Preparation method of porous fiber non-woven fabric
A technology of porous fibers and non-woven fabrics, applied in the field of industrial textiles, can solve the problems of fiber mechanical performance degradation, low output, easy cracking and plugging, etc., to reduce the cost of raw materials, increase specific surface area, reduce die and heat Effect of Air Temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1 polypropylene / liquid paraffin solid-liquid phase separation system
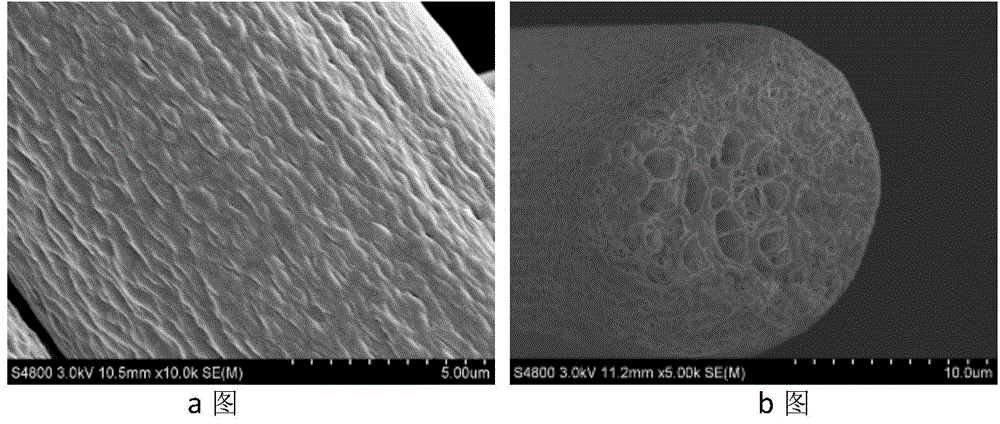
[0033] The polymer raw material is polypropylene T30S produced by Qilu Petrochemical, the diluent is liquid paraffin, and the extractant is n-hexane. The mass percent concentration of polypropylene is 30%. Firstly, the polypropylene and liquid paraffin are uniformly blended with a high-speed mixer at normal temperature. Then use a screw extruder to granulate, the aspect ratio of the screw extrusion granulator is 42, the compression ratio is 3, the screw speed is 400rpm, the extrusion temperature is 180°C, the extrusion speed is 150kg / h, and the polypropylene / liquid is obtained by cooling in the air. Paraffin meltblown masterbatch. The masterbatch is produced by melt blowing, the process parameters are slit nozzle, spinneret diameter 0.42mm, air groove angle 30°, slit width 0.62mm, die temperature 185°C, hot air temperature 200°C, gas pressure 0.1 Mpa, the receiving distance is 15cm, the ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Embodiment 2 polypropylene / n-butyl phthalate / n-octyl phthalate liquid-liquid phase separation system
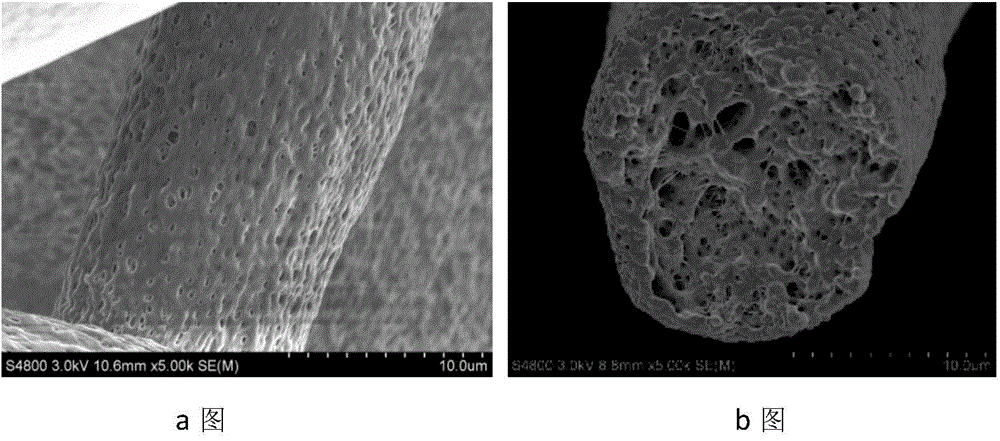
[0035] The polymer raw material is polypropylene S1003 produced by Yanshan Petrochemical, the diluent is a mixture of n-octyl phthalate and n-butyl phthalate, and the extractant is isopropanol. The mass percentage concentration of polypropylene is 20%, the mass percentage concentration of n-octyl phthalate is 64%, and the mass percentage concentration of n-butyl phthalate is 16%. Firstly, polypropylene, n-octyl phthalate and n-butyl phthalate are blended uniformly with a high-speed mixer at room temperature. Then use a screw extruder to granulate, the aspect ratio of the screw extrusion granulator is 20, the compression ratio is 4, the screw speed is 600rpm, the extrusion temperature is 200°C, the extrusion speed is 300kg / h, and the polypropylene / ortho N-octyl phthalate / n-butyl phthalate meltblown masterbatch. The masterbatch is produced by melt blowing, the process ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Embodiment 3 polypropylene / diphenyl ether liquid-liquid phase separation system
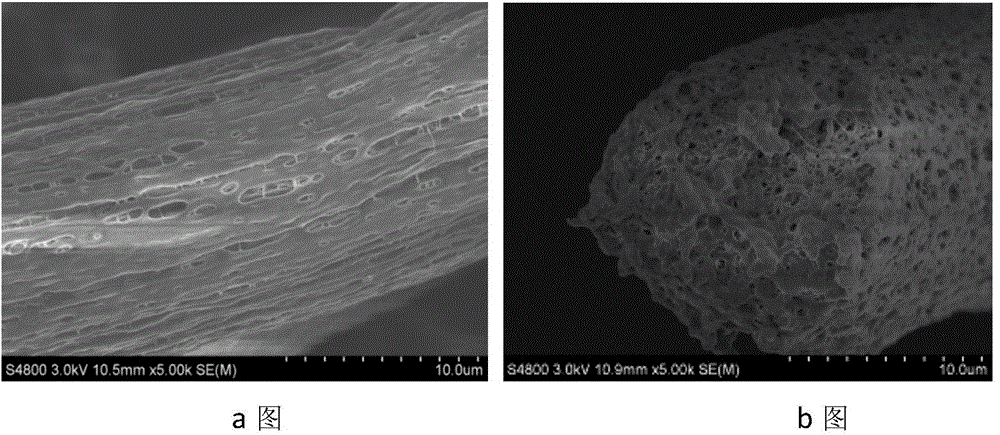
[0037] The basic process parameters are the same as in Example 1, diphenyl ether is selected as the diluent, and the fiber surface and cross-sectional morphology are as follows: image 3 As shown, the size distribution of pores in the fiber ranges from 300nm to 650nm. This system only undergoes liquid-liquid (L-L) phase separation, and the L-L phase separation temperature is 135°C, so elliptical openings are formed on the surface of the fiber, and the cross-section of the fiber is a double continuous pore structure.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Basis weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com