Patents
Literature
2690results about How to "Accurate diagnosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
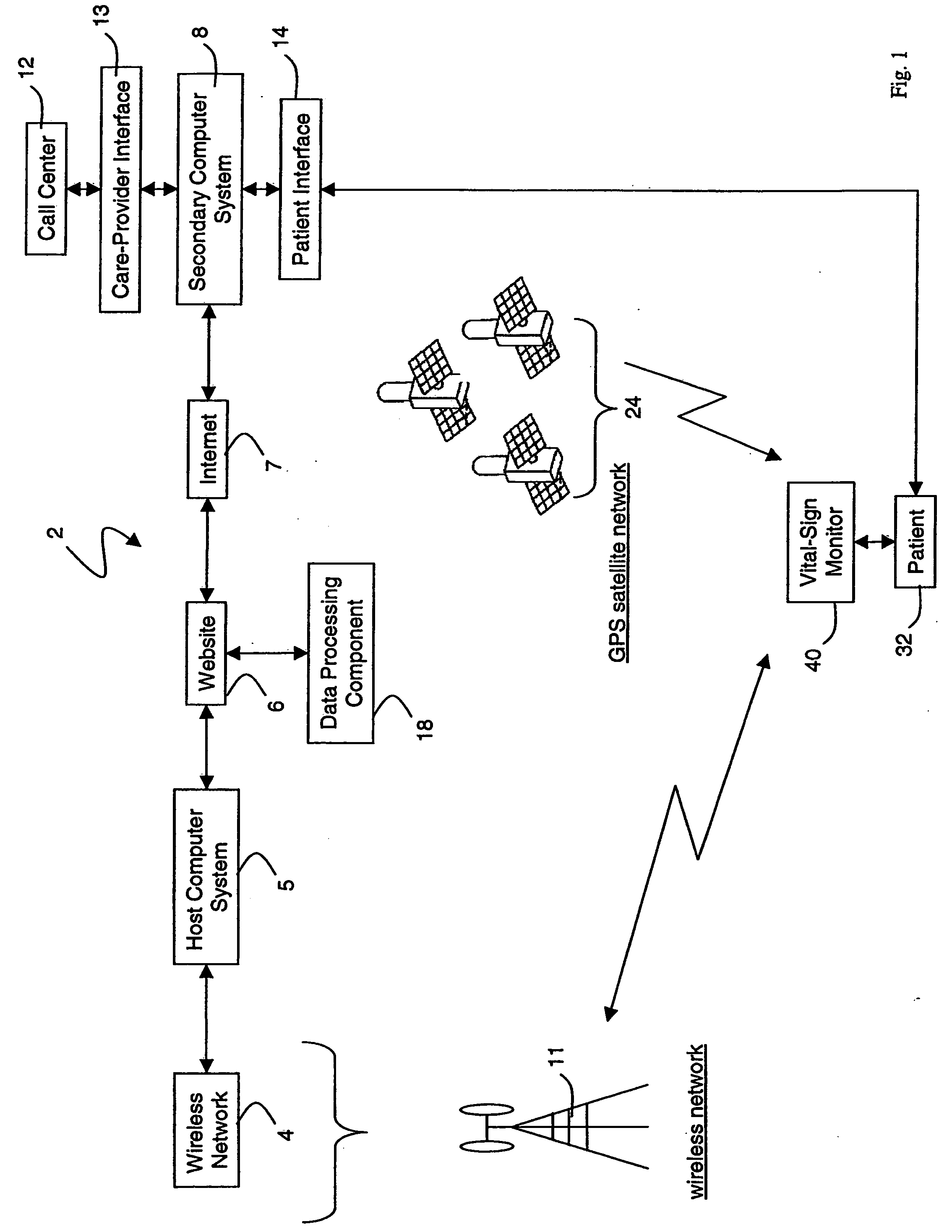
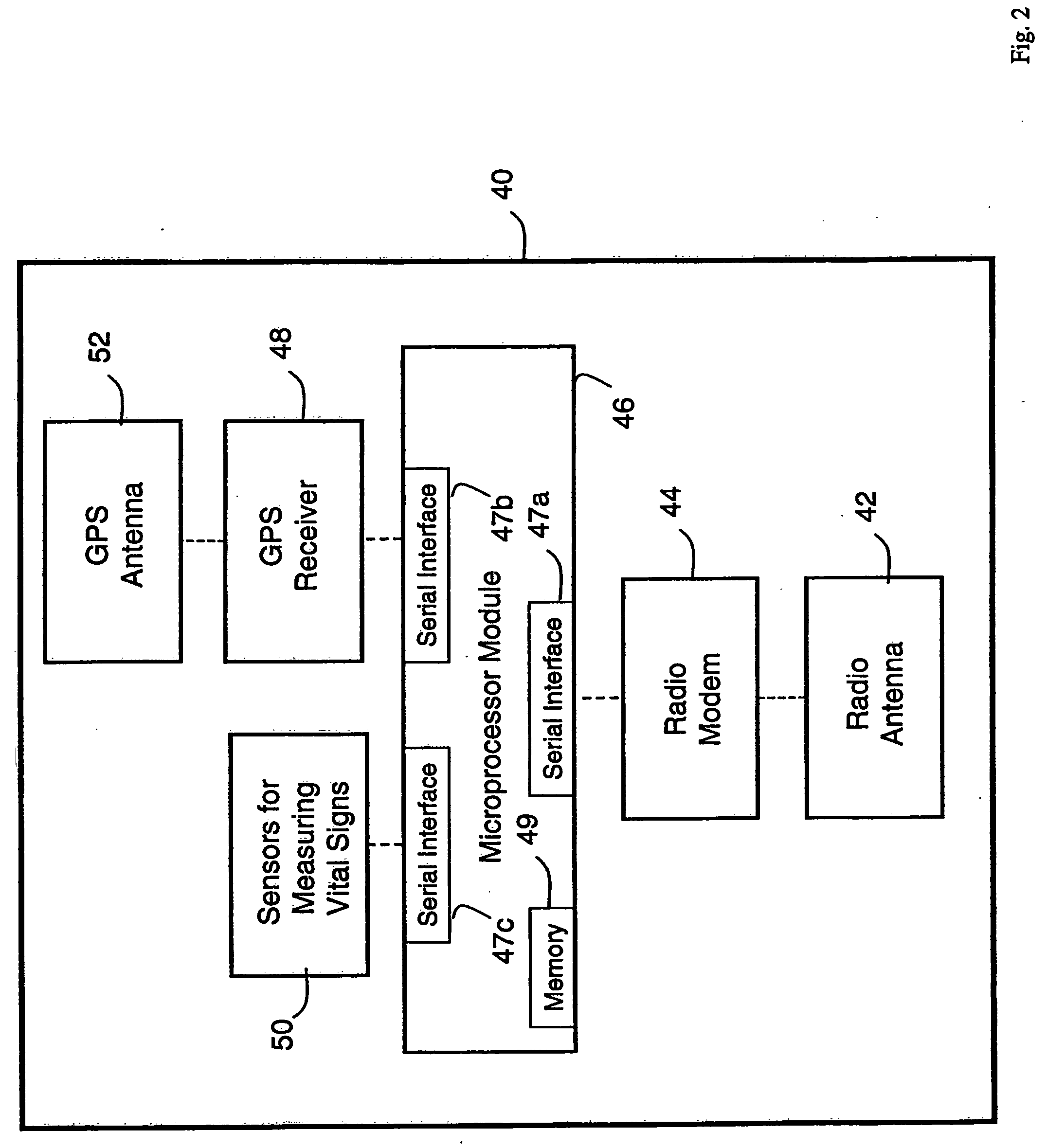
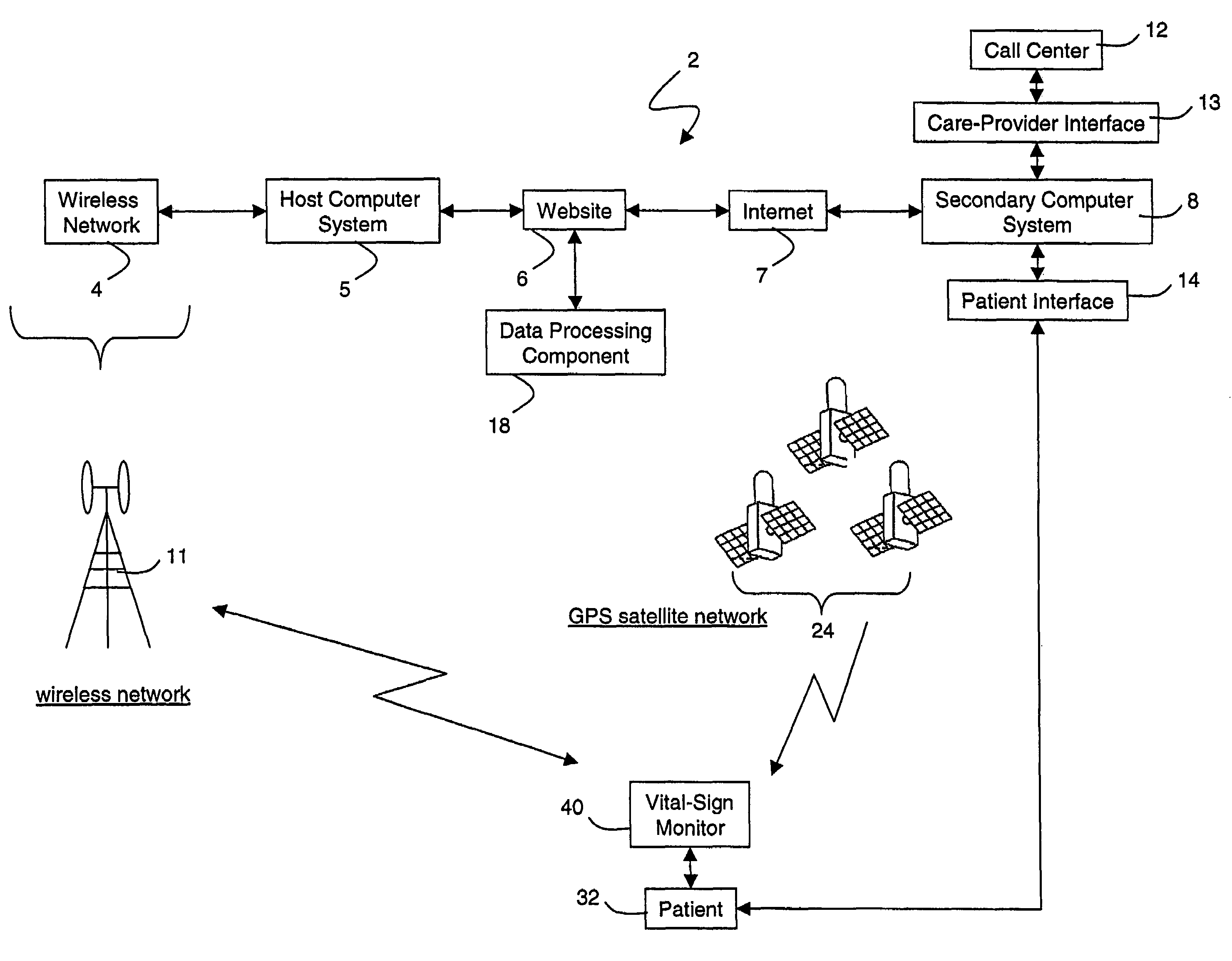
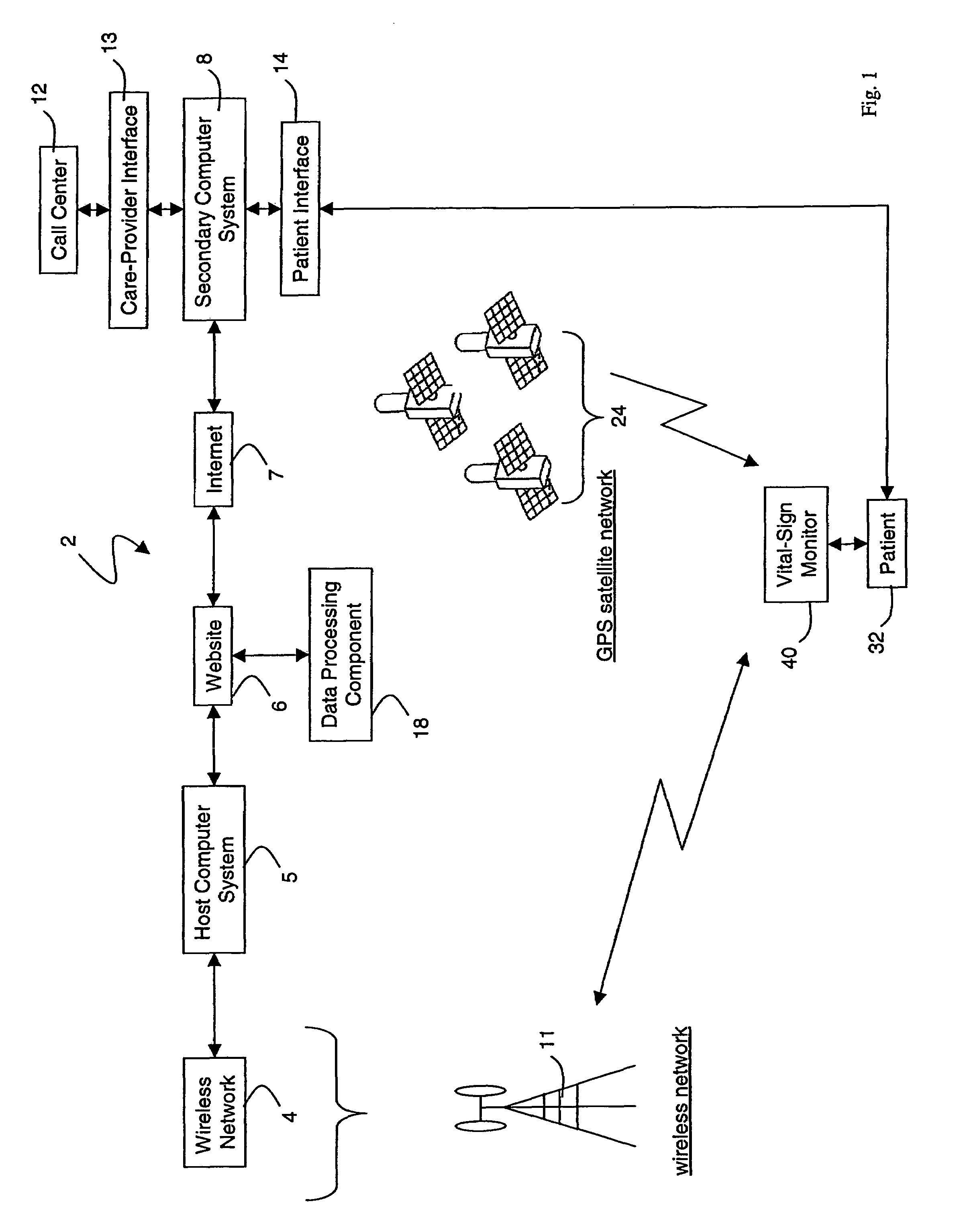
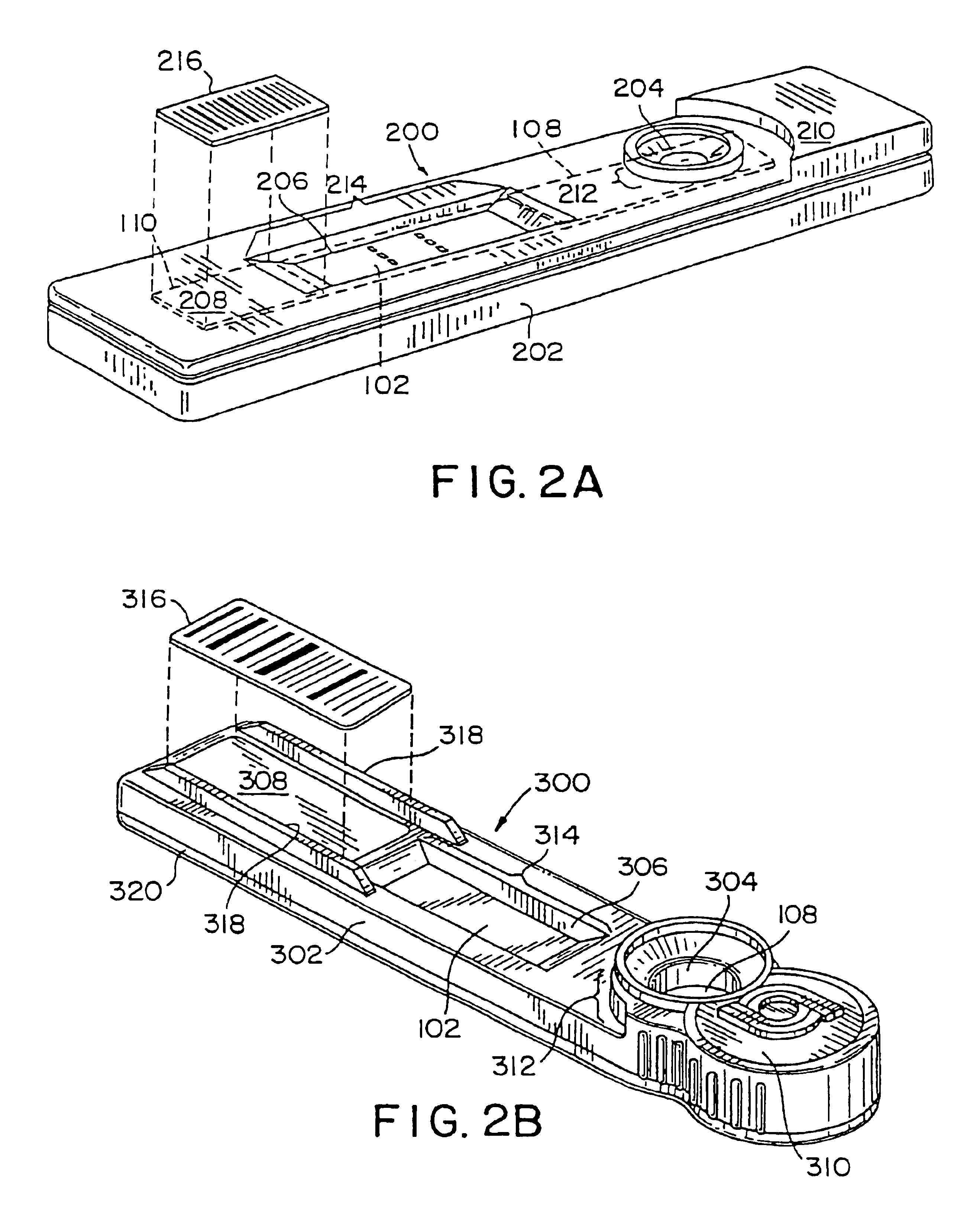
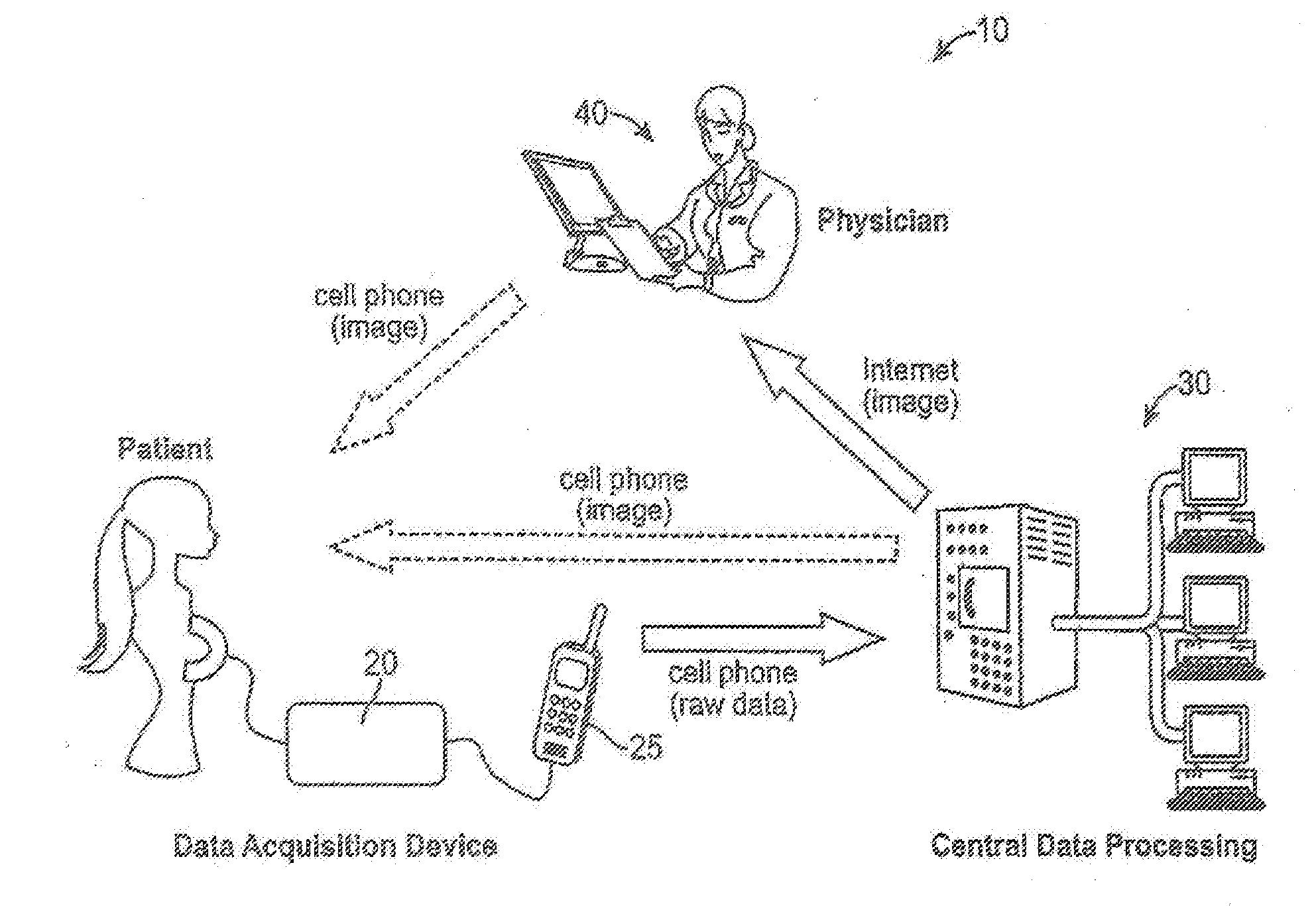
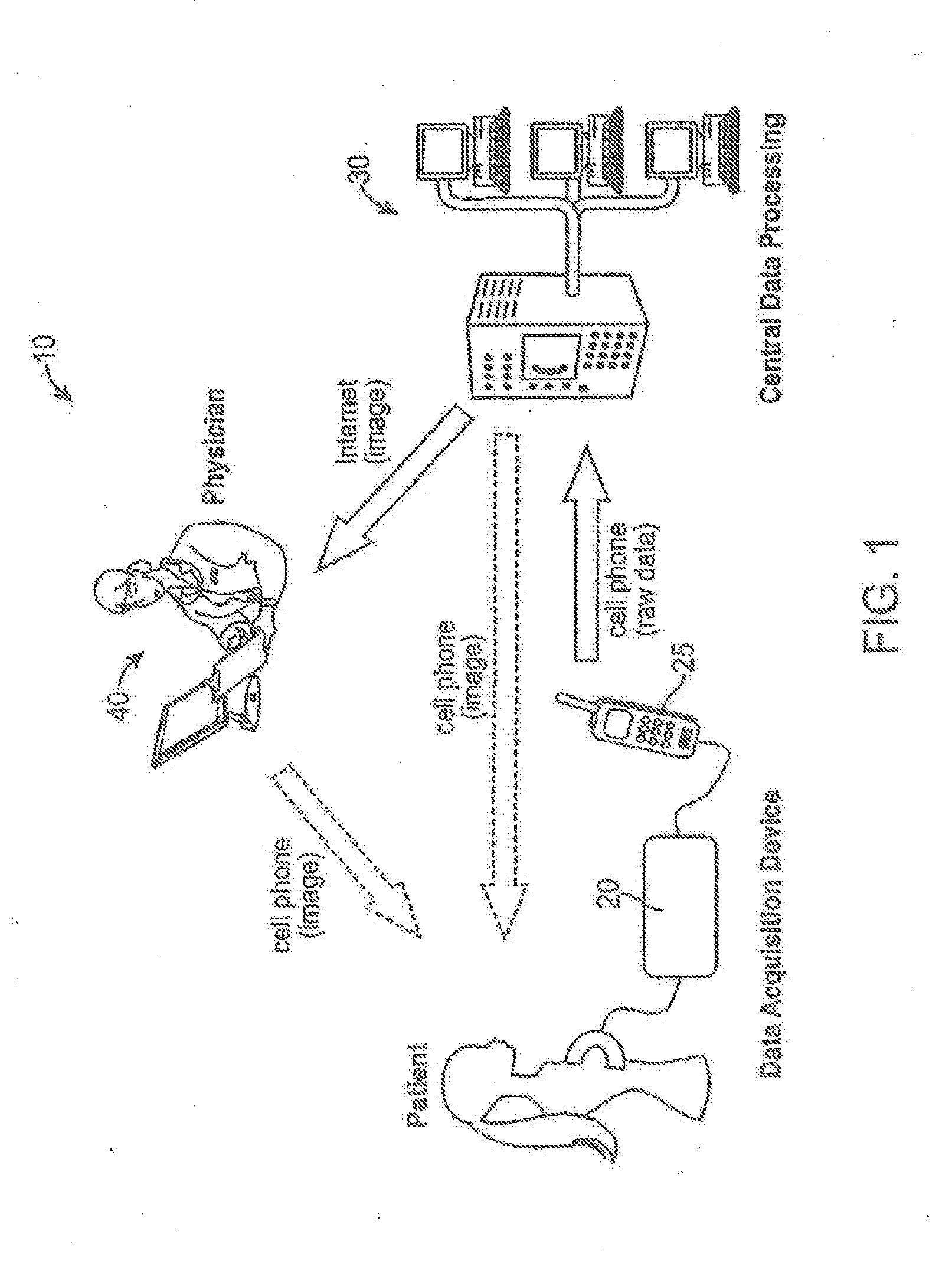
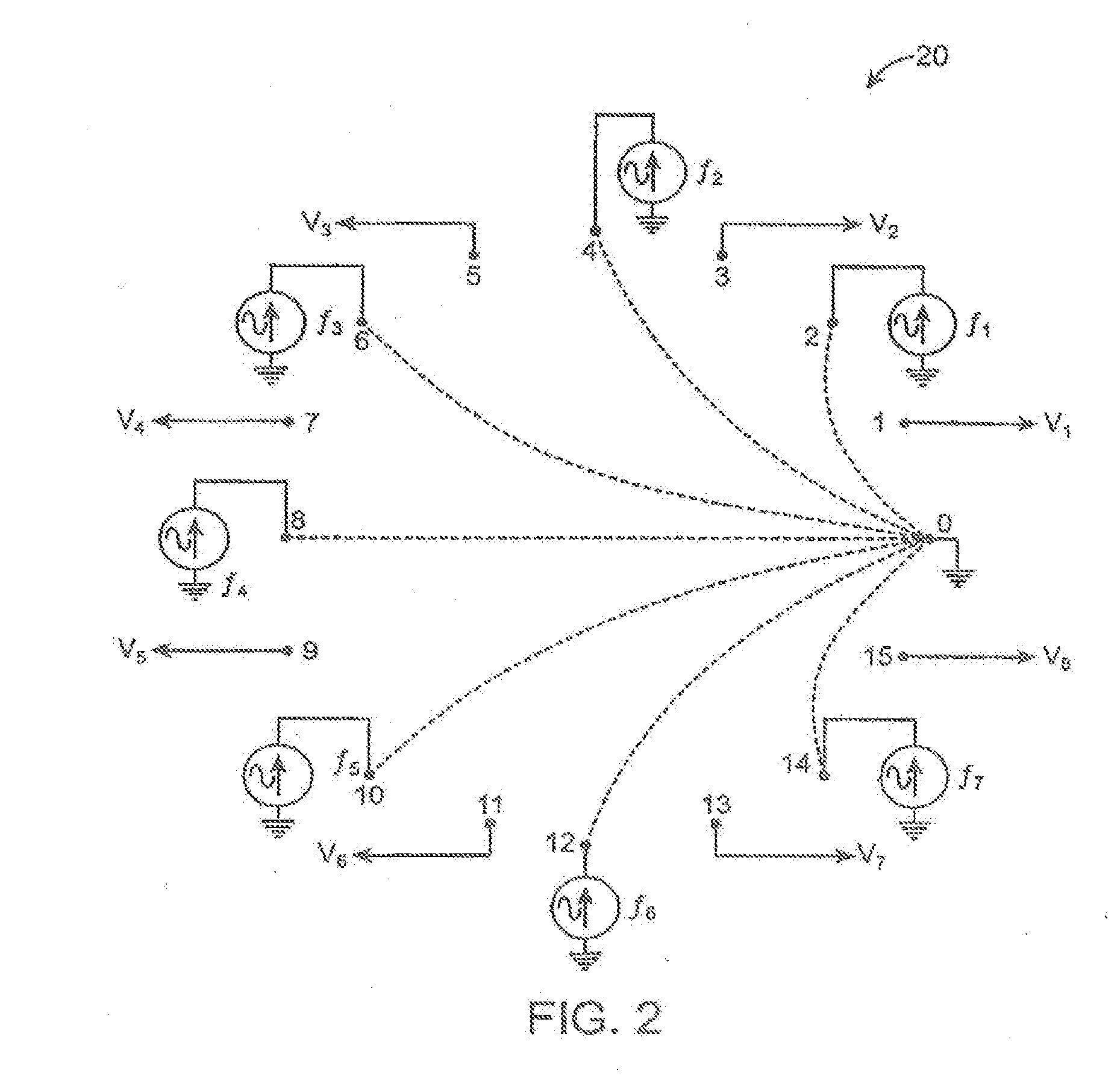
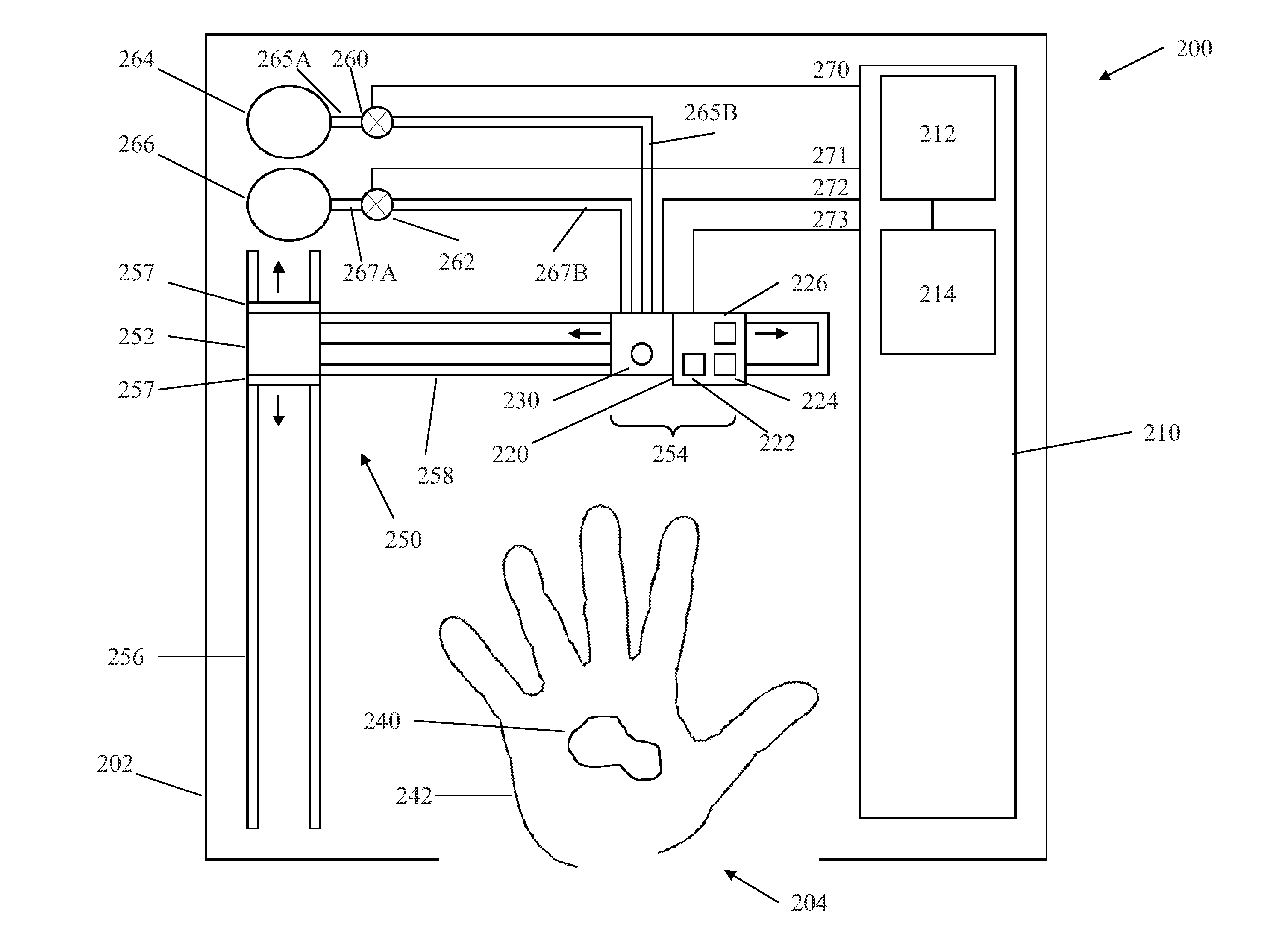
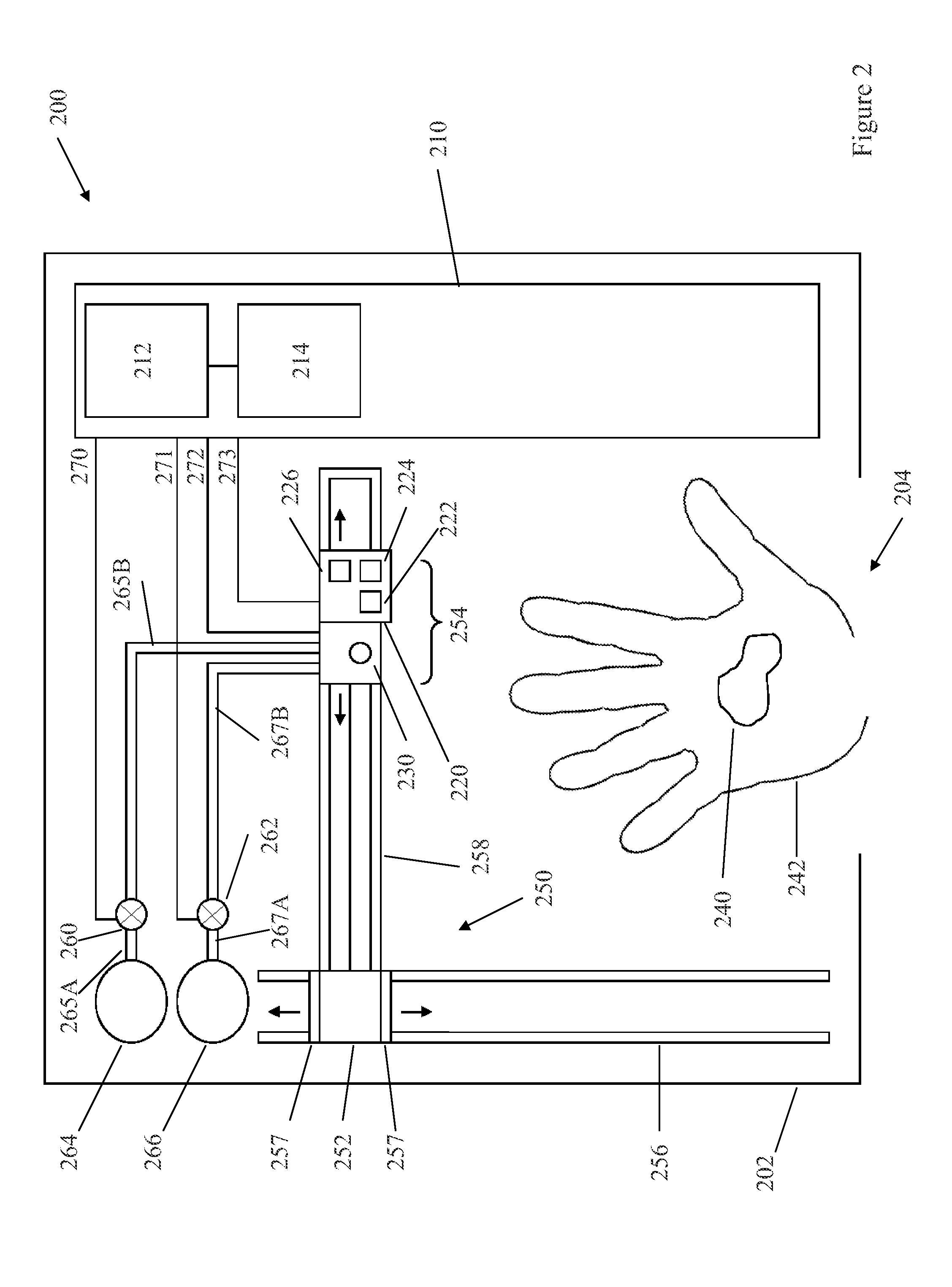
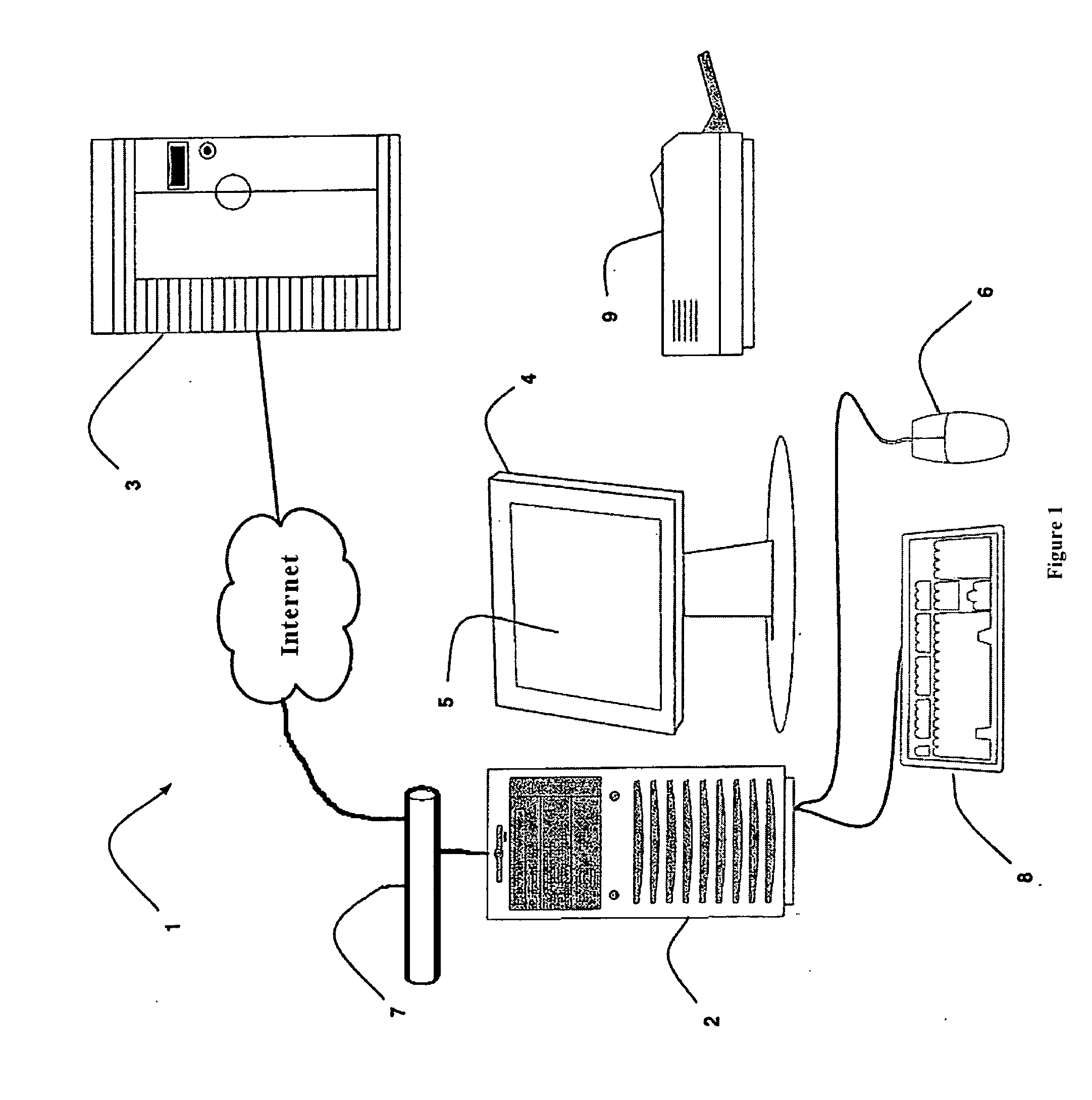
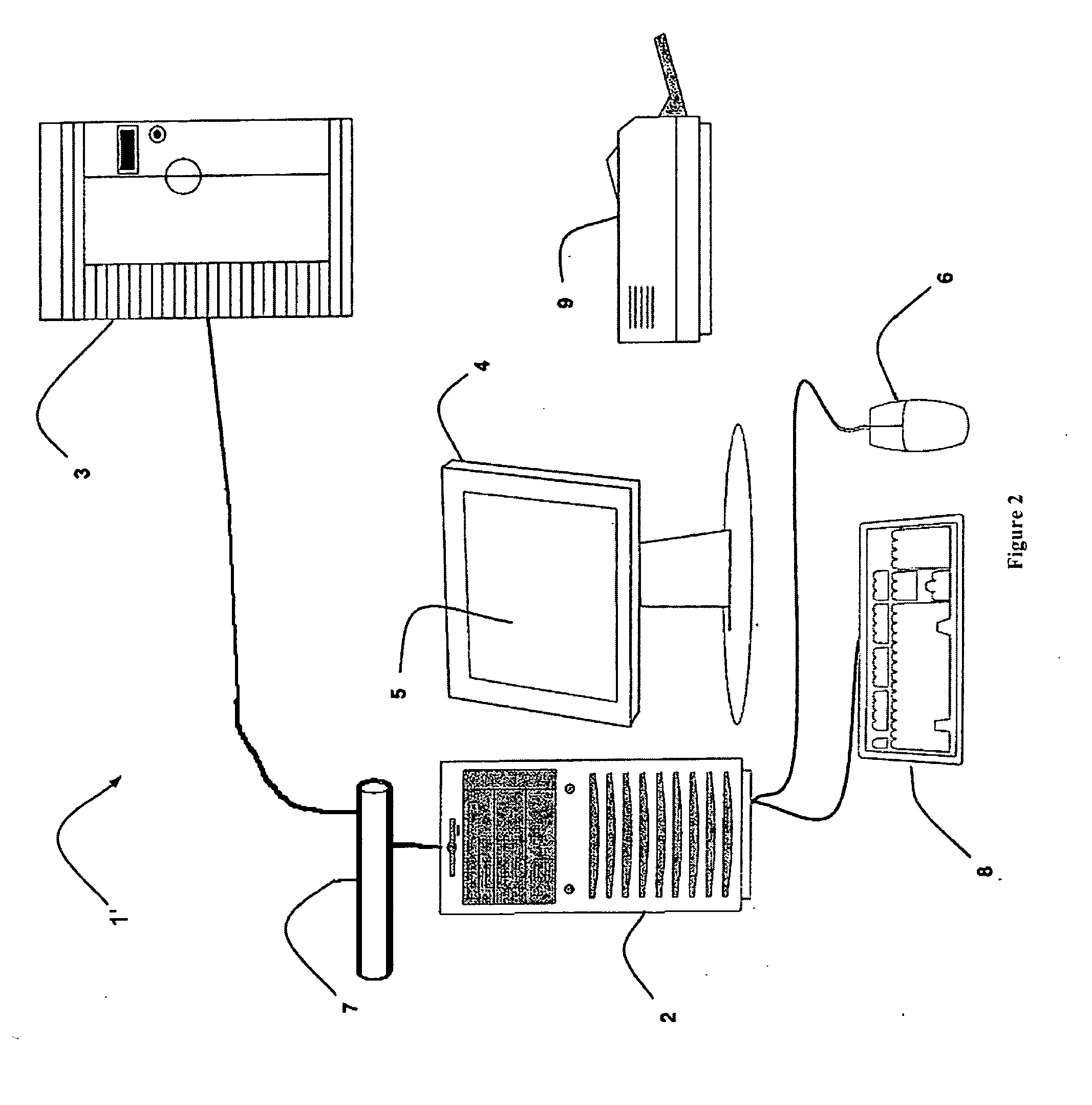
Wireless, internet-based medical-diagnostic system
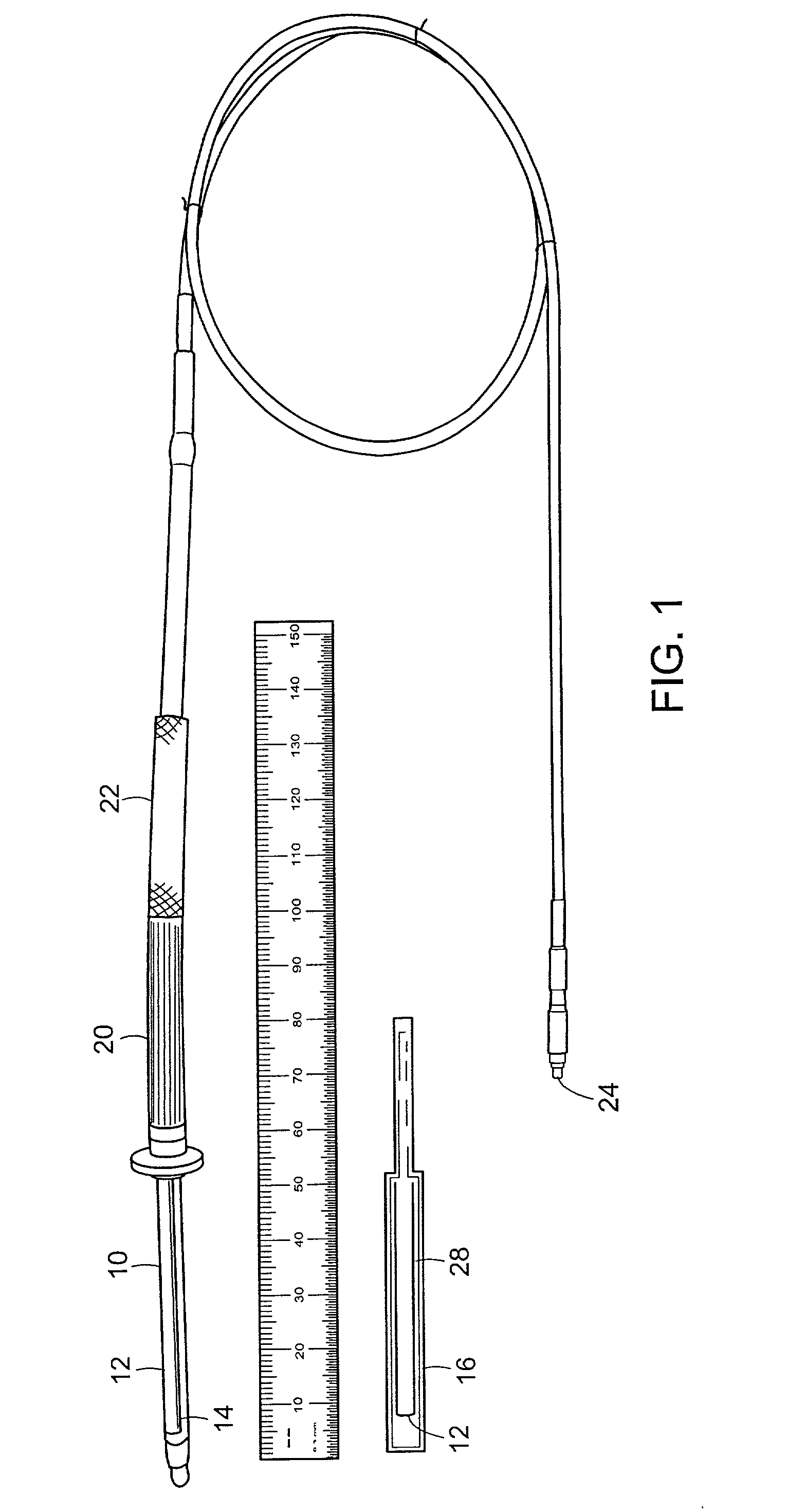
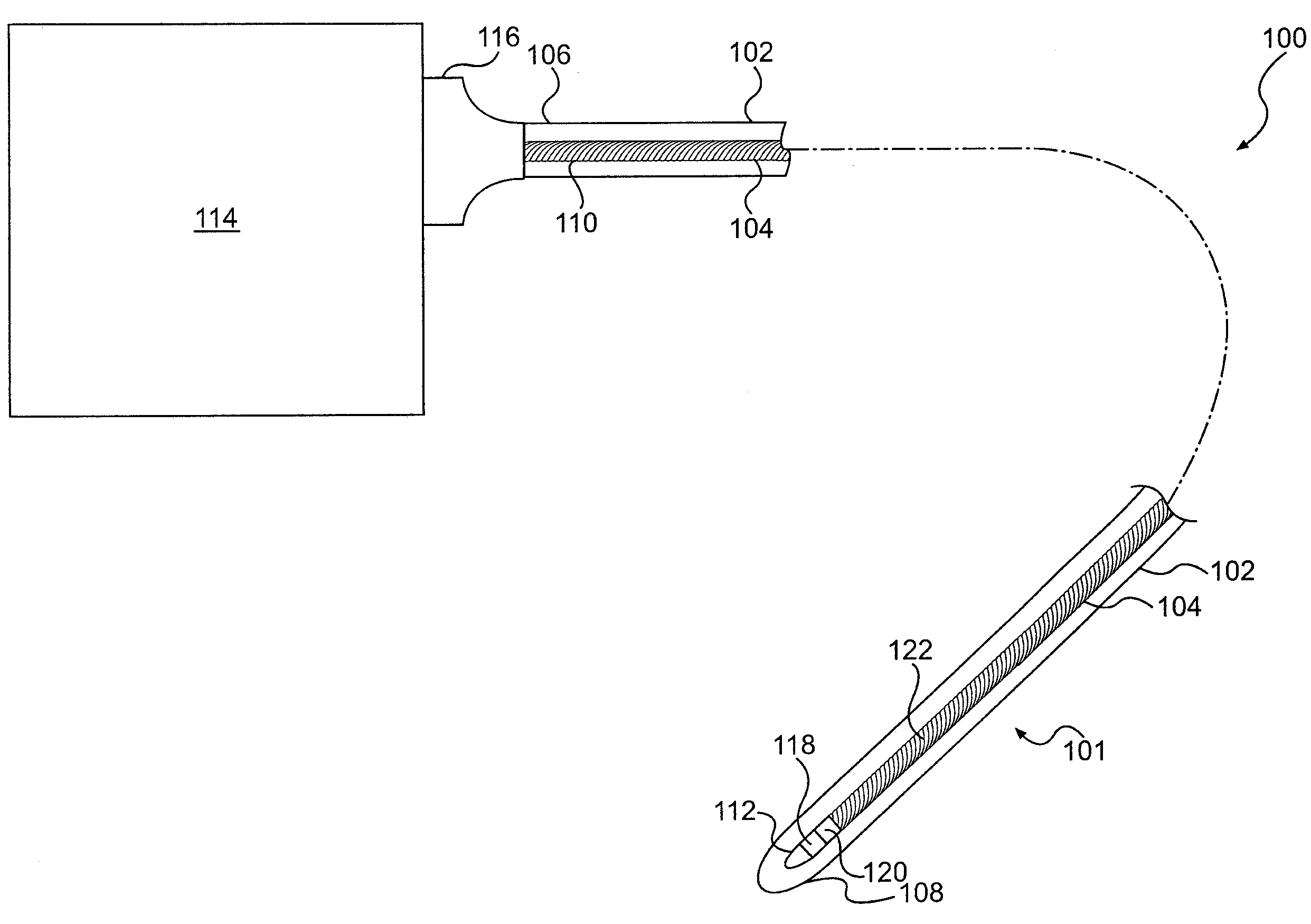
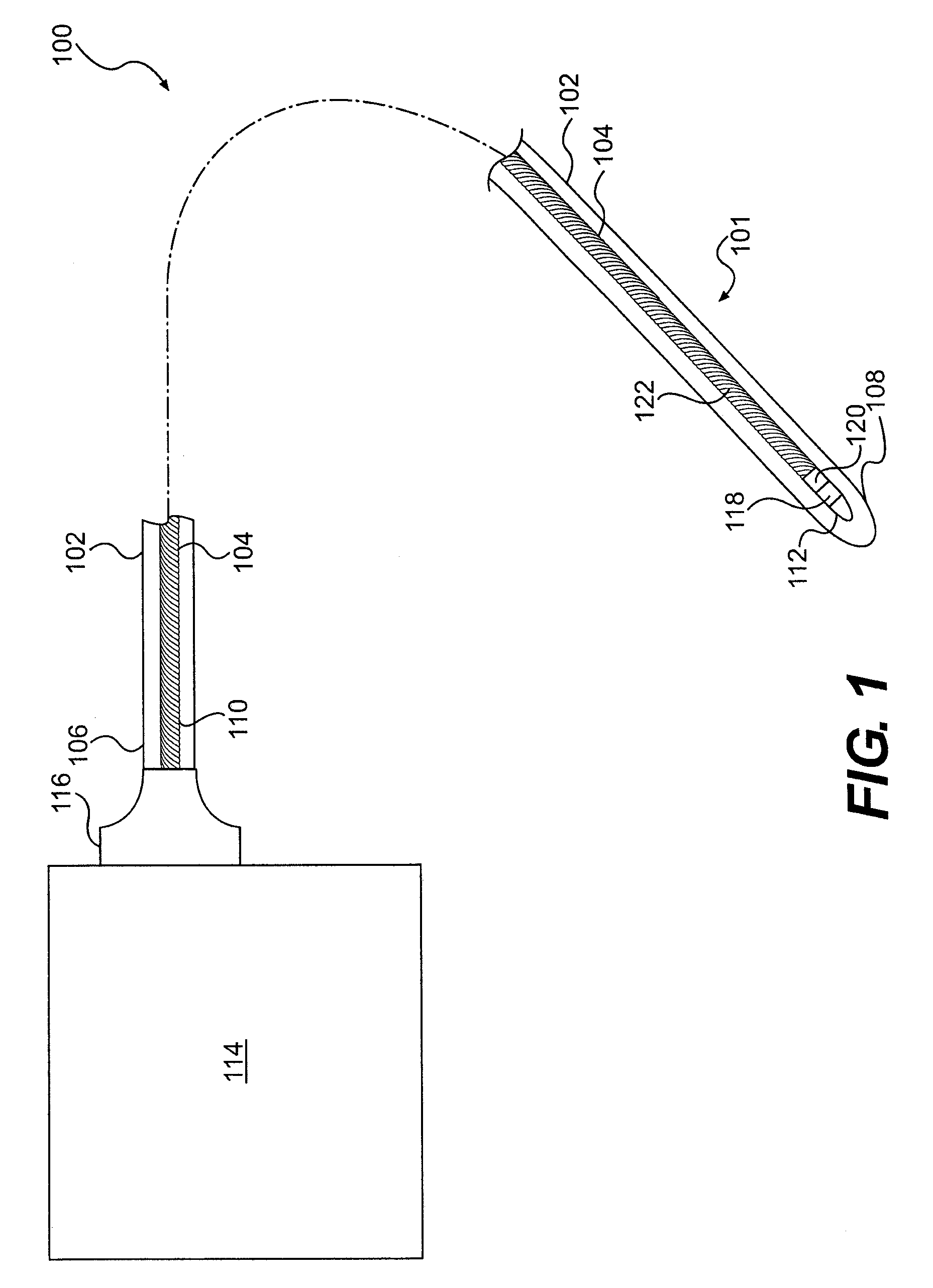
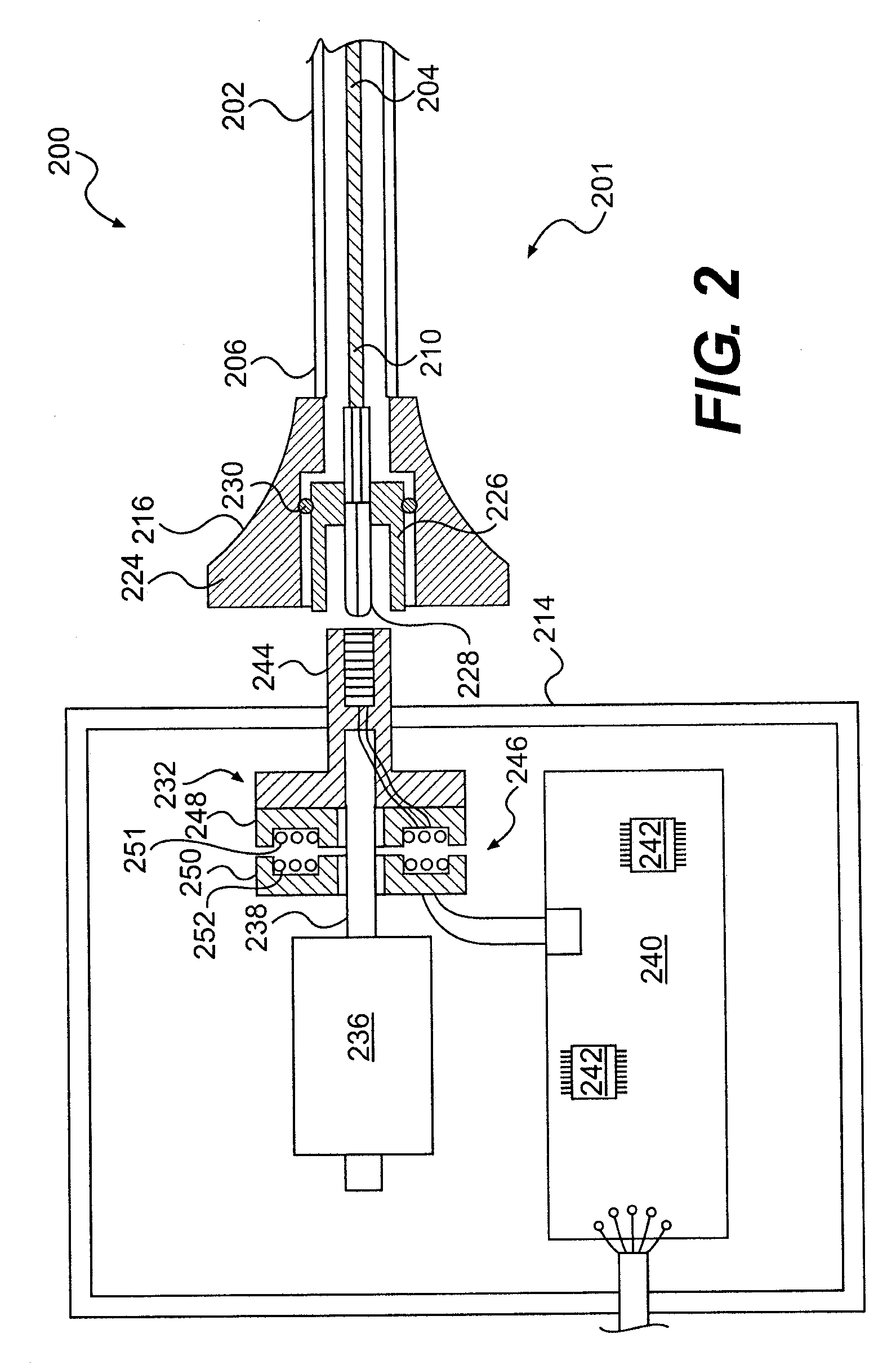
ActiveUS20050010087A1Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactSurgeryCatheterGlobal Positioning SystemUser interface
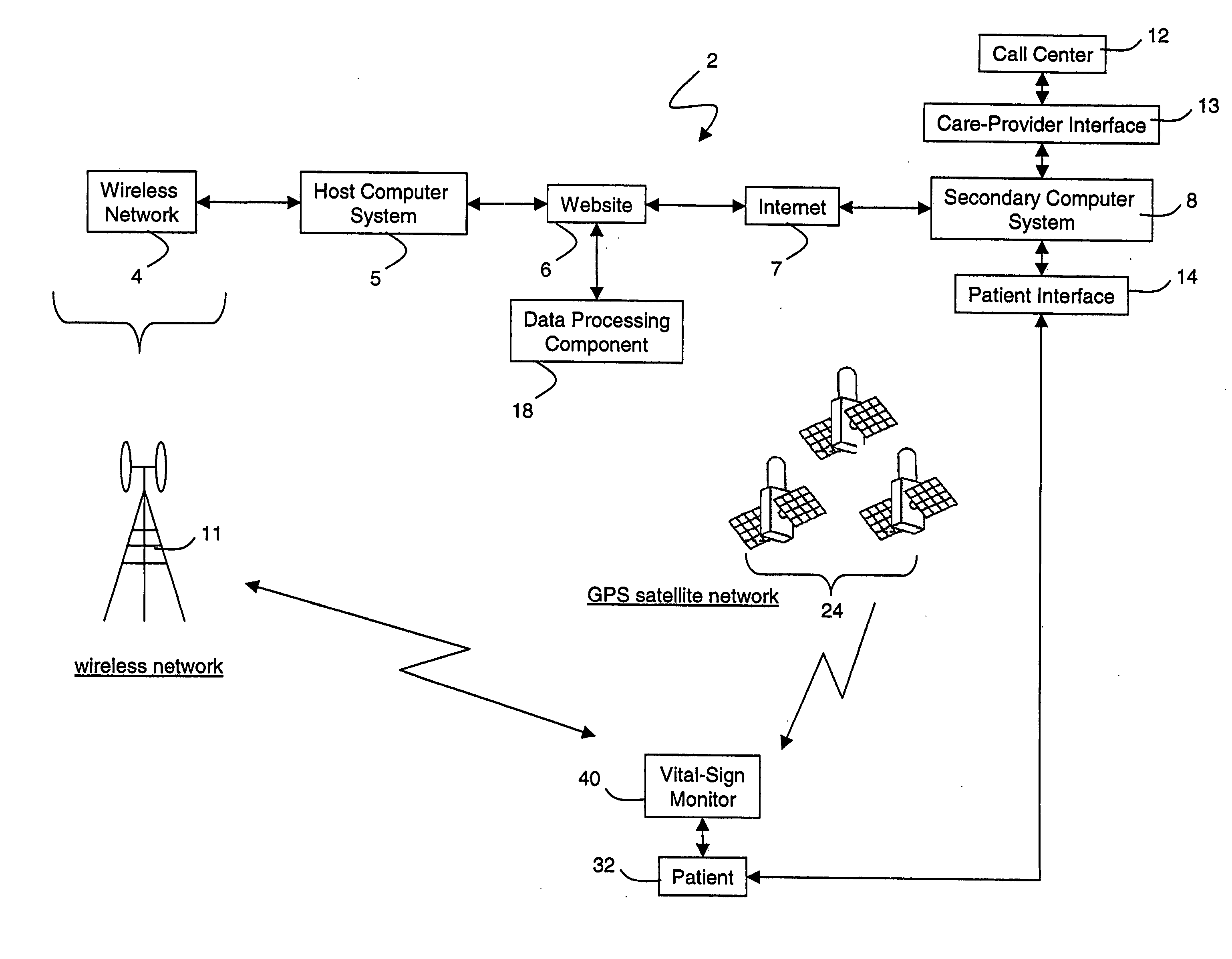
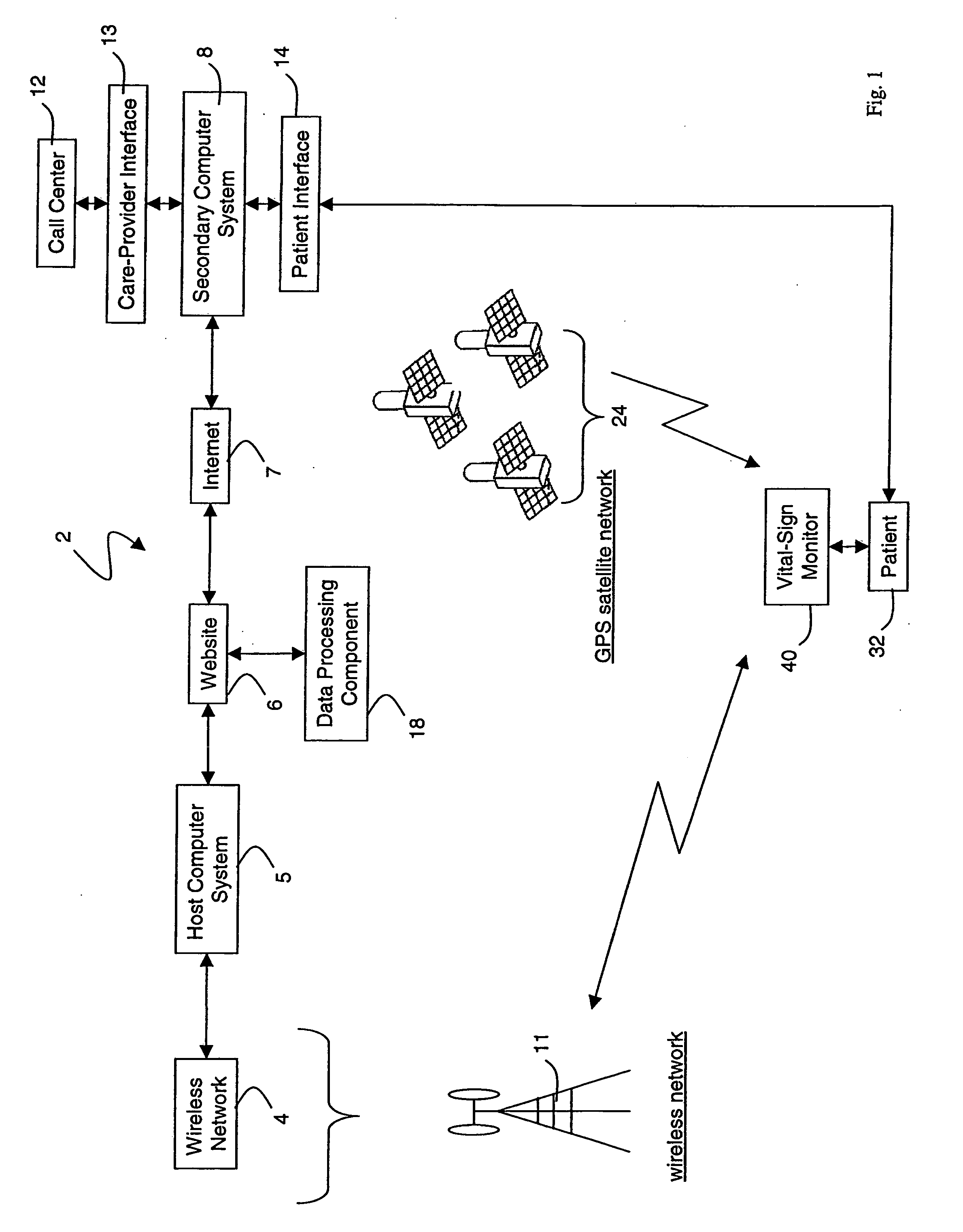
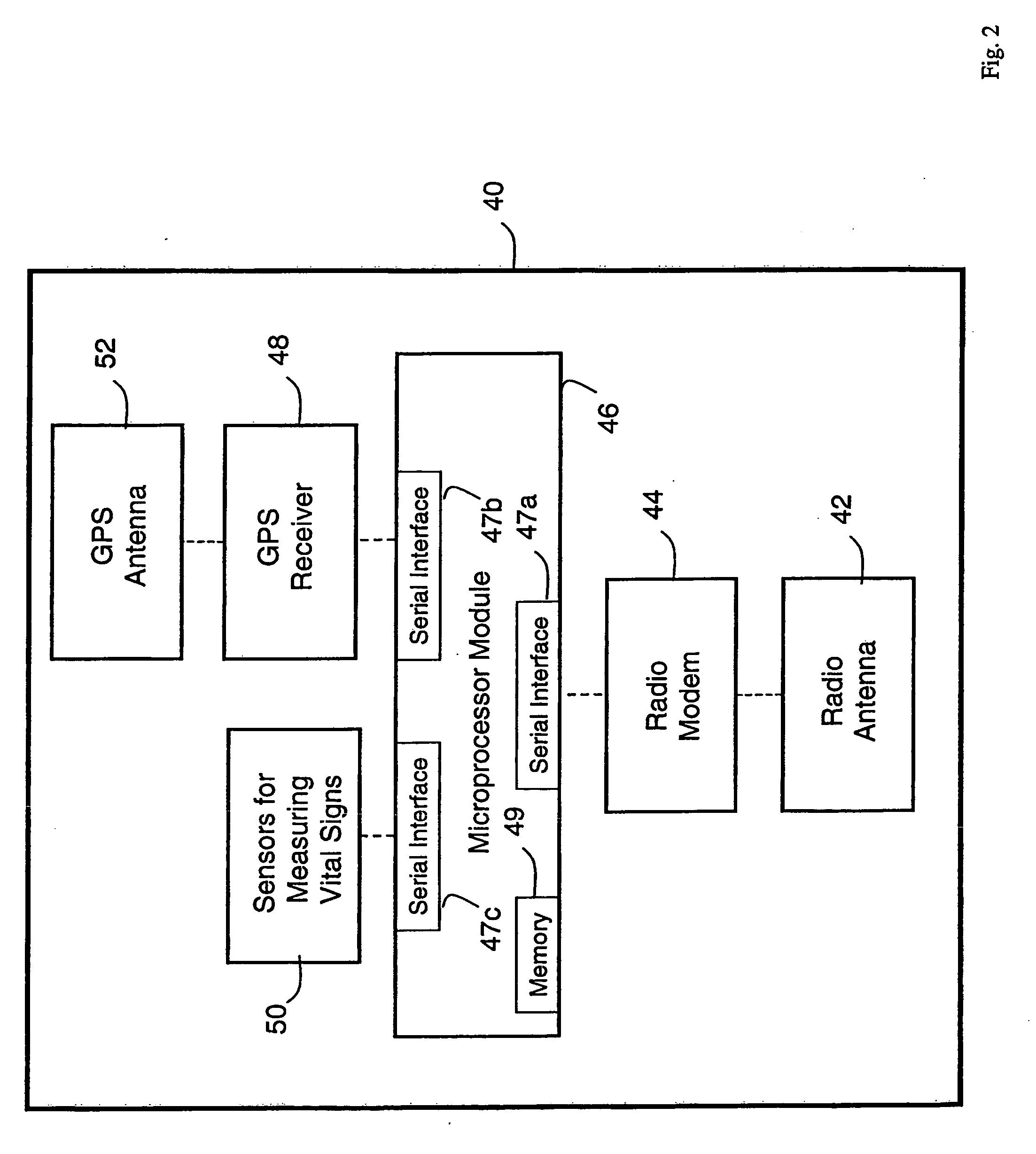
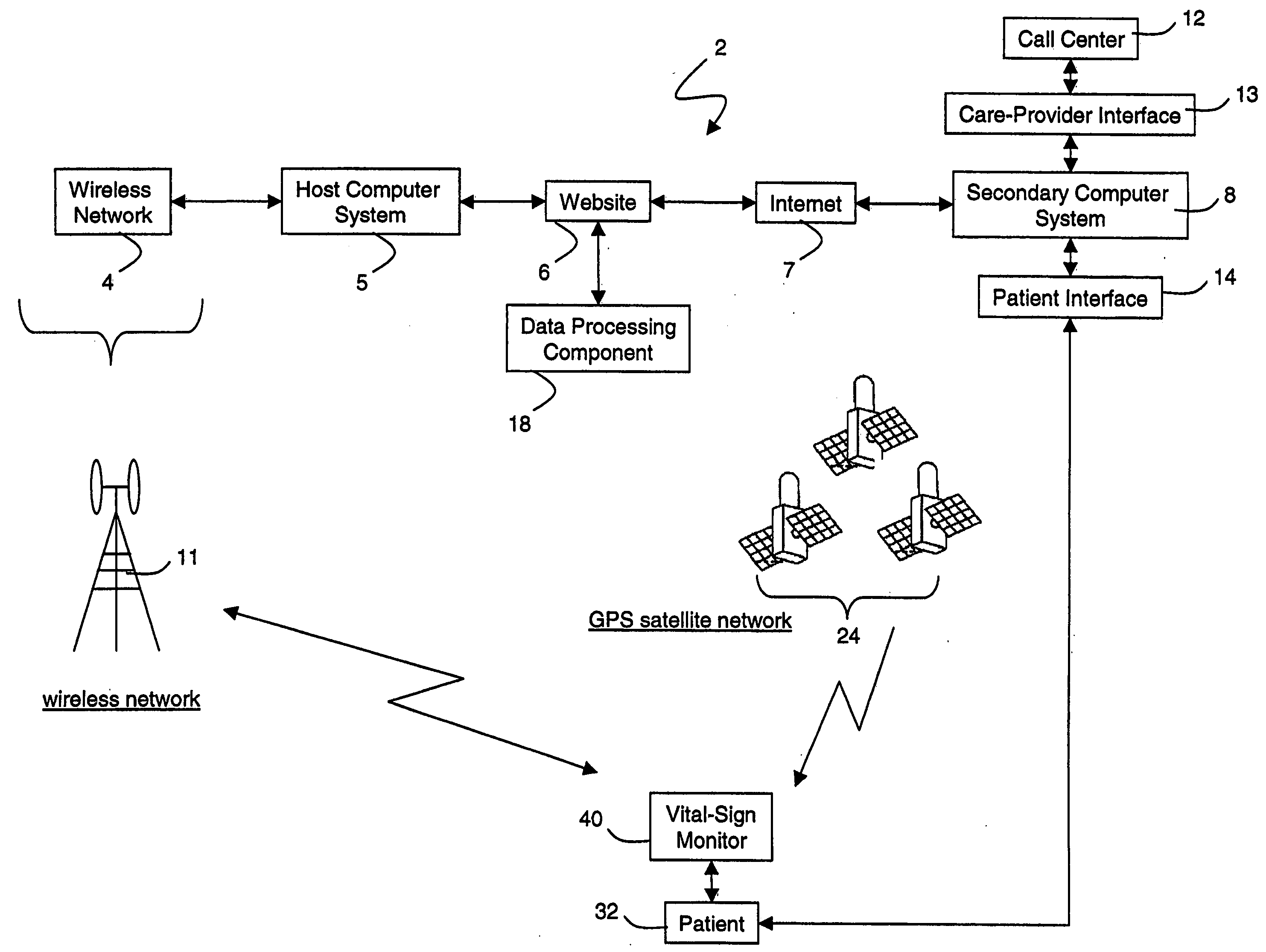
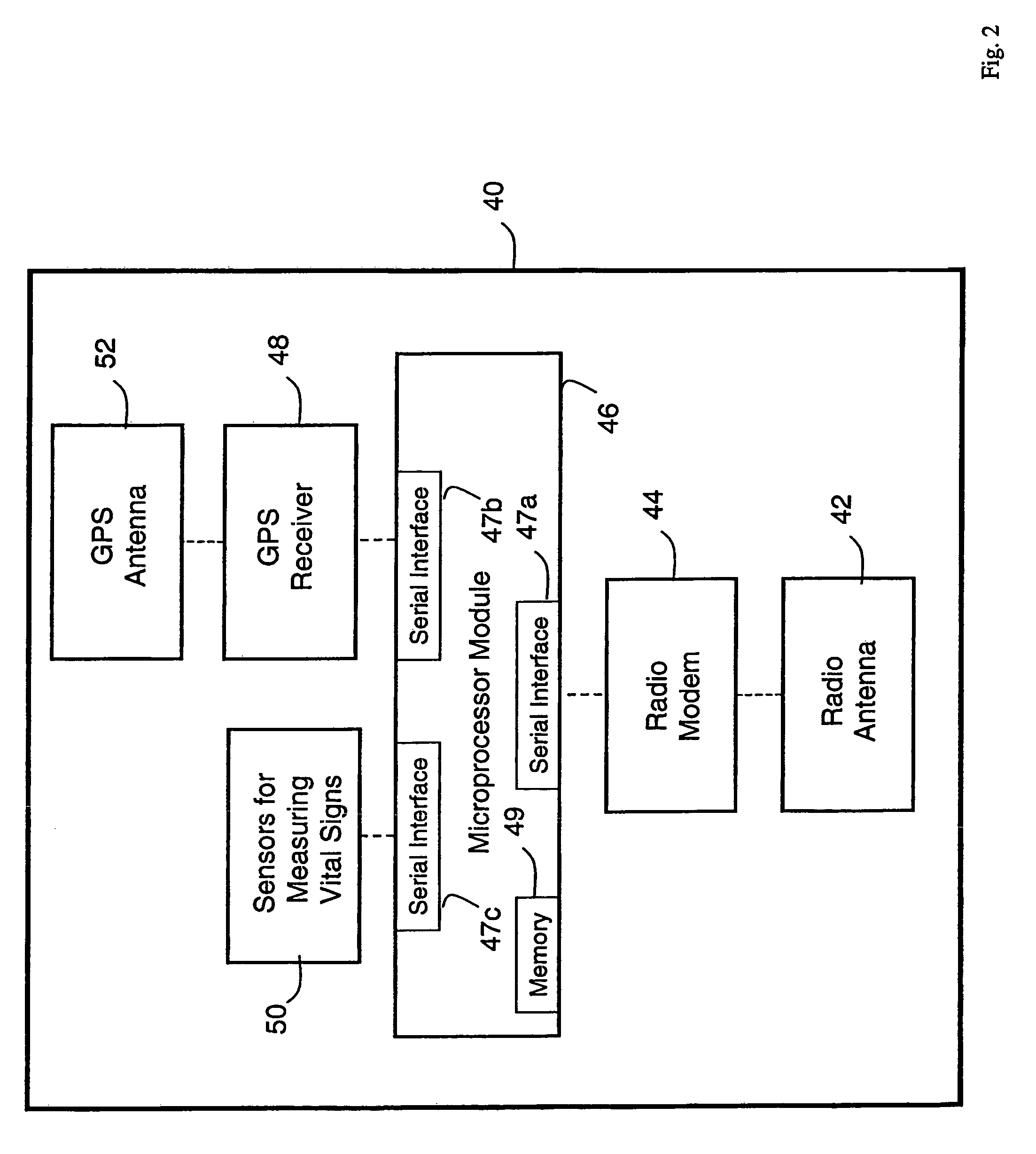
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electro-cardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Wireless, internet-based, medical diagnostic system
InactiveUS20060142648A1Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsEmergency medicineGlobal Positioning System
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:TRIAGE DATA NETWORKS
Wireless, internet-based medical-diagnostic system
ActiveUS7396330B2Accurate diagnosisMinimize impactSurgeryCatheterGlobal Positioning SystemUser interface
A system for monitoring a patient's vital signs that features a vital-sign monitor including sensors for measuring from the patient at least one of the following vital-sign data: O2 saturation, blood pressure, electro-cardiogram, respirator rate, and blood glucose level. The system also includes a global positioning system that determines location-based data. A wireless transmitter, in electrical contact with the vital-sign monitor and global positioning system, receives the vital-sign and location-based data and wirelessly transmits these data through a conventional wireless network. A gateway software piece receives and processes the data from the wireless network and stores these data in a computer memory associated with a database software piece. The system also includes an Internet-based user interface that displays the vital sign data for both individual patients and care-providers.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Point of care diagnostic systems
InactiveUS6867051B1Accurate concentrationAccurately presenceComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionMedical imagesPoint of careDiagnostic test
Systems and methods for medical diagnosis or risk assessment for a patient are provided. These systems and methods are designed to be employed at the point of care, such as in emergency rooms and operating rooms, or in any situation in which a rapid and accurate result is desired. The systems and methods process patient data, particularly data from point of care diagnostic tests or assays, including immunoassays, electrocardiograms, X-rays and other such tests, and provide an indication of a medical condition or risk or absence thereof. The systems include an instrument for reading or evaluating the test data and software for converting the data into diagnostic or risk assessment information.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
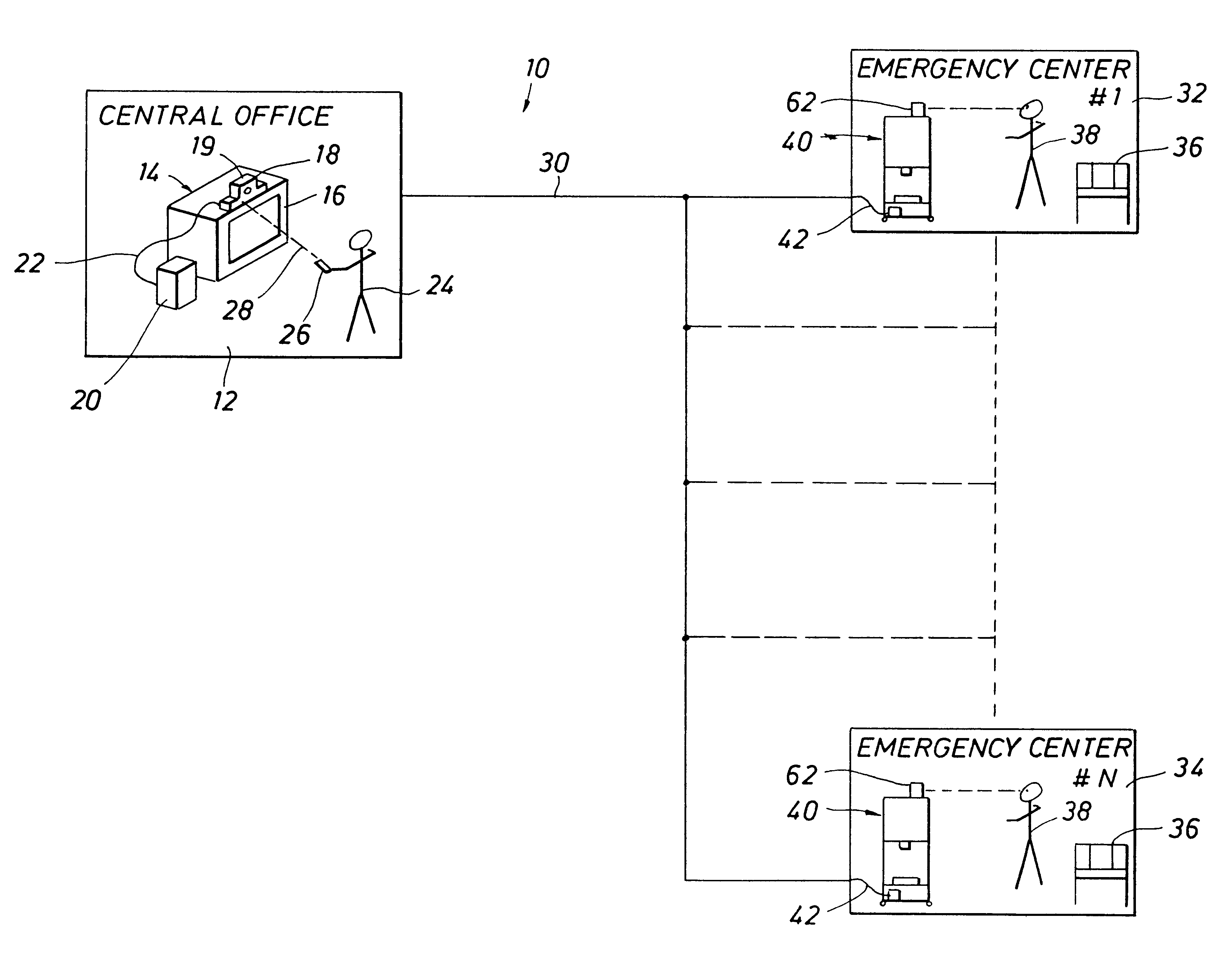
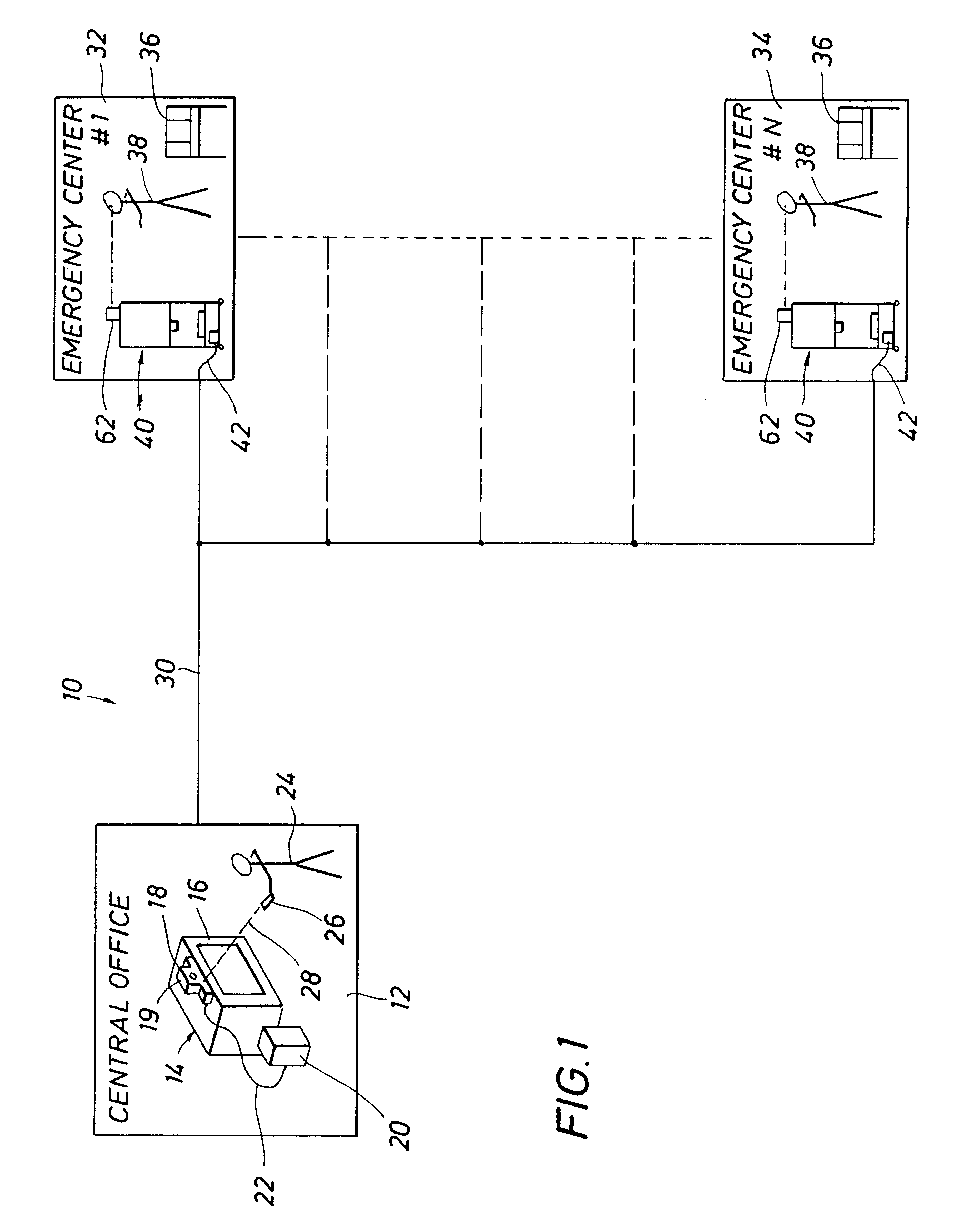
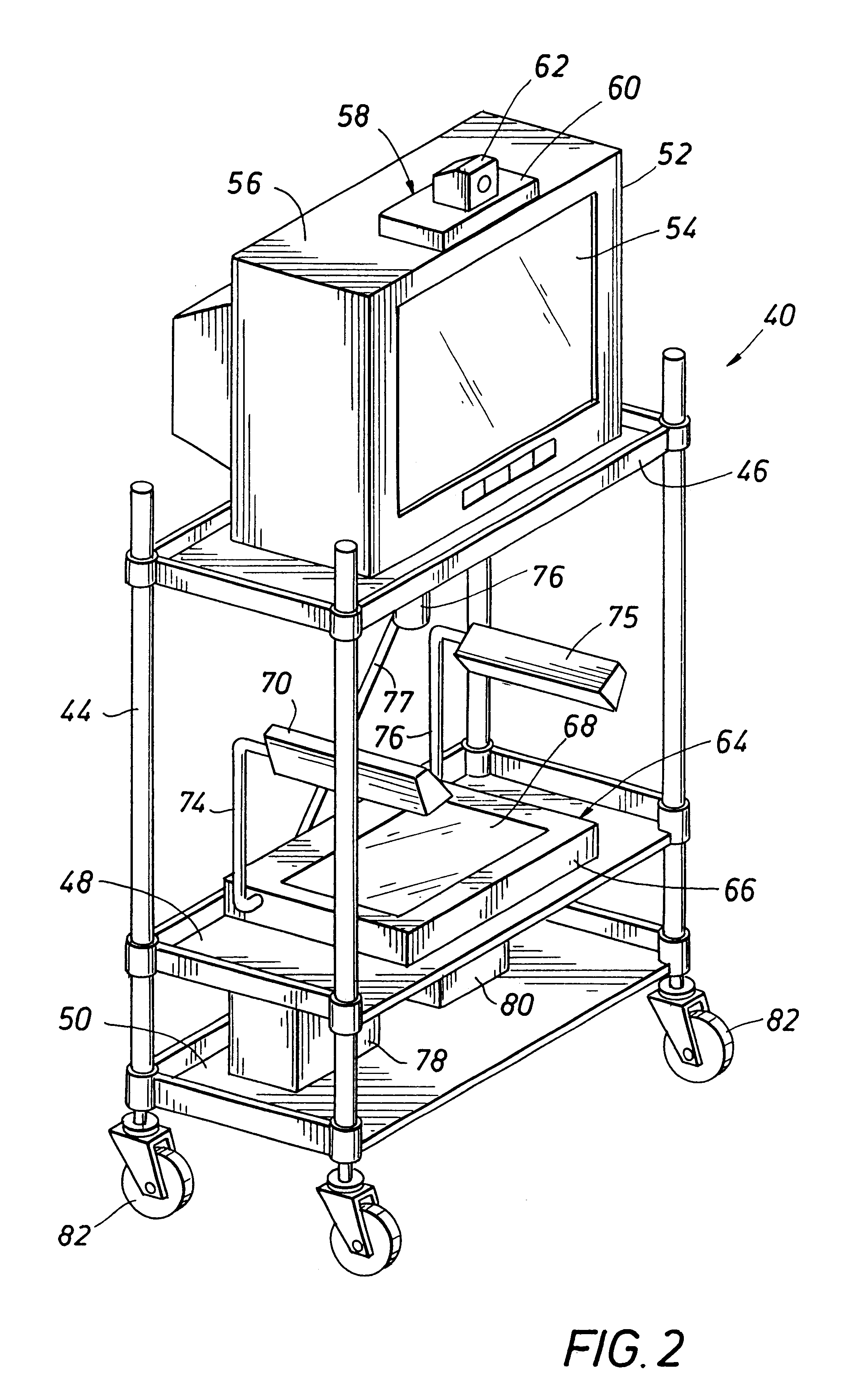
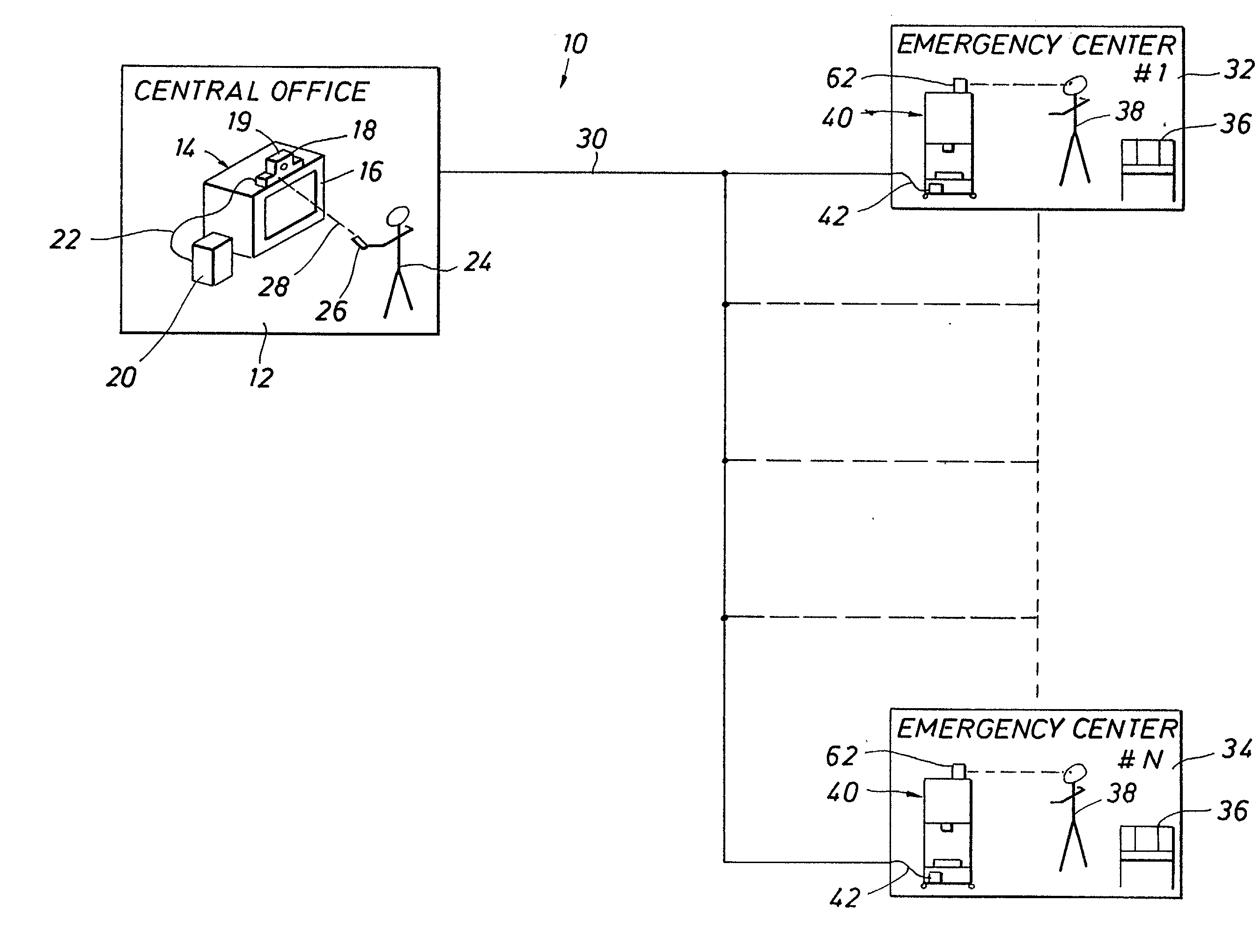
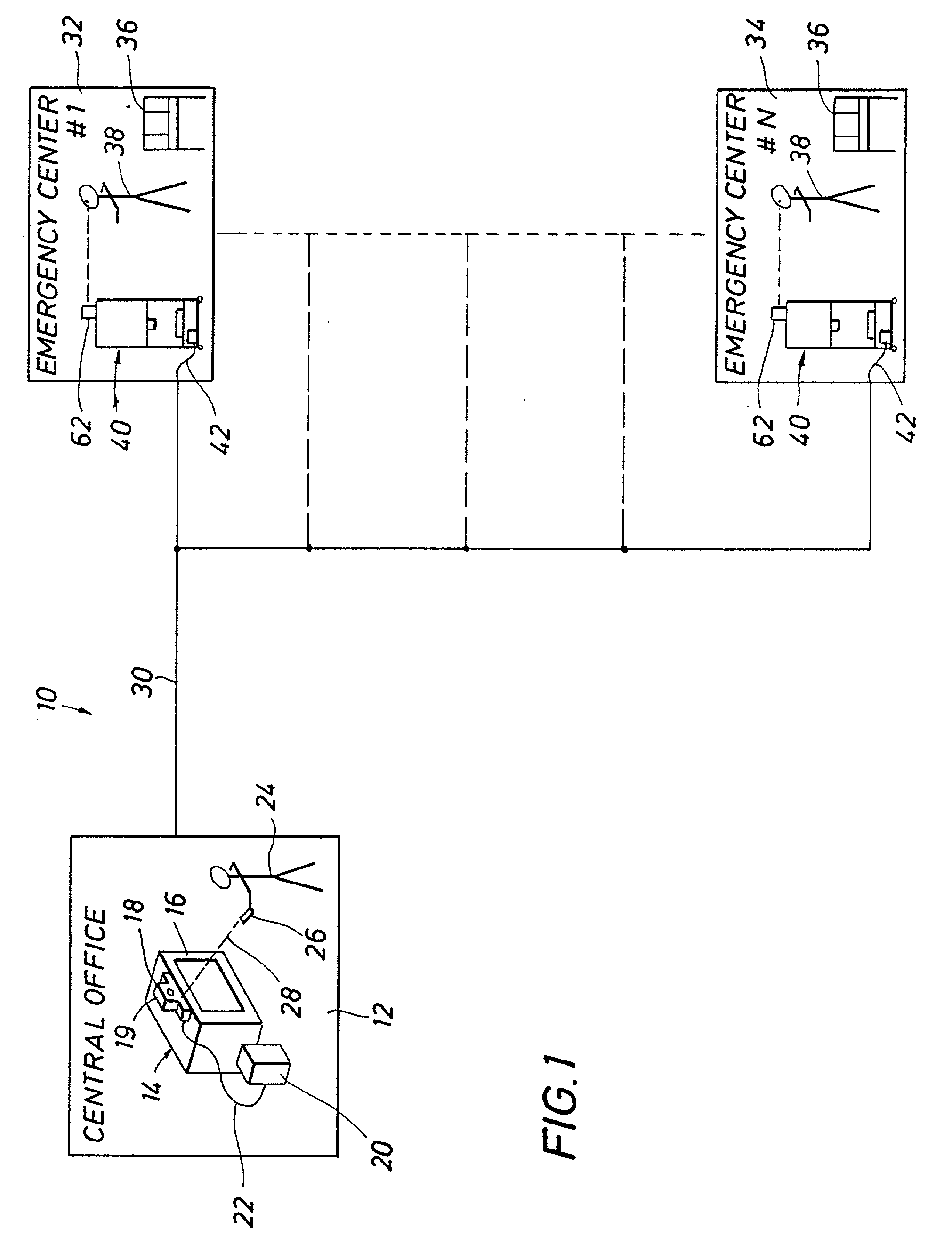
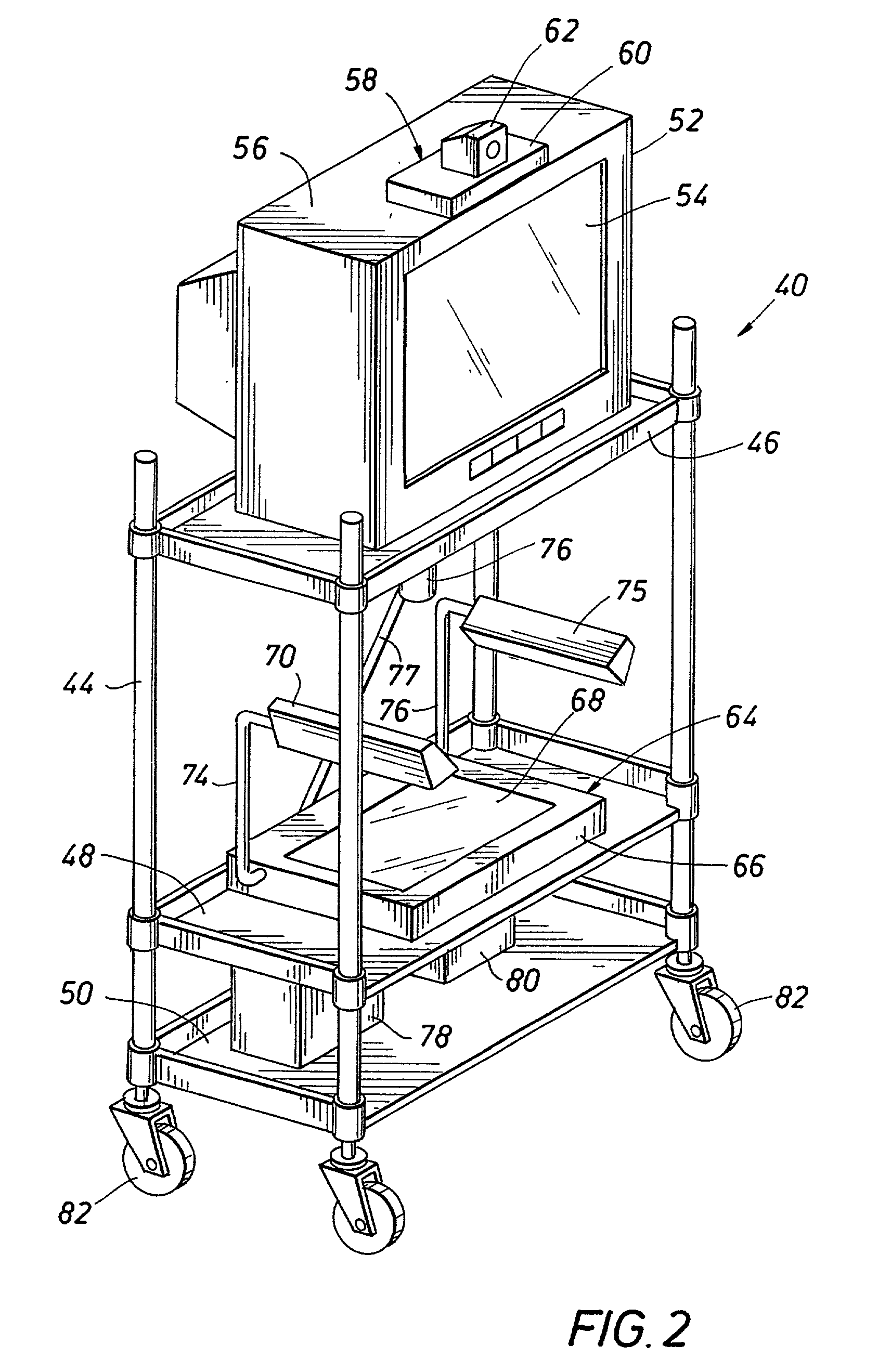
Emergency facility video-conferencing system
InactiveUS6369847B1Accurate diagnosisMedical communicationTelevision conference systemsCamera controlTelecommunications link
A medical video-teleconferencing and treatment system, having a central video-conferencing station and one or more remote video-conferencing stations and a communications link establishing video-conferencing communication therebetween. A central video monitor and audio system is located at the central video-conferencing station, and a controller unit is coupled with the communications link. The remote video-conferencing stations each have a mobile emergency center cart including a remote video monitor and audio system and a video-conferencing camera controlled by the controller unit via the communications link and capable of responding to control signals of the controller unit for panning and zoom movement of said video-conferencing camera by a medical practitioner located at the central video-conferencing station. The arrangement enables the medical practitioner to observe and to diagnose the condition of the patient and direct the medical personnel of the selected video-conferencing station to provide treatment of the patient.
Owner:EMTEL
Physiological monitoring device
InactiveUS20140206977A1Avoid mechanical stressPrecise positioningElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsPhysiological monitoringLong term monitoring
The present invention relates to a physiological monitoring device. Some embodiments of the invention allow for long-term monitoring of physiological signals. Further embodiments may also allow for the monitoring of secondary signals such as motion.
Owner:IRHYTHM TECH
In-situ method of analyzing cells
InactiveUS6165734AWidespread samplingEasy to masterRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryHistological stainingBiology
A method of in situ analysis of a biological sample comprising the steps of (a) staining the biological sample with N stains of which a first stain is selected from the group consisting of a first immunohistochemical stain, a first histological stain and a first DNA ploidy stain, and a second stain is selected from the group consisting of a second immunohistochemical stain, a second histological stain and a second DNA ploidy stain, with provisions that N is an integer greater than three and further that (i) if the first stain is the first immunohistochemical stain then the second stain is either the second histological stain or the second DNA ploidy stain; (ii) if the first stain is the first histological stain then the second stain is either the second immunohistochemical stain or the second DNA ploidy stain; whereas (iii) if the first stain is the first DNA ploidy stain then the second stain is either the second immunohistochemical stain or the second histological stain; and (b) using a spectral data collection device for collecting spectral data from the biological sample, the spectral data collection device and the N stains are selected such that a spectral component associated with each of the N stains is collectable.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Intraoral appliances with sensing
ActiveUS20180000563A1Patient compliance is goodGood curative effectMobile data collection deviceOthrodonticsBiomedical engineeringIntraoral appliance
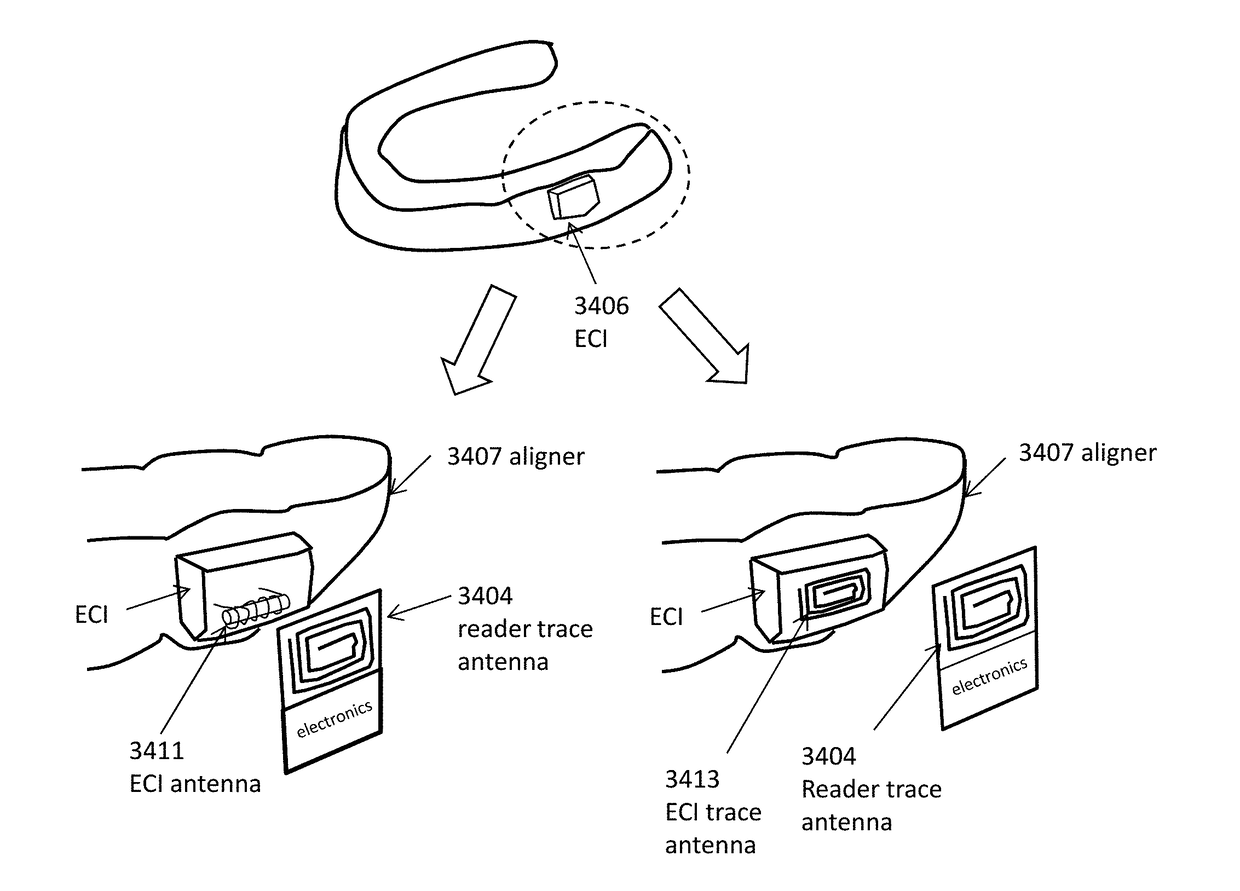
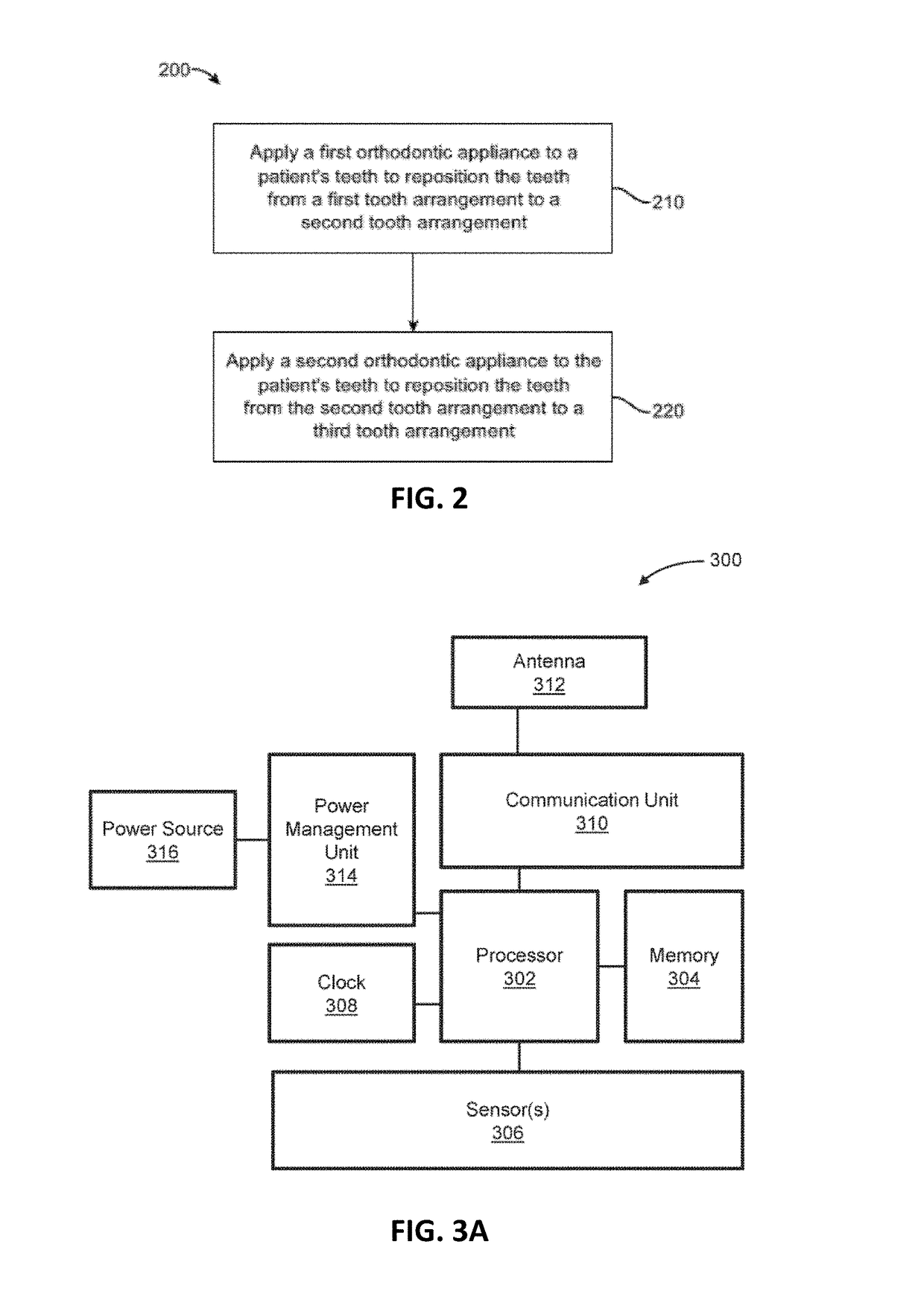
Detection of placement of dental aligners in patient mouth on teeth for indication of wearing compliance. Described herein are apparatuses and methods for detecting wearing, including compliance, and for reliably transferring data, by wired or wireless direct or indirect communication of electronic compliance information to a smartphone. Also described herein are dental appliances that can detect physiological parameters related to respiration and sleep. Also described herein are aligner cases that enable NFC communication with electronic compliance indicator (ECI) devices and Bluetooth communication with smartphones.
Owner:ALIGN TECH
Method and system for guided, efficient treatment
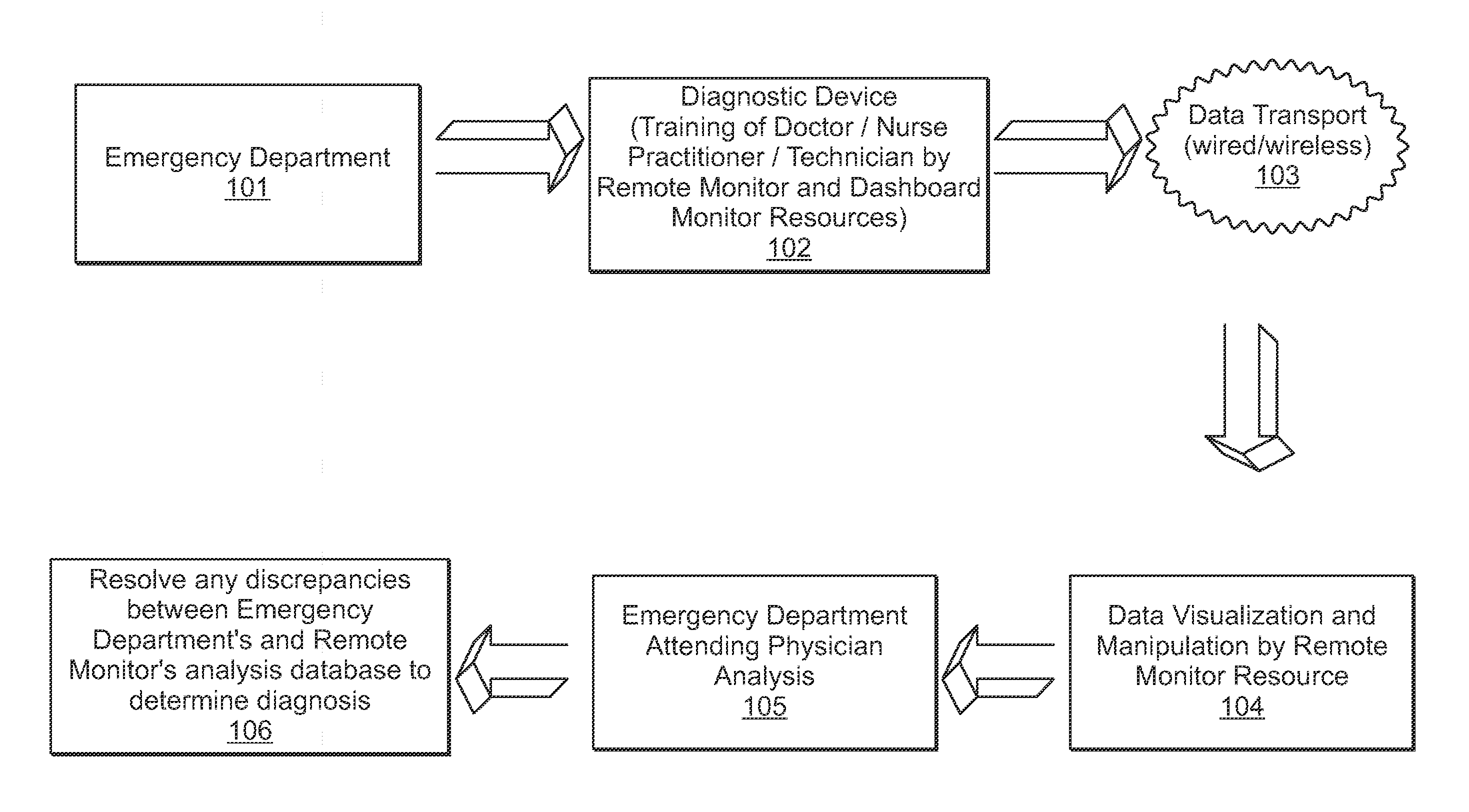
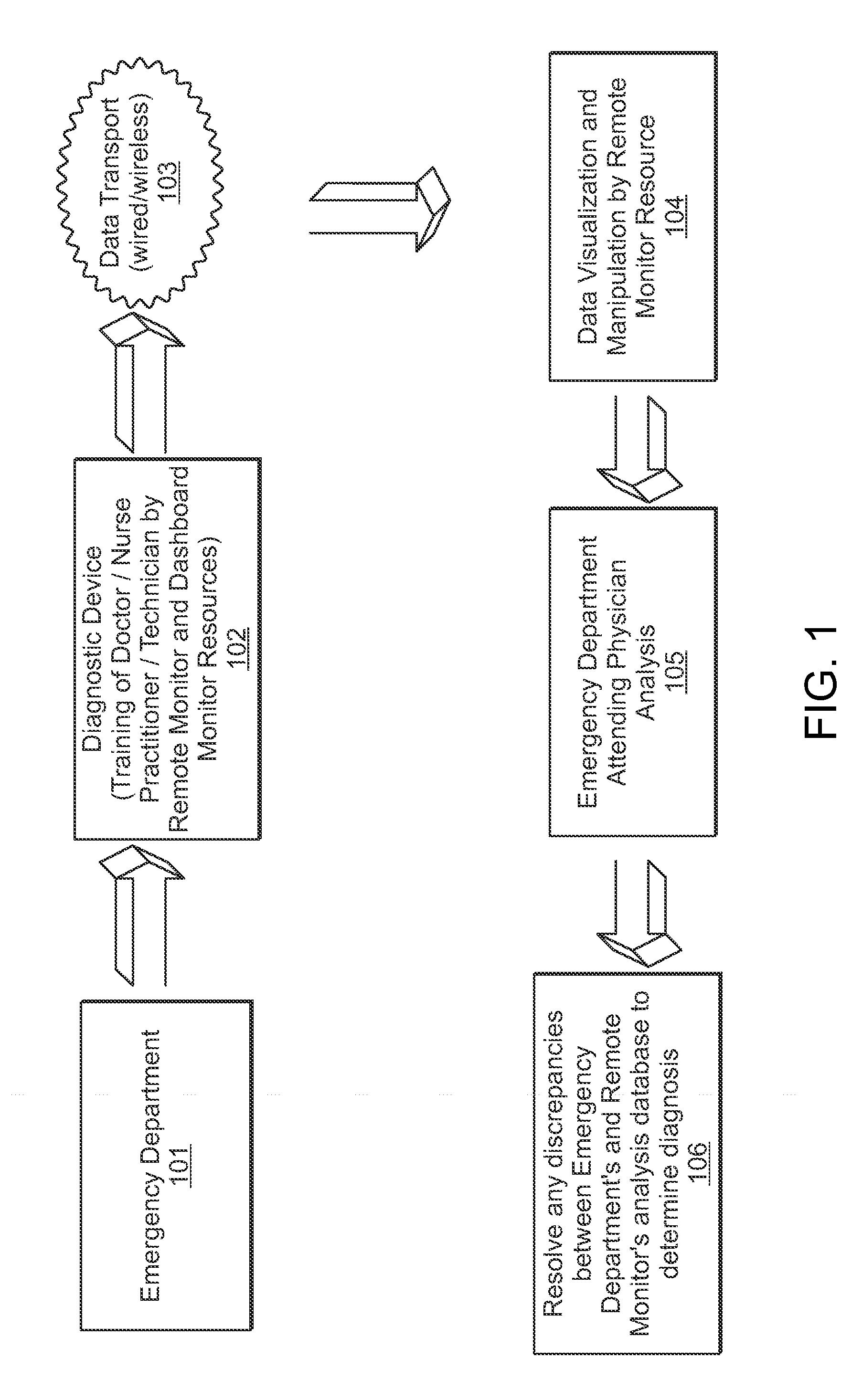
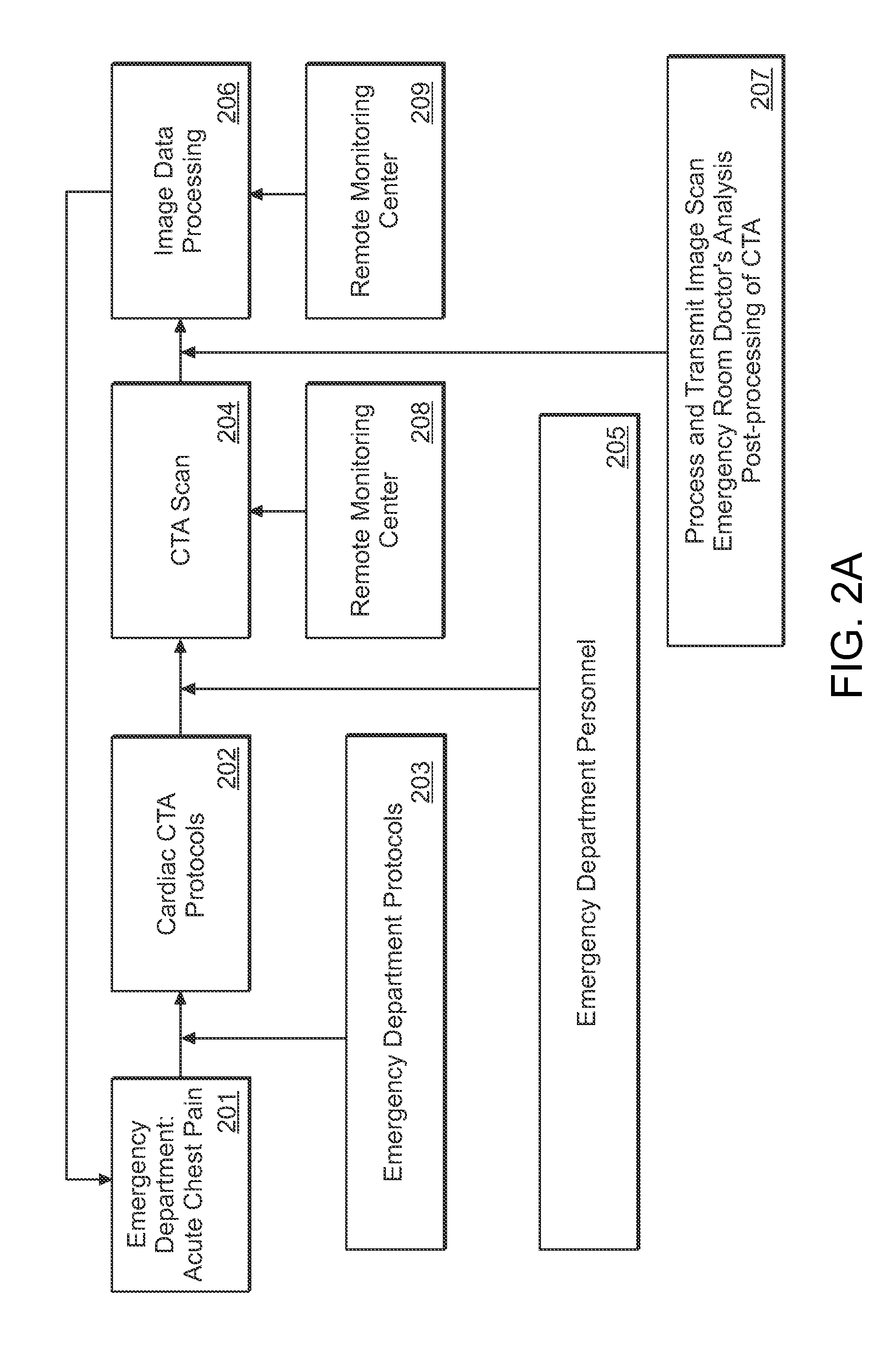
InactiveUS20130024213A1Accurate and efficientAccurate diagnosisRadiation diagnosis data transmissionMedical imagesDashboardMedical record
A system and method is provided in which medical treatment of a patient is effected in a systematic and guided fashion. From a patient's symptoms and electronic medical record, a specific diagnostic test may be recommended. Upon execution of the diagnostic test, the diagnostic scan results may be forwarded to a remote location for assistance in analysis. Once analyzed, the results are transmitted to the attending medical personnel. The results, and information which led to the decision to have a diagnostic test, are also sent to a repository for use in future diagnoses and other determinations. A monitor or dashboard is used to keep track of the various steps of the procedure, to provide on the job guidance in using a diagnostic test device, and the ensure a specific efficiency and protocol are followed. A remote location of experts may also be monitoring the dashboard, as a quality control.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Systems and methods for evaluating the urethra and the periurethral tissues
InactiveUS20020040185A1Accurate diagnosisImprove clinical outcomesGastroscopesOesophagoscopesDiseaseUrethra
The present invention provides systems and methods for the evaluation of the urethra and periurethral tissues using an MRI coil adapted for insertion into the male, female or pediatric urethra. The MRI coil may be in electrical communication with an interface circuit made up of a tuning-matching circuit, a decoupling circuit and a balun circuit. The interface circuit may also be in electrical communication with a MRI machine. In certain practices, the present invention provides methods for the diagnosis and treatment of conditions involving the urethra and periurethral tissues, including disorders of the female pelvic floor, conditions of the prostate and anomalies of the pediatric pelvis.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
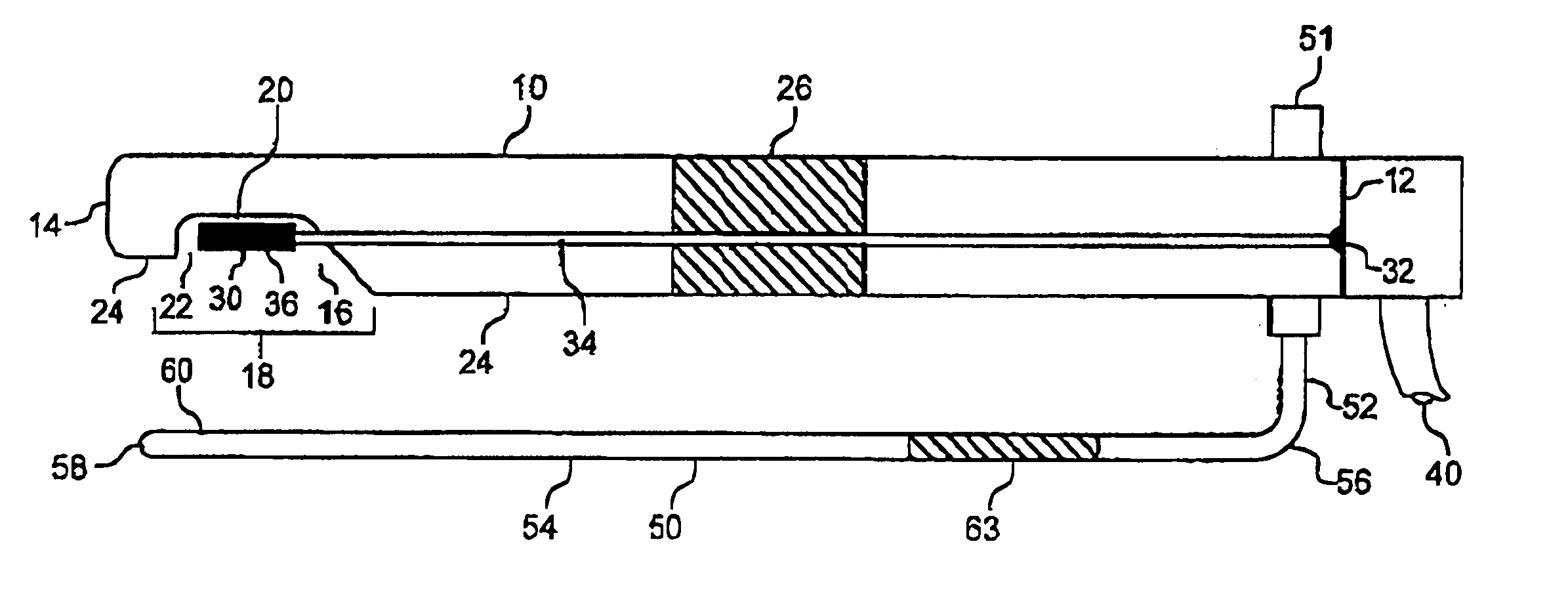
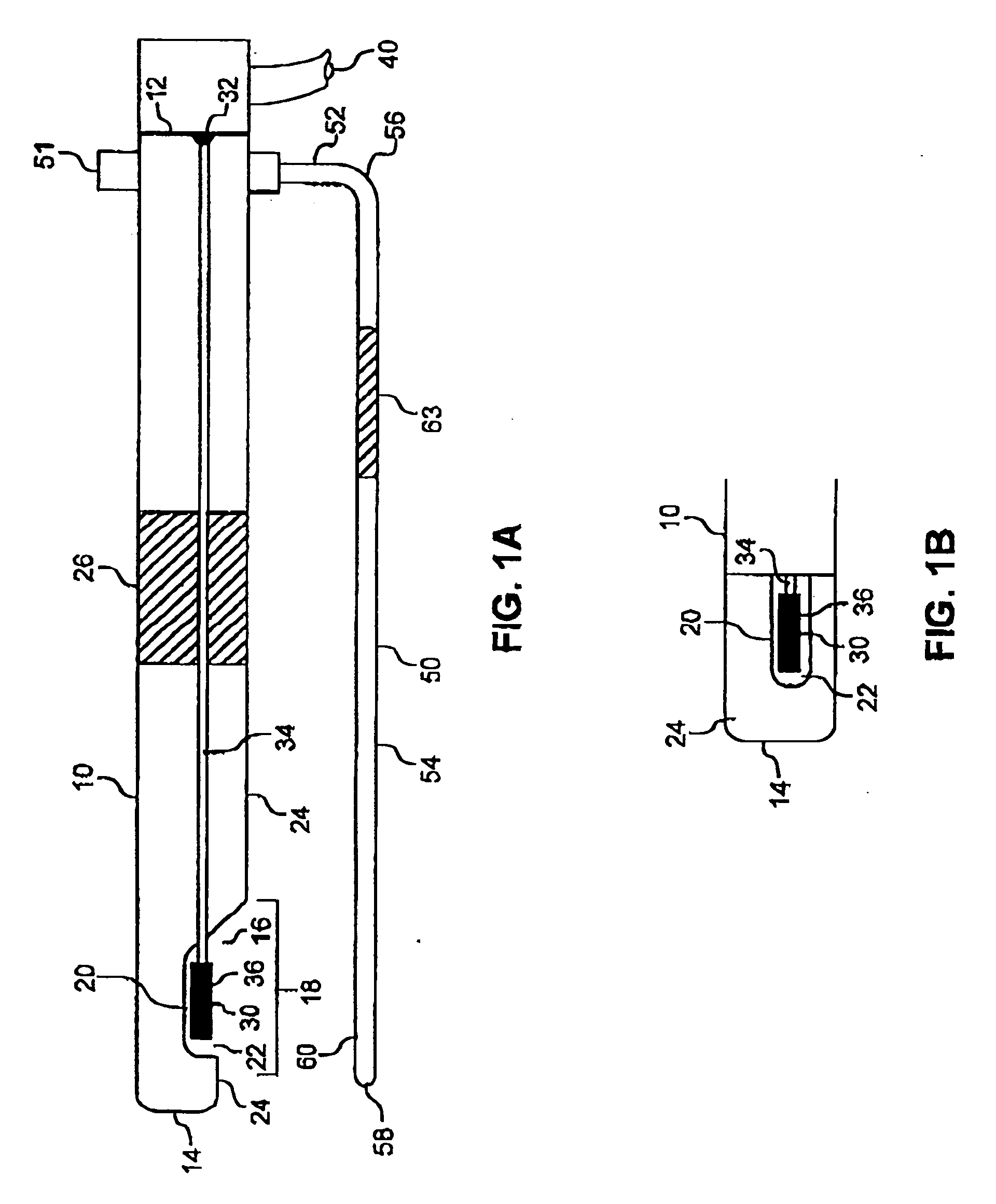
Noninvasive detection of a physiologic parameter with a probe
InactiveUS20060020179A1Non-invasive and accurate determinationPreventing application of excessive pressureBlood flow measurement devicesCatheterAnalyteBlood flow
The invention provides a device for contacting a surface of a patient's body to determine a physiologic parameter in a measurement region of a tissue of the patient. The device typically comprises a sensor responsive to the physiologic parameter and a probe housing the sensor. The probe is constructed to allow the sensor to be secured at a sensing site adjacent to the measurement region, without disturbing the blood flow within the measurement region of the tissue. The device may also include a means for reducing interference in the sensing area. Preferably, the device further comprises an indicating means operably connected to the sensor for indicating an analyte quantity and / or concentration associated with the physiologic parameter.
Owner:EXOSTAT MEDICAL
Emergency facility video-conferencing system
InactiveUS20020130950A1Accurate diagnosisMedical communicationTelevision conference systemsCamera controlTelecommunications link
A medical video-teleconferencing and treatment system, having a central video-conferencing station and one or more remote video-conferencing stations and a communications link establishing video-conferencing communication therebetween. A central video monitor and audio system is located at the central video-conferencing station, and a controller unit is coupled with the communications link. The remote video-conferencing stations each have a mobile emergency center cart including a remote video monitor and audio system and a video-conferencing camera controlled by the controller unit via the communications link and capable of responding to control signals of the controller unit for panning and zoom movement of said video-conferencing camera by a medical practitioner located at the central video-conferencing station. The arrangement enables the medical practitioner to observe and to diagnose the condition of the patient and direct the medical personnel of the selected video-conferencing station to provide treatment of the patient.
Owner:LASCO FITTINGS
Rotational intravascular ultrasound probe with an active spinning element
ActiveUS20100234736A1Improve image qualityAccurate diagnosis of medicalCatheterInfrasonic diagnosticsManufacturing cost reductionSonification
An intravascular ultrasound probe is disclosed, incorporating features for utilizing an advanced transducer technology on a rotating transducer shaft. In particular, the probe accommodates the transmission of the multitude of signals across the boundary between the rotary and stationary components of the probe required to support an advanced transducer technology. These advanced transducer technologies offer the potential for increased bandwidth, improved beam profiles, better signal to noise ratio, reduced manufacturing costs, advanced tissue characterization algorithms, and other desirable features. Furthermore, the inclusion of electronic components on the spinning side of the probe can be highly advantageous in terms of preserving maximum signal to noise ratio and signal fidelity, along with other performance benefits.
Owner:VOLCANO CORP
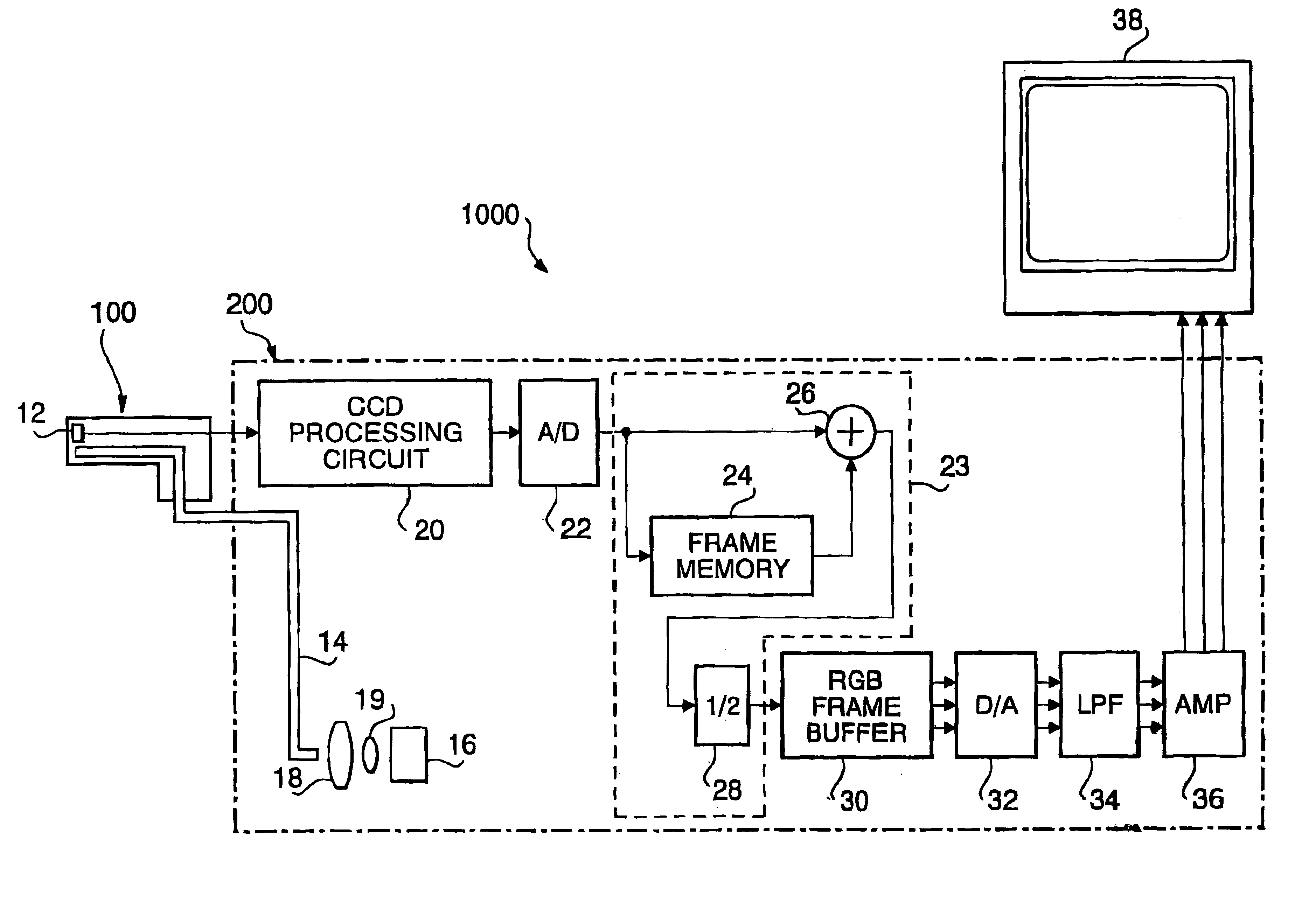
Electronic endoscope system for reducing random noise of a video signal
InactiveUS6900829B1Reduce random noiseClear imagingImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionColor image
An electronic endoscope system which captures an image of an object and displays the same on a display device is provided with a noise reduction system. The noise reduction system reduces noise included in a frame of an image signal for each color component. The noise-reduced color components are stored in a buffer, and then output as a video signal to be transmitted to a display where a color image of the object is displayed.
Owner:HOYA CORP
Point of care diagnostic systems
InactiveUS6936476B1Accurate concentrationAccurately presenceScattering properties measurementsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionPoint of careDiagnostic test
Systems and methods for medical diagnosis or risk assessment for a patient are provided. These systems and methods are designed to be employed at the point of care, such as in emergency rooms and operating rooms, or in any situation in which a rapid and accurate result is desired. The systems and methods process patient data, particularly data from point of care diagnostic tests or assays, including immunoassays, electrocardiograms, X-rays and other such tests, and provide an indication of a medical condition or risk or absence thereof. The systems include an instrument for reading or evaluating the test data and software for converting the data into diagnostic or risk assessment information.
Owner:CYTYC CORP
Wireless technology as a data conduit in three-dimensional ultrasonogray
InactiveUS20110034209A1Low costHigh technology costTelemedicineCharacter and pattern recognitionOriginal dataData acquisition
An imaging system, having: an imaging data acquisition device; a remote image reconstruction and data processing facility; and a wireless data transfer to transmit raw data from the data acquisition device to the remote facility. At the facility, the raw data is processed to prepare a diagnostic image that can be transmitted to an expert or non-expert, or transmitted back to the display of the wireless data transfer device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Automated Cryogenic Skin Treatment
InactiveUS20100087806A1Density of pulse will decreaseHigh densityDiagnosticsSurgical instruments for coolingProximateSkin treatments
An apparatus and methods for treating lesions on skin are presented. The apparatus collects information about a lesion and can automatically determine a course of treatment for the lesion. The device can include a controller that positions the nozzle proximate to a surface region of the lesion and automatically dispenses a pulse of the cryogenic fluid from the nozzle. The controller then positions the nozzle proximate to another surface region of the lesion and automatically dispenses a pulse of the cryogenic fluid from the nozzle.
Owner:VANDOLAY INC
Point-of-care information entry
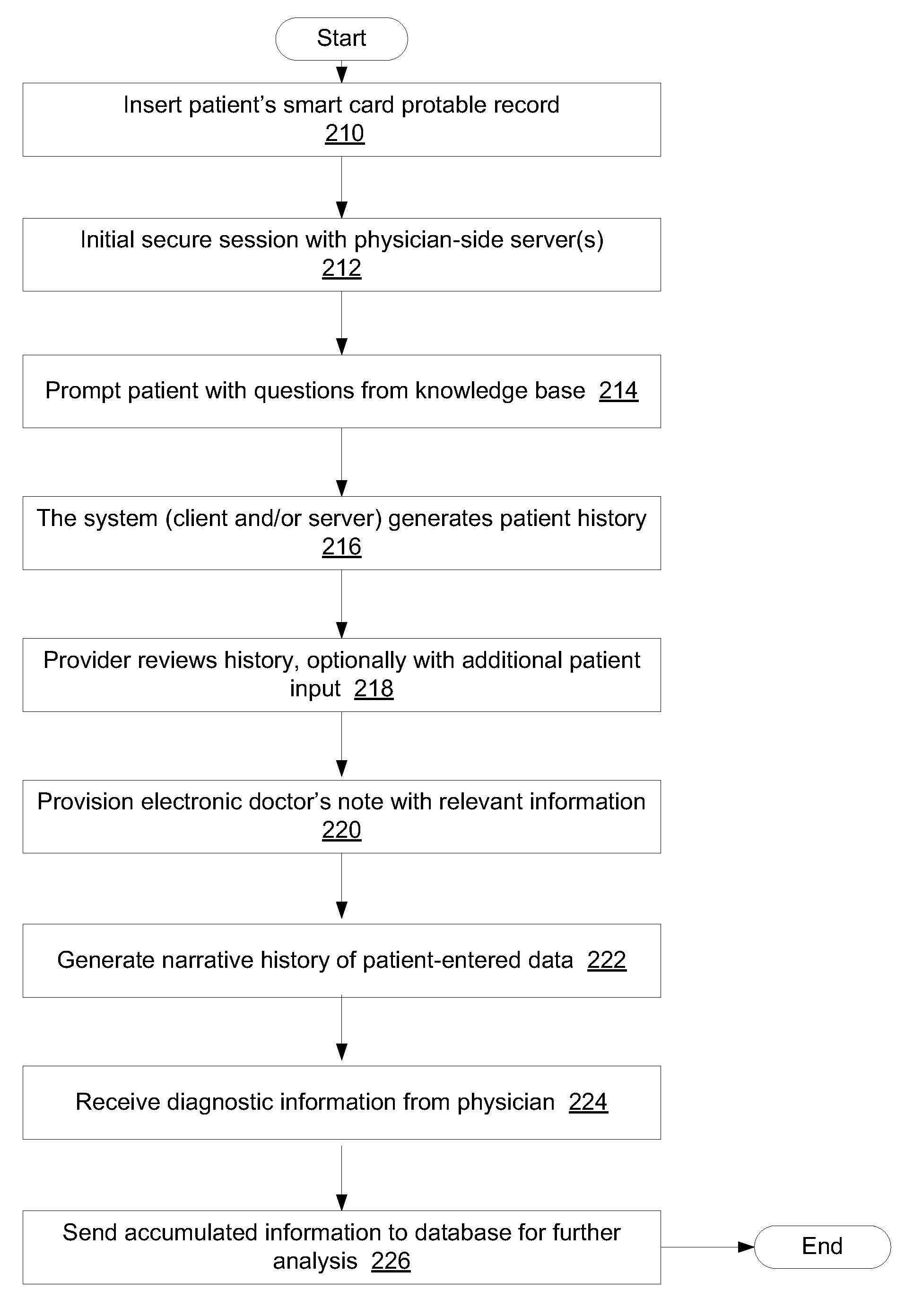
InactiveUS20080183504A1Easy to storeImprove extrapolationComplete banking machinesTelephonic communicationMedical recordPoint of care
A point-of-care touch / click entry system can be used to replace and / or augment standard dictation transcription models in medical record systems (which comprise institution-centric data). Key word entry can better standardized medical record display, can be linked directly to diagnostic and billing codes to automate billing thus decreasing payers claims of fraud and can be used to insert data variables directly into relational databases to improve outcome analysis. In total the “clinical operating system (COS) and clinical information system (CIS) can quickly and accurately produce “longitudinal” lifetime medical records (which comprise patient-centric data). The longitudinal medical record can be used in accordance with medical record systems to connect patients, providers, pharmacies, clinics, hospitals, payers, and producers through a secure private network that operates in real-time at the point of care on-line or off-line.
Owner:CHI SQUARE TECH
ESR1 and Cervical Cancer
InactiveUS20090023137A1High sensitivityAccurate diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyMethylation
The present invention provides methods and kits for detecting susceptibility to, or the incidence of, cervical cancer in a sample comprising determining the methylation status of the ESR1 gene, optionally as part of a panel of genes. Also provided are methods and kits which involve determining the expression levels of genes including the ESR1 gene in order to diagnose cervical cancer.
Owner:ONCOMETHYLOME SCI
Machine learning based system for identifying and monitoring neurological disorders
InactiveUS20190110754A1Accurate and Rapid DiagnosisGood curative effectMathematical modelsMedical data miningDiseaseNervous system
A system and methods of diagnosing and monitoring neurological disorders in a patient utilizing an artificial intelligence based system. The system may comprise a plurality of sensors, a collection of trained machine learning based diagnostic and monitoring tools, and an output device. The plurality of sensors may collect data relevant to neurological disorders. The trained diagnostic tool will learn to use the sensor data to assign risk assessments for various neurological disorders. The trained monitoring tool will track the development of a disorder over time and may be used to recommend or modify the administration of relevant treatments. The goal of the system is to render an accurate evaluation of the presence and severity of neurological disorders in a patient without requiring input from an expertly trained neurologist.
Owner:RAO SATISH +1
System and method of implementing multi-level marketing of weight management products
InactiveUS20050240434A1Maximize chanceReducing attritionMedical communicationHealth-index calculationWeight managementPersonalization
A system and method of driving weight management product sales in a multi-level marketing environment using a body impedance data acquisition device, a weight management software program, nutritional supplements and a standardized sales pathway software program, resulting in direct sales, lead generation and new distributor sign up. A prospect's personal information and lean body mass data are input to the weight management computer software program for determining an individualized weight management plan, where the lean body mass data are obtained using the body impedance data acquisition device. The prospect is presented weight management product packages for purchase, individualized according to the derived weight management plan and becomes a client upon purchasing a product package. The new customer is presented a business opportunity in becoming a new distributor of the weight management products and, if enlisted, is provided product discounts and sales software tools for facilitating weight management product sales.
Owner:HEALTHPORT
Performance analysis support system
A performance analysis support system is disclosed that provides one or more recommended solutions of a performance improvement project to management and the expected improvement benefit of each solution. The performance analysis support system guides a user through a detailed, consistent analysis process, helping organizational leaders accurately diagnose critical performance or productivity issues. Then, the performance analysis support system estimates the personnel and equipment requirements, time, costs, and return on investment associated with each solution generated based on the analysis results. In addition, the performance analysis support system provides management immediate access to ongoing and past analyses.
Owner:PROOFPOINT SYST INC
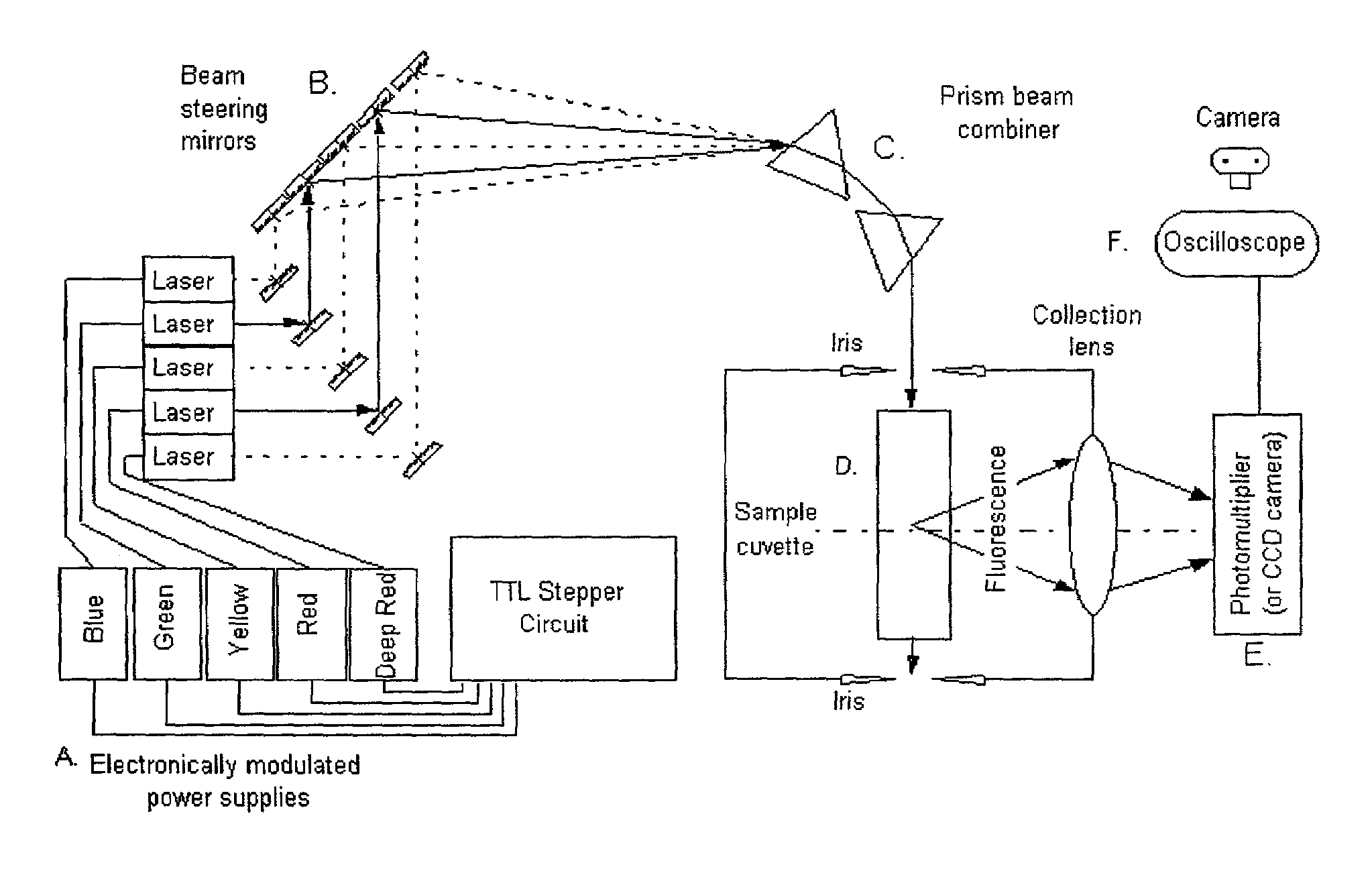
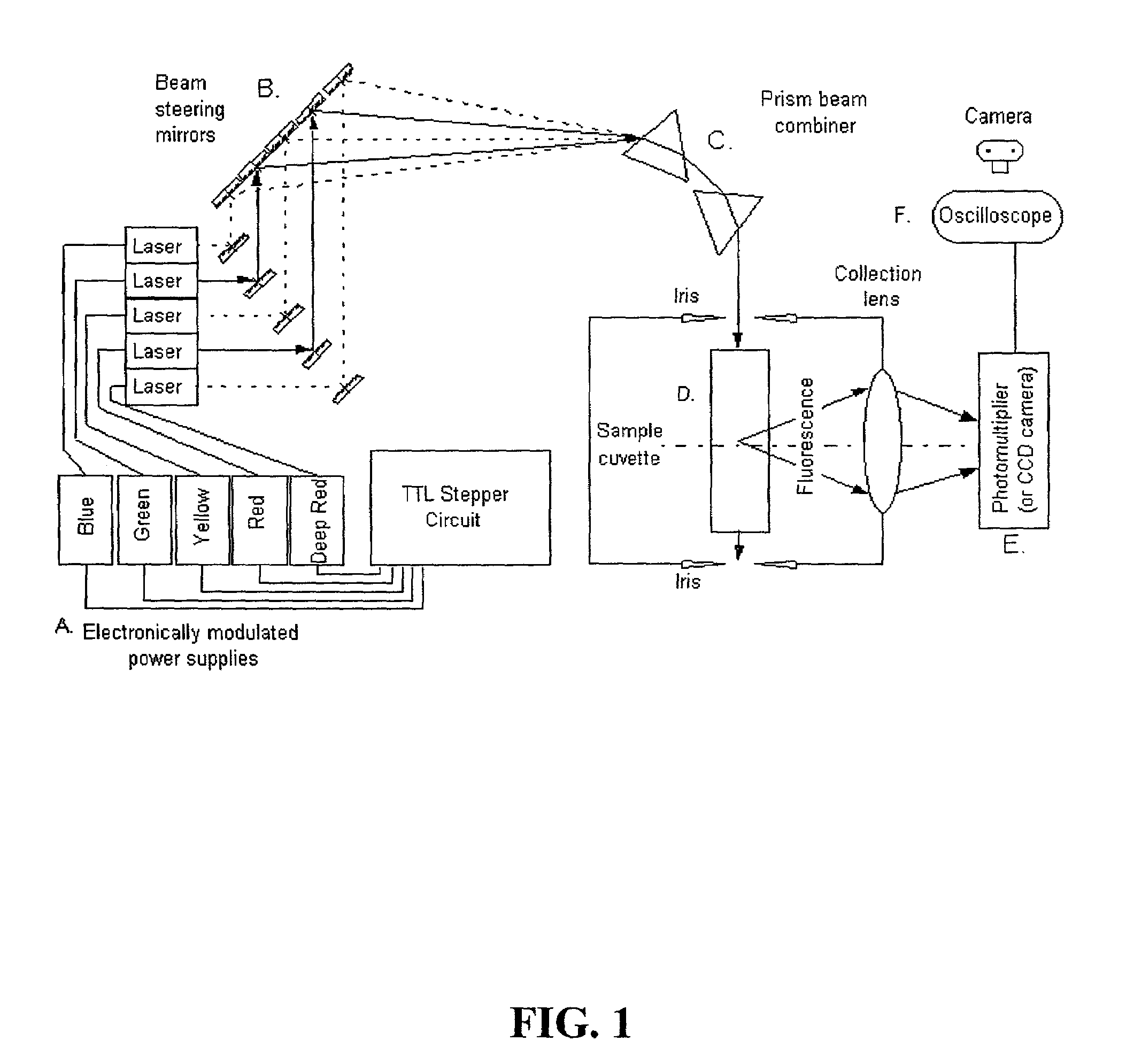
Pulsed-multiline excitation for color-blind fluorescence detection
InactiveUS6995841B2Accurate diagnosisImproved prognosisRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryFluorophoreCrowds
The present invention provides a technology called Pulse-Multiline Excitation or PME. This technology provides a novel approach to fluorescence detection with application for high-throughput identification of informative SNPs, which could lead to more accurate diagnosis of inherited disease, better prognosis of risk susceptibilities, or identification of sporadic mutations. The PME technology has two main advantages that significantly increase fluorescence sensitivity: (1) optimal excitation of all fluorophores in the genomic assay and (2) “color-blind” detection, which collects considerably more light than standard wavelength resolved detection. Successful implementation of the PME technology will have broad application for routine usage in clinical diagnostics, forensics, and general sequencing methodologies and will have the capability, flexibility, and portability of targeted sequence variation assays for a large majority of the population.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE +1
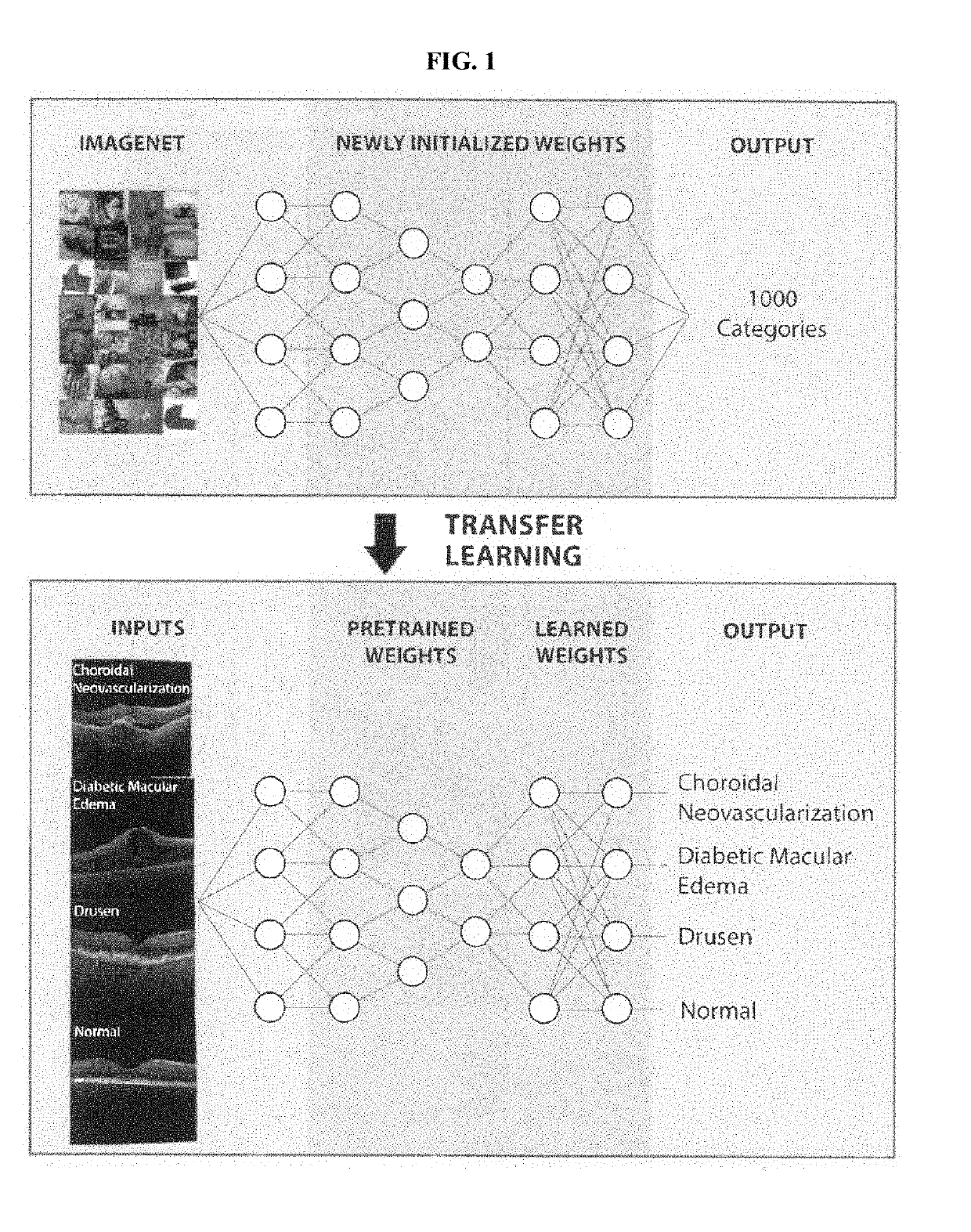
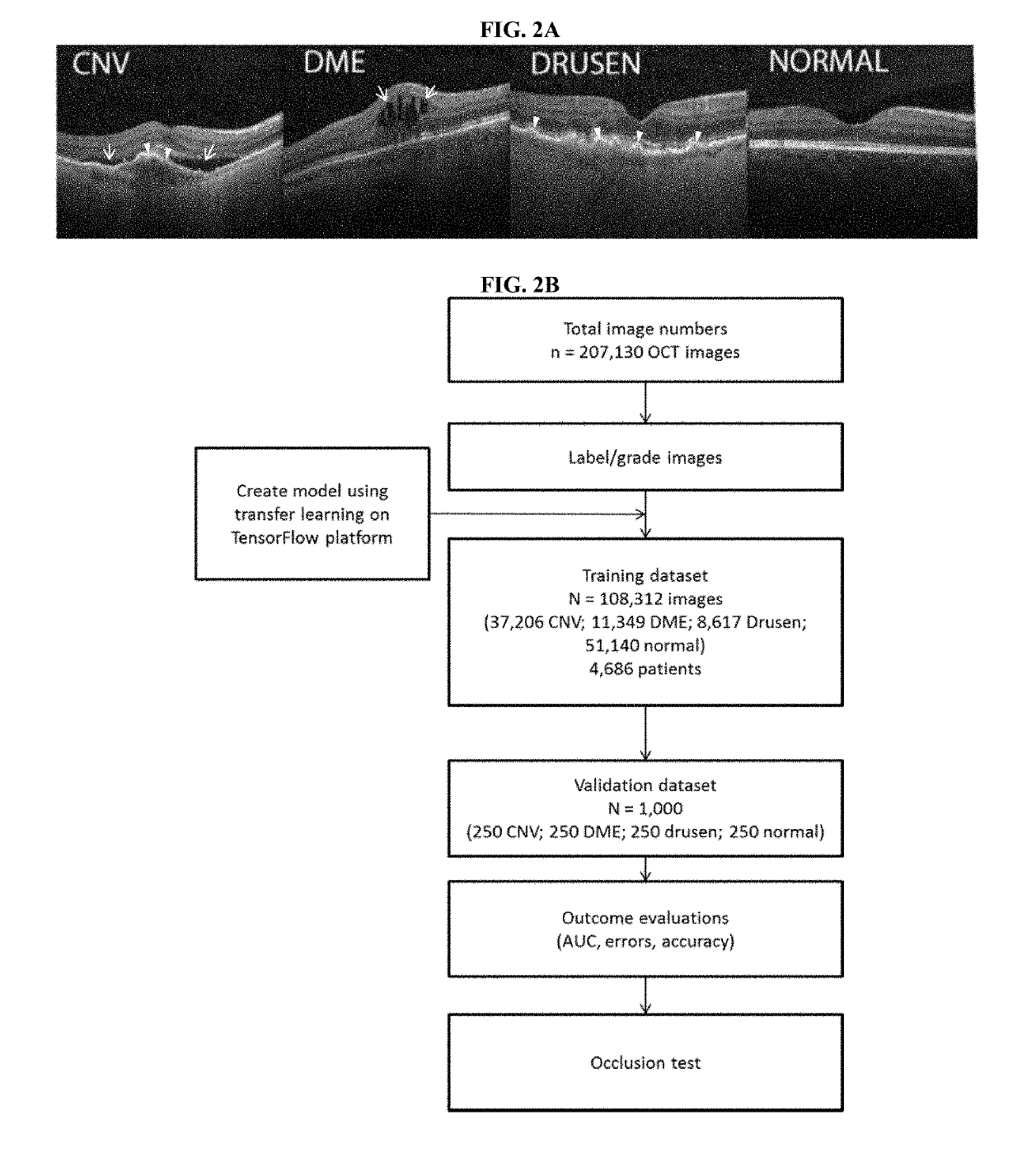
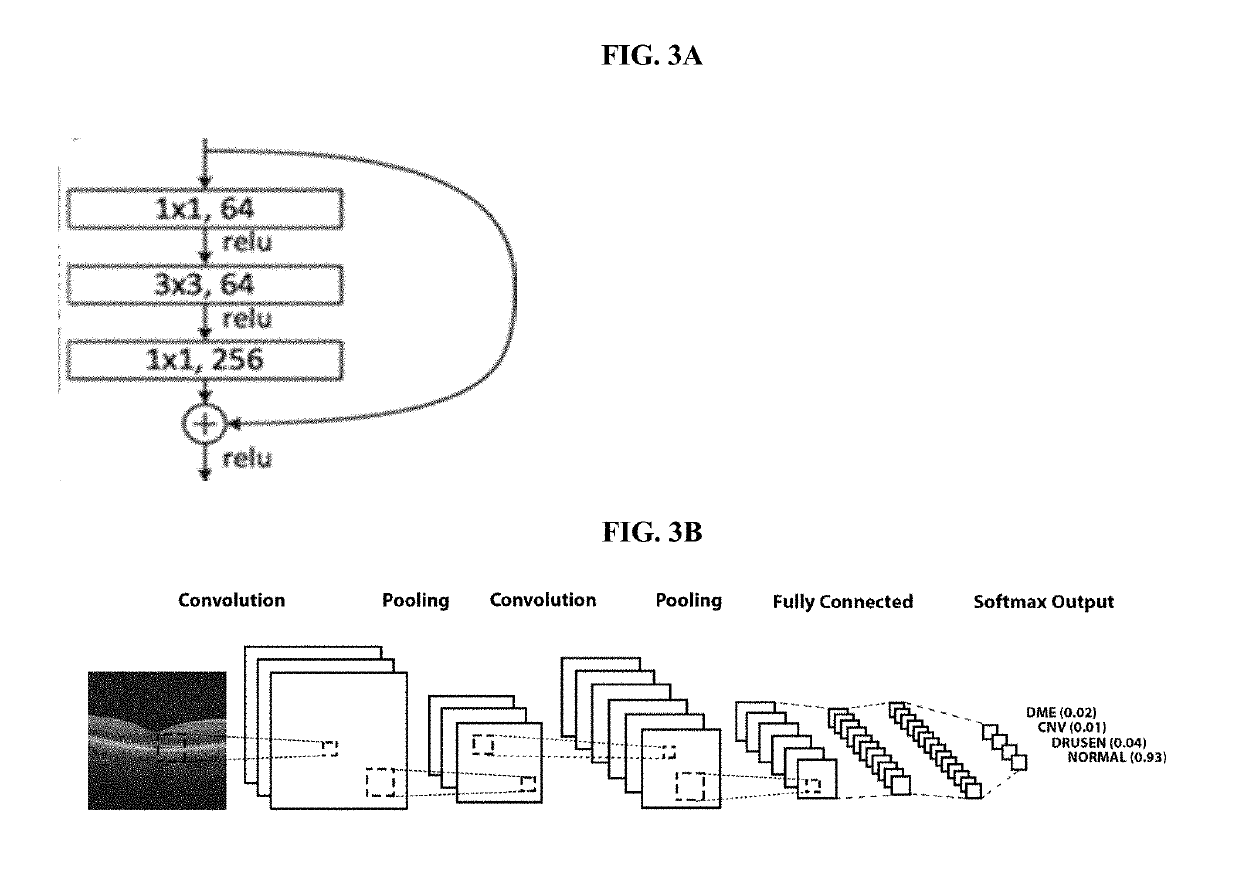
Deep learning-based diagnosis and referral of ophthalmic diseases and disorders
ActiveUS20190110753A1Efficient analysisLess computing powerMedical imagingEvaluation of blood vesselsDiseaseLearning based
Disclosed herein are systems, methods, devices, and media for carrying out medical diagnosis of ophthalmic diseases and conditions. Deep learning algorithms enable the automated analysis of ophthalmic images to generate predictions of comparable accuracy to clinical experts.
Owner:AITECH +1
Catheter for inserting into a vessel
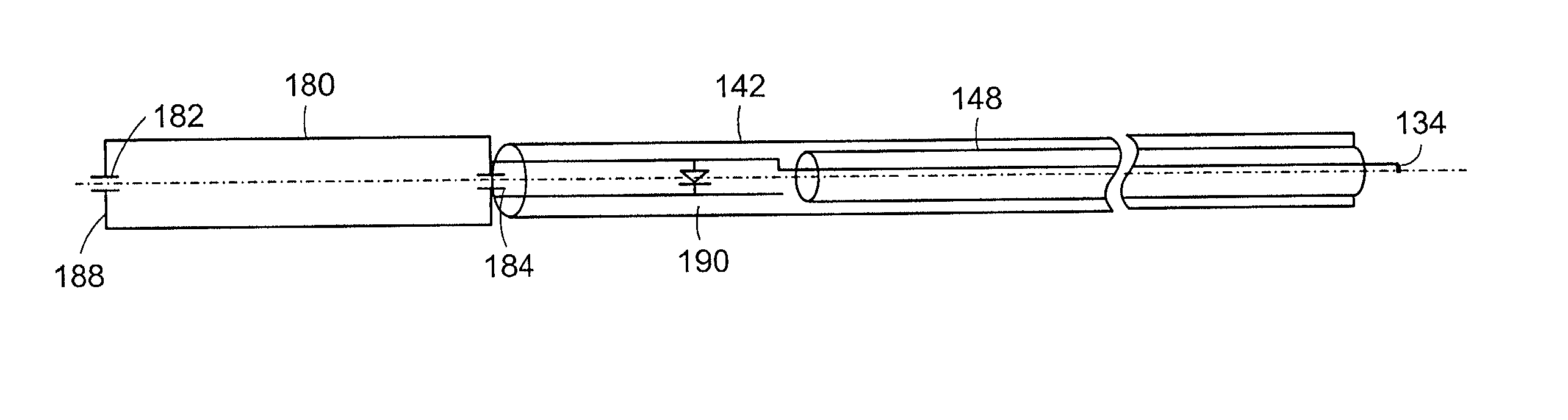
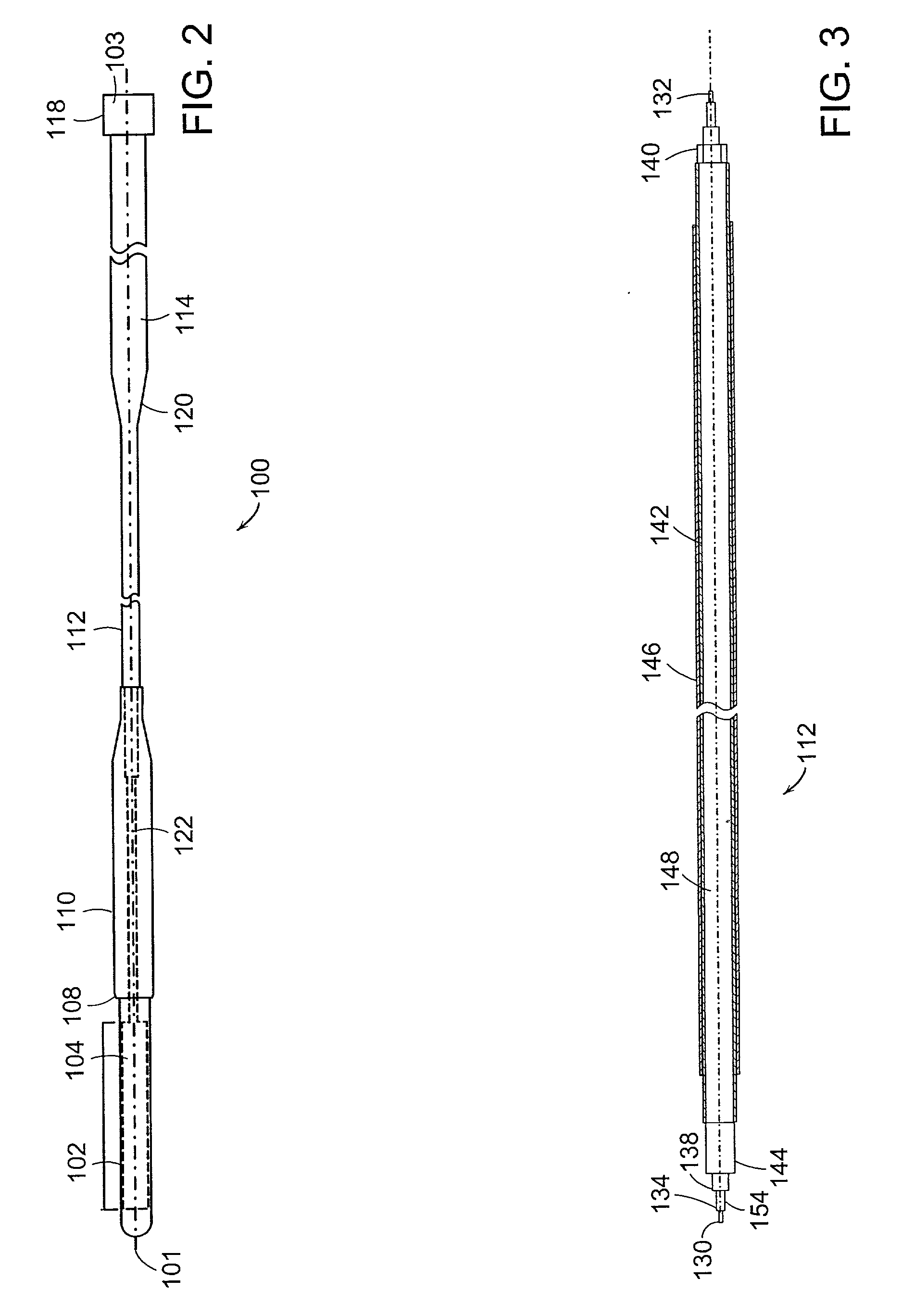
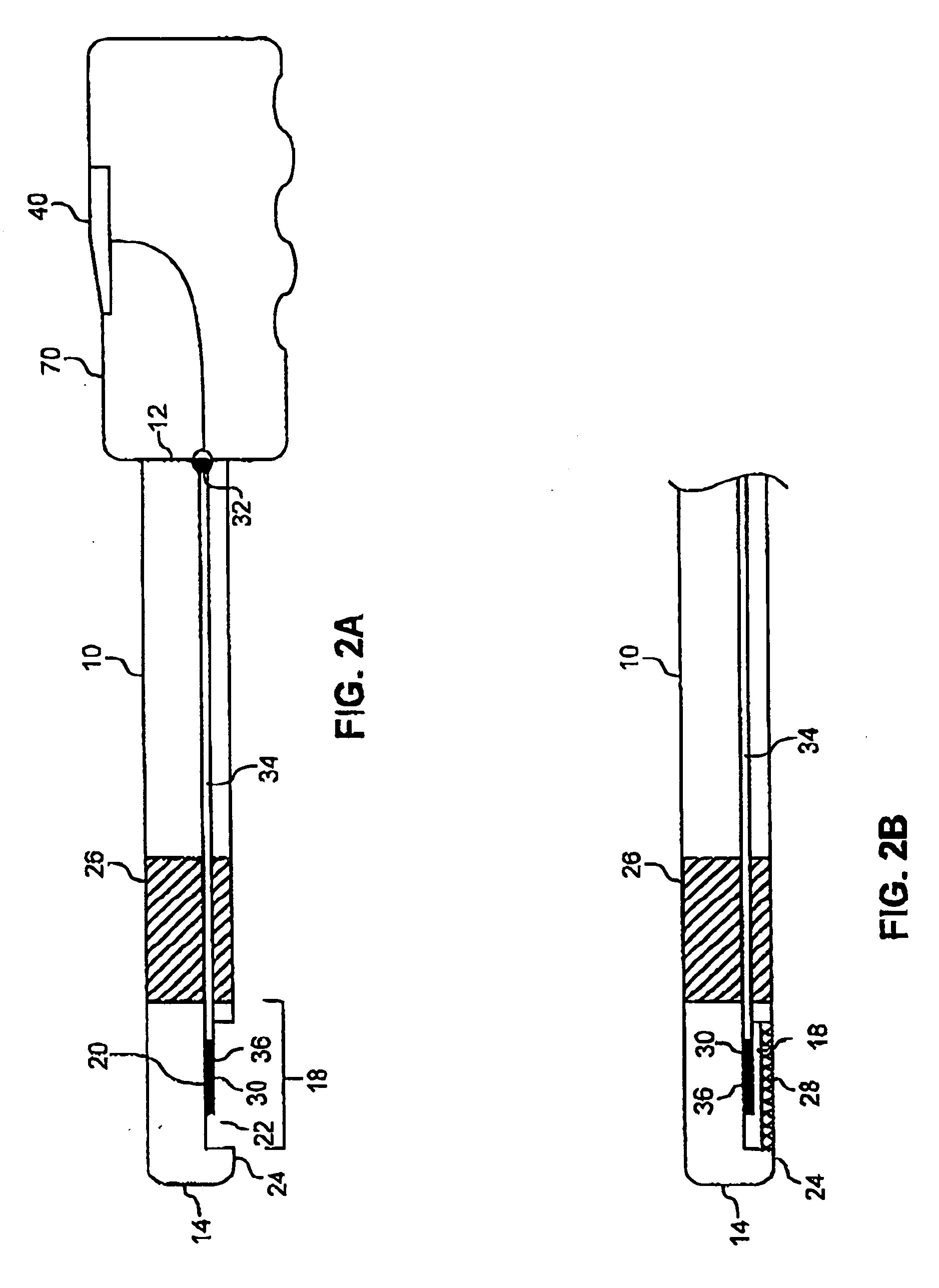
InactiveUS20050192496A1Easy to catchAccurate diagnosisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsStentsInsertion stentTomography
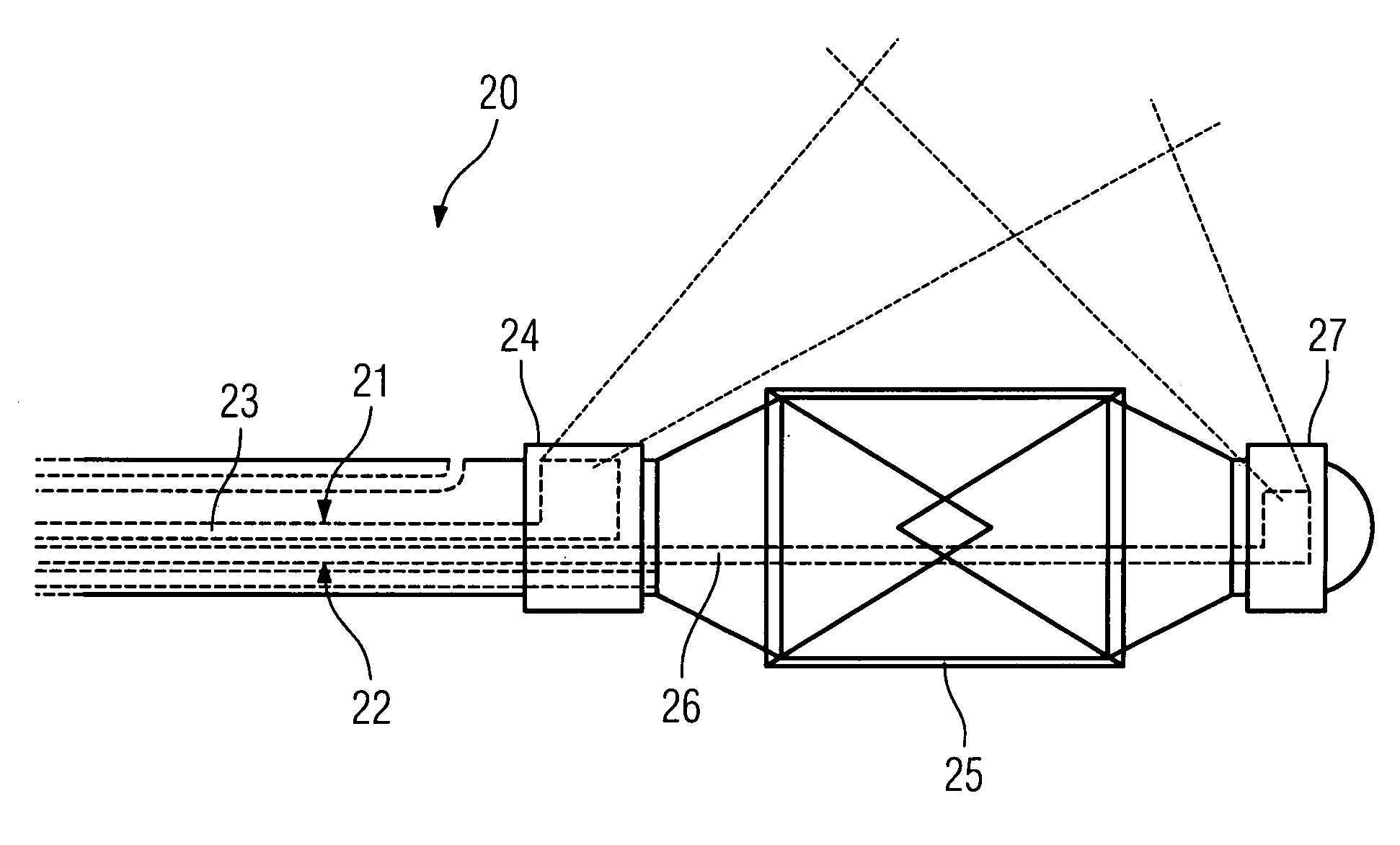
Catheter for insertion into a vessel, comprising a reversibly inflatable balloon (10, 25) provided in the area of the catheter tip, on the outside of which a stent (11) to be implanted in the vessel is arranged, and at least one imaging device (14, 21, 22) arranged in the area of the catheter tip for optical coherence tomography, which is arranged or configured such that the area of the vessel, in which the balloon (10, 25) is positioned, can be captured.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
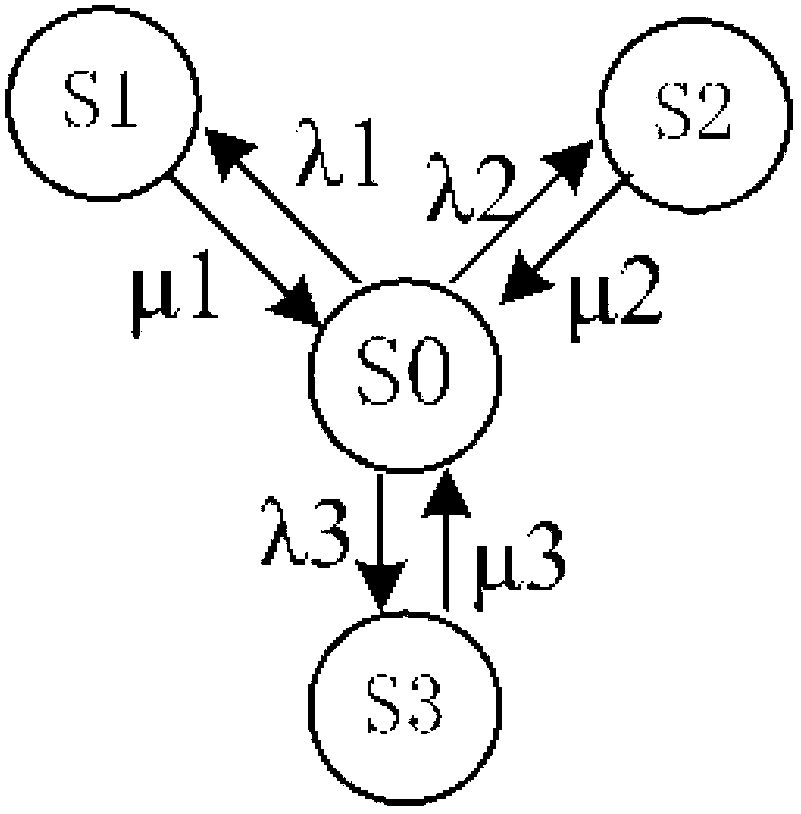
Fault diagnosis and assessment method of intelligent substation
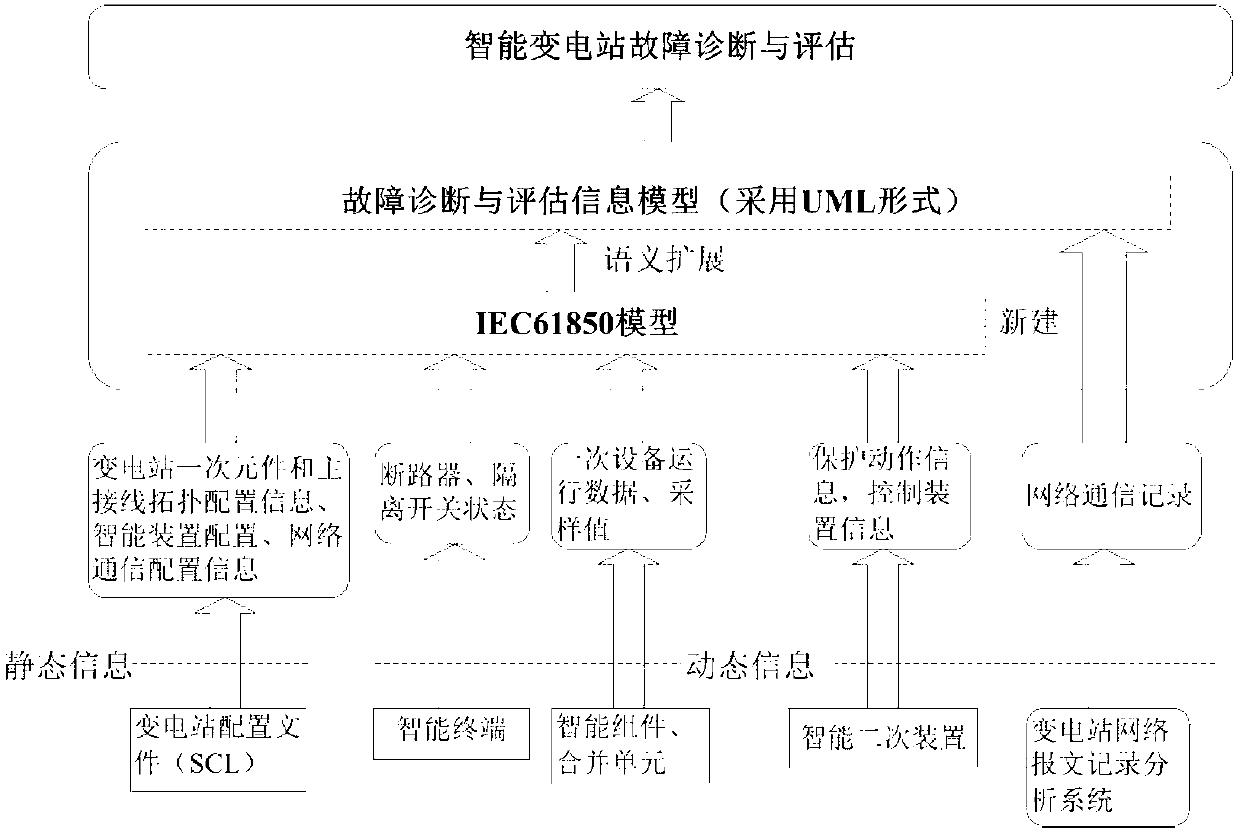
InactiveCN103001328AAccurate diagnosisClear structureCircuit arrangementsInformation technology support systemAssessment methodsSmart substation
The invention discloses a fault diagnosis and assessment method of an intelligent substation. The fault diagnosis and assessment method is characterized by including the specific steps that a fault diagnosis and assessment information model of the intelligent substation is constructed; fault and assessment indexes of a primary device, a secondary device and a network device in the intelligent substation are calculated on the basis of the fault diagnosis and assessment information model; a Petri net is used to perform primary fault diagnosis and assessment to the intelligent substation; and final diagnosis and assessment are performed by means of a distributed type expert system based on a knowledge base. The fault diagnosis and assessment method has the advantages of being clear in the diagnosis process, fast and practical in diagnosis methods and accurate and reliable in diagnosis results.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
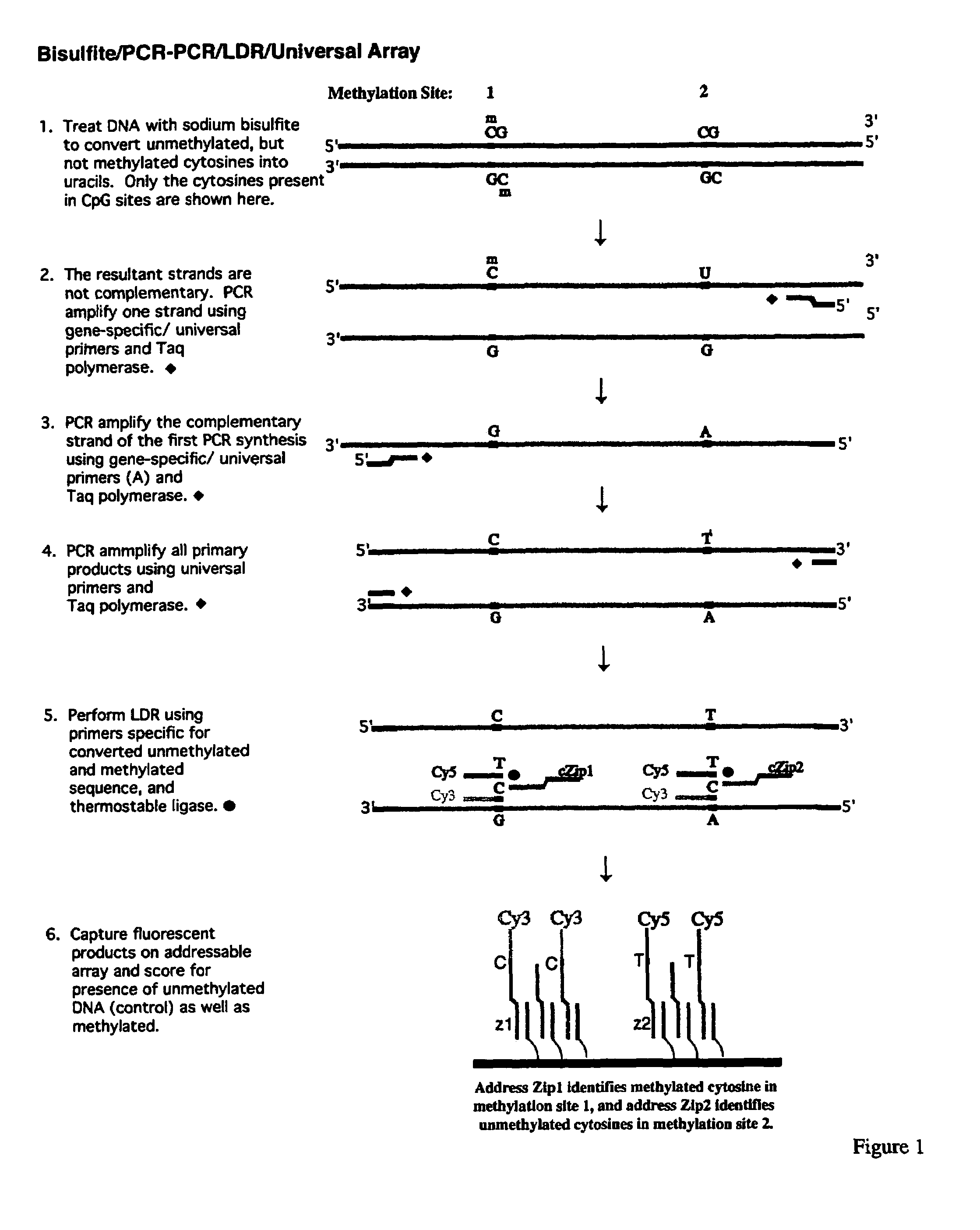
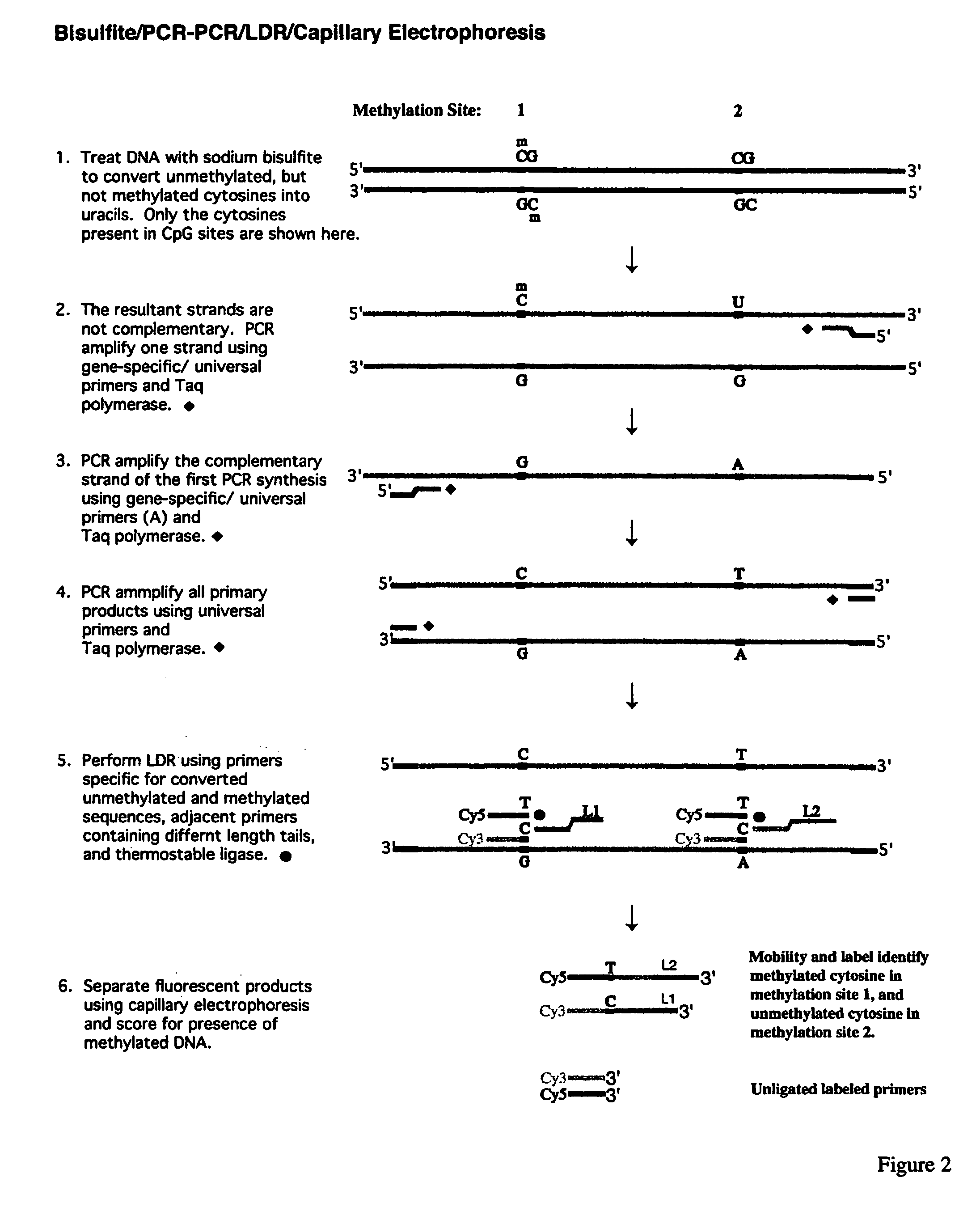
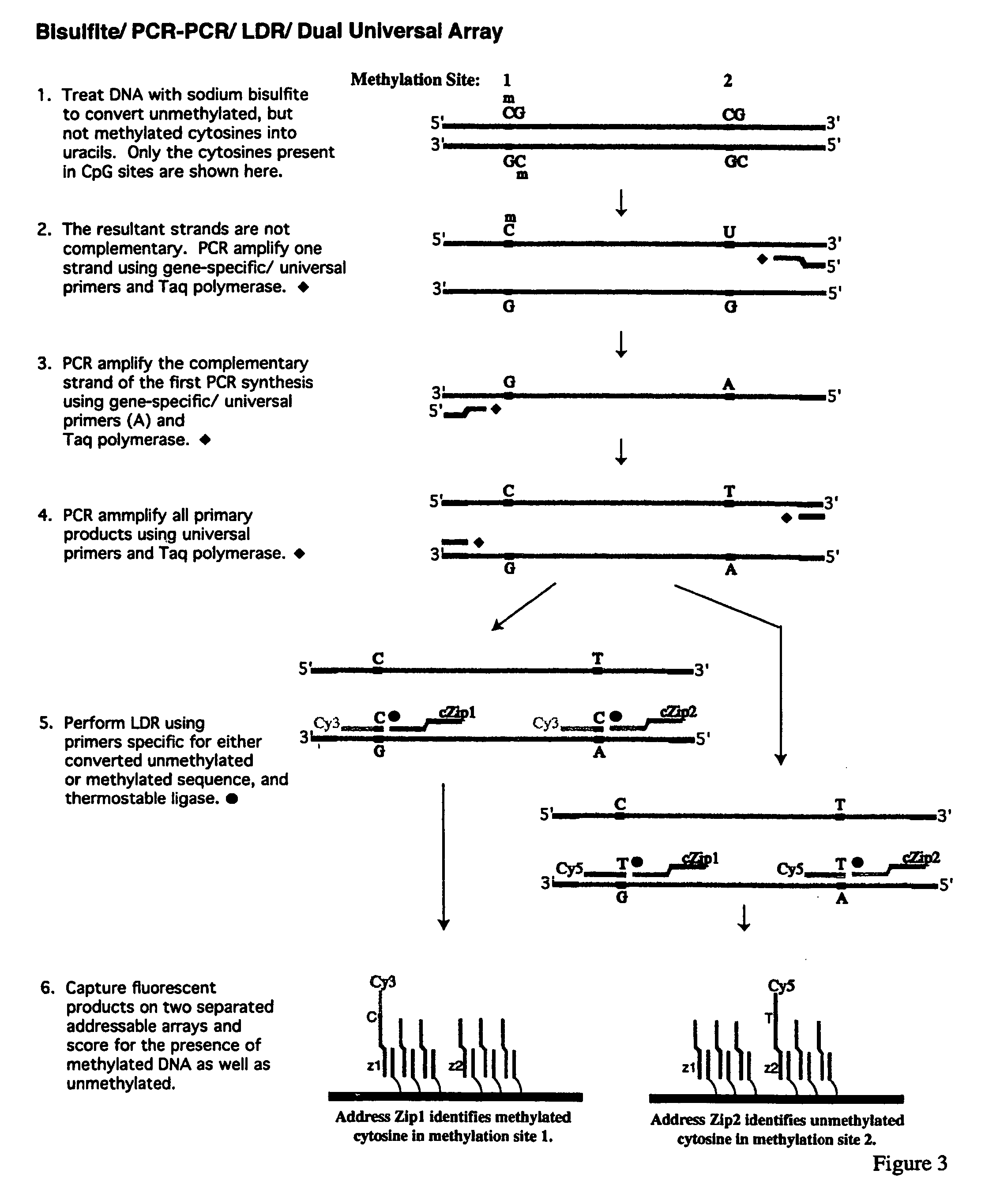
Method for detection of promoter methylation status
InactiveUS7358048B2Precise “ molecular signature ”Accurately methylation statusMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationCapillary electrophoresisElectrophoresis
The present invention relates to the detection of promoter methylation status using a combination of either modification of methylated DNA or restriction endonuclease digestion, multiplex polymerase chain reaction, ligase detection reaction, and a universal array or capillary electrophoresis detection.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
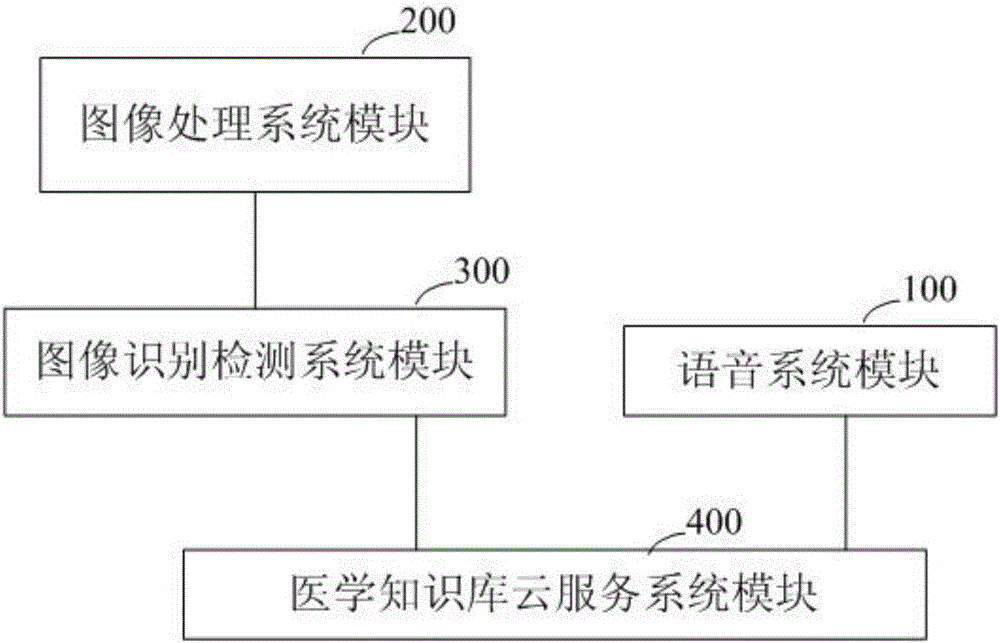
Medical diagnostic robot system
ActiveCN106709254AShorten treatment timeImprove quality of lifeMedical automated diagnosisSpecial data processing applicationsRobotic systemsMedical physics
The present invention discloses a medical diagnosis robot system. The system comprises a voice system module, an image processing system module, an image recognition detection system module and a medical knowledge base cloud service system module. The voice system module is used for collecting language information of a patient that needs to be diagnosed; the image recognition detection system module is connected with the image processing system module; and the medical knowledge base cloud service system module is connected with the voice system module and the image recognition detection system module respectively, and is used for storing the preset medical knowledge base, selecting corresponding diagnostic data in the medical knowledge base, and sending the data to the user. According to the medical diagnosis robot system disclosed by the present invention, diagnosis can be accurately performed on the disease and etiology of the patient, an ideal diagnosis and treatment plan can be provided for the patient, valuable treatment time of the patient can be saved, the patient can be ensured to be treated in time, the urgent need of the patient for medical diagnosis can be satisfied, and quality of life for people can be improved.
Owner:天津中科智能识别有限公司
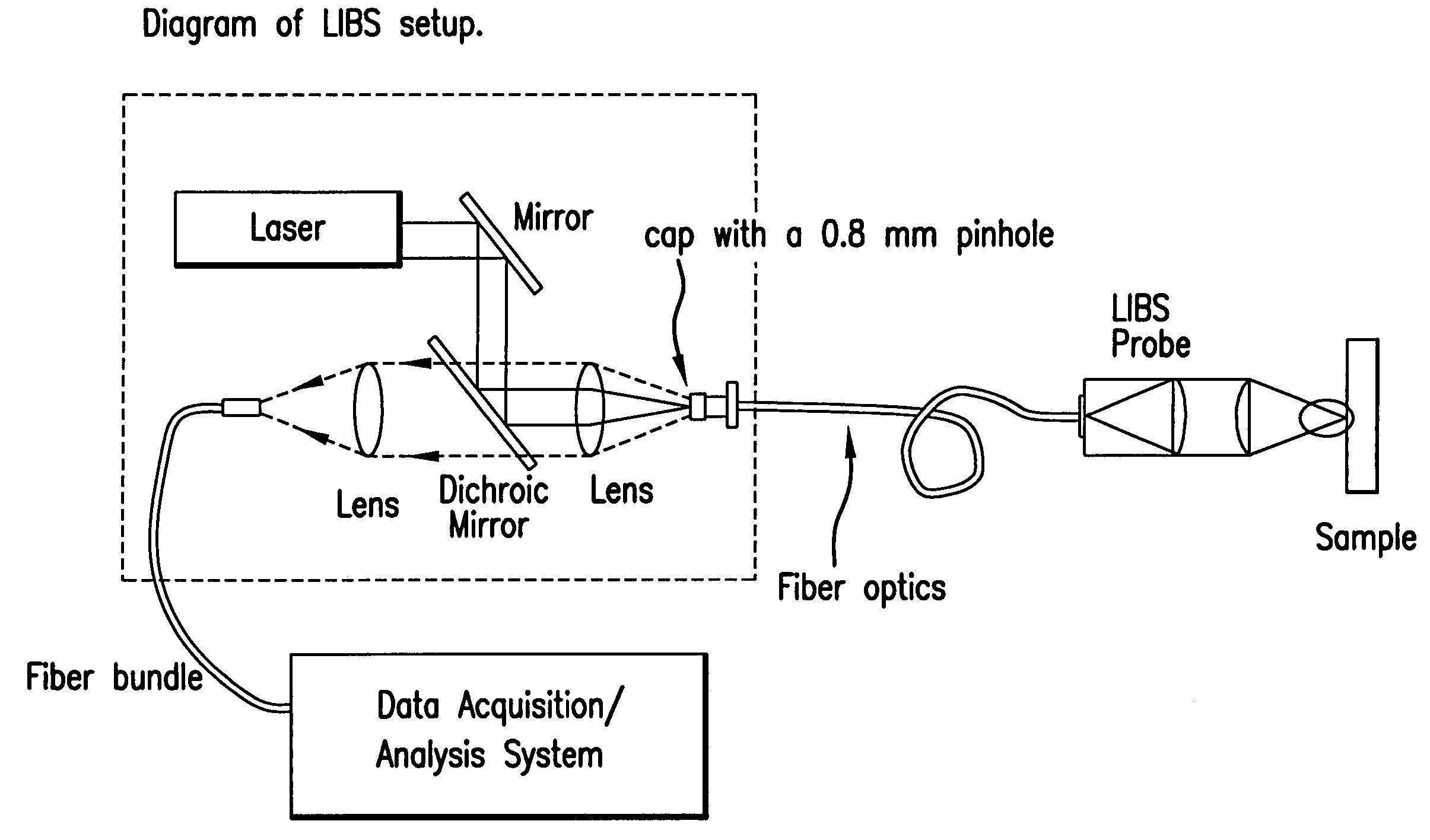
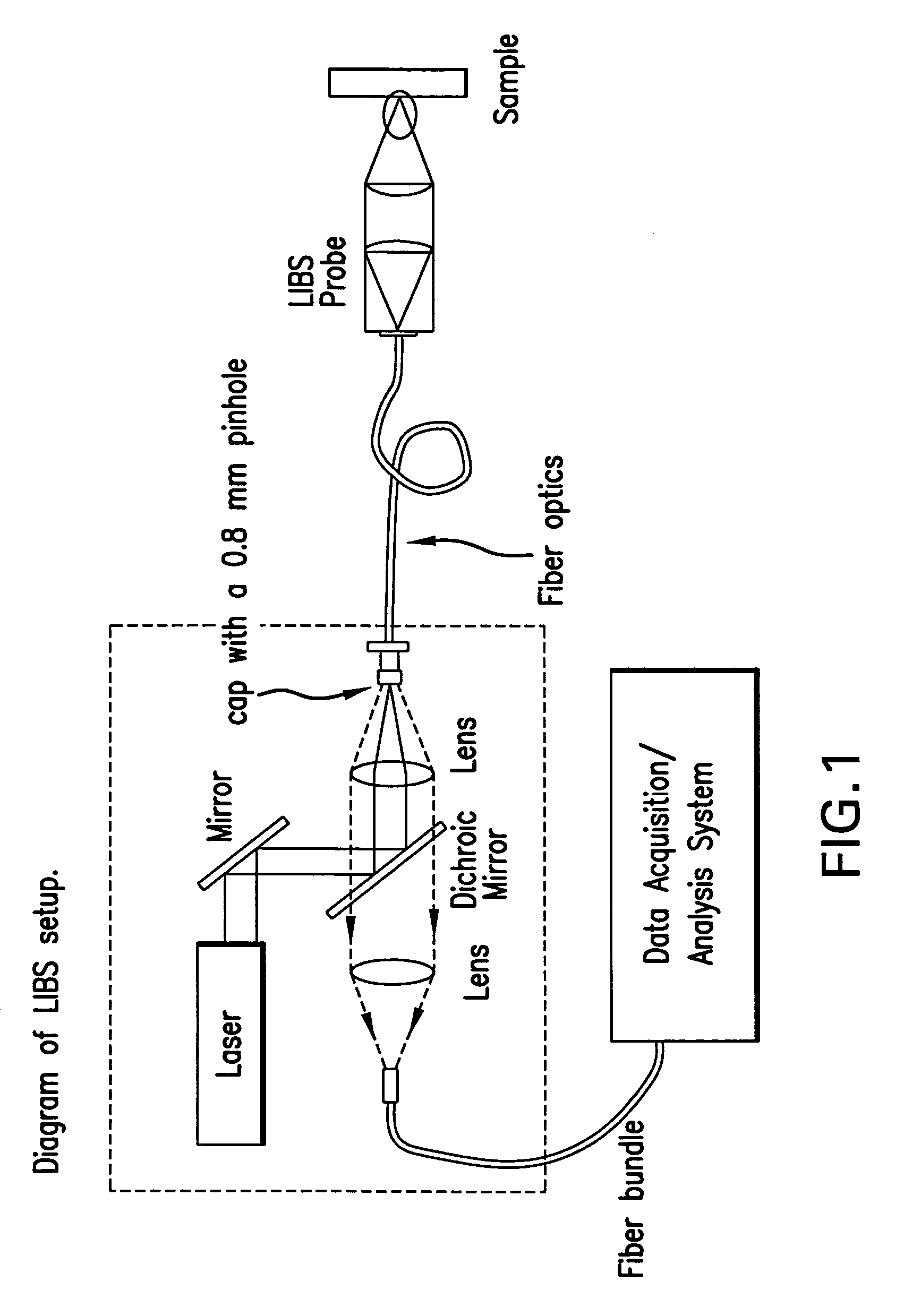
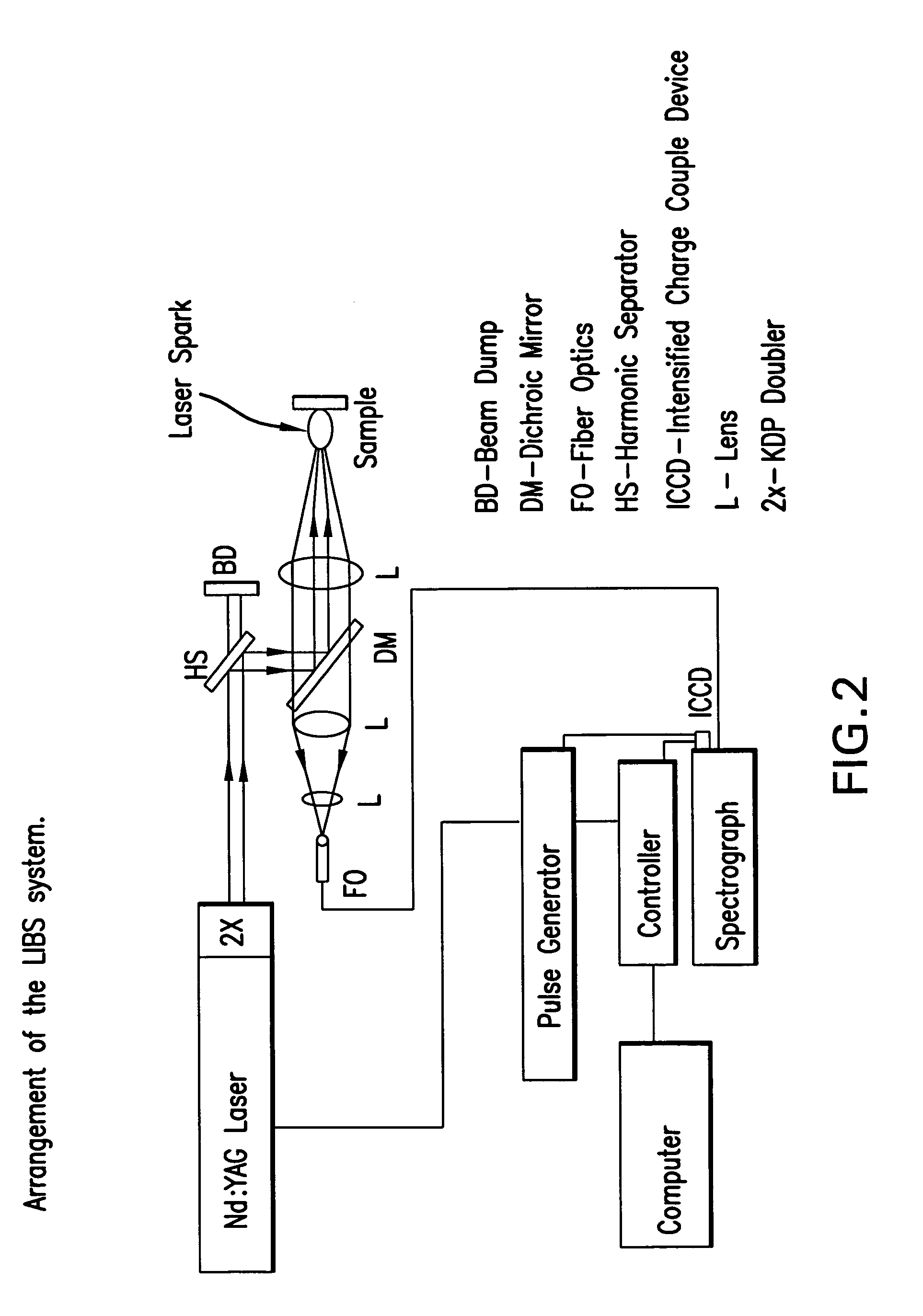
Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for specimen analysis
InactiveUS7092087B2Minimally traumaticRapid accurate diagnosisEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryCancer cellTrace element
Owner:MISSISSIPPI STATE UNIVERSITY
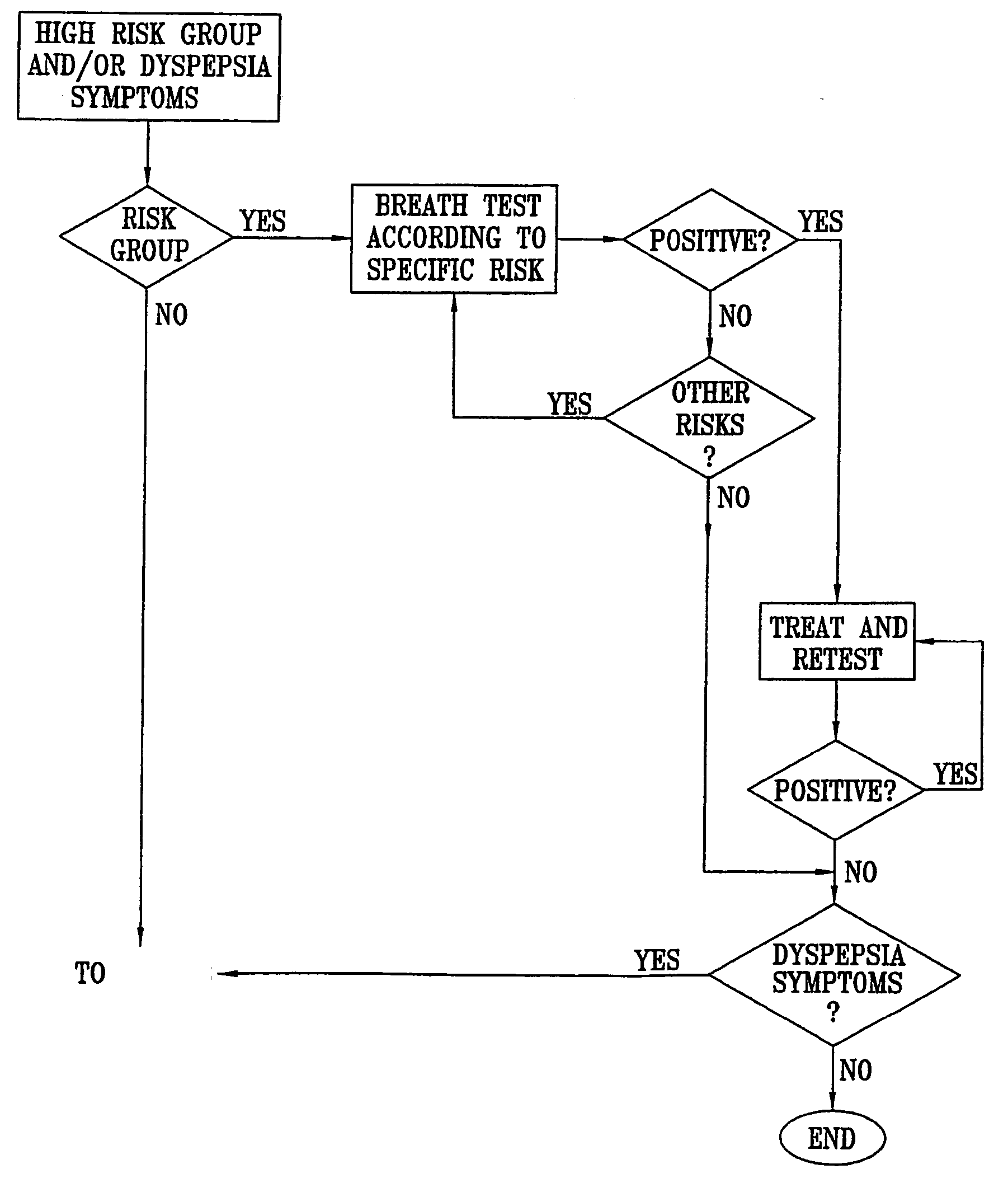
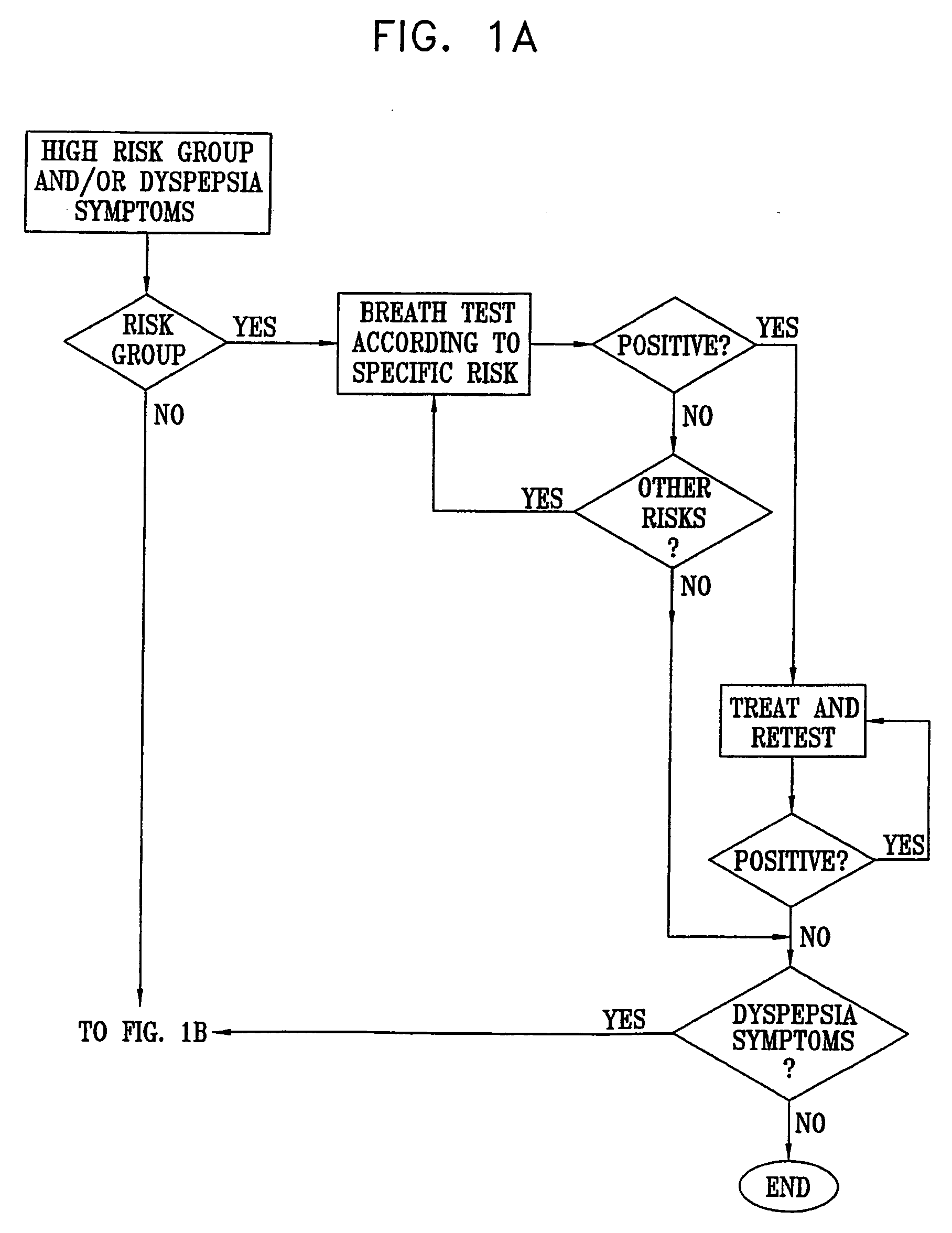
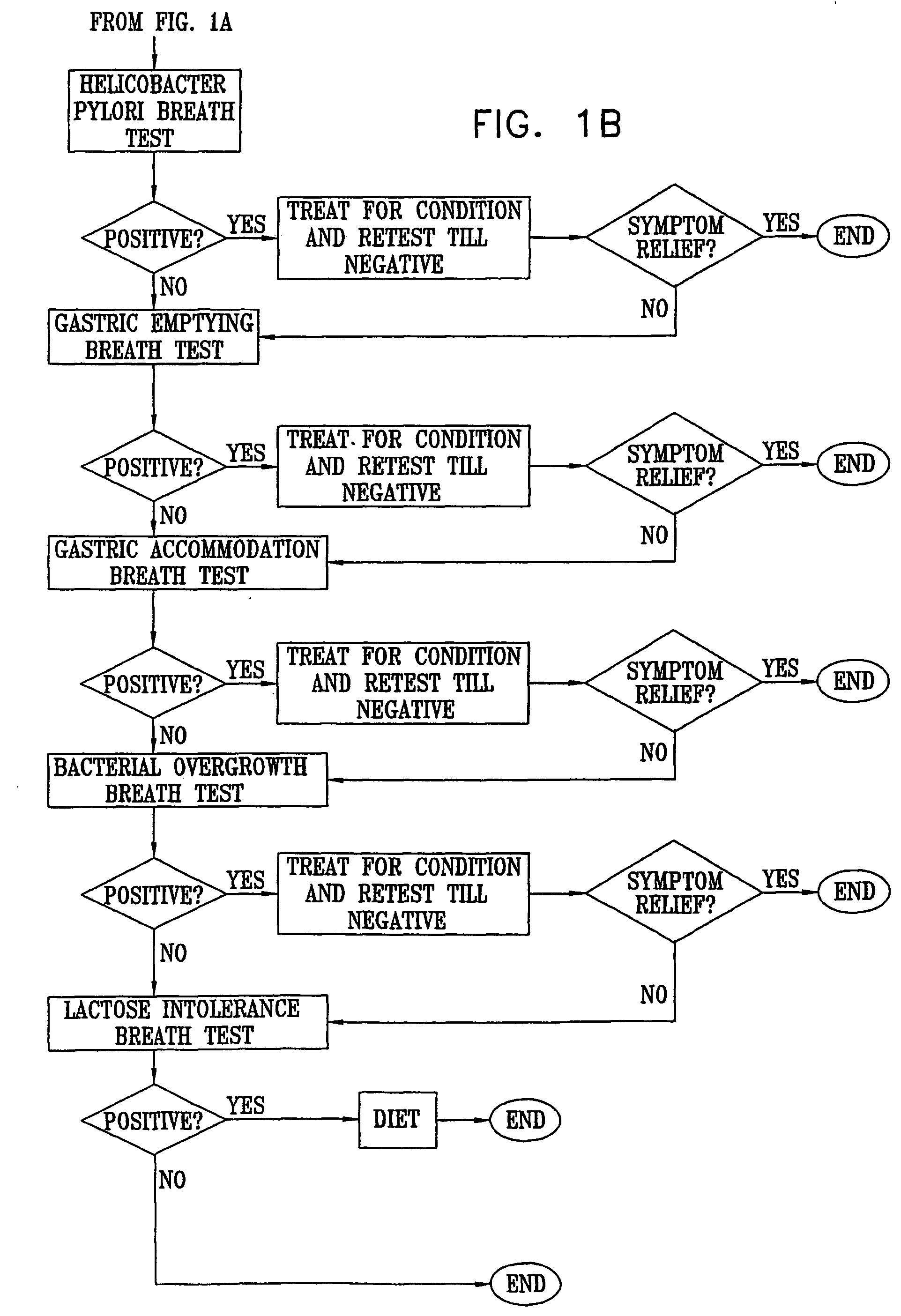
Management of gastro-intestinal disorders
InactiveUS20060074335A1Easily toleratedQuick testCompounds screening/testingPerson identificationDiseaseGastrointestinal dysfunction
The present invention relates to the field of methods and apparatus for the determination of various conditions of gastric and gastro-intestinal malfunction, especially those performed by means of breath tests.
Owner:EXALENZ BIOSCIENCE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com