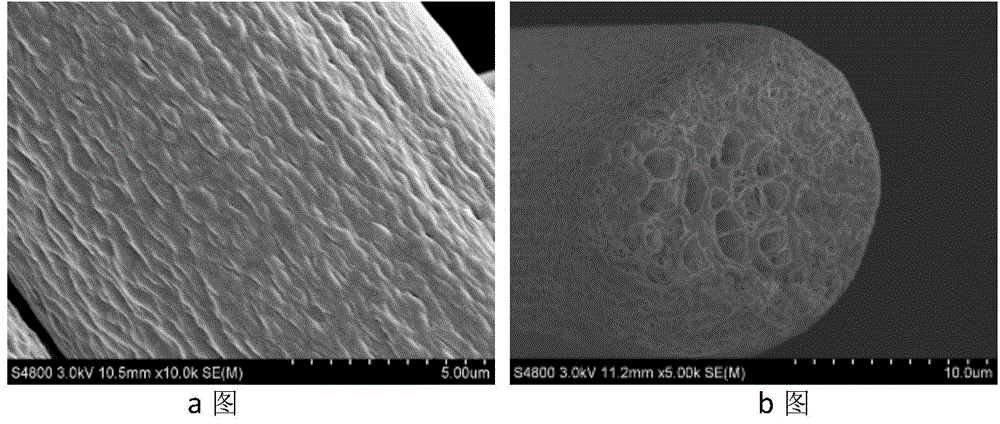
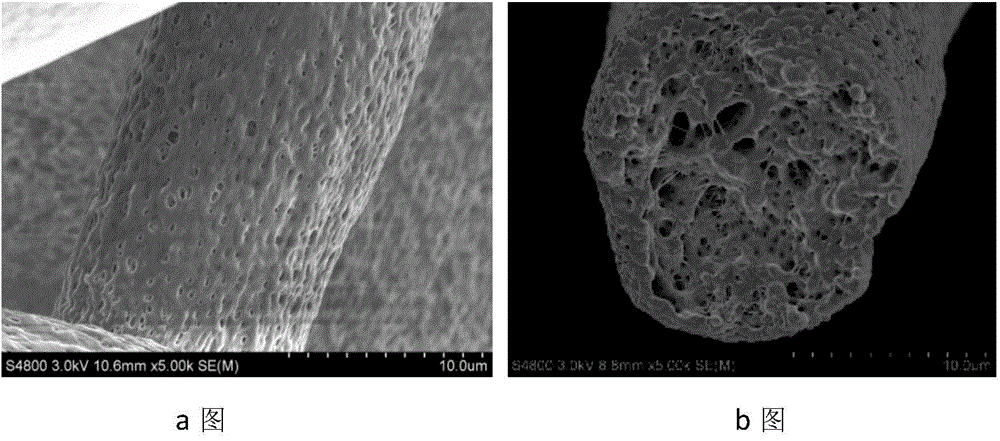
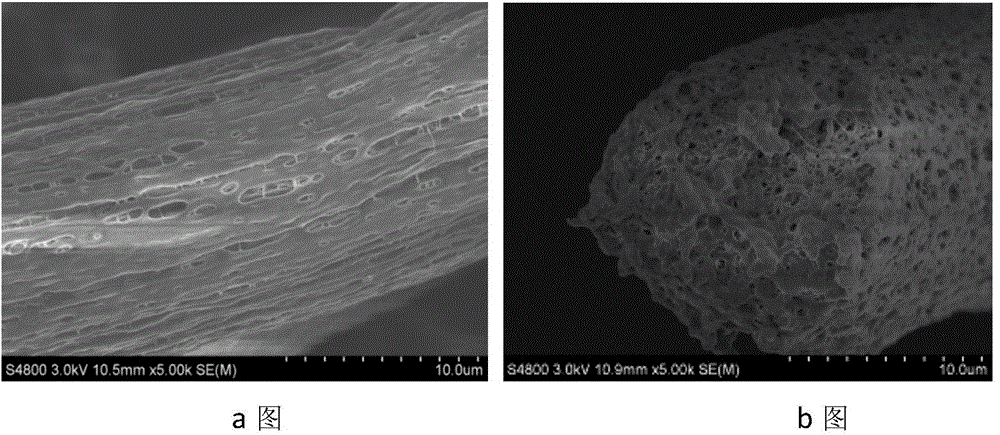
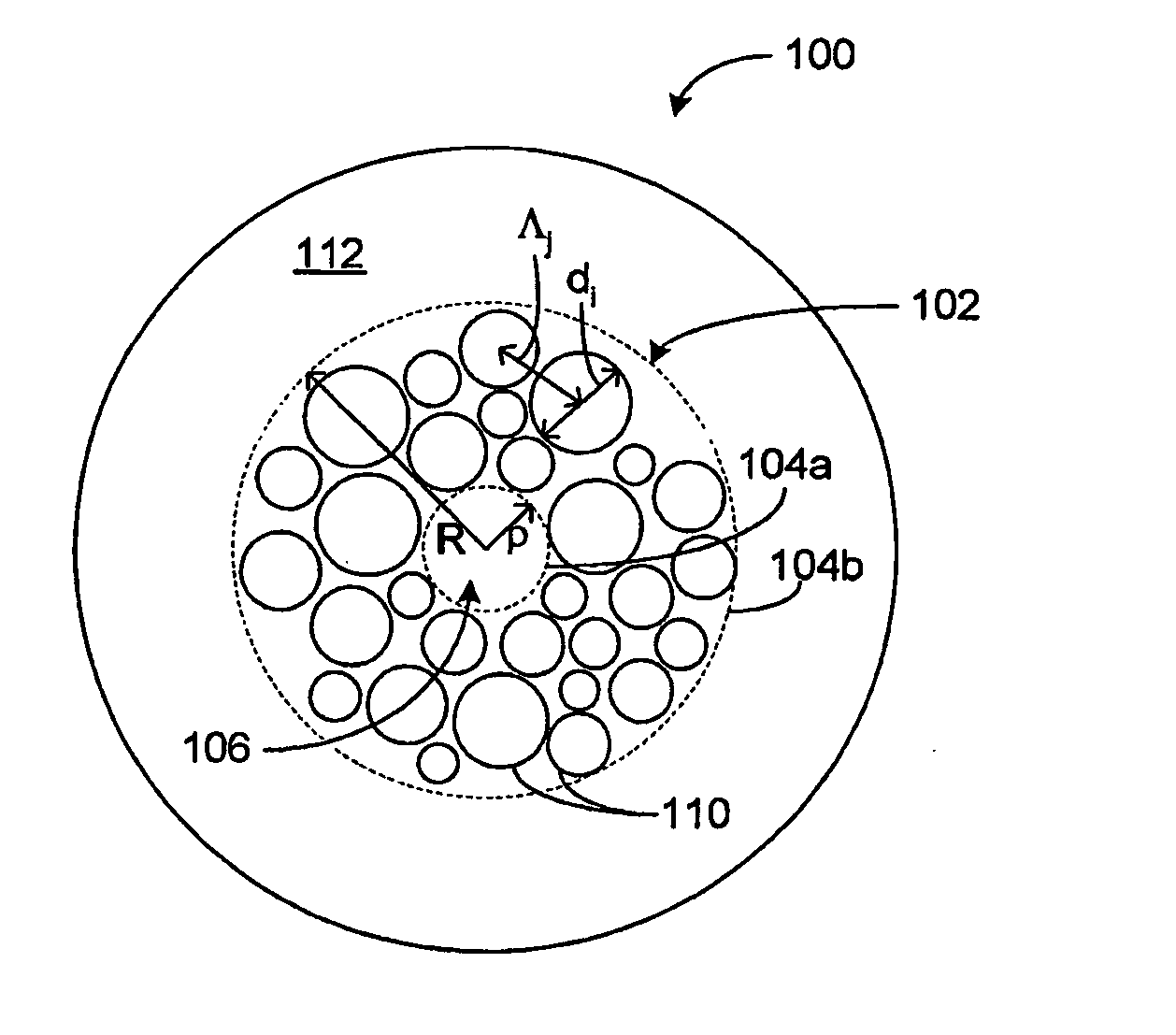
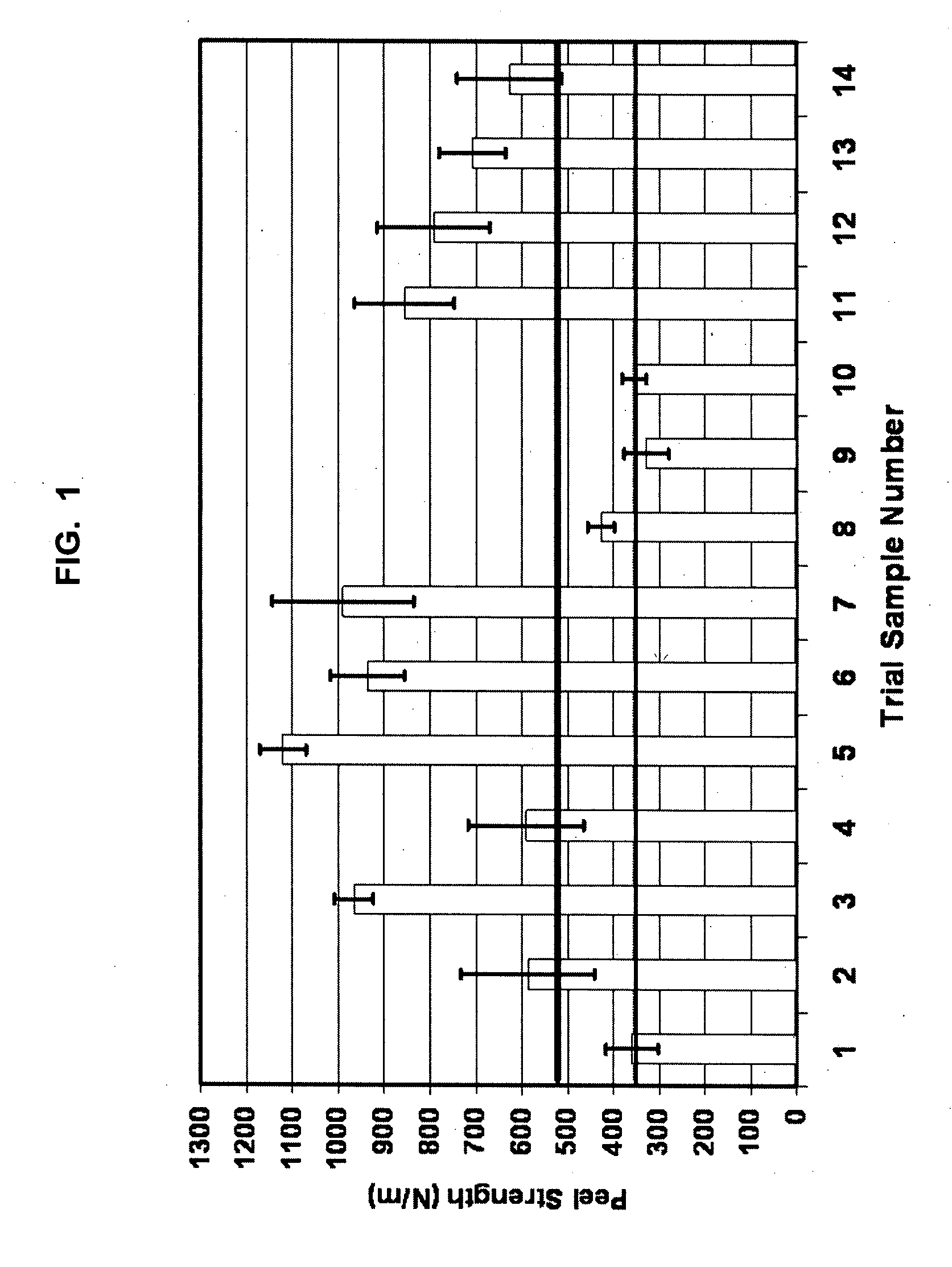
Patents
Literature
659 results about "Porous fiber" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Preparation method of porous fiber non-woven fabric
ActiveCN103981635AReduce melt viscosityReduce degradationFilament forming substance formingMelt spinning methodsDiluentNonwoven fabric
The invention relates to a preparation method of a porous fiber non-woven fabric. The aim of the preparation method is to improve the product performance of the conventional non-woven fabric, so that the non-woven fabric meets the requirements on high-precision and high-performance filter. The technical scheme is that the preparation method of the porous fiber non-woven fabric comprises the following steps in sequence: (1) uniformly mixing a polymer and a diluent to obtain a blend with 10 to 60 percent of polymer; (2) melting and extruding the blend in the step (1) by adopting a screw extruder granulator, and directly cooling and granulating in air; (3) producing master batches in the step (2) by melt-down equipment to obtain a primary non-woven fabric; (4) extracting to remove the diluent from the primary non-woven fabric in the step (3), performing pore-forming on fibers in the non-woven fabric, and drying to obtain the porous fiber non-wave fabric; (5) recovering mixed waste liquid of the diluent and an extraction agent for reuse.
Owner:浙江省轻工业品质量检验研究院
Large core holey fibers
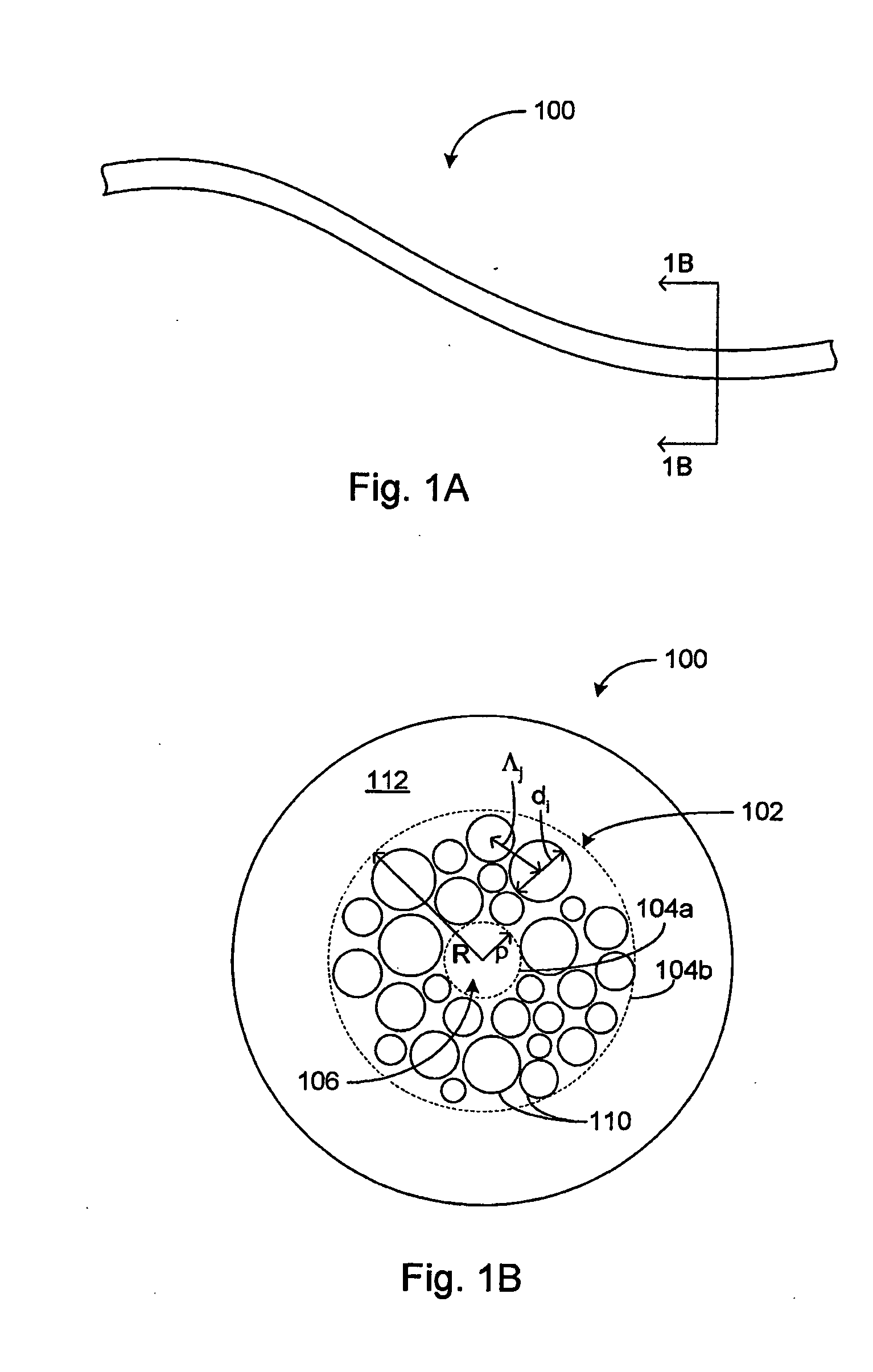
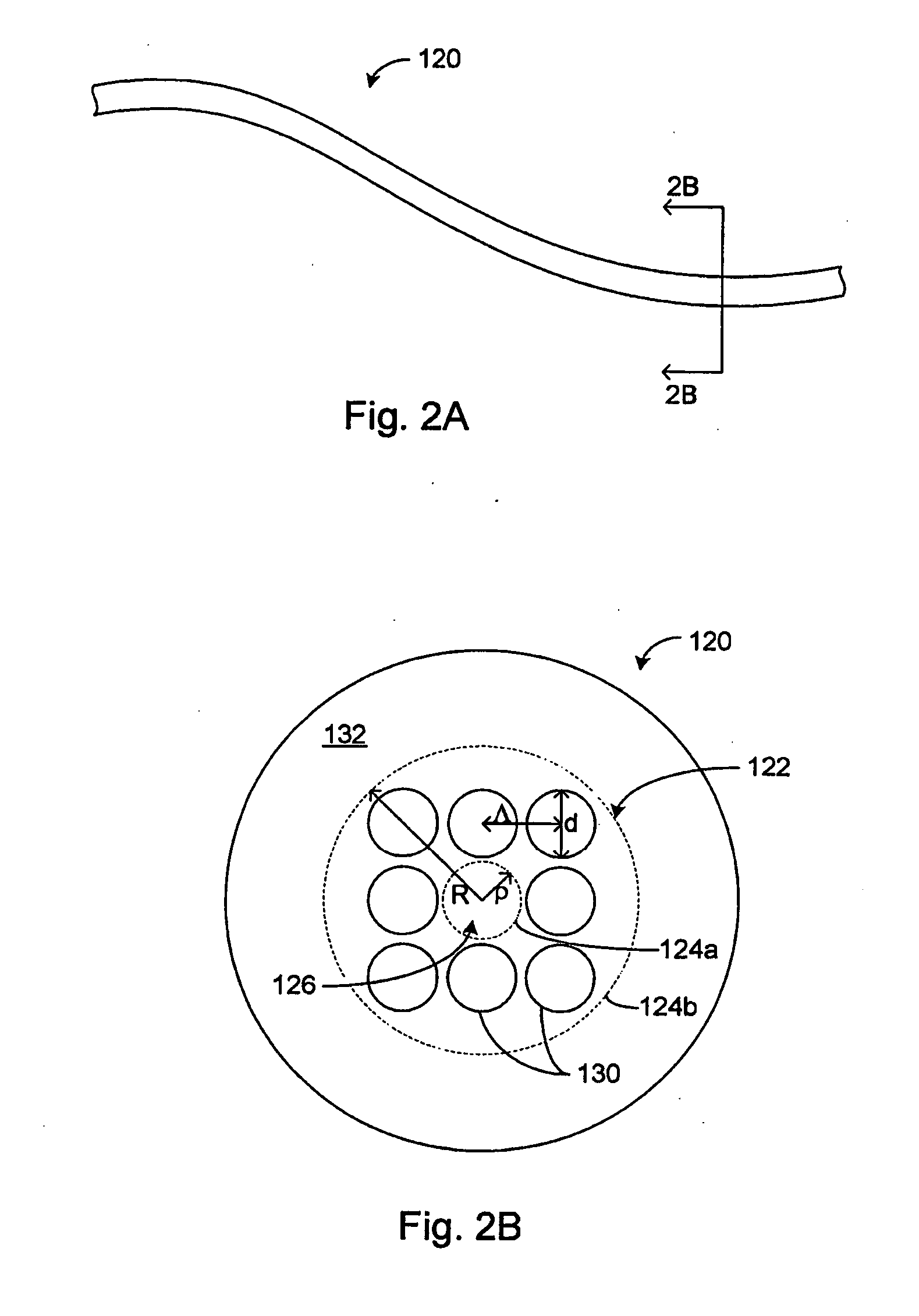
Various types of holey fiber provide optical propagation. In various embodiments, for example, a large core holey fiber comprises a cladding region formed by large holes arranged in few layers. The number of layers or rows of holes about the large core can be used to coarse tune the leakage losses of the fundamental and higher modes of a signal, thereby allowing the non-fundamental modes to be substantially eliminated by leakage over a given length of fiber. Fine tuning of leakage losses can be performed by adjusting the hole dimension and / or the hole spacing to yield a desired operation with a desired leakage loss of the fundamental mode. Resulting holely fibers have a large hole dimension and spacing, and thus a large core, when compared to traditional fibers and conventional fibers that propagate a single mode. Other loss mechanisms, such as bend loss and modal spacing can be utilized for selected modes of operation of holey fibers. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Decorative interior sound absorbing panel
A multi-layered fiber reinforced thermoplastic sound absorbing panel includes a porous fiber reinforced thermoplastic core layer having a first surface and a second surface, and includes a thermoplastic material and from about 20 weight percent to about 80 weight percent fibers, a tie layer covering the second surface of the core layer and including a thermoplastic material, and a barrier layer covering the tie layer. The barrier layer includes a thermoplastic material having a melting temperature higher than the melting temperature of the core layer thermoplastic material. The tie layer bonds the barrier layer to the core layer. The panel also includes a non-woven layer including a fabric bonded to the barrier layer. The non-woven layer forms an outer surface of the panel.
Owner:HANWA AZDEL INC
Porous fiber
InactiveUS7097904B2Good color propertiesMaintain good propertiesFilament/thread formingNanotechnologyMetallurgyNanopore
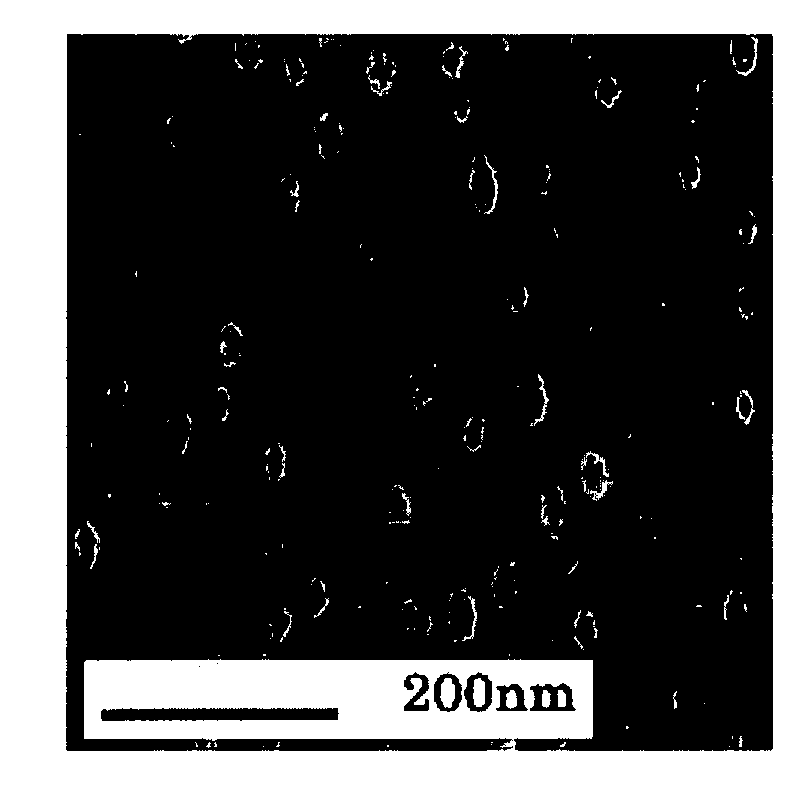
The present invention provides a nanoporous fiber being substantially free from coarse pores and having homogeneously dispersed nanopores, unlike conventional porous fibers. A porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, and the pores are unconnected pores, or a porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, the pores are connected pores, and the fiber has a strength of 1.0 cN / dtex or more.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Porous fibrous sheets of nanofibers
Owner:DUPONT SAFETY & CONSTR INC
Fiber-reinforced, porous, biodegradable implant device
InactiveUS20050240281A1Promote regenerationProvide strengthBone implantLaminationArticular cartilagePolymer
A fiber-reinforced, polymeric implant material useful for tissue engineering, and method of making same are provided. The fibers are preferably aligned predominantly parallel to each other, but may also be aligned in a single plane. The implant material comprises a polymeric matrix, preferably a biodegradable matrix, having fibers substantially uniformly distributed therein. Inorganic particles may also be included in the implant material. In preferred embodiments, porous tissue scaffolds are provided which facilitate regeneration of load-bearing tissues such as articular cartilage and bone. Non-porous fiber-reinforced implant materials are also provided herein useful as permanent implants for load-bearing sites.
Owner:OSTEOBIOLOGICS
Porous fiber
ActiveUS20050260911A1Good color propertiesExcellent moisture adsorptionWarp knittingCeramic shaping apparatusMetallurgyNanopore
The present invention provides a nanoporous fiber being substantially free from coarse pores and having homogeneously dispersed nanopores, unlike conventional porous fibers. A porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, and the pores are unconnected pores, or a porous fiber has pores each having a diameter of 100 nm or less, in which the area ratio of pores each having a diameter of 200 nm or more to the total cross section of the fiber is 1.5% or less, the pores are connected pores, and the fiber has a strength of 1.0 cN / dtex or more.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Decorative interior sound absorbing panel
A multi-layered fiber reinforced thermoplastic sound absorbing panel includes a porous fiber reinforced thermoplastic core layer having a first surface and a second surface, and includes a thermoplastic material and from about 20 weight percent to about 80 weight percent fibers, a tie layer covering the second surface of the core layer and including a thermoplastic material, and a barrier layer covering the tie layer. The barrier layer includes a thermoplastic material having a melting temperature higher than the melting temperature of the core layer thermoplastic material. The tie layer bonds the barrier layer to the core layer. The panel also includes a non-woven layer including a fabric bonded to the barrier layer. The non-woven layer forms an outer surface of the panel.
Owner:HANWA AZDEL INC
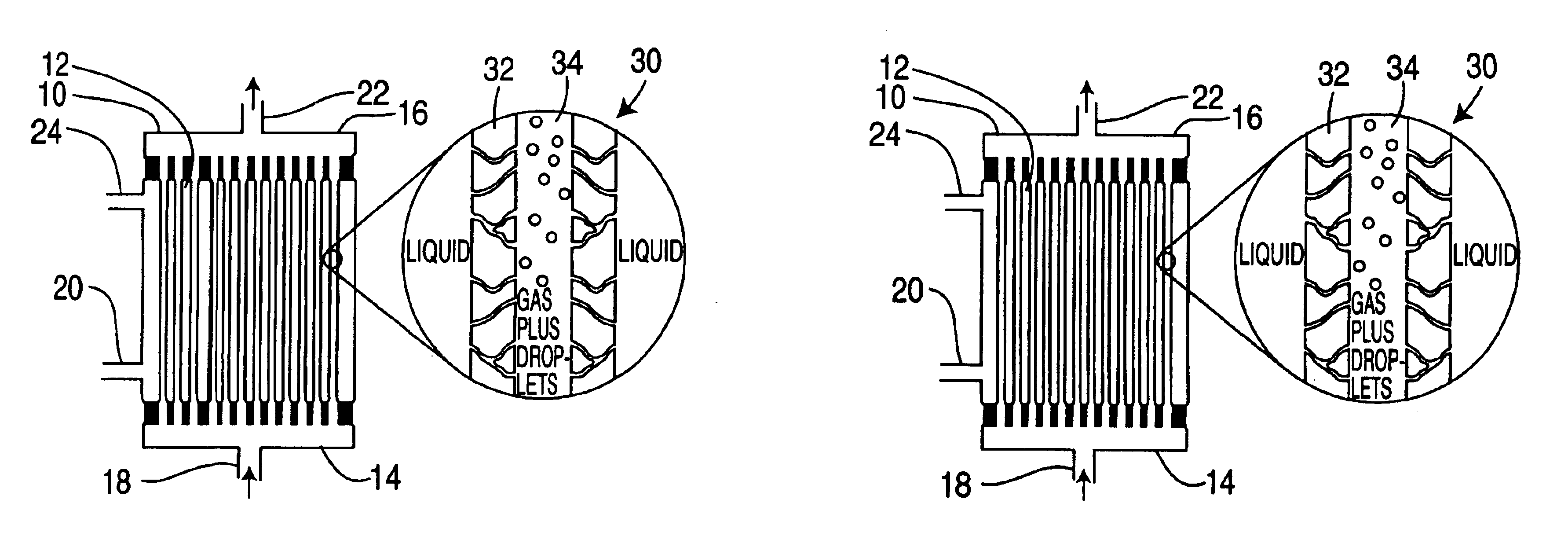
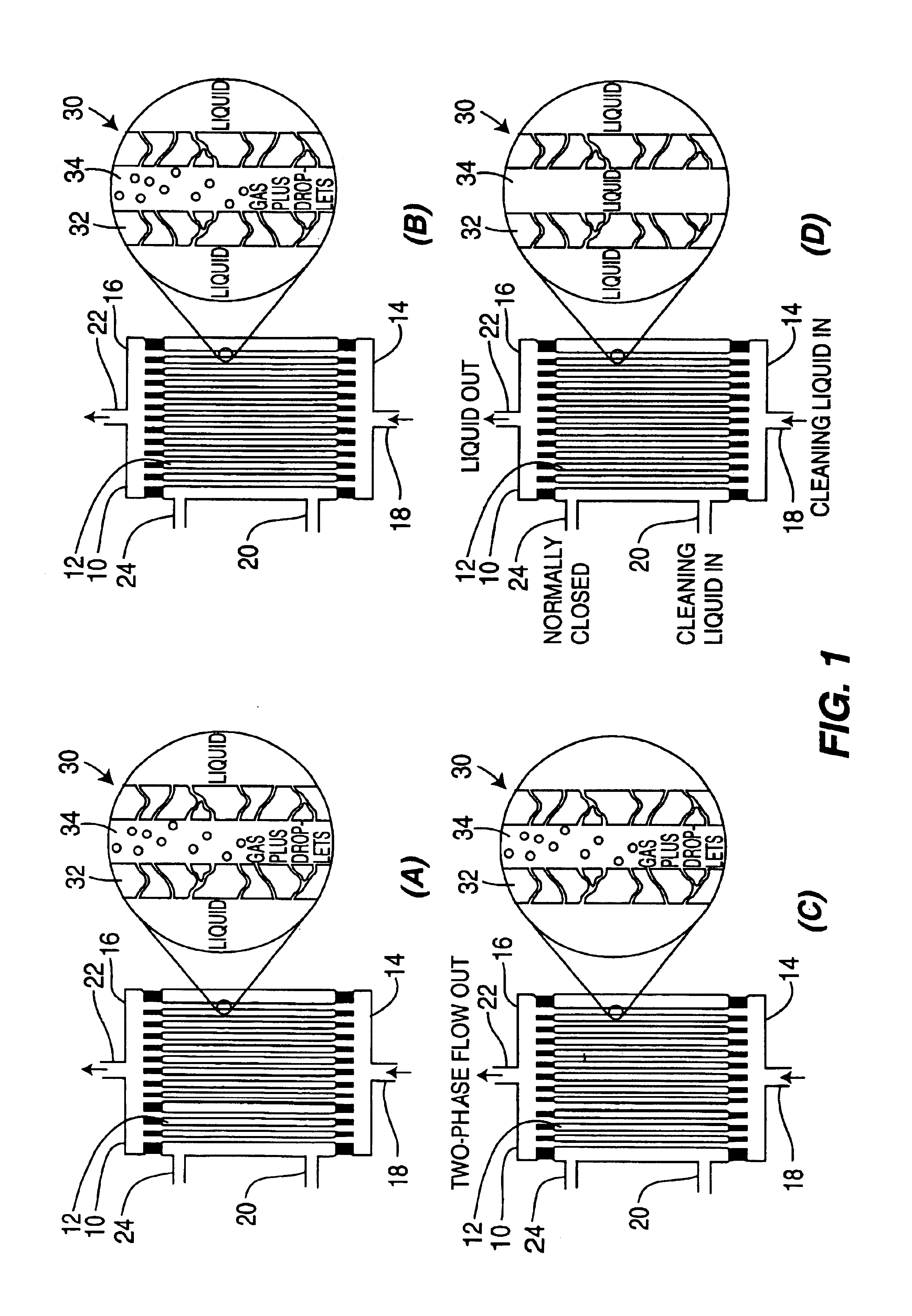
Method for cleaning hollow tubing and fibers
InactiveUS20050150831A1High aspect ratioReadily flushed awayInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsSemi-permeable membranesHollow fibreLiquid bubble
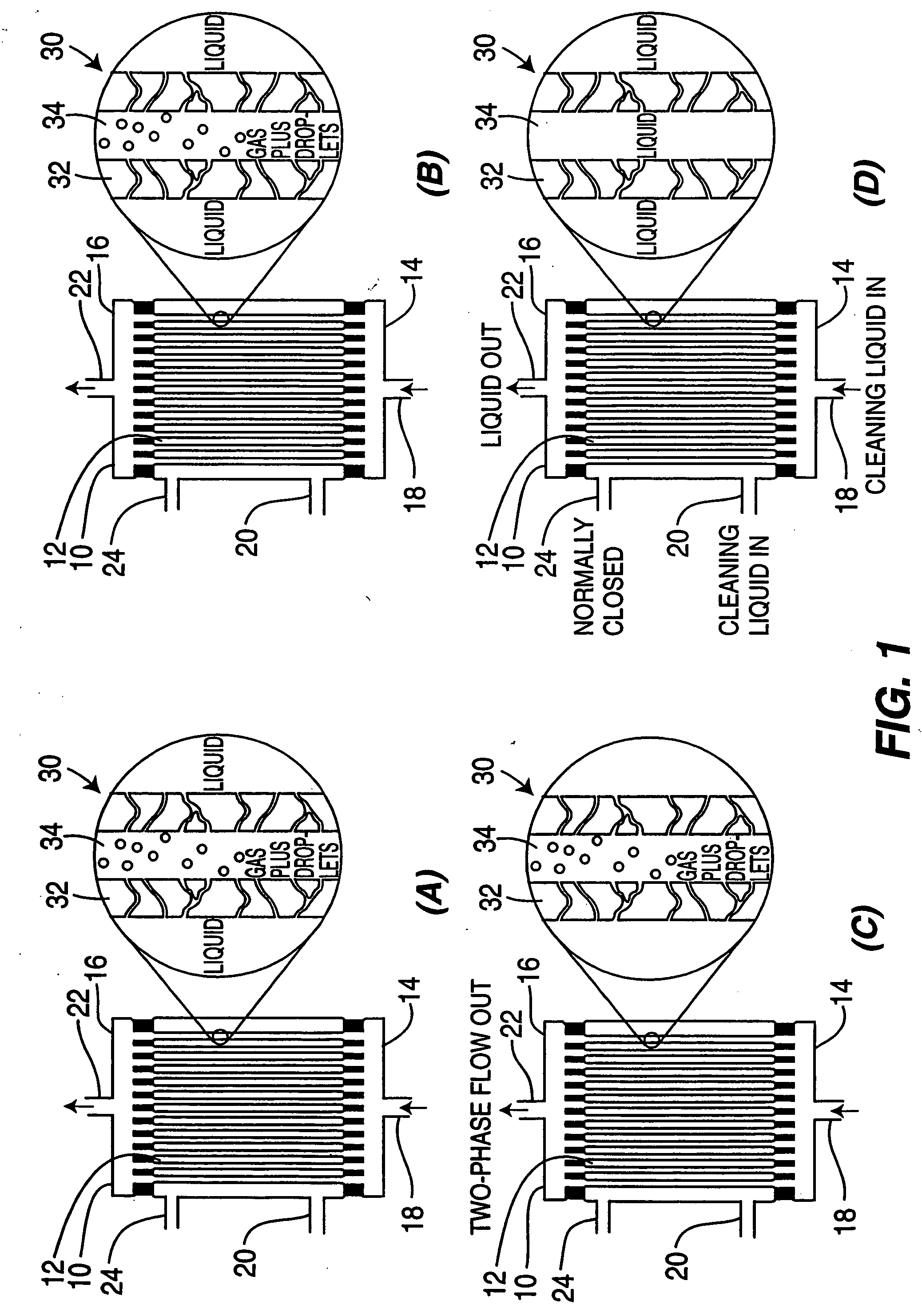
Hollow porous fibers containing adhered contaminants are cleaned to remove the contaminants by backflushing a liquid to fill the pores, and adding a flow of gas so as to form a two-phase mixture of gas and bubbles of liquid that can scrub the fibers, loosening the contaminants and allowing them to be flushed from the hollow fibers. The method is particularly useful for cleaning hemodialyzers used for dialysis and hollow fiber modules used in water treatment and separations. The two phase flow method is specifically effective in cleaning piping systems having high length to diameter (l / d) ratios.
Owner:NOVAFLUX INC
Poly-dopamine based porous carbon fiber/MoSe2 composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105742074AGentle preparationThe preparation process is environmentally friendlyHybrid capacitor electrodesCell electrodesElectro catalystCarbon fibers
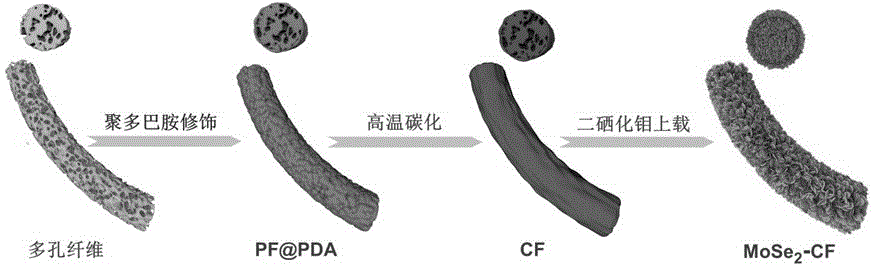
The invention belongs to the technical field of a composite fiber material, in particular relates to a poly-dopamine based porous carbon fiber / MoSe2 nanosheet composite material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of preparing a spinning solution with a spinnable high-polymer material, and preparing to obtain porous fiber with an uniform structure by an electrostatic spinning device; immersing the porous fiber in a dopamine solution, and controlling the thickness of a poly-dopamine cladding layer by adjusting the concentration and the reaction time of the dopamine solution; carrying out high-temperature carbonization to achieve carbonization on the poly-dopamine modified porous fiber material; and uniformly arranging MoSe2 nanosheets on the surface of the porous fiber by a hydrothermal method. The method disclosed by the invention is safe and environment-friendly, and the prepared porous carbon fiber / MoSe2 has the advantages of high active substance content, high specific area, high conductivity, stable physical and chemical performance and the like, and is an ideal electrode material for preparing an active electric catalyst for a hydrogen evolution reaction.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Enhanced sound absorption in thermoplastic composites
InactiveUS20080008869A1Good sound-absorbing propertiesEnhanced sound absorption characteristicNatural cellulose pulp/paperSynthetic resin layered productsMetal formingMicrosphere
A moldable composite sheet having enhanced sound absorption characteristics and attenuation of transmitted sound intensities. In one aspect, the composite sheet may be a porous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic comprising discontinuous reinforcing fibers, expandable polymeric beads such as microspheres, and, optionally, one or more thermoplastic skins. Generally, the composite sheet may have a void content or porosity from greater than 0% to about 95% by volume of the sheet, an areal weight between about 400 g / m2 to about 4000 g / m2 (gsm), a fiber content from about 20% to about 80% by weight, and an expandable polymeric bead content from greater than 0 gsm to about 25 gsm. The composite sheet can be molded via low pressure processes, such as thermoforming, match metal molding on stops, vacuum forming and pressure forming, to produce durable automotive interior trim parts and construction articles having enhanced sound absorption capabilities in addition to other beneficial characteristics.
Owner:AZDEL INC
Technique for reducing impurity content in gas phase hydrogenchloride from hydrolysis of dimethyldichlorosilane
InactiveCN101423193ALow impurity contentHigh yieldChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationGas phaseHydrolysate
The invention discloses a process method used for reducing the content of impurities in gas-phase hydrogen chloride after hydrolysis of dichlorodimethyl silane, comprising the steps as follows: a two-step device is used for separating the impurities; a vapour liquid separator leads the mixed hydrogen chloride gas generated after the hydrolysis of dichlorodimethyl silane to enter a washing tower of a guide structure so as to remove most of impurities; subsequently, the hydrogen chloride gas with most of impurities removed is arranged into the bottom of a demister; the adsorption medium at the internal layer of the demister is porous fiber which is used to adsorb the siloxane impurity in the hydrogen chloride gas; and the hydrogen chloride gas with the siloxane impurity removed is sent to a methyl chloride device to carry out the subsequent process. The method reduces the content of the impurities in the hydrogen chloride gas, improves the yield of hydrolysate of the dichlorodimethyl silane, keeps the pressure of the hydrogen chloride gas at a high level after purification, does not generate a great deal of waste acid, avoids the disposal of waste acid, and has low energy consumption and low equipment expense.
Owner:浙江恒业成有机硅有限公司
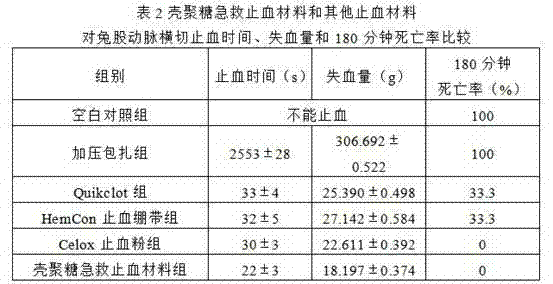
Chitosan emergent hemostasis material
ActiveCN102648985AStrong water absorptionSpeed up penetrationAbsorbent padsBandagesSuction forceTissue repair
The invention provides a chitosan emergent hemostasis material, which is provided with at least two layers of structures: a chitosan hemostasis layer as an upper layer, and a polyacrylic acid grafting chitosan lining layer as a lower layer, wherein the chitosan hemostasis layer is of a structure of a porous microsphere, porous fiber, porous sponge, or a compound of the porous microsphere, the porous fiber and the porous sponge; and the polyacrylic acid grafting chitosan lining layer is of a structure of porous fiber, porous sponge, or a compound of the porous fiber and the porous sponge. According to the chitosan emergent hemostasis material, the polyacrylic acid grafting chitosan is used as the lining layer of the chitosan, so that powerful water suction force can be provided, seepage velocity of blood in the chitosan hemostasis material is improved, blood is further concentrated, the density of the hemostasis material is improved simultaneously, the hemostasis material is easier to sink to arrive at a bleeding point, gravity press of a bleeding part is formed, pressurization is convenient, and the hemostasis effect is improved. Meanwhile, the polyacrylic acid grafting chitosan layer also can be used as a medicine-carrying substrate, can be used for carrying antibacterial drug, acesodyne, factors for promoting tissue repair and the like, and is good for preventing and controlling infection while stopping bleeding, relieving pains, and accelerating wound tissue healing.
Owner:欣乐加生物科技温州有限公司
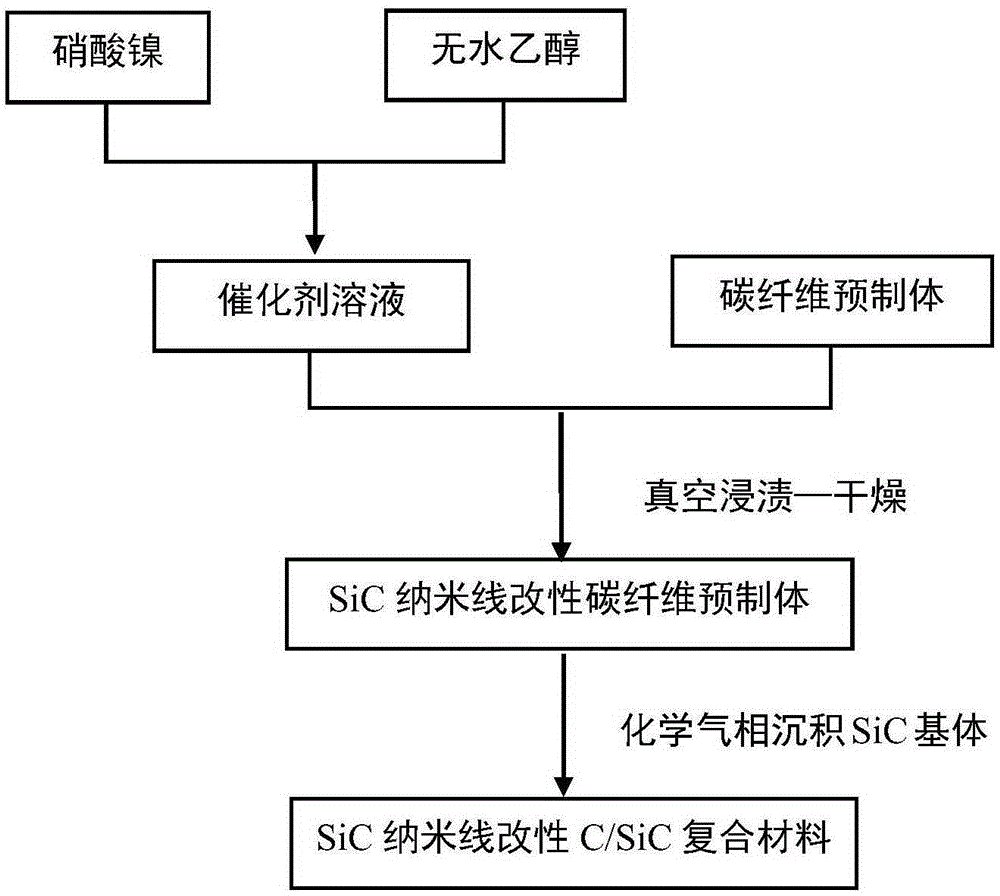
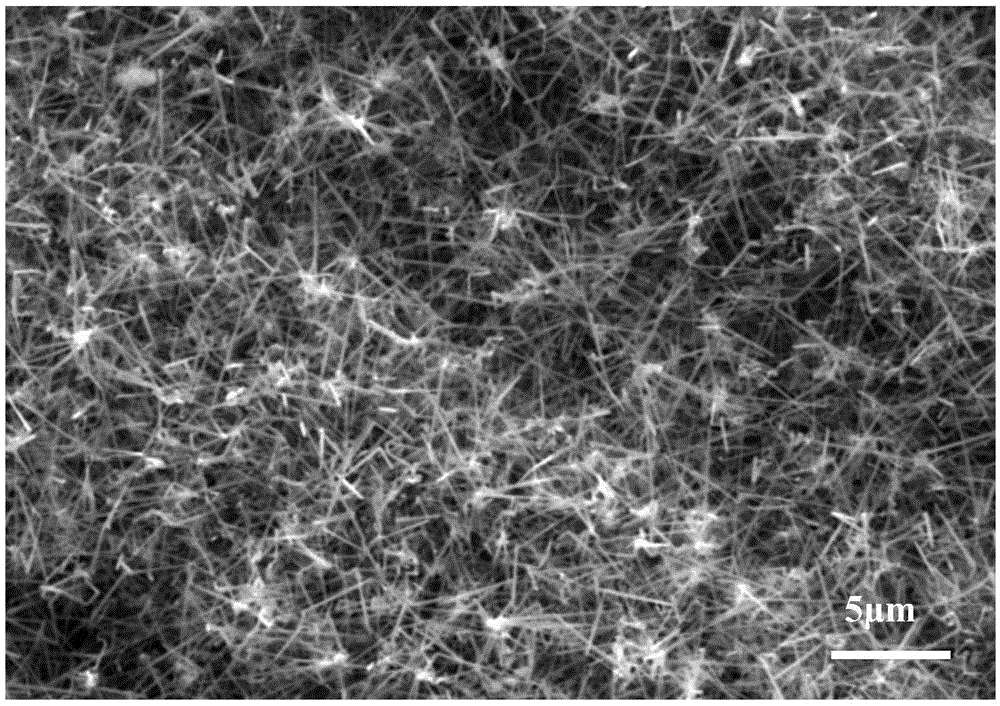
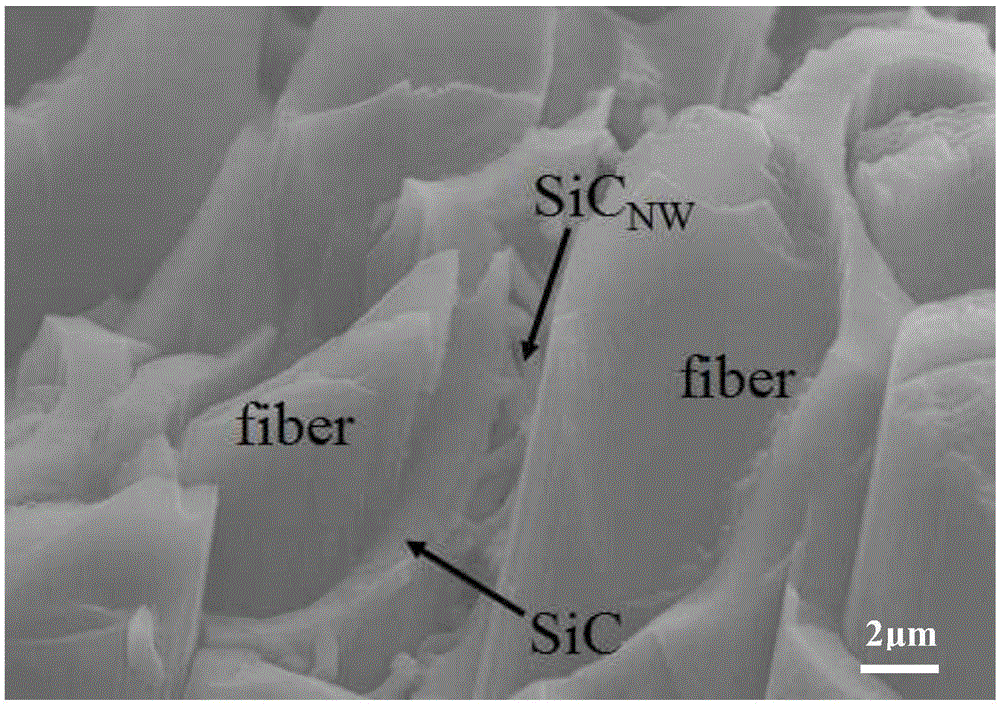
Method for preparing ceramic matrix composite material through SiC nano-wire modified ceramic matrix composite material interface
InactiveCN105237021AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove bending strengthHydrogenMethyltrichlorosilane
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a ceramic matrix composite material through a SiC nano-wire modified ceramic matrix composite material interface. The method comprises: immersing a porous fiber preform in a catalyst solution; in a CVD furnace, carrying out in-situ SiC nano-wire deposition by using methyltrichlorosilane MTS as a silicon source, using argon Ar as a dilution gas, and using hydrogen as a carrier gas, wherein the dilution ratio is 30-90; and preparing a SiC matrix by using a CVI process, using methyltrichlorosilane MTS as a silicon source, and using argon Ar as a dilution gas so as to obtain the compact SiC nano-wire modified ceramic matrix composite material, wherein the dilution ratio is 9-11. According to the present invention, the reinforcing and toughening mechanism of the SiC nano-wire is used to improve the mechanical property of the material; and the bending strength of the composite material adopting the SiC nano-wires as the interface is increased by 26.7% (Figure 6) compared with the PyC interface composite material under the same process, and the interface antioxidant property of the interface can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
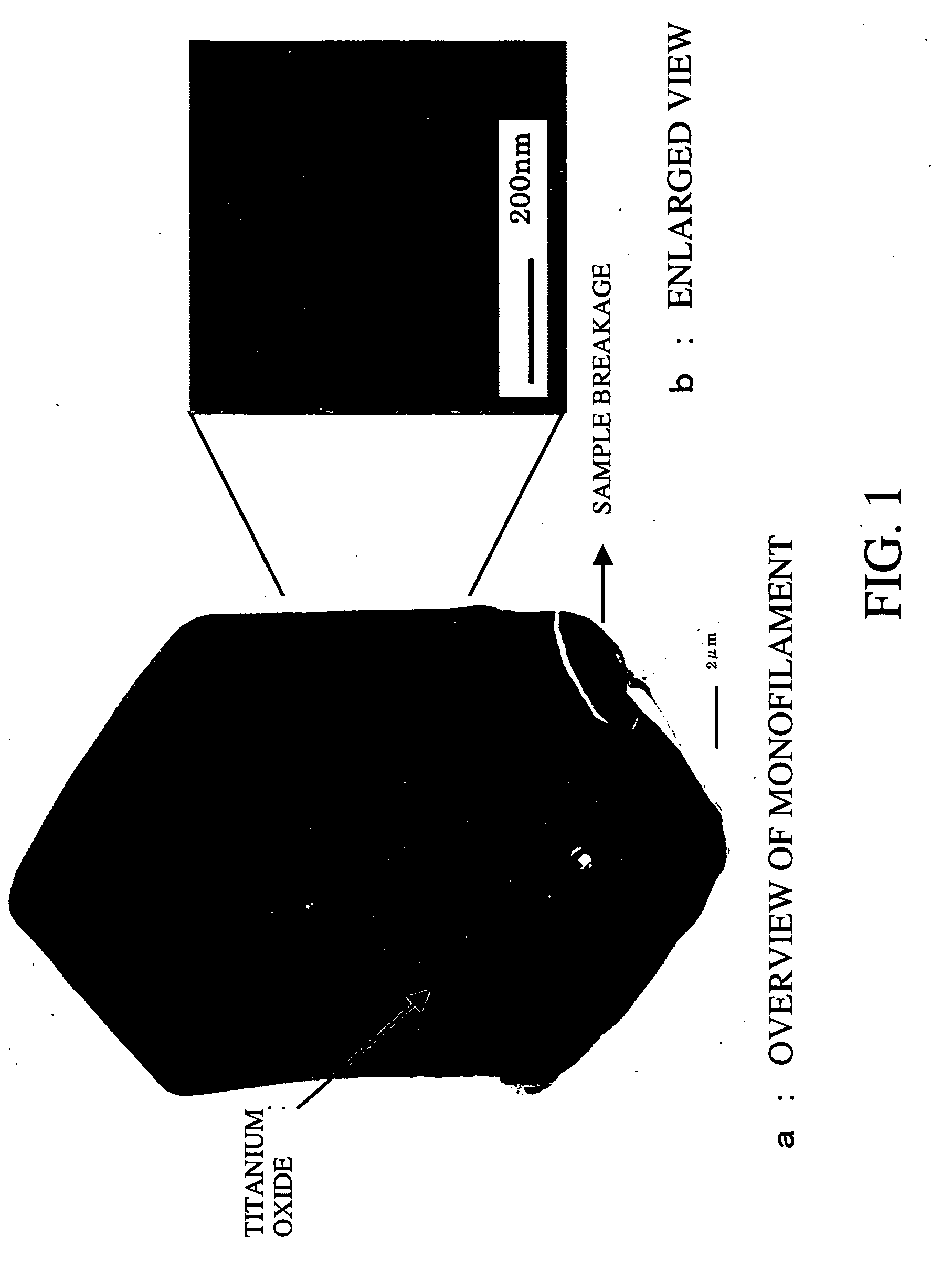
Method of preparing titanium dioxide, stannum dioxide and doping composite fiber material thereof
InactiveCN101033082AGood lookingSimple structureNanostructure manufactureTitanium dioxideTin dioxideNitrogen gas
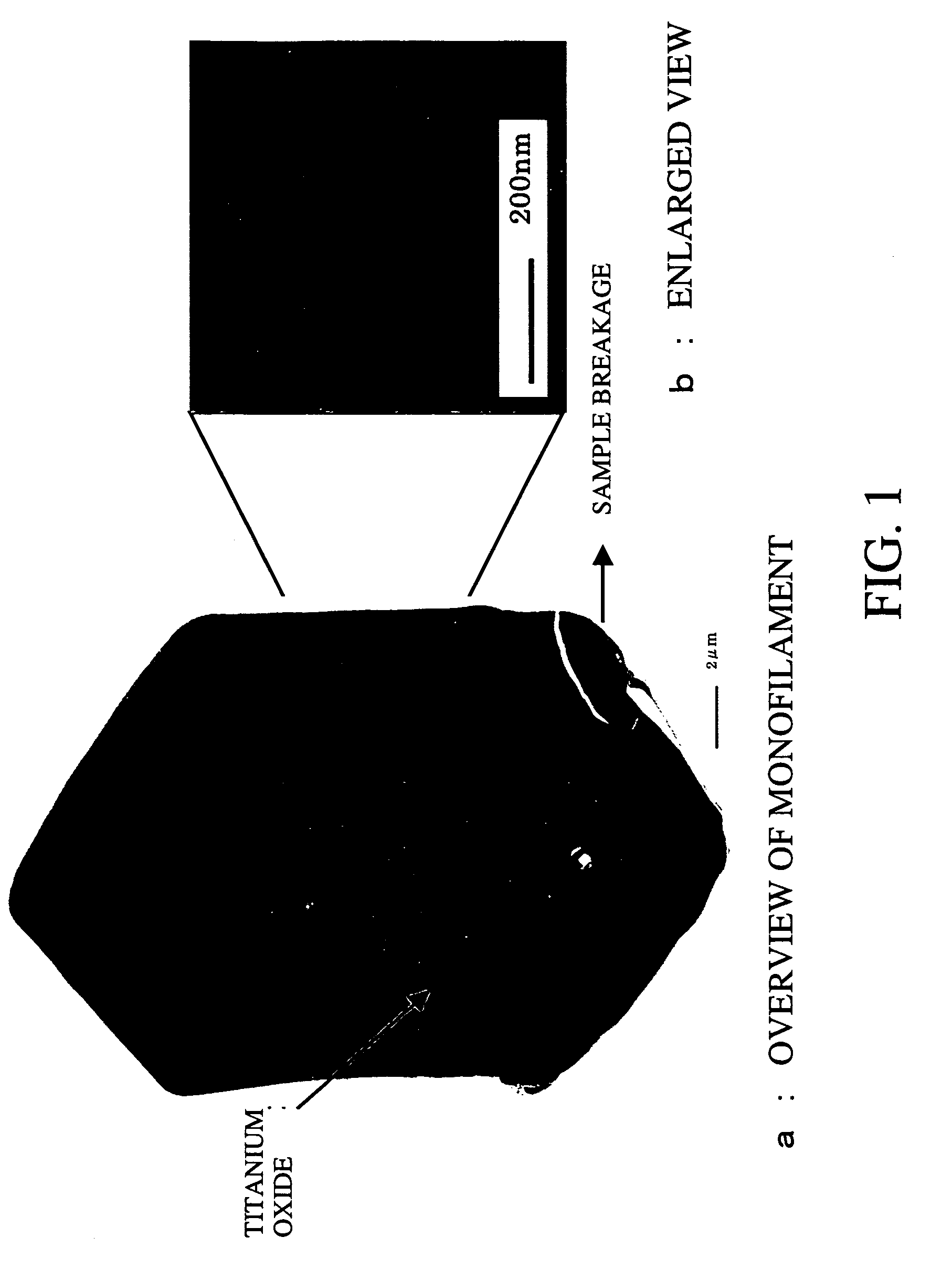
This invention relates to a method for preparing fiber TiO2, SnO2 and its doped compound material characterizing in utilizing a fiber material as a template, taking TBT, titanium tetrahalide, tin tetrachloride or a mixture as a precursor, which is carried by nitrogen or argon and enters into a reactor with a gas containing ammonia for chemical gaseous phase deposition, in which, the gas flow, deposition temperature and the sinter atmosphere and temperature are controlled, the inert gas is heated to get load-type fiber material to be sintered under the atmosphere of oxidation and reaction to remove the fiber template and form an oxide fiber material, and utilize the active carbon fiber template and ignition process to form porous fiber or tubular fiber material.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing polyimide porous nanofiber electrode diaphragm
ActiveCN104752665AImprove stabilityHigh mechanical strengthHybrid capacitor separatorsCell component detailsMetal oxide nanoparticlesAcid anhydride formation
The invention discloses a method for preparing a polyimide porous nanofiber electrode diaphragm. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out condensation reaction by adopting binary organic amine and binary organic acid anhydride in an organic solvent, thereby obtaining a polyamide acid solution; adding a soluble metal salt to prepare a spinning precursor, preparing a polyamide acid-metal salt electrostatic spinning fiber diaphragm by virtue of high-voltage electrostatic spinning, and performing thermal imidization treatment, thereby obtaining a polyimide-metallic oxide fiber composite diaphragm; and dissolving the composite diaphragm in an inorganic acid aqueous solution for performing acid treatment, so that metallic oxide nanoparticles are converted into soluble metal salts so as to be dissolved in the inorganic acid aqueous solution so as to obtain the polyimide nano / micron porous fiber diaphragm. The method has the advantages that according to the polyimide nano / micron porous fiber diaphragm, the mechanical strength, thermal stability, liquid holdup, permeability, wettability and migration rate of conductive ions of the diaphragm can be effectively improved, and the liquid junction resistance of the diaphragm and electrolyte and the contact resistance of the diaphragm and the electrode can be reduced, so that the electrochemical performance of a supercapacitor is improved.
Owner:锦州凯美能源有限公司
Method for preparing macromolecule hollow porous fiber membrane by using chemical reaction inductive phase conversion method
InactiveCN103212302AImprove performanceIncrease membrane fluxSemi-permeable membranesPhase conversionHollow fibre
The invention discloses a method for preparing a macromolecule hollow porous fiber membrane by using a chemical reaction inductive phase conversion method, and belongs to the field of membrane preparation. The method for preparing the macromolecule hollow porous fiber membrane by using the chemical reaction inductive phase conversion method comprises the following steps of: preparing a homogeneous membrane casting liquid; extruding the membrane casting liquid and a core liquid from a spinning nozzle, and forming a membrane in outer gel bath; and carrying out chemical post treatment on the prepared membrane, so as to obtain the hollow porous fiber membrane which is uniform in pore diameter, high in membrane flux and high in pollution resistance. The method for preparing the macromolecule hollow porous fiber membrane by using the chemical reaction inductive phase conversion method, provided by the invention, is characterized in that pores are formed by chemical reaction induction through changing the composition of the core liquid and the outer gel bath or types of chemical reaction porogens and utilizing the reaction among the core liquid, the outer gel bath and the chemical porogens, and therefore, the macromolecule hollow porous fiber membrane which is uniform in pore diameter distribution, good in pollution resistance, and high in flux.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Oil-water emulsion separation membrane of metal organic framework compound/polyacrylonitrile
InactiveCN107983180AImprove oil stain resistanceEasy to separateSemi-permeable membranesMembranesYarnMetal-organic framework
The invention relates to an oil-water emulsion separation membrane of a metal organic framework compound / polyacrylonitrile. According to the oil-water emulsion separation membrane, polyacrylonitrile is used as a raw material and is prepared into a fiber membrane with the yarn diameter of about 300 nanometers and extremely high porosity by utilizing an electrostatic spinning technology; then the fiber membrane is subjected to a hydrolytic action so that functional groups including hydroxyl, carboxyl and the like are formed on surfaces of fibers; furthermore, the fiber membrane and amino on hydrophilic UIO-66-NH2 can form hydrogen bonding and electrostatic adsorption; finally, a porous fiber membrane with a hydrophilic multi-grade structure is prepared. The porous fiber membrane can be usedfor carrying out efficient separation on oil-water emulsion and has extremely low oil adhesion and relatively high oil stain resistance; furthermore, a preparation method of the oil-water emulsion separation membrane is simple and feasible, is safe and environmentally friendly and has very good application value.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Holey fiber and method of manufacturing the same
A holey fiber includes a core region and a cladding region surrounding the core region and having air holes arranged around the core region. The cladding region includes an inner cladding layer surrounding the core region and an outer cladding layer surrounding the inner cladding layer. Furthermore, viscosities of the core region and the inner cladding layer are set lower than a viscosity of the outer cladding layer.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Functional porous fibres
InactiveUS20060099414A1Ion-exchanger regenerationMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentOrganic compoundActive particles
The invention relates to a method for the preparation of porous polymeric fibres comprising functionalized or active particles. By extruding a mixture of one or more dissolved polymers with particulate material a porous fibre is obtained in which the particulate material is entrapped. Extrusion of the fibre occurs under two-step phase inversion conditions. In particular the porous fibres can be used for the isolation of macromolecules such as peptides, proteins, nucleic acids or other organic compounds from complex reaction mixtures, in particular from fermentation broths. Another application is the immobilization of a catalyst in a reaction mixture.
Owner:NEOKIDNEY HLDG
Preparation method of porous fiber with controllable degradation rate for tissue engineering scaffold
InactiveCN101781815AEasy to prepareLow costHollow filament manufactureSurgeryDistilled waterVacuum drying
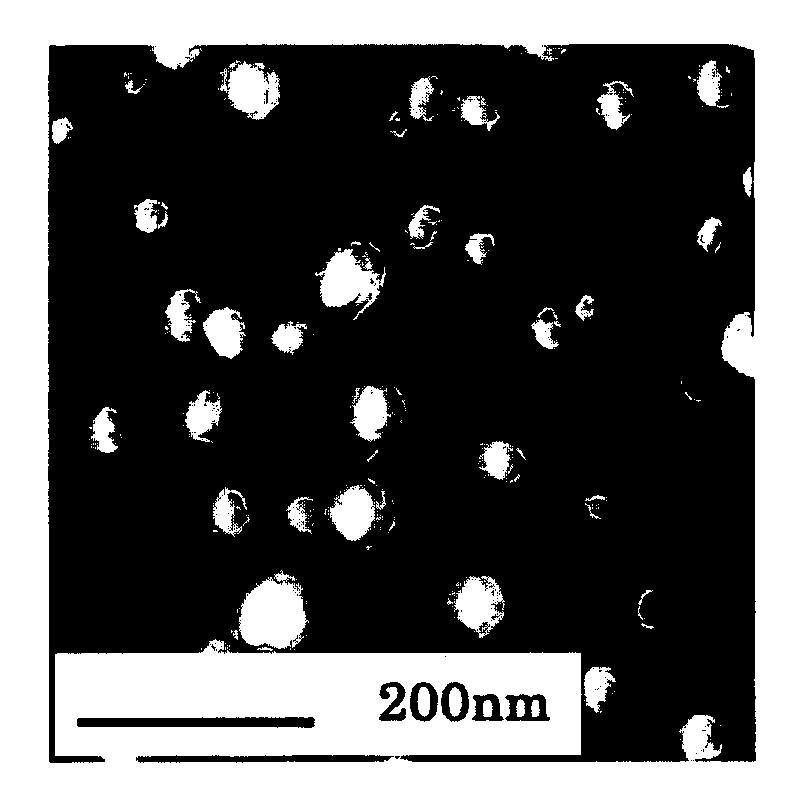
The invention relates to a preparation method of porous fiber with a controllable degradation rate for a tissue engineering scaffold, which comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing a biodegradable polymer and a pore-forming agent, vacuum drying, melt spinning, drawing, immersing into hydrochloric acid or distilled water to remove the pore-forming agent, and vacuum drying, thereby obtainingthe porous fiber with micro pores with the diameters of 10-100mum uniformly distributed on the surface thereof. The preparation method of the invention is simple and is applicable to industrial production. The diameters of the micro pores of the prepared fiber are matched with cell sizes, so that cells can be easily adhered into the micro pores on the surface of the fiber for growth. Simultaneously, the degradation rate is controllable.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Moldable composite sheet with improved adhesion at elevated service temperatures
InactiveUS20080032094A1Improved thermal adhesive characteristicImprove adhesionThin material handlingMetal layered productsThermoplasticMetal forming
A moldable composite sheet having improved adhesion characteristics, particularly at elevated service temperatures, as well as improved sound absorption and attenuation of transmitted sound intensities. In one aspect, the composite sheet may be a porous fiber-reinforced thermoplastic comprising discontinuous reinforcing fibers and having an adhesive skin layer covering. Generally, the-composite sheet may have a void content or porosity from about 5% to about 95% by volume of the sheet, an areal weight between about 400 g / m2 to about 4000 g / m2 and a fiber content from about 20% to about 98% by weight. The composite sheet can be molded via low pressure processes, such as thermoforming, match metal molding on stops, vacuum forming and pressure forming, to produce durable automotive interior trim parts capable of withstanding service temperatures exceeding 100° C. for extended periods of time along with improved sound absorption capabilities exceeding a noise reduction coefficient (NRC) rating of 0.5.
Owner:AZDEL INC
Fibril solar cell and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050194035A1Reduce manufacturing costHigh light conversion efficiencyLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureFibrilCarbon nanotube
A fibril solar cell includes: a fiber-shaped inner core having a porous fiber composed of first carbon nanotubes and a cathode material, in which pores of the porous fiber are filled with second carbon nanotubes, titanium dioxide, a photosensitive dye, and an electron transfer electrolyte; a photoconductive layer formed on a surface of the fiber-shaped inner core and composed of at least one photoconductive polymer; a transparent electrode layer formed on a surface of the photoconductive layer; and a transparent protective layer formed on a surface of the transparent electrode layer and composed of at least one transparent polymer. The fibril solar cell can be mass-produced inexpensively using a polymer. Also, the fibril solar cell has a high efficiency and can be converted into various shapes. The fibril solar cell can be attached to clothing, and be used as a portable power source for mobile electronics.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Composite filtration article
InactiveUS20060070950A1Reduce porosityIncreased operating system pressureIon-exchange process apparatusIon-exchanger regenerationParticulatesSorbent
A composite filter medium comprising a filter element comprising at least one porous fibrous filtration layer, and at least one layer of a sorbent, stationary phase particulates selected from organic or inorganic particulates having an average diameter of less than 50 micrometers, soft particulates, and ground monolithic particulates. The particulates are capable of binding target molecule by, for example, adsorption, ion exchange, hydrophobic binding, and affinity binding. The particulates provide higher binding capacities than can be achieved using filter media incorporating conventional process scale chromatography resin particulates.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method of increasing loft in a porous fiber reinforced thermoplastic sheet
A method of fabricating a porous, fiber-reinforced thermoplastic sheet having increased lofting properties is provided. The method includes adding reinforcing fibers having an average length of about 5 mm to about 50 mm, and thermoplastic resin powder particles to an agitated aqueous foam to form a dispersed mixture, laying the dispersed mixture of reinforcing fibers and thermoplastic resin particles down onto a support structure, evacuating the water to form a web, generating a z-axis orientation of a portion of the reinforcing fibers, heating the web above the glass transition temperature of the thermoplastic resin, and pressing the web to a predetermined thickness to form a porous thermoplastic composite sheet having a void content of about 1 percent to about 95 percent.
Owner:AZDEL INC
Method for cleaning hollow tubing and fibers
InactiveUS6945257B2High aspect ratioReadily flushed awayInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsSemi-permeable membranesHollow fibreProduct gas
Hollow porous fibers containing adhered contaminants are cleaned to remove the contaminants by backflushing a liquid to fill the pores, and adding a flow of gas so as to form a two-phase mixture of gas and bubbles of liquid that can scrub the fibers, loosening the contaminants and allowing them to be flushed from the hollow fibers. The method is particularly useful for cleaning hemodialyzers used for dialysis and hollow fiber modules used in water treatment and separations. The two phase flow method is specifically effective in cleaning piping systems having high length to diameter (l / d) ratios.
Owner:NOVAFLUX INC
Nano carbon-doped porous fiber single electrode, membrane electrode and preparation method
InactiveCN105261767AQuality improvementLight in massMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesElectrospinningNanofiber
The invention relates to a nano carbon-doped porous fiber single electrode, a membrane electrode and a preparation method. According to the nano carbon-doped porous fiber single electrode, a semi-ordered porous nano fiber thin film is deposited at one side of a gas diffusion layer material; and a layer of metal nanoparticles with catalytic activity is evenly deposited on the nanofiber surface of the semi-ordered porous nano fiber thin film to form the nano carbon-doped porous fiber single electrode, wherein the semi-ordered porous nano fiber thin film is formed by a co-spun high-molecular polymer nano charged superfine fiber attached with a nano carbon material on the surface, and comprises a co-spun high-molecular polymer doped with the nano carbon material as the component. According to the nano carbon-doped porous fiber single electrode, the semi-ordered porous nano fiber layer is formed by the nano carbon material and a high-molecular polymer solution through electrostatic spinning and cospinning for the first time; a catalyst is sprayed on the porous nano fiber layer; and a mico-pore layer and a catalyst layer are combined into one, so that the properties of a prepared single battery are greatly improved; and the lifetime is greatly prolonged.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Mineral micro powder lasting aldehyde and odor removing bag
The invention relates to a lasting aldehyde and odor removing bag with mineral micro powder which is a solid control product for removing air odor pollutions, i.e. formaldehyde, benzene, TVOC, and the like which are generated due to decoration. The lasting aldehyde and odor removing bag with the mineral micro powder is formed in such a way that aldehyde and odor removing mineral micro powder is manufactured into swelling hollow beads (strips), and then the swelling hollow beads (strips) are respectively packaged into porous fibre bags. The swelling hollow beads (strips) are prepared from the follow four groups of components: 60-98 percent of mineral micro powder combined by one or several of meerschaum with the particle diameter of 500-2000 meshes, fluorspar, sodium bentonite, kaoline, diatomite, activated clay, tourmaline powder, white mica power, titanium pigment, expansion graphite, corundum, and the like, 1-40 percent of aldehyde and odor removing matters, 0.01-5 percent of bonding agent, and the balance of 5-15 percent of water. The lasting aldehyde and odor removing bag with the mineral micro powder can be conveniently and neatly placed at air pollution sources, thereby achieving the purpose of lasting aldehyde and odor removal.
Owner:王岚
Porous silicon carbide fibers and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101876095ALarge specific surface areaRealize electrospinningSpinning head liquid feederFilament/thread formingElectrospinningFractionation
The invention discloses porous SiC fibers and a preparation method thereof. The porous SiC fibers are characterized in that the content of Si accounts for 50-60wt%, the content of C accounts for 30-40wt%, and the balance is O, the fibers are felty, the diameter of the fibers is 0.5-2.0 mu m, the porosity is greater than 60vol%, wherein the mesopore volume is greater than 50vol%, and the specific surface area is 400-800 m<2> / g. The preparation method is characterized in that poly carbon silicon alky suspension solution which can spin electrically is prepared by utilizing a precipitation fractionation principle, electrostatic spinning of the extremely dilute carbon silicon alky solution is realized, a large number of mesopore structures are introduced, thus firstly preparing poly carbon silicon alky porous fibers, and then after non-melting and sintering, the porous SiC fibers are prepared. The porous SiC fibers have good application prospects in fields such as high-temperature catalysis, heat insulation, heat preservation, sound insulation and the like. The method has universality and can be used for realizing electrostatic spinning of extremely dilute solution of other precursor polymers and for preparing corresponding porous ceramic fibers.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Fiber-reinforced, porous, biodegradable implant device
InactiveUS7524335B2Promote regenerationProvide strengthBone implantLaminationArticular cartilageInorganic particle
A fiber-reinforced, polymeric implant material useful for tissue engineering, and method of making same are provided. The fibers are preferably aligned predominantly parallel to each other, but may also be aligned in a single plane. The implant material comprises a polymeric matrix, preferably a biodegradable matrix, having fibers substantially uniformly distributed therein. Inorganic particles may also be included in the implant material. In preferred embodiments, porous tissue scaffolds are provided which facilitate regeneration of load-bearing tissues such as articular cartilage and bone. Non-porous fiber-reinforced implant materials are also provided herein useful as permanent implants for load-bearing sites.
Owner:OSTEOBIOLOGICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com