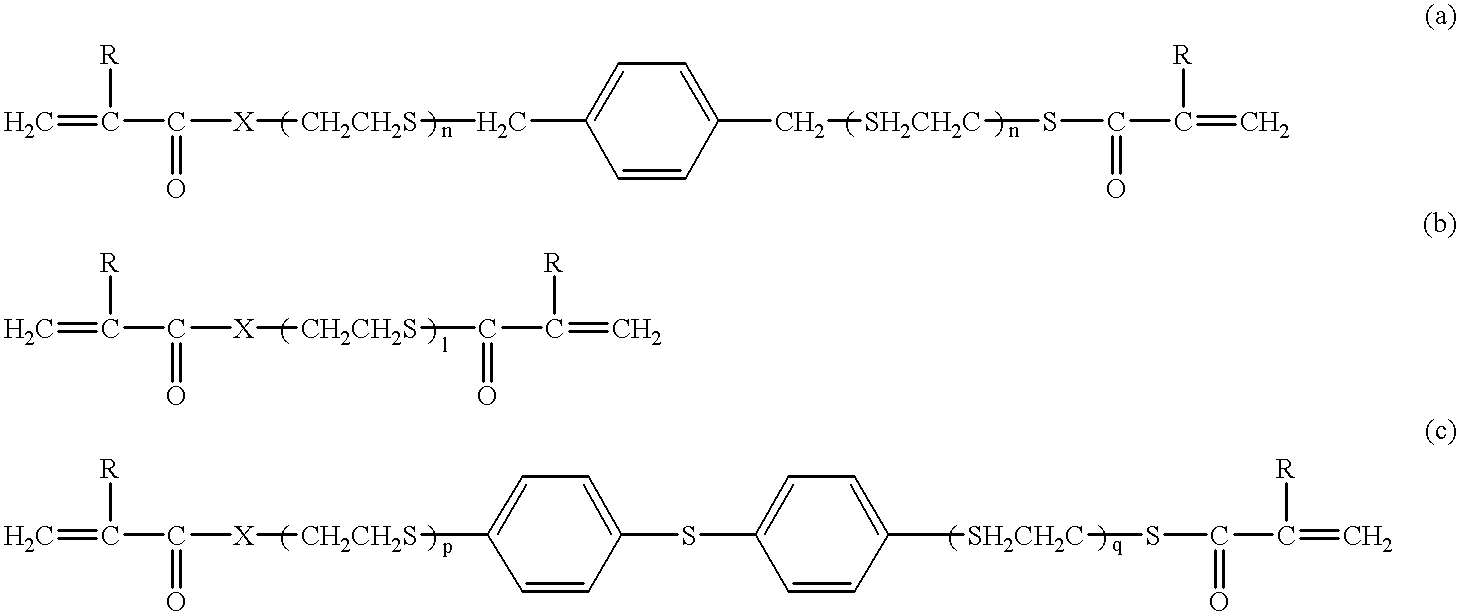
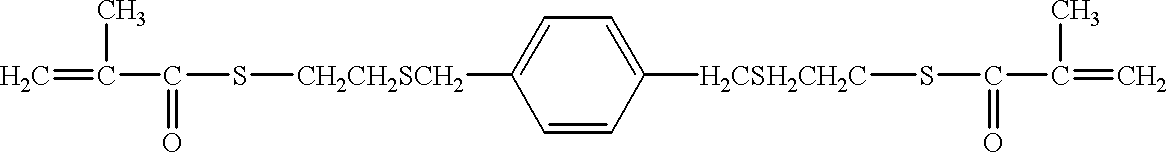
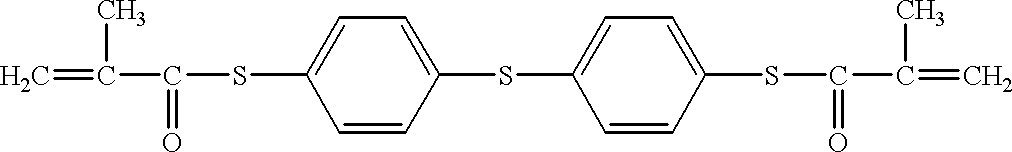
Patents
Literature
691results about How to "Deformation Minimization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
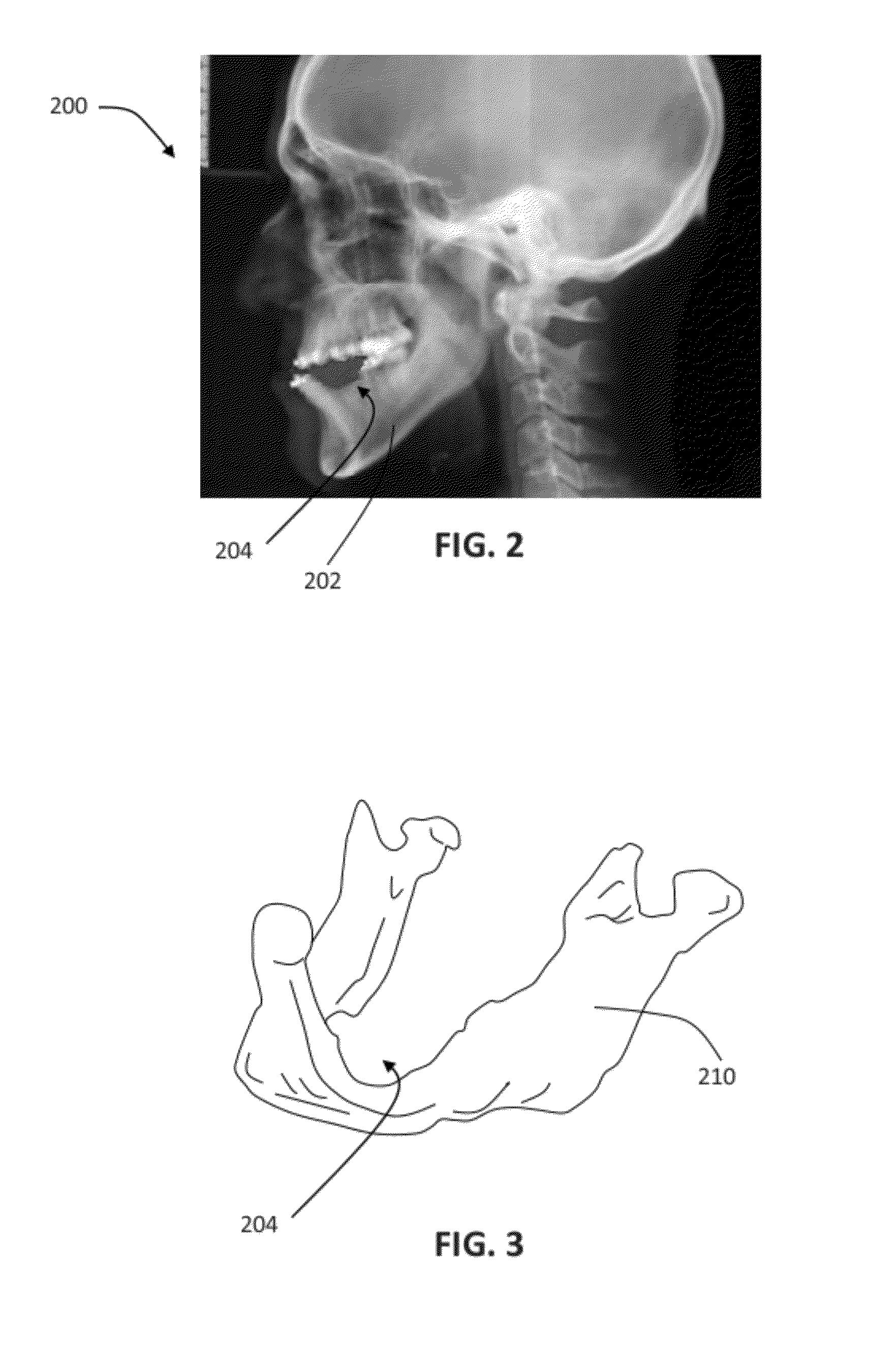
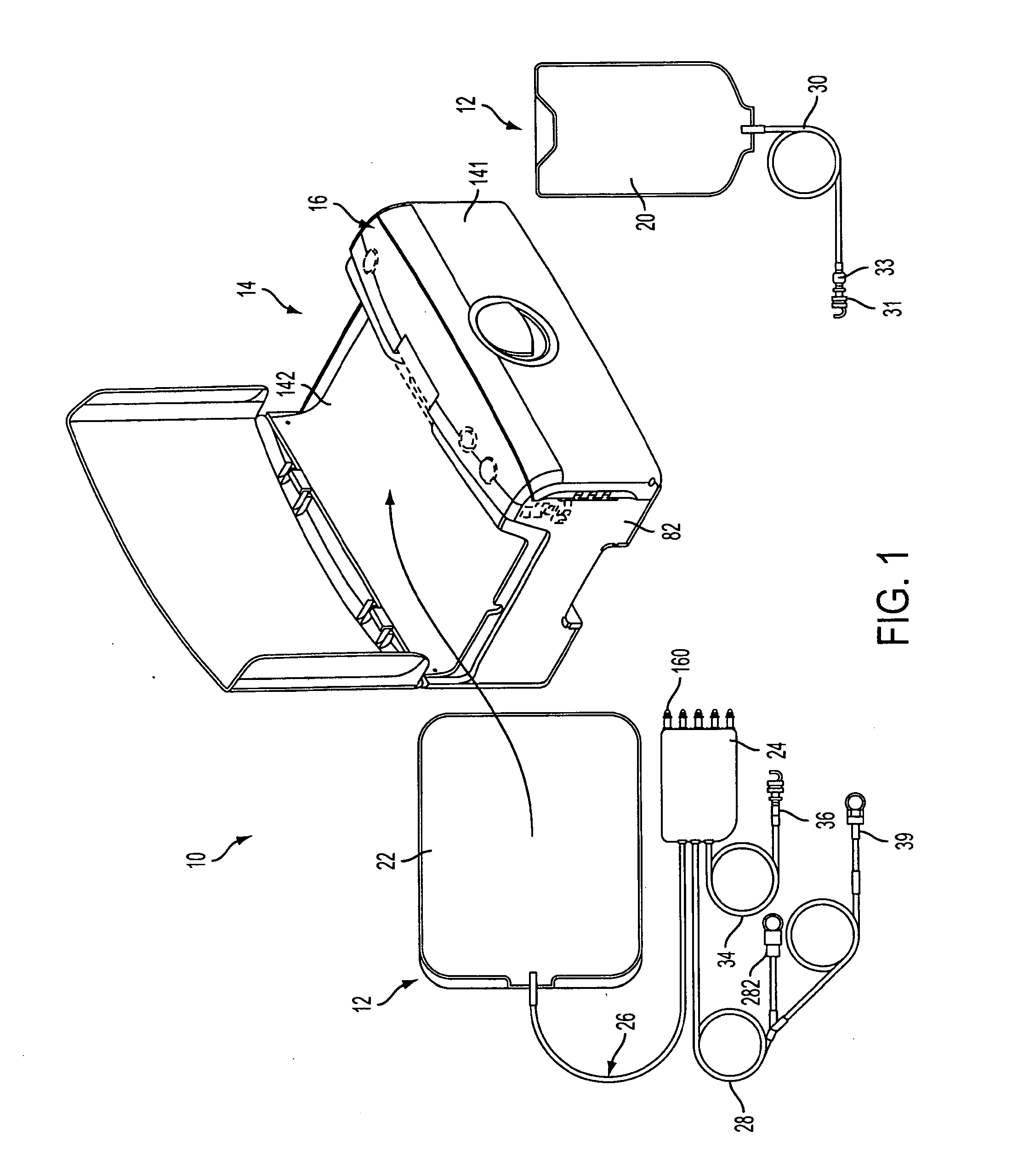
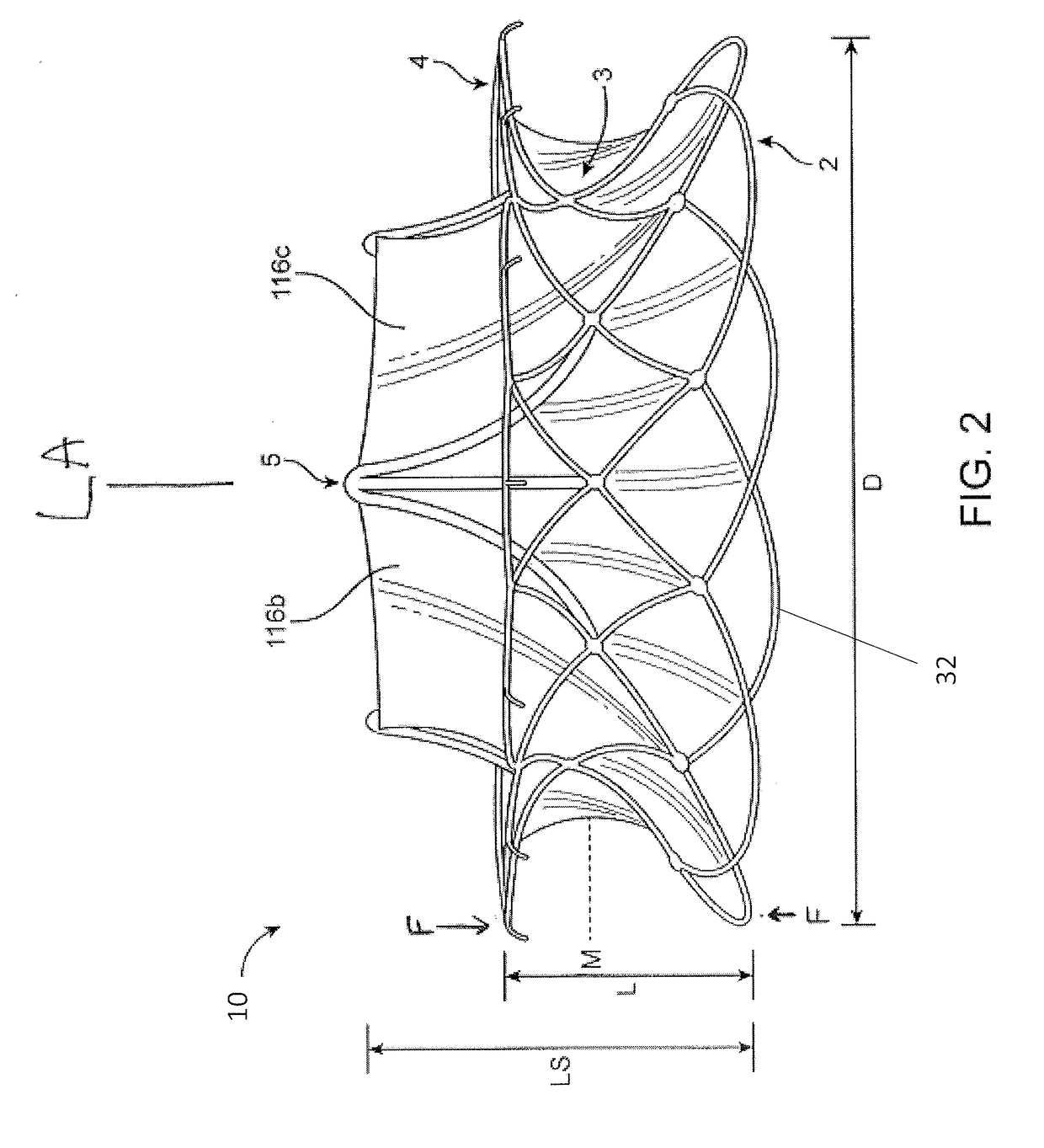
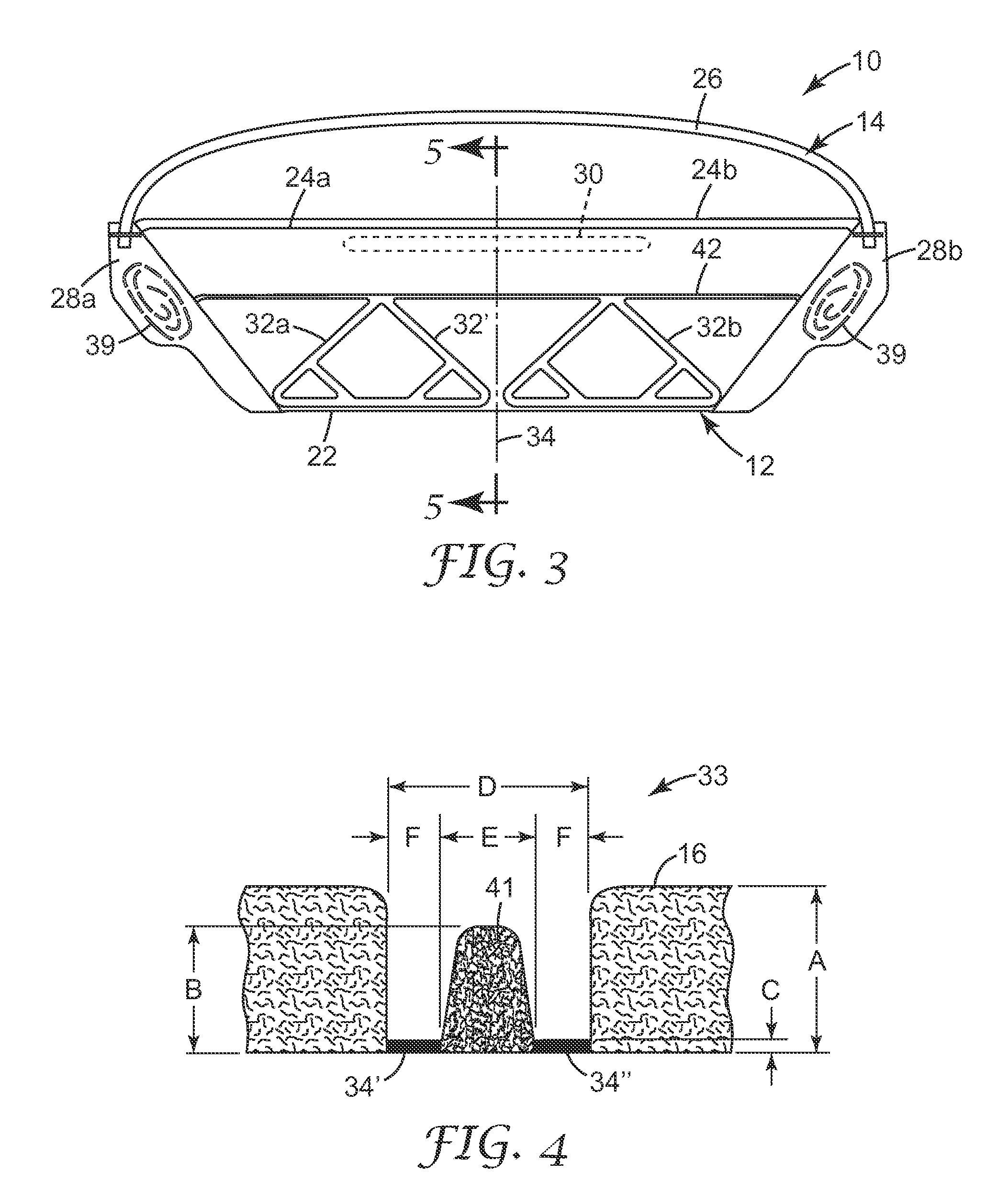
A surgical sealing device
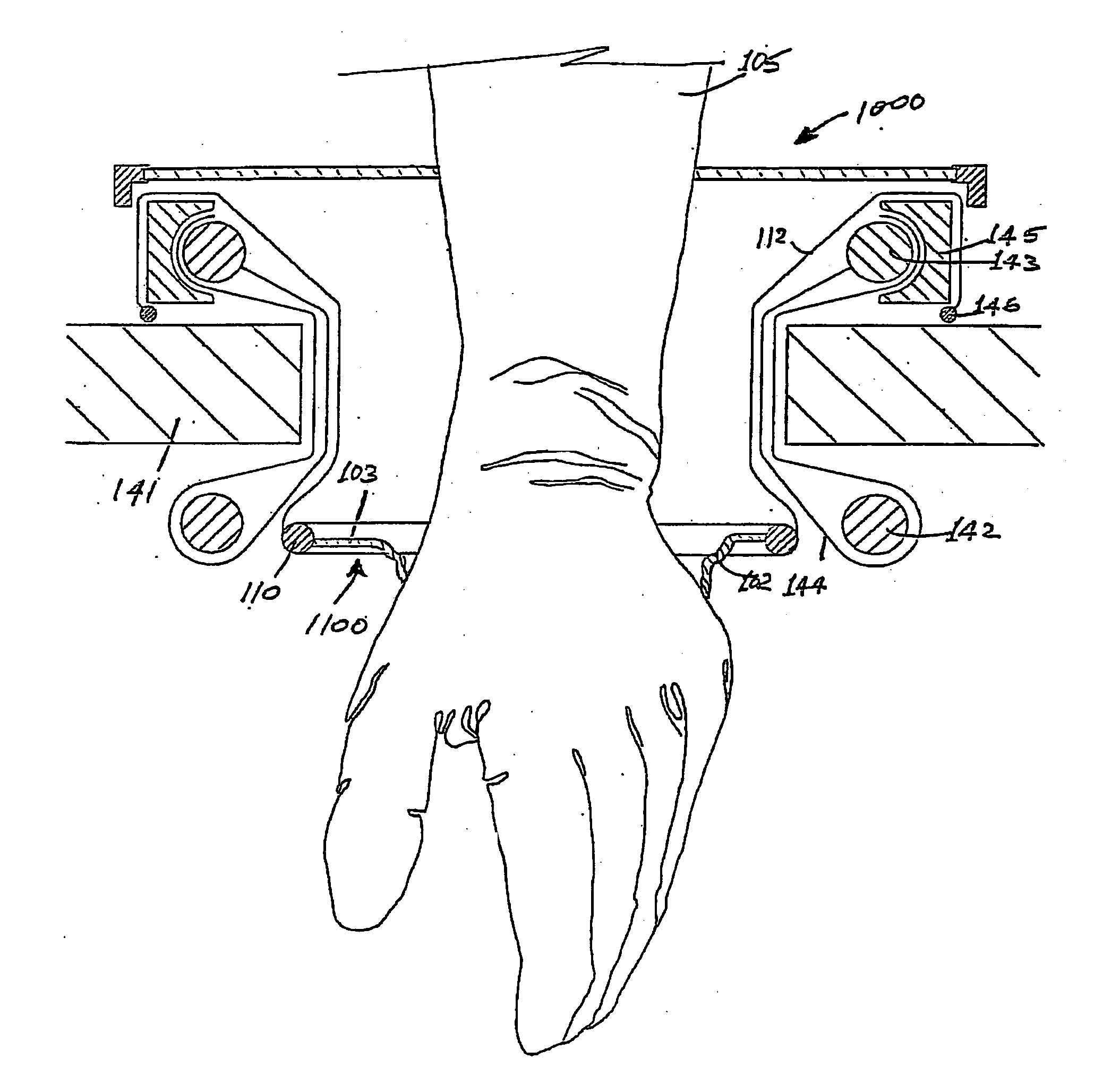
A surgical sealing device (405), suitable for use during a surgical procedure such as a laparoscopic procedure or a hand-assisted laparoscopic procedure, comprises a first sealing member (5) and a second sealing member (6). A thin slit is defined between the sealing members (5, 6). In a closed configuration, the first sealing member (5) overlaps the distal end opening of a passageway (2) through the second sealing member (6) to prevent leakage of insufflation gases out of an abdomen (4). In an open configuration, the first sealing member (5) is retracted to reveal the distal end opening of the passageway (2) and thus facilitate passage of an object, such as a surgeon's hand or forearm (3), into the abdomen (4). The device (405) comprises a planar support element (406) fixedly attached to the proximal exterior surface (408) of the first sealing member (5). The first sealing member (5) is fixedly attached to the second sealing member (6) at an attached region (409), with a detached region (407) remaining detached from the second sealing member (6). The support element (406) acts as a stiffening element to increase the stiffness of the detached region (407) of the first sealing member (5) to minimise the deformation of the detached region (407) of the first sealing member (5) when the surgeon's hand / forearm (3) is pushed through the passageway (2). It is thus easier for the surgeon to retract the first sealing member (5) laterally to reveal the distal end opening of the passageway (2) by pushing the hand / forearm (3) through the passageway (2) and easier for the surgeon to pass the hand / forearm (3) through the device (405) and gain access to the abdomen (4).
Owner:ATROPOS LTD
Fluid volume determination for medical treatment system
ActiveUS20110071465A1Deformation MinimizationPreventing sticking of the membraneMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesFlexible member pumpsPump chamberMathematical model
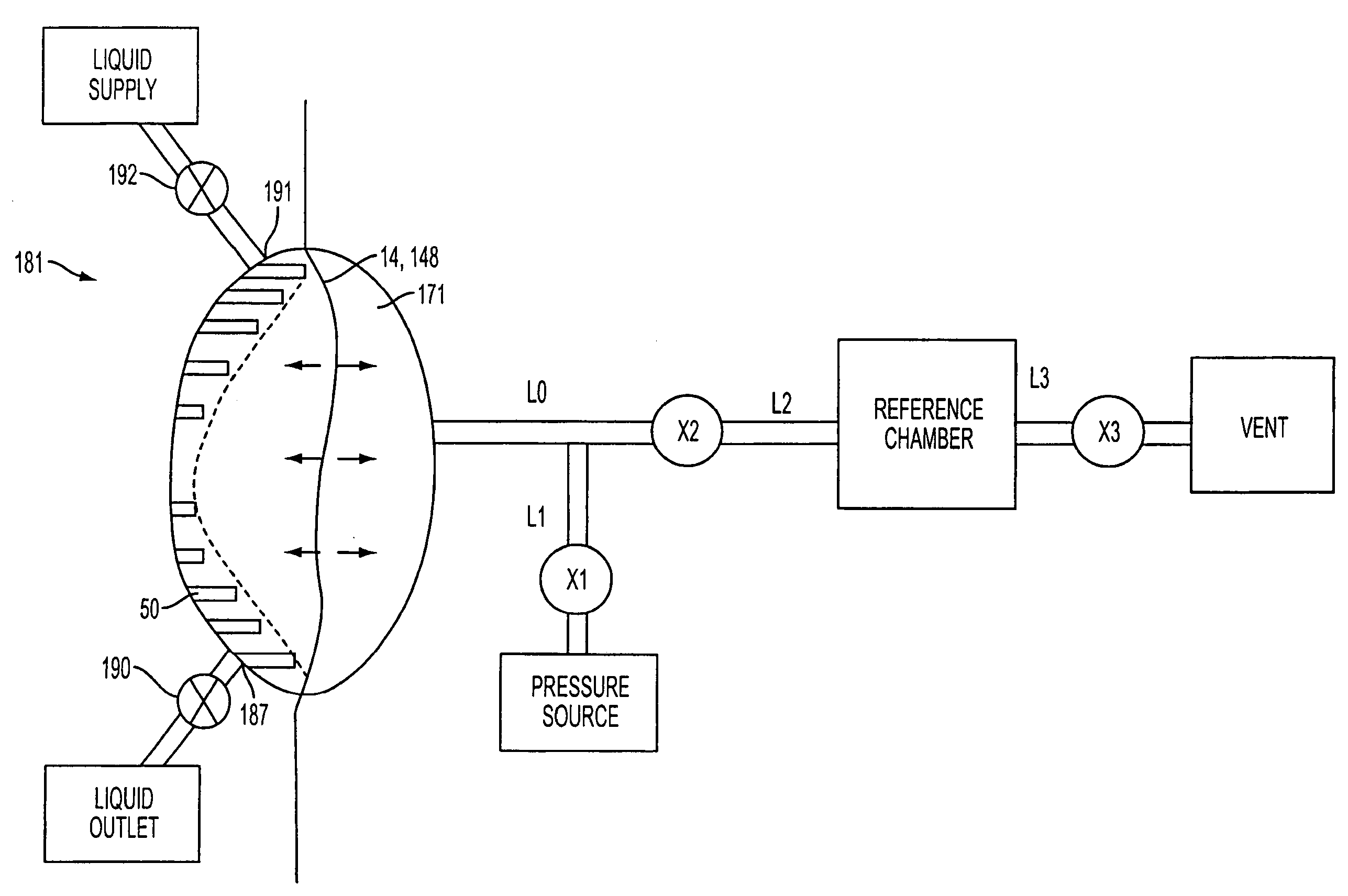
A volume of fluid moved by a pump, such as a pump in an APD system, may be determined without direct measurement of the fluid, such as by flow meter, weight, etc. For example, a volume of a pump chamber (181) (having a movable element that varies the volume of the pump chamber) may be determined by measuring pressure in the pump chamber and a reference chamber, both while the two chambers are isolated from each other, and after the two chambers are fluidly connected so that pressures in the chambers may equalize. Equalization of the pressures may be assumed to occur in an adiabatic way, e.g., a mathematical model of the system that is based on an adiabatic pressure equalization process may be used to determine the pump chamber volume. In one embodiment, pressures measured after the chambers are fluidly connected may be measured at a time before complete pressure equalization has occurred, and thus the pressures for the pump and reference chambers measured after the chambers are fluidly connected may be unequal, yet still be used to determine the pump chamber volume.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
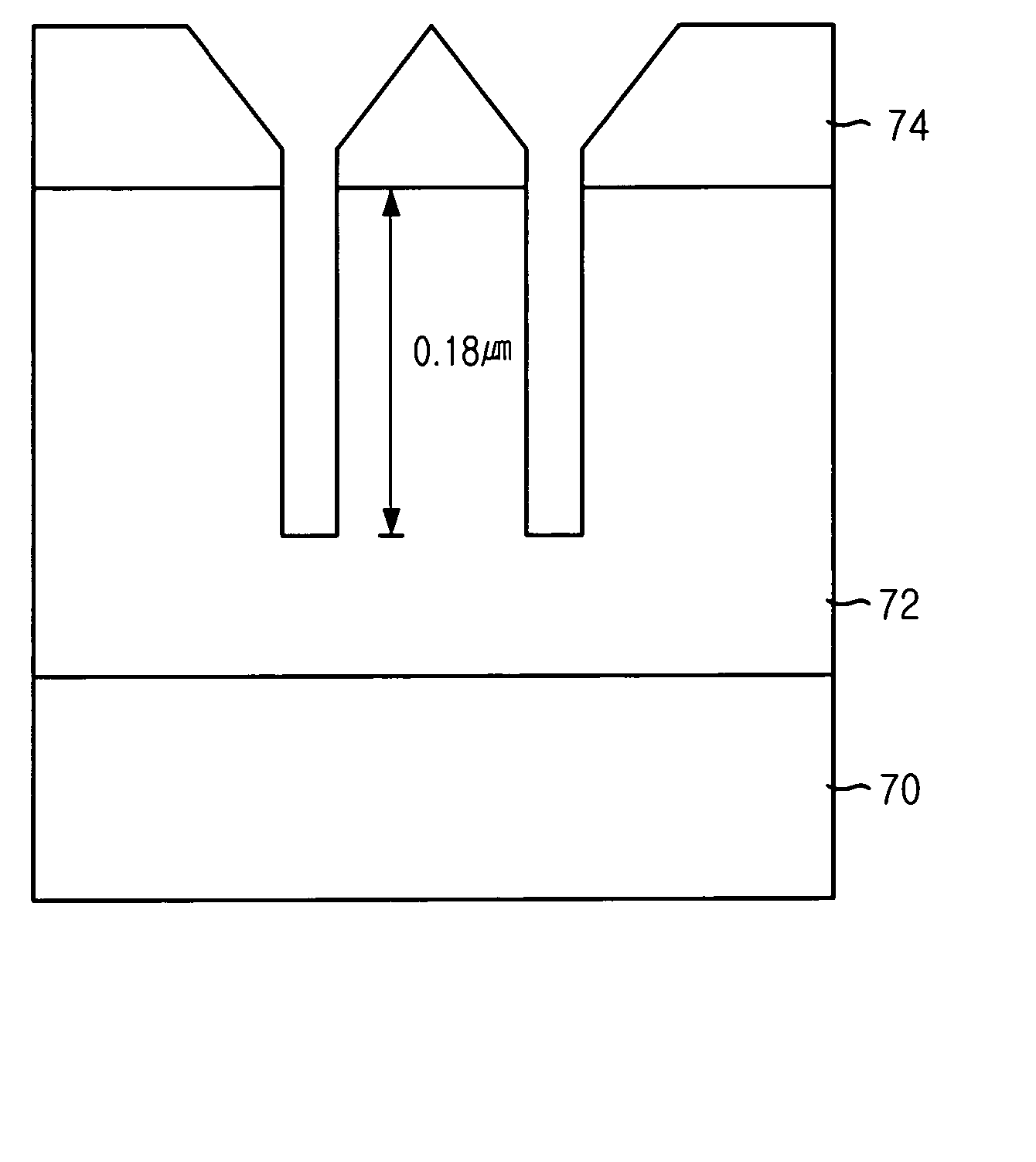
Method for fabricating semiconductor device using amorphous carbon layer as sacrificial hard mask
ActiveUS20060024945A1Minimizing pattern deformationEtch selectivity of hardSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistDevice material
Disclosed is a method for fabricating a semiconductor device by using an amorphous carbon layer as a sacrificial hard mask. The method includes the steps of: forming an amorphous carbon layer on an etch target layer; forming a photoresist pattern on the amorphous carbon layer; etching the amorphous carbon layer by using the photoresist pattern to form a sacrificial hard mask; and etching the etch target layer by using the sacrificial hard mask to form a predetermined pattern.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
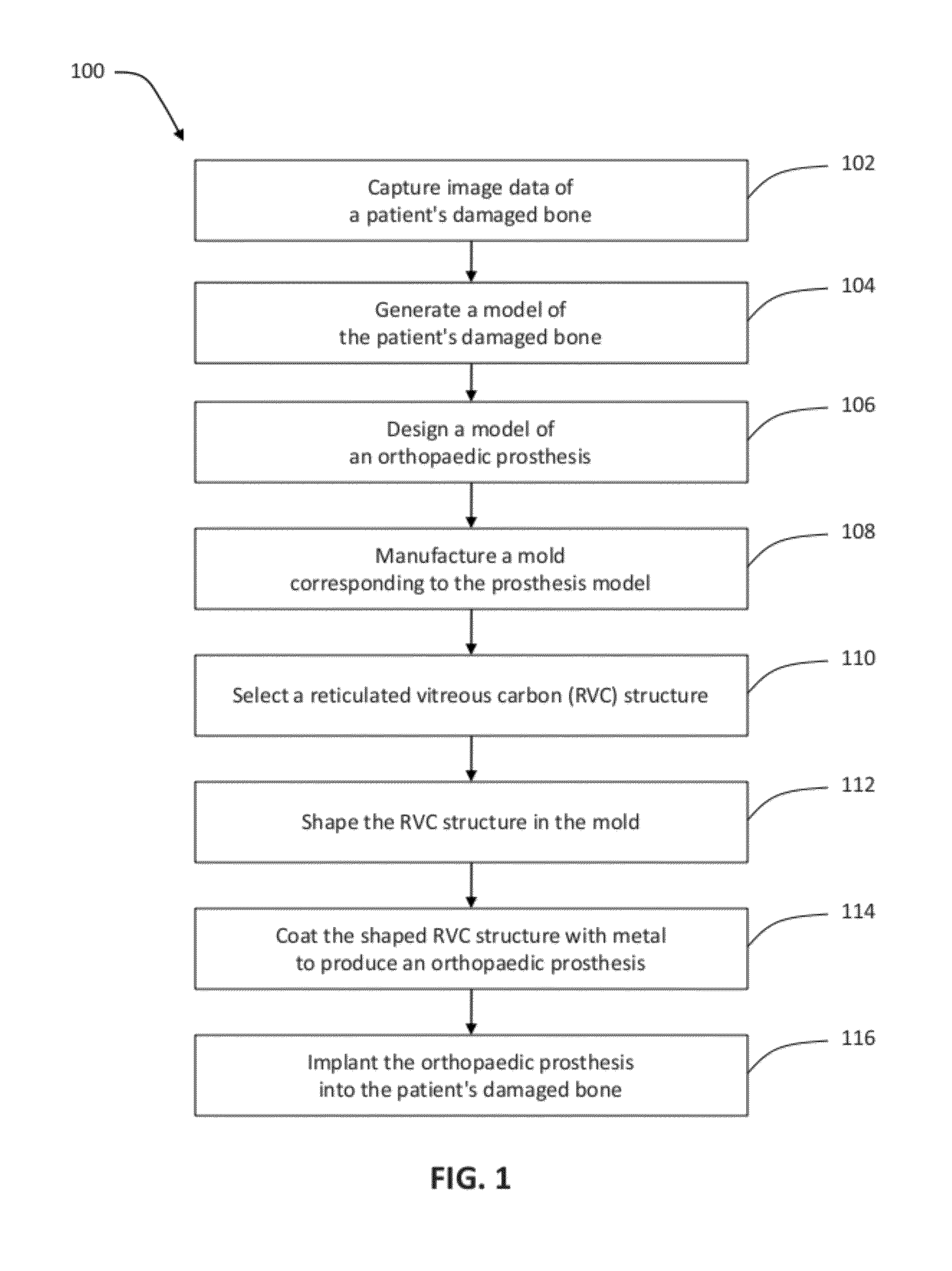
Patient-specific manufacturing of porous metal prostheses
ActiveUS20120310364A1Low efficiencyAvoid substantially changing porosityImpression capsPretreated surfacesProsthesisPlastic surgery
A patient-specific porous metal prosthesis and a method for manufacturing the same are provided. The orthopaedic prosthesis may be metallic to provide adequate strength and stability. Also, the orthopaedic prosthesis may be porous to promote bone ingrowth.
Owner:ZIMMER INC
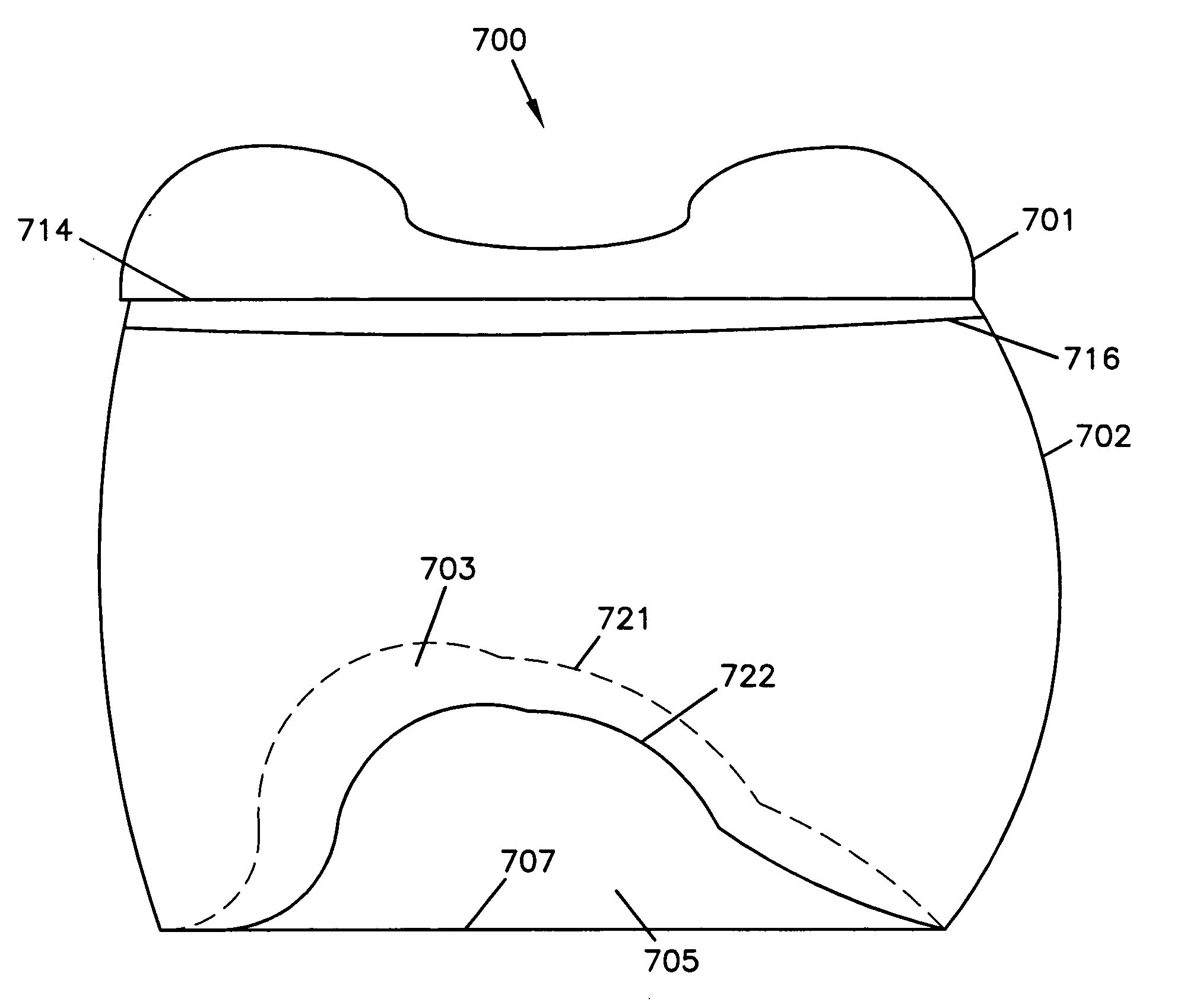
Pressurized plastic bottle for dispensing an aerosol
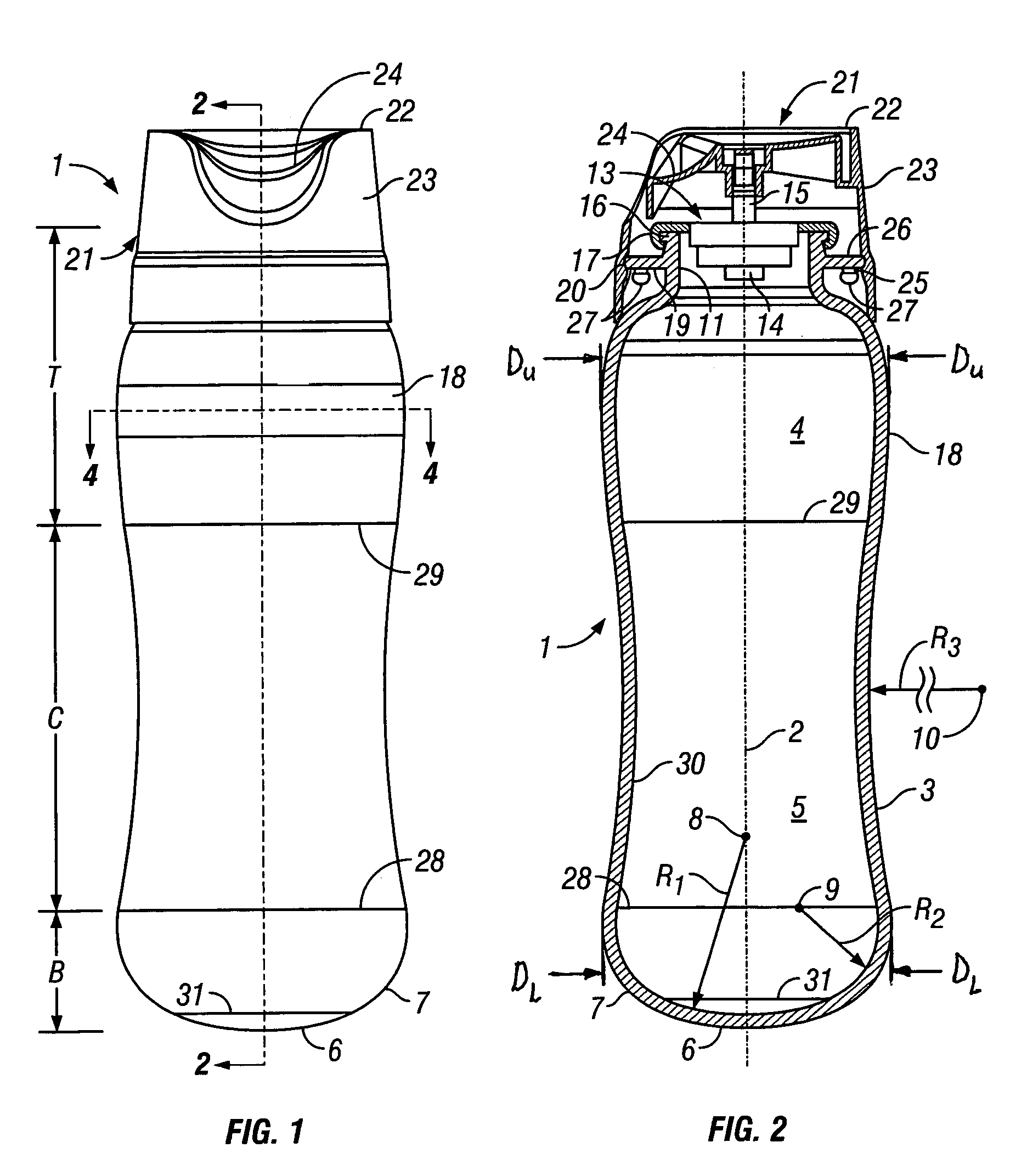
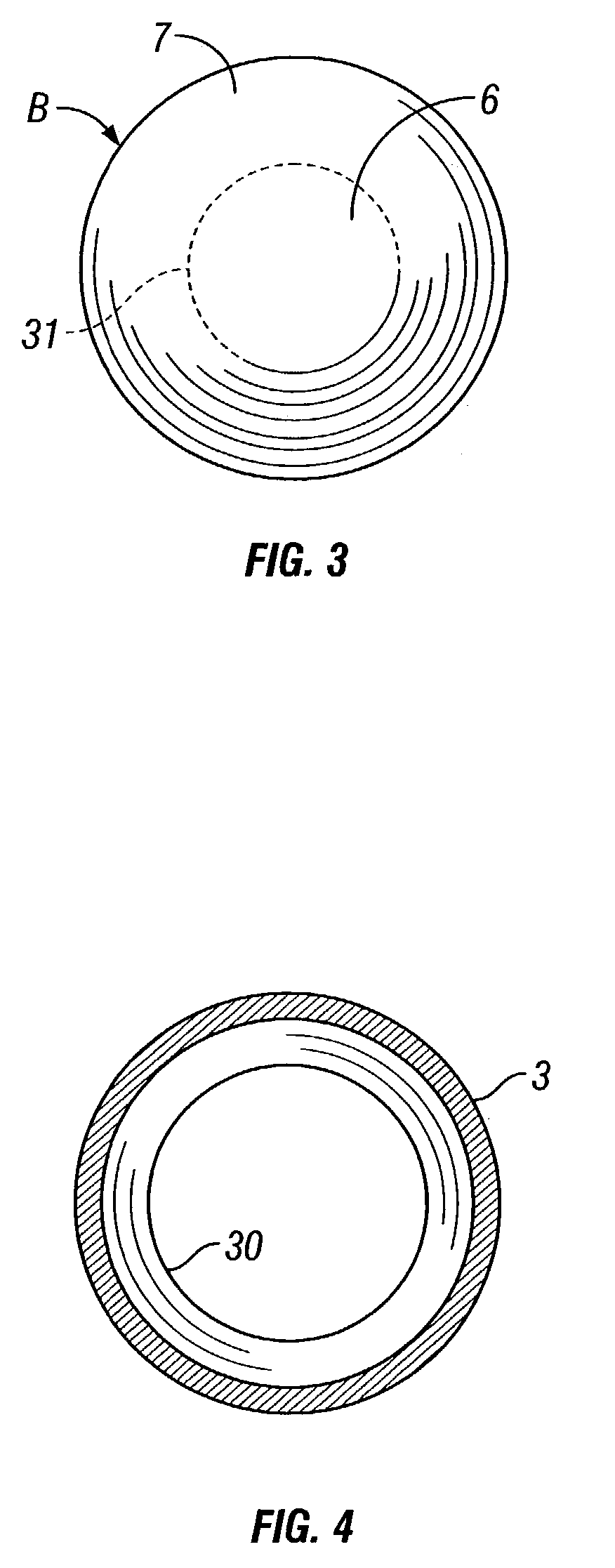
InactiveUS7028866B2Deformation MinimizationUniform changeLarge containersLiquid dispensingEngineeringAerosol composition
A pressure resistant plastic bottle for containing and dispensing an aerosol composition. The plastic bottle is comprised of a hollow elongate body having a central portion, a top portion and an opposite bottom portion with the central portion having an inwardly concave configuration extending along its longitudinal direction. The bottom portion of the elongate body is integral with the central portion and defines an outwardly projecting convexly shaped configuration. The top portion of the bottle is integral with the central portion and has an outwardly convex configuration extending along its longitudinal direction and defines a neck having an opening for receiving and dispensing the aerosol composition. A closure covers the opening and is sealingly attached to the neck to contain the aerosol within the plastic bottle.
Owner:SC JOHNSON & SON INC
Showerhead assembly and apparatus for manufacturing semiconductor device having the same
InactiveUS20050000430A1Minimizes thermal expansion-induced deformationUniform propertyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
A showerhead assembly of an apparatus for manufacturing a semiconductor device includes a backing plate having a gas inlet, a showerhead combined with the backing plate at an end portion thereof, wherein the showerhead has a plurality of holes, and a sub heater equipped at a peripheral portion of the showerhead.
Owner:JUSUNG ENG
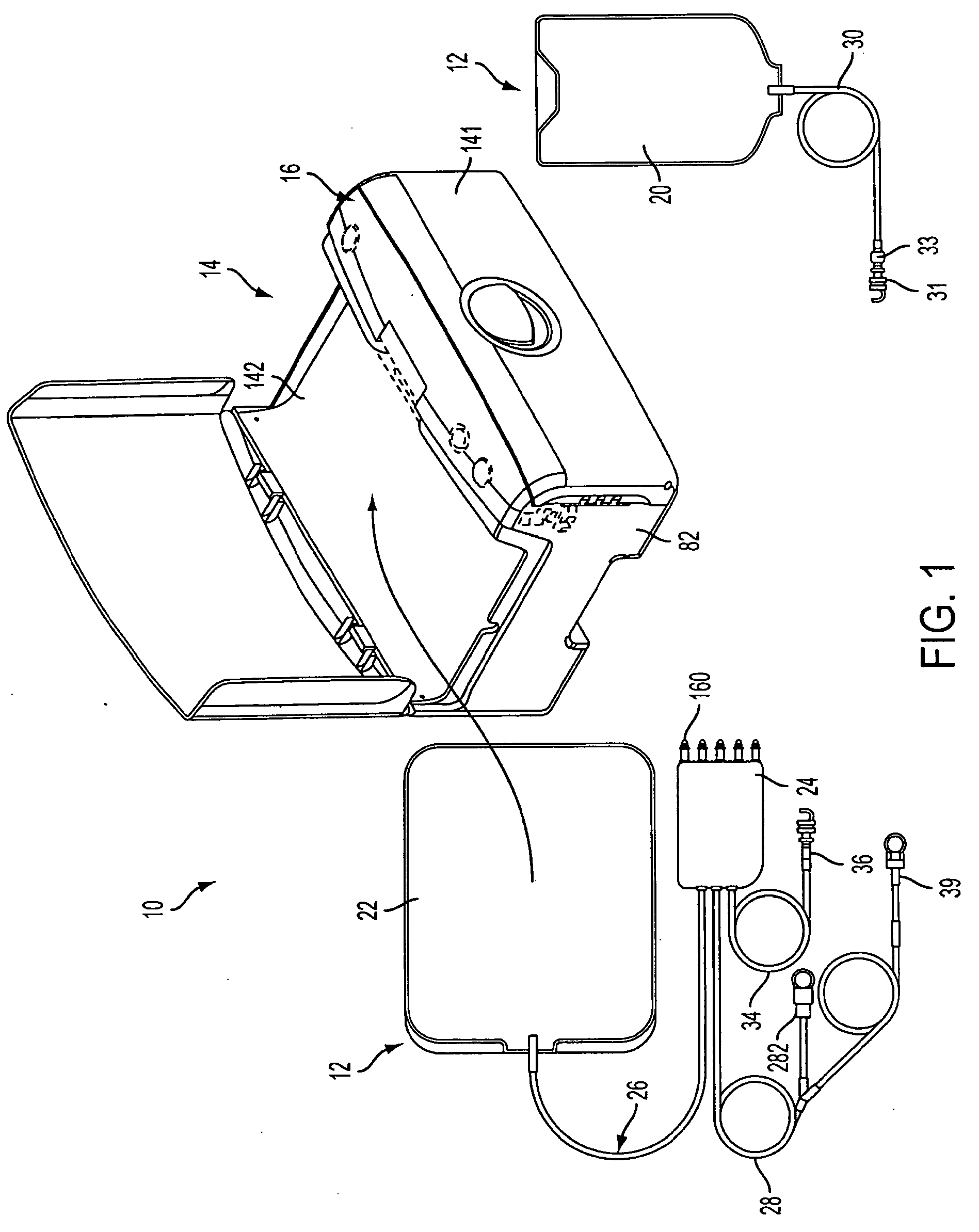
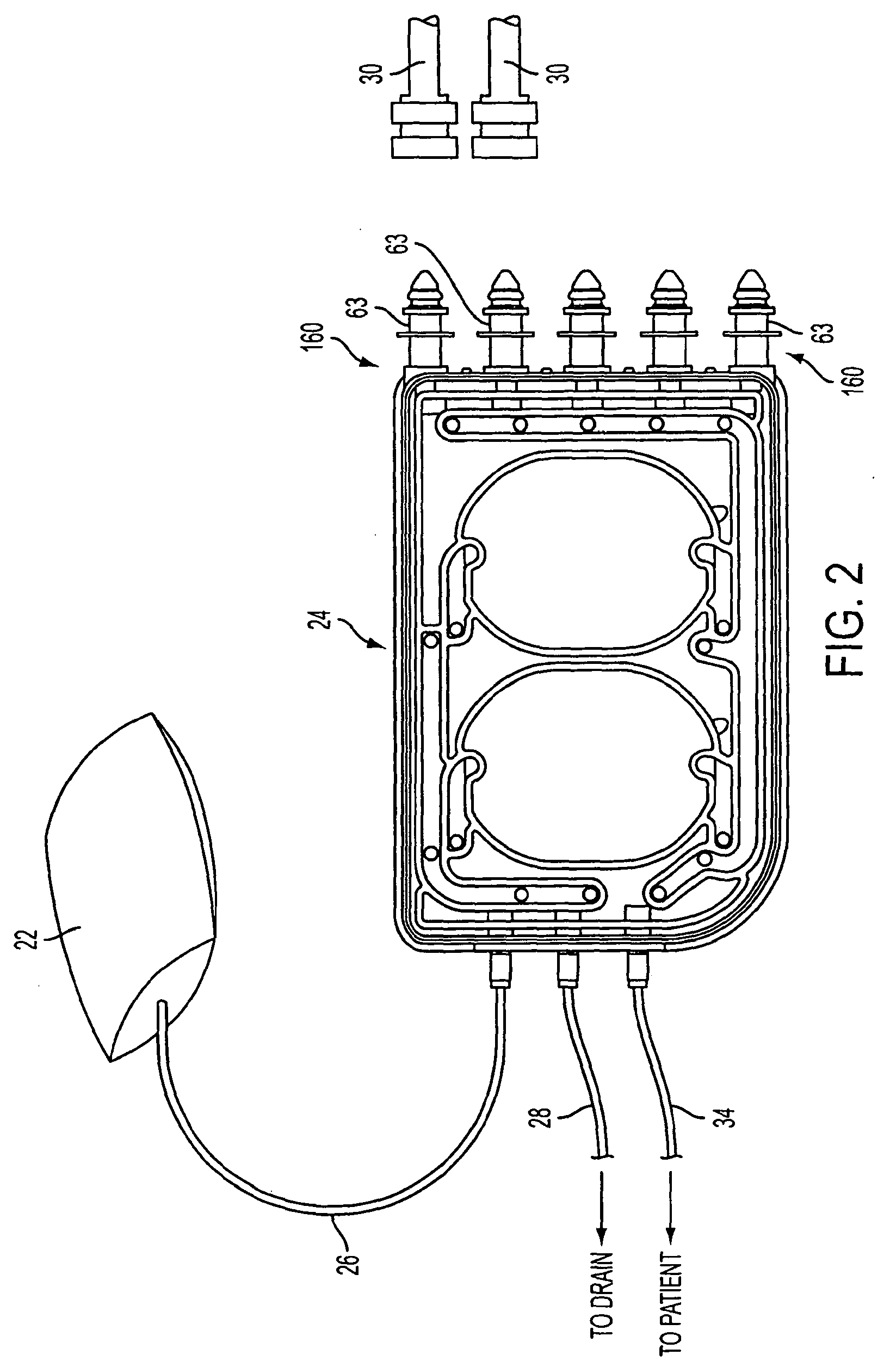
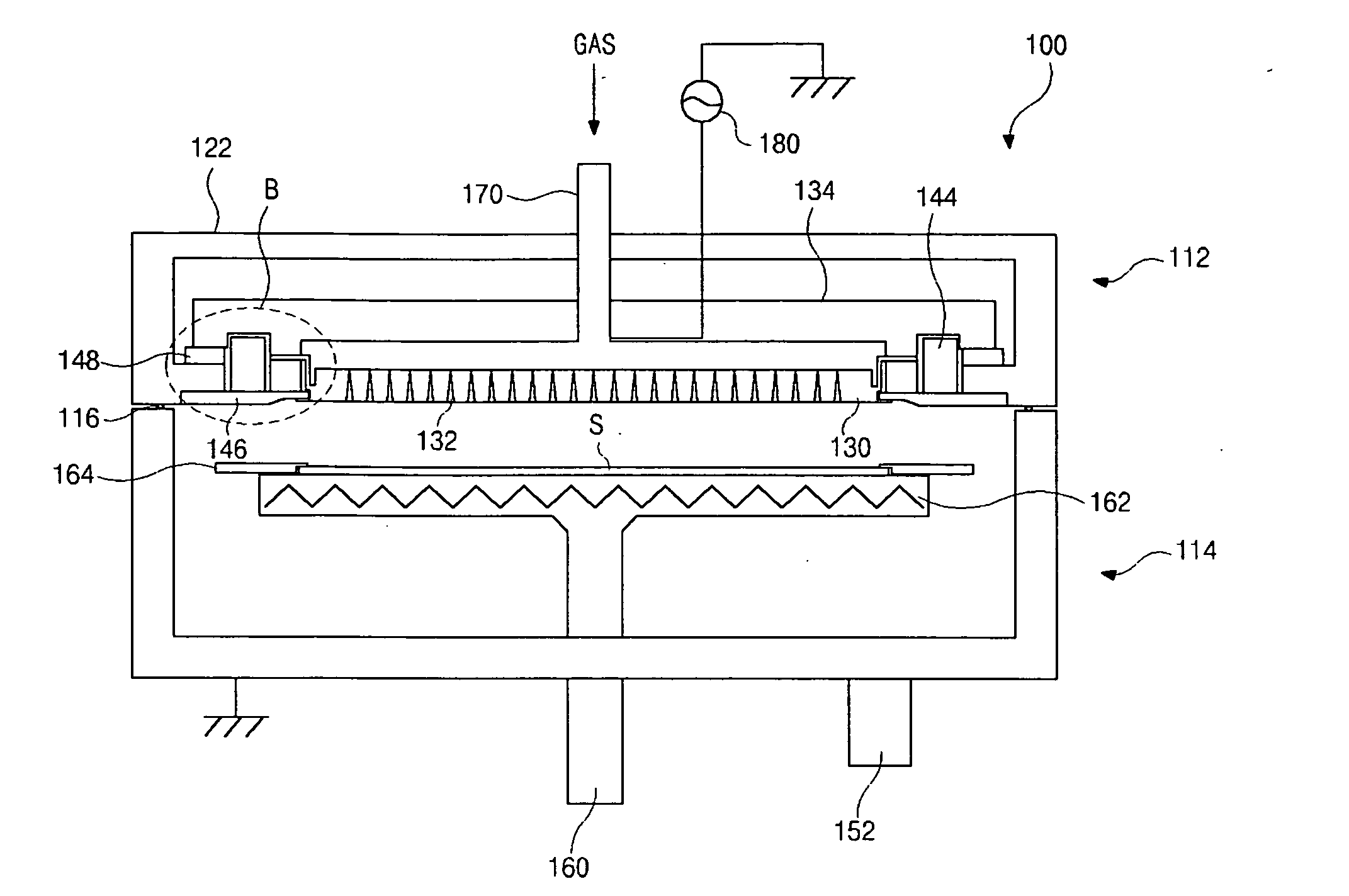
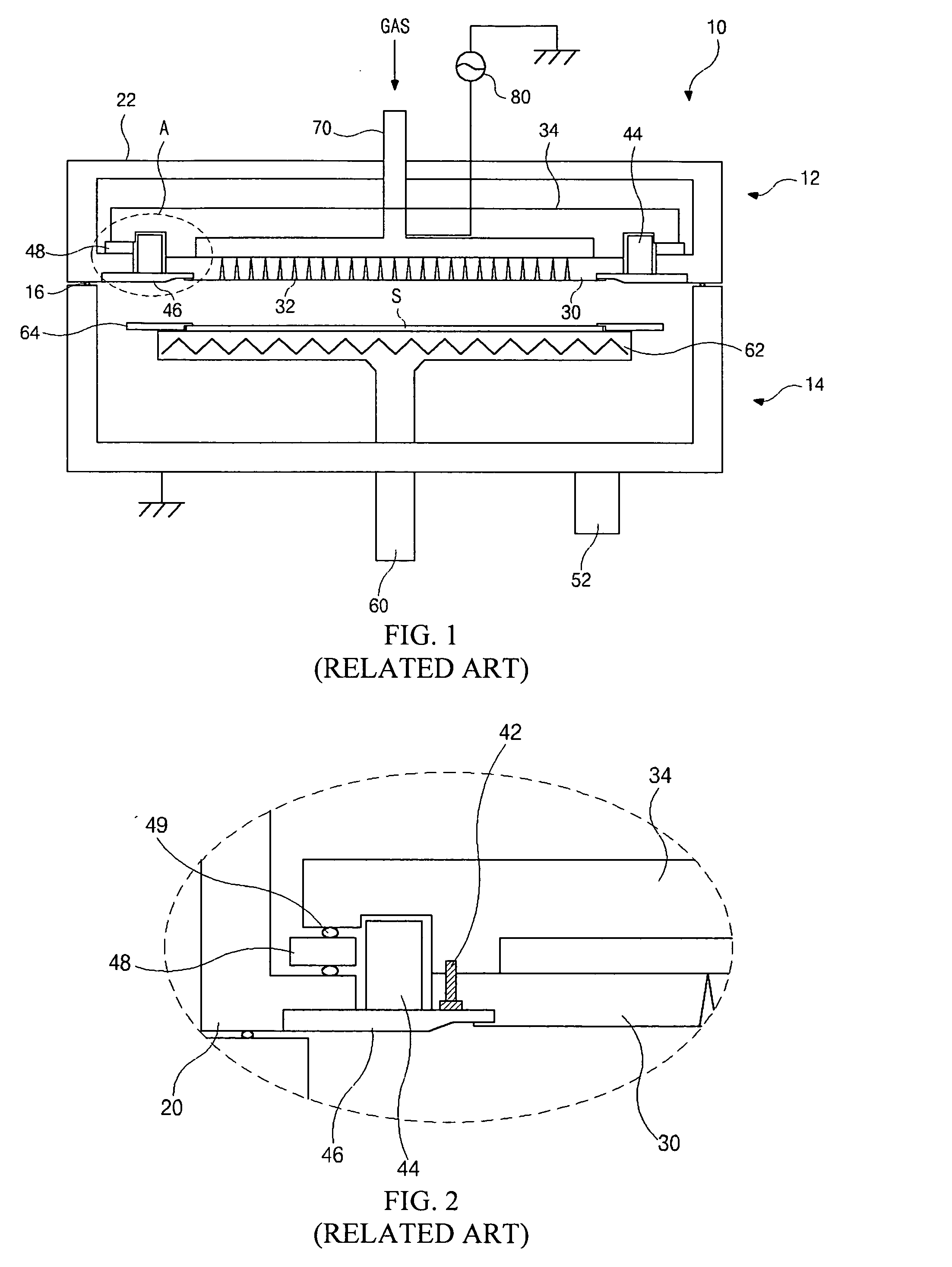
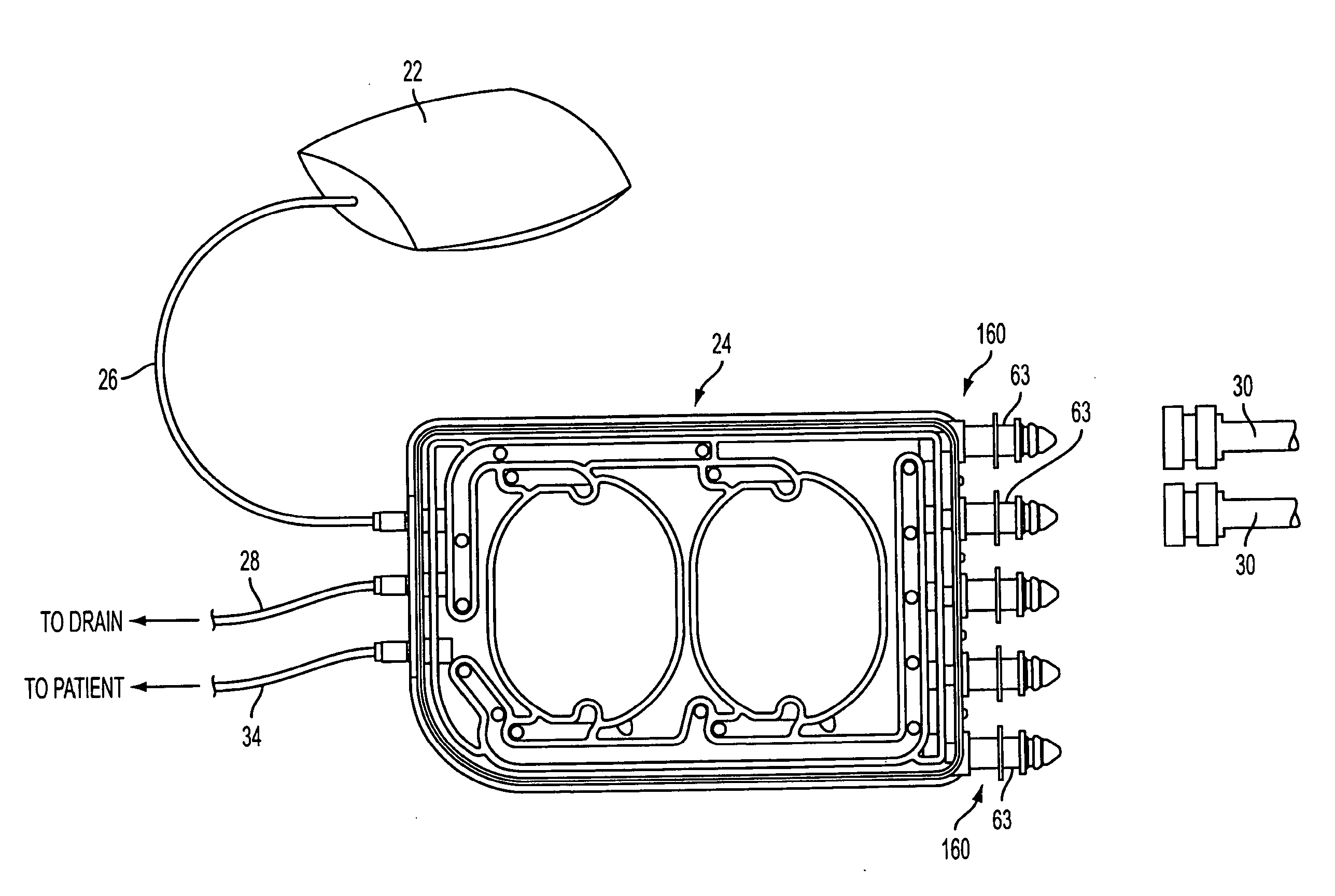
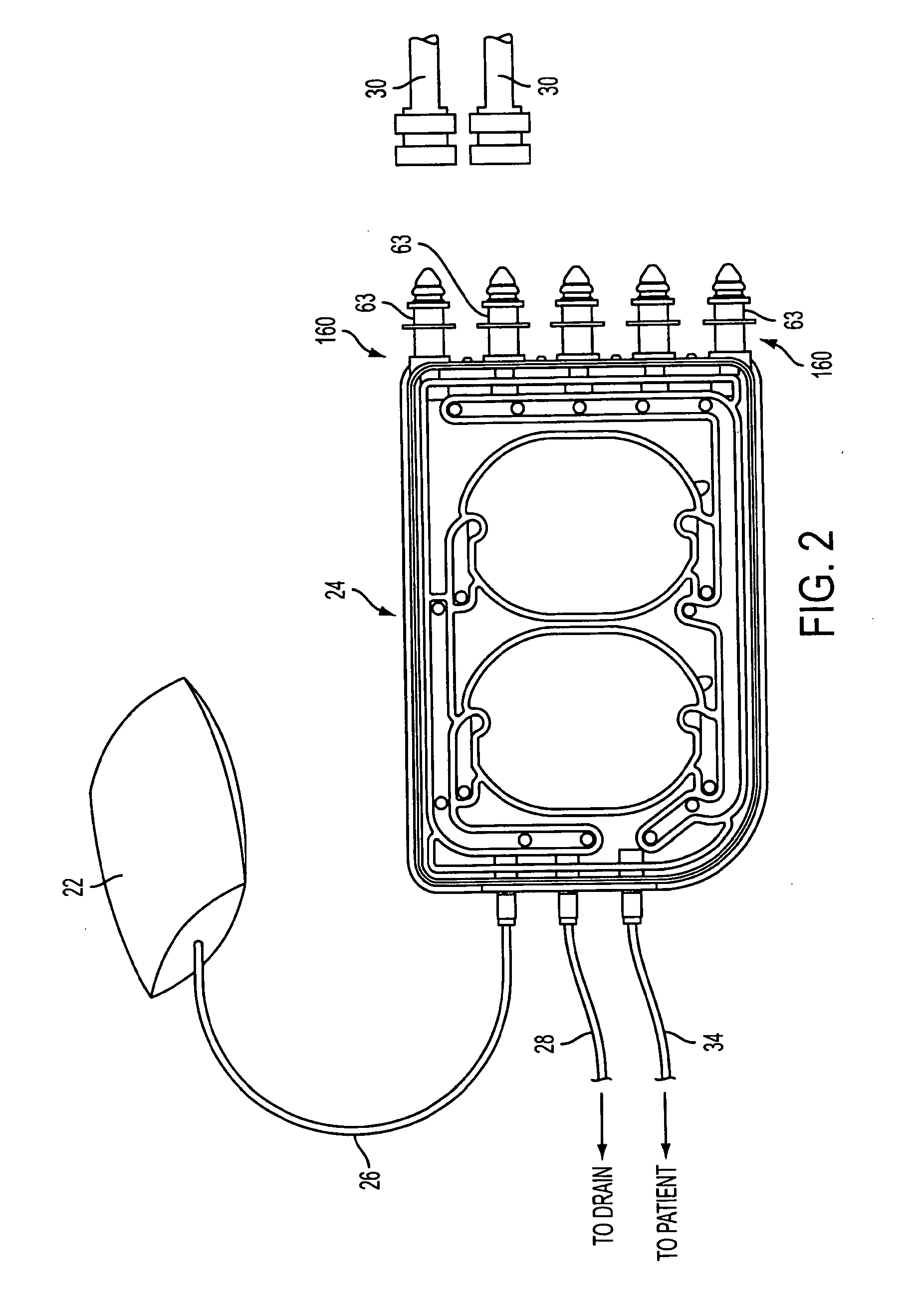
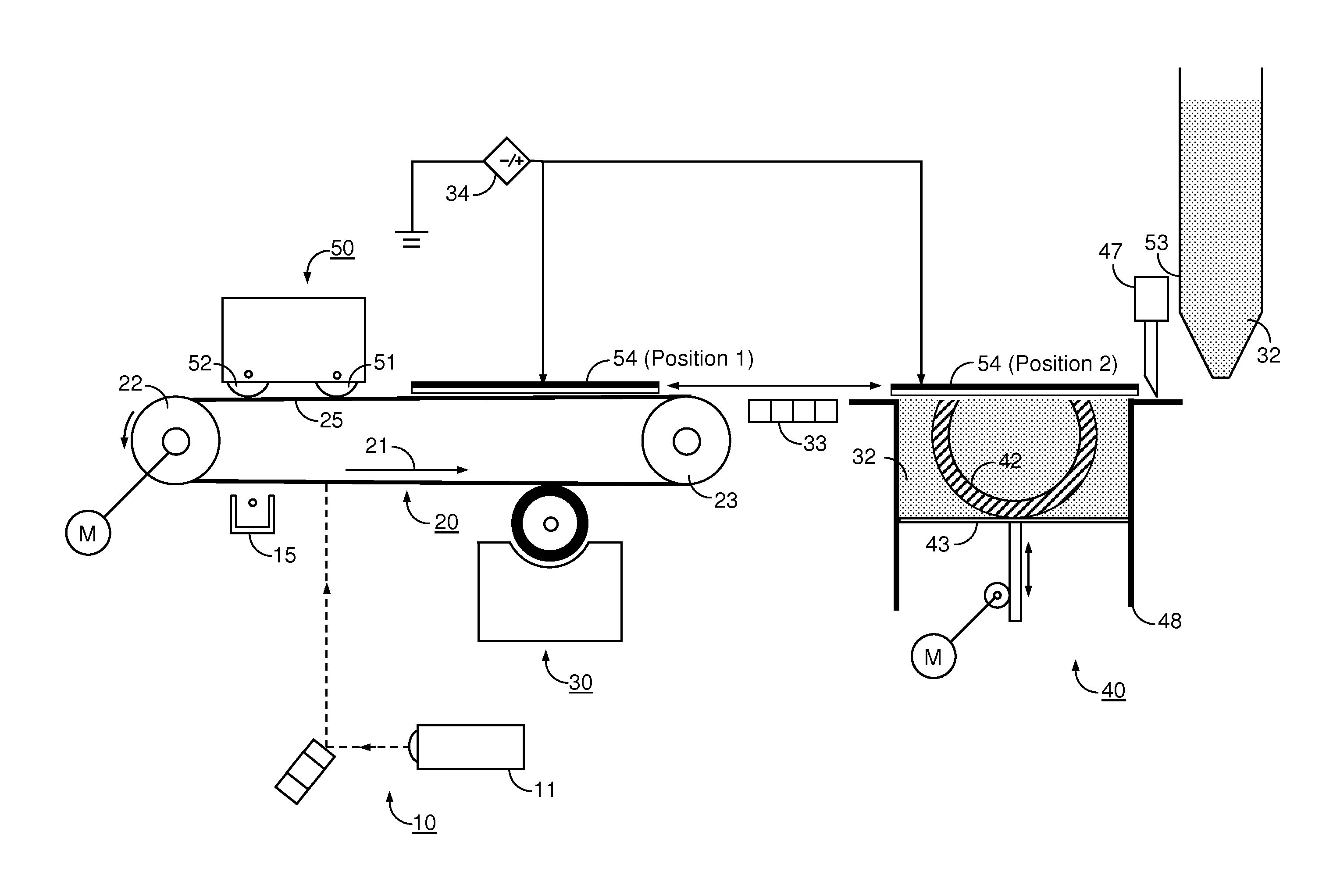
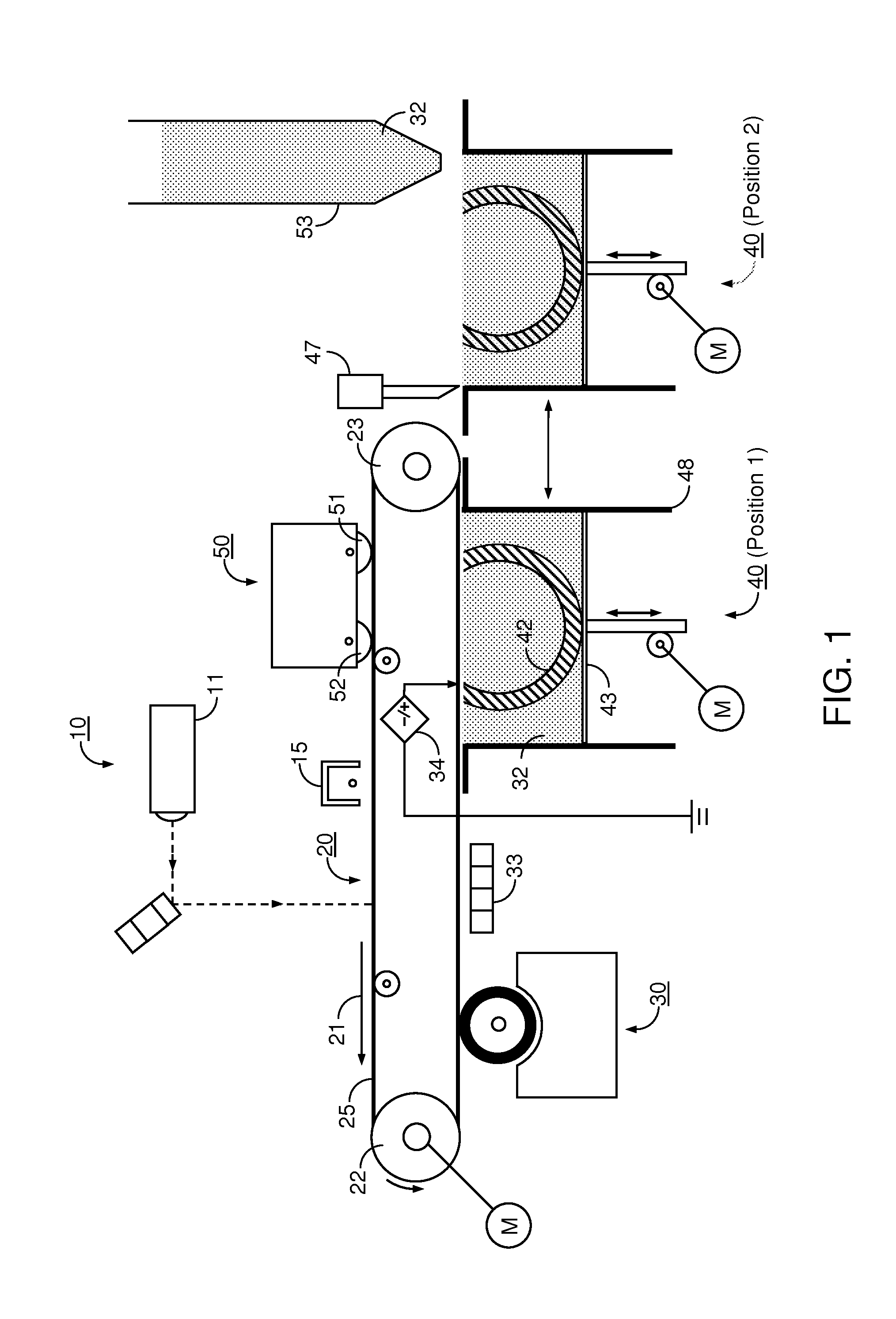
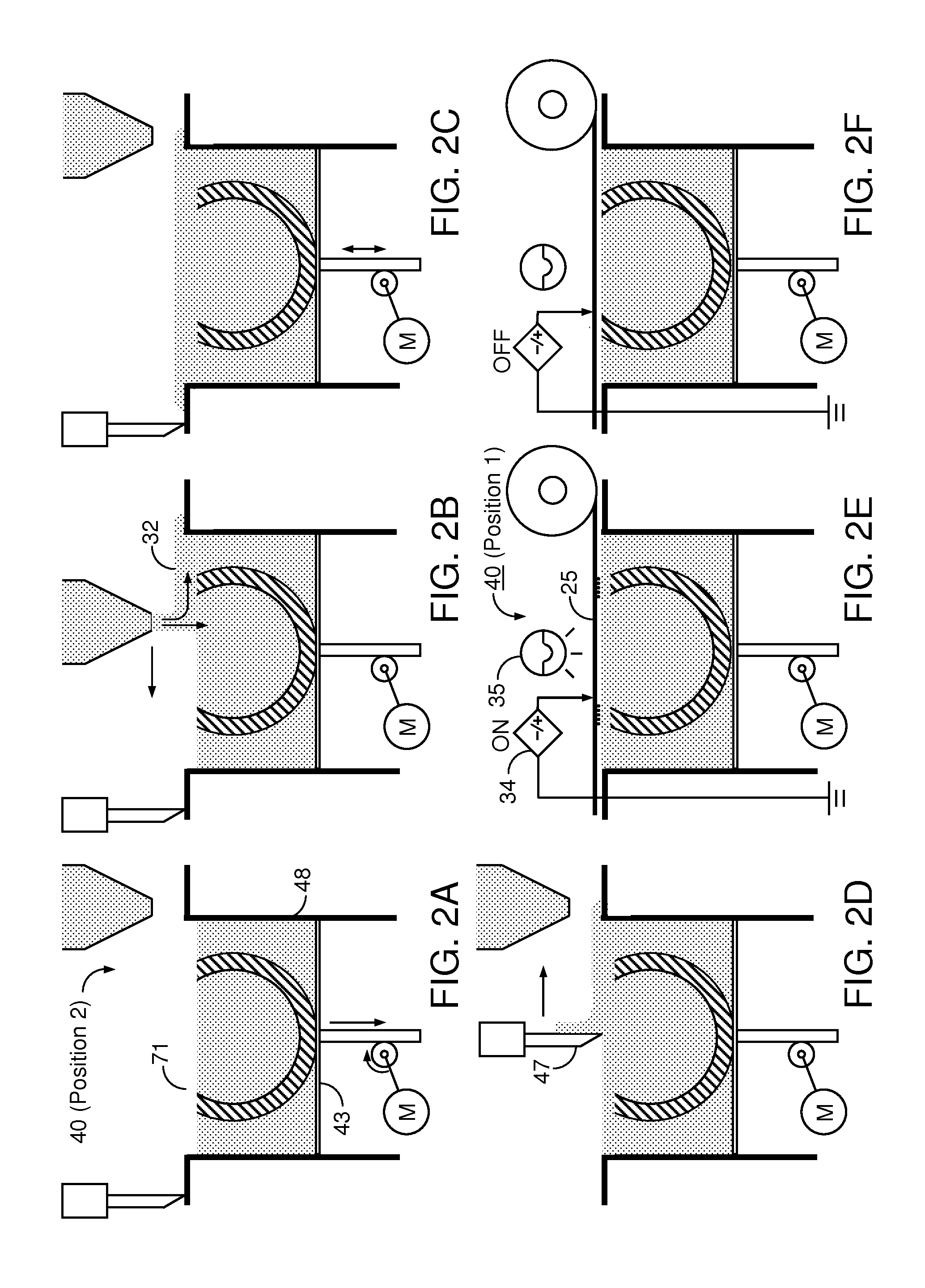
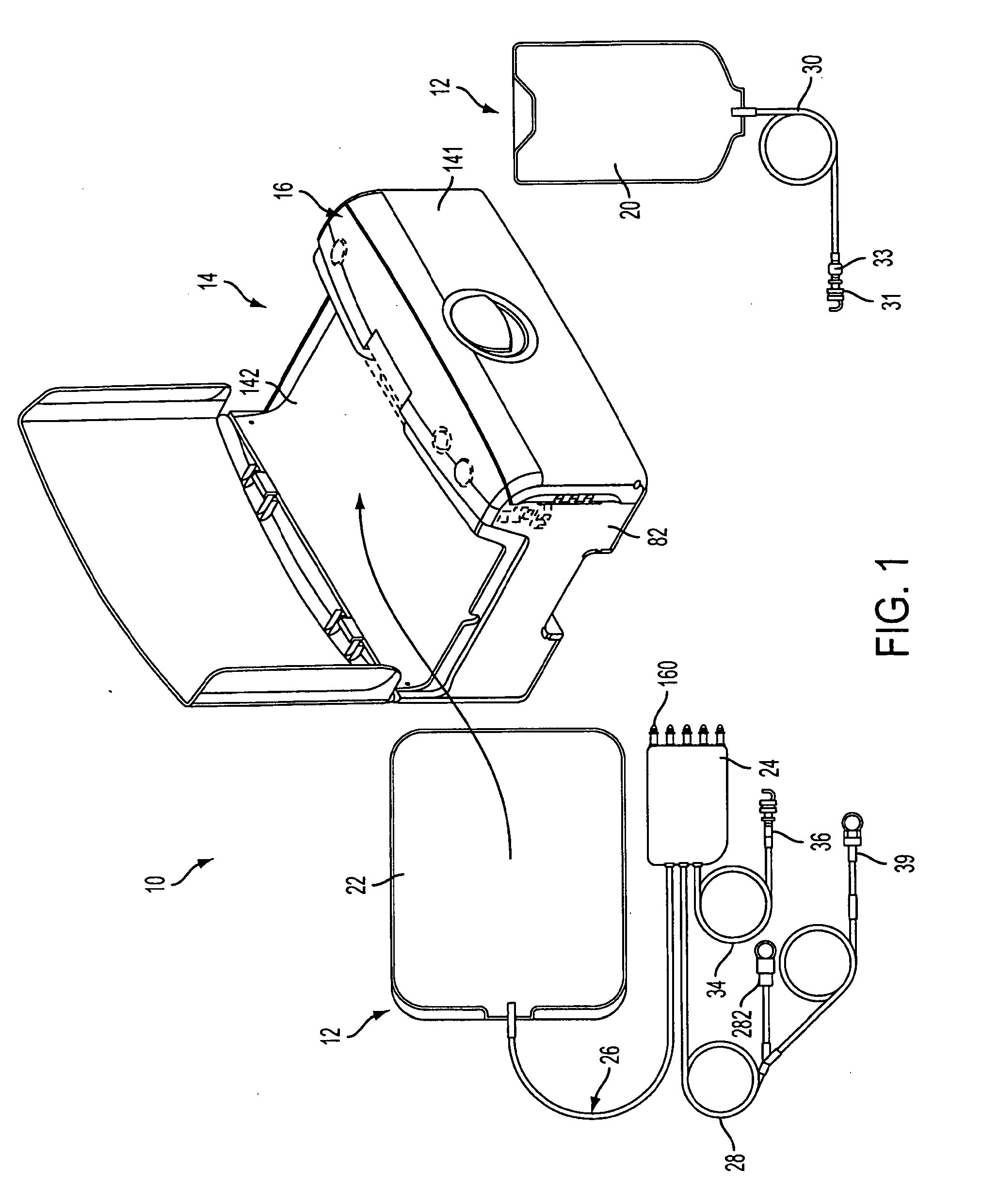
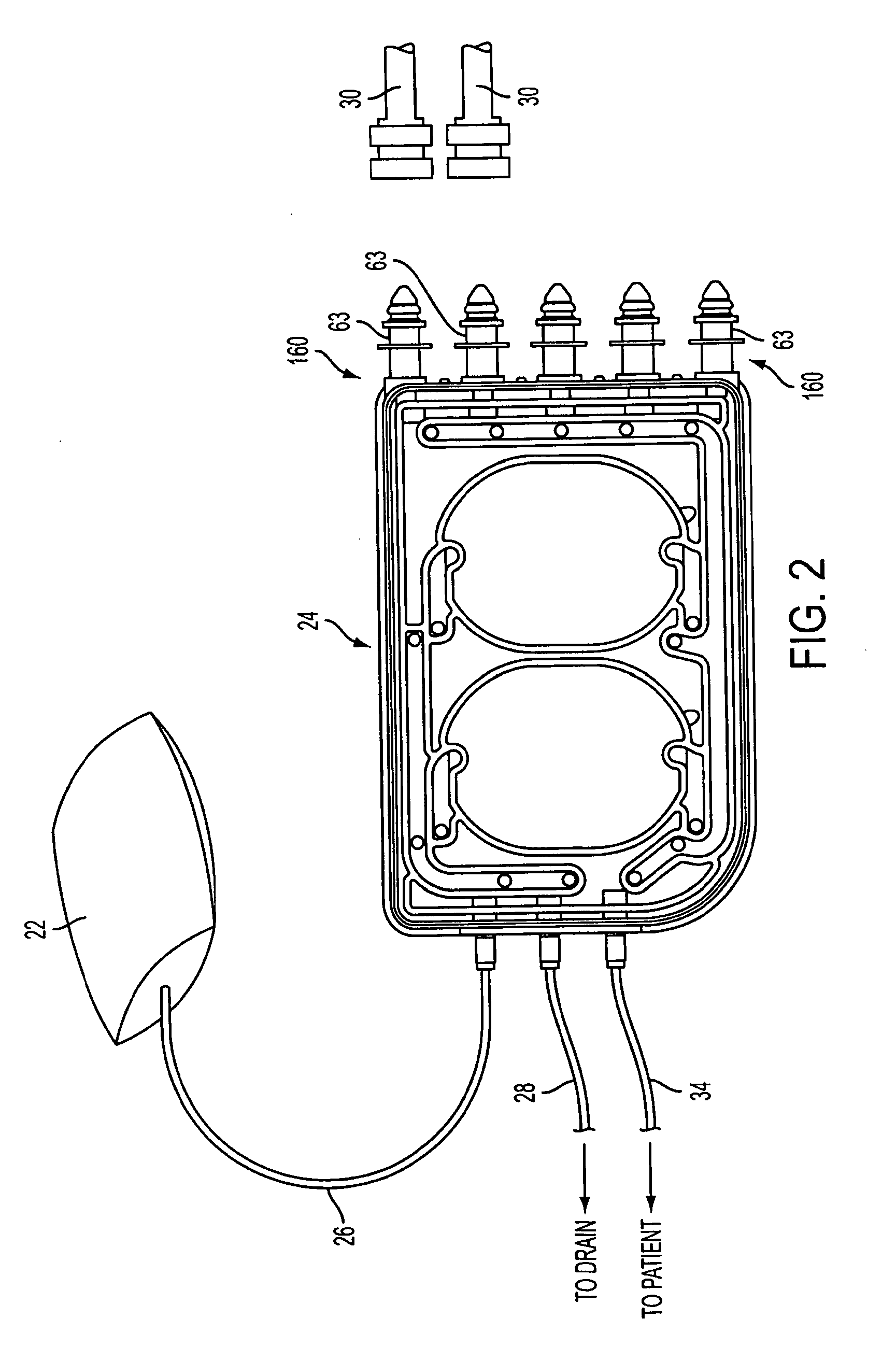
Pump cassette and methods for use in medical treatment system using a plurality of fluid lines
ActiveUS20110092894A1Deformation MinimizationPreventing sticking of the membraneMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPositive displacement pump componentsPump chamberBiomedical engineering
A fluid handling cassette (24), such as that useable with an APD cycler device or other infusion apparatus, may include a generally planar body having at least one pump chamber (181) formed as a depression in a first side of the body and a plurality of flowpaths for fluid that includes a channel. A patient line port may be arranged for connection to a patient line (34) and be in fluid communication with the at least one pump chamber via at least one flowpath, and an optional membrane (15) may be attached to the first side of the body over the at least one pump chamber. In one embodiment, the membrane may have a pump chamber portion (151) with an unstressed shape that generally conforms to the pump chamber depression in the body and is arranged to be movable for movement of fluid in the useable space of the pump chamber. One or more spacers (50) may be provided in the pump chamber to prevent a pump membrane from contacting an inner wall of the pump chamber. Patient, drain (28) and / or heater bag lines (26) may be positioned to be separately occludable in relation to one or more solution lines (30) that are connectable to the cassette.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Photosensitive paste, a plasma display, and a method for the production thereof
InactiveUS6197480B1Reduce processDeformation MinimizationPhotography auxillary processesCoatingsInorganic particleDisplay device
To provide a photosensitive paste that permits pattern formation with a high aspect ratio and a high accuracy and to provide a plasma display including the photosensitive paste, by using a photosensitive paste that includes, as essential components, an inorganic particles and an organic component that contains a photosensitive compound with the difference between the average refractive index of the organic component and the average refractive index of the inorganic particles being 0.1 or less.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
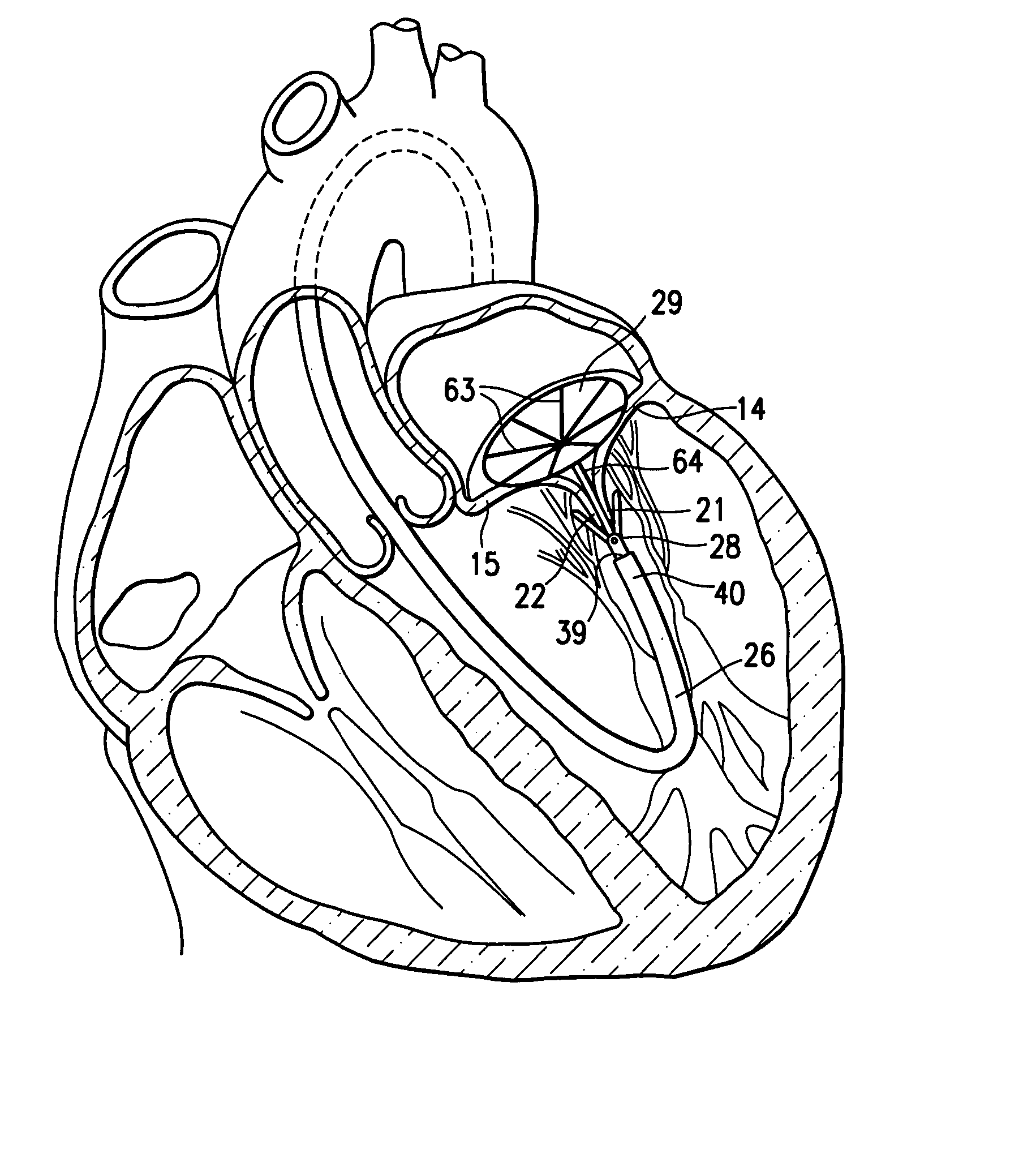
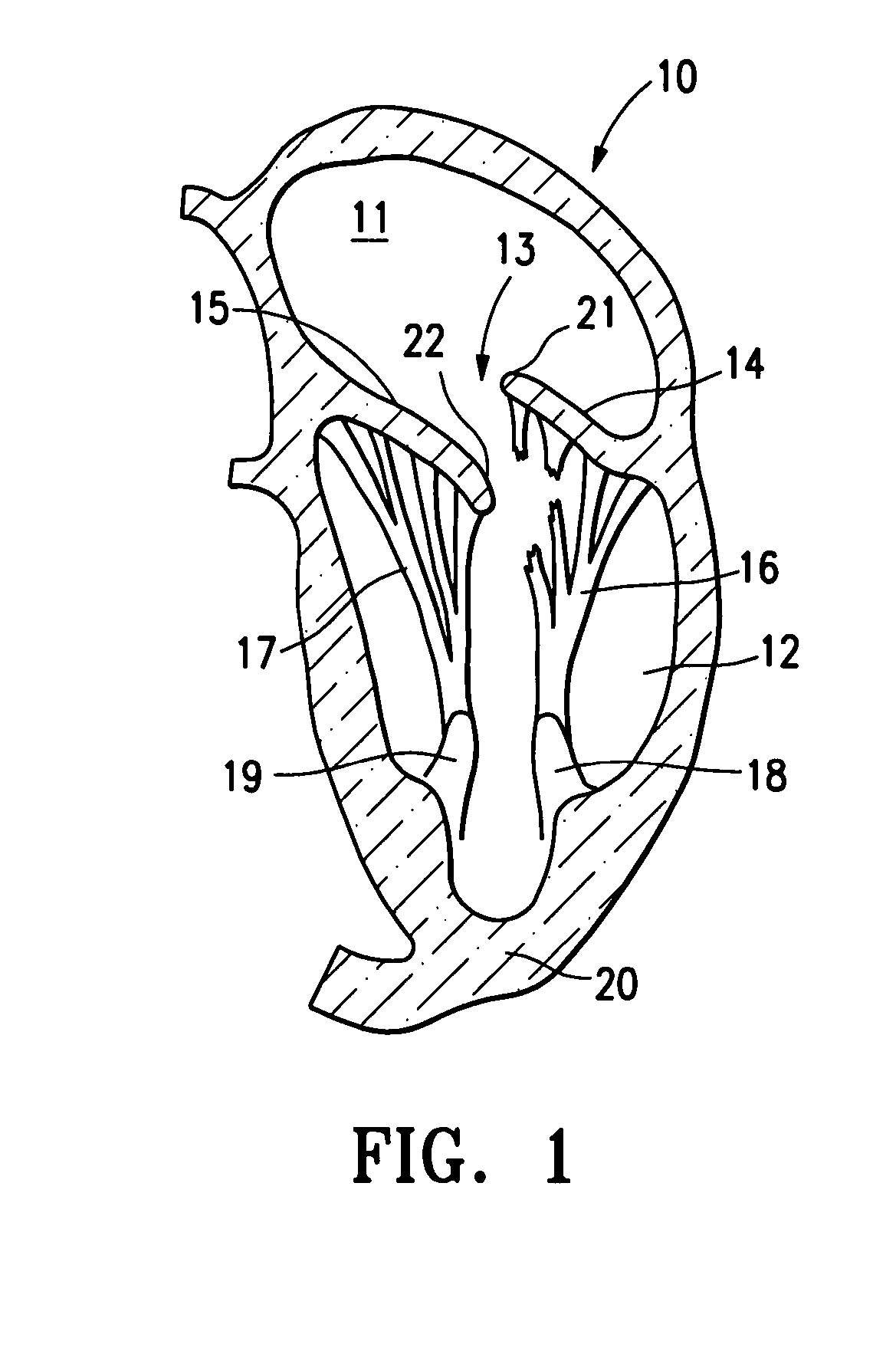
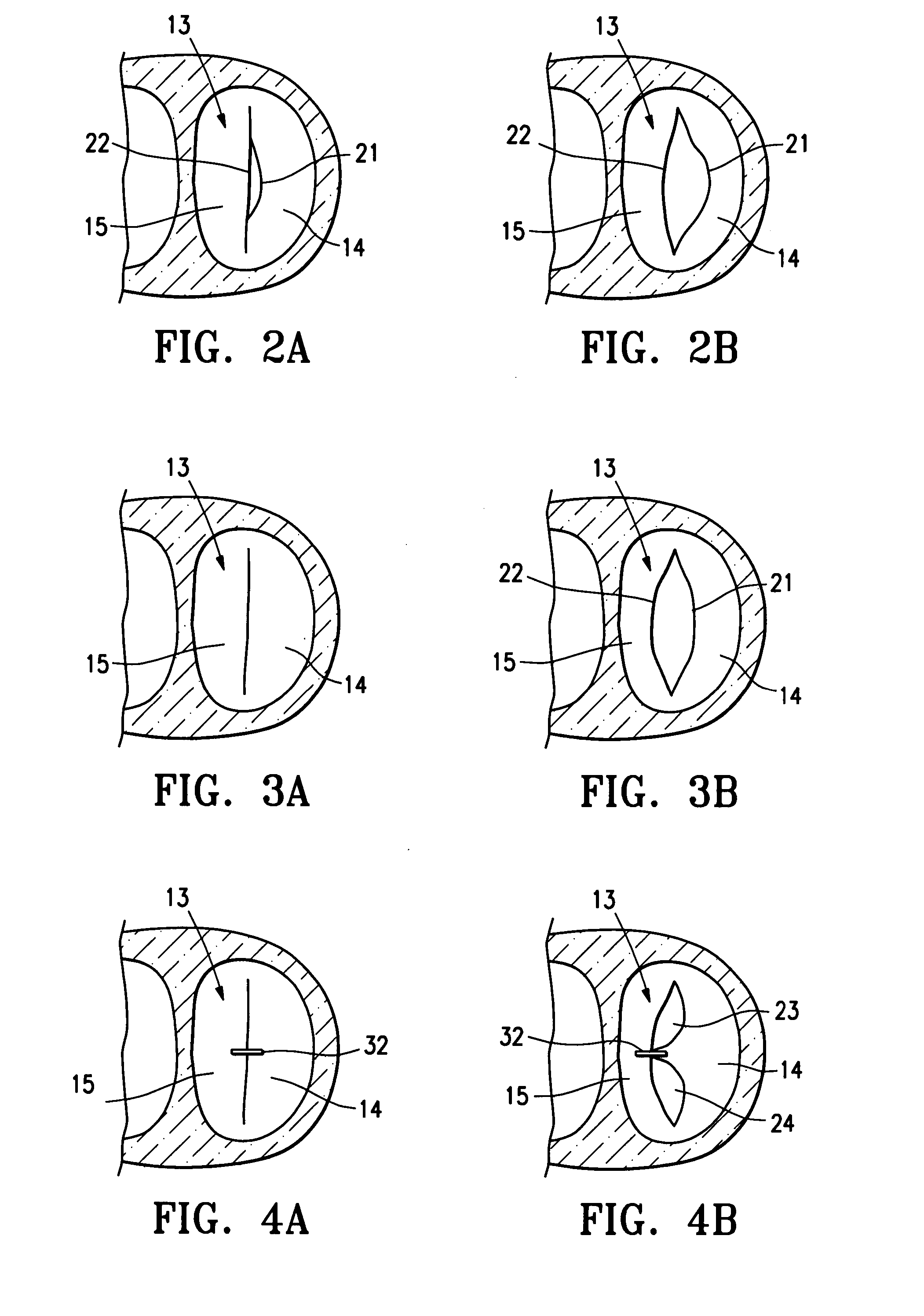
Replacement mitral valves
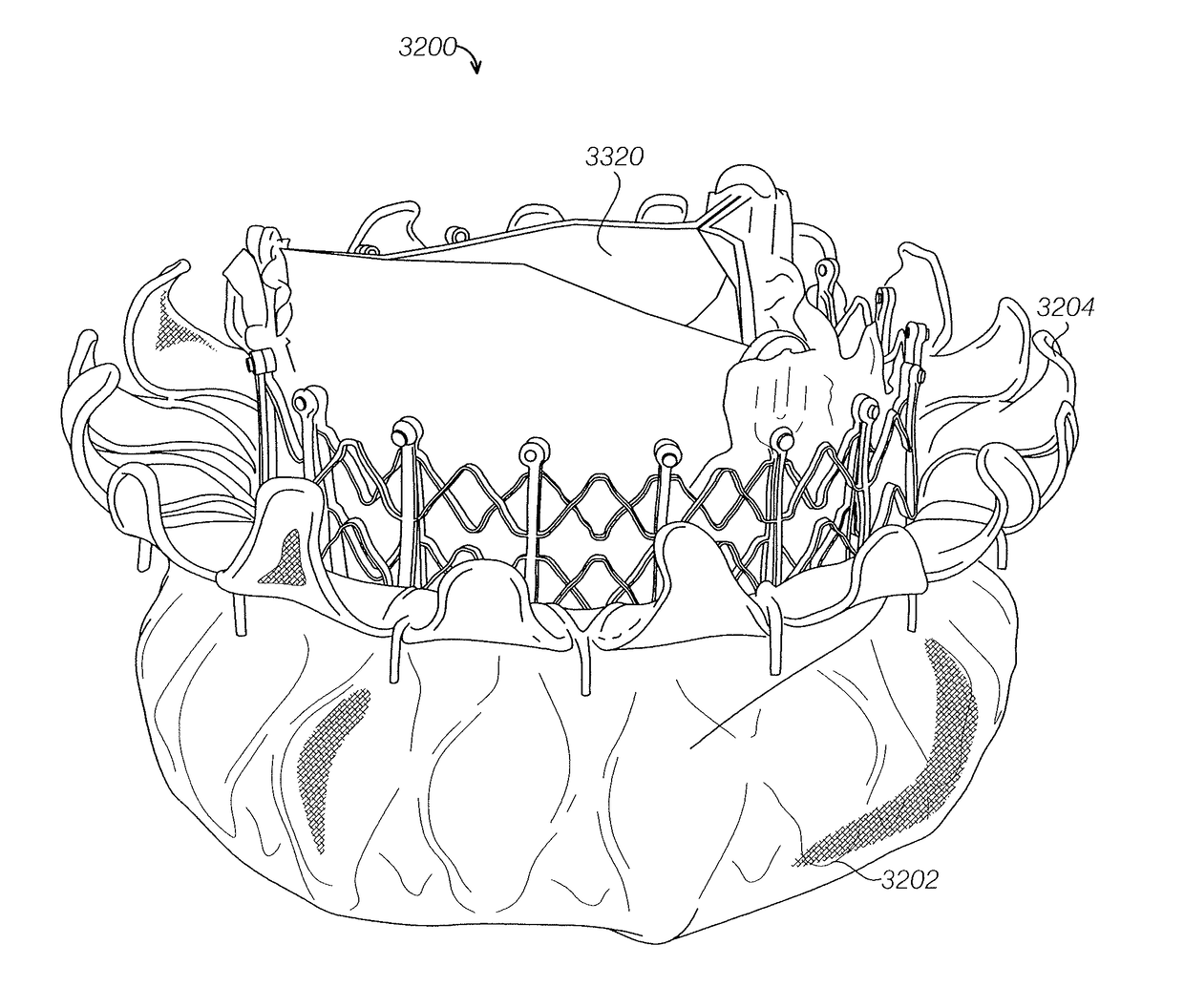
ActiveUS20180000580A1Spring constantIncrease the spring constantStentsHeart valvesEngineeringMitral valve leaflet
Owner:CEPHEA VALVE TECH
Replacement mitral valves
ActiveUS20170325948A1Spring constantIncrease the spring constantStentsHeart valvesEngineeringMitral valve leaflet
A prosthetic mitral valve includes an anchor assembly, an annular strut frame, and a plurality of replacement leaflets secured to the annular strut frame. The anchor assembly includes a ventricular anchor, an atrial anchor, and a central portion therebetween. The annular strut frame is disposed radially within the anchor assembly. An atrial end of the annular strut frame is attached to the anchor assembly such that a ventricular end of the annular strut frame is spaced away from the anchor assembly.
Owner:CEPHEA VALVE TECH
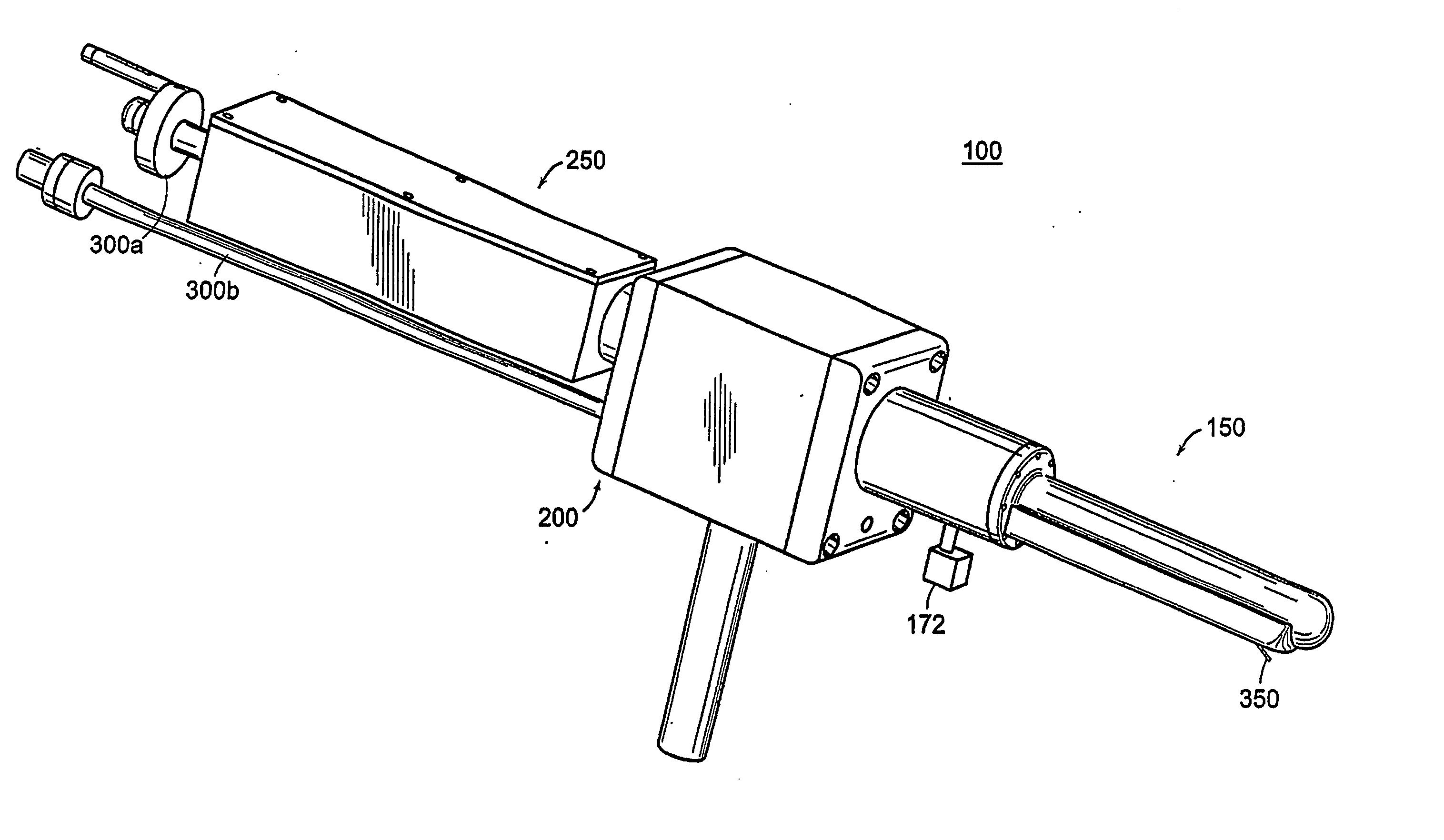
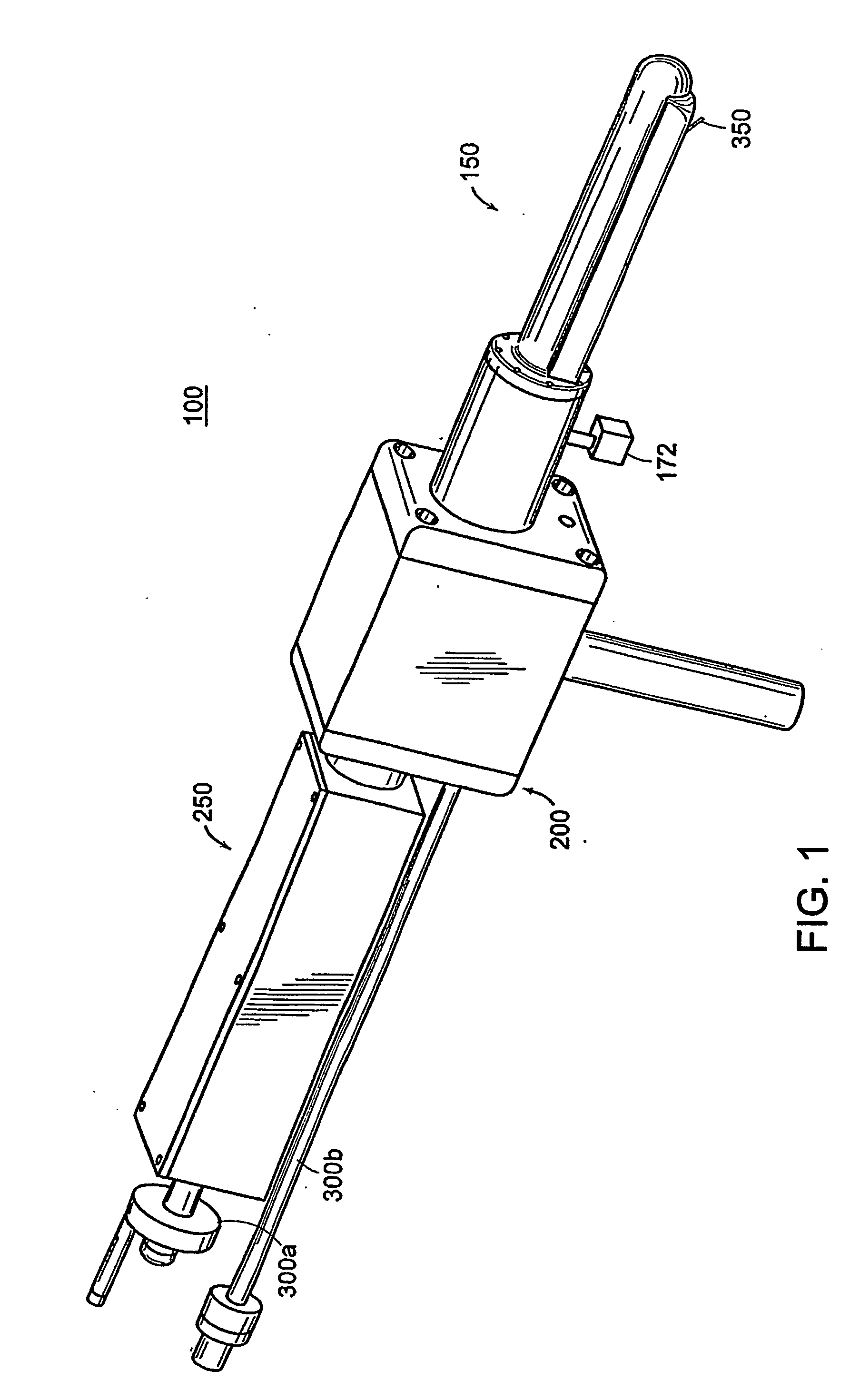
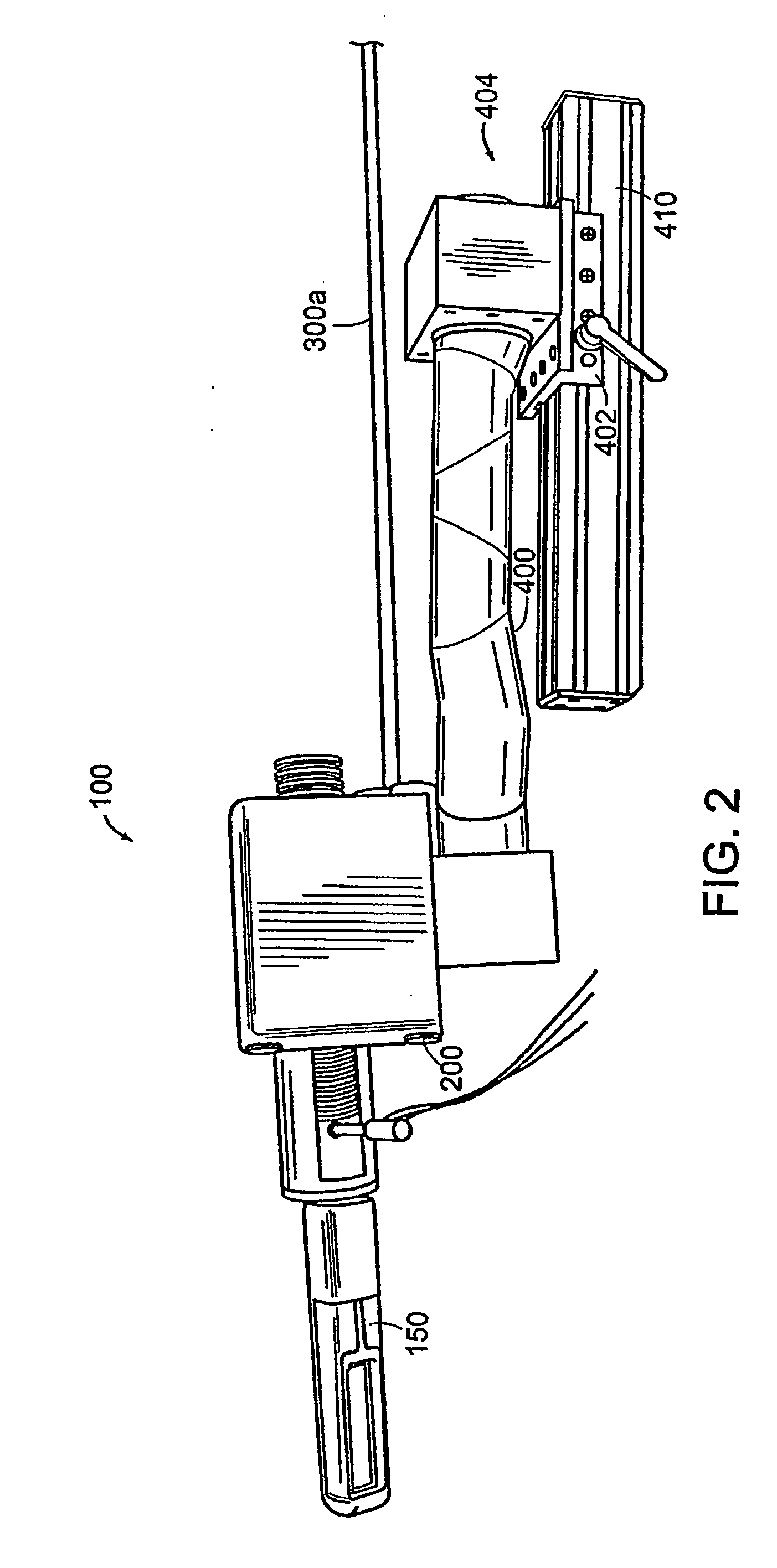
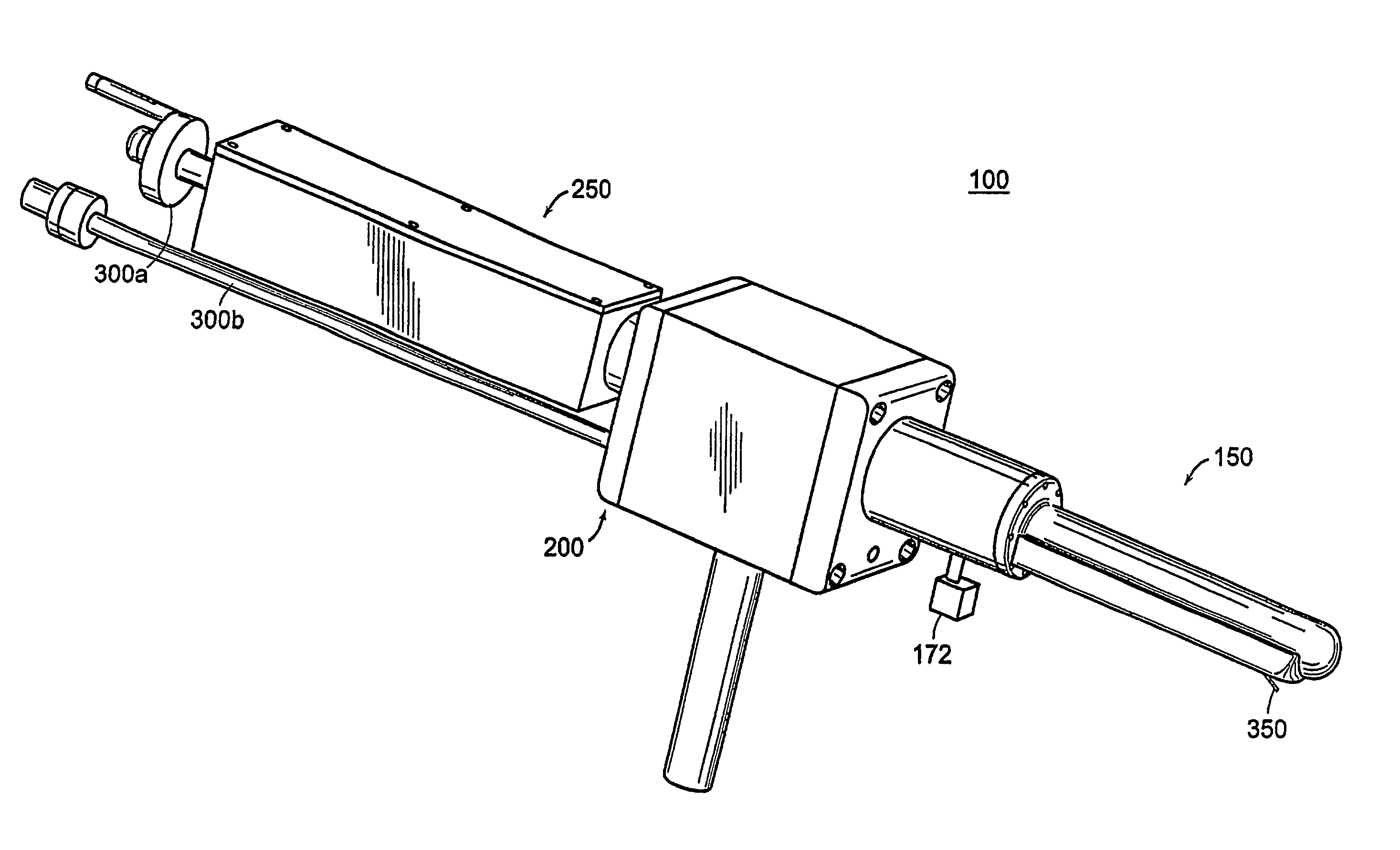
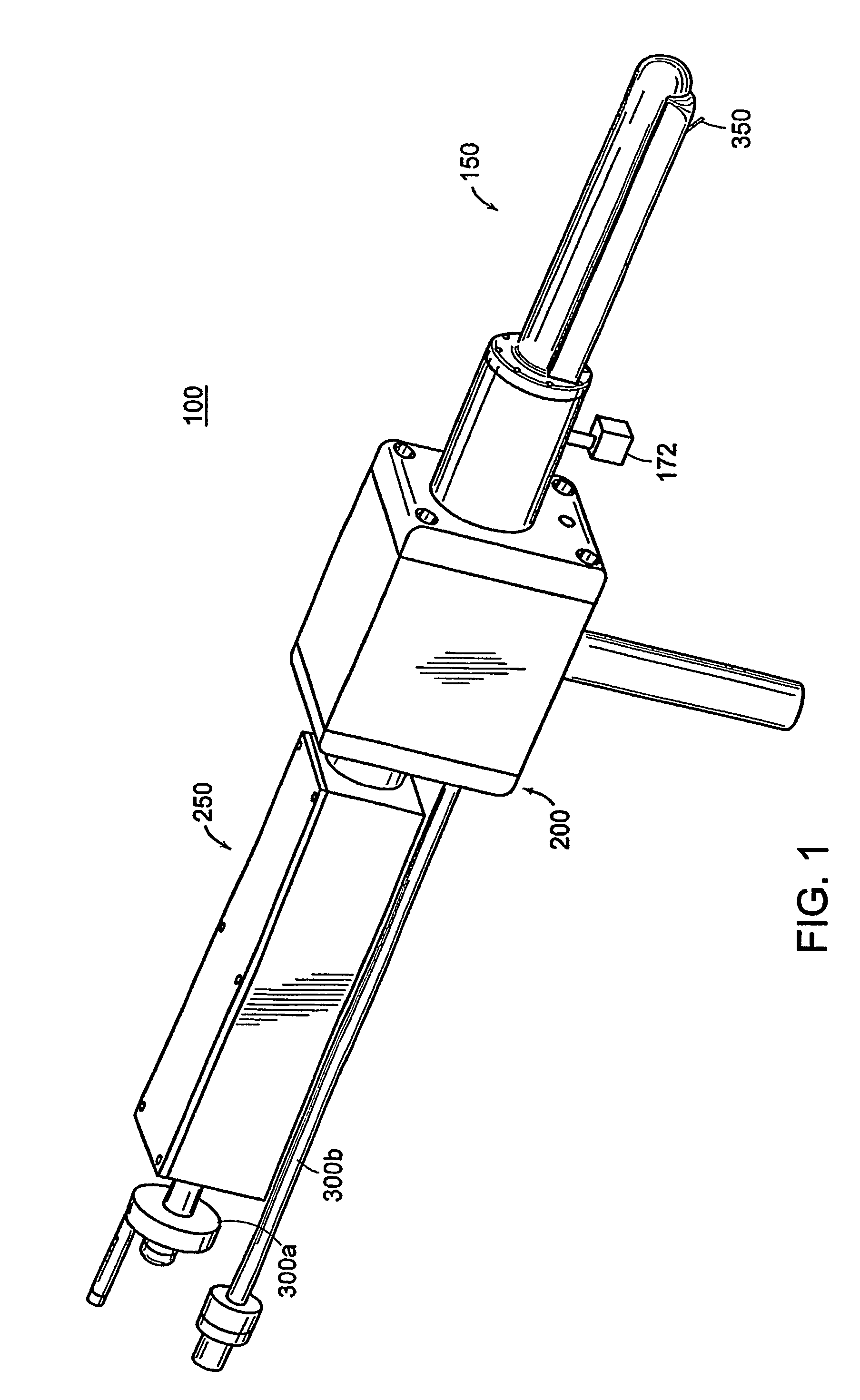
Apparatus for insertion of a medical device during a medical imaging process
ActiveUS20060241368A1Easy accessMaximize accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesMedical imagingMedical device
The end-effector (150) includes a sheath (152) and a medical device or needle carrier (154) that is disposed within the interior compartment (166) of the sheath. Aperture (162) is located in a portion of the sheath proximal a distal end of the sheath that is inserted into a natural or artificial cavity. This device is guided by a real-time imager.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Process for building three-dimensional objects
InactiveUS20120231175A1Deformation MinimizationLiquid surface applicatorsElectrographic process apparatusObject basedEngineering
A process for building three-dimensional objects based on electrophotographic printing is disclosed, comprising the steps of depositing a first layer of powdered base material on a substrate, operating an imaging member, a charging device, an image generating device and an image developing device, in that order, to deliver and deposit filler material onto the layer of powdered base material in an image-wise manner to produce a layer of bonded base material that correspond to the first cross-section of the three-dimensional object being built, repeating all the above steps for as many times as required to form successive layers that constitute the three-dimensional object, said filler material further causing adjacent layers to be bonded with one another; and removing unbonded material to cause the three-dimensional object to appear.
Owner:TAN YU EN
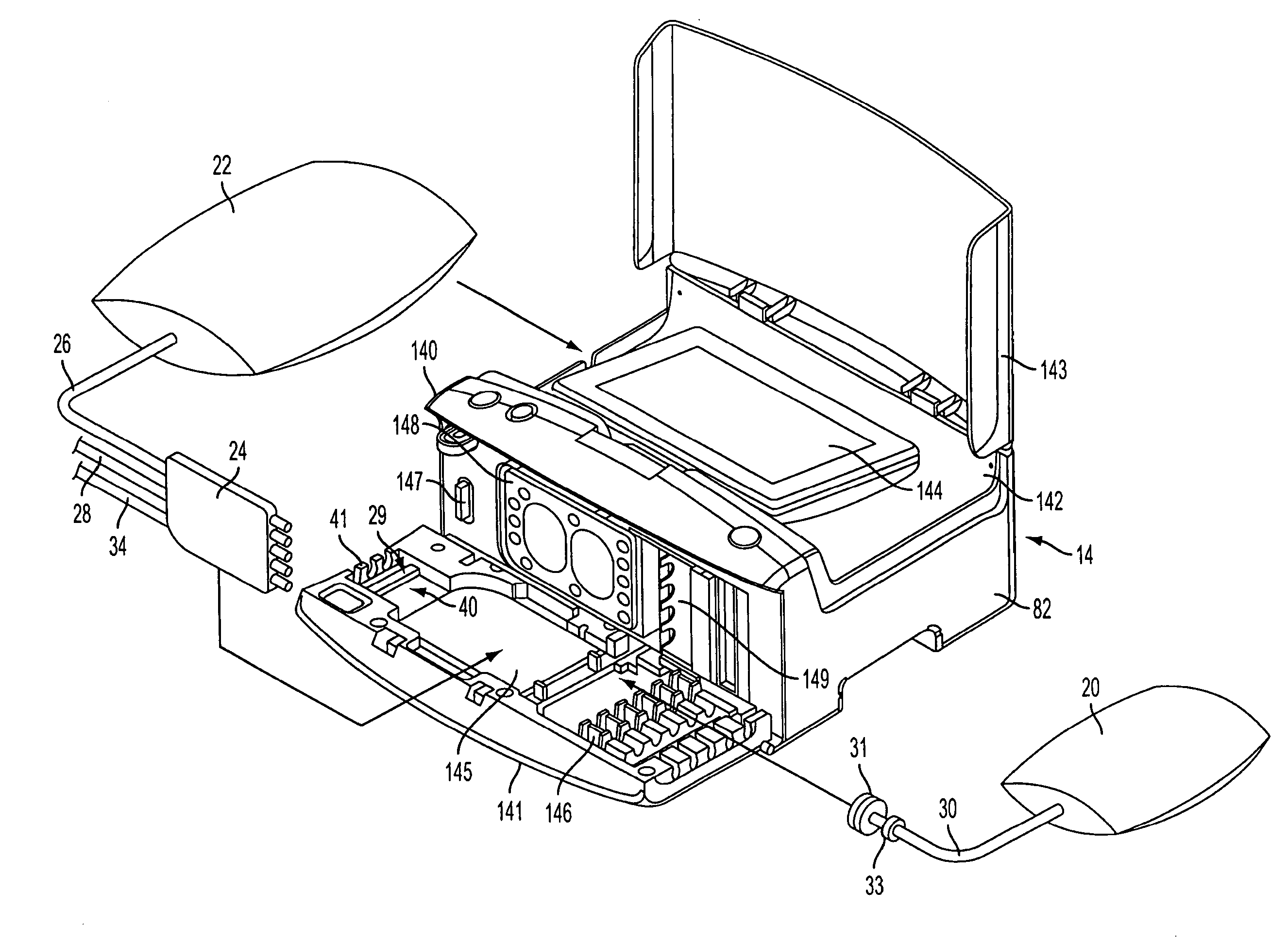
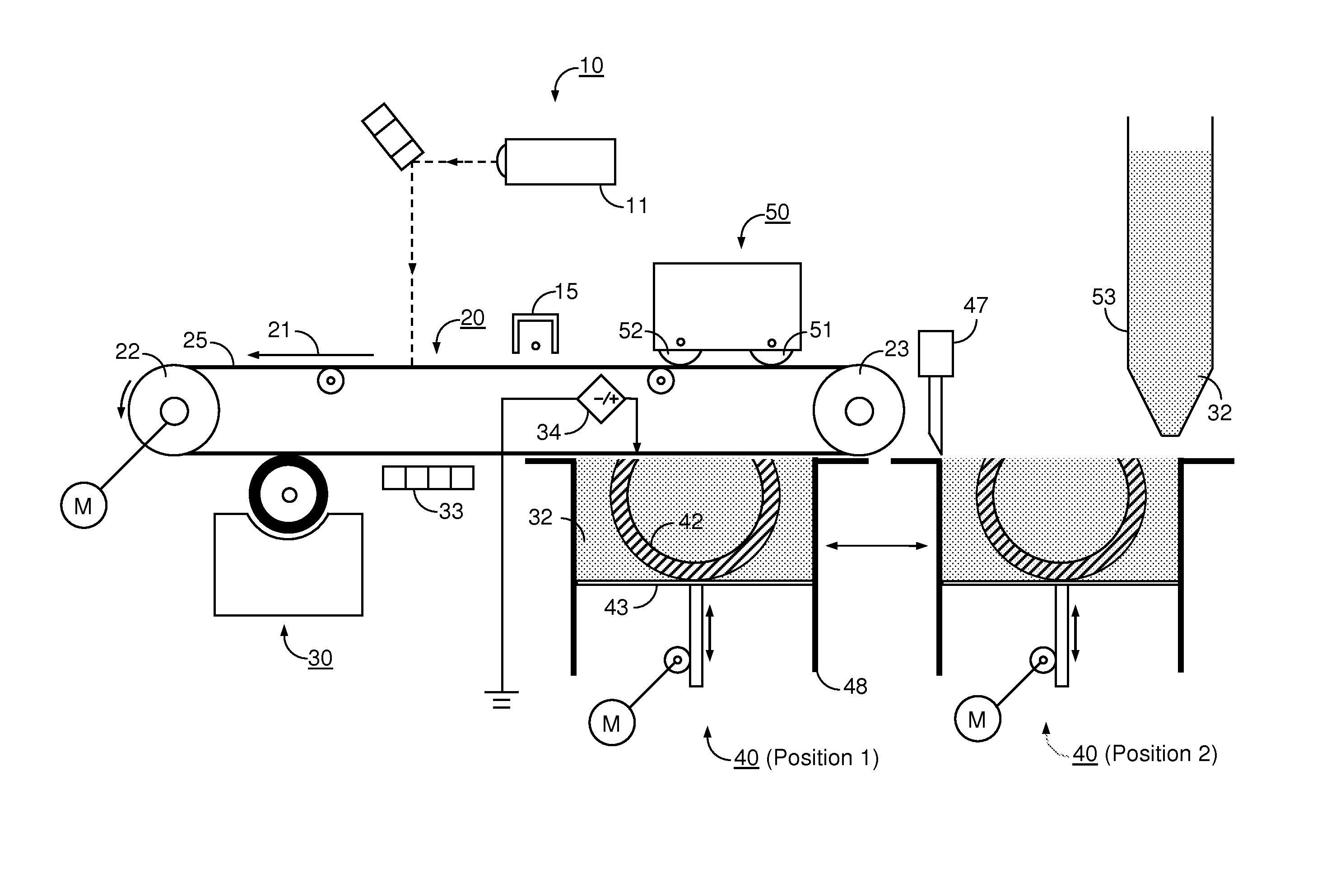
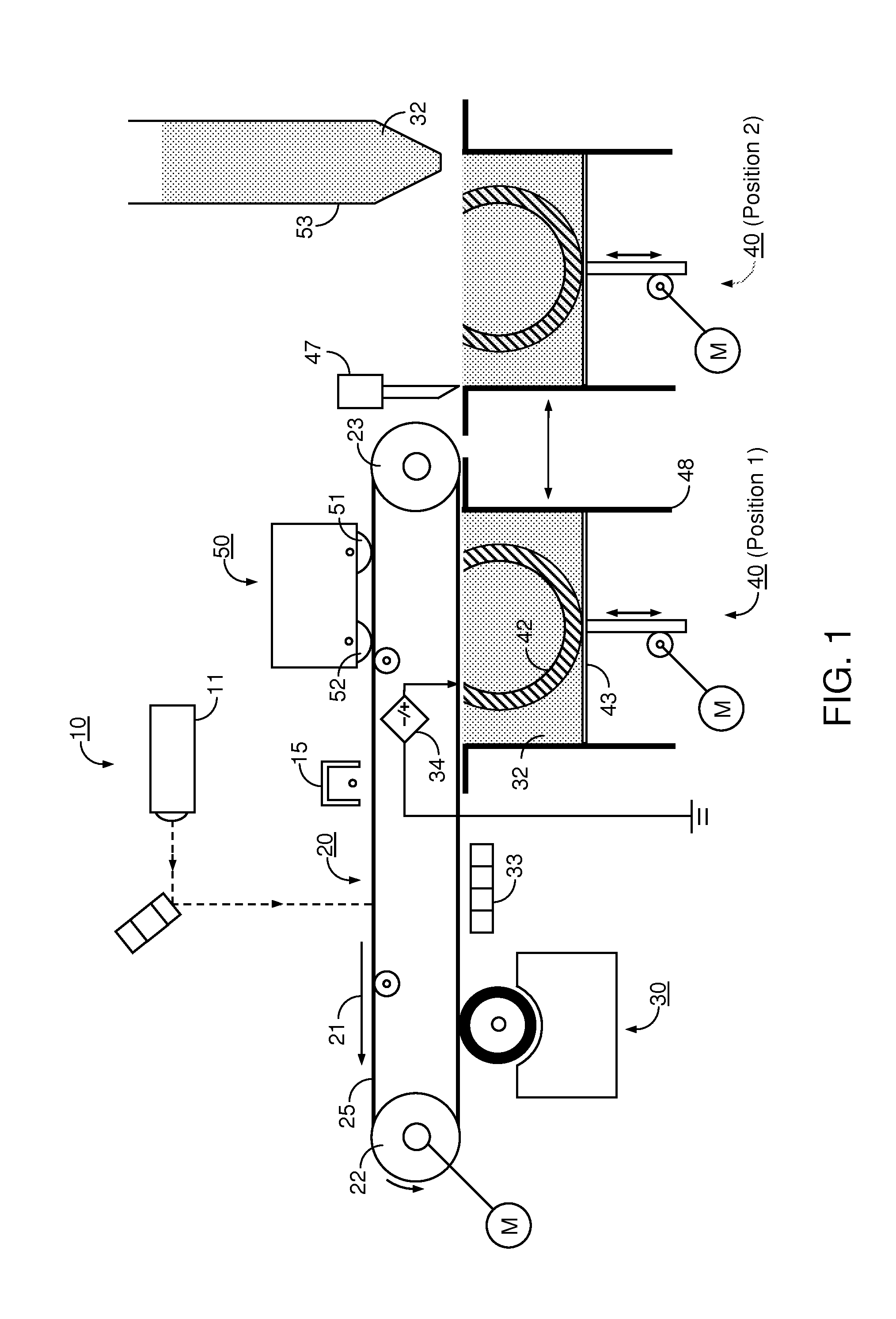
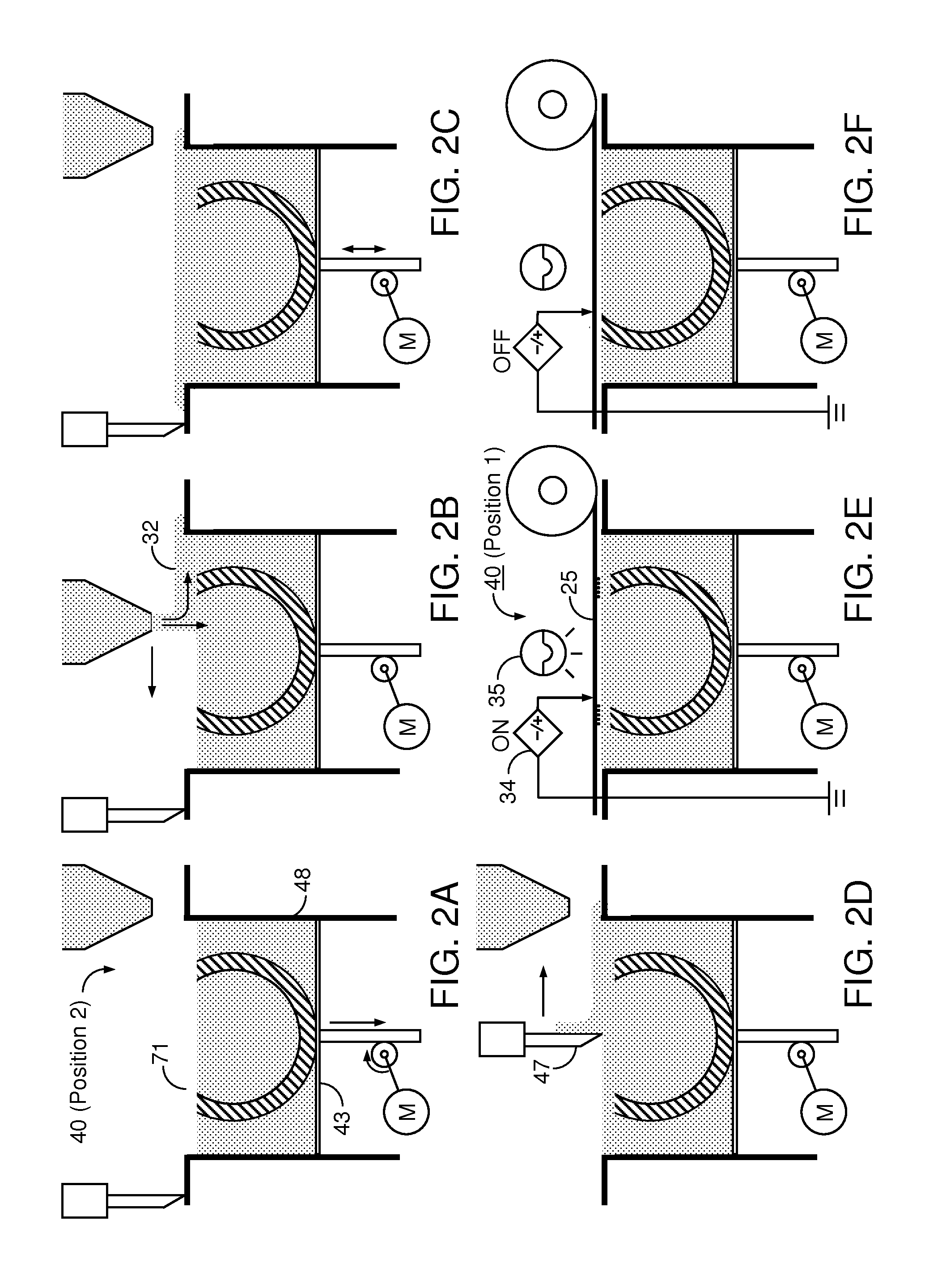
Medical treatment system and methods using a plurality of fluid lines
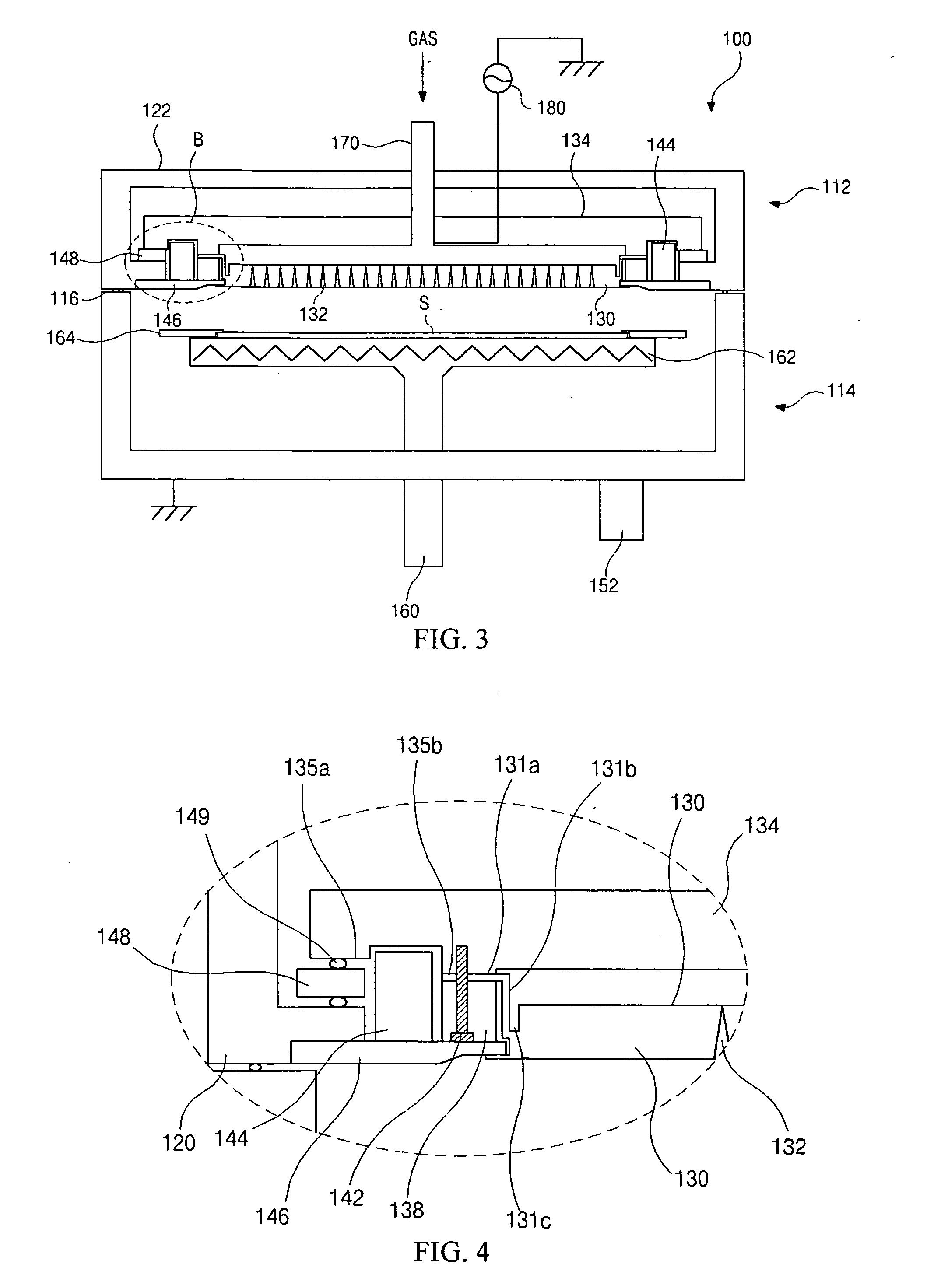
ActiveUS20110092893A1Deformation MinimizationPreventing sticking of the membraneMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPositive displacement pump componentsPeritoneal dialysisPatient comfort
A medical treatment system, such as peritoneal dialysis system, may include control and other features to enhance patient comfort and ease of use. For example, a cycler device (14) may include a heater bag receiving section (142) and a lid (143) mounted to cover and uncover the heater bag receiving section, potentially enabling faster heating of dialysate. A user interface (144) may be moveable to be received into the receiving section and covered by the Hd, if desired. The system may detect anomalous conditions, such as tilting of the system housing, and automatically recover without terminating a treatment. The system may include noise reduction features, such as porting pneumatic outputs to a common chamber, and others. The system may also automatically detect any one of several different solution lines (30) connected to the system, and control operation accordingly, e.g., to mix solutions provided by two or more lines and form a needed dialysate solution. A cassette control (148) surface may be arranged to have one or more ports that can detect the presence of liquid, e.g., to identify if the cassette (24) is leaking or has otherwise been compromised.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Apparatus and method for two stage ejection of a molded preform from a mold
InactiveUS7128865B2Quickly and efficiently removingDeformation MinimizationMouldsFood shapingEngineeringCycle time
Injection molding method and apparatus for ejecting a molded plastic preform from a mold. A first lifting structure and / or step is configured to have an inner surface with an area for sealing and aligning with a complementary surface on a core, and to have an upper surface with an area for sealing and aligning with a complementary surface on a second lifting structure, said upper surface of said first lifting structure being configured to lift a molded plastic preform from the injection mold in a lifting direction for a first period of time, the lower portion of the molded plastic preform lying in a plane substantially perpendicular to the lifting direction. A second lifting structure and / or step is configured to have an inner surface configured to lift an outer surface of the molded plastic preform from the injection mold in the lifting direction for a second period of time, the outer surface of the molded plastic preform including structure lying in a plane substantially parallel with the lifting direction.Since the molded plastic preform is lifted by its end, the preform does not have to be solidified at its interior, thus allowing earlier removal of the preform from the mold, reducing cycle time.
Owner:HUSKY INJECTION MOLDING SYST LTD
Mounting device for an optical element
InactiveUS6552862B2Deformation MinimizationAcceleration-induced deformations of the optical surface are likewise minimizedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIn planeCompensation effect
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Fixing device with resistance heating element capable of accurately generating heat and image forming apparatus with fixing device
InactiveUS20120237273A1Deformation MinimizationElectrographic process apparatusElectrical resistance and conductanceImage formation
In a fixing device, a heating element is extended along a fixing member at a location other than a nip on an inner circumferential surface side of the fixing member to generate heat. The fixing member contacts the heating element either indirectly via a gap of a prescribed size or directly contacts the heating element by with a prescribed pressure when the fixing member is rotating, and continuously separates from the heating element by a prescribed distance greater than the size of the gap when the fixing member stops rotating.
Owner:RICOH KK
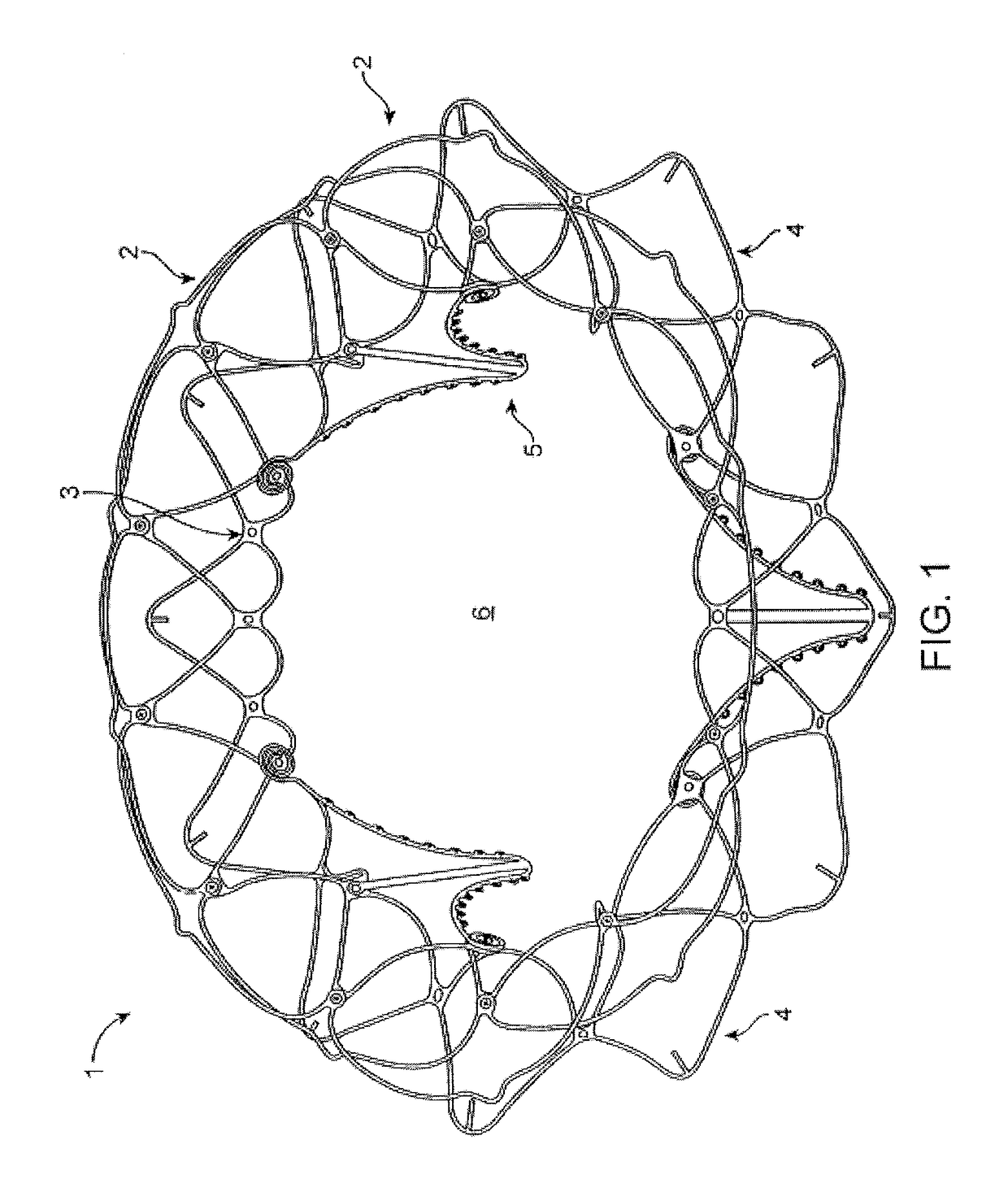
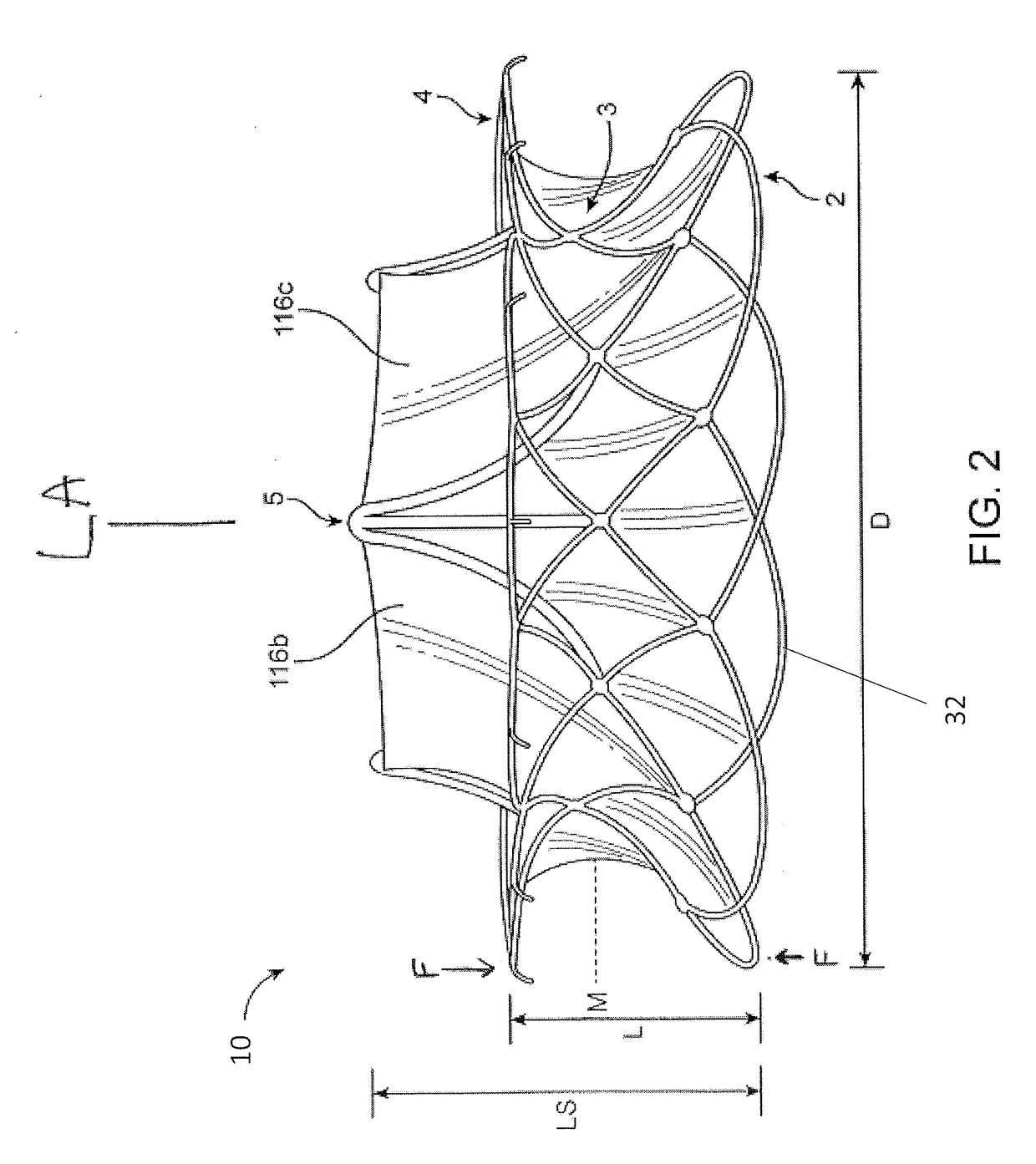
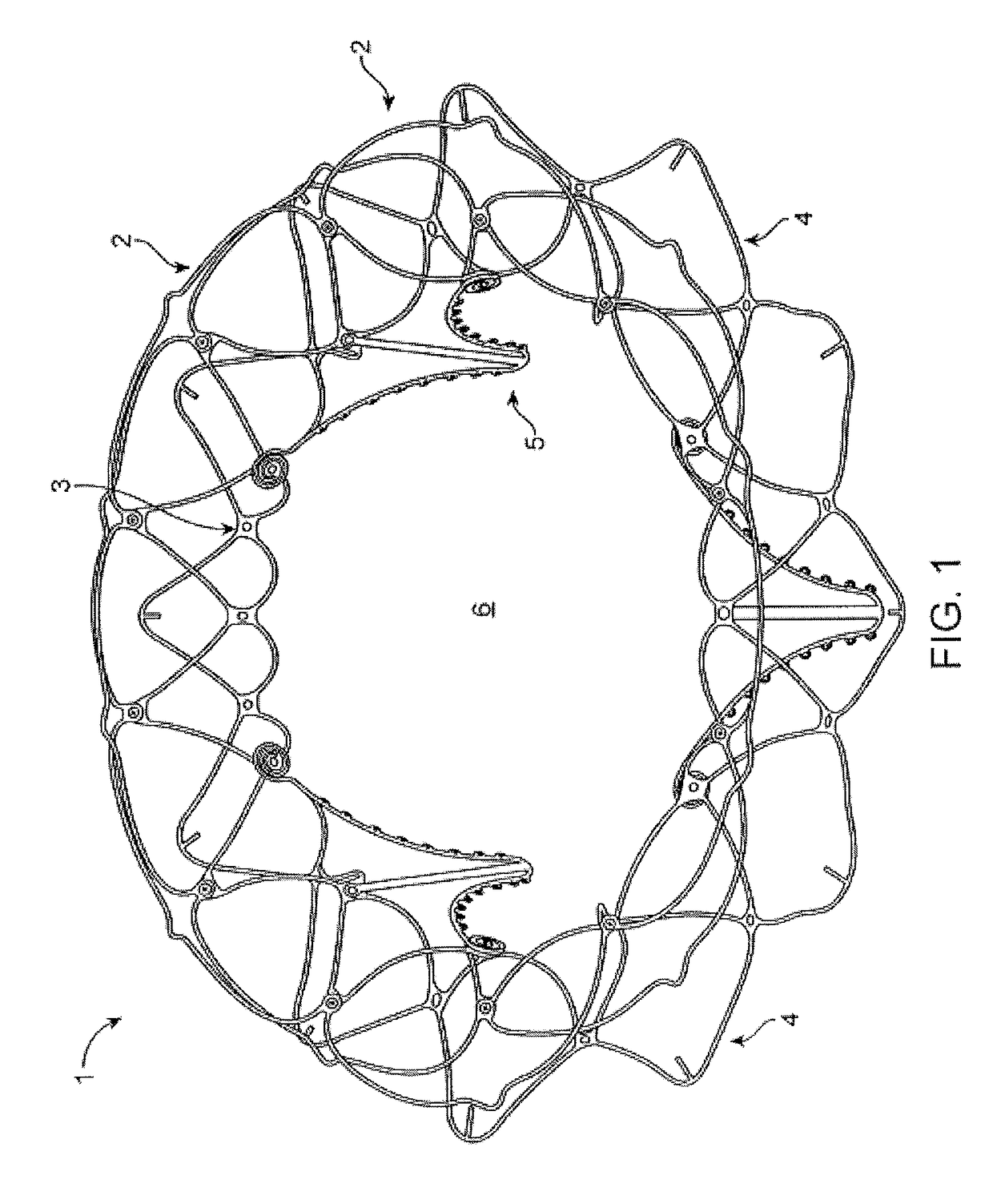
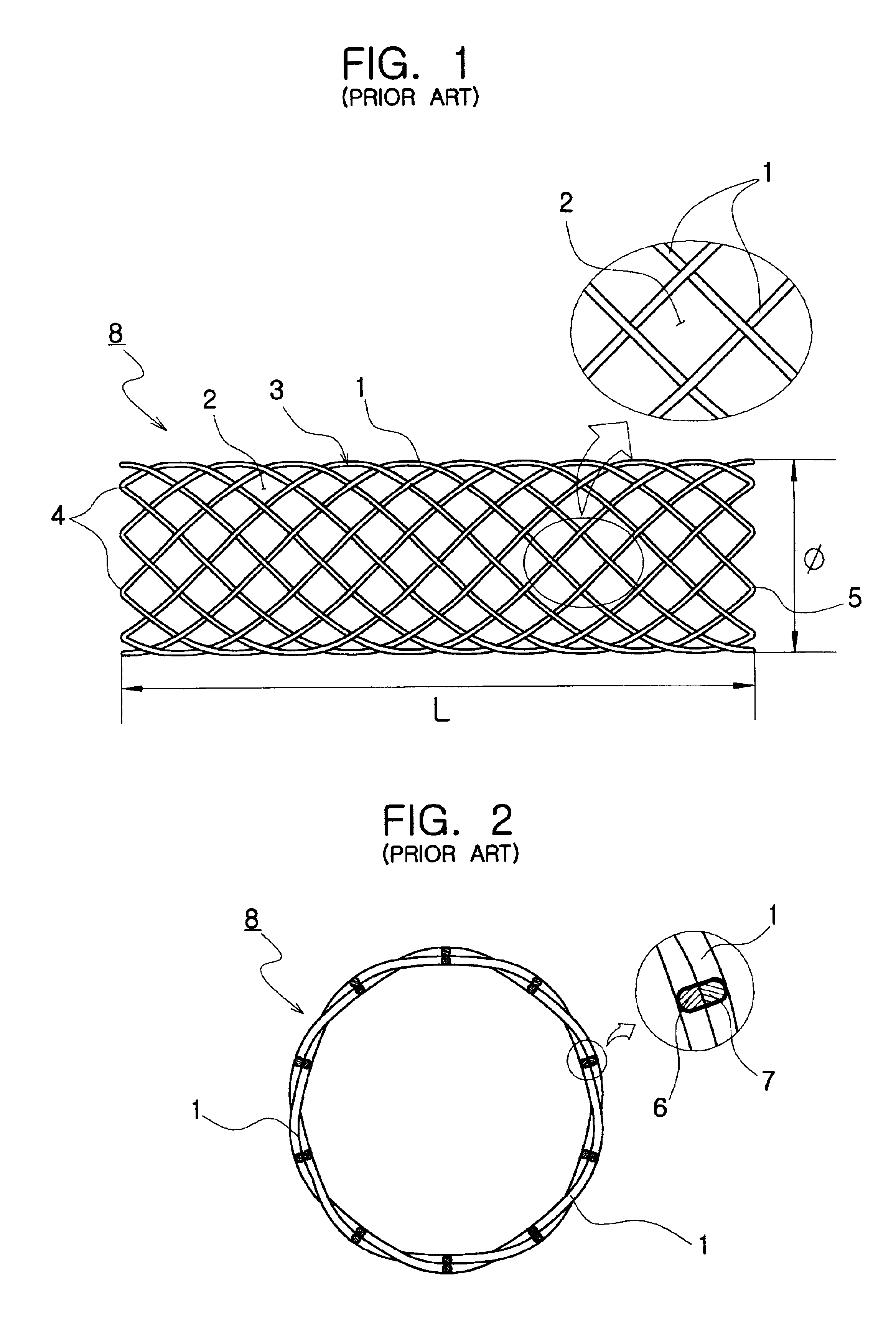
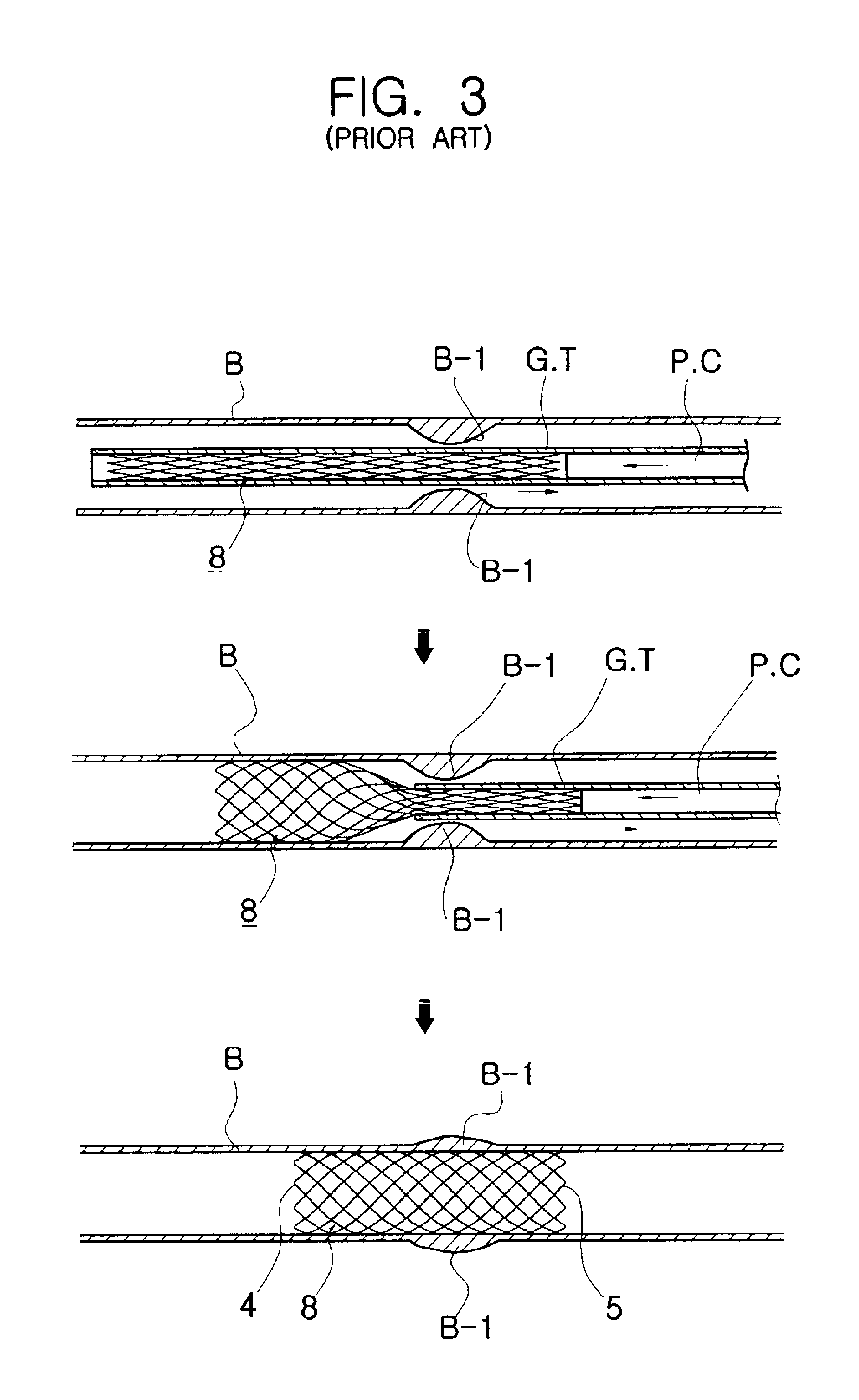
Flexible self-expandable stent using shape memory alloy and method and apparatus for fabricating the same
Disclosed herein is a flexible self-expandable stent using shape memory alloy for expanding stenosal portions and method and apparatus for fabricating the same. The self-expandable stent using shape memory allow, comprises a first cylindrical stent member comprised of a first wire formed of super elastic shape memory alloy, the first wire being bent a large number of times while being extended upwardly and downwardly a large number of times, so the first wire forms a plurality of variable rhombic spaces by forming a plurality of intersections for causing the first wire to be intersected with itself to resist longitudinal constriction of the first cylindrical stent member and a plurality of interlocked points for causing the first wire to be interlocked with itself at spaced positions to allow longitudinal constriction of the first cylindrical stent member; and a second cylindrical stent member comprised of a second wire formed of super elastic shape memory alloy, the second wire being diagonally extended in parallel with the previously positioned first wire and passed alternately under and over the first wire so as to divide each of a plurality of rhombic spaces formed in the first cylindrical stent member into four equal parts, thereby preventing the first and second cylindrical stent members from being separated from each other.
Owner:TAEWOONG MEDICAL CO LTD
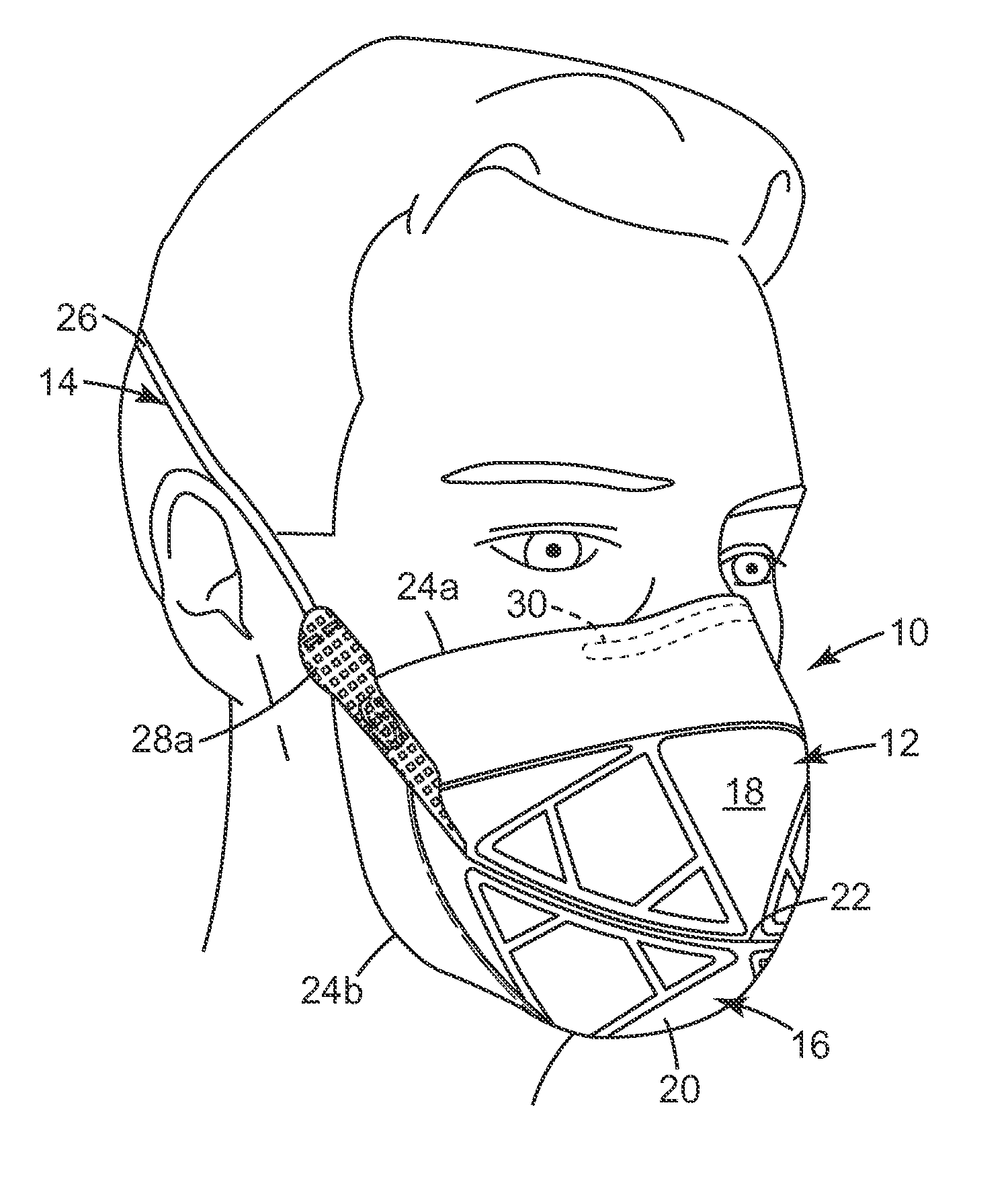
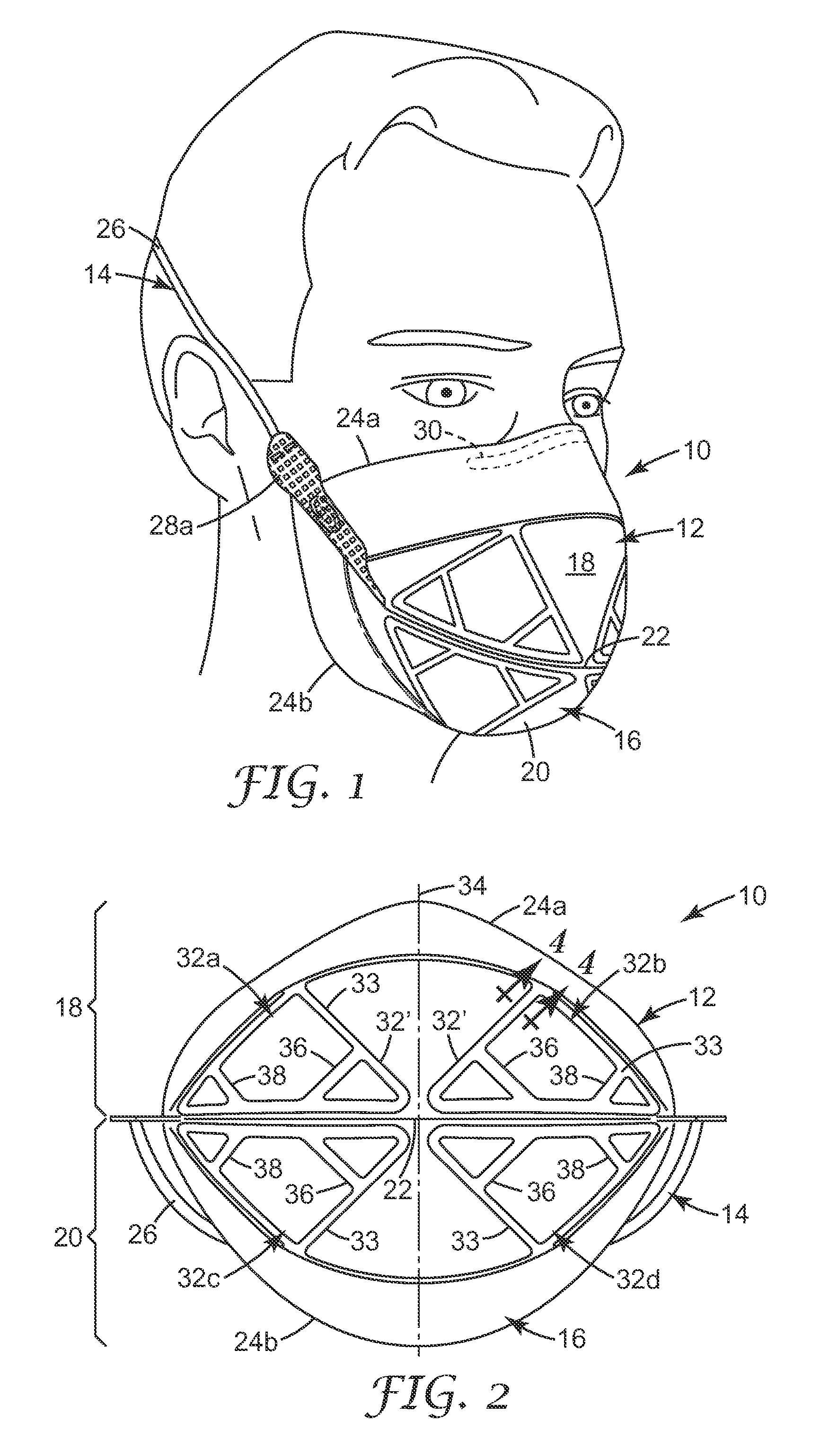
Filtering face-piece respirator having parallel line weld pattern in mask body
ActiveUS20110094515A1Reduce usageDeformation MinimizationBreathing filtersBreathing masksRespiratorEngineering
A respirator 10 that has a harness 14 and a mask body 12 that is joined to the harness 14. The mask body 12 includes a filtering structure 16 that may contain a plurality of layers of nonwoven fibrous material 58, 60, 62. The layers of nonwoven fibrous material 58, 60, 62 have a thickness A and are welded together by at least two parallel weld lines 34′, 34″ that are spaced at 0.5 to 6 times A. A mask body that uses parallel weld lines may exhibit better resistance to collapse and may be manufactured at faster speeds than similar structures which use single weld lines of comparable width.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
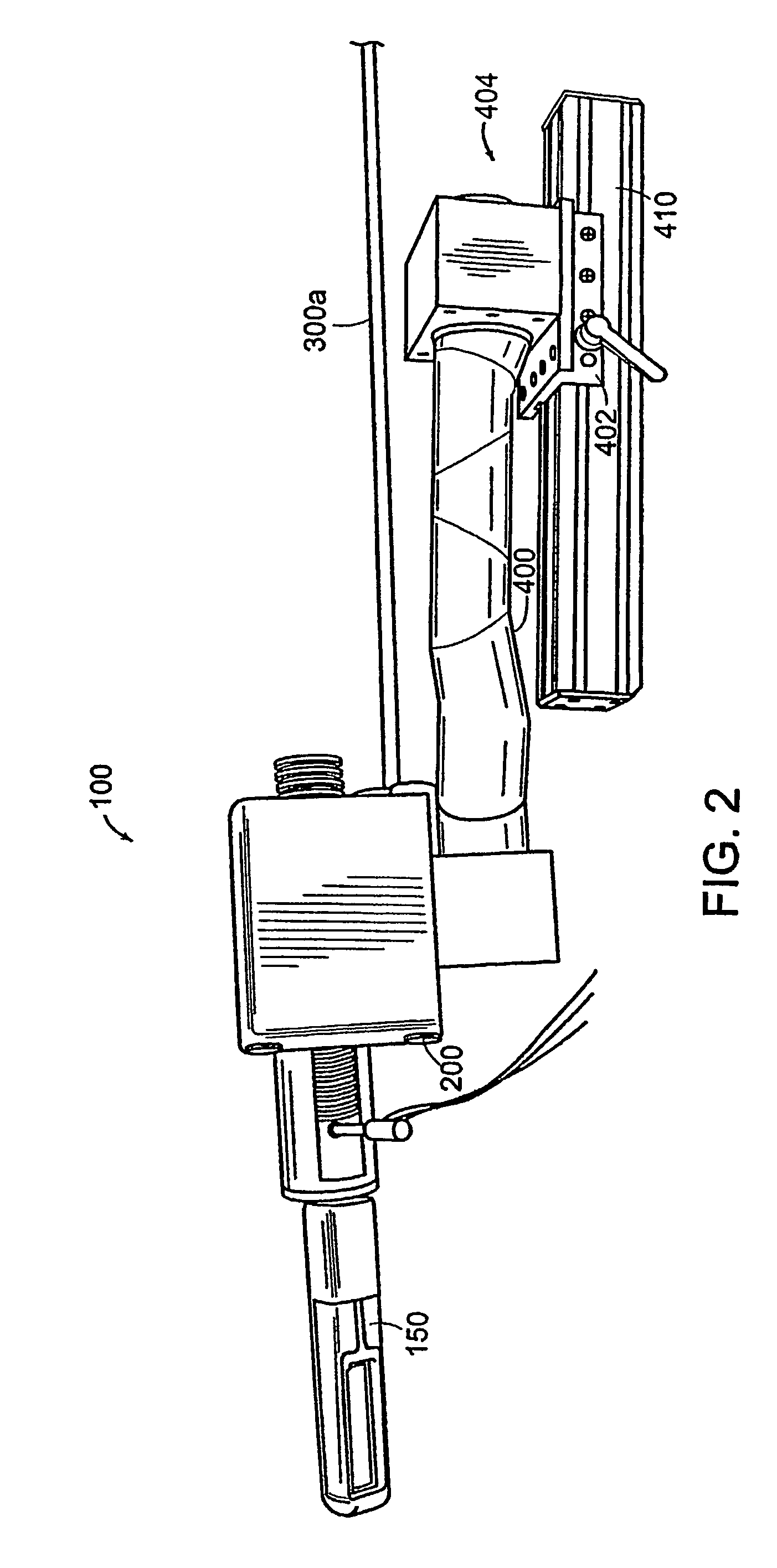
Apparatus for insertion of a medical device within a body during a medical imaging process and devices and methods related thereto
ActiveUS20100056900A1Minimizes motion and deformationEasy accessSurgical navigation systemsVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsX-rayMedical treatment
A device, system, and method for entering a medical device such as a needle into the body inside a medical imager such as a MRI scanner, CT, X-ray fluoroscopy, and ultrasound imaging, from within a body cavity (such as the rectum, vagina, or laparoscopically accessed cavity). A three degree-of-freedom mechanical device translates and rotates inside the cavity and enters a needle into the body, and steers the needle to a target point selected by the user. The device is guided by real-time images from the medical imager. Networked computers process the medical images and enable the clinician to control the motion of the mechanical device that is operated within the imager, outside of the imager or remotely from outside the imager.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Percutaneous treatment for heart valves
InactiveUS20070265702A1Avoid problemsReduce ventricular outputSuture equipmentsHeart valvesCongestive heart failure chfBlood vessel
The invention is directed to percutaneous transvascular therapeutic procedures, particularly for patients with congestive heart failure, and systems for such procedures. A system of the invention for a “Bow-tie” procedure has an elongated guide catheter, a leaf stabilizing device and a tissue grasping device for grasping the free edges of the patient's heart valve slidably disposed within the guide catheter. Preferably, an artificial cordae tendenae is provided if a natural cordae tendenae of the patient has been torn.
Owner:TRANSCARDIAC THERAPEUTICS
Dielectric resonator antenna embedded in multilayer substrate for enhancing bandwidth
ActiveUS20110248890A1Easy to manufactureMinimize changesSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric resonator antennaDielectric resonator
Disclosed herein is a dielectric resonator antenna embedded in a multilayer substrate for enhancing bandwidth. The dielectric resonator antenna includes a multilayer substrate, a first conductive plate, a second conductive plate, a plurality of first metal via holes, a feeding part configured to feed a dielectric resonator, and a conductive pattern part inserted into the dielectric resonator so that a vertical metal interface is formed in the dielectric resonator. Accordingly, the dielectric resonator antenna has low sensitivity to fabrication errors and an external environment, and can enhance the radiation characteristics of the antenna when multiple resonances occur.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Lighting apparatus having light emitting diodes for light source
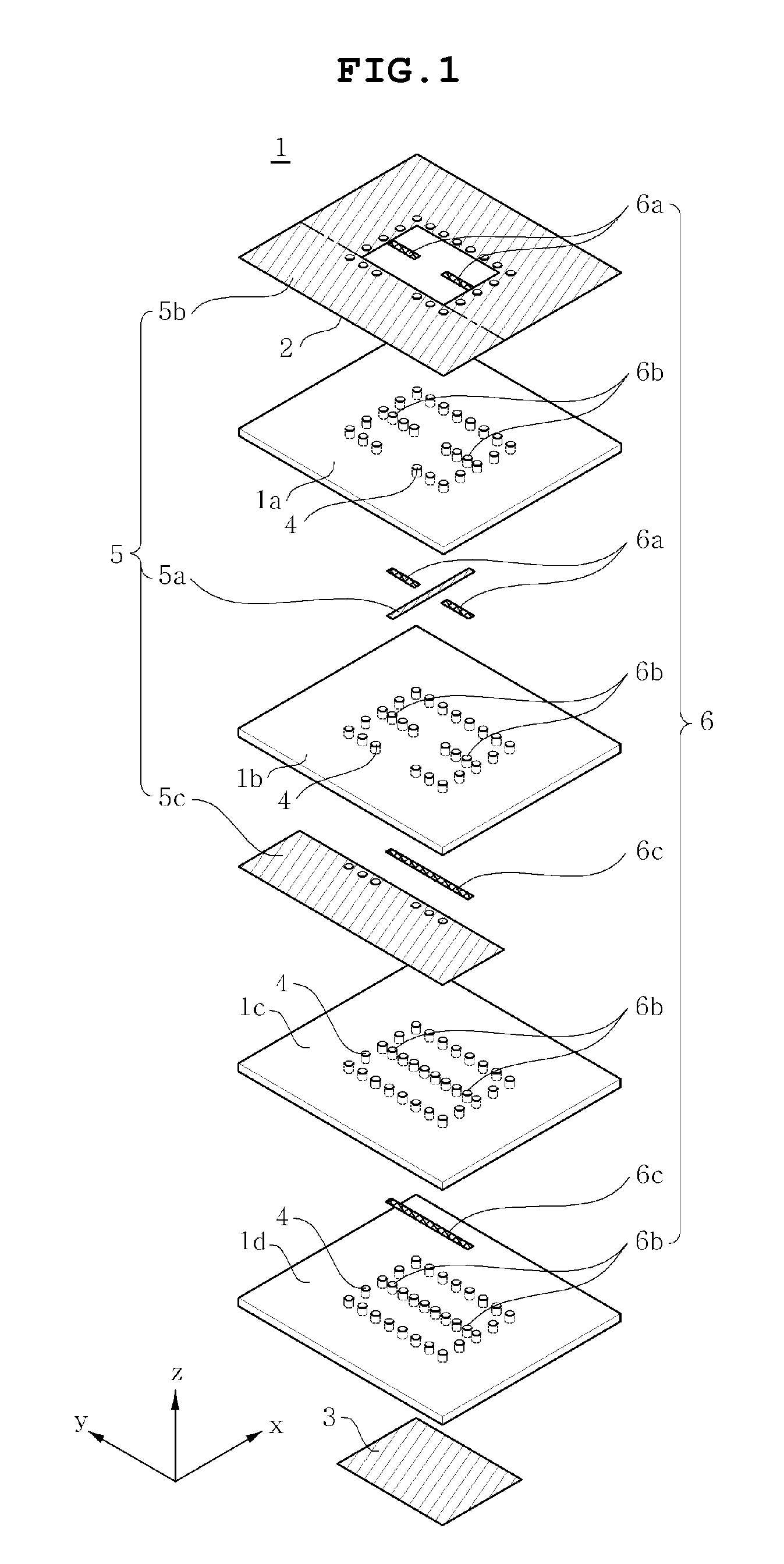
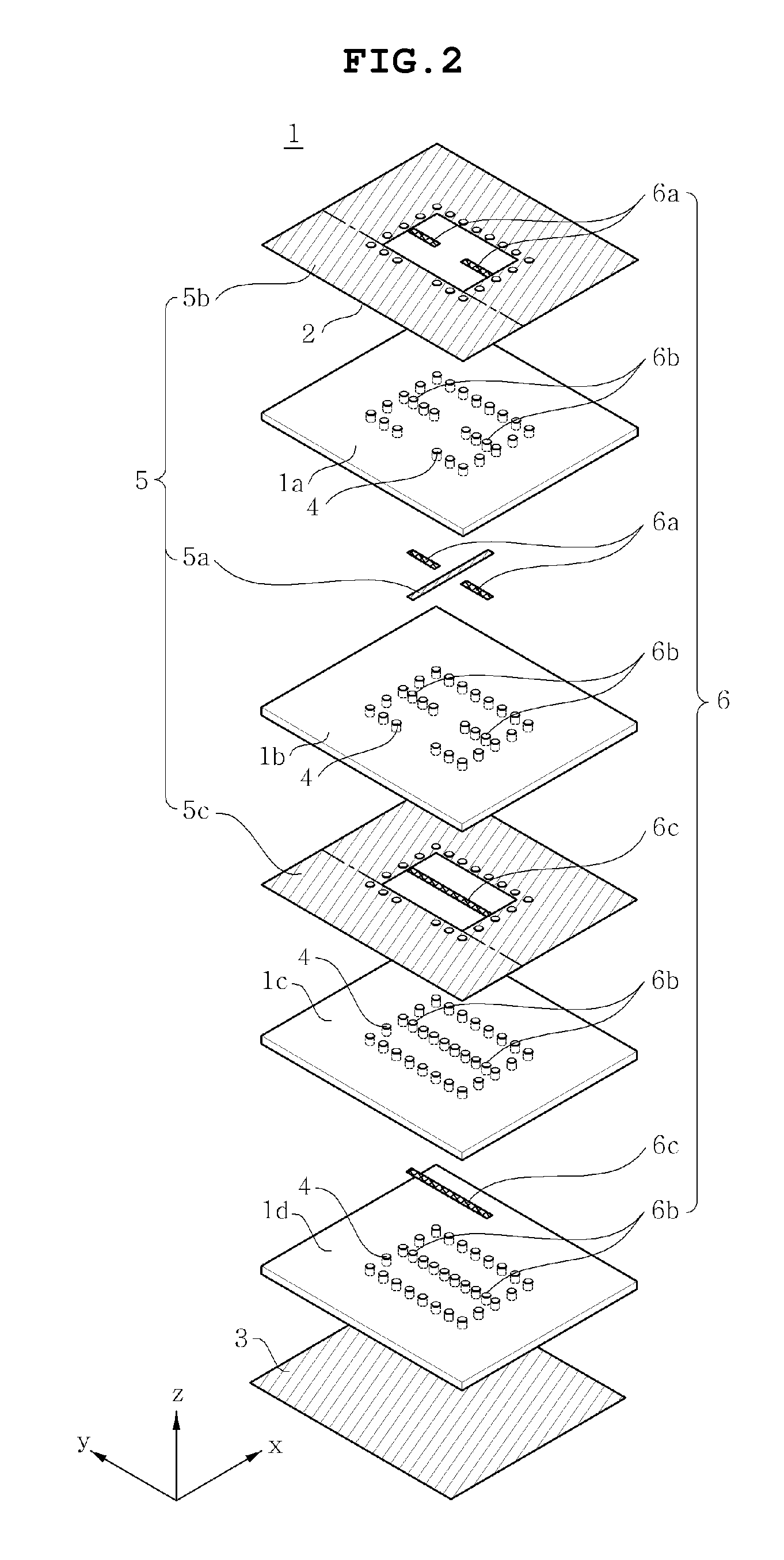
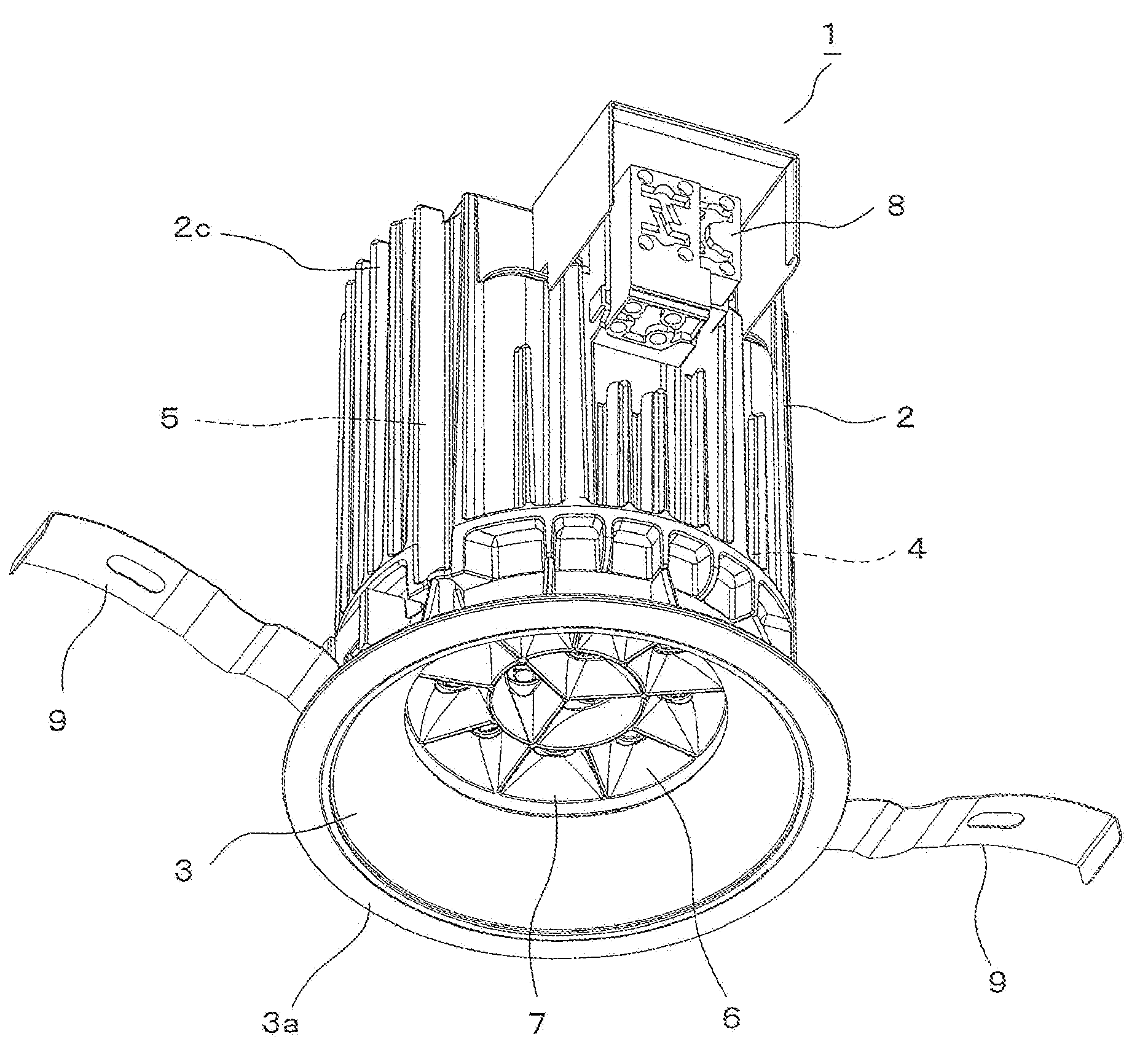
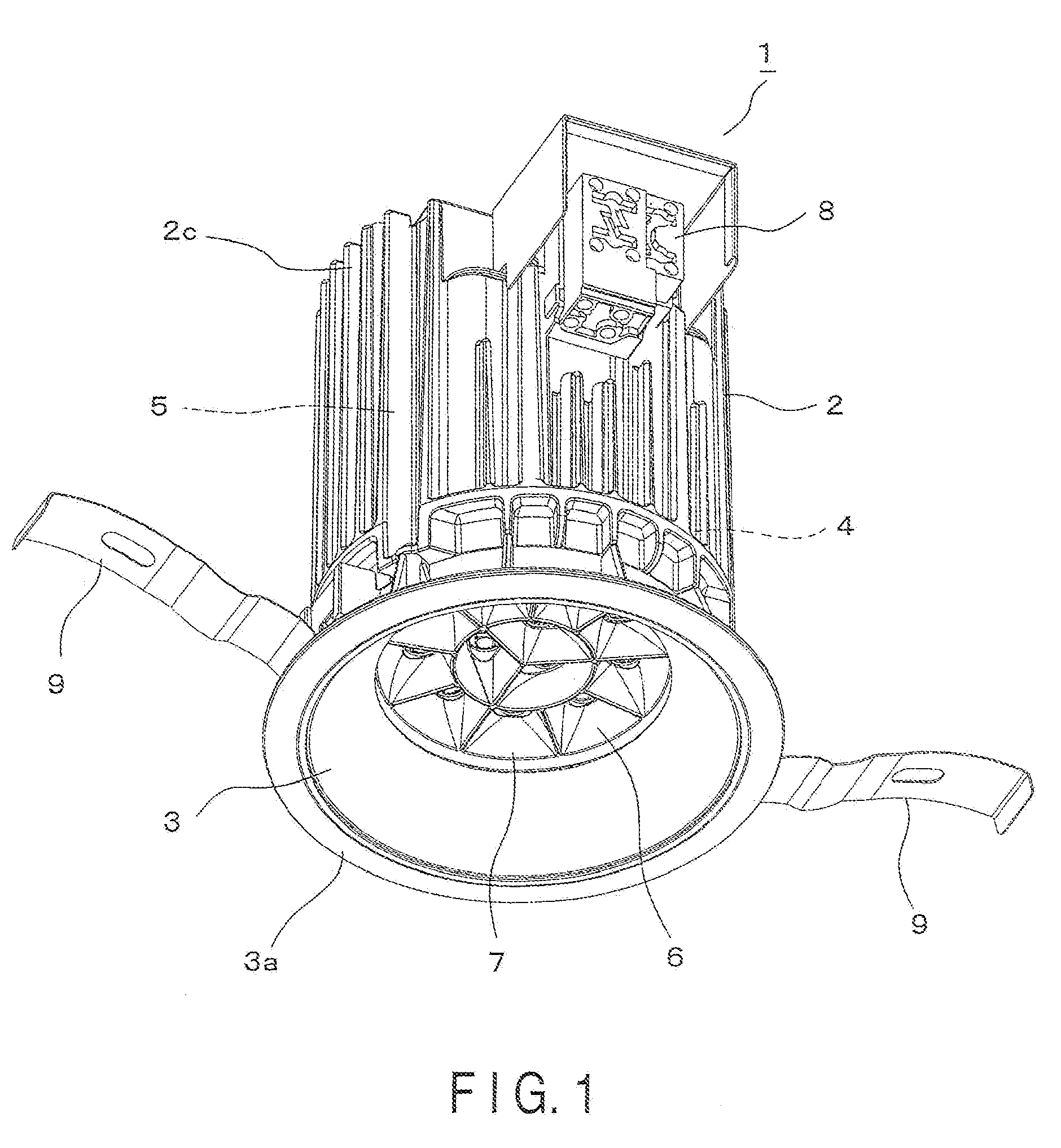
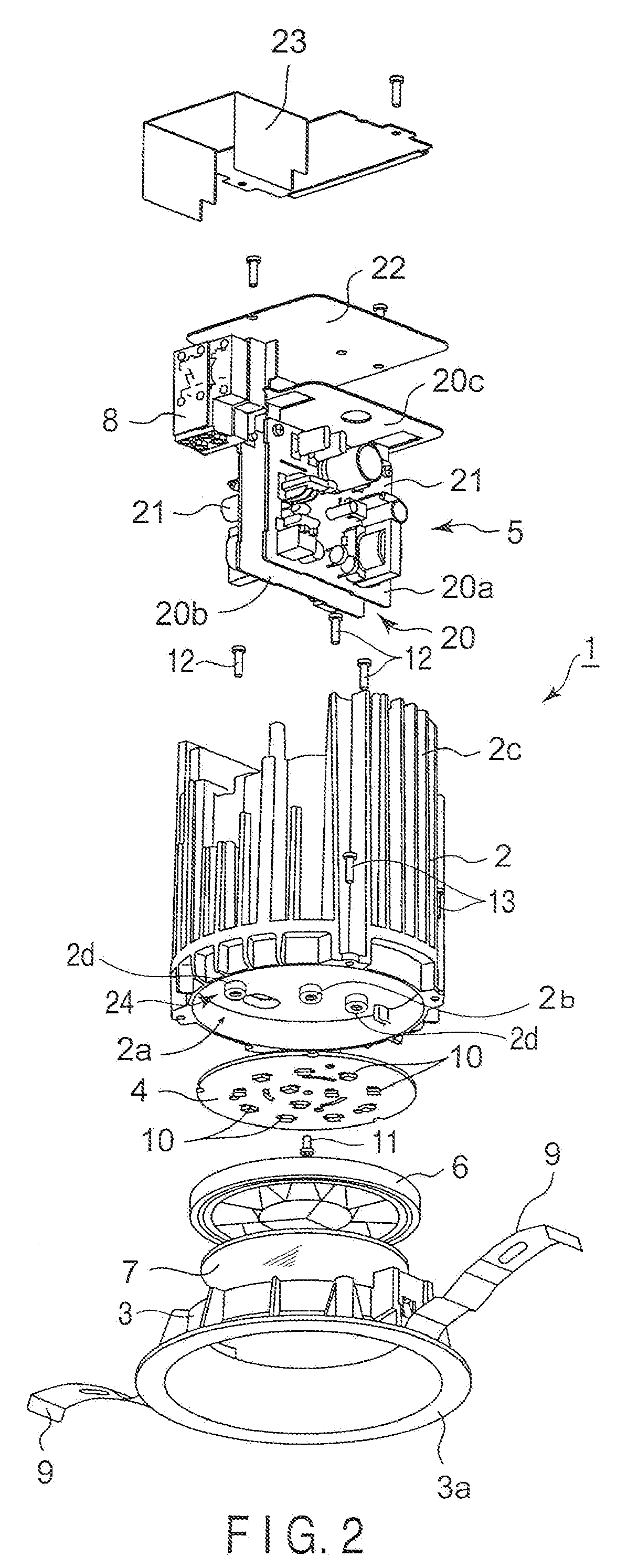
InactiveUS20100053950A1Deformation MinimizationEasy to installPlanar light sourcesPoint-like light sourceEngineeringLight source
A down-light has a main body, a substrate, a plurality of LEDs, a reflector, a central boss, a central screw and peripheral screws. The main body has a mounting area. The substrate having LEDs is assembled in the mounting area. The reflector is attached to the main body with the substrate interposed therebetween, and reflects light emitted from the LEDs. The central boss is formed on the mounting area to correspond to a central part of the substrate. The central screw fixes the central part of the substrate to the central boss from the reflector side. Peripheral screws fix the substrate to the main body by pulling the reflector from the main body side.
Owner:TOSHIBA LIGHTING & TECH CORP
Process for building three-dimensional objects
InactiveUS8968625B2Deformation MinimizationLiquid surface applicatorsElectrographic process apparatusObject basedEngineering
A process for building three-dimensional objects based on electrophotographic printing is disclosed, comprising the steps of depositing a first layer of powdered base material on a substrate, operating an imaging member, a charging device, an image generating device and an image developing device, in that order, to deliver and deposit filler material onto the layer of powdered base material in an image-wise manner to produce a layer of bonded base material that correspond to the first cross-section of the three-dimensional object being built, repeating all the above steps for as many times as required to form successive layers that constitute the three-dimensional object, said filler material further causing adjacent layers to be bonded with one another; and removing unbonded material to cause the three-dimensional object to appear.
Owner:TAN YU EN
Apparatus for insertion of a medical device during a medical imaging process
ActiveUS8244327B2Easy accessMaximize accuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesMedical imagingActuator
The end-effector (150) includes a sheath (152) and a medical device or needle carrier (154) that is disposed within the interior compartment (160) of the sheath. Aperture (162) is located in a portion of the sheath proximal a distal end of the sheath that is inserted into a natural or artificial cavity. This device is guided by a real-time imager.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Multi-component dental appliances and a method for constructing the same
ActiveUS20060115795A1Deformation MinimizationAdditive manufacturing apparatusDental articulatorsEngineeringDental appliances
Dental appliances including multiple components and a system and method for constructing the same are disclosed herein. The dental components are designed to fit together to form the dental appliance. The components of the dental appliance are electronically modeled, printed, and pressed sequentially, separately, or as a unitary piece. Forming the dental appliance from multiple components enables each component of the dental appliance to be formed from a different material, each material having different features associated with it. In various embodiments, different materials have different colors, textures, opacities, and transformation factors associated with them. Furthermore, each component can be formed from multiple components. In some other embodiments, a support structure is designed and constructed in order to minimize deformation of a dental component during fabrication of the component.
Owner:NAT DENTEX LLC
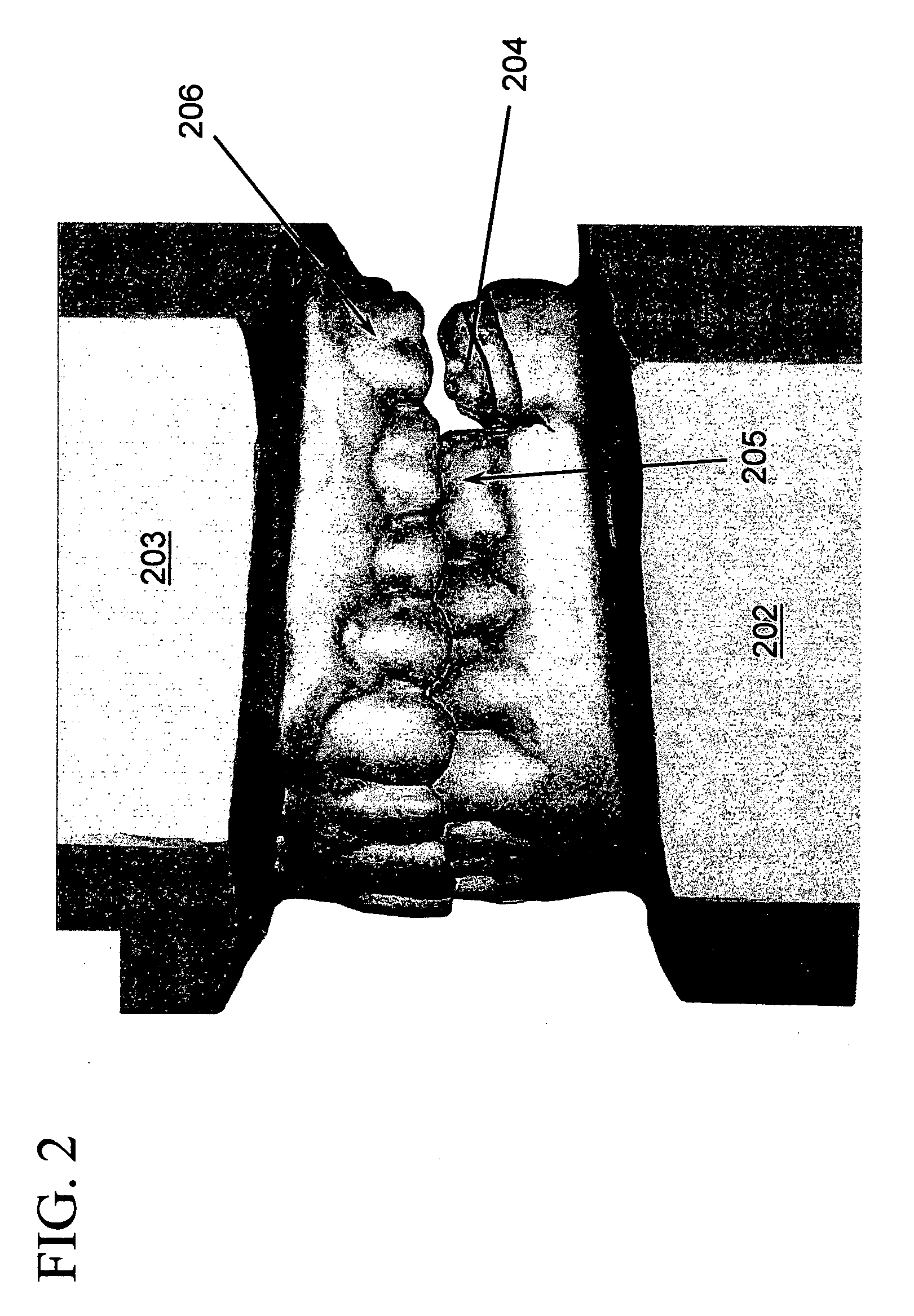
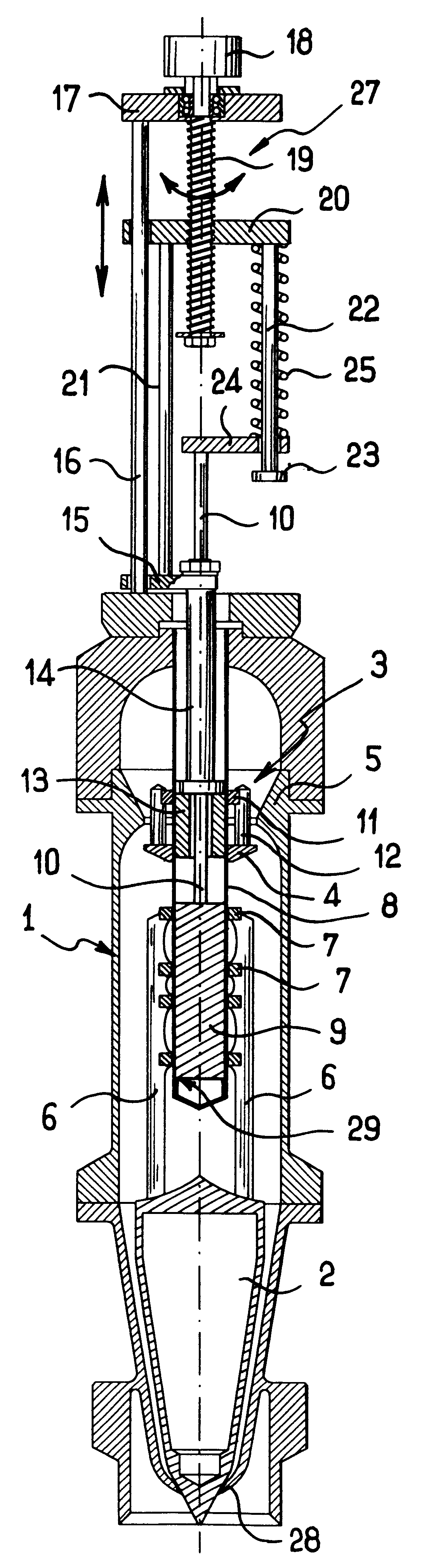
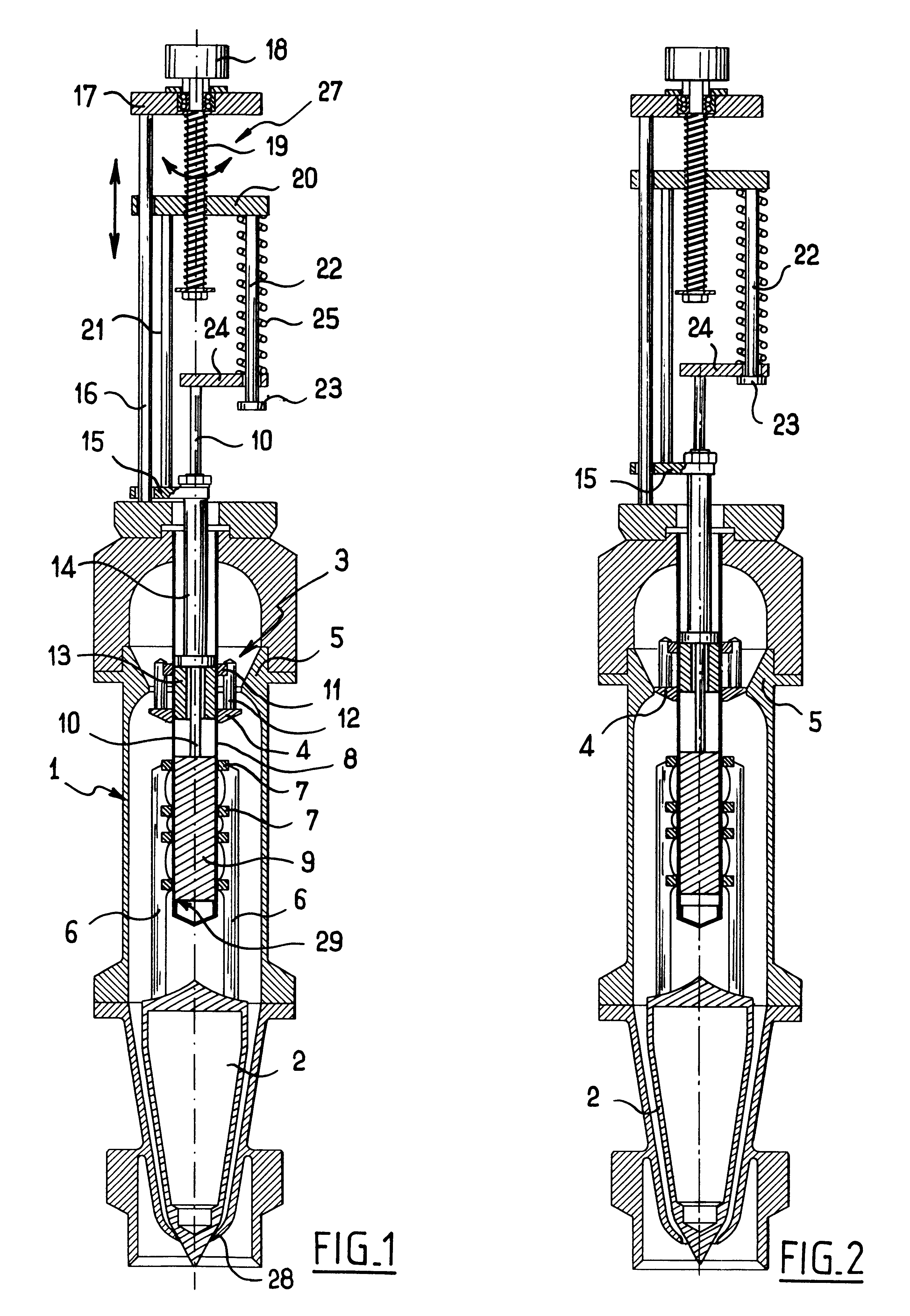
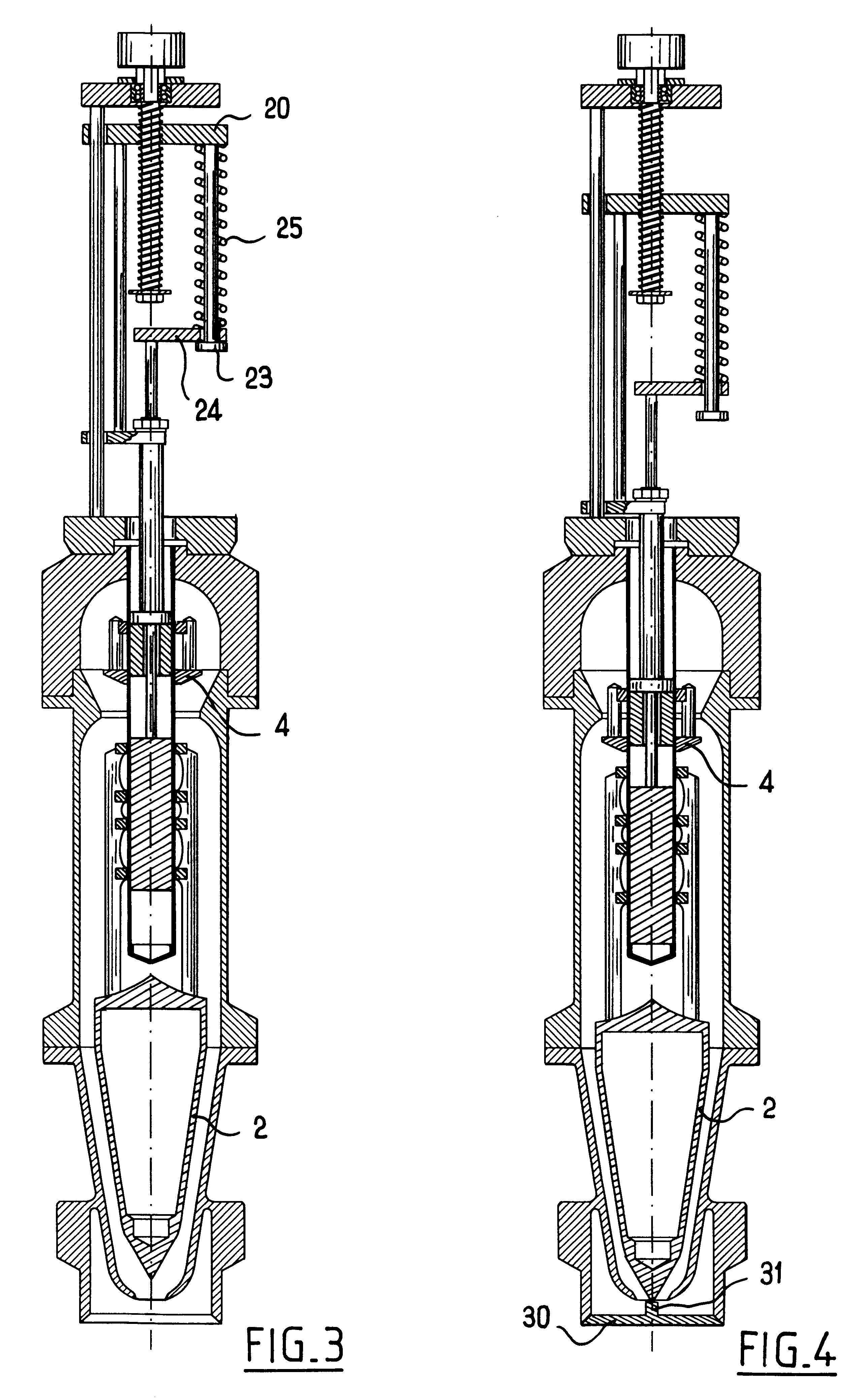
Filling spout whose flow rate can be adjusted by a single actuator device
InactiveUS6375050B1Risk minimizationDeformation MinimizationLiquid fillingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringActuator
A filling spout having an adjustable flow rate and comprising a valve body receiving a valve member extending facing a valve seat, and a flow-rate adjustment member disposed upstream from the valve member and extending in register with a constriction in the valve body, the valve member and the flow-rate adjustment member being connected to a single actuator device via means allowing limited axial movement by enabling the adjustment member and the valve member to move axially relative to each other to a limited extent.
Owner:SERAC GROUP
Disposable acetabular reamer from flat stock
ActiveUS20090163921A1Easy to moldMinimizing stress-induced deformationSurgeryStress inducedMetallic materials
A disposable reamer is provided, made up of a base and a thin-walled, perforated cutting body of flat metal stock affixed thereto. The base and body may be molded together or assembled together in a mechanical manner. The body is optionally formed so as to comprise a plurality of appendages connected at a center so as to improve die forming of the body into a final desired shape while at the same time minimizing stress-induced deformation in the body.
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
Supporting substrate for manufacturing flexible information display device, manufacturing method thereof, and flexible information display device
InactiveUS20150060870A1Low investment costIncrease equipment costLamination ancillary operationsLayered product treatmentDisplay deviceEngineering
Disclosed are a supporting substrate for manufacturing a flexible information display device capable of easily separating the flexible information display device from the supporting substrate without deforming or damaging the flexible information display device, a manufacturing method thereof, and a flexible information display device manufactured thereby. The supporting substrate for manufacturing a flexible information display device includes: a coating layer formed therein with a plurality micro-protrusions formed on the supporting substrate; and a temporary bonding / debonding layer formed on the coating layer and including an adhesive material mechanically interlocked with and bonded to the supporting substrate through Van der Waals bonding force. The method provides a method capable of economically manufacturing the display device having a high resolution while reviewing a cost competitive force by reducing a device investment cost and improving the yield rate in the flexible flat panel information display device.
Owner:LEE KEUN SOO +2
Method and compression apparatus for introducing residual compression into a component having a regular or an irregular shaped surface
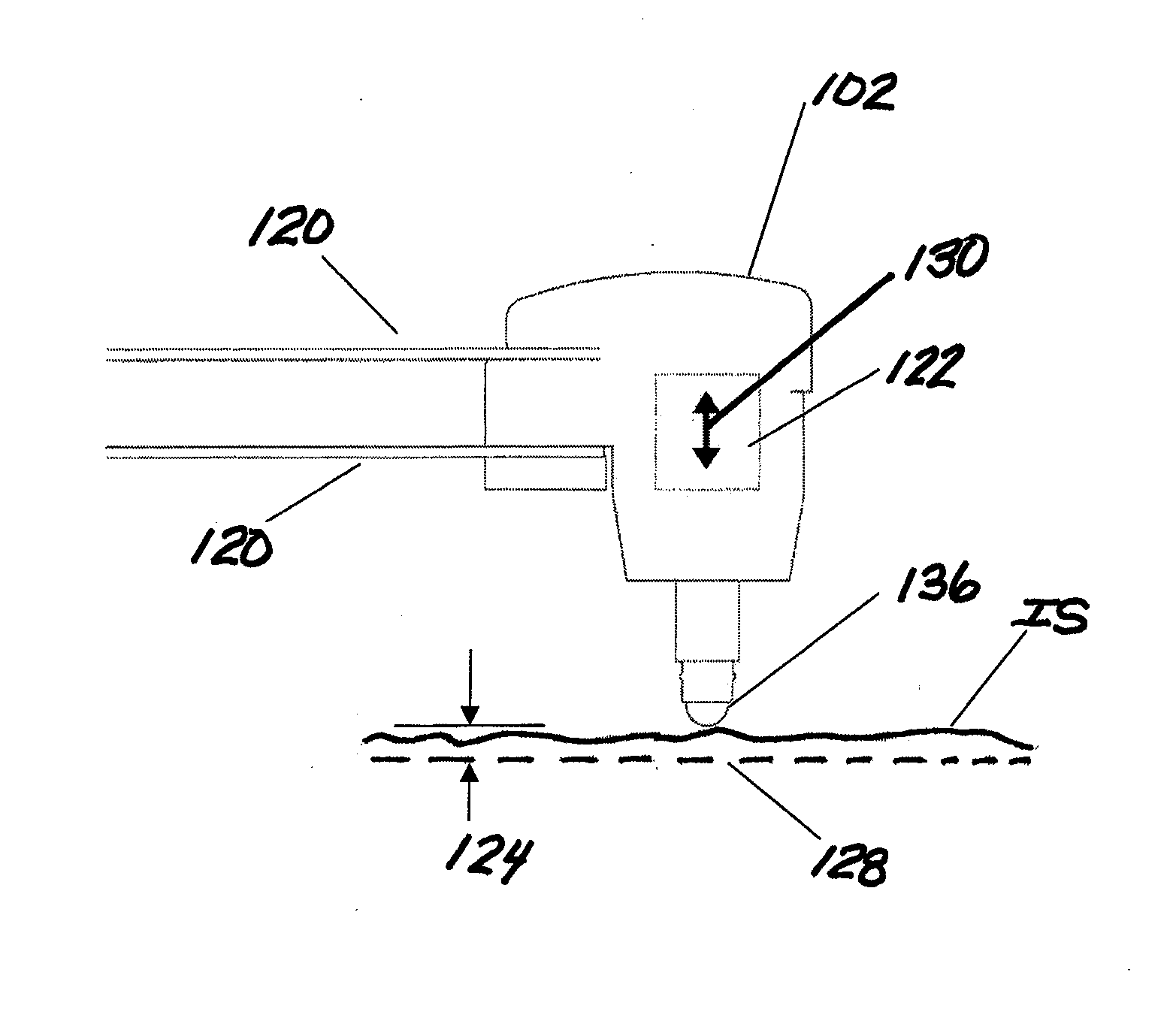
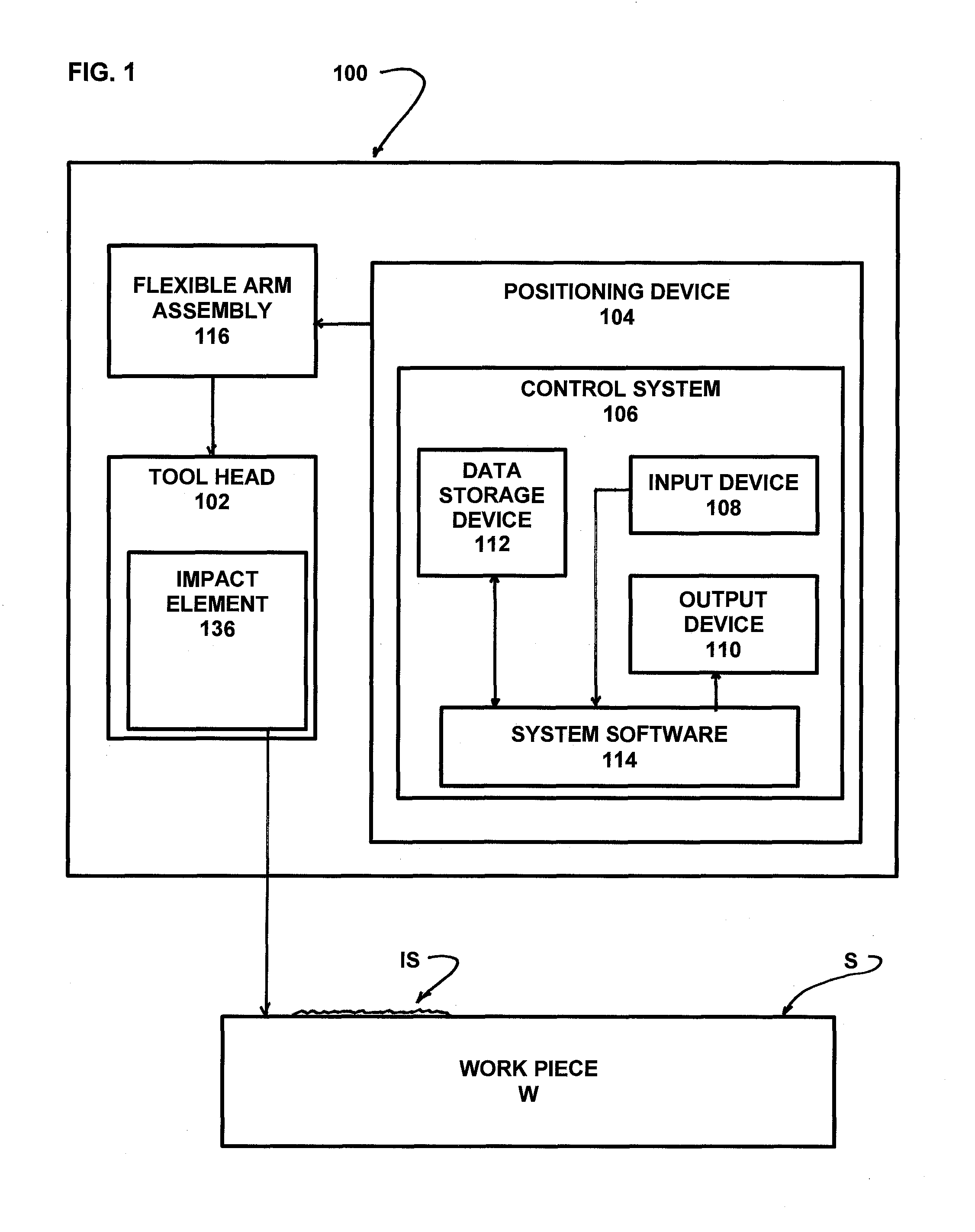
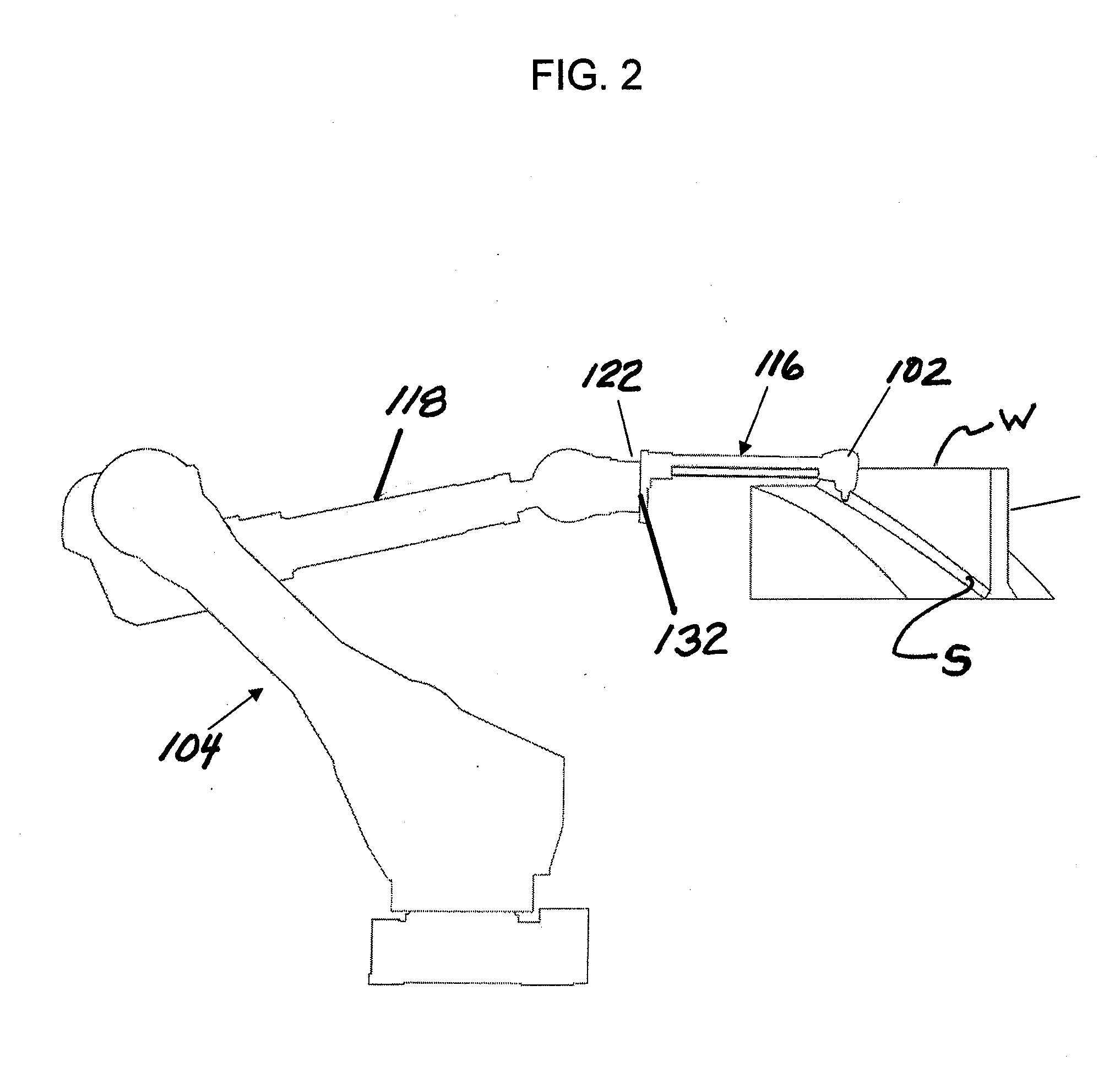
ActiveUS20140007394A1Freedom of movementDeformation MinimizationBurnishing machinesGrinding machinesCompression deviceClosed loop
A method and apparatus for improving the fatigue and stress corrosion cracking performance of irregular surfaces, such as welds assemblies of components, using a positioning system, such as a robotic or CNC machine, to position a tool head for inducing compression along and into the surface of a workpiece to automatically follow the surface irregularities. The method and apparatus operates to follow a virtual control surface located below the actual surface of the workpiece thereby allowing the irregular topography surface to be uniformly processed with closed loop process control.
Owner:SURFACE TECH HLDG
Multilength tubular transporter
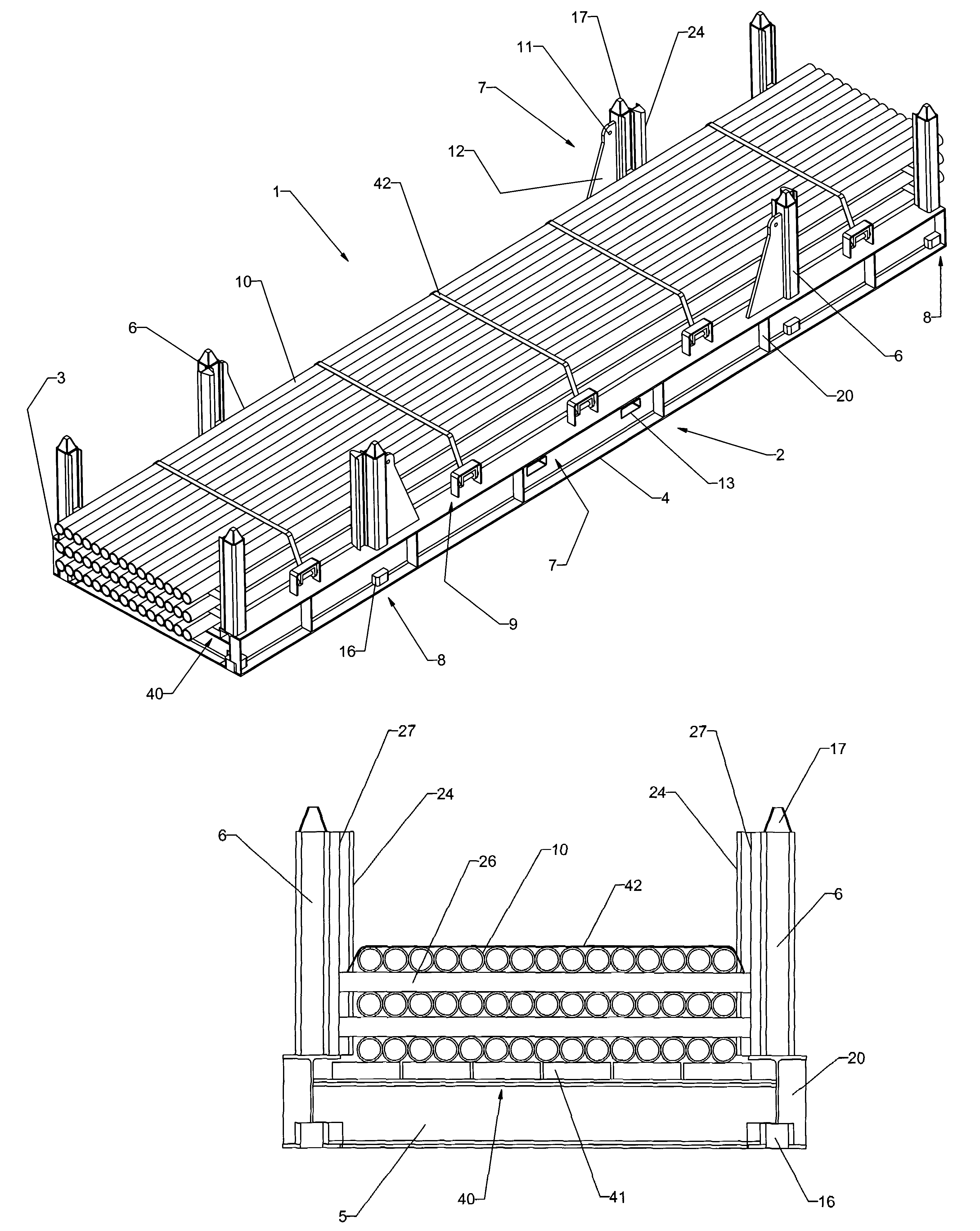
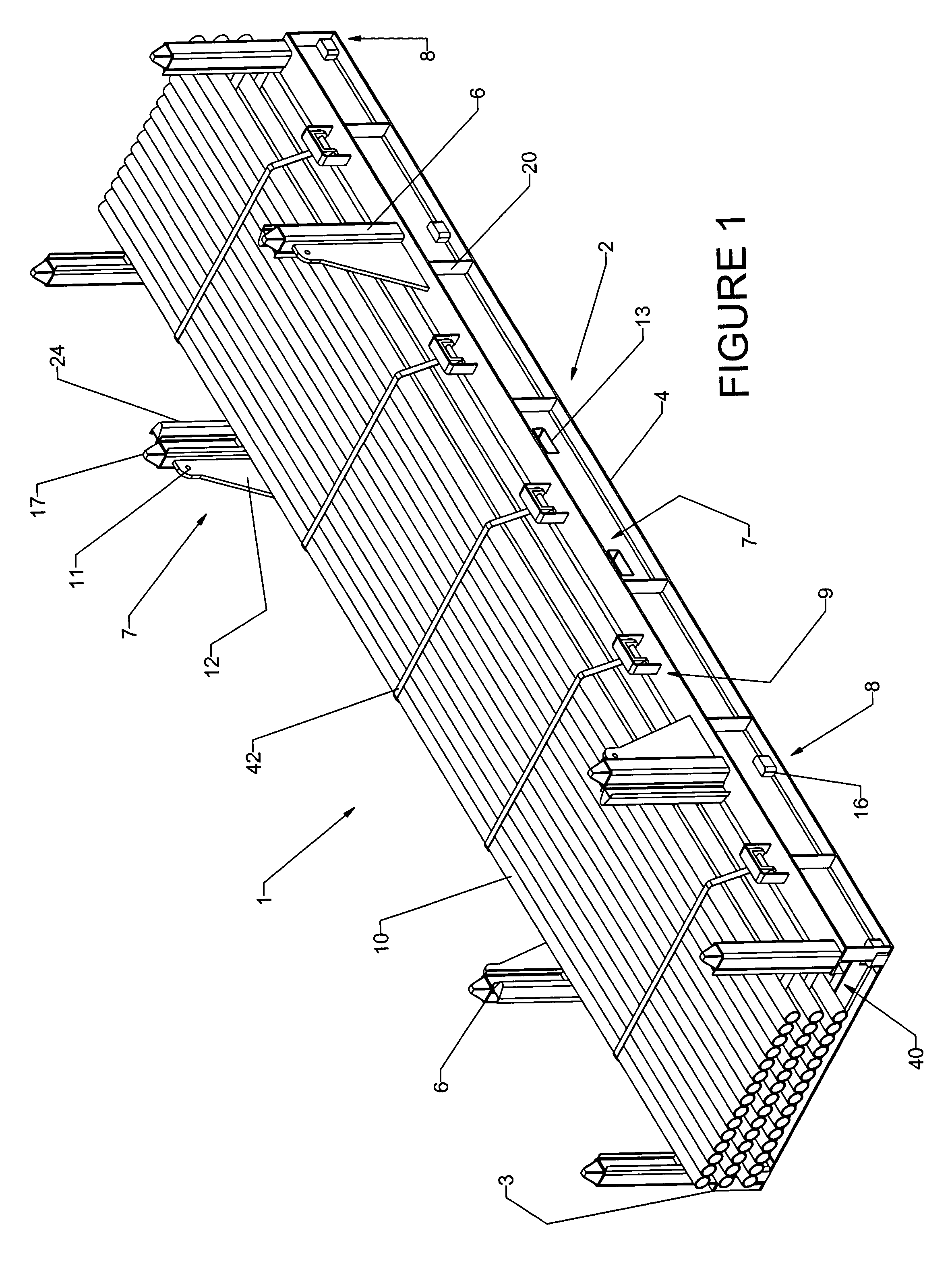
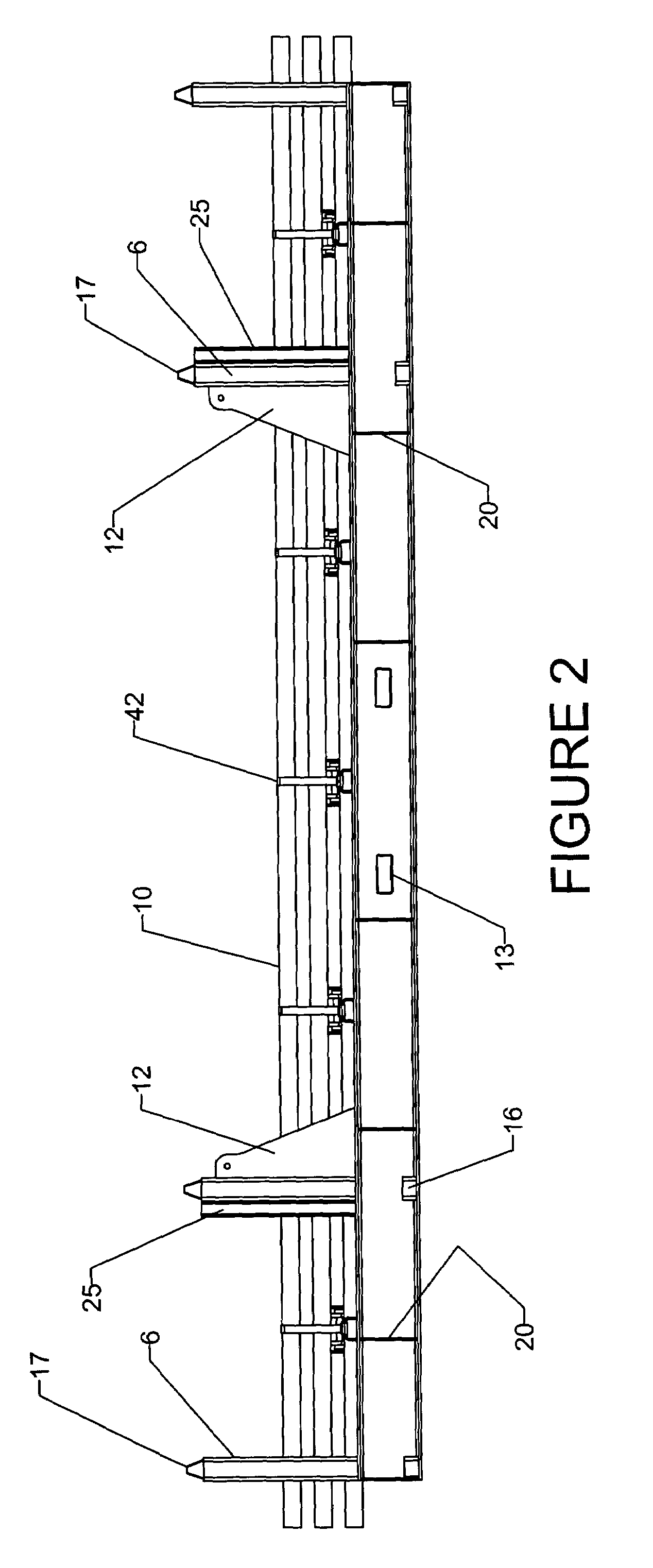
InactiveUS7131803B2Easy to liftIncreased payload capacityLarge containersFlexible elementsEngineeringWinch
A multilength tubular transporter is provided, comprising a base frame, including at least two main beams, wherein the main beams are connected by a plurality of cross members, a floor substantially covering the areas defined by the main beams and cross members; a plurality of substantially vertical guide members connected to each of the main beams; a lifting arrangement operatively connected to the base frame for enabling the transporter to be lifted to and from a vehicle; a stacking device operatively connected to the base frame for engaging the guide members of a second transporter, wherein the transporters may be securely stacked; and wherein the base frame includes one or more winches for securing tubulars within the transporter.
Owner:PARAGON INDS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com