Patents
Literature
147results about How to "Avoid mechanical stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
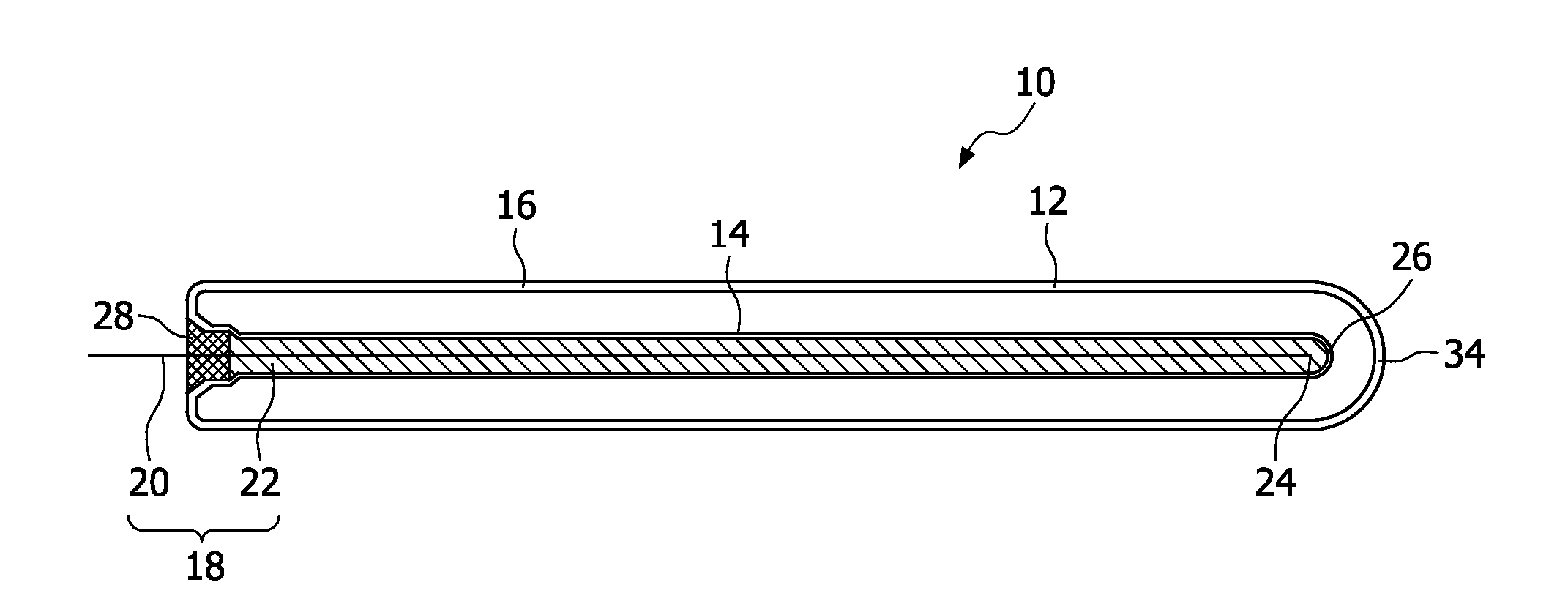
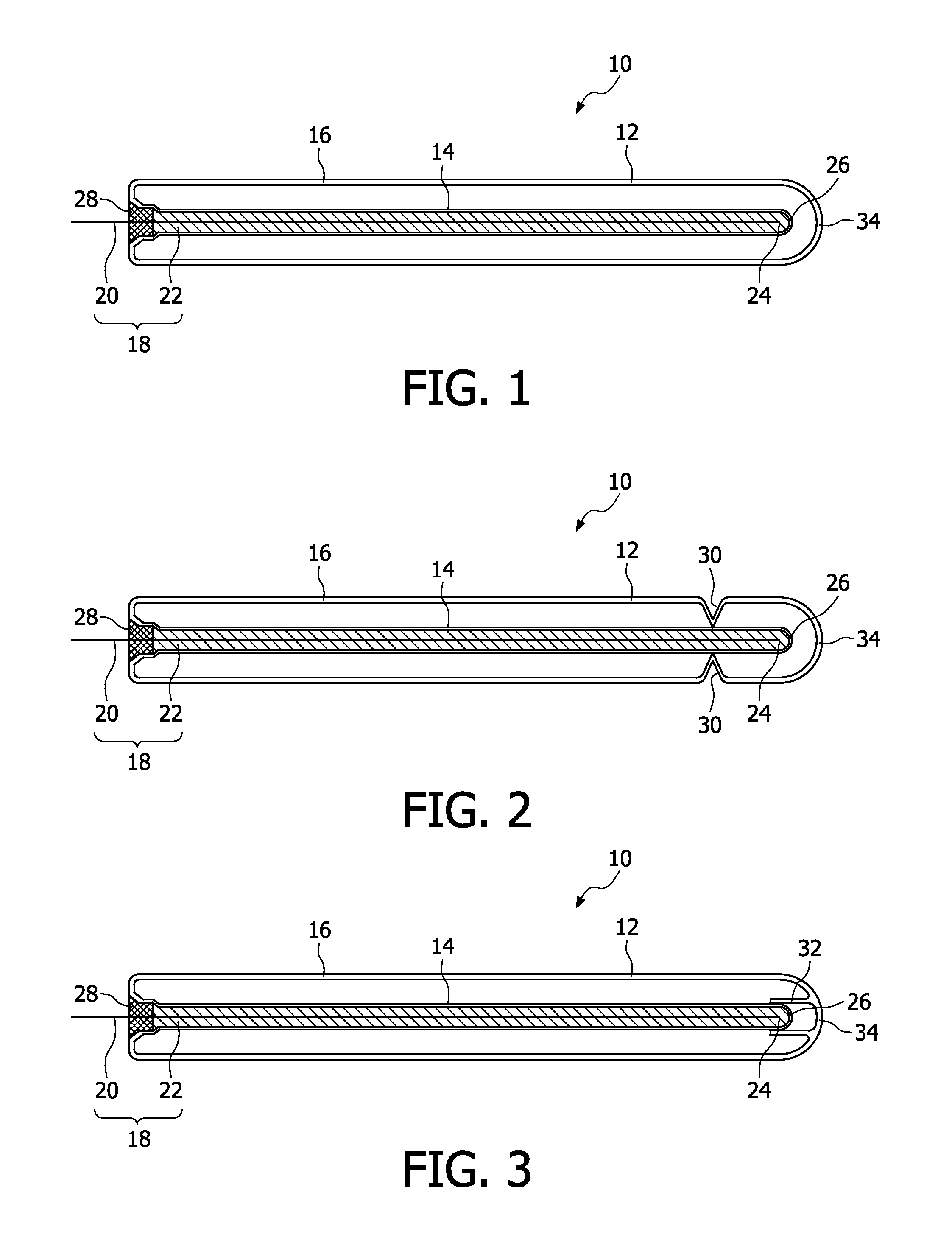
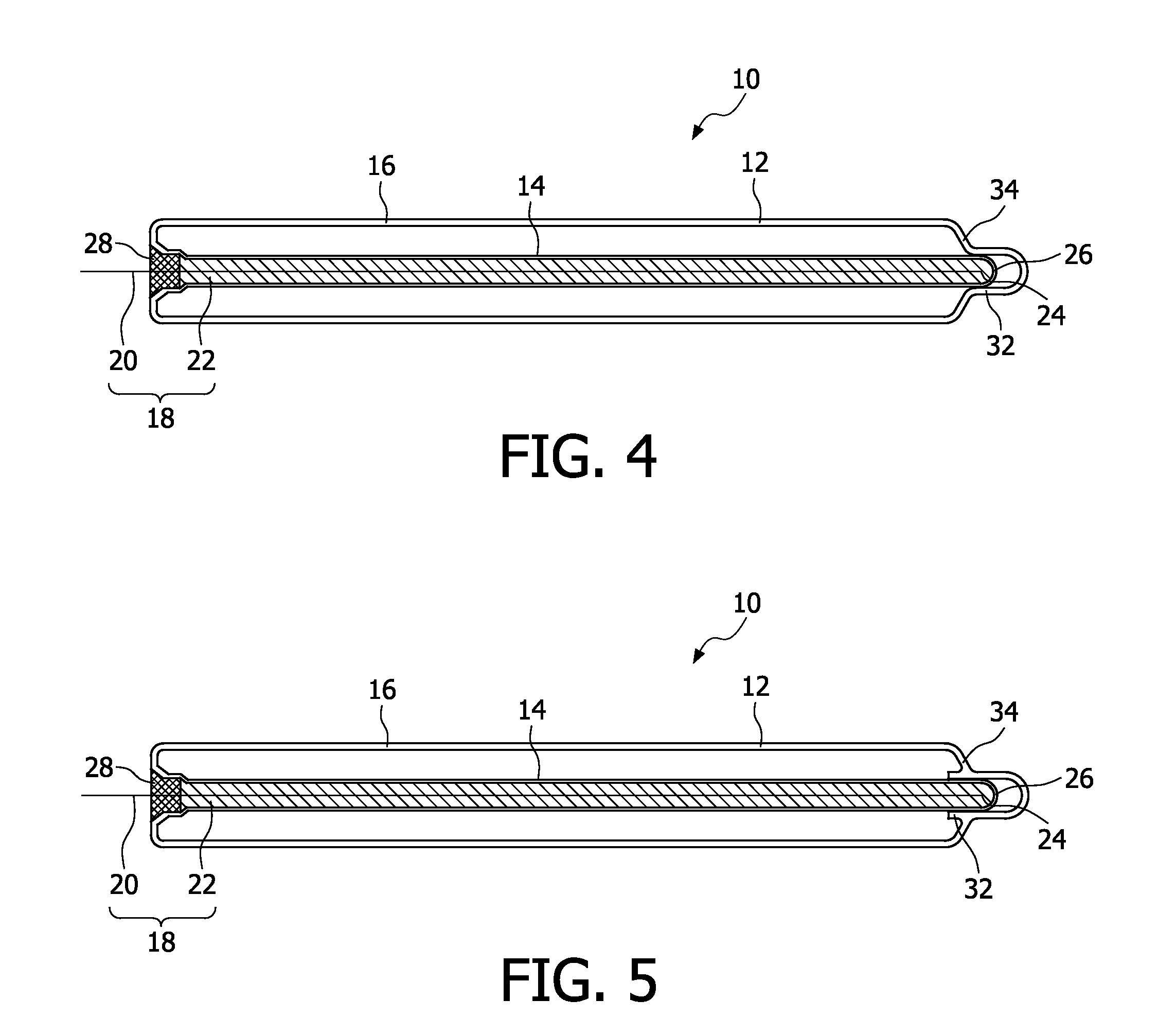
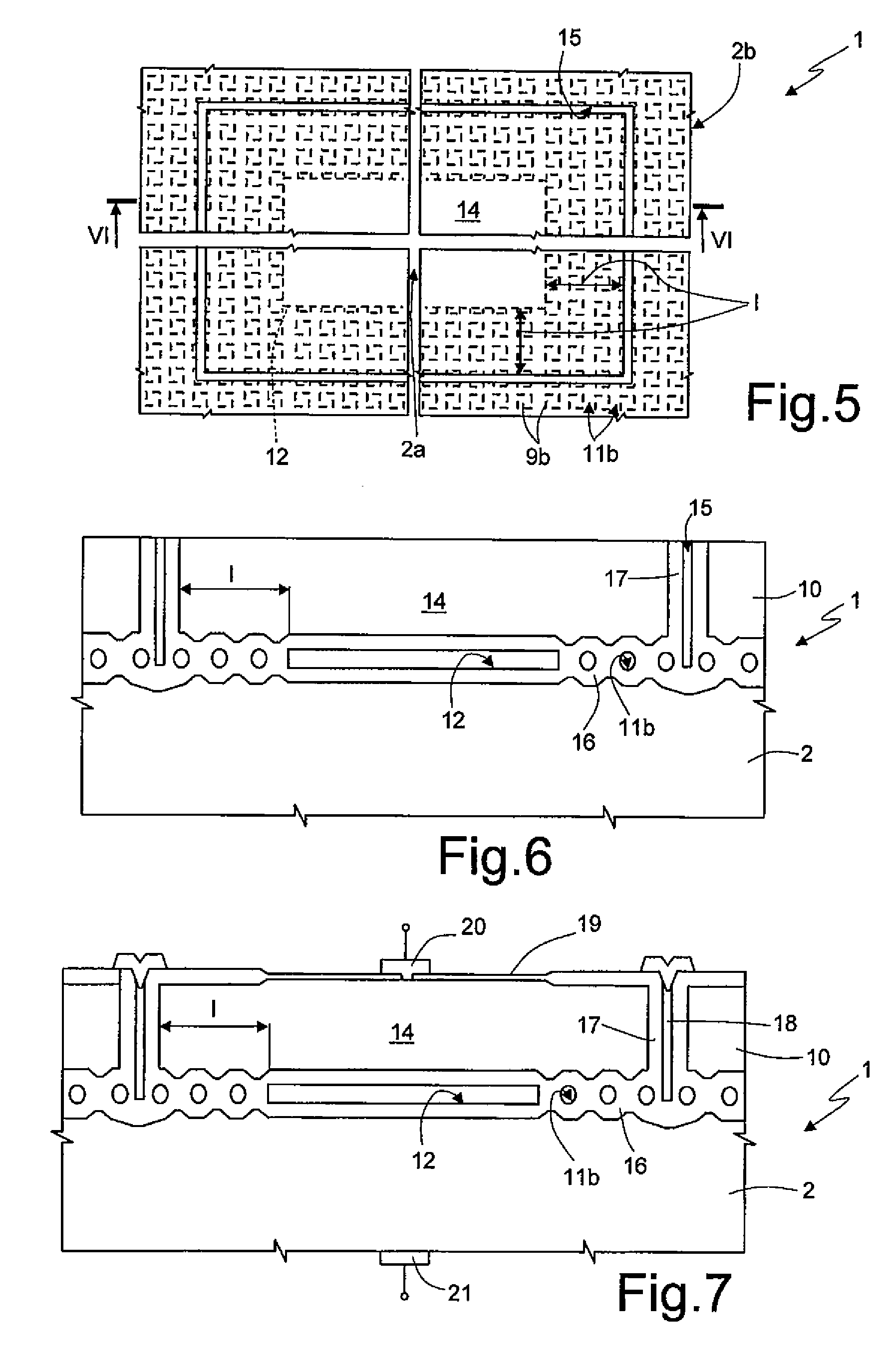
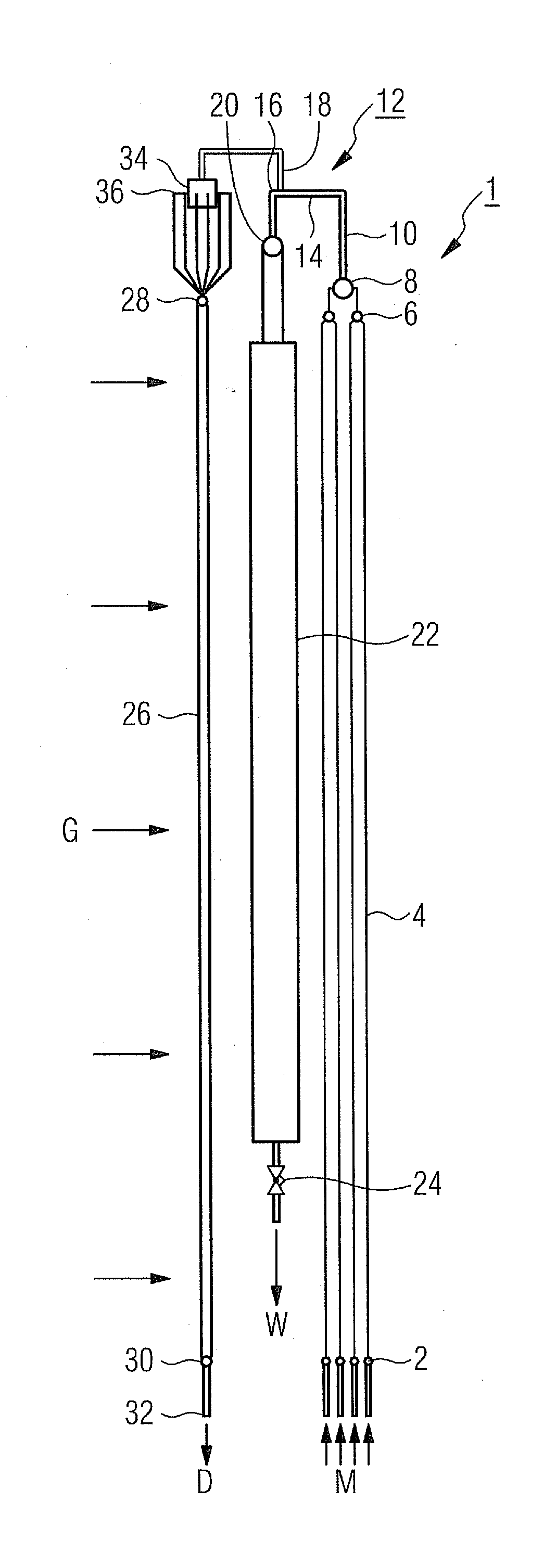
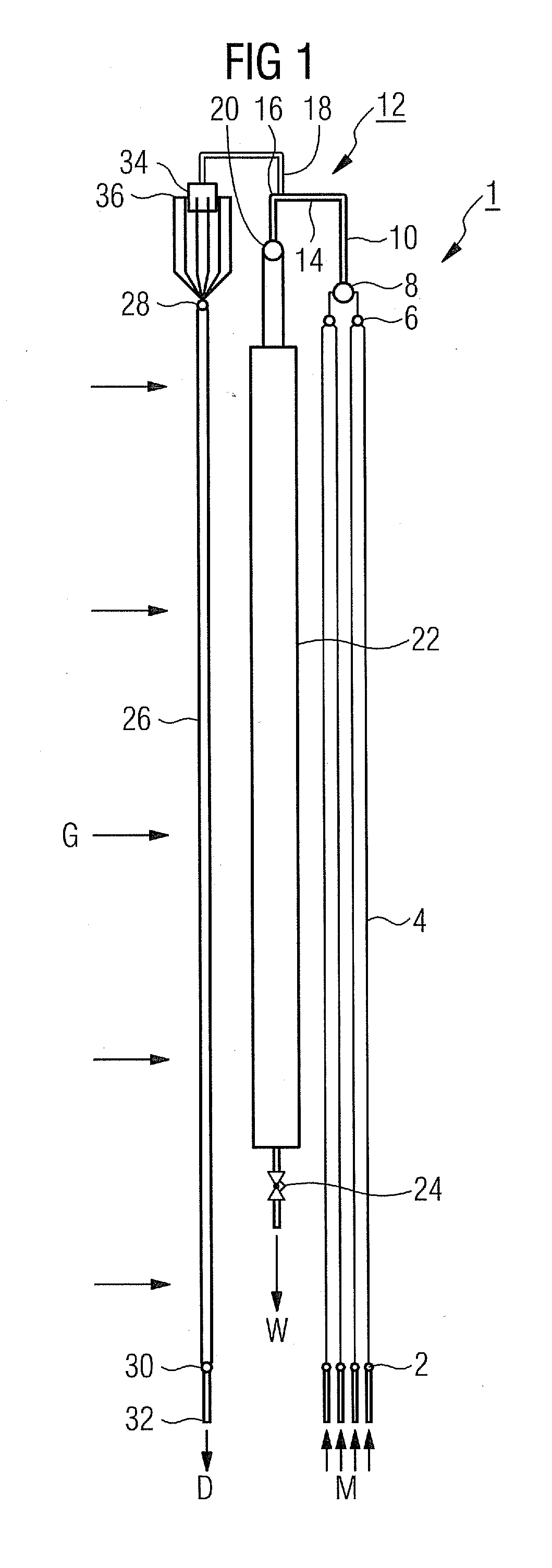
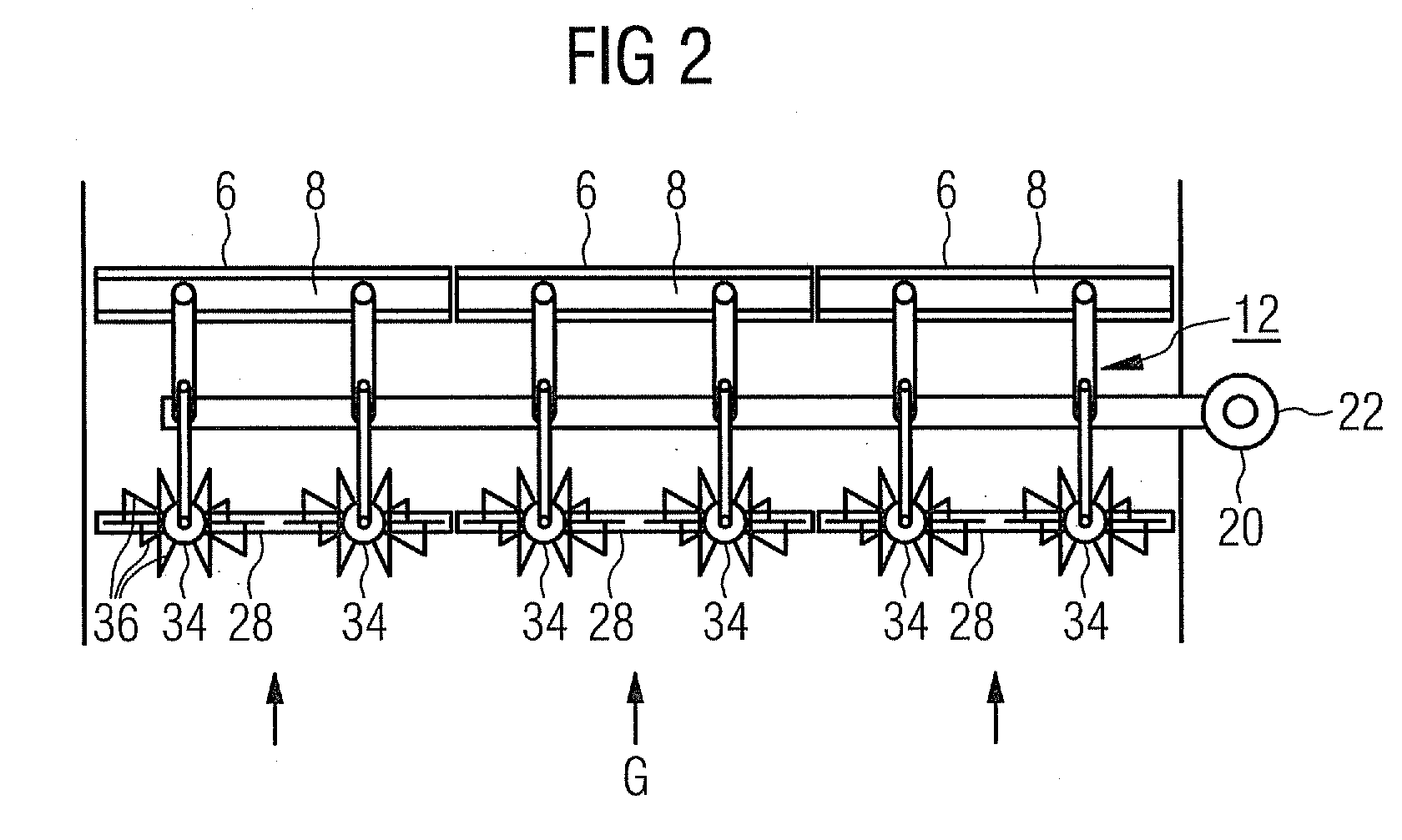
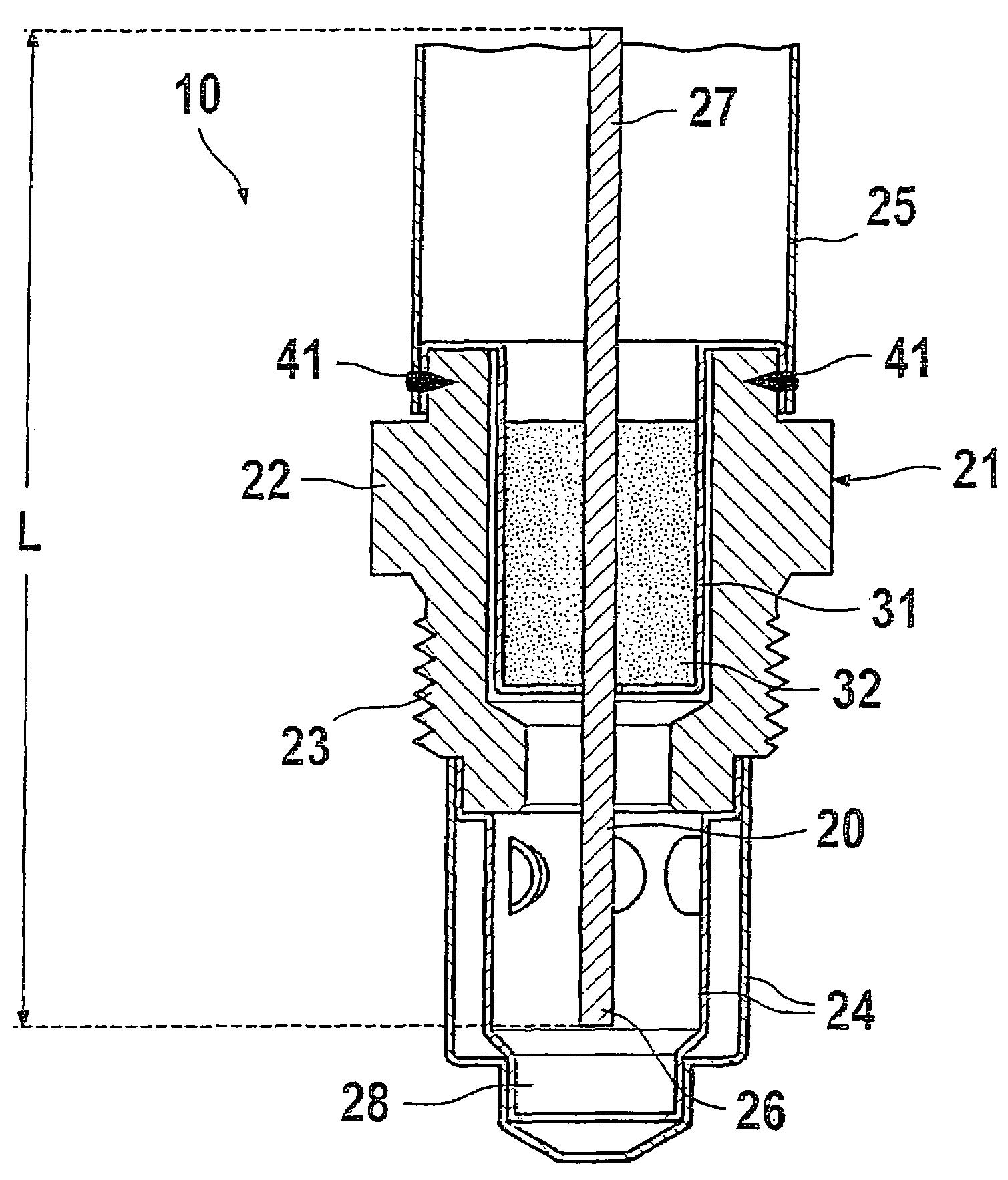
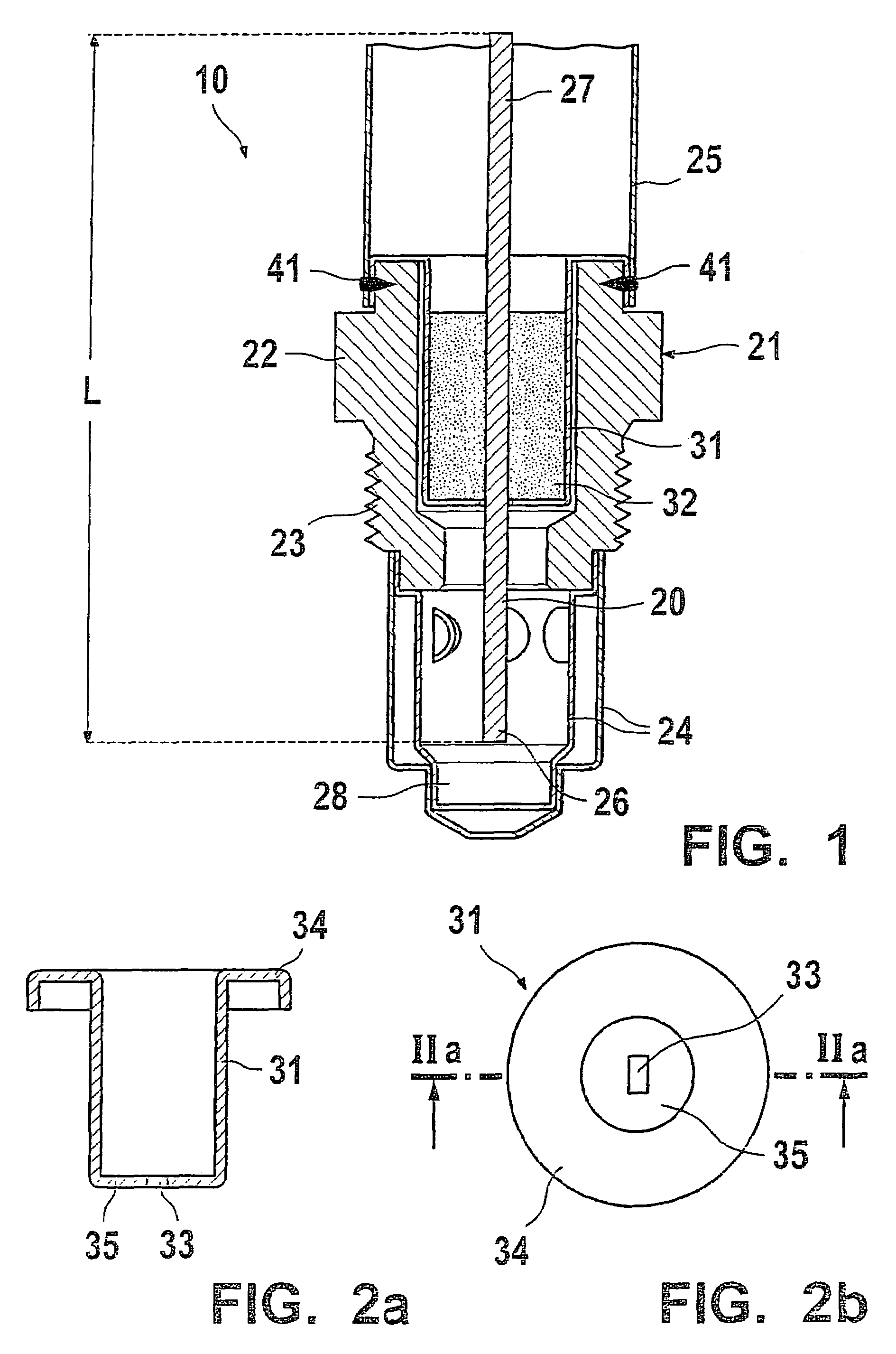
Dielectric barrier discharge lamp
InactiveUS20100244688A1Easy to replaceExtended service lifeSolid cathode detailsGas discharge lamp detailsDielectric barrier dischargeEngineering
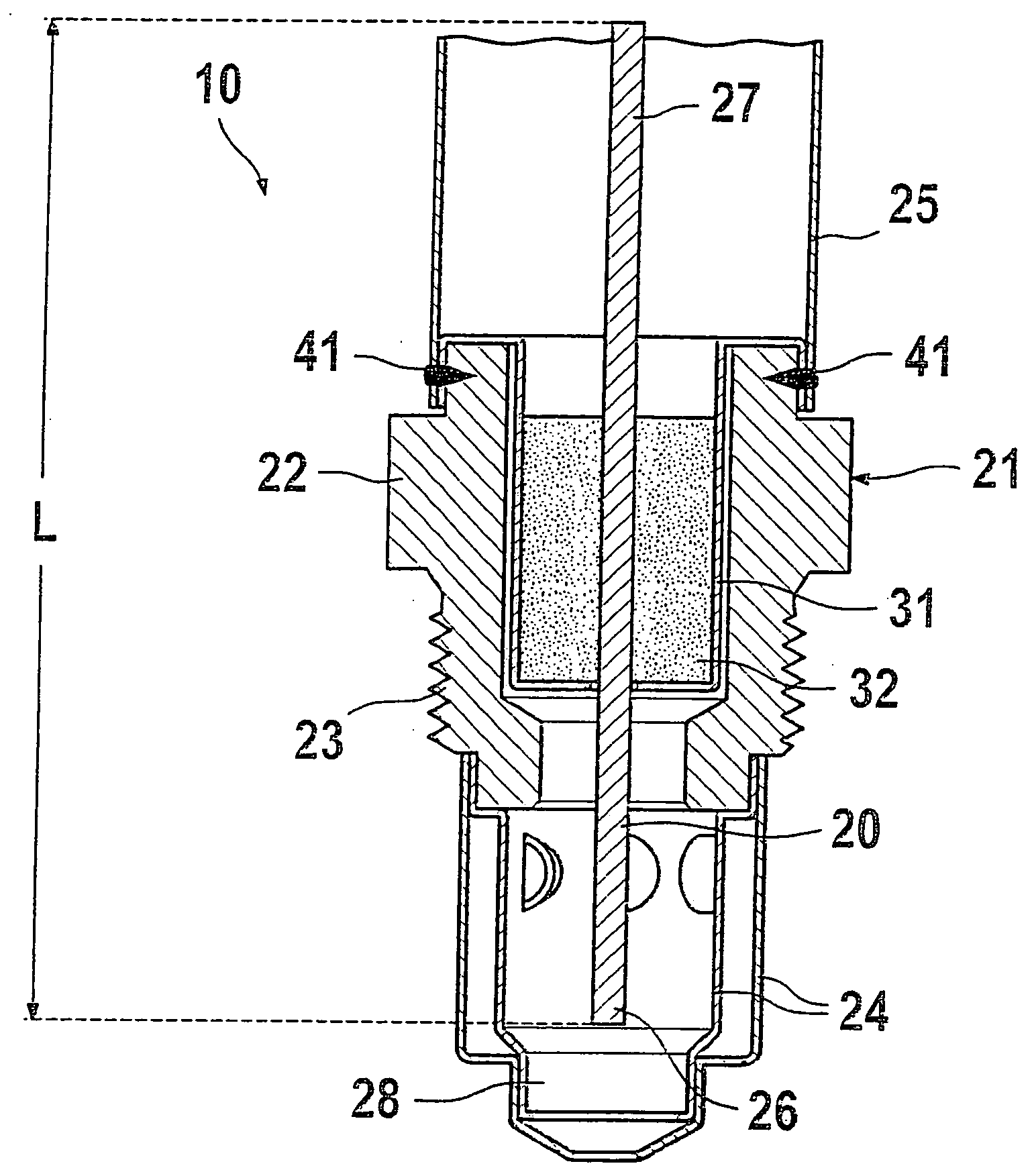
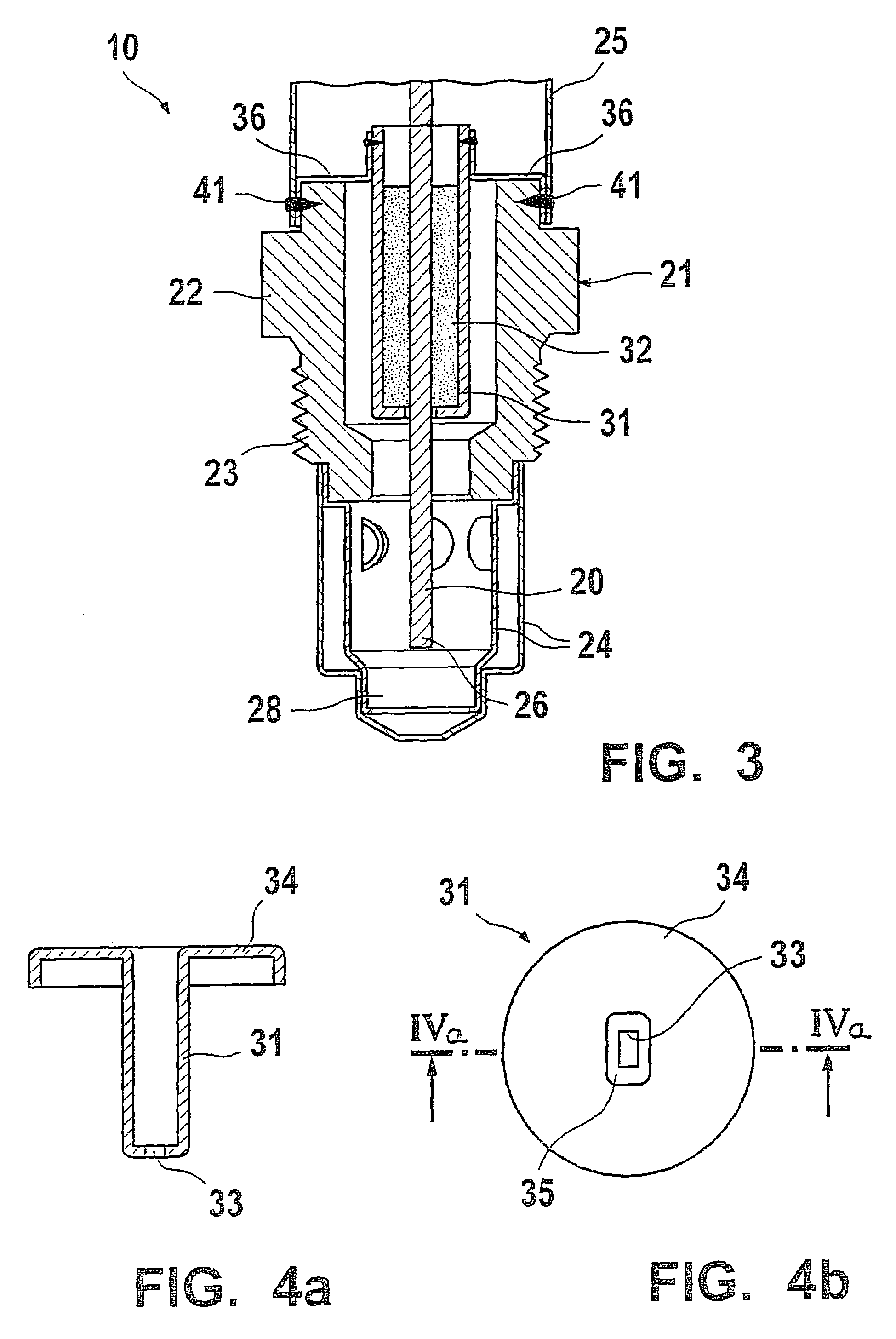
It is provided a dielectric barrier discharge lamp (10) for providing ultraviolet light, comprising an outer tube (12) filled with a discharge gas for providing ultraviolet light, an inner tube (14) arranged at least partially inside the outer tube (12), an outer electrode (16) electrically connected to the outer tube (12) and an inner electrode (18) electrically connected to the inner tube (14), wherein the inner electrode (18) comprises a conductor (20) and a plurality of an conductive granulated material (22) for providing an electrical contact between the conductor (20) and the inner tube (14). Due to the conductive granulated material (22) an electrical contact between the conductor (20) and the inner tube (14) is safeguarded and different thermal expansions of the inner electrode (18) and the inner tube (14) are compensated at the same time without applying mechanical stress to the inner tube (14). This leads to a dielectric barrier discharge lamp (10), which comprises an increased life time without the need for external cooling.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
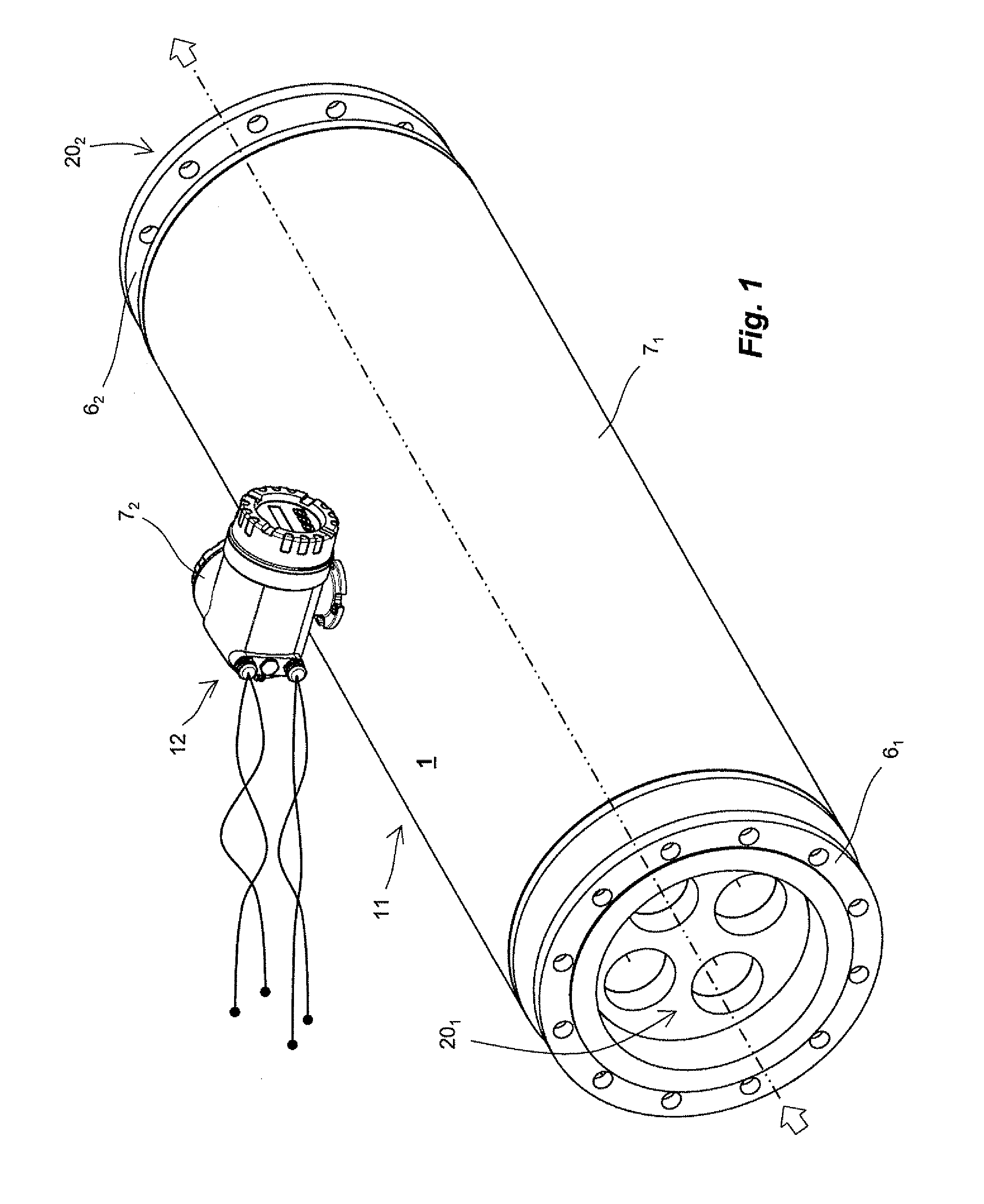
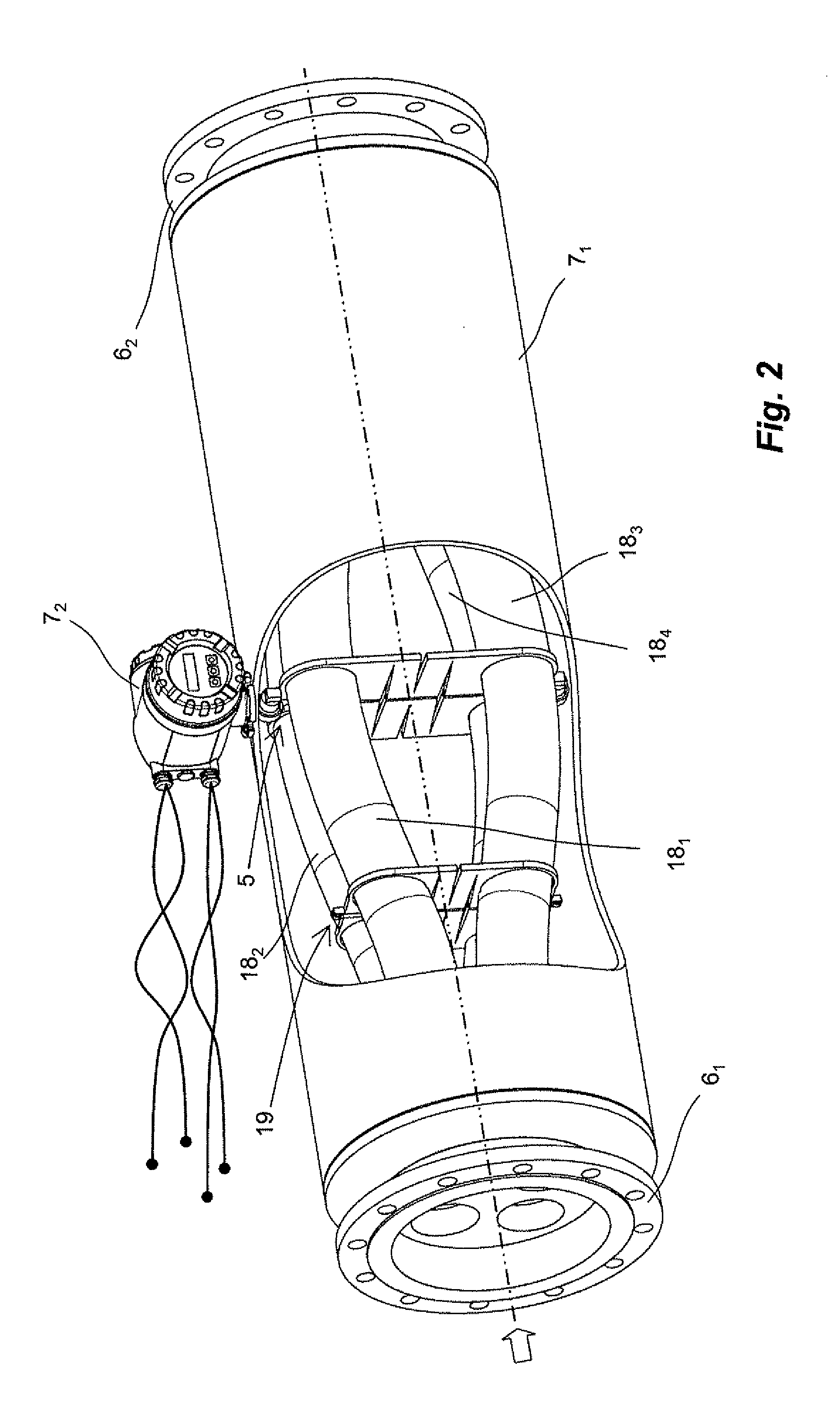
Measuring transducer of vibration-type
ActiveUS20110167907A1Impairs accuracy of measurementMeasurement accuracySpecific gravity using flow propertiesVolume variation compensation/correction apparatusSection planeTransducer
The measuring transducer comprises: a transducer housing, of which an inlet-side, housing end is formed by means of a flow divider including four flow openings spaced, and an outlet-side, formed by means of a flow divider including four flow openings spaced, from one another. A tube arrangement including four curved measuring tubes connected to the flow dividers for guiding flowing medium along flow paths connected in parallel. Each measuring tubes opens with an inlet-side, measuring tube end into one of the flow openings of the flow divider and with an outlet-side, measuring tube end into one the flow openings of the flow divider. The two flow dividers are embodied and arranged in the measuring transducer, so that the tube arrangement extends both between a first and a second of the measuring tubes and between a third and a fourth of the measuring tubes. An imaginary longitudinal-section plane, with respect to which the tube arrangement is mirror symmetric and perpendicular to the imaginary longitudinal-section plane, an imaginary longitudinal-section plane, with respect to which the tube arrangement likewise is mirror symmetric. An electromechanical exciter mechanism of the measuring transducer serves for producing and / or maintaining mechanical oscillations of the four measuring tubes.
Owner:ENDRESS HAUSER FLOWTEC AG
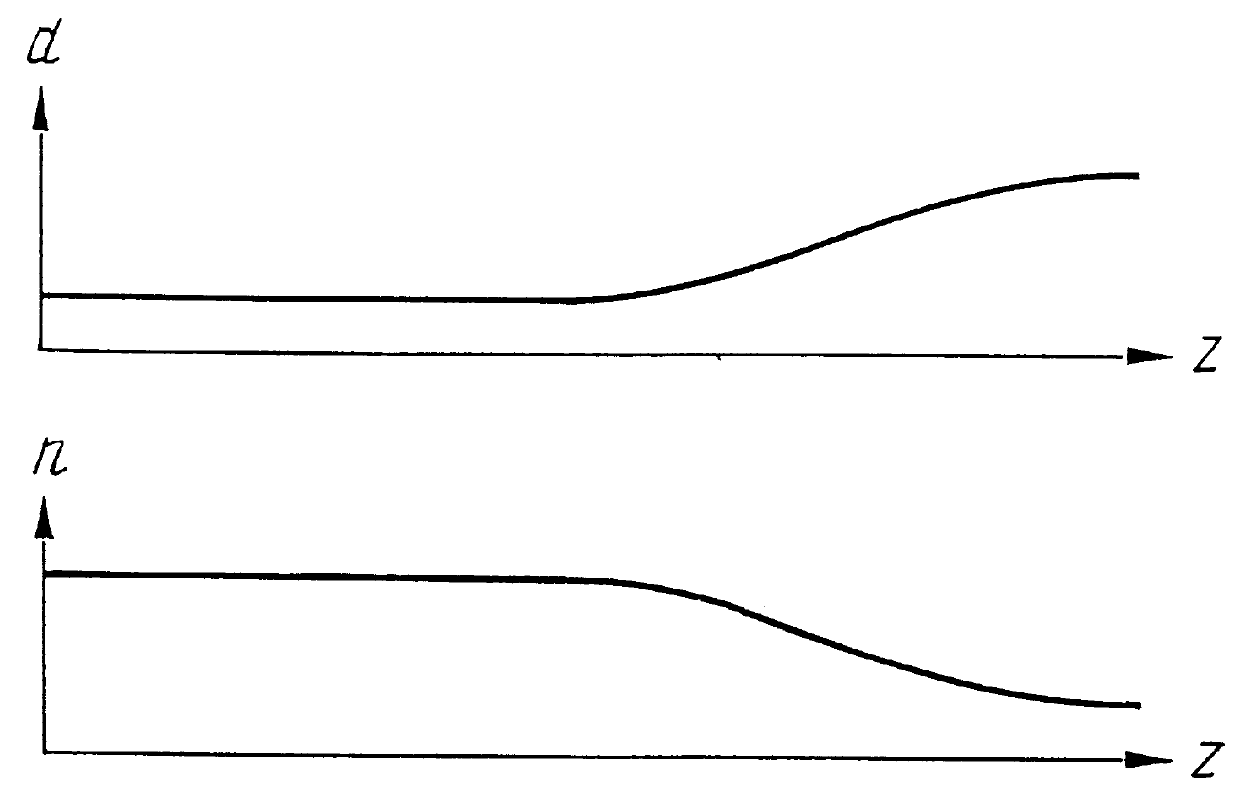
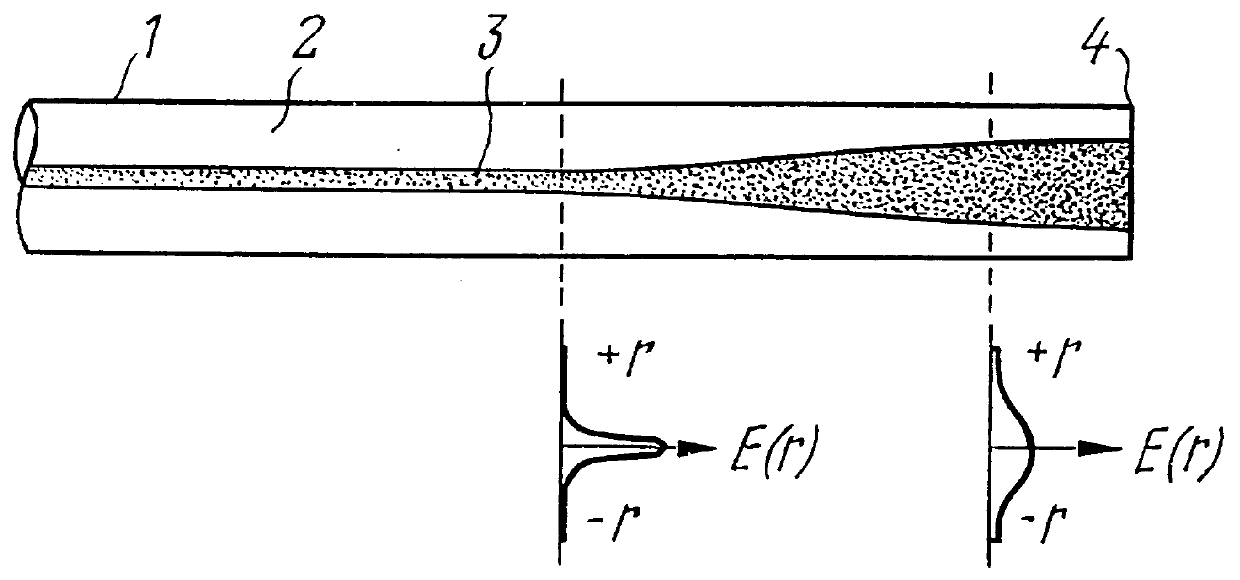
Mode field diameter conversion fiber, method for locally changing a refractive index of optical waveguides and method for fabricating optical waveguide preforms
InactiveUS6125225AAvoid mechanical stressGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingGratingRefractive index
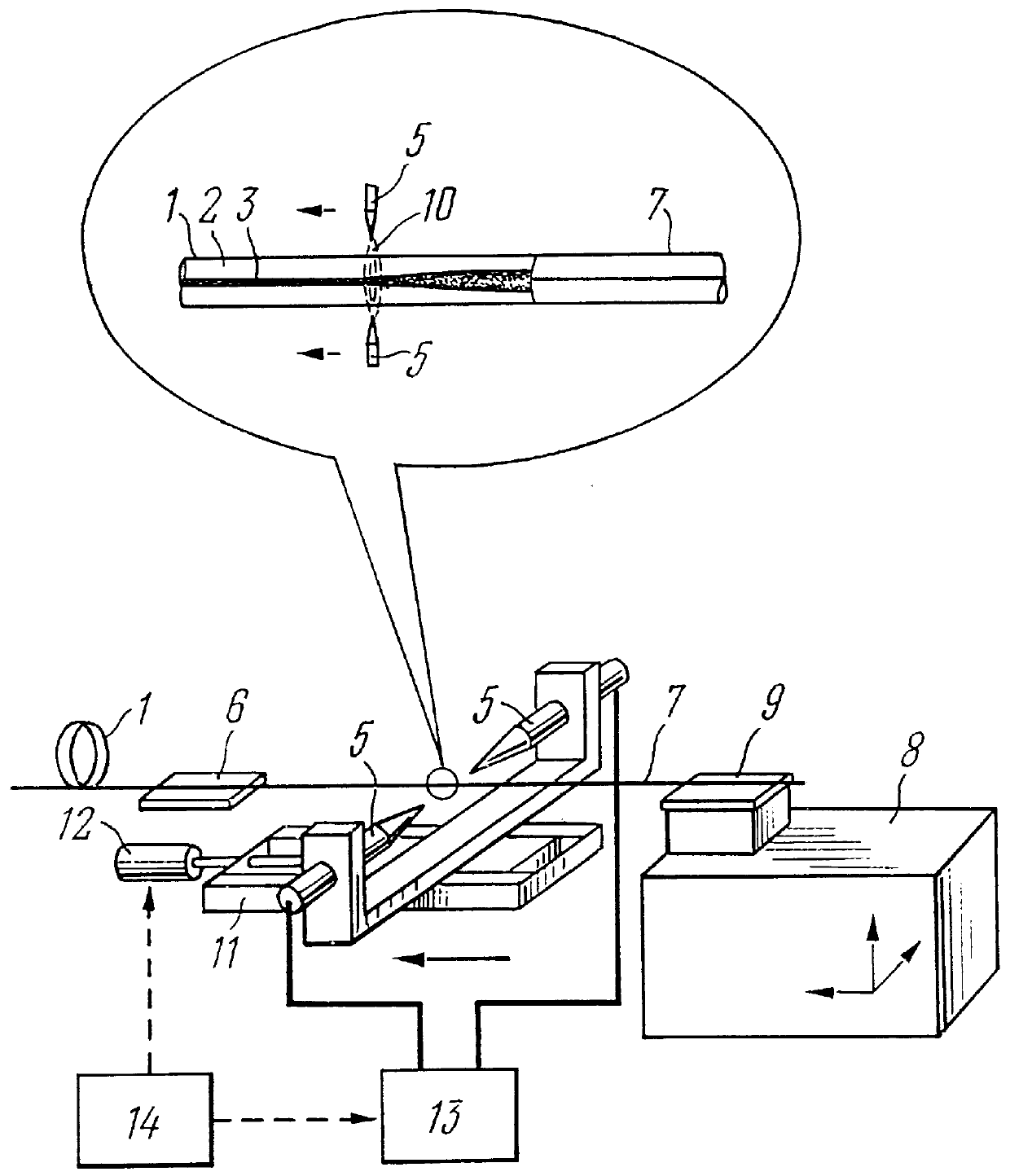
PCT No. PCT / RU97 / 00278 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 9, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 9, 1998 PCT Filed Sep. 3, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 28643 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 2, 1998The invention relates to fiber optics and can be employed in fiber radiation collimators, optical waveguide couplers, spectral filters, optical isolators, long-period gratings, dispersion compensators, cascade mode field diameter conversion fibers on simulated Raman effect, physical value sensors, radiation suppression units for predetermined wavelengths, and for smoothing the gain spectrum in erbium fiber amplifiers. The invention facilitates fabrication of optical waveguides and apparatuses based on them. To produce preforms for optical waveguides (1) by a plasma chemical vapor deposition method, molecular gaseous agents, fed to a substrate tube (24), are mixed so that less than five atoms of oxygen fall on every atom of silicon and more than one atom of nitrogen falls on every 1000 atoms of oxygen. The refractive index is locally changed by heating a length of an optical waveguide (1). This causes a local thermal diffusion of elements contained in a core (3) into a cladding (2), or vice versa. The length of the optical waveguide (1) is heated by current of an electric arc (10) or by radiation (16) of an infrared laser (15). The core (3) is doped with nitrogen at concentration from 0.01 at. % to 5 at. %. In the mode field diameter conversion fiber, a diameter of the core (3) changes along the length of the optical waveguide (1), increasing towards its end (4).
Owner:VOLOKONNO OPTICHESKAYA TEKHNIKA KAPITAL +2
Manufacturing method of heat-assisted magnetic head constituted of slider and light source unit
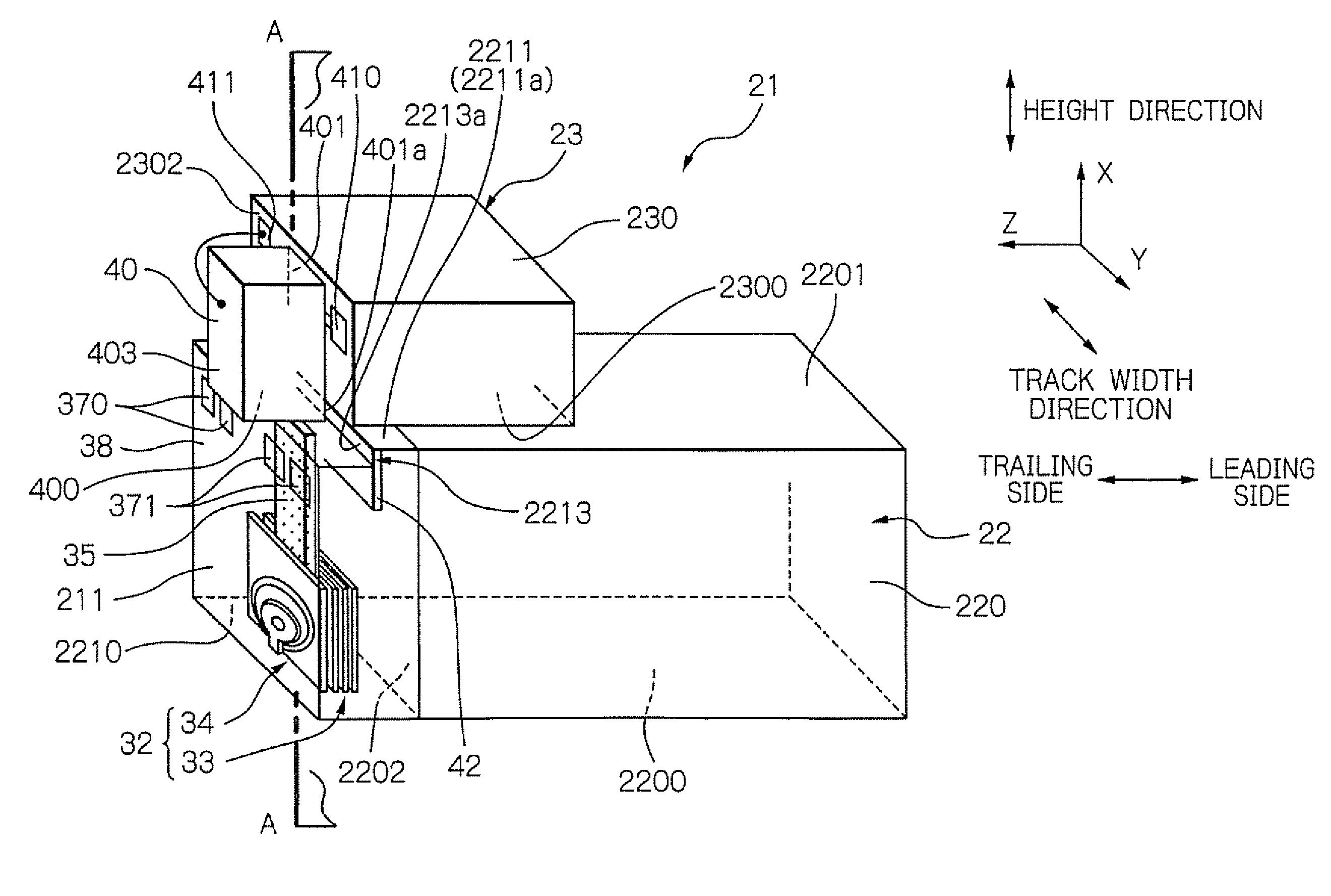
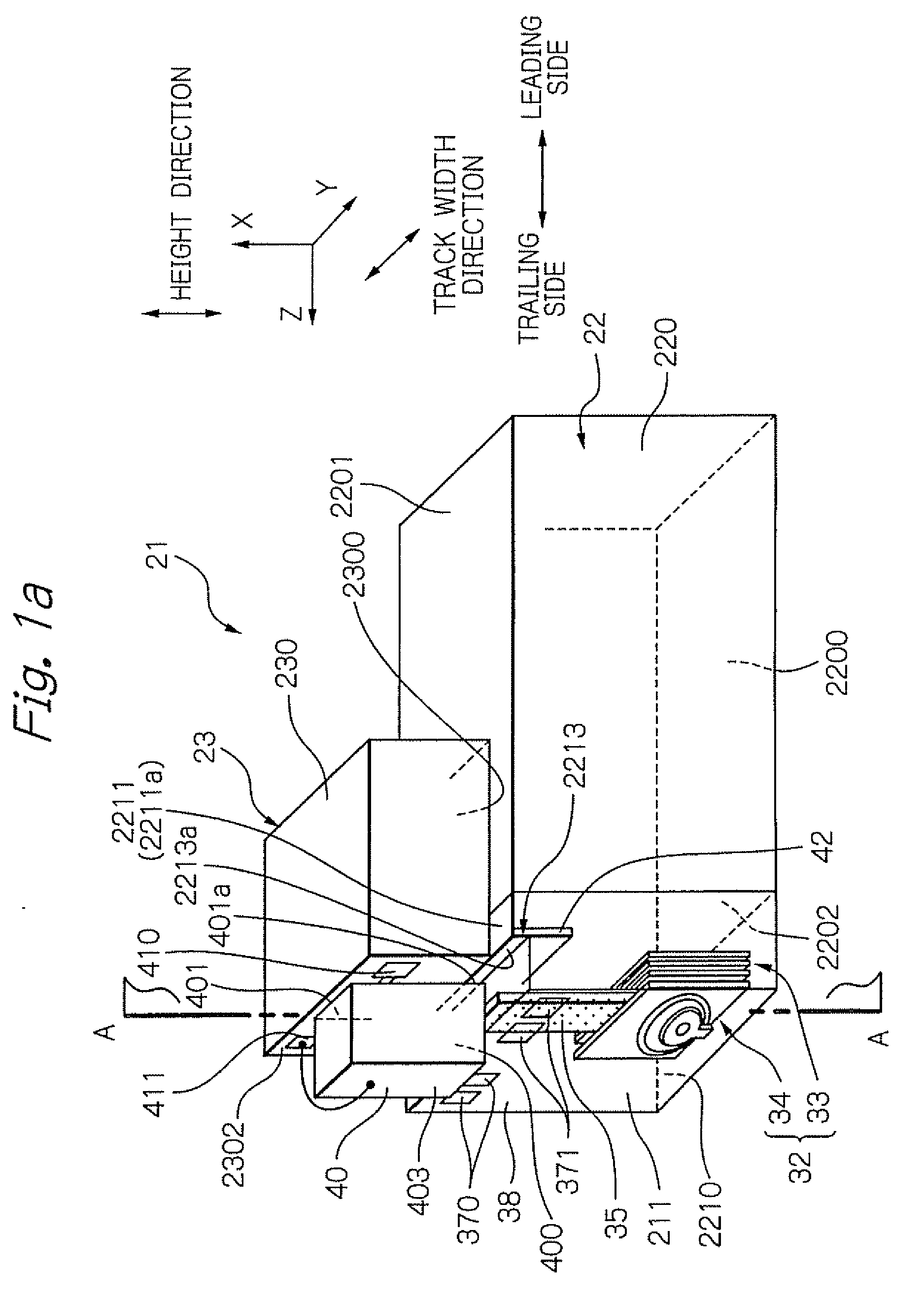
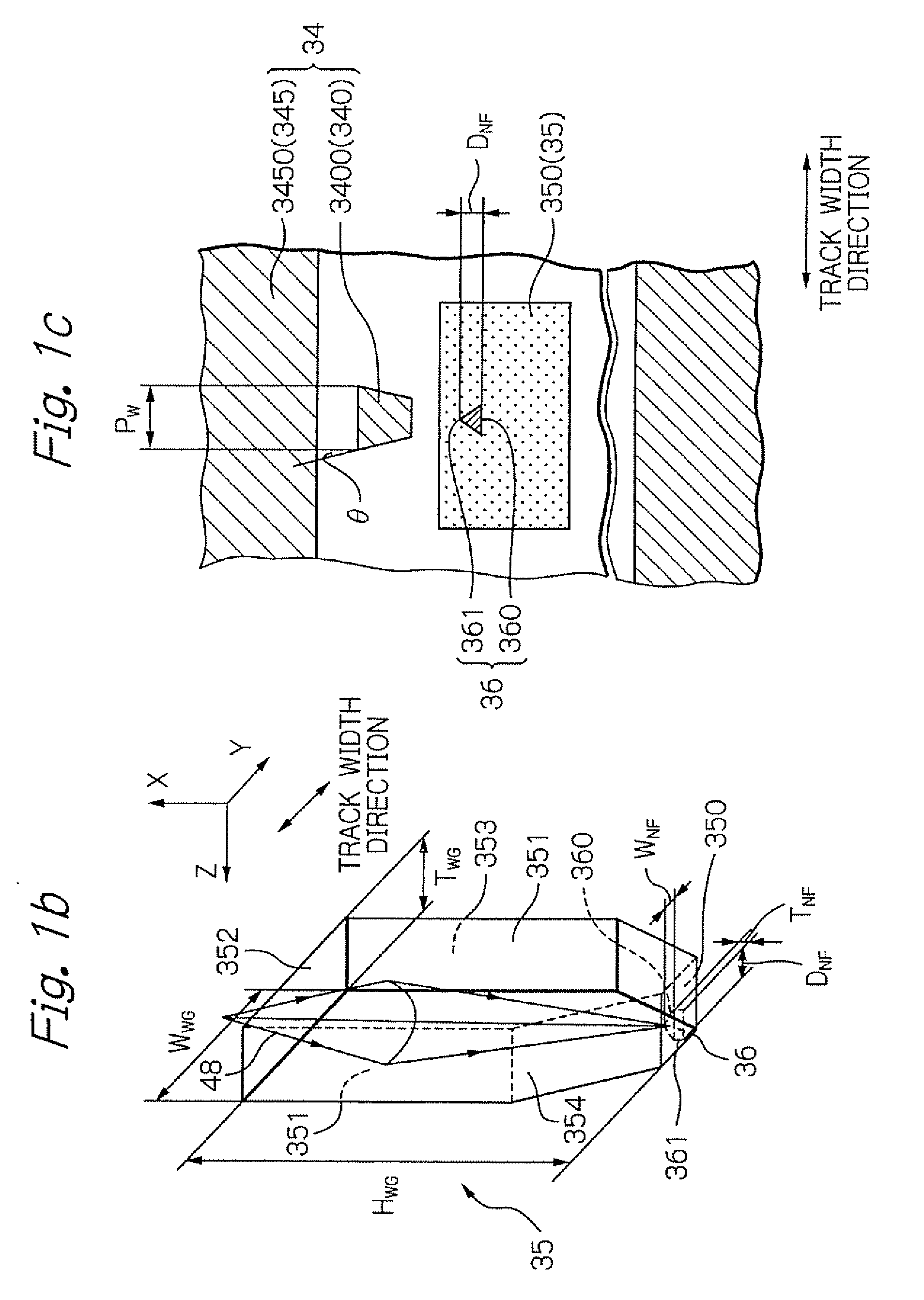
ActiveUS20090266789A1Easy to joinAvoiding excessive mechanical stressDecorative surface effectsRecord information storageLight sourceEngineering
Provided is a manufacturing method of heat-assisted magnetic recording head, in which a light source unit can be easily joined to a slider with sufficiently high accuracy, under avoiding the excessive mechanical stress. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of: moving relatively the light source unit and the slider, while applying a sufficient voltage between an upper electrode of the light source and an electrode layer provided in the slider; and setting the light source unit and the slider in desired positions in a direction perpendicular to the element-integration surface of the slider substrate. The desired positions are positions where the light source just emits due to a surface contact between: the protruded portion of the lower surface of the light source; and the upper surface of the electrode layer, which is a portion of the wall surface of a step formed on the head part.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Keyboard with key supporting structure for portable electronics devices
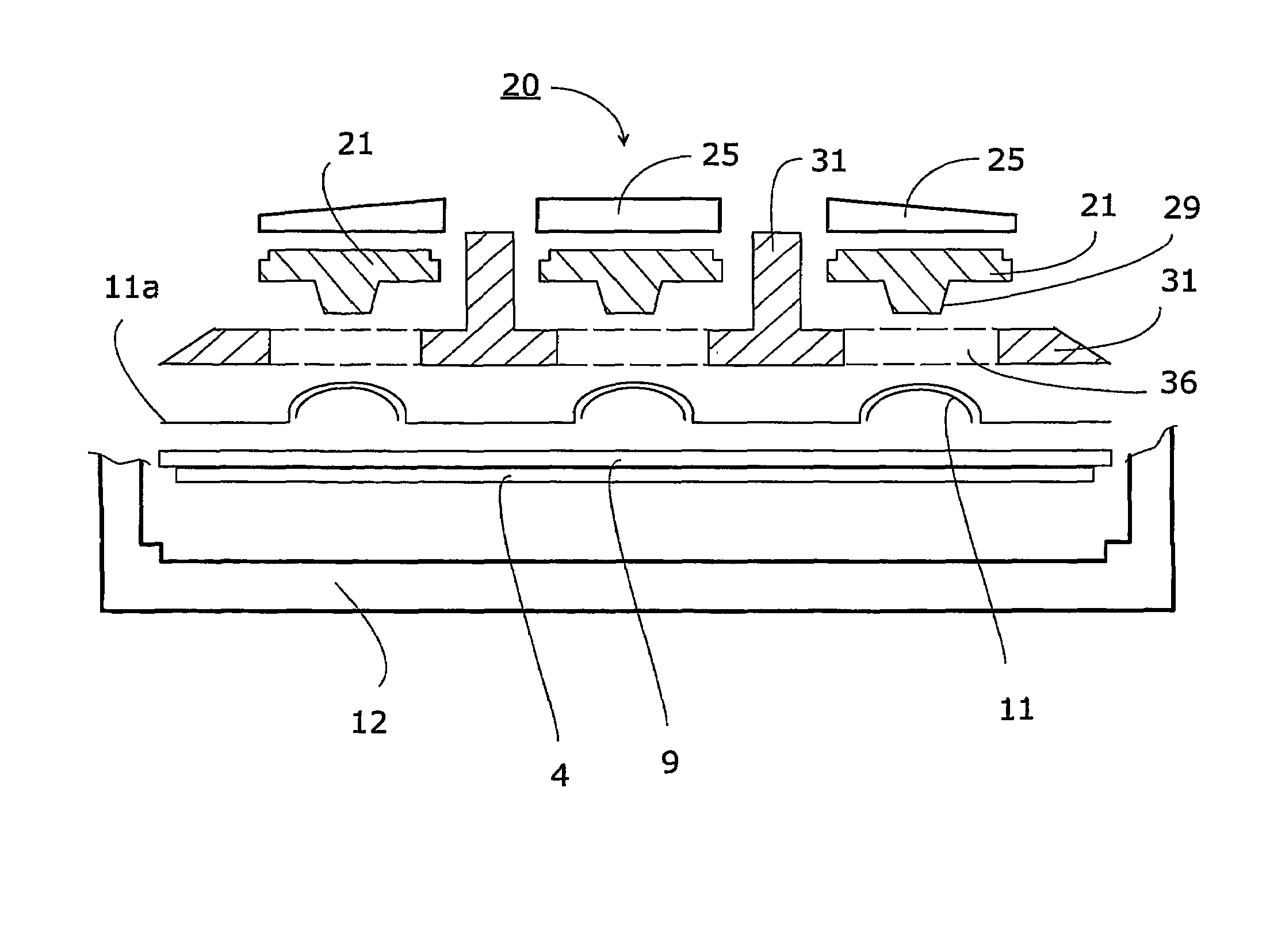
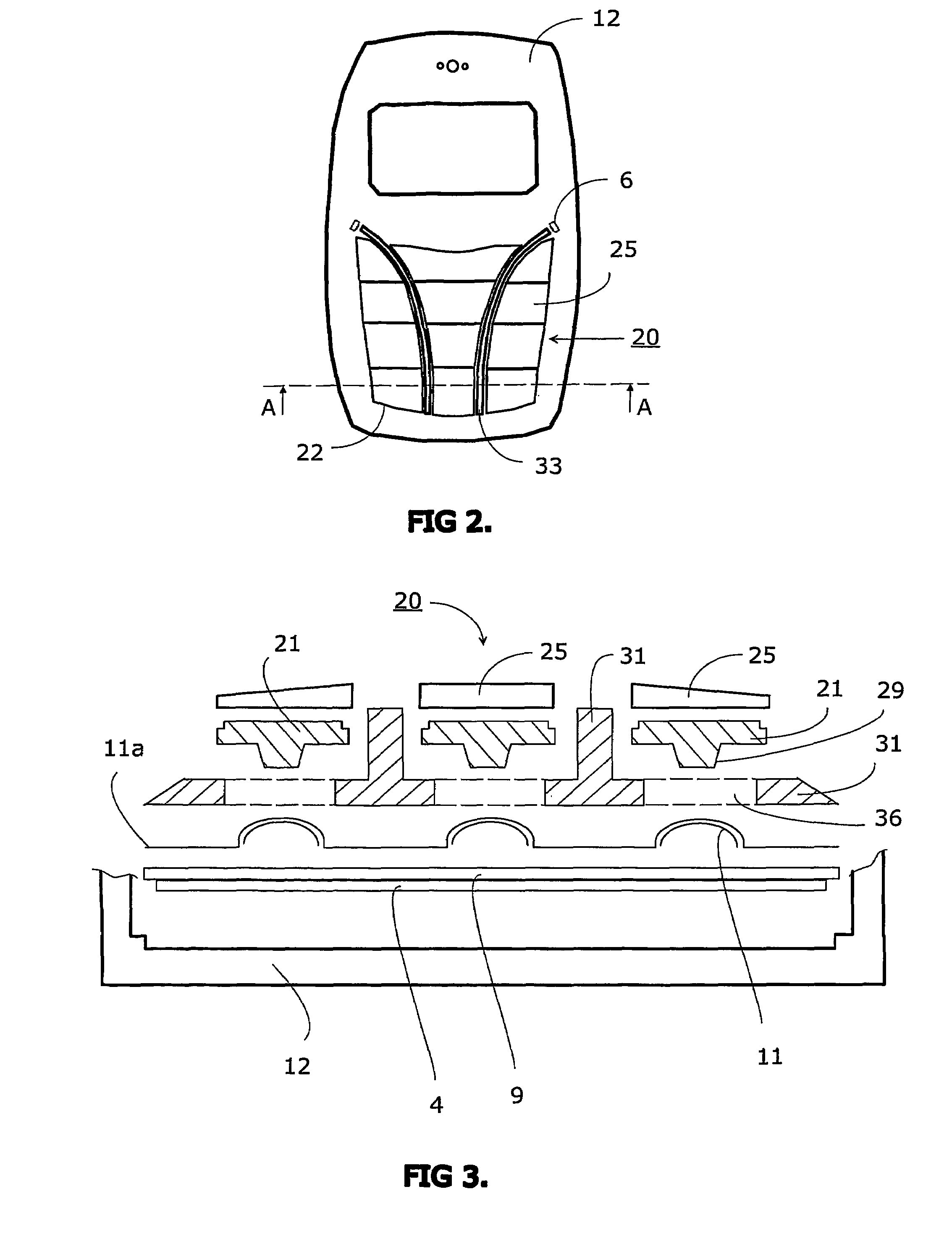
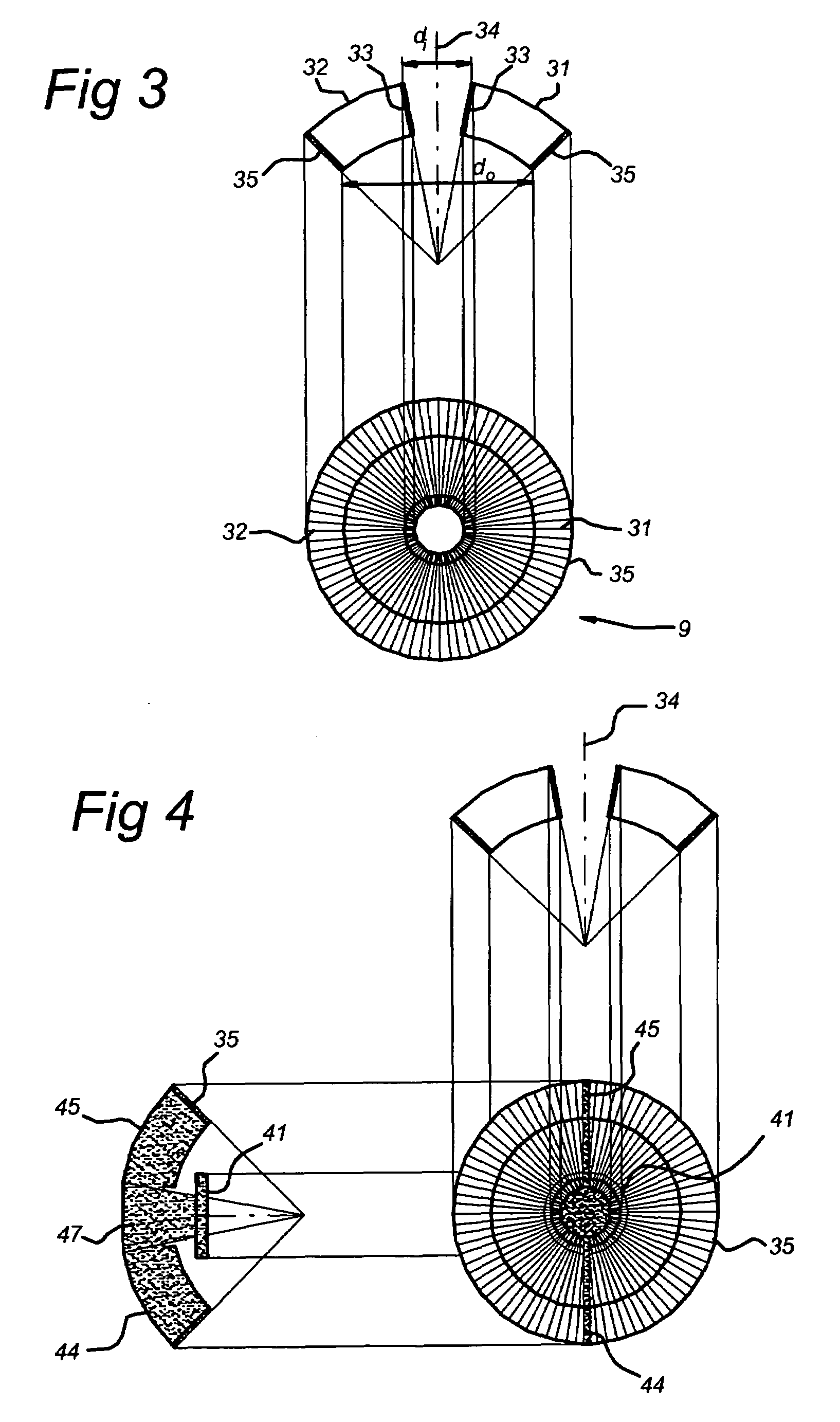
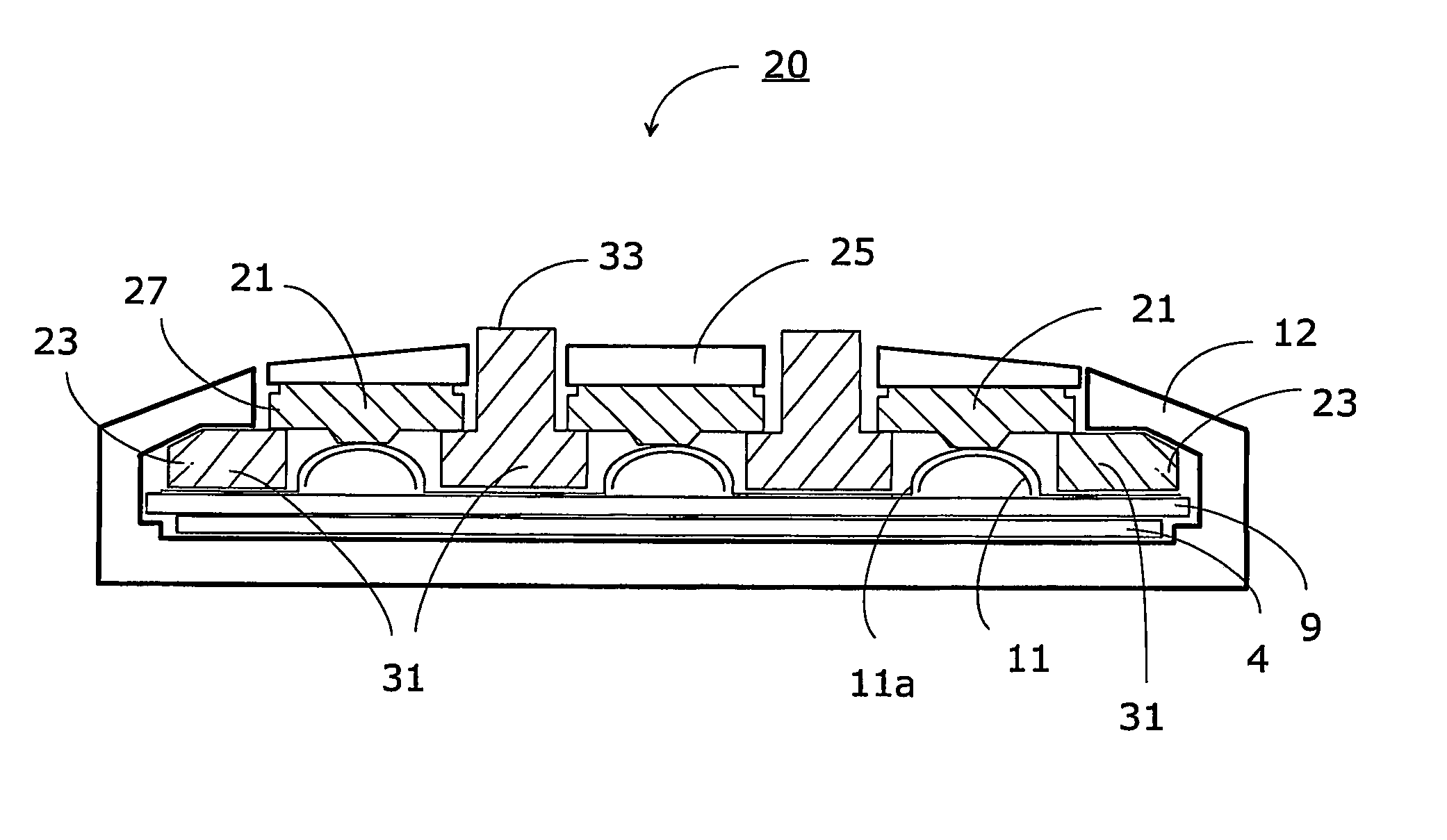
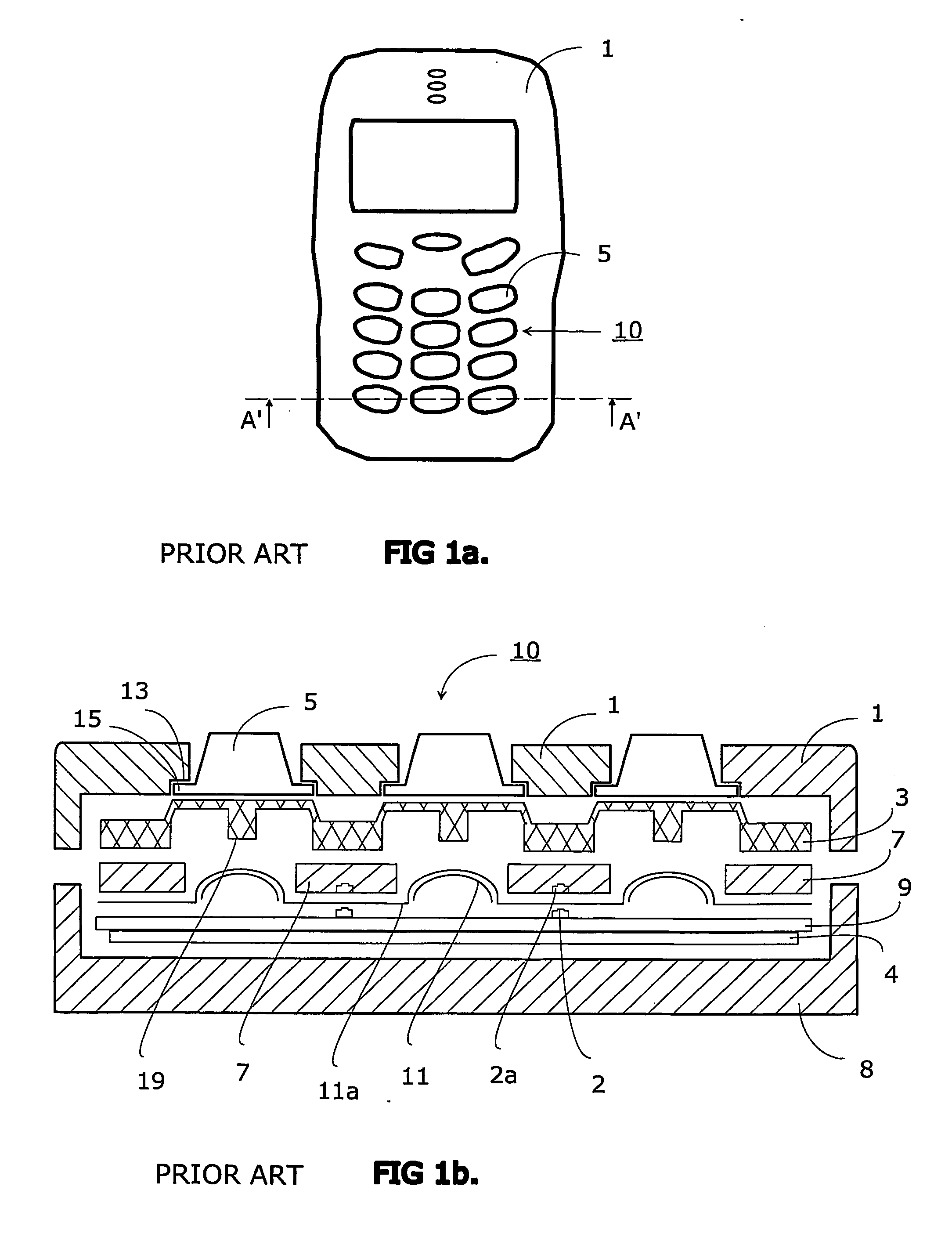
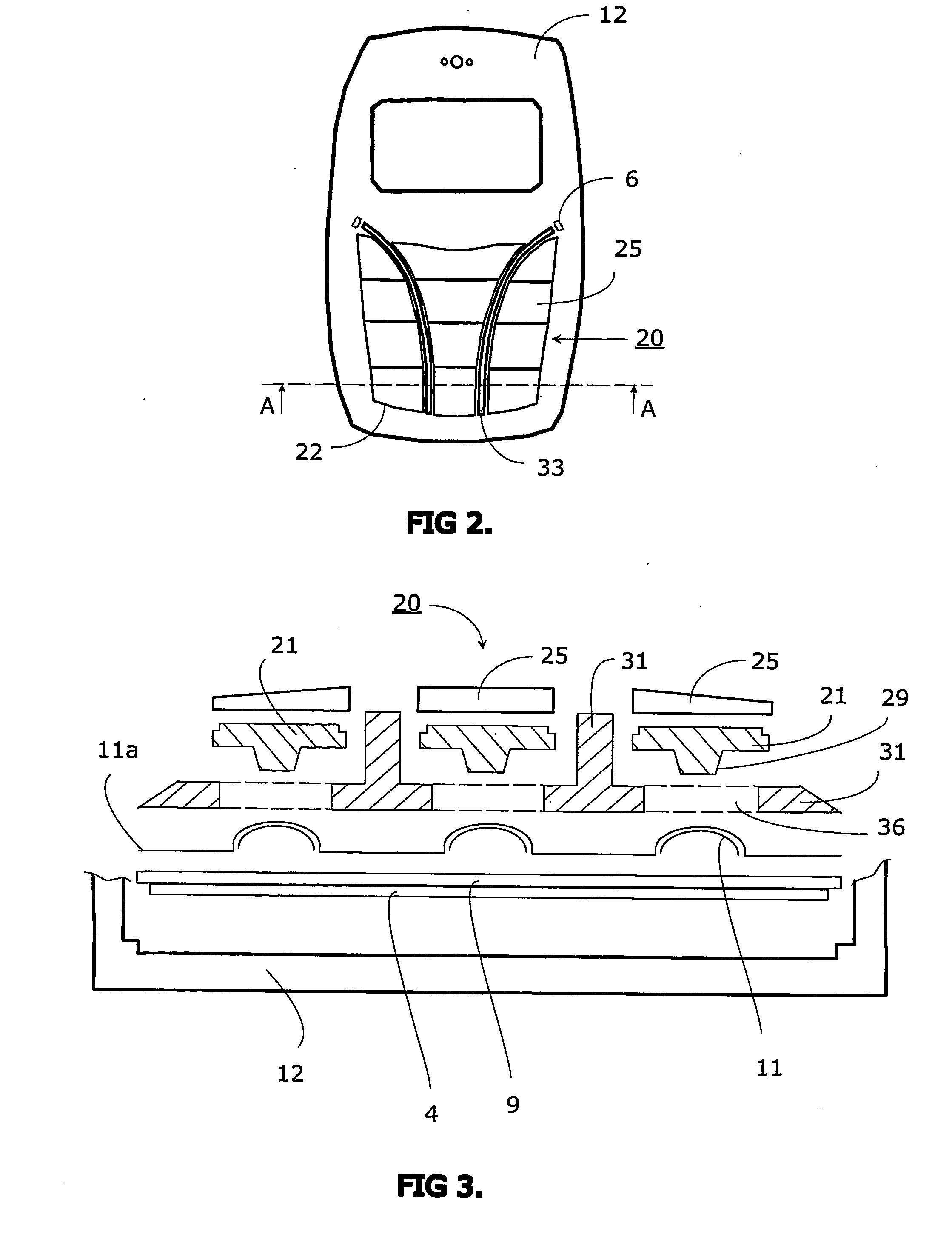
InactiveUS7345250B2Avoid mechanical stressSimple structureInput/output for user-computer interactionContact surface shape/structureLight guideEngineering
A keyboard assembly (20) has a light guide (23, 31, 33) and a supporting structure (23, 33) arranged to provide an illuminated and integrated keyboard assembly (20). A light guide (23, 31, 33) provides an integrated supporting, protecting and illuminating structure for keyboard assemblies (20). The keyboard assembly (20) has a layer of rigid material (31) which separates the elastic layer (21) from the printed wired board (9) located under the rigid layer (31). The layers are bonded together. The protection rib (33) is part of the combination of the elastic layer (21) and rigid layer (31) which is supported against the printed wired board (9) by the rigid layer (31). The combined structure of the light guide and supporting frame forms an integrated structure (23, 31, 33) which illuminates an array of keys (22), supports the keyboard assembly (20) and protects the keys (22) and key tops 25 from mechanical stress.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
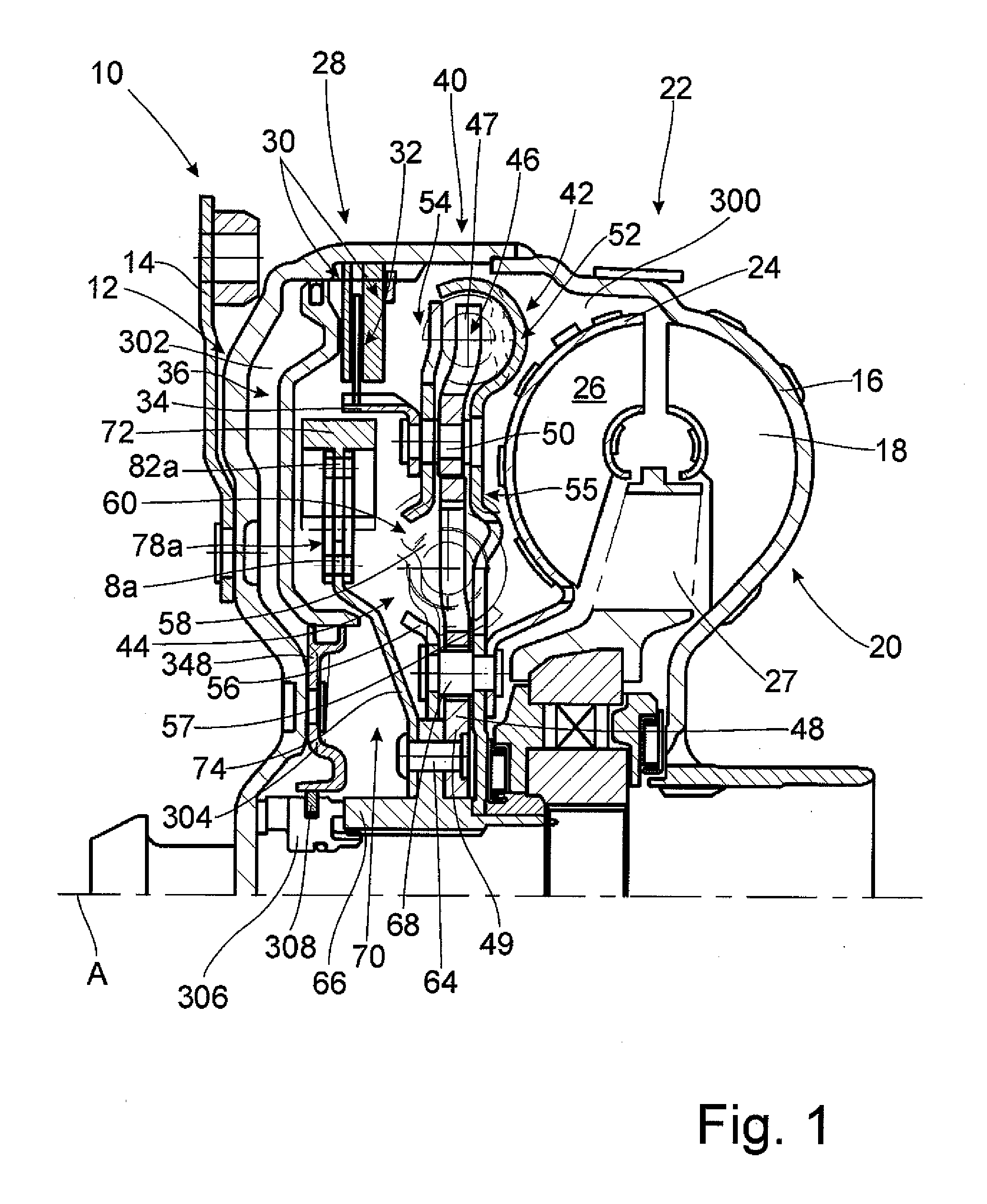
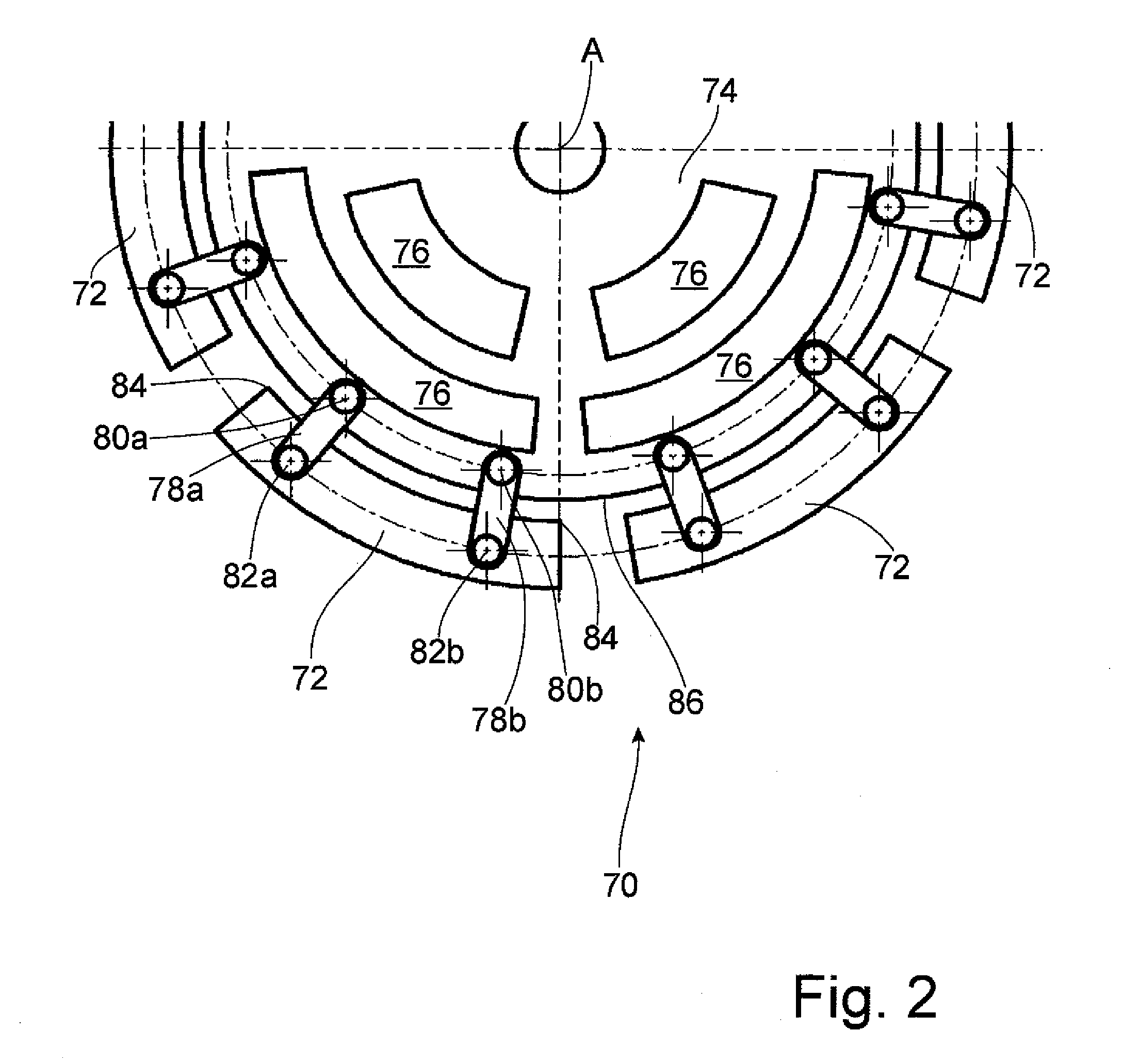
Hydrodynamic Coupling Arrangement, In Particular A Torque Converter
ActiveUS20110240429A1Large intermediate spaceEnabling displaceabilityRotary clutchesFluid gearingsImpellerRadial position
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
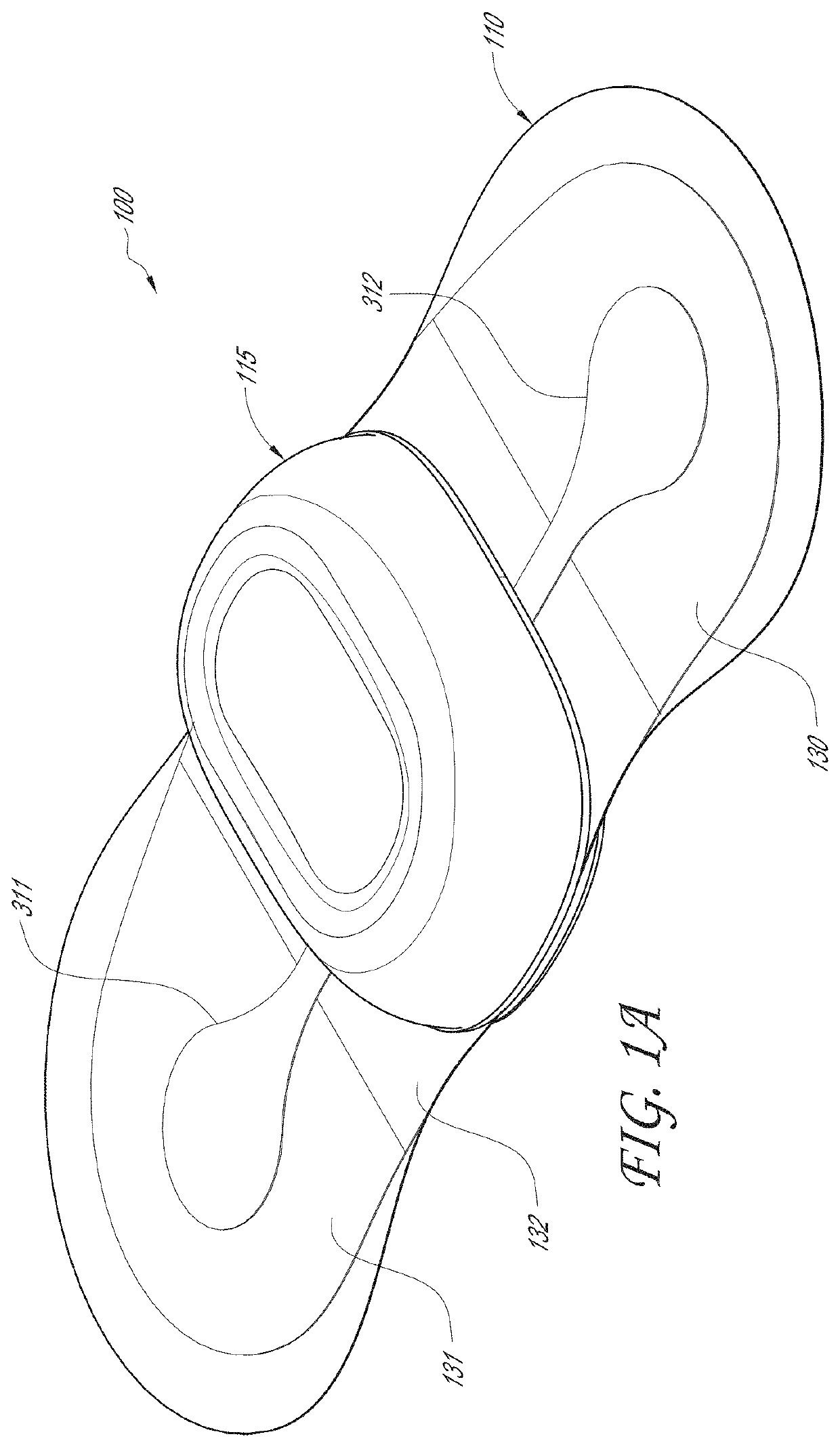
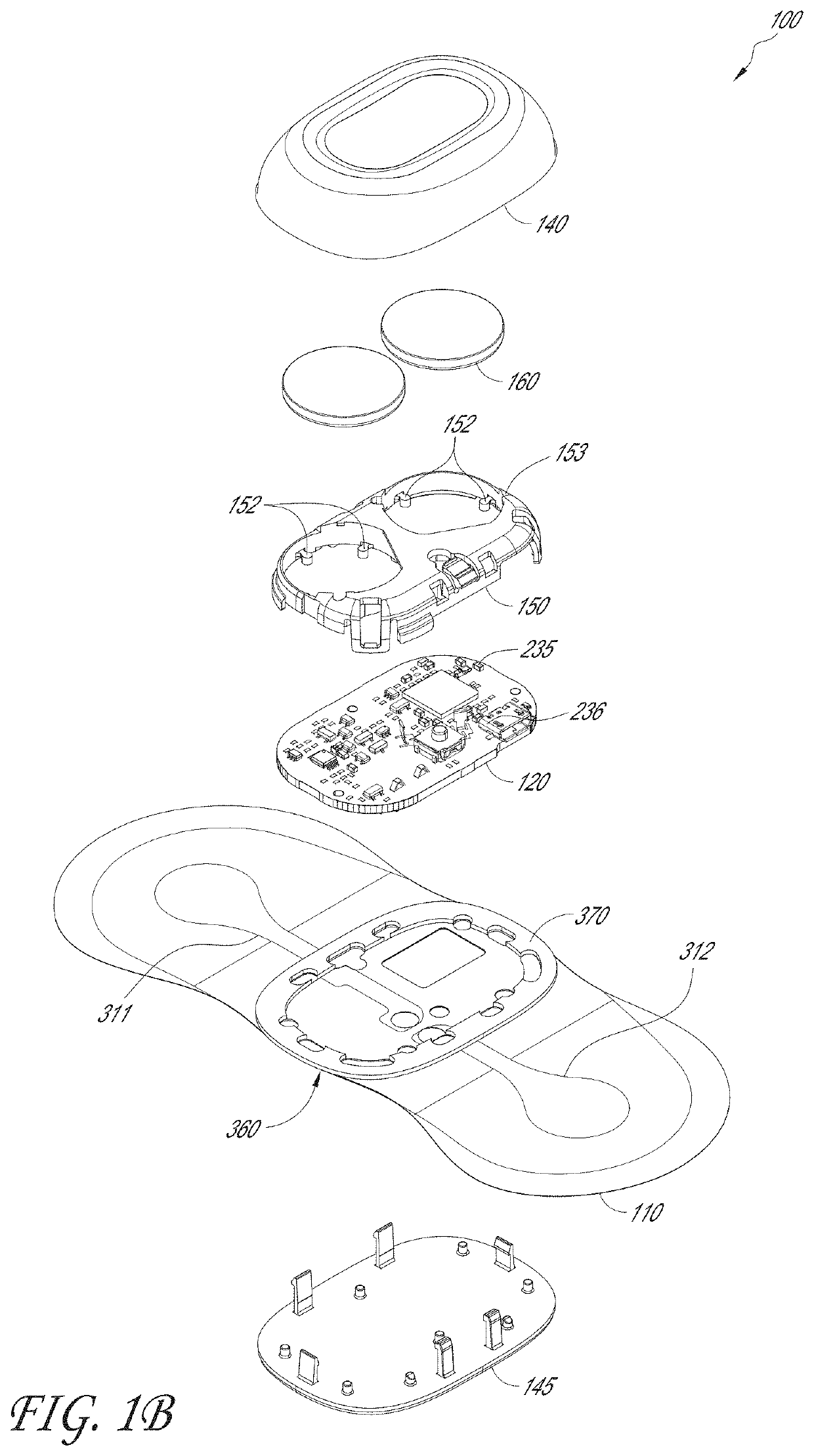
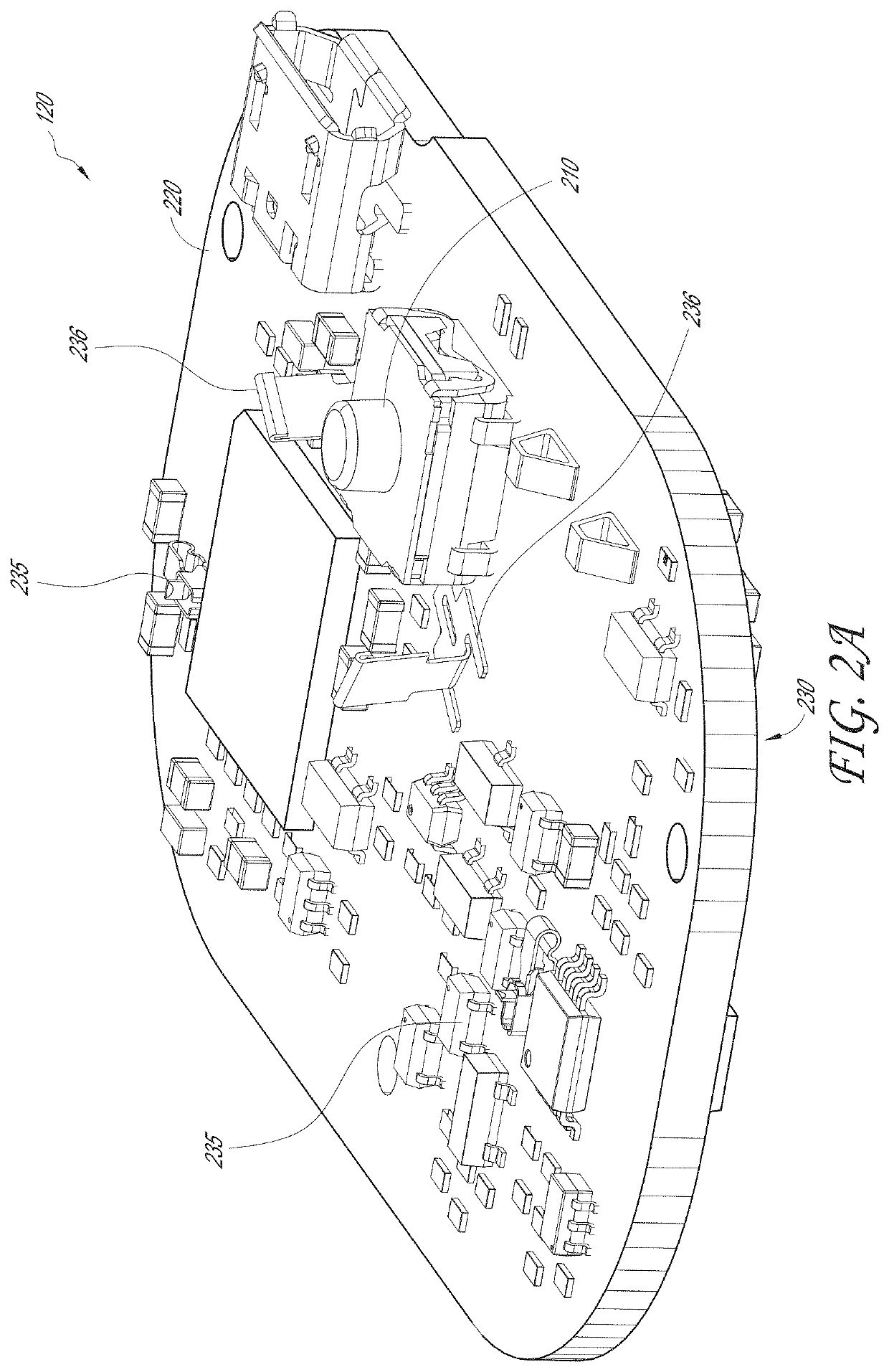
Wearable monitor
ActiveUS20190274574A1Facilitate and enhance experienceAccurate diagnosisMedical communicationElectrocardiographyHealth related informationEngineering
The present disclosure relates to a wearable monitor device and methods and systems for using such a device. In certain embodiments, the wearable monitor records cardiac data from a mammal and extracts particular features of interest. These features are then transmitted and used to provide health-related information about the mammal.
Owner:IRHYTHM TECH
Process for manufacturing a membrane of semiconductor material integrated in, and electrically insulated from, a substrate
ActiveUS20080224242A1Overcome disadvantagesOvercome problemsFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsBiomedical engineering
A process for manufacturing an integrated membrane made of semiconductor material includes the step of forming, in a monolithic body of semiconductor material having a front face, a buried cavity, extending at a distance from the front face and delimiting with the front face a surface region of the monolithic body, the surface region forming a membrane that is suspended above the buried cavity. The process further envisages the step of forming an insulation structure in a surface portion of the monolithic body to electrically insulate the membrane from the monolithic body; and the further and distinct step of setting the insulation structure at a distance from the membrane so that it will be positioned outside the membrane at a non-zero distance of separation.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Opto-electric module and method of assembling
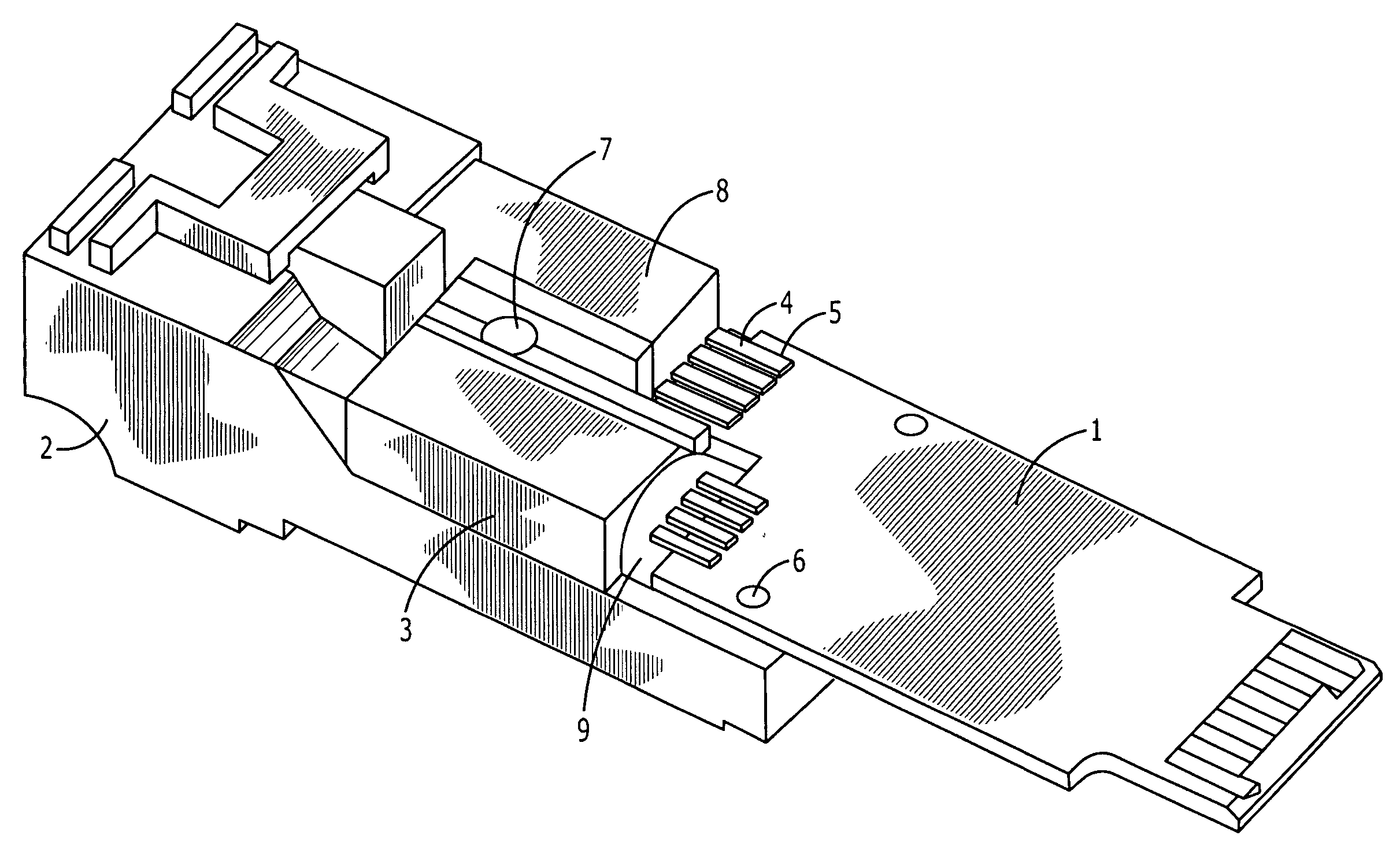
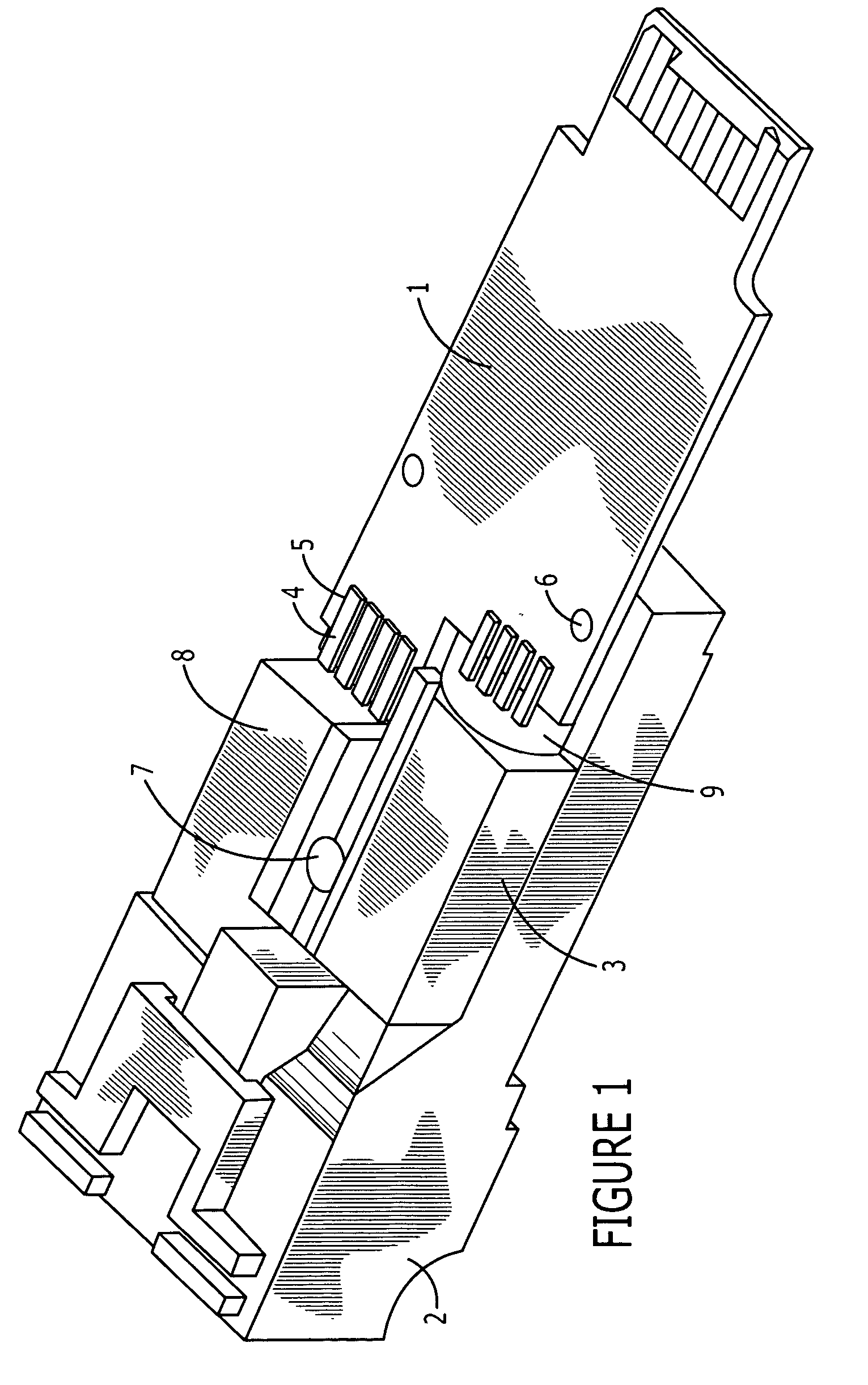
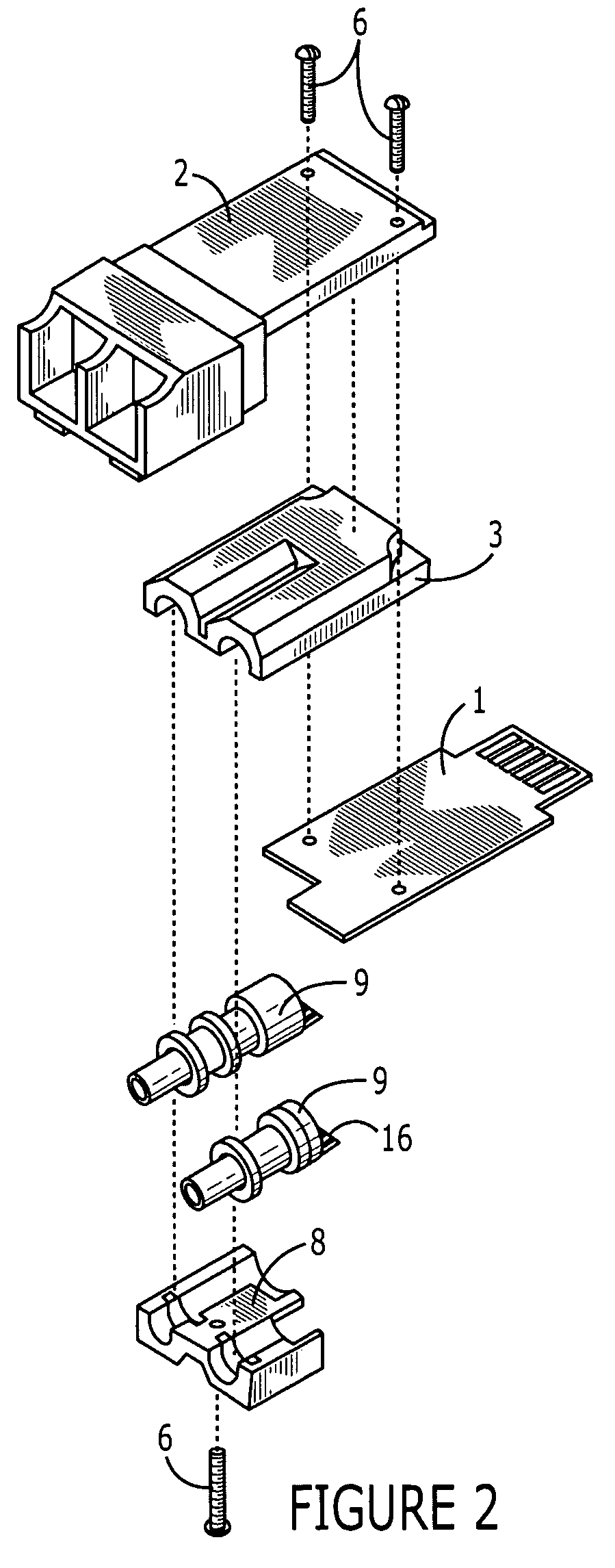
InactiveUS20050018978A1Maintain structural integrityMaintain integrityCoupling light guidesElectricityElectrical conductor
An opto-electric module comprising: (a) an OSA having an optical axis, and optical end, an electrical end; (b) a planar circuit board having top and bottom surfaces and one or more electrical contacts on at least one of the surfaces of the circuit board; (c) a connector interface for receiving a mating connector; (d) a substrate connected to the connector interface, the OSA and the circuit board, the substrate holding the circuit board parallel to the optical axis of the OSA; and (e) an electrical interface between the electrical end of the OSA and the electrical contacts of the circuit board, the electrical interface comprising a flexible conductor extending orthogonally from the optical axis of the OSA and bending around to overlay the electrical contacts on the circuit board.
Owner:TE CONNECTIVITY CORP
Physiological monitoring device
ActiveUS20180289274A1Facilitate and enhance experienceAccurate diagnosisElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsPhysiological monitoringLong term monitoring
The present invention relates to a physiological monitoring device. Some embodiments of the invention allow for long-term monitoring of physiological signals. Further embodiments may also allow for the monitoring of secondary signals such as motion.
Owner:IRHYTHM TECH
Process for manufacturing a membrane of semiconductor material integrated in, and electrically insulated from, a substrate
ActiveUS7678600B2Avoid mechanical stressFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsMembrane configuration
A process for manufacturing an integrated membrane made of semiconductor material includes the step of forming, in a monolithic body of semiconductor material having a front face, a buried cavity, extending at a distance from the front face and delimiting with the front face a surface region of the monolithic body, the surface region forming a membrane that is suspended above the buried cavity. The process further envisages the step of forming an insulation structure in a surface portion of the monolithic body to electrically insulate the membrane from the monolithic body; and the further and distinct step of setting the insulation structure at a distance from the membrane so that it will be positioned outside the membrane at a non-zero distance of separation.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
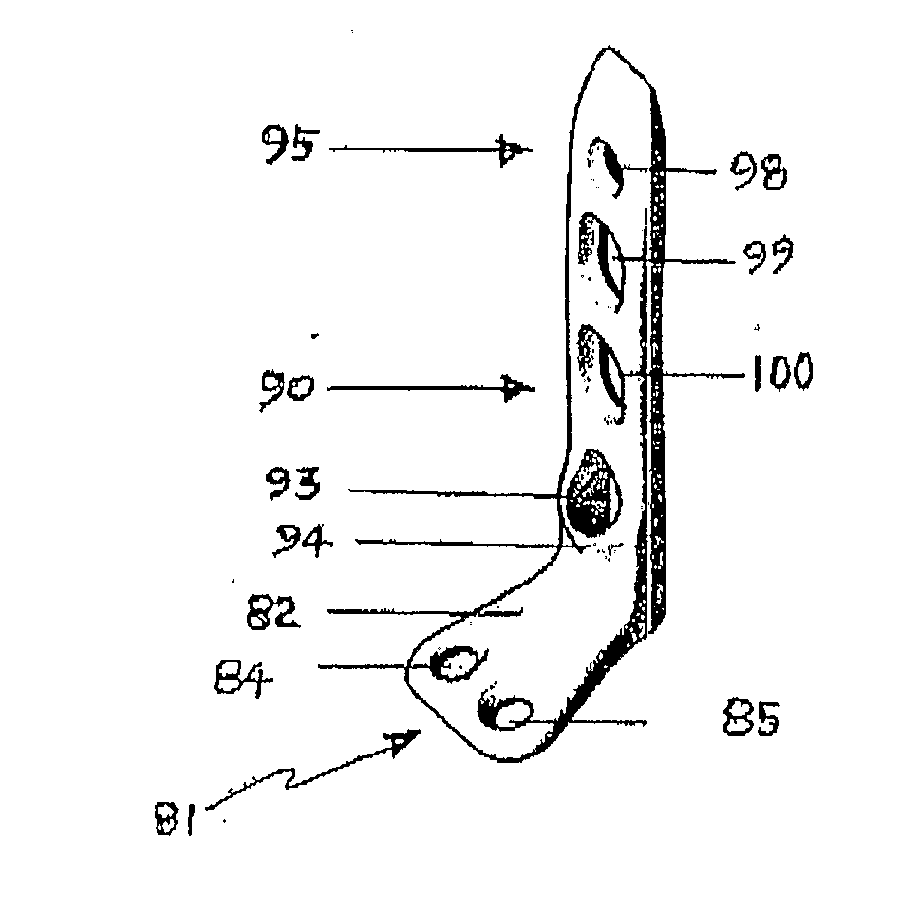
Ankle Fusion Plate
InactiveUS20110184413A1Reduce thicknessPermit recalcification and bondingJoint implantsBone platesJoint arthrodesisAnkle fusions
Owner:SLATER GORDON
Wearable monitor
ActiveUS10667712B2Facilitate and enhance experienceAccurate diagnosisMedical communicationElectrocardiographyHealth related informationEngineering
The present disclosure relates to a wearable monitor device and methods and systems for using such a device. In certain embodiments, the wearable monitor records cardiac data from a mammal and extracts particular features of interest. These features are then transmitted and used to provide health-related information about the mammal.
Owner:IRHYTHM TECH
Waste Heat Steam Generator
ActiveUS20110162594A1Reduce stepsEasy constructionSteam generation heating methodsSteam separation arrangementsSeparation systemWaste heat
A waste heat steam generator including evaporator tubes is provided. The evaporator tubes are connected in parallel on the flow medium side, a plurality of overheating tubes are mounted downstream of the evaporator tubes using a water separation system. The water separation system includes water separation elements, each water separation element being respectively mounted downstream of the plurality of evaporator tubes and / or upstream of a plurality of overheating tubes. Each water separating element includes an inlet pipe which is respectively connected upstream to the evaporator tubes, the inlet pipe extending into a water evacuation pipe when seen in the longitudinal direction. A plurality of outflow pipes branch off in the transitional area, the pipes being connected to an inlet collector of the overheating tubes which are respectively connected downstream. A distribution element is arranged on the steam side between the respective water separating element and the inlet collector.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY GLOBAL GMBH & CO KG
Contamination barrier with expandable lamellas
InactiveUS7247866B2Deformation MinimizationNo deformationRadiation/particle handlingNanoinformaticsContaminationPhysics
A contamination barrier that passes through radiation from a radiation source and captures debris coming from the radiation source is disclosed. The contamination barrier includes an inner ring, an outer ring, and a plurality of lamellas. The lamellas extend in a radial direction from a main axis, and each of the lamellas is positioned in a respective plane that include the main axis. At least one outer end of each of the lamellas is slidably connected to at least one of the inner and outer ring.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Keyboard with key supporting structure for portable electronics devices
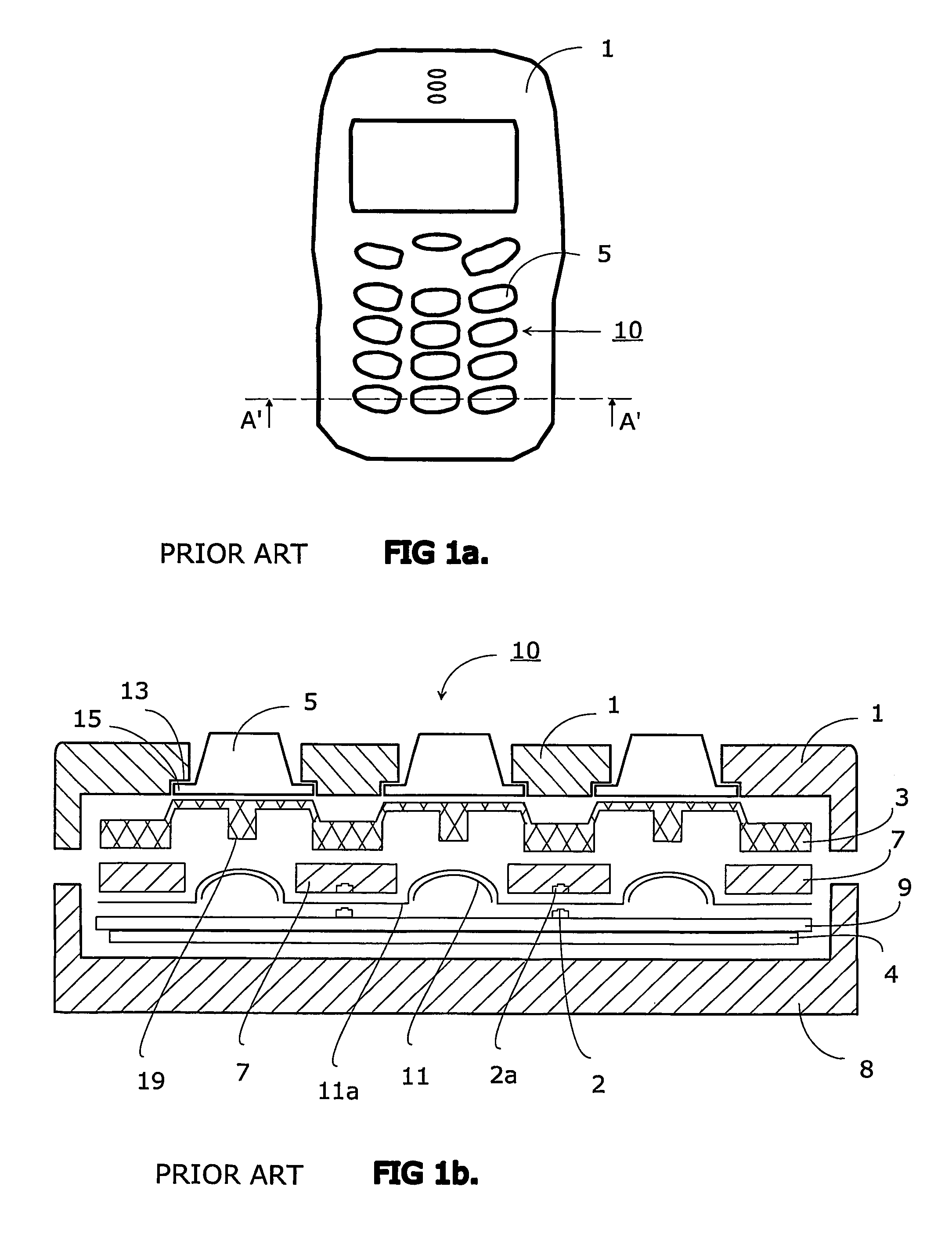
InactiveUS20070051603A1Simple structureAvoid mechanical stressInput/output for user-computer interactionLegendsLight guideEngineering
A keyboard assembly (20) has a light guide (23, 31, 33) and a supporting structure (23, 33) arranged to provide an illuminated and integrated keyboard assembly (20). A light guide (23, 31, 33) provides an integrated supporting, protecting and illuminating structure for keyboard assemblies (20). The keyboard assembly (20) has a layer of rigid material (31) which separates the elastic layer (21) from the printed wired board (9) located under the rigid layer (31). The layers are bonded together. The protection rib (33) is part of the combination of the elastic layer (21) and rigid layer (31) which is supported against the printed wired board (9) by the rigid layer (31). The combined structure of the light guide and supporting frame forms an integrated structure (23, 31, 33) which illuminates an array of keys (22), supports the keyboard assembly (20) and protects the keys (22) and key tops 25 from mechanical stress.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Electrode unit for rechargeable electrochemical cells
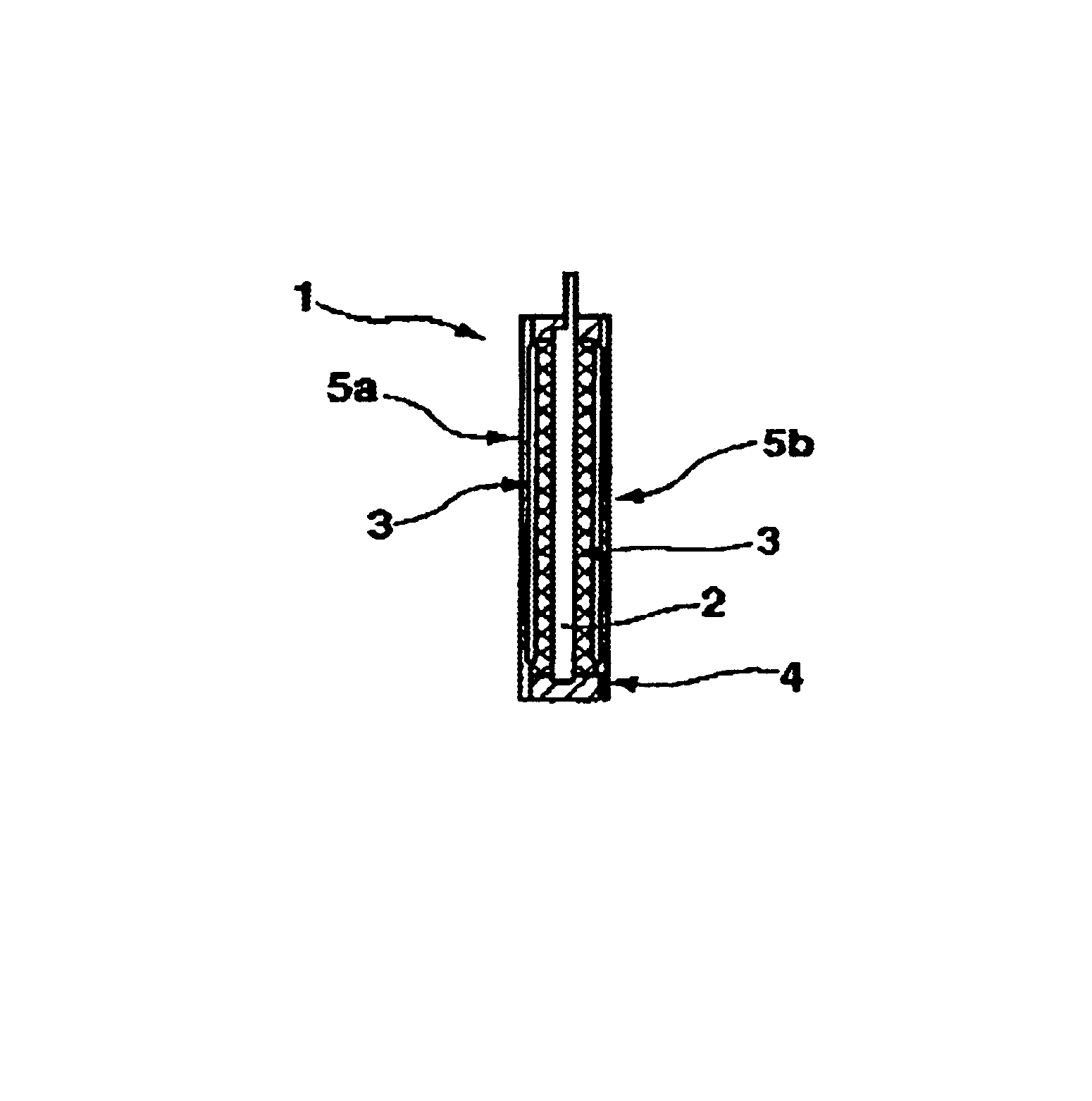
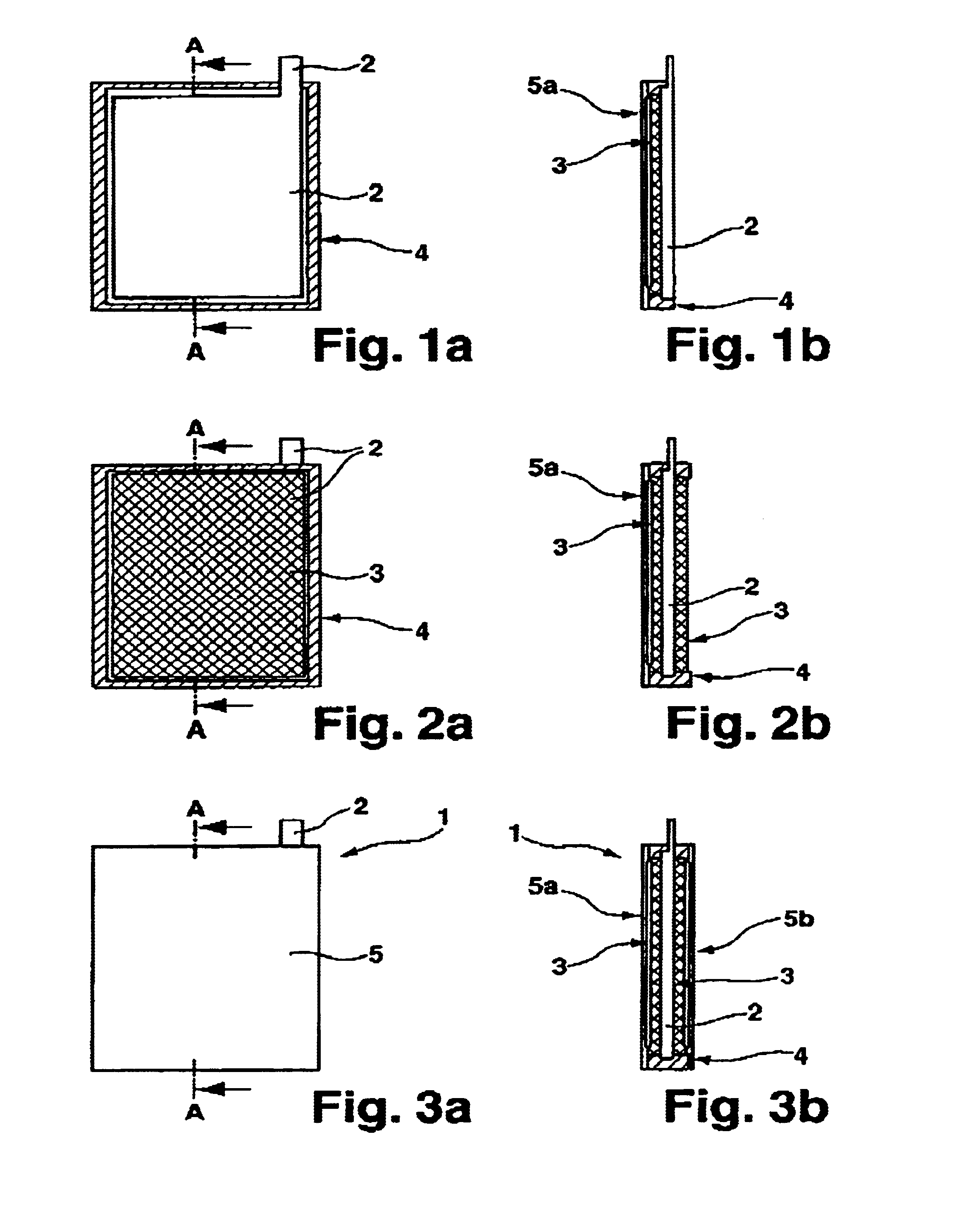
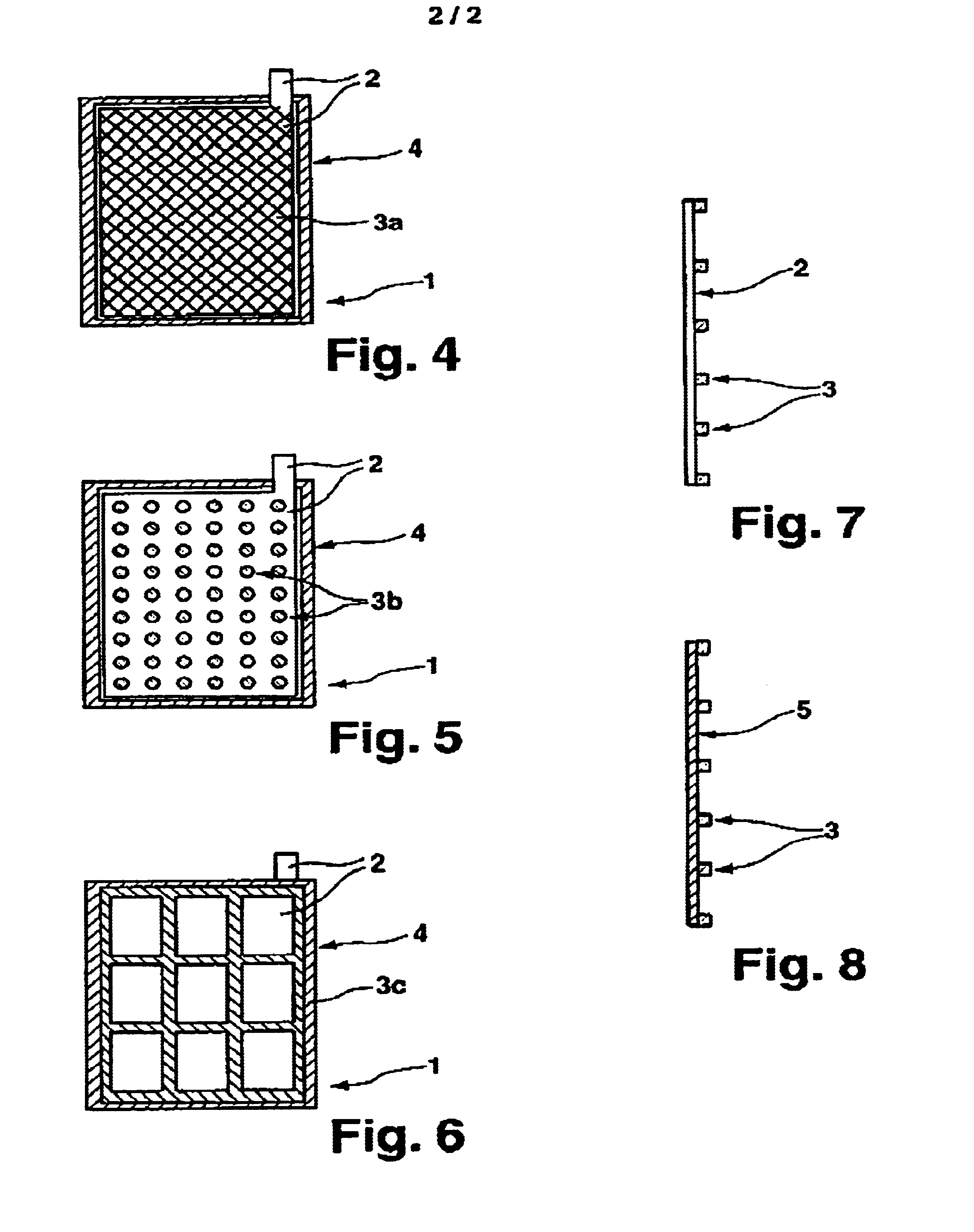
InactiveUS6855455B1Avoids mechanical pressure build-upLoad moreLead-acid accumulatorsCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersElectricityElectrochemical cell
The invention relates to an electrode unit for rechargeable electrochemical cells, e.g. accumulator cells, whose energy storage properties are drawn from the deposition of an element such as metal or an alloy. The electrode unit has an electrode (2) and a porous separator (5a) nearly completely surrounding said electrode, wherein an electrically insulating spacer (3) covering at least one face of the electrode is disposed between the electrode and the separator. The spacer according to the invention makes it possible to provide the necessary space for the metal or alloy deposited on the electrode, particularly during charging of the accumulator cell. The mechanical pressure as a result of changes in the volume of the electrode due to the deposited metal or alloy are intercepted, thereby reliably preventing short circuits.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
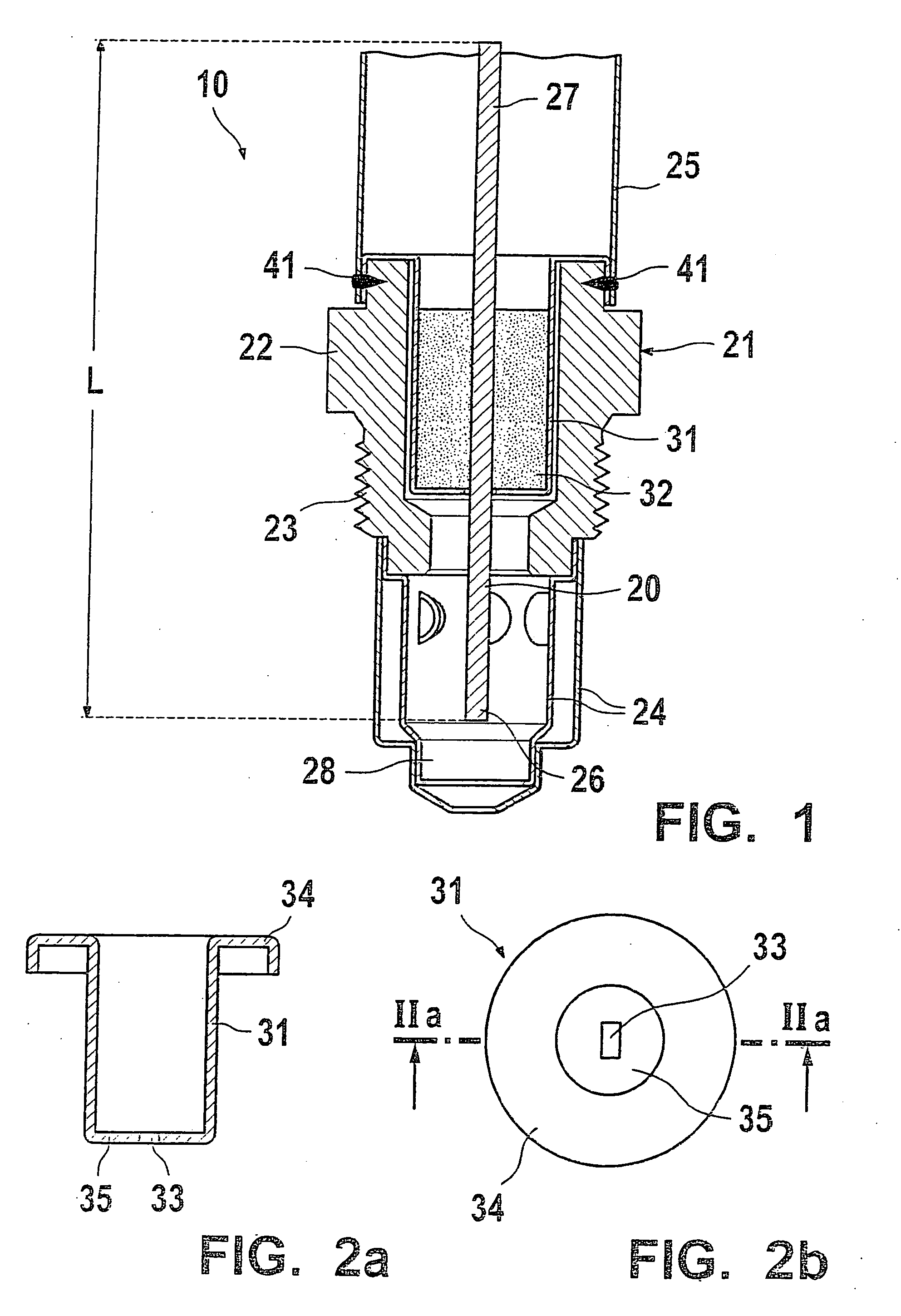
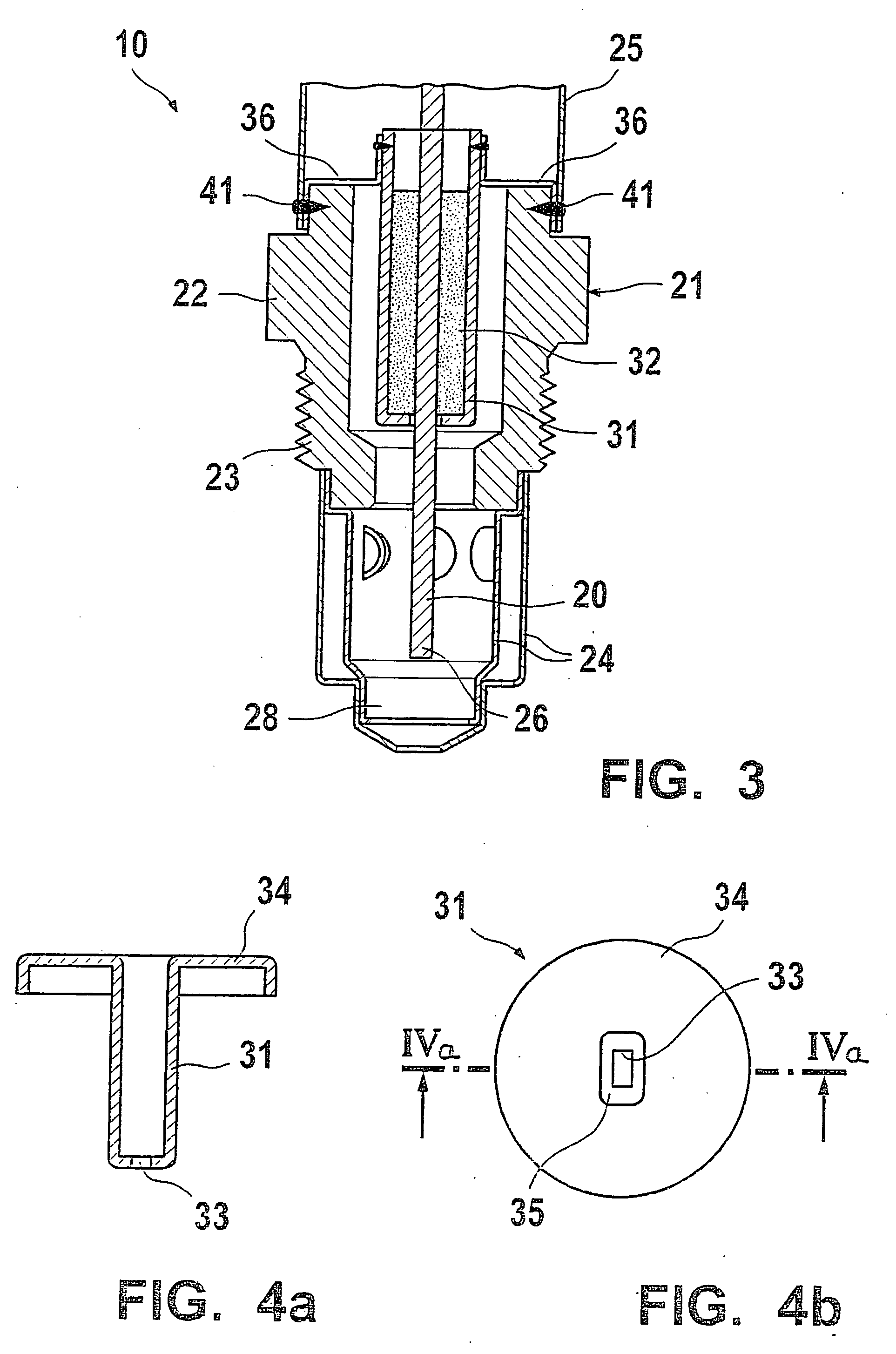
Gas sensor and method for production thereof
InactiveUS20060162422A1Cost-effectiveSimple technologyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringMetal
A gas sensor, whose purpose is to determine a physical property of a measuring gas, e.g., to determine the concentration of a gas component or the temperature of an exhaust gas. The gas sensor includes a sensor element arranged in a metal housing which is sealed by at least one sealing element arranged in a metal receptacle. The metal receptacle is affixed to the housing. The sealing element surrounds the sensor element in a centered position along its longitudinal extension L or on its half facing the measuring gas.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
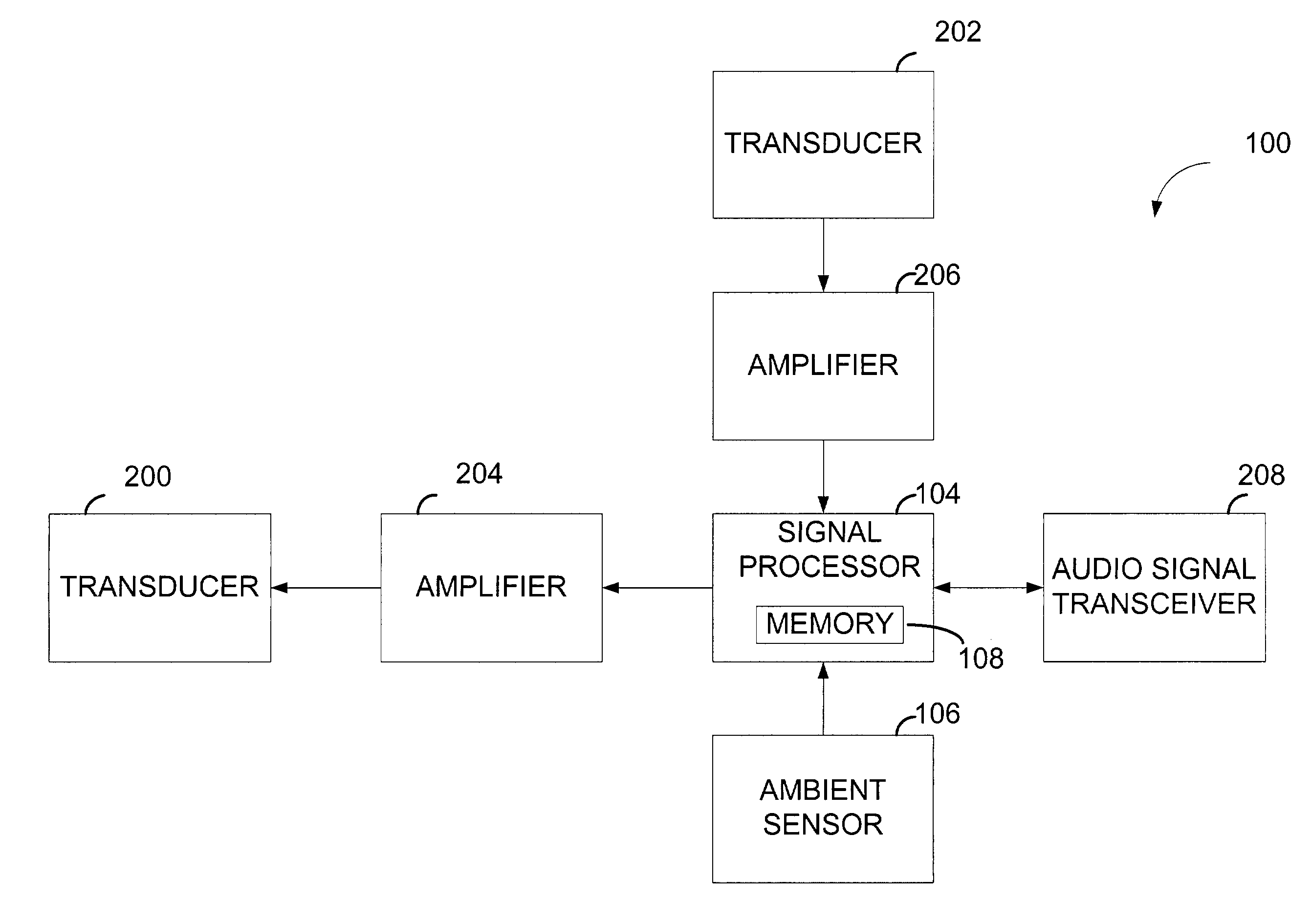
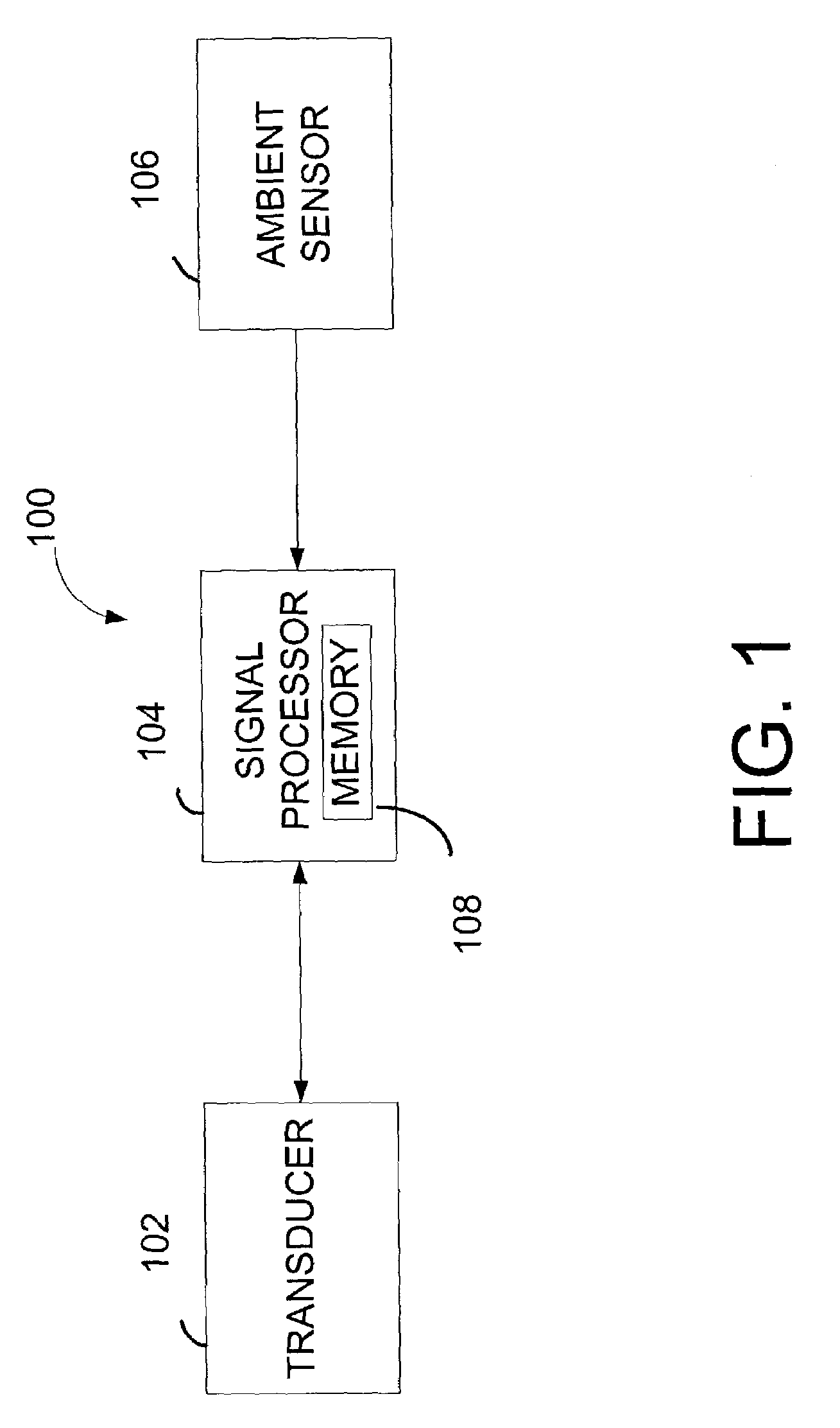
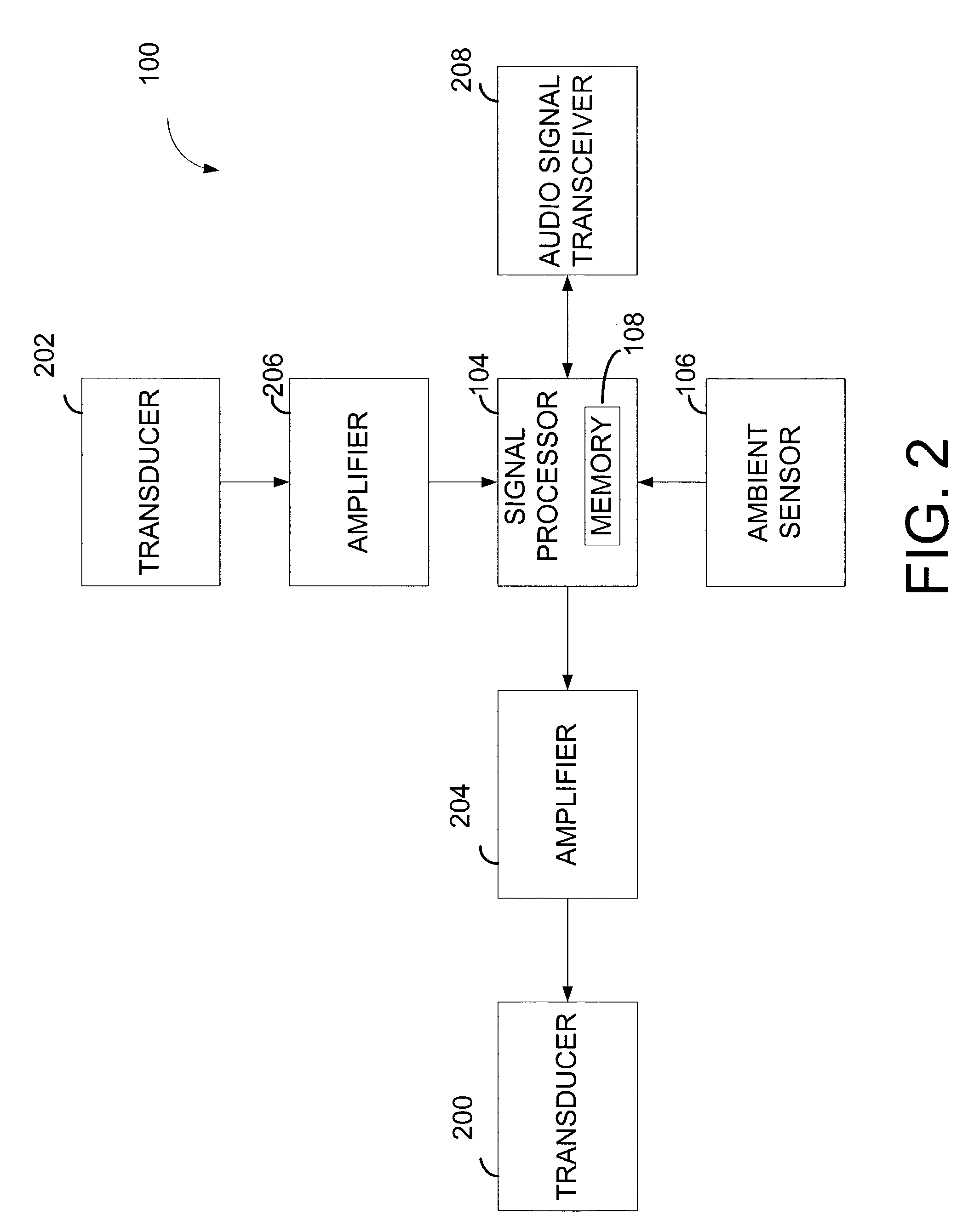
System for transducer compensation based on ambient conditions
ActiveUS7092536B1Improve performanceAvoid mechanical stressFrequency response correctionLimiting amplitudeTransducerEngineering
A system for transducer compensation based on ambient conditions includes a transducer, a signal processor and an ambient condition sensor. The signal processor may process audio signals for the transducer. In addition, the signal processor may receive signals from the ambient condition sensor. The signals may represent ambient conditions being experienced by the transducer. The signal processor may dynamically adjust the equalization of the audio signals based on the ambient conditions to optimize operation of the transducer.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
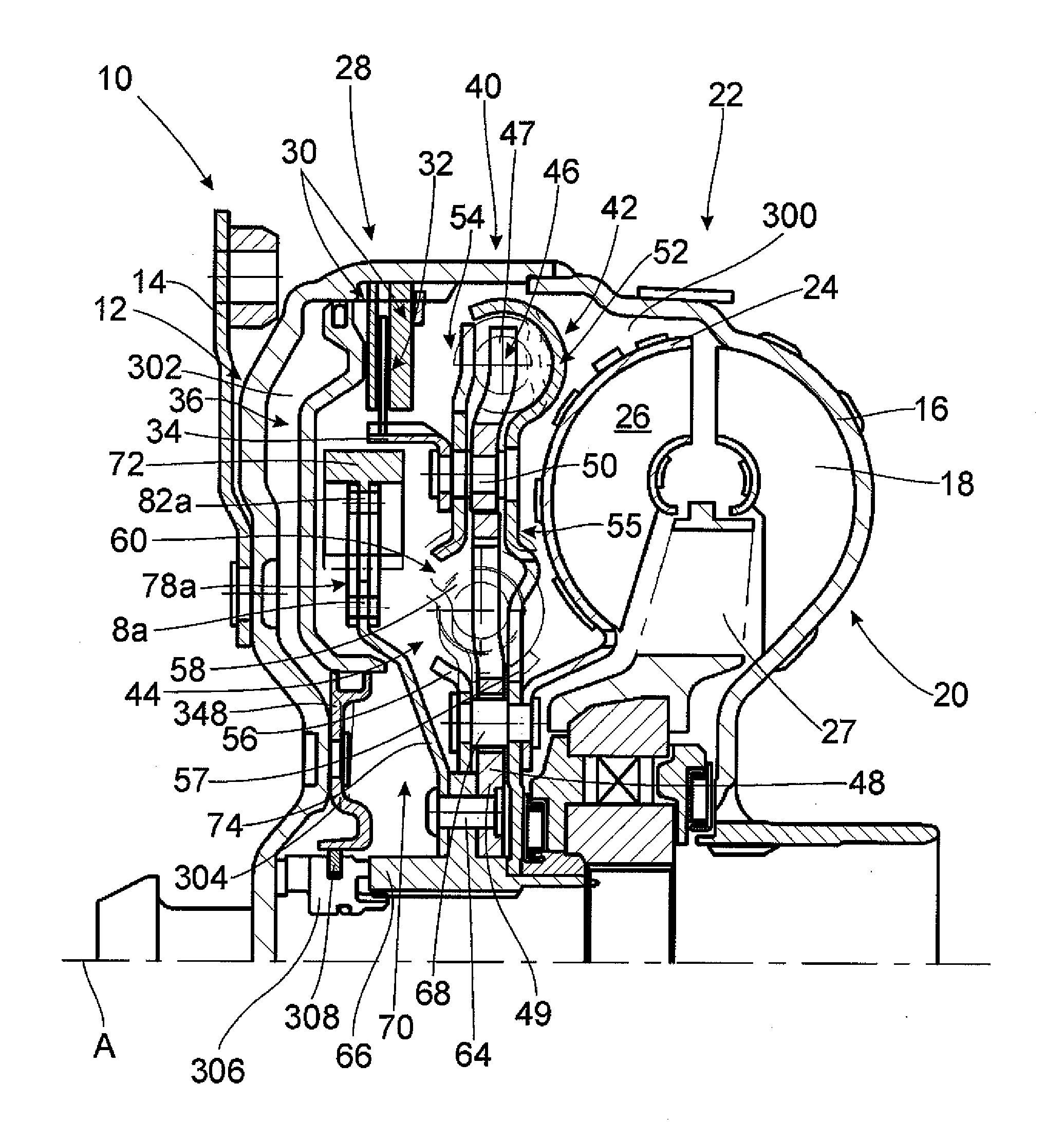
Method for producing a turbine casing
InactiveCN101480705AFast and unified quality checksCutting costsEngine manufactureFoundry mouldsTurbine
A method for producing a turbine casing for a rotating machine is provided. The casing is manufactured by a casting process, and is cast in two casing halves which are separated by a parting plane which passes axially through the turbine casing. Each casing half is first cast in one piece in each case, and each casing half is separated into at least two casing sections which are joined together for forming a casing half in each case.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Component of a fuel cell unit
In order to provide a component of a fuel cell unit that has an electric insulation effect at the operating temperature of the fuel cell unit and that has an adequate electrically insulating effect and an adequate mechanical strength also at a high operating temperature of the fuel cell unit, it is proposed that the component comprises a basic body and at least one electrically insulating insulation layer, which is disposed on the basic body and contains aluminium oxide, wherein the insulation layer is produced by anodizing an aluminium-containing layer disposed on the basic body.
Owner:ELRINGKLINGER AG
Pressure bulkhead and method for subdivision of an aircraft or spacecraft
ActiveCN101801783AProtects against stress and deformationAvoid deformationFuselage bulkheadsAirplaneSpacecraft
The present invention provides a pressure bulkhead for subdivision of an aircraft or spacecraft into an internal-pressure area and an external-pressure area. The pressure bulkhead comprises a pressure plate which has a rim which is shaped corresponding to an internal contour of the aircraft or spacecraft, a supporting device which supports the rim such that it can be tilted on the inner contour, and a seal which seals the rim with the internal contour. A further aspect of the invention provides a method for subdivision of an aircraft or spacecraft into an internal-pressure area and an external-pressure area. First of all, a pressure plate is provided which has a rim which is shaped to correspond to an internal contour of the aircraft or spacecraft. In further steps, the rim is supported such that it can be tilted on the internal contour, and is sealed with the internal contour.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Method of Forming Isolation Layer of Semiconductor Device
InactiveUS20090170280A1Avoid mechanical stressAvoid electrical stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIsolation layerDielectric layer
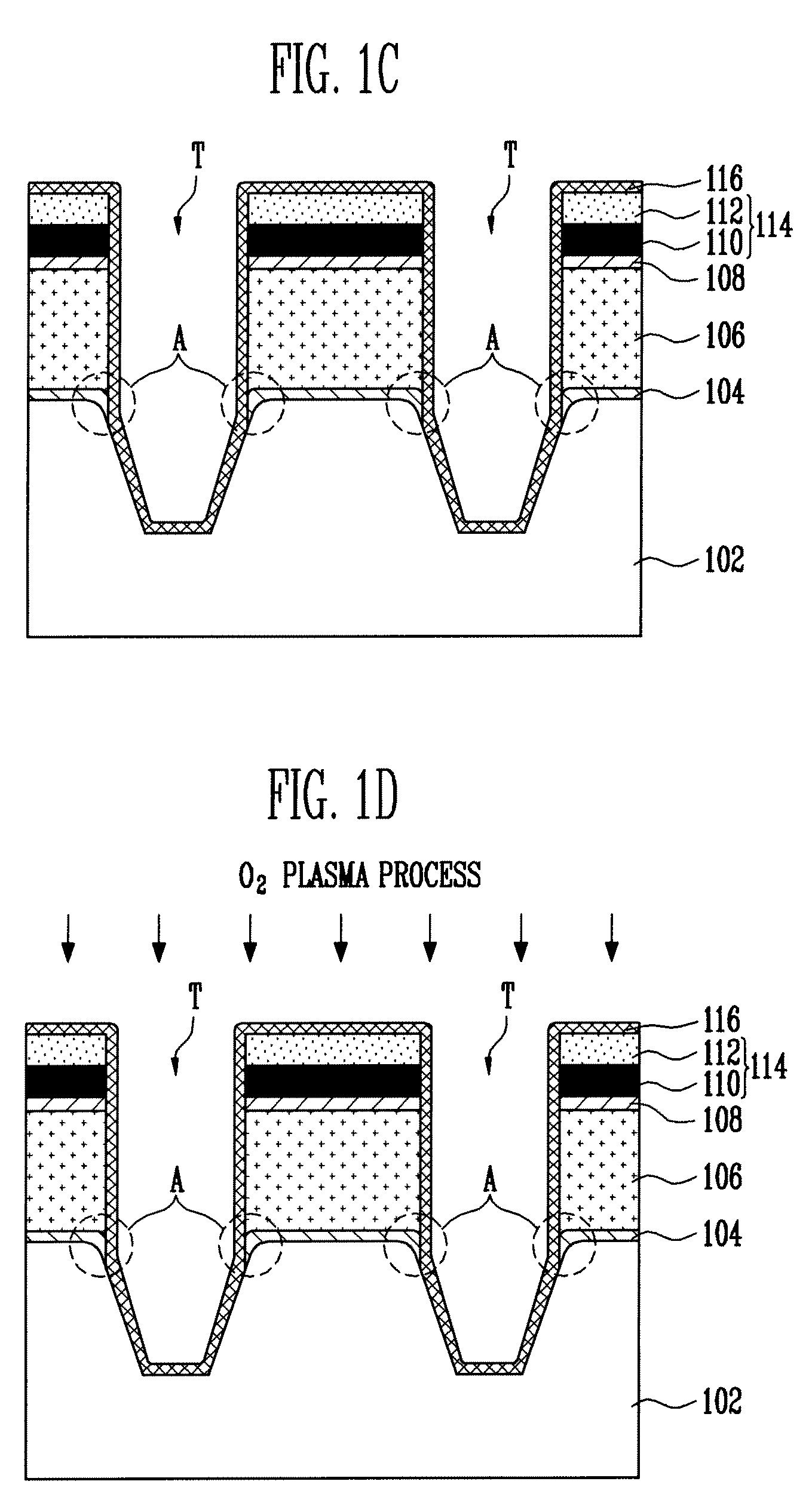
A method of forming isolation layers of a semiconductor device, comprising providing a semiconductor substrate in which a tunnel dielectric layer and a conductive layer are formed in active regions having two ends and trenches are formed in isolation regions; rounding both ends of each active region by performing an O2 plasma process on the semiconductor substrate; forming a first insulating layer on sidewalls of each trench; and, forming a second insulating layer, preferably having a greater fluidity than that of the first insulating layer, on the first insulating layer.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Integrated arrangement of optical fibers in a conductor
InactiveUS20050082084A1Reduce manufacturing costEasy to produceThermometer detailsNon-insulated conductorsElectrical conductorTransformer
An electrical conductor and in particular a conductor bar of an electrical machine, particularly a generator or transformer, in which an optical measuring device can be integrally arranged. A measuring unit includes an electrical conductor and an optical measuring device arranged in the conductor, and a production method for producing such an electrical conductor is described. The electrical conductor (10), having a conductor cross section and also an extent in the conductor longitudinal direction, includes a recess (11, 12, 13) in the conductor longitudinal direction at least along a section of the conductor, for integrated arrangement of a signal conductor, in particular an optical waveguide.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Manufacturing method of heat-assisted magnetic head constituted of slider and light source unit
ActiveUS8065786B2More stressImprove accuracyDecorative surface effectsRecord information storageHeat-assisted magnetic recordingEngineering
Provided is a manufacturing method of heat-assisted magnetic recording head, in which a light source unit can be easily joined to a slider with sufficiently high accuracy, under avoiding the excessive mechanical stress. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of: moving relatively the light source unit and the slider, while applying a sufficient voltage between an upper electrode of the light source and an electrode layer provided in the slider; and setting the light source unit and the slider in desired positions in a direction perpendicular to the element-integration surface of the slider substrate. The desired positions are positions where the light source just emits due to a surface contact between: the protruded portion of the lower surface of the light source; and the upper surface of the electrode layer, which is a portion of the wall surface of a step formed on the head part.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Accumulator current sensor for automobile
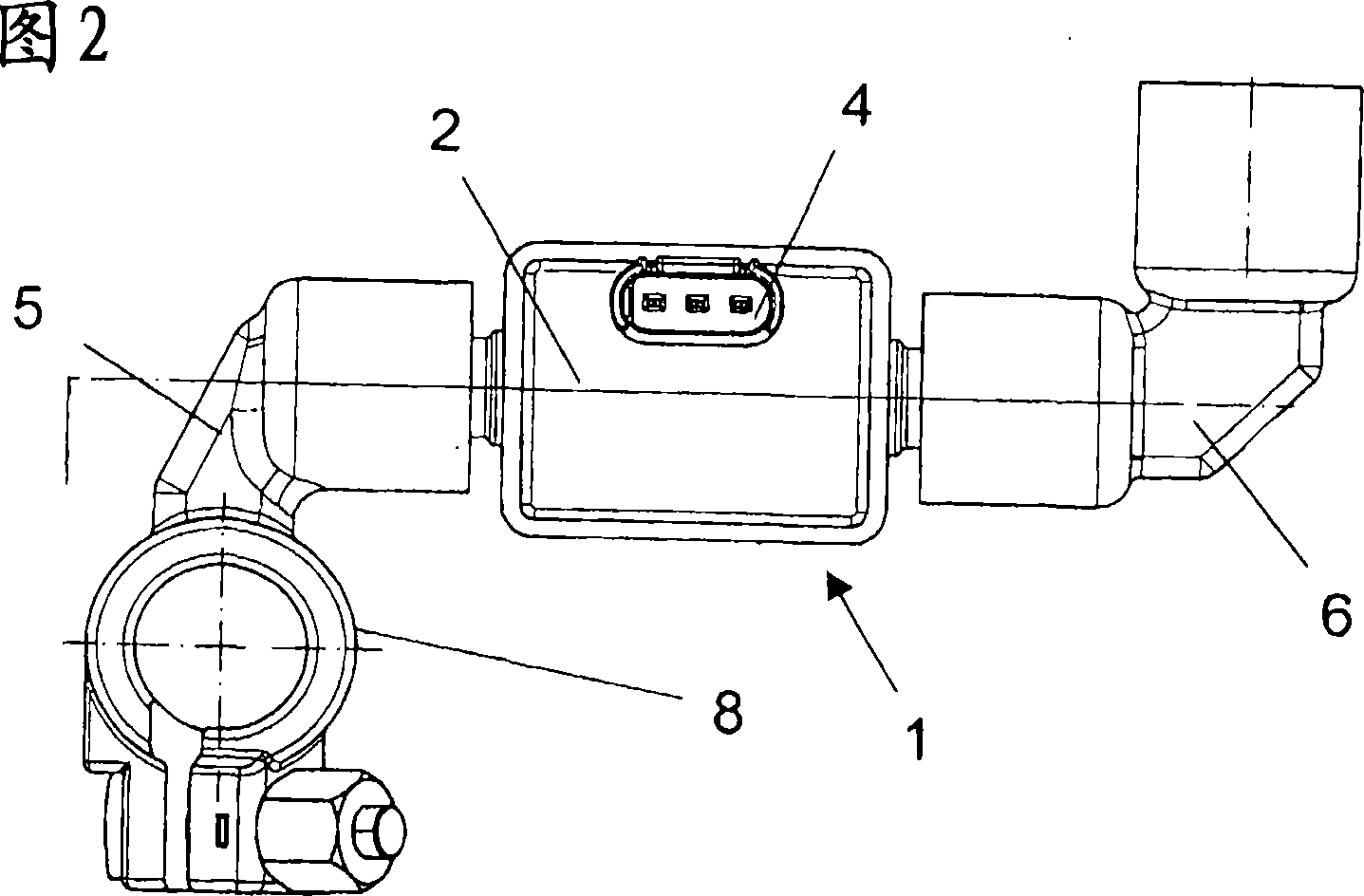
InactiveCN101052885AAvoid mechanical stressCoupling device detailsBase element modificationsCurrent sensorElectric current flow
The invention relates to a battery current sensor for automobiles, which includes a measurement sensor embedded in a battery circuit and a measurement circuit device connected to the measurement sensor. In the sensor, at least components of the measurement circuit device are arranged on a circuit substrate. , the circuit substrate is electrically and mechanically connected to the measuring sensor in a positionally fixed manner via connecting elements, wherein each connecting element has at least one press-in contact via which the connecting element is connected to the circuit substrate and / or to the measuring sensor. connected.
Owner:LEOPOLD KOSTAL GMBH & CO KG
Method for fabricating semiconductor device with use of partial gate recessing process
InactiveUS7074661B2Avoid mechanical stressSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricIon implantation
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Developer supplying device, developing roller, developing device, image forming apparatus and process cartridge
Owner:RICOH KK
Stress-free clamping flexible device for high-precision standard lenses
PendingCN107621678AReduce the effect of surface shapeSolve the sticky effectMountingsMultiple injectionEngineering
The invention relates to a stress-free clamping flexible device for high-precision standard lenses, which includes a flexible frame, a pressing ring, and a standard lens frame. The flexible frame is provided with a plurality of circular arc slits of the same radius which divide the flexible frame into an inner ring and an outer ring, and the inner ring and the outer ring are connected by a flexible member. Multiple injection holes are arranged in the side of the inner ring of the flexible frame. A standard lens is fixed to the inner ring of the flexible frame through adhesive in the injectionholes. The standard lens frame is a barrel-shaped part with a round hole in the bottom, and the radius of the round hole is smaller than that of the standard lens. The flexible frame is sheathed in the standard lens frame. The joint portion of the bottom of the standard lens frame and one end face of the outer ring of the flexible frame is provided with a boss. The pressing ring is arranged on theother end face of the outer ring of the flexible frame. The joint portion of the pressing ring and the outer ring of the flexible frame is provided with a boss. The standard lens frame is provided with a standard interface connected with an interferometer. The thermal characteristic mismatch between the standard lens and the supporting structure thereof is compensated through the deformation of the flexible structure. The influence of temperature change on the surface shape is reduced.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gas sensor and method for production thereof
InactiveUS7454949B2Cost-effectiveSimple technologyEngine testingMaterial resistanceProduct gasEngineering
A gas sensor, whose purpose is to determine a physical property of a measuring gas, e.g., to determine the concentration of a gas component or the temperature of an exhaust gas. The gas sensor includes a sensor element arranged in a metal housing which is sealed by at least one sealing element arranged in a metal receptacle. The metal receptacle is affixed to the housing. The sealing element surrounds the sensor element in a centered position along its longitudinal extension L or on its half facing the measuring gas.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com