Patents
Literature
129results about How to "Thermal conductivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
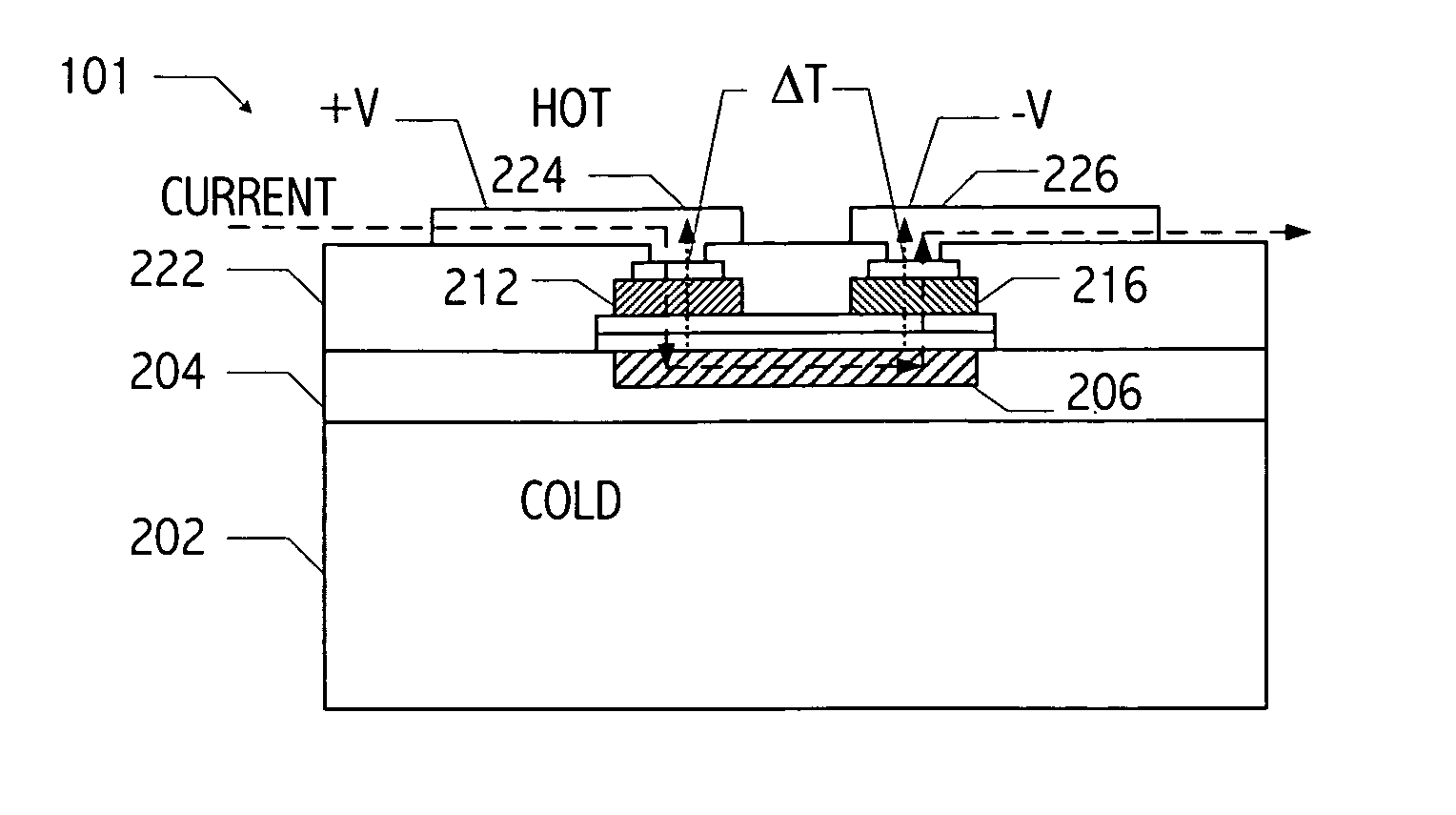
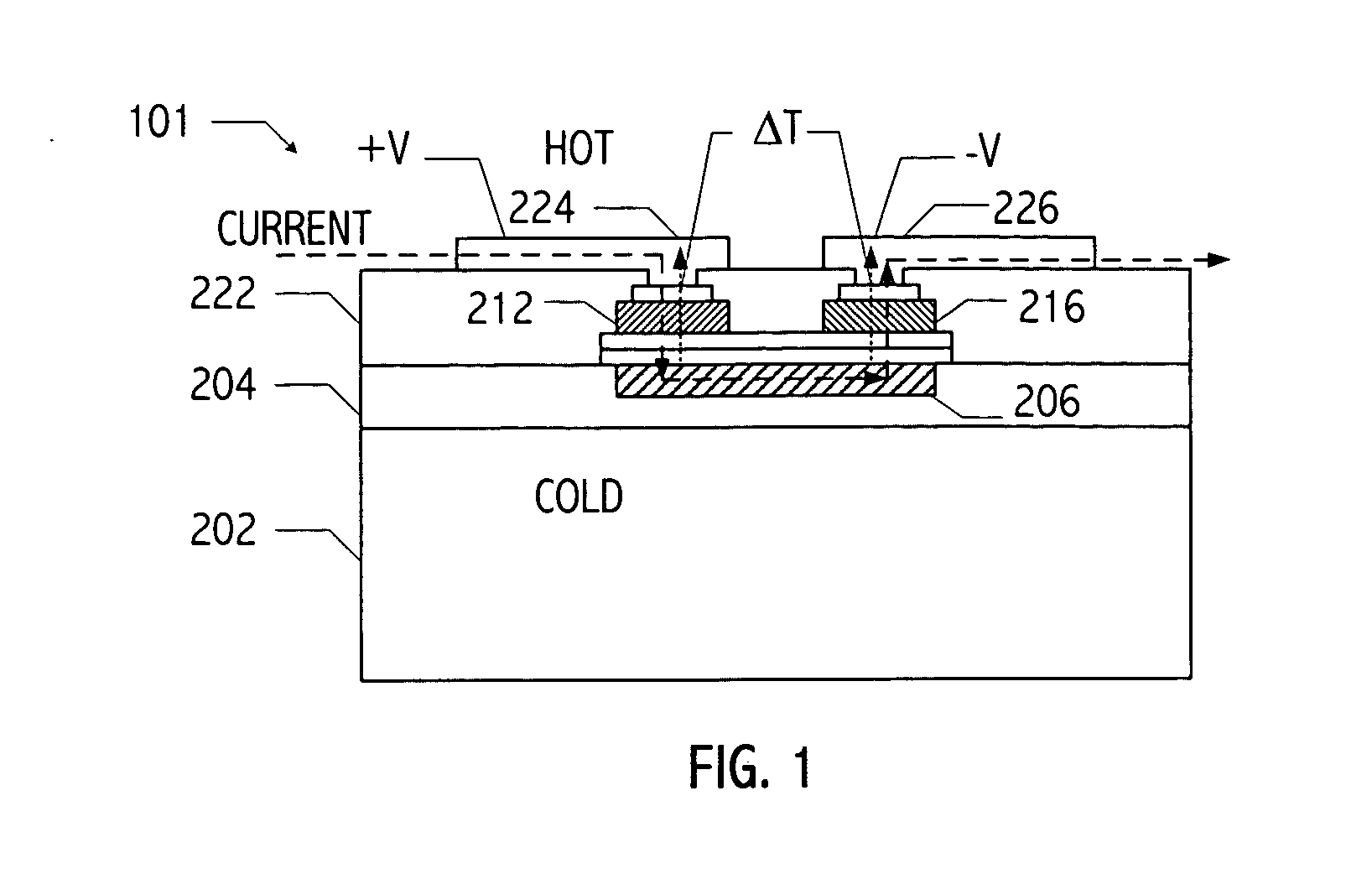
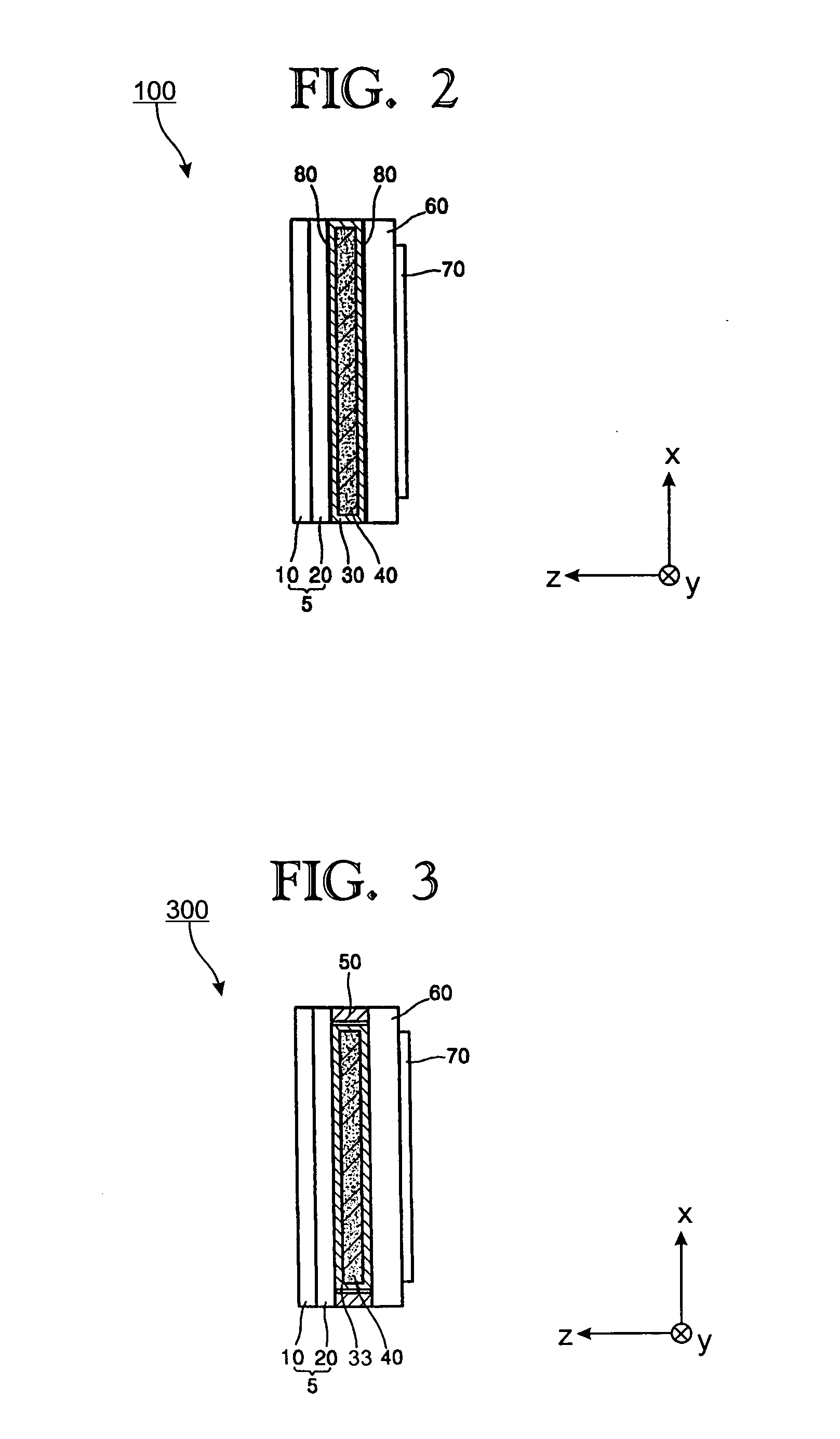
Method for forming a thin-film thermoelectric device including a phonon-blocking thermal conductor
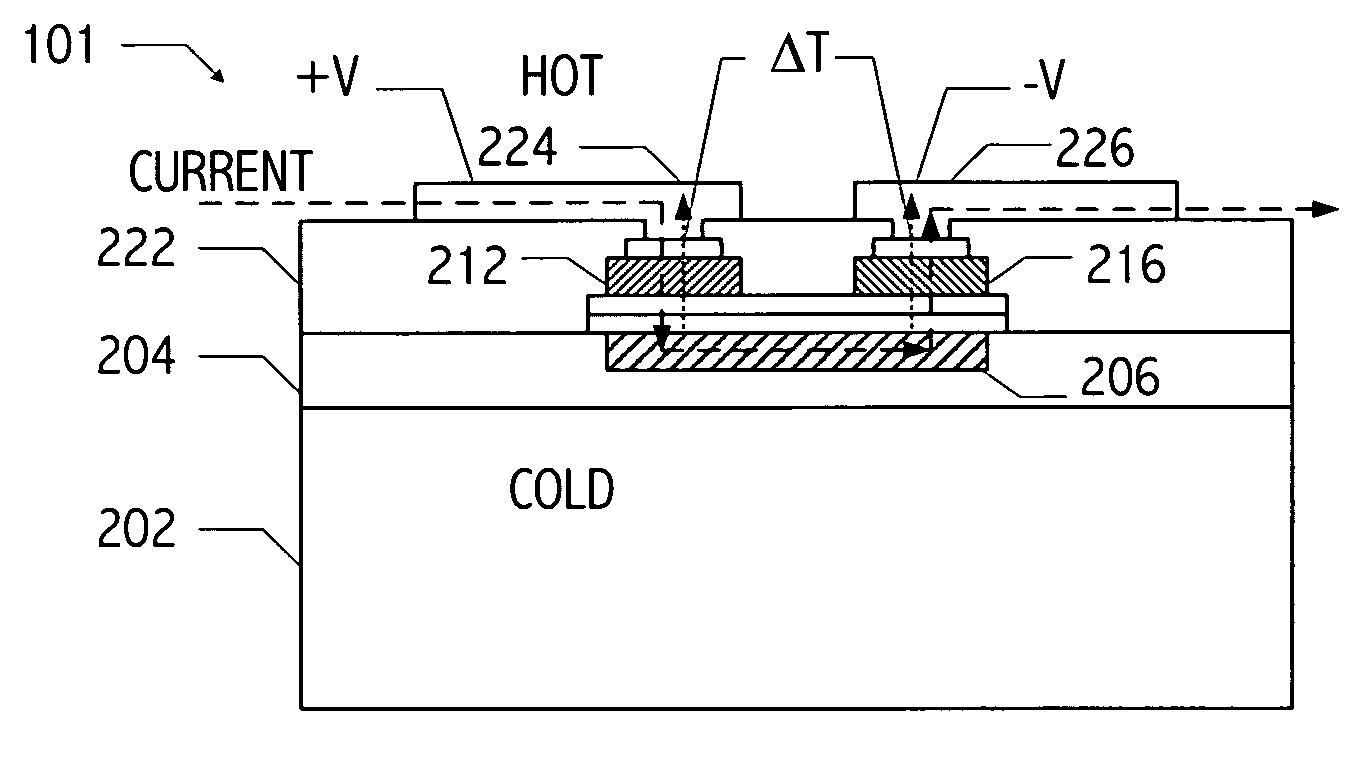
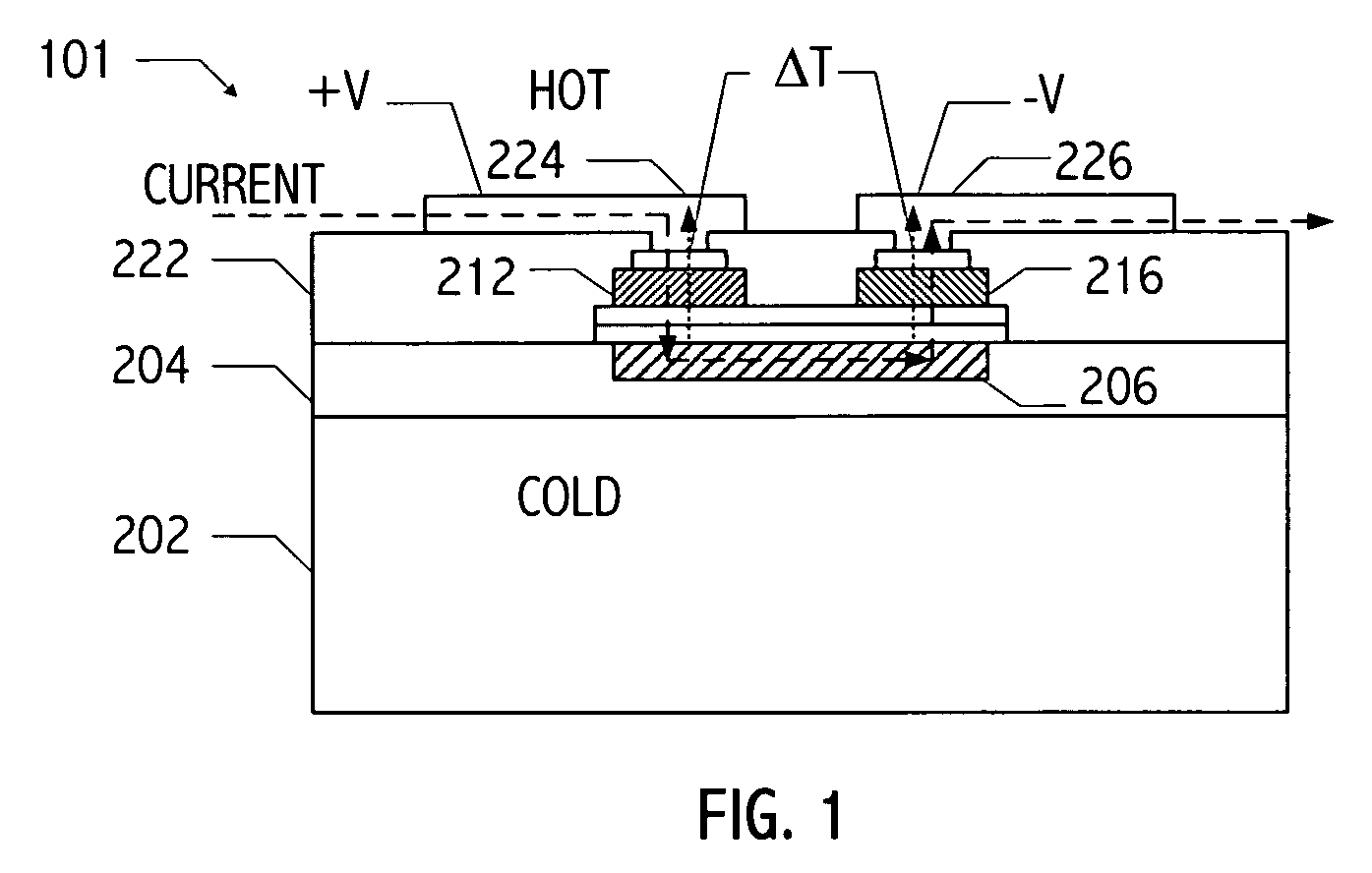
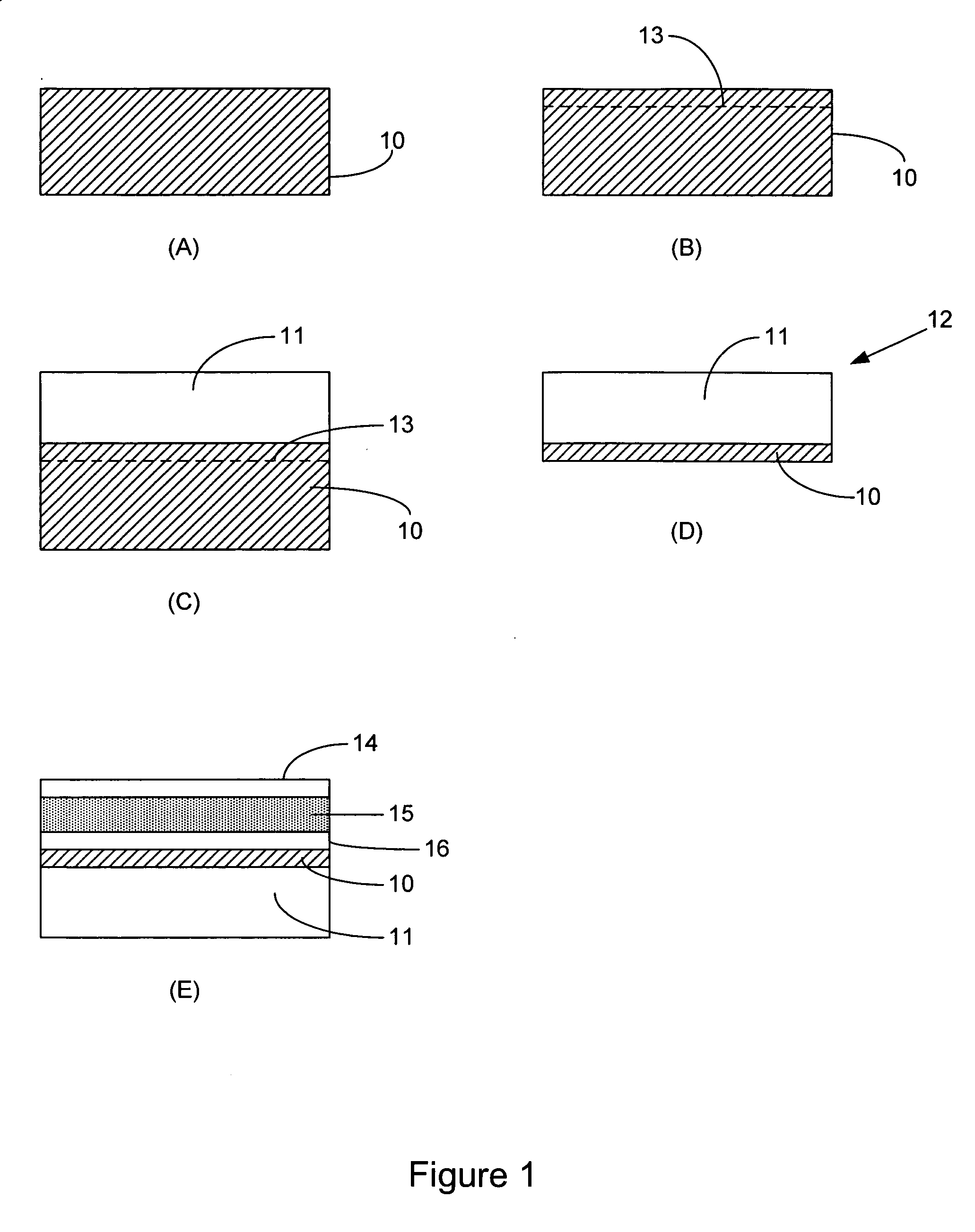
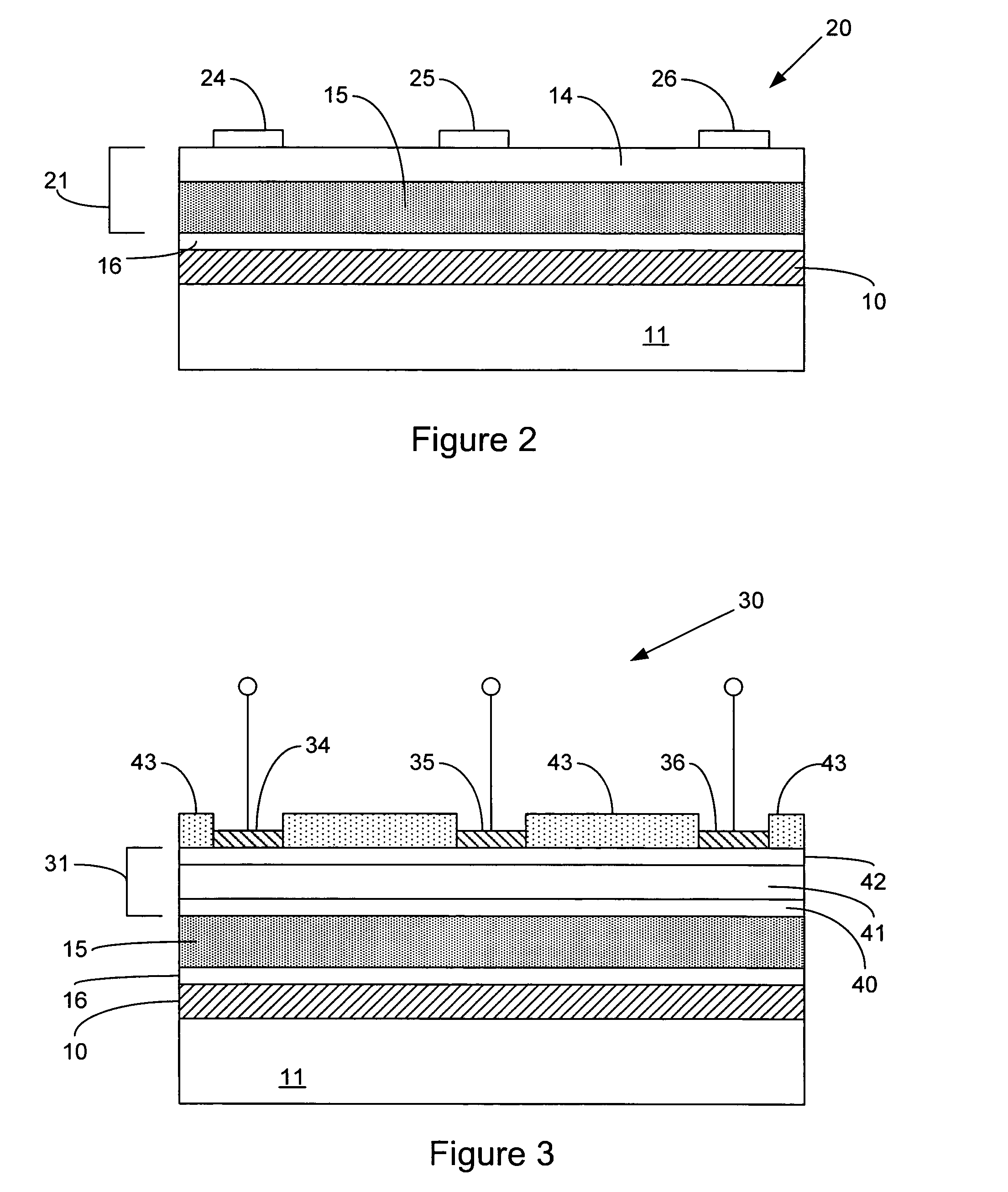
InactiveUS20050150535A1Reduce needReduction in electron thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentElectrical conductorLiquid metal
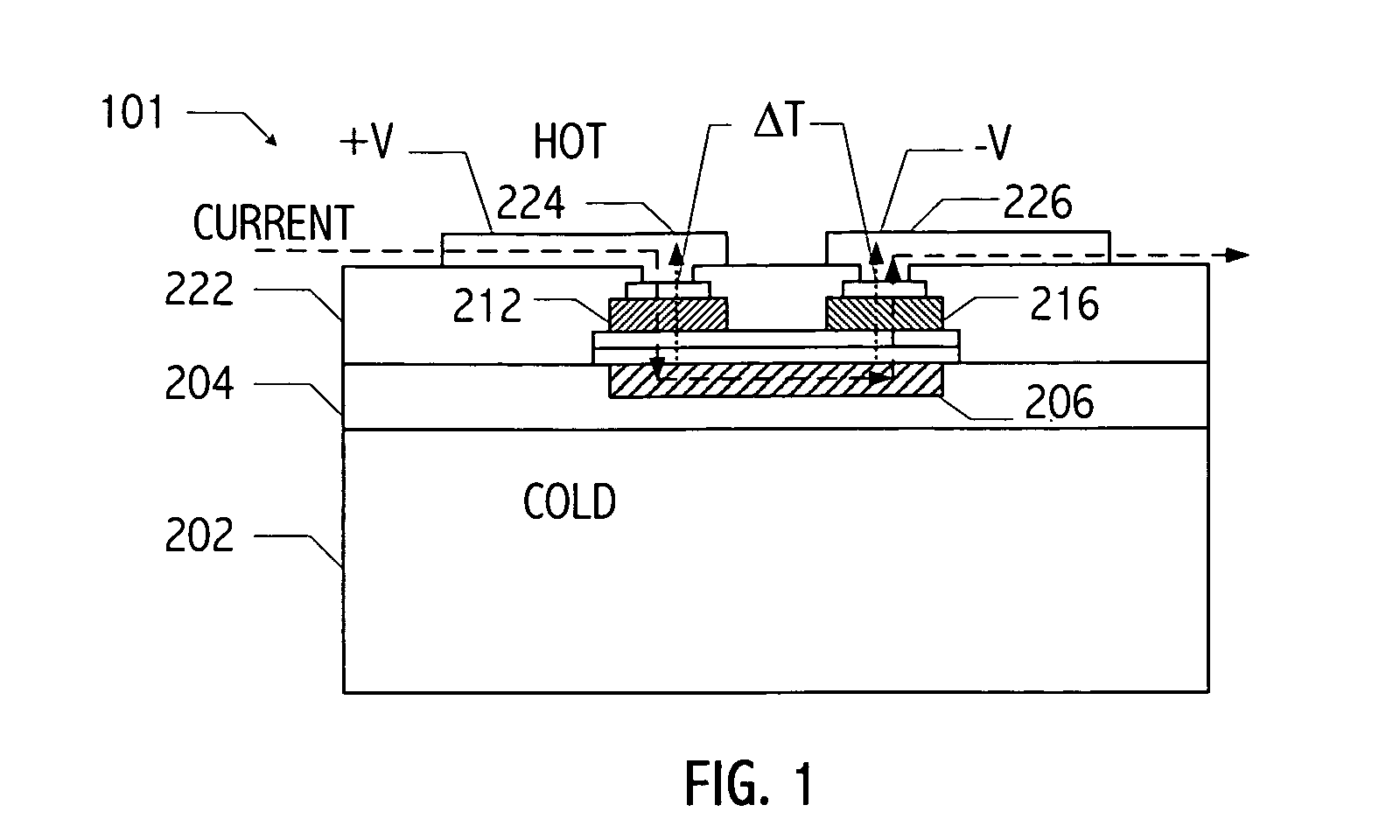
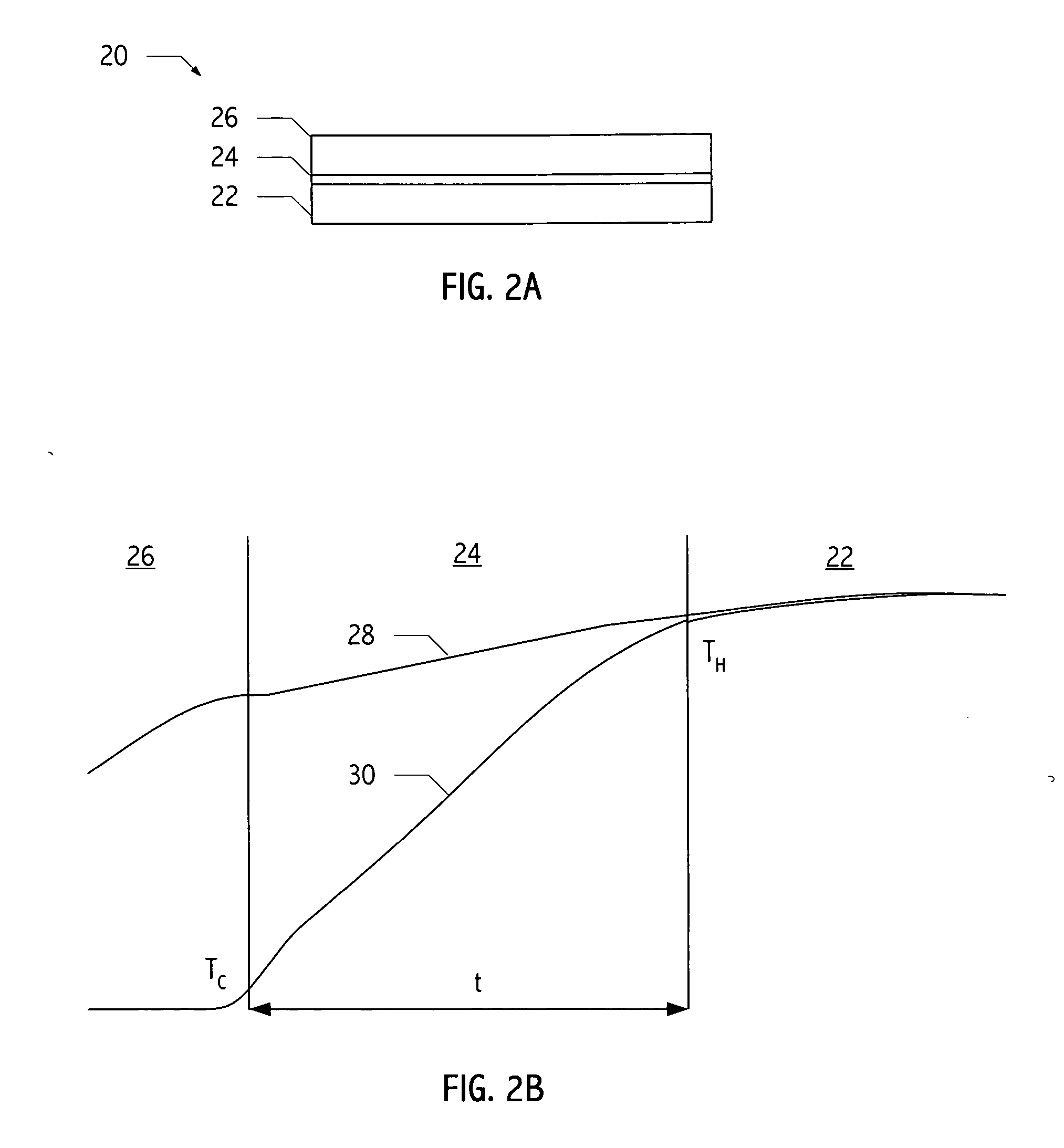
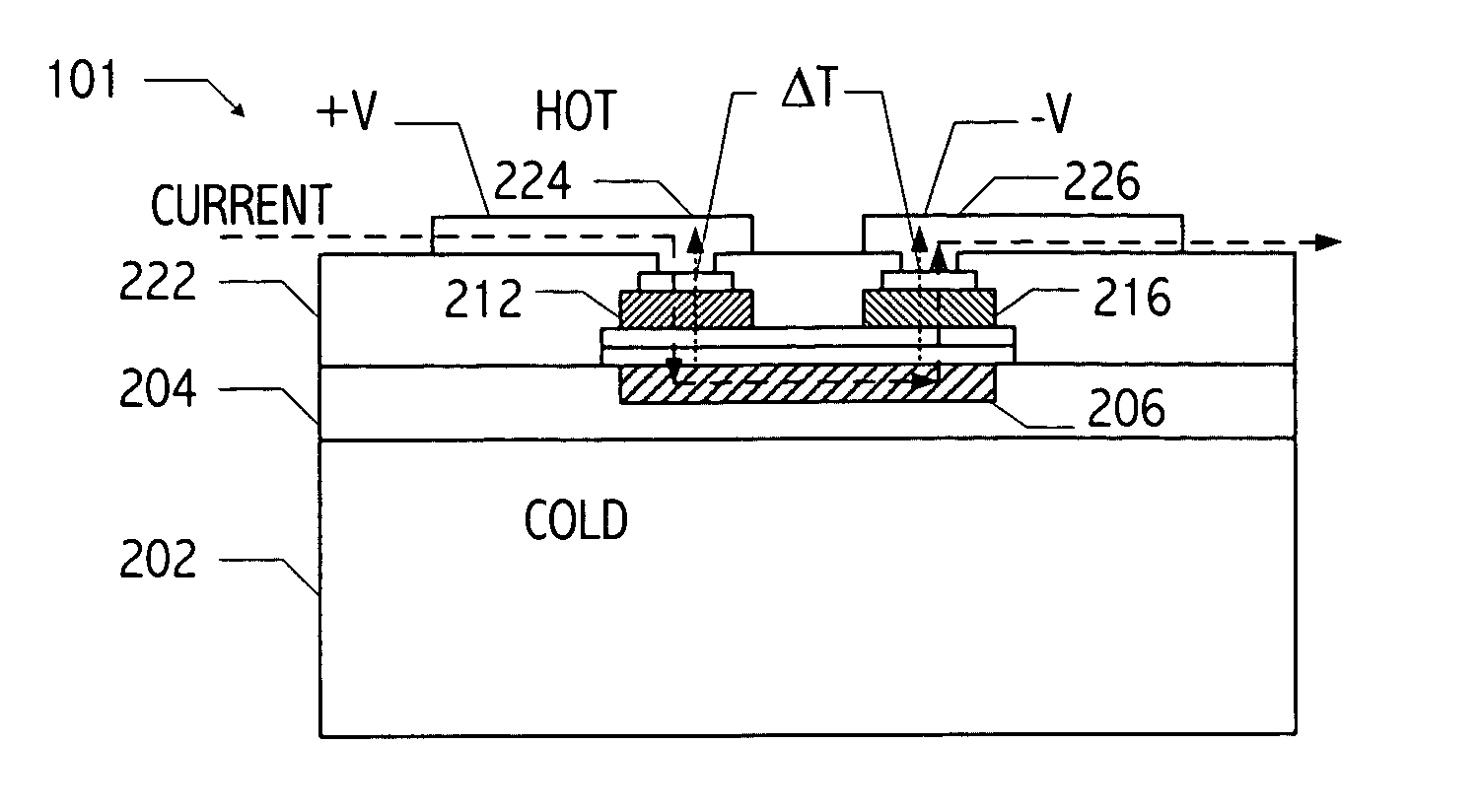
A vertical, monolithic, thin-film thermoelectric device is described. Thermoelectric elements of opposing conductivity types may be coupled electrically in series and thermally in parallel by associated electrodes on a single substrate, reducing the need for mechanisms to attach multiple substrates or components. Phonon transport may be separated from electron transport in a thermoelectric element. A thermoelectric element may have a thickness less than an associated thermalization length. An insulating film between an electrode having a first temperature and an electrode having a second temperature may be a low-thermal conductivity material, a low-k, or ultra-low-k dielectric. Phonon thermal conductivity between a thermoelectric element and an electrode may be reduced without a significant reduction in electron thermal conductivity, as compared to other thermoelectric devices. A phonon conduction impeding material may be included in regions coupling an electrode to an associated thermoelectric element (e.g., a liquid metal).
Owner:NANOCOOLERS
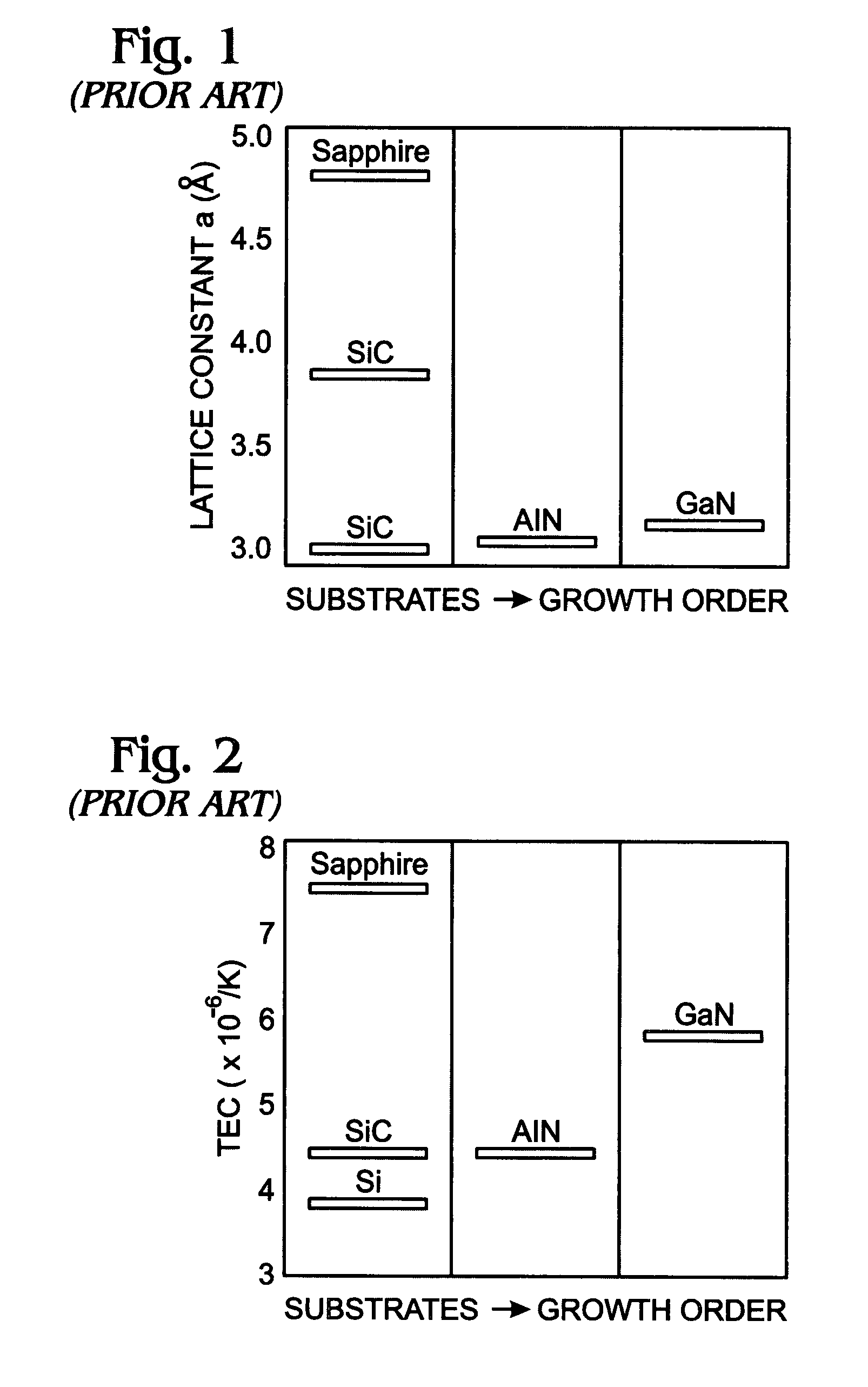
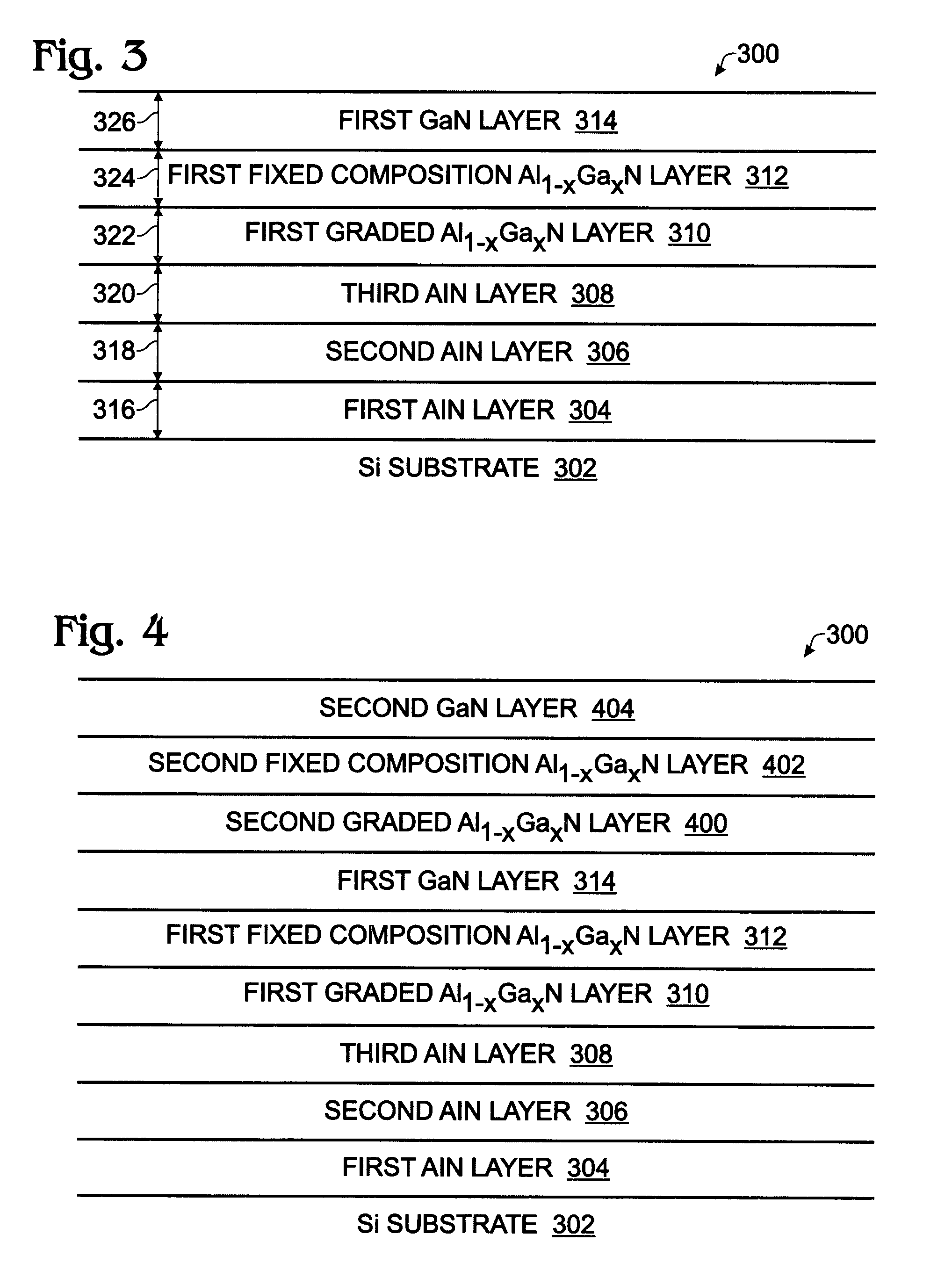
Gallium nitride-on-silicon interface using multiple aluminum compound buffer layers
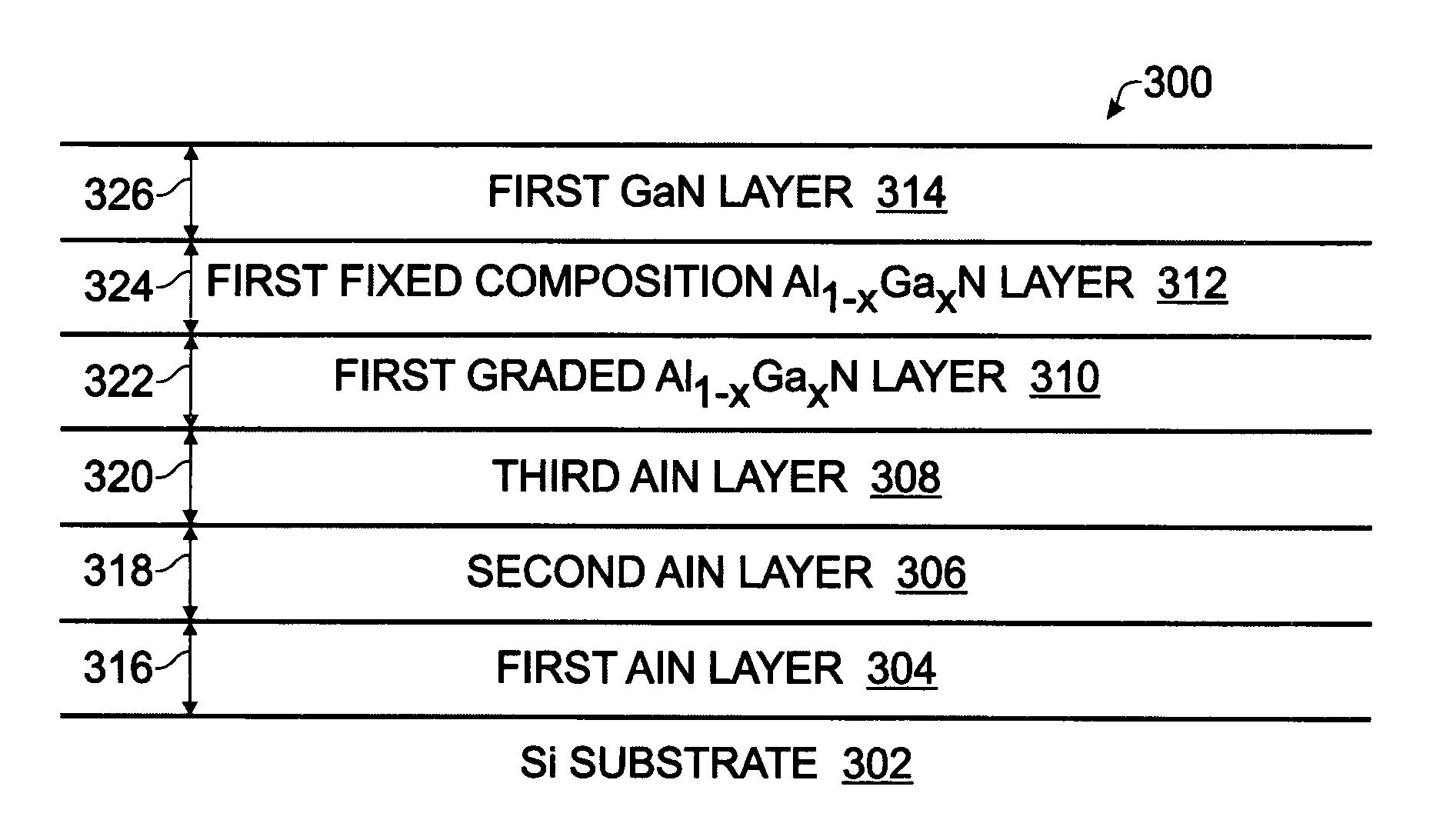
InactiveUS7598108B2Thermal conductivityIncrease powerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesThermal expansionGallium nitride
A thermal expansion interface between silicon (Si) and gallium nitride (GaN) films using multiple buffer layers of aluminum compounds has been provided, along with an associated fabrication method. The method provides a (111) Si substrate and deposits a first layer of AlN overlying the substrate by heating the substrate to a relatively high temperature of 1000 to 1200° C. A second layer of AlN is deposited overlying the first layer of AlN at a lower temperature of 500 to 800° C. A third layer of AlN is deposited overlying the second layer of AlN by heating the substrate to the higher temperature range. Then, a grading Al1-XGaXN layer is formed overlying the third layer of AlN, where 0<X<1, followed by a fixed composition Al1-XGaXN layer overlying the first grading Al1-XGaXN layer. An epitaxial GaN layer can then be grown overlying the fixed composition Al1-XGaXN layer.
Owner:SHARP KK
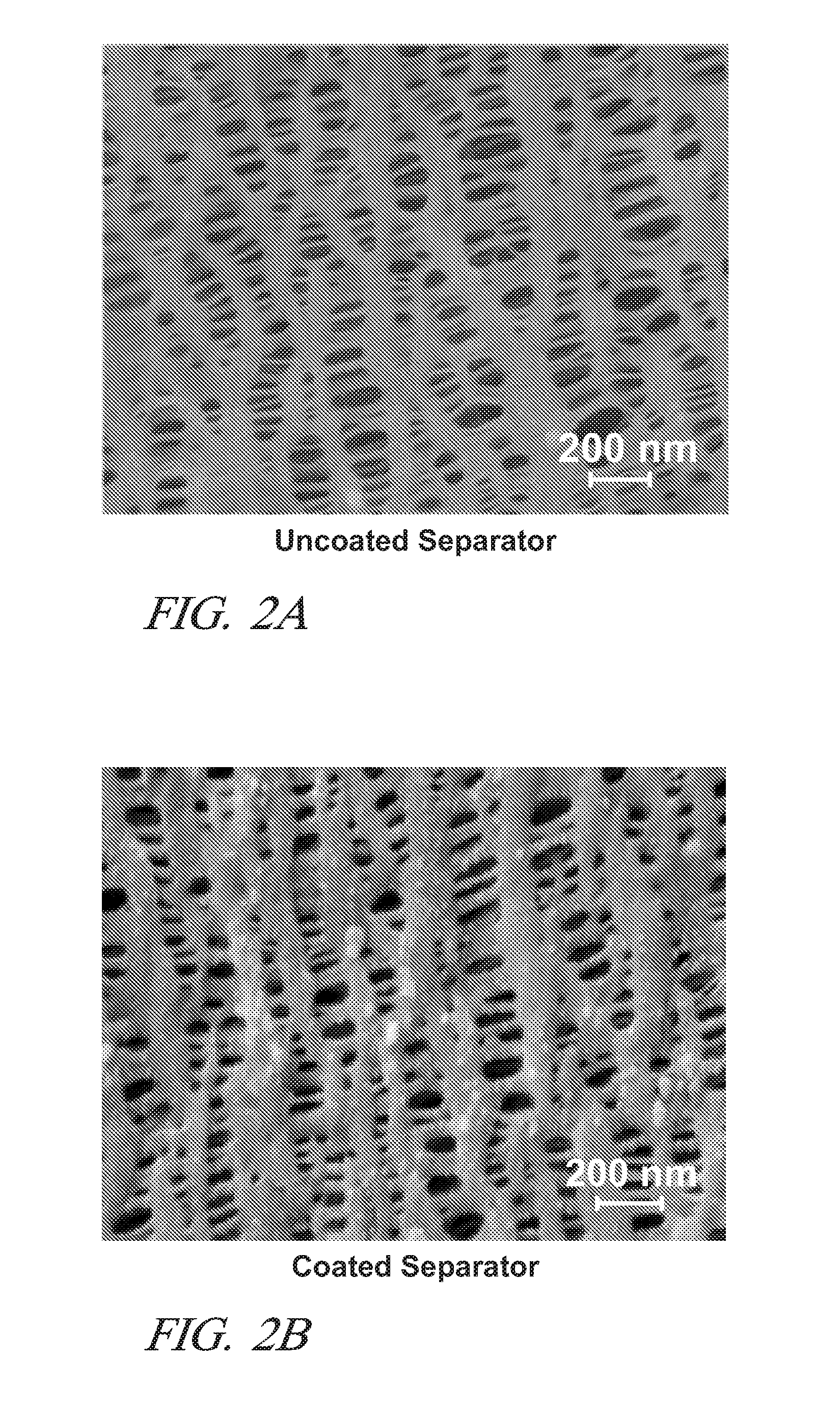
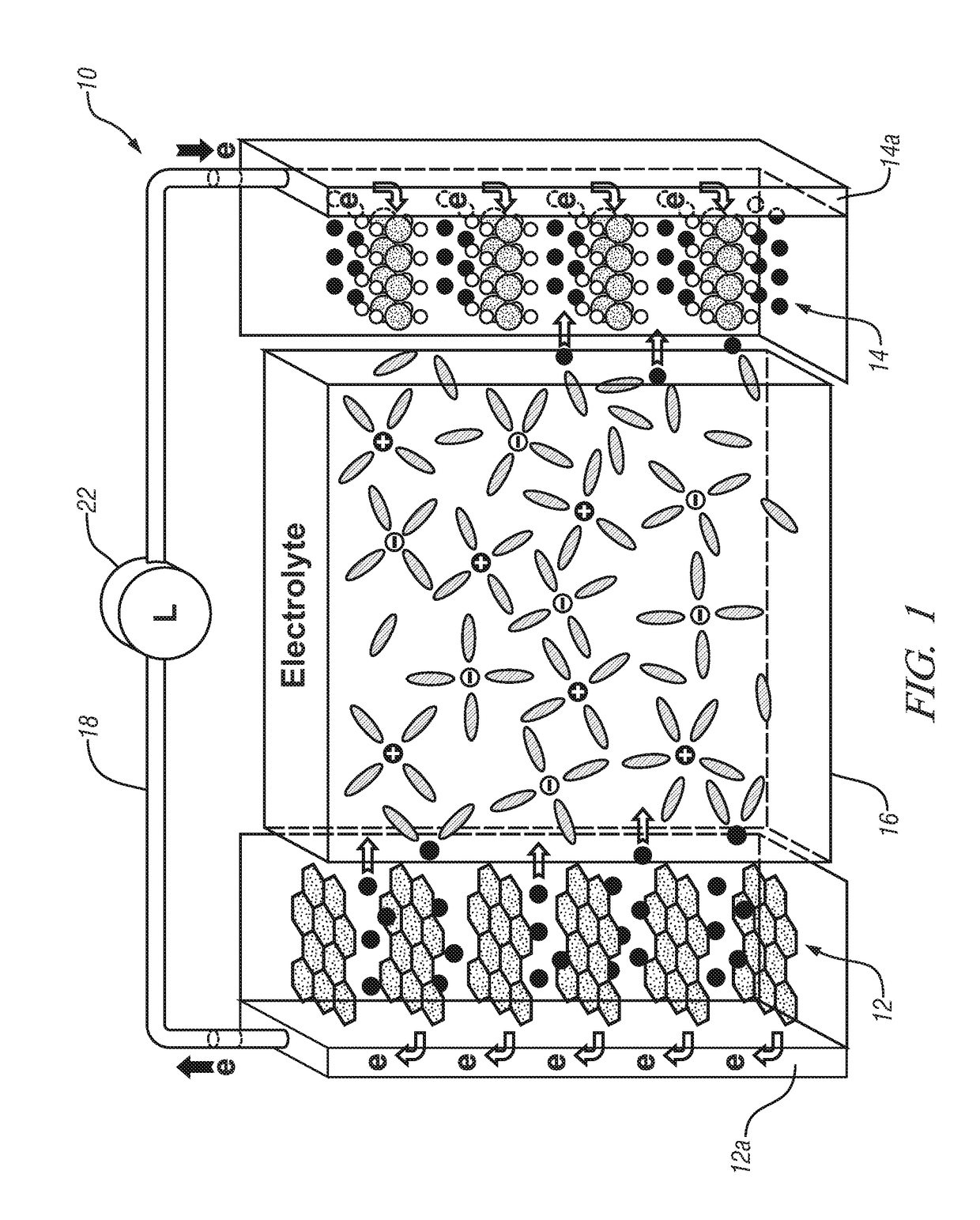
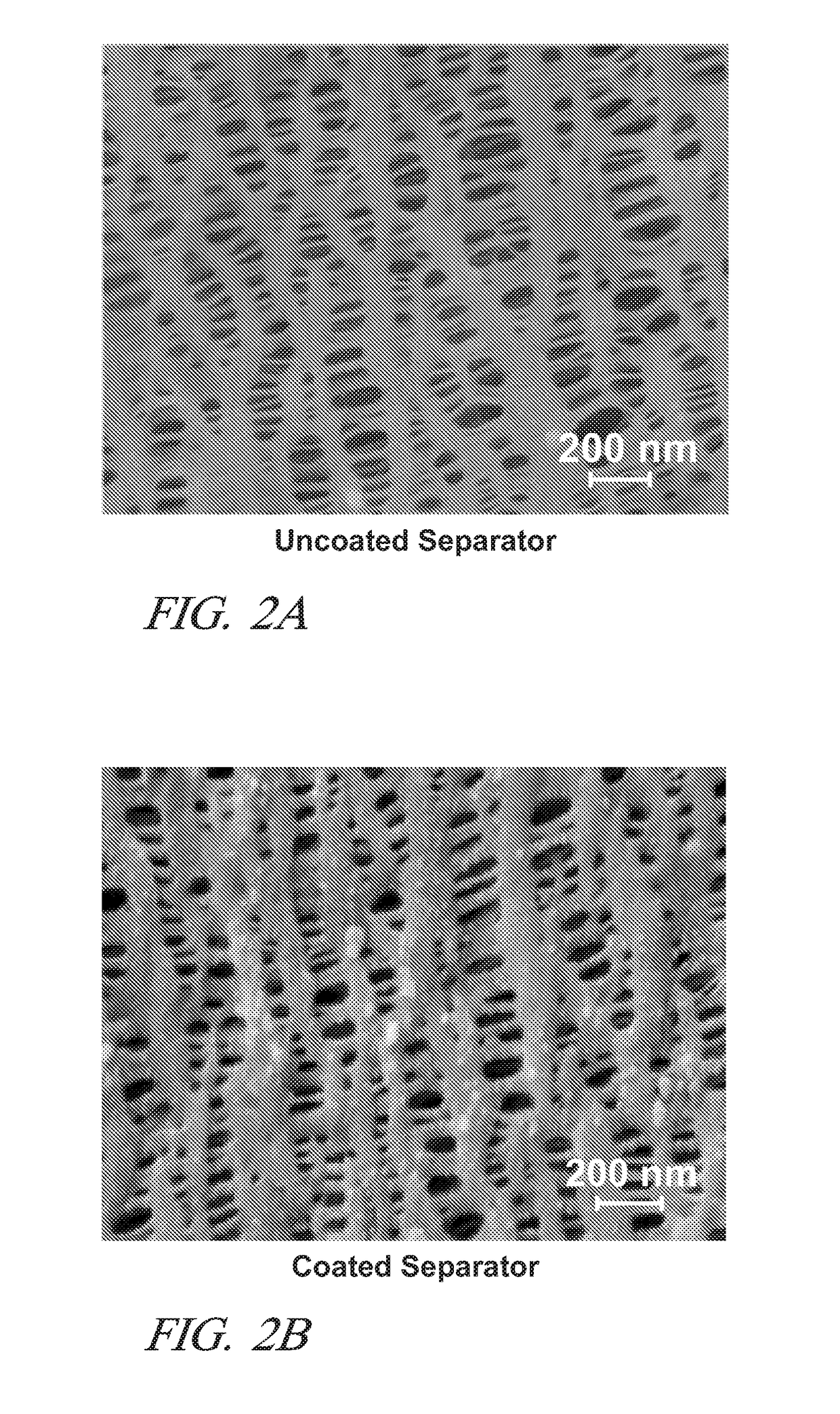
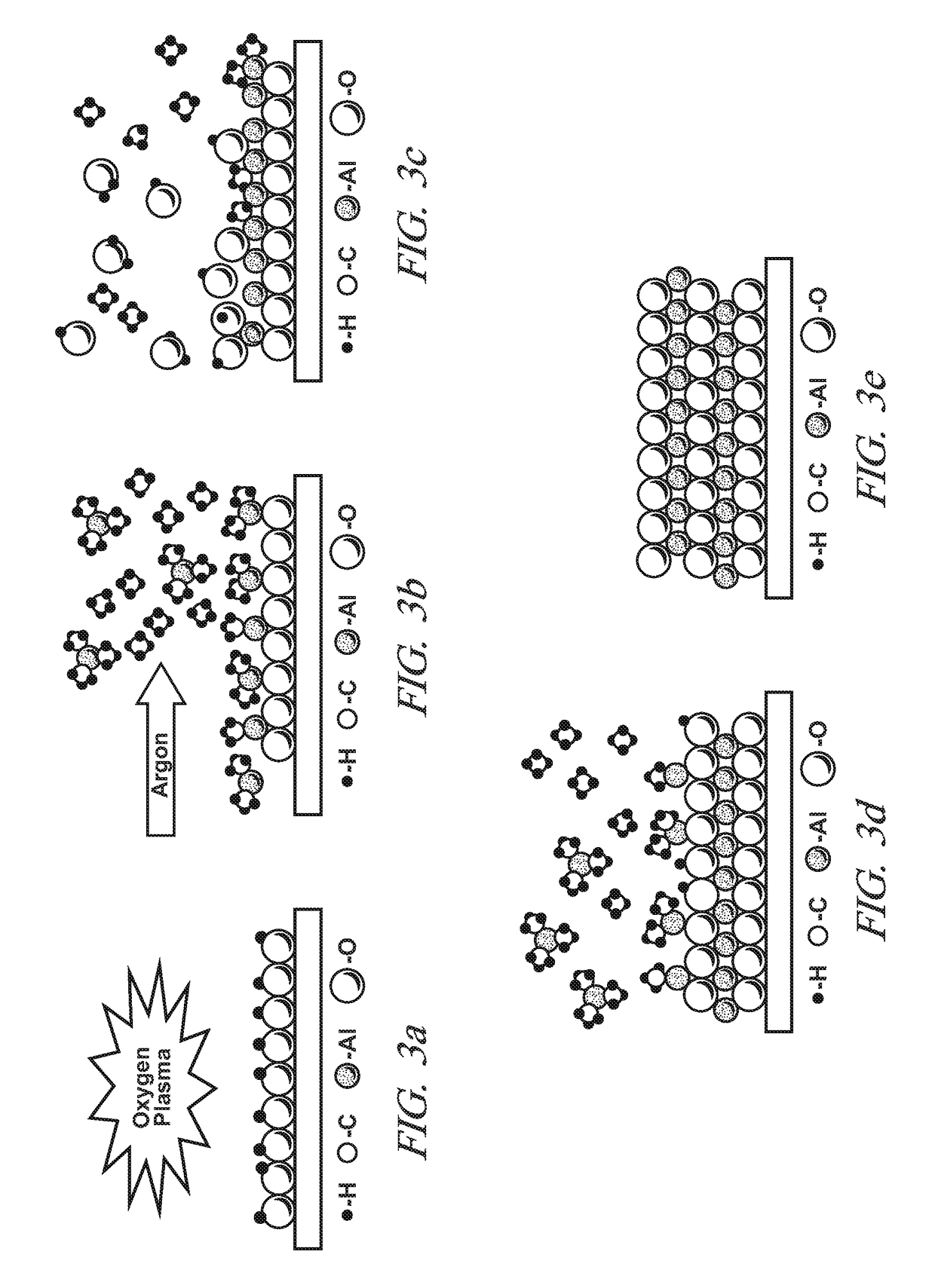
Lithium-ion batteries with coated separators
ActiveUS20110200863A1Low environmental impactThermal conductivityCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersLi-accumulatorsCoated membraneGas phase
A porous polymer sheet or membrane is provided with a thin coating of an electrically non-conductive ceramic composition and the coating conforms to all surfaces, including the pore surfaces, of the membrane. Such a coated membrane serves well, for example, as an intra-cell separator in a lithium ion battery. The coating increases the mechanical properties and thermal stability of the separator in battery operation and retains electrolyte. The coating may be formed by a two-step vapor-phase process in which atoms of one or more metals such as aluminum, calcium, magnesium, titanium, silicon and / or zirconium are deposited in a conformal layer on a workpiece surface. The metal atoms may then be reacted with ammonia, carbon dioxide, and or water to form their respective non-conductive nitrides, carbides, and / or oxides on the surface. The two-step process is repeated as necessary to obtain a ceramic material coating of desired thickness.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
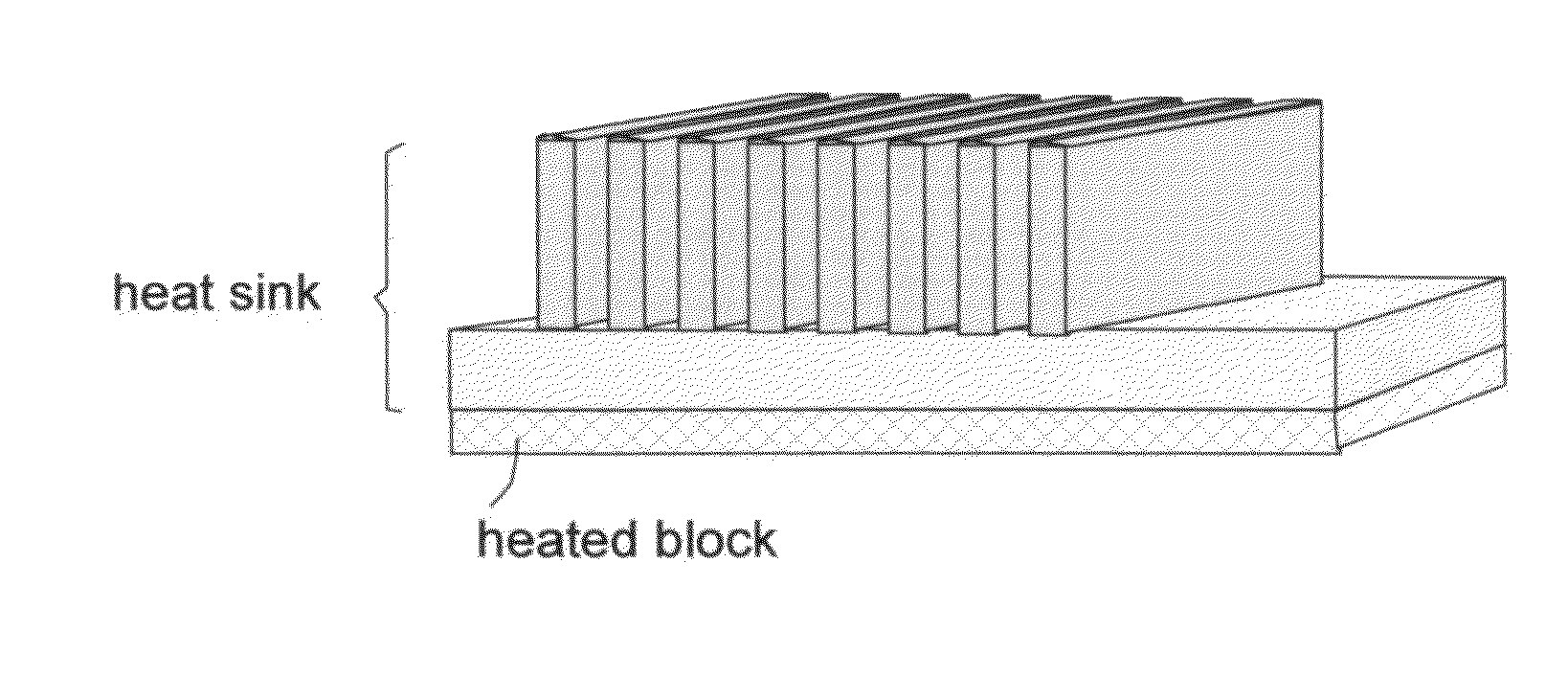
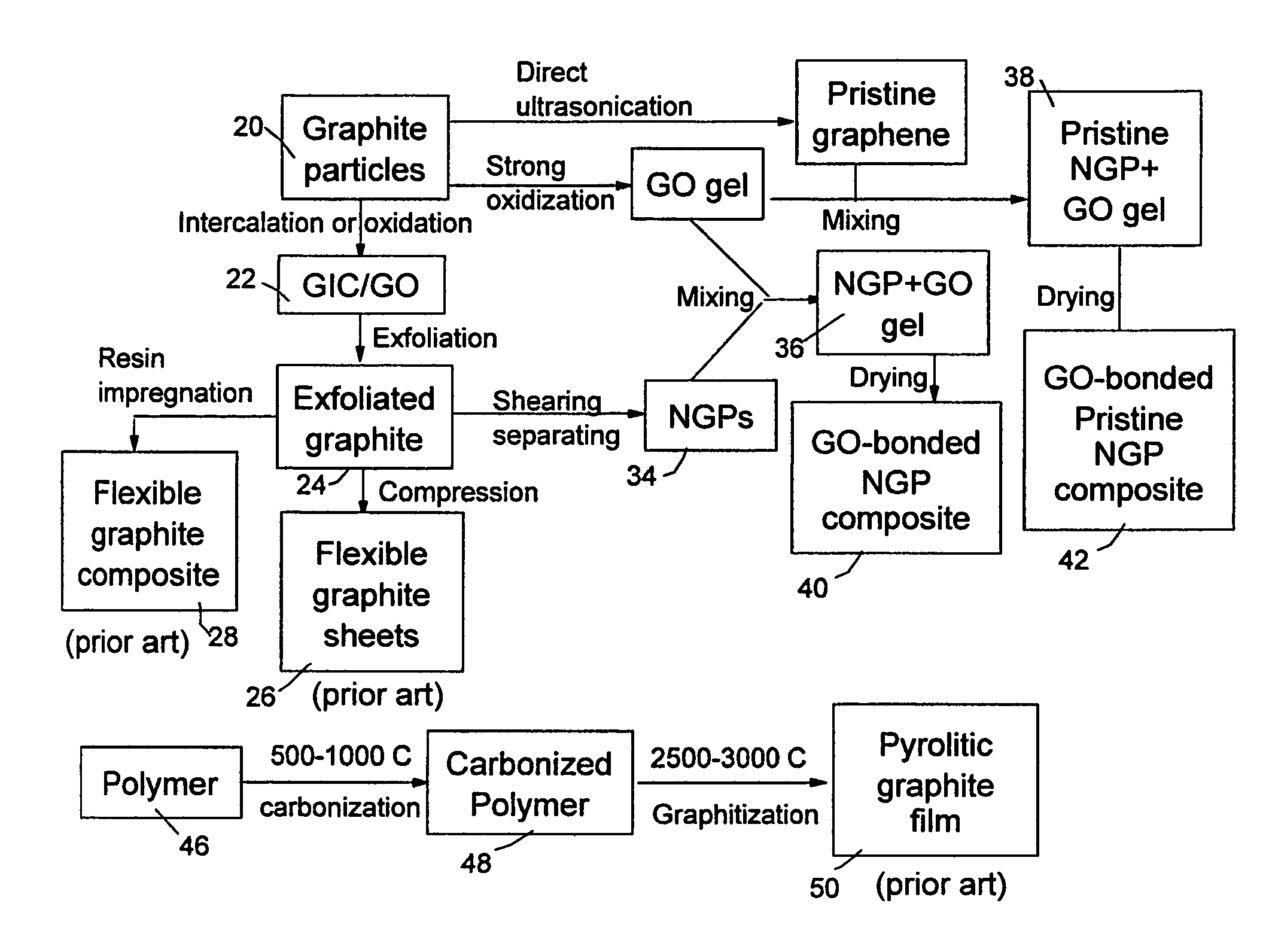
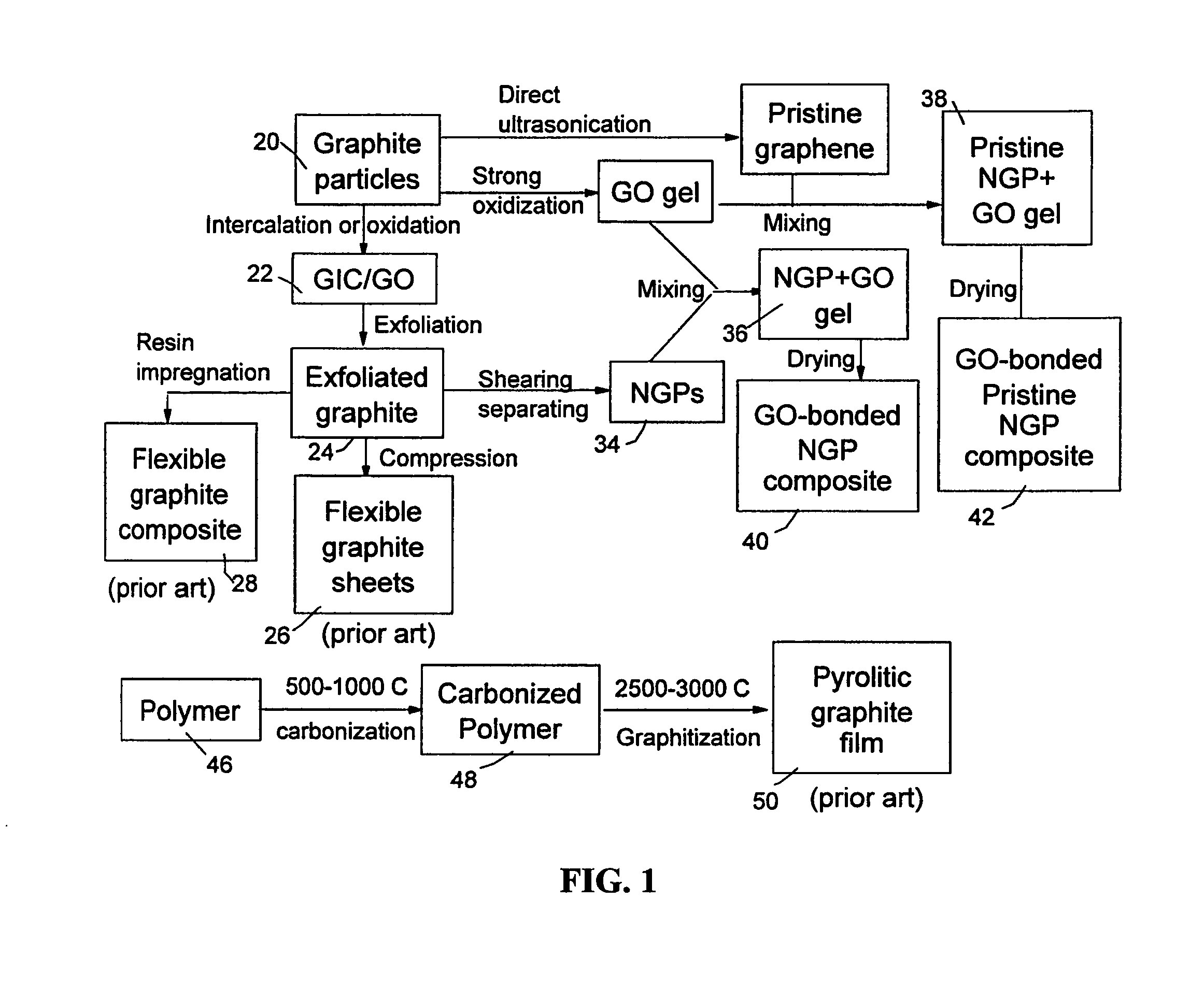
Nano graphene platelet-reinforced composite heat sinks and process for producing same
ActiveUS20140224466A1Improve surface scratch resistanceReduced/eliminated possibilityMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringGraphite
An integrated heat sink article composed of a heat collection member and at least one heat dissipation member integral to the heat collection member, wherein the heat collection member is configured to be in thermal contact with a heat source, collects heat from the heat source, and dissipates heat through the at least one heat dissipation member, and further wherein the heat sink is formed of a nano graphene platelet-reinforced composite having nano graphene platelets or sheets (NGPs) as a first reinforcement phase dispersed in a matrix material and the first reinforcement phase occupies a weight fraction of 1-90% based on the total composite weight. Preferably, these NGPs, alone or in combination with a second reinforcement phase, are bonded by an adhesive and constitute a continuous 3-D network of electron- and phonon-conducting paths.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
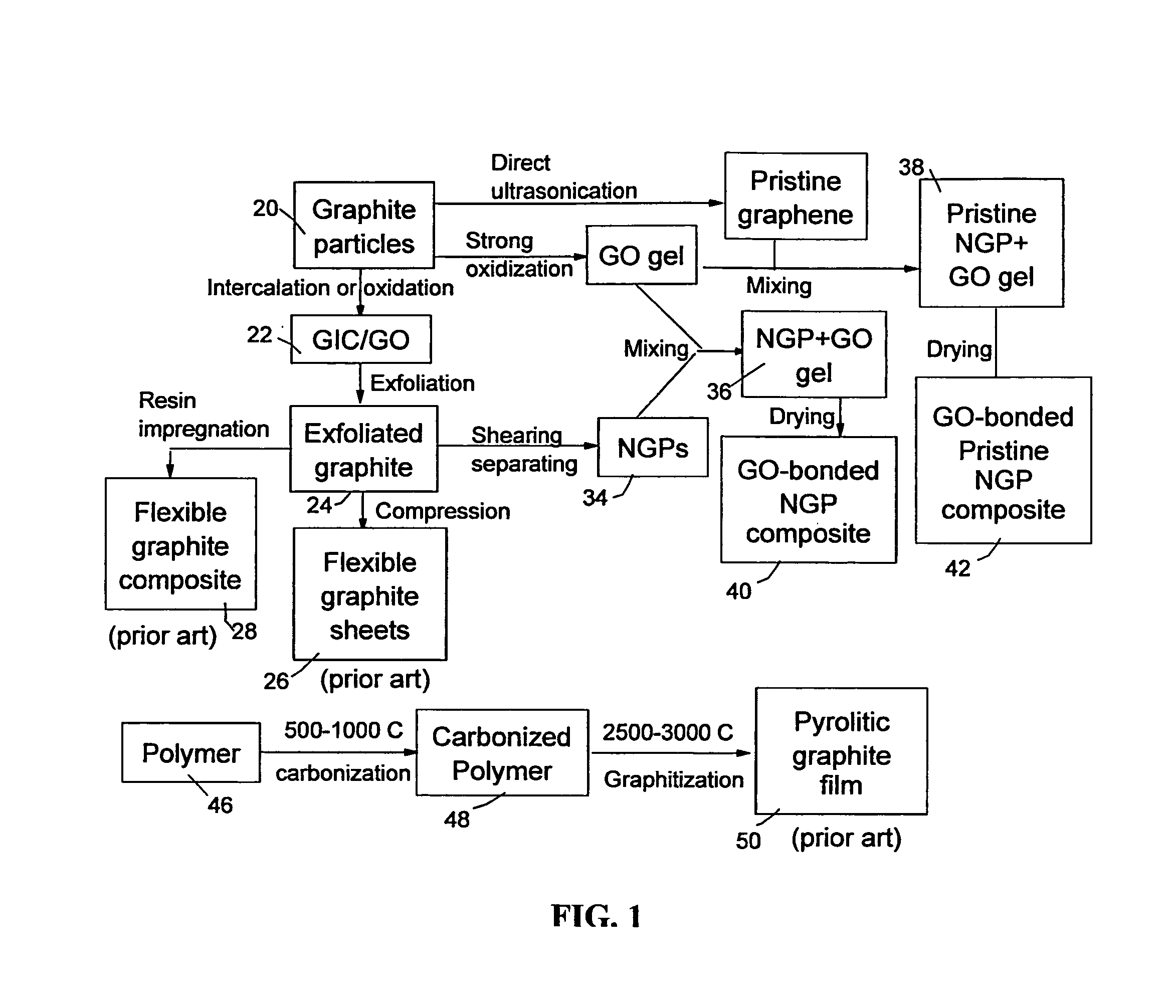
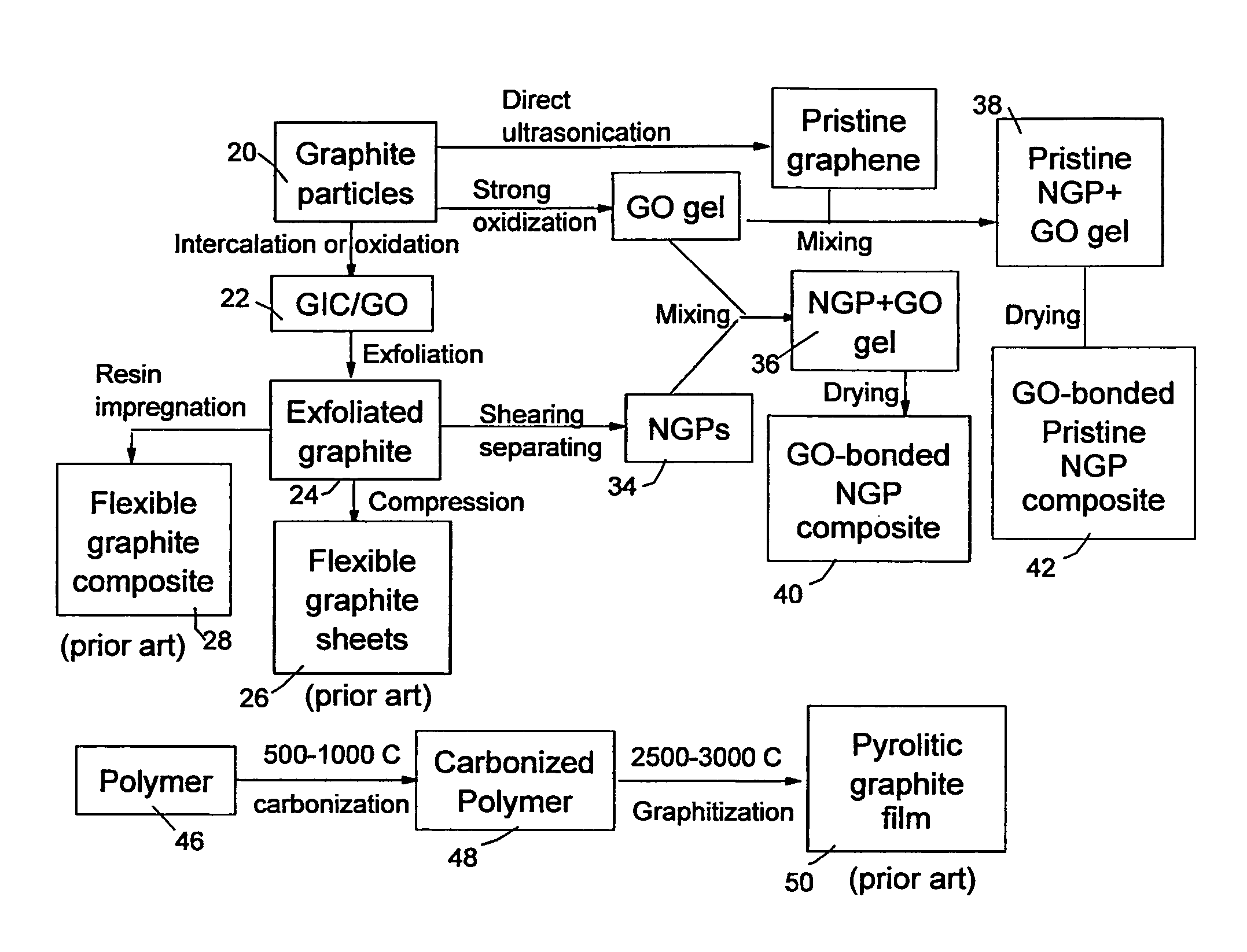
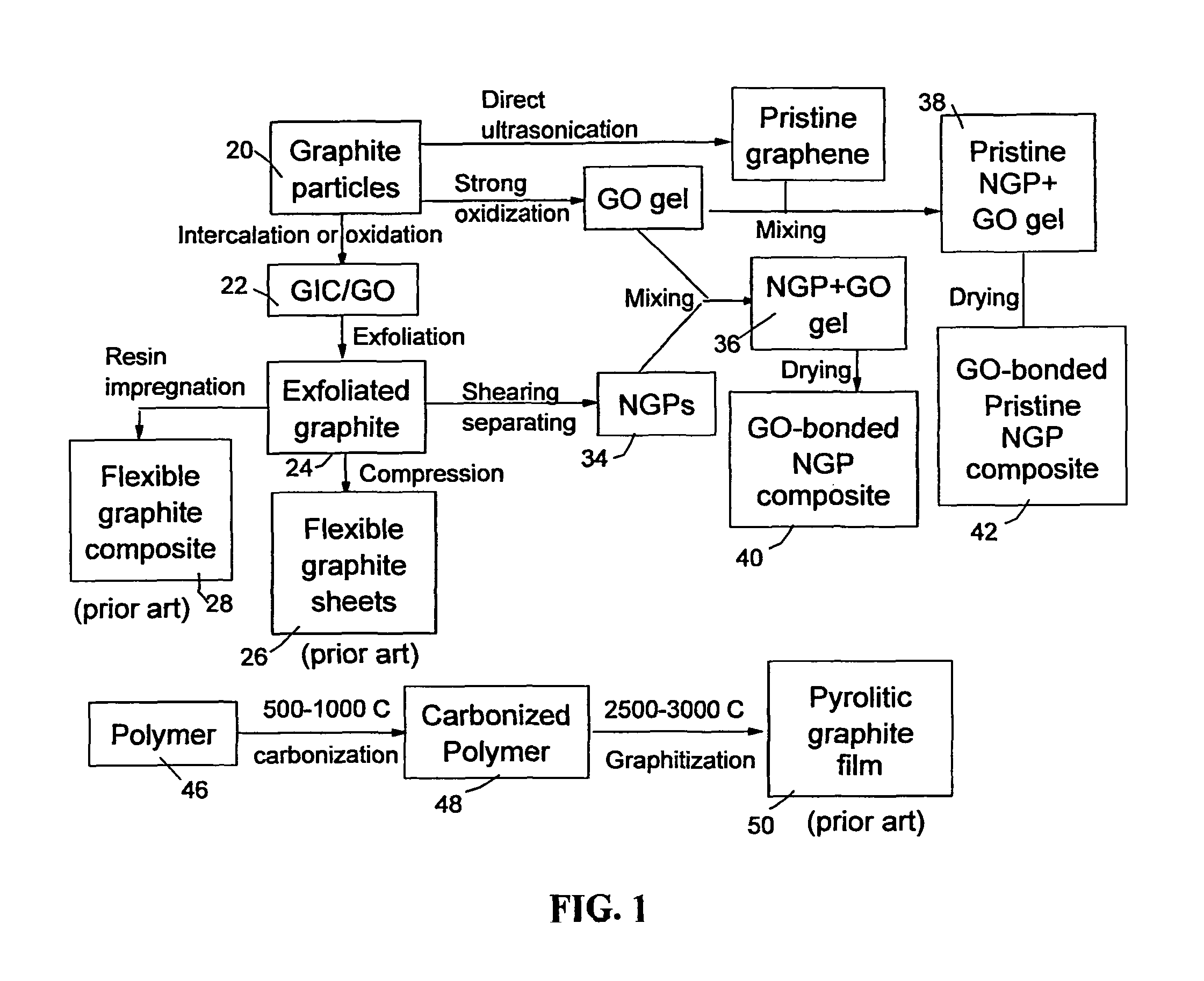
Graphene oxide gel bonded graphene composite films and processes for producing same
ActiveUS20130236715A1Low densityThermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyNon-metal conductorsPhysical chemistryThin membrane
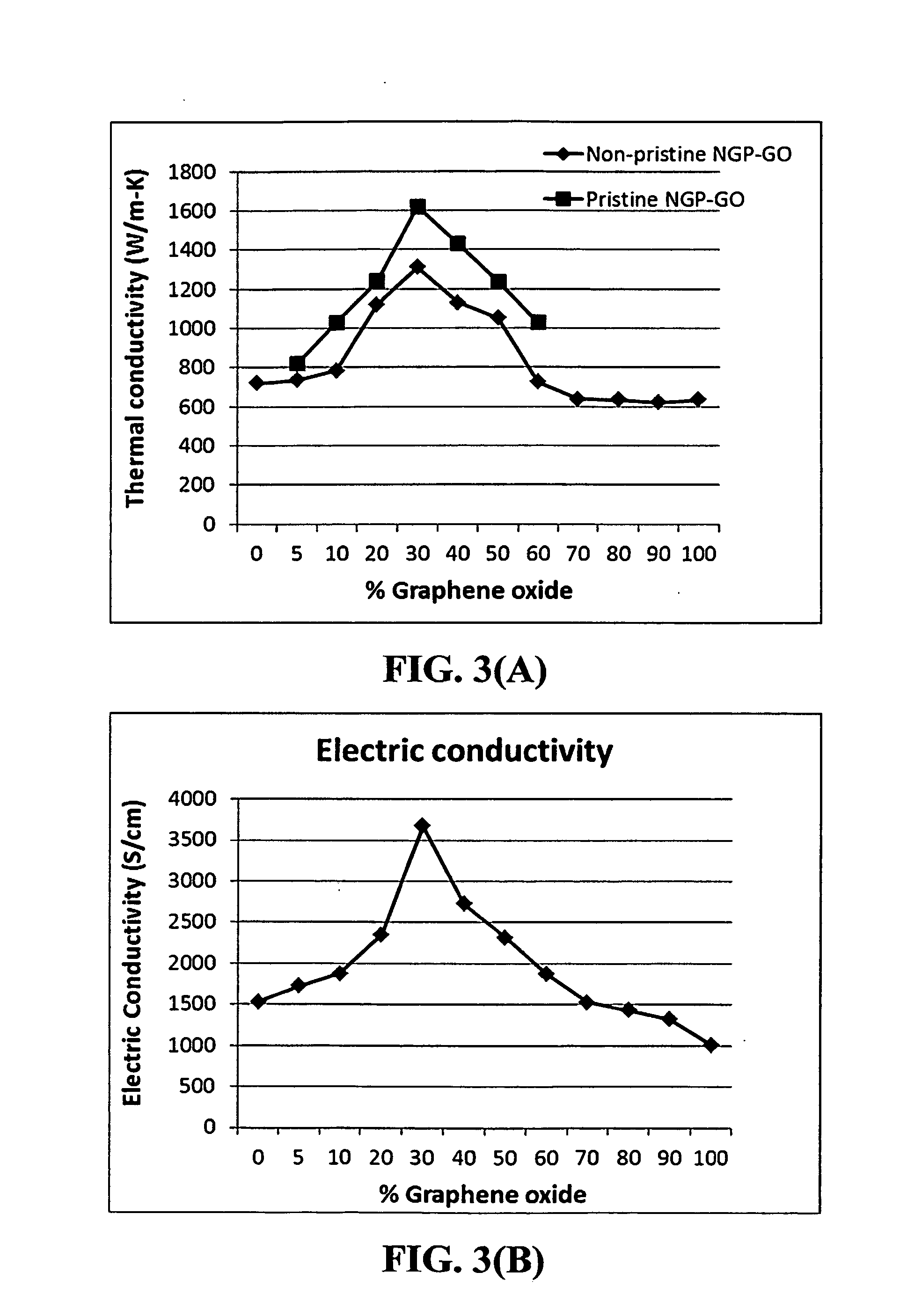
Disclosed is a graphene composite thin film composition composed of nano graphene platelets (NGPs) bonded by a graphene oxide binder, wherein the NGPs contain single-layer graphene or multi-layer graphene sheets having a thickness from 0.335 nm to 100 nm. The NGPs occupy a weight fraction of 1% to 99.9% of the total composite weight. The graphene oxide binder, having an oxygen content of 1-40% (preferably <10%) by weight based on the total graphene oxide weight, is obtained from a graphene oxide gel. The composite forms a thin film with a thickness no greater than 1 mm, but preferably no greater than 100 μm and no less than 10 μm. This composition has a combination of exceptional thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength unmatched by any thin-film material of comparable thickness range.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Silicon Carbide on Diamond Substrates and Related Devices and Methods
ActiveUS20050164482A1Improve thermal conductivityReduce thicknessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesWaferingSemiconductor structure
A method of forming a high-power, high-frequency device in wide bandgap semiconductor materials with reduced junction temperature, higher power density during operation and improved reliability at a rated power density is disclosed, along with resulting semiconductor structures and devices. The method includes adding a layer of diamond to a silicon carbide wafer to increase the thermal conductivity of the resulting composite wafer, thereafter reducing the thickness of the silicon carbide portion of the composite wafer while retaining sufficient thickness of silicon carbide to support epitaxial growth thereon, preparing the silicon carbide surface of the composite wafer for epitaxial growth thereon, and adding a Group III nitride heterostructure to the prepared silicon carbide face of the wafer.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
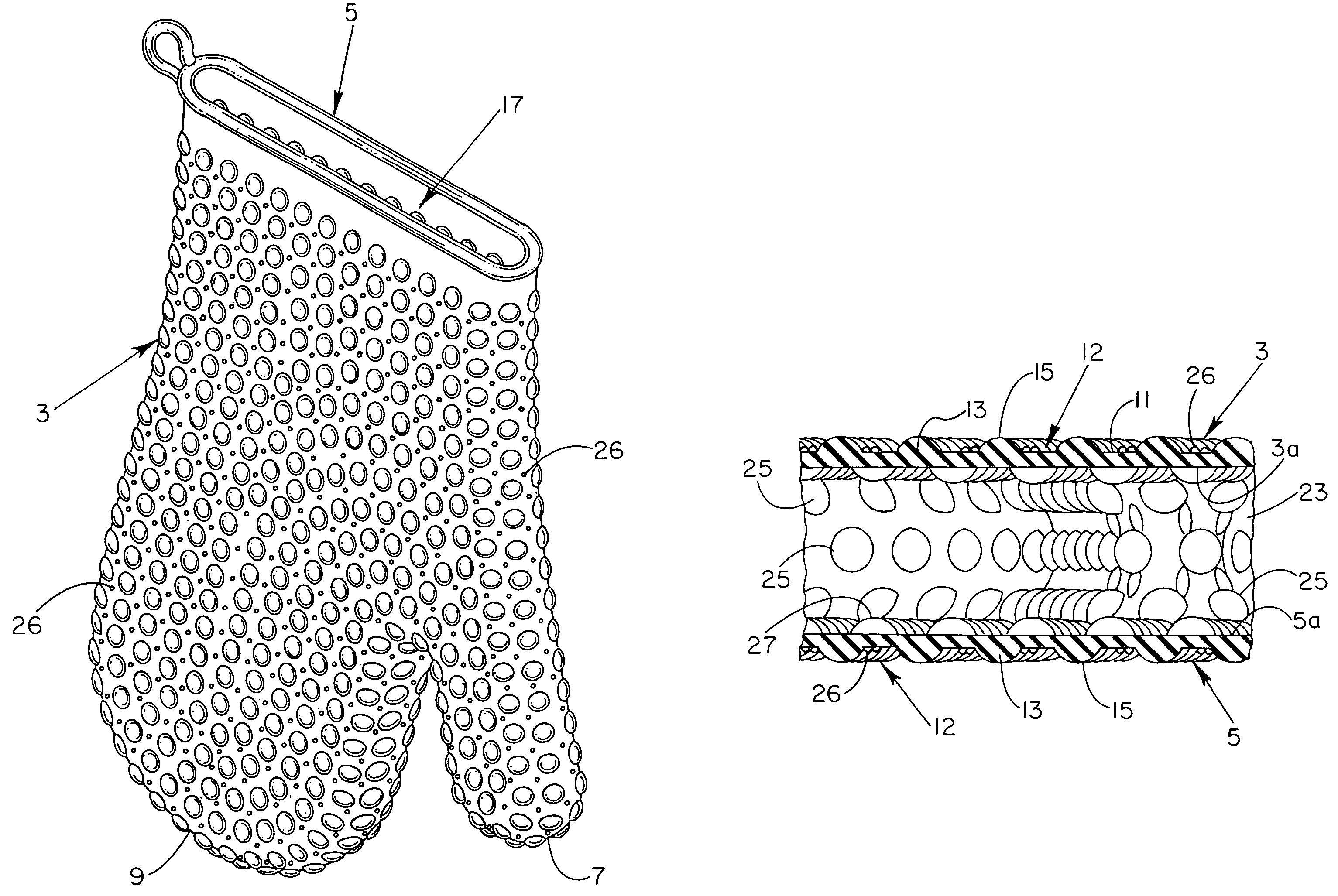
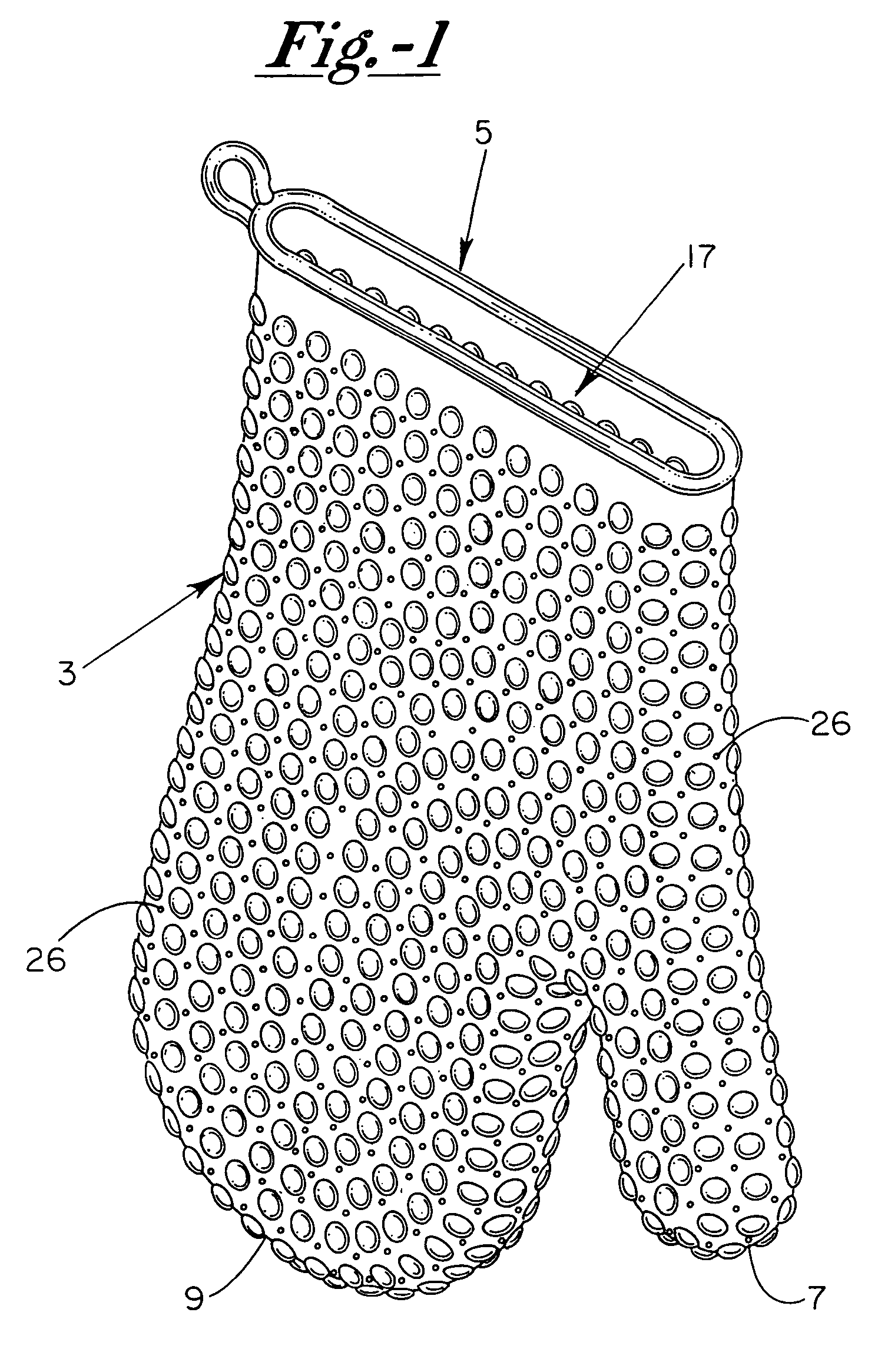
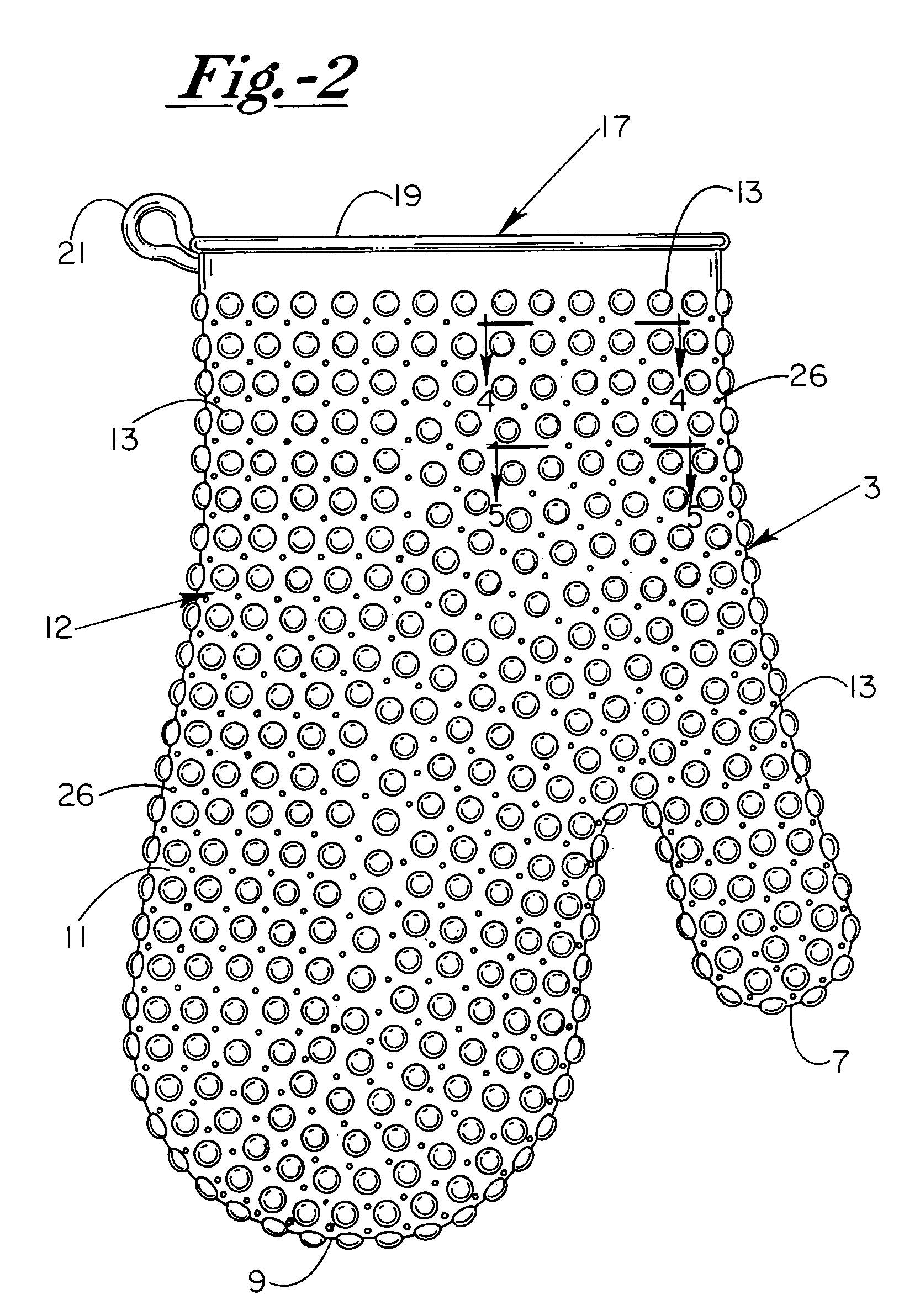
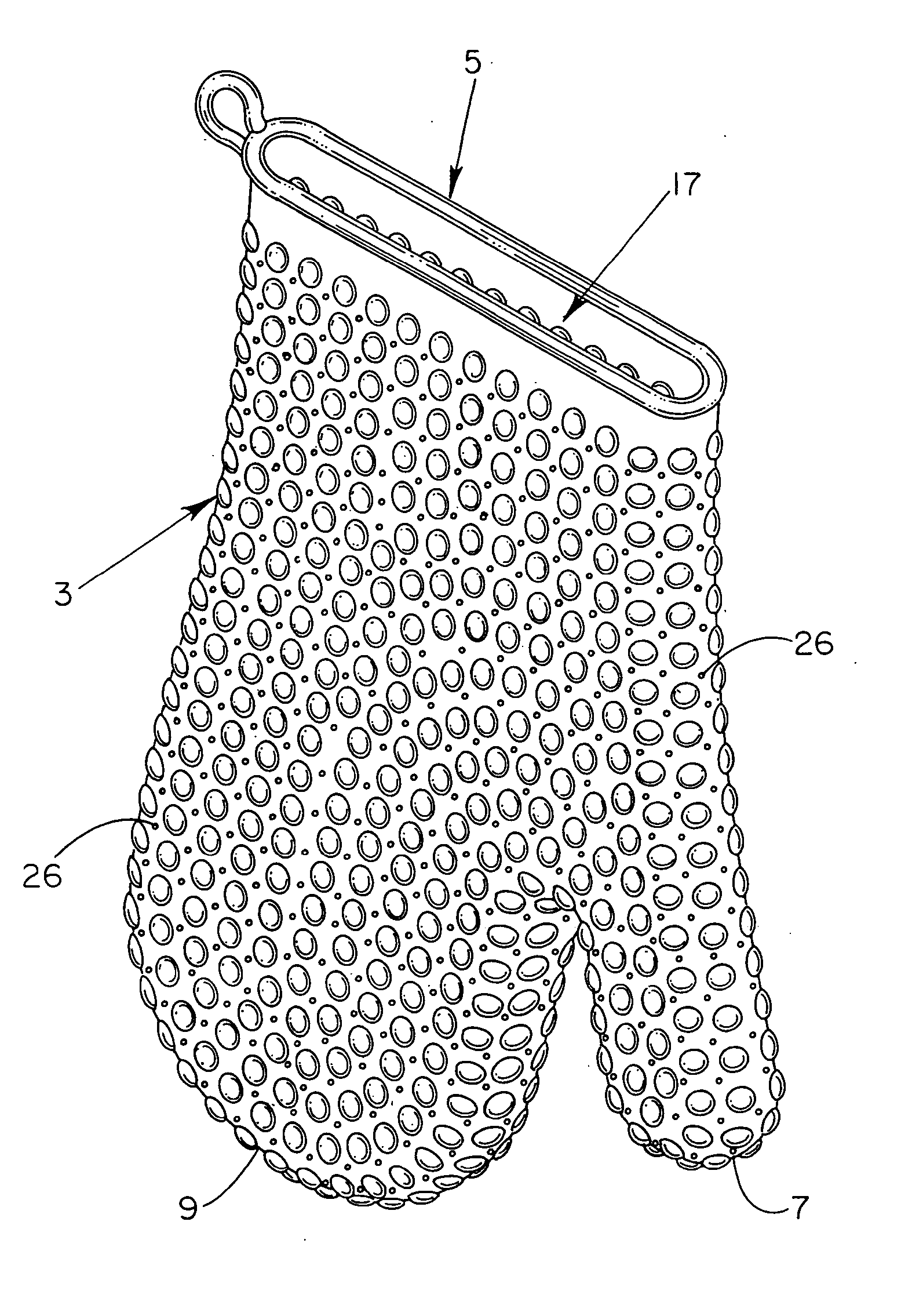
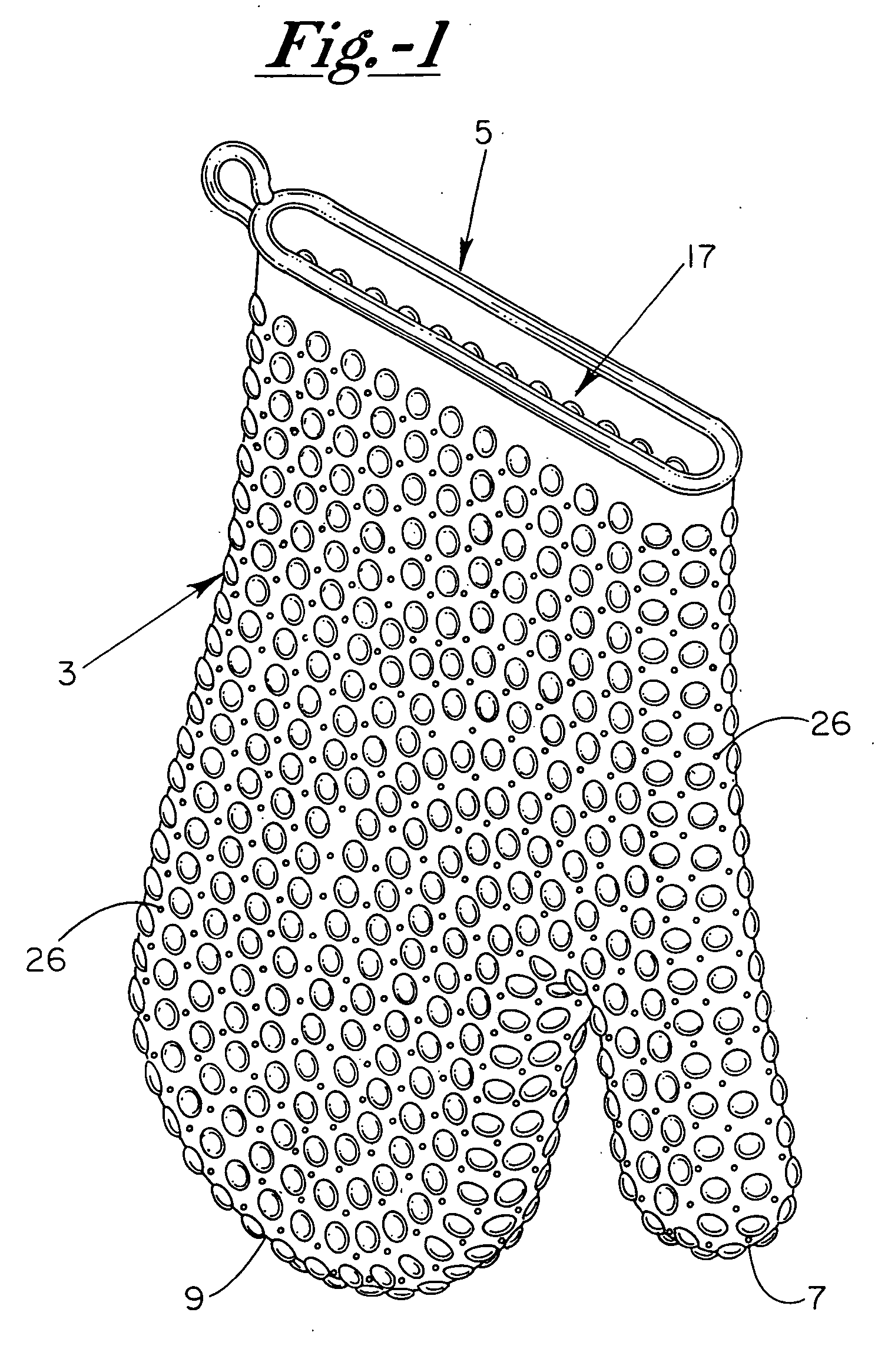
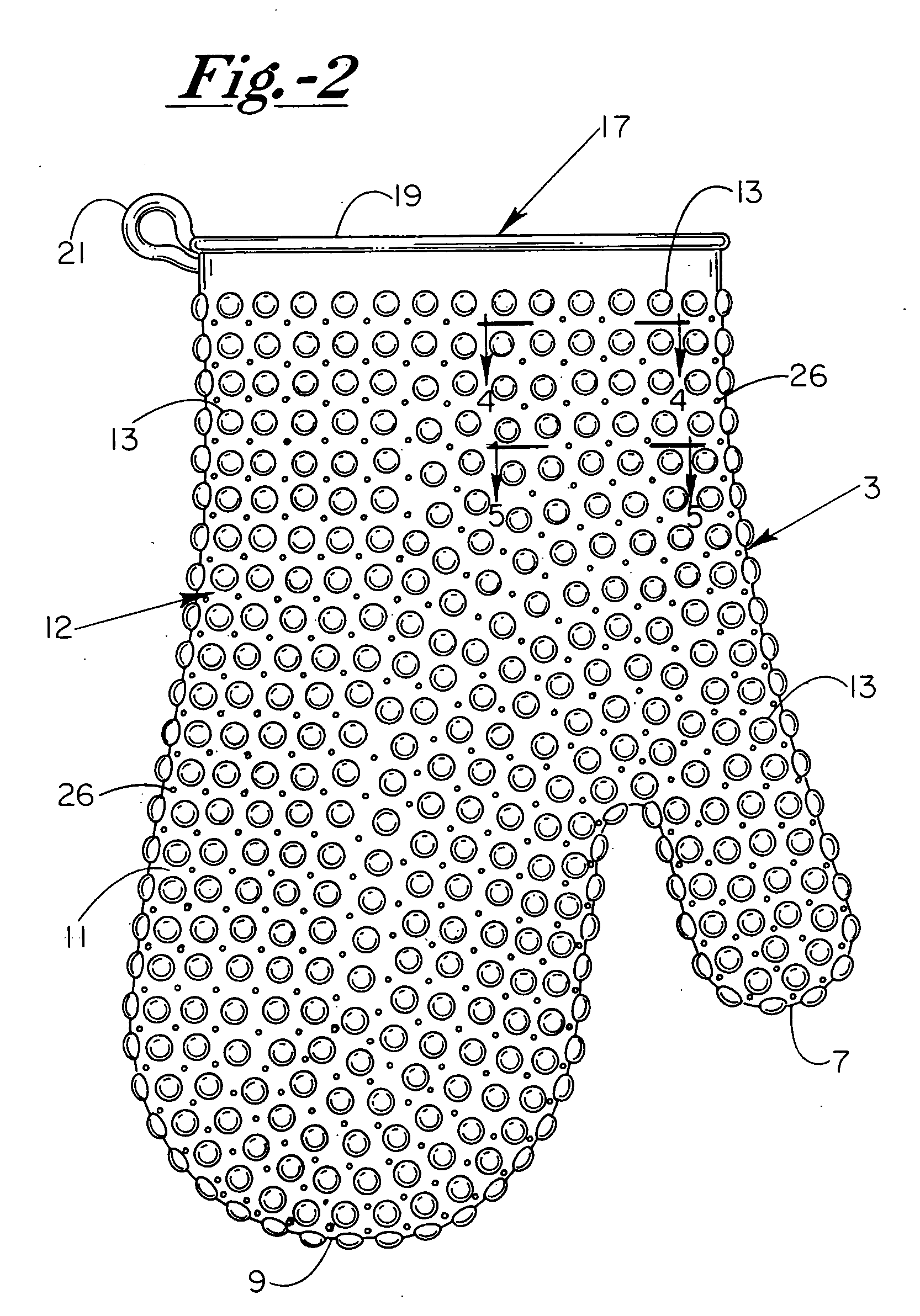
Heat/cold resistant protective hand covering
InactiveUS7234170B2Effective thermal barrierThermal conductivityGlovesEye treatmentTransverse axisEngineering
Owner:QUADION CORP
Thermal management system containing an integrated graphene film for electronic devices
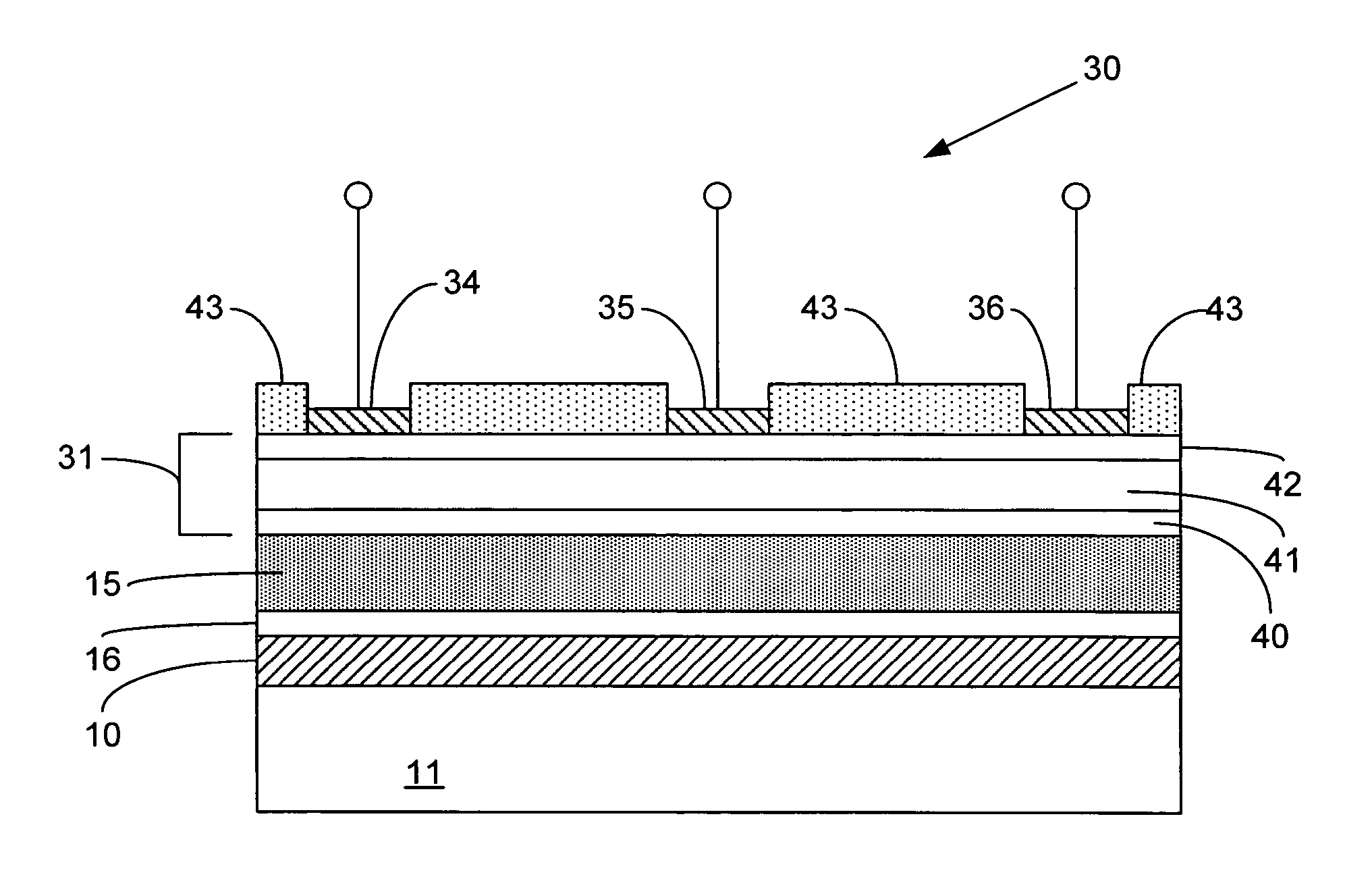
ActiveUS20130264041A1Low densityThermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyDigital data processing detailsHeat conductingThermal management system
Disclosed is a graphene-based heat dissipation system for an electronic device, comprising: (a) an electronic device comprising a heat source, wherein the heat source transmits heat to a second component or an external surface of the electronic device; (b) a heat-conducting layer comprising two major surfaces, the heat-conducting layer being positioned such that one of its major surfaces is in operative contact with the heat source such that it is interposed between the heat source and the second component or the external surface of the electronic device; wherein the heat-conducting layer comprises at least one sheet of integrated graphene film which thermally shields the second component or the external surface of the electronic device from heat generated by the heat source.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Monolithic thin-film thermoelectric device including complementary thermoelectric materials
InactiveUS20050150539A1Reduce needReduction in electron thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentLiquid metalThermoelectric element
A vertical, monolithic, thin-film thermoelectric device is described. Thermoelectric elements of opposing conductivity types may be coupled electrically in series and thermally in parallel by associated electrodes on a single substrate, reducing the need for mechanisms to attach multiple substrates or components. Phonon transport may be separated from electron transport in a thermoelectric element. A thermoelectric element may have a thickness less than an associated thermalization length. An insulating film between an electrode having a first temperature and an electrode having a second temperature may be a low-thermal conductivity material, a low-k, or ultra-low-k dielectric. Phonon thermal conductivity between a thermoelectric element and an electrode may be reduced without a significant reduction in electron thermal conductivity, as compared to other thermoelectric devices. A phonon conduction impeding material may be included in regions coupling an electrode to an associated thermoelectric element (e.g., a liquid metal).
Owner:NANOCOOLERS
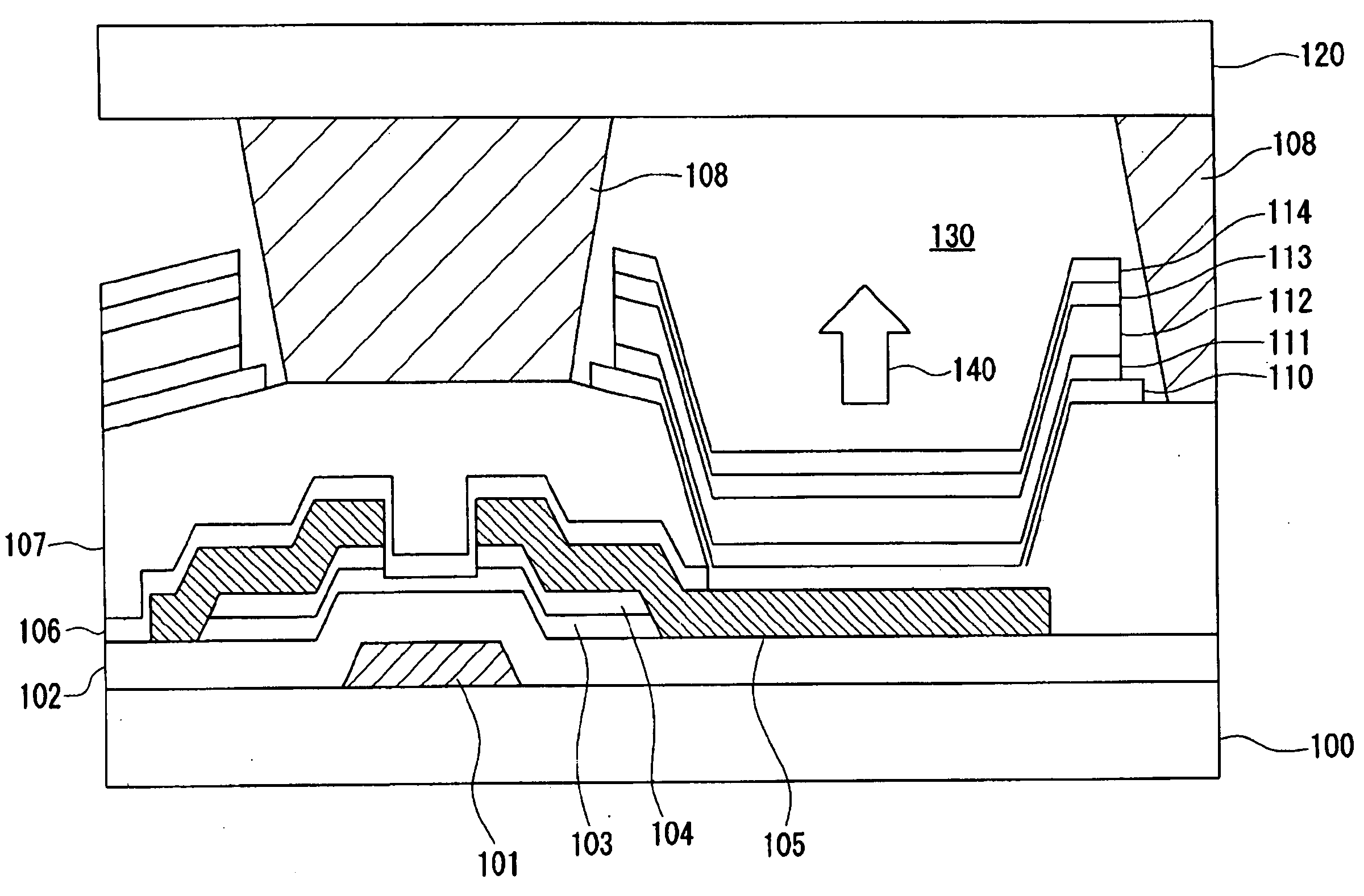
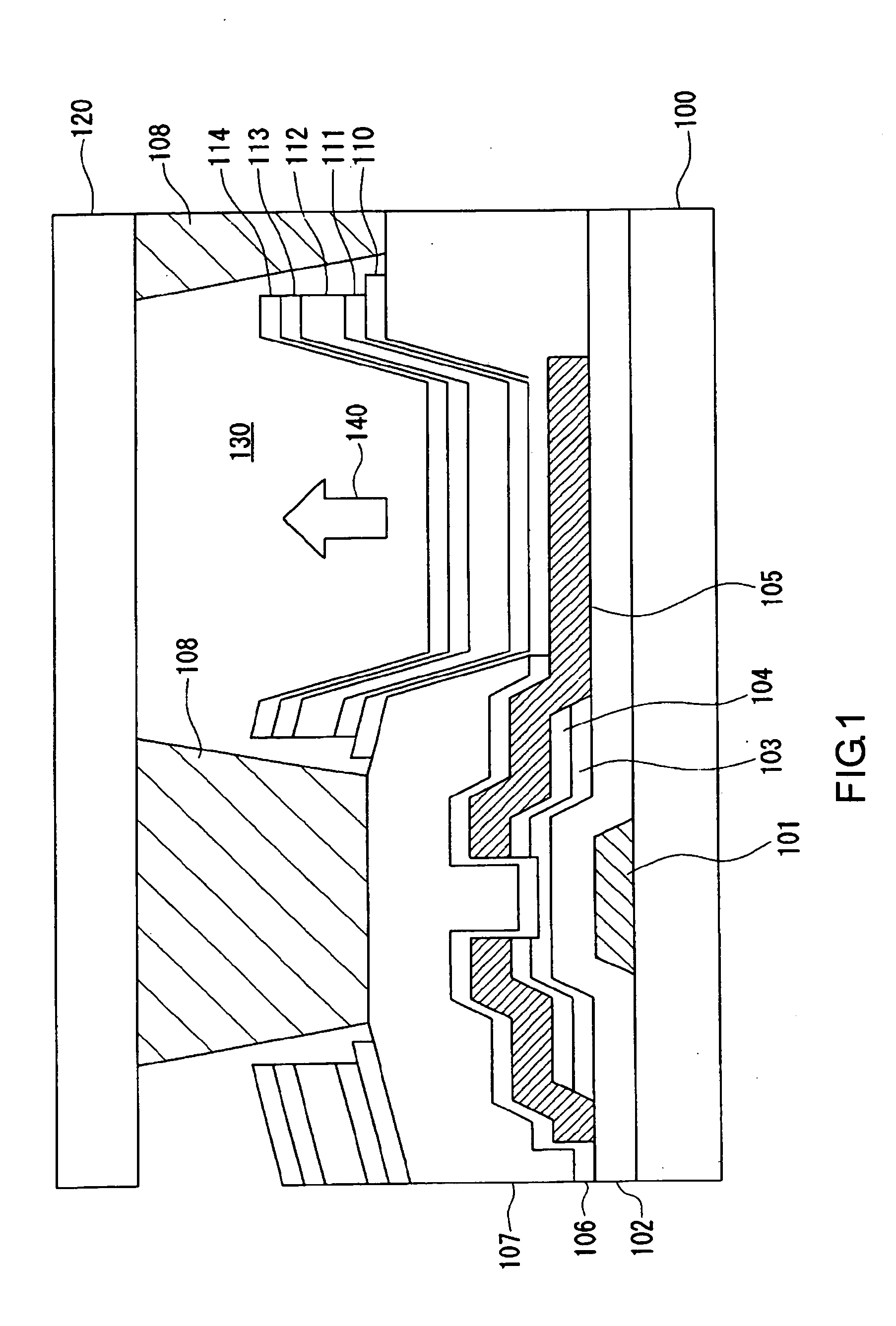
Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
InactiveUS20050172904A1Improve consistencyThermal conductivityElectric discharge tubesVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringPlasma processing
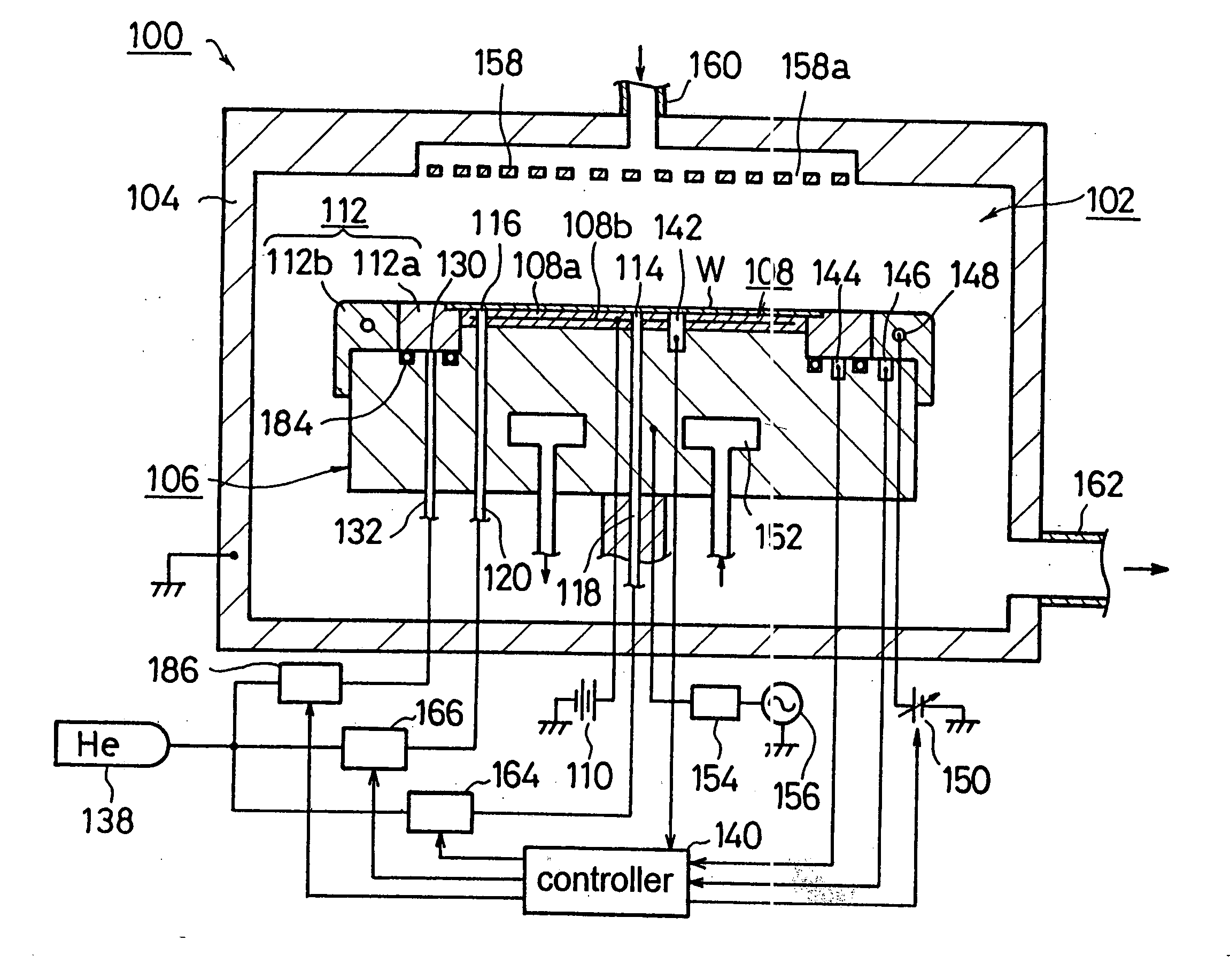
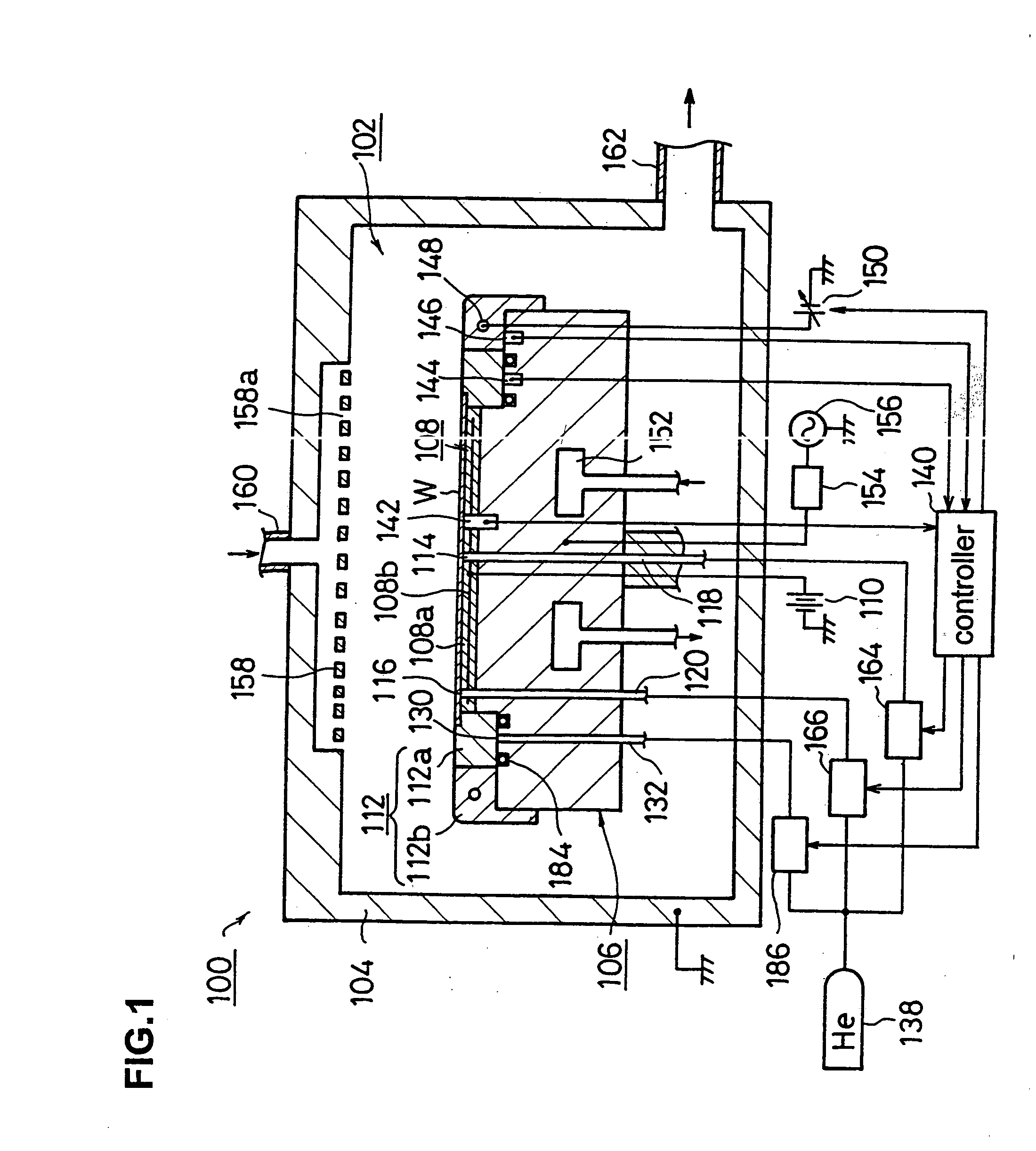
An electrostatic chuck 108 is provided on a lower electrode 106 provided inside a processing chamber 102 of an etching apparatus 100, and a conductive inner ring body 112a and an insulating outer ring body 112b are encompassing the outer edges of a wafer W mounted on the chuck surface. The temperatures of the wafer W and the inner and outer ring bodies 112a and 112b are detected by first third temperature sensors 142, 144 and 146. A controller 140 controls the pressure levels of He supplied to the space between the center of the wafer W and the electrostatic chuck 108 via first gas outlet ducts 114 and to the space between the outer edges of the wafer W and the electrostatic chuck 108 via second gas outlet ducts 116 and the quantity of heat generated by a heater 148 inside the outer ring body 112b based upon the information on the temperatures thus detected so that the temperatures of the wafer W and the inner ring body 112a are set roughly equal to each other.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON AT +1
Electronic apparatus having structure for protecting flexible printed circuit and chip thereon
InactiveUS6972963B1Easy to installLow costDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMetal frameworkFlexible electronics
An electronic apparatus having a structure for protecting a flexible printed circuit (FPC) and a chip thereon is described, including a metal backplate, a first circuit and a second circuit respectively on the front side and the back side of the backplate, a metal frame plate at the periphery of the backplate, at least one FPC with at least one chip thereon, a metal screen plate, and at least one insulating elastic ring disposed around the FPC. The FPC has a first end connected to the first circuit and a second end connected to the second circuit over the frame plate, and the screen plate is disposed on the frame plate screening the FPC and the chip. The inner periphery of the insulating elastic ring closely contacts with the chip, and the outer periphery of the ring closely contacts with the frame plate and the screen plate.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
Heat/cold resistant protective hand covering
InactiveUS20050177923A1Effective thermal barrierThermal conductivityGlovesEye treatmentTransverse axisEngineering
An ambidextrous protective hand covering monolithically formed from a heat / cold resistant flexible silicone material, the opposing interior and exterior surfaces of which each include a plurality of integrally-formed raised nodules that are positionally off-set relative to one another with non-aligning transverse axes. The positionally off-set exterior and interior nodules act to oppose thermal conductivity and provide an effective thermal barrier so as to protect the hand and wrist during handling of articles of differing or uncomfortable temperatures. Optionally, the formulation of the heat / cold resistant material may be chemically enhanced to provide a thermal luminescent change in color of the hand protective covering upon detection of excessive hot / cold temperatures.
Owner:QUADION CORP
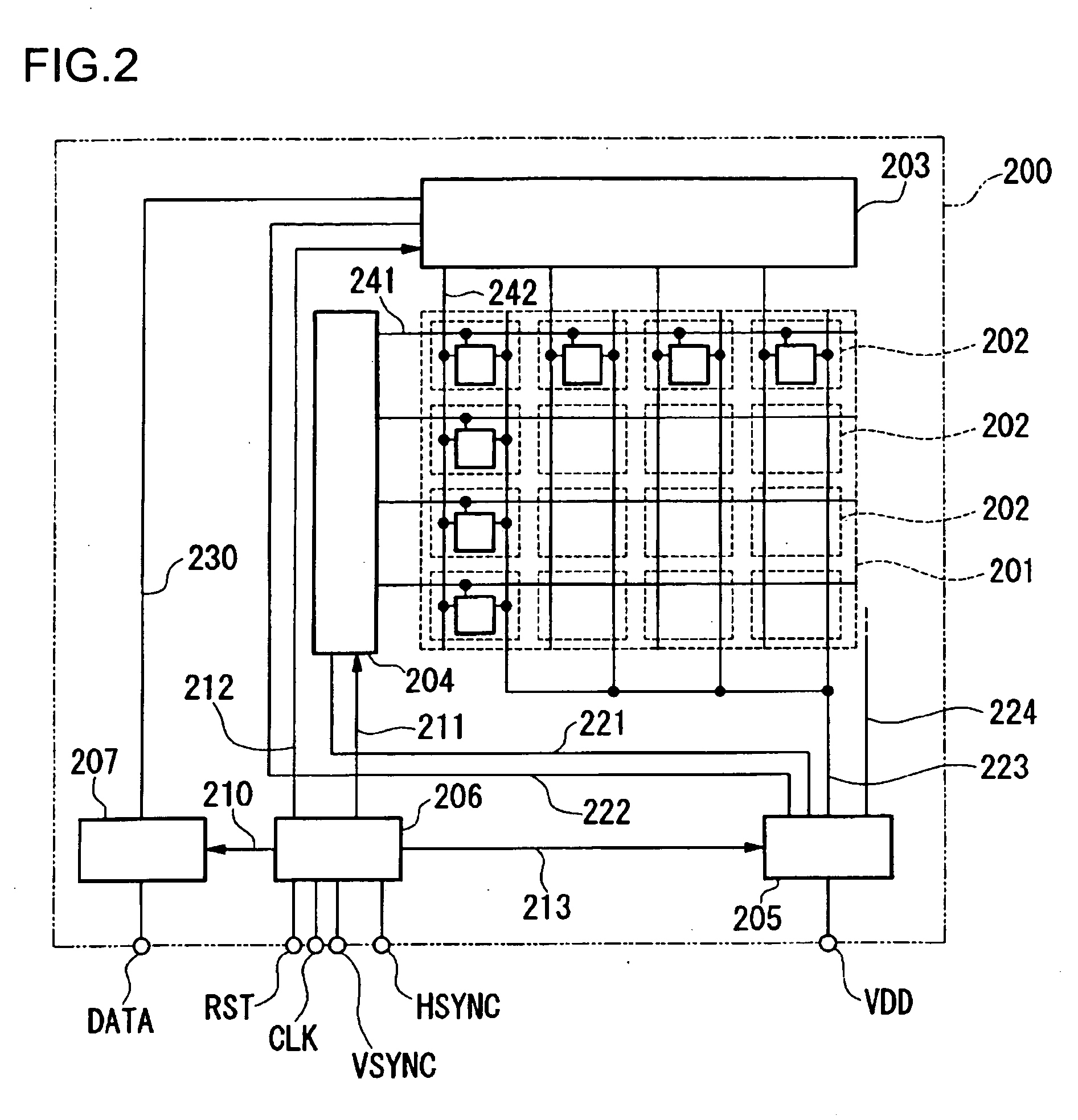
Electro-optical device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20050001247A1Avoid heatImprove thermal conductivityStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesEnvironmental resistanceEngineering
The invention provides an electro-optical device that can include a plurality of scanning lines, a plurality of signal lines, a plurality of pixels arranged corresponding to intersections of the scanning lines and the signal lines, and heat-release sections. The pixels can each include corresponding transistors and corresponding light-emitting elements, the light-emitting elements emit light in the direction that light is withdrawn, and the heat-release sections include heat release portions, located on the side opposite to the light-withdrawing direction of the light-emitting elements, having electrical conductivity. Accordingly, the invention can enhance the environmental resistance of an electro-optical device including light-emitting elements.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Carbon fiber composite sheet, use thereof as a heat conductor and pitch-based carbon fiber web sheet for use in the same
InactiveUS20090061193A1Suitable thermal conductivityImproved three-dimensional thermal conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyMagnetic/electric field screeningFiberElectrical conductor
A carbon fiber composite sheet comprising a pitch-based carbon fiber web and a matrix resin, whereincarbon fibers constituting the pitch-based carbon fiber web have a crystallite size in the hexagonal net plane direction of 5 nm or more and a thermal conductivity in the thickness direction of 1 W / (m·K) or more.This carbon fiber composite sheet is used for radio shielding and heat conduction.
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Magnetic core, inductor and module including inductor
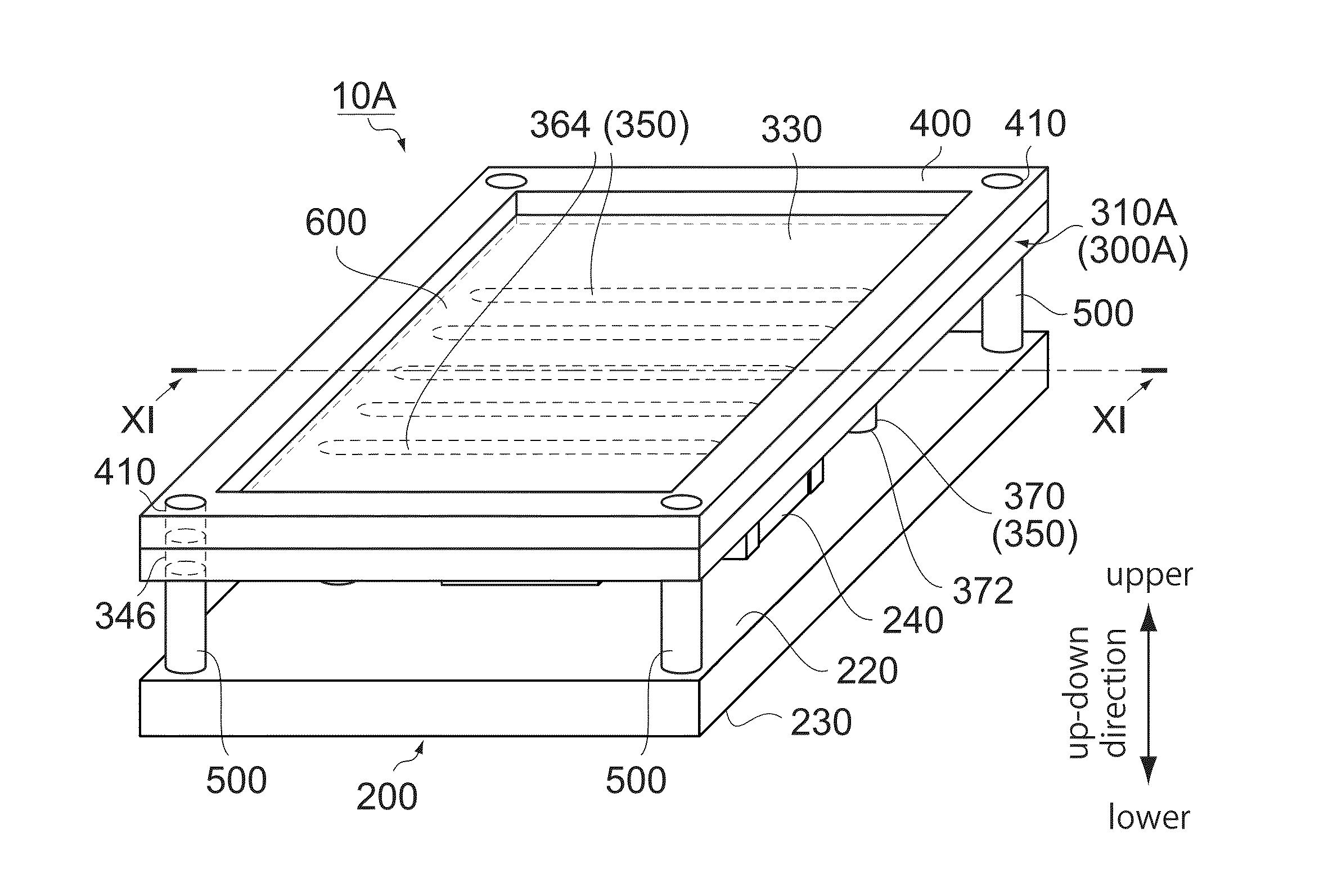
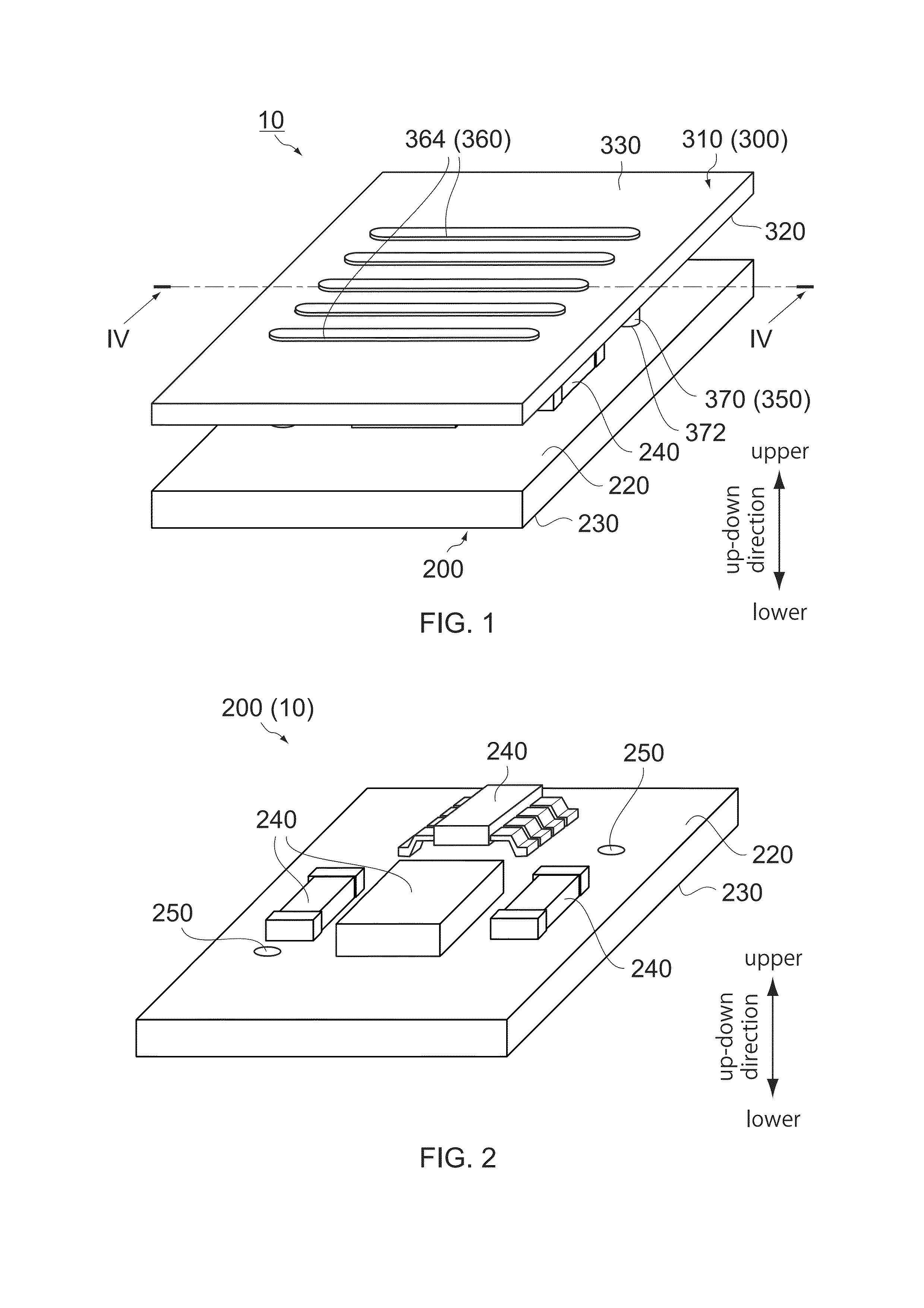
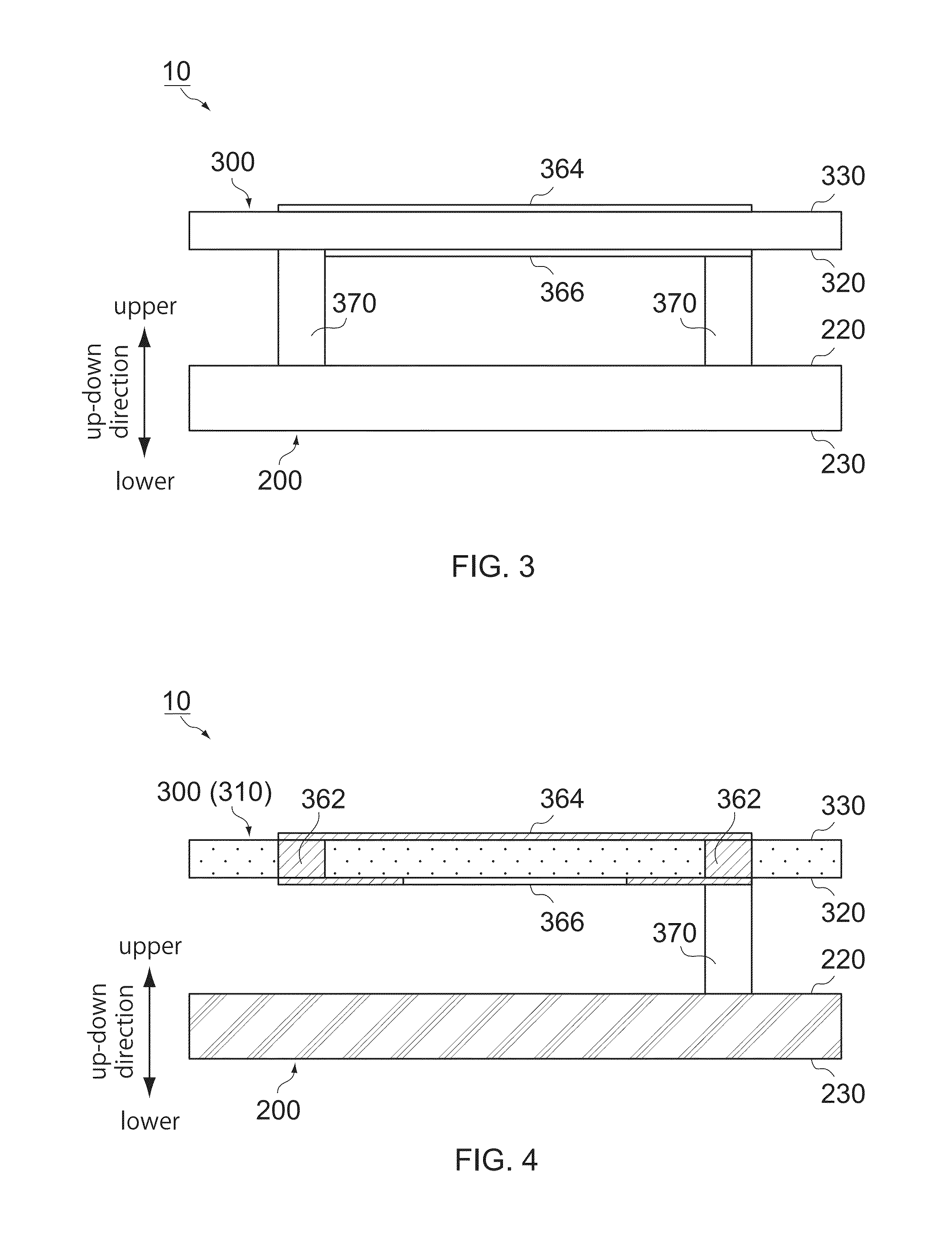
ActiveUS20140218147A1Simple structureEffective coolingTransformers/inductances coolingTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsInductorInductance
A module comprises a circuit board and an inductor. The circuit board has a facing surface and a rear surface which are located at opposite sides to each other in an up-down direction. The inductor has a magnetic core and a coil. The magnetic core is made of a soft magnetic metal material. The magnetic core has a facing surface and a radiating surface which are located at opposite sides to each other in the up-down direction. The facing surface of the magnetic core is arranged to face the facing surface of the circuit board in the up-down direction. The radiating surface of the magnetic core is arranged to be radiatable heat outward. The coil has a coil portion and a connection end. The coil portion winds, at least in part, the magnetic core. The connection end is connected to the facing surface of the circuit board.
Owner:TOKIN CORP
Method for forming a monolithic thin-film thermoelectric device including complementary thermoelectric materials
InactiveUS20050150536A1Reduce needReduction in electron thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentLiquid metalThermoelectric element
A vertical, monolithic, thin-film thermoelectric device is described. Thermoelectric elements of opposing conductivity types may be coupled electrically in series and thermally in parallel by associated electrodes on a single substrate, reducing the need for mechanisms to attach multiple substrates or components. Phonon transport may be separated from electron transport in a thermoelectric element. A thermoelectric element may have a thickness less than an associated thermalization length. An insulating film between an electrode having a first temperature and an electrode having a second temperature may be a low-thermal conductivity material, a low-k, or ultra-low-k dielectric. Phonon thermal conductivity between a thermoelectric element and an electrode may be reduced without a significant reduction in electron thermal conductivity, as compared to other thermoelectric devices. A phonon conduction impeding material may be included in regions coupling an electrode to an associated thermoelectric element (e.g., a liquid metal).
Owner:NANOCOOLERS
Isocyanate-based polymer foams with nano-scale materials
Isocyante-based polymer foams containing functionalized nano-scale materials in which the functional groups are OH, NH2, COOH or NCO groups. The incorporation of such functionalized nano-scale materials into the isocyanate-based polymer foams provides foams with improved properties such as insulation values, mechanical properties and flame retardancy performance properties, including but not limited to k-factor and dimensional stability.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Plasma display module with improved heat dissipation characteristics
InactiveUS20050046618A1Improve temperature uniformityAttach and detachTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesEngineeringGraphite
Provided are designs for a plasma display module (PDM) that has a plasma display panel (PDP) and a chassis base with circuits mounted thereon. Heat dissipating layers and plane structures are formed between the PDP and the chassis base. The heat dissipating layer and the plane structure have novel shapes and sizes and are made out of specific materials or combinations of materials to improve the heat dissipating characteristics for the PDM. Preferably, a high-orientation graphite material having a high thermal conductivity is used for the heat dissipating layer. The plane structure is a highly conductive metal that is positioned between the graphite layer and the glass PDP to form a better contact to the PDP, to better draw heat away from the PDP and to allow for easy attachment and detachment of the graphite layer to the PDP.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Lithium-ion batteries with coated separators
ActiveUS8470468B2Thermal conductivityLow environmental impactCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersLi-accumulatorsCoated membraneGas phase
A porous polymer sheet or membrane is provided with a thin coating of an electrically non-conductive ceramic composition and the coating conforms to all surfaces, including the pore surfaces, of the membrane. Such a coated membrane serves well, for example, as an intra-cell separator in a lithium ion battery. The coating increases the mechanical properties and thermal stability of the separator in battery operation and retains electrolyte. The coating may be formed by a two-step vapor-phase process in which atoms of one or more metals such as aluminum, calcium, magnesium, titanium, silicon and / or zirconium are deposited in a conformal layer on a workpiece surface. The metal atoms may then be reacted with ammonia, carbon dioxide, and or water to form their respective non-conductive nitrides, carbides, and / or oxides on the surface. The two-step process is repeated as necessary to obtain a ceramic material coating of desired thickness.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Liquid heating vessels
ActiveUS20090001070A1Realized cost-effectivelyImprove thermal conductivityBoiling over preventionWater-boiling vesselsLiquid temperatureEngineering
A liquid heating vessel comprising heating means for heating liquid in the vessel, electronic control means, electromagnetic switching means for interrupting or reducing power to the heating means, and temperature sensing means for providing a signal dependent on the temperature of liquid in the vessel to the control means. The control means is arranged to operate the electromagnetic switching means to interrupt or reduce power to the heating means in response to the control means determining that a pre-determined temperature condition has been reached.
Owner:STRIX LTD
Apparatus And Method For Holding A Cryogenic Fluid And Removing Cryogenic Fluid Therefrom With Reduced Heat Leak
ActiveUS20070000259A1Reduce heat leakageExtended hold timeInternal combustion piston enginesFuel supply apparatusDrive shaftHeat leak
The apparatus comprises a double walled vacuum insulated vessel defining a cryogen space for holding a cryogenic fluid, a pump assembly comprising a pump with a suction inlet disposed within the cryogen space, and at least one elongated member extending from the pump to a drive unit disposed outside the cryogen space. The elongated member comprises an elongated non-metallic section that has a thermal conductivity that is less than that of a structurally equivalent elongated stainless steel member of the same length. In preferred embodiments, the elongated member can be one or both of a drive shaft or a rigid structural member for supporting the pump and holding it in a fixed relationship to the drive unit. The method employs the apparatus to increase hold times for holding cryogenic fluids by reducing heat leak into the cryogen space.
Owner:WESTPORT FUEL SYST CANADA INC
Silicon submount for light emitting diode and method of forming the same
InactiveUS20130105978A1Reduce light lossSimplify manufacturing stepsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSilicon basedReflective layer
A silicon submount for a light emitting diode (LED) including a silicon base, a first insulating layer, a first electrode, a second electrode, and a reflective layer is provided. The silicon base has an upper surface and a lower surface, and a recess is disposed at the upper surface. The first insulating layer covers the upper surface and the lower surface of the silicon base. The first electrode and the second electrode are disposed on the first insulating layer on a bottom of the recess. The reflective layer is disposed on the first insulating layer on a sidewall of the recess. The first electrode, the second electrode, and the reflective layer are separated from one another and formed by the same material.
Owner:EPISIL TECH
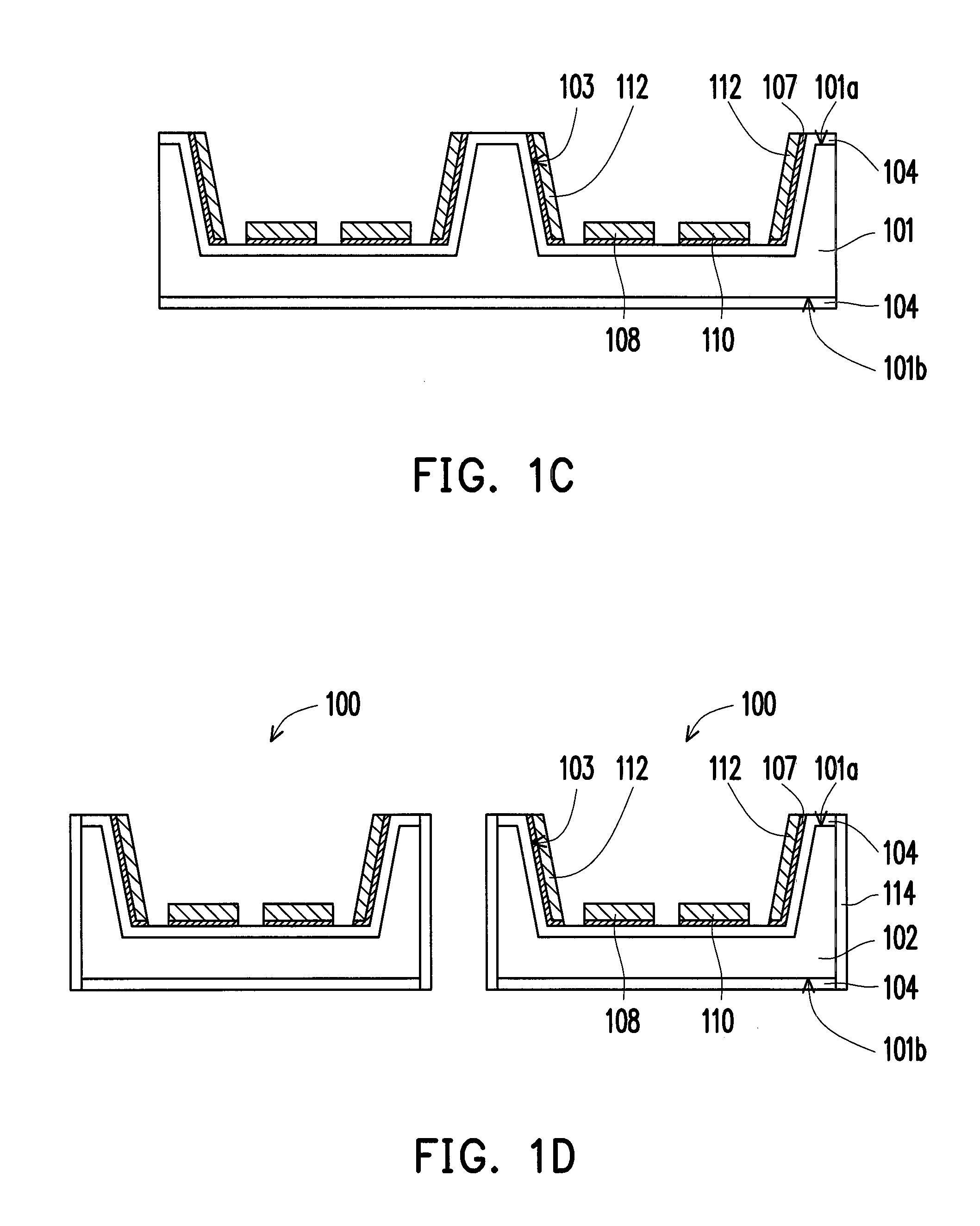
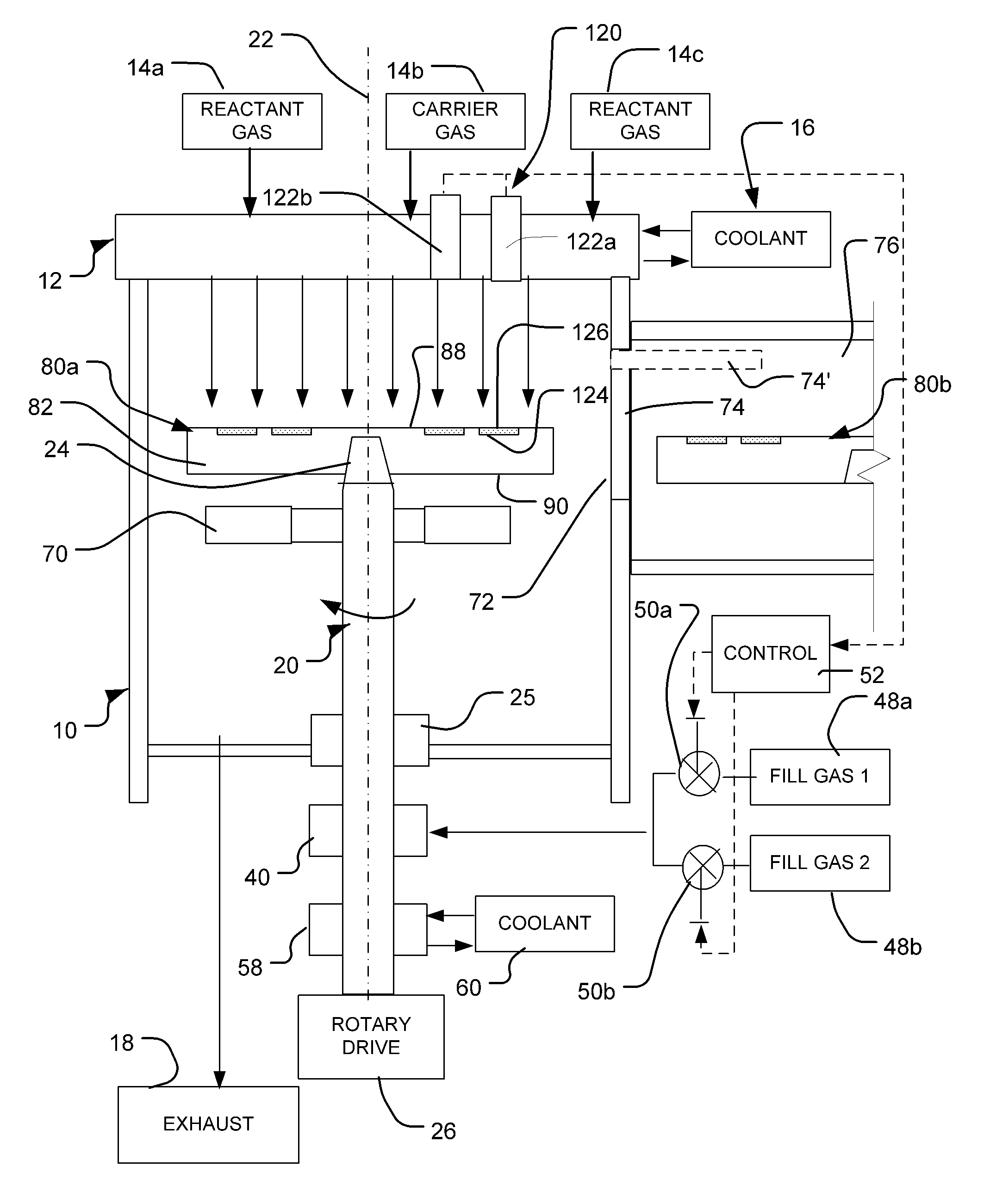
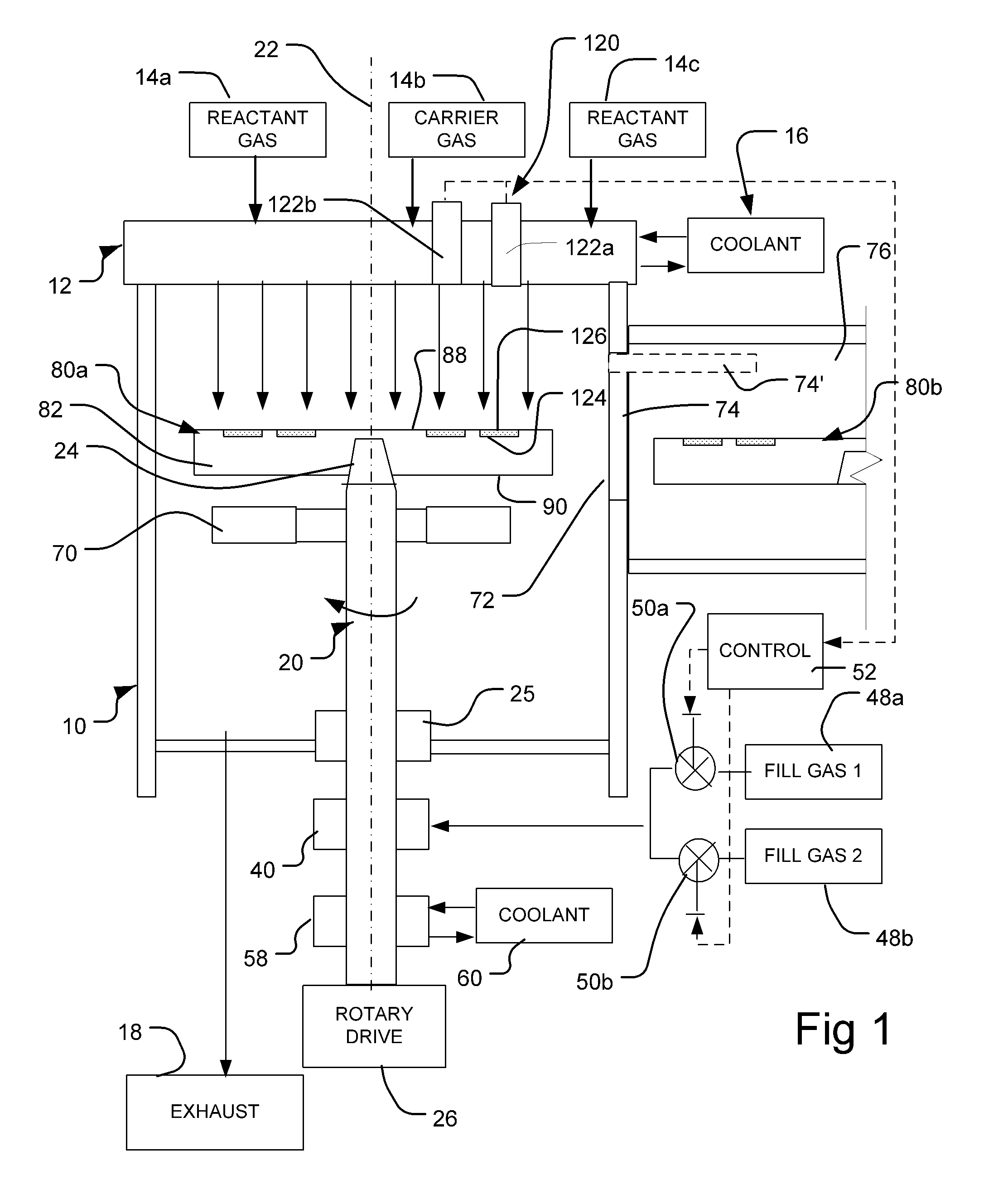
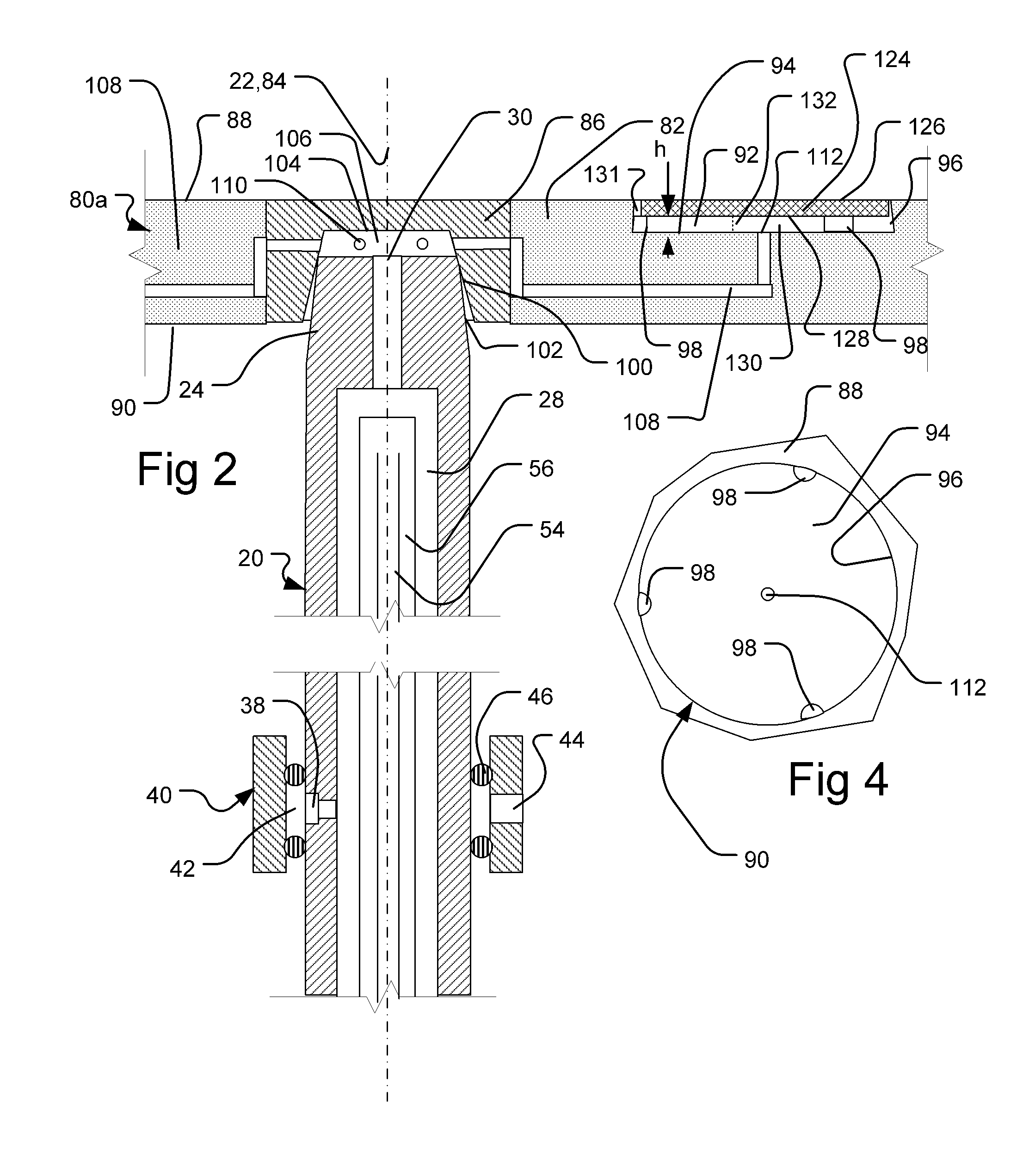
Processing methods and apparatus with temperature distribution control
ActiveUS20110206843A1Minimize changesThermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDistribution controlEngineering
Wafer treatment process and apparatus is provided with a wafer carrier arranged to hold wafers and to inject a fill gas into gaps between the wafers and the wafer carrier. The apparatus is arranged to vary the composition, flow rate, or both of the fill gas so as to counteract undesired patterns of temperature non-uniformity of the wafers.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Vacuum insulation panel
InactiveUS8765247B2Avoid deformationThermal conductivityThermal insulationLayered productsEngineeringAtmospheric pressure
Owner:XL CO LTD
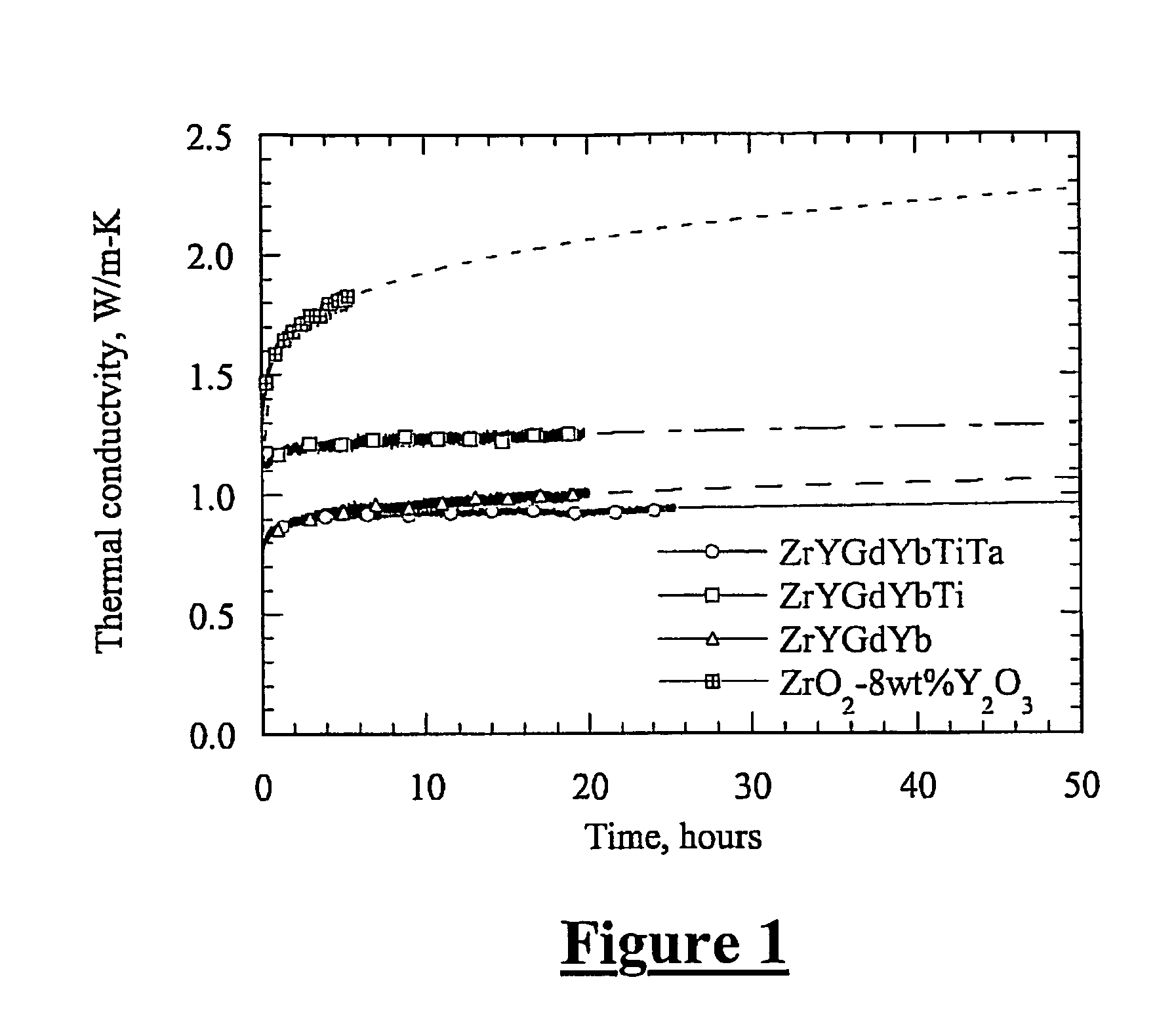
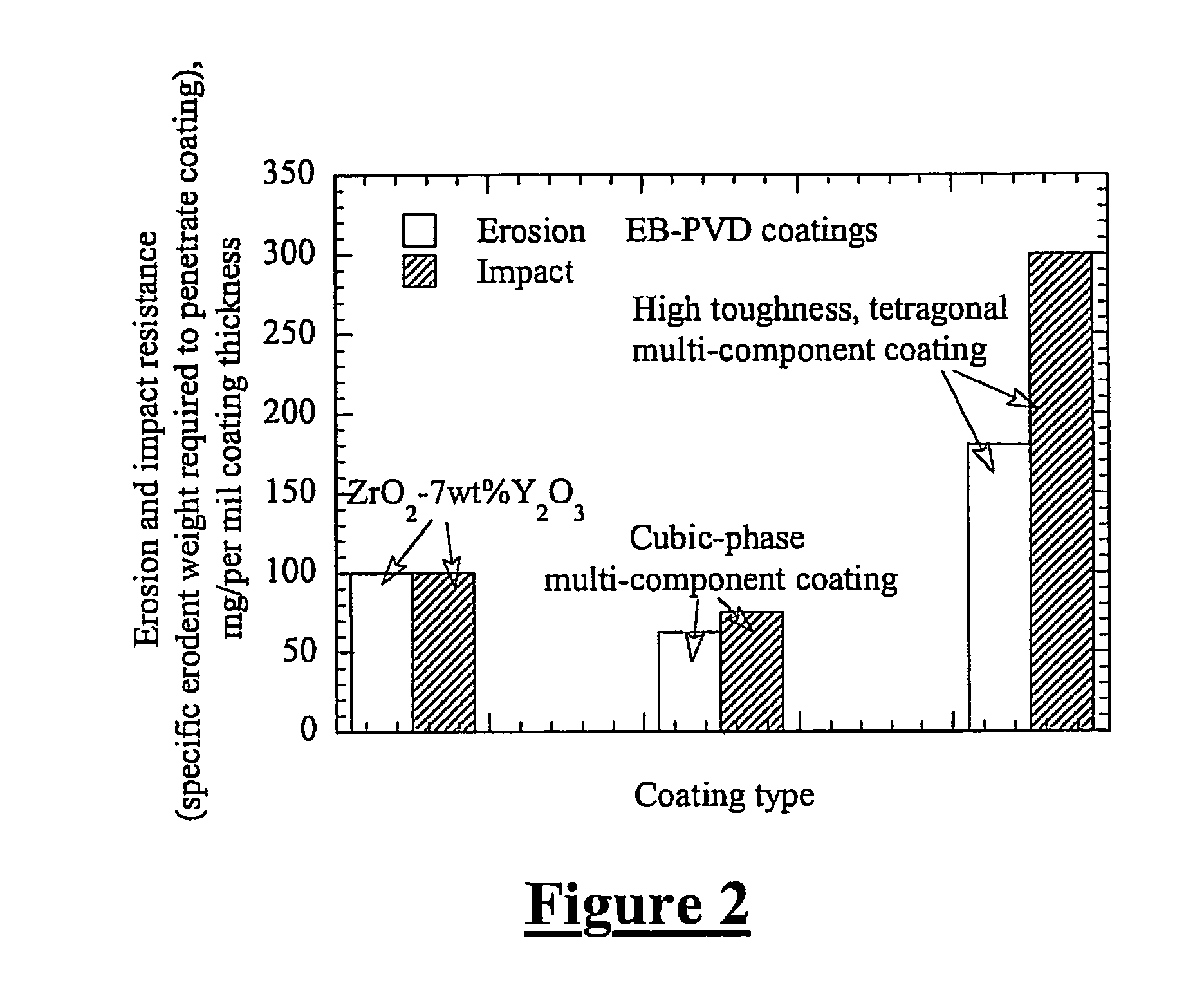
Low conductivity and high toughness tetragonal phase structured ceramic thermal barrier coatings
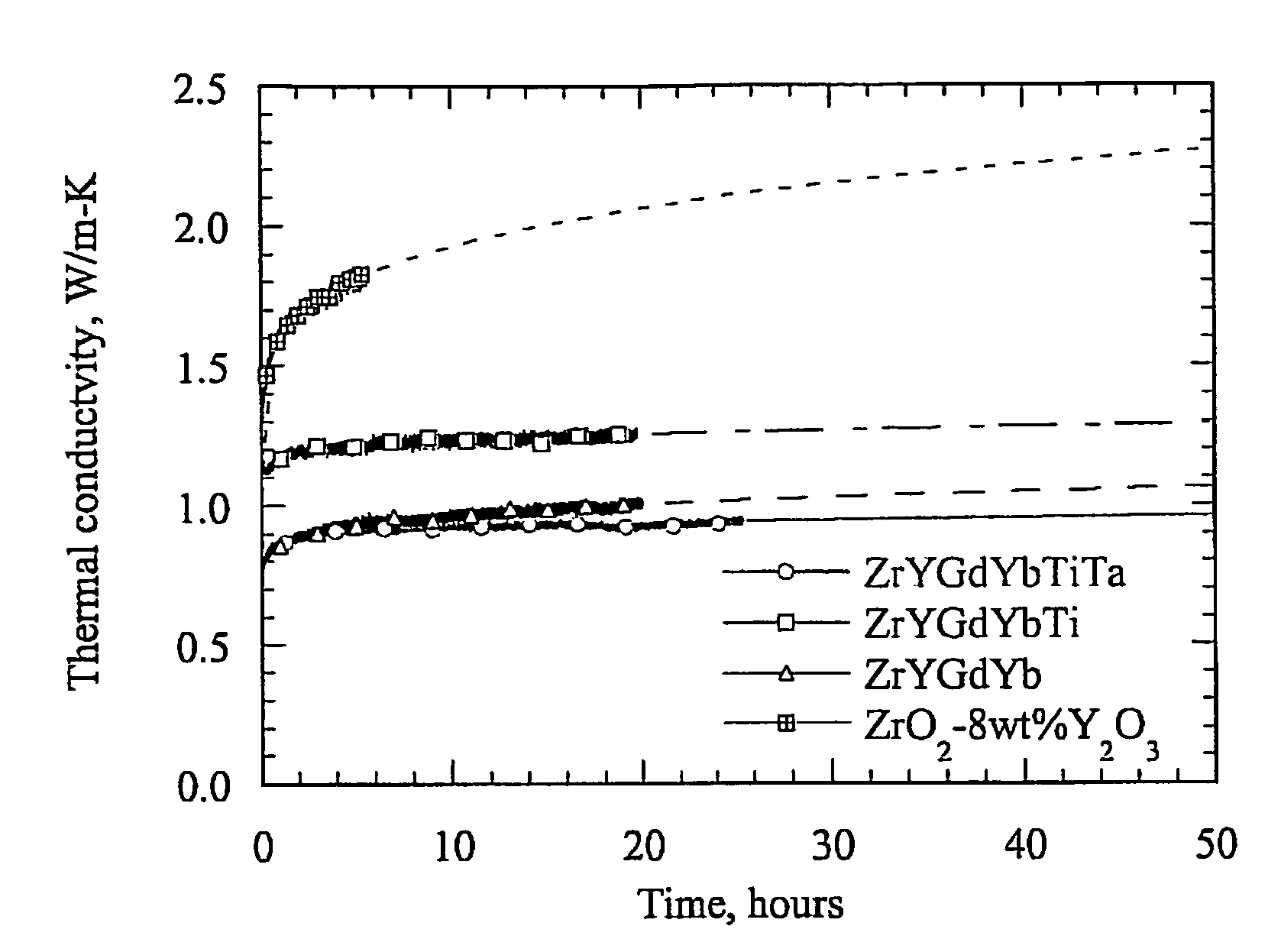
InactiveUS7700508B1Improve thermal conductivityImprove toughnessMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingRare earthDoped oxide
A composition for thermal barrier coatings exhibiting improved thermal conductivity and toughness is provided. The composition is comprised of a base majority oxide, a first dopant oxide, at least one small rare earth oxide, at least one large rare earth oxide and at least one toughening oxide. Compared to traditional thermal barrier coatings, a composition of the present invention provides approximately twice the toughness one-third to one-half the thermal conductivity.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Waterproof coating of carton
ActiveCN102704330AGood chemical stabilityImprove insulation performanceCoatingsPaper forming aids additionParaffin waxEmulsion
The invention relates to a waterproof coating, in particular to a waterproof coating of a carton, which comprises the following components in weight part: 30-120 parts of paraffin micro-emulsion, 50-90 parts of simethicone, and 4-8 parts of emulsifier. The waterproof coating is prepared according to a method as follows: (1) heating the paraffin micro-emulsion to 50-180 degree C; (2) adding simethicone and stirring for 0.5-3 hours; and (3) adding the emulsifier, stirring at a high speed for 10-40 minutes, and cooling to the room temperature. The waterproof coating of the carton, disclosed by the invention, has no pollution on the human body and the environment, can be combined with the base material firmly, and has excellent waterproof property.
Owner:ANHUI JINDUN PAINT
Production method of metallized substrate
ActiveUS20120321805A1Inhibit migrationImprove conductivityConductive materialPretreated surfacesTitanium nitrideSilver copper
A production method for a metallized substrate to produce a metallized substrate which comprises: a sintered nitride ceramic substrate; a titanium nitride layer formed on the sintered substrate; and a metal layer containing copper, silver and titanium formed on the titanium nitride layer. The method comprises: a step of layering a first paste layer containing copper powder and titanium hydride powder on the sintered nitride ceramic substrate, to produce a first layered body; a step of layering a second paste layer containing silver-copper alloy powder on the first paste layer of the first layered body, to produce a second layered body; and a step of firing the second layered body, to thereby form the titanium nitride layer and the metal layer on the sintered nitride ceramic substrate.
Owner:TOKUYAMA CORP
Semiconductor module
InactiveUS20140339693A1Improve moisture resistanceExcellent in voltage enduranceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor packageEngineering
Provided is an improved cooler-integrated semiconductor module.A semiconductor module (100) includes a plurality of cooling plates (12), and a plurality of flat-plate semiconductor packages (5) and flat-plate device packages (2). The semiconductor packages (5) each include a semiconductor element housed therein. The device packages (2) each include an electronic component housed therein, the electronic component being different in type from the semiconductor element housed in the semiconductor elements. The cooling plates (12) are laminated alternately with the semiconductor packages (5) or the device packages (2). Connecting tubes (13a, 13b) having refrigerant flowing therein are provided between the cooling plates (12) adjacent to each other.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Graphene oxide gel bonded graphene composite films and processes for producing same
ActiveUS9561955B2Low densityThermal conductivityNon-metal conductorsMaterial nanotechnologyComposite filmSingle layer graphene
Disclosed is a graphene composite thin film composition composed of nano graphene platelets (NGPs) bonded by a graphene oxide binder, wherein the NGPs contain single-layer graphene or multi-layer graphene sheets having a thickness from 0.335 nm to 100 nm. The NGPs occupy a weight fraction of 1% to 99.9% of the total composite weight. The graphene oxide binder, having an oxygen content of 1-40% (preferably <10%) by weight based on the total graphene oxide weight, is obtained from a graphene oxide gel. The composite forms a thin film with a thickness no greater than 1 mm, but preferably no greater than 100 μm and no less than 10 μm. This composition has a combination of exceptional thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength unmatched by any thin-film material of comparable thickness range.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
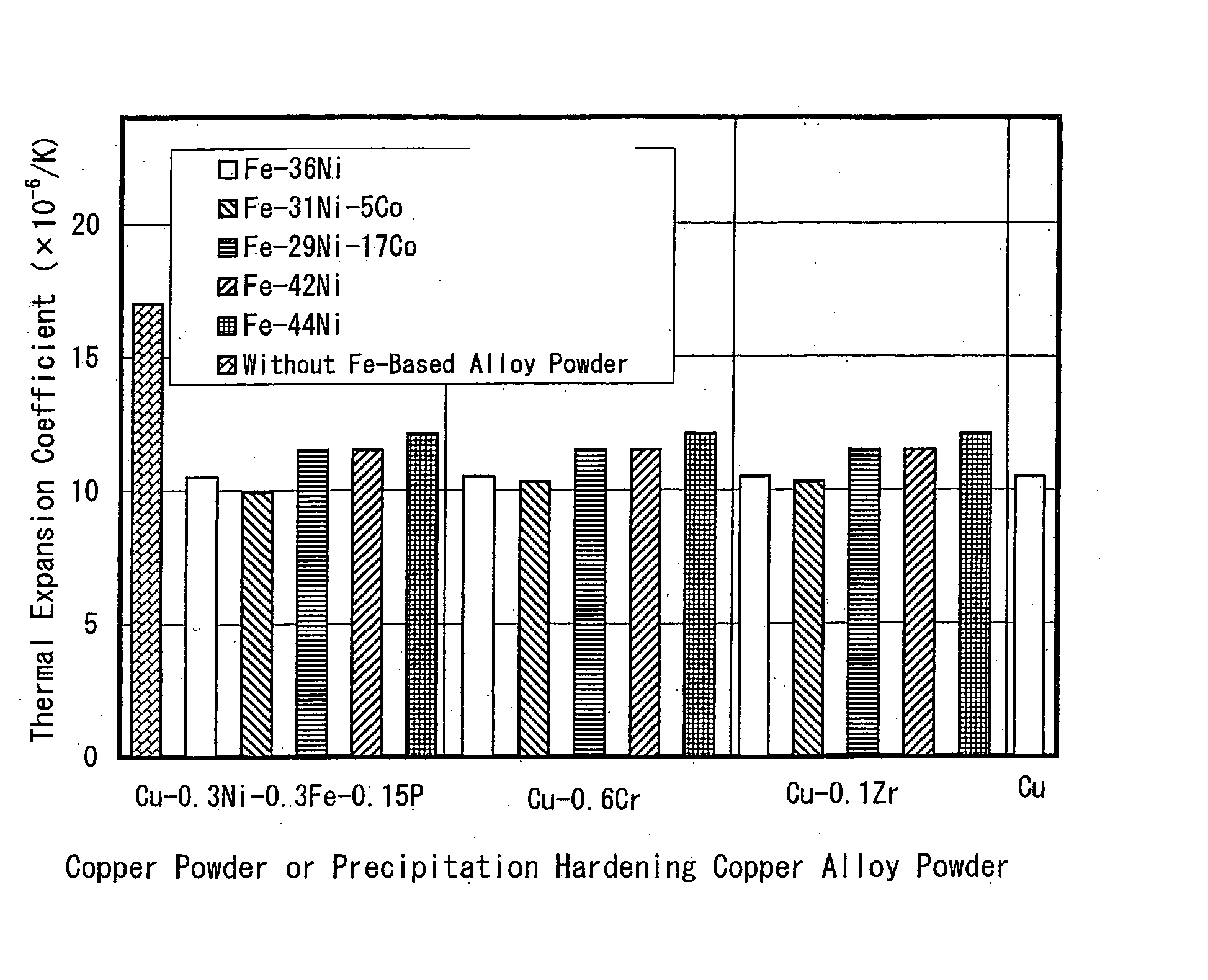
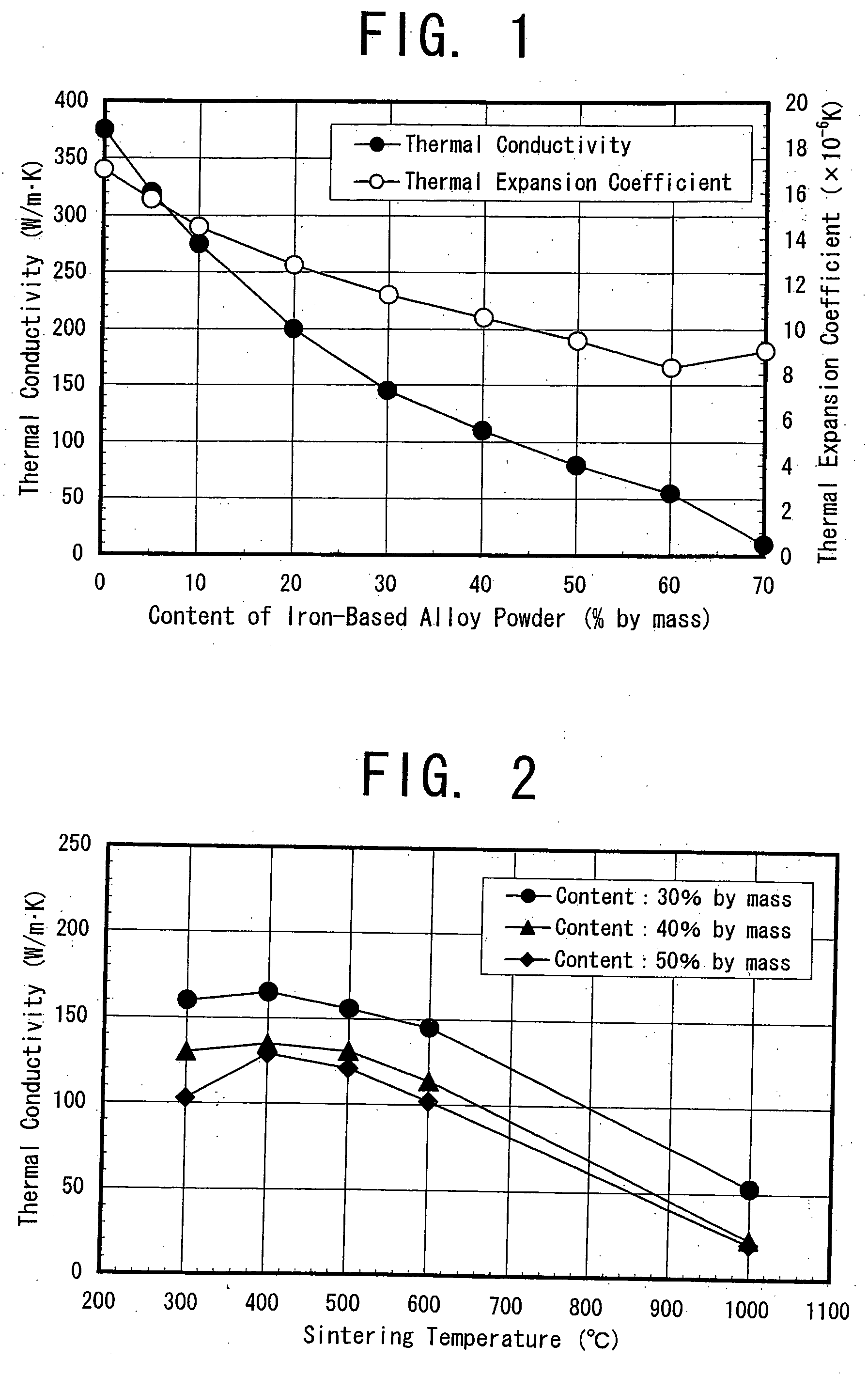
Copper based material of law thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity and method for producing the same
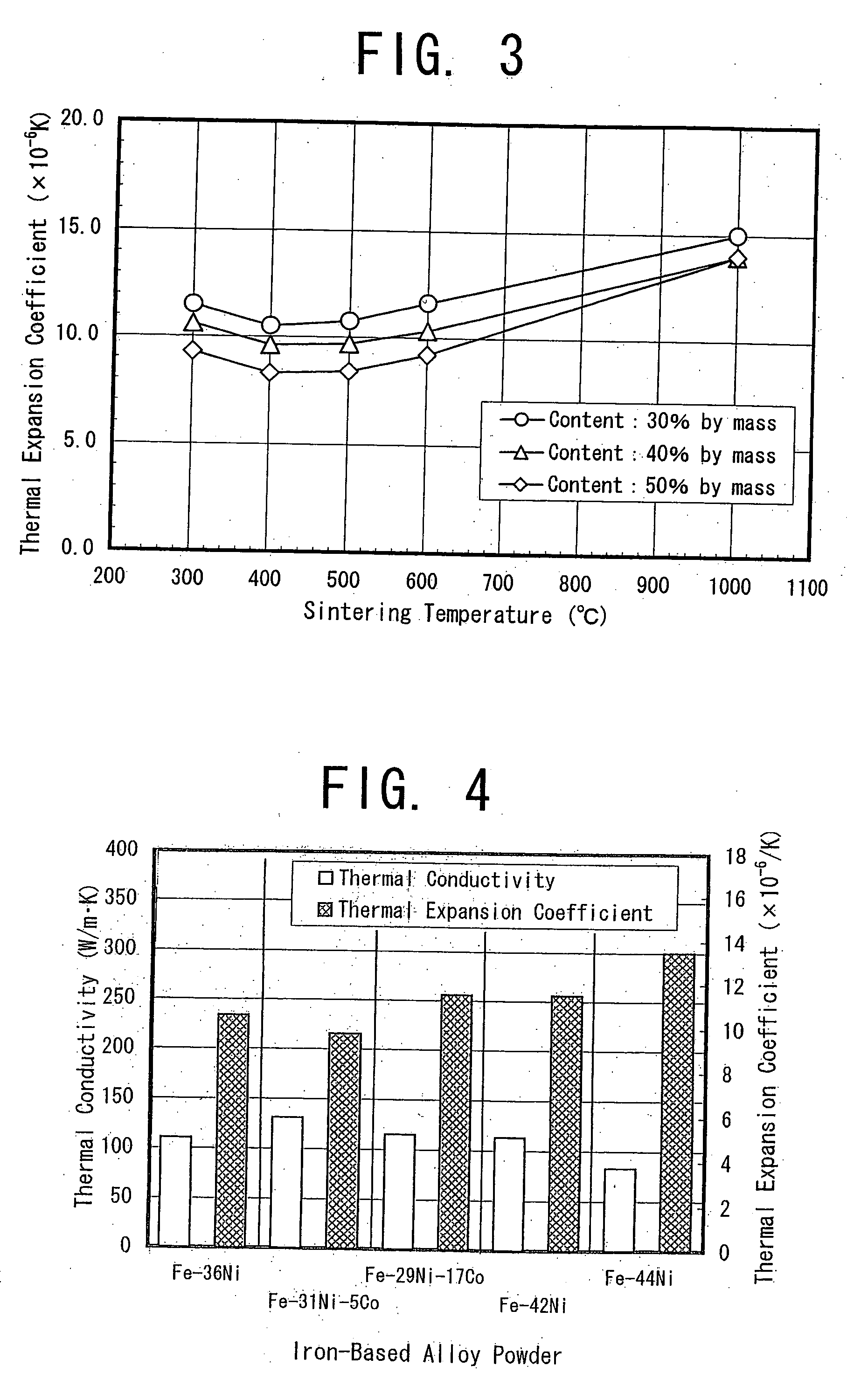
InactiveUS20040213692A1Maintain good propertiesHigh production costTransportation and packagingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPowder mixtureMachinability
The invention proposes a copper-based material with low thermal expansion and high thermal conductivity having good machinability and adaptability to nickel plating and also proposes a method for producing the same. The copper-based material is prepared through the steps of: adding 5 to 60% of iron-based alloy power having a certain value in thermal expansion coefficient into a matrix powder of pure copper phase powder and / or a precipitation hardening copper alloy powder; mixing the powders together; compacting the obtained powder mixture into a green compact and sintering it at temperatures of 400 to 600° C.
Owner:HITACHI POWDERED METALS COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com