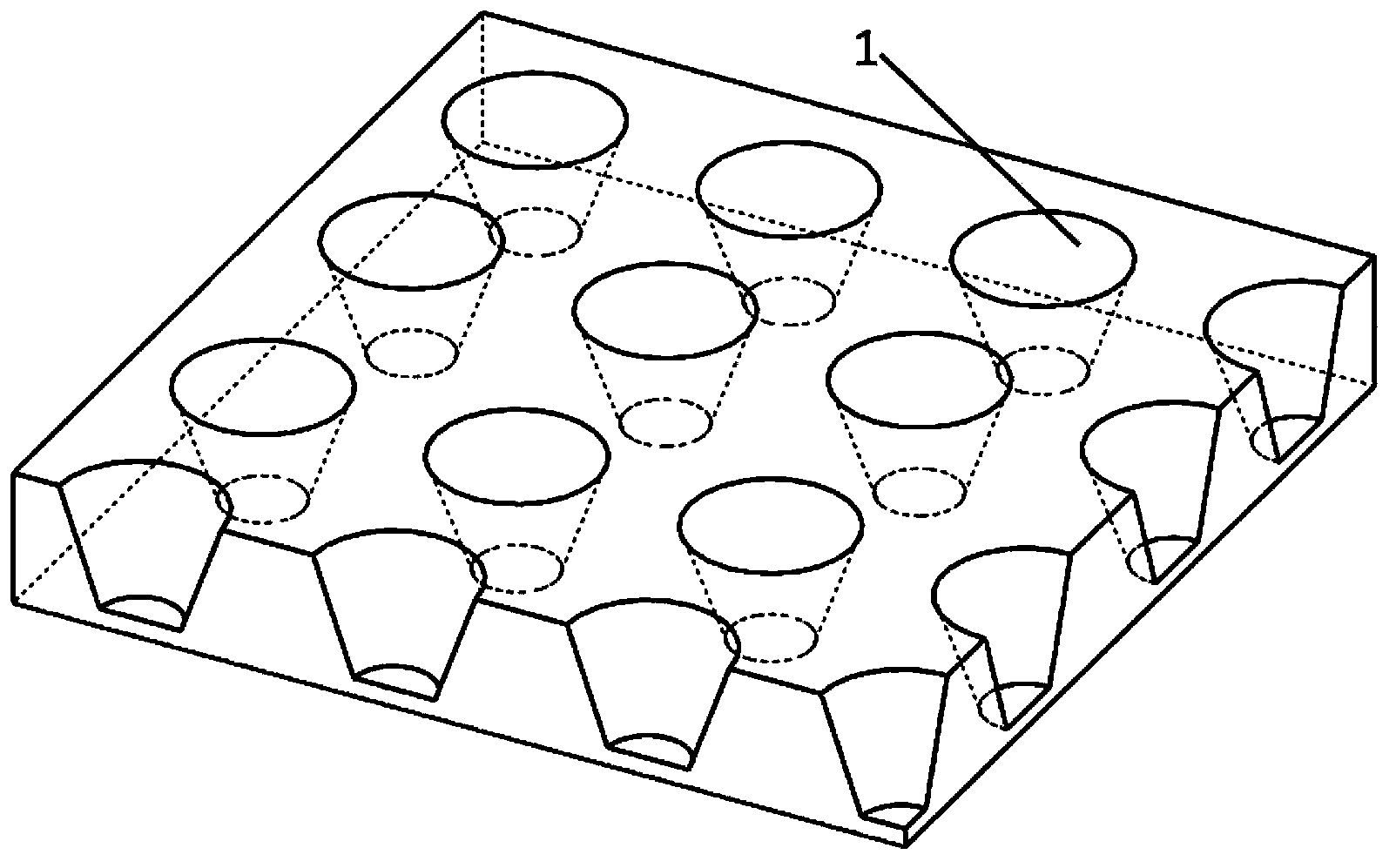
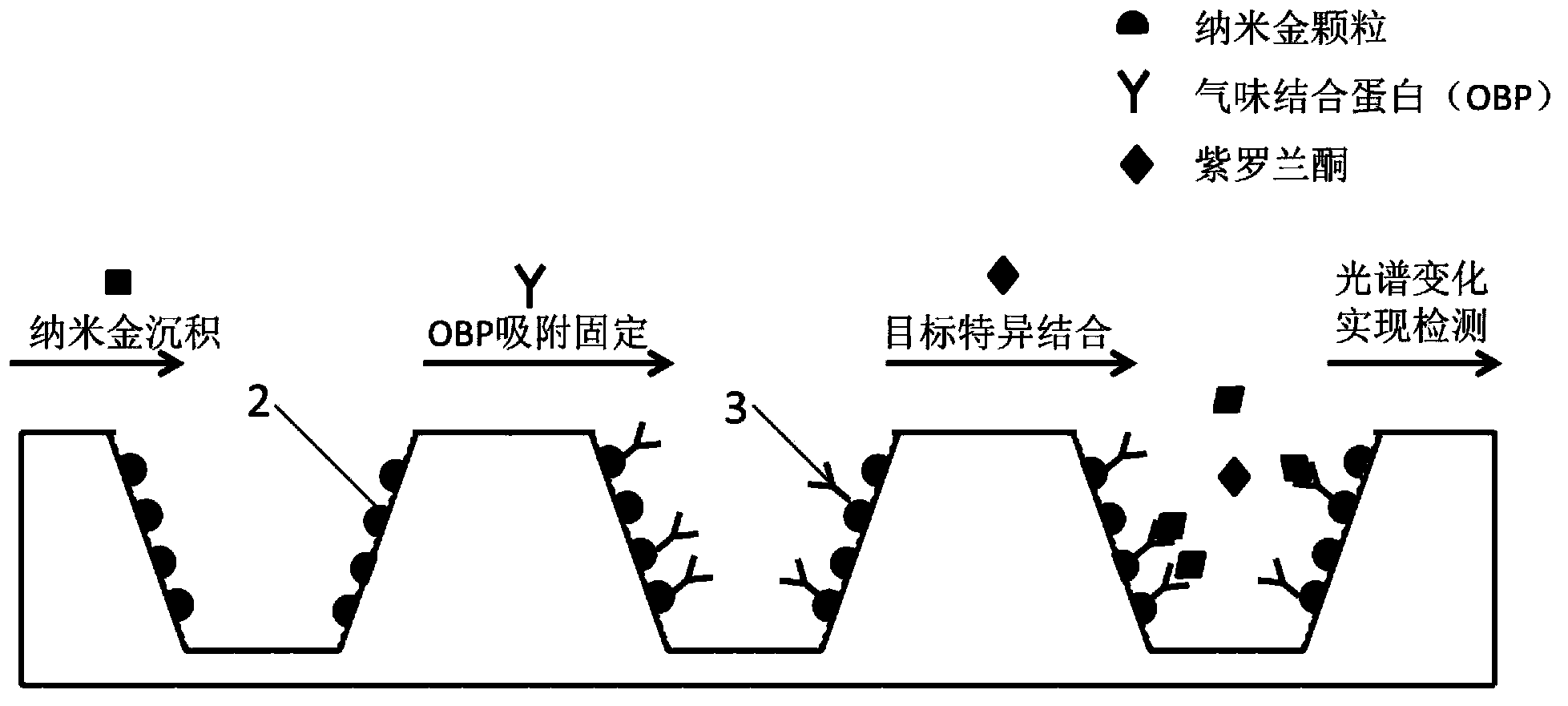
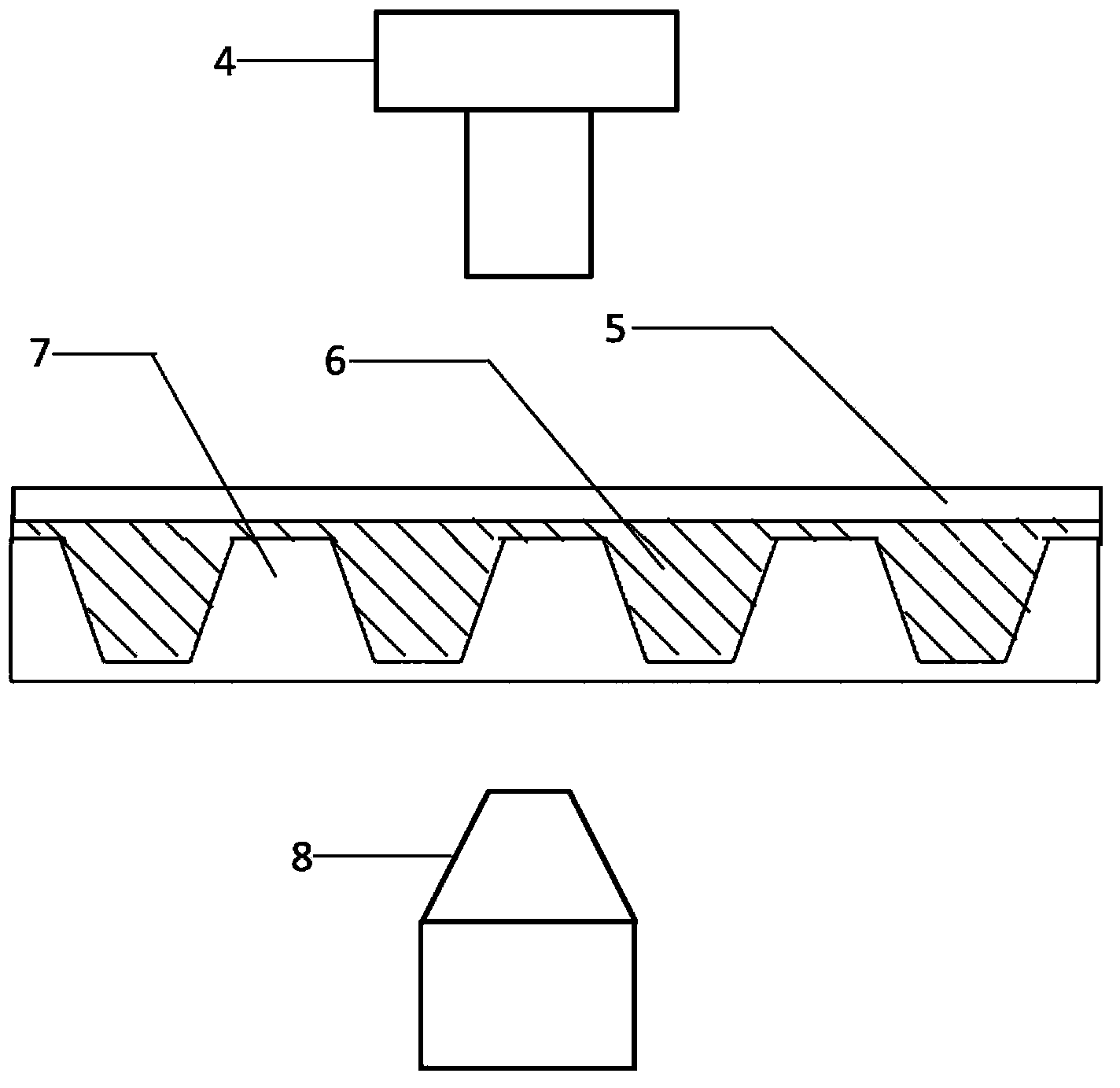
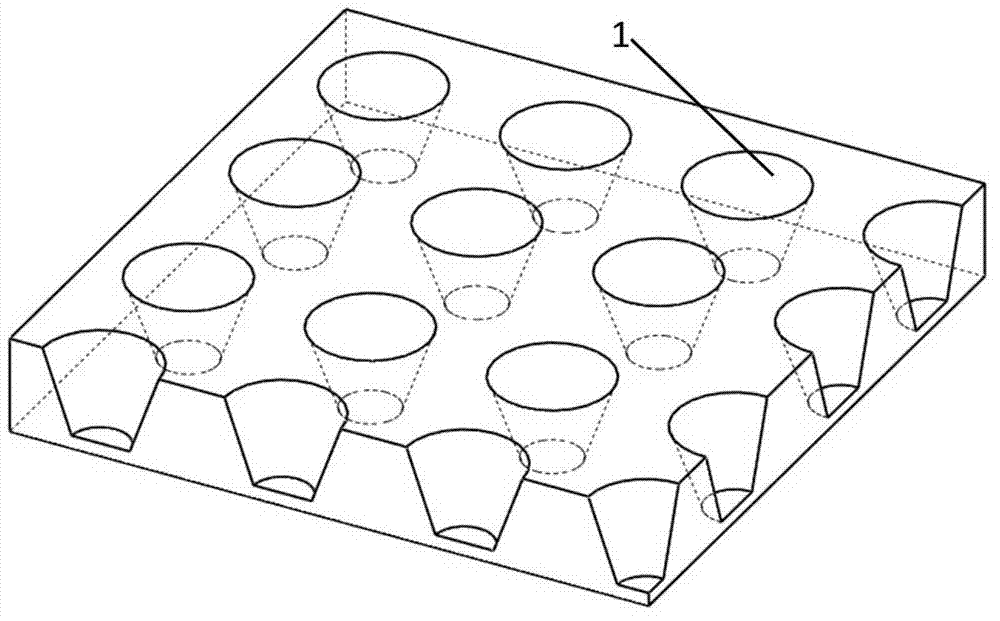
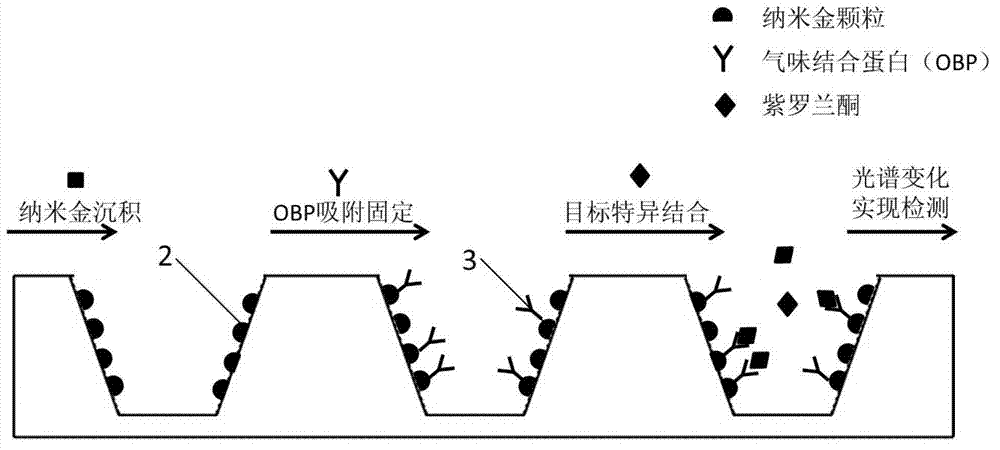
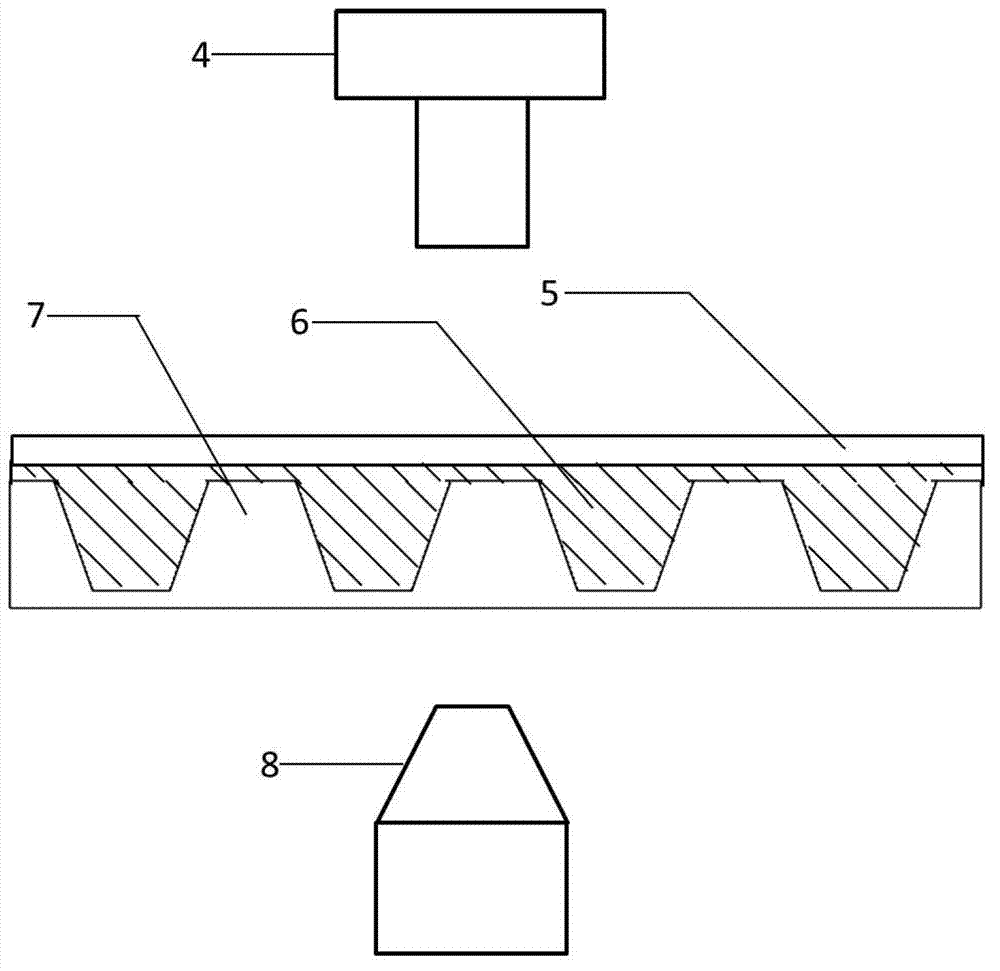
Preparation method of nano cup array biosensor for ionone detection
ActiveCN103439255ARealize detectionHigh sensitivityColor/spectral properties measurementsIononeOdorant-binding protein
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano cup array biosensor for ionone detection. The method comprises the steps that a nanoscale cup-shaped structure is constructed by a nano impressing technology; gold nanoparticles are deposited on a side wall of a nano cup; odorant binding protein Acer-ASP2 is fixed on the side wall of the nano cup by electrostatic adsorption of the gold nanoparticles; during detection, a target molecule ionone is specifically bound with the odorant binding protein to result in change of an optical refraction characteristic of the side wall of the nano cup; and a spectrum of transmission light passing through the biosensor is changed correspondingly, so that the detection of the target molecule ionone is realized. Compared with the traditional ionone detection means, the nano cup array biosensor avoids a complicated light path required by optical detection and is simple, convenient and quick to operate based on the advantages of high sensitivity and specificity of the optical detection means.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High efficiency expression of smell molecule combined protein of migratory locust in pronucleus system
InactiveCN1782073AHigh expressionSimple procedureFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMigratory locustPronucleus
The present invention discloses a method of expressing recombinant odorant binding protein (OBP) of insect in prokaryotic cell, and vector containing target nucleic acid sequence is transformed to competent prokaryotic cell. The present invention also discloses new OBP-coding nucleic acid sequence obtained from Locusta migratoria antenna.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Smell activator screening method based on apis cerana odorant binding protein
The invention discloses a plant fragrance smell activator formula screening method based on apis cerana odorant binding protein. The method comprises the following process steps: 1) extracting working bee antenna total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of apis cerana; 2) designing an apis cerana odorant binding protein gene primer, and acquiring the full length of an apis cerana odorant binding protein gene through RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction); 3) building a prokaryotic expression vector of the apis cerana odorant binding protein gene; 4) inducing recombinant expression of the apis cerana odorant binding protein through IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside), and performing purification through a Ni Sepharose FF affinity column; 5) acquiring a combined response spectrum of the apis cerana odorant binding protein and plant fragrance smell through a competitive fluorescent combination method, and determining the combined response spectrum as the plant fragrance smell activator suitable for the apis cerana when the dissociation constant KD is lower than 20mummol / L.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
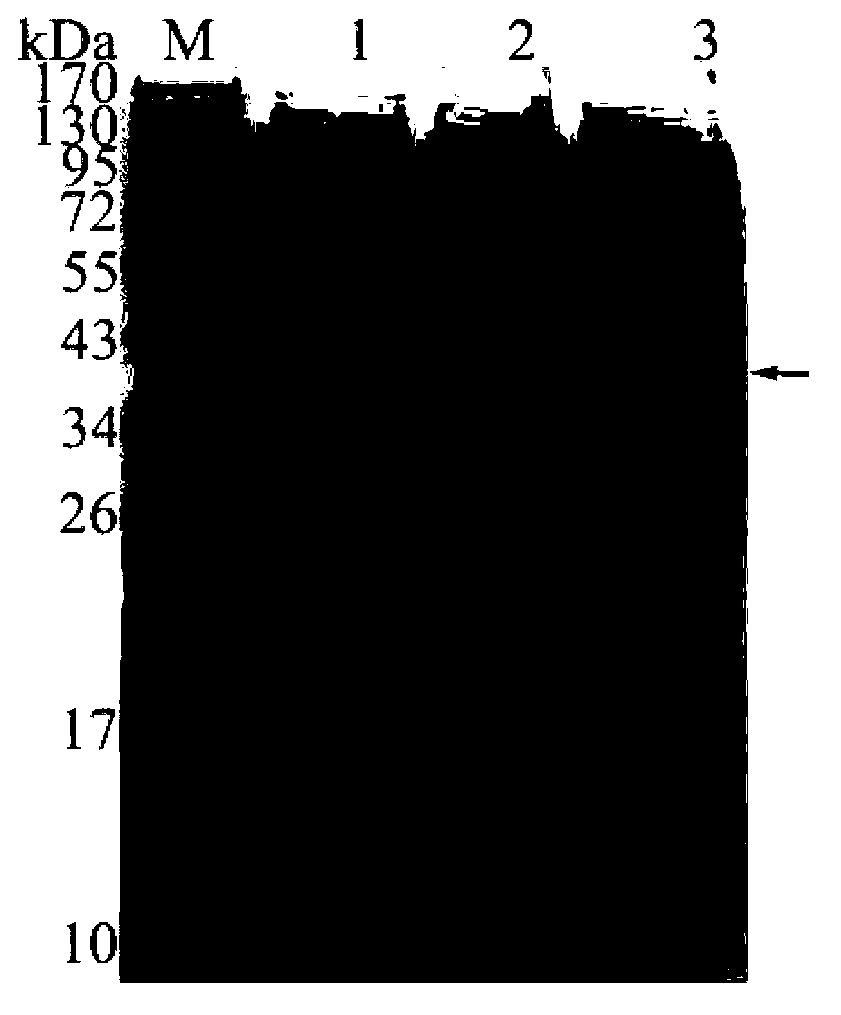
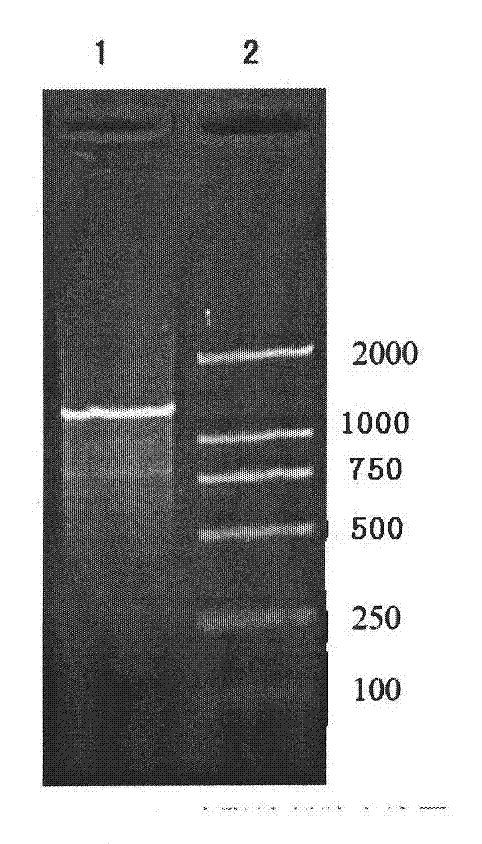
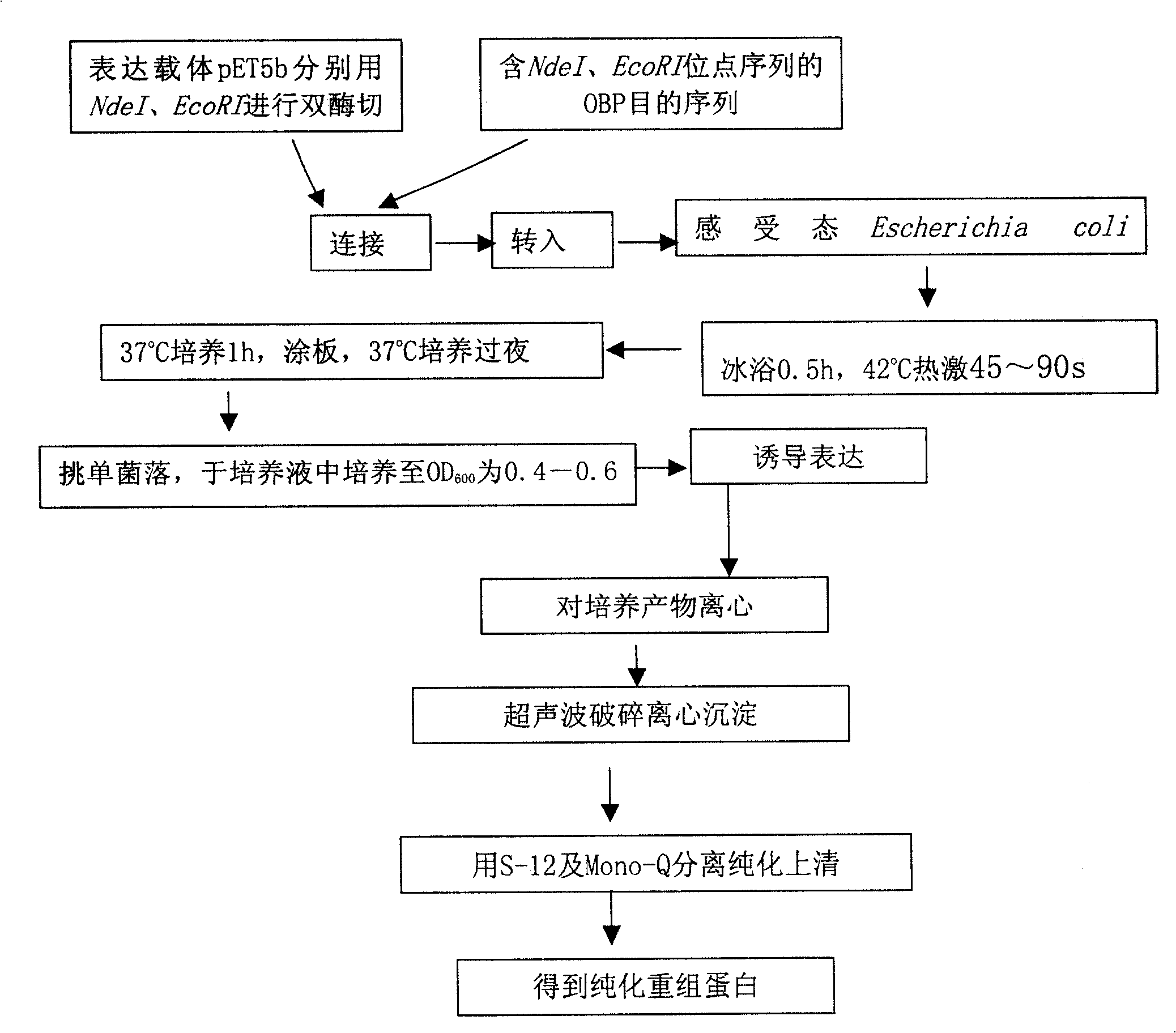
Expression and purification method for bombyx mori odorant binding protein (BmOBP2)
InactiveCN103103209AHigh purityLow expressionPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesPurification methodsBombyx mori
The invention relates to an expression and purification method for bombyx mori odorant binding protein (BmOBP2). By designing a primer, an expression vector Pet-32a-BmOBP2 is constructed and recombined, a great quantity of recombined interest protein is obtained through inducible expression, and high-purity recombined protein can be obtained by carrying out two simple purification technologies namely nickel ion affinity chromatography and anion displacement chromatography on the recombined protein, so that the method lays a very important foundation for research of the three dimensional structure and biological function of the recombined protein, and the problem that the natural membrane protein has low expression quantity and is difficult to purify is solved.
Owner:TIANJIN YAOYU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method for detecting self-mutilation rate of insects by using odorant binding protein 15 gene
InactiveCN103060467BEasy to buyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMetapopulationAmino acid
The invention discloses a method for detecting the self-mutilation rate of insects by using an odorant binding protein 15 gene. The invention provides an application of a substance for detecting the expression level of an odorant binding protein 15 coding gene in insect populations fed with different substances in detection of the self-mutilation rate of the insect populations fed with different substances; and the amino acid sequence of an odorant binding protein 15 is sequence 2 in a sequence table. According to the method disclosed by the invention, experiments prove that the detection method provided by the invention can be used for detecting the self-mutilation rate of the insects, in particular to the self-mutilation rate of arma chinensis with different nutrient sources; and the detection of the self-mutilation rate of the insects by the detection method disclosed by the invention only requires 2-3 days. However, the use of a traditional biological method requires about 30-60 days. The detection method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of wide range of involved material sources, easiness in purchase, simplicity in operation, and time-saving and labor-saving properties, and is suitable for popularization and application in commodity inspection and detection of insects.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method
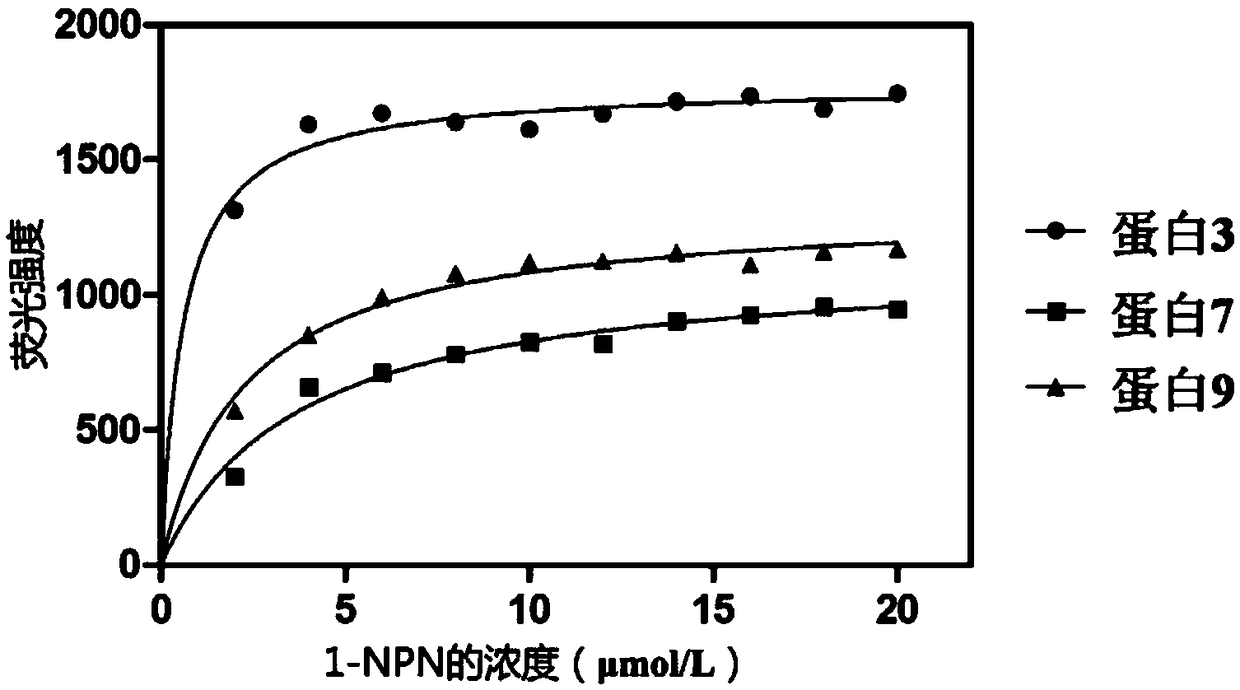
The invention discloses a tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method comprises the following processes of collecting tea geometrid antenna total RNA, acquiring total length of a tea geometrid odorant binding protein by RT-PCR, constructing a prokaryotic expression vector of the tea geometrid odorant binding protein, inducing the expression of the recombinant tea geometrid odorant binding protein by IPTG, carrying out the purification of the recombinant tea geometrid odorant binding protein by nickel sepharose gel affinity column, acquiring a binding reaction spectrum of the recombinant tea geometrid odorant binding protein and tea leaf smell volatiles by a competitive fluorescent combination method, and determining that the tea leaf smell volatile reducing relative fluorescence intensity of 1-NPN to less than 50% and having the binding constant of 13-45 micromoles per liter is the plant attractant of tea geometrid. The tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method provides a novel means for screening and designing a formula of a plant tea geometrid smell information attractant.
Owner:HANGZHOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Coding gene OBP11 for OBPs (odorant binding proteins) of brown planthopper and application
InactiveCN109336961AReduce pesticide useReduce human inputFermentationAnimals/human peptidesBrown planthopperOdorant binding
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly discloses a coding gene OBP11 for OBPs (odorant binding proteins) of brown planthopper and an application. The amino acid sequence of the OBPs of the brown planthopper is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The OBPs play an essential role in growth and development processes of the brown planthopper, a lethal effect can be realized on the brown planthopper by silencing the gene, the sequence has stronger target specificity, and the killing effect on other types of insects and species is avoided. Therefore, a new direction and theoretical basis are provided for control of the brown planthopper and culture of resistant varieties.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Apparatus and method for detecting combination process of odorant-binding protein and pheromone
ActiveCN104034761ALow costLow detection limitMaterial electrochemical variablesApis ceranaHigh resistance
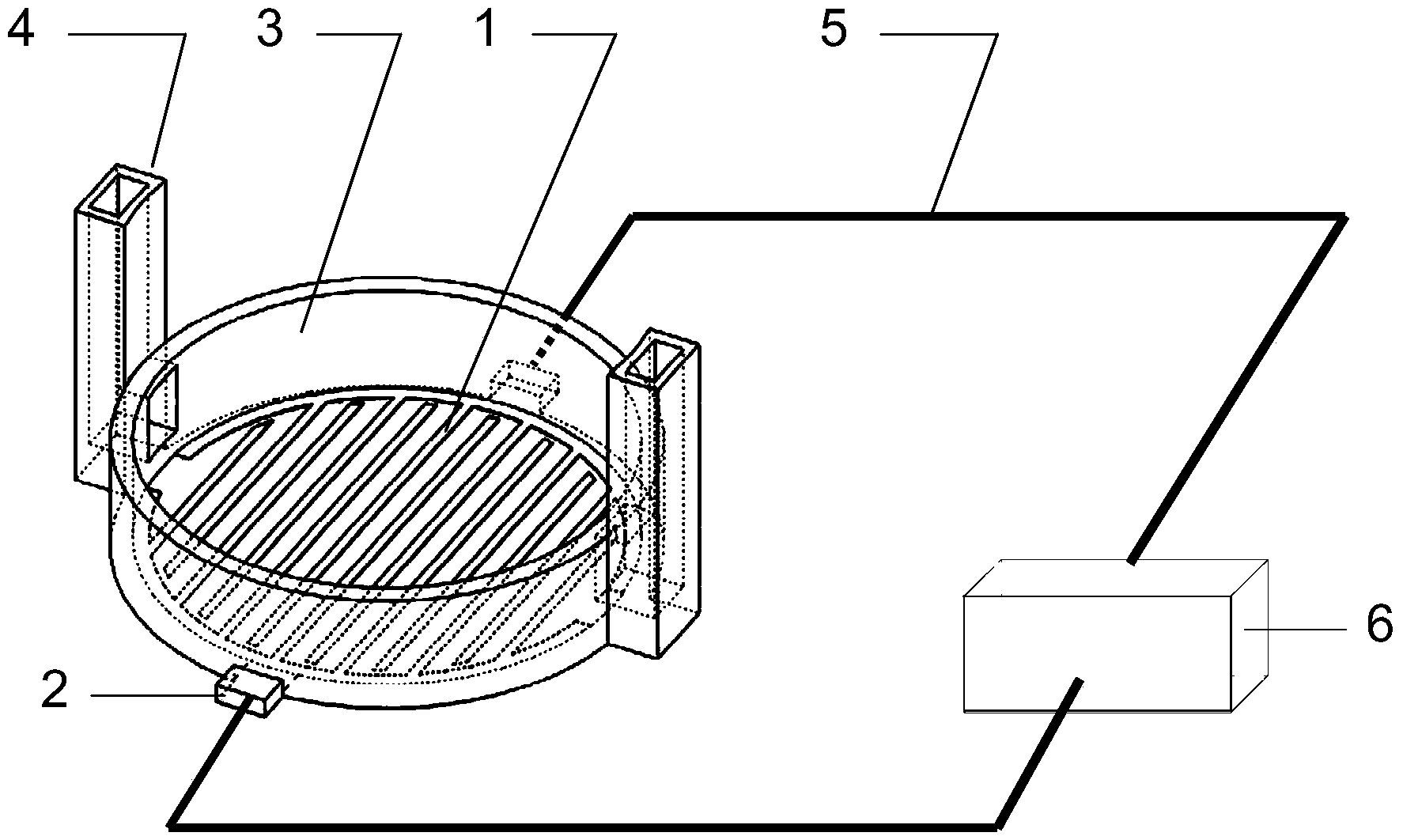
The invention discloses an apparatus and a method for detecting a combination process of odorant-binding protein and pheromone. The apparatus comprises a sample introduction system, a measure transition system, a counter electrode, a reference electrode, a working electrode, a measure groove, an oscillator, a liquid-outlet peristaltic pump, a waste liquid groove and a computer; the sample introduction system consists of a first peristaltic pump, a second peristaltic pump, a third peristaltic pump, a first injector, a second injector, a third injector and a controller; and the measure transition system consists of a measure circuit, a high-resistance electrometer and a measure circuit. The method comprises preparing honeybee pheromone isoamyl-acetate standard solutions with different concentration, an apis-cerana-ceraca odorant-binding protein (Acer-ASP2) standard solution, and mixed solutions of apis-cerana-ceraca odorant-binding protein (Acer-ASP2) and honeybee pheromone isoamyl acetate and with different concentration, and detecting variation of electrochemical impedance of the three kinds of solutions along with time, so as to obtain corresponding electrochemical impedance spectrograms, and further to obtain the combination of odorant-binding protein and pheromone.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
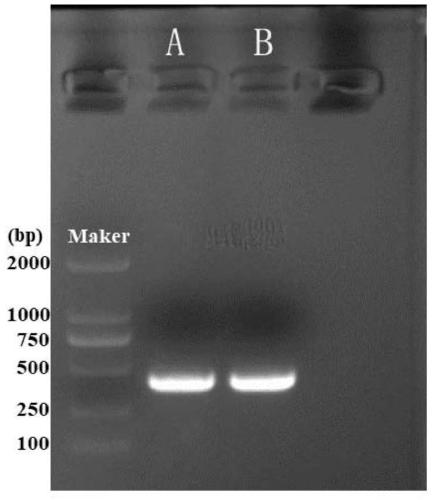
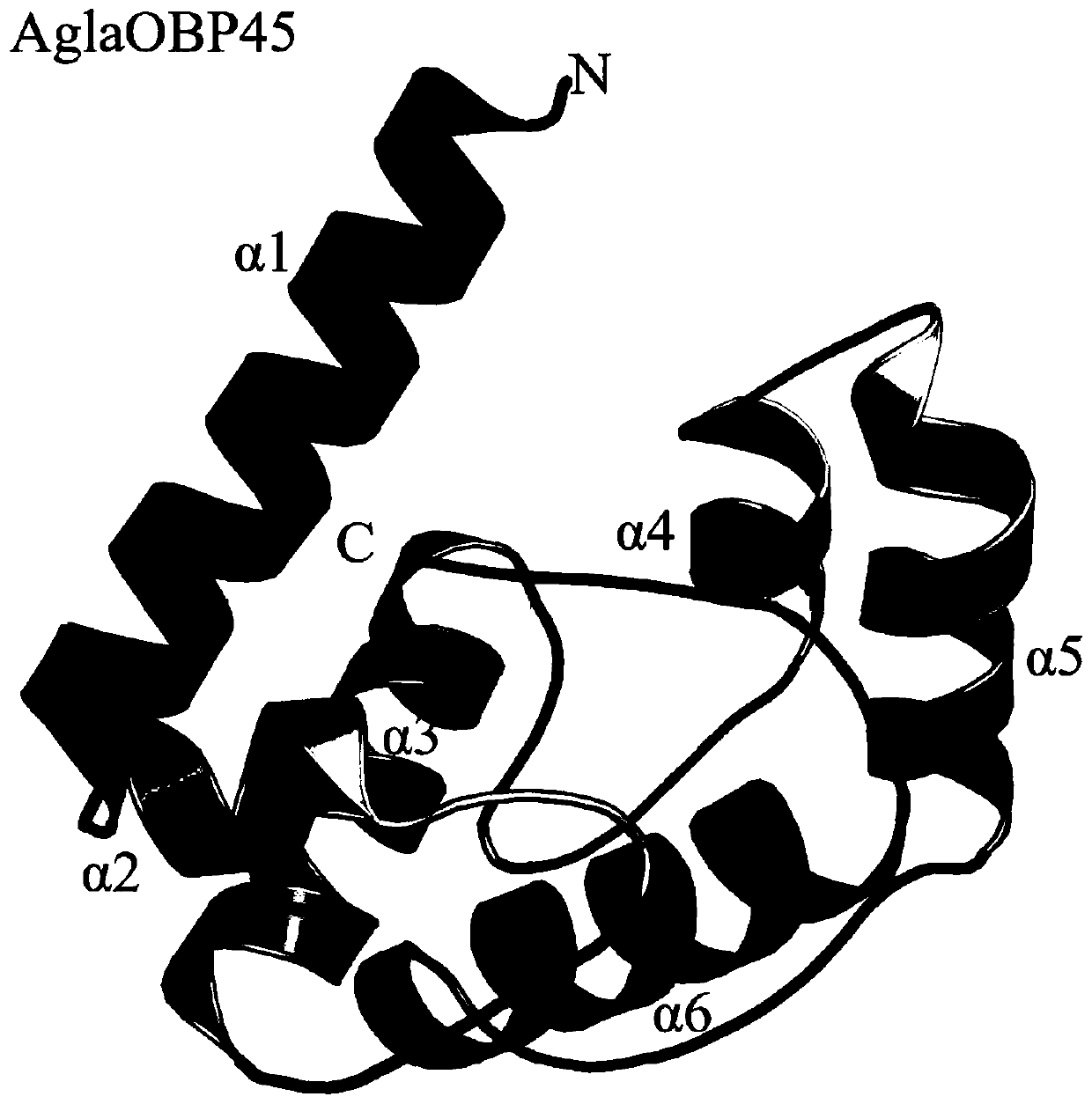
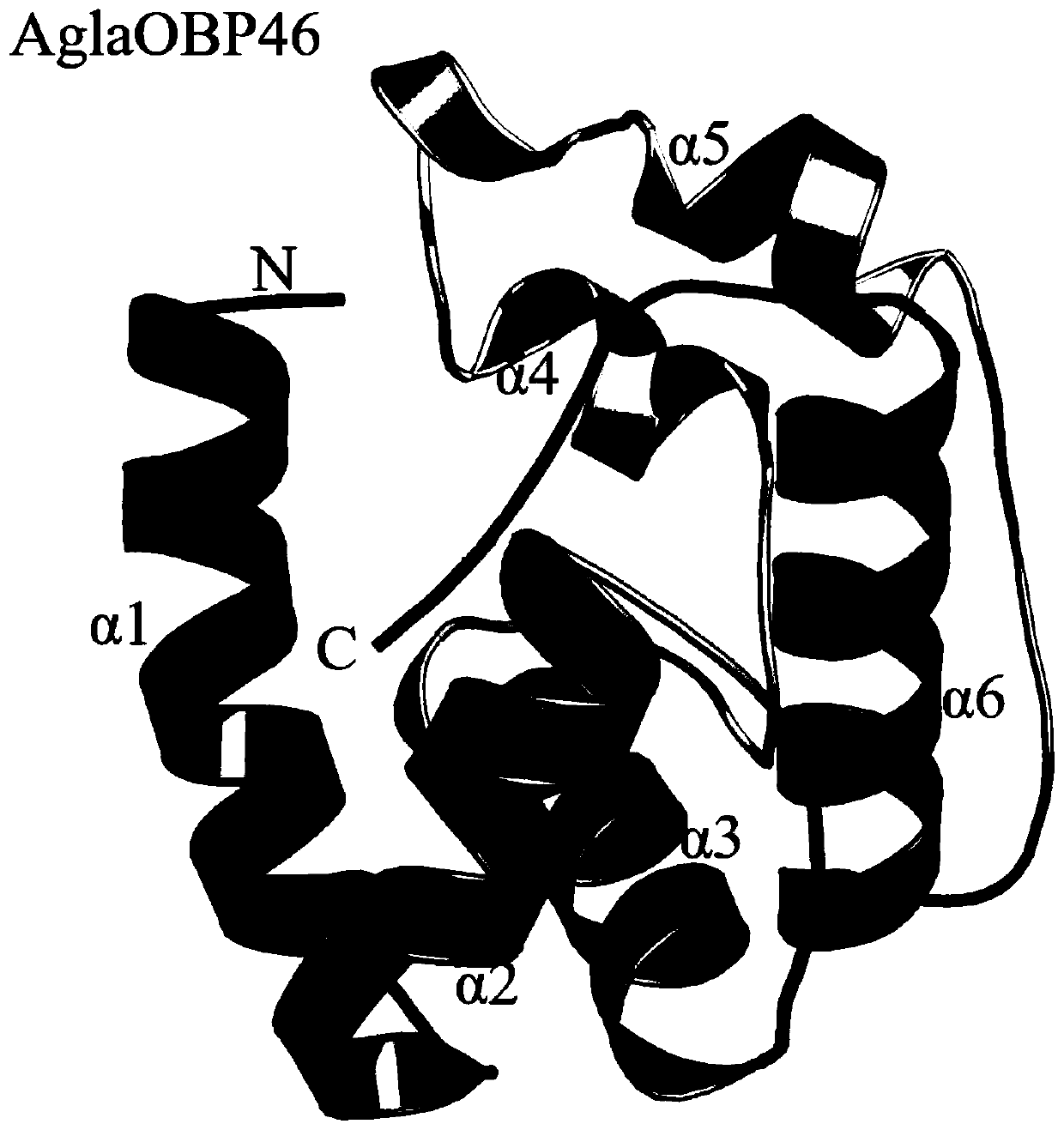
Anoplophora glabripennis odorant binding protein OBP45, OBP46 and application in screening attractants thereof
InactiveCN110272475AImprove screening efficiencyEfficient screeningProteomicsGenomicsFluorescenceScreening method
The invention discloses anoplophora glabripennis odorant binding protein OBP45, OBP46 and genes thereof. The invention further discloses an attractant screening method based on the anoplophora glabripennis odorant binding protein OBP45, OBP46. The anoplophora glabripennis odorant binding protein OBPs homology modeling, computer virtual screening and a fluorescence competition experiment are combined, the screening efficiency of odor molecules is greatly improved, and a new strategy is provided for the screening and design of a formula of an anoplophora glabripennis olfactory attractant. According to a fluorescence competitive combination method, the combining capacity of 34 anoplophora glabripennis host main volatiles and 7 pheromone molecules is determined, a fluorescence competitive compound with an IC50 value (20 [mu] mol / L, or the dissociation constant KD is (20 [mu] mol / L) is determined as the olfactory attractant suitable for anoplophora glabripennis.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for separation and identification of odorant binding protein (OBP) genes in insect's antenna
InactiveCN102399773AHelps elucidate the mechanism of recognitionLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsSmart technologyOrganism
The invention discloses a method for antenna cDNA library construction adopting a SMART technology, and separation and identification of odorant binding protein (OBP) genes in an insect's antenna. The method can realize effective separation and identification of the OBP genes in adelphocoris lineolatus through a bioinformatic method. Through the method, nucleotide sequences of 14 OBP genes of adelphocoris lineolatus are screened out. Because of important effects of the OBP genes on insect olfactory identification, the OBP genes have important effects on insect biological control.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Attractant screening method based on citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein
The invention discloses an attractant screening method based on citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein, and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps of collecting citrus fruit fly tentacle total RNA; obtaining the whole length of the citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein through RT-PCR; building a prokaryotic expression vector of the citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein; inducing the citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein through IPTG; performing purification through a nickel agarose gel affinity chromatographic column; obtaining a combination reaction spectrum of the citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein and the host fruit odorant volatile matter by a competitive fluorescent combination method; when the dissociation constant KD is lower than 10 mumol / L of host fruit smell, and the fluorescence competition IC50 value is smaller than 30mumol / L, determining the attractant to be the host fruit smell Attractant suitable for the citrus fruit fly. The invention provides a novel strategy for the screening and the designing of the citrus fruit fly host fruit smell odorant information attractant recipe.
Owner:四川科劲生物科技有限公司
Vegetable leafminer odorant-binding protein and application thereof
The invention relates to a separated vegetable leafminer odorant-binding protein, its encoding protein and an application thereof. The protein can bind to odors matters of 4-ethyl benzaldehyde, azulene, 3,4-dimethyl acetophenone and p-ethylacetophenone, and combination of the protein and the odors matters can be used for preventing and treating vegetable leafminer.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
OBPs originated from Adelphocoris lineolatus and its coding gene
InactiveCN102399277BHelps elucidate the mechanism of recognitionLow costBiocidePest attractantsCDNA libraryOdorant binding
The invention discloses odorant binding proteins (OBPs) originated from Adelphocoris lineolatus and its coding genes. According to the invention, an antenna cDNA library is constructed by utilizing the technology of SMART, and OBPs are effectively separated and identified from antenna of Adelphocoris lineolatus by using an information biological method. Since OBPs have a critical effect on olfactory recognition of insects, and the genes related in the invention can play an important role in biological control of insects.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting self-mutilation rate of insects by using odorant binding protein 15 gene
InactiveCN103060467AEasy to buyEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMetapopulationAmino acid
The invention discloses a method for detecting the self-mutilation rate of insects by using an odorant binding protein 15 gene. The invention provides an application of a substance for detecting the expression level of an odorant binding protein 15 coding gene in insect populations fed with different substances in detection of the self-mutilation rate of the insect populations fed with different substances; and the amino acid sequence of an odorant binding protein 15 is sequence 2 in a sequence table. According to the method disclosed by the invention, experiments prove that the detection method provided by the invention can be used for detecting the self-mutilation rate of the insects, in particular to the self-mutilation rate of arma chinensis with different nutrient sources; and the detection of the self-mutilation rate of the insects by the detection method disclosed by the invention only requires 2-3 days. However, the use of a traditional biological method requires about 30-60 days. The detection method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of wide range of involved material sources, easiness in purchase, simplicity in operation, and time-saving and labor-saving properties, and is suitable for popularization and application in commodity inspection and detection of insects.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A device and method for detecting the binding process of odorant binding protein and pheromone
ActiveCN104034761BLow costLow detection limitMaterial electrochemical variablesPeristaltic pumpHigh resistance
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for detecting expression of odorant-binding protein gene OBP6 of Italian bees by using fluorescent RT-PCR technology
ActiveCN108660219AGuaranteed reliabilityGuaranteed repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementItalian beeFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for detecting expression of an odorant-binding protein gene OBP6 of Italian bees by using fluorescent RT-PCR technology, and particularly relates to the technical field of biology. The method for detecting the expression of the odorant-binding protein gene OBP6 of the Italian bees by using the fluorescent RT-PCR technology comprises the following steps that (1), OBP6 genes are detected by using primers; (2), total RNA extraction is performed; (3), cDNA synthesis is performed; (4), real-time fluorescent PCR is performed; and (5), the relative expression quantityof OBP6 of the Italian bees is calculated before and after benomyl treatment. The real-time fluorescent RT-PCR adopted by the method for detecting the expression of the odorant-binding protein gene OBP6 of the Italian bees by using the fluorescent RT-PCR technology is compared with conventional PCR, and the real-time fluorescent PCR technology collects fluorescent signals by automated instruments, the subjectivity of visual judgment is avoided, and the sensitivity is further improved; and at the same time, the real-time fluorescent RT-PCR technology reacts in a fully closed mode without post-treatment of PCR, pollution is avoided, and the reliability and repeatability of the results are ensured. At the same time, the following tedious steps such as electrophoresis and quantitative scanning in routine PCR are eliminated, and the experiment time is greatly shortened.
Owner:SERICULTURAL RES INST ANHUI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
A kind of Liriomyza sativae odorant binding protein and its application
The invention relates to a separated vegetable leafminer odorant-binding protein, its encoding protein and an application thereof. The protein can bind to odors matters of 4-ethyl benzaldehyde, azulene, 3,4-dimethyl acetophenone and p-ethylacetophenone, and combination of the protein and the odors matters can be used for preventing and treating vegetable leafminer.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Expression and purification method for bombyx mori odorant binding protein (BmOBP2)
InactiveCN103103209BHigh purityPeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesPurification methodsBombyx mori
The invention relates to an expression and purification method for bombyx mori odorant binding protein (BmOBP2). By designing a primer, an expression vector Pet-32a-BmOBP2 is constructed and recombined, a great quantity of recombined interest protein is obtained through inducible expression, and high-purity recombined protein can be obtained by carrying out two simple purification technologies namely nickel ion affinity chromatography and anion displacement chromatography on the recombined protein, so that the method lays a very important foundation for research of the three dimensional structure and biological function of the recombined protein, and the problem that the natural membrane protein has low expression quantity and is difficult to purify is solved.
Owner:TIANJIN YAOYU BIOLOGICAL TECH
Preparation method of nanocup array biosensor device for ionone detection
ActiveCN103439255BRealize detectionHigh sensitivityColor/spectral properties measurementsNanoparticleOrganic chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nano cup array biosensor for ionone detection. The method comprises the steps that a nanoscale cup-shaped structure is constructed by a nano impressing technology; gold nanoparticles are deposited on a side wall of a nano cup; odorant binding protein Acer-ASP2 is fixed on the side wall of the nano cup by electrostatic adsorption of the gold nanoparticles; during detection, a target molecule ionone is specifically bound with the odorant binding protein to result in change of an optical refraction characteristic of the side wall of the nano cup; and a spectrum of transmission light passing through the biosensor is changed correspondingly, so that the detection of the target molecule ionone is realized. Compared with the traditional ionone detection means, the nano cup array biosensor avoids a complicated light path required by optical detection and is simple, convenient and quick to operate based on the advantages of high sensitivity and specificity of the optical detection means.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High efficiency expression of smell molecule combined protein of migratory locust in pronucleus system
InactiveCN100424173CFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionMigratory locustPronucleus
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Odorant-binding protein of Myzus persicae and application of odorant-binding protein
ActiveCN108333156AEnrich chemical ecology theoryAchieve the purpose of preventionFluorescence/phosphorescenceMyzus persicaeAmino acid
The invention relates to an odorant-binding protein of Myzus persicae and an application of the odorant-binding protein. Amino acid sequence is at least one selected from amino acid sequences shown asSEQ ID No.2, SEQ ID No.4 and SEQ ID No.6.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Urine protein marker for asthma and application thereof
The invention relates to a urine protein marker for asthma and application thereof. The present application relates to the application of a urine protein marker selected from a group consisting of epidermal growth factor receptor substrate 15, Cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide, haptoglobin, alpha-1-acidic glycoprotein 1, prolactin-inducing protein homolog, odorant binding protein 2a, protein LEG1homolog, complement factor B, retinoid beta, beta-2 microglobulin, prothrombin, eosinophilic granulocyte cationic protein 1, protein AMBP, plasminogen, a procollagen C-endopeptidase enhancer 1, a sodium channel and gridding protein connecting agent 1 and vitamin D binding protein. According to the application, an animal model for screening the asthma-related urine protein marker is established, the asthma-related urine protein marker is obtained by using the established animal model, and an application of a detection reagent of the marker in preparation of a kit for diagnosing asthma of a subject is also established.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A method for detecting the expression of the odorant-binding protein gene obp6 in Apis mellifera using fluorescent RT-PCR
ActiveCN108660219BGuaranteed reliabilityGuaranteed repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementItalian beeFluorescence
Owner:SERICULTURAL RES INST ANHUI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
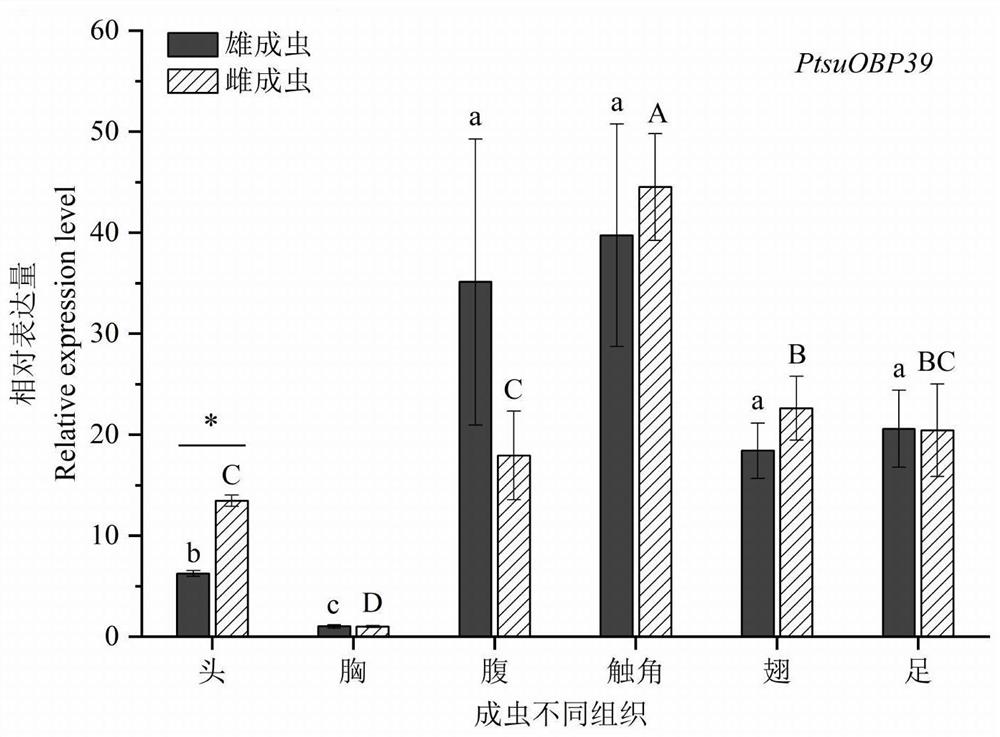
Protein PtsuOBP39 bound with volatile compounds of Cinnamomum camphora and insect pheromone, attractant and application of protein PtsuOBP39 and attractant
The invention provides a protein PtsuOBP39 bound with volatile compounds of Cinnamomum camphora and insect pheromone, an attractant and application of the protein PtsuOBP39 and the attractant and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. The odorant-binding protein is PtsuOBP39, an amino acid sequence of the odorant-binding protein is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and a coding gene of the odorant-binding protein is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The protein and the gene can be used for reversely verifying and screening key components of the attractant for the pest Pagiophloeus tsushimanus, a foundation is laid for analyzing an olfactory molecular mechanism of the Pagiophloeus tsushimanus, and a reference basis is also provided for developing a pest prevention and control technology taking a pest olfactory key gene as a target. The screened (1alpha,3alpha,4alpha,6alpha)-4,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-3-ol Cinnamomum-camphora volatile compounds capable of being specifically bound with the protein are used for preparing the attractant, and a new way of think is provided for monitoring, preventing and controlling the Pagiophloeus tsushimanus.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV +1
A screening method for plant-derived attractants based on tea geometrid odor-binding protein
The invention discloses a tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method comprises the following processes of collecting tea geometrid antenna total RNA, acquiring total length of a tea geometrid odorant binding protein by RT-PCR, constructing a prokaryotic expression vector of the tea geometrid odorant binding protein, inducing the expression of the recombinant tea geometrid odorant binding protein by IPTG, carrying out the purification of the recombinant tea geometrid odorant binding protein by nickel sepharose gel affinity column, acquiring a binding reaction spectrum of the recombinant tea geometrid odorant binding protein and tea leaf smell volatiles by a competitive fluorescent combination method, and determining that the tea leaf smell volatile reducing relative fluorescence intensity of 1-NPN to less than 50% and having the binding constant of 13-45 micromoles per liter is the plant attractant of tea geometrid. The tea geometrid odorant binding protein-based plant attractant screening method provides a novel means for screening and designing a formula of a plant tea geometrid smell information attractant.
Owner:HANGZHOU ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein-based attractant screening method
The invention discloses a citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein-based attractant screening method belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. The citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein-based attractant screening method comprises the following steps of: collecting the total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of antennae of a citrus fruit fly; obtaining the overall length of a citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein through RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction); constructing a prokaryotic expression vector of the citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein; inducing the expression of a citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein through IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside), and purifying the citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein through a nickel sepharose gel affinity column; obtaining a conjugation reaction spectrum of the citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein and a host fruit odor volatile matter through a competitive fluorescence combing method, wherein a dissociation constant (KD) is lower than below 10 mu mol / L host fruit smell; and the IC 50 value of fluorescence competition is less than 30 mu mol / L, determining a host fruit smell attractant suitable for the citrus fruit fly. The invention provides a new strategy for screening and designing a citrus fruit fly odorant host fruit smell odor information attractant formula.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
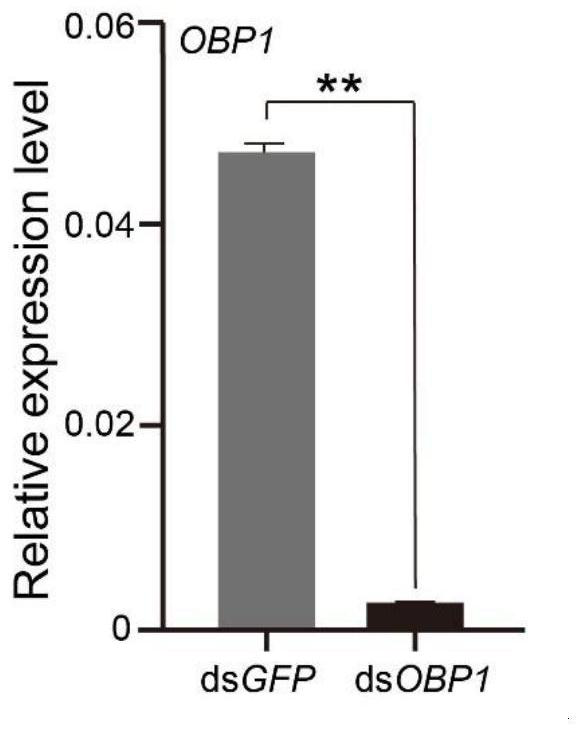
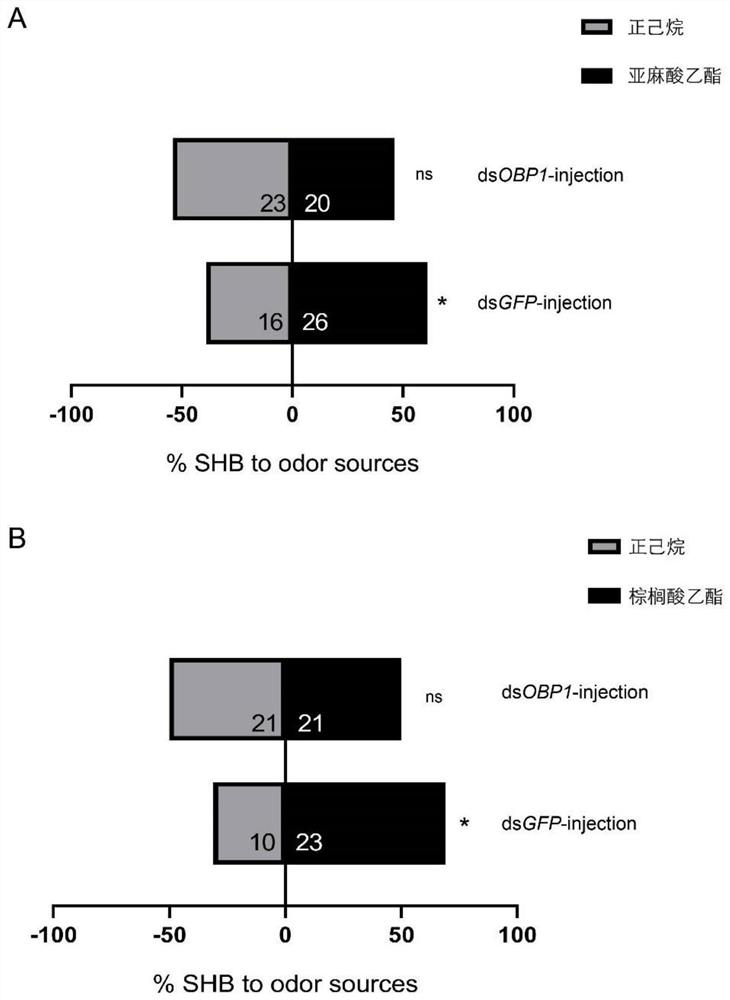
Application of knockout or silencing odorant binding protein gene 1 of aethina tumida to prevention and treatment of aethina tumida
The invention discloses an application of a knockout or silencing odorant binding protein gene 1 of aethina tumida to prevention and treatment of the aethina tumida. The nucleotide sequence of the odorant binding protein gene 1 of the aethina tumida is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. A RNA interference technology is adopted, dsRNA is used for silencing the OBP1 gene of the aethina tumida, selection of the aethina tumida on food source pollen volatile matter can be affected, the protein gene 1 can be used for preventing and treating the aethina tumida, and plays an important role in the prevention and treatment process of the aethina tumida.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com