Patents
Literature
4598 results about "Thermoplastic materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermoplastic materials are those materials that are made of polymers linked by intermolecular interactions or van der Waals forces, forming linear or branched structures.
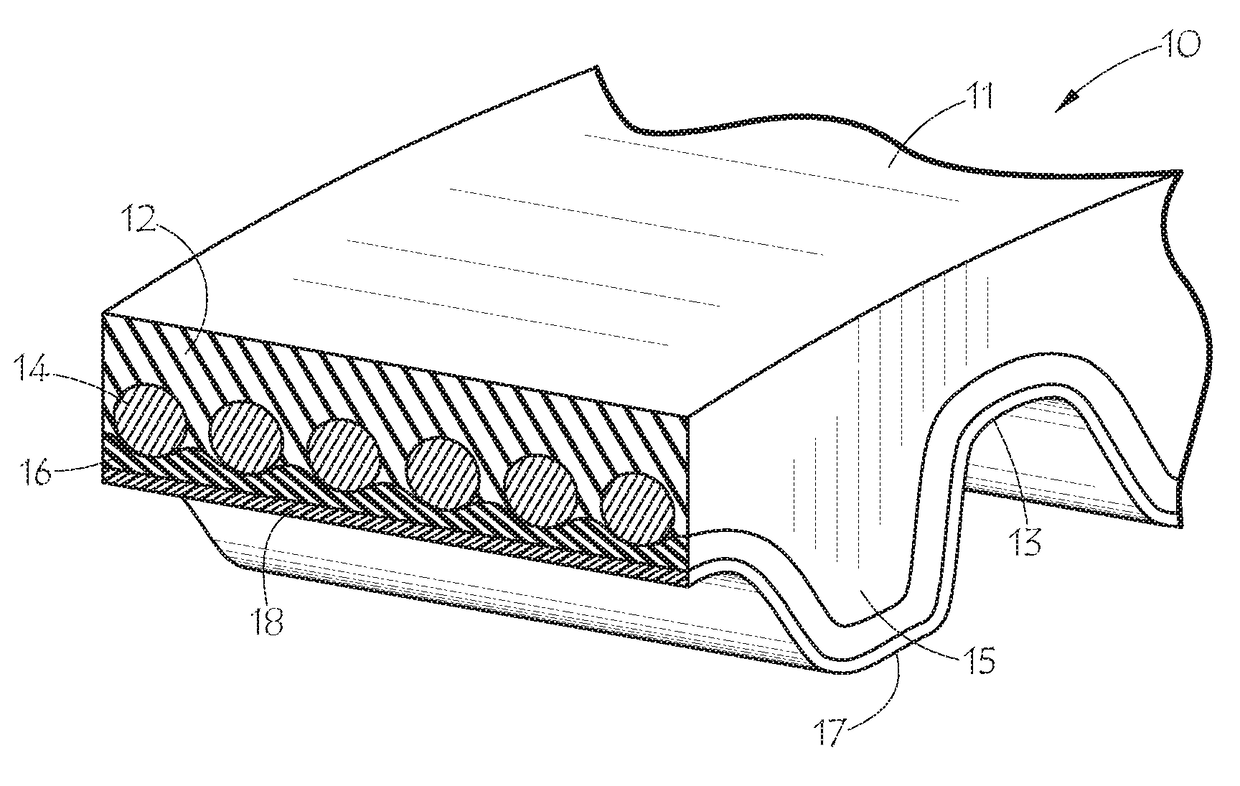
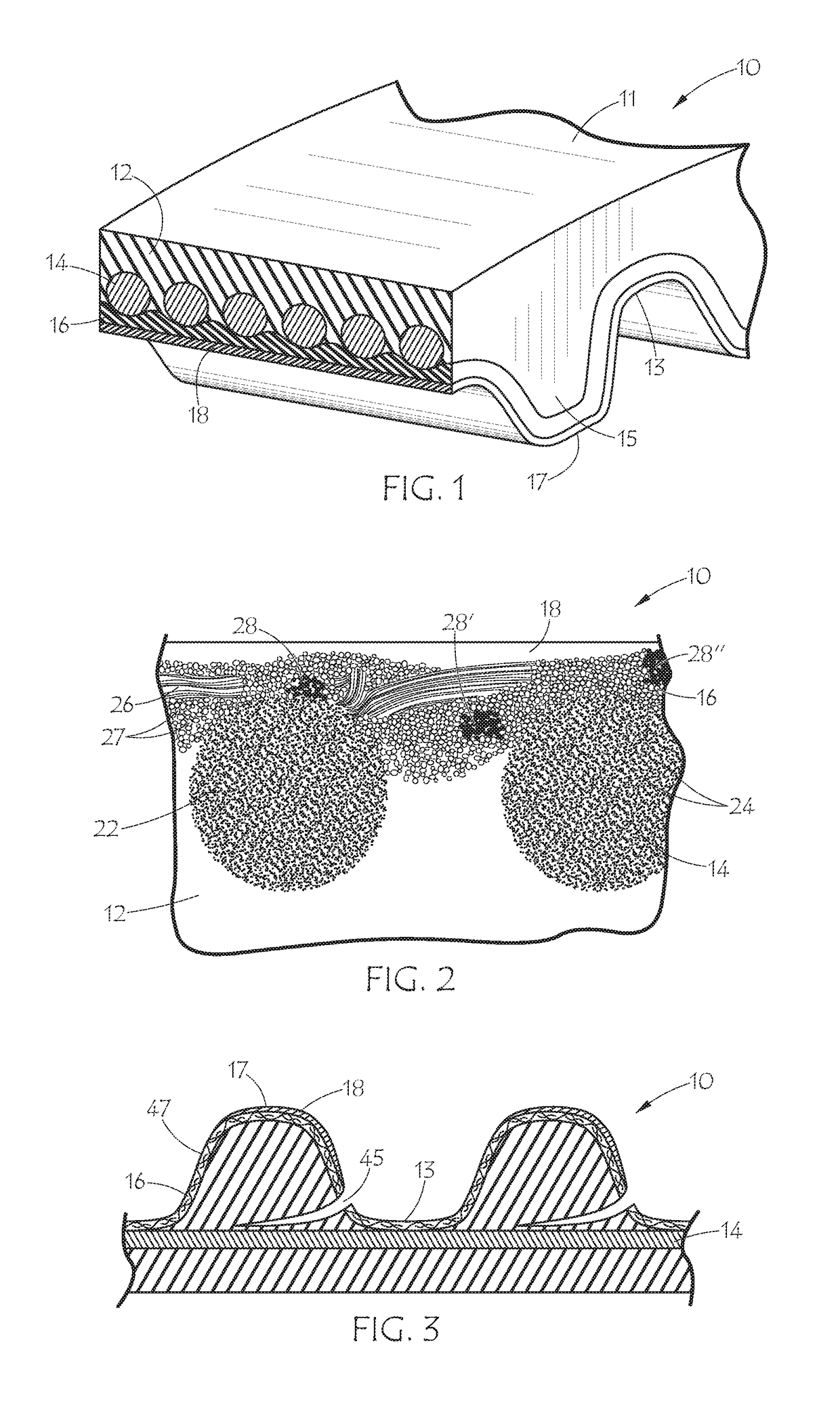
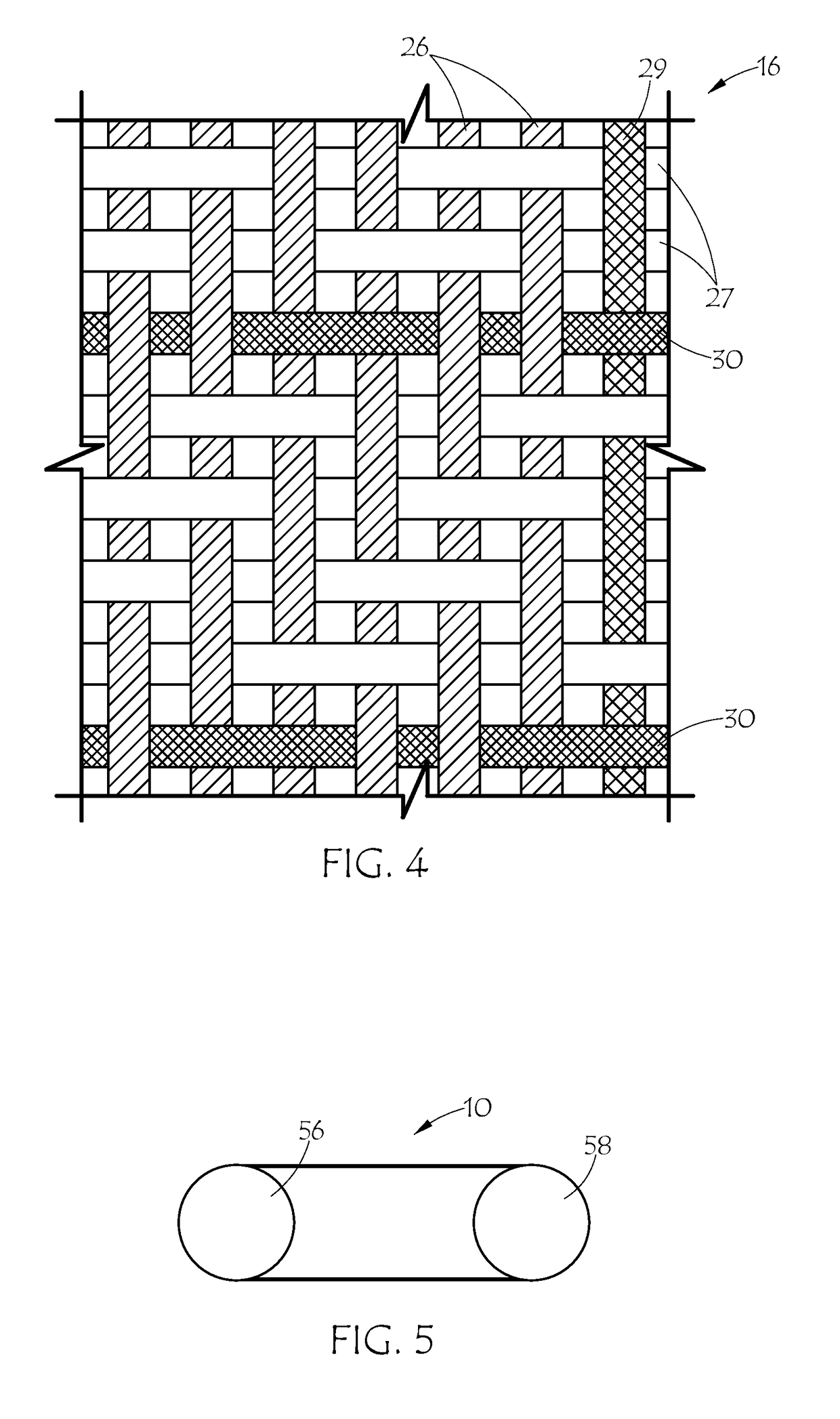
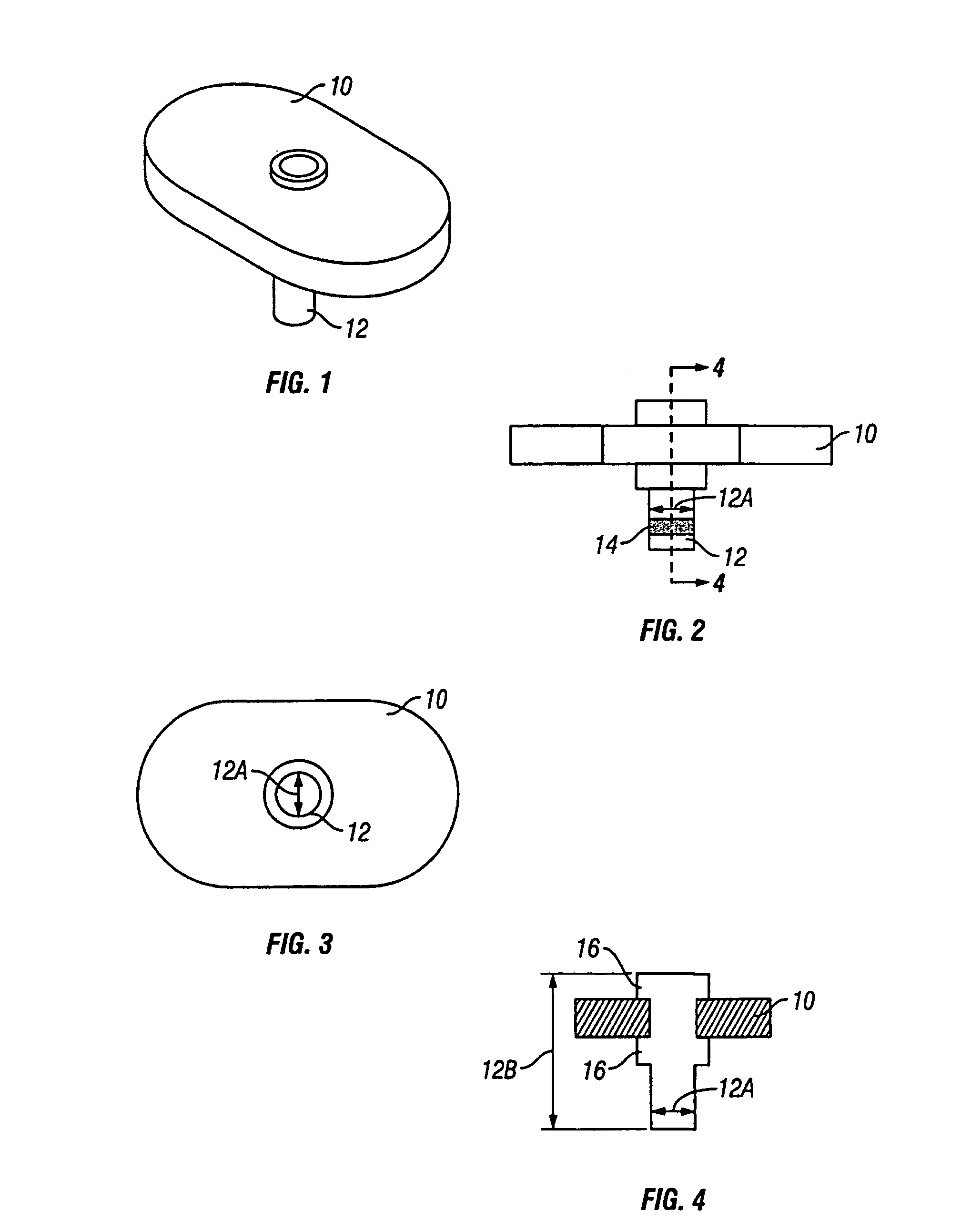
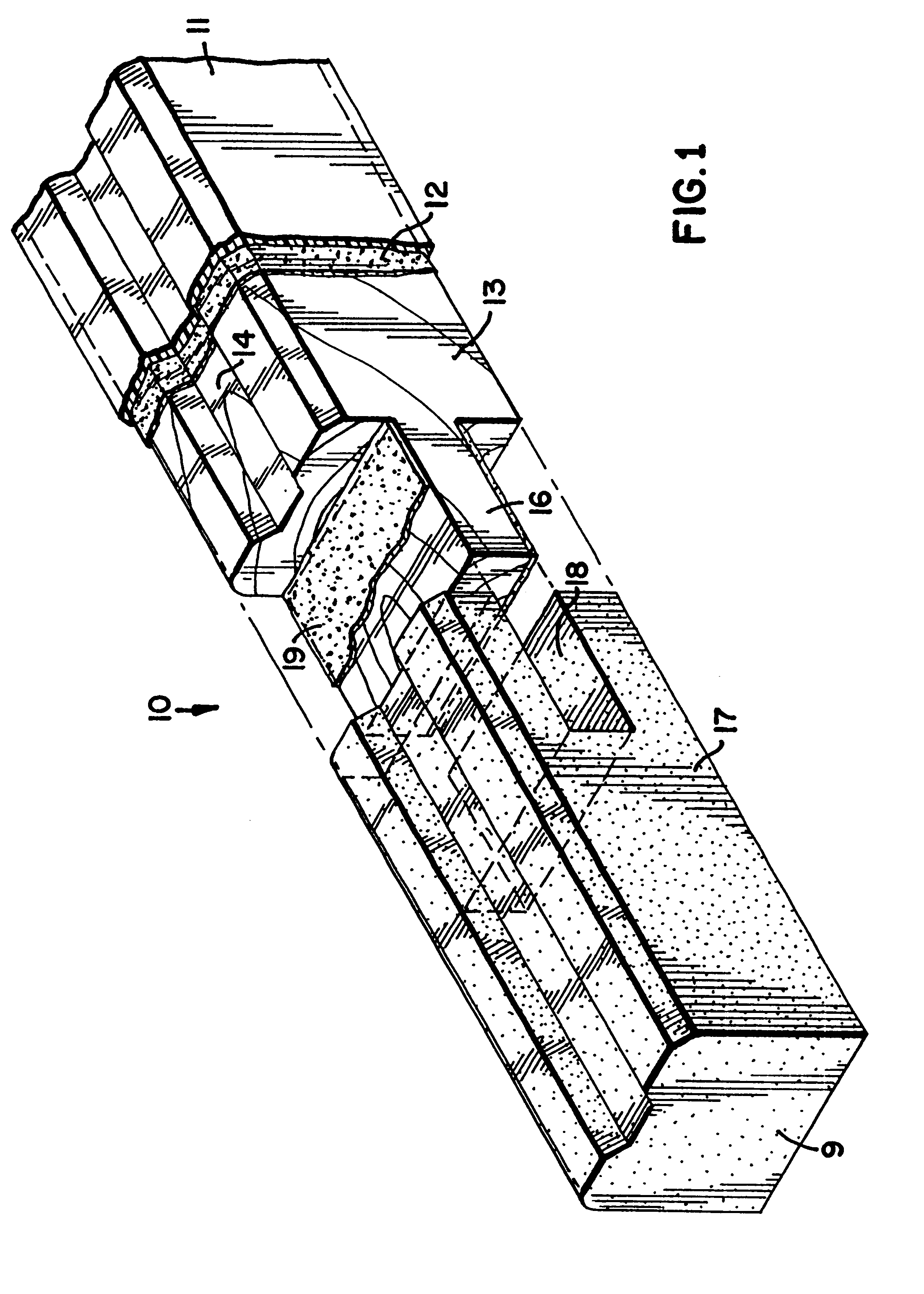
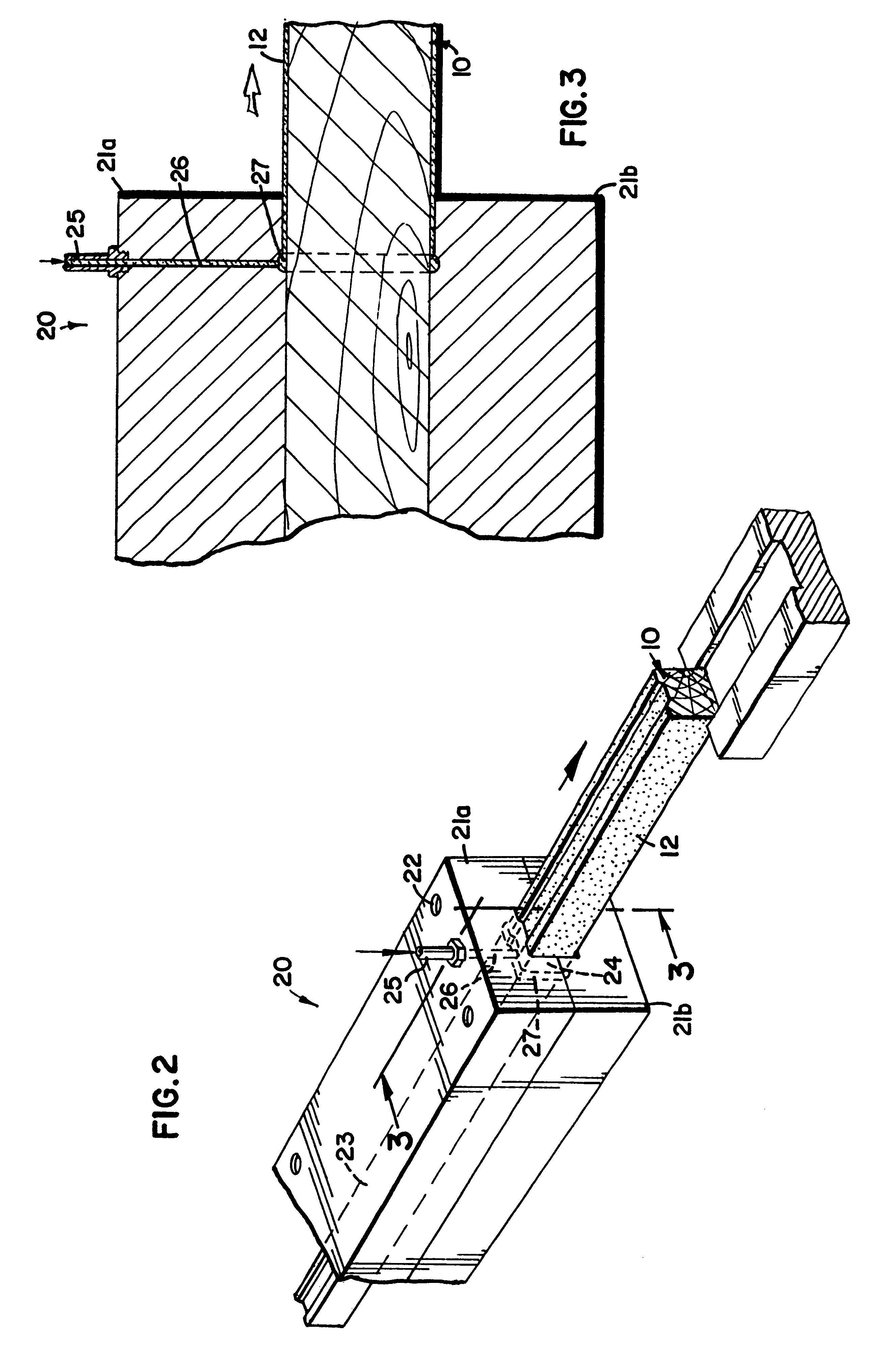
Surgical stapler and method of applying plastic staples to body tissue
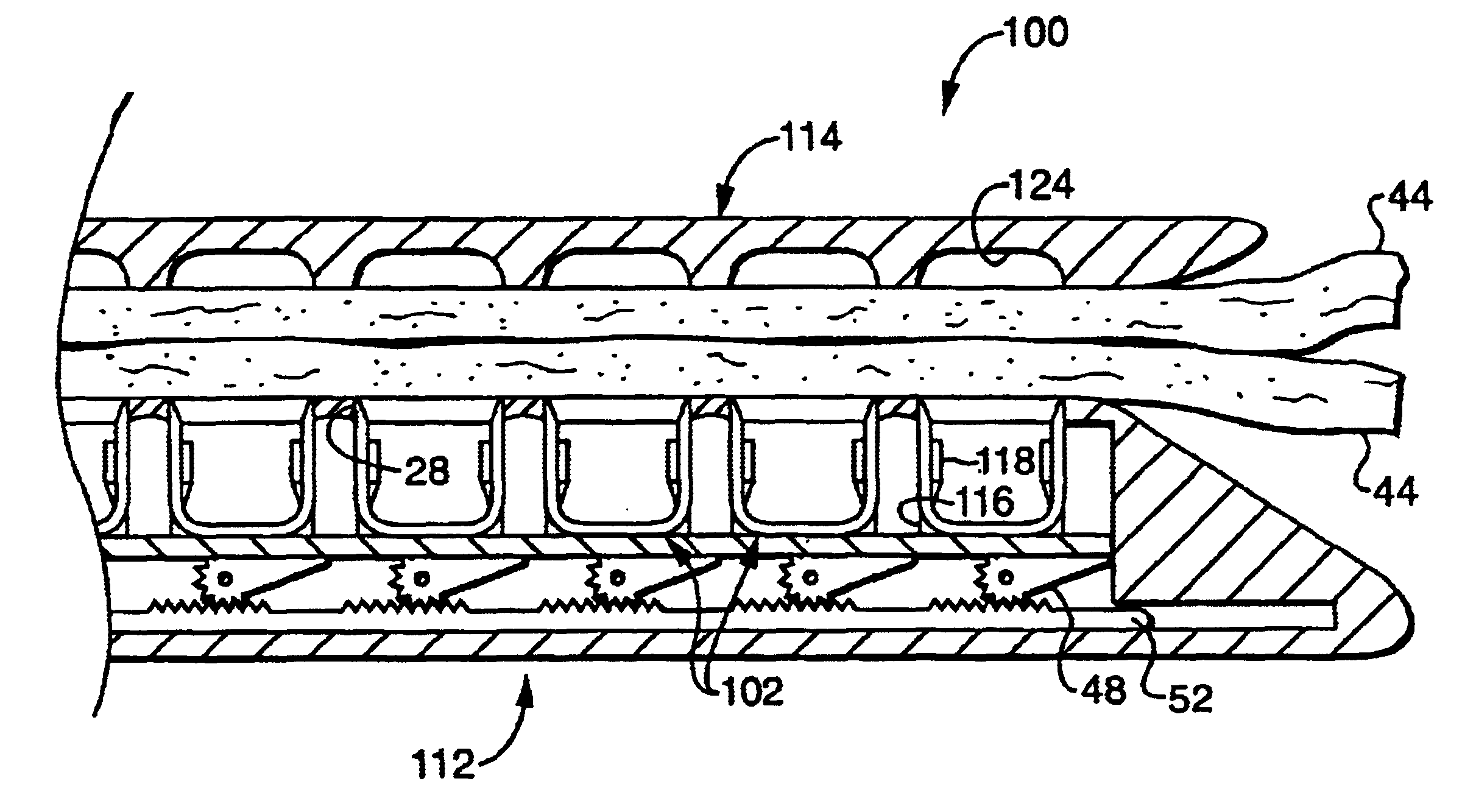
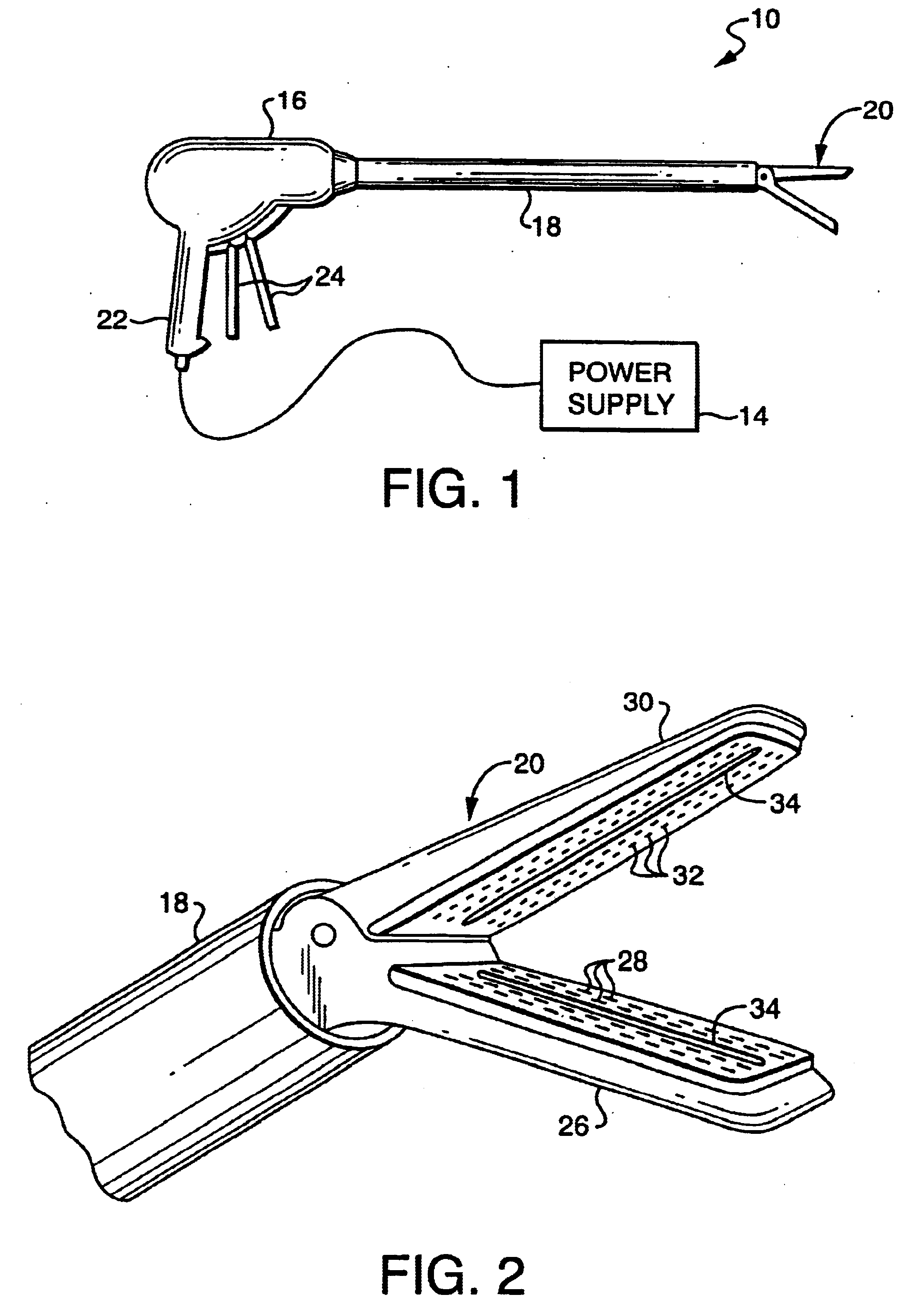
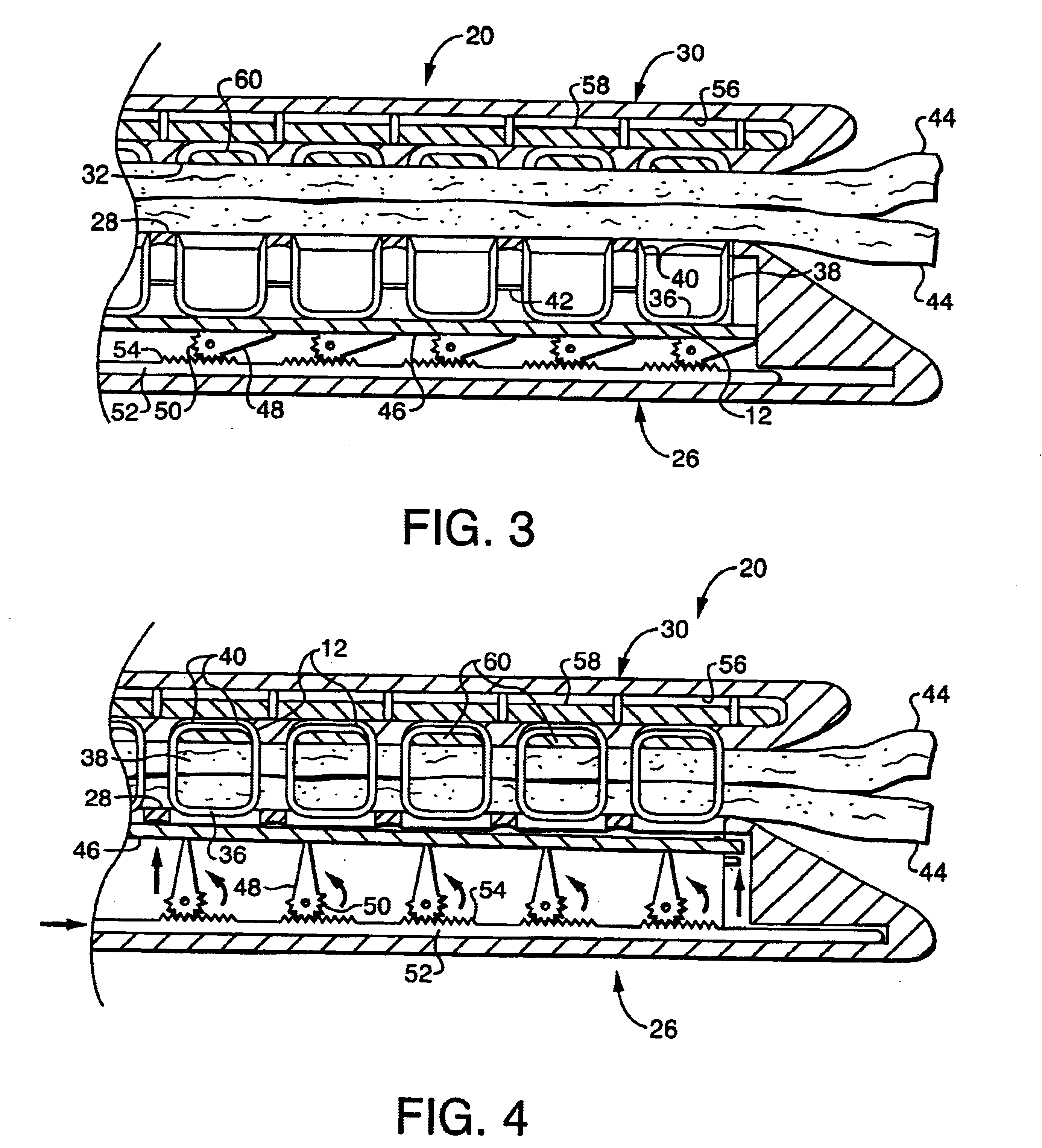
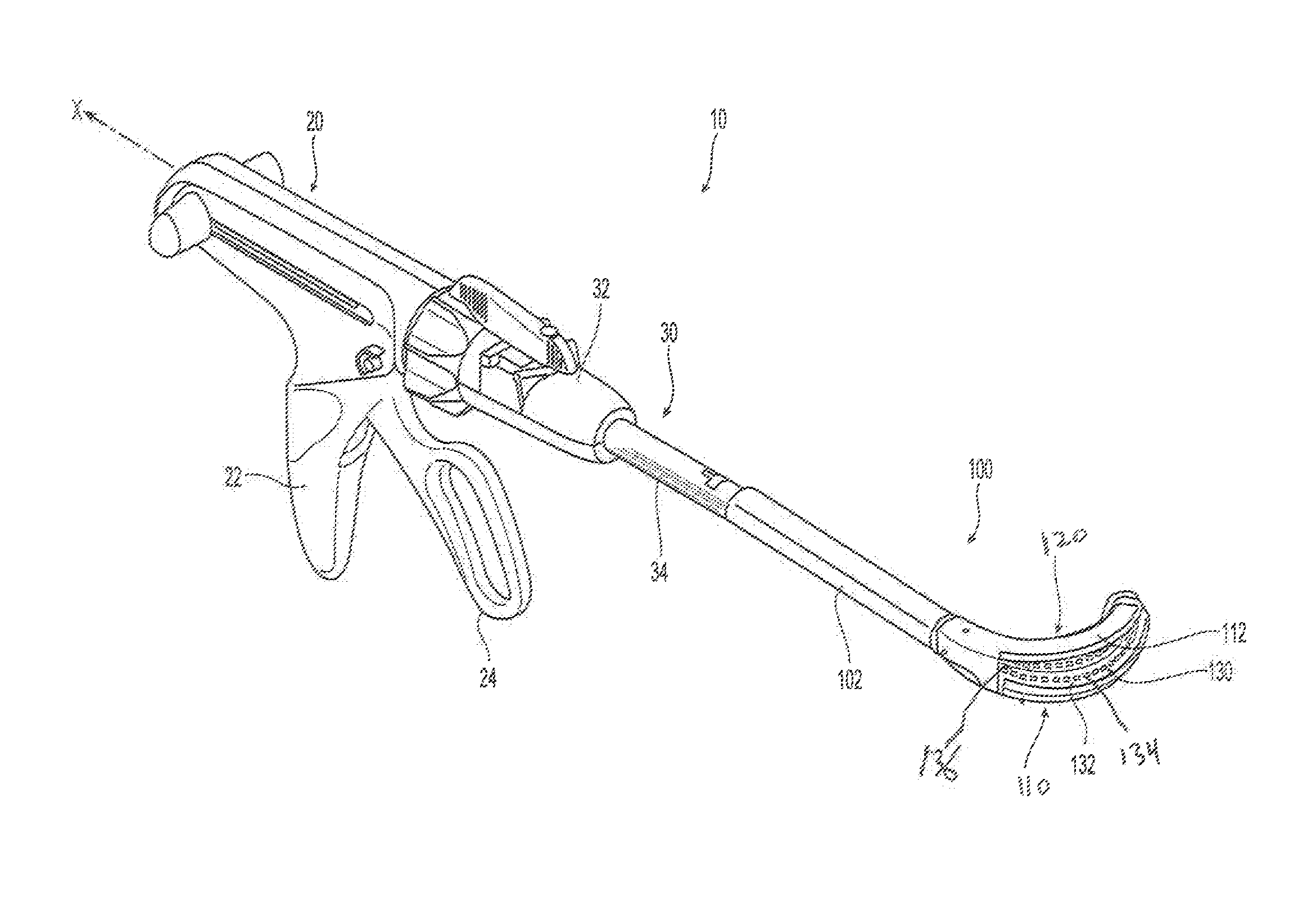
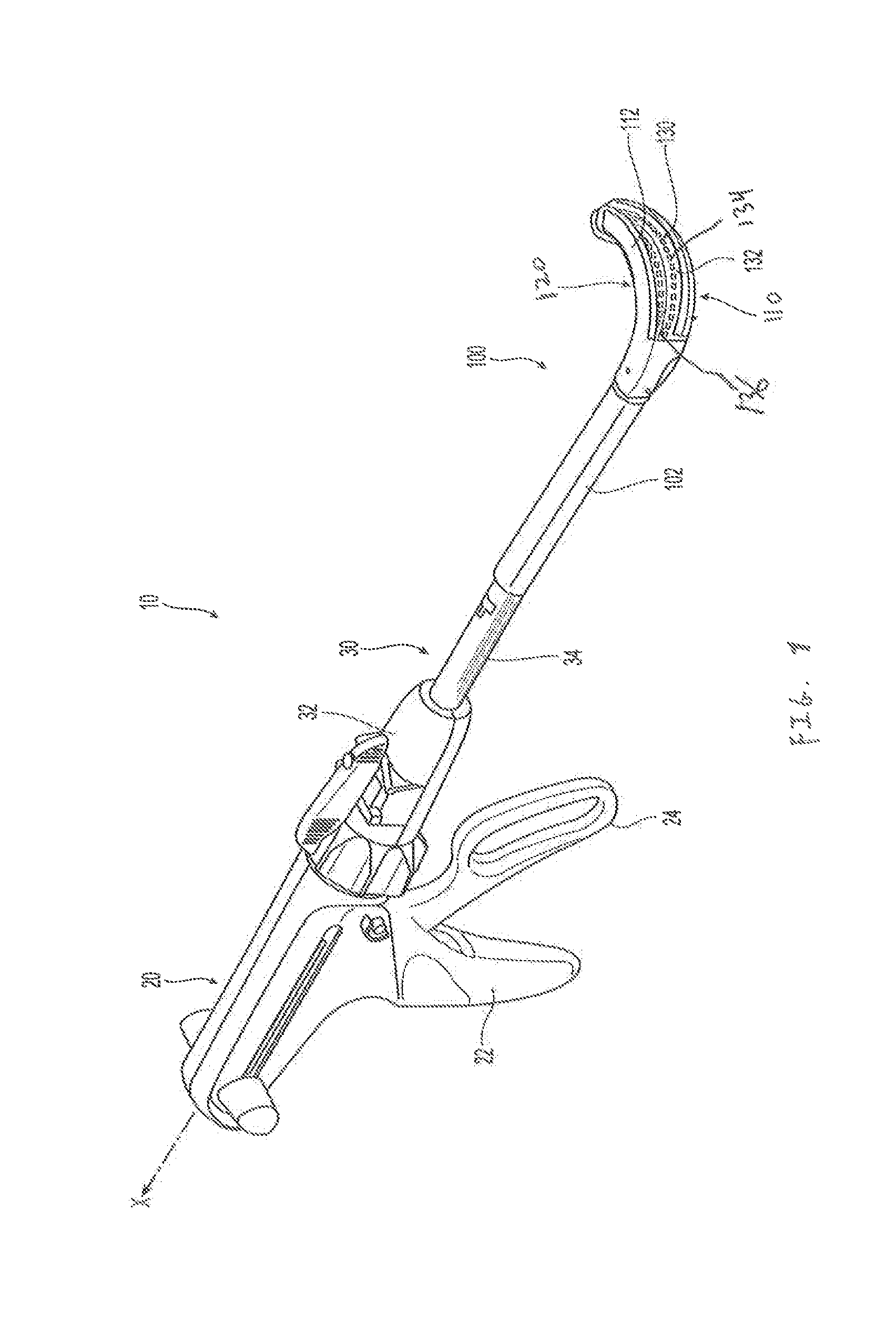
A stapler for ejecting at least one staple of resilient thermoplastic material having a base member and two legs extending from the base member to sharp ends and wherein the legs include overlapping distal portions for engaging body tissue. The stapler includes a pair of jaws movable between open and closed positions, a handle and trigger assembly for controlling operation of the jaws, an elongated tubular structure connecting the handle and trigger assembly to the jaws, an ejector for ejecting at least one staple from one of the jaws against the other of the jaws, and posts for holding normally overlapping distal portions of legs of the staple generally parallel until after the staple is ejected from the stapler.
Owner:TORNIER INC
Jaw members and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20160256159A1Domestic articlesSurgical staplesBiomedical engineeringThermoplastic materials
An anvil assembly for use with a surgical stapling instrument includes an anvil plate and an anvil cover each being fabricated from a thermoplastic material. The anvil plate includes a first surface and a second surface opposite the first surface. The first surface has a plurality of beads disposed along a periphery thereof. The anvil cover is configured to be coupled to a distal end of the surgical stapling instrument. The anvil cover includes a surface having at least one elongate surface feature disposed along a periphery thereof. The beads of the anvil plate and the elongate surface feature of the anvil cover are configured for abutting engagement upon assembly thereof.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Thermoplastic starch compositions incorporating a particulate filler component
InactiveUS6231970B1Reduce molecular weightAvoid hydrolysisProtein adhesivesPaper coatingParticulatesCross-link
Thermoplastic starch compositions that include a particulate filler, e.g. an inorganic filler component, and optional fibrous component The compositions include a thermoplastic phase comprising a thermoplastic starch melt that contains, at a minimum, starch blended with an appropriate plasticizing agent under conditions in order for the starch to form a thermoplastic melt. The thermoplastic phase may also include one or more additional thermoplastic polymers and other optional reactants, liquids or cross-linking agents to improve the water-resistance, strength, and / or other mechanical properties of the thermoplastic melt, particularly upon solidification. The inorganic filler component may affect the mechanical properties but will mainly be added to reduce the cost of the thermoplastic starch compositions by displacing a significant portion of the more expensive starch or starch / polymer melt. Fibers may optionally be included in order to improve the mechanical properties of the thermoplastic starch compositions. The thermoplastic starch compositions may be shaped into a wide variety of useful articles, such as sheets, films, containers, and packaging materials. Because the thermoplastic starch compositions will typically include a thermoplastic phase that is biodegradable, and because the other components will either constitute a naturally occurring mineral and optionally a natural fiber, the overall composition will typically be more environmentally friendly compared to conventional thermoplastic materials.
Owner:BIO TEC BIOLOGISCHE NATURVERPACKUNGEN
Multiple material golf club head
InactiveUS6491592B2Large coefficientImprove complianceMetal-working apparatusGolf clubsCoefficient of restitutionMetallic materials
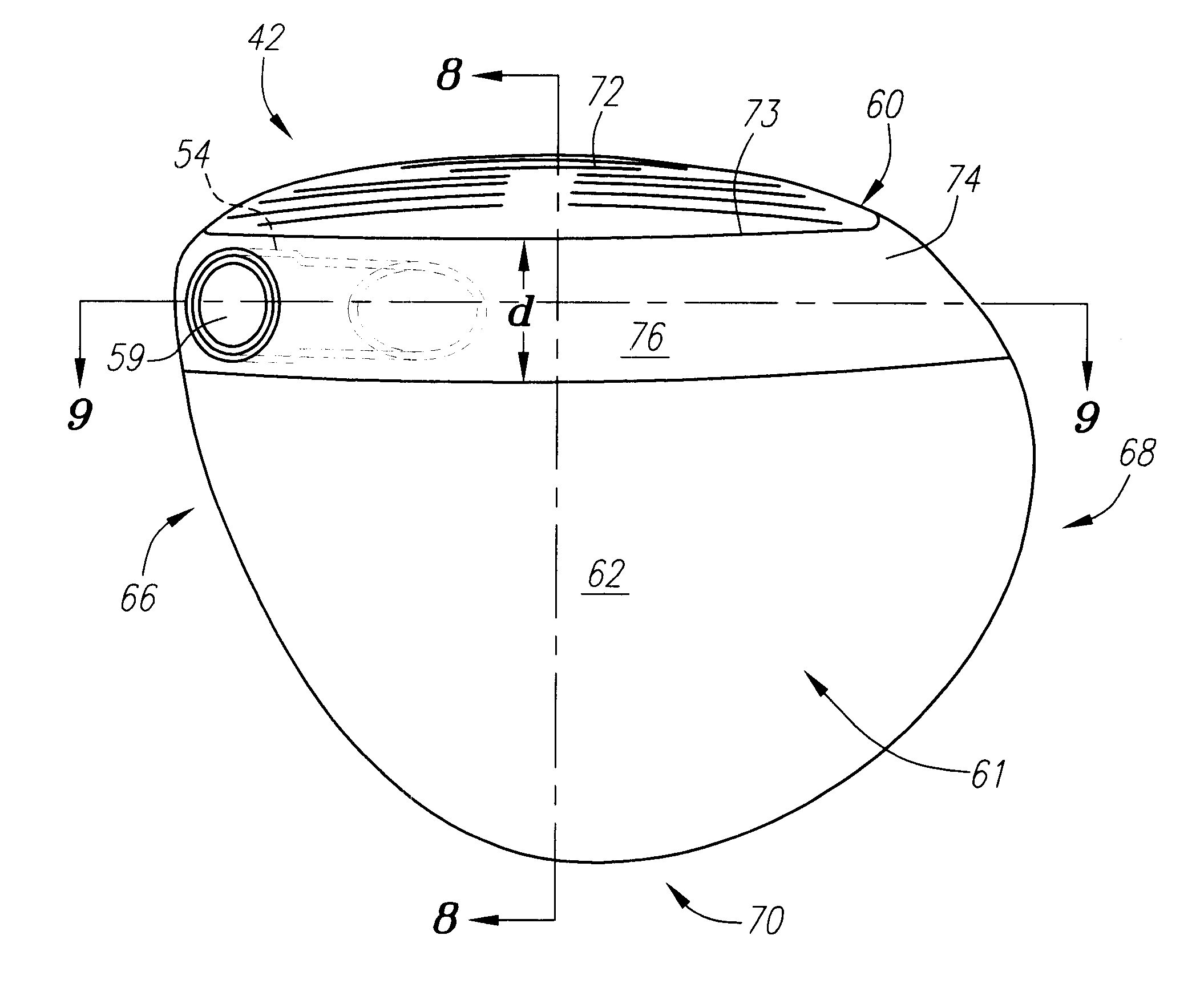
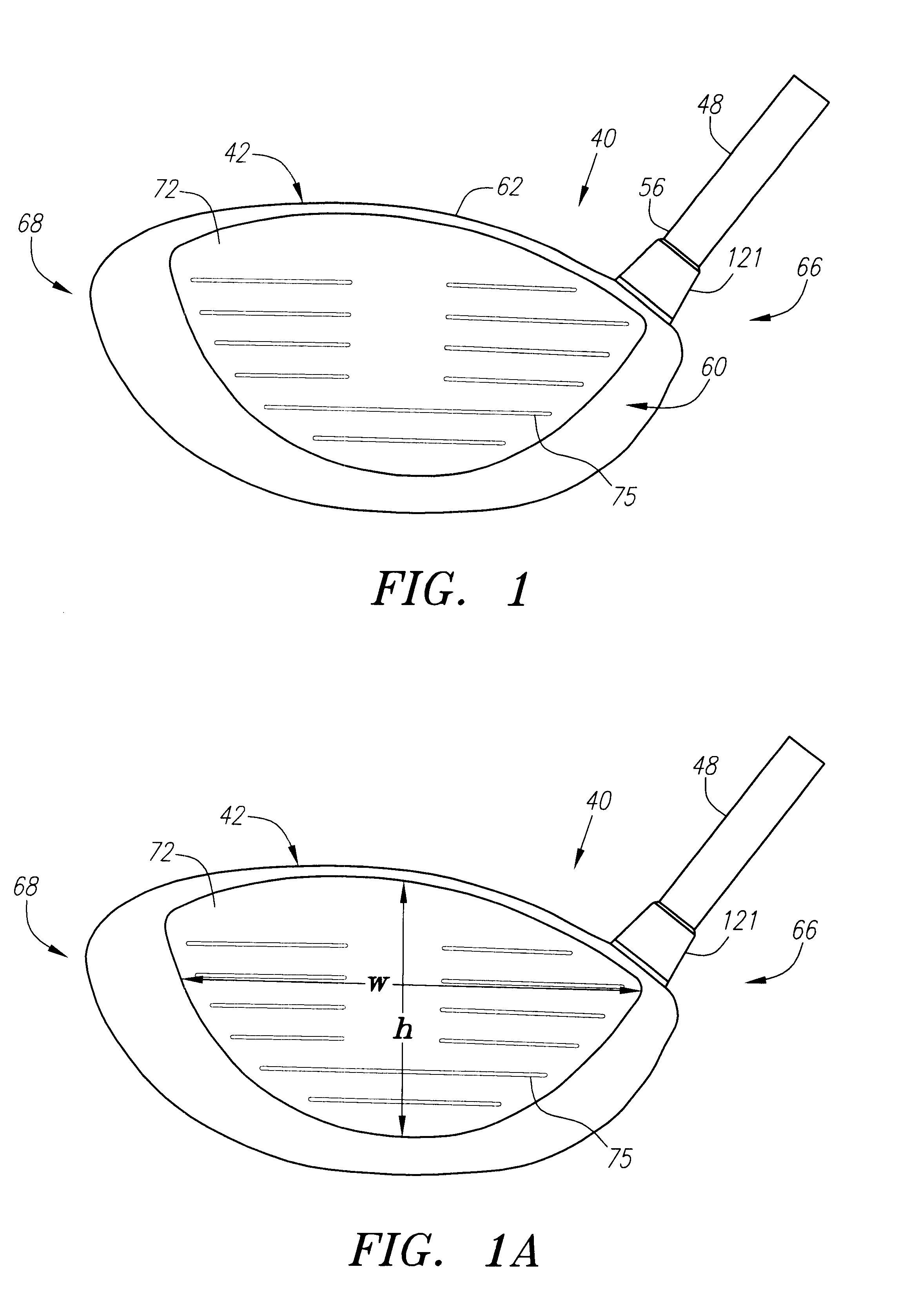
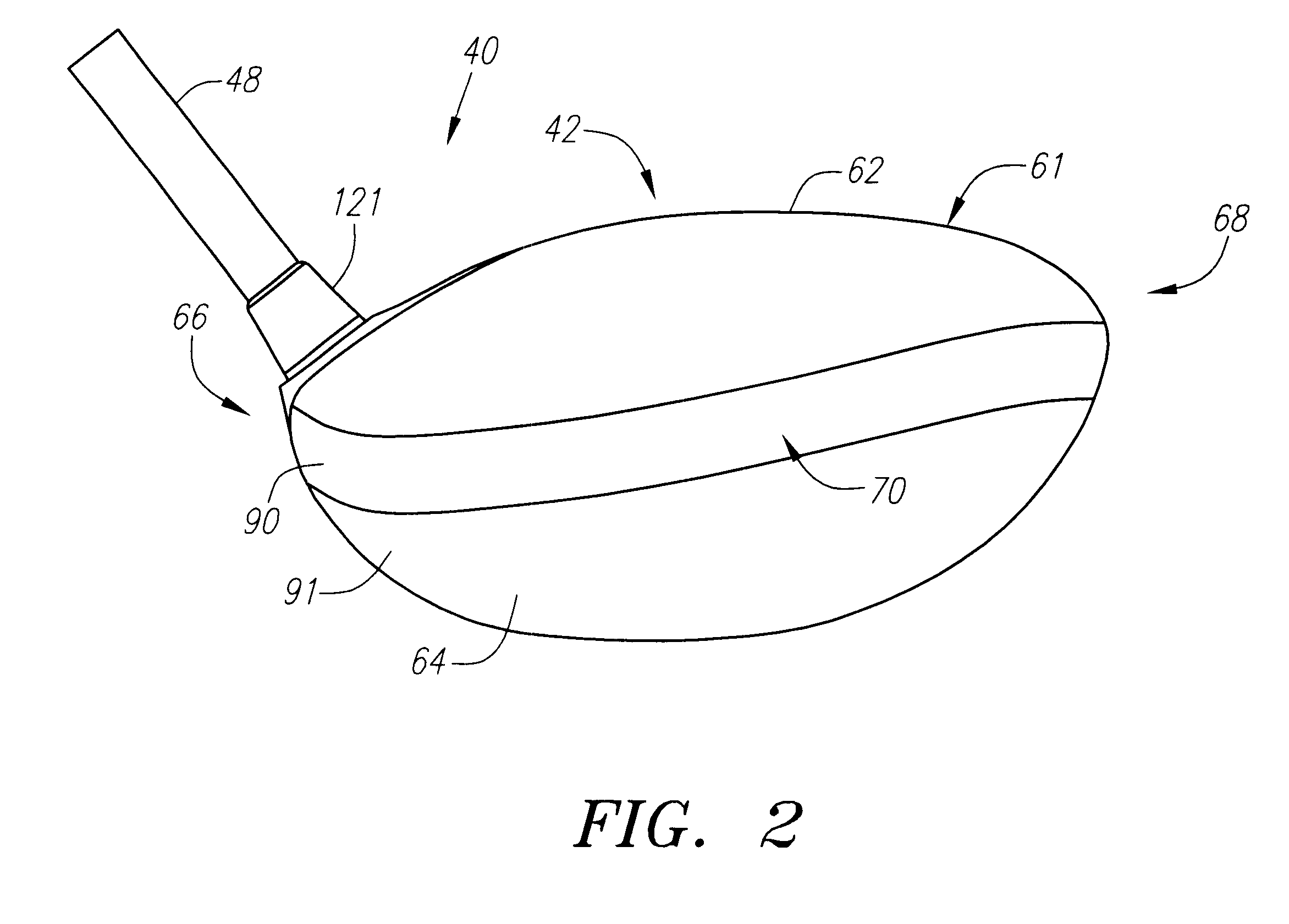
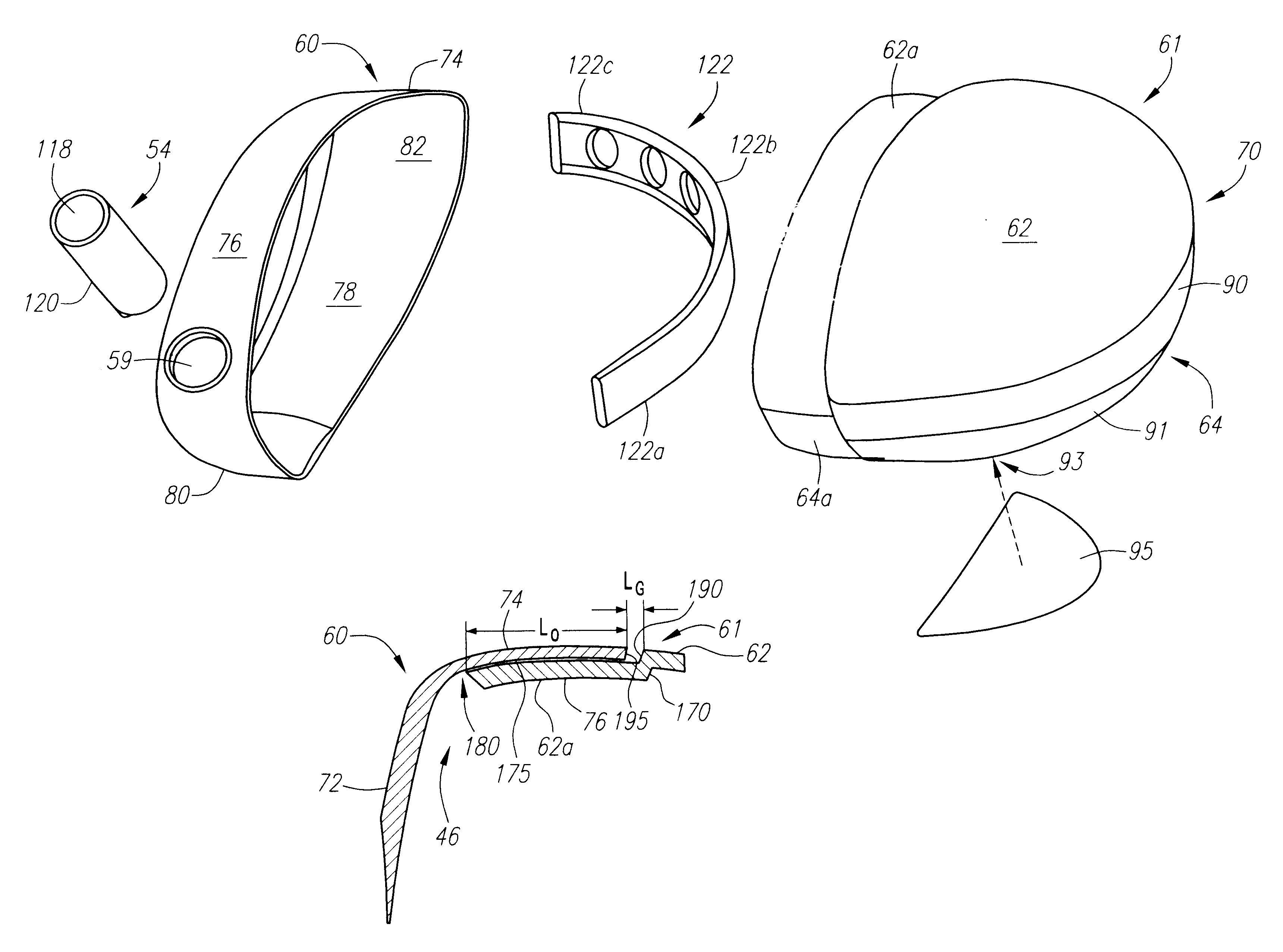
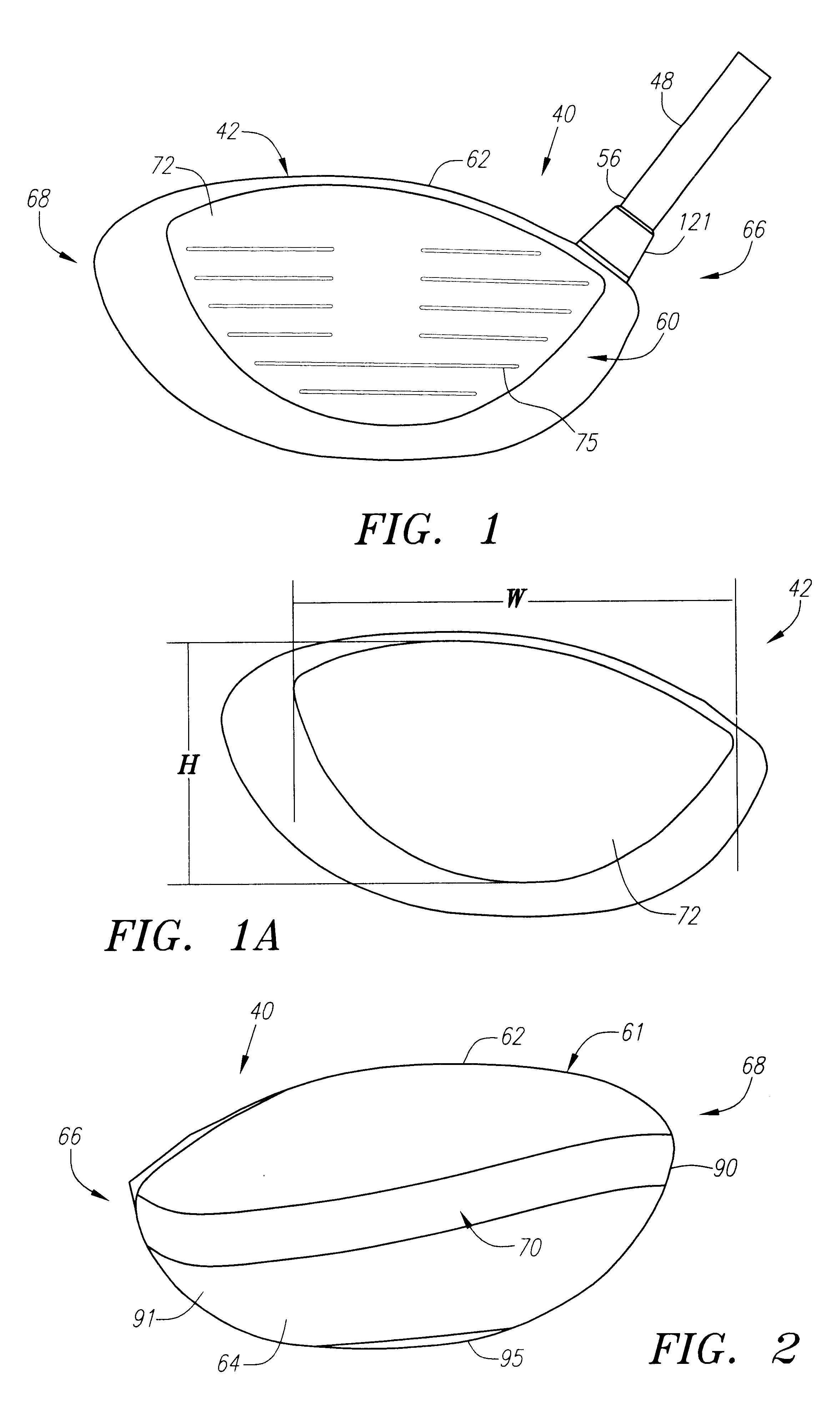
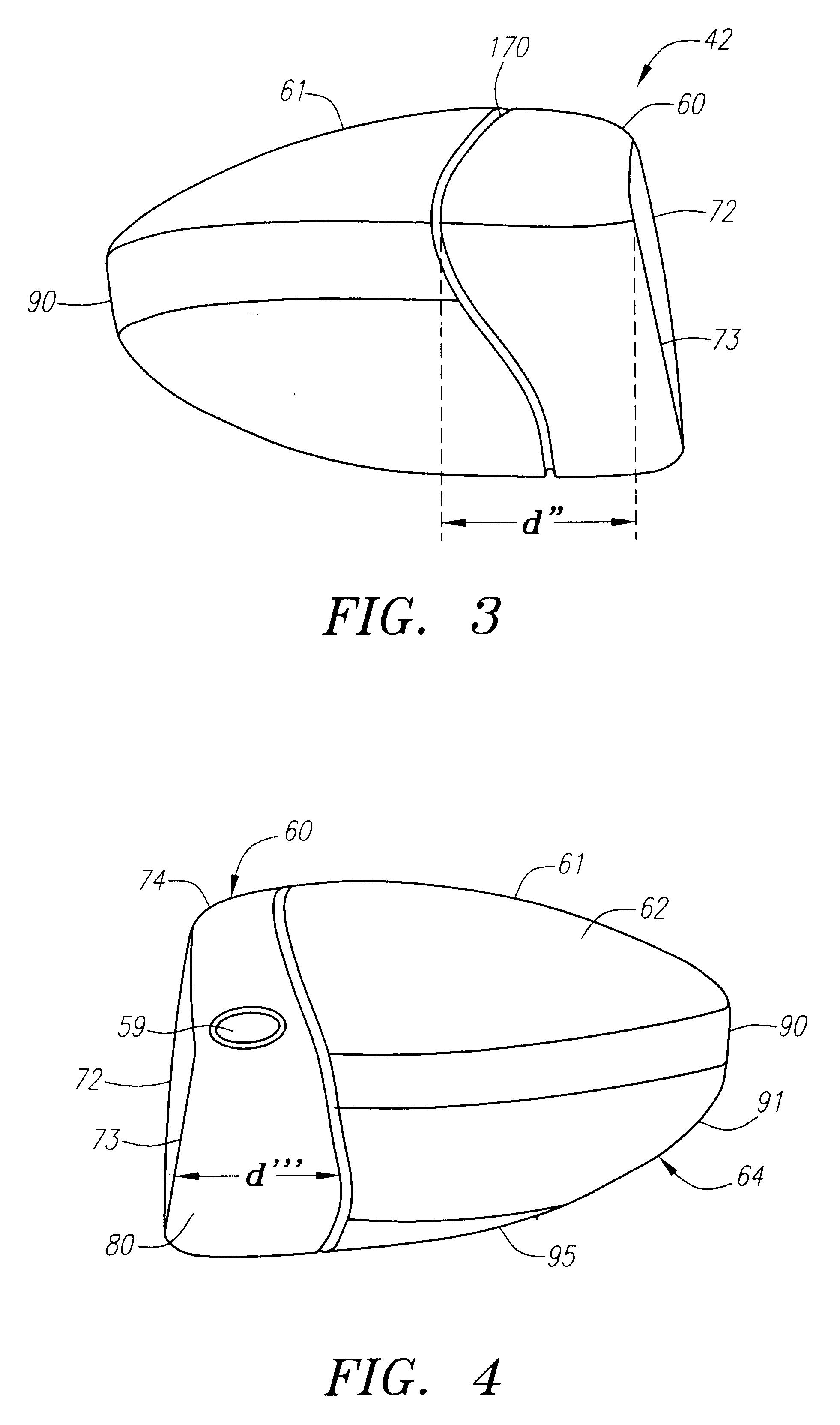
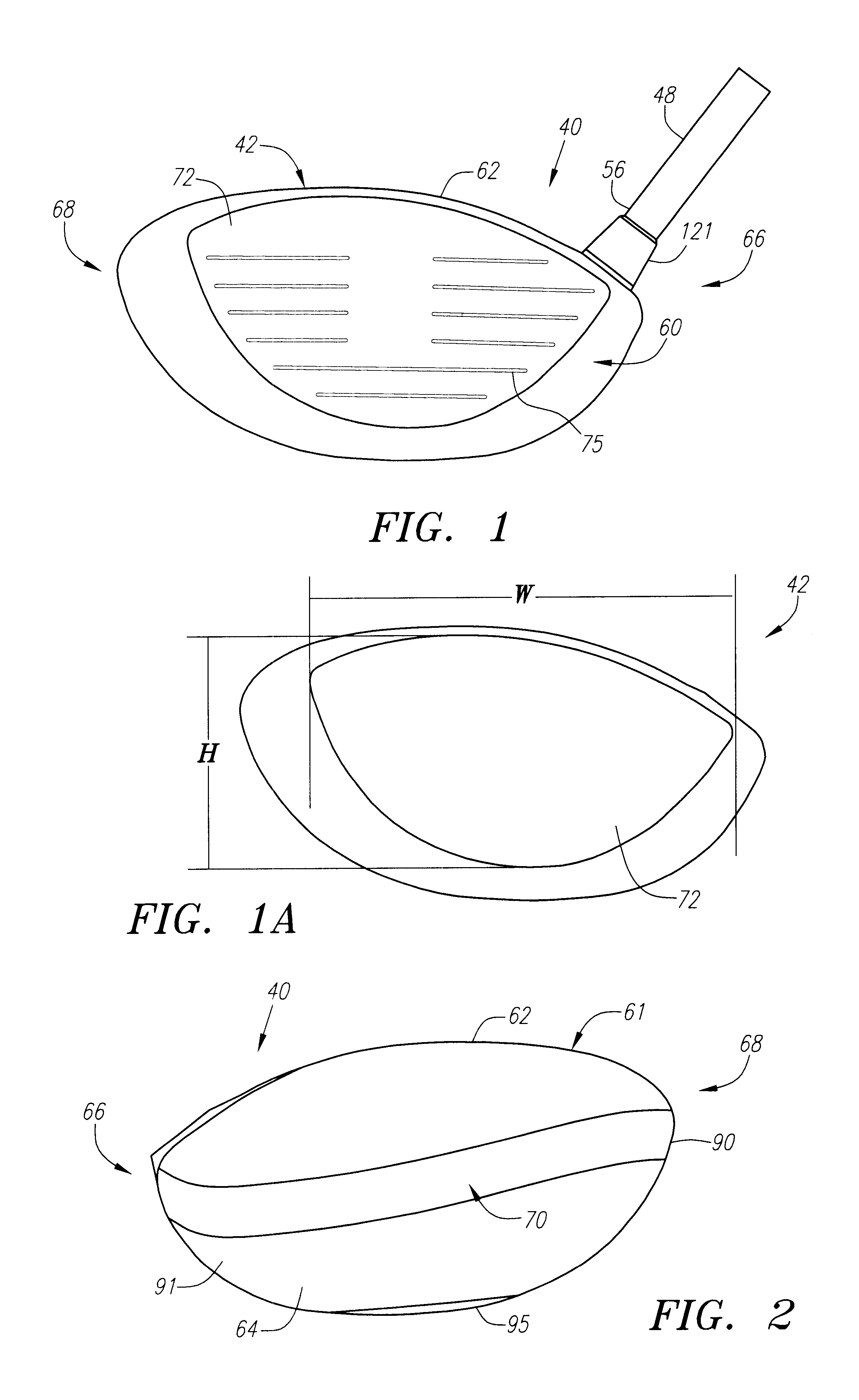
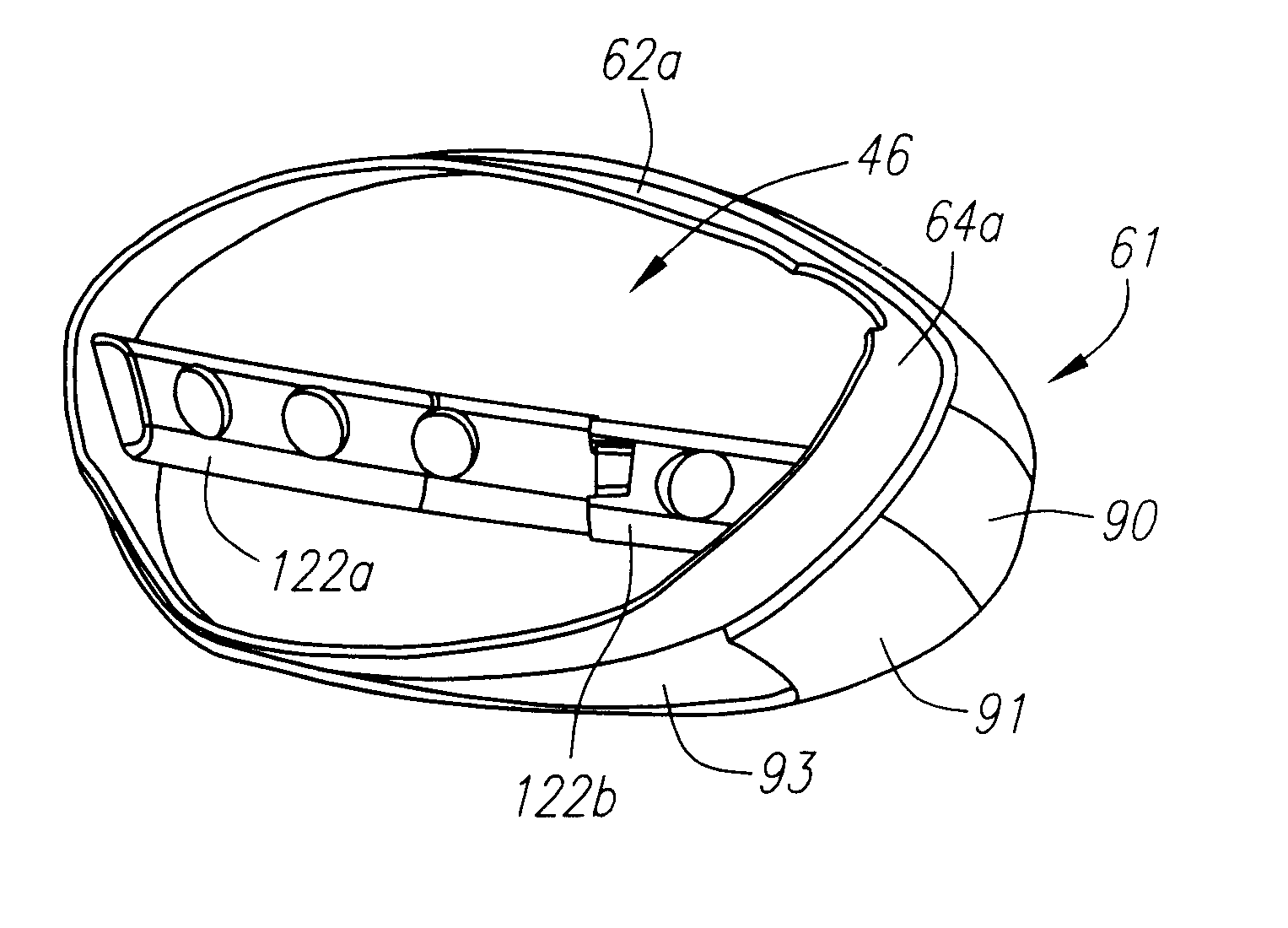
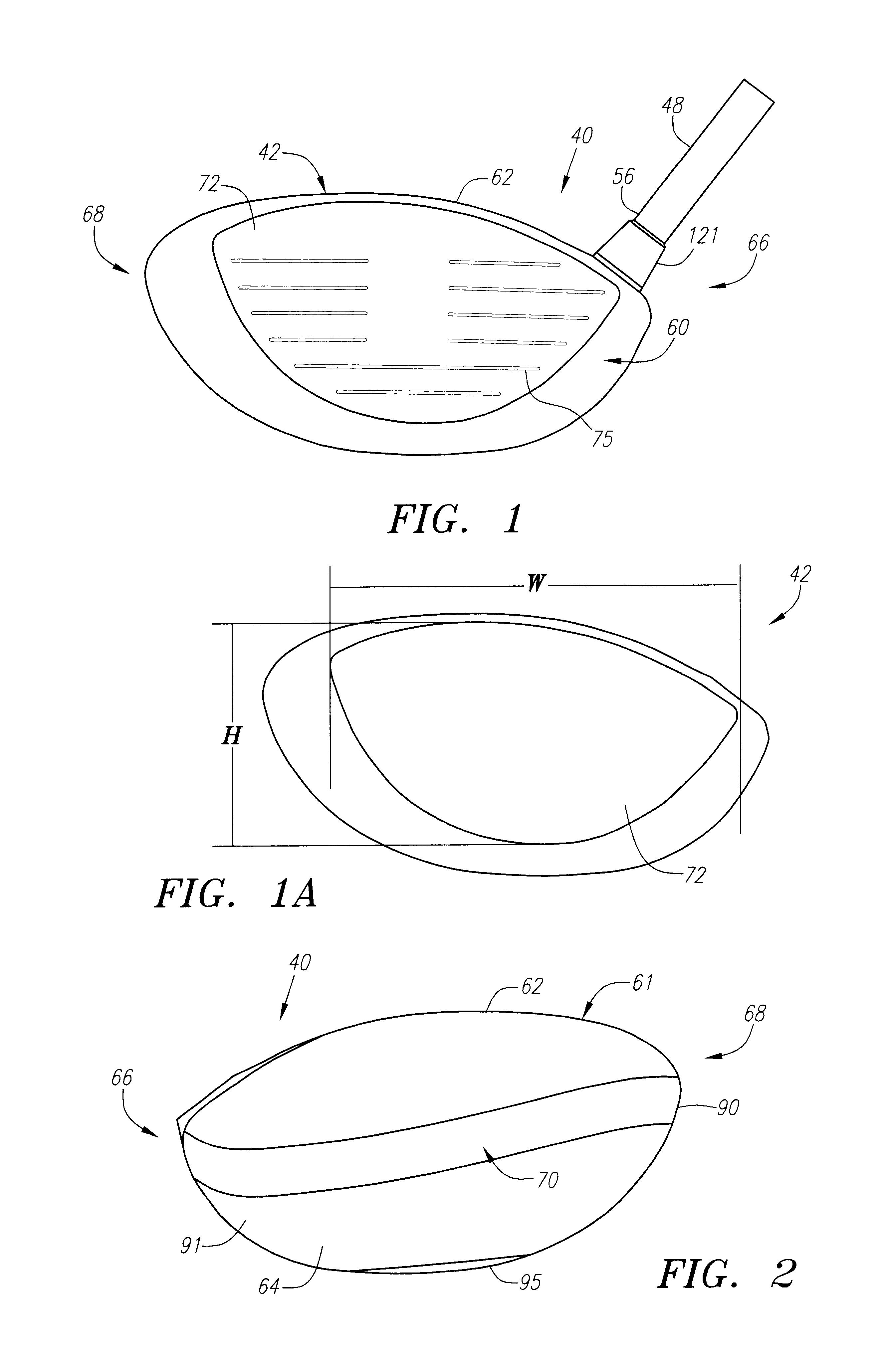
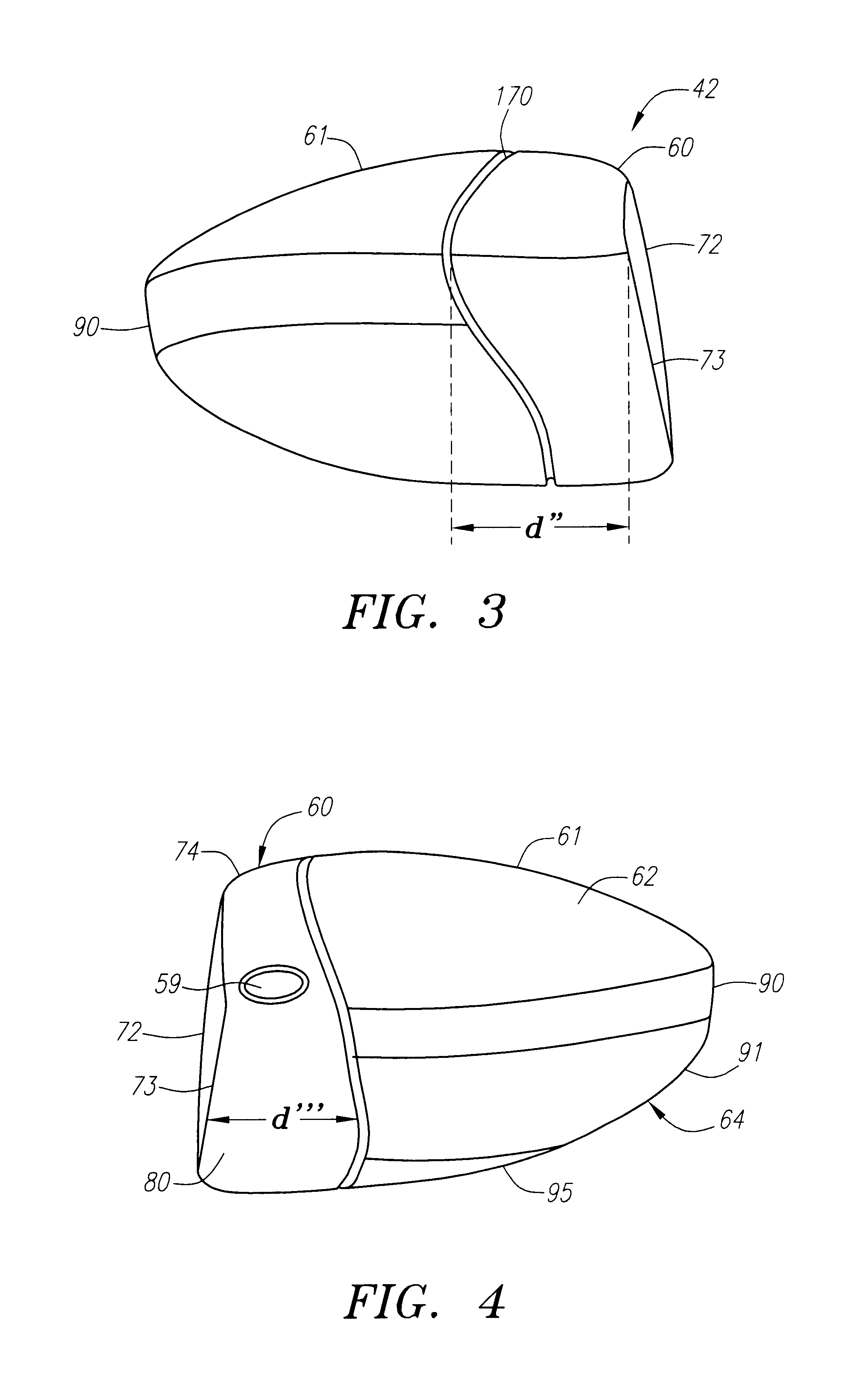
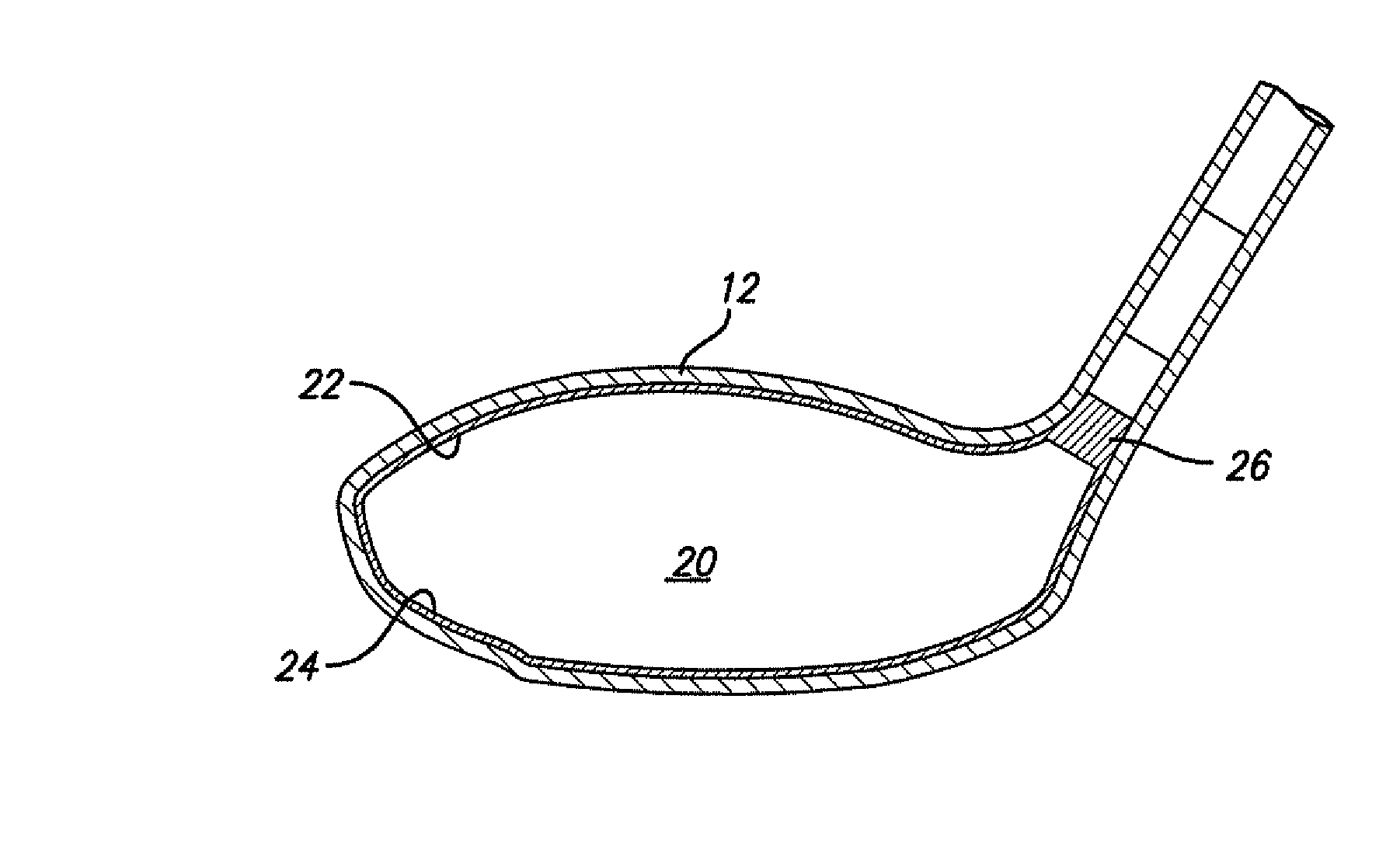
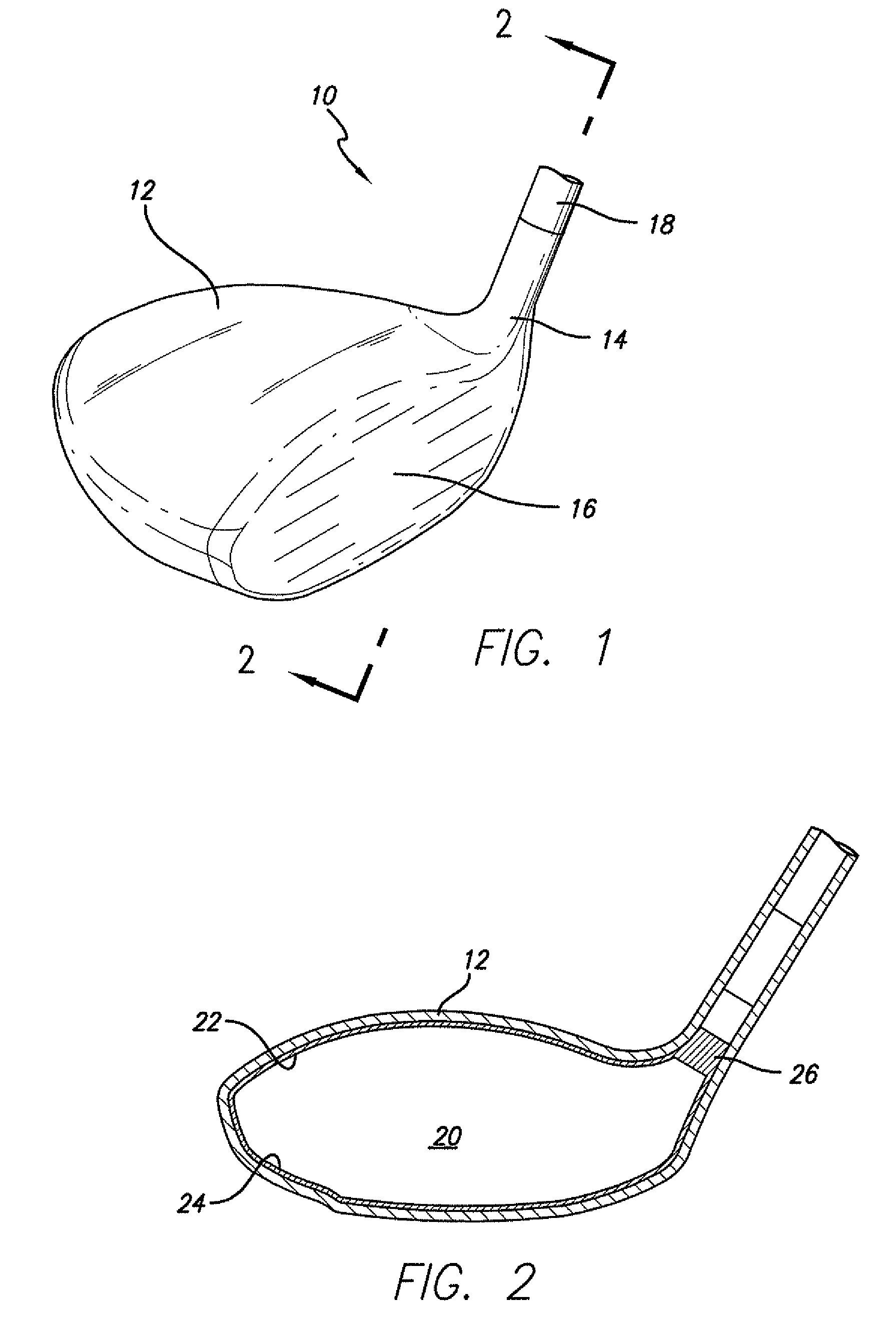
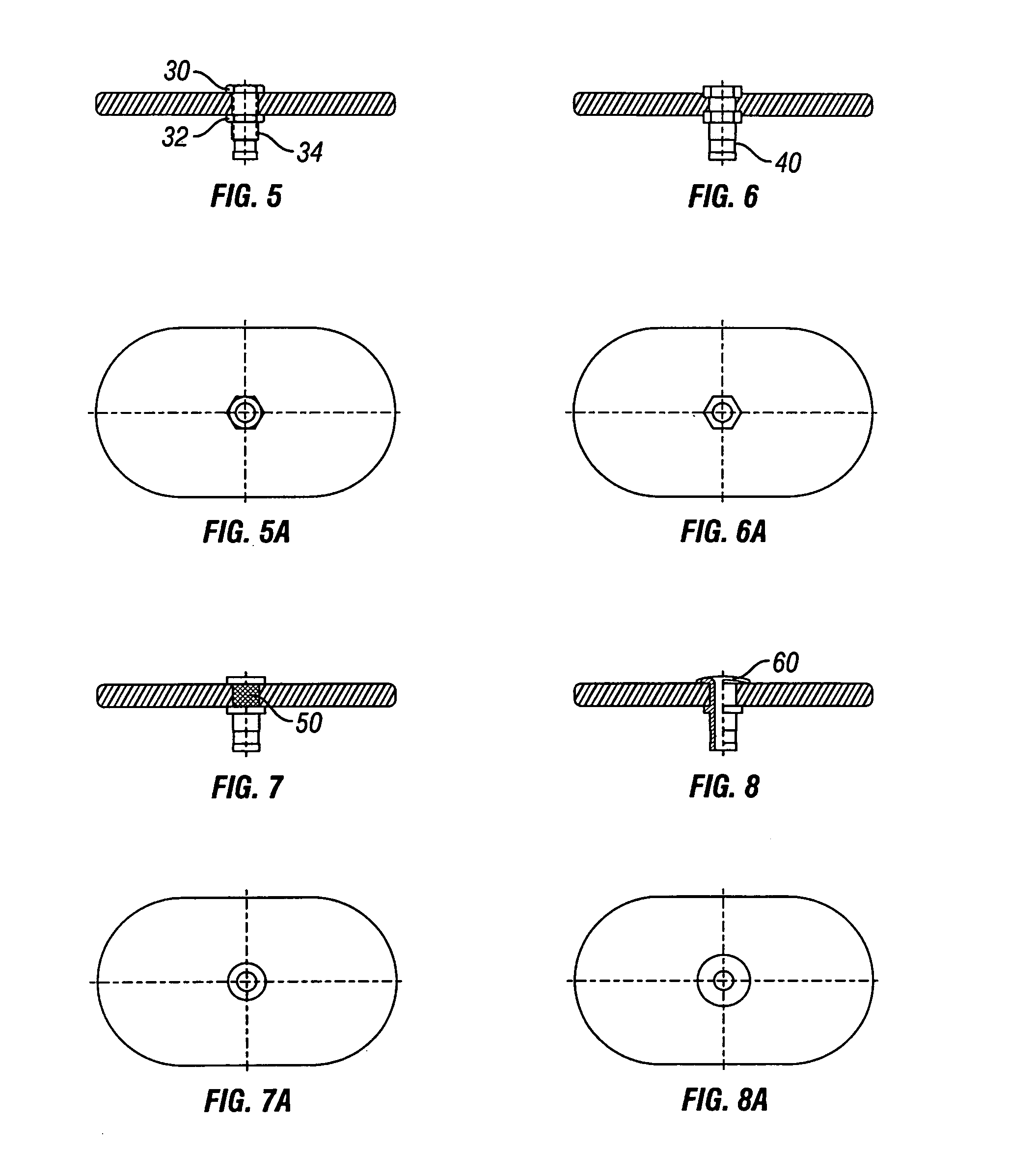
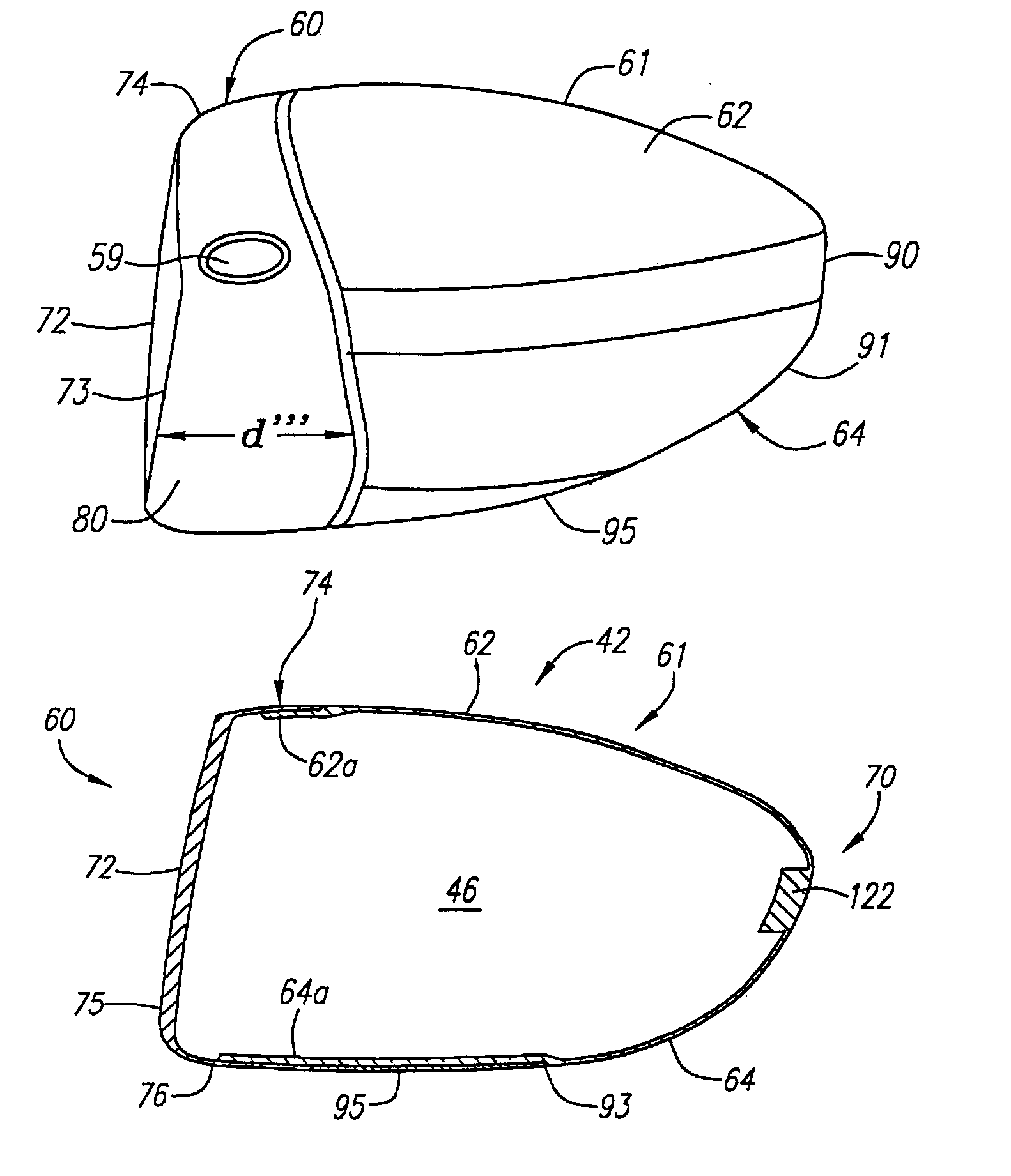
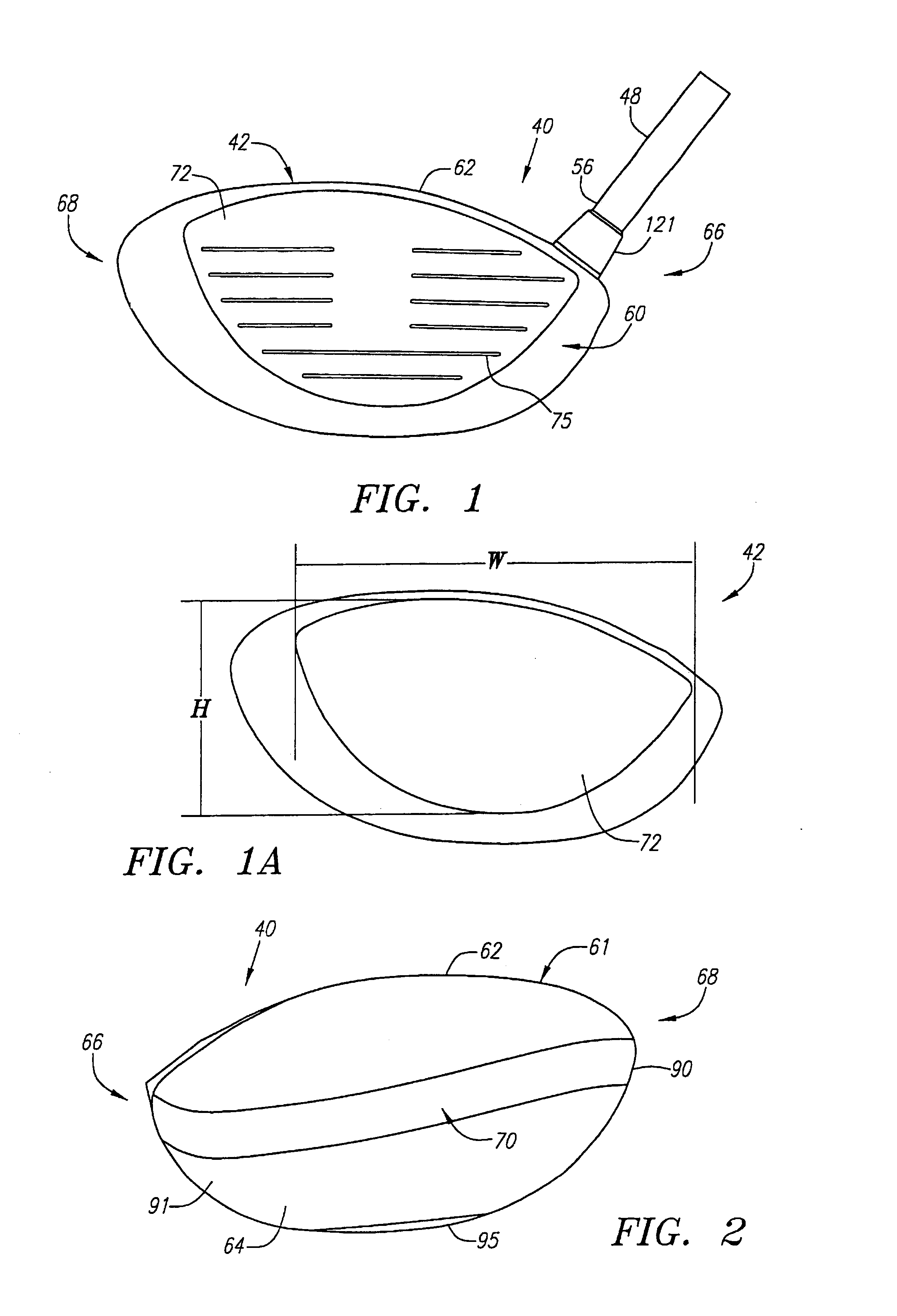
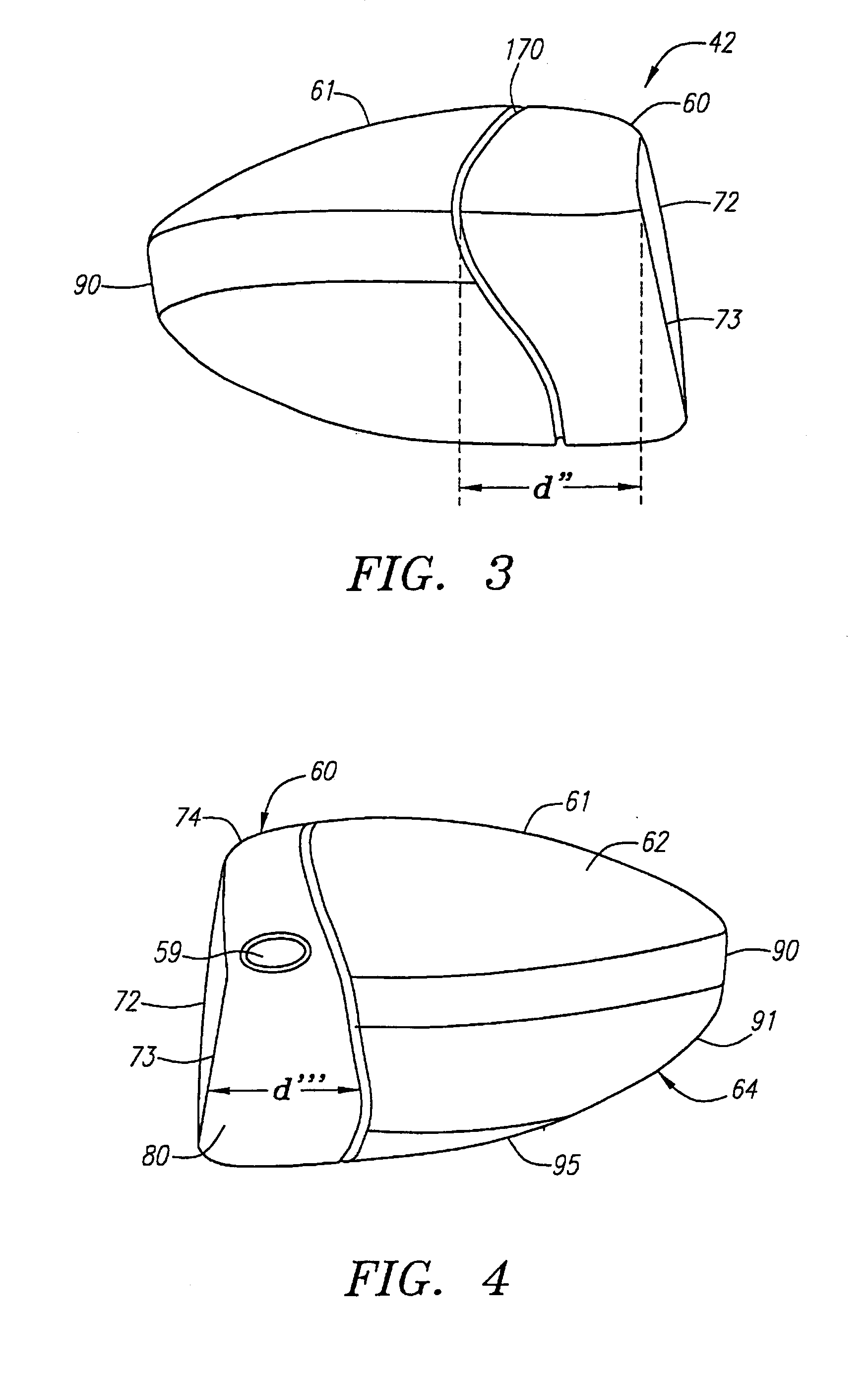
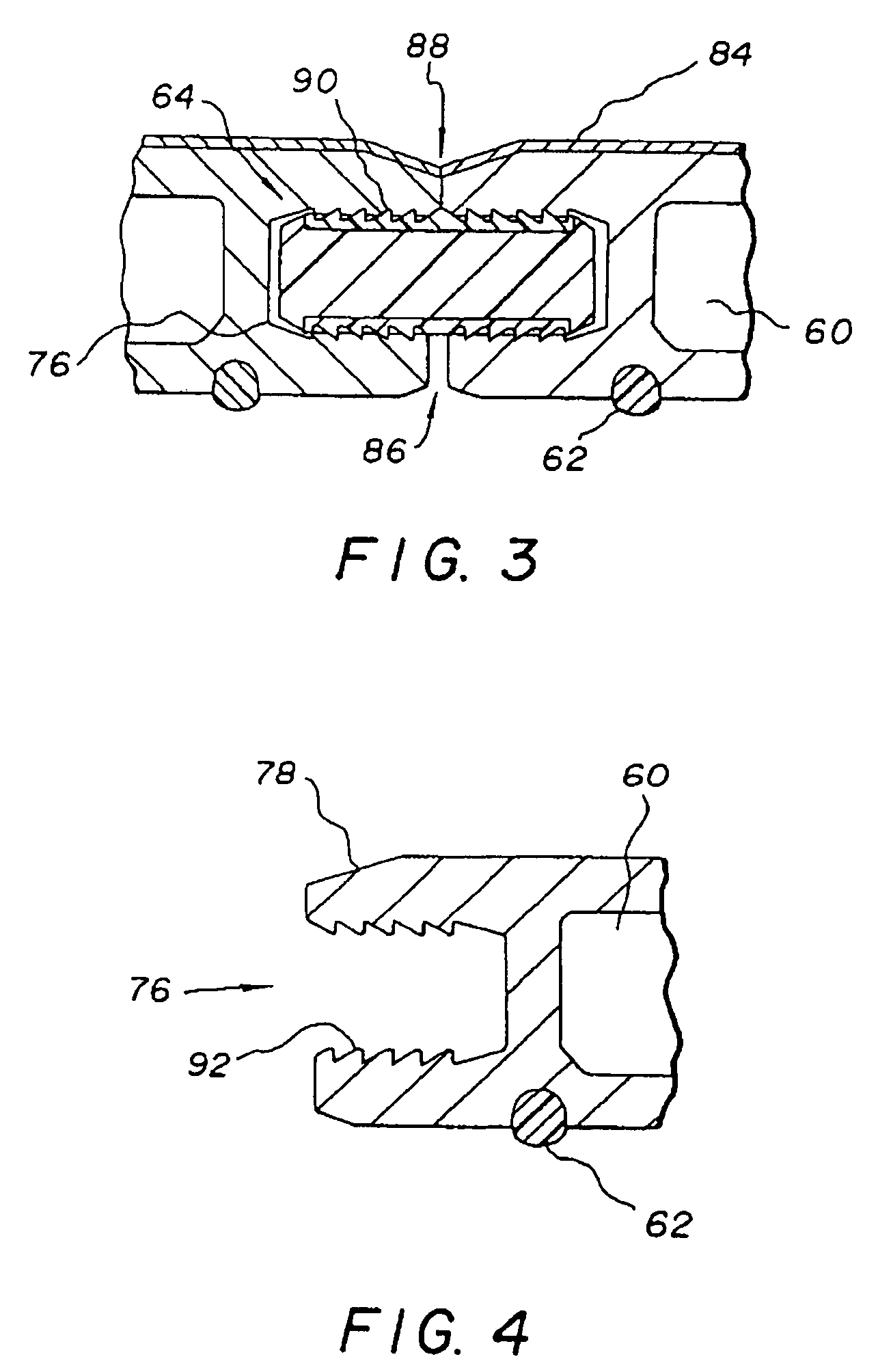
A golf club (40) having a club head (42) with a face component (60) and an aft-body (61) is disclosed herein. The face component (60) has a striking plate portion (72) and a return portion (74). The aft-body (61) is composed of a crown portion (62), a sole portion (64) and optionally a ribbon section (90). The face component (60) is composed of a metal material, and the aft-body (61) is composed of a non-metal material such as a composite material or a thermoplastic material. The striking plate portion (72) preferably has an aspect ratio less than 1.7. The striking plate portion (72) preferably has concentric regions of thickness with the thickness portion in the center (102). The club head (42) has a volume in the range of 300 cubic centimeters to 600 cubic centimeters, a weight in the range of 165 grams to 300 grams, and a striking plate portion (72) surface area in the range of 4.00 square inches to 7.50 square inches. The golf club head (42) has a coefficient of restitution greater than 0.81 under test such as the USGA test conditions specified pursuant to Rule 4-1e, Appendix II, of the Rules of Golf for 1998-1999.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Bonded joint design for a golf club head
A golf club (40) having a club head (42) with a face component (60) and an aft body (61) is disclosed herein. The face component (60) has a striking plate port ion (72) and a return portion (74). The aft-body (61) is composed of a crown portion (62), a sole portion (64) and optionally a ribbon section (90). The face component (60) is composed of a metal material, and the aft-body (61) is preferably composed of a non-metal material such as a composite material or a thermoplastic material. The face component (60) is bonded to the aft-body (61) with a leading edge (180) of an undercut portion (62a and 64a) of the aft-body positioned a distance of 0.100 inch to 0.500 inch from the interior surface (60a) of the face component (60) in order to reduce the stress on the bonded joint of between the face component (60) and the aft-body (61). The club head (42) has a volume in the range of 290 cubic centimeters to 600 cubic centimeters, a weight in the range of 165 grams to 300 grams, and a striking plate portion (72) surface area in the range of 4.00 square inches to 7.50 square inches.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
LED lighting assemblies with thermal overmolding
ActiveUS20070121326A1Thermal conductivityPoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsEffect lightEngineering
One or more light emitting diode diodes (LEDs) are attached to a printed circuit board. The attached LEDs are connectable with a power source via circuitry of the printed circuit board. An overmolding material is insert molded an over at least portions of the printed circuit board proximate to the LEDs to form a free standing high thermal conductivity material overmolding that covers at least portions of the printed circuit board proximate to the LEDs. The free standing high thermal conductivity material has a melting temperature greater than about 100° C. and has a thermal conductivity greater than or about 1 W / m·K. In some embodiments, the free standing high thermal conductivity material is a thermoplastic material.
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
Multiple material golf club head with face insert
A golf club (40) having a club head (42) with a face component (60) and an aft body (61) is disclosed herein. The face component (60) has a striking plate insert (72) within an opening (45) of a return portion (74). The aft-body (61) is composed of a crown portion (62), a sole portion (64) and optionally a ribbon section (90). The return portion (74) is preferably composed of a cast metal material, the striking plate insert (72) is preferably composed of a formed or forged metal material, and the aft-body (61) is preferably composed of a non-metal material such as a composite material or a thermoplastic material. The golf club head (42) preferably has a volume in the range of 250 cubic centimeters to 600 cubic centimeters and a weight in the range of 165 grams to 300 grams.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Golf club having a hollow pressurized metal head
ActiveUS20080188322A1Avoid passingPrevent escapeFilling using counterpressureMetal rolling stand detailsShell moldingPlastic materials
A golf club having a hollow golf club head which is filled with a gas under pressure. The interior surface of the golf club head is coated with a solidified layer of plastic material. The pressurized gas permits the use of thinner face plates by compensating for forces generated when the face plate strikes a golf ball. The plastic layer is preferably applied through the process of rotational molding using a thermoplastic material.
Owner:BLOWERS ALDEN J
Multiple material golf club head
InactiveUS6582323B2Increase flexibilityGood coefficientMetal-working apparatusGolf clubsGramMetallic materials
A golf club (40) having a club head (42) with a face component (60) and an aft body (61) is disclosed herein. The face component (60) has a striking plate portion (72) and a return portion (74). The aft-body (61) is composed of a crown portion (62), a sole portion (64) and optionally a ribbon section (90). The face component (60) is composed of a metal material, and the aft-body (61) is composed of a non-metal material such as a composite material or a thermoplastic material. The striking plate portion (72) preferably has an aspect ratio less than 1.7. The striking plate portion (72) preferably has concentric regions of thickness with the thickness portion in the center (102). The club head (42) has a volume in the range of 290 cubic centimeters to 600 cubic centimeters, a weight in the range of 165 grams to 300 grams, and a striking plate portion (72) surface area in the range of 4.00 square inches to 7.50 square inches. The golf club head (42) has a coefficient of restitution greater than 0.81 under test conditions such as the USGA test conditions specified pursuant to Rule 4-1e, Appendix II, of the Rules of Golf for 1998-1999.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Golf club having a hollow pressurized metal head
ActiveUS8663026B2Prevent escapeMetal rolling stand detailsPackaging under special atmospheric conditionsPlastic materialsEngineering
A golf club having a hollow golf club head which is filled with a gas under pressure. The interior surface of the golf club head is coated with a solidified layer of plastic material. The pressurized gas permits the use of thinner face plates by compensating for forces generated when the face plate strikes a golf ball. The plastic layer is preferably applied through the process of rotational molding using a thermoplastic material.
Owner:BLOWERS ALDEN J
Method of thermoforming a bladder structure
InactiveUS6837951B2Increase awarenessImprove efficiencySolesOrnamental textile articlesBladder structureThermal contact
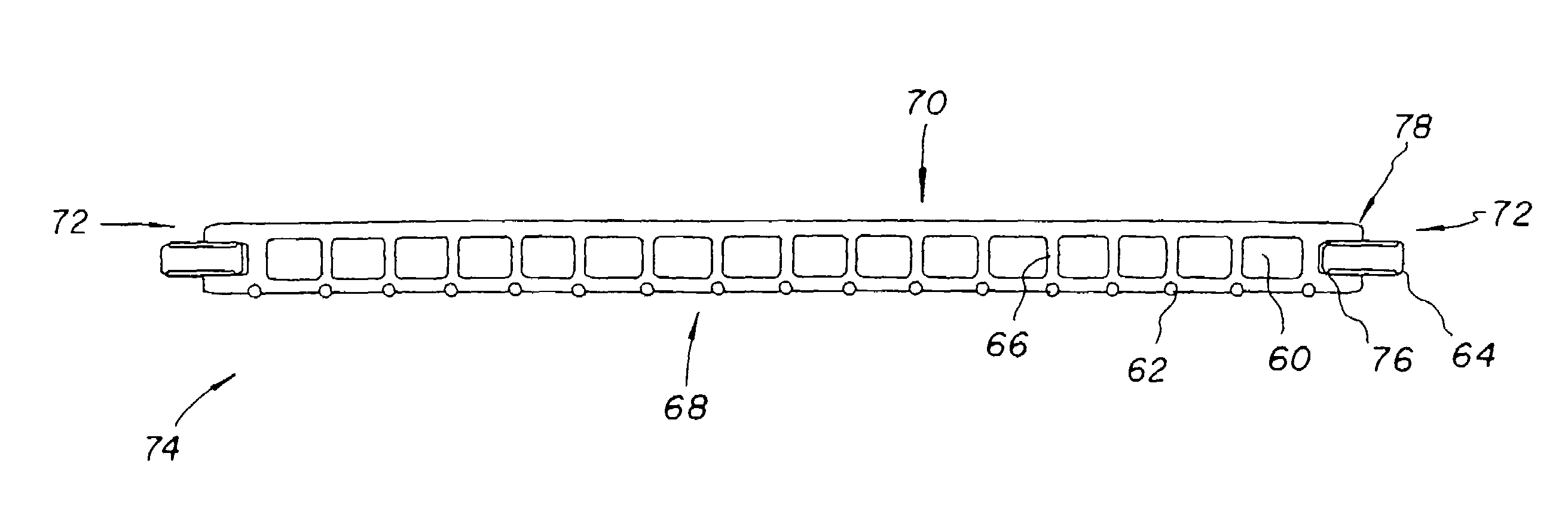
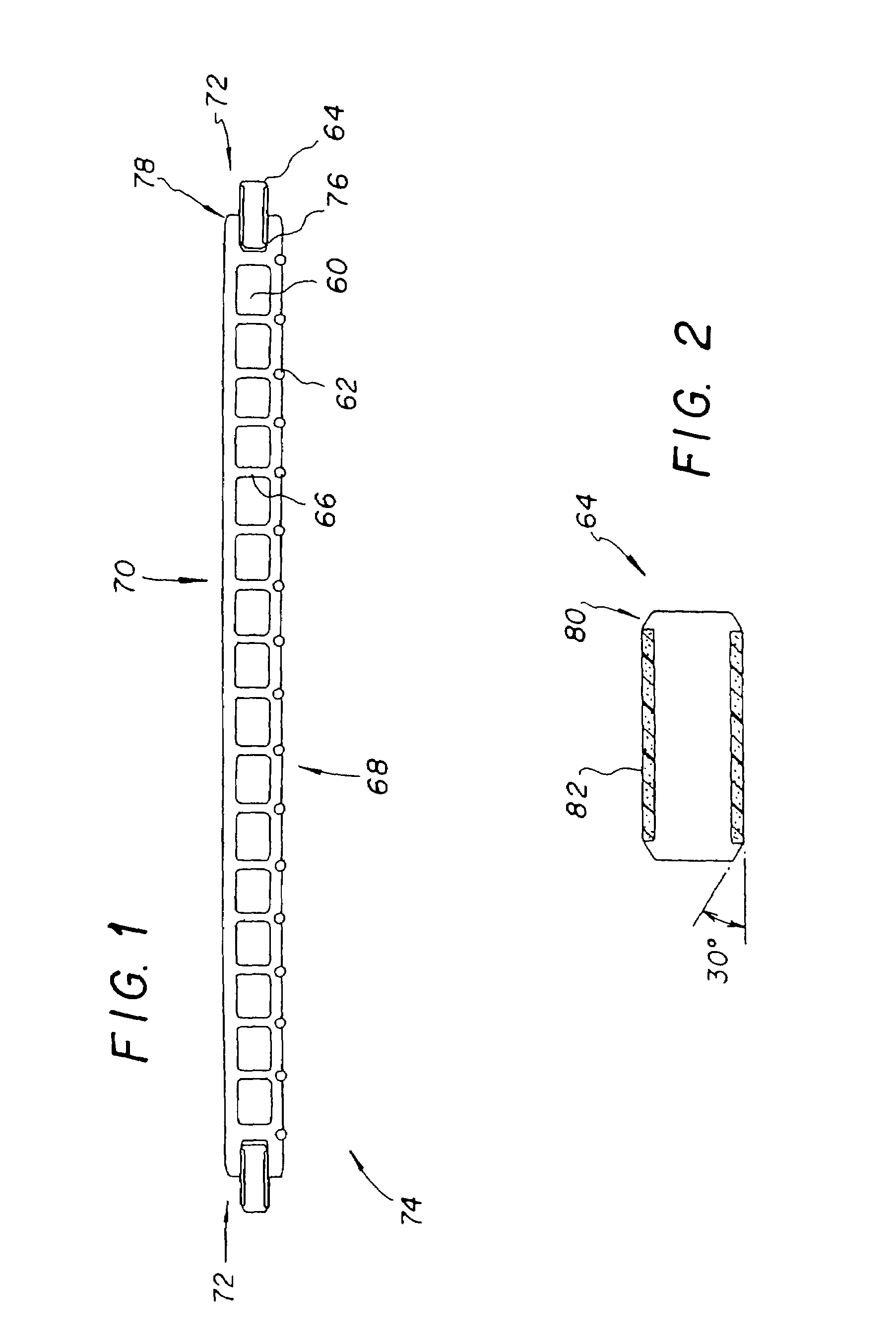
A method for thermoforming a resilient, fluid-filled bladder structure with thermal contact molding is disclosed. The bladder includes two sheets of thermoplastic material that are separated by at least one core formed of two spaced outer layers connected together by a plurality of connecting members. The bladder is formed by bonding the sheets to the core, bonding the sheets to each other around the periphery of the core and forming a sidewall between the sheets in a single mold. A fluid is then inserted into the space bounded by the peripheral bond and the two sheets such that the connecting members are extended.
Owner:NIKE INC
Method for Making Advanced Smart Cards With Integrated Electronics Using Isotropic Thermoset Adhesive Materials With High Quality Exterior Surfaces
InactiveUS20080096326A1Speed up the flowPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsIntegrated electronicsSmart card
Advanced Smart Cards and similar form factors (e.g. documents, tags) having high quality external surfaces of Polyvinylchloride (PVC), Polycarbonate (PC), synthetic paper or other suitable material can be made with highly sophisticated electronic components (e.g. Integrated Circuit chips, batteries, microprocessors, Light Emitting Diodes, Liquid Crystal Displays, polymer dome switches, and antennae), integrated in the bottom layer of the card structure, through use of injection molded thermosetting or thermoplastic material that becomes the core layer of said Advanced Smart Cards. A lamination finishing process can provide a high quality lower surface, and the encapsulation of the electronic components in the thermosetting or thermoplastic material provides protection from the lamination heat and pressure.
Owner:CARDXX
Method for making memory cards and similar devices using isotropic thermoset materials with high quality exterior surfaces
InactiveUS7225537B2Shorten the timeQuality improvementPrinted circuit assemblingLine/current collector detailsEngineeringInjection moulding
Memory Cards containing Integrated Circuits and other electronic components (e.g. resistors) in a variety of form factors having high quality external surfaces of polycarbonate, synthetic paper (e.g. Teslin), or other suitable material (e.g. PVC) can be made through use of injection molded thermoplastic material or thermosetting material that becomes the core layer of said Memory Cards and similar devices. The object of the invention is to provide the following properties to Memory Cards: rapid production cycle, high volume manufacturing throughput, security, electronics protection, better tamper resistance, durability, and highly reliable complex electronics encapsulation, achieved through a process utilizing low temperature and low pressure.
Owner:CARDXX
Air gas analyzer window and a method for producing such a window
ActiveUS7629039B2Uniform material thicknessSatisfactory transmission propertyLayered productsRespiratory organ evaluationPlastic materialsLight beam
A window for use in an adapter for an IR gas analyser for analysing breathing gases, where the gases flow through a through-penetrating passageway in the adapter, which includes windows disposed on opposite sides of the passageway so as to enable an IR beam to be sent through the windows and through the passageway containing said breathing gases. Each window is a one-piece structure comprised of plastic material and has a round basic shape that includes a surrounding edge and a central part which is sunken in relation to the surrounding edge and which forms the window through which the IR beams or rays shall be able to pass. A method of producing such a window, by injection moulding a thermoplastic material in a mould where injection of the plastic material is also disclosed.
Owner:PHASEIN
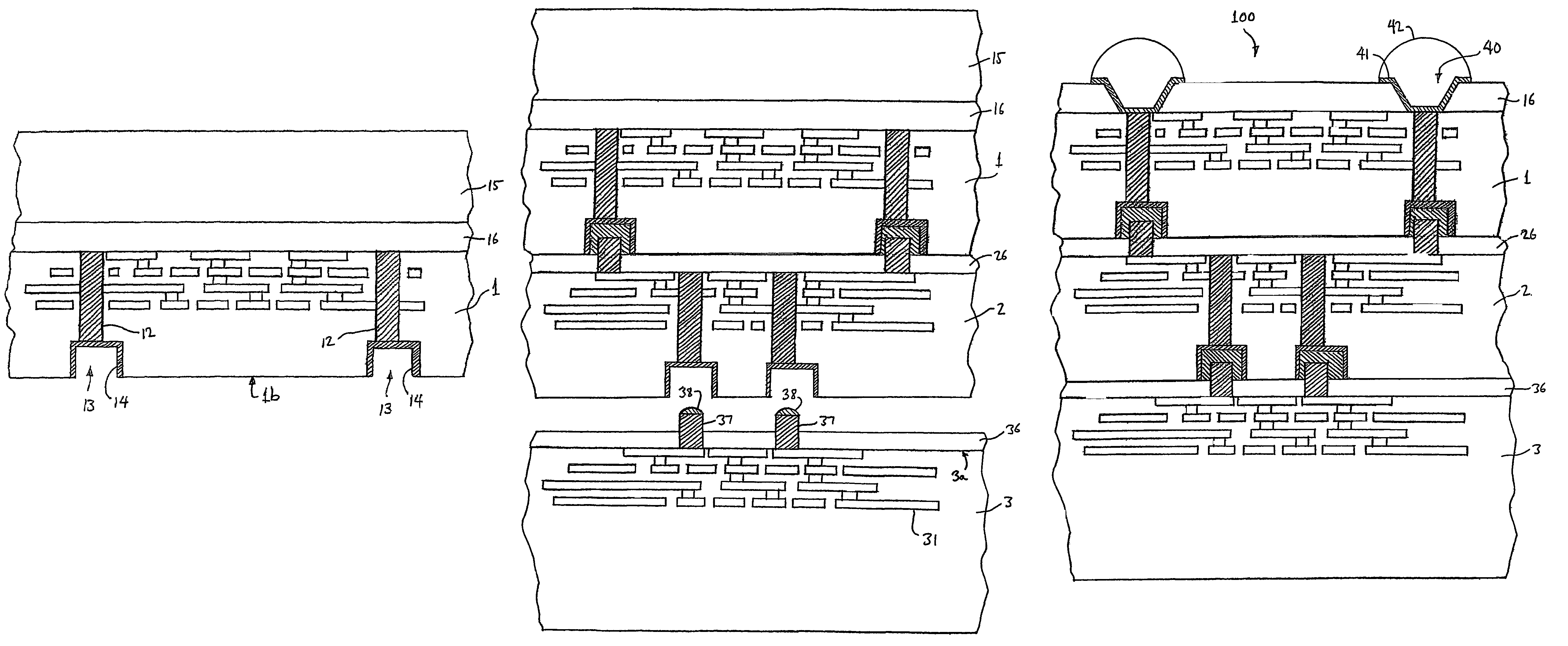
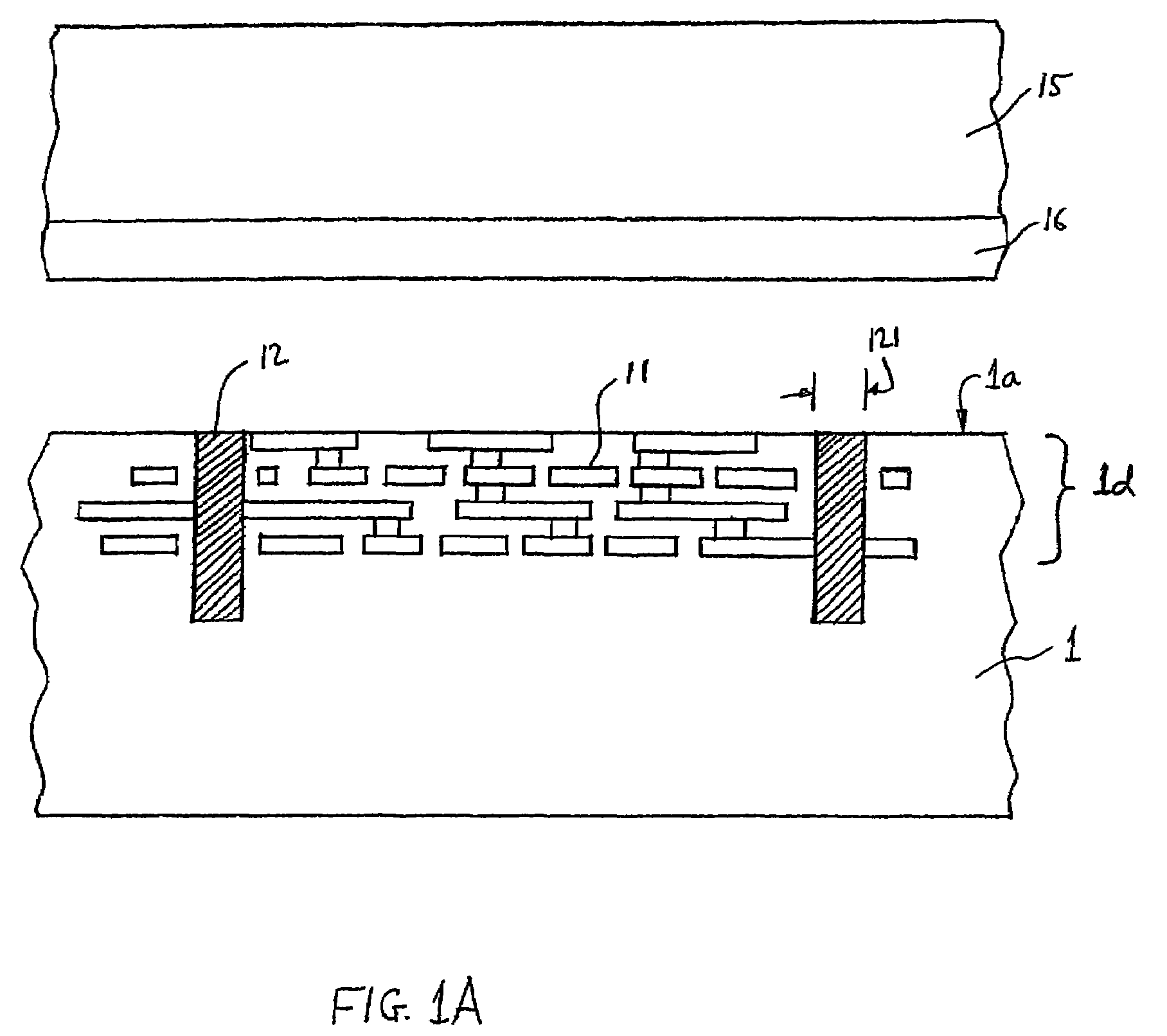
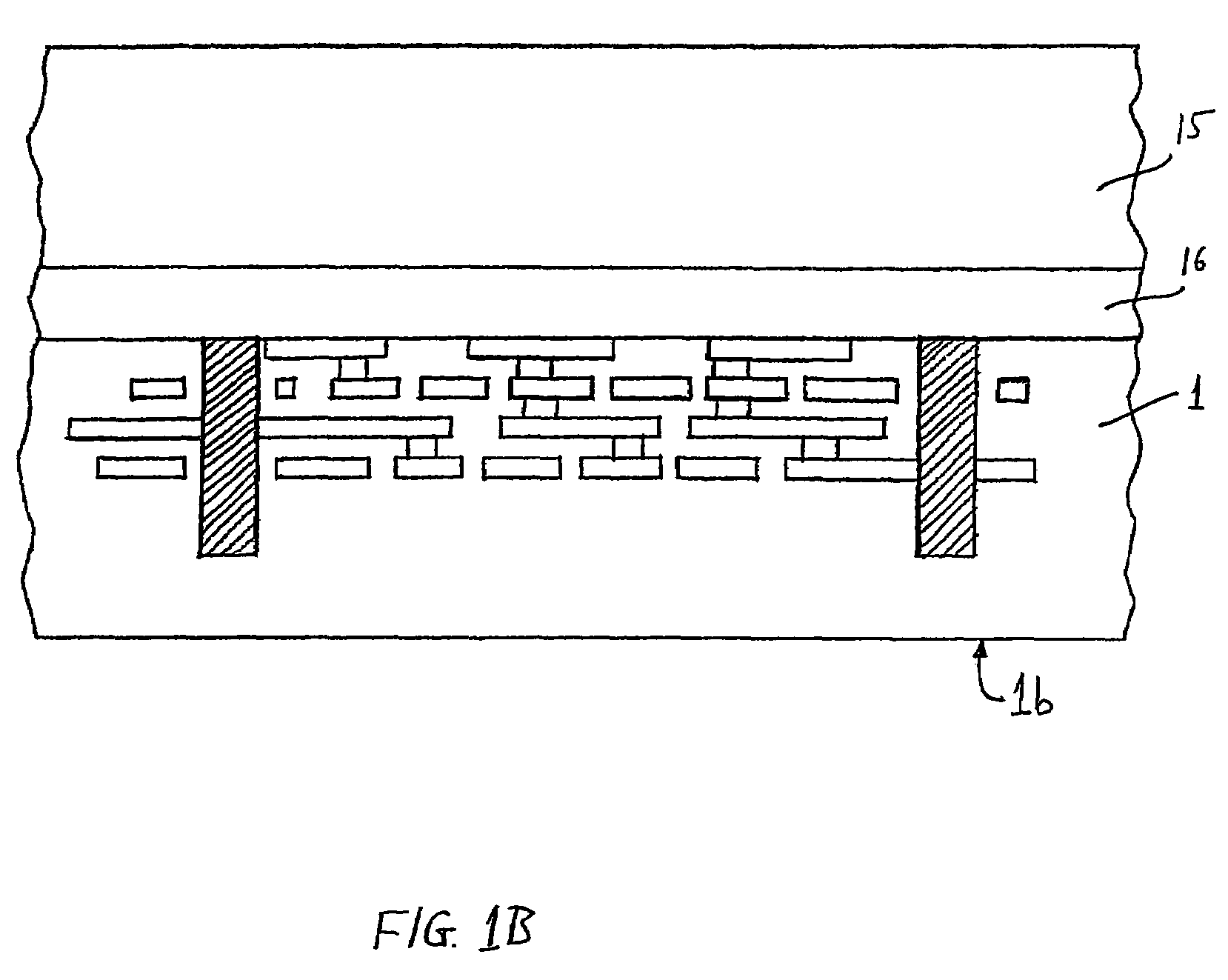
Three-dimensional device fabrication method
InactiveUS7354798B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesConduction pathwayElectrical connection
A method is described for fabricating a three-dimensional integrated device including a plurality of vertically stacked and interconnected wafers. Wafers (1, 2, 3) are bonded together using bonding layers (26, 36) of thermoplastic material such as polyimide; electrical connections are realized by vias (12, 22) in the wafers connected to studs (27, 37). The studs connect to openings (13, 23) having a lateral dimension larger than that of the vias at the front surfaces of the wafers. Furthermore, the vias in the respective wafers need not extend vertically from the front surface to the back surface of the wafers. A conducting body (102) provided in the wafer beneath the device region and extending laterally, may connect the via with the matallized opening (103) in the back surface. Accordingly, the conducting path through the wafer may be led underneath the devices thereof. Additional connections may be made between openings (113) and studs (127) to form vertical heat conduction pathways between the wafers.
Owner:IBM CORP
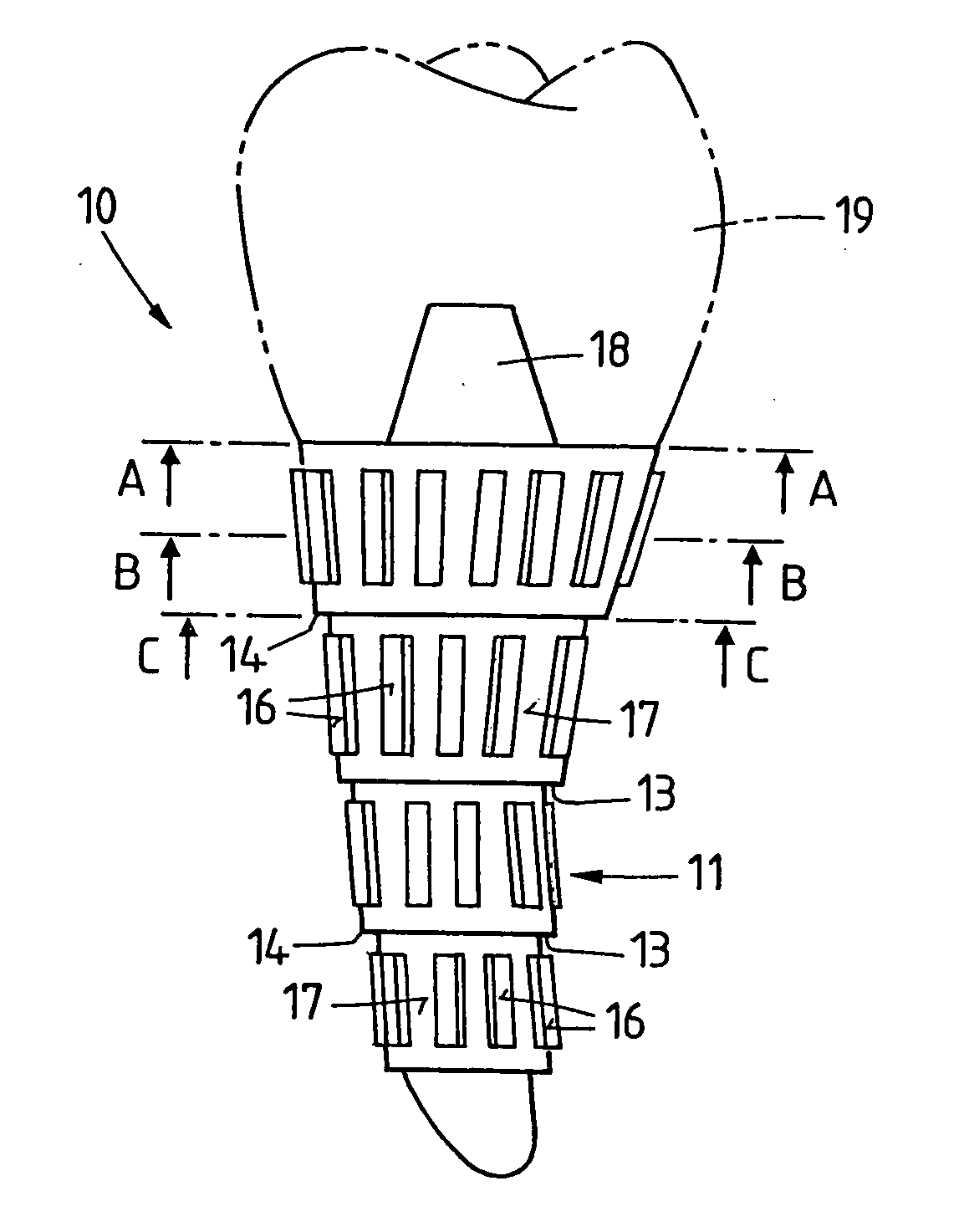
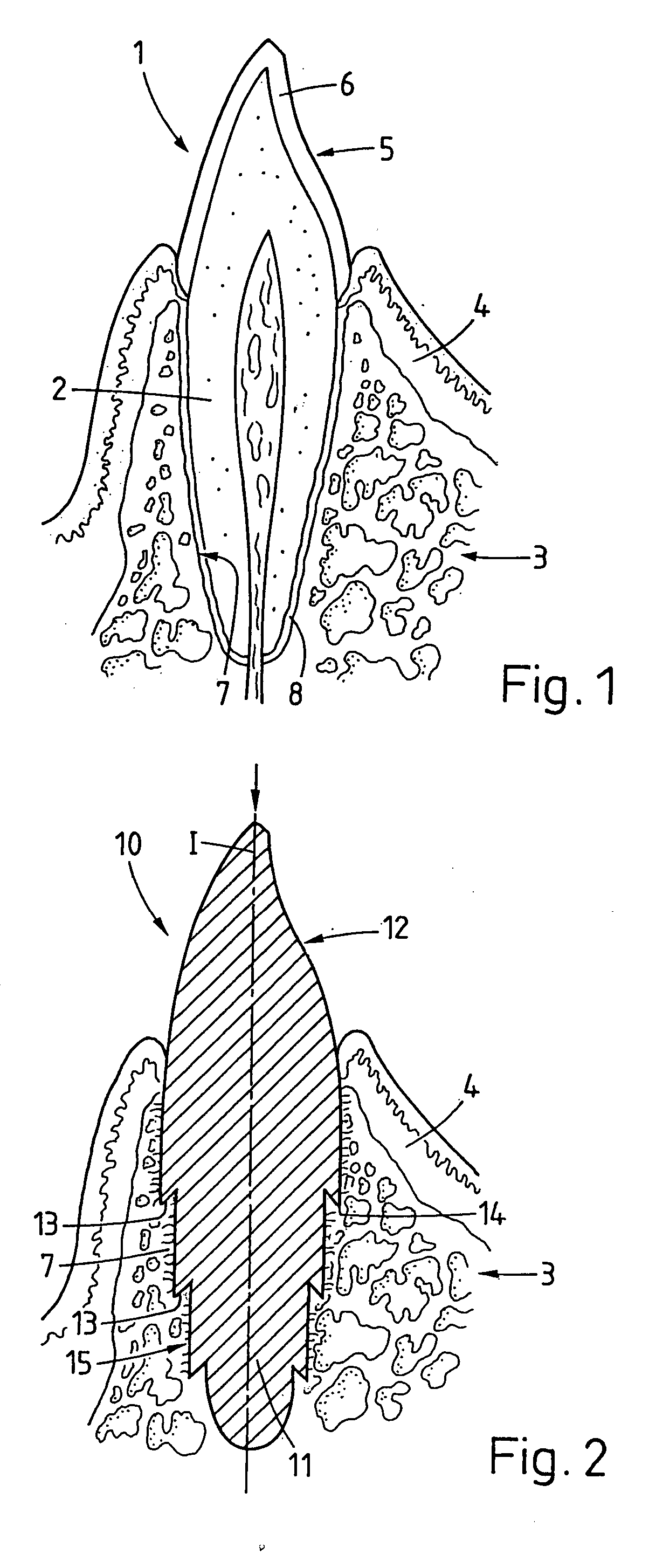
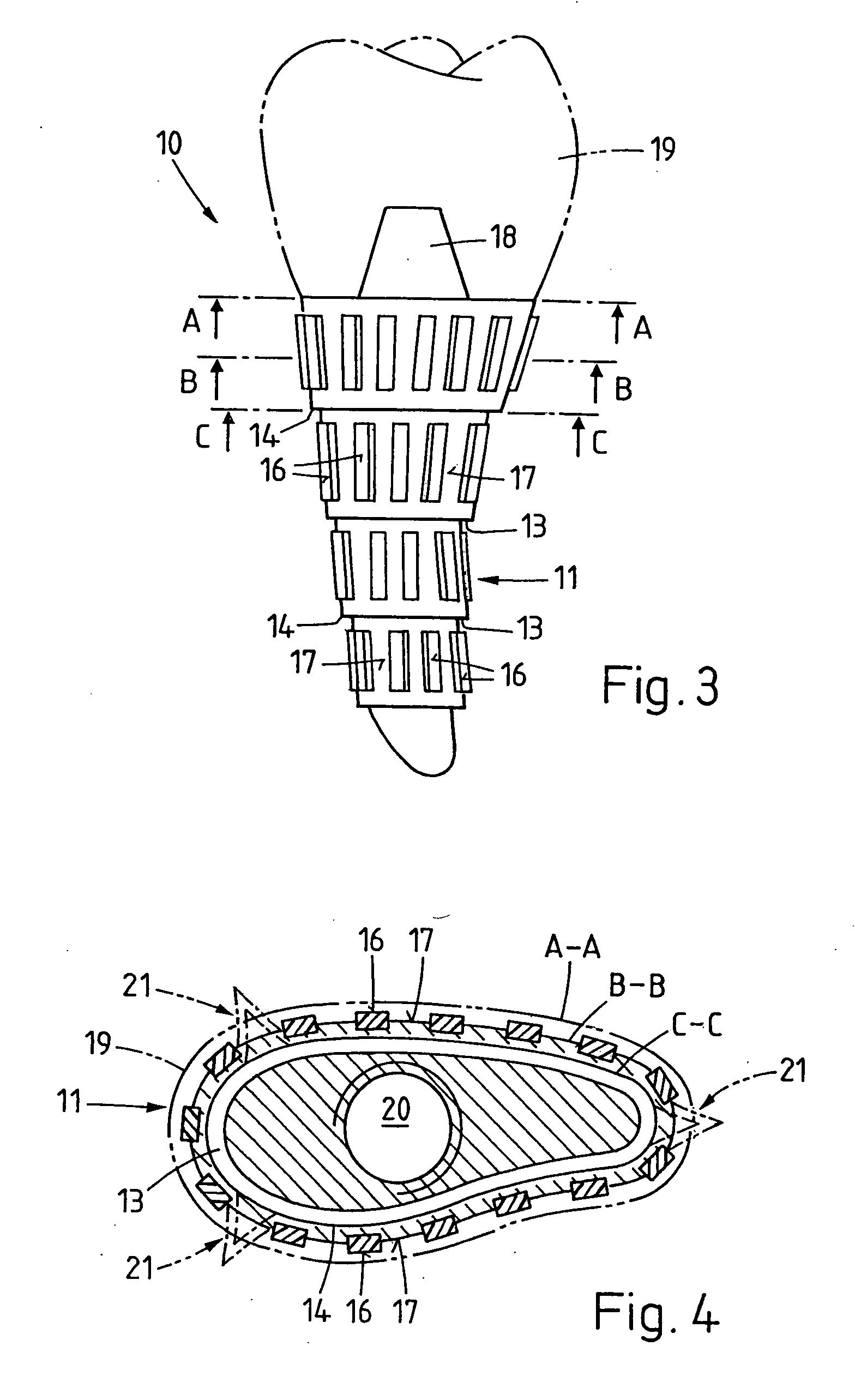
Implant that can be implanted in osseous tissue and method for producing said implant corresponding implant
ActiveUS20060105295A1Strong long-term anchoringProcess stabilityDental implantsInternal osteosythesisBone implantCavity wall
A bone implant (10) is implanted in a cavity parallel to an implant axis (I) and without substantial rotation. The implant includes, on an implant portion to be implanted, cutting edges (14), which do not extend in a common plane with the implant axis and are facing toward the distal end of the implant. The implant also includes surface ranges (16) of a material that is liquefiable by mechanical oscillations. The cutting edges (14) are dimensioned such that they are lodged in the cavity wall after implantation. For implantation, the implant is impinged with mechanical oscillations, resulting in the thermoplastic material being at least partially liquefied and pressed into unevennesses and pores of the cavity wall to form a form-fit and / or material-fit connection between implant (10) and cavity wall, when re-solidified. The cutting edges (14) anchor the implant in the cavity wall.
Owner:WOODWELDING
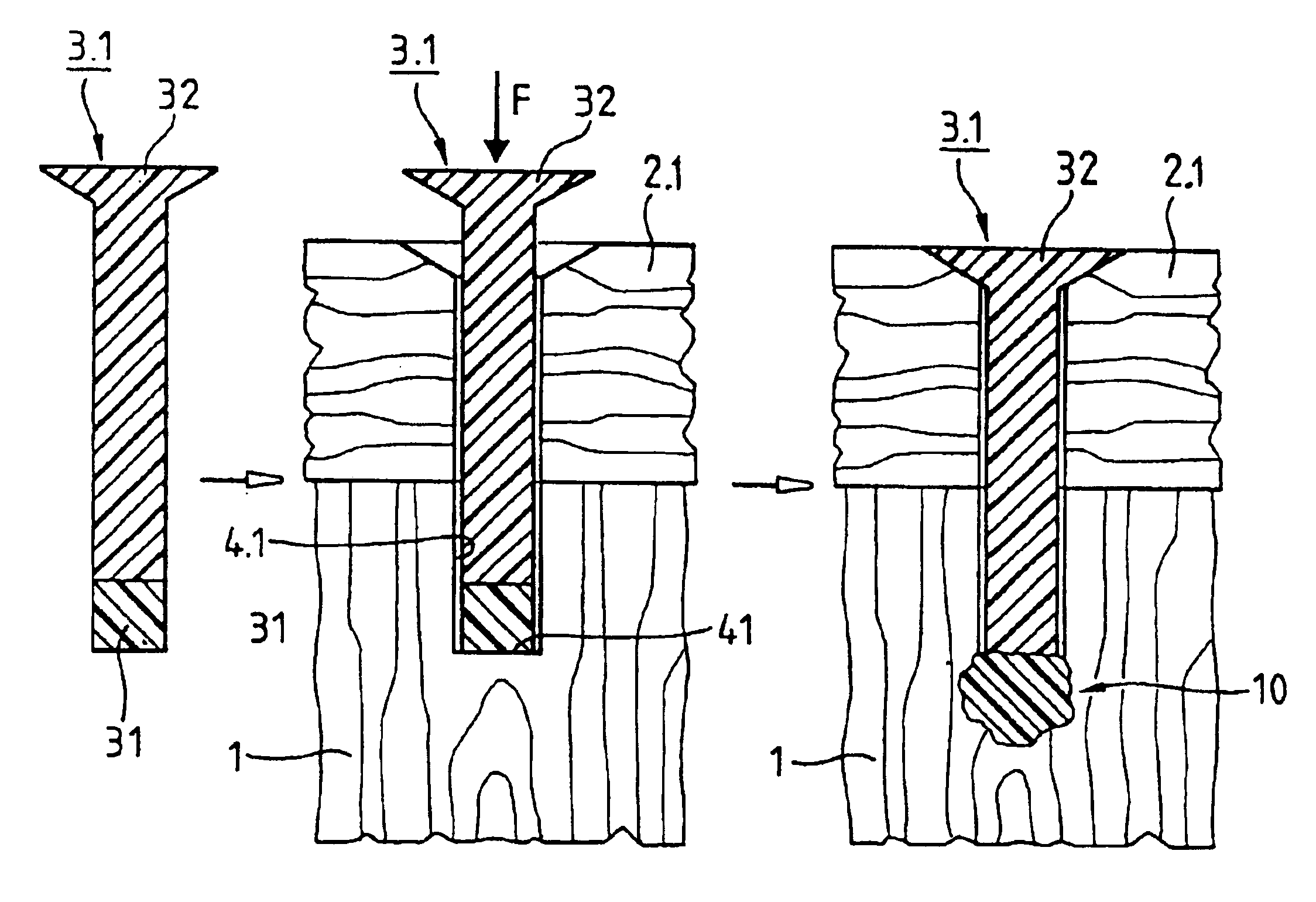
Process for anchoring connecting elements in a material with pores or cavities and connecting elements therefor
InactiveUS6913666B1Easy to reachReduce disadvantagesRivetsCylinder headsEngineeringUltrasonic vibration
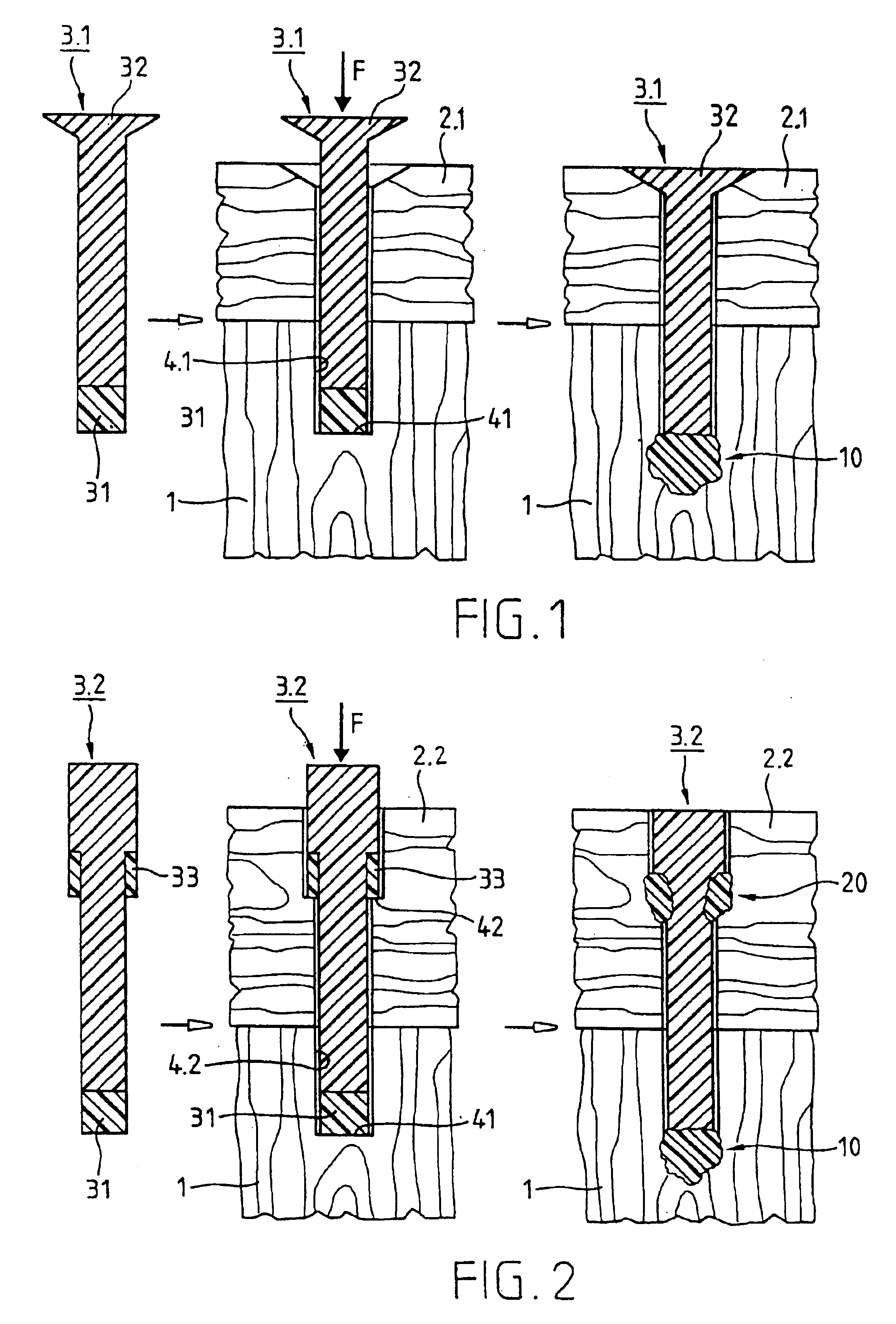
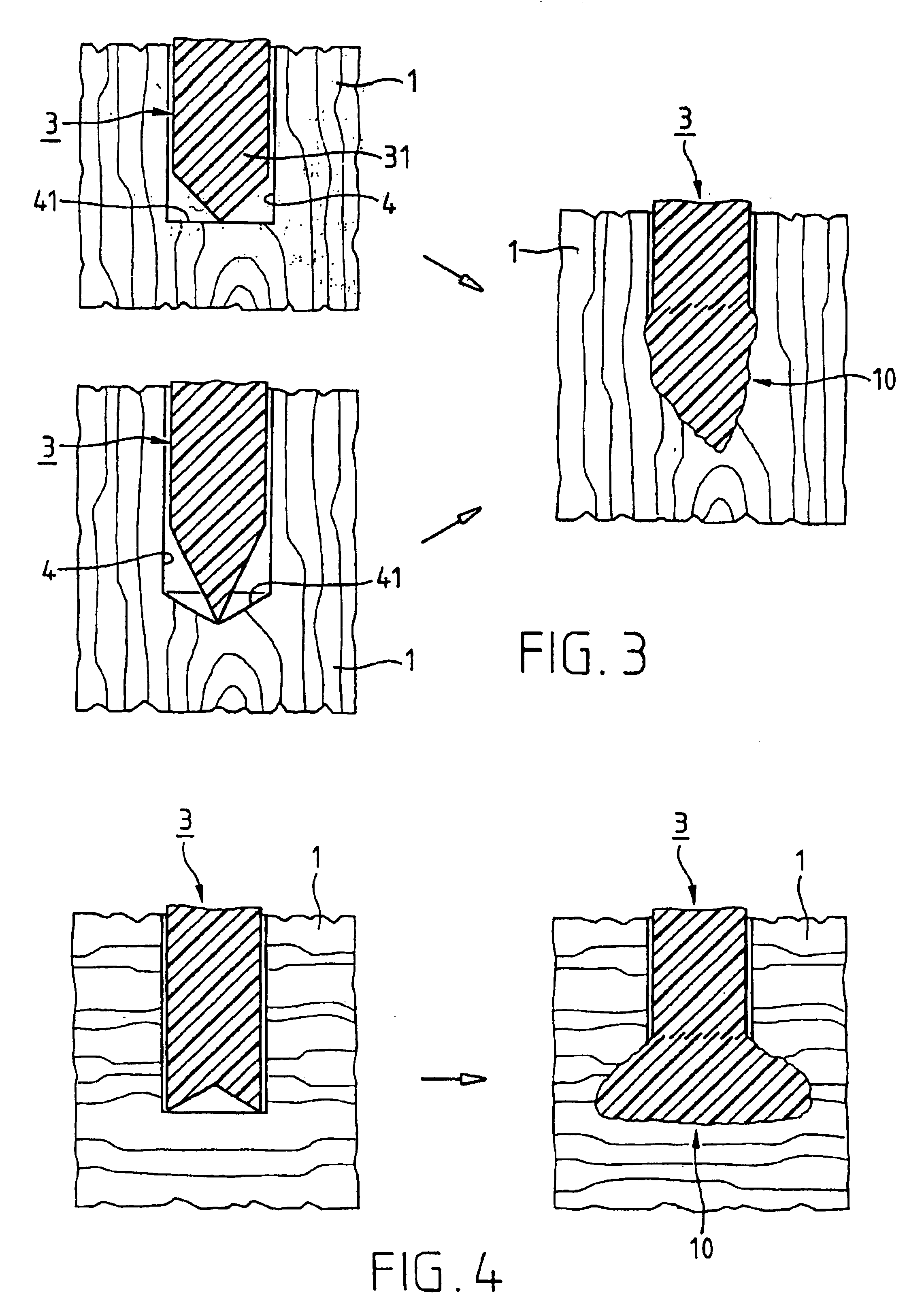
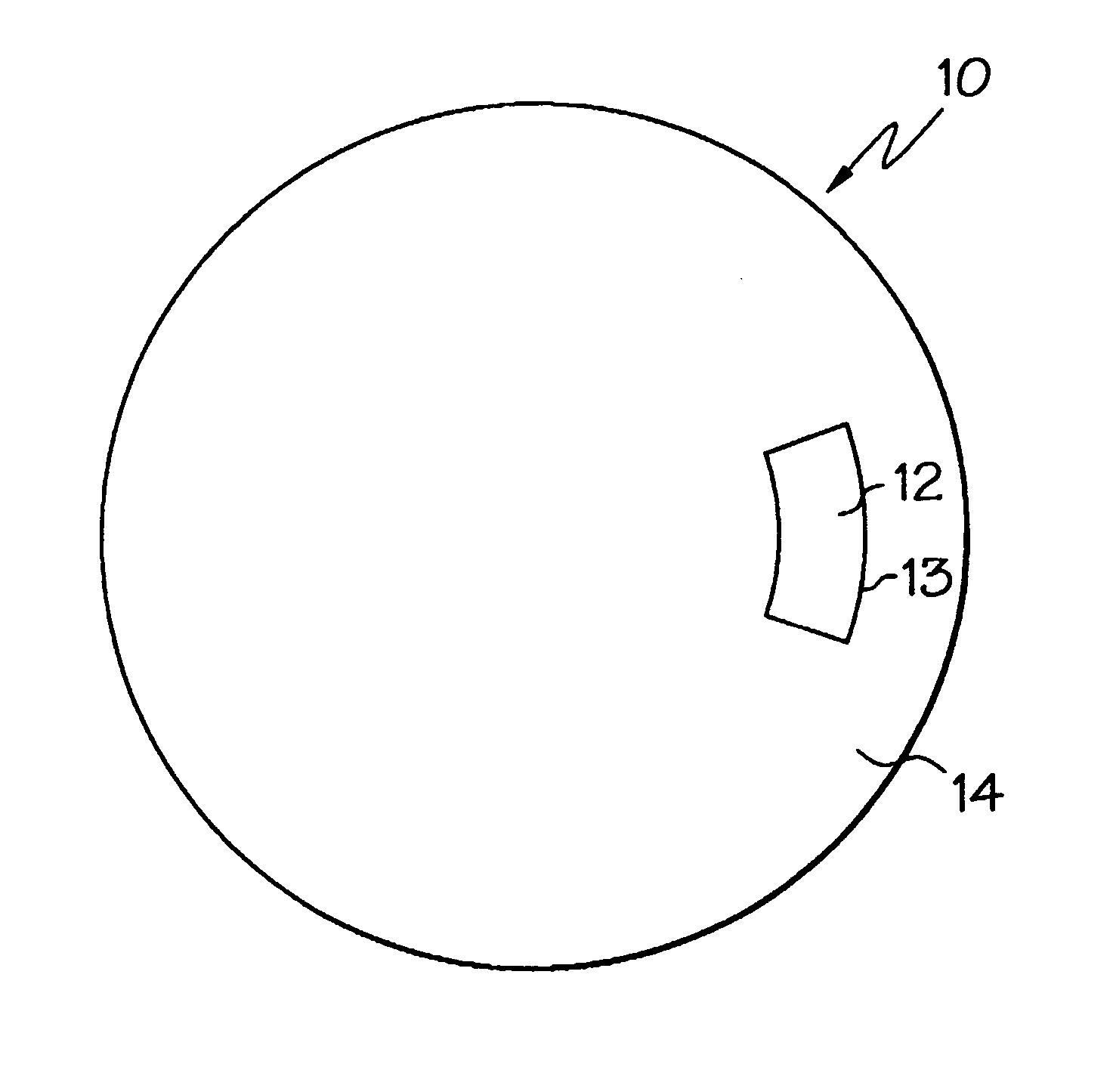
A joining pin (3.2) with which two parts (1 and 2) made from a porous material, particularly wood or a wood-like material, are to be joined together, is anchored in the porous material at predetermined anchoring points (31, 33). For this purpose, a bore (4.2) with a closed inner end (41) is made in the parts (1 and 2). The shape of this bore (4.2) is so matched to the joining pin (3.2) that it can be introduced substantially without force expenditure into the bore and is positionable in a first position. At least one predetermined anchoring point (31, 33) between the joining pin (3.2) and the wall of the bore (4.2) is formed when pressure is built up by pressing the joining pin (3.2) with a pressing force (F) more deeply into the bore to a second position. Energy is supplied in a planned manner to the joining pin (3.2) so that at the predetermined anchoring points (31, 33) the thermoplastic material of the joining pin (3.2) is plasticized. The locally plasticized plastic material is pressed by the local pressure into the porous material of the parts and forms local, macroscopic anchors (10, 20). The joining pin (3.2) is, e.g., made entirely from a thermoplastic material and the energy for plasticizing is supplied thereto by ultrasonic vibration.
Owner:WOODWELDING
Molded polishing pad having integral window
A polishing pad is formed as a one-piece article having a region which is transparent and an adjacent region which is opaque. The article is formed by solidifying a flowable polymeric material which at least initially has a uniform composition. The flowable polymeric material is processed during a molding operation to provide the transparent region and the adjacent opaque region. Types of polymeric material suitable for making the polishing pad include a single thermoplastic material, a blend of thermoplastic materials, and a reactive thermosetting polymer.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
Electrically conductive power transmission belt
A belt made up of an elastomeric belt body, an electrically conductive tensile cord such as carbon fiber cord in a cord layer reinforcing the belt body, an outer layer of electrically conductive thermoplastic material such as polypropylene film, and an electrically conductive fabric layer residing between the tensile cord layer and the outer layer and providing electrical continuity between the outer layer and the tensile cord. An electrically conductive thread may be woven in the fabric and may present at both surfaces of the fabric and contact both the outer layer and the tensile cord to provide the electrical continuity there between.
Owner:THE GATES CORP
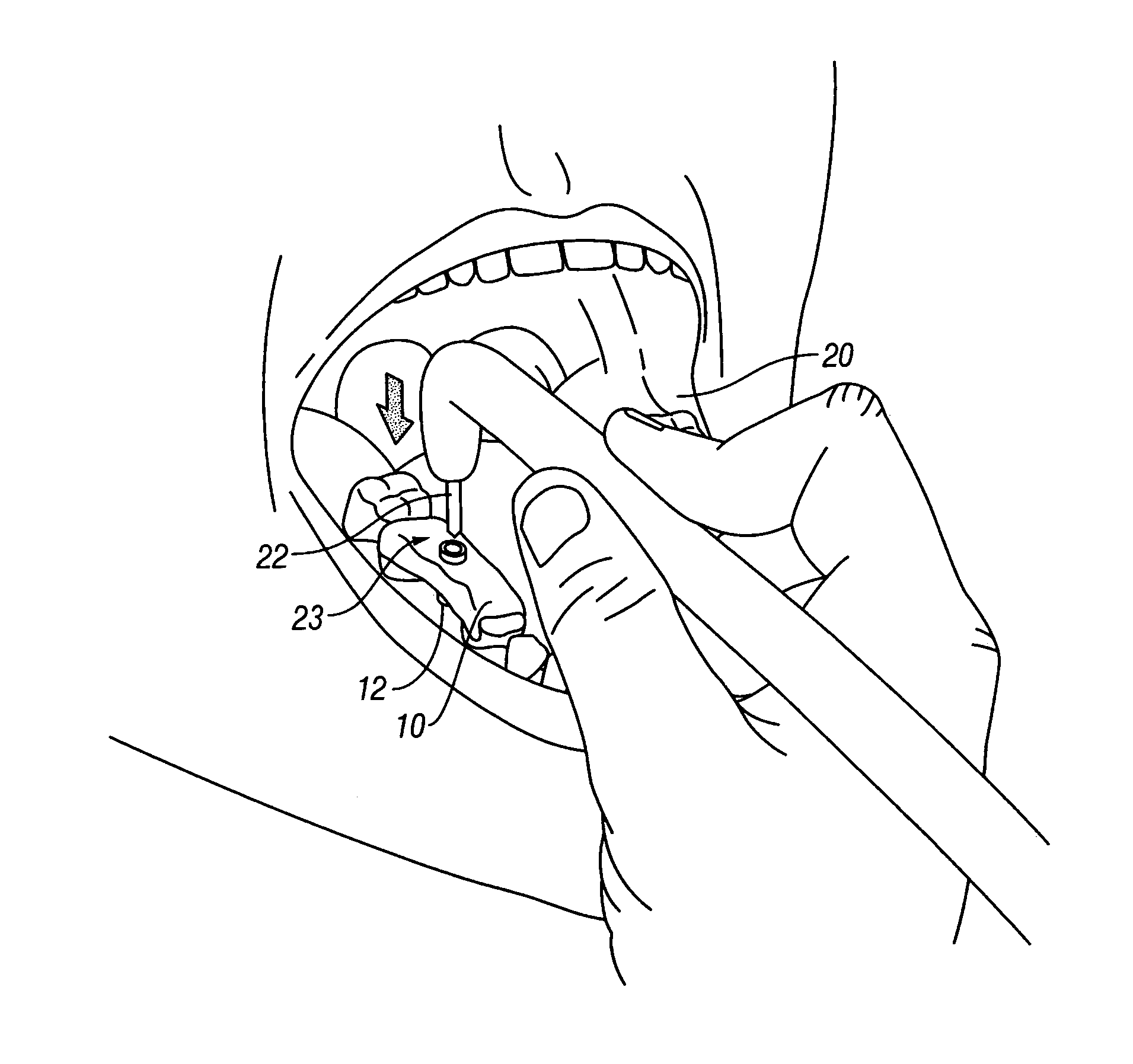
Thermoplastic surgical template for performing dental implant osteotomies and method thereof
A surgical template for performing dental implant osteotomies comprises a malleable, resinous, thermoplastic base, at least one non-thermoplastic, rigid drill guide attached to the base, and a securing mechanism between the base and the drill guide. The template may reversibly melt to a malleable state and can be handled by hand without additional tools so as to conform to the adjacent teeth of the edentulous ridge, either directly in the patient's mouth or on a cast model. Dental osteotomies using the template can then be performed. The surgical template may be manufactured of a thermoplastic material having a sharp and low melting point but high rigidity in the solid state at room temperature.
Owner:TANG BRIAN
Bonded joint design for a golf club head
A golf club (40) having a club head (42) with a face component (60) and an aft body (61) is disclosed herein. The face component (60) has a striking plate portion (72) and a return portion (74). The aft-body (61) is composed of a crown portion (62), a sole portion (64) and optionally a ribbon section (90). The face component (60) is composed of a metal material, and the aft-body (61) is preferably composed of a non-metal material such as a composite material or a thermoplastic material. The face component (60) is bonded to the aft-body (61) with a leading edge (180) of an undercut portion (62a and 64a) of the aft-body positioned a distance of 0.100 inch to 0.500 inch from the interior surface (60a) of the face component (60) in order to reduce the stress on the bonded joint of between the face component (60) and the aft-body (61). The club head (42) has a volume in the range of 290 cubic centimeters to 600 cubic centimeters, a weight in the range of 165 grams to 300 grams, and a striking plate portion (72) surface area in the range of 4.00 square inches to 7.50 square inches.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
Fibers and methods for use in solid freeform fabrication
ActiveUS20110143108A1Easy to produceSpecific characteristicAdditive manufacturing apparatusSynthetic resin layered productsFiberRapid prototyping
A shaped body comprised of individual, interconnected layers may be produced from fibers in accordance with a solid freeform fabrication or rapid prototyping method. The fibers may be produced by extrusion molding a thermoplastic material.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
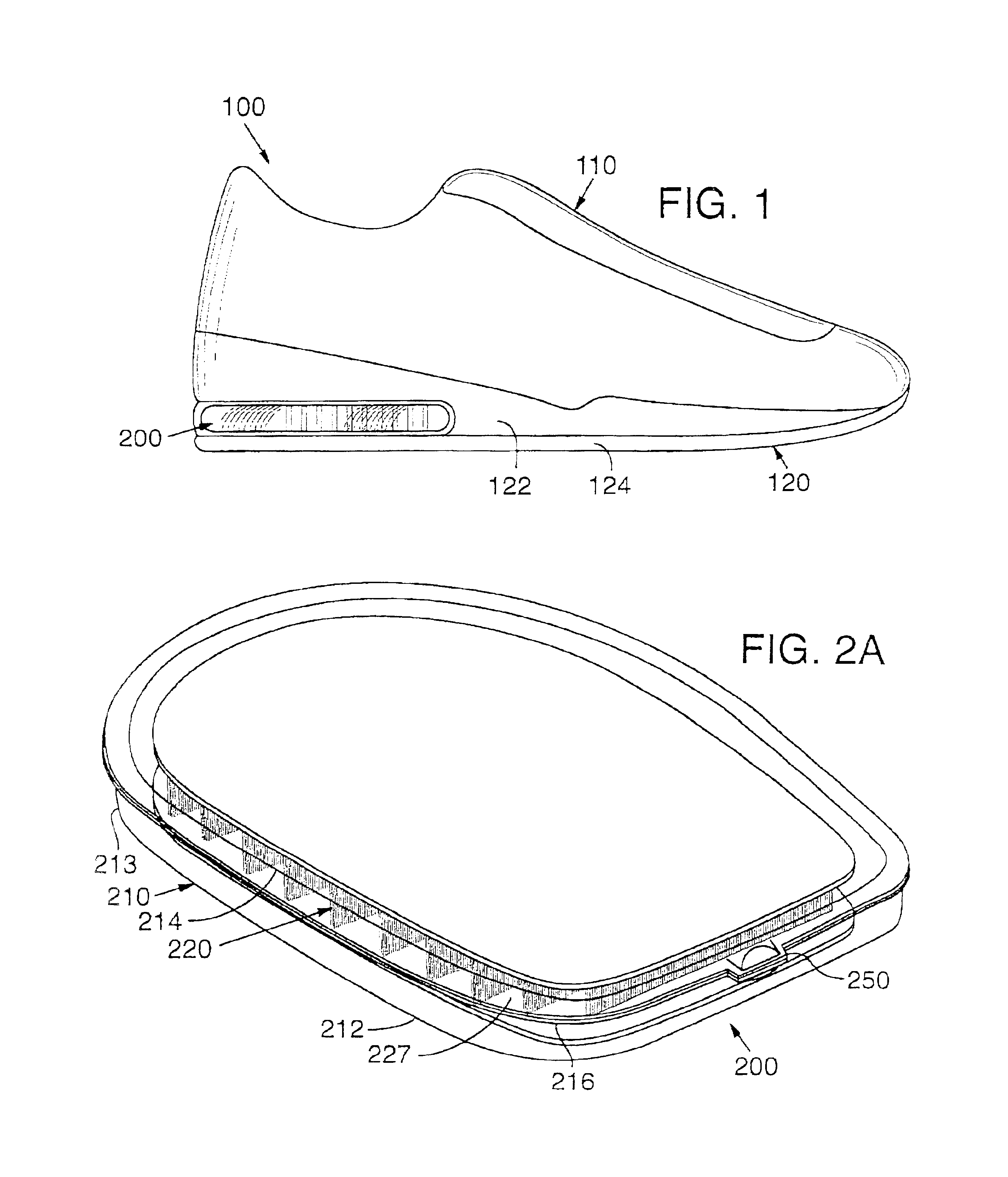
Footwear uppers and other textile components including reinforced and abutting edge joint seams
ActiveUS20100077634A1Strong and stable and durable constructionShoemaking devicesLeather sewingEngineeringMechanical engineering
Textile Components, such as upper members for articles of footwear, include: (a) a first portion having a first edge, wherein the first edge includes a first portion of material engaged with a first seam support material via a first thermoplastic material; (b) a second portion having a second edge, wherein the second edge includes a second portion of material engaged with a second seam support material via a second thermoplastic material; and (c) structure to engage the first and second edges in an abutting edge joint (such as a zig-zag stitch). The resulting textile components may be lightweight and breathable (e.g., due to use of lightweight upper fabric), having a comfortable fit (e.g., due to the abutting edge joint), while still providing a strong, stable, and durable construction (e.g., due to the presence of the seam support member(s)).
Owner:NIKE INC
Polymer covered advanced polymer/wood composite structural member
InactiveUS6357197B1Corner/edge jointsMetal rolling stand detailsComposite constructionMoisture absorption
A composite structural member of the invention comprises a linear member having a first end and a second end attached to each end of the linear member as an end piece or end cap structure. Covering the composite member is a thermoplastic envelope preferably adherently bonded to the composite member. The end caps or end pieces are preferably thermoplastic materials typically thermoplastic composites comprising a thermoplastic resin and a fiber. Such a member is environmentally stable, resists moisture absorption, forms strong mitered joints and can be used in the assembly of fenestration products for commercial and residential real estate.
Owner:ANDERSEN CORPORATION
Thermoplastic planks and methods for making the same
InactiveUS6986934B2Improve moisture resistanceEasy flexibilityDecorative surface effectsSpecial ornamental structuresEngineeringThermoplastic materials
A thermoplastic laminate plank is described wherein the thermoplastic laminate plank comprises a core, a print layer, and optionally an overlay. The core comprises at least one thermoplastic material and has a top surface and bottom surface wherein a print layer is affixed to the top surface of the core and an overlay layer is affixed to the top surface of the print layer. Optionally, an underlay layer can be located and affixed between the bottom surface of the print layer and the top surface of the core. In addition, a method of making the thermoplastic laminate plank is further described which involves extruding at least one thermoplastic material into the shape of the core and affixing a laminate on the core, wherein the laminate comprises an overlay affixed to the top surface of the print layer and optionally an underlay layer affixed to the bottom surface of the print layer.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
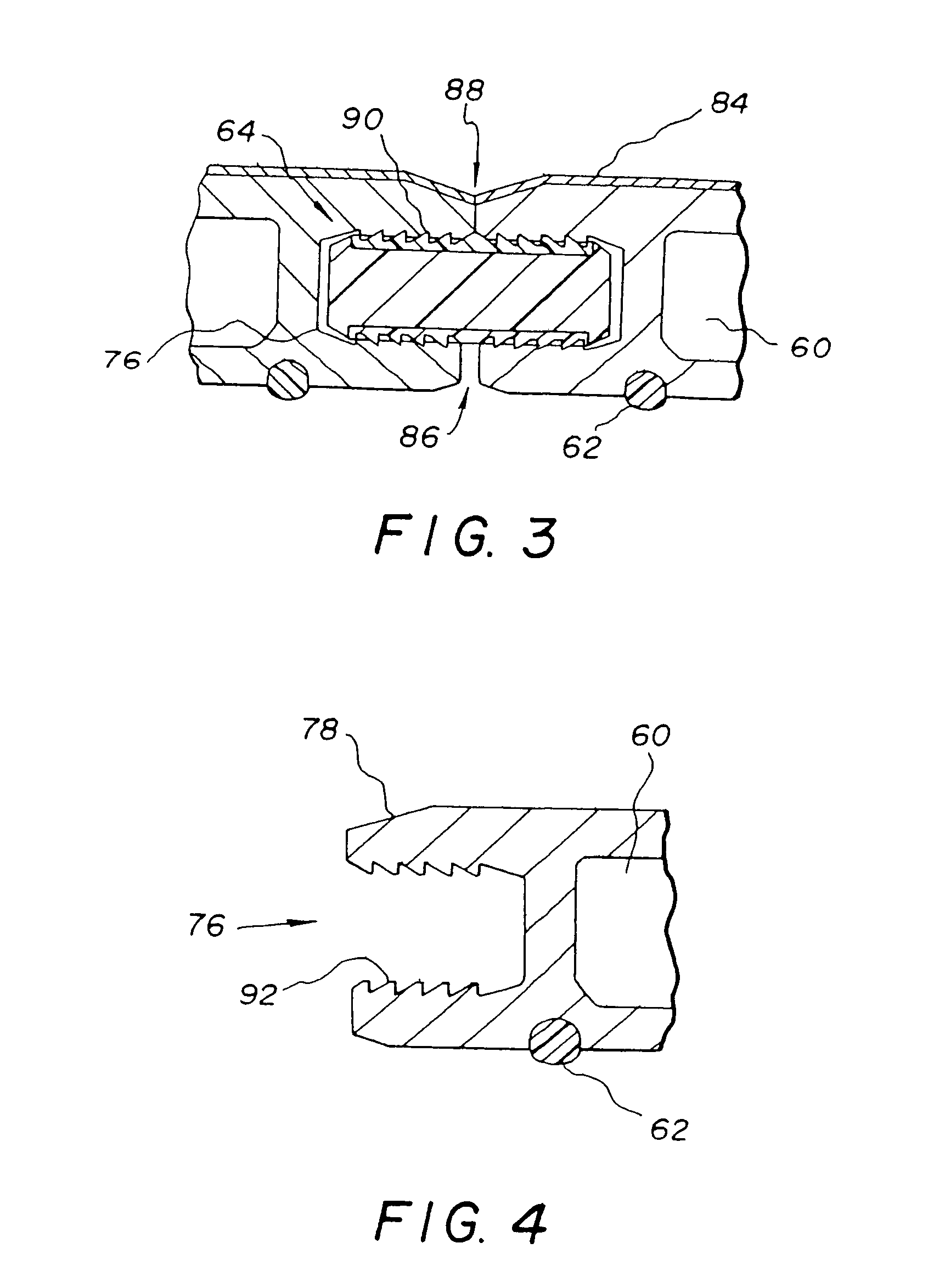
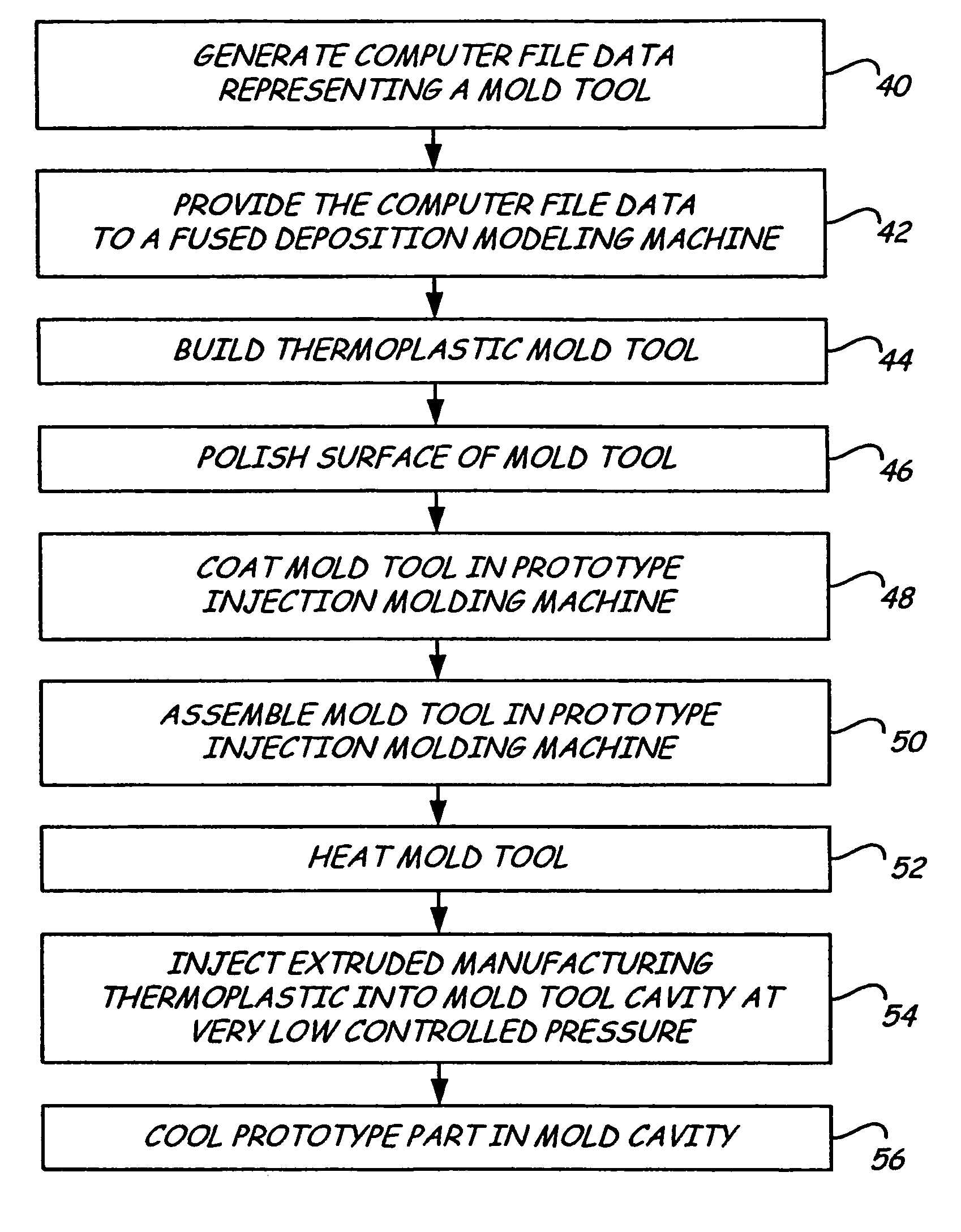
Rapid prototype injection molding
InactiveUS7125512B2Additive manufacturing apparatusMechanical vibrations separationInjection mouldingRapid prototyping
Owner:STRATSYS INC
Apparatus and method for making form-fitted molded protective cases for products
A method and apparatus for making inexpensive, form-fitted, protective cases of thermal plastic or polycarbonate material that can be easily printed with decorative imagery and / or electronic circuitry for a variety of products, such as portable music players or radios, cell phones, lap-top computers, and the like. The method involves creating a tool having substantially the same surface dimensions of a product. An element is then molded from bulk film of thermoplastic material using the tool. Once the element is molded, it is trimmed from the bulk film. The resulting apparatus is a protective case intended to form-fit over the surface features and dimensions of the actual product used to define the tool.
Owner:SIK
Embolectomy capture sheath
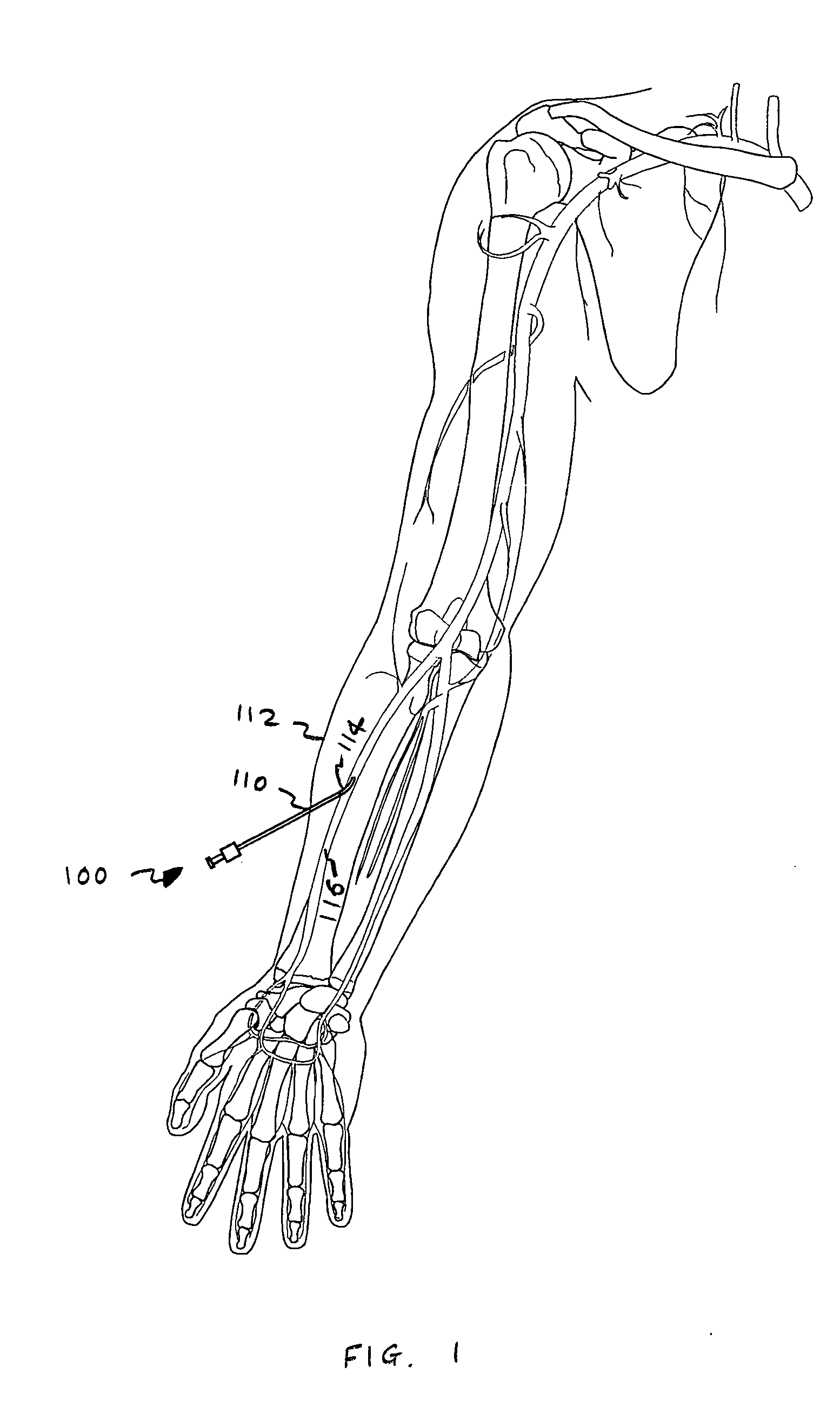
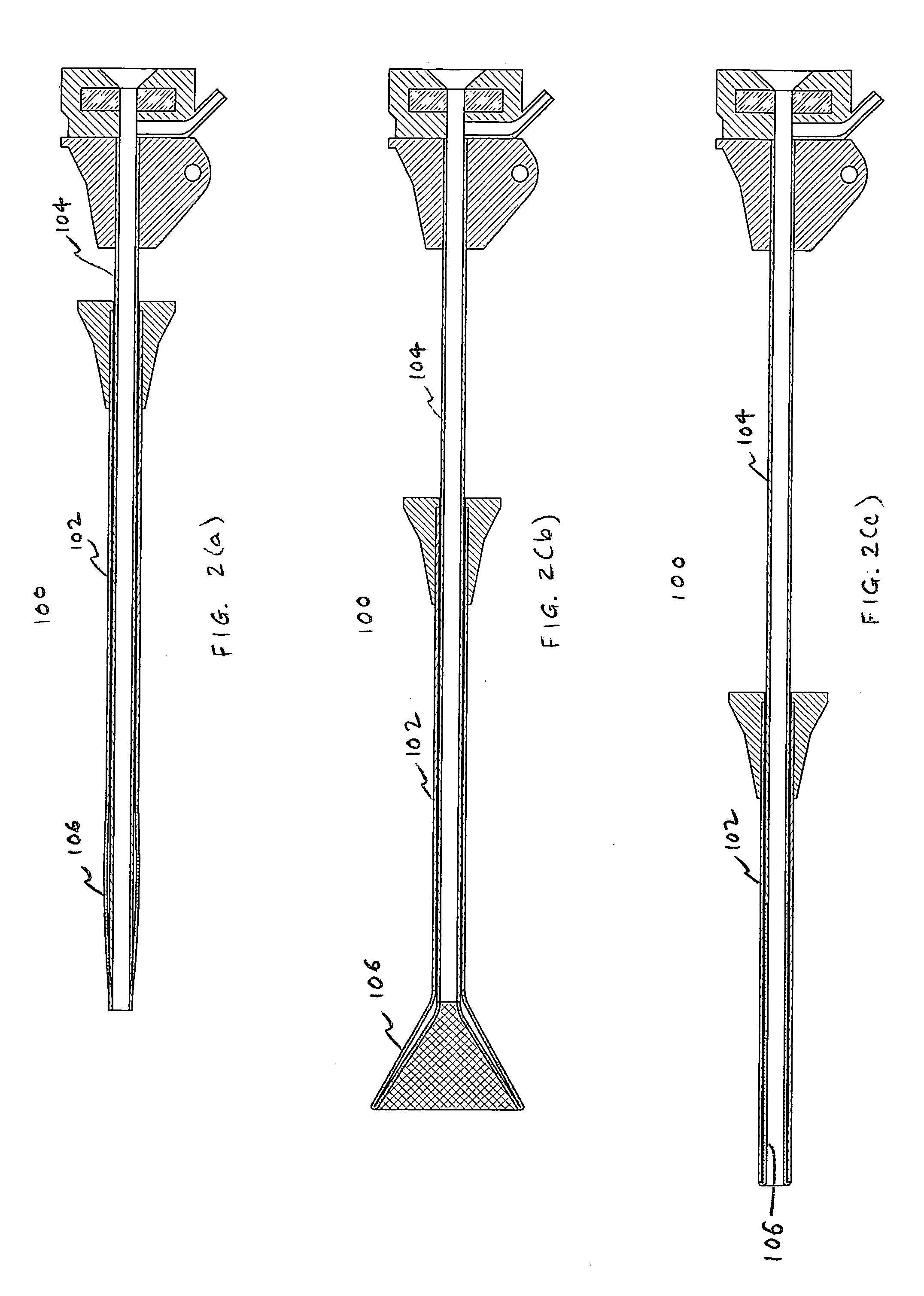
InactiveUS20050187570A1Variable flexibilityVariable kink-resistanceGuide needlesCannulasPlastic materialsActuator
An access device adapted for use in a body conduit is provided comprising an outer tube having a proximal end and a distal end, an inner tube disposed coaxially with the outer tube having a proximal end and a distal end, and an expandable portion having a first end coupled to the distal end of the outer tube and a second end coupled to the distal end of the inner tube. The outer tube and the inner tube are movable relative to each other to transform the expandable portion between a low-profile state and a high-profile state, and at least one of the outer and inner tubes comprises a wire-reinforced tube or is formed from a plurality of individual, discrete, generally ring-shaped elements arranged in series and fused or bonded together to form a continuous tubular structure. The access device may further comprise an actuator coupled to one of the outer and inner tubes and being movable relative to the other of the outer and inner tubes to transform the expandable portion between the low- and high-profile states. The expandable portion may be formed with a braid material and has the shape of a cone. The ring-shaped elements may be formed of a thermoplastic or a thermoset material, and they may include at least one of plastic rings, metallic rings, un-reinforced plastic rings and metal reinforced plastic rings assembled along the length of at least one of the tubes to provide variable flexibility and kink-resistance. The wire-reinforced tube is formed by coating a wire with a plastic material, wrapping the coated wire around a mandrel forming a plurality of windings, and heating the wound coated wire until the plastic material melts and bonds the windings forming the wire-reinforced tube.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Thermoplastic planks and methods for making the same
InactiveUS7763345B2Improve moisture resistanceEasy flexibilityCovering/liningsDecorative surface effectsThick plateEngineering
A thermoplastic laminate plank is described wherein the thermoplastic laminate plank comprises a core, a print layer, and optionally an overlay. The core comprises at least one thermoplastic material and has a top surface and bottom surface wherein a print layer is affixed to the top surface of the core and an overlay layer is affixed to the top surface of the print layer. Optionally, an underlay layer can be located and affixed between the bottom surface of the print layer and the top surface of the core. In addition, a method of making the thermoplastic laminate plank is further described which involves extruding at least one thermoplastic material into the shape of the core and affixing a laminate on the core, wherein the laminate comprises an overlay affixed to the top surface of the print layer and optionally an underlay layer affixed to the bottom surface of the print layer.
Owner:VÄLINGE INNOVATION AB
Substrate mounting for organic, dielectric, optical film
A method for optically coupling a thermoplastic material to an outer surface layer of an organic, dielectric, optical film and the resulting optical filter. Initially, a dielectric film is selected that includes (i) repeating optical layers of at least two polymers having different refractive indexes from each other, (ii) an exterior film surface, (iii) a refractive boundary along the exterior film surface, and (iv) a delamination threshold based on total thermal energy delivered to the film. A thermoplastic material which is miscible with the exterior film surface is fused to the refractive boundary with thermal energy below the delamination threshold to form a polydisperse region having a higher optical transmission than the refractive boundary. Add-on filters in the form of hardcoat layers, anti-reflection layers, holograms, metal dielectric stacks and combinations of these may be combined with the thermoplastic-film construct.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com