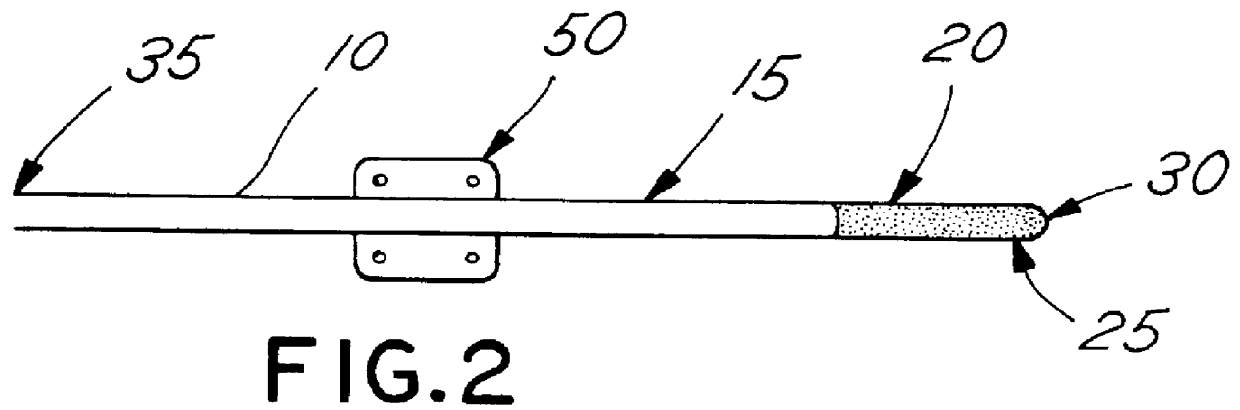
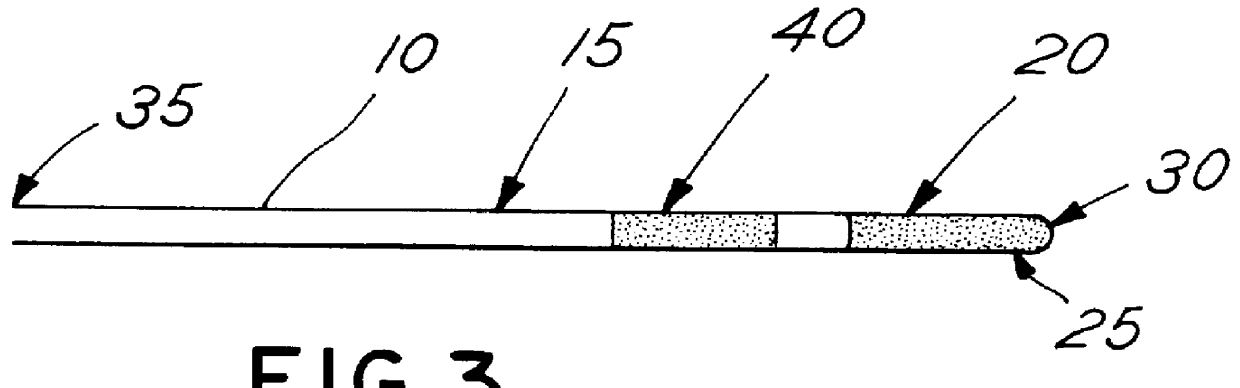
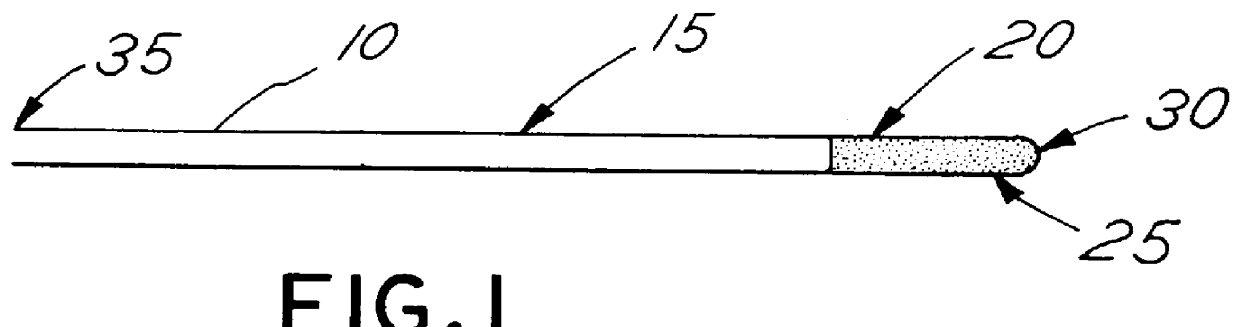
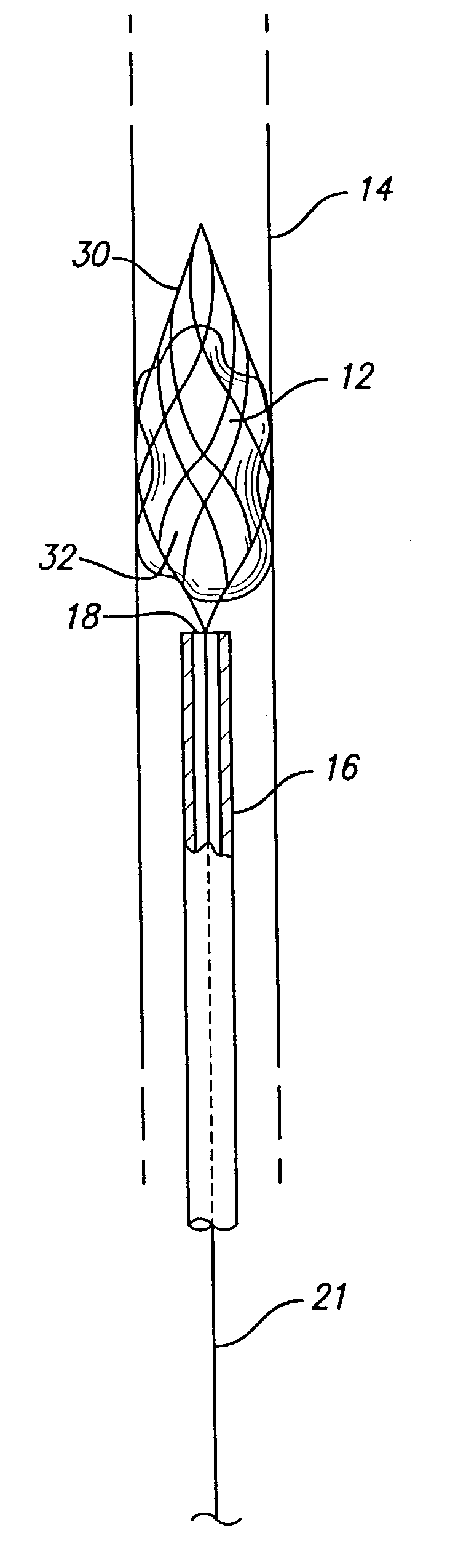
Patents
Literature
7015results about How to "Small diameter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
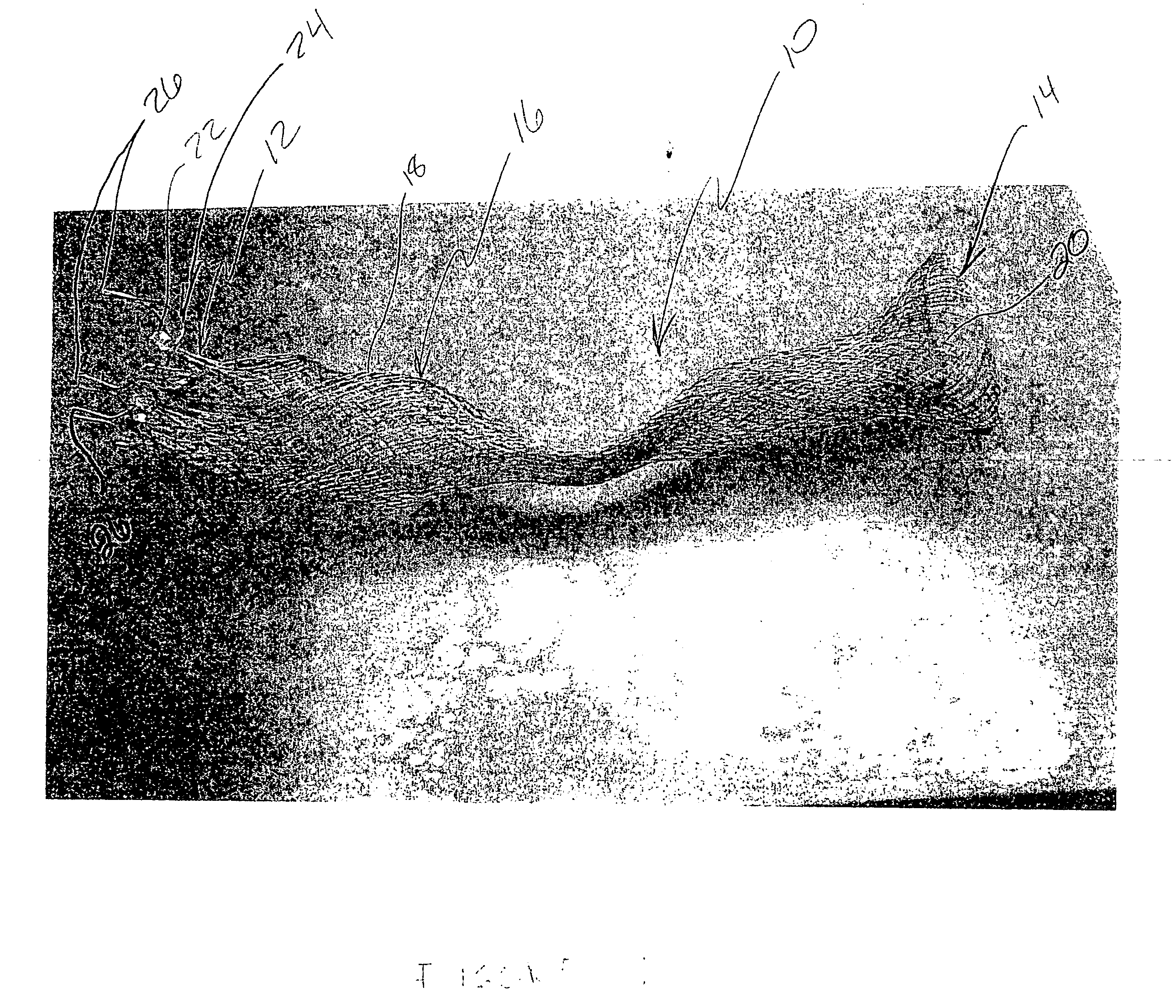
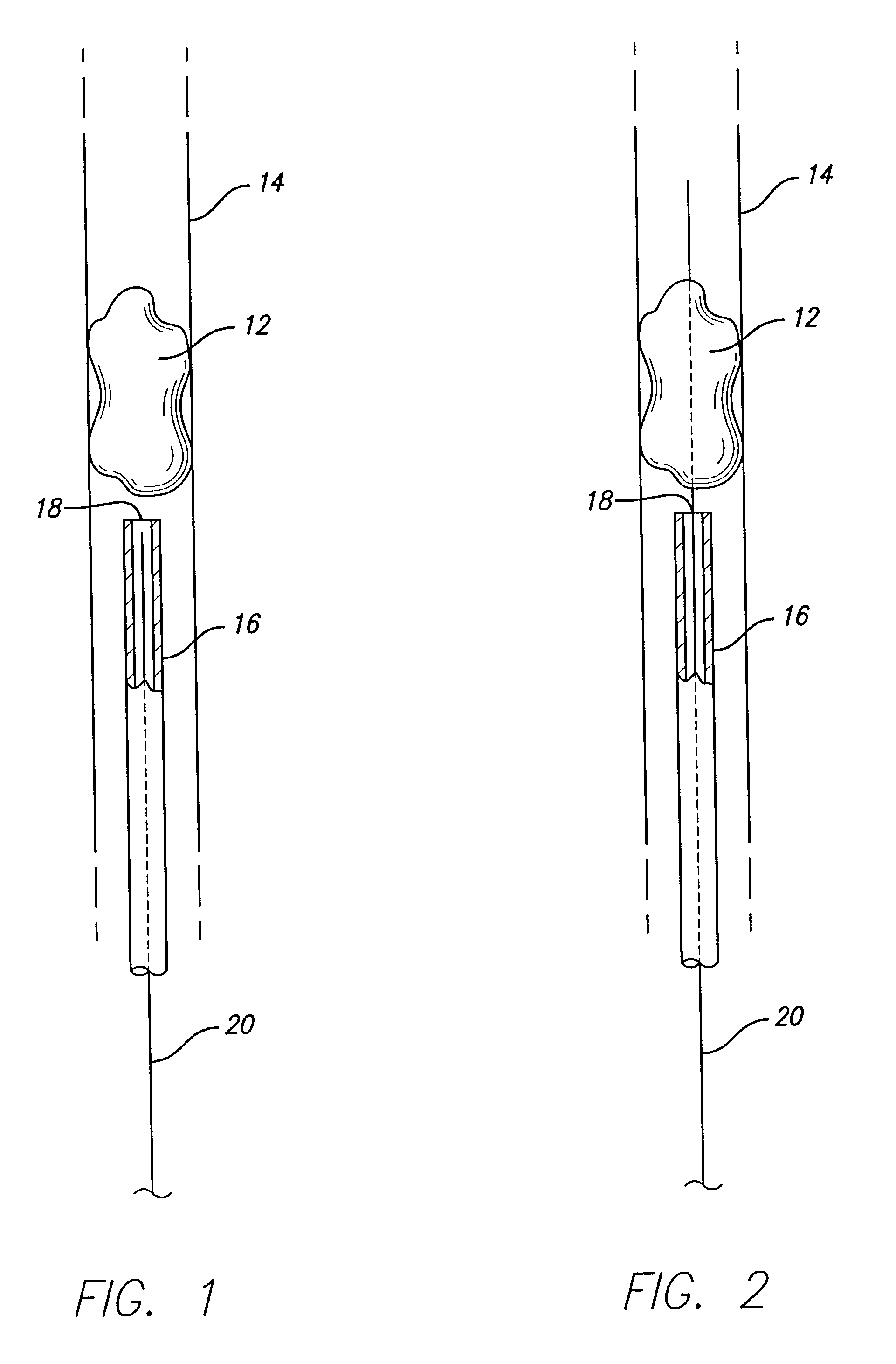
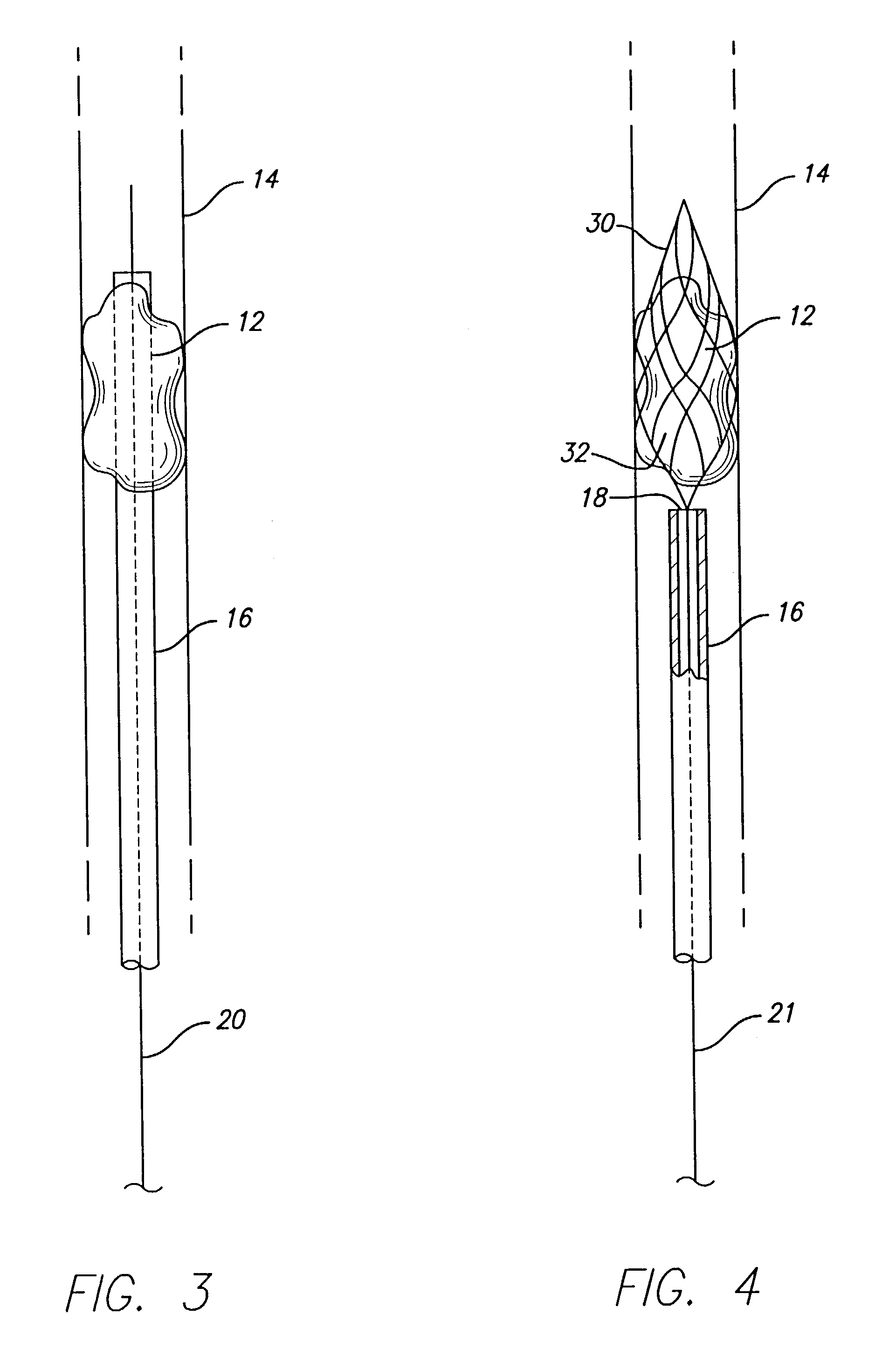
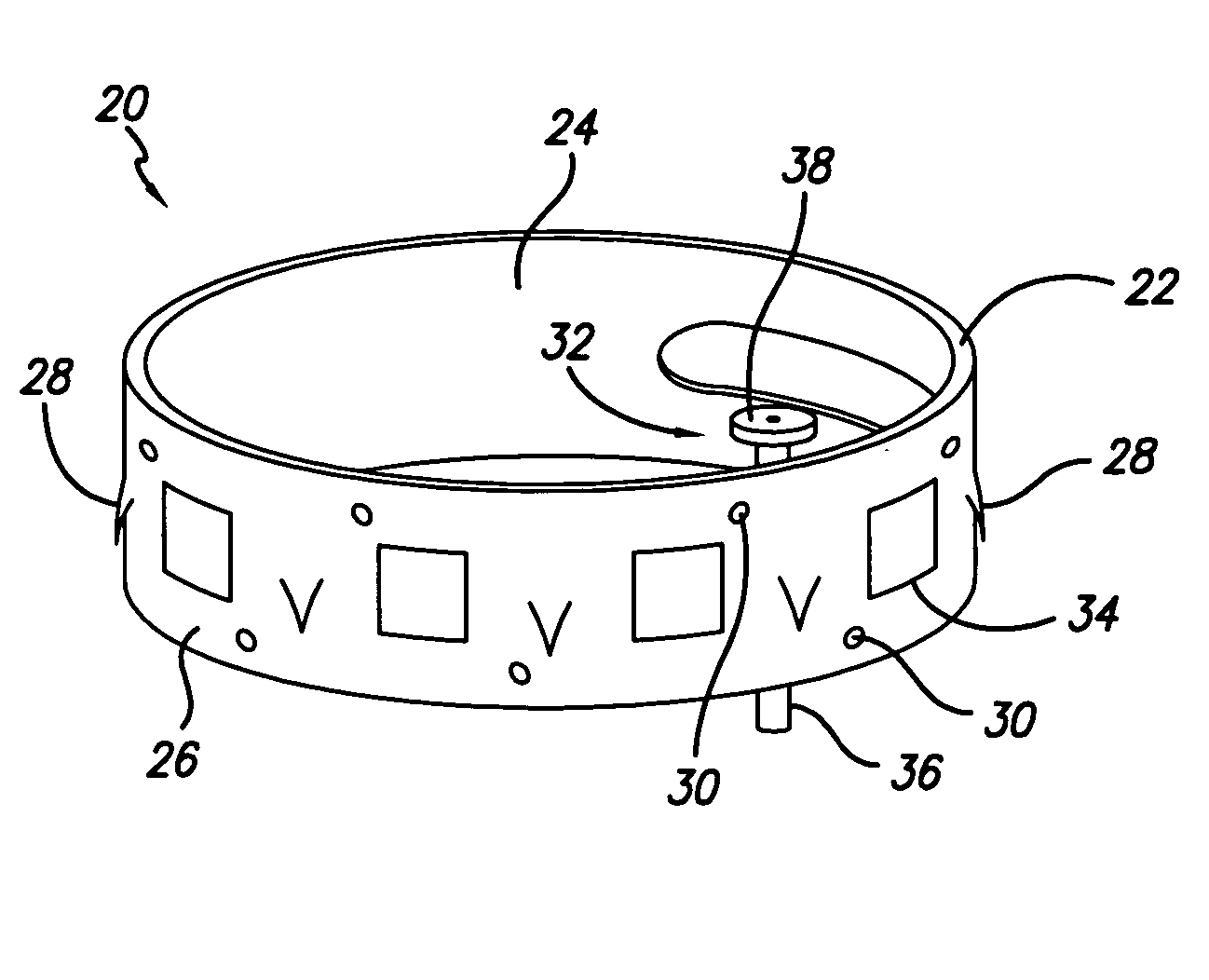
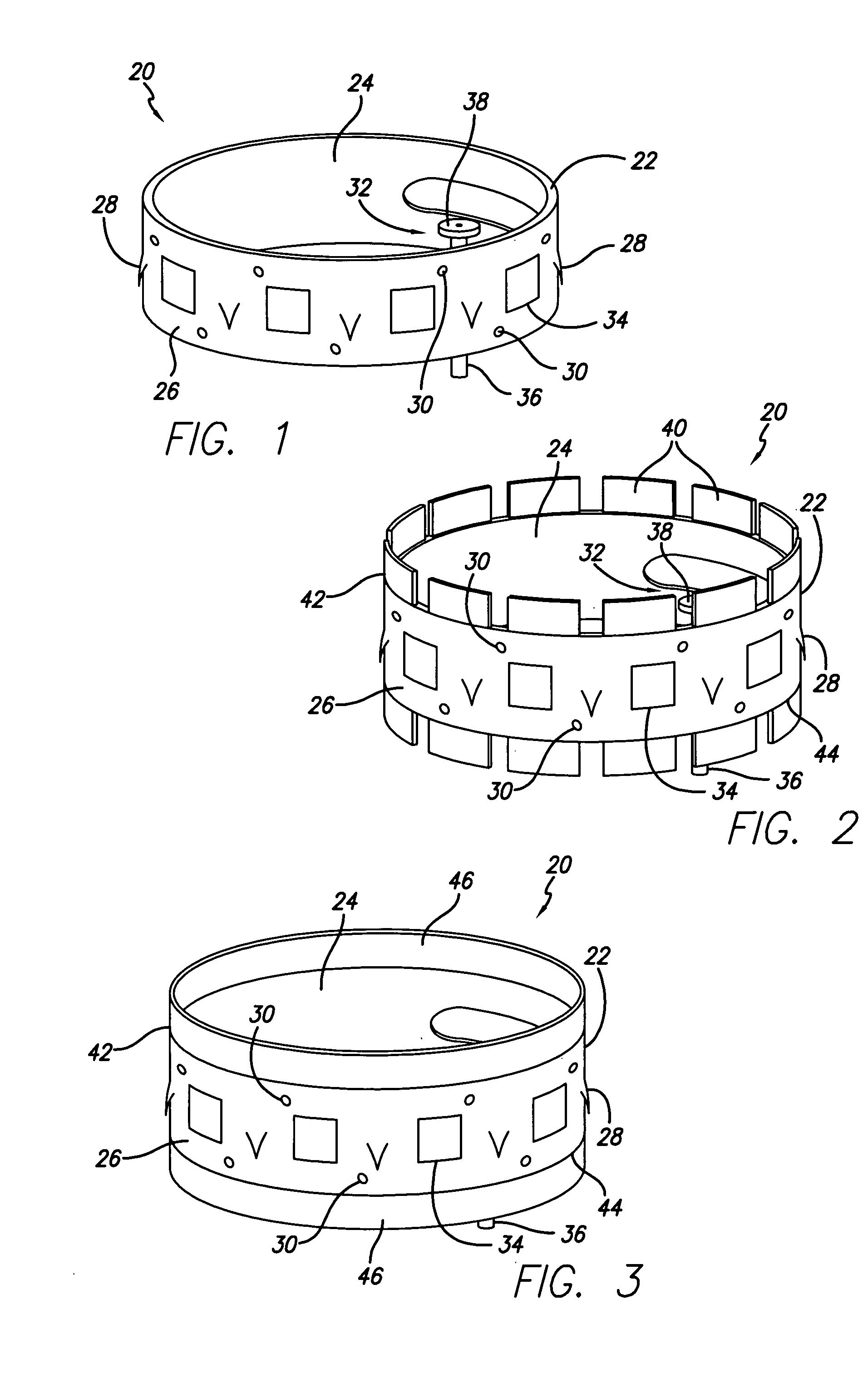
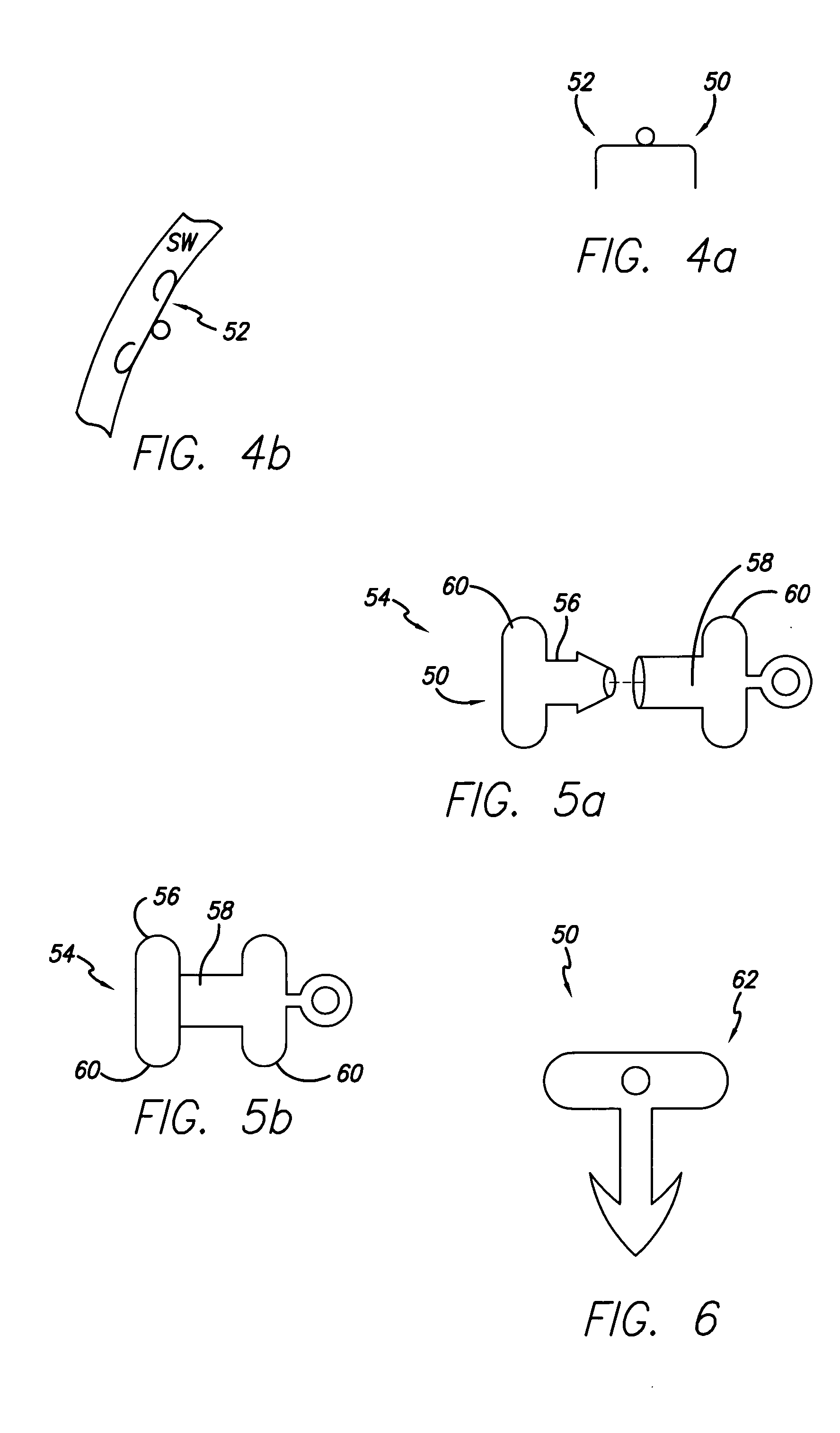
Flexible instrument
InactiveUS7090683B2Small diameterSufficient flexibilitySuture equipmentsProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringComputer algorithm
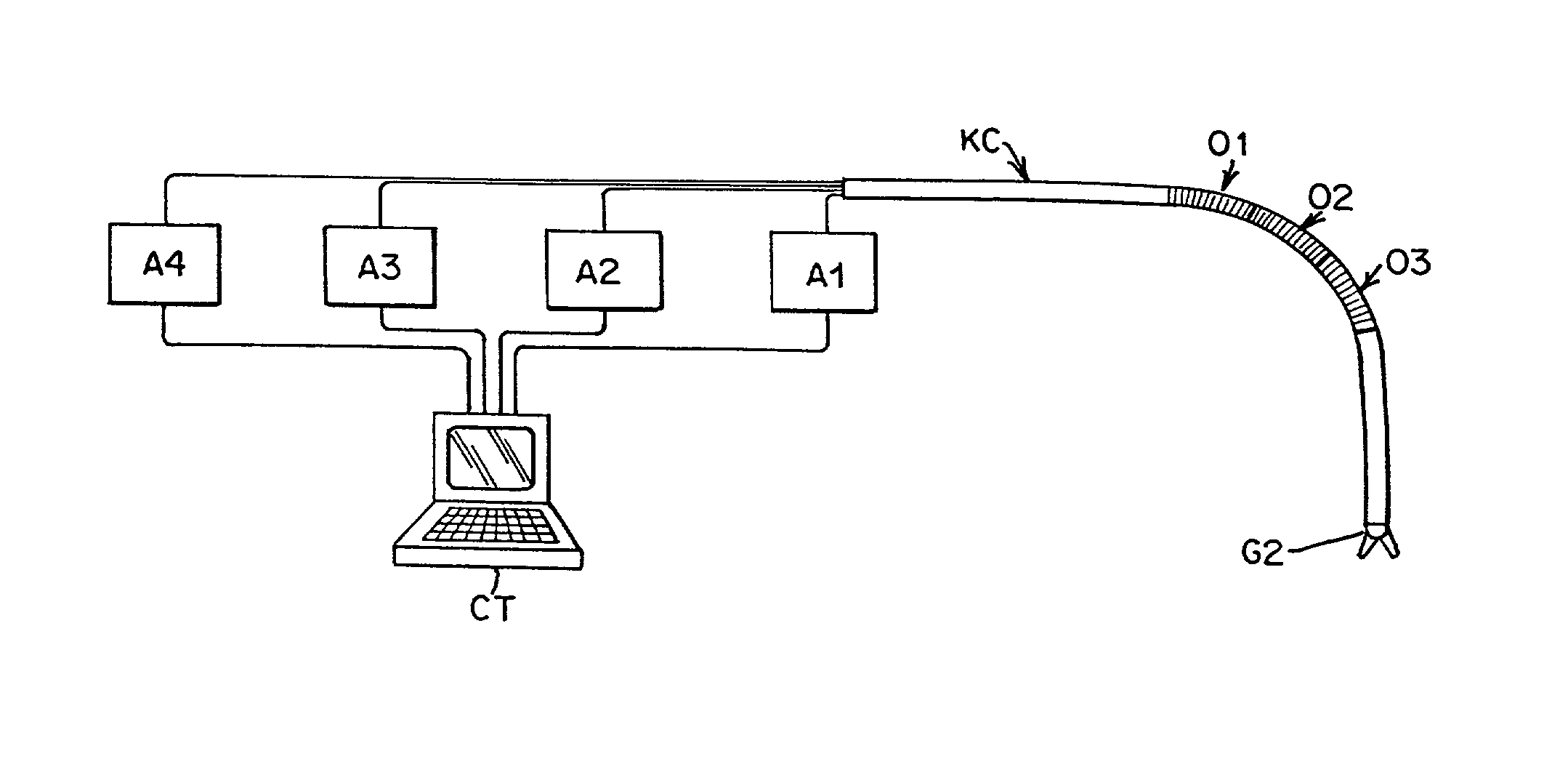
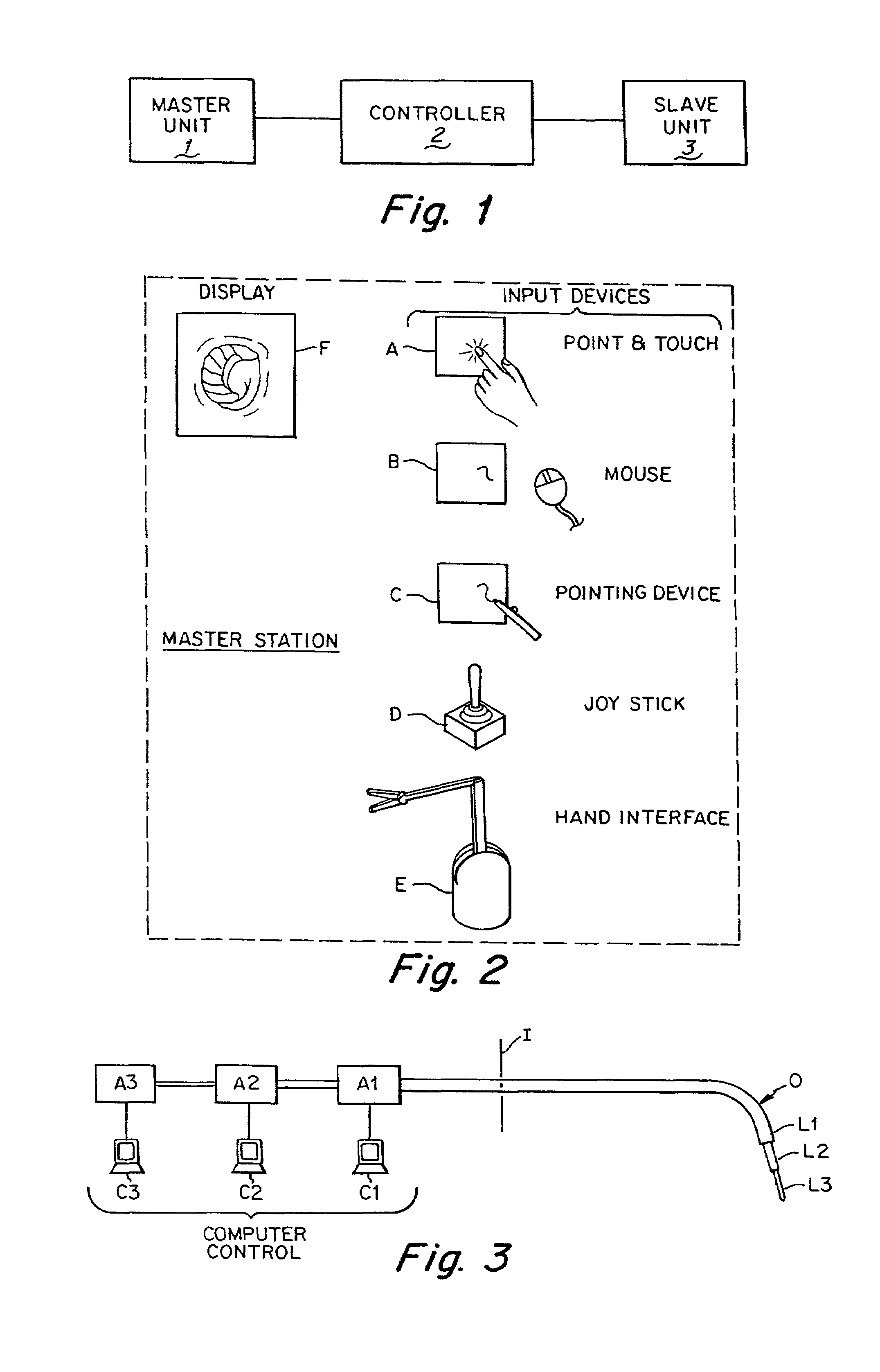
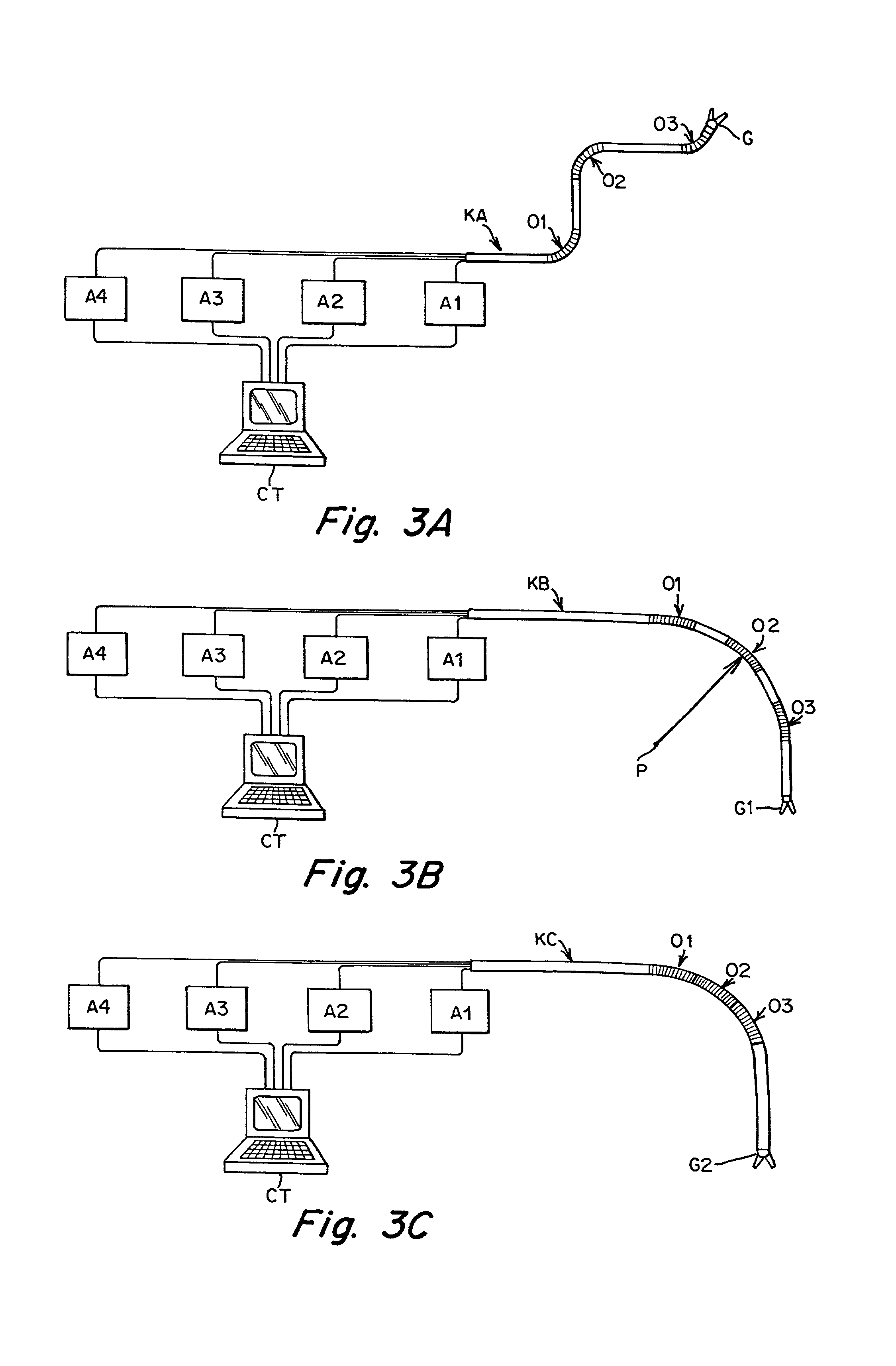
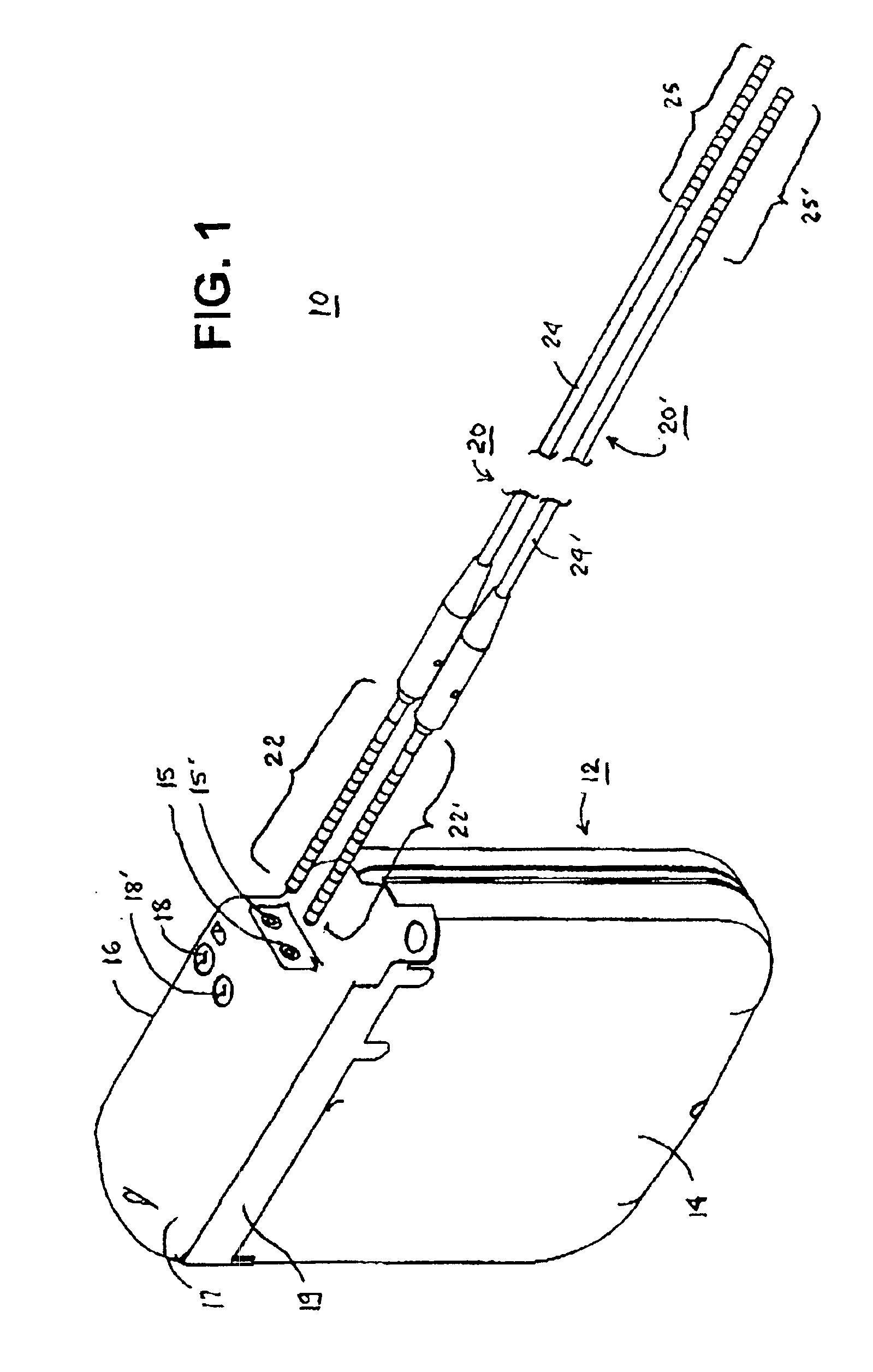
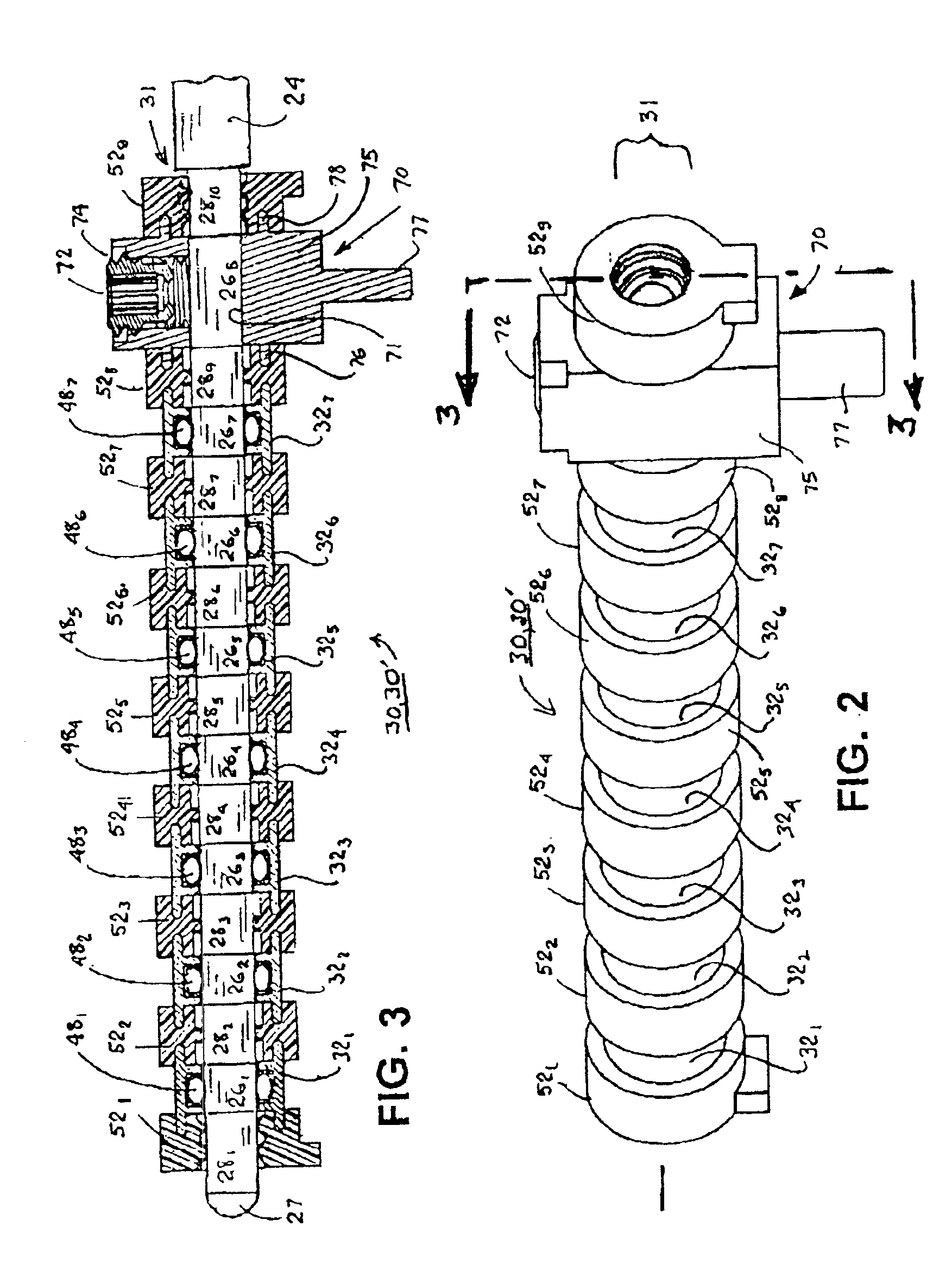
A remote control flexible instrument system, employing a shaft which supports a tool, is described in which the has proximal and distal ends with at least a portion thereof extending through a lumen of the human body so as to locate the shaft at an internal target site. A master station including an input device provides control of the instrument situated at a slave station. The master station can control at least one degree-of-freedom of the flexible instrument. A controller intercouples the master and slave stations and is operated in accordance with a computer algorithm that receives a command from the input device for controlling at least one degree-of-freedom of the catheter so as to respond in accordance with action at the input device. The flexible instrument further comprises a controlled flexible segment along the shaft, for controlled bending at the flexible segment to guide the shaft and to dispose the tool at an operative site.
Owner:HANSEN MEDICAL INC
Cardiac tissue ablation instrument with flexible wrist
InactiveUS20060199999A1Promotes convenient, simplified manufacturing and assembly processesShorten the counting processEndoscopesSurgical manipulatorsWristInstrumentation
An articulate minimally invasive surgical instrument with a flexible wrist to facilitate the safe placement and provide visual verification of the ablation catheter or other devices in Cardiac Tissue Ablation (CTA) treatments is described. In one embodiment, the instrument is an endoscope which has an elongate shaft, a flexible wrist at the working end of the shaft, and a vision scope lens at the tip of the flexible wrist. The flexible wrist has at least one degree of freedom to provide the desired articulation. It is actuated and controlled by a drive mechanism located in the housing at the distal end of the shaft. The articulation of the endoscope allows images of hard-to-see places to be taken for use in assisting the placement of the ablation catheter on the desired cardiac tissue. The endoscope may further include couplings to releasably attach an ablation device / catheter or a catheter guide to the endoscope thereby further utilizing the endoscope articulation to facilitate placement of the ablation catheter on hard-to-reach cardiac tissues. In another embodiment, the articulate instrument is a grasper or any other instrument with a flexible wrist and a built-in lumen to allow an endoscope to insert and be guided to the distal end of the instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
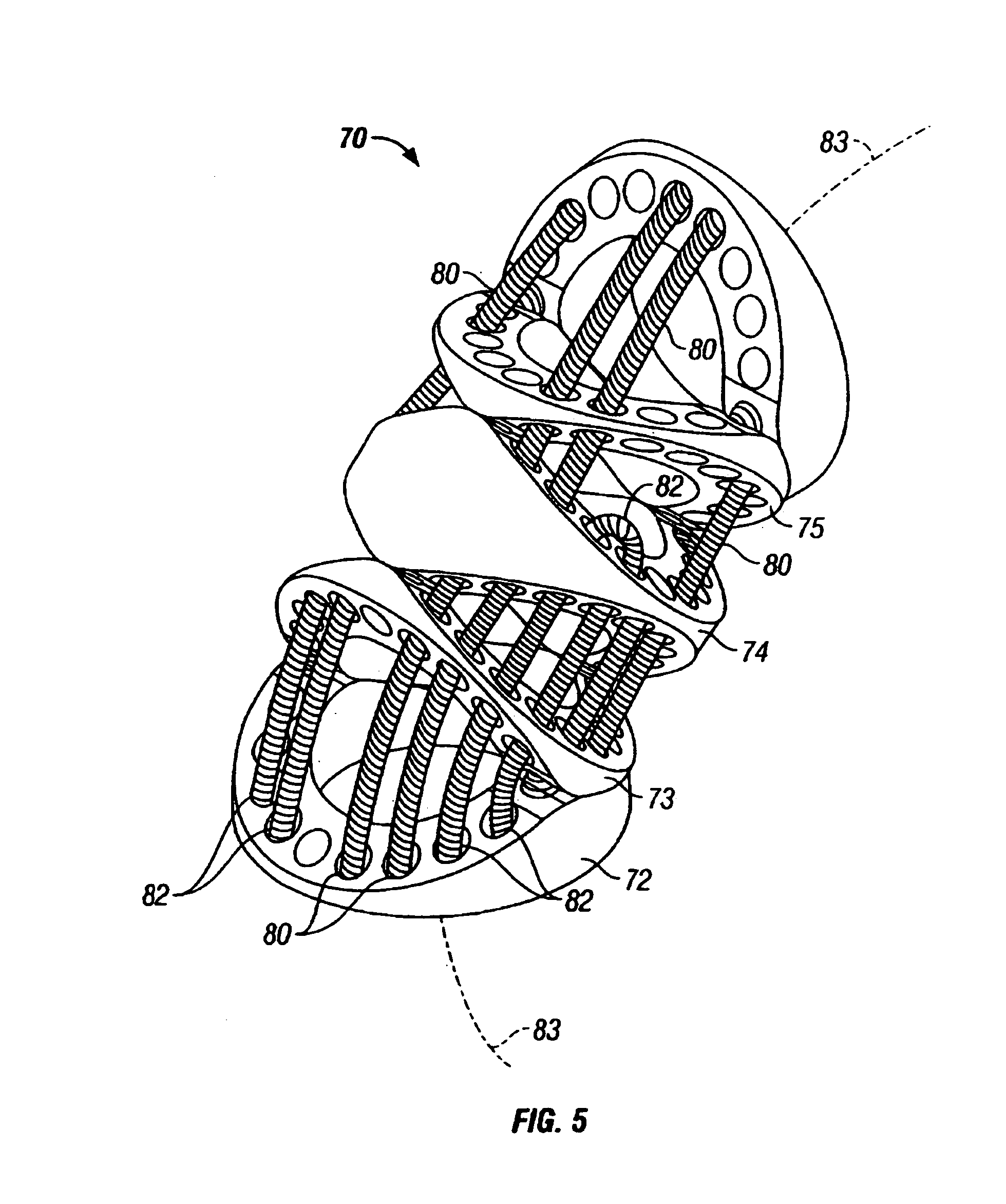
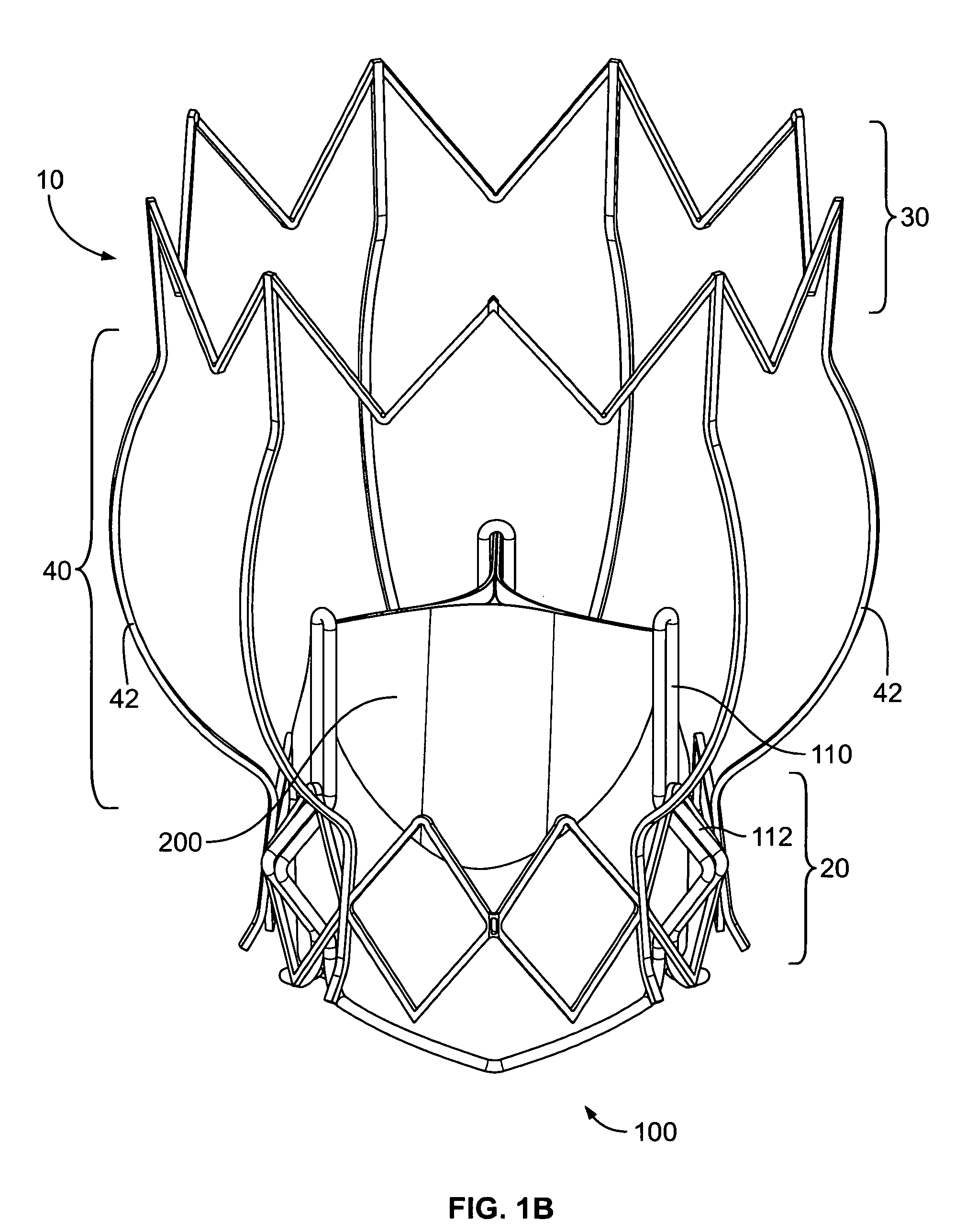
Assembly for setting a valve prosthesis in a corporeal duct
The invention concerns an assembly comprising a valve prosthesis to be implanted and a support receiving said valve. The support comprises: at least a tubular portion made of a pliable material slightly stretchable in the circumferential direction; means for fixing said tubular portion to the wall of the corporeal duct; and a plurality of elongated reinforcing elements, arranged on the circumference of said tubular portion and linked to said tubular portion independently of one another; the valve is linked at least partly to said elongated reinforcing elements, in particular at the commissures of its leaflets, and said elongated reinforcing elements jointly form, in extended position, a structure having a predetermined diameter that ensures sufficient extension of said valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
Surgical stapler with circumferential firing
A surgical stapler is provided. The stapler employs circumferential channels through which staples are deployed along an arc pathway against an anvil surface. The curved channels allow staples with relatively longer legs to be used in the stapler having a smaller diameter at the jaws. Also, by utilizing a curved path, a much larger staple can be placed in the same diameter device. Specialized curved staples for use with the stapler of the present invention are also provided. To further enable the benefits of the stapler with circumferential channels and method of staple deployment, novel jaw reinforcement structures are provided in the present invention. The jaw reinforcement structures are located towards the center or bladeline of the device instead of around the circumference as in conventional staplers, thereby clearing the outer area near the circumference of the device to provide room for longer staples and staple firing components.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Preparation method of porous fiber non-woven fabric
ActiveCN103981635AReduce melt viscosityReduce degradationFilament forming substance formingMelt spinning methodsDiluentNonwoven fabric
The invention relates to a preparation method of a porous fiber non-woven fabric. The aim of the preparation method is to improve the product performance of the conventional non-woven fabric, so that the non-woven fabric meets the requirements on high-precision and high-performance filter. The technical scheme is that the preparation method of the porous fiber non-woven fabric comprises the following steps in sequence: (1) uniformly mixing a polymer and a diluent to obtain a blend with 10 to 60 percent of polymer; (2) melting and extruding the blend in the step (1) by adopting a screw extruder granulator, and directly cooling and granulating in air; (3) producing master batches in the step (2) by melt-down equipment to obtain a primary non-woven fabric; (4) extracting to remove the diluent from the primary non-woven fabric in the step (3), performing pore-forming on fibers in the non-woven fabric, and drying to obtain the porous fiber non-wave fabric; (5) recovering mixed waste liquid of the diluent and an extraction agent for reuse.
Owner:浙江省轻工业品质量检验研究院
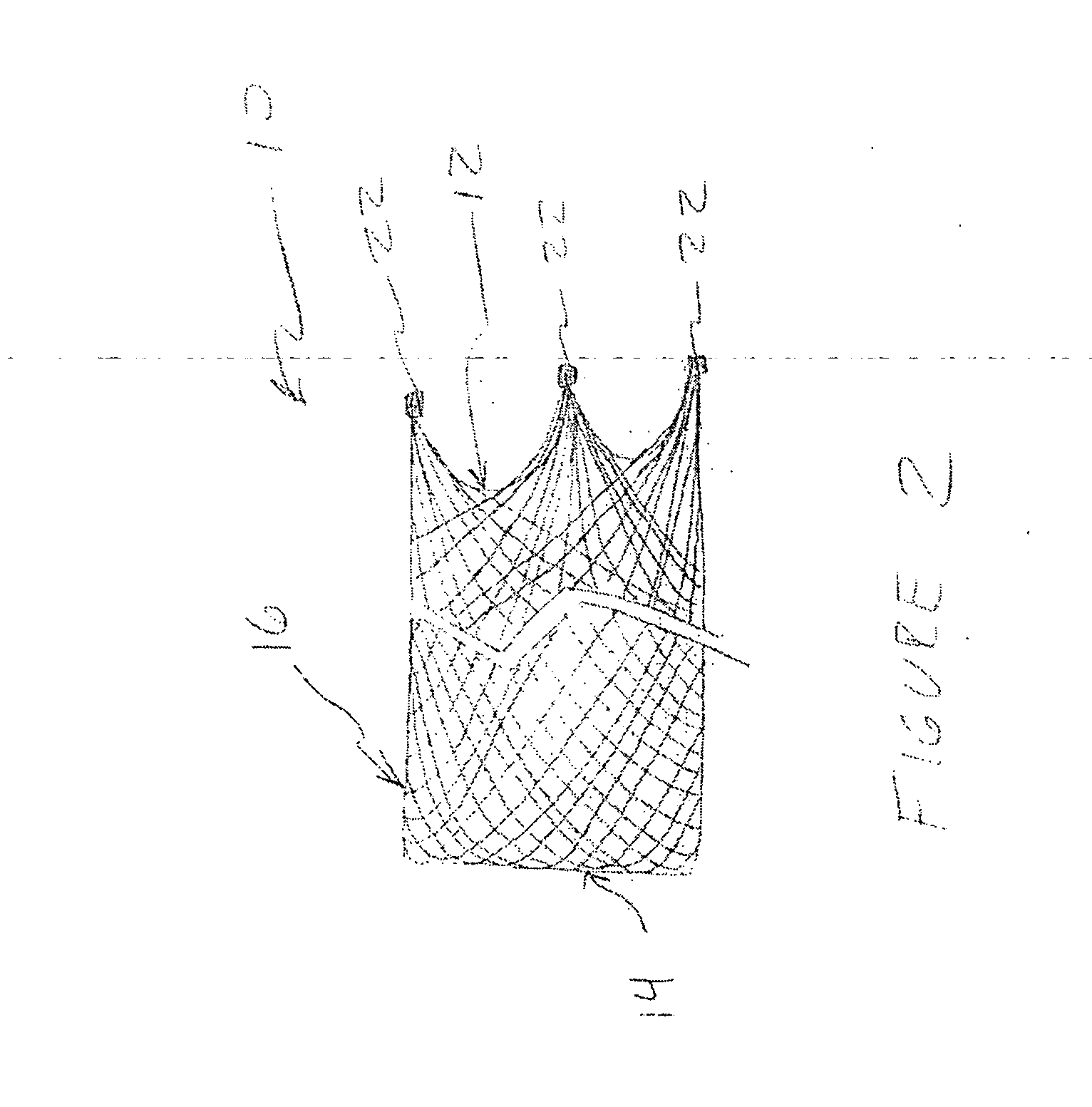
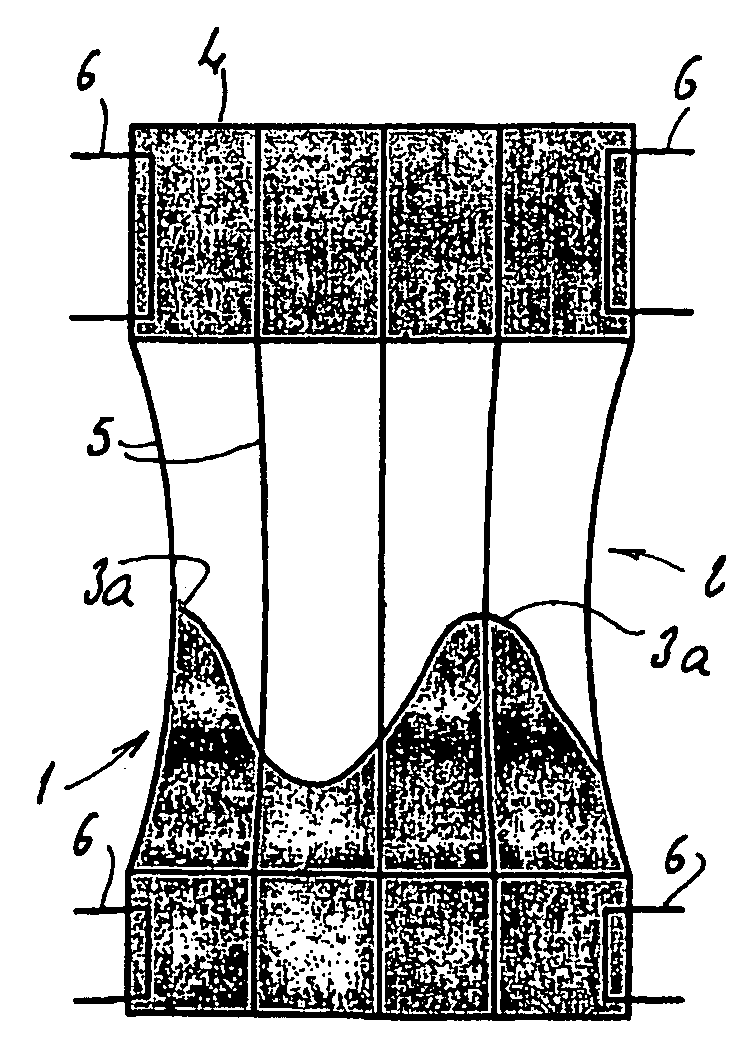
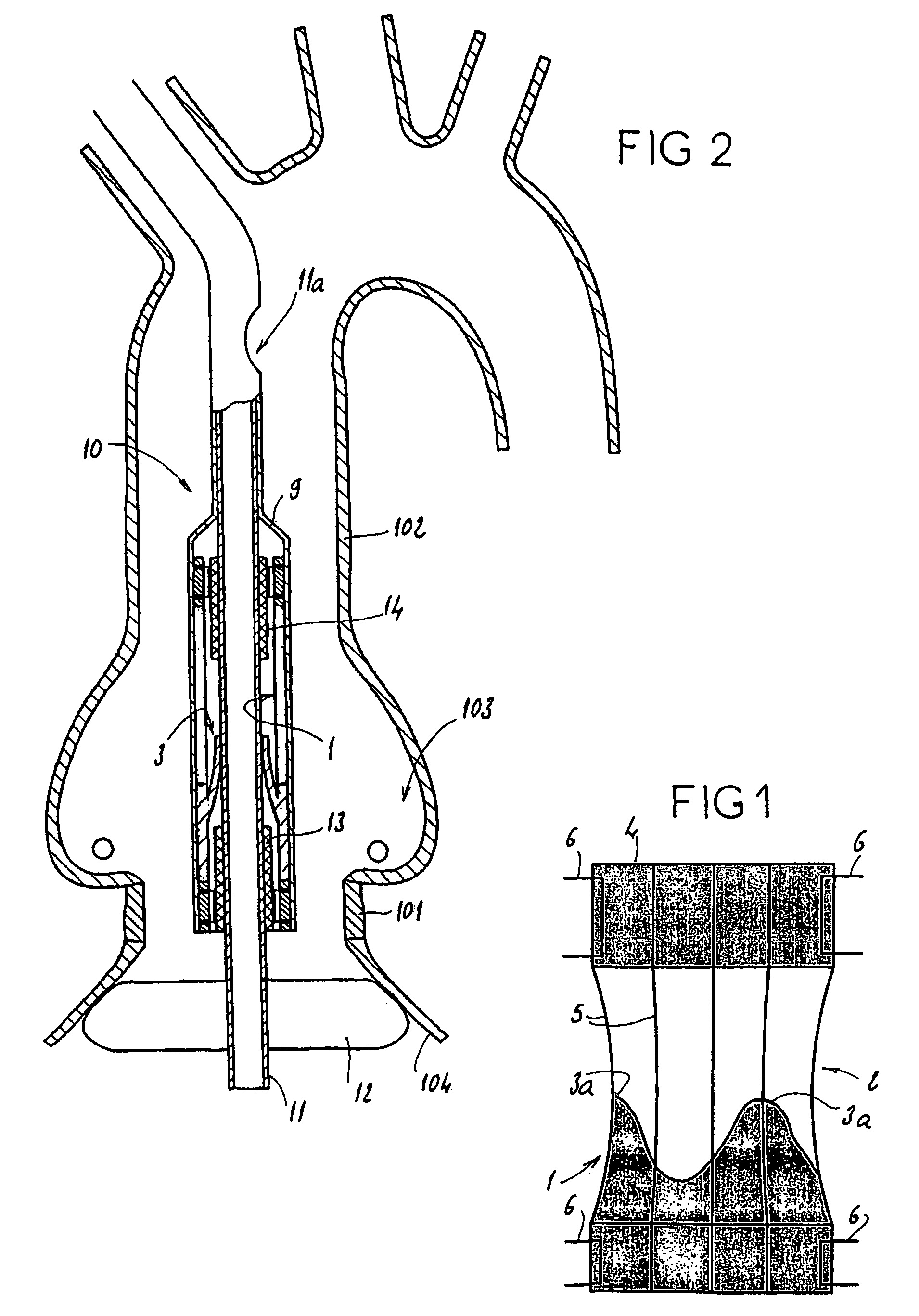
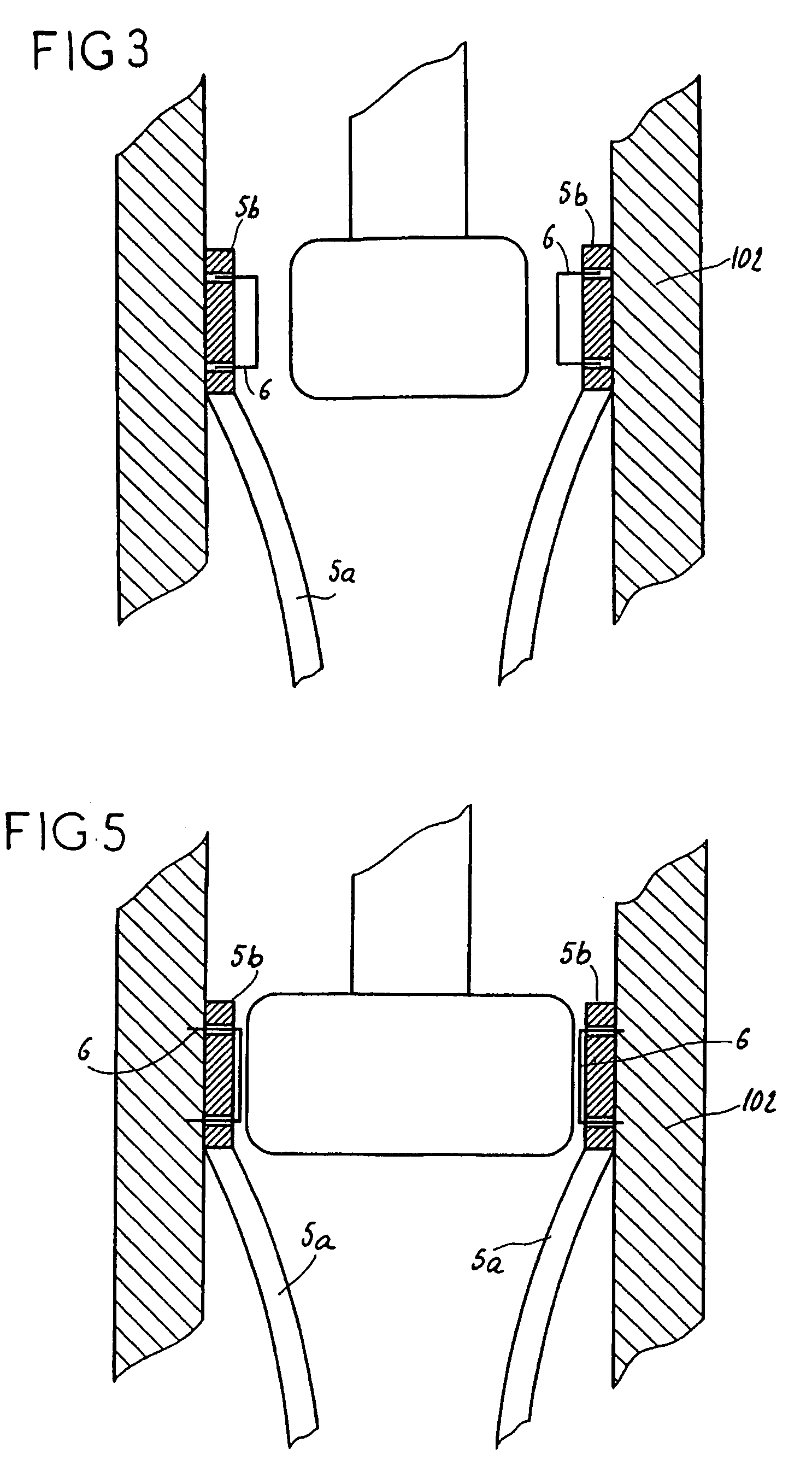
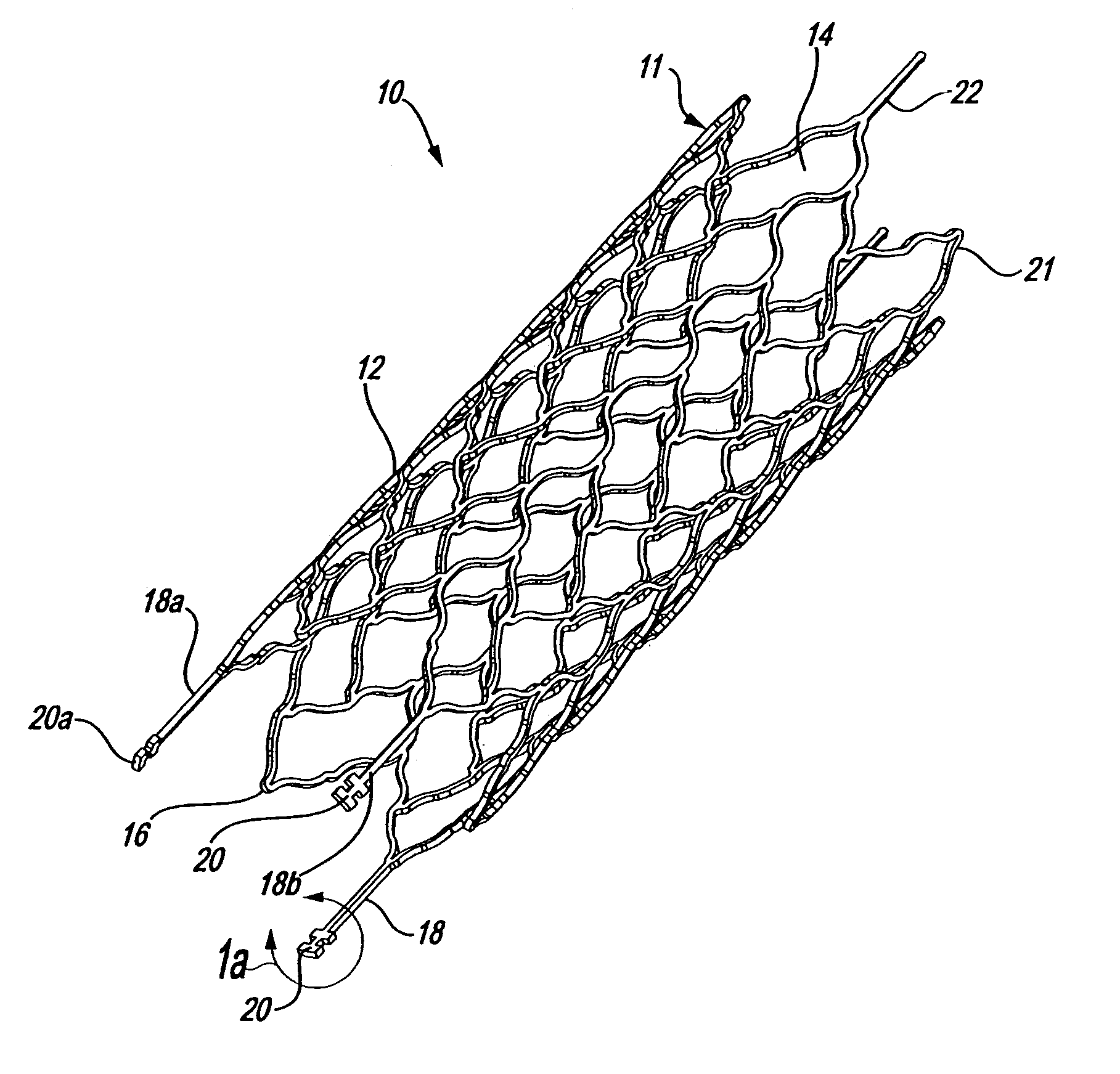
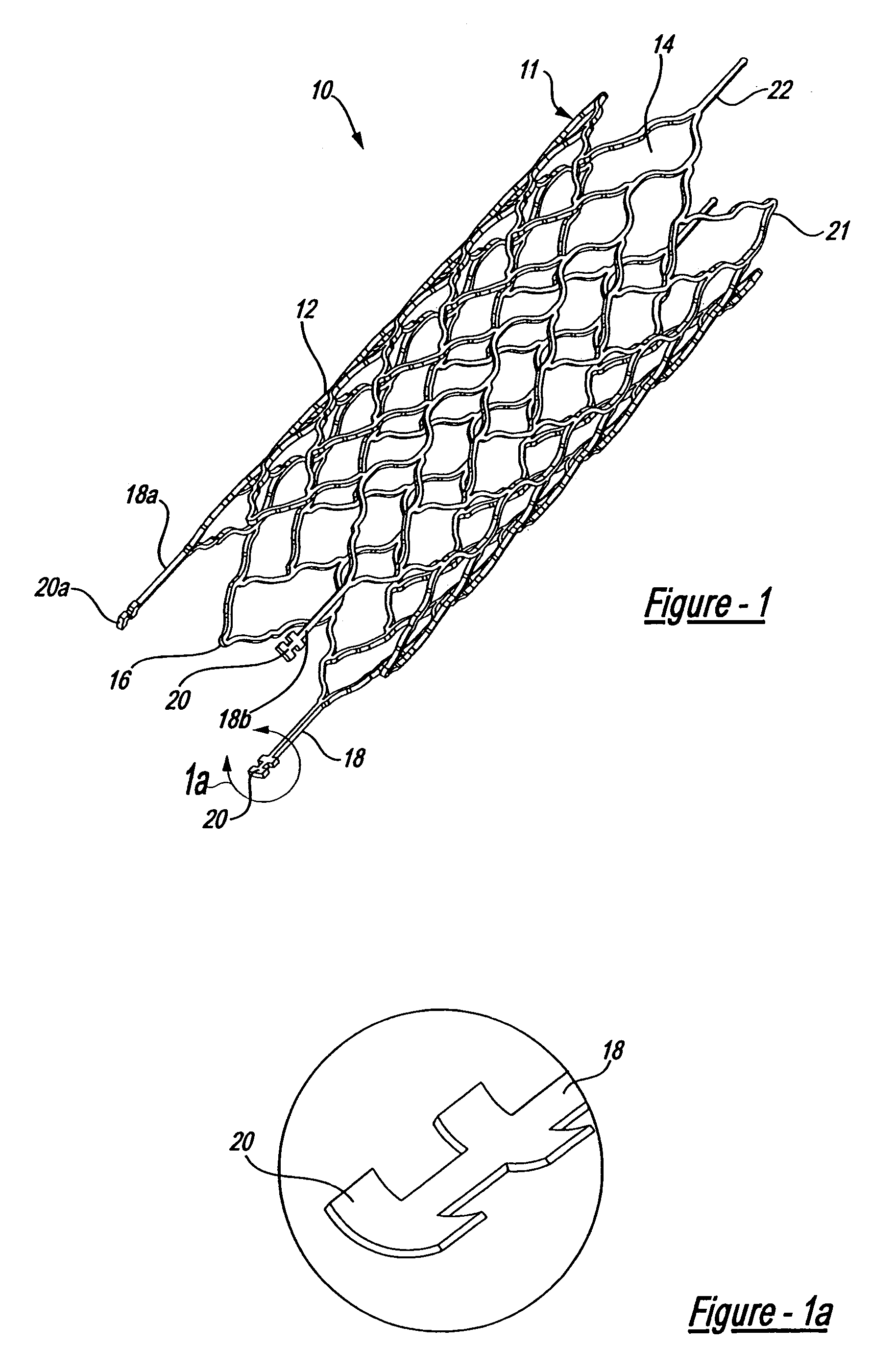
Stentless support structure
ActiveUS20060271166A1Avoid damageSmall diameterStentsHeart valvesProsthetic valveUltimate tensile strength
A stentless support structure capable of being at least partly assembled in situ. The support structure comprises a braided tube that is very flexible and, when elongated, becomes very long and very small in diameter, thereby being capable of placement within a small diameter catheter. The support structure is preferably constructed of one or more thin strands of a super-elastic or shape memory material such as Nitinol. When released from the catheter, the support structure folds itself into a longitudinally compact configuration. The support structure thus gains significant strength as the number of folds increase. This radial strength obviates the need for a support stent. The support structure may include attachment points for a prosthetic valve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Assembly for setting a valve prosthesis in a corporeal duct
InactiveUS7682390B2Eliminate riskRisk is exacerbatedBalloon catheterHeart valvesCommissureBiomedical engineering
The invention concerns an assembly comprising a valve prosthesis to be implanted and a support receiving said valve. The support comprises: at least a tubular portion made of a pliable material slightly stretchable in the circumferential direction; means for fixing said tubular portion to the wall of the corporeal duct; and a plurality of elongated reinforcing elements, arranged on the circumference of said tubular portion and linked to said tubular portion independently of one another; the valve is linked at least partly to said elongated reinforcing elements, in particular at the commissures of its leaflets, and said elongated reinforcing elements jointly form, in extended position, a structure having a predetermined diameter that ensures sufficient extension of said valve.
Owner:MEDTRONIC COREVALVE
Methods and apparatus for anchoring within the gastrointestinal tract
ActiveUS20050125020A1Minimize traumaLarge caliberSuture equipmentsStentsIntestinal structureMedical device
The present invention relates to an anchor configured for minimally-invasive implantation and sized to remain securely positioned within at least a portion of the gastrointestinal tract of an animal. The anchor includes a radial spring formed from an elongated resilient member shaped into an annular wave pattern about a central axis. The anchor defines a central lumen and provides an outward radial force, while allowing for substantial flexure about its perimeter. The anchor is generally removable, but can include fasteners, such as barbs, to further secure it to the surrounding anatomy. In some embodiments, the anchor includes a connector coupling a fixed portion to a removable portion. Further, the anchor can be used to secure a medical device within the body, such as a flexible sleeve within the intestine.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
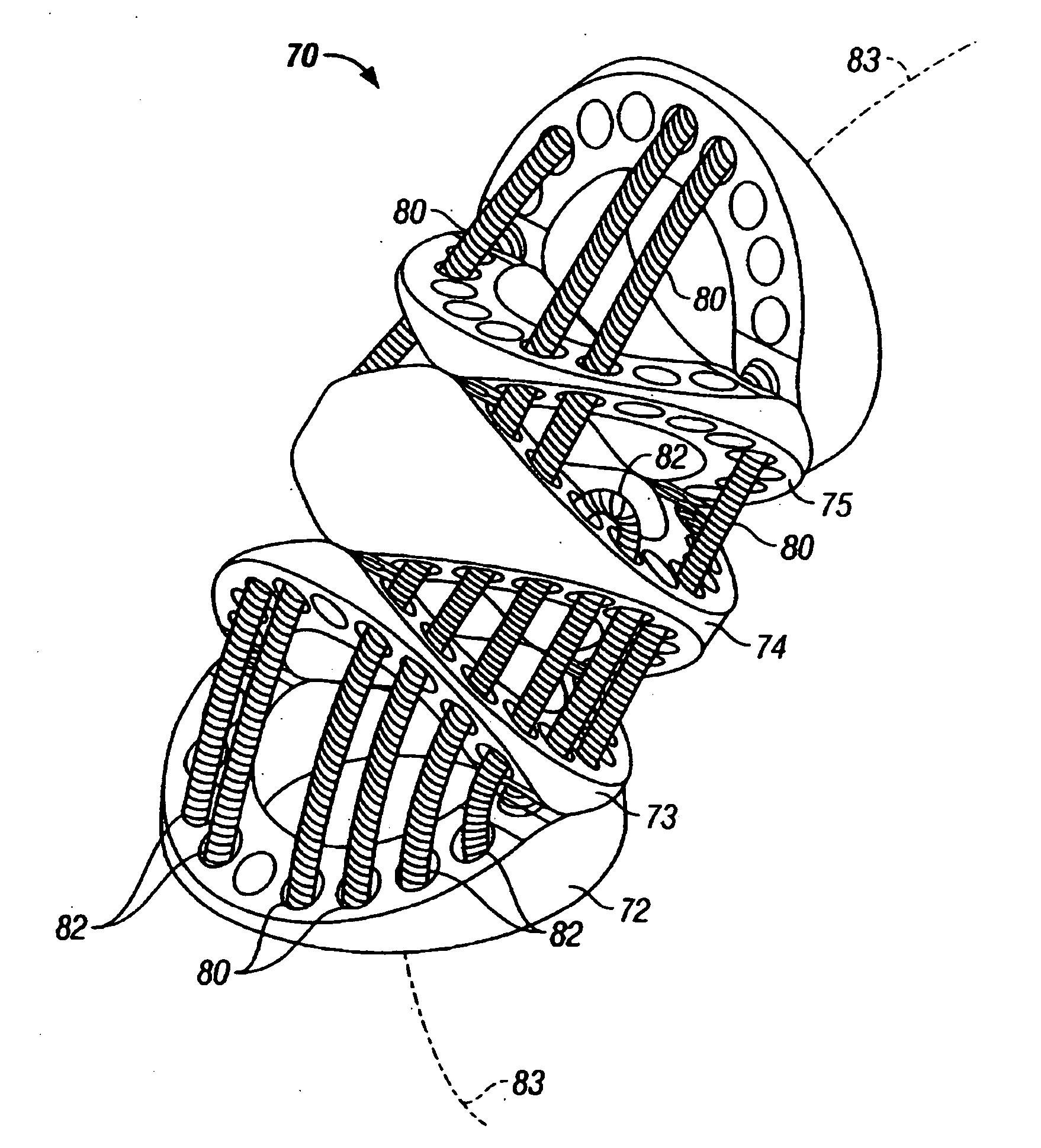
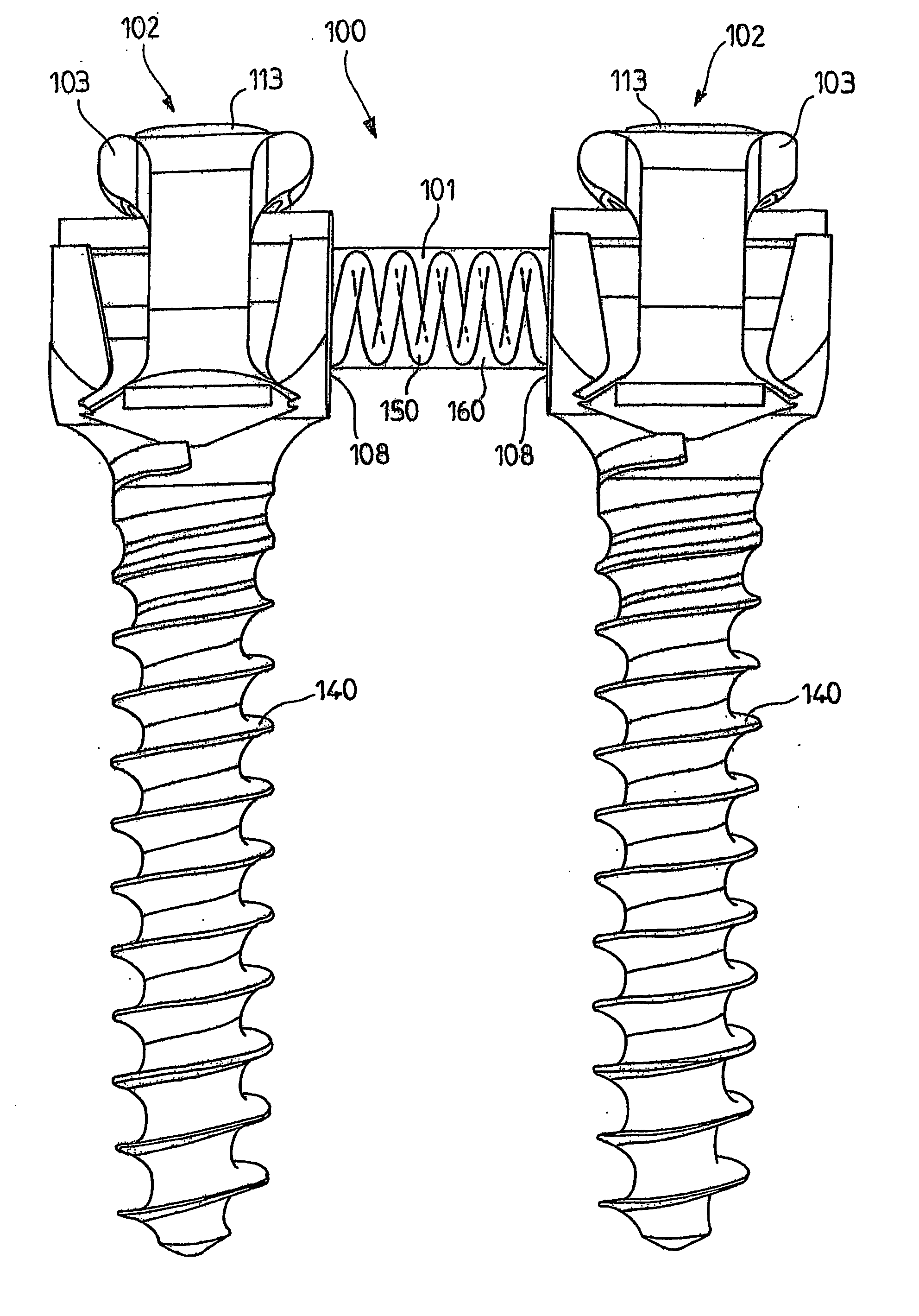
Linking element for dynamically stabilizing a spinal fixing system and spinal fixing system comprising same
InactiveUS20060142758A1Small diameterEasily interchangeableInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringEngineering
A linking element for a spinal fixing system is designed to link at least two implantable connecting assemblies. The linking element consists at least partly of a support made of polymeric material and a rod, bent or not, substantially coaxial with the support. The invention also concerns a spinal fixing system comprising at least two implantable connecting assemblies linked by at least one linking element of the invention.
Owner:NORGINE VENTURES BV +1
Cardiac Tissue Ablation Instrument with Flexible Wrist
InactiveUS20110028991A1Promotes convenient, simplified manufacturing and assembly processesShorten the counting processEndoscopesSurgical manipulatorsInstrumentationWrist
An articulate minimally invasive surgical instrument with a flexible wrist to facilitate the safe placement and provide visual verification of the ablation catheter or other devices in Cardiac Tissue Ablation (CTA) treatments is described. In one embodiment, the instrument is an endoscope which has an elongate shaft, a flexible wrist at the working end of the shaft, and a vision scope lens at the tip of the flexible wrist. The flexible wrist has at least one degree of freedom to provide the desired articulation. It is actuated and controlled by a drive mechanism located in the housing at the distal end of the shaft. The articulation of the endoscope allows images of hard-to-see places to be taken for use in assisting the placement of the ablation catheter on the desired cardiac tissue. The endoscope may further include couplings to releasably attach an ablation device / catheter or a catheter guide to the endoscope thereby further utilizing the endoscope articulation to facilitate placement of the ablation catheter on hard-to-reach cardiac tissues. In another embodiment, the articulate instrument is a grasper or any other instrument with a flexible wrist and a built-in lumen to allow an endoscope to insert and be guided to the distal end of the instrument.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
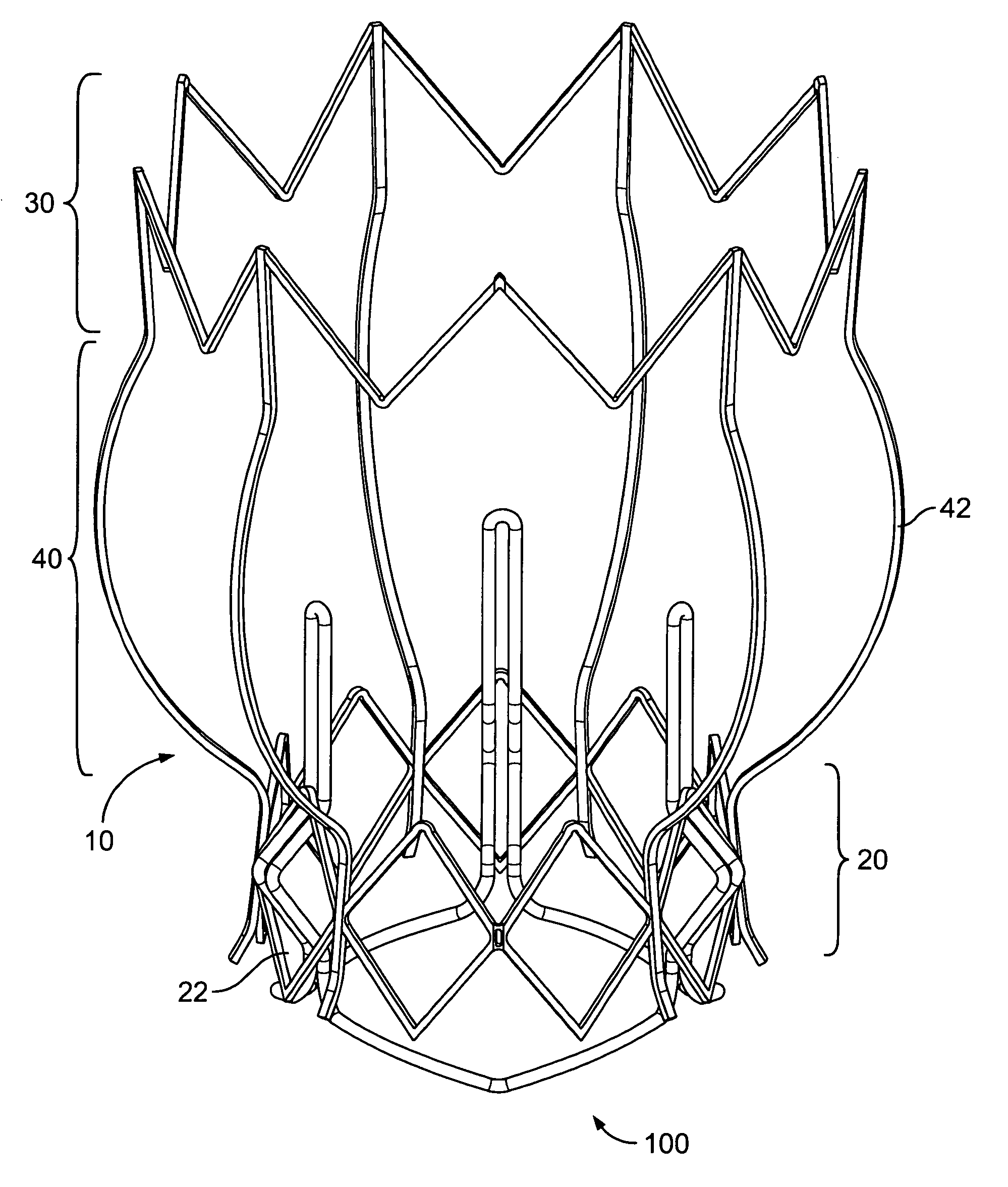
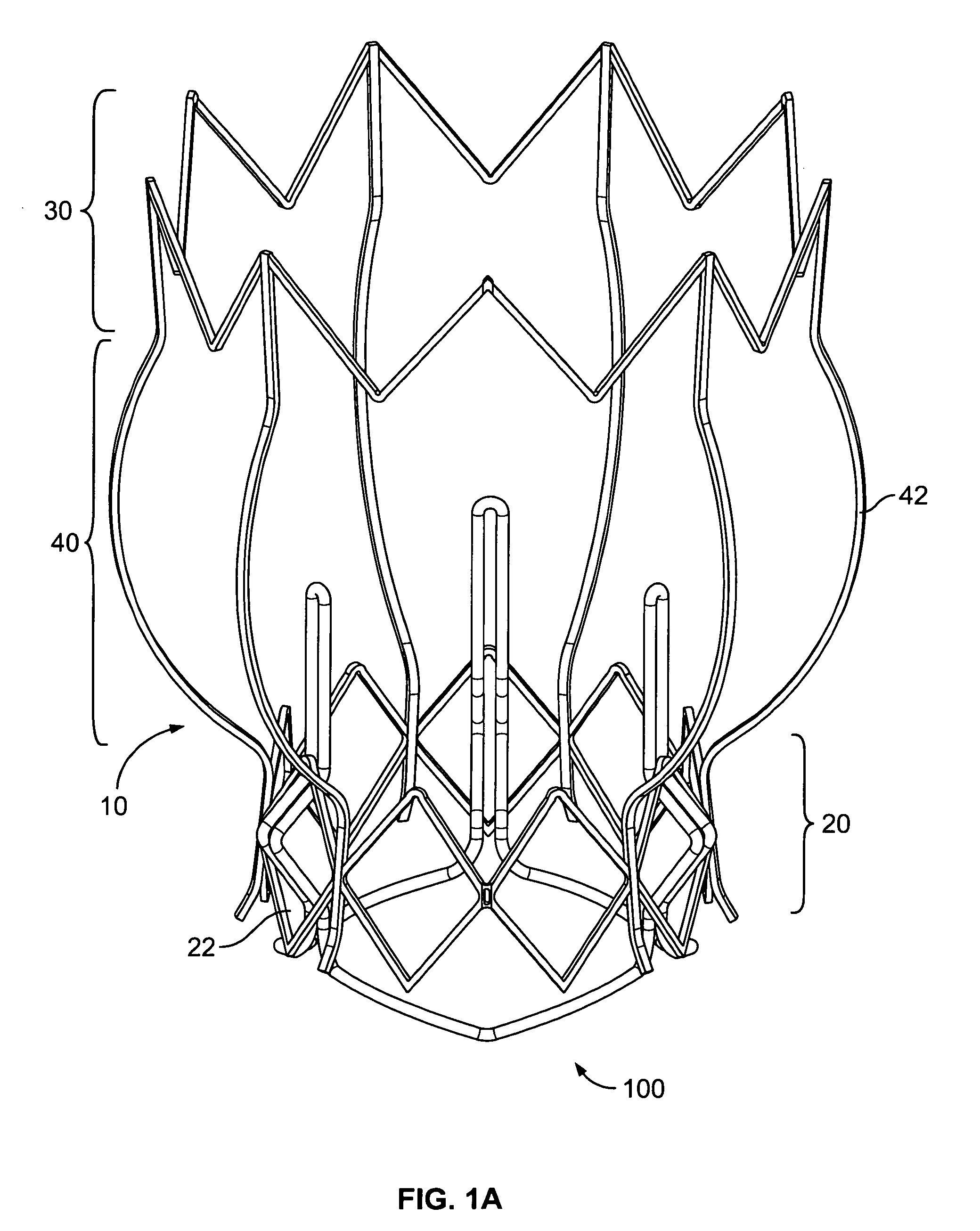
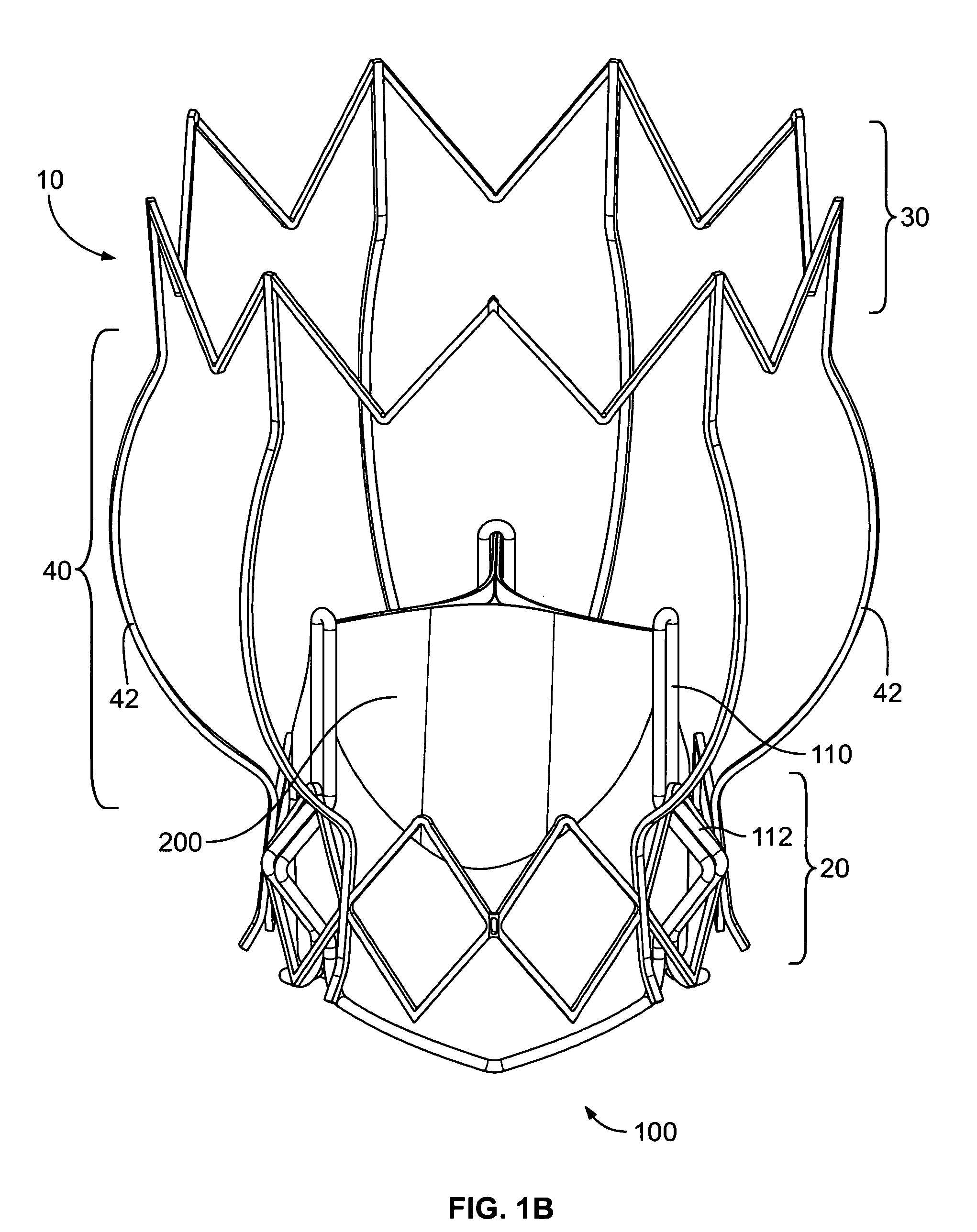
Two-stage collapsible/expandable prosthetic heart valves and anchoring systems
ActiveUS8454686B2Small diameterLow profileBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthetic heartImplantation Site
Prosthetic heart valve apparatus is adapted for delivery into a patient in a circumferentially collapsed condition, followed by circumferential re-expansion at the implant site in the patient. The apparatus includes an annular anchoring structure that can be implanted in the patient first. The apparatus further includes an annular valve support structure, which supports a flexible leaflet structure of the valve. The support and leaflet structures are initially separate from the anchoring structure, but they can be implanted in the patient by interengagement of the support structure with the already-implanted anchoring structure.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LLC
Single and multi-polar implantable lead for sacral nerve electrical stimulation
InactiveUS6055456ALess sensitivitySimple procedureSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorSacral nerve stimulation
An implantable medical lead for stimulation of the sacral nerves comprises a lead body which includes a distal end and a proximal end, and the distal end having at least one electrode contact having a length of between 0.10 and 1.50 inches extending longitudinally from the distal end toward the proximal end. The lead body at its proximal end may be coupled to a pulse generator, additional intermediate wiring, or other stimulation device. The implantable medical lead can comprise a first and second electrode contacts. The second electrode contact has a length of between 0.030 and 1.00 extending longitudinally from a point approximately 1.00 from the distal end toward the proximal end. The first and second electrode contacts do no overlap longitudinally. The implantable lead is implanted by taking the lead and implanting near the sacral nerves and then connecting to a pulse generator.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Device for removal of thrombus through physiological adhesion
InactiveUS7004954B1Raise the level of performanceRestoring native blood flowBalloon catheterSurgeryMedicineThrombus
A device that is useful for removing obstructions from vessels. Various embodiments and methods of use are contemplated for the effective removal of obstructions. The disclosed devices utilize a thrombogenic material to promote the formation of fibrin bonds, thus enhancing adhesion. It is further contemplated that the disclosed devices may be used in all vasculature including the cerebral vasculature and the neurovasculature.
Owner:ENDOVASCULAR TECH
Intravascular stent device
A very small diameter intravascular stent device which may be used to occlude or partially occlude an aneurysm in the human brain which is comprised of a thin-walled skeletal cylindrical tube formed of undulating or sinusoidal elements which, when compressed, nest tightly with each other.
Owner:CODMAN & SHURTLEFF INC
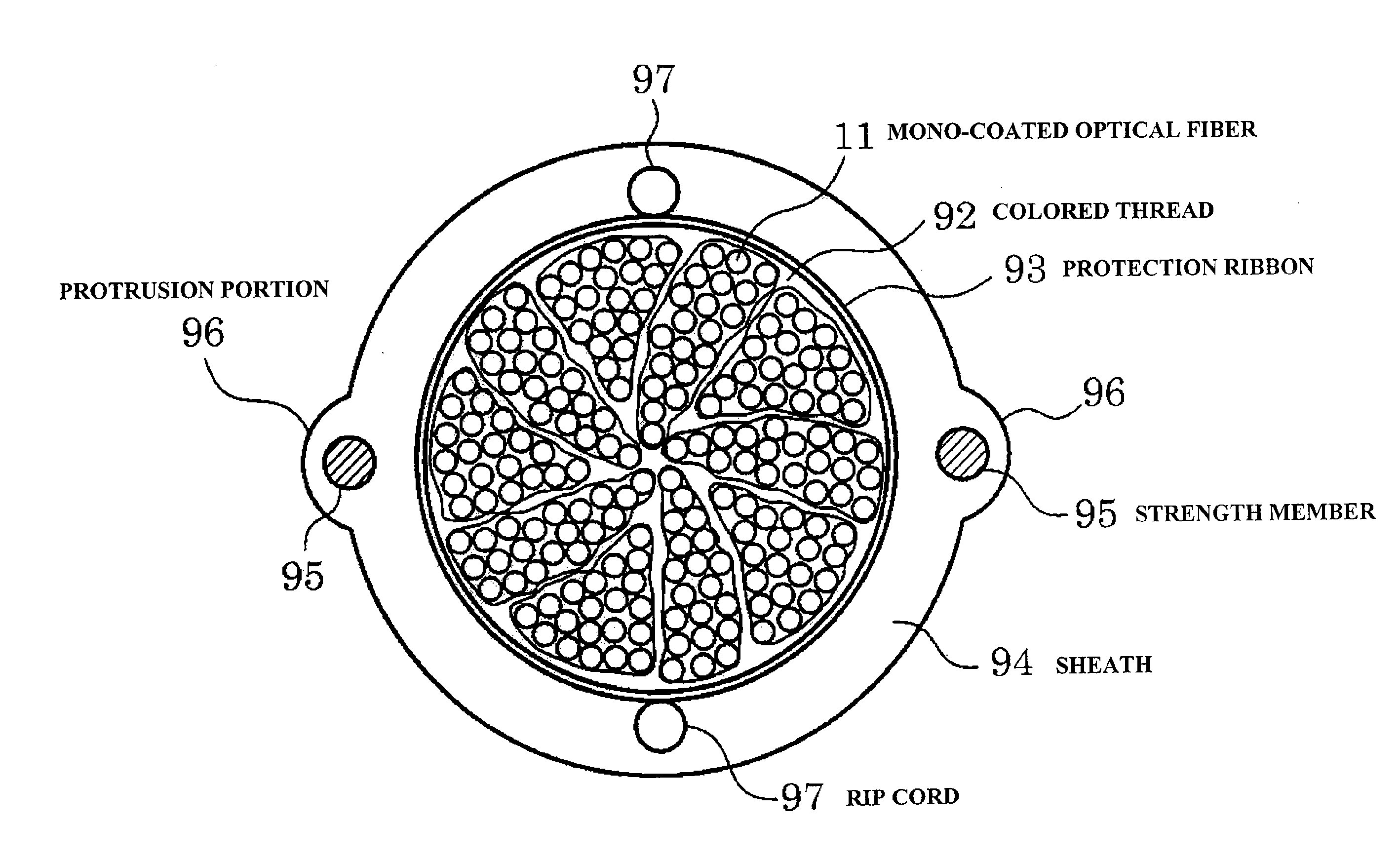
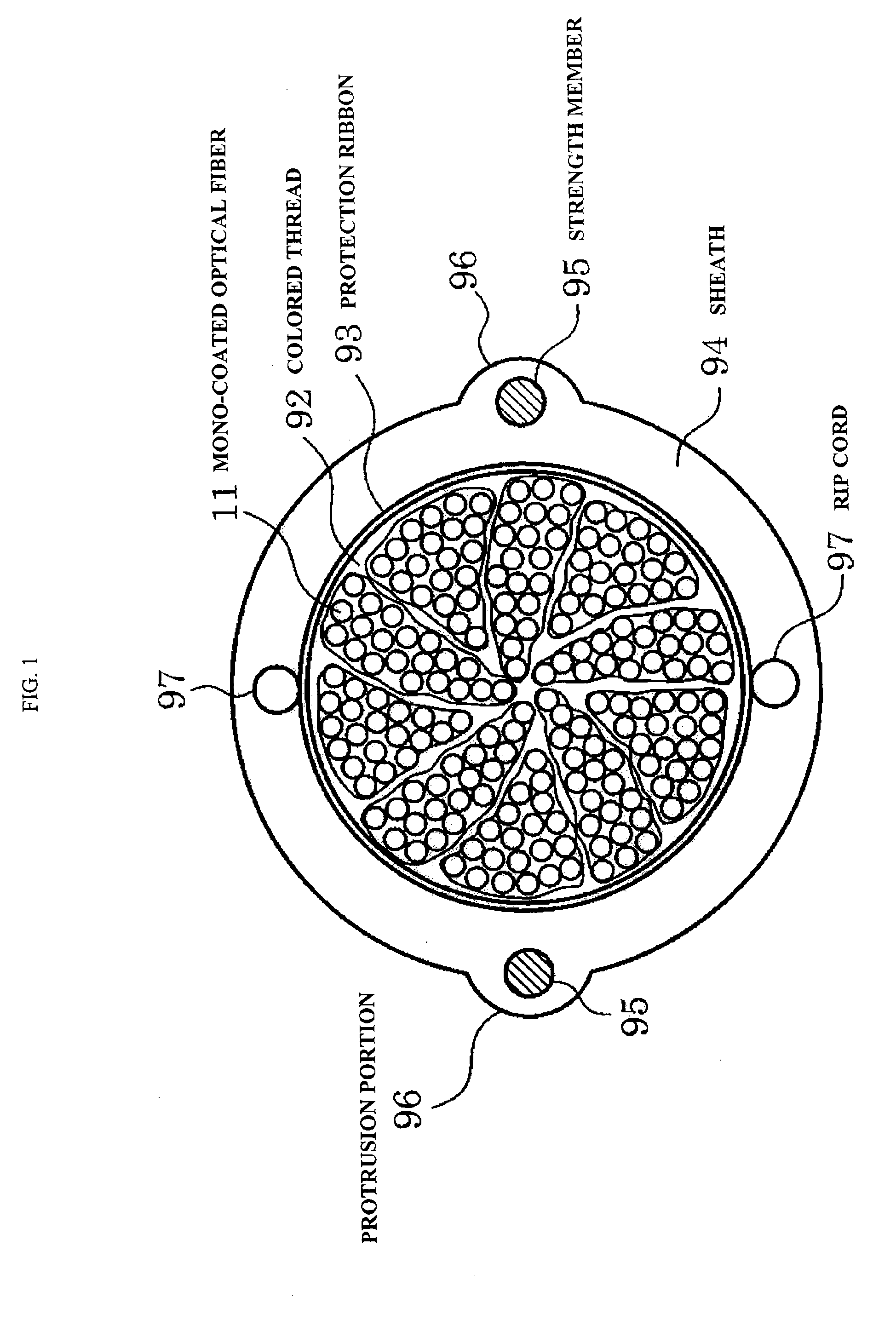
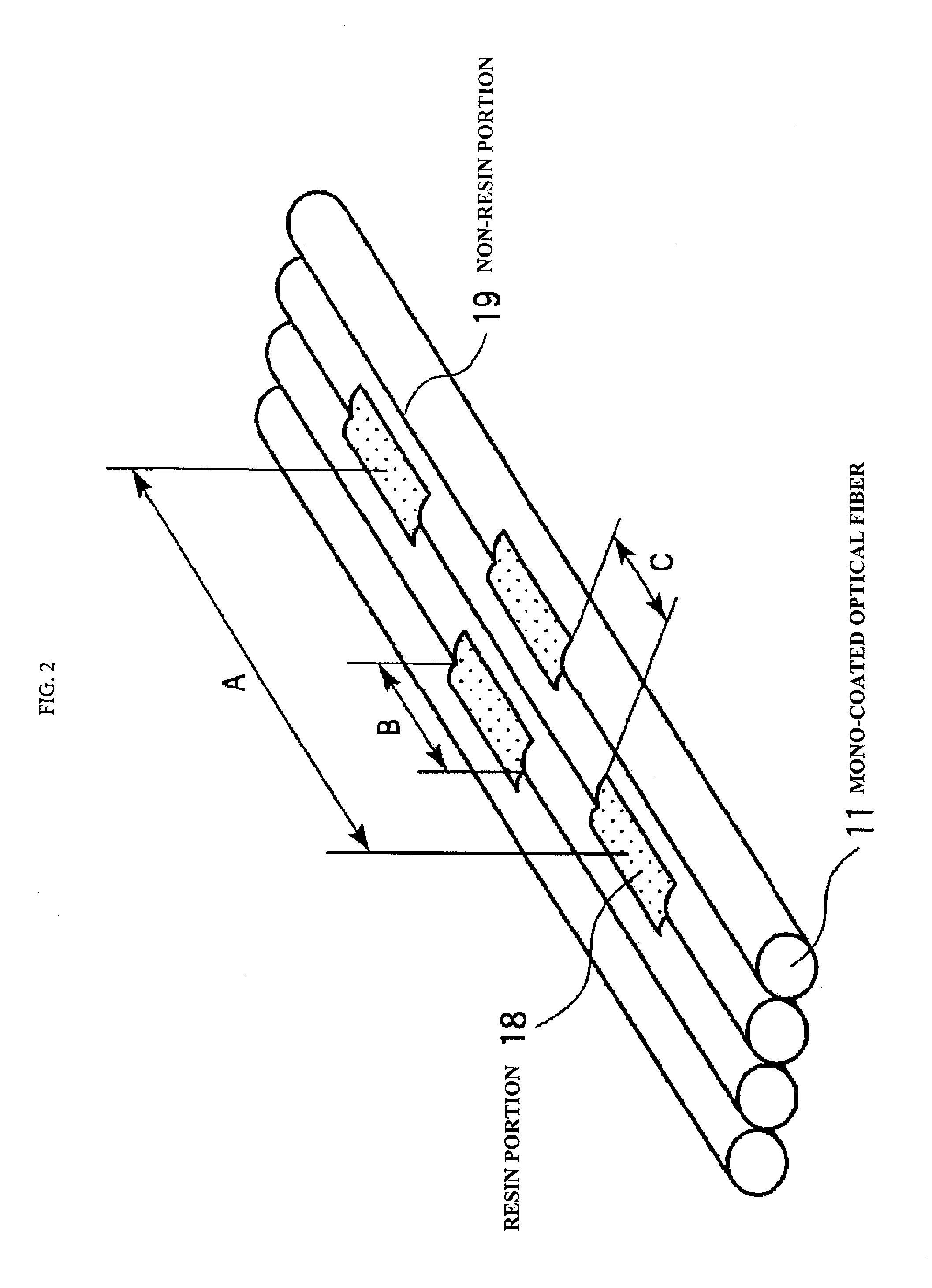
Optical fiber cable and optical fiber ribbon
ActiveUS8548294B2Stable optical loss characteristicReduce warpageFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringBend radius
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
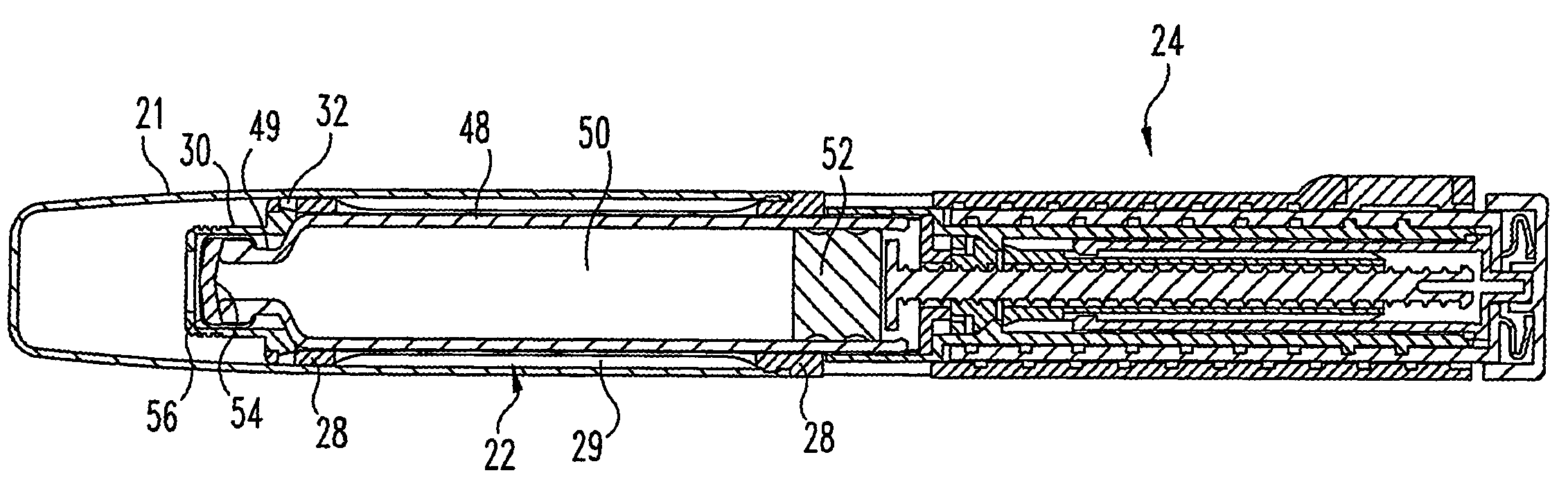
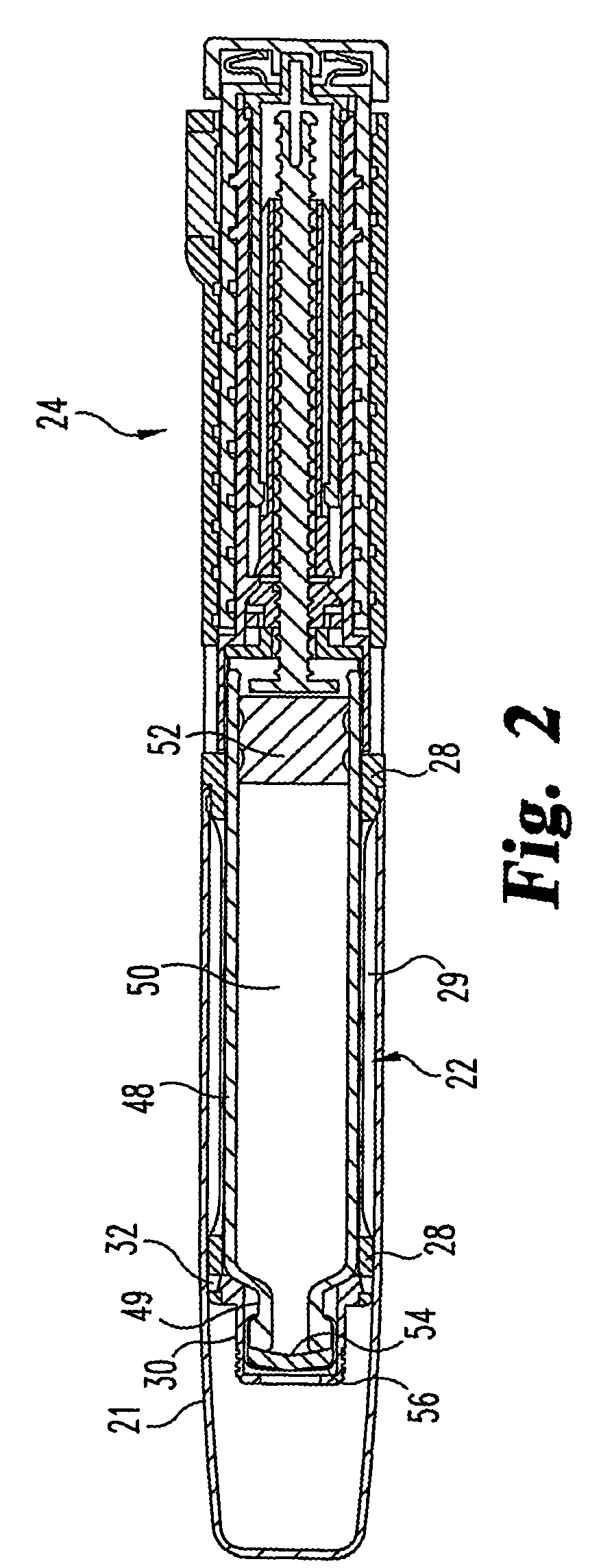
Medication dispensing apparatus with triple screw threads for mechanical advantage
A medication dispensing apparatus that provides a mechanical advantage. During dose preparing, a nut rotating element (410) and a screw element (368) are in a first axial arrangement such that a screwing motion of the nut rotating element and screw element relative to the apparatus housing that moves the elements a first axial distance from a home position screws a nut (364) along a drive member threaded shaft (362) a second axial distance different than the first axial distance. During dose dispensing, the nut rotating element and the screw element are in a second axial arrangement, whereby a screwing motion of the screw element relative to the housing back toward the home position advances a plunger (366) in the distal direction to axially advance the nut and thereby the drive member and a fluid container piston to dispense medicine.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Method of forming barbs on a suture and apparatus for performing same
InactiveUS6848152B2Maximum anchoring propertyMore suitedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesEngineeringBlade geometry
A method of making a barbed suture by varying the blade geometry and / or the movement of the blade when cutting a suture. The method can also be accomplished with a cutting device to create a plurality of barbs on the exterior of surgical suture. The barbs produced using the method with the cutting device can be the same or random configurations.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Two-stage collapsible/expandable prosthetic heart valves and anchoring systems
ActiveUS20100204785A1Improve securityLow profileBalloon catheterHeart valvesProsthesisProsthetic heart
Prosthetic heart valve apparatus is adapted for delivery into a patient in a circumferentially collapsed condition, followed by circumferential re-expansion at the implant site in the patient. The apparatus includes an annular anchoring structure that can be implanted in the patient first. The apparatus further includes an annular valve support structure, which supports a flexible leaflet structure of the valve. The support and leaflet structures are initially separate from the anchoring structure, but they can be implanted in the patient by interengagement of the support structure with the already-implanted anchoring structure.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LLC
Surgical instrument access device
ActiveUS7163510B2High tear strengthHigh elongationCannulasInfusion syringesSurgical departmentVALVE PORT
A surgical access device includes a single valve that forms a seal with a body wall and provides an access channel into a body cavity. The valve has properties for creating a zero seal in the absence of an instrument as well as an instrument seal for an instrument having a diameter up to about 37 mm. The valve can include a gel material and the access channel can include a protective sleeve to provide for wound protection during insertion and withdrawal of a sharp surgical instrument. The valve further comprises a cap ring which may be inserted or molded with the gel material. The protective sleeve may be bonded or molded around an inner diameter of the cap ring. The protective sleeve may be a single tubular member, or may comprise a plurality of axially extending sleeve members having a plurality of axial slits. The protective sleeve and the cap ring may comprise of the same or different materials. The surgical access device further comprises at least one support ring disposed circumferentially of the valve forming a hollow space, and a wound retractor operatively placed in the hollow space. The wound retractor includes an inner ring, an outer ring, and a flexible sleeve connecting the inner ring and the outer ring.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050184377A1Increase freedomFunction increaseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTectorial membraneElectrical conductor
In a semiconductor device, via holes are formed around a chip buried in a package, and conductor layers are respectively formed to be connected to one end and another end of the conductor filled in the individual via hole. Portions (pad portions) of the conductor layers which correspond to the conductors are exposed from protective films, or external connection terminals are bonded to the pad portions. The chip is mounted with flip-chip technology so that at least some of electrode terminals thereof are electrically connected to the conductor layers.
Owner:SHINKO ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
In-line lead header for an implantable medical device
InactiveUS6895276B2Small diameterEasy to insertElectrotherapyCoupling contact membersElectricityElectrical connector
Implantable medical devices (IMDs) comprising a monitor or implantable pulse generator (IPG) having an IPG header to which lead connector assemblies of electrical medical leads are coupled, particularly, an improved in-line IPG header providing enhanced durability, ease of manufacture, and ease of use. A stack of alternating, substantially tubular electrically insulating fluid seals and header connector elements is assembled in axial alignment to form a common, elongated axial stack bore sized in diameter and length to receive the lead connector assembly. Each adjacent electrical connector element and fluid seal are interlocked with one another during assembly of the stack to maintain the axial alignment and the length and diameter dimensions. Fluid seals are located at each end of the stack, and the stack can be inserted as a unit into a cavity of the IPG header.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Electronic Apparatus
InactiveUS20100232100A1Simple designSmall diameterInput/output for user-computer interactionElectric spark ignitersEngineeringMechanical engineering
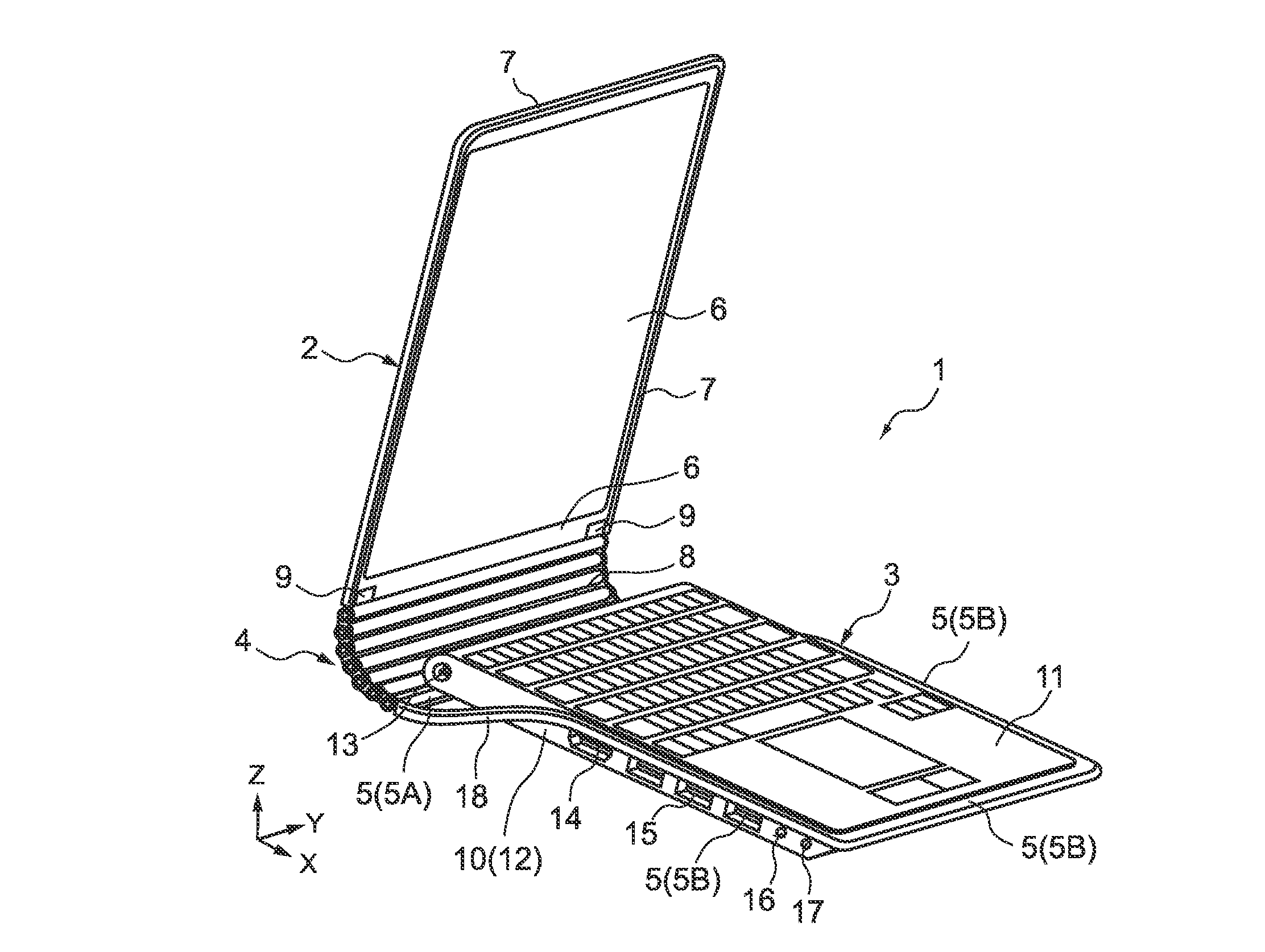
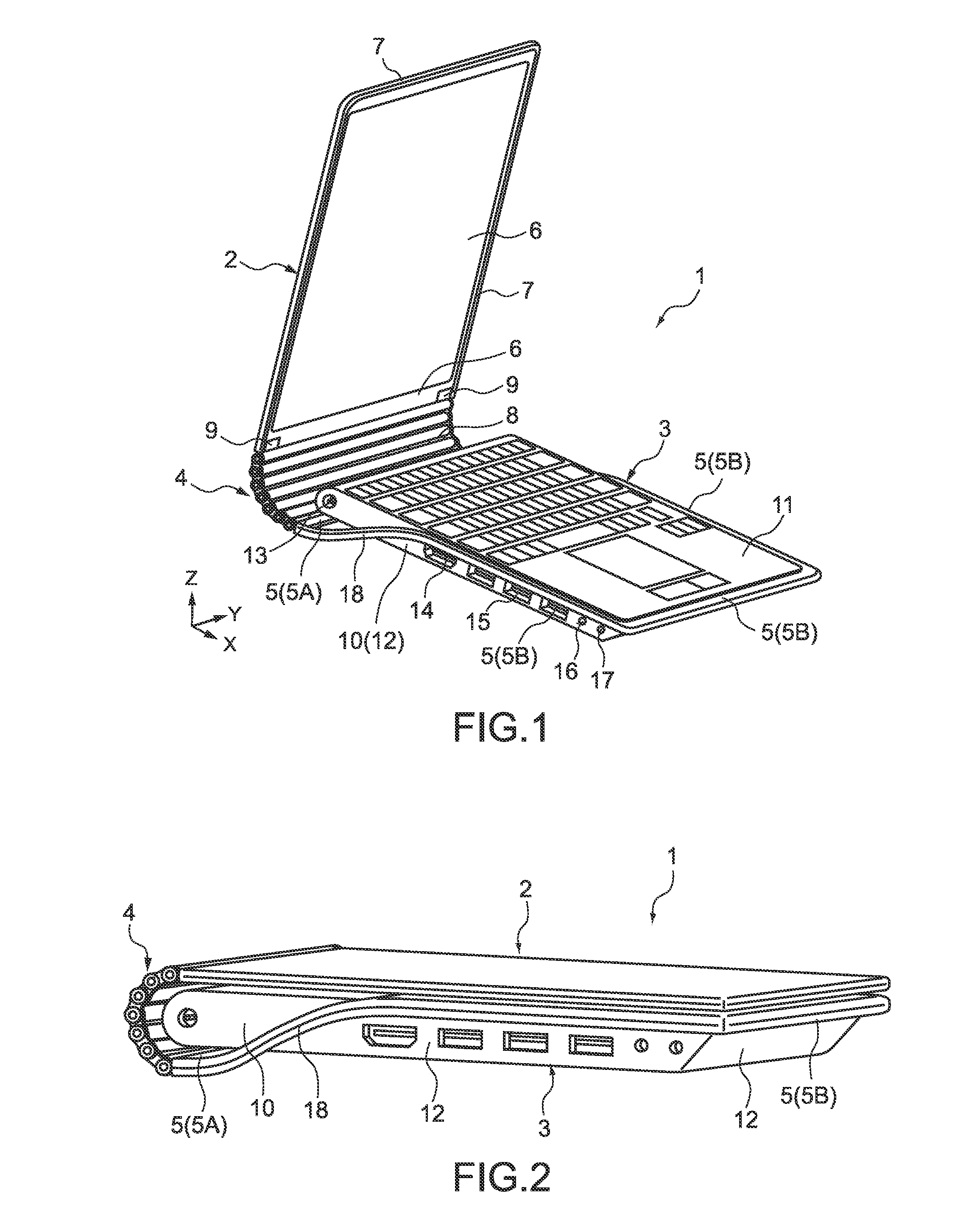
An electronic apparatus includes a display portion, a main body portion, an articulated coupling mechanism, and an interlock mechanism. The display portion includes a display screen. The main body portion is coupled to the display portion. The articulated coupling mechanism includes, at each of end portions, a plurality of coupling members each having a rotation axis and being rotatably coupled to one another in series about the rotation axis, the plurality of coupling members coupled in series having one end coupled to the main body portion side and the other end coupled to the display portion side. The interlock mechanism interlocks rotations of the plurality of coupling members with one another in the articulated coupling mechanism.
Owner:SONY CORP
Valvuloplasty Catheter And Methods
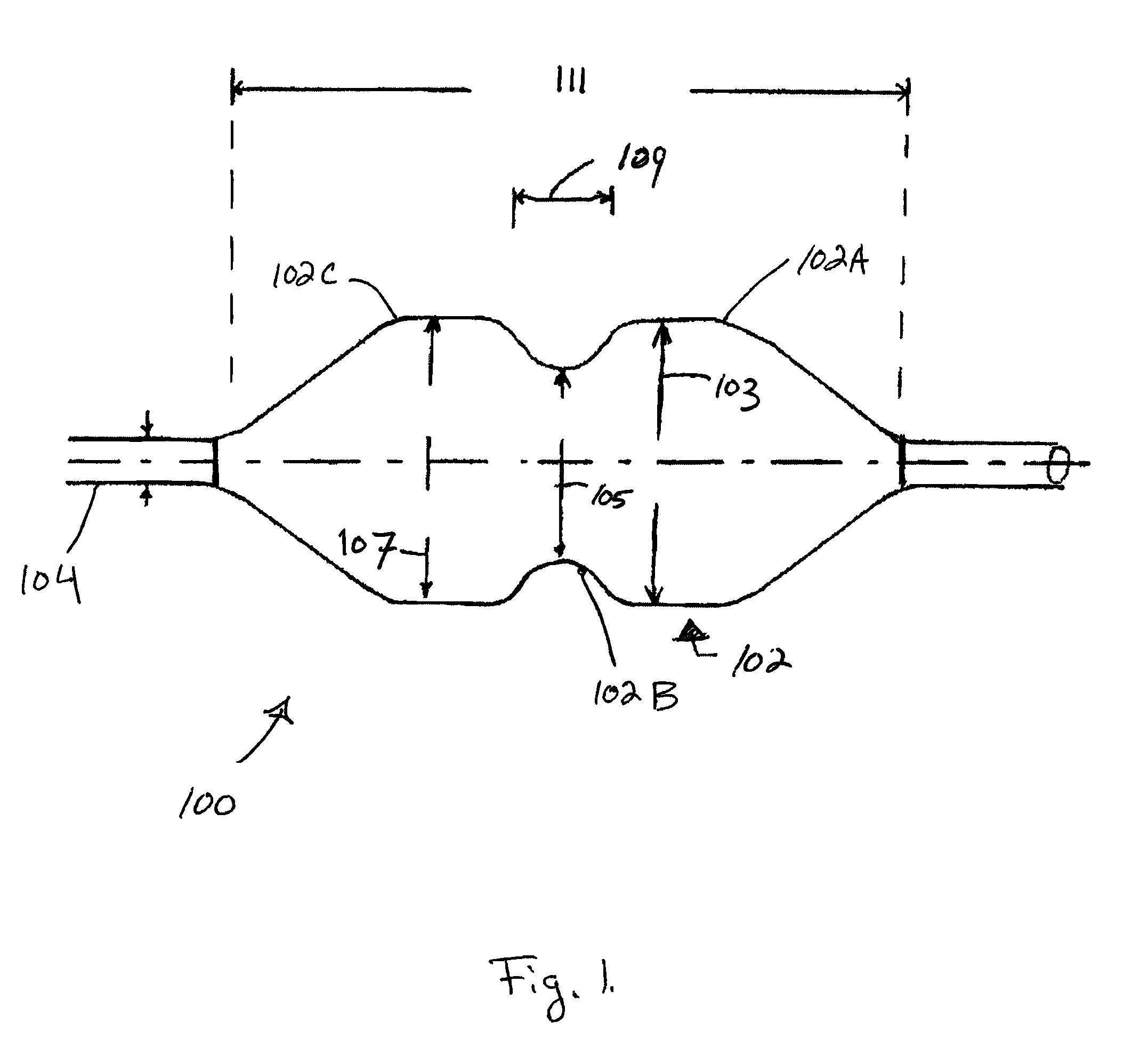
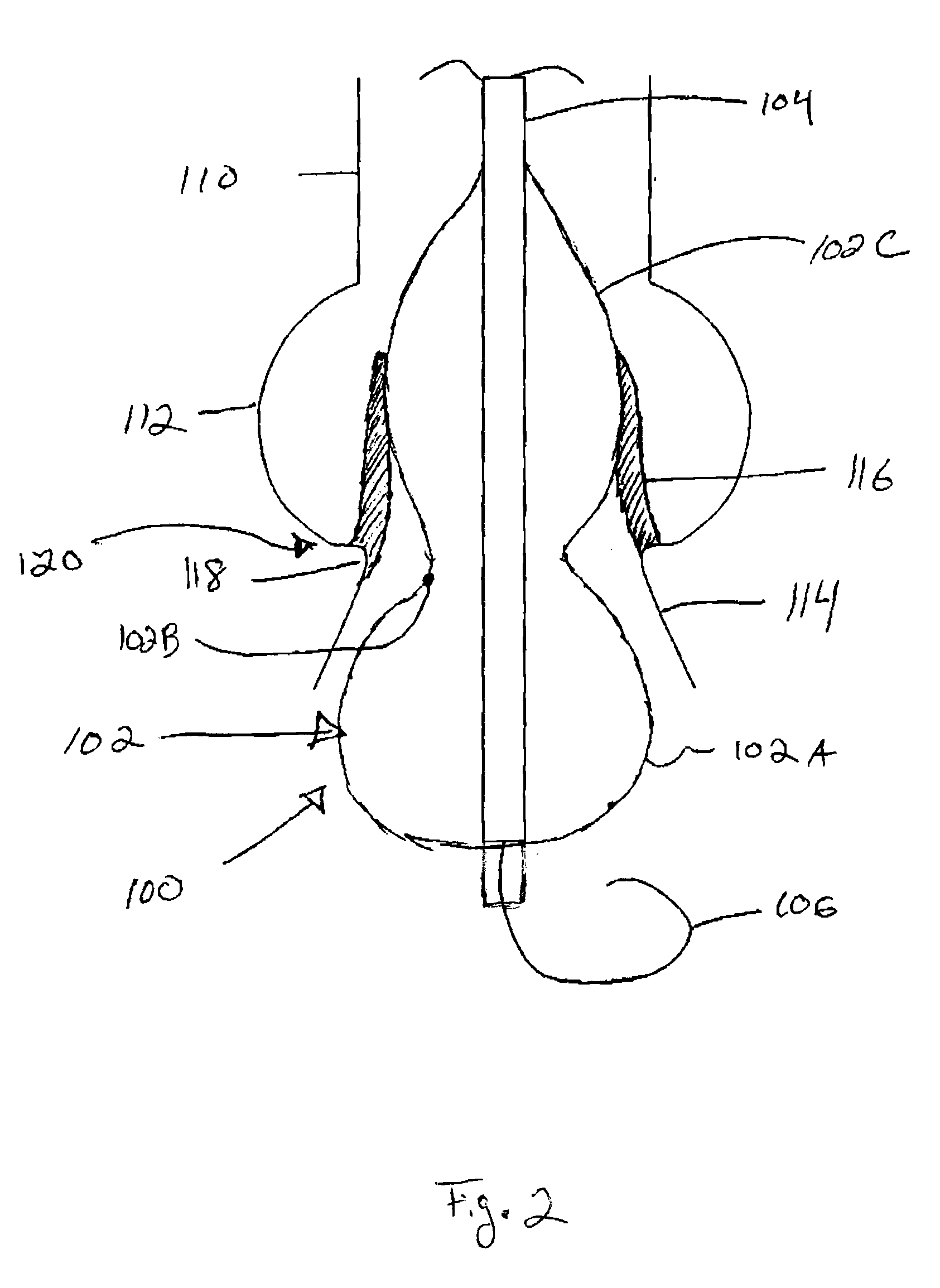
ActiveUS20100094209A1Small diameterAccurate measurementBalloon catheterSurgeryVolume CurveBone shape
A valvuloplasty catheter has a dog-bone shaped balloon with semi-compliant smaller diameter waist and non-compliant larger diameter bulbous end regions. The balloon centers across the valve with the waist adjacent to the annulus. One bulbous region serves to hyperextend the valve leaflets and the other assists in stabilizing the balloon position to reduce migration. The semi-compliant waist increases in diameter as fluid enters the balloon until it comes into contact with the valve annulus. The pressure within the balloon per unit of volume delivery has a greater slope after contact with the annulus than before resulting in a change in slope for the pressure versus volume curve. The diameter of the balloon and annulus are determined at this inflection point when the balloon contacts the annulus.
Owner:INTERVALVE MEDICAL INC
Methods and devices for reducing hollow organ volume
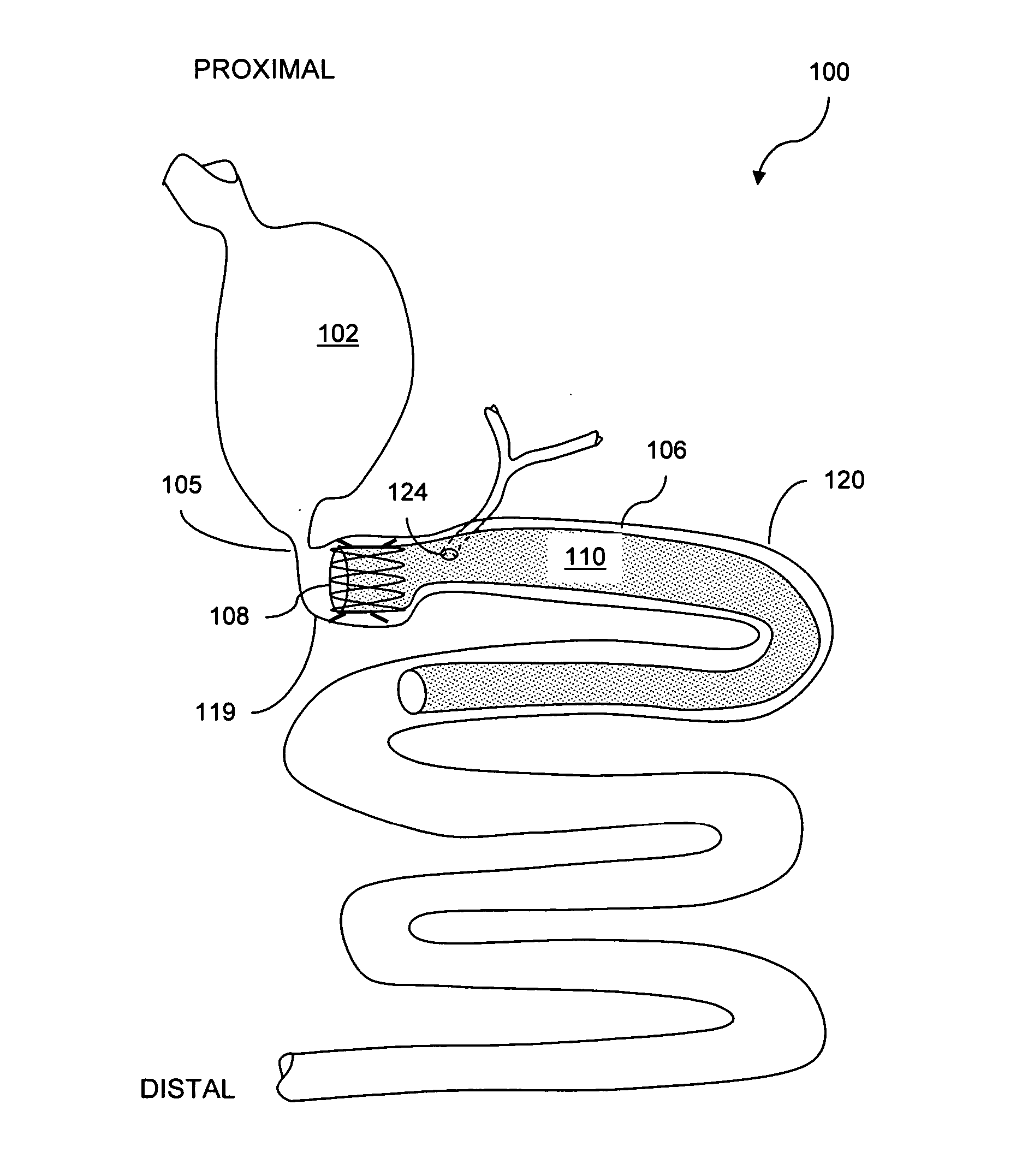
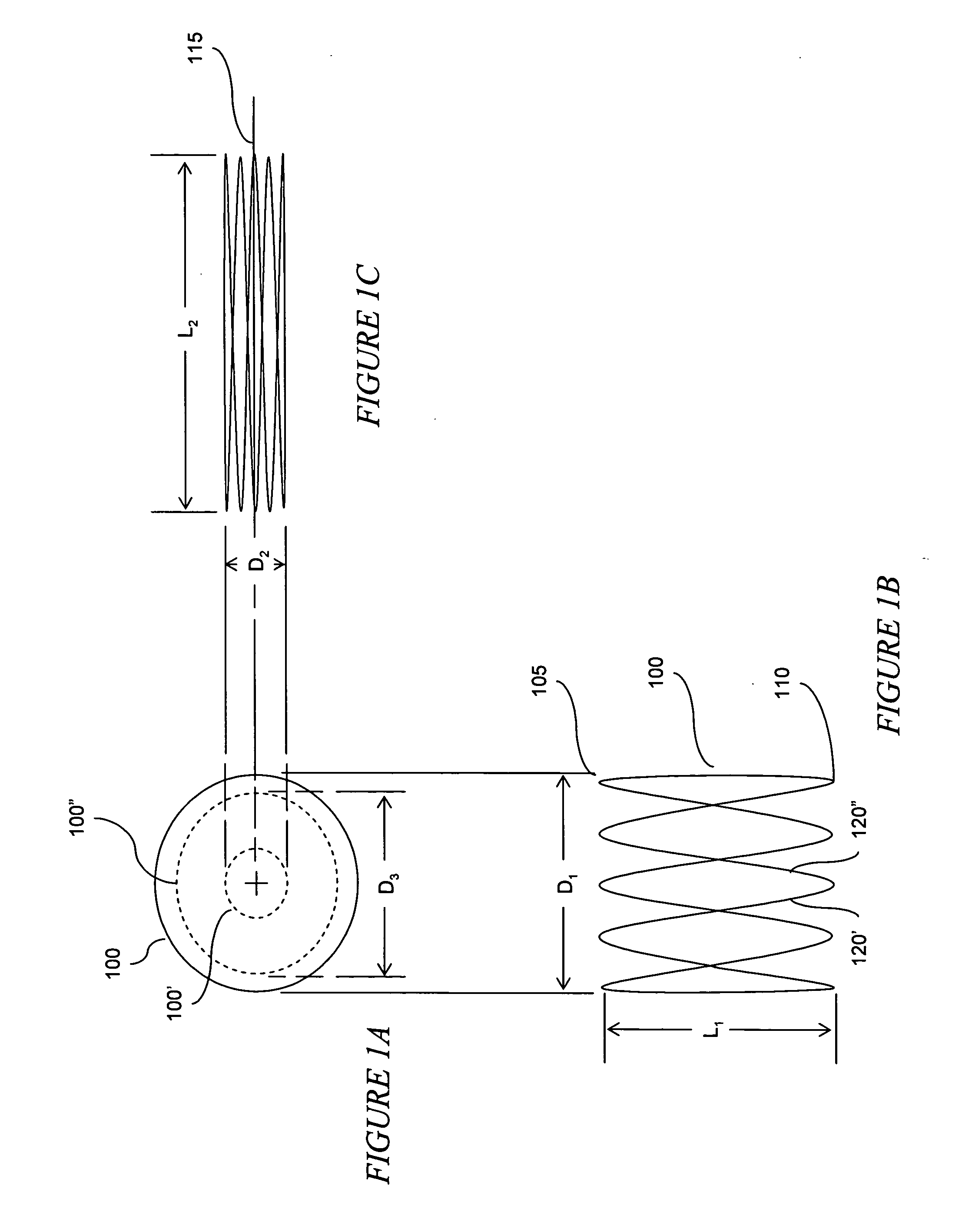
ActiveUS20050192601A1Reducing stomach volumeOvercomes shortcomingSuture equipmentsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesOrgan VolumeBody organs
Methods and devices for providing a minimally-invasive placement of a mechanical structure for reducing the volume of a hollow body organ. Intragastric bands may be secured within the hollow body organ and then reduced in diameter to form a stricture within the hollow body organ. The strictures may be placed anywhere within the hollow body organ, and more than one stricture may be formed within the hollow body organ.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
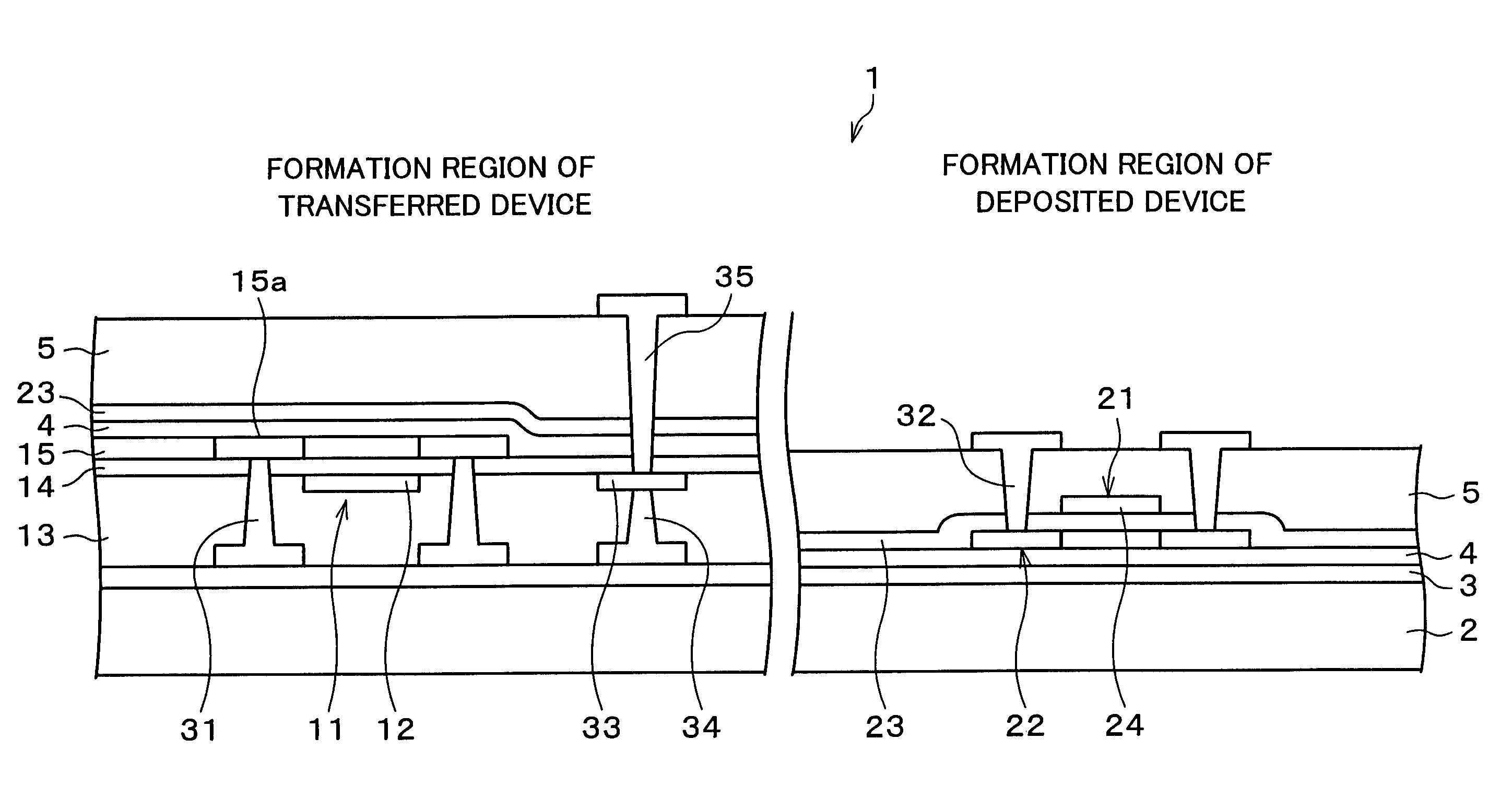
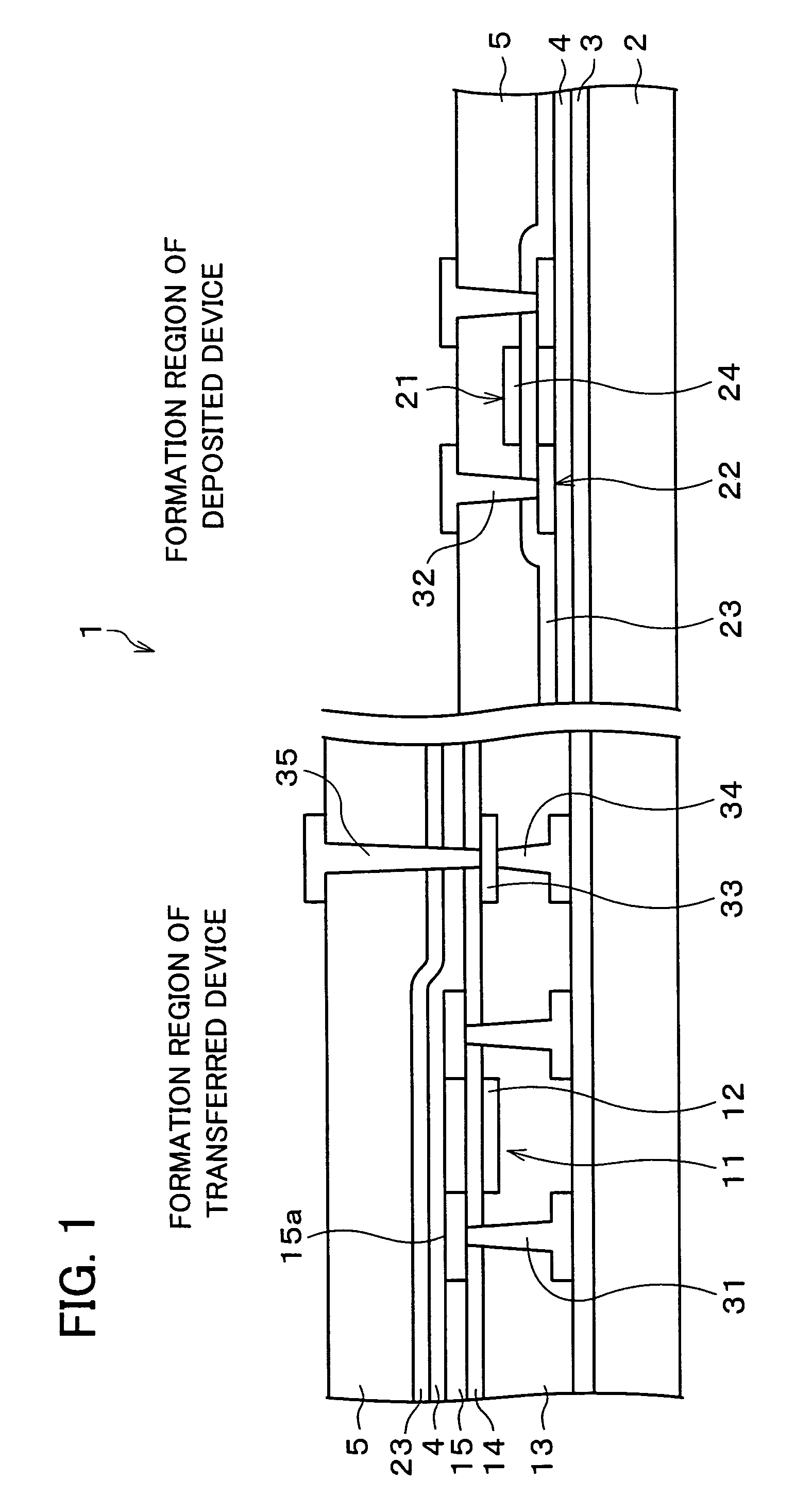
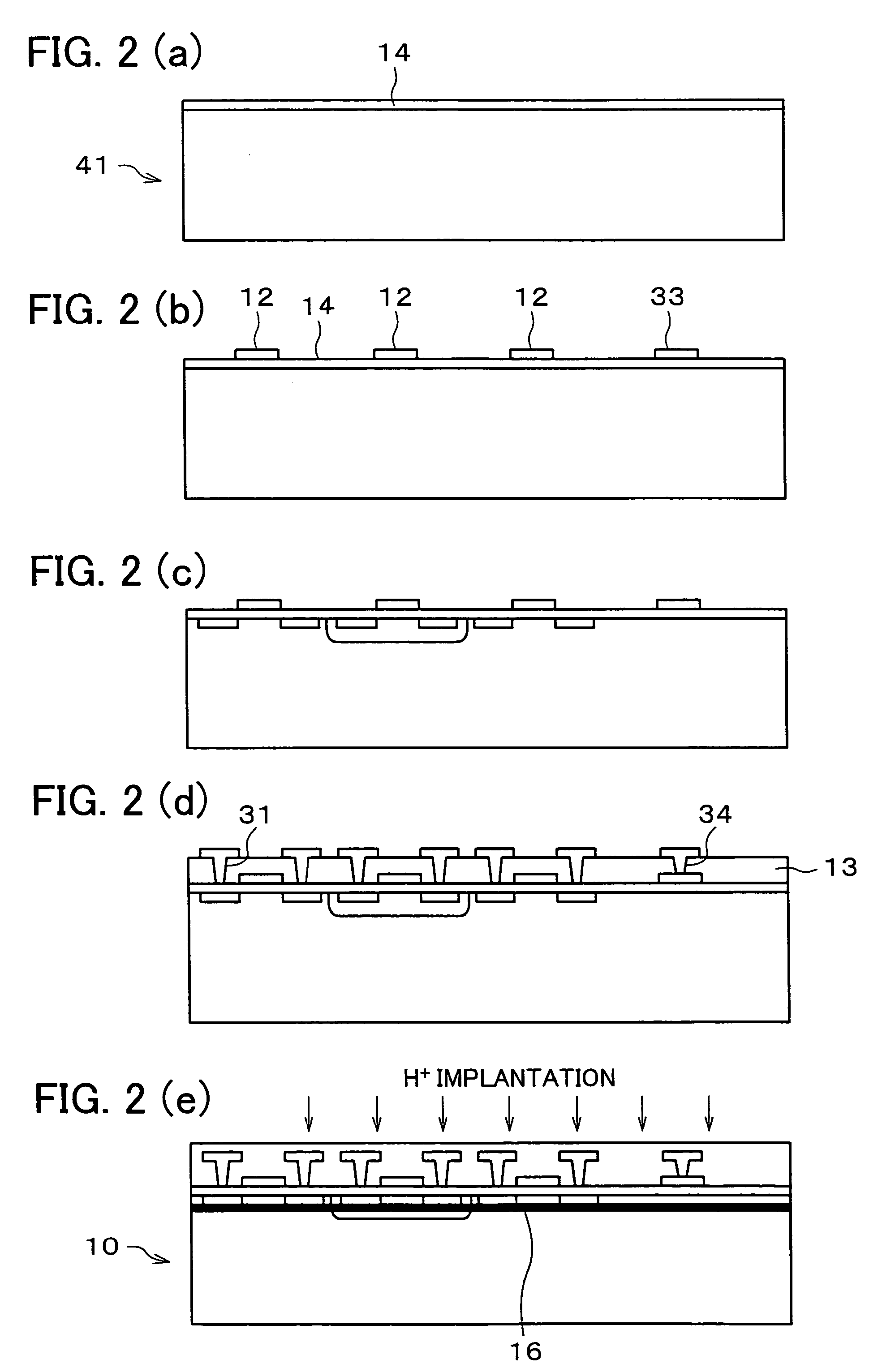
Thin film semiconductor device and fabrication method therefor
InactiveUS7488980B2Restraining aspect ratioSmall sizeTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInsulation layerEngineering
A relaying pad is formed in a predetermined portion in an insulation layer of the single-crystal thin film device, in a region where the single-crystal thin film device is formed. The relaying pad is for providing connection wiring through the insulator substrate. With this configuration it is possible to prevent an increase in an aspect ratio of a contact hole formed in an insulation layer in a region in which a transferred device is formed, the semiconductor device including a substrate on which the transferred device and a deposited device coexist.
Owner:SHARP KK
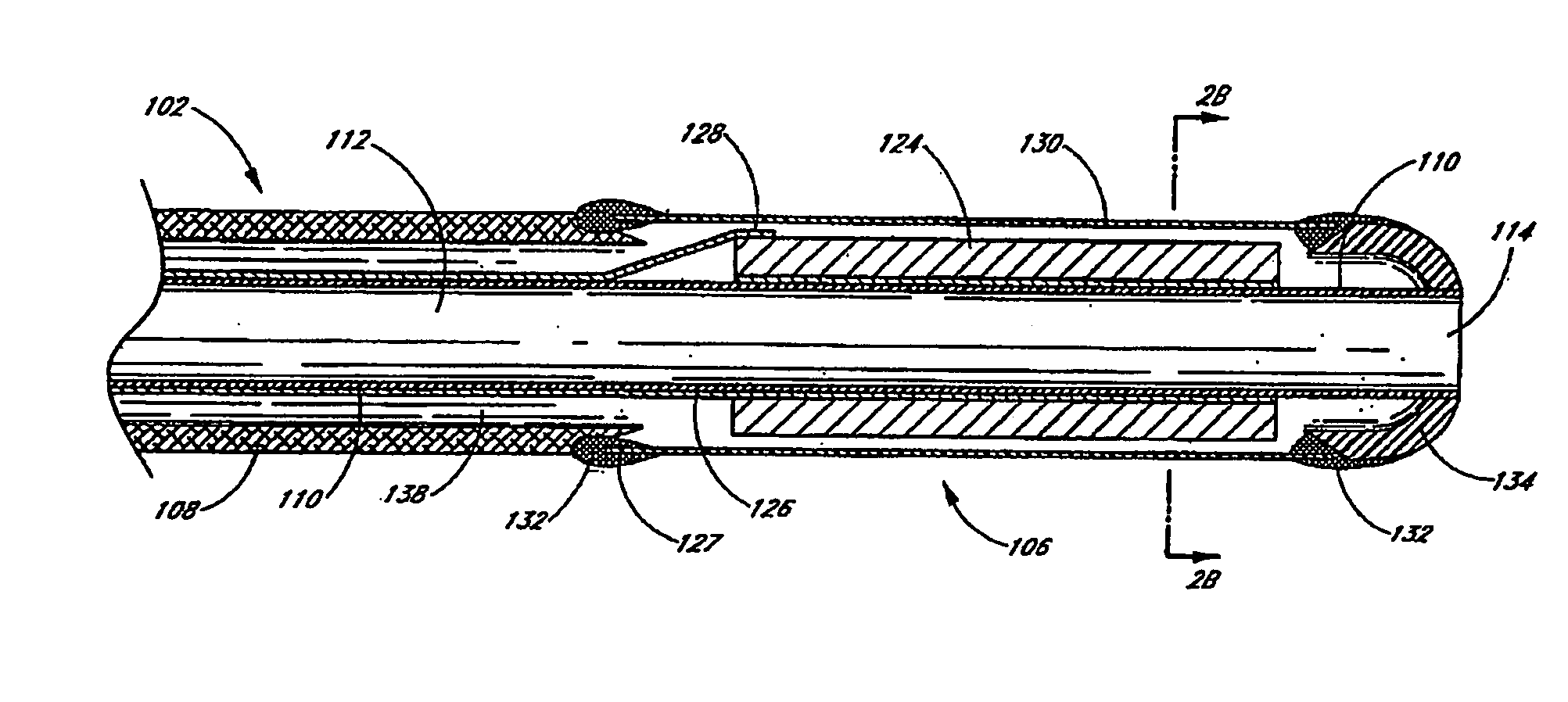
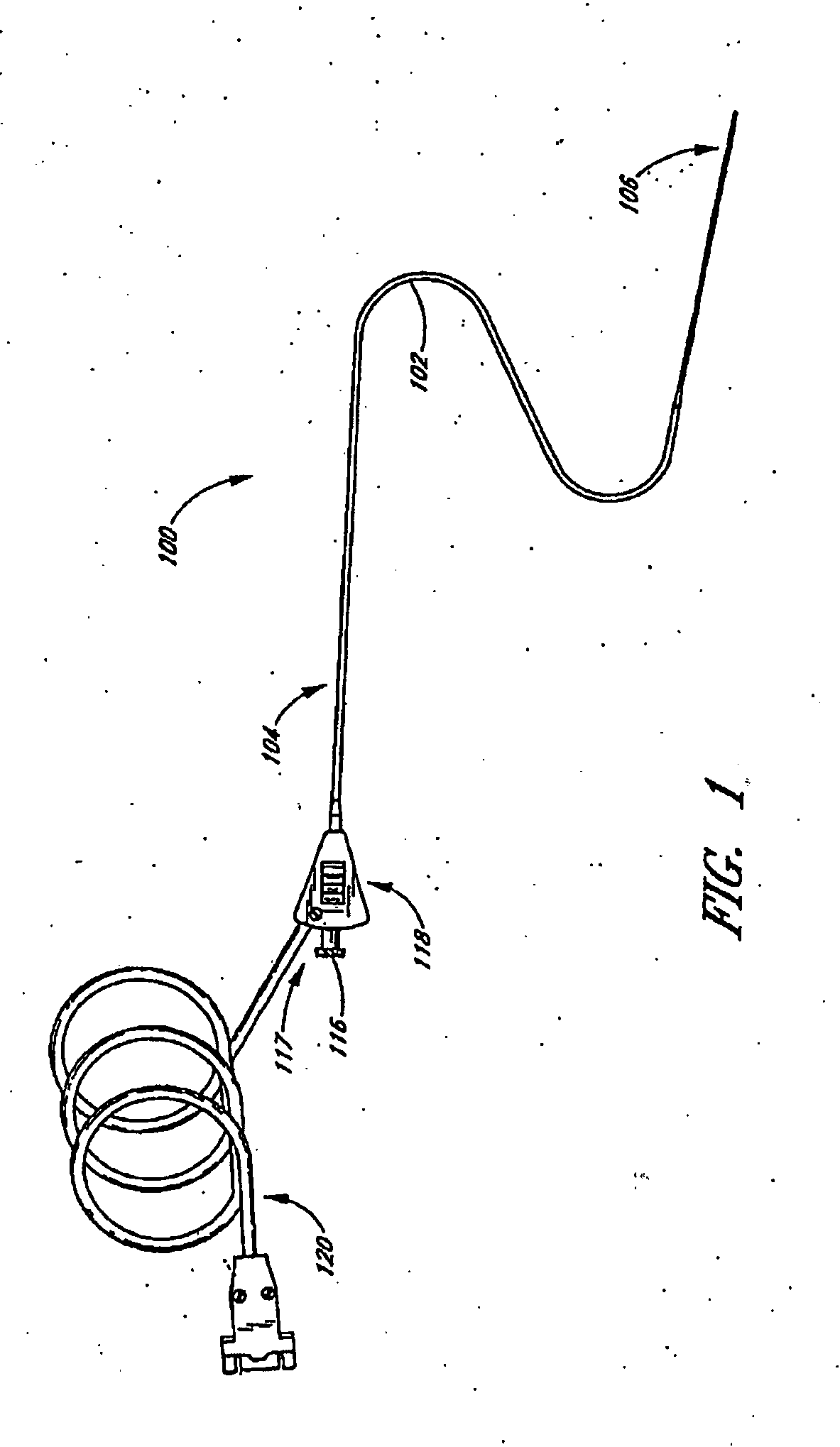
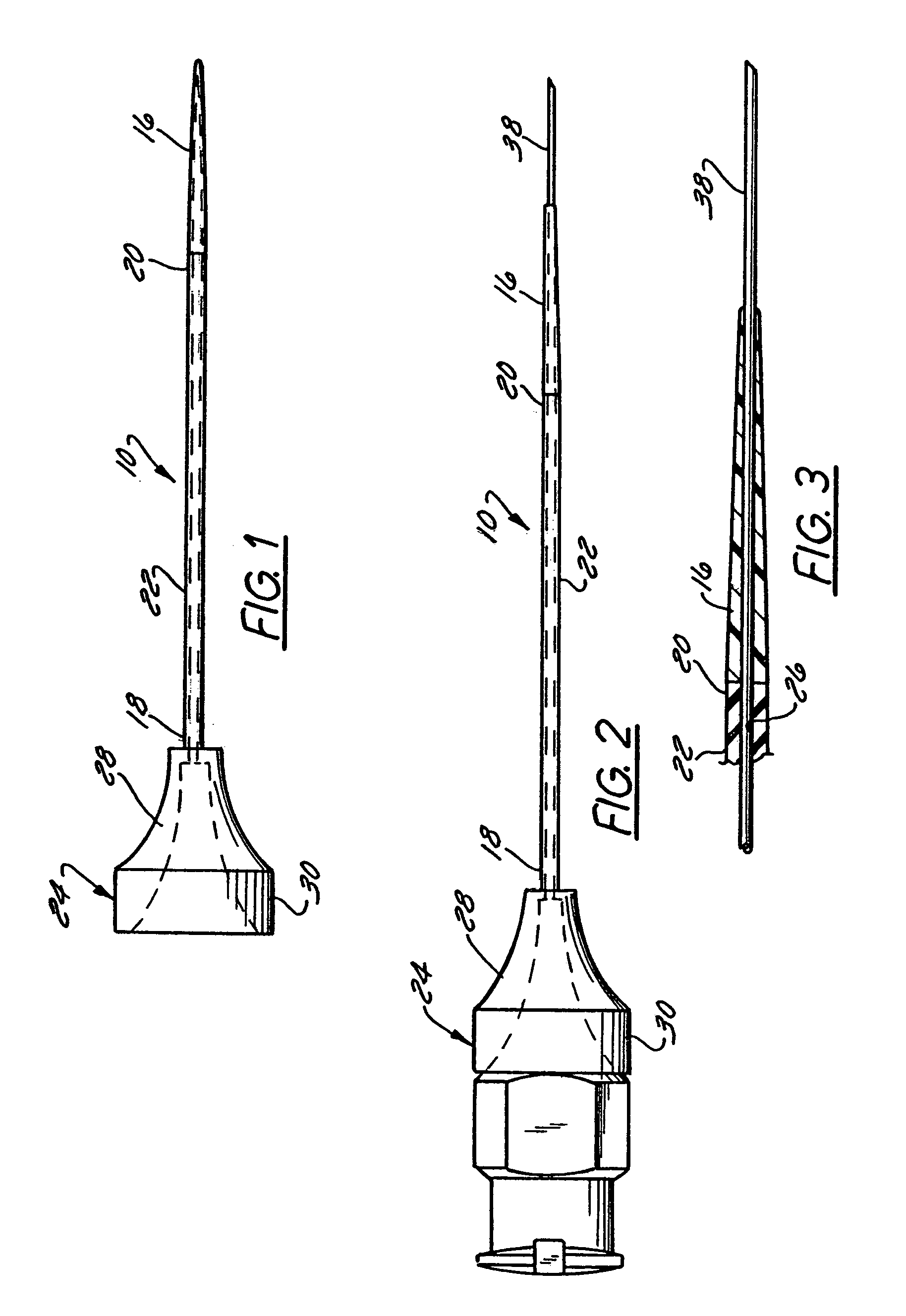
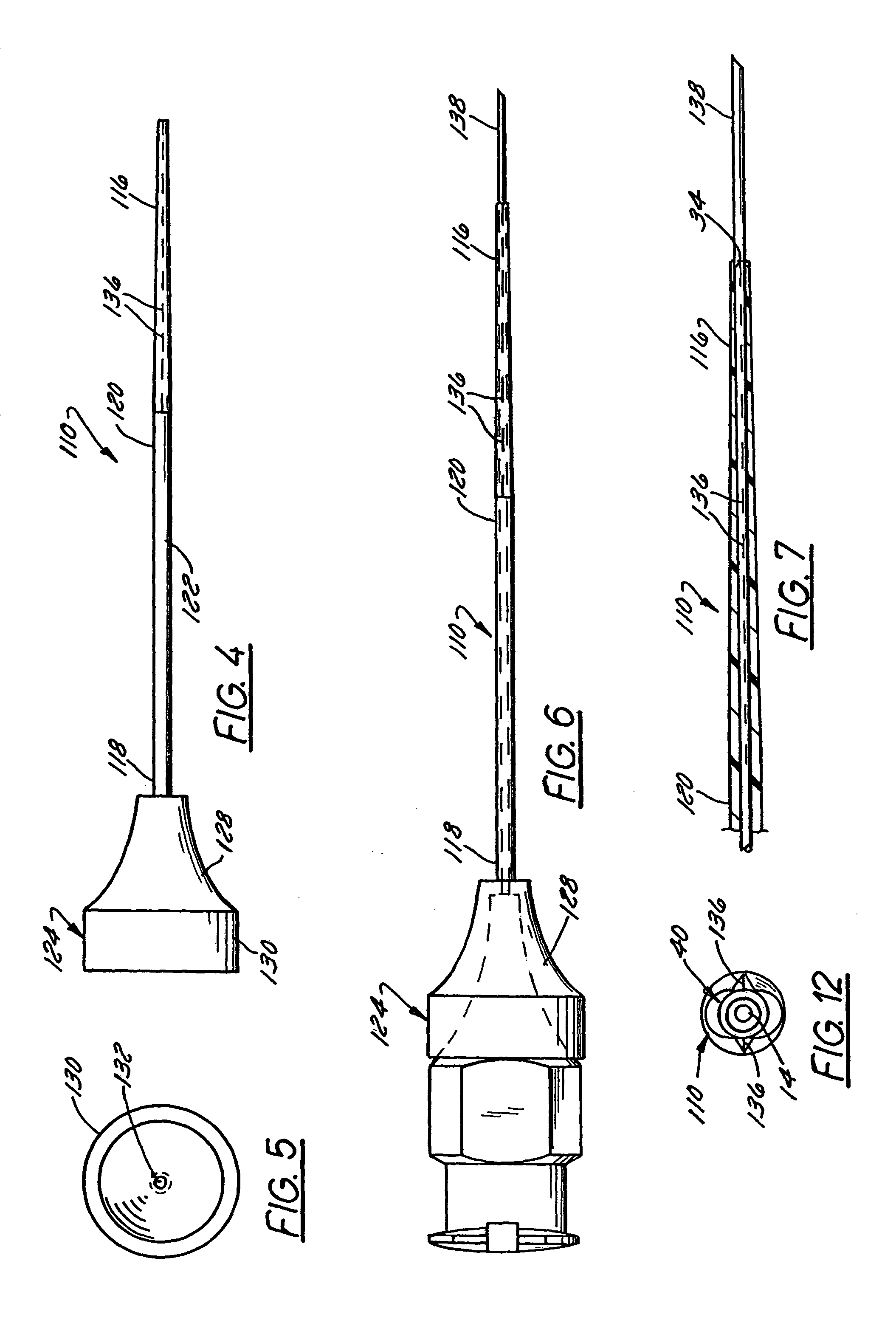
Small vessel ultrasound catheter
InactiveUS20050215942A1Increase stiffnessSufficient flexibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyDrugs solutionVascular ultrasound
An ultrasound catheter adapted for accessing small vessels in the distal anatomy is disclosed. The ultrasound catheter comprises an elongate tubular body formed with a delivery lumen. The flexibility and dimensions of the tubular body allow access to the distal anatomy by advancement over the guidewire. An ultrasound radiating member is provided along the distal end portion of the tubular body for emitting ultrasound energy at a treatment site. A drug solution may also be delivered through the delivery lumen and out an exit port to the treatment site.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Implantable coronary sinus lead and lead system
InactiveUS6968237B2Increase flexibilitySmall diameterTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesElectrical conductorCoronary sinus
An implantable stimulation lead is disclosed for placement in the coronary sinus region and its associated coronary vessels overlying the left side of a patient's heart. The lead comprises at least one proximal connector; at least one tissue stimulation electrode; at least one conductor coupled between the at least one proximal connector and the at least one stimulation electrode; and a lead body including a housing of insulating material enclosing the at least one conductor, the lead body having a relatively flexible distal portion of, for example, silicone rubber, having a length corresponding to the coronary sinus region of the heart, and a stiffer proximal portion of, for example, polyurethane. A robust transition joint comprising telescoped sections of the distal and proximal portions of the lead body couples the two portions of the lead body.Also provided is a versatile lead delivery system including a stylet stop disposed within the distal portion of the lead body. The stylet stop defines an aperture dimensioned to pass a guide wire but not the enlarged distal tip of a stylet. The lead includes a tip electrode having a longitudinally extending bore dimensioned to permit passage of the guide wire through the tip electrode.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Stent delivery system
The present invention relates to a system for delivering a medical prosthesis into a body lumen. A preferred embodiment of the invention utilizes a catheter having a stent mounted at the distal end that is released into the body lumen by movement of an outer sheath covering the stent in the proximal direction. The stent expands to conform to the inner wall of the lumen and the catheter is withdrawn.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Catheter introducer having an expandable tip
InactiveUS7144386B2Small initial tip diameterReduce manufacturing costGuide needlesInfusion syringesCatheter introducerBiomedical engineering
A catheter includes a body having an outer surface defining a lumen and an expandable tip on a distal end thereof. The tip includes an opening axially extending therethrough. Upon insertion of a device having a larger outer diameter than the inner diameter of the expandable tip, the opening permits passage of the device therethrough. The tip expands commensurately with a difference between the outer diameter of the device and the inner diameter of the expandable tip. The expandable tip includes a tubular wall having an axially extending weakened portion formed from (1) at least two axially aligned slit segments and (2) at least two axially aligned segments that are strengthened when compared to the slit segments. One of the strengthened segments is positioned between two of the slit segments. Another of the strengthened segments is formed between a distal-most slit segment and a distal end of the expandable tip.
Owner:A B KORKOR MEDICAL
Expandable transluminal sheath
ActiveUS20060052750A1Reduce manufacturing costMinimize abrasion and damageGuide needlesStentsStone removalBiomedical engineering
Disclosed is an expandable transluminal sheath, for introduction into the body while in a first, low cross-sectional area configuration, and subsequent expansion of at least a part of the distal end of the sheath to a second, enlarged cross-sectional configuration. The distal end of the sheath is maintained in the first, low cross-sectional configuration and expanded using a radial dilatation device. In an exemplary application, the sheath is utilized to provide access for a diagnostic or therapeutic procedure such as ureteroscopy or stone removal.
Owner:ONSET MEDICAL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com