Patents
Literature
141 results about "Haptoglobin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
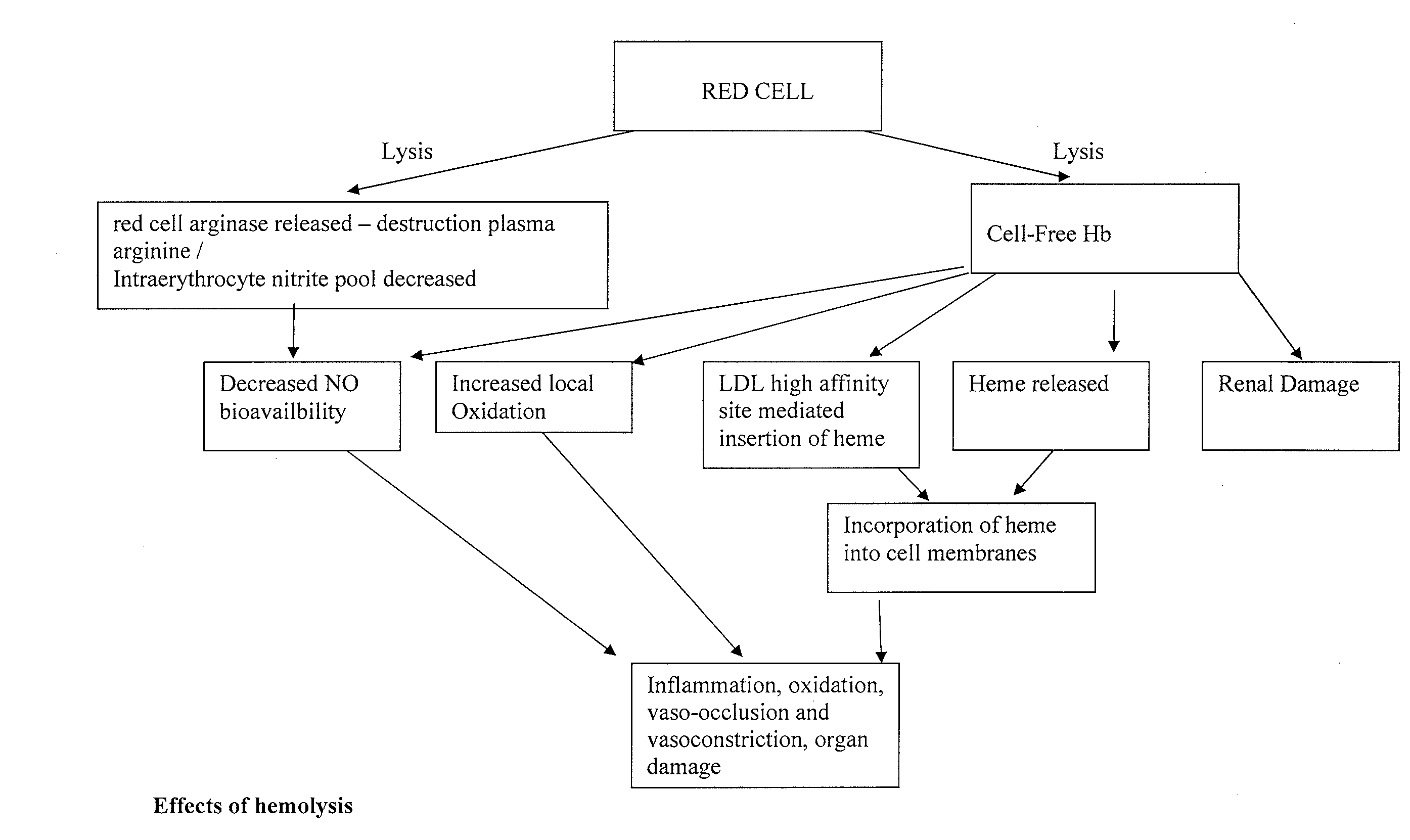
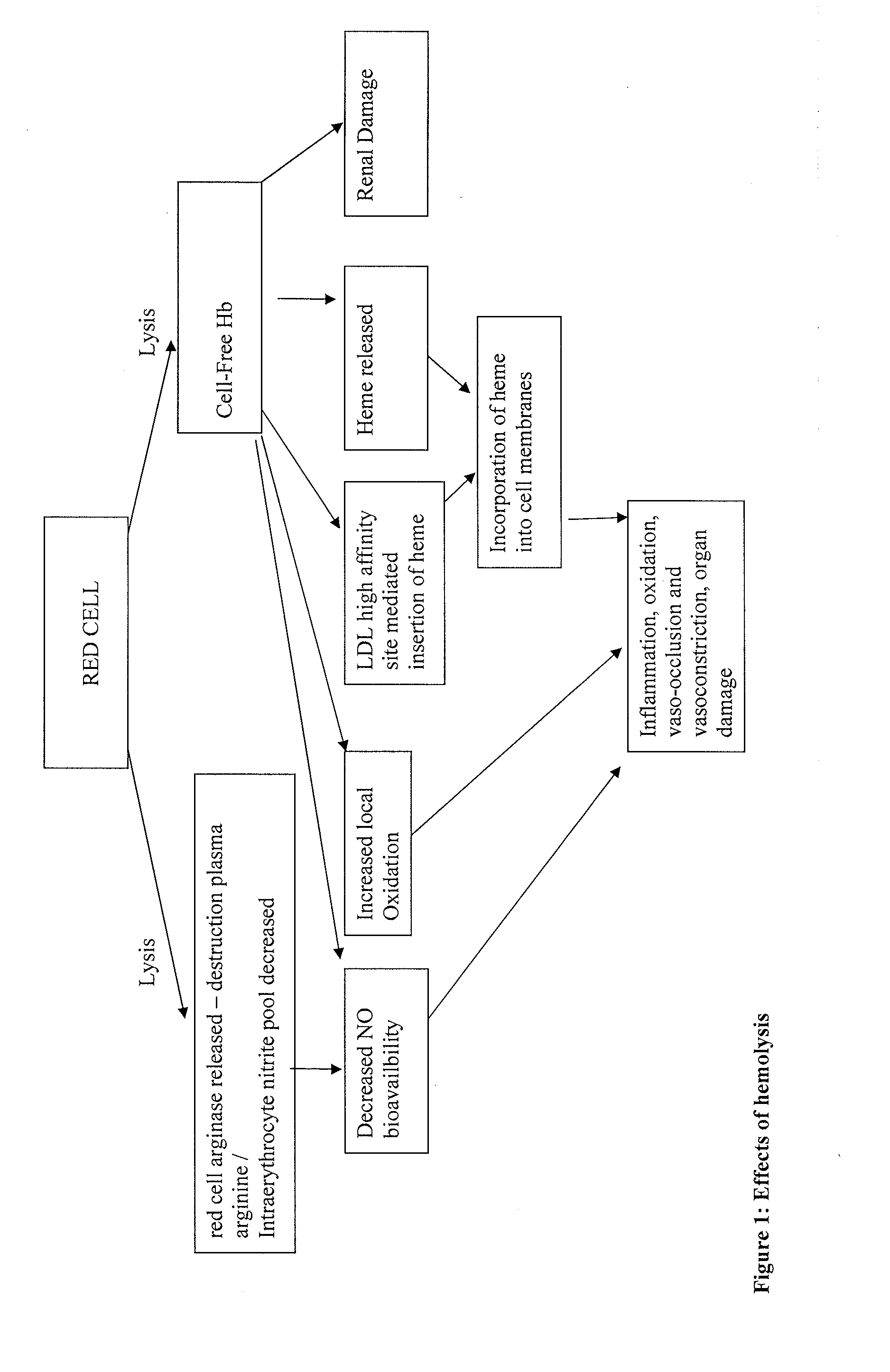
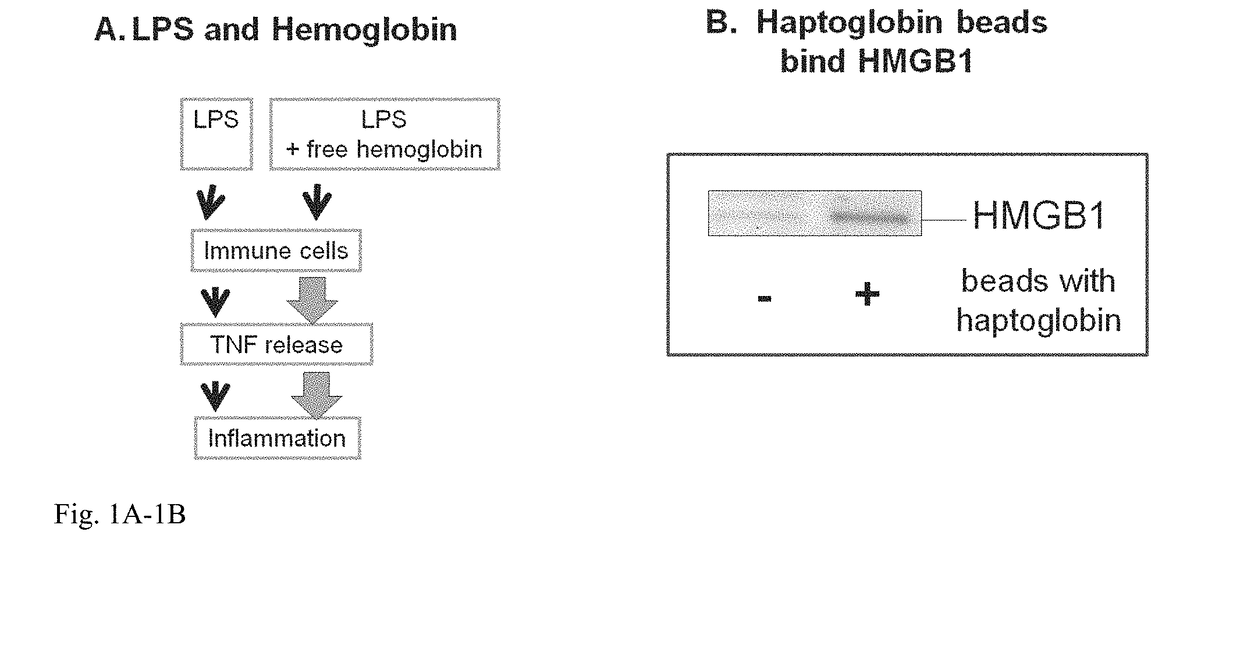
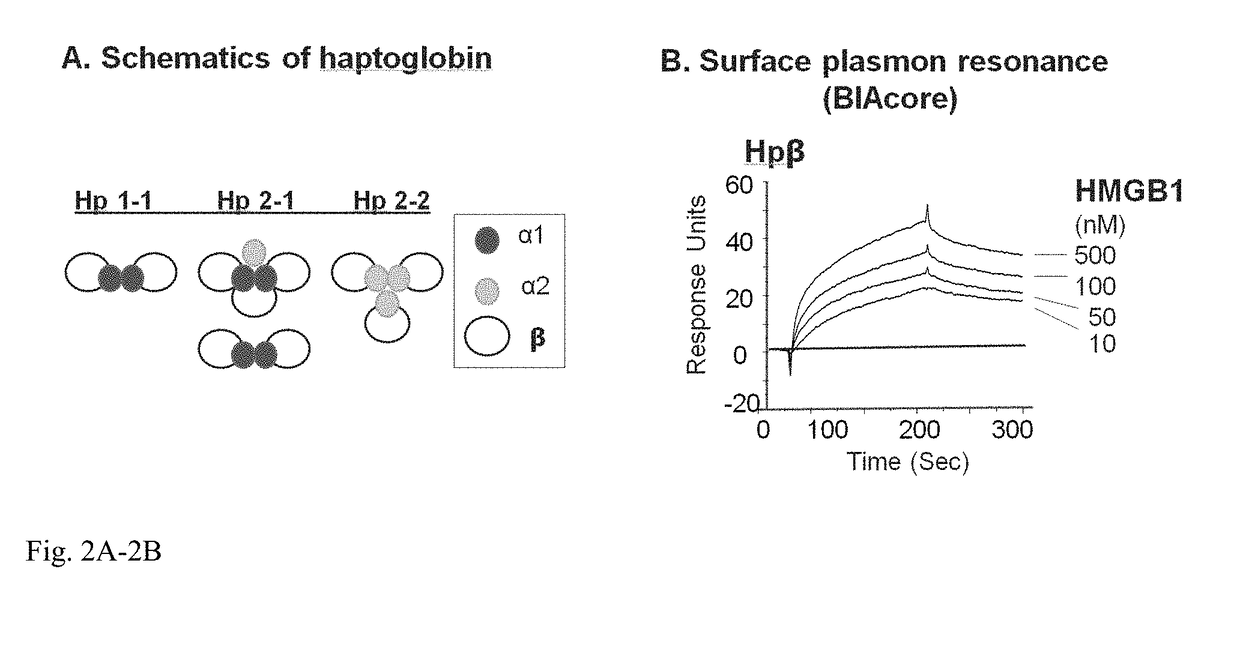
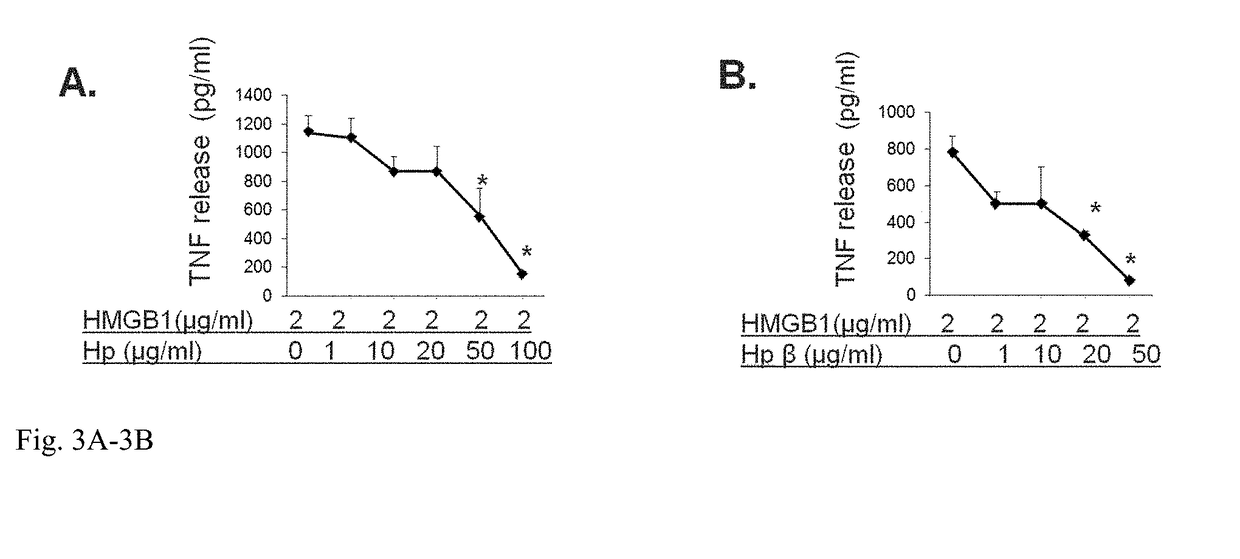
Haptoglobin (abbreviated as Hp) is the protein that in humans is encoded by the HP gene. In blood plasma, haptoglobin binds to free hemoglobin, compared to hemopexin that binds to free heme, released from erythrocytes with high affinity and thereby inhibits its oxidative activity. The haptoglobin-hemoglobin complex will then be removed by the reticuloendothelial system (mostly the spleen).
Diagnostic marker for ovarian cancer
InactiveUS20070053896A1Easy accessEarly detectionPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhysiologyNucleic Acid Probes
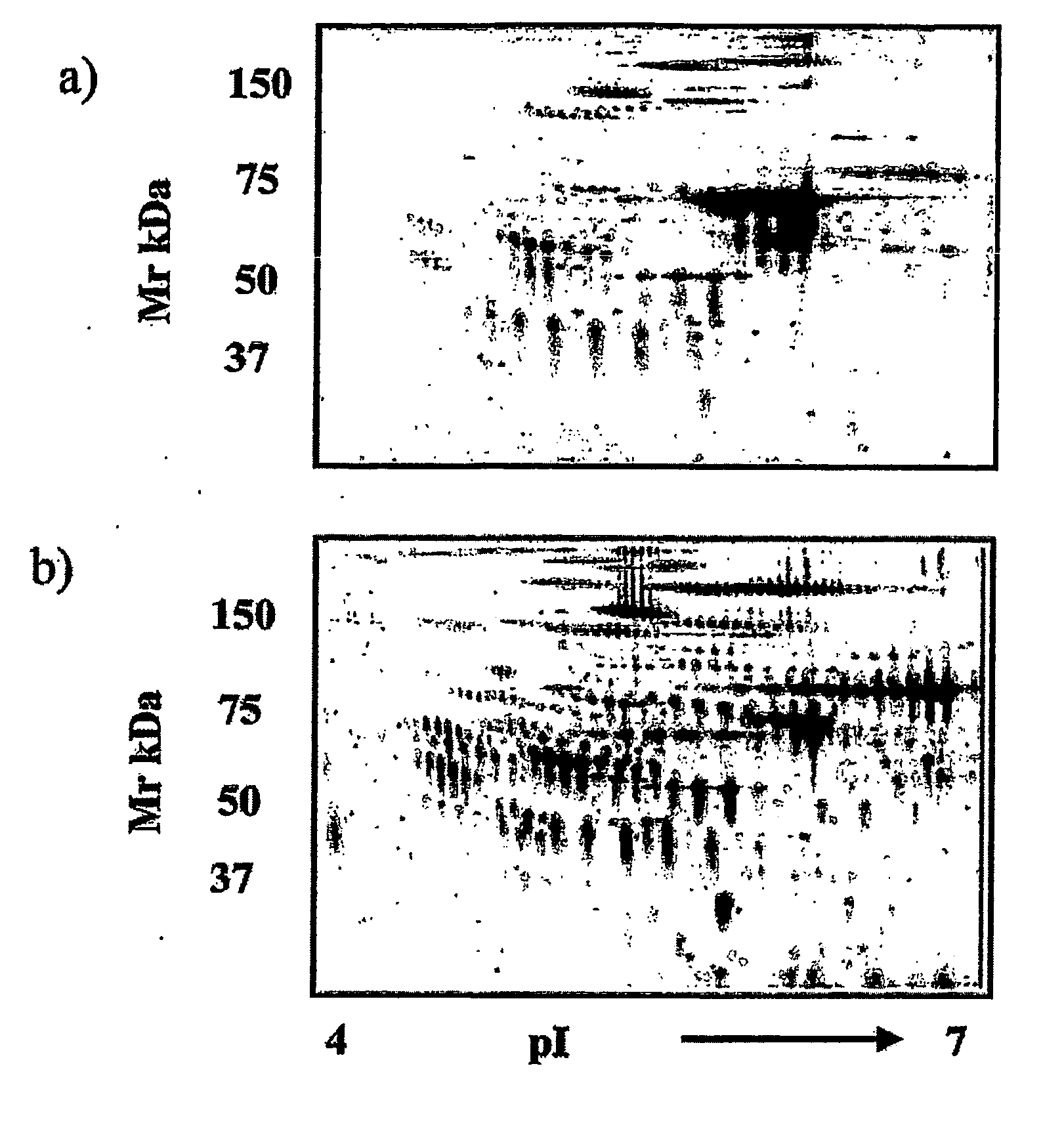
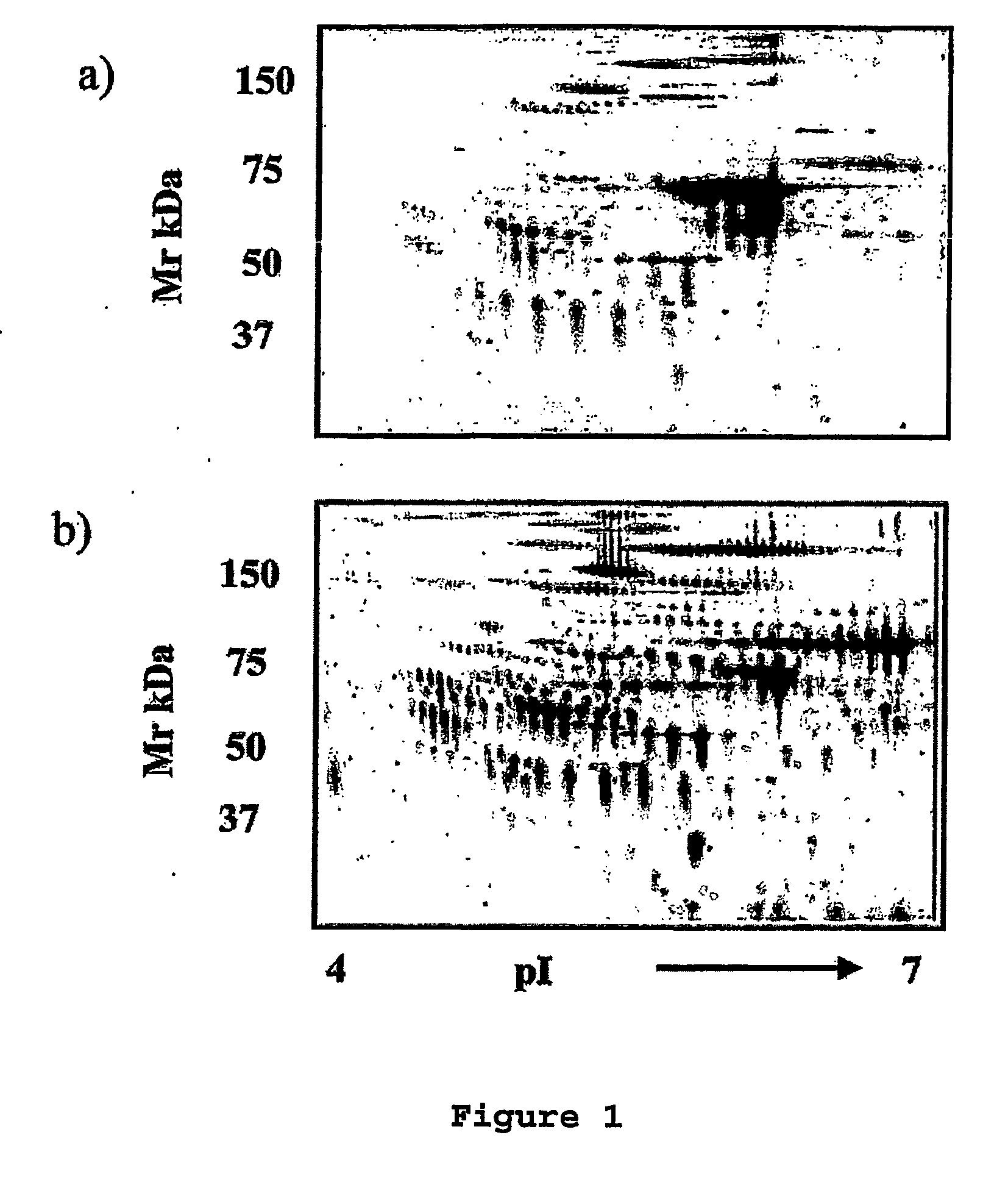
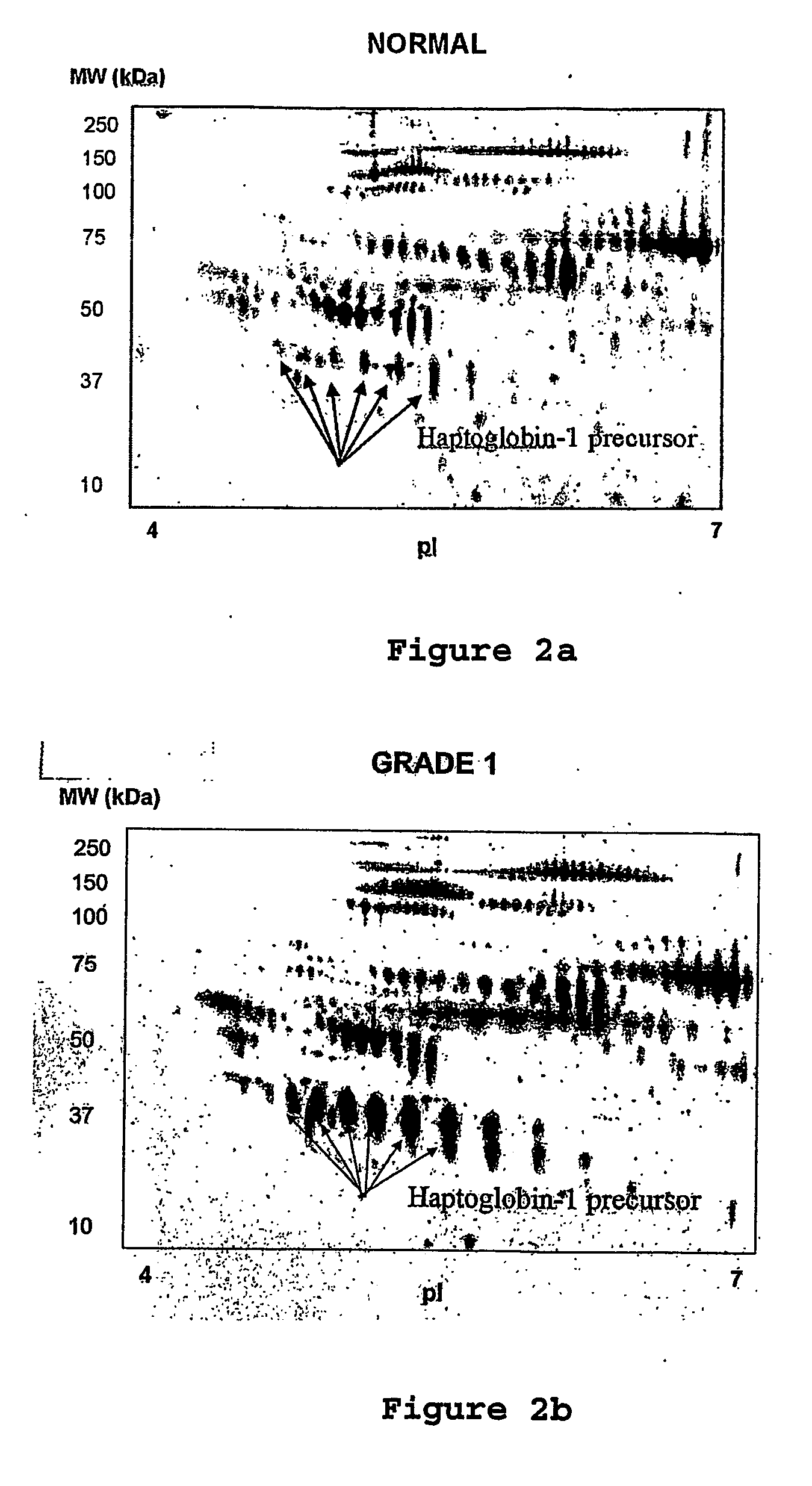
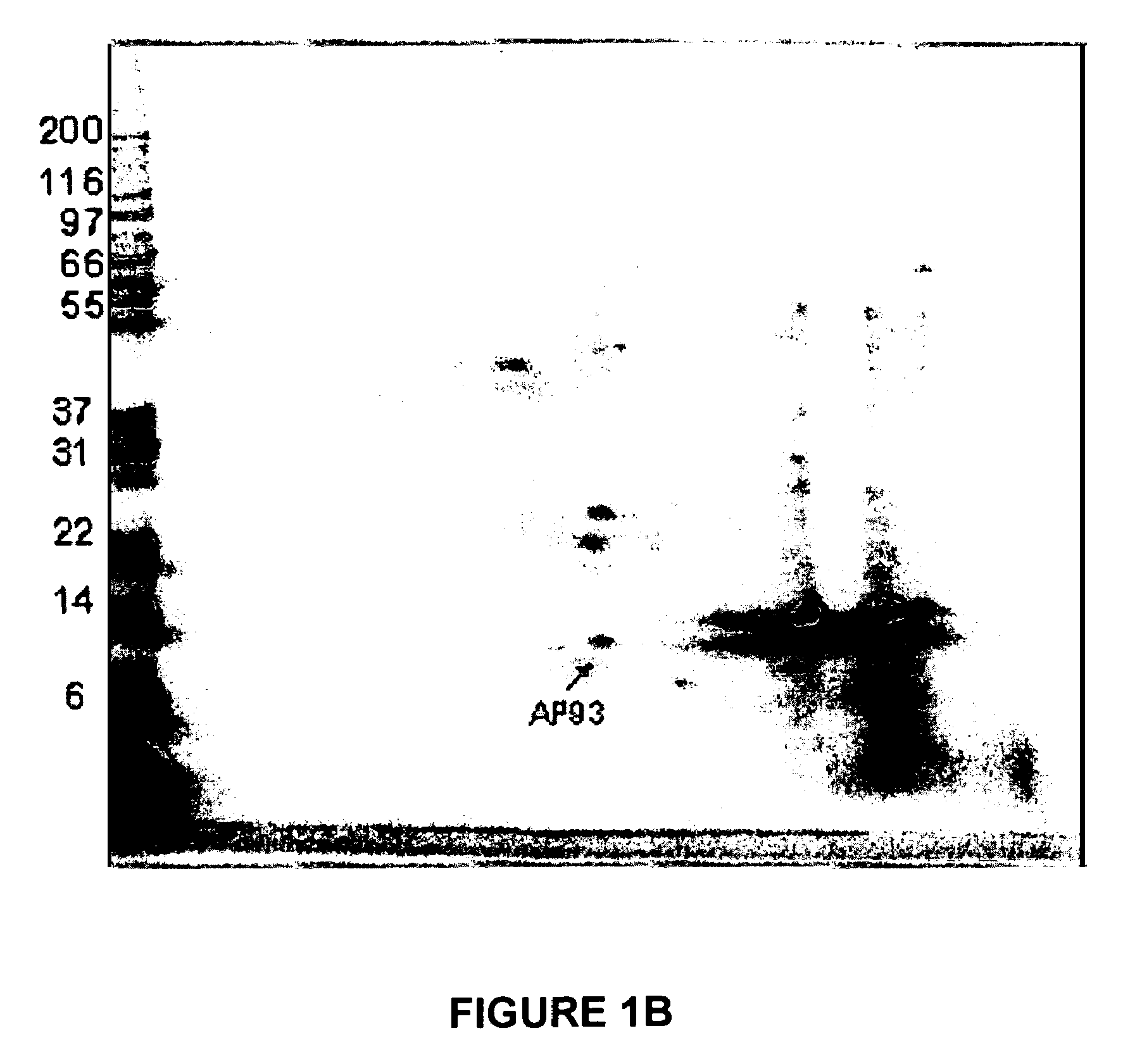
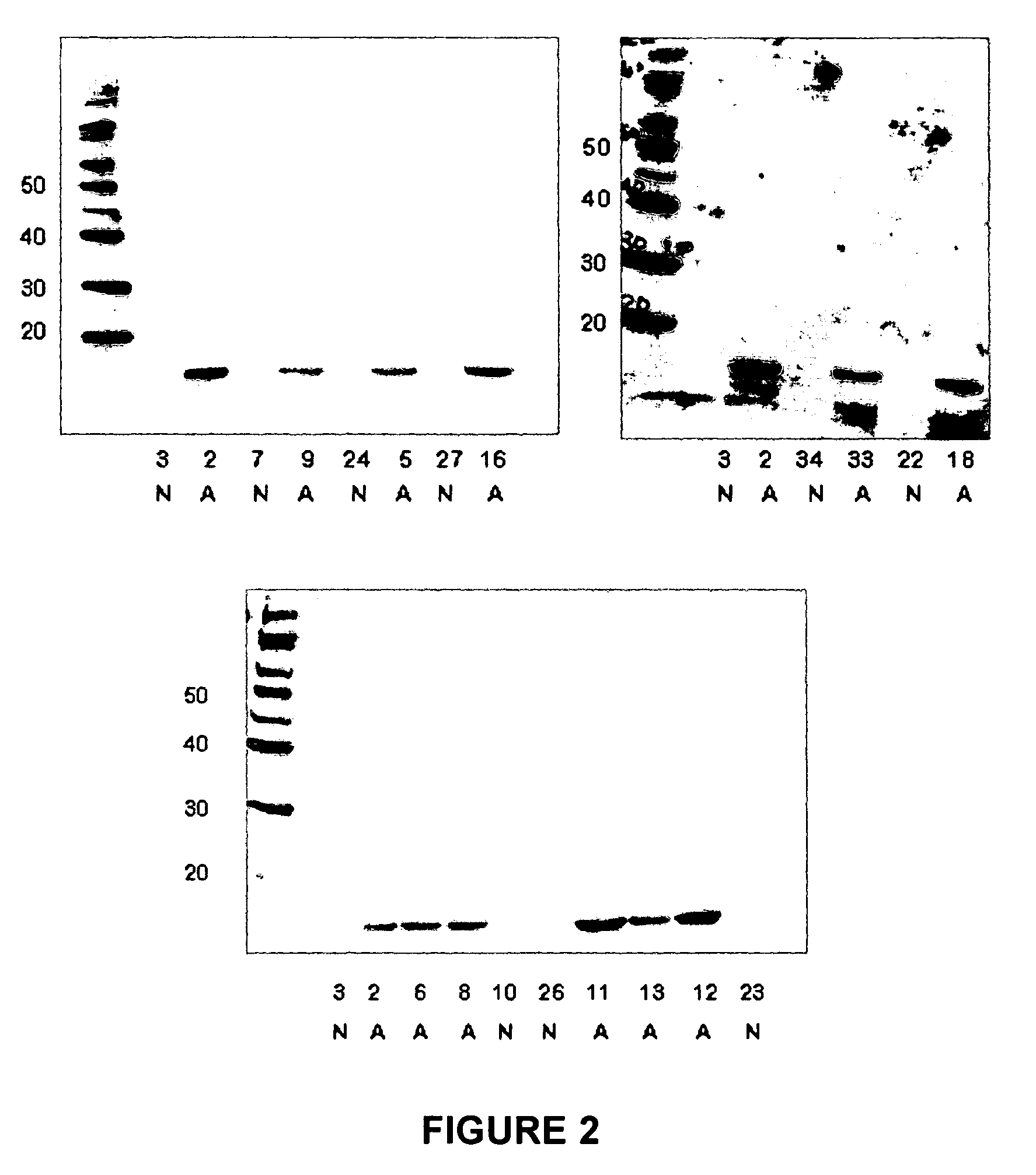
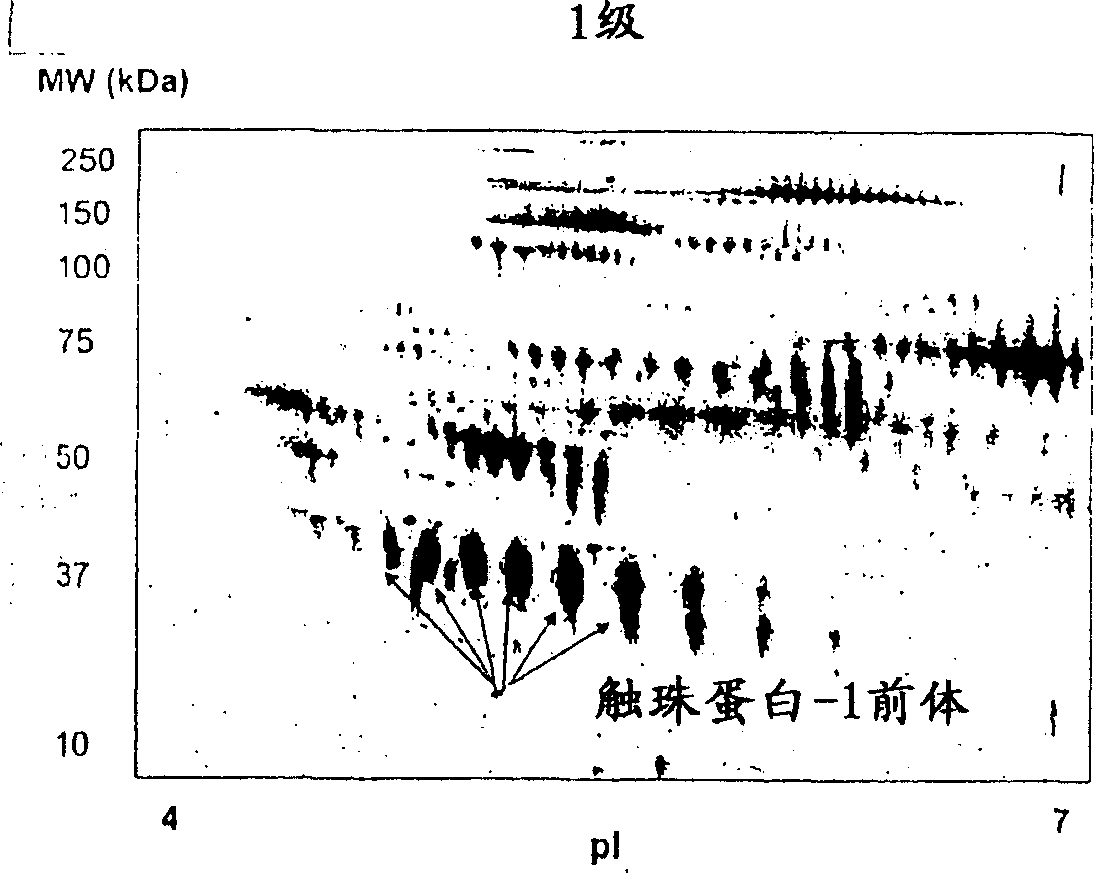
The present invention relates to methods of detecting, monitoring the efficacy of treatment of, and assessing the severity of ovarian cancer, by assessing the concentration of haptoglobin-1 precursor in a sample of biological fluid. The invention also relates to a kit comprising an antibody or nucleic acid probe specific for haptoglobin-1 precursor for use in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer, monitoring the efficacy of treatment of ovarian cancer, or assessing the severity of ovarian cancer.
Owner:ROYAL WOMENS HOSPITAL
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
ActiveUS20110195429A1Eliminate needEasy to adaptDisease diagnosisBiological testingSoluble P-SelectinFactor ii
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using assays that detect one or more markers selected from the group consisting of soluble p-selectin, protein NOV homolog, soluble epidermal growth factor receptor, netrin-4, haptoglobin, heat shock protein beta-1, alpha-1-antitrypsin, leukocyte elastase, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 6, soluble tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 6, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule 2, active caspase-3, and soluble platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
Method of determining a potential of a hyperglycemic patients of developing vascular complications
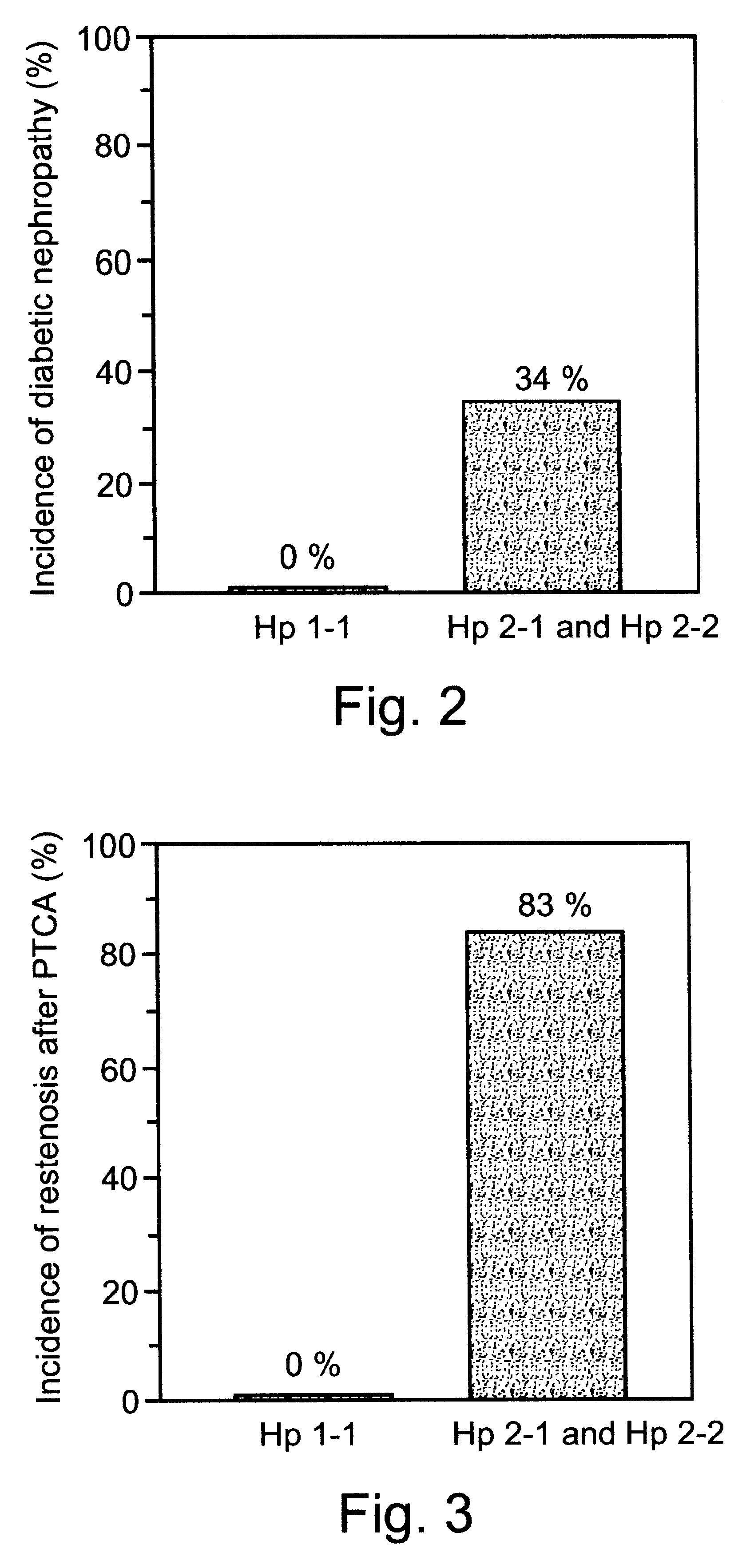
Methods for determining a potential of a hyperglycemic patient to develop vascular complications in response to oxidative stress and for determining the importance of reducing oxidative stress in a specific hyperglycemic patient are disclosed. Each method includes the step of determining a haptoglobin phenotype of the patient. A variety of means of making this determination are further disclosed.
Owner:RAPPAPORT FAMILY INSTITUTE FOR RESEACH IN THE MEDICAL SCIENCES
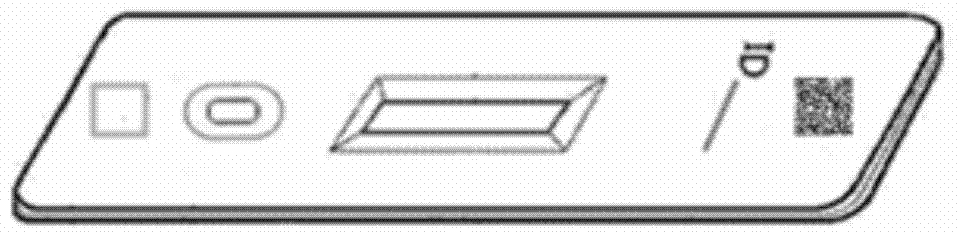
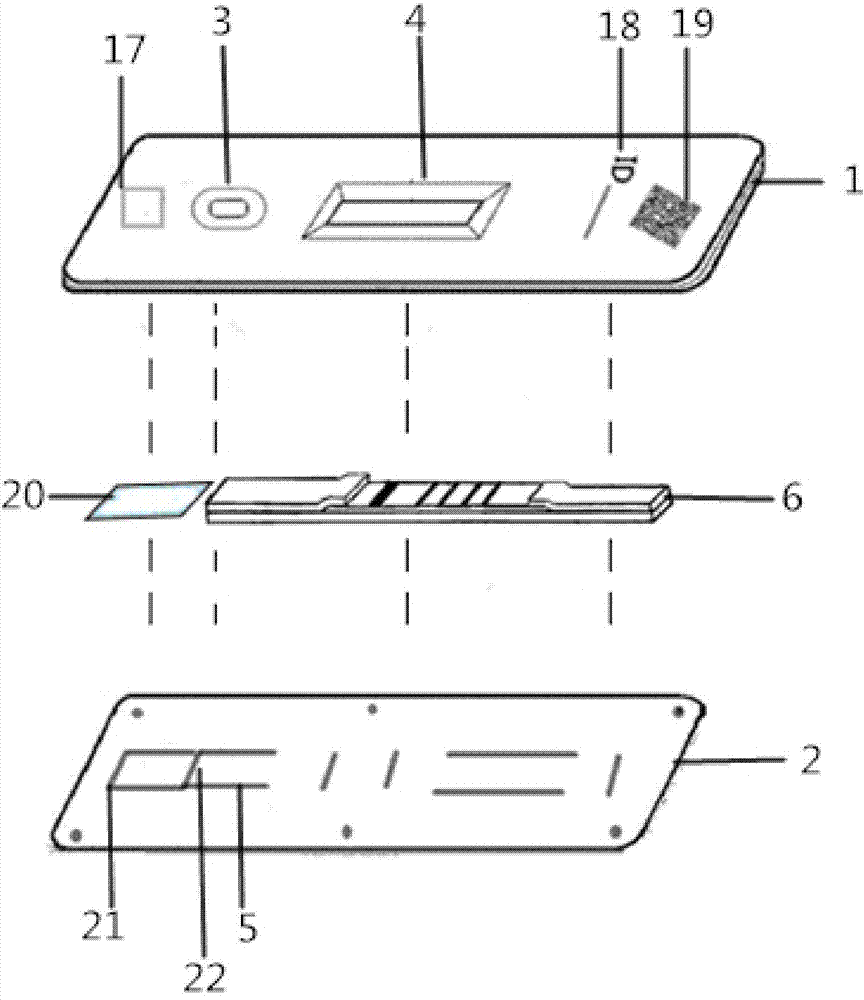
Hemoglobin, hemoglobin-haptoglobin composite and transferrin joint examination kit and preparation method and detection method thereof
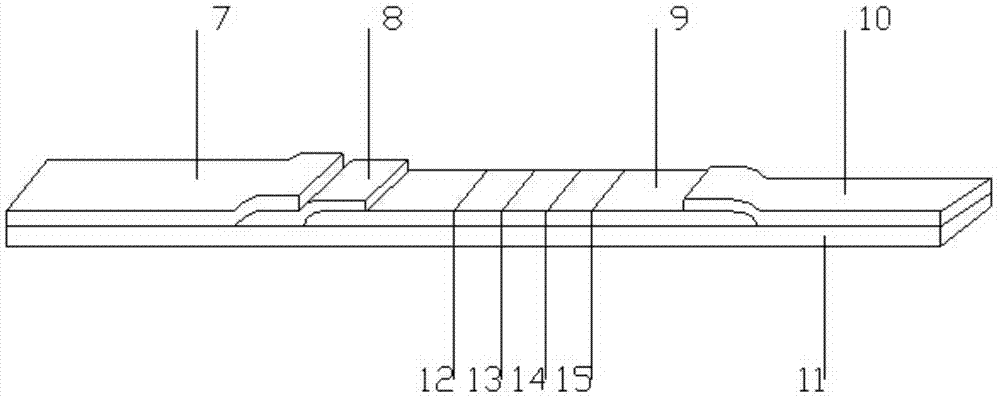
The invention provides a hemoglobin, hemoglobin-haptoglobin composite and transferrin joint examination kit. The hemoglobin, hemoglobin-haptoglobin composite and transferrin joint examination kit comprises an upper shell, a lower shell, an immunostrip, test paper and the like; a gold-labeled composite containing a hemoglobin monoclonal antibody, a hemoglobin-haptoglobin composite monoclonal antibody and a transferrin monoclonal antibody is scribed on a nitrocellulose membrane; 3 test lines, a quality control line (15) and a gold-labeled composite membrane scribing line (8) are arranged on the nitrocellulose membrane in parallel. The invention further provides a preparation method and a detection method of the hemoglobin, hemoglobin-haptoglobin composite and transferrin joint examination kit. The hemoglobin, hemoglobin-haptoglobin composite and transferrin joint examination kit is convenient and simple in operation, stable in performance and accurate in result, has a relatively good reference value for early diagnosis and identification of colorectal cancer or colon cancer tumor or other tumors with lower gastrointestinal bleeding symptoms in clinic, significantly improves the positive detection rate of digestive hemorrhagic diseases, is suitable for clinical hospital examination and household self-examination, and provides measures for large-scale general examination of such diseases.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUIYUANTAI MEDICAL DEVICES
Glycoprotein Profiling of Bladder Cancer
InactiveUS20100184049A1Simple and rapid and reliable and accurate and cost-effectiveEasy to identifyElectrolysis componentsMicrobiological testing/measurementHaptoglobinBiomarker (petroleum)
The present invention relates to a method for the diagnosis, prognosis, and monitoring of bladder cancer, such as early or late stage bladder cancer, by detecting in a urine sample from a subject at least one biomarker for bladder cancer identified herein, such as alpha-1B-glycoprotein, haptoglobin, serotransferrin, or alpha-1-antitrypsin. The biomarkers may be detected and, optionally, measured using an agent that detects or binds to the biomarker protein or an agent that detects or binds to encoding nucleic acids, such as antibodies specifically reactive with the biomarker protein or a portion thereof. The invention further relates to kits for carrying out the methods of the invention. The invention further relates to a device for the rapid detection of one or more bladder cancer biomarkers in urine and methods for rapidly measuring bladder cancer biomarkers in urine.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method of determining a risk of hyperglycemic patients of developing a cardiovascular disease
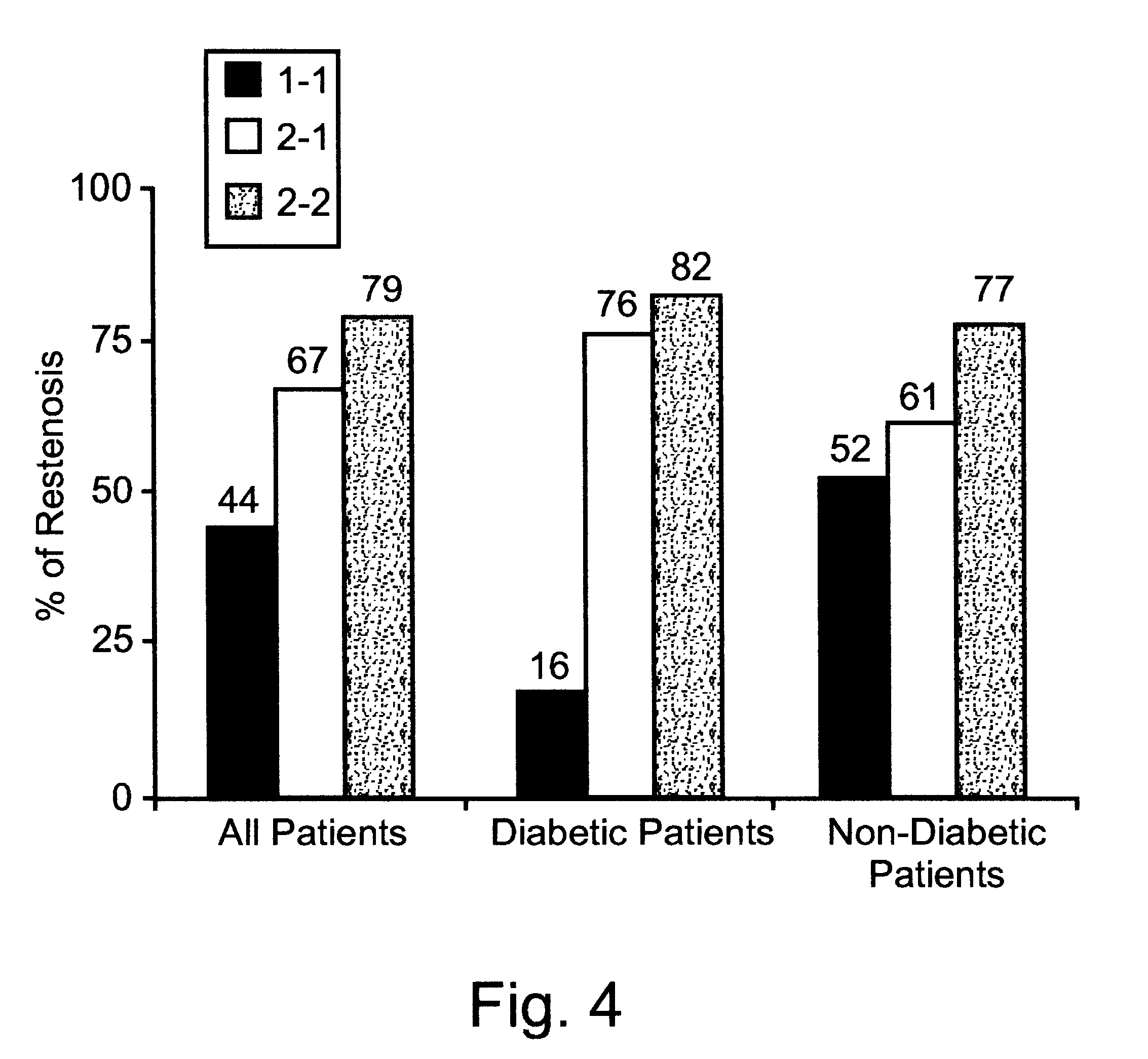
A method and kit of evaluating a risk of a diabetic patient to develop cardiovascular disease (CVD) is disclosed. The method comprises determining a haptoglobin phenotype of the diabetic patient and thereby evaluating the risk of the diabetic patient to develop the cardiovascular disease (CVD), wherein the risk is decreased in diabetic patients with haptoglobin 1-1 phenotype as compared to patients with haptoglobin 1-2 or haptoglobin 2-2 phenotypes. The risk is also decreased in diabetic patients with haptoglobin 1-2 phenotype as compared to patients with haptoglobin 2-2 phenotype. The kit comprises packaged reagents for determining a haptoglobin phenotype of the diabetic patient and the kit is identified for use in evaluating a risk of a diabetic patient to develop cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Owner:RAPPAPORT FAMILY INSTITUTE FOR RESEACH IN THE MEDICAL SCIENCES
Methods and kits for the diagnosis of sickle cell
InactiveUS20080255766A1Quick checkRapid accurate diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAnalyteIl 12p40
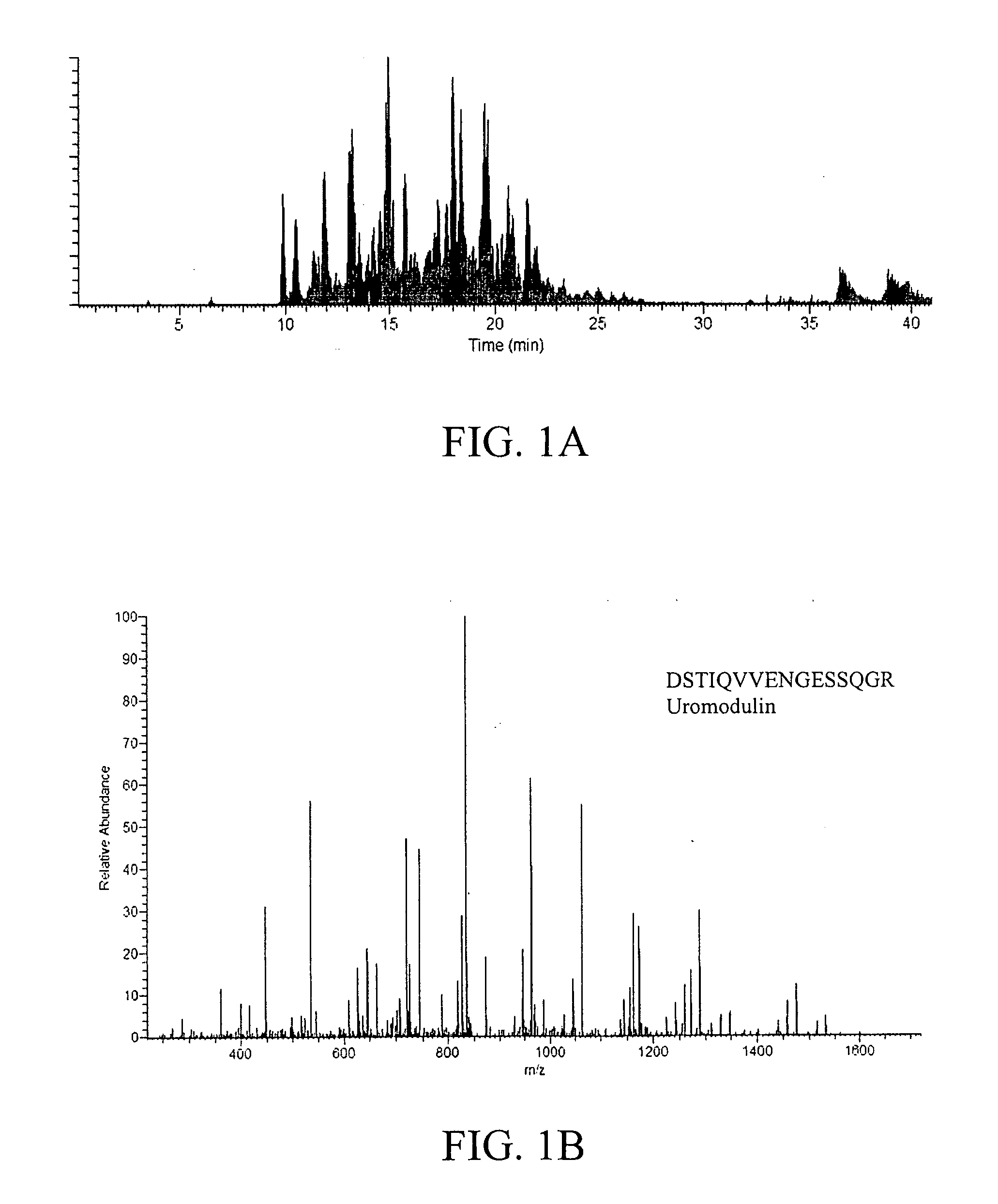
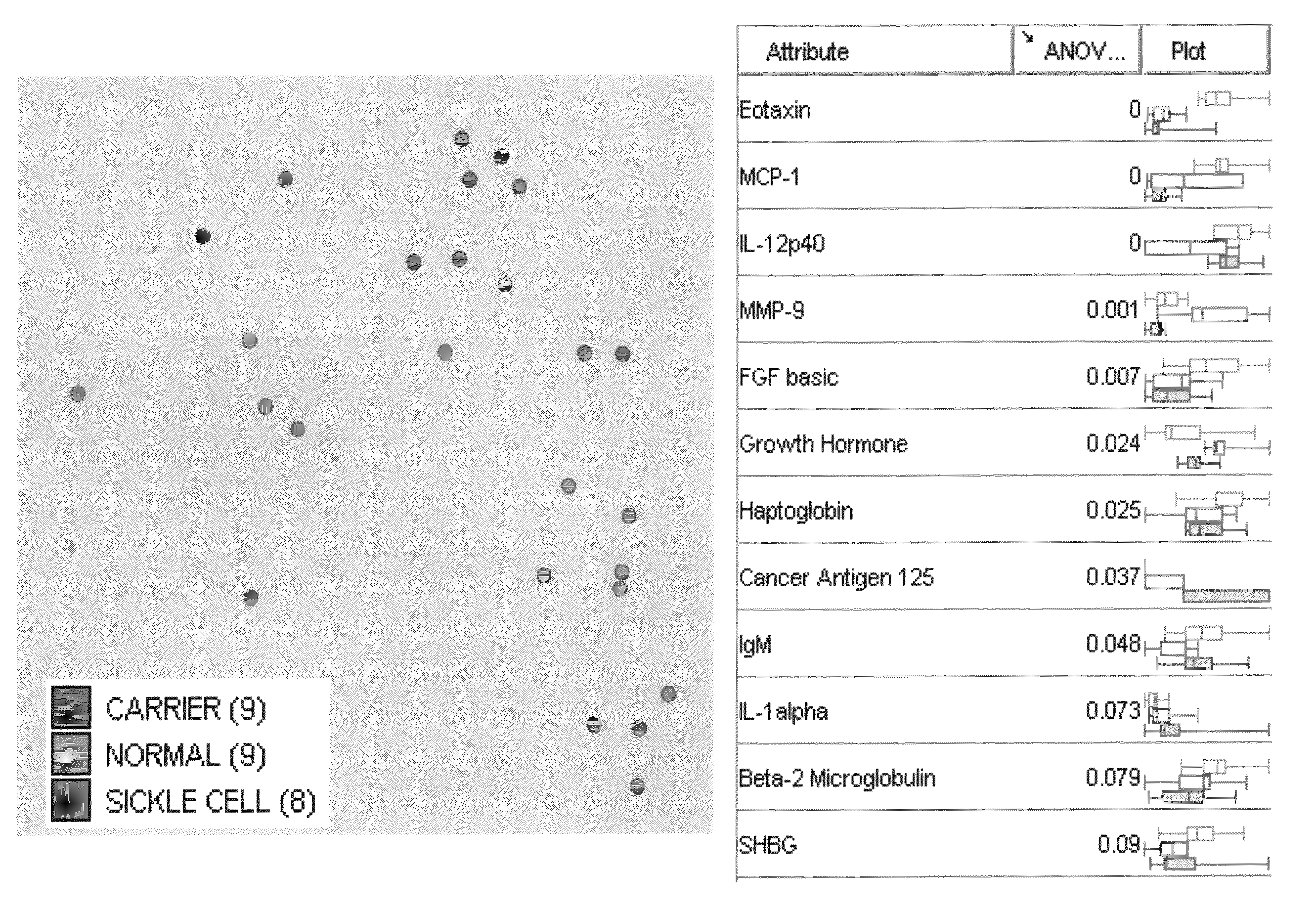
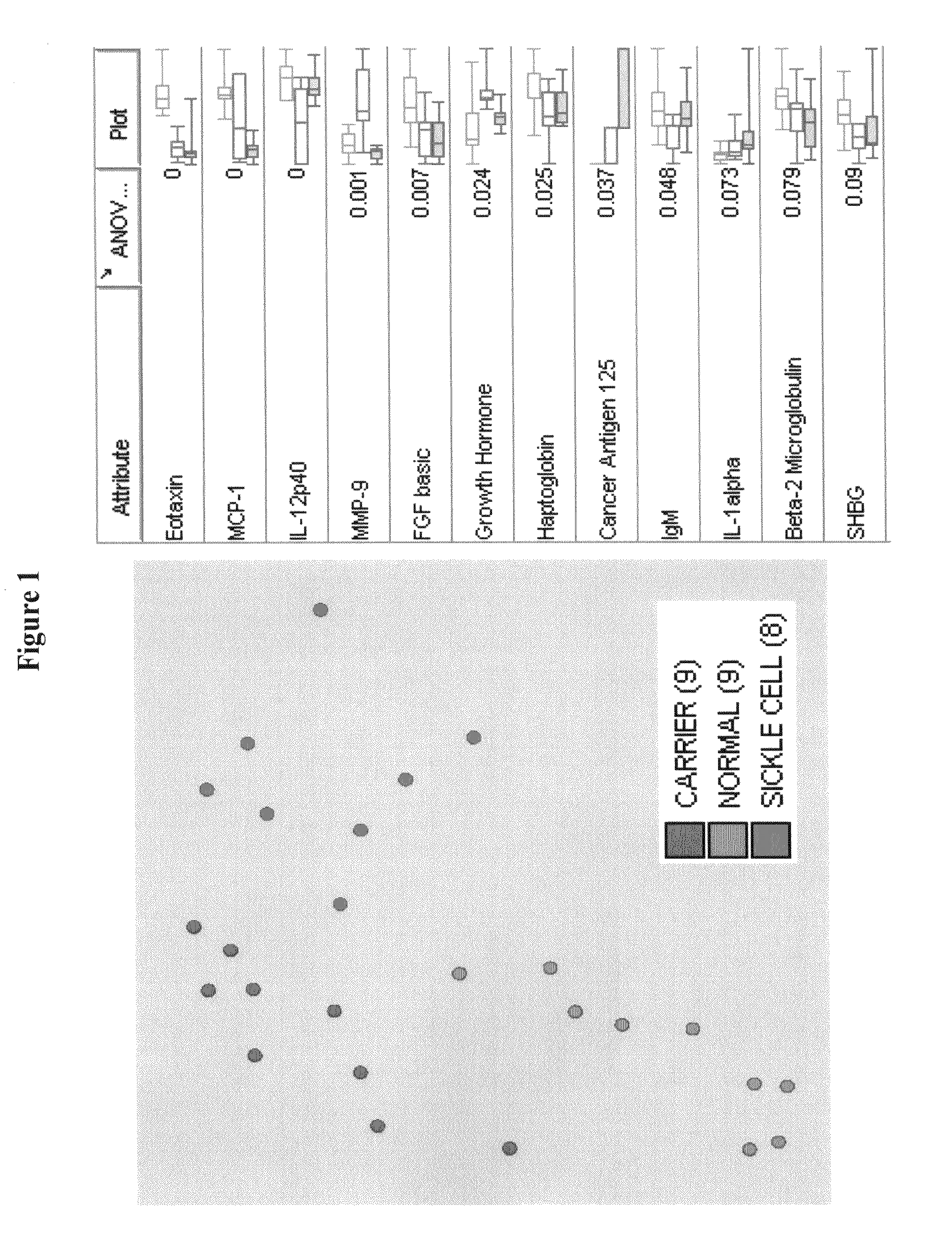
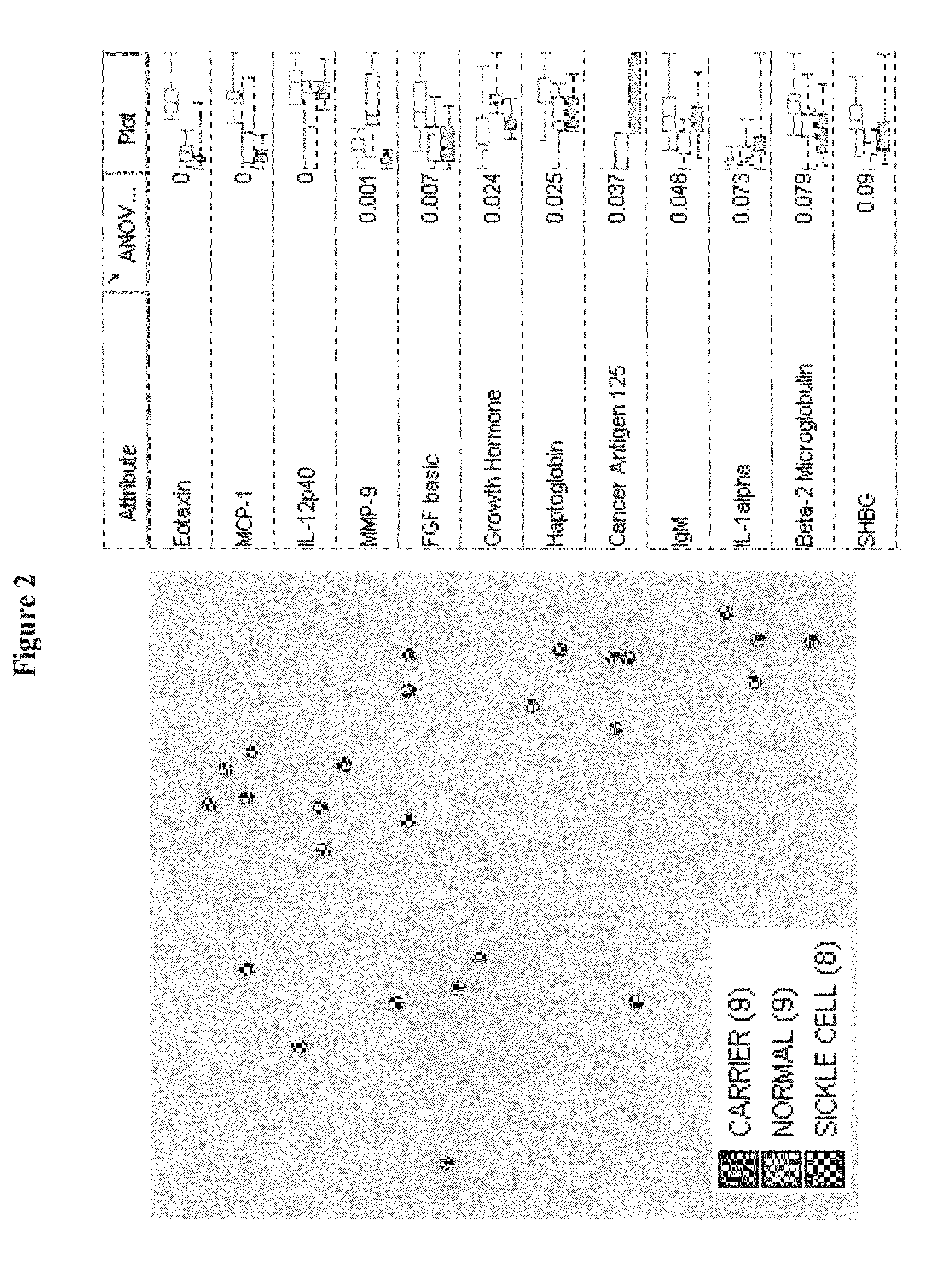
Provided are methods for the detection and diagnosis of sickle cell. The methods are based on the discovery that abnormal levels of selected analytes in sample fluid, typically blood samples, of patients who are at risk are supportive of a diagnosis of sickle cell. At least two new biomarkers for sickle cell are thus disclosed, Eotaxin and Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1. Altogether the concentrations of eleven analytes provide a sensitive and selective picture of the patient's condition, namely, whether the patient is suffering from sickle cell. Other important biomarkers for sickle cell are described, including but not limited to IL-12p40, SHBG, MMP-9, Adiponectin, Haptoglobin, FGF basic, IgM, Growth Hormone, Factor VII. Kits containing reagents to assist in the analysis of fluid samples are also described.
Owner:RULES BASED MEDICINE +1
Rapid joint inspection reagent for hemoglobin -haptoglobin complex and occult blood in stool
Owner:王学生 +1
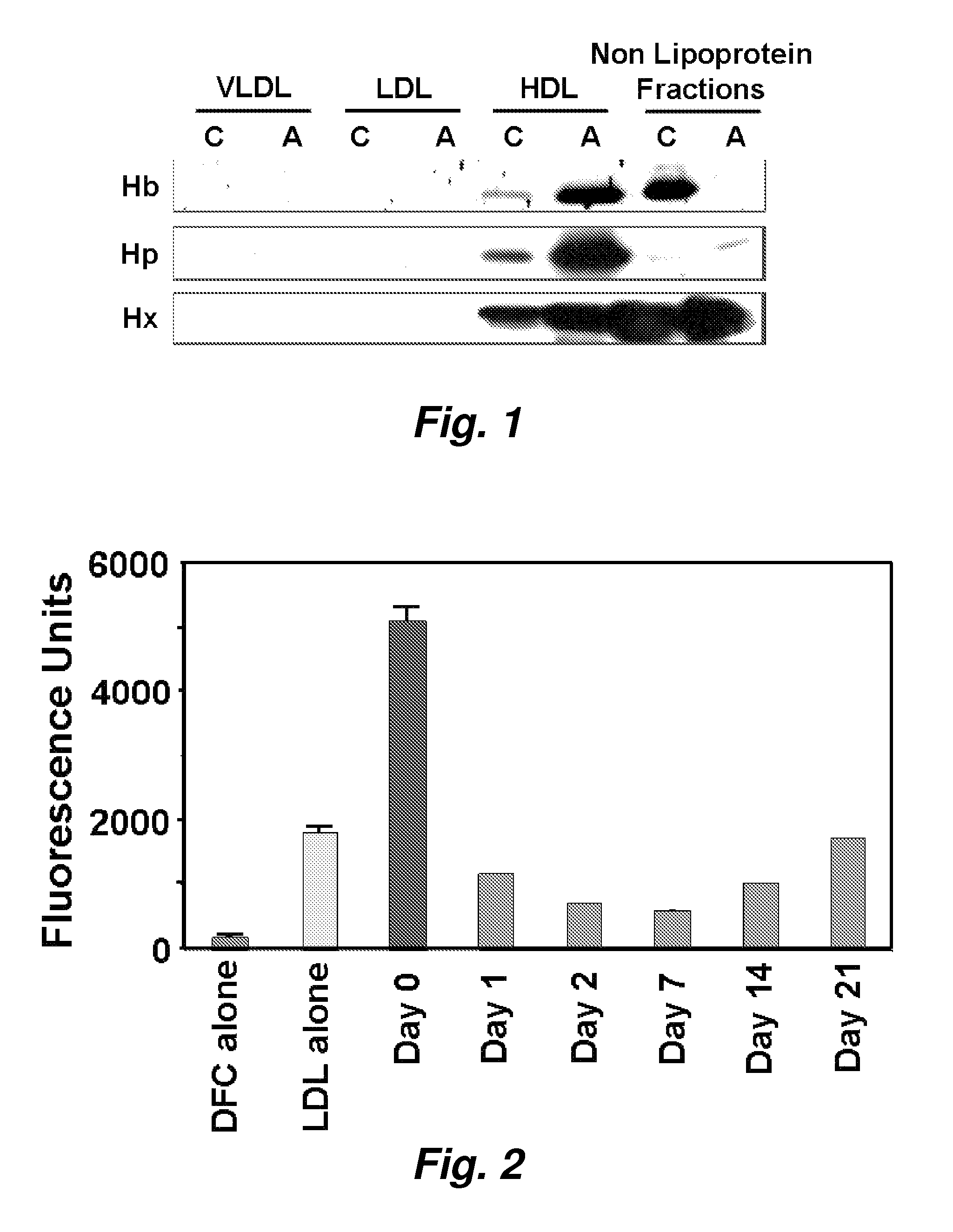
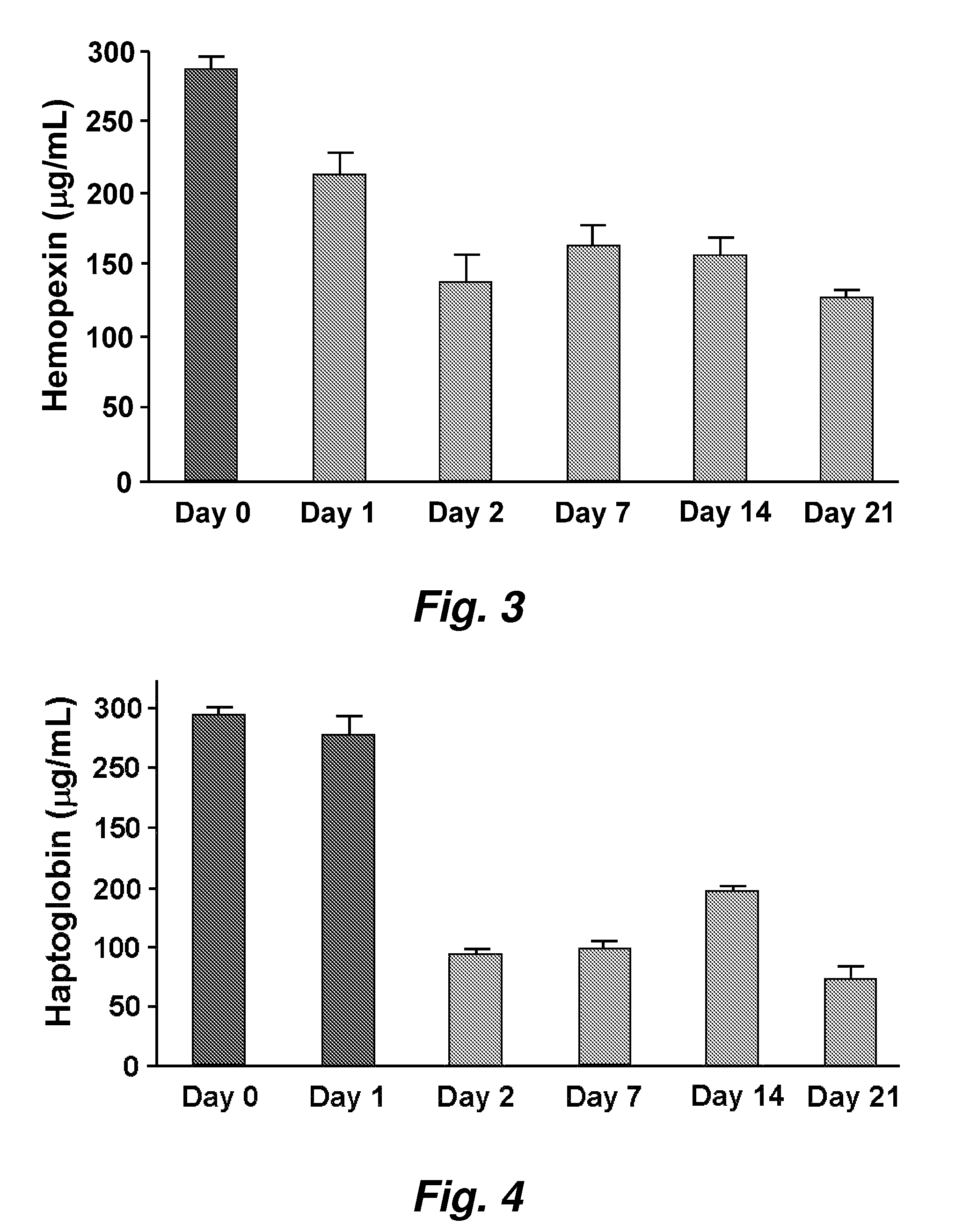
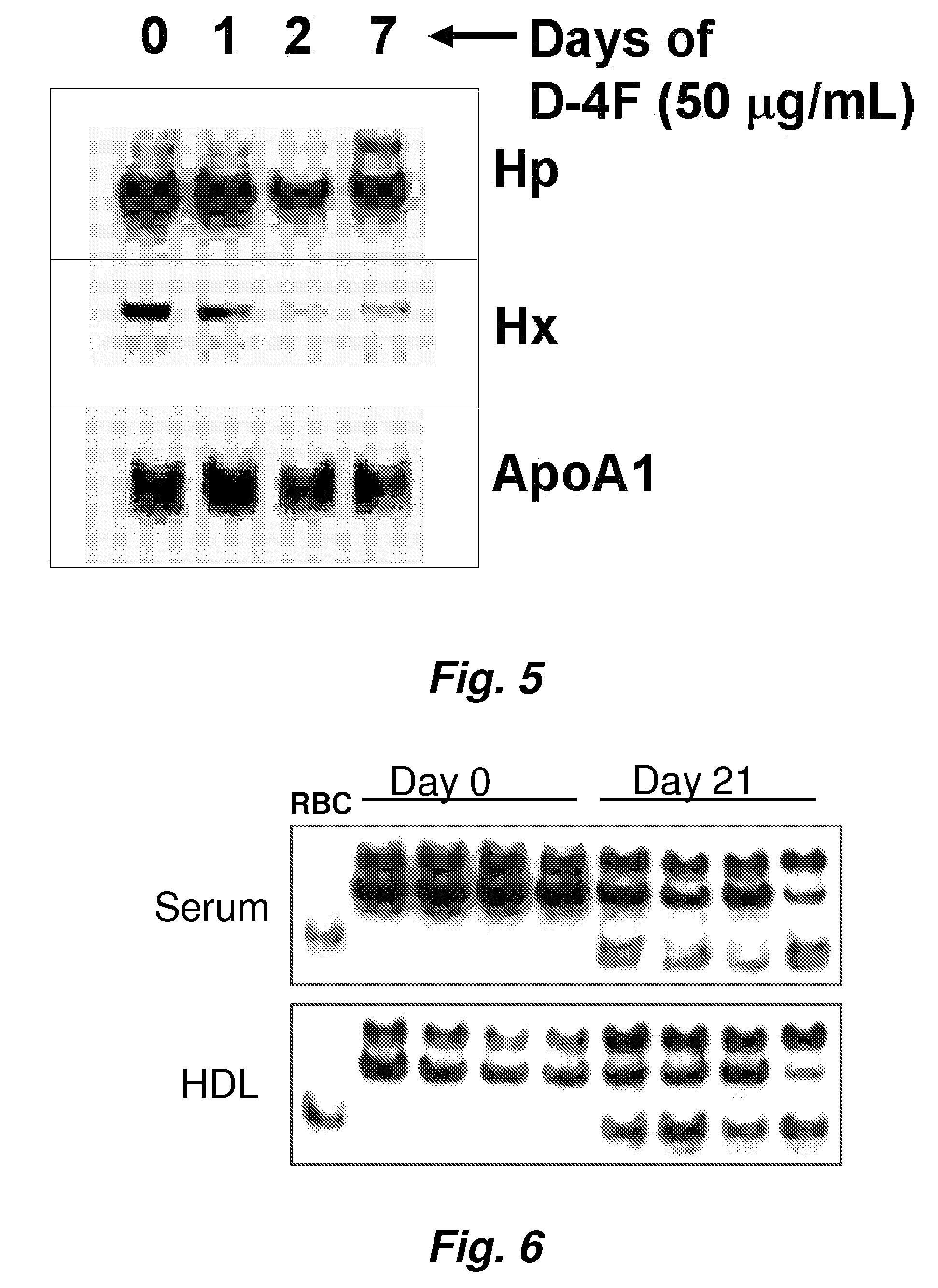
Assays to predict atherosclerosis and dysfunctional high-density lipoprotein
ActiveUS20070218501A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNitric oxideAtheroma
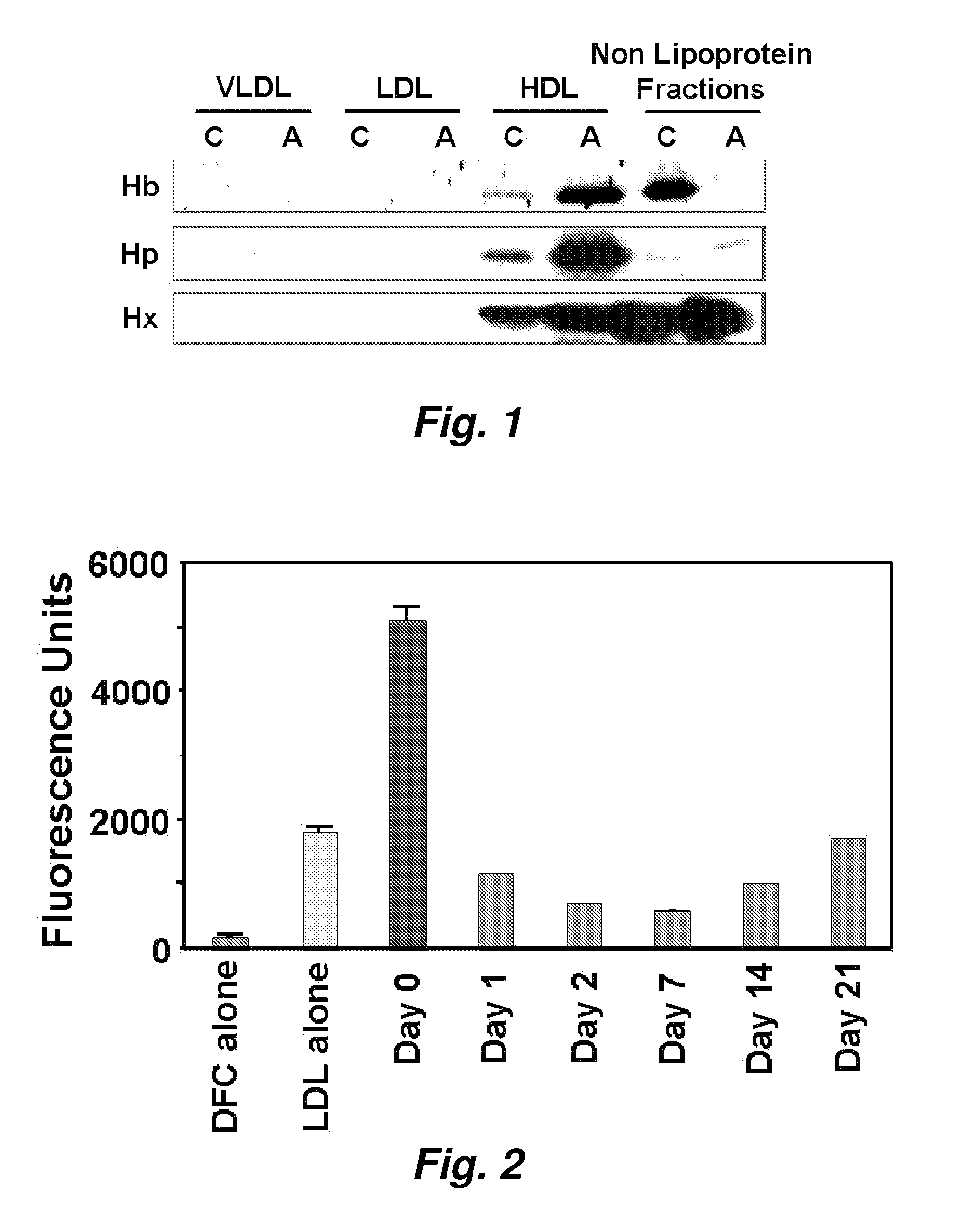
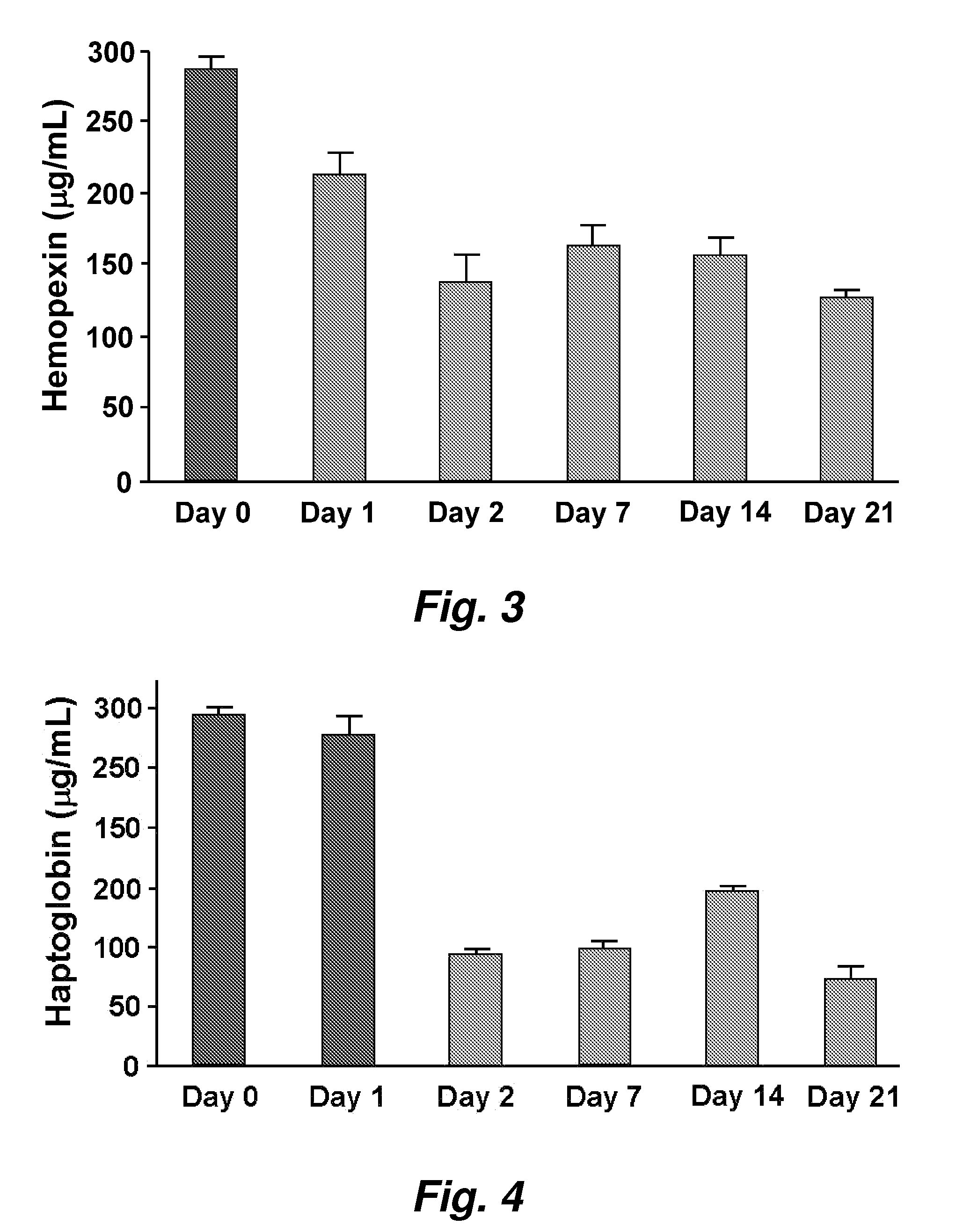
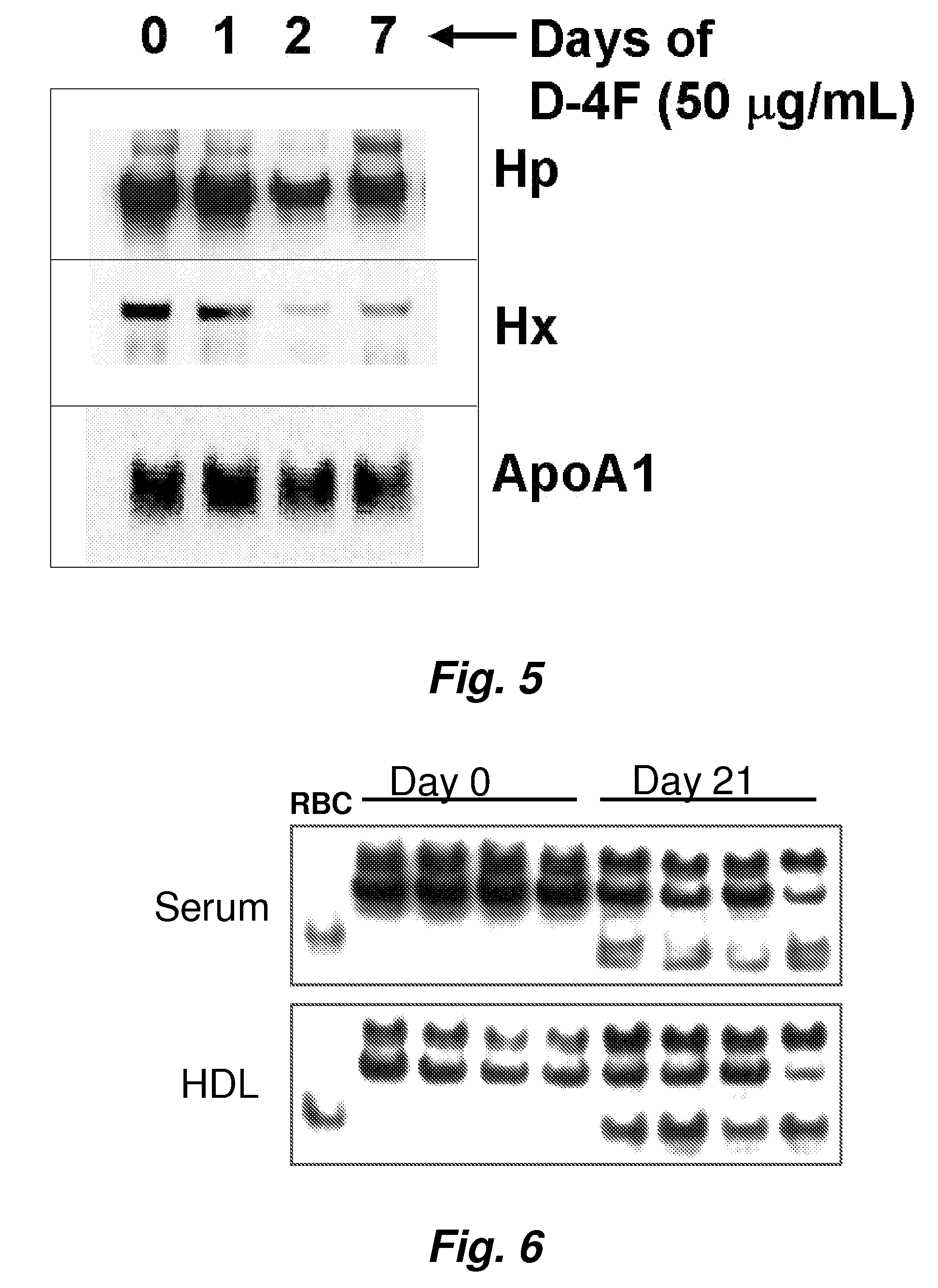
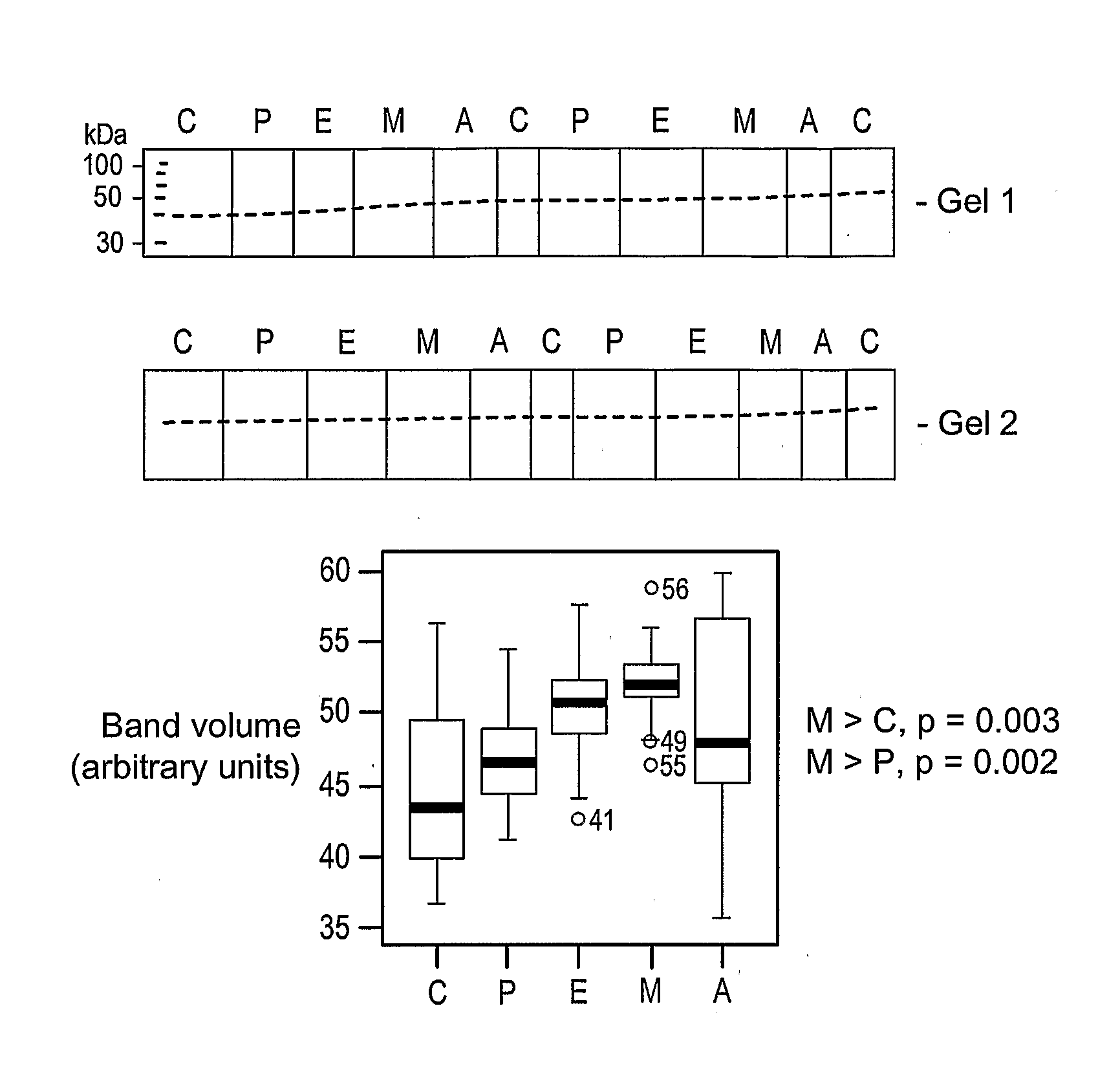
This invention provides novel assays for the detection of dysfunctional HDL. The assays are good diagnostics and / or prognostics for atherosclerosis or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiments the methods involve measurements of heme-related HDL-associated proteins (e.g., haptoglobin, hemopexin, etc.), and / or measurements of the relative distribution of HDL-associated proteins between HDL and the non-lipoprotein fractions of plasma / serum, and / or measurements of the ability of pro-inflammatory HDL to consume nitric oxide, and / or measurement of the ability of HDL to inhibit LDL aggregation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Detection of ovarian cancer based upon alpha-haptoglobin levels
The present invention is directed to a method for determining whether a woman has, or is likely to develop, ovarian cancer based upon assays of the alpha subunit of haptoglobin.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Diagnosis Of Neurodegenerative Diseases
InactiveUS20080286263A1Improve trustNervous disorderElectrolysis componentsHemoglobin Beta ChainApolipoprotein C-II
The invention relates to a method of diagnosis of Huntington's Disease in a diagnostic sample of a valid body tissue taken from a human subject, which comprises detecting an altered concentration of a protein in the diagnostic sample, compared with a sample of a control human subject, the protein being selected from: Swiss Prot accession number: Protein name; P10909: Clusterin precursor; P00738: Haptoglobin precursor; P01009: Alpha-1-antitrypsin precursor; P01024: Complement C3 precursor; P01620: 1 g kappa chain V-III region; P01834: 1 g kappa chain C region P01842: 1 g lambda chain C regions; P01857: 1 g gamma-1 chain C region; P01859: Ig gamma-2 chain C region; P01876: 1 g alpha-1 chain C region P02647: Apolipoprotein A-I precursor; P02649: Apolipoprotein E precursor; P02652: Apolipoprotein A-II precursor; P02655: Apolipoprotein C-II precursor; P02656: Apolipoprotein C-II precursor P02671: Fibrinogen alpha / alpha-E chain precursor; P02763: Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 1 precursor; P02766: Transthyretin precursor; P02768: Serum albumin precursor; P02787: Serotransferrin precursor; P04196: Histidine-rich glycoprotein precursor; P06727: Apolipoprotein A-IV precursor; P19652: Alpha-1-acid glycoprotein 2 precursor; P68871 / P02042: Hemoglobin beta chain / Hemoglobin delta chain; P60709: Beta actin.
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD
Method of evaluating a risk of a subject of developing vascular complications
InactiveUS6599702B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHaptoglobinVascular complication
A method of evaluating a risk of a subject to develop vascular complications is disclosed. The method is effected by determining a haptoglobin phenotype of the subject and thereby evaluating the risk of the subject to develop vascular complications. The risk is decreased in patients with haptoglobin 1-1 phenotype as compared to patients with haptoglobin 1-2 or haptoglobin 2-2 phenotypes.
Owner:RAPPAPORT FAMILY INSTITUTE FOR RESEACH IN THE MEDICAL SCIENCES
Tumor marker for pancreatic cancer and method of testing the same
ActiveUS20090181461A1Improve accuracyUseful in detectionBiological testingImmunoassaysFucosylationHaptoglobin
The determination (test, diagnosis) of pancreatic cancer can be performed with high accuracy by detecting a fucosylated sugar chain (N-glycan) present in a specific site of the human haptoglobin and using an amount of the fucosylated sugar chain as a tumor marker for pancreatic cancer.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Endometriosis-specific secretory protein
InactiveUS7122322B2Immunoglobulins against animals/humansPreparing sample for investigationEndometriosisHaptoglobin
A method and kit of diagnosing endometriosis in a female patient suspected of having endometriosis. The method includes obtaining a sample from the patient. The sample is analyzed to detect the presence of a purified and isolated endometriotic haptoglobin designated ENDO-I and functional analogs thereof. A therapeutic for treating endometriosis by modulating the expression of a purified and isolated endometriotic haptoglobin designated ENDO-I and functional analogs thereof and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
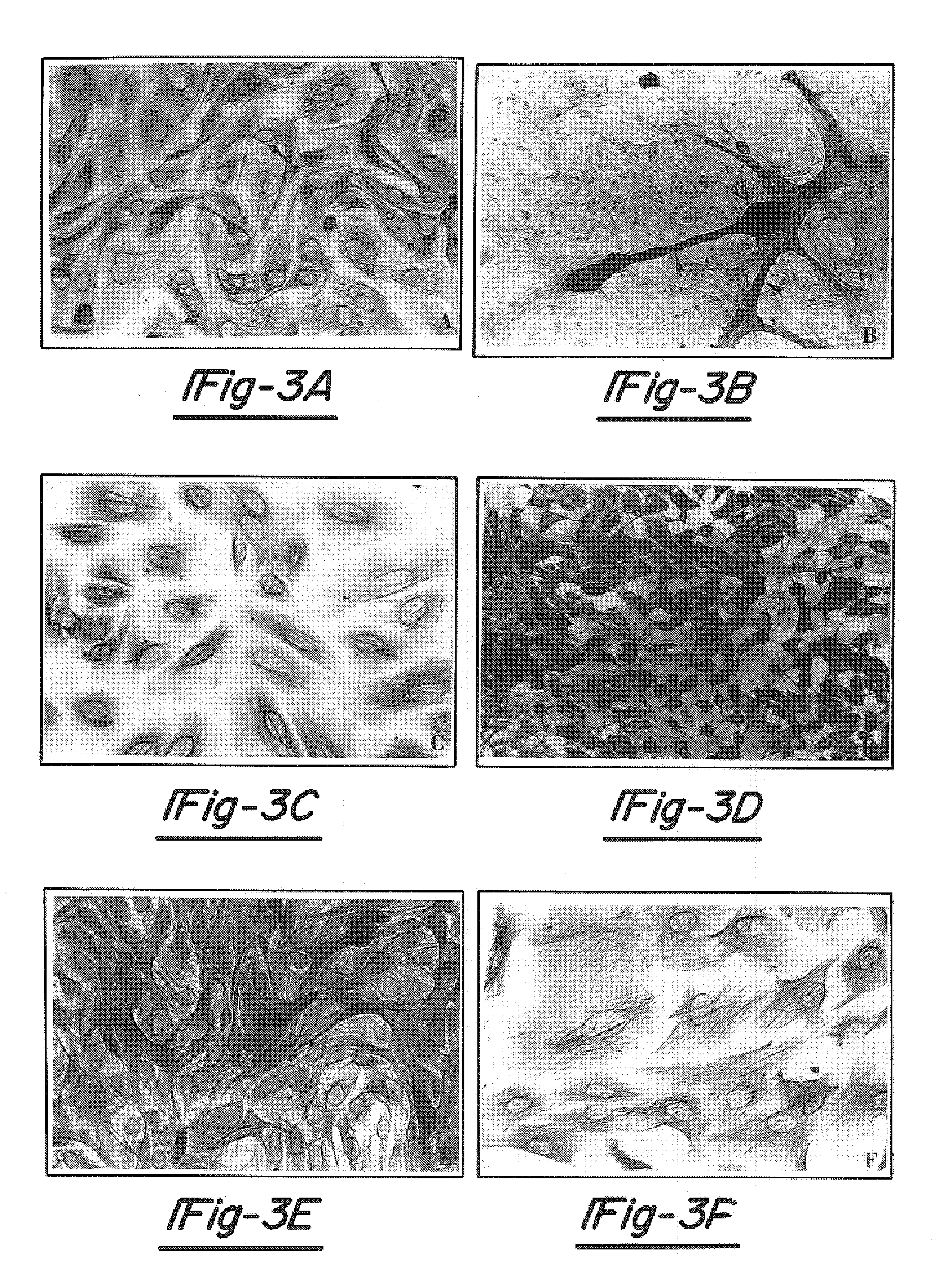
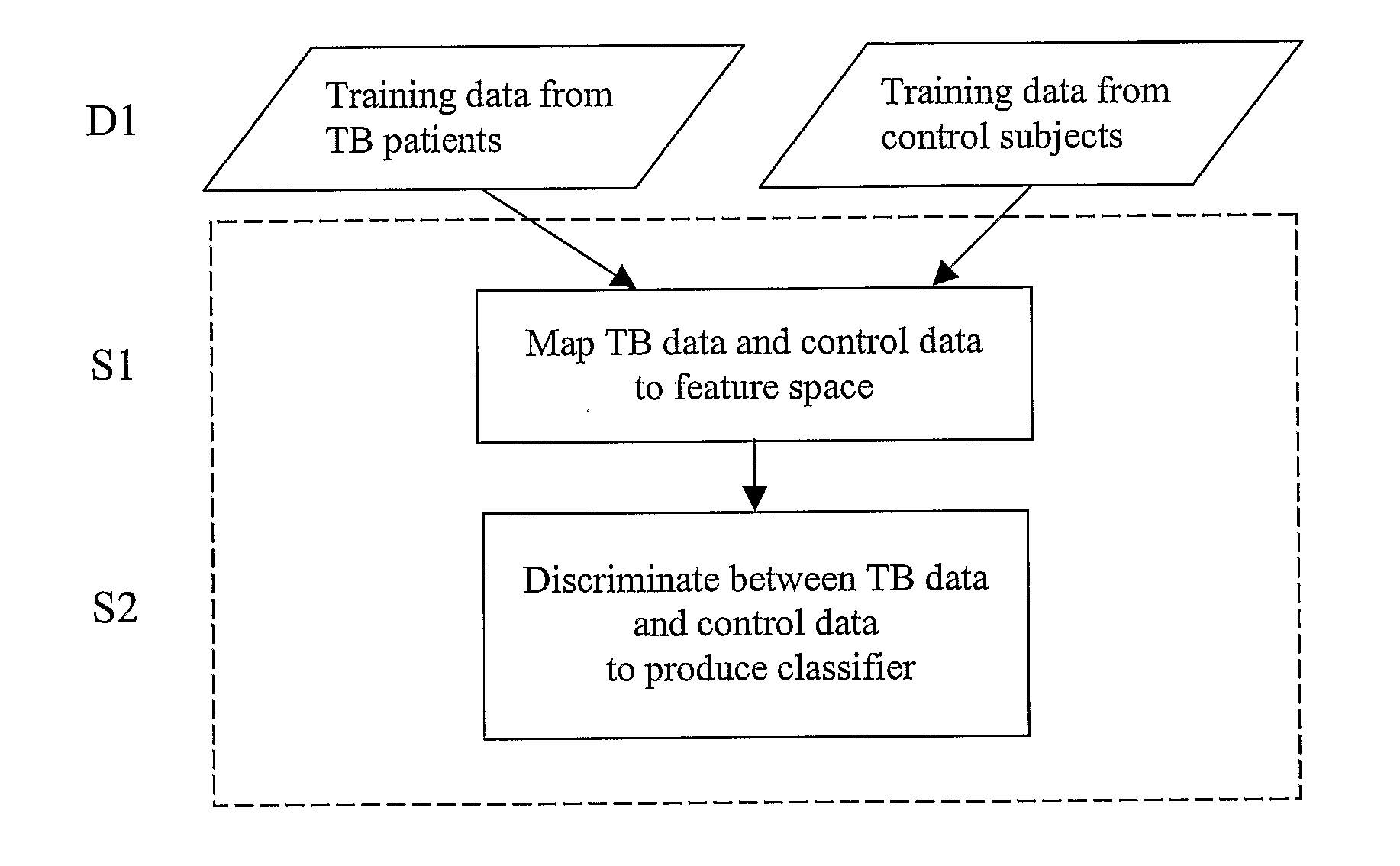
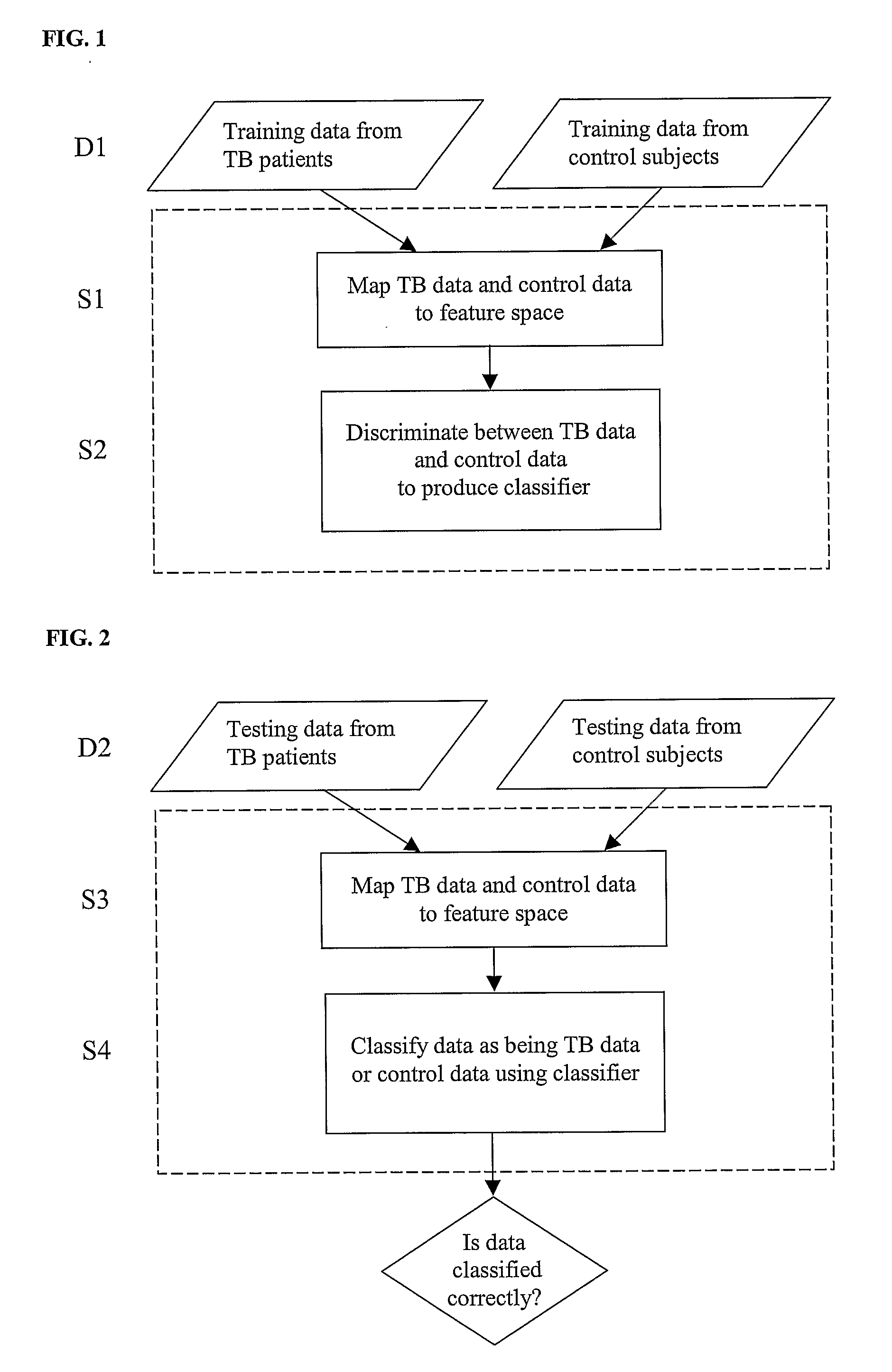
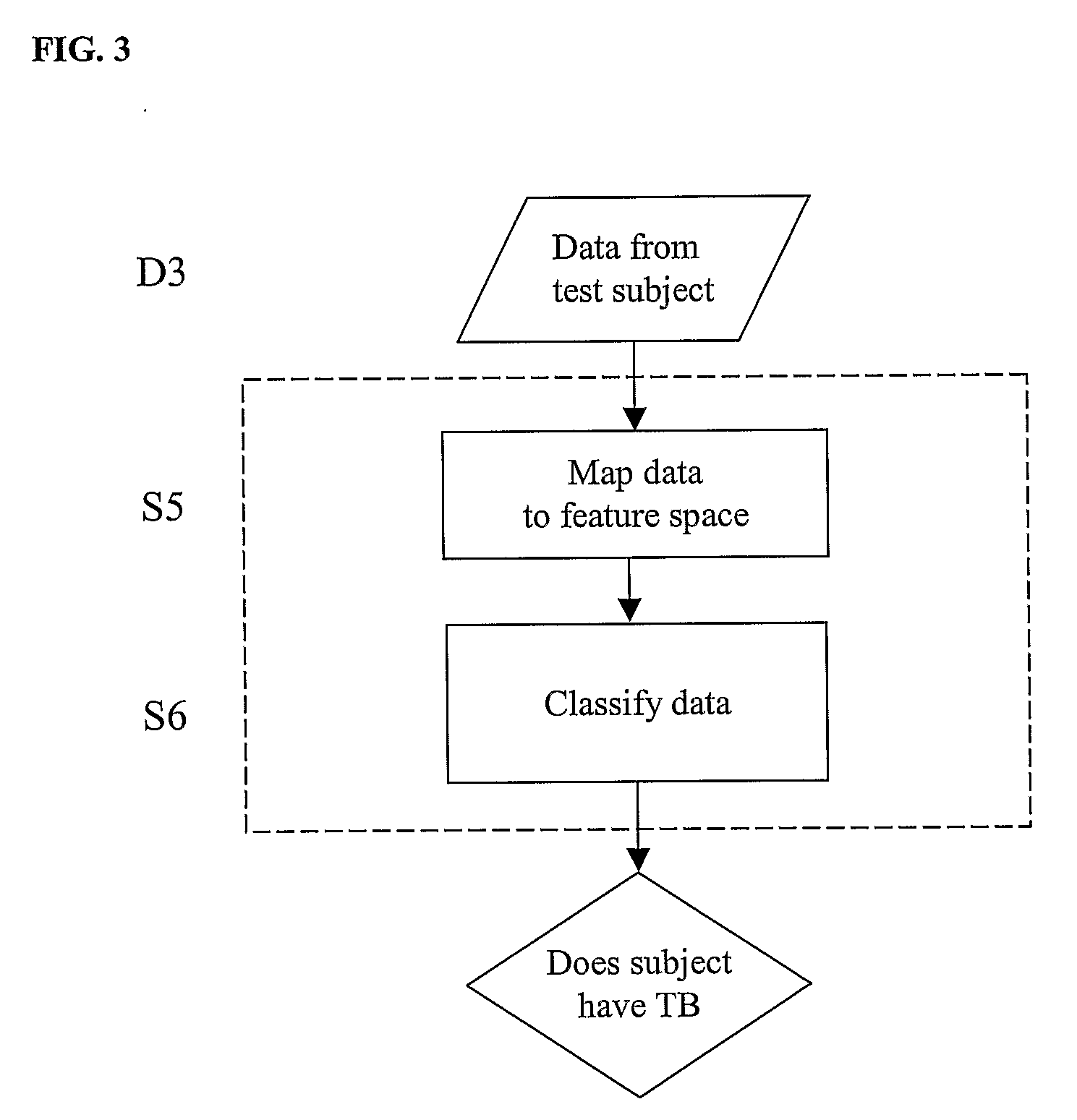
Diagnosis of Tuberculosis
InactiveUS20090104602A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisSerum protein albuminApolipoproteins E
The invention provides a method of diagnosing tuberculosis (TB) in a test subject, said method comprising: (i) providing expression data of two or more markers in a subject, wherein at least two of said markers are selected from transthyretin, neopterin, C-reactive protein (CRP), serum amyloid A (SAA), serum albumin, apoliopoprotein-A1 (Apo-A1), apolipoprotein-A2 (Apo-A2), hemoglobin beta, haptoglobin protein, DEP domain protein, leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein (A2GL) and hypothetical protein DFKZp667I032; and (ii) comparing said expression data to expression data of said marker from a group of control subjects, wherein said control subjects comprise patients suffering from inflammatory conditions other than TB, thereby determining whether or not said test subject has TB.
Owner:FERNANDEZ REYES DELMIRO +3
Kit for determining haptoglobin and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106053839AHigh analytical sensitivityRapid responseBiological material analysisBiological testingSuspending AgentsSurface-active agents
The invention discloses a kit for determining haptoglobin and a preparation method thereof. The kit comprises dual-liquid components of a reagent R1 and a reagent R2 which are independent from each other. The reagent R1 is prepared from a buffer solution, an accelerator, a surface active agent, inorganic salt ions and a corrosion remover, and a solvent of the reagent R1 is purified water; the reagent R2 is prepared from a buffer solution, a suspending agent, a surface active agent, inorganic salt ions, a corrosion remover and haptoglobin antibodies, and a solvent of the reagent R2 is purified water. The preparation method comprises the steps that the reagents are prepared according to the component content; a to-be-tested sample is mixed with the reagent R1 and the reagent R2 to be subjected to a sufficient reaction; a fully automatic biochemical analyzer is used for determining an absorptivity difference obtained after the reaction; according to an absorptivity change value, the concentration of haptoglobin in the sample is worked out. The kit has the advantages of being convenient to operate, high in accuracy and the like.
Owner:ANHUI IPROCOM BIOTECH CO LTD
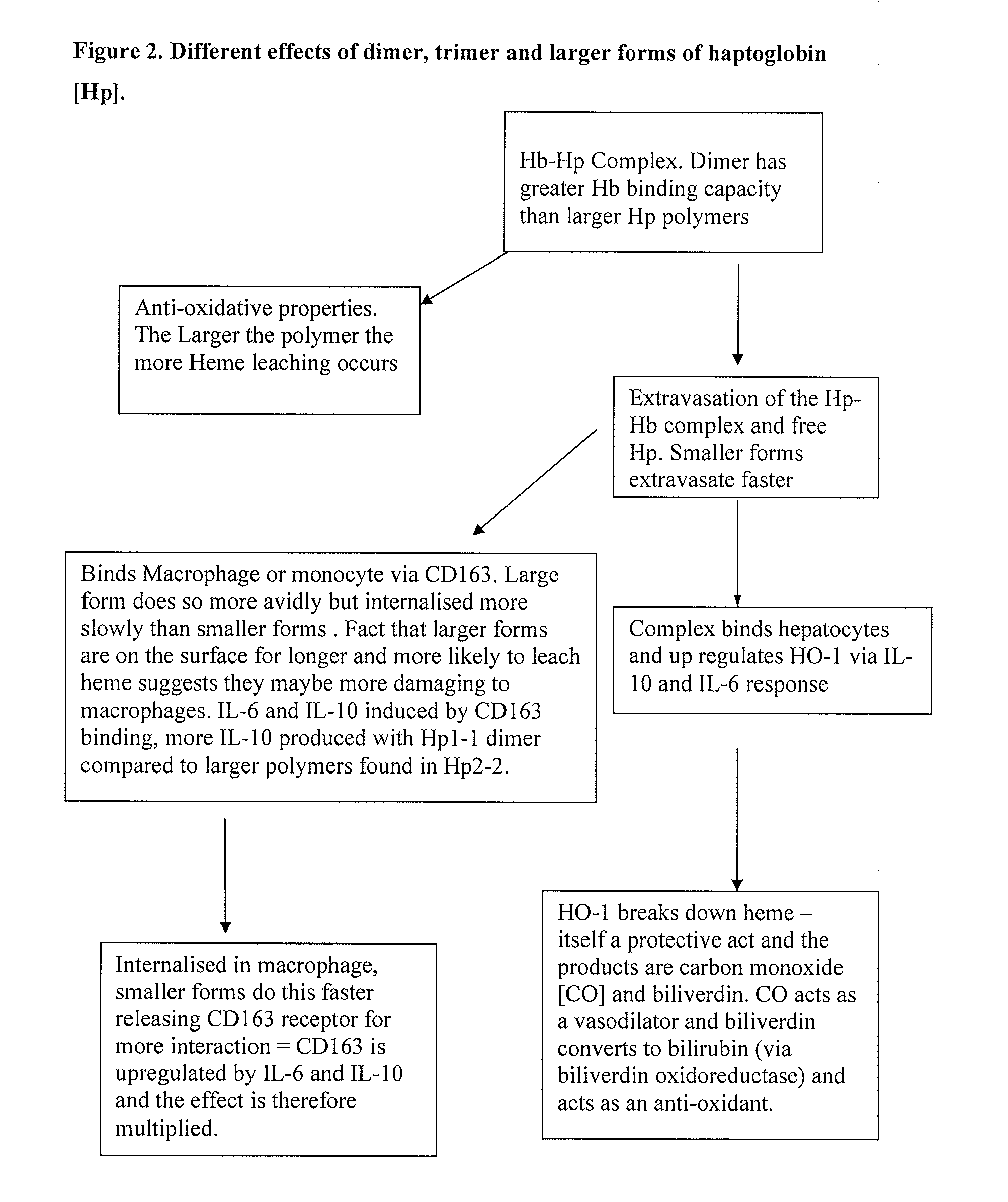
Enriched haptoglobin polymers for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20080293623A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseAntioxidant
Haptoglobin (Hp) removes cell-free Hemoglobin (Hb), with different physiological effects depending on the particular Hp polymer. We propose that material enriched for alpha 1 chain Hp polymeric forms, such as those made from Cohn fraction V precipitate, will be more suitable for the treatment of certain diseases benefiting from both an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory component, such as for hemolytic disease. Material enriched for alpha-2 chain Hp polymeric forms, made for example from Cohn fraction IV precipitate, will be more suitable for treatment of diseases where an angiogenic, and / or inflammatory affect, and / or limited extravasation is desirable.
Owner:NHS BLOOD & TRANSPLANT
Assays to predict atherosclerosis and dysfunctional high-density lipoprotein
ActiveUS7723045B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNitric oxideAtheroma
This invention provides novel assays for the detection of dysfunctional HDL. The assays are good diagnostics and / or prognostics for atherosclerosis or other pathologies characterized by an inflammatory response. In certain embodiments the methods involve measurements of heme-related HDL-associated proteins (e.g., haptoglobin, hemopexin, etc.), and / or measurements of the relative distribution of HDL-associated proteins between HDL and the non-lipoprotein fractions of plasma / serum, and / or measurements of the ability of pro-inflammatory HDL to consume nitric oxide, and / or measurement of the ability of HDL to inhibit LDL aggregation.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Haptoglobin derivative for treatment of sepsis and acetaminophen-induced liver damage
InactiveUS20180344808A1Reduce the possibilityProlonged plasma half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntisepticsHaptoglobinGastroenterology
Methods for treating sepsis of acetaminophen-induced liver damage in a subject sing a haptoglobin derivative are provided. Compositions containing a haptoglobin derivative for treating sepsis of acetaminophen-induced liver damage are provided.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
Methods and devices for diagnosis of appendicitis
InactiveUS7501256B2Diagnosing appendicitisAccurate diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyTissue sampleSuspected appendicitis
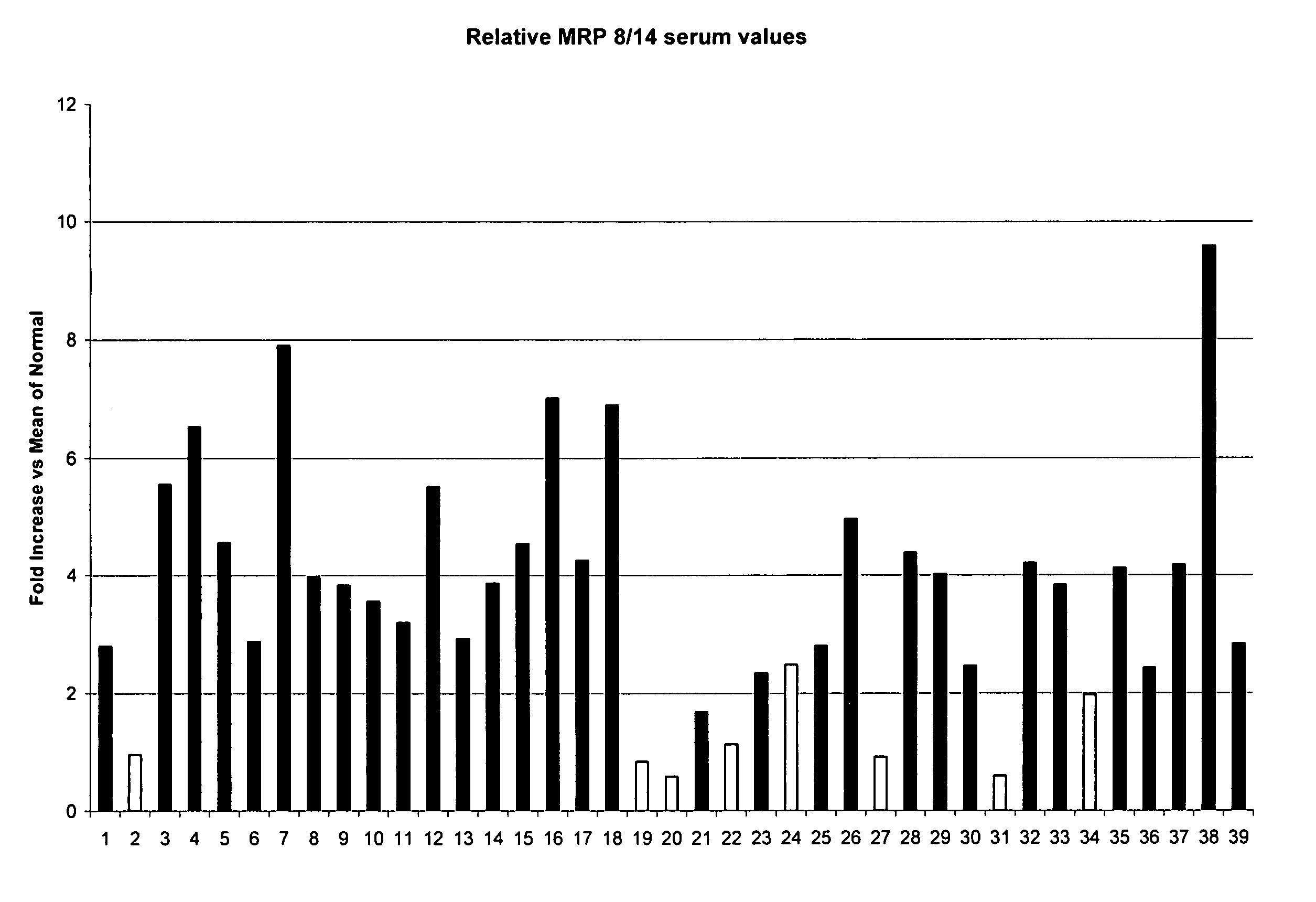
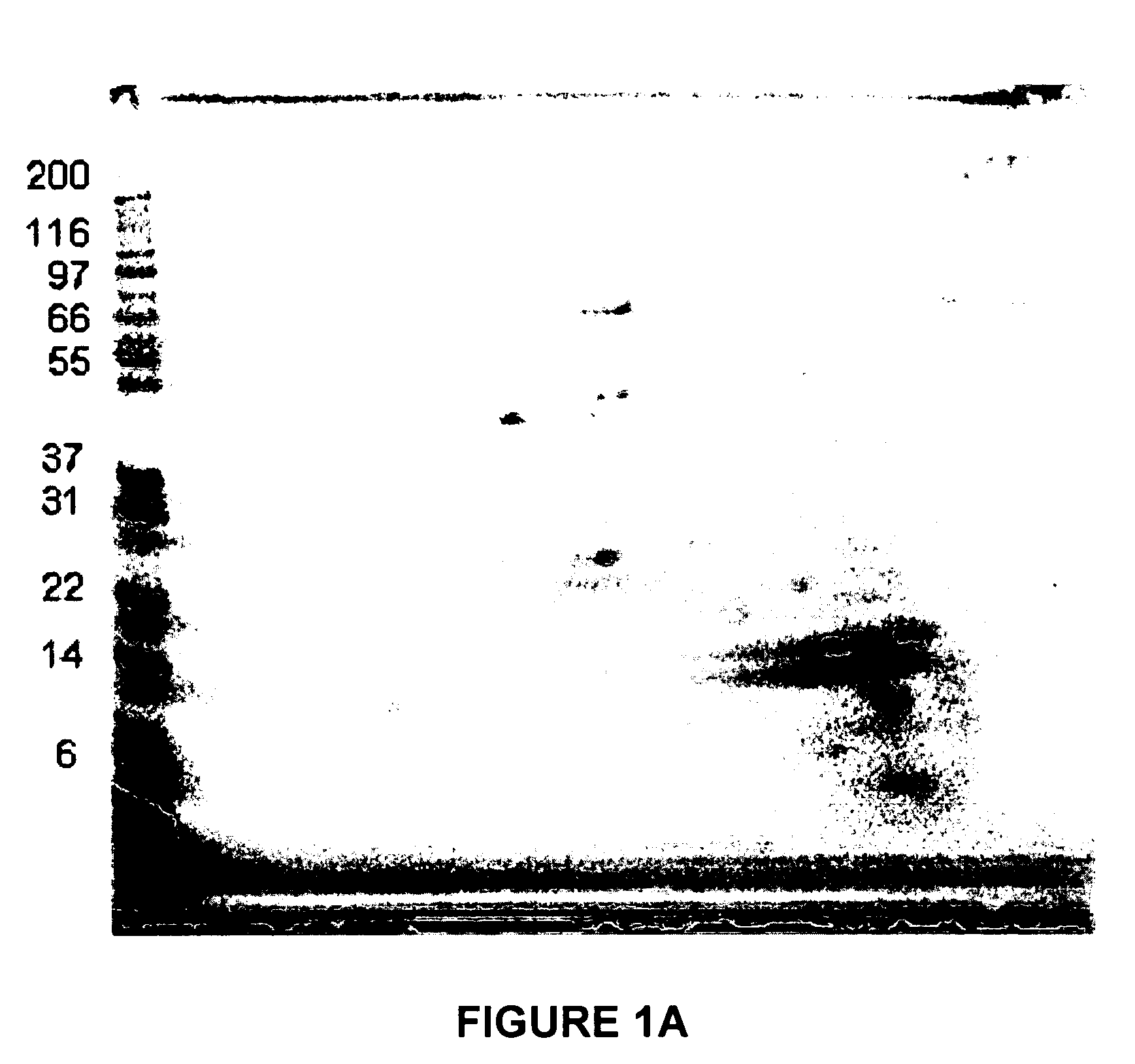
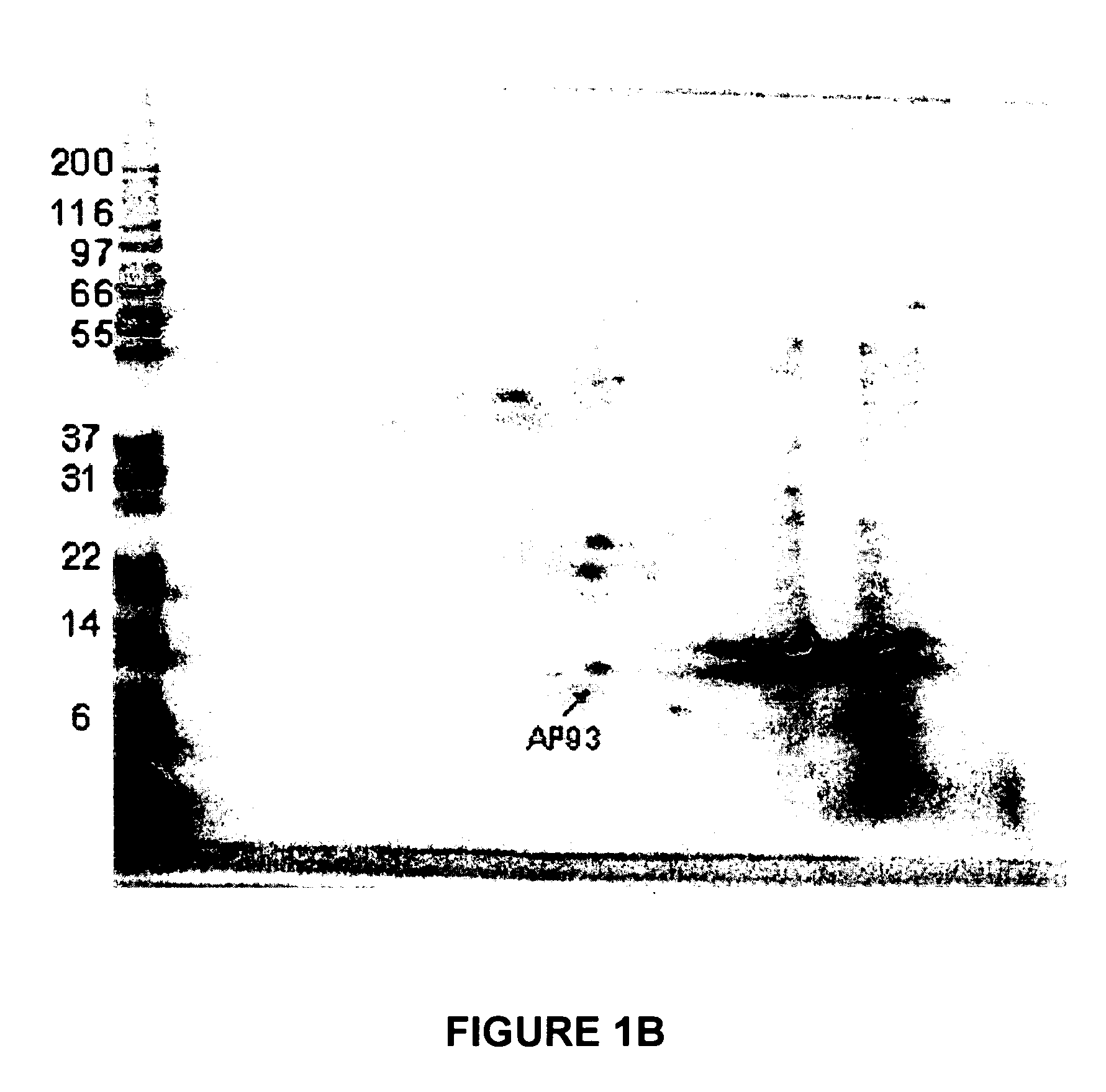
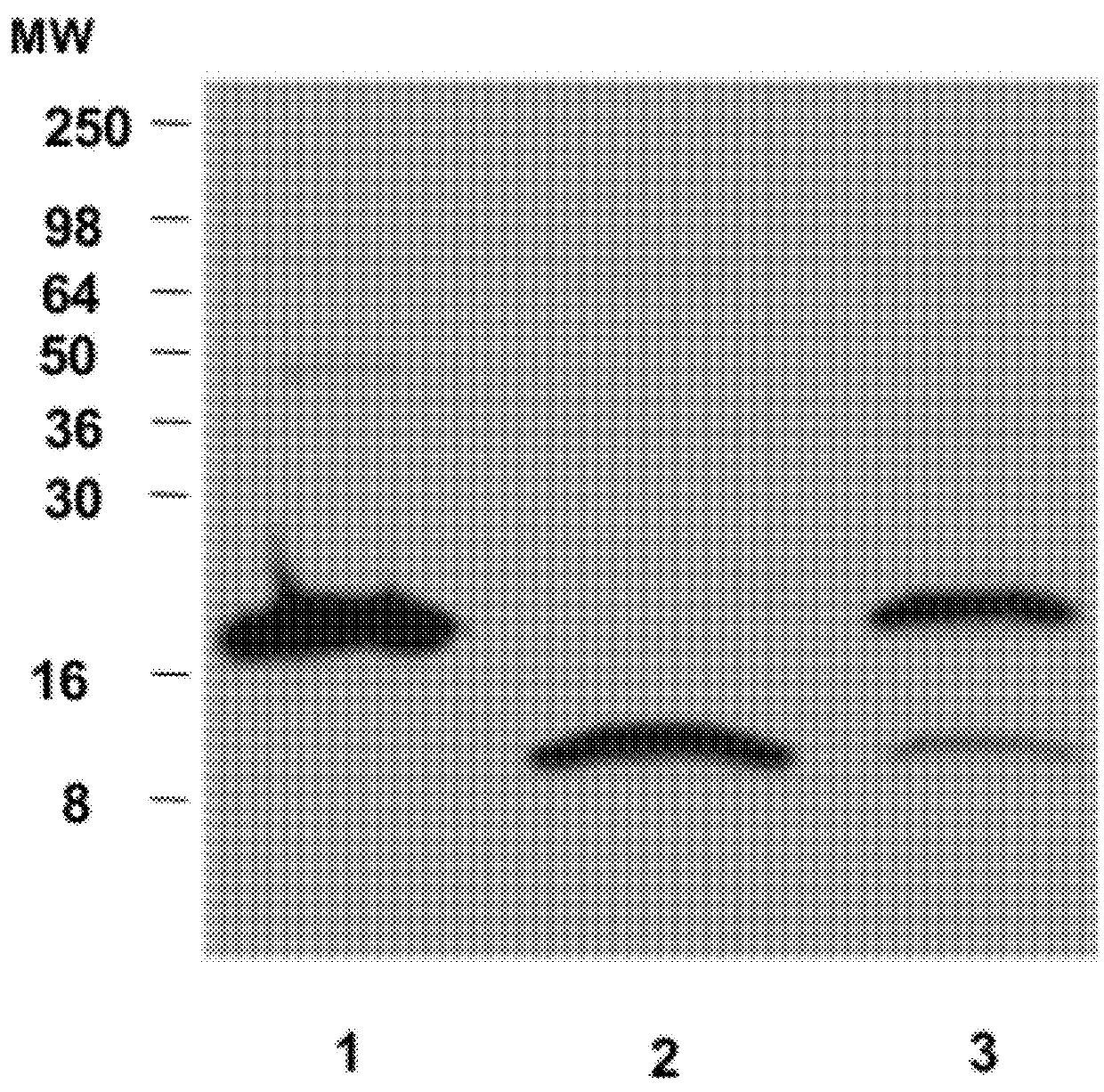
A method is provided for diagnosing appendicitis in a patient that includes identifying at least one symptom of appendicitis in the patient and identifying the presence of at least one molecule differentially associated with appendicitis in a fluid or tissue sample of said patient. MRP-8 / 14 and haptoglobin are examples of molecules differentially associated with appendicitis. Devices and kits for performing the appendicitis assays of this invention are also provided. In one embodiment, the device is in a flow-through immunoassay format for testing blood samples. Further, methods for screening for molecules differentially associated with appendicitis are provided that include the use of samples from patients being operated on for suspected appendicitis.
Owner:ASPENBIO PHARMA
Diagnostic marker for ovarian cancer
The present invention relates to methods of detecting, monitoring the efficacy of treatment of, and assessing the severity of ovarian cancer, by assessing the concentration of haptoglobin-1 precursor in a sample of biological fluid. The invention also relates to a kit comprising an antibody or nucleic acid probe specific for haptoglobin-1 precursor for use in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer, monitoring the efficacy of treatment of ovarian cancer, or assessing the severity of ovarian cancer.
Owner:ROYAL WOMENS HOSPITAL
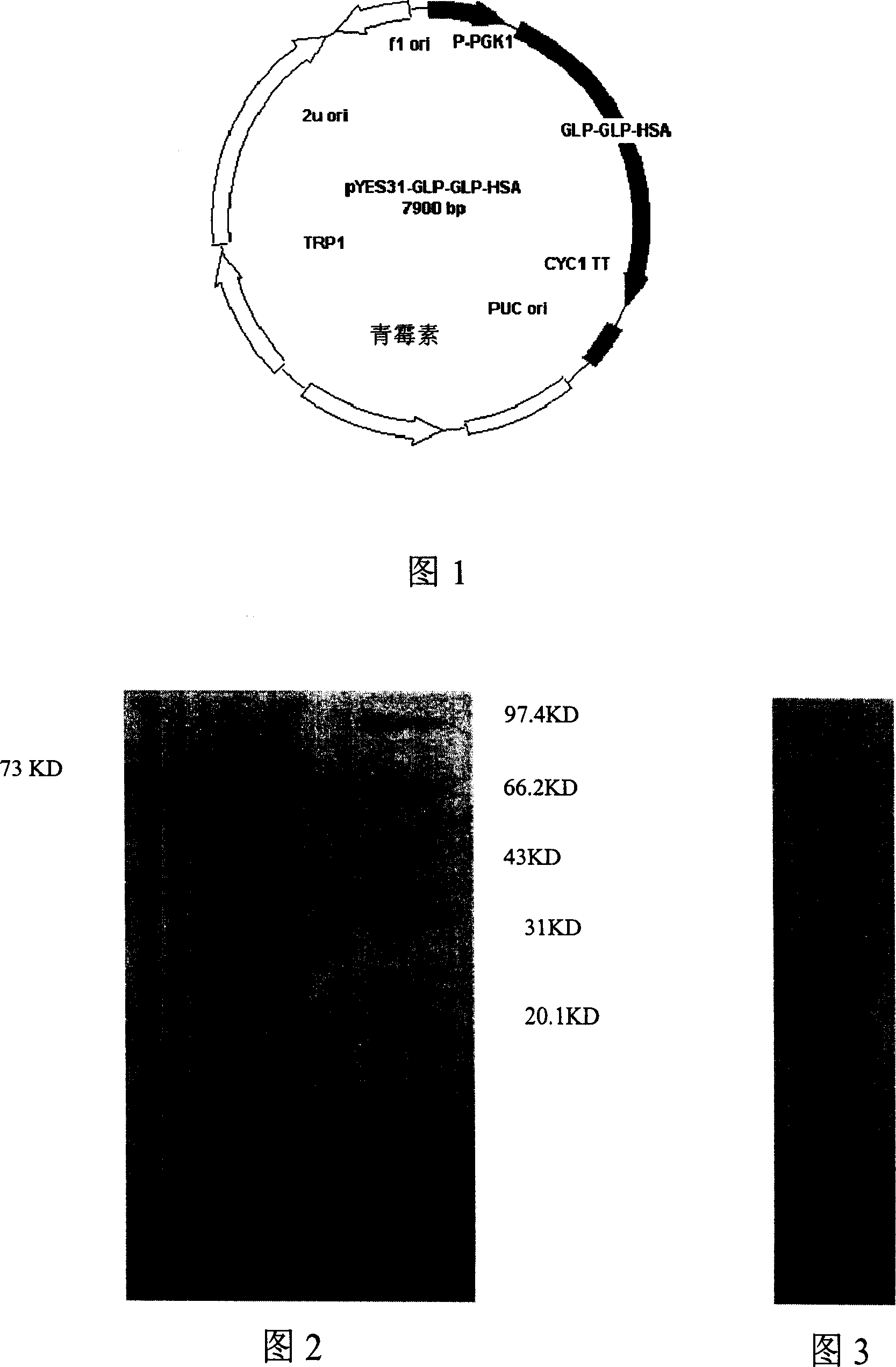
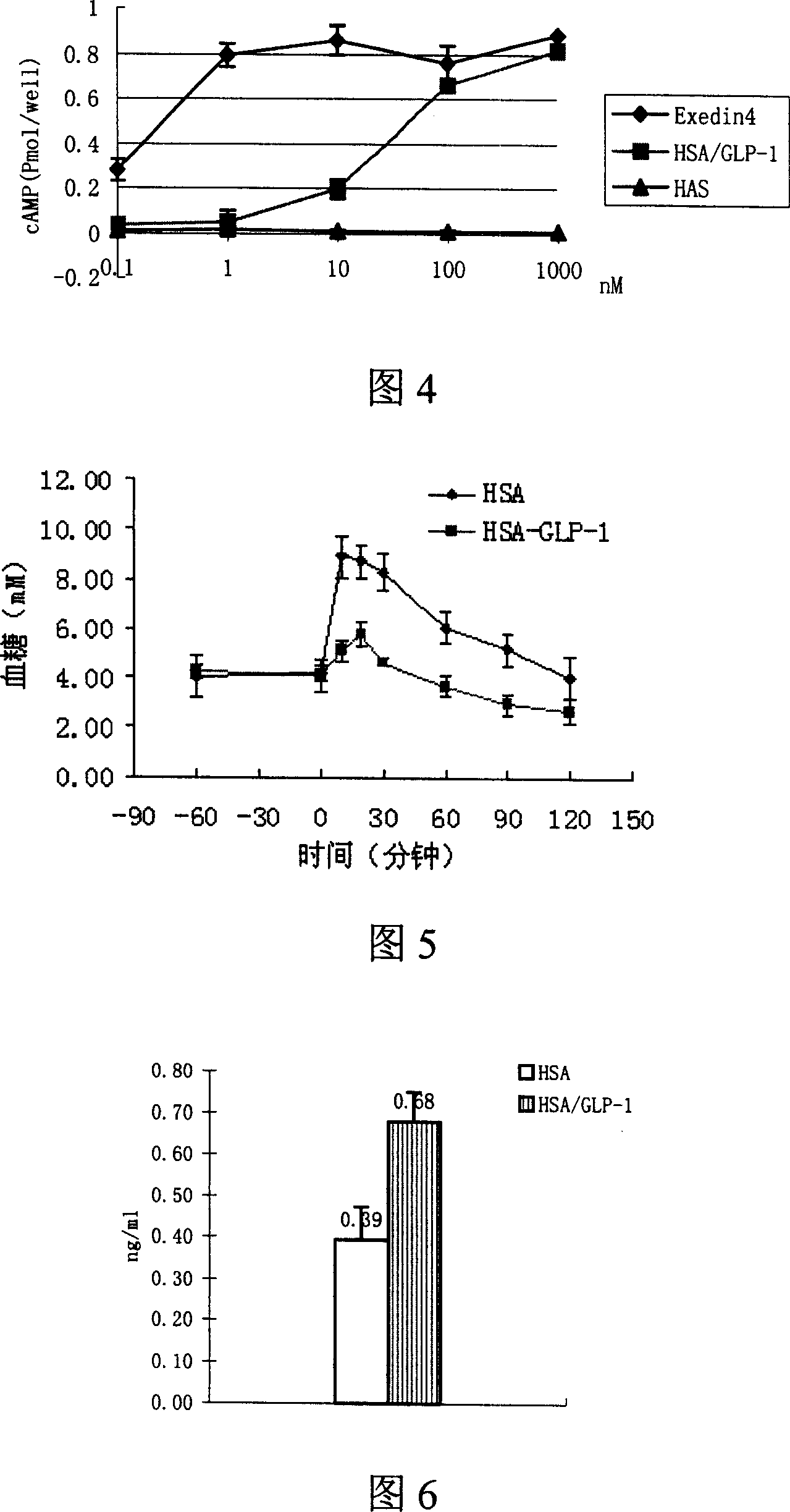
GLP-1 infusion proteins, their preparation and use
ActiveCN1962695AProlong the action timeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsHalf-lifeThyroxine-binding proteins
The invention discloses a fusing protein and preparing method and application, which is combined of para-insanguinin peptide 1 repeating sequence and human serum albumin, immune globulin, ferritin, steroid connecting protein, transferrin, thyroid connecting protein, alpha-2 macroglobulin and haptoglobin. The invention also provides the coding sequence of fusing protein and carrier and host with the coding chain, which possesses better stability and internal half-life.
Owner:ZHEJIANG WOLWO BIOTECH
Method of predicting a benefit of antioxidant therapy for prevention or treatment of vasclar disease in hyperglycemic individuals
InactiveUS20080213785A1Improve welfareReduce oxidative stressMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisVascular diseaseHaptoglobin
This invention relates to methods and compositions of determining the benefit of therapy using antioxidant for the treatment of cardiovascular events in individuals with diabetes mellitus based on their haptoglobin phenotype and the treatment of the cardiovascular events using antioxidants based on the haptoglobin phenotype.
Owner:RAPPAPORT FAMILY INSTITUTE FOR RESEACH IN THE MEDICAL SCIENCES
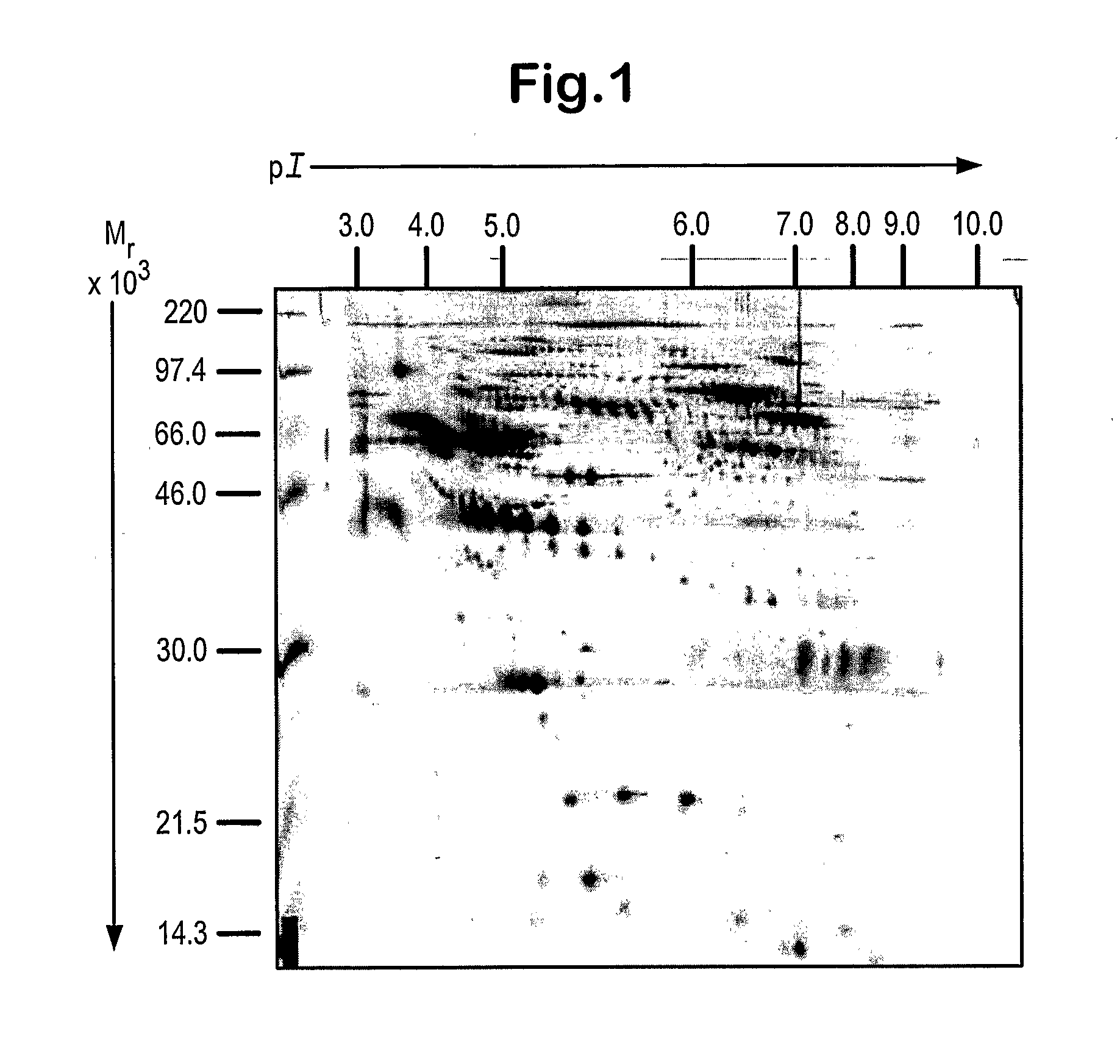
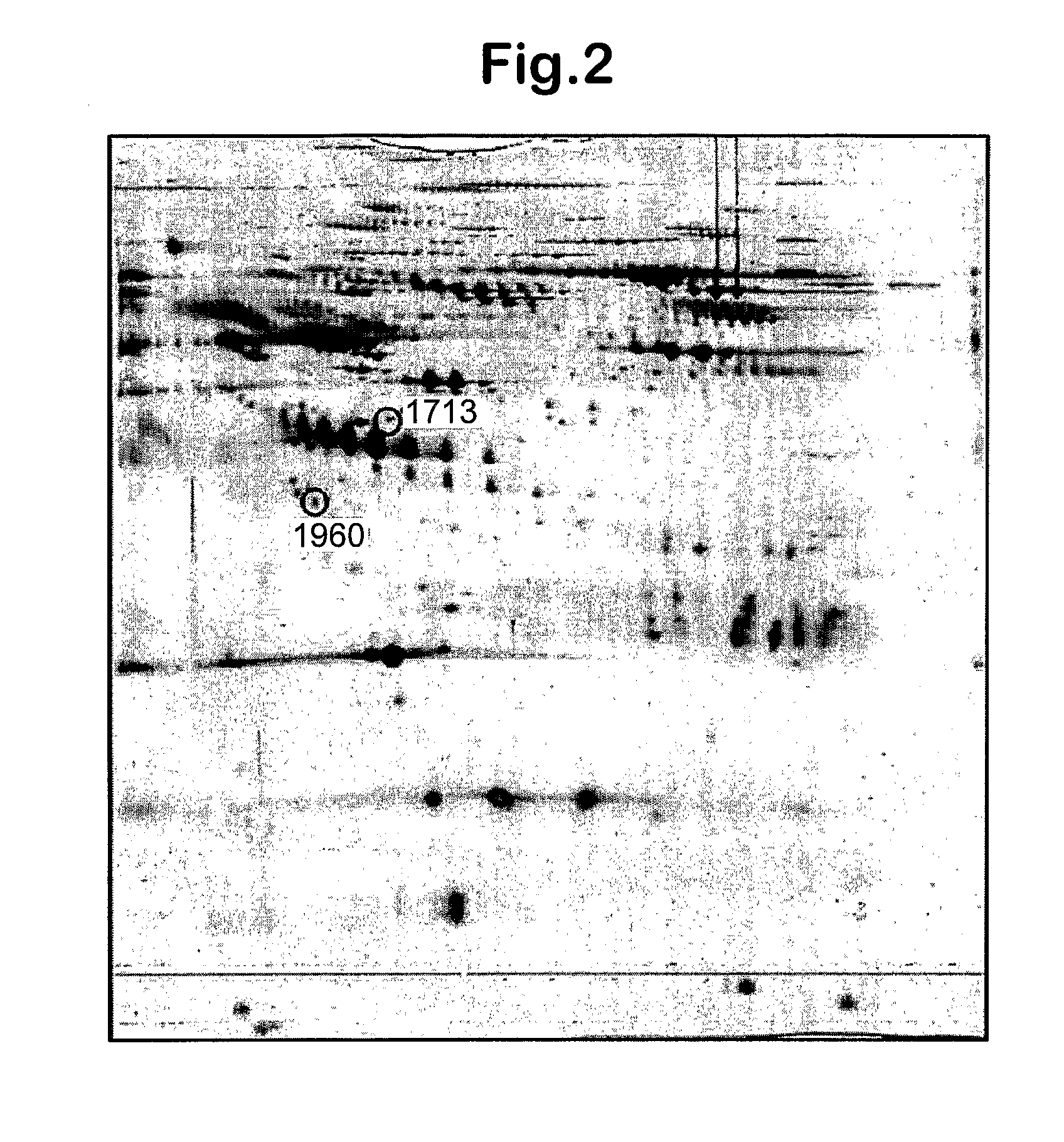
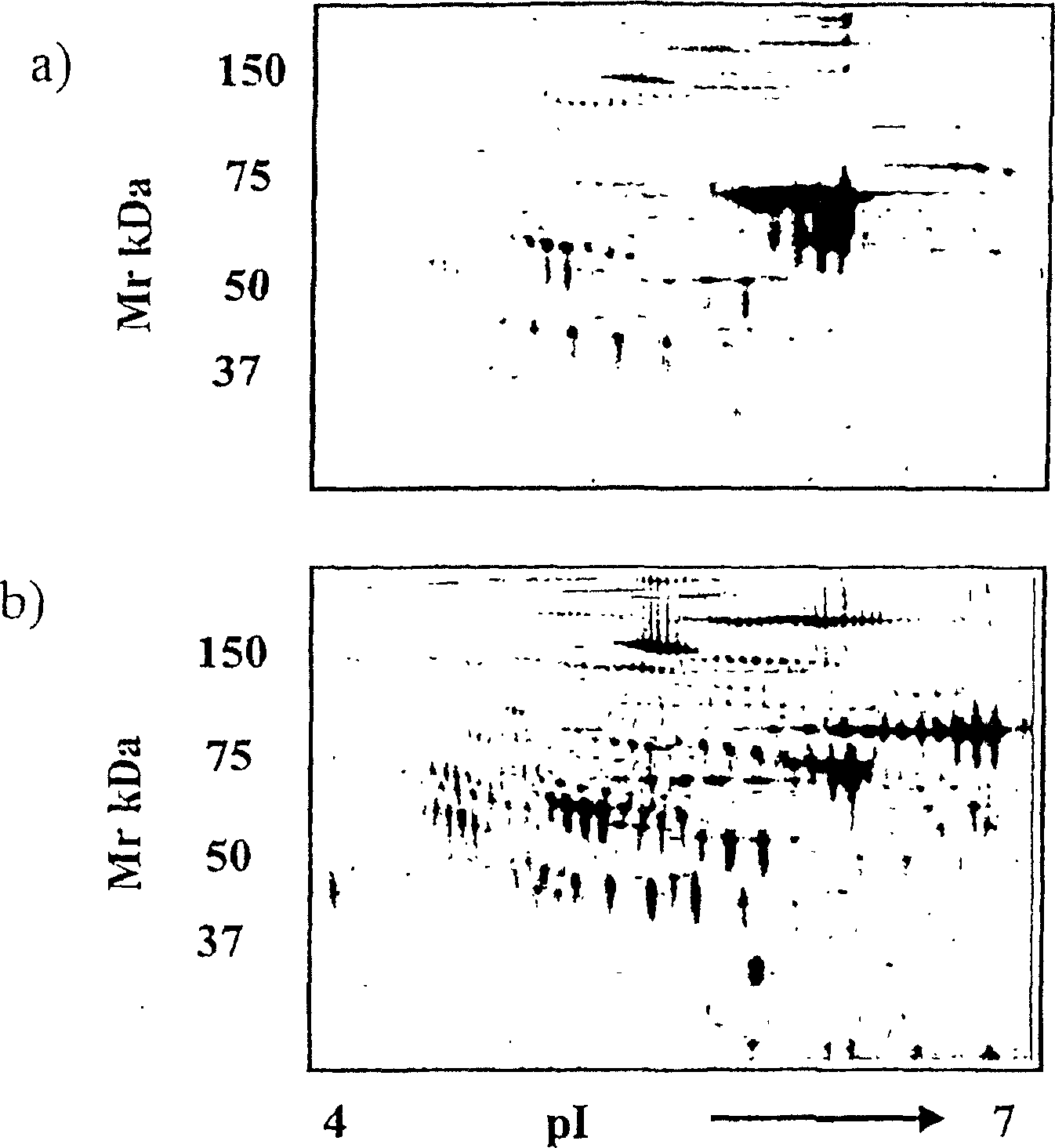
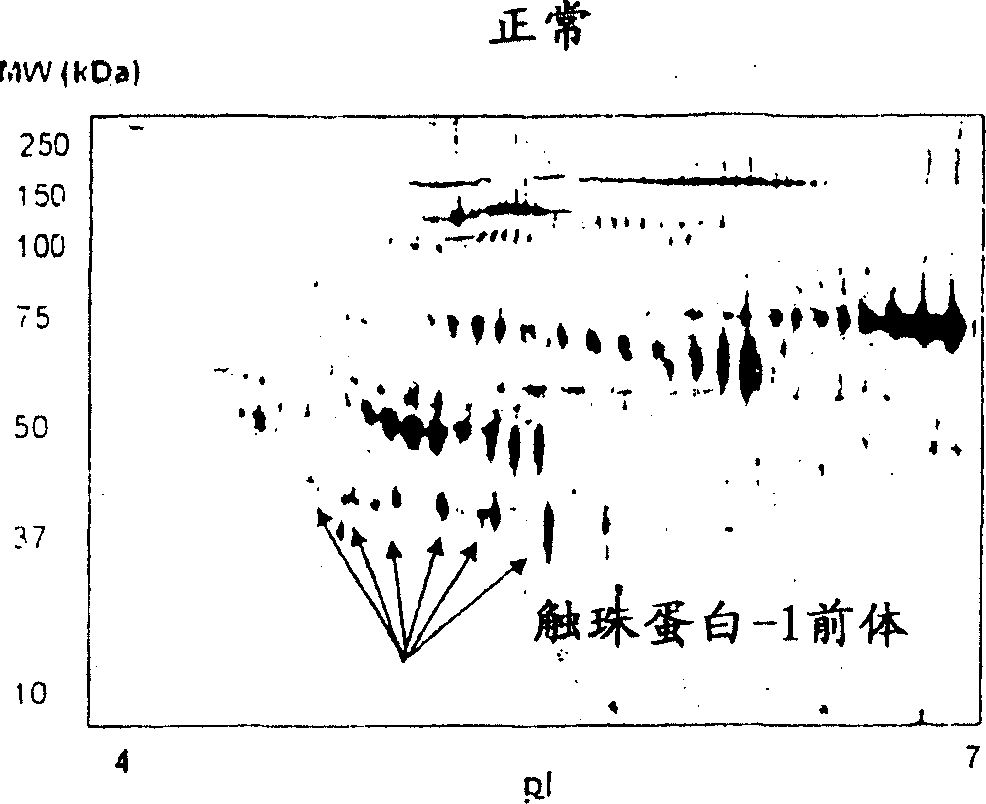
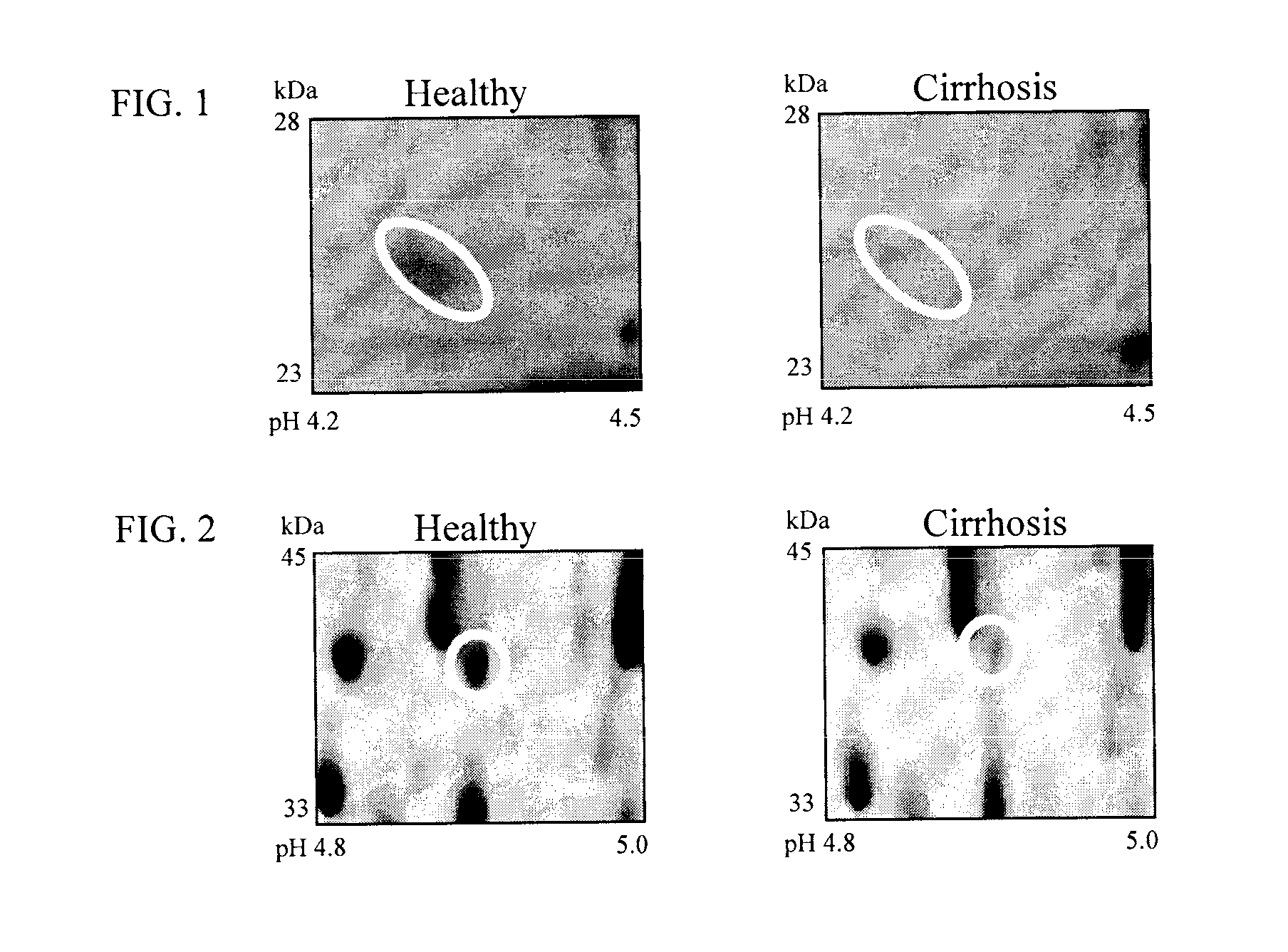
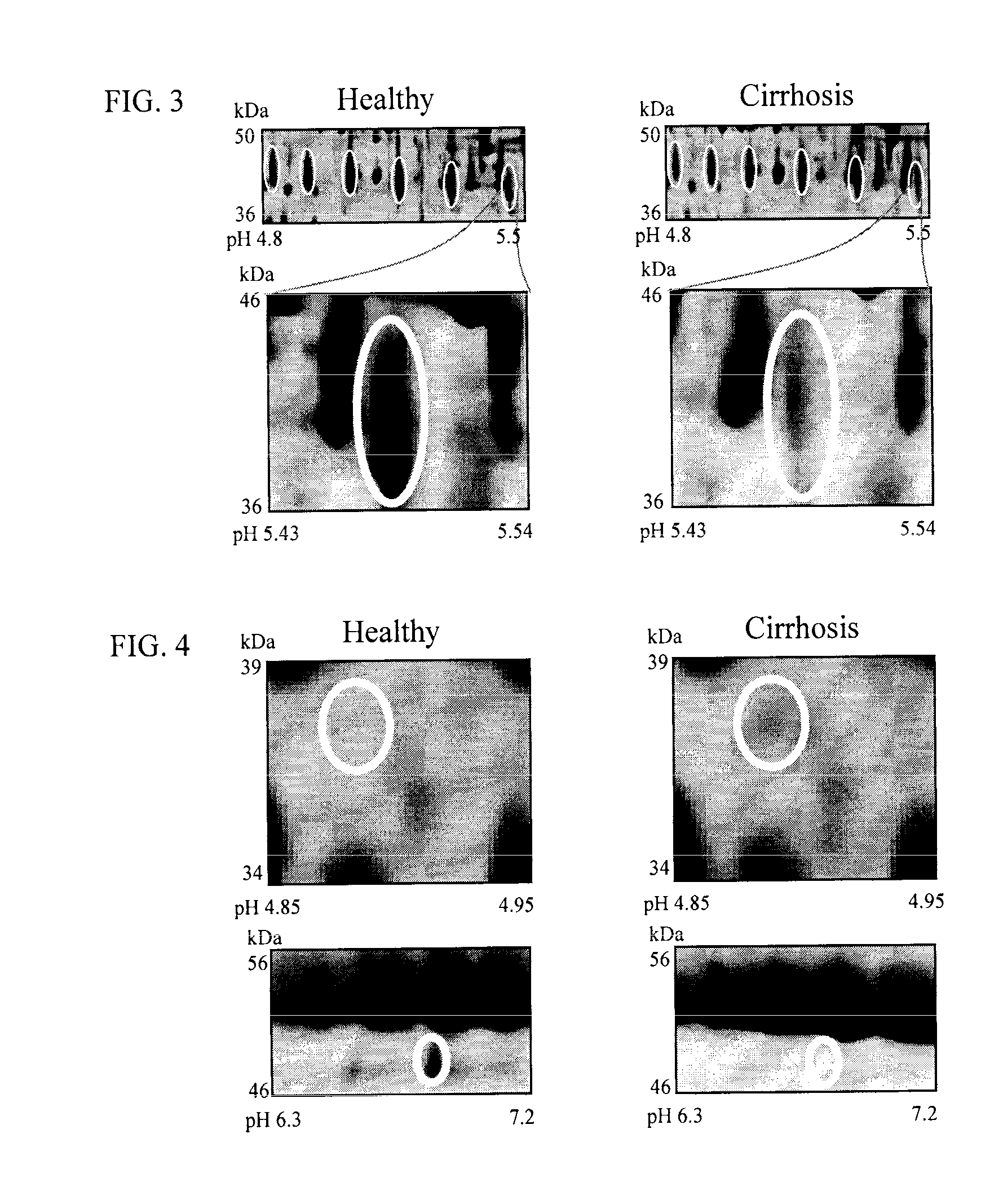
Clinical diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis using a novel panel of low abundant human plasma protein biomarkers
The inventors have proposed a novel panel of human plasma protein biomarkers for diagnosing hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. Presently there is no reliable non-invasive way of assessing liver fibrosis. A 2D-PAGE based proteomics study was used to identify potential fibrosis biomarkers. Plasma from patients with hepatic cirrhosis induced by infection with the hepatitis C virus (HCV) were analysed. Several proteins associated with liver scarring and potentially also related to viral infection were identified. These proteins include 14-3-3 protein zeta / delta, adiponectin, afamin, alpha-1-antitrypsin, alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein, apolipoprotein C-III, apolipoprotein E, C4b-binding protein beta chain, intact / cleaved complement C3dg, corticosteroid-binding globulin, fibrinogen gamma chain, beta haptoglobin at pH 5.46-5.49, haptoglobin-related protein, hemopexin, immunoglobulin J chain, leucine-rich alpha-2-glycoprotein, lipid transfer inhibitor protein, retinol-binding protein 4, serum paraoxonase / arylesterase 1, sex hormone-binding globulin and zinc-alpha-2-glycoprotein. These biomarkers can be used in conjunction with polypeptides in WO / 2008 / 031051. The concentrations of these novel biomarkers can be determined using an immunoassay where the concentrations would reflect the extent of fibrosis. A fibrosis scoring scale for each of the novel biomarkers is proposed. The additive result from the scores of all the novel biomarkers would give a more reliable indication of the degree of fibrosis rather than examining individual biomarkers.
Owner:UNIV OF OXFORD
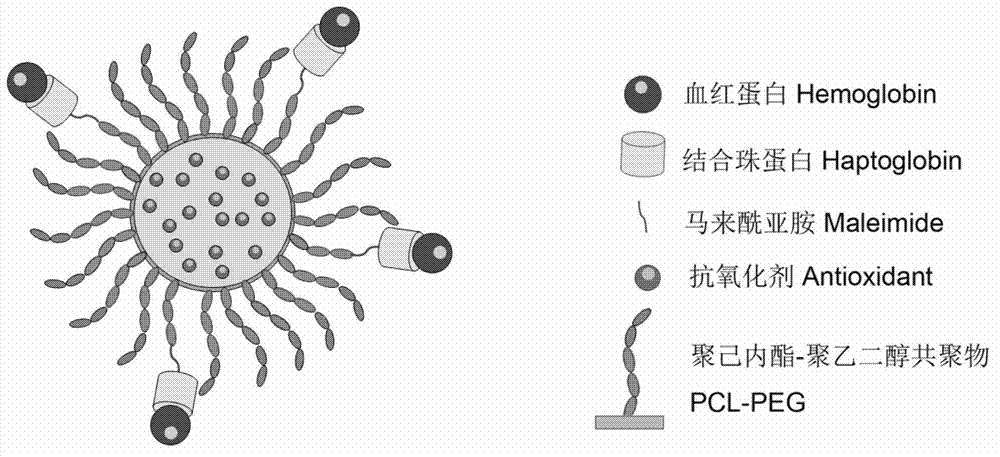
Hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102861322ARealize fixed-point quantitative combinationQuality improvementPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFree hemoglobinPolyester
The invention discloses a hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier, which comprises hemoglobin, haptoglobin and polyethyleneglycol-polyester nanoparticles. Hemoglobin is connected on the surfaces of the polyethyleneglycol-polyester nanoparticles by haptoglobin. The hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier provided by the invention has no obvious toxicity on the cells, the blood plasma does not have obvious free hemoglobin in the blood plasma after the hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier is infused, and no hypertension reaction is produced, so that the defect that the traditional hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier is high in side effects is overcome. The hemoglobin-based oxygen carrier has a good application prospect and a economic benefit.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Methods of predicting a benefit of antioxidant therapy for prevention of cardiovascular disease in hyperglycemic patients
InactiveUS20040229244A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHaptoglobinDiabetic patient
A method of determining a potential of a diabetic patient to benefit from anti oxidant therapy for treatment of a vascular complication, the method comprising determining a haptoglobin phenotype of the diabetic patient and thereby determining the potential of the diabetic patient to benefit from said anti oxidant therapy, whereby a patient having a haptoglobin 2-2 phenotype benefits from anti oxidant therapy more than a patient having a haptoglobin 1-2 phenotype or a patient having a haptoglobin 1-1 phenotype.
Owner:RAPPAPORT FAMILY INSTITUTE FOR RESEACH IN THE MEDICAL SCIENCES
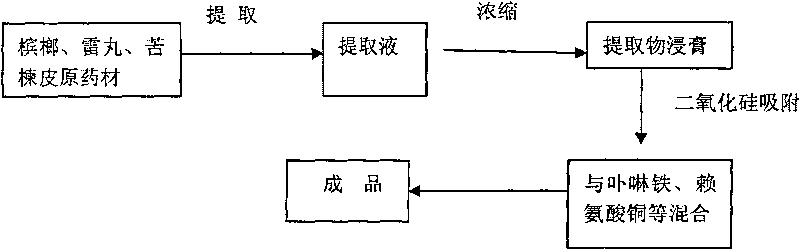
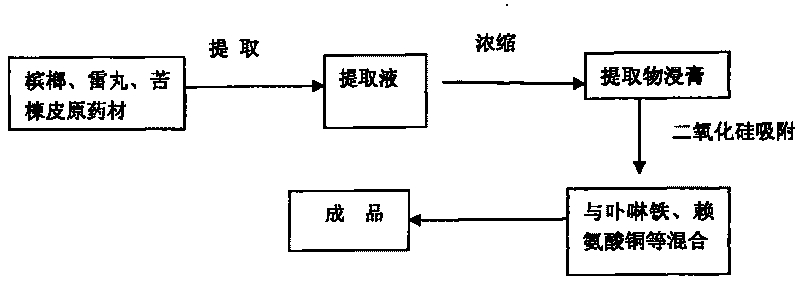
Method for producing feed additive for preventing and curing pig anemia
ActiveCN101690548AIncrease the number ofHigh biological potencyAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsFood additivePink color
The invention discloses a method for producing feed additive for preventing and curing pig anemia and comprises the following technique steps: 1. preparing traditional Chinese medicine extract; 2. absorbing the traditional Chinese medicine extract with an absorbent; 3. mixing the absorbed semi-finished product with porphyrin iron, copper lysine, zinc glycinate and auxiliary materials to obtain the finished product. The invention has the advantages that porphyrin iron can be directly absorbed by an organism and can be synthesized with haptoglobin (Hp) into hemoglobin with low energy consumption, high efficiency and fast blood enrichment speed so as to effectively prevent and cure piglet anemia; the traditional Chinese medicine extract can effectively kill pig endoparasite; the product has good efficacy both for pig anemia and parasite infection; the product accelerates synthesis of in vivo hemoglobin and increases hemoglobin quantity to promote in vivo blood circulation, eliminate striving for nutrients from parasite, eliminate anemia symptom, improve metabolic rate of pig organism, and cause the skin of pig to show healthy pink color.
Owner:WUXI ZHENGDA POULTRY
Novel method for gastric cancer diagnosis
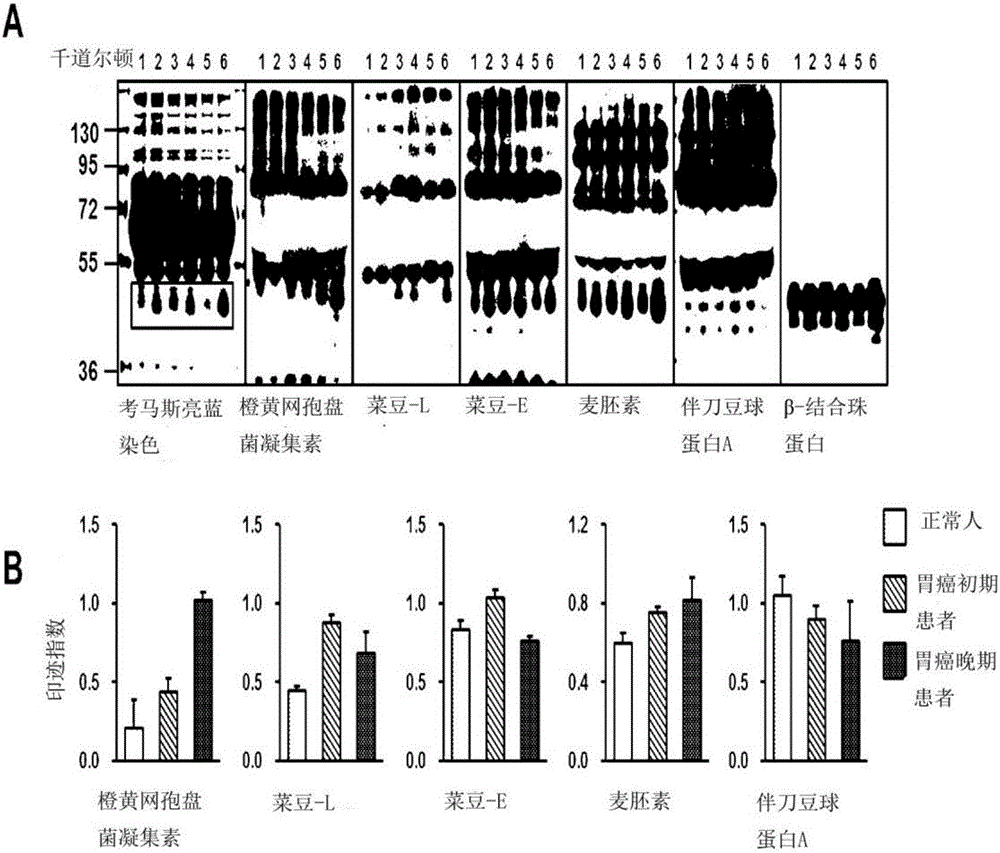
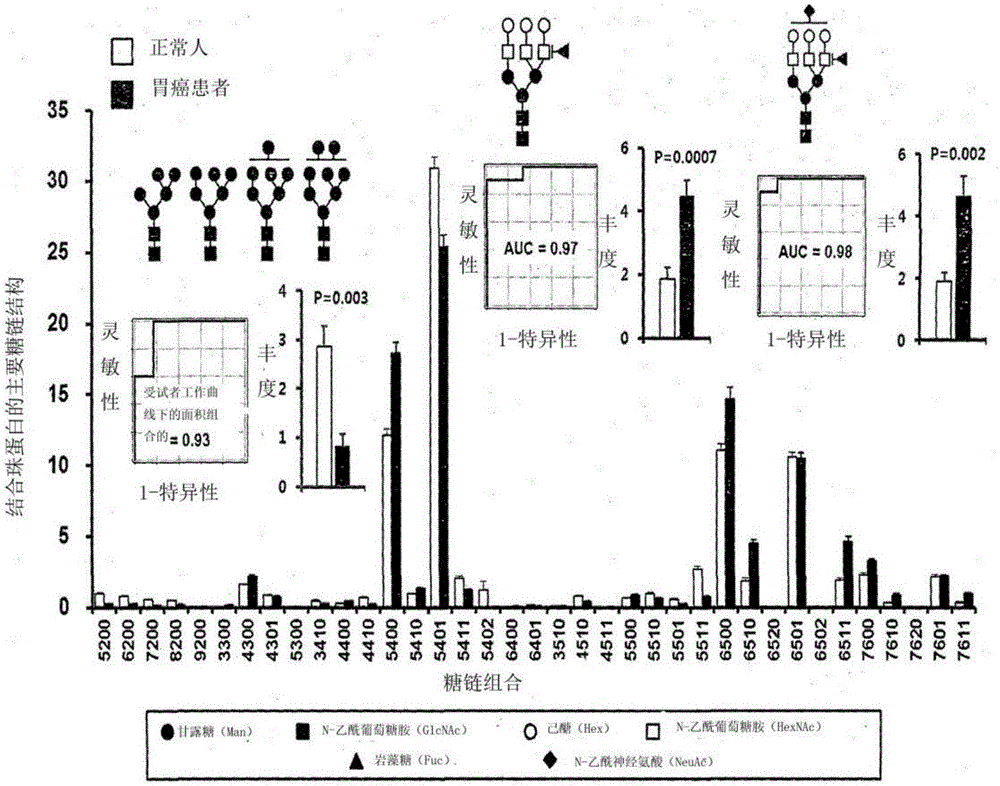
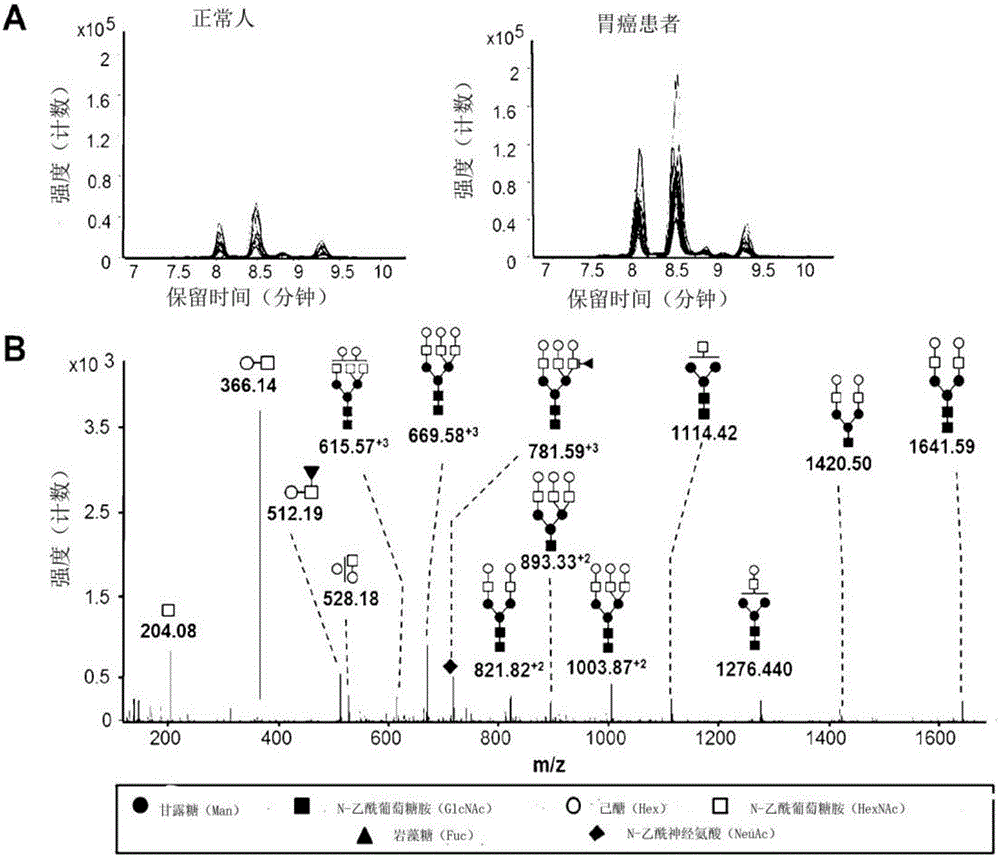
InactiveCN106029906AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFucosylationHigh mannose
The present invention relates to a method for gastric cancer diagnosis through the detection of glycan changes, and to a kit for gastric cancer diagnosis. More specifically, based on, among the changes in N-linked glycosylation of the gastric cancer patient-derived haptoglobin, which are detected through lectin and mass spectrometry, the increase in fucosylation, the increases or significant changes in particular glycan structures according to the classification of antennary, or the reduction in high-mannose structure of the N-linked glycan compared with normal persons, the discovered N-glycosylation structures can be favorably used for a method for gastric cancer diagnosis using lectin, as a diagnostic marker, or mass spectrometry, and a kit for diagnosing gastric cancer.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Methods and devices for diagnosis of appendicitis
InactiveUS20060024719A1Diagnosing appendicitisAccurate diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymologyTissue sampleSuspected appendicitis
A method is provided for diagnosing appendicitis in a patient that includes identifying at least one symptom of appendicitis in the patient and identifying the presence of at least one molecule differentially associated with appendicitis in a fluid or tissue sample of said patient. MRP-8 / 14 and haptoglobin are examples of molecules differentially associated with appendicitis. Devices and kits for performing the appendicitis assays of this invention are also provided. In one embodiment, the device is in a flow-through immunoassay format for testing blood samples. Further, methods for screening for molecules differentially associated with appendicitis are provided that include the use of samples from patients being operated on for suspected appendicitis.
Owner:ASPENBIO PHARMA
EGFR and PAR2 Regulation of Intestinal Permeability
InactiveUS20120107329A1Inhibition releaseReduce penetrationOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementAutoimmune conditionAllergy
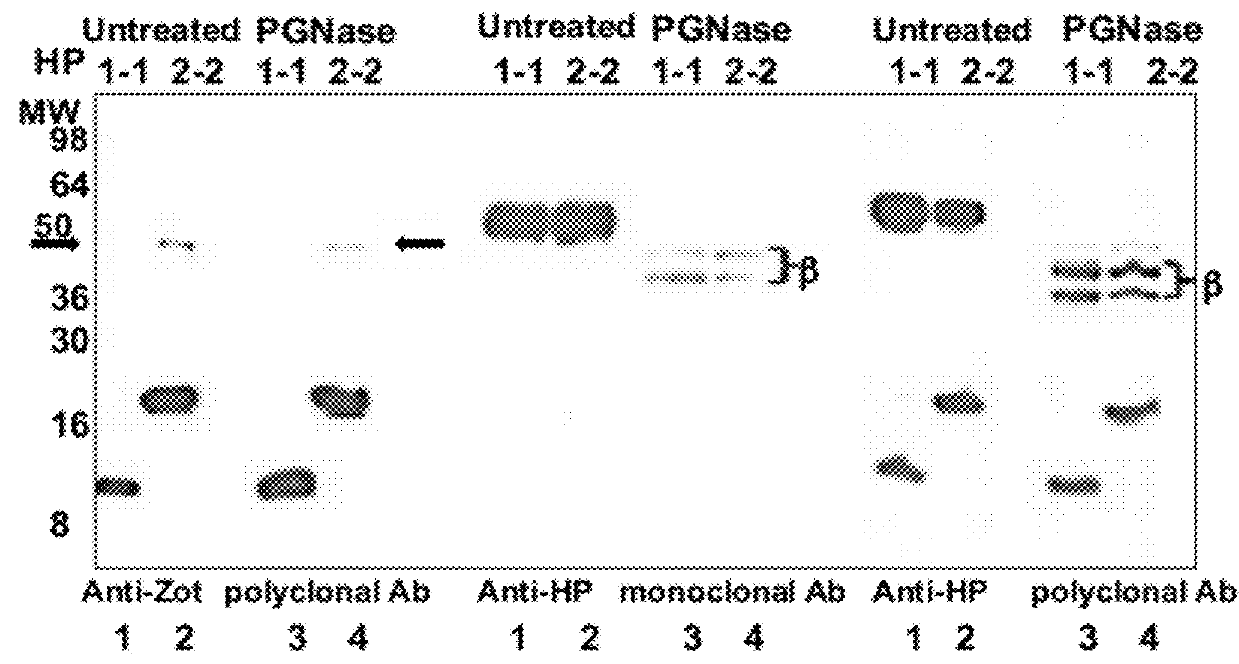
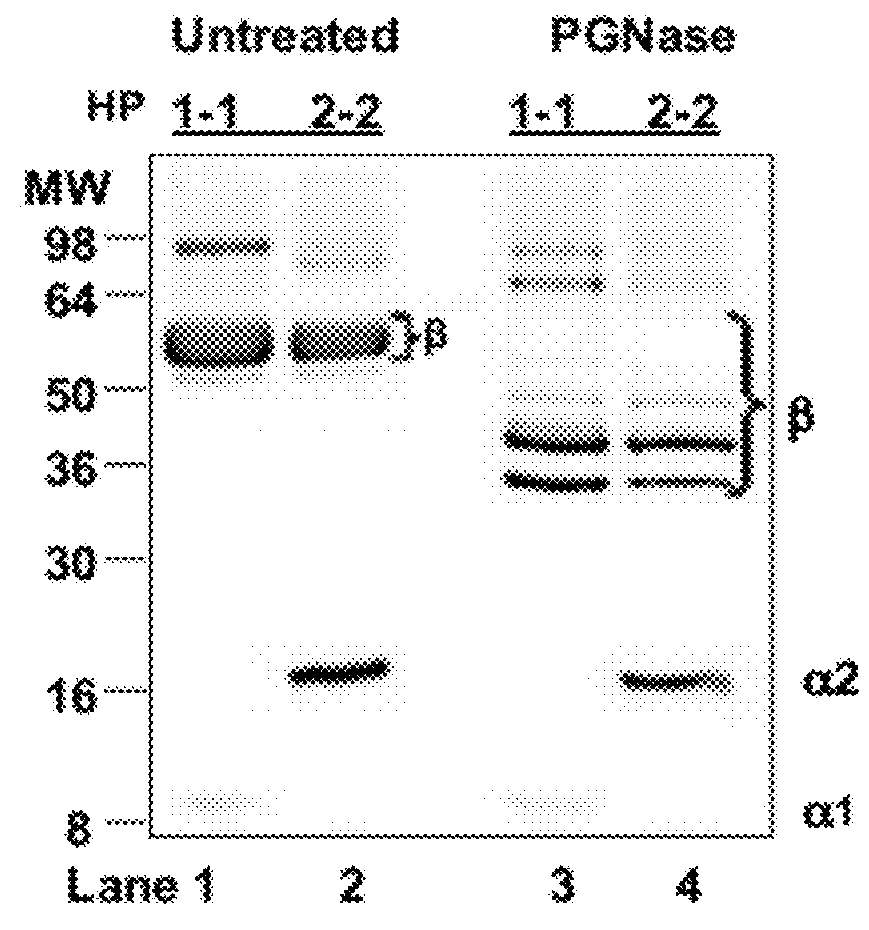
The present invention provides methods for diagnosing and treating an immune-mediated disease, e.g., an autoimmune disease, an allergy or an inflammatory disease. Diagnosis is made by detecting a heterozygous or homozygous genotype of haptoglobin 2 or by detecting and quantifying pre-haptoglobin 2 mRNA or protein. After diagnosis, the disease may be treated by decreasing cell permeability leading to increased transepithelial electrical resistance, for example, by administering an antibody directed against single chain zonulin thereby inhibiting epidermal growth factor receptor and inhibiting proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR2).
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com